Patents
Literature
91 results about "Acute ischemia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acute mesenteric ischemia (AMI) is a syndrome caused by inadequate blood flow through the mesenteric vessels, resulting in ischemia and eventual gangrene of the bowel wall. Although relatively rare, it is a potentially life-threatening condition.
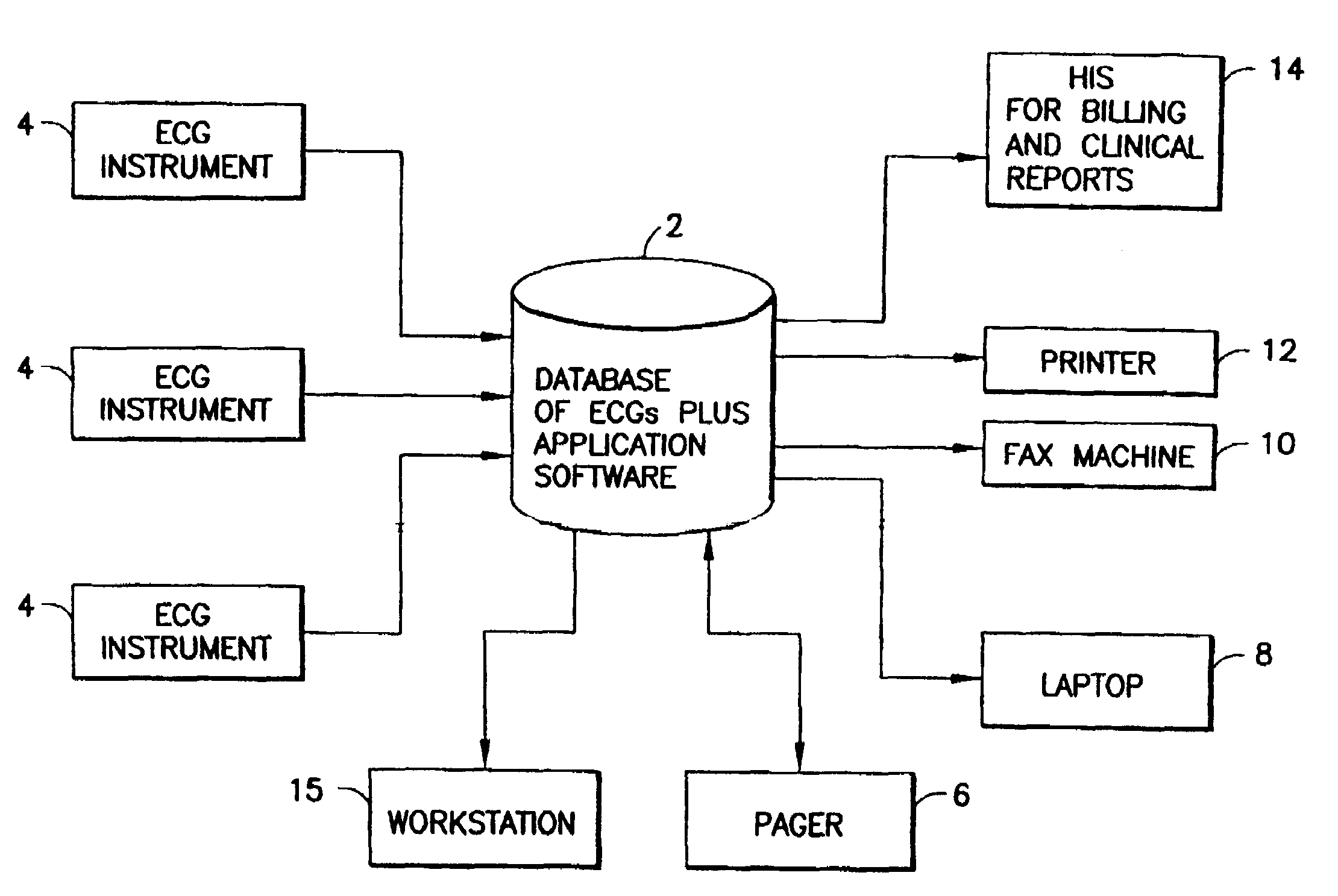
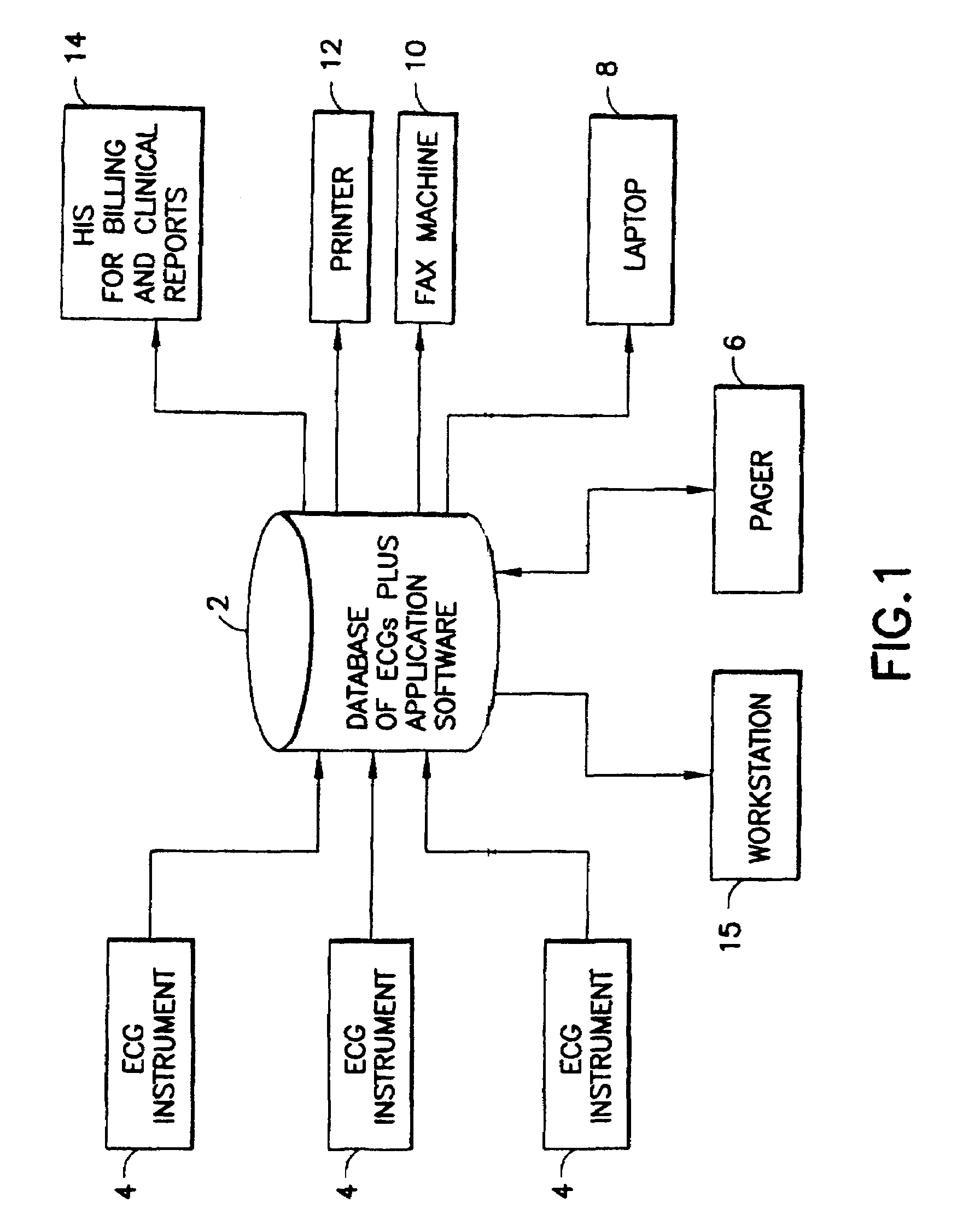
Automated scheduling of emergency procedure based on identification of high-risk patient
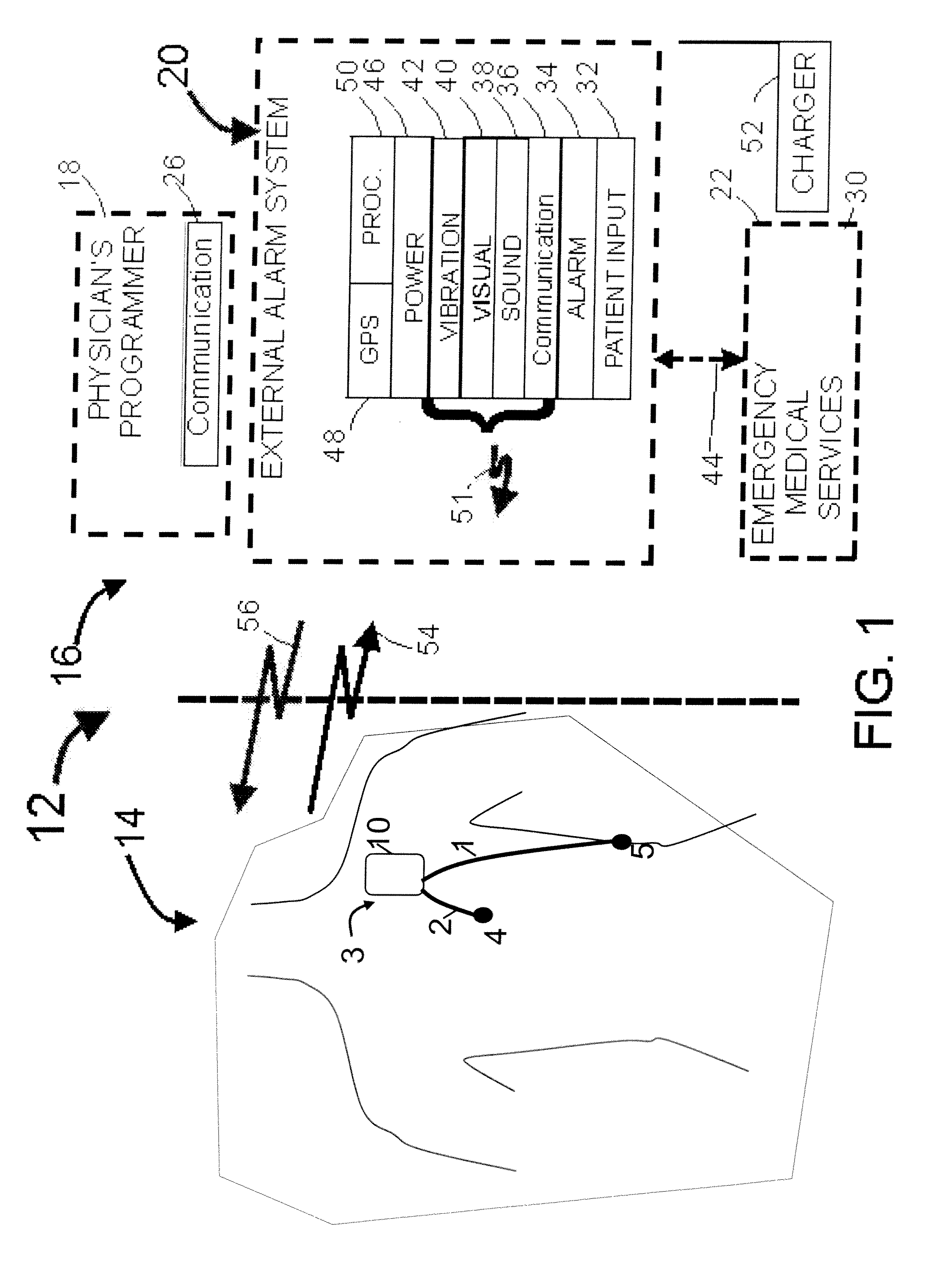
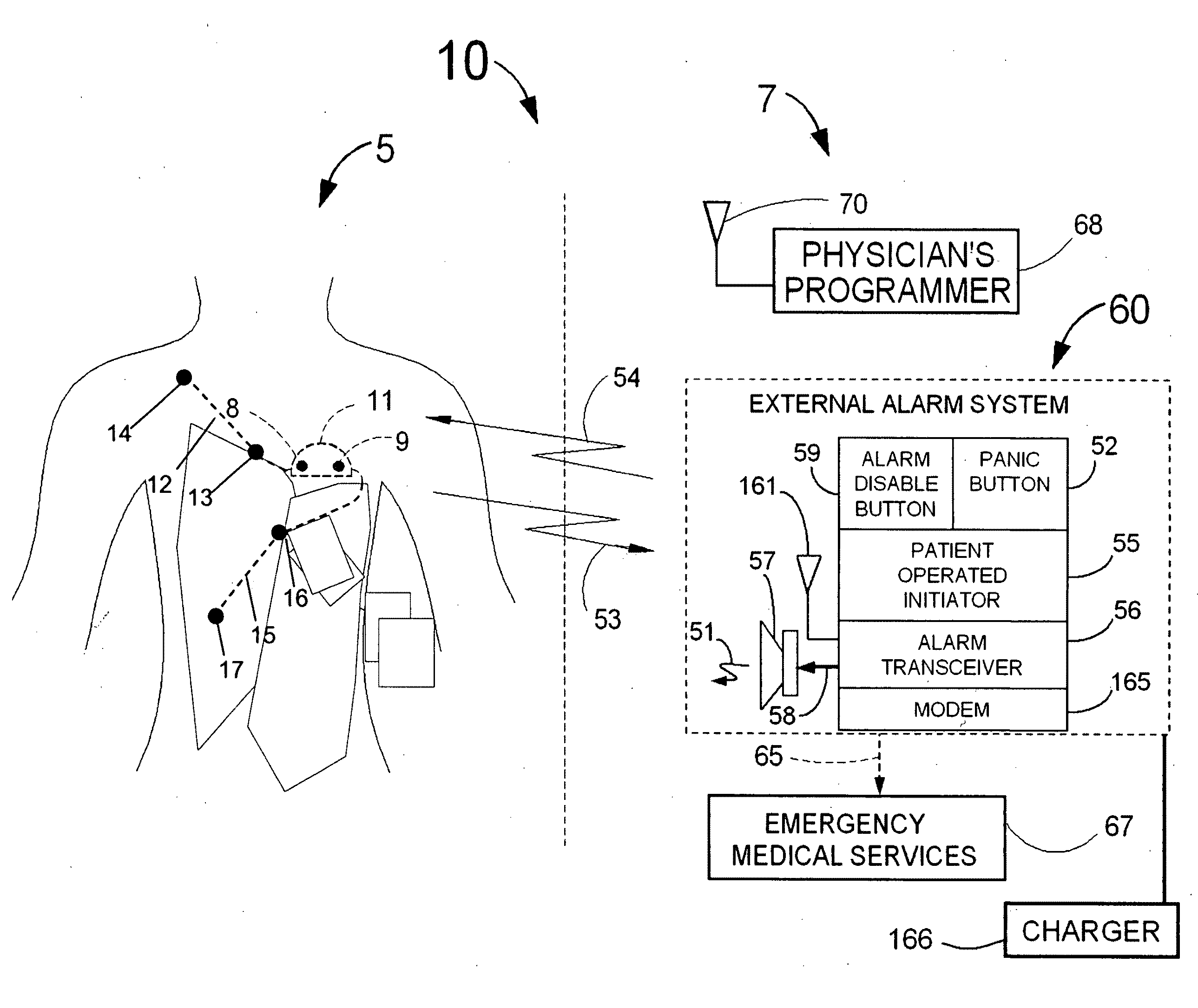
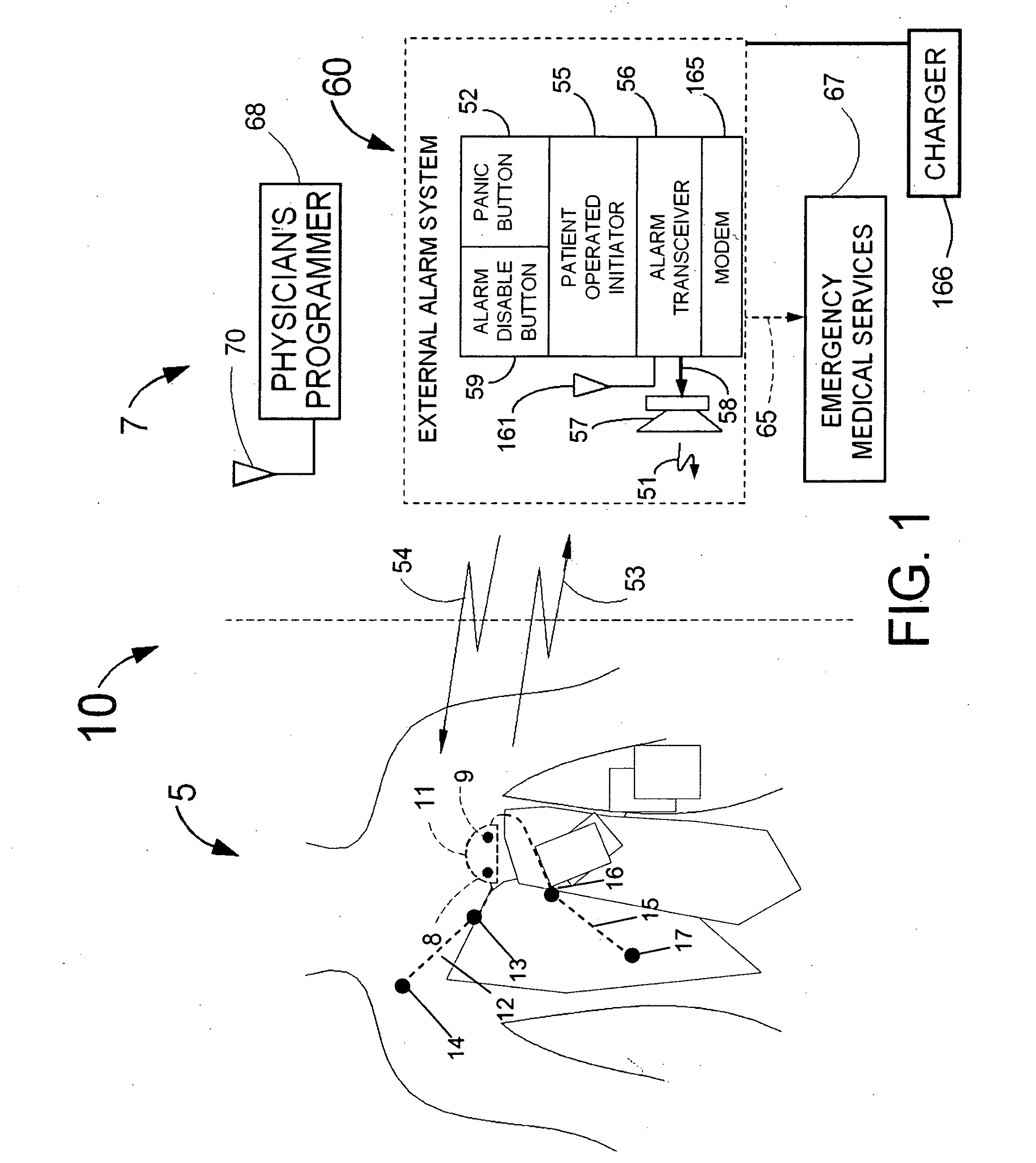
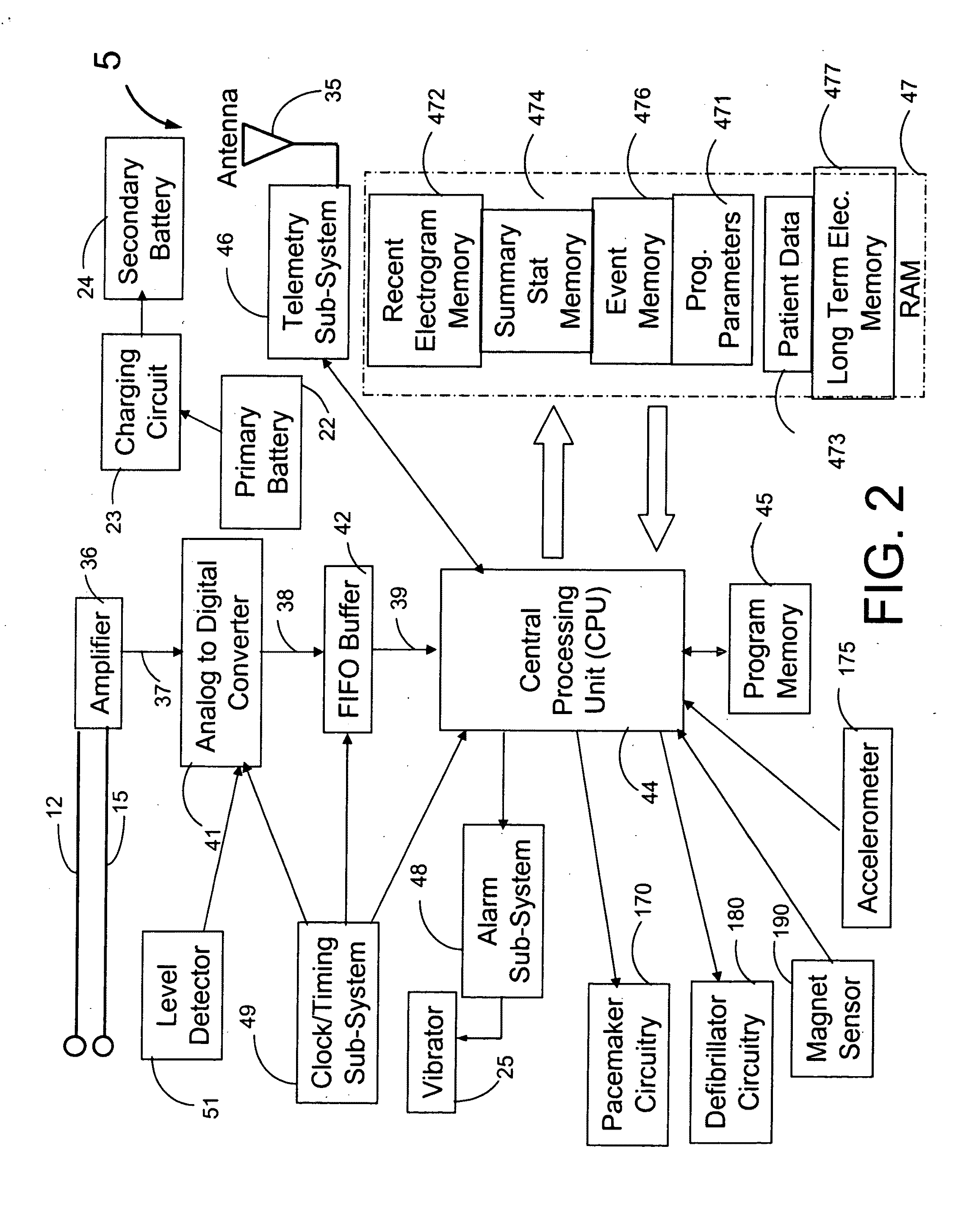
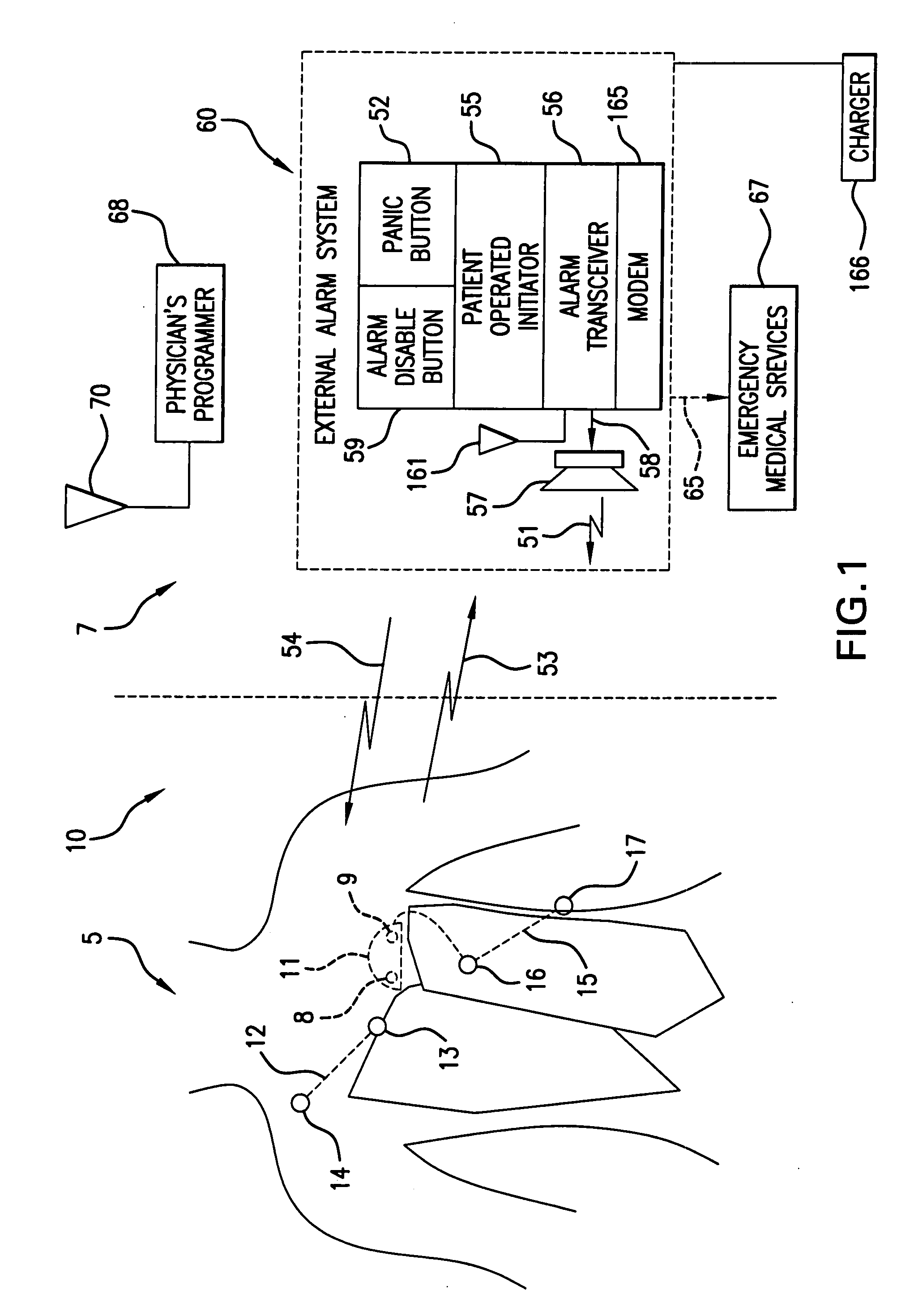
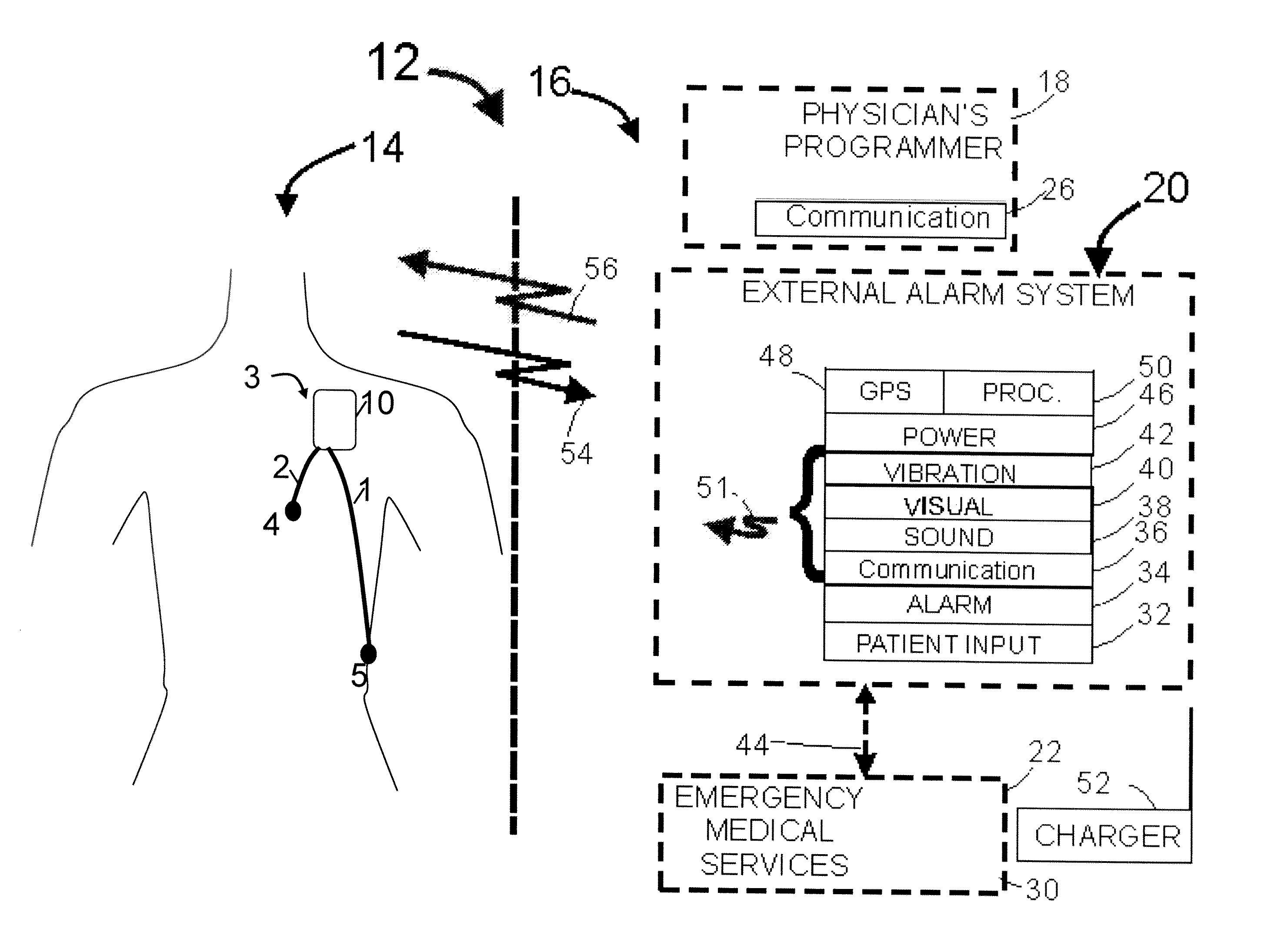
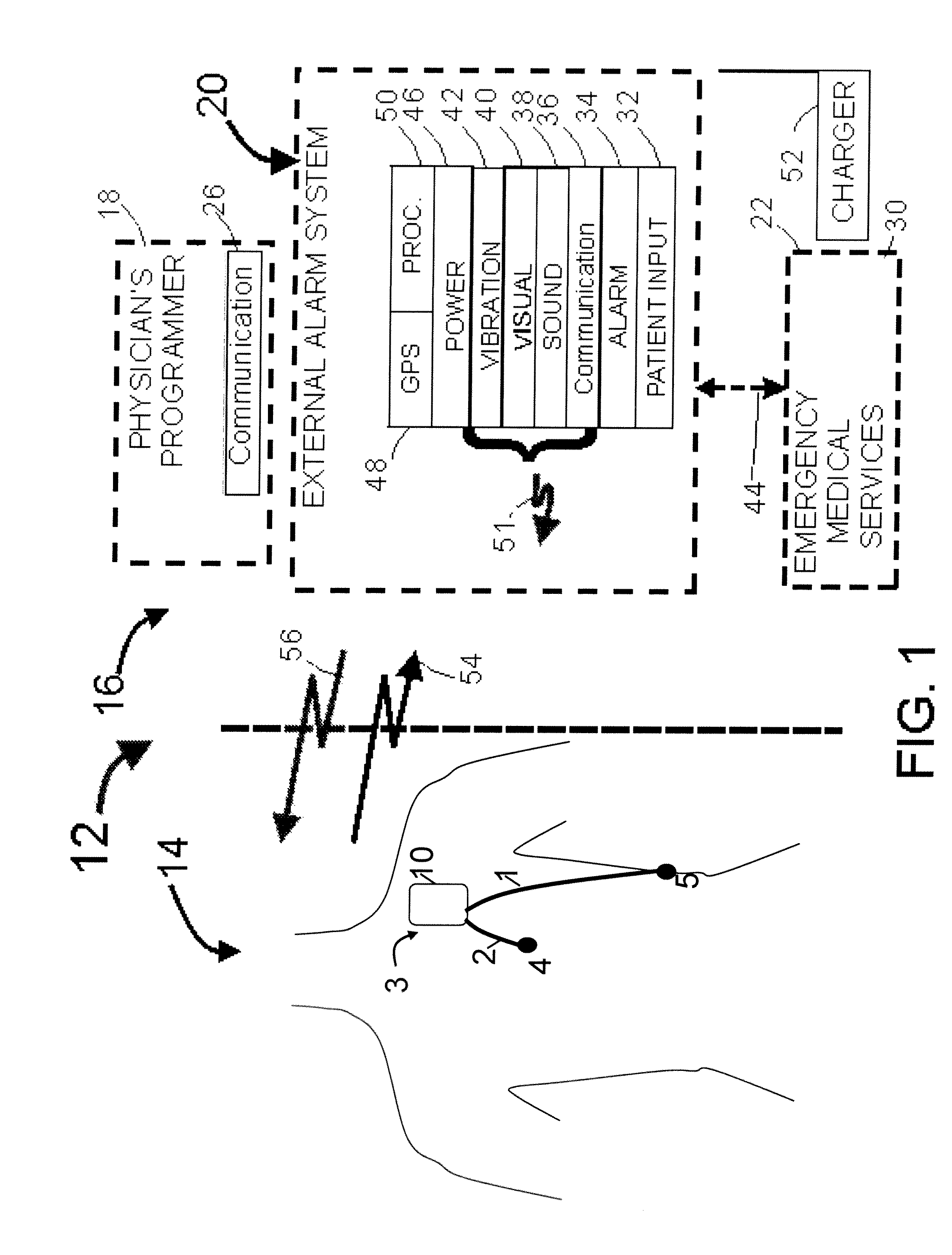
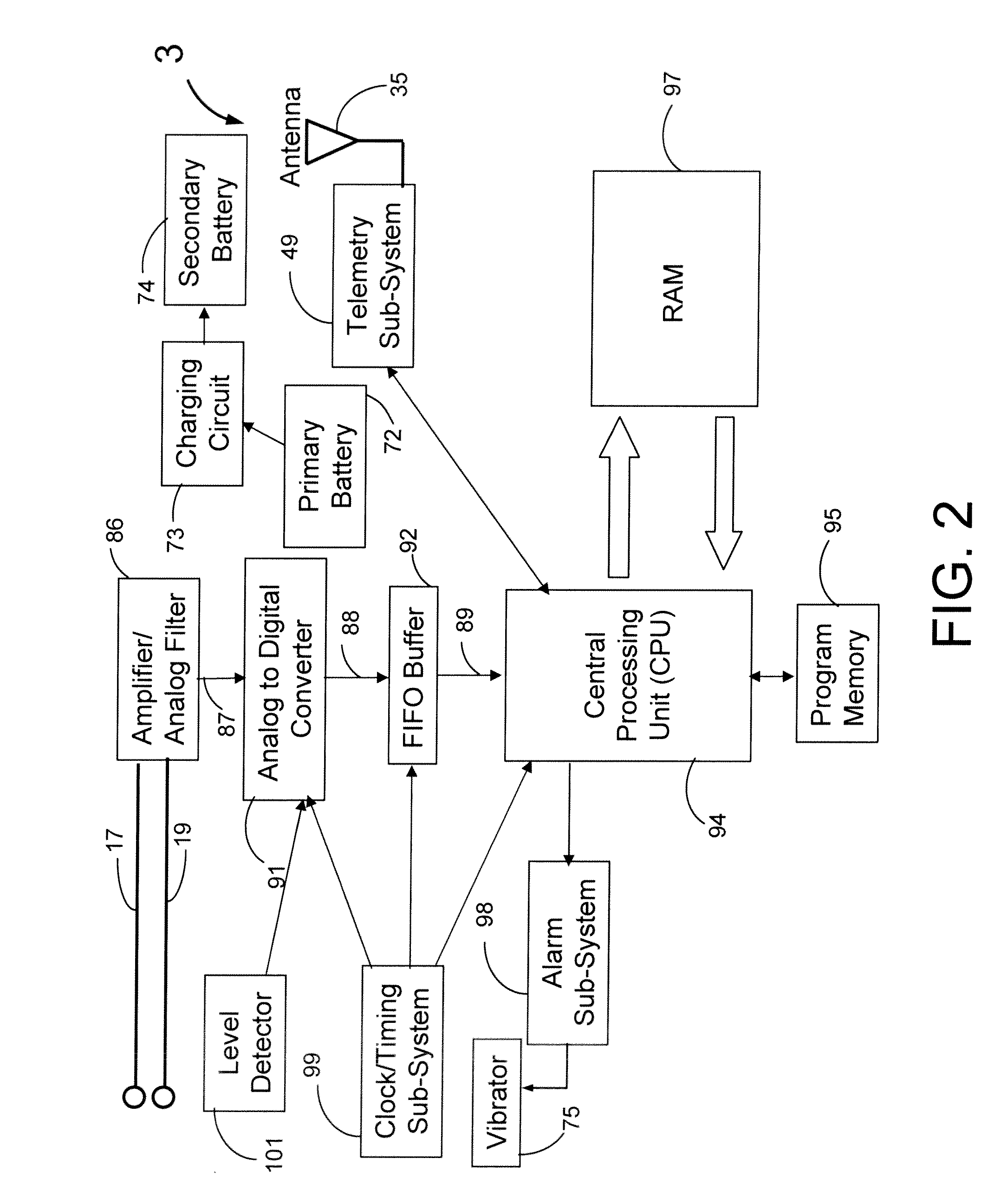
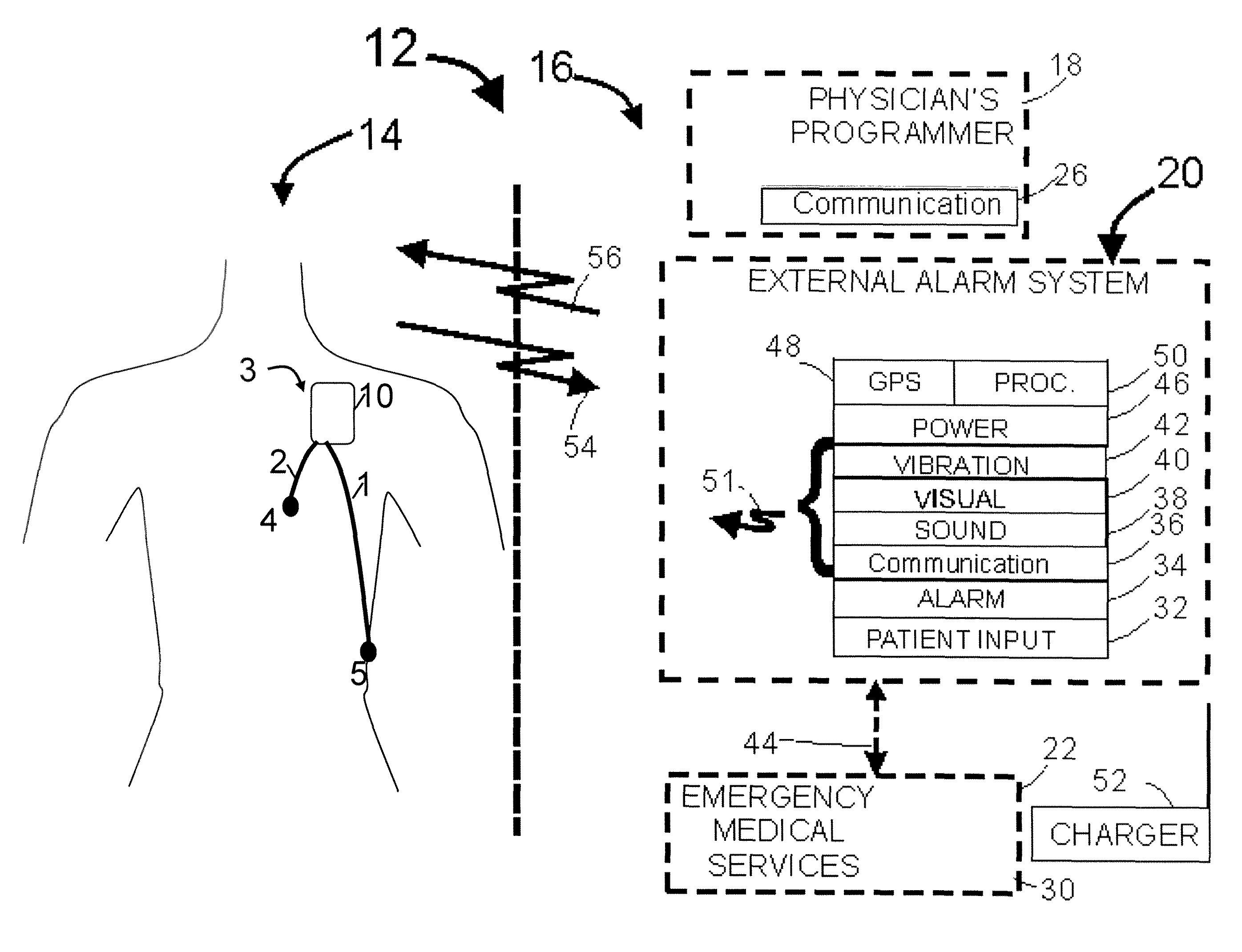
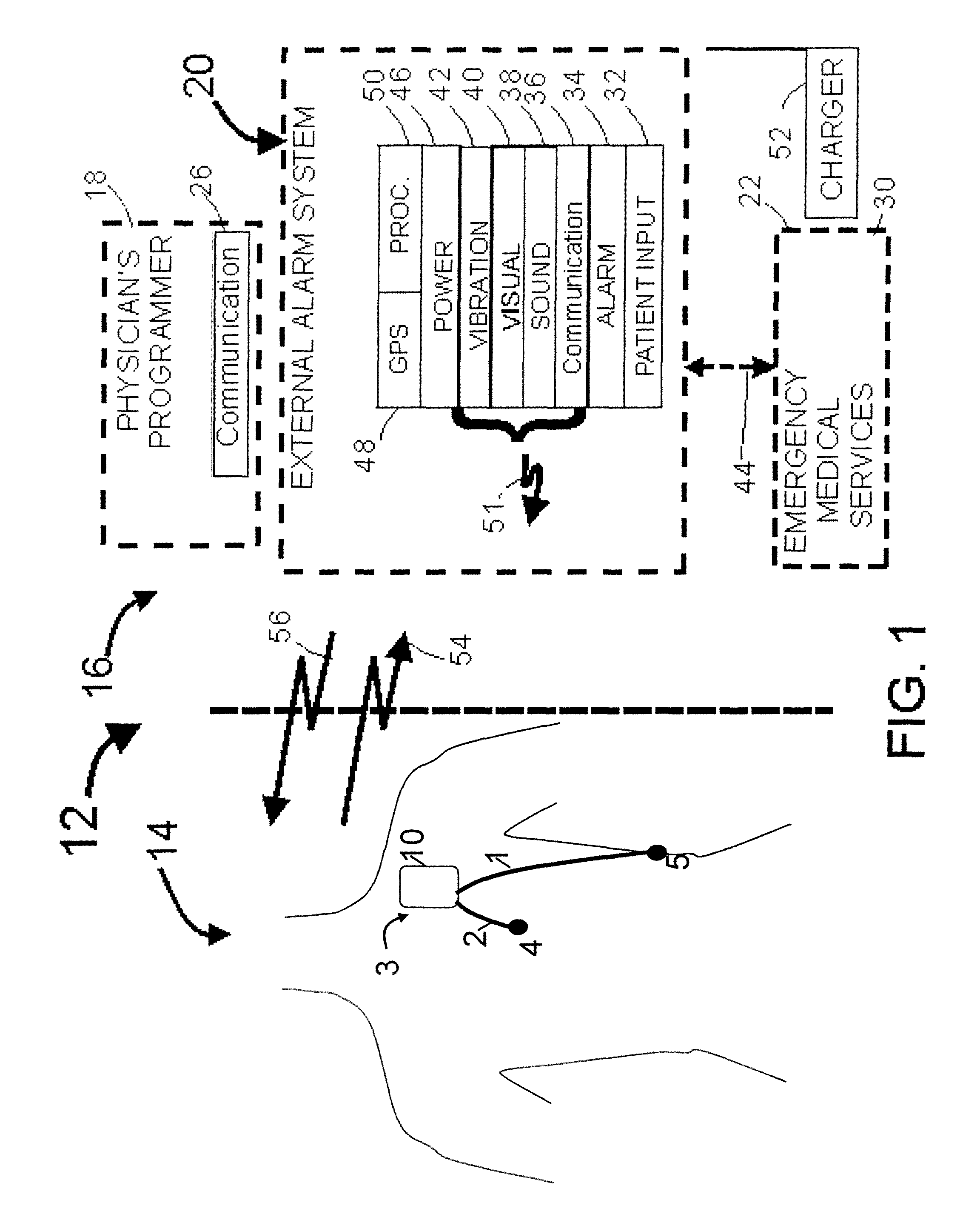
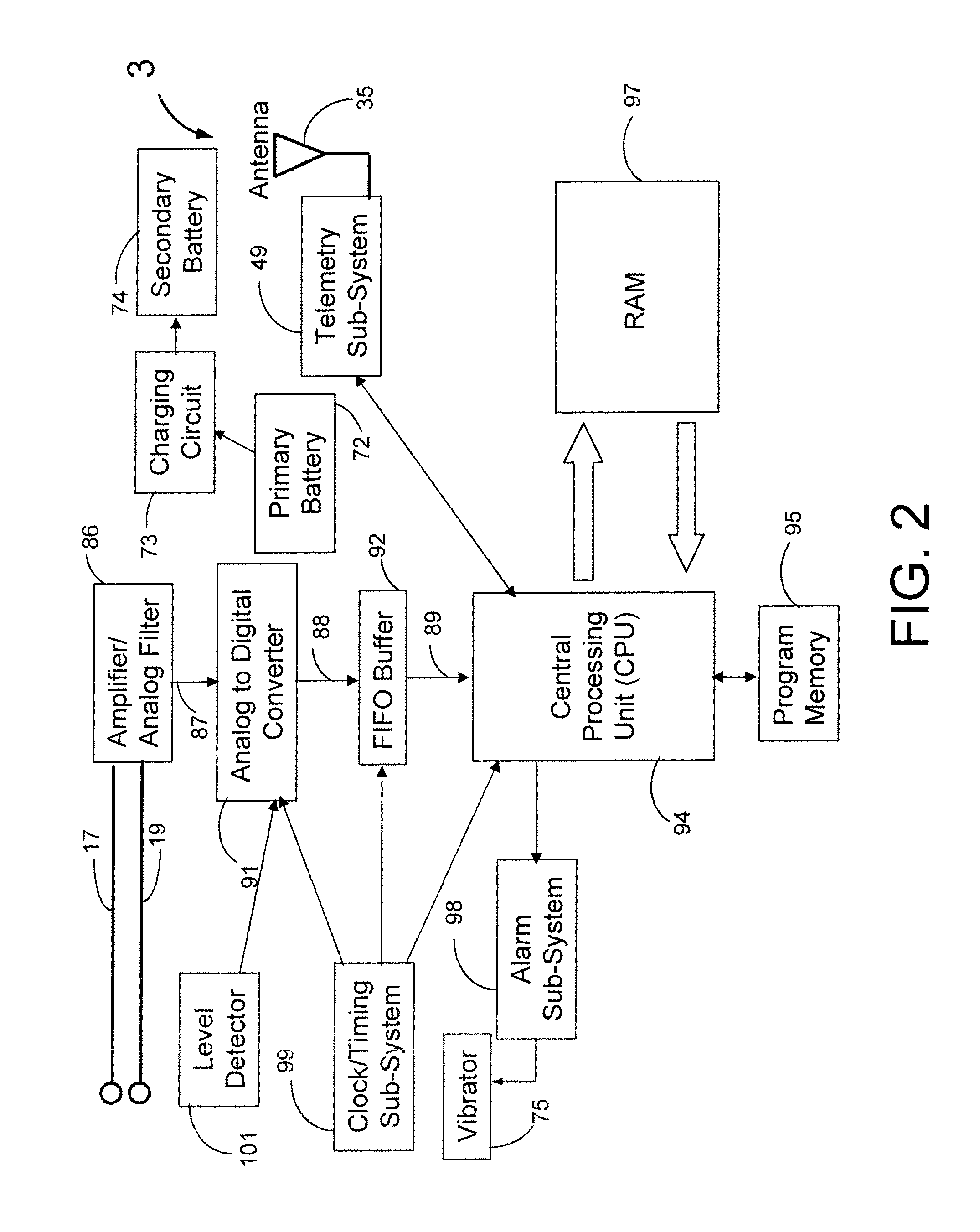
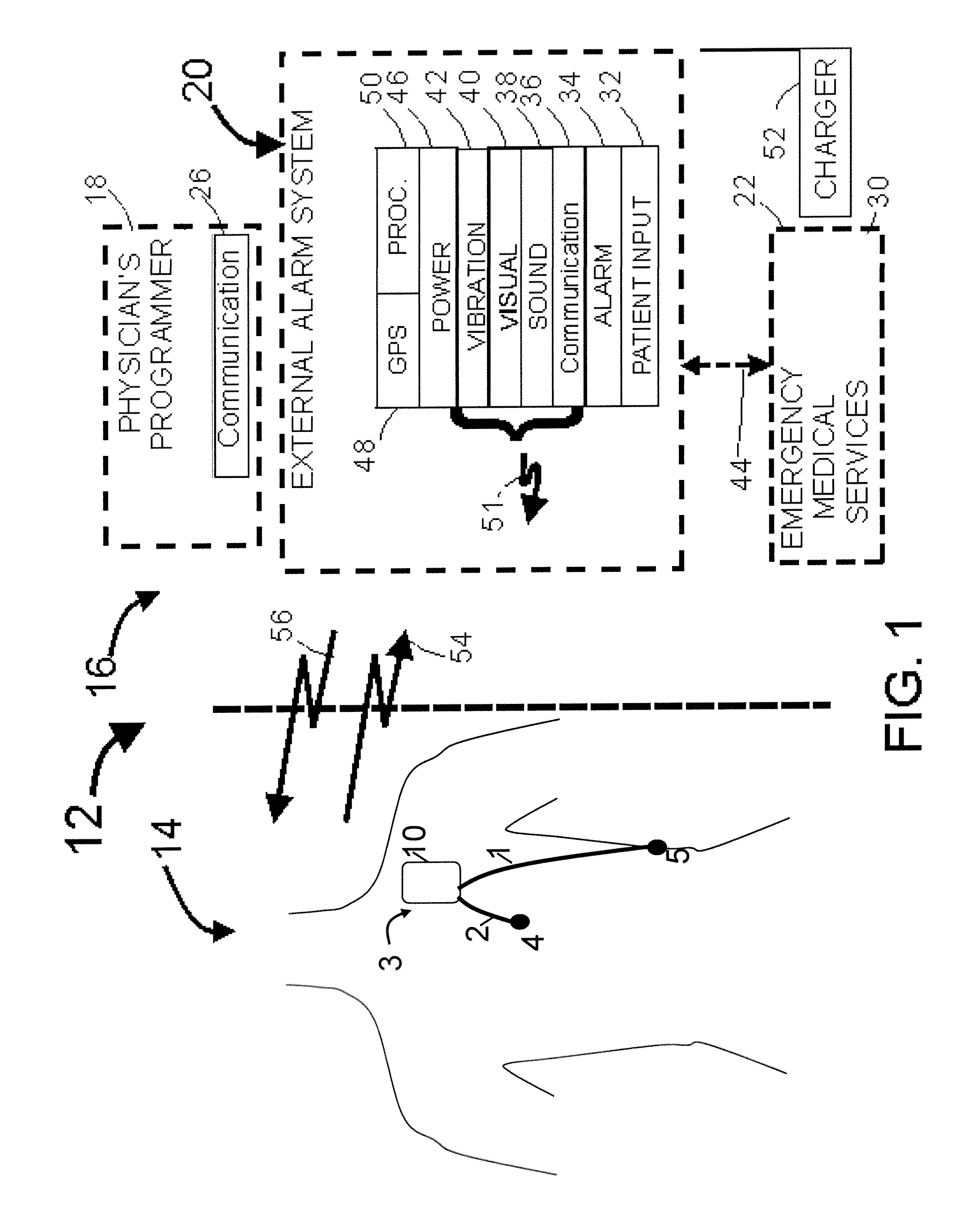
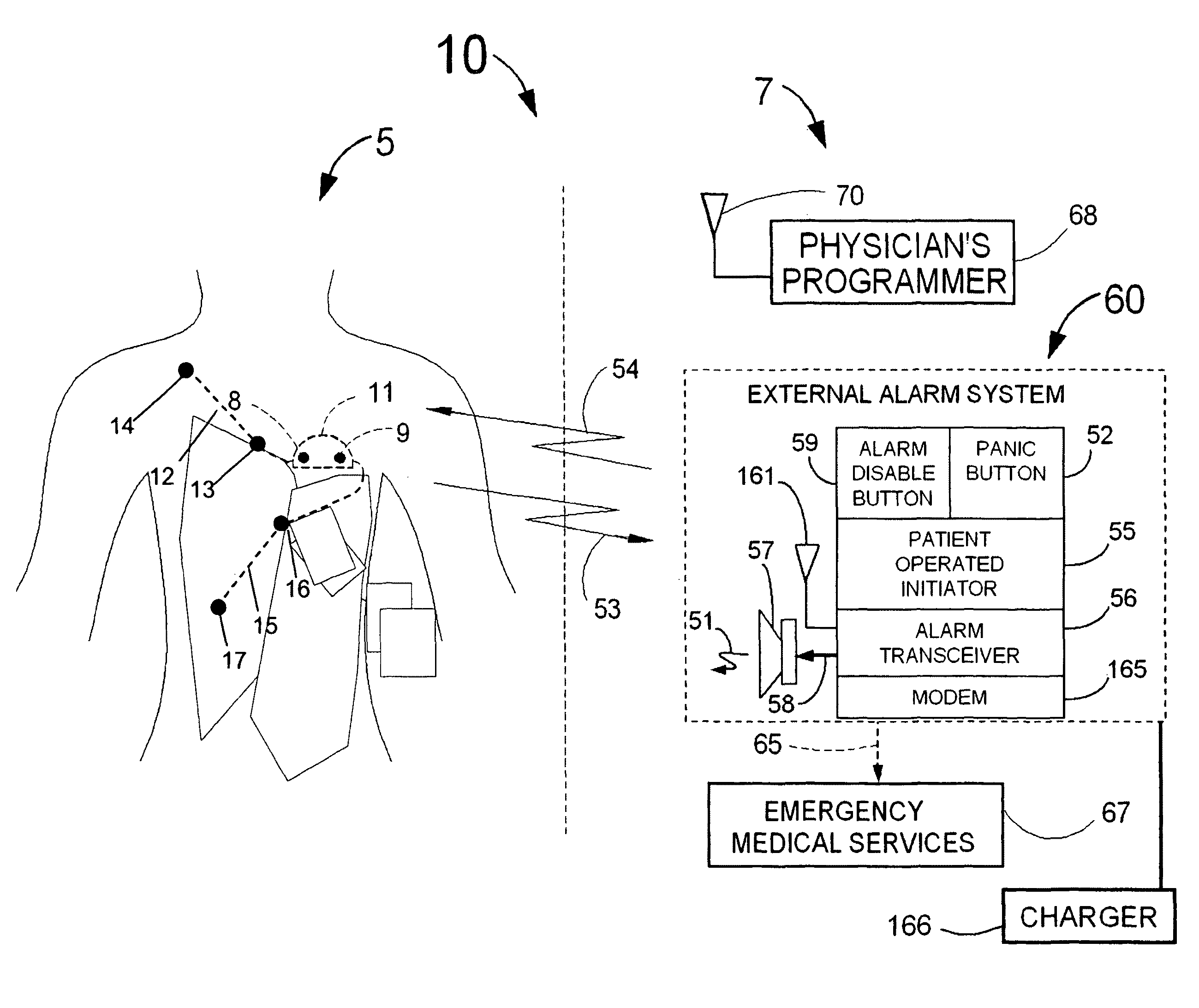
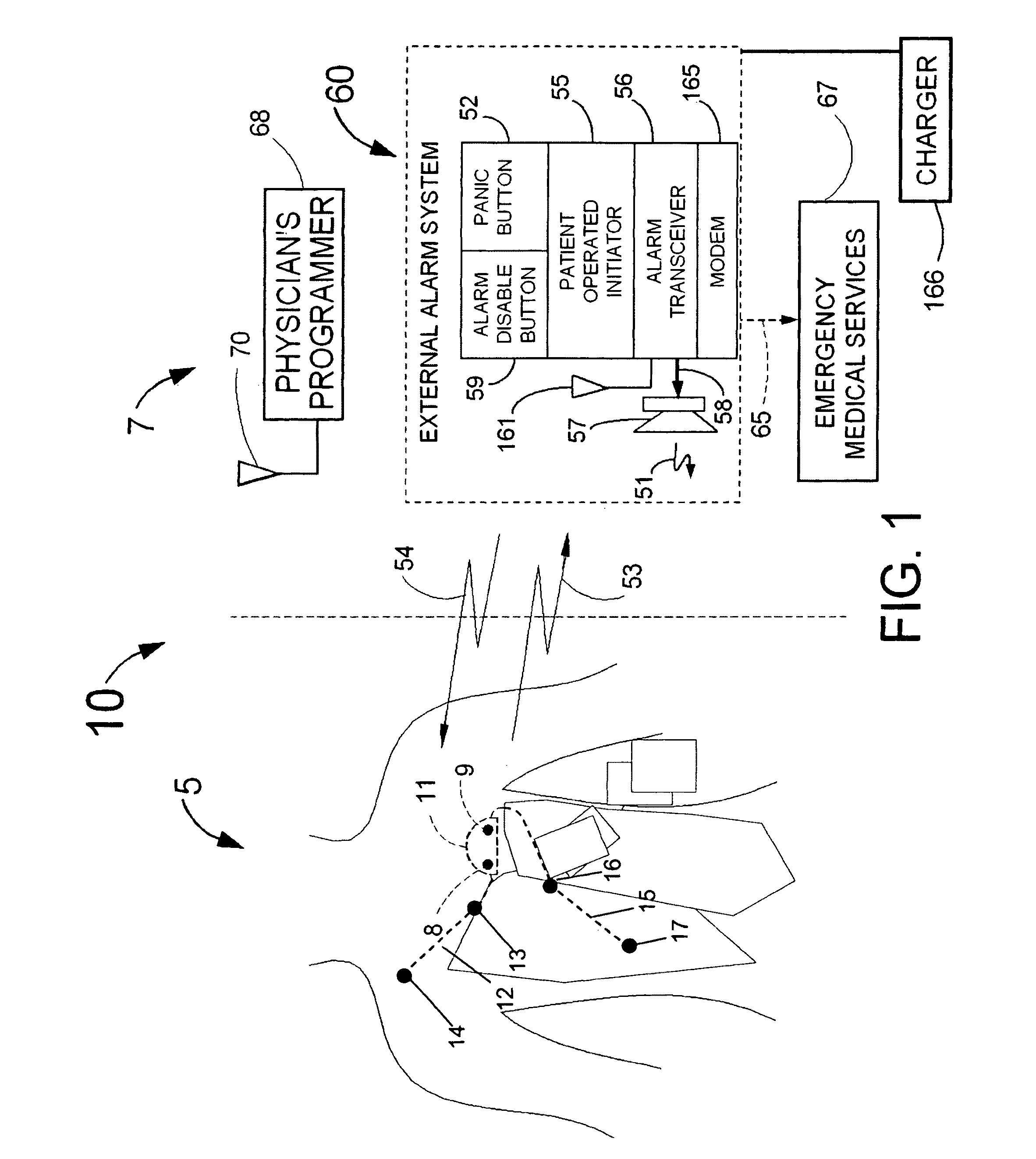
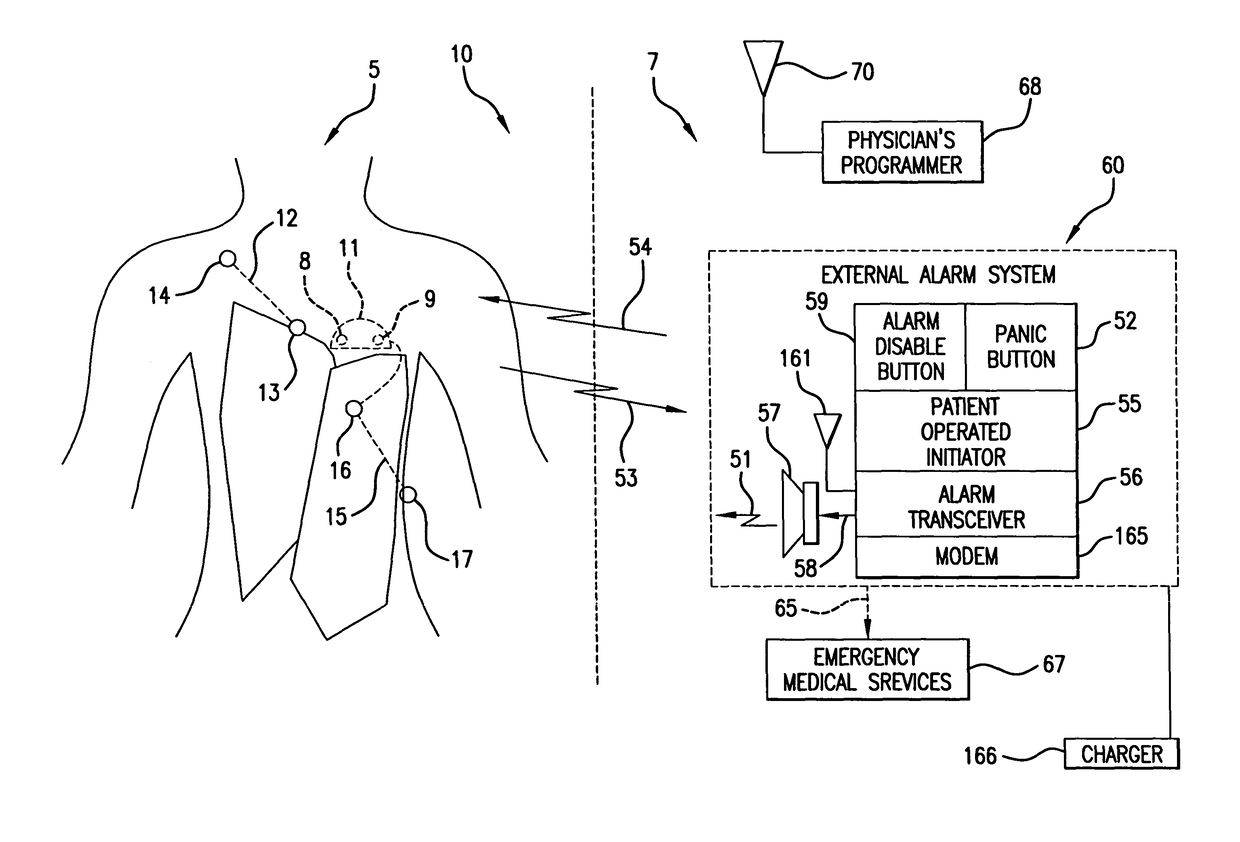
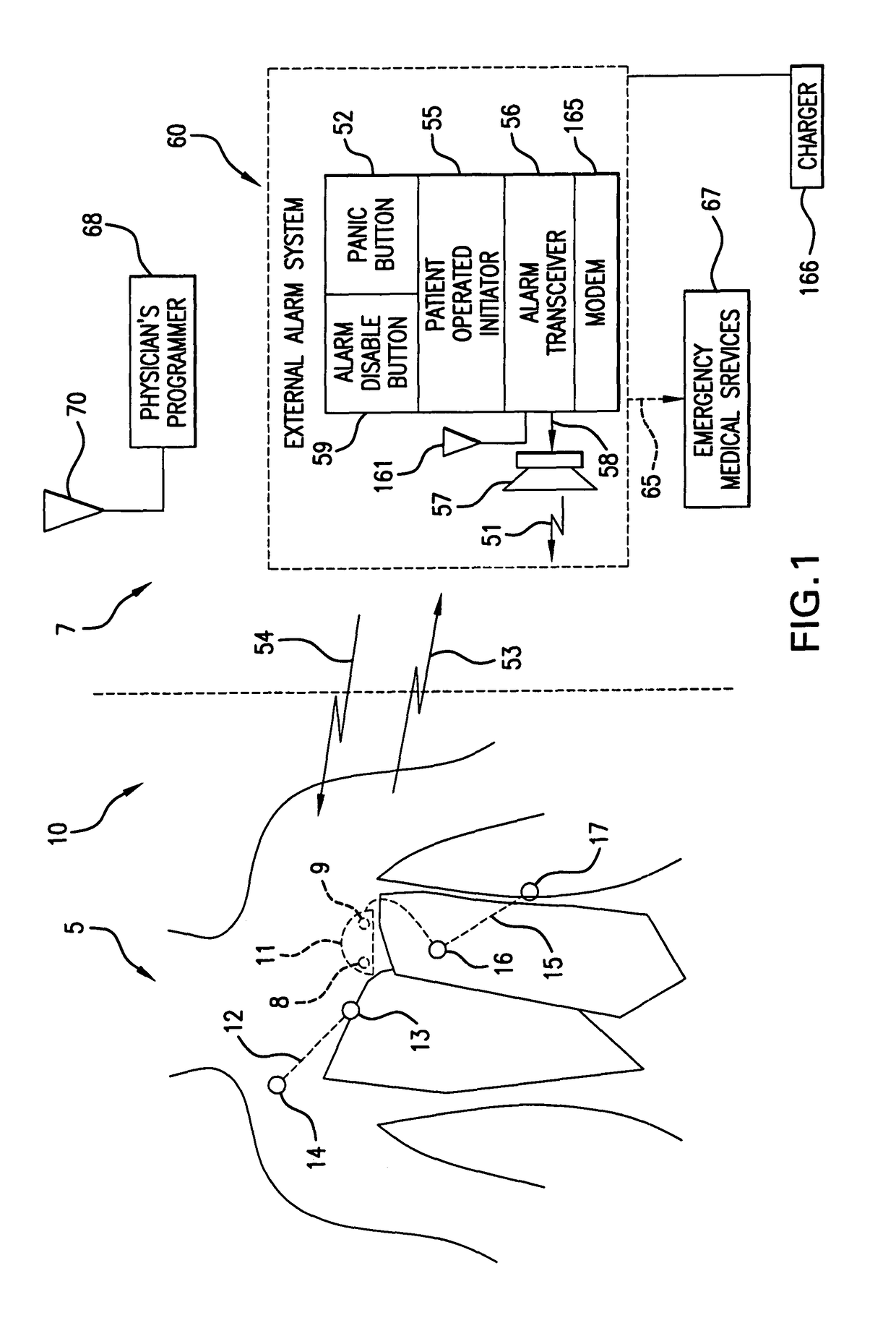
A system and a method for scheduling an emergency procedure in response to detecting that a patient has a high probability of acute myocardial infarction. The system is able to identify patients that are suspected of having acute myocardial infarction (or acute ischemia). The system uses one or more expert software tools or algorithms to analyze received ECG records. Each software tool has logic (e.g., thresholds and / or settings) for automatic routing which is configurable by the customer via a graphical user interface. If any sufficient condition for automatic routing is satisfied, the system routes the data (including the underlying ECG record) and an alert to an electronic device which is accessible by the cardiologist “on call” via a bidirectional pager. If the cardiologist decides that the requested emergency treatment or procedure should be performed, the system accesses the schedules of all associated catheterization labs across multiple hospitals to identify a lab having optimum time-to-treatment. Then the system automatically contacts the selected catheterization lab via a network to schedule the PTCA procedure.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
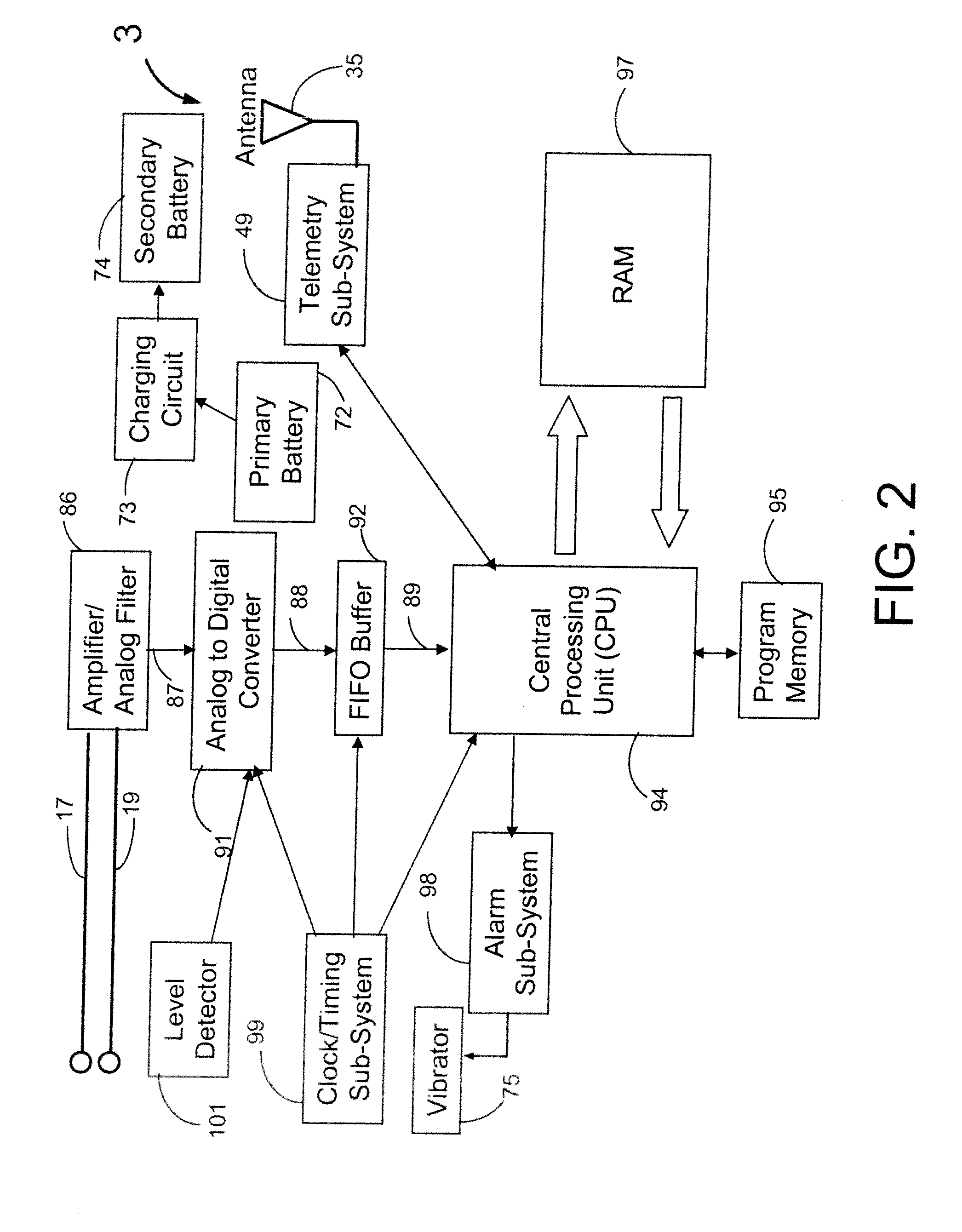
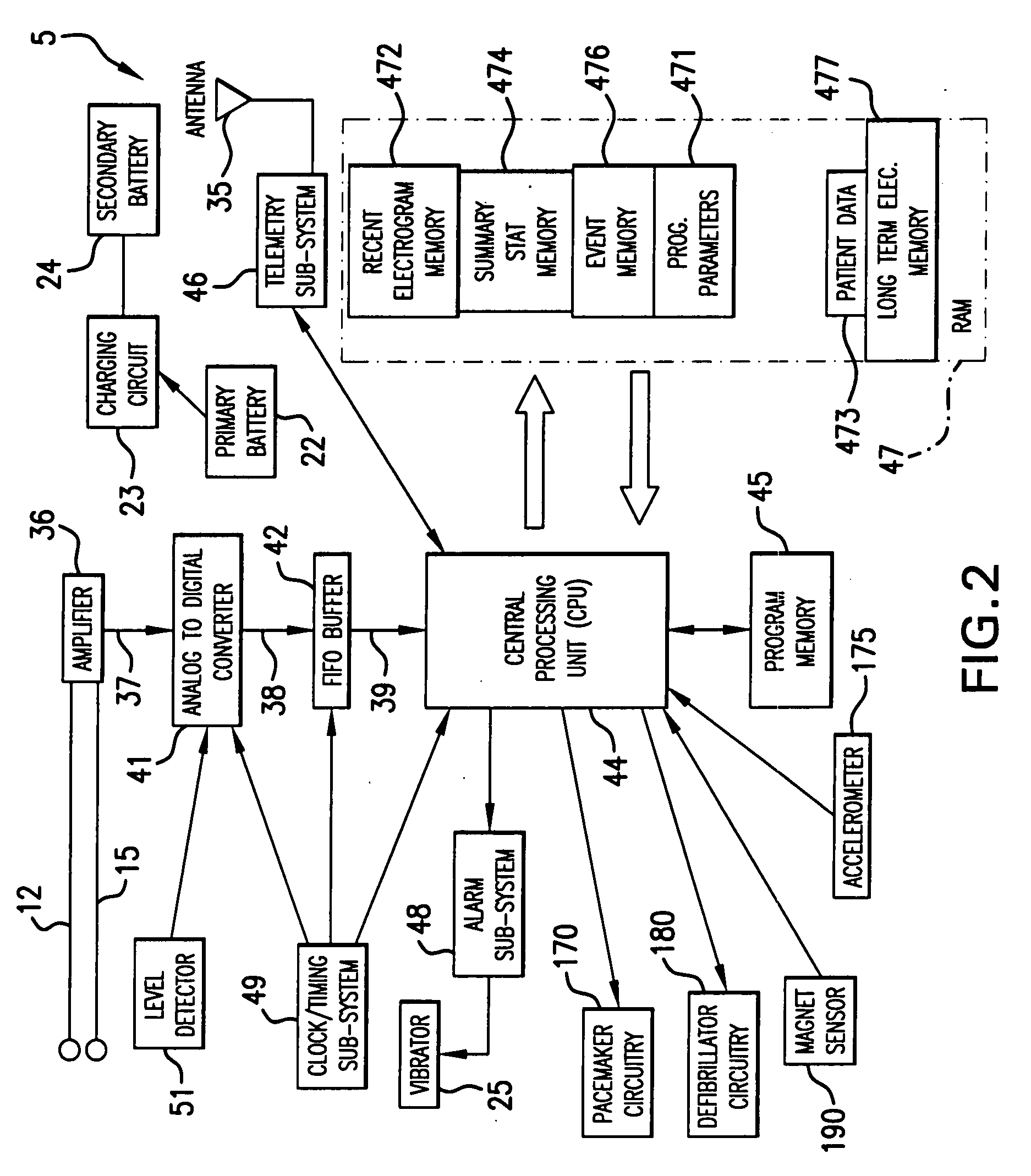
Acute ischemia detection based on parameter value range analysis
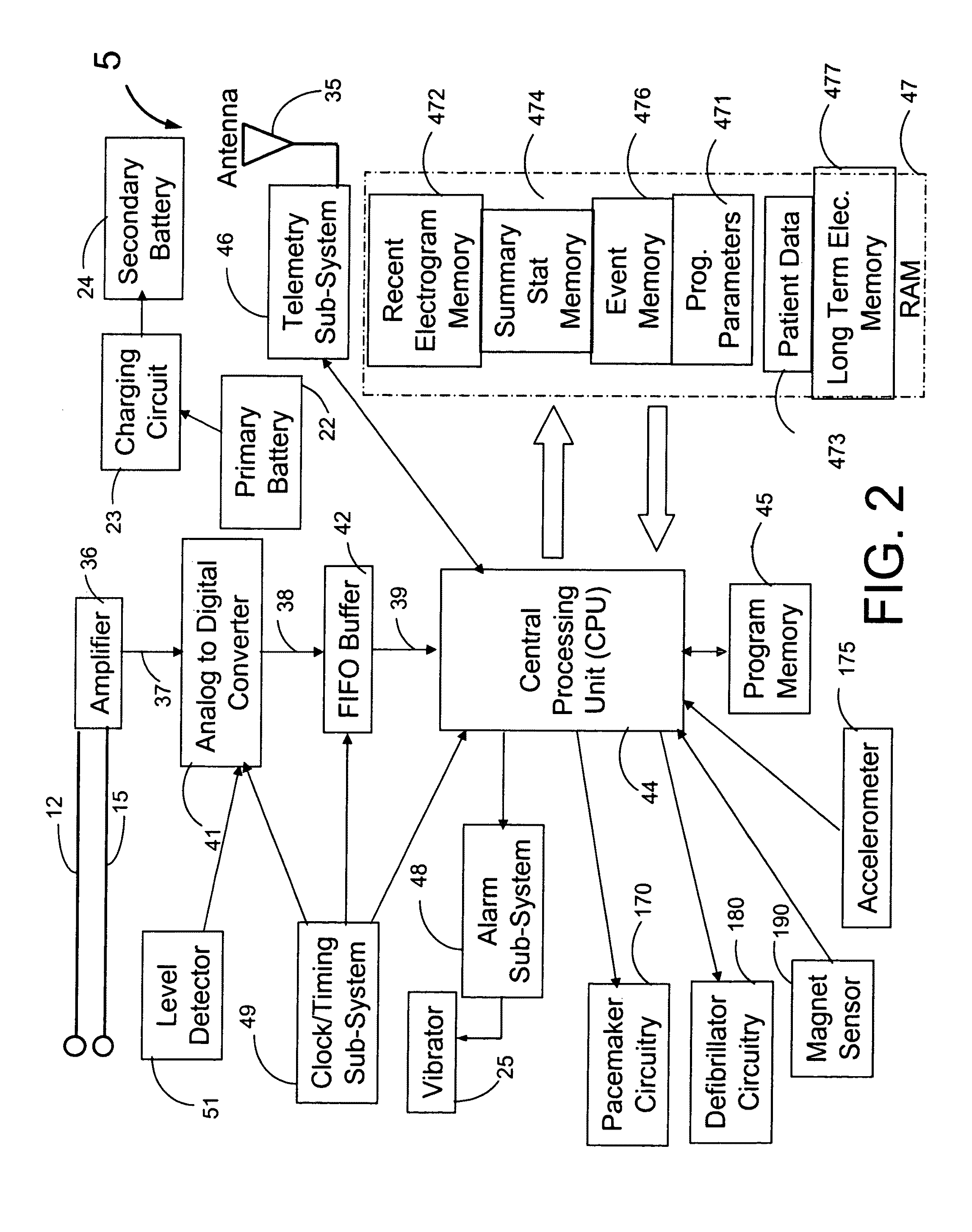
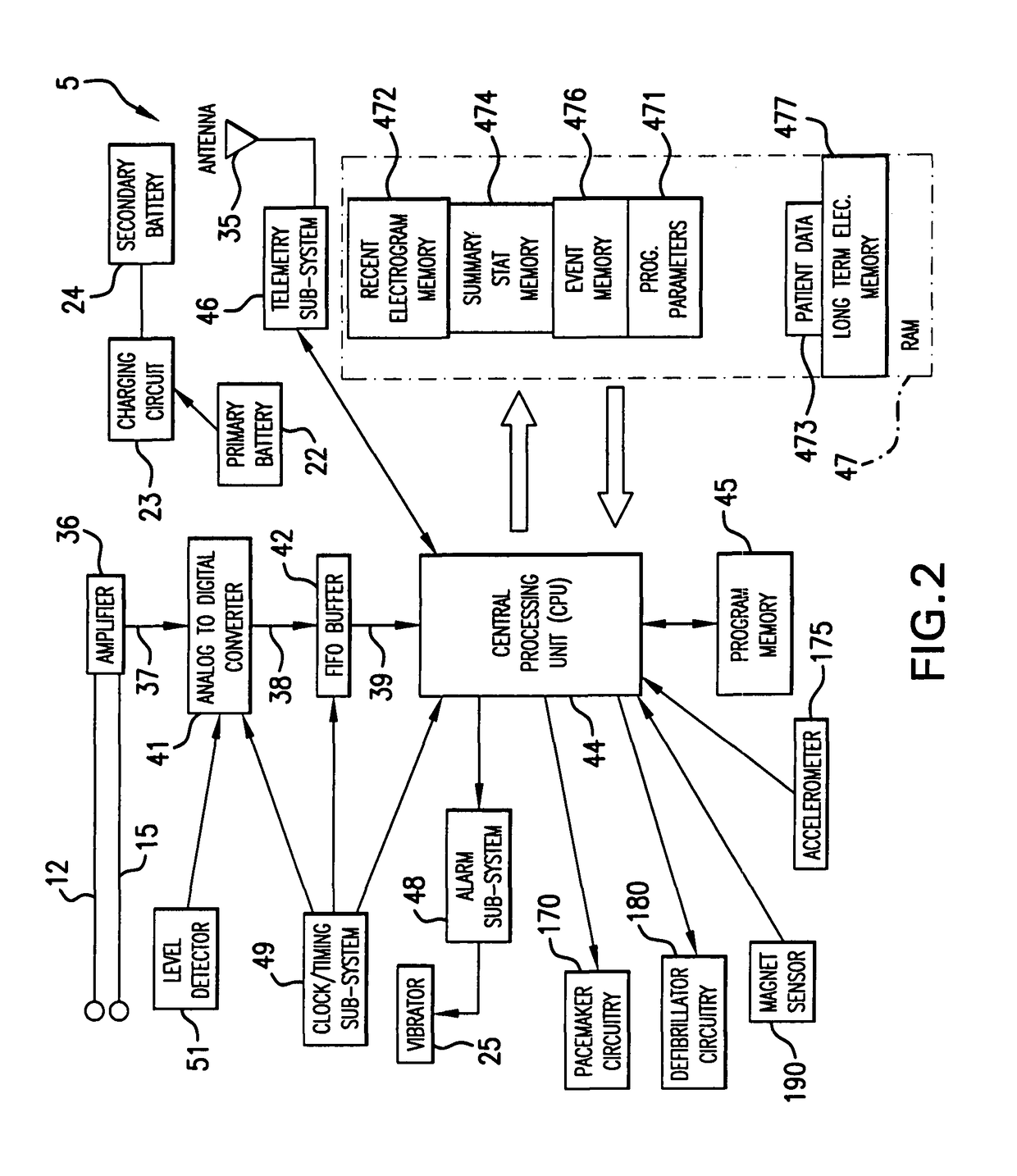
A heart monitor is disclosed. The monitor computes ST segment deviations and stores the results in heart rate based histograms. Periodically, the monitor analyzes the histogram data to determine a normal range of ST deviation for a particular heart rate range. The monitor computes heart rate dependent ischemia detection thresholds based on the upper and lower boundaries of the normal range.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Heart rate correction system and methods for the detection of cardiac events
ActiveUS20110040199A1Strong specificityEliminate high frequency noiseElectrocardiographySensorsBlood vessel spasmAcute ischemia
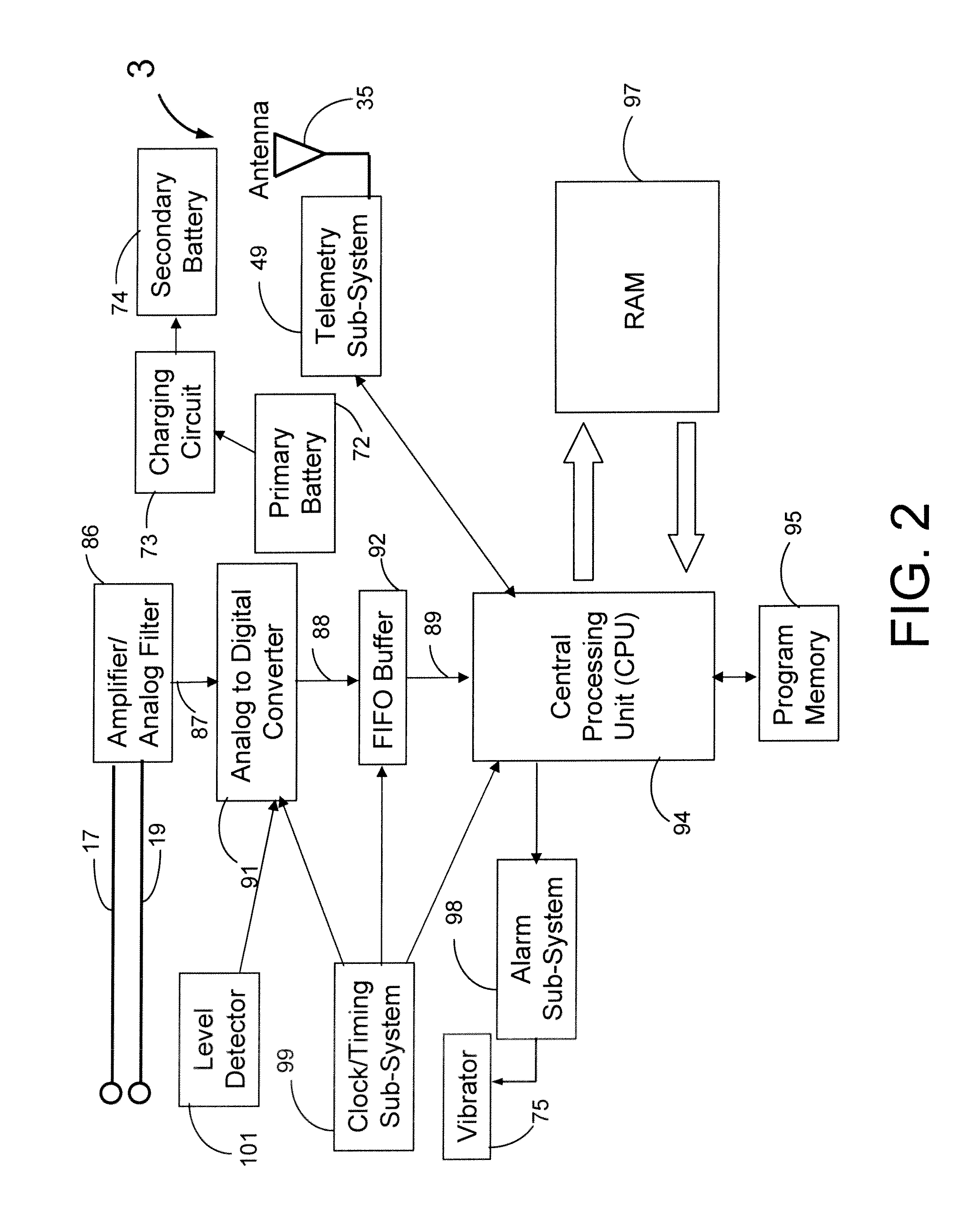
A device for detecting a cardiac event is disclosed. Detection of an event is based on a test applied to a parameter whose value varies according to heart rate. Both the parameter value and heart rate (RR interval) are filtered with an exponential average filter. From these filtered values, the average change in the parameter and the RR interval are also computed with an exponential average filter. Before computing the average change in the parameter, large changes in the parameter over short times, which may be caused by body position shifts, are attenuated are removed, so that the average change represents an average of small / smooth changes in the parameter's value that are characteristic of acute ischemia, one of the cardiac events that may be detected. The test to detect the cardiac event depends on the heart rate, the difference between the parameter's value and its upper and lower normal values, and its average change over time, adjusted for heart rate changes. The upper and lower normal parameter values as a function of heart rate are determined from long term stored data of the filtered RR values and parameter values. Hysteeresis related data and transitory deviations from normal (e.g. vasospasm related data) are excluded from the computation of normal upper and lower parameter bounds.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
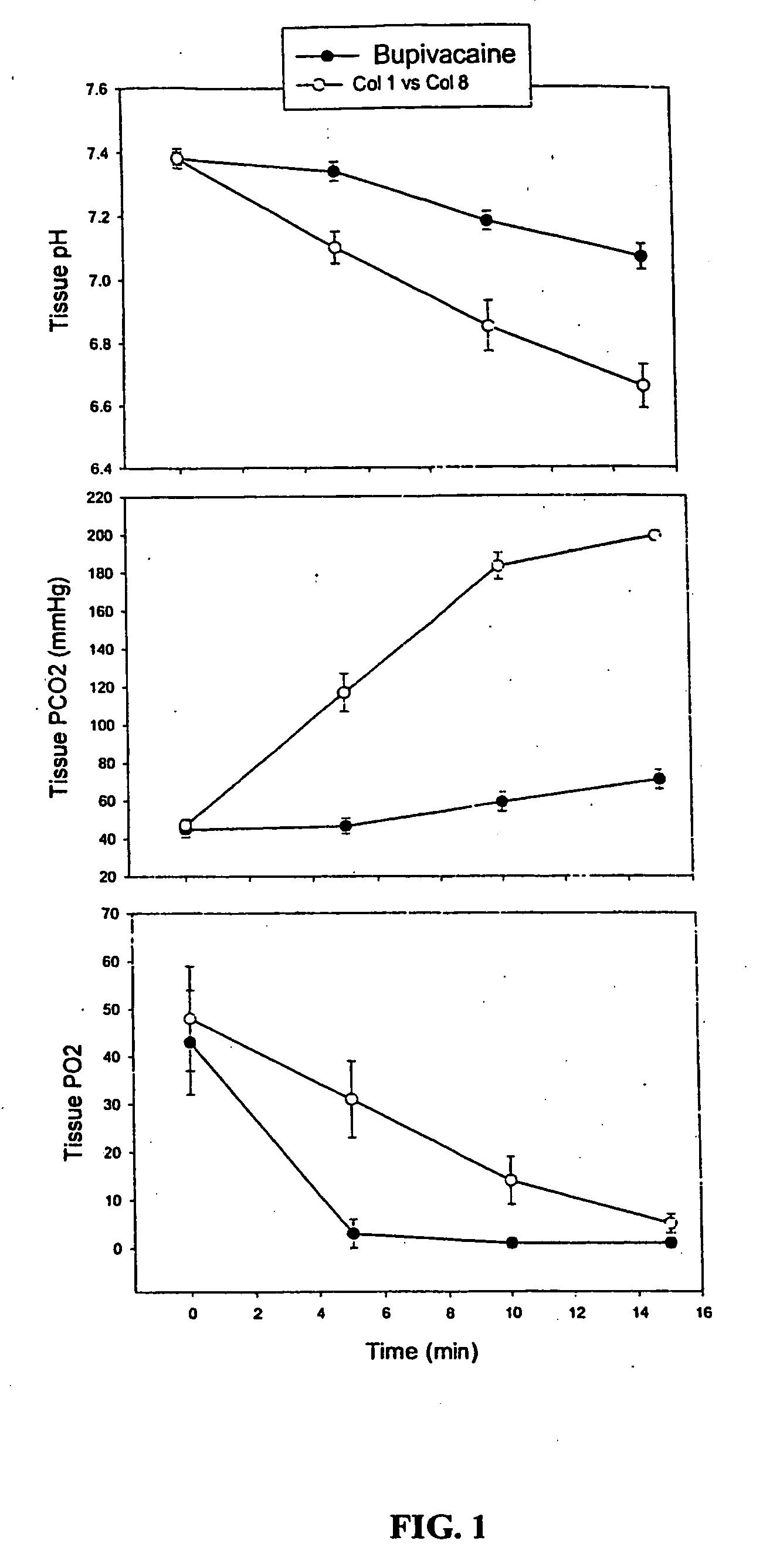
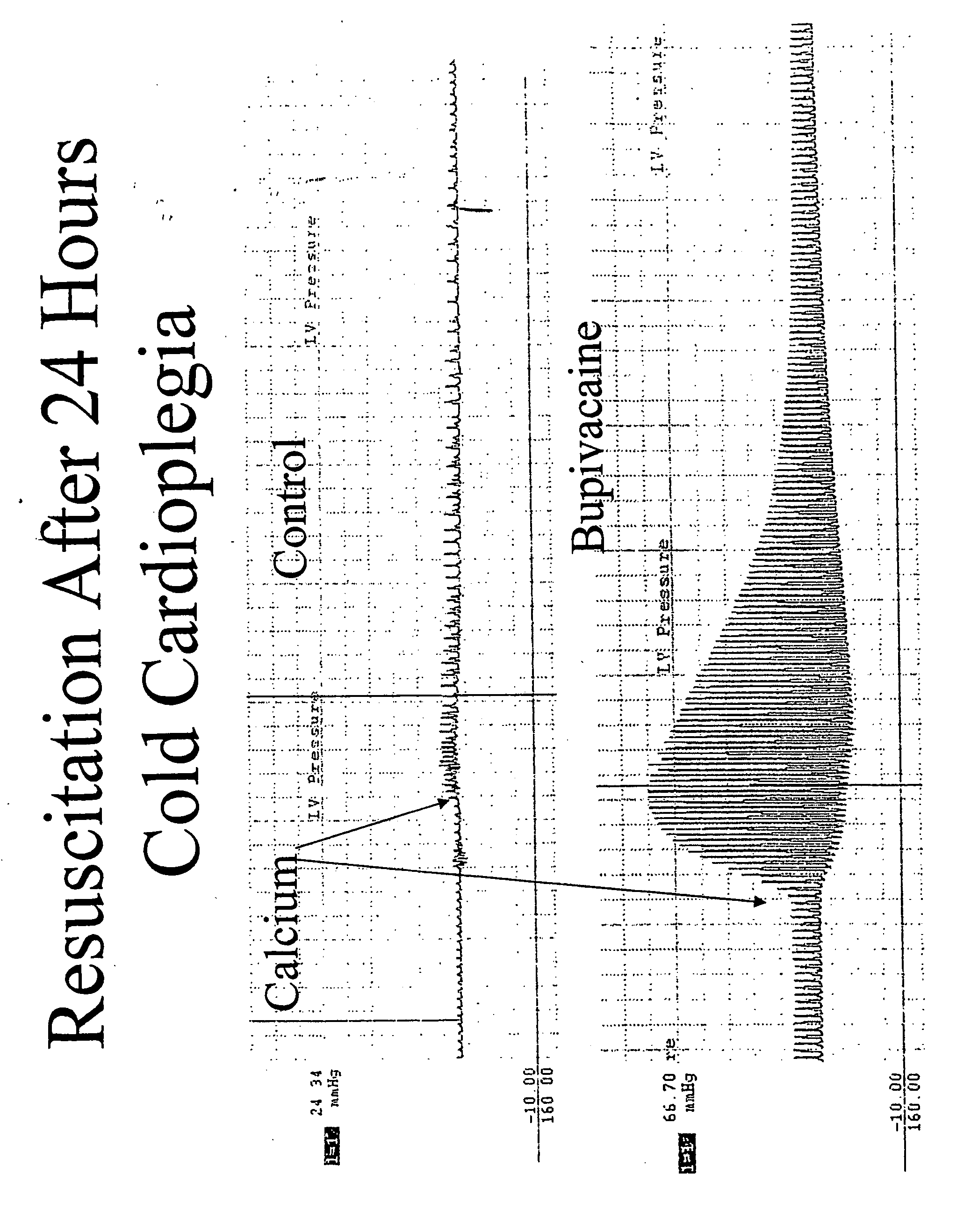
Tissue and organ preservation, protection and resuscitation
InactiveUS20060166182A1Protection from damageReverses effectDead animal preservationReperfusion injurySurgery procedure
The present invention provides compositions and methods for protecting tissues and organs from damage during transplantation or from acute ischemia due to, e.g., injury or surgery. The compositions protect the tissue or organ from acidosis, oxidative damage, ischemia and repurfusion injury while the organ is isolated from the normal circulation or receives inadequate arterial flow.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Waveform feature value averaging system and methods for the detection of cardiac events
Disclosed is a system for detecting pathophysiological cardiac conditions. The system comprises a diagnostic device that contains electronic circuitry that can detect a cardiac event such as an acute ischemia. The cardiac diagnostic device receives electrical signals from subcutaneous or body surface sensors. The cardiac diagnostic device includes a processor that computes QRS onset and offset points and fiducial points associated with T and U waves. The processor than baseline corrects the original signal / waveform by fitting a polynomial function to QRS offset points, and subtracting this function from the original waveform. Based on the baseline adjusted signal and / or the above mentioned fiducial points, the processor then computes averages of various waveform feature values, including a QRS measure sensitive to QRS curvature, T wave timing measures, ST segment deviation (difference between signal amplitudes at QRS offset and onset and / or minimum amplitude between QRS offset and peak T wave); and T / U wave amplitudes. These averages are computed by exponential averaging. From the exponential averages, the processor computes an average of the change in the averages over time. Based on the averages and the change in the averages, the processor applies an ischemia test to determine a likelihood of ischemia.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Threshold adjustment schemes for acute ischemia detection
A heart monitor is disclosed. The monitor computes ST segment deviations and stores the results in heart rate based histograms. Periodically, the monitor analyzes the histogram data to determine heart rate dependent acute ischemia detection thresholds. If the statistical distribution associated with a heart rate range is insufficient, the threshold for that heart rate range is set as a function of the threshold for a neighboring heart rate range. Thresholds are also increased for heart rate ranges associated with statistical distributions that are sufficient but that have a relatively small number of entries.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Ischemia detection based on combination of parameters associated with different sensors
An acute ischemia monitor is disclosed. The monitor, which includes an analog to digital convertor and a processor that performs beat detection, monitors the time course of a heart signal parameter, namely ST segment deviation, computed from an electrocardiogram. The device stores ST deviation statistics for multiple leads. For each lead, upper and lower ST deviation boundaries are computed. For each lead, current ST deviation values are compared with the statistical values to determine a metric indicative of the degree of abnormality of a current ST deviation value. The metric is equal to the difference between the current ST deviation value and the upper or lower boundary, normalized according to the dispersion of the ST deviation. Metrics from different leads are summed and compared to a threshold to determine whether the combined metric is indicative of a cardiac event.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
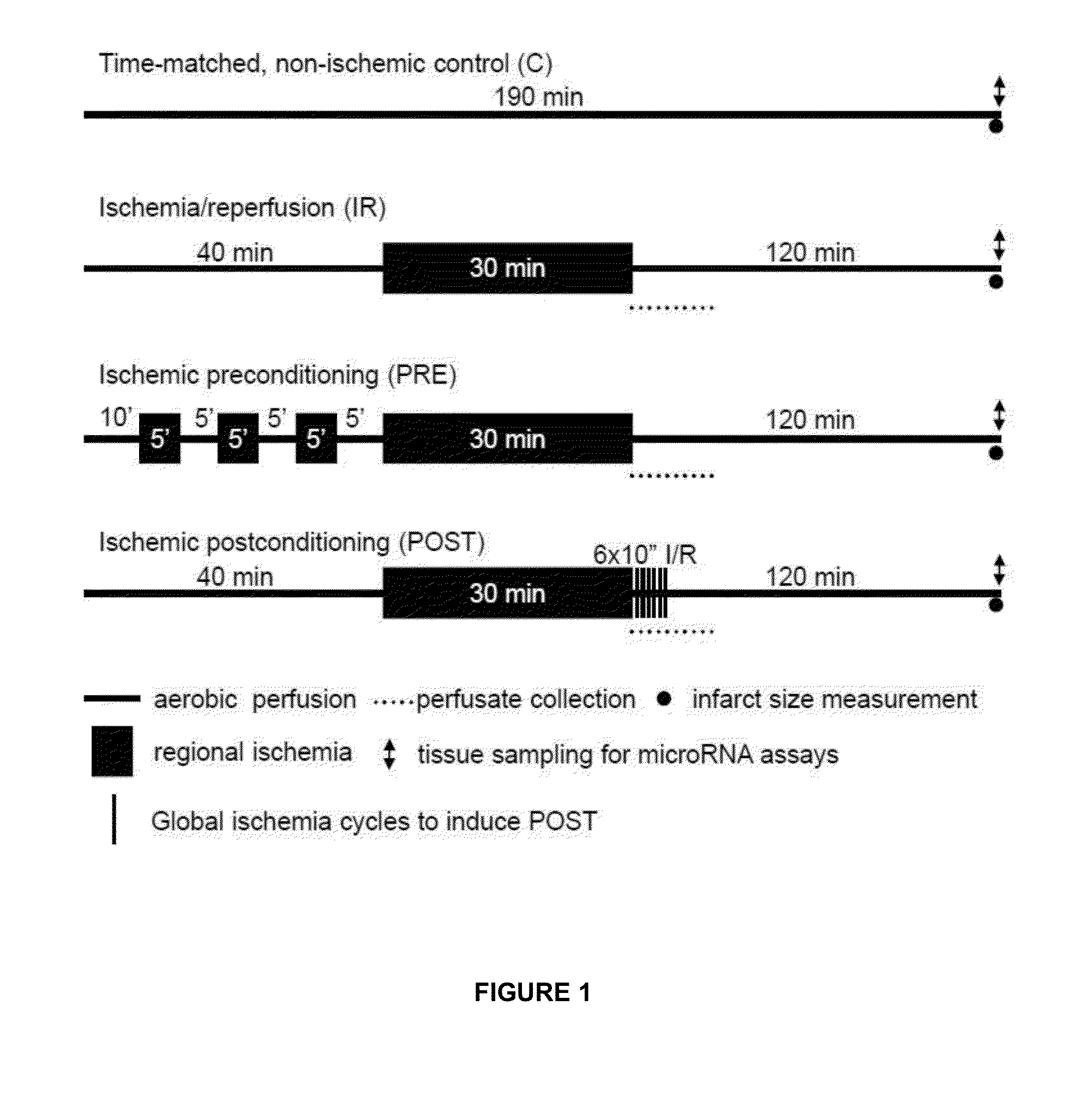
Compounds for treatment of ischemic injury
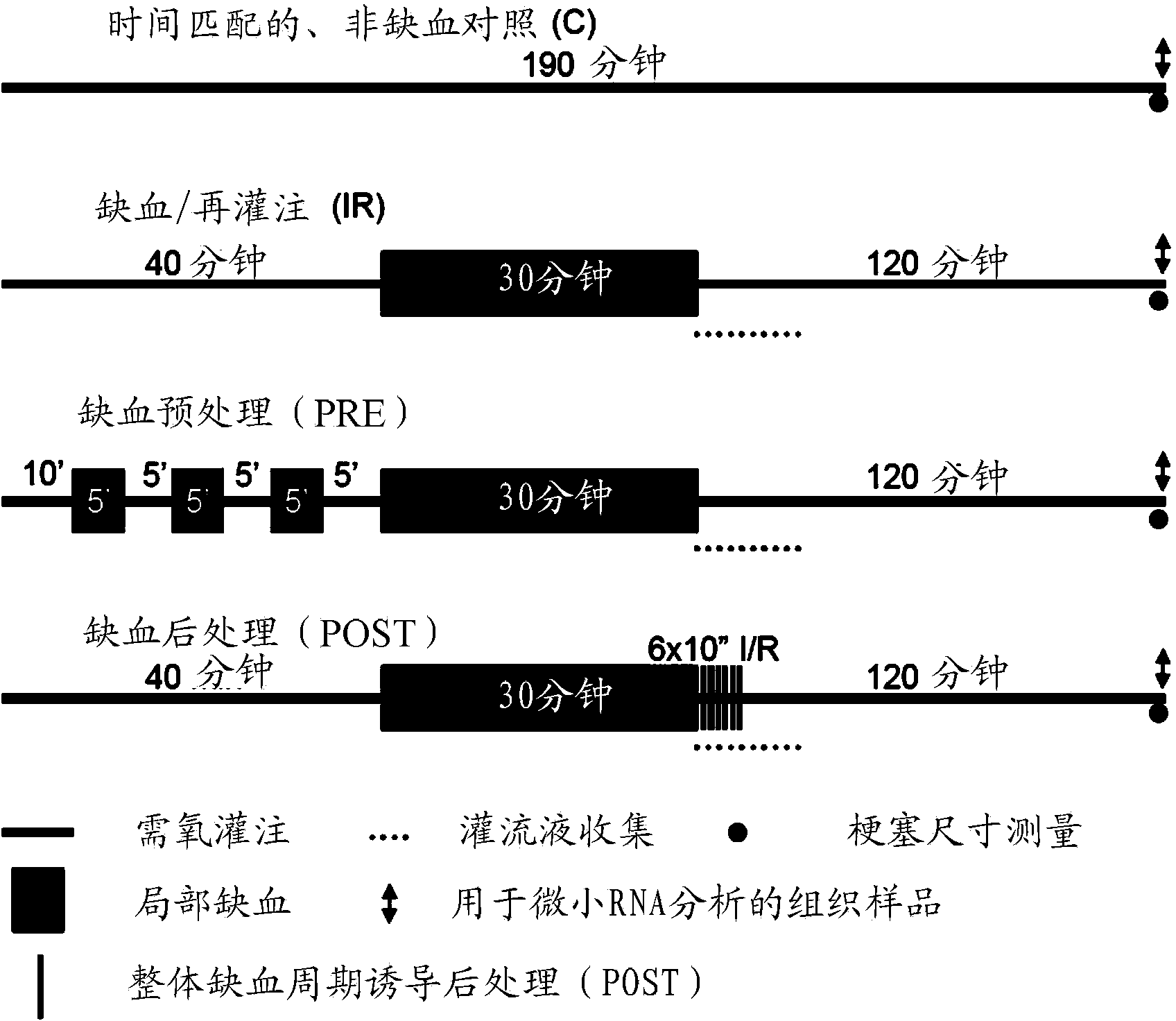
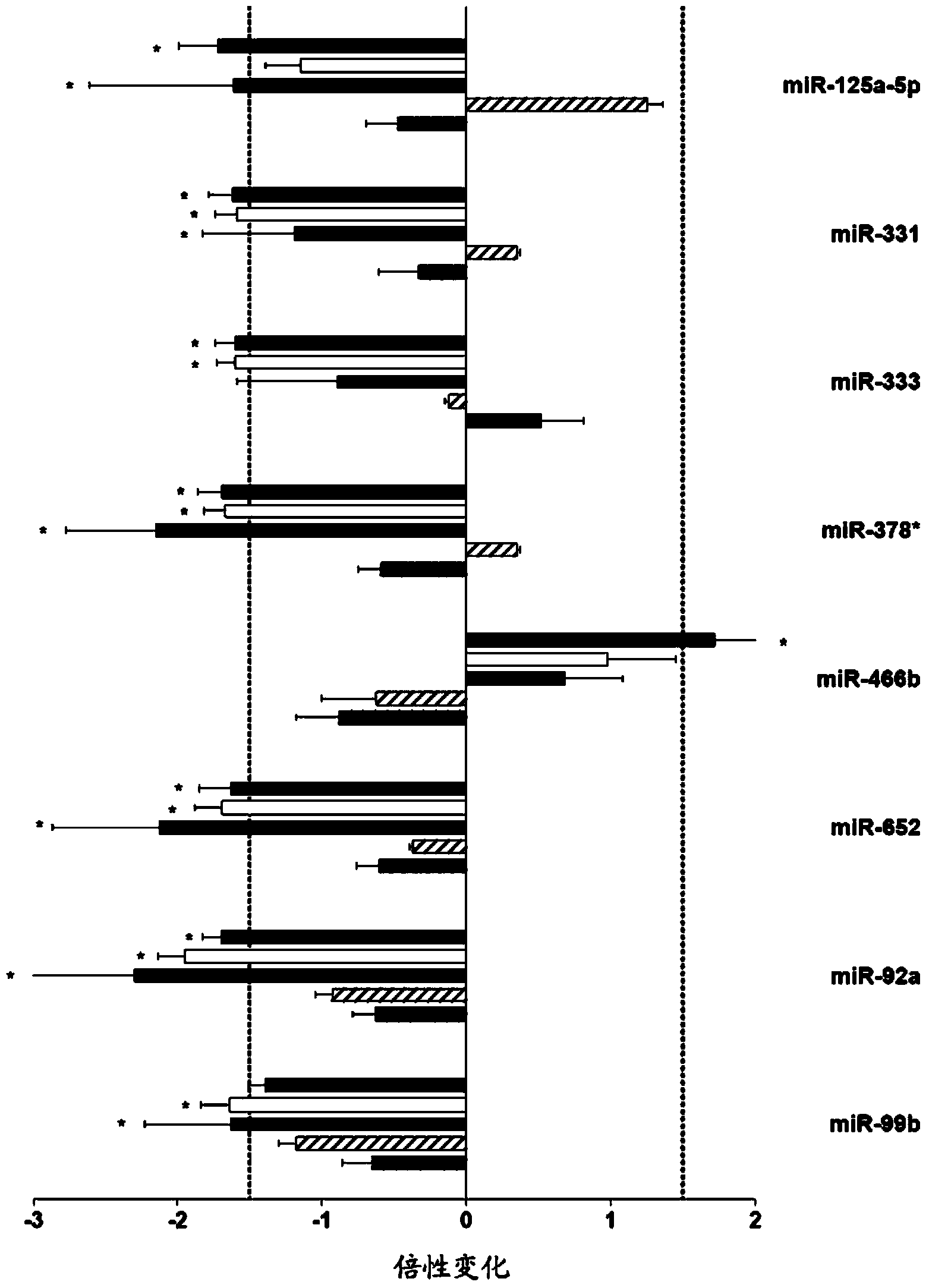
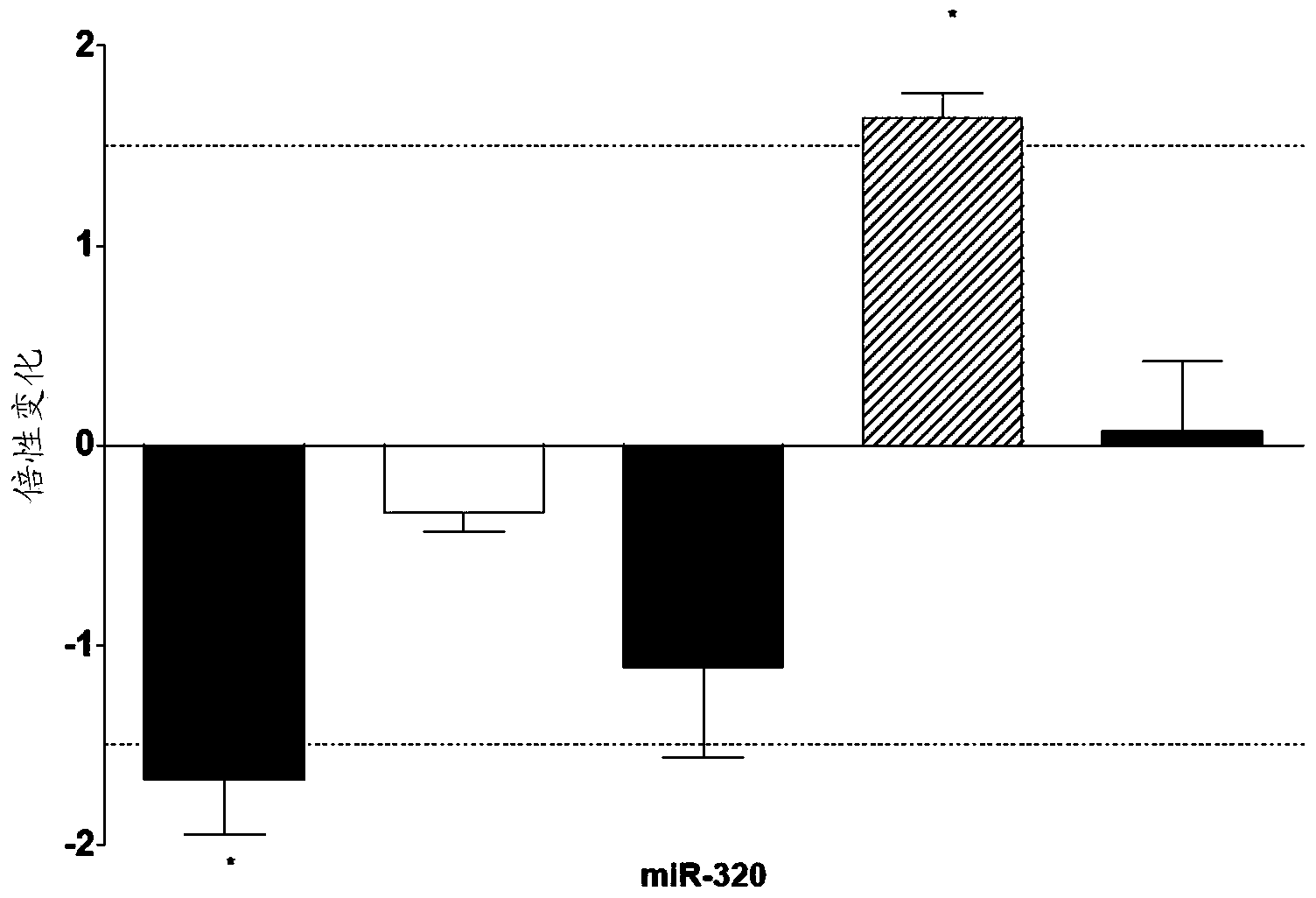
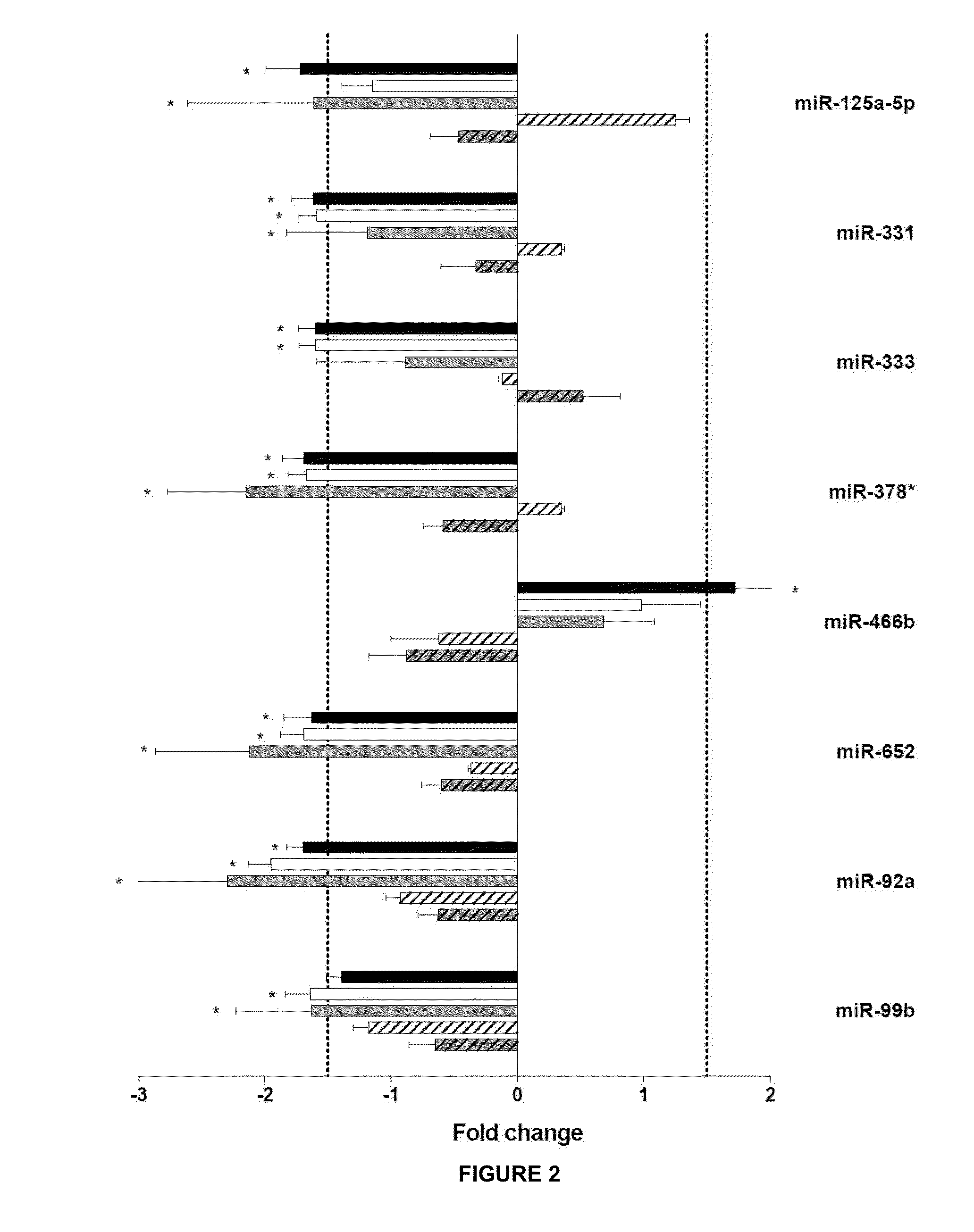
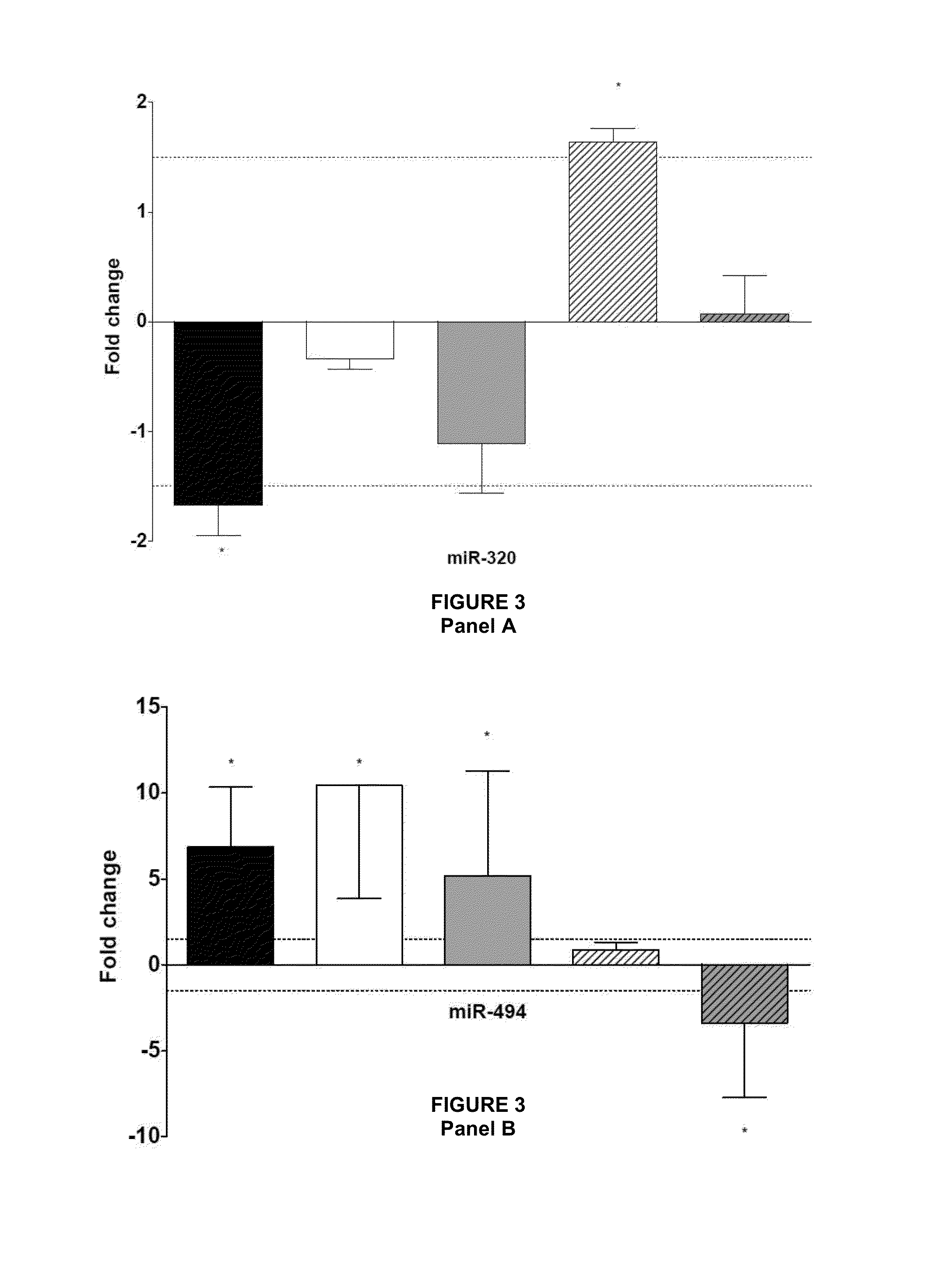
The present invention relates to microRNA (miRNA) compounds for use in the treatment of consequences of acute ischemia / reperfusion, a method for preparing miRNA compounds by using test ischemia-reperfusion, test preconditioning and test postconditioning of biological samples, use of the miRNA compounds in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions having cytoprotective and / or anti-ischemic effect in ischemic cardiac diseases.
Owner:PHARMAHUNGARY 2000
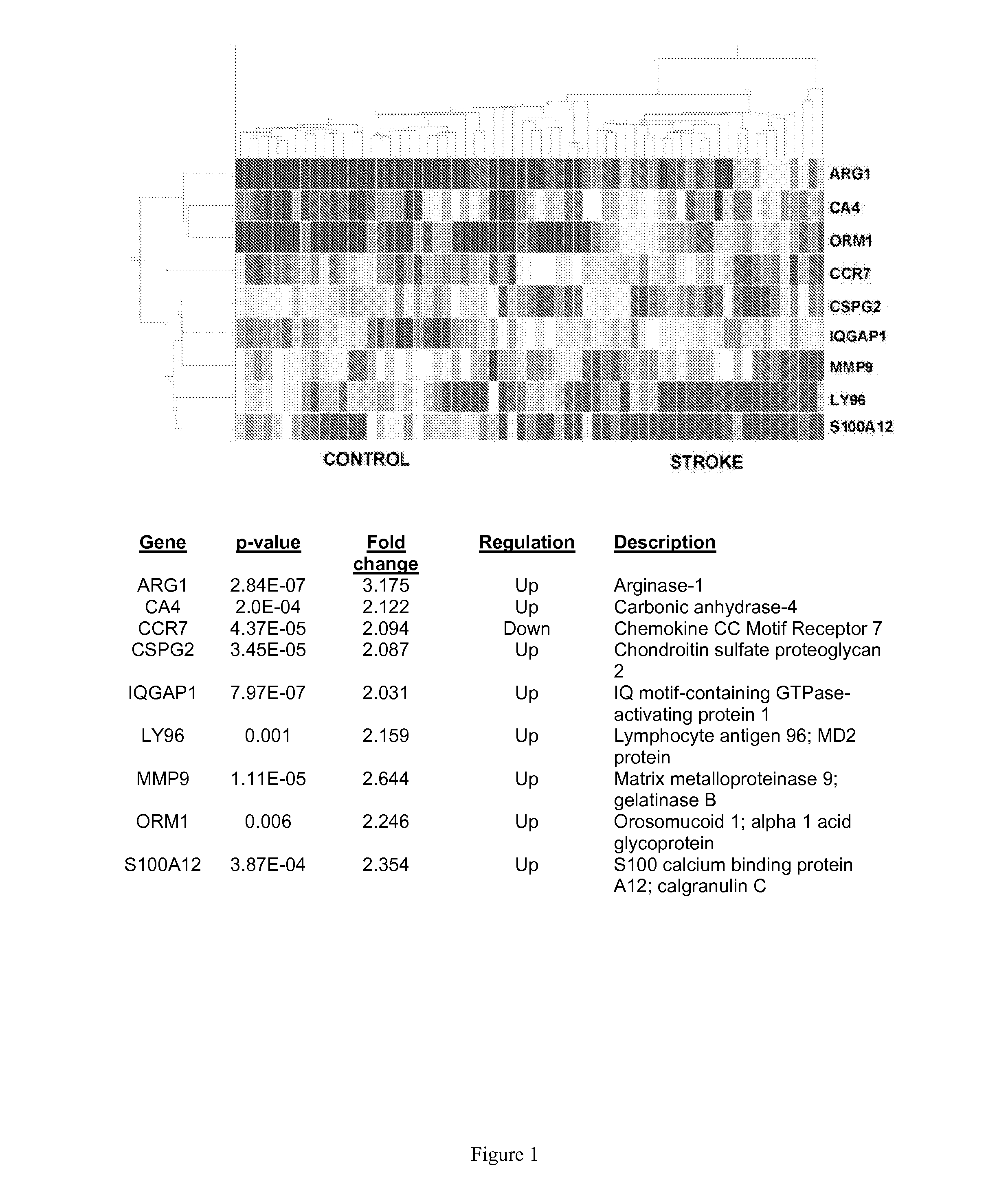
Biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke
ActiveUS20130189243A1Convenient treatmentAdditional diagnostic and/or prognostic indicatorsPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiomarker (petroleum)Ischemic stroke
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke. The invention further provides methods and compositions for distinguishing acute ischemic stroke from other forms of stroke and TIAs and “stroke mimic” events. Moreover, methods and compositions are provided to facilitate the treatment of acute ischemic stroke patients.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Two bromophenol compounds and application of pharmaceutically-acceptable salts of two bromophenol compounds in preparation of protection drug
ActiveCN102423308AImprove antioxidant capacity (SOD)Improve complianceKetone active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderVeinMedicine
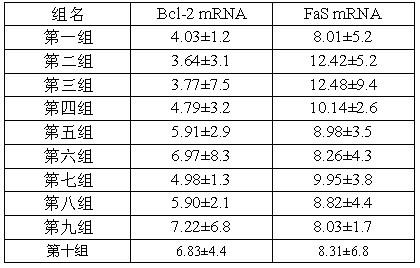
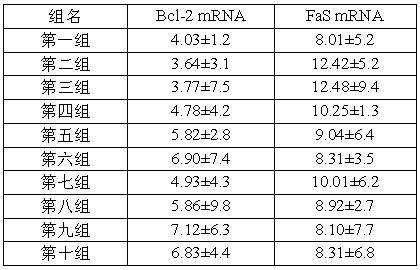
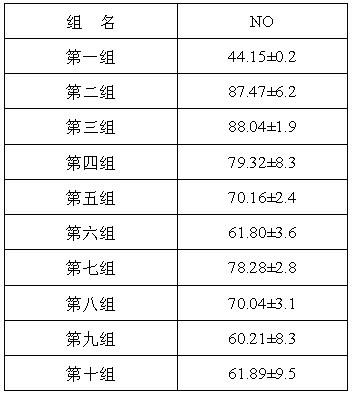
The invention discloses two bromophenol compounds and a pharmaceutical application of their pharmaceutically-acceptable salts, specifically an application in the preparation of a myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury protection drug. The two compounds and their pharmaceutically-acceptable salts can protect cardiomyocytes during rat heart acute ischemia so as to make rat heart functions complete.After routine intravenous administration, SOD activity after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion is raised, myocardial compliance is improved, serum LDH, serum CK, serum cTnT and MDA level after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion is remarkably reduced, myocardial injury is minimized, and FasmRNA after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion can be remarkably inhibited and reduced so as to inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Therefore, the two bromophenol compounds and their pharmaceutically-acceptable salts have a clear myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury protection function, thus providing a new method and means for the clinical treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and opening up a new direction for clinical medication.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
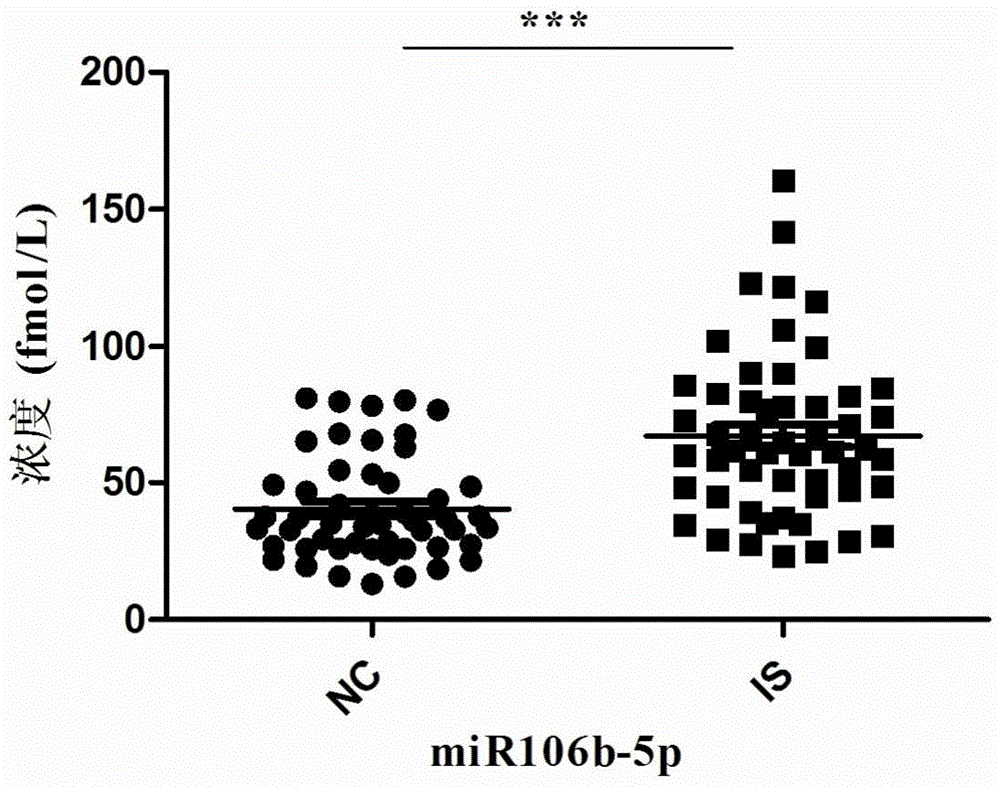
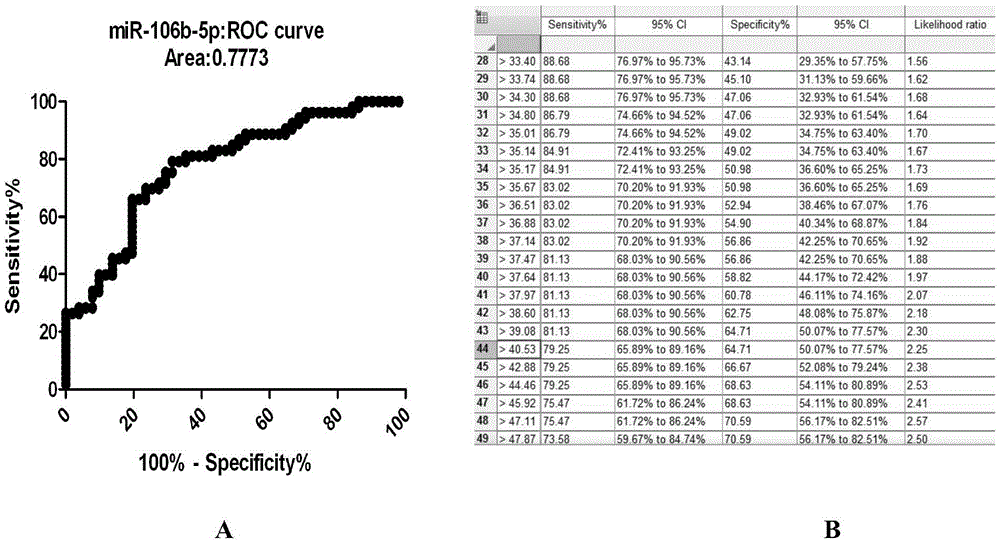
Mir-106b-5p, detection primer thereof and application of antisense nucleotide sequence thereof in fields of ischemic cerebral stroke diagnosis and treatment
InactiveCN105543394AGood diagnostic sensitivityImprove featuresOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseSide effect
The invention discloses miR-106b-5p, a detection primer thereof and application of the antisense nucleotide sequence thereof in the fields of ischemic cerebral stroke diagnosis and treatment, and belongs to the field of application of micro ribonucleic acid. The sequence of a reverse transcription primer in the detection primer of the miR-106b-5p is 5'-CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCAGTTGAGATCTGCAC-3'. The antisense nucleotide sequence of the miR-106b-5p is 5'-AUCUGCACUGUCAGCACUUUA-3'. The miR-106b-5p, the detection primer thereof and the antisense nucleotide sequence thereof are associated with acute ischemic cerebral strokes, the miR-106b-5p can become an auxiliary index of acute ischemic cerebral stroke clinical detection, and a therapeutic target is provided for prevention of the disease. The miR-106b-5p has the advantages of being good in treatment effect, easy to operate, free of toxic and side effects and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL OF TCM
Ischemia detection based on combination of parameters associated with different sensors
An acute ischemia monitor is disclosed. The monitor, which includes an analog to digital convertor and a processor that performs beat detection, monitors the time course of a heart signal parameter, namely ST segment deviation, computed from an electrocardiogram. The device stores ST deviation statistics for multiple leads. For each lead, upper and lower ST deviation boundaries are computed. For each lead, current ST deviation values are compared with the statistical values to determine a metric indicative of the degree of abnormality of a current ST deviation value. The metric is equal to the difference between the current ST deviation value and the upper or lower boundary, normalized according to the dispersion of the ST deviation. Metrics from different leads are summed and compared to a threshold to determine whether the combined metric is indicative of a cardiac event.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
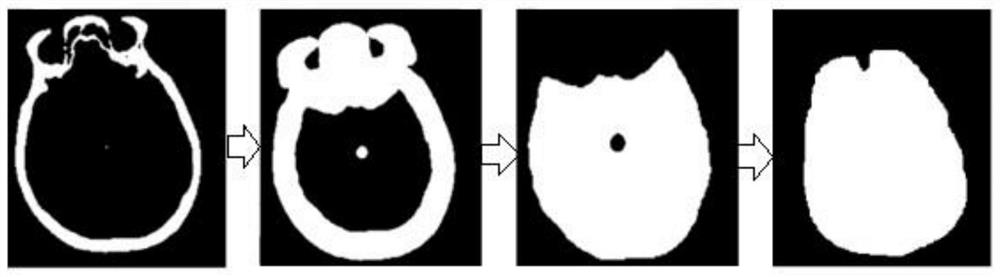
Acute ischemic stroke focus automatic segmentation method and system, terminal and medium
PendingCN113077479AAccurate segmentationImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelFeature Dimension
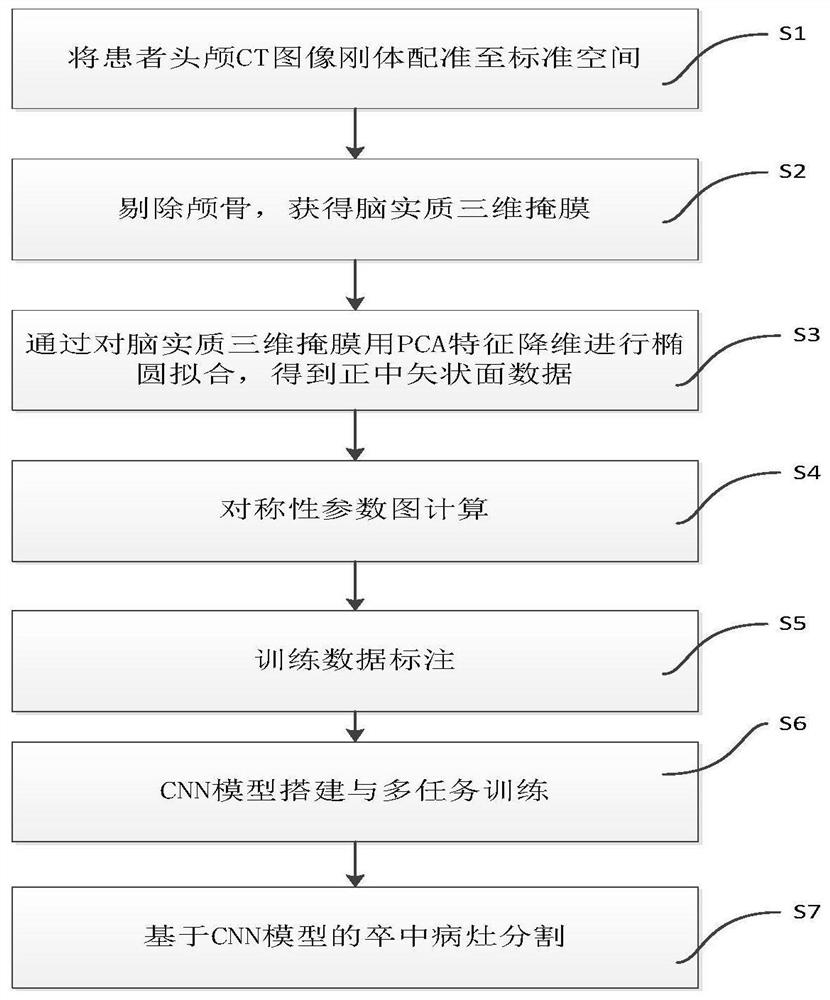
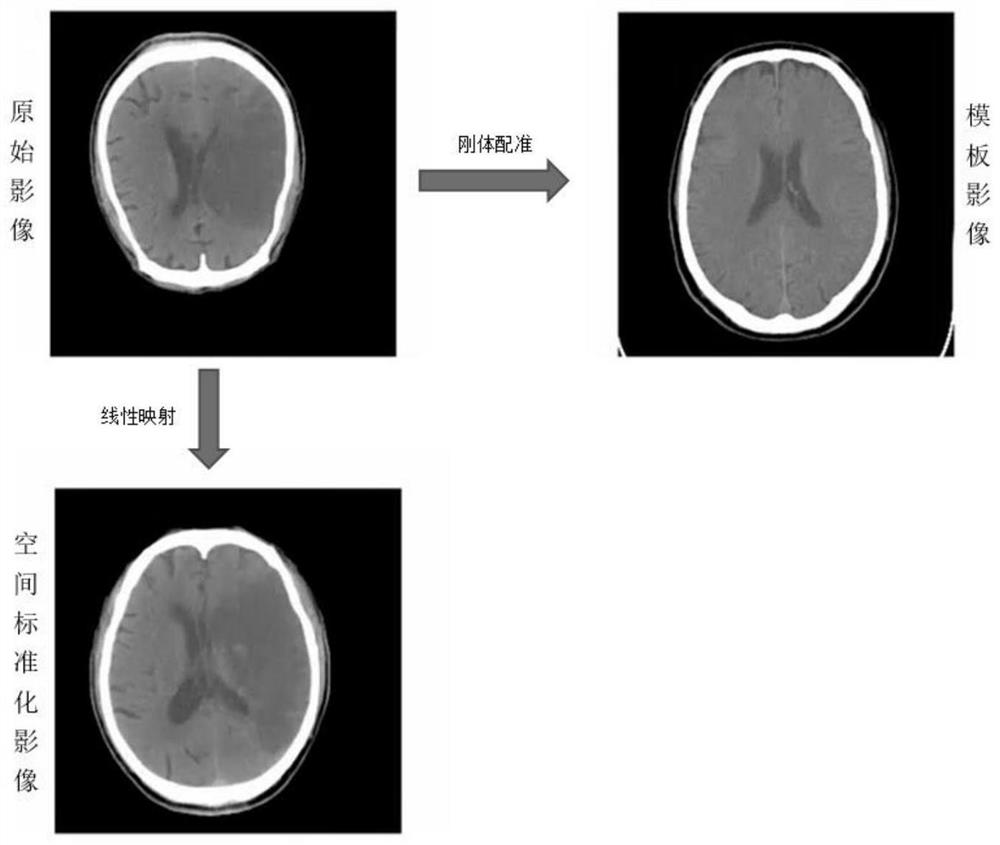
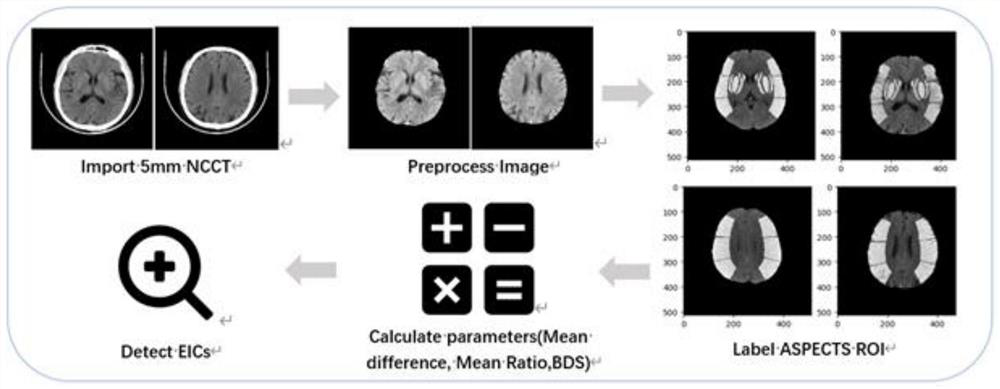
The invention discloses an acute ischemic stroke focus automatic segmentation method and system. The method comprises the following steps of: registering a head CT (Computed Tomography) image; removing the skull to obtain a brain parenchyma three-dimensional mask; performing ellipse fitting on the brain parenchyma three-dimensional mask through PCA feature dimension reduction to obtain median sagittal plane data; calculating left and right symmetric parameter diagrams of the brain; setting different window widths and window levels for the median sagittal plane data to obtain multi-level window width and window level image data; marking training data; training a segmentation convolutional neural network model; inputting test data into the trained segmentation model for segmentation to obtain a segmentation probability graph of the brain parenchyma, the cerebrospinal fluid and the stroke focus of the corresponding voxel and a prediction probability of whether the stroke focus exists in the corresponding two-dimensional image; and outputting different segmentation results according to different prediction probabilities. According to the method, multi-task training is carried out in combination with brain anatomy priori knowledge, the performance of the convolutional neural network in the NCCT stroke focus automatic segmentation method is improved, and the acute ischemic stroke focus can be accurately segmented.
Owner:深圳市铱硙医疗科技有限公司
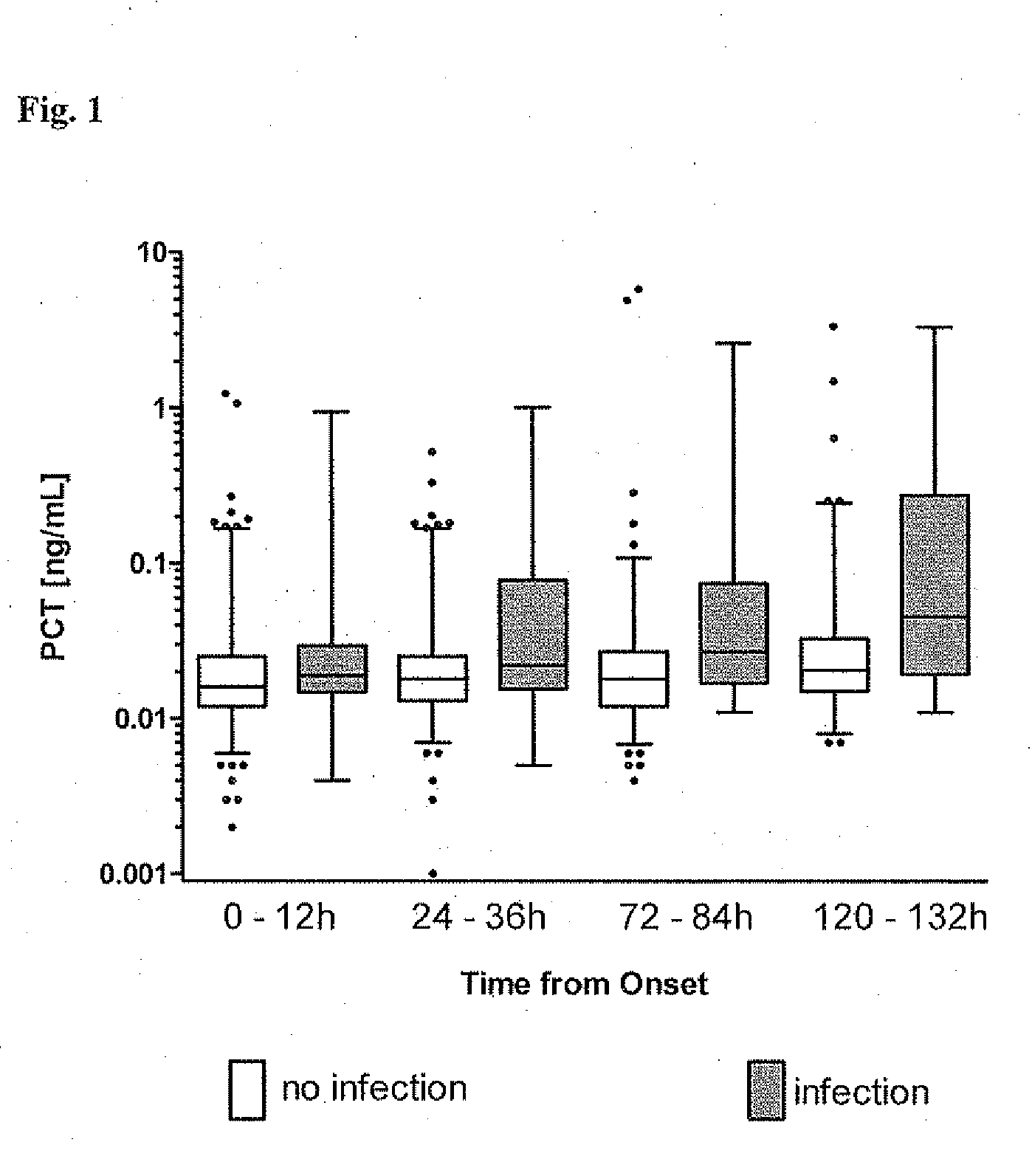
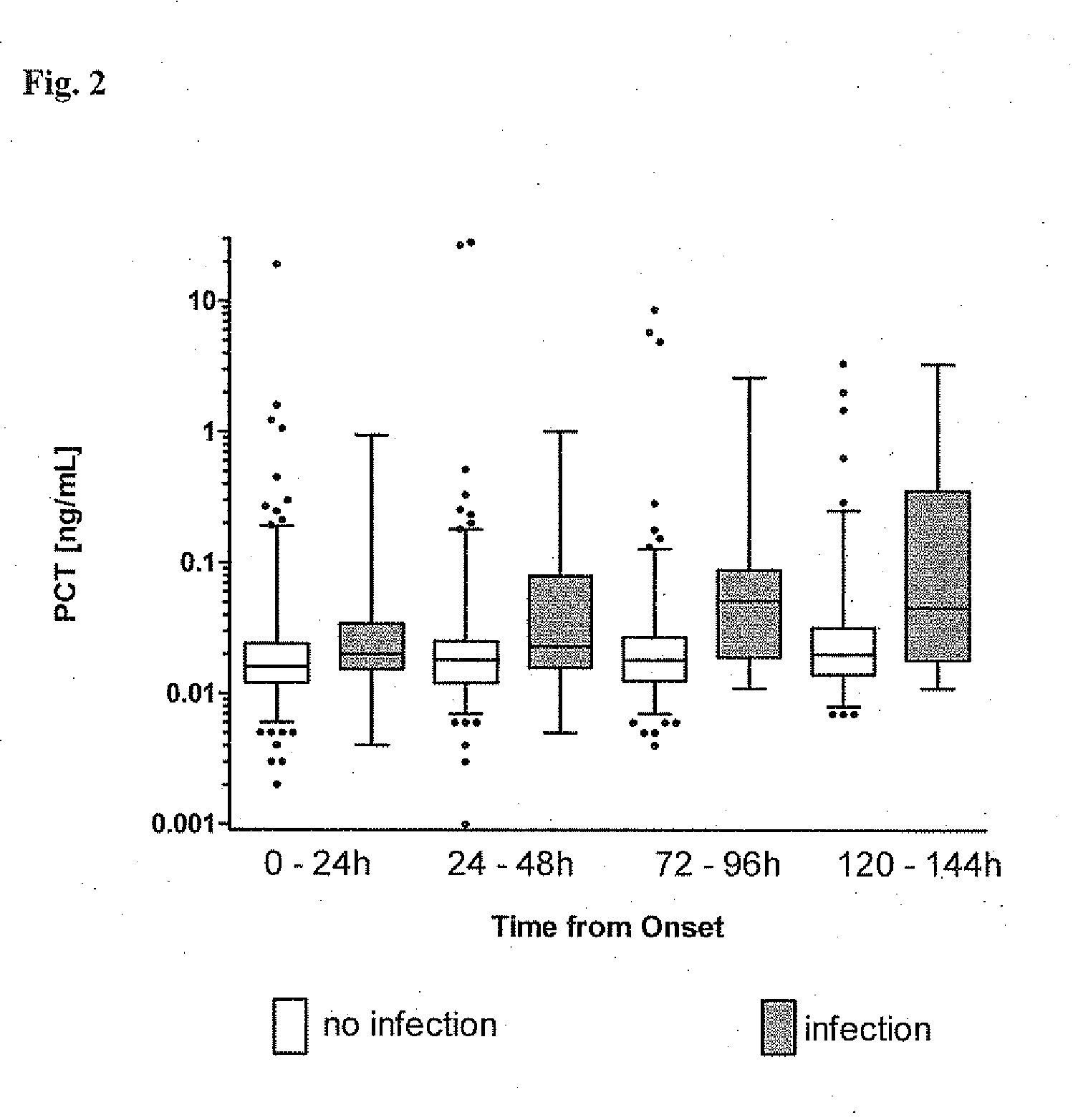
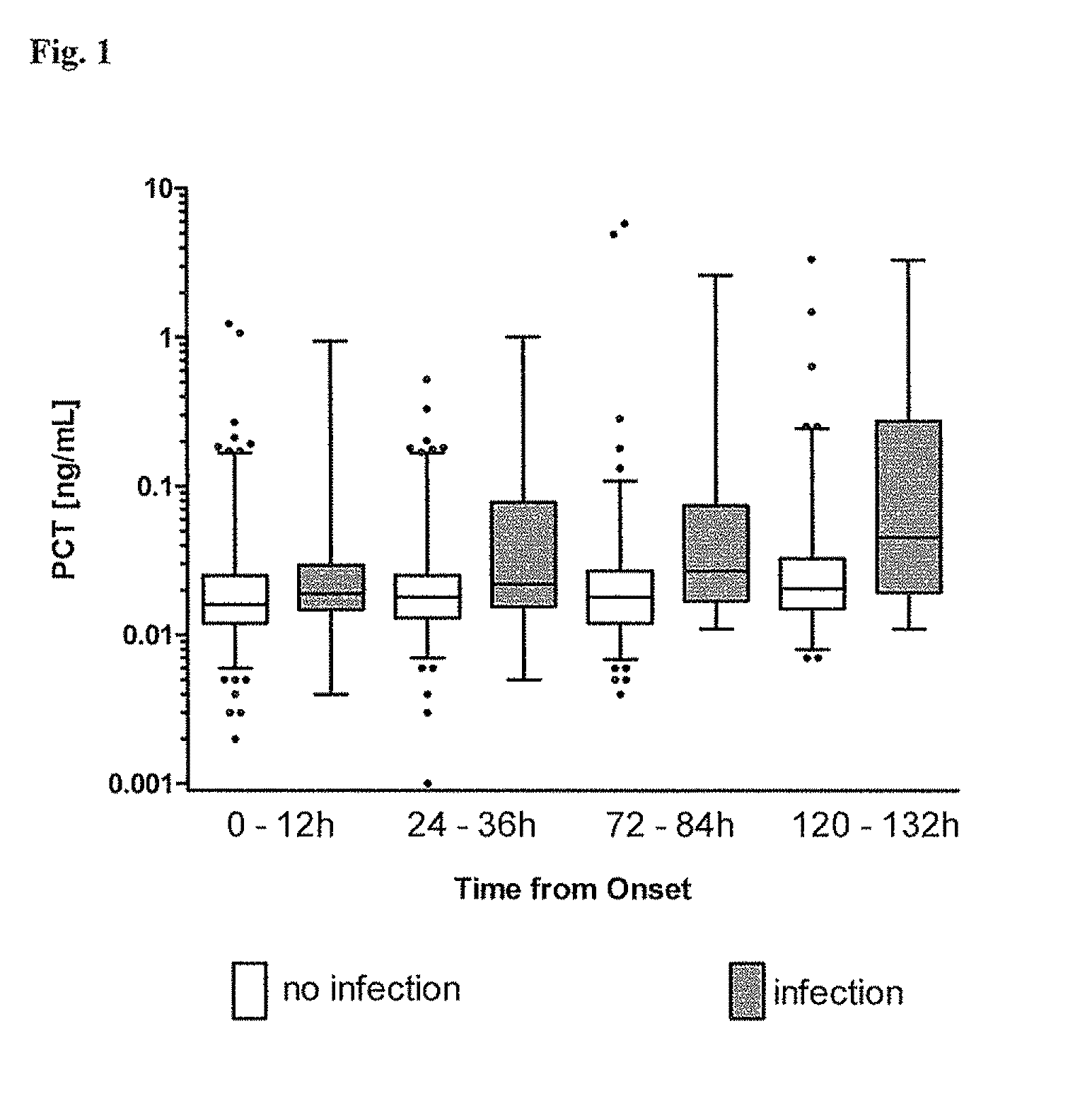
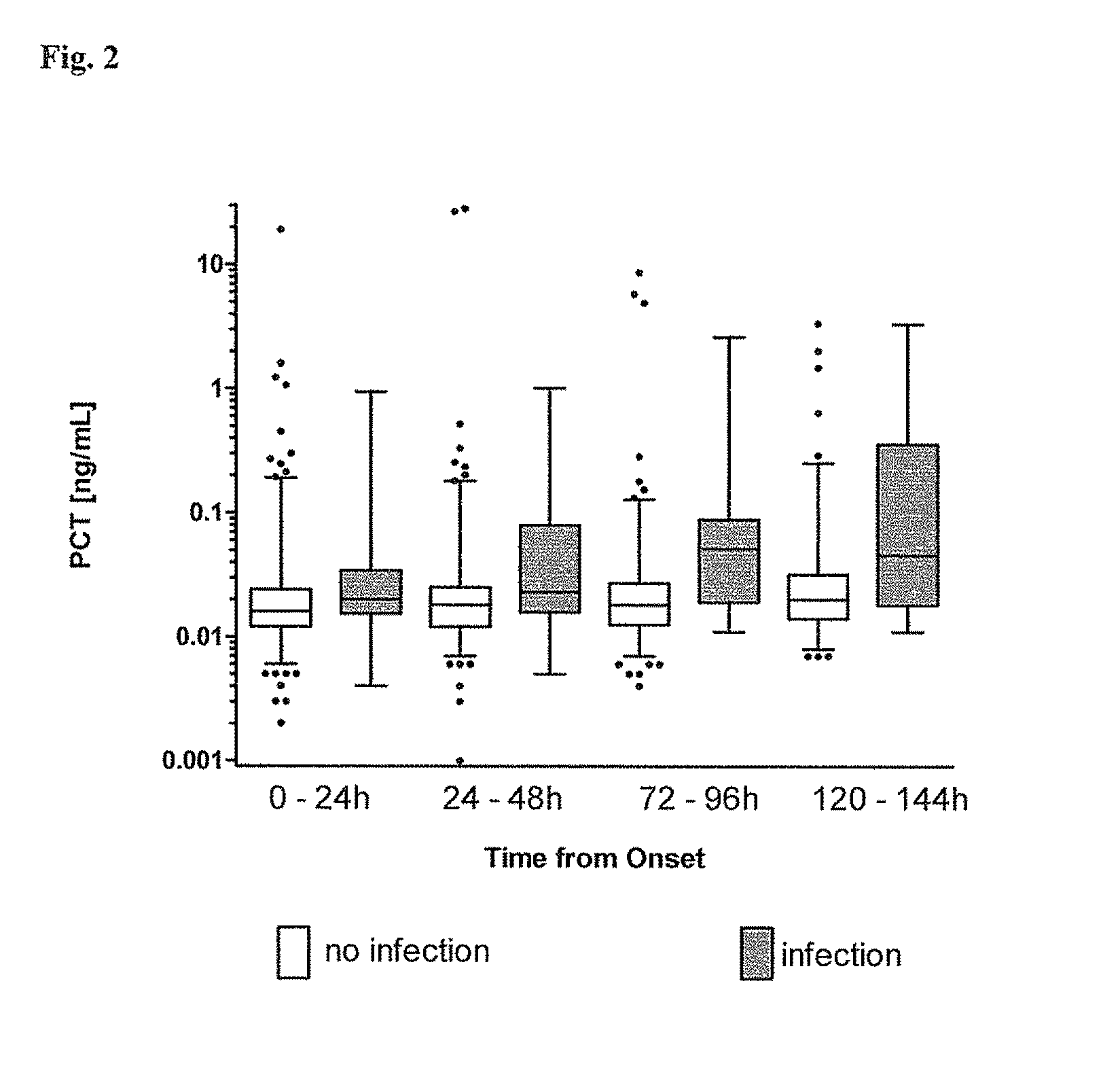
Procalcitonin for the diagnosis of bacterial infections and guidance of antibiotic treatment in patients with acute stroke or transient ischemic attack
ActiveUS20110086831A1Improve patient outcomesHigh sensitivityAntibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibioticsAcute ischemia
The present invention relates to an in vitro method for the diagnosis and treatment guidance of a bacterial infection in patients suffering from an acute ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, comprising the determination of the level of Procalcitonin (PCT) or a fragment thereof having at least 12 amino acid residues in a sample of a bodily fluid from said patient and the correlation of the determined level to the diagnosis of a bacterial infection in said patient.
Owner:BRAHMS GMBH
Compounds for the treatment of ischemic injury
ActiveUS20140256792A1Easy to detectFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMedicineIschemic injury
The present invention relates to microRNA (miRNA) compounds for use in the treatment of consequences of acute ischemia / reperfusion, a method for preparing miRNA compounds by using test ischemic-reperfusion, test preconditioning and test postconditioning of biological samples, use of the miRNA compounds in the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions having cytoprotective and / or anti-ischemic effect in ischemic cardiac diseases.
Owner:PHARMAHUNGARY 2000
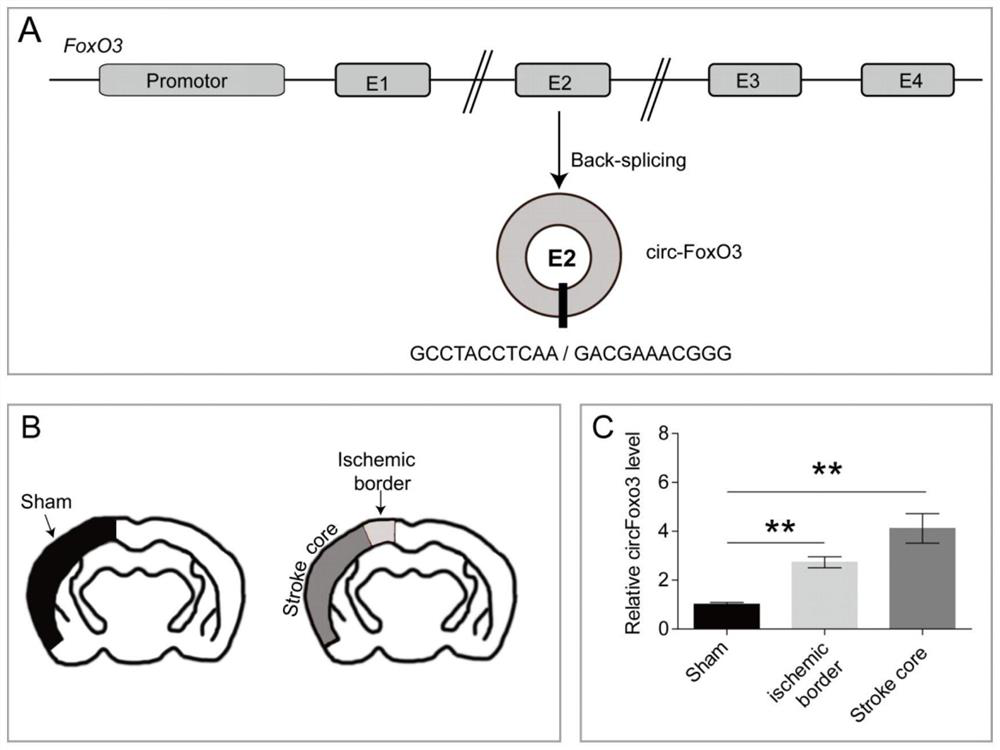
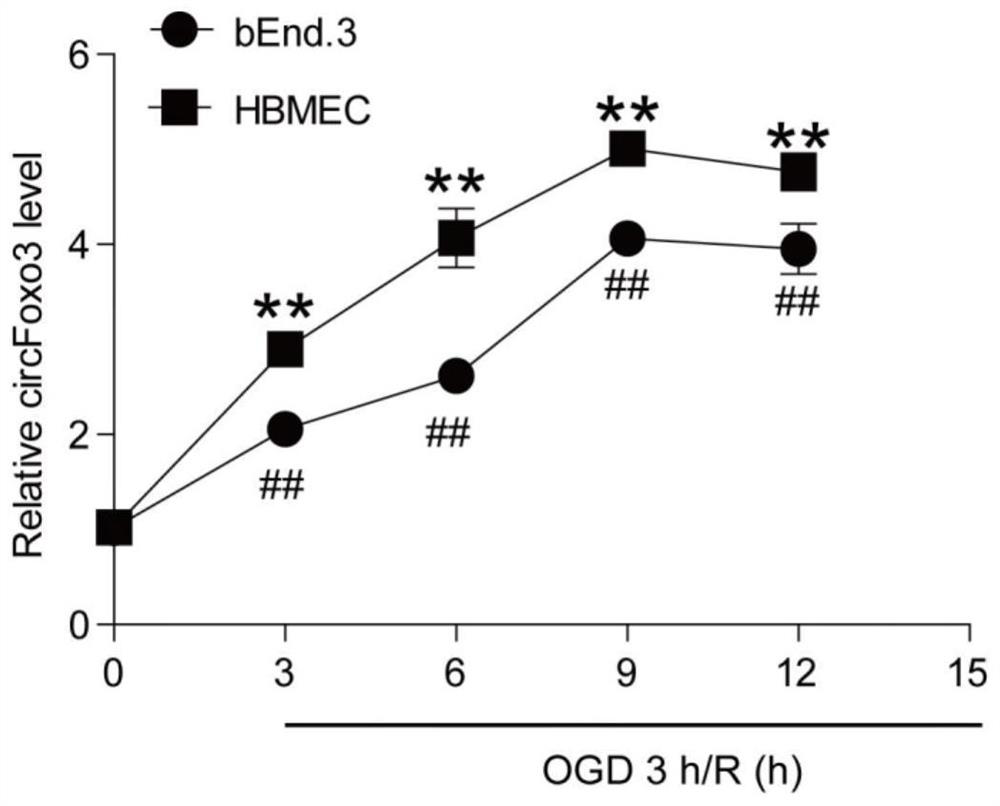
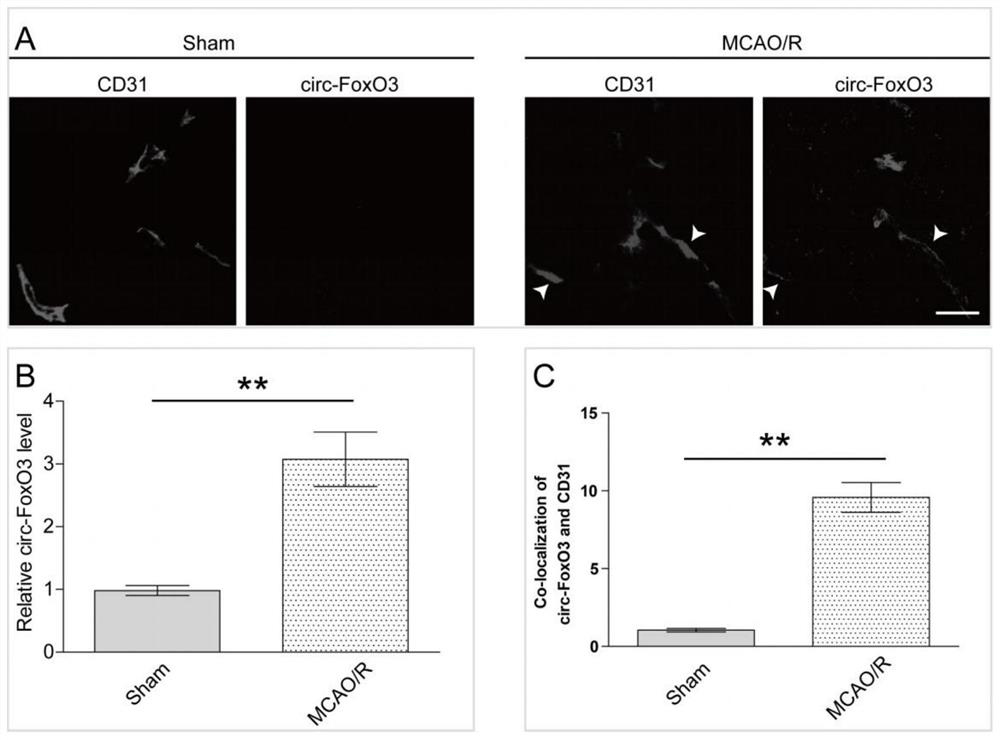
Application of circular RNA circ-FoxO3 in preparation of products for preventing and treating cerebral arterial thrombosis
ActiveCN112156103AImprove permeabilityPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCerebral arterial thrombosisAcute ischemia
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and cerebral arterial thrombosis, and particularly relates to application of circular RNA circ-FoxO3 in preparation of products for preventing and treating cerebral arterial thrombosis. The circular RNA is highly conservative and has the same reverse shearing site in human-derived or mouse-derived species. The application proves that the circ-FoxO3 is highly expressed in cerebrovascular endothelial cells of a MCAO / R mouse and the cerebrovascular endothelial cell line subjected to OGD / R treatment; A certain effect of the circ-FoxO3 in the endothelial barrier treated by OGD / R is shown by knockdown or over-expression of the circFoxO3. The application of the circular RNA circ-FoxO3 provides a new thought for prevention of hemorrhagic transformation after acute ischemic stroke, and provides a new target for development of a neurovascular protective agent.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF JINAN UNIV
Procalcitonin for the diagnosis of bacterial infections and guidance of antibiotic treatment in patients with acute stroke or transient ischemic attack
ActiveUS8383332B2High sensitivityImprove patient outcomesAntibacterial agentsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibioticsAcute ischemia
The present invention relates to an in vitro method for the diagnosis and treatment guidance of a bacterial infection in patients suffering from an acute ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, comprising the determination of the level of Procalcitonin (PCT) or a fragment thereof having at least 12 amino acid residues in a sample of a bodily fluid from said patient and the correlation of the determined level to the diagnosis of a bacterial infection in said patient.
Owner:BRAHMS GMBH
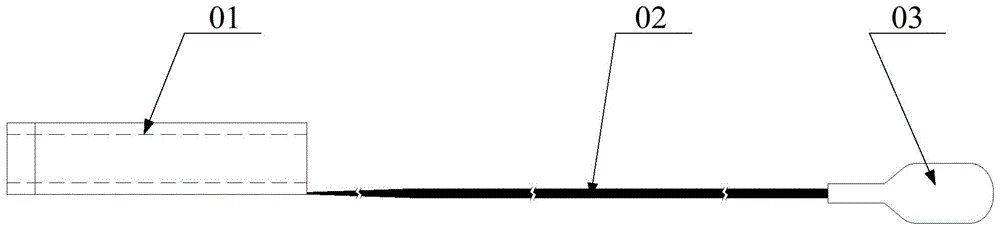
Son-mother extending catheter and son catheter thereof
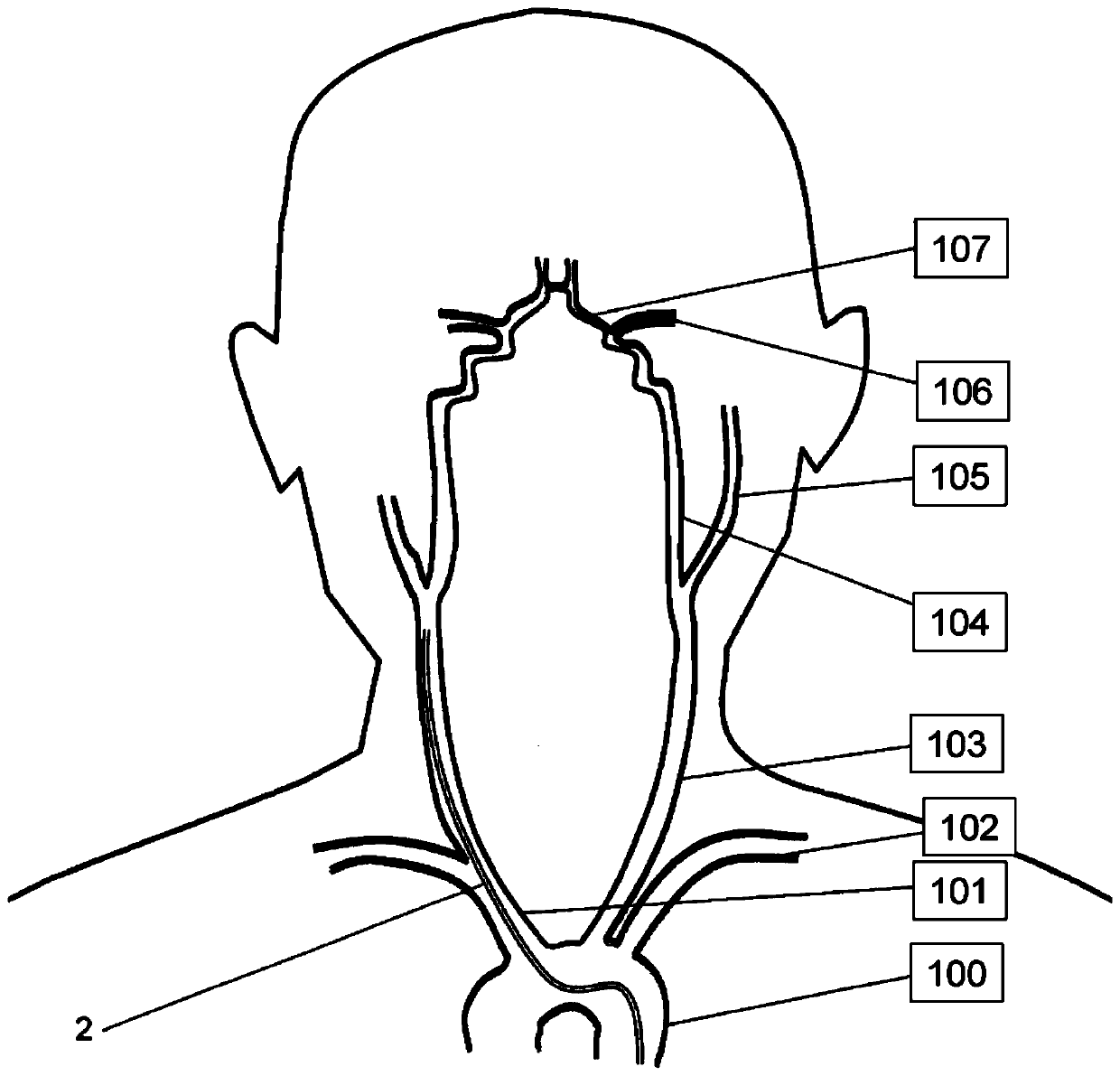
The invention discloses a son-mother extending catheter and a son catheter thereof. The son catheter comprises a catheter body and a catheter seat, wherein an opening is formed in the end part, far away from the catheter seat, of the catheter body; side holes are formed in the side walls of the catheter body. The son catheter moves along a guide wire in a mother catheter until the son catheter stretches out of the mother catheter, at the moment, the outer wall of the son catheter is in contact with the inner wall of the blood vessel to cause the blockage of the blood vessel, when the contact part of the son catheter and the blood vessel is positioned between each side hole and the end part, far away from the catheter seat, of the catheter body, blood can flow into the catheter body from the side holes in the side walls of the catheter body, and then the blood in the catheter body can bleed from the end part, far away from the catheter seat, of the son catheter to realize the circulation of the blood, so that the condition that the blood vessel is blocked by the son catheter is avoided, the condition of causing acute ischemia is prevented, and the surgical risk is reduced.
Owner:APT MEDICAL HUNAN INC +1
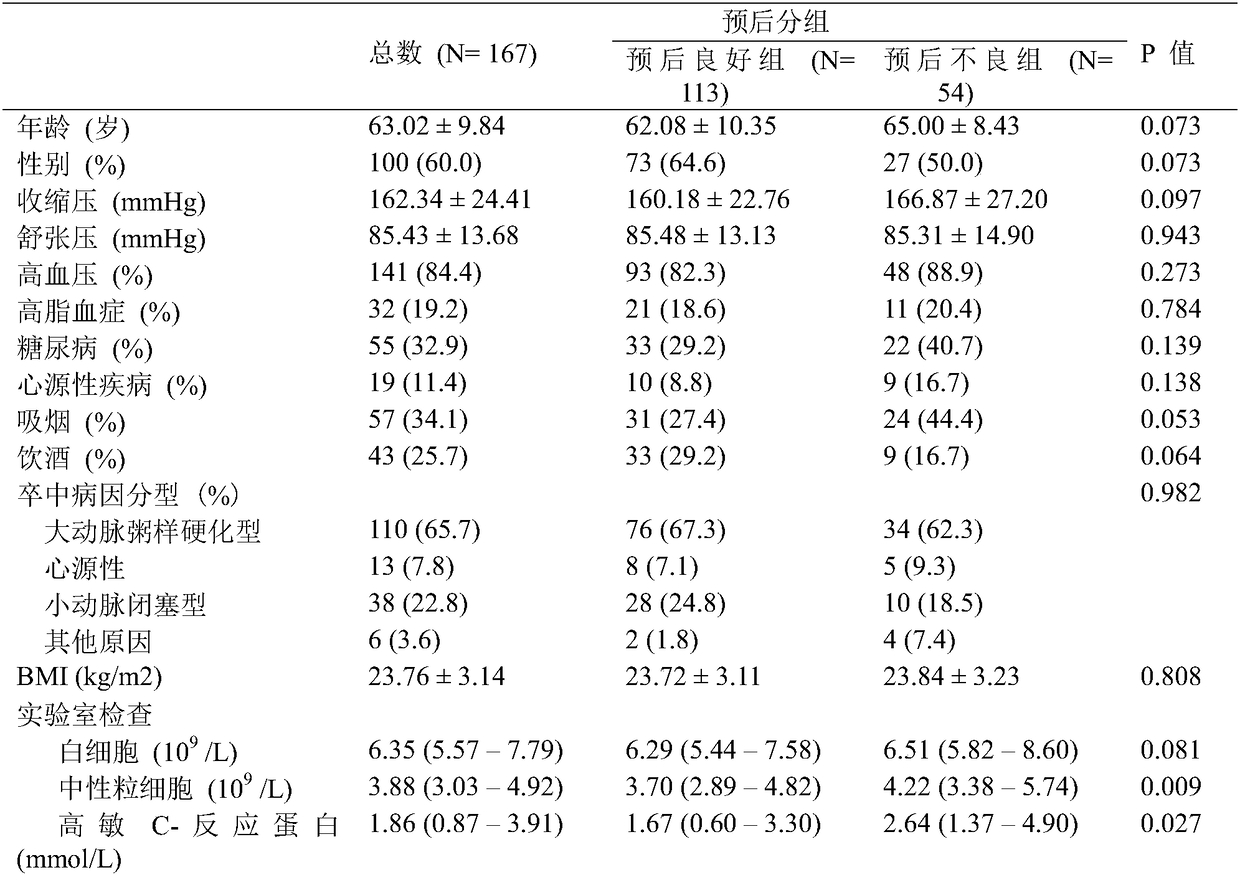
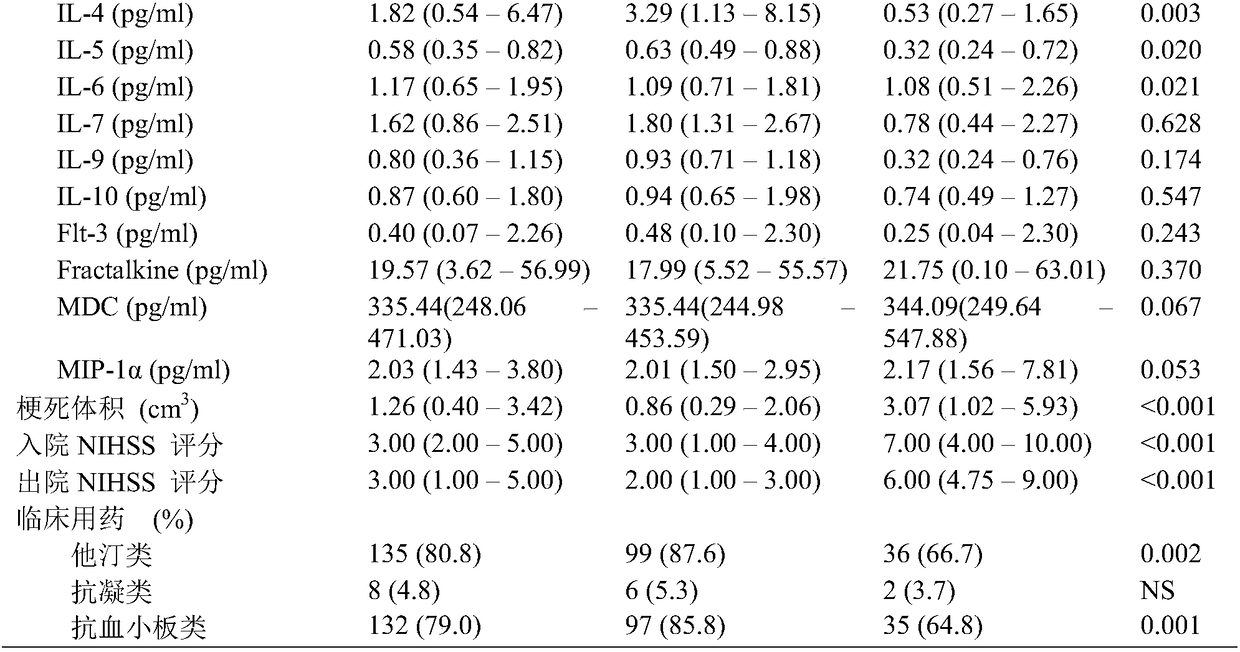
Application of serum inflammatory biomarkers in prevention and treatment of acute ischemic cerebral infarction
InactiveCN109061139ALower rate of poor prognosisPredict neurological outcomeMaterial analysisAcute cerebral infarctionInflammatory biomarkers
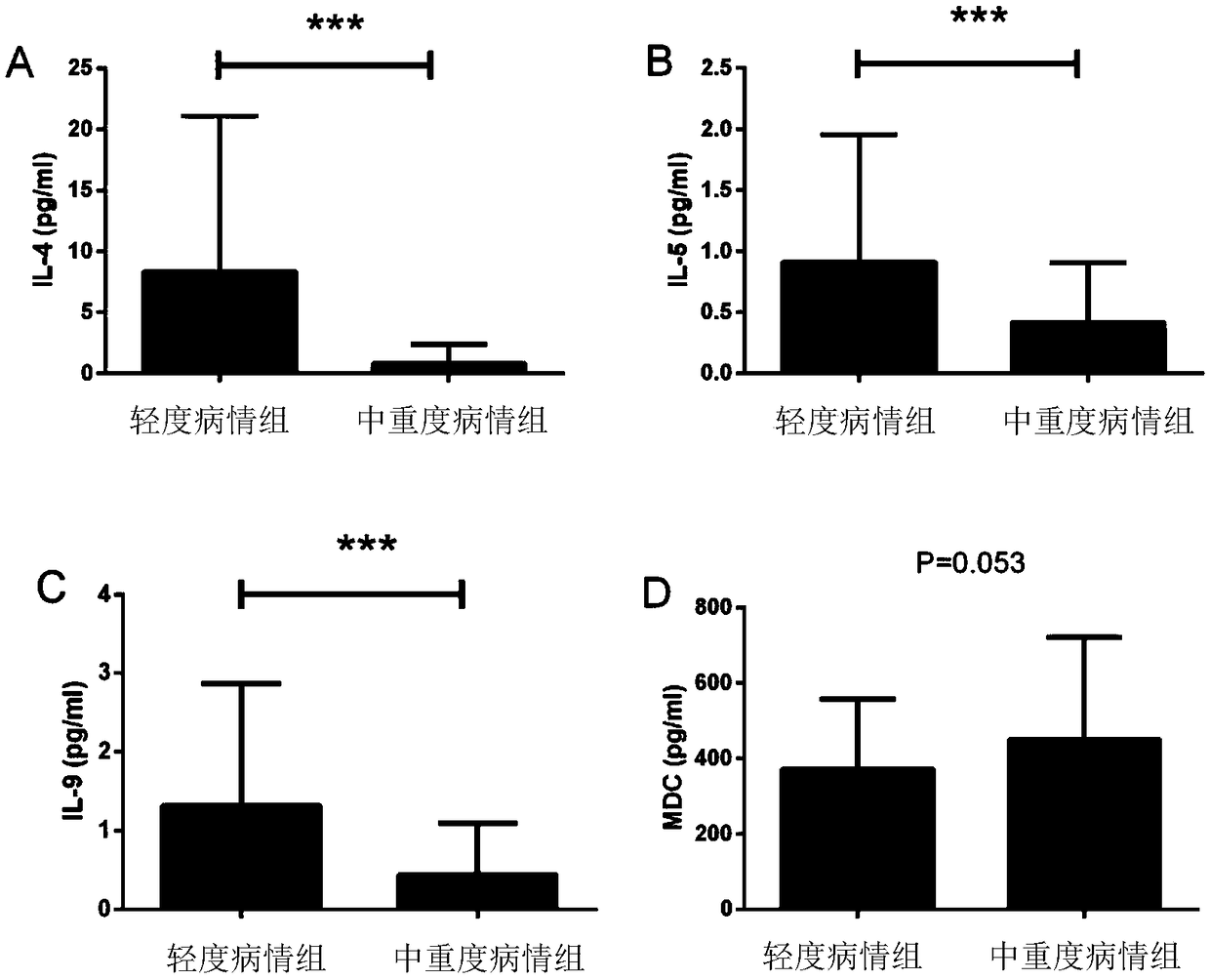
The invention discloses application of serum inflammatory biomarkers in prevention and treatment of acute ischemic cerebral infarction. The biomarkers include at least one cytokine of IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, MDC, MIP-1 alpha, sLOX-1, IL-33, Trx and YKL-40. The application of the serum inflammatory biomarkers in the prevention and treatment of the acute ischemic cerebral infarction verifies that the cytokines IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, MDC, MIP-1 alpha, sLOX-1, IL-33, Trx and YKL-40 are associated with functional prognosis of the cerebral infarction, the reject ratio of the prognosis of patients with the cerebral infarction can be reduced through the regulation of the cytokines, especially levels of IL-4, IL-5 and MDC, and the application can be used for preventing and treating the acute ischemic cerebral infarction by regulating the serum cytokines and related pathways thereof to predict neural functional prognosis of the patients with the cerebral infarction.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Inhibitor of ischemic disorders
ActiveUS8242302B2High melting pointGood water solubilityBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsBrain edemaDepressant
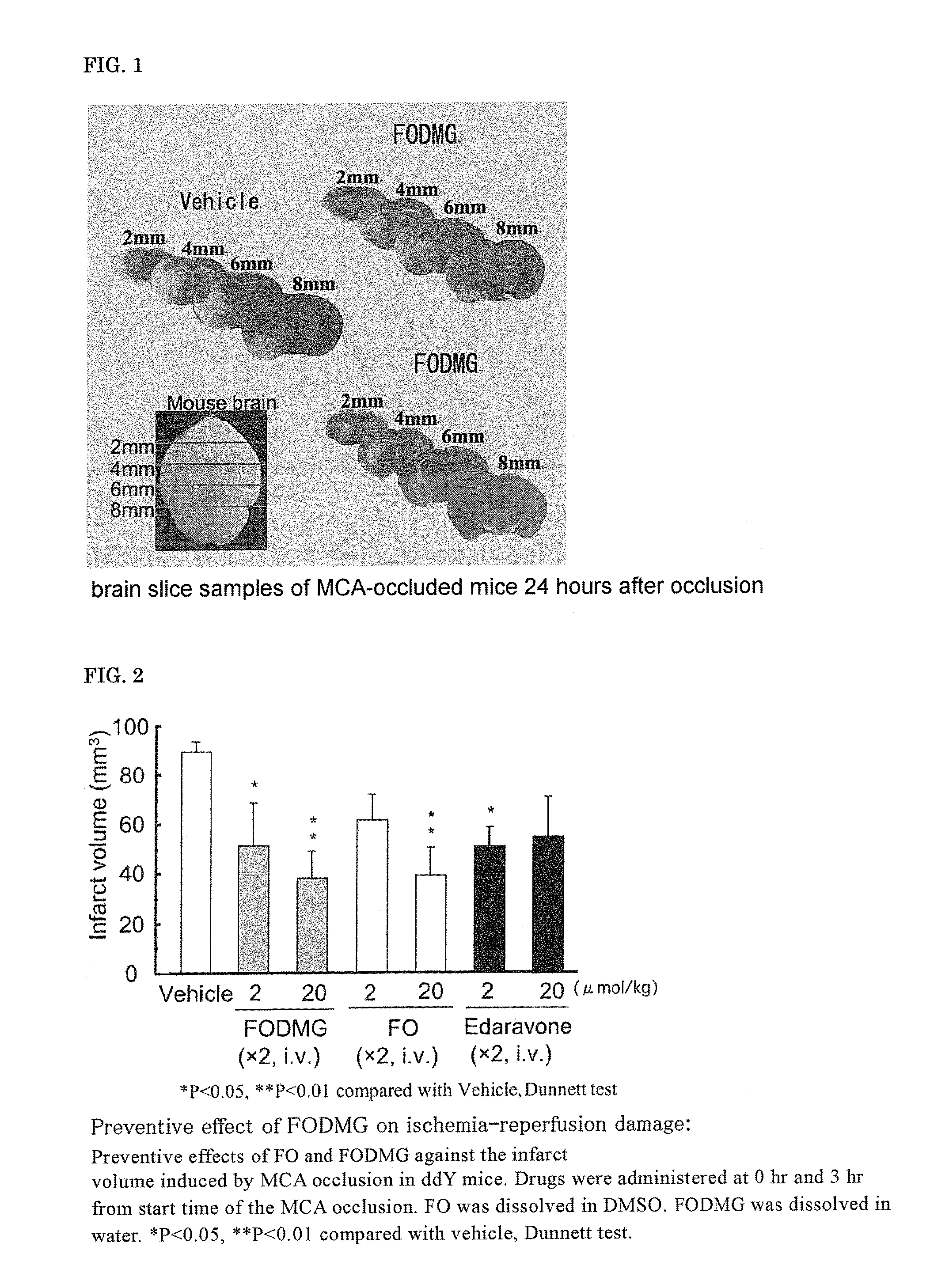
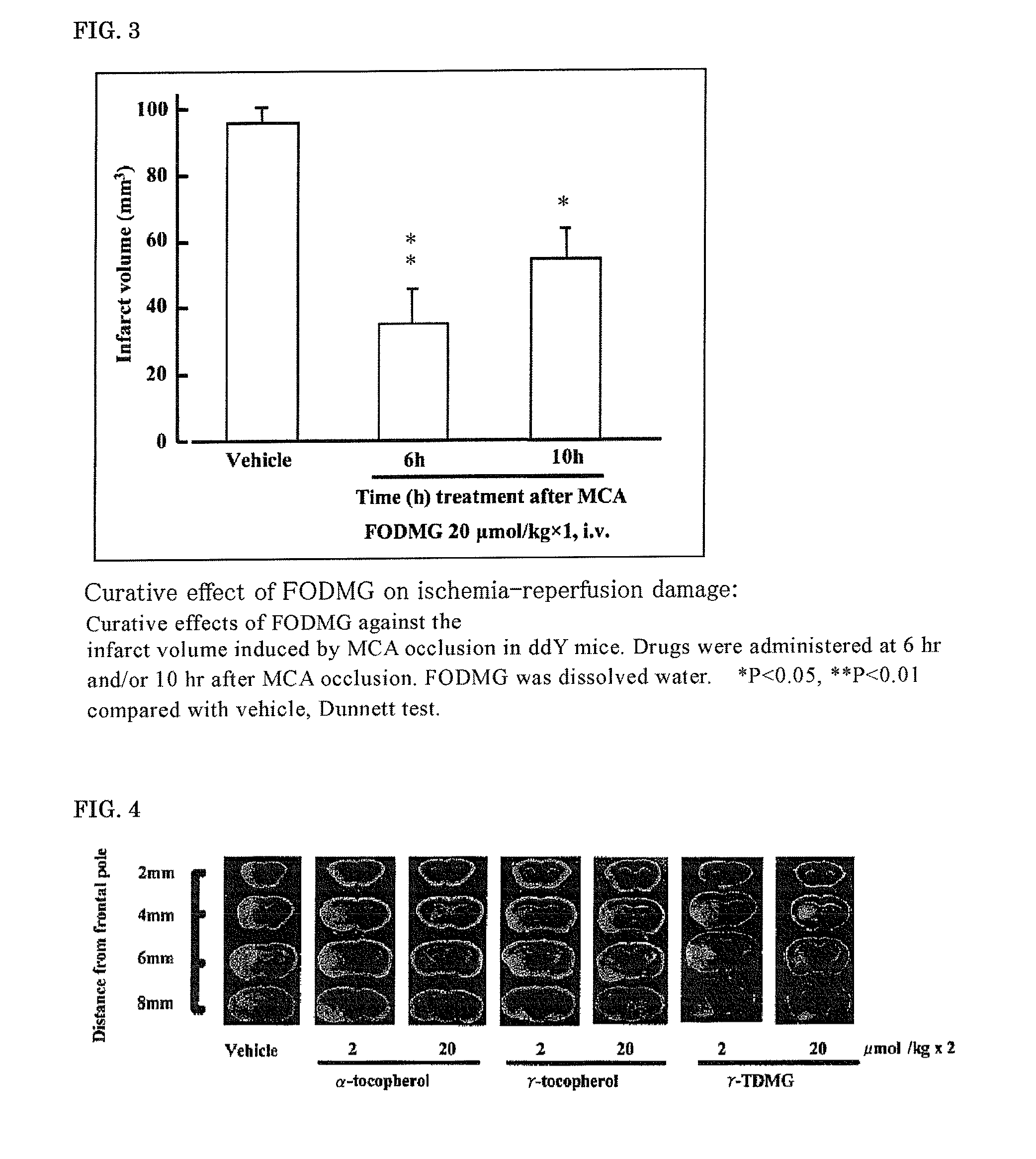
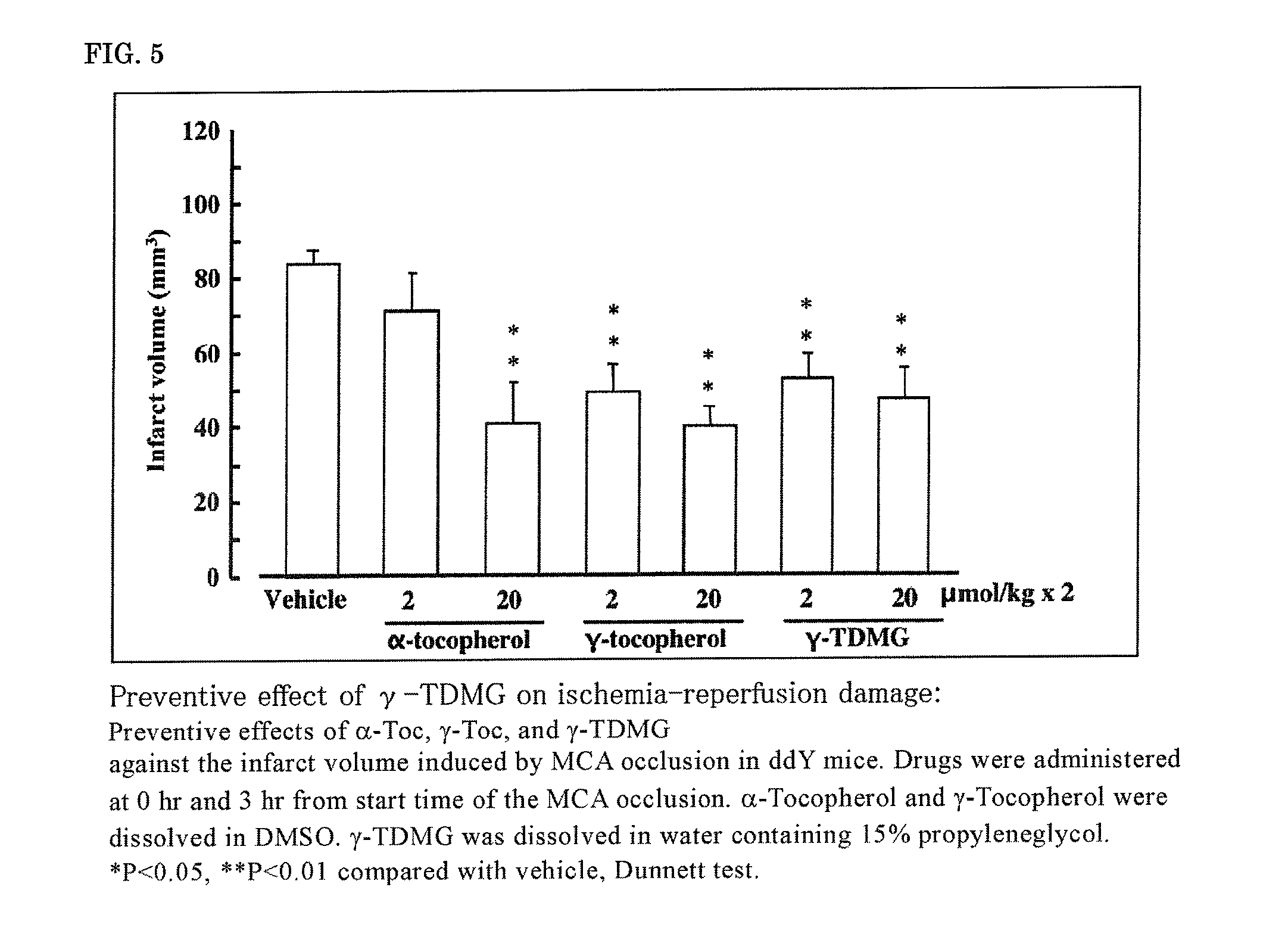
It is intended to provide a drug which is efficacious in treating and preventing diseases wherein ischemia or an inflammatory substance associated with ischemia participates in the onset or worsening thereof. Because of containing as the active ingredient a substance selected from among farnesol, a farnesol derivative, a tocopherol derivative, a tocotrienol derivative, pharmacologically acceptable salts thereof and solvates thereof, the above-described inhibitor of ischemic disorders can exert therapeutic and preventive effects on diseases wherein ischemia or an inflammatory substance associated with ischemia participates in the onset or worsening thereof (for example, brain infarction, brain edema, cardiac infarction, etc.) not only by the administration in the acute ischemic stage but also by the therapeutic administration in subacute and / or chronic stages after ischemia-reperfusion. It is also intended to provide a farnesol carboxylic acid ester derivative and a method of producing the same.
Owner:FUKUOKA UNIV
Mother-son extension catheter and son catheter thereof
The invention discloses a mother-son extension catheter and a son catheter thereof. The son catheter comprises a catheter body and a catheter base, wherein a hole is formed at the end, far away from the catheter base, of the catheter body; side holes are formed in the side wall of the catheter body. The son catheter moves along a guide wire in a mother catheter until the son catheter extends out of the mother catheter, and at the moment, if a blood vessel is blocked and the contact site of the son catheter and the blood vessel is located between the side holes and the end, far away from the catheter base, of the catheter body due to contact of the outer wall of the son catheter and the inner wall of the blood vessel, blood can flow into the catheter body via the side holes in the side wall of the catheter body and then the blood in the catheter body can flow out via the hole at the end, far away from the catheter base, of the son catheter, thus achieving blood circulation and then avoiding the condition that the blood vessel is blocked by the son catheter, preventing causing acute ischemia and reducing the surgical risks.
Owner:孙英贤 +1
Chinese medicinal preparation for treating acute ischemic stroke
InactiveCN104383038AGood treatment effectImprove securityAnthropod material medical ingredientsDispersion deliveryTreatment effectNeurological impairment
Owner:胡万华
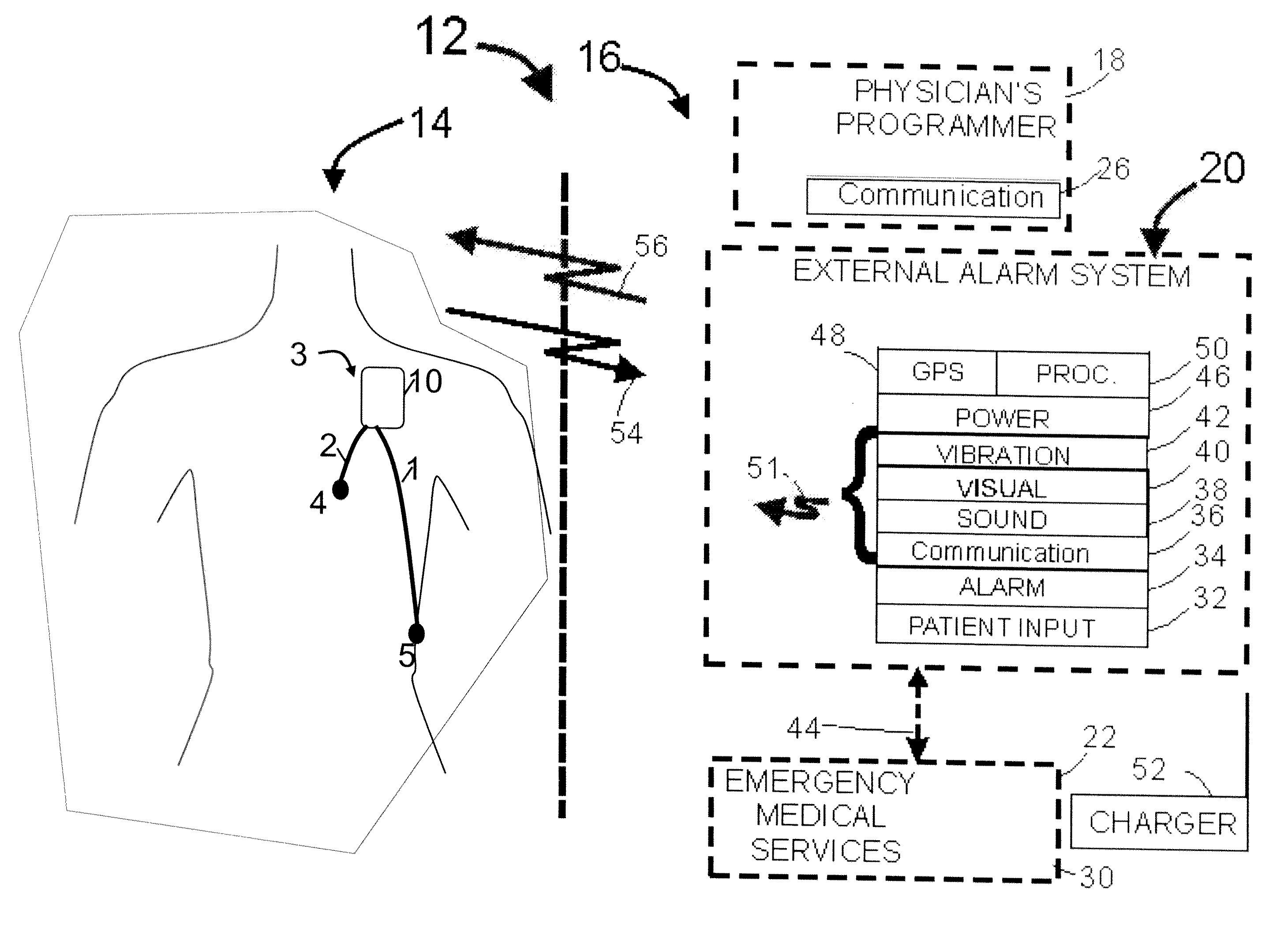
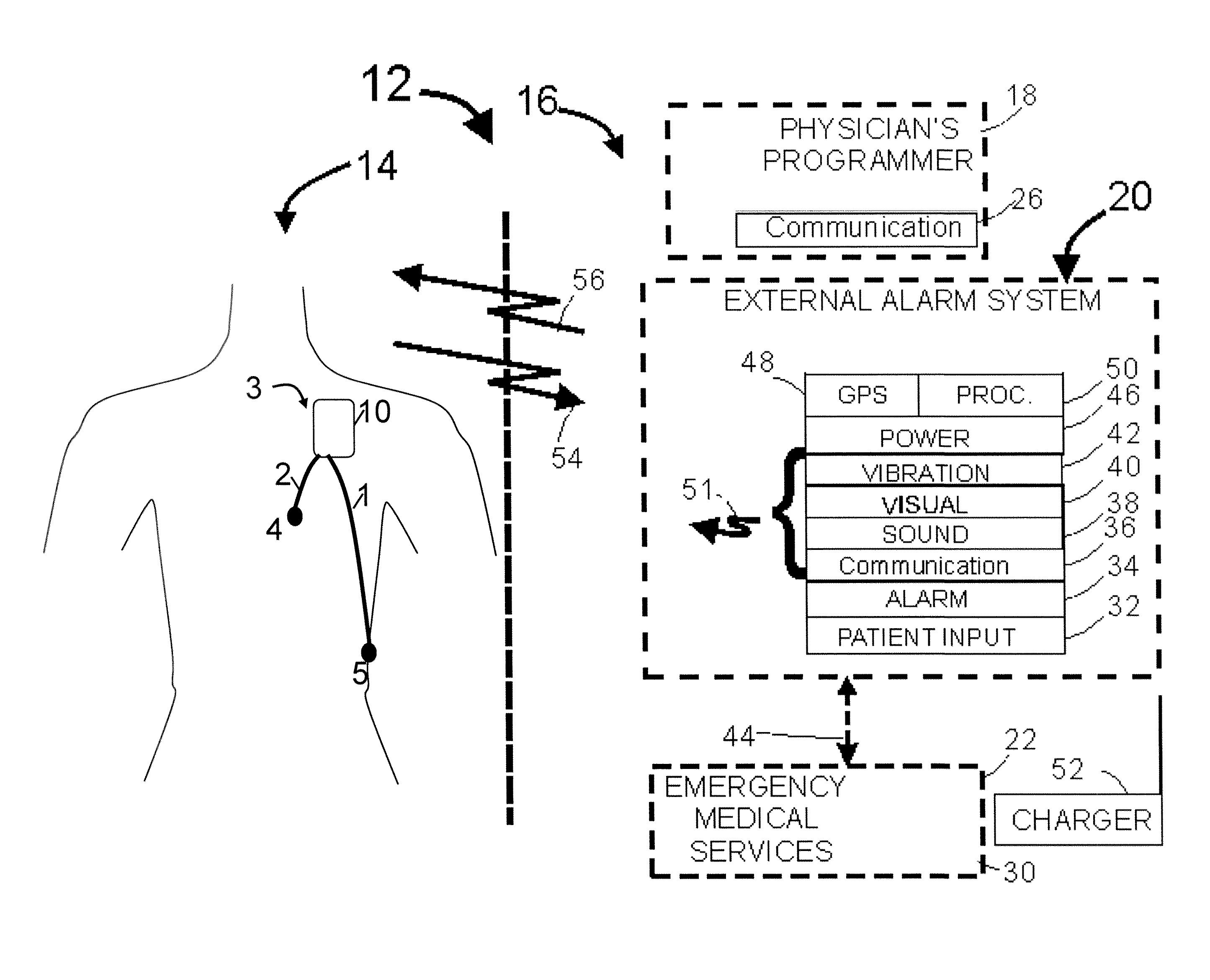
Apparatus for managing acute ischemic events
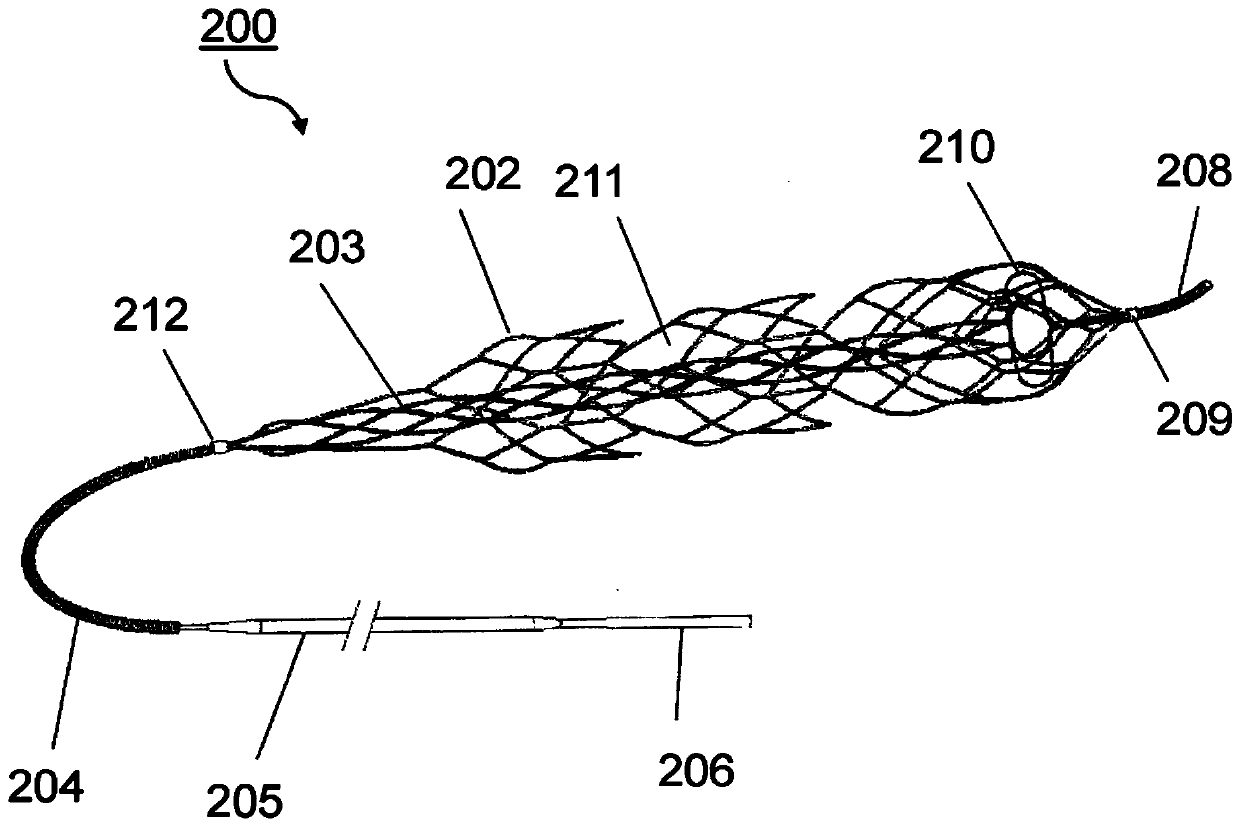
A method or use for managing one or more acute ischemic events. The method can include determining criteria of a clot; classifying the clot based on the criteria and generating a classification; determining an individualized treatment protocol for the clot based on the classification, the individualized treatment protocol comprising one or more techniques selected from using aspiration, restoring perfusion using a first reperfusion device, and / or restoring perfusion using a second reperfusion device; and treating the clot based on the individualized treatment protocol.
Owner:NEURAVI
Heart rate correction system and methods for the detection of cardiac events
ActiveUS9042969B2Strong specificityEliminate high frequency noiseElectrocardiographySensorsRR intervalAverage filter
A device for detecting a cardiac event is disclosed. Detection of an event is based on a test applied to a parameter whose value varies according to heart rate. Both the parameter value and heart rate (RR interval) are filtered with an exponential average filter. From these filtered values, the average change in the parameter and the RR interval are also computed with an exponential average filter. Before computing the average change in the parameter, large changes in the parameter over short times, which may be caused by body position shifts, are attenuated are removed, so that the average change represents an average of small / smooth changes in the parameter's value that are characteristic of acute ischemia, one of the cardiac events that may be detected. The test to detect the cardiac event depends on the heart rate, the difference between the parameter's value and its upper and lower normal values, and its average change over time, adjusted for heart rate changes. The upper and lower normal parameter values as a function of heart rate are determined from long term stored data of the filtered RR values and parameter values. Hysteeresis related data and transitory deviations from normal (e.g. vasospasm related data) are excluded from the computation of normal upper and lower parameter bounds.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Method and apparatus for managing acute ischemic event
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for managing an acute ischemic event. The method for managing one or more acute ischemic events can include determining the criteria of a clot;classifying the clot based on the criteria and generating a classification; determining an individualized treatment protocol for the clot based on the classification, the individualized treatment protocol comprising one or more techniques selected from using aspiration, restoring perfusion using a first reperfusion device, and / or restoring perfusion using a second reperfusion device; and treatingthe clot based on the individualized treatment protocol.
Owner:NEURAVI
Ingestible compositions system and method
PendingUS20190328699A1Nitrous oxide captureHydroxy compound active ingredientsCrohn's diseaseMedicine
The ingestible compositions system includes the co-production of orally-ingestible compositions usable as inhalable respiratory agents including delivery apparatus and related methods. The invention comprises a healthy alternative delivery system to smoking. THC / CBD fits like a key in a lock into CB1 and CB2 receptors. The H2O solution (with THC / CBD) can also be consumed orally for a slight euphoric effect. As designed, the present invention can be useful in treating cancers, acute ischemic neurological insults or chronic neurodegenerative diseases, Crohn's disease, Lupus, and PTSD, but is not limited to just the mentioned diseases / ailments.
Owner:FORDE TANIA
Application of 5-bromo-2-(alpha-hydroxy amyl) sodium benzoate in medicine for curing cardiovascular disease
InactiveCN108283633AReduce infarct sizeImprove protectionOrganic active ingredientsPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesReperfusion injuryHeart disease
The invention discloses application of compound 5-bromo-2-(alpha-hydroxy amyl) sodium benzoate (BZP) in medicine for curing cardiovascular disease, and belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry. Experiments prove that BZP has a protective effect for acute and chronic myocardial ischemia reperfusion injuries of a mouse, so that the overall animal acute myocardial infarction area is reduced through BZP oral administration and intravenous injection, the myocardial infarction area of the acute ischemia reperfusion injury of the isolated perfusion heart of the mouse is reduced through BZP, the function of myocardial contraction is improved, and the haematological myocardial injury markers are reduced; moreover, the invention also relates to application for delaying a process of the conversionfrom myocardial hypertrophy to cardiac failure after chronic orally taken administration of BZP for acute myocardial infarction of the mouse and reducing ventricular remodeling caused by ischemic heart disease of the mouse, the therapeutic action of the cardiac function is improved obviously; moreover, the invention also relates to the transient effect of the compound BZP for reducing the blood pressure of the hypertension mouse (SHR mouse), and these results indicate that the BZP has effective research and development prospects of myocardial damage protection medicine for clinically acute and chronic myocardial infarctions.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV +1
Waveform feature value averaging system and methods for the detection of cardiac events
Disclosed is a system for detecting pathophysiological cardiac conditions. The system comprises a diagnostic device that contains electronic circuitry that can detect a cardiac event such as an acute ischemia. The cardiac diagnostic device receives electrical signals from subcutaneous or body surface sensors. The cardiac diagnostic device includes a processor that computes QRS onset and offset points and fiducial points associated with T and U waves. The processor than baseline corrects the original signal / waveform by fitting a polynomial function to QRS offset points, and subtracting this function from the original waveform. Based on the baseline adjusted signal and / or the above mentioned fiducial points, the processor then computes averages of various waveform feature values, including a QRS measure sensitive to QRS curvature, T wave timing measures, ST segment deviation (difference between signal amplitudes at QRS offset and onset and / or minimum amplitude between QRS offset and peak T wave); and T / U wave amplitudes. These averages are computed by exponential averaging. From the exponential averages, the processor computes an average of the change in the averages over time. Based on the averages and the change in the averages, the processor applies an ischemia test to determine a likelihood of ischemia.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Method for auxiliary diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke based on CT flat scanning images
PendingCN112599236AHelp check outIncreased sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisComputed tomographyImaging processing
The invention discloses an image processing method based on a CT (computed tomography) flat scanning image. The method assists in evaluating the CT early ischemic change degree of the head of an AIS (acute ischemic stroke) patient. According to the invention, the risk assessment of the automatic zoning and quantitative treatment of the acute ischemic stroke from the CT flat scanning images is realized, and an effective assessment method is provided for the early screening, early diagnosis and early treatment of patients with the acute ischemic stroke (AIS).
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Medicine for treating acute ischemic cerebral apoplexy and its preparing method
ActiveCN1290491CThe prescription process is reasonable and feasibleQuality improvementPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsActivated carbonBenzene
The medicine for treating acute ischemic cerebral apoplexy is prepared with butyl benzene phthalein, emulsifier, co-emulsifier, excipient and water for injection in certain proportion. The preparation process includes weighing materials in certain proportion; mixing butyl benzene phthalein, emulsifier and co-emulsifier in partial water for injection via high speed stirring; dissolving the excipient in other water for injection, adding active carbon, heating at 100 deg.c for 15 min before eliminating carbon; mixing two kinds of solution, adding active carbon, filtering and eliminating carbon; adding water for injection to full amount, measuring pH value and content; fine filtering, bottling and freeze drying to obtain the powder for injection. The present invention provides medicine for salvage of serious cerebral apoplexy patient clinically.
Owner:CSPC ZHONGQI PHARM TECH (SHIJIAZHUANG) CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com