Patents
Literature
1026 results about "Split lines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
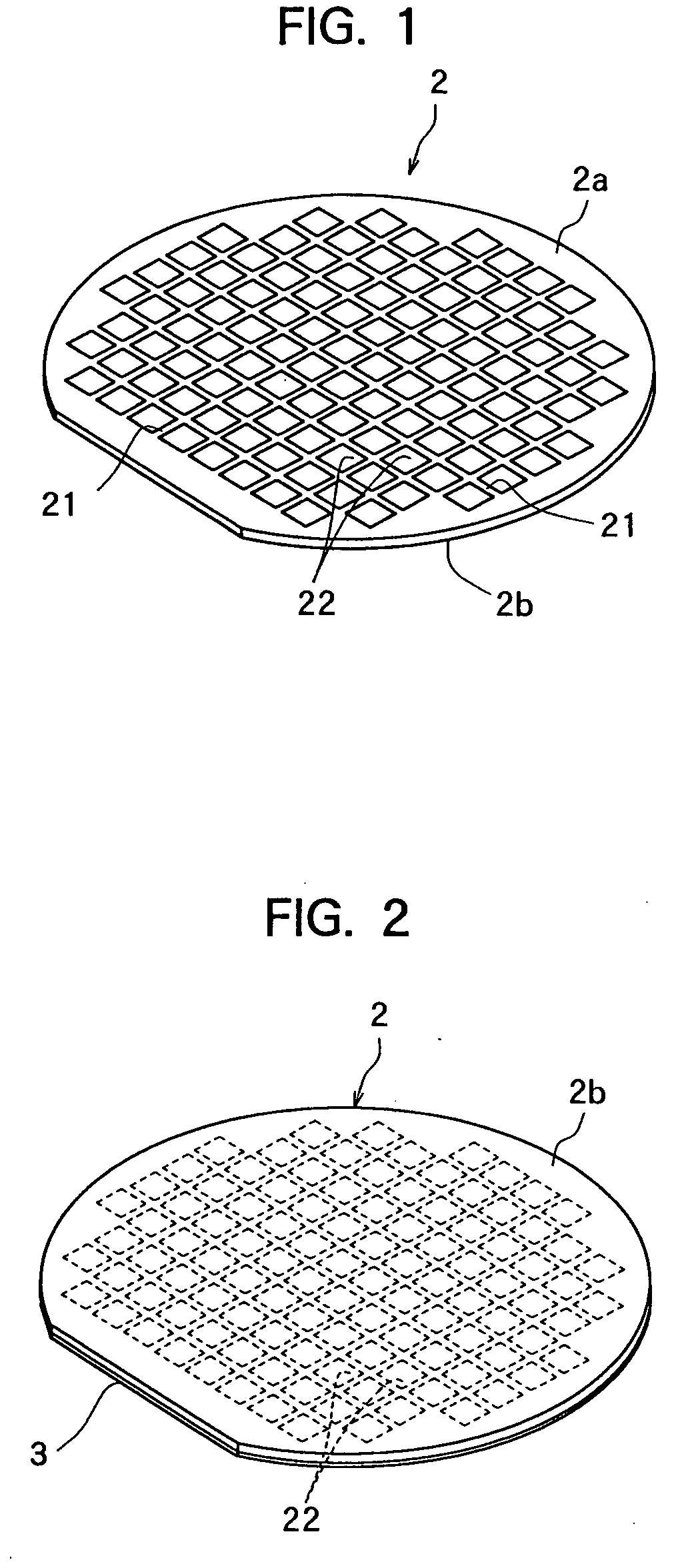
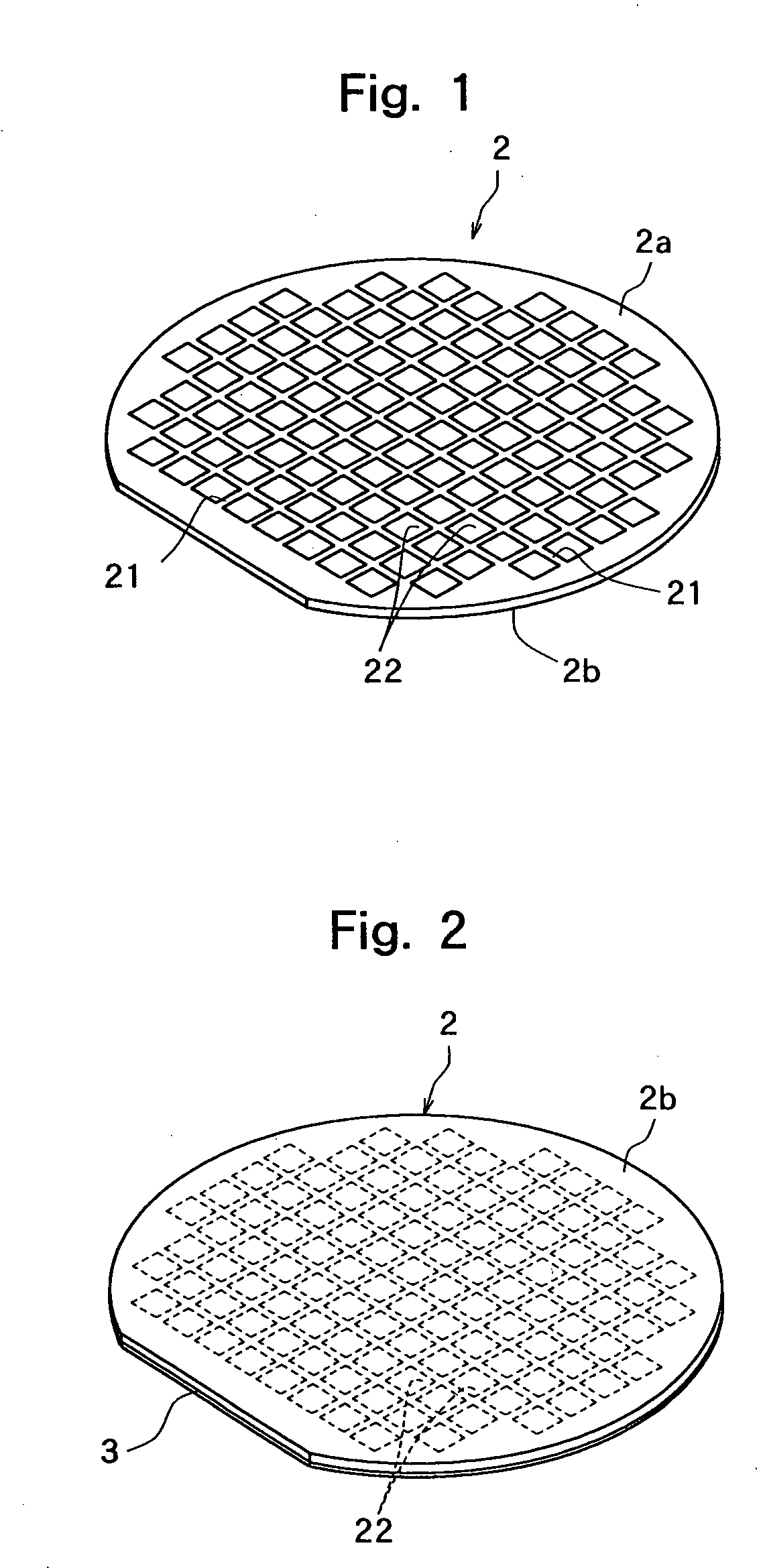
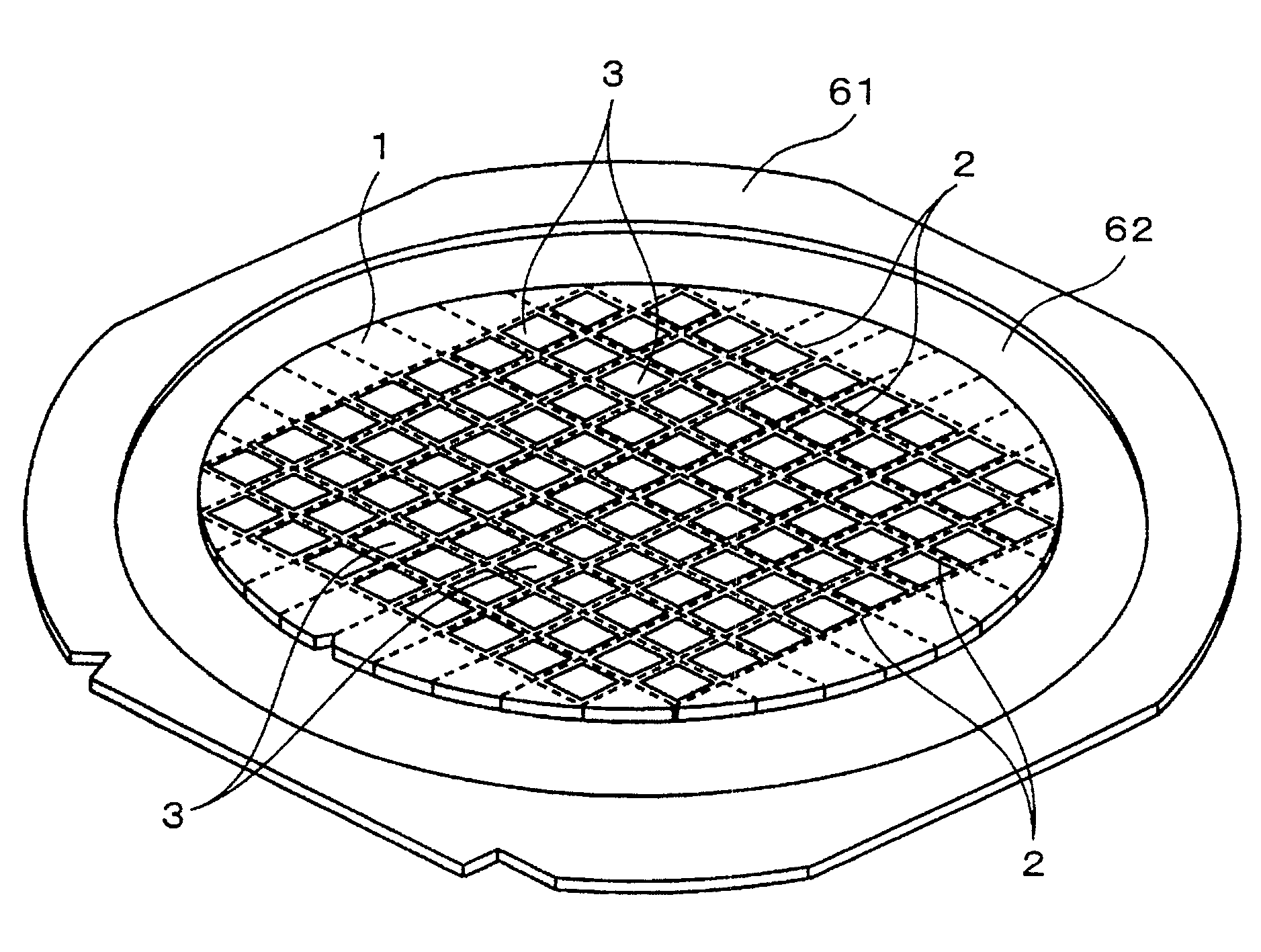
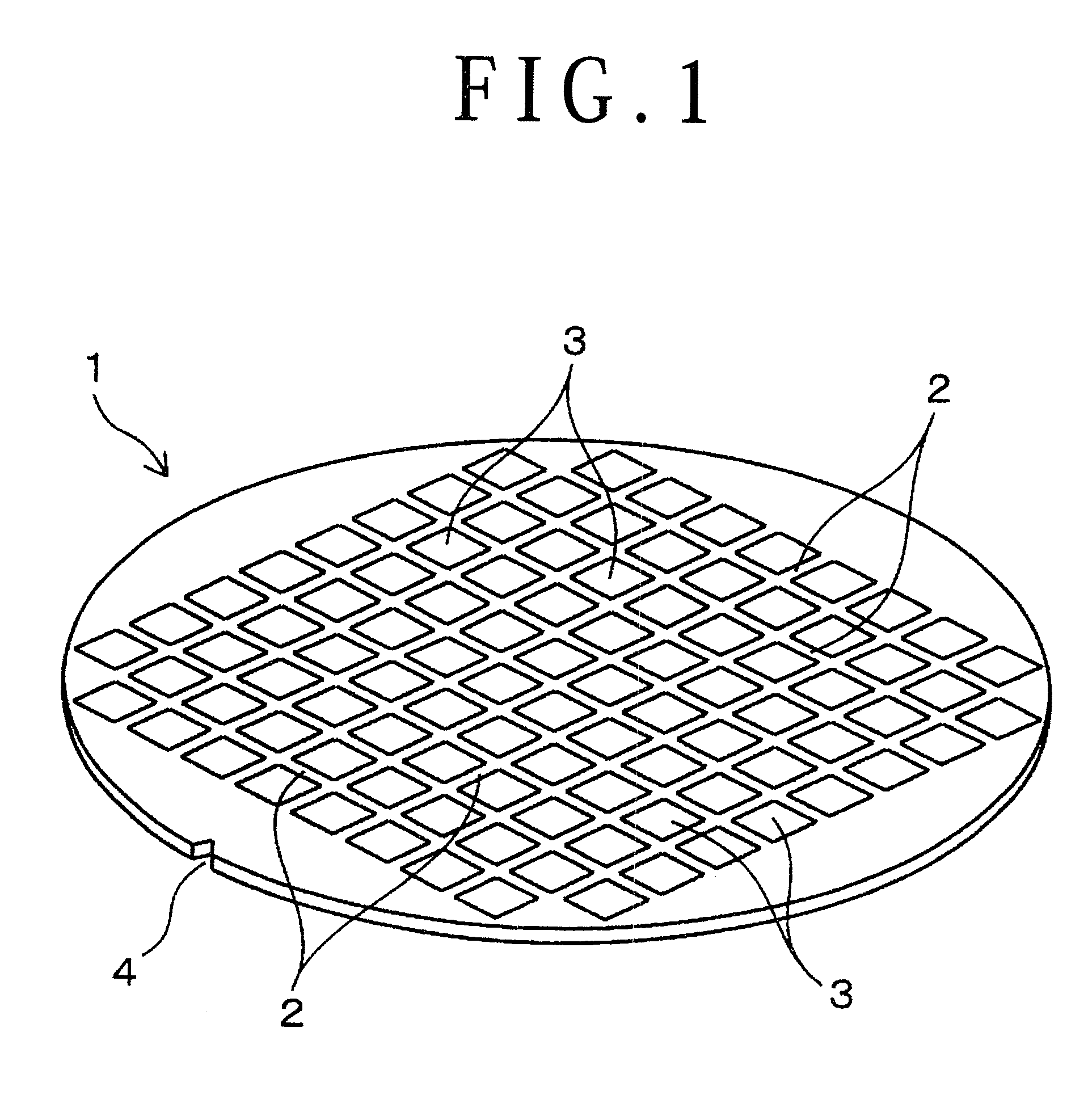
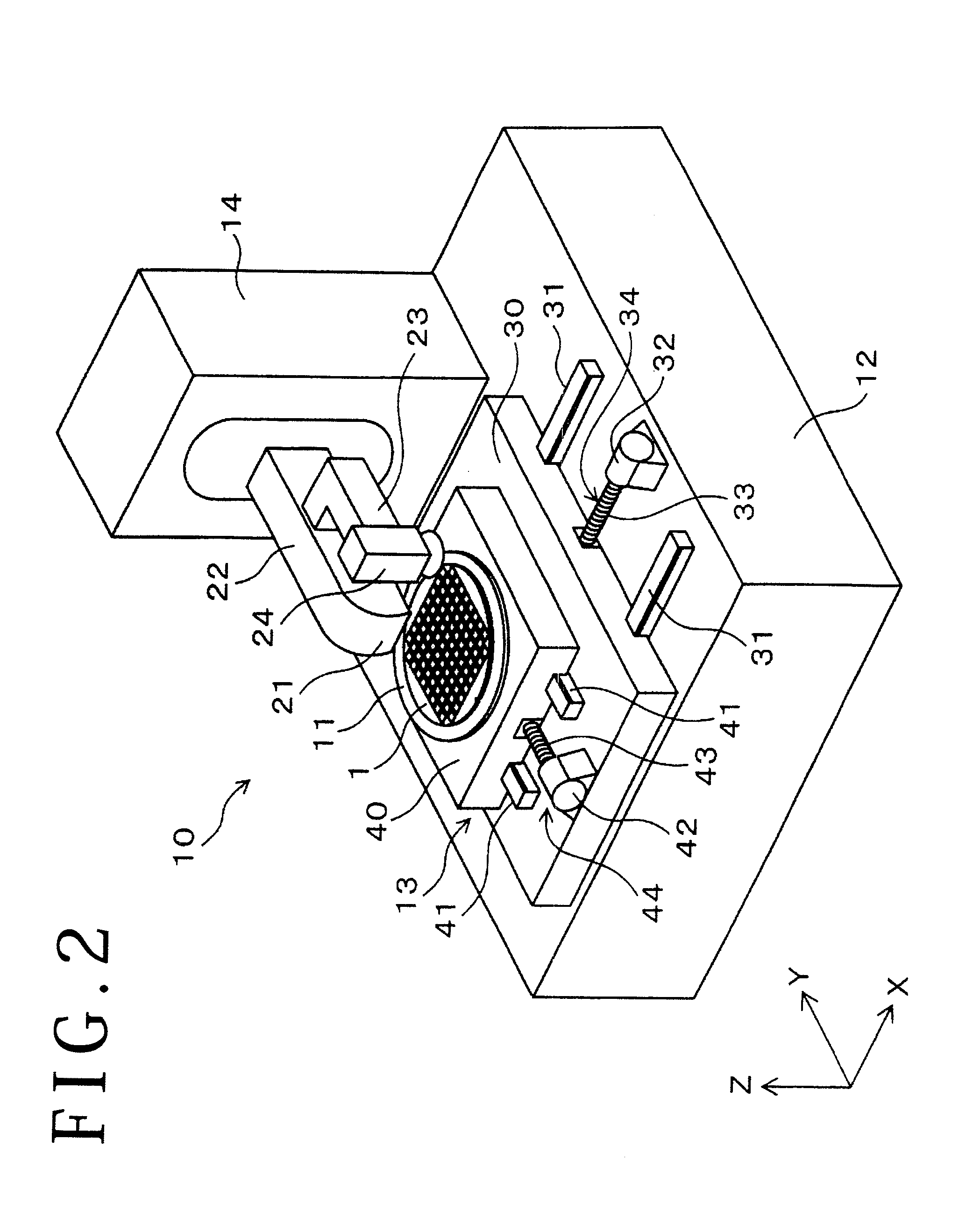
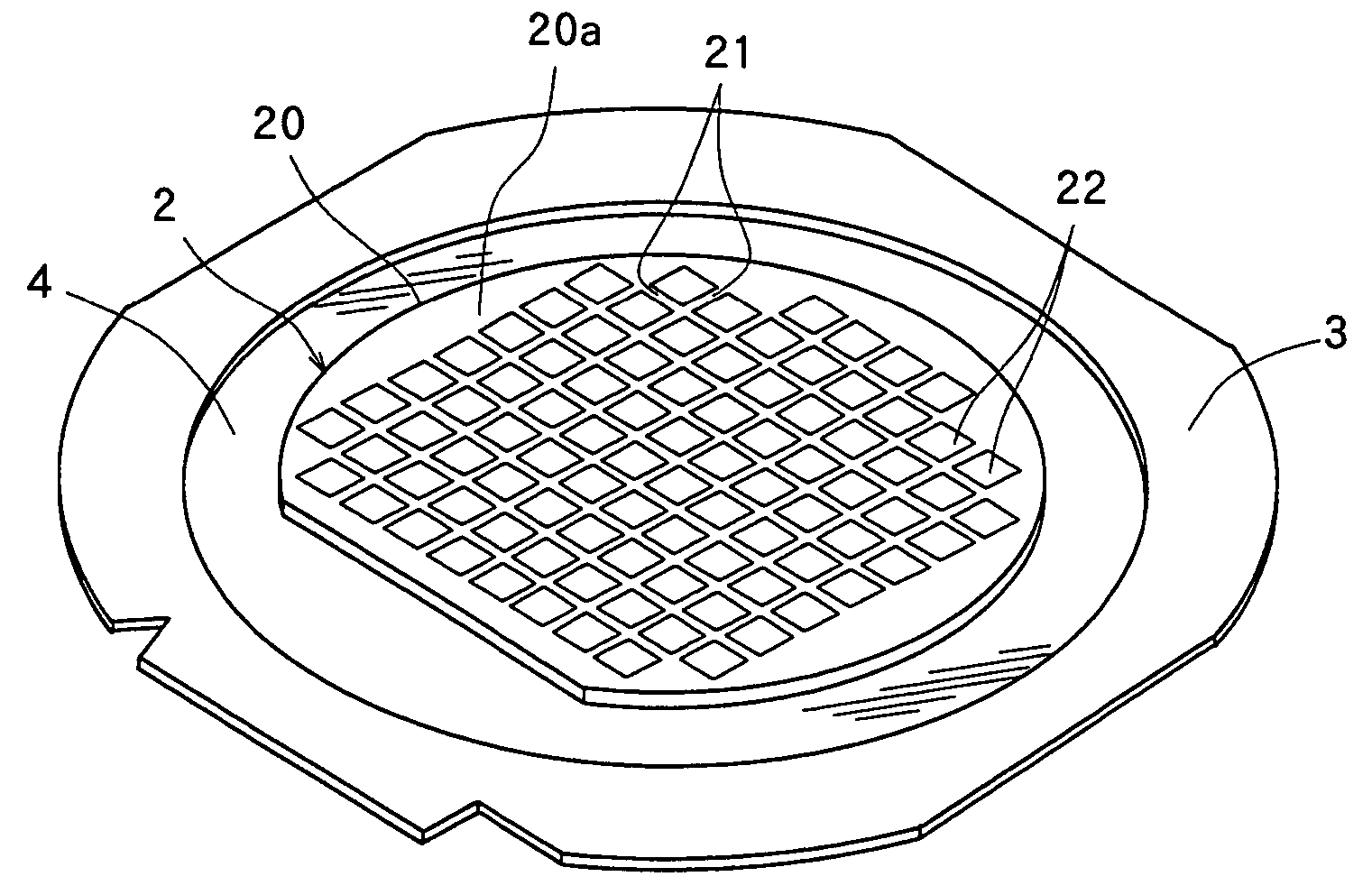
Split Lines. The Split Line tool projects an entity (sketch, solid, surface, face, plane, or surface spline) to surfaces, or curved or planar faces. It divides a selected face into multiple separate faces.
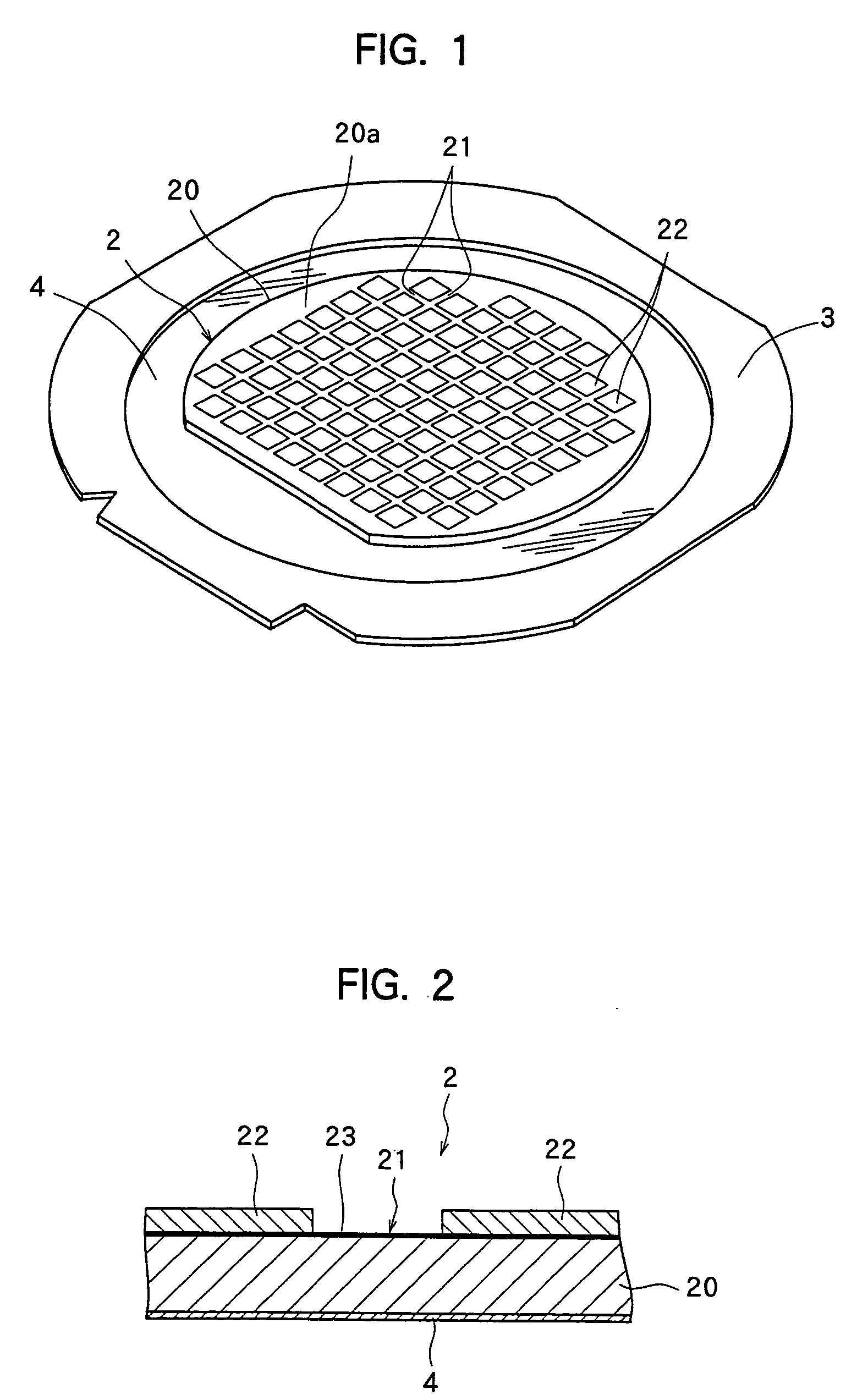
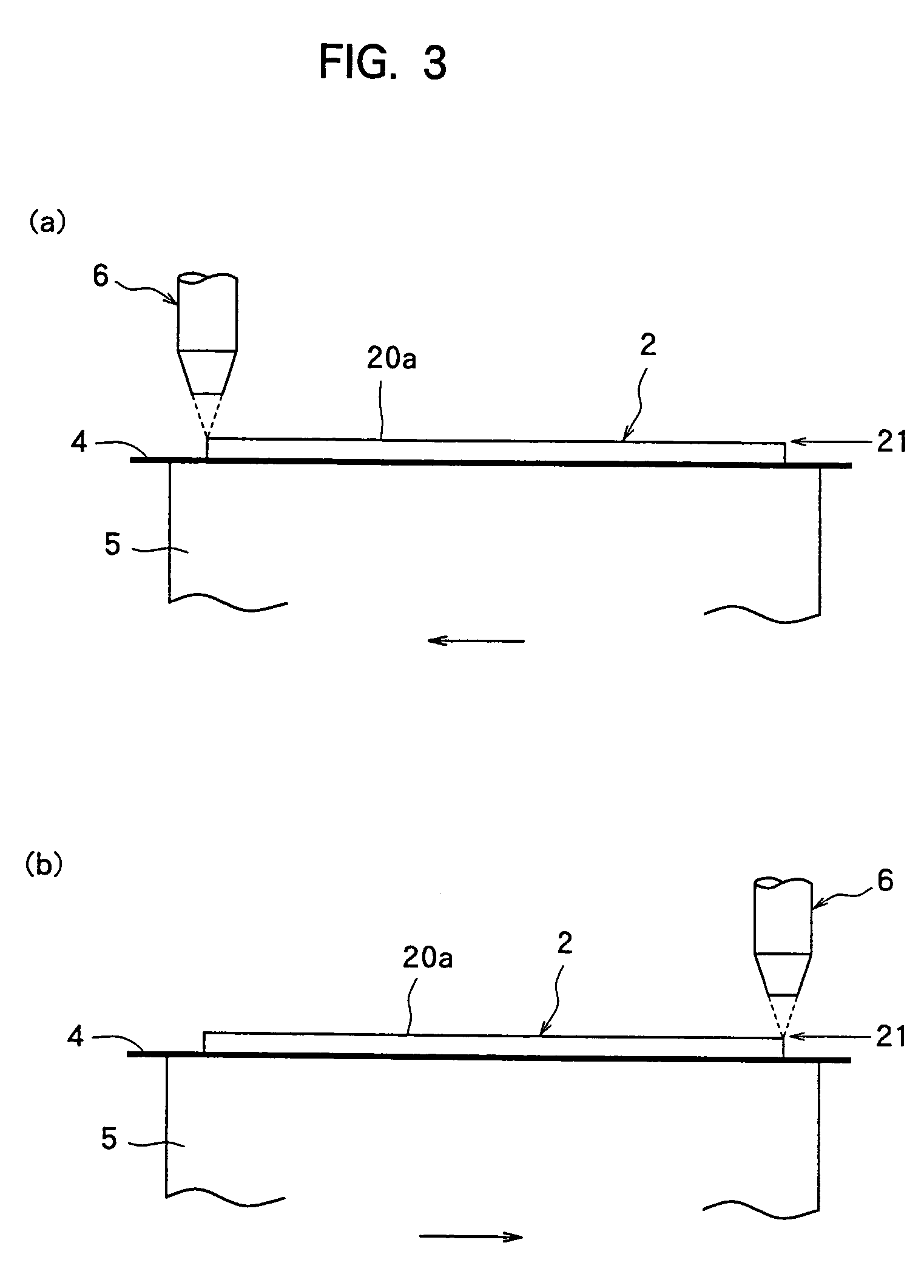
Semiconductor light-emitting device and method for separating semiconductor light-emitting devices
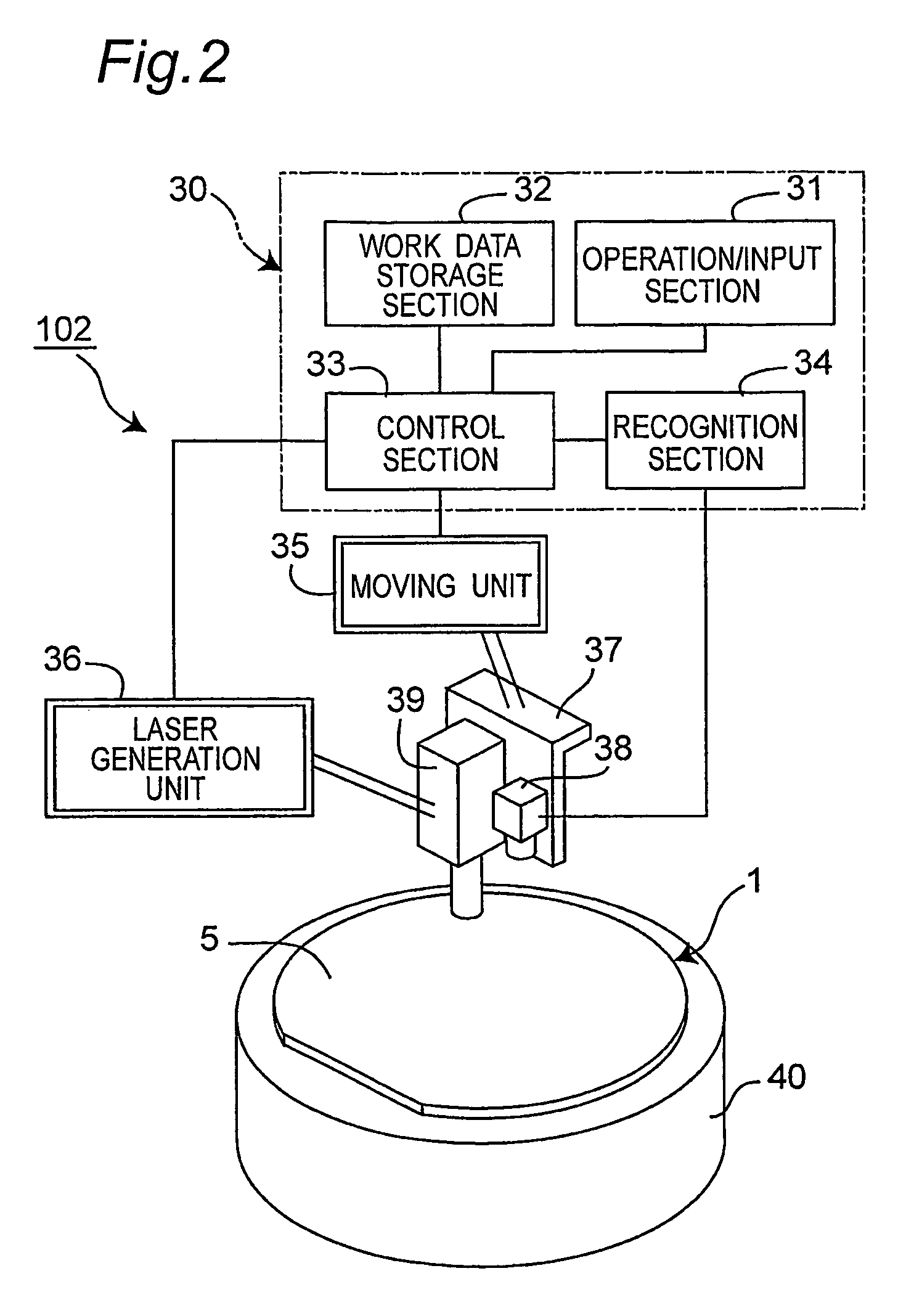
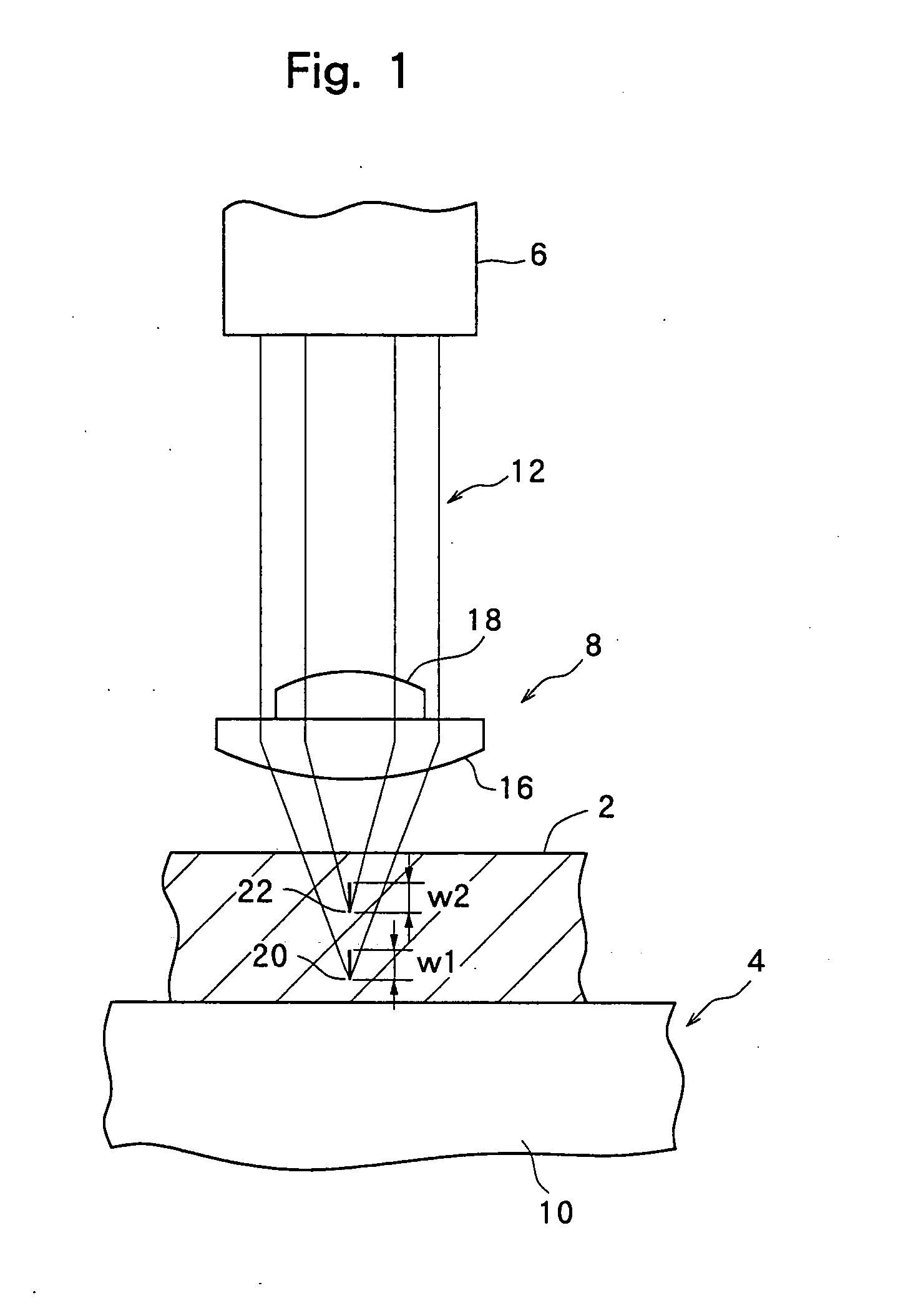
InactiveUS20070298529A1Reliably splitLight absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSplit linesPulsed laser beam
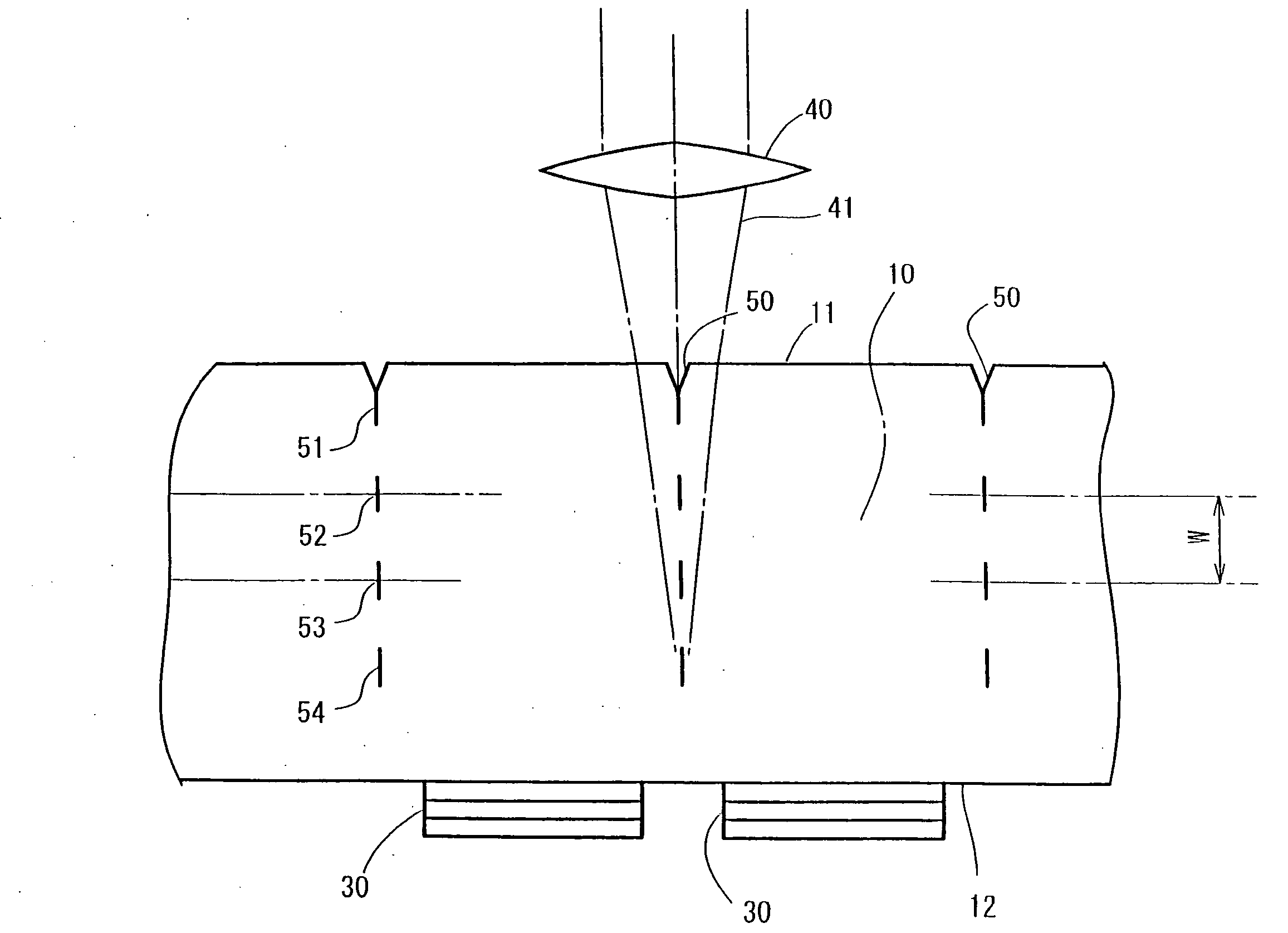
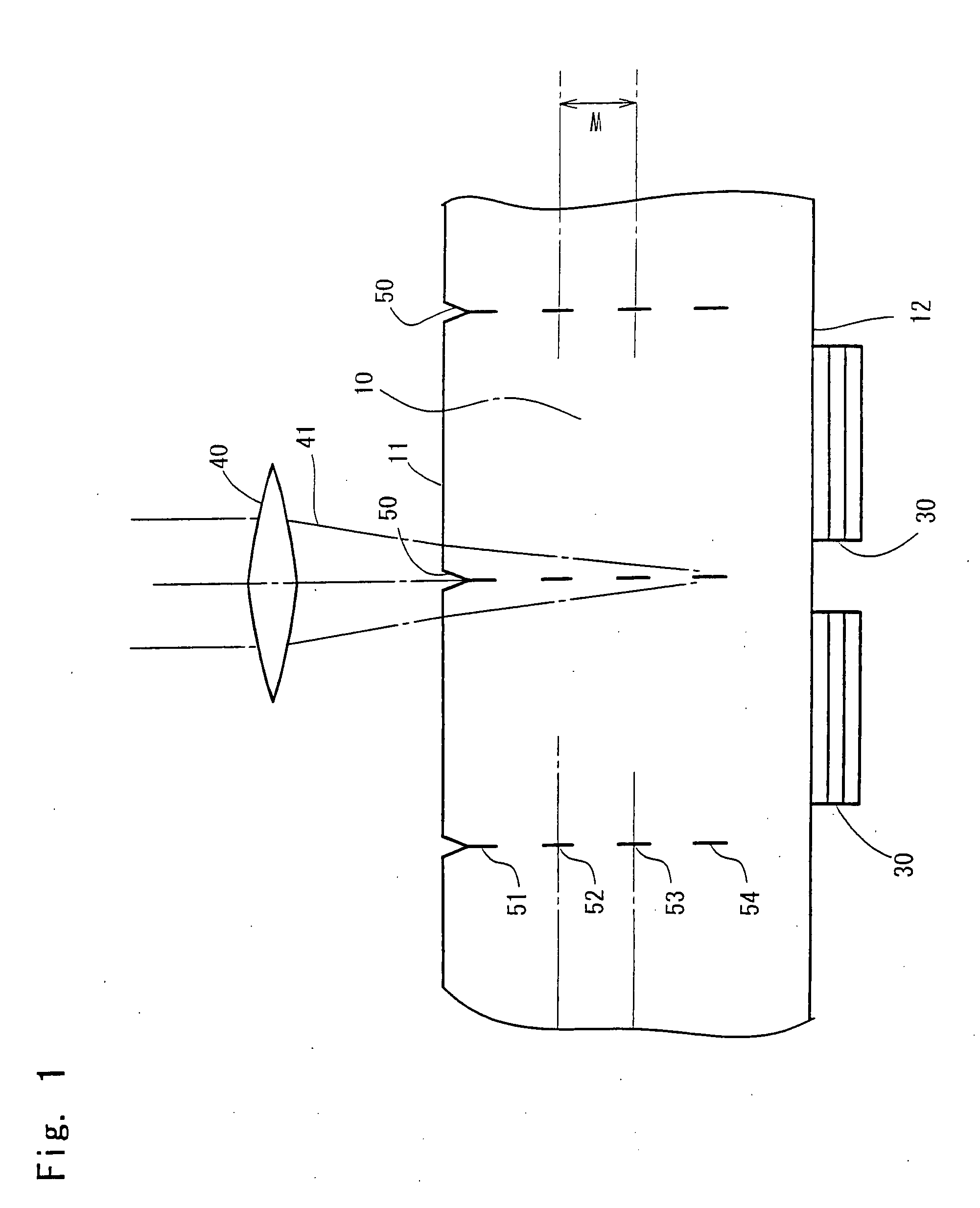
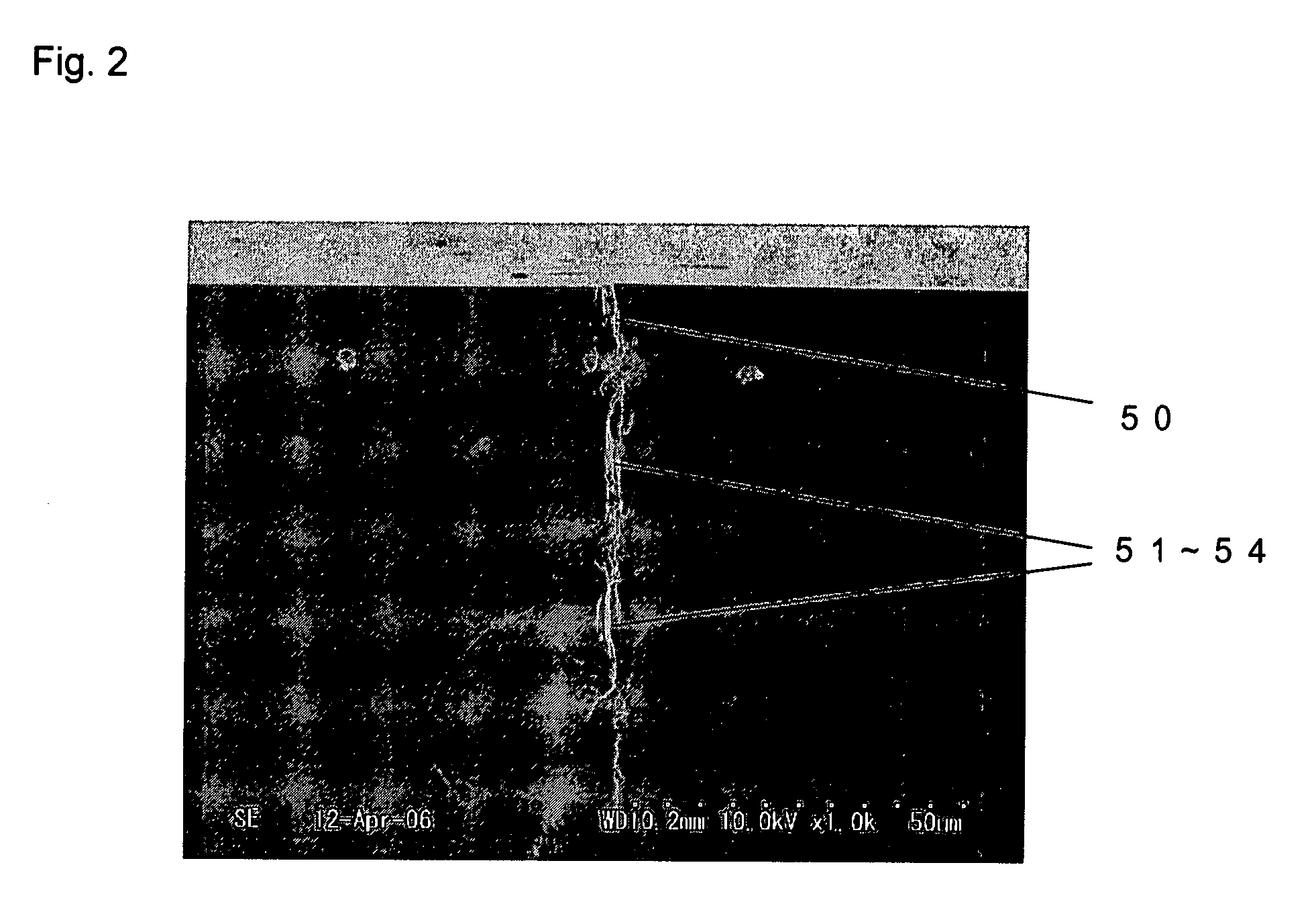
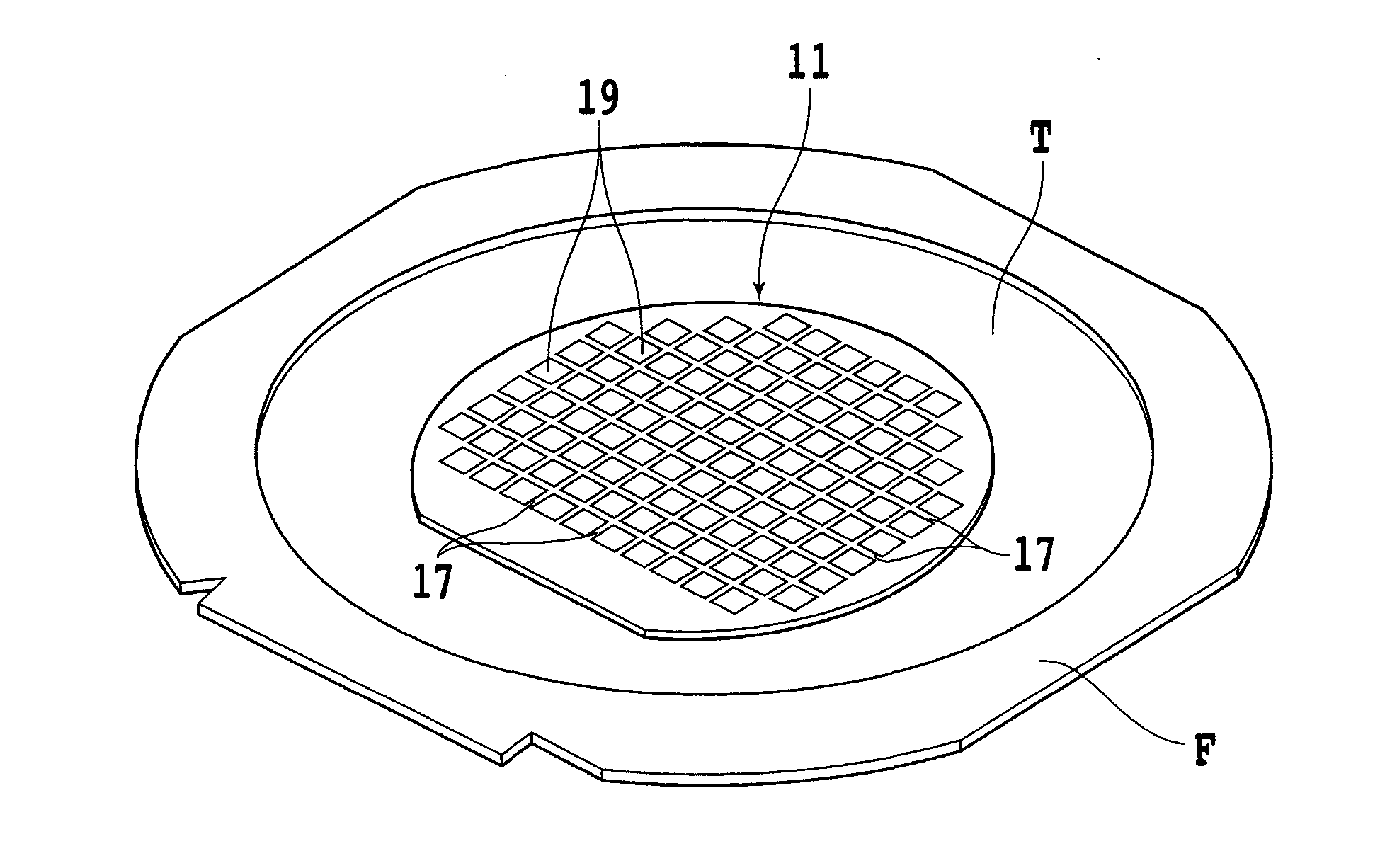
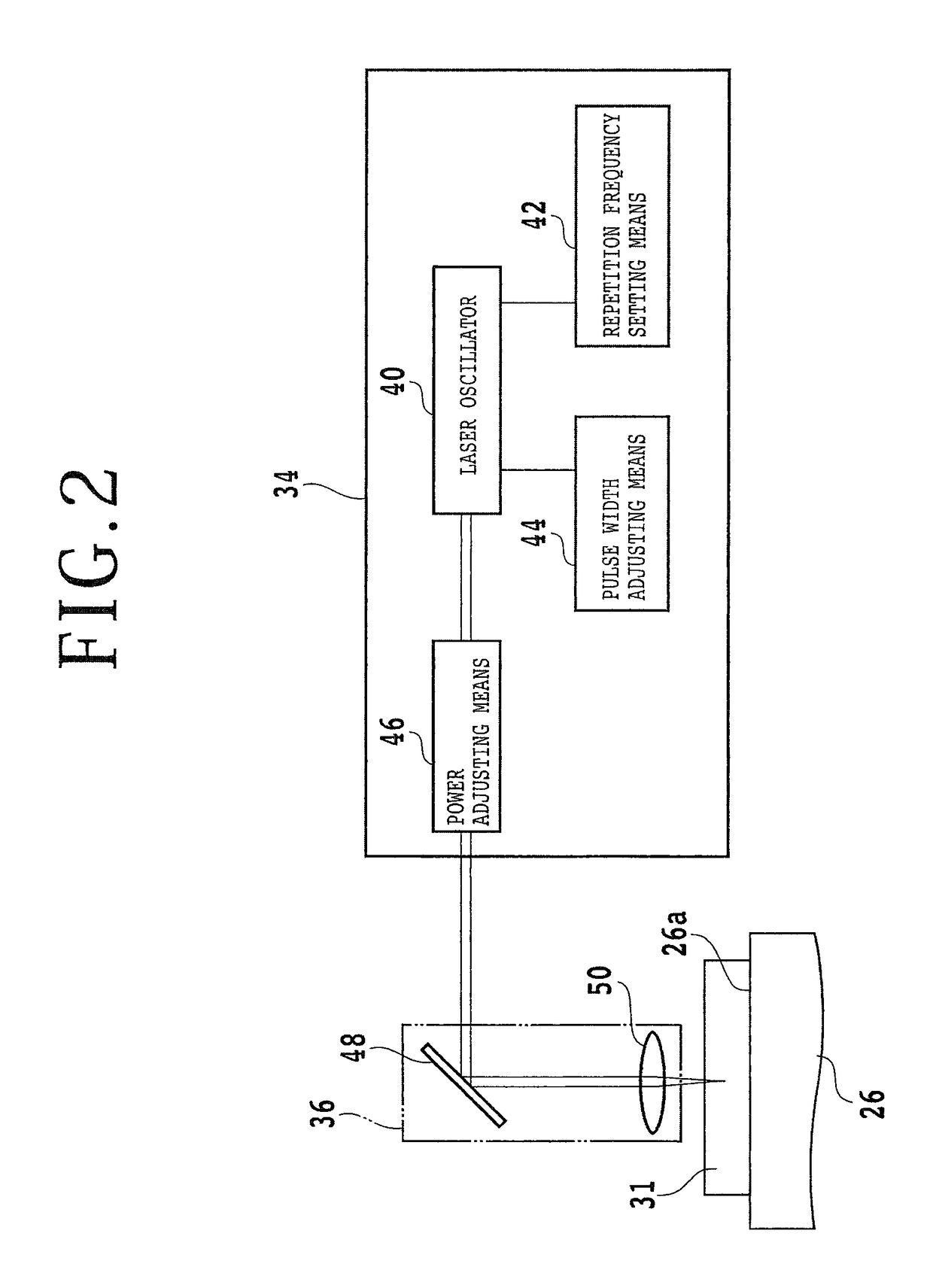
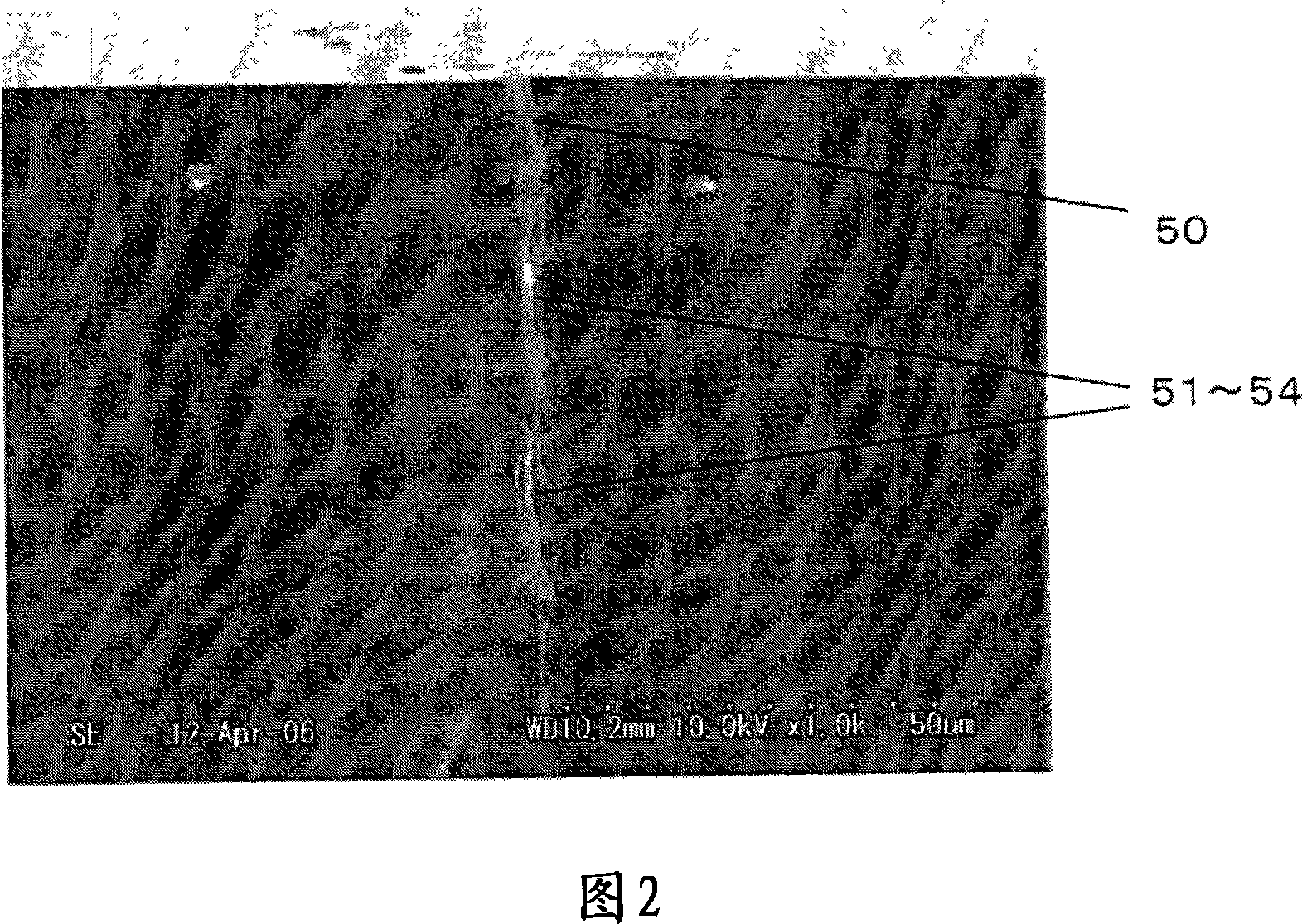
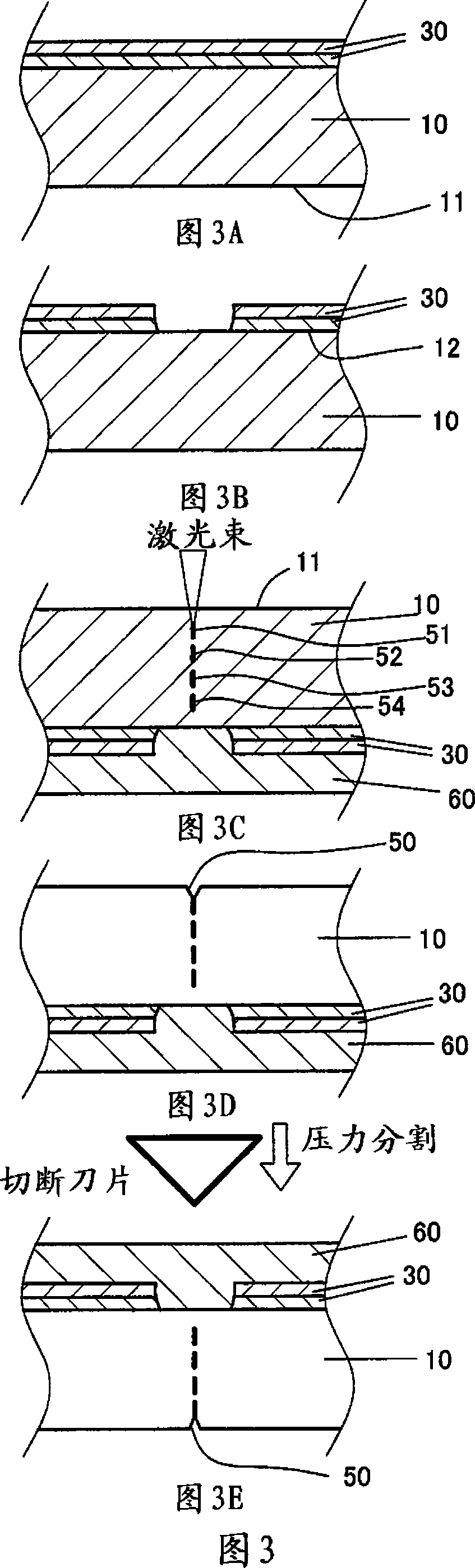
The invention provides a method for separating semiconductor light-emitting devices formed on a substrate. In the method, a pulse laser beam having a pulse width less than 10 ps in a substrate is focused on the substrate, to thereby cause multi-photon absorption in the substrate. Through multi-photon absorption, a groove is formed through the pulse laser beam along a split line predetermined on a surface of the substrate, the groove being substantially continuous in the direction of the predetermined split line. In addition, internal structurally changed portions are formed through the pulse laser beam at a predetermined depth of the substrate on a predetermined split face, the structurally changed portions being discontinuous in the direction of the predetermined split line. Subsequently, an external force is applied to thereby form a split face along the continuous groove and the discontinuous internal structurally changed portions, whereby the semiconductor light-emitting devices are separated from one another
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
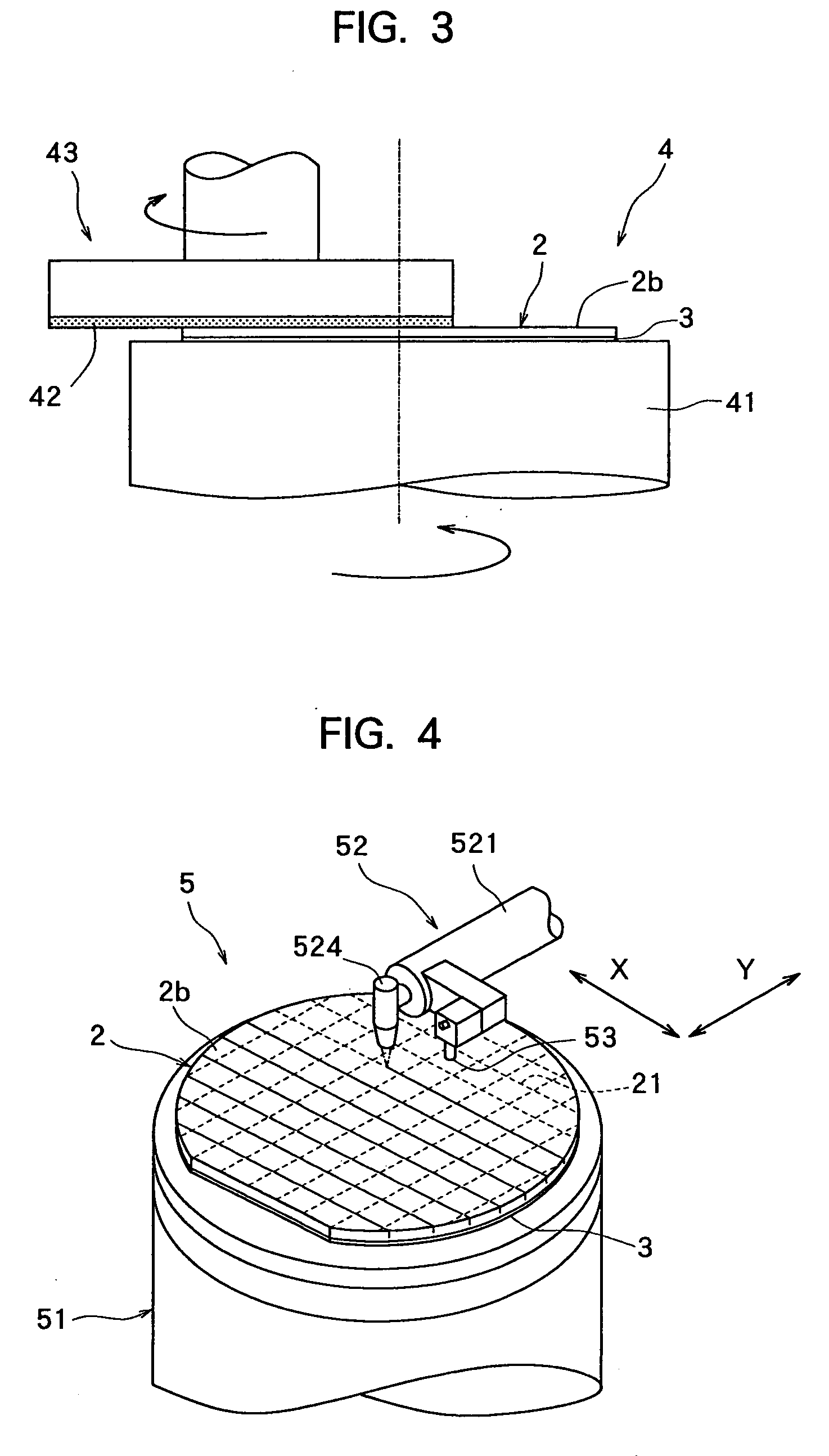
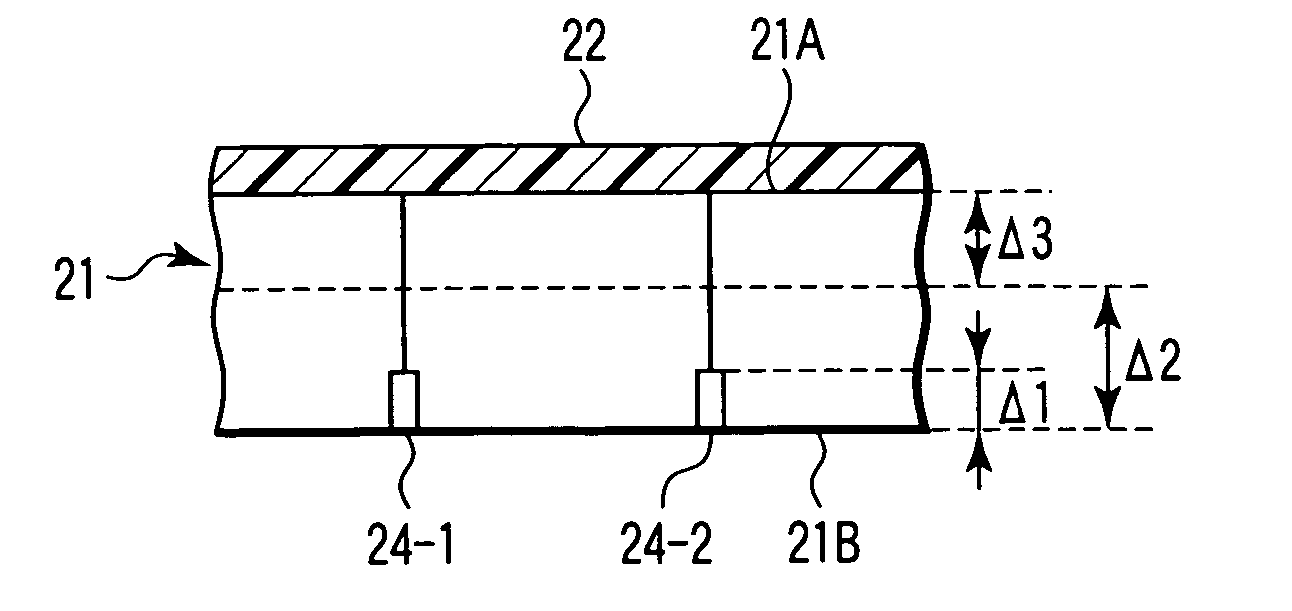
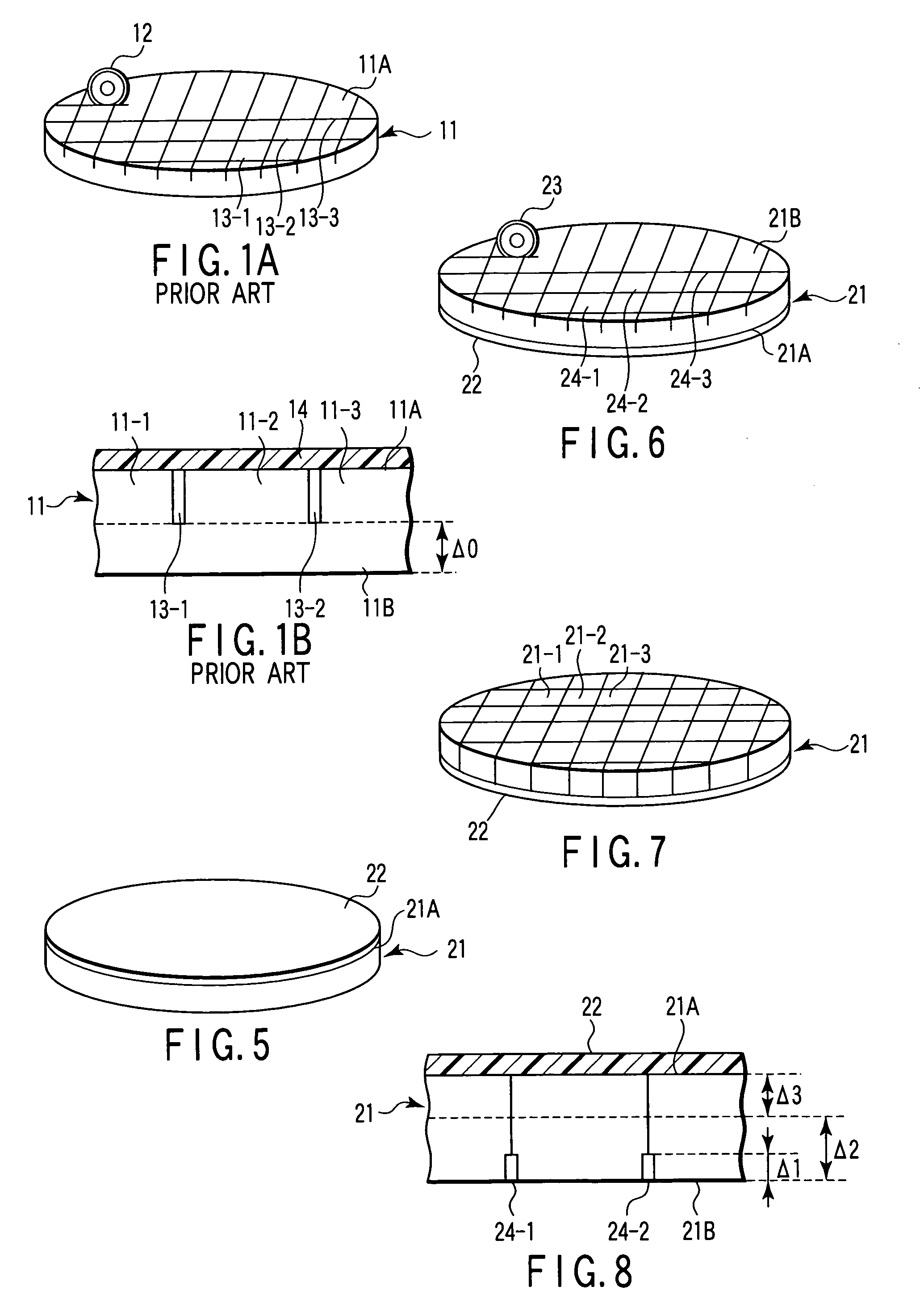
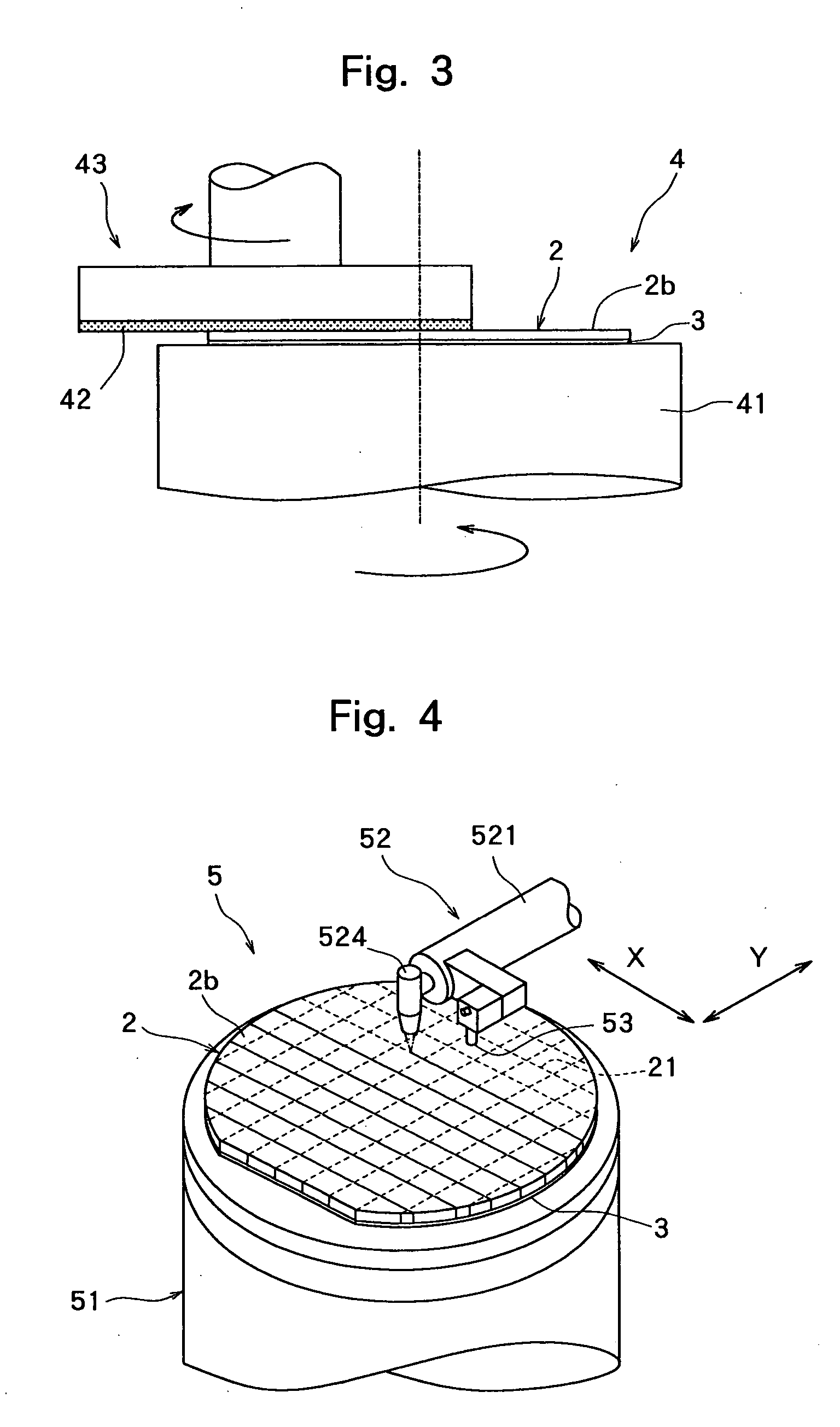
Wafer dividing method
ActiveUS7507639B2Reduced adhesion strengthIncrease spacingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesSplit linesDevice form
A method of dividing a wafer having devices formed in a plurality of areas sectioned by a plurality of dividing lines, into individual chips along the dividing lines, comprising a deteriorated layer forming step for forming a deteriorated layer by applying a laser beam of a wavelength having permeability for the wafer along the dividing lines; a wafer supporting step for putting the rear surface of the wafer on the surface of an adhesive tape which is mounted on an annular frame and whose adhesive strength is reduced by applying ultraviolet radiation thereto; and a chips-spacing forming step for reducing the adhesive strength of the adhesive tape and shrinking a shrink area between the inner periphery of the annular frame and the area to which the wafer has been affixed, of the adhesive tape by applying ultraviolet radiation to the adhesive tape to which the wafer has been affixed so as to divide the wafer into individual chips along the dividing lines where the deteriorated layer has been formed and widen the space between adjacent chips.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Method for dividing semiconductor wafer and manufacturing method for semiconductor devices
ActiveUS7927973B2Formation of comparatively small pieces in the semiconductor wafer can be preventedInhibition formationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSplit linesEngineering
In a semiconductor wafer including a plurality of imaginary-divided-regions which are partitioned by imaginary-dividing-lines that are respectively arranged in a grid-like arrangement on the semiconductor wafer and a circumferential line that is the outer periphery outline of the semiconductor wafer, a mask is placed so as to expose an entirety of surfaces of the wafer corresponding to respective removal-regions. The removal-regions are regions in approximately triangular form partitioned by the circumferential line of the wafer and the imaginary-dividing-lines. Then, plasma etching is performed on a mask placement-side surface of the wafer, by which the semiconductor wafer is divided into the individual semiconductor devices along dividing lines while portions corresponding to the removal-regions of the wafer are removed.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Machining apparatus utilizing laser beam
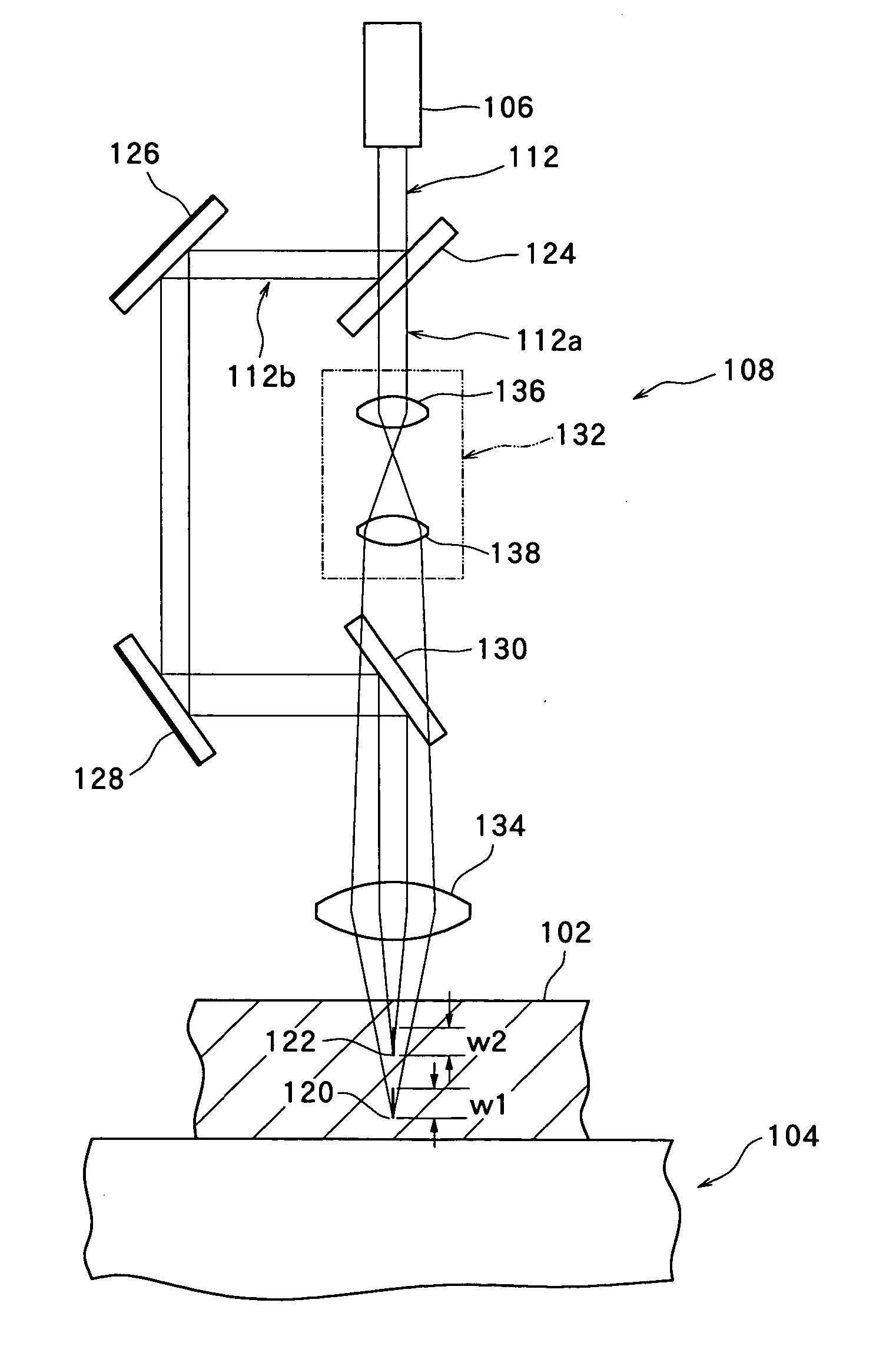
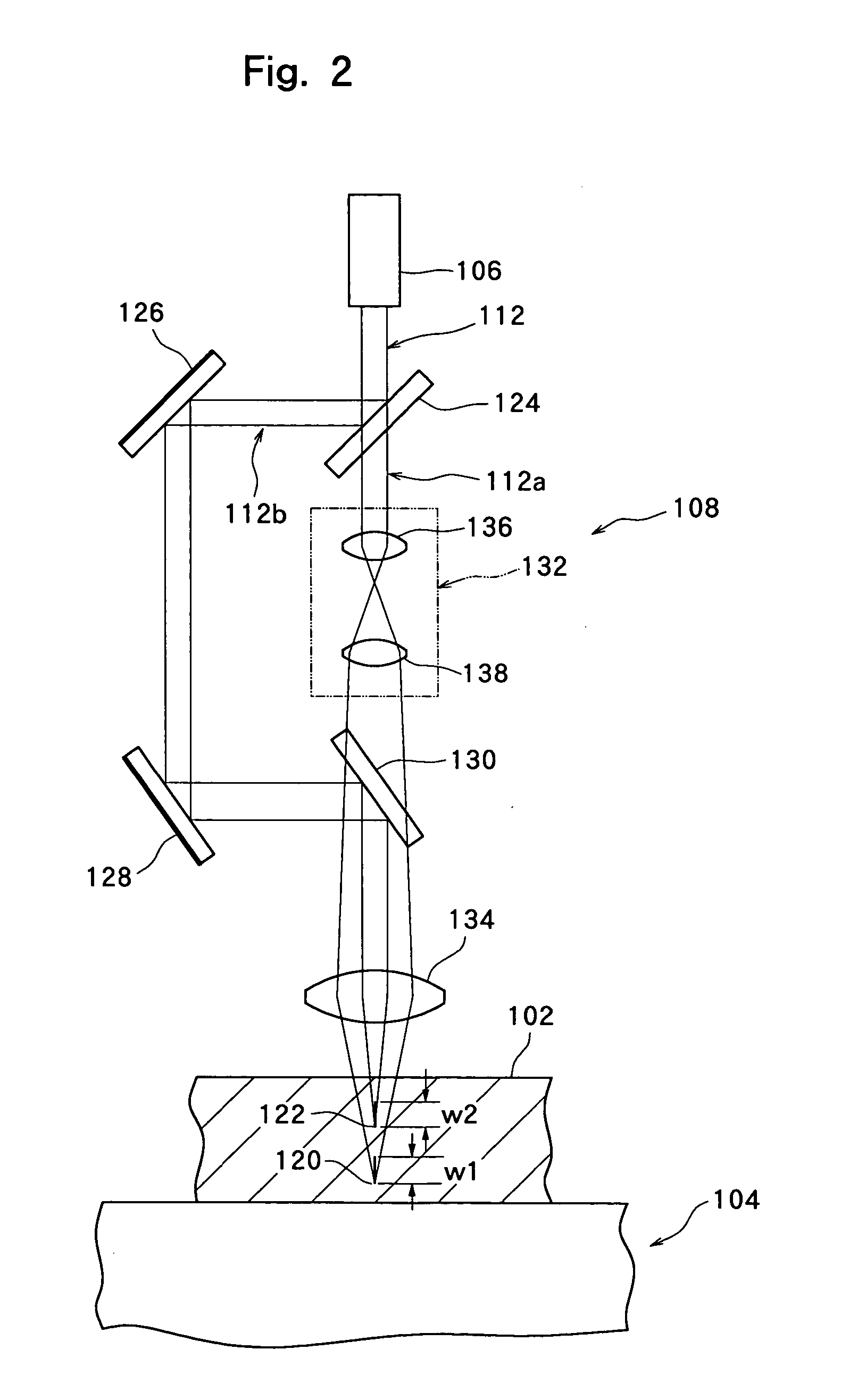
InactiveUS20050006361A1Efficiently formedDeterioration zones of a required thickness can be formed sufficiently efficientlySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSplit linesOptical axis
A machining apparatus utilizing a laser beam, the machining apparatus being capable of efficiently forming a deterioration zone of a required thickness along a division line. A laser beam from laser beam generation means is focused not to a single focused spot, but to at least two focused spots displaced in the direction of an optical axis.
Owner:DISCO CORP
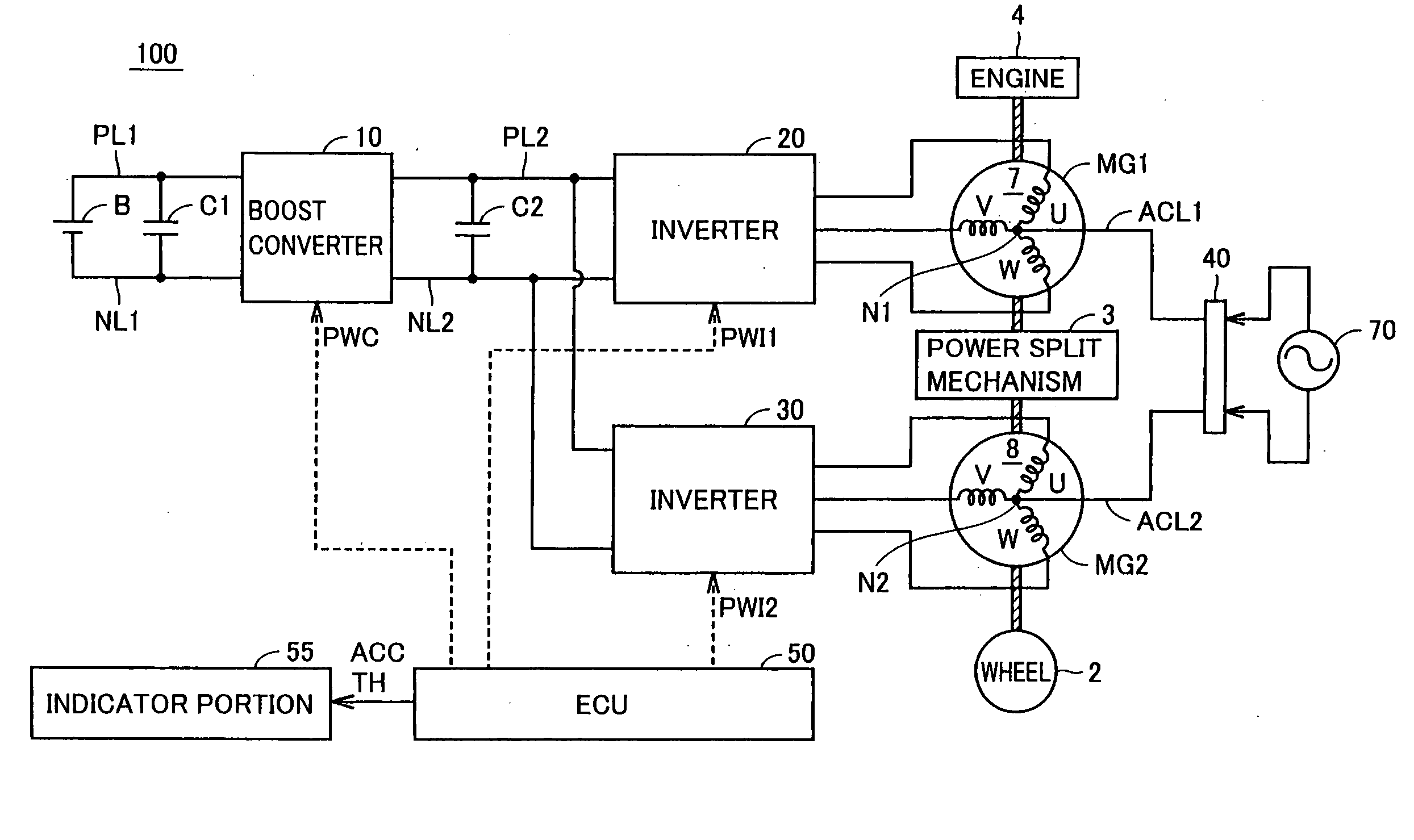
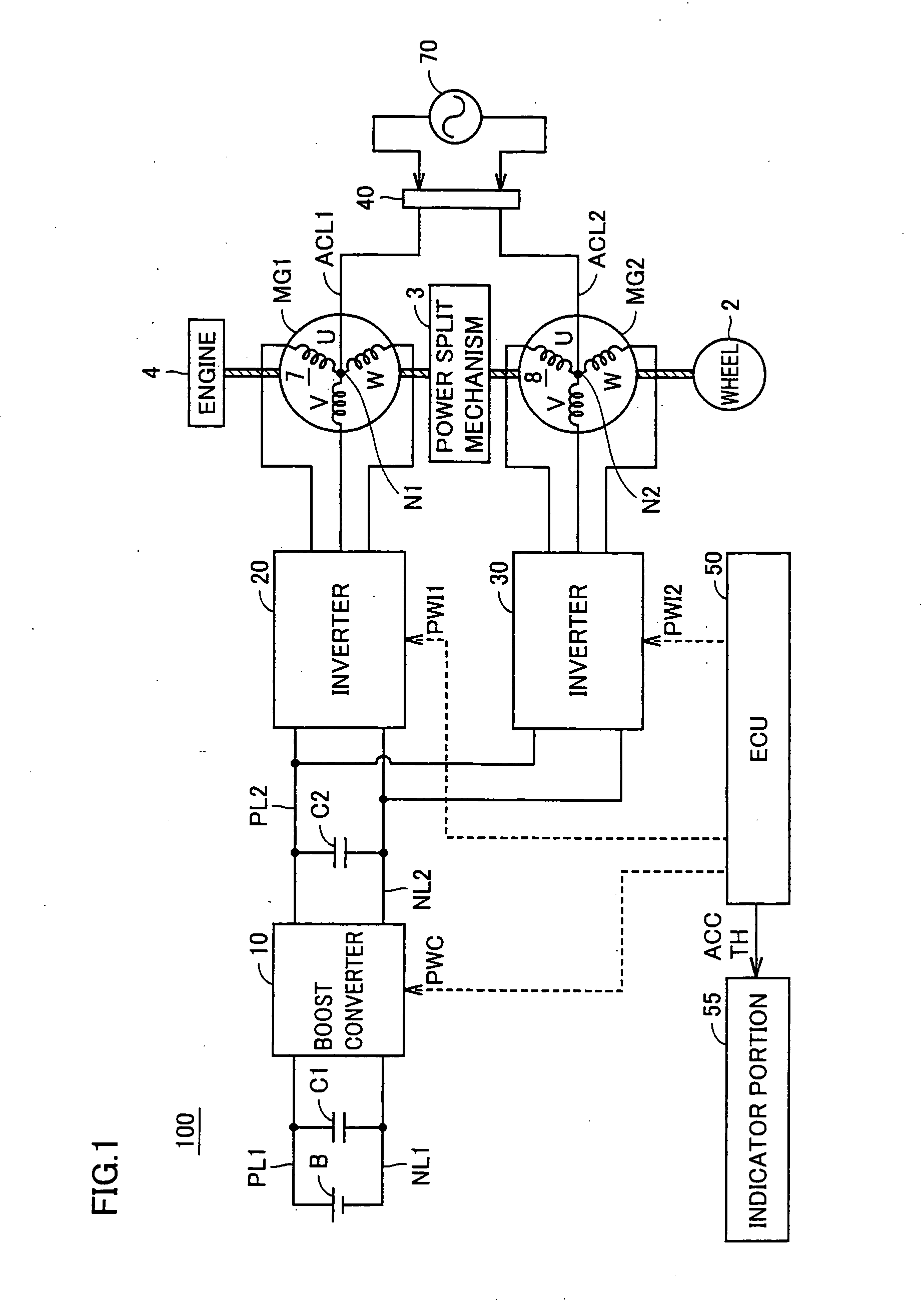
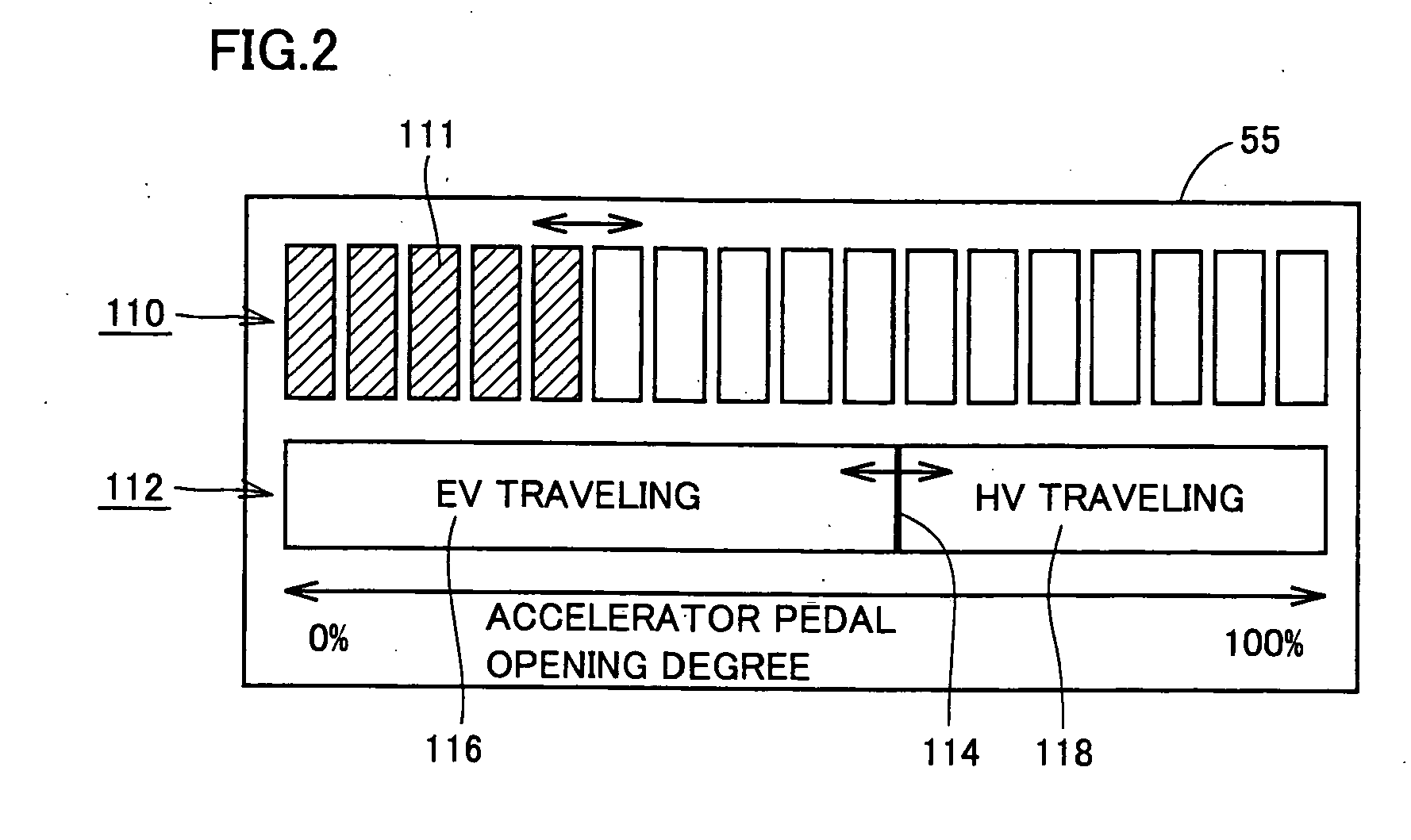
Indicator apparatus for hybrid vehicle, hybrid vehicle, indicating method for hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS20090322503A1Increase rangeHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingTravel modeSplit lines
An indicator portion (55) includes a first indicator portion (110) and a second indicator portion (112). The first indicator portion (110) indicates an accelerator pedal opening degree that changes in accordance with an operated amount of the accelerator pedal by the driver. The second indicator portion (112) includes a division line (114) and regions (116, 118) divided by the division line (114). The division line (114) shows an accelerator pedal opening degree where traveling modes (EV mode and HV mode) are switched. The regions (116, 118) show the ranges of accelerator pedal opening degrees where traveling is performed in EV mode and HV mode, respectively.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
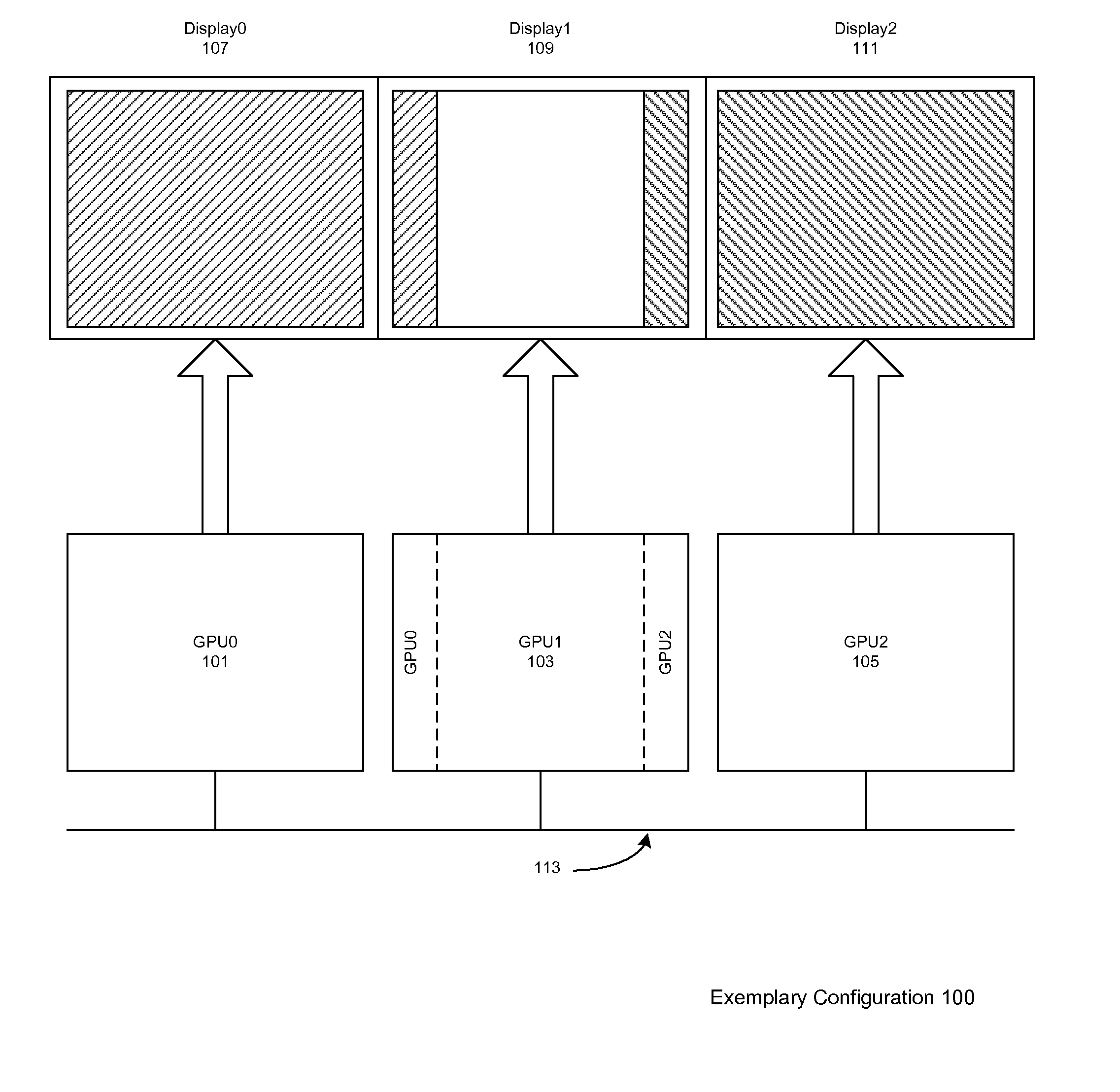
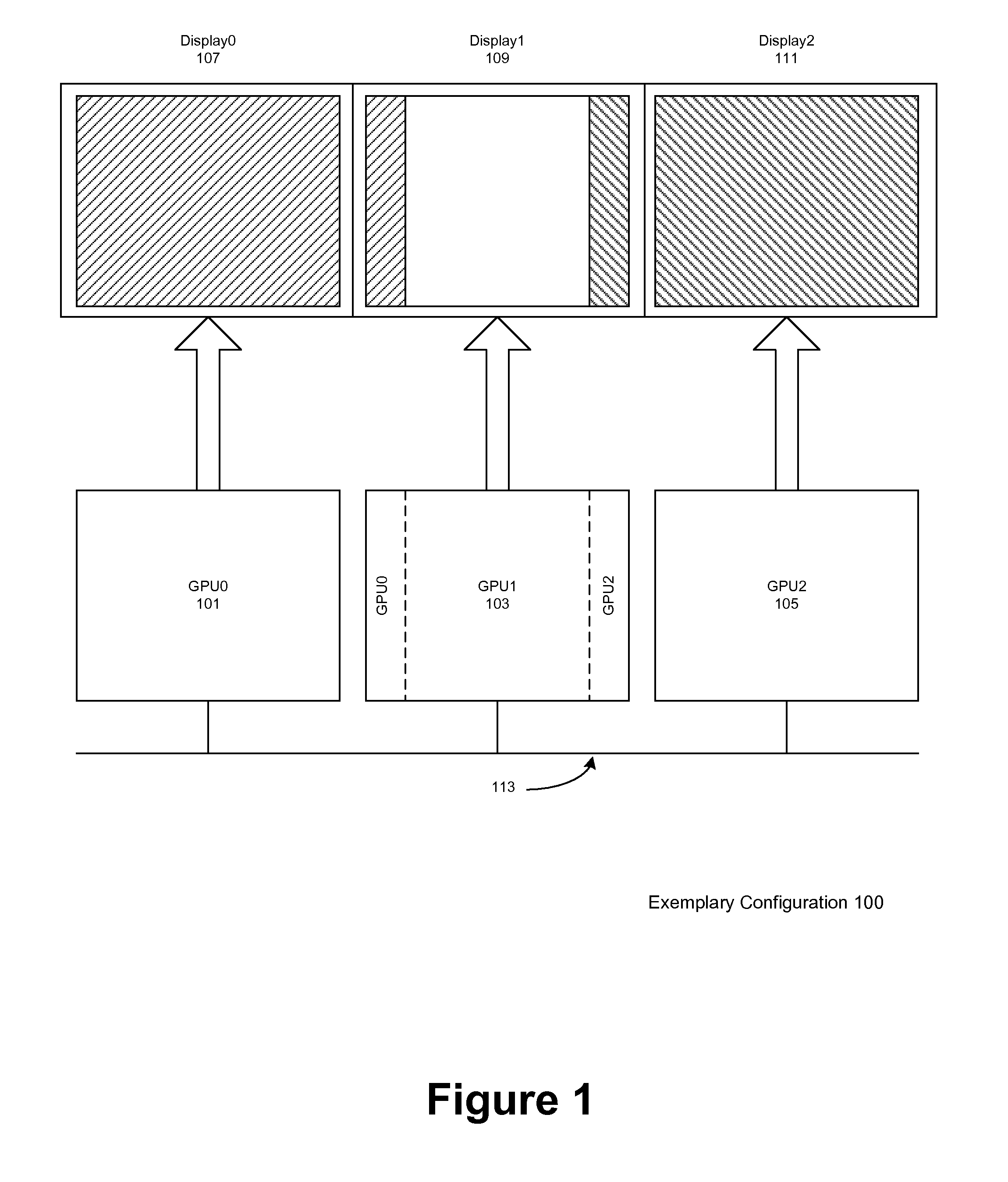
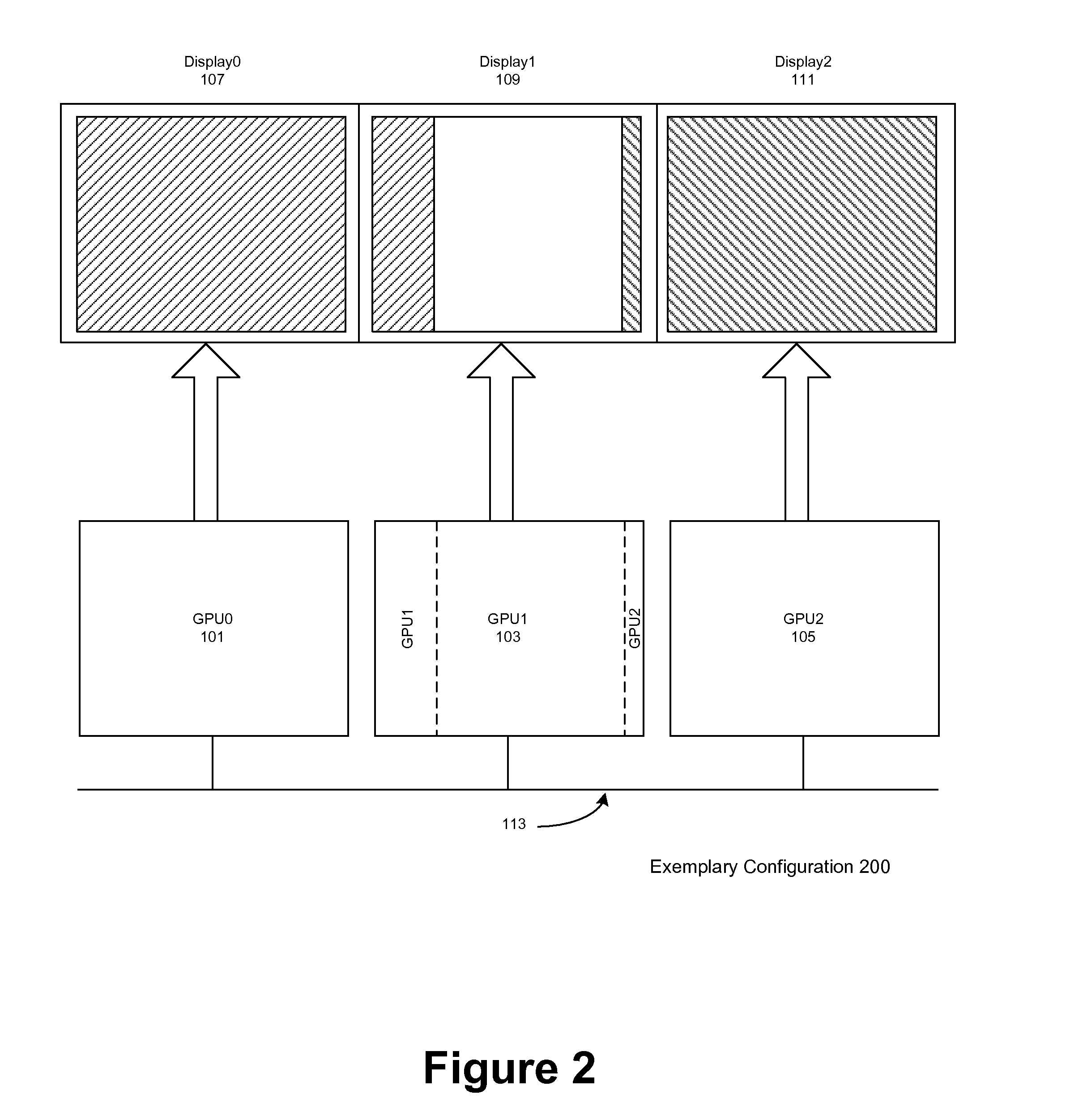
Load balancing in a system with multi-graphics processors and multi-display systems
ActiveUS20110157193A1Optimize allocationLow efficiencyCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsSplit lines
In typical embodiments a three GPU configuration is provided comprising three discrete video cards, each connected to a standard monitor placed horizontally for a 3× horizontal resolution. In this configuration, depending on the load on each GPU, the vertical split lines are dynamically adjusted. To adjust the load balancing according to these virtual split lines, the rendering clip rectangle of each GPU is adjusted, in order to reduce the number of pixels rendered by the heavily loaded GPU. These split lines define the boundary of the scene to be rendered by each GPU, and, according to some embodiments, may be moved horizontally. Thus for example if a GPU has a more complex rendering clip polygon to render than the other GPUs, the neighboring GPUs may render the rendering clip polygon it displays plus a portion of the rendering clip polygon to be displayed by heavily loaded GPU. The assisting GPUs transmit to the heavily loaded GPU the portion of the rendering clip polygon to be displayed by GPU via the chipset with a peer-to-peer protocol or through a communication bus. The split line is dynamically adjusted after each scene.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Ultrasound endoscope
A rigid tip end section which is connected to an angle section at the fore distal end of an insertion instrument of an ultrasound endoscope is housed in a casing which can be split into a main casing and a separable head block to facilitate maintenance and service of internal component parts of the rigid tip end section. An ultrasound transducer is accommodated in a front side portion of the main casing, while endoscopic observation means including an illumination means and an optical image pickup means are fitted in an inclined wall rising obliquely upward on the rear side of the ultrasound transducer. An outlet opening of a biopsy channel outlet passage is located between the ultrasound transducer and the endoscopic observation means. The main casing is adapted to accommodate the ultrasound transducer and its wiring, while the separable head block is adapted to accommodate at least part of component parts of the endoscopic observation means. The main casing and the separable head block are joined with each other through joint wall portions provided along split lines at the opposite lateral sides and at the front side thereof. A foremost one of angle rings of the angle section is detachably fitted on base end portions of the main casing and separable head block to retain these parts in a fixedly connected state.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
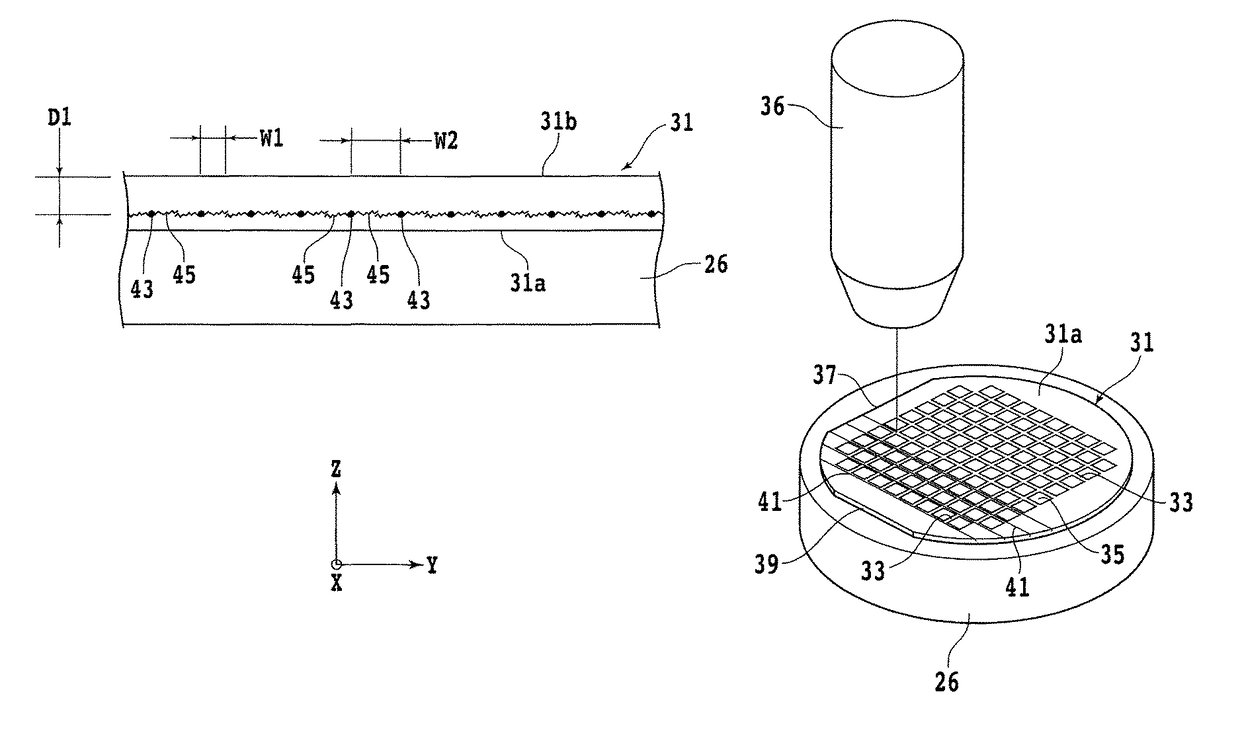
Method of singulating a microelectronic wafer
A method of singulating a microelectronic wafer. The method comprises: providing a microelectronic wafer; focusing a laser beam in an interior region of the wafer from the backside of the wafer to form a modified region extending along the severance lines of the wafer dividing the wafer IC chips, the modified region further extending from an undersurface of the active surface and ending at a predetermined depth with respect to the backside. The modified region comprises a plurality of modified sites of the wafer molten by the laser and resolidified. The method further includes reducing a thickness of the wafer in a direction from the backside toward the active surface by a reduction amount equal to at least the predetermined depth; and dividing the wafer into individual IC chips along the severance lines at the modified sites.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Processing method for wafer
ActiveUS20130189806A1So as not to breakSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesSplit linesLight beam
A wafer has, on a front face thereof, a device region in which a device is formed in regions partitioned by a plurality of scheduled division lines. An outer peripheral region surrounds the device region. A reflecting film of a predetermined width is formed from the outermost periphery of the wafer on a rear face of the wafer corresponding to the outer peripheral region. The front face side of the wafer is held in a chuck table, and a focal point of a pulsed laser beam of a wavelength having permeability through the wafer is positioned in the inside of the wafer corresponding to the scheduled division lines. The pulsed laser beam is irradiated from the rear face side of the wafer to form modified layers individually serving as a start point of division along the scheduled division lines in the inside of the wafer.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Brittle workpiece splitting system and brittle workpiece splitting method
InactiveUS8104385B2Improve processing qualityAchieving splitting processGlass blowing apparatusGlass reforming apparatusSplit linesMechanical engineering
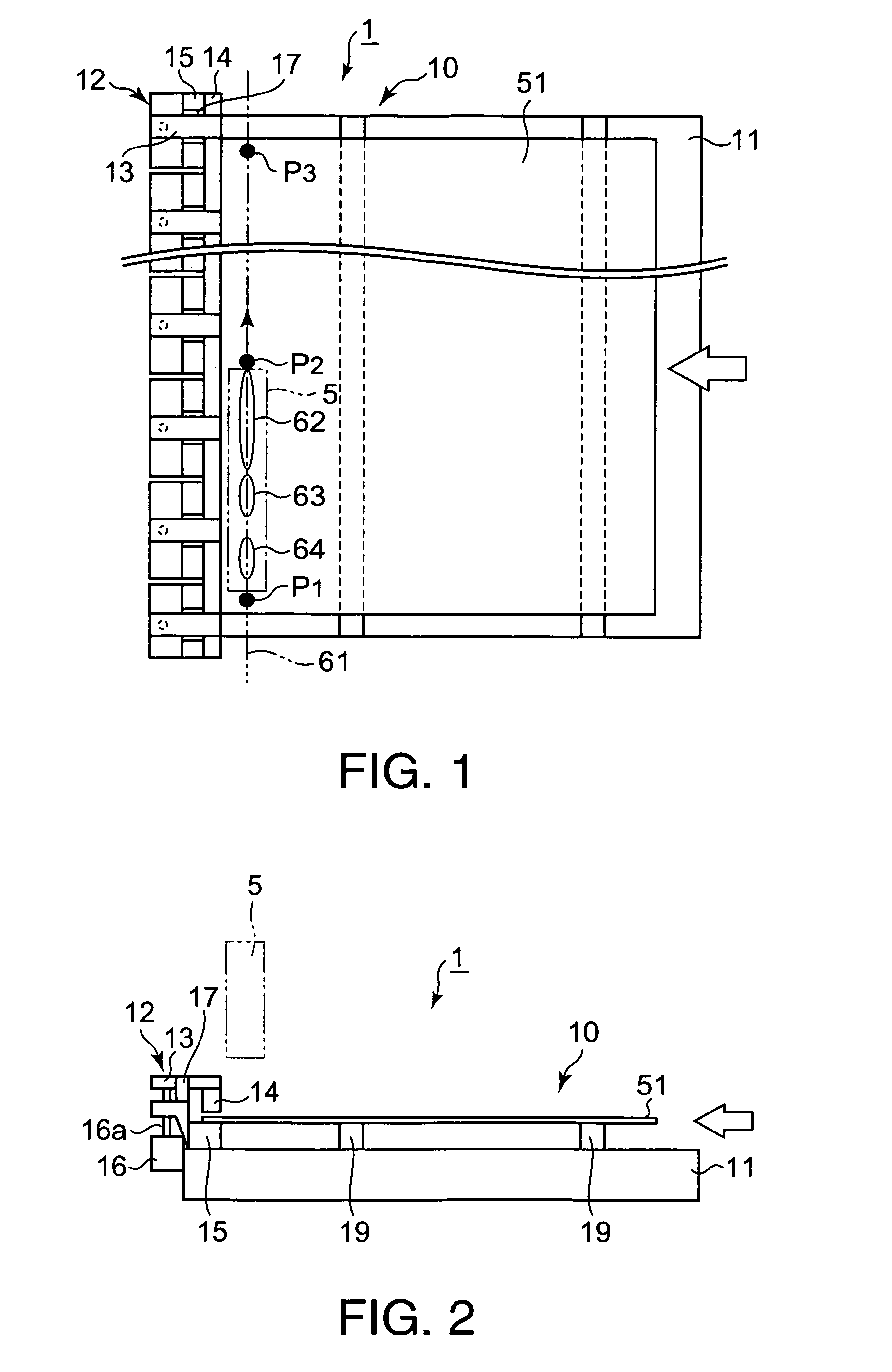
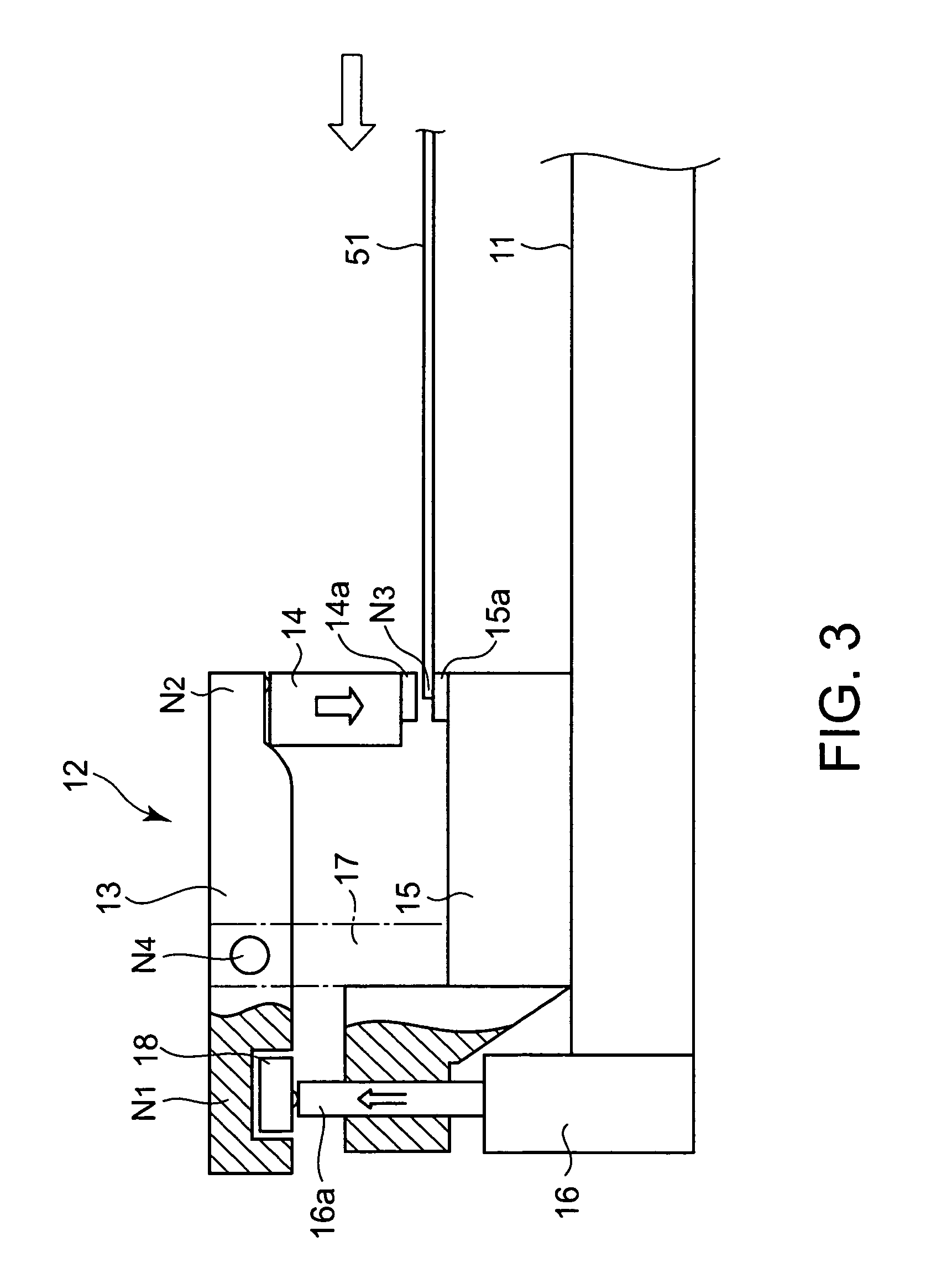
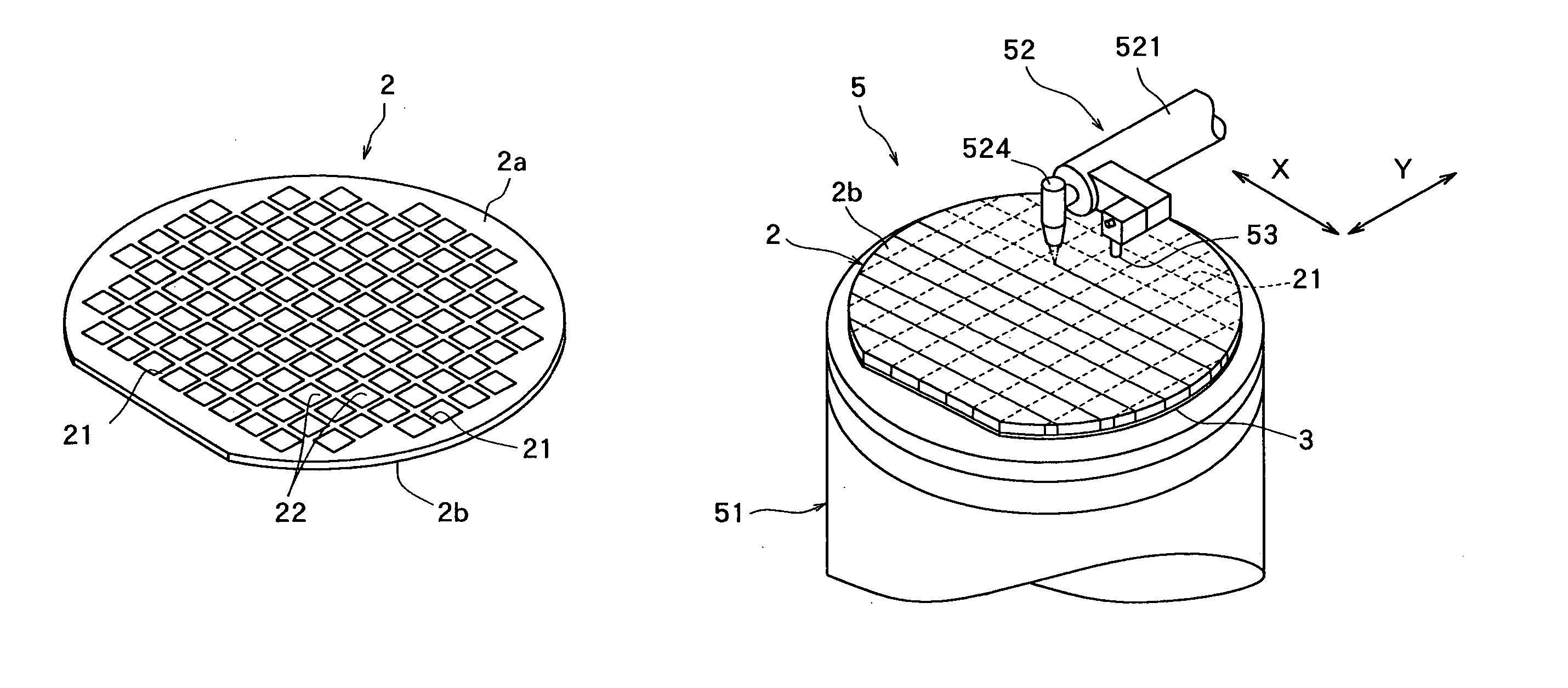
The brittle workpiece splitting system 1 includes a substrate holding mechanism 10 for holding a substrate 51, and a processing unit 5 for splitting the substrate 51 held by the substrate holding mechanism 10 by a splitting process. The substrate holding mechanism 10 has an edge damper 12 adapted to clamp an edge part of the substrate 51 from the sides of the opposite surfaces of the edge part, and support members 19 for supporting the substrate 51 thereon at a predetermined height. The support members 19 are disposed on the side opposite the side of the edge damper 12 with respect to the intended split line 61 parallel to the edge part of the substrate 51. The edge damper 12 has an edge holder 15 on which the substrate 51 is seated, and a pressure bar 14 for pressing the substrate 51 against the edge holder 15 to hold the substrate 51 between the edge holder 15 and the pressure bar 14. Resin members 14a and 15a made of an elastic material having comparatively high rigidity are attached to parts, to be brought into contact with the substrate 51, of the pressure bar 14 and the edge holder 15, respectively. The support members 19 are made of a low-friction material to permit the horizontal movement of the substrate 51 during the splitting process.
Owner:SHIBAURA MECHATRONICS CORP +1
Lane Departure Warning Apparatus and Lane Departure Warning System
InactiveUS20120212612A1Prevent false warningRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionLane departure warning systemSplit lines
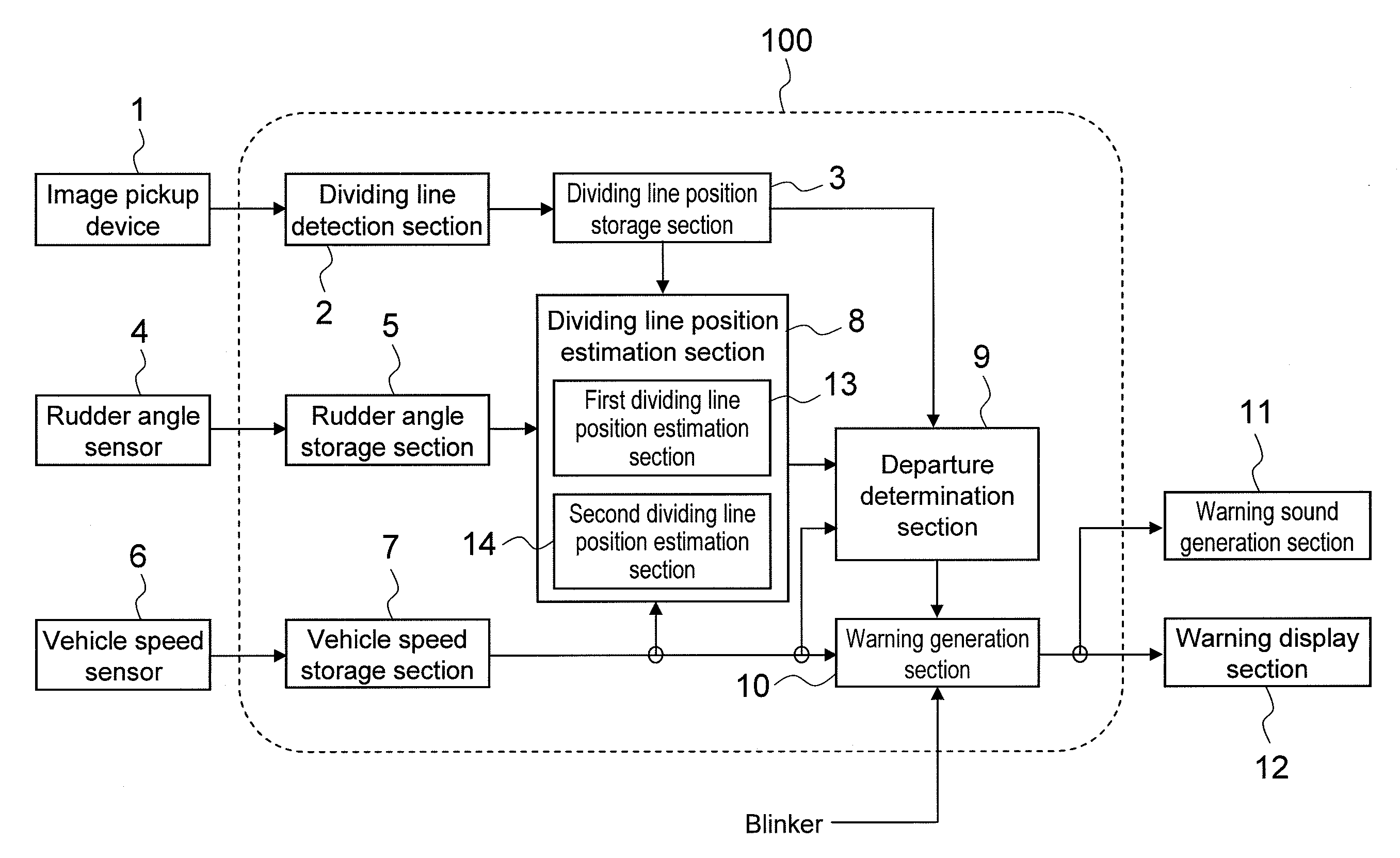
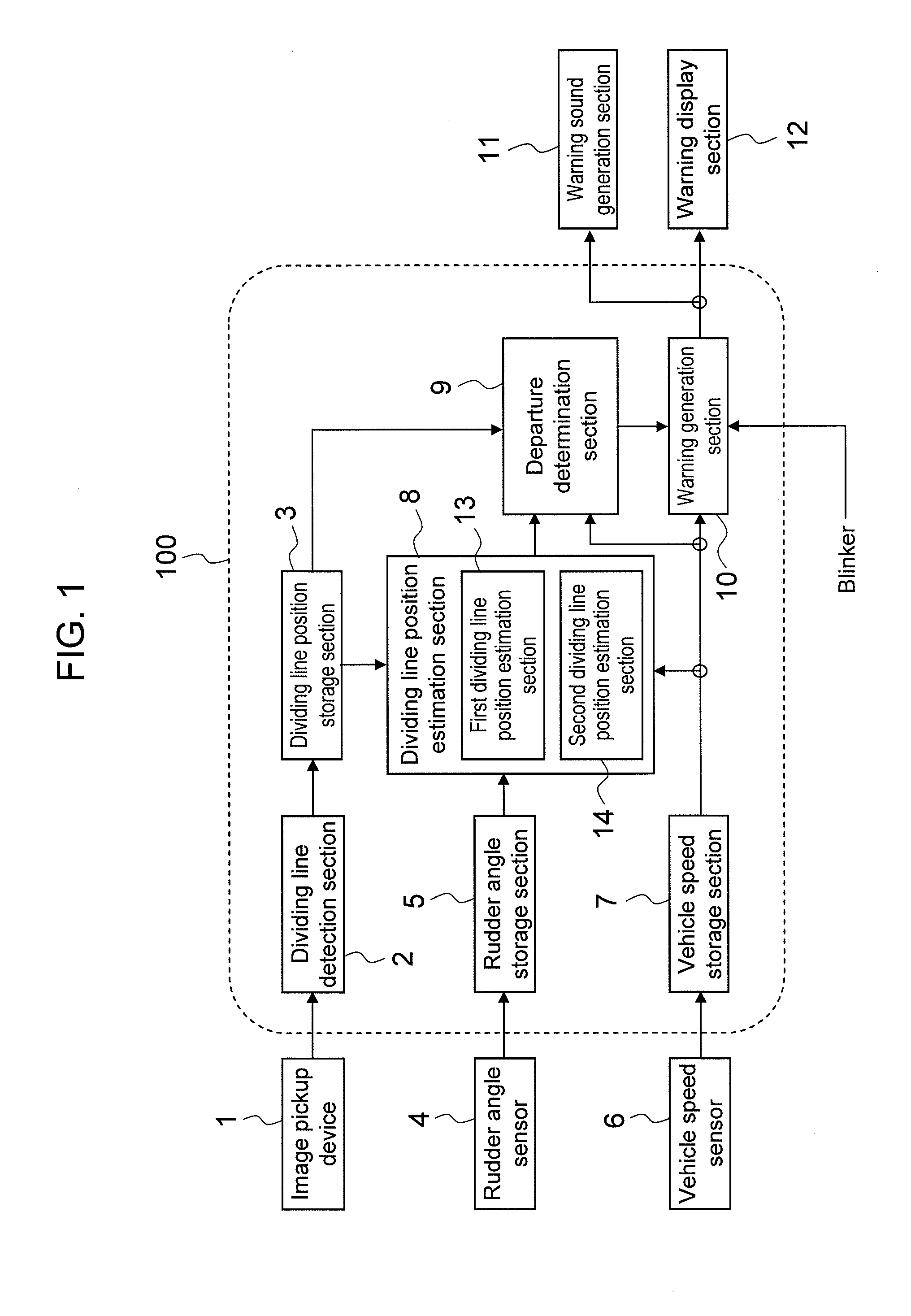
There is provided a lane departure warning apparatus capable of preventing false warnings and absence of a warning regarding lane departure which is attributed to special road geometries such as junctions and tollgates. The lane departure warning apparatus for outputting a warning signal upon determining departure of a vehicle from a lane, performing the steps of: when one dividing line in a vehicle width direction of the vehicle is non-detected, estimating a position of the one dividing line based on a position of the other dividing line as a first estimation dividing line; estimating a position of the non-detected one dividing line based on a position of the one dividing line prior to non-detection as a second estimation dividing line; and comparing the first estimation dividing line with the second estimation dividing line to determine lane departure.
Owner:CLARION CO LTD
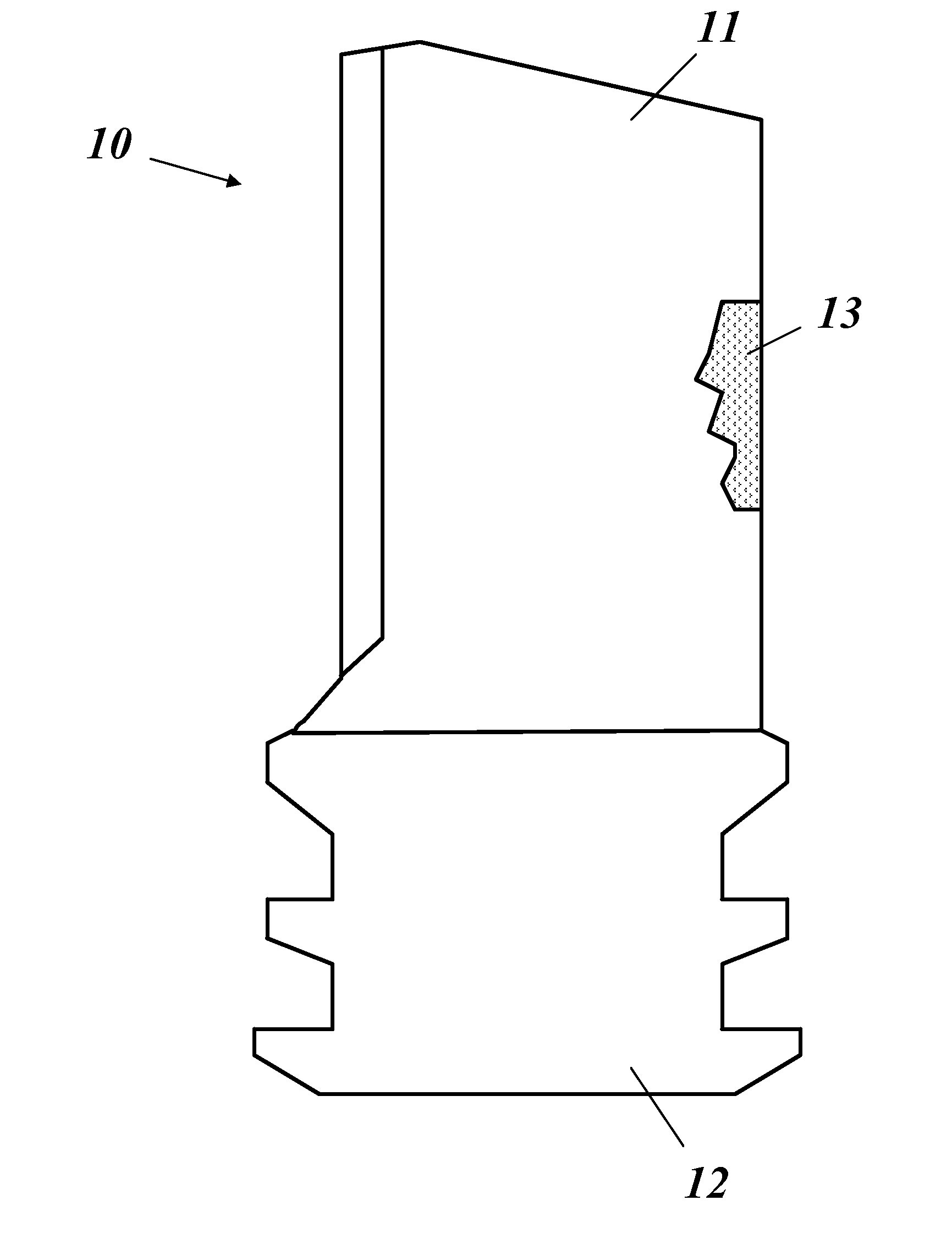
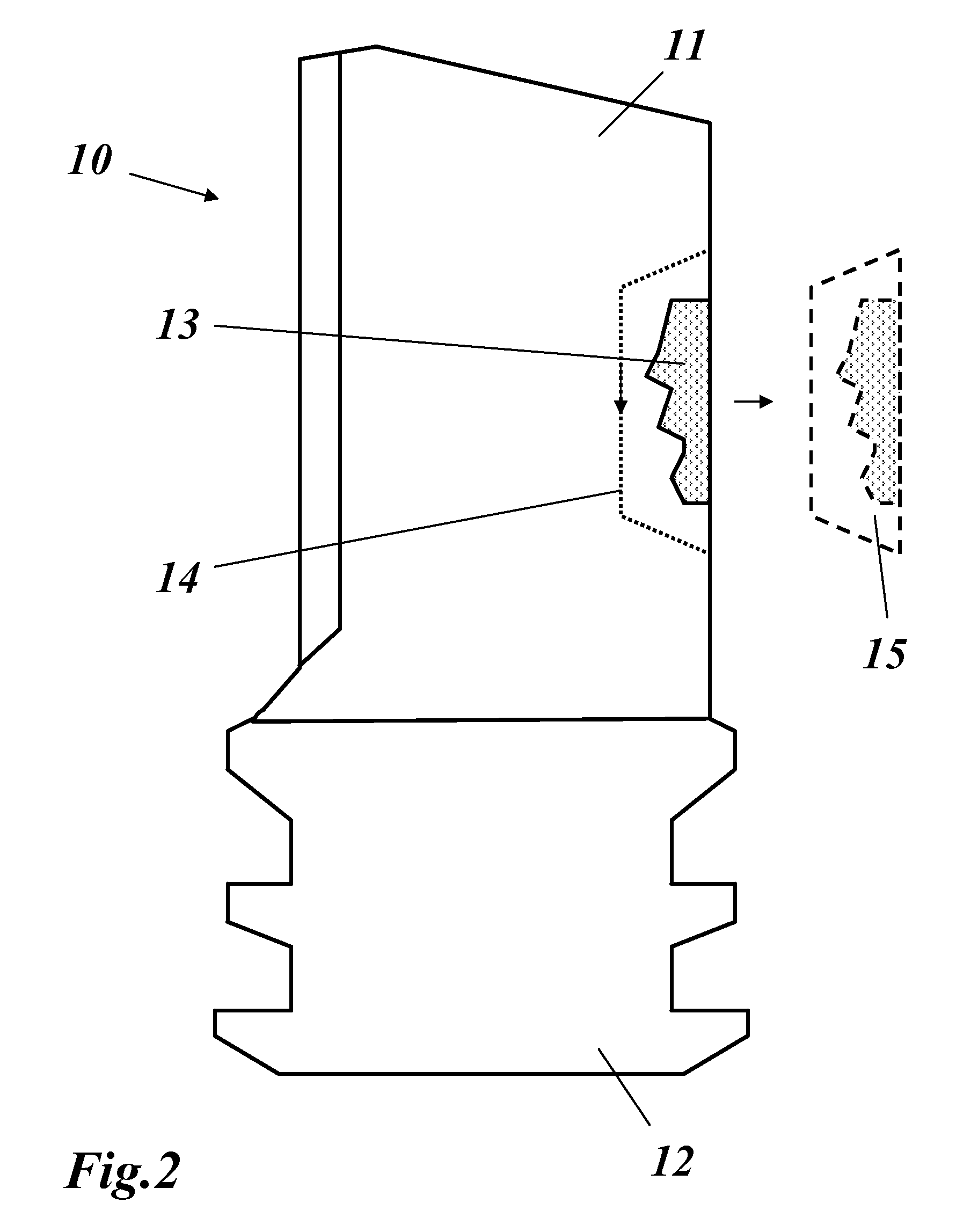
Method for repairing a gas turbine component
InactiveUS20110099810A1Low costQuality improvementTurbinesAdditive manufacturingProduction rateSplit lines
A method for repairing an ex-service gas turbine component (10) includes the steps of: removing a damaged section (13) from the gas turbine component (10), manufacturing a 3-D article, which fits in the gas turbine component (10) to replace the removed damaged section (13), and joining the gas turbine component (10) and the 3-D article inserted therein. Reduced cost, improved flexibility and productivity, and simplified handling are achieved by removing the damaged section (13) in the form of a cut-out section along a split line (14) as one single cut-out piece (15), measuring the cut-out piece (15) to obtain the actual non-parametric geometry data set of the cut-out piece (15), and manufacturing the 3-D article based on the geometry data set of the cut-out piece (15).
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Wafer processing method
ActiveUS20170053829A1Wear amount of abrasiveImprove economySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSplit linesOptoelectronics
A wafer formed from an SiC substrate having a first surface and a second surface is divided into individual device chips. A division start point formed by a laser has a depth corresponding to the finished thickness of each device chip along each division line formed on the first surface. The focal point of the laser beam is set inside the SiC substrate at a predetermined depth from the second surface, and the laser beam is applied to the second surface while relatively moving the focal point and the SiC substrate to thereby form a modified layer parallel to the first surface and cracks extending from the modified layer along a c-plane, thus forming a separation start point. An external force is applied to the wafer, thereby separating the wafer into a first wafer having the first surface and a second wafer having the second surface.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Image type automatic analysis method for mesh adhesion rice corn
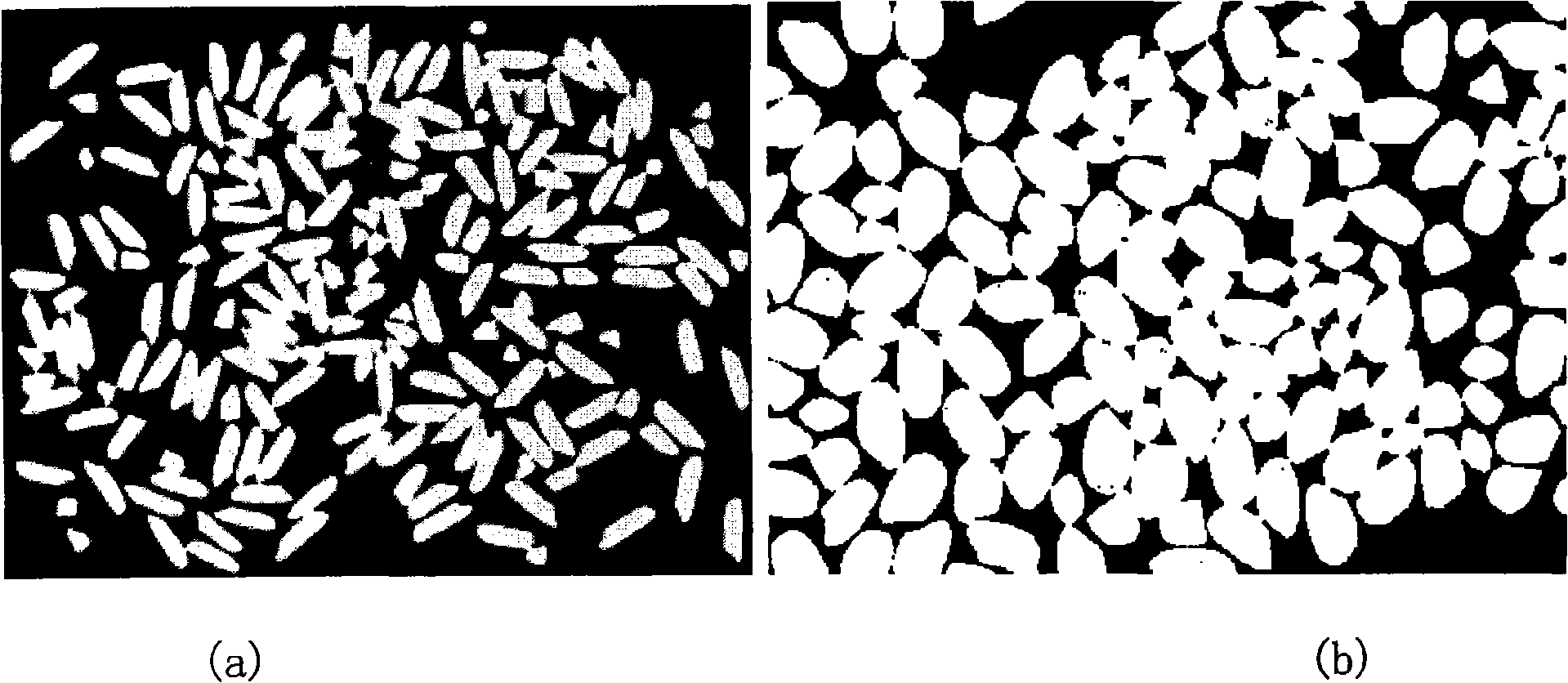
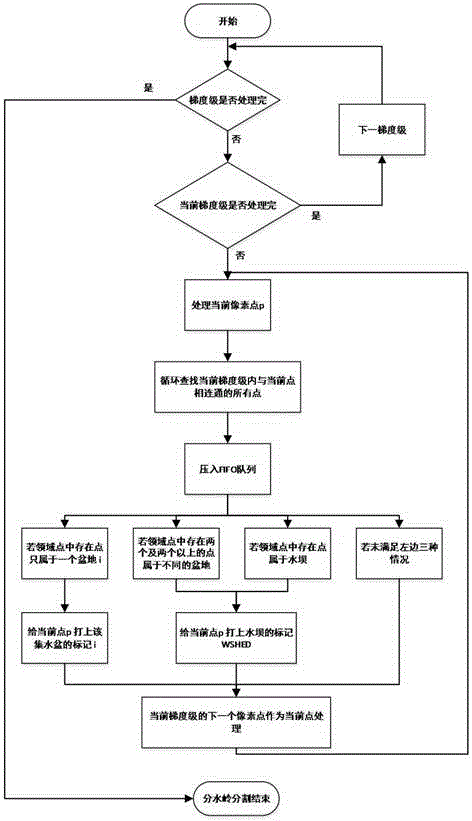
InactiveCN101281112AOvercoming problems that are difficult to analyze automaticallyRemove the restriction of non-stick placementImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansAutomatic segmentationSplit lines
The invention discloses an image automatic analysis method for reticulate adhesion rice. The method firstly images rice under the grade of a reference backlight, and enables the reticulate adhesion rice to belong to the different local regions separately through an automatic segmentation. Secondly, the automatic segmentation includes that fat circular rice is carried on a distance transformation and a watershed transformation to be divided, as well as to use a circular template to get the concave angle point of long rice after the long rice is carried out watershed transformation, and the separation line can be determined and the wrong separation line can be removed according to the concave angle point. Different colors is using to color complete polished rice, broken rice and the rice whose length is in the critical region and to color background and chalkiness so as to figure out the grain number, the length, the width and the length to width ratio of each grain, finally, and the entire polished rice rate, the broken rice rate, the chalkiness degree and the chalkiness grain rate, and to form an analysis report. The invention overcomes the problem that the reticulate adhesion rice is difficult to be carried on automated analysis, and removes the limit of the request analysis sample is not in adhesion placing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for planning a dental component
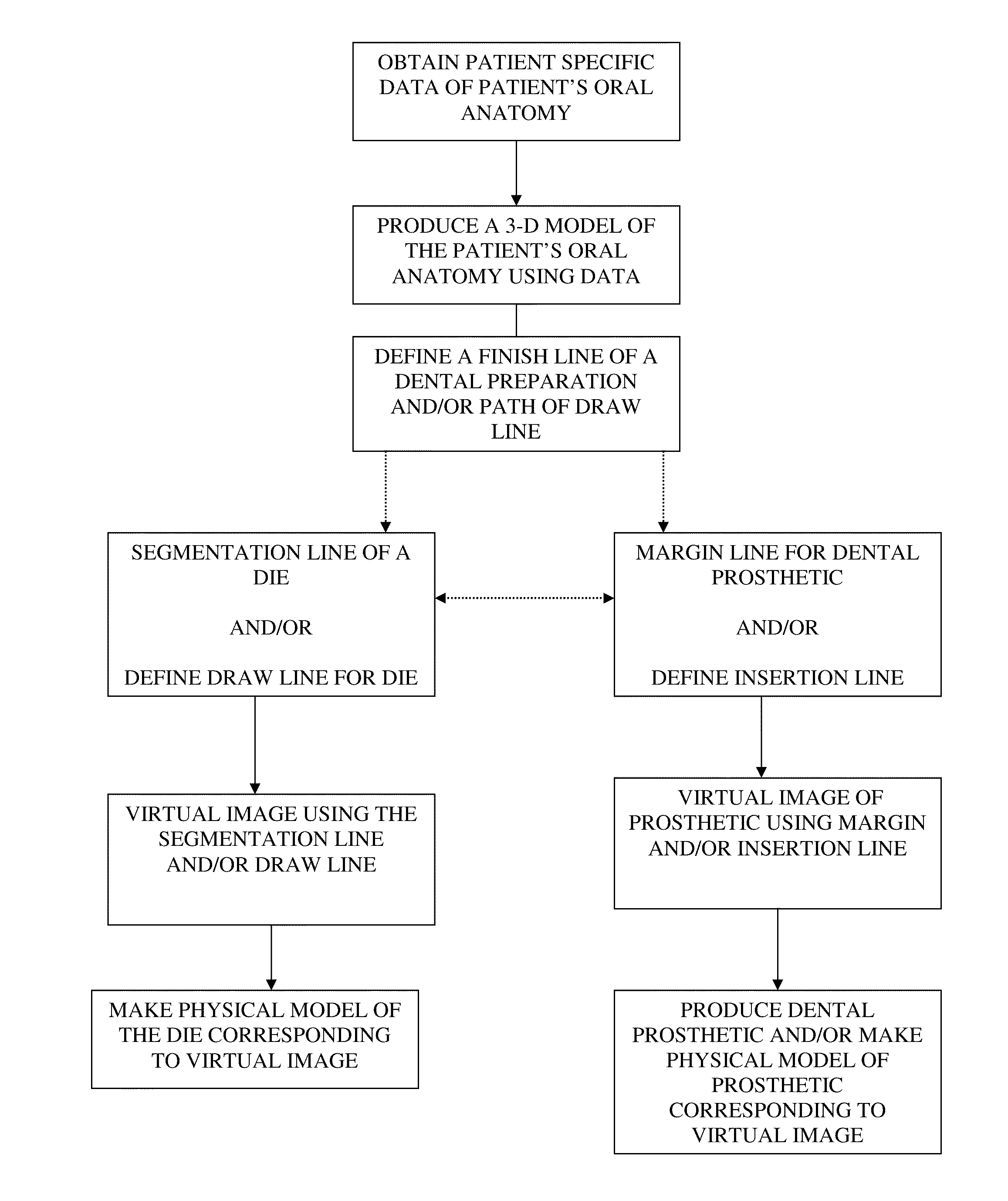
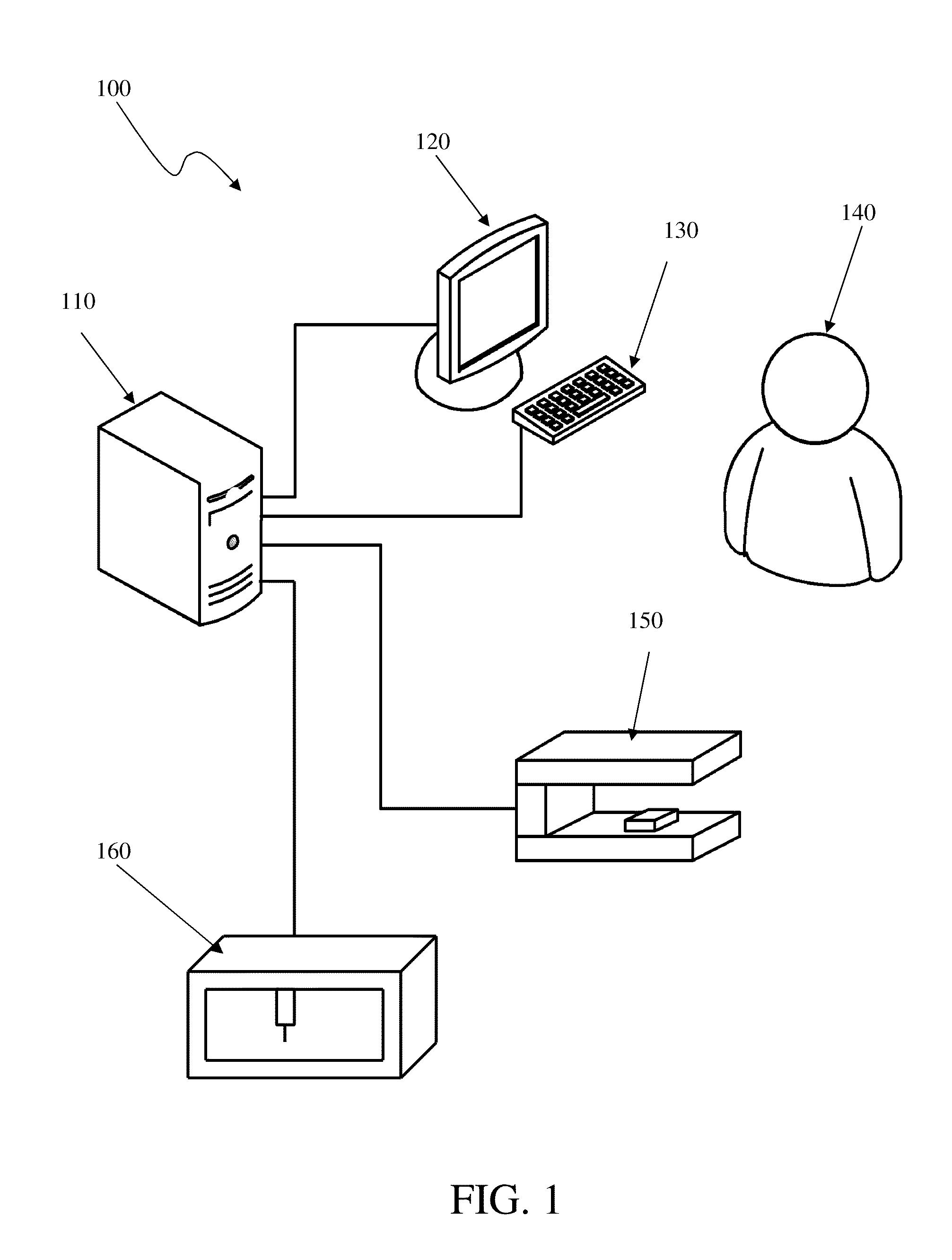
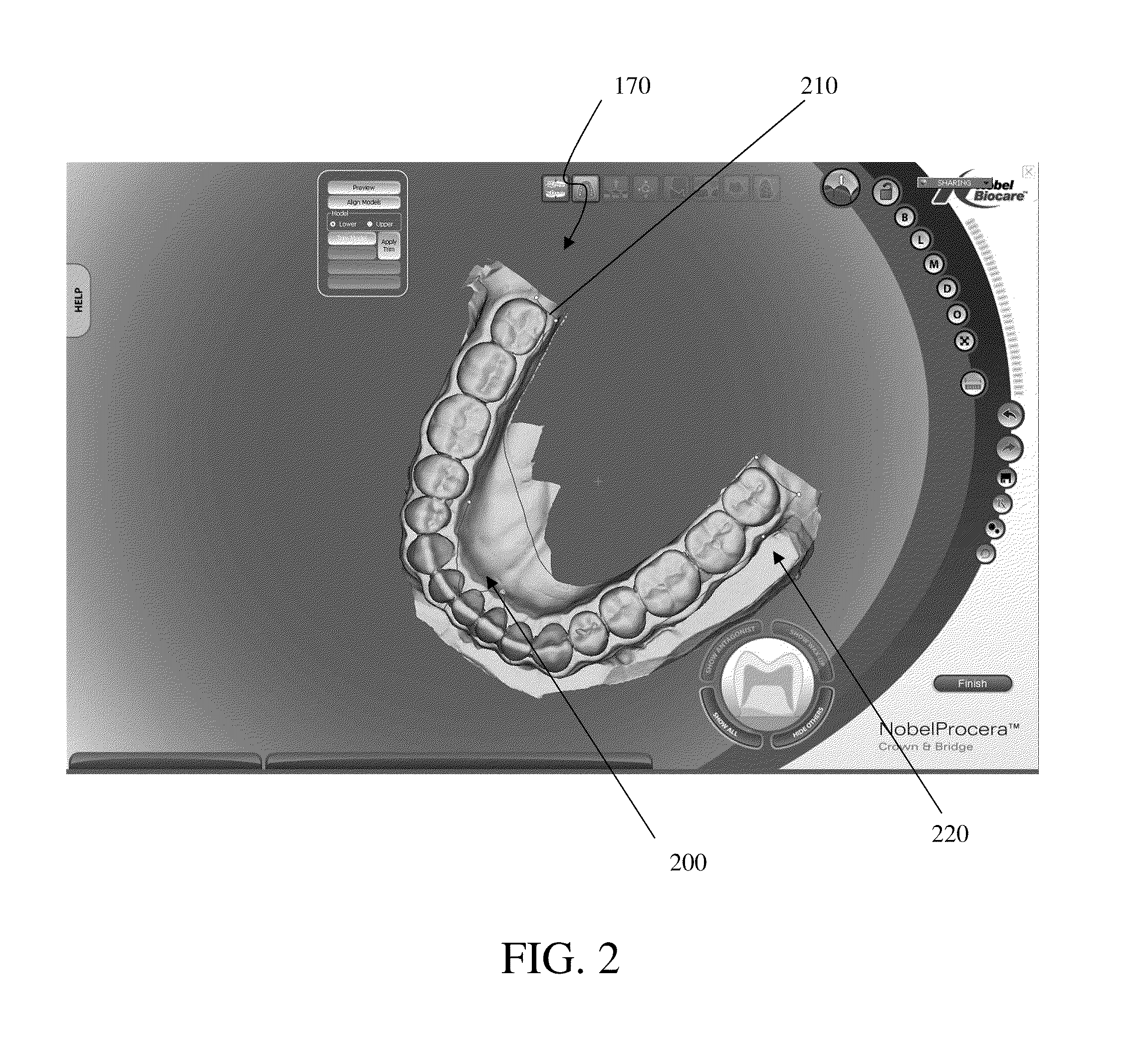
Presented herein are methods and devices for designing dental components, such as physical models of a patient's anatomy, crowns and bridges. An operator of a prosthetic designing system can receive information, such as from a scanner, which provides information on the topology of the patient's dentition. The operator can use this information to design a custom prosthetic to fit the patient. Part of the designing process involves using a finish line defined for a preparation as a segmentation line for a physical die corresponding to the preparation, and using a path of draw line as an insertion axis line for a dental prosthetic.
Owner:BIOCAD MEDICAL
Wafer processing method
ActiveUS20050282359A1Transverse rupture strength of does not lowerHigh strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSplit linesWafer backgrinding
A wafer processing method for dividing a wafer having function elements in area sectioned by dividing lines formed on the front surface in a lattice pattern into individual chips along the dividing lines, comprising a deteriorated layer forming step for forming a deteriorated layer on the side of the back surface of a position at a distance corresponding to the final thickness of the chip from the front surface of the wafer by applying a laser beam capable of passing through the wafer along the dividing lines from the back surface of the wafer; a dividing step for dividing the wafer into individual chips along the dividing lines by applying external force to the wafer in which the deteriorated layer has been formed along the dividing lines; and a back surface grinding step for grinding the back surface of the wafer divided into individual chips to the final thickness of the chip.
Owner:DISCO CORP
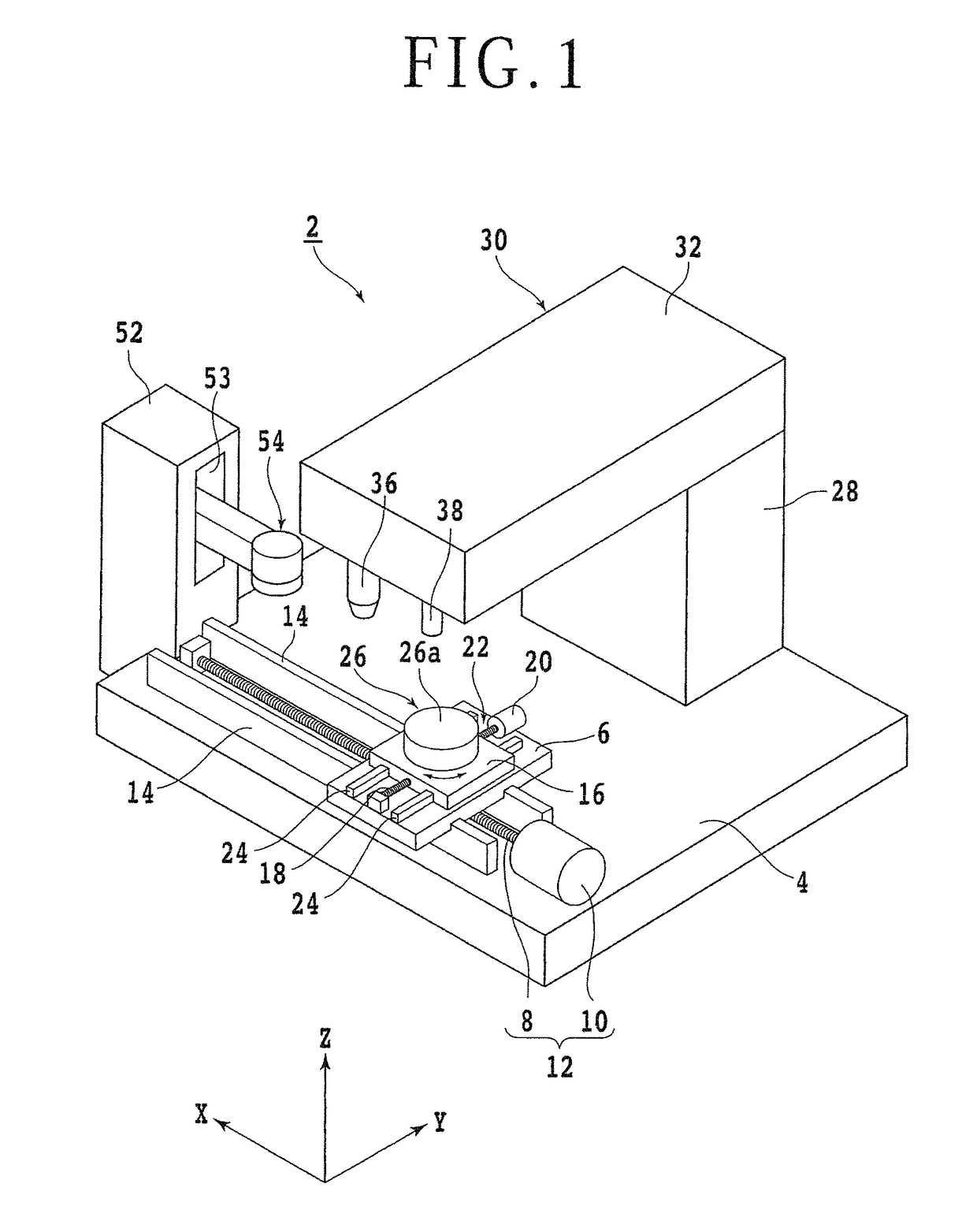
Semiconductor wafer dividing apparatus and semiconductor device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050023260A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesSplit linesManufactured apparatus
A semiconductor device manufacturing apparatus includes etching equipment, damage forming equipment, dividing equipment and removing equipment. The etching equipment etches a film formed on an element forming surface of a semiconductor wafer, thereby defining a dicing line or a chip-dividing line. The damage forming equipment forms damage layers used as starting points to divide a semiconductor wafer into discrete semiconductor chips on a rear surface side of the semiconductor wafer which is opposite to an element forming surface. The dividing equipment divides the semiconductor wafer into discrete semiconductor chips with the damage layers used as the starting points. The removing equipment removes a rear surface portion of the semiconductor wafer to at least a depth where the damage layers are no more present.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Split line moving platform
ActiveCN102074915ATimely detection of defectsFlexibleManipulatorApparatus for overhead lines/cablesSplit linesHardware tool
The invention relates to a split line moving platform. A power transmission lead is used as a working path in the platform, various barriers (a vibration damper, a crimping pipe, a spacing bar, a suspension line clamp, an insulator string and the like) are spanned and avoided, the platform is provided with a camera which can observe the condition of the running line and timely discover the defects of the line and hardware tools, and other working mechanical arms can be expanded to finish clearing line barriers and the like. A robot has flexible action and large working range, has the effect of protecting devices during jumping the barriers, and has high safety and reliability. The platform mainly consists of a traveling device, a driving arm device, an anti-tilting device and a power supply control box; and the traveling device is arranged on an electric cable and connected with the driving arm device, and the anti-tilting device is arranged at the tail end of the traveling device.
Owner:STATE GRID INTELLIGENCE TECH CO LTD
Multiple-picture display control method, multiple-picture display control device and multiple-picture display control system
ActiveCN102750122AIntuitive settingsFlexible settingsData processing applicationsTelevision conference systemsSplit linesControl objective
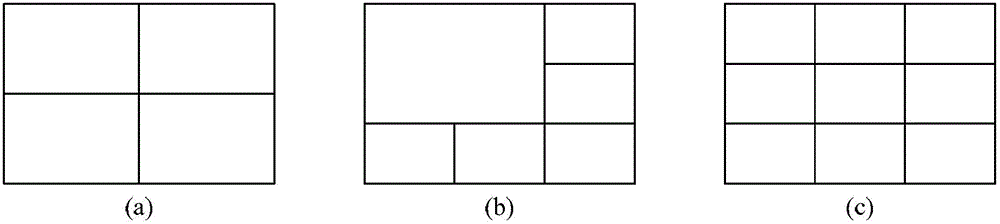
An embodiment of the invention provides a multiple-picture display control method, a multiple-picture display control device and a multiple-picture display control system. The method comprises the steps of receiving sliding tracks operated by a user, performing multiple-picture split line operation according to the sliding tracks operated by the user and controlling a target screen to perform picture displaying according to a multiple-picture display mode formed by operated multiple-picture split lines. By means of the multiple-picture display control method, the multiple-picture display control device and the multiple-picture display control system, the multiple-picture display mode can be intuitively and flexibly arranged.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Wafer dividing method
ActiveUS20050170616A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSplit linesDicing tape
A method of dividing, along dividing lines, a wafer having function elements formed in areas sectioned by the dividing lines formed in a lattice pattern on the front surface, which comprises: a protective member affixing step for affixing a protective member to the front surface of the wafer; a polishing step for polishing the back surface of the wafer having the protective member affixed to the front surface; a deteriorated layer formation step for forming a deteriorated layer along the dividing lines in the inside of the wafer by applying a pulse laser beam capable of passing through the wafer to the wafer along the dividing lines from the polished back surface side of the wafer; a frame holding step for affixing the back surface of the wafer in which the deteriorated layers have been formed along the dividing lines, to a dicing tape mounted on an annular frame; a dividing step for dividing the wafer into individual chips along the dividing lines by exerting external force along the dividing lines where the deteriorated layers have been formed, of the wafer held on the frame; an expansion step for enlarging the interval between chips by stretching the dicing tape affixed to the wafer divided into individual chips; and a pick up step for picking up the chips from the stretched dicing tape.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Wafer processing method
ActiveUS9620415B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSplit linesOptoelectronics
A wafer formed from an SiC substrate having a first surface and a second surface is divided into individual device chips. A division start point formed by a cutting blade has a depth corresponding to the finished thickness of each device chip along division lines formed on the first surface. A separation start point is formed by a laser beam having a focal point set inside the SiC substrate at a predetermined depth from the second surface, and the laser beam is applied to the second surface while relatively moving the focal point and the SiC substrate to thereby form a modified layer parallel to the first surface and cracks extending from the modified layer along a c-plane. An external force is applied to the wafer, thereby separating the wafer into a first wafer having the first surface and a second wafer having the second surface.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Circular masking-out area rate determination-based adhesive particle image concave point segmentation method
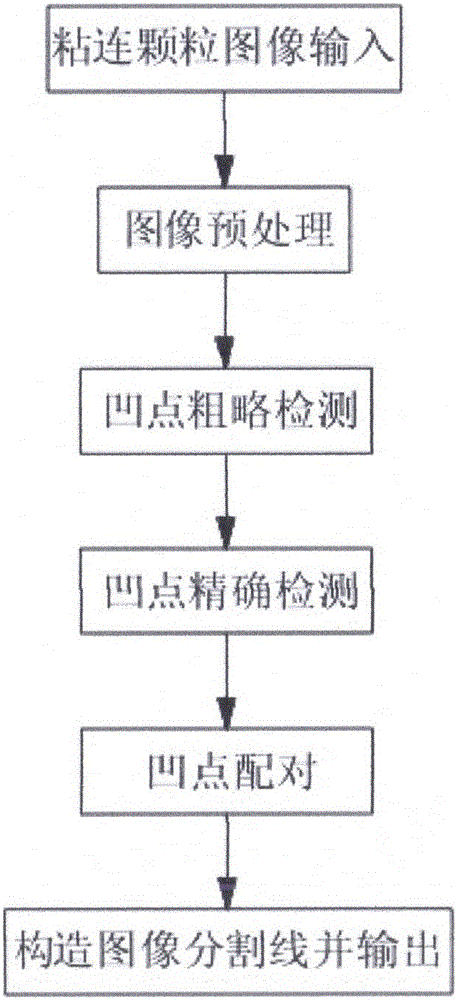
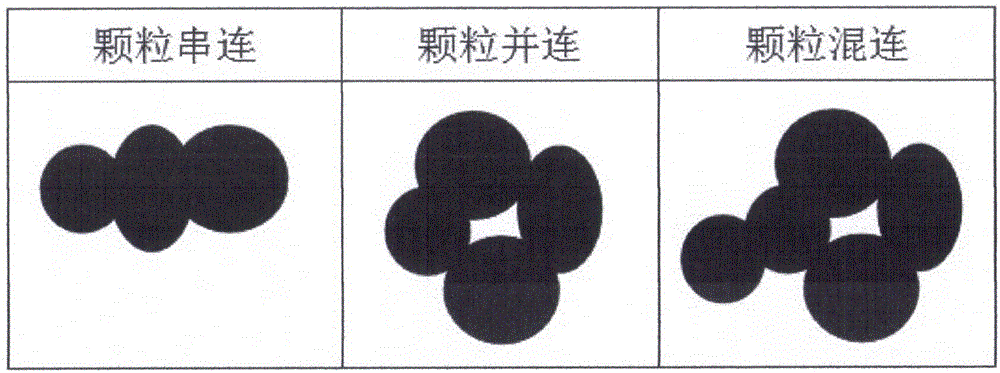
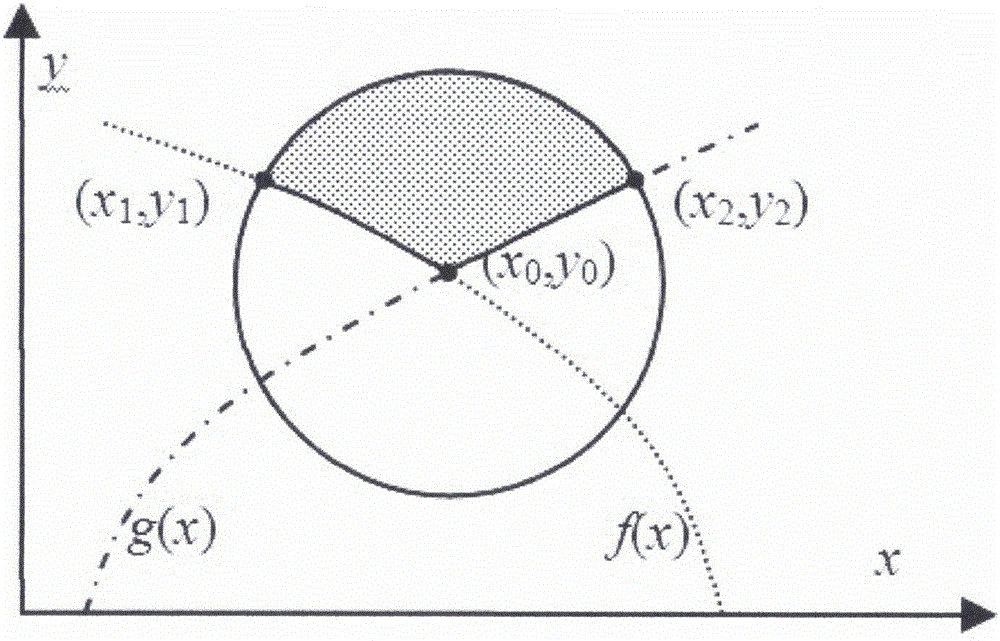
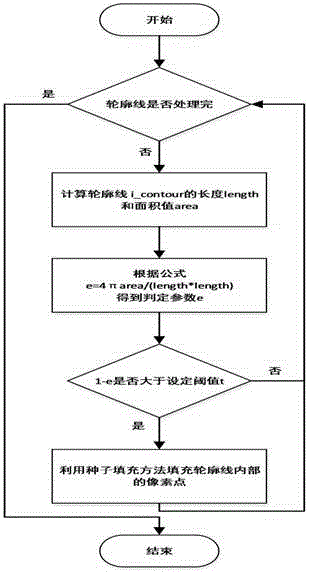
The present invention relates to a circular masking-out area rate determination-based adhesive particle image concave point segmentation method. The method comprises the following steps of 1) carrying out the image pre-processing to obtain a binary image of a particle image; 2) carrying out the concave point rough detection to obtain an angular point image of the particle image; 3) carrying out the concave point accurate detection, and utilizing an area rate method to obtain all concave points capable of being used for the particle segmentation in a regional contour; 4) carrying out the concave point pairing, wherein the selected concave point pairs are used as the segmentation points of an adhesive particle image; 5) constructing a segmentation line of the particles, obtaining the contour coordinates of individual particles, and combining the coordinates of two segmentation points to obtain the complete particle contour. According to the present invention, by combining an angular point detection method and a method based on concave point analysis, an operand problem brought by purely utilizing the concave point search based on area is avoided; by setting few parameters, a lot of sample training is not needed; at the same time, the segmentation paths can be replanned, thereby being able to adapt to the different shape and size change of the images.
Owner:WEIFANG UNIVERSITY
Wafer dividing method
ActiveUS20120289028A1Avoid quality lossRule out the possibilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSplit linesEngineering
Owner:DISCO CORP
Semiconductor light-emitting device and method for separating semiconductor light-emitting devices
InactiveCN101083292AIncrease productionReduce processing timeLaser detailsSolid-state devicesSplit linesLight beam
The invention provides a method for separating semiconductor light-emitting devices formed on a substrate. In the method, a pulse laser beam having a pulse width less than 10 ps in a substrate is focused on the substrate, to thereby cause multi-photon absorption in the substrate. Through multi-photon absorption, a groove is formed through the pulse laser beam along a split line predetermined on a surface of the substrate, the groove being substantially continuous in the direction of the predetermined split line. In addition, internal structurally changed portions are formed through the pulse laser beam at a predetermined depth of the substrate on a predetermined split face, the structurally changed portions being discontinuous in the direction of the predetermined split line. Subsequently, an external force is applied to thereby form a split face along the continuous groove and the discontinuous internal structurally changed portions, whereby the semiconductor light-emitting devices are separated from one another.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Substrate dividing method
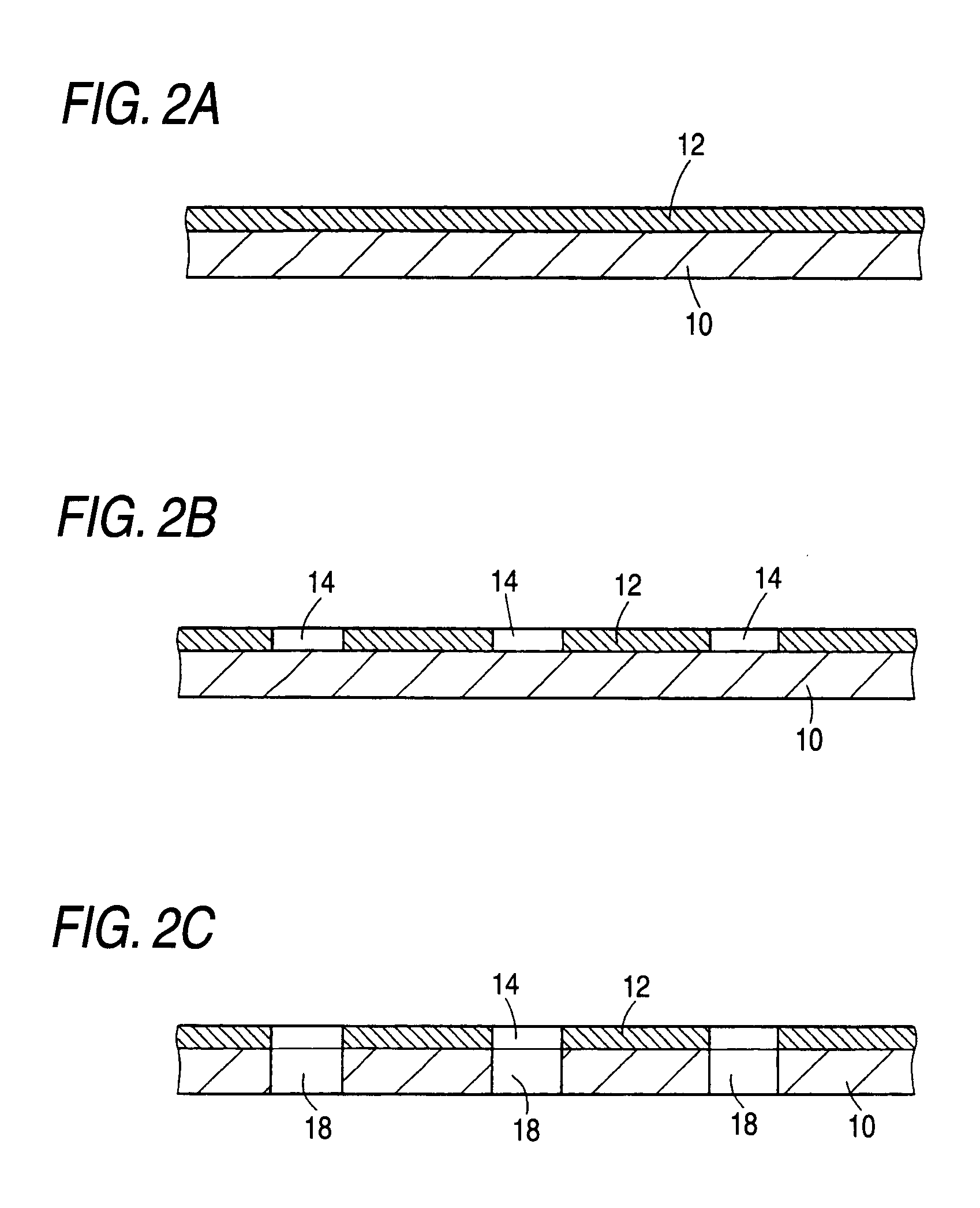
InactiveUS20090098712A1High strengthEasy to handlePrinted circuit aspectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSplit linesEngineering
A method of dividing a substrate 10 into individual pieces by setting dividing lines A used to dividing the substrate 10 into individual pieces at a predetermined interval in a vertical direction and a horizontal direction and then dividing the substrate 10 along the dividing lines A, includes a step of forming chamfering patterns 14 to form through holes, which are used to chamfer corner portions of individual pieces of the substrate, in respective intersection points between the dividing lines on the substrate, a step of forming chamfering through holes by etching the substrate 10, and a step of obtaining the individual pieces of the substrate by separating the substrate in the vertical direction and the horizontal direction along the dividing lines A respectively.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Method for manufacturing semiconductor element
ActiveUS20110298084A1Accurate segmentationAccurate divisionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSplit linesEngineering
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor element of the present invention, has: a laser irradiation step of focusing a pulsed laser beam inside of a substrate constituting a wafer, thereby forming a plurality of isolated processed portions along an intended dividing line inside of the substrate, and creating a fissure that runs from the processed portions at least to the surface of the substrate and links adjacent processed portions; and a wafer division step of dividing the wafer along the intended dividing line.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Method for cutting portable data file (PDF) 417 standard two-dimensional bar code image
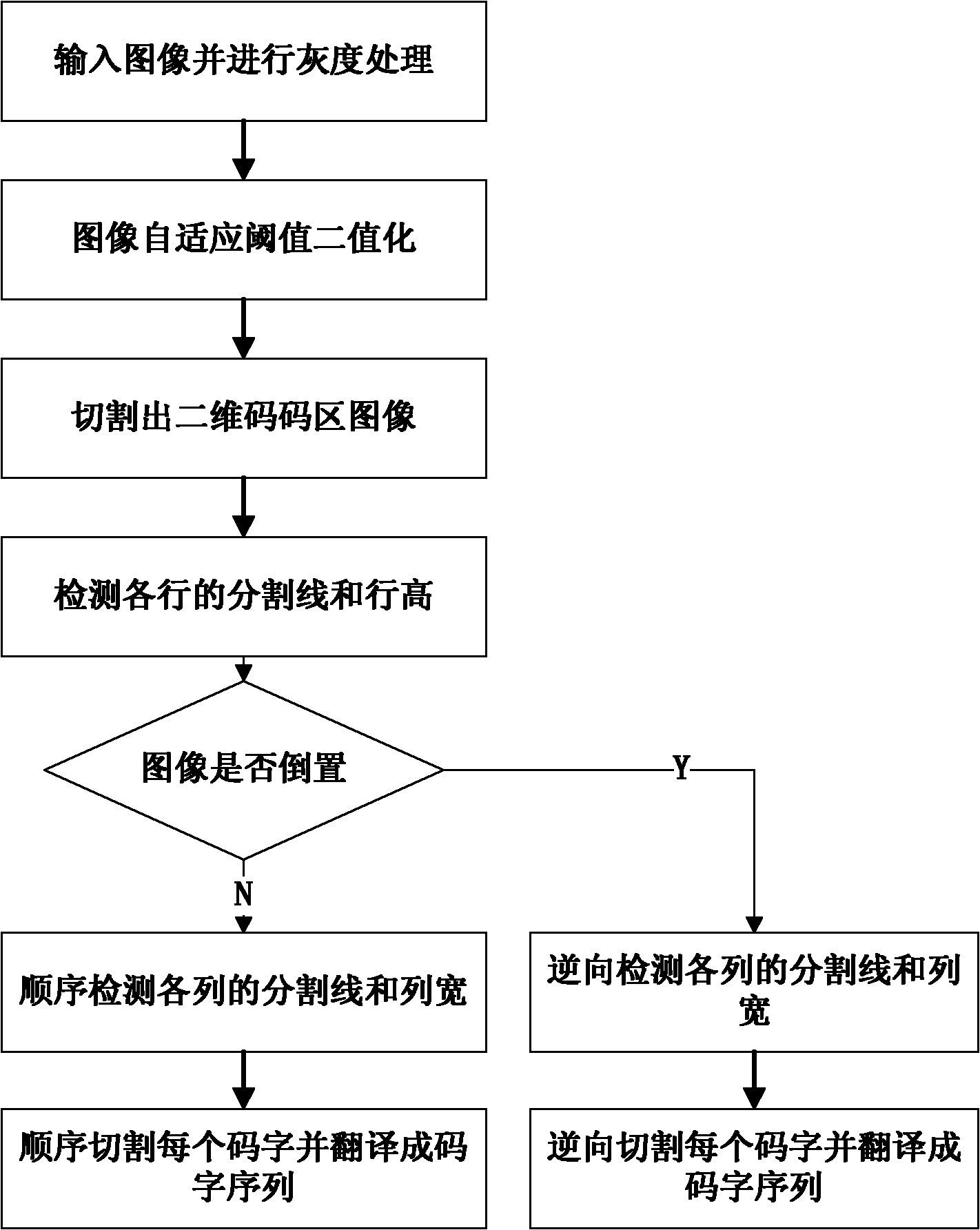
InactiveCN102184378AImprove fouling resistanceImprove efficiencySensing by electromagnetic radiationSplit linesLine width
The invention discloses a method for cutting a portable data file (PDF) 417 standard two-dimensional bar code image based on a projection mode by using image profile information. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting the normal PDF417 standard two-dimensional bar code image, carrying out grey processing, and binarizing a grey image by using a self-adaptive global threshold value to obtain a two-dimensional code binary image; cutting two-dimensional code areas of the processed image to obtain the image which only has the code areas; identifying the obtained two-dimensional code image, detecting coordinates of partition lines of each row, and calculating row height; detecting whether the two-dimensional code image is inversed, cutting each code word image sequentially from top to bottom and from right to left according to the detected coordinates of the partition lines of the row, the row height, the coordinates of the partition lines of a line, and line width; and identifying code words from right to left reversely, and converting the code words into corresponding code word sequences. By the method, each code word can be cut accurately in the situation that the image is partially contaminated, lost or even inclined slightly at an angle of less than 0.1 degree. The method is high in robustness and high in reliability.
Owner:MAOMING POLYTECHNIC
Recognition and counting method for cells
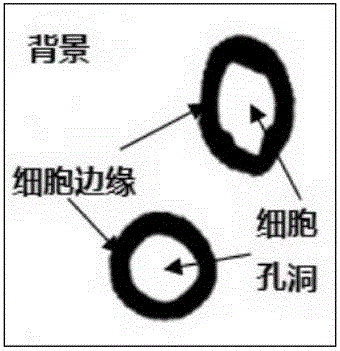
ActiveCN106056118AImprove recognition rateReduce the effects of image noiseRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsSplit linesChamfer distance
The invention discloses a recognition and counting method for cells, comprising nine steps: preprocessing an image in a micron-order microscopic acquisition environment; extracting cell holes from the preprocessed image; performing closed hole filling of cells by using the knowledge of a connected domain; extracting a contour point sequence of cells from the image filled in step 3; filling non-closed holes of cells by adopting a non-closed hole filling method based on circularity determination; performing chamfer distance transformation on the filled image; performing extreme value uniqueness marking on cell hole positions; segmenting the image after extreme value uniqueness by using a marked watershed method; and quantifying and marking the segmented result. The method has the advantages that the influence of image noise can be greatly reduced, the phenomena of over-segmentation and discontinuous segment lines are eliminated, the segmentation effect is improved, and the cell recognition rate is improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Laser beam machining method for wafer
ActiveUS20090004828A1Carry-out smoothly and easilyMachining efficiency can be moreSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesSplit linesLaser beam machining
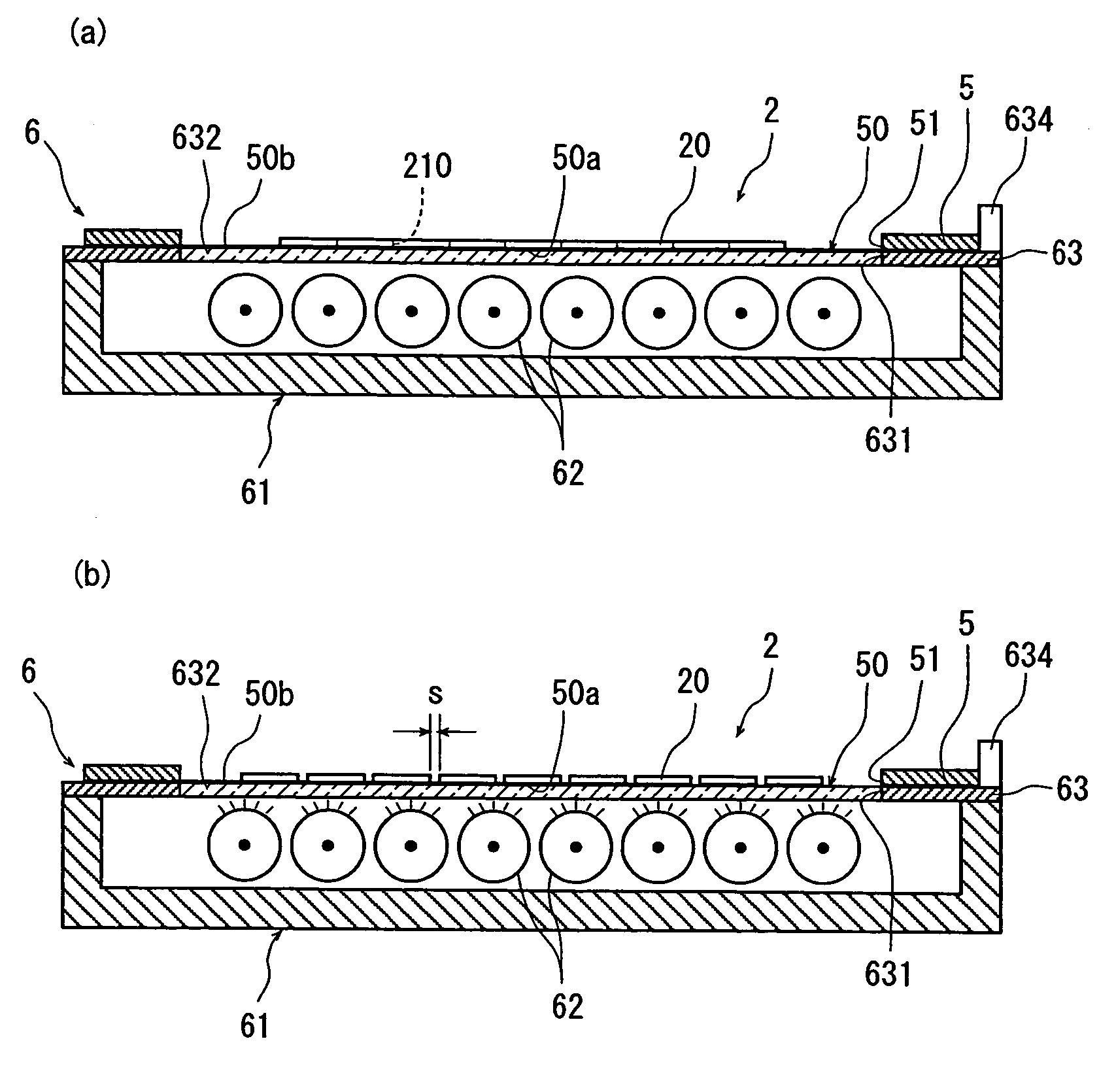
A laser beam machining method for a wafer, wherein an operation of irradiating the inside of a wafer with a laser beam L along each of planned dividing lines is repeated a plural number of times from a position proximate to a back-side surface of the wafer toward a face-side surface of the wafer so that a plurality of composite layers each including a denatured layer and a cracked layer extending from the denatured layer toward the face-side surface are formed stepwise at intervals (first laser beam irradiation step). Subsequently, each of some of non-cracked layers between the composite layers is irradiated with the laser beam L so as to extend the cracked layer of a given one of the composite layers and to cause the cracked layer to reach the denatured layer of the composite layer which is adjacent to the given one composite layer. The denatured layers and the cracked layers which are sufficient for enabling the wafer to be split are formed by a reduced number of laser beam irradiation operations.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Method of dividing a plate-like workpiece
InactiveUS20050035100A1Improve accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesSplit linesMechanical engineering
A method of dividing a plate-like workpiece having a layer that is made of a different material from that of a substrate and is formed on the front surface of the substrate along predetermined dividing lines, comprising a laser beam application step for applying a laser beam along the dividing lines formed on the plate-like workpiece to form a plurality of grooves deeper than the layer and a cutting step for cutting the plate-like workpiece with a cutting blade along the plurality of grooves formed in the laser beam application step, wherein a length between the outer sides of grooves on both sides formed in the laser beam application step is set to be larger than the thickness of the cutting blade and the cutting blade cuts the area between the outer sides of the grooves on both sides in the cutting step.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com