Patents
Literature
300 results about "Soda lime" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
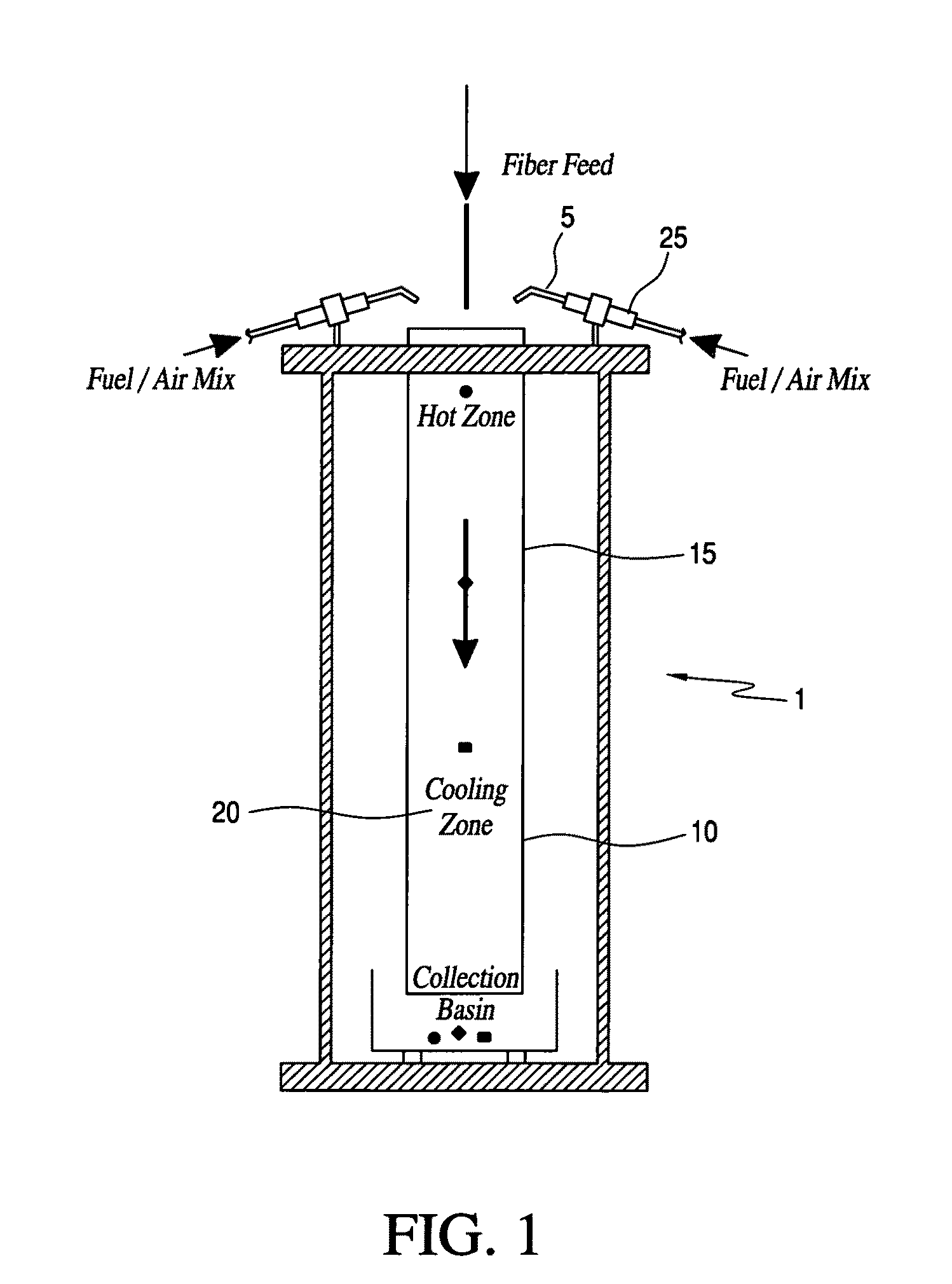
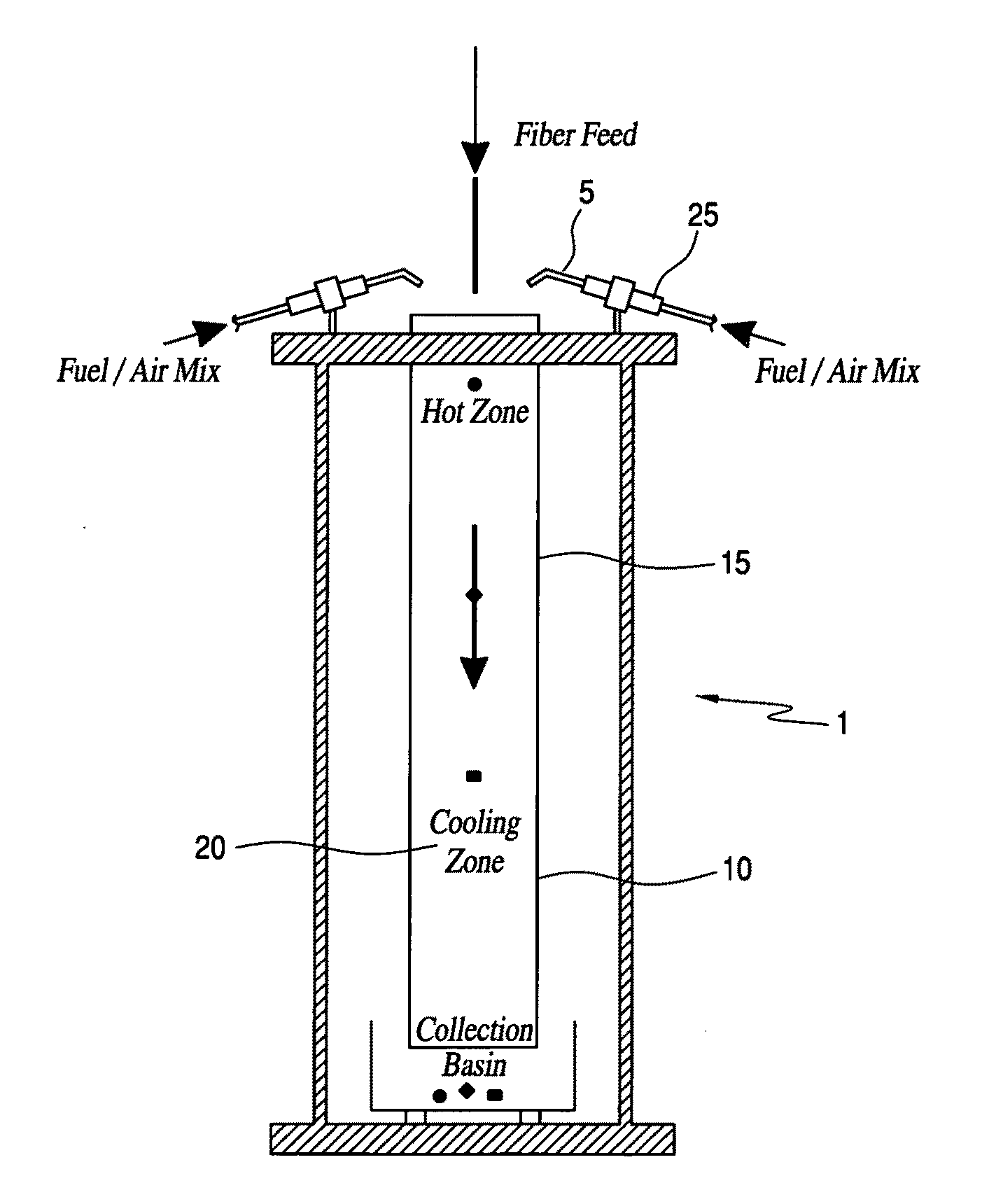
Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH & CaO chemicals, used in granular form in closed breathing environments, such as general anaesthesia, submarines, rebreathers and recompression chambers, to remove carbon dioxide from breathing gases to prevent CO₂ retention and carbon dioxide poisoning.
Electrode structure for use in electronic device and method of making same
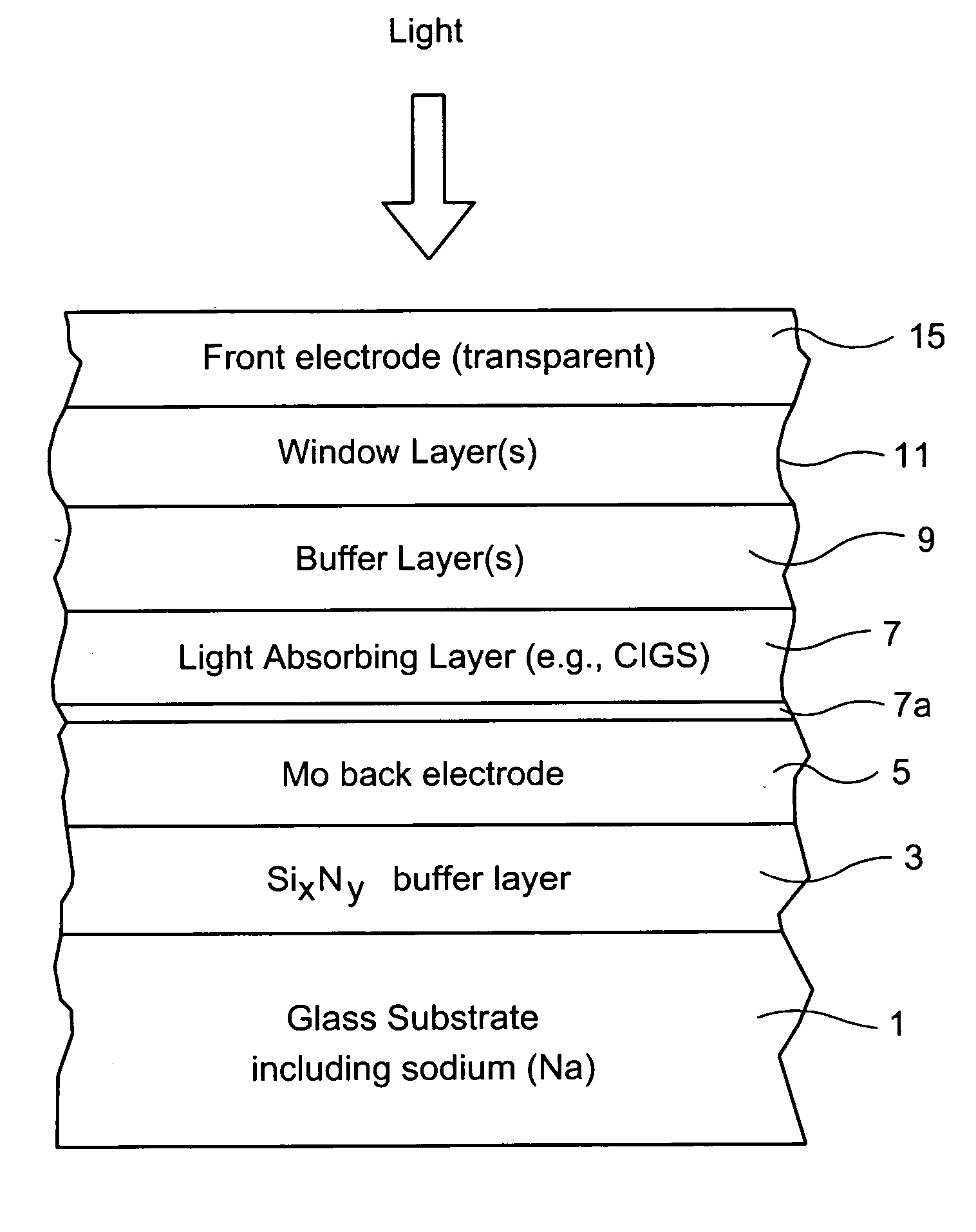
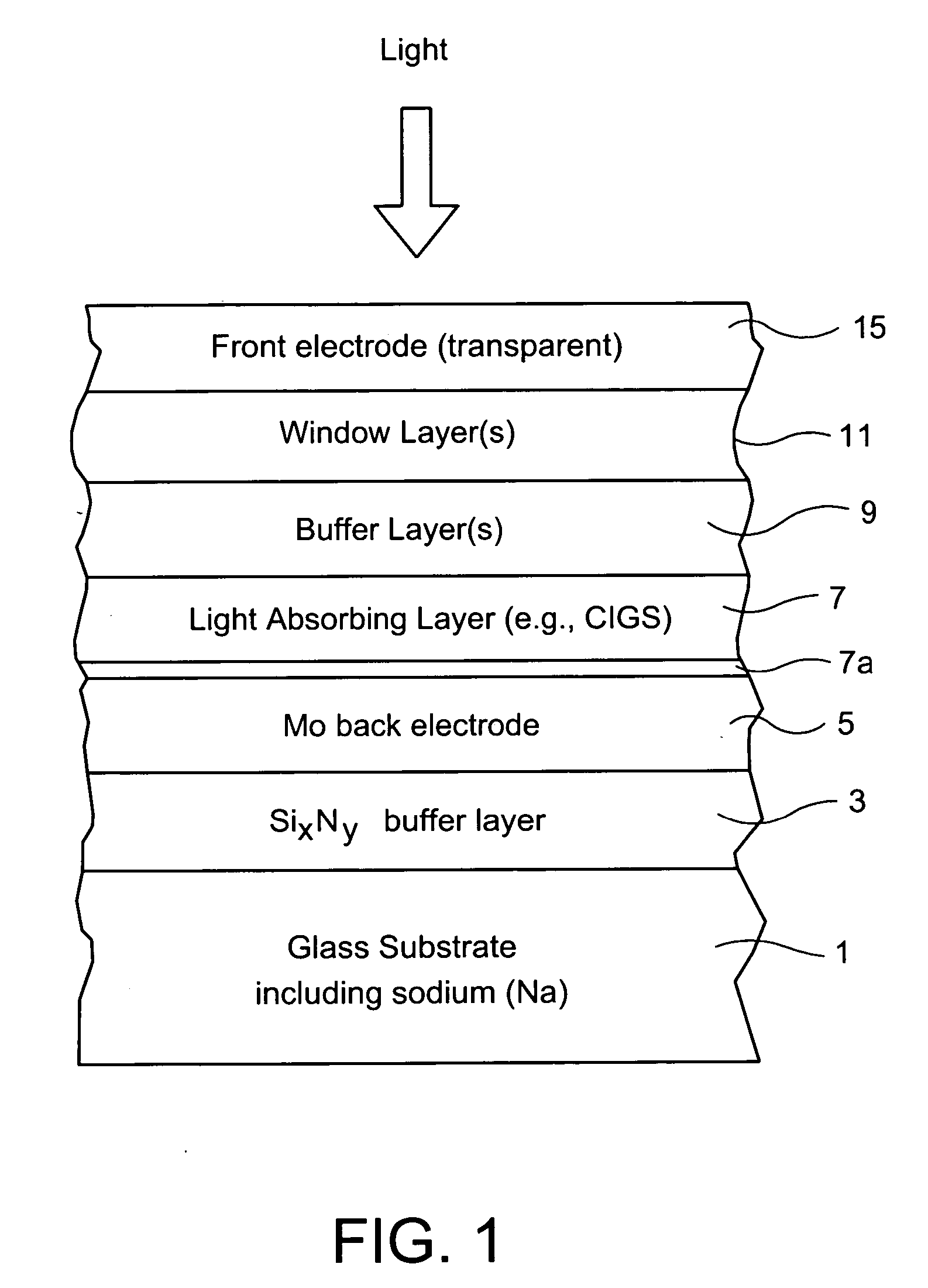
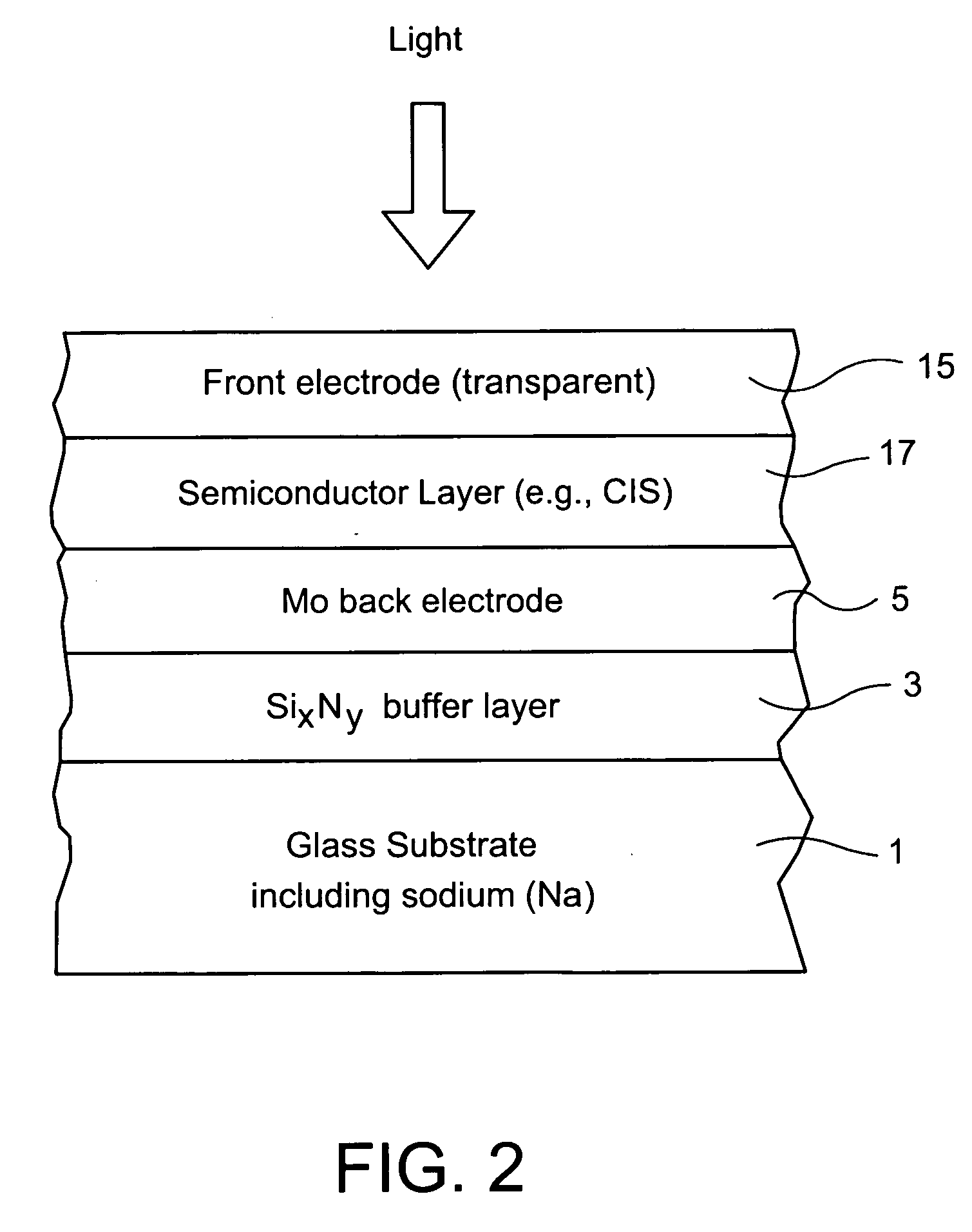
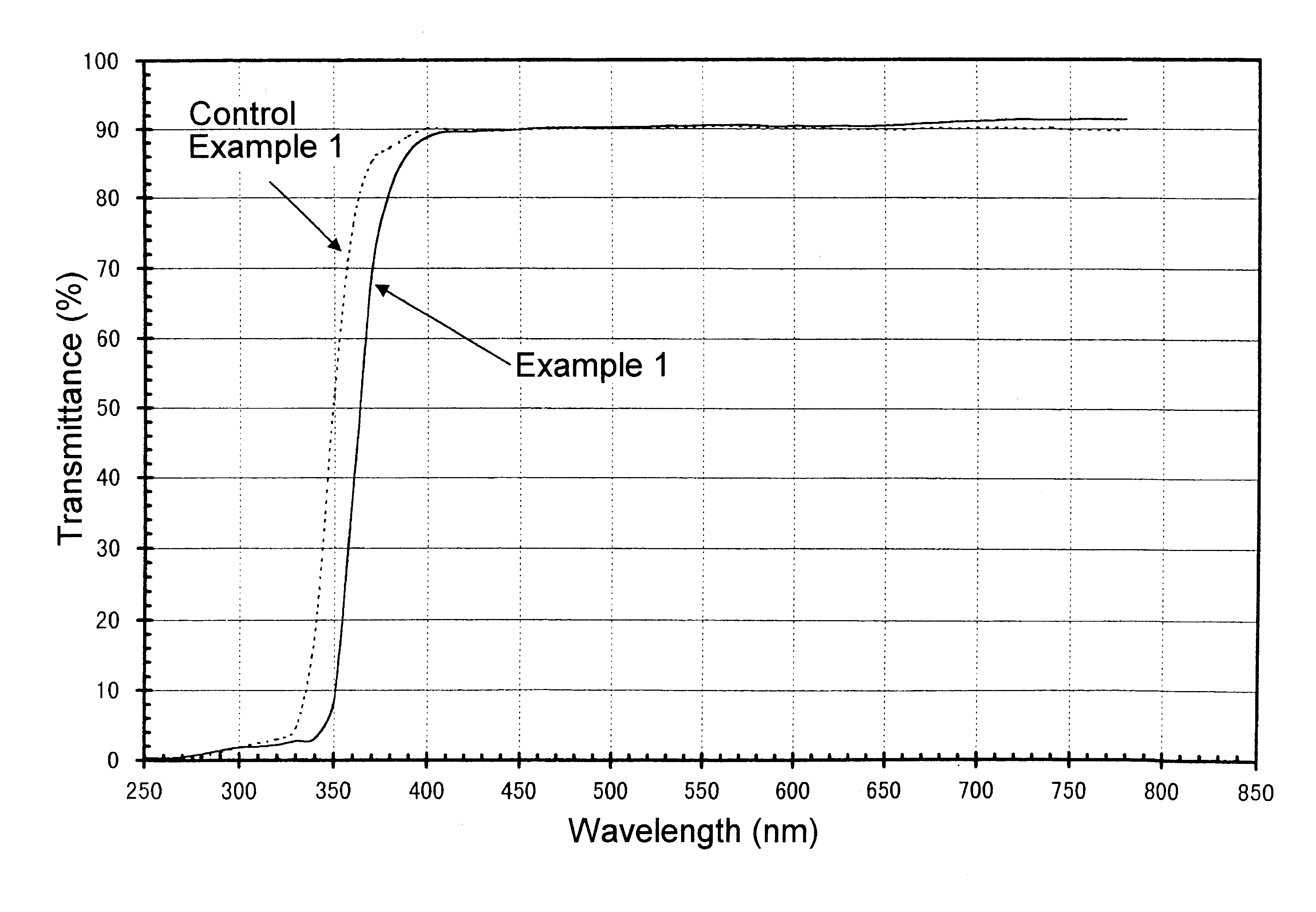
InactiveUS20070193623A1Reduce and prevent migrationControl of mechanical and efficiency propertyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationOptoelectronicsSoda lime
An electrode structure is provided for use in an electronic device. In certain example embodiments, an electrode structure includes a supporting glass substrate (e.g., soda-lime silica based float glass), a buffer layer (e.g., SixNy), and a conductive electrode (e.g., Mo) provided in this order. The buffer layer is advantageous in that it prevents or reduces sodium (Na) migration from the glass substrate into semiconductor layer(s) of the electronic device.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
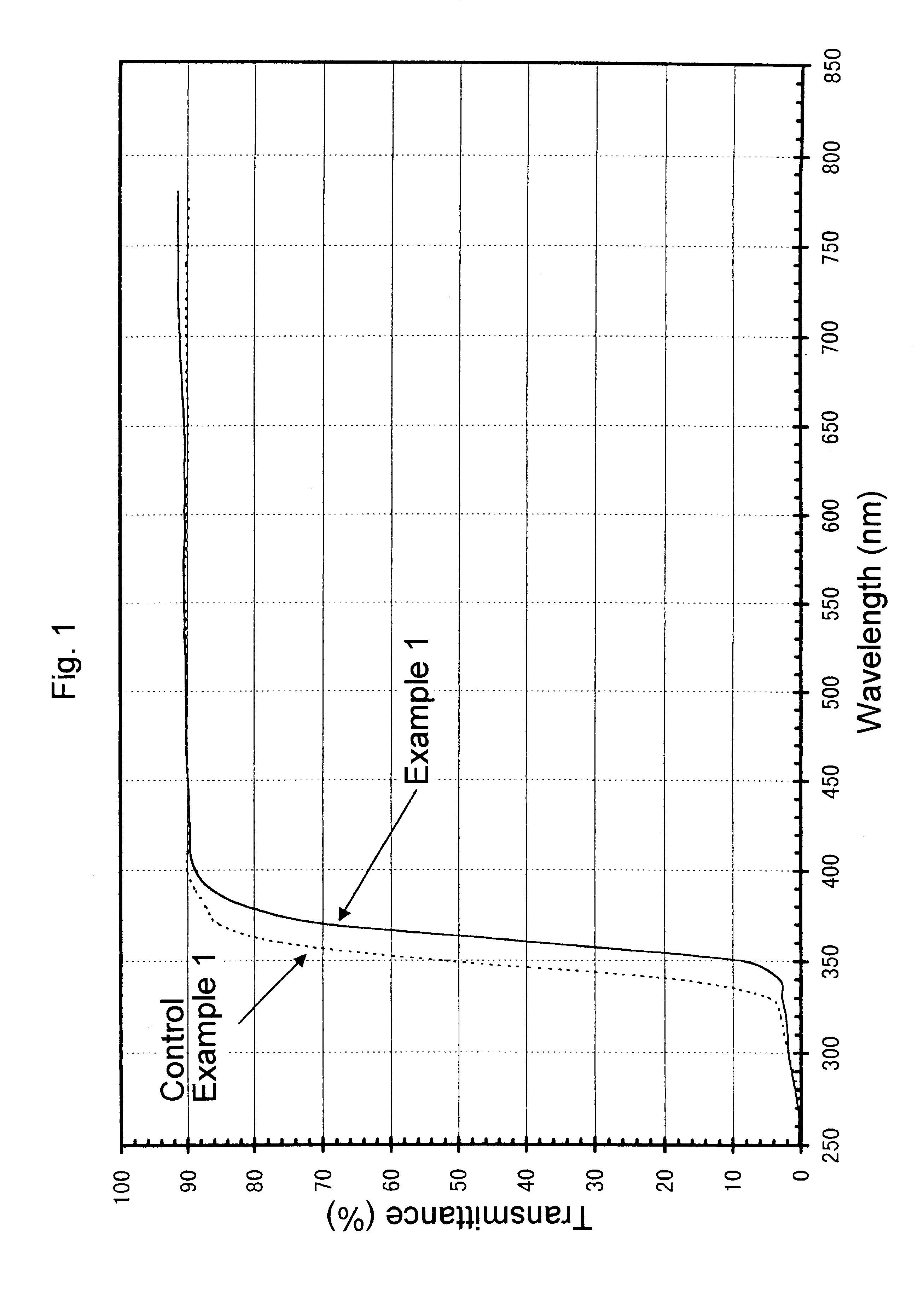
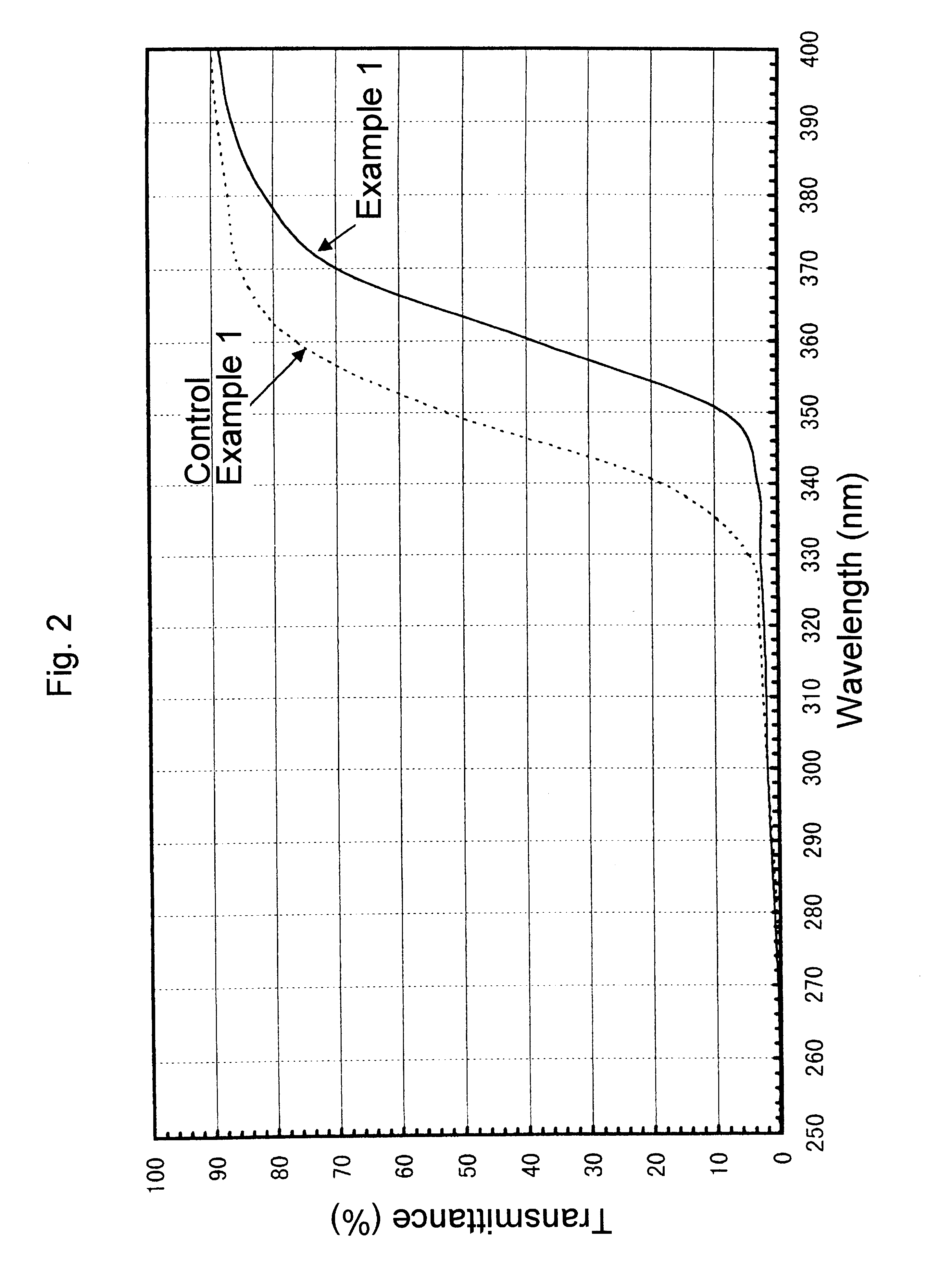
Ultraviolet radiation-absorbing, colorless, transparent soda-lime silica glass
An ultraviolet radiation-absorbing, colorless, transparent soda-lime-silica glass as well as glass bottles formed out of the glass are disclosed which, while maintaining high transmittance to light in the visible region and thereby allowing the contents to be seen clearly, absorbs ultraviolet radiation and thus prevents coloration, discoloration, fading in color or deterioration of the flavor of the contents caused by ultraviolet radiation. The glass is characterized in that its composition includes, in % by weight, SO3 . . . 0.15-0.4%; Cerium oxide . . . 0.2-1% (calculated as CeO2); Fe2O3 . . . 0.01-0.08%; FeO . . . 0-0.008%; Manganese oxide . . . 0.01-0.08% (calculated as MnO); and Cobalt oxide . . . 0-0.0005% (calculated as CoO).
Owner:NIHON YAMAMURA GLASS CO LTD
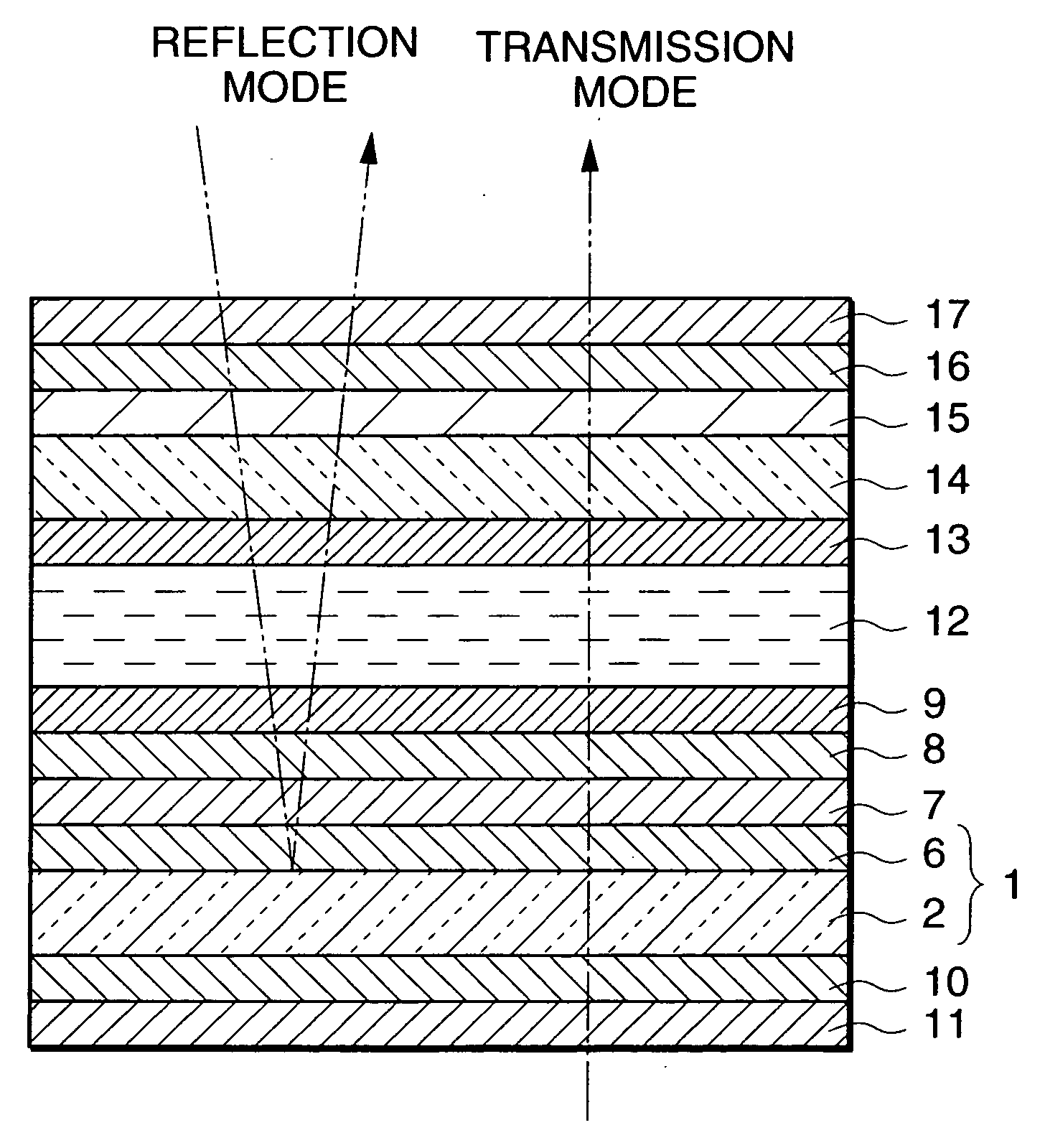
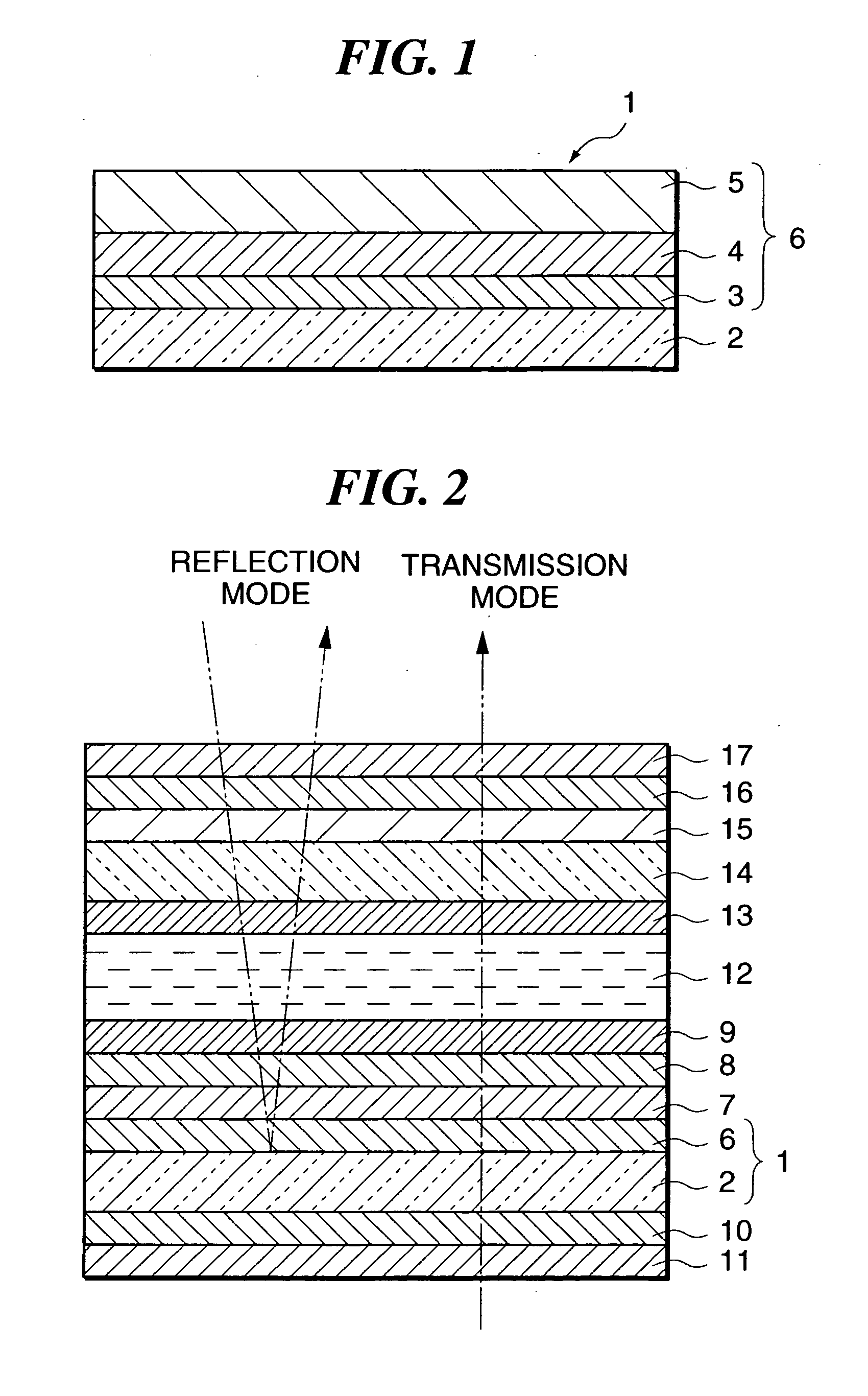
Semi-transmitting mirror-possessing substrate, and semi-transmitting type liquid crystal display apparatus
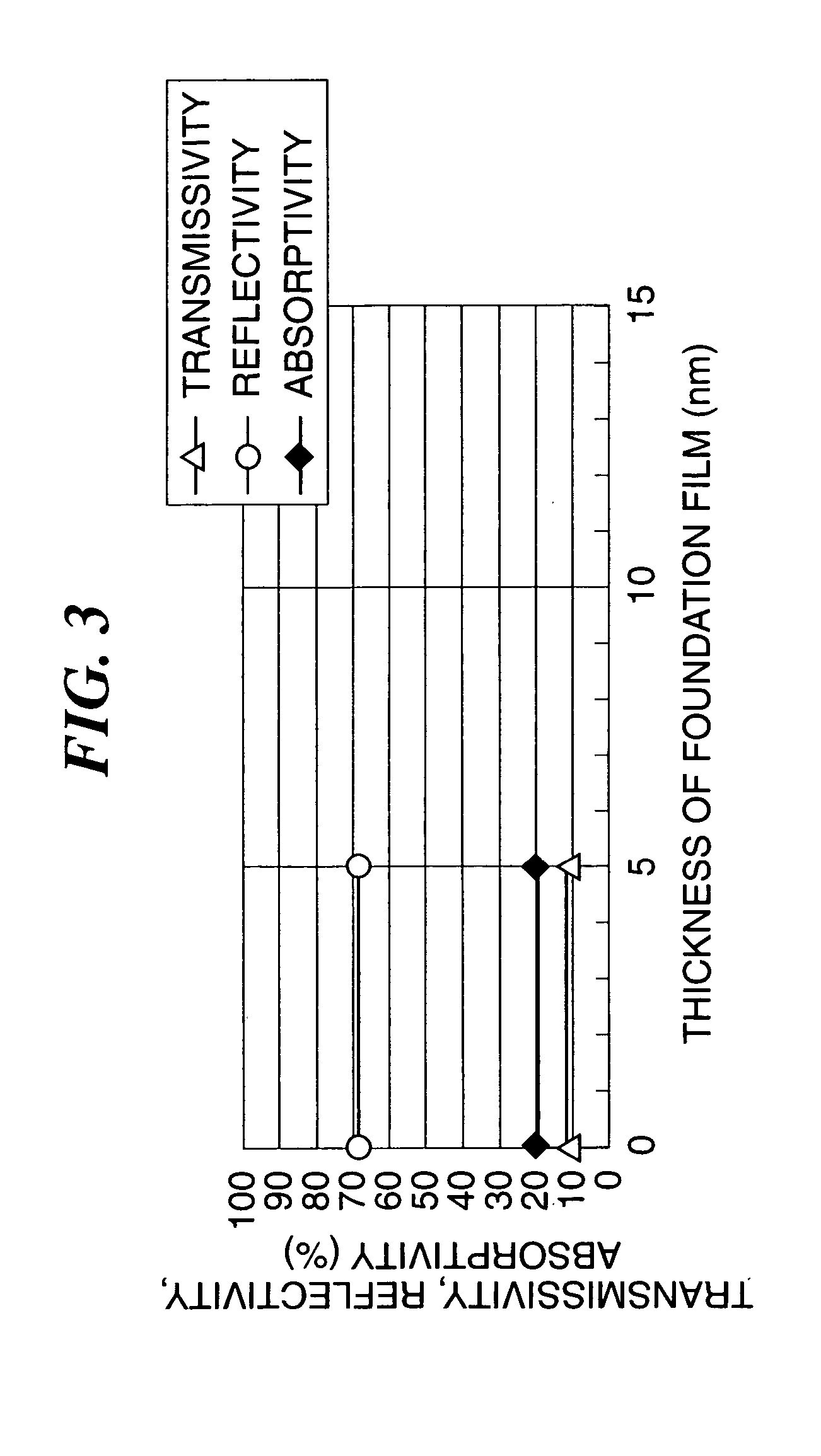
There is provided a semi-transmitting mirror-possessing substrate that has high reflectivity while maintaining high transmissivity, whereby transmission display performance and reflection display performance can both be improved. The semi-transmitting mirror-possessing substrate 1 has a transparent glass substrate 2 made of a soda lime silicate glass, a foundation film 3 made of silicon oxide (SiOx) formed on the glass substrate 2, a semi-transmitting reflective film 4 made of aluminum (Al) formed on the foundation film 3, and a protective film 5 made of silicon dioxide (SiO2) formed on the semi-transmitting reflective film 4. The film thickness of the SiOx used as the foundation film 3 is in a range of 0 to 8 nm. Moreover, the chemical composition ratio x of oxygen (O) to silicon (Si) in the SiOx is in a range of 1.5 to 2.0.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Soda-lime-silicate glass composition
A neutral-colored soda-lime-silicate glass with high light transmission in the visible region. The glass has a basic composition which contains at least the following constituents: SiO2, 66-75 weight %; Na2O, 10-20 weight %; CaO, 5-15 weight %; MgO, 0-6 weight %; Al2O3, 0-5 weight %; and K2O, 0-5 weight %; and incorporates a colorant portion comprising the following constituents: Co, 0.1-1 ppm; Fe2O3, <=0.03 weight % (total iron content); and FeO / Fe2O3, >0.4. The glass possesses a light transmittance (illuminant D 65 according to DIN 67 507) of at least 89% at a reference thickness of 4 mm.
Owner:PILKINGTON DEUTLAND
Method of making oxide thin film transistor array, and device incorporating the same
InactiveUS20120074399A1Improve conductivityImprove economyTransistorSolid-state devicesOxide thin-film transistorRoom temperature
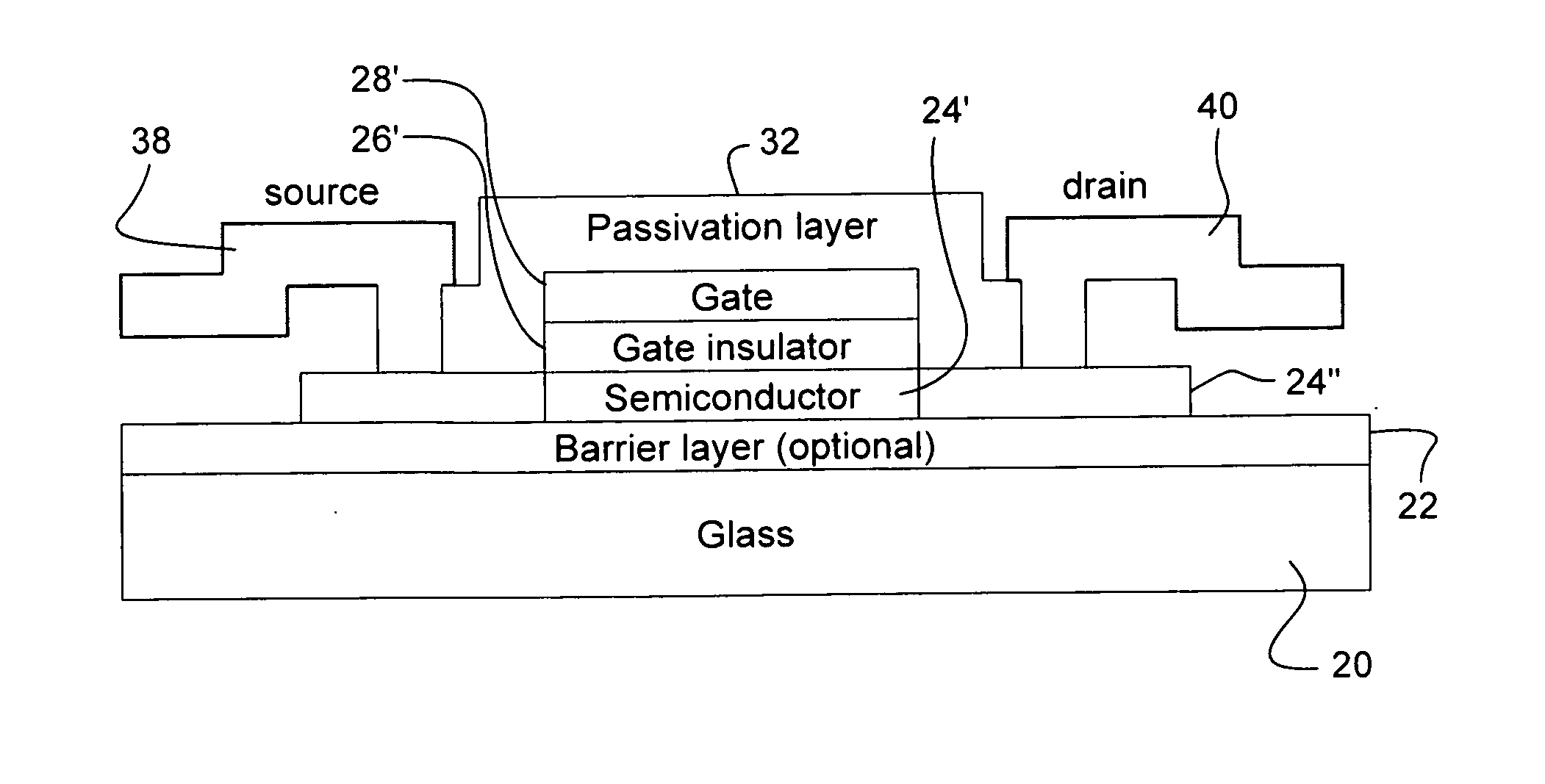
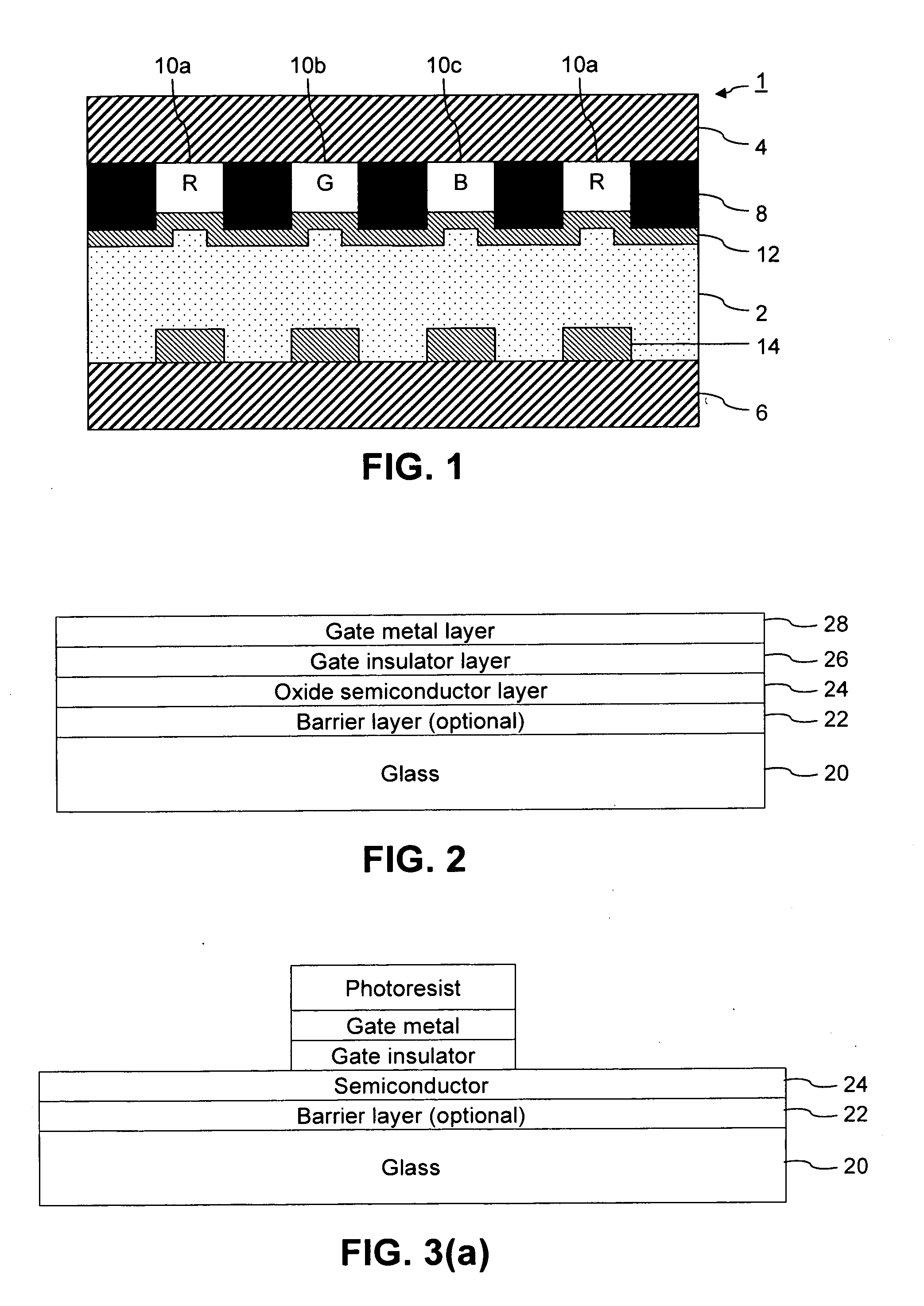
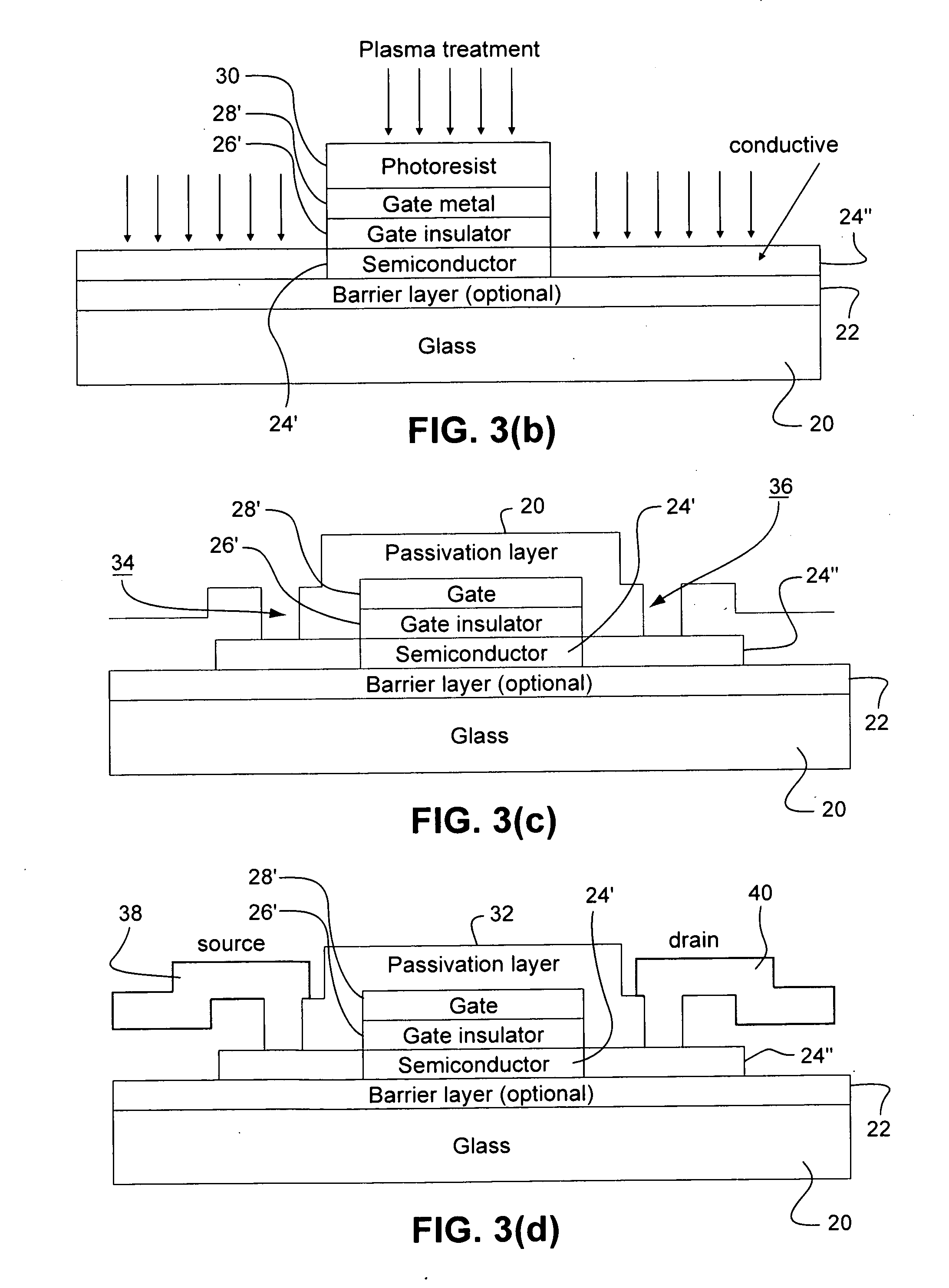
Certain example embodiments relate to methods of making oxide thin film transistor arrays (e.g., IGZO, amorphous or polycrystalline ZnO, ZnSnO, InZnO, and / or the like), and devices incorporating the same. Blanket layers of an optional barrier layer, semiconductor, gate insulator, and / or gate metal are disposed on a substrate. These and / or other layers may be deposited on a soda lime or borosilicate substrate via low or room temperature sputtering. These layers may be later patterned and / or further processed in making a TFT array according to certain example embodiments. In certain example embodiments, all or substantially all TFT processing may take place at a low temperature, e.g., at or below 150 degrees C., until a post-annealing activation step, and the post-anneal step may take place at a relatively low temperature (e.g., 200-250 degrees C.).
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Clear glass composition
Glass is provided so as to have high visible transmission and / or fairly clear or neutral color. In certain example embodiments, the glass may include a base glass (e.g., soda lime silica base glass) and, in addition, by weight percentage, from 0.01 to 0.30% total iron (expressed as Fe2O3). The glass may be made using a batch redox of at least +7.5.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Method for preparing silicon dioxide and aluminum oxide from coal ash
ActiveCN101993084AMild desilication reactionWeak corrosiveSilicaSolid waste disposalFoam concreteHigh pressure
Owner:CHINACOAL PINGSHUO GRP
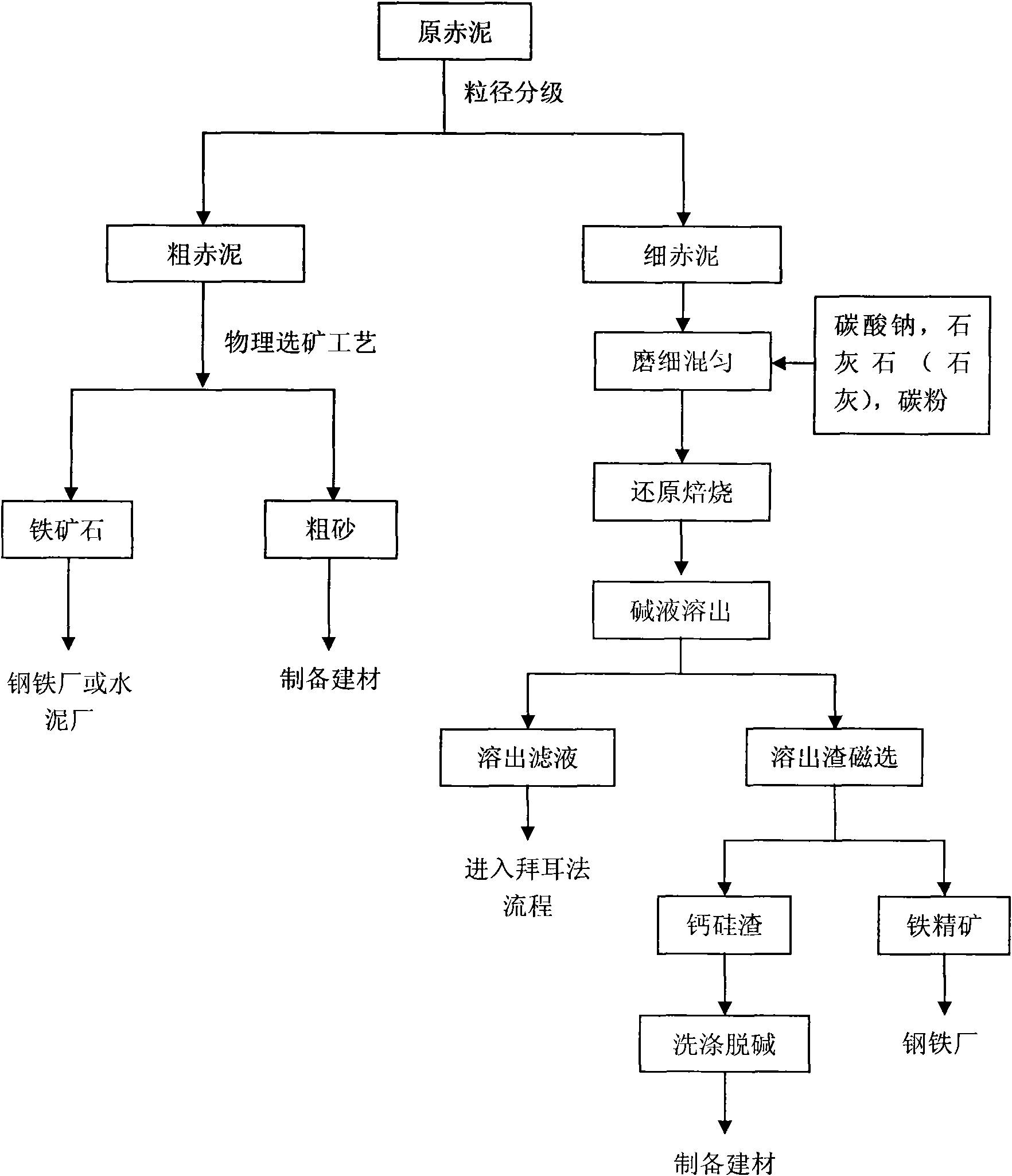
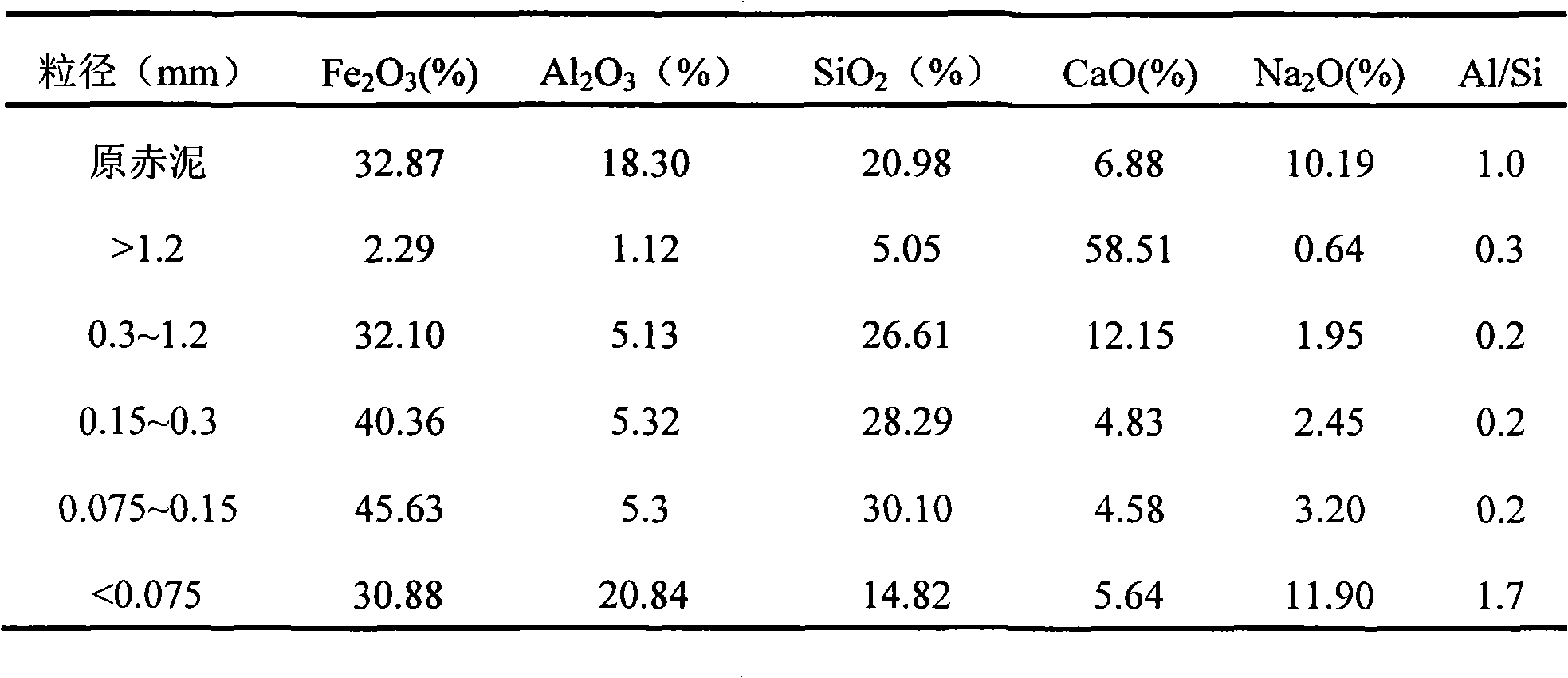
Method for recycling iron and aluminum by particle size grading pretreatment of Bayer process red mud
InactiveCN101624654AReduce difficultyReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementSlagRed mud
The invention relates to a method for recycling iron and aluminum by particle size grading pretreatment of Bayer process red mud, belonging to the technology for recycling red mud resources. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, Bayer process red mud is graded in terms of the particle size by using a physical method into coarse red mud and refined red mud; the coarse red mud is processed using physical mineral dressing processes, such as magnetic separation, gravity separation and the like, in order to obtain iron ore having high iron quality and coarse-grained sand, which are made use of respectively; the refined red mud is mixed with sodium carbonate, limestone and carbon power and is then subjected to reduction sintering, and two processes of magnetizing reduction roasting of iron and soda lime sintering of aluminum are implemented synchronously by means of the control of sintering conditions; sodium aluminate is dissolved out of clinker through dilute alkali solution, dissolved slag is subjected to magnetic separation to recover iron ore concentrate, and after being subjected to dealkalized cleaning, the residual calcium silicon slag is applied to building material industry. The method realizes combined recovery of iron, aluminum and other elements, magnificently achieves the comprehensive utilization of the Bayer process red mud, is capable of effectively relieving environment pollution resulting from the accumulation of the Bayer process red mud, and has excellent economic and social benefits.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
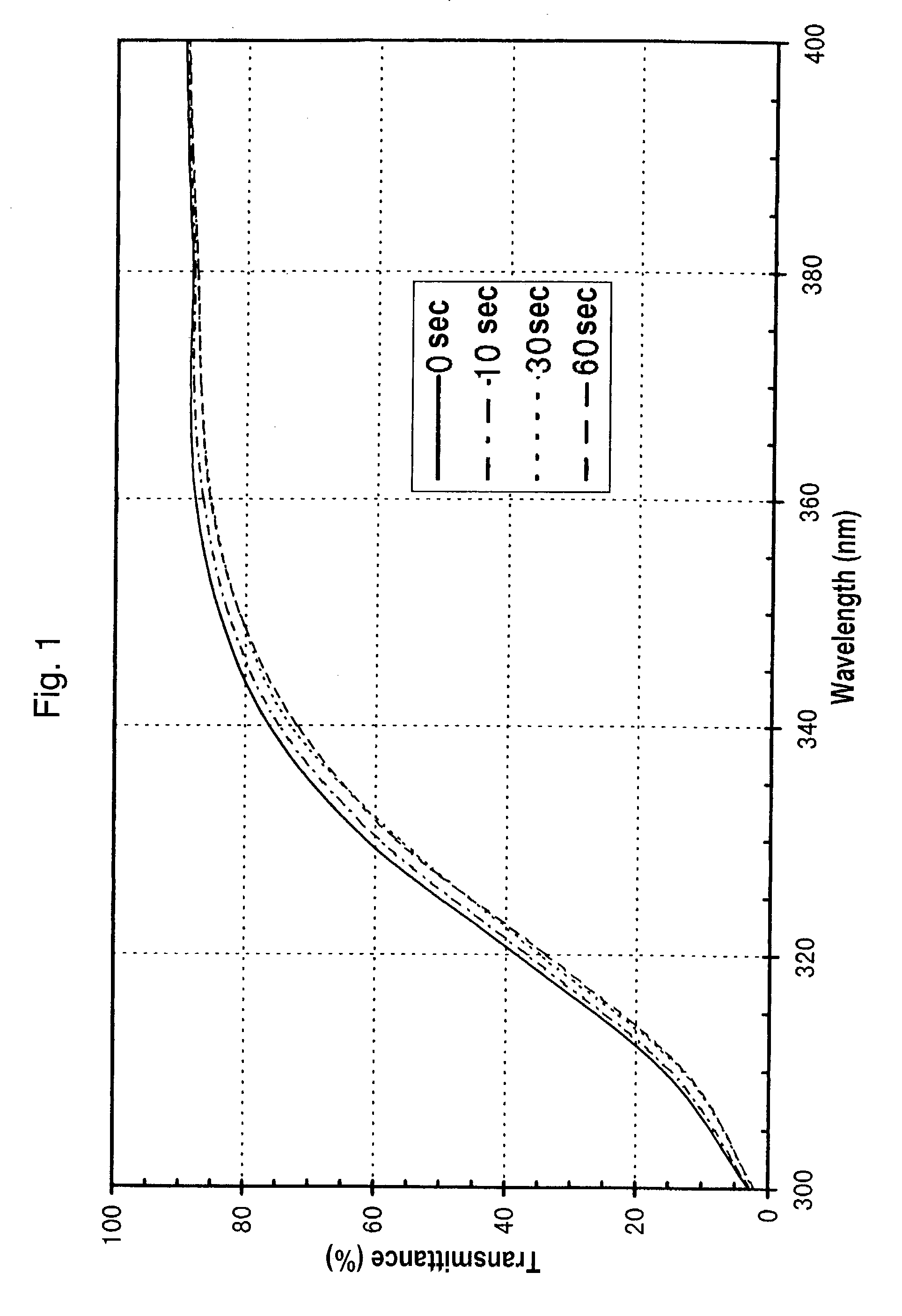
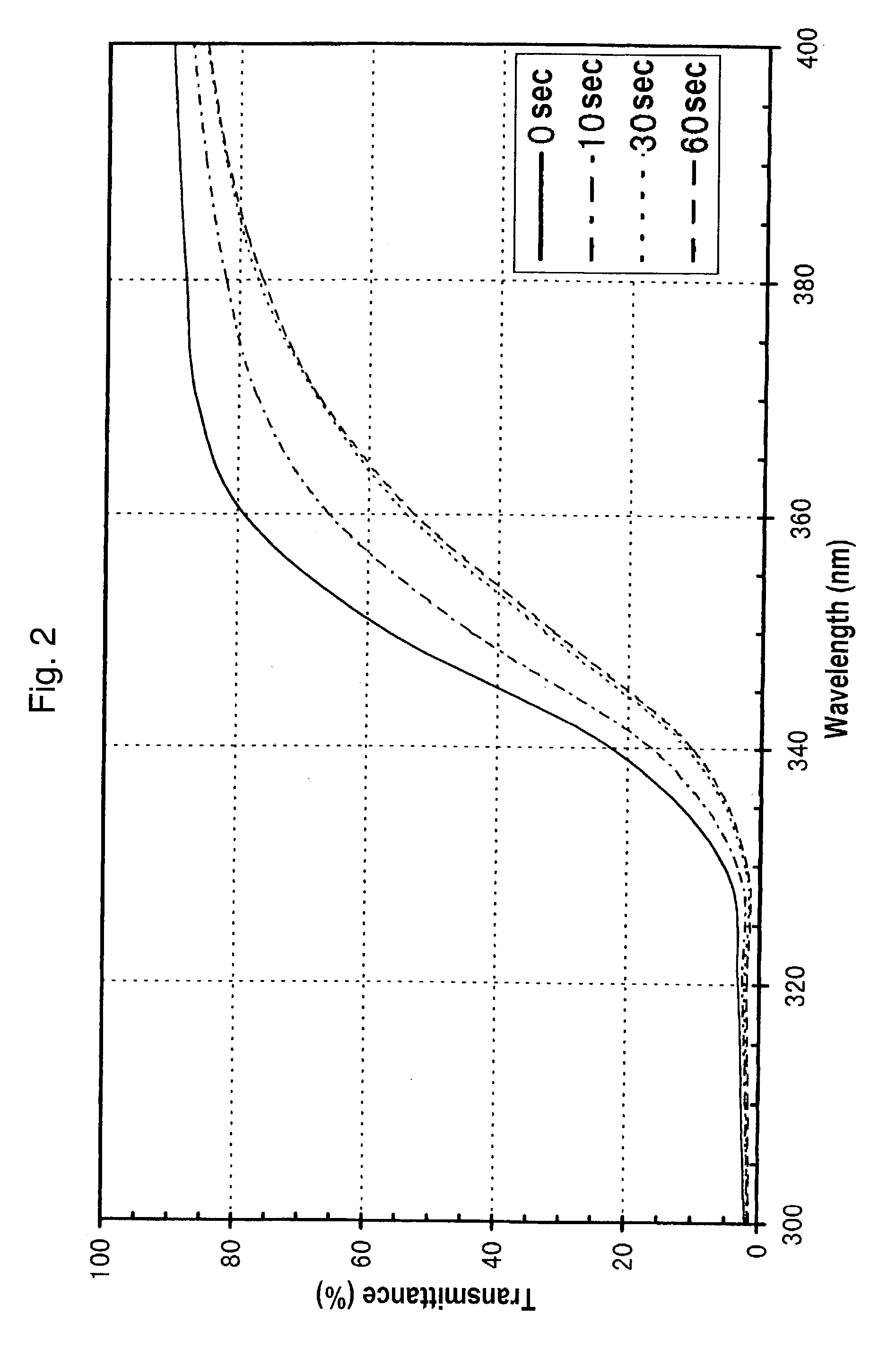
Ultraviolet ray-absorbing, colorless and transparent soda-lime-silica glass
An ultraviolet ray-absorbing, colorless and transparent soda-lime-silica glass is disclosed, which glass is prepared by irradiating a cerium containing soda-lime-silica glass with light having wavelengths in far- to near-ultraviolet region and thereby reducing transmittance to light with wavelengths in the region of 300-400 nm.
Owner:NIHON YAMAMURA GLASS CO LTD
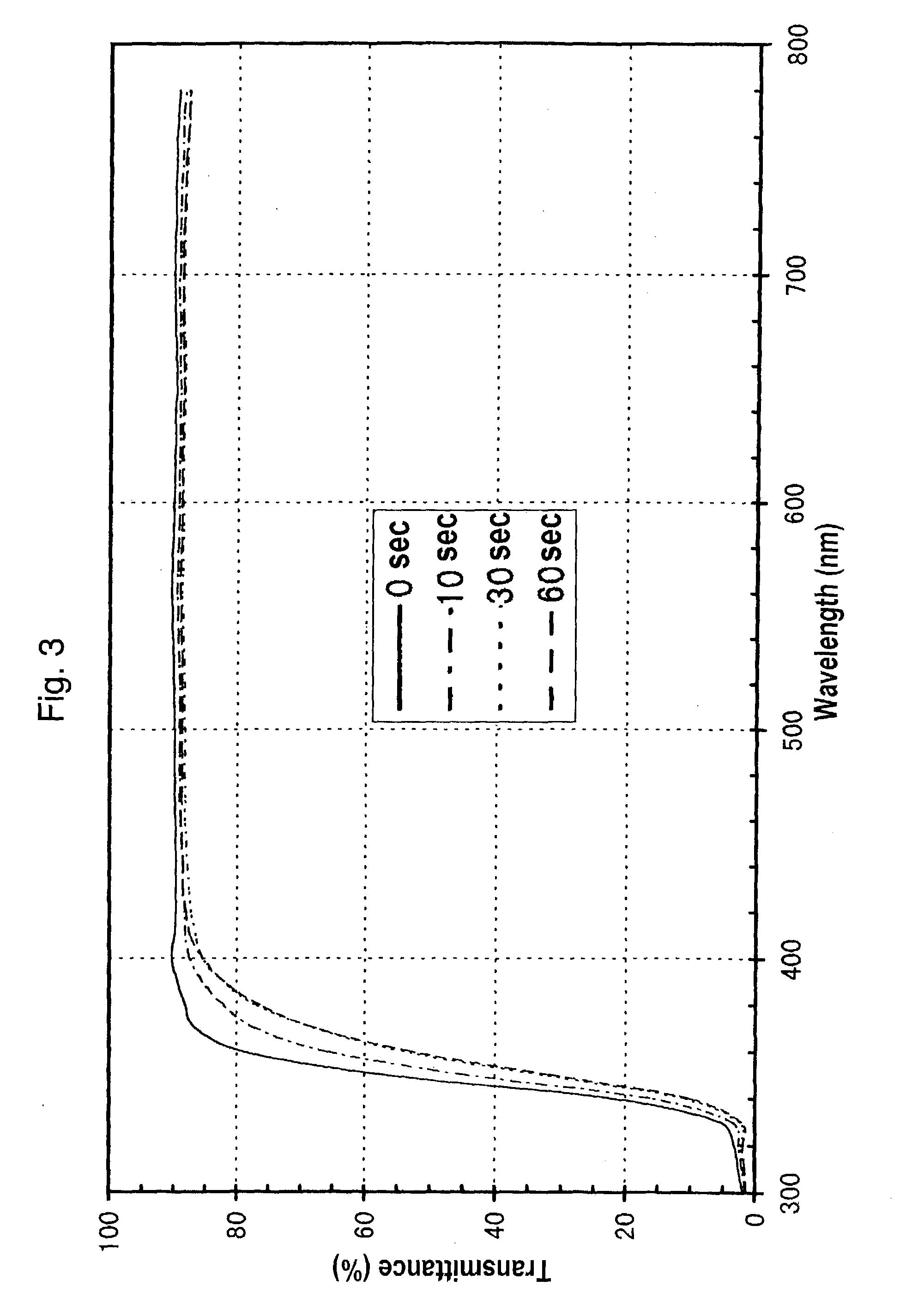
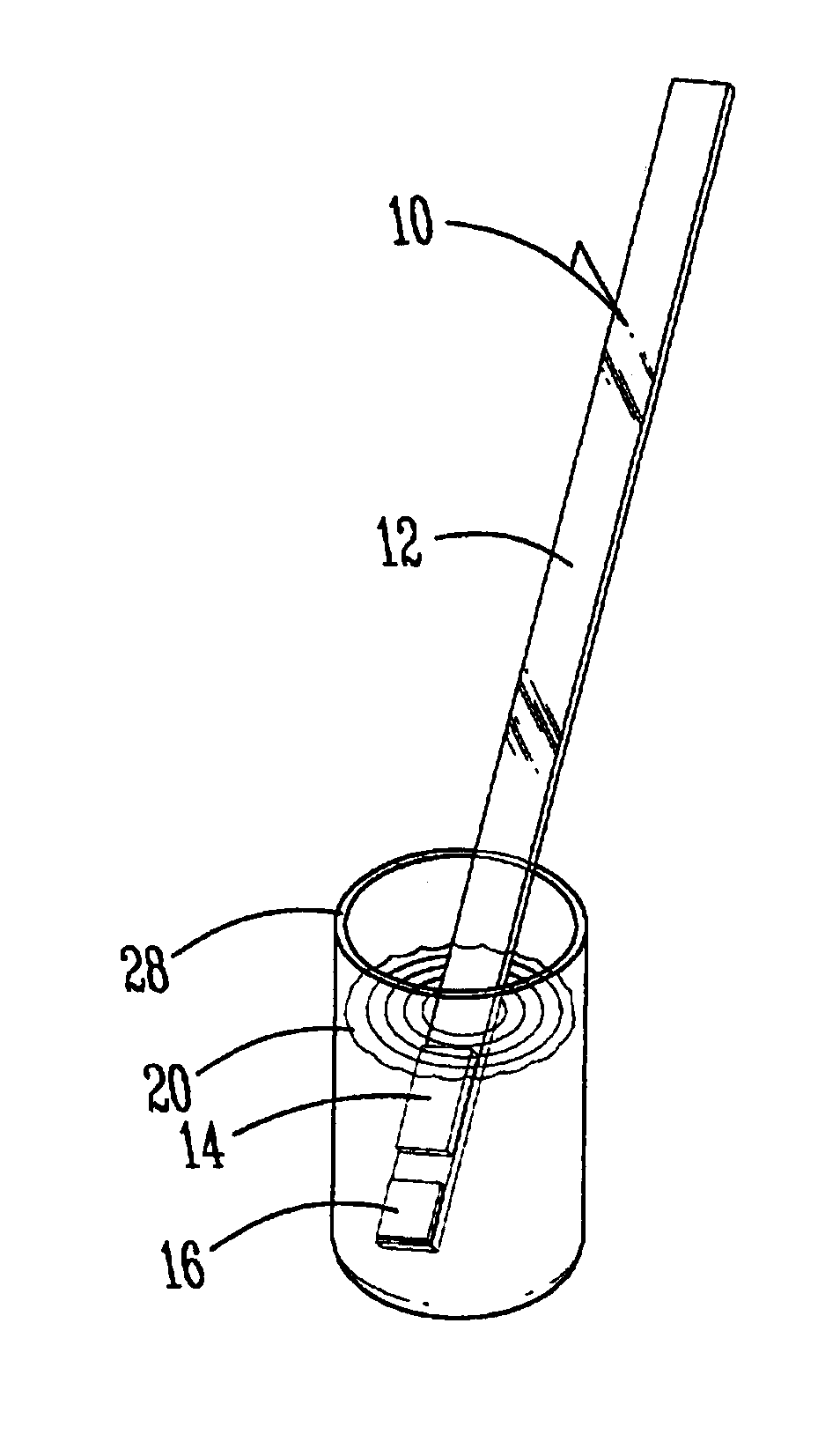
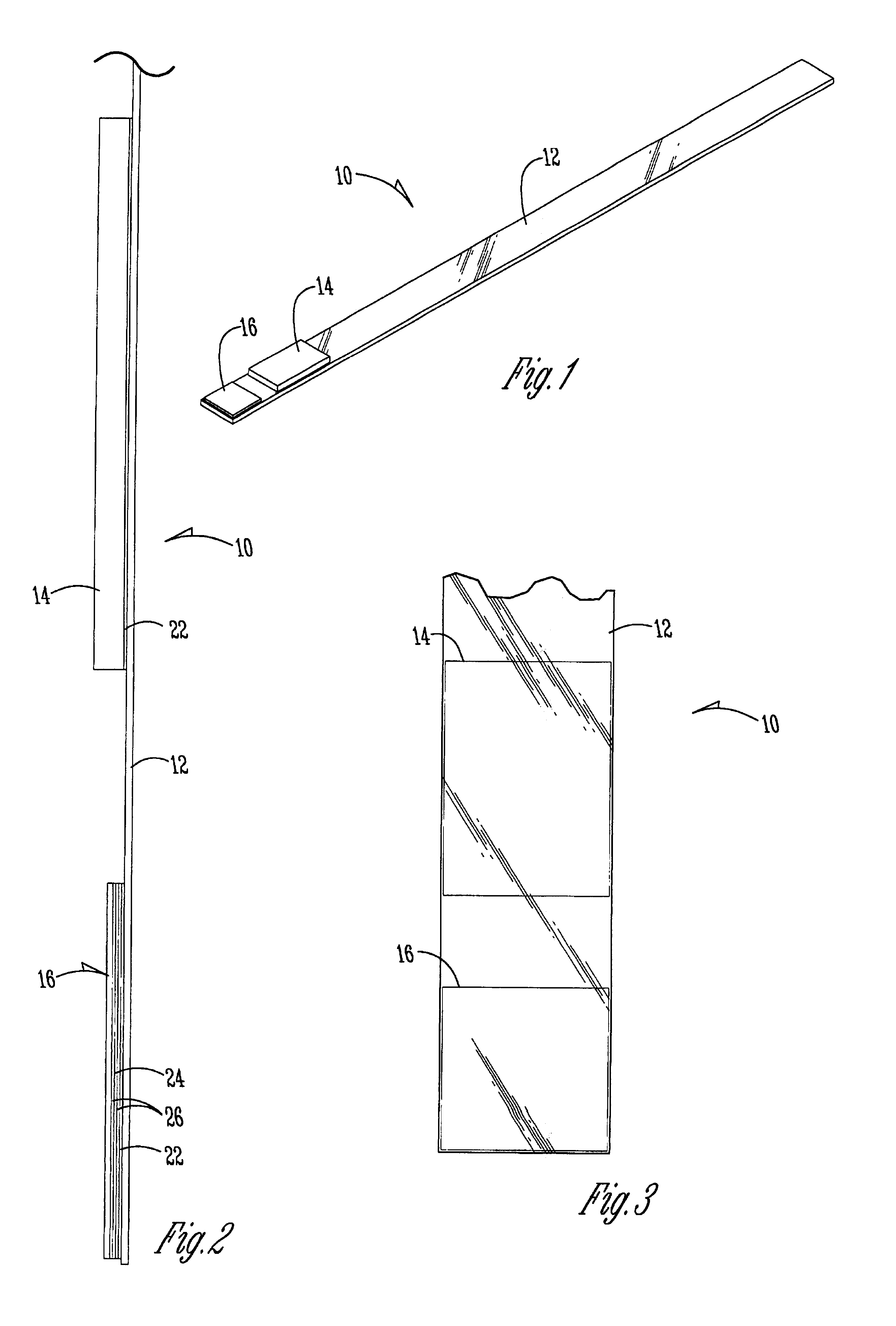
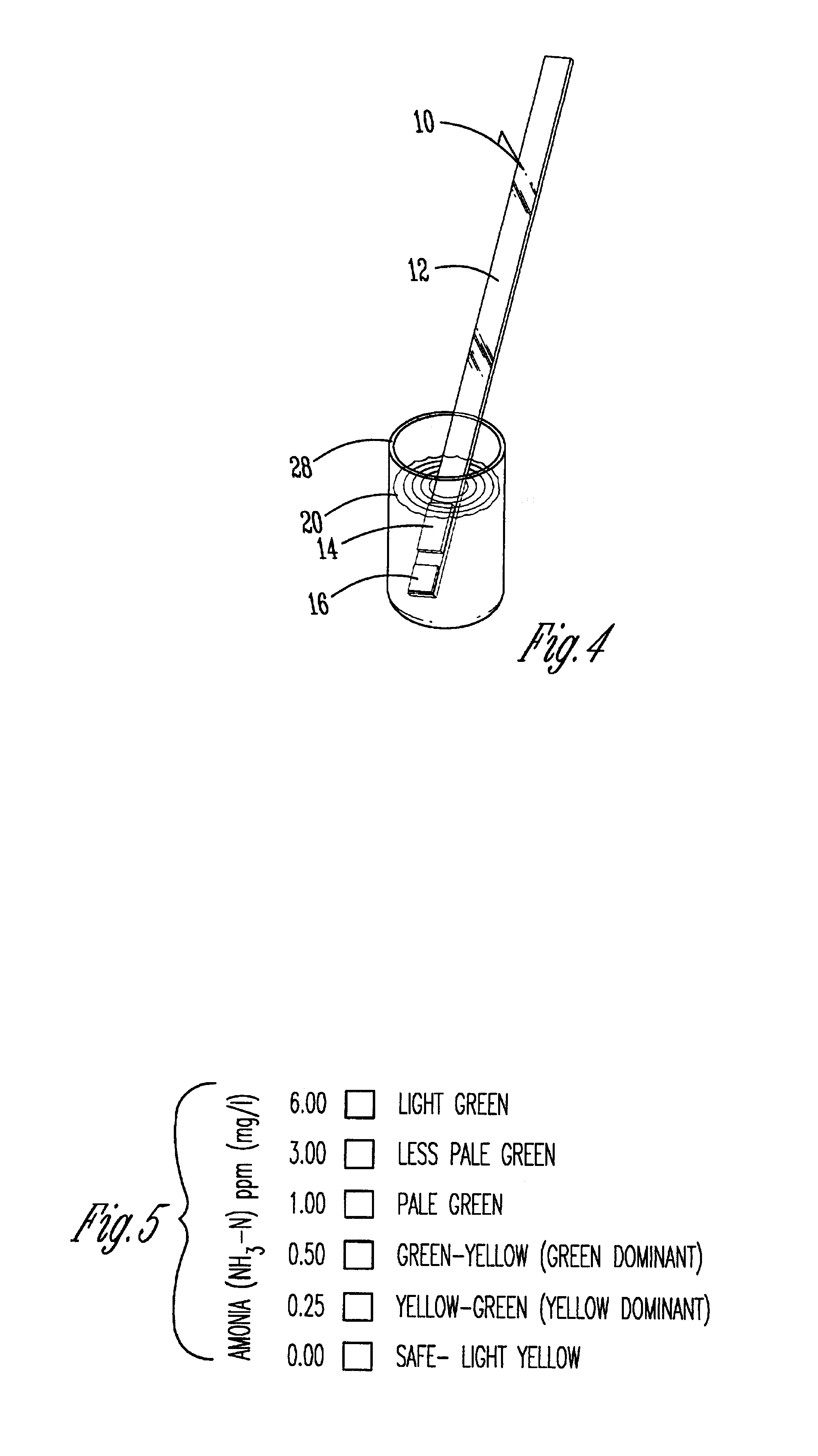
Quick acting toxic ammonia test for aqueous samples
InactiveUS7033839B1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorWater/sewage treatmentAmmonia levelsColor response
A method, test reagent and device usable as a test strip for detecting toxic ammonia levels in water samples such as aquarium water. The volume of the water to be tested contacted with a soda lime reagent to raise the pH to at least 10, and simultaneously contacted with a hydrophobic barrier membrane capable of allowing only ammonia gas to pass through. The membrane is coated with a pH chromogenic indicator mixture which changes color if ammonia gas passes through. The color response of the sample is compared with standard color charts to determine the toxic ammonia potential.
Owner:HACH CO
Treatment of particles for improved performance as proppants
ActiveUS8193128B2Reduce the amount requiredDecreased fractionFluid removalFlushingMolten saltIon exchange
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Treatment of particles for improved performance as proppants
ActiveUS20100326657A1Reduce the amount requiredDecreased fractionFluid removalFlushingMolten saltIon exchange
The disclosed invention relates to a process of using molten salt ion exchange to treat particles such as spherically shaped soda-lime-silica glass particles. The treated particles may be used as proppants in hydrofractured oil and natural gas wells.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Soda-lime-silica glass compositions and applications
The subject of the invention is a glass composition of the silica-soda-lime type, intended for the manufacture of substrates or sheets, the said glass composition having a φ coefficient of between 0.50 and 0.85 N / (mm2.° C.) and a working point of less than 1200° C.
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
Synthetic cork compound
A synthetic cork compound includes a methyl vinyl silicone polymer with a microsphere agent such as soda lime borosilicate in an amount of approximately 5 to 50 weight percent. The microsphere agent gives the compound a low density. The methyl vinyl silicone polymer preferably includes polydimethylvinylsiloxane polymer from about 45 to 90 weight percent and fumed silica from about 5 to 50 weight percent. Preferably, the compound is catalyzed using chloro-platanic acid from about 0.1 to 5 percent. Additional components of the compound include toasted oak dust from about 0.1 to 25 weight percent, ground cork from about 5 to 50 weight percent, a pigment from about 0.1 to 5 weight percent, silicon hydride from about 0.1 to 25 weight percent, and ethynyl cyclohexanol from about 0.05 to 5 weight percent.
Owner:M MANAGEMENT TEX
Cyclopropene preservative with double functions of anticorrosion and keeping freshness
The cyclopropene consists of: 1-methyl cyclopropene 0.3-4 weight portions, preservative 5-40 weight portions, stabilizer 60-90 weight portions, slow releasing agent 0-20 weight portions and excipient 0-5 weight portions. The preservative is one or several of 2-aminobutane, phosphate of 2-aminobutane, hydrochloride of 2-aminobutane, sulfate of 2-aminobutane, lactate of 2-aminobutane, sodium pyrosulfite, potassium pyrosulfite, sodium bisulfite, potassium bisulfite and propyl isothiocyanate; the release controlling agent is one or several of lime, sodium bicarbonate, soda lime, reductive microcrystal alditol acid lignin polyacrylamide; and the stabilizer is one or several of cyclodextrin, rosin, silica gel and lac. The slow releaseing preservative has obvious functions of resisting rot and keeping freshness.
Owner:NAT ENG AN TECH RES CENT FOR PRESERVATION OF AGRI PROD TIANJIN
Method for producing 4A molecular sieve
InactiveCN101445254ALower requirementRemoval of Synthetic Affecting FactorsAluminosilicate zeolite type-ASodium aluminateSODIUM SILICATE SOLN
A method for producing a 4A molecular sieve comprises the following steps: (a) an intermediate product sodium silicate solution or a product carbon white obtained in the process of extracting silicon dioxide by a fly ash alkali solution method, (b) an intermediate product sodium aluminate solution or products aluminum hydroxide and aluminum oxide obtained in the process of extracting aluminum oxide by a fly ash soda lime sintering method, (c) NaOH and (d). H2O are taken as raw materials which meet the following mol ratios: Na2O:SiO2=1.6-3.8:1 and SiO2:Al2O3=1.7-2.1:1, and water added is controlled at the mol ratio of H2O:Na2O=30-60:1; and the raw materials are evenly mixed, stirred and gelled at 50-80 DEG C, heated to 90-120 DEG C, kept standing and crystallized for 3-6 hours, filtered, washed and dried to obtain the 4A molecular sieve. The calcium exchange capacity of the produced 4A molecular sieve is not less than 310mgCaCO3 / g, and the sieving rate of a 1.25mm sieve is not lower than 90%.
Owner:PINGSHUO INDAL
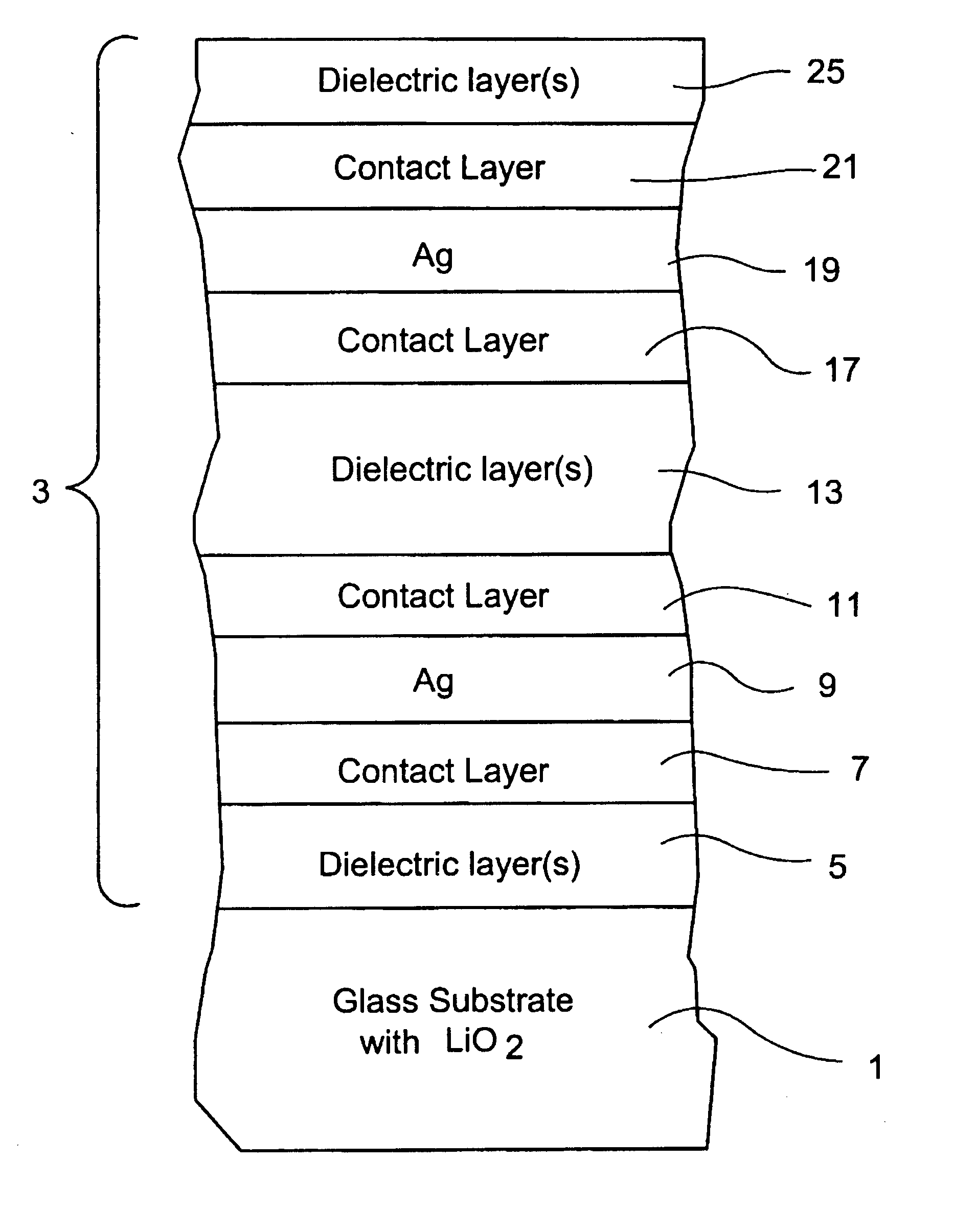
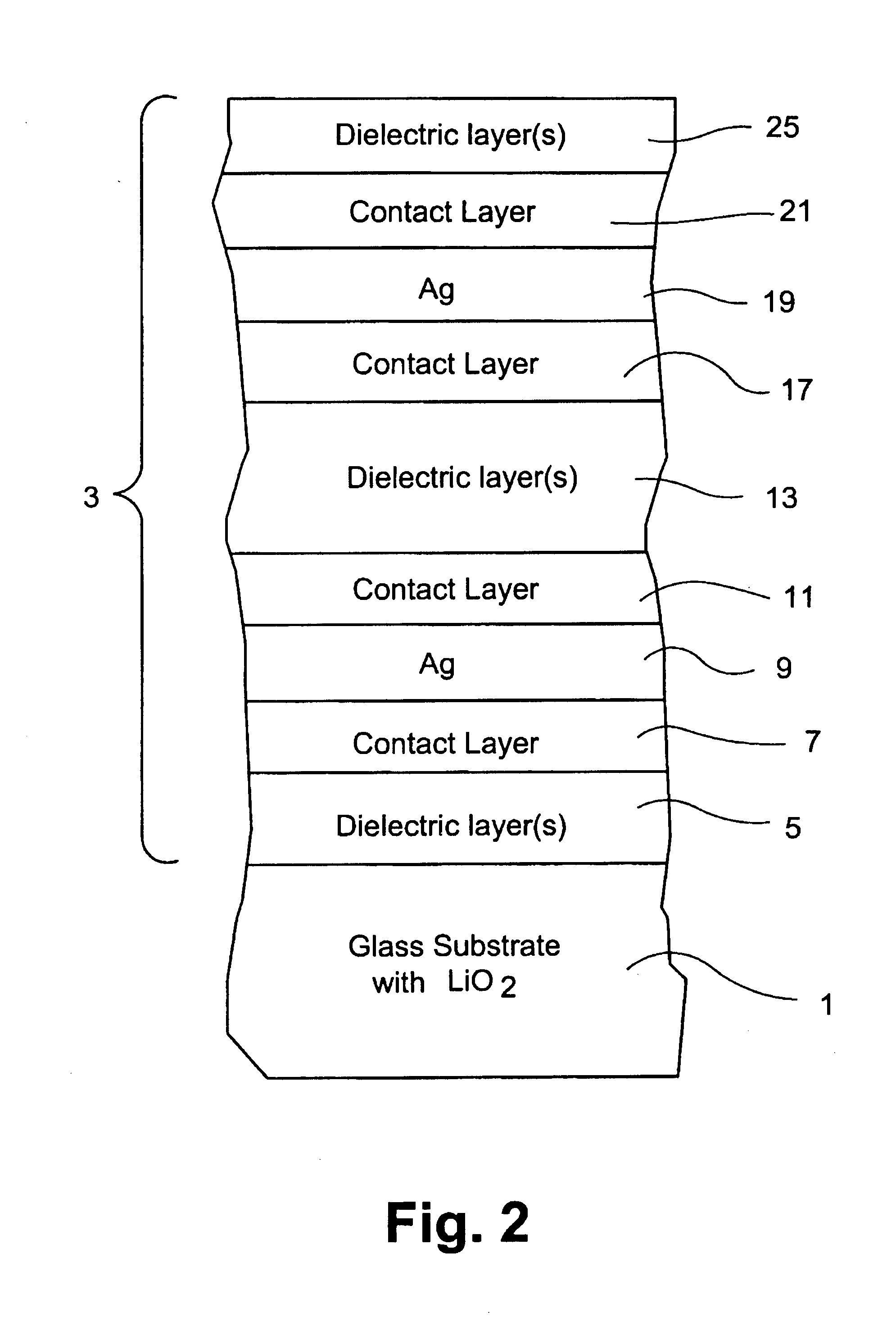
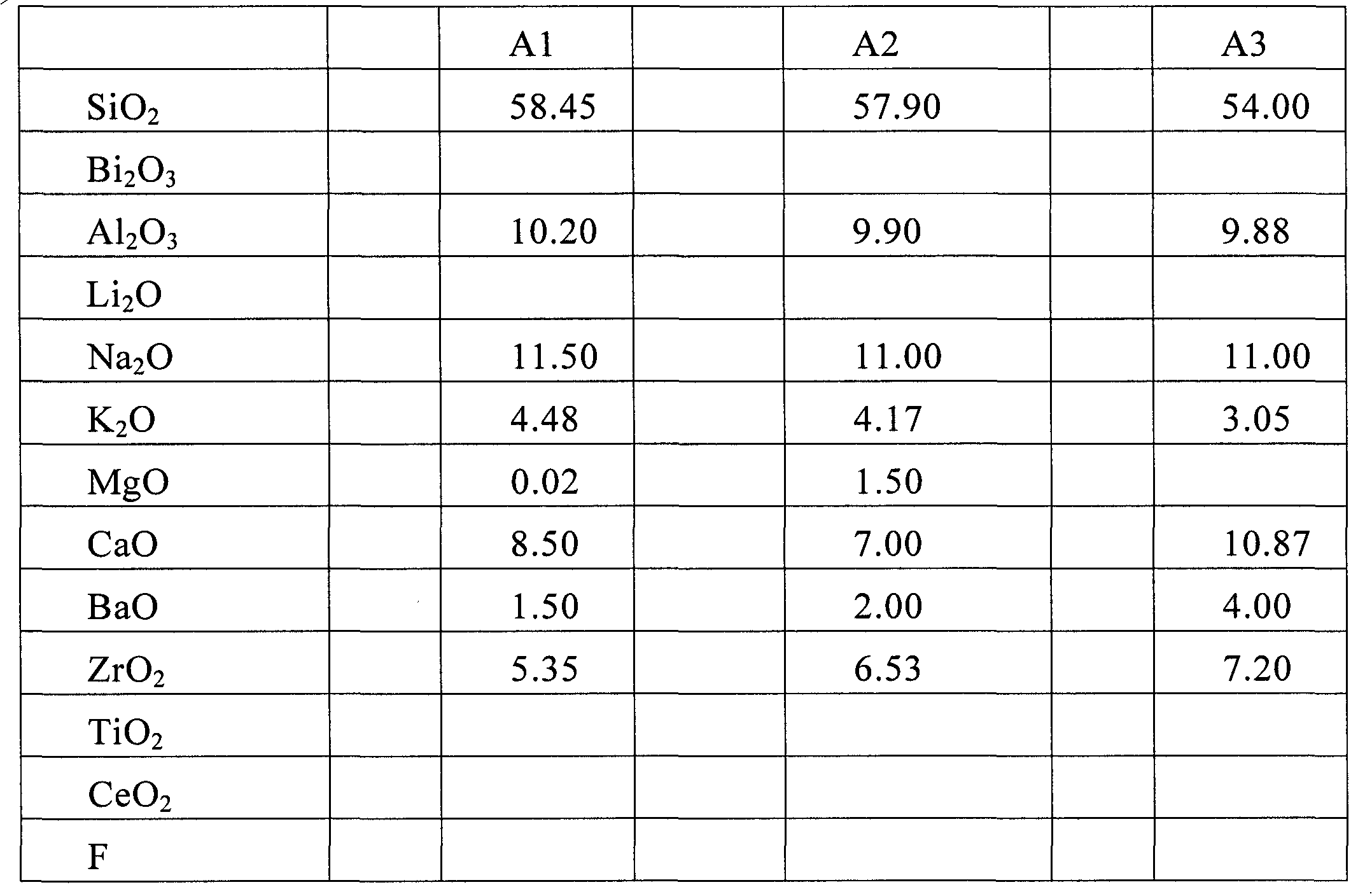
Coated article including soda-lime-silica glass substrate with lithium and/or potassium to reduce sodium migration and/or improve surface stability and method of making same
InactiveUS20070036987A1Reduce sodium migrationImprove surface stabilityGlass/slag layered productsCoatingsLithium oxideLow emissivity
A coated article includes a glass substrate that supports a coating such as a low-E (low emissivity) coating. In certain example embodiments, the glass substrate is formed of a soda-lime-silica based glass composition manufactured using a float process. In certain example embodiments, lithium oxide (e.g., LiO2) and / or potassium oxide (K2O) is used in the soda-lime-silica based glass substrate in order to reduce sodium migration and / or improve surface stability. Such coated articles are useful, for example and without limitation, in architectural, vehicular and / or residential glass window applications.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Aluminosilicate glass having high thermal stability and low processing temperature
ActiveCN102548919AImprove efficiencyRaise the processing temperatureThermal dilatationSoda-lime glass
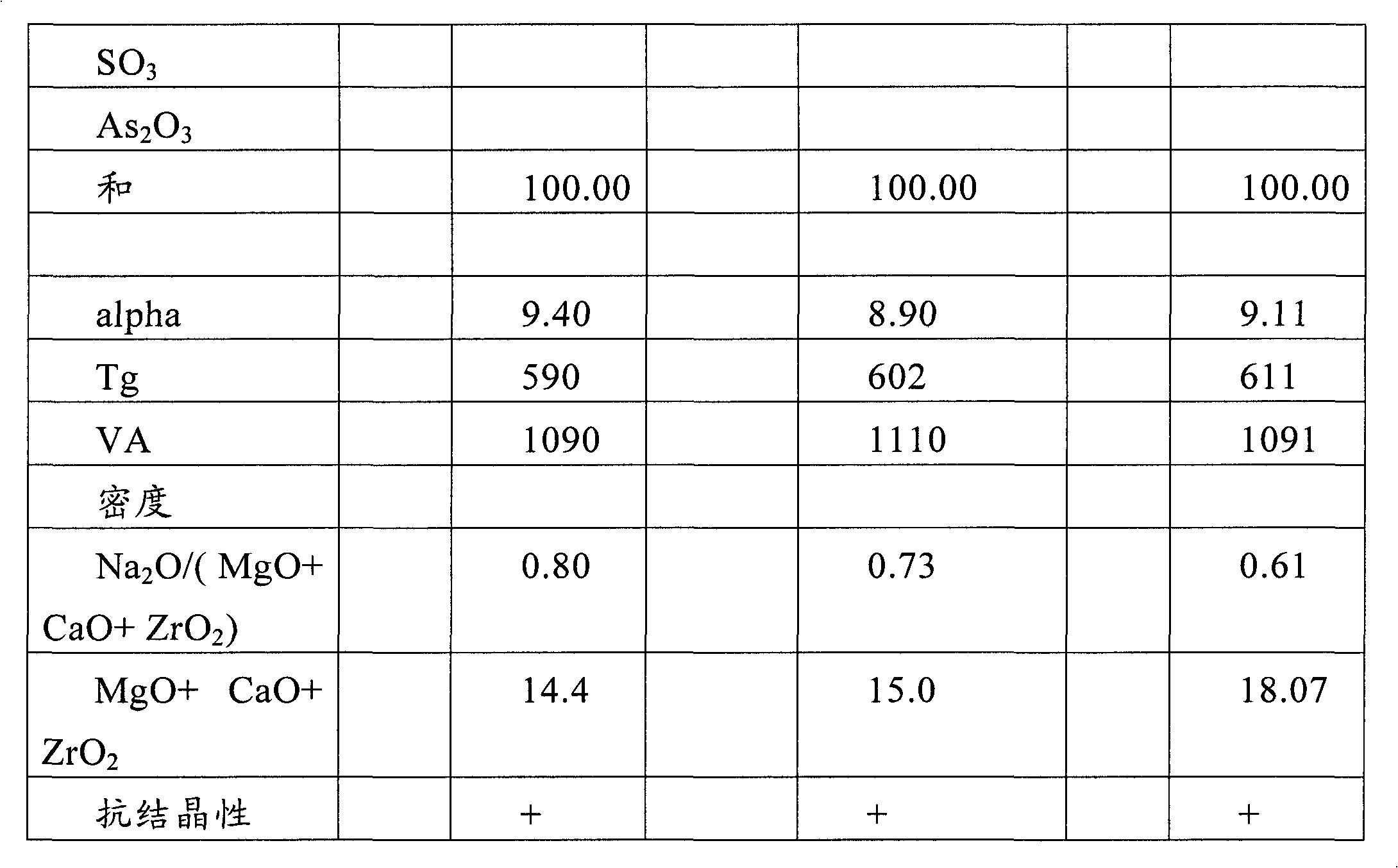
The invention relates to an aluminosilicate glass having a thermal expansion coefficient ranging from 8 to 10 x 10-6 / K in a temperature range of 20 to 300 DEG C, a transformation temperature Tg ranging from 580DEG C; C to 640DEG C; C, and a processing temperature VA ranging from 1065DEG C; C to 1140DEG C; C, and thus can be used as an alternative to soda lime glass. The invention further relates to the use of the glass according to the invention in applications where high thermal resistance of the glass is advantageous, in particular as substrate glass, superstrate glass and / or cover glass in the field of semiconductor technology, preferably for Cd-Te or for CIS and / or CIGS photovoltaic applications, and for other applications in solar technology.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Alumino-silicate glass having high thermal stability and low processing temperature
The invention relates to an alumino-silicate glass which has a thermal expansion coefficient in the range of 8 to 10×10−6 / K in a temperature range of 20 to 300° C., a transformation temperature Tg in a range of 580° C. to 640° C., and a processing temperature VA in a range of 1065° C. to 1140° C. and which can therefore be used as an alternative for soda lime glasses. An object of the invention is also the use of the inventive glasses in applications where a high temperature stability of the glasses is advantageous, in particular as substrate glass, superstrate glass and / or cover glass in the field of semiconductor technology, preferably for Cd—Te or for CIS or CIGS photovoltaic applications and for other applications in solar technology.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method of making glass including use of boron oxide for reducing glass refining time
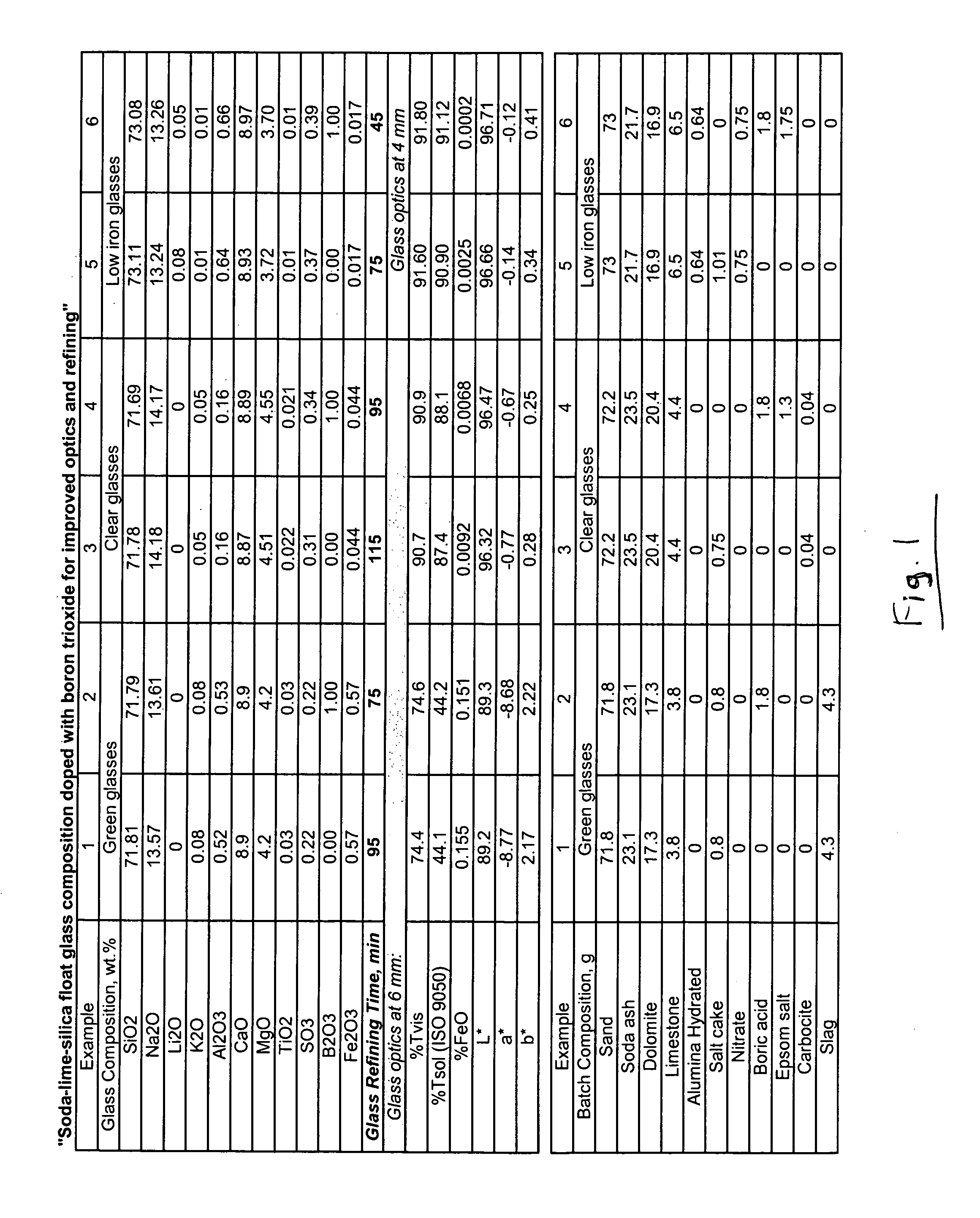
InactiveUS20070207912A1Reduce refining timeIncrease ratingsGlass furnace apparatusBoric acidBoron oxide
This invention relates to a method of making soda-lime-silica based glass. In certain example embodiments, boron oxide (e.g., B2O3) is used in the glass for reducing the refining time (or increasing the refining rate) thereof. The boron oxide may be introduced into the glass batch or melt in the form of boric acid, sodium tetraborate pentahydrate, sodium tetraborate decahydrate, sodium pentahydrate, or in any other suitable form. In certain example embodiments, the resulting soda-lime-silica based glass ends up including from about 0.1 to 3%, more preferably from about 0.1 to 2.5%, and most preferably from about 0.5 to 2.0% (e.g., about 1%), boron oxide. It has been found that the use of boron oxide, and / or the form in which the same is introduced into the glass, is advantageous in that it permits the refining time of the glass to be substantially reduced.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Light scattering reflection substrate?use photosensitive resin composition, light scattering reflection substrate, and production methods therefor
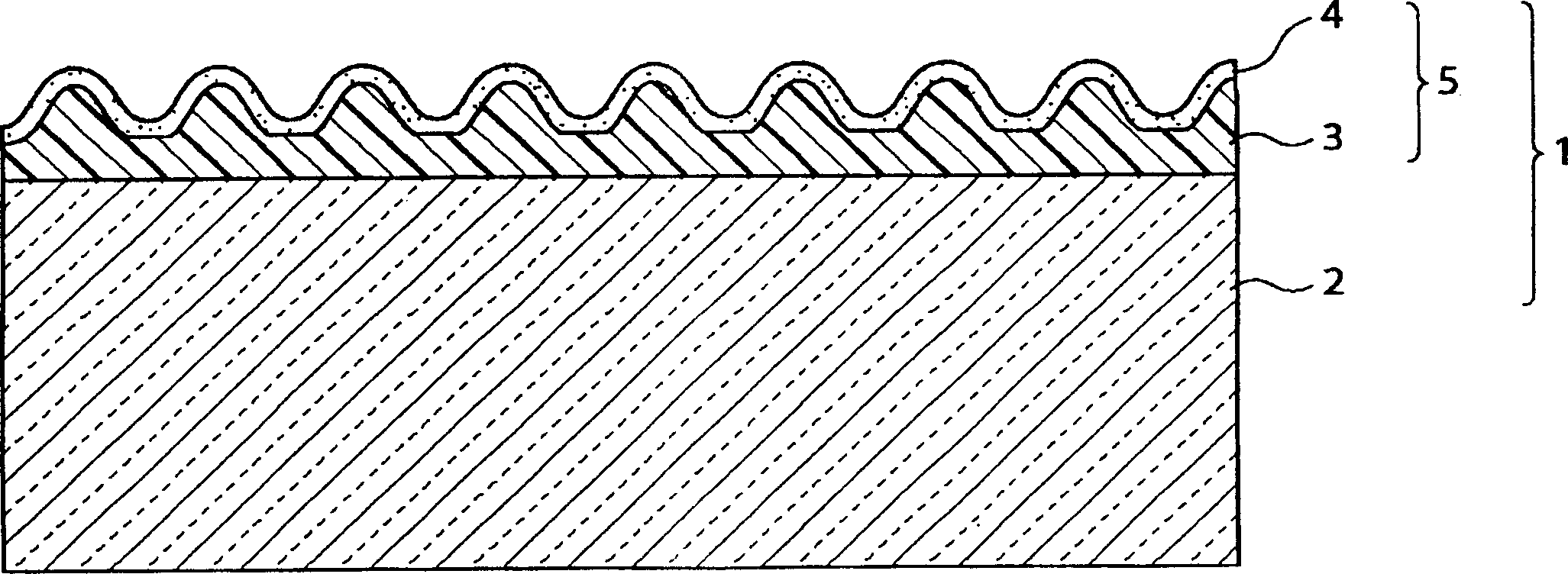
InactiveCN1468383AImprove adhesionIncreased durabilityMirrorsDiffusing elementsSilicate glassSilicon oxide
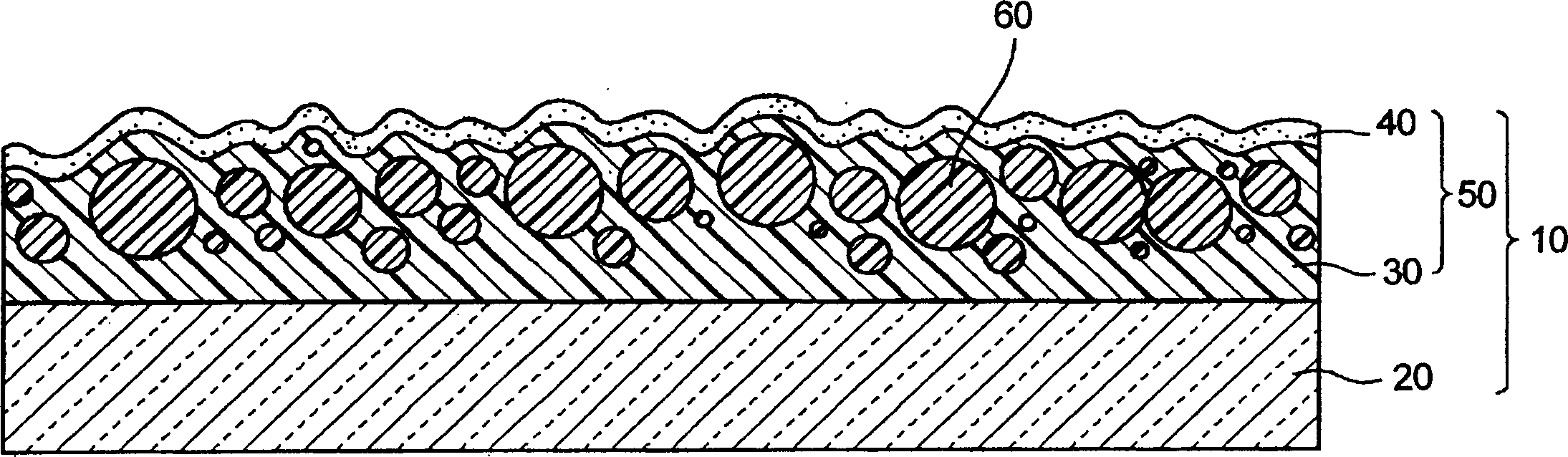
A first object of the present invention is to provide a light-scattering / reflecting substrate according to which adhesion between a light-scattering film and a reflecting film can be improved, and durability and chemical resistance can be improved. A light-scattering / reflecting substrate 1 is comprised of a soda lime silicate glass substrate 2, a light-scattering film 3 that has an undulating shape and is formed on the glass substrate 2, and a reflecting film 4 that is formed on the light-scattering film 3 following the undulating shape of the light-scattering film 3. The light-scattering film 3 is formed into the desired undulating shape by applying, onto a surface of the glass substrate 2, a material obtained by adding a photosensitive resin made of an organic material as a binder to an inorganic material such as silicon oxide (silica), aluminum oxide (alumina) or titanium oxide (titania), and then using a photolithography method.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Fruit and vegetable preserving backing
InactiveCN1505935AReduce mechanical damageSuppresses aging symptomsFruit and vegetables preservationChlorine dioxidePotassium
The fruit and vegetable preserving backing consists of preferably: preservative 4-40 weight portions, physiological regulator 0-30 weight portions and gas regulator 0-30 weight portions. The preservative is one or two of 2-aminobutane, hydrochloride of 2-aminobutane, sulfate of 2-aminobutane, sodium pyrosulfite, potassium pyrosulfite, sodium bisulfite, potassium bisulfite, stable chlorine dioxide, propyl isothiocyanate, cinamic aldehyde and acetyldehyde; the physiological regulator is potassium permanganate and / or potassium bromate; and the gas regulator one or several of soda lime, sodium hydroxide, lime and active carbon. The present invention has the functions of reducing mechanical damage of fruits and vegetables, suppressing softening, yellowing and other senility symptoms of fruits and vegetables during storage and transportation, reducing rot of fruits and vegetables during transportation caused by vibration and pressure and regulating humidity inside the package.
Owner:NAT ENG AN TECH RES CENT FOR PRESERVATION OF AGRI PROD TIANJIN
Ion exchange process for thin glass chemical tempering and fused salt
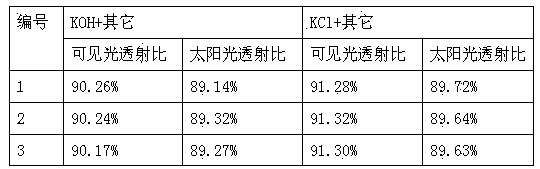
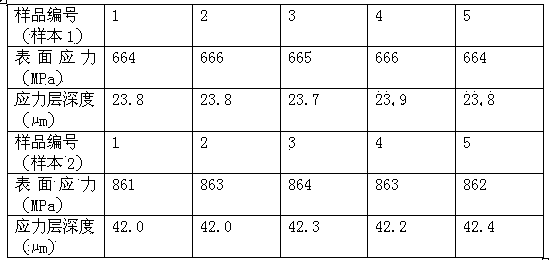
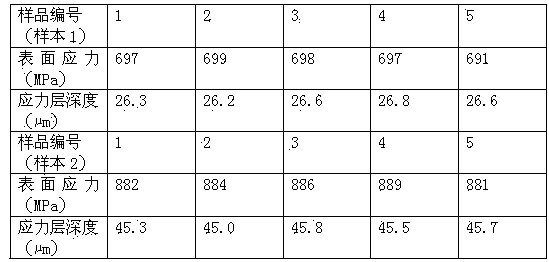
The invention relates to a thin glass tempering treatment technology, and in particular relates to fused salt for thin glass chemical tempering and a production process thereof. The main component of the fused salt is KNO3, and the auxiliary component is KCl, K2CO3, KSb(OH)6 and gamma-Al2O3, the warming speed of a pre-heating furnace in the production process is 5+ / -0.5 DEG C per minute, heat preservation is performed for 30+ / -5 minutes after the temperature is raised to 350+ / -5 DEG C, and then the glass is placed in the fused salt so as to be subjected to the ion exchange; the glass subjected to the ion exchange is placed in an annealing furnace so as to be cooled, and the temperature of the annealing furnace is 300+ / -5 DEG.C; a power source is turned off after the glass is placed therein, so as to slowly cool to 50+ / -5 DEG.C, and then the glass is taken out so as to be cleaned, dried and packaged. The surface stress of the normal soda lime silica glass produced by the invention can achieve 650MPa and more, the stress layer depth can achieve 23microns and more; the surface stress of alkaline alumina silicate glass can achieve 850MPa and more, and the stress layer depth can achieve 40 microns and more.
Owner:CHINA LUOYANG FLOAT GLASS GROUP
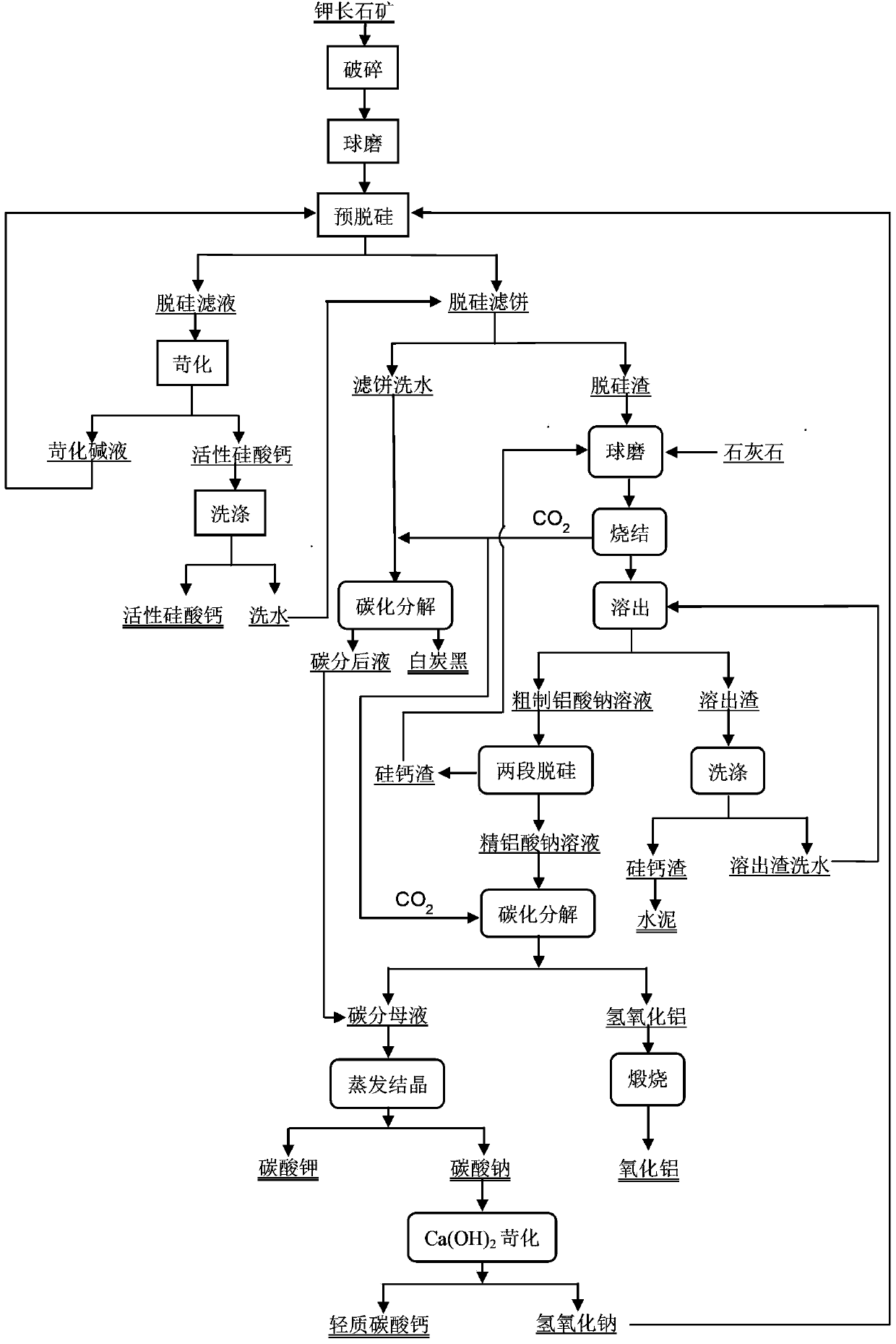
New technology using potash feldspar ore for production of potash, sodium carbonate and alumina
ActiveCN104211094AReasonable product planIncrease production costAlkali metal carbonatesAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationCalcium silicateSlag
The invention discloses a new technology using potash feldspar ore for production of potash, sodium carbonate and alumina, and a method comprising pre-desiliconization, soda-lime sintering dissolution, aluminum extraction by carbon and evaporation crystallization for separation of potassium and sodium is used for comprehensive recovery of aluminum, potassium and sodium resources. The new technology has the following advantages: the technical scheme of the new technology is reasonable, and active calcium silicate, white carbon black, sodium carbonate potassium carbonate and alumina can be produced. In carbonation decomposition process of the new technology, CO2 gas produced by sintering is used, the raw material cost is very low, and the greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced. During the sintering, the amount of a pre-desiliconization raw material is reduced by about 35%, the amount of silicon calcium slag is reduced by about 30%; desilicification slag needs no addition of sodium carbonate for raw material proportioning; washing water for washing active calcium silicate can be used for desiliconization slag washing, the amount of process water and waste water can be reduced, the silica product form can be enriched, the white carbon black and activated calcium silicate with the high added value can be outputted; by causticization regeneration of the sodium carbonate, alkali self-sufficiency and equilibrium cycle of the whole process can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
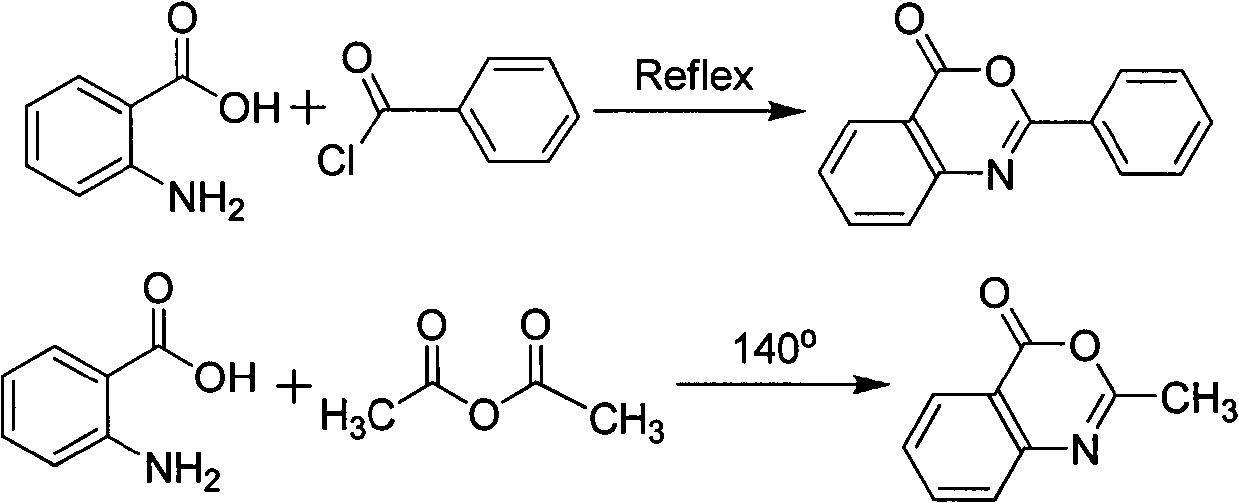
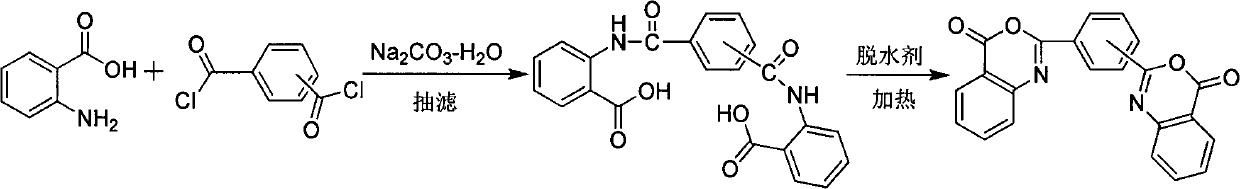
Novel synthetic method of bis-benzoxazine ketone ultraviolet absorbent
The invention provides a novel synthetic method of a bis-benzoxazine ketone ultraviolet absorbent, and belongs to the technical field of fine chemical engineering. The method comprises the following steps: A, stirring, anhydrides, used as raw materials, of o-aminobenzoic acid and (o-, m-, p-) phthaloyl dichloride or (o-, m-, p-)phthalic acid for a certain time in a non-polar solvent; B, adding chemical dehydrating agent or physical dehydrating agent in a reaction system without separating, slowly heating and refluxing for a certain time to obtain (o-, m-, p-)substituted bis-benzoxazine ketone ultraviolet absorbent; wherein the stirring time in the step A is not less than 1 hour, the refluxing time is 5-10 hours in the step B, the chemical dehydrating agent used in the step B is various dehydrating agents reacted with the water, including but not limited to alkaline calcium oxide, soda lime, acidic concentrated sulfuric acid, concentrated phosphoric acid, polyphosphoric acid, phosphorus pentoxide, thionyl chloride, acetic anhydride and the like, neutral molecular sieve, water-absorbent, anhydrous cupric sulfate and the like; the physical dehydrating agent comprises but not limited to non-protonic solvent such as benzene, methylbenzene, xylene and the like. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple in operation flow, low in cost, simple in equipment, and suitable for the scale industrial production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High transmittance glass sheet and method of manufacturing the same
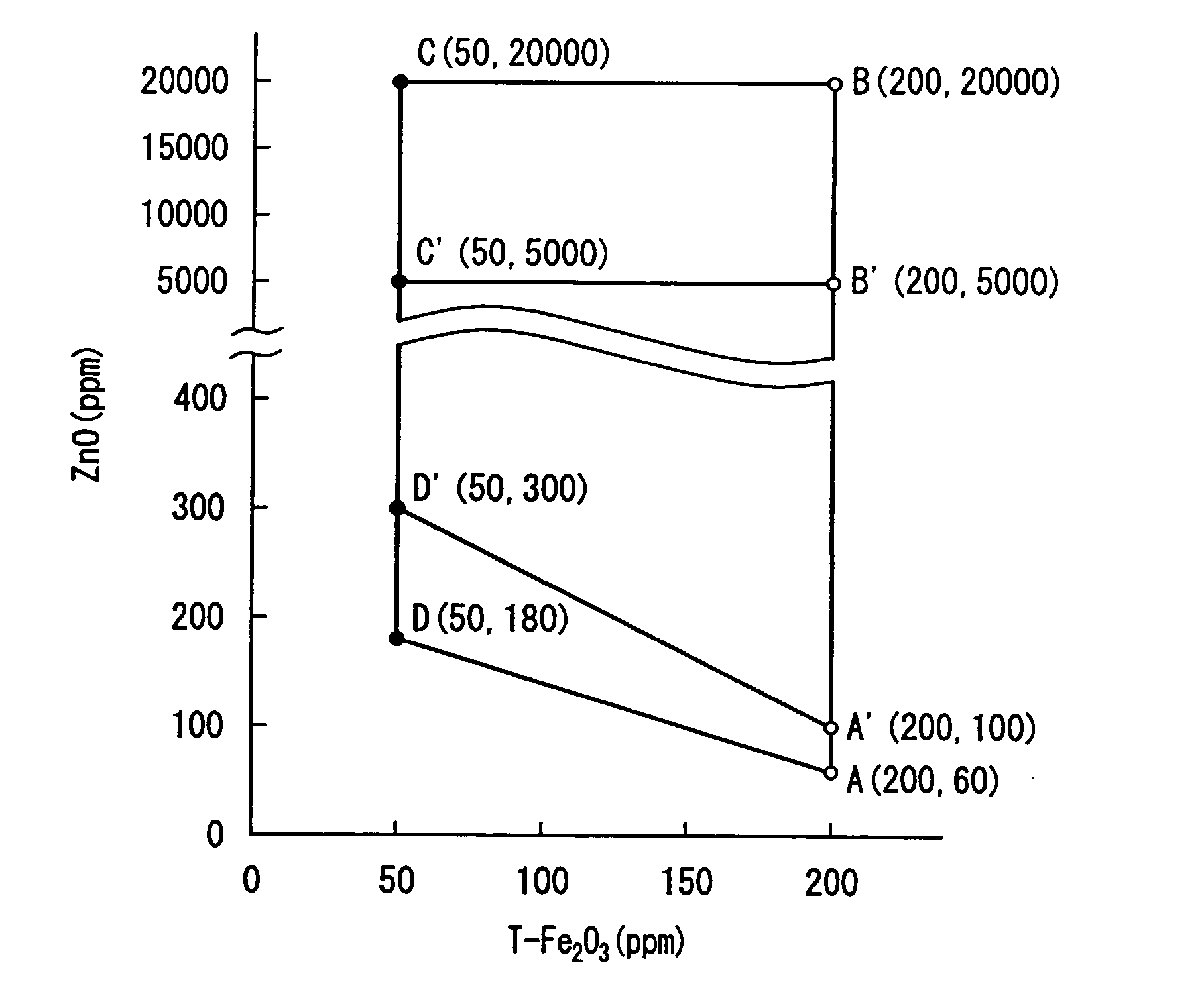
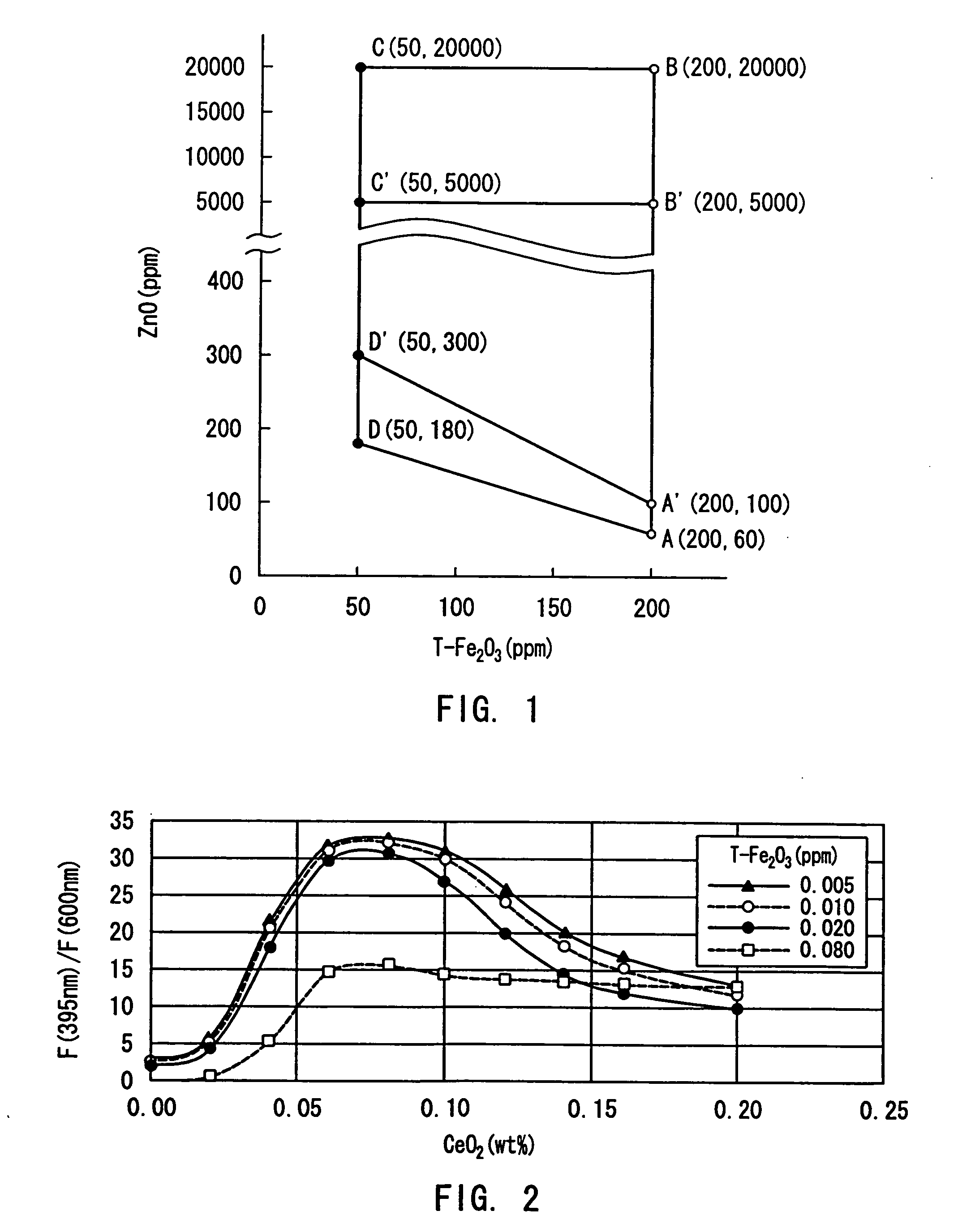
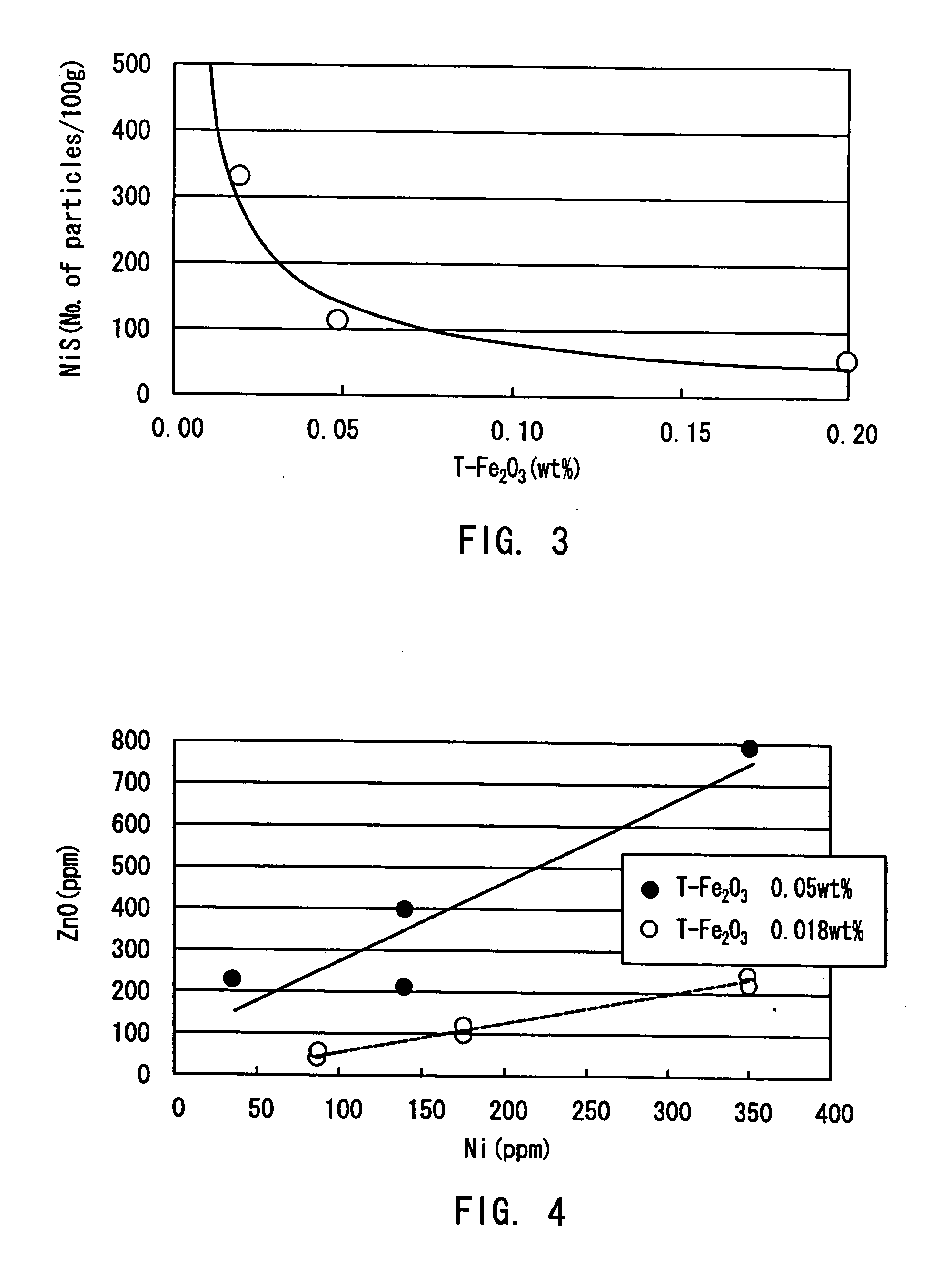
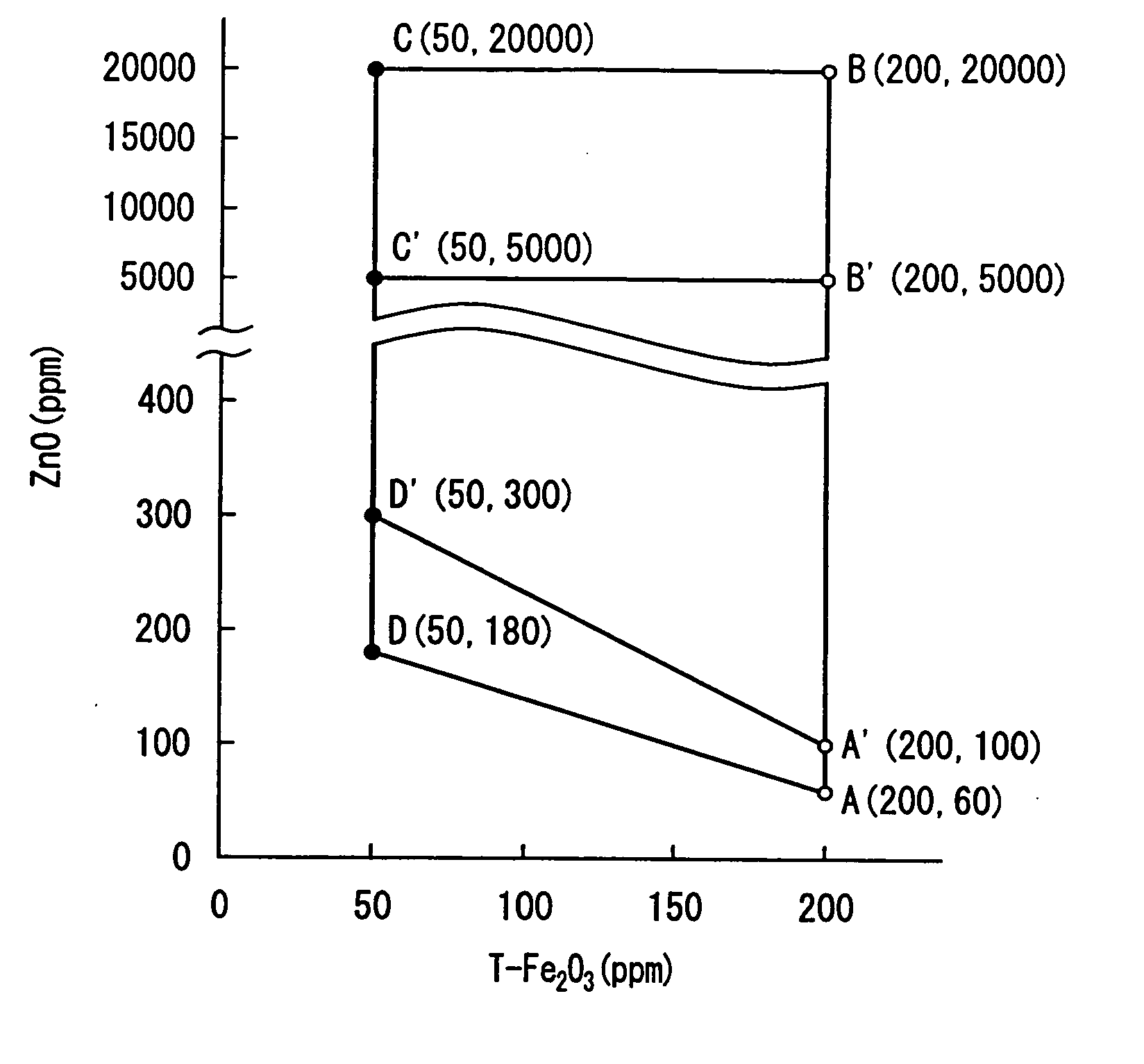
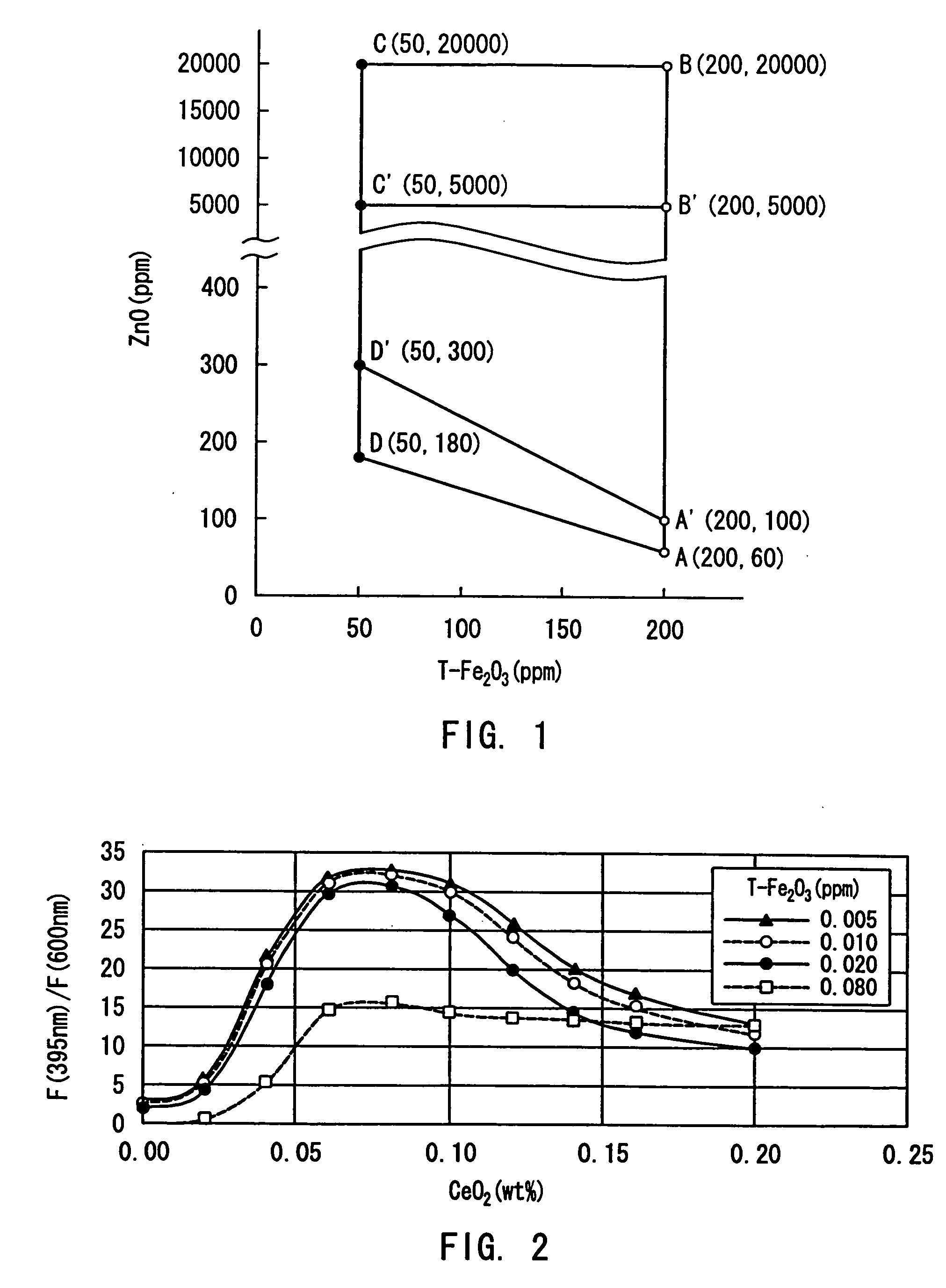
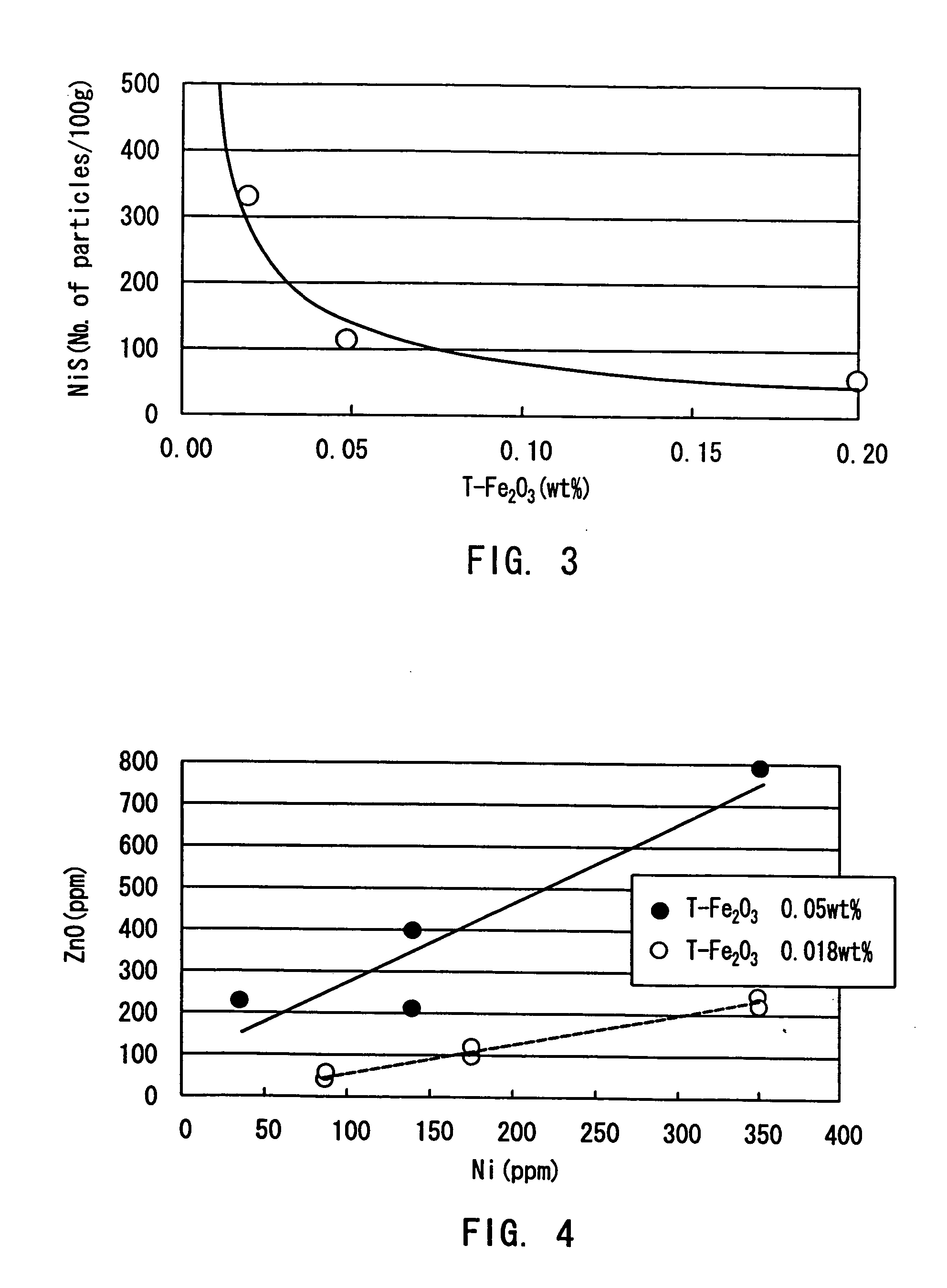
InactiveUS20040162212A1Reduce formationQuality improvementGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusZinc compoundsNickel sulfide
A high transmittance glass sheet is provided that is formed of a soda-lime-silica glass composition containing, expressed in wt. %, less than 0.020% of total iron oxide in terms of Fe2O3 and 0.006 to 2.0% of zinc oxide. The glass sheet allows the formation of nickel sulfide particles to be suppressed by the addition of a zinc compound to a glass raw material.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
High transmittance glass sheet and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20040157722A1Reduce formationQuality improvementGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusZinc compoundsNickel sulfide
A high transmittance glass sheet is provided that is formed of a soda-lime-silica glass composition containing, expressed in wt. %, less than 0.020% of total iron oxide in terms of Fe2O3 and 0.006 to 2.0% of zinc oxide. The glass sheet allows the formation of nickel sulfide particles to be suppressed by the addition of a zinc compound to a glass raw material.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Water-based paint useful for windshields
The invention is directed to a water-based paint composition comprising sodium silicate, water, water-soluble base, metal oxide pigment, a fused silica and, optionally, a low-melting glass frit, soda-lime-silica glass particles and / or zinc oxide. It may further optionally include surfactants and aluminum hydroxide. The paint composition is particularly useful as a black-out paint on automotive vehicle windshields and has been shown to impart improved stone chip resistance to the glass.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
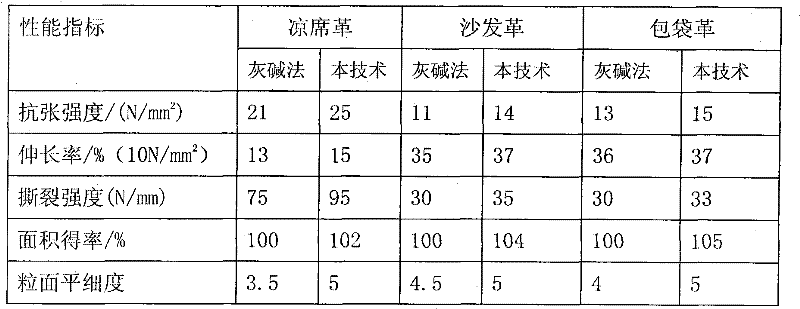
Clean tanning hair removal expansion method
InactiveCN102344975AEasy to operateGood hair removal effectLeather manufacturingPre-tanning chemical treatmentEnzymeHair removal
The invention discloses a clean tanning hair removal expansion method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: loosening hair roots while raw leather is immersed in water and softened under the synergistic action of various proteases; making hairs on the leather fall under the action of a fleshing machine during the fleshing of the conventional machine; and uniformly andappropriately loosening leather fibers under the actions of alkali and enzyme. The method is suitable for pollution-free production of hair removal expansion in the process of tanning cow leather. Bythe method, the defects of high content of suspended matters, chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) in waste liquor, heavy pollution and the like due to high using amount of sodium sulphide and lime in a barilla hair removal process are overcome, and the problems of uncompleted hair removal, damages to leather grain surfaces, loose surfaces and the like in the conventional enzyme hair removal process are solved.
Owner:LONGCHANG YANGZHOU LEATHER MAKING
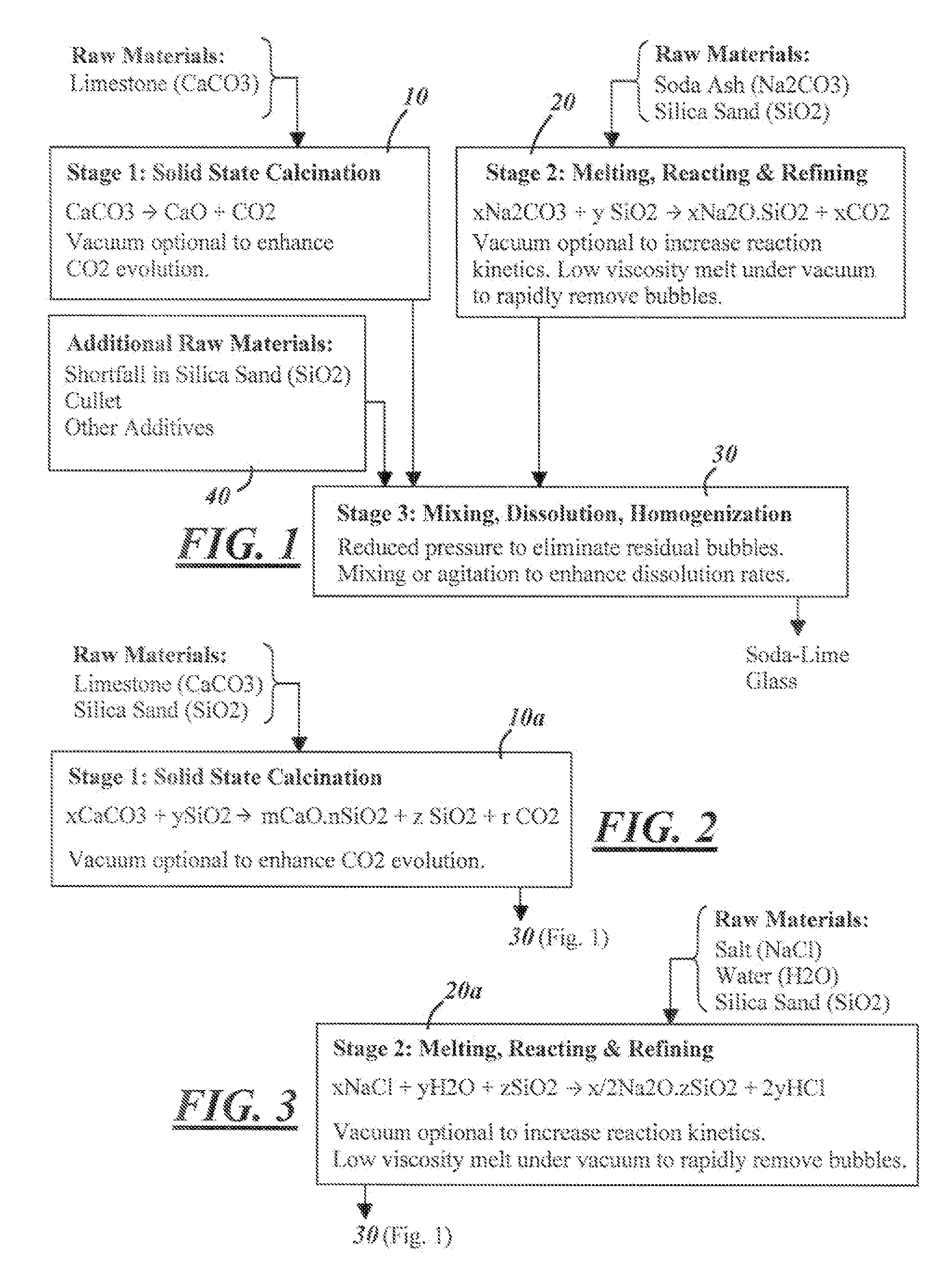
Process for Melting and Refining Soda-Lime Glass
ActiveUS20120216574A1High energy inputCharging furnaceGlass furnace apparatusSolid phasesSodium silicate
A process for making soda-lime glass includes calcinating calcium carbonate in solid phase and at elevated temperature to form calcium oxide and release gases such as carbon dioxide. Sodium silicate glass is formed separately in liquid phase while releasing gaseous reaction products. The calcium oxide and the sodium silicate glass intermediate products are mixed in liquid phase to form a soda-lime glass melt. Formation of sodium silicate glass as an intermediate product before mixing with the calcium oxide has the advantage of promoting release of gaseous reaction products in the sodium silicate due at least in part to the relatively low viscosity of the sodium silicate glass. The calcination step and / or the sodium silicate-forming step and / or the final mixing step can be carried out under reduced pressure further to promote release of gases and reduce bubble formation.
Owner:OWENS-BROCKWAY GLASS CONTAINER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com