Patents
Literature
1177results about "Glass blowing apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and methods for manufacturing cigarettes
ActiveUS20060272655A1Precise alignmentCut excess tobacco filler awayCigarette manufactureGlass pressing apparatusBiomedical engineering
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
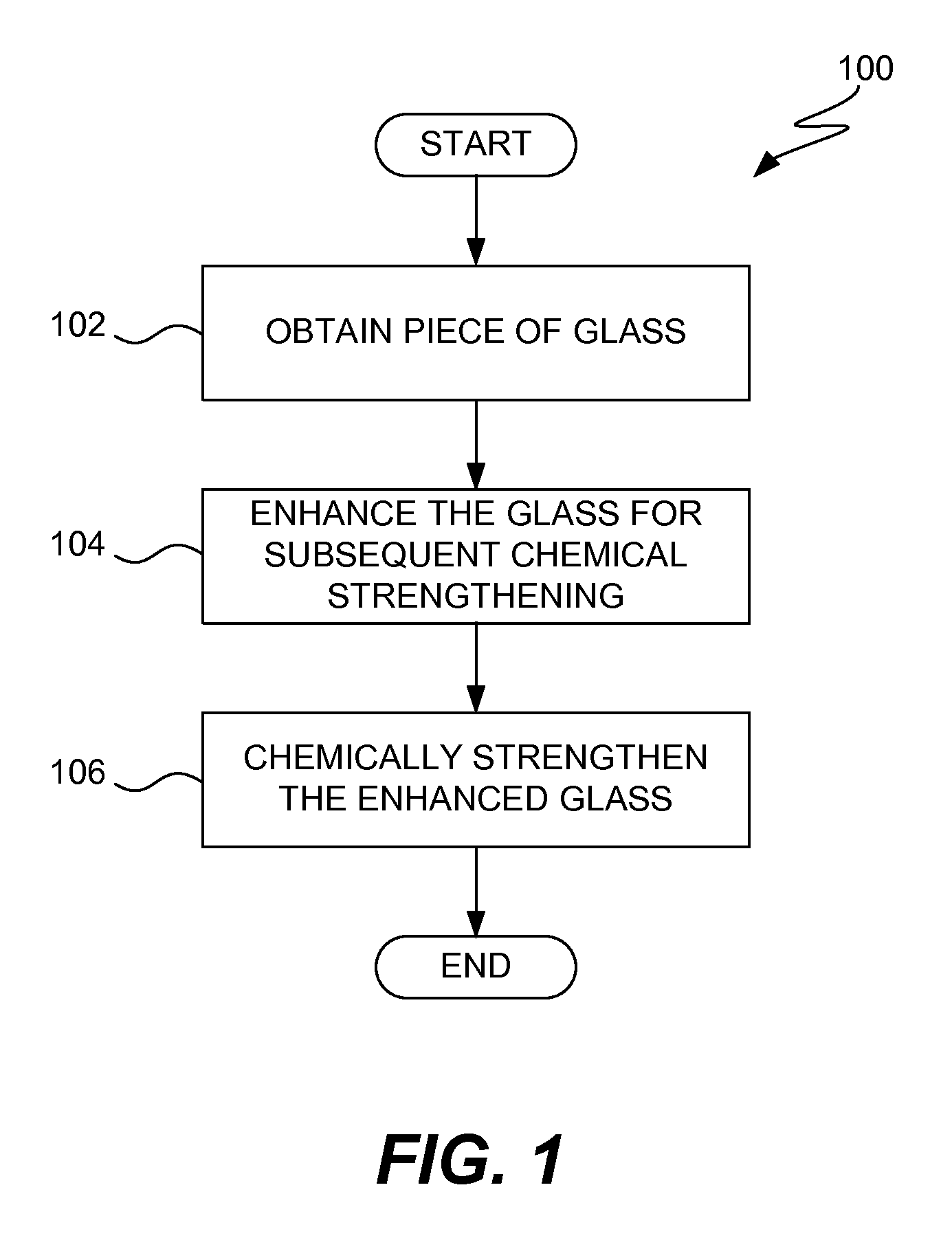
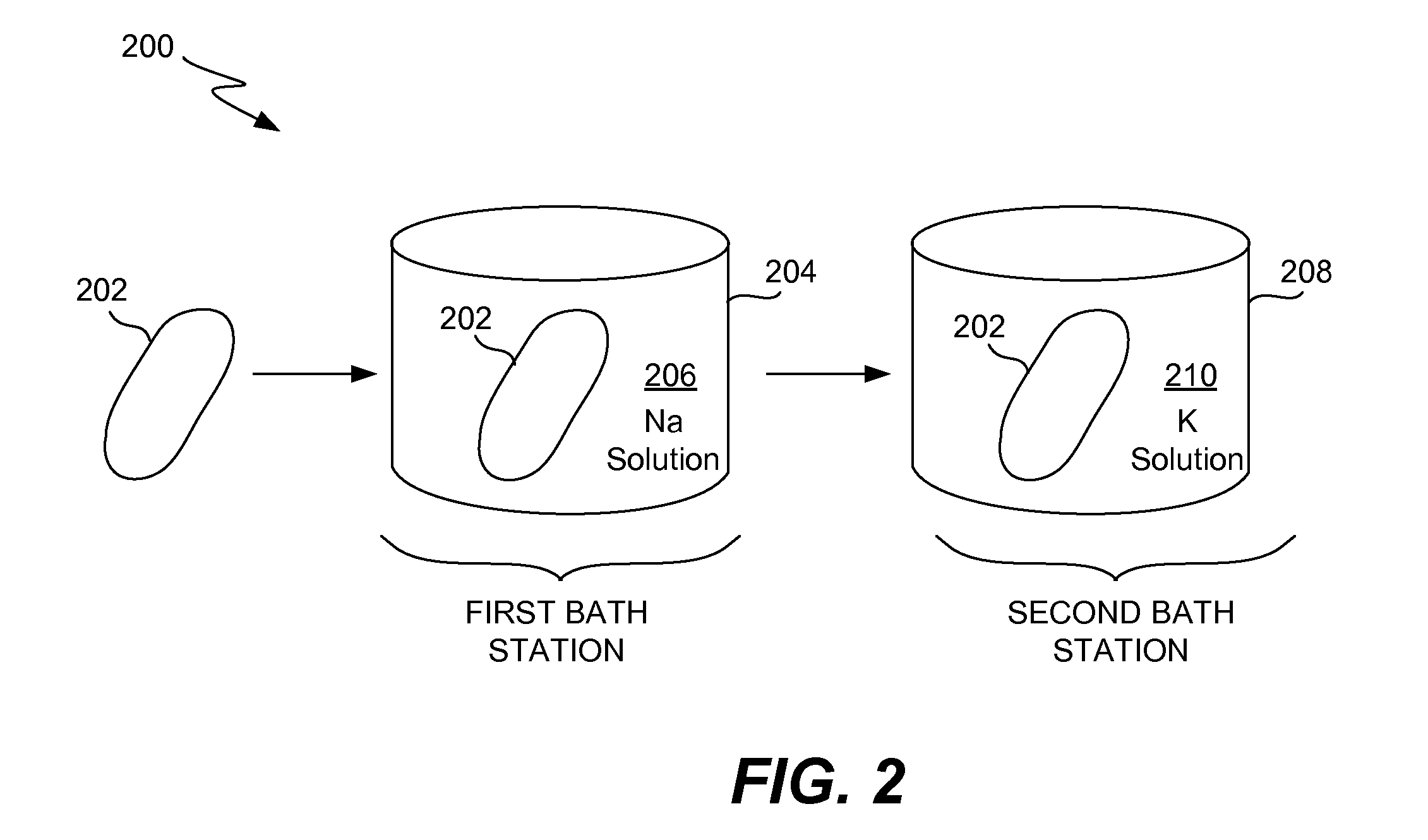
Enhanced Strengthening of Glass
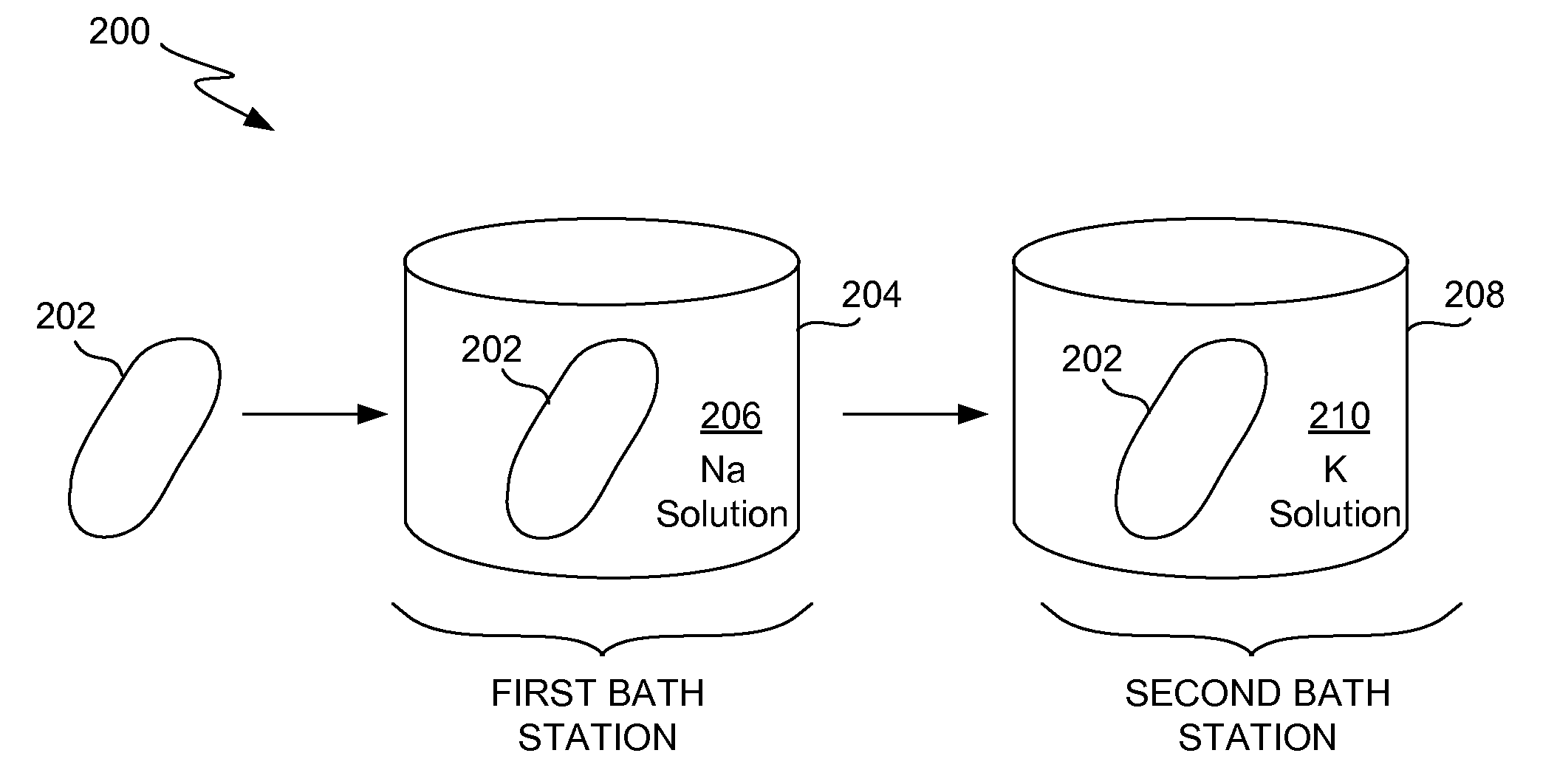
ActiveUS20110067447A1Improve glass strengthImprove the level ofGlass drawing apparatusGlass transportation apparatusChemical treatmentGlass cover
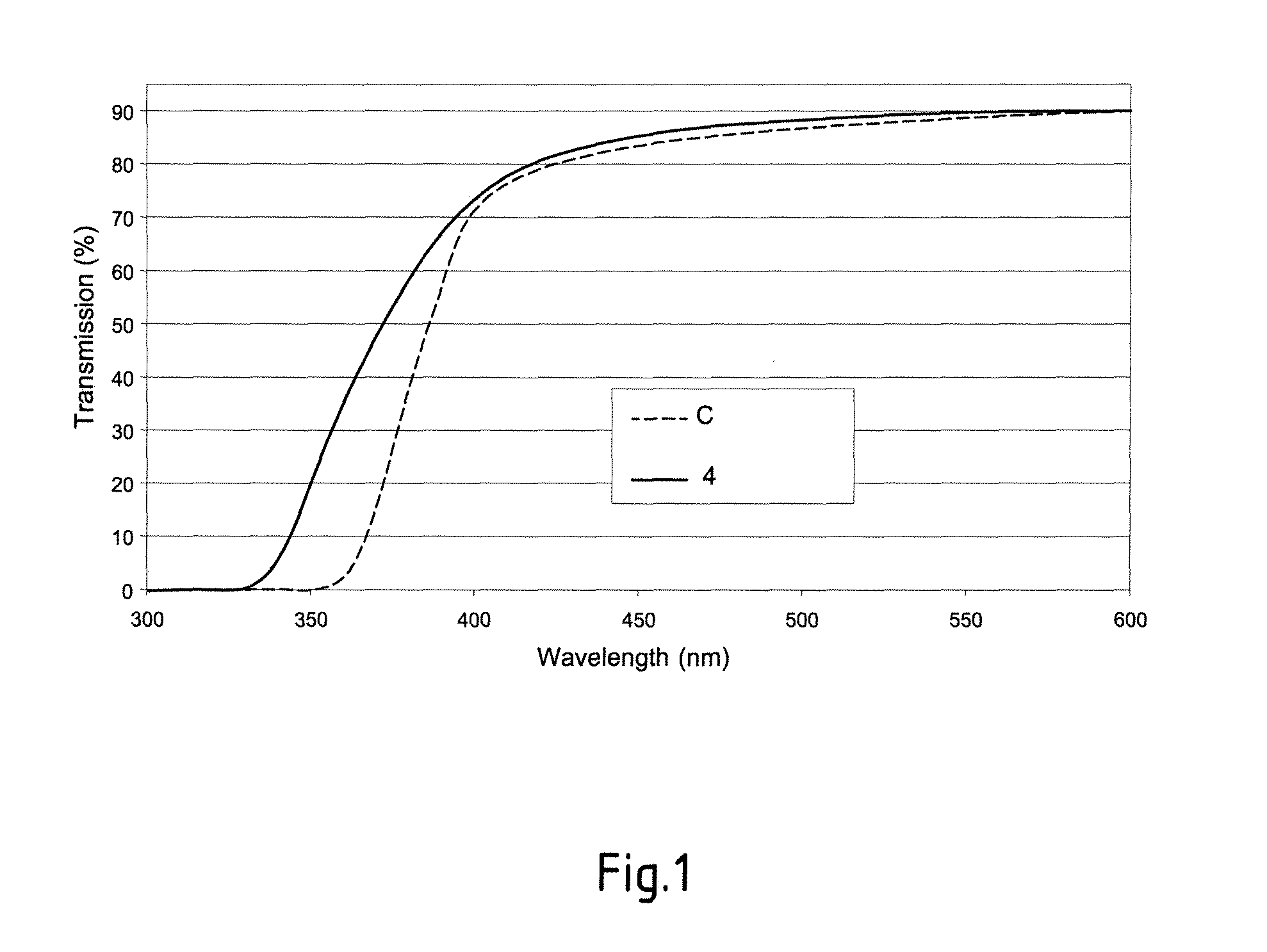
Apparatus, systems and methods for improving strength of a thin glass member for an electronic device are disclosed. In one embodiment, the glass member can have improved strength by using multi-bath chemical processing. The multi-bath chemical processing allows greater levels of strengthening to be achieved for glass member. In one embodiment, the glass member can pertain to a glass cover for a housing of an electronic device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Al2O3-Y2O3-ZrO2/HfO2 materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS7507268B2Facilitates formation and homogeneityEliminates and minimizes heat transferPigmenting treatmentGlass drawing apparatusFiberThermal insulation
Al2O3—Y2O3—ZrO2 / HfO2 ceramics (including glasses, crystalline ceramics, and glass-ceramics) and methods of making the same. Ceramics according to the present invention can be made, formed as, or converted into glass beads, articles (e.g., plates), fibers, particles, and thin coatings. The particles and fibers are useful, for example, as thermal insulation, filler, or reinforcing material in composites (e.g., ceramic, metal, or polymeric matrix composites). The thin coatings can be useful, for example, as protective coatings in applications involving wear, as well as for thermal management. Certain ceramic particles according to the present invention can be are particularly useful as abrasive particles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Overflow downdraw glass forming method and apparatus
ActiveUS20060016219A1Process can be modifiedMinimizing thickness variationGlass furnace apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementThermal creepEngineering
The present invention significantly modifies “The Overflow Process”. It includes a method and apparatus for measuring glass flow rate and maintaining a constant glass flow rate. It also embodies design features and methods that support and stress the forming apparatus in a manner such that the deformation that results from thermal creep is corrected, thus minimizing the effect of the thermal creep on the thickness variation of the glass sheet. The present invention also embodies design features that change the process from a single step (combined flow distribution and cooling) to a two step process; step one being flow distribution and step two being cooling.
Owner:CORNING INC
Cleaving method for a glass film, manufacturing method for a glass roll, and cleaving apparatus for a glass film
ActiveUS20120017642A1Efficient cuttingGlass drawing apparatusGlass transportation apparatusMaterials scienceGlass film
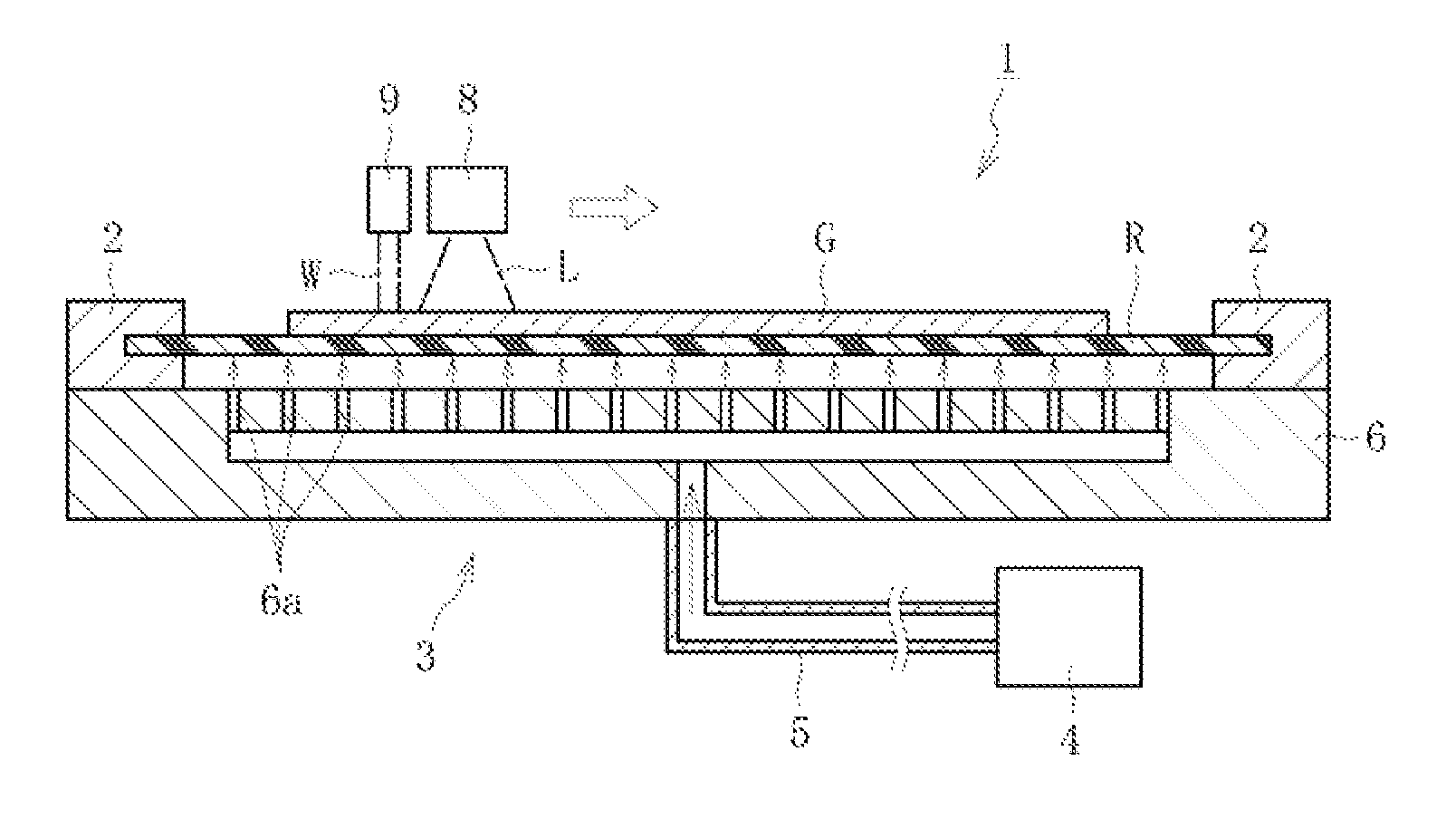
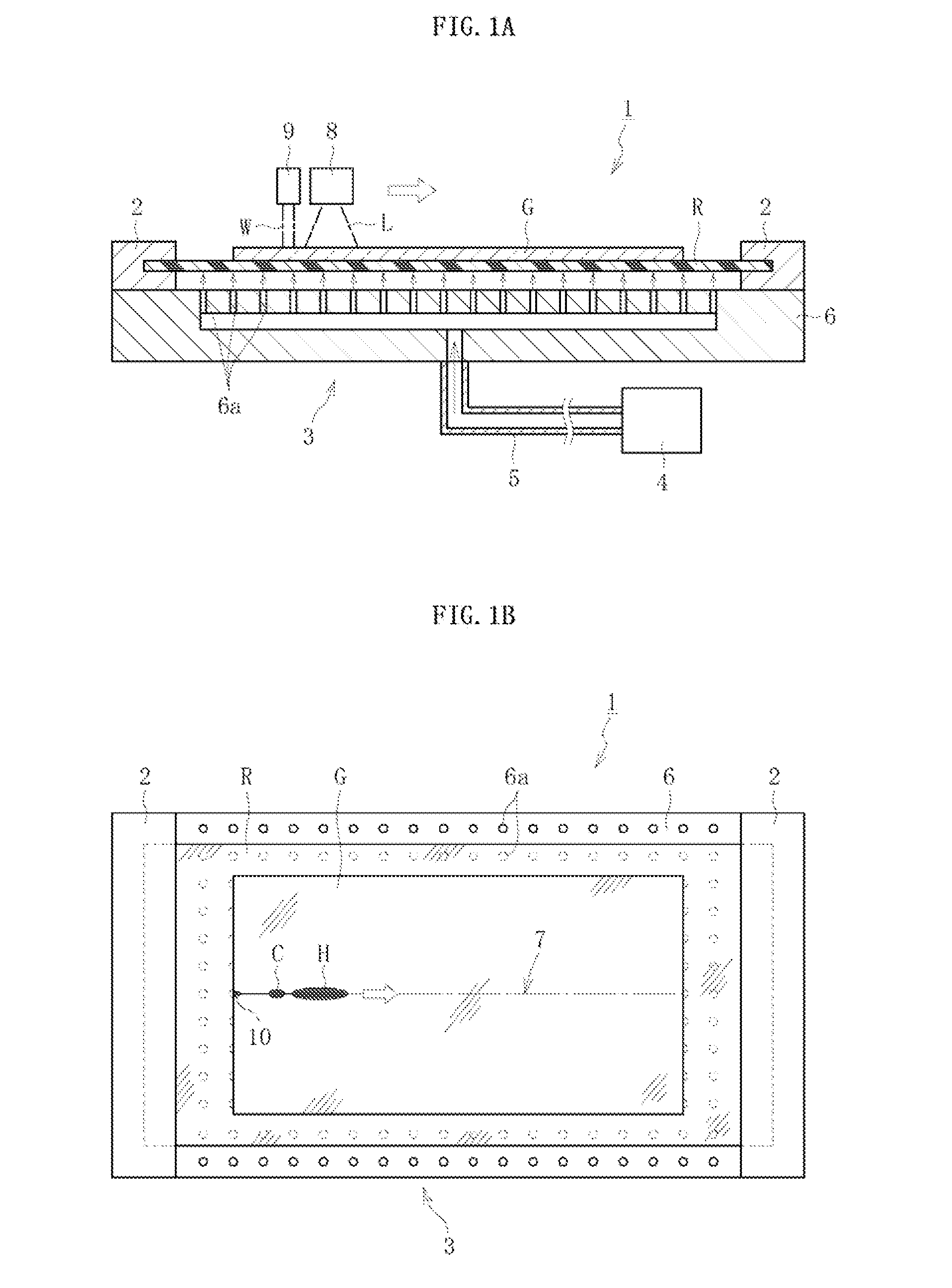
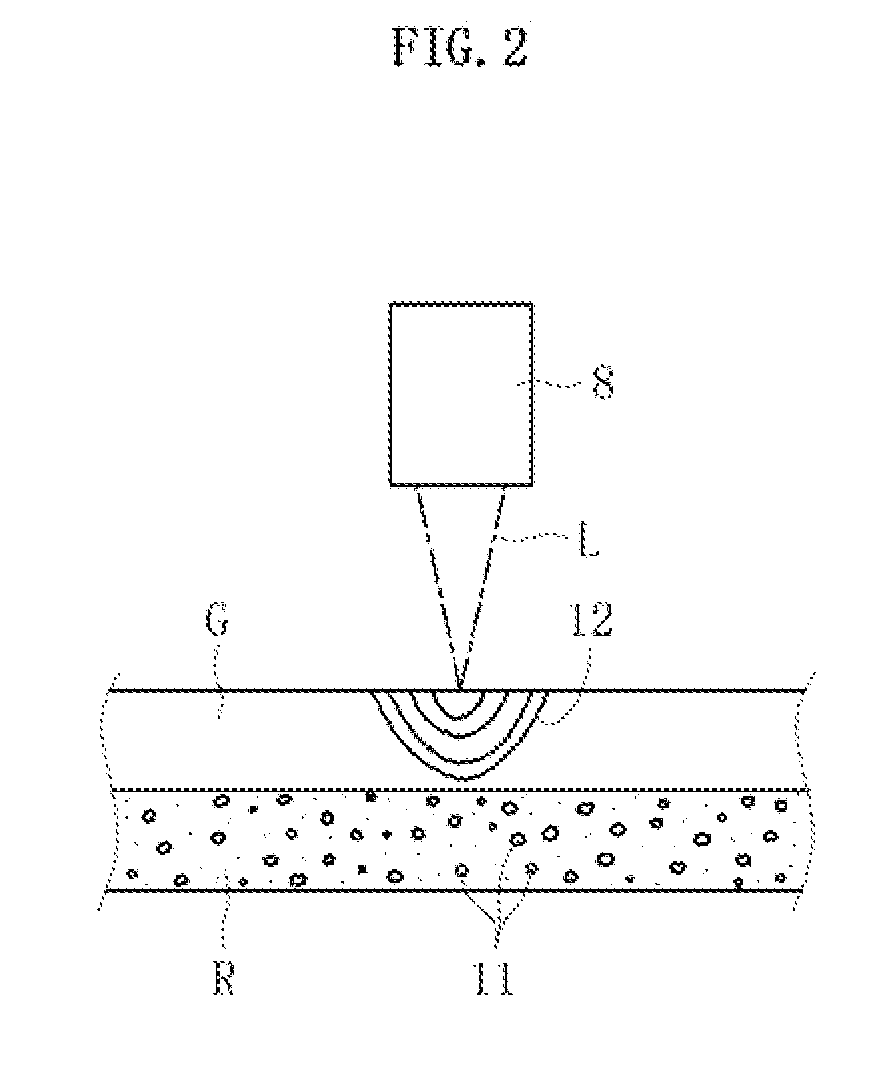
In a cleaving apparatus (1) for a glass film, an initial crack (10), which is formed at a leading end portion of a preset cleaving line (7) of a glass film (G), is propagated along the preset cleaving line (7) by a thermal stress generated in the glass film (G) through localized heating performed along the preset cleaving line (7) and cooling of a heated region resulting from the localized heating. At this time, a resin sheet (R) having higher flexibility than the glass film (G) is arranged in a cleaving region, and the resin sheet (R) is floated by blowing a gas on a lower surface of the resin sheet (R) by a floating unit (3). Then, a preset cleaving portion of the glass film (G) including the preset cleaving line (7) is lifted and supported while being covered with the floated resin sheet (R) from below, and in this state, the glass film (G) is cleaved.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Oxygen-fired front end for glass forming operation
A front end for a glass forming operation comprises an open channel and at least one burner. The channel has at least one surface. The surface has at least one hole therein. The burner is oriented in the hole at an acute angle relative to the surface. In another embodiment of the invention, the channel has a top and a pair of sidewalls each having a surface. At least one hole is in at least one of the surfaces. The hole is at an acute angle relative to at least one surface. The burner is an oxygen-fired burner. In yet another embodiment of the invention, the top and sidewalls each have a super structure surface constructed of refractory material. The channel has an upstream end and a downstream end. At least one of the surfaces has a plurality of holes therein. The burners extend at an acute angle relative to at least one surface and in a plane extending between the upstream end and the downstream end and perpendicular to at least one surface. Oxygen-fired burners extend axially through corresponding holes.
Owner:OCV INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Method and device for parting glass substrate, liquid crystal panel, and liquid crystal panel manufacturing device
InactiveUS20050056127A1High mechanical strengthPrevent peelingLiquid crystal compositionsBox making operationsLiquid-crystal displayCutting glass
A method for cutting apart a glass substrate is provided whereby scribing of the glass substrate is possible without being affected by the presence or thickness of a deposited film formed thereon and without scratching the deposited film. To treat a glass substrate (1) having a deposited film (1a), such as a thin film or resin film, formed on one surface thereof, there are provided a shaving means (202), which is a blade that removes strip-shaped portions of the deposited film (1a) to expose strip-shaped regions on the glass substrate (1), and a wheel cutter (14a) that forms scribed lines along the strip-shaped regions exposed on the glass substrate (1). The glass substrate (1) is cut apart along the scribed lines.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Silicon Casting Apparatus and Method of Producing Silicon Ingot
InactiveUS20070227189A1Good reproducibilityLow costFinal product manufactureGlass drawing apparatusIngotTemperature gradient
A silicon casting apparatus for producing polycrystal silicon ingot by heating a silicon melt (8) held in a mold (4) from above by a heater (3) and cooling it from below while changing the heat exchange area of a heat exchange region (HE), defined between a pedestal (5) having the mold (4) placed thereon and a bottom cooling member (6), in such a manner as to keep pace with the rise of the solid-liquid interface of the silicon melt (8), thereby causing unidirectional solidification upward along the mold (4); and a method of producing polycrystal silicon ingot using such apparatus. According to this production method, the temperature gradient given to the silicon melt (8) can be maintained at constant by adjusting the heat exchange area, so that polycrystal silicon ingot having good characteristics can be produced with good reproducibility.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Method for low energy separation of a glass ribbon
Owner:CORNING INC
Molten glass delivery and refining system
Methods and apparatus for refining and delivering a supply of molten glass include melting a supply of glass in a melter and discharging a stream of molten glass. A refining section is provided to refine the molten glass discharged by the melter and to deliver the molten glass downstream to a glass forming apparatus. The refining section is mounted for movement into and out of contact with the stream of molten glass to connect and disconnect the glass forming apparatus with the stream of molten glass.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Al2O3-Y2O3-ZrO2/HfO2 materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20030110708A1Facilitates formation and homogeneityOxide formationPigmenting treatmentGlass drawing apparatusFiberThermal insulation
Al2O3-Y2O3-ZrO2 / HfO2 ceramics (including glasses, crystalline ceramics, and glass-ceramics) and methods of making the same. Ceramics according to the present invention can be made, formed as, or converted into glass beads, articles (e.g., plates), fibers, particles, and thin coatings. The particles and fibers are useful, for example, as thermal insulation, filler, or reinforcing material in composites (e.g., ceramic, metal, or polymeric matrix composites). The thin coatings can be useful, for example, as protective coatings in applications involving wear, as well as for thermal management. Certain ceramic particles according to the present invention can be are particularly useful as abrasive particles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Low heat capacity gas oxy fired burner
A front end for a glass forming operation including an open channel and at least one burner. The channel surface has at least one burner port and a burner oriented in the burner port at an acute angle relative to the channel surface. The surface may be a top, side or end wall and the burner port is at an acute angle relative to the surface of the wall.
Owner:OCV INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
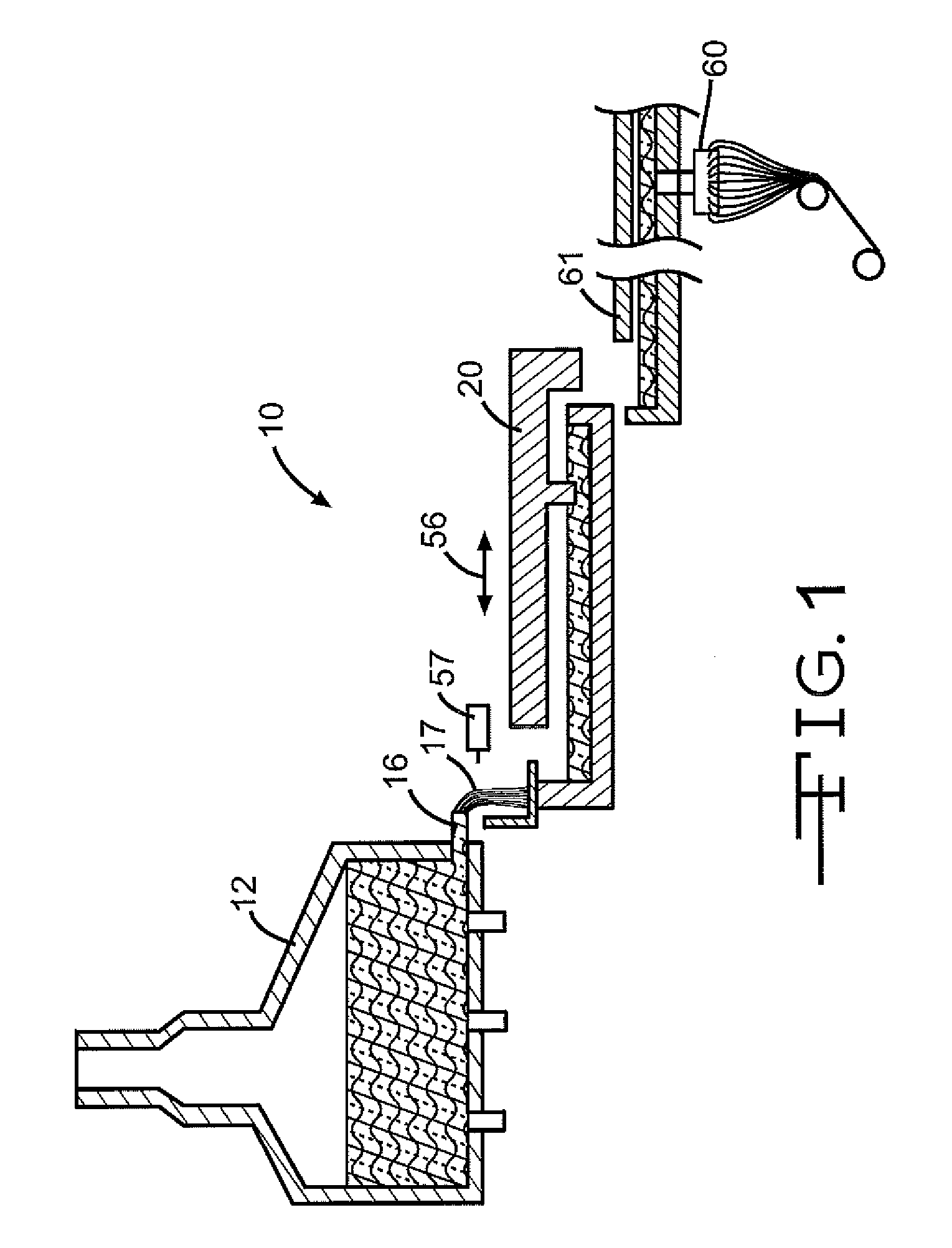
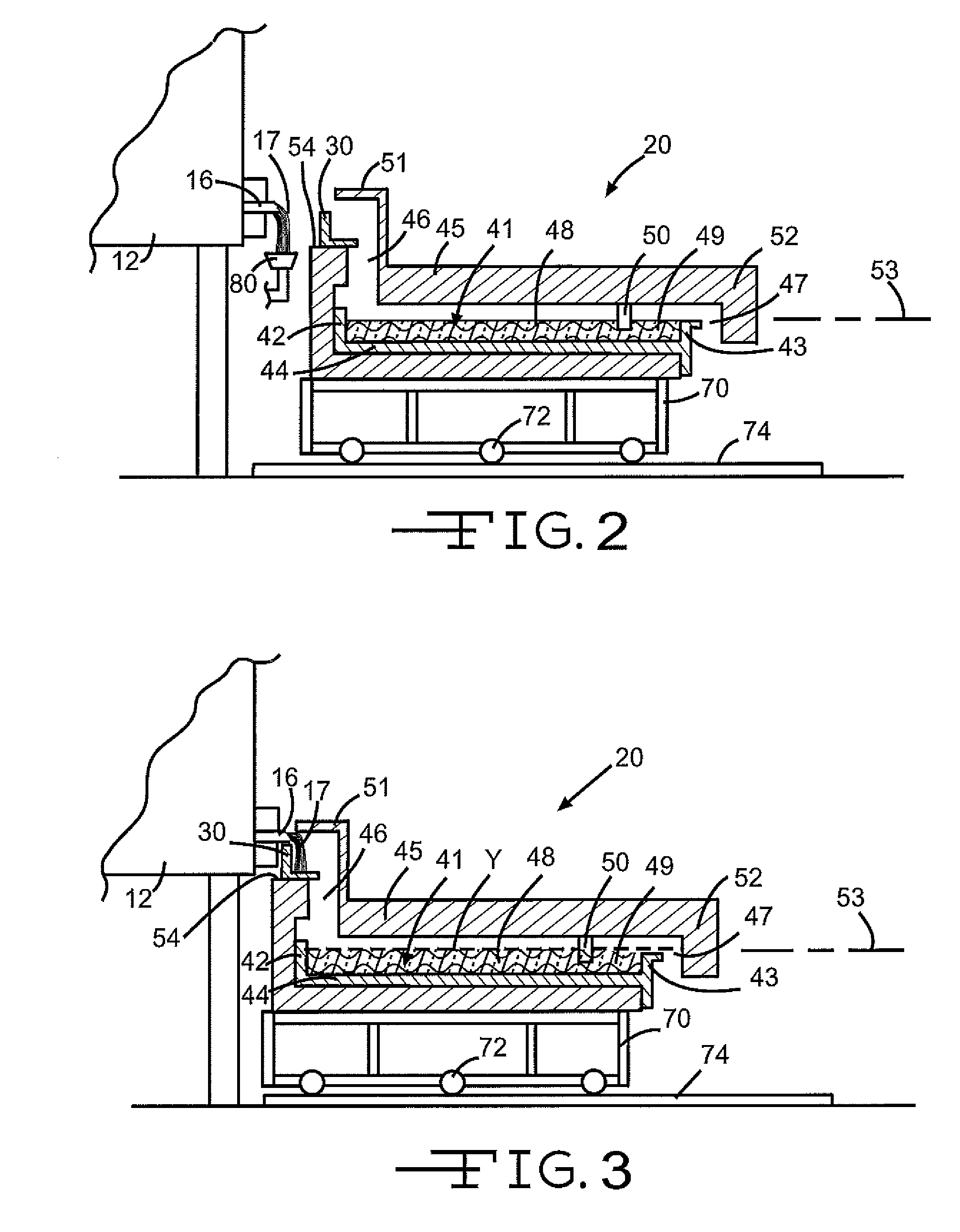
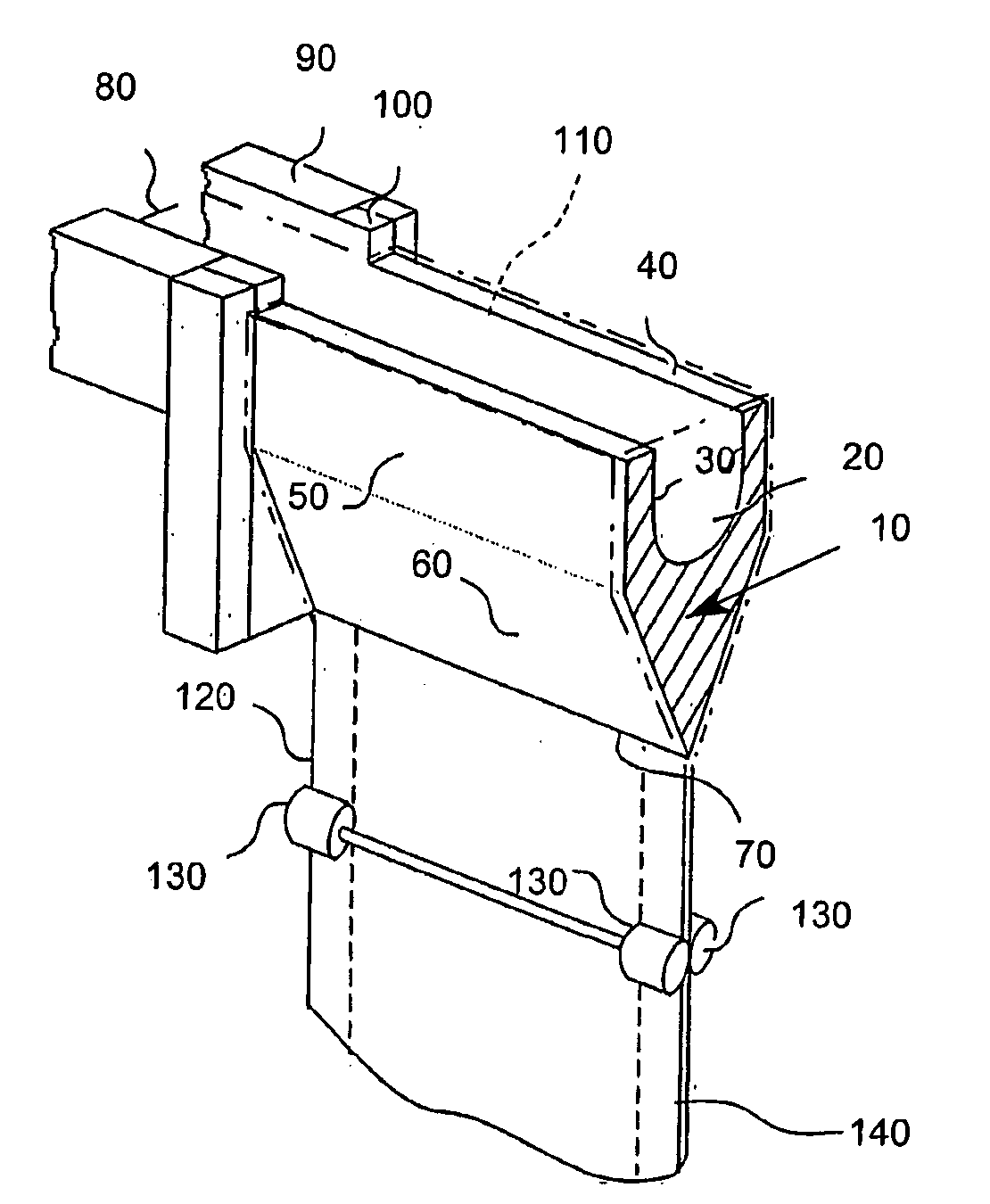
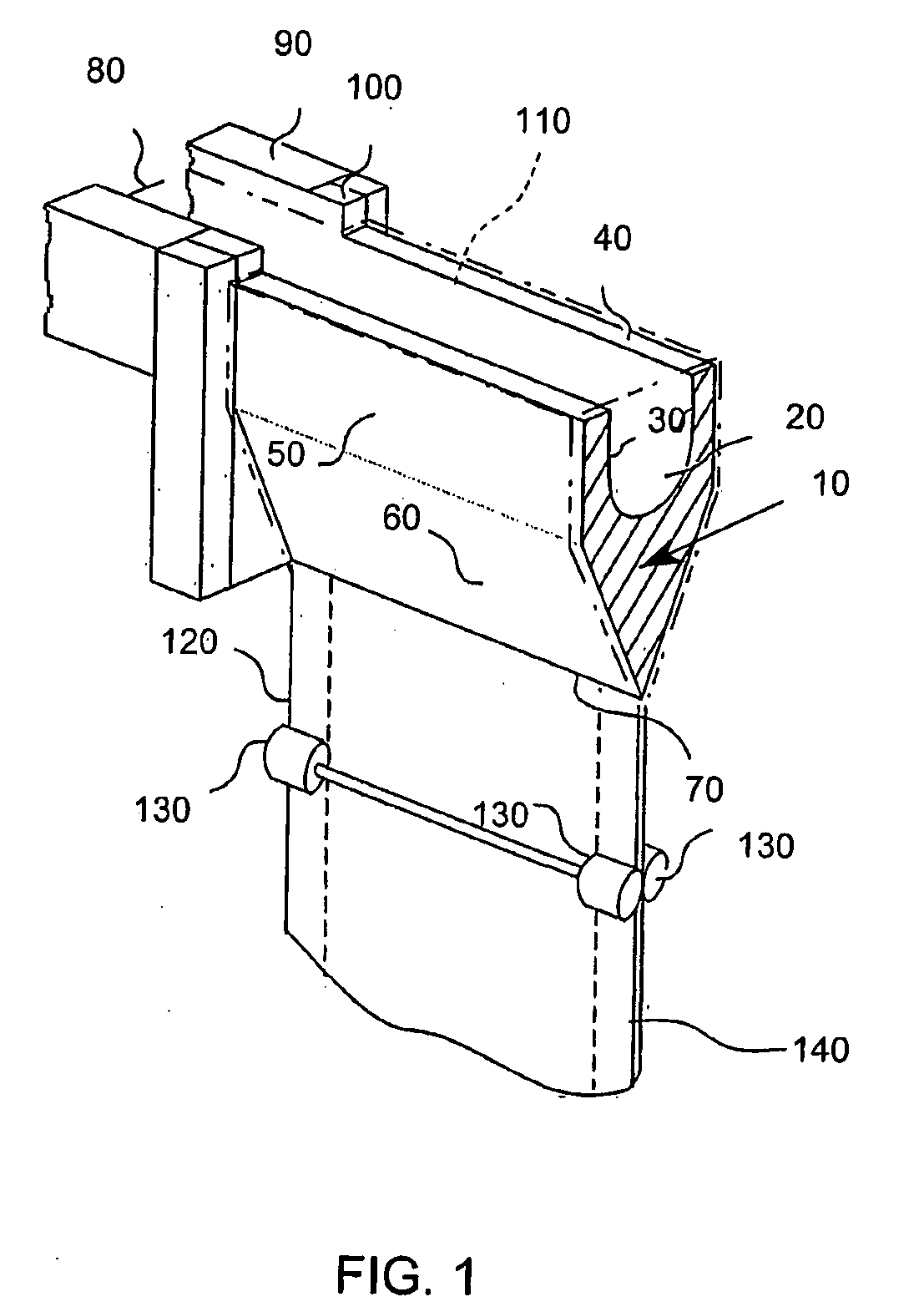
Method of making a glass sheet using controlled cooling
InactiveUS20090100873A1Increase rate increaseHigh trafficGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusFluid phaseEngineering
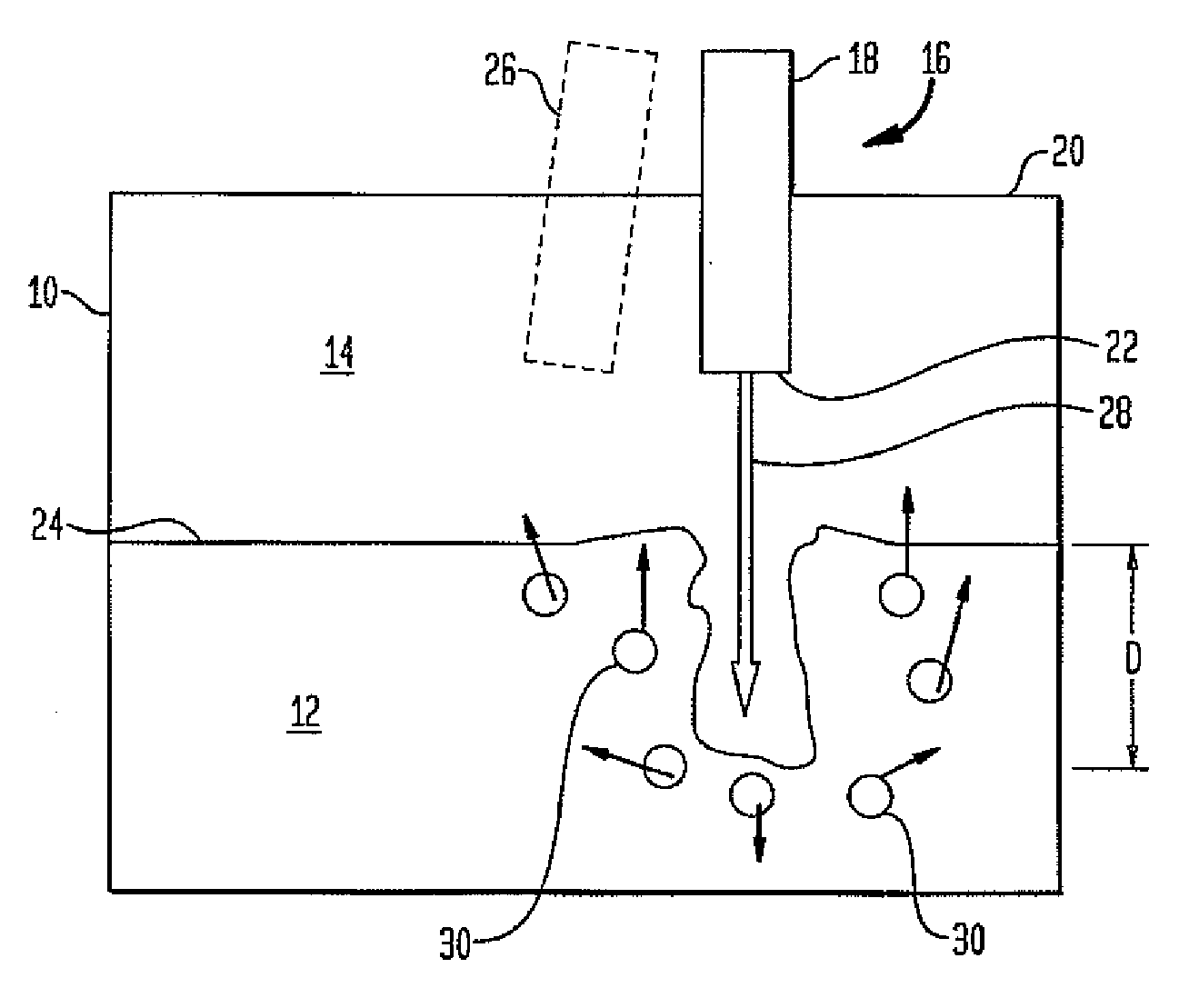
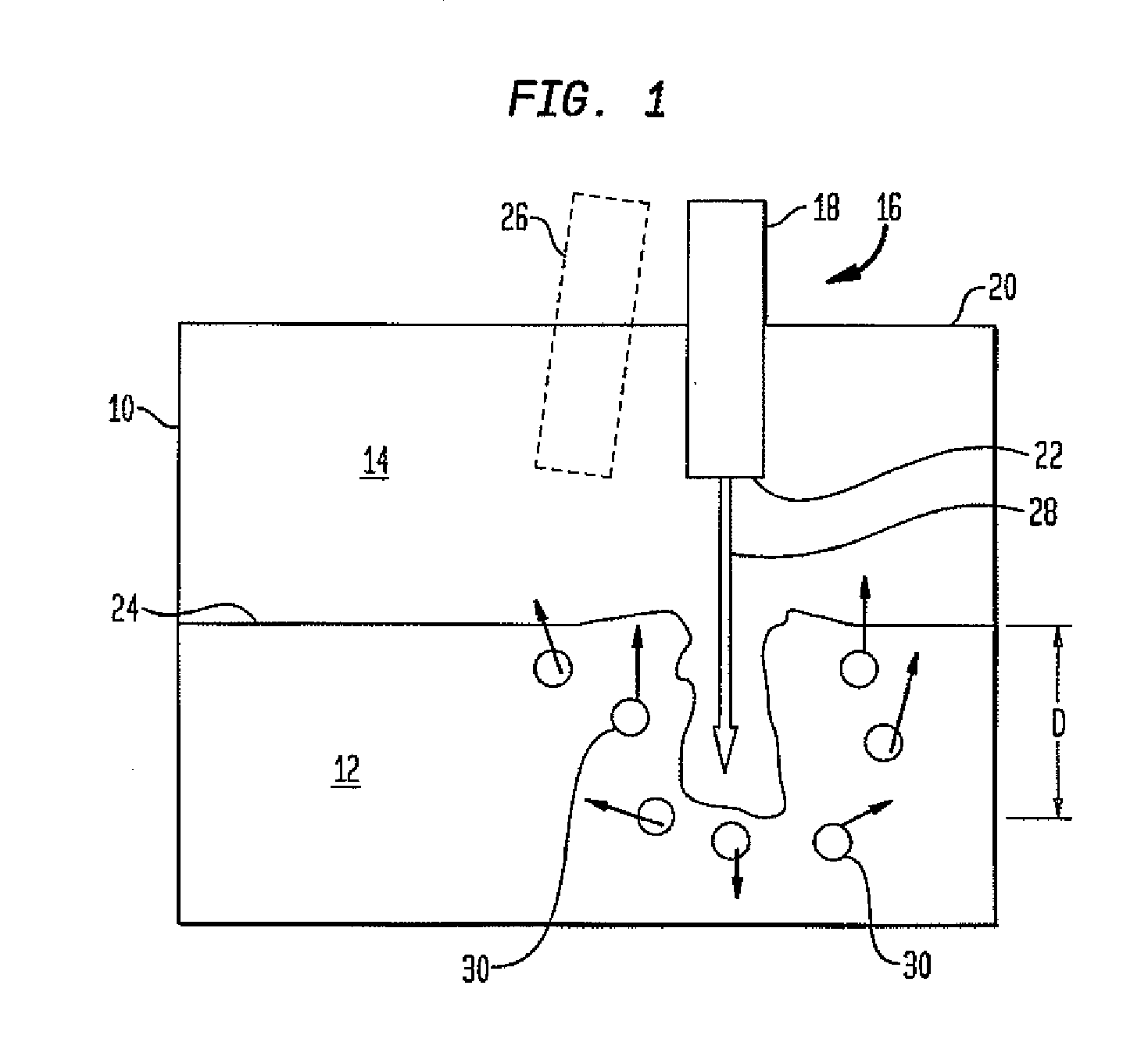
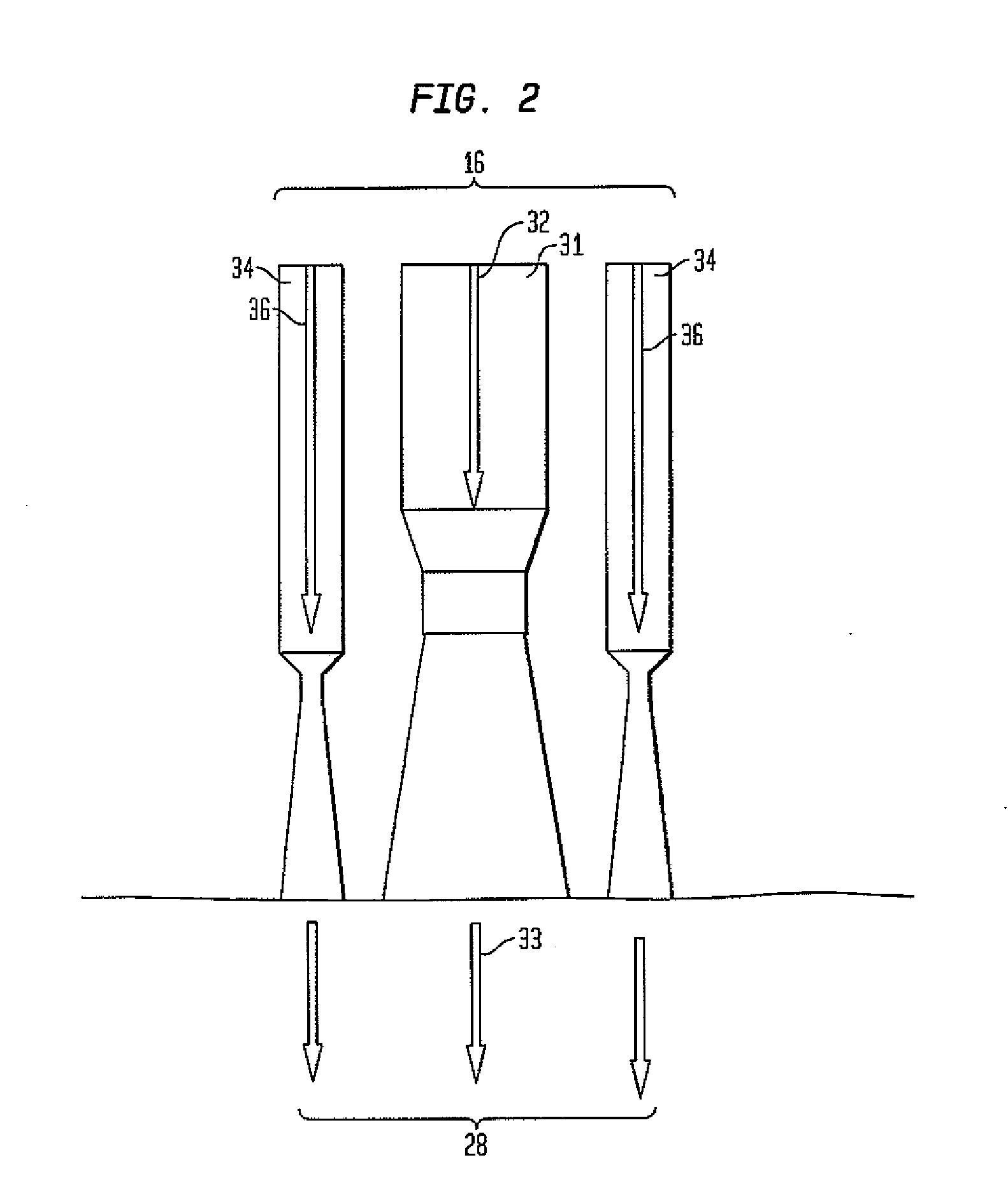
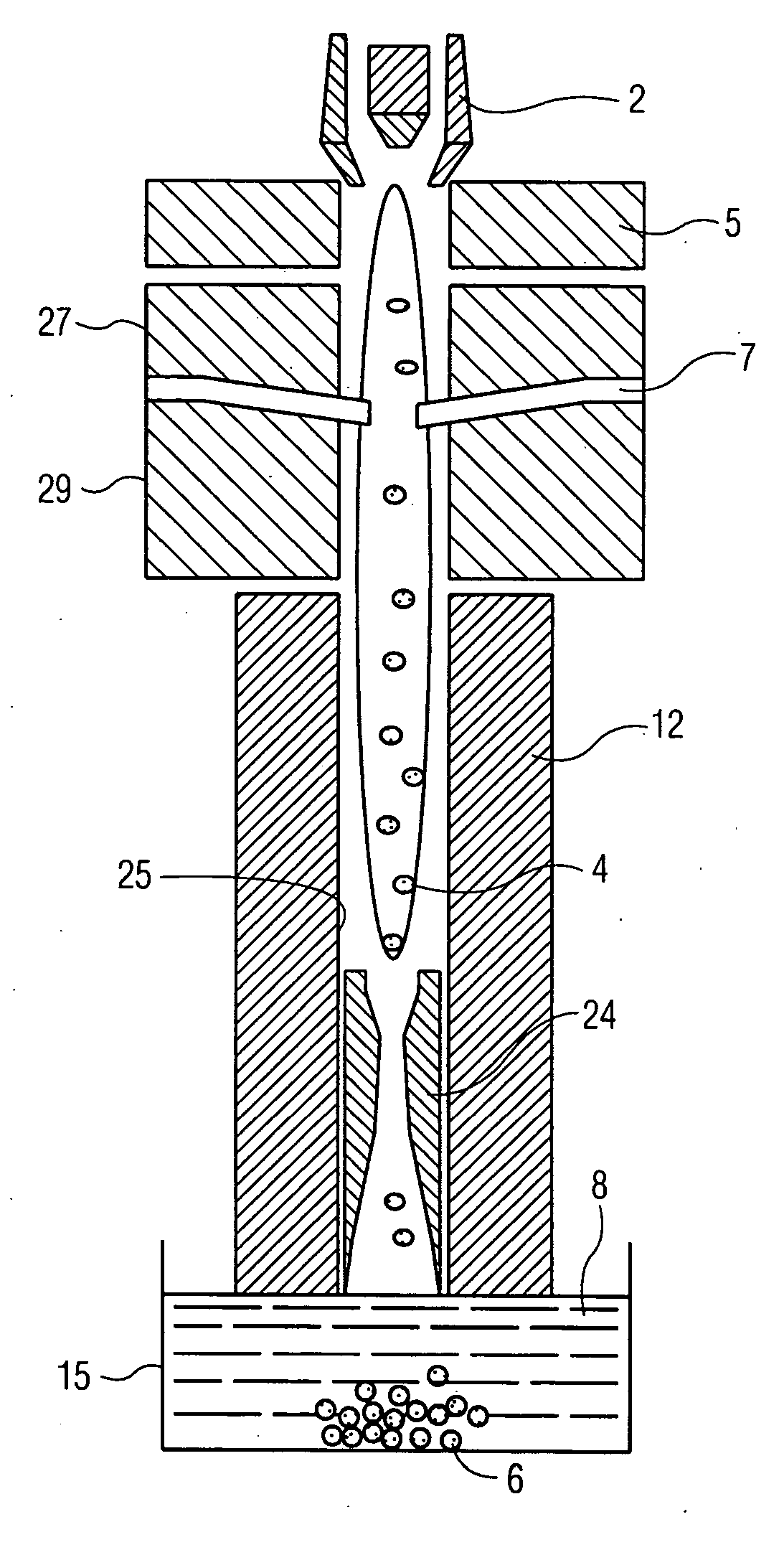
Methods of drawing glass sheet via a downdraw process are provided. In certain aspects, the methods utilize rapid cooling below the root (70) of the forming apparatus (10). Such rapid cooling can, for example, facilitate the use of glass having a liquidus viscosity less than about 100,000 poise. In other aspects, the methods utilize slow cooling between the viscosities of 1011 poises and 1014 poises. Such slow cooling can facilitate the production of glass substrates which exhibit low levels of compaction. In further aspects, substrates are removed from the glass sheet at elevated temperatures which can facilitate increases in the production rates of downdraw machines. In still further aspects, rapid cooling below the root, slow cooling between the viscosities of 1011 poises and 1014 poises, and / or substrate removal at elevated temperatures are combined. Such combinations can facilitate economically effective utilization of downdraw equipment.
Owner:CORNING INC
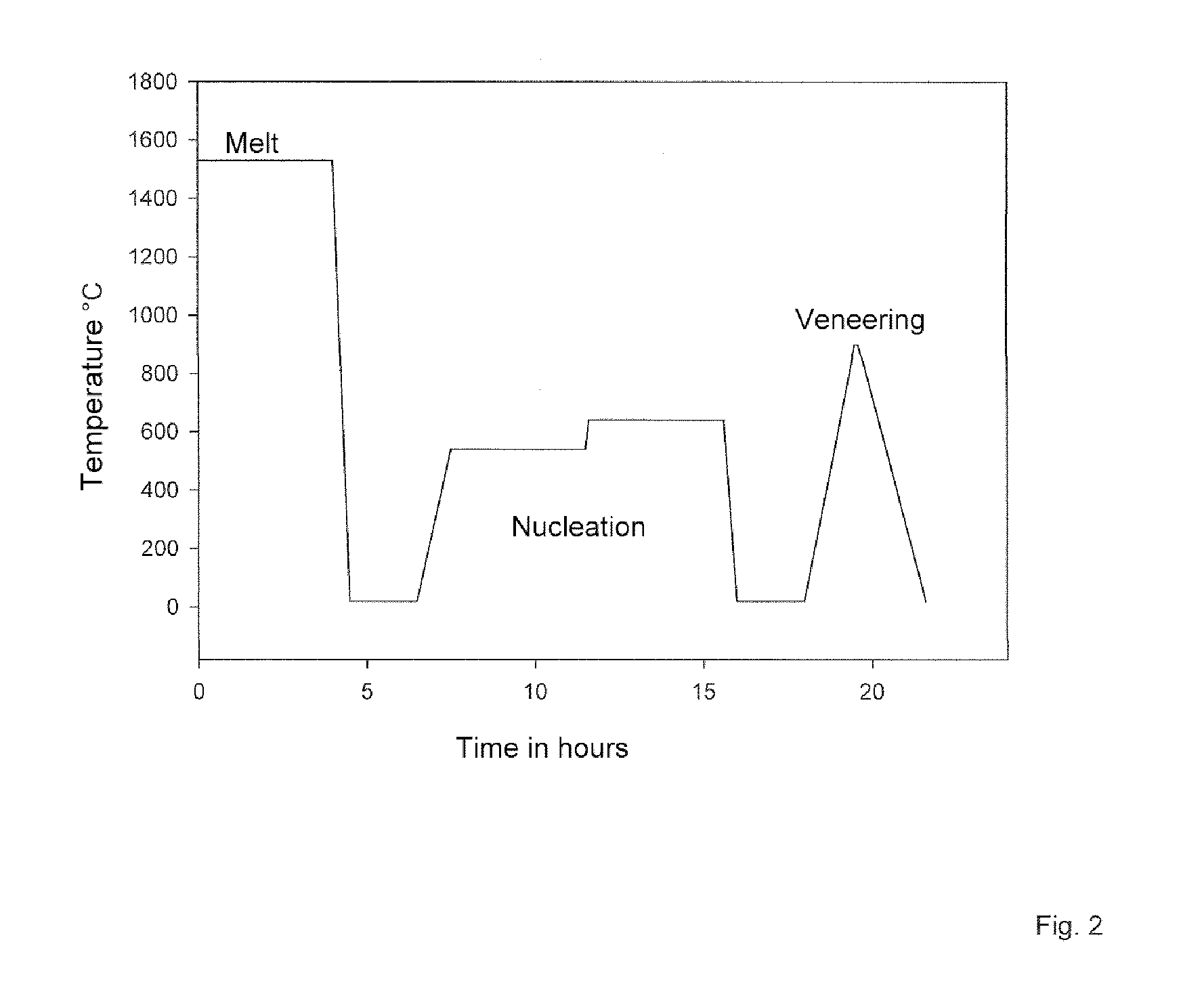
Veneer Ceramic for Dental Restorations and Method for Veneering Dental Restorations
ActiveUS20110030423A1Improve flexural strengthImprove adhesionDental implantsImpression capsFlexural strengthYttrium
The invention is directed to veneer ceramics for dental restorations of framework ceramics comprising yttrium-stabilized zirconium dioxide. It is the object of the invention to make possible a translucent veneer ceramic which has high flexural strength as well as excellent adhesion to the framework ceramic of yttrium-stabilized zirconium dioxide. According to the invention, this object is met in a veneer ceramic for dental restorations made of yttrium-stabilized zirconium dioxide which is produced from the following components:a)SiO258.0-74.0 percent by weightb) Al2O3 4.0-19.0 percent by weightc)Li2O 5.0-17.0 percent by weightd)Na2O 4.0-12.0 percent by weighte) ZrO2 0.5-6.0 percent by weight.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
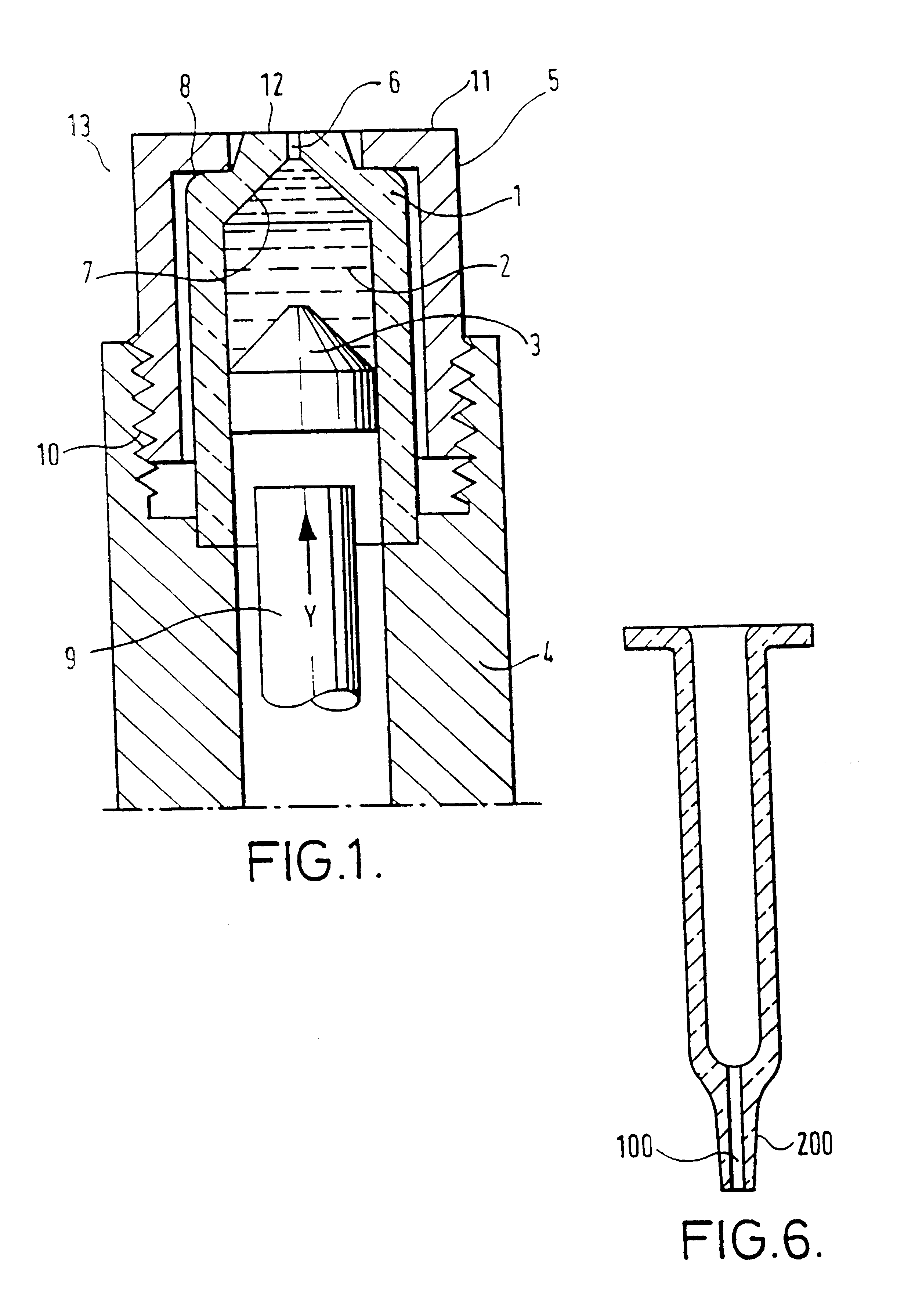
Method and apparatus for making an article from a formable material
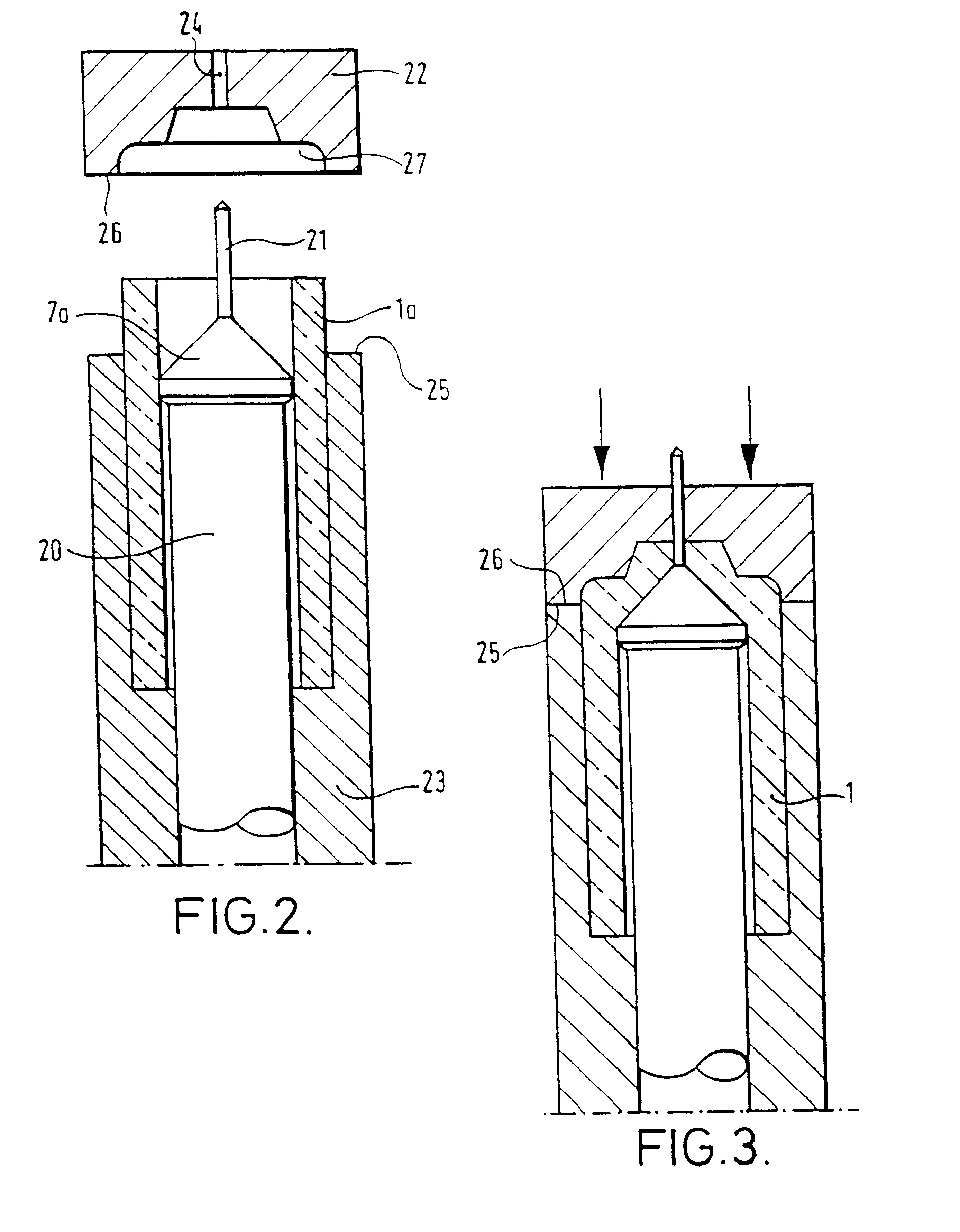
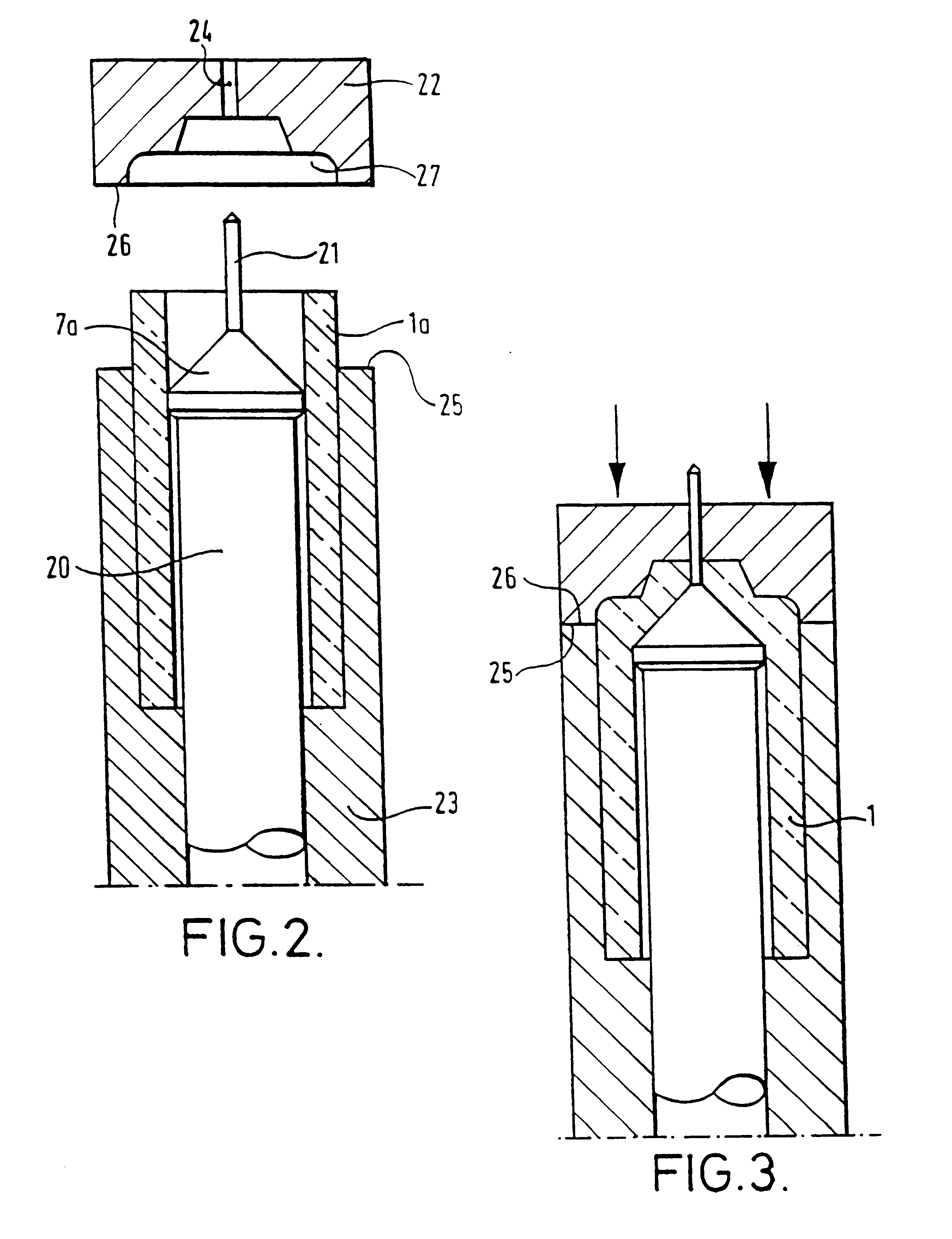
InactiveUS6415631B1Good repeatabilityHigh speed productionButtonsAmpoule syringesEngineeringInjector
A method and apparatus are described for making an article such as the body of a needleless injector capsule, from a formable material, such as glass, the article having a cavity communicating with the exterior via an orifice. A blank having an open end is mounted on a first forming tool, and the open end is engaged by a second forming tool while an end region of the blank adjacent the open end is in a condition to permit it to be formed. One of the tools has a pin extending therefrom, and when the tools are brought together to form the end region into the desired shape the pin defines the orifice.
Owner:ZOGENIX INC
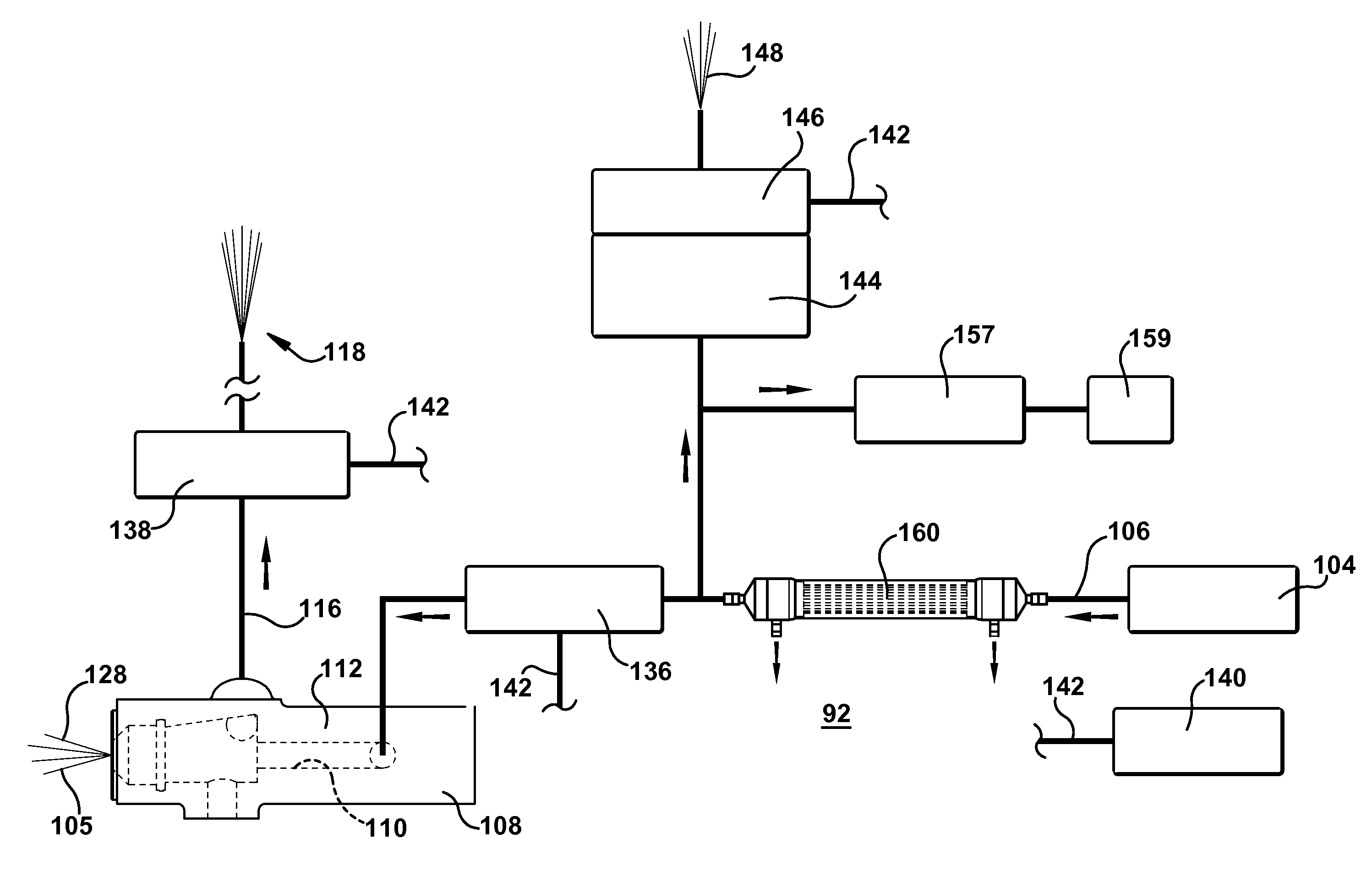
Preventing gas from occupying a spray nozzle used in a process of scoring a hot glass sheet
ActiveUS20100287991A1Improve spraying effectImprove performanceGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusSolubilityHigh energy
A spray nozzle is used in a process of quenching a hot glass sheet during a laser scoring process or other high energy glass heating process. The scoring is conducted by a high energy means such as a laser. The nozzle is located in proximity to the glass sheet, creating gas in liquid used to quench the glass located in the nozzle (e.g., water). The gas (e.g., air bubbles) is removed from the quenching liquid. Then, the spray nozzle is used to spray the quenching liquid onto the sheet at a location trailing laser scoring of the sheet, such as using a traveling anvil machine at the bottom of the draw. The spray nozzle (purge nozzle) has a purge opening and tubing leading to a discharge location. The purge nozzle can have a sloped passageway that pre-stages gas bubbles near the purge opening in the nozzle. The spray nozzle can include a cooling coil passing around the nozzle passageway that enables a coolant to travel along the coil. This cools the quenching liquid passing through the nozzle, and increases the solubility of bubbles in the quenching liquid in the nozzle. A gas filter can receive gas-rich quenching liquid from the pressurized quenching liquid source, remove gas from the liquid, and send gas-depleted quenching liquid to the spray nozzle.
Owner:CORNING INC
Methods of separating strengthened glass substrates
ActiveUS8720228B2Avoid it happening againGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusSurface layerWhole body
Methods of separating a strengthened glass substrate having a compressive surface layer and an inner tension layer include translating a laser beam on a surface of the strengthened glass substrate along a line of desired separation from a first edge of the strengthened glass substrate toward a second edge of the strengthened glass substrate. Methods further include backward-propagating a controlled full-body crack within the strengthened glass substrate from the second edge toward the first edge substantially along the line of desired separation. A scribe line may be formed on a surface of the strengthened glass substrate such that the strengthened glass substrate self-separates along the scribe line. A residual stress field may be created within the strengthened glass substrate such that a full-body crack backward-propagates from an exit defect located at the second edge toward the first edge along a line of desired separation, thereby separating the strengthened glass substrate.
Owner:CORNING INC
Thermal laser scribe cutting for electrochromic device production
The disclosure is directed to a cutting process involving: (a) creating a starter crack using a scribe wheel, (b) application of laser or electrothermal heating, and (c) subsequent cooling from a gas or an aerosol jet, as the laser beam and cooling jet move along the desired cutting line. The cutting process can be implemented for cutting a glass panel or other substrate into a plurality of smaller panels. The starter crack may be created on any of the smaller panels within about 10 mm to about 20 mm from the corner of the smaller panel.
Owner:SAGE ELECTROCHROMICS
Method of producing glass substrate for information recording medium
InactiveUS6332338B1Avoid deformationIncrease speedGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusProduction ratePoise
Disclosed is a process for producing a glass substrate for an information recording medium by press-shaping a molten glass which gives a glass containing 0.1 to 30 mol % of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol % of CaO, 5 to 40 mol % of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol % of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol % of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol % of SiO2 and having properties of a liquidus temperature of 1,360° C. or lower and a viscosity of at least 10 poise in a shaping-allowable temperature range, or by preparing a preform formed of a glass which contains 0.1 to 30 mol % of TiO2, 1 to 45 mol % of CaO, 5 to 40 mol % of total of MgO and the above CaO, 3 to 30 mol % of total of Na2O and Li2O, 0 to 15 mol % of Al2O3 and 35 to 65 mol % of SiO2 and has properties of a liquidus temperature of 1,360° C. or lower and shaping the preform in the form of a disc by a re-heat pressing method. According to the above process, there can be mass-produced, with high productivity, high-quality glass substrates to be used for information recording media such as a magnetic disc, an optical disc, a magneto-optic disc, and the like.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Process for producing glass substrate and glass substrate
ActiveUS20090226733A1Easy to distortReadily warpedGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusBand shapeMolten glass
Provided are a process for producing a glass substrate usable for low-temperature p-SiTFT substrates directly in accordance with a down draw method, and the glass substrate obtained by the process. The process for producing a glass substrate includes a forming step of forming a molten glass into a ribbon shape in accordance with a down draw method, an annealing step of annealing the glass ribbon, and a cutting step of cutting the glass ribbon to give a glass substrate, in which, in the annealing step, an average cooling rate from the annealing point to the (annealing point −50° C.) is lower than an average cooling rate from the (annealing point +100° C.) to the annealing point.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
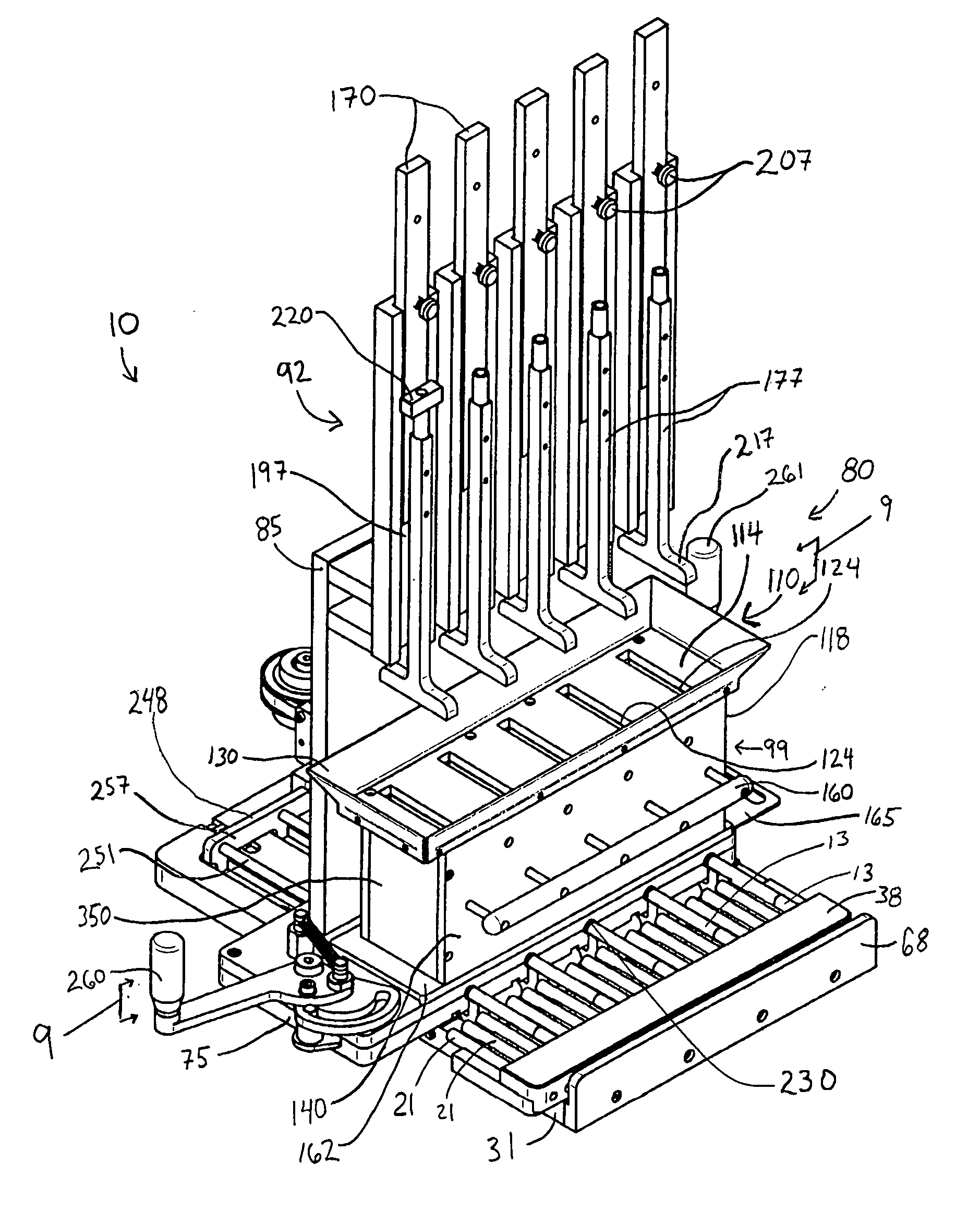
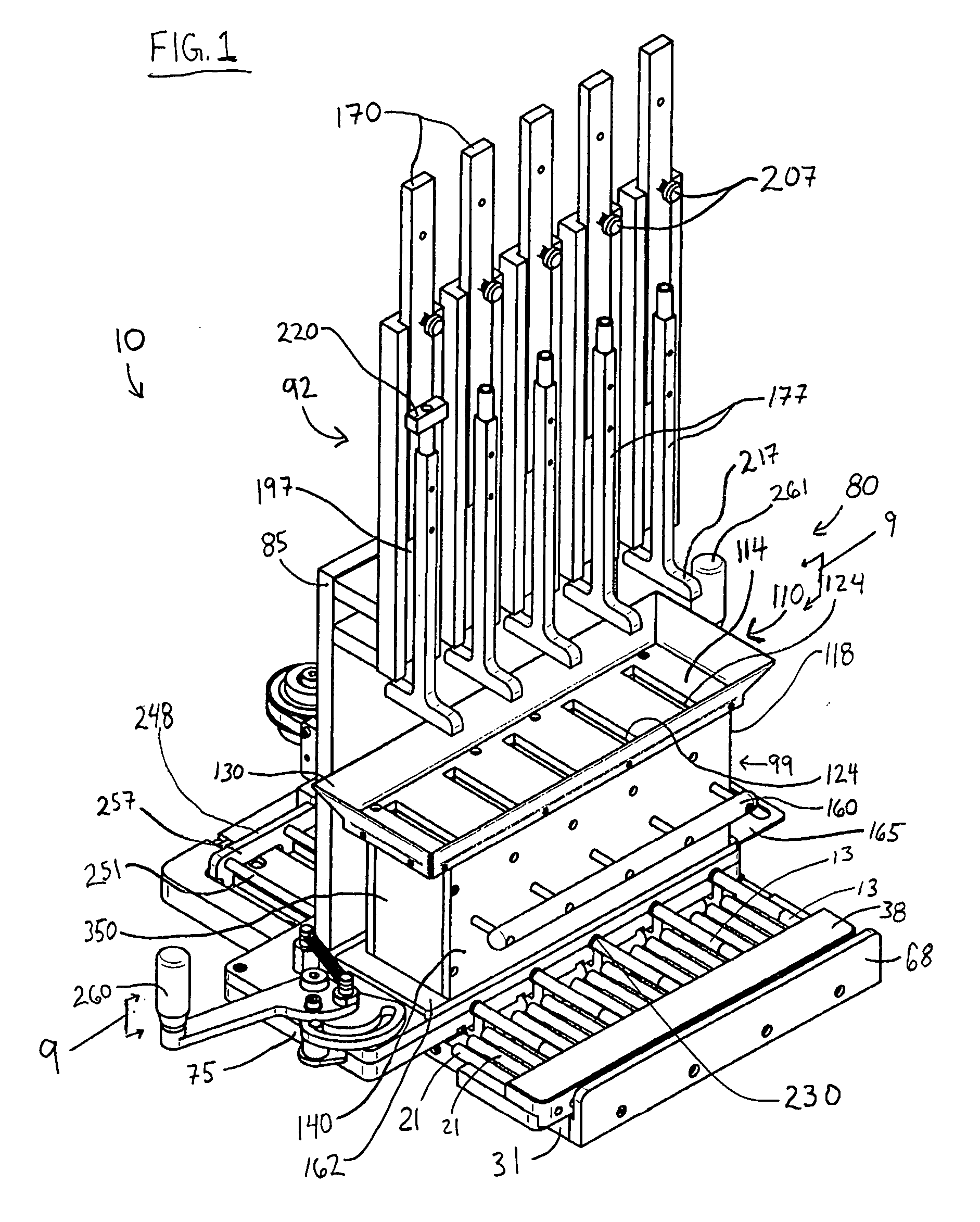
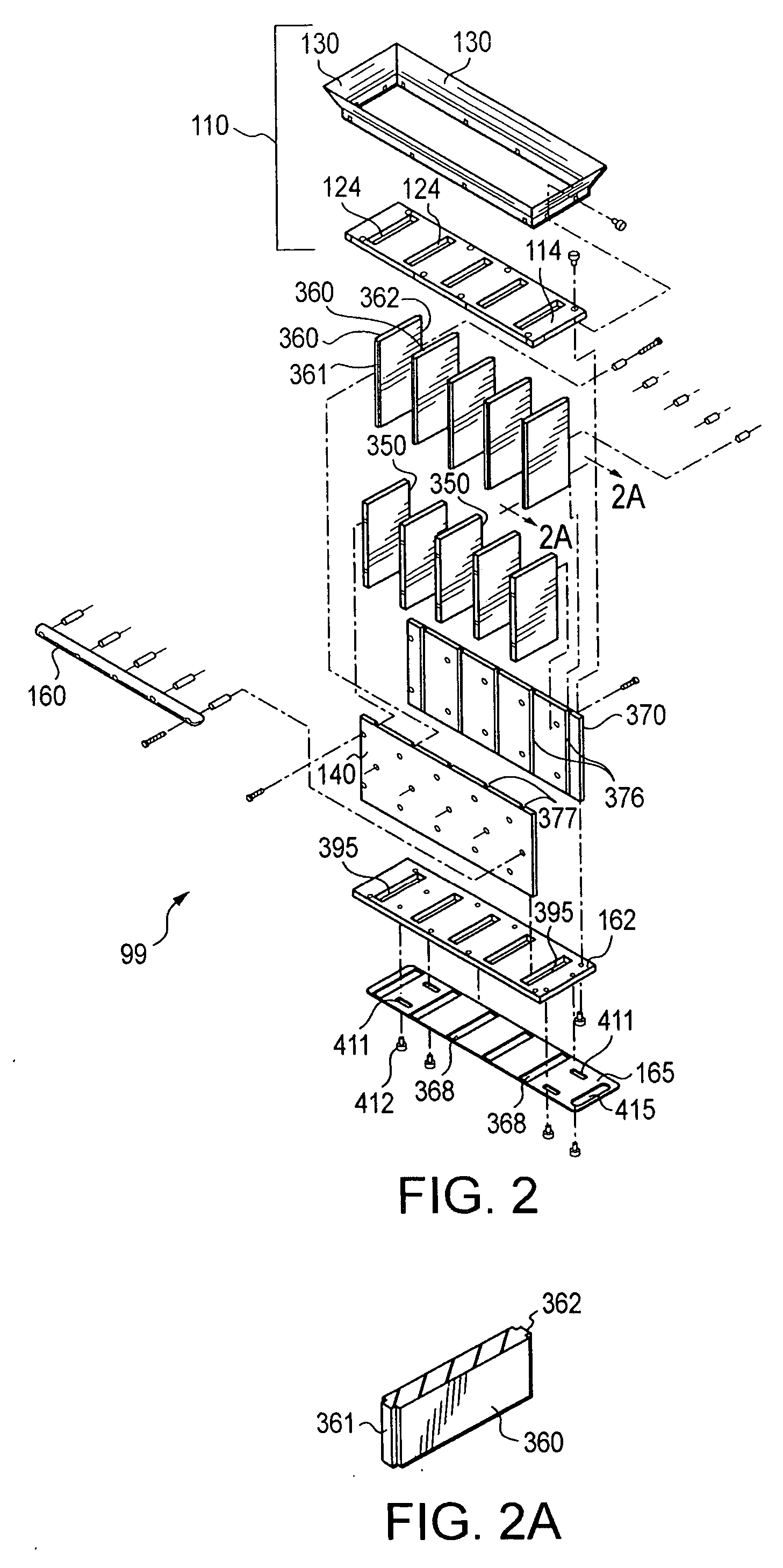
Apparatus and methods for manufacturing cigarettes
ActiveUS7565818B2Cut excess tobacco filler awayPrecise alignmentCigarette manufactureGlass pressing apparatusBiomedical engineering
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Burner injection system for glass melting
A burner for melting glass forming batch material includes a burner assembly constructed and arranged with a first passage for providing a fuel stream and a second passage for providing an oxidant stream, the first and second streams coacting to produce a supersonic combustion jet flame penetrable into glass melt. A method for melting glass forming batch material is also provided and includes providing a fuel stream; providing an oxidant stream; mixing the fuel and oxidant streams with sufficient force for providing a supersonic combustion jet flame; directing the supersonic combustion jet flame to contact the glass forming batch material; and penetrating the glass forming batch material to a select depth with the supersonic combustion jet flame.
Owner:LINDE AG
Shrouded-plasma process and apparatus for the production of metastable nanostructured materials
InactiveUS20070044513A1Improve compactnessImprove sintering performanceMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsLiquid jetShort range order
A method and apparatus for producing metastable nanostructured materials employing a ceramic shroud surrounding a plasma flame having a steady state reaction zone into which an aerosol or liquid jet of solution precursor or powder material is fed, causing the material to be pyrolyzed, melted, or vaporized, followed by quenching to form a metastable nanosized powder that has an amorphous (short-range ordered), or metastable microsized powder that has a crystalline (long-range ordered) structure, respectively.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method and apparatus for making an article from a formable material
InactiveUS6216493B1Good repeatabilityHigh speed productionButtonsAmpoule syringesEngineeringInjector
A method and apparatus are described for making an article such as the body of a needleless injector capsule, from a formable material, such as glass, the article having a cavity communicating with the exterior via an orifice. A blank (1a) having an open end is mounted on a first forming tool, and the open end is engaged by a second forming tool (22) while an end region of the blank (1a) adjacent the open end is in a condition to permit it to be formed. One of the tools (7a) has a pin (21) extending therefrom, and when the tools are brought together to form the end region into the desired shape of the pin (21) defines the orifice.
Owner:ZOGENIX INC
Method and device for refining a glass melt using negative pressure
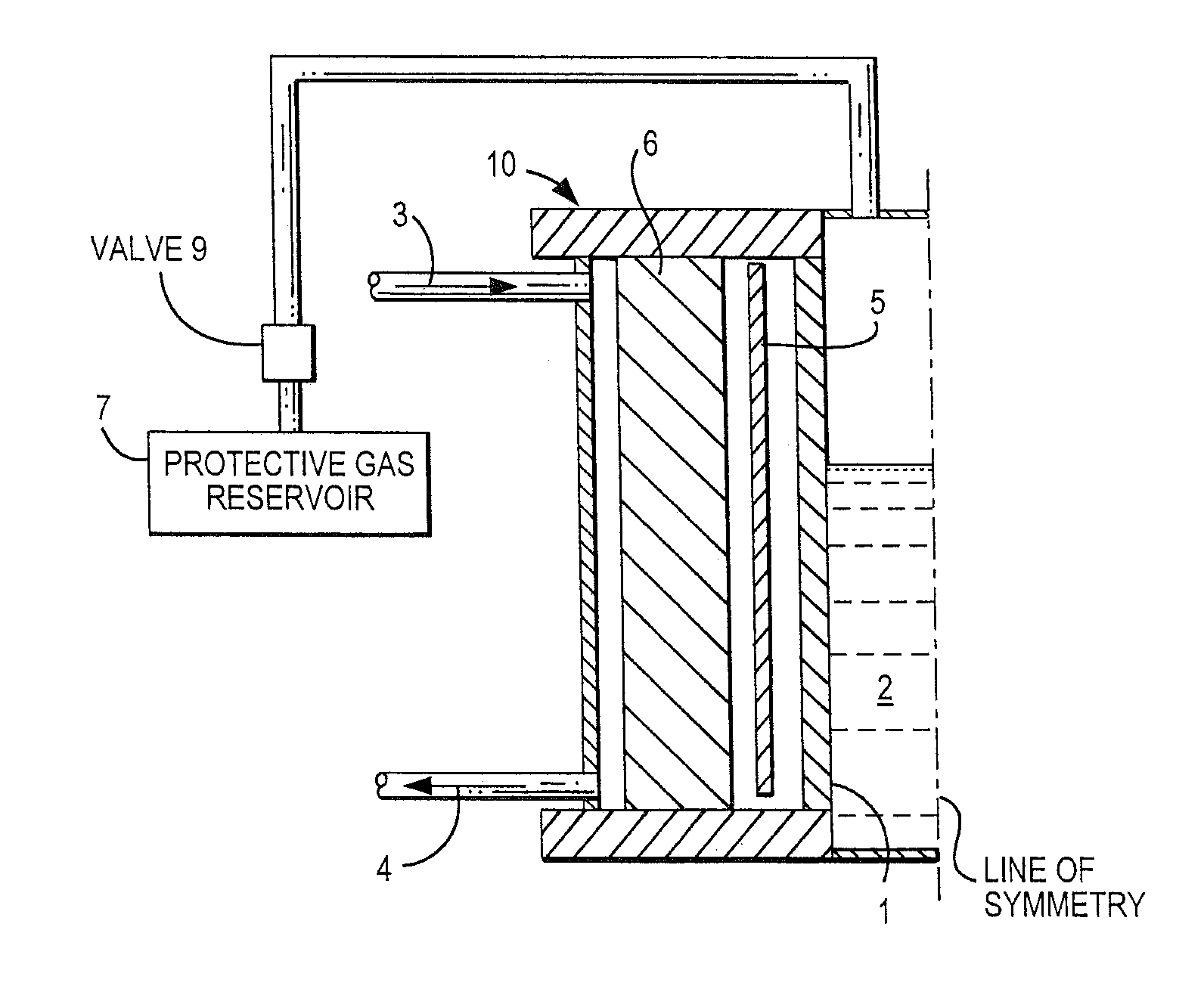
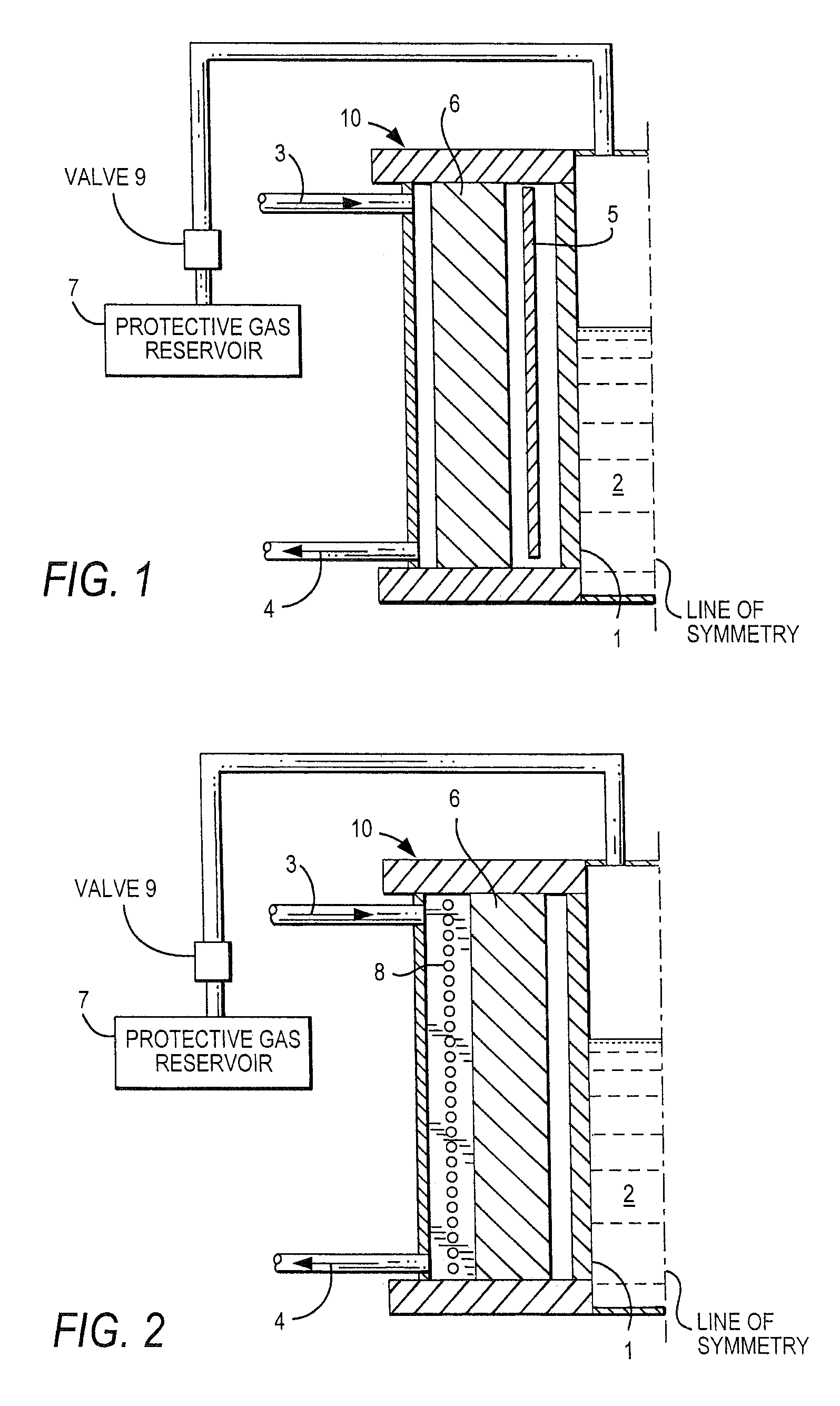
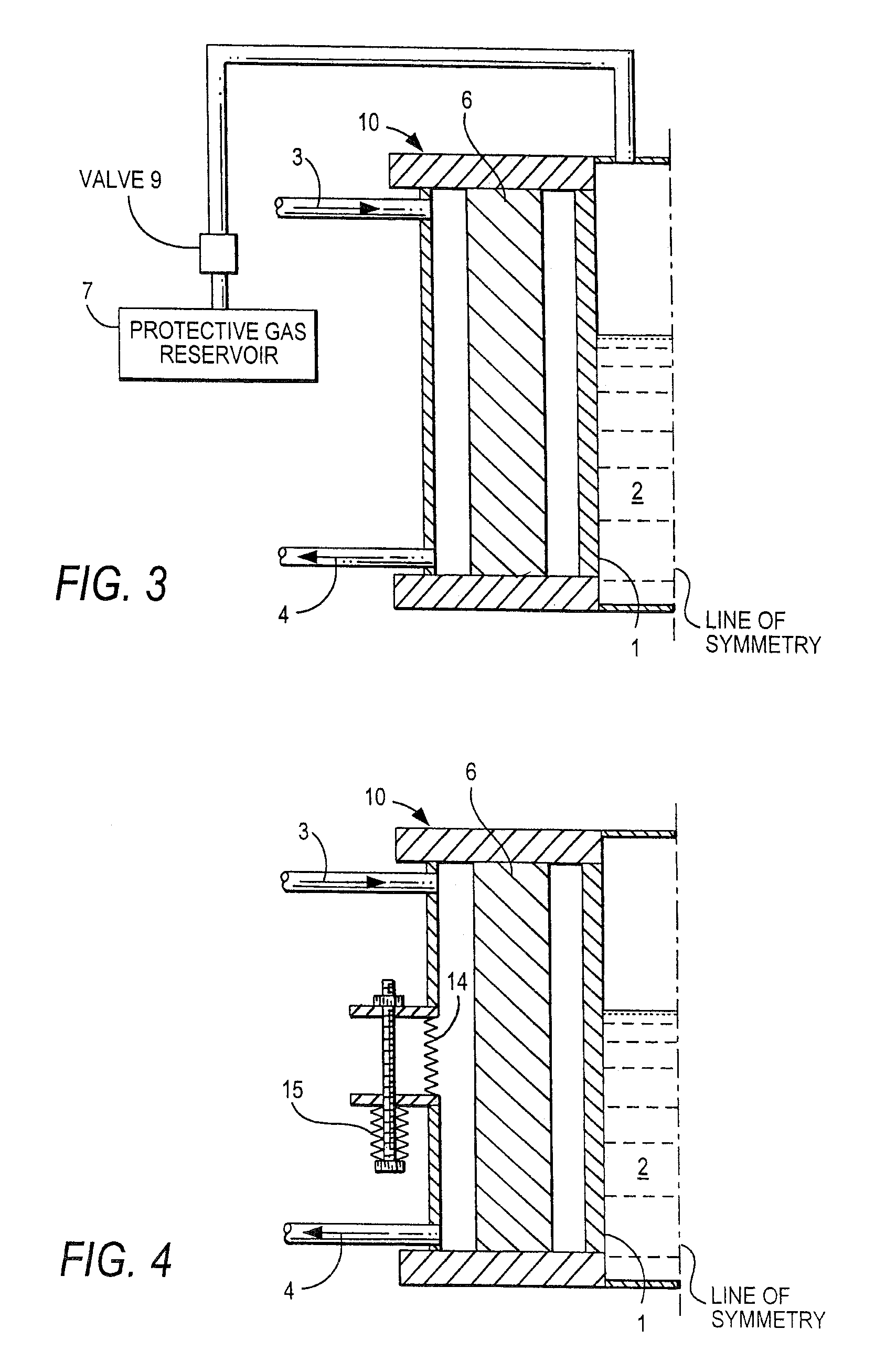
InactiveUS7231788B2Possible operating costPossible procurement costGlass furnace apparatusGlass blowing apparatusPressure riseShielding gas
The apparatus for reduced-pressure refining of a glass melt includes a refining bank formed so that a reduced pressure is generated by a glass flow in it. The refining bank has a component, which is made from a refractory metal or refractory alloy acting as glass-contact material. The refractory metal or alloy contains molybdenum, tungsten, tantalum, and / or hafnium. The device of the present invention includes a protective gas reservoir for a protective gas and an automatically operating valve connecting the reservoir with the refining bank so that an inner side of the component that would otherwise be exposed when a pressure rise or a falling glass melt column occurs is protected from oxidation by the protective gas. A process for using the device during refining of the glass melt is also part of the invention.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Transparent, colorless low-titania beta-quartz glass-ceramic material
Owner:EUROKERA SOC & NOM COLLECTIF
Coefficient of thermal expansion filler for vanadium-based frit materials and/or methods of making and/or using the same
ActiveUS20120213954A1Improve sealingReduce sealClimate change adaptationWindows/door improvementMetal chlorideFrit
Certain example embodiments relate to seals for glass articles. Certain example embodiments relate to a composition used for sealing an insulted glass unit. In certain example embodiments the composition includes vanadium oxide, barium oxide, zinc oxide, and at least one additional additive. For instance, another additive that is a different metal oxide or different metal chloride may be provided. In certain example embodiments, a composition may be combined with a binder solution that substantially or completely burns out by the time the composition is melted. In certain example embodiments, a CTE filler is included with a frit material. In certain example embodiments, a vacuum insulated glass unit includes first and second glass substrates that are sealed together with a seal that includes the above-described composition.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
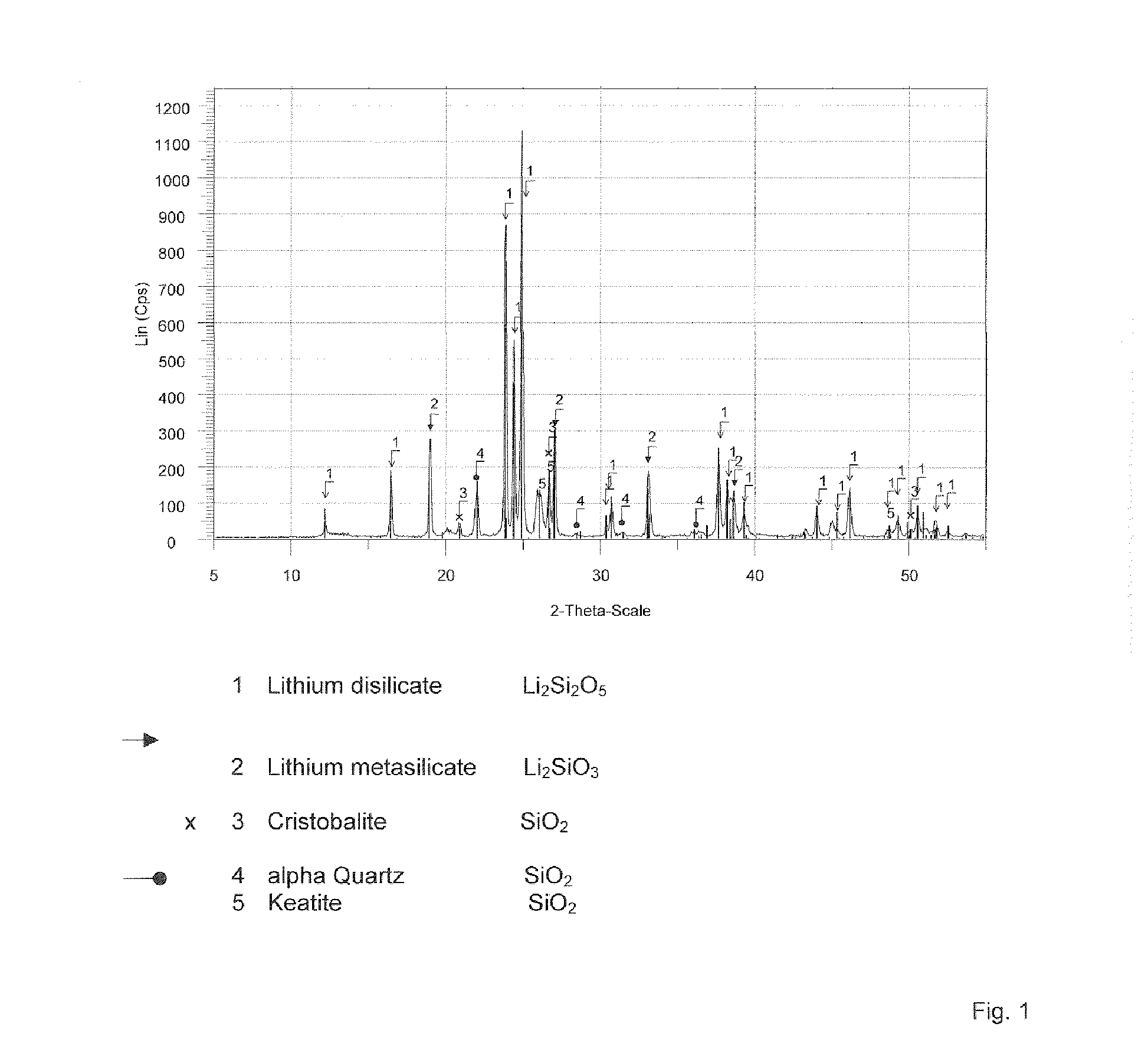
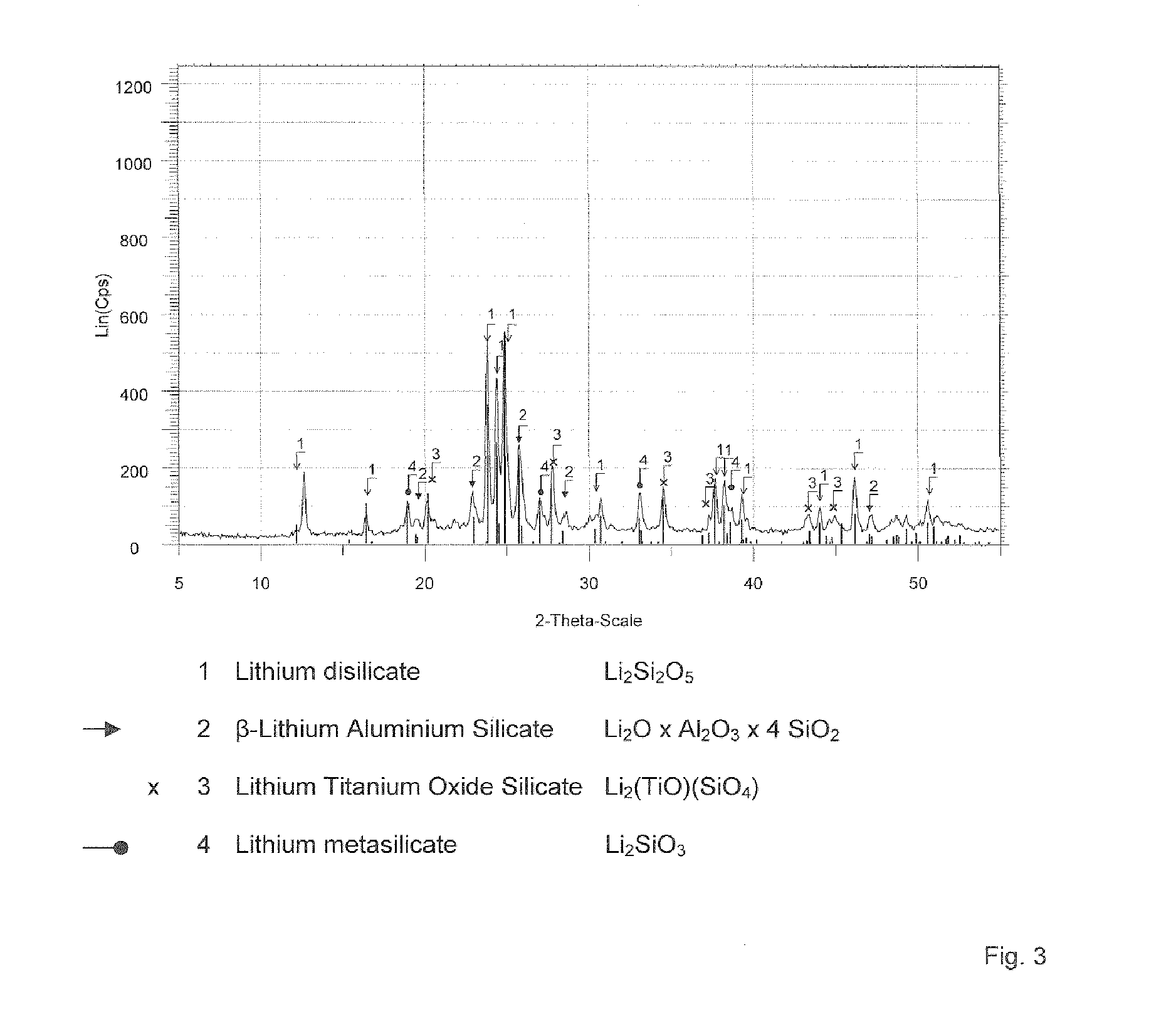
Lithium silicate glass ceramic
ActiveUS7867930B2Easy to shapeExcellent chemical durabilityDental implantsGlass drawing apparatusSilicate glassPhysical chemistry
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Porous silica granule, method for producing the same, and method for producing synthetic quartz glass powder using the porous silica granule
InactiveUS6849242B1Minimizes pore diameterHigh bulk densitySilicaGlass blowing apparatusMean diameterSlurry
The granule consists of individual granules approximately spherical in shape, having a pore volume of 0.5 cm3, a mean diameter of pores of 50 nm or less, a specific surface area of 100 m2 / g or less, and a bulk density of 0.7 g / cm3 or higher. It is produced by dispersing a fumed silica obtained by hydrolysis of a silicon compound into pure water to obtain a slurry, and drying the slurry. The granule is used for producing high purity synthetic quartz glass powder. The method further comprises: a first heat treatment under an oxygen-containing atmosphere, a second heat treatment in a temperature range of from 600 to 1100° C., and a third heat treatment in a temperature range of from 1100 to 1300° C. under an atmosphere containing hydrogen chloride; and a step of densification comprising calcining the product at a temperature not higher than 1500° C. under vacuum or in an atmosphere of gaseous hydrogen or gaseous helium. To calcine the powder without causing fusion adhesion of the particles, bubbling fluidization of said porous silica granule is conducted by supplying gaseous helium and calcining thereof in a temperature range of from 1000 to 1600° C.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS +1
Glass-ceramics and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090162608A1Suitability for press formingImprove productivityMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersGlass-ceramicAntimony
For providing glass-ceramics having properties suitable for use as a substrate of an information storage medium of next generation such as one for the perpendicular magnetic recording system without employing arsenic and antimony components which adversely affect human beings and the environment, there are provided glass-ceramics comprising SiO2, Li2O and Al2O3 on oxide basis, comprising lithium disilicate as a crystal phase, and comprising one or more elements selected from the group consisting of Sn, Ce, Mn, W, Ta, Bi, Nb, S, Cl and F.
Owner:OHARA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com