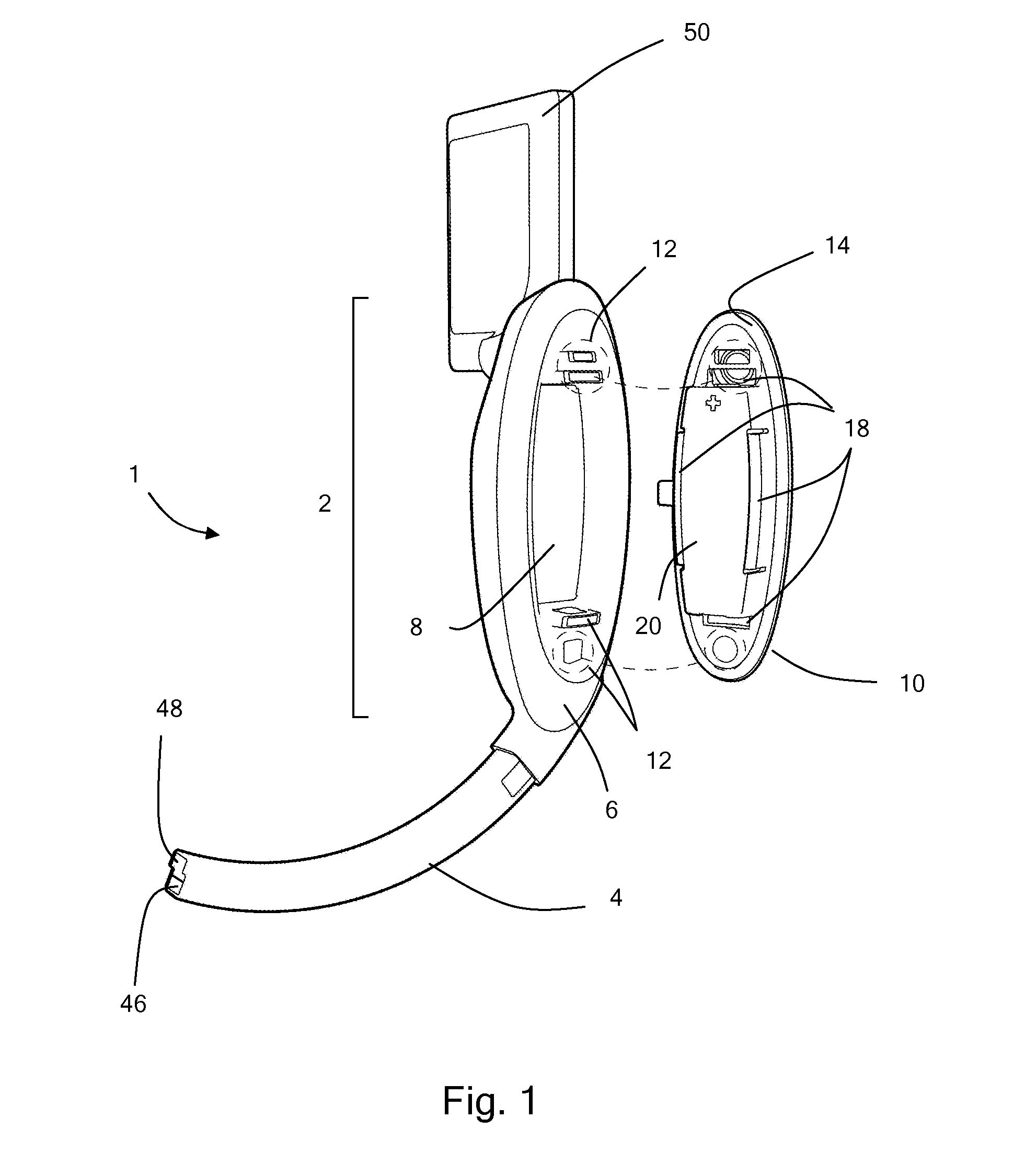
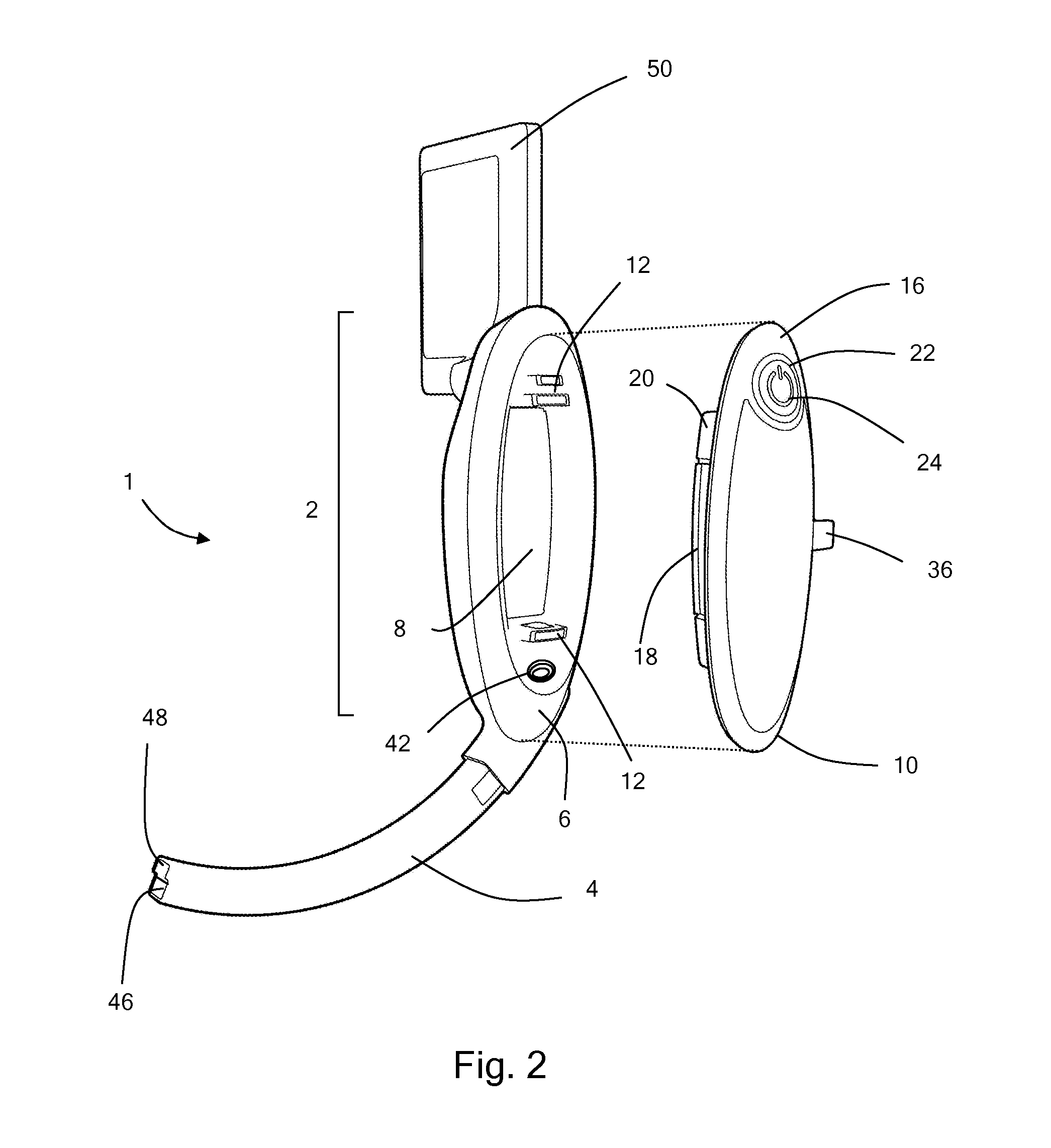
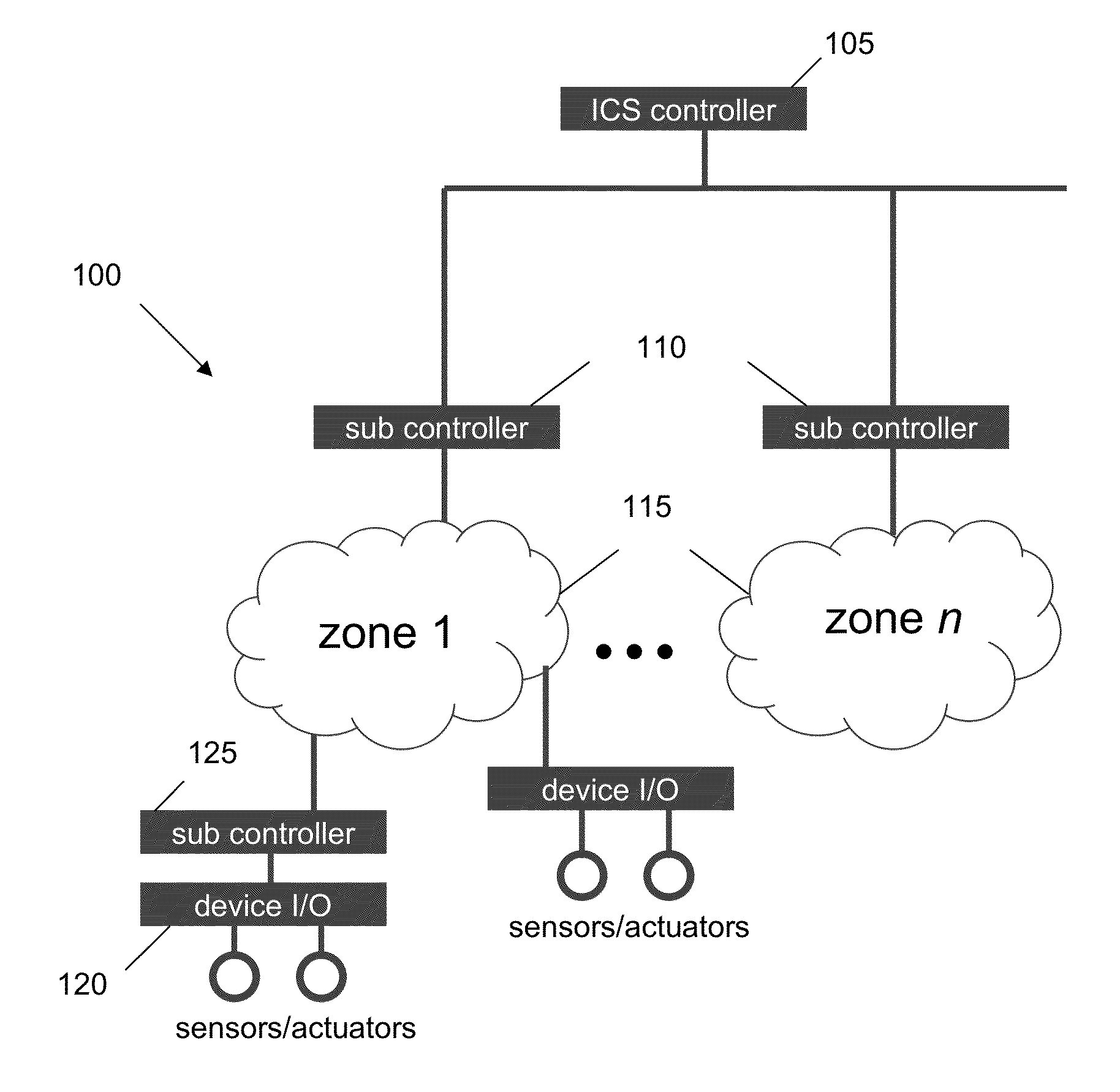
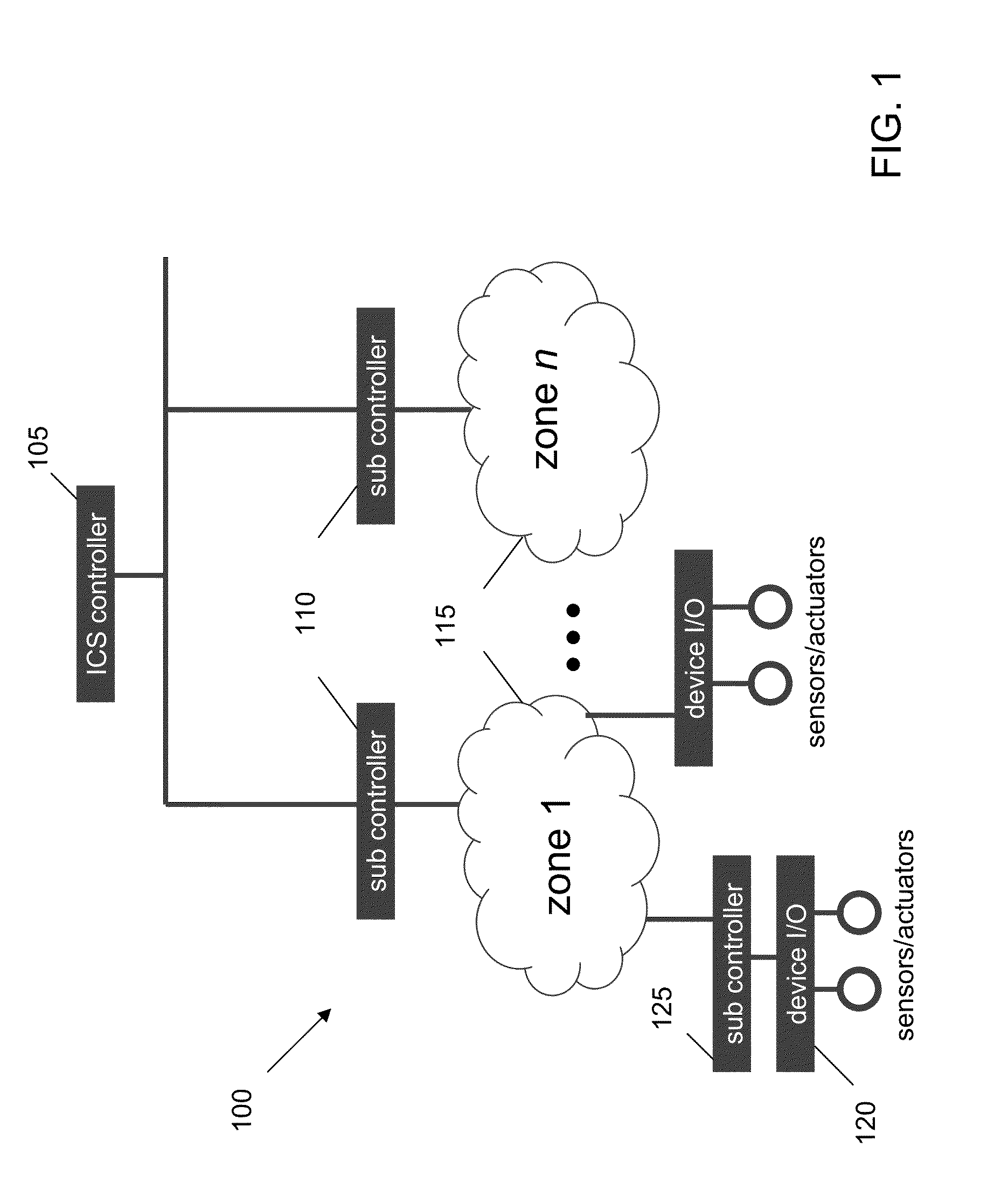
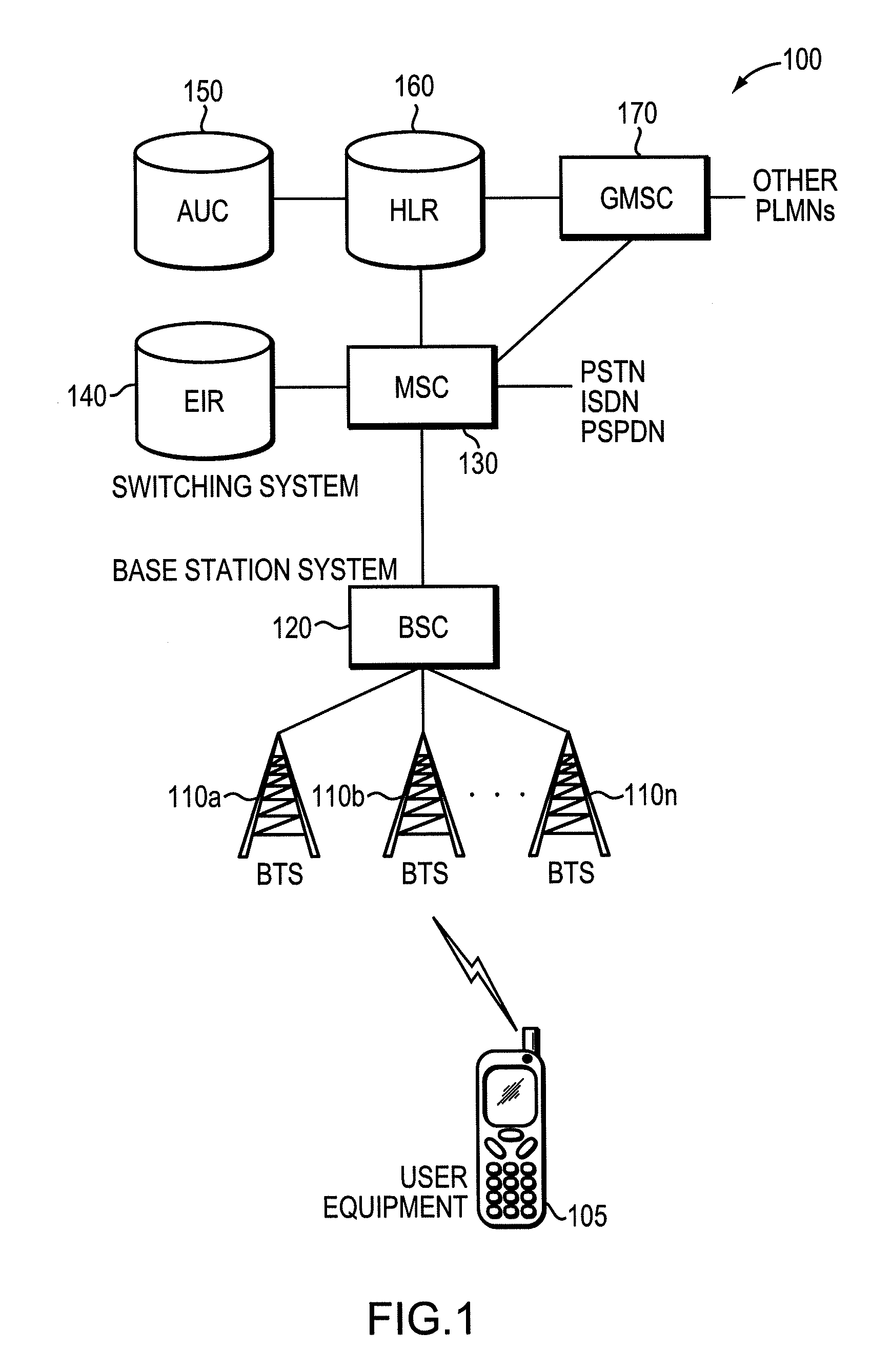
Patents
Literature
60 results about "Emergency procedure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An emergency procedure is a plan of actions to be conducted in a certain order or manner, in response to a specific class of reasonably foreseeable emergency, a situation that poses an immediate risk to health, life, property, or the environment. Where a range of emergencies are reasonably foreseeable, an emergency plan may be drawn up to manage each threat. Most emergencies require urgent intervention to prevent a worsening of the situation, although in some situations, mitigation may not be possible and agencies may only be able to offer palliative care for the aftermath. The emergency plan should allow for these possibilities.
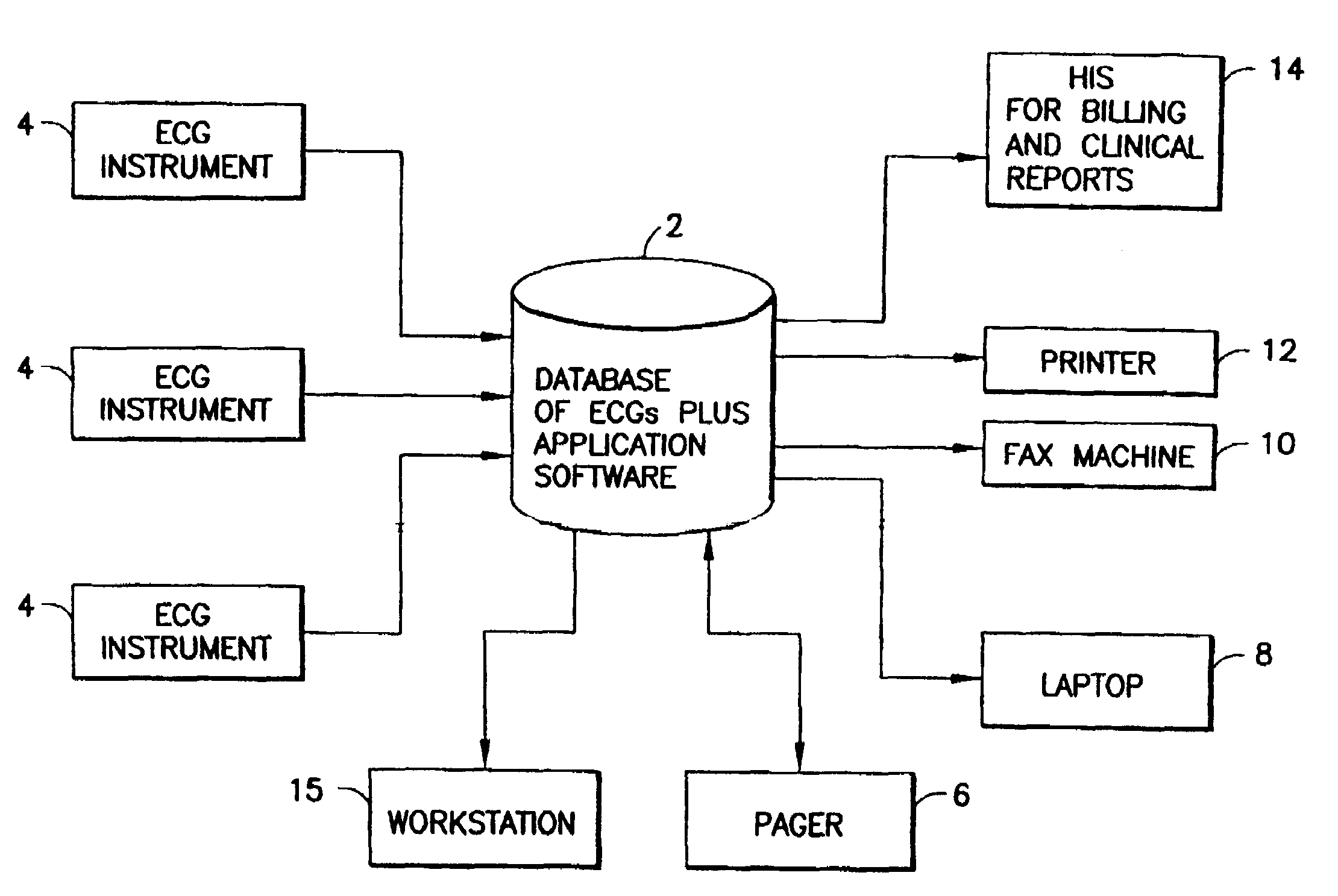
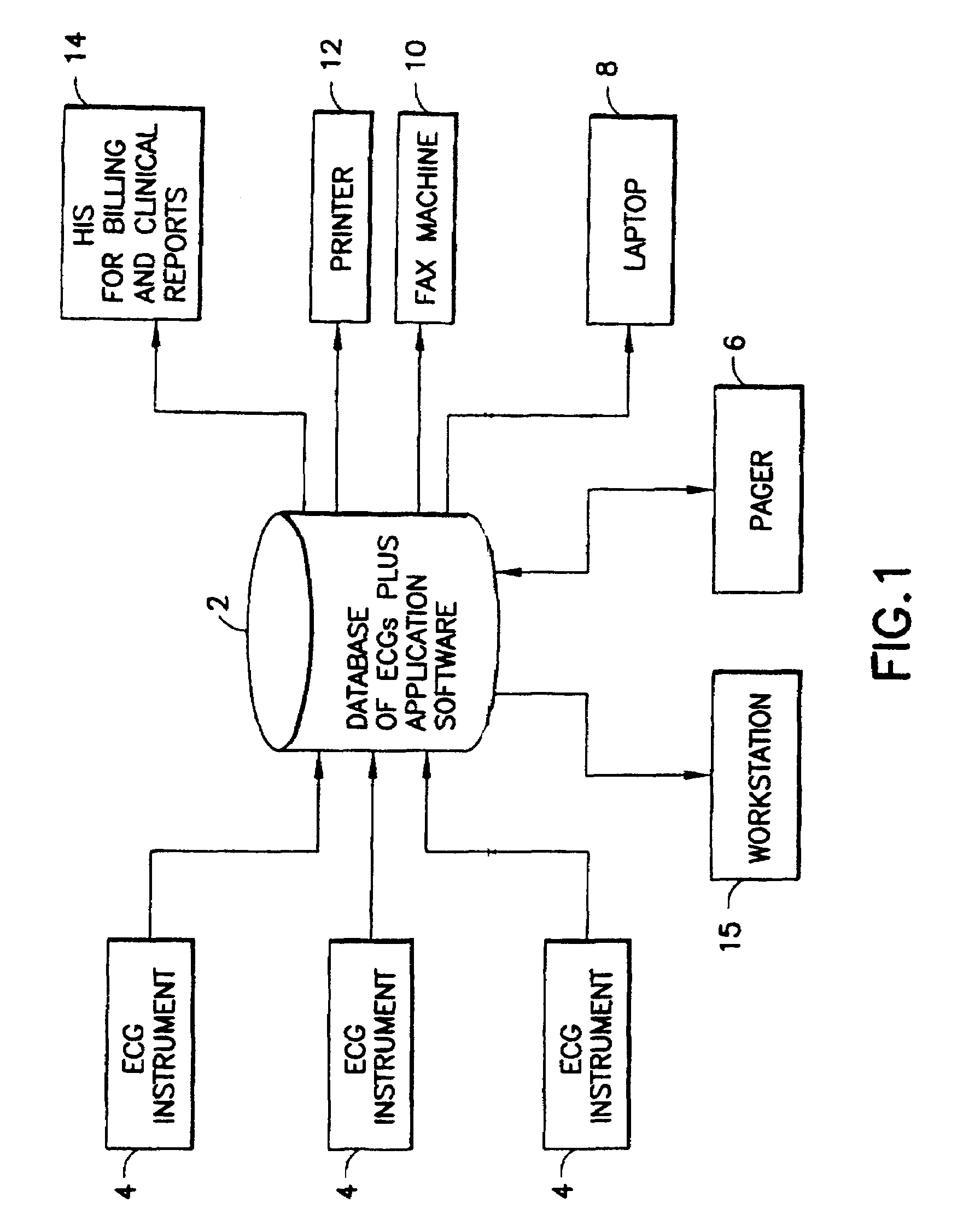
Automated scheduling of emergency procedure based on identification of high-risk patient
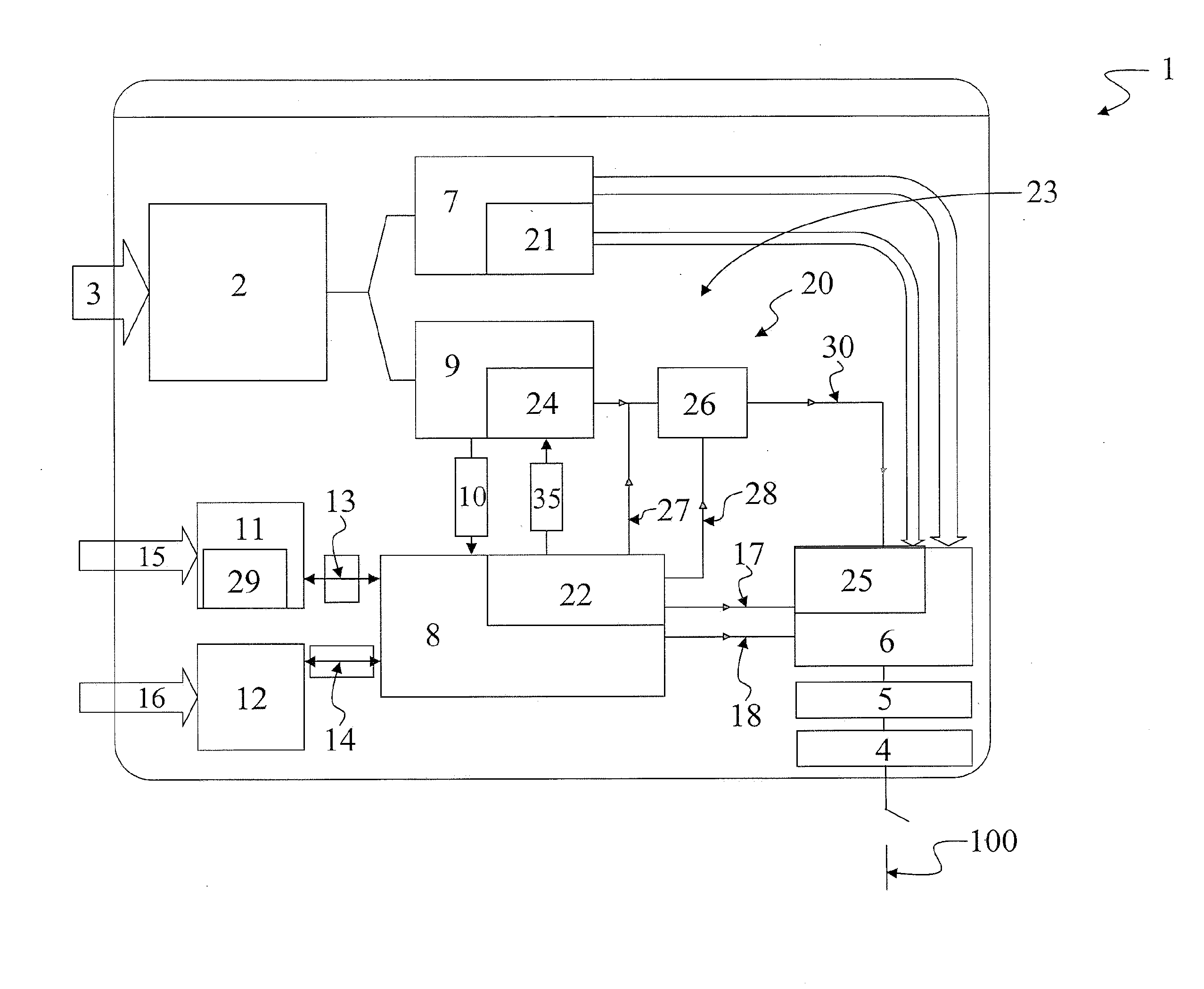
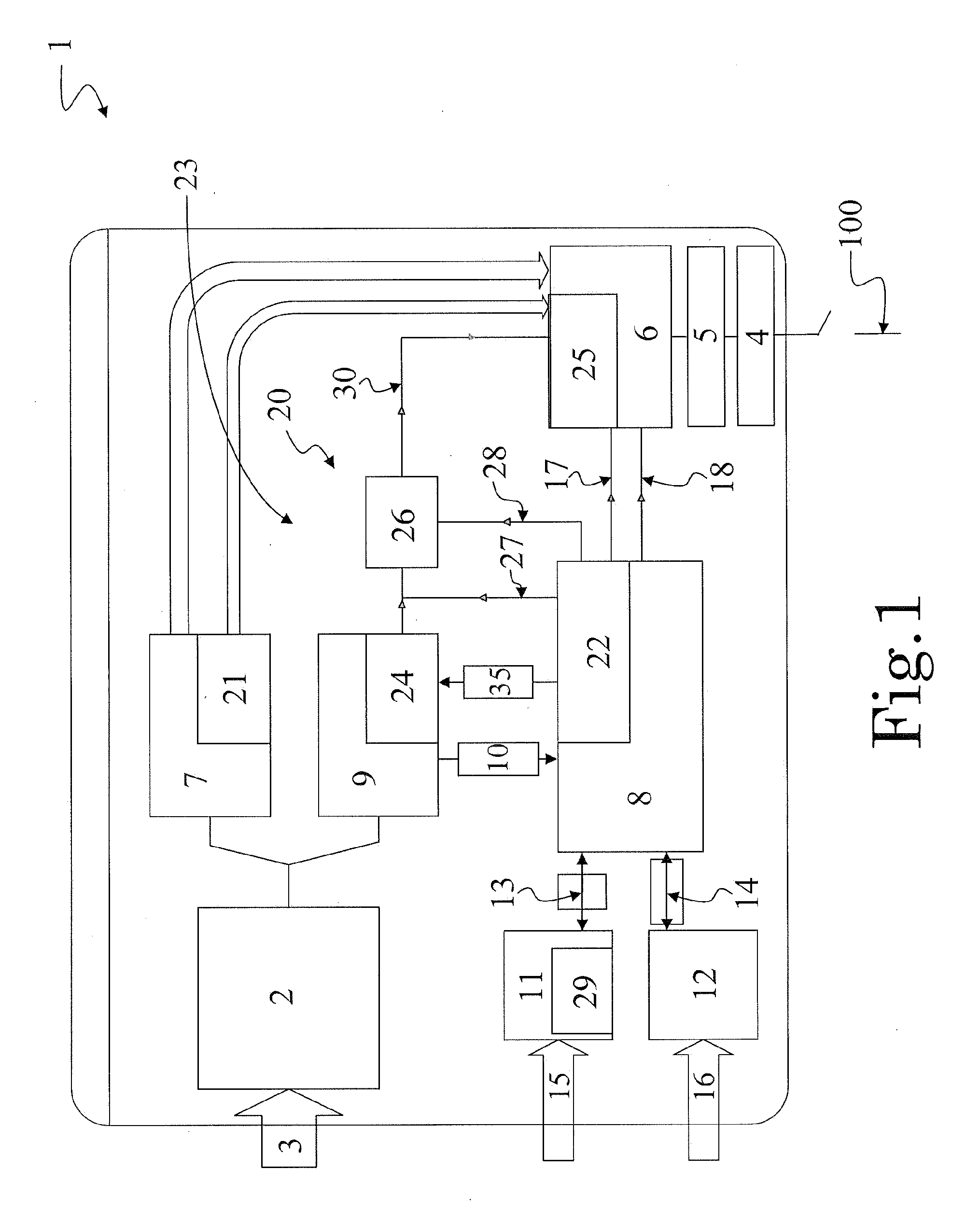
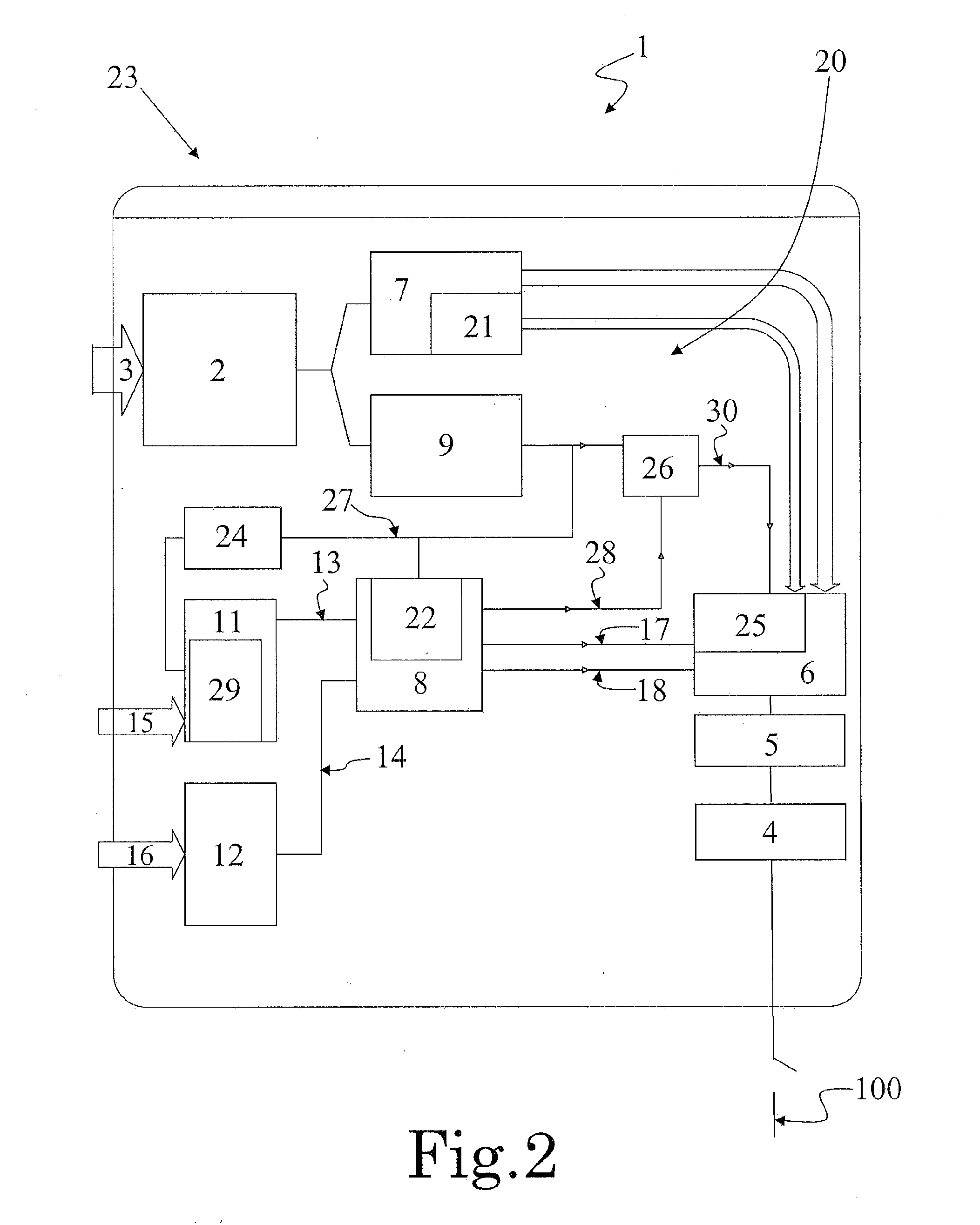
A system and a method for scheduling an emergency procedure in response to detecting that a patient has a high probability of acute myocardial infarction. The system is able to identify patients that are suspected of having acute myocardial infarction (or acute ischemia). The system uses one or more expert software tools or algorithms to analyze received ECG records. Each software tool has logic (e.g., thresholds and / or settings) for automatic routing which is configurable by the customer via a graphical user interface. If any sufficient condition for automatic routing is satisfied, the system routes the data (including the underlying ECG record) and an alert to an electronic device which is accessible by the cardiologist “on call” via a bidirectional pager. If the cardiologist decides that the requested emergency treatment or procedure should be performed, the system accesses the schedules of all associated catheterization labs across multiple hospitals to identify a lab having optimum time-to-treatment. Then the system automatically contacts the selected catheterization lab via a network to schedule the PTCA procedure.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
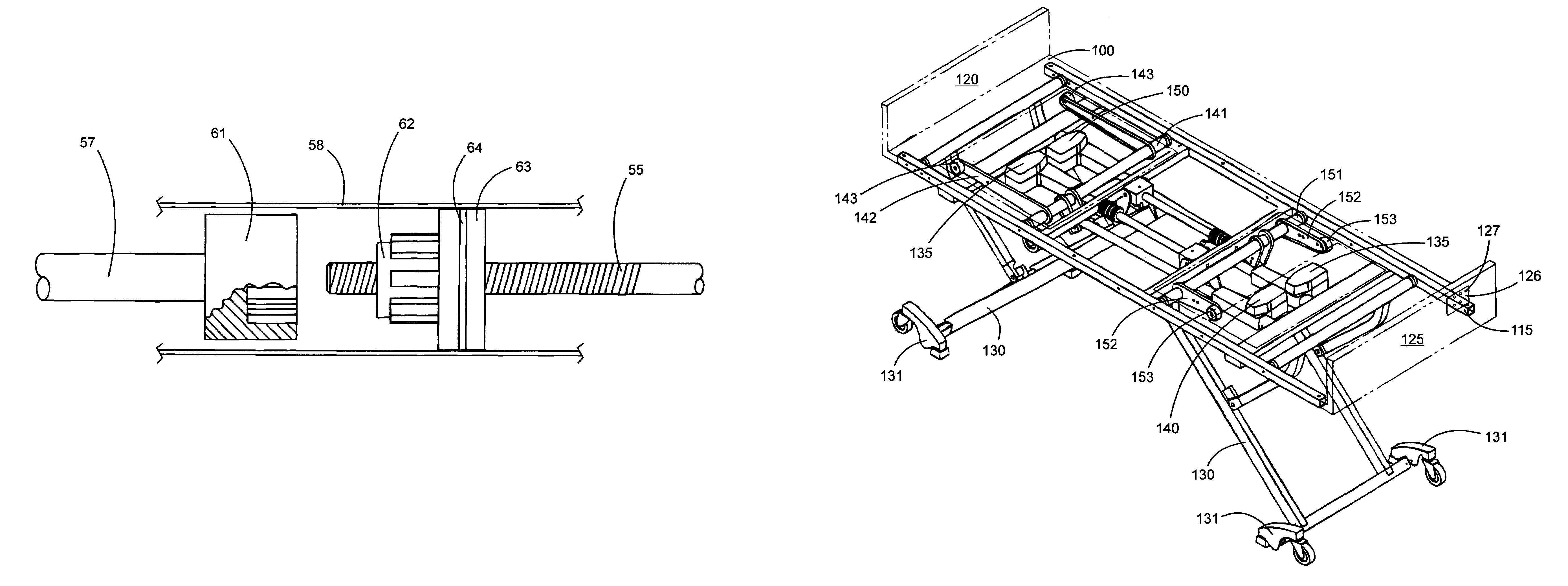
Patient bed with CPR system
An electrically activated emergency system for a patient bed comprises: an electrically powered linear actuator for driving a back rest of the patient bed from a lowered back rest position to a raised back rest position and operable to permit the back rest to lower from the raised back rest position to the lowered back rest position without being driven by the linear actuator; and, an independent emergency back rest lowering feature comprising an electrical activation means for activating the linear actuator to permit the back rest to lower from the raised back rest position to the lowered back rest position without being driven by the linear actuator, the electrical activation means not requiring continued operator attendance for continued lowering of the back rest. The present invention permits an attendant, for example a nurse, to press a single button to bring the back rest to a lowered back rest position without having to keep the button pressed so that the attendant is free to immediately begin administering emergency procedures while the back rest is lowering.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
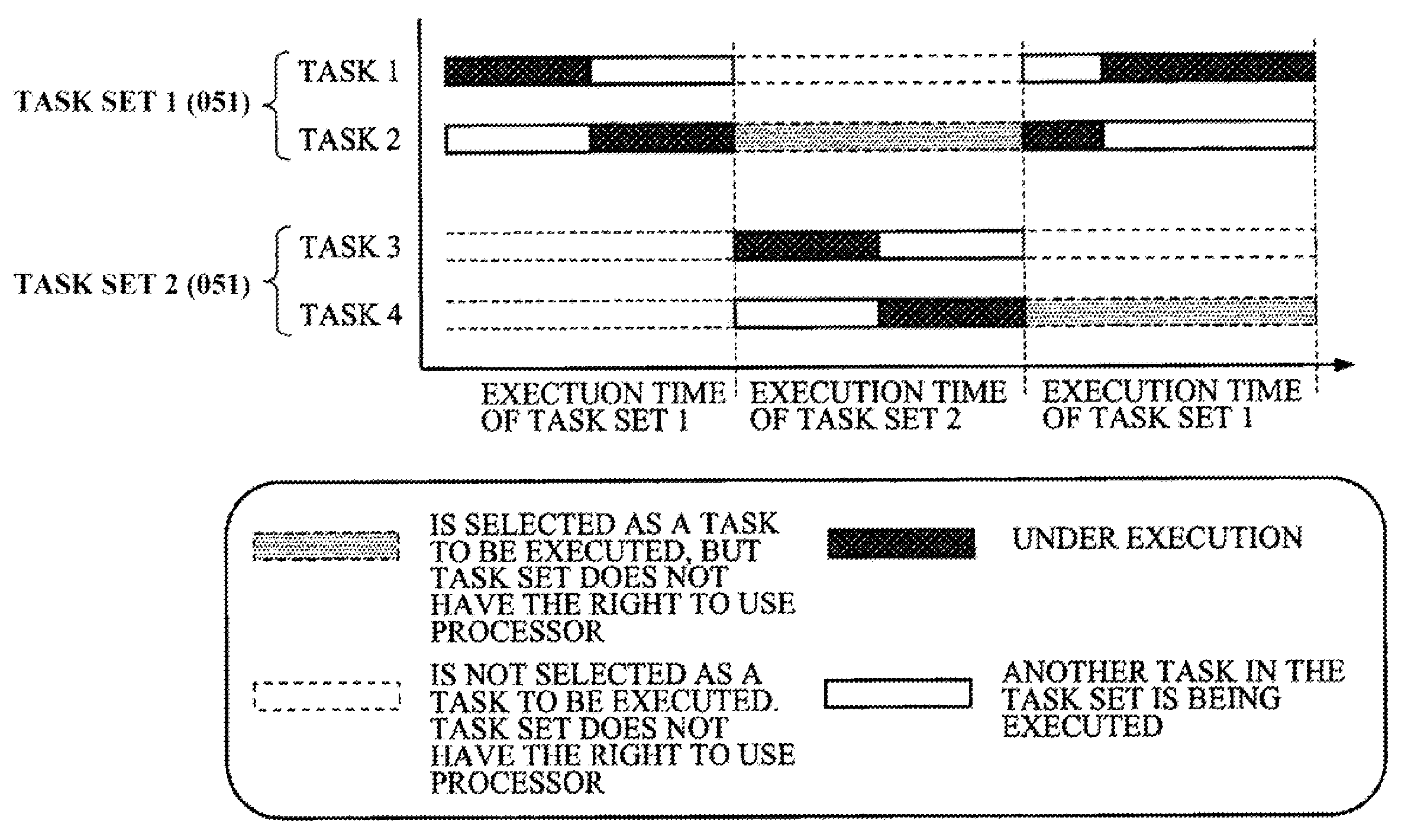
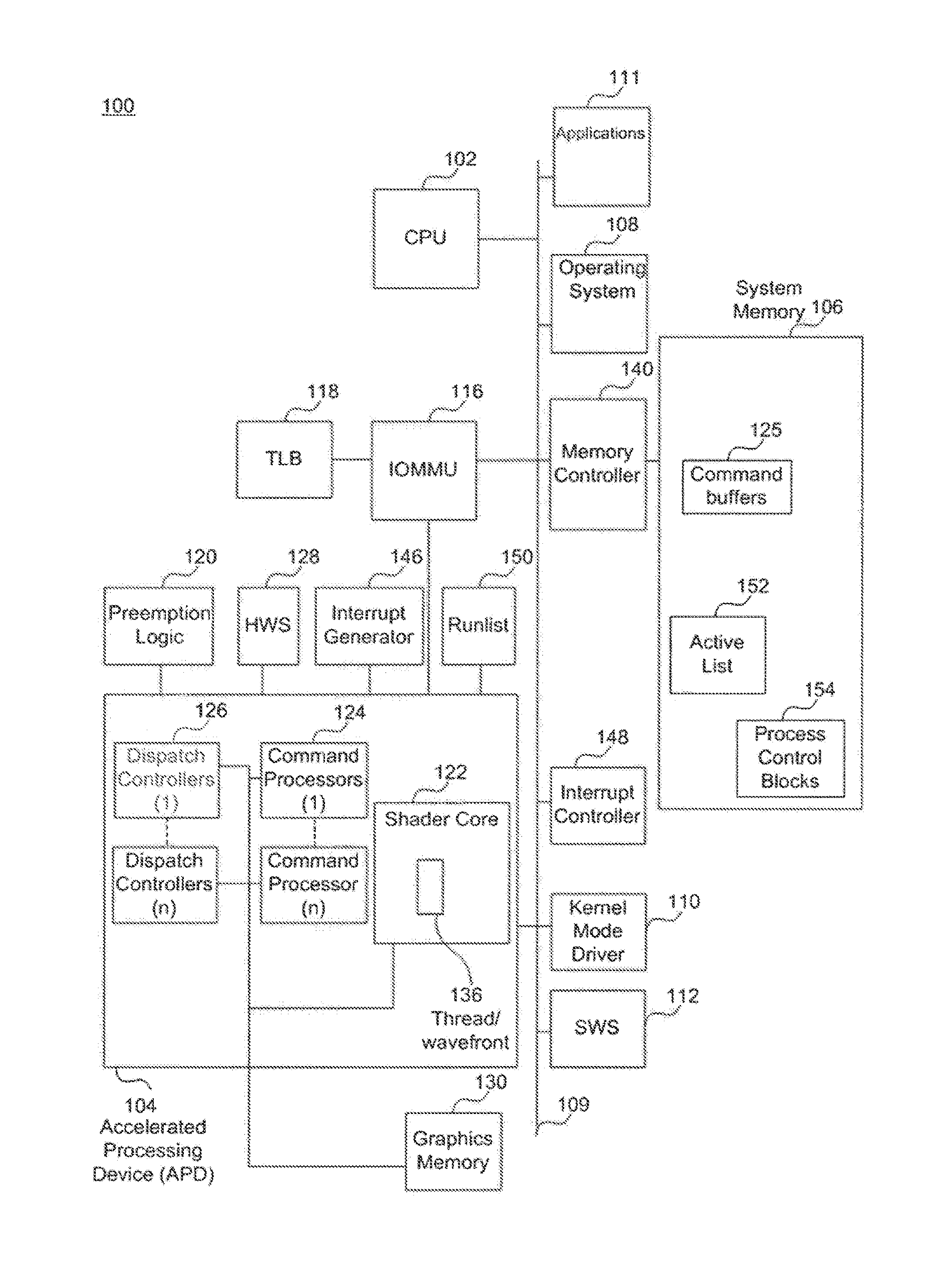
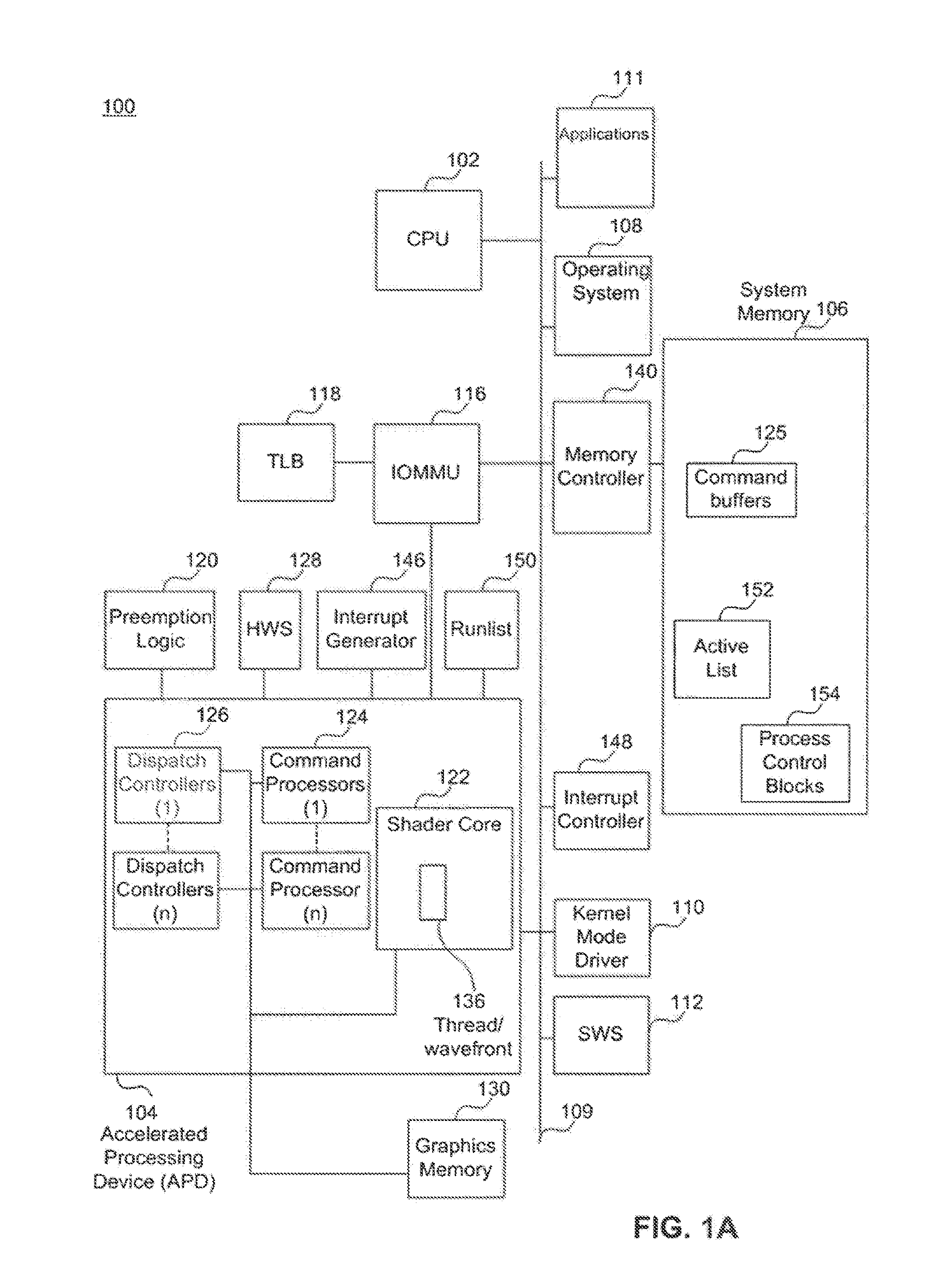
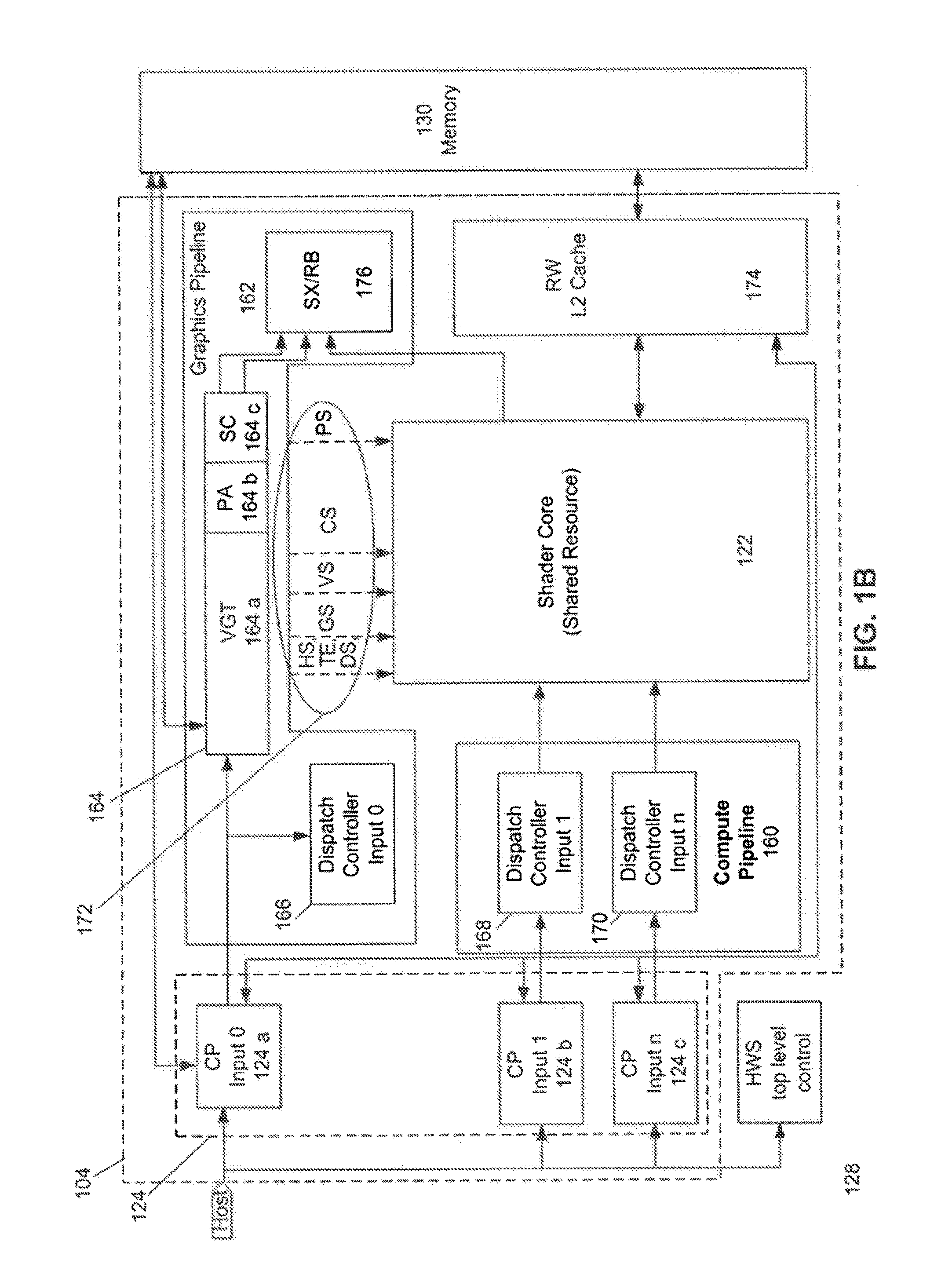
Processor system, task control method on computer system, computer program
InactiveUS7647594B2Simple methodProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationEmergency procedureComputer architecture
A mechanism for recording a timing in which a high urgency process is started is provided, and upon entry to a critical section in the middle of a low urgency process, by referencing the record, it is inspected whether a high urgency process will be started during execution of the critical section. If it will not be started, the critical section is entered, and if it will be started, control is exerted so that entry to the critical section is postponed until the high urgency process is completed. Exclusive access control in a critical section can be performed suitably under conditions where a plurality of task execution environments exist.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for urgency-based preemption of a process
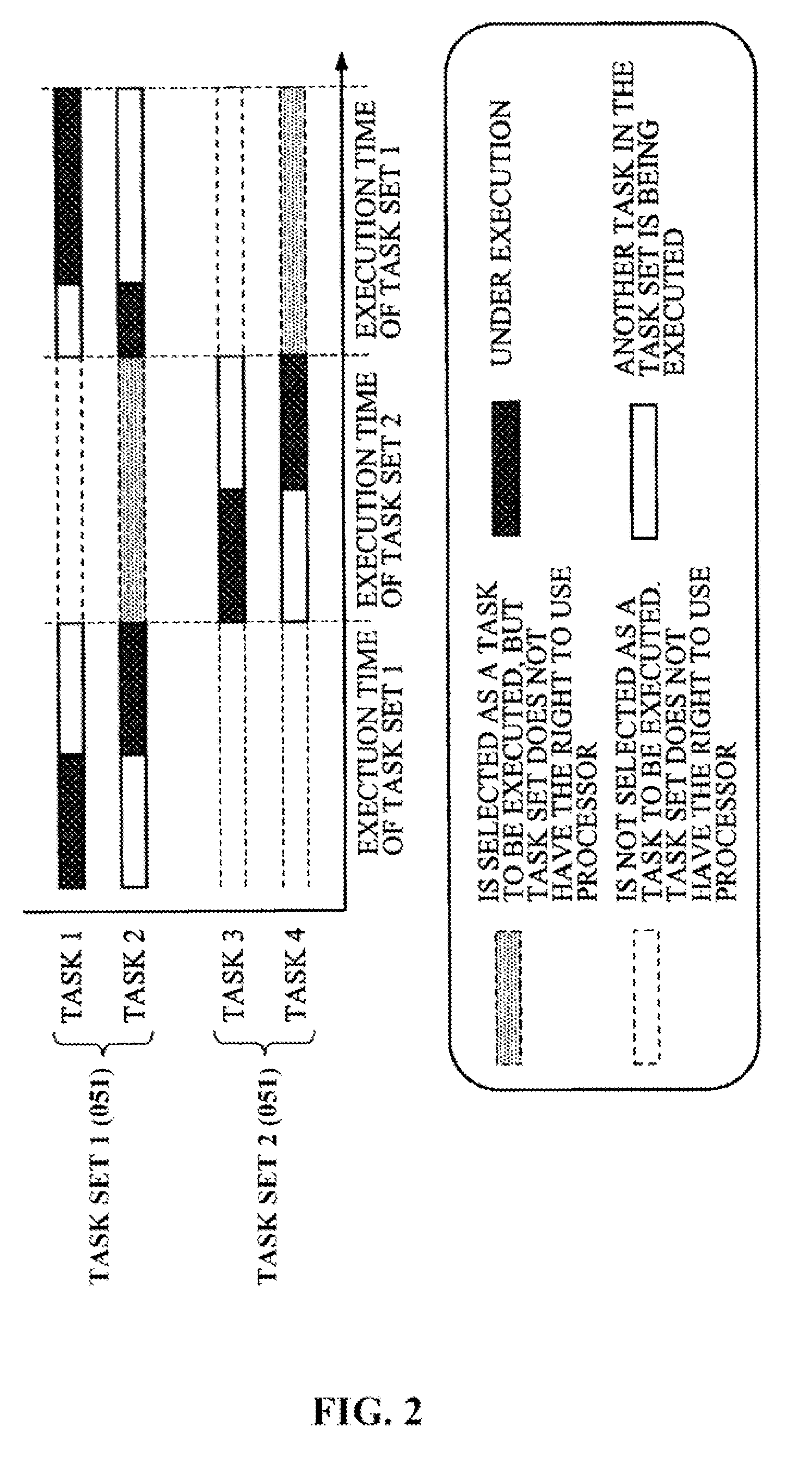
ActiveUS20140022263A1Efficiently preemptingProgram initiation/switchingMultiple digital computer combinationsEmergency procedureSystem capacity
The desire to use an Accelerated Processing Device (APD) for general computation has increased due to the APD's exemplary performance characteristics. However, current systems incur high overhead when dispatching work to the APD because a process cannot be efficiently identified or preempted. The occupying of the APD by a rogue process for arbitrary amounts of time can prevent the effective utilization of the available system capacity and can reduce the processing progress of the system. Embodiments described herein can overcome this deficiency by enabling the system software to pre-empt a process executing on the APD for any reason. The APD provides an interface for initiating such a pre-emption. This interface exposes an urgency of the request which determines whether the process being preempted is allowed a grace period to complete its issued work before being forced off the hardware.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
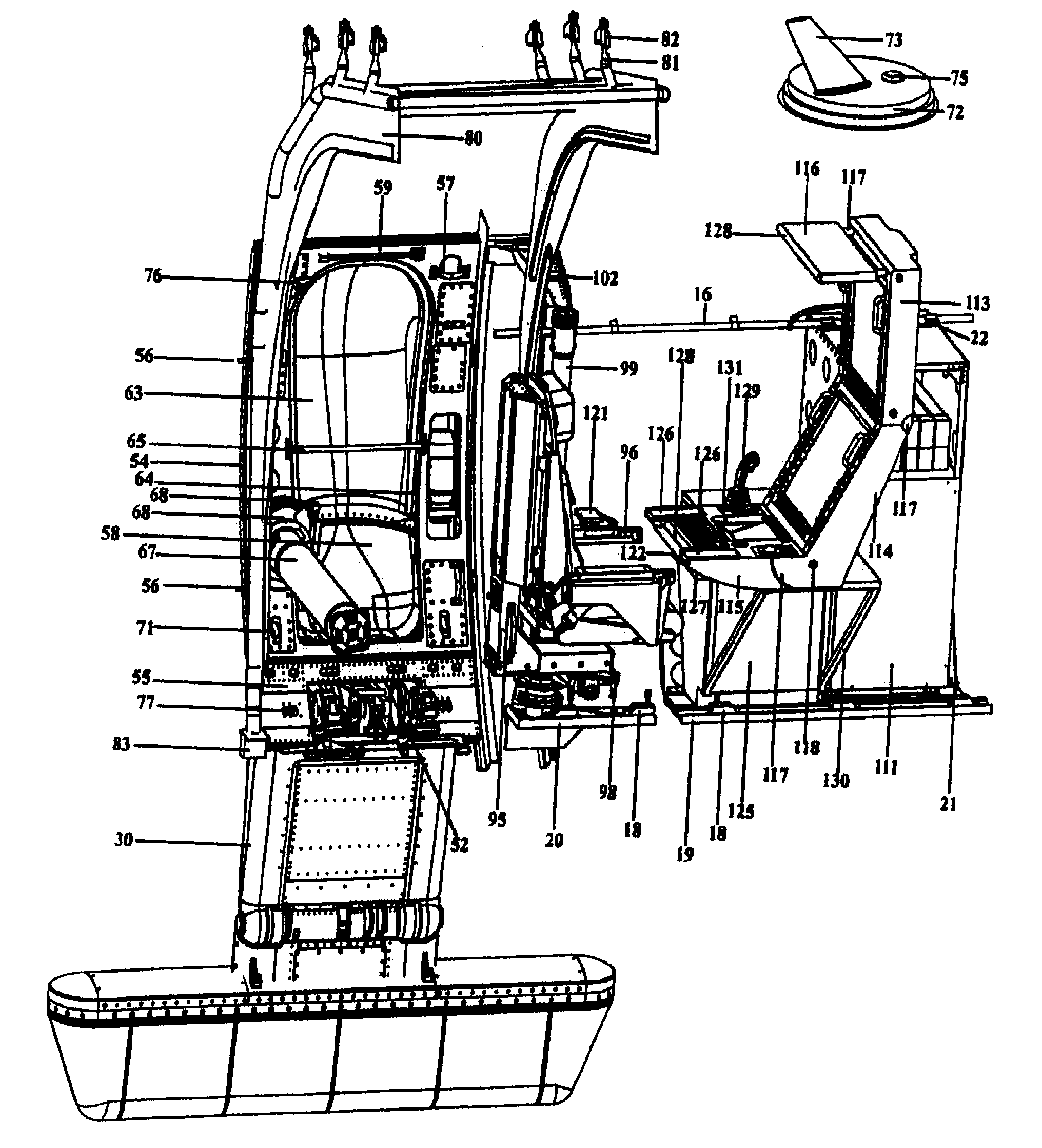
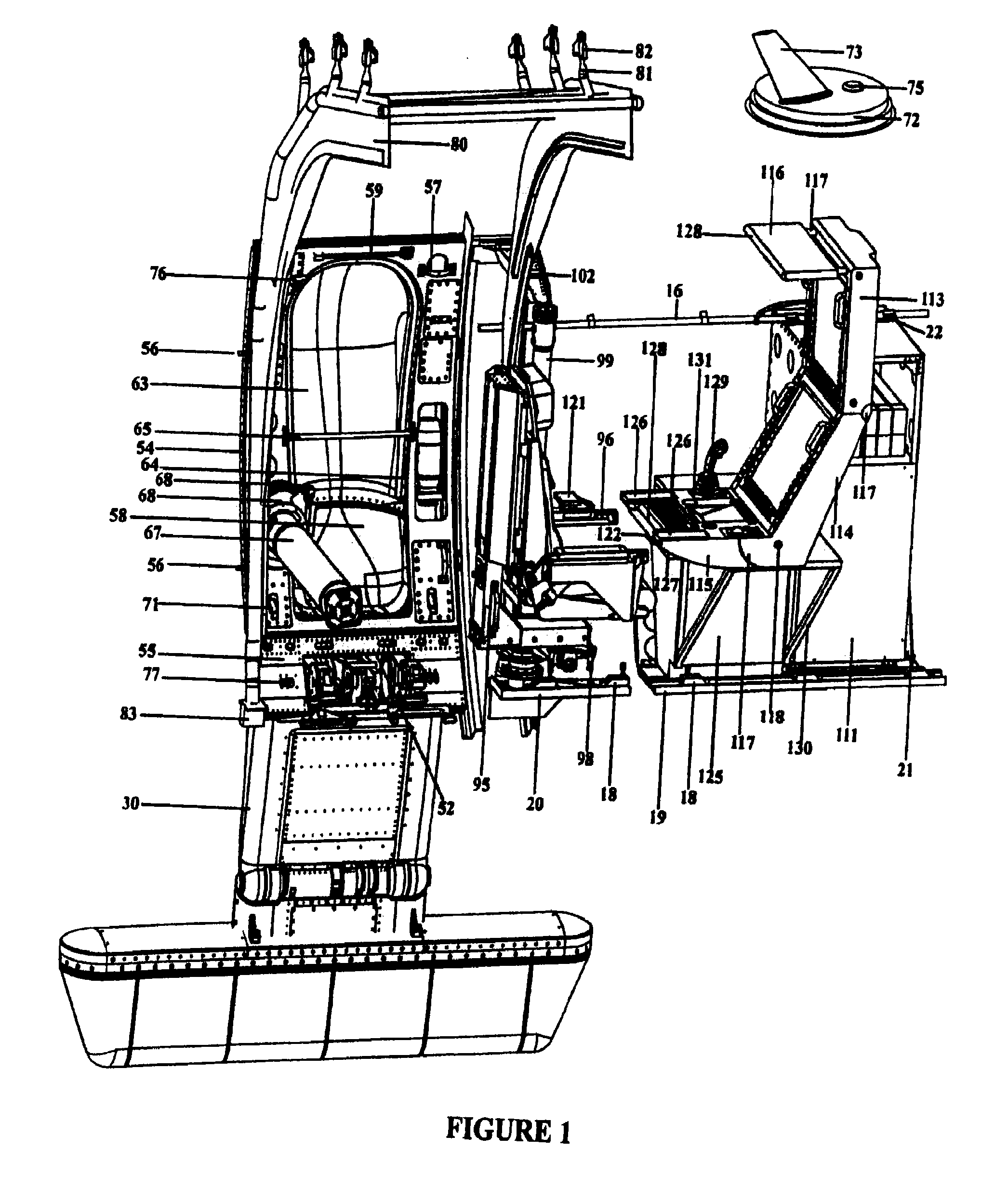
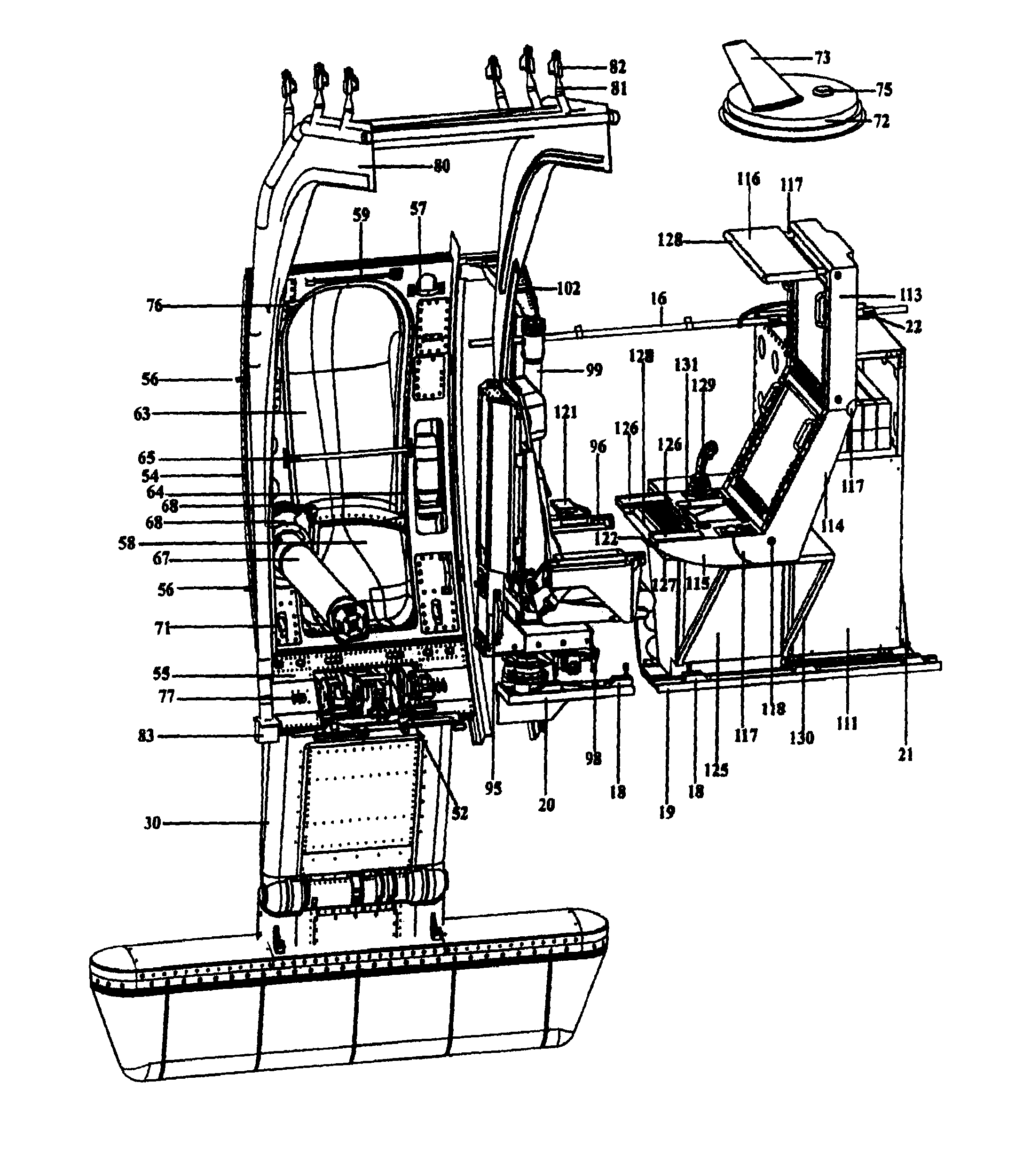
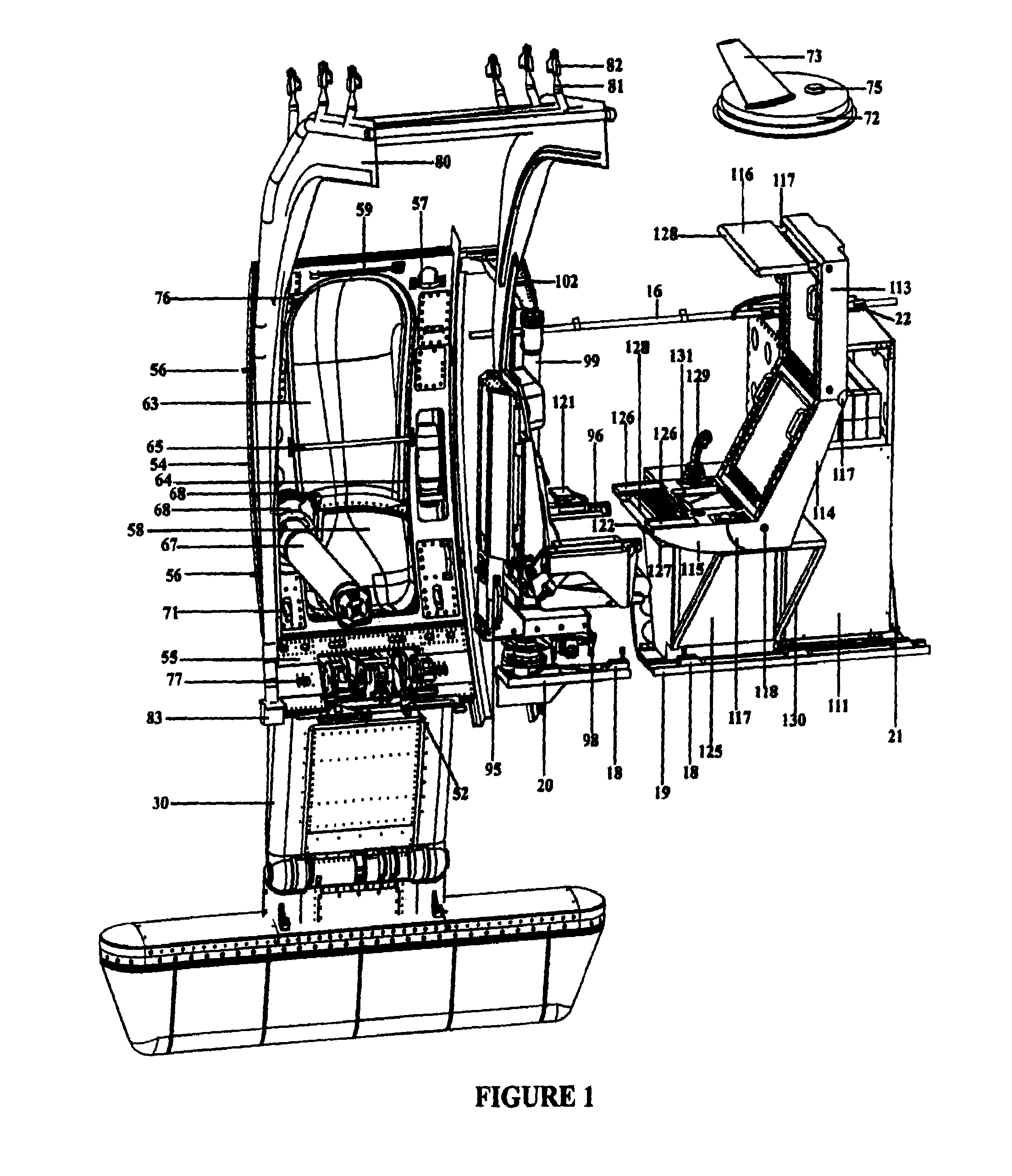
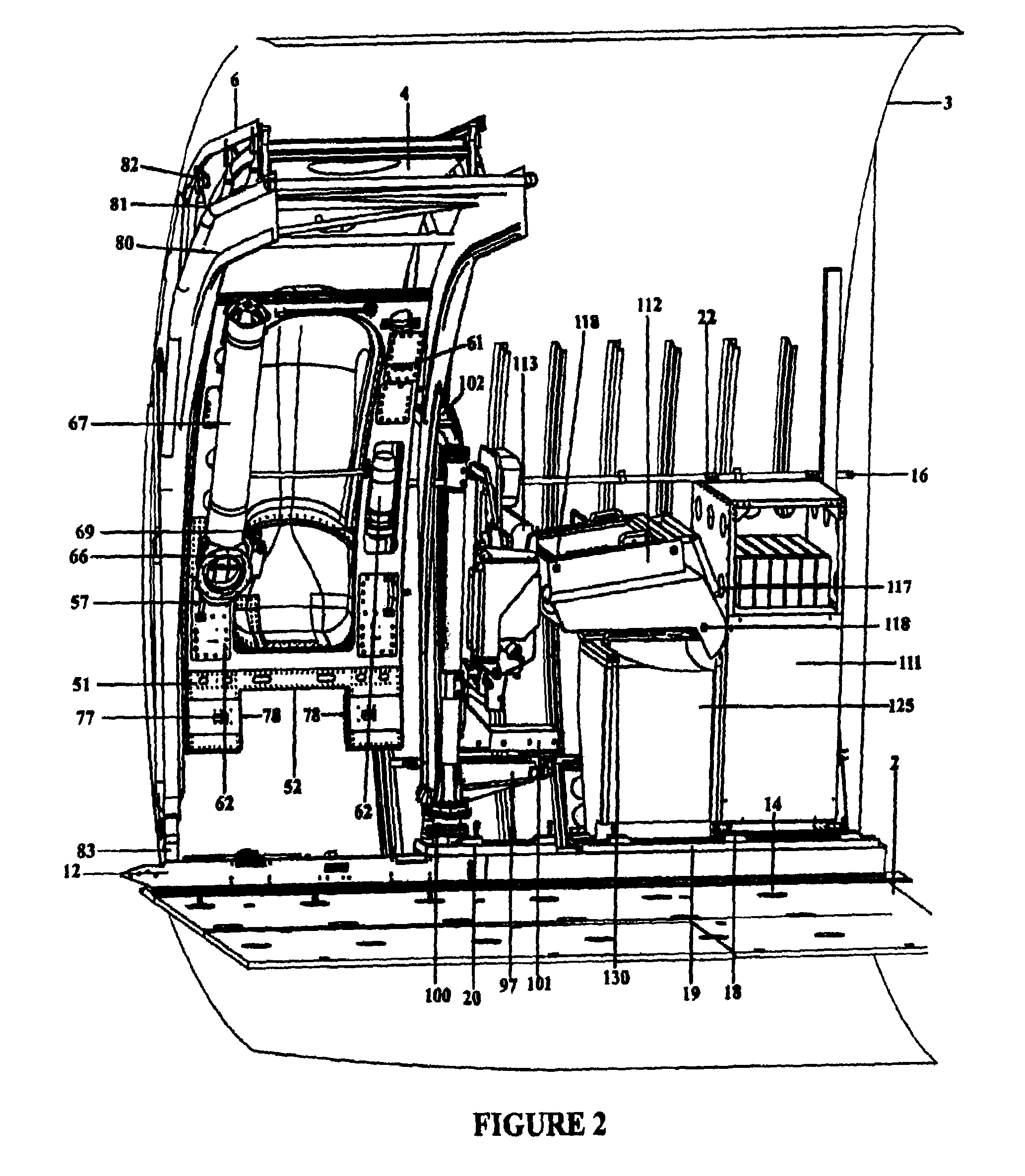
Temporarily installed aircraft observer door plug, chair, sonotube ejection and control system
ActiveUS20100206988A1Quick installationCost-effective utilizationSeating arrangementsMilitary adjustmentSeat beltMissile defense
The system and apparatus of the present invention is generally comprised of a non-dedicated, temporarily installed, aircraft observer bubble door, chair, sonotube ejection system, mission electronics LRU rack and workstation assembly which are affixed to the Air Deployment System (ADS) rails, cargo tie down “D” rings, seat belt restraint ring bolt sockets, and litter bar of a host aircraft, thereby precluding the requirement for dedicated airframe modifications. One embodiment of the present invention also utilizes a multi-axis, articulated, foldable chair temporarily installed in conjunction with a segmented or one piece pressurized observer bubble door plug and door retraction system. The door plug assembly is designed to accommodate the simultaneous use of a sonotube stores launch system, a missile defense system, and an observer bubble window. The door plug also accommodates fitment around the envelope of a special mission strut which extends through the interior to the exterior of the host aircraft beneath the door plug's lower periphery. The door plug is also moveably mounted within a temporary retraction rail system which interfaces mechanically to the permanent door retraction rails and the aircraft floor or ADS rail system. When the host aircraft is not equipped with an ADS rail system, the retract rails, chair stanchion, mission electronics racks, and workstation assemblies are mounted to an adaptive floor plate (AFP) which can be modified to interface with various cargo floor “D” rings, or other cargo tie down mechanisms and bolt patterns such that several types of dissimilar aircraft can utilize the subject apparatus either with or without ADS rails installed. Once installed the subject apparatus can be stowed outboard of the fuselage cargo transit envelope to permit use of the ADS rail system in-flight, without affecting normal air drop operations, crew egress, the flight performance envelope, or emergency procedures of the host aircraft.
Owner:1281329 ALBERTA
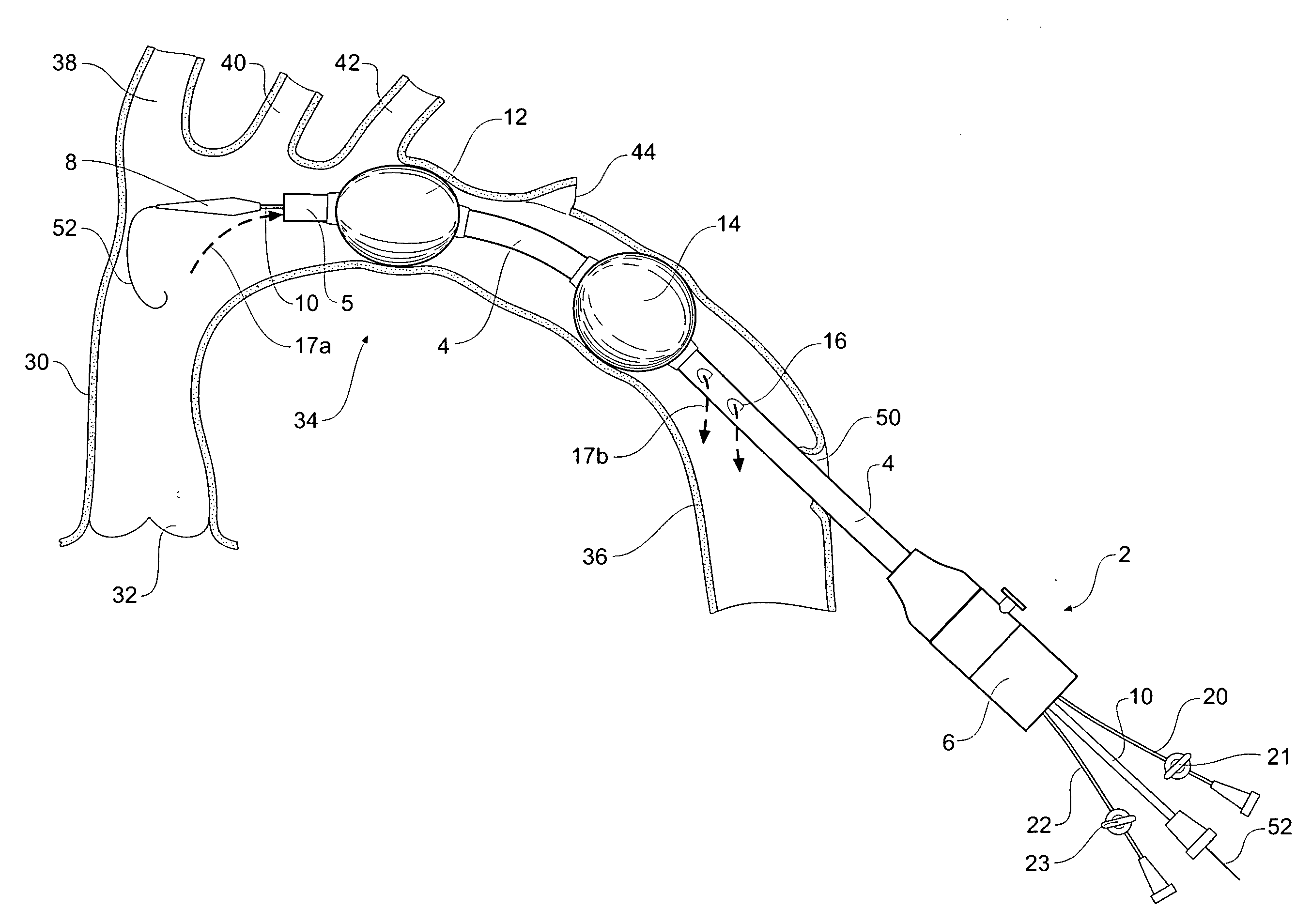
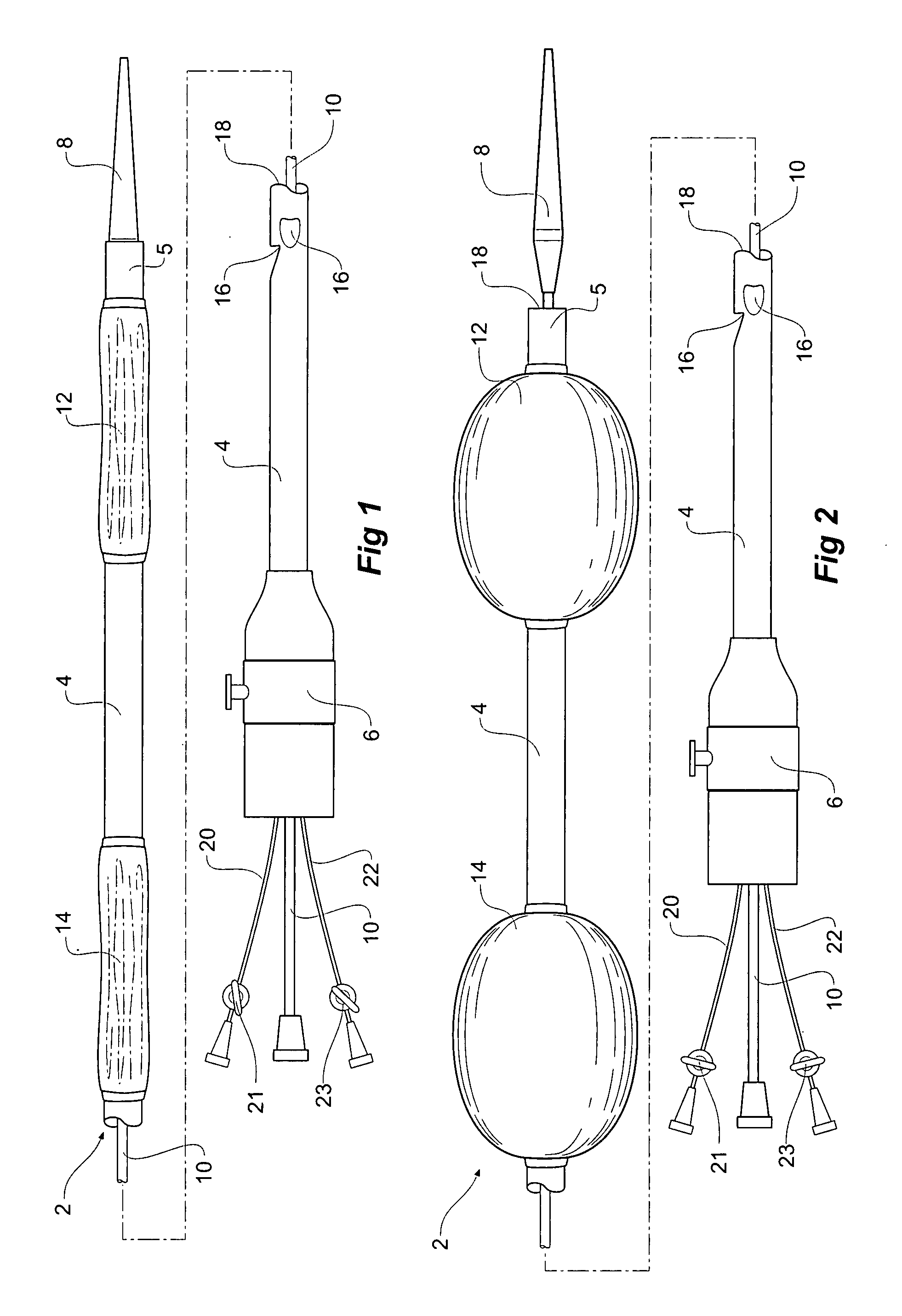
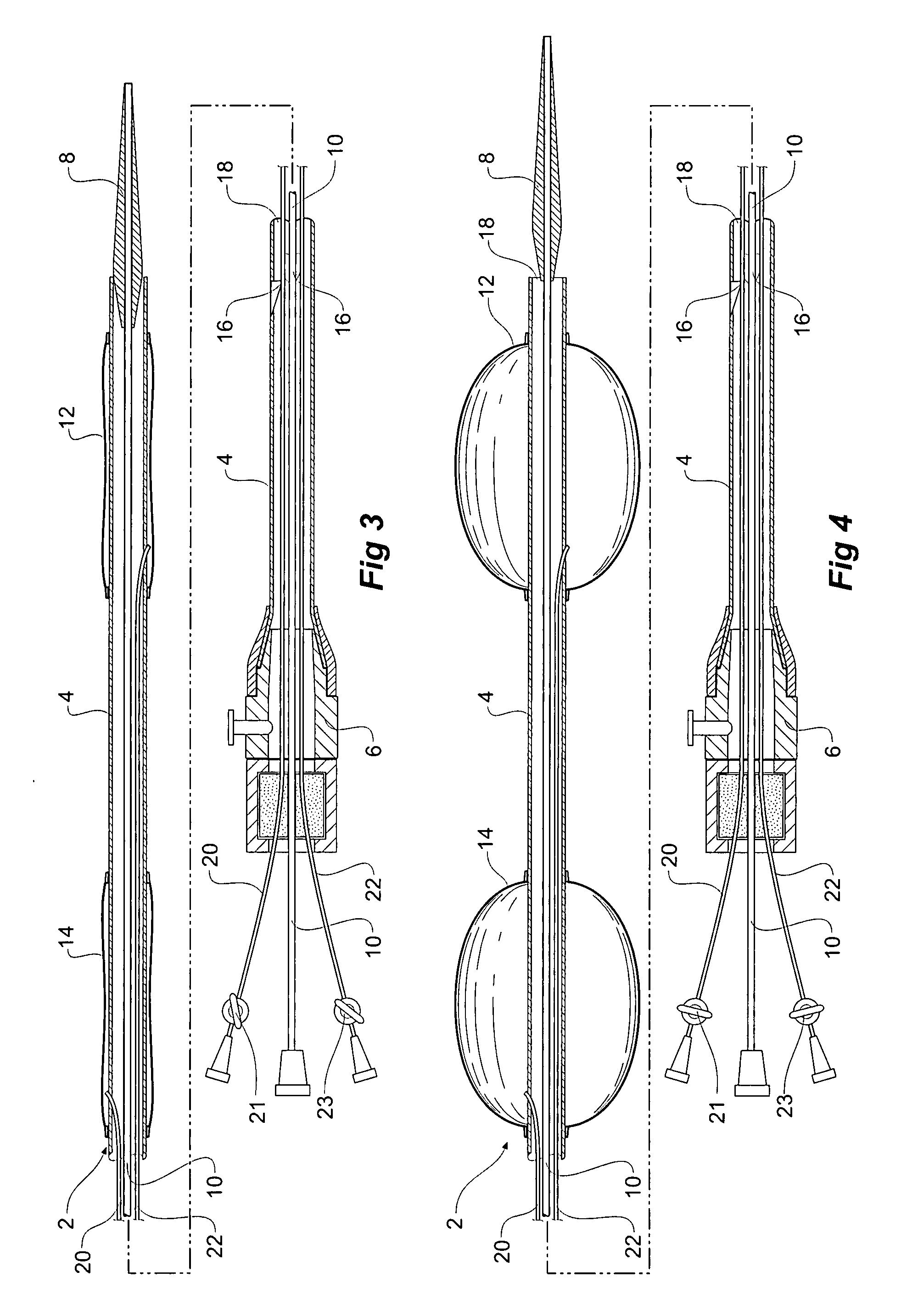
Emergency transection device
An emergency transection intervention device has an elongated catheter ( 4 ) with a movable nose cone dilator ( 8 ) temporarily closing off the first end of the elongate catheter, a haemostatic seal ( 6 ) on a second end of the catheter and closing off the second end of the elongate catheter. First and second inflatable balloons ( 12, 14 ) are spaced apart on the elongate catheter, and there is an aperture ( 16 ) in the elongate catheter between the balloons and the haemostatic seal. The emergency transection intervention device can be deployed into a blood vessel of the human or animal body, during an emergency procedure for instance, with the balloons positioned either side of a damaged portion of the vessel and the balloons inflated such that a region of the vessel between the balloons is isolated. The nose cone dilator can then be advanced to allow blood flow through the elongate catheter and exit through the aperture in the elongate catheter to bypass the damaged portion of the vessel during repair.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
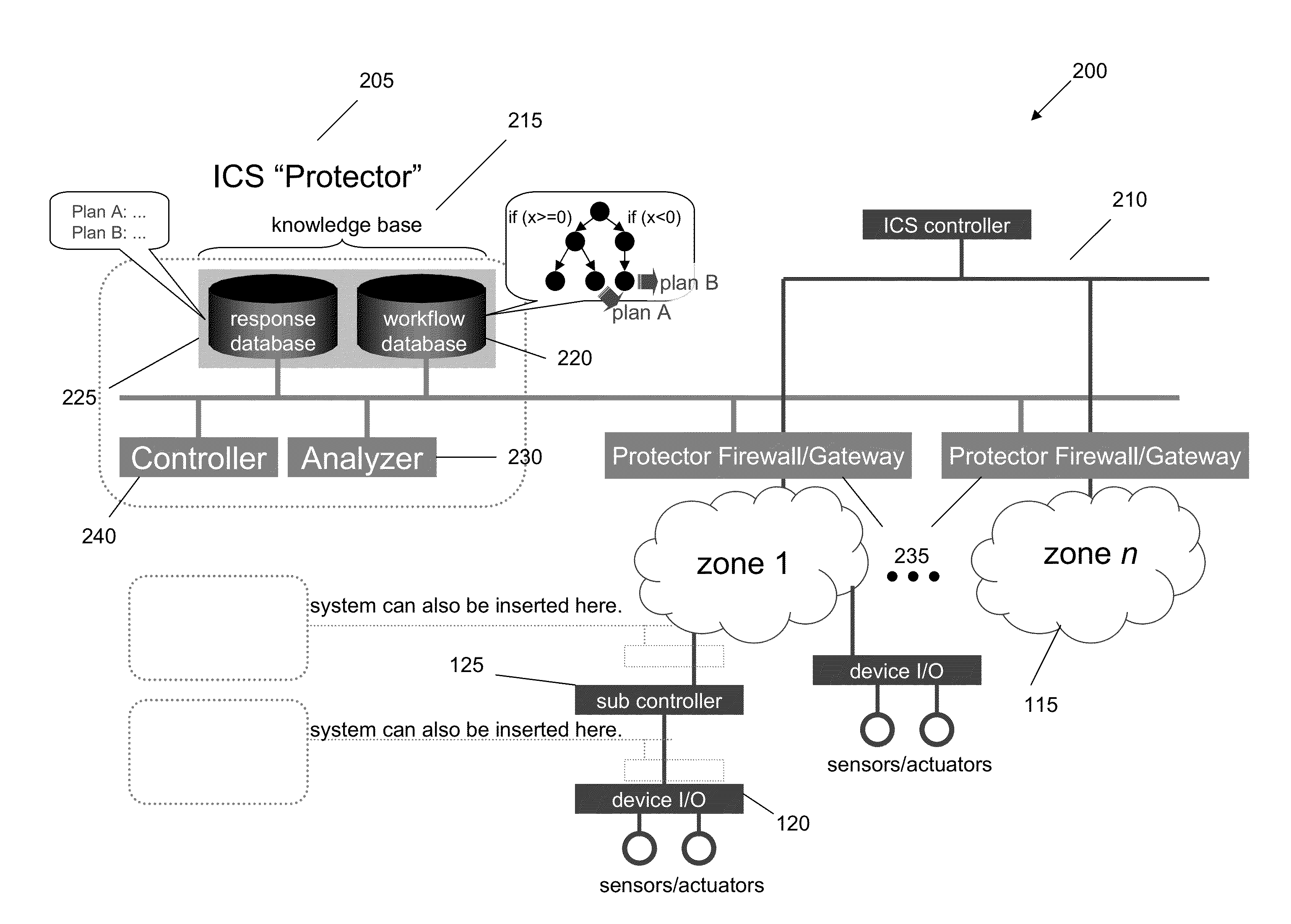
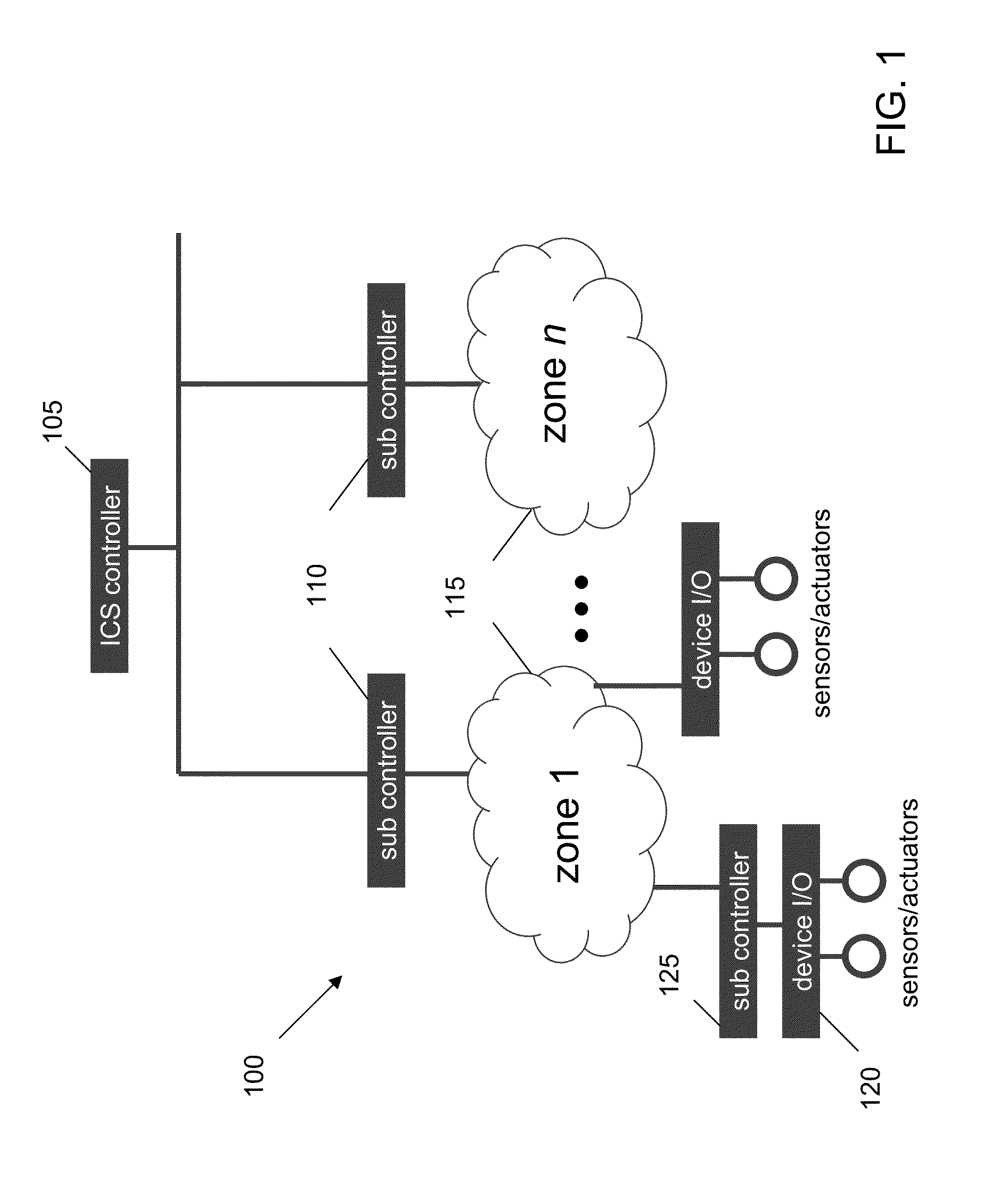
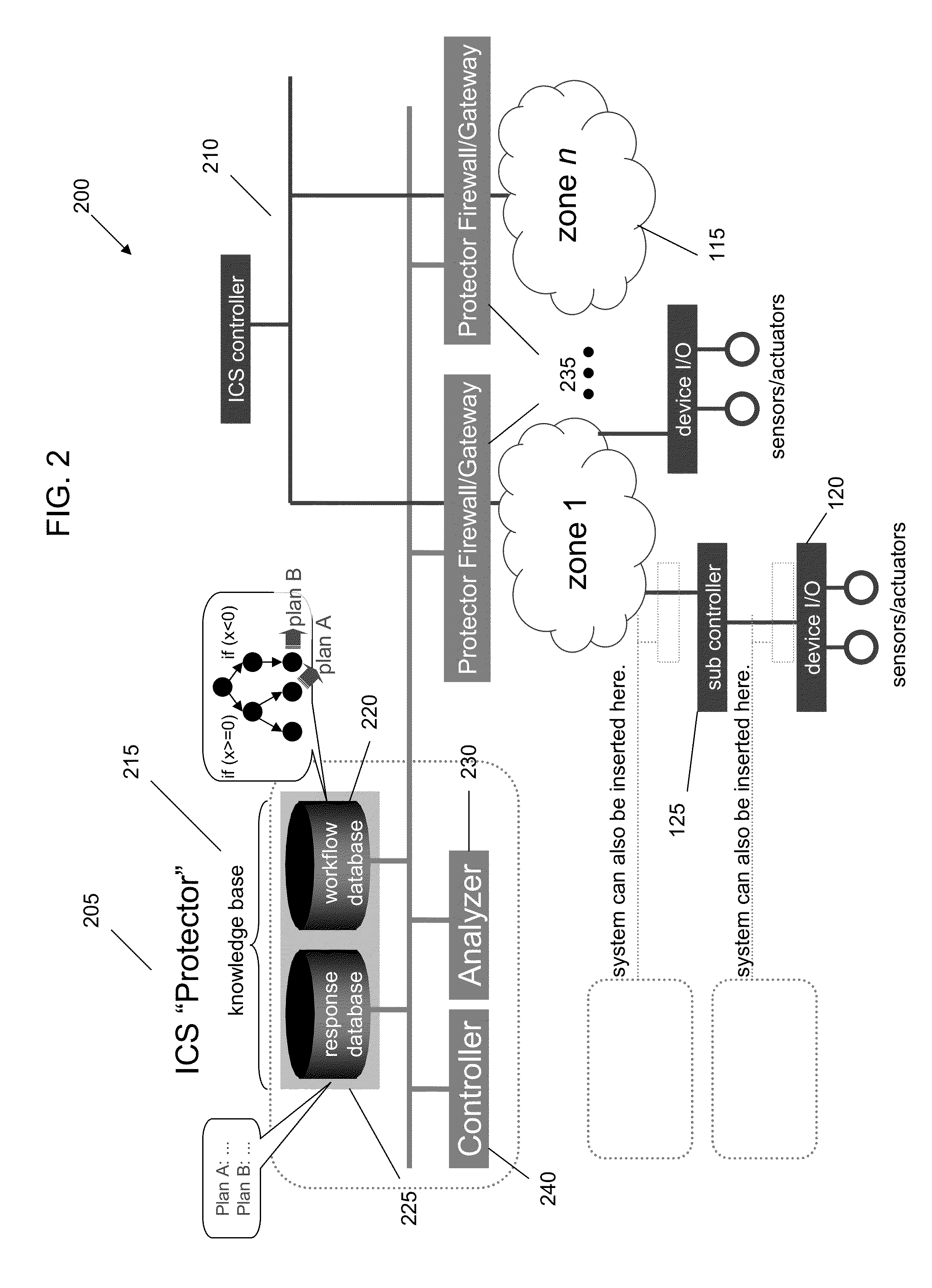
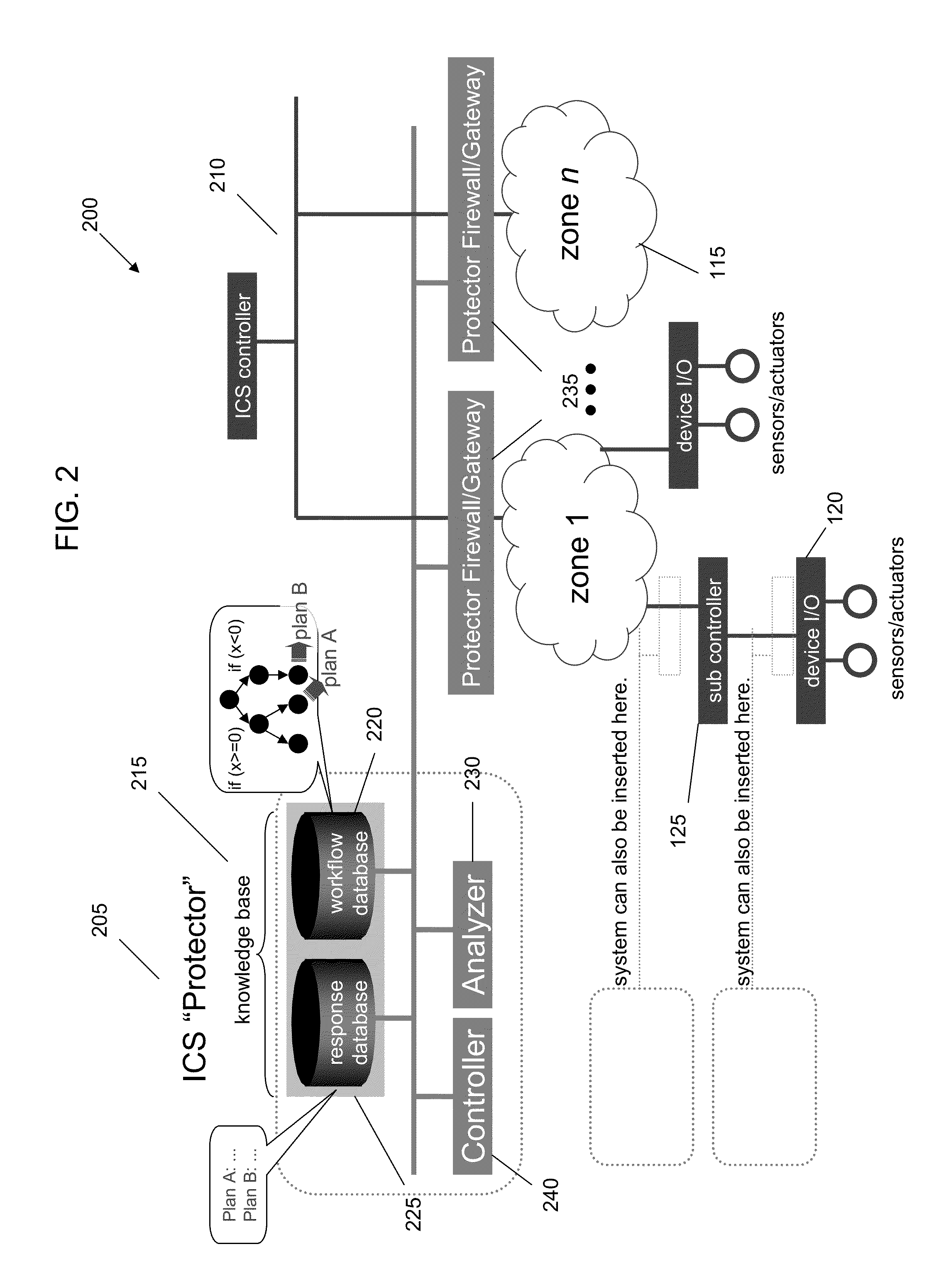
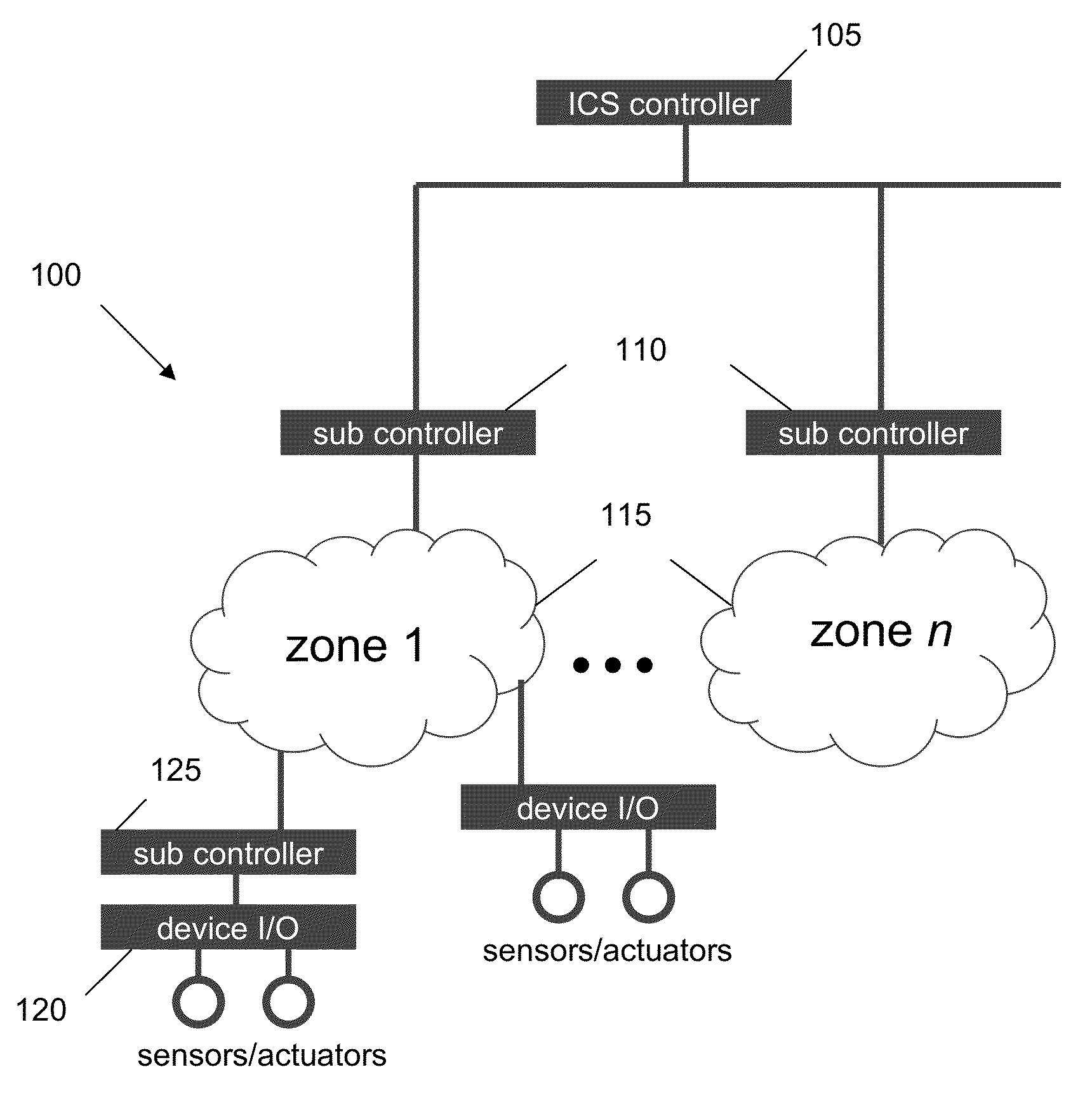
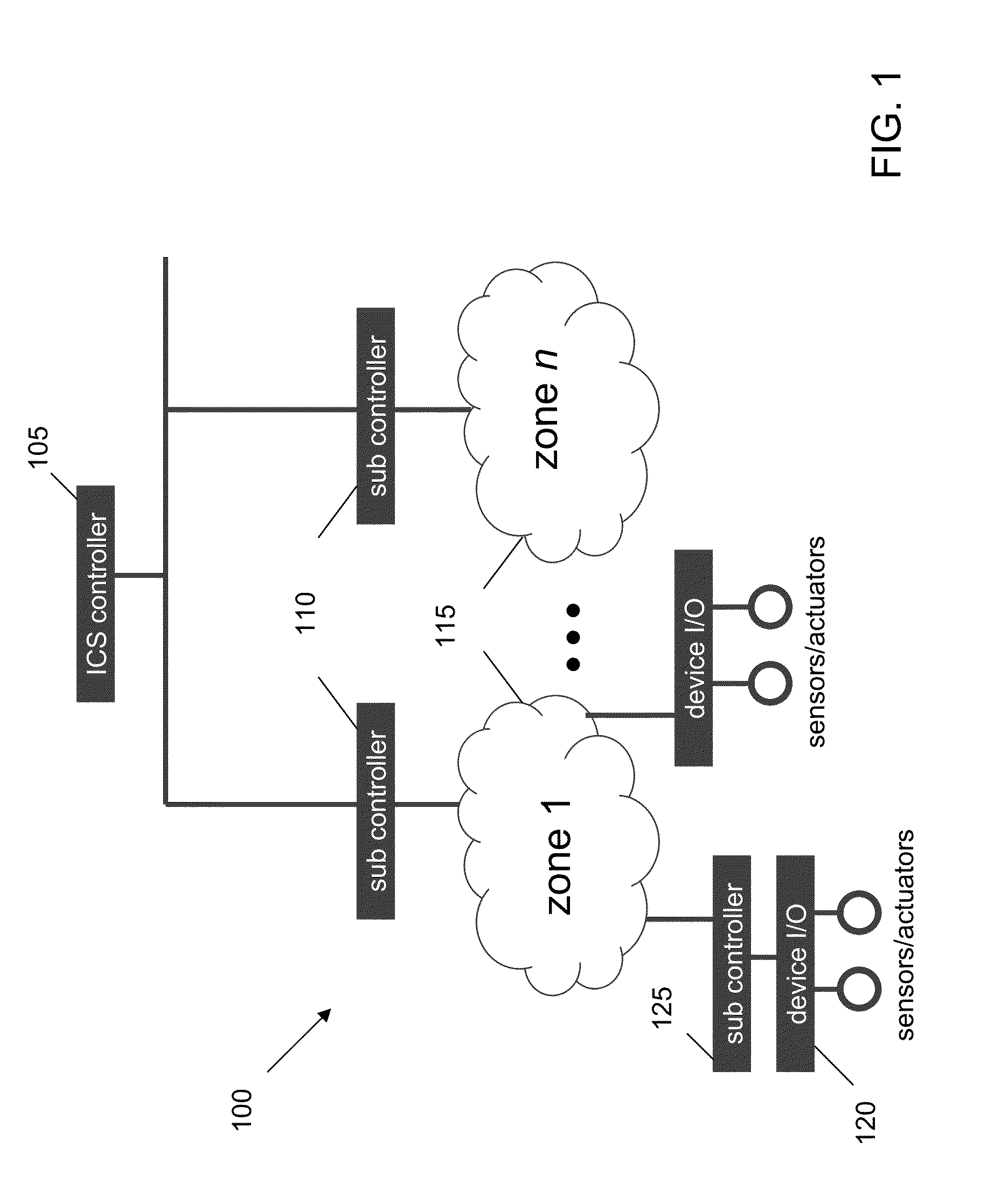
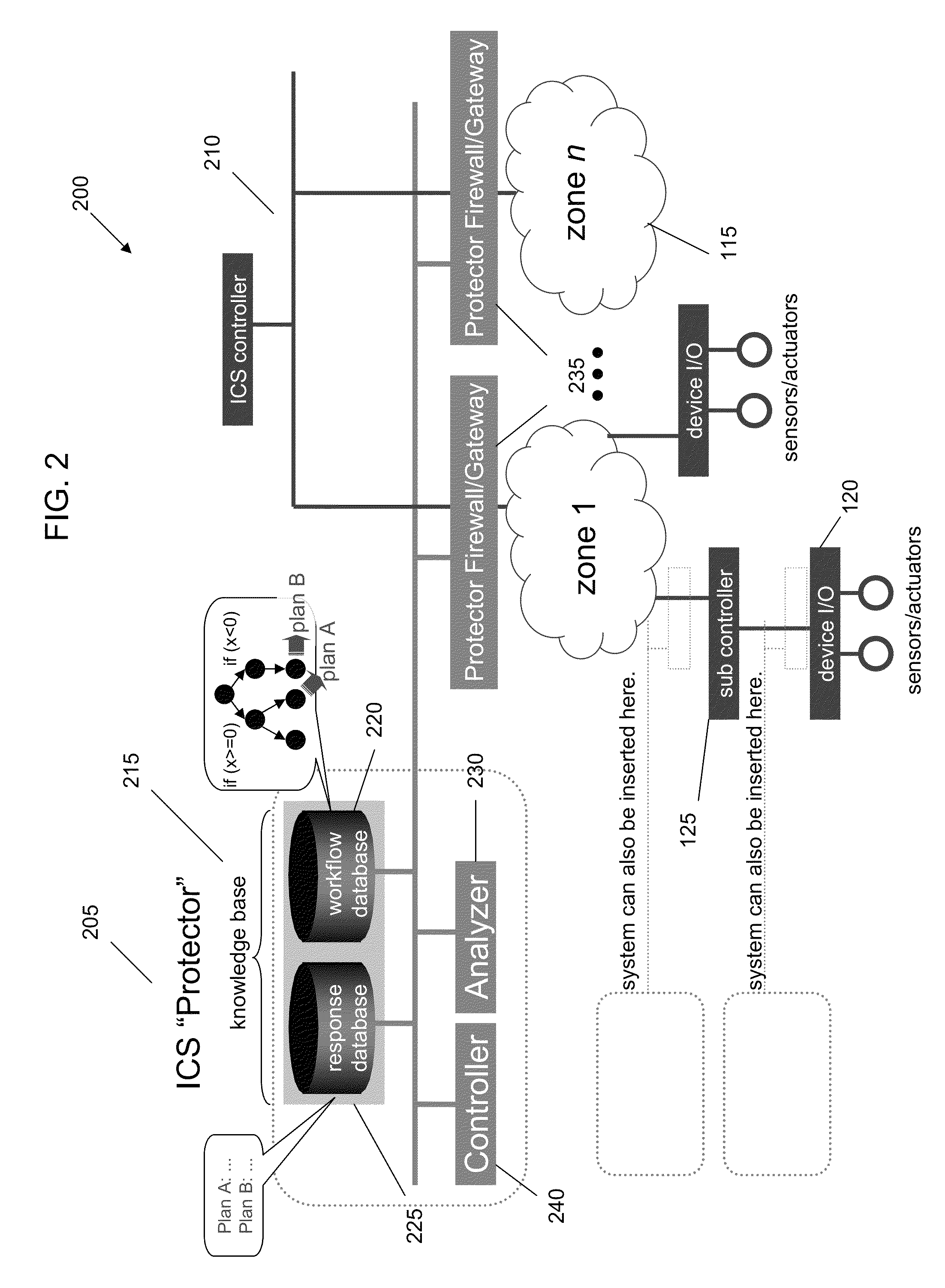
Detecting and Combating Attack In Protection System of an Industrial Control System
InactiveUS20130212669A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionEmergency procedureProtection system
A method for detecting and combating an attack in an industrial control system includes sending a command stream from a protection network of an industrial control system to at least one zone, the command stream comprising at least one command; concatenating the at least one command into at least one sequential command package comprising units or work; passing the at least one sequential command package to a crypto hash generator; generating at least one of unit of work hash codes or sequence hash codes; comparing the generated hash codes against a database of existing valid unit of work hash codes and sequence hash codes; and if a command stream fault is detected, generating an alert and accessing a database comprising emergency procedures.
Owner:IBM CORP
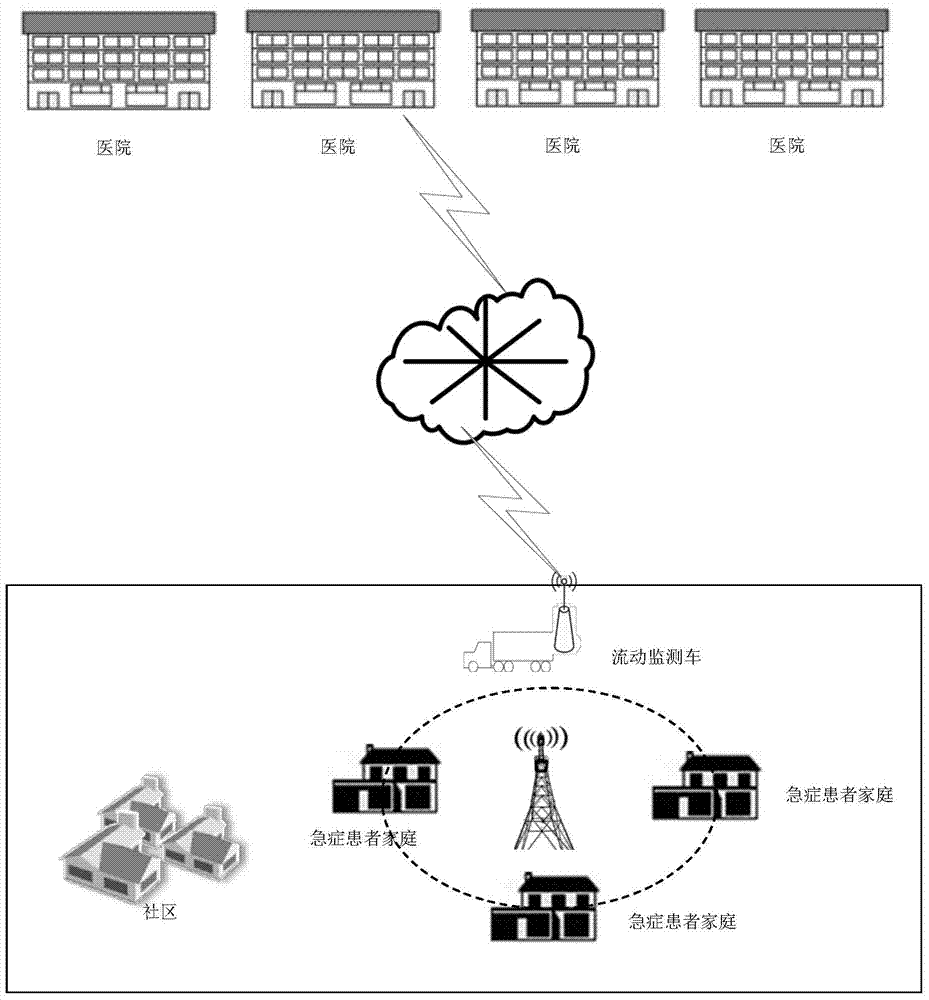
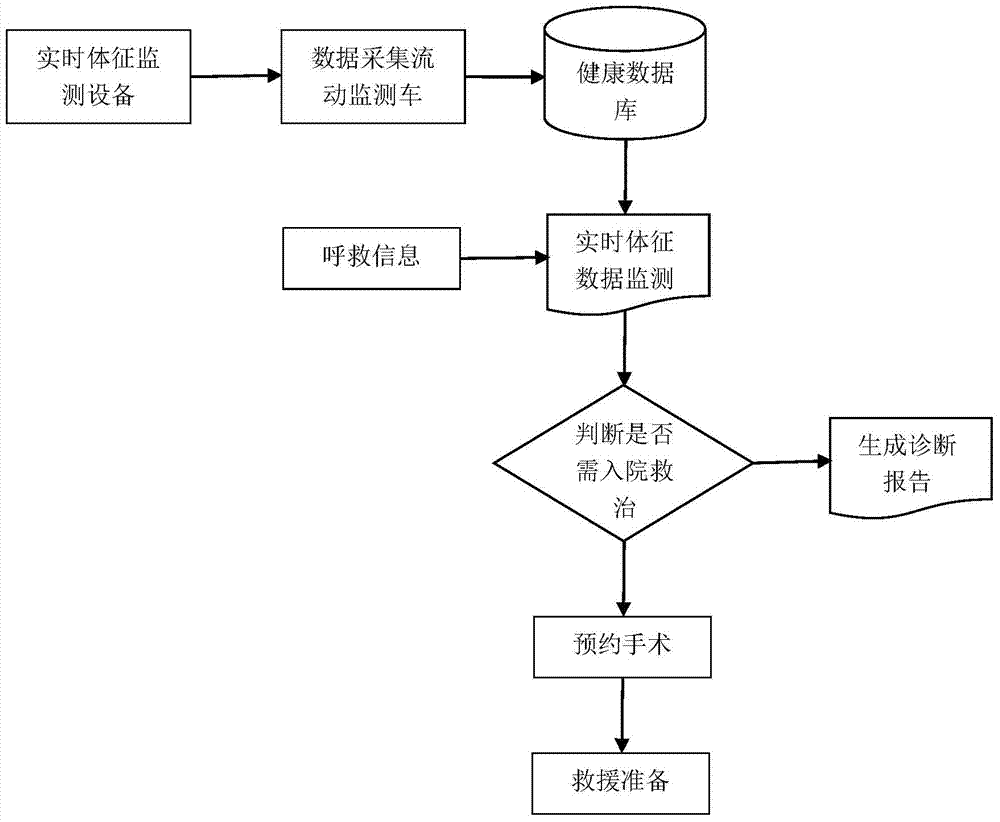
Emergency patient emergency rescue system based on mobile monitoring car
InactiveCN103942454AEarly Access to Physiological DataReduce mortalitySpecial data processing applicationsMedical recordEmergency rescue
The invention discloses an emergency patient emergency rescue system based on a mobile monitoring car. The mobile monitoring car is connected with a community user medical device and a hospital information system through a wireless network, obtains sign information of monitored users and related information of hospitals in real time, and monitors the health states of the users; the mobile monitoring car instantly enter the emergency rescue state when the users send out distress call information or when the medical device for monitoring the users automatically gives an alarm, so that the patients are automatically positioned and tracked in real time; the mobile monitoring car obtains information of the patients through electronic medical records, comprehensively evaluates all collaboration hospitals for the patients who need to be admitted to hospitals, sends the patients to different hospitals to be treated, orders operations and sends all the information of the patients to the hospitals, so that medical workers can make rescue preparation in advance. Doctors and experts in the hospitals can know illness states of the patients and participate in emergency work as early as possible, so that emergency procedures are optimized, and the therapeutic effect is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Improvements to body area networks
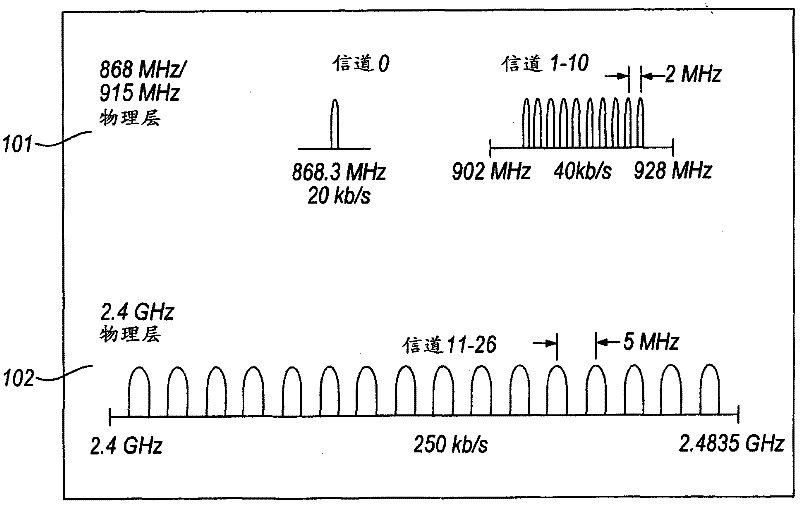
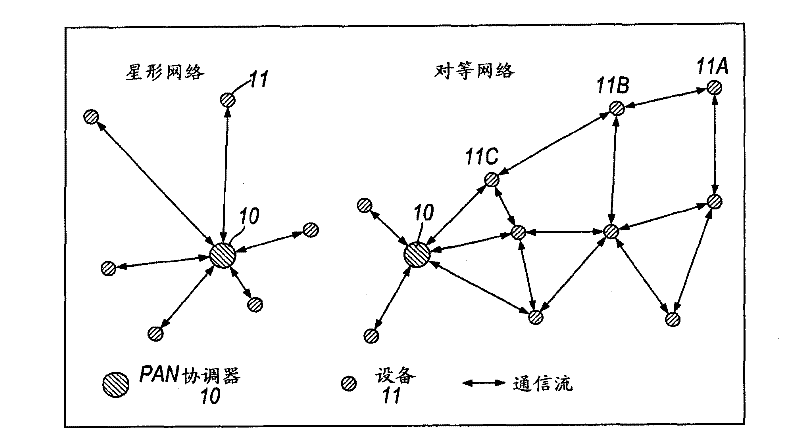
A method of declaring an emergency condition in a wireless sensor network, the wireless sensor network comprising a plurality of devices (10, 11, 12) including sensors (11) arranged for monitoring at least one living body or other entity, the method comprising steps of: sensing a value of parameter related to the living body by one of the sensors (11); wirelessly transmitting information by said sensor to another device (10) in the network; determining existence or non-existence of an emergency condition affecting said living body by using said sensed value or said transmitted information; and declaring existence or non-existence of the emergency condition to at least one other device (e.g. 10) in the network. The determining step may be carried out in any of the sensor (11), a coordinator (10) of the wireless sensor network, or a central monitor (12) in communication with the coordinator. The declaring step may be performed by setting a frame control field of a frame-based wireless sensor network to a value predefined as denoting an emergency frame. An acknowledgement frame may be used by the recipient to acknowledge receipt of the emergency declaration, after which an emergency procedure is followed. The emergency procedure can involve, for example, increasing the bandwidth allocated to the sensor so as to ensure reliability of subsequent information from the sensor. The method may be applied, for example, to monitoring of patients in a hospital using MBANs operating in accordance with IEEE 802.15.6.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
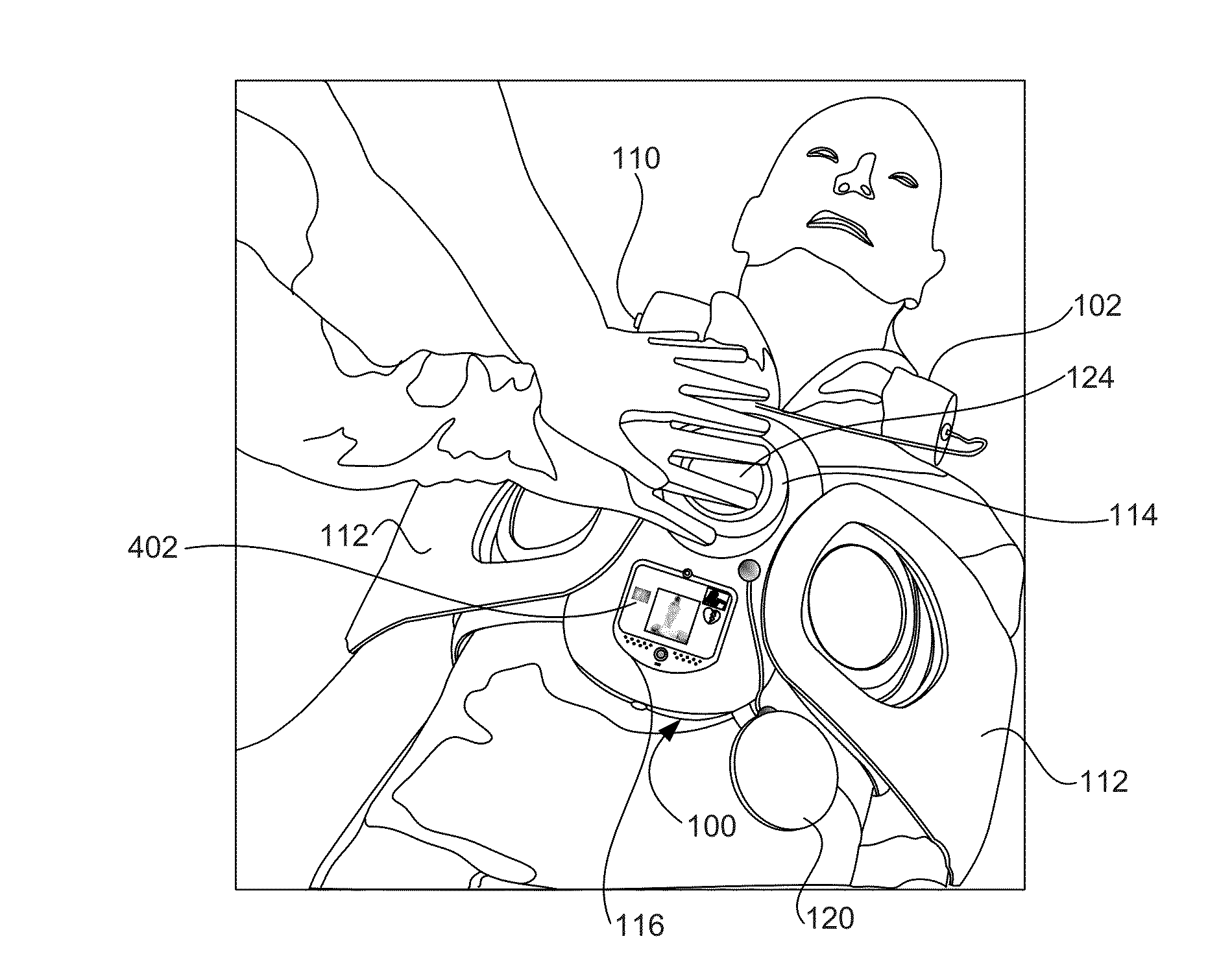
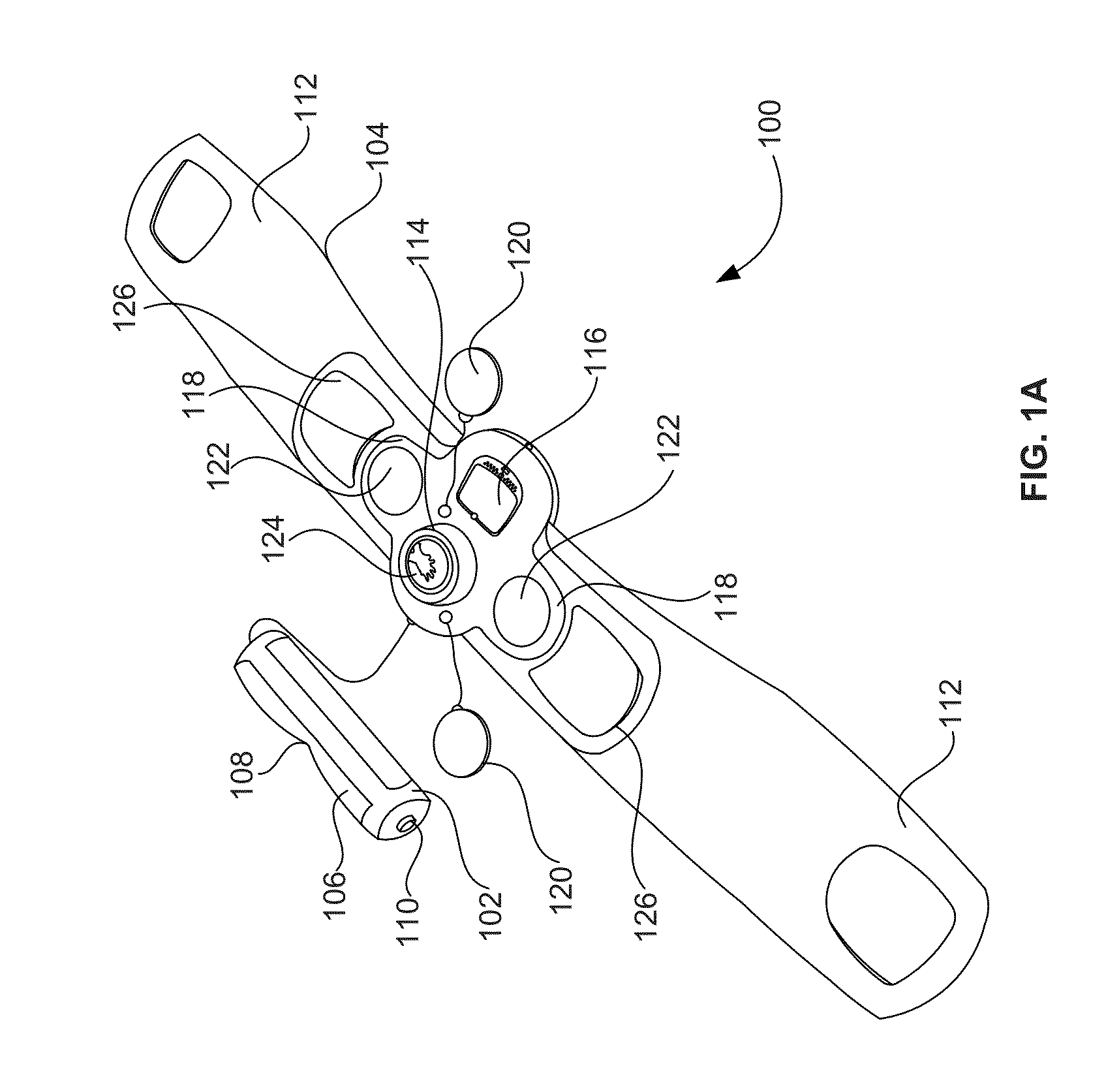
Combined Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Apparatus and Method
A combined cardio pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) system for performing an emergency procedure over the clothing of a patient is provided. The system includes a spinal support rest having a cushion that accommodates a neck portion of the patient, a compression pad operatively connected to the spinal support rest and is adapted to be placed over the patient such that the compression pad is aligned above the heart and chest of the patient. A first arm strap and a second arm strap operatively connected to the compression pad. A power button automatically dials an emergency number to contact a medical professional. An interactive communication unit activates a two way real time video conference with the medical professional on the display to receive a set of instructions from the medical professional in real time to enable a user to perform the emergency procedure on the patient.
Owner:MADANAT SAHAR ANIS
Electrical device power management
ActiveUS20130066153A1Many changeConfidenceBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesEmergency procedureElectrical battery
An electrical device includes a memory storing a value indicative the remaining available rated capacity of one or more batteries. The stored value is changed in use to reflect reducing capacity. The initial stored value is chosen so that there is a very high (e.g. >99.9%) confidence that the one or more batteries will provide at least the capacity indicated by the initial stored value. This reduces the chance of failure during emergency procedures. The one or more batteries may be integral to the electrical device. An override facility is provided.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
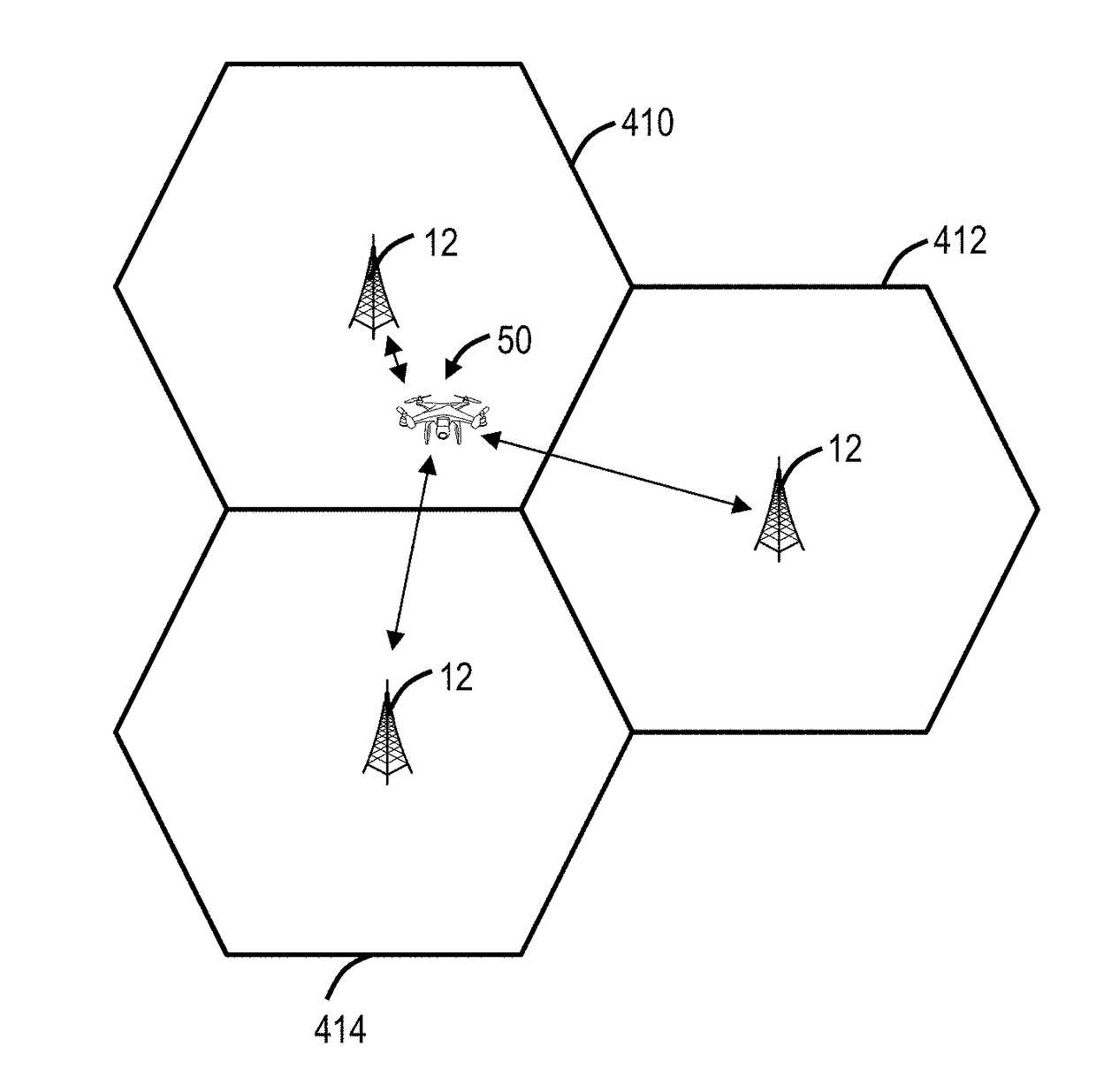
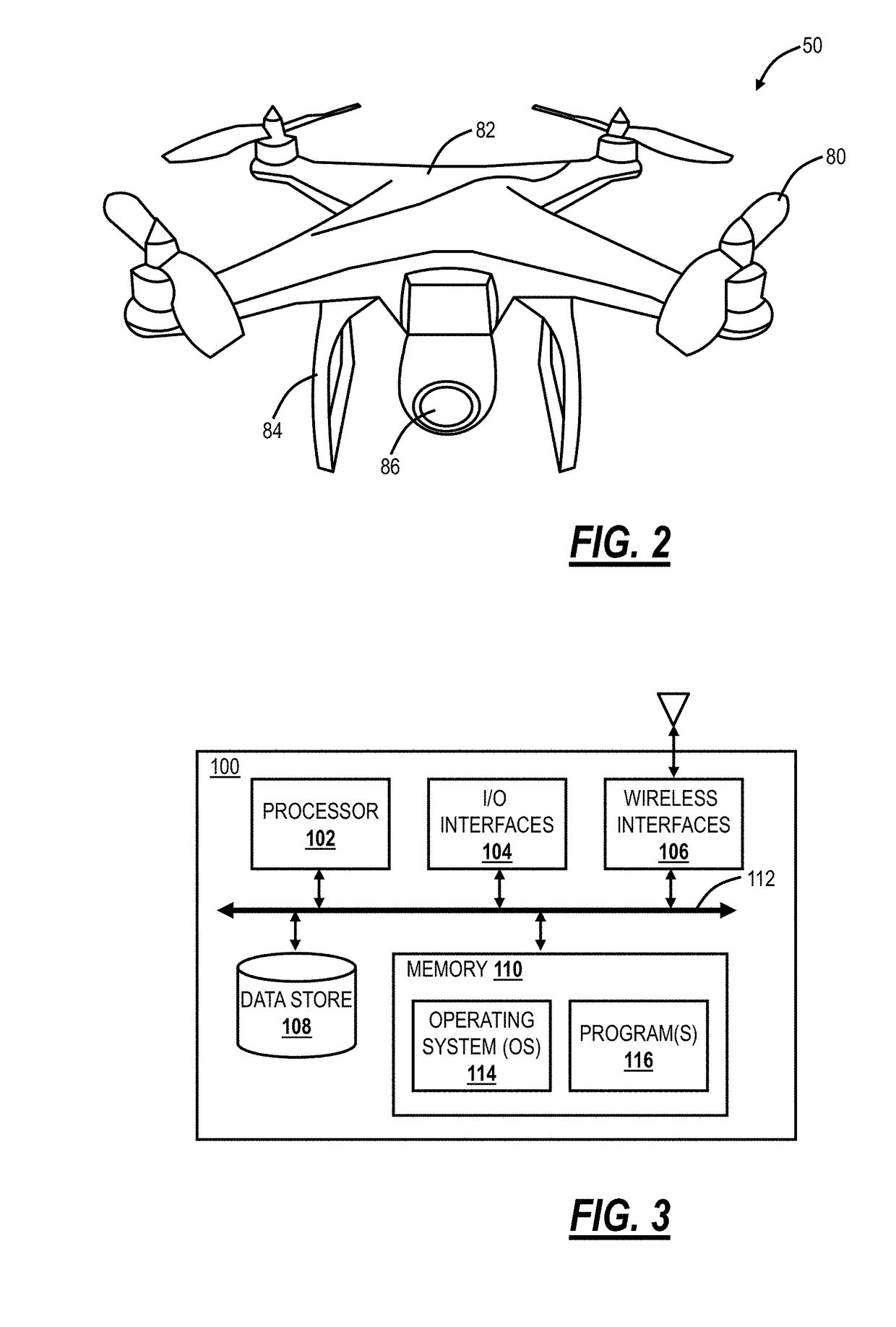
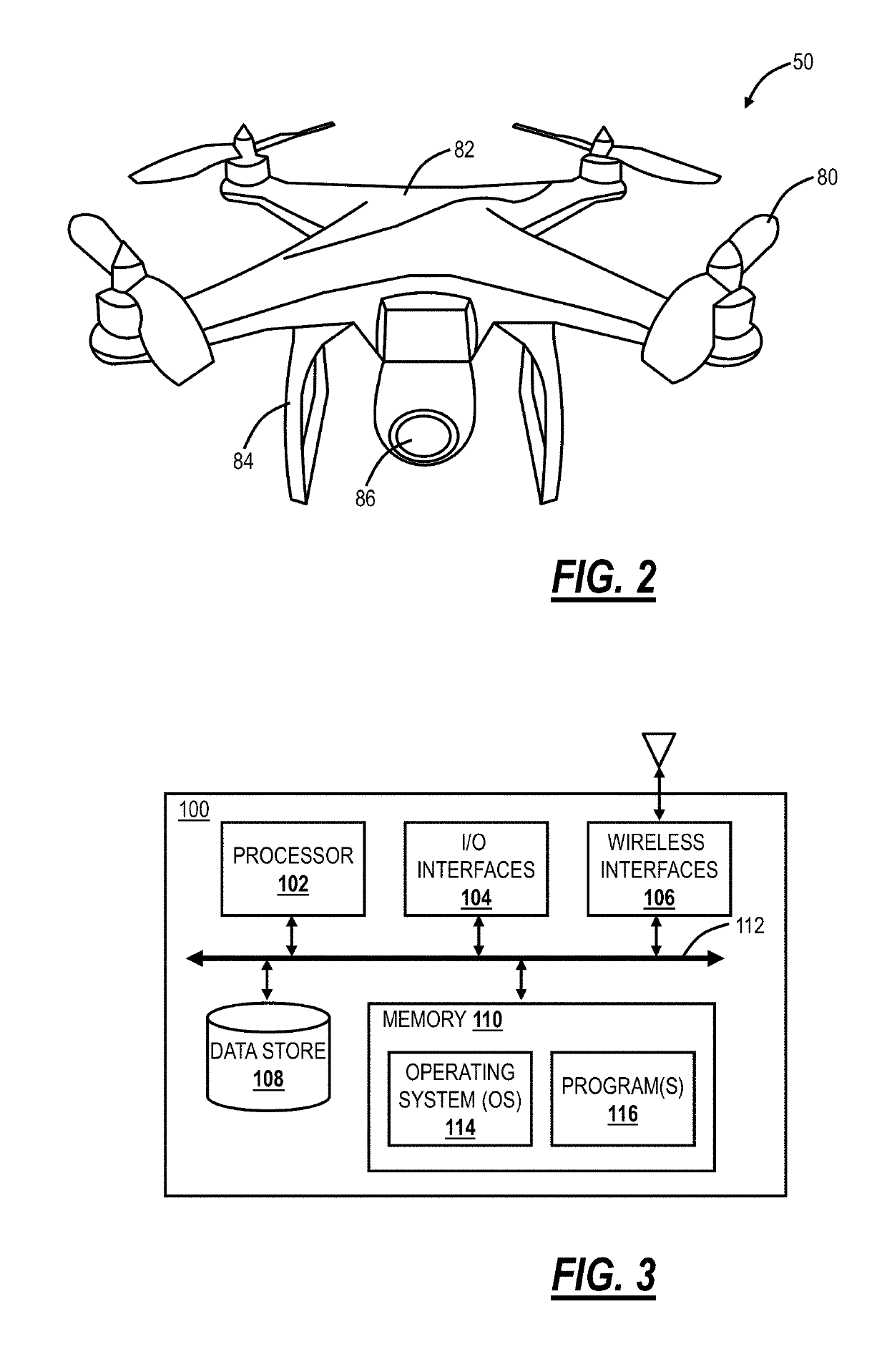
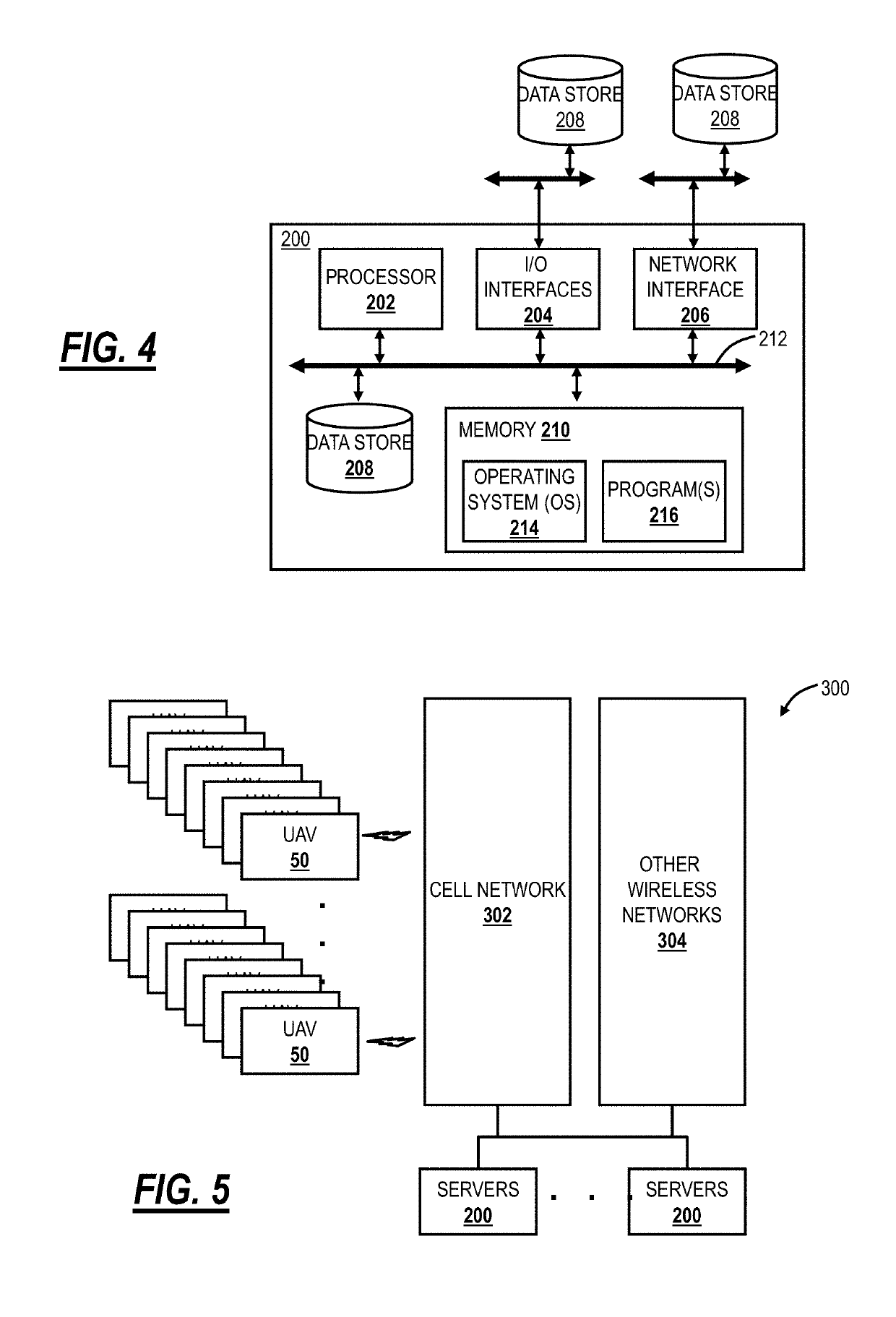
Drone network switchover between wireless networks
ActiveUS20180026708A1Avoid flyingUnmanned aerial vehiclesParticular environment based servicesEmergency procedureWireless mesh network
Systems and methods for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) network switchover and emergency procedures, implemented by a UAV includes communicating to an Air Traffic Control (ATC) system via a primary wireless network; receiving and storing emergency instructions from the ATC system; detecting communication disruption on the primary wireless network to the ATC system; responsive to the detecting, switching to a backup wireless network to reestablish communication to the ATC system; and, responsive to failing to reestablish communication to the ATC system via the backup wireless network, implementing the emergency instructions.
Owner:METAL RAPTOR LLC
Battery pack and electrical device with demountable battery pack
A battery pack (10) for an electrical device (60) has a cover portion which forms part of the assembled electrical device (60) and a seal (78) for forming a waterproof seal between the battery pack (10) and the electrical device (10). Thus, every new battery pack can form a fresh seal with the electrical device (60), allowing effective waterproofing. A battery pack (10) for an electrical device (60) includes a memory storing a value indicative the remaining available rated capacity of the battery pack (10). The stored value is changed in use to reflect reducing capacity. The initial stored value is chosen so that there is a very high (e.g. >99.9%) confidence that the battery pack will provide at least the capacity indicated by the initial stored value. This reduces the chance of failure during emergency procedures. An override facility is provided. A laryngoscope (60) comprising a handle comprising a demountable battery pack (10) comprising one or more batteries (20) and an arm (49) operable to retain a demountable laryngoscope blade.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Detecting and Combating Attack In Protection System of an Industrial Control System
InactiveUS20130212078A1Digital data processing detailsTransmissionIndustrial control systemEmergency procedure
A method for detecting and combating an attack in an industrial control system includes sending a command stream from a protection network of an industrial control system to at least one zone, the command stream comprising at least one command; concatenating the at least one command into at least one sequential command package comprising units or work; passing the at least one sequential command package to a crypto hash generator; generating at least one of unit of work hash codes or sequence hash codes; comparing the generated hash codes against a database of existing valid unit of work hash codes and sequence hash codes; and if a command stream fault is detected, generating an alert and accessing a database comprising emergency procedures.
Owner:IBM CORP
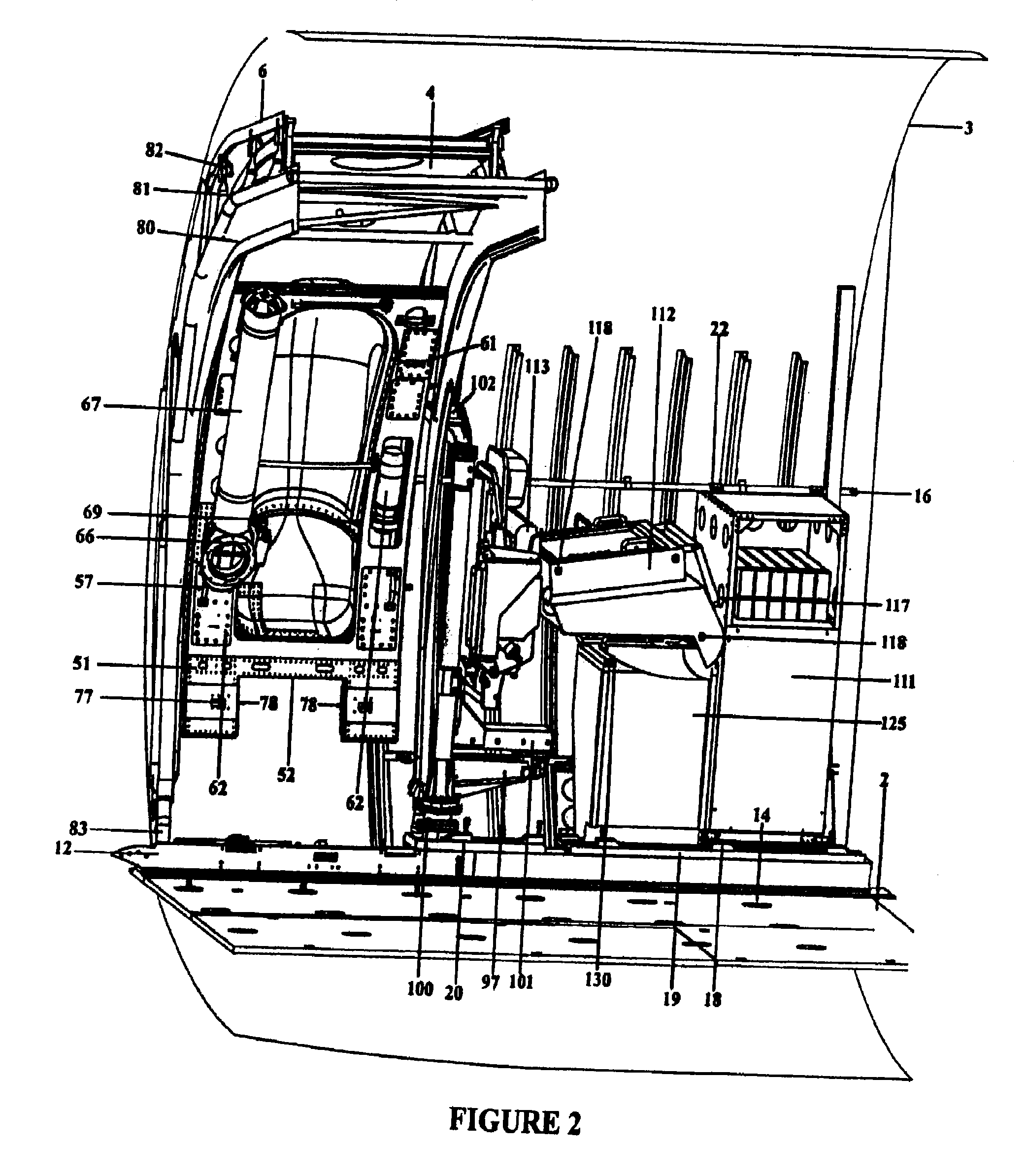
Aircraft based non-dedicated special mission pod mounting apparatus
ActiveUS20100206992A1Avoid insufficient thicknessMilitary adjustmentFreight handlingEmergency procedureCam
The system and apparatus of the present invention is generally comprised of a non-dedicated, temporarily installed, airborne special mission payload mounting system which is mechanically interfaced to the Air Deployment System (ADS) rails of a host cargo aircraft. Where a host aircraft does not possess ADS rails, an Adaptive ADS rail section typical of those used by the host aircraft, is installed to the existing cargo floor “D” rings using adjustable cam locks familiar to those skilled in the art of aircraft cargo restraint systems. Where the host aircraft does not have the required cargo “D” rings installed they are then temporarily installed within the “D” ring bolt sockets to enable the aircraft to accommodate mounting of the Adaptive ADS rail section plate. Once the ADS rail section and plate are installed, an Adaptive Mounting Plate (AMP) is placed over the ADS rail section and restrained in position by using multiple bolts, and the cargo “D” rings integral to the ADS rail securing the AMP in position using adjustable cam locks hooked through the ADS rail “D” rings thereby precluding the requirement for a load transfer (torque) pallet, or dedicated airframe modifications. Once the AMP is secured, an articulated or fixed position strut can be attached to it through the opened side doorway without removing the original door. Once the fixed position or articulated strut is bolted to the AMP, a one piece or segmented two piece pressurized door plug indented along its lower periphery to accommodate the protruding form factor of the fixed position or articulated strut is installed within the vacant doorway above the strut providing an airtight seal and thereby permitting pressurization of the aircraft. In-flight dynamic loads exerted upon the various mission payload pods are transferred through the strut to the interior ADS rail by the AMP and to various cargo “D” rings located on the aircraft floor by a plurality of removable Load Transfer Braces (LTB) hinged to the inboard side of the AMP which in turn transfers said dynamic loads to a Floor Loads Plate (FLP) secured to multiple cargo tie down “D” rings on the floor of the host aircraft by means of adjustable cam locks. Said removable load transfer braces being able to rapidly disconnect from the adjustable cam locks, “D” rings, and FLP for stowage in the vertical position, outboard of the cargo transit envelop as to permit in flight air drop operations. In flight, the articulated strut assembly can be extended below the fuselage to achieve a 360 degree unobstructed field of view (FOV) for a given payload, or retracted into the fuselage to change sensor payloads or re-load jettisonable stores. The preferred embodiment of the present invention can be installed or removed in minutes, does not interfere with crew egress, the aircraft flight performance envelope, or emergency procedures of the host aircraft while installed and further possesses redundant primary drive retraction systems along with a manual retraction system, and payload jettisoning system to preclude any danger in landing the aircraft should there be a problem retracting the various mission payloads.
Owner:1281329 ALBERTA
Detecting and combating attack in protection system of an industrial control system
InactiveUS8812466B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsEmergency procedureProtection system
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
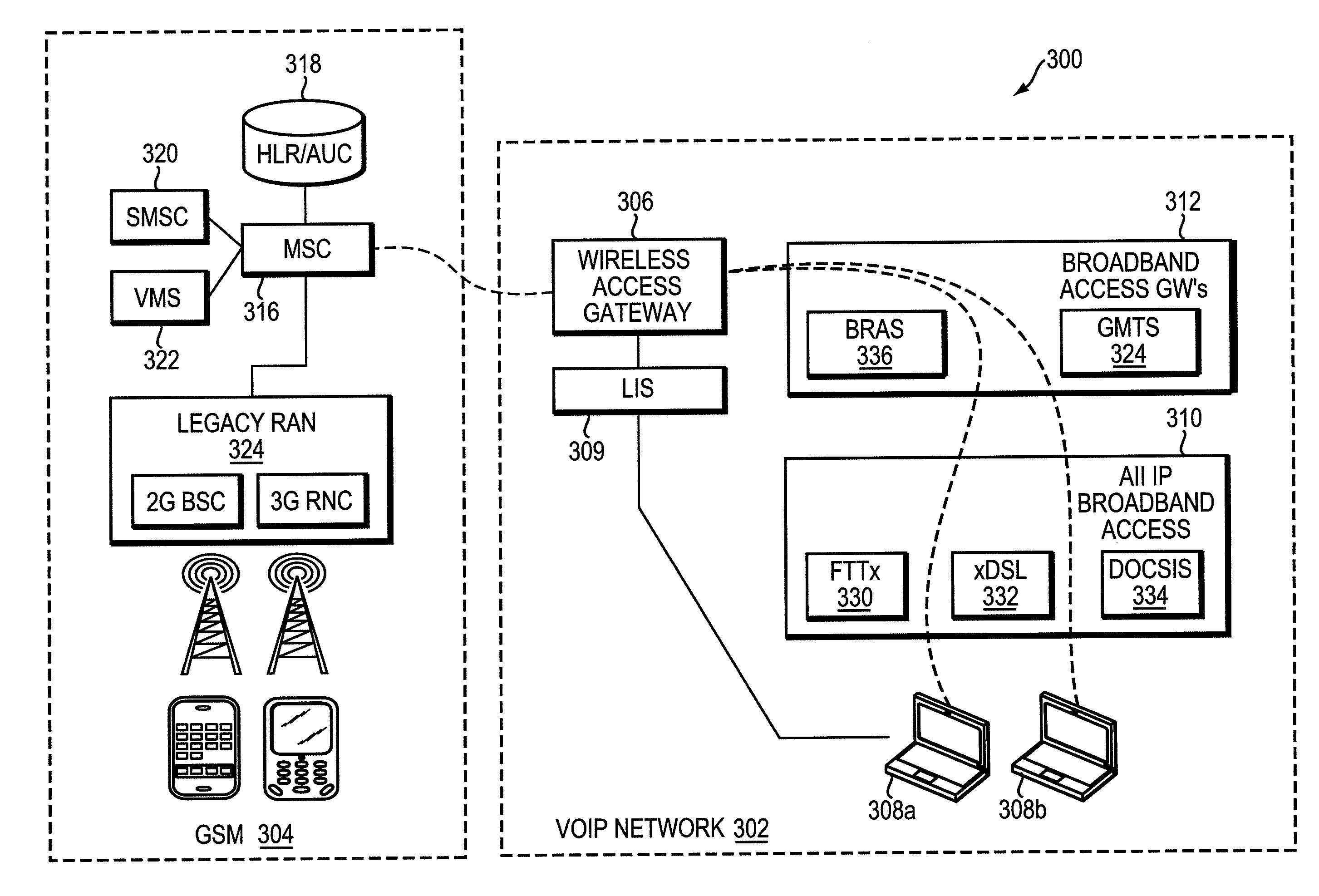
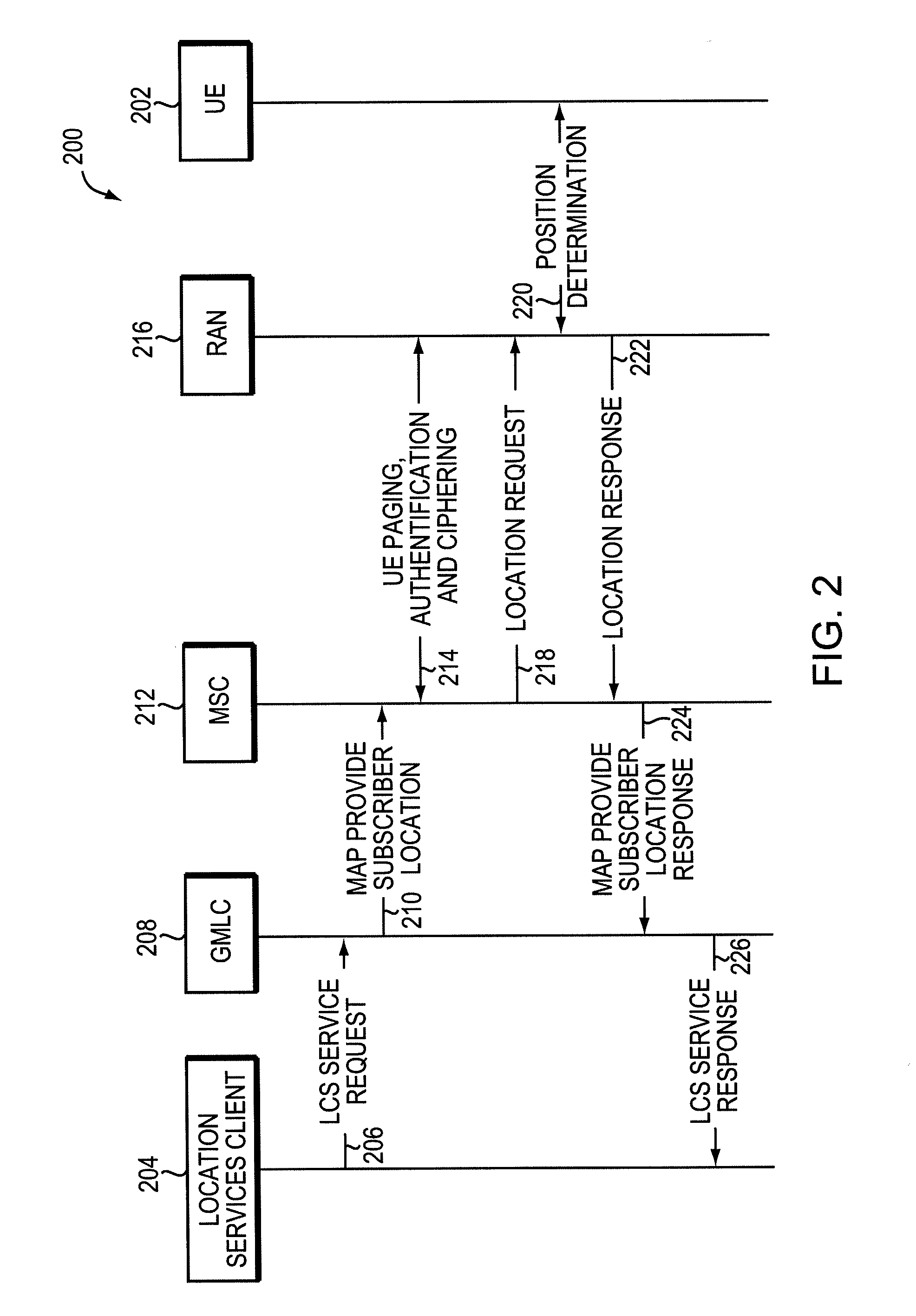
Utilizing Emergency Procedures to Determine Location Information of a Voice Over Internet Protocol Device
ActiveUS20110292870A1Apparent advantageMore accessEmergency connection handlingInformation formatEmergency procedureInternet protocol suite
Described are methods and apparatuses, including computer program products for utilizing emergency procedures to determine location information for a Voice Over Internet Protocol (VOIP) device. A wireless access gateway (WAG) determines location information of the VOIP device and stores the location information. A request for a location of the VOIP device from a Mobile Switching Center (MSC) is received by the WAG. The WAG translates the stored location information into a format used by the MSC to receive location information from a Radio Access Network (RAN). The WAG provides the translated location information to the MSC.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
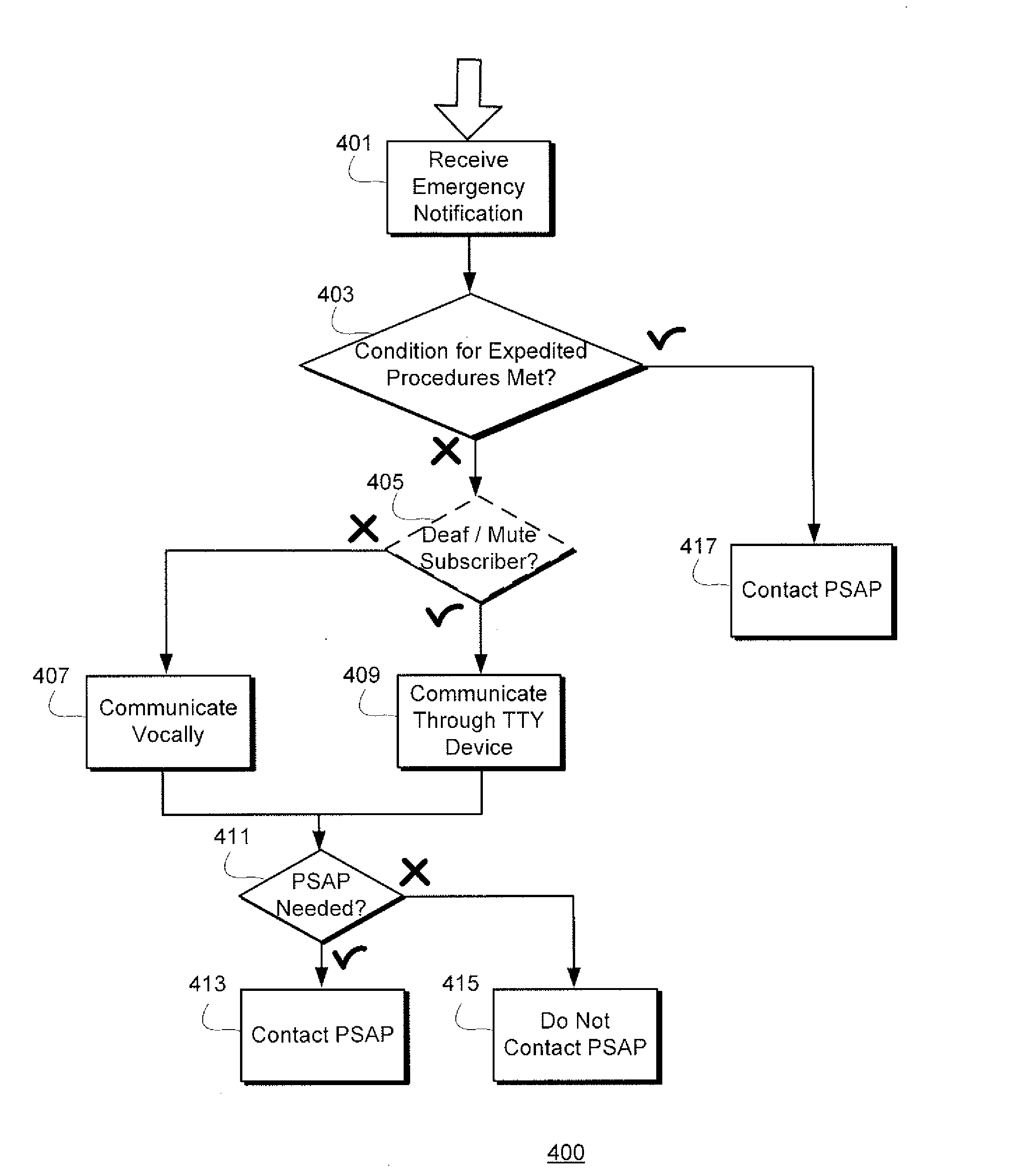
Tyy interface module signal to communicate equipment disruption to call center
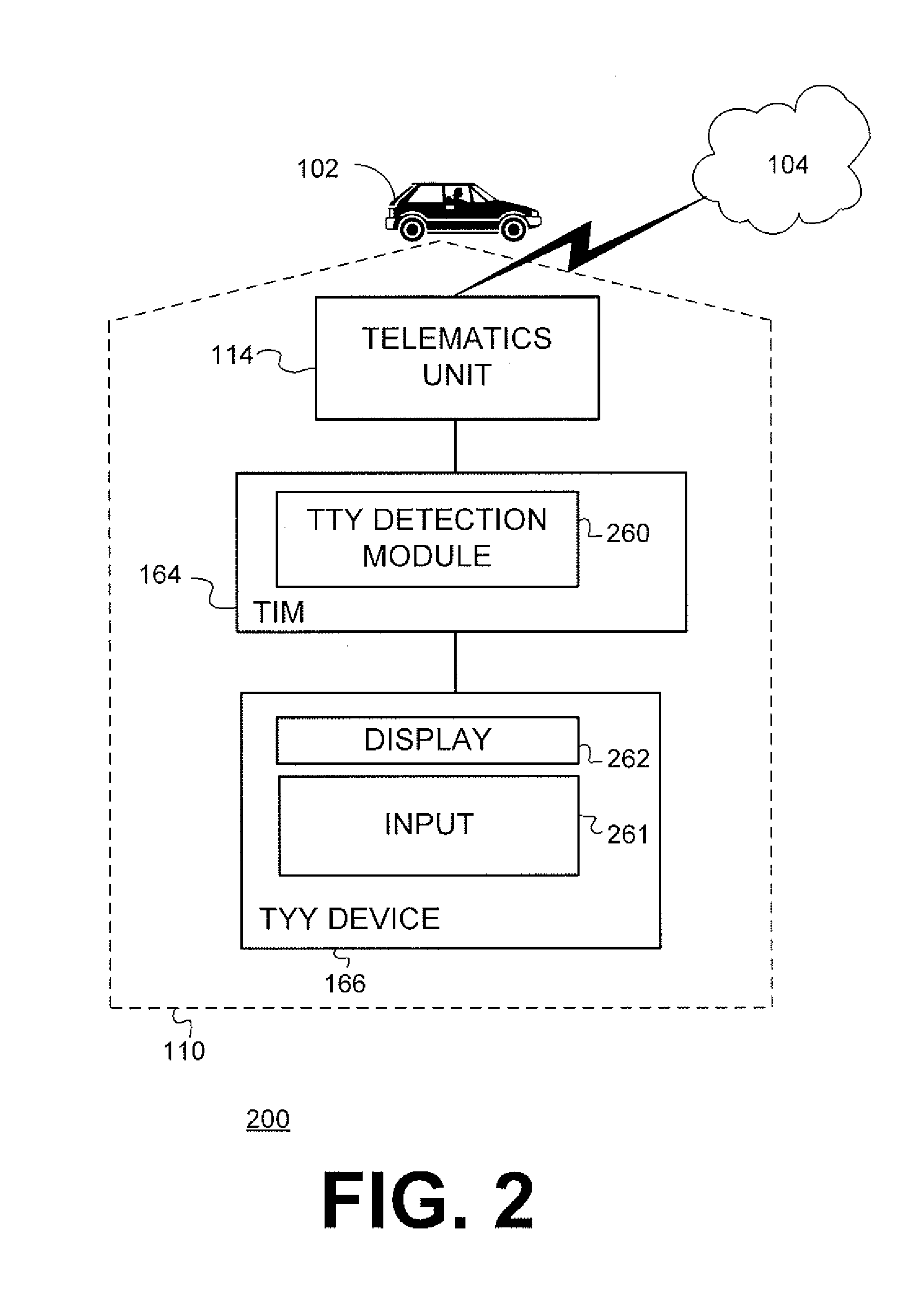
InactiveUS20130017800A1Emergency connection handlingParticular environment based servicesEmergency procedureTelematics
The described method and system provide for determining whether to immediately contact a PSAP (Public Safety Answering Point) or attempt to communicate with a telematics services subscriber before contacting the PSAP in the event of an emergency. If a subscriber associated with the telematics unit is deaf and / or mute, and a TIM (TTY (TeleTYpewriter) Interface Module) or TTY device is not available to the subscriber, the subscriber may not be able to communicate with a call center regarding an emergency situation. Thus, expedited emergency procedures are executed by the call center in such a situation to avoid delay and facilitate the arrival of assistance as soon as possible.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC
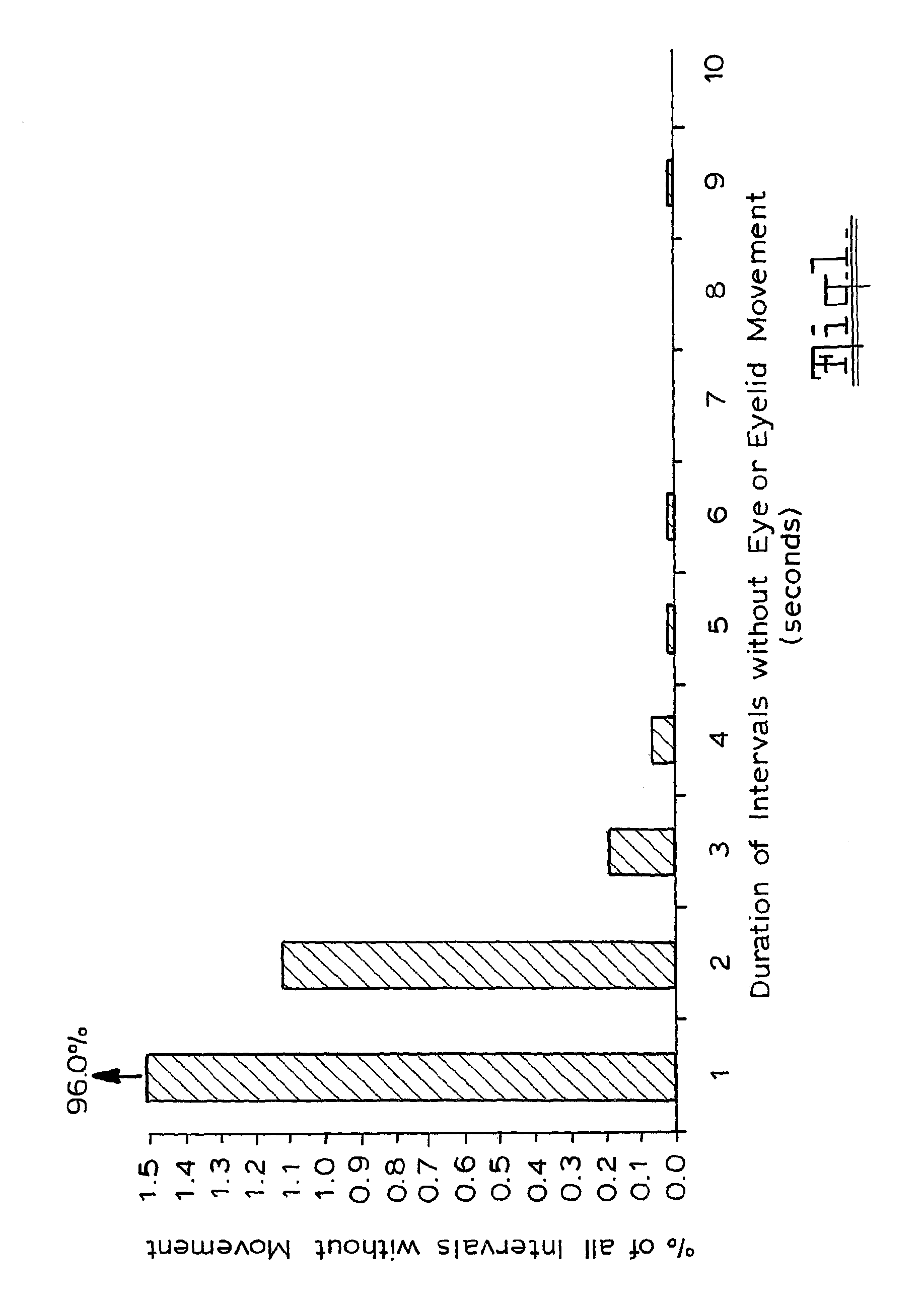
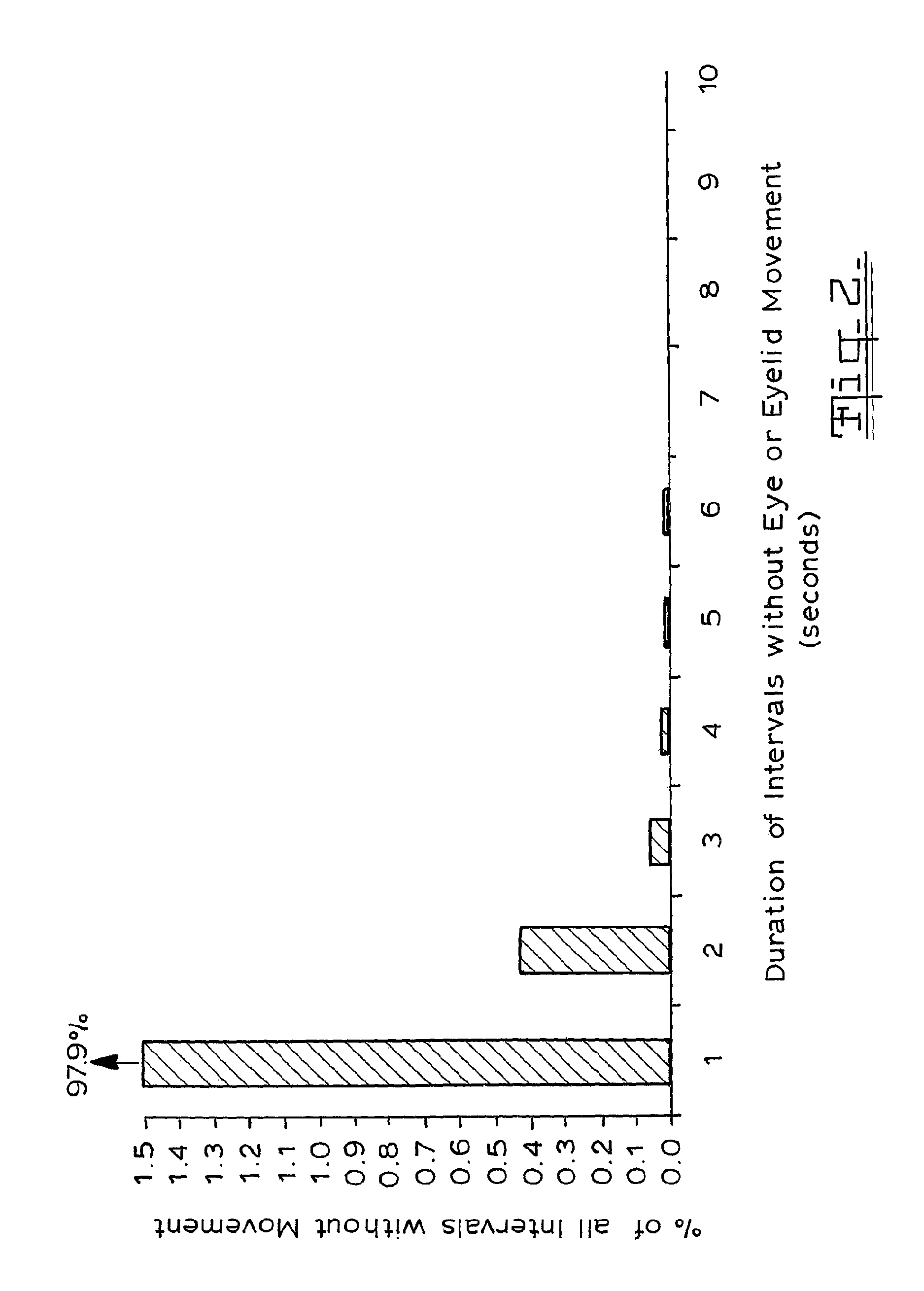
Incapacity monitor
InactiveUS20090034796A1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsEmergency procedureEyelid
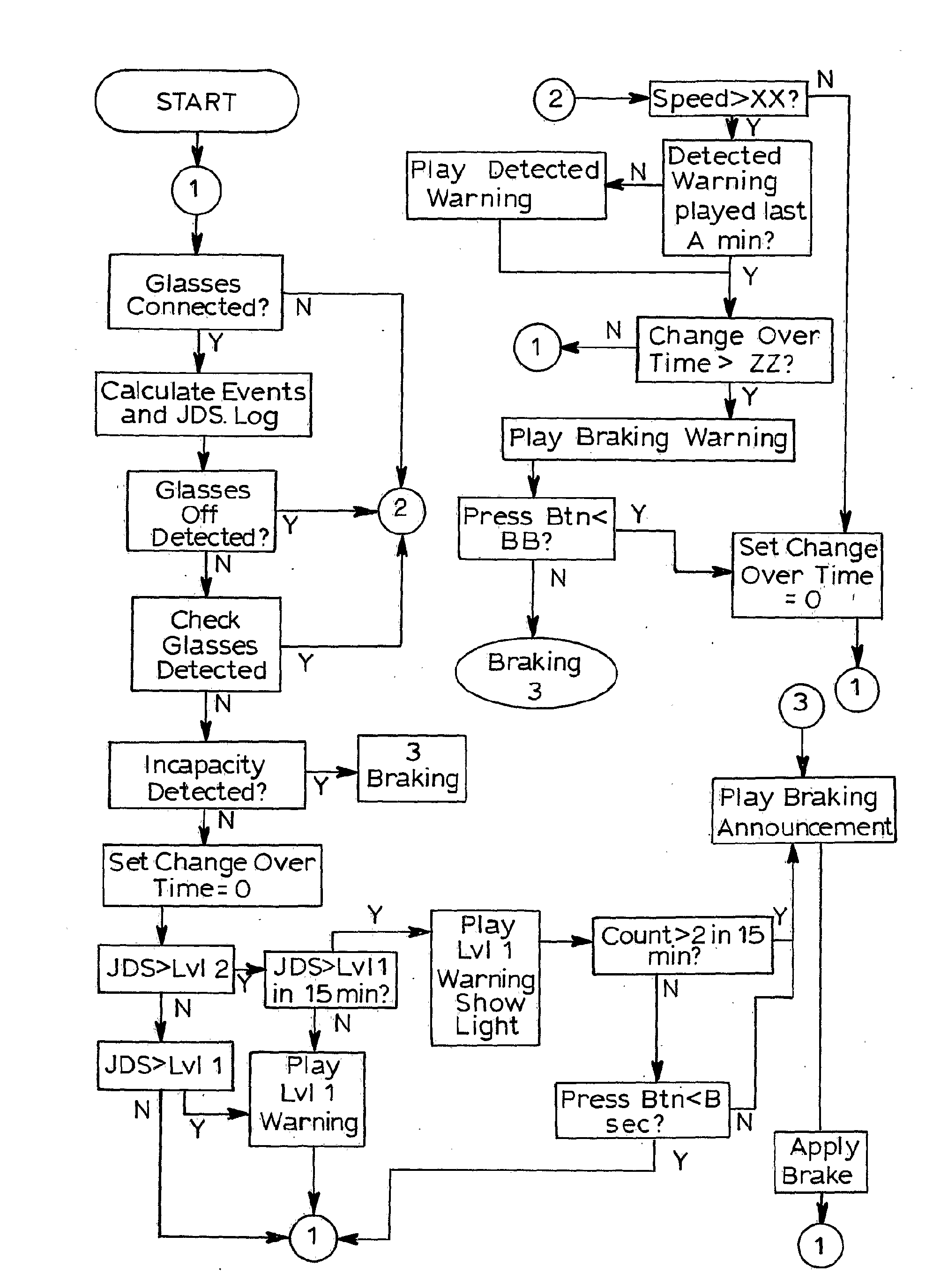
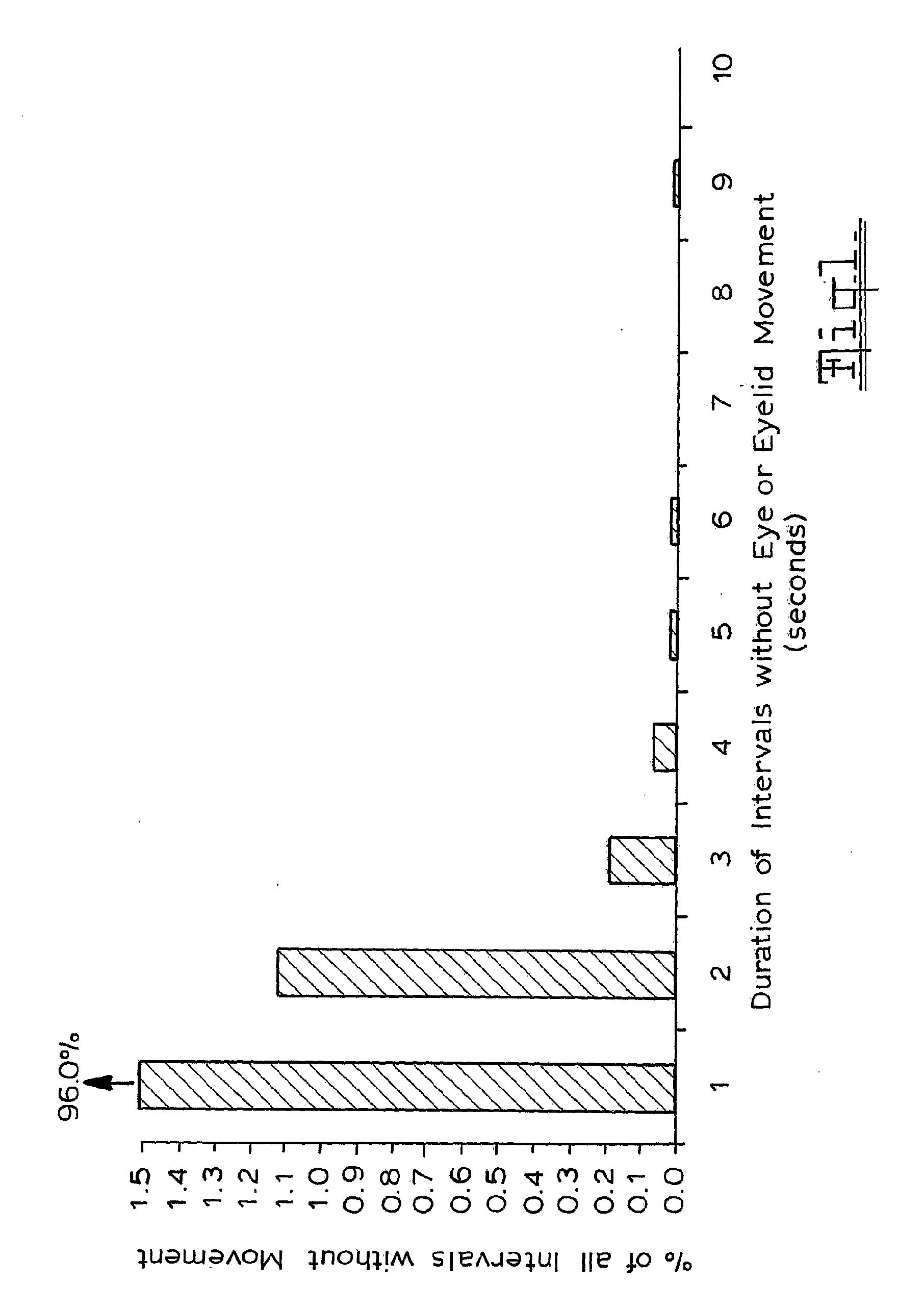
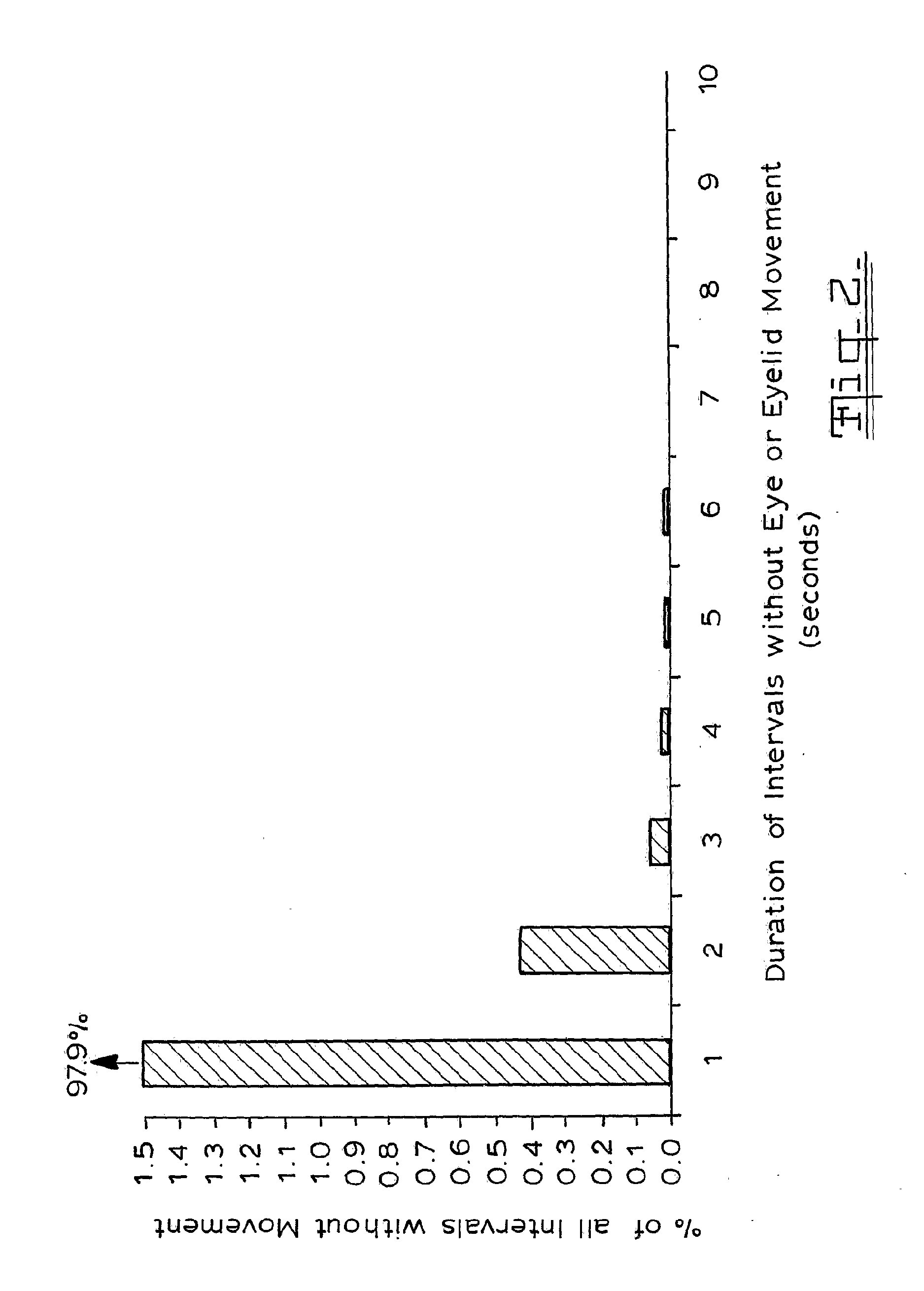
A method of monitoring incapacity of a subject which includes the steps of continuously monitoring eye and eyelid movement of at least one eye of the subject; analyzing eye and eyelid movements to obtain measures of ocular quiescence and the duration of an interval of no eye or eyelid movement; and if the duration of ocular quiescence exceeds a predetermined value providing a potential incapacity warning and requesting a response within a predetermined period, and applying an emergency procedure if no response is made within a predetermined interval.
Owner:OPTALERT
Method of implementing essential service of electric playbill
InactiveCN101179565ASpecial service provision for substationTwo-way working systemsEmergency procedureUser authentication
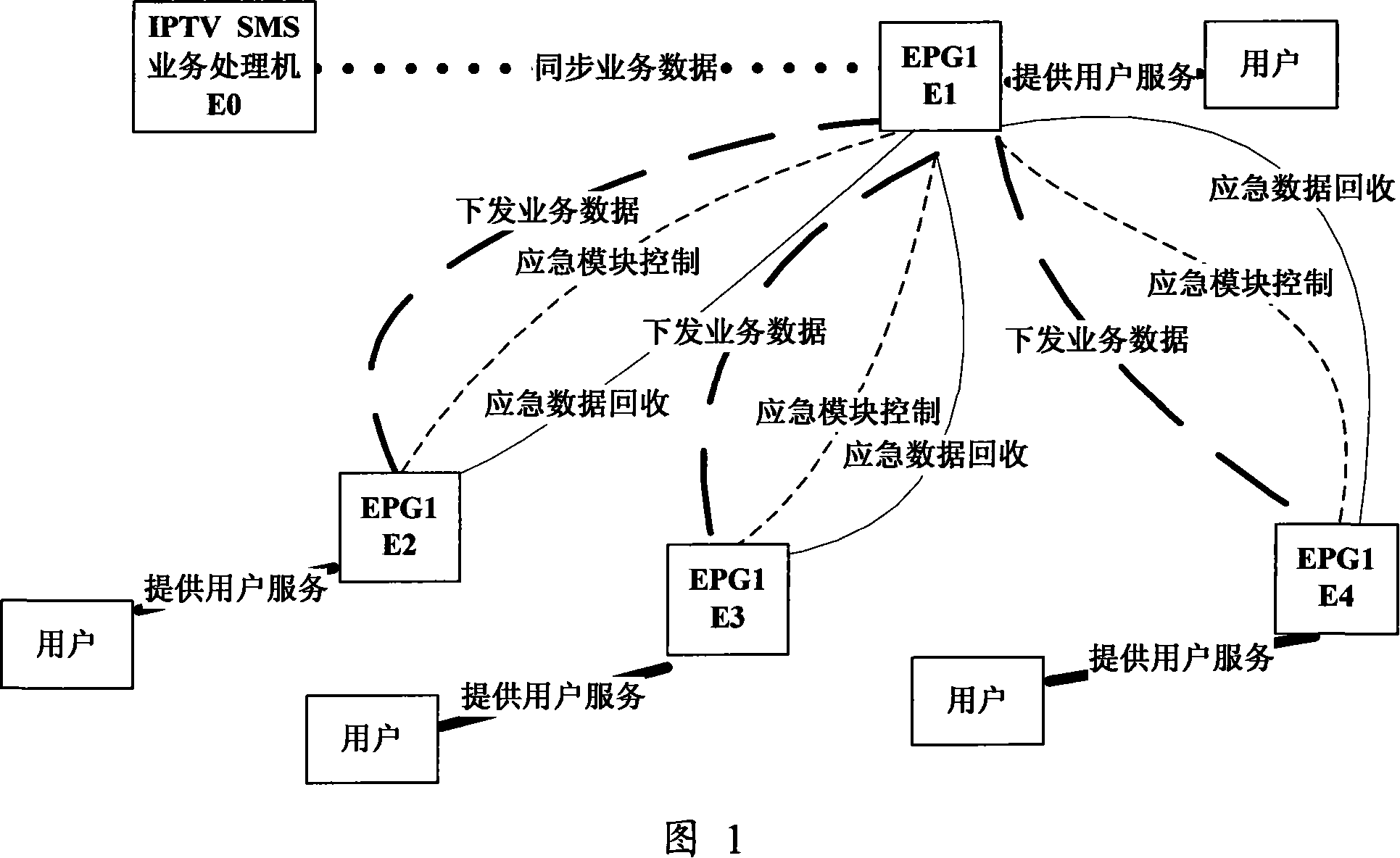
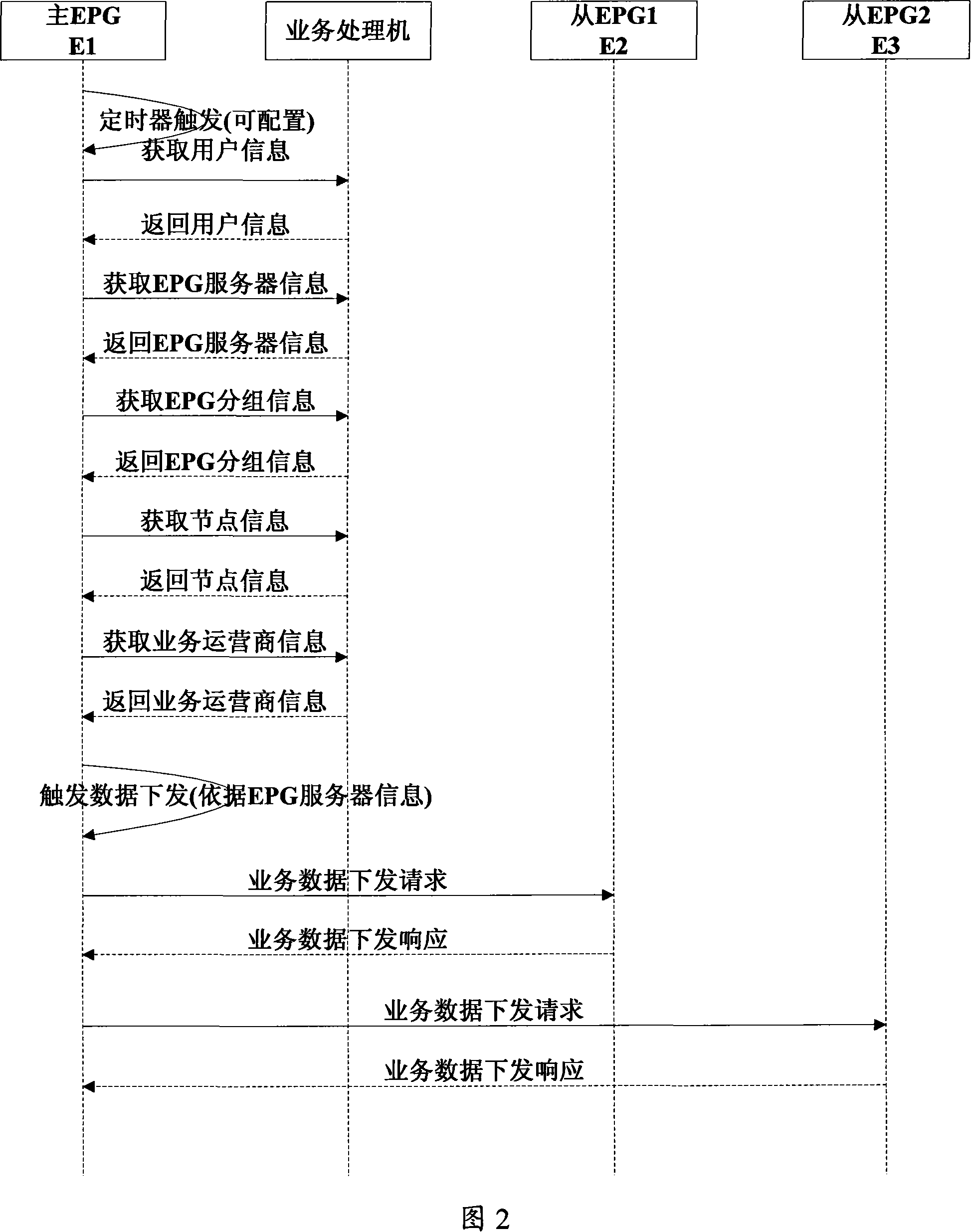
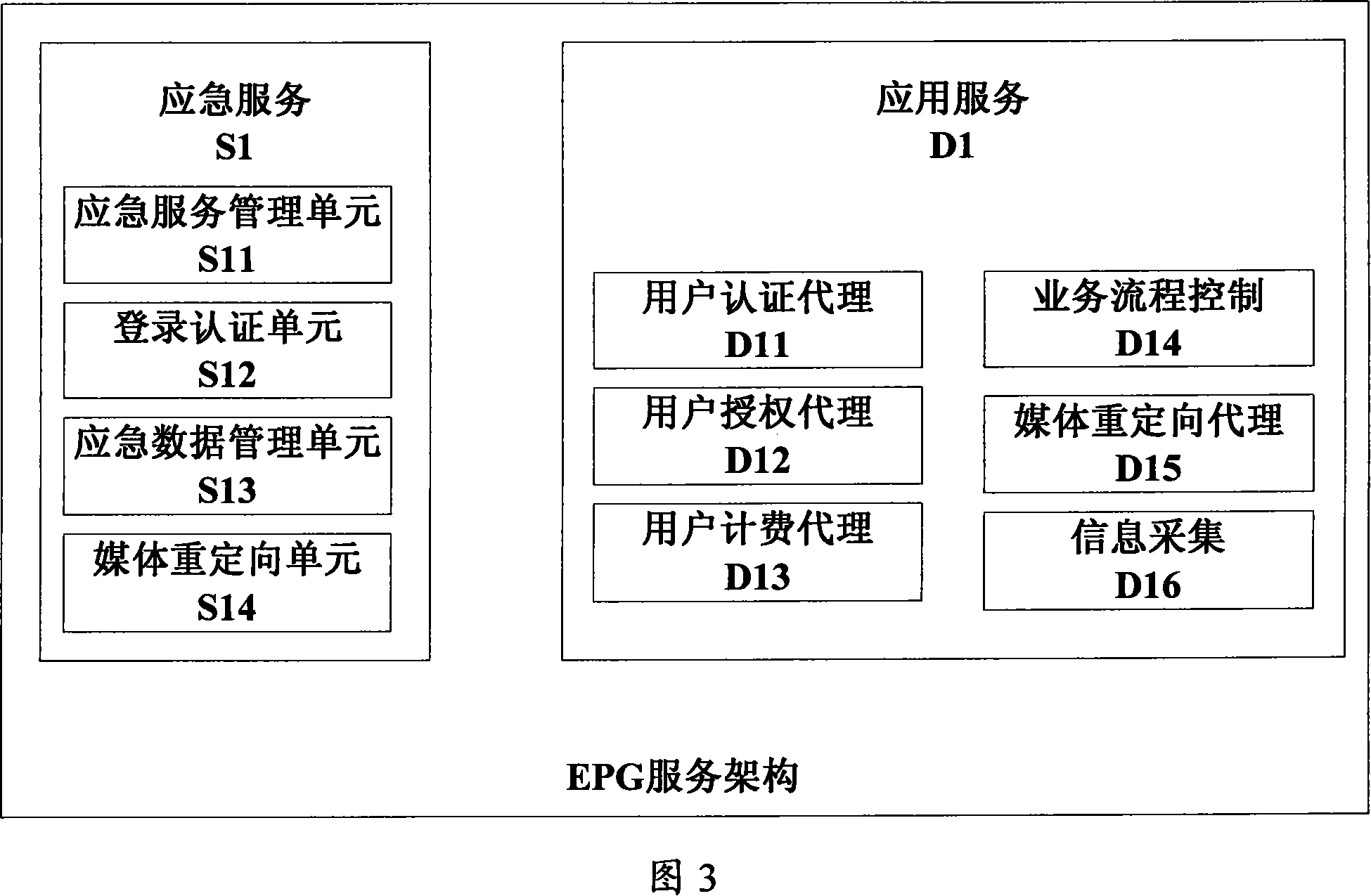
The invention discloses a method for realizing the basic business of an electronic program guide. The method is as follows: A. Log in to the management page of the main EPG (electronic program guide server), select an emergency plan and the EPG to start the emergency process, and start its emergency process; B. The EPG that has started the emergency process downloads the business data required for emergency services from the business processor and stores them in their respective databases; C. intercepts the user login authentication request sent by the above-mentioned EPG to the business processor, and saves the business data from each server Query user information in the data, and perform user login authentication judgment according to the information; D. Each EPG processes the user's media playback request and provides media services to the user. With the present invention, the administrator can start the emergency process in advance before the business processor goes down, and can also start the emergency process after it goes down, which ensures that when the business processor cannot provide services, the user can log in through the EPG and continue to use the EPG. business is not affected.
Owner:ZTE CORP
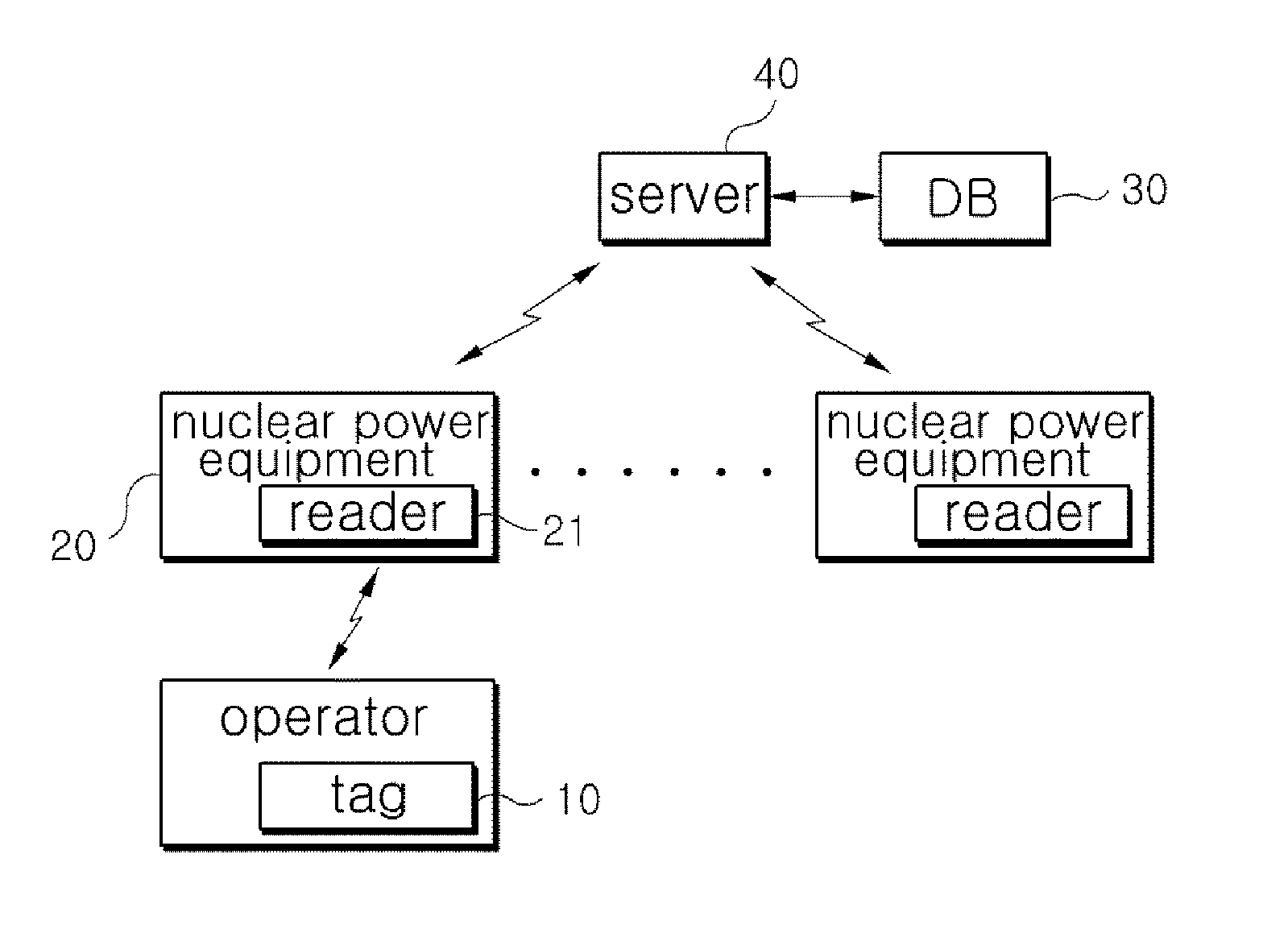
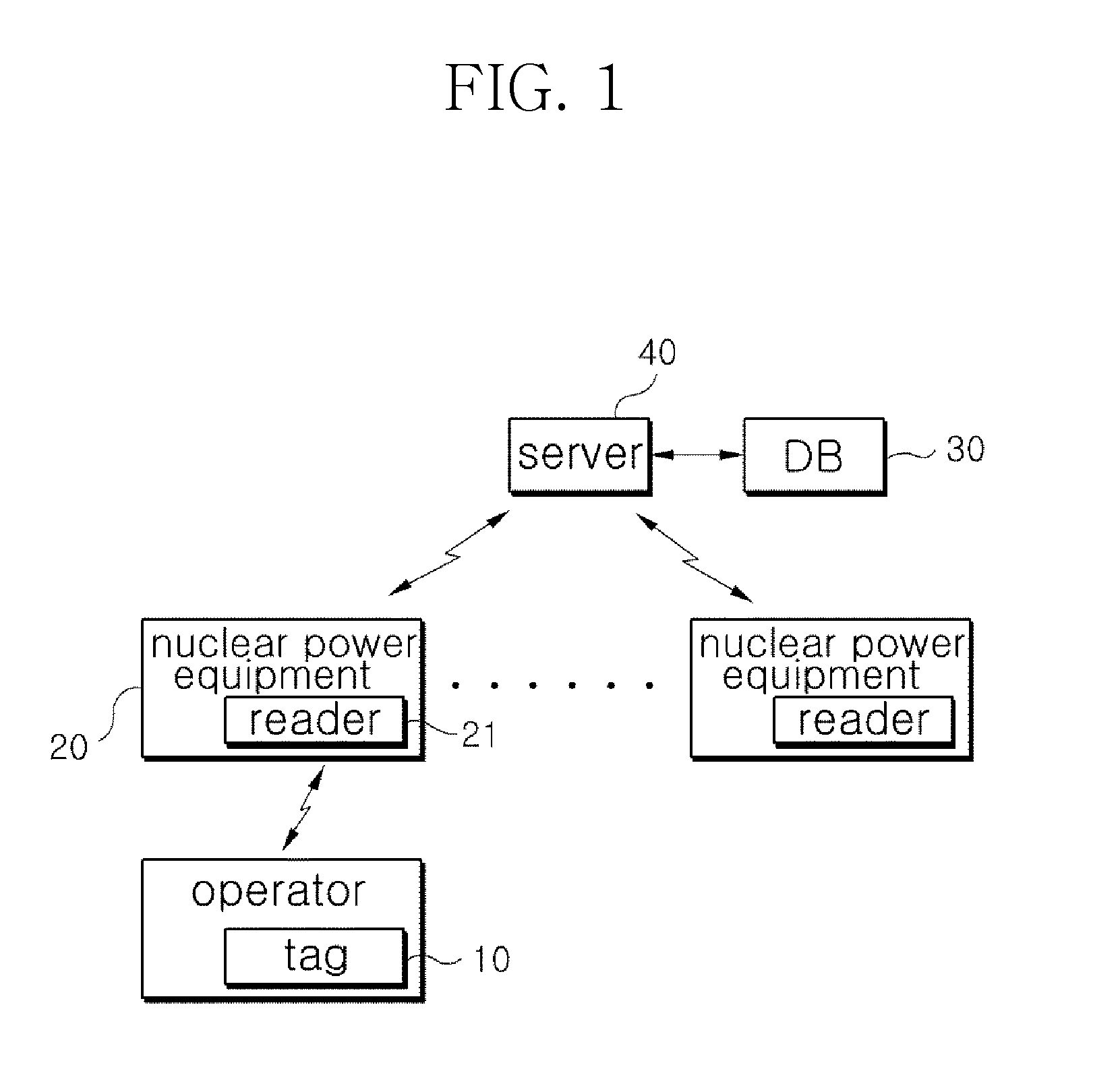
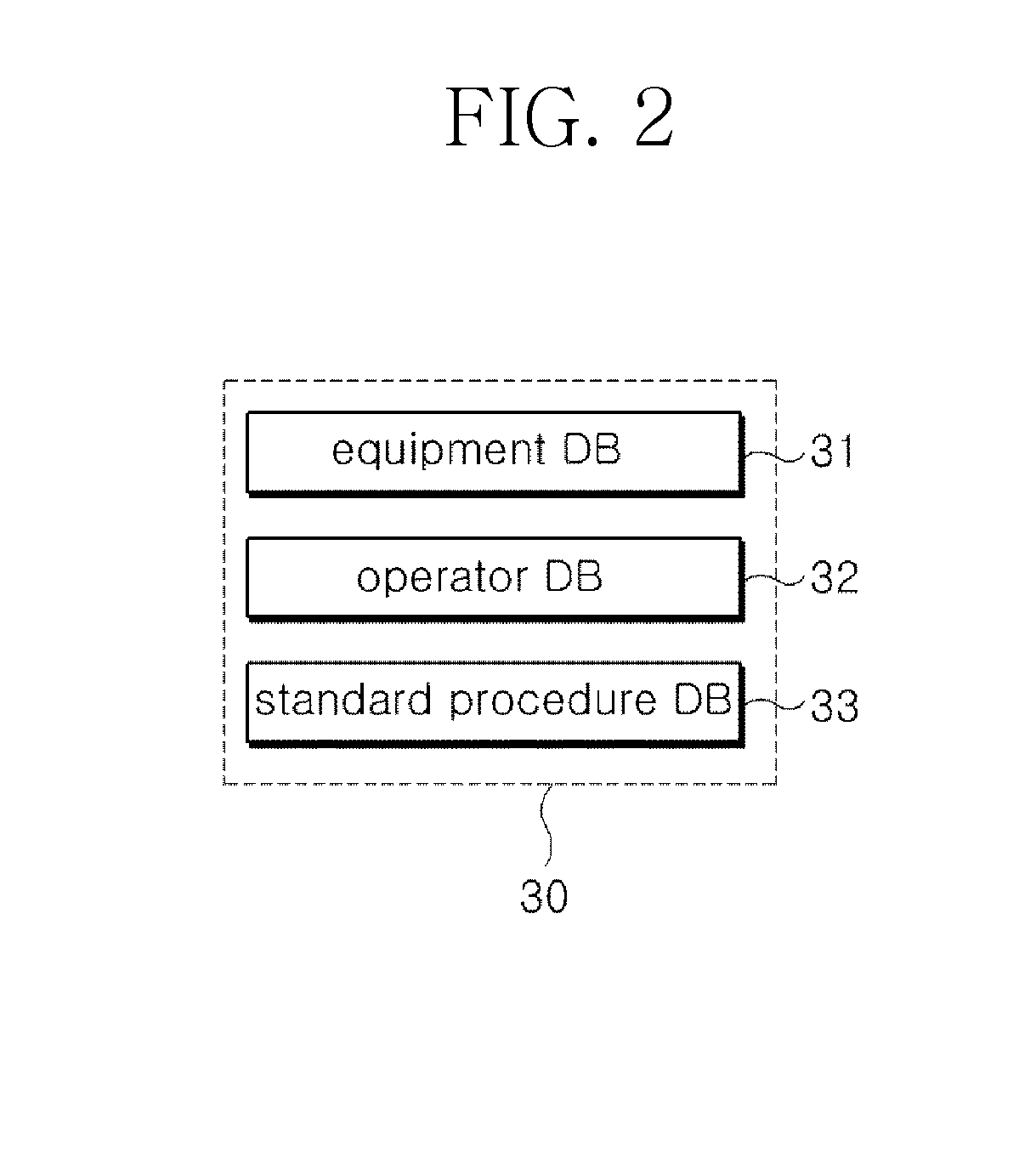
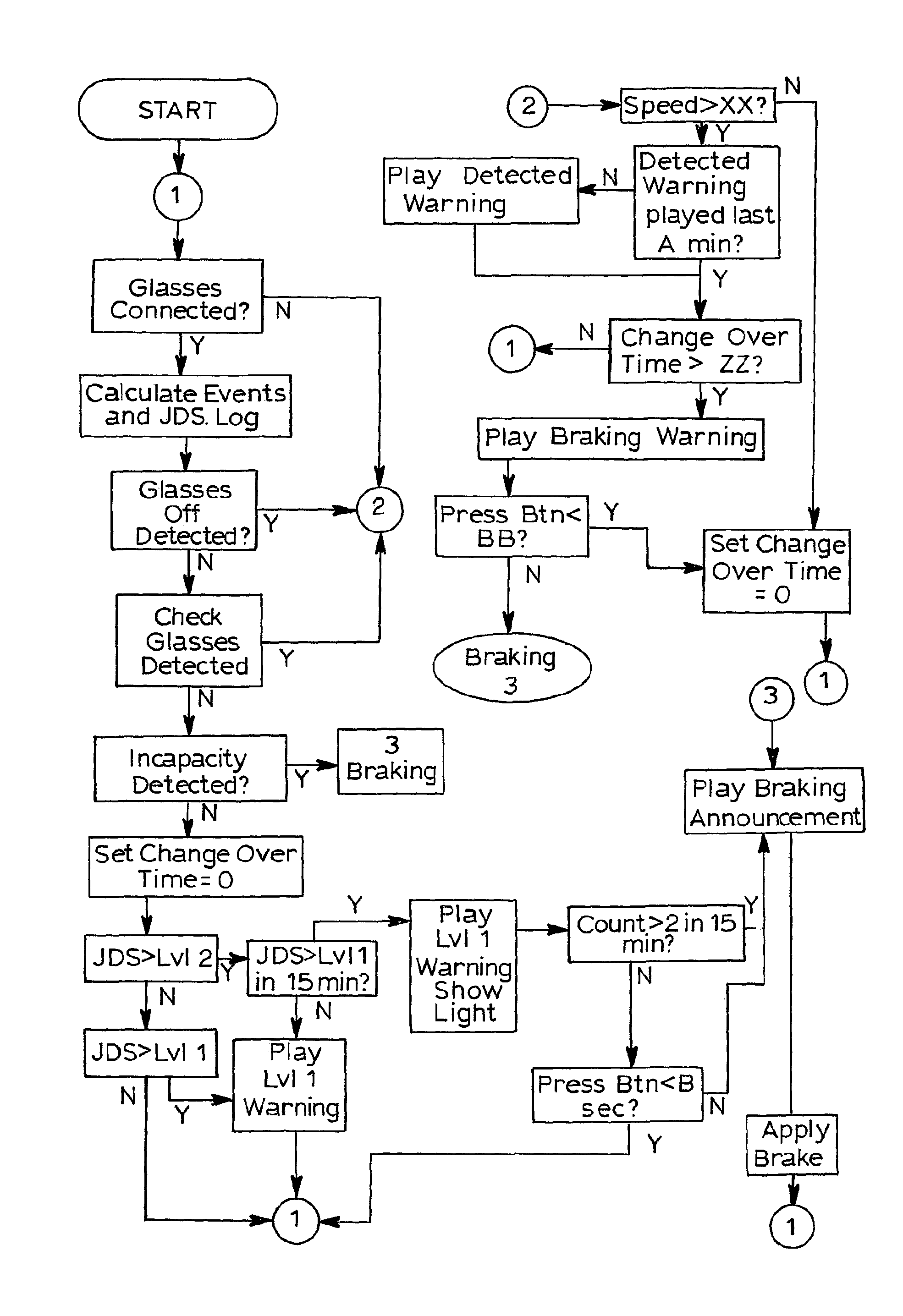
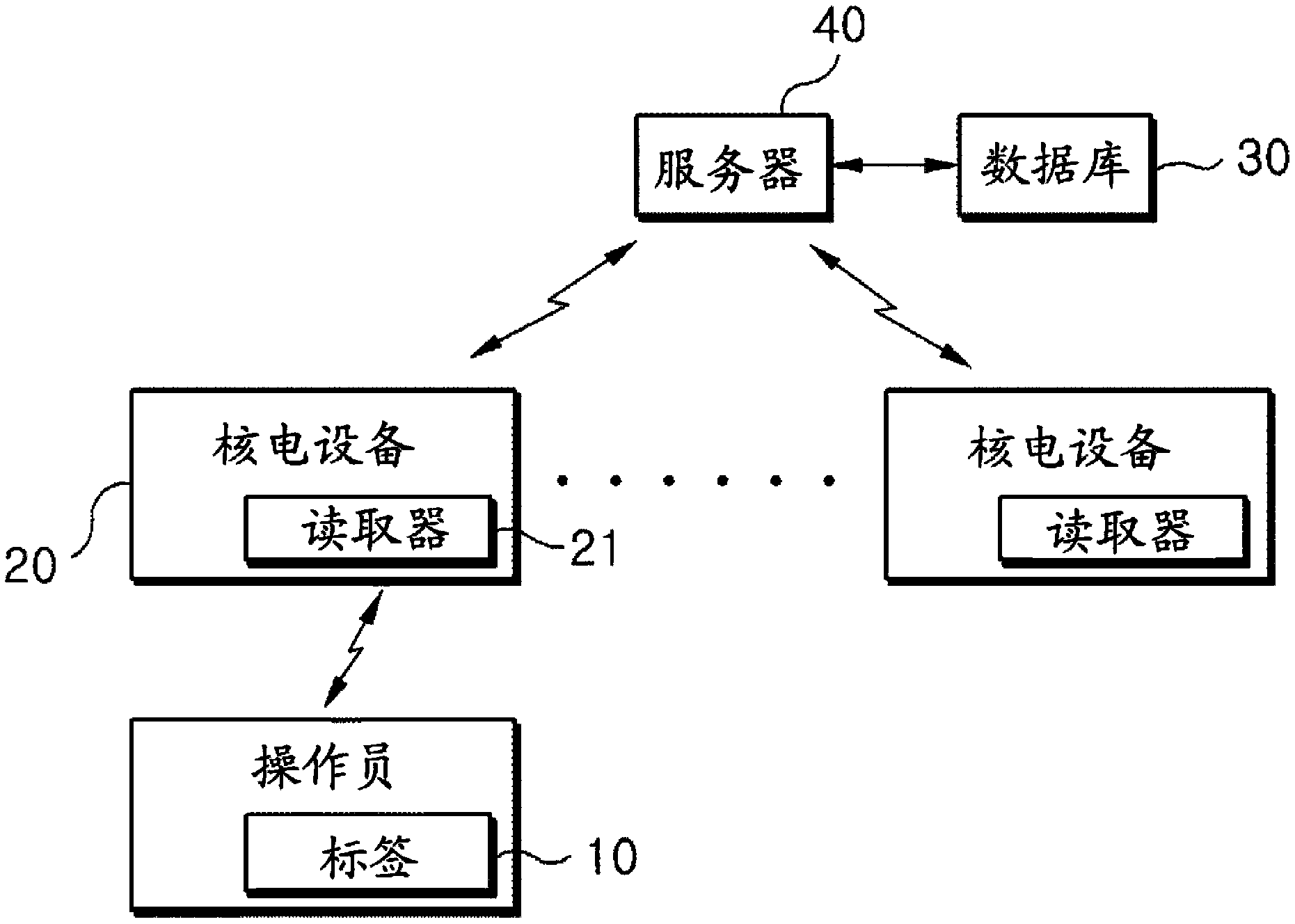
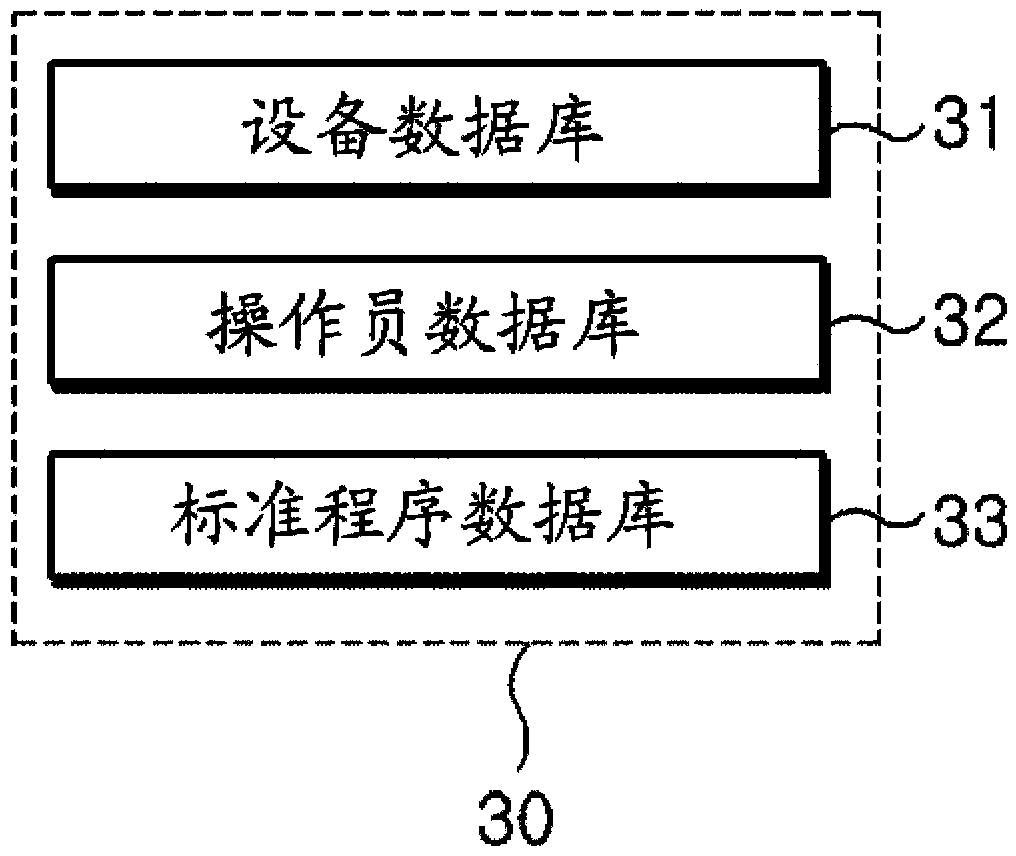
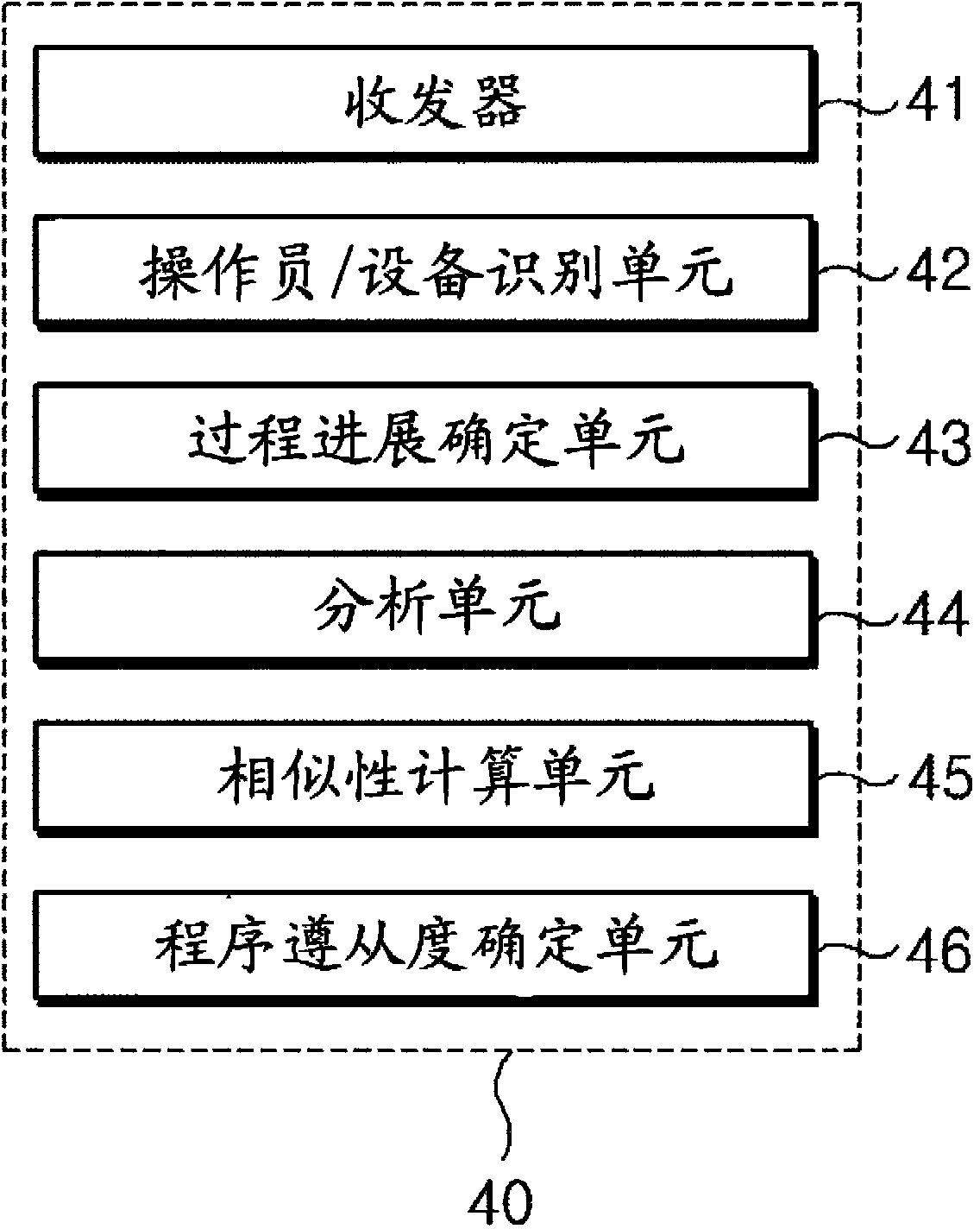
System for assessing procedure compliance level of human operators in nuclear power plants and method thereof
Disclosed are a system for assessing the procedure compliance level of a human operator in a nuclear power plant, which quantitatively detects if the human operator complies with a standard procedure written in an emergency procedure guideline for the nuclear power plant, and a method thereof. The system includes a first recognizing unit attached to each of human operators, a second recognizing unit that is mounted on each of nuclear power equipments and able to make communication with the first recognizing unit, a database storing information of a standard procedure to be performed by the human operator with respect to the nuclear power equipment, and a server that is able to make communication with the second recognizing unit, and assesses the standard procedure stored in the database and an actual procedure performed by the human operator, which is received from the second recognizing unit.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
Combined cardio pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) apparatus and method
A combined cardio pulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) system for performing an emergency procedure over the clothing of a patient is provided. The system includes a spinal support rest having a cushion that accommodates a neck portion of the patient, a compression pad operatively connected to the spinal support rest and is adapted to be placed over the patient such that the compression pad is aligned above the heart and chest of the patient. A first arm strap and a second arm strap operatively connected to the compression pad. A power button automatically dials an emergency number to contact a medical professional. An interactive communication unit activates a two way real time video conference with the medical professional on the display to receive a set of instructions from the medical professional in real time to enable a user to perform the emergency procedure on the patient.
Owner:MADANAT SAHAR ANIS
Systems and Methods of Mapping Locales
InactiveUS20150088937A1Encourage public participationMuch effortDigital data processing detailsMaps/plans/chartsEmergency procedureWeb site
The present invention relates to one or more applications and / or programs that may be used on a smart phone, on a computer, or on a computer like device. The one or more applications and / or programs are able to receive input from one or more users or may automatically receive information from web sites that allows the mapping of establishments and may also create a database that contains relevant information that can be used by consumers and various establishments. When a user accesses the one or more applications and / or programs, the one or more applications and / or programs can provide the user with information such as the best route to take so that the user will arrive at a given product. The present invention may also be able to map other locales. Other advantages that may be provided by the one or more applications and / or programs include raising revenue, offering better service to the public, auditing emergency procedures and other procedures, inventorying goods and / or products, studying the effects of marketing, testing the effectiveness of staging, reducing costs, and / or evaluating vender and / or service providers.
Owner:LONS DARRIN K +2
Switch unit, and related method
ActiveUS20130015712A1Continuous monitoringBatteries circuit arrangementsSwitch power arrangementsEmergency procedureElectronic controller
A switch unit includes a current switching device drivable by an electromagnetic actuator for opening / closing an electric circuit associated with the switch unit, a first energy storage for storing electric energy for the electromagnetic actuator, and electronic controller means which are supplied by an external power line and control a supply of the electric energy from the energy storage means to the electromagnetic actuator. The switch unit includes emergency procedure operating means associated with the electronic controller means and provided with a second energy storage means. The emergency procedure operating means are configured for enabling driving of the current switching device and opening the associated electric circuit in an emergency condition in which a lack or drop or irregular supply of the external power line is experienced.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Drone network switchover between wireless networks
ActiveUS10312994B2Unmanned aerial vehiclesParticular environment based servicesEmergency procedureAir traffic control
Systems and methods for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) network switchover and emergency procedures, implemented by a UAV includes communicating to an Air Traffic Control (ATC) system via a primary wireless network; receiving and storing emergency instructions from the ATC system; detecting communication disruption on the primary wireless network to the ATC system; responsive to the detecting, switching to a backup wireless network to reestablish communication to the ATC system; and, responsive to failing to reestablish communication to the ATC system via the backup wireless network, implementing the emergency instructions.
Owner:METAL RAPTOR LLC
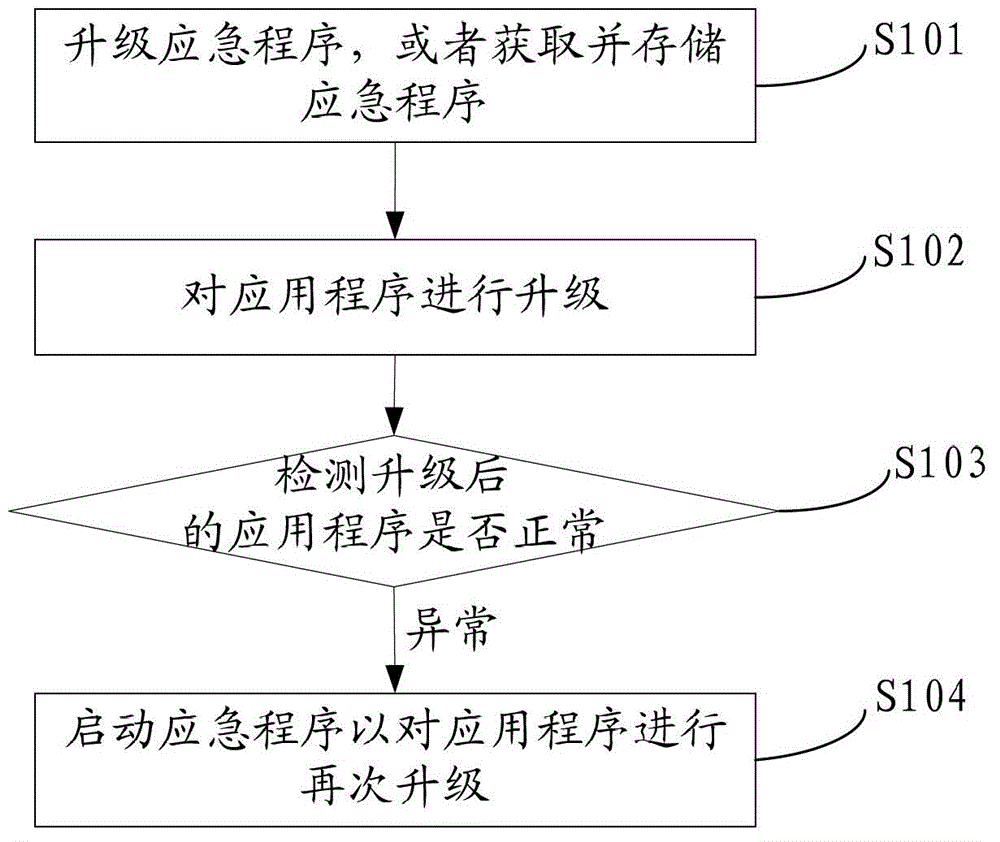
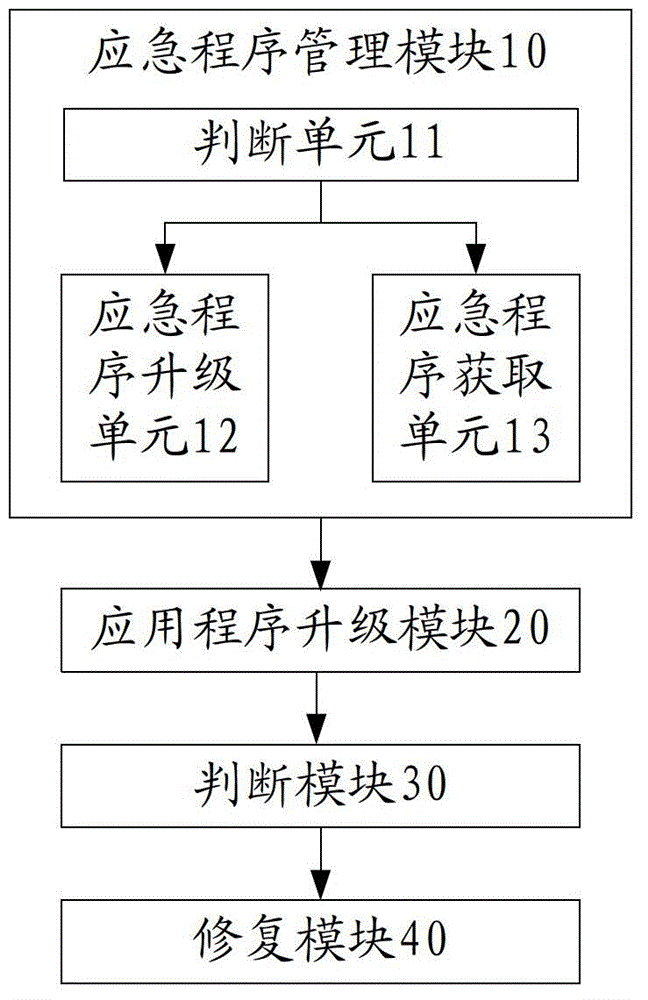
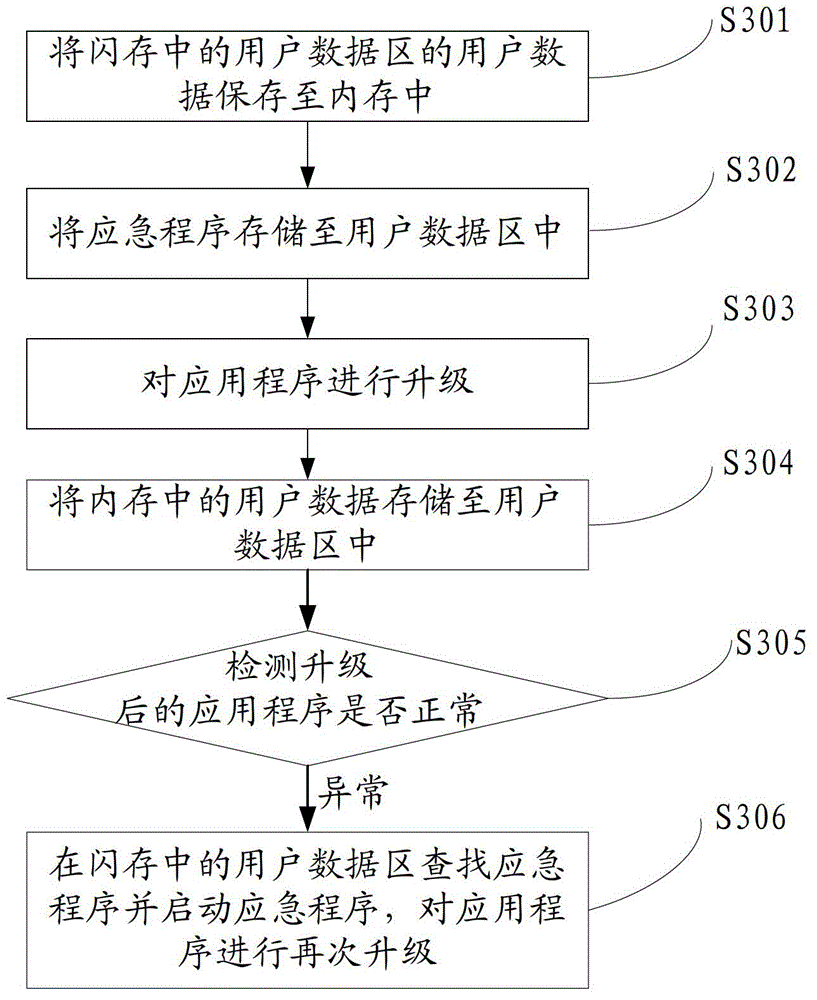
Set-top box upgrading method and device
InactiveCN102917267AAvoid failure to startTakes up little storage spaceProgram loading/initiatingSelective content distributionEmergency procedureApplication procedure
The invention discloses a set-top box upgrading method and device. The set-top box upgrading method comprises the following steps: upgrading an application procedure; detecting whether the upgraded application procedure is normal or not; and starting an emergency procedure to re-upgrade the application procedure if the upgraded application procedure is not normal. Due to the mode, if the upgrading of the application procedure fails, the emergency procedure can be started, and the application procedure can be re-updated or repaired in the emergency procedure, so that the situation that the set-top box can not be started normally if the upgrading of the application procedure of the set-top box fails and is damaged is avoided.
Owner:SHENZHEN SKYWORTH DIGITAL TECH CO LTD +1
Temporarily installed aircraft observer door plug, chair, sonotube ejection and control system
ActiveUS8807482B2Simple technologyQuick installationSeating arrangementsMilitary adjustmentEmergency procedureSeat belt
The system and apparatus of the present invention is generally comprised of a non-dedicated, temporarily-installed, aircraft observer bubble door, chair, sonotube ejection system, mission electronics LRU rack and workstation assembly which are affixed to the Air Deployment System (ADS) rails, cargo tie down “D” rings, seat belt restraint ring bolt sockets, and litter bar of a host aircraft, thereby precluding the requirement for dedicated airframe modifications. One embodiment of the present invention also utilizes a multi-axis, articulated, foldable chair temporarily-installed in conjunction with a segmented or one piece pressurized observer bubble door plug and door retraction system. Once installed the subject apparatus can be stowed outboard of the fuselage cargo transit envelope to permit use of the ADS rail system in-flight, without affecting normal air drop operations, crew egress, the flight performance envelope, or emergency procedures of the host aircraft.
Owner:1281329 ALBERTA
Incapacity monitor
InactiveUS8311284B2Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsEyelidEmergency procedure
Owner:OPTALERT
System for assessing procedure compliance level of human operators in nuclear power plants and method thereof
Disclosed are a system for assessing the procedure compliance level of a human operator in a nuclear power plant, which quantitatively detects if the human operator complies with a standard procedure written in an emergency procedure guideline for the nuclear power plant, and a method thereof. The system includes a first recognizing unit attached to each of human operators, a second recognizing unit that is mounted on each of nuclear power equipments and able to make communication with the first recognizing unit, a database storing information of a standard procedure to be performed by the human operator with respect to the nuclear power equipment, and a server that is able to make communication with the second recognizing unit, and assesses the standard procedure stored in the database and an actual procedure performed by the human operator, which is received from the second recognizing unit.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST +1
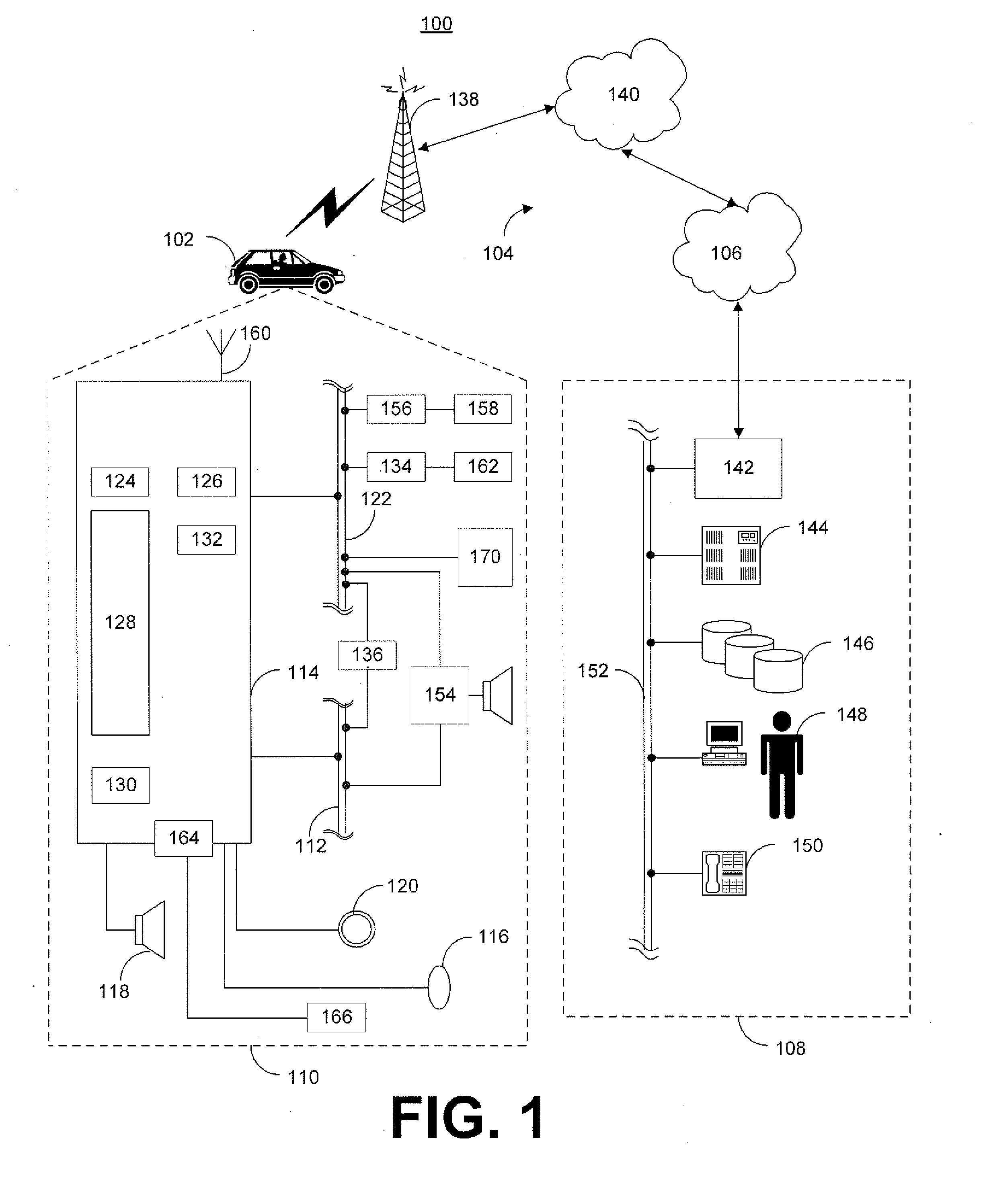
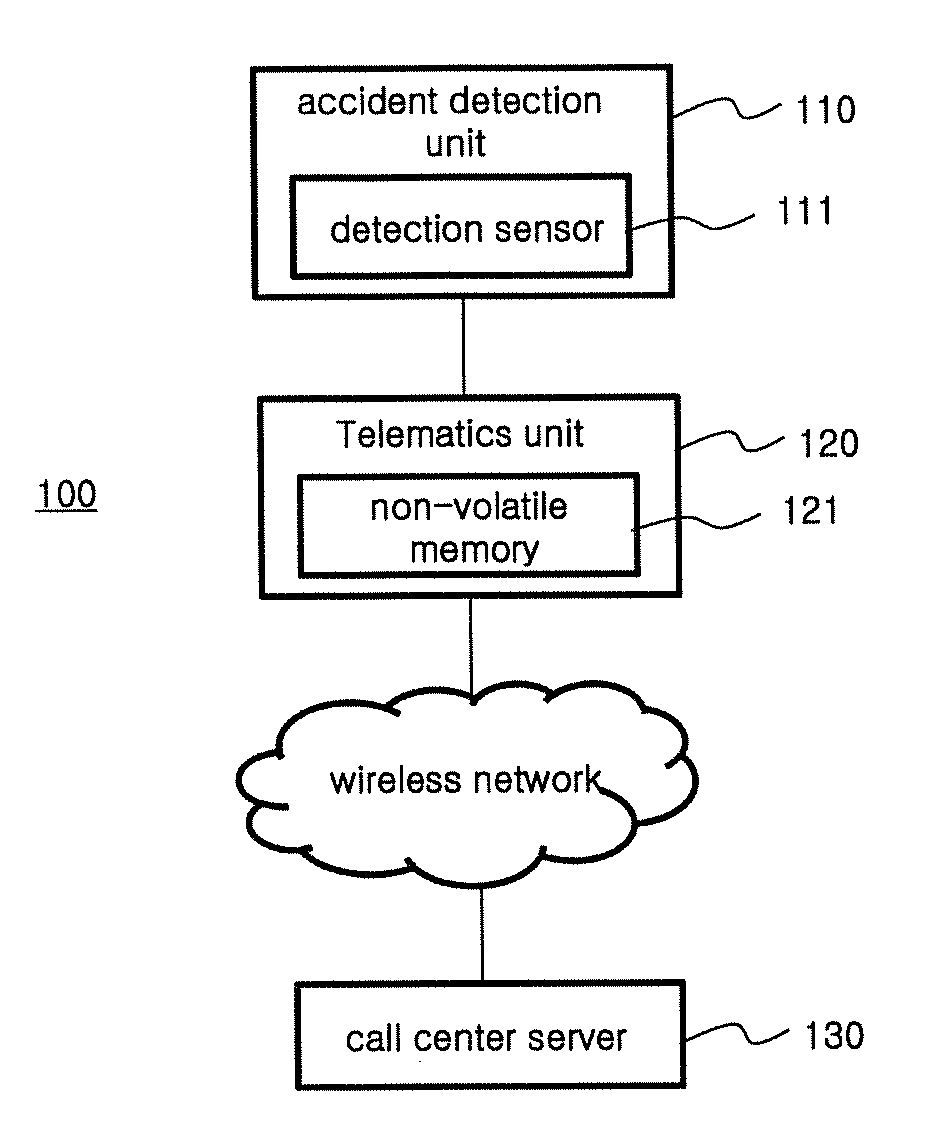
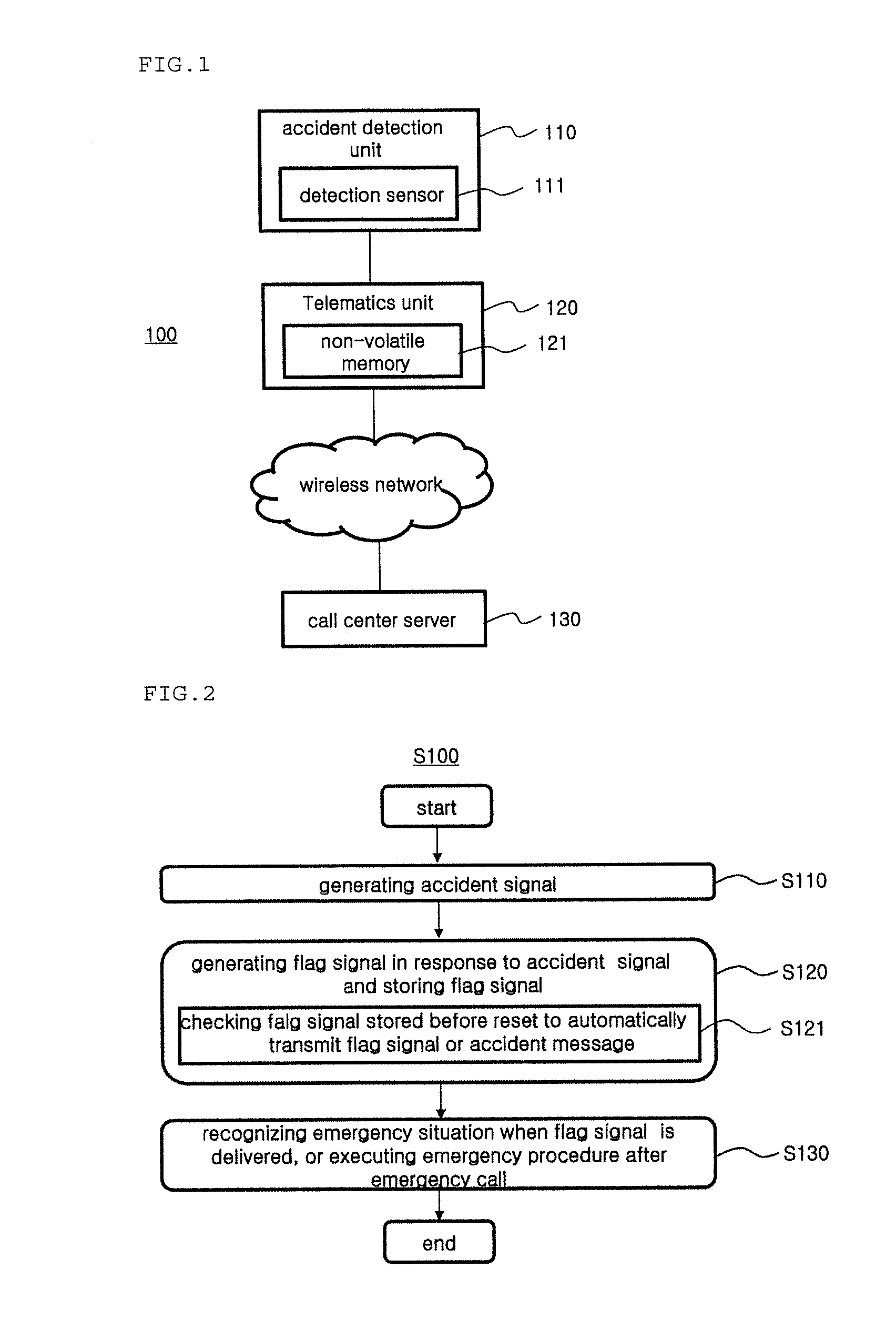
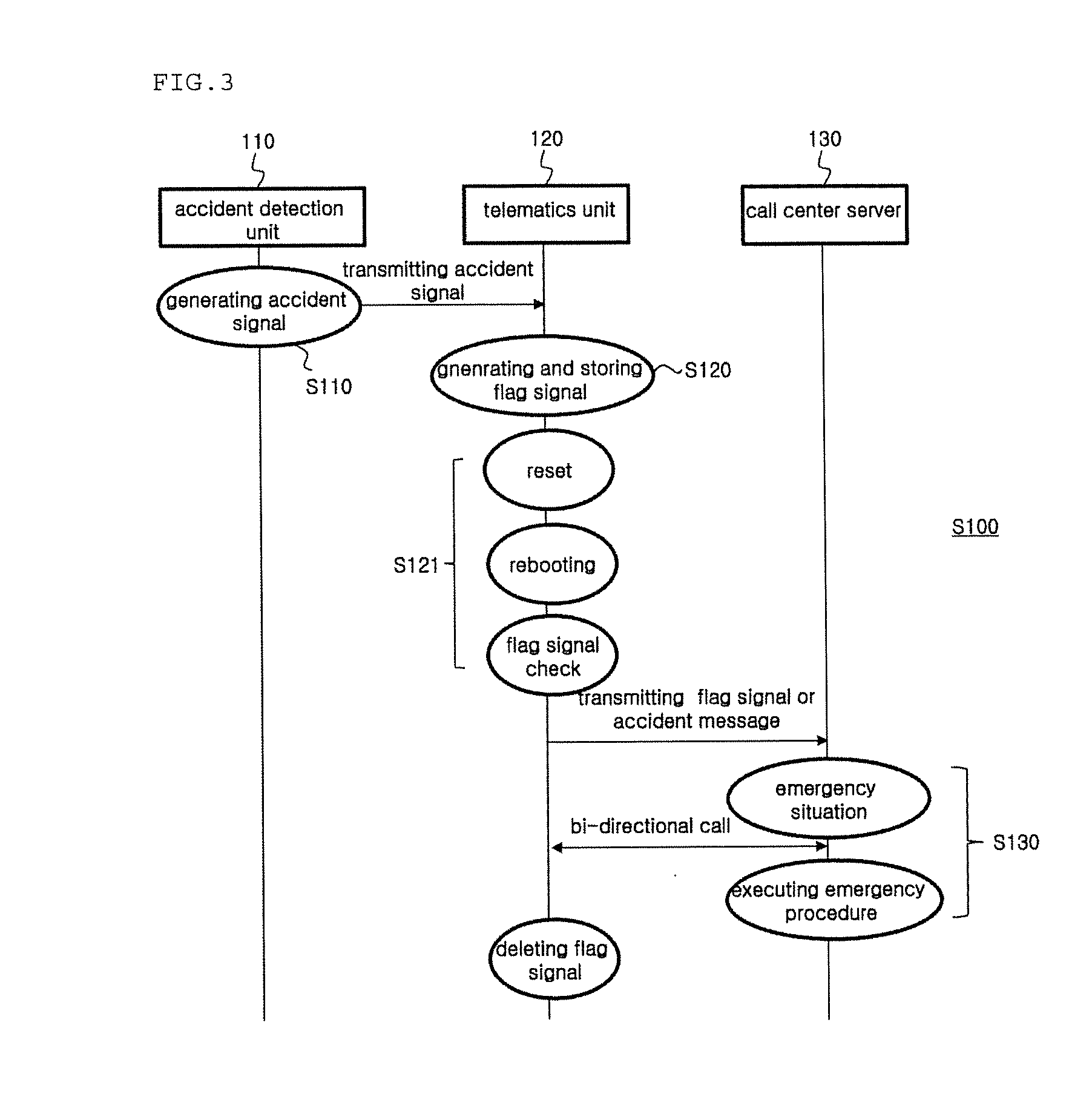
Car emergency system and method of emergency measures using the car emergency system
ActiveUS20160150083A1Pedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSpecial service for subscribersEmergency procedureEngineering
A vehicle emergency system includes an accident detection unit for detecting a collision strength to generate an accident signal, a telematics unit for generating a flag signal in response to the accident signal and for storing the flag signal, and a call center server for recognizing an emergency situation when the flag signal is delivered, and for executing an emergency procedure after emergency call, wherein the telematics unit, even when reset by the accident signal, checks the flag signal stored before reset, and automatically transmits at least one of the flag signal and an accident message generated based on the flag signal into the call center server.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com