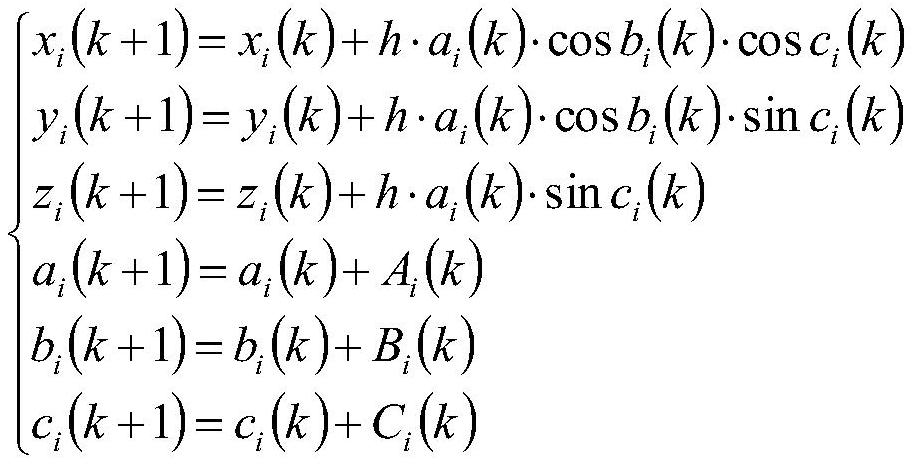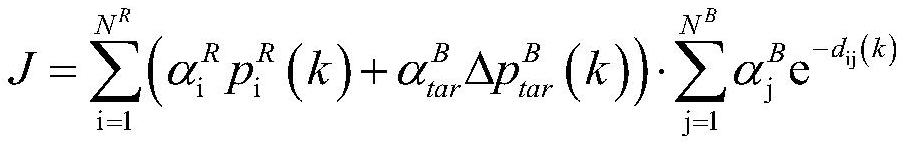Patents
Literature
36 results about "Missile defense" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
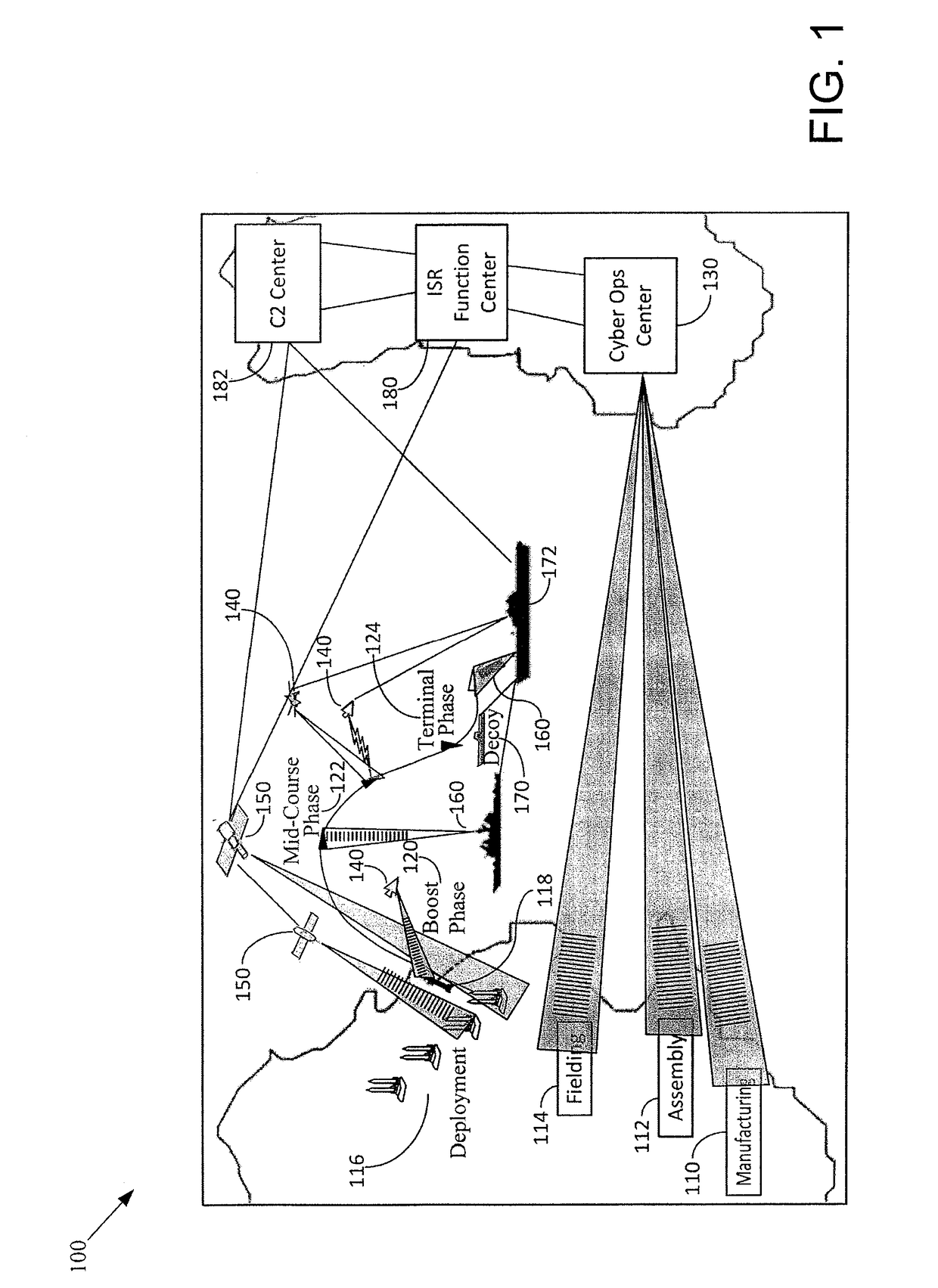
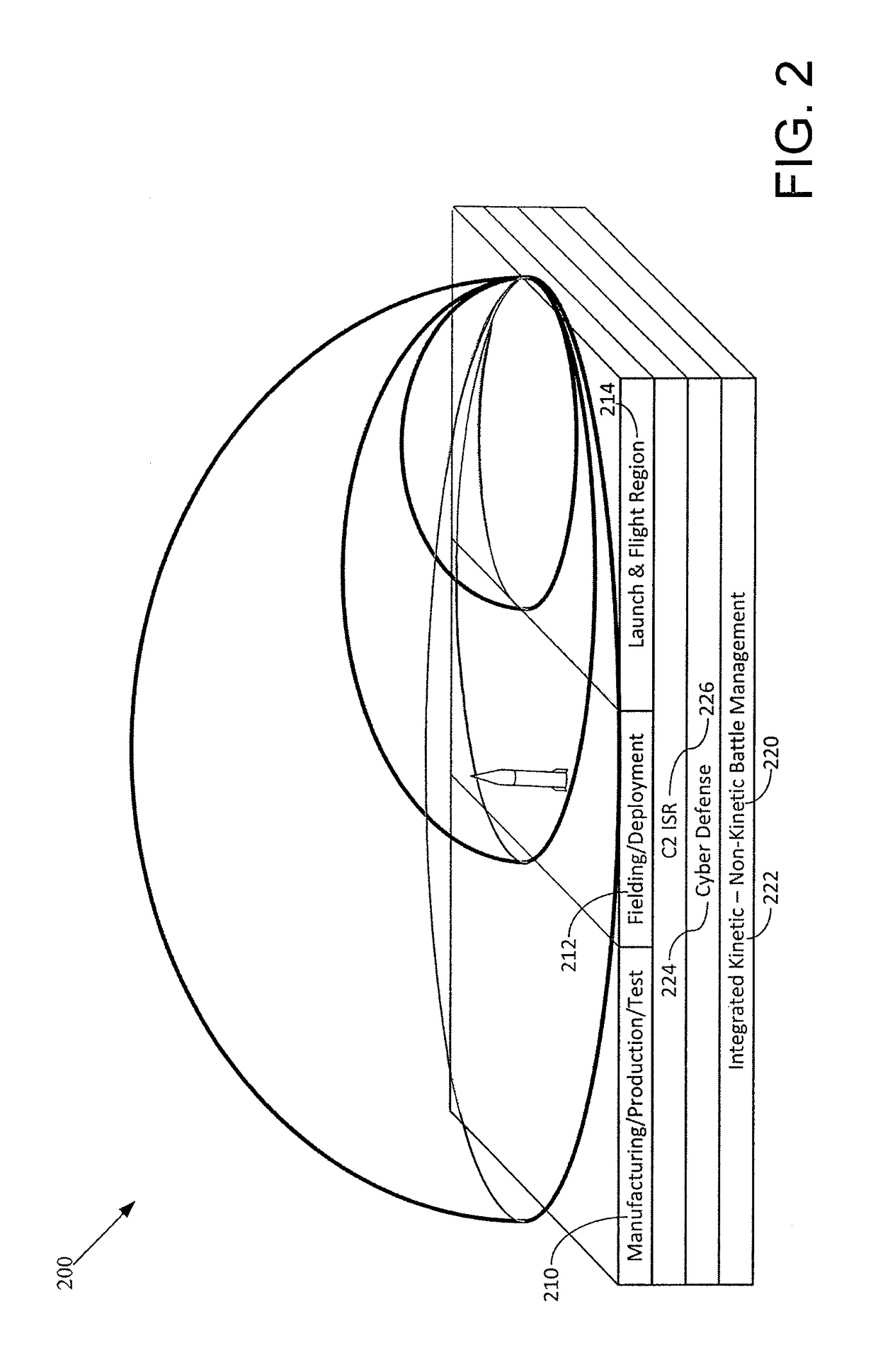
Missile defense is a system, weapon, or technology involved in the detection, tracking, interception, and destruction of attacking missiles. Originally conceived as a defense against nuclear-armed intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), its application has broadened to include shorter-ranged non-nuclear tactical and theater missiles.
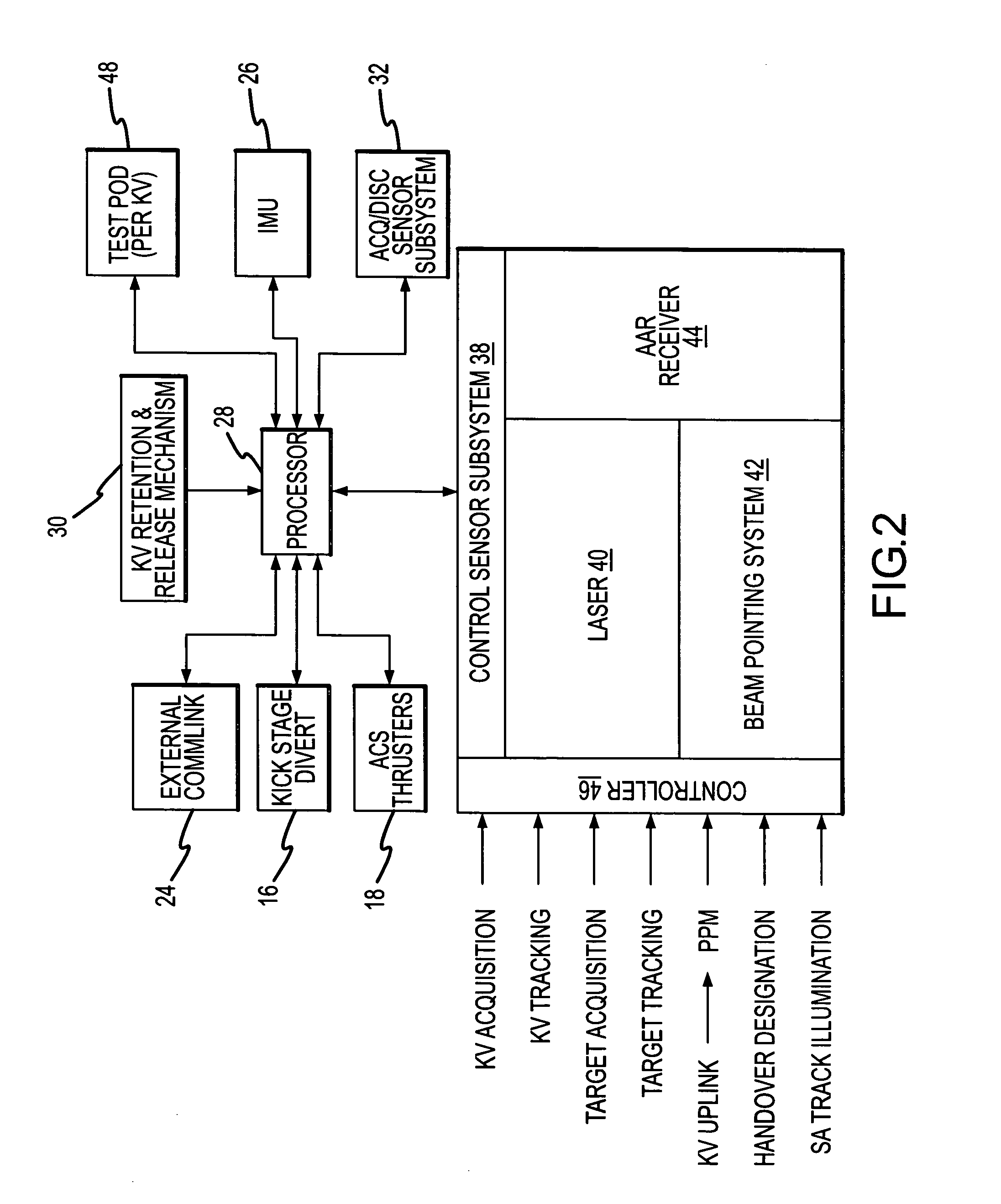
Multi-target-tracking optical sensor-array technology
ActiveUS7551121B1Highly accurate positional metricWide field-of-viewDirection controllersWeapon control systemsSensor arrayAviation
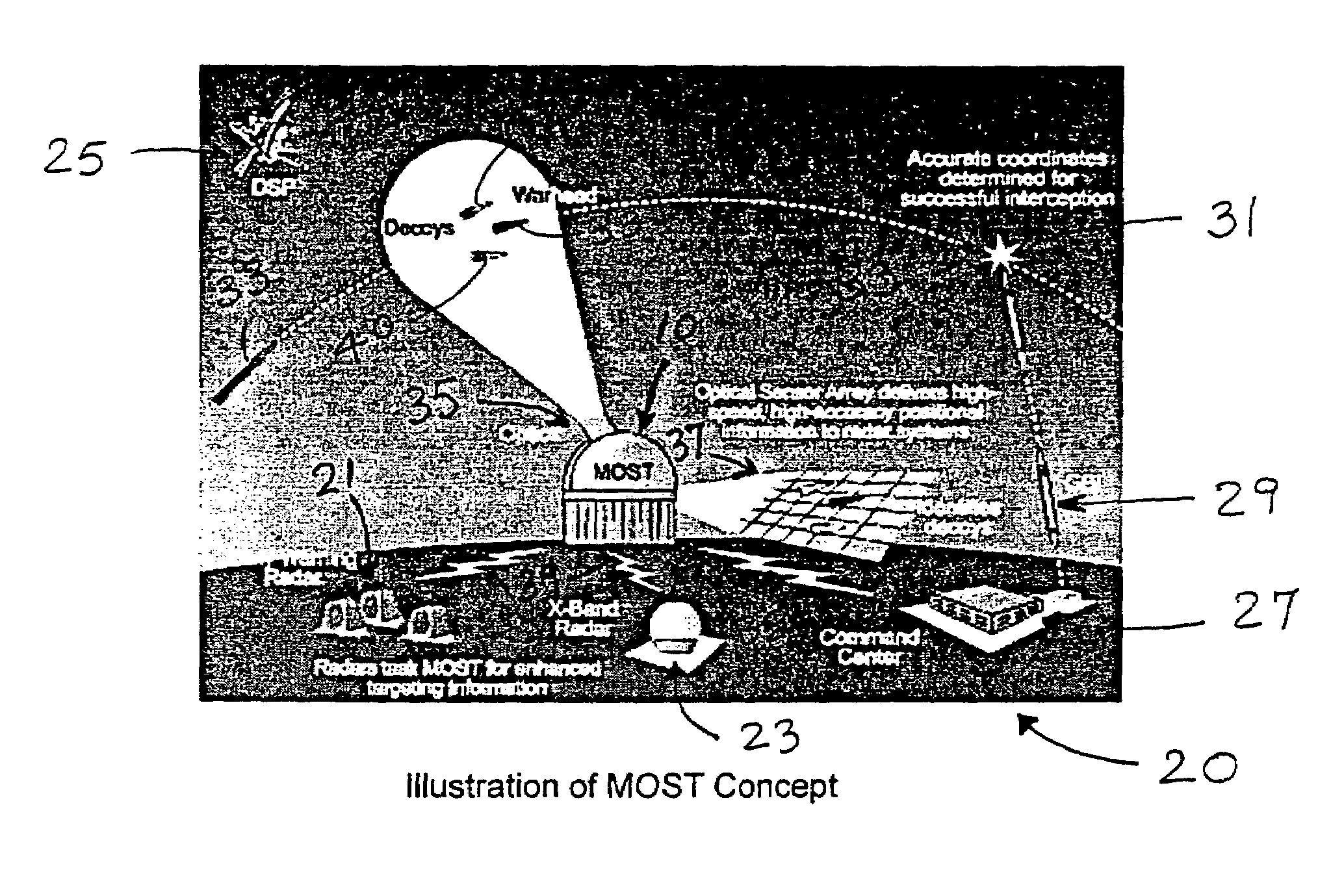
The multi-target tracking and discrimination system (MOST) fuses with and augments existing BMDS sensor systems. Integrated devices include early warning radars, X-band radars, Lidar, DSP, and MOST which coordinates all the data received from all sources through a command center and deploys the GBI for successful interception of an object detected anywhere in space, for example, warheads. The MOST system integrates the optics for rapid detection and with the optical sensor array delivers high-speed, high accuracy positional information to radar systems and also identifies decoys. MOST incorporates space situational awareness, aero-optics, adaptive optics, and Lidar technologies. The components include telescopes or other optical systems, focal plane arrays including high-speed wavefront sensors or other focal plane detector arrays, wavefront sensor technology developed to mitigate aero-optic effects, distributed network of optical sensors, high-accuracy positional metrics, data fusion, and tracking mounts. Field applications include space monitoring, battlefield artillery, battlefield management, ground defense, air defense, space protection, missile defense, gunfire detection, and the like.
Owner:OCEANIT LAB
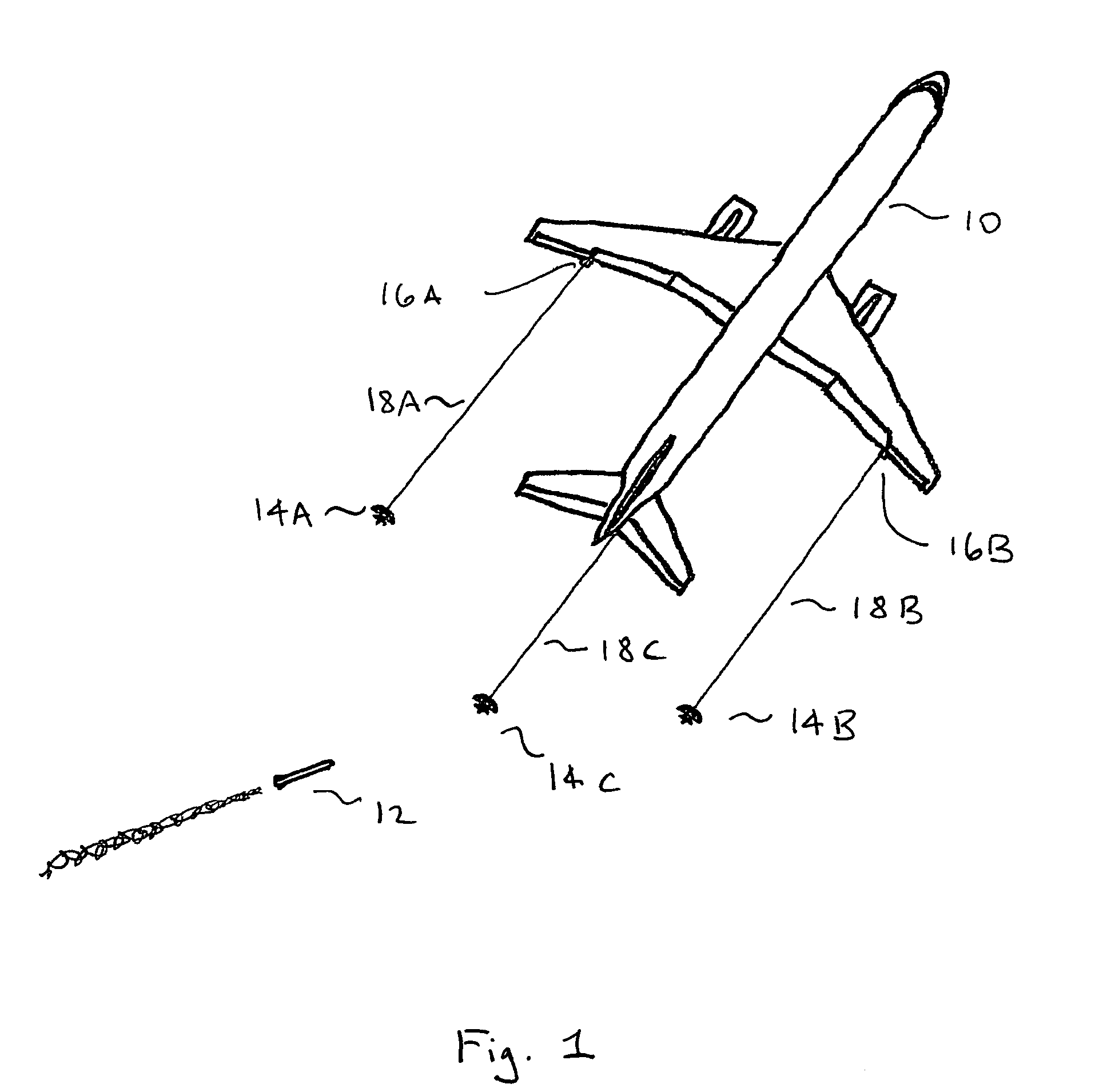
Self-powered tethered decoy for heat-seeking transport aircraft missile defense
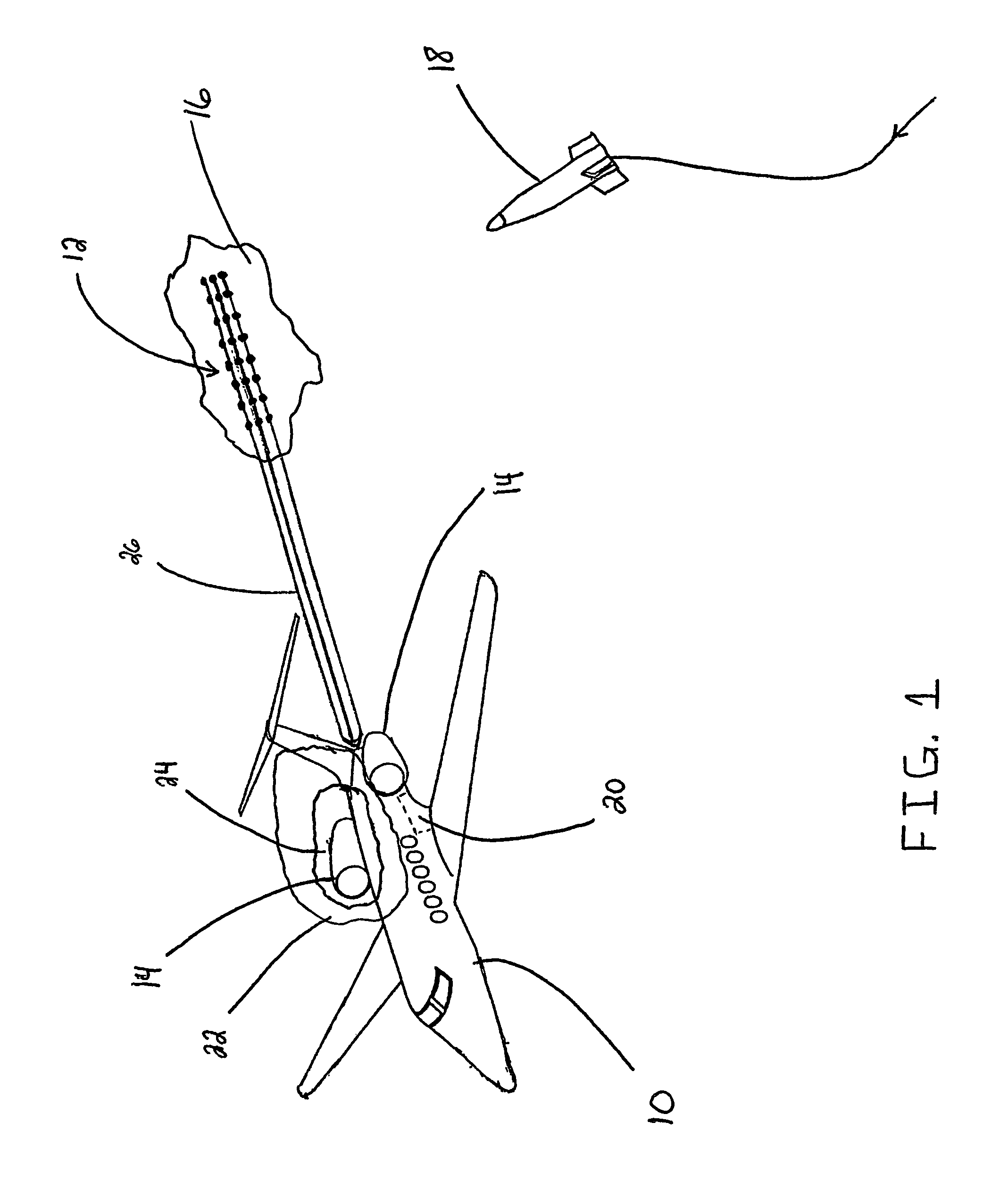
A low-cost airliner defense system utilizing self powered, retrievable, towed decoys against man portable heat-seeking missile (MANPAD) systems provides both high power and a large IR radiating surface area. An efficient and lightweight integrated turbine-alternator extracts sufficient electric power from an air stream directed through a small decoy deployed and towed behind an aircraft during the vulnerable phases of a flight to power a large and intense IR emitter. Unfurled IR radiator “petals” present large area arrays of rear-facing IR emitters. During the high-altitude cruise phase the radiating petals furl down folding around the retrieved decoy body as it is stowed in a streamlined housing for minimizing fuel consumption and maneuverability penalties.
Owner:BURNS ALAN ALEXANDER
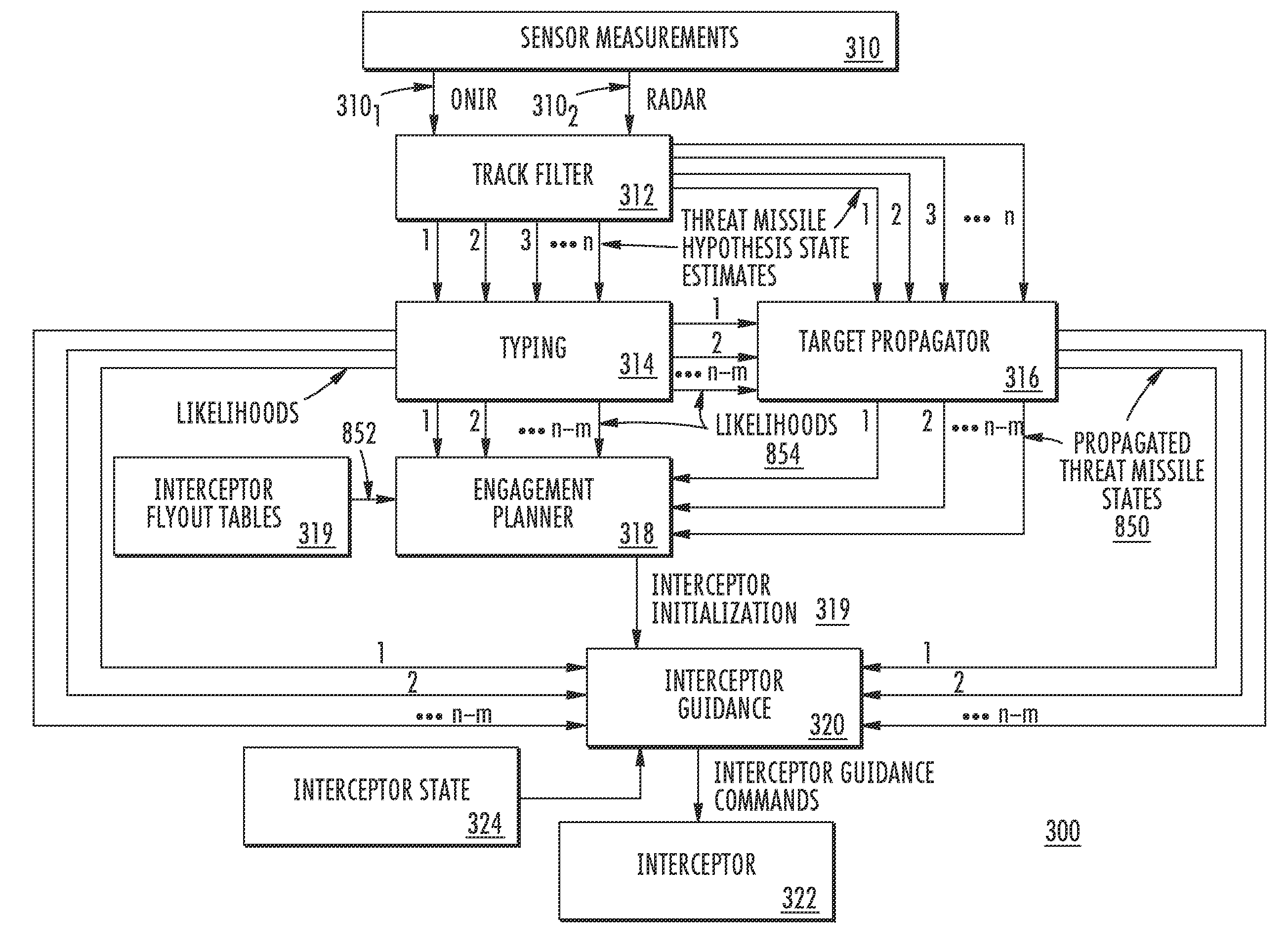
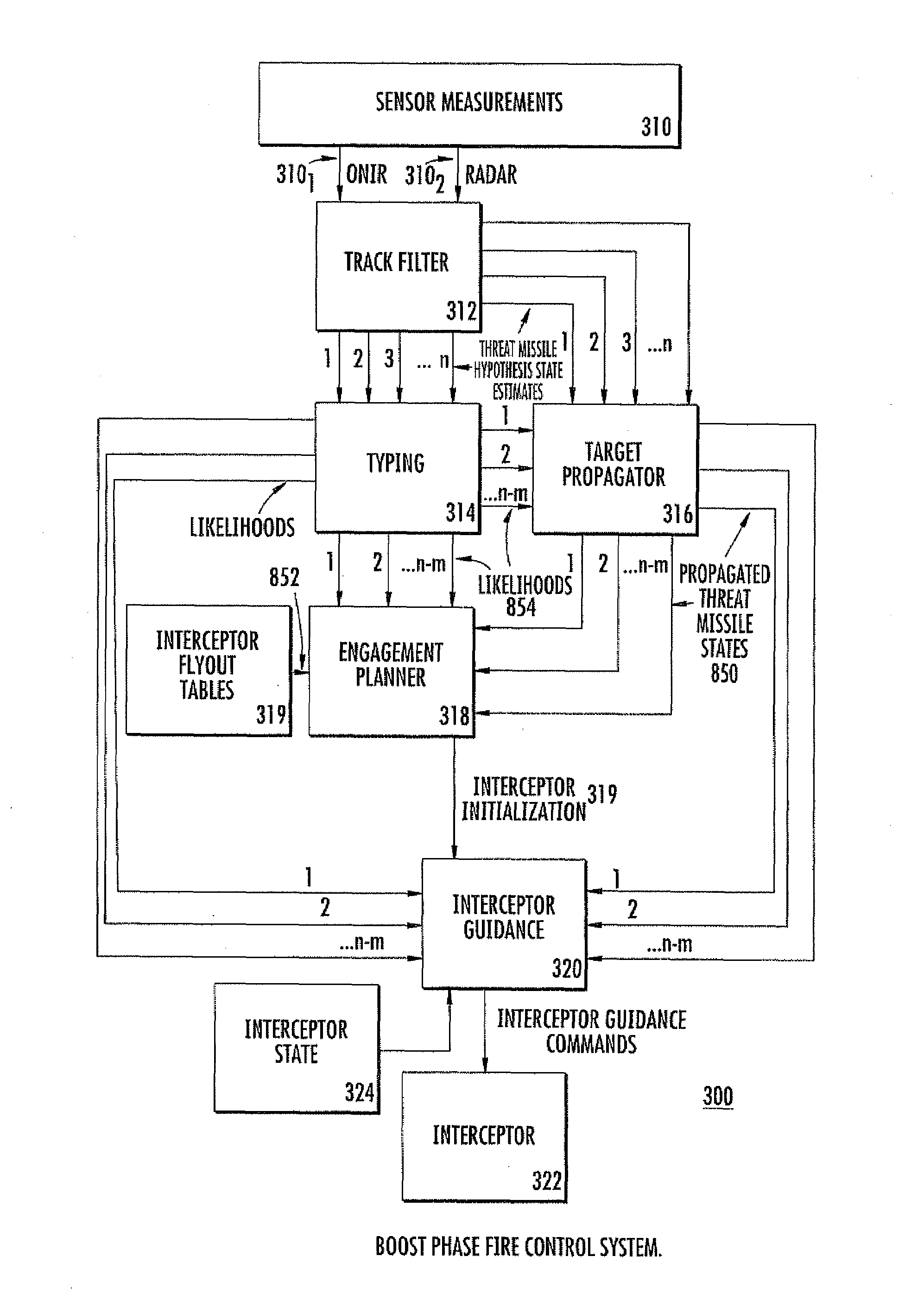
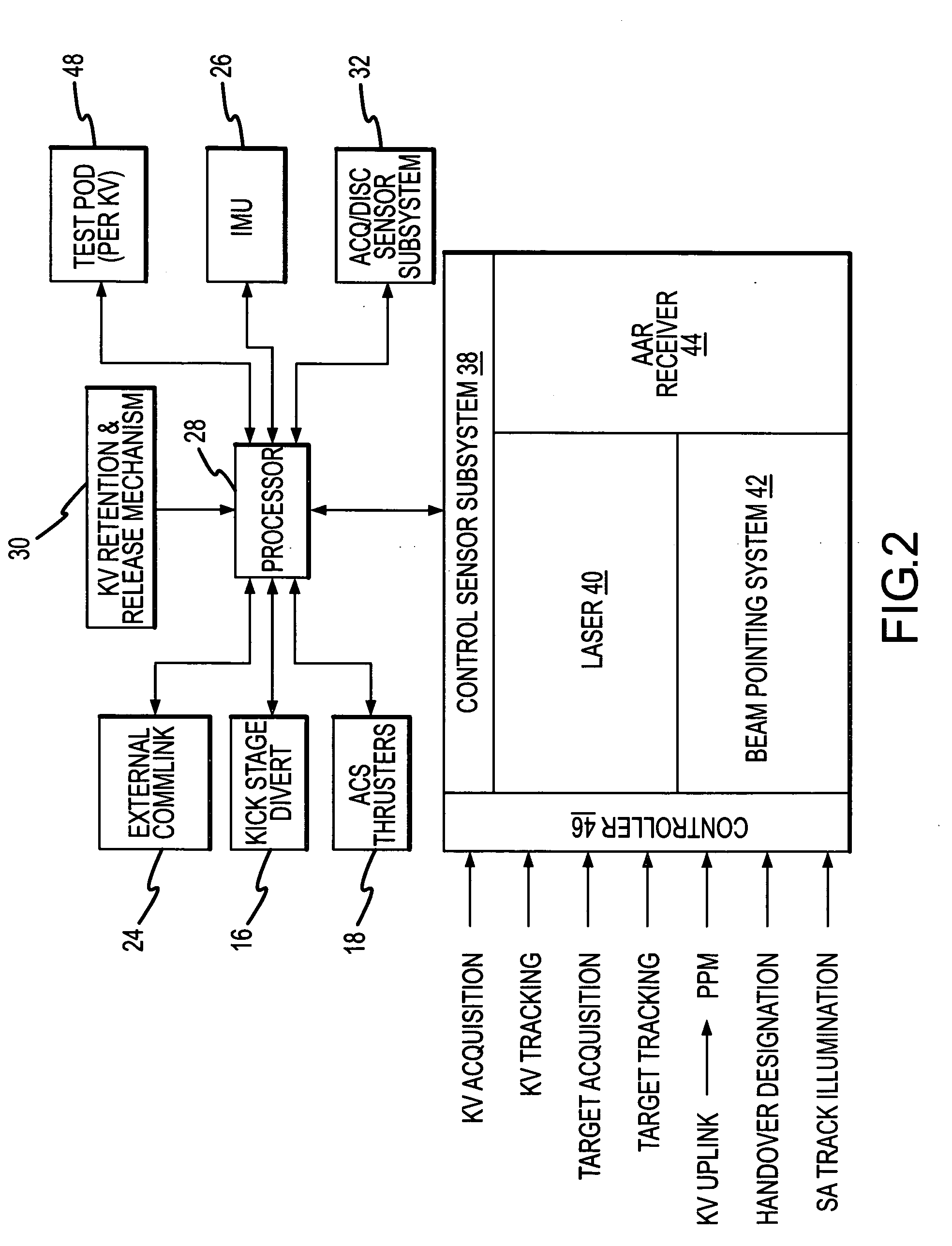
Interceptor guidance for boost-phase missile defense
A fire control system for a boost phase threat missile includes sensors for generating target-missile representative signals, and a multi-hypothesis track filter, which estimates the states of various target hypotheses. The estimated states are typed to generate hypotheses and their likelihoods. The states, hypotheses and likelihoods are applied to a multihypothesis track filter, and the resulting propagated states are applied to an engagement planner, together with the hypotheses and likelihoods. The engagement planner initializes the interceptor(s). Interceptor guidance uses the initialization and the propagated states and typing information to command the interceptor.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
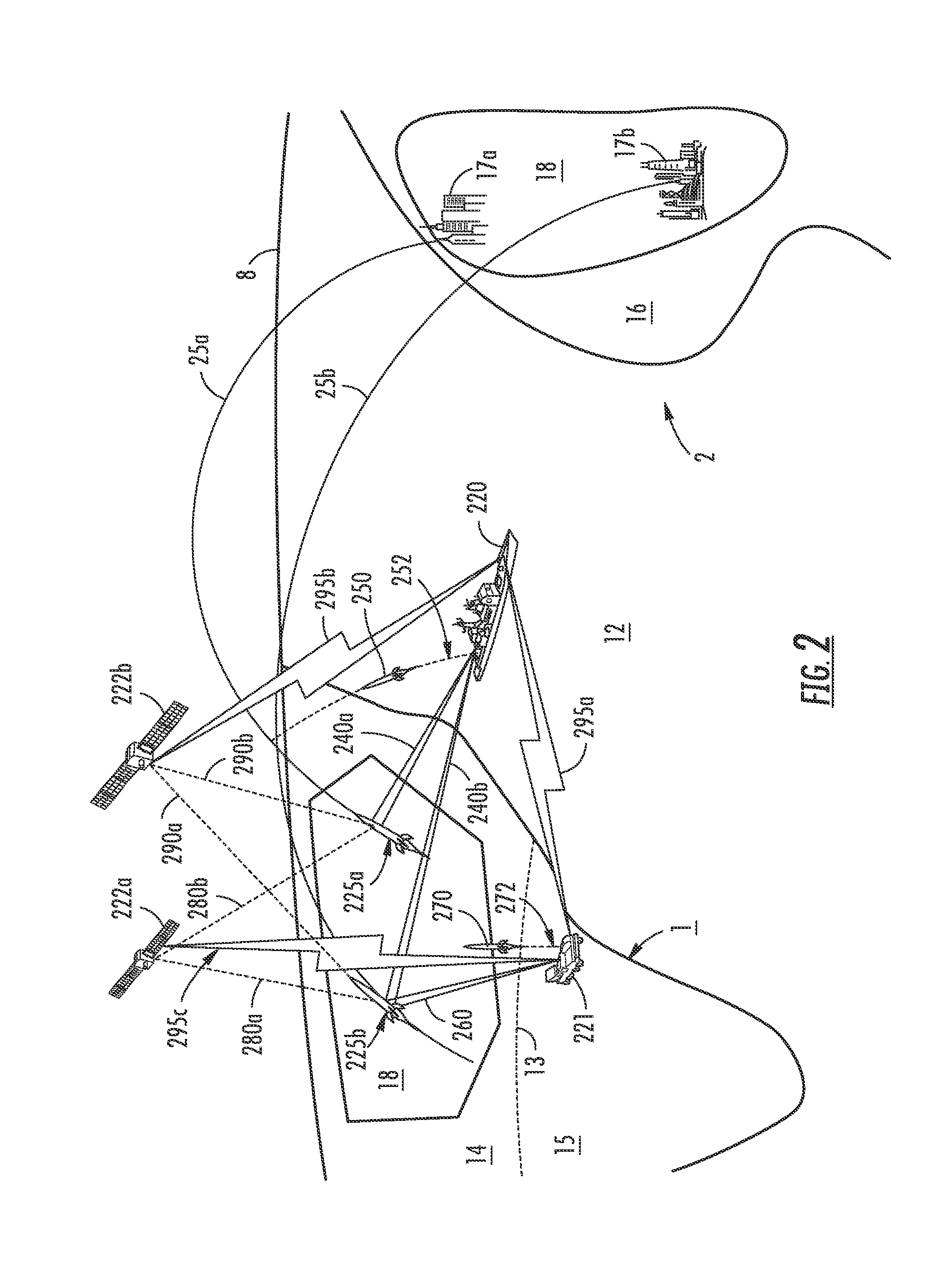
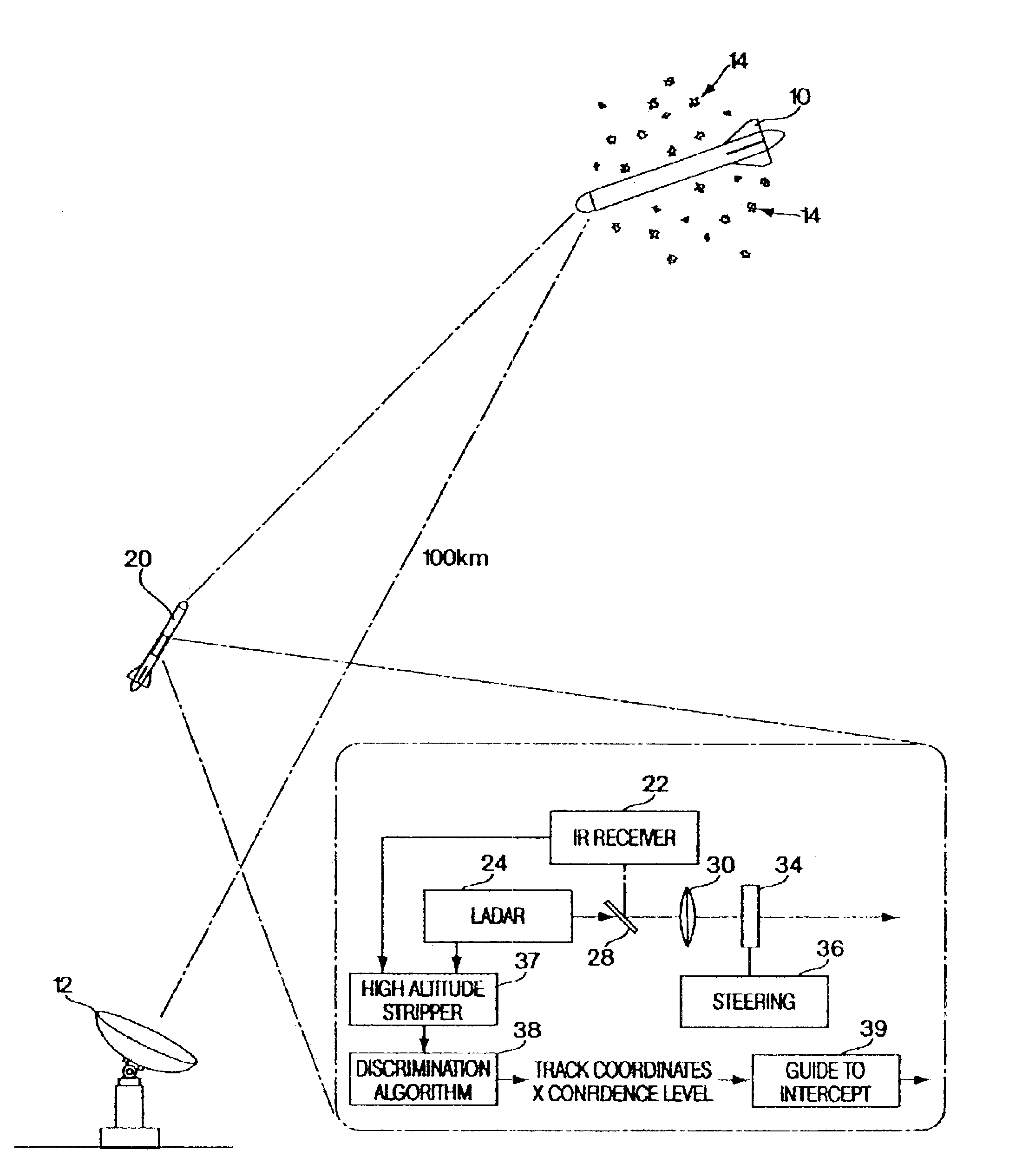
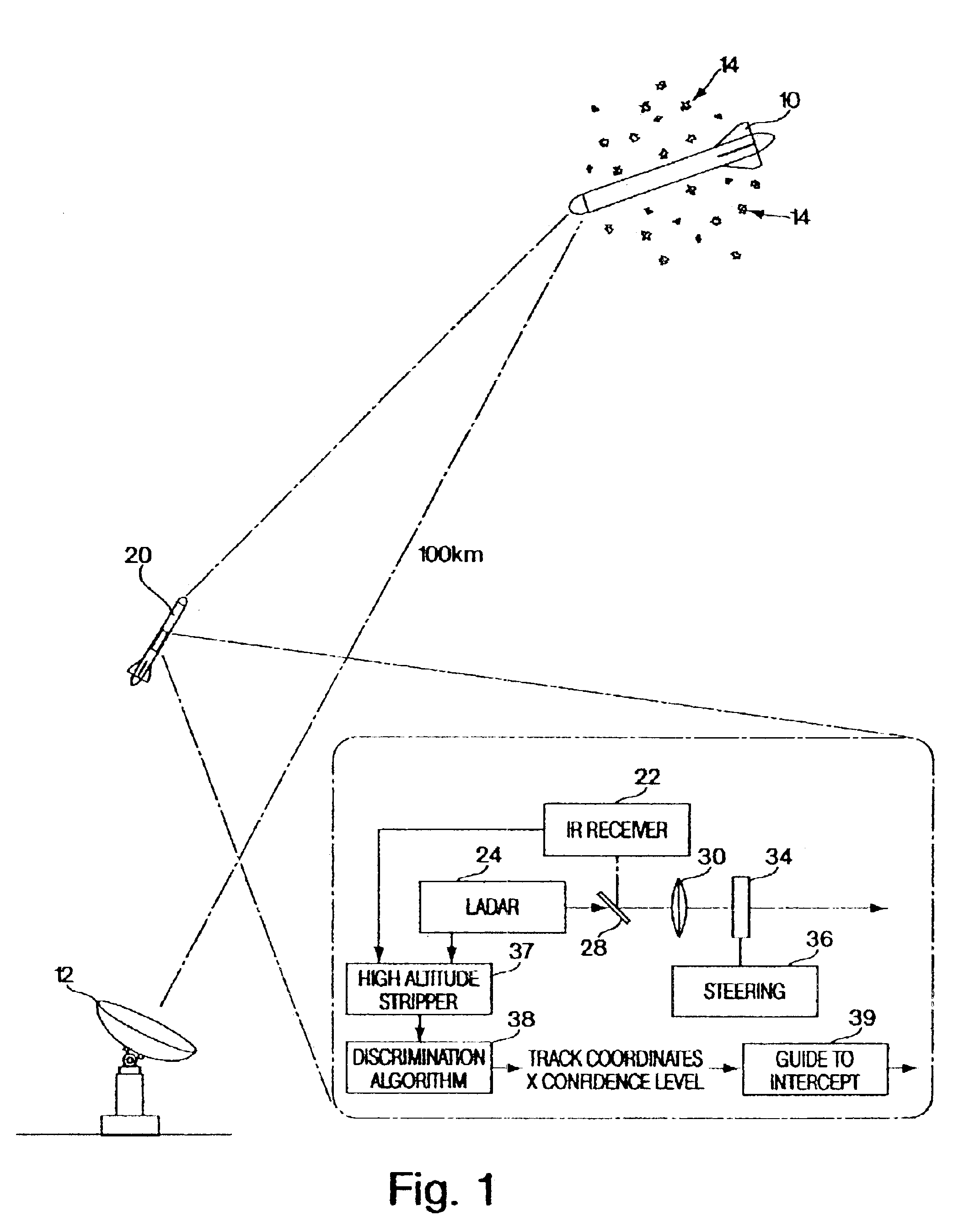
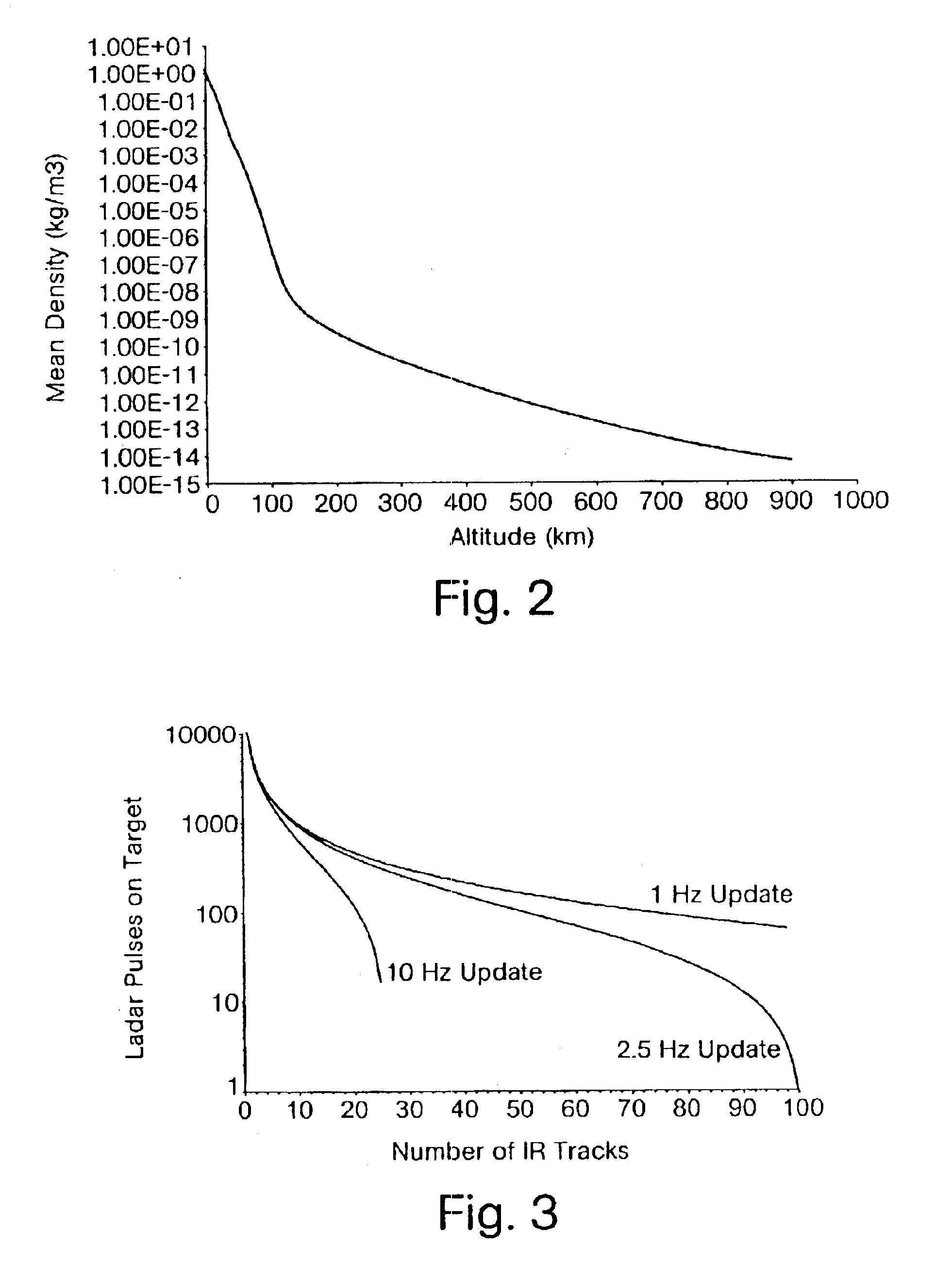
High altitude stripping for threat discrimination
InactiveUS6877691B2Improve spatial resolutionPrecise target dynamic measurementDirection controllersSelf-propelled projectilesGround based radarDecoy
A technique is provided that uses a dual mode seeker (IR and LADAR) for precise target dynamics measurement, which extends stripping to a much higher altitude than ground based radar. Initial results show that this approach works to altitudes in excess of 100 km. Stripping becomes a reliable way to discriminate lighter weight decoys from reentry vehicles at altitudes and ranges consistent with planned divert capabilities for terminal phase missile defense. It is a finding of this invention that the LADAR will improve the spatial resolution by a factor of five over typical missile defense IR seekers using a common aperture. The LADAR provides a 3D angle, angle, range (AAR) image for each laser pulse which is used to extract the precise target state vectors.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
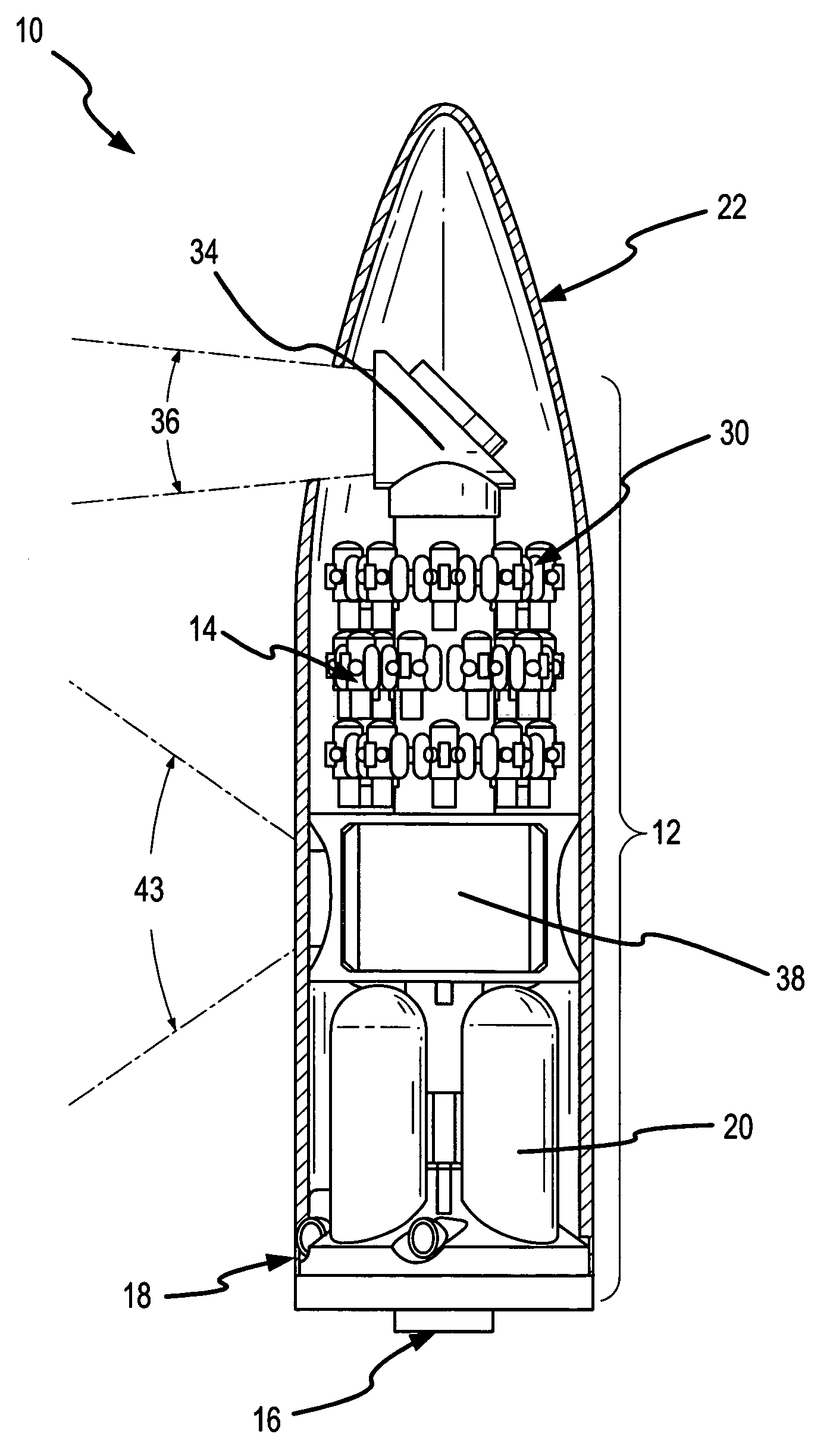
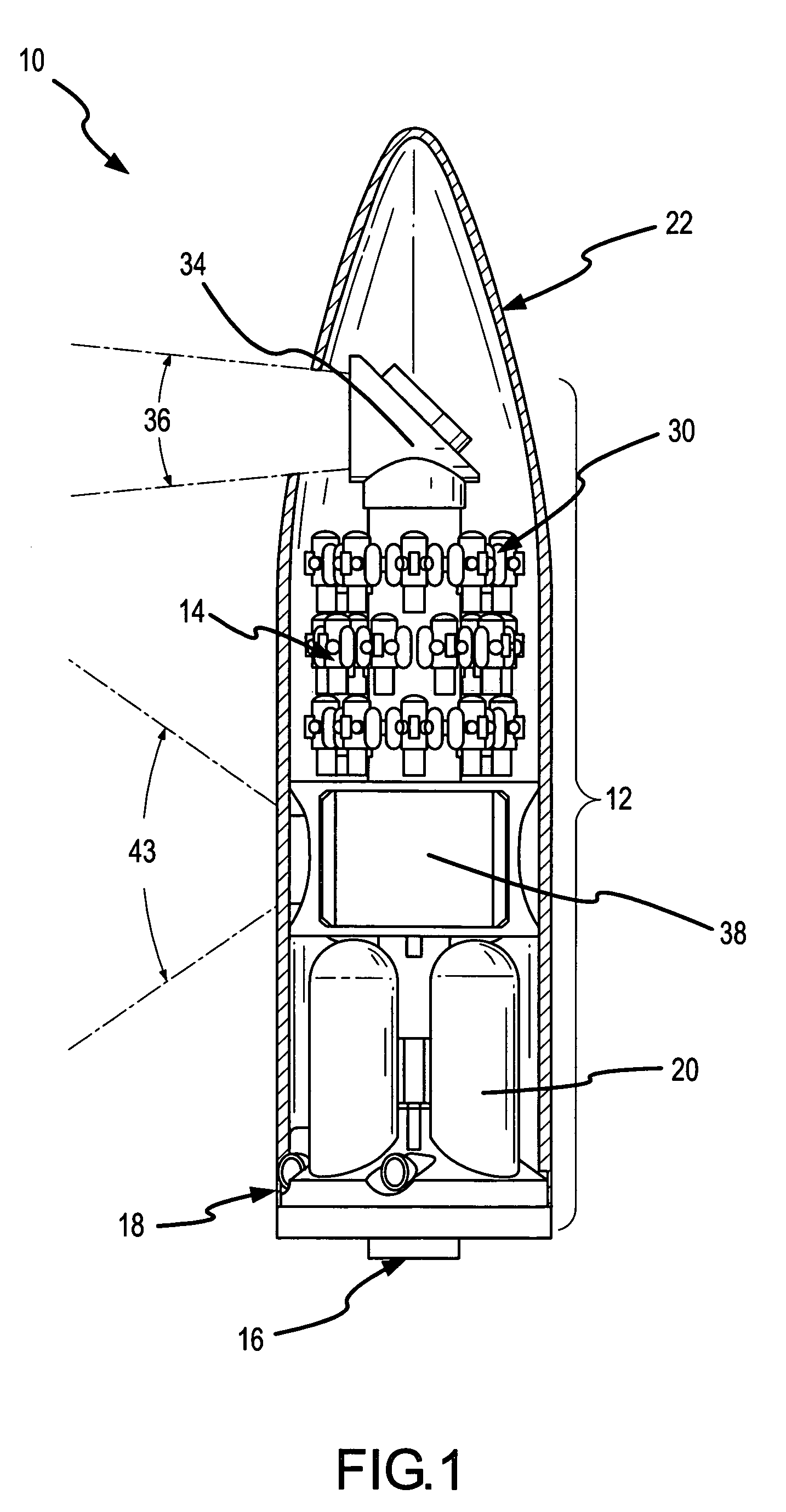
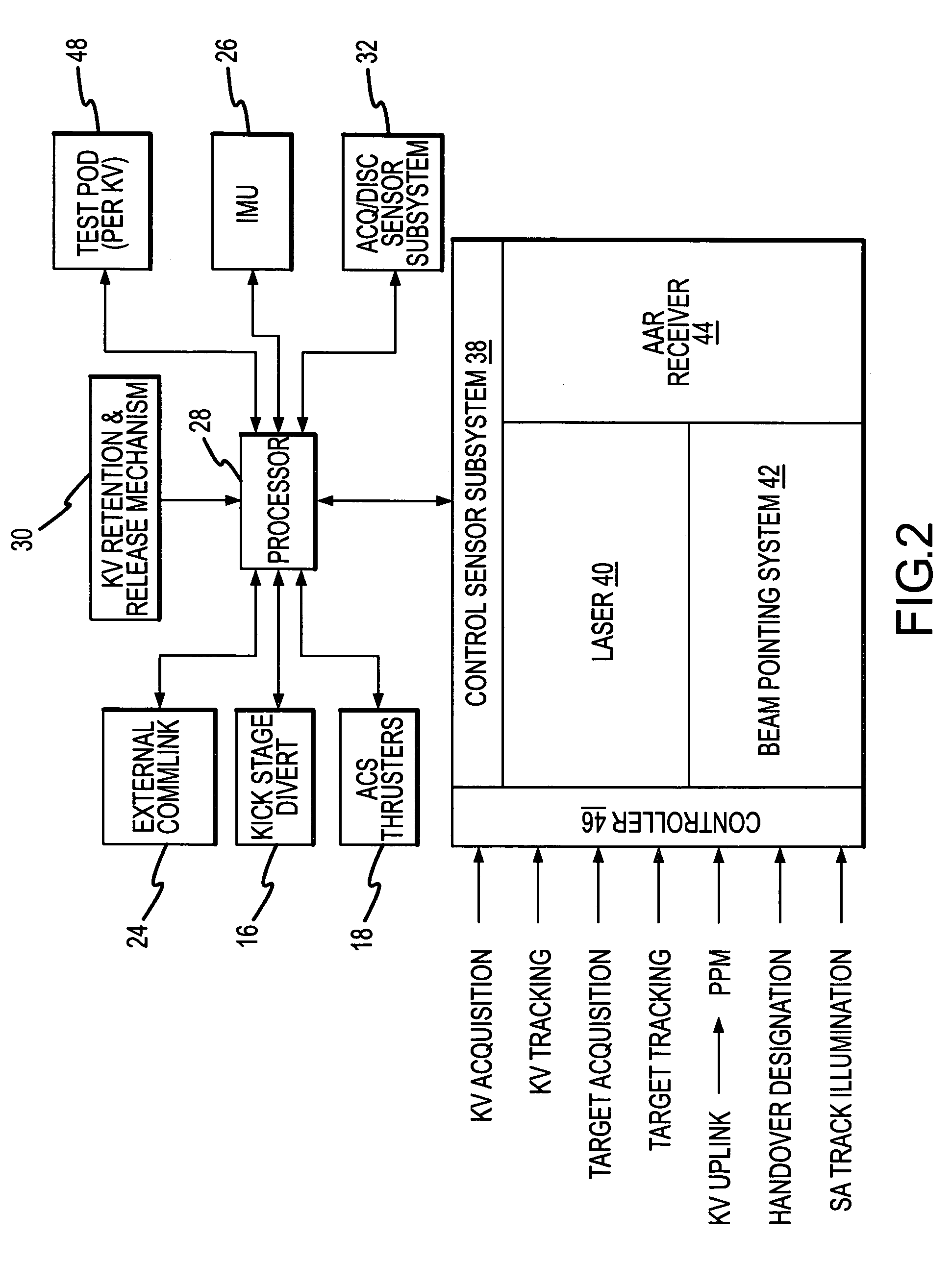
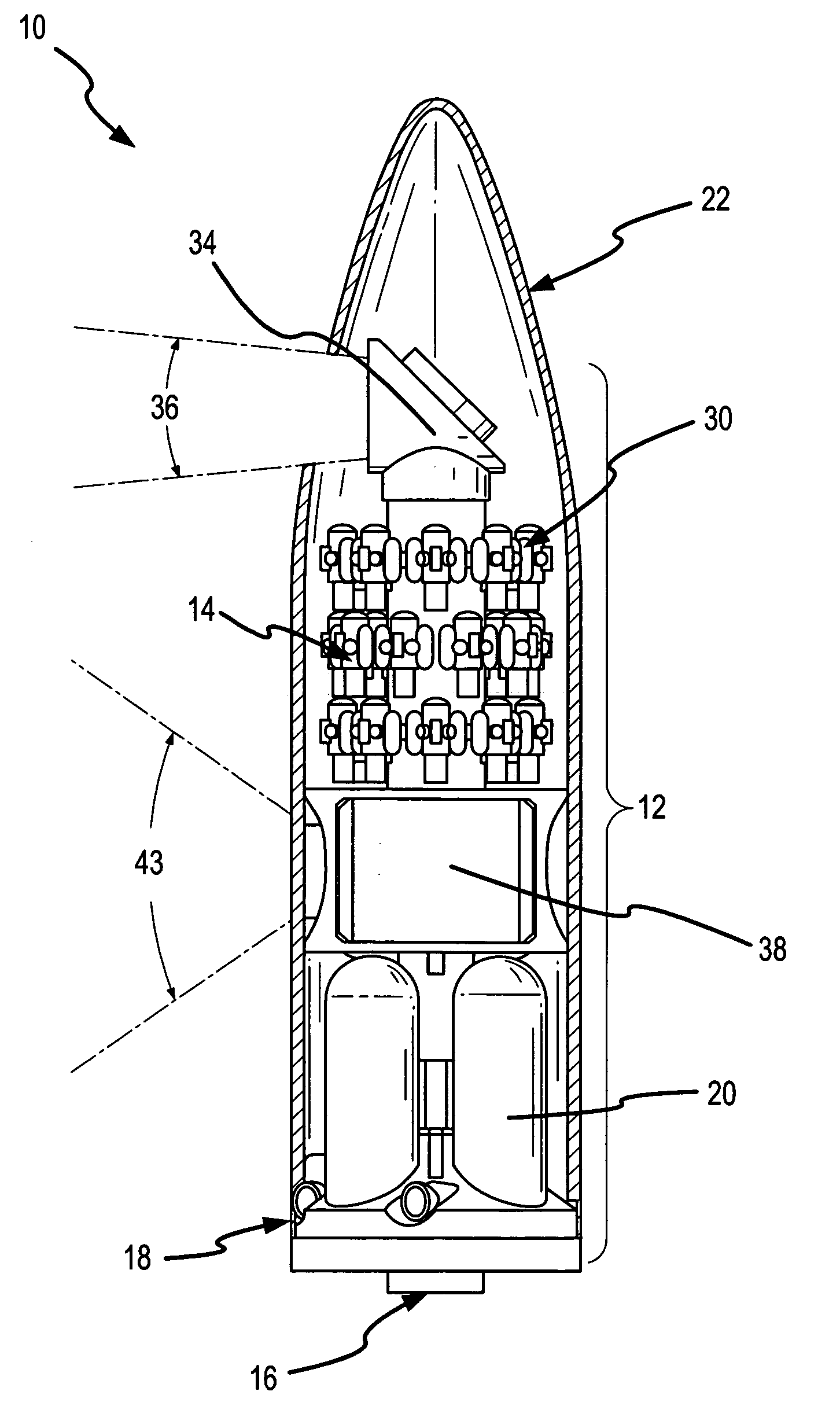
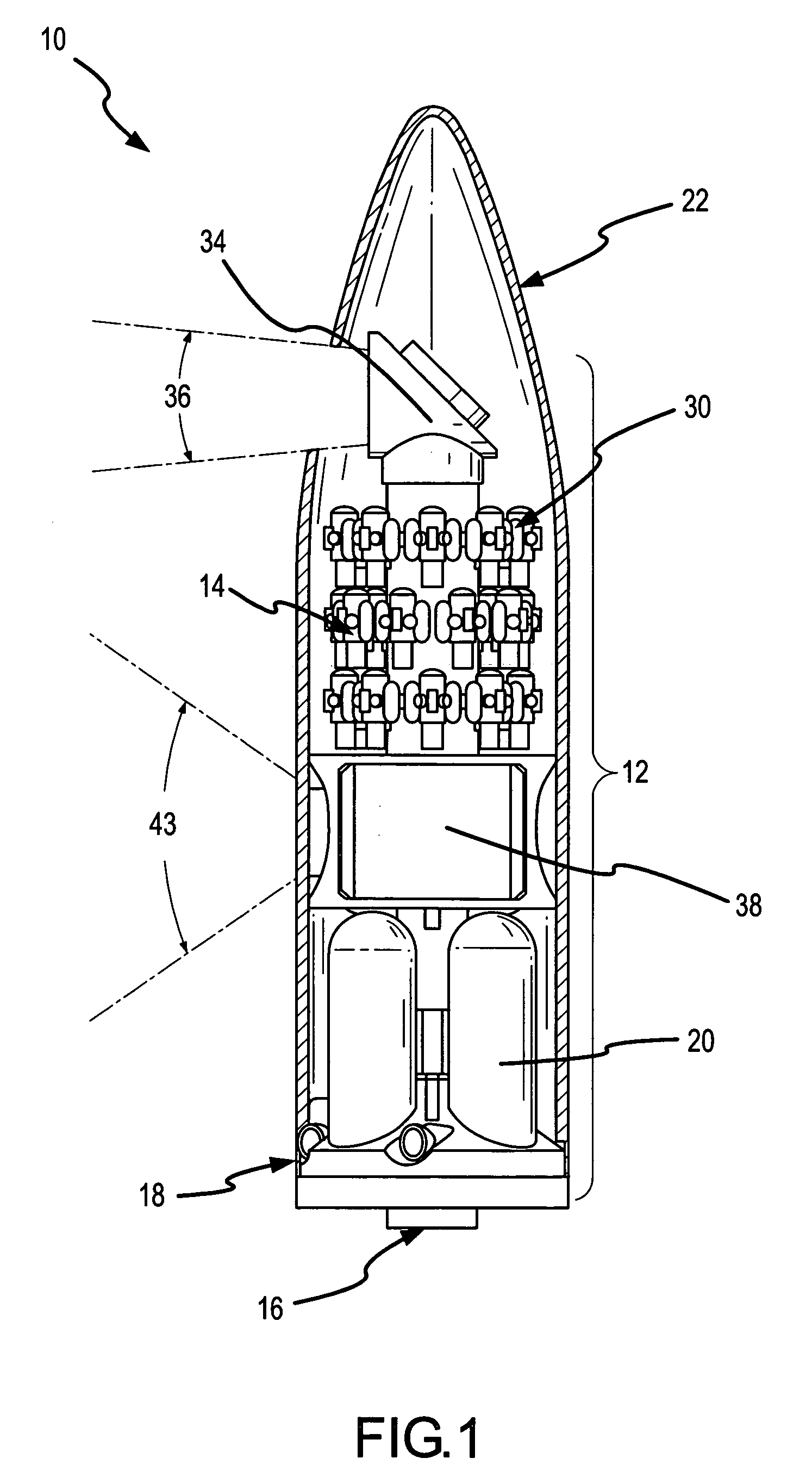
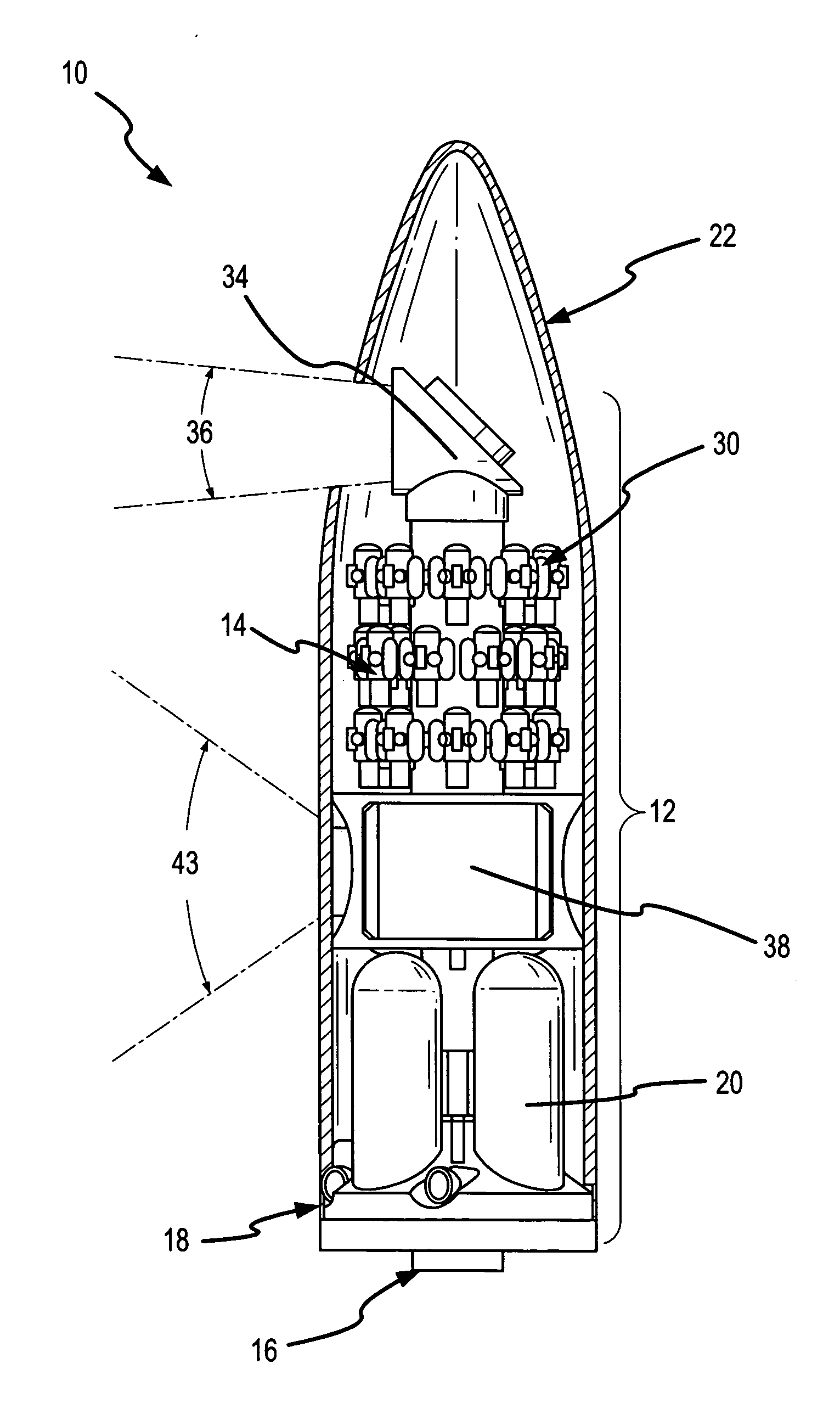
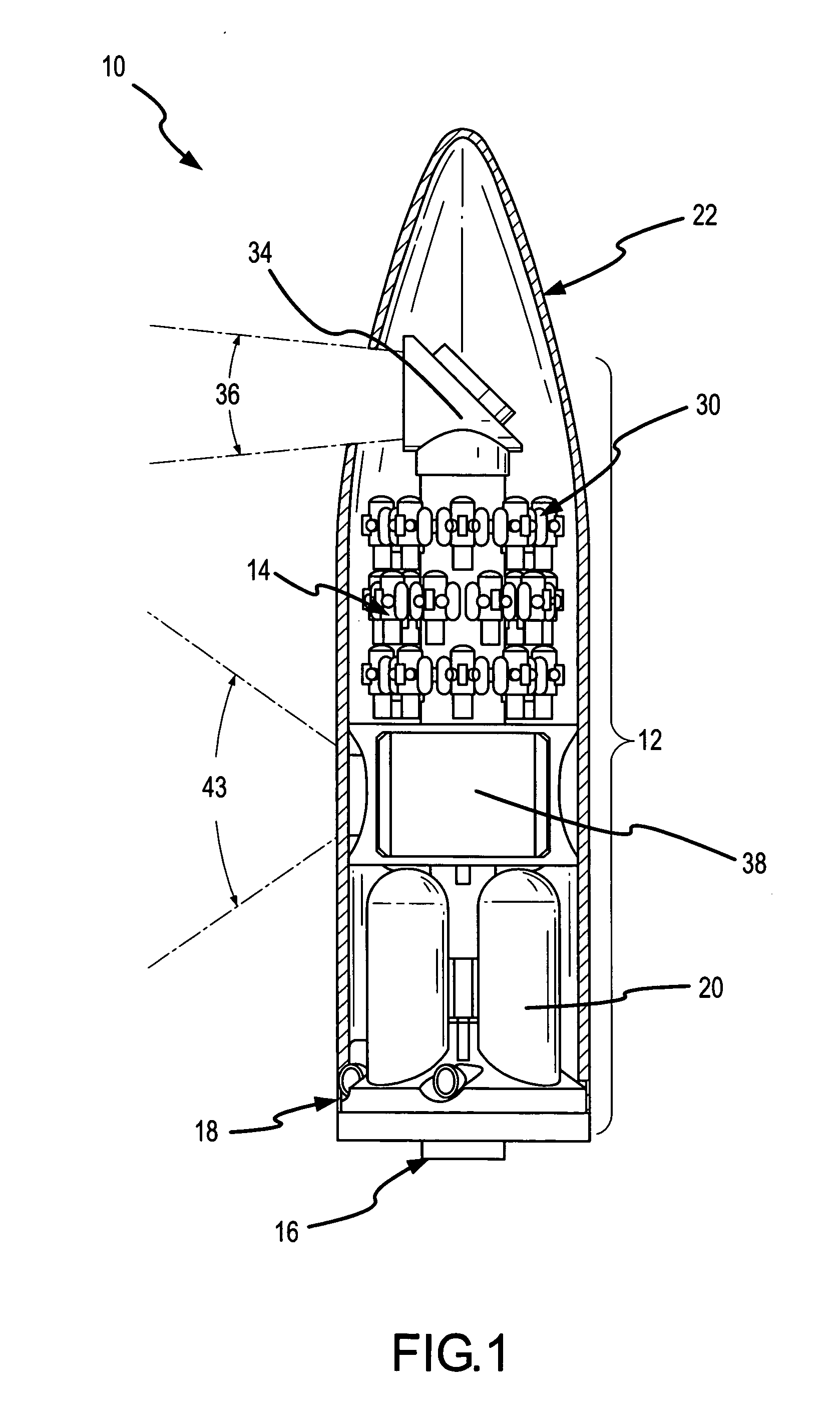
Multiple kill vehicle (MKV) interceptor and method for intercepting exo and endo-atmospheric targets
ActiveUS7494089B2Overcomes of bandwidthAvoid complexityAmmunition projectilesCosmonautic vehiclesCost effectivenessImage resolution
By sharing tasks between the CV and the KVs, the MKV interceptor provides a cost-effective missile defense system capable of intercepting and killing multiple targets. The placement of the acquisition and discrimination sensor and control sensor on the CV to provide target acquisition and discrimination and mid-course guidance for all the KVs avoids the weight and complexity issues associated with trying to “miniaturize” unitary interceptors. The placement of a short-band imaging sensor on each KV overcomes the latency, resolution and bandwidth problems associated with command guidance systems and allows each KV to precisely select a desirable aimpoint and maintain track on that aimpoint to impact.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Temporarily installed aircraft observer door plug, chair, sonotube ejection and control system
ActiveUS20100206988A1Quick installationCost-effective utilizationSeating arrangementsMilitary adjustmentSeat beltMissile defense
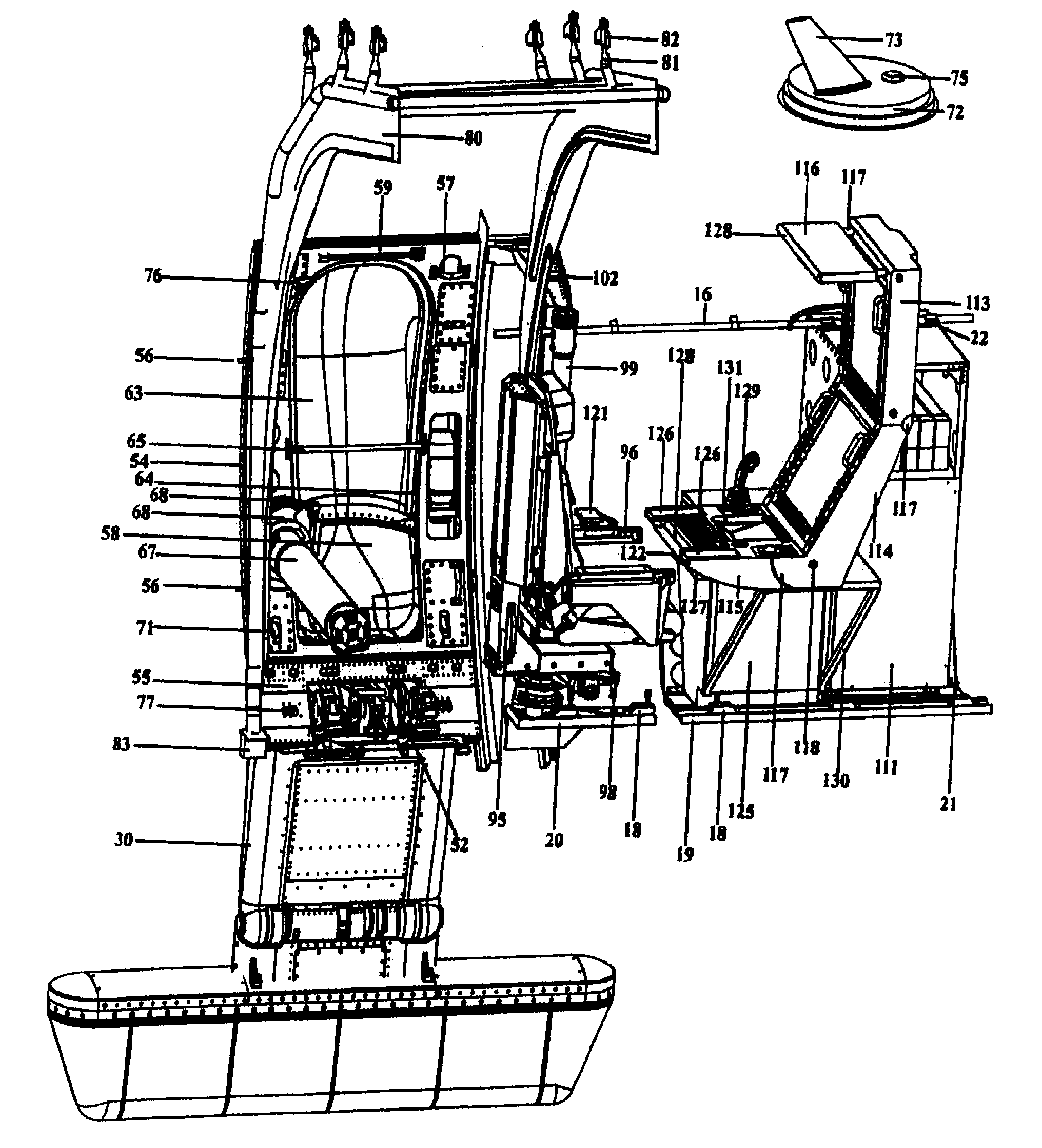
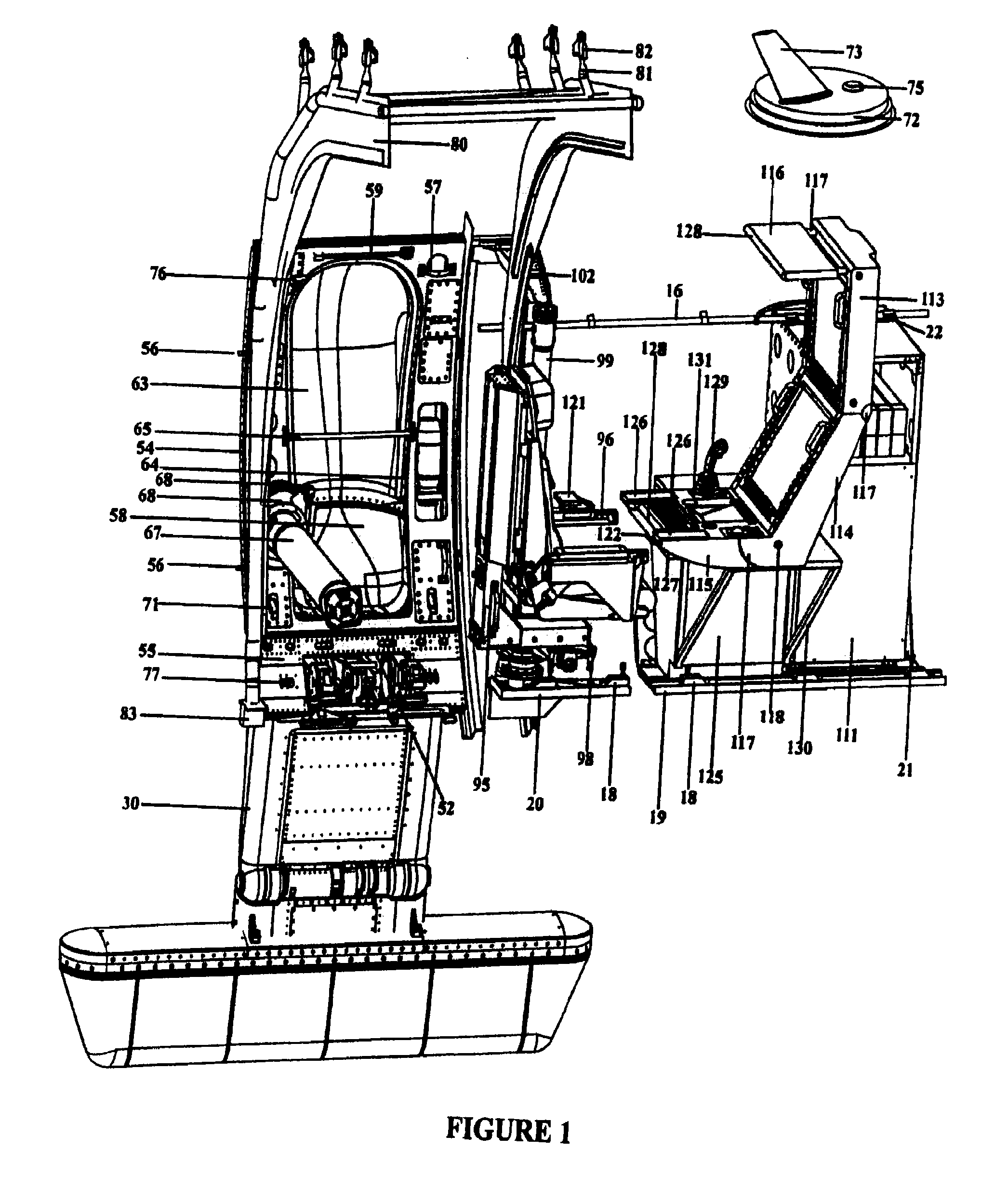
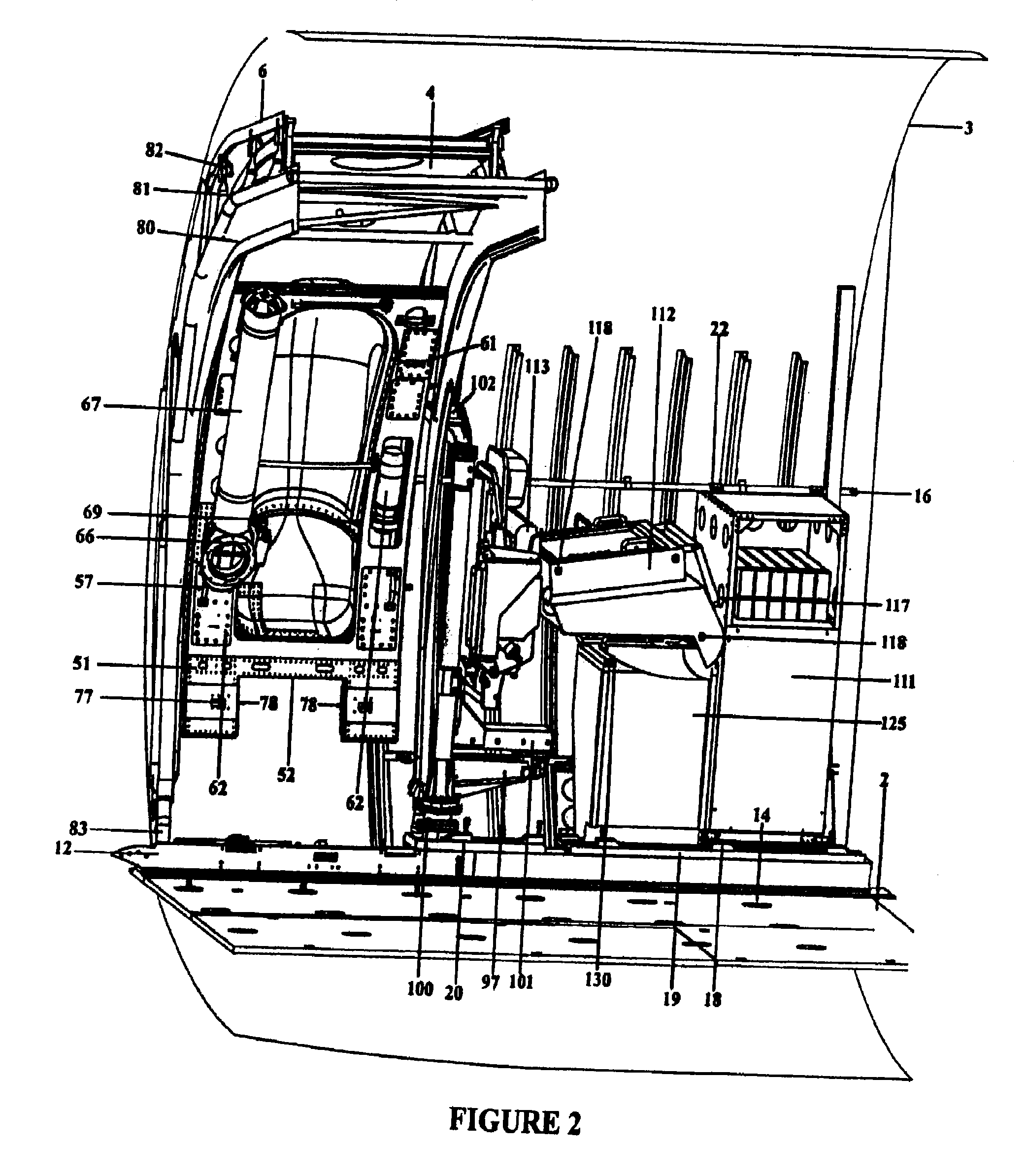
The system and apparatus of the present invention is generally comprised of a non-dedicated, temporarily installed, aircraft observer bubble door, chair, sonotube ejection system, mission electronics LRU rack and workstation assembly which are affixed to the Air Deployment System (ADS) rails, cargo tie down “D” rings, seat belt restraint ring bolt sockets, and litter bar of a host aircraft, thereby precluding the requirement for dedicated airframe modifications. One embodiment of the present invention also utilizes a multi-axis, articulated, foldable chair temporarily installed in conjunction with a segmented or one piece pressurized observer bubble door plug and door retraction system. The door plug assembly is designed to accommodate the simultaneous use of a sonotube stores launch system, a missile defense system, and an observer bubble window. The door plug also accommodates fitment around the envelope of a special mission strut which extends through the interior to the exterior of the host aircraft beneath the door plug's lower periphery. The door plug is also moveably mounted within a temporary retraction rail system which interfaces mechanically to the permanent door retraction rails and the aircraft floor or ADS rail system. When the host aircraft is not equipped with an ADS rail system, the retract rails, chair stanchion, mission electronics racks, and workstation assemblies are mounted to an adaptive floor plate (AFP) which can be modified to interface with various cargo floor “D” rings, or other cargo tie down mechanisms and bolt patterns such that several types of dissimilar aircraft can utilize the subject apparatus either with or without ADS rails installed. Once installed the subject apparatus can be stowed outboard of the fuselage cargo transit envelope to permit use of the ADS rail system in-flight, without affecting normal air drop operations, crew egress, the flight performance envelope, or emergency procedures of the host aircraft.
Owner:1281329 ALBERTA
Multihypothesis threat missile propagator for boost-phase missile defense
A fire control system for a boost phase threat missile includes sensors for generating target-missile representative signals, and a multi-hypothesis track filter, which estimates the states of various target hypotheses. The estimated states are typed to generate hypotheses and their likelihoods. The states, hypotheses and likelihoods are applied to a multihypothesis track filter, and the resulting propagated states are applied to an engagement planner, together with the hypotheses and likelihoods. The engagement planner initializes the interceptor(s). Interceptor guidance uses the initialization and the propagated states and typing information to command the interceptor.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method and system for defence against surface-to-air missiles
InactiveUS20080174469A1Verify validityMore powerDefence devicesWave based measurement systemsMissile defenseElectromagnetic interference
A method and a system for defense against surface-to-air missiles (Manpads), which represent a threat to military and civil aircraft during takeoff and landing. For missile defense, the missile is jammed by irradiating it with electromagnetic jamming radiation. This jamming radiation may be constituted of continuous-wave irradiation or frequency packets with a defined pulse repetition rate.
Owner:DIEHL BGT DEFENCE GMBH & CO KG
Multiple kill vehicle (MKV) interceptor and method for intercepting exo and endo-atmospheric targets
ActiveUS20090001214A1Overcomes of bandwidthAvoid complexityAmmunition projectilesDirection controllersCost effectivenessImage resolution
By sharing tasks between the CV and the KVs, the MKV interceptor provides a cost-effective missile defense system capable of intercepting and killing multiple targets. The placement of the acquisition and discrimination sensor and control sensor on the CV to provide target acquisition and discrimination and mid-course guidance for all the KVs avoids the weight and complexity issues associated with trying to “miniaturize” unitary interceptors. The placement of a short-band imaging sensor on each KV overcomes the latency, resolution and bandwidth problems associated with command guidance systems and allows each KV to precisely select a desirable aimpoint and maintain track on that aimpoint to impact.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Pulsed detonation engines for reaction control systems
InactiveUS20060201134A1Improve performanceEffectiveCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusControl systemMissile defense
Pulsed detonation engines (PDEs) are adapted for use in reaction control systems (RCS), such as thrusters for orbital correction and control (e.g., for earth-orbiting satellites), divert thrust generation and control for space-based interceptor devices, and for missile trajectory correction and motion control. According to one aspect of the invention, PDEs are adapted for motion control of so-called “kill vehicles,” which are small devices, typically launched from satellites, for strategic missile defense.
Owner:LEIDOS
System and method for asymmetric missile defense
ActiveUS20160253590A1Accurate responseAccurately determineDefence devicesProbabilistic networksSoftware engineeringMissile defense
A method for accurately determining whether a response tool will be effective for responding to a given enemy threat object. Embodiments described herein provide a method and system for responding to a threat object, for example, negating missile threats. Embodiments may include validating effectiveness of a response to the threat object. Other embodiments may include verifying the continued effectiveness of a response to the threat object. Further embodiments may include providing feedback to re-perform the method for responding to the threat object. The system may include a mathematical method, and associated algorithms, to assess, in an automated fashion, the performance of non-kinetic techniques with respect to negating the threat object.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
A Method for Analyzing Force Scale Requirements of Ground Air Defense Weapons
InactiveCN106508044BImprove collaboration efficiencyImprove the combat effectiveness of comprehensive defenseData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsForce structureMissile defense
The invention belongs to the field of force utilization of air defense and anti-missile weapons and equipment, and in particular relates to a method for analyzing the force scale demand of ground air defense weapons. The present invention takes the air defense confrontation between the enemy and the enemy as the background, and comprehensively considers factors such as the enemy's attack direction, the tactical and technical indicators of the enemy's weapons, the combat use mode, the characteristics of different defensive locations or areas, different firepower connection conditions, and different firepower density requirements. , analyze and calculate the force scale and structure requirements of ground air defense weapons in three basic combat deployment styles of ring, sector and linear for different defense areas, and construct the analysis and calculation model of ground air defense force scale structure, which is aimed at single type and multiple types respectively Mixed ground air defense weapons calculate the force scale requirements, and obtain a reasonable number of troops and equipment structure required for ground air defense weapons to defend a specific target, effectively improving the coordination efficiency of the ground air defense firepower network and the effectiveness of comprehensive defense operations.
Owner:GROUND TO AIR DEFENSE EQUIP INST OF AIRFORCE EQUIP INST OF THE PLA
Pulsed detonation engines for reaction control systems
InactiveUS7278611B2Improve performanceEffective controlCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusControl systemMissile defense
Owner:LEIDOS
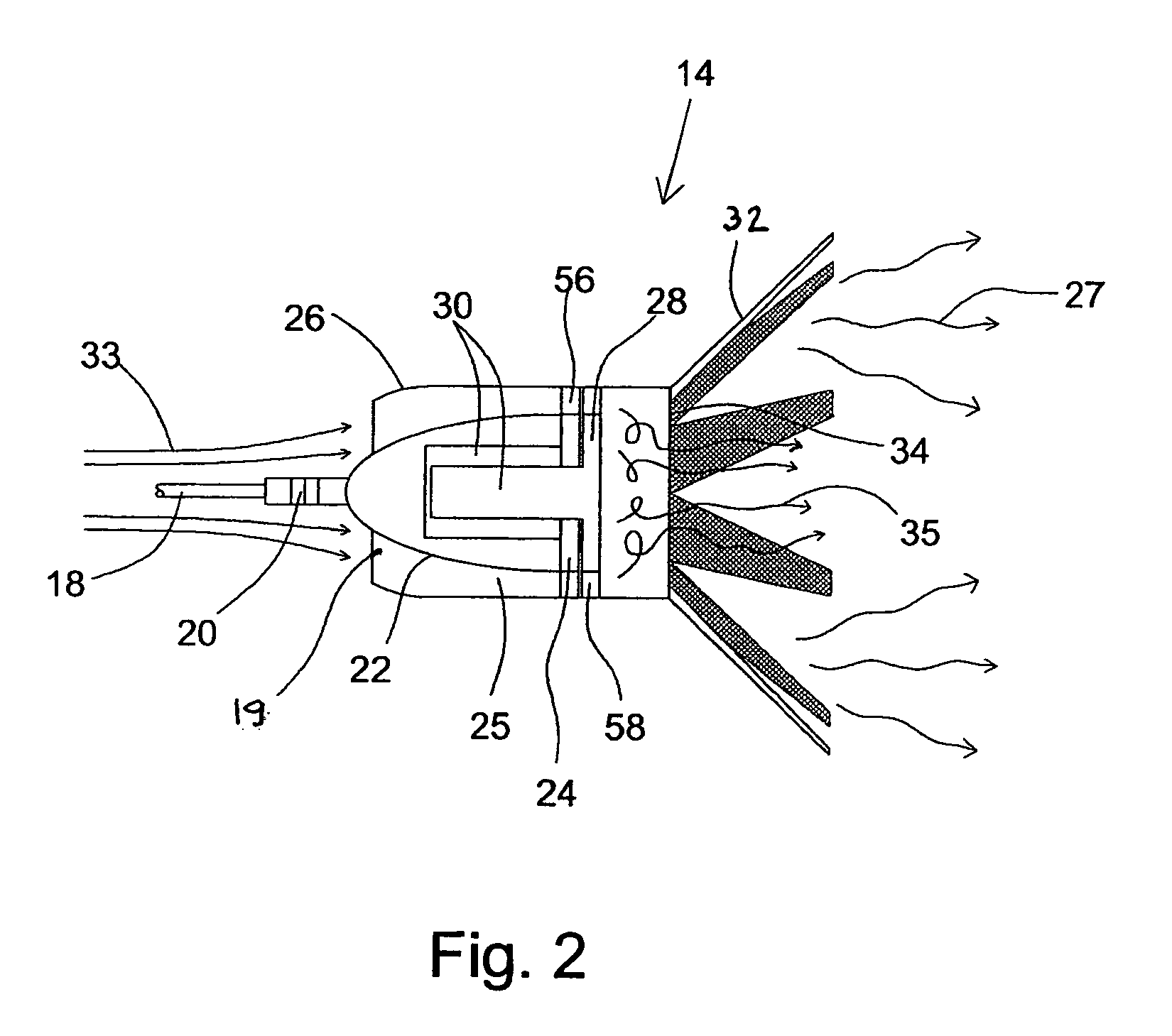
Anti-missile defense suite
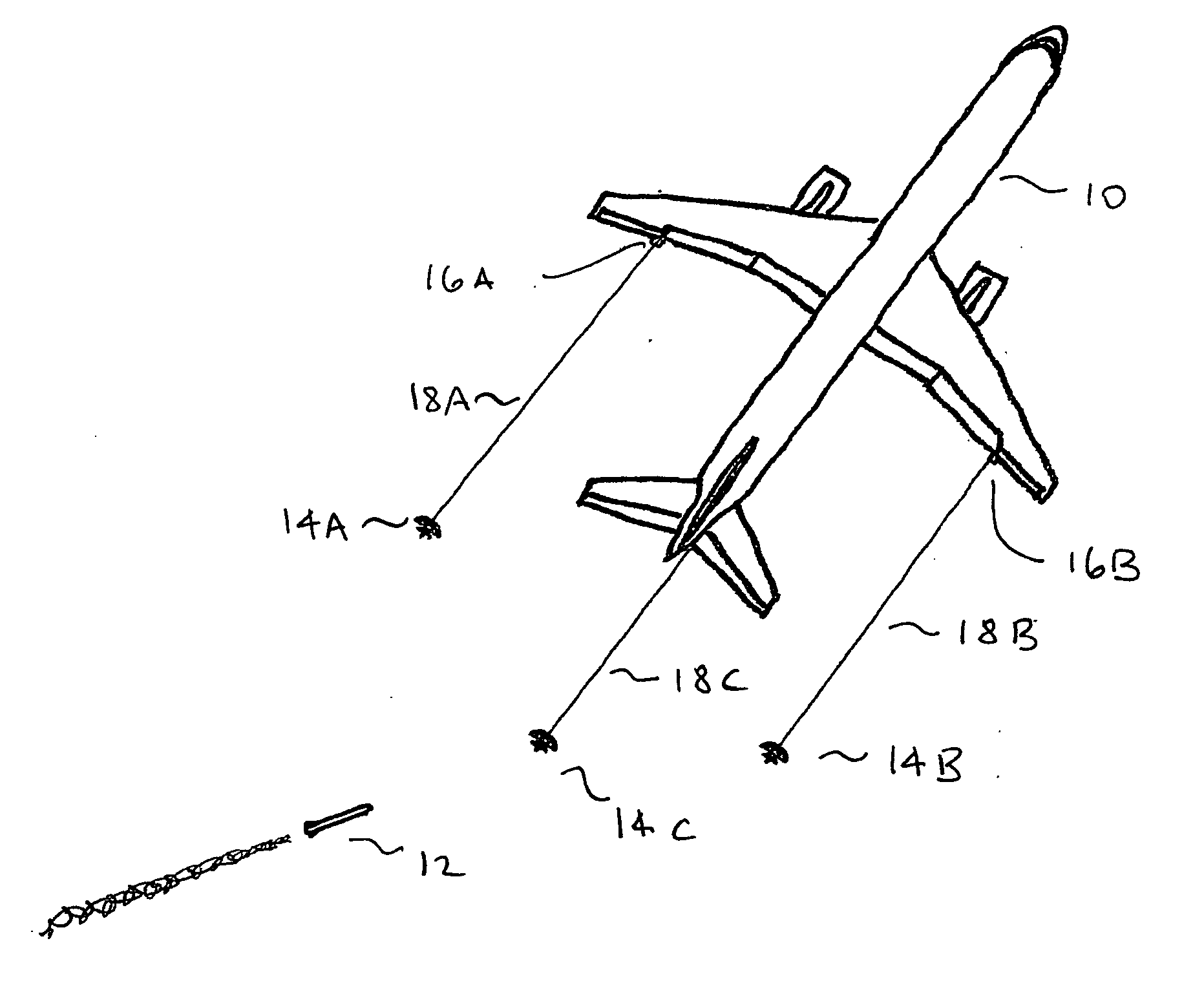
InactiveUS8066218B2Increase radiation intensityBrighter, stronger, and largerDefence devicesFirework flares/torchesDecoyMissile defense
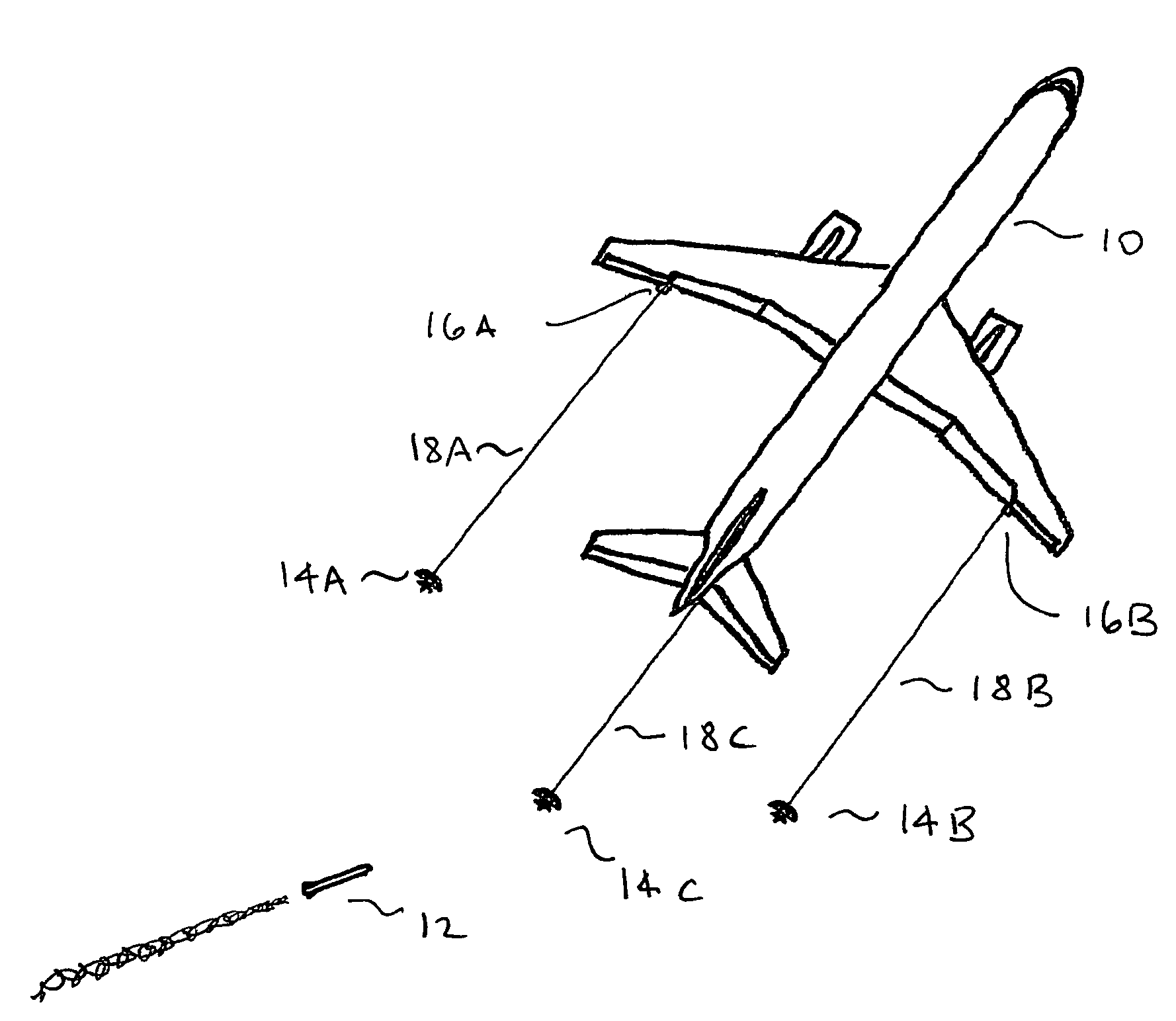
A system and method for an aircraft (10) that provides an IR decoy (12) for an incoming missile (18) to track instead of an engine (14) of the aircraft (10) is disclosed. The IR decoy (12) is deployed during or just after take off, and prior to landing to provide a signature (16) for any incoming missile (18). The IR decoy (12) provides a heat source (16) that has a higher radiant intensity than the hottest heat source on the aircraft (10), which is typically the engine (14), thereby providing a more attractive heat source for the missile (18). In another embodiment, a warning system (20) for an aircraft (10) detects an incoming missile (18), and deploys IR decoy (12) and creates an engine mask (22) by injecting an additive into the exhaust stream of the engine (14), thereby obscuring the radiation emanating from the engine (14).
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Systems and/or methods for using coherent electromagnetic waves in a missile defense shield
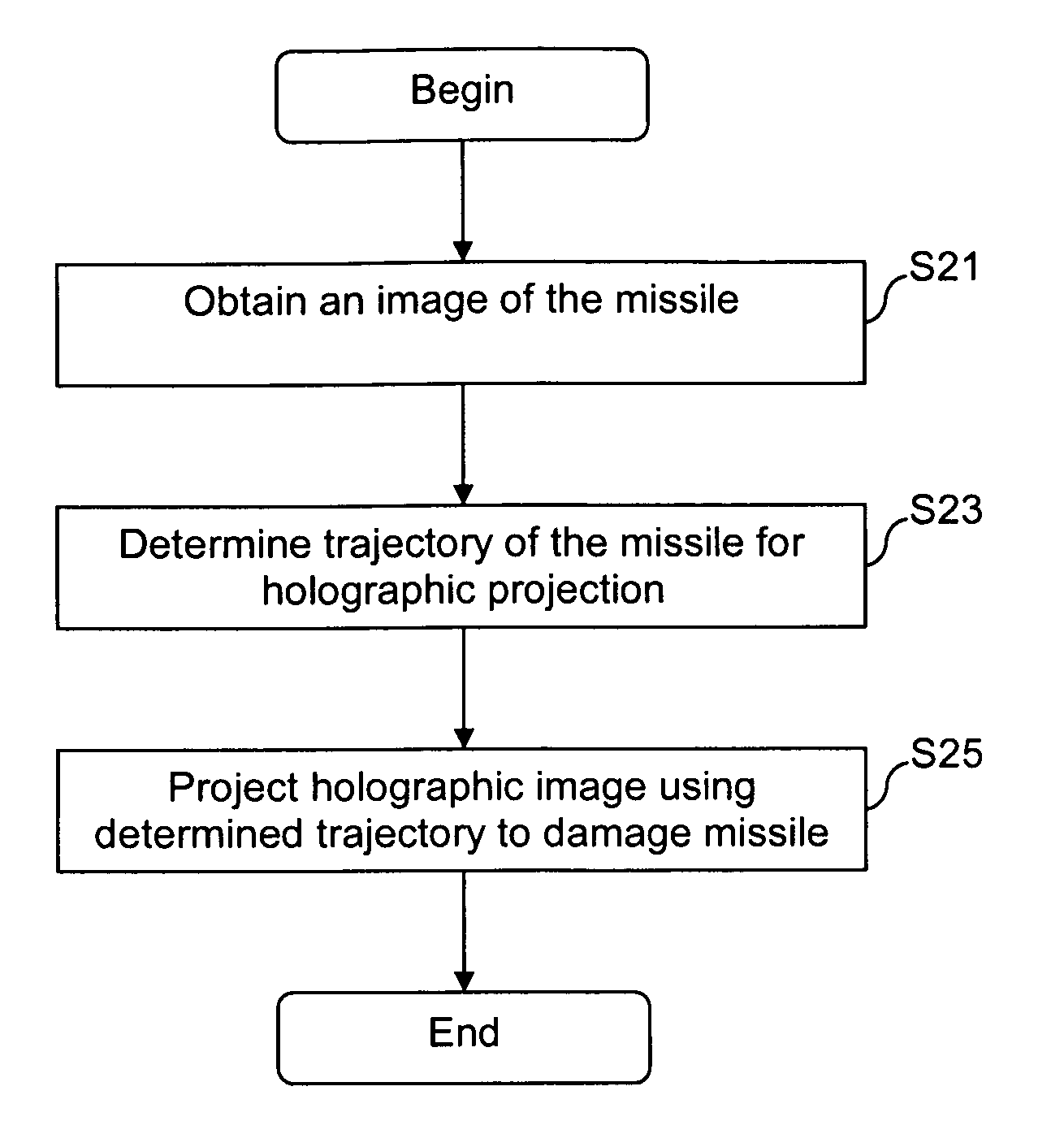
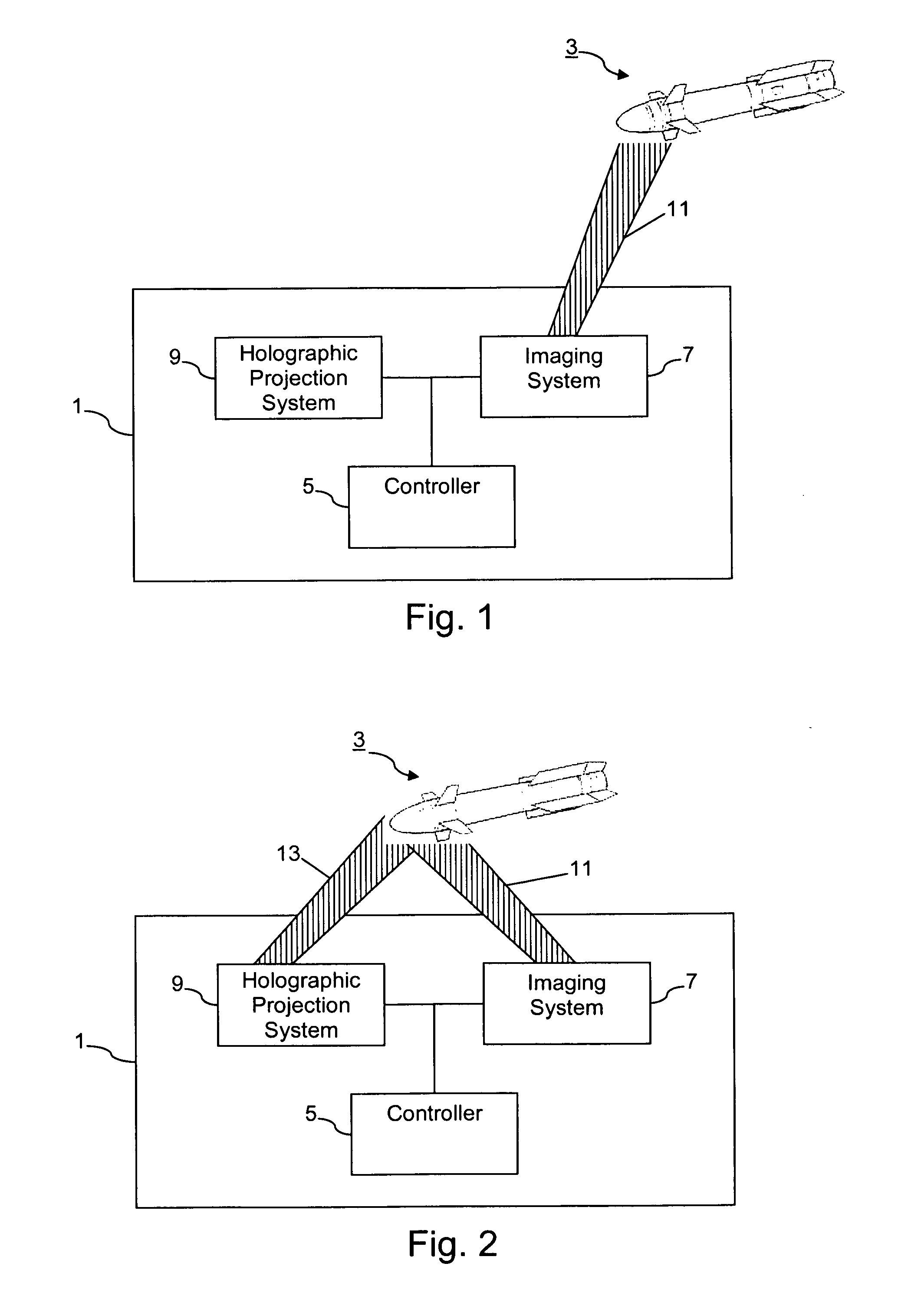
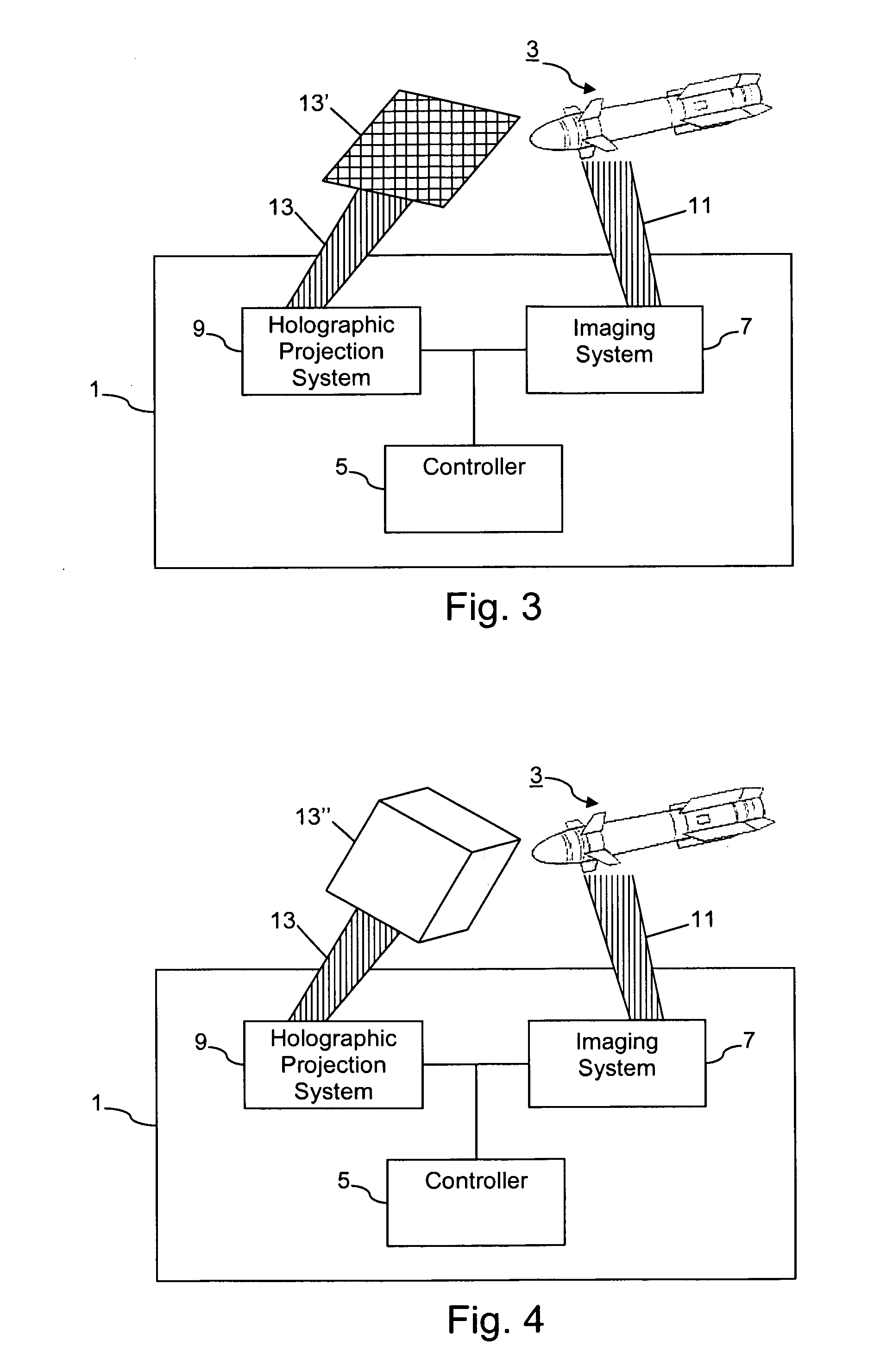
Certain example embodiments of this invention relate to a holography-based missile defense shield. In certain example embodiments, an EM field is created on or proximate to a missile. Based on imaging and / or trajectory data, a holographic plate is prepared such that a holographic projection may be generated therefrom. Electromagnetic waves are then focused on the holographic plate as a reference beam so that the holographic image is generated. In certain example embodiments, the holographic image may correspond to the missile itself, a portion of the missile, a substantially planar shape, a substantially three-dimensional shape, and / or the like. In certain example embodiments, the holographic image focused on or near the missile will interfere with the operation of the missile such that it is damaged, destroyed, or otherwise rendered less of a threat.
Owner:AVOGADRO MAXWELL BOLTZMAN
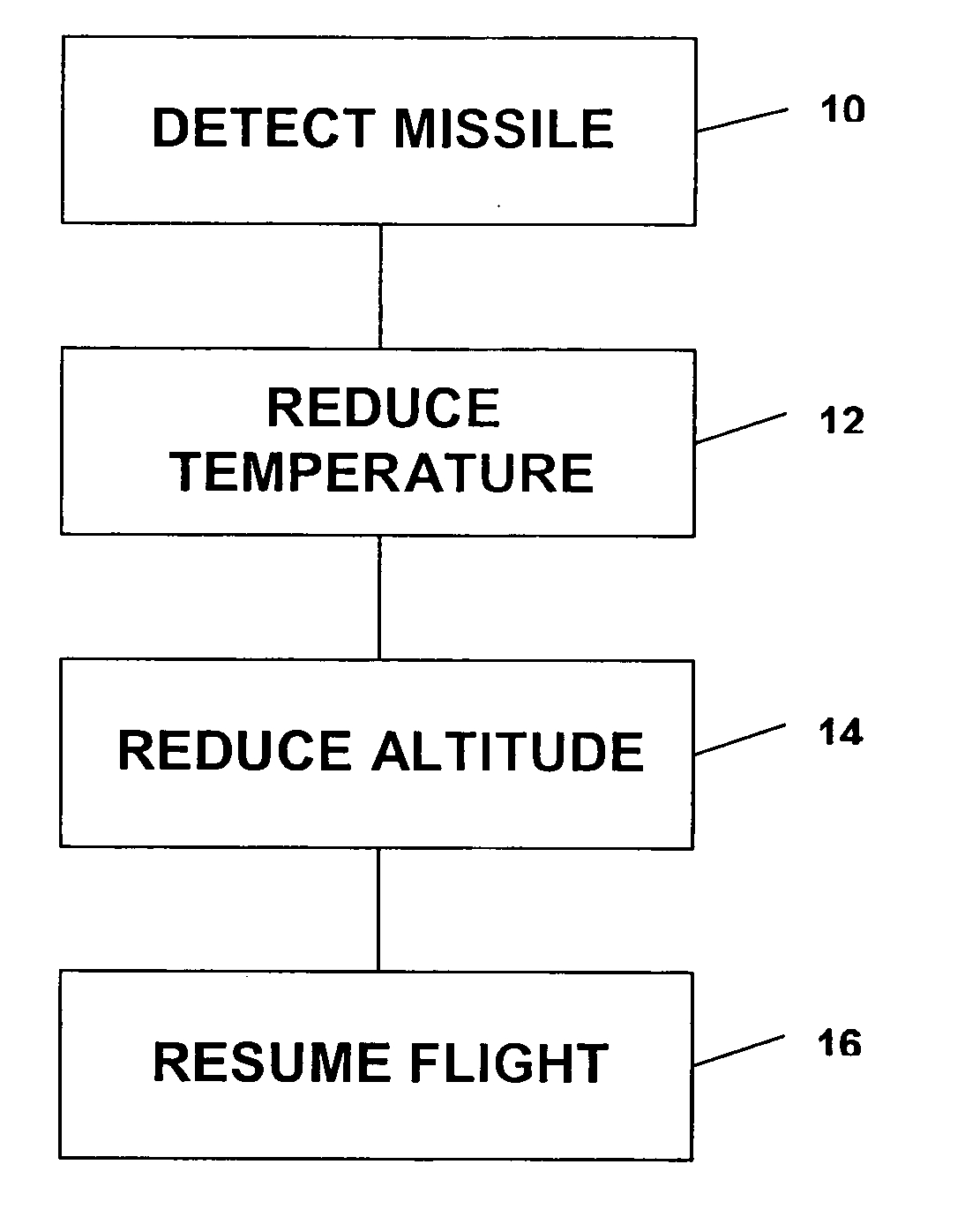
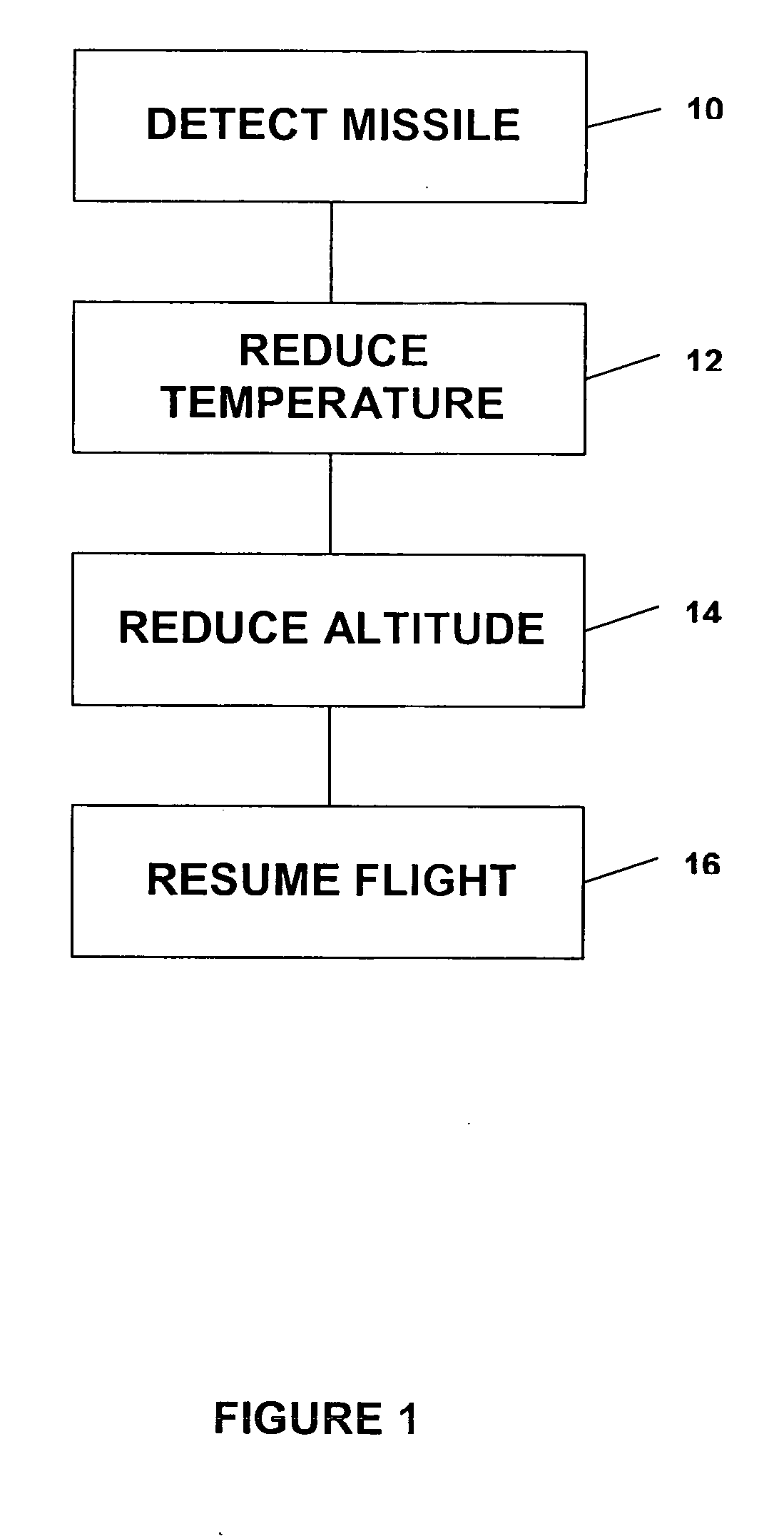
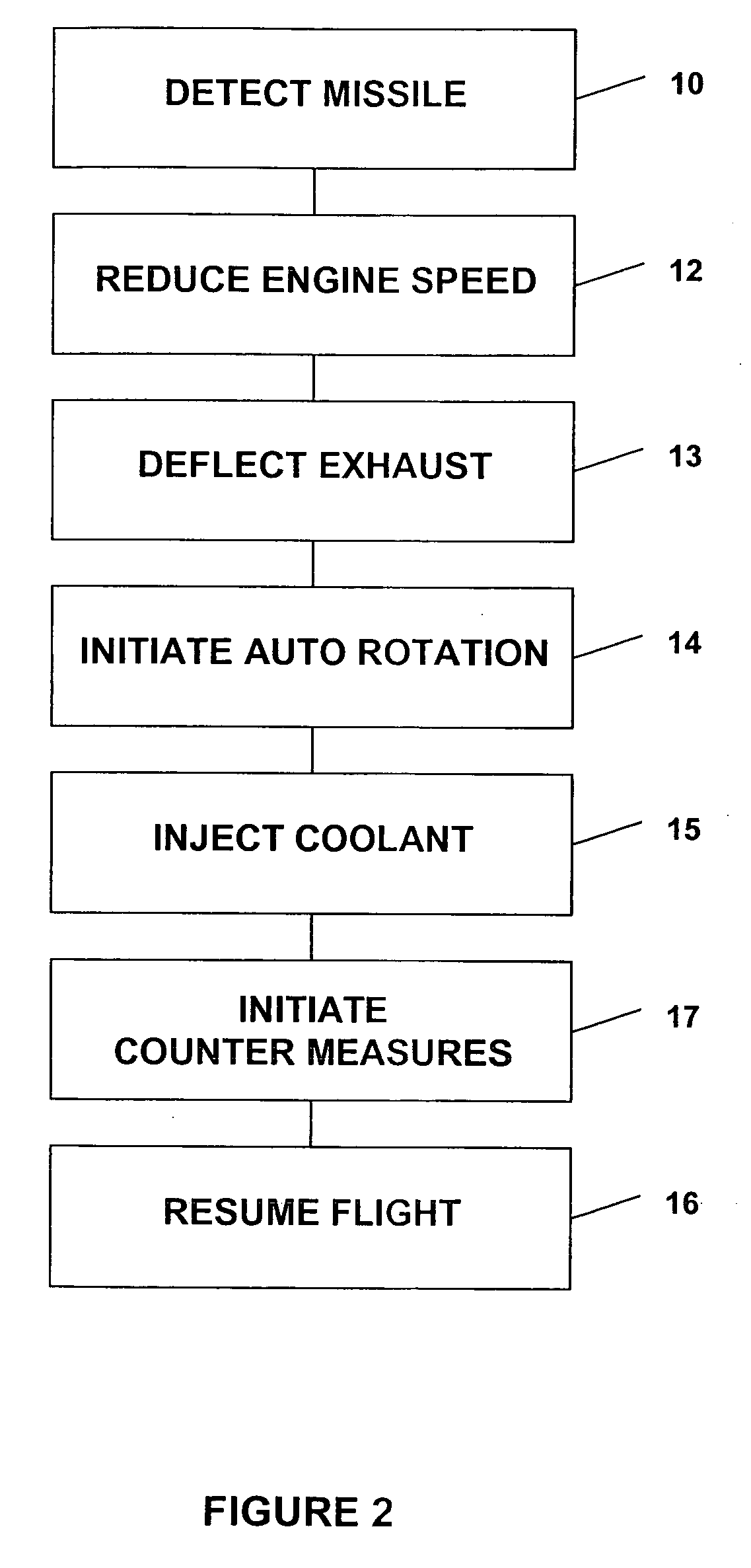
Missile defense system and methods for evading heat seeking missiles
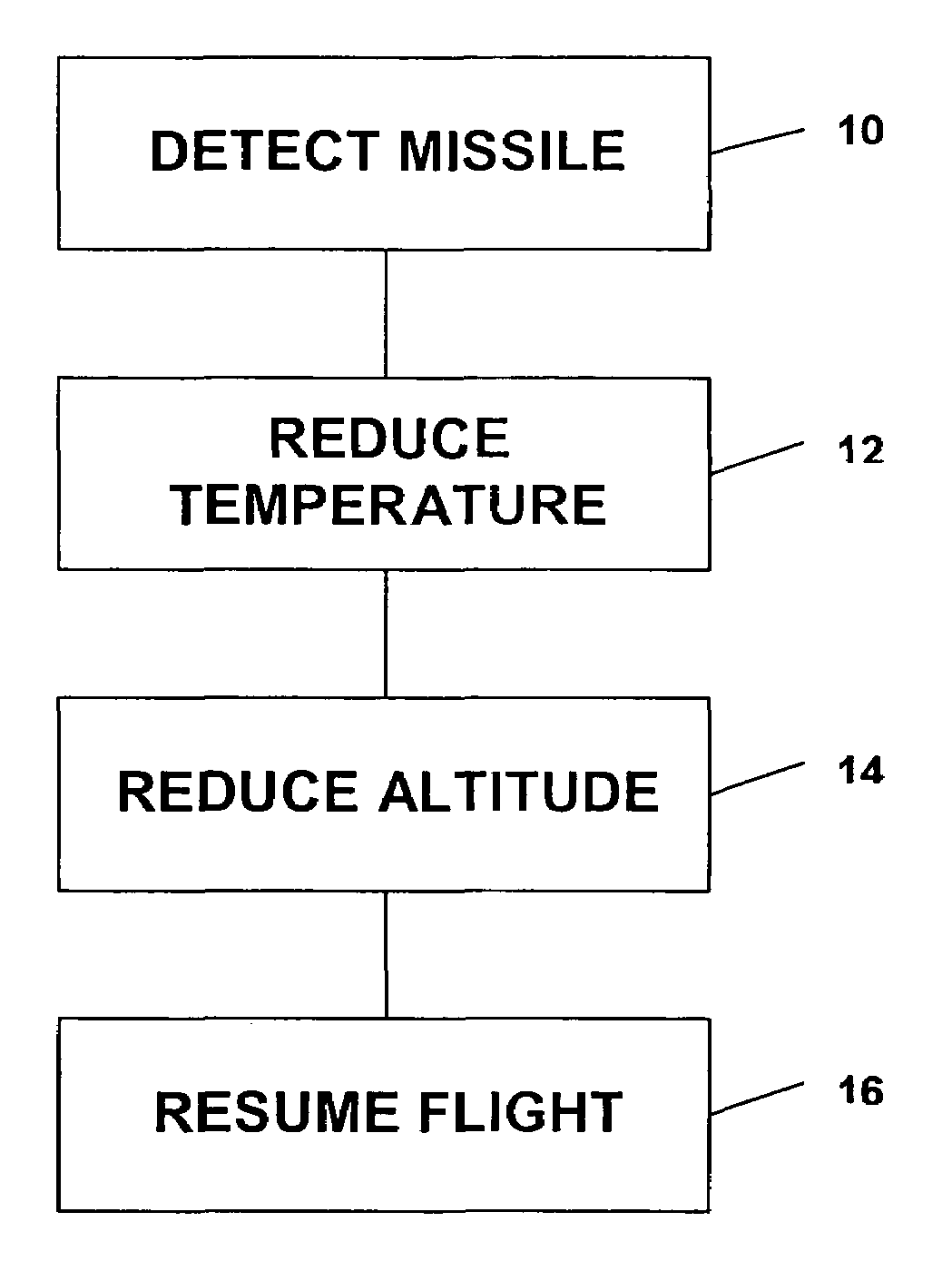
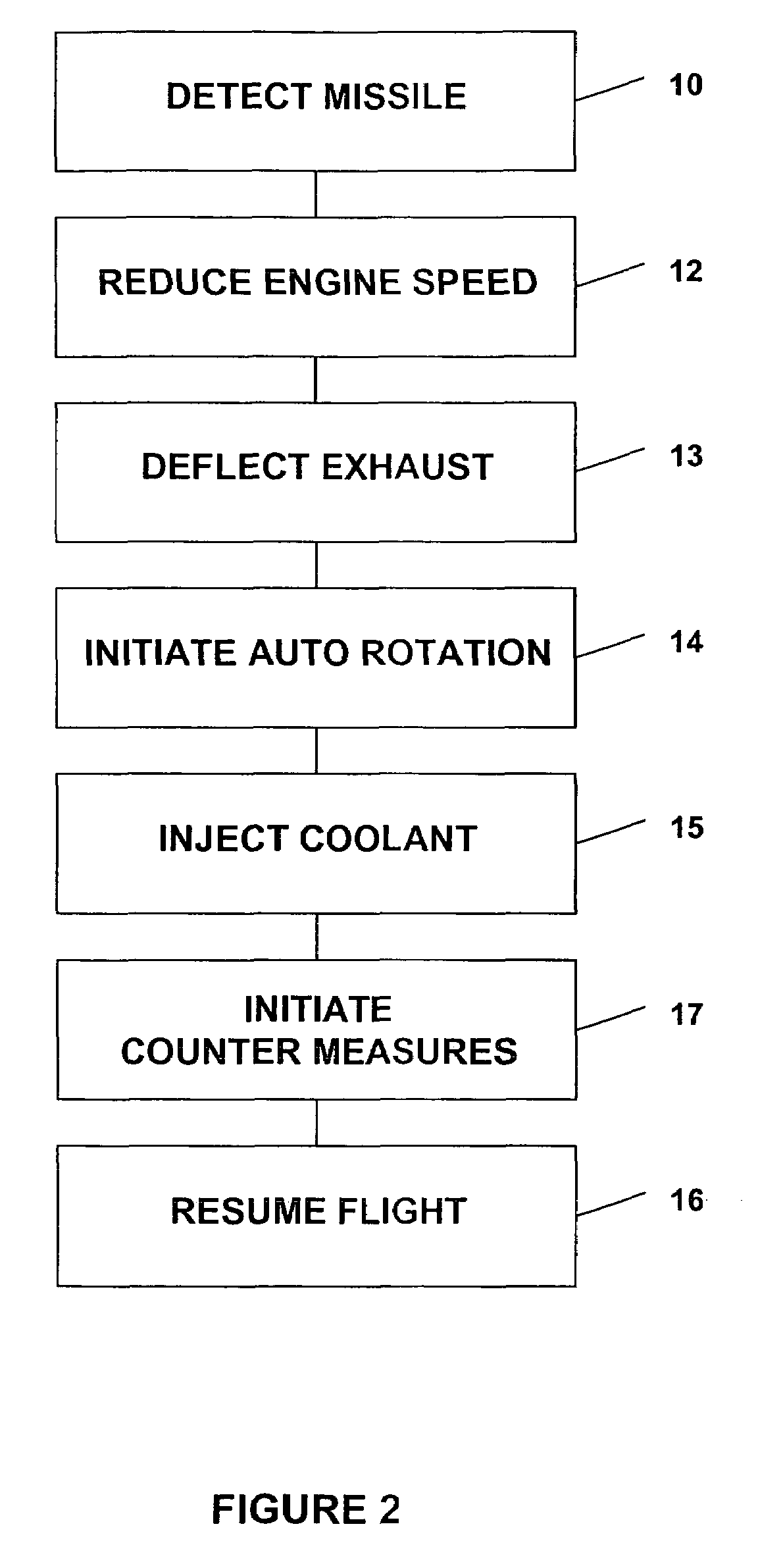
InactiveUS7370836B2Reduce heatRapid temperaturePropellersAircraft controlCountermeasureMissile defense
A method for aiding a helicopter pilot to avoid a heat seeking missile includes the step of detecting a threat from a missile. The method also includes the step of reducing heat emanating from the helicopter's engine and rapidly reducing altitude. Then, when the threat has passed flight is resumed. A system for accomplishing the above is also described which simultaneously reduces engine temperature, deflects the exhaust gases, injects water into the exhaust gases, reduces altitude and launches a countermeasure.
Owner:SAFE FLIGHT INSTR
Self-powered tethered decoy for heat-seeking transport aircraft missile defense
A low-cost airliner defense system utilizing self powered, retrievable, towed decoys against man portable heat-seeking missile (MANPAD) systems provides both high power and a large IR radiating surface area. An efficient and lightweight integrated turbine-alternator extracts sufficient electric power from an air stream directed through a small decoy deployed and towed behind an aircraft during the vulnerable phases of a flight to power a large and intense IR emitter. Unfurled IR radiator “petals” present large area arrays of rear-facing IR emitters. During the high-altitude cruise phase the radiating petals furl down folding around the retrieved decoy body as it is stowed in a streamlined housing for minimizing fuel consumption and maneuverability penalties.
Owner:BURNS ALAN ALEXANDER
Airplane missile defense system
InactiveCN101554923AImprove survival rateImprove mobilityRocket launchersMilitary adjustmentJet aeroplaneSurvivability
The invention relates to an airplane missile defense system for smashing missiles or enemy planes striking at the rear part of an airplane. The airplane missile defense system comprises a rear view radar, a special backward aerogun and a special missile. The rear view radar is used for observing, targeting an object at the rear of the airplane and directing the missile. Radar guidance is unnecessary if infrared guidance is used for a homing missile. The aerogun is used for launching the missile in a pipe, solving zero-crossing velocity when the missile is launched backwards; causing the missile to complete the process of zero-crossing velocity in a gun bore to travel forward after the missile is out of the gun bore, and ensuring the stability of missile flight. The rear part of the missile is made into a gun shell form so as to be suitable for aerogun launch. When the airplane is chased by the enemy plane or stricken by the missile, the distance is so near that a short-distance micro-missile can be adopted, thus solving the problem that the existing air-to-air missile can not be launched backwards, greatly lowering the technical difficulty of over-the-shoulder launch and improving airplane survivability in wars.
Owner:寿国伟
Probabilistic Sampling Method For Track Association
ActiveUS20200090011A1Quick buildImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsMissile defenseEngineering
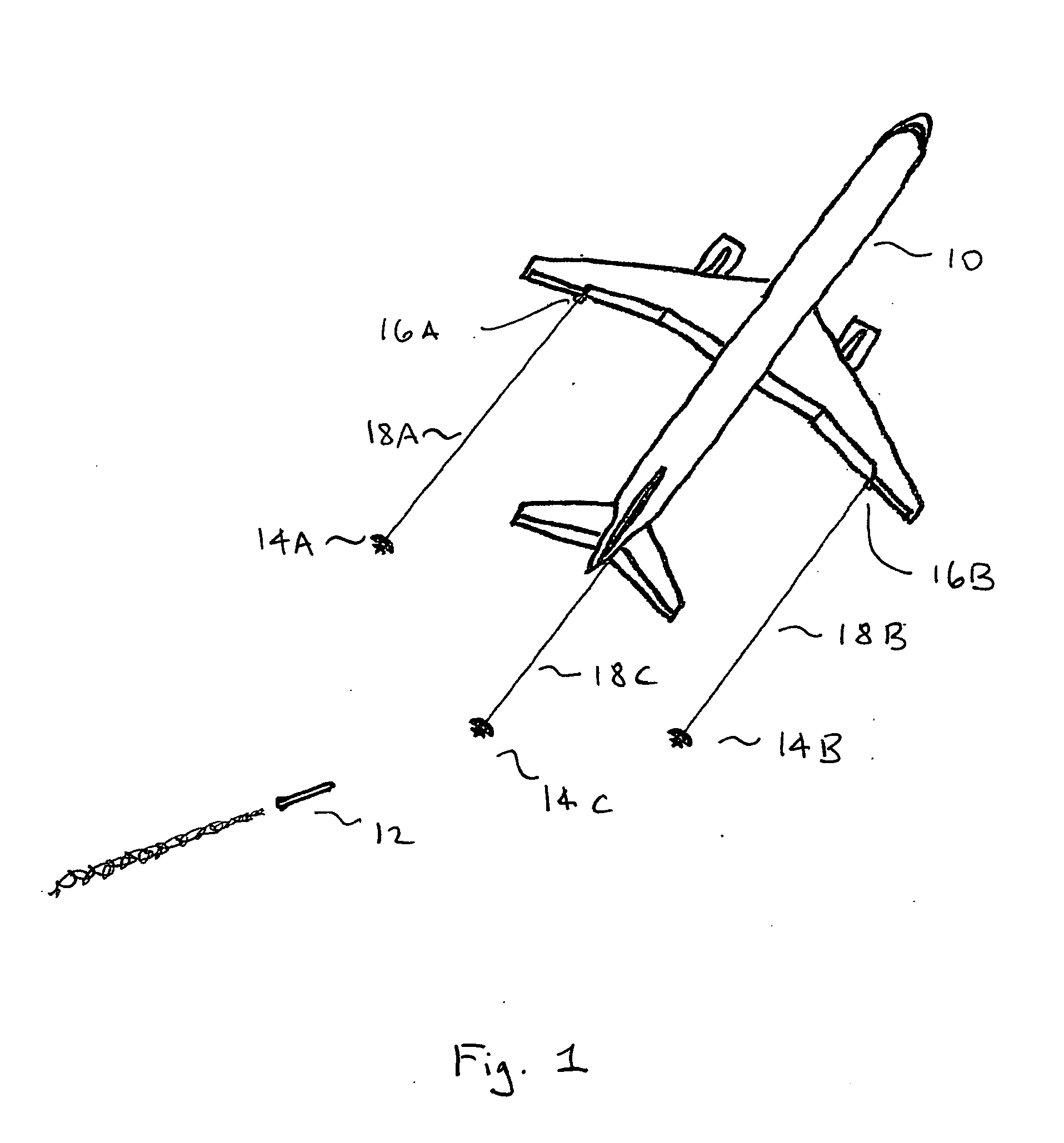
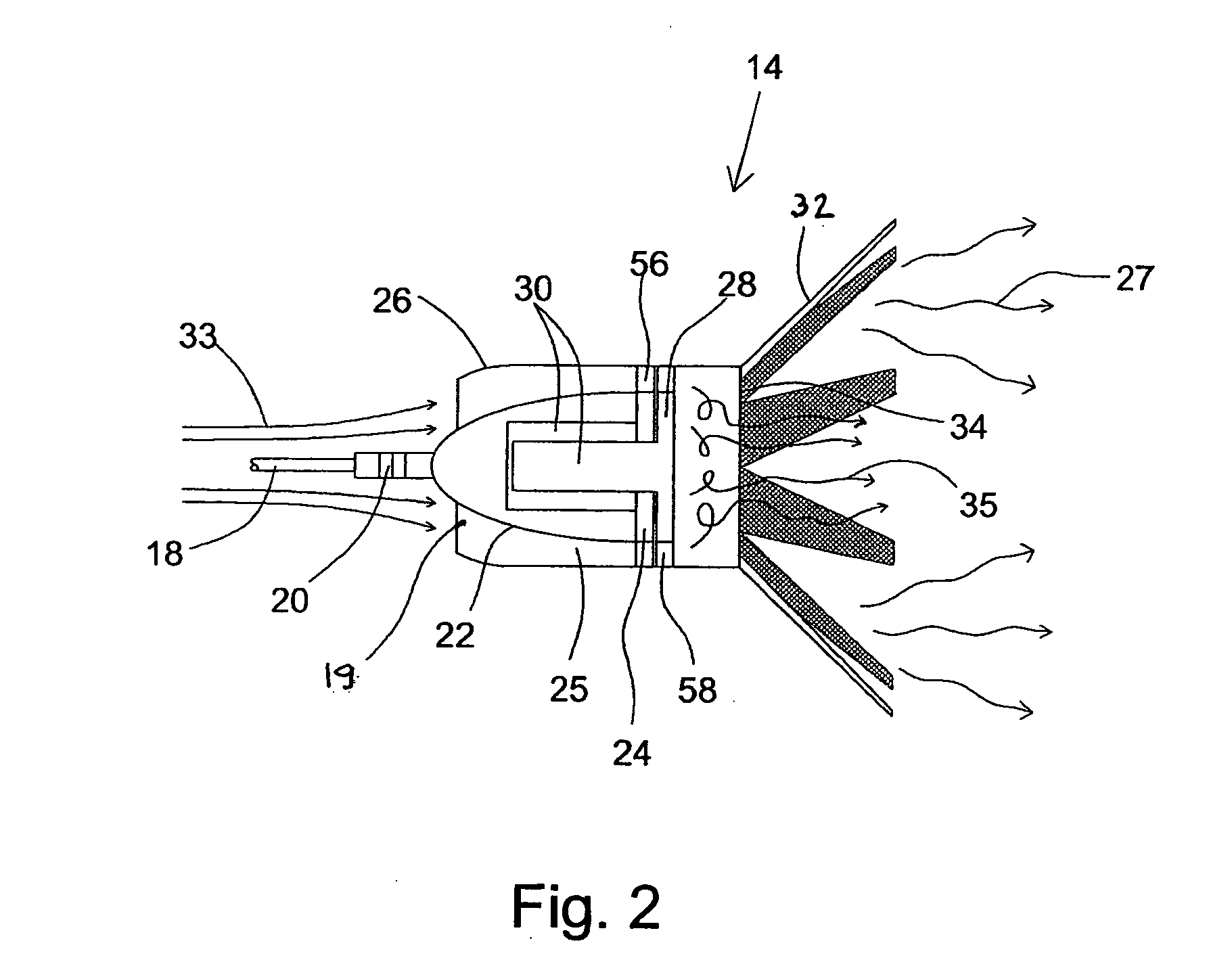
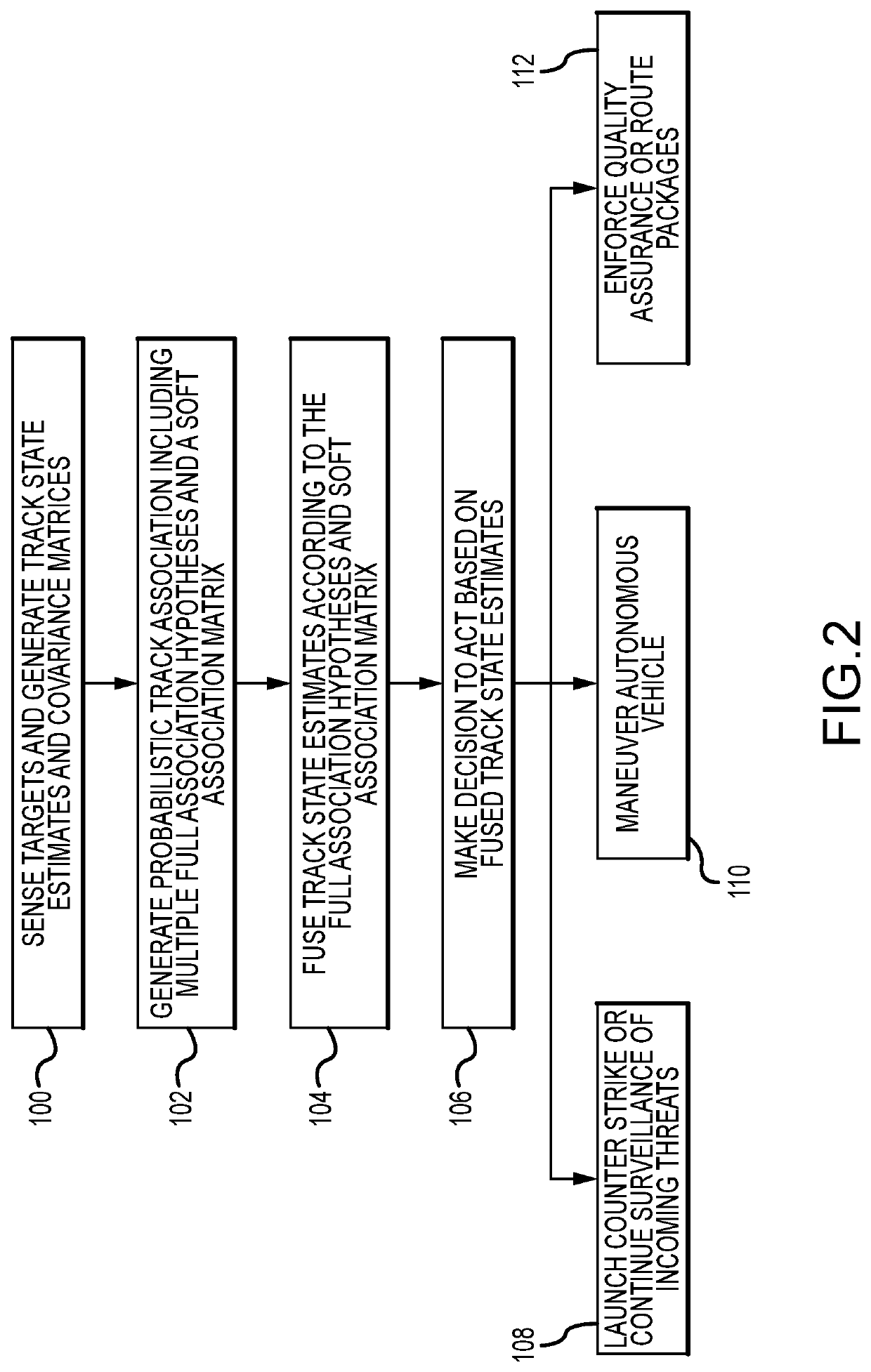
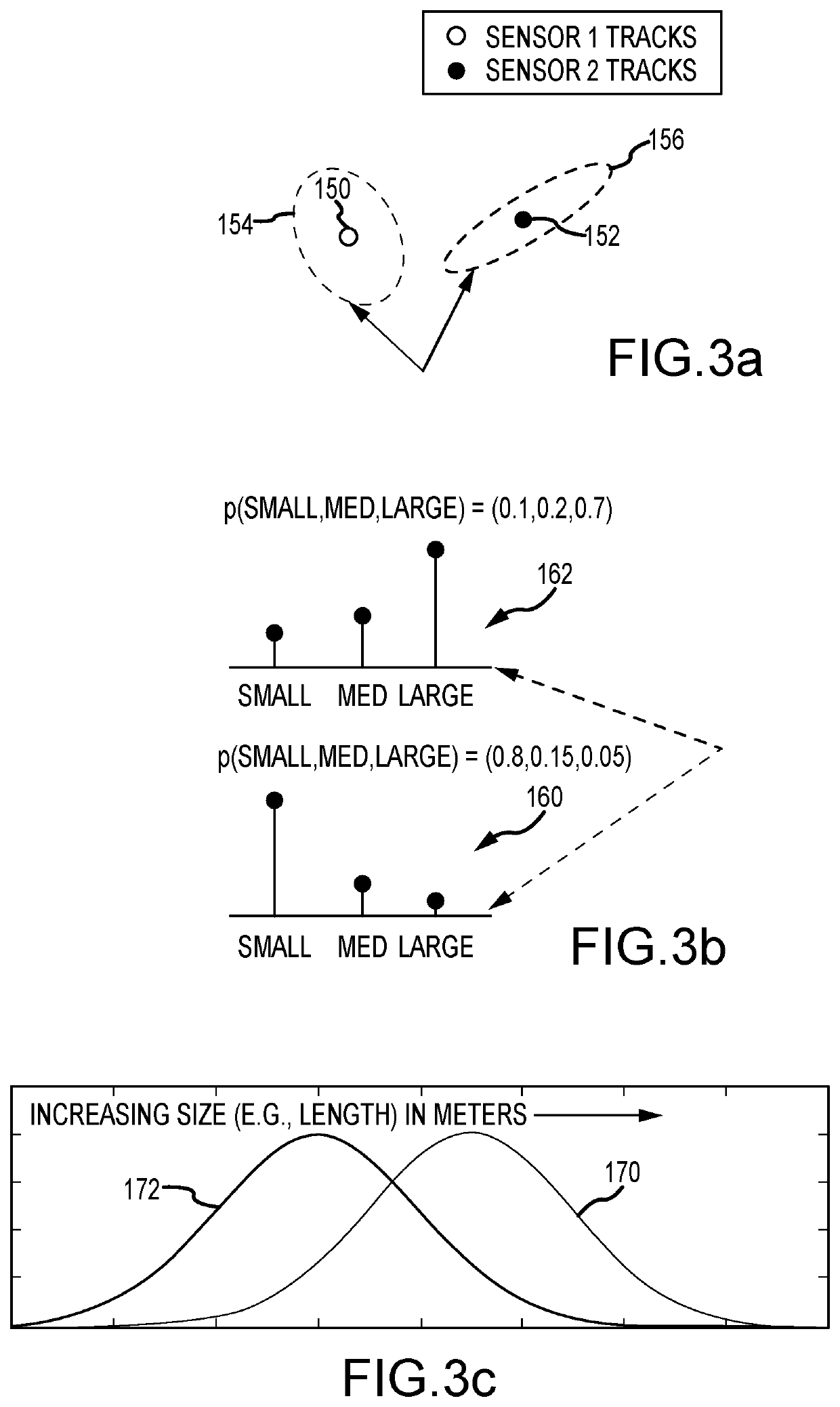
A method for solving the track association problem updates and samples a marginal association likelihood conditioned upon existing track assignments and marginalized over possible sensor biases to assign tracks and build a full association hypothesis. The “sampling” is repeated multiple times for a given seed track pair and for different seed track pairs to quickly generate hypotheses that approximate the solution space. The probabilistic track association includes a plurality of likely full association hypotheses and a soft association matrix that probabilistically reflects the likelihood of the track association for a pair of sensors. Efficacy can be enhanced by sensing and processing non-metric features (e.g. size, shape, color) to supplement the metric features (e.g. location, velocity). Efficiency may be enhanced by prioritizing the list of seed track pairs in order of decreasing likelihood, saving only full association hypotheses that are both unique and close to the current most likely hypothesis and terminating the search based on a staleness criteria. Probabilistic sampling may be used for such diverse applications as missile defense, autonomous vehicles and package handling.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Remote interception launch data acquisition method and system based on single-sided launch table
ActiveCN113642122AReduce workloadImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationClassical mechanicsMissile defense
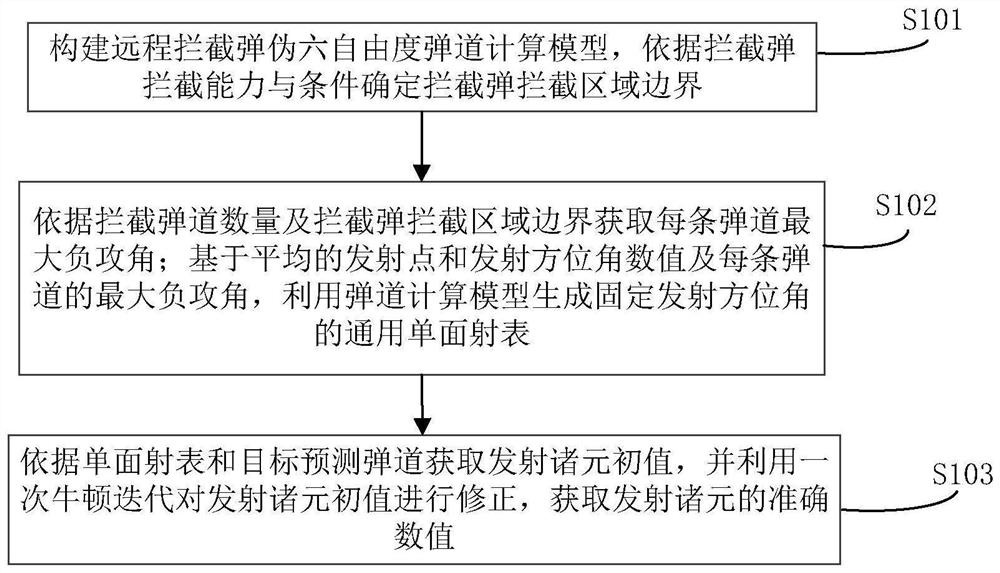
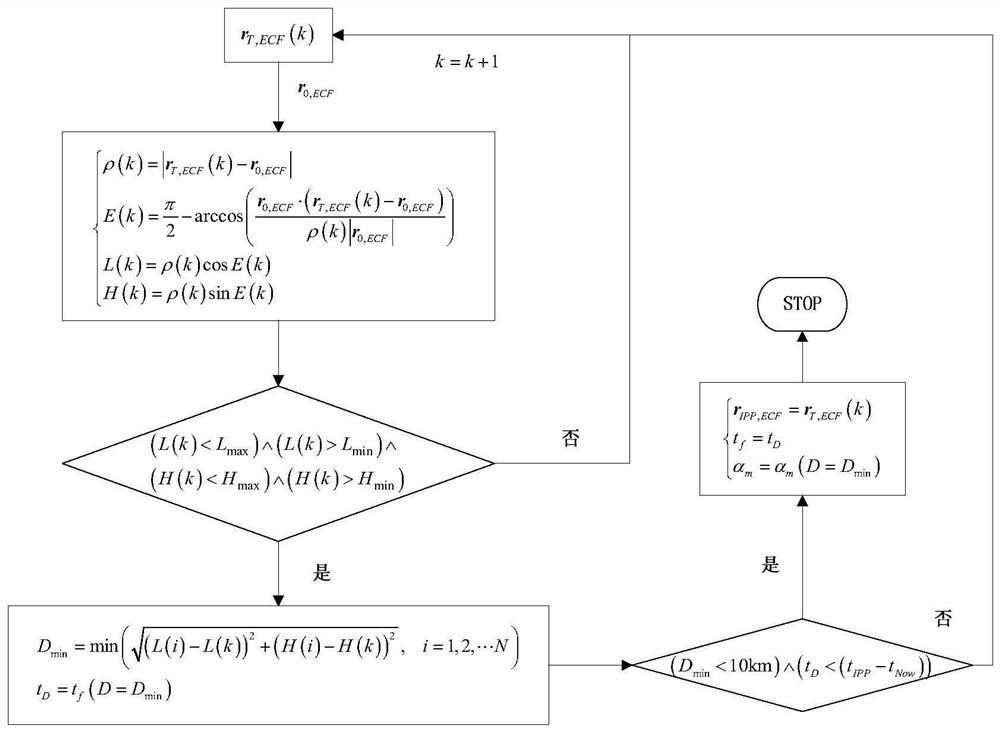
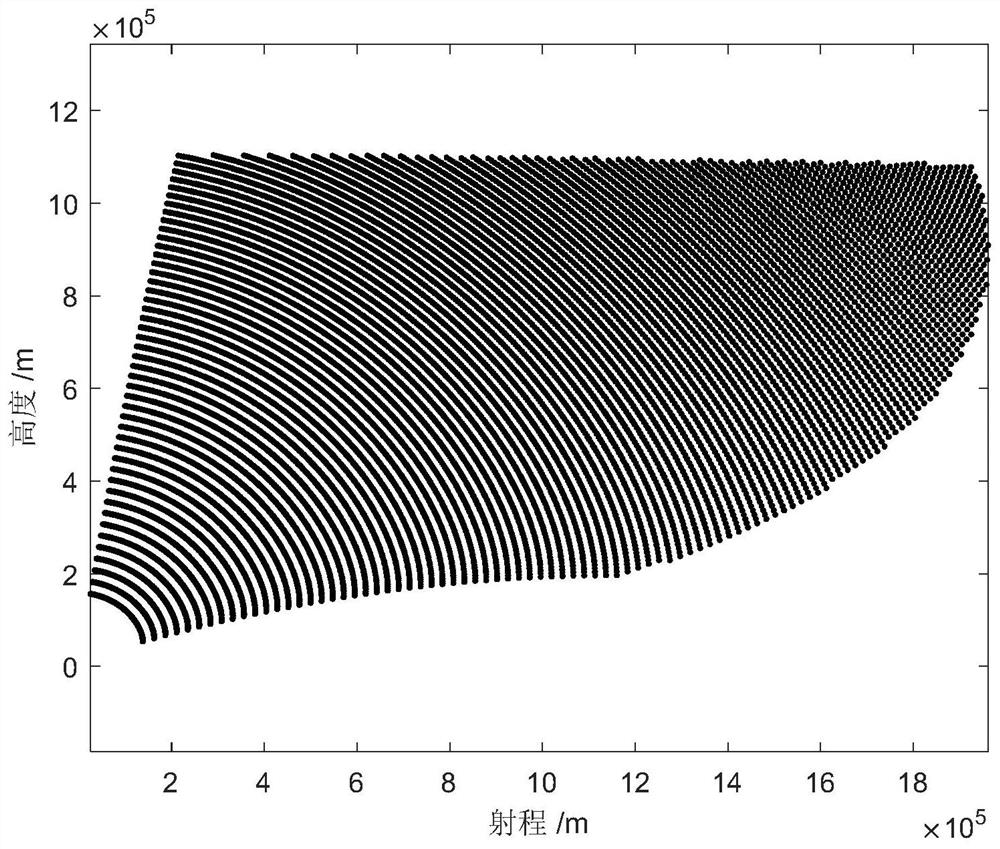
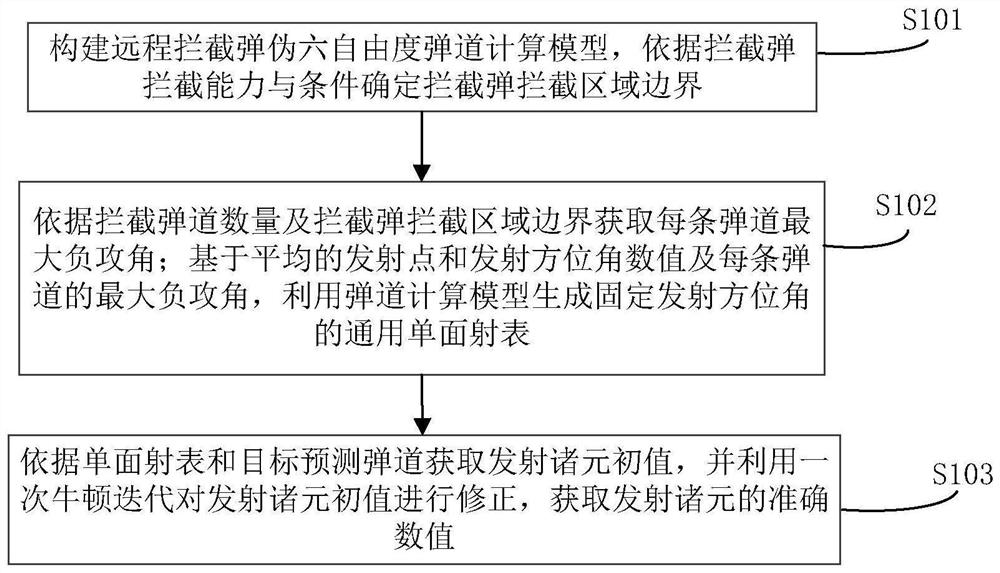
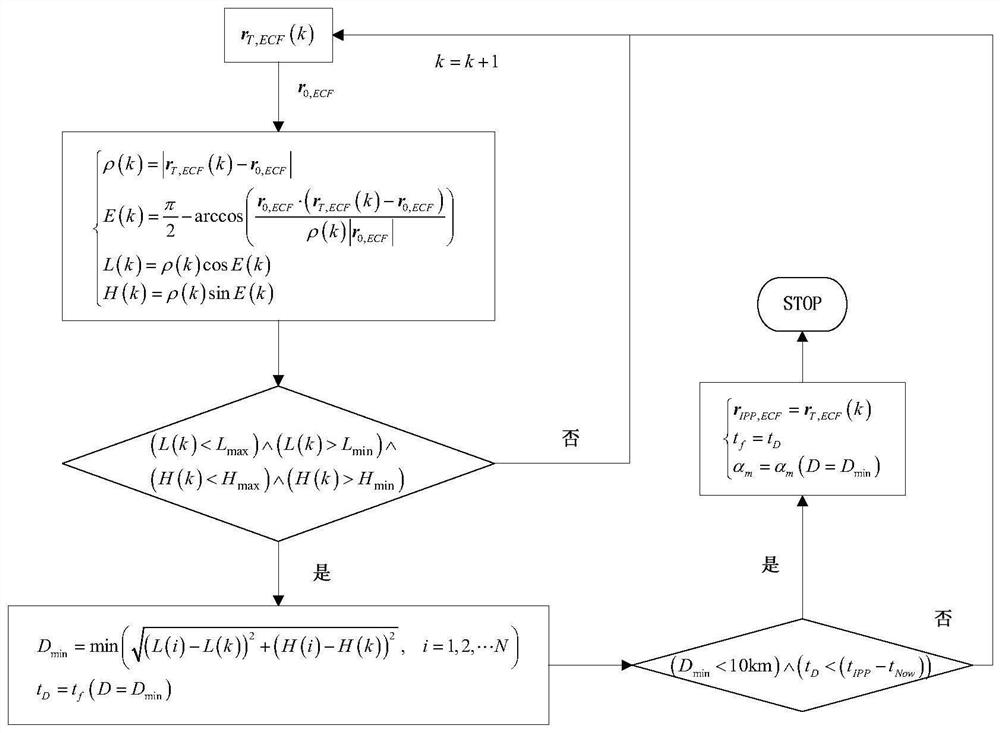
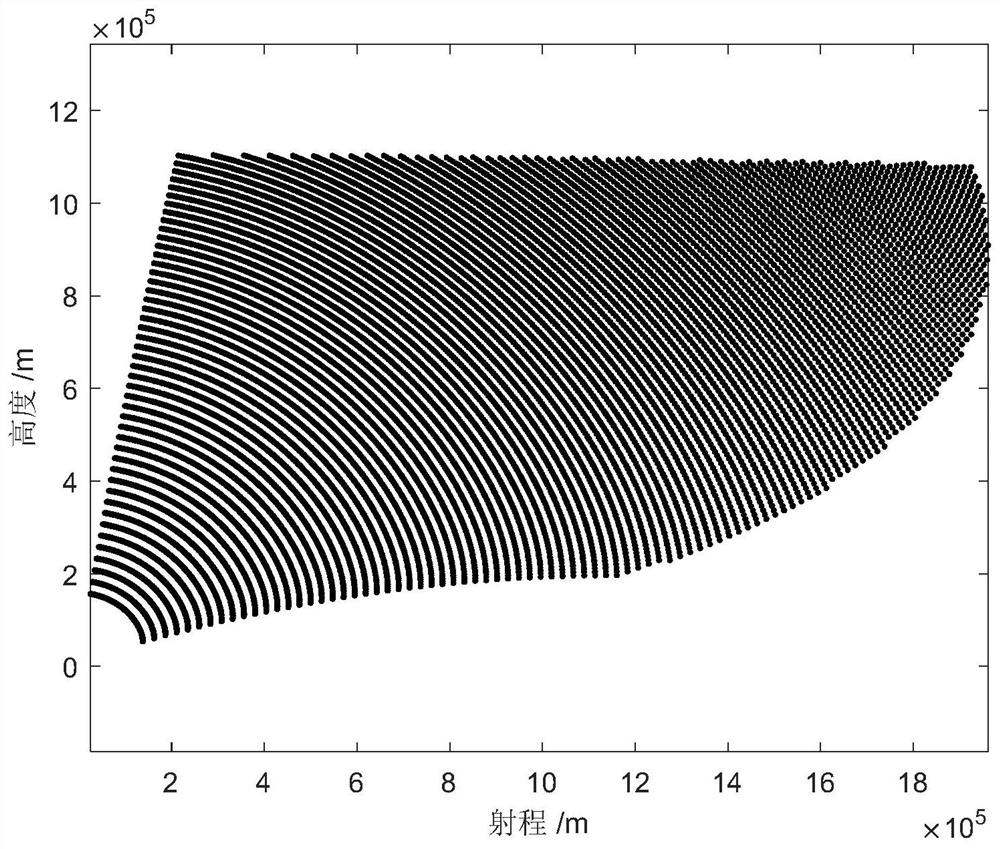
The invention belongs to the technical field of missile defense, and particularly relates to a remote interception launch data acquisition method and system based on a single-sided launch table, and the method comprises the steps: constructing a remote interception missile pseudo-six-degree-of-freedom trajectory calculation model, and determining an interception region boundary of an interception missile according to the interception capability and conditions of the interception missile; obtaining the maximum negative attack angle of each trajectory according to the number of the intercepted trajectories and the boundary of the intercepted region of the intercepted projectiles; based on the average launching point and launching azimuth angle values and the maximum negative angle of attack of each trajectory, generating a general single-sided launching table of a fixed launching azimuth angle by using a trajectory calculation model; and according to the single-sided firing table and the target prediction trajectory, initial values of the firing data are obtained, correcting the initial values of the firing data through one-time Newton iteration, and accurate values of the firing data are obtained. The problems of remote interception missile data calculation with an uncertain launching point and the like are solved, the calculation amount is reduced, the stability and efficiency of calculation equipment are improved, the real-time requirement of remote interception missile launching data calculation can be met, and the invention has high engineering application value and prospect.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Long range KV-to-KV communications to inform target selection of follower KVS
A KV-based missile defense system and method of strategic engagement provides performance improvement for both singleton and raid scenarios by launching multiple interceptors that place a follower KV in a trailing position with respect to a lead KV. Knowledge of the target cloud gained by the lead KV is transmitted to the follower KV and incorporated to inform the target selection of the follower KV. The follower KV trails the lead KV with sufficient spacing in time and distance to select a target and maneuver to engage the target pre-acquisition. This also allows the follower KV to receive and incorporate knowledge of target impact by the lead KV. This knowledge may be transmitted back to another follower KV and so forth in a “string” of KVs to inform target selection and down to the ground to inform strategic engagement. Updated non-KV observational data can be uplinked and transmitted forward along the string to the lead KV.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Manufacturing method of ground-interception missile defense system and application of missile defense system
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a ground-interception missile defense system and application of the missile defense system. The manufacturing method of the ground-interception missile defense system is characterized in that the base and the inner layer of the ground-interception missile defense system are cast by use of an alloy steel, a plurality of layers are formed for mounting an outer layer, a second layer is made of a composite bullet resistant material composed of a soft bullet resistant material and a shock-absorptive material in addition to the alloy steel, a third layer is knitted by use of carbon fibers and a c / c composite material, an outer layer is coiled by use of a high-strength alloy steel, welded by use of steel hoops at intervals and hooped section by section, the joint of each layer is hooped by use of one steel hoop and fastened by use of a screw button, each layer is spaced with a fire-resistant antiknock glue, a groove is formed in the inner layer of a device head, sleeves a connection and is tightened by use of a screw, an outer opening is in a flaring shape, and an additional interception protective layer is mounted in the device; the ground-interception missile defense system is mounted on a heavy traction vehicle; a vehicle-mounted radar is combined with optical detection to realize tracking of a defense penetration missile and to transmit inducing signals; a vehicle-mounted navigation system is used for realizing tracking the defense penetration missile along with a phased array radar, and correcting and commanding the traction vehicle to move by use of alignment and calibration so that the missile is capable of falling into the device.
Owner:刘卓韬
System and method for asymmetric missile defense
ActiveUS9726460B2Accurately determineDefence devicesInference methodsSoftware engineeringMissile defense
A method for accurately determining whether a response tool will be effective for responding to a given enemy threat object. Embodiments described herein provide a method and system for responding to a threat object, for example, negating missile threats. Embodiments may include validating effectiveness of a response to the threat object. Other embodiments may include verifying the continued effectiveness of a response to the threat object. Further embodiments may include providing feedback to re-perform the method for responding to the threat object. The system may include a mathematical method, and associated algorithms, to assess, in an automated fashion, the performance of non-kinetic techniques with respect to negating the threat object.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Missile defense system and methods for evading heat seeking missiles
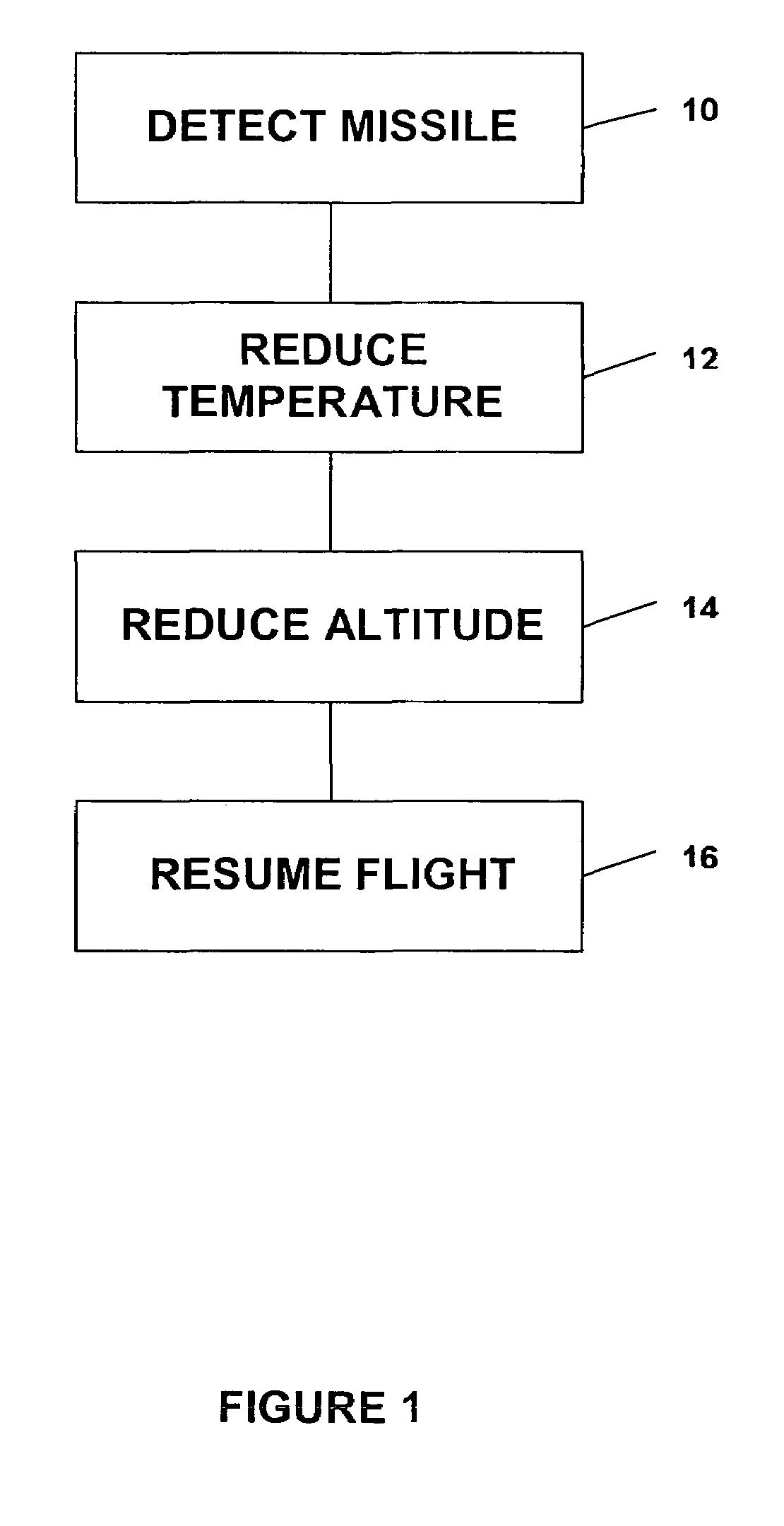
InactiveUS20070034072A1Reduce heatRapidly low temperaturePropellersAircraft controlCountermeasureMissile defense
A method for aiding a helicopter pilot to avoid a heat seeking missile includes the step of detecting a threat from a missile. The method also includes the step of reducing heat emanating from the helicopter's engine and rapidly reducing altitude. Then, when the threat has passed flight is resumed. A system for accomplishing the above is also described which simultaneously reduces engine temperature, deflects the exhaust gases, injects water into the exhaust gases, reduces altitude and launches a countermeasure.
Owner:SAFE FLIGHT INSTR
Enhanced multiple kill vehicle (MKV) interceptor for intercepting exo and endo-atmospheric targets
ActiveUS20120001015A1Overcomes of bandwidthAvoid complexityAmmunition projectilesCosmonautic vehiclesImage resolutionFlight vehicle
By sharing tasks between the CV and the KVs, the MKV interceptor provides a cost-effective missile defense system capable of intercepting and killing multiple targets. The placement of the acquisition and discrimination sensor and control sensor on the CV to provide target acquisition and discrimination and mid-course guidance for all the KVs avoids the weight and complexity issues associated with trying to “miniaturize” unitary interceptors. The placement of either a short-band imaging sensor and headlamp or a MWIR sensor on each KV overcomes the latency, resolution and bandwidth problems associated with command guidance systems and allows each KV to precisely select a desirable aimpoint and maintain track on that aimpoint to impact. An implicit divert and attitude control system (DACS) using tow or more divert thrusters performs KV divert and attitude maneuvers to respond to the command guidance pre-handover and to maintain track on the aimpoint to terminal intercept post-handover
Owner:SCI APPL INT CORP +1
Pulsed Detonation Engines For Reaction Control Systems
InactiveUS20080053058A1Improve performanceEffective controlCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusControl systemMissile defense
Owner:LEIDOS INC
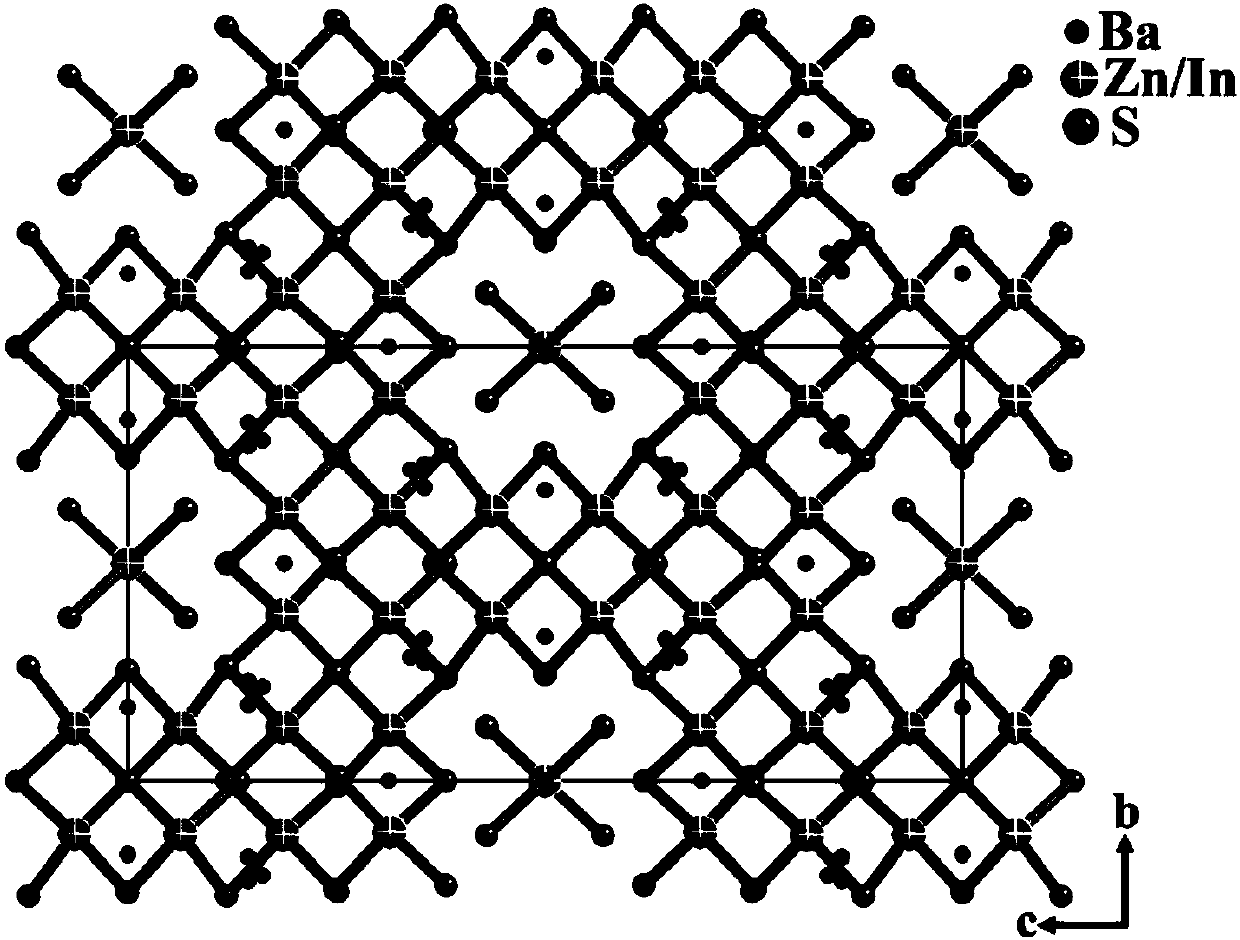
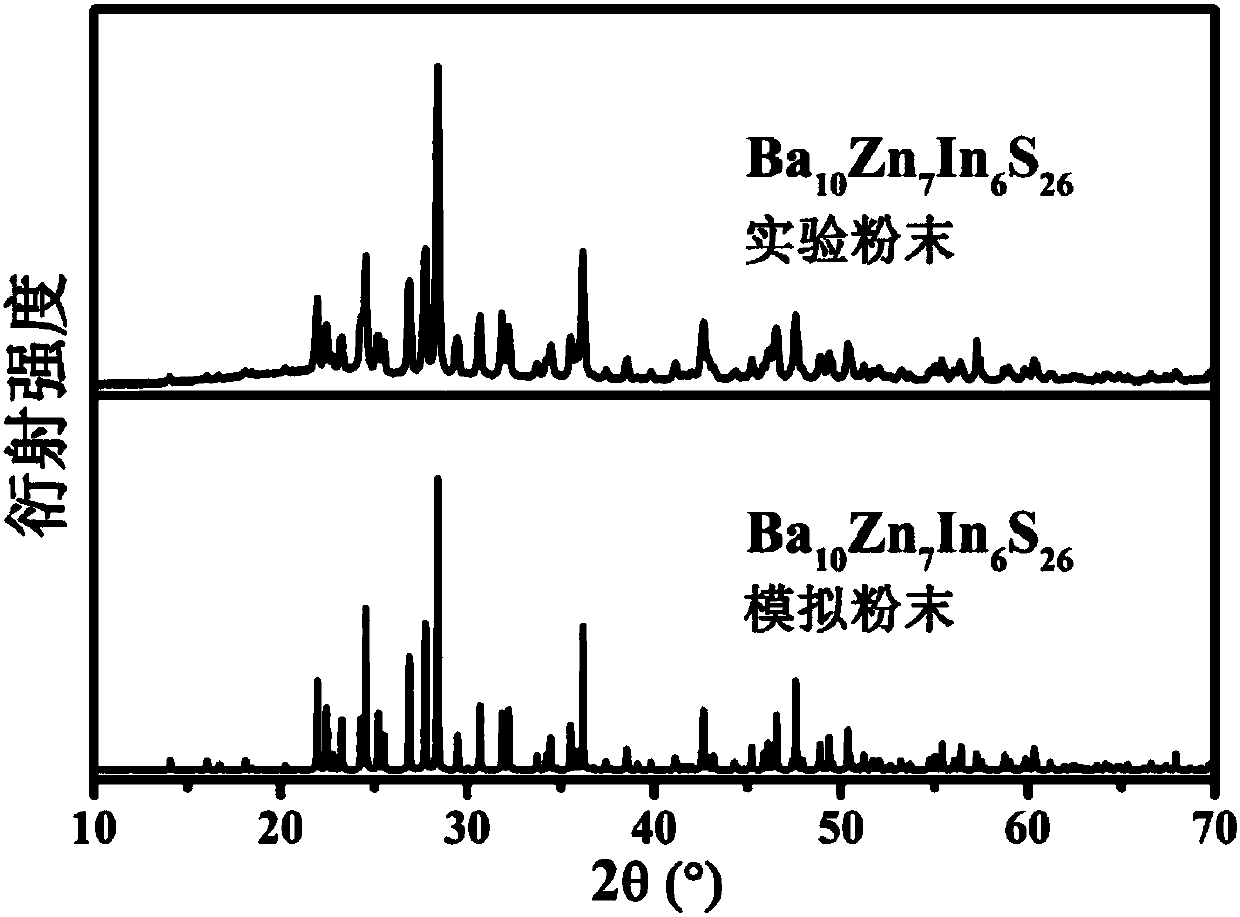
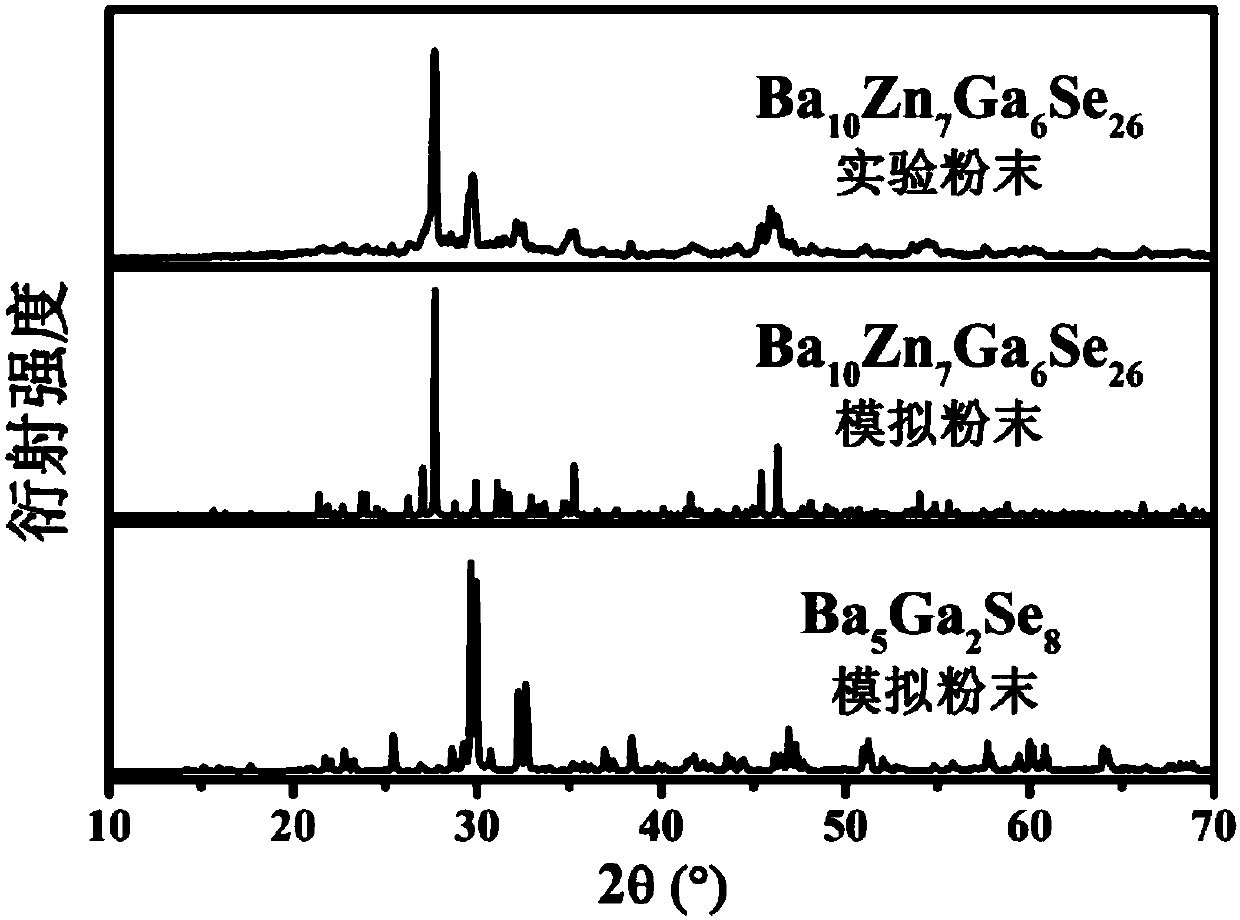
Infrared nonlinear optical crystal Ba10Zn7M6Q26 and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109750357AFluorescentIncreased Laser Damage ThresholdPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateNonlinear optical crystalTetragonal crystal system
The invention discloses infrared nonlinear optical crystal Ba10Zn7M6Q26 and a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular formula of the infrared nonlinear optical crystal is Ba10Zn7M6Q26, wherein M is selected from In or Ga, and Q is selected from S or Se. The infrared nonlinear optical crystal belongs to a tetragonal system, and the space group of the infrared nonlinear optical crystal is I-42m. By taking a crystal compound with the molecular formula being Ba10Zn7In6S26 as an example, the compound is an I type non-phase-match nonlinear optical material under the laser of 2.05 micrometers, the powder frequency doubling response of the compound is 4.1 times of that of commercial AgGaS2 in the particle size range of 30-46 micrometers, and the laser-induced damage threshold ofthe compound is 37.2 times of that of AgGaS2 in the particle size range of150-210 micrometers. The compound is promising in application prospect in military and civil fields and applicable to fields such as electro-optical countermeasure, resource detection, space missile defense and communication.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
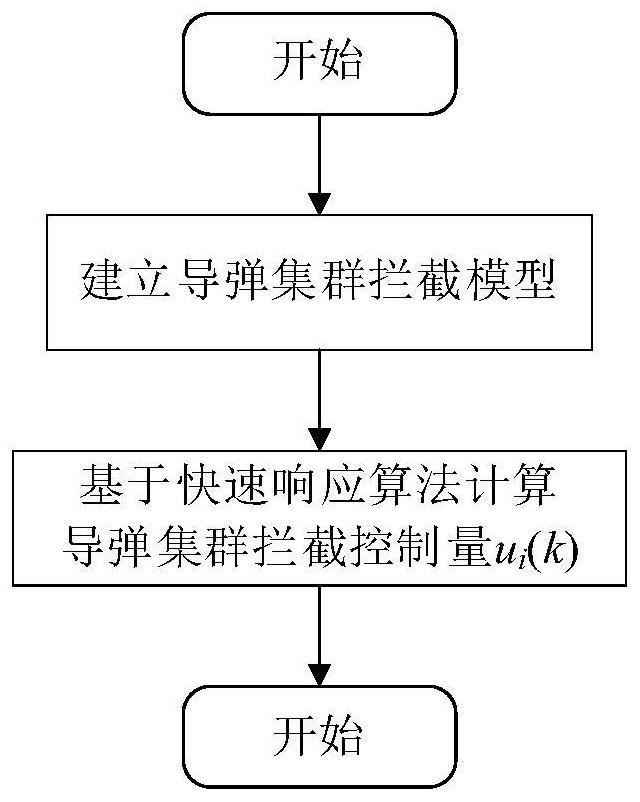
Missile cluster interception method based on quick response algorithm
PendingCN114329316AImprove effectivenessAccurate descriptionDefence devicesComplex mathematical operationsSimulationMissile defense
The invention discloses a missile cluster interception method based on a quick response algorithm. Aiming at a missile cluster attack problem, establishing a missile cluster interception model; and calculating missile cluster interception control quantity according to the missile cluster interception model, establishing an objective function to optimize the missile cluster interception control quantity, and further controlling a defense system to finish accurate and rapid interception of the missile cluster. The accuracy and rapidity of missile cluster interception are improved, and the missile interception capability of a missile defense system is enhanced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and system for acquiring elements for remote interception and launch based on single-sided shooting table
ActiveCN113642122BReduce workloadImprove accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationClassical mechanicsMissile defense
The invention belongs to the technical field of missile defense, and in particular relates to a method and system for obtaining elements of long-range interception and launching based on a single-sided shooting table, constructing a pseudo six-degree-of-freedom ballistic calculation model of a long-range interceptor, and determining the interceptor according to the interception capability and conditions of the interceptor The boundary of the interception area; the maximum negative angle of attack of each trajectory is obtained according to the number of intercepted trajectory and the boundary of the interception area of the interceptor missile; based on the average launch point and launch azimuth value and the maximum negative angle of attack of each trajectory, the trajectory calculation model is used to generate a fixed launch azimuth The general single-sided shooting table of angle; according to the single-sided shooting table and the predicted trajectory of the target, the initial values of the launching elements are obtained, and the initial values of the launching elements are corrected by a Newton iteration to obtain the accurate values of the launching elements. The invention solves the problems of element calculation of long-range interceptor bombs with uncertain launch points, reduces the amount of calculation, improves the stability and efficiency of computing equipment, and can meet the real-time requirements of element calculation of remote interceptor bombs, and has strong engineering application value and prospects .
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com