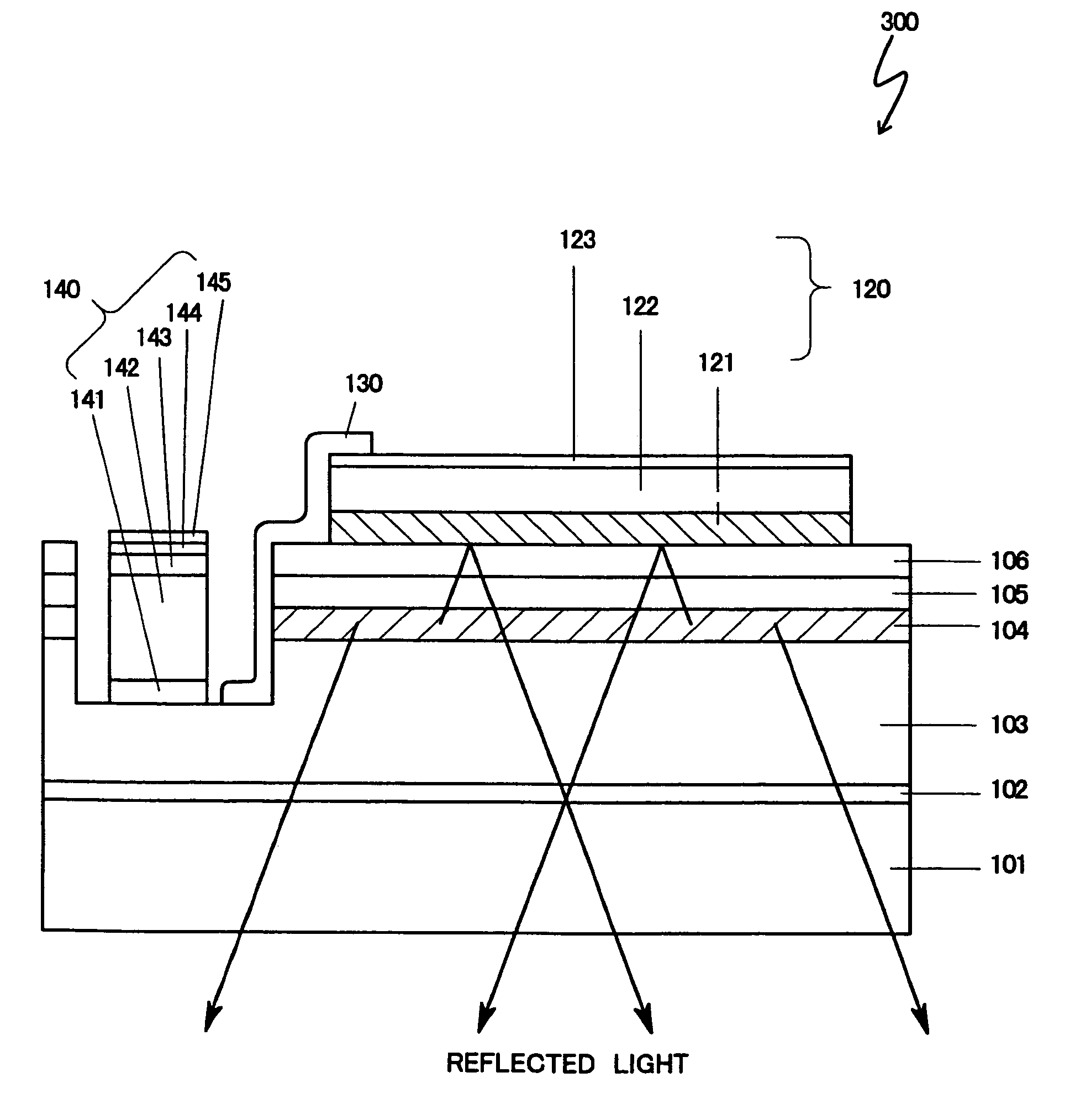
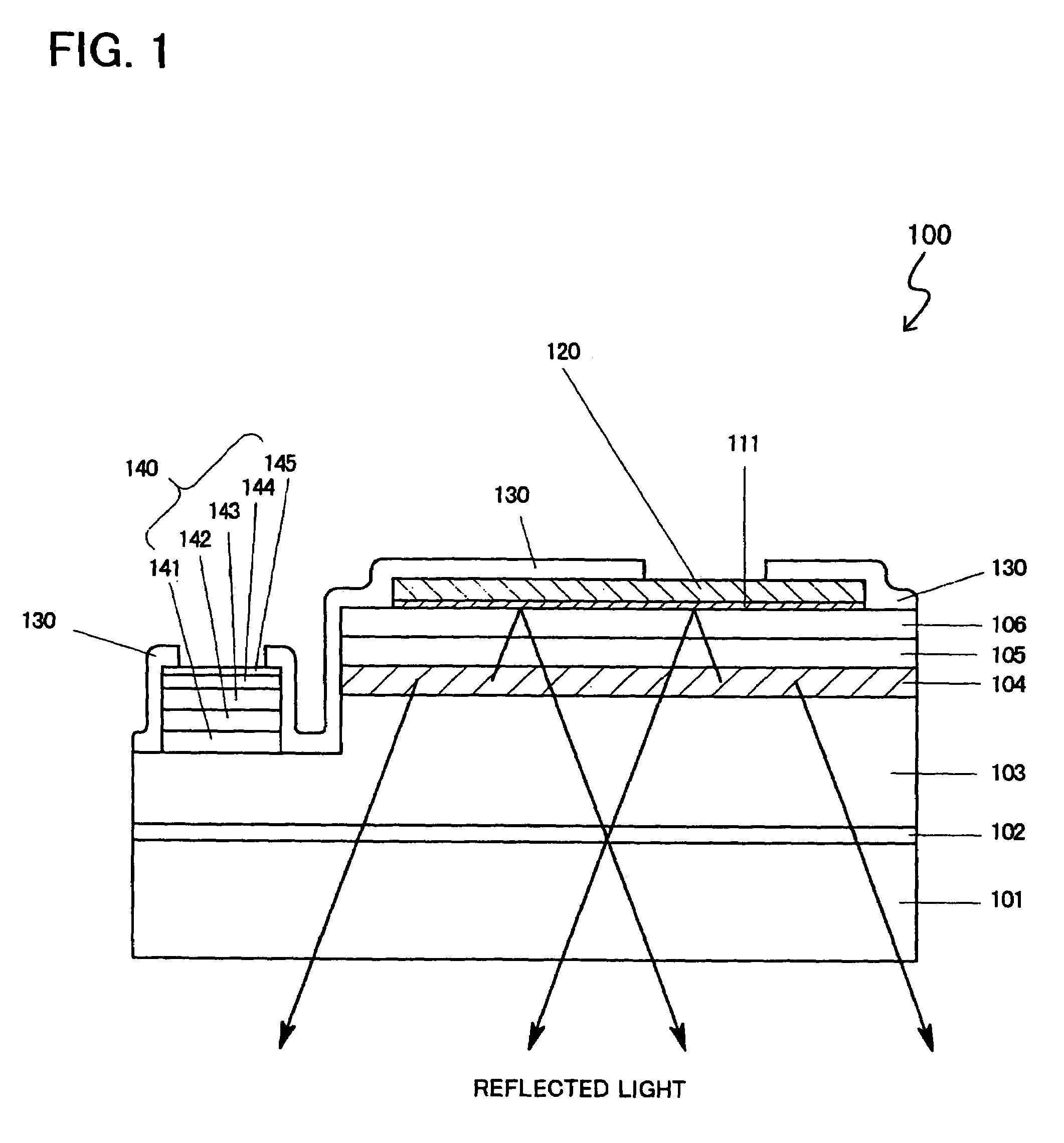
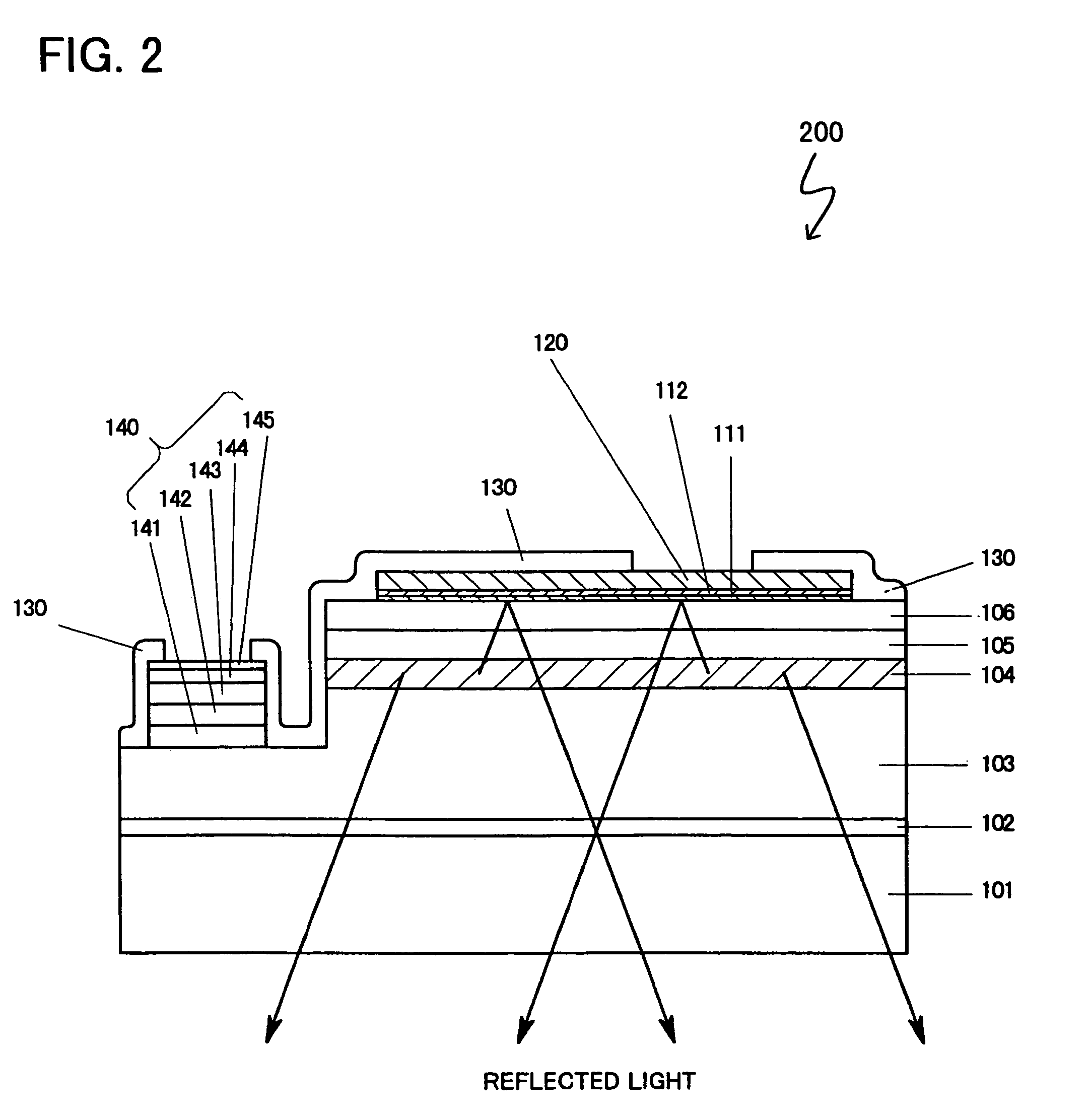
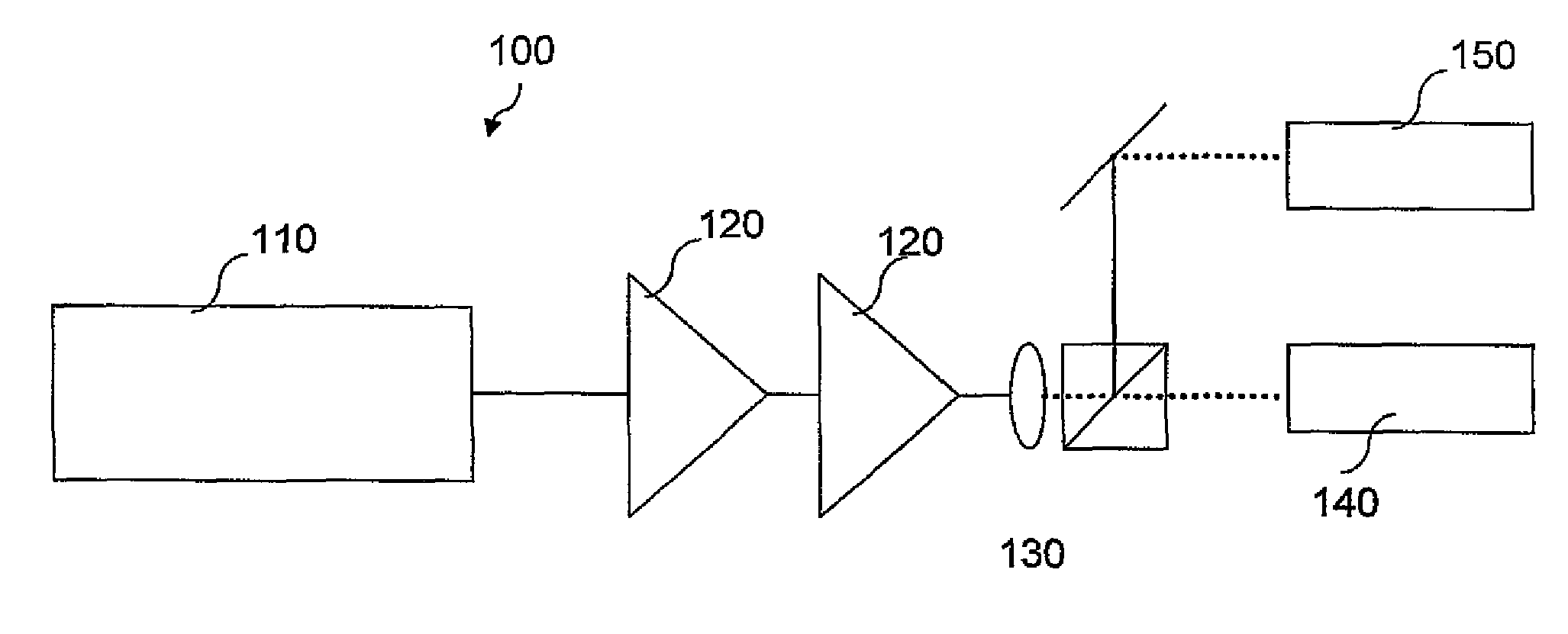
Patents
Literature
2620 results about "High reflectivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
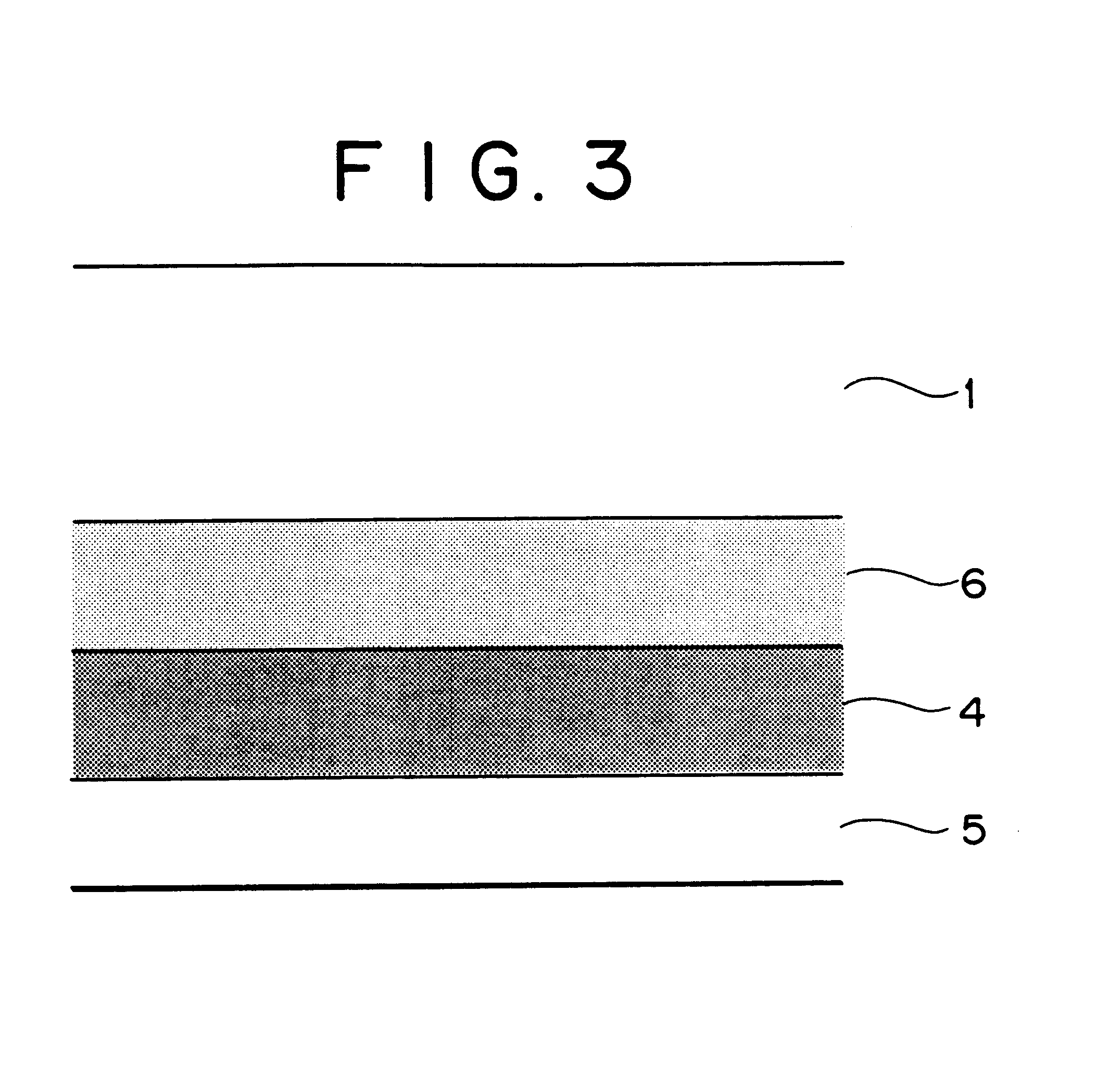
Multistage-spreading heat-dissipation fire-proof heat-insulation composite fabric, preparation method and application
ActiveCN102783741AImprove permeabilityPromote absorptionLaminationLamination apparatusInsulation layerMetal foil
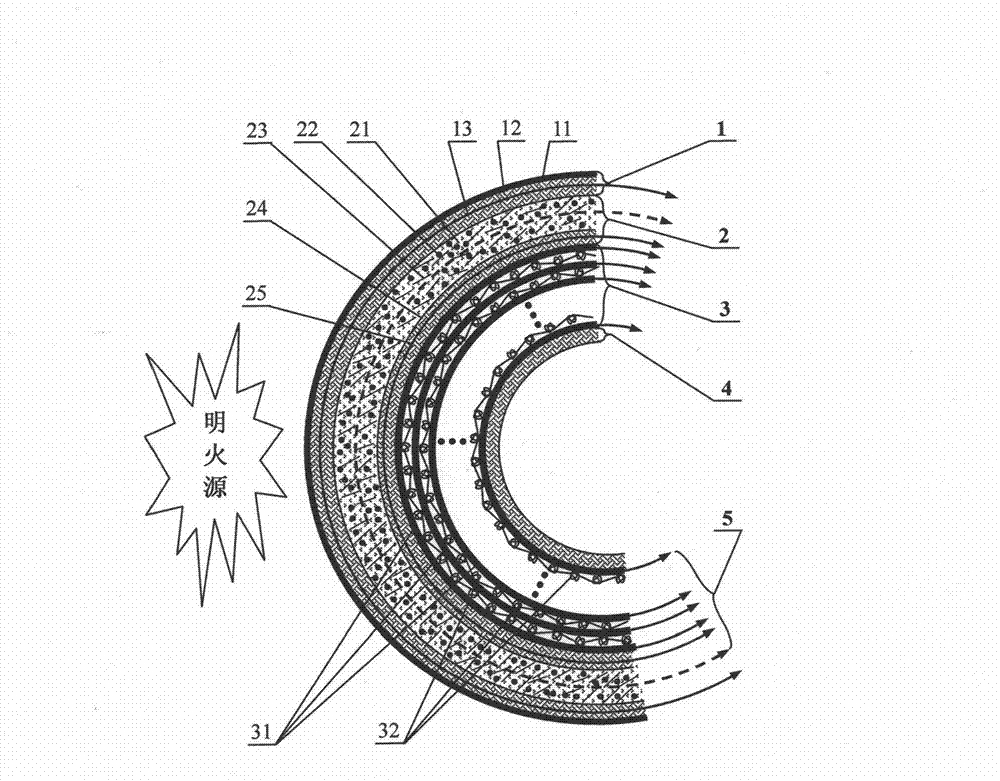
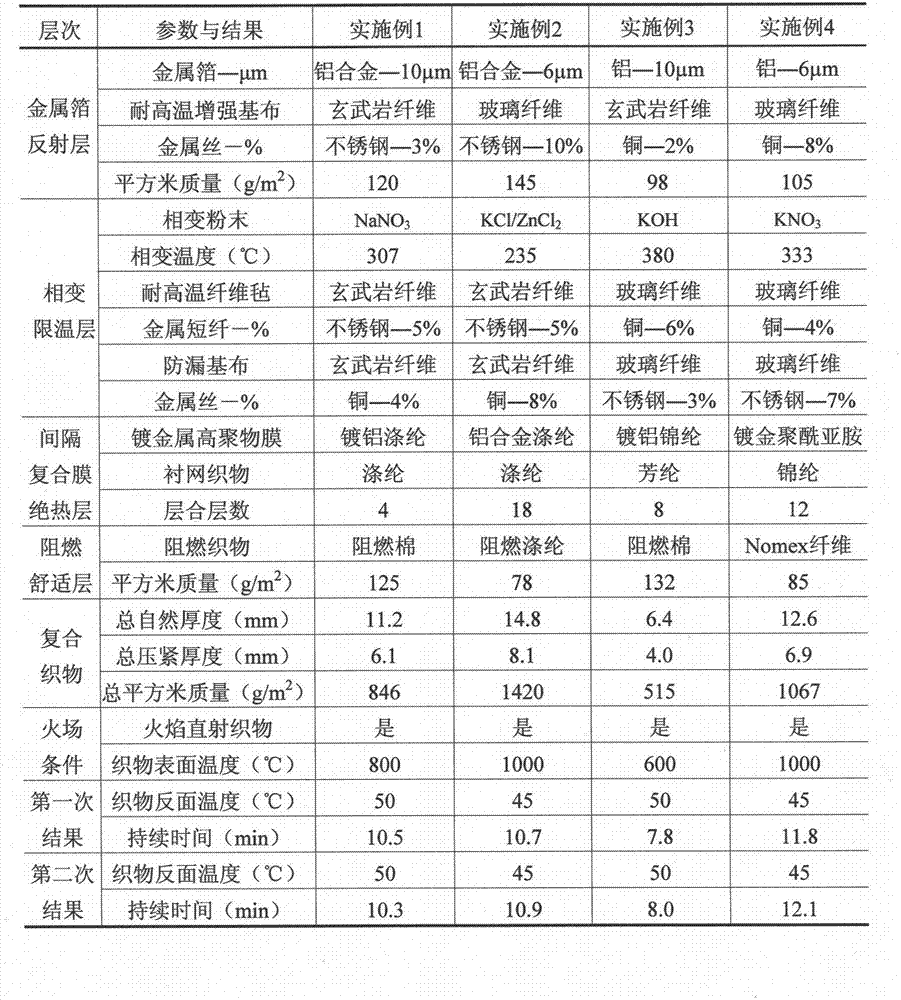
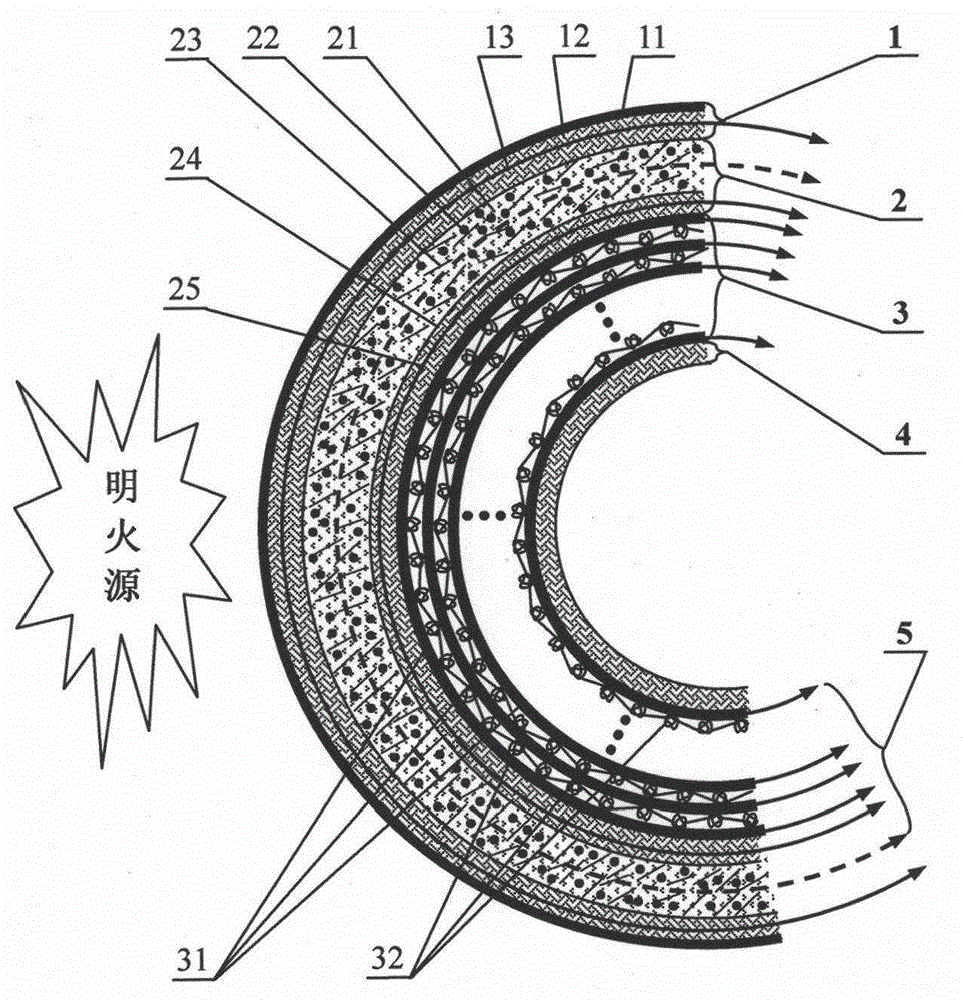
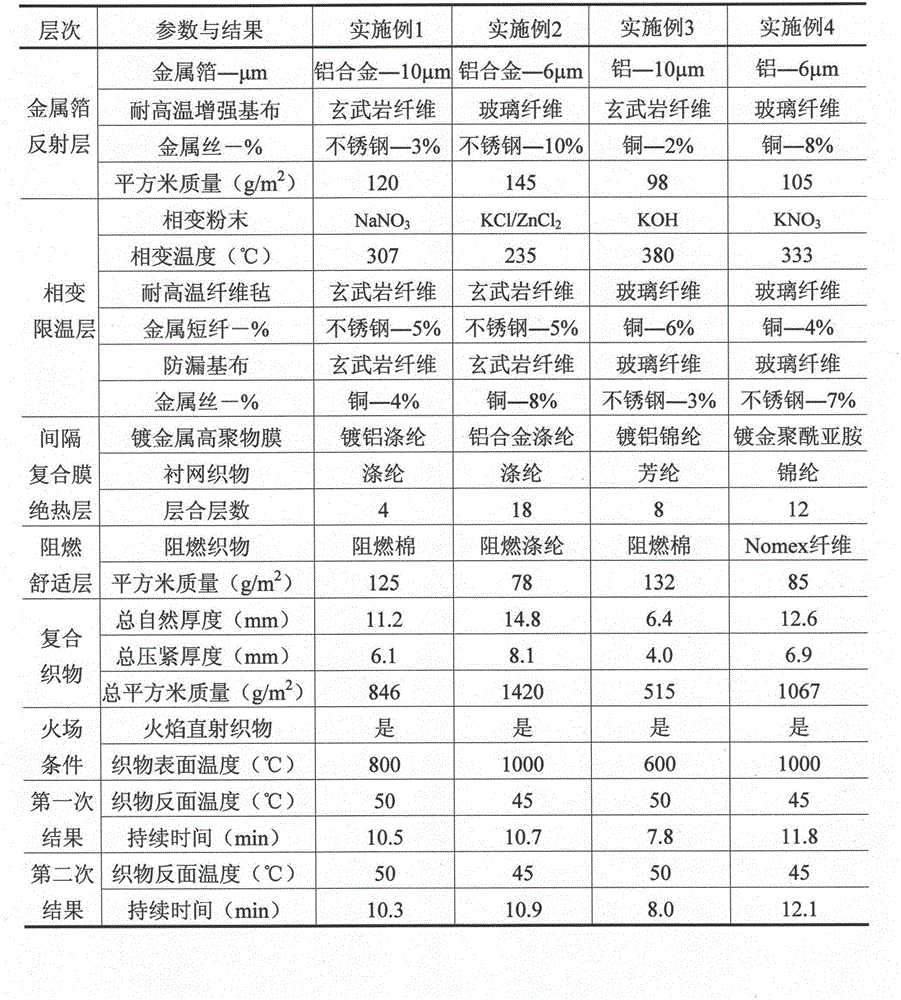
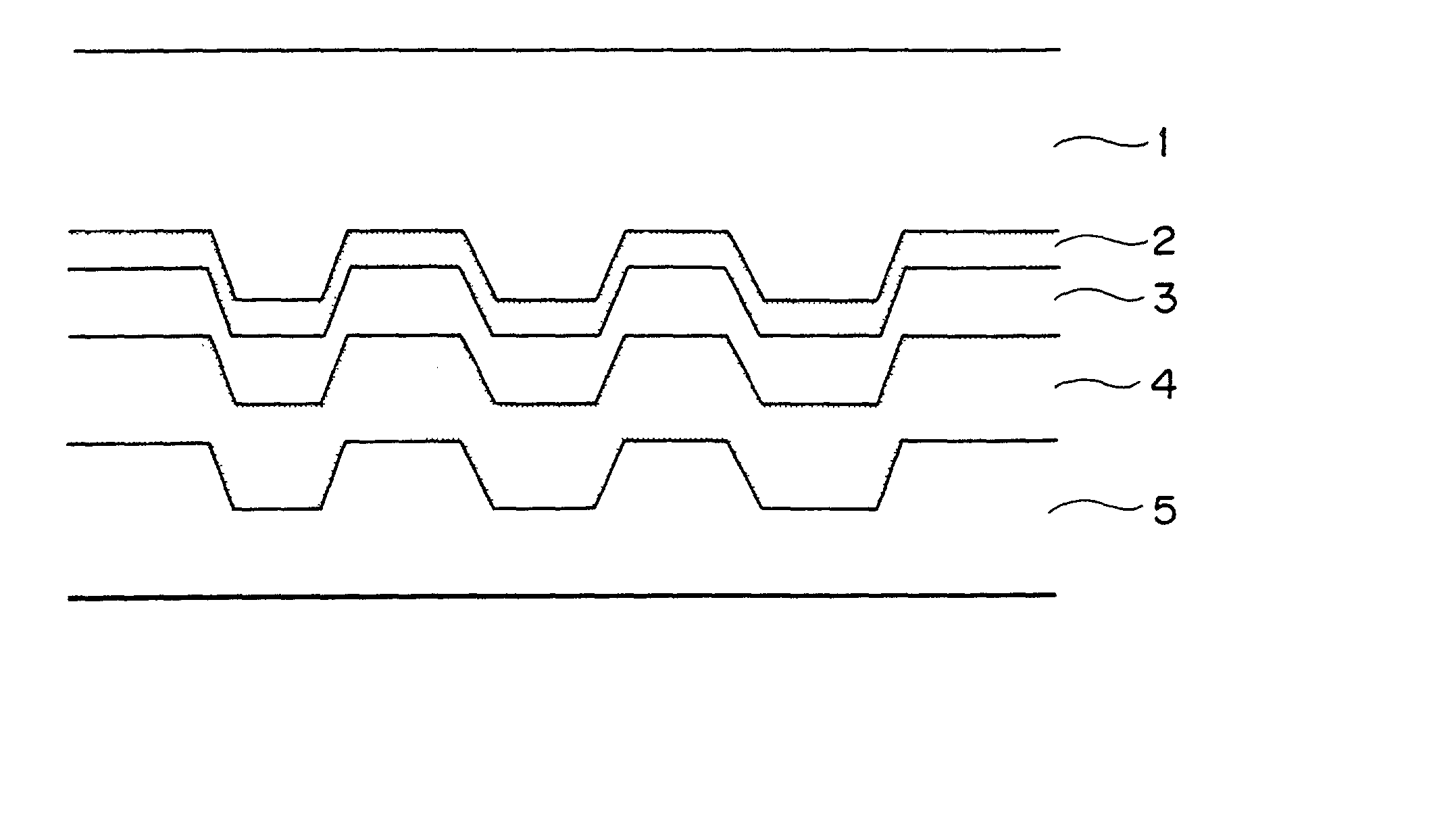
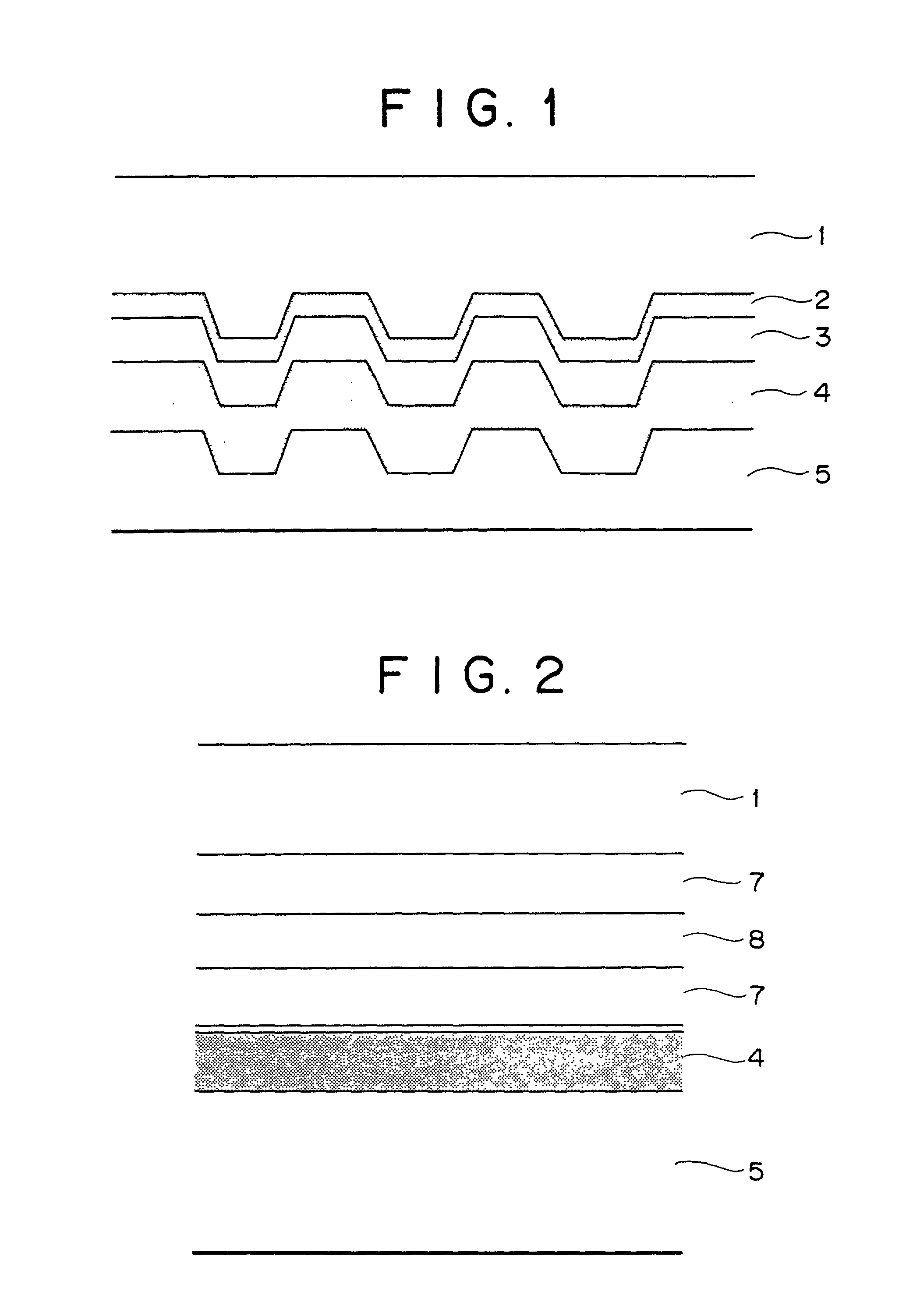
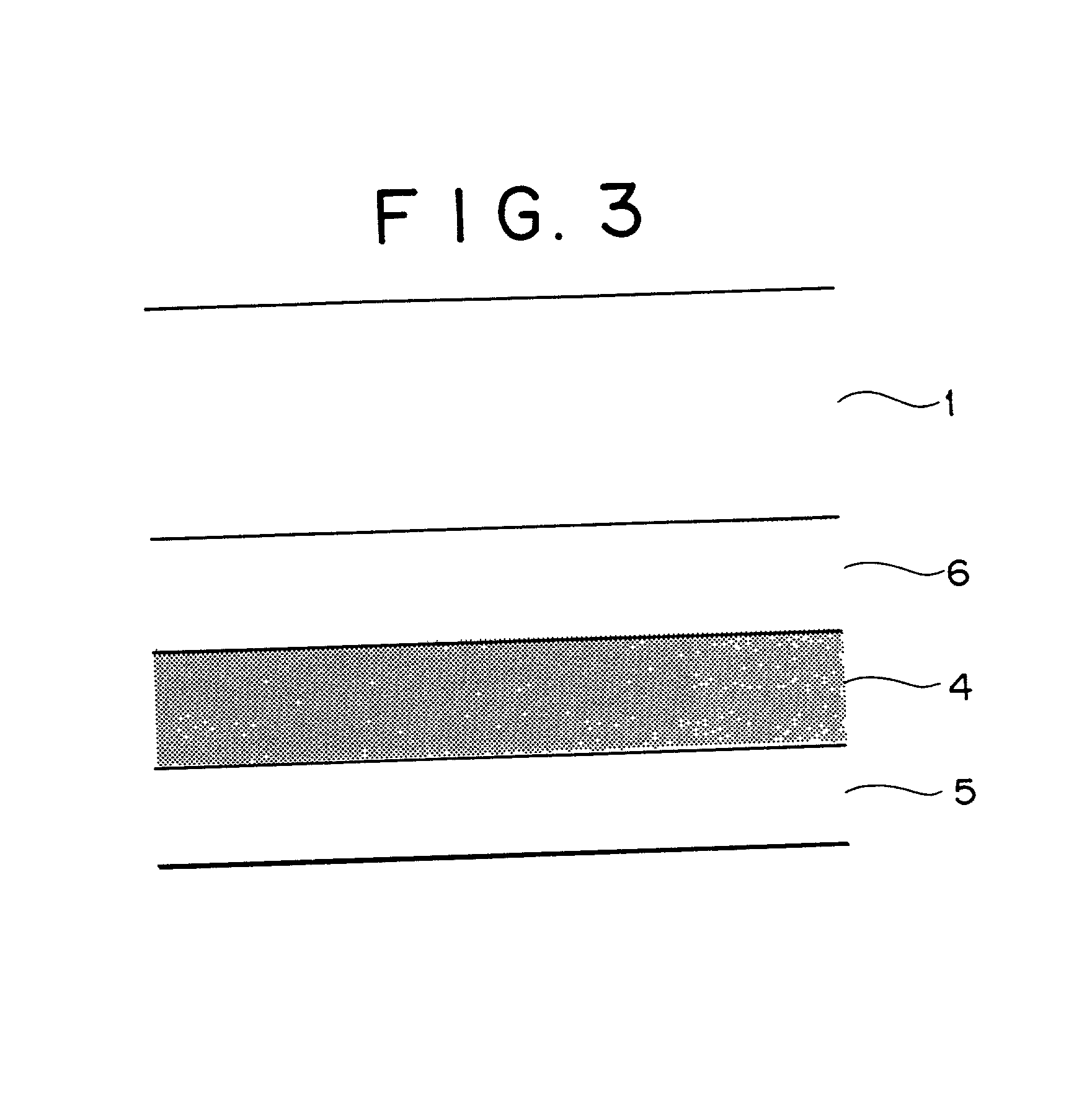
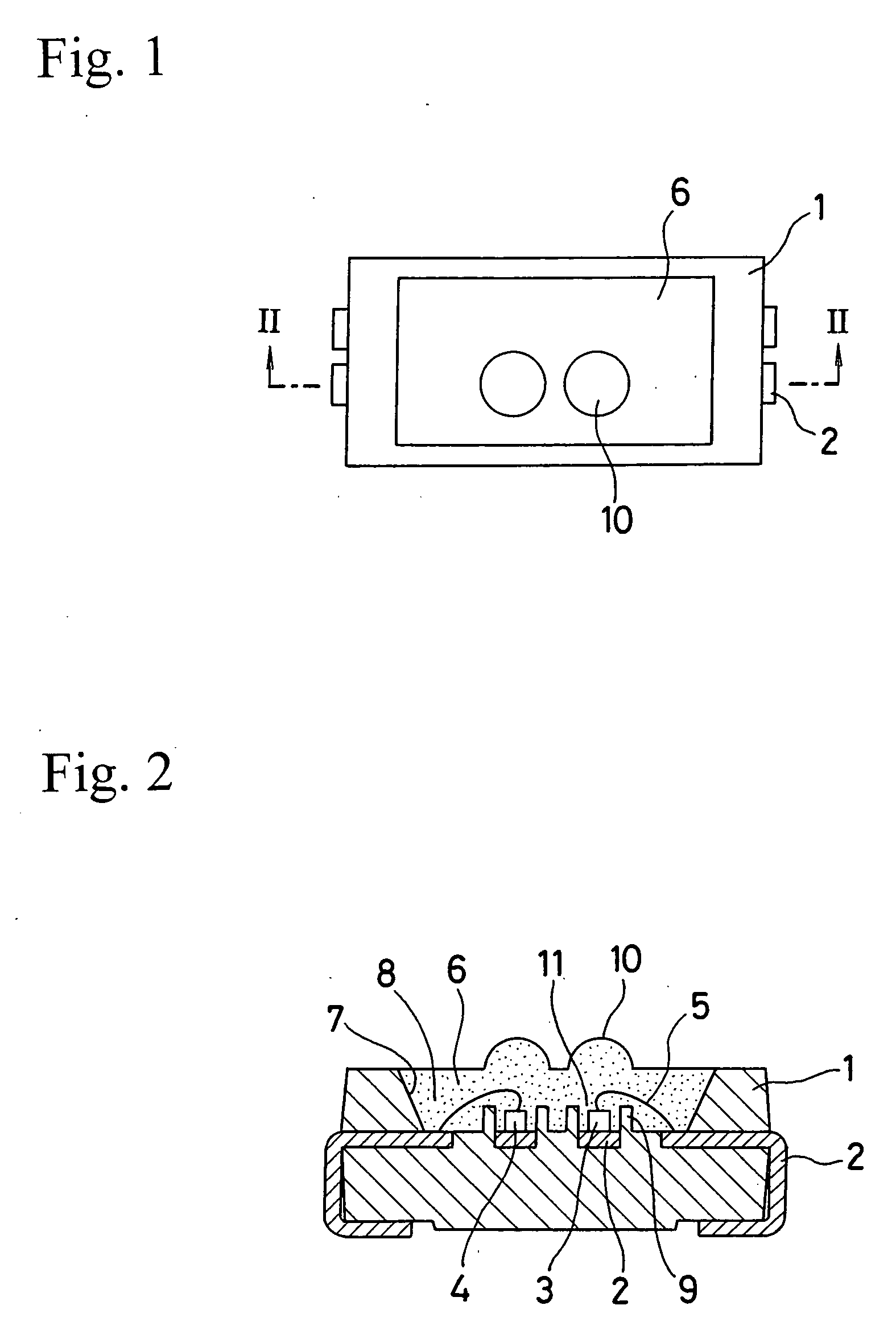
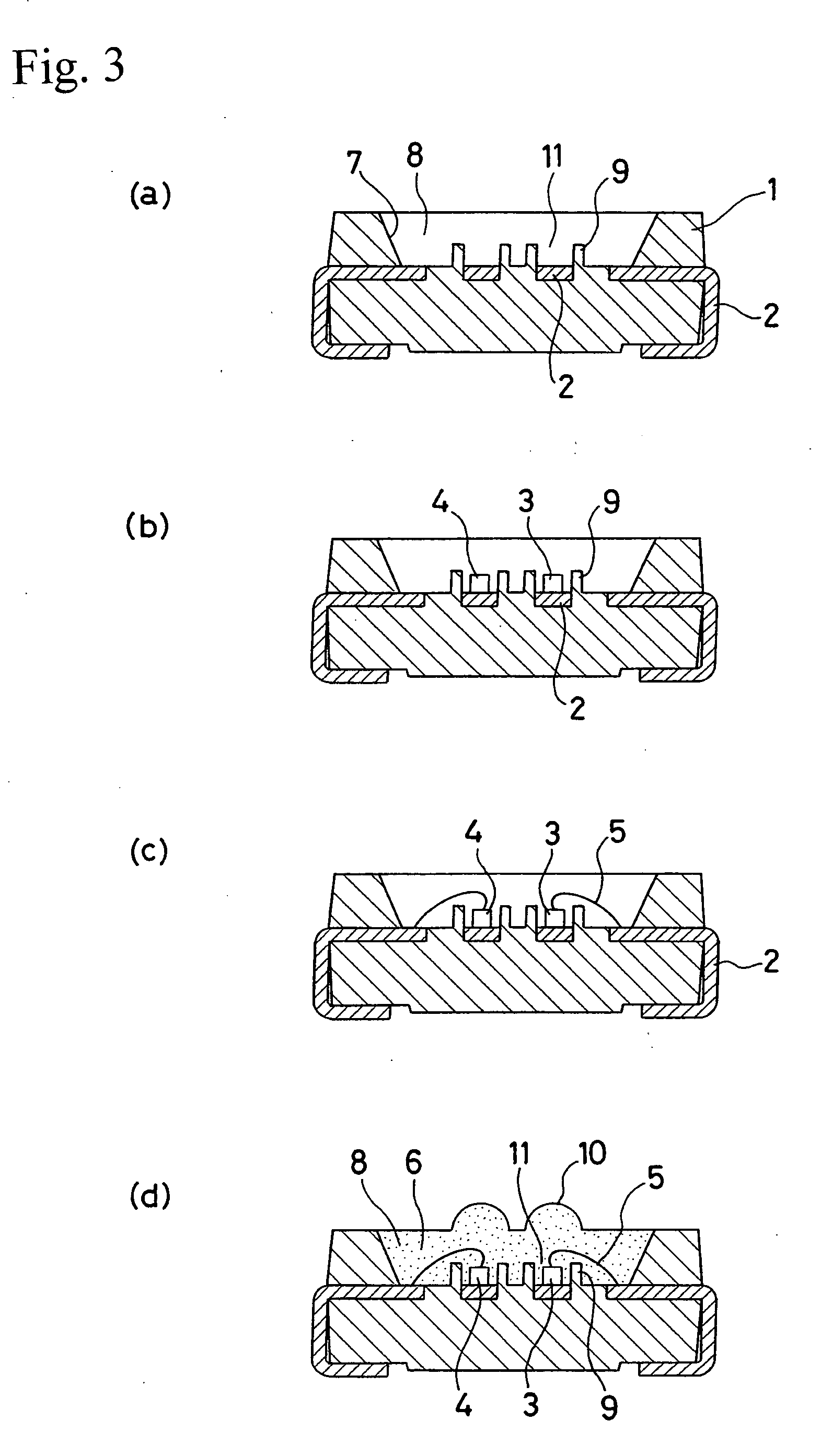
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of multistage-spreading heat-dissipation fire-proof heat-insulation composite fabric. The multistage-spreading heat-dissipation fire-proof heat-insulation composite fabric is formed by successively arranging and laminating a metal foil reflection layer, a phase change temperature limitation layer, an interval composite membrane heat-insulation layer and a flame-retardant comfortable layer, wherein the metal foil reflection layer has high reflectivity and an enhanced heat-dissipation function; the phase change temperature limitation layer has functions of high energy consumption absorption and evenly-distributed heat conduction; the interval composite membrane heat-insulation layer has the functions of reflection insulation and even distribution of heat; and the flame-retardant comfortable layer has the functions of low-contact heat conduction, heat insulation and comfort. When the front side of the multistage-spreading heat-dissipation fire-proof heat-insulation composite fabric is under the action of open fire and strong heat flow environment, the back side of the multistage-spreading heat-dissipation fire-proof heat-insulation composite fabric can be kept below 50DEG C which is near the safe temperature state of the human skin, and the integral structural form and the mechanical property are stable. The natural thickness of the composite fabric is 5-15mm, the compression thickness of the composite fabric is 3-8mm, and the square meter quality of the composite fabric is 400-1500g / m<2>. The composite fabric is fire-proof heat-insulation material which is totally sealed, stuck and sewn and can be used for individual protection and environment heat insulation in special high-temperature occasions, such as fire control, military, exploration, safe escape and industry and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Fire-proof and heat-insulating composite fabric with multi-stage expansion and heat dissipation, preparation method and application
ActiveCN102783741BImprove permeabilityPromote absorptionLaminationLamination apparatusInsulation layerMetal foil
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of multistage-spreading heat-dissipation fire-proof heat-insulation composite fabric. The multistage-spreading heat-dissipation fire-proof heat-insulation composite fabric is formed by successively arranging and laminating a metal foil reflection layer, a phase change temperature limitation layer, an interval composite membrane heat-insulation layer and a flame-retardant comfortable layer, wherein the metal foil reflection layer has high reflectivity and an enhanced heat-dissipation function; the phase change temperature limitation layer has functions of high energy consumption absorption and evenly-distributed heat conduction; the interval composite membrane heat-insulation layer has the functions of reflection insulation and even distribution of heat; and the flame-retardant comfortable layer has the functions of low-contact heat conduction, heat insulation and comfort. When the front side of the multistage-spreading heat-dissipation fire-proof heat-insulation composite fabric is under the action of open fire and strong heat flow environment, the back side of the multistage-spreading heat-dissipation fire-proof heat-insulation composite fabric can be kept below 50DEG C which is near the safe temperature state of the human skin, and the integral structural form and the mechanical property are stable. The natural thickness of the composite fabric is 5-15mm, the compression thickness of the composite fabric is 3-8mm, and the square meter quality of the composite fabric is 400-1500g / m<2>. The composite fabric is fire-proof heat-insulation material which is totally sealed, stuck and sewn and can be used for individual protection and environment heat insulation in special high-temperature occasions, such as fire control, military, exploration, safe escape and industry and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
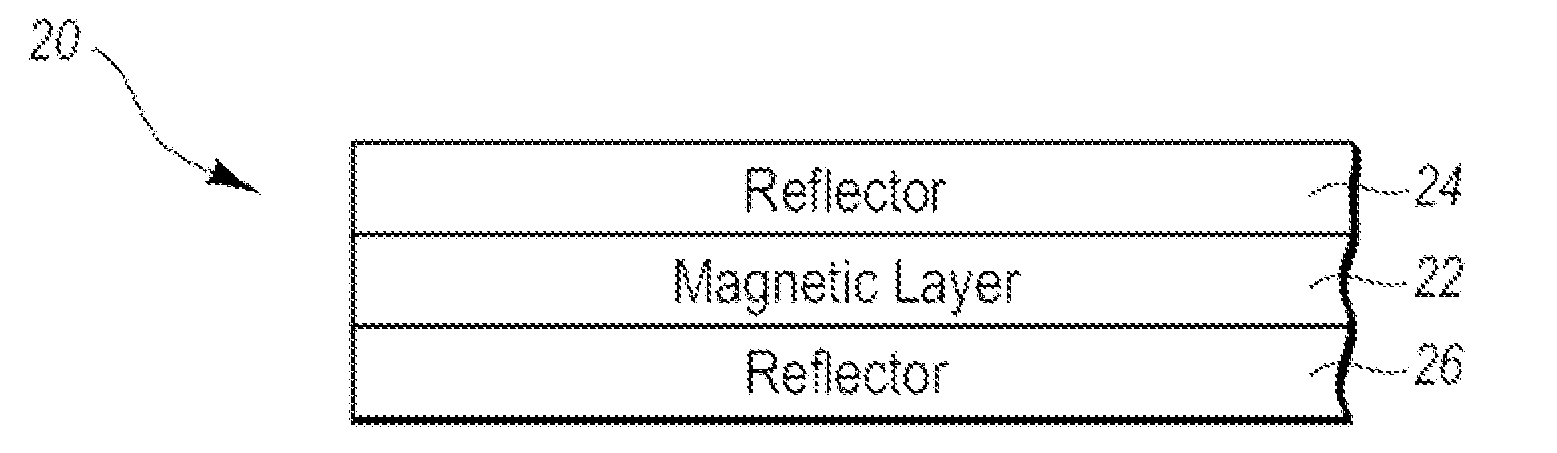
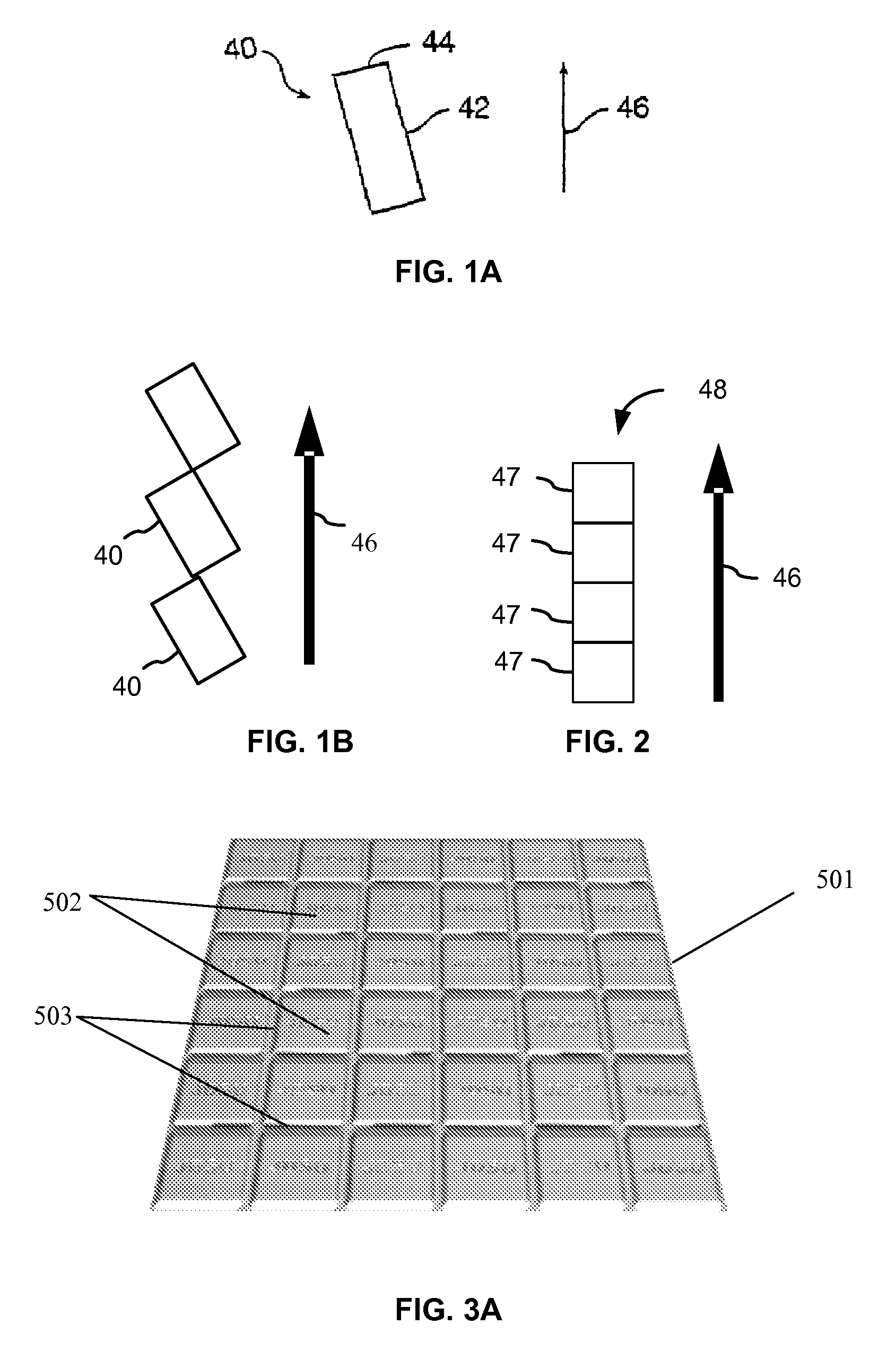
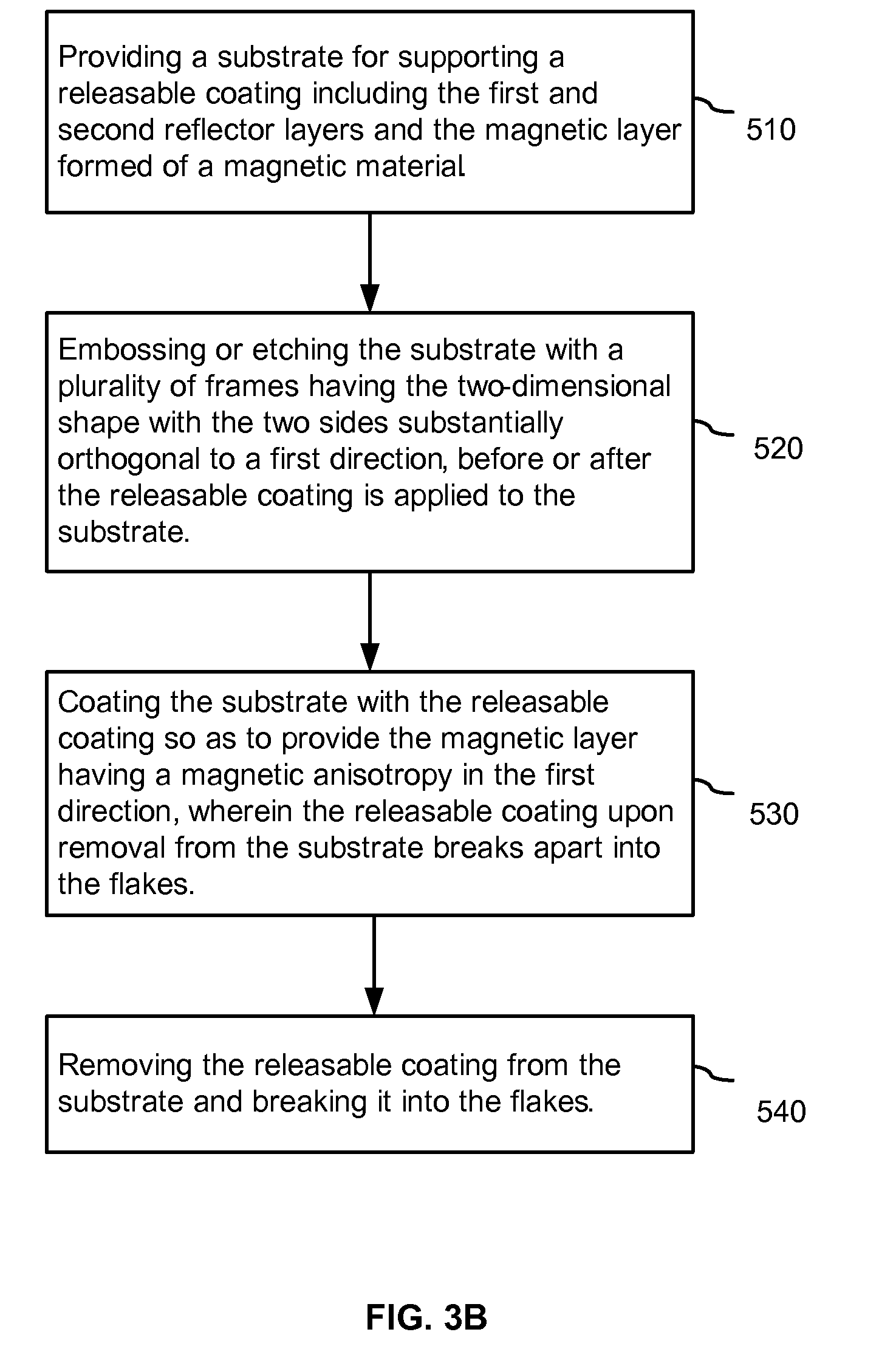
Anisotropic Magnetic Flakes
ActiveUS20090072185A1Cost effectiveMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsHigh reflectivityMaterials science
The invention relates to anisotropic, reflective, magnetic flakes. In a liquid carrier and under influence of an external magnetic field, the flakes attract to one another side-by-side and form ribbons which provide higher reflectivity to a coating and may be used as a security feature for authentication of an object.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Sub-wavelength grating integrated VCSEL
InactiveUS20070153860A1Good optical performanceEasy to manufactureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is described using a sub-wavelength grating (SWG) structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity. The grating comprises segments of high and low refractive index materials with an index differential between the high and low index materials. By way of example, a SWG reflective structure is disposed over a low index cavity region and above another reflective layer (either SWG or DBR). In one embodiment, the SWG structure is movable, such as according to MEMS techniques, in relation to the opposing reflector to provide wavelength selective tuning. The SWG-VCSEL design is scalable to form the optical cavities for a range of SWG-VCSELs at different wavelengths, and wavelength ranges.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
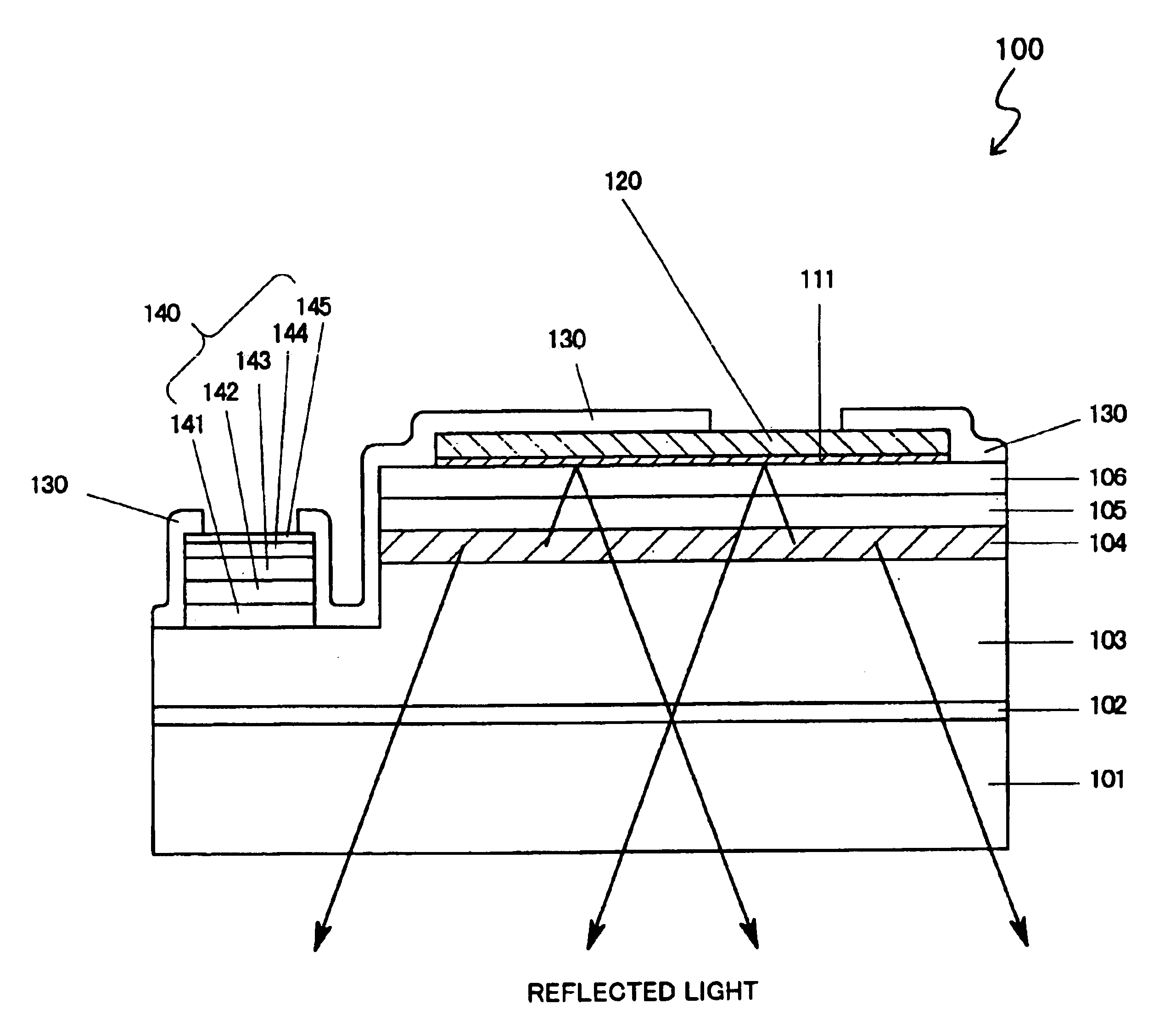
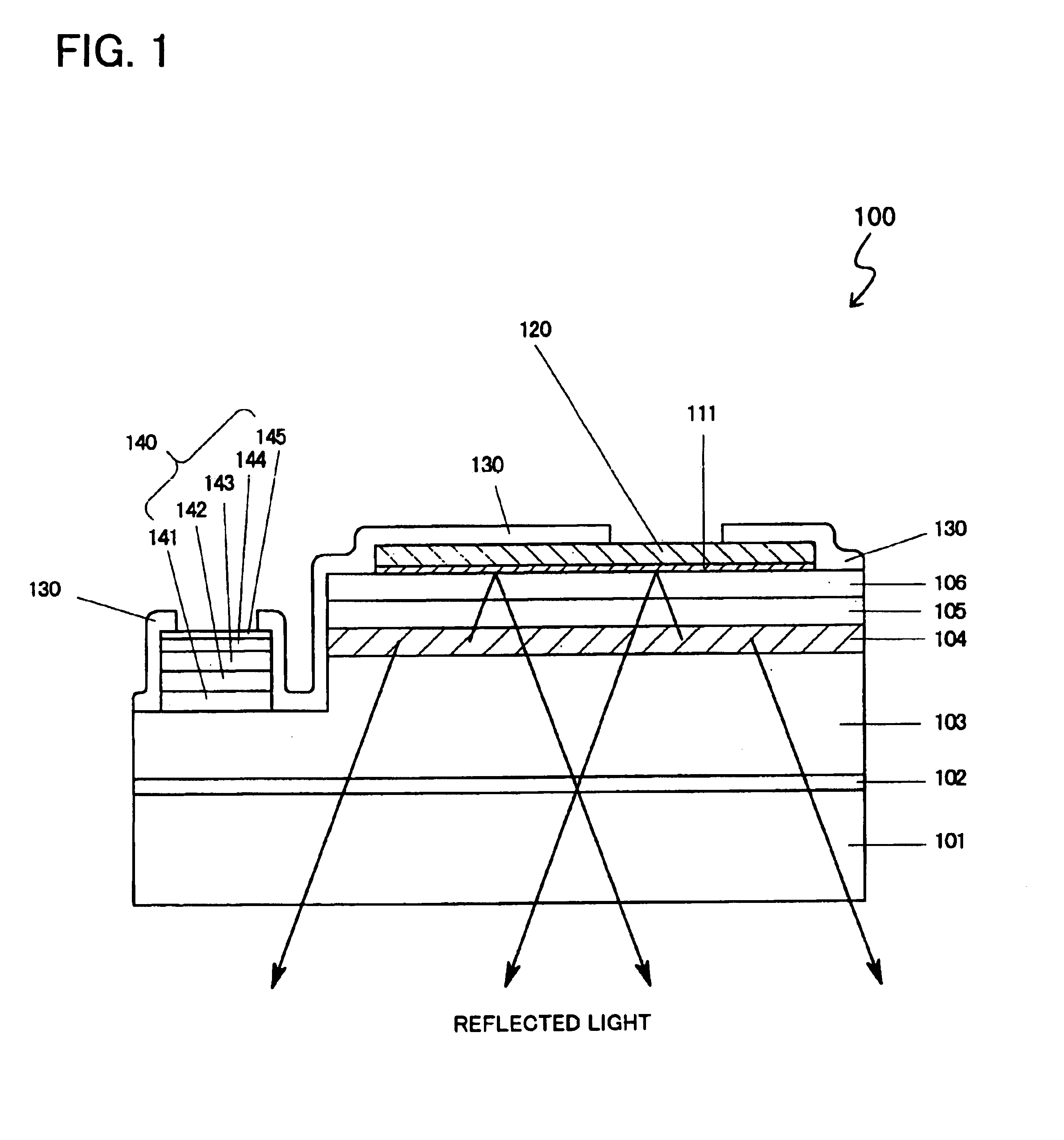
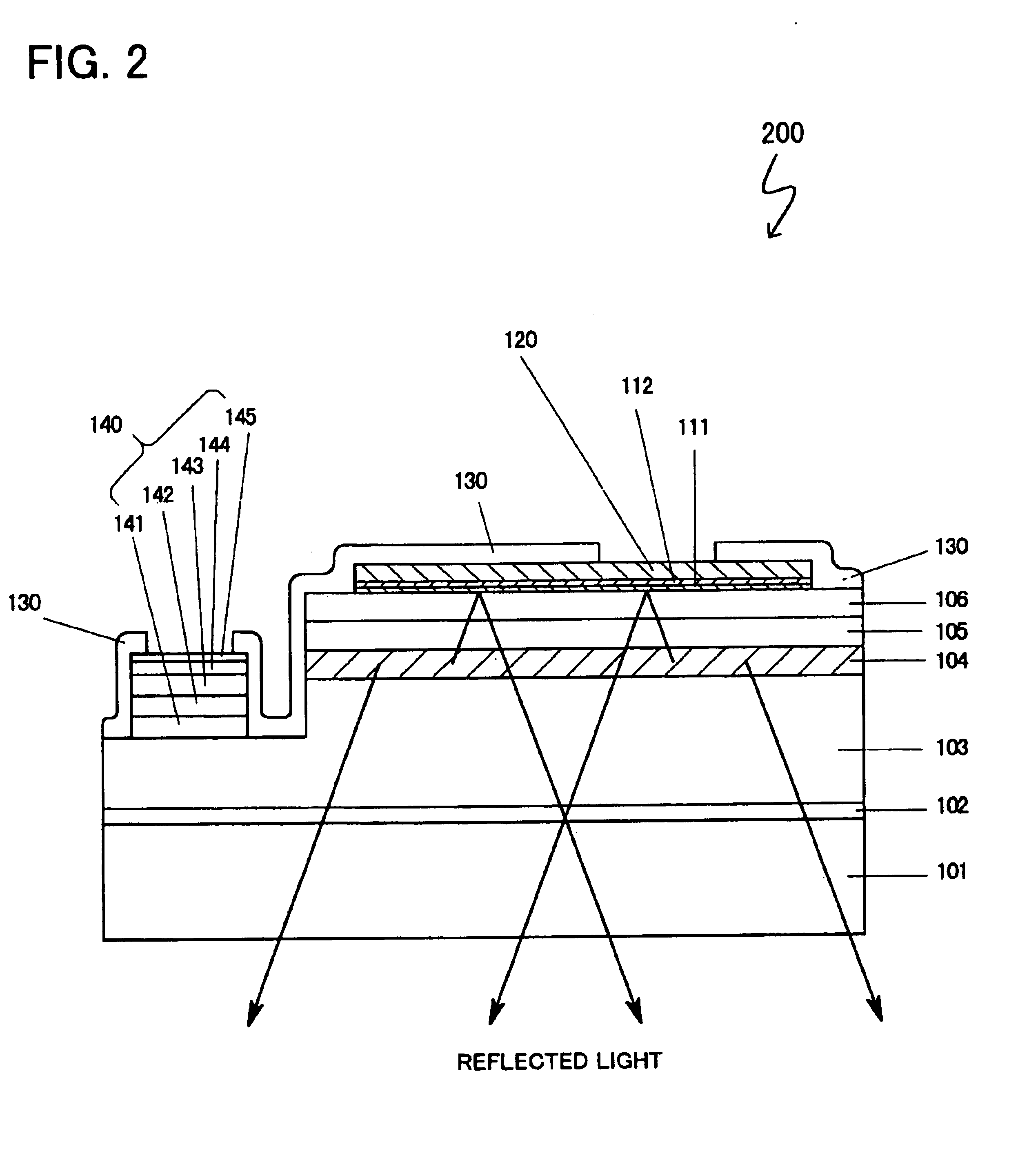
Light emitting diodes with high light extraction and high reflectivity
InactiveUS20070018184A1Improve extraction efficiencyConvenient lightingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureHigh reflectivity
The invention is a light emitting diode that exhibits high reflectivity to externally incident light and high extraction efficiency for internally generated light. The light emitting diode includes a first reflecting electrode that reflects both externally incident light and internally generated light. The first reflecting electrode can be a metal layer; or a transparent layer and a metal layer; or a transparent layer and a metal layer with a plurality of metal contacts extending from the reflecting metal layer through the transparent layer. A multi-layer semiconductor structure is in contact with the first reflecting layer and has an active region that emits the internally generated light in an emitting wavelength range. The multi-layer semiconductor structure has an absorption coefficient less than 50 cm−1. A second reflecting electrode underlies the multi-layer semiconductor structure and reflects both the externally incident light and the internally generated light. The second reflecting electrode can be a first transparent layer and a reflecting metal layer; or a second transparent layer, a first transparent layer and a reflecting metal layer; or a second transparent layer, a first transparent layer and a reflecting metal layer with a plurality of metal contacts extending from the reflecting metal layer through the first transparent layer to the second transparent layer. An array of light extracting elements extends at least part way through the multi-layer semiconductor structure and improves the extraction efficiency for the internally generated light.
Owner:GOLDENEYE
Semiconductor light emitting element, semiconductor light emitting device, and method for fabricating semiconductor light emitting element
InactiveUS20050285132A1Light extraction efficiencyLow efficiencyNanoopticsOptical light guidesHigh reflectivityMetal electrodes
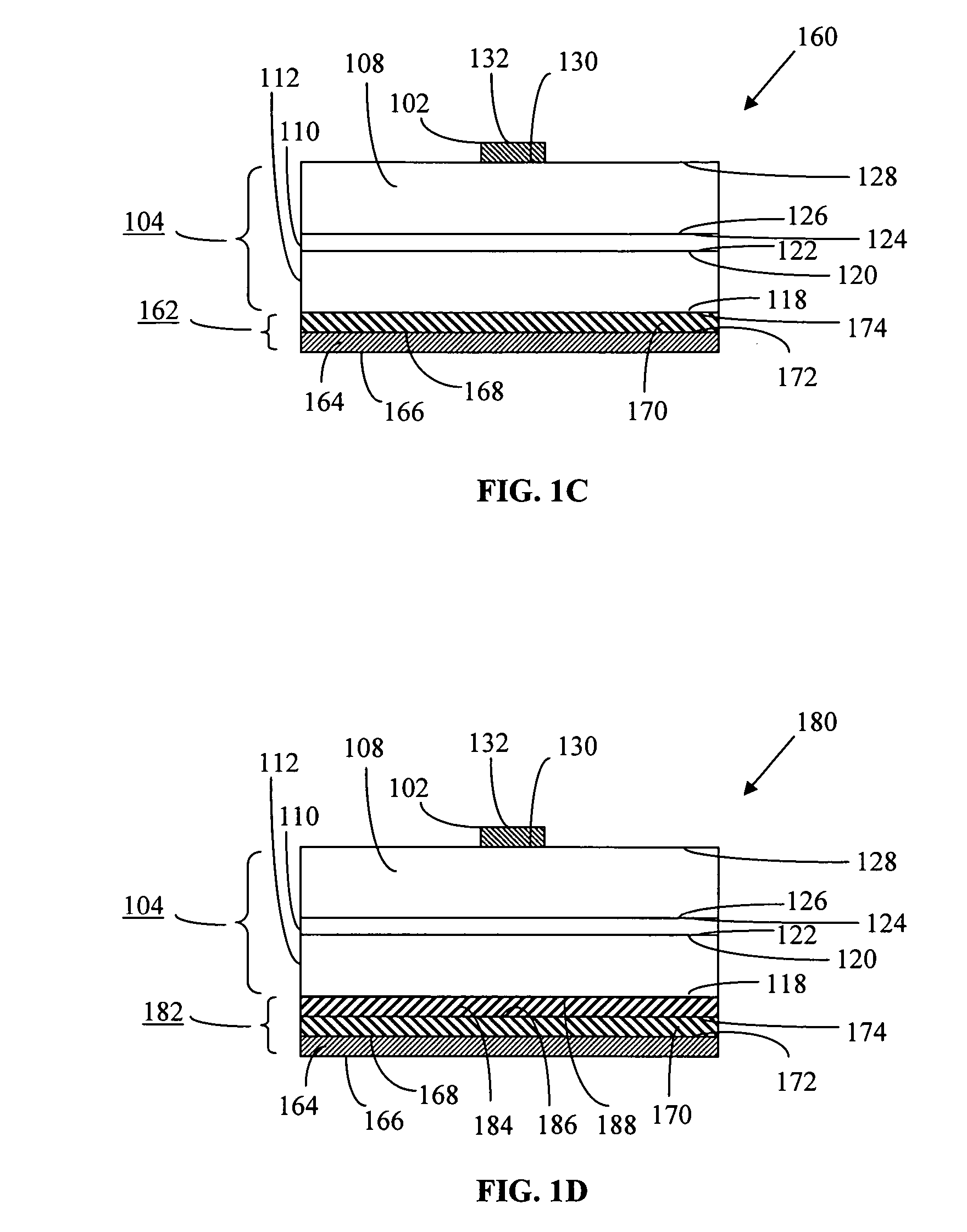
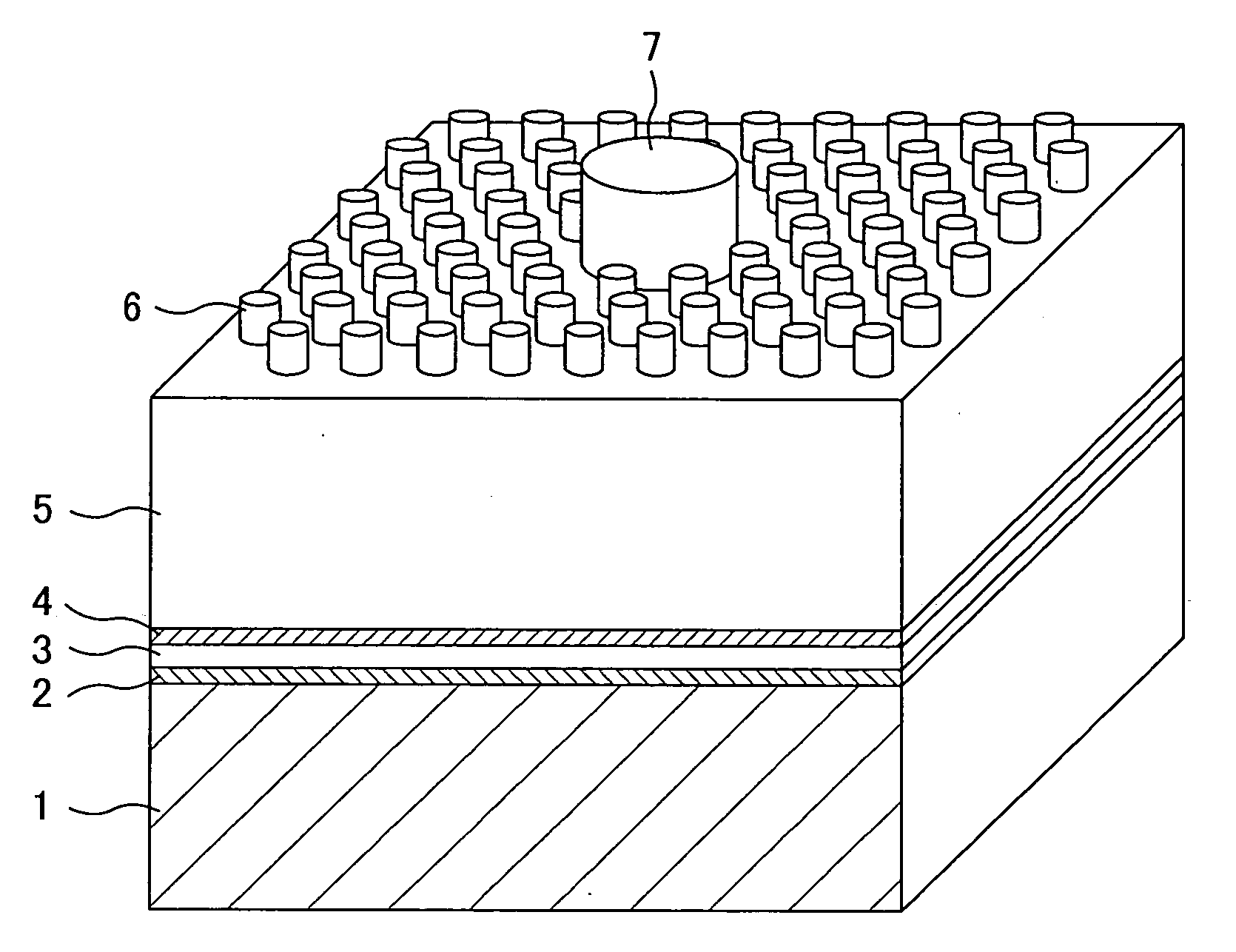
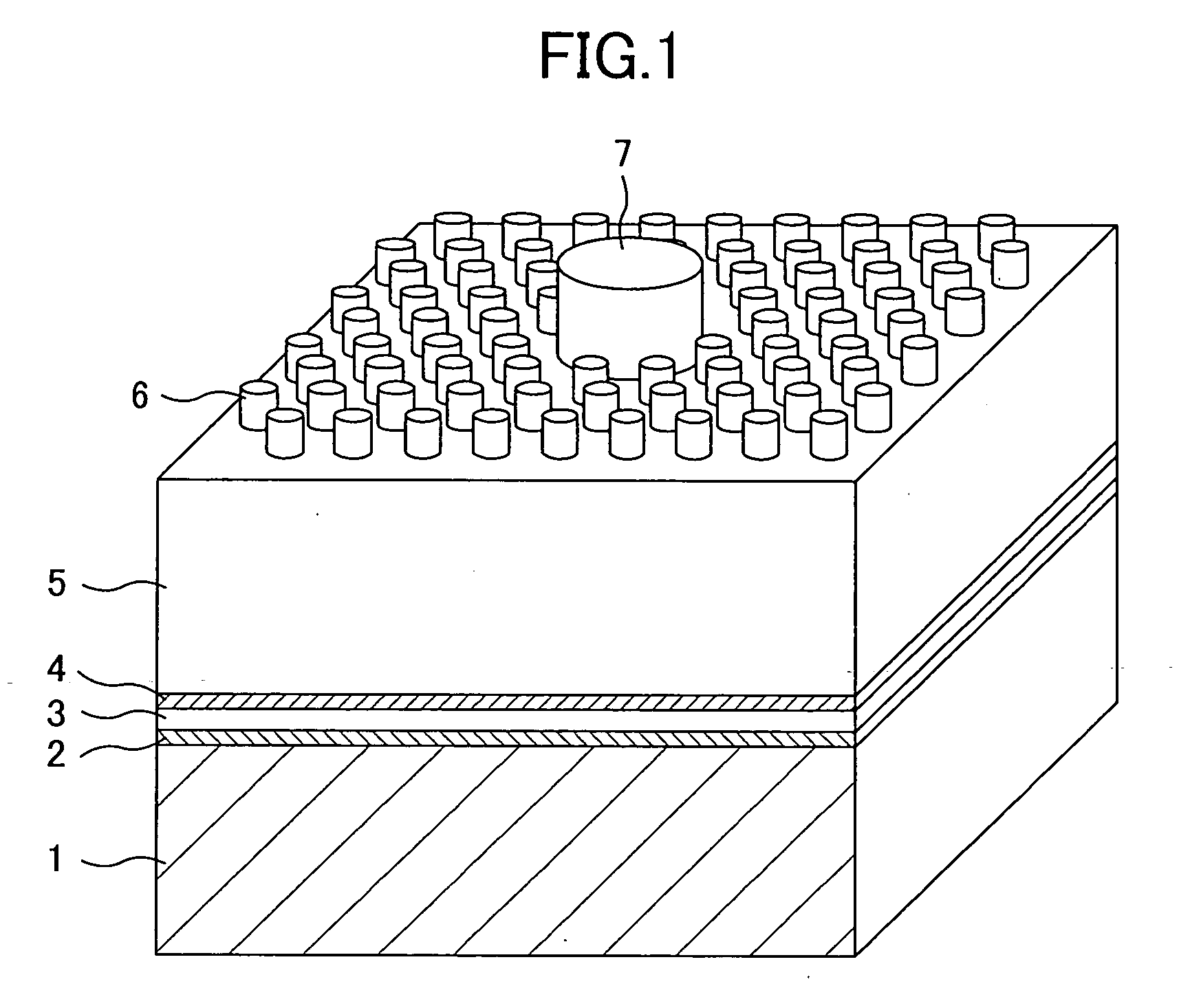
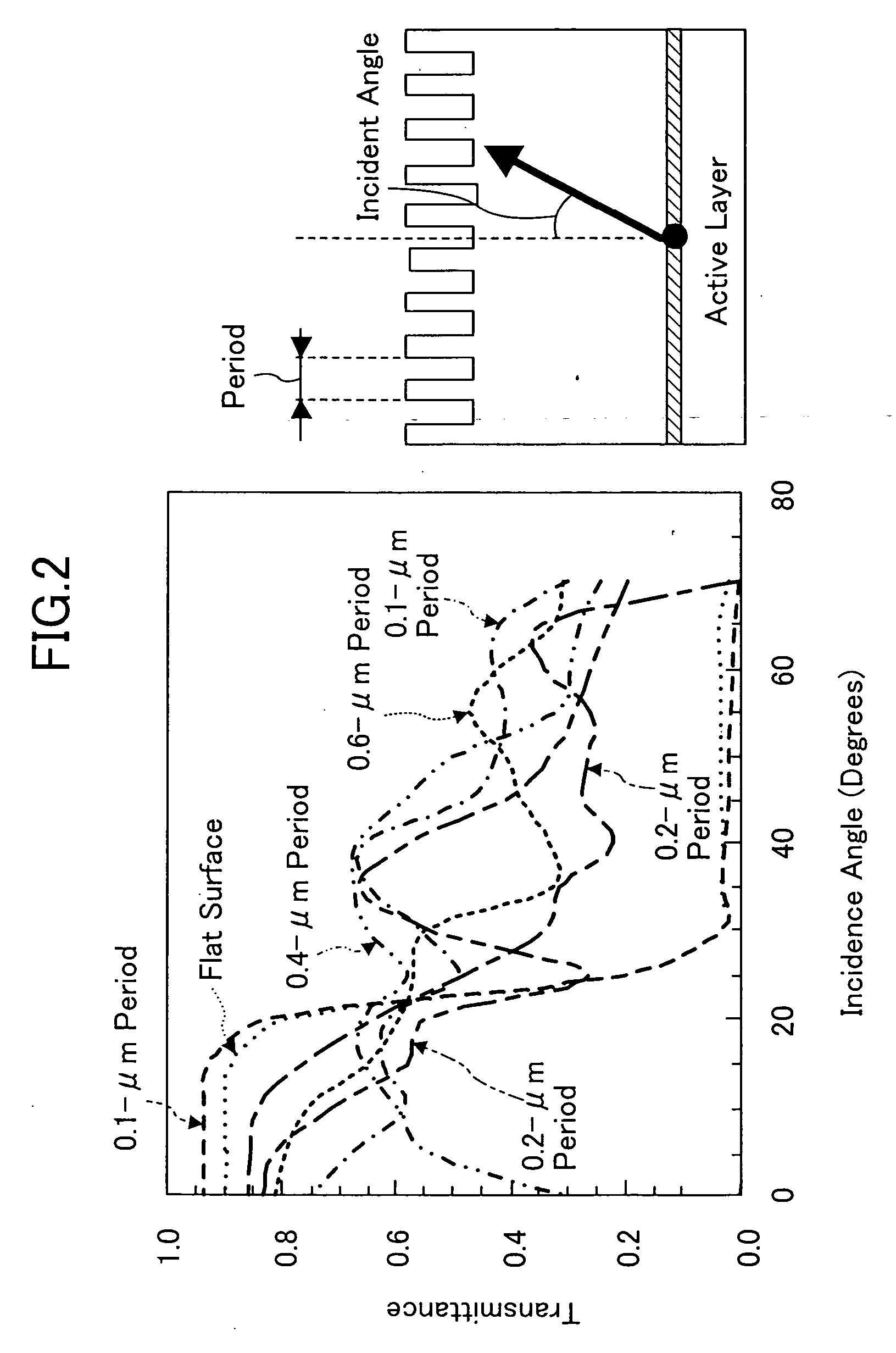
Projections / depressions forming a two-dimensional periodic structure are formed in a surface of a semiconductor multilayer film opposing the principal surface thereof, while a metal electrode with a high reflectivity is formed on the other surface. By using the diffracting effect of the two-dimensional periodic structure, the efficiency of light extraction from the surface formed with the projections / depressions can be improved. By reflecting light emitted toward the metal electrode to the surface formed with the projections / depressions by using the metal electrode with the high reflectivity, the foregoing effect achieved by the two-dimensional periodic structure can be multiplied.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Universal vehicle head display (HUD) device and method for using the same
InactiveUS20070019297A1Low costFunctionalCathode-ray tube indicatorsOptical elementsHead-up displayActive matrix
The invention generally relates to an integrated head up displaying (HUD) device including a housing that houses an active-matrix image projecting system and its accompanying electronics, and an optical combiner (for providing a see-through image thereon) connected to the housing via a retractable arm attached at one end to the main body and holds the HUD optical panel at its other end. In particular, the telescopically retractable arm allows the assembly to extend or retract for a desirable combiner height. Further, the LED backlighting array is placed within a reflective light chamber which is lined with a safe, light-weight, low cost, specular, reflective sheet for high reflectivity. The non-conductive, reflective sheet also covers the LED printed circuit board.
Owner:STEWART ROBERT J +2
Highly reflective mounting arrangement for LEDs
InactiveUS7622746B1Improves overall device light emissionLow possible additional manufacturing costSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceSemiconductor materials
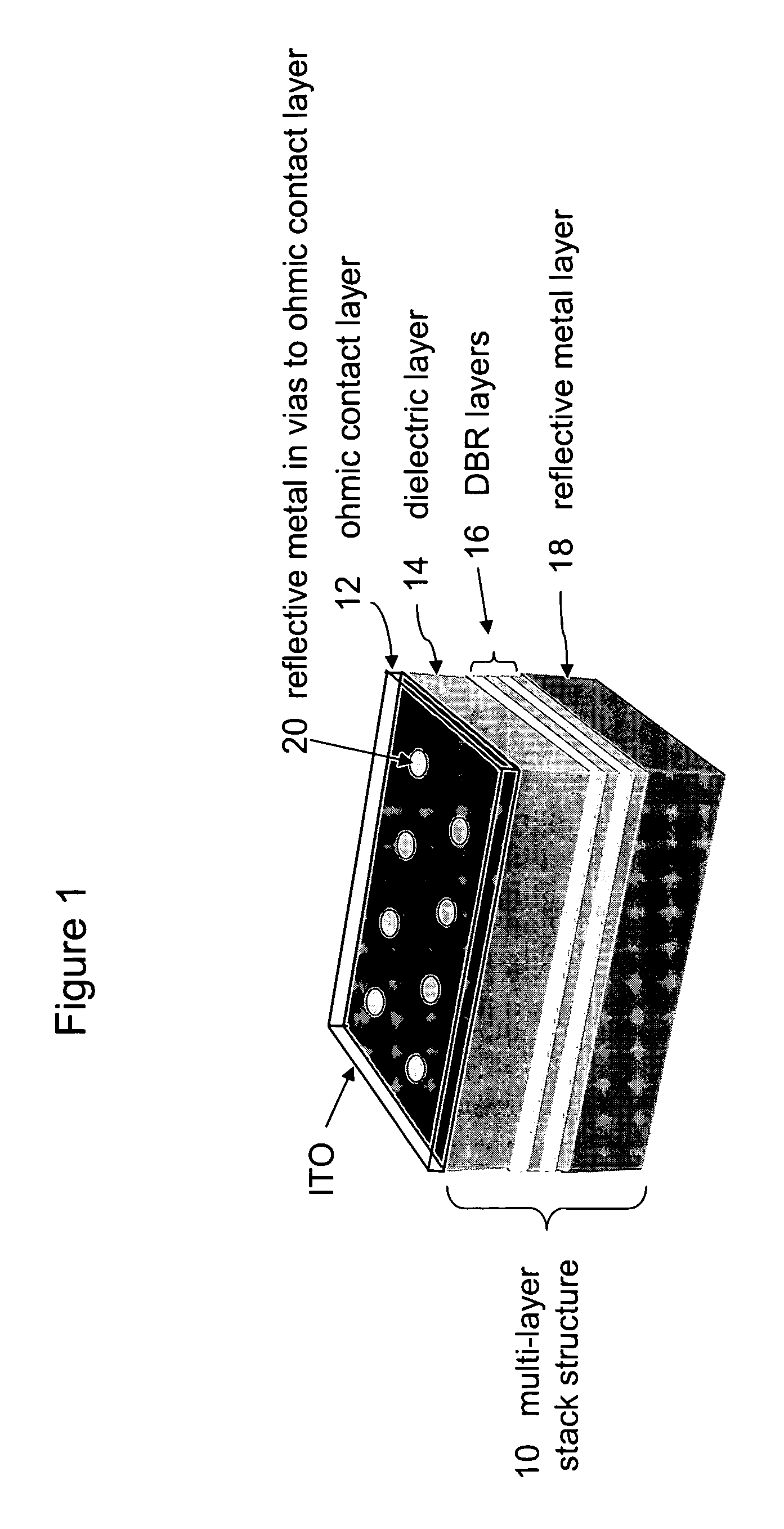
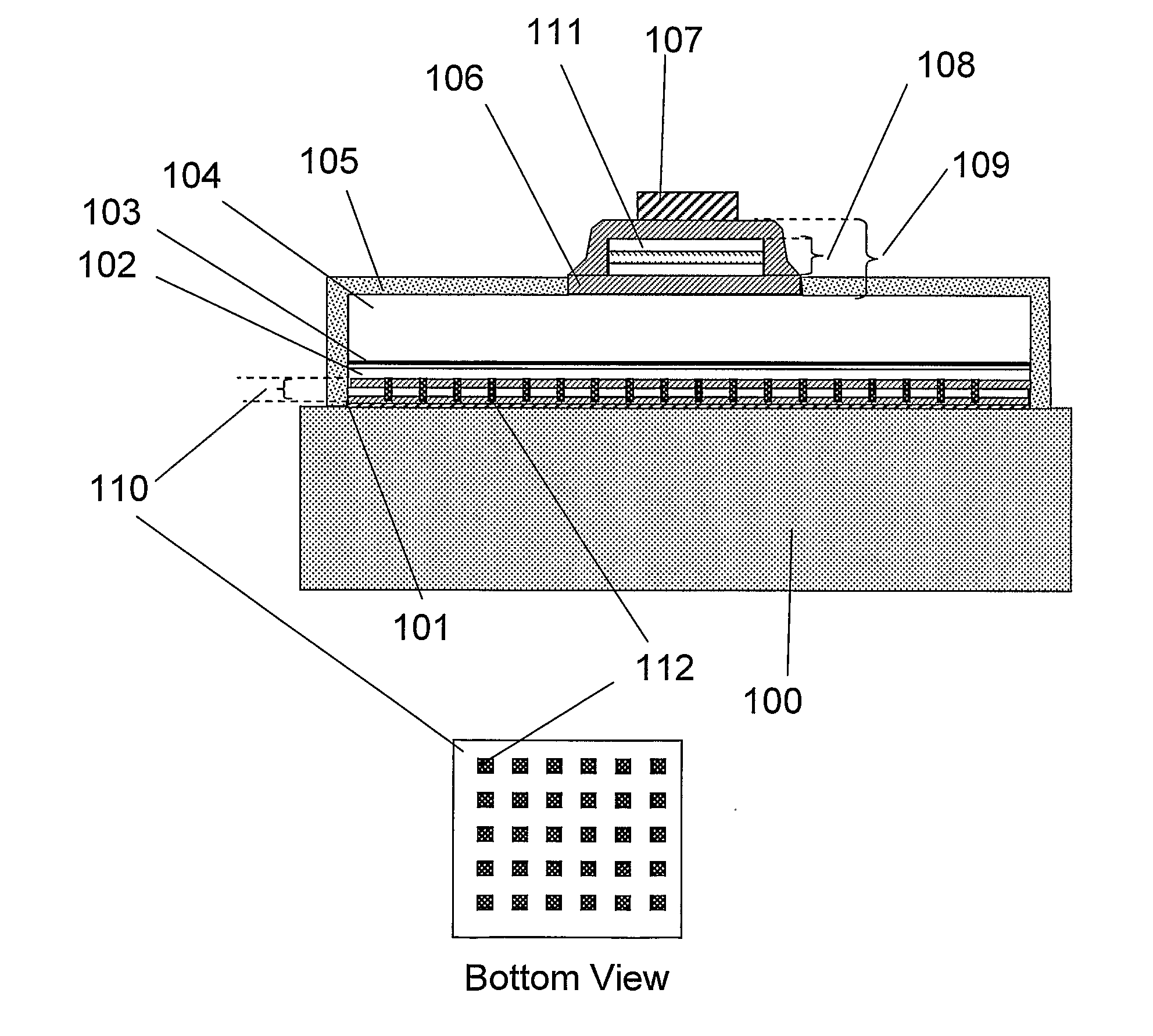
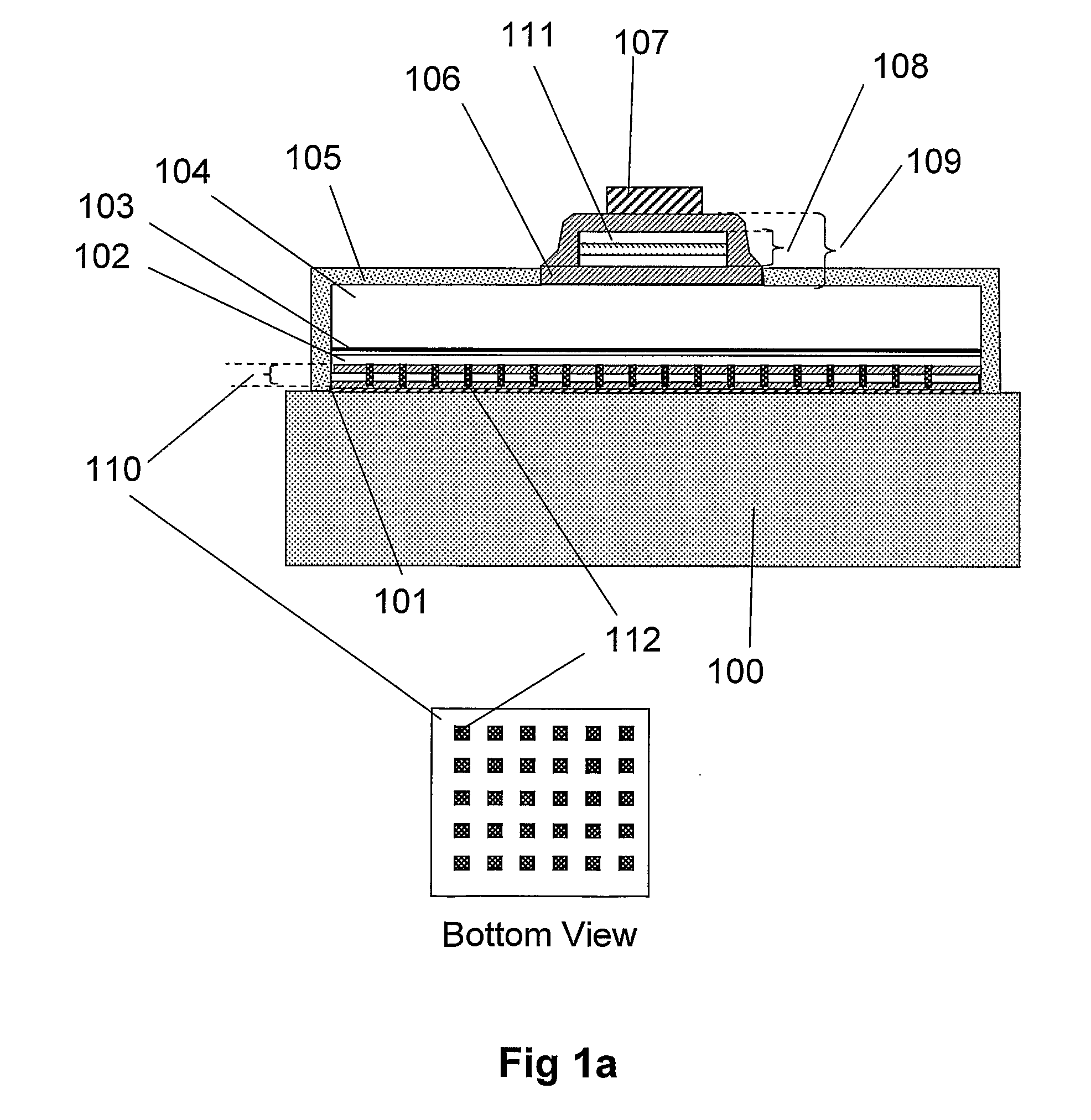
A semiconductor device emitting light about a predetermined wavelength comprising a structure comprising a plurality of layers, sometimes referred to as a stack, providing low resistance, high reflectivity and ohmic contacts to at least one semiconductor material.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Vertical LED with conductive vias
ActiveUS20100213485A1Maximizing light extractionLight extraction efficiency can be improvedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface plasmonHigh reflectivity
A light emitting device comprises a novel low-loss array of conductive vias embedded in a dielectric multilayer stack, to act as an electrically-conductive, low-loss, high-reflectivity reflector layer (CVMR). In one example the CVMR stack is employed between a reflective metal bottom contact and a p-GaN semiconductor flip chip layer. The CVMR stack comprises at least (3) layers with at least (2) differing dielectric constants. The conductive vias are arranged such that localised and propagating surface plasmons associated with the structure reside within the electromagnetic stopband of the CVMR stack, which in turn inhibits trapped LED modes coupling into these plasmonic modes, thereby increasing the overall reflectivity of the CVM R. This technique improves optical light extraction and provides a vertical conduction path for optimal current spreading in a semiconductor light emitting device. A light emitting module and method of manufacture are also described.
Owner:LUMILEDS HLDG BV
Flip-chip light emitting diode with resonant optical microcavity
InactiveUS6969874B1Improve efficiencyAccelerate emissionsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDielectric substrateGallium nitride
A flip-chip light emitting diode with enhanced efficiency. The device structure employs a microcavity structure in a flip-chip configuration. The microcavity enhances the light emission in vertical modes, which are readily extracted from the device. Most of the rest of the light is emitted into waveguided lateral modes. Flip-chip configuration is advantageous for light emitting diodes (LEDs) grown on dielectric substrates (e.g., gallium nitride LEDs grown on sapphire substrates) in general due to better thermal dissipation and lower series resistance. Flip-chip configuration is advantageous for microcavity LEDs in particular because (a) one of the reflectors is a high-reflectivity metal ohmic contact that is already part of the flip-chip configuration, and (b) current conduction is only required through a single distributed Bragg reflector. Some of the waveguided lateral modes can also be extracted with angled sidewalls used for the interdigitated contacts in the flip-chip configuration.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS6544616B2Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicMagnetic materials for record carriersVacuum evaporation coatingMetal alloyManganese
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective coating layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include zinc, aluminum, zinc plus aluminum, manganese, germanium, and copper plus manganese. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS20080246047A1Improve reflectivityGood ohmic contactSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactHigh reflectivity
A semiconductor light-emitting device comprises an N-type semiconductor layer, an active layer formed on the surface of the N-type semiconductor layer, a P-type semiconductor layer formed on the surface of the active layer, and a reflective layer formed on the surface of the P-type semiconductor layer. A plurality of ohmic contact blocks with electrical properties of ohmic contact are on the surface of the reflective layer adjacent to the P-type semiconductor layer, and the remaining part of the surface acts as the reflective regions with higher reflectivity, and the reflective regions can effectively reflect the light generated from the active layer.
Owner:ADVANCED OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Process of producing group III nitride based reflectors
InactiveUS20070128743A1Improve reflectivityBroad stopbandLaser detailsSolid-state devicesVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPhotovoltaic detectors
To solve the existing problems in distributed Bragg reflectors (DBR) used in the prior art, the present invention provides a fabrication method of group III nitride based distributed Bragg reflectors (DBR) for vertical cavity surface emitting lasers (VCSELs), which suppresses the generation of cracks, and a distributed Bragg reflector with high reflectivity, broad stopband, and adaptability to optical devices such as vertical cavity surface emitting lasers, micro-cavity light emitting diodes, resonance cavity light emitting diodes and photodetectors.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Metal alloys for the reflective or the semi-reflective layer of an optical storage medium
InactiveUS20020034603A1Improve reflectivitySimilar sputtering characteristicMagnetic materials for record carriersVacuum evaporation coatingManganeseHigh reflectivity
A silver-based alloy thin film is provided for the highly reflective or semi-reflective coating layer of optical discs. Alloy additions to silver include zinc, aluminum, zinc plus aluminum, manganese, germanium, and copper plus manganese. These alloys have moderate to high reflectivity and reasonable corrosion resistance in the ambient environment.
Owner:TARGET TECH
Display device
InactiveUS20090219734A1Big spaceReduce lightPlanar/plate-like light guidesIlluminated signsLight guideDisplay device
A display device has a light guide plate formed with a display pattern by a plurality of diffusion dots having translucency in a display pattern formed region, a light shielding layer, and a light source. A plurality of the light guide plates are arranged facing each other, and the light shielding layer is sandwiched between the light guide plates. Light from the light source is selectively introduced to one of the light guide plates to display the display pattern of the light guide plate. The light shielding layer has a surface facing an observer's side formed by a low reflectivity material and a surface facing a side opposite to the observer's side formed by a high reflectivity material. A region facing the display pattern of the light guide plate positioned on the side opposite to the observer's side than the light shielding layer is cut out.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Wide angle mirror system
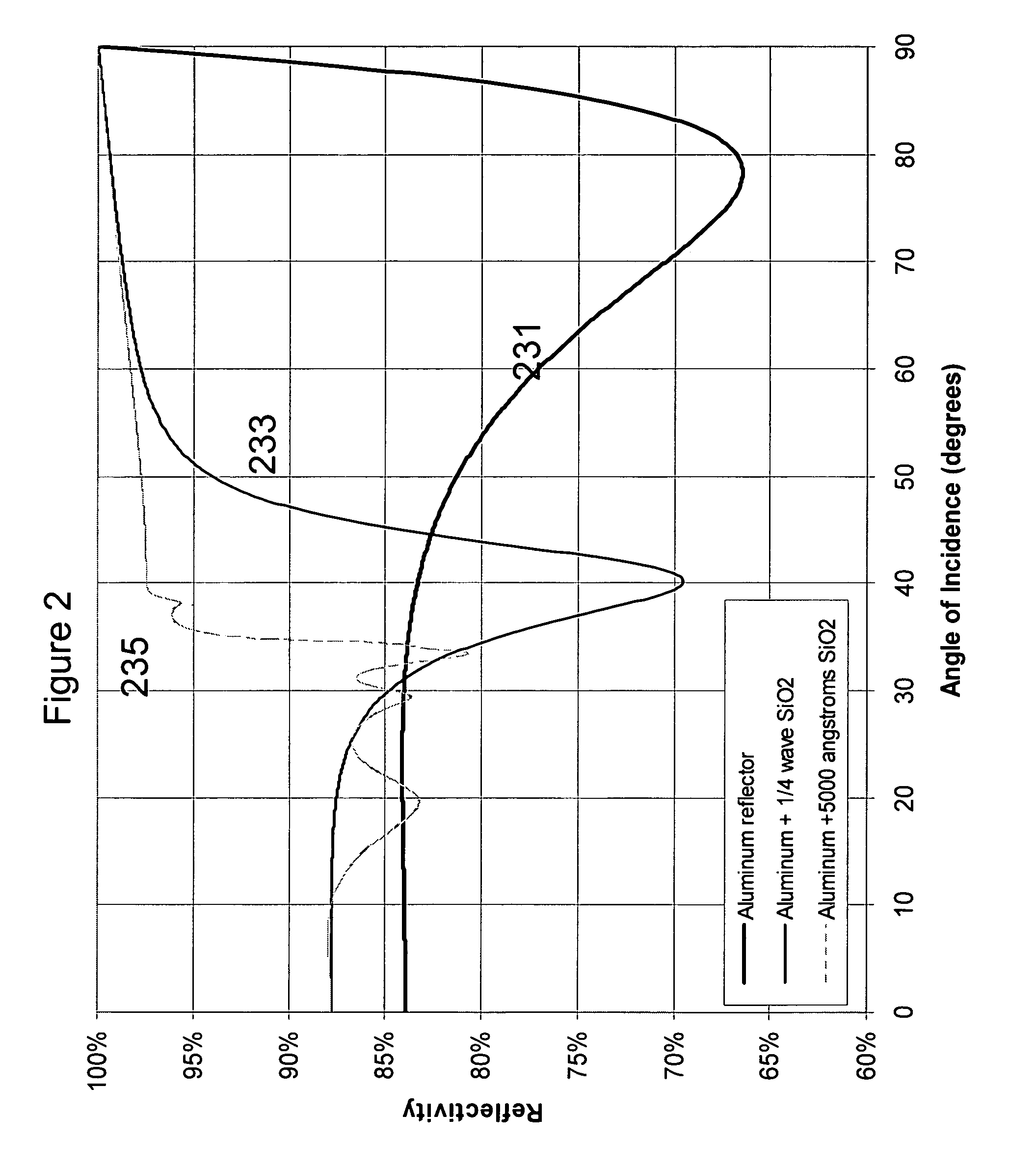
InactiveUS20080037127A1Improve reflectivityWide angle of incidenceMirrorsPlanar/plate-like light guidesBroadbandAbsorbent material
Composite mirror systems include a wideband thin film interference stack having a plurality of microlayers and an optically thick layer having a refractive index greater than air but less than the smallest refractive index of the stack. The mirror systems can provide high reflectivity for light propagating in the stack and in the optically thick layer at supercritical angles, while avoiding degradation in reflectivity if dirt or other disturbances such as absorbing materials are present at the mirror backside for example due to contact with a support structure.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Semi-transmitting mirror-possessing substrate, and semi-transmitting type liquid crystal display apparatus
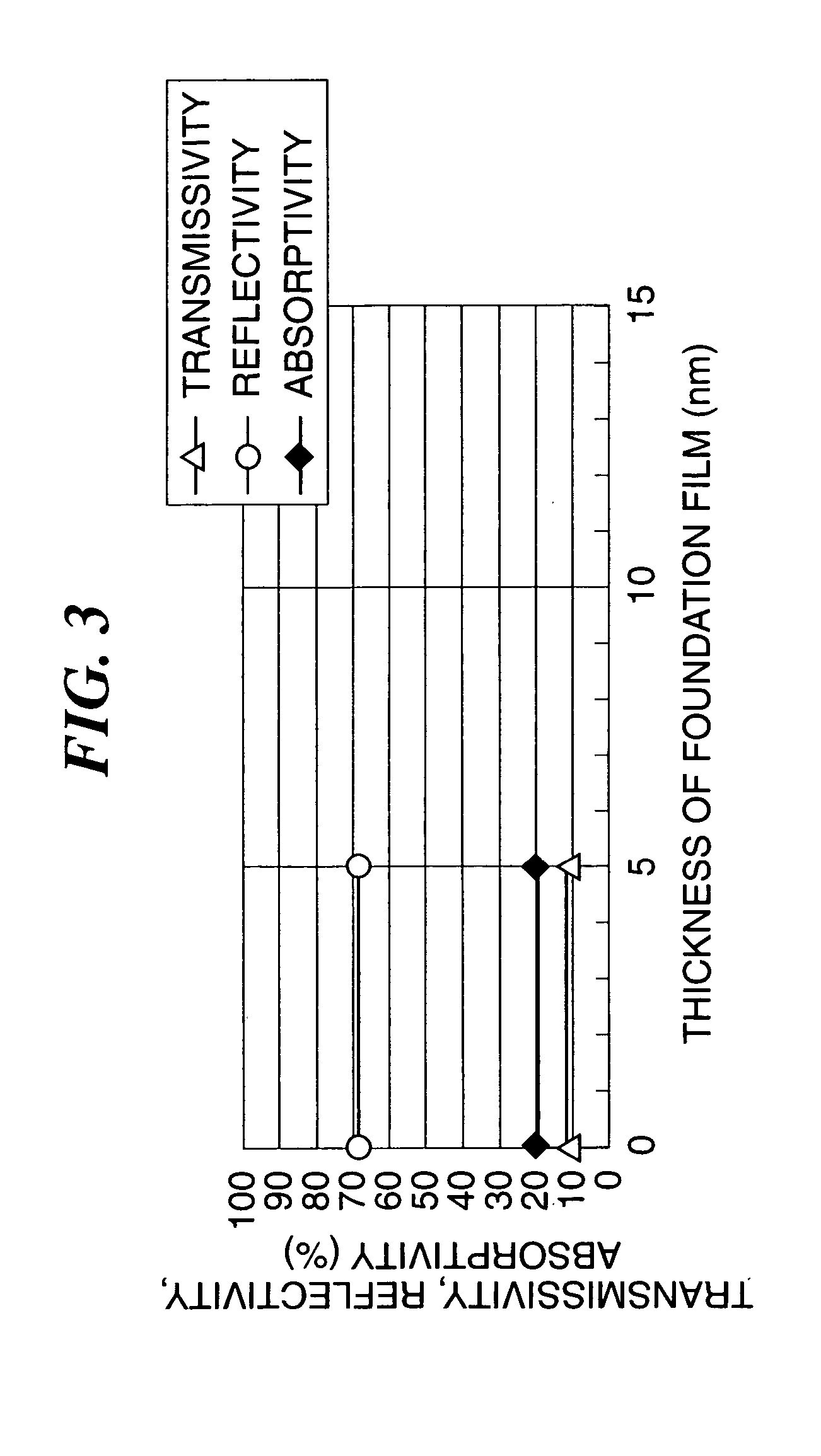
There is provided a semi-transmitting mirror-possessing substrate that has high reflectivity while maintaining high transmissivity, whereby transmission display performance and reflection display performance can both be improved. The semi-transmitting mirror-possessing substrate 1 has a transparent glass substrate 2 made of a soda lime silicate glass, a foundation film 3 made of silicon oxide (SiOx) formed on the glass substrate 2, a semi-transmitting reflective film 4 made of aluminum (Al) formed on the foundation film 3, and a protective film 5 made of silicon dioxide (SiO2) formed on the semi-transmitting reflective film 4. The film thickness of the SiOx used as the foundation film 3 is in a range of 0 to 8 nm. Moreover, the chemical composition ratio x of oxygen (O) to silicon (Si) in the SiOx is in a range of 1.5 to 2.0.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Mirror structure and laser device comprising such a mirror structure
InactiveUS7778305B2Efficient solutionPoor spatial coherenceOptical resonator shape and constructionDiffraction gratingsGratingMicrochip laser
For increasing the power emitted by surface emitting lasers and for improving the spatial coherence of the laser beam, emitted in particular by disk lasers, microchip lasers and VCSELs having a relatively wide emitting area, the invention proposes to select a low order transverse cavity mode by means of a mirror structure (12) of high reflectivity, and of high angular selectivity. The mirror structure comprises a multilayer (14) receiving the optical beam (24) and a resonant grating mirror (16) following the multilayer and arranged for highly reflecting the optical beam in a narrow angular range at each side of a determined incidence angle.
Owner:UNIV JEAN MONNET
Reflection layer or semi-transparent reflection layer for use in optical information recording media, optical information recording media and sputtering target for use in the optical information recording media
InactiveUS20020150772A1Improve stabilityIncreased durabilityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingRare-earth elementAlloy
A novel reflective layer or semi-transparent reflective layer for use in optical information recording media with suppressed growth of Ag crystal grains and having a high reflectivity and excellent structural stability comprising an Ag based alloy containing from 0.1 to 3.0% of Nd in total of at least one element selected from the group consisting of Nd, Sn and Ge; and / or containing 0.1% or more of at least one rare earth element.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Light emitting diodes with improved light extraction and reflectivity
InactiveUS20070018182A1Improve extraction efficiencyGood light extractionSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureHigh reflectivity
The invention is a light emitting diode that exhibits high reflectivity to externally incident light and high extraction efficiency for internally generated light. The light emitting diode includes a first reflecting electrode that reflects both externally incident light and internally generated light. A multi-layer semiconductor structure is in contact with the first reflecting layer and has an active region that emits the internally generated light in an emitting wavelength range. The multi-layer semiconductor structure has an absorption coefficient less than 50 cm−1. A second reflecting electrode underlies the multi-layer semiconductor structure and reflects both the externally incident light and the internally generated light. An array of light extracting elements extends at least part way through the multi-layer semiconductor structure and improves the extraction efficiency for the internally generated light. The light emitting diode has a reflectivity greater than 60 percent for externally incident light in the emitting wavelength range and has an extraction efficiency greater than 40 percent.
Owner:GOLDENEYE
Reflection layer or semi-transparent reflection layer for use in optical information recording media, optical information recording media and sputtering target for use in the optical information recording media
InactiveUS6689444B2Improve stabilityIncreased durabilityCellsVacuum evaporation coatingRare-earth elementAlloy
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
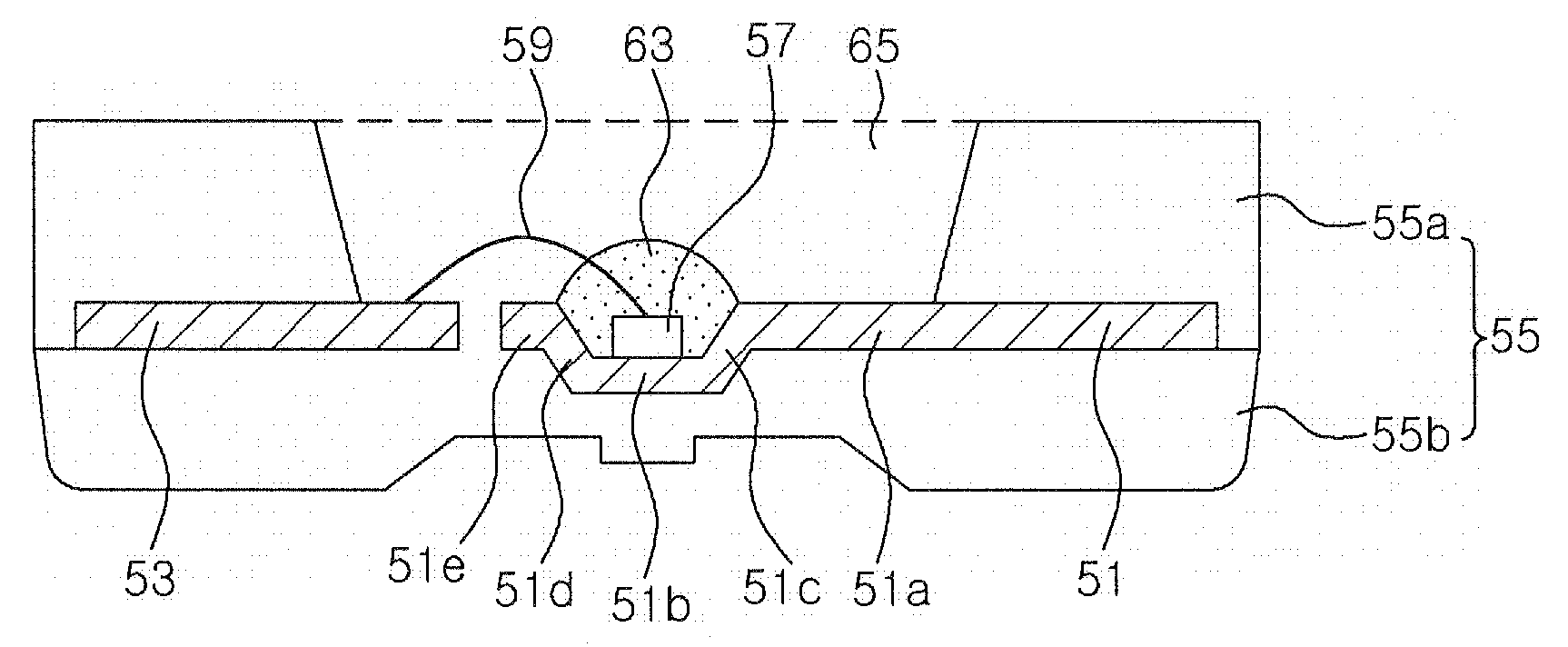
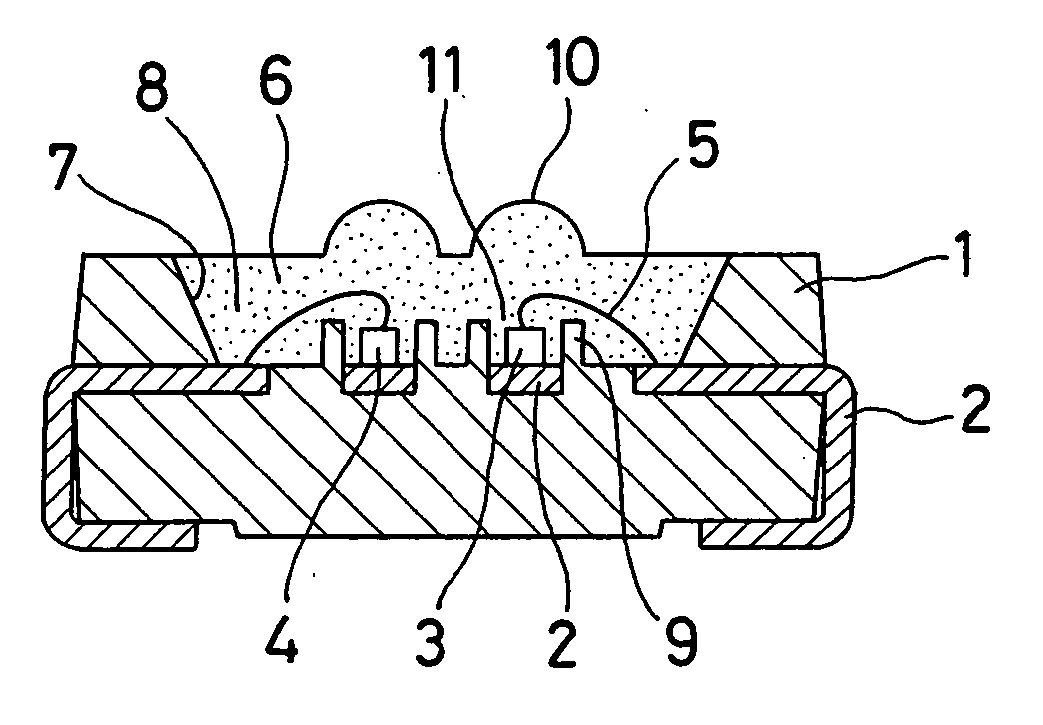
Light emitting diode package employing lead terminal with reflecting surface
InactiveUS20080048201A1Improved light emissionWell formedDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsEngineeringHigh reflectivity
Disclosed is a light emitting diode (LED) package employing a lead terminal with a reflecting surface. The package includes first and second lead terminals that are spaced apart from each other. The first lead terminal has a lower portion with an LED chip mounting area, and at least one reflecting surface formed by being bent from the lower portion. Meanwhile, a package body supports the first and second lead terminals and forms a cavity through which the LED chip mounting area and the reflecting surface of the first lead terminal and a part of the second lead terminal are exposed. The first and second lead terminals extend outside of the package body. Accordingly, light emitted from an LED chip can be reflected on the reflecting surface with high reflectivity, so that the optical efficiency of the package can be improved.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Ultra broadband mirror using subwavelength grating
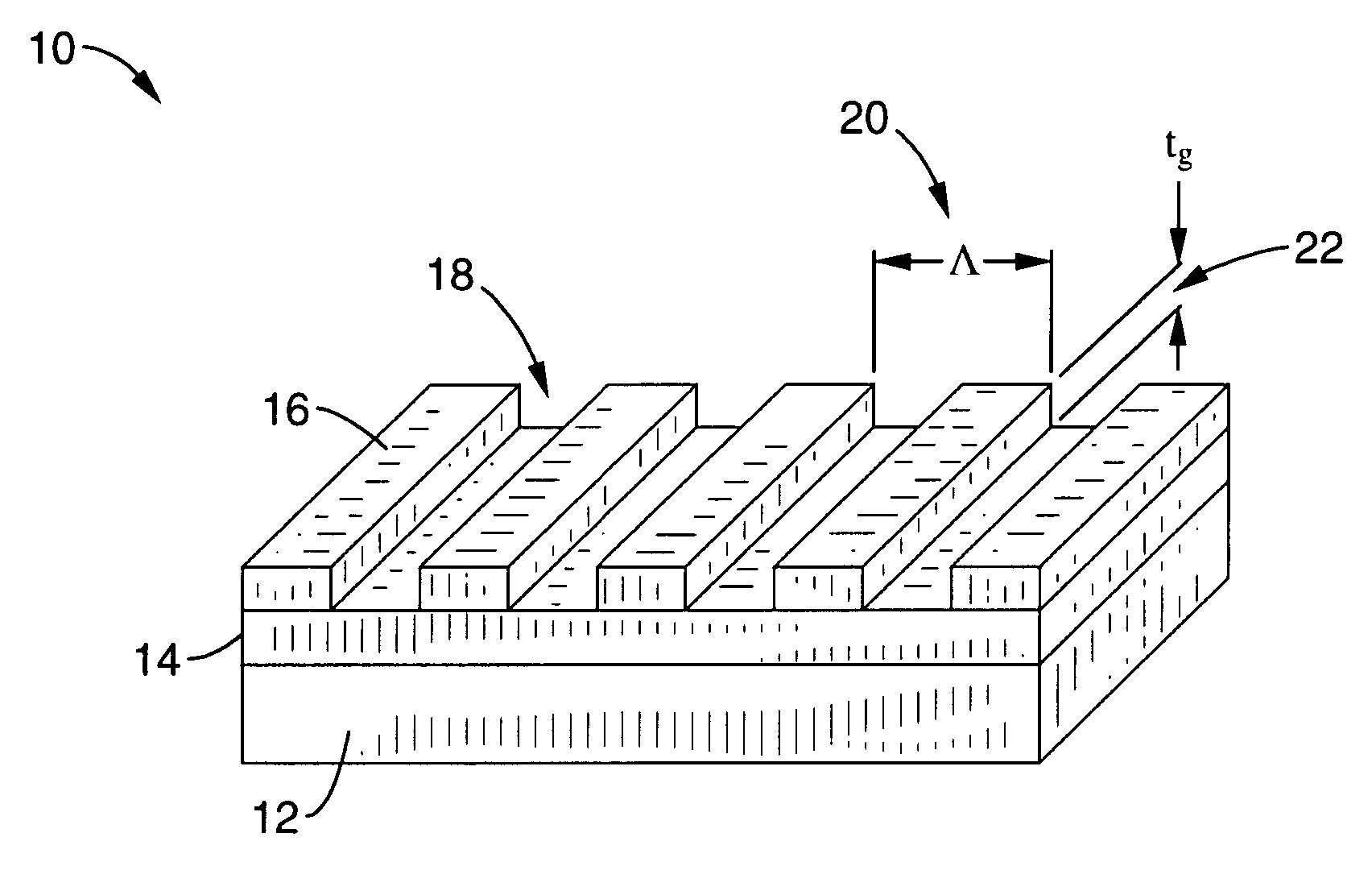
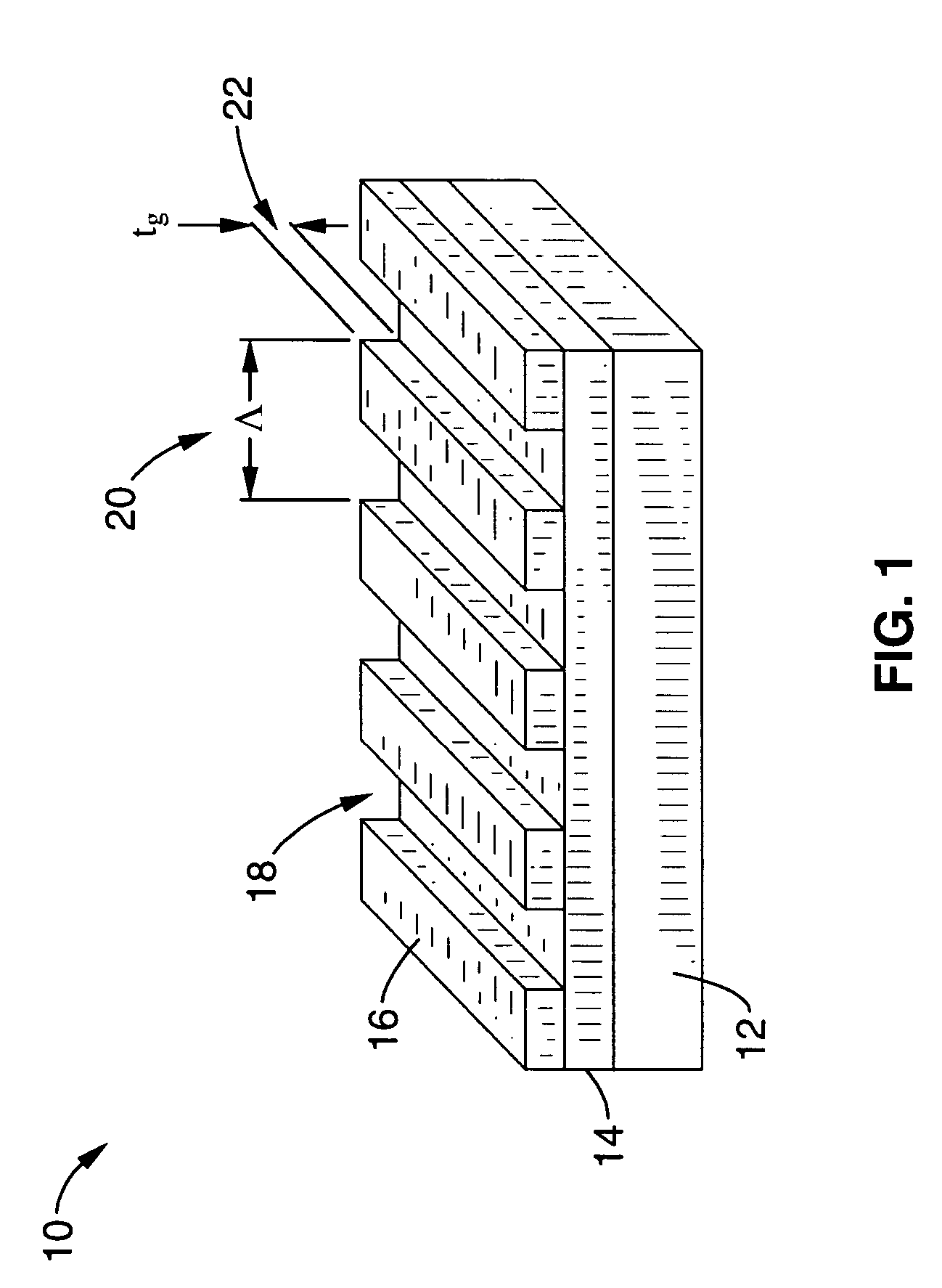
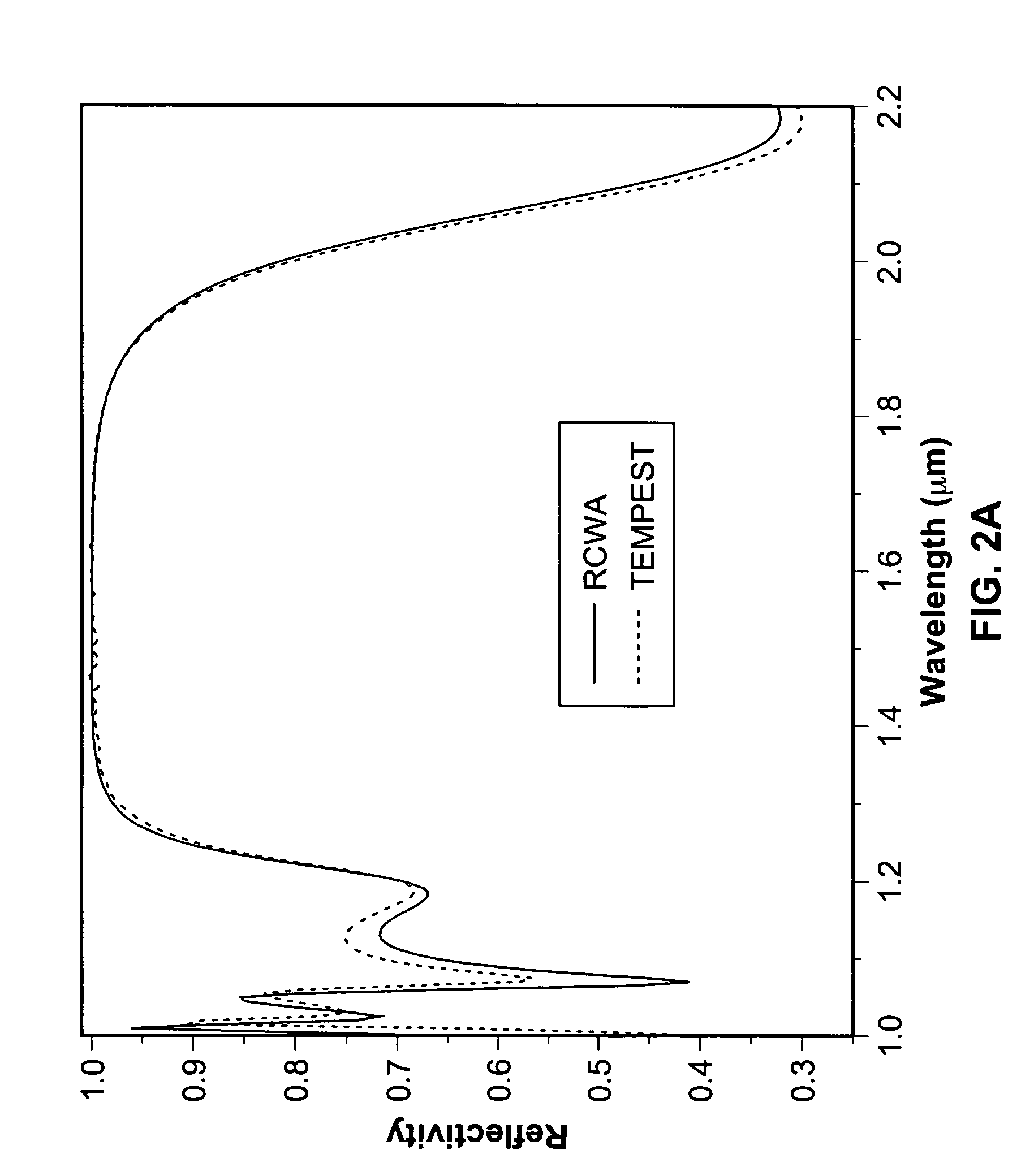
ActiveUS20070115553A1Broad reflection spectrumImprove reflectivityLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingRefractive index
A sub-wavelength grating structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity comprising segments made of high refractive index material disposed on a layer of low refractive index material and a low refractive index material disposed above and between the segments. The index differential between the high and low index materials determines the bandwidth and modulation depth. The larger difference in refractive indices gives rise to wider reflection bands. The reflection is sensitive to parameters such as the grating period, the grating thickness, the duty cycle of the grating, the refractive index and the thickness of the low index layer underneath the grating. The design is scalable for different wavelengths, and facilitates monolithic integration of optoelectronic devices at a wide range of wavelengths from visible to far infrared. The sub-wavelength grating reflectors may be used in a variety of settings such as tunable etalon filters and as a replacement for conventional distributed Bragg reflectors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Light emitting diode device
InactiveUS20060065957A1Efficient ConcentrationDistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringLead frame
A plurality of separate lead frames can be insert-molded in a reflector composed of a white resin having a high reflectivity to form a package for an LED device. A cavity is formed in the reflector. The cavity can have an inner circumferential surface that opens wider in an upward direction. Cups can be located in the cavity. Each cup has an outer wall that can be in the form of a cylinder with the bottom formed of each of two separate lead frames. A red LED chip and a green LED chip can be adhesively fixed to the lead frames located on the bottoms of the respective cups. The LED chips can have lower electrodes, which are electrically brought into conduction with the lead frames one by one. The LED chips can also have upper electrodes, which are electrically brought into conduction with the lead frames one by one via bonding wires. A light transmissive resin can be filled in the cavity.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
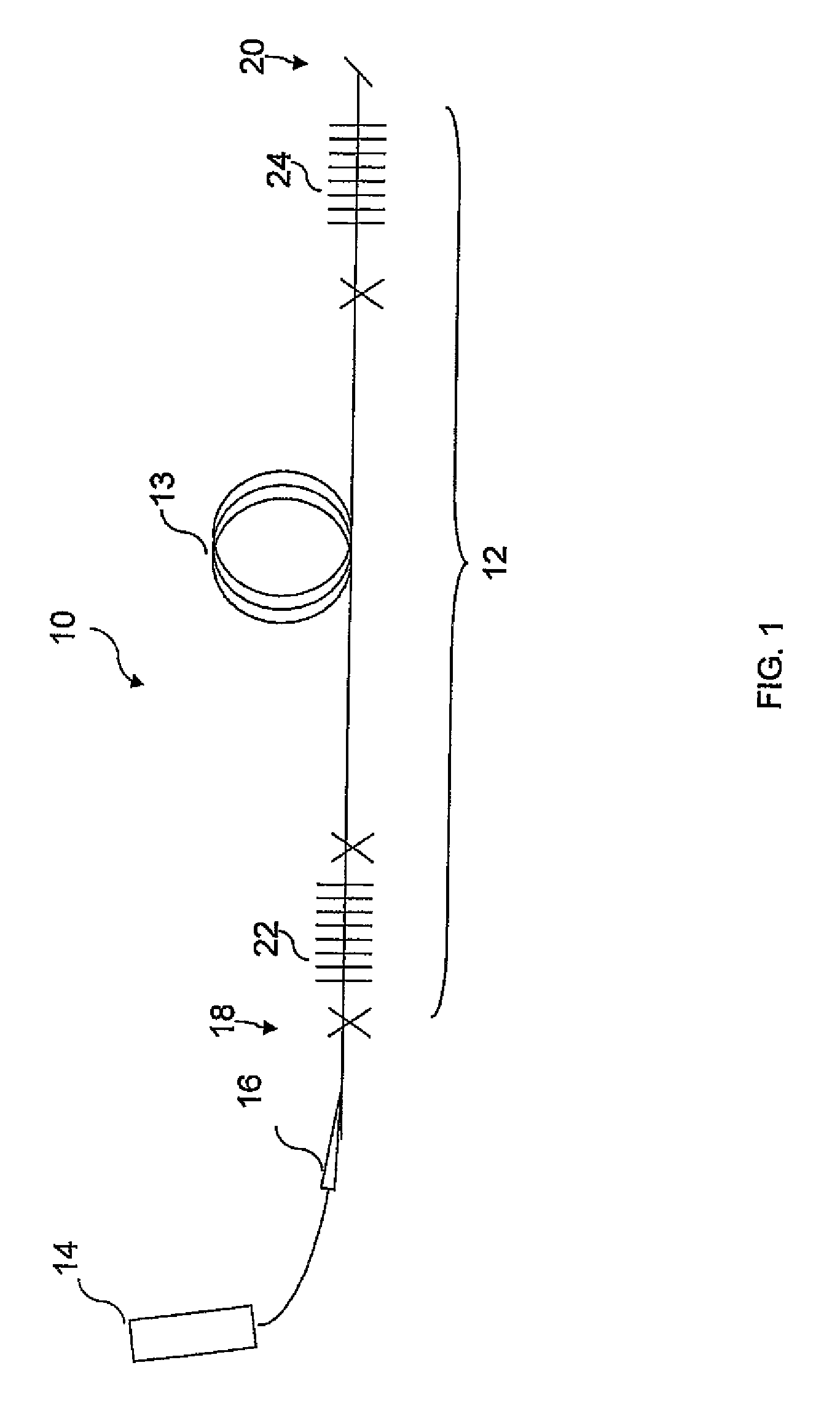
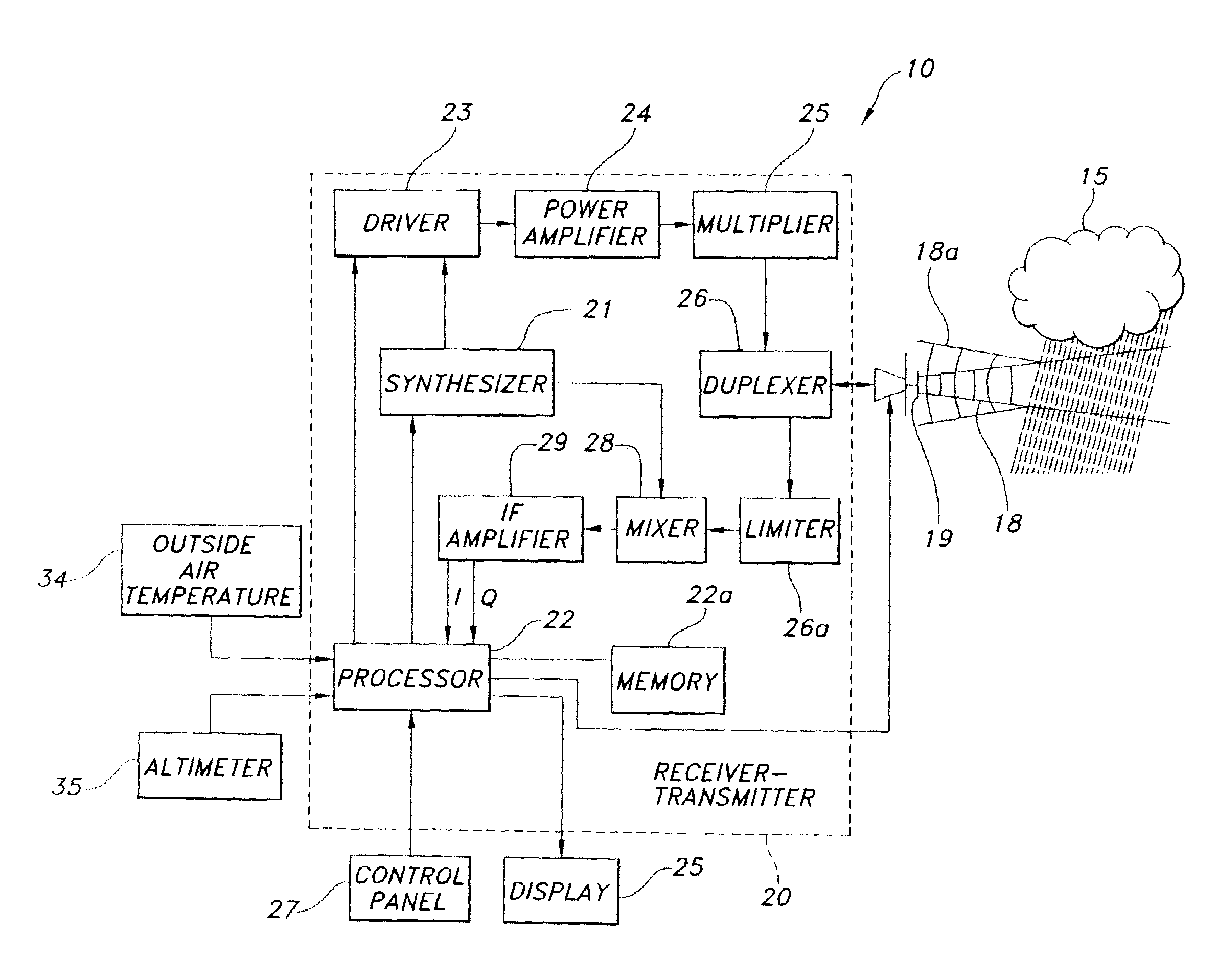
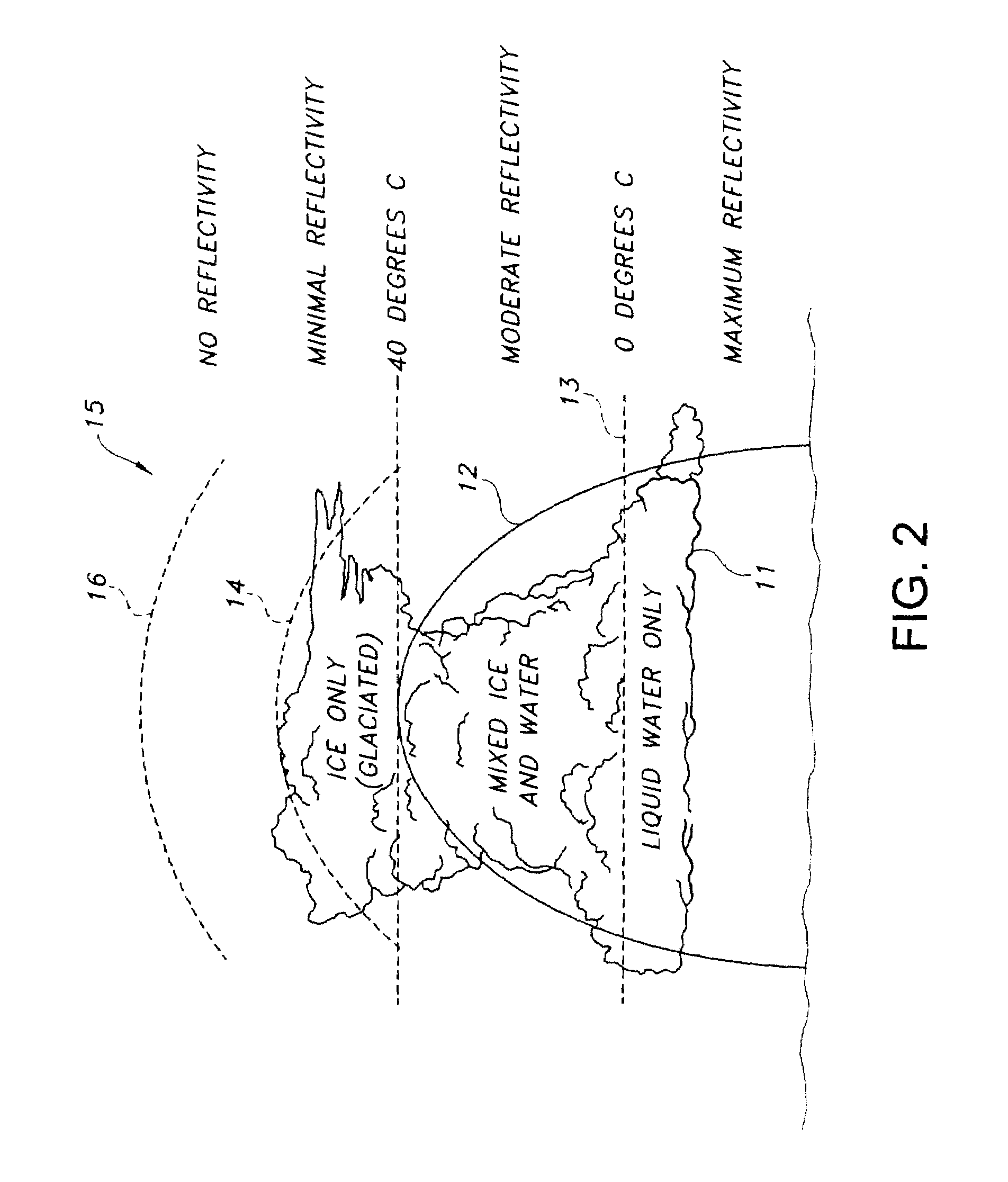
Automatic bright band detection and compensation
ActiveUS7492304B1Small modificationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationWave bandHigh reflectivity
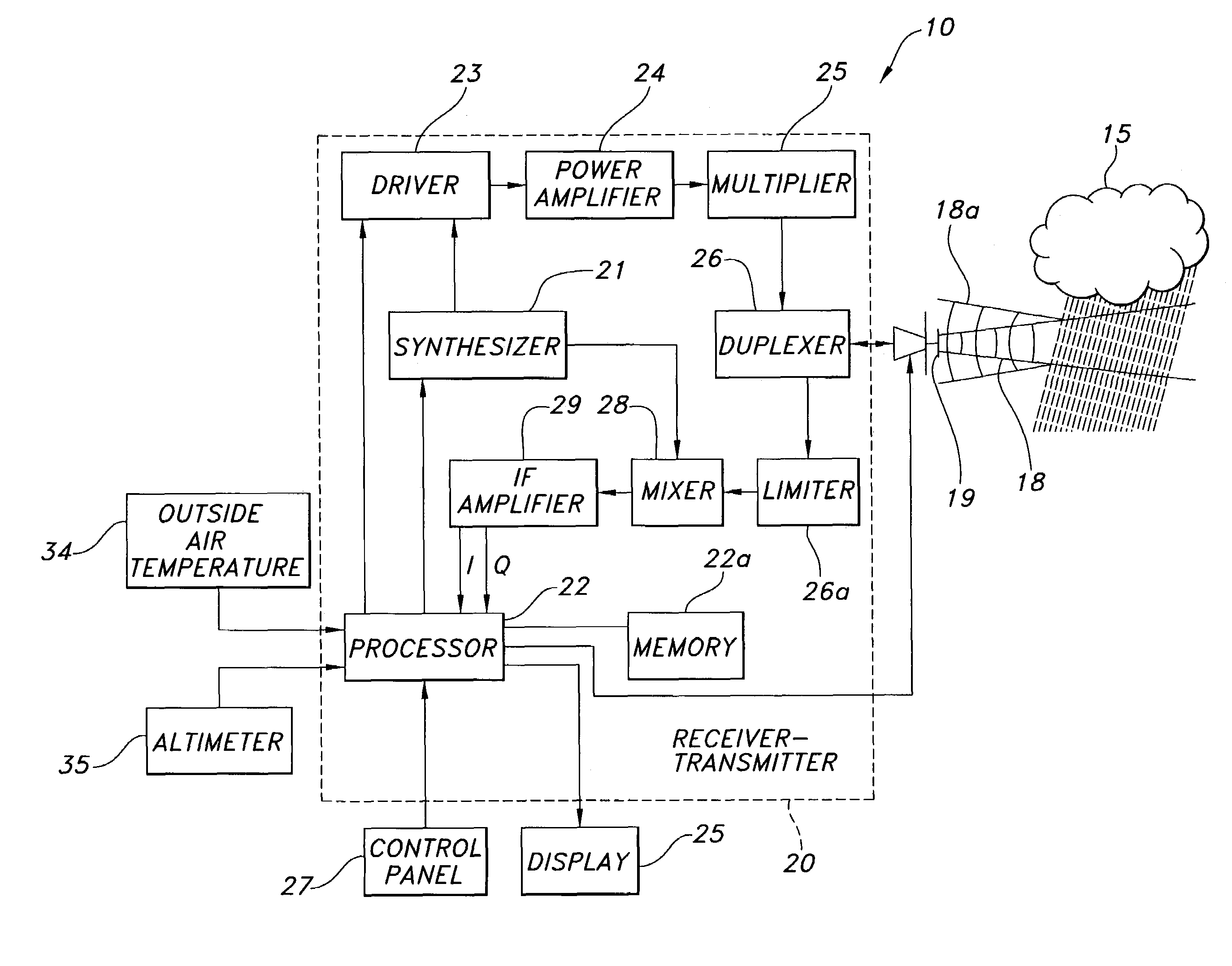
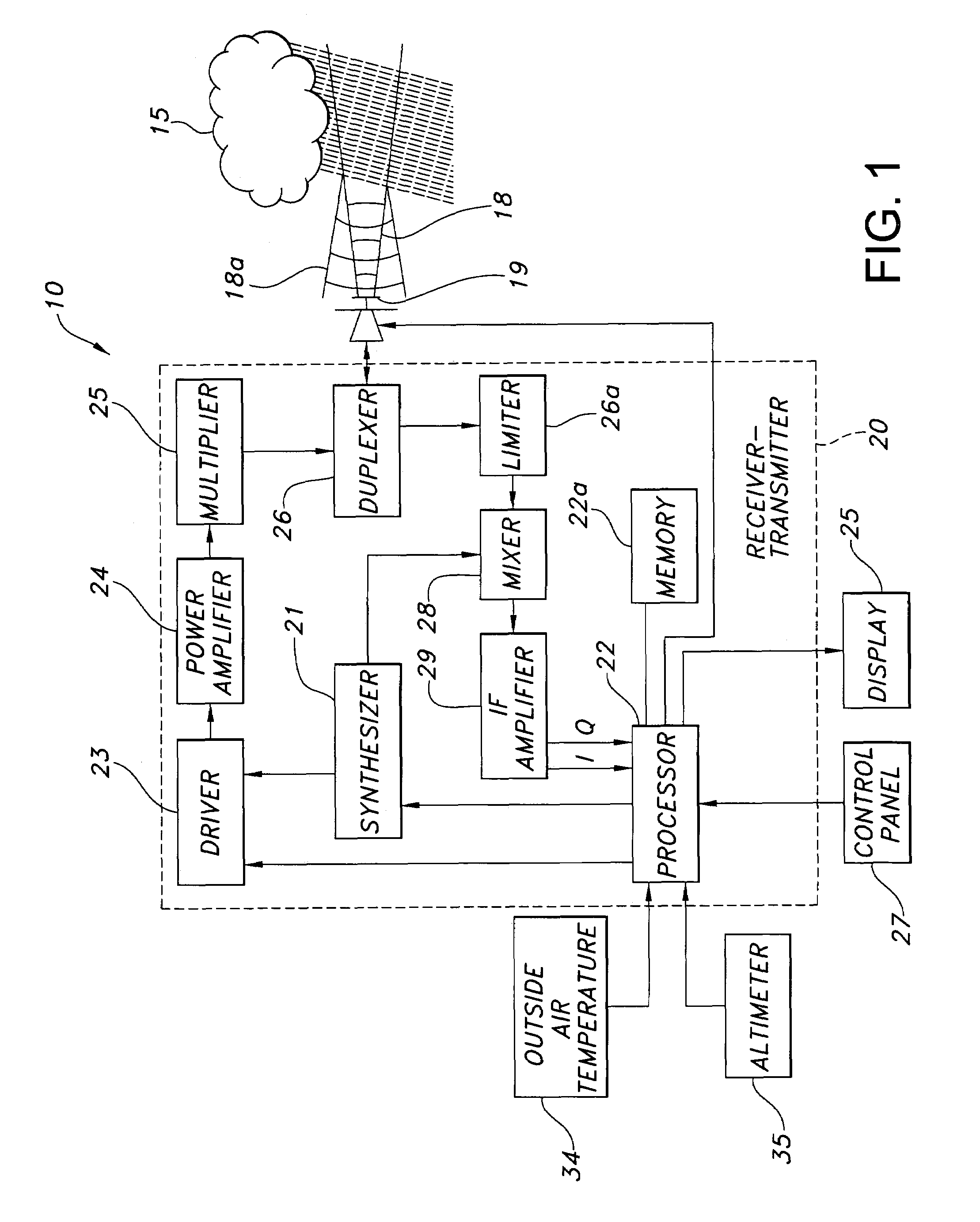
A weather radar system has bright band detection and compensation. The weather radar system determines that high reflectivity in weather is a bright band and reduces an encoded return level from the bright band to compensate for it on a display. The weather radar system detects the presence of the bright band using an inference system that uses outside air temperature, aircraft altitude, and an assumed lapse rate to estimate the bright band location relative to the aircraft and uses antenna elevation to estimate bright band range to reduce the encoded radar return level on the display. The weather radar system may also detect the presence of the bright band using a detection system that uses radar estimates from normal reflectivity scan operation of the system. The weather radar system may also use an active detection process separate from a normal radar sampling process to detect the bright band.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Light-emitting semiconductor device using group III nitride compound
InactiveUS6936859B1Improve reflectivityIncreased durabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAlloyContact layer
A flip chip type of light-emitting semiconductor device using group III nitride compound comprising a thick positive electrode. The positive electrode, which is made of at least one of silver (Ag), rhodium (Rh), ruthenium (Ru), platinum (Pt) and palladium (Pd), and an alloy including at least one of these metals, is adjacent to a p-type semiconductor layer, and reflect light toward a sapphire substrate. Accordingly, a positive electrode having a high reflectivity and a low contact resistance can be obtained. A first thin-film metal layer, which is made of cobalt (Co) and nickel (Ni), or any combinations of including at least one of these metals, formed between the p-type semiconductor layer and the thick electrode, can improve an adhesion between a contact layer and the thick positive electrode. A thickness of the first thin-film metal electrode should be preferably in the range of 2 Å to 200 Å, more preferably 5 Å to 50 Å. A second thin-film metal layer made of gold (Au) can further improve the adhesion.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Light-emitting semiconductor device using group III nitride compound
InactiveUS7109529B2Improve reflectivityIncreased durabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAlloyContact layer
A flip chip type of light-emitting semiconductor device using group III nitride compound includes a thick positive electrode. The positive electrode, which is made of at least one of silver (Ag), rhodium (Rh), ruthenium (Ru), platinum (Pt) and palladium (Pd), and an alloy including at least one of these metals, is adjacent to a p-type semiconductor layer, and reflect light toward a sapphire substrate. Accordingly, a positive electrode having a high reflectivity and a low contact resistance can be obtained. A first thin-film metal layer, which is made of cobalt (Co) and nickel (Ni), or any combinations of including at least one of these metals, formed between the p-type semiconductor layer and the thick electrode, can improve an adhesion between an contact layer and the thick positive electrode. A thickness of the first thin-film metal electrode should be preferably in the range of 2 Å to 200 Å, more preferably 5 Å to 50 Å. A second thin-film metal layer made of gold (Au) can further improve the adhesion.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
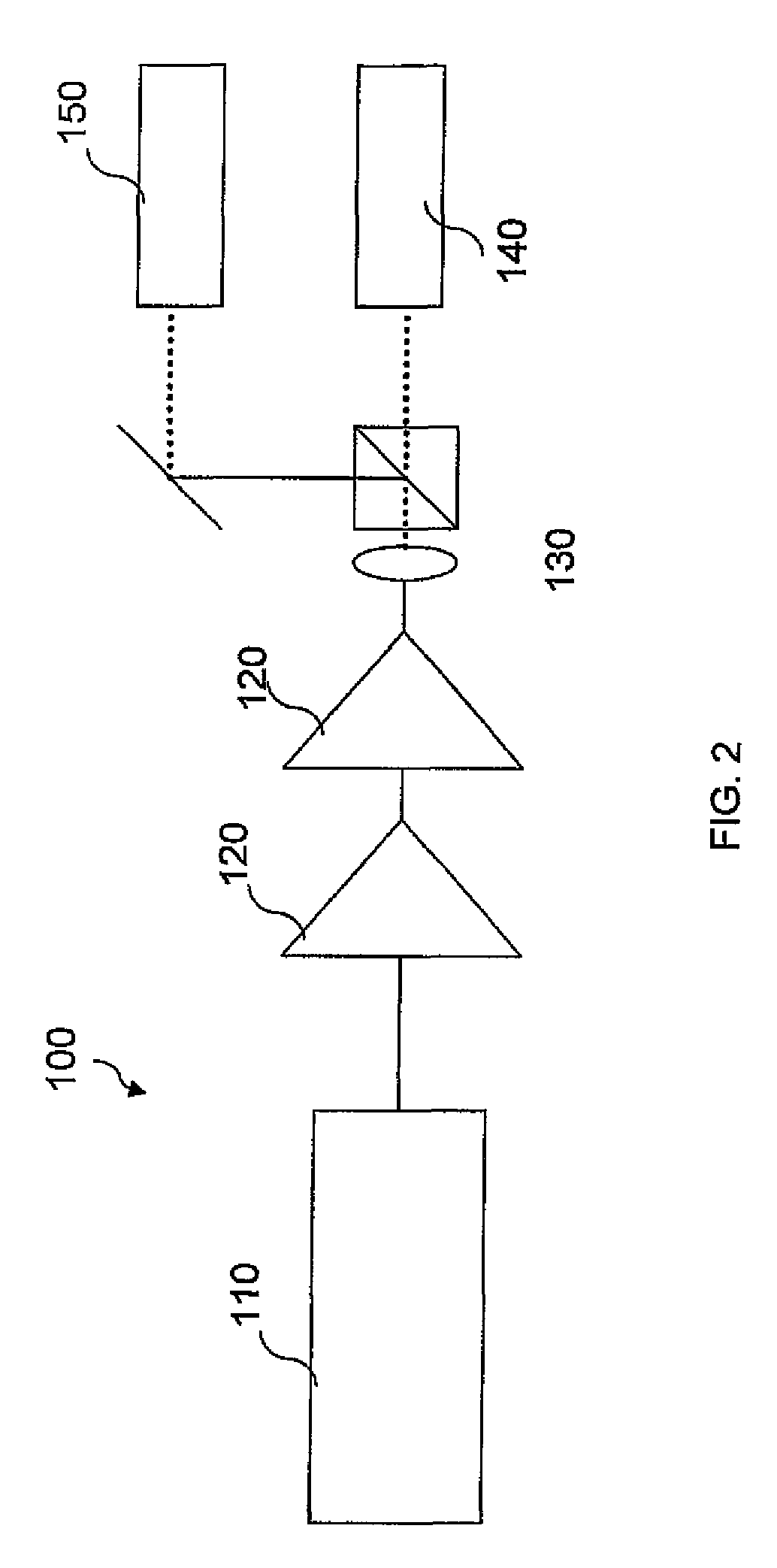
Fiber lasers
ActiveUS7778290B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove abilitiesLaser using scattering effectsDouble-clad fiberPolarizer
Fiber lasers for producing Band I wavelengths include a laser cavity having an optical fiber with specific parameters in length and thickness and doping concentration, and having high reflectivities. Examples show the feasibility of producing such fiber lasers. Fiber lasers for producing Band IV wavelengths include a depolarized laser oscillator, at least one amplifier and a polarizer. Depolarized laser oscillator is an inherently depolarized CW laser, or a depolarized laser diode, which is depolarized by a depolarizer. Additional fiber lasers in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include a double clad active optical fiber having a pump power entry point for sending pump energy through the active optical fiber in a first direction, and a loop portion at a second end of the fiber for sending pump energy through the active optical fiber in a second direction which is opposite to the first direction. A system for coupling light into a fiber in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include a first fiber, a second double clad fiber, and a bulk optic component positioned between the first and second fibers. A mode stripper included within the second fiber allows for removal of high power light which is propagated through the outer clad rather than launched into the core of the second fiber.
Owner:ELBIT SYST ELECTRO OPTICS ELOP
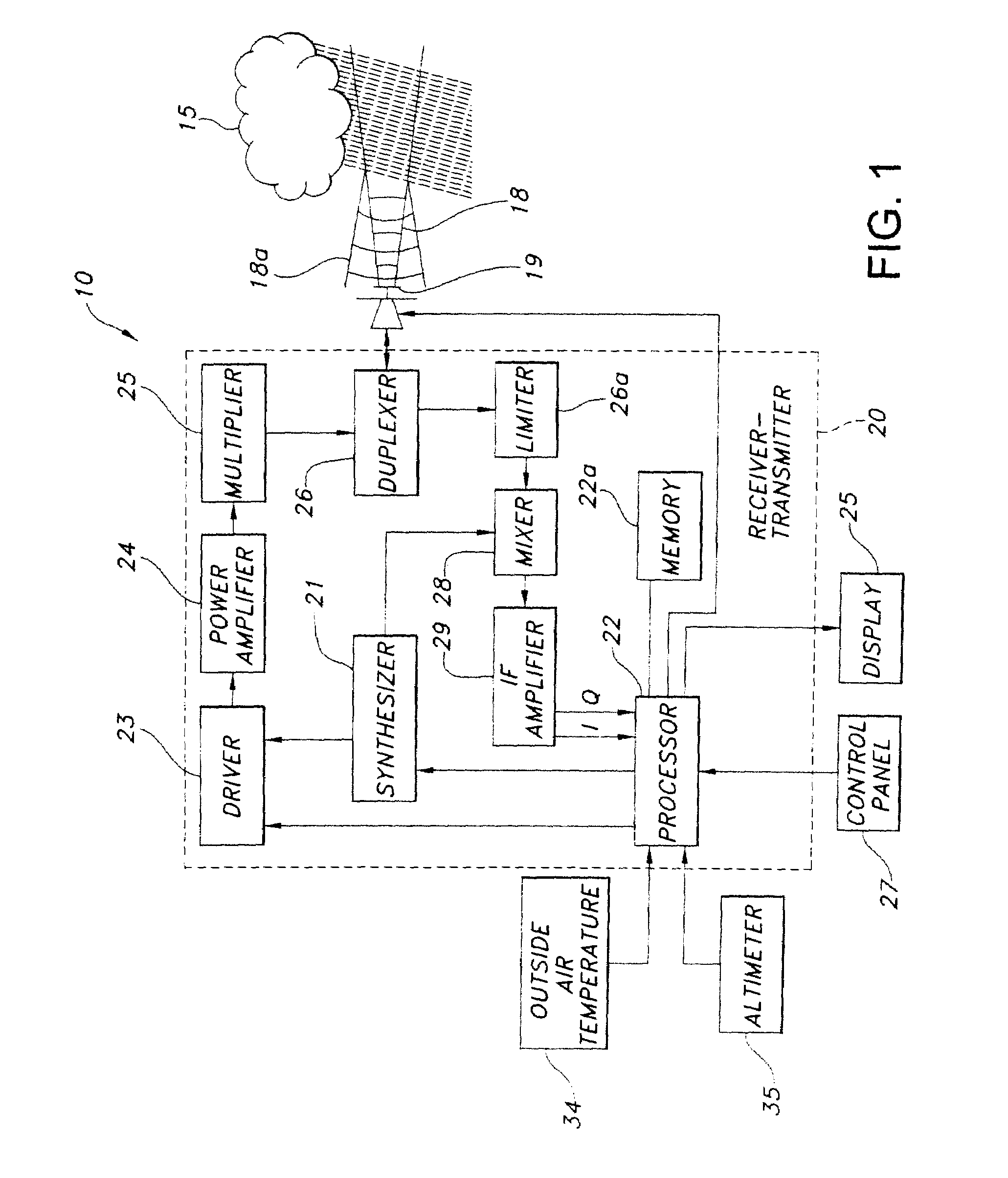
Automatic bright band detection and compensation
ActiveUS7541971B1Small modificationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationFailure rateRadar systems
A weather radar system has bright band detection and compensation. The weather radar system determines that high reflectivity in weather is a bright band and reduces an encoded return level from the bright band to compensate for it on a display. The weather radar system detects the presence of the bright band using an inference system that uses outside air temperature, aircraft altitude, and an assumed lapse rate to estimate the bright band location relative to the aircraft and uses antenna elevation to estimate bright band range to reduce the encoded radar return level on the display. The weather radar system may also detect the presence of the bright band using a detection system that uses radar estimates from normal reflectivity scan operation of the system. The weather radar system may also use an active detection process separate from a normal radar sampling process to detect the bright band.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Light recycling illumination systems utilizing light emiting diodes
InactiveUS20060066192A1Improve reflectivityIncrease brightness efficiencyIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensPolarizerHigh reflectivity
This invention is an illumination system that incorporates a light emitting diode and a partially reflecting optical element. The light emitting diode emits internally generated light and reflects incident light with high reflectivity. The partially reflecting optical element transmits a first portion of the internally generated light and reflects a second portion of the internally generated light back to the light emitting diode, where the second portion is reflected by the light emitting diode. The partially reflecting optical element can be a non-absorbing reflecting polarizer or a wavelength conversion layer. Utilizing a partially reflecting optical element and light recycling can increase the effective brightness and the output efficiency of the illumination system.
Owner:GOLDENEYE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com