Patents
Literature
1767 results about "Ultraviolet radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
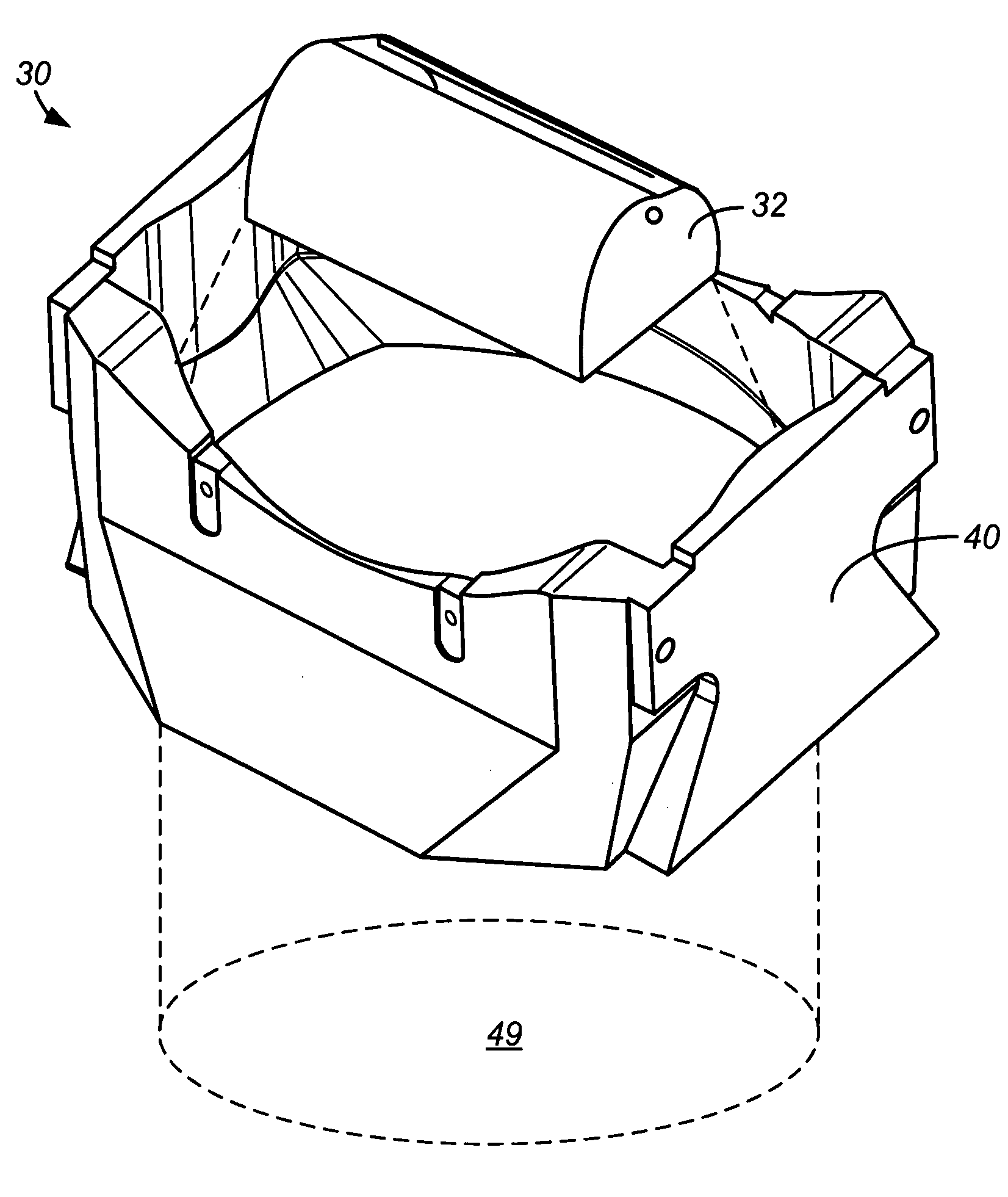
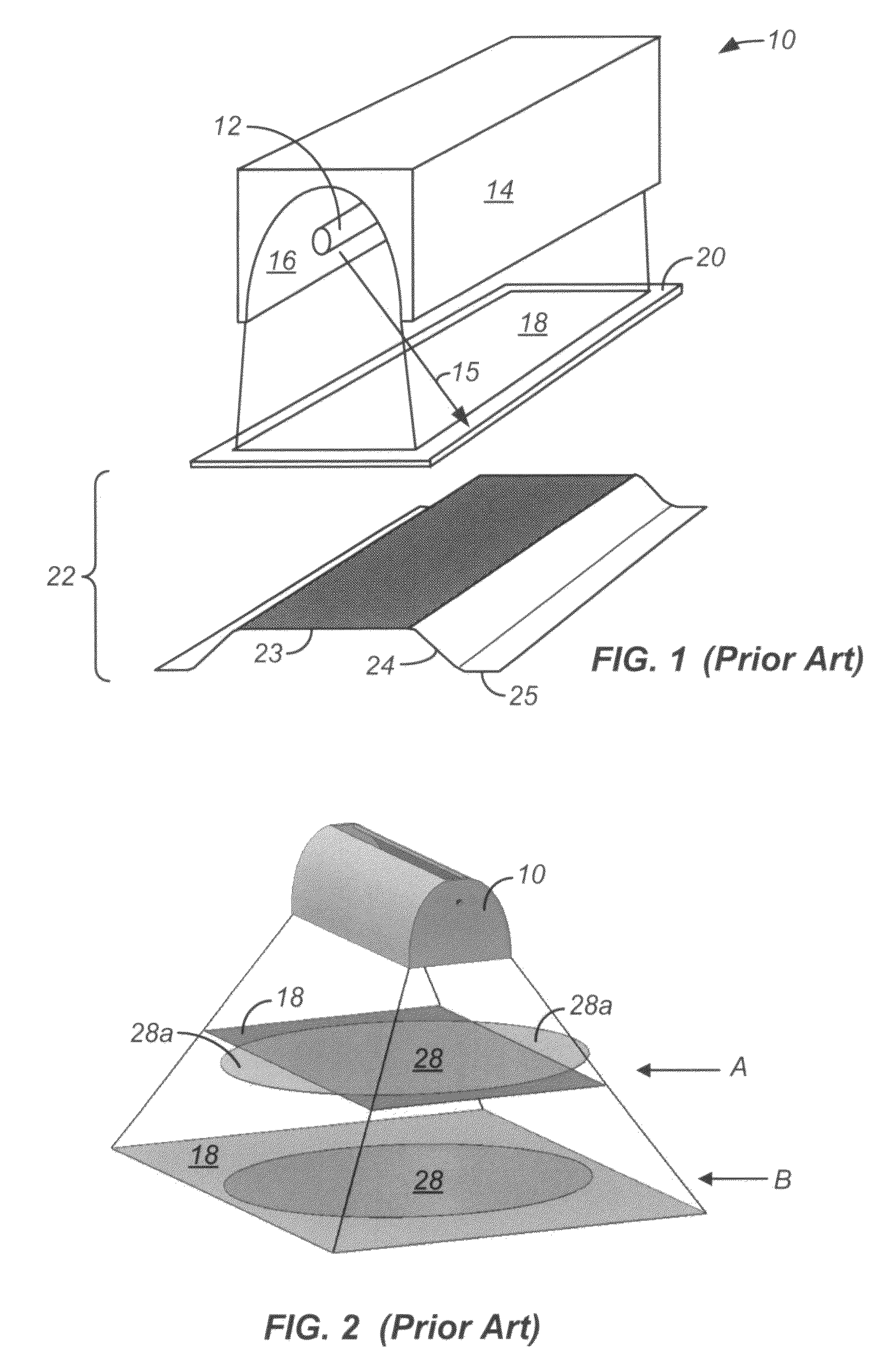
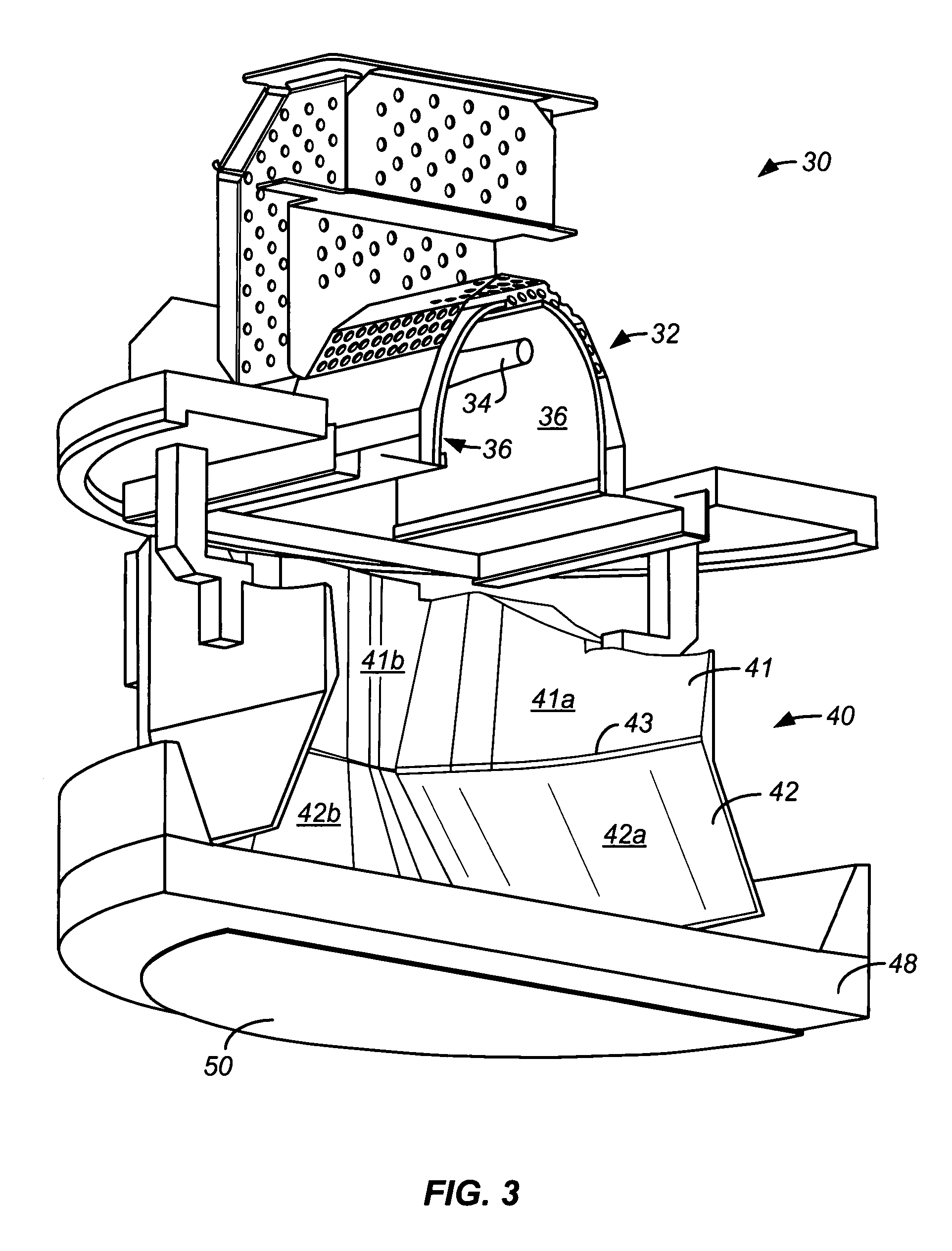
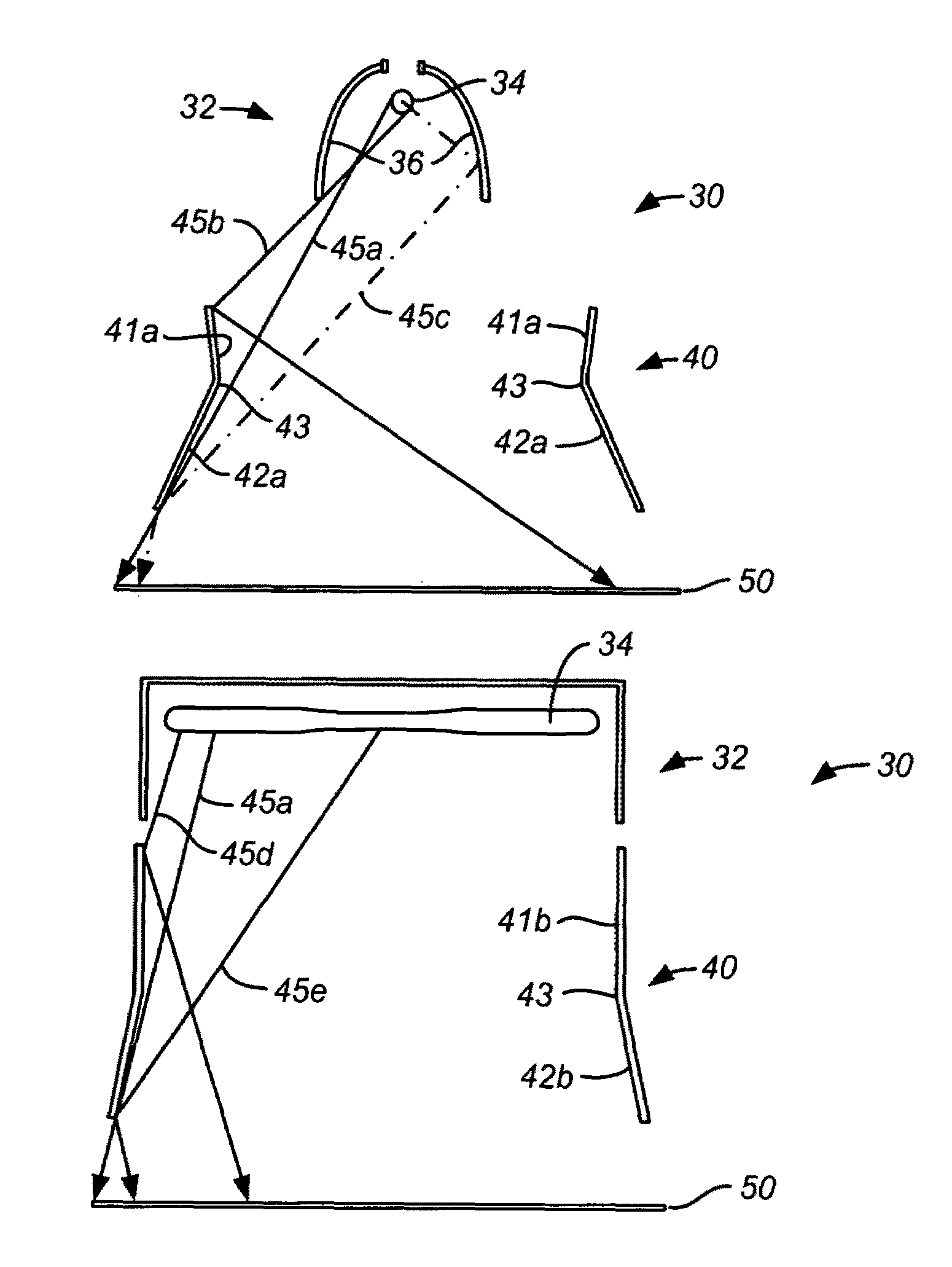
Apparatus and method for treating a substrate with UV radiation using primary and secondary reflectors
ActiveUS7566891B2Reduce light lossRadiation pyrometryPretreated surfacesProcess regionUltraviolet radiation
Embodiments of the invention relate generally to an ultraviolet (UV) cure chamber for curing a dielectric material disposed on a substrate and to methods of curing dielectric materials using UV radiation. A substrate processing tool according to one embodiment comprises a body defining a substrate processing region; a substrate support adapted to support a substrate within the substrate processing region; an ultraviolet radiation lamp spaced apart from the substrate support, the lamp configured to transmit ultraviolet radiation to a substrate positioned on the substrate support; and a motor operatively coupled to rotate at least one of the ultraviolet radiation lamp or substrate support at least 180 degrees relative to each other. The substrate processing tool may further comprise one or more reflectors adapted to generate a flood pattern of ultraviolet radiation over the substrate that has complementary high and low intensity areas which combine to generate a substantially uniform irradiance pattern if rotated. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus and method for exposing a substrate to UV radiation using asymmetric reflectors
ActiveUS7692171B2Reduce light lossNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess regionUltraviolet radiation
Embodiments of the invention relate generally to an ultraviolet (UV) cure chamber for curing a dielectric material disposed on a substrate and to methods of curing dielectric materials using UV radiation. A substrate processing tool according to one embodiment comprises a body defining a substrate processing region; a substrate support adapted to support a substrate within the substrate processing region; an ultraviolet radiation lamp spaced apart from the substrate support, the lamp configured to transmit ultraviolet radiation to a substrate positioned on the substrate support; and a motor operatively coupled to rotate at least one of the ultraviolet radiation lamp or substrate support at least 180 degrees relative to each other. The substrate processing tool may further comprise one or more reflectors adapted to generate a flood pattern of ultraviolet radiation over the substrate that has complementary high and low intensity areas which combine to generate a substantially uniform irradiance pattern if rotated. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Microstructure-bearing articles of high refractive index
InactiveUS6844950B2High refractive indexLiquid crystal compositionsImpression capsPolymer scienceMeth-
Blends of oligomeric urethane multi(meth)acrylate; optionally at least one other monomer selected from the group consisting of acrylic monomers, styrenic monomers and ethylenically unsaturated nitrogen heterocycles, preferably a polyol multi(meth)acrylate; and nanoparticles of an ethylenically unsaturated, preferably (meth)acrylic-functionalized, titanium or zirconium compound can be cured by ultraviolet radiation in contact with a photoinitiator to produce optical resinous articles having high refractive indices, haze ratings of at most 5% and other properties which may be tailored according to the desired use.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Novel antioxidants
This invention comprises administering to a human or animal in need of treatment an effective amount of an antioxidant lipoic acid derivative and / or pharmaceutically acceptable salts and solvates thereof for the treatment or prevention of pathological (inflammatory, proliferative and degenerative diseases, e.g. diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease and chronic viral diseases) and non-pathological (e.g. skin aging and wrinkle formation) conditions caused by oxidative damage. Methods of synthesizing novel antioxidant lipoic acid derivatives and their use in preventing or treating diseases or conditions caused by oxidative stress and other free radical mediated conditions are described. Another aspect of this invention is the use of these antioxidant compositions for the protection of skin from damage caused by ultraviolet radiation and dessication, and to provide improved skin feel by desquamating, cleansing and clarifying the skin. The compositions described in this invention increase cellular viability of epidermal cells, promote cytoprotection, and decrease the production of inflammatory mediators such as inflammatory cytokines in these cells. The antioxidant compositions are incorporated into sunscreen products, soap, moisturizing lotions, skin toners, and other skin care products.
Owner:BETHESDA PHARMA
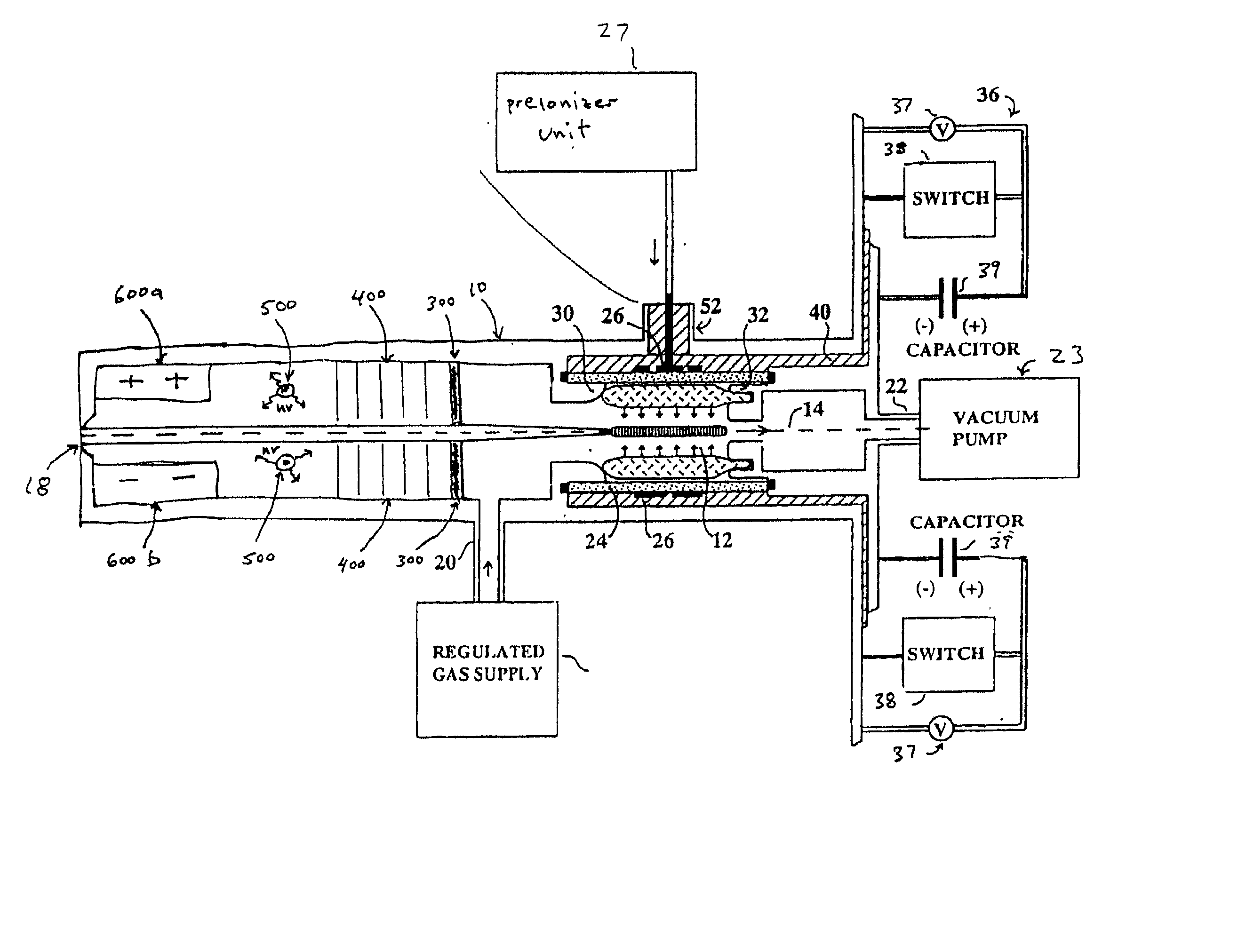
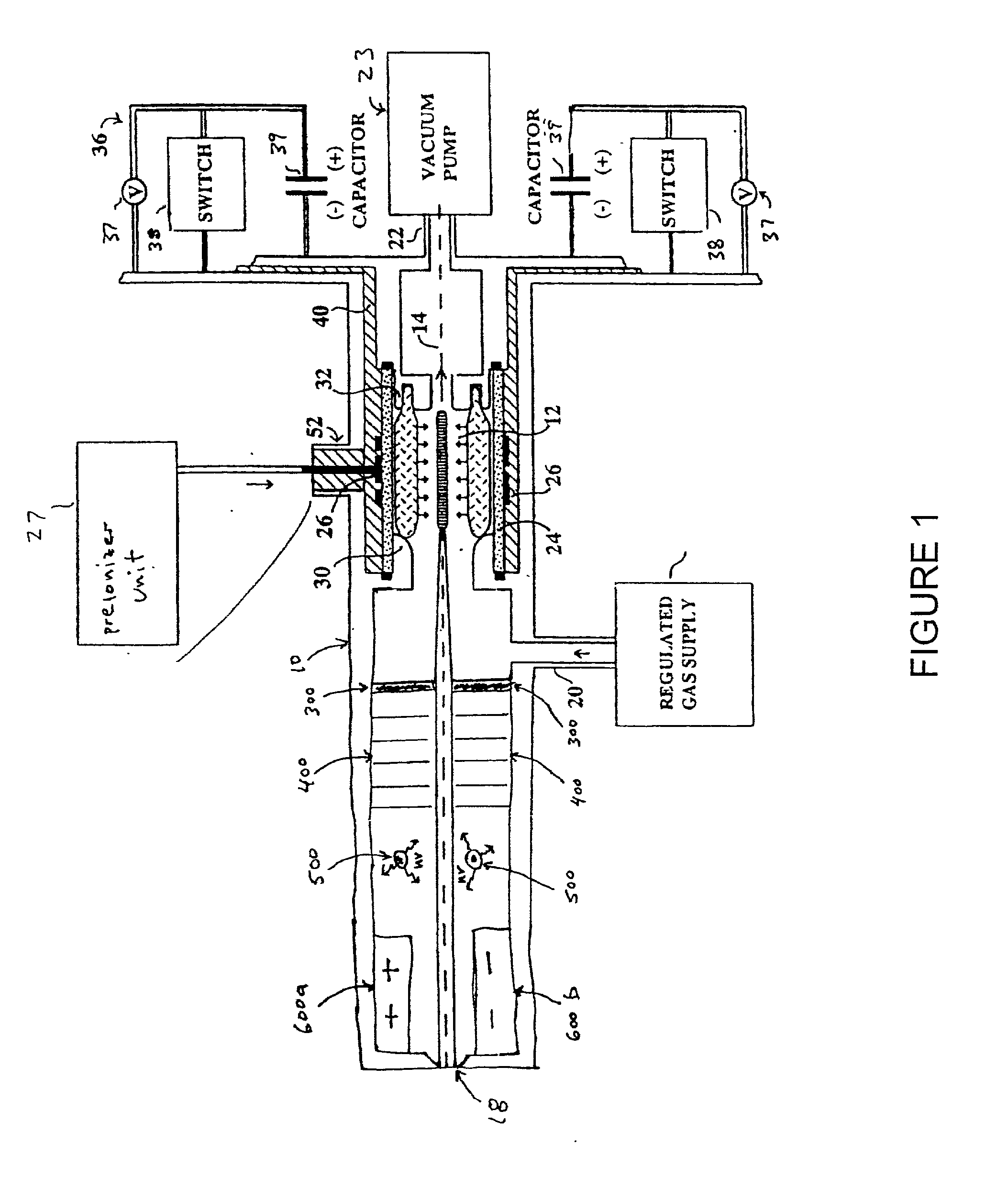
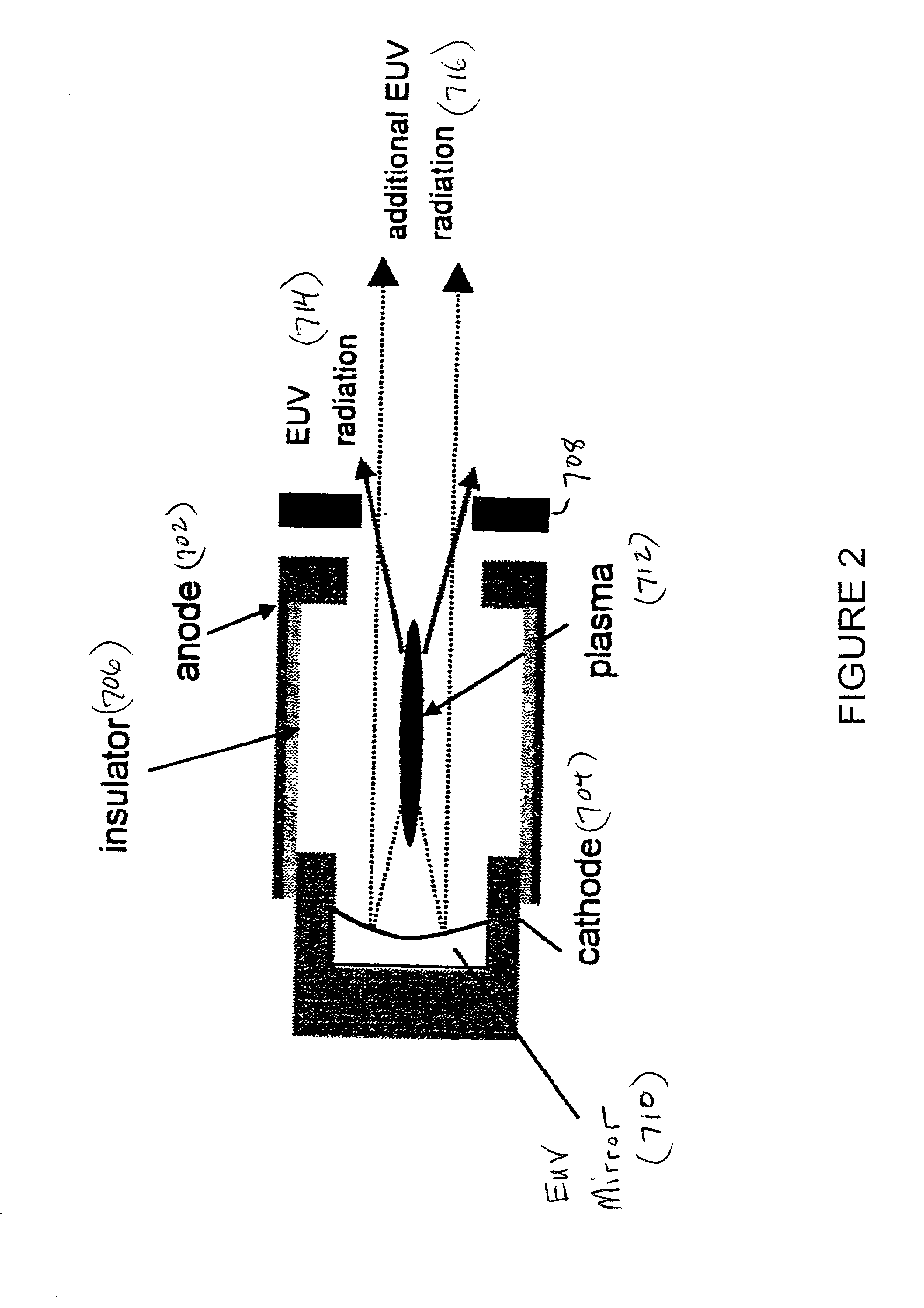
Method and apparatus for generating high output power gas discharge based source of extreme ultraviolet radiation and/or soft x-rays
InactiveUS20020168049A1Avoid reflectionsReduce reflectionRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsSoft x rayUltraviolet radiation
An EUV photon source includes a plasma chamber filled with a gas mixture, multiple electrodes within the plasma chamber defining a plasma region and a central axis, a power supply circuit connected to the electrodes for delivering a main pulse to the electrodes for energizing the plasma around the central axis to produce an EUV beam output along the central axis, and a preionizer for ionizing the gas mixture in preparing to form a dense plasma around the central axis upon application of the main pulse from the power supply circuit to the electrodes. The EUV source preferably includes an ionizing unit and precipitator for collecting contaminant particulates from the output beam path. A set of baffles may be disposed along the beam path outside of the pinch region to diffuse gaseous and contaminant particulate flow emanating from the pinch region and to absorb or reflect acoustic waves emanating from the pinch region away from the pinch region. A clipping aperture, preferably formed of ceramic and / or Al2O3, for at least partially defining an acceptance angle of the EUV beam. The power supply circuit may generates the main pulse and a relatively low energy prepulse for homogenizing the preionized plasma prior to the main pulse. A multi-layer EUV mirror is preferably disposed opposite a beam output side of the pinch region for reflecting radiation along the central axis for output along the beam path of the EUV beam. The EUV mirror preferably has a curved contour for substantially collimating or focusing the reflected radiation. In particular, the EUV mirror may preferably have a hyperbolic contour.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
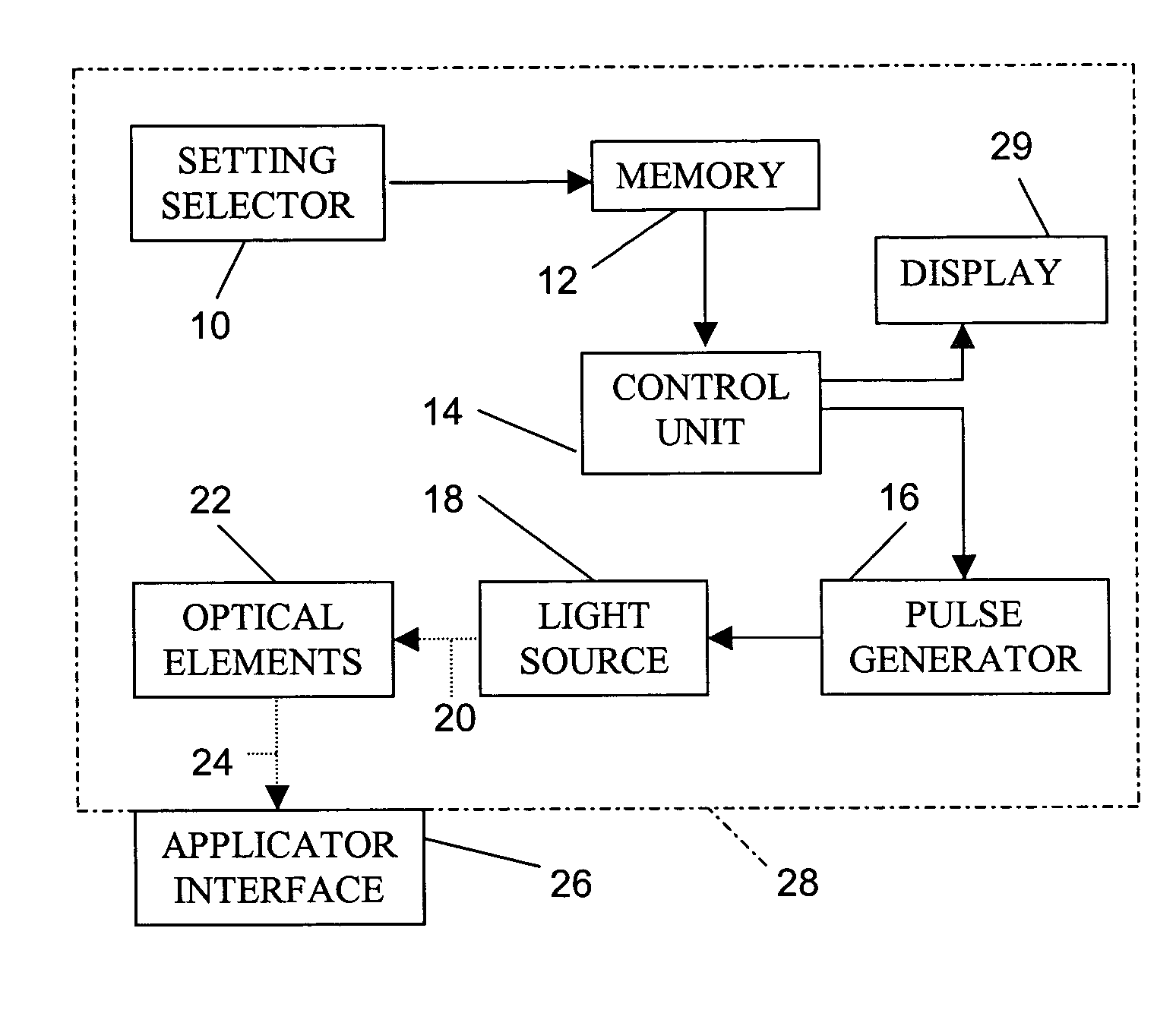
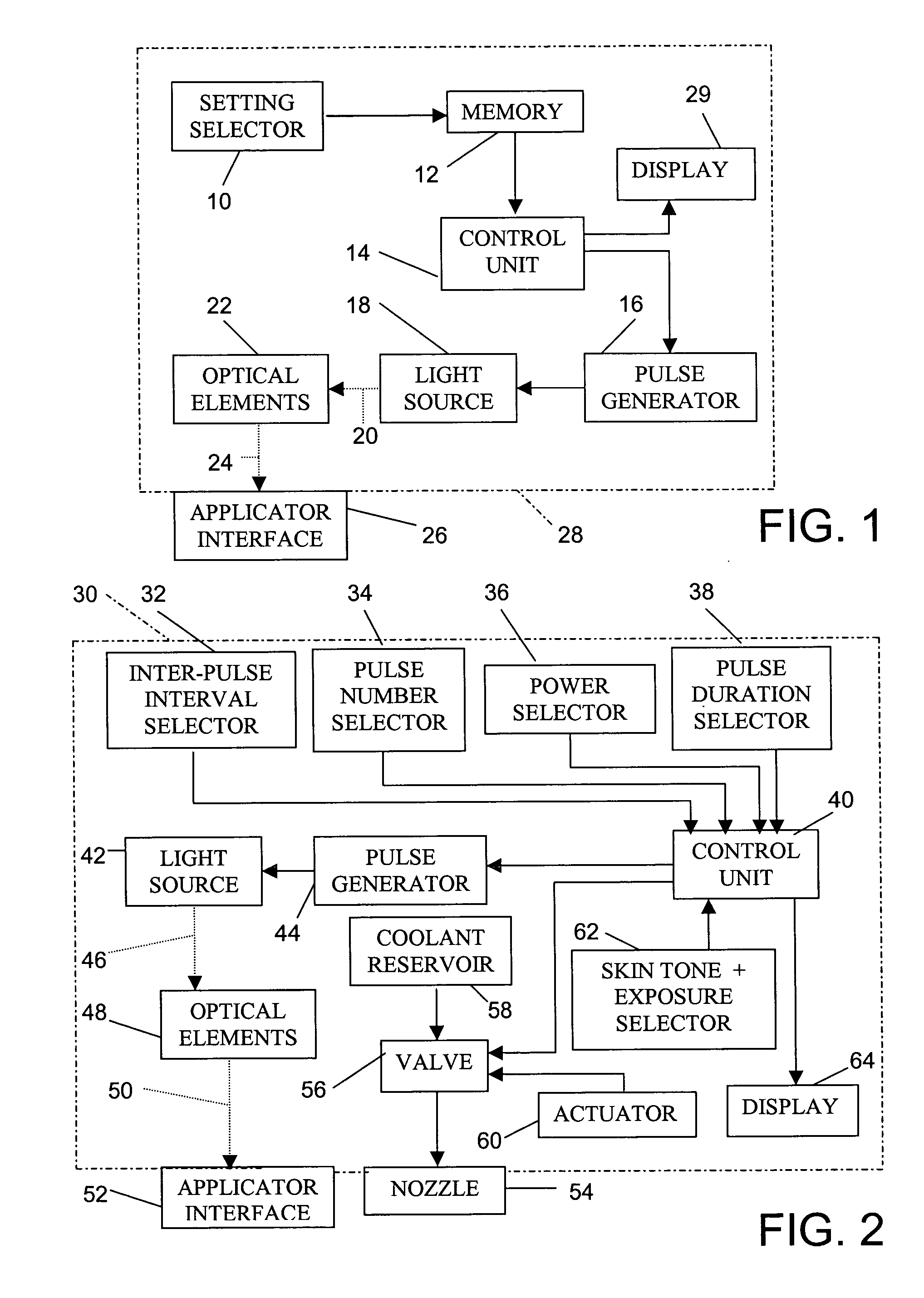
Skin treatment with optical radiation
InactiveUS20050045189A1Promote protect healthReduces and inhibits tissue damageElectrotherapyDiagnostics using lightOptical radiationFrequency spectrum
A hand held device generates a predetermined number of pulses of electromagnetic radiation having a predetermined electromagnetic spectrum, a predetermined duration, a predetermined inter-pulse interval, and a predetermined total energy. The pulse sequence is delivered to a skin surface to reduce or eliminate Xray or ultraviolet radiation damage to the skin surface.
Owner:JAY HARVEY H
Light-Emitting Planar Body-Structured Body
InactiveUS20070297045A1Increase the areaEfficient light emissionLighting applicationsPoint-like light sourceInorganic particlePhosphor
A light-emitting planar body-structured body characterized in that it comprises an LED (light-emitting diode) light source which radiates ultraviolet radiation or near ultraviolet radiation and a planar body provided disposed in front thereof, and that the planar body is a light-transmitting resin molding containing dispersed therein at least one type of phosphors and light-storing bodies together with light-transmitting inorganic particles.
Owner:DOPPEL
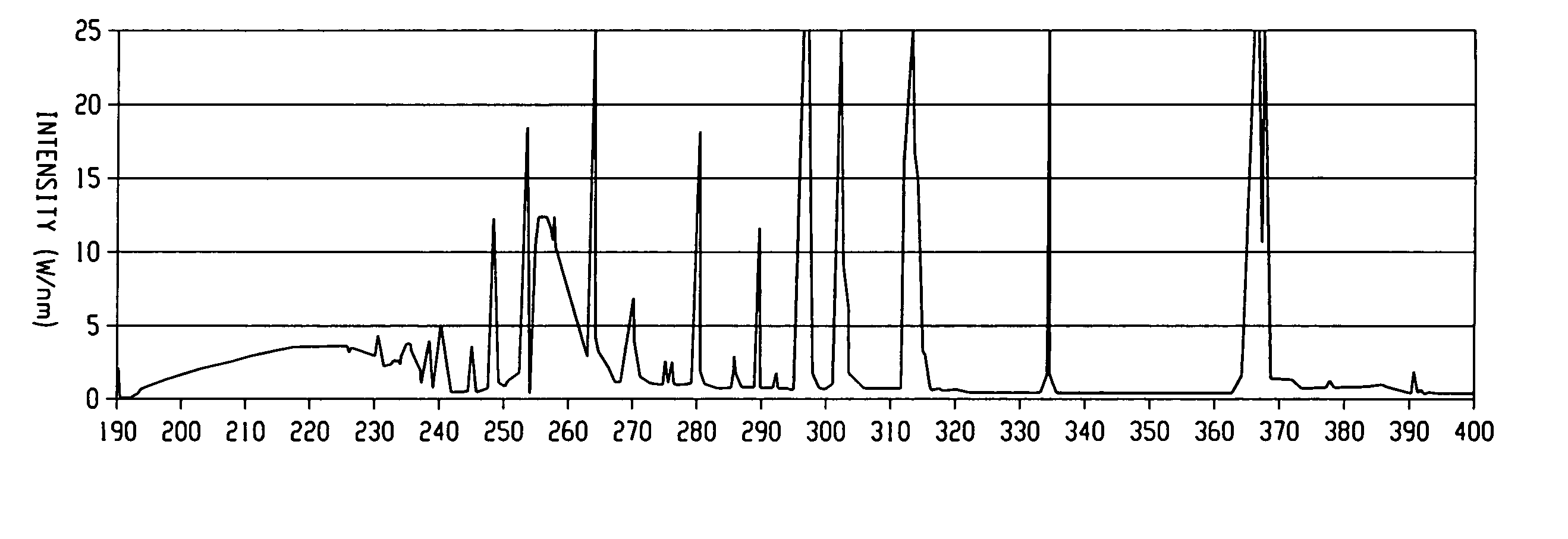
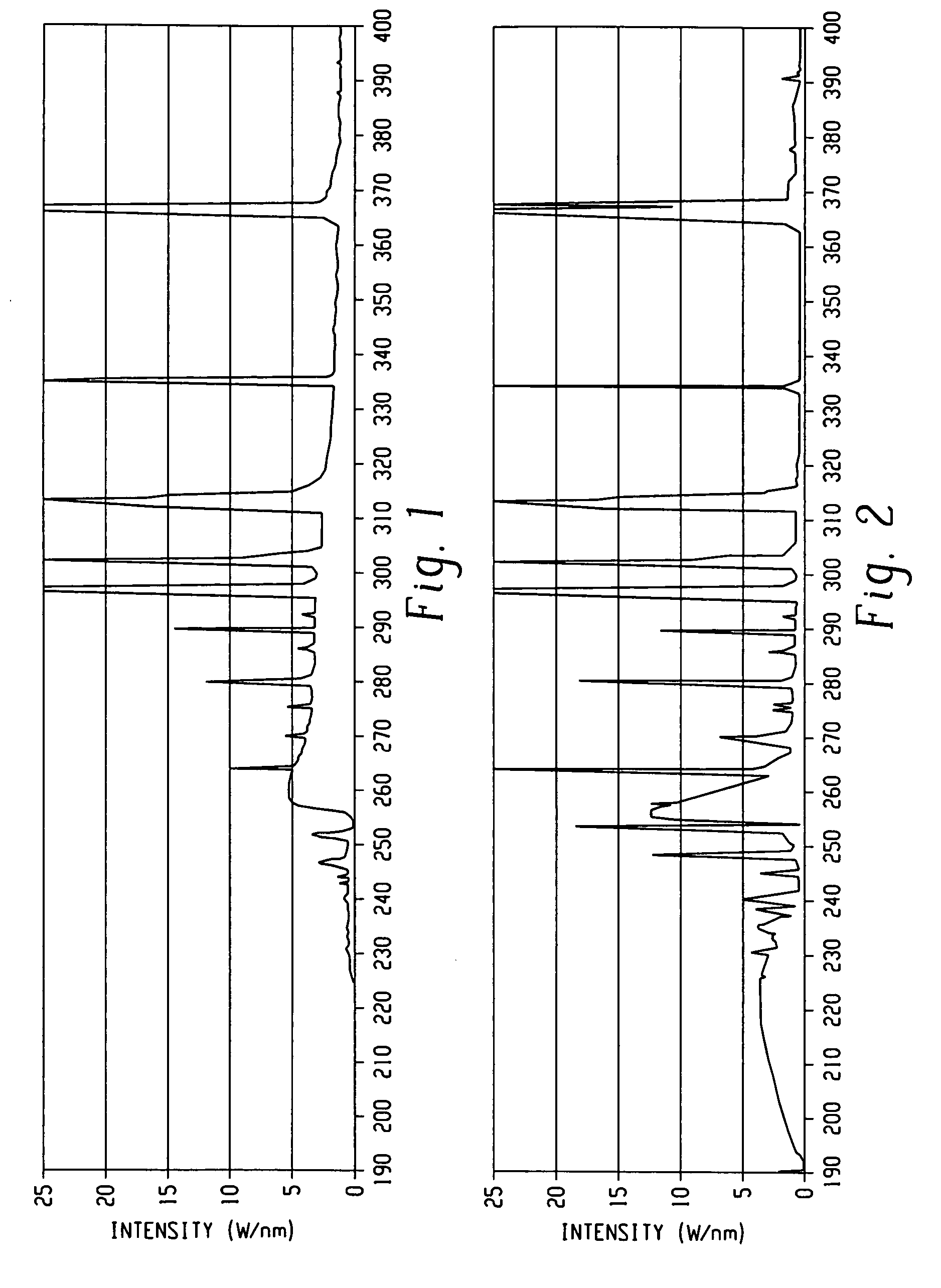
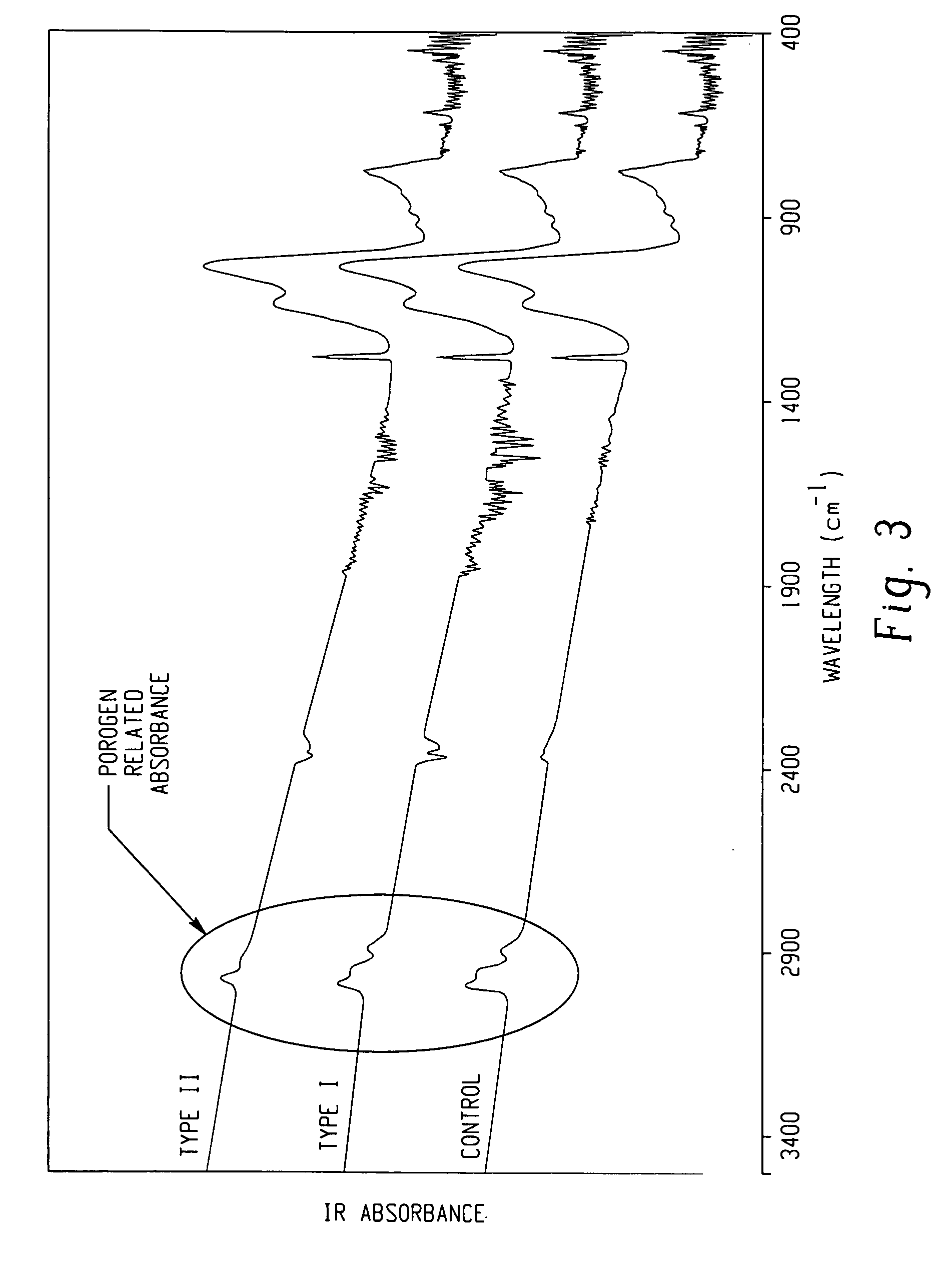
Ultraviolet assisted porogen removal and/or curing processes for forming porous low k dielectrics
InactiveUS20060024976A1Material removalIncrease crosslink densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal interconnectUltraviolet radiation
Processes for forming porous low k dielectric materials from low k dielectric films containing a porogen material include exposing the low k dielectric film to ultraviolet radiation. In one embodiment, the film is exposed to broadband ultraviolet radiation of less than 240 nm for a period of time and intensity effective to remove the porogen material. In other embodiments, the low k dielectric film is exposed to a first ultraviolet radiation pattern effective to increase a crosslinking density of the film matrix while maintaining a concentration of the porogen material substantially the same before and after exposure to the first ultraviolet radiation pattern. The low k dielectric film can be then be processed to form a metal interconnect structure therein and subsequently exposed to a second ultraviolet radiation pattern effective to remove the porogen material from the low k dielectrics film and form a porous low k dielectric film.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
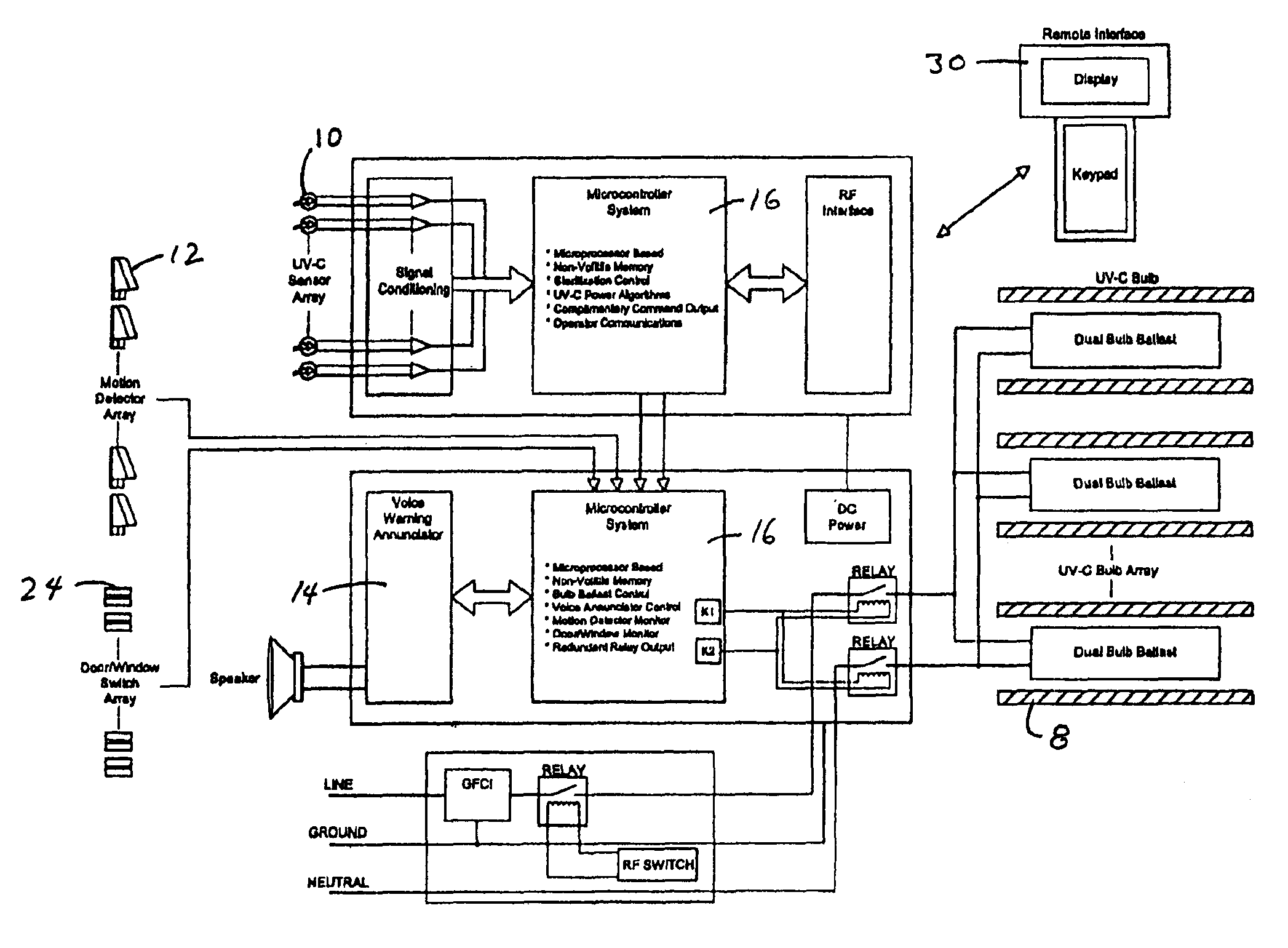
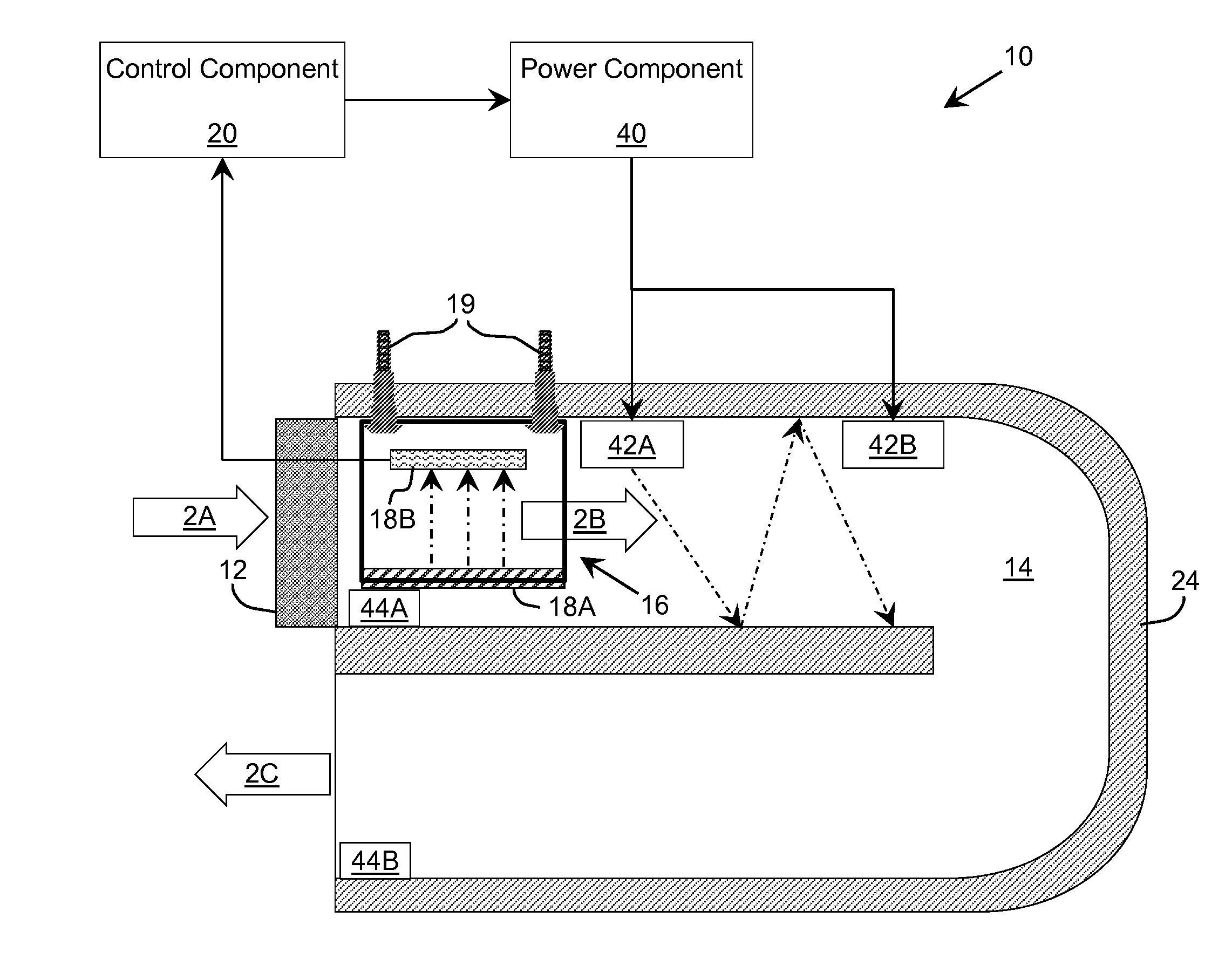
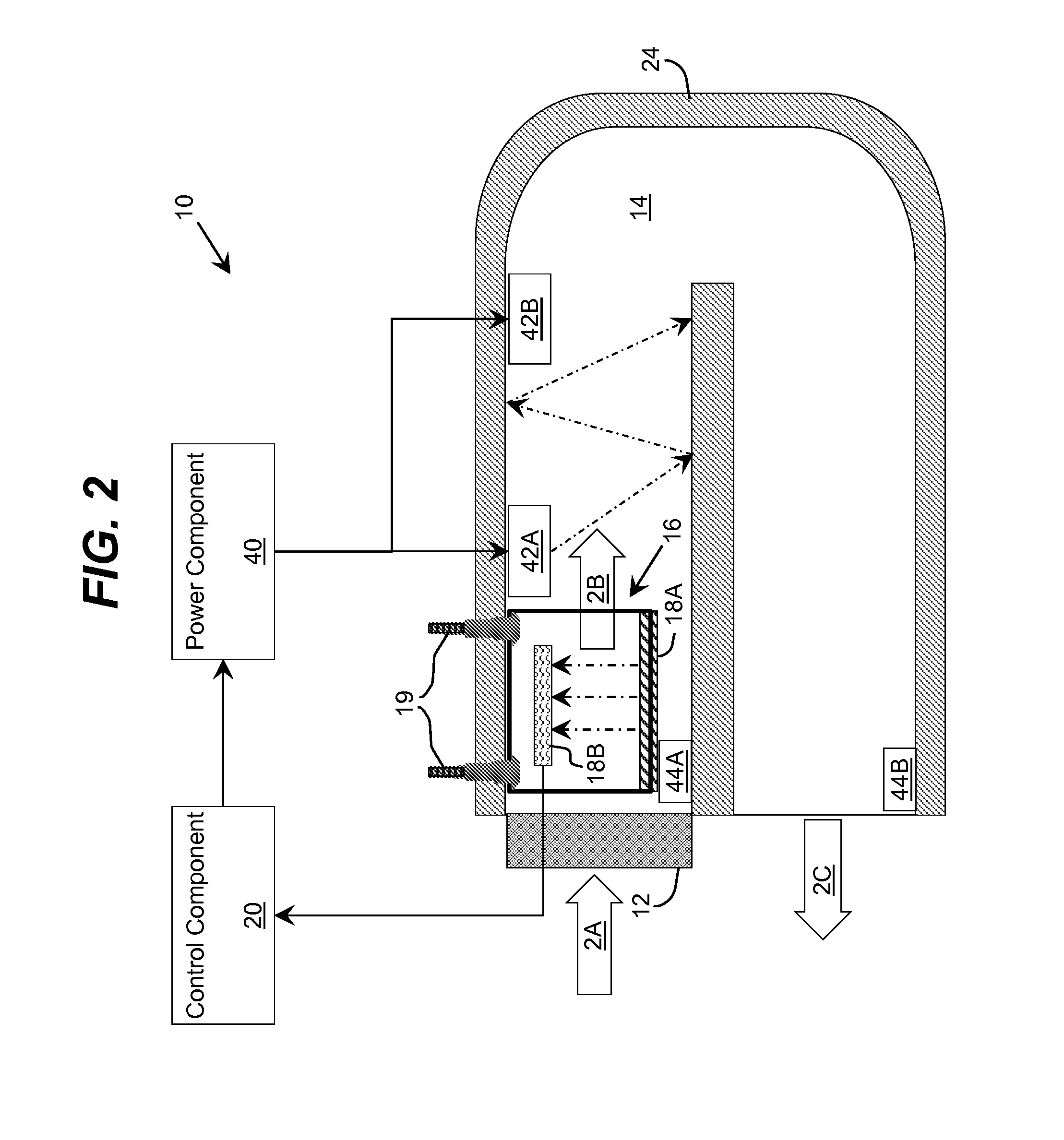
Ultraviolet area sterilizer and method of area sterilization using ultraviolet radiation
An ultraviolet area sterilizer (UVAS) is mobile or stationary. The UVAS is positioned in a room, such an operating room or intensive care unit. Motion detectors sense movement, to assure that personnel have evacuated the space to be sterilized. Subsequently, UV-C generators, such mercury bulbs, generate UV-C from multiple locations within the room or other enclosed space. Multiple UV-C sensors scan the room, and determine the area reflecting the lowest level of UV-C back to the sensors. The device calculates the time required to obtain a bactericidal dose of UV-C reflected back to the sensors. Once an effective bactericidal dose has been reflected to all the sensors, the unit notifies the operator and shuts down.
Owner:UVAS
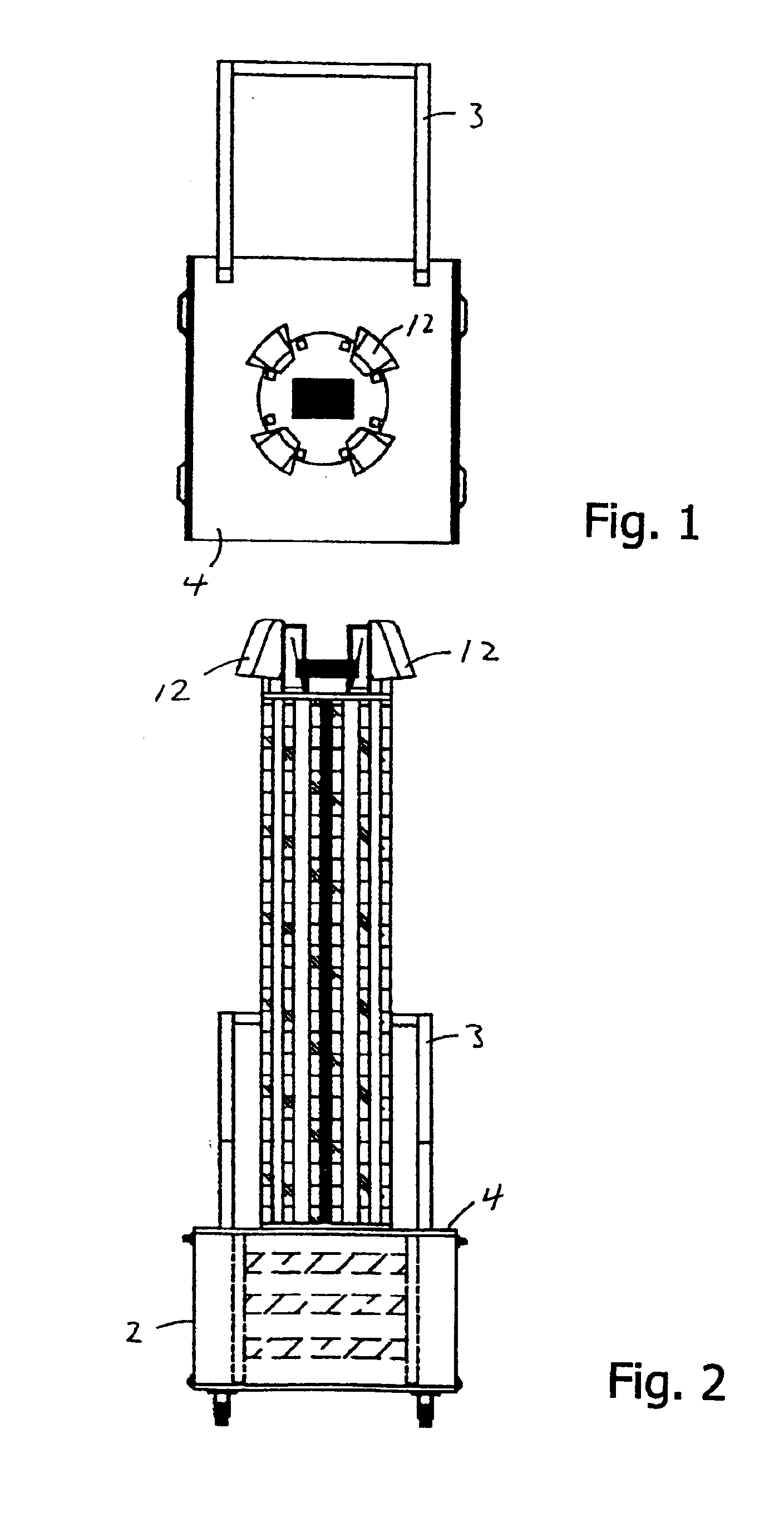
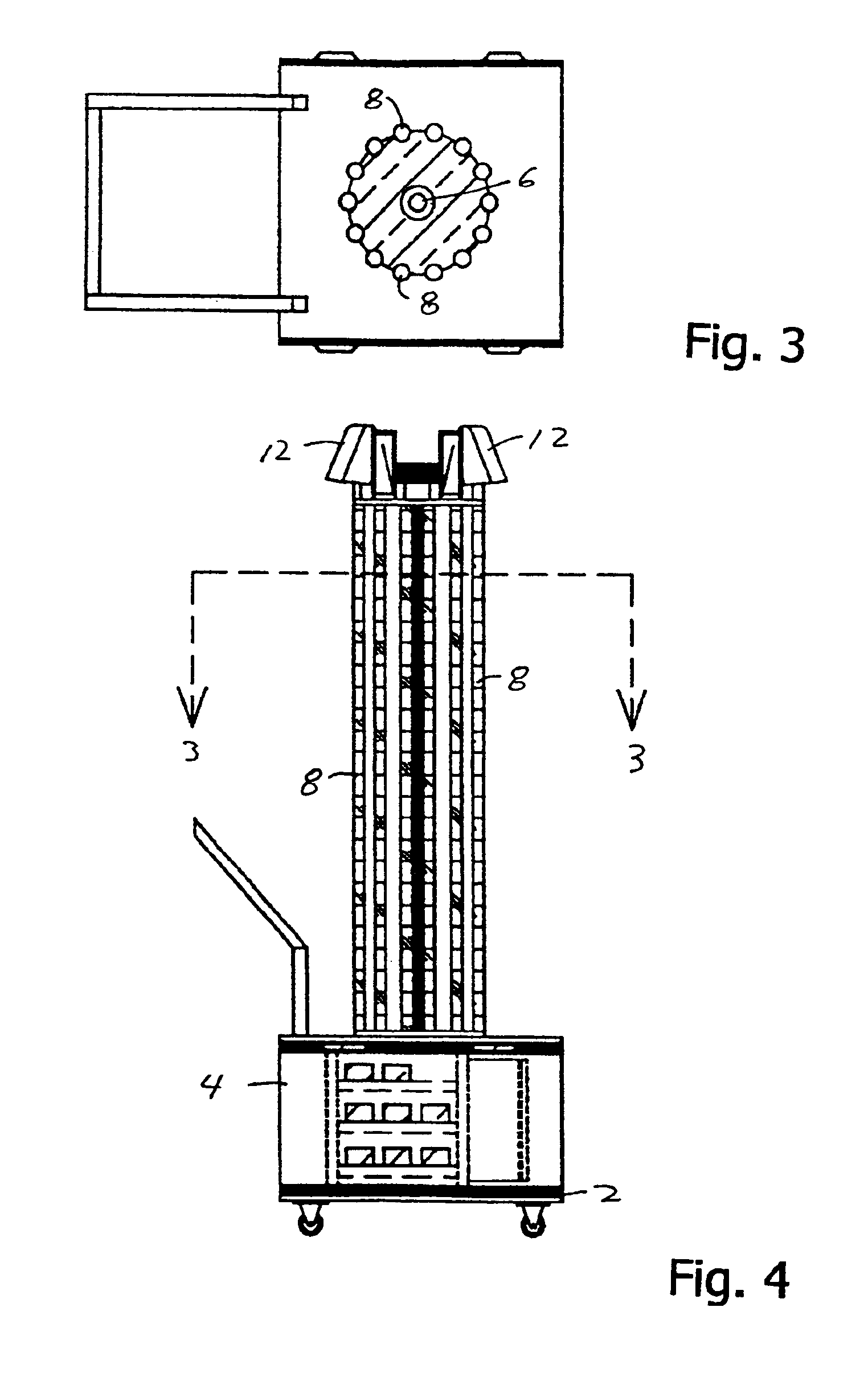
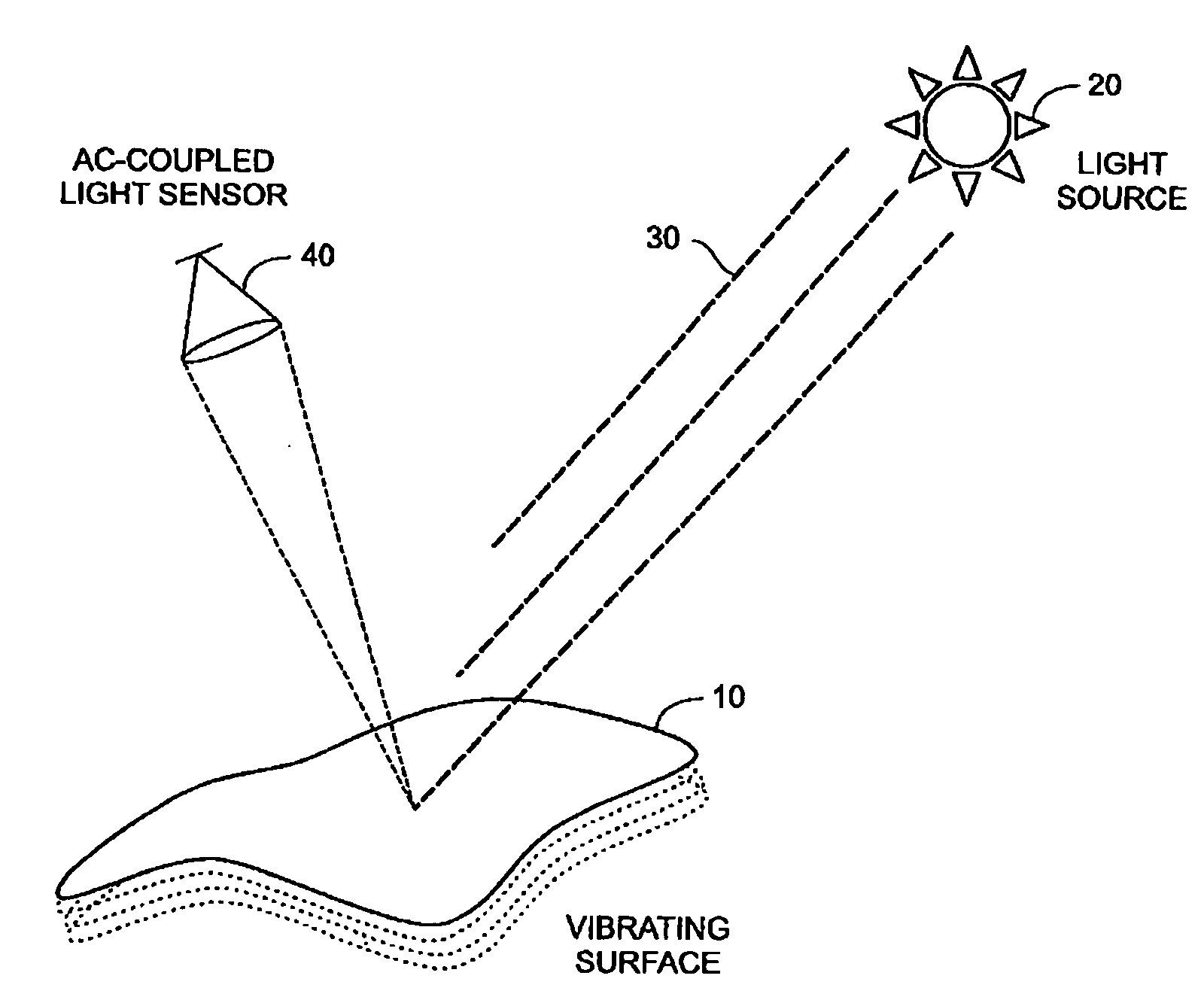
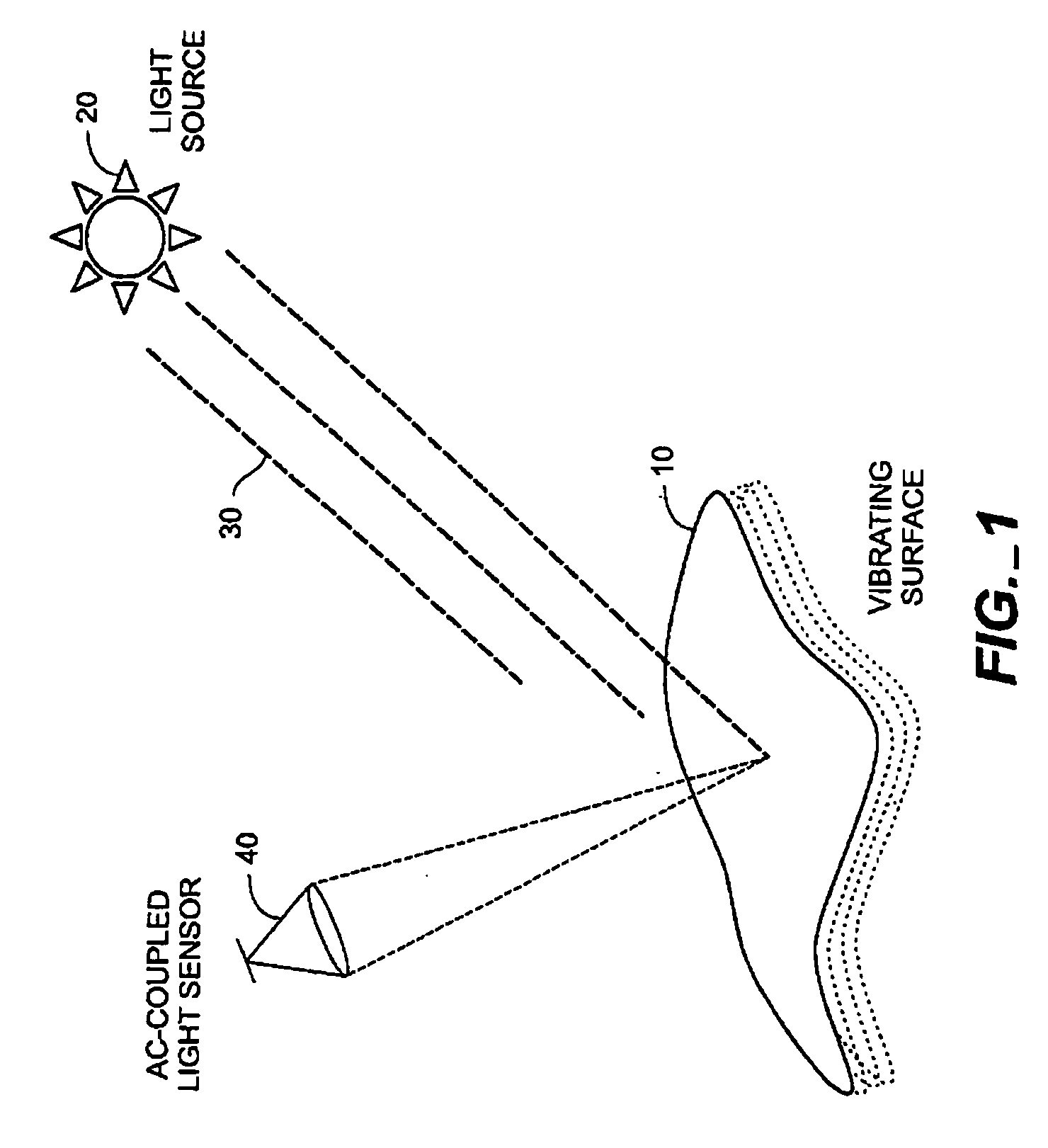
Method for detecting vibrations in a biological organism using real-time vibration imaging
InactiveUS20060209631A1Vibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis by observing immersed bodiesUltravioletDetector array
The present invention provides a method for detecting vibration information by receiving electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from a biological organism at a light amplitude modulation detector array to provide real-time imaging of the target object. The detected radiation may be visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, and / or of other desired frequency ranges. The detected radiation is preferably AC-coupled to isolate components relating to oscillations of the biological organism from components relating to ambient radiation, e.g. background sunlight. The isolated oscillations may then be digitized, stored, and subjected to processing such as a Fourier transform to generate outputs representative of frequencies of oscillation. This output can then be used for analysis of the target object.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Antioxidants
This invention comprises administering to a human or animal in need of treatment an effective amount of an antioxidant lipoic acid derivative and / or pharmaceutically acceptable salts and solvates thereof for the treatment or prevention of pathological (inflammatory, proliferative and degenerative diseases, e.g. diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease and chronic viral diseases) and non-pathological (e.g. skin aging and wrinkle formation) conditions caused by oxidative damage. Methods of synthesizing novel antioxidant lipoic acid derivatives and their use in preventing or treating diseases or conditions caused by oxidative stress and other free radical mediated conditions are described. Another aspect of this invention is the use of these antioxidant compositions for the protection of skin from damage caused by ultraviolet radiation and dessication, and to provide improved skin feel by desquamating, cleansing and clarifying the skin. The compositions described in this invention increase cellular viability of epidermal cells, promote cytoprotection, and decrease the production of inflammatory mediators such as inflammatory cytokines in these cells. The antioxidant compositions are incorporated into sunscreen products, soap, moisturizing lotions, skin toners, and other skin care products.
Owner:BETHESDA PHARMA
Thermal processing system for curing dielectric films
InactiveUS20080063809A1Easy to optimizeIncrease temperatureVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle stageUltraviolet radiation
A thermal processing system and method for curing a dielectric film. The thermal processing system is configured to treat the dielectric film with ultraviolet (UV) radiation and infrared (IR) radiation in order to cure the dielectric film. The thermal processing system can include an array if IR and UV light-emitting devices (LEDs) configured to irradiate a substrate having a low dielectric constant (low-k) film. The method dries the dielectric film to remove contaminants from the film and exposes the dielectric film at a single stage to ultraviolet radiation and IR radiation.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
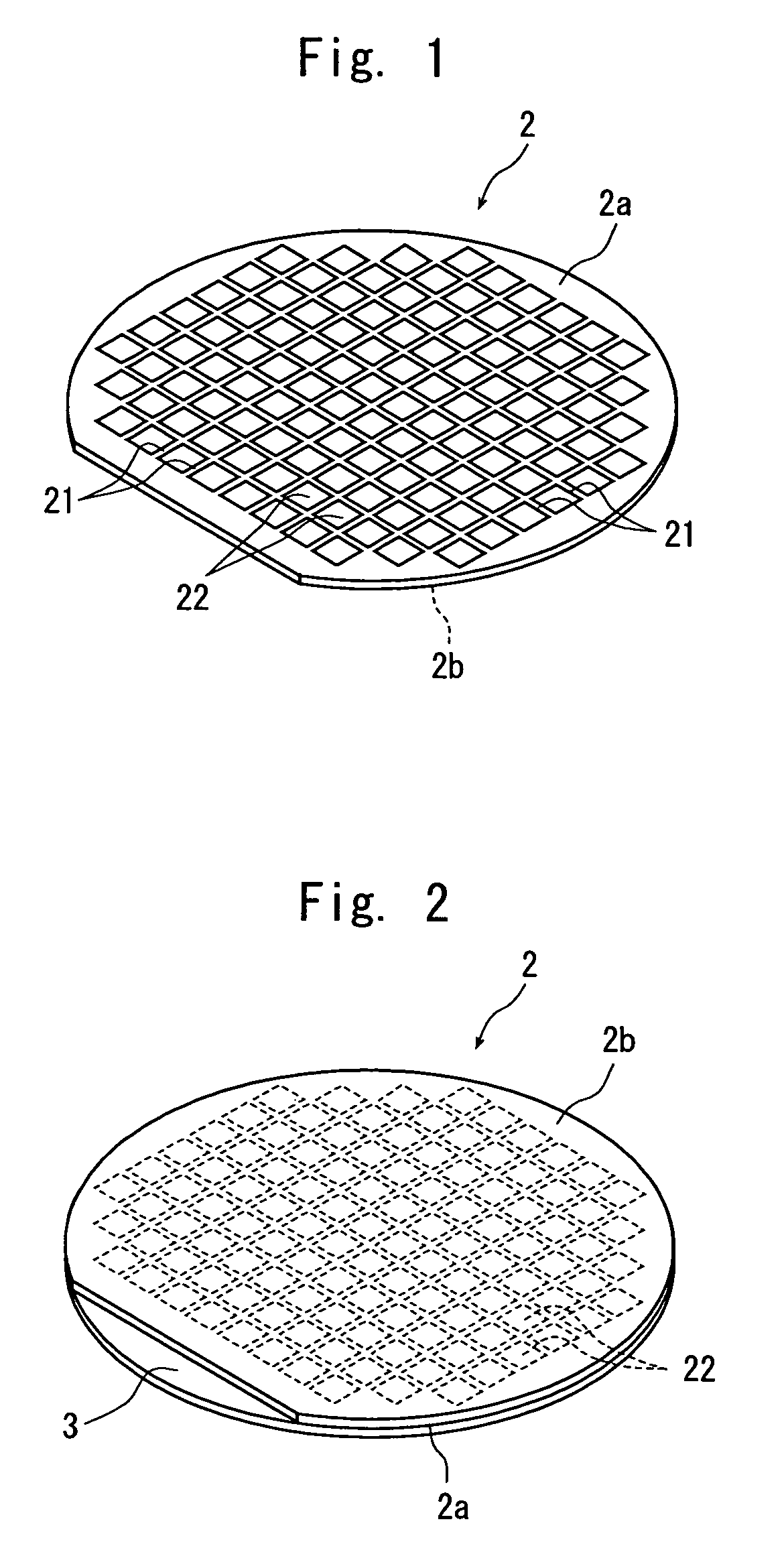
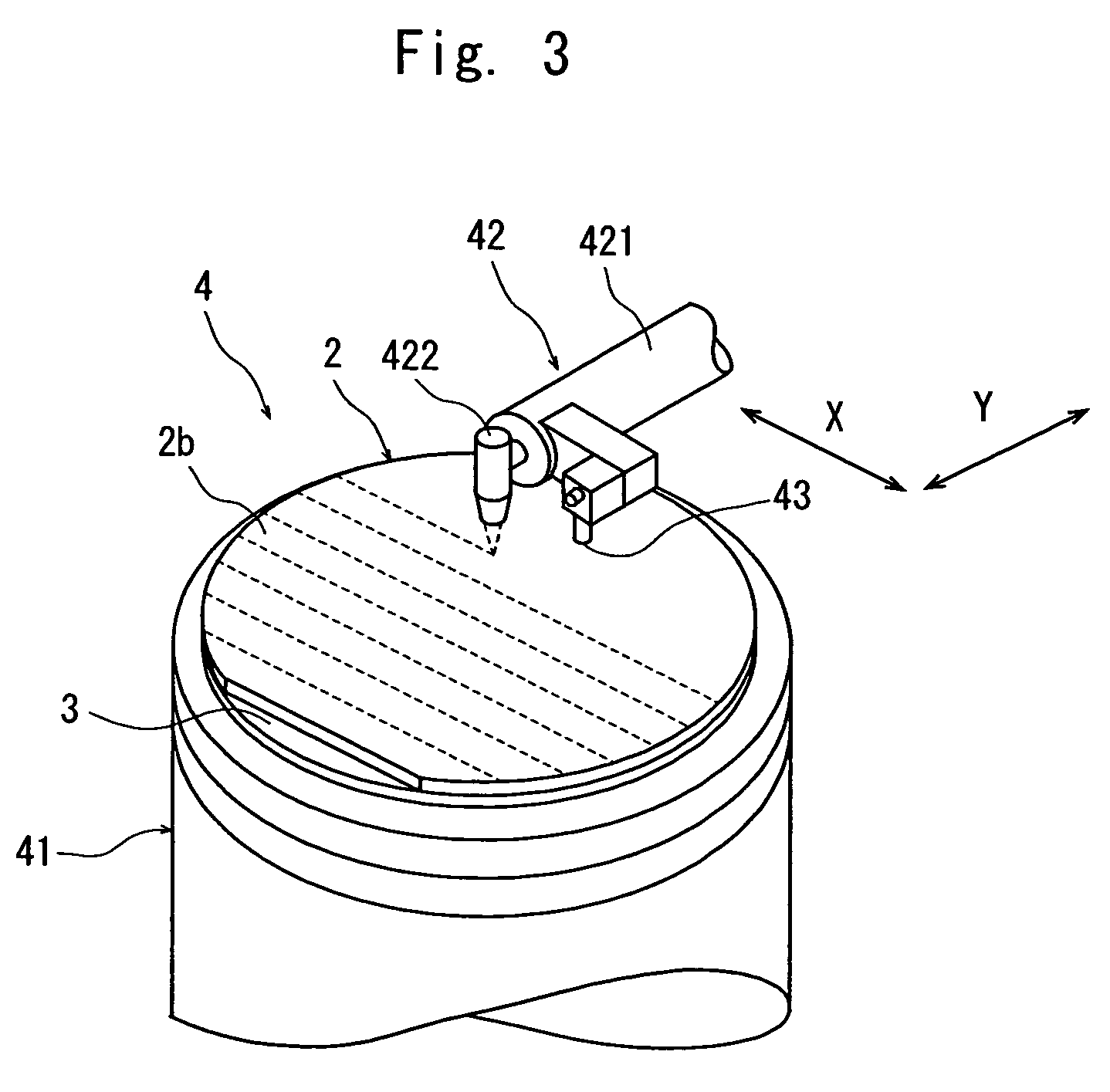
Wafer dividing method
ActiveUS7507639B2Reduced adhesion strengthIncrease spacingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesSplit linesDevice form
A method of dividing a wafer having devices formed in a plurality of areas sectioned by a plurality of dividing lines, into individual chips along the dividing lines, comprising a deteriorated layer forming step for forming a deteriorated layer by applying a laser beam of a wavelength having permeability for the wafer along the dividing lines; a wafer supporting step for putting the rear surface of the wafer on the surface of an adhesive tape which is mounted on an annular frame and whose adhesive strength is reduced by applying ultraviolet radiation thereto; and a chips-spacing forming step for reducing the adhesive strength of the adhesive tape and shrinking a shrink area between the inner periphery of the annular frame and the area to which the wafer has been affixed, of the adhesive tape by applying ultraviolet radiation to the adhesive tape to which the wafer has been affixed so as to divide the wafer into individual chips along the dividing lines where the deteriorated layer has been formed and widen the space between adjacent chips.
Owner:DISCO CORP
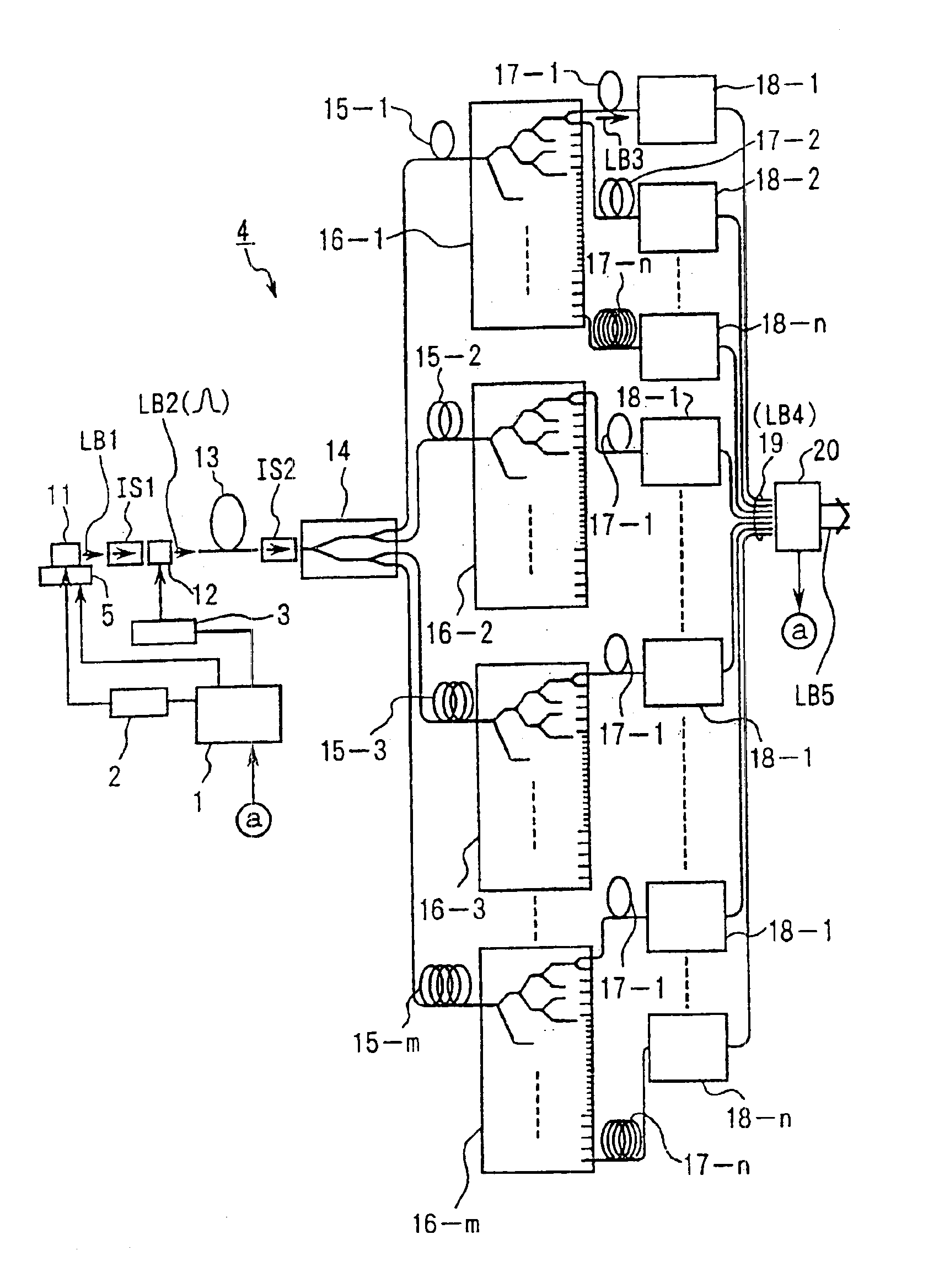
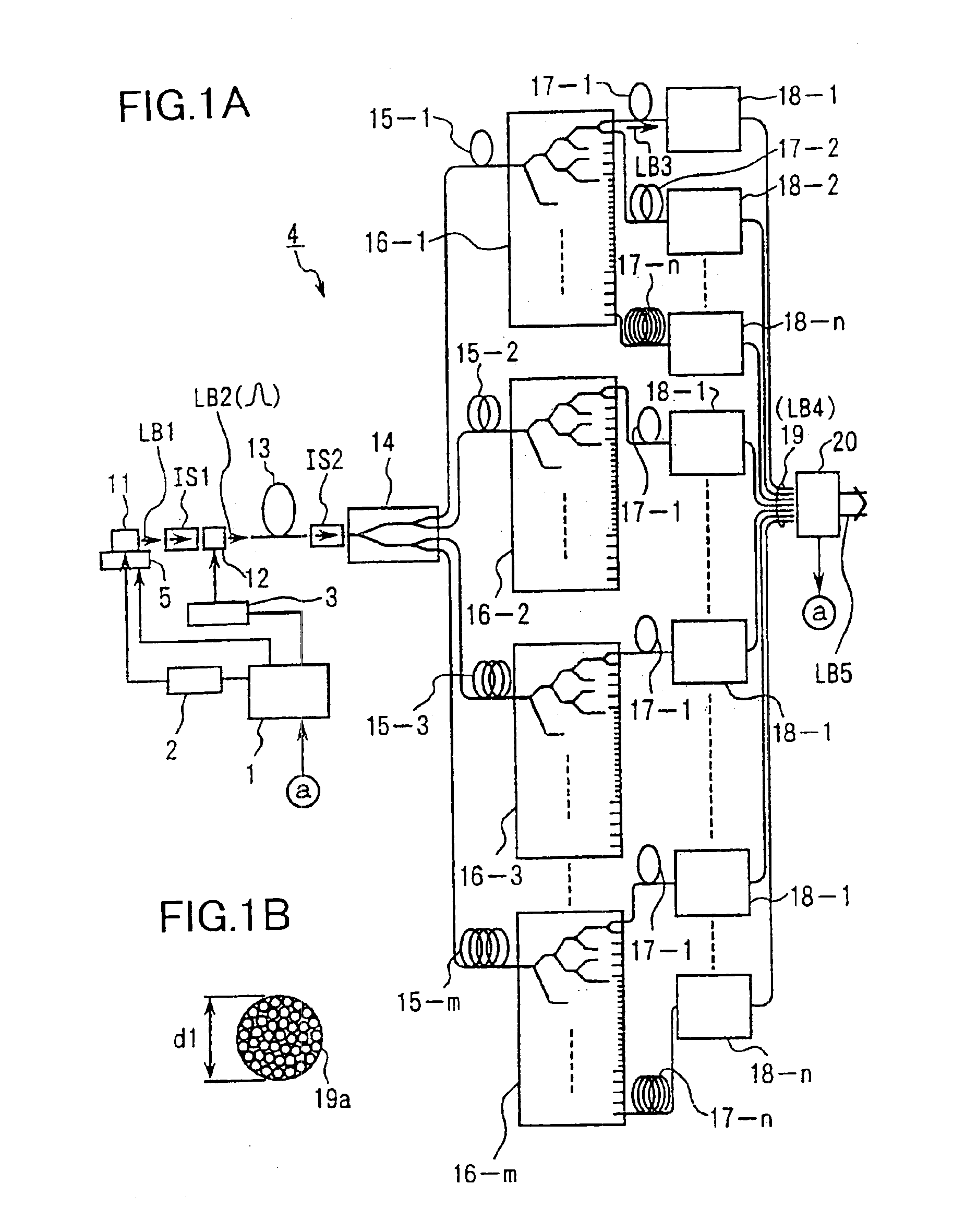
Exposure apparatus with laser device
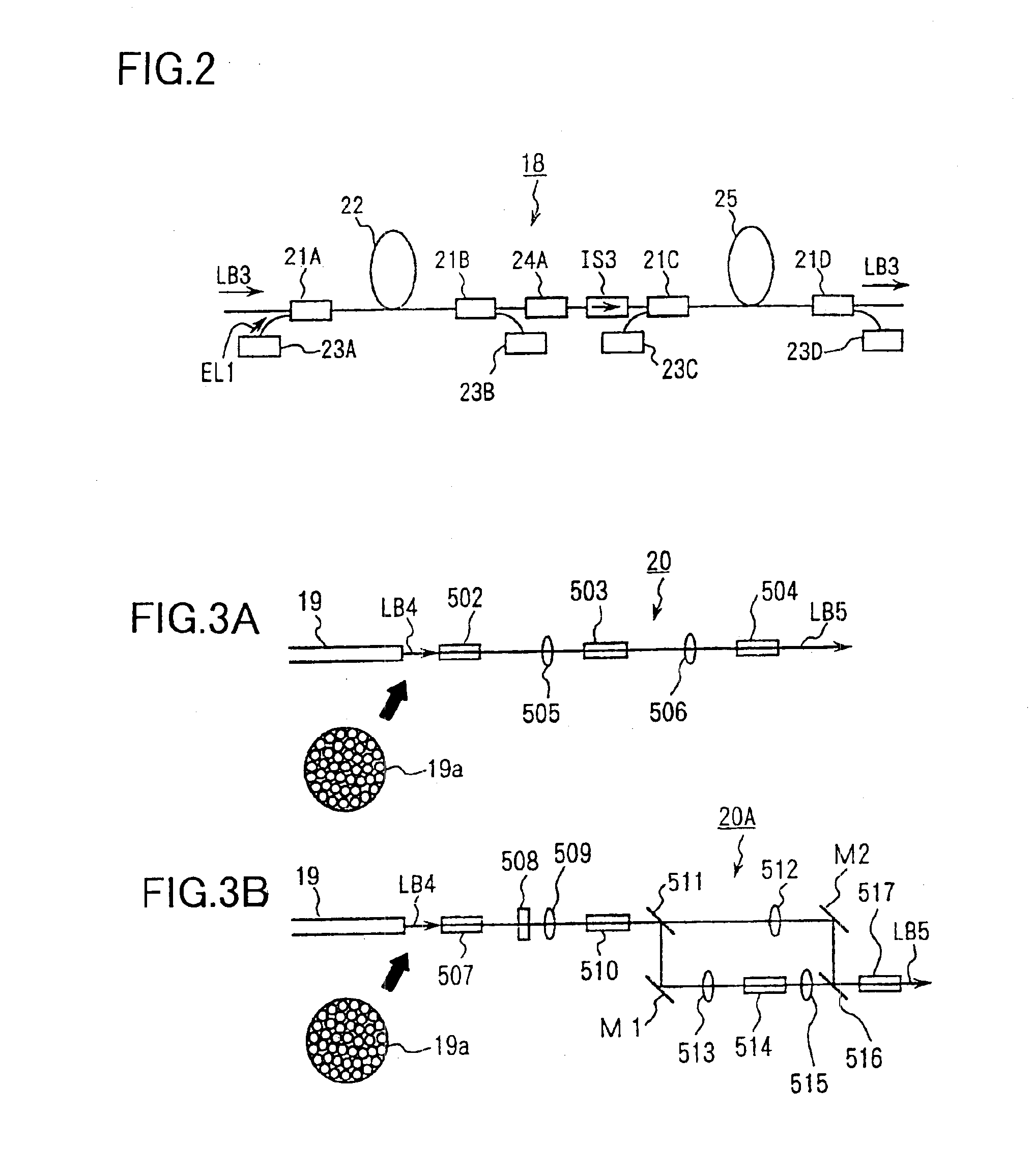
InactiveUS6901090B1Improve maintainabilityEasy alignmentLaser detailsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusFiber bundleAudio power amplifier
An exposure apparatus has a laser device that is small, easy to maintain, and capable of producing an output that is unlikely to be affected by optical surges occurring in the beginning of operation. A single-wavelength laser oscillator (11) supplies a laser beam (LB1) to a fiber optic amplifier (13) through an optical modulator (12). The amplified laser beam is split by splitters (14, 16-1 to 16-m), amplified by optical amplifier units (18-1 to 18-n) and supplied through a fiber bundle (19) to a wavelength converter (20), which in turn converts the split beams into ultraviolet laser radiation (LB5) for use as exposure light. The optical modulator (12) outputs light pulses during the generation of ultraviolet light. The optical modulator (12) also produces laser radiation during the absence of ultraviolet light, but the laser radiation has substantially the same average output and a considerably low peak compared with that during the generation of ultraviolet light.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Ultraviolet Fluid Disinfection System with Feedback Sensor
ActiveUS20140202962A1Effective exposureHigh disinfection rateWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by irradiationUltraviolet radiationUv disinfection
A solution for treating a fluid, such as water, is provided. The solution determines an ultraviolet transparency of a fluid before or as the fluid enters a disinfection chamber. In the disinfection chamber, the fluid can be irradiated by ultraviolet radiation to harm microorganisms that may be present in the fluid. One or more attributes of the disinfection chamber, fluid flow, and / or ultraviolet radiation can be adjusted based on the transparency to provide more efficient irradiation and / or higher disinfection rates.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Ultraviolet Gradient Sterilization, Disinfection, and Storage System
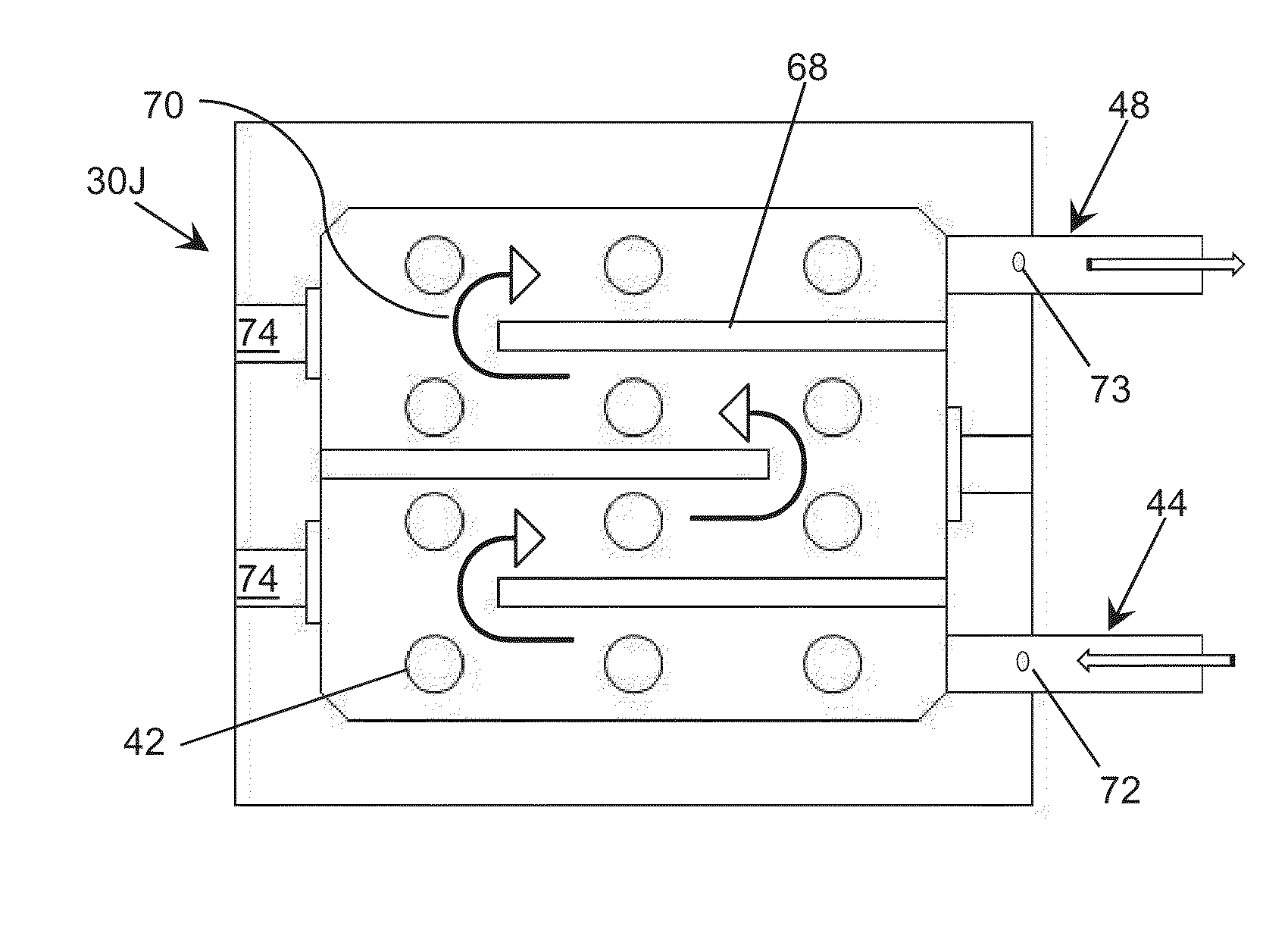
ActiveUS20140060104A1Milk preservationLighting and heating apparatusUltraviolet radiationUltraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation is directed within an area. The storage area is scanned and monitored for the presence of biological activity within designated zones. Once biological activity is identified, ultraviolet radiation is directed to sterilize and disinfect designated zones within the storage area.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Water Disinfection Using Deep Ultraviolet Light
InactiveUS20130048545A1Microorganism can be damagedHigh disinfection rateGeneral water supply conservationIon-exchanger regenerationUltraviolet radiationUltraviolet lights
A solution for treating a fluid, such as water, is provided. The solution first removes a set of target contaminants that may be present in the fluid using a filtering solution. The filtered fluid enters a disinfection chamber where it is irradiated by ultraviolet radiation to harm microorganisms that may be present in the fluid. An ultraviolet radiation source and / or the disinfection chamber can include one or more attributes configured to provide more efficient irradiation and / or higher disinfection rates.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
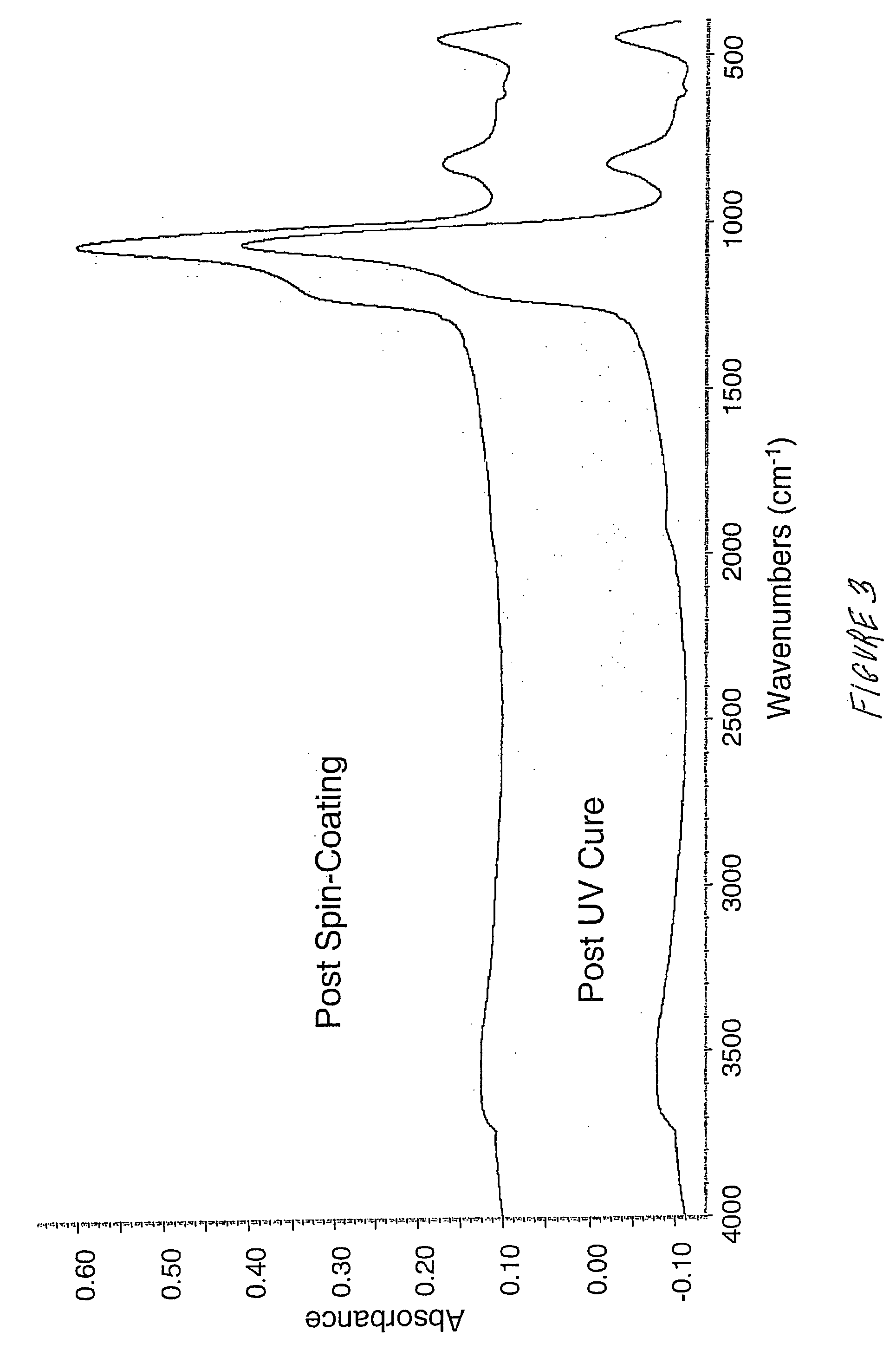
Ultraviolet curing process for spin-on dielectric materials used in pre-metal and/or shallow trench isolation applications
InactiveUS20050272220A1Reduce organic contentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUV curingUltraviolet radiation
A UV curing process for a dielectric material used in pre-metal and shallow trench isolation applications comprises coating a suitable dielectric material onto a substrate; and exposing the dielectric material to ultraviolet radiation in an amount effective to reduce an organic content and / or increase a density and. / or increase a wet etch resistance of the dielectric material. Optionally, the UV cured dielectric material may be exposed to multiple ultraviolet radiation patterns.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
Apparatus and process for mediated electrochemical oxidation of materials
A unique apparatus unique apparatus and process that uses mediated electrochemical oxidation (MEO) for: (1) Destruction of: a) nearly all organic solid, liquid, and gases materials, except fluorinated hydrocarbons; b) all biological solid, liquid, and gases materials; c) and / or dissolution and decontamination (such as cleaning equipment and containers, etc.) of nearly all inorganic solid, liquid, or gas where higher oxidation states exist which includes, but is not limited to, halogenated inorganic compounds (except fluorinated), inorganic pesticides and herbicides, inorganic fertilizers, carbon residues, inorganic carbon compounds, mineral formations, mining tailings, inorganic salts, metals and metal compounds, etc.); and d) combined materials (e.g. a mixture of any of the foregoing with each other); henceforth collectively referred to as materials. (2) Sterilization / disinfection of equipment, glassware, etc., by destroying all existing infectious materials. (3) Dissolution of transuranic / actinide materials and / or destruction of the oxidizable components in the hazardous waste portion of mixed waste. (4) Generation of hydrogen and oxygen from MEO of materials. (5) Alteration of organic, biological, and inorganic materials by MEO to produce other compounds from these materials. The materials are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the materials with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized forms of any other redox couples present are produced either by similar anodic oxidation or reaction with the oxidized form of other redox couples present and capable of affecting the required redox reaction. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the materials molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable material species, including intermediate reaction products, have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures between ambient and approximately 100° C. The oxidation process may be enhanced by the addition of reaction enhancements, such as: ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
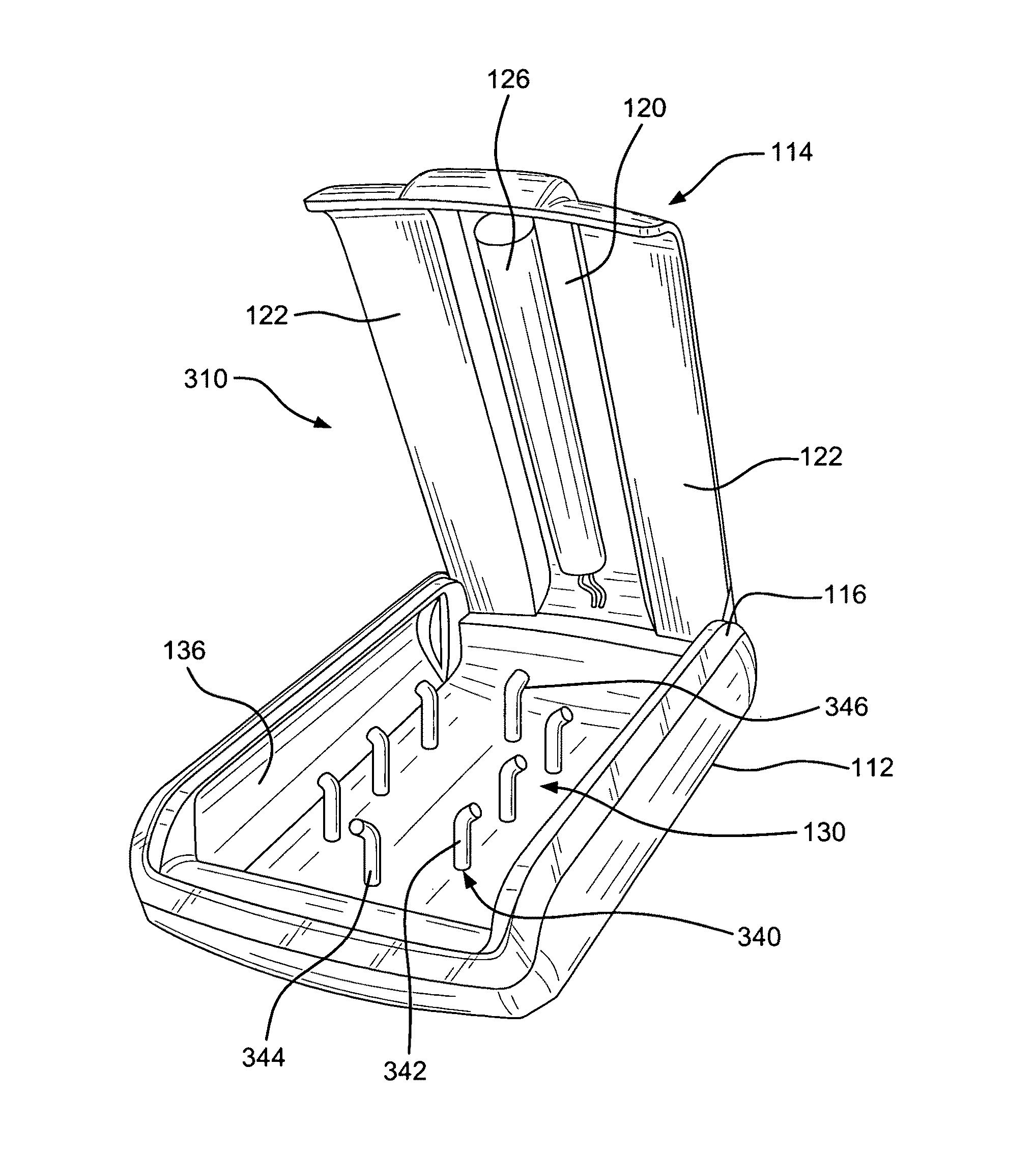
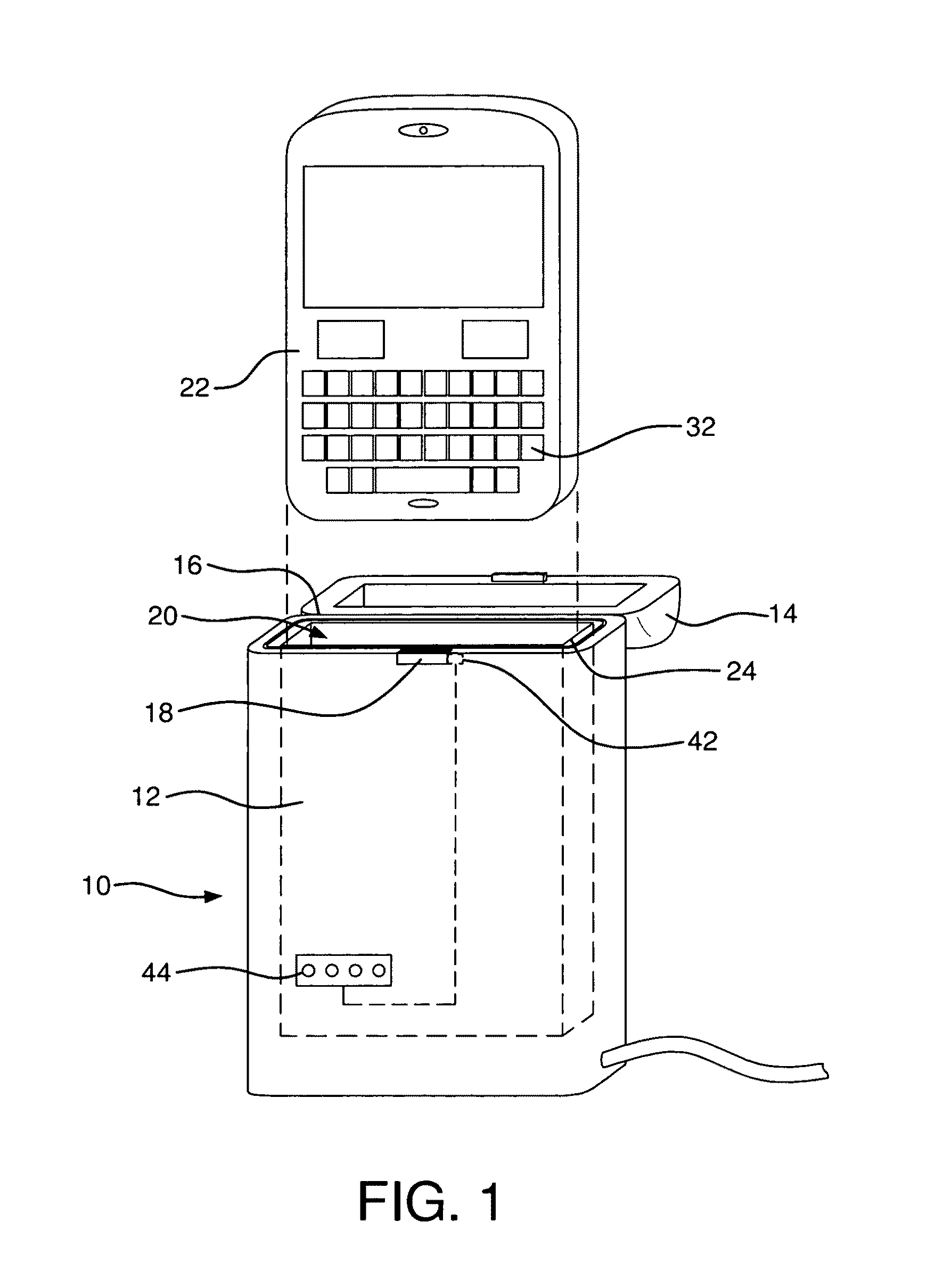
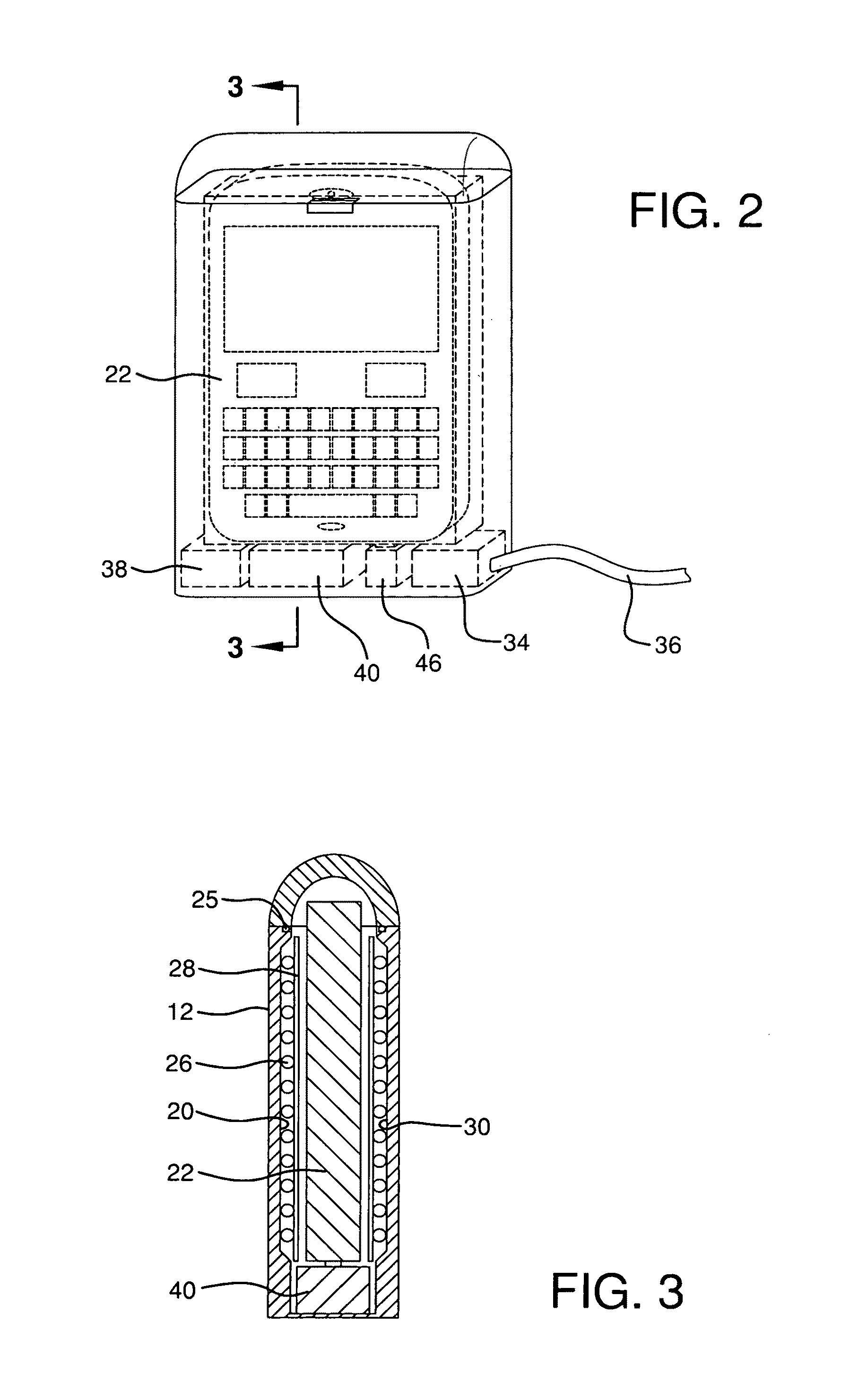
Sanitizer for portable electronic devices
InactiveUS8481970B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltraviolet radiationUltraviolet
A sanitizer for sanitizing a portable electronic device is provided, the sanitizer having a base including a cavity for receiving the electronic device, at least one ultraviolet radiation source for emitting ultraviolet radiation into the cavity, a cover cooperating with the base, the cover moving between an open position wherein the electronic device can be inserted into or removed from the cavity and a closed position wherein the cavity is enclosed so as to substantially maintain the ultraviolet radiation within the cavity, and a controller for enabling the ultraviolet radiation source to be activated only when the cover is closed.
Owner:SPECTRONICS
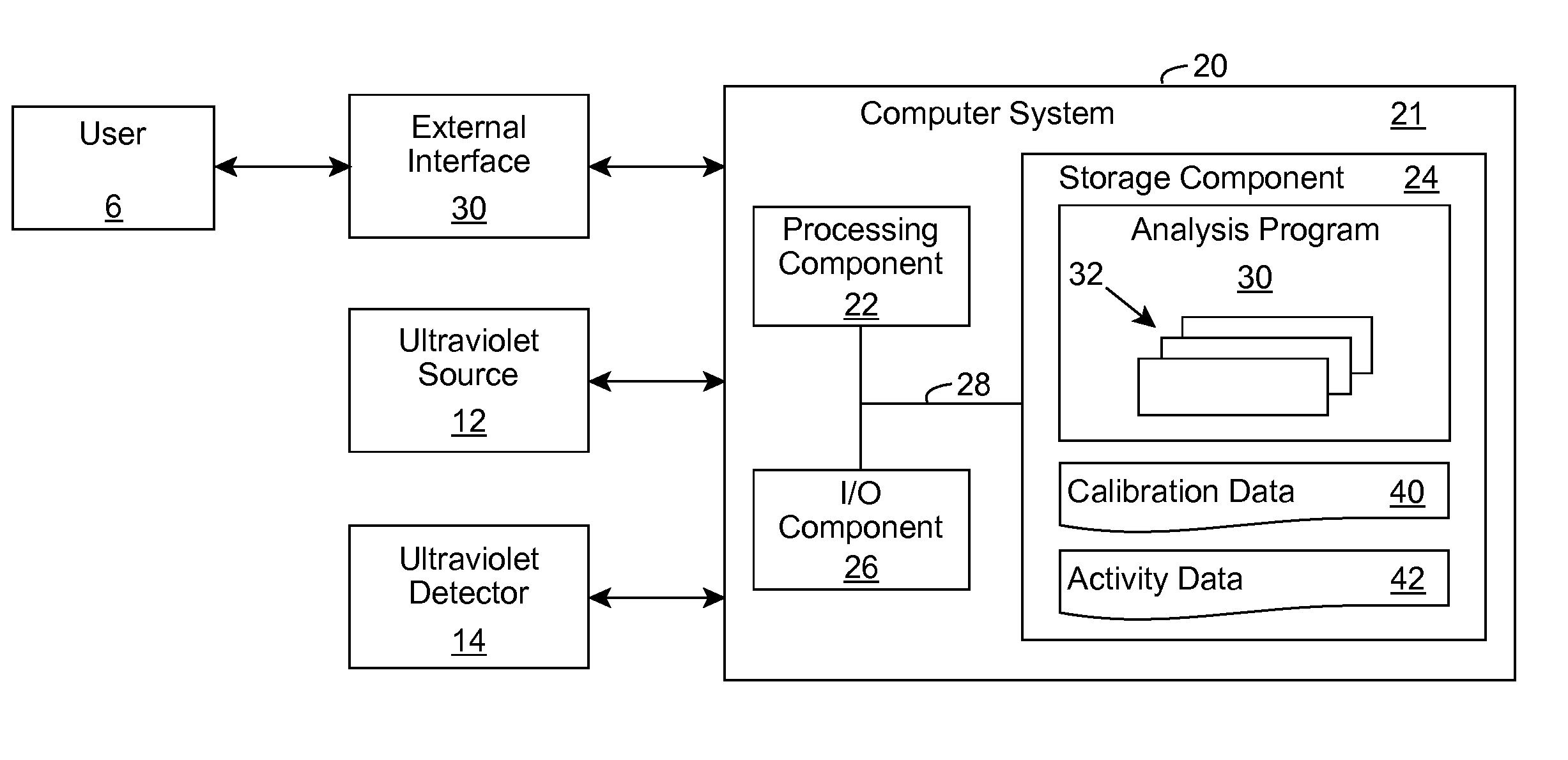
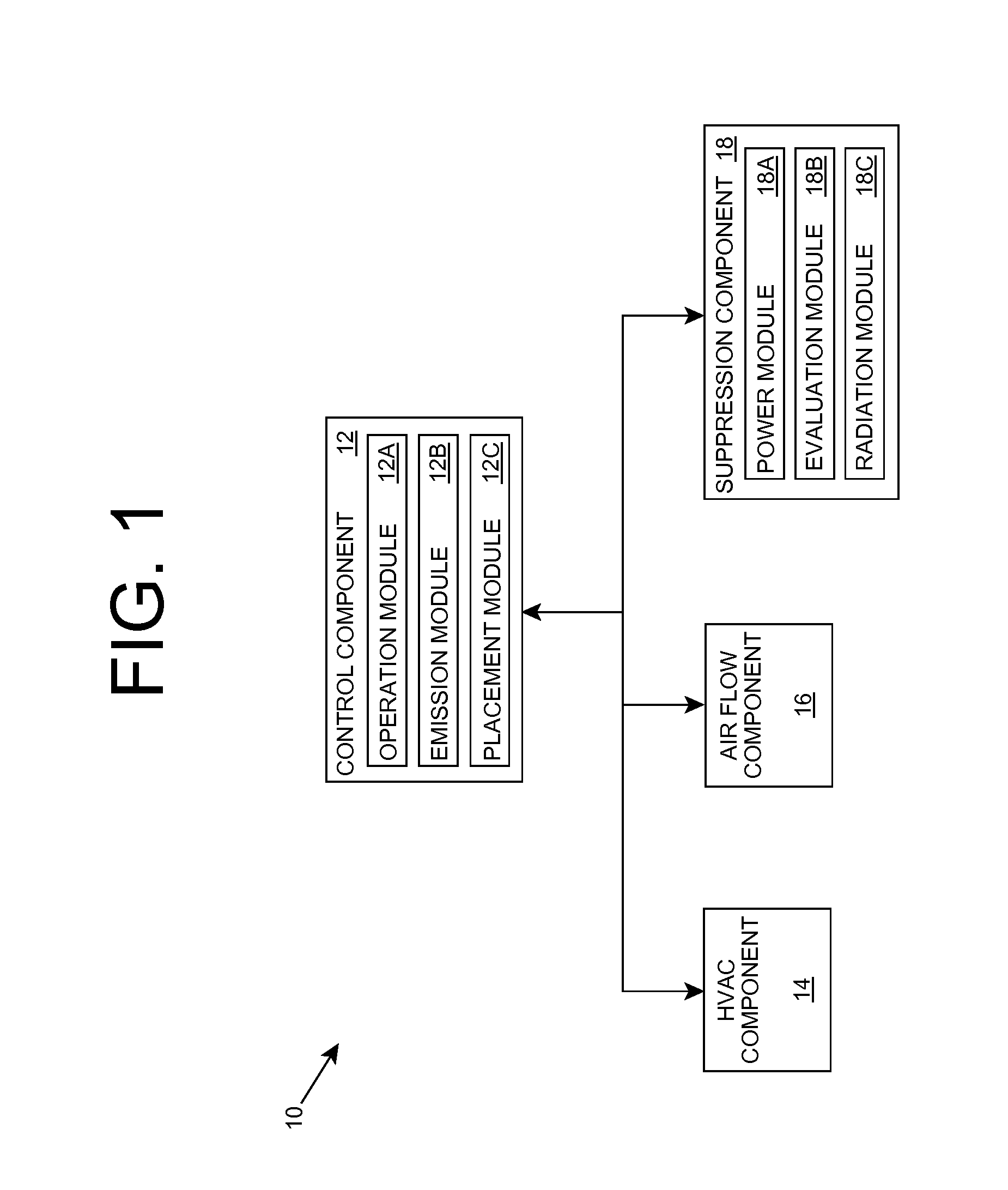
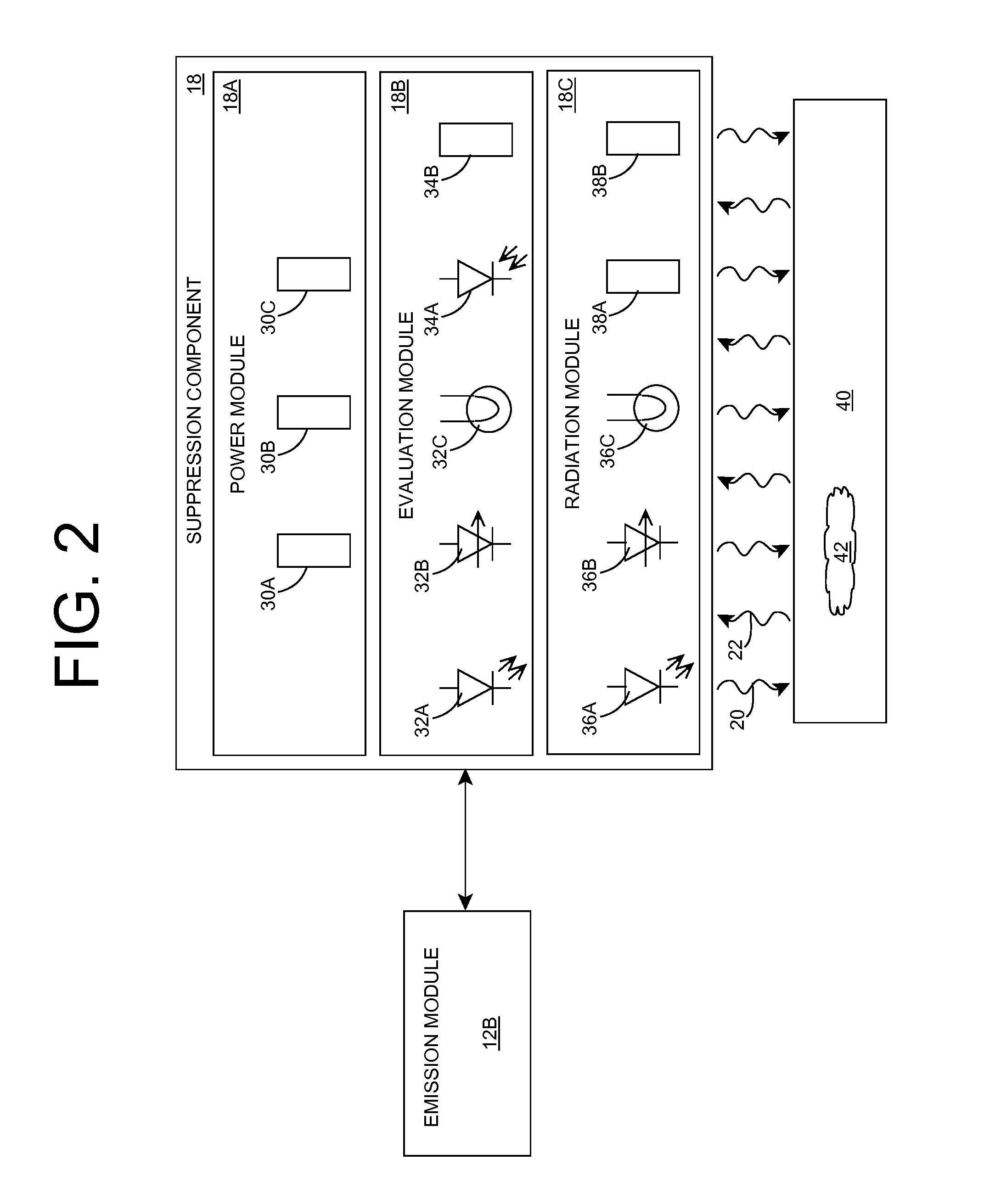
Biological activity monitoring and/or suppression
ActiveUS8277734B2Without affecting quality of foodMonitor and suppress bacteria multiplicationSpace heating and ventilationExhaust apparatusUltravioletUltraviolet radiation
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
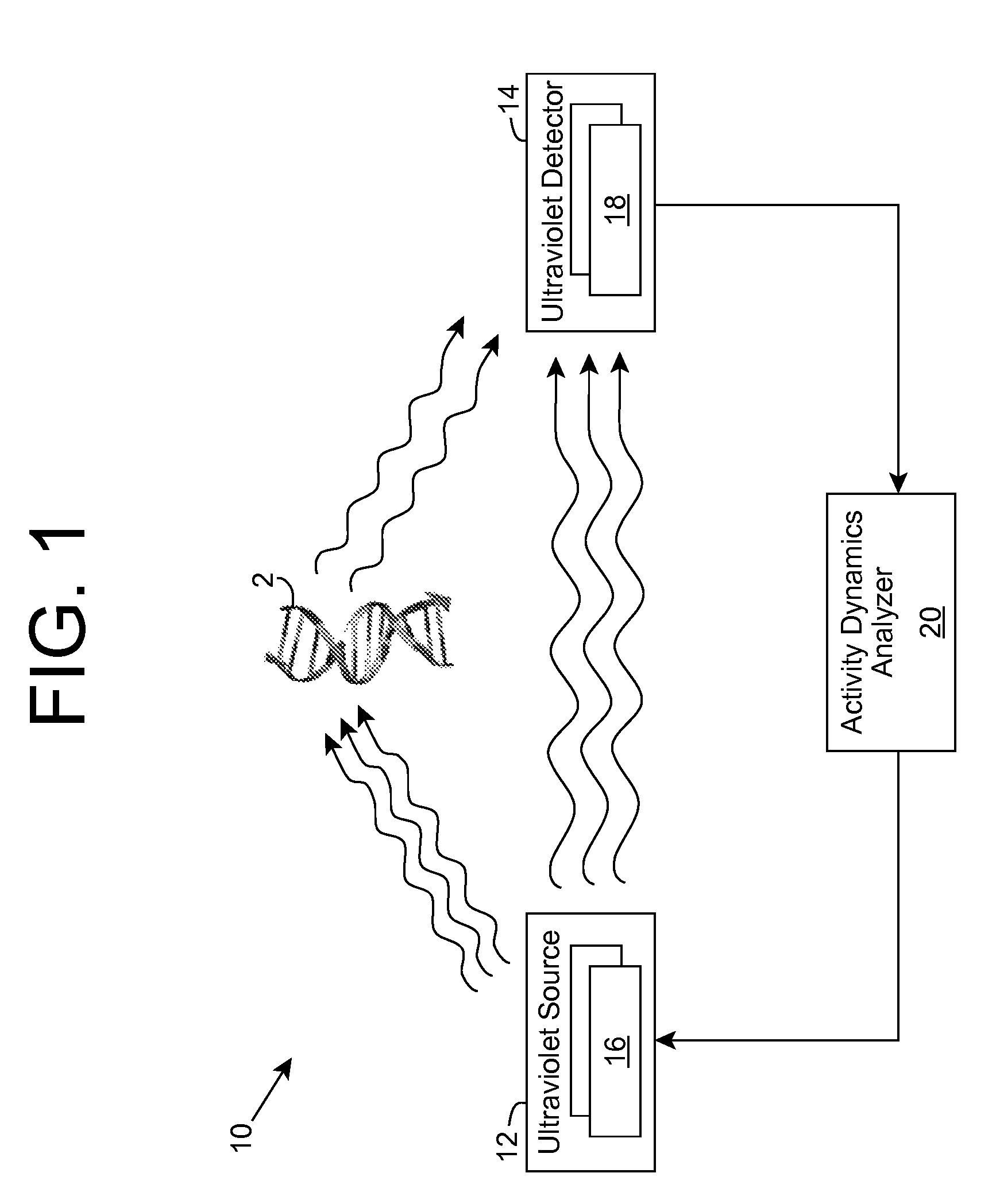
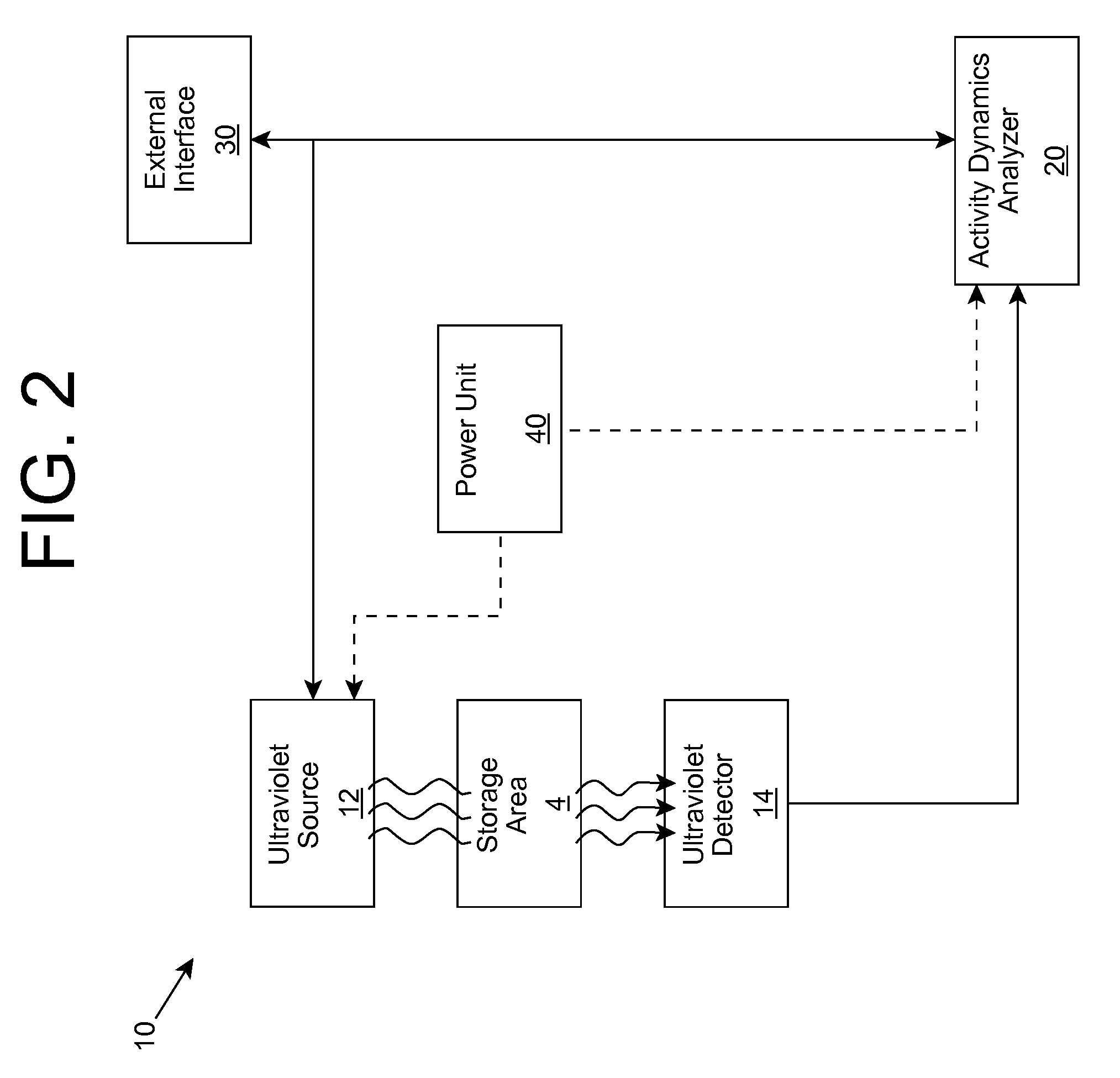
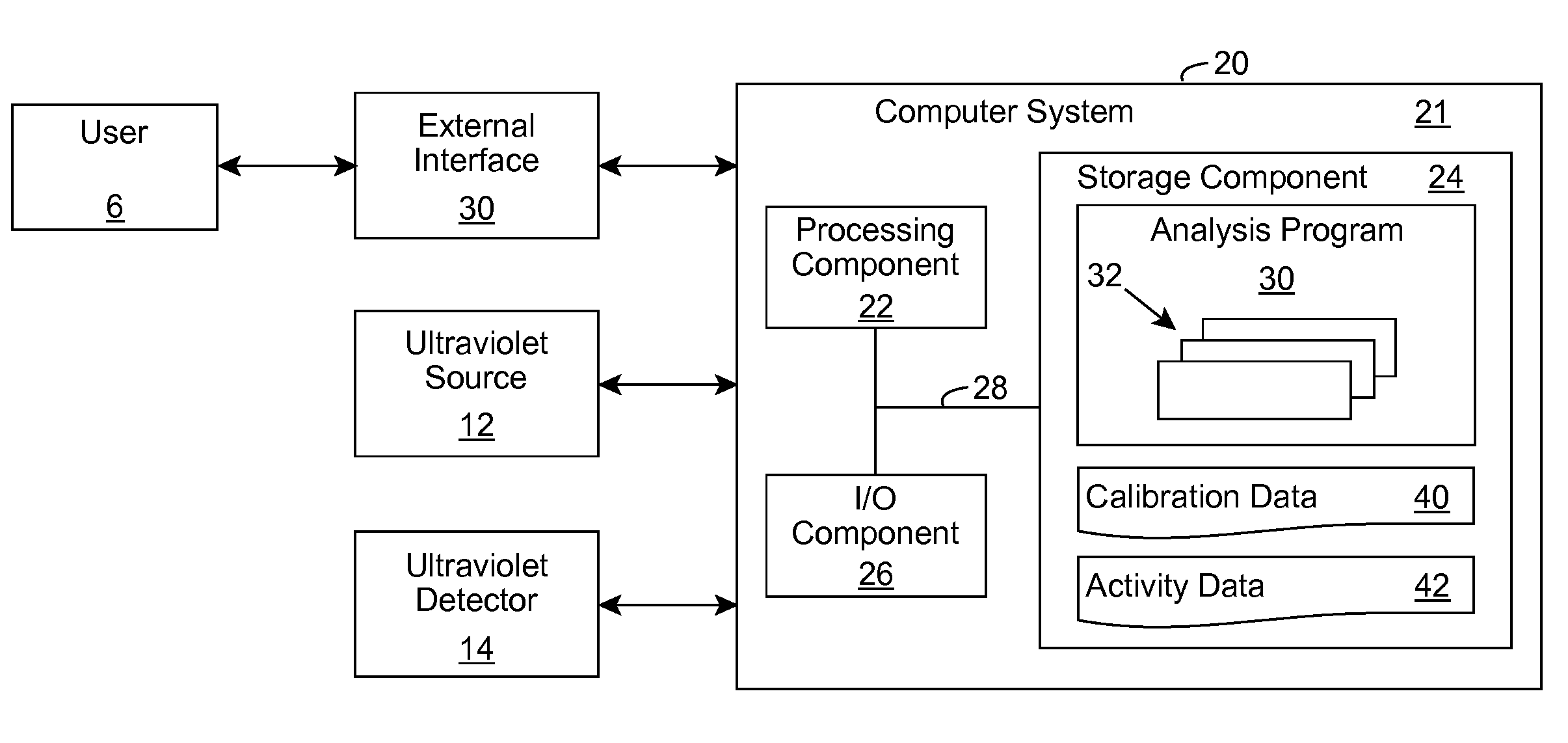
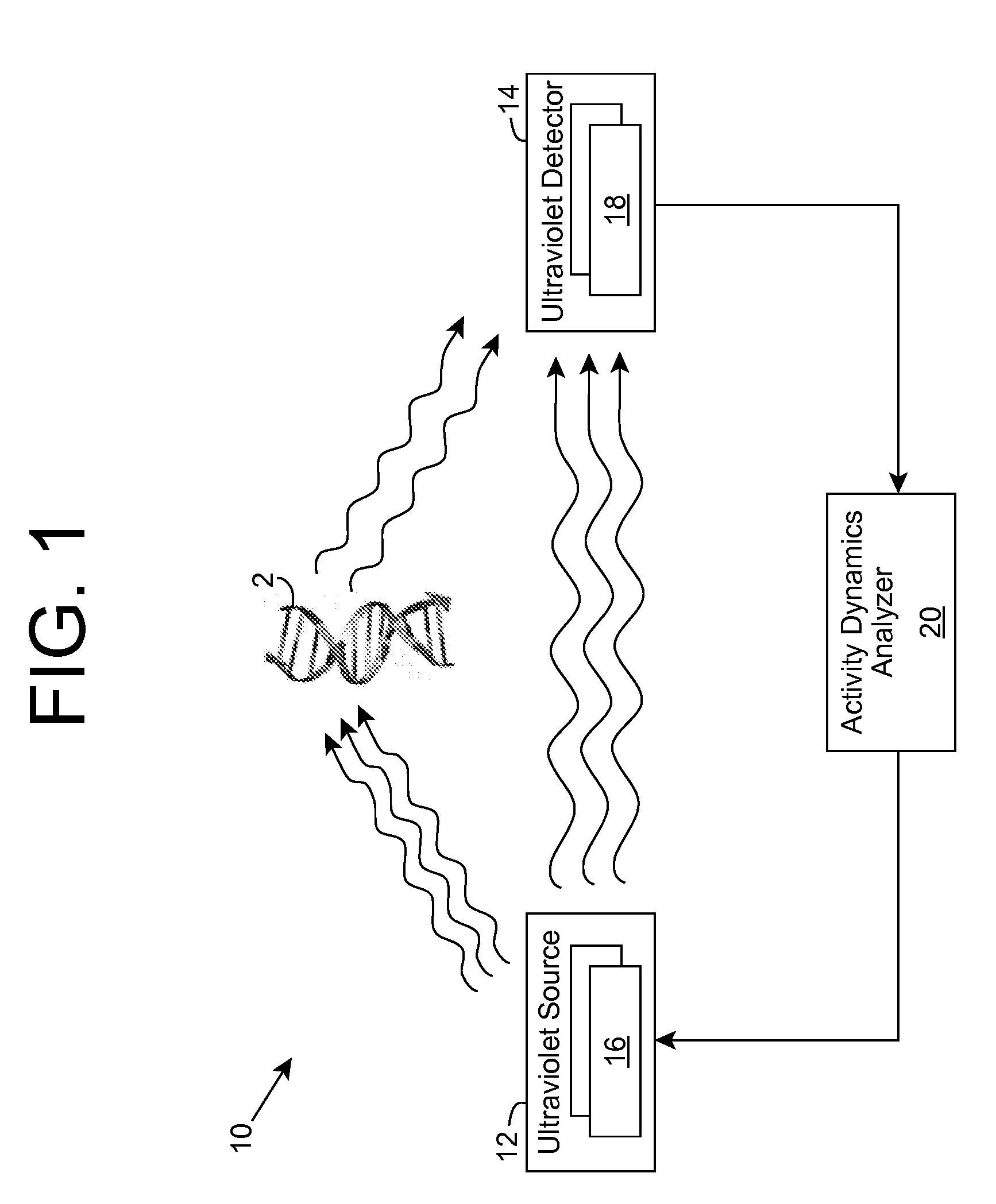
Biological activity monitoring and/or suppression
ActiveUS20090280035A1Without affecting quality of foodMonitor and suppress bacteria multiplicationSpace heating and ventilationExhaust apparatusUltravioletUltraviolet radiation
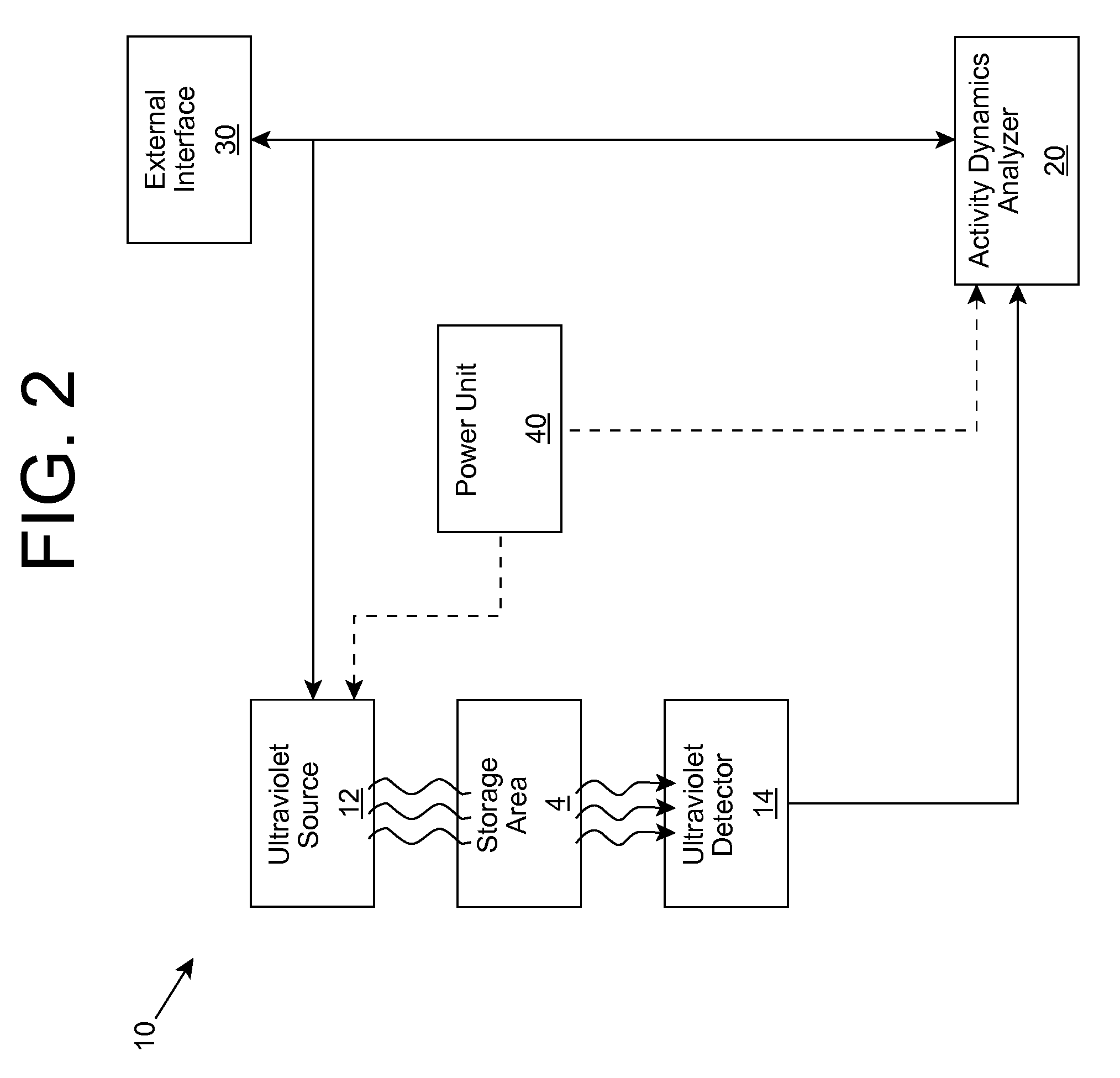
Ultraviolet radiation is shone within an area and detected. The detected ultraviolet radiation is monitored over a period of time to determine a set of biological activity dynamics for the area. Ultraviolet radiation detected during a calibration period can be used to provide a baseline with which analysis of subsequently detected ultraviolet radiation is compared and analyzed. When the presence of biological activity is determined within the area, ultraviolet radiation and / or one or more other approaches can be utilized to suppress the biological activity.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Ultraviolet Water Disinfection System
ActiveUS20150008167A1Effective exposureHigh disinfection rateIon-exchanger regenerationTreatment involving filtrationUltravioletUltraviolet radiation
A solution for treating a fluid, such as water, is provided. An ultraviolet transparency of a fluid can be determined before or as the fluid enters a disinfection chamber. In the disinfection chamber, the fluid can be irradiated by ultraviolet radiation to harm microorganisms that may be present in the fluid. One or more attributes of the disinfection chamber, fluid flow, and / or ultraviolet radiation can be adjusted based on the transparency to provide more efficient irradiation and / or higher disinfection rates. In addition, various attributes of the disinfection chamber, such as the position of the inlet(s) and outlet(s), the shape of the disinfection chamber, and other attributes of the disinfection chamber can be utilized to create a turbulent flow of the fluid within the disinfection chamber to promote mixing and improve uniform ultraviolet exposure.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
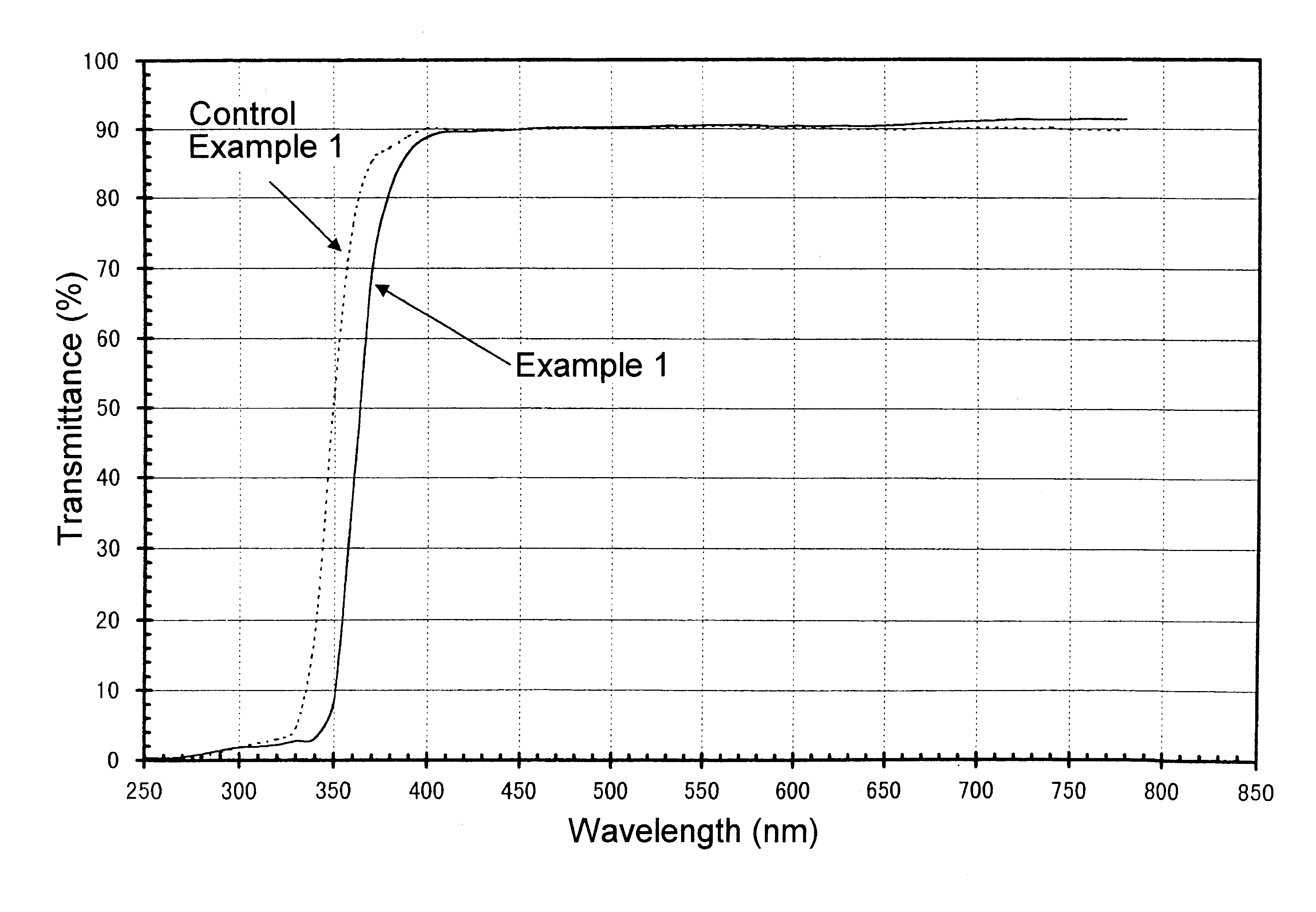
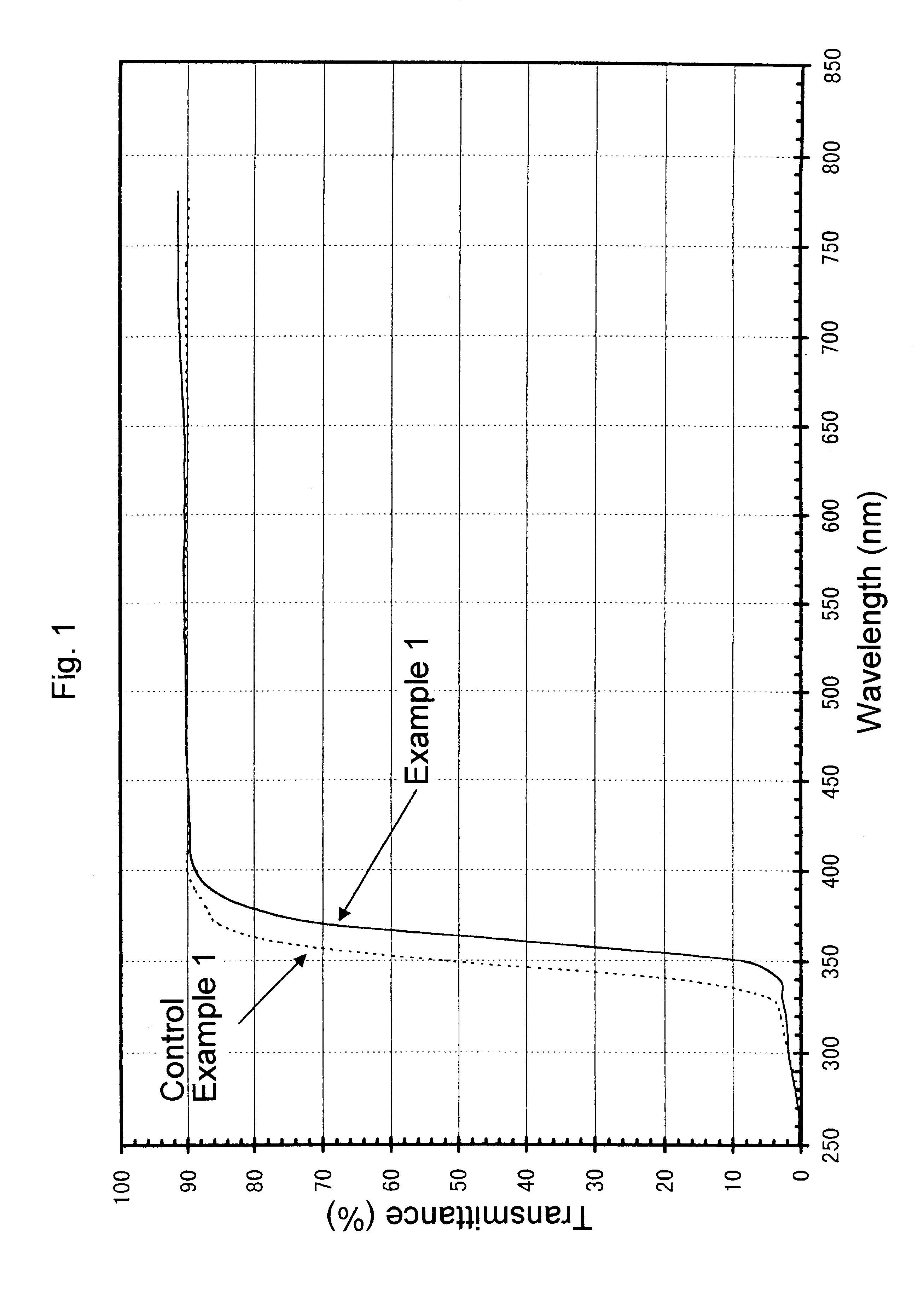
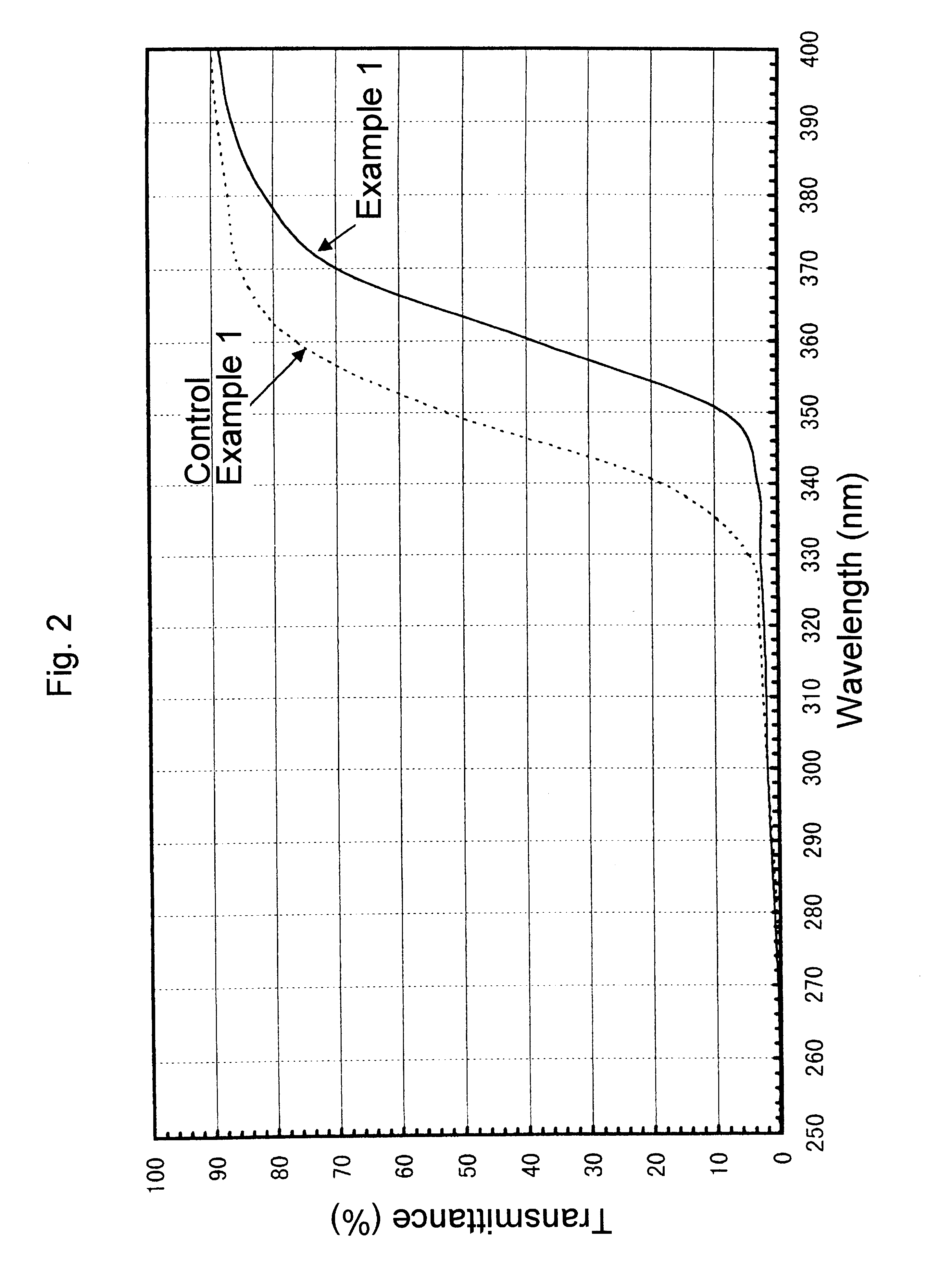
Ultraviolet radiation-absorbing, colorless, transparent soda-lime silica glass
An ultraviolet radiation-absorbing, colorless, transparent soda-lime-silica glass as well as glass bottles formed out of the glass are disclosed which, while maintaining high transmittance to light in the visible region and thereby allowing the contents to be seen clearly, absorbs ultraviolet radiation and thus prevents coloration, discoloration, fading in color or deterioration of the flavor of the contents caused by ultraviolet radiation. The glass is characterized in that its composition includes, in % by weight, SO3 . . . 0.15-0.4%; Cerium oxide . . . 0.2-1% (calculated as CeO2); Fe2O3 . . . 0.01-0.08%; FeO . . . 0-0.008%; Manganese oxide . . . 0.01-0.08% (calculated as MnO); and Cobalt oxide . . . 0-0.0005% (calculated as CoO).
Owner:NIHON YAMAMURA GLASS CO LTD
Ultraviolet-curable polysiloxane composition and method for the formation of cured patterns therefrom
InactiveUS6051625AImprove the immunityImprove heat resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoatingsUltravioletEther
The instant invention pertains to a curable composition comprising (a) substance that generates free radicals under the action of ultraviolet radiation and (b) polymer molecule bearing functionality capable of polymerization under the action of said free radicals wherein (a) is a benzoin ether and makes up from 0.001 to 10 wt % of the total composition and (b) has the following formula(R3SiO1 / 2)a(R'2SiO2 / 2)b(R''SiO3 / 2)c(SiO4 / 2)din which R, R', and R'' are each H or C1 to C10 hydrocarbyl possibly containing a heteroatom and at least 10% is, for example, a vinyl group, and a+b+c+d=1. The composition of the instant invention is a storage-stable UV-curable composition that does not suffer from cure inhibition by air or oxygen, that is very efficiently cured by low doses of UV radiation, and provides a highly heat-resistant cured pattern by heating after pattern formation.
Owner:DOW CORNING ASIA
Organism growth suppression using ultraviolet radiation
ActiveUS20070205382A1Suppress and prevent growthGrowth inhibitionRadiation pyrometryFire rescueBiological bodyBiofilm
A solution for suppressing organism growth using ultraviolet radiation generated by solid state ultraviolet radiation emitters, such as ultraviolet diodes is provided. The invention includes a connection structure that includes a plurality of solid state ultraviolet radiation emitters disposed thereon. Each of the plurality of solid state ultraviolet radiation emitters emits ultraviolet radiation having a wavelength less than or equal to four hundred nanometers to harm a target organism that may be present on a surface. In one embodiment, the connection structure comprises a two-dimensional mesh that may be placed adjacent an air filter, incorporated in a cover, and / or moved with respect to a surface, such as the interior of an air duct. In this manner, the invention can suppress and / or prevent the growth of organisms, such as biofilms and mold, in locations that are susceptible to such growth.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
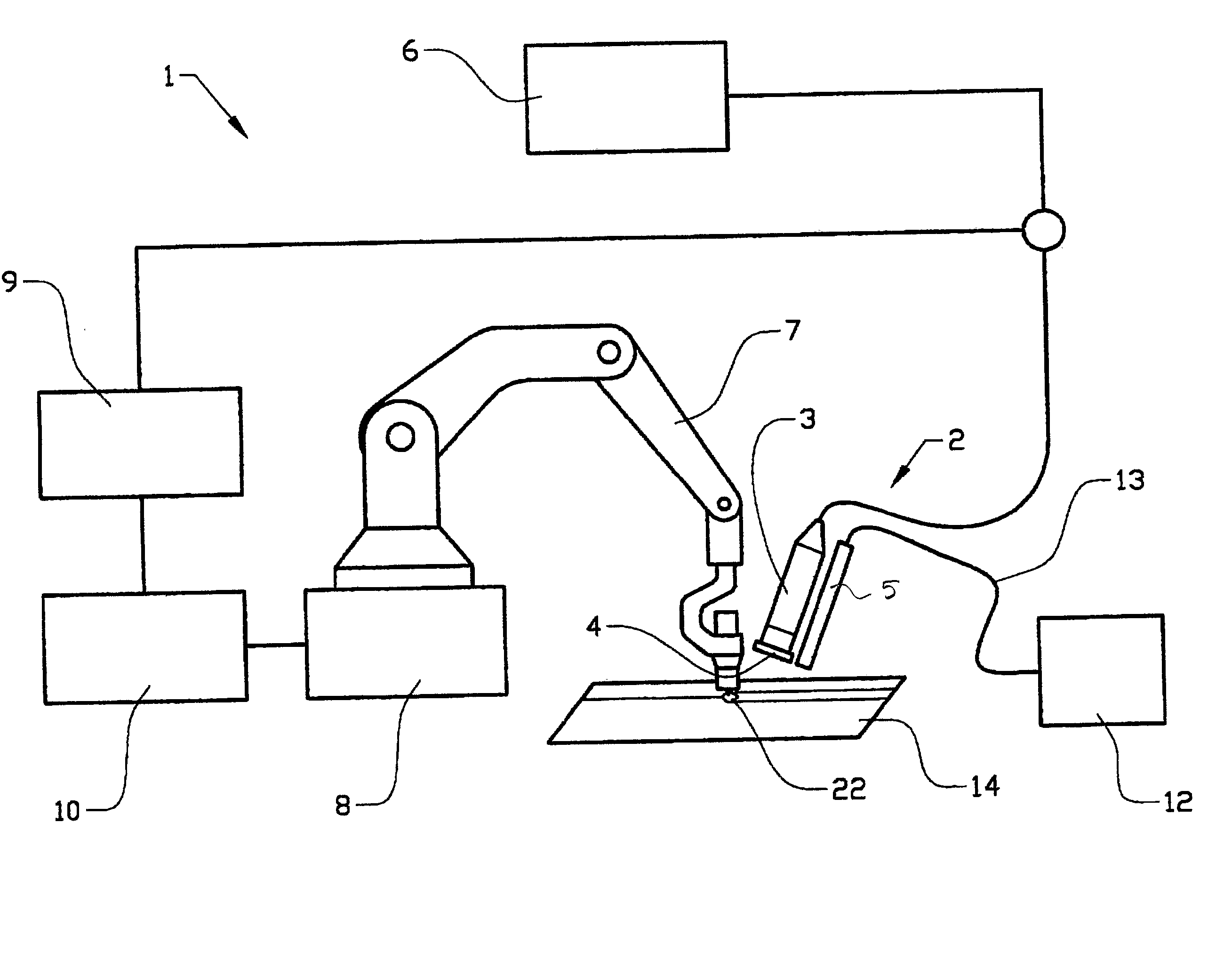
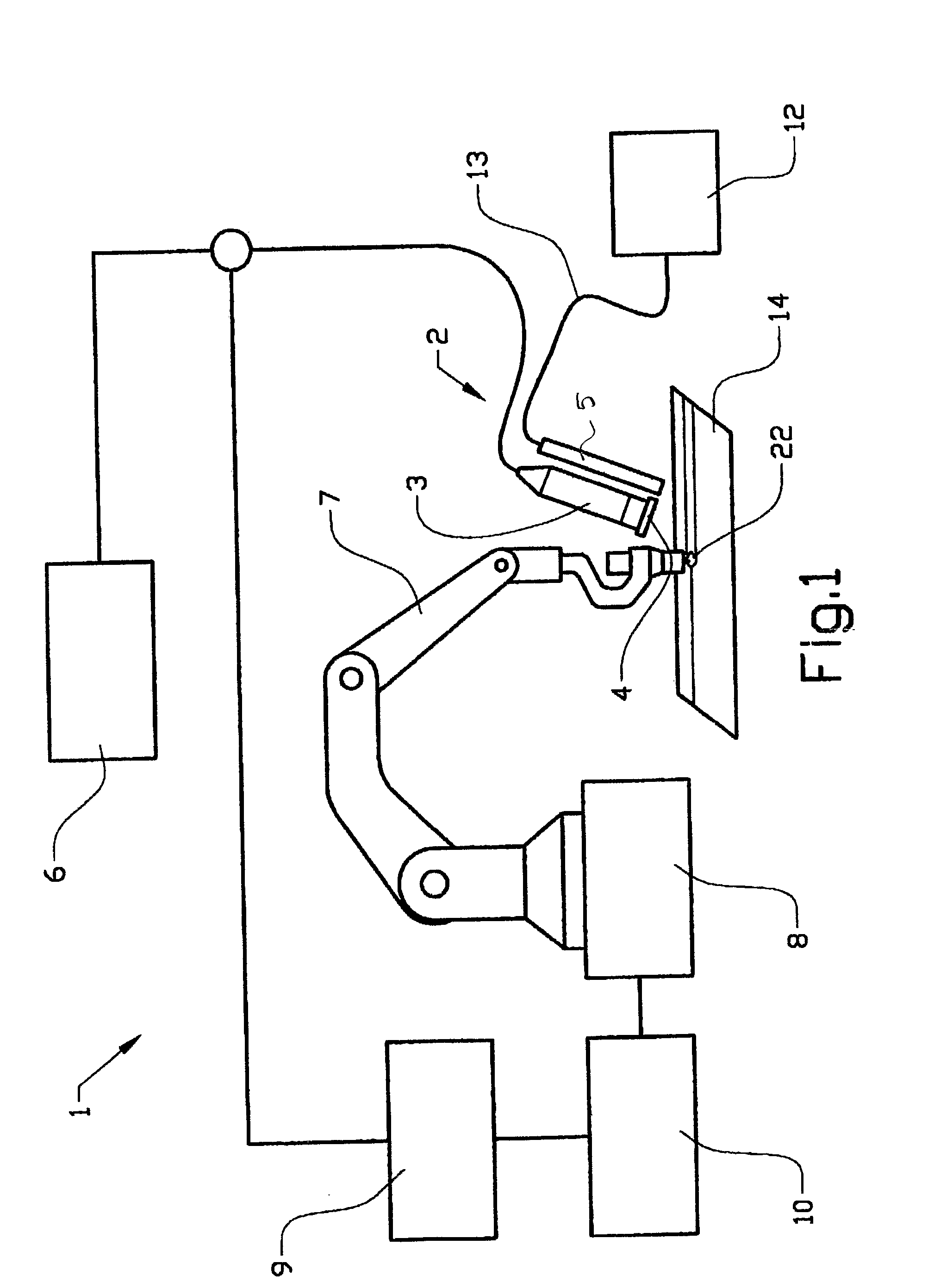
Device and method for monitoring a welding area and an arrangement and a method for controlling a welding operation
InactiveUS20050029326A1Great amount of detailed information and precisionImprove welding qualityAutomatic control devicesPrecision positioning equipmentBand-pass filterUltraviolet
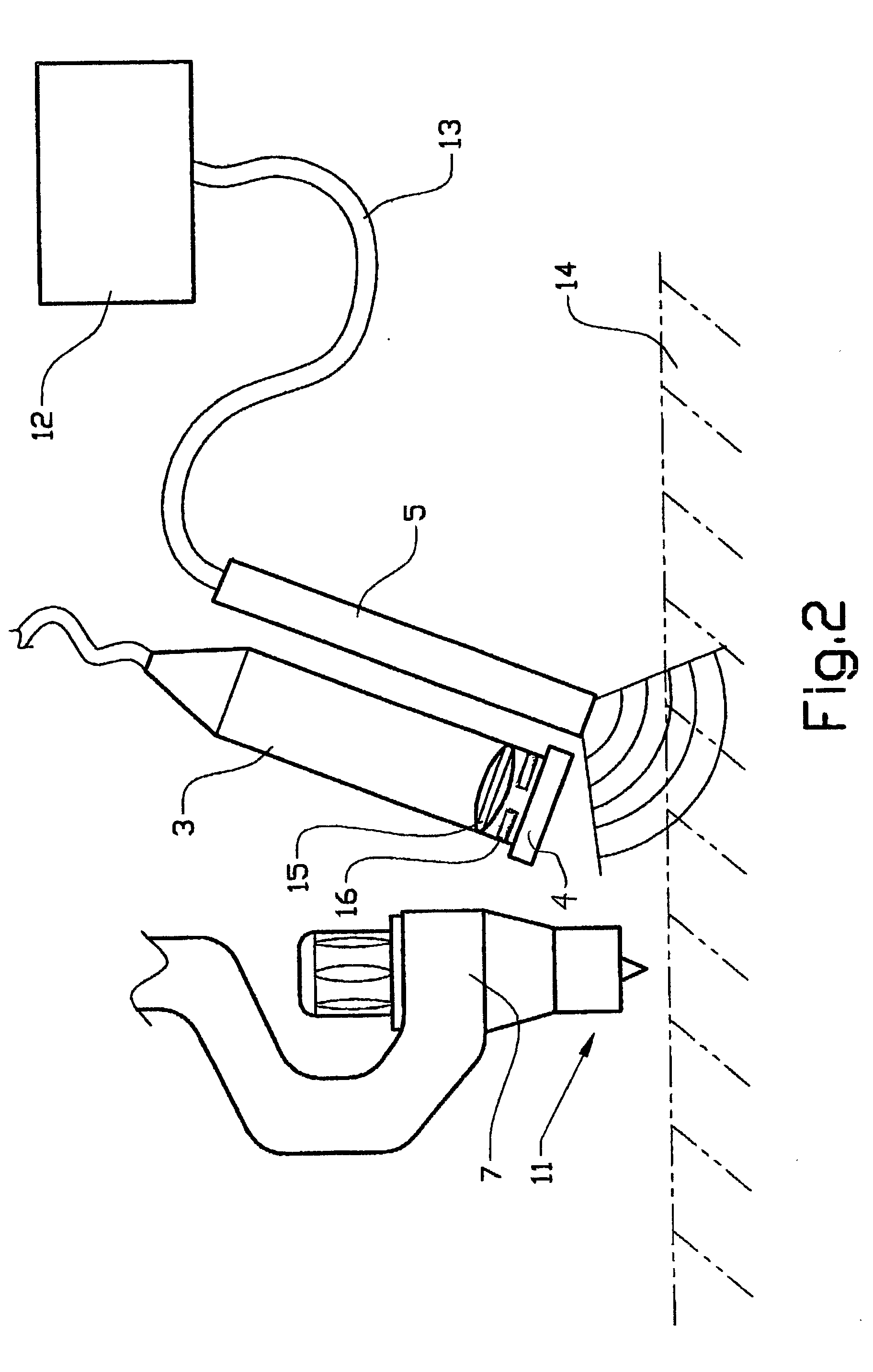
Method and device (2) for monitoring a welding area of an object (14) in connection with welding, which device includes arrangements (3) for reproduction of the welding area, at least one filter (4) arranged in front of or in the reproduction arrangement (3), and an illumination arrangement (5) of the welding area with ultraviolet radiation. The filter (4) consists of a band-pass filter which is adapted for filtering around a wavelength within the ultraviolet wavelength range.
Owner:GKN AEROSPACE SWEDEN AB
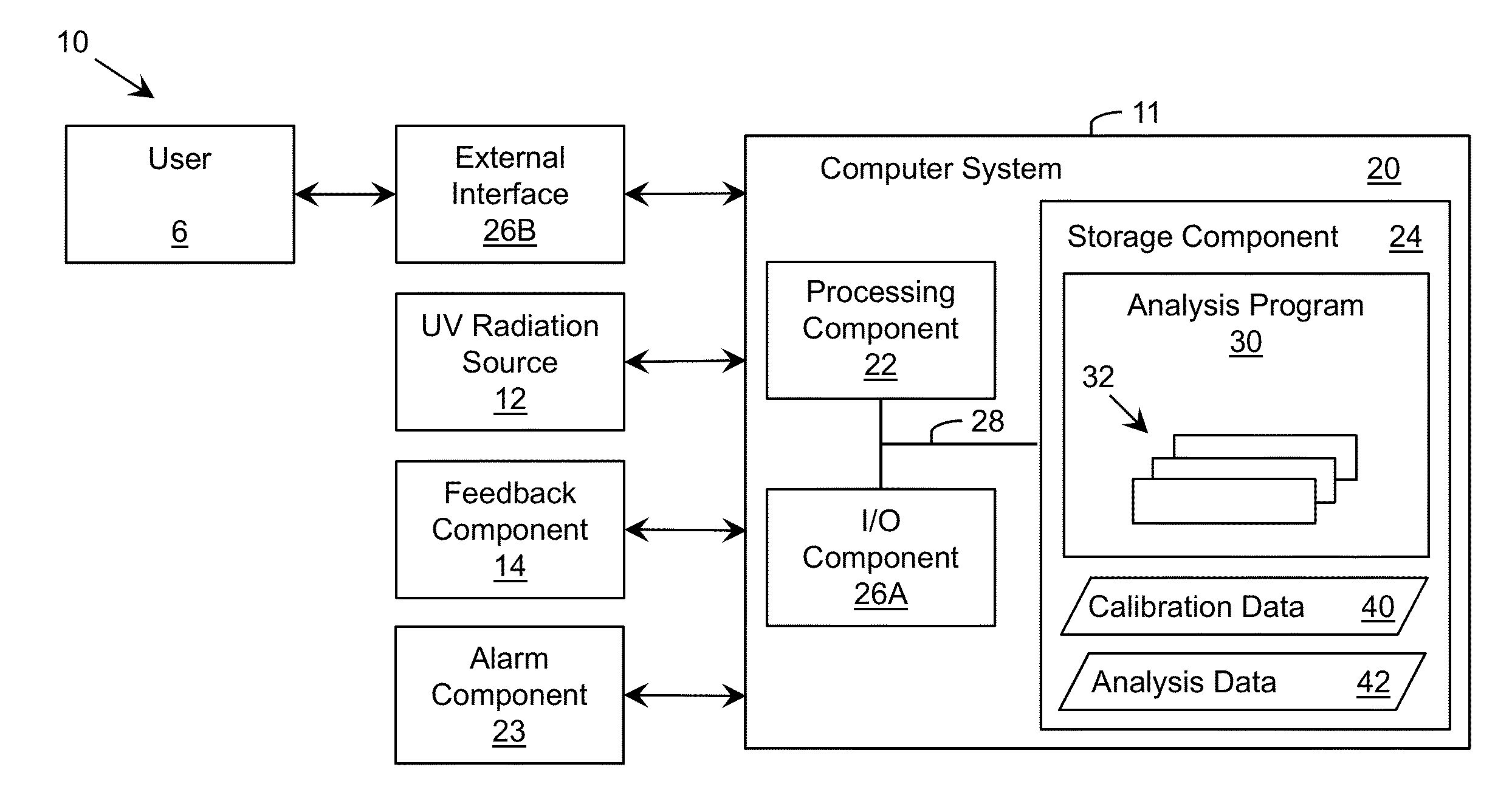
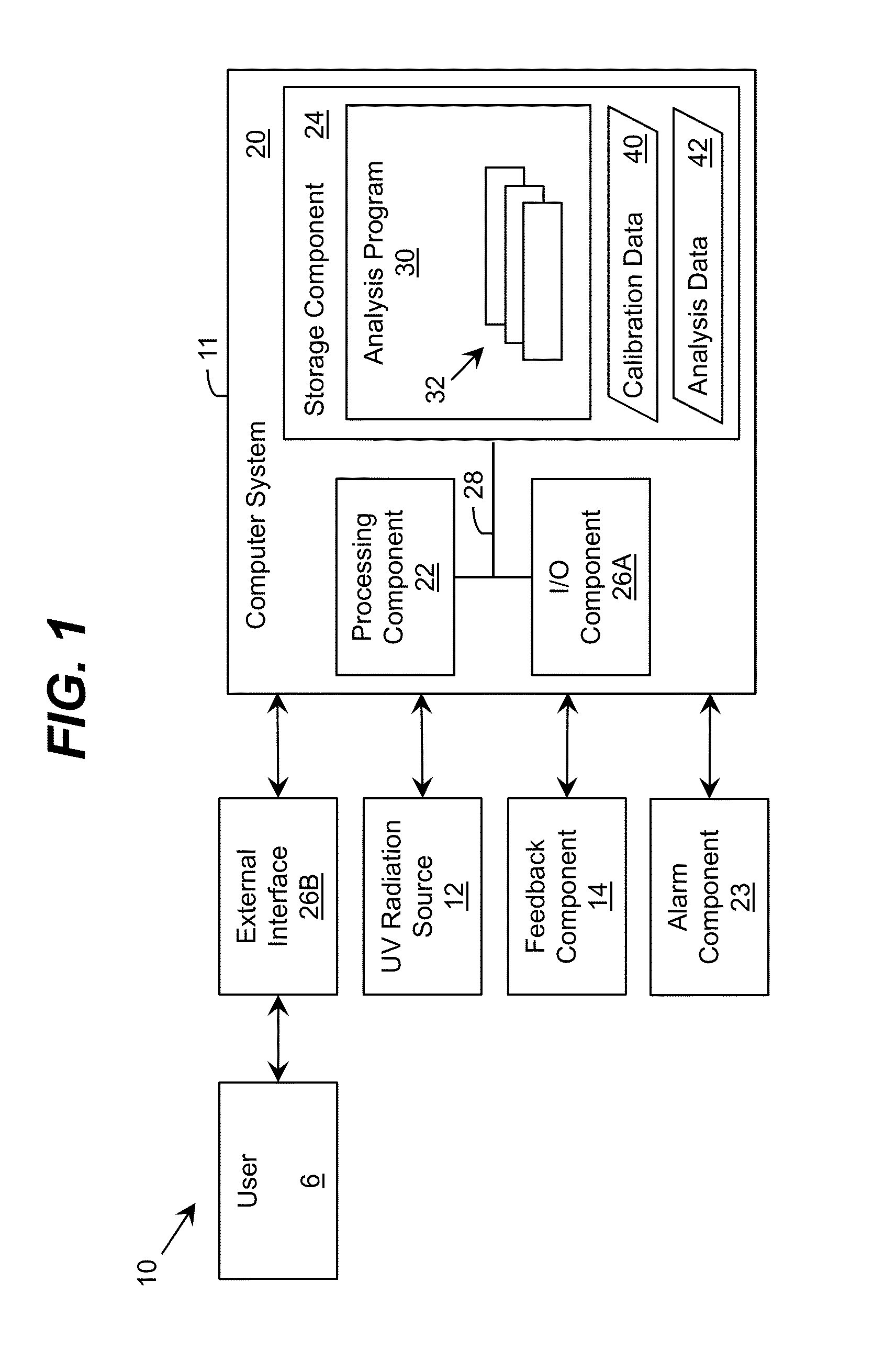
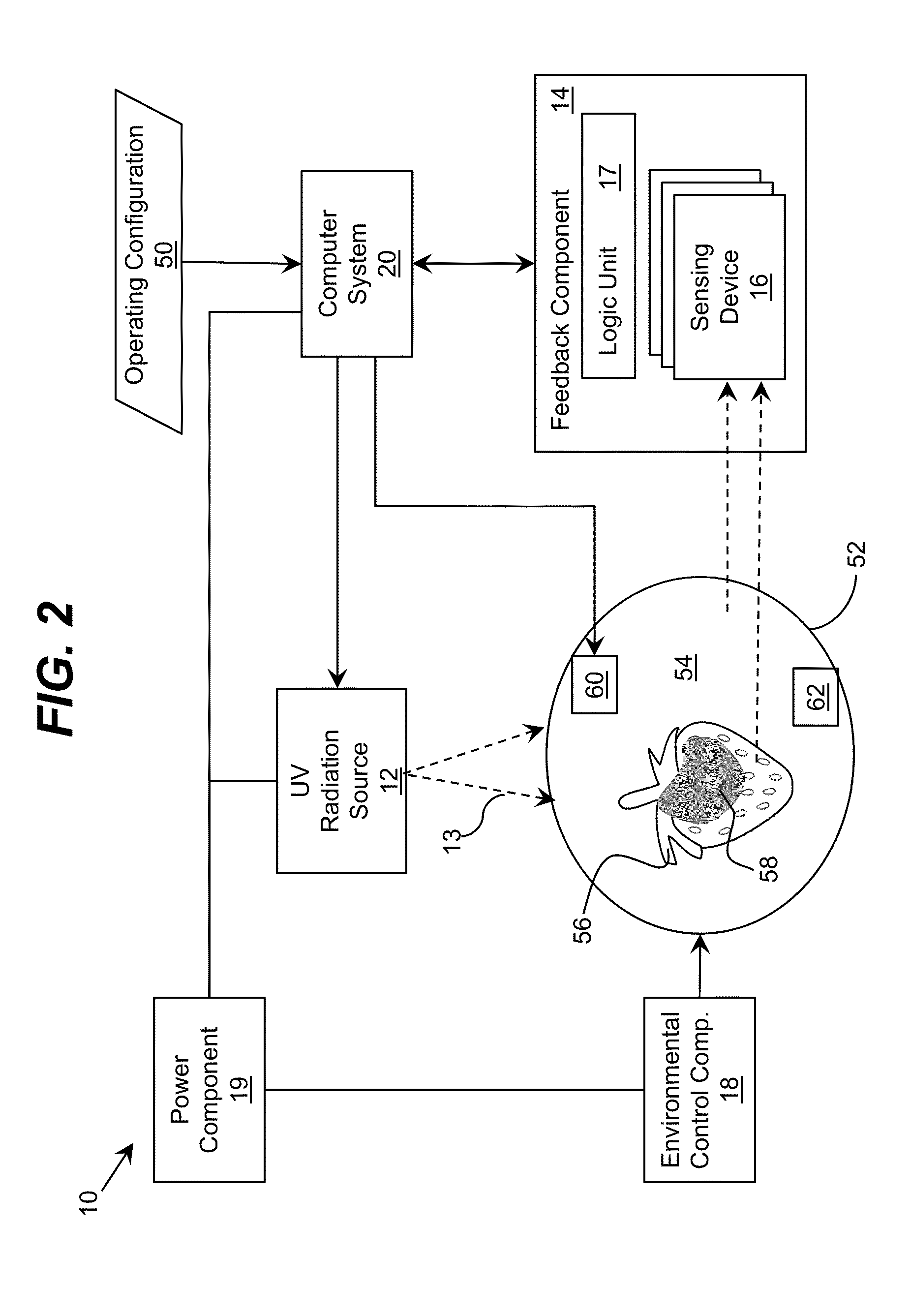
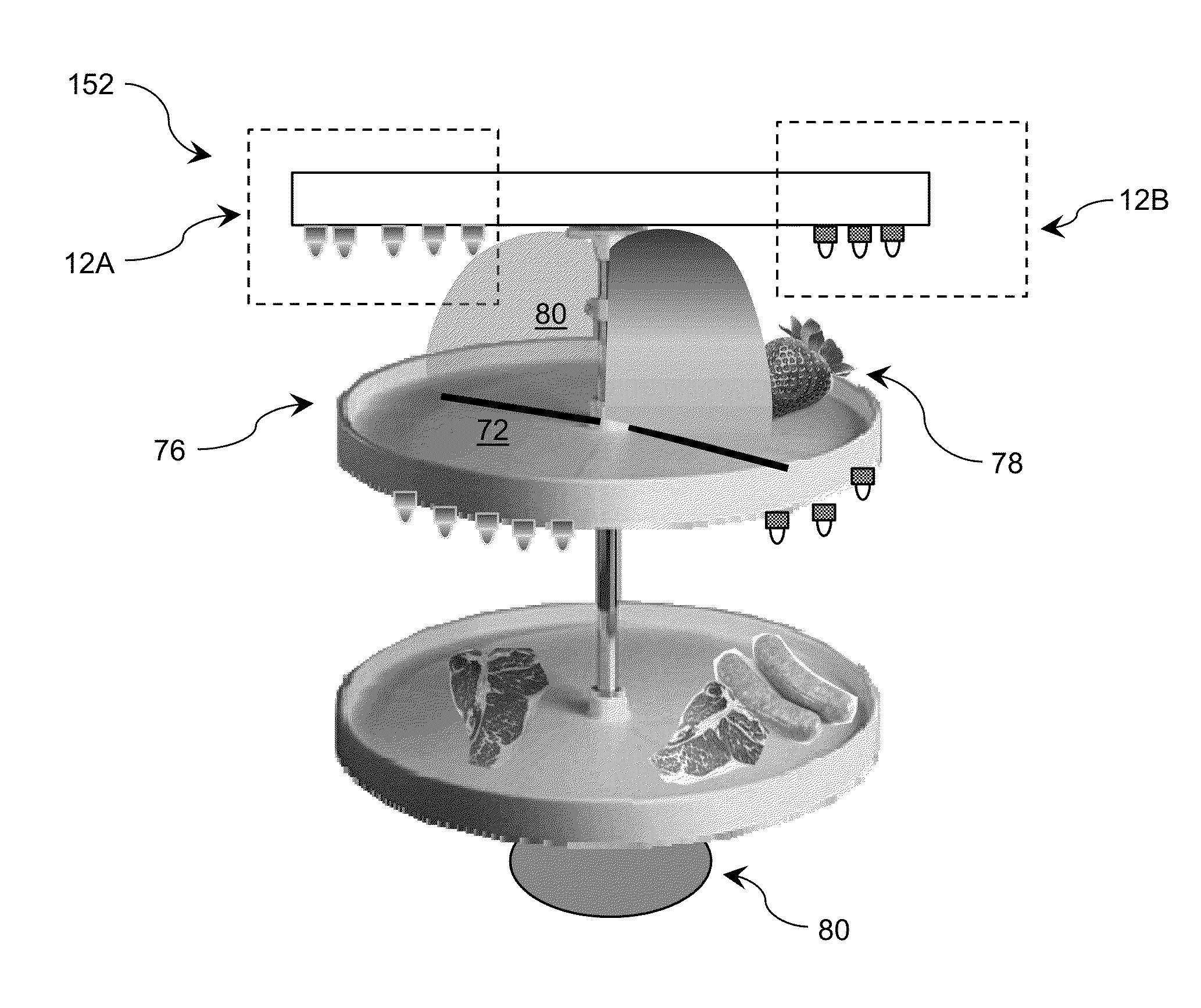
Storage device including target UV illumination ranges
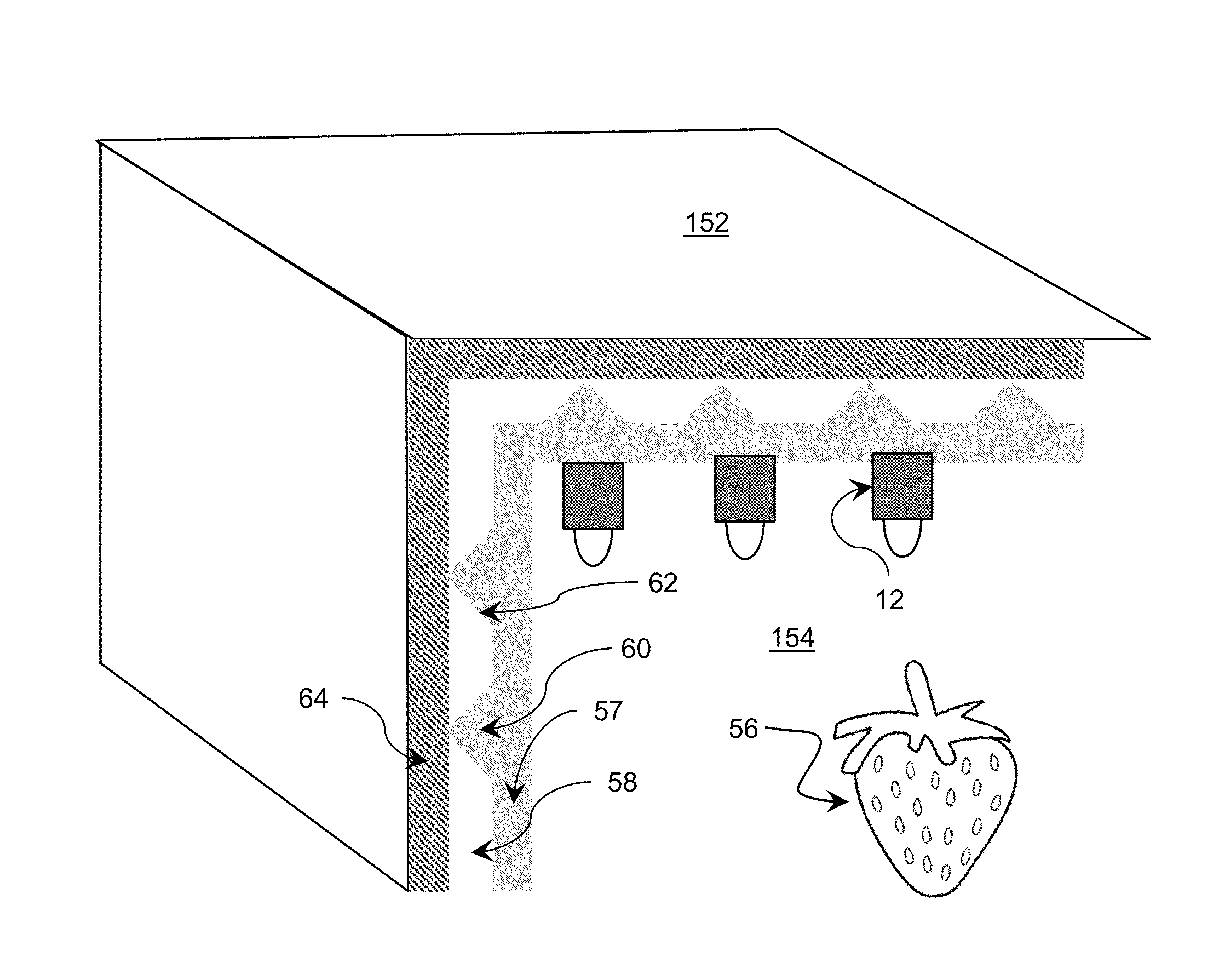
ActiveUS20140060094A1Lighting and heating apparatusMaterial analysis by optical meansDecompositionUltraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet radiation is directed within an area at target wavelengths and / or target intensities. The target wavelength ranges and / or target intensity ranges of the ultraviolet radiation sources can correspond to at least one of a plurality of selectable operating configurations including a storage life preservation operating configuration, a disinfection operating configuration, and an ethylene decomposition operating configuration.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
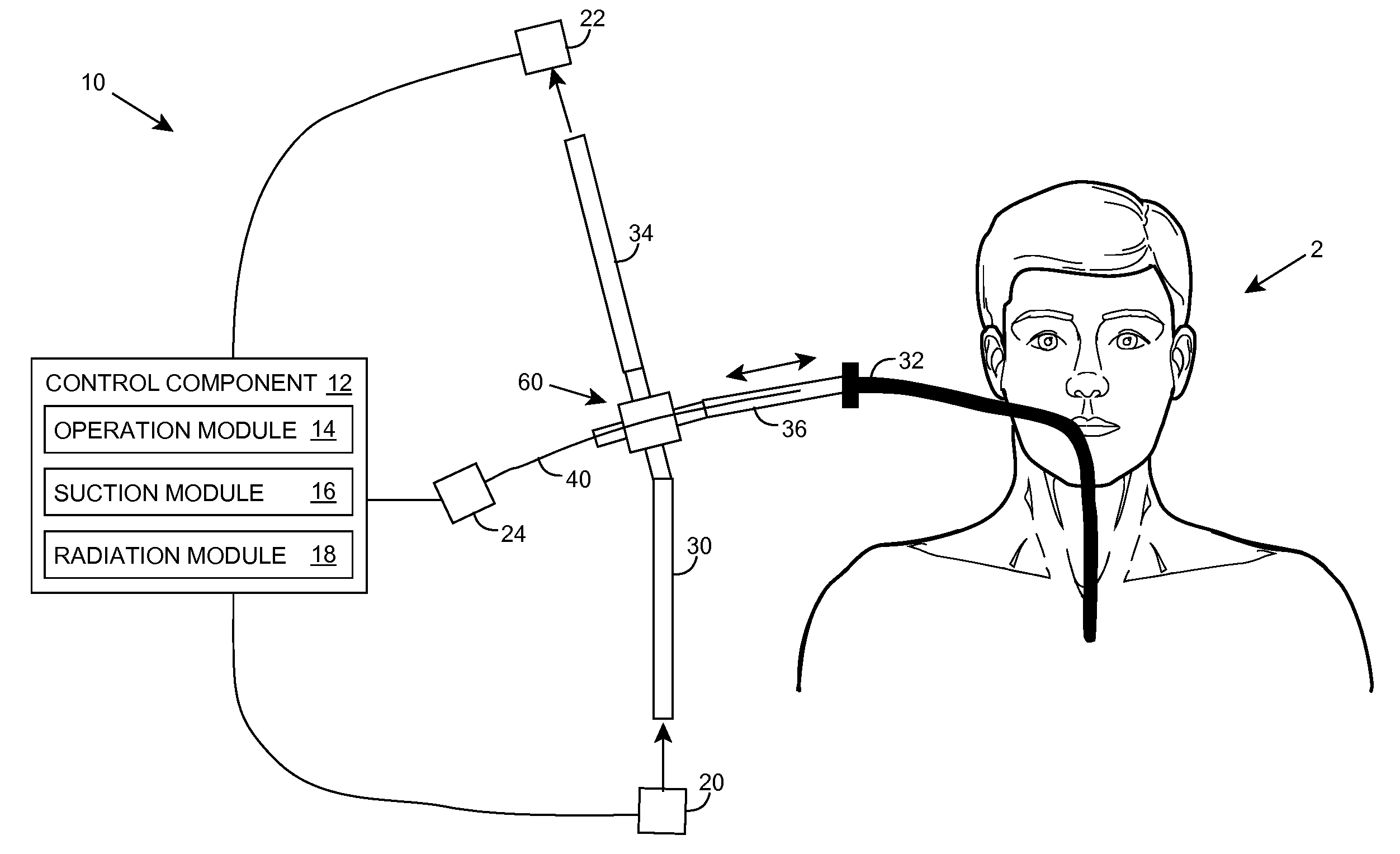
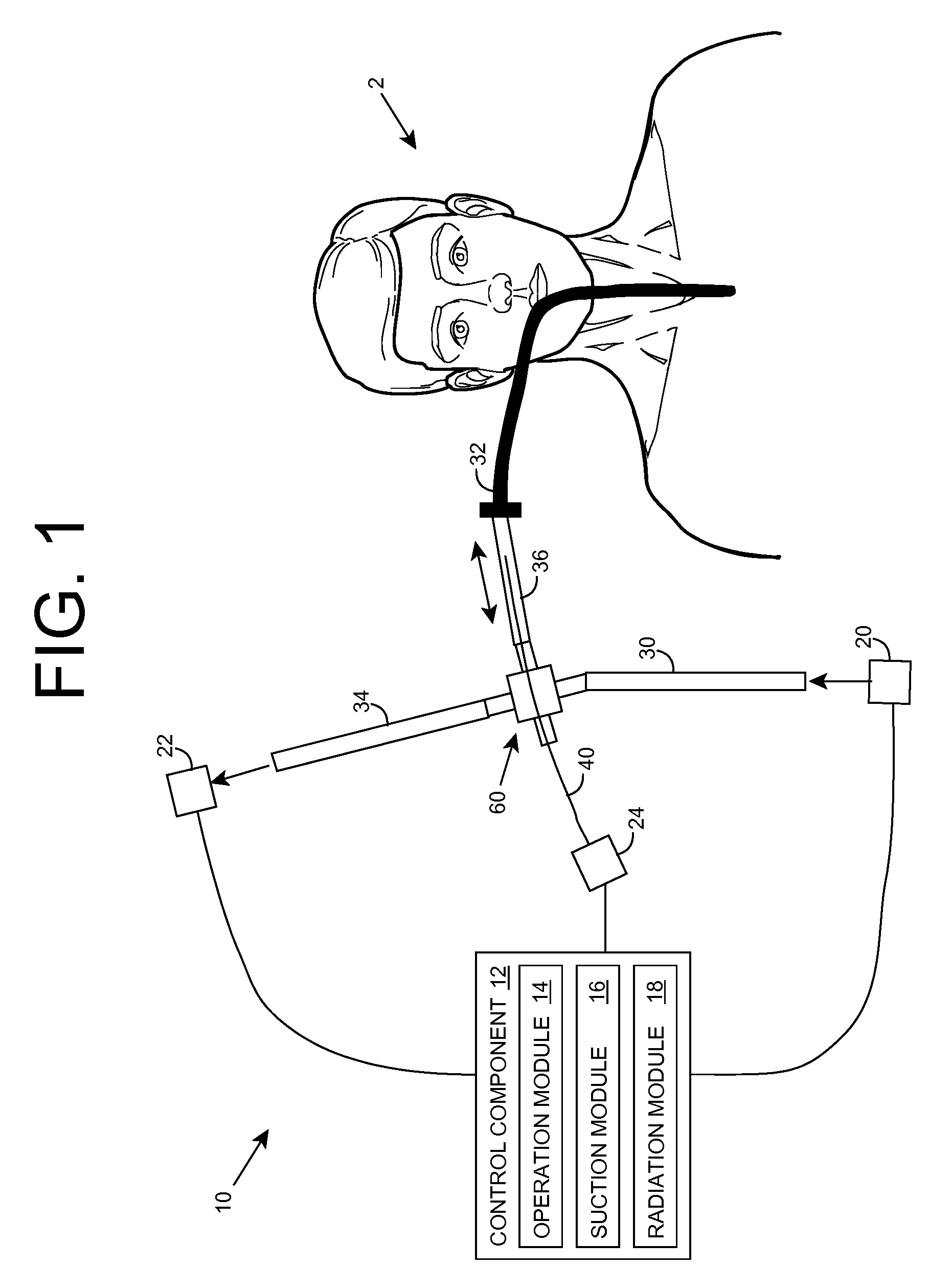
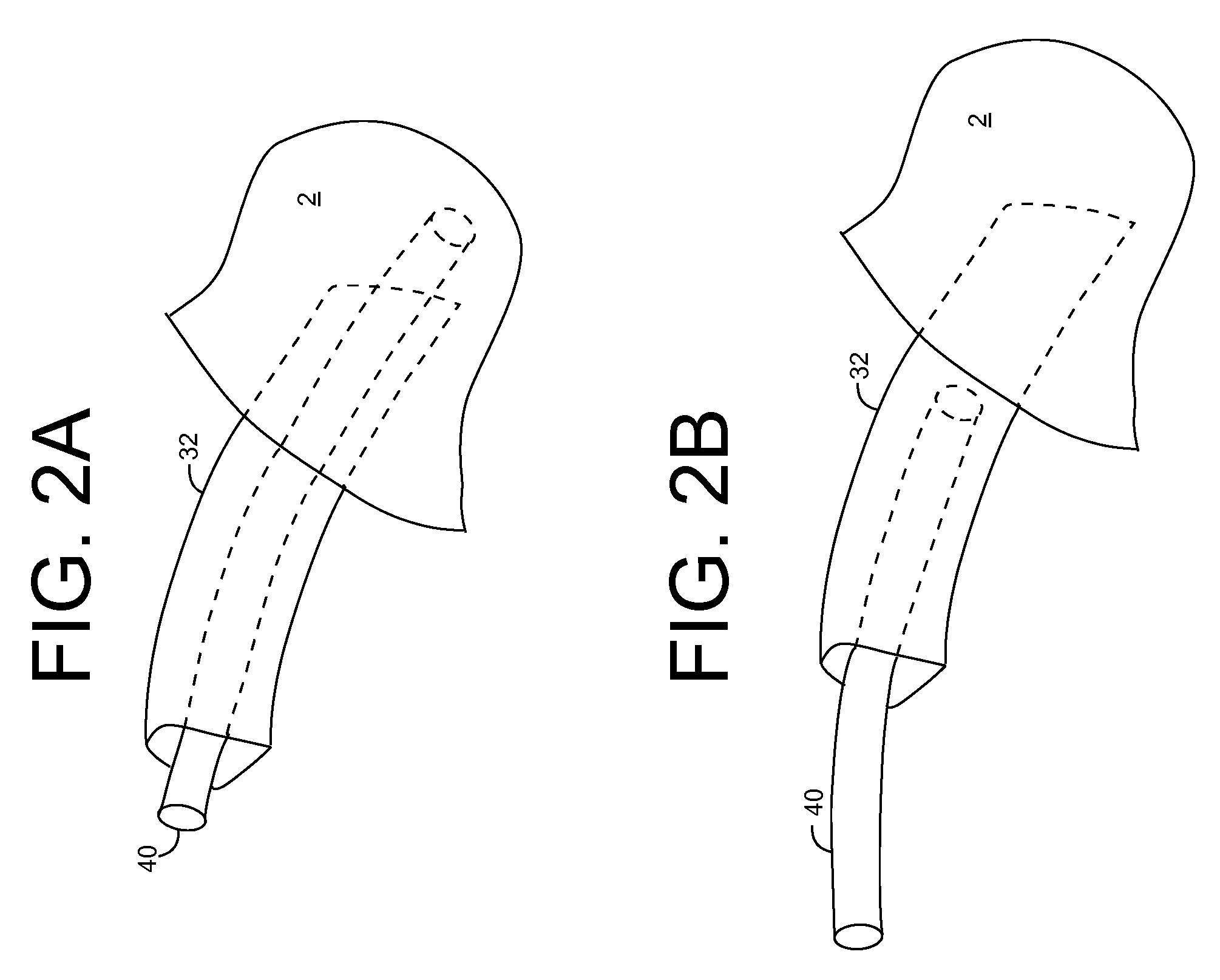
Ultraviolet radiation sterilization
ActiveUS7634996B2Guaranteed to continue to useTracheal tubesMedical devicesUltraviolet radiationUltraviolet
A solution for sterilizing one or more hollow components of a device, such as a medical device, is provided. Ultraviolet radiation having one or more predominant wavelength(s) and a sufficient dose is generated and directed to an interior side of the hollow component(s). The predominant wavelength(s) is / are selected to harm one or more target organisms that may be present on the interior side. The ultraviolet radiation can be delivered by a structure that is periodically inserted and retracted into the hollow component. The structure can be configured to provide additional cleaning capability, such as suction, for removing matter that may be present in the hollow component.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Multi Wave Sterilization System
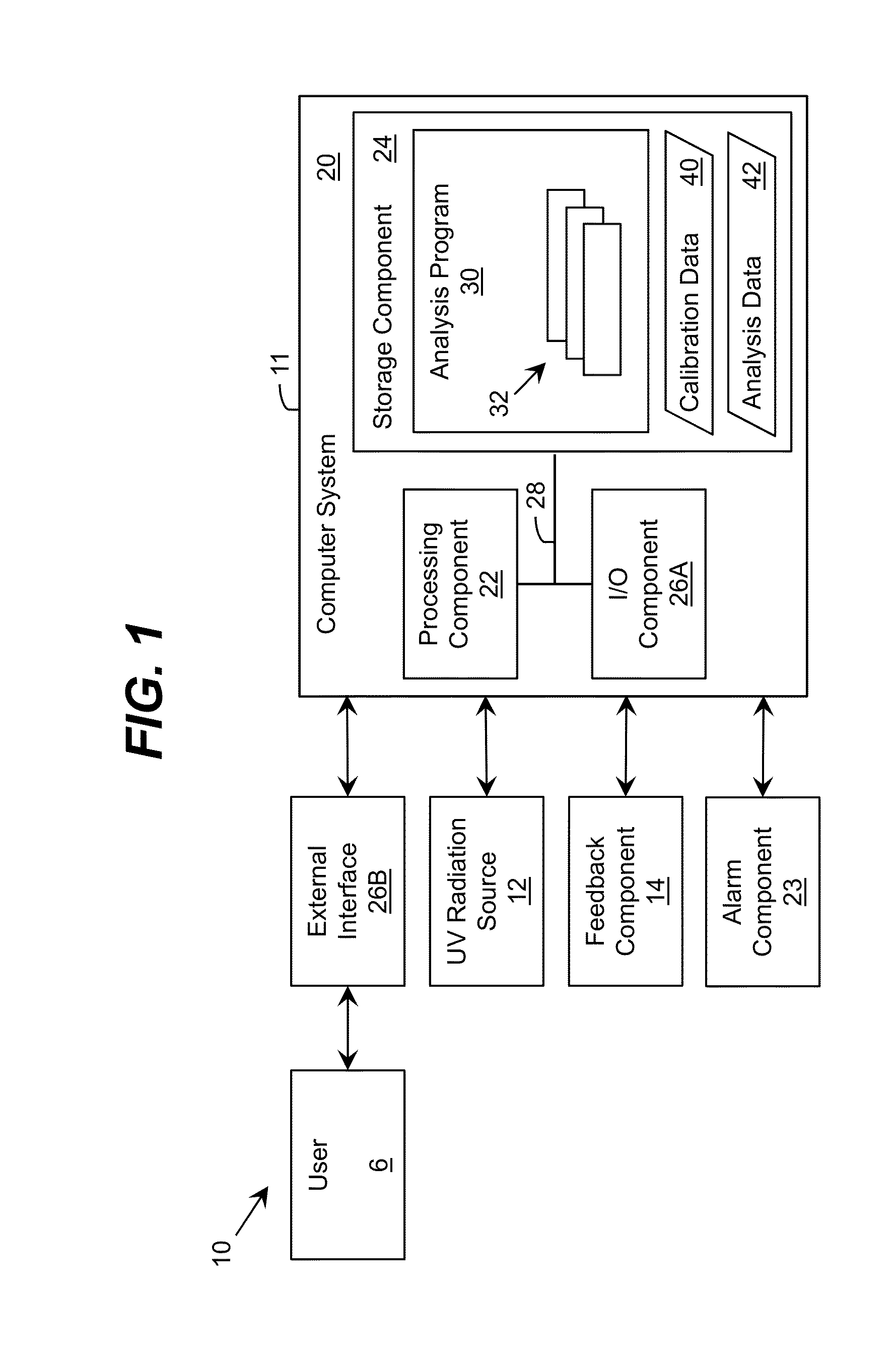
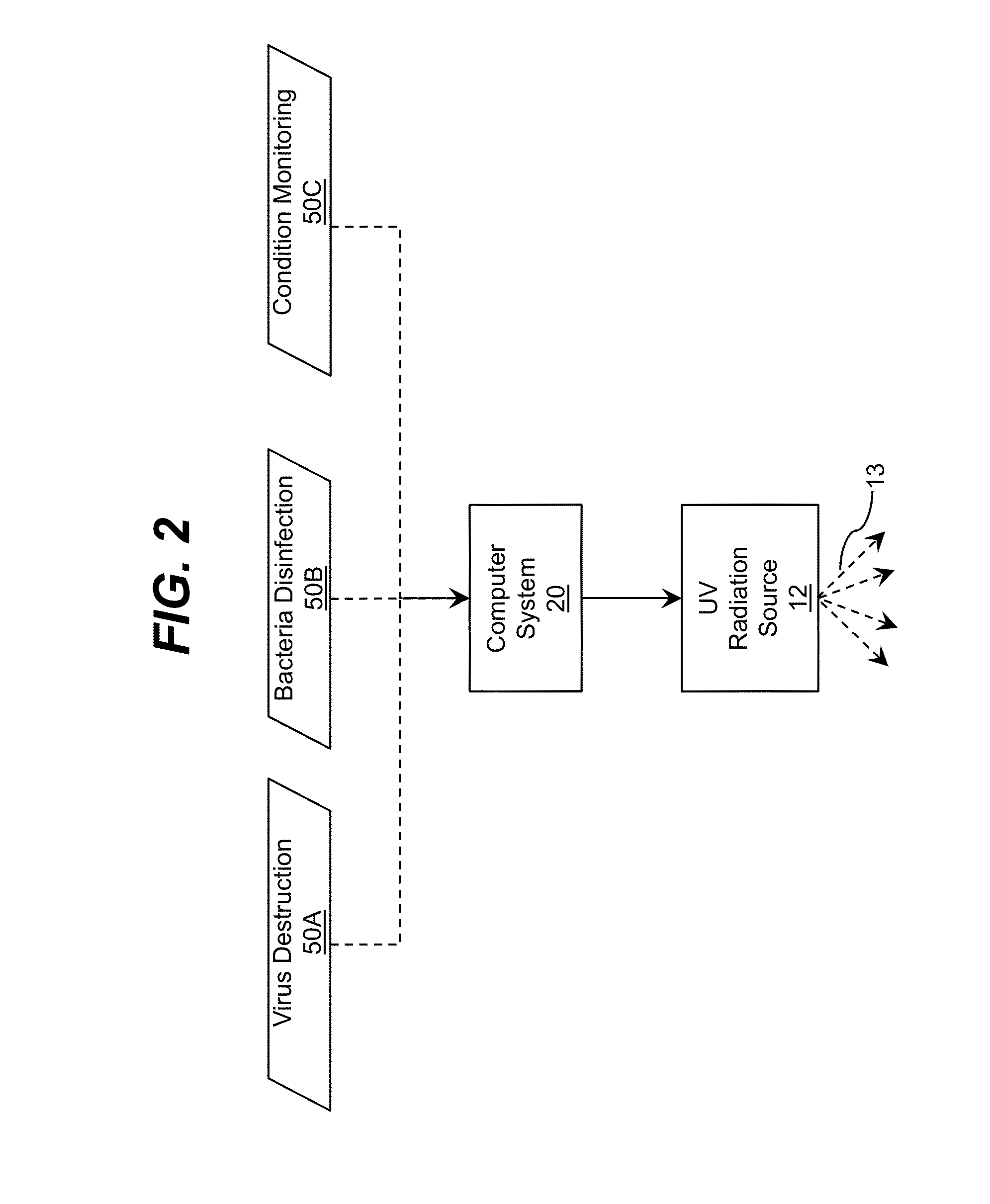
Ultraviolet radiation is directed within an area. The target wavelength ranges and / or target intensity ranges of the ultraviolet radiation sources can correspond to at least one of a plurality of selectable operating configurations including a virus destruction operating configuration and a bacteria disinfection operating configuration. Each configuration can include a unique combination of the target wavelength range and target intensity range.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com