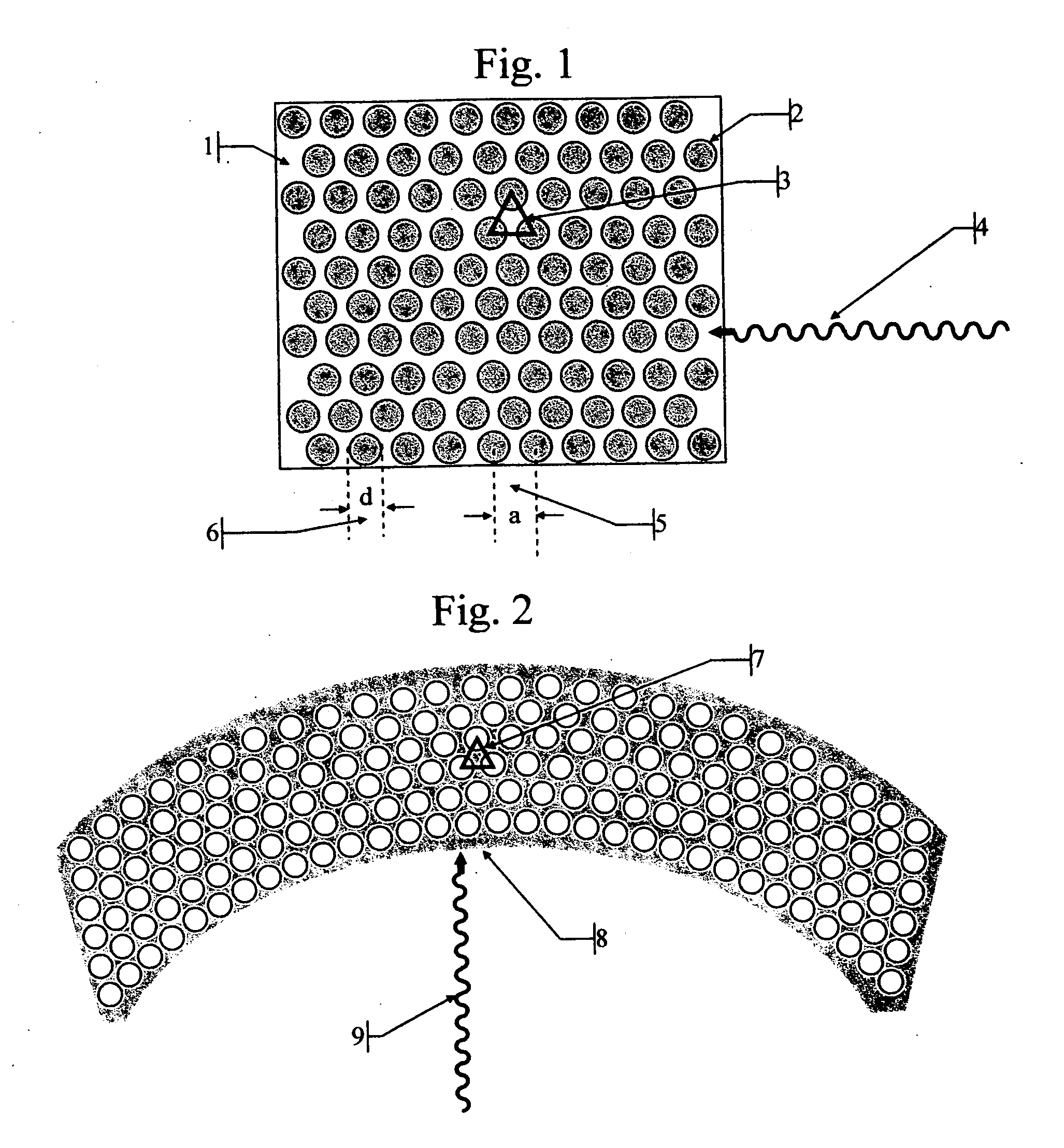
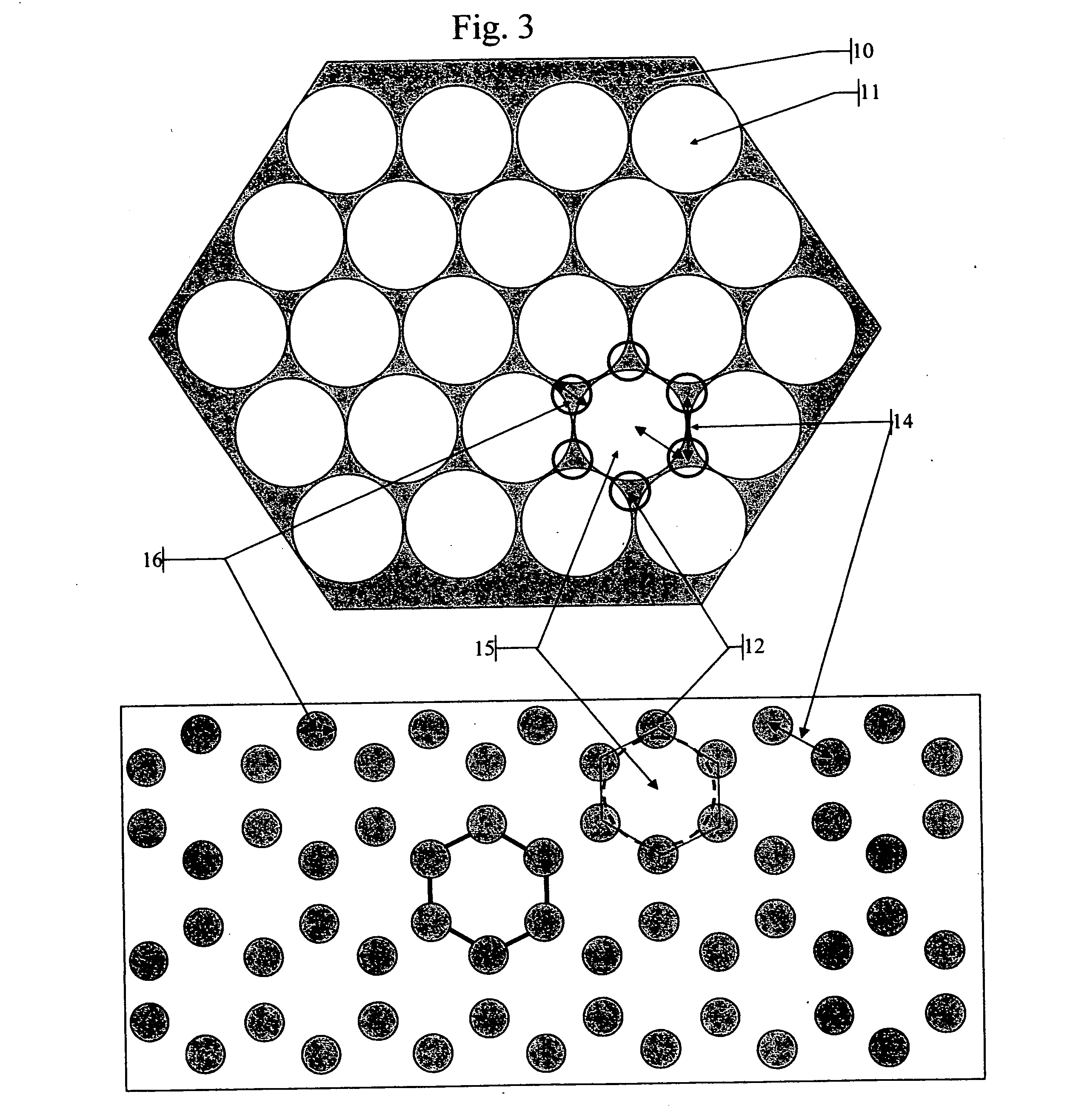
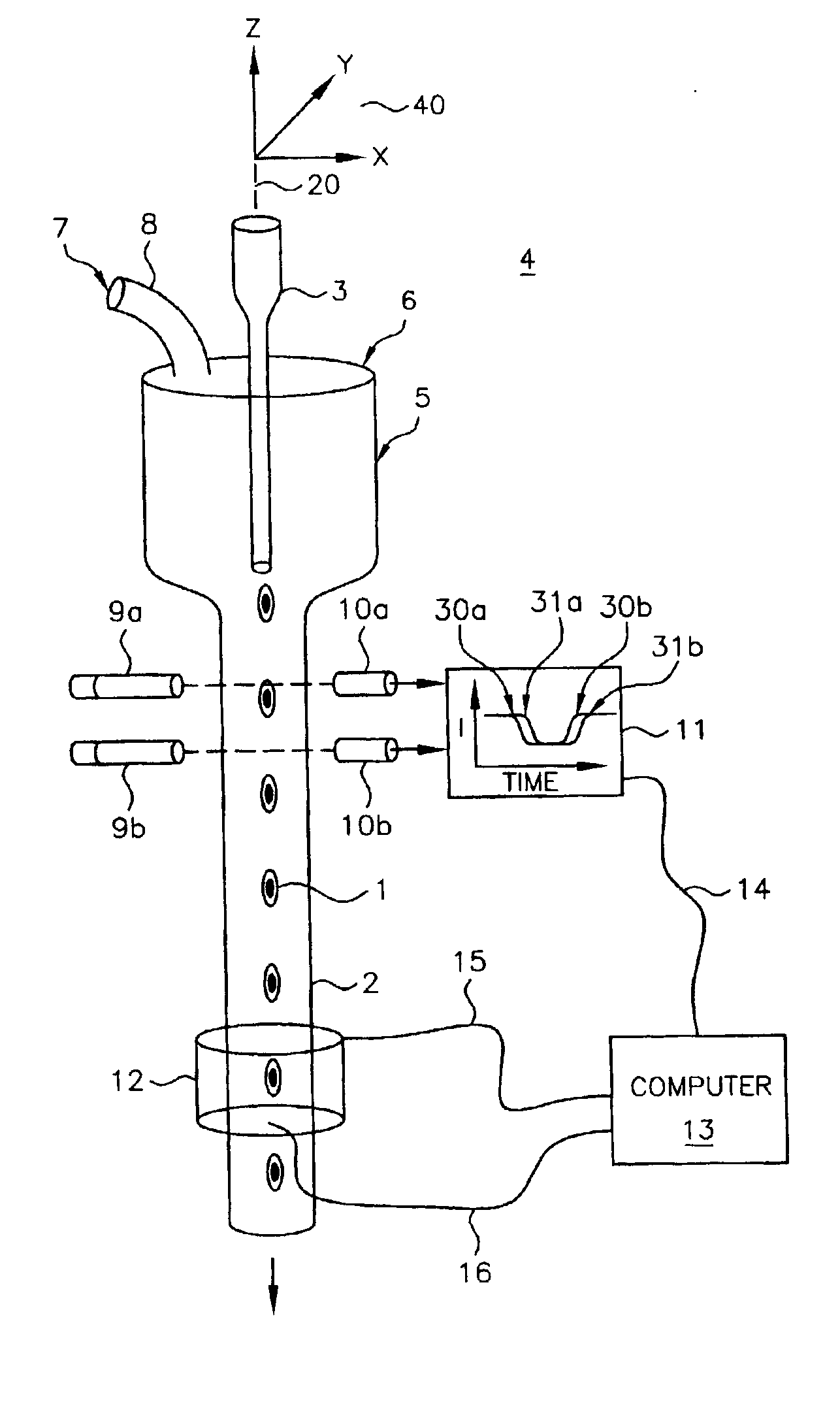
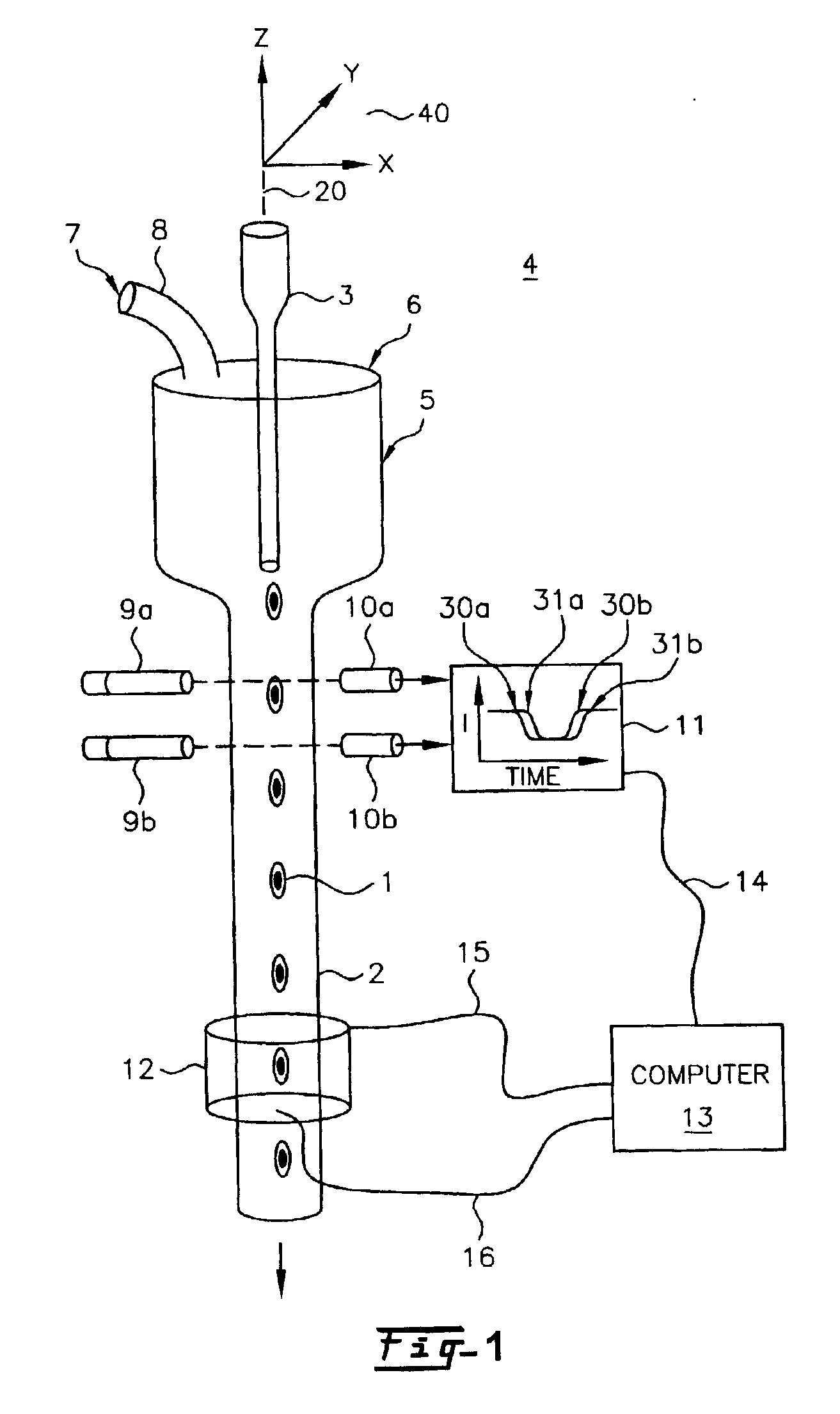
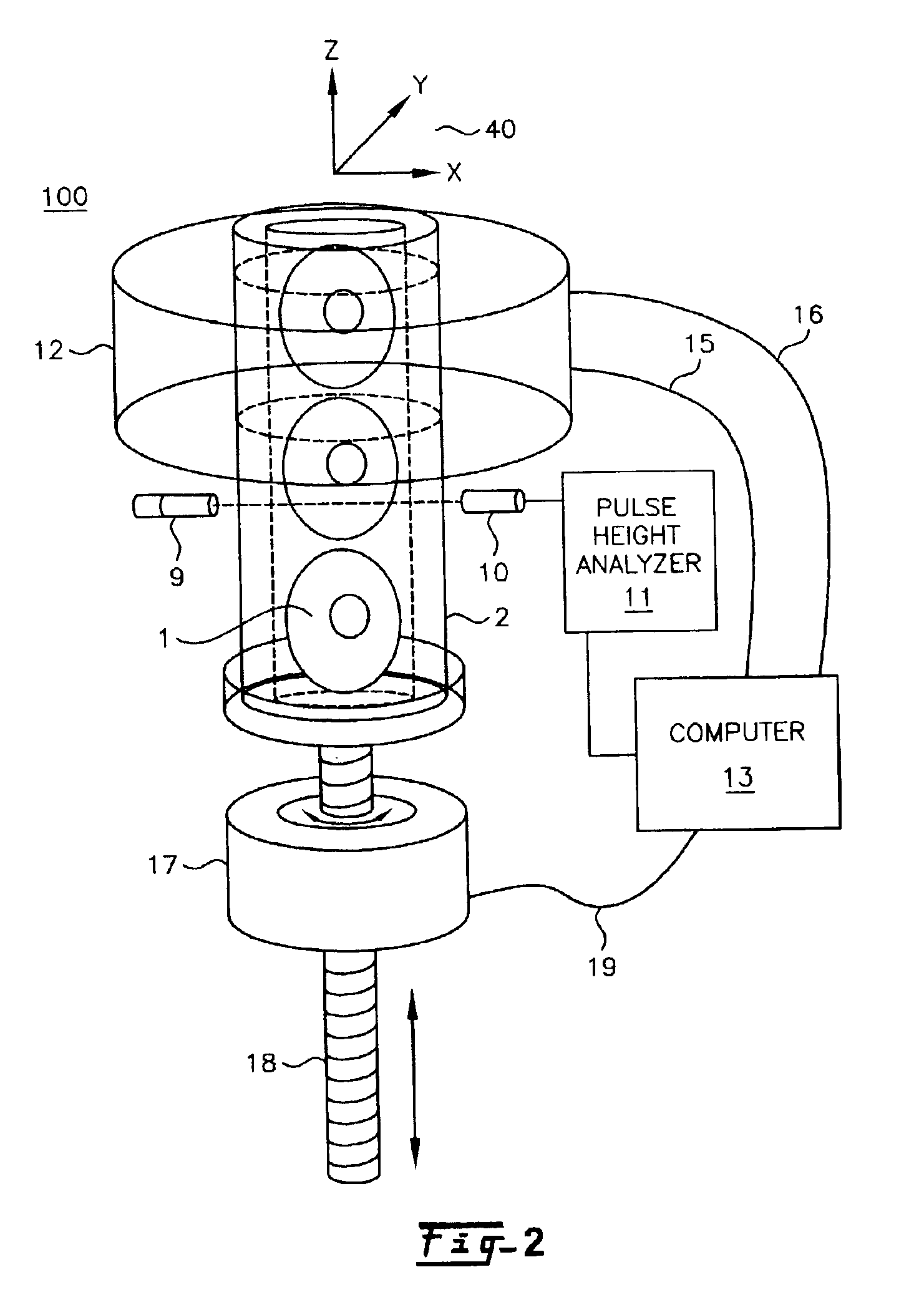
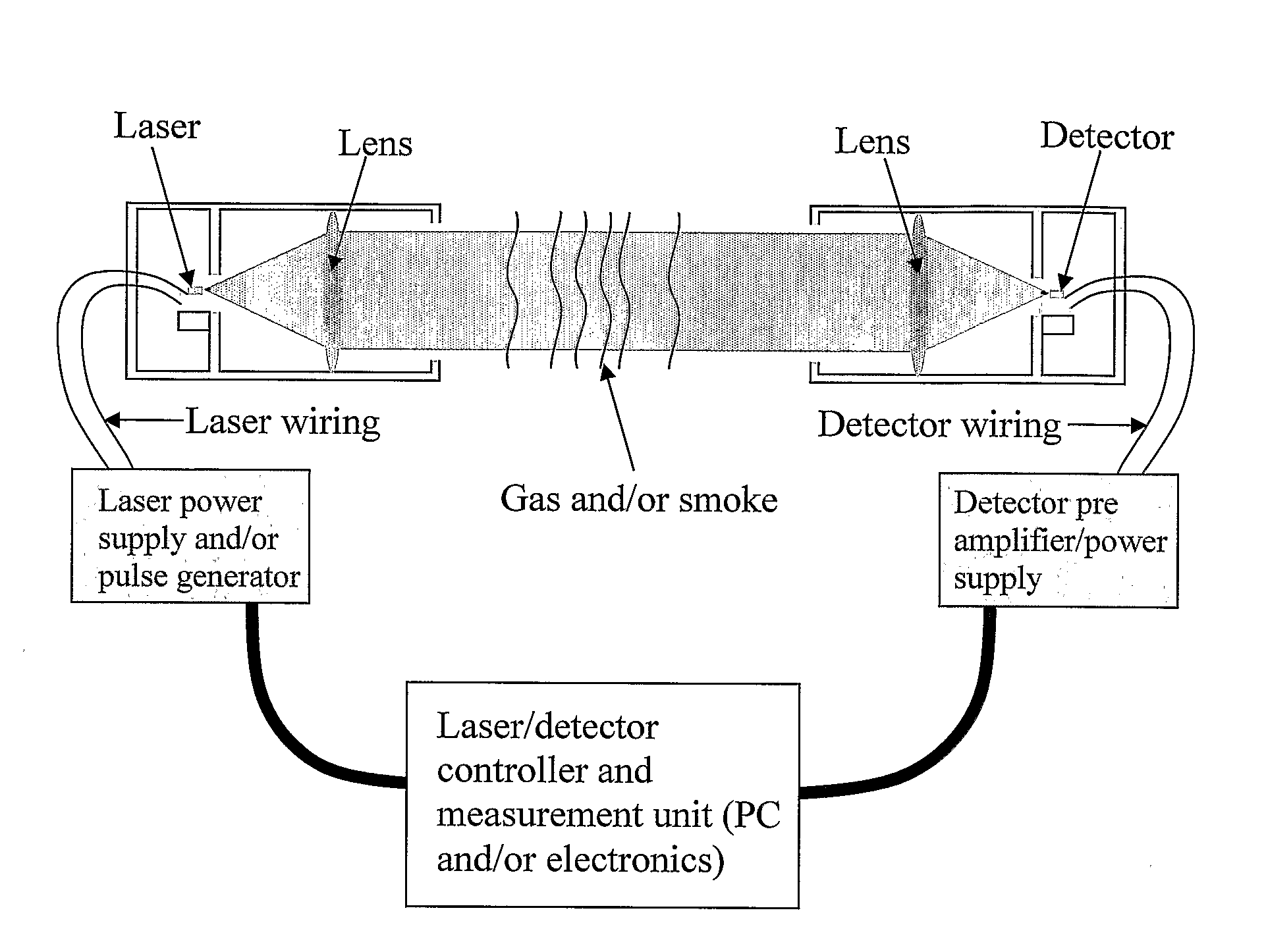
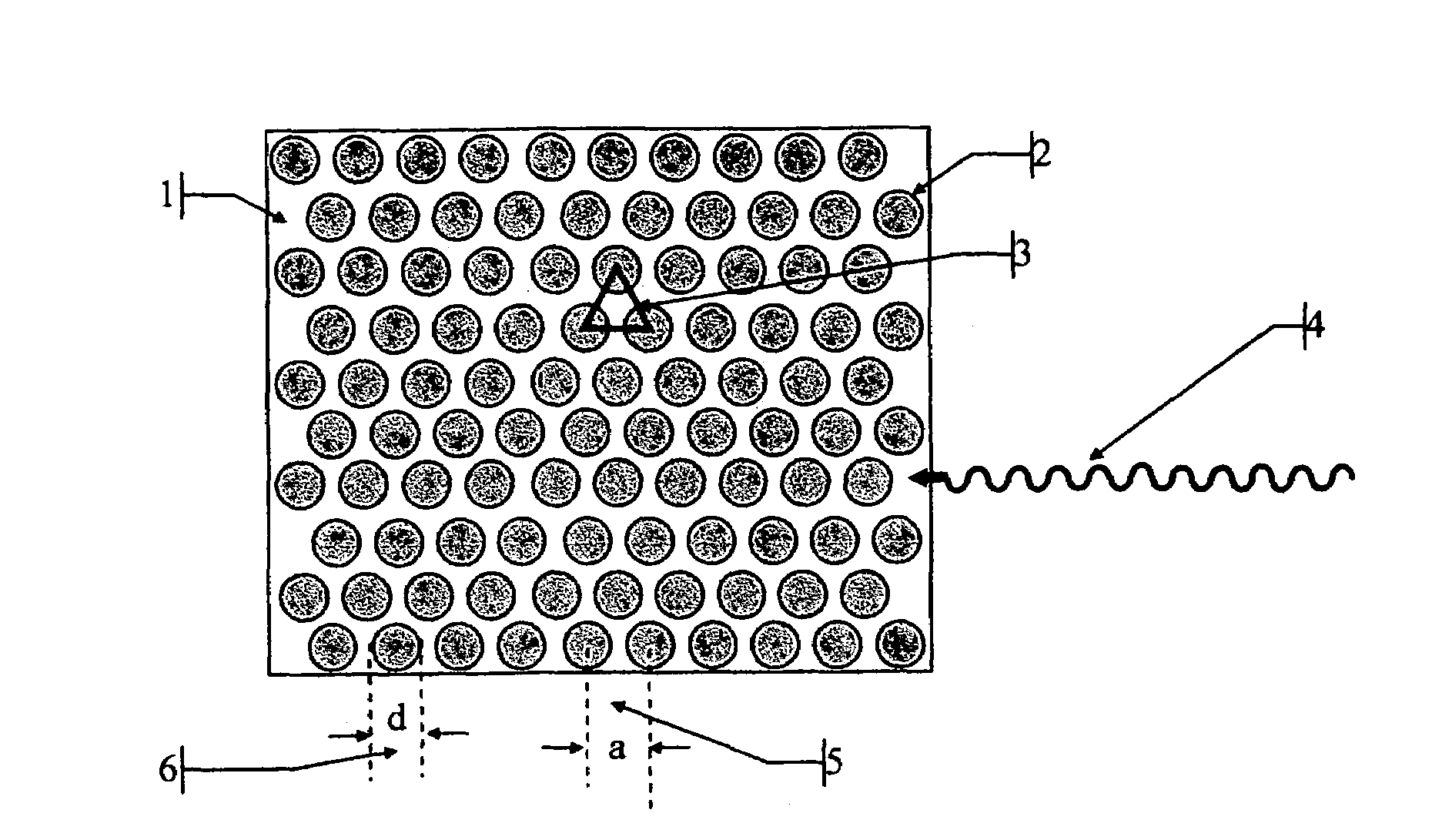
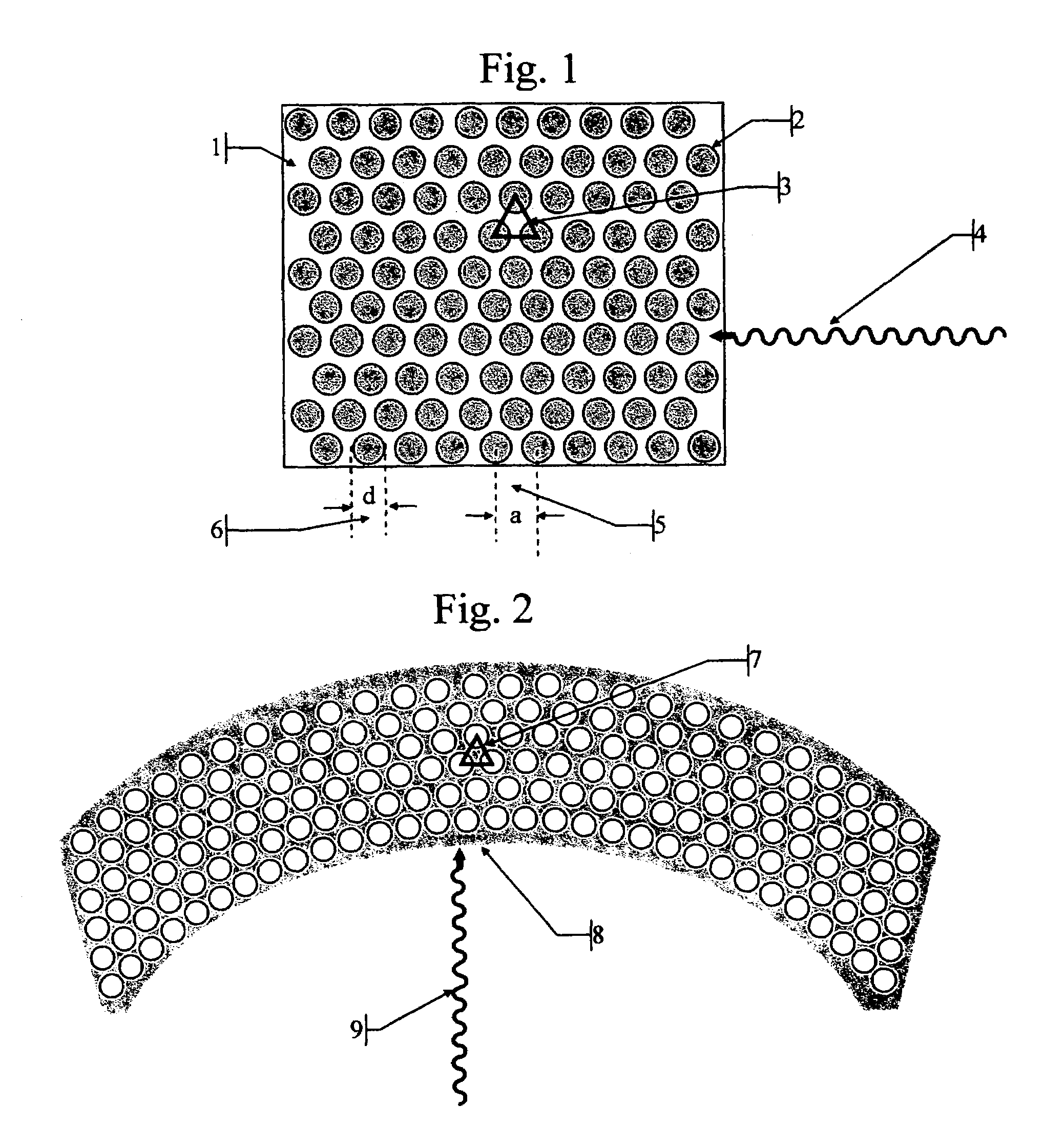
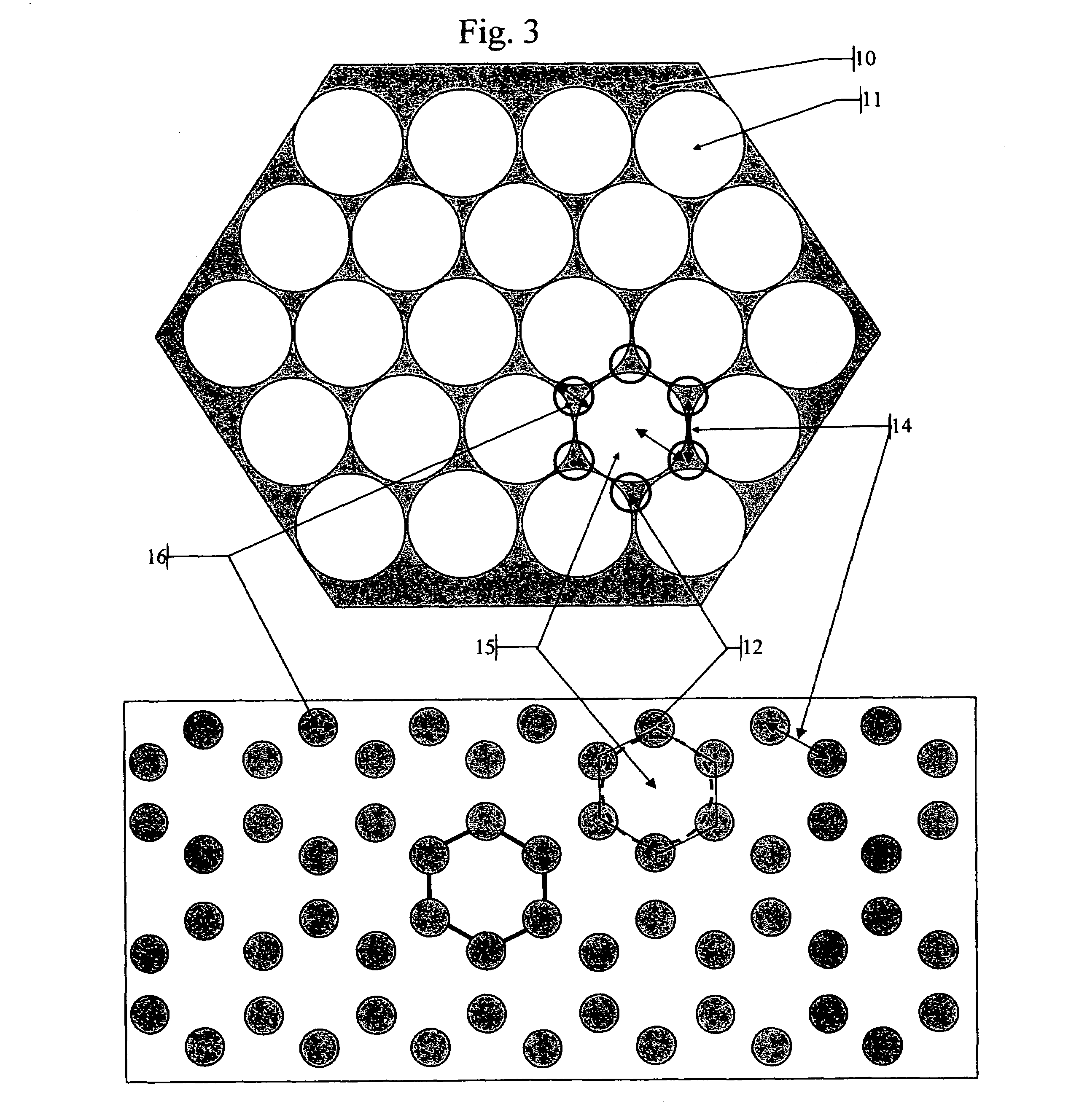
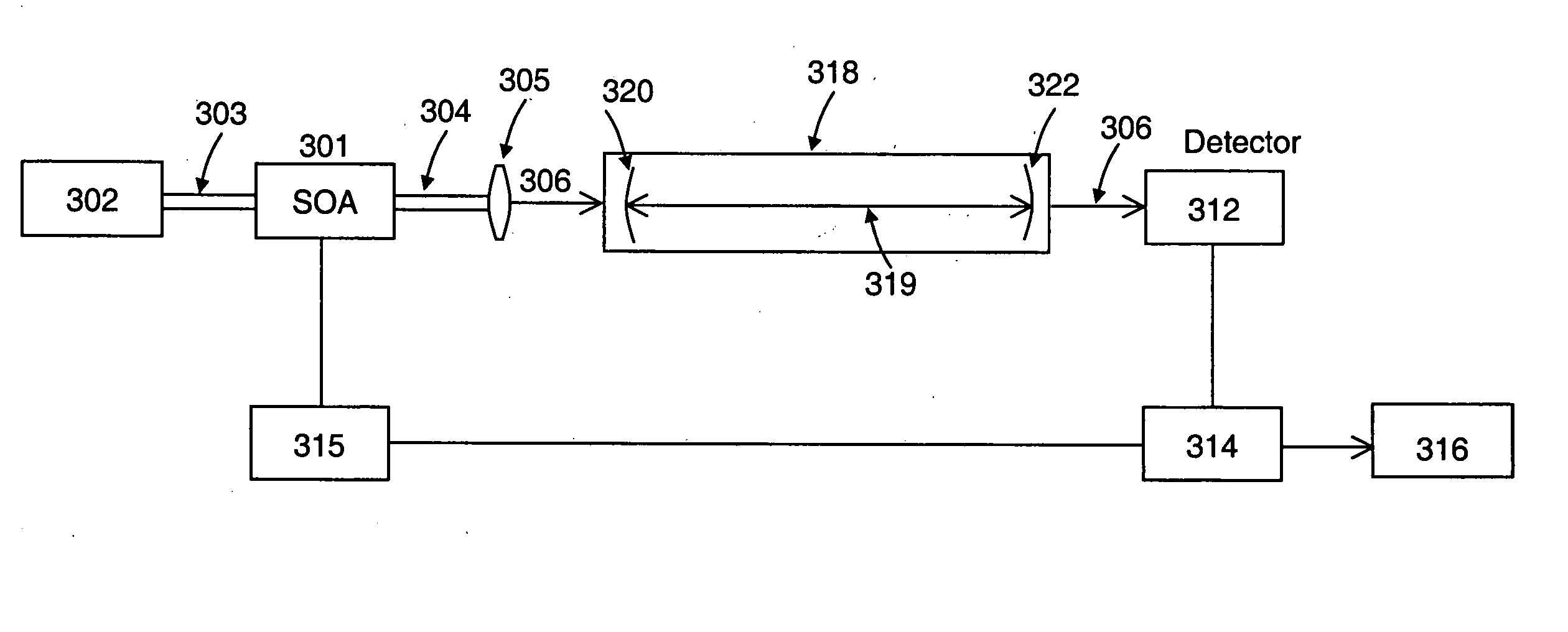
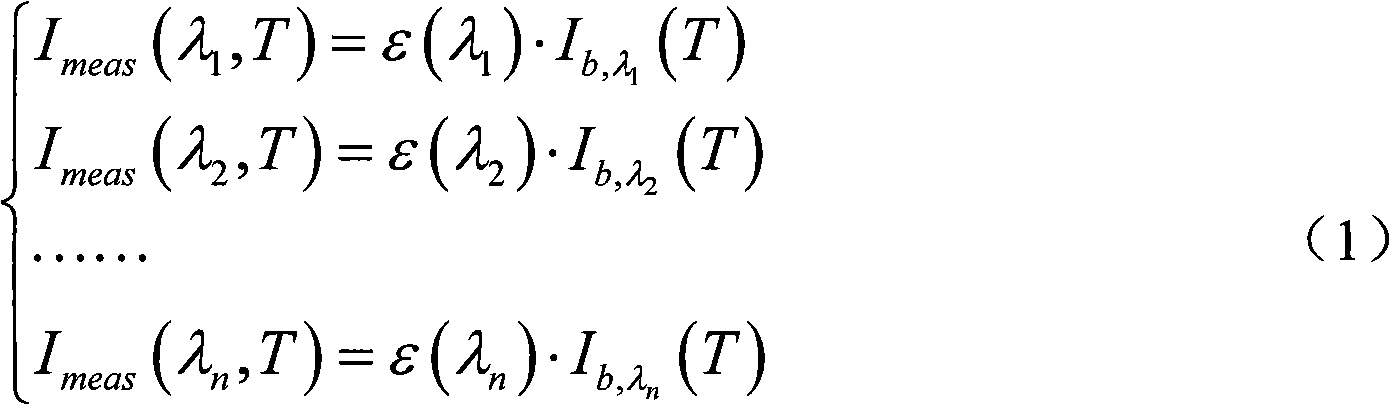Patents
Literature
563 results about "Radiant intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In radiometry, radiant intensity is the radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit solid angle, and spectral intensity is the radiant intensity per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. These are directional quantities. The SI unit of radiant intensity is the watt per steradian (W/sr), while that of spectral intensity in frequency is the watt per steradian per hertz (W·sr⁻¹·Hz⁻¹) and that of spectral intensity in wavelength is the watt per steradian per metre (W·sr⁻¹·m⁻¹)—commonly the watt per steradian per nanometre (W·sr⁻¹·nm⁻¹). Radiant intensity is distinct from irradiance and radiant exitance, which are often called intensity in branches of physics other than radiometry. In radio-frequency engineering, radiant intensity is sometimes called radiation intensity.
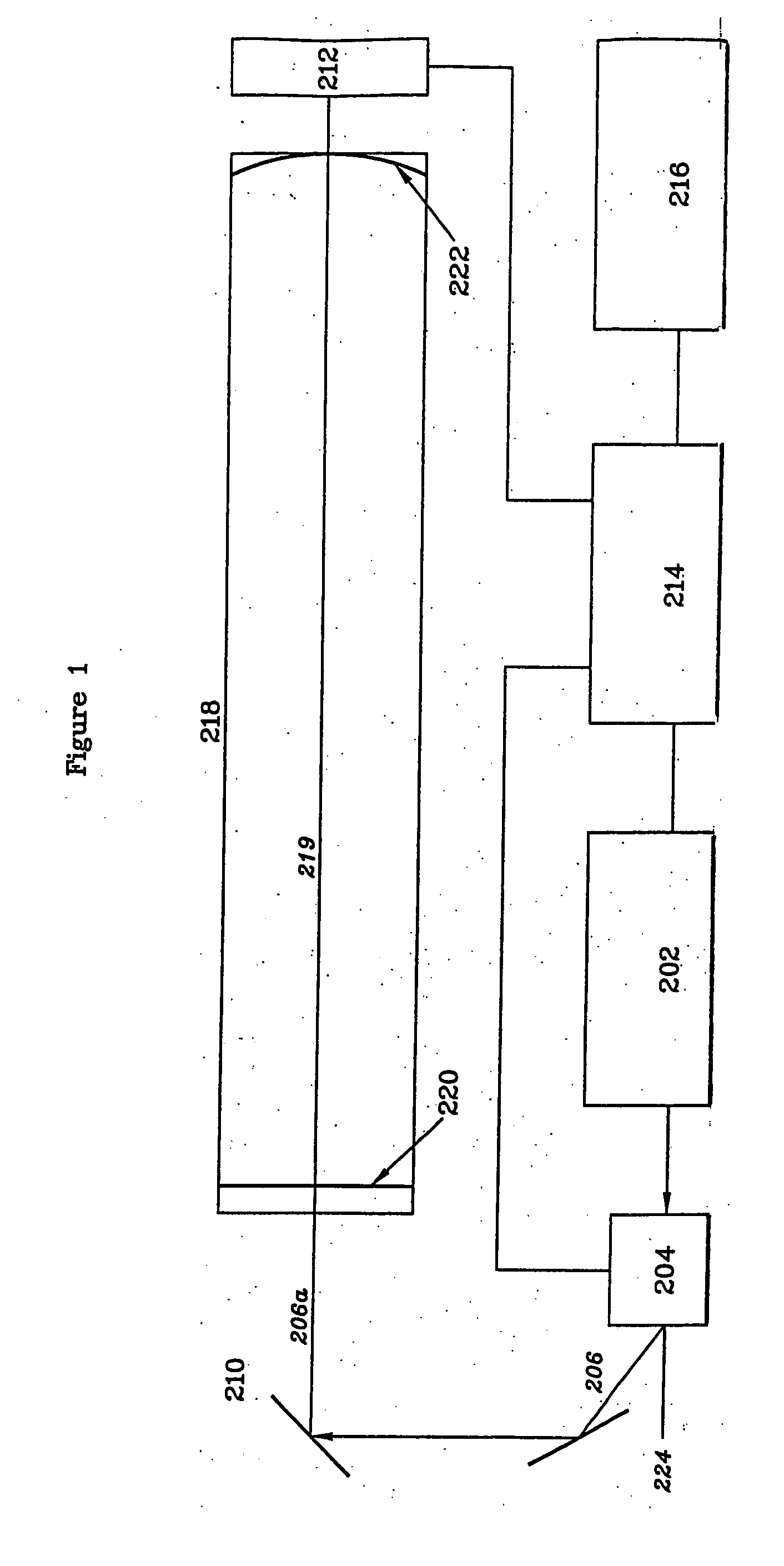
Multi-dimensional image reconstruction
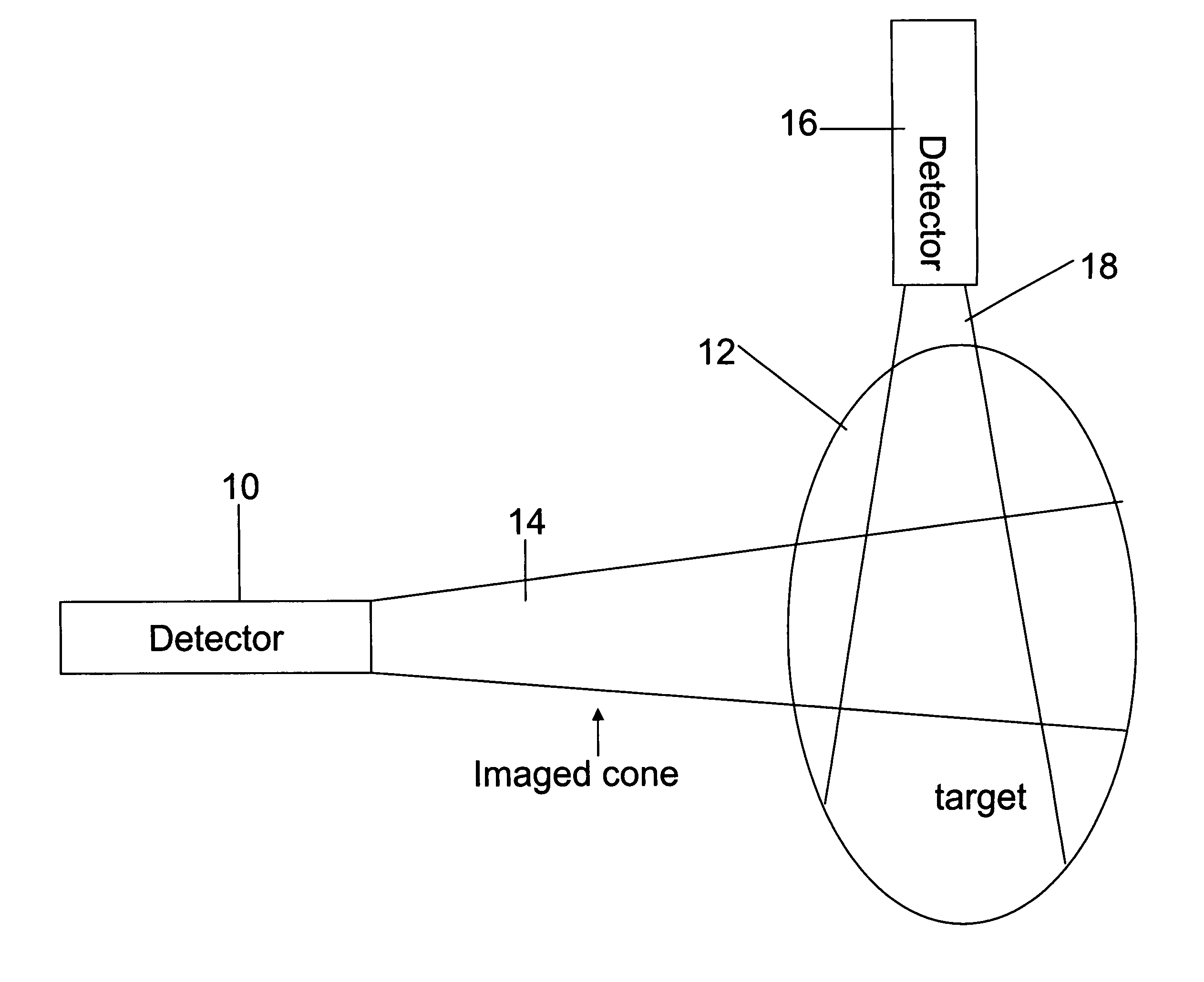
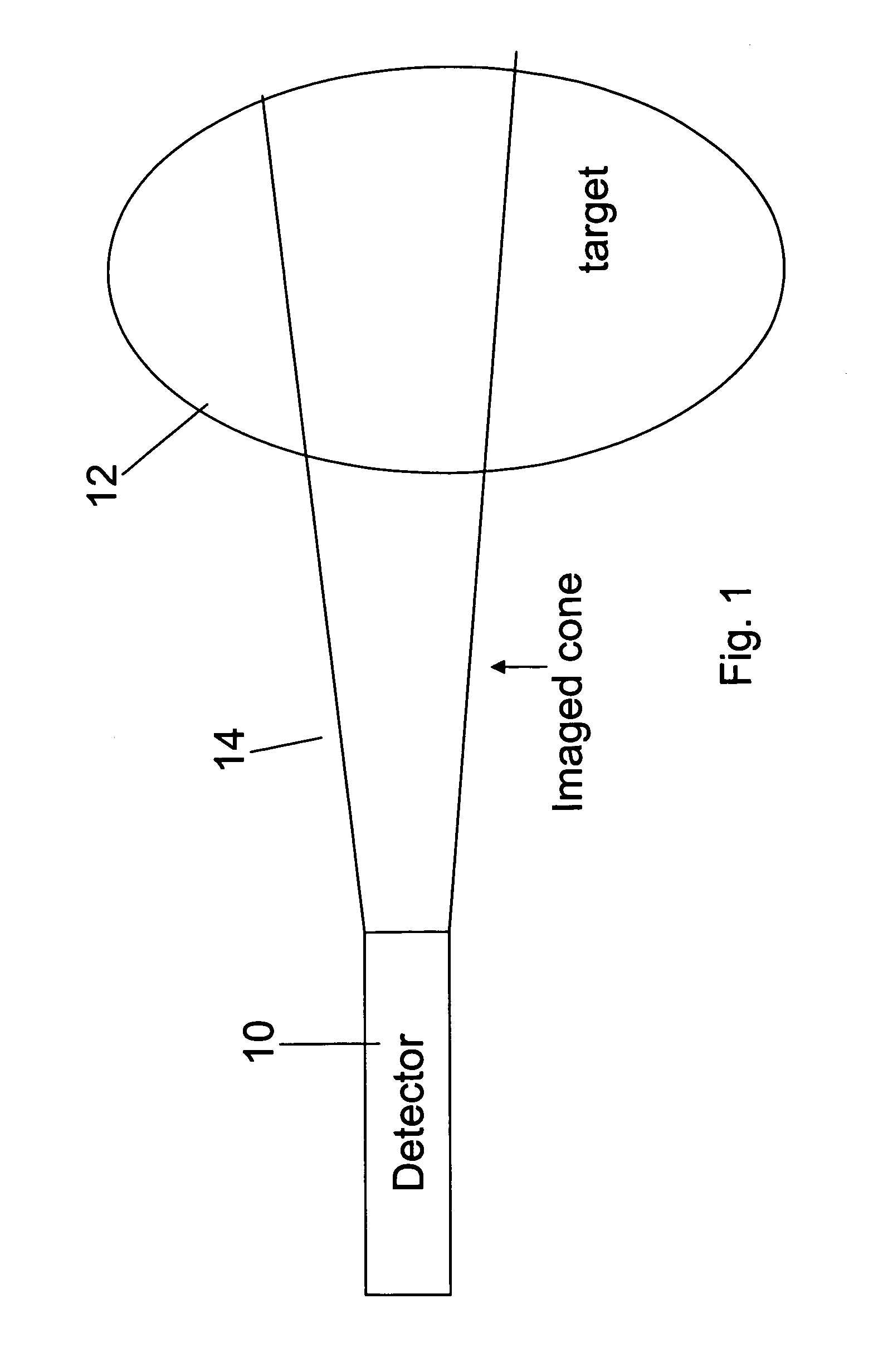
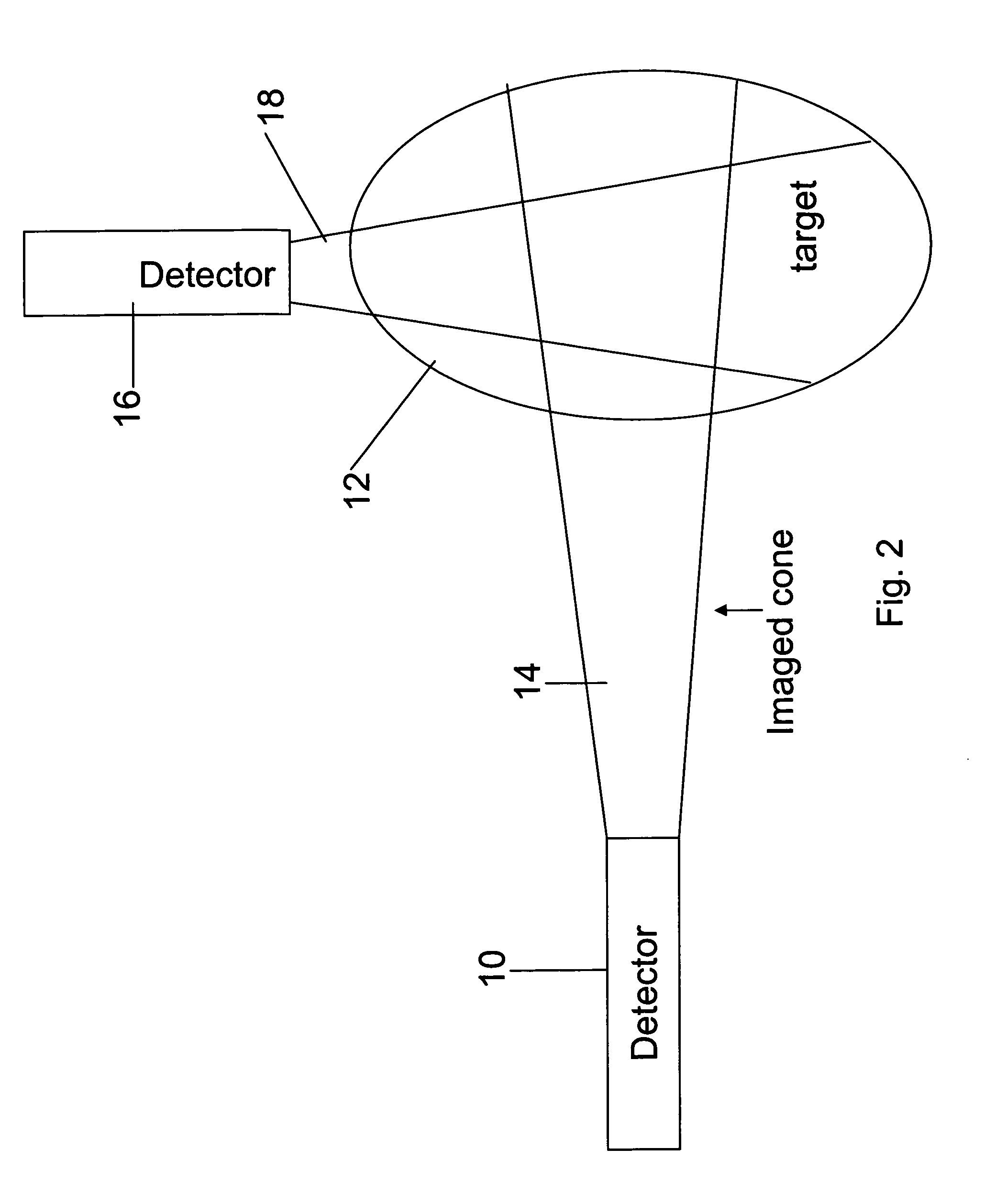
Apparatus for radiation based imaging of a non-homogenous target area having distinguishable regions therein, comprises: an imaging unit configured to obtain radiation intensity data from a target region in the spatial dimensions and at least one other dimension, and an image four-dimension analysis unit analyzes the intensity data in the spatial dimension and said at least one other dimension in order to map the distinguishable regions. The system typically detects rates of change over time in signals from radiopharmaceuticals and uses the rates of change to identify the tissues. In a preferred embodiment, two or more radiopharmaceuticals are used, the results of one being used as a constraint on the other.
Owner:SPECTRUM DYNAMICS MEDICAL LTD
Radiation detectors
InactiveUS20060202125A1Thinner sliceImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsRecoil electronPhotonic bandgap
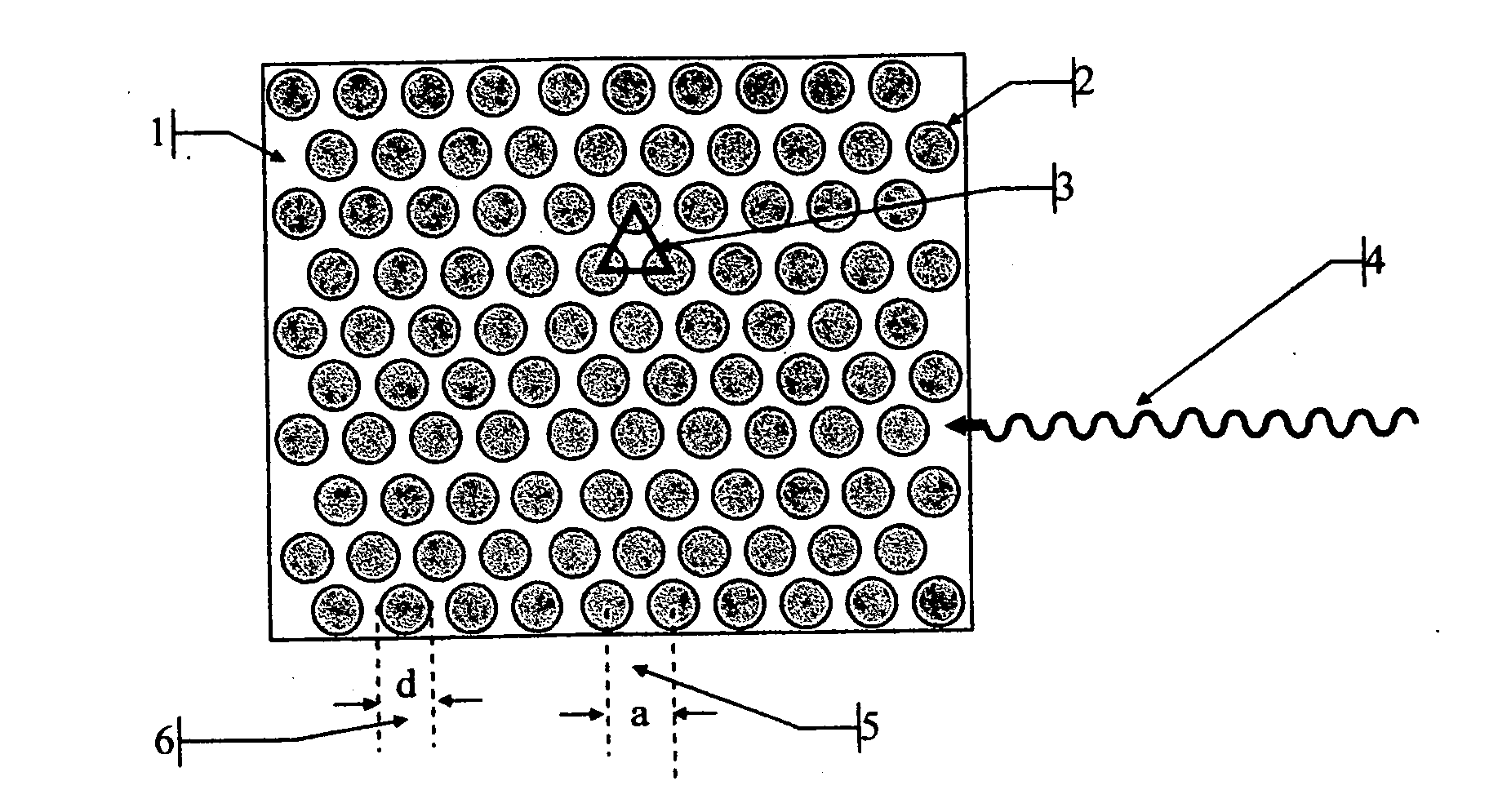
The invention consists in structuring scintillation radiation detectors as Photonic Bandgap Crystals or 3D layers of thin filaments, thus enabling extremely high spatial resolutions and achieving virtual voxellation of the radiation detector without physical separating walls. The ability to precisely measure the recoil electron track in a Compton camera enables to assess the directions of the gamma rays hitting the detector and consequently dispensing with collimators that strongly reduce the intensity of radiation detected by gamma cameras. The invention enables great enhancements of the capabilities of gamma cameras, SPECT, PET, CT and DR machines as well as their use in Homeland Security applications. Methods of fabrication of such radiation detectors are decribed.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
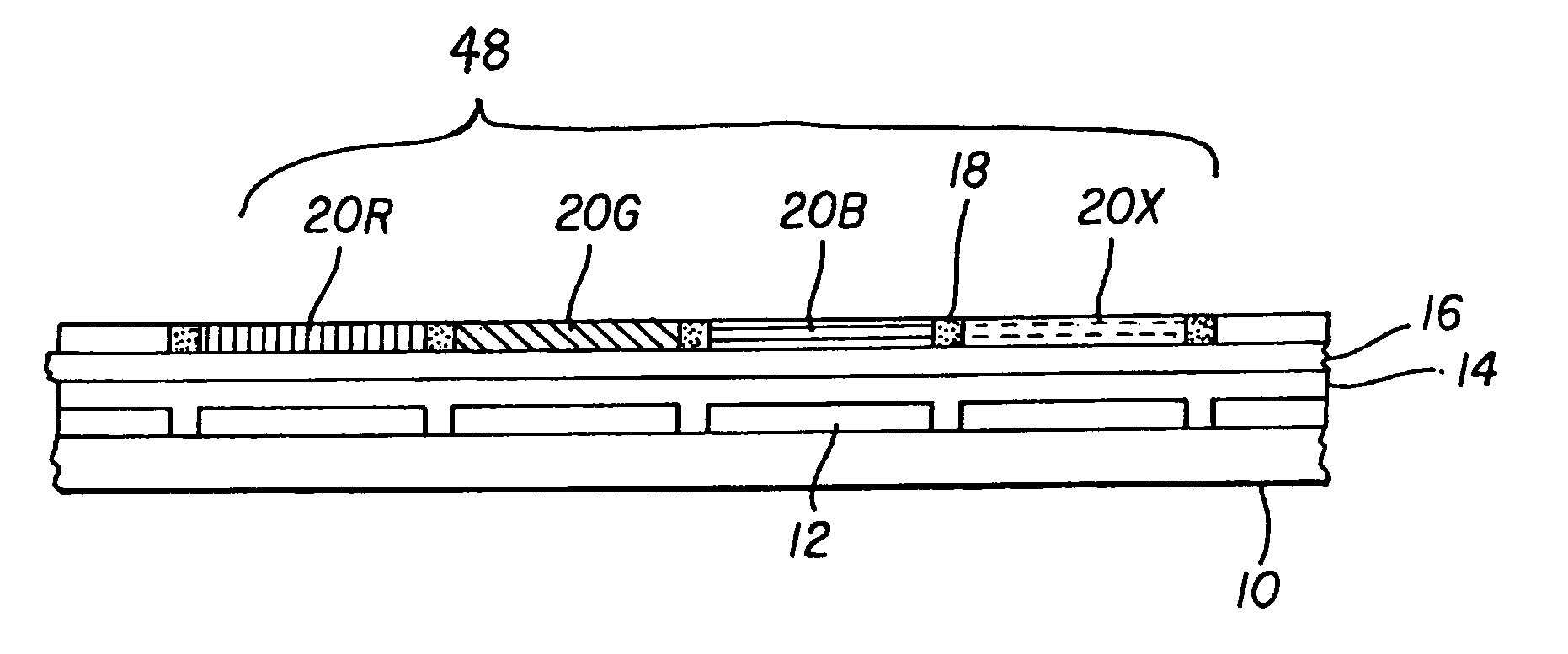
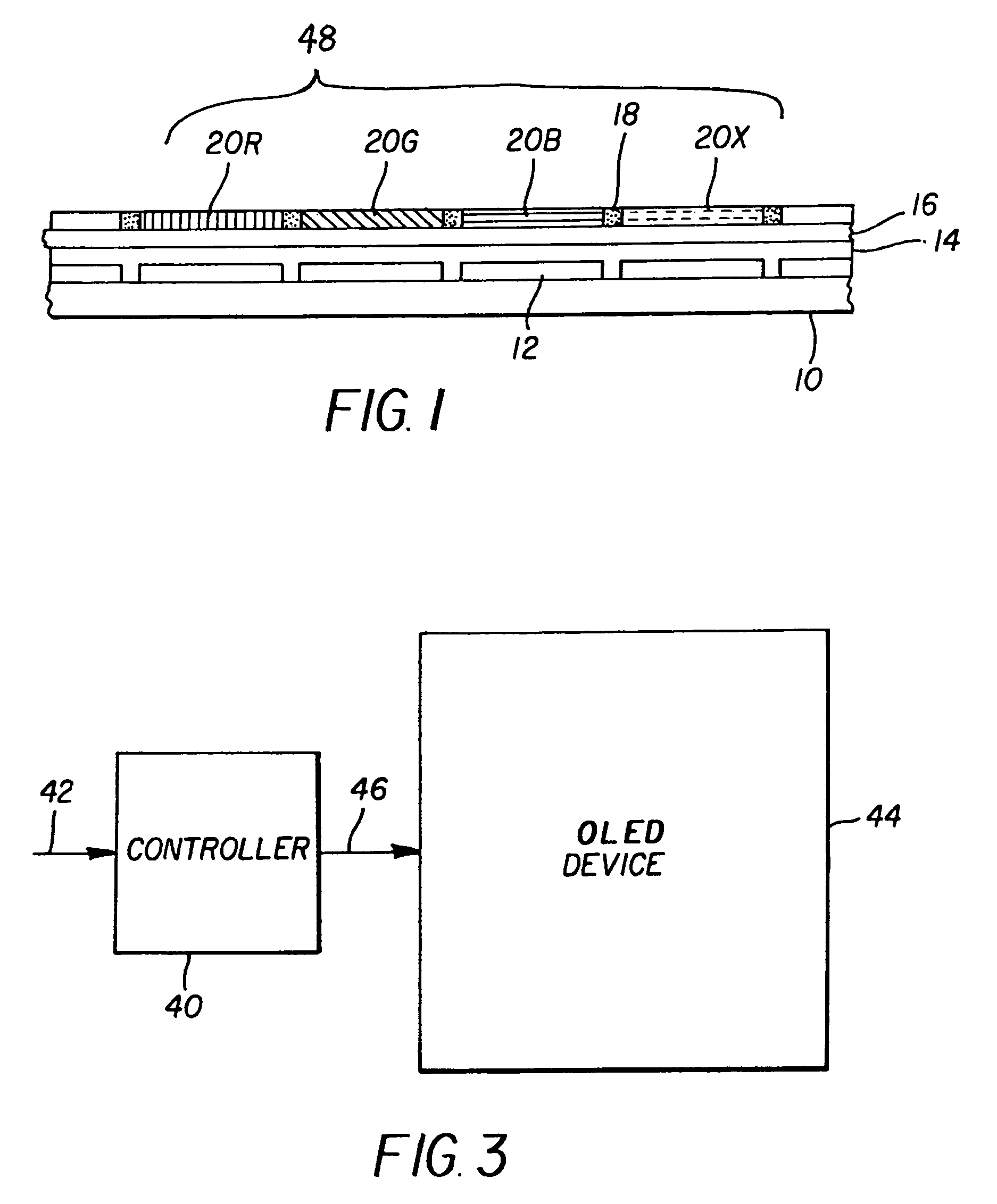
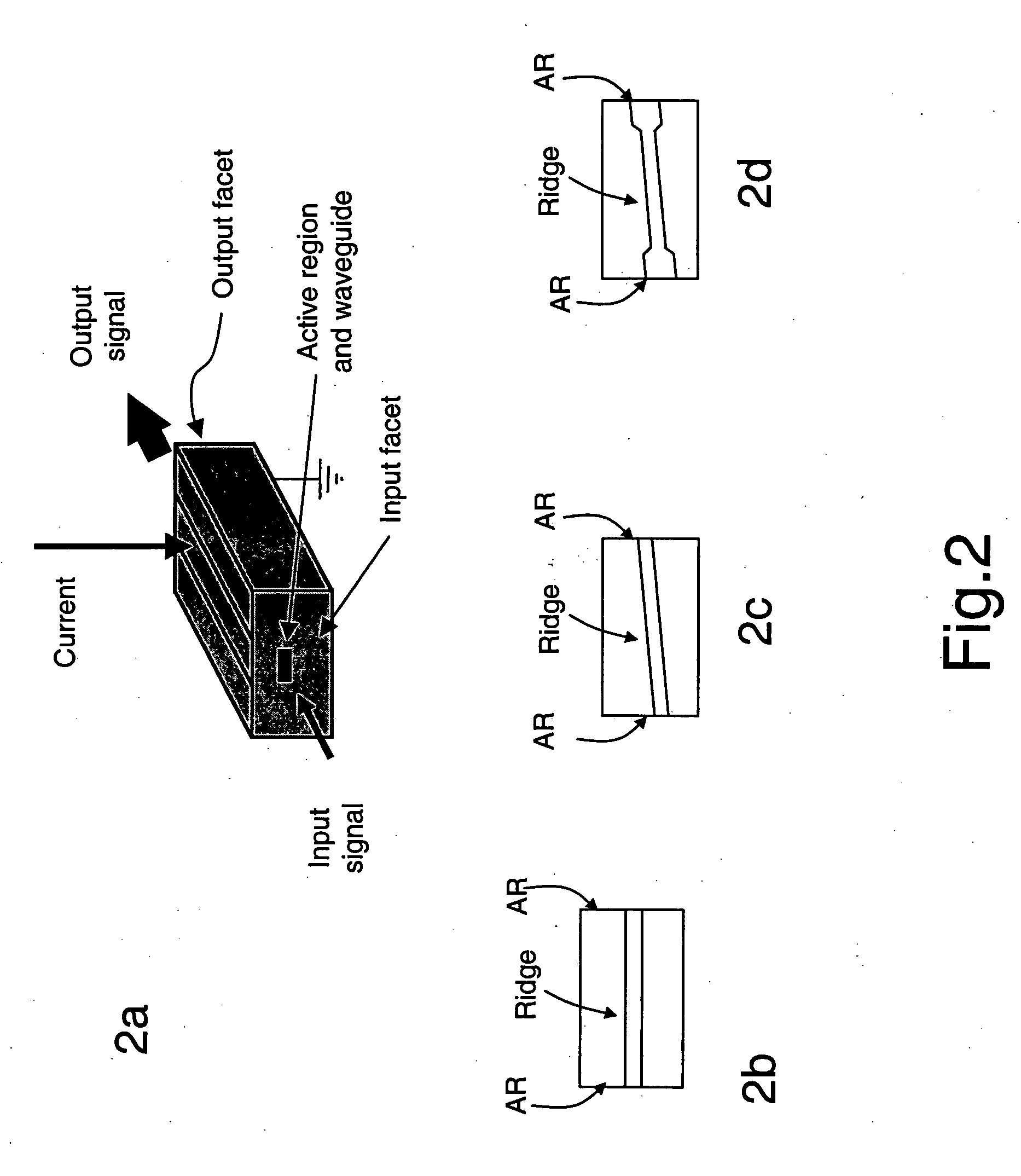
Color OLED device having improved performance
ActiveUS7091523B2Improve color gamutElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesGamutBroadband
A color OLED device is described having one or more pixels, at least one pixel comprising: four or more light-emitting elements, each light-emitting element comprising one or more layers of electroluminescent organic material producing a broadband light having a variable frequency-dependent luminous efficacy emission spectrum, and each light-emitting element further comprising a filter for filtering the broadband light and emitting a different color of light; wherein the different colors of light emitted by three of the light-emitting elements specify a first color gamut of the OLED device, and an additional one or more of the light-emitting elements emit at least one additional different color of light and wherein the frequency range of the filter of the additional light emitting element is matched to a portion of the broadband light frequency range having a radiant intensity greater than the radiant intensity of the frequency range of at least one of the filters of the three light-emitting elements specifying the first color gamut of the OLED device, and the additional one or more light emitting elements having luminous efficiency greater than that of at least one of the three light emitting elements specifying the first color gamut.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Method and devices for creating a multiplicity of holes in workpieces
InactiveUS20130209731A1Quality improvementReduce material strengthLayered productsGlass reforming apparatusThermal DestructionsLaser beams
Methods and apparatuses for producing a multiplicity of holes in thin workpieces made of glass or glass-like materials and semiconductors are provided. The method includes directing multiple laser beams onto predetermined perforation points of the workpiece in a wavelength range between 1600 and 200 nm and with a radiation intensity that causes local non-thermal destruction of the workpiece material along respective filamentary channels. Subsequently, the filamentary channels are widened to the desired diameter of the holes.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Optical tomography of small objects using parallel ray illumination and post-specimen optical magnification
InactiveUS6944322B2Easy to controlUniform intensity distributionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorOptical tomographyMagnifying glass
A parallel-beam optical tomography system for imaging an object of interest includes a parallel ray beam radiation source that illuminates the object of interest with a plurality of parallel radiation beams. After passing through the object of interest the pattern of transmitted or emitted radiation intensities is magnified by a post specimen optical element or elements. An object containing tube is located within an outer tube, wherein the object of interest is held within or flows through the object containing tube. A motor may be coupled to rotate and / or translate the object containing tube to present differing views of the object of interest. One or more detector arrays are located to receive the emerging radiation from the post specimen magnifying optic. Two- or three-dimensional images may be reconstructed from the magnified parallel projection data.
Owner:VISIONGATE
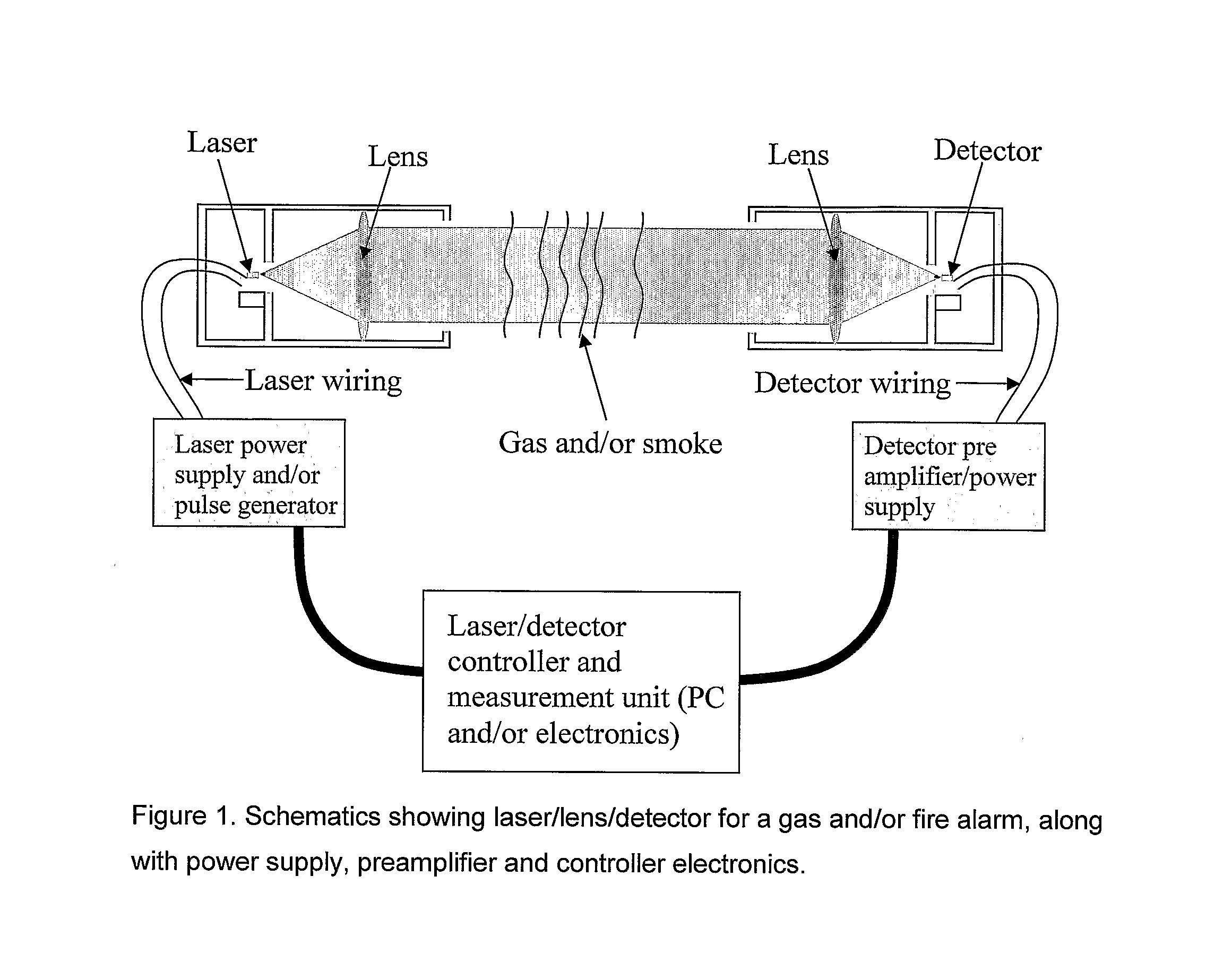
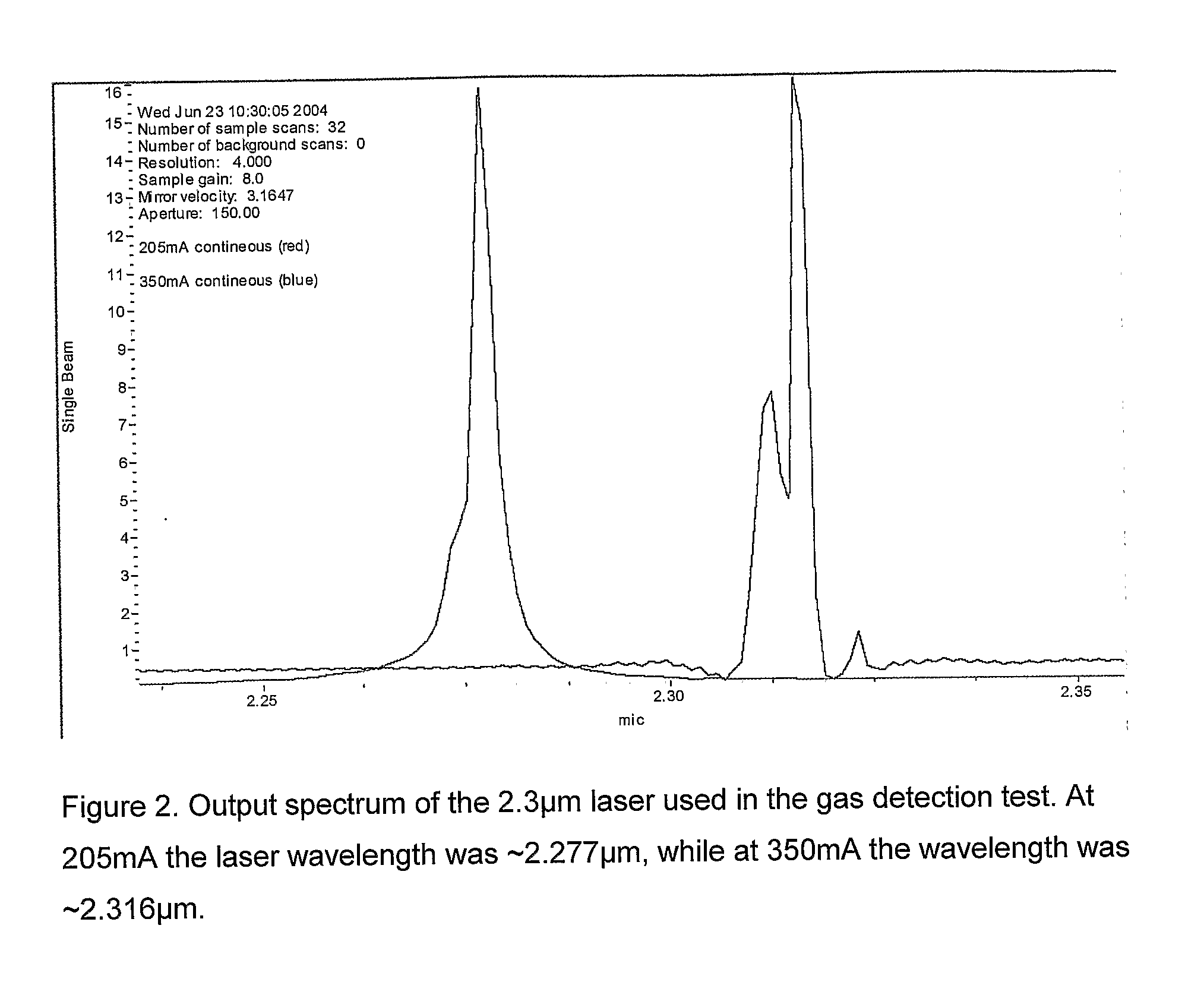
Infrared Laser Based Alarm
InactiveUS20080198027A1Avoid frostAvoid corrosion damageInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsGas compositionParticle density
The subject invention relates to a new alarm which is based on using a quarternary tunable Mid-IR laser to measure both particles and gas at the same time. The measurement is done within an area of which the gas of interest will absorb the Mid-IR radiation. By widely tuning the emission wavelength of the laser, several wavelengths can be measured in order to accurately find both gas composition and particle density with one laser based sensor. We tested a new device which use radiation between 2.27 μm and 2.316 μm. Methane gas reduces intensity of the radiation at certain wavelengths in this device, while particles / fog reduce intensity for all wavelengths. In this case, fog should not trigger an alarm, while methane leaks should. This can also be applied for CO and smoke in which one sensor will measure both parameters to sound an alarm instead of just one parameter.
Owner:INTEGRATED OPTOELECTRONICS
Radiation sources and radiation scanning systems with improved uniformity of radiation intensity
InactiveUS6954515B2Uniform radiation intensityImproved intensity distributionRadiation/particle handlingCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingFluenceX-ray
A radiation source is disclosed comprising a source of charged particles that travel along a path. Target material lies along the path to generate radiation upon impact by the beam. A magnet is provided to deflect the beam prior to impacting the target. The magnet may generate a time-varying magnetic field or a constant magnetic field. A constant magnetic field may be varied spatially across the beam. The magnet may be an electromagnet or a permanent magnet. In one example, deflection of the beam results in impact of the beam on the target along a plurality of axes. In another example, portions of the beam are differentially deflected. The source may thereby irradiate an object to be scanned with more uniform radiation. The charged particles may be electrons or protons and the radiation may be X-ray or gamma ray radiation, or neutrons. Scanning systems incorporating such sources, methods of generating radiation and methods of examining objects are disclosed, as well.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
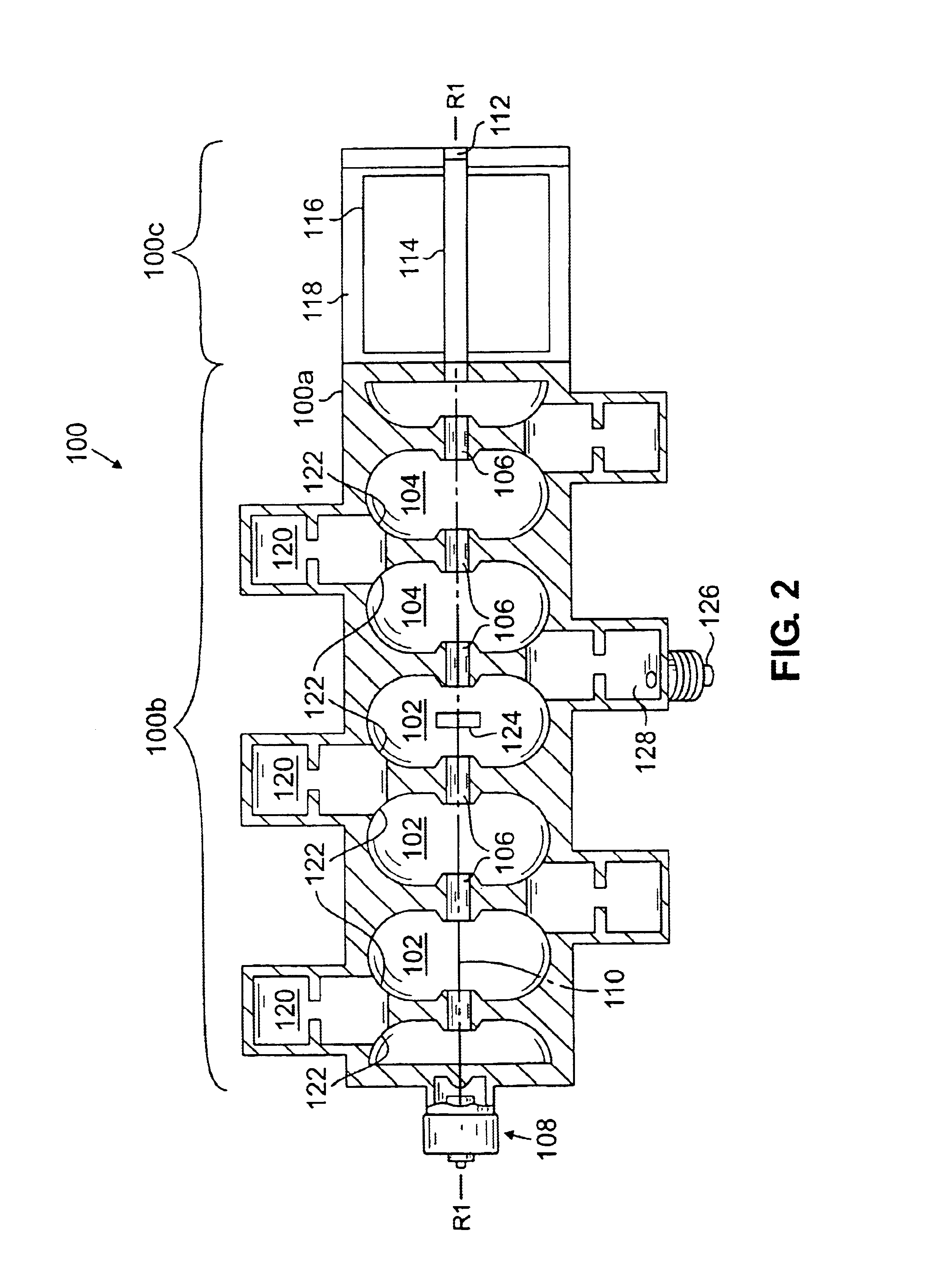
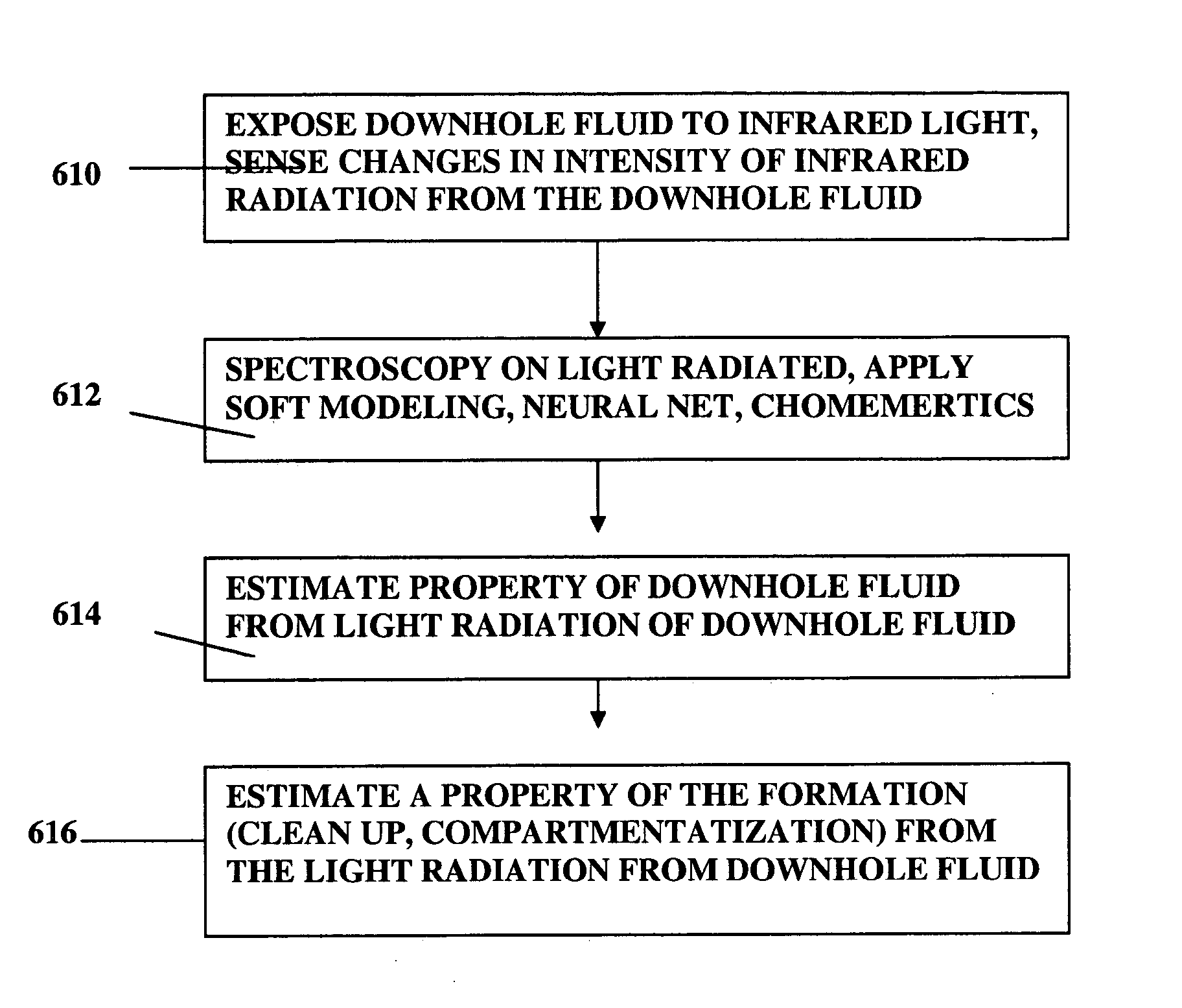
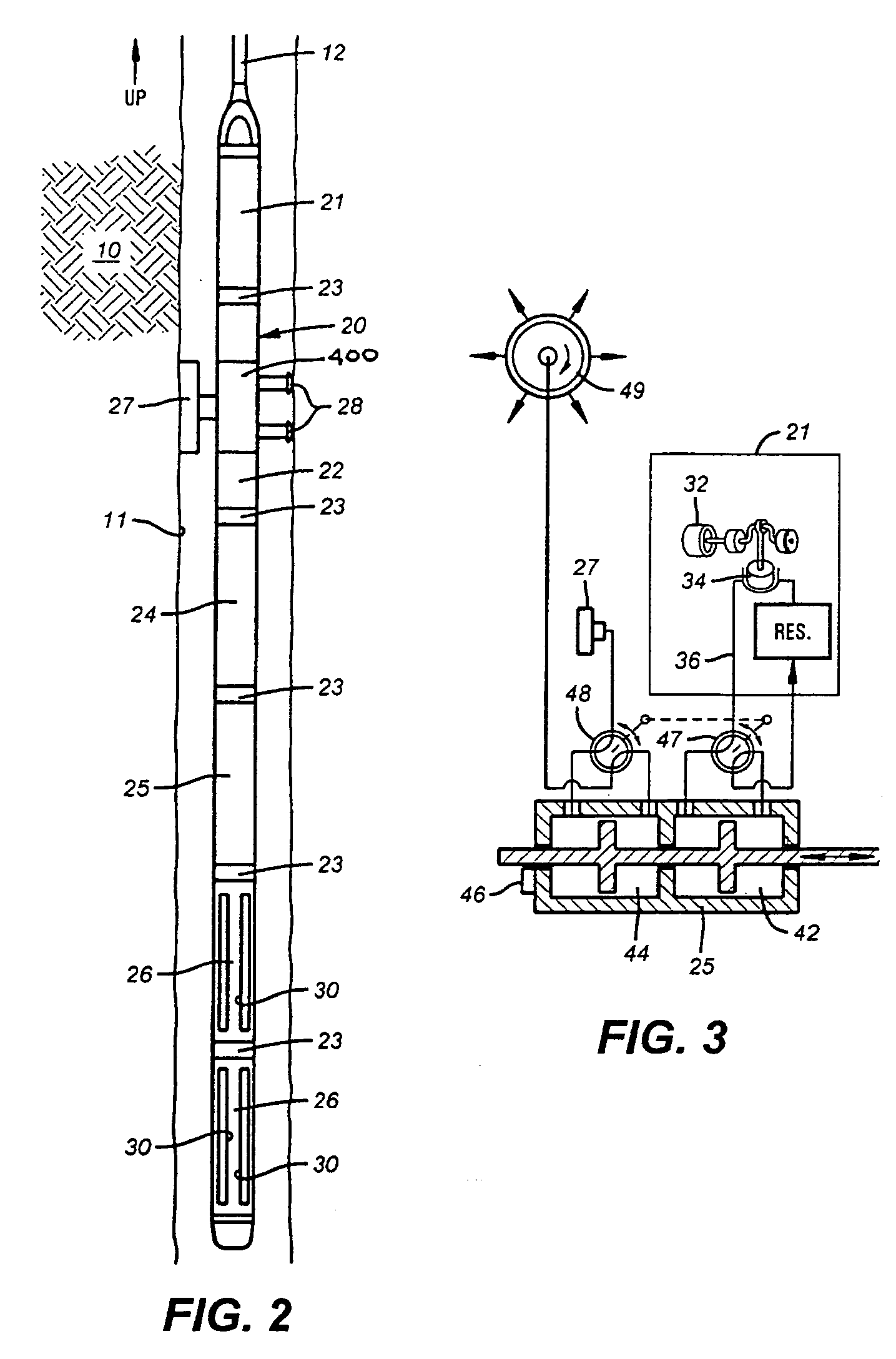
Method and apparatus for analyzing a downhole fluid using a thermal detector
InactiveUS20060175547A1Material analysis by optical meansAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyElectricityPath length
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for estimating a property of a fluid downhole by exposing the fluid to modulated light downhole and sensing changes in intensity of infrared radiation from the downhole fluid to estimate the property of the downhole fluid. The present invention senses changes in intensity of light by converting the changes to transient changes in temperature of a detector, such as a pyroelectric detector. The present invention performs spectroscopic analysis of fluids by optically filtering the light allowed to impinge on a pyroelectric detector, converting the changes in temperature of the pyroelectric detector to a signal and converting the signal to estimate the property of the downhole fluid. The light source is modulated by mechanically chopping the beam or by electrically pulsing the light source or by steering the beam between different path lengths of sample or between a reference cell (filled with a reference fluid or empty) and a sample-filled cell.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Radiation detectors
InactiveUS7304309B2Improve efficiencyEasy accessMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsRecoil electronPhotonic bandgap
The invention consists in structuring scintillation radiation detectors as Photonic Bandgap Crystals or 3D layers of thin filaments, thus enabling extremely high spatial resolutions and achieving virtual voxellation of the radiation detector without physical separating walls. The ability to precisely measure the recoil electron track in a Compton camera enables to assess the directions of the gamma rays hitting the detector and consequently dispensing with collimators that strongly reduce the intensity of radiation detected by gamma cameras. The invention enables great enhancements of the capabilities of gamma cameras, SPECT, PET, CT and DR machines as well as their use in Homeland Security applications. Methods of fabrication of such radiation detectors are described.
Owner:SUHAMI AVRAHAM
System and method for controlling the light source of a cavity ringdown spectrometer
InactiveUS20050254056A1Reduce repetition rateEasy to controlRadiation pyrometryTransmissivity measurementsHigh reflectivitySpectrometer
A system and method for controlling the light source of a cavity ring-down spectrometer (CRDS). The system comprises a resonant optical cavity having at least two high reflectivity mirrors; a source for providing a continuous wave optical signal into the optical cavity, the source comprising an electrically pumped semiconductor gain medium; and a SOA interposed between the optical signal source and the optical cavity. The SOA receives the optical signal and transmits it to the resonant optical cavity. The system also includes a first detector for monitoring the intensity of radiation emitted from said cavity and generating a first detection signal based thereon; and at least a first controller for deactivating the optical signal based on a comparison of the first detection signal and a predetermined threshold and for thereafter reactivating the optical signal after a delay period in excess of the ring-down time of the optical cavity, the deactivating and reactivating being achieved by respectively turning off and then turning on electrical current to the SOA.
Owner:PICARRO
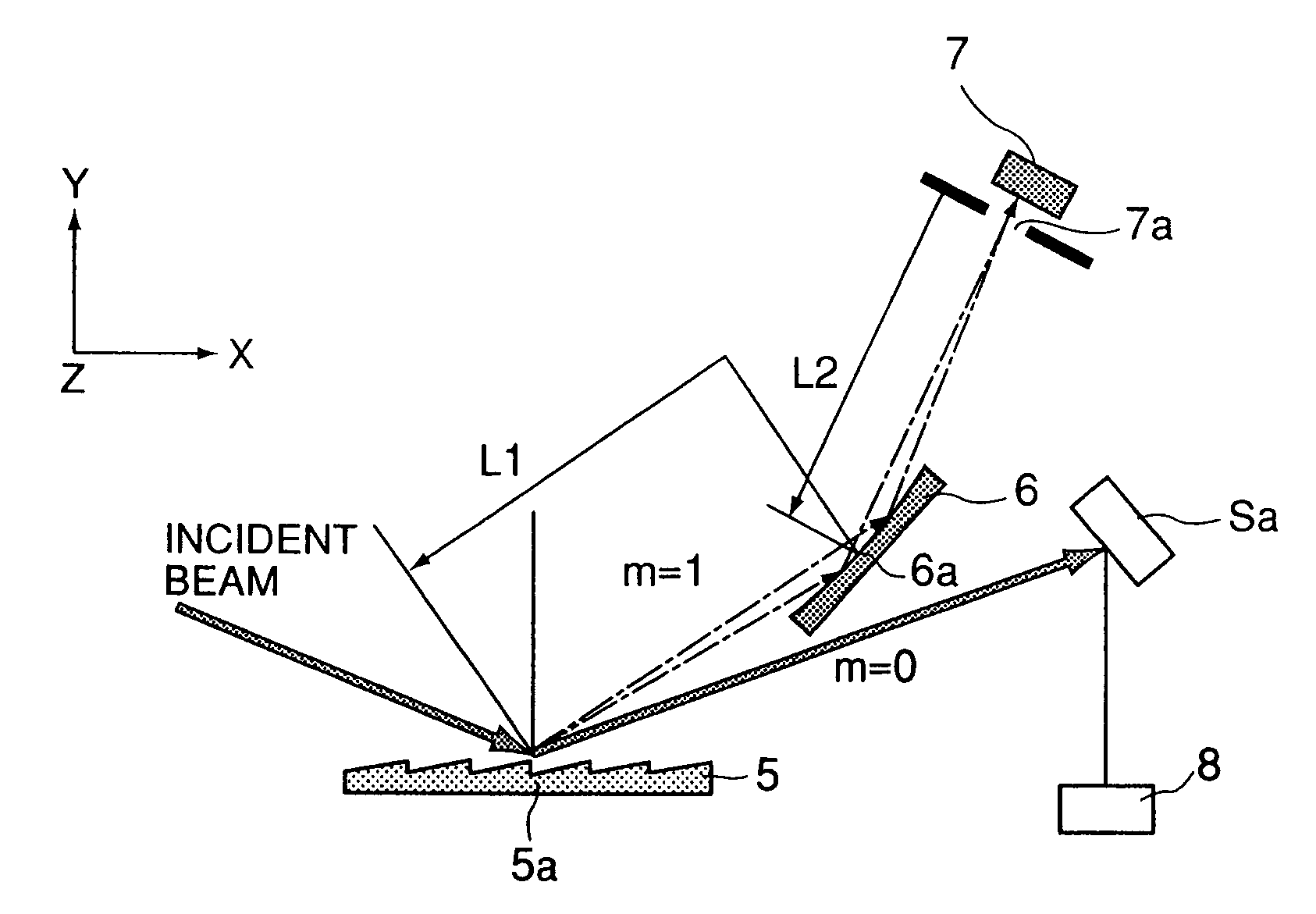
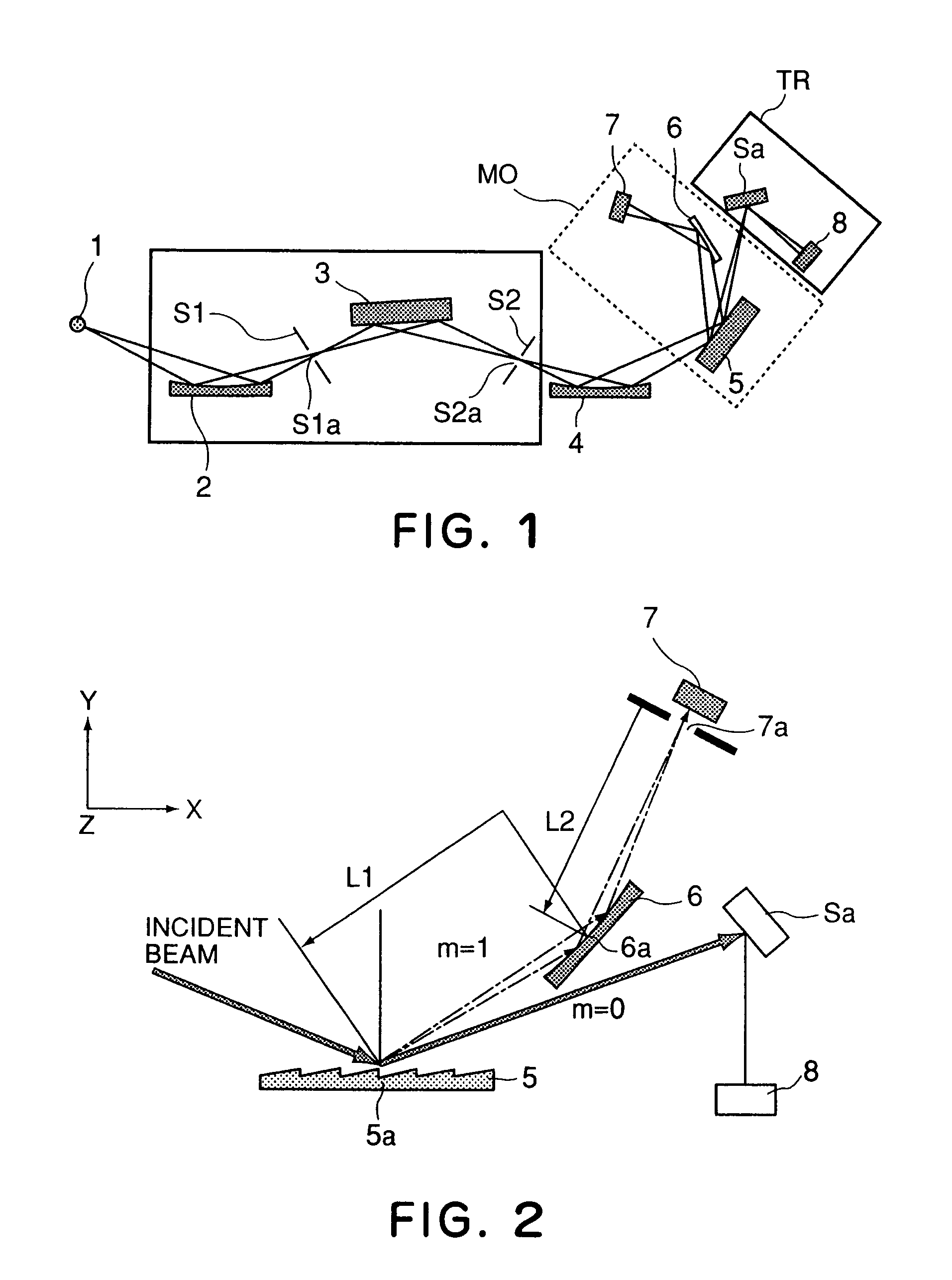
Optical measuring device
ActiveUS7003075B2Accurate measurementRadiation pyrometryX-ray spectral distribution measurementMeasurement deviceOptical property
The present invention provides a measuring device by which, even if a radiation intensity from a light source, a beam size or a beam intensity distribution of the light source changes, an optical characteristic of an optical element to be measured can be measured very precisely. In a measuring device according to the present invention, to this end, light from a light source is diffracted by a diffracting grating to thereby resolve the same into plural light beams, and by using different light beams, the object to be measured is measured and the intensity of incident light from the light source is measured. With this structure, even if the light from the light source changes, the intensity of the light from the light source is specified concurrently, and therefore, the optical characteristic of the object to be measured can be measured very accurately.
Owner:CANON KK
Neutron/gamma ray survey instrument with directional gamma ray sensitivity
ActiveUS20050121618A1High detection sensitivitySufficient thermalizationMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsSurvey instrumentMeasuring instrument
A portable survey instrument and methodology yield intensity of neutron radiation, intensity of gamma radiation, and a direction of impinging gamma radiation. The instrument uses a neutron detector surrounded by an essentially rectangular moderator with preferably four gamma ray detectors disposed symmetrically about the neutron detector and within the moderator. Material and dimensions of the moderator are selected so that the neutron-measurement is equally sensitive to fast and thermal neutrons. The moderator also induces angular responses to the gamma ray detectors. Responses of the gamma ray detectors are combined to yield a parameter indicative of the angular position of a source. The survey instrument is portable and suited for hand held use.
Owner:DELTA EPSILON INSTR
Airplane infrared radiation and atmospheric transmittance modeling method
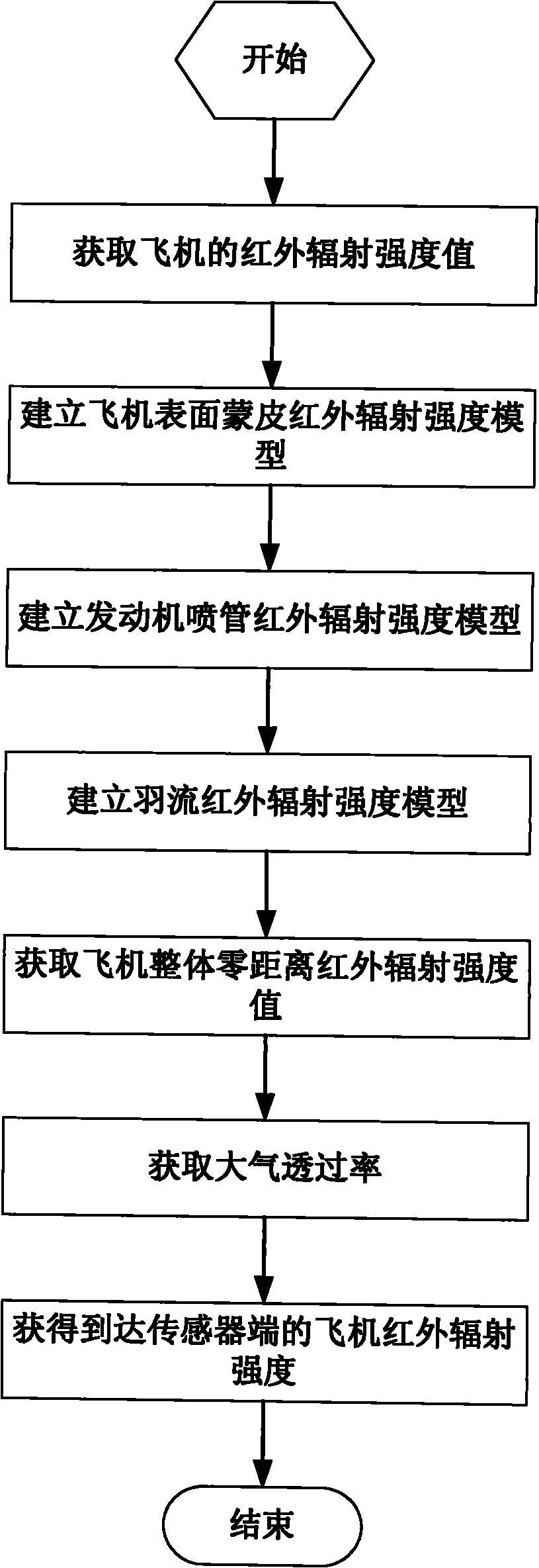
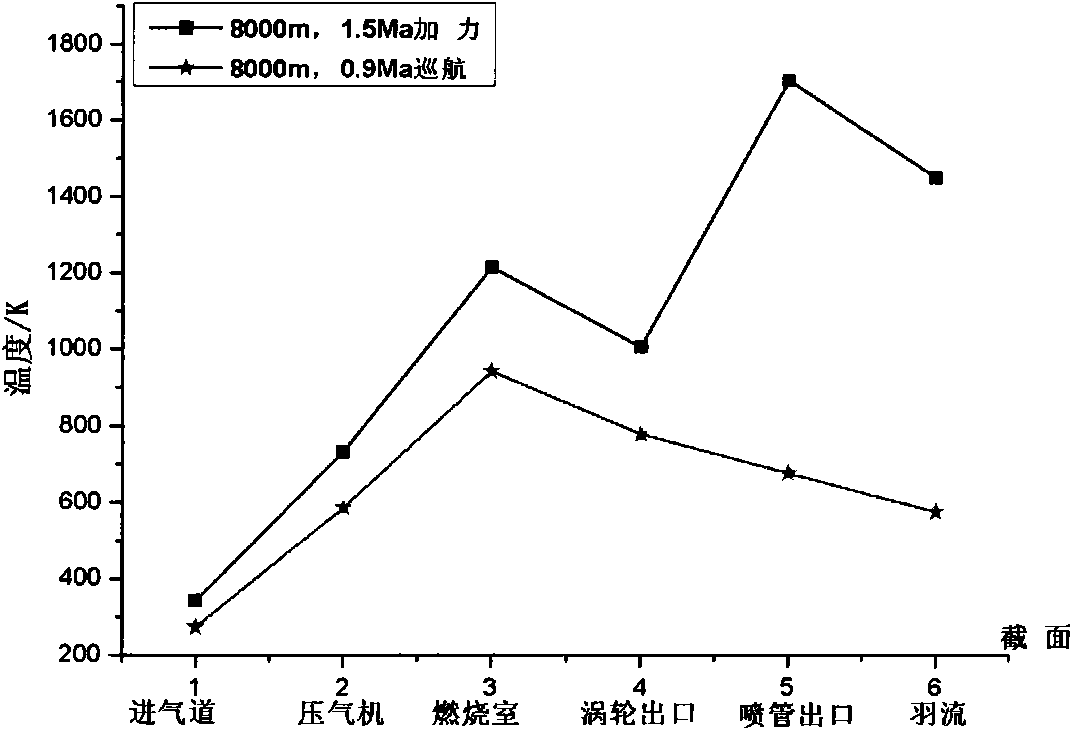
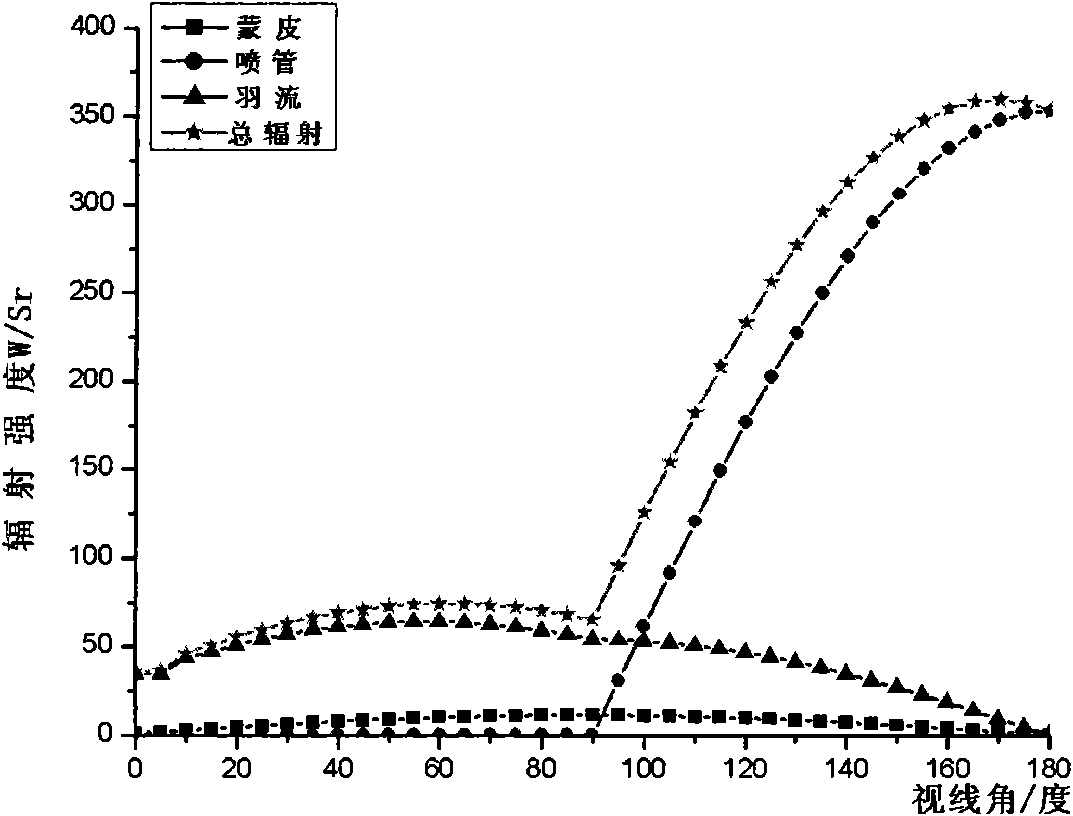
InactiveCN101976275ABig contributionSpecial data processing applicationsTransmittanceAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses an airplane infrared radiation and atmospheric transmittance modeling method, belonging to the field of airplane infrared radiation modeling and simulation in computer simulation. The modeling method comprises the following steps of: firstly acquiring an airplane infrared radiation intensity interface, establishing an airplane surface skin temperature model by integrating surrounding environmental radiation, and calculating airplane surface skin infrared radiation intensity according to an area model; and then establishing an engine effuser infrared radiation intensity model; and finally establishing an plume input parameter model and plume temperature model and calculating plume infrared radiation intensity. After acquiring an airplane zero-distance infrared radiation intensity model, the invention adopts software Modtran4 to establish a transmission radiation model of infrared radiation in an atmospheric environment to acquire atmospheric transmittance and further obtain an infrared radiation intensity signal reaching an sensor terminal. In the modeling method, the models are simple, and experiment data accords with real conditions. The modeling method can be applied to platform infrared scene generation and infrared target detection platforms easily.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and apparatus of calibrating multi-position SLM elements
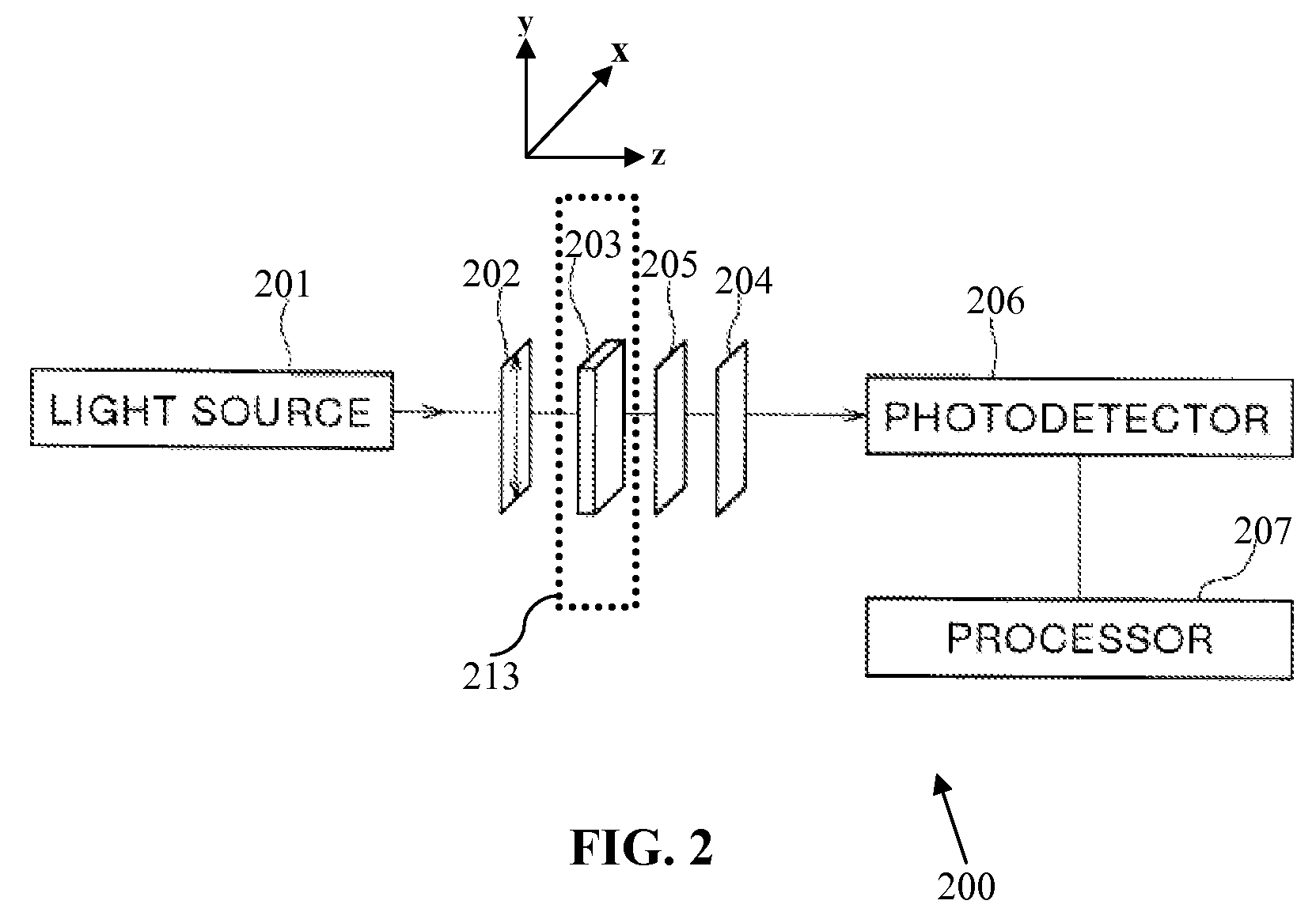
InactiveUS6965119B2Improving Imaging AccuracyImprove accuracyBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInvestigating moving sheetsSpatial light modulatorControl signal
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating elements in a spatial light modulator (SLM) as a function of an applied element control signal. A plurality of elements are calibrated simultaneously. A beam of electromagnetic radiation is projected onto at least a part of the SLM. An image of said part of said SLM is formed on a device for measuring intensity of electromagnetic radiation. Element calibrating data is generated by using the intensity data as a function of the applied element control signal by either driving a sub-matrix comprising at least two elements out of said part of the SLM to a sequence of applied element control signals or by seeking out the control signal for each element which give the same predetermined intensity value on the device for measuring the intensity of electromagnetic radiation and stepping through N different predetermined intensity values. The invention also relates to an apparatus for patterning a workpiece having such a calibration method. Other aspects of the present invention are reflected in the detailed description.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
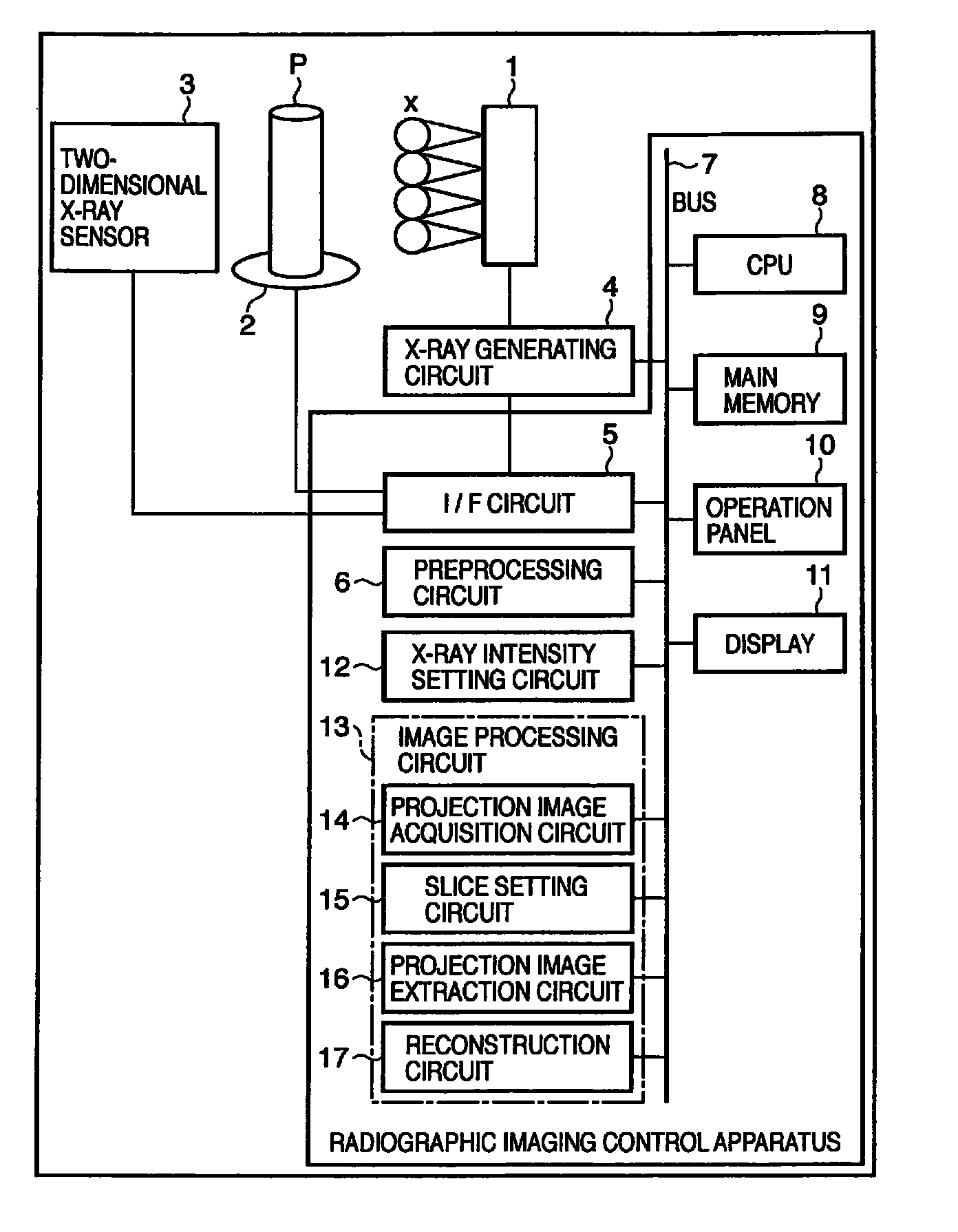
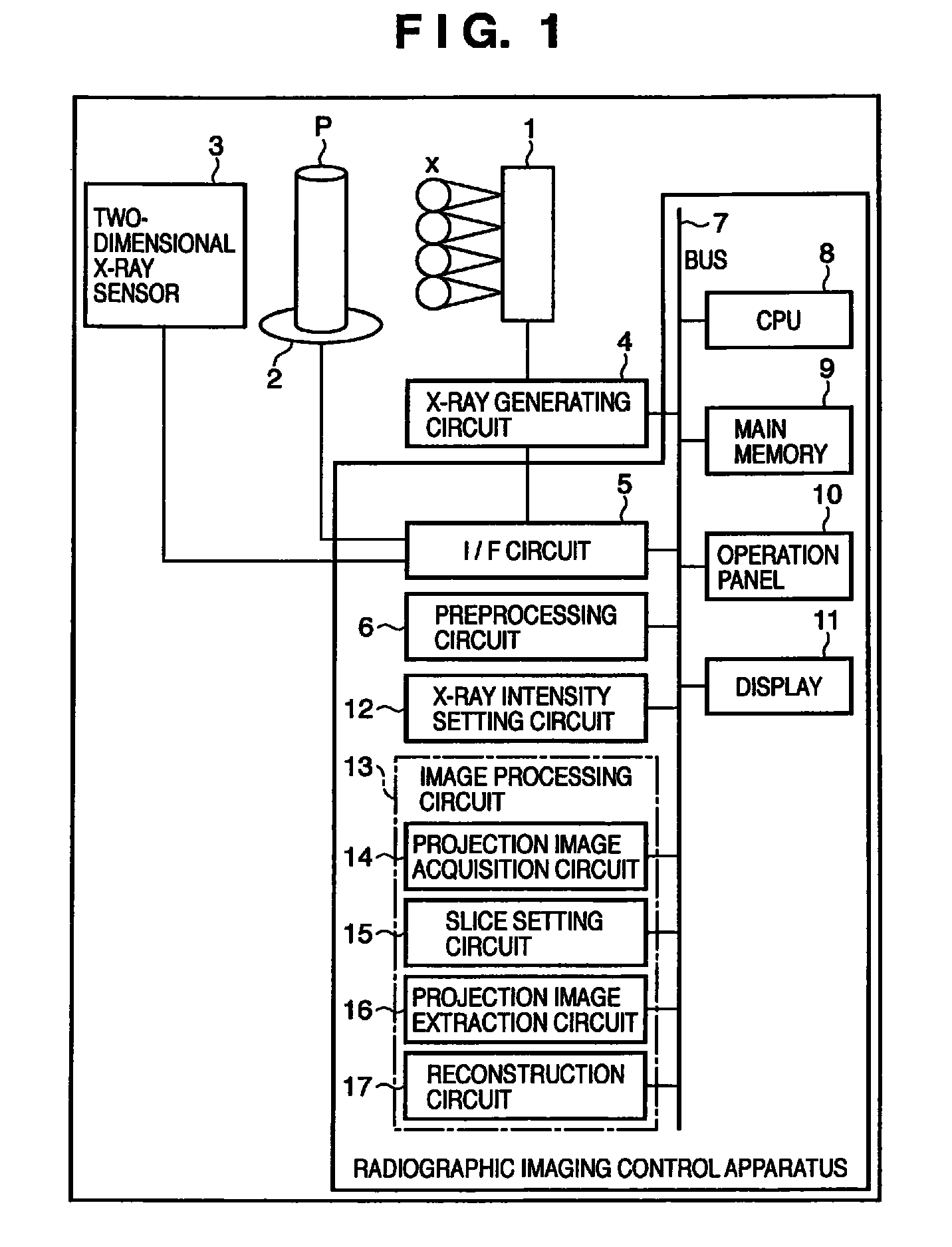
Radiographic imaging control apparatus using multi radiation generating apparatus
InactiveUS7978816B2Suppresses degradation of image qualityInhibition effectPatient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsFluenceRadiography
Owner:CANON KK
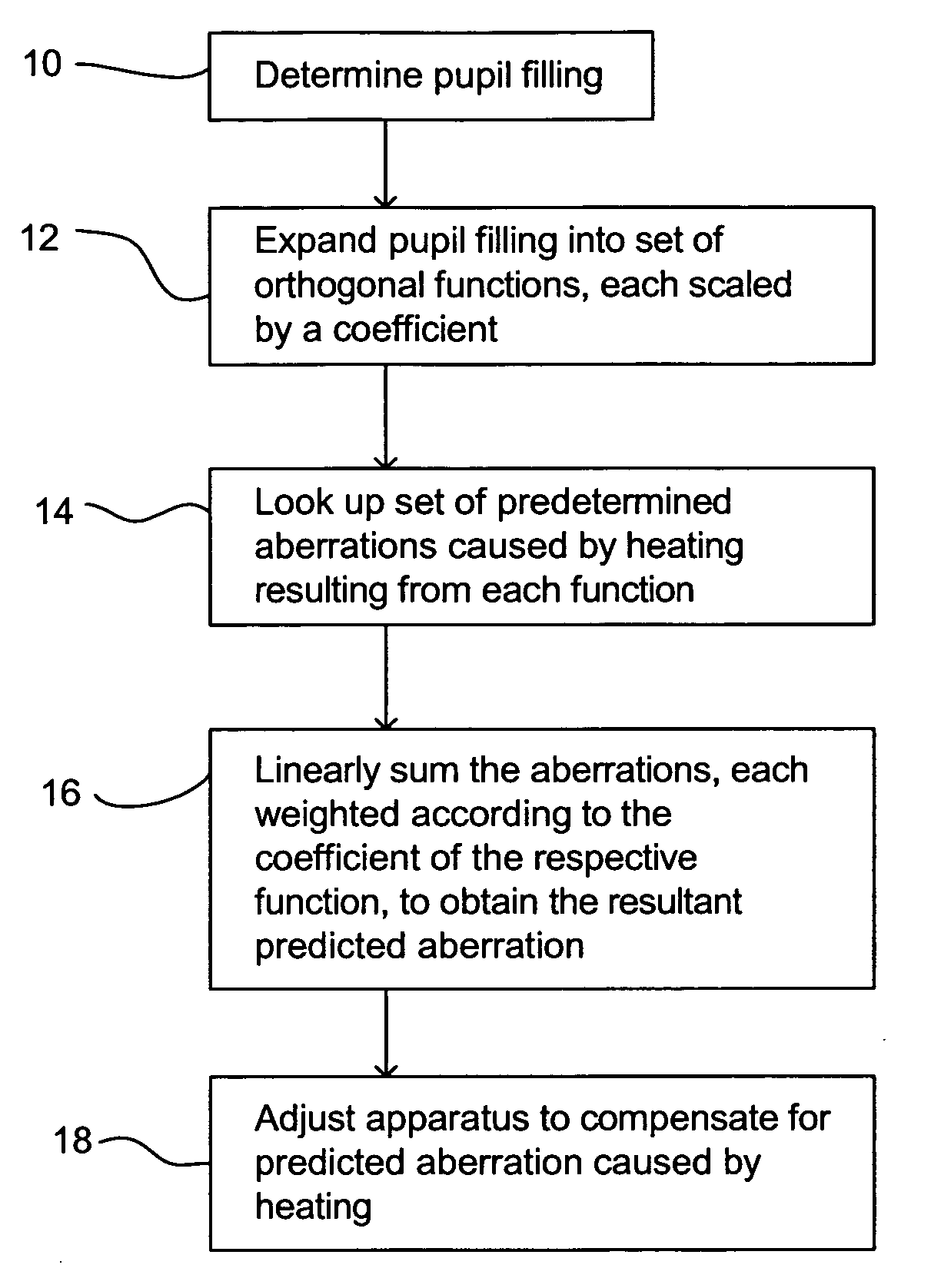
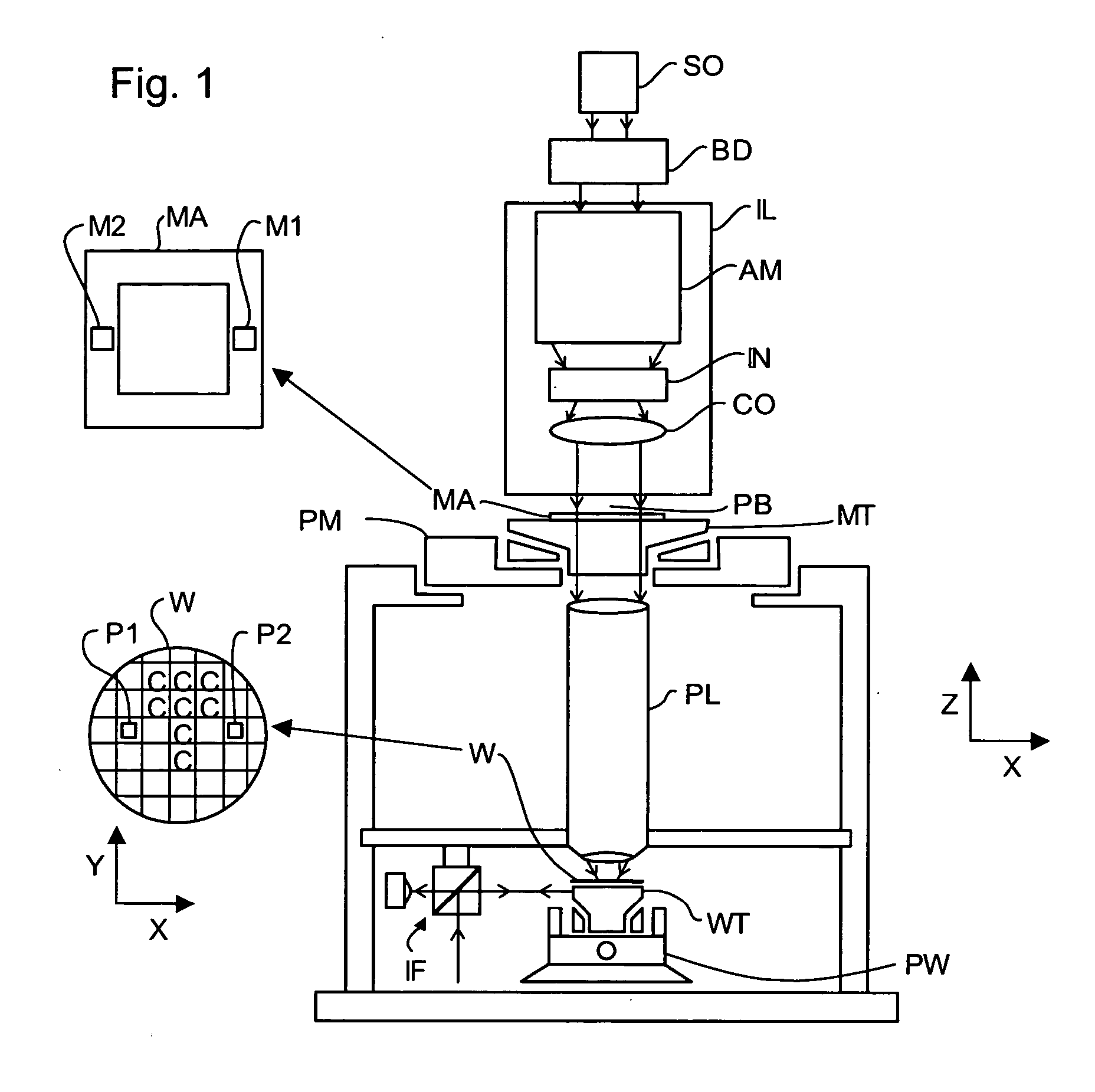
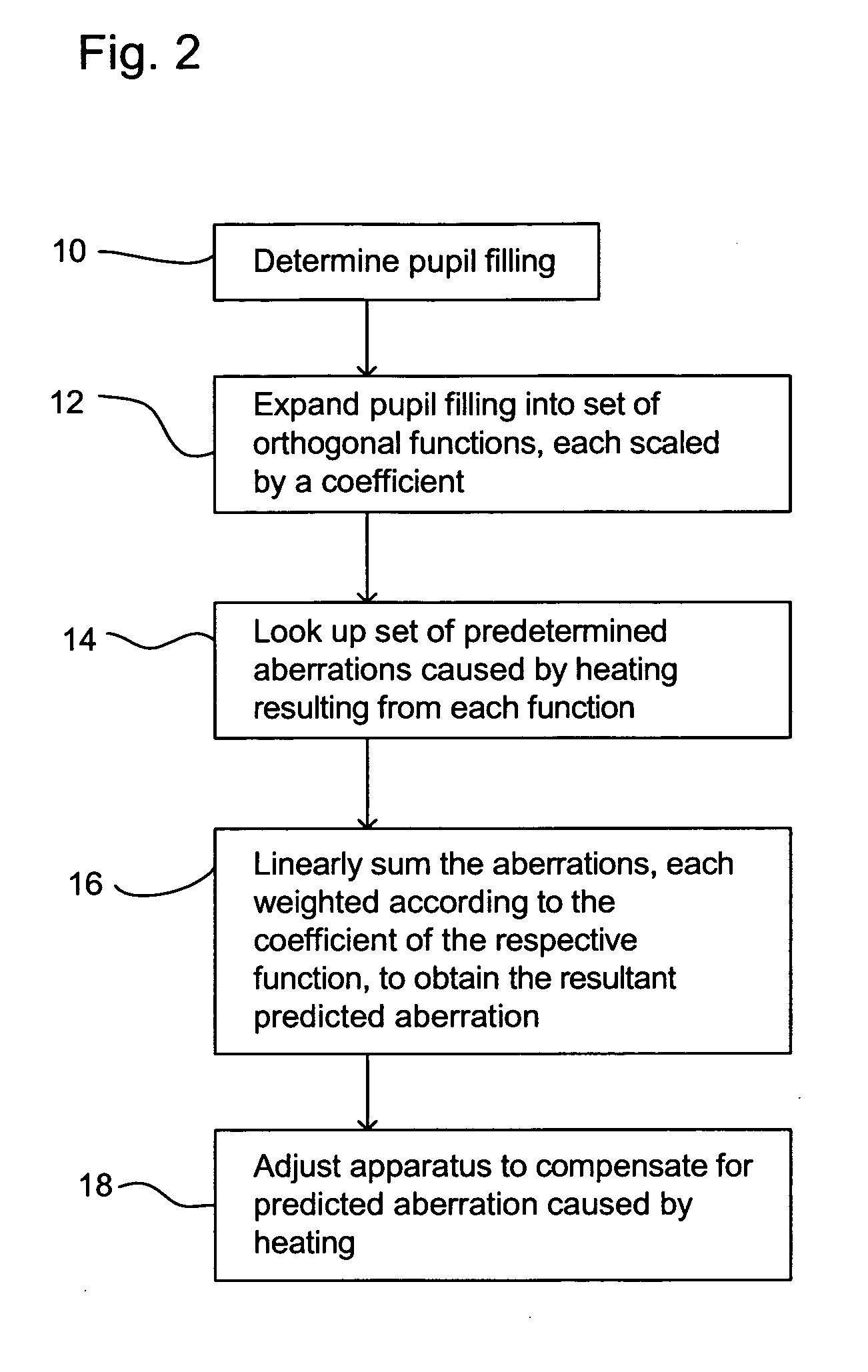
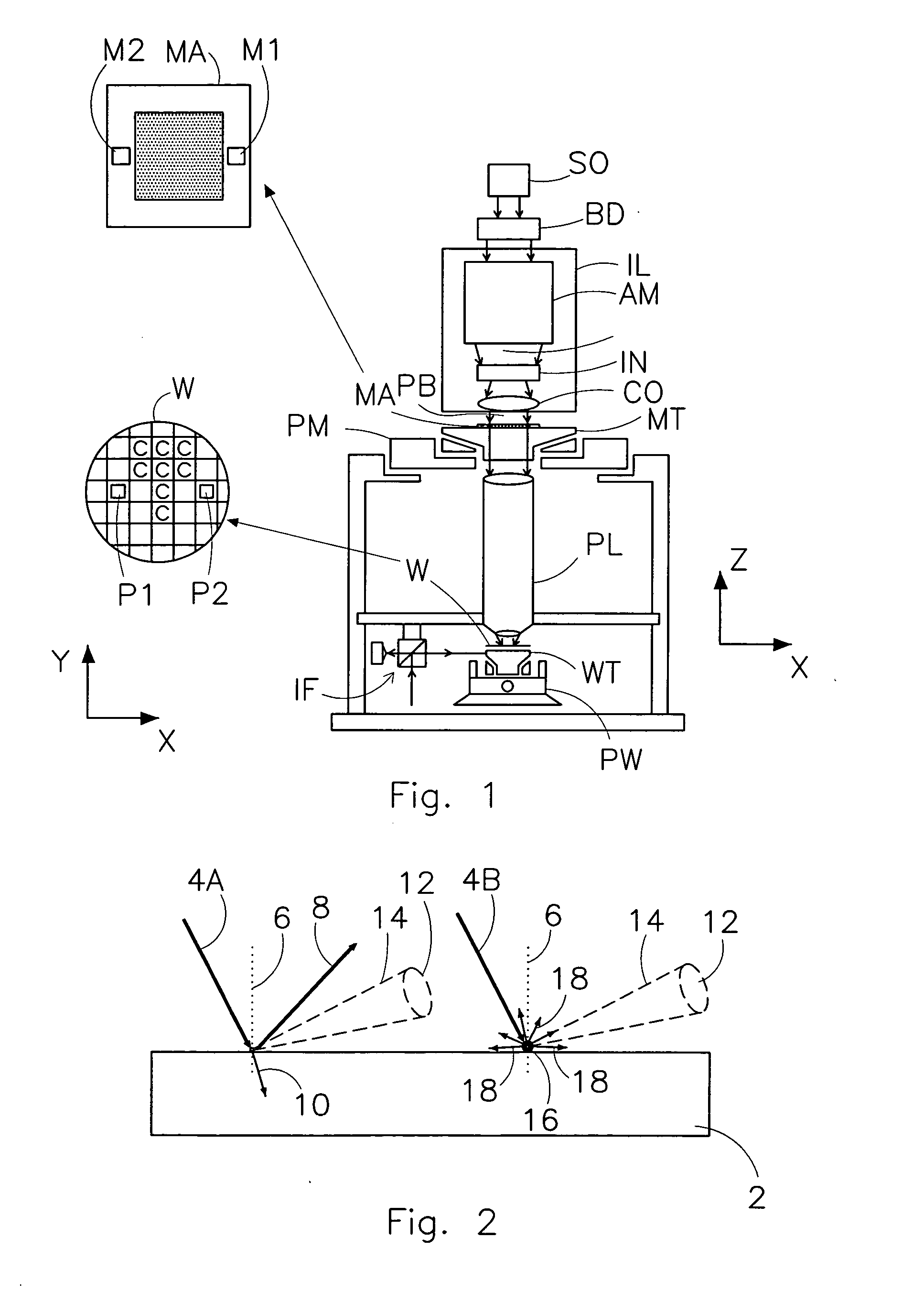
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
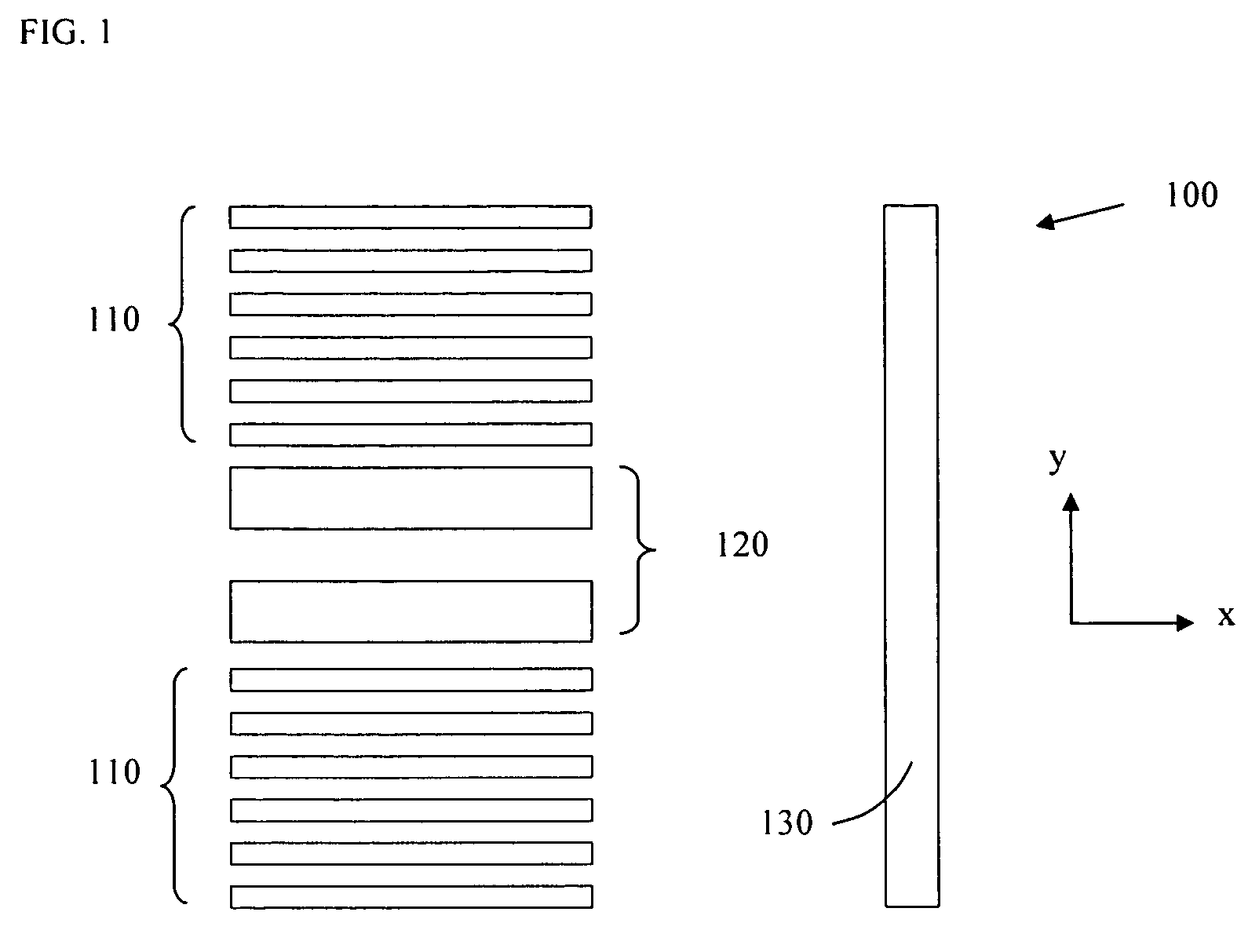
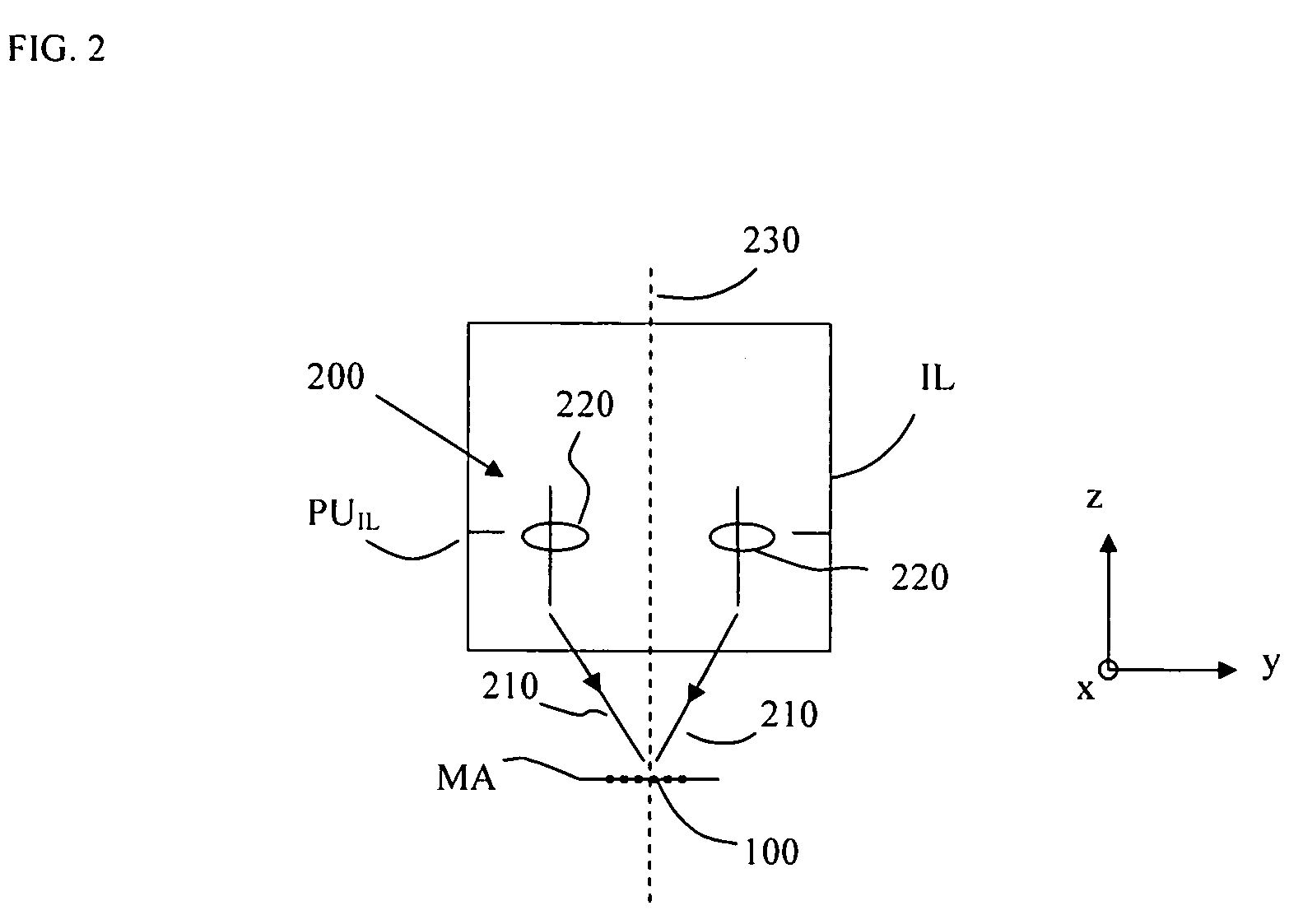
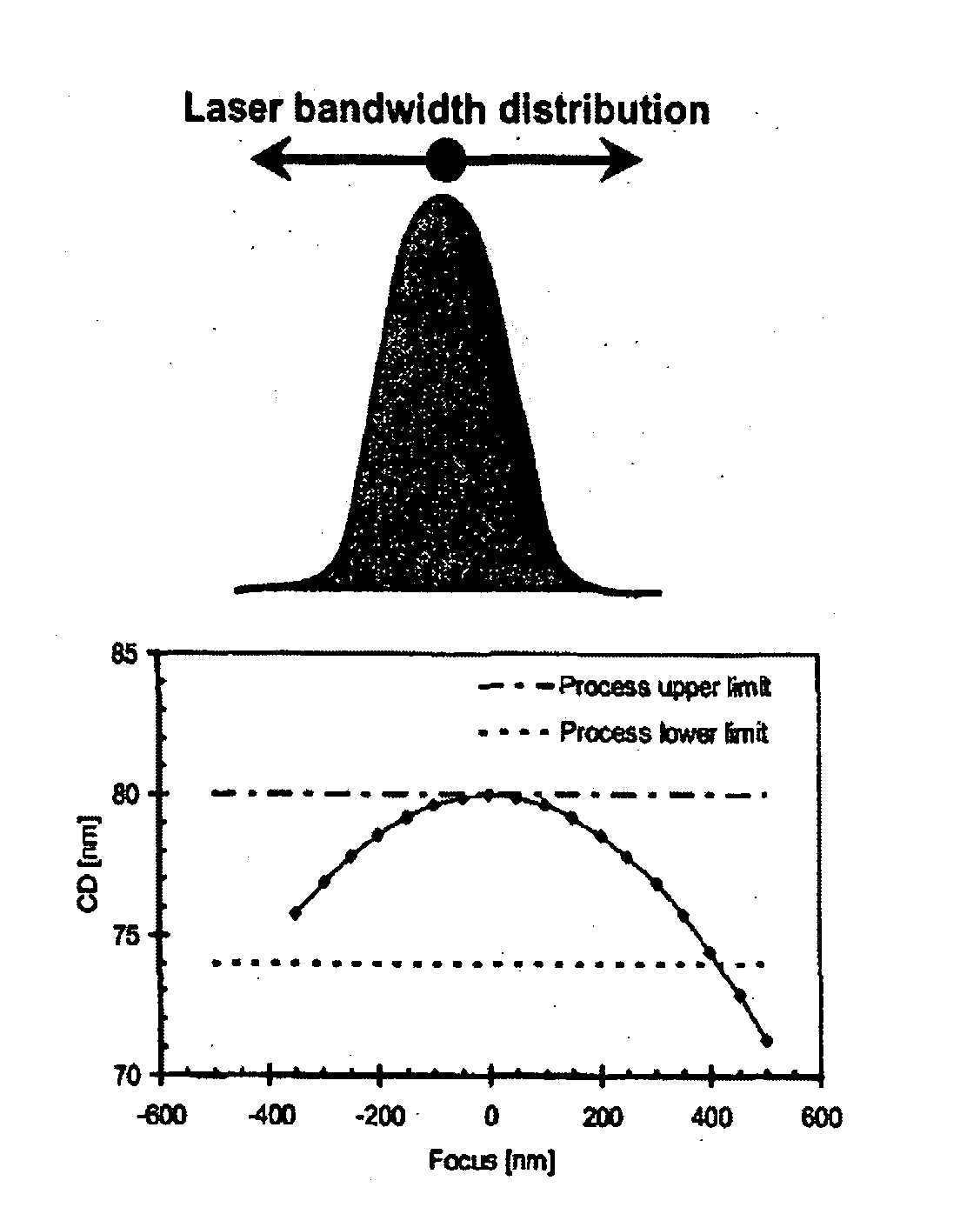
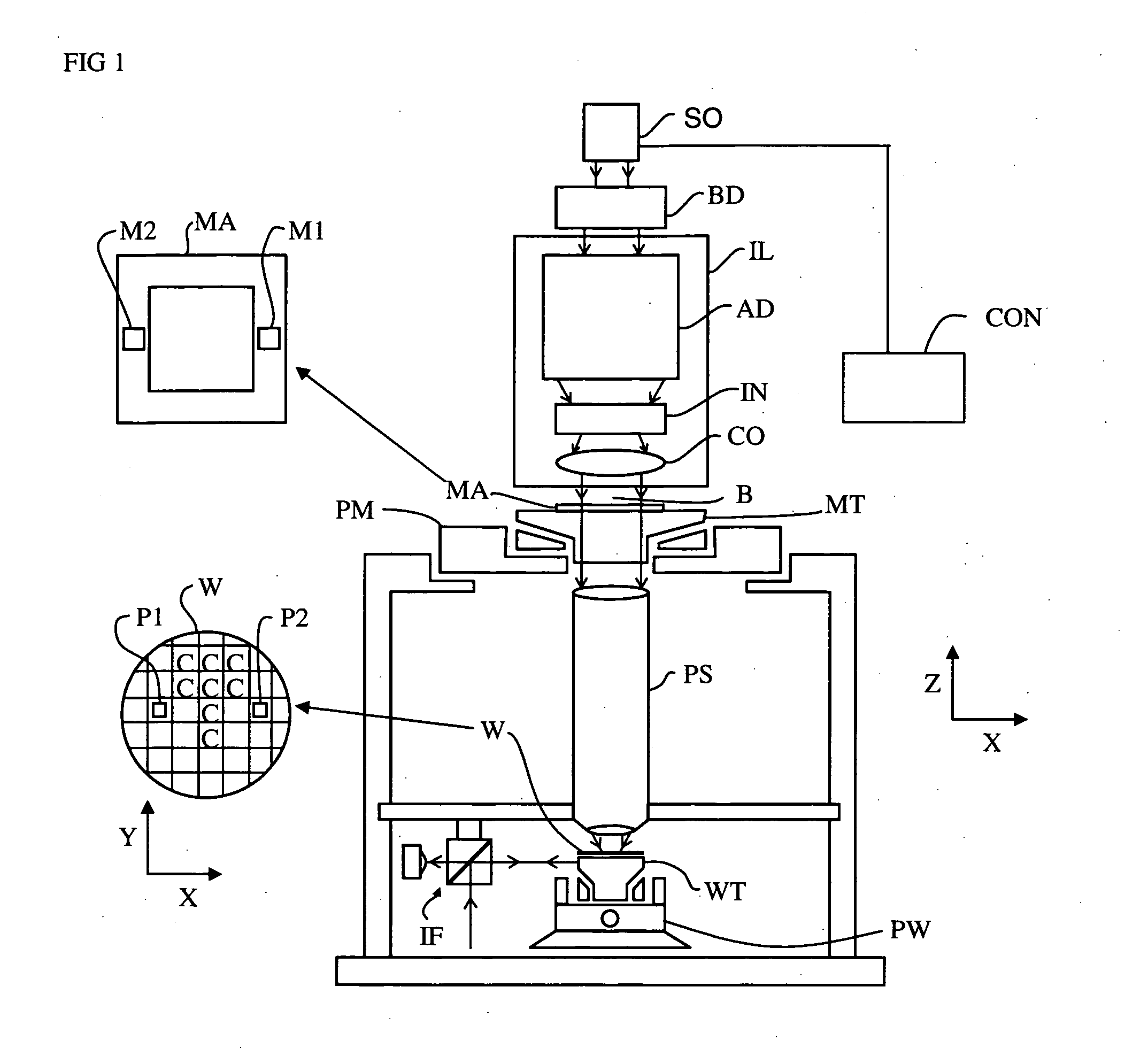
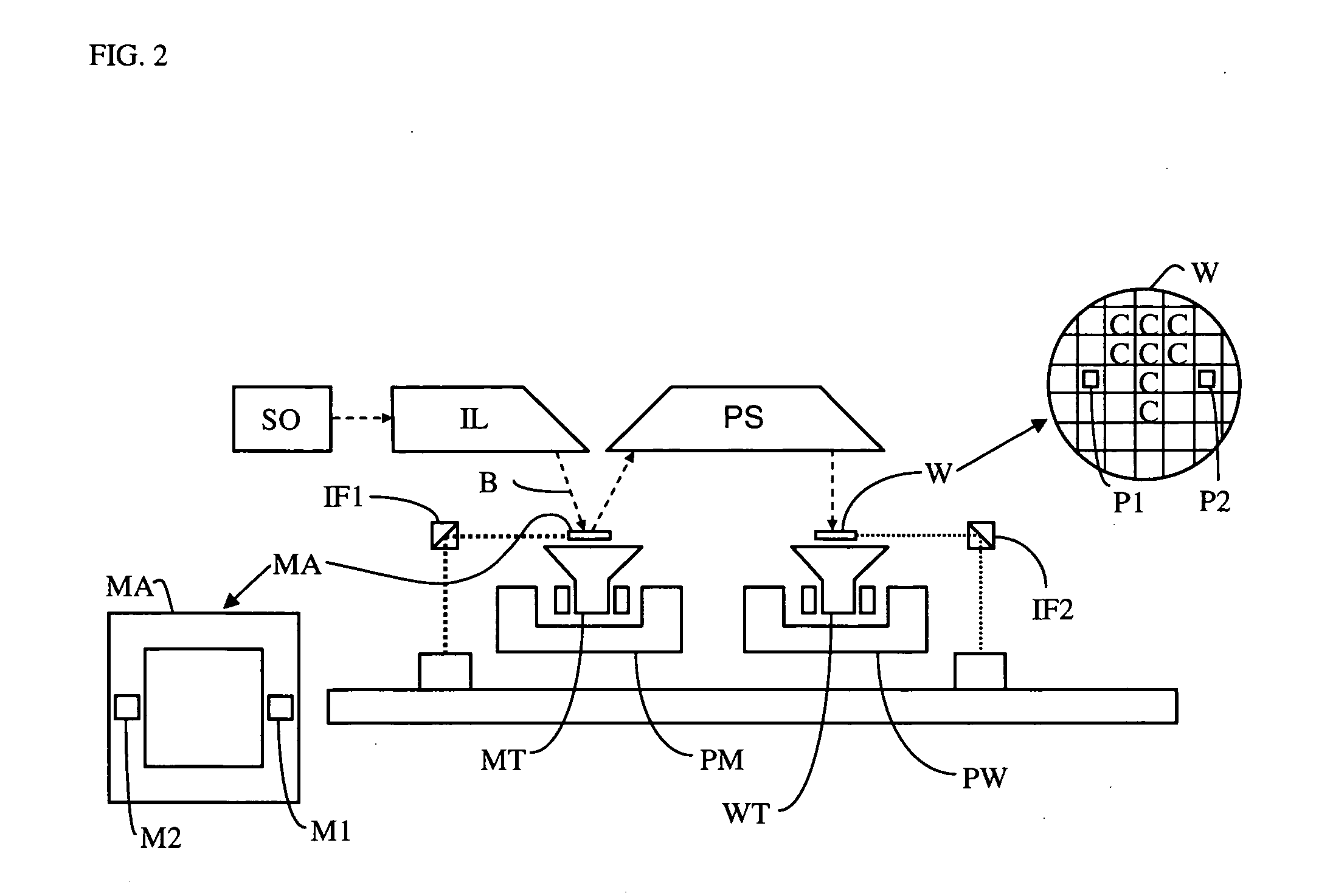
InactiveUS20050254024A1Easy to predictReduce in quantitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLight beamProjection system
A lithographic apparatus includes an instrument for determining the radiation intensity distribution at a pupil plane of the projection system while a patterning device is imparting the projection beam with a pattern, a calculation apparatus for calculating the effect on the imaging by the projection system of heating resulting from the projection beam in the projection system having the determined intensity distribution and a controller for adjusting the lithographic apparatus to compensate for the calculated effect of heating.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Measuring instrument and method for determination of the properties of an item and its surface
ActiveUS20120206710A1Affect qualityClear impact both on the production process quality assuranceCaliper-like sensorsOptical rangefindersOptical radiationMeasurement device
A measurement device for the determination of the characteristics of the object's surface by means of the optical radiation, wherein a measurement device comprises an optical radiation source and a detector to receive the radiation reflected from the surface being measured. In addition, a measurement device comprises an emitted optical radiation processing unit, which is adjusted to split optical radiation emitted by an optical source into separate wavelengths and to direct said separate wavelengths to the object being measured in a direction, that differs from the normal of the surface being measured so, that at least the shortest and the longest wavelengths of said wavelengths are focused on different halves and different heights of the measured object's surface, in the direction of the normal of the surface being measured. In addition, a measurement device comprises a reflected optical radiation processing unit, which is adjusted to receive an optical radiation reflected from the measured object at least in the direction of a specular reflection, which differs from the normal of the surface being measured, and to direct received optical radiation to said detector. Still further, the measurement device is adjusted to analyze an electric signal produced by the detector and proportional to the intensity of the radiation focused thereto, and to further determine a surface gloss (gloss degree) and / or thickness characteristic property of the measured object, based on the intensity of its wavelength, the focus point of which was located on the measured surface, and which wavelength was the strongest reflected from that point to the detector in the specular geometry.
Owner:FOCALSPEC
System for measuring normal spectral emissivity of high-temperature material
ActiveCN102042993ASimple designLess interference with radiometric measurementsSpectrum investigationMaterial thermal analysisData acquisitionEngineering
The invention discloses a system for measuring the normal spectral emissivity of a high-temperature material, comprising a vacuum heating unit, a water cooling sleeve unit, an optical fiber sensor measurement unit and a data acquisition and analysis unit, wherein a test sample is arranged on the upper part of the vacuum heating unit, and the vacuum heating unit performs radiant heating on the lower surface of the test sample; the water cooling sleeve unit is sleeved on the upper part of the test sample, and the upper surface of the test sample is placed in a constant-temperature cold environment; the optical fiber sensor measurement unit is arranged above the test sample to measure the normal spectral radiant intensity of the upper surface of the test sample; and the data acquisition and analysis unit is connected with the optical fiber sensor measurement unit and is used for calculating the normal spectral emissivity through a multi-spectrum inversion algorithm according to the measured normal spectral radiant intensity. The invention realizes material normal spectral emissivity measurement in a spectrum range of 0.4-1.7mum and a temperature range of 600-1,500 DEG C without on-line radiometric calibration, is accurate and reliable to realize the technology, and overcomes limitations on high price, complicated structure, high difficulty in technical implementation and other applications of the conventional spectral emissivity device.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
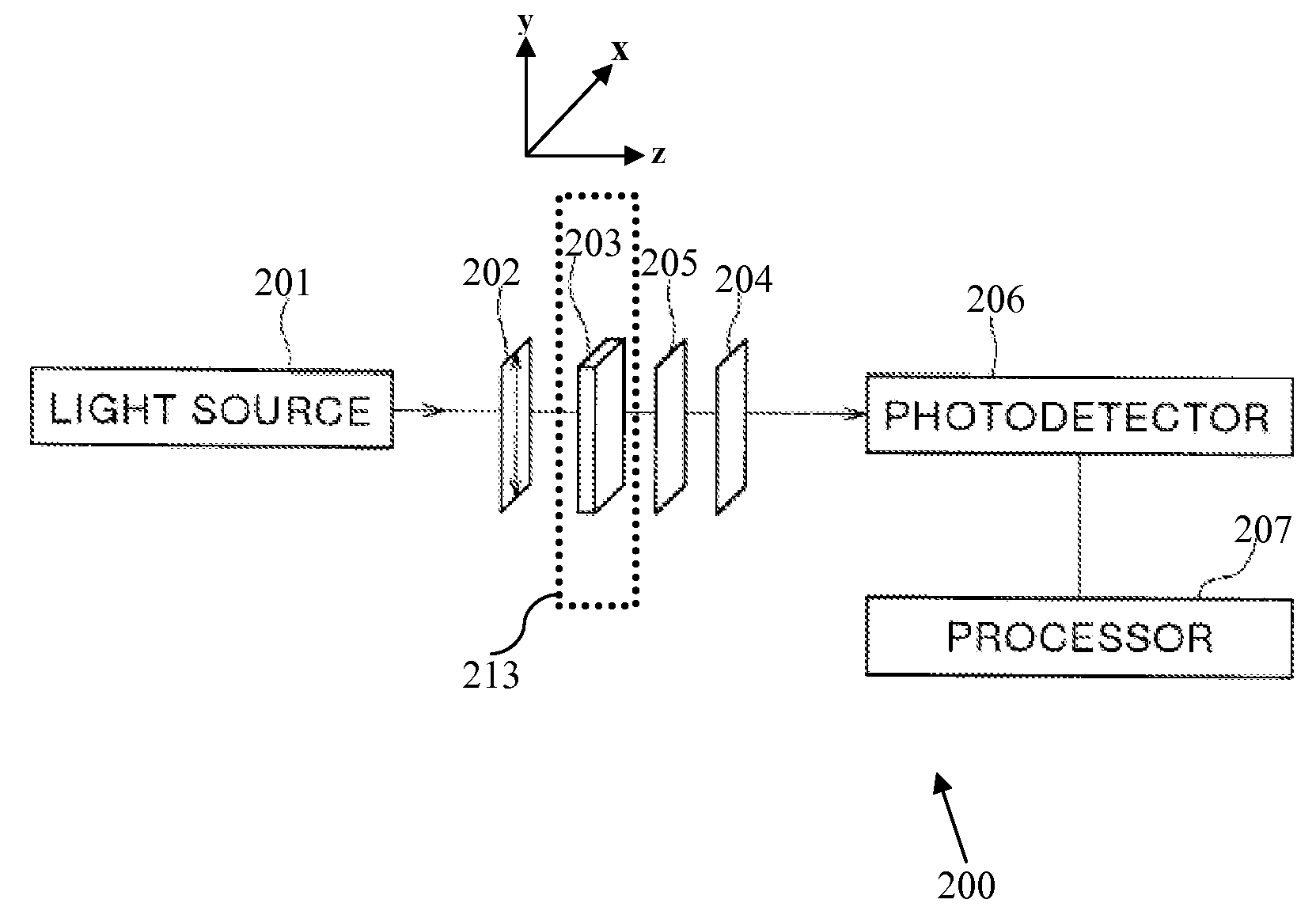
System and method for characterizing fibrous materials using stokes parameters
ActiveUS20090101297A1Material analysis using microwave meansInvestigating moving sheetsPhotodetectorPolarimeter
An apparatus (200) for determining fiber orientation parameters of a sheet of material during a production process includes a polarized radiation generating system (201, 202) operable for providing polarized radiation having a frequency of at least 1×108 Hz. The radiation is aligned to be incident on a sheet of material to be characterized (203). A polarimeter (204, 205) is aligned to receive the radiation transmitted by the sheet of material (203). A photodetector (206) is provided for measuring radiation received after polarization processing by the polarimeter. A processor (207) is coupled to the photodetector (206) for calculating Stokes parameters of the moving sheet (203) based upon intensities of the radiation received and determines at least one parameter relating to fiber orientation of the moving sheet based upon the Stokes parameters.
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC +1
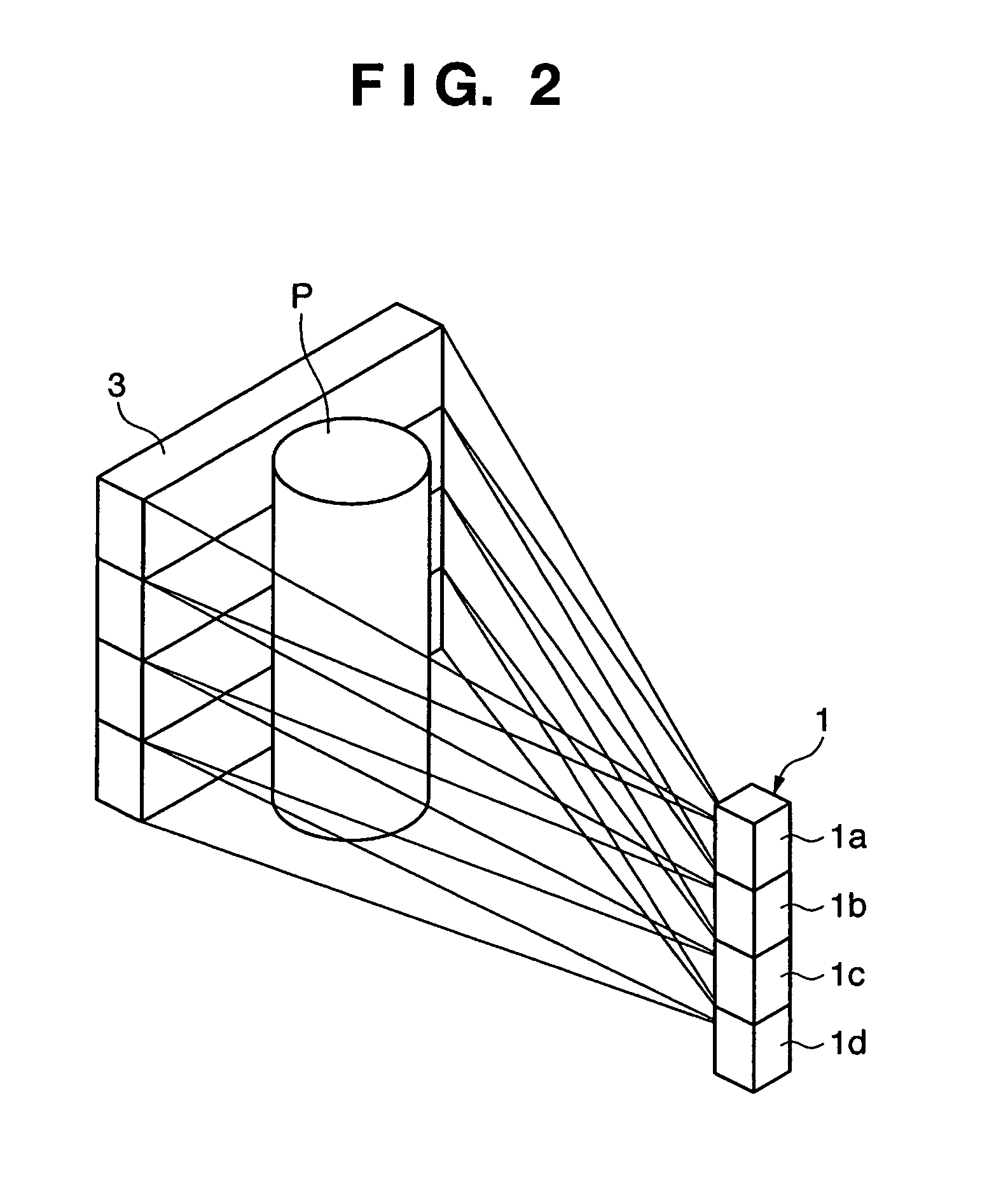
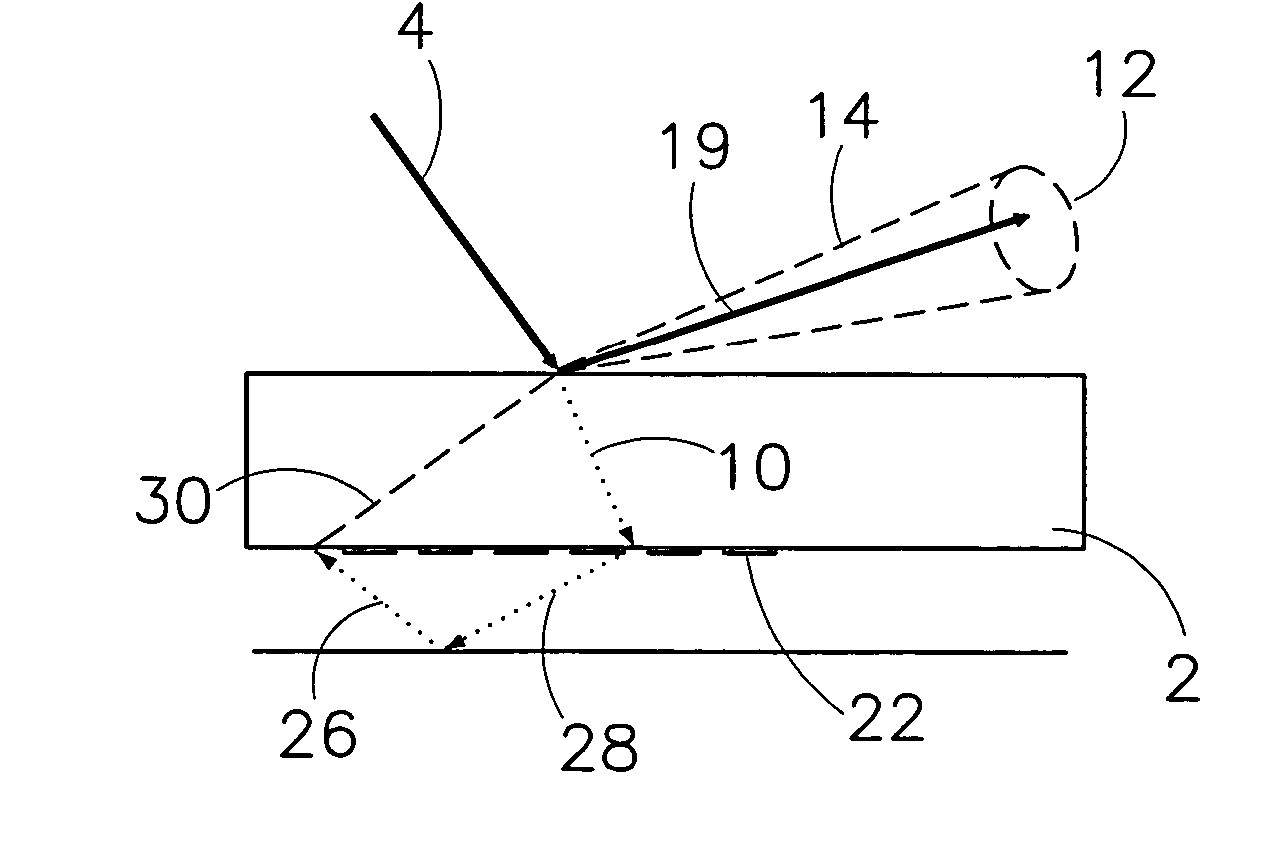
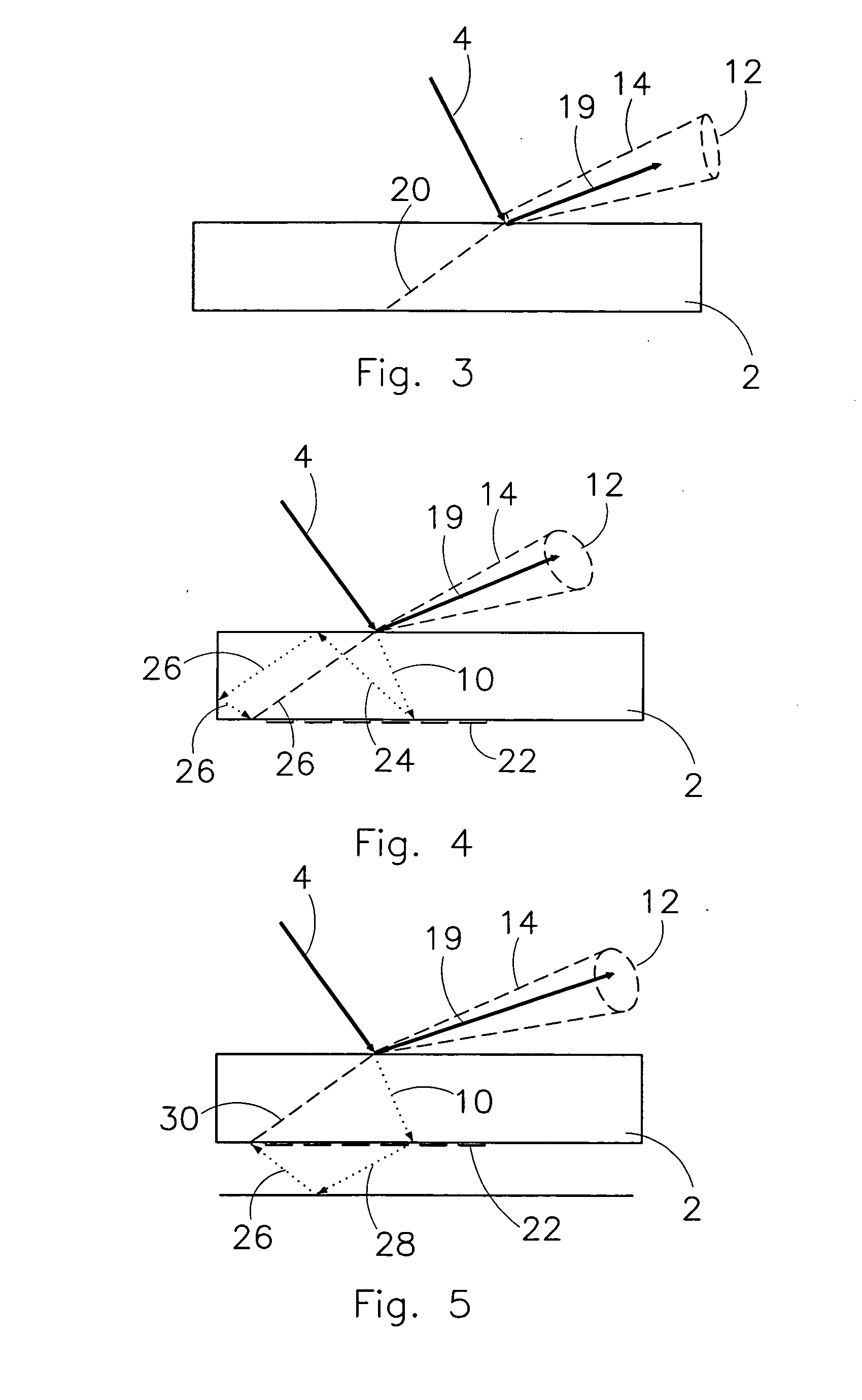
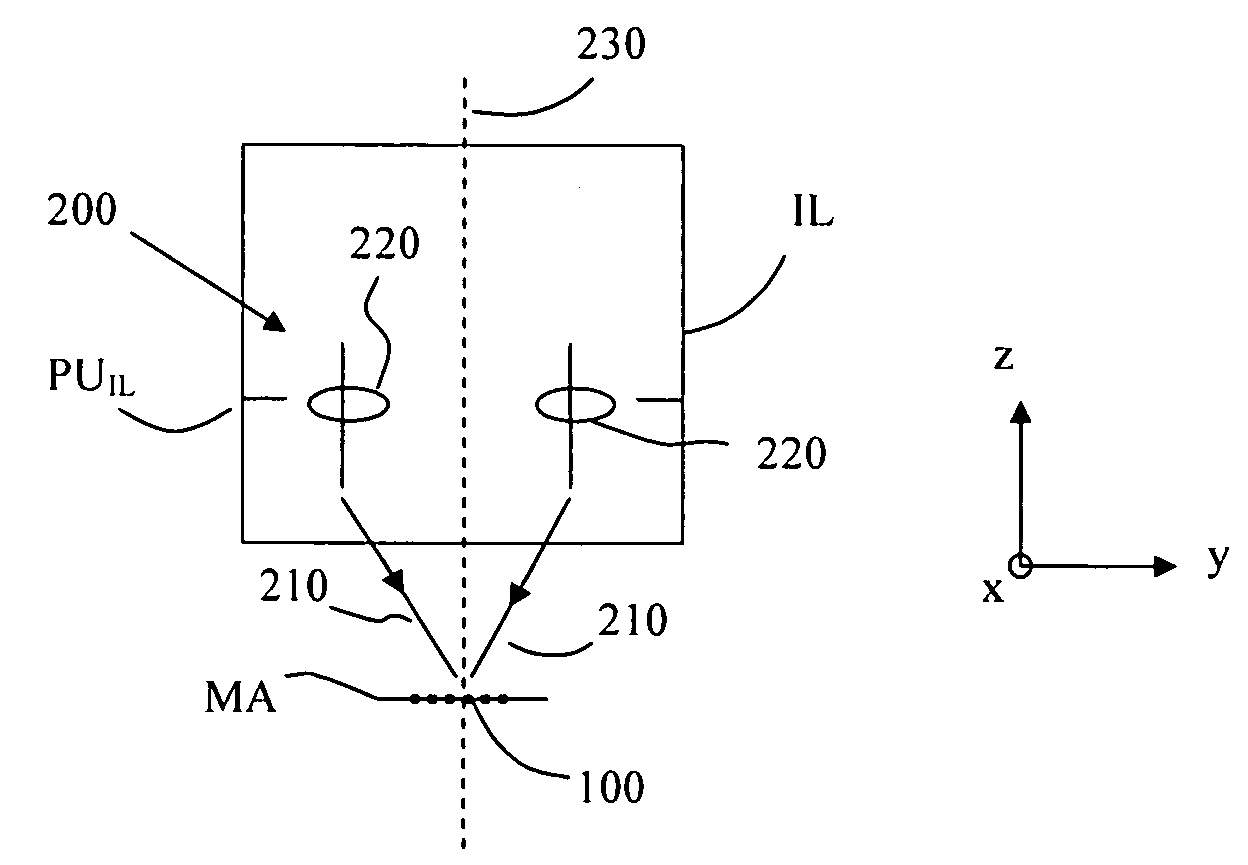
Particle detection device, lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20060072108A1Simple and cost-effectivePhotomechanical apparatusOptically investigating flaws/contaminationParticle physicsLength wave
To enable differentiation between a particle and a ghost particle, a detector system resolves radiation from a ghost particle from radiation from an actual particle. The detector system outputs at least two detector signals corresponding to intensities of radiation being incident on different parts of the detector system or the detector system outputs at least two detector signals corresponding to intensities of radiation with different wavelengths being incident on the detector system. If radiation is received from a ghost particle, not each of the at least two detector signals has a level above a predetermined threshold level, whereas radiation received from a particle results in the signals having substantially a same level above a threshold level. The detector system may include a radiation detector device configured to generate the first detector signal in response to radiation incident on at least one predetermined part of the radiation detector device and a radiation blocking assembly configured to prevent radiation not originating from a particle from being incident on the predetermined part of the detector device.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
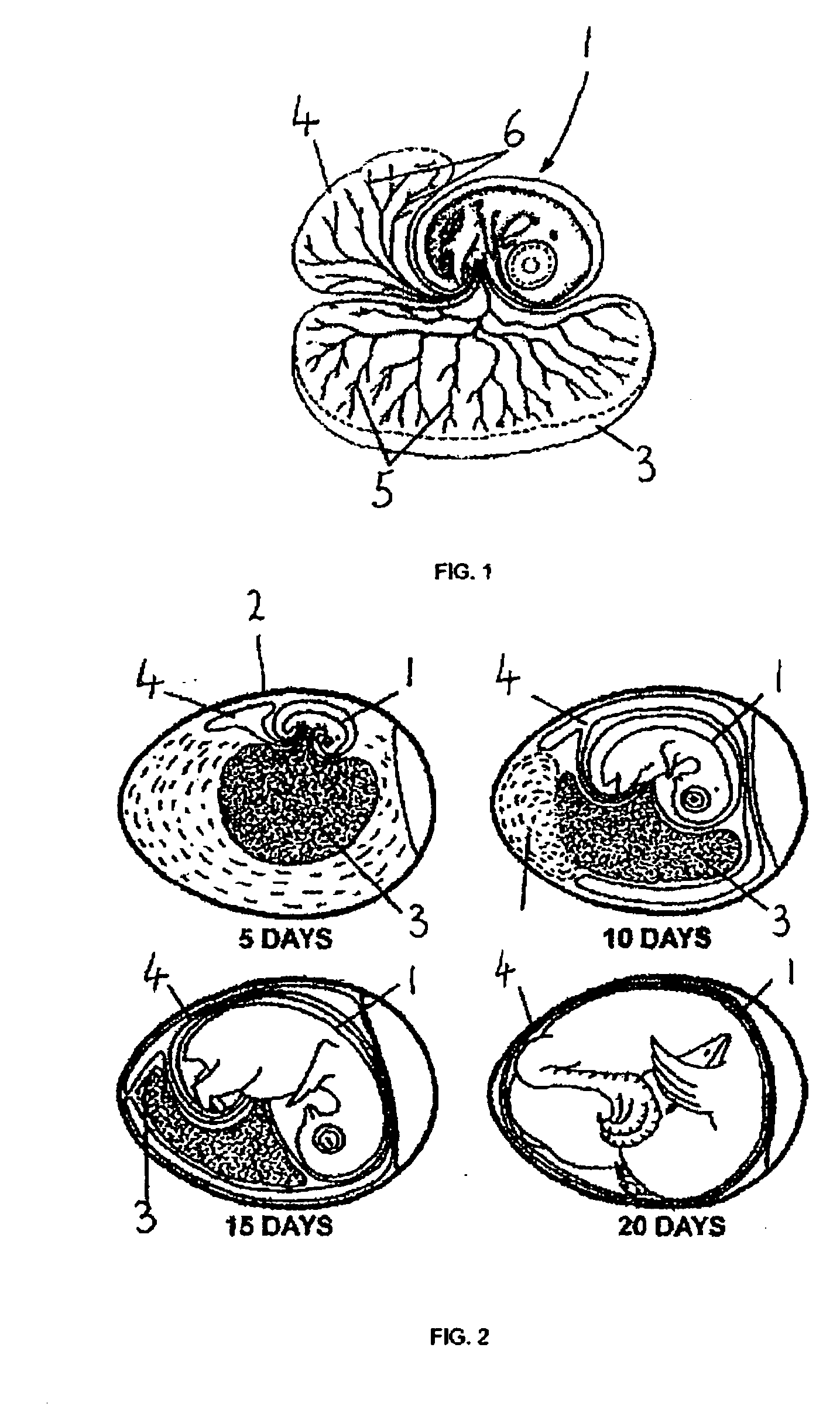
Method and apparatus for determining the viability of eggs
InactiveUS20050206876A1Determine viabilityViability can be determinedTesting eggsScattering properties measurementsAnimal scienceEggs per gram
A method of determining the viability of an egg at least approximately 50% through its incubation period, which method comprises the steps of: (a) causing electromagnetic radiation to impinge upon the egg, the electromagnetic radiation having one or more wavelengths in the infra-red part of the spectrum; (b) receiving at least a part of the infra-red radiation that has passed through the egg and generating an output signal representative of the received infra-red radiation; and (c) processing said output signal to determine whether there is a cyclical variation in the intensity of the infra-red radiation leaving the egg corresponding to action of a heart, the existence of said cyclical variation indicating that the egg is viable; wherein step (a) is performed by directing infra-red radiation so that it passes through the shell for reflection from an outer surface of a vascular structure adjacent an inner surface of said shell, and step (b) is performed by receiving any infra-red radiation so reflected.
Owner:VISCON BV
Method of reducing a wave front aberration, and computer program product
ActiveUS20070296938A1Reduce optical effectsReduce decreasePhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansPupilProjection system
A method of reducing a wave front aberration is provided for a lithographic process whereby the reducing is based on the selected pattern to be printed and the selected illumination mode used for exposure. Wave front aberrations of a projection system of a lithographic apparatus are measured and reduced by calculating adjustments of optical elements of the projection system and applying the calculated adjustments to the projection system. The calculation of adjustments is based on information on a spatial distribution of radiant intensity in a pupil of the projection system as present during exposing the radiation sensitive layer, and is limited to aberrations in projection lens pupil areas of relative high radiant flux.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Compensation of actinic radiation intensity profiles for three-dimensional modelers
ActiveUS8048359B2Reduce build timeImprove throughputLiquid surface applicatorsAdditive manufacturing apparatusUltimate tensile strengthPhysics
There is provided methods and apparatus for compensation of intensity profiles of imagers used in three-dimensional modelers. The intensity profile of the actinic radiation projected from the imager is determined by a variety of techniques, including but not limited to manually operated sensors, exposed and scanned actinic radiation-sensitive paper, and intensity profilers. Once the intensity profile of the imager is determined, each layer of the solidifiable liquid material is cured by projecting a plurality of patterns (as opposed to a single pattern) defining the two-dimensional cross-section of the part being cured. The patterns vary in duration, number, and / or shape to correlate to the intensity profile so that a single layer of selectively cured solidifiable liquid material is cured with a substantially equivalent (or otherwise controlled) amount of actinic radiation per unit of surface area to provide generally controlled and consistent part quality.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Optical transmitter
InactiveUS20070206952A1Improve optical output powerIncrease output powerDiffusing elementsElectromagnetic transmissionOptical axisEngineering
An optical transmission apparatus is provided in which high optical output power is secured in an optical transmitter, the fine adjustment of the optical axis is unnecessary, and the propagation range of the optical output signal can be adaptively changed. A diffusing liquid lens includes a first liquid and a second liquid containing a scattering material that scatters light, and the curvature of the boundary surface between the first and the second liquids is changed according to the control voltage applied from a controlling unit. A first optical signal outputted from a light emitting device is diffused in the first liquid, and emitted as a second optical signal having a spread angle corresponding to the curvature of the boundary surface and a substantially uniform radiant intensity distribution.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Lithographic apparatus, excimer laser and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060146310A1Increase depth of focusEffect on the image contrast at wafer levelPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLight beamVolumetric Mass Density
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
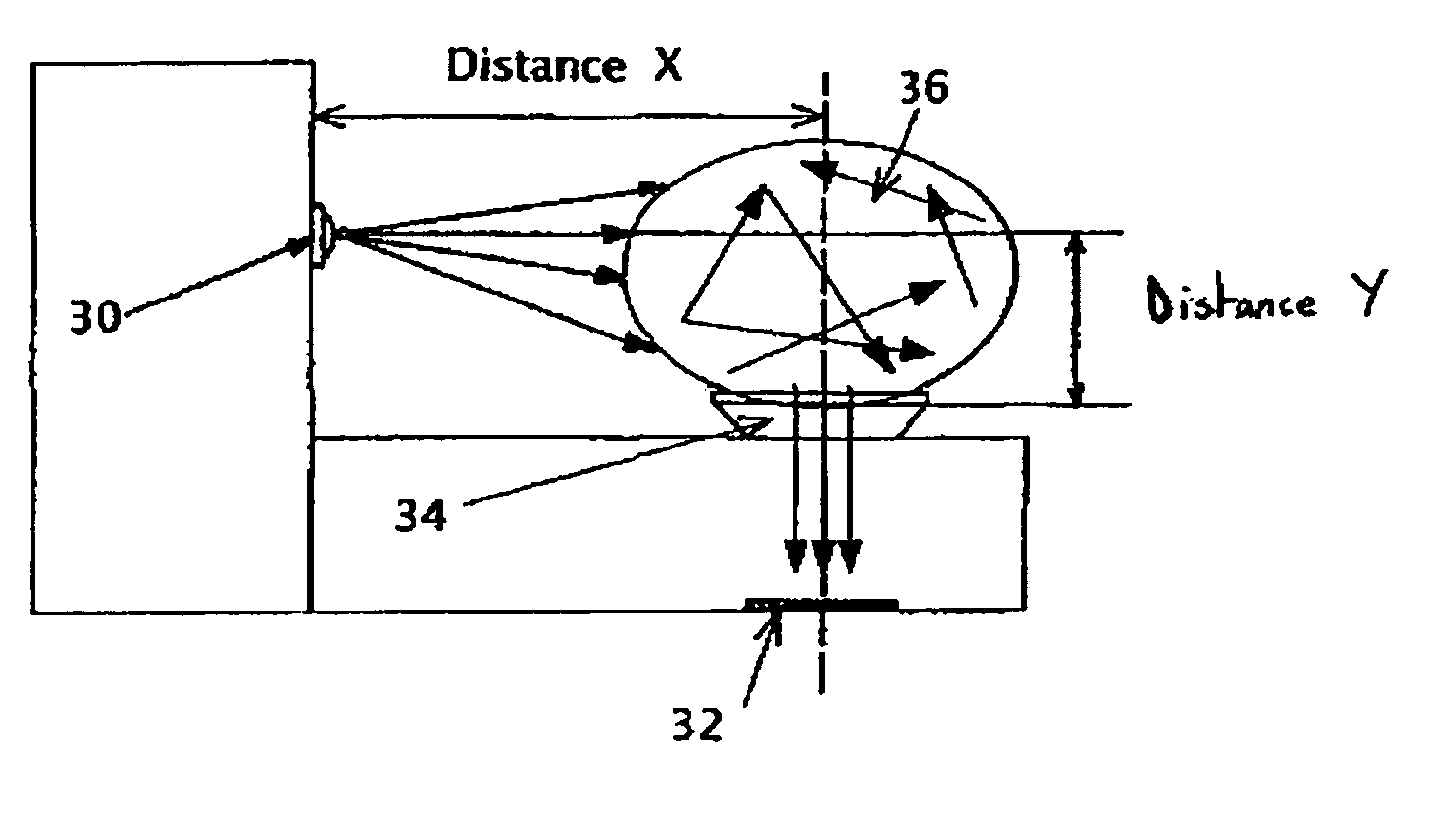
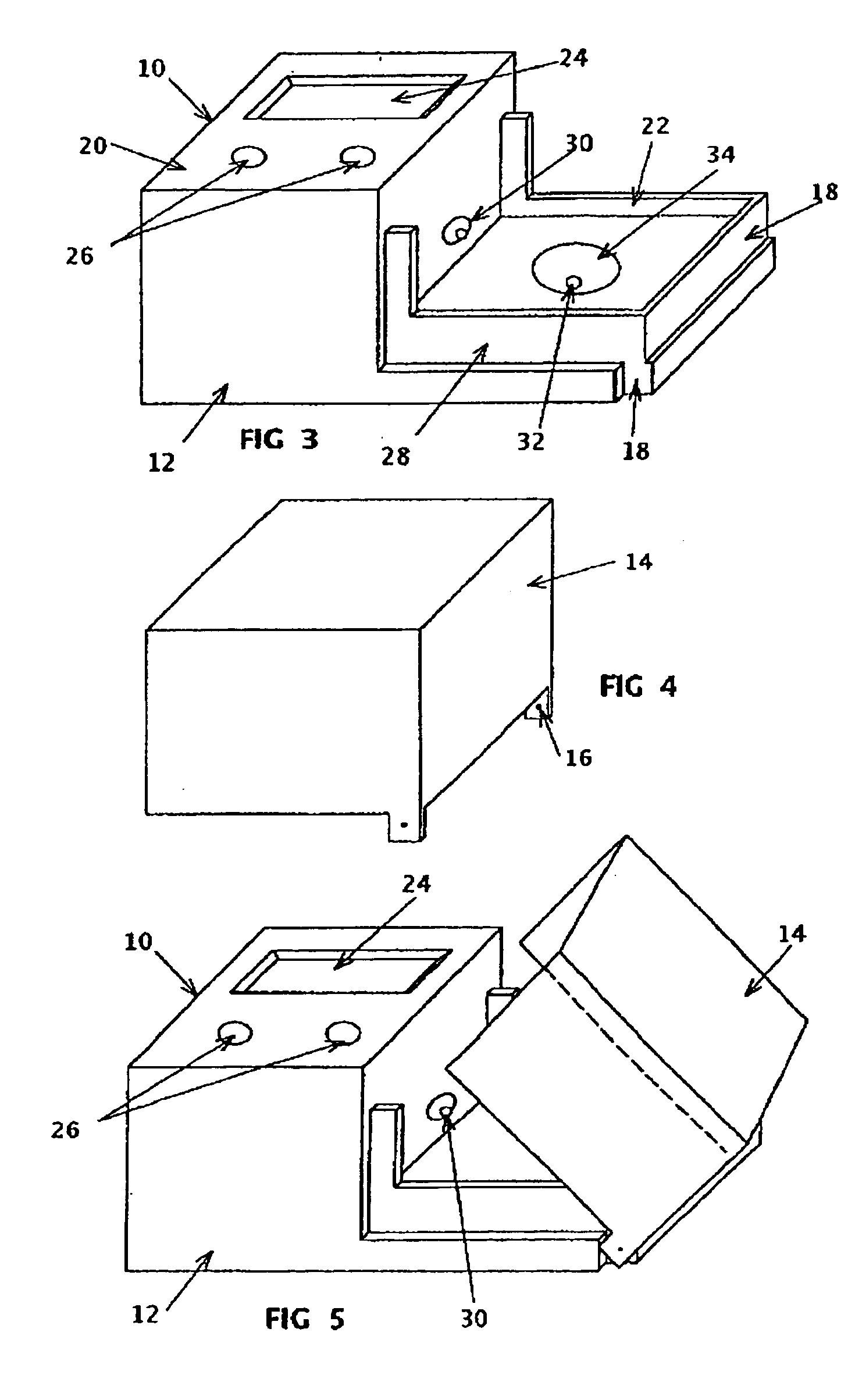
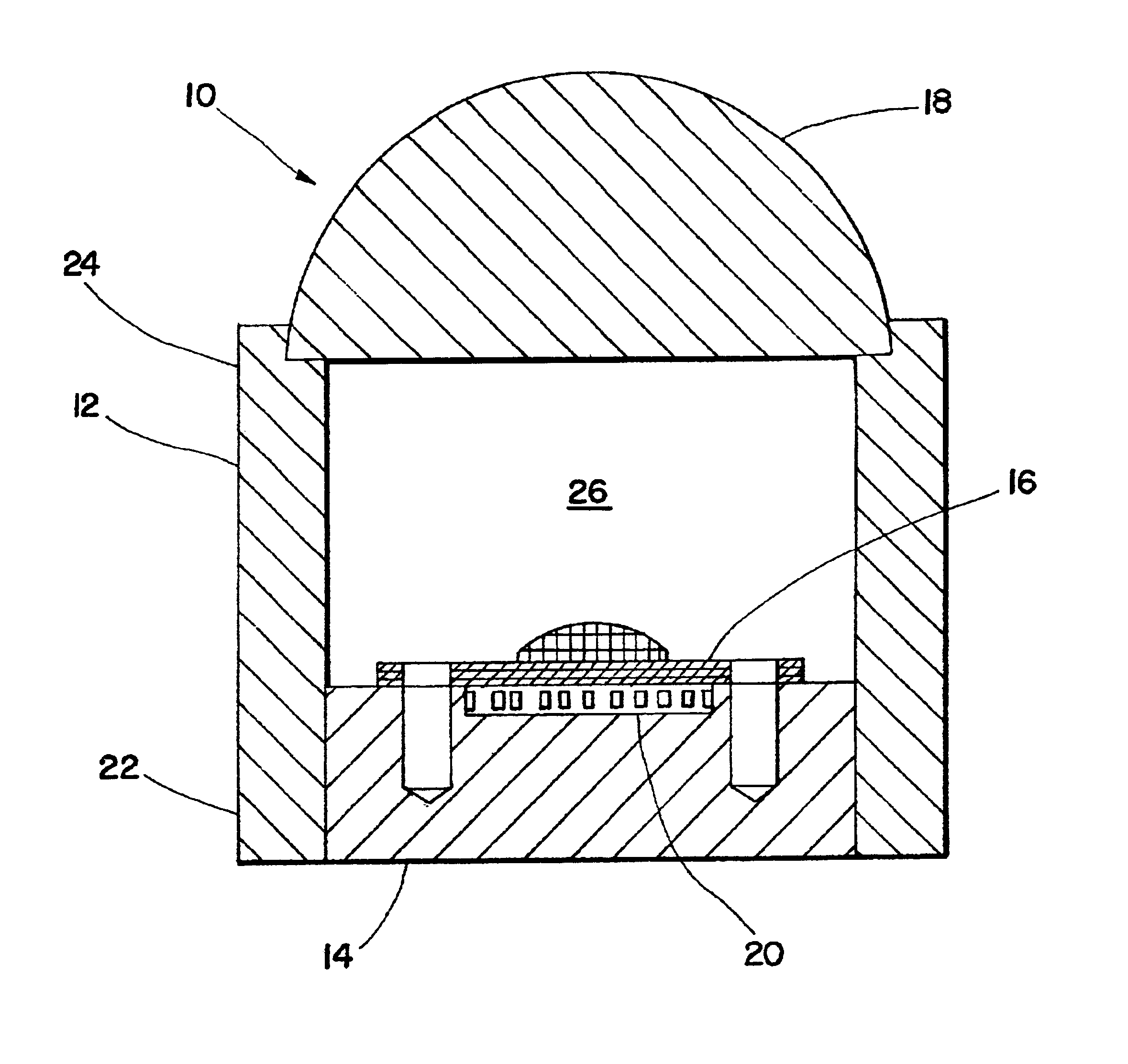
IR diode based high intensity light
InactiveUS6960776B2Increased complexityIncrease costPoint-like light sourceSemiconductor devices for light sourcesLow intensity lightAspheric lens
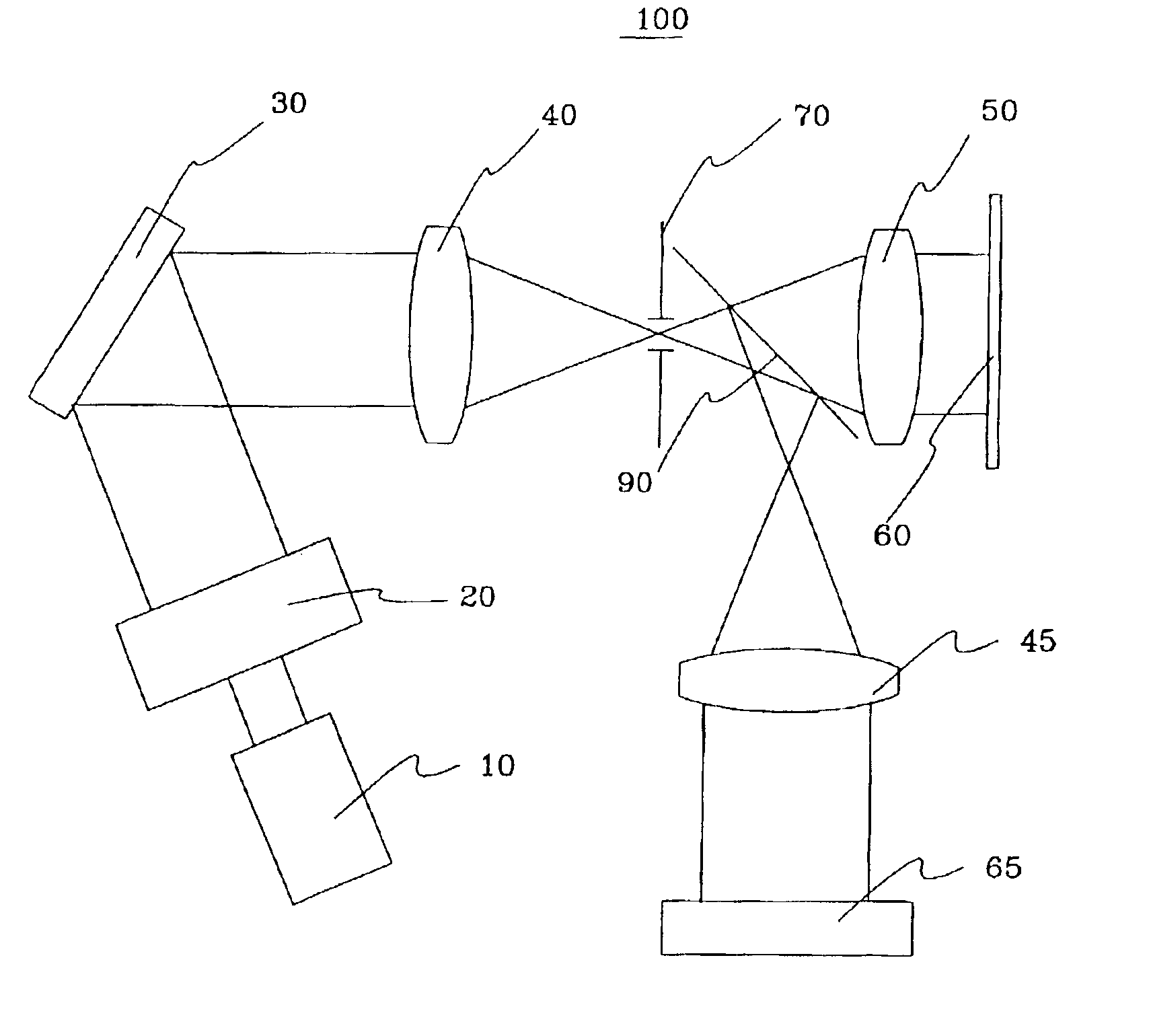
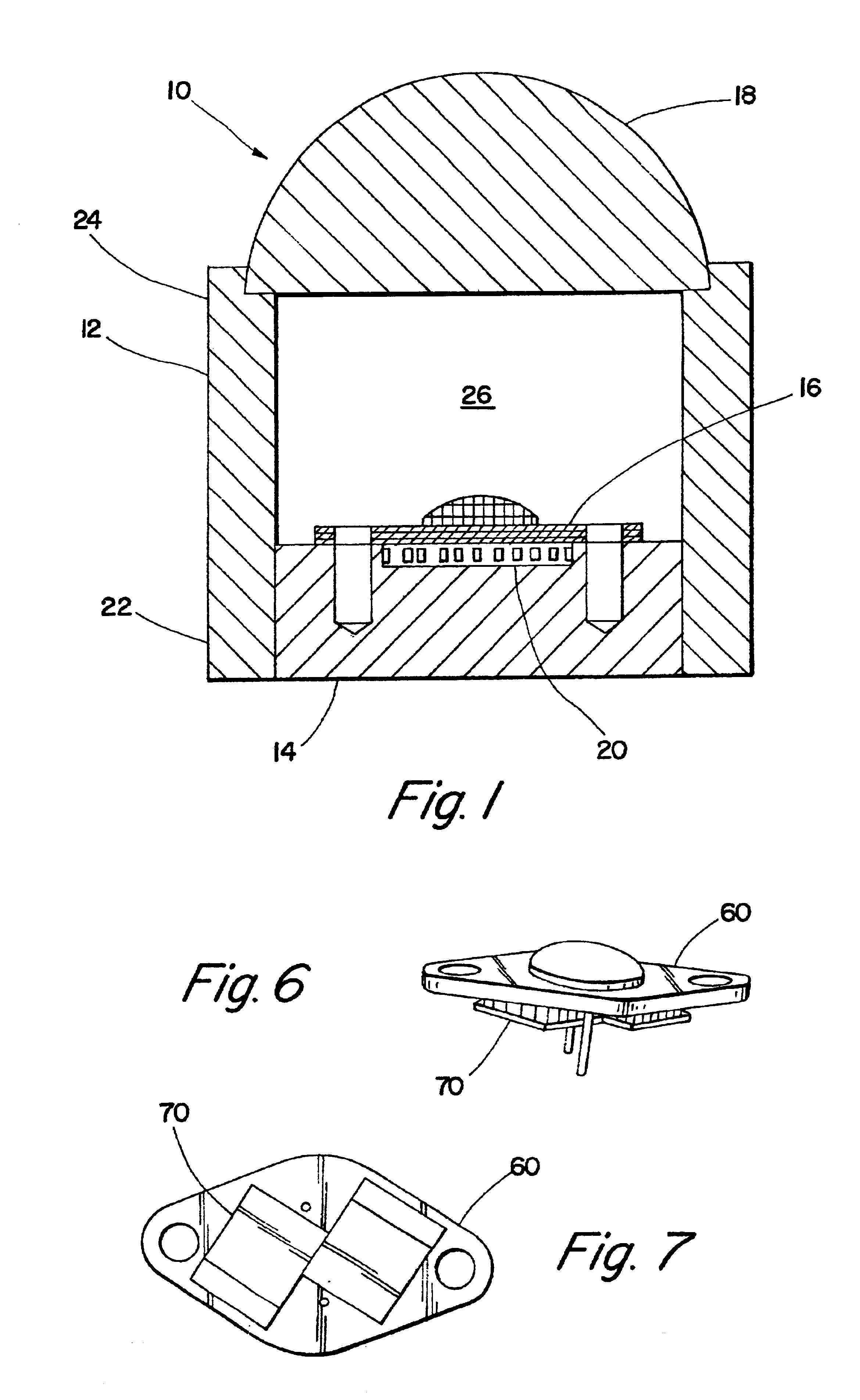
The present invention is directed to an infrared light assembly (10, 30, 80, 90). A preferred embodiment of the light assembly (10, 30, 80, 90) may be used on aircraft or other vehicles for landing, taxi mode, or search operations. The light assembly (10, 30, 80, 90) preferably only requires about 10 to 20 watts of power. The light assembly (10, 30, 80, 90) may include a housing (12, 32, 82), a base (14, 34, 50), an IR diode (16, 36, 60), and an aspheric lens (18, 38). The base (14, 34, 50) is preferably connected to the bottom portion (22) of the housing(12, 32, 82), and the aspheric lens (18, 38) is preferably connected to the top portion (24) of the housing (12, 32, 82). The IR diode (16, 36, 60) may be mounted on the base (14, 34, 50). The housing (12, 32, 82) and the base (14, 34, 50) preferably have high thermal conductivity, and they preferably act as heat sinks. In addition, a plurality of thermal electric coolers (20, 40, 70) may be positioned between the base (14, 34, 50) and the IR diode (16, 36, 60) for additional dissipation of the heat generated by the light assembly. The IR diode (16, 36, 60) is adapted to emit infrared light. The light assembly (10, 30, 80, 90) preferably maintains a substantially constant operating temperature so that the peak emission of the IR diode (16, 36, 60) is substantially maintained. The infrared light may radiate through the hollow of the housing(12, 32, 82) to the aspheric lens (18, 38). The aspheric lens (18, 38) is preferably adapted to collimate infrared light. As a result, the light assembly (10, 30, 80, 90) may provide a collimated beam of infrared light having a NVIS radiant intensity greater than about 2.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Blackbody fitting for temperature determination
ActiveUS20100246631A1Simple and straightforward and robust self-calibration techniqueSimple, straightforward, and robust self-calibration techniquesRadiation pyrometryThermometer testing/calibrationCurve fittingTemperature monitoring
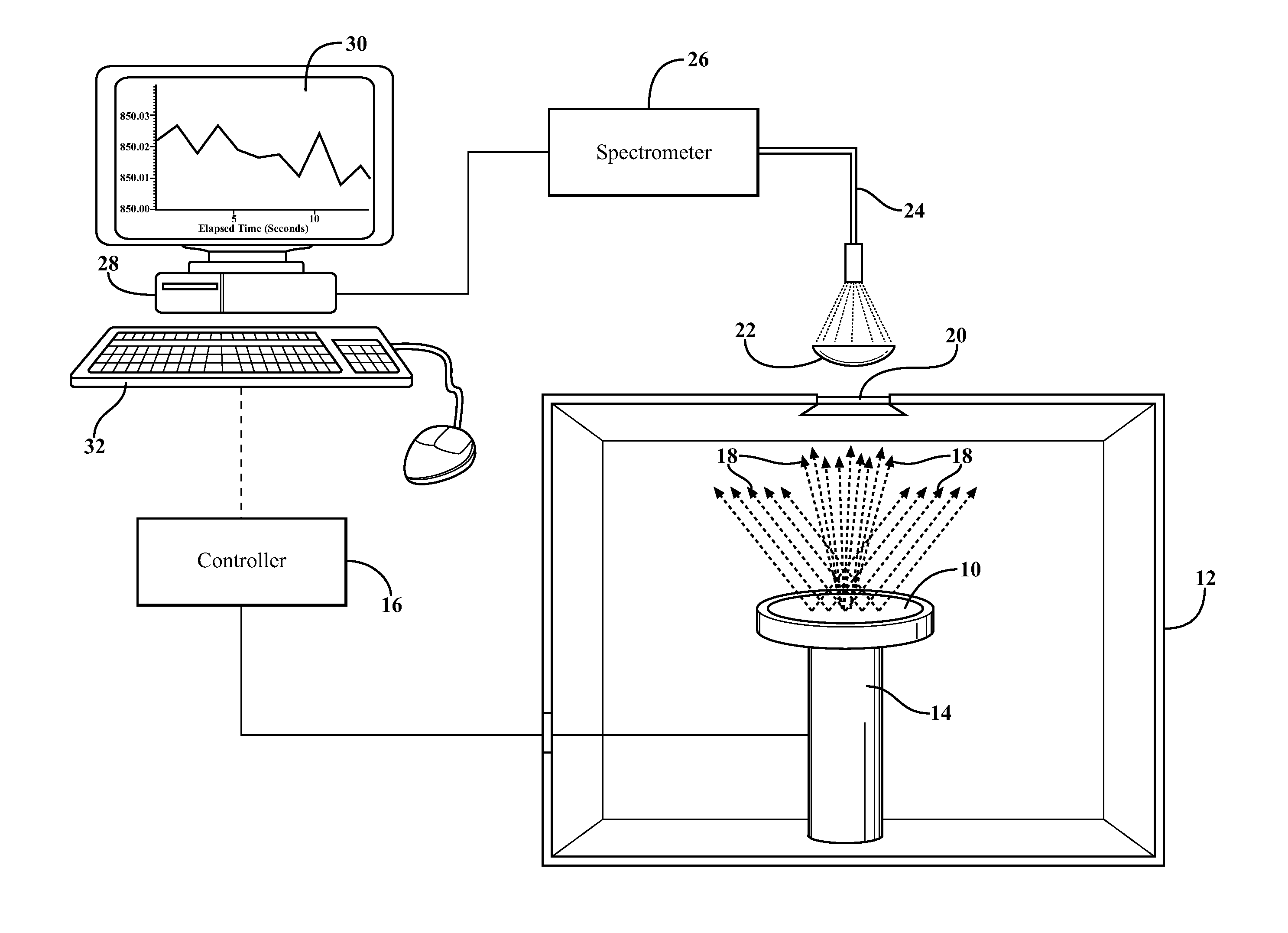
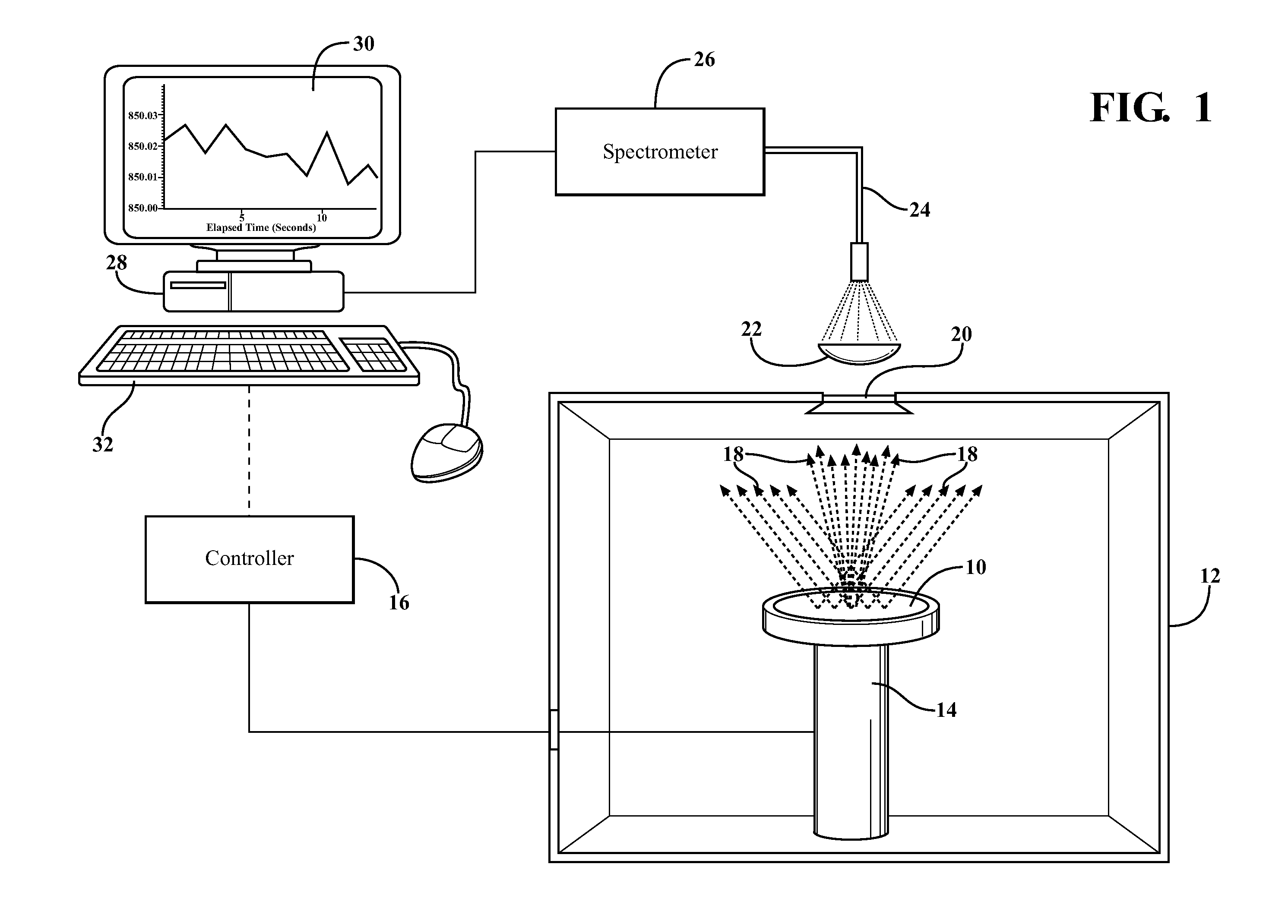
A temperature monitoring technique for collecting radiation intensity (blackbody emission) across a broad wavelength range. A solid state spectrometer (26) acquires spectra from a sample (10) in real time and resolves the spectra to a radiation intensity (I) versus wavelength (λ) curve. This curve is fitted to Planck's equation using a non-linear least squares fitting analysis. The system can be configured to self-calibrate and then lock in an amplitude value (A) which is used in subsequent temperature measurements by fitting to the blackbody emission curve. Preferably, the spectrometer (26) is flat field corrected (36) in an initial step to counteract variations in the spectrometer response with wavelength.
Owner:K SPACE ASSOCS
Multiple Aperture Hand-Held Laser Therapy Apparatus
ActiveUS20130317571A1Easy to changeIncrease the areaLaser detailsControlling energy of instrumentHigh energyHand held
A hand-held therapeutic laser apparatus with a special opto-mechanical construction, which enables changeability of a front collimating lens to create different effective laser apertures. A smaller effective aperture has a comparatively higher radiant flux density for treatment of a small area that requires a higher energy dose, while a larger effective aperture facilitates treatment of a large area at a relatively reduced radiant intensity.
Owner:MEDICAL COHERENCE
Calibration of a probe in ptychography
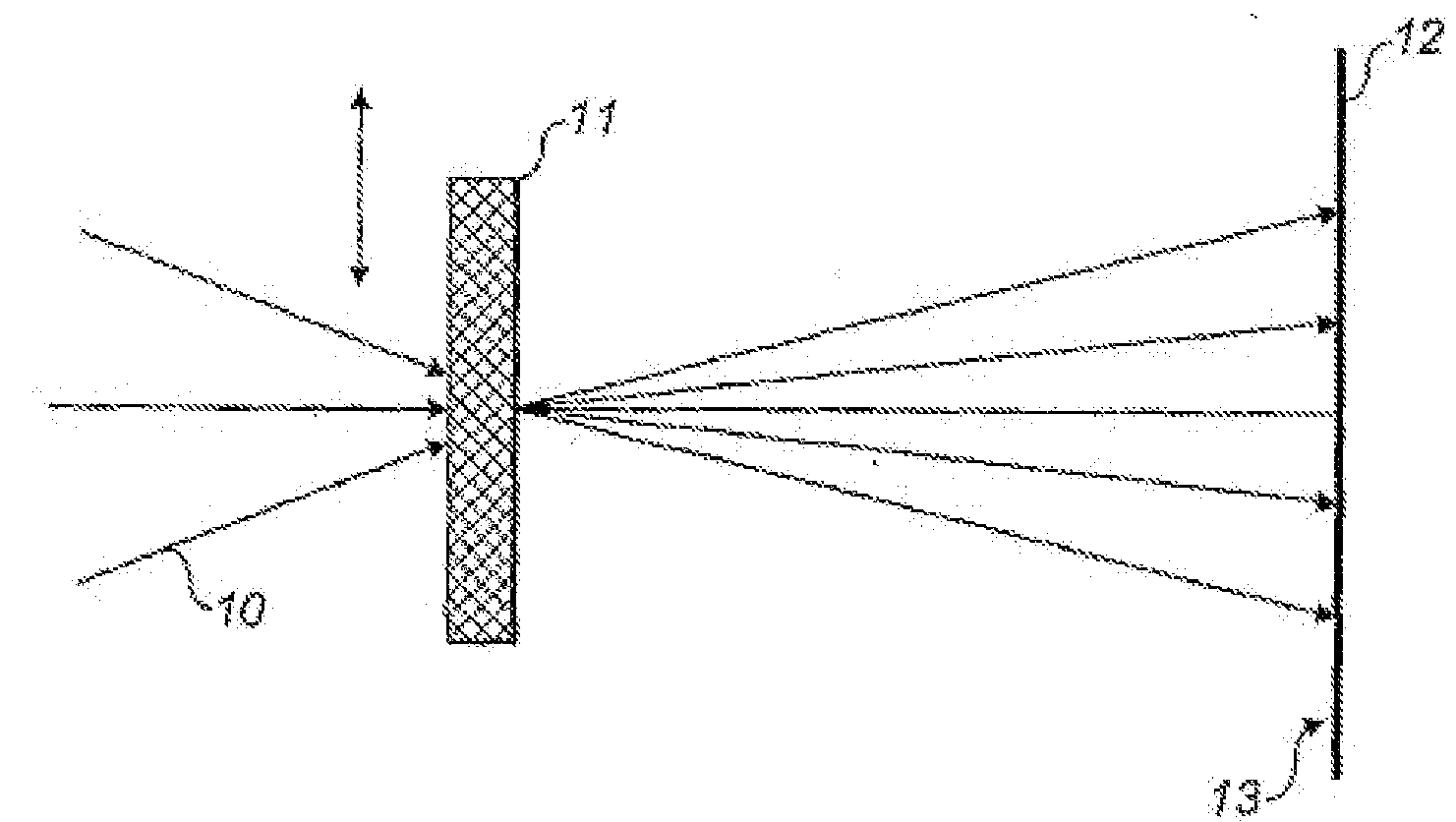
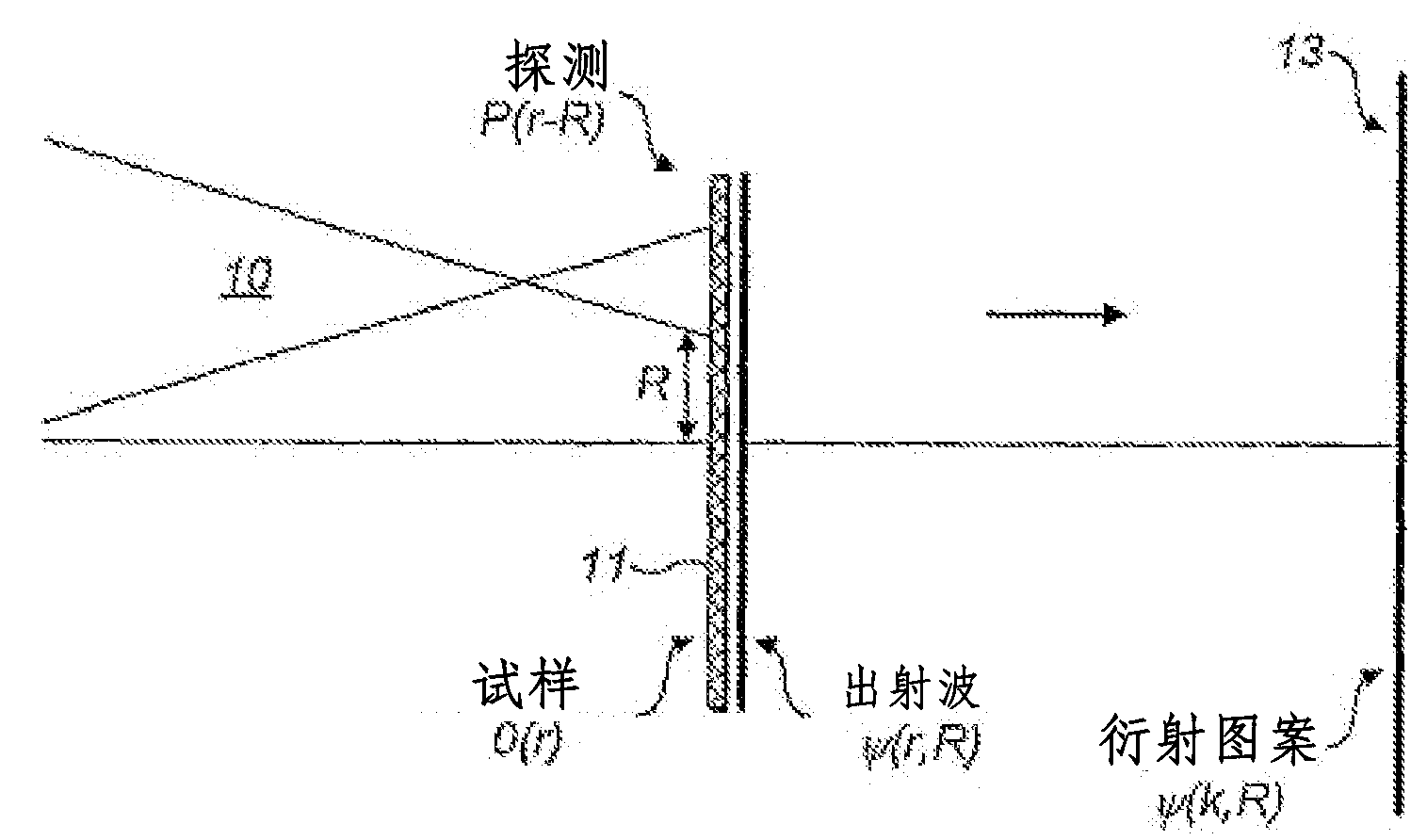
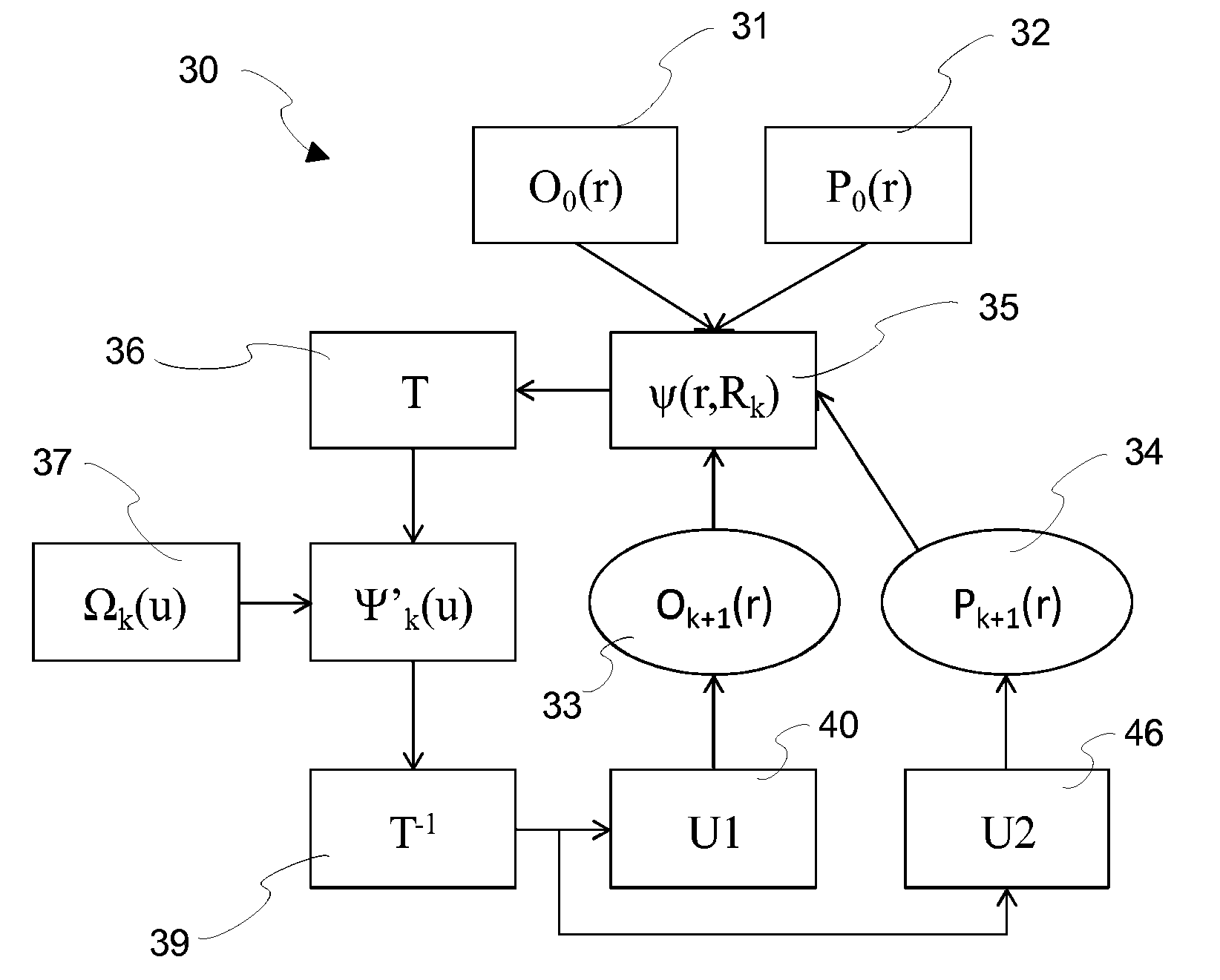
ActiveCN103201648AImprove performanceReduced or eliminated potential for divergenceCharacter and pattern recognitionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentPtychographyRadiology
A method of providing image data for constructing an image of a region of a target object, comprising providing a reference diffraction pattern of a reference target object; determining an initial guess for a probe function based upon the reference diffraction pattern; and determining, by an iterative process based on the initial guess for the probe function and an initial guess for an object function, image data for a target object responsive to an intensity of radiation detected by at least one detector.
Owner:PHASE FOCUS
High-Speed Random Number Generator
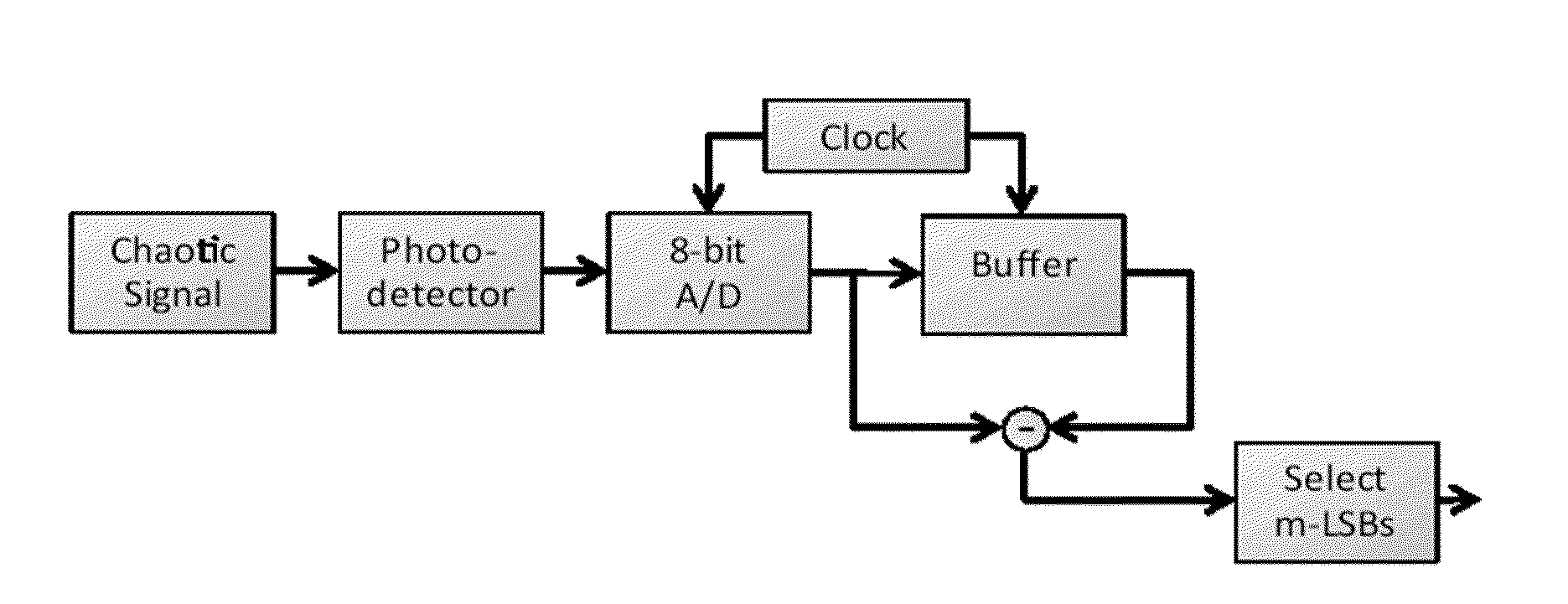
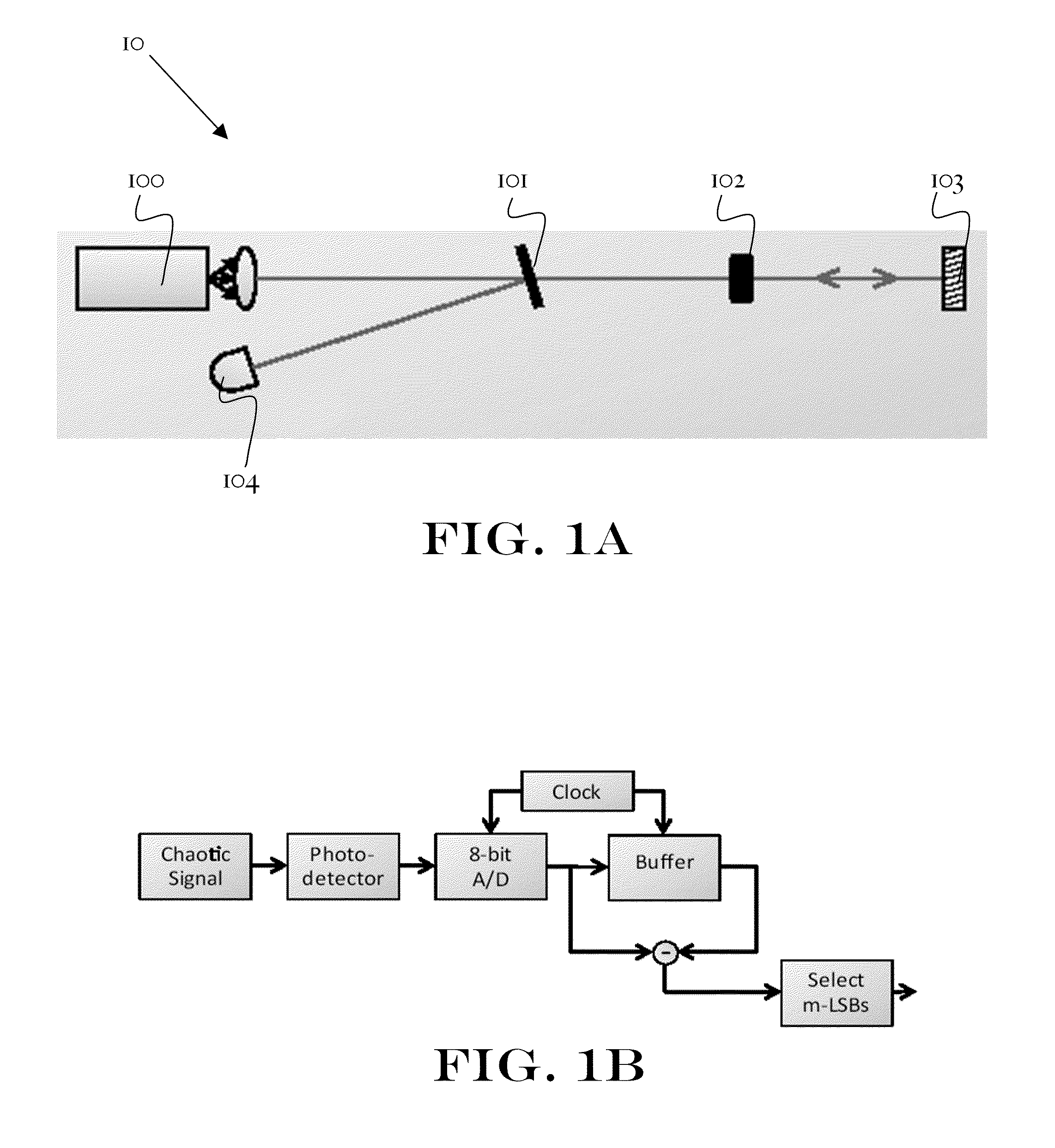
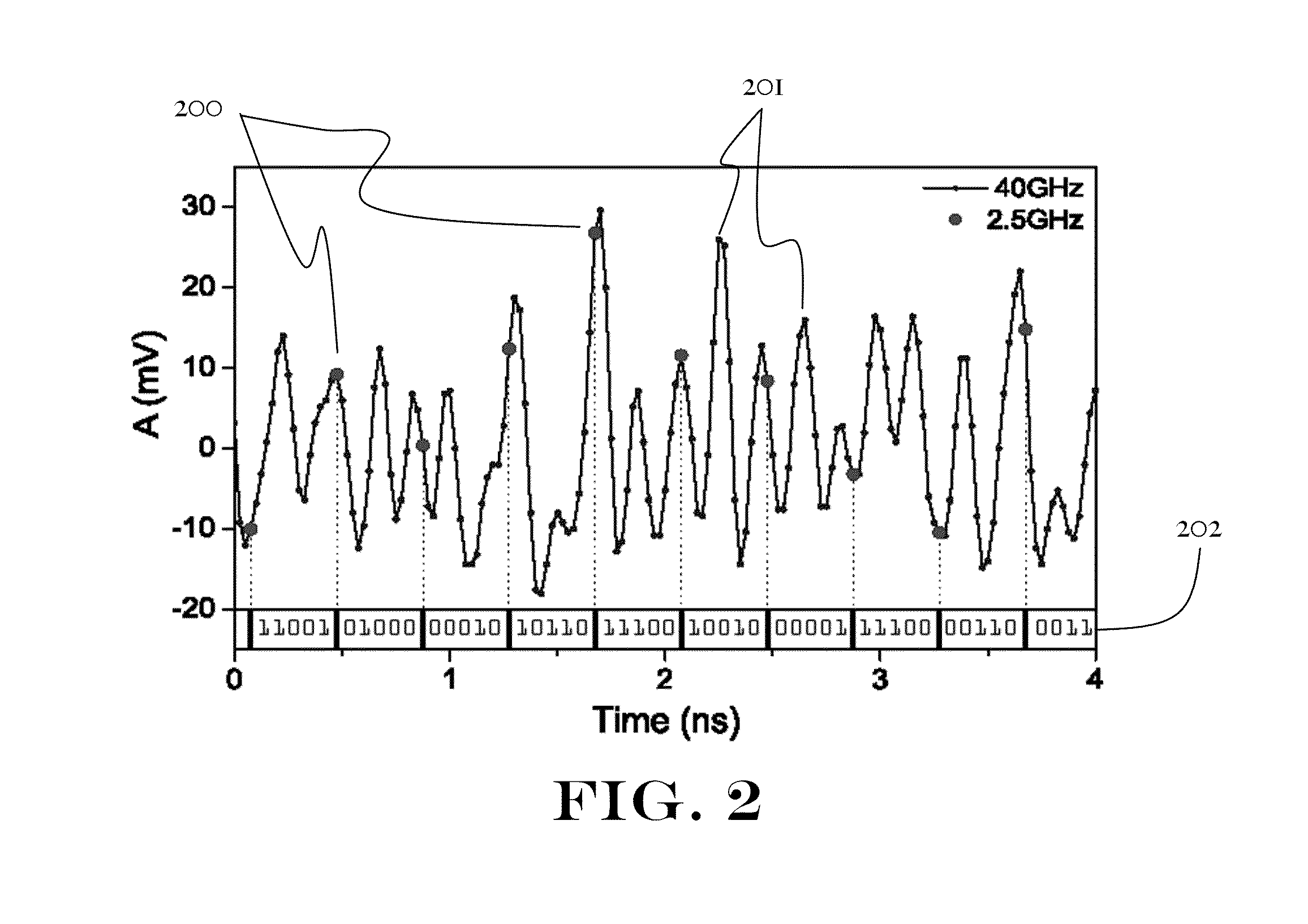
InactiveUS20100332575A1Random number generatorsSecuring communication by chaotic signalsLeast significant bitNumber generator
A method of generating a sequence of random bits is disclosed. The method comprises steps of (a) generating a stream of photons using a laser; (b) attenuating said series of photons; (c) reflecting at least a part of said stream of photons from a reflector positioned such that at least part of said stream of photons is directed from said reflector into the cavity of said laser; (d) directing a part of said stream of photons to a detector such that a signal proportional to the intensity of the radiation falling on said detector is produced; (e) sampling the AC component of said signal at a plurality of times, thereby obtaining a sampled signal comprising a sequence of data points; (f) obtaining the nth time derivative of said sampled signal over at least a portion of said sample signal; and (g) adding the m least significant bits (LSBs) of said nth time derivative to said sequence. By this method, truly random sequences of bits can be obtained at rates of up to at least 300 GBits / s.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com