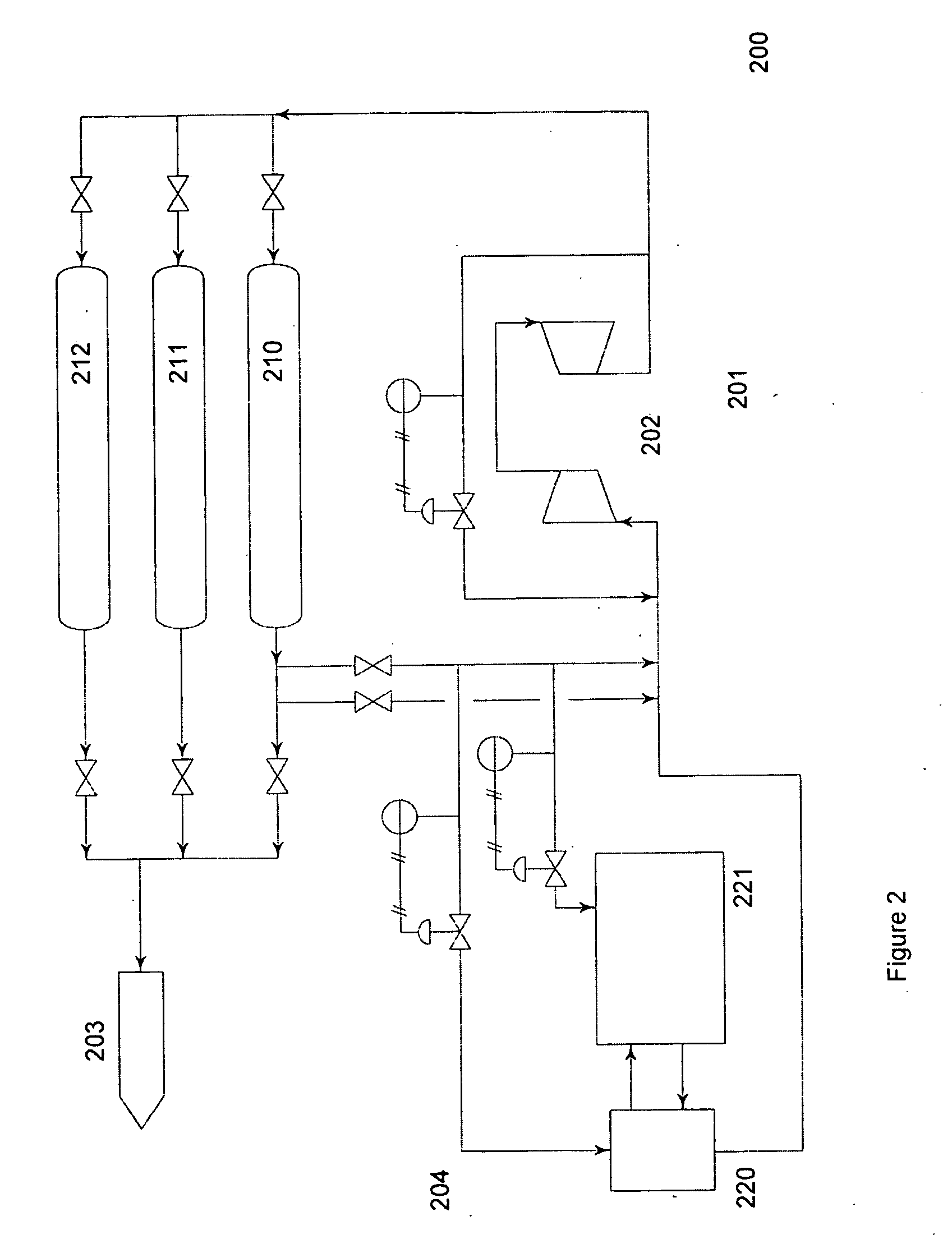
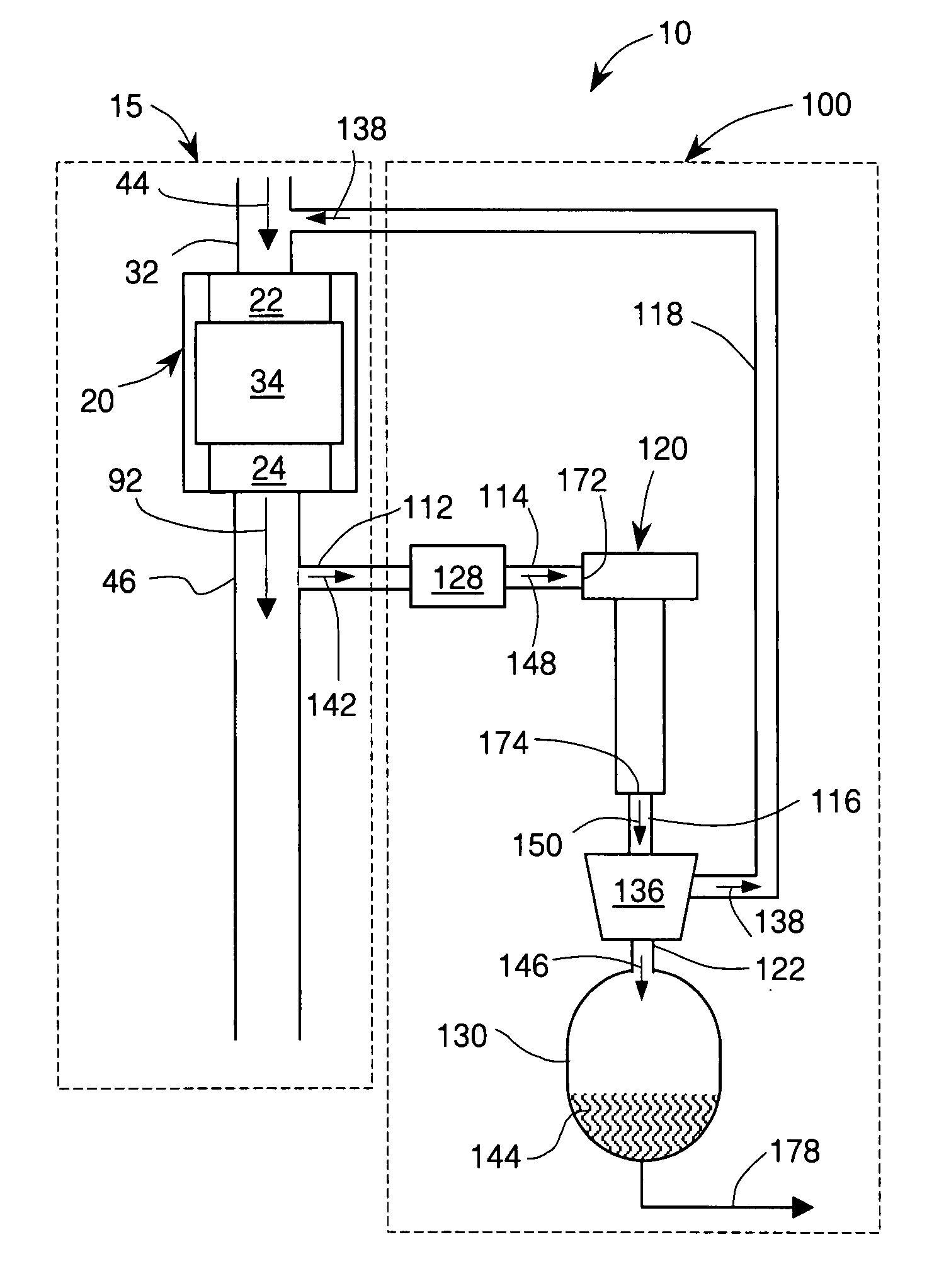
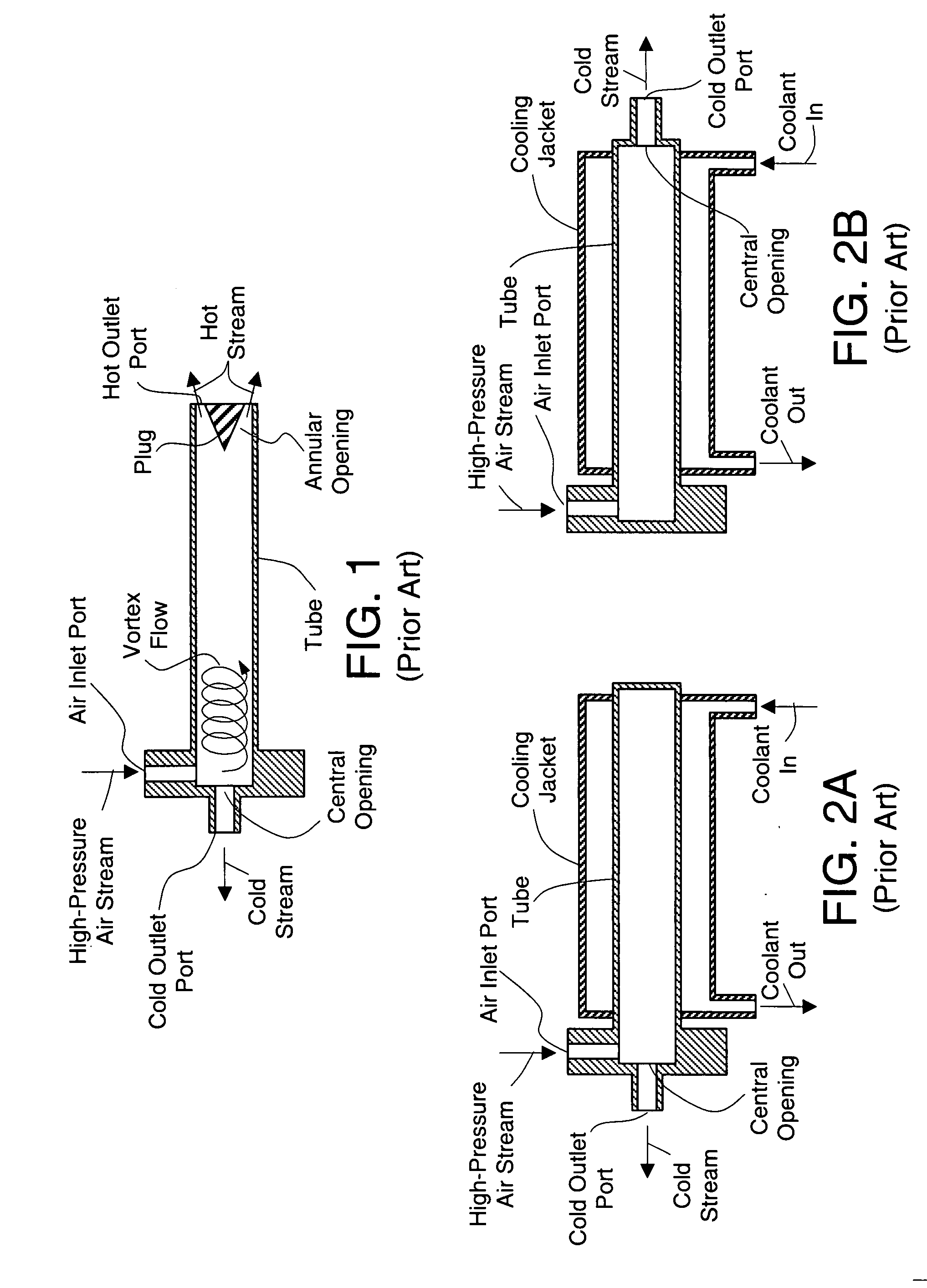
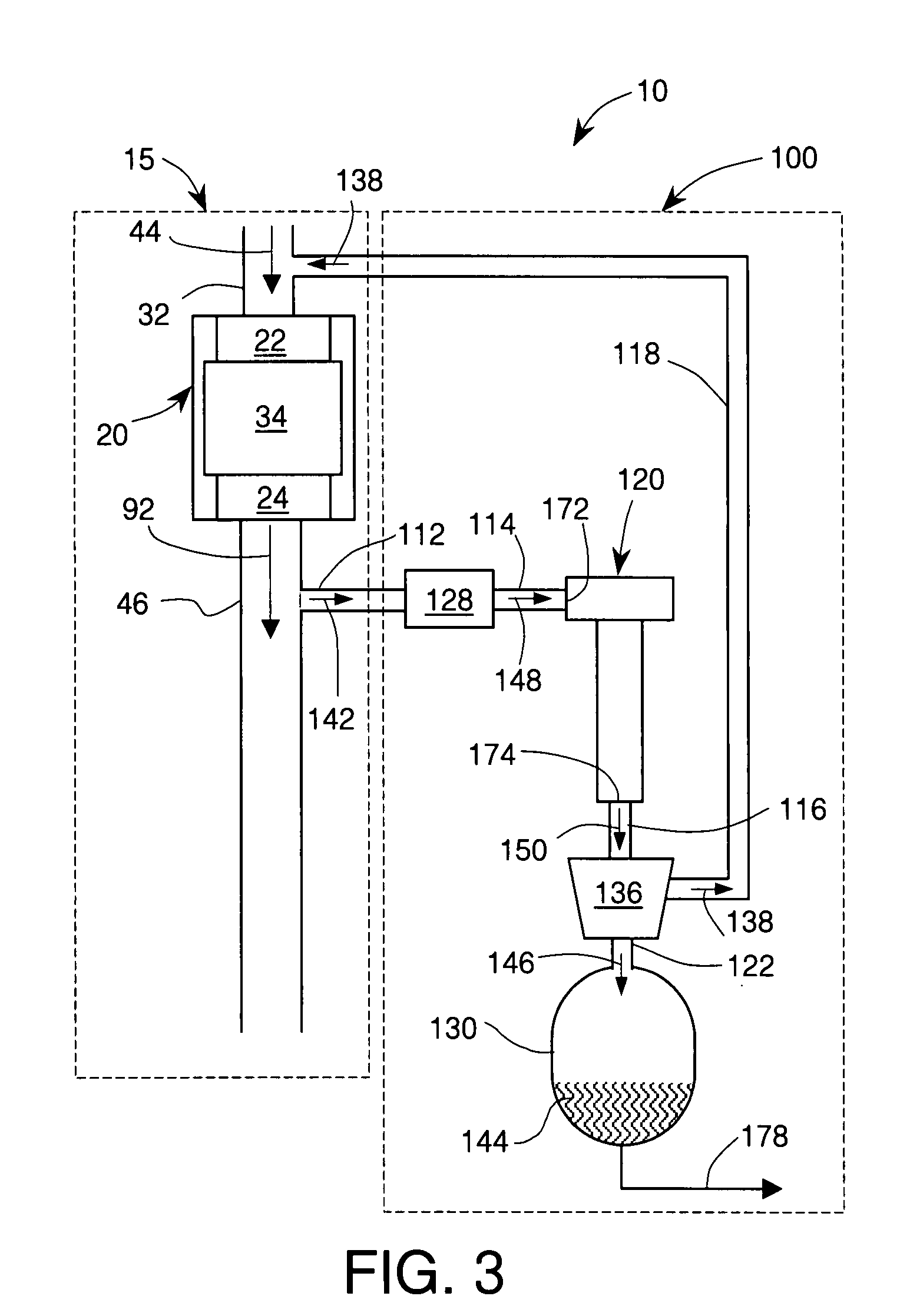
Patents
Literature
398 results about "Gaseous hydrogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydrogen (H), a colourless, odourless, tasteless, flammable gaseous substance that is the simplest member of the family of chemical elements. The hydrogen atom has a nucleus consisting of a proton bearing one unit of positive electrical charge; an electron, bearing one unit of negative electrical charge,...
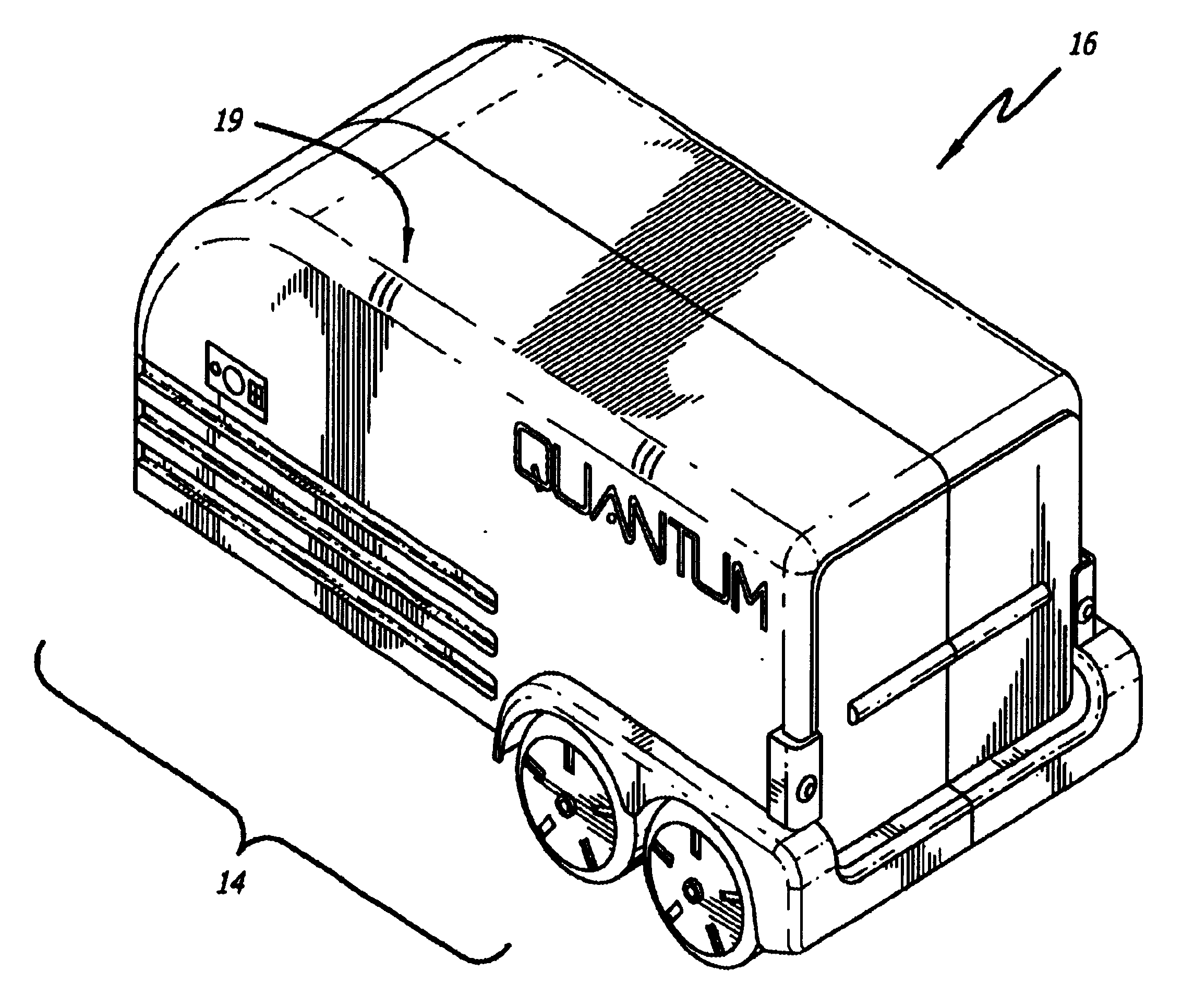
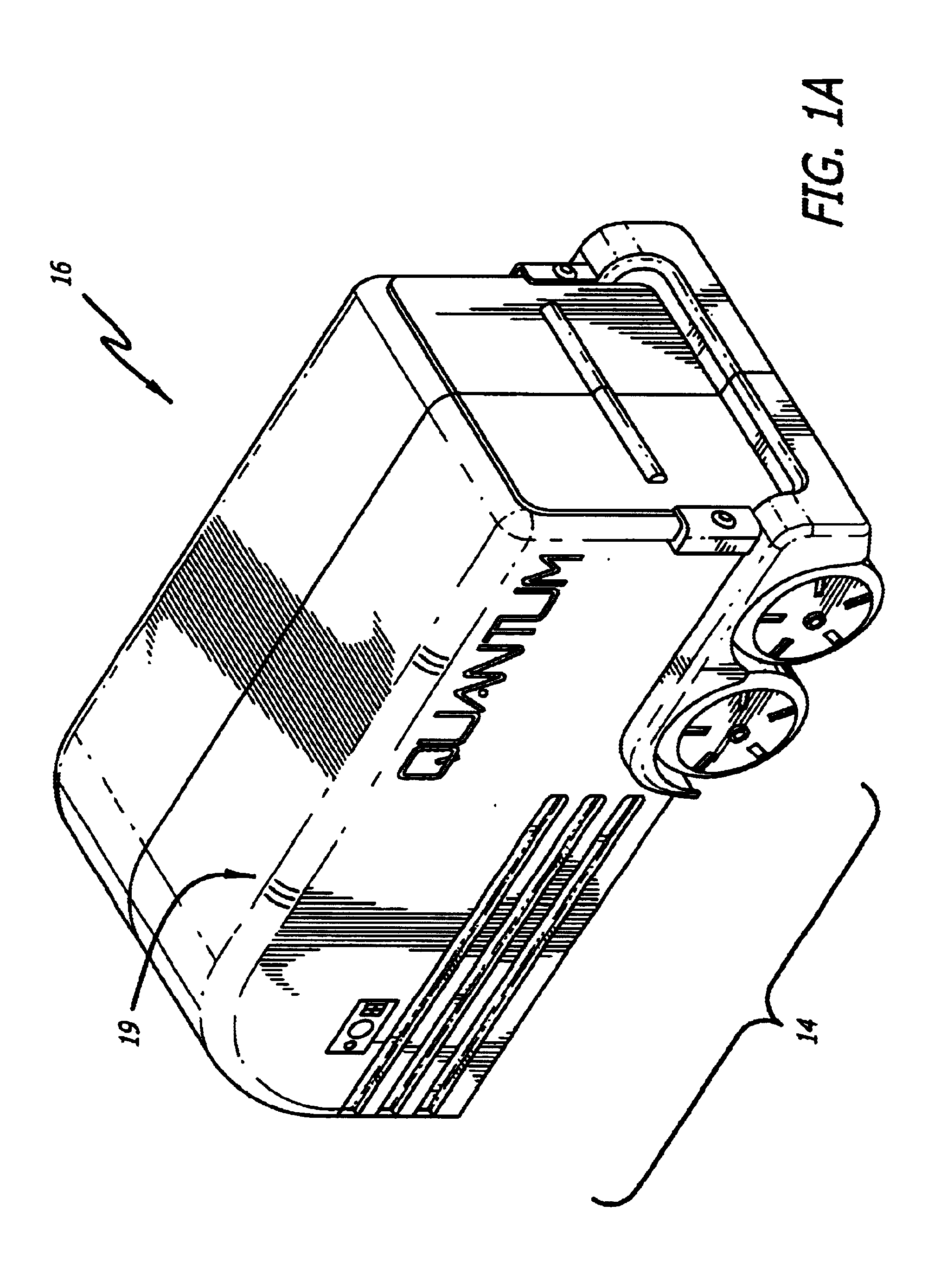
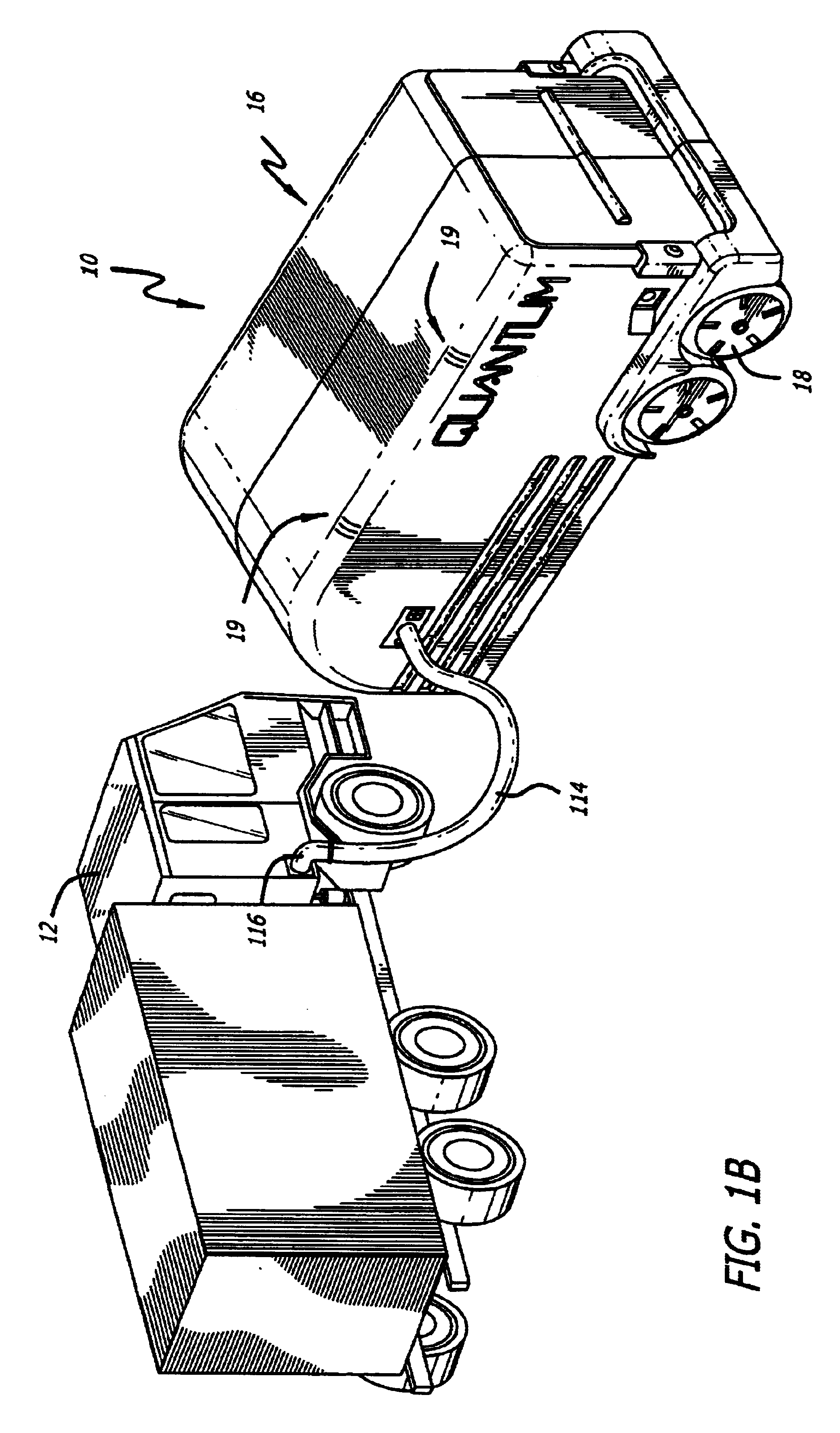
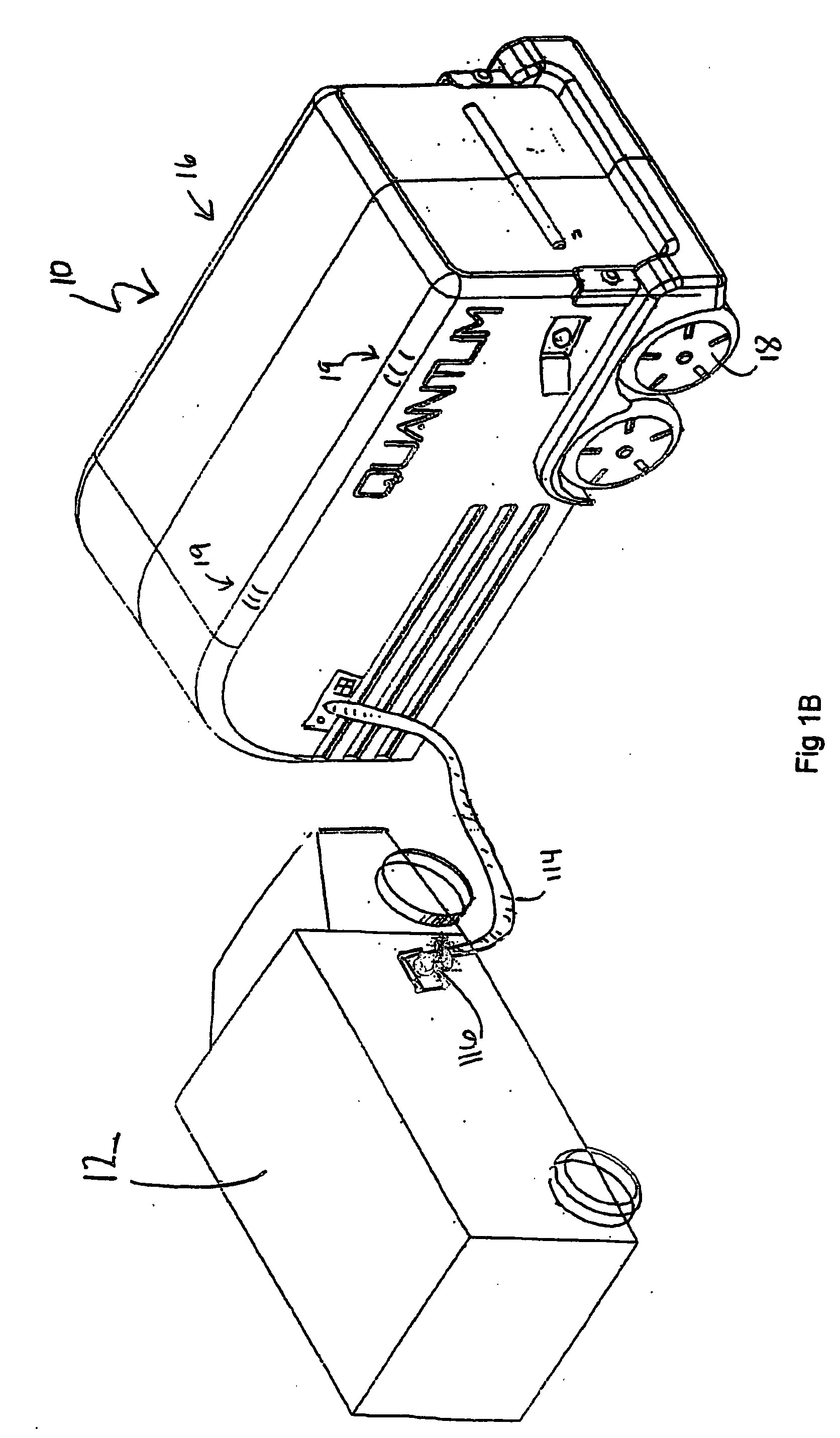
Transportable hydrogen refueling station
InactiveUS6755225B1Easy to monitorReduce riskTank vehiclesGas handling applicationsHigh pressureGaseous hydrogen
A portable hydrogen refueling stations which can dispense gaseous hydrogen from one or more internal high pressure tanks. The refueling station can be refilled with a lower pressure hydrogen gas feed and then compressed for storage within the refueling station.
Owner:QUANTUM FUEL SYST TECH WORLDWIDE INC
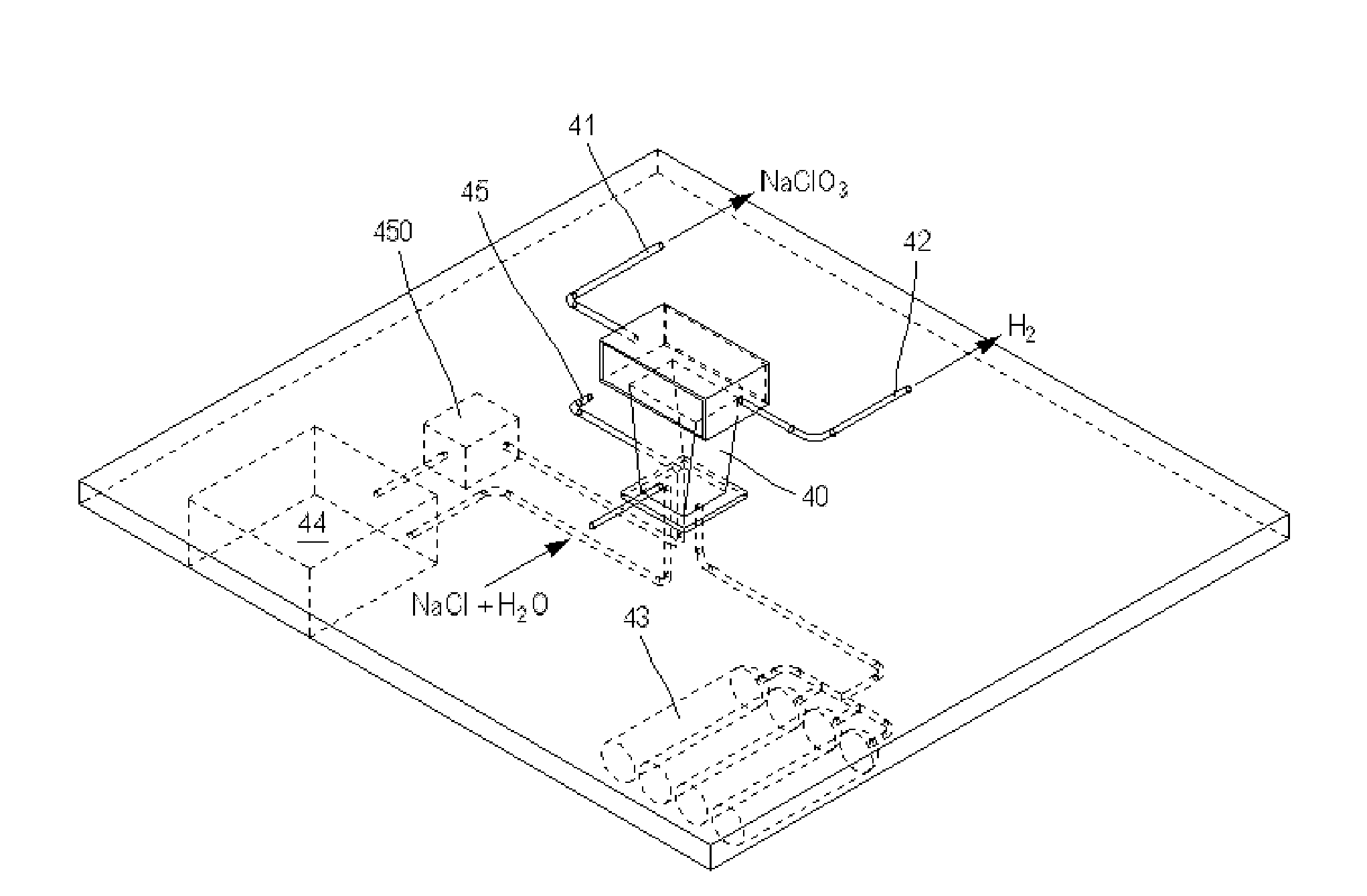
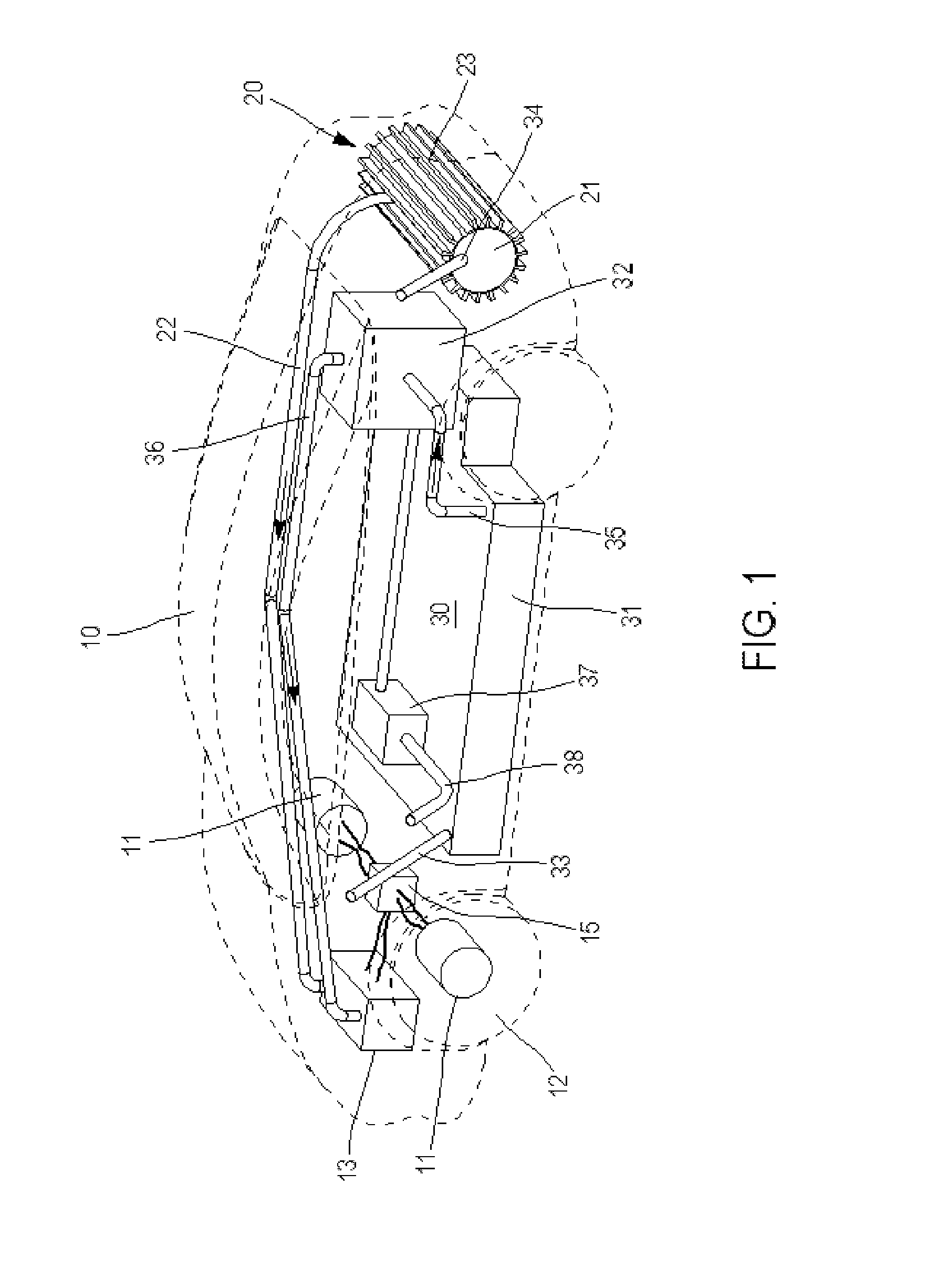
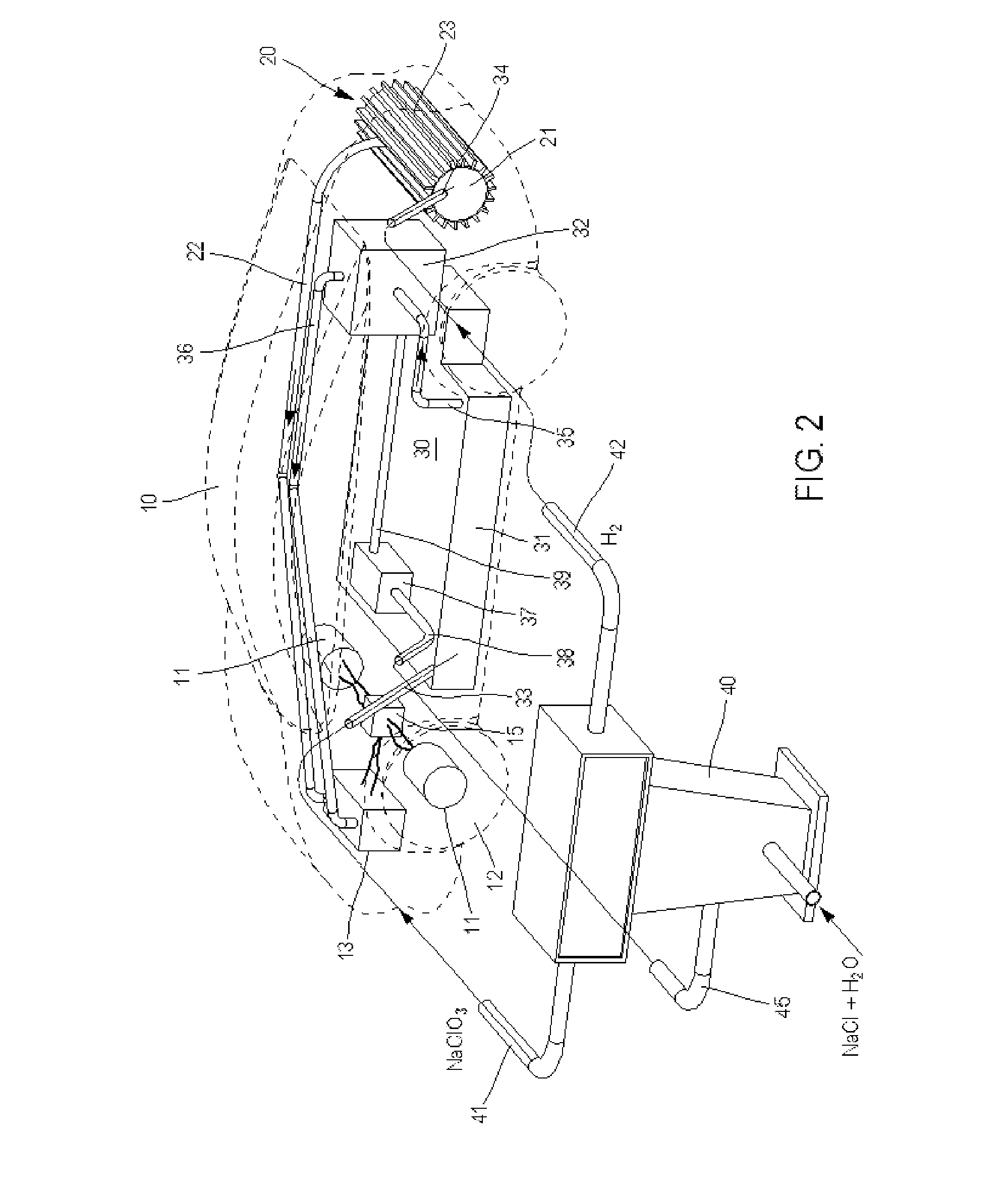
System for Producing and Supplying Hydrogen and Sodium Chlorate, Comprising a Sodium Chloride Electrolyser for Producing Sodium Chlorate
InactiveUS20130115535A1Increase supplyIncrease productionCellsReactant parameters controlElectrolysisSodium chlorate
A system is provided for producing hydrogen and oxygen based on decomposition of sodium chlorate (NaClO3). In a service station, NaClO3 is produced by a sodium chloride (NaCl) electrolyser. The service station is supplied with water (H2O), NaCl, and energy in order to carry out an electrolysis reaction in the electroyser, to produce NaClO3 and gaseous hydrogen (H2). The NaClO3 and H2 are supplied to vehicles. Each vehicle includes a reactor for decomposing the NaClO3 and producing reaction products of NaCl and oxygen, with the oxygen being supplied to a fuel cell.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
Heat and hydrogen peroxide gas sterilization of container
The present invention discloses a method and apparatus for sterilizing containers with gas-phase hydrogen peroxide and heat on a linear form, fill and seal packaging machine. A partially formed container is subjected to multiple applications of gaseous hydrogen peroxide and hot air within a sterilization tunnel. The sterilization tunnel is maintained at a temperature greater than the condensation temperature of hydrogen peroxide. The present invention sterilizes the container allowing for filling of the container with a high acid product such as orange juice for ambient distribution. The container may be any number of possibilities such as TETRA REX TM gable top cartons, plastic bottles, and the like. The invention allows for the efficacious use of hydrogen peroxide gas having a concentration of up to 53%.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
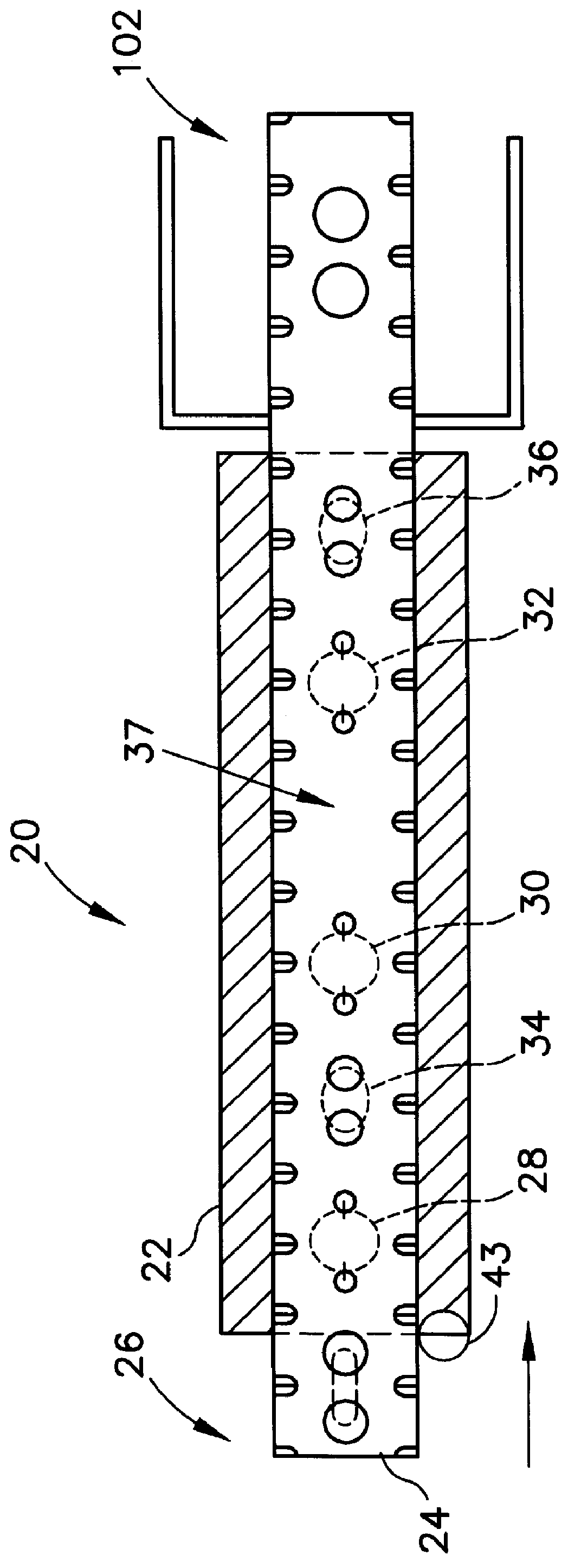
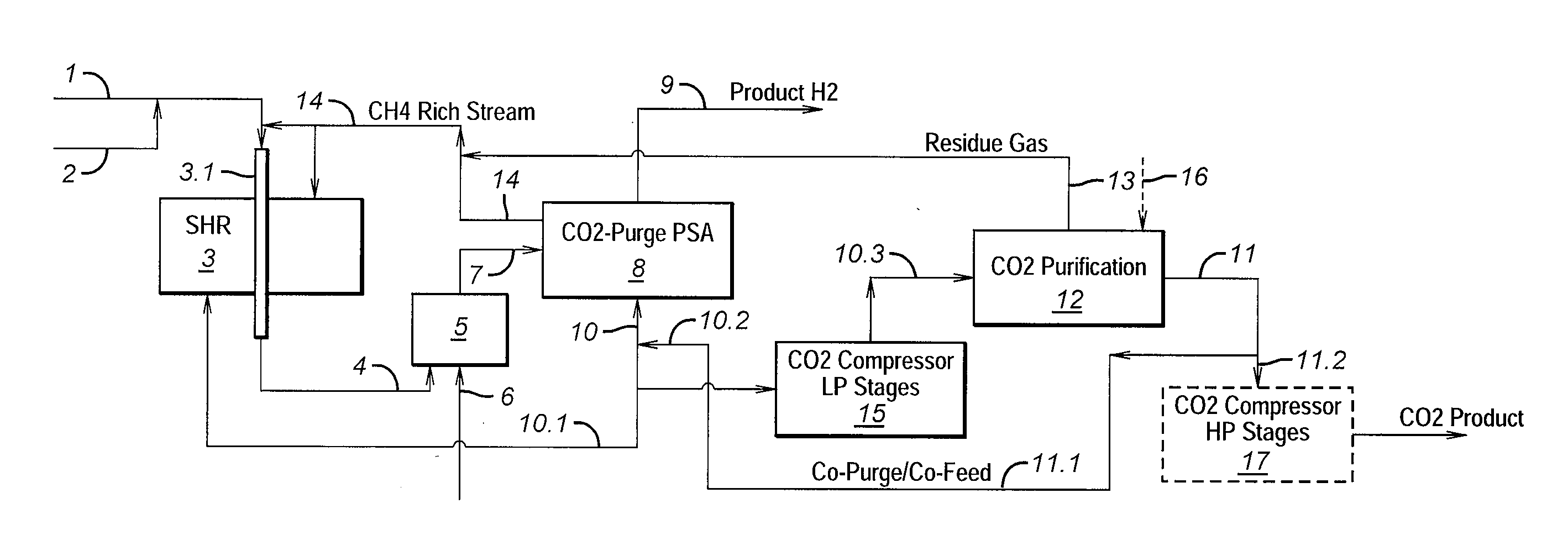
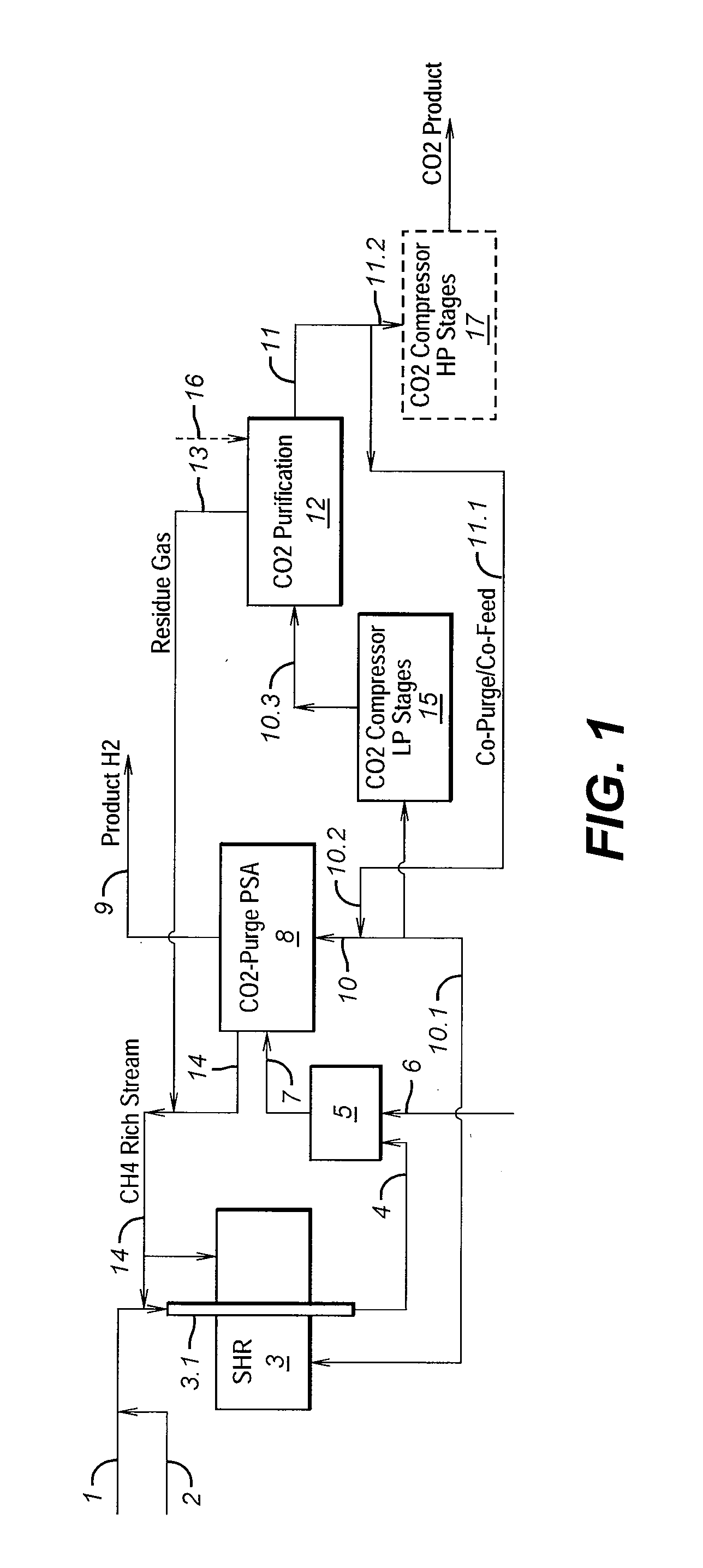
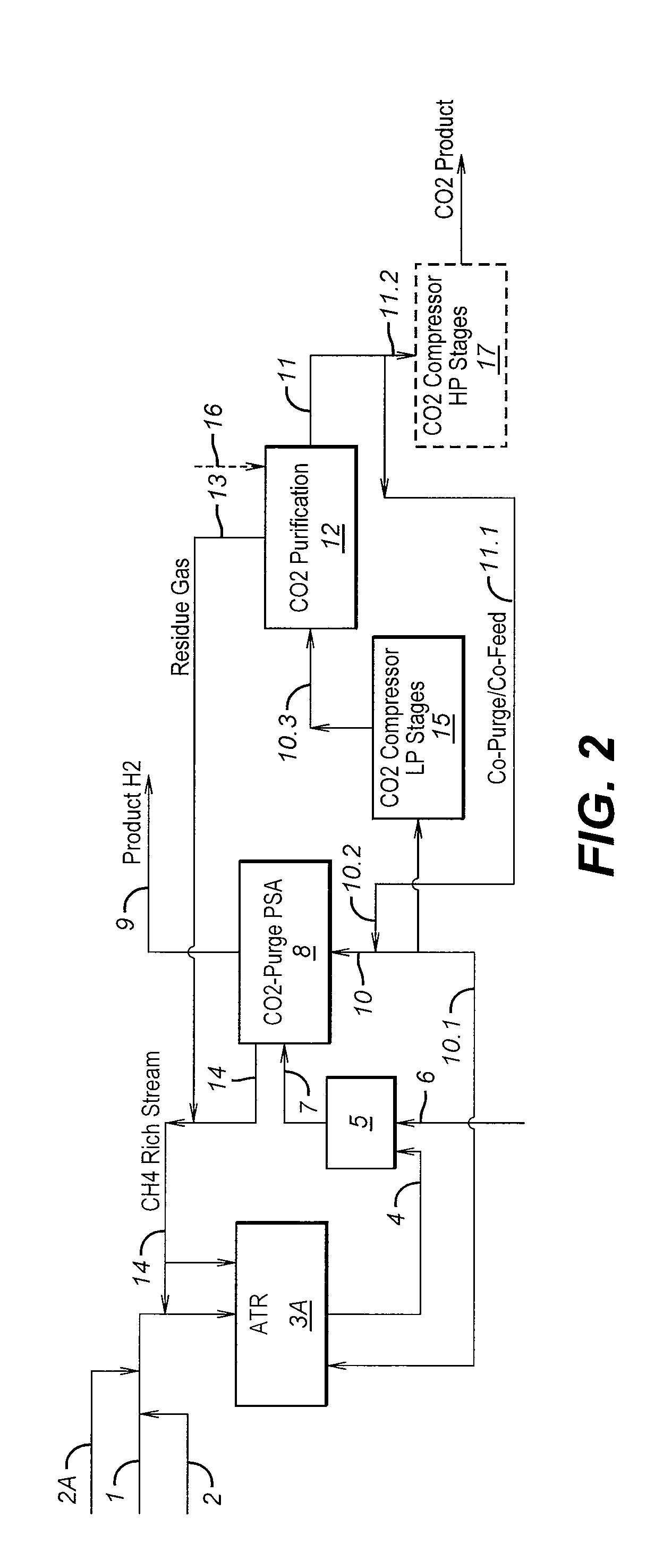
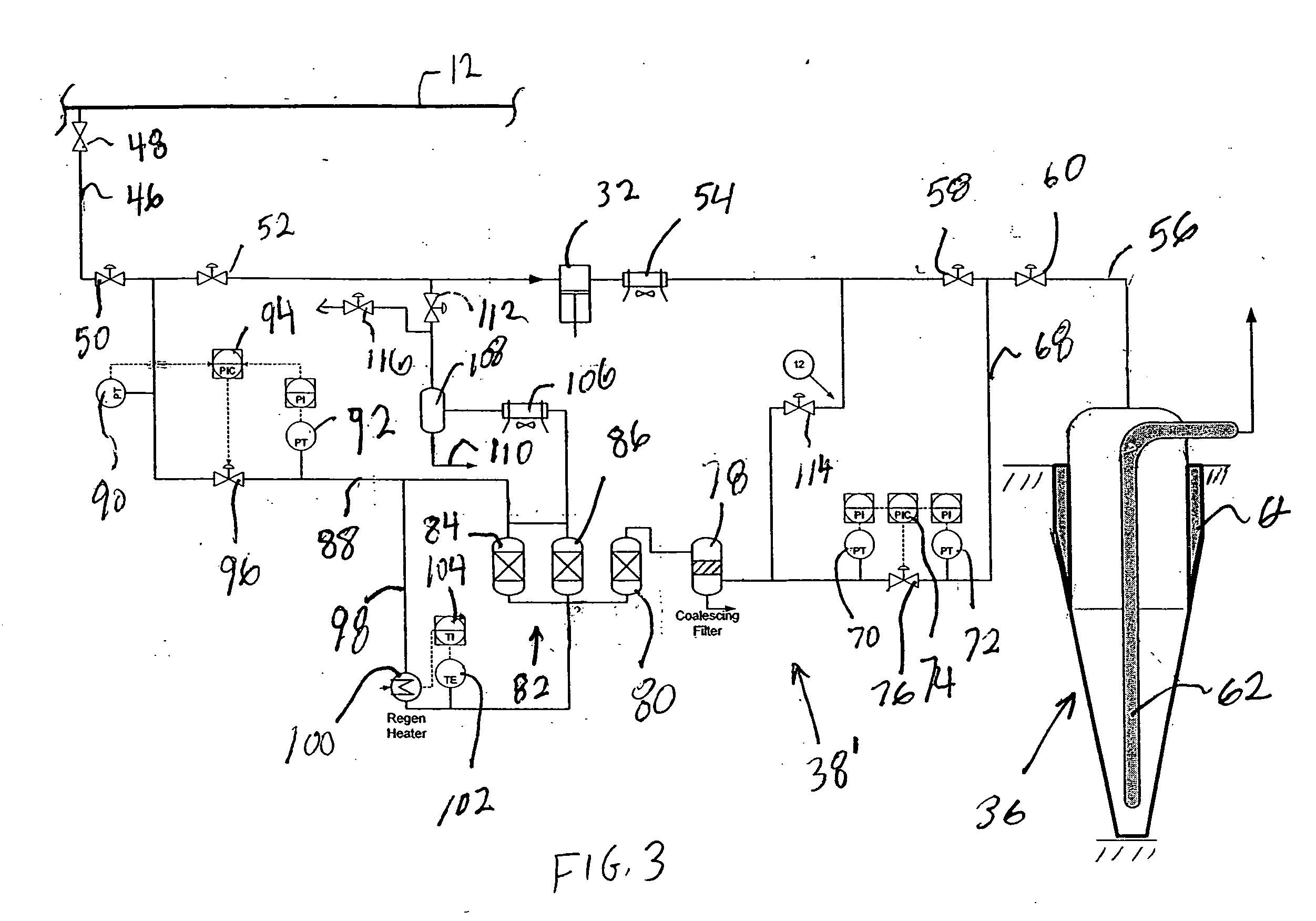
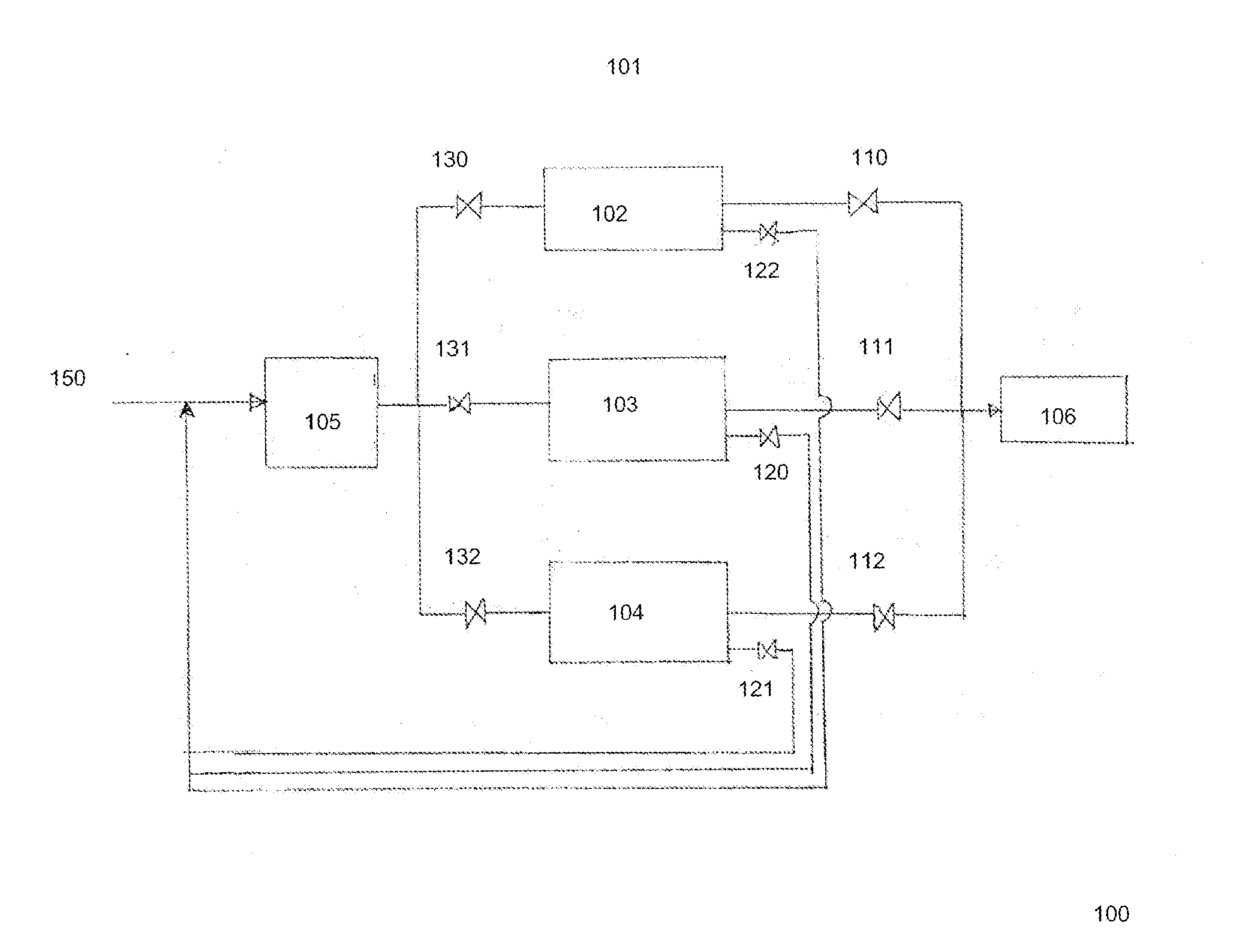
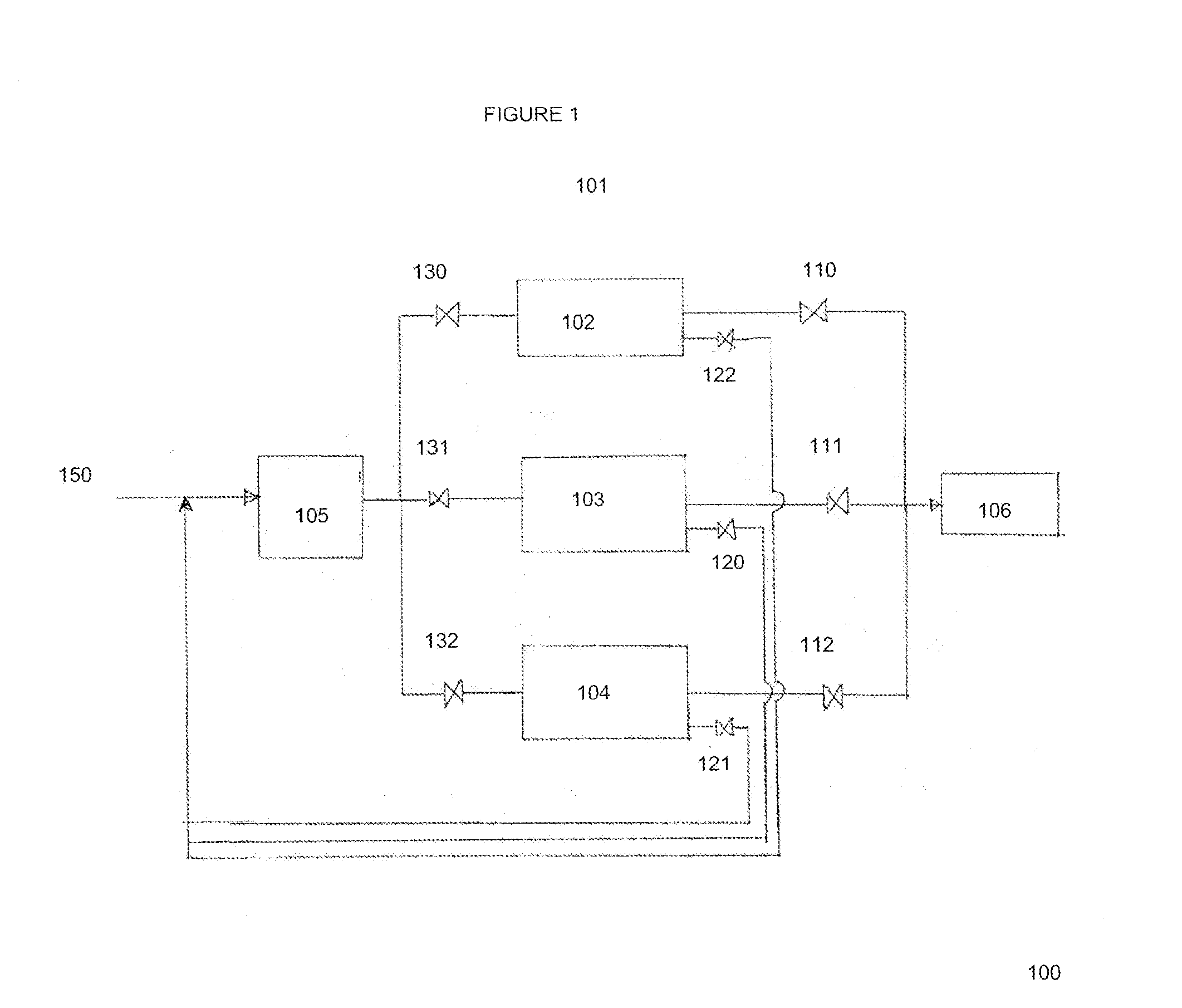
Process For The Production Of Carbon Dioxide Utilizing A Co-Purge Pressure Swing Adsorption Unit
The present invention provides a process for recovering gaseous hydrogen and gaseous carbon dioxide from a mixture of hydrocarbons by utilizing a system that includes a reformer unit, an optional water gas shift reactor, and a pressure swing adsorption unit in conjunction with a carbon dioxide purification unit such as a cryogenic purification unit or a catalytic oxidizer. In this process, purified CO2 from the CO2 purification unit is used as a co-feed / co-purge in the pressure swing adsorption unit in order to produce a CO2 tail gas that includes a higher concentration of CO2.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
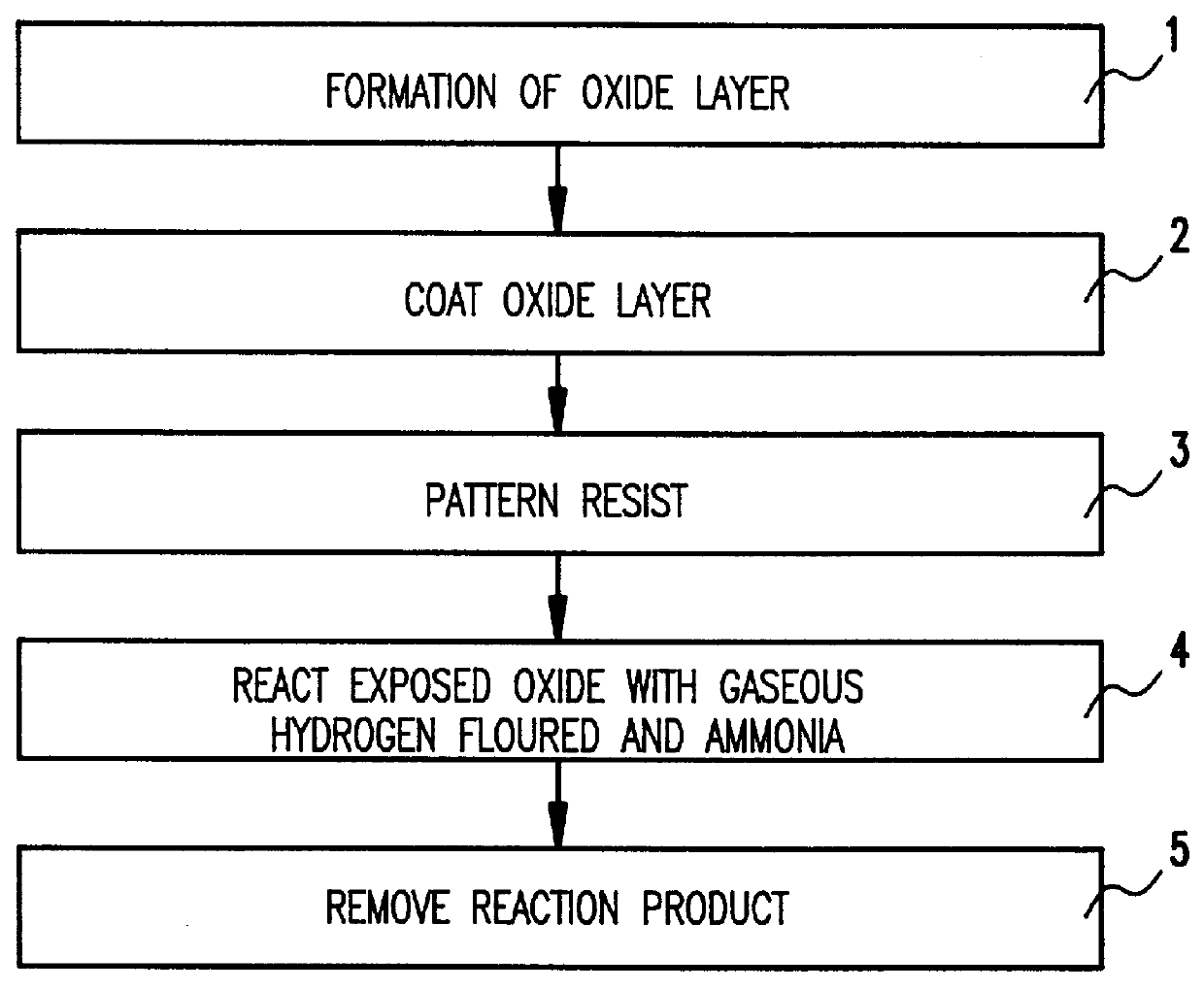
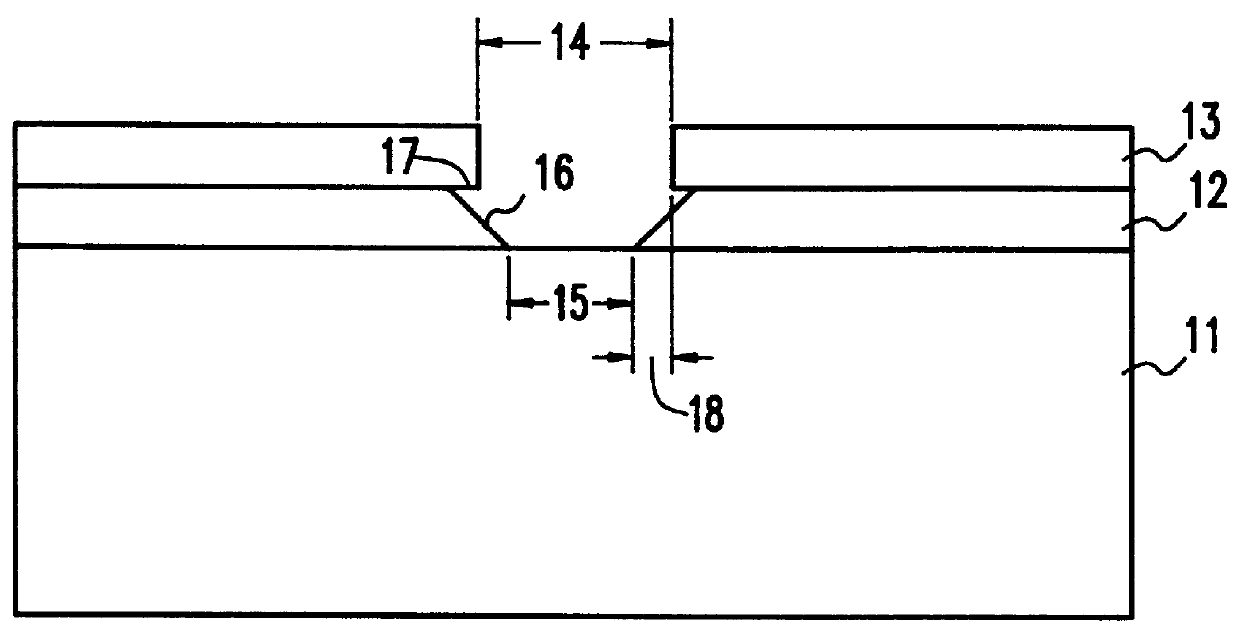
Vapor phase etching of oxide masked by resist or masking material
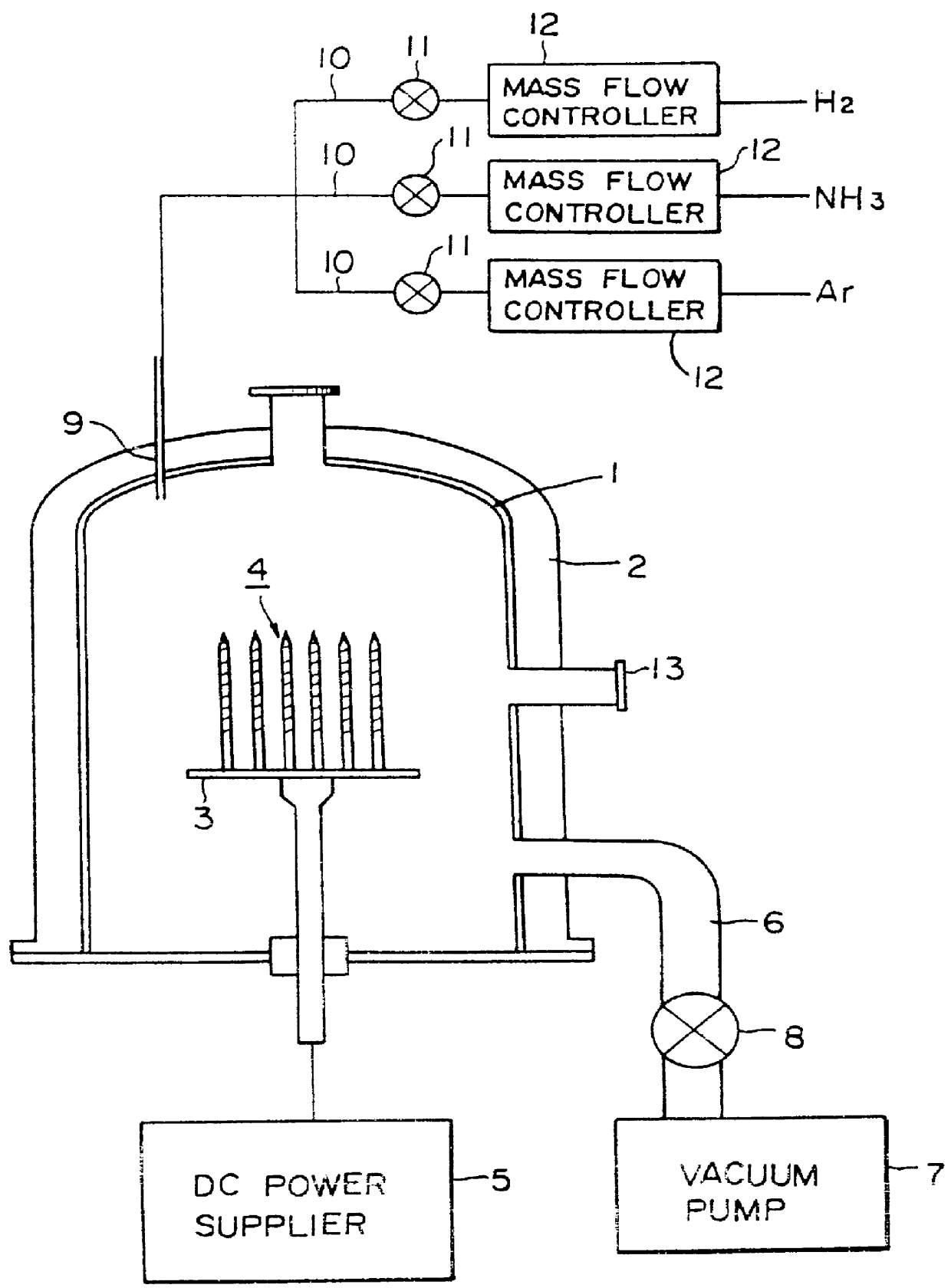
Hydrogen fluoride undercut of oxide layers may be reduced by using a low pressure mixture of gaseous hydrogen fluoride and gaseous ammonia mixture. Organic photoresists can be used as a masking material when using the gaseous hydrogen fluoride / ammonia mixture without resulting in an enhanced reaction rate. In addition, because of the reaction conditions, the dimensions in the oxide layer being etched can be specifically sized smaller than openings made in the overcoating masking material.
Owner:IBM CORP
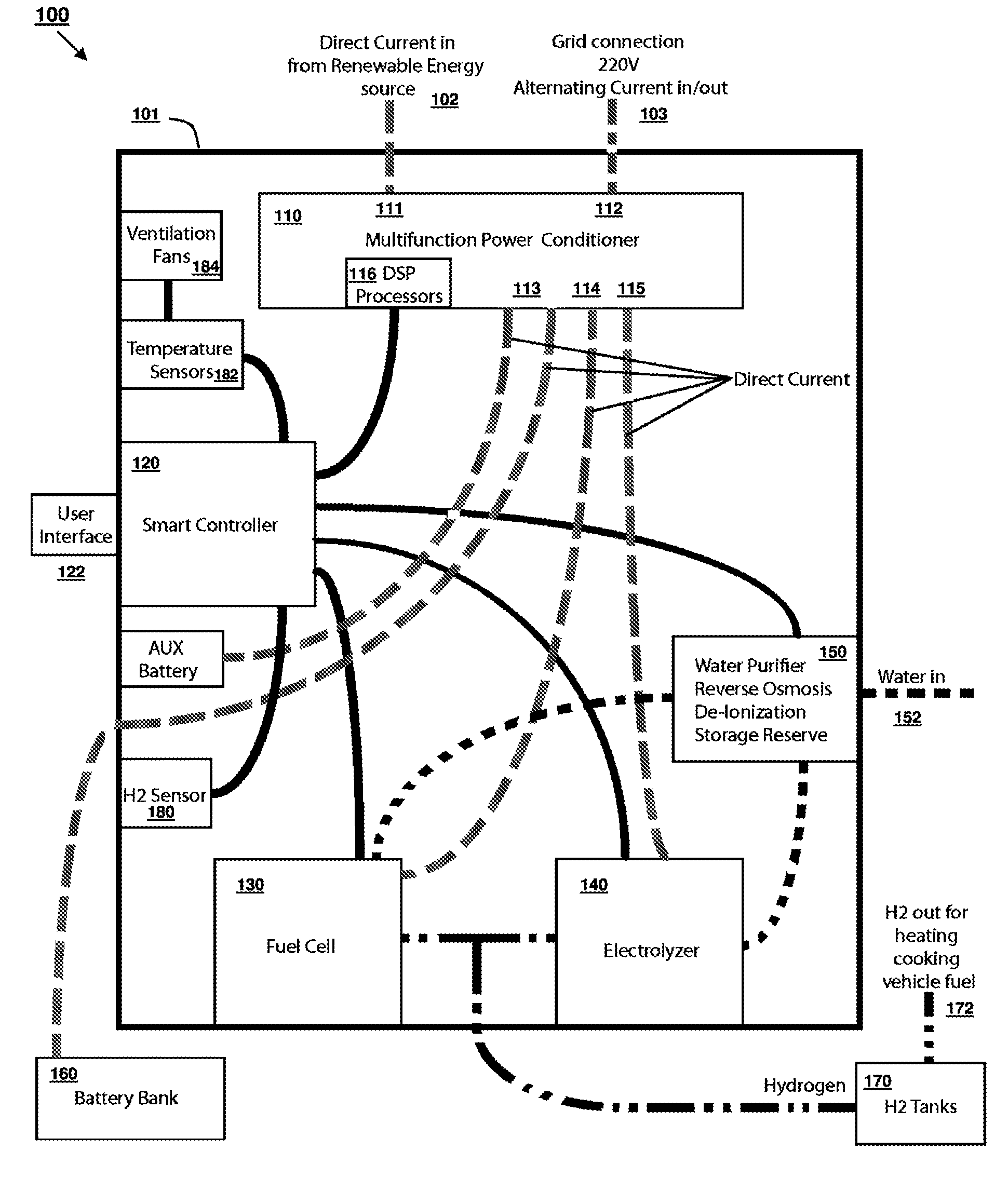
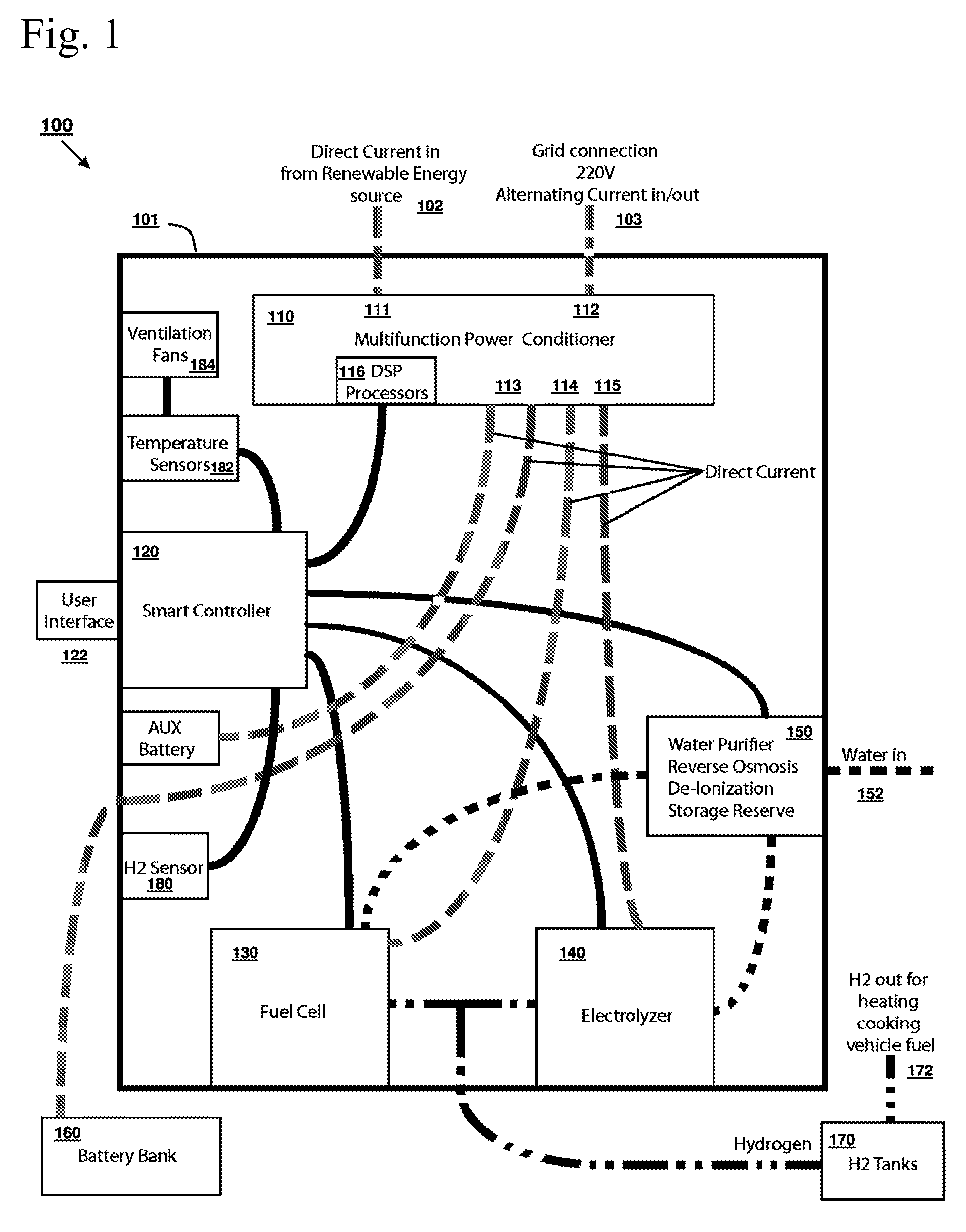
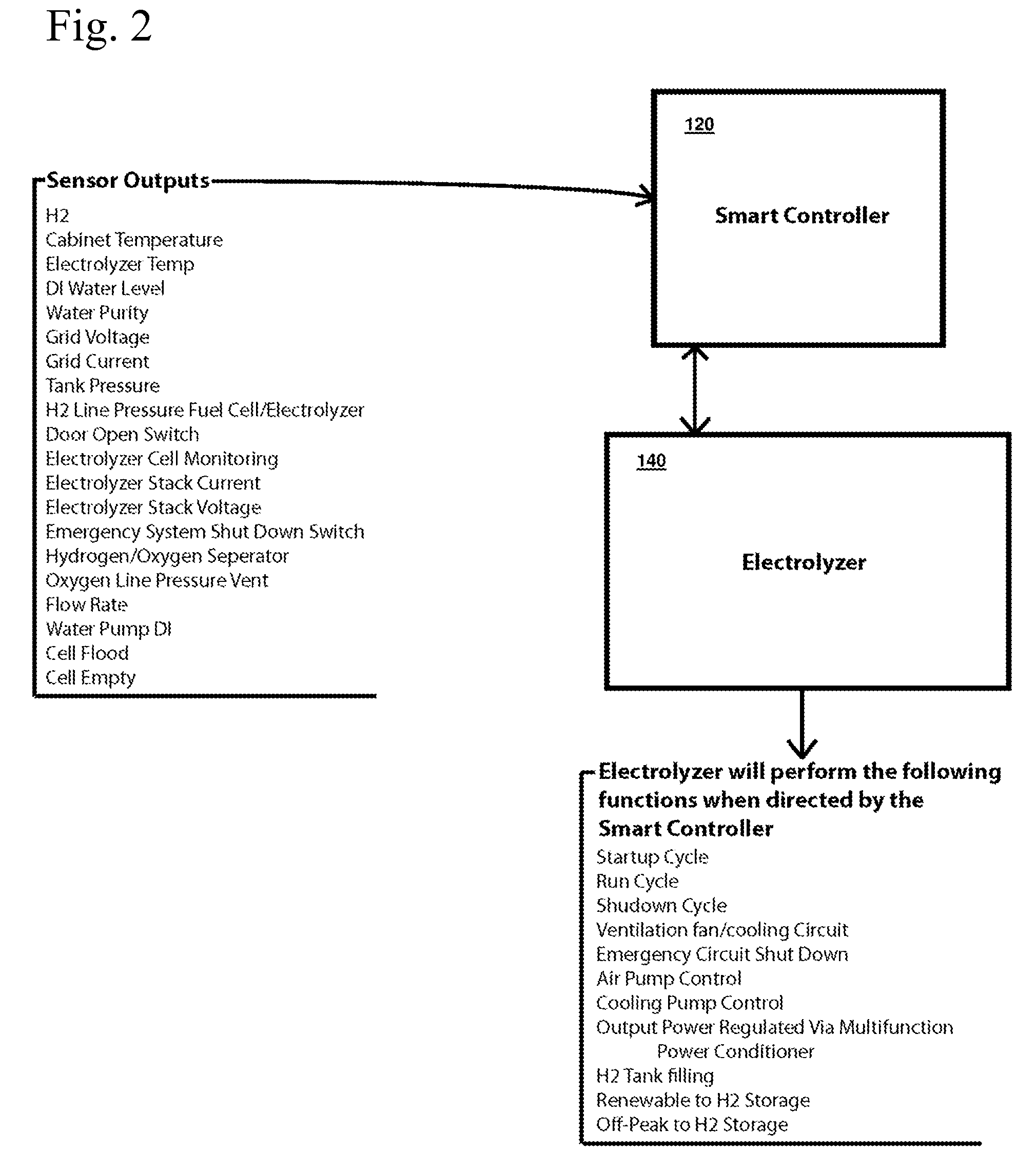
Renewable energy management and storage system
InactiveUS20090189445A1Firmly connectedBatteries circuit arrangementsEnergy industryElectricityAlternating current
An integrated system of renewable energy management and storage that receives direct current generated from renewable sources and intelligently routes the electrical power between a direct current circuit and an alternating current circuit, and at the same time determines the optimal routing for electrical storage based on usage and demand. Electrical power from the direct current circuit can be converted to alternating current electrical power and supplied to the alternating current circuit, or vice versa. Electrical power from either the direct current circuit or the alternating current can be stored in the energy storage subsystem. Electric energy can be further converted to and stored as gaseous hydrogen and can supply for other applications that consume gaseous hydrogen. The system can work with a connection to a utility grid or as a stand-alone system.
Owner:RENEWABLE ENERGY HLDG
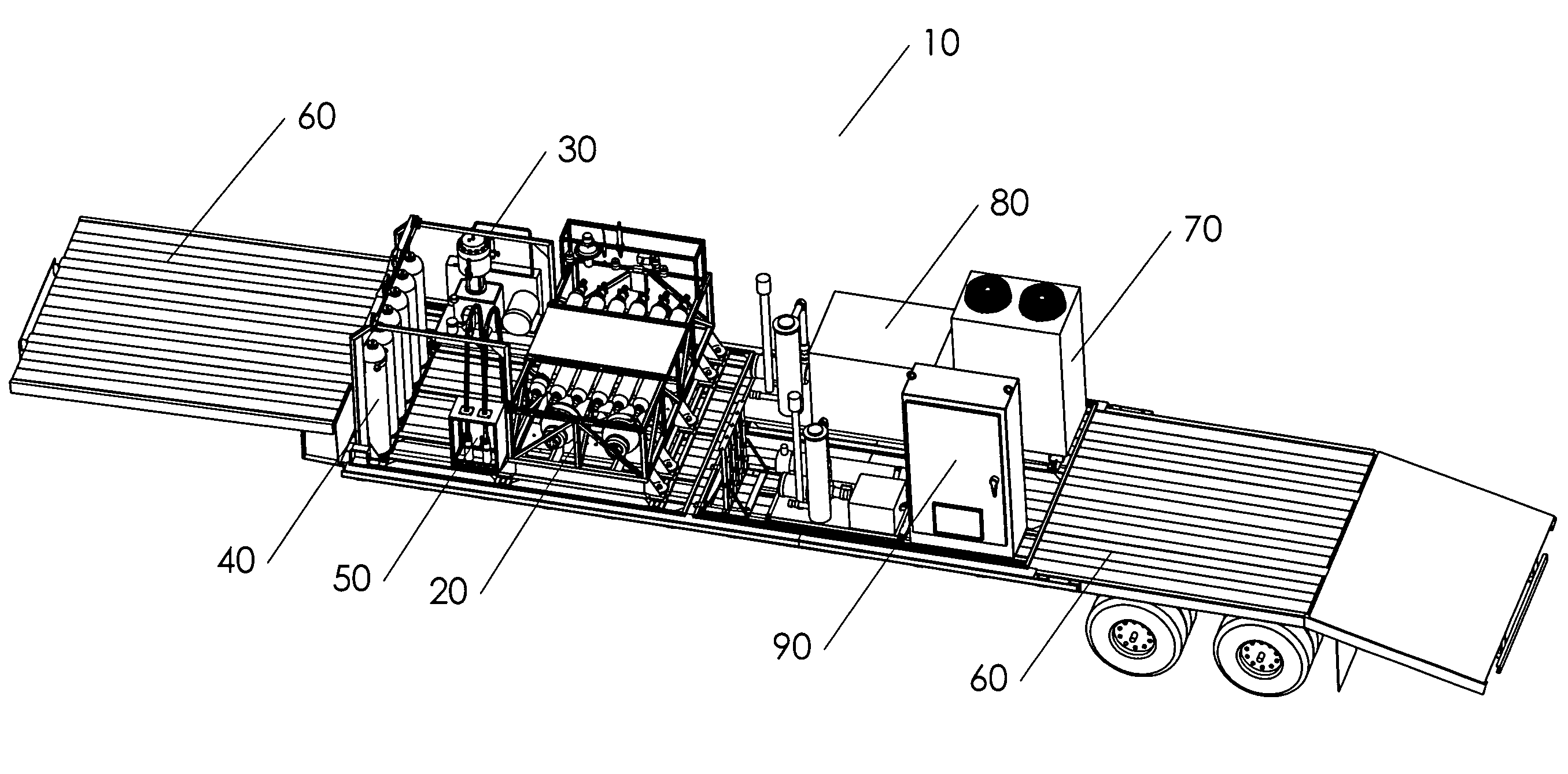
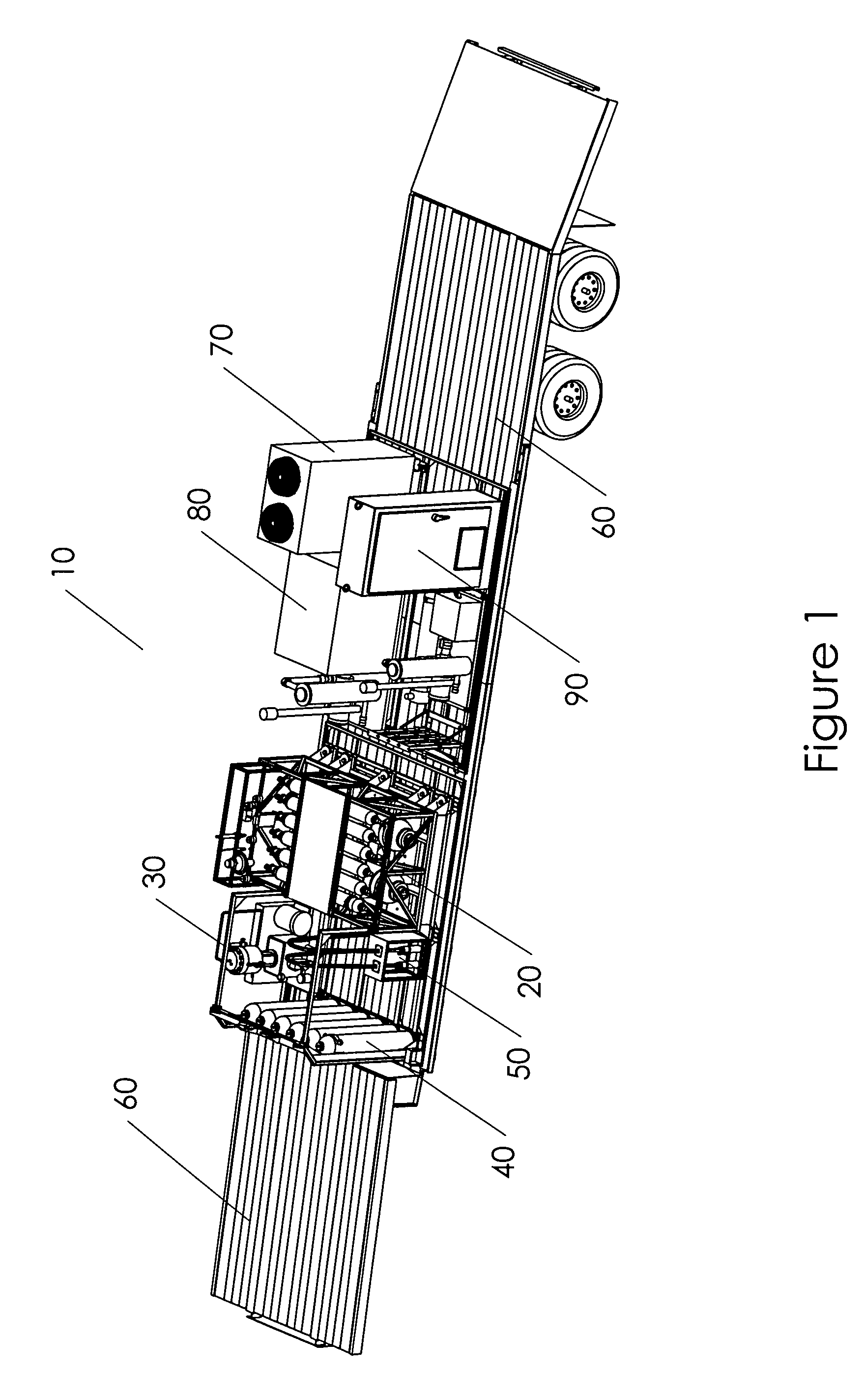
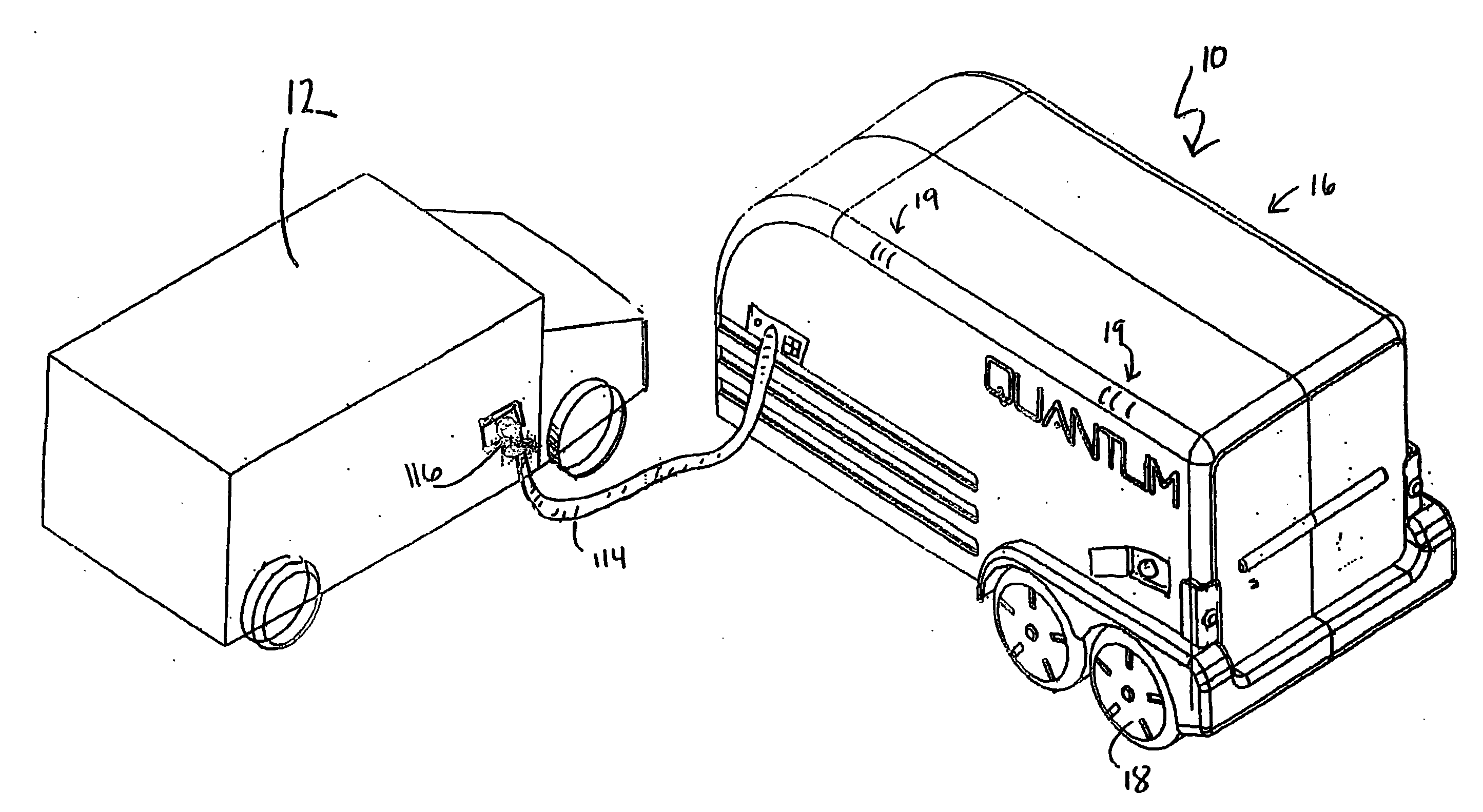
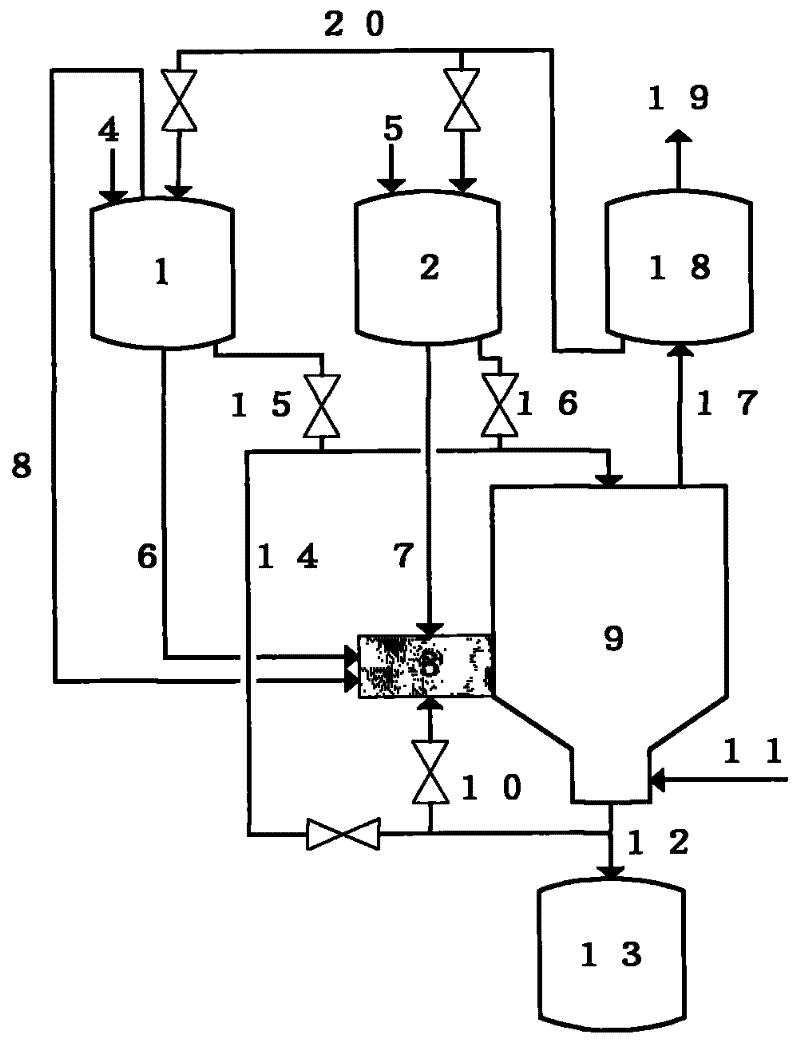
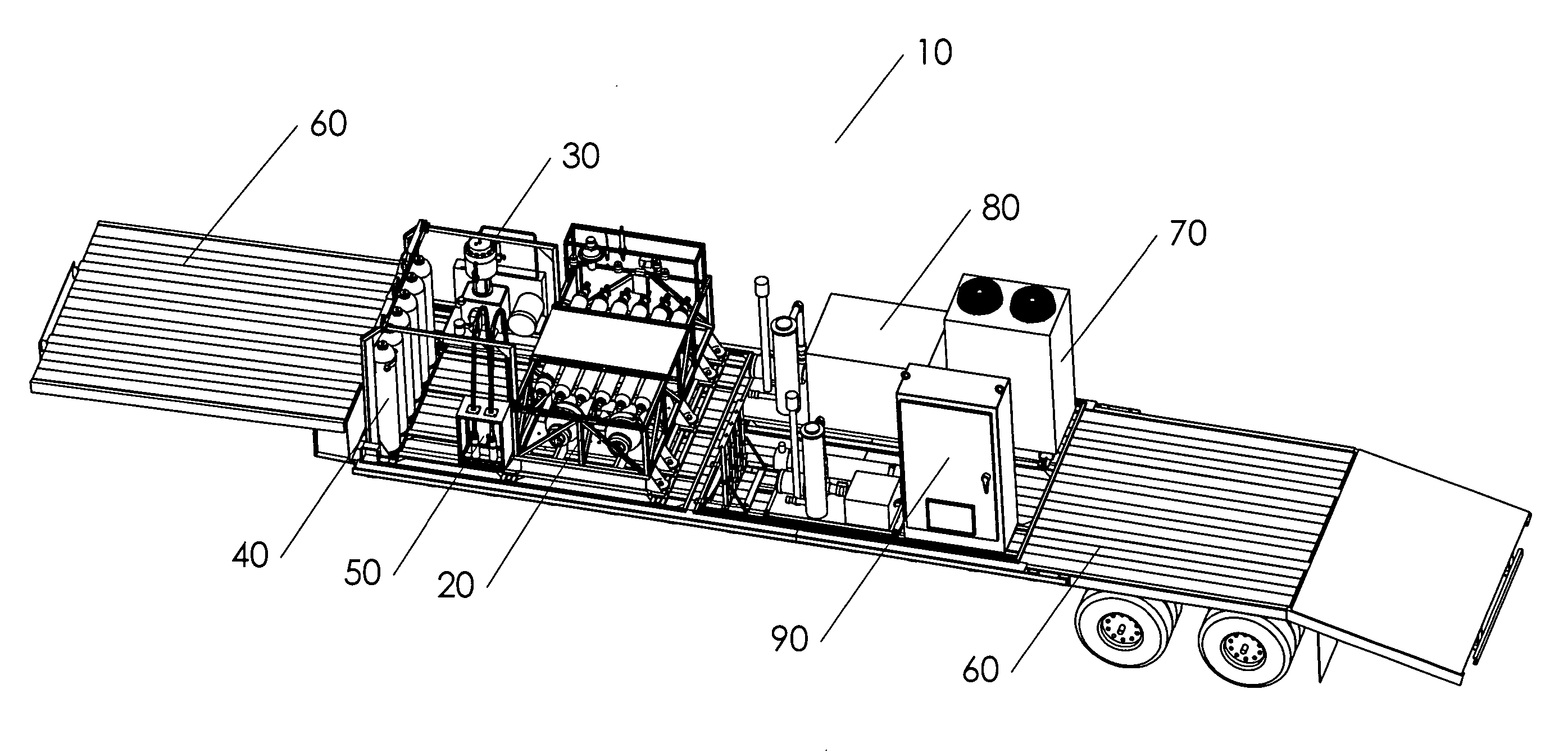
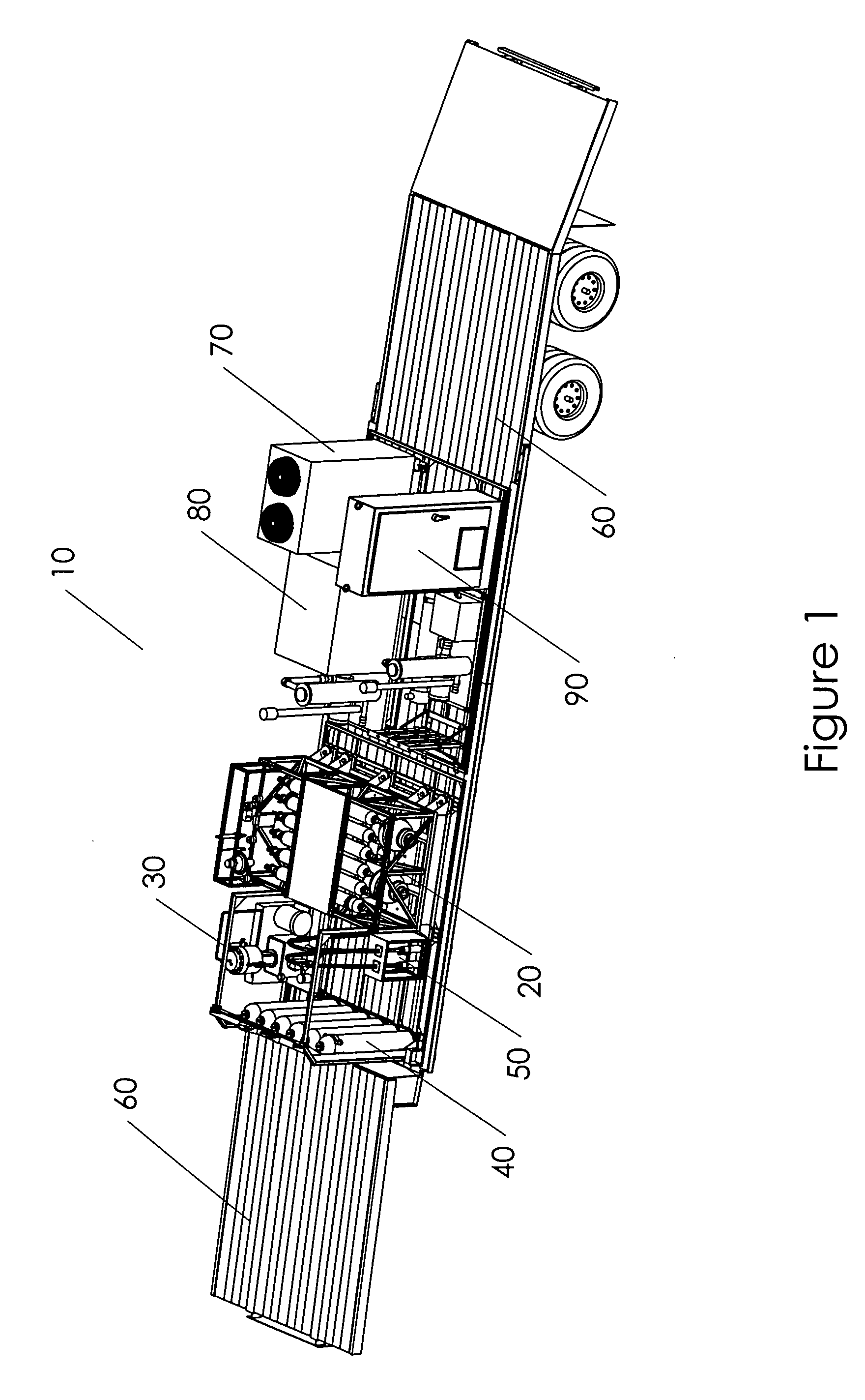
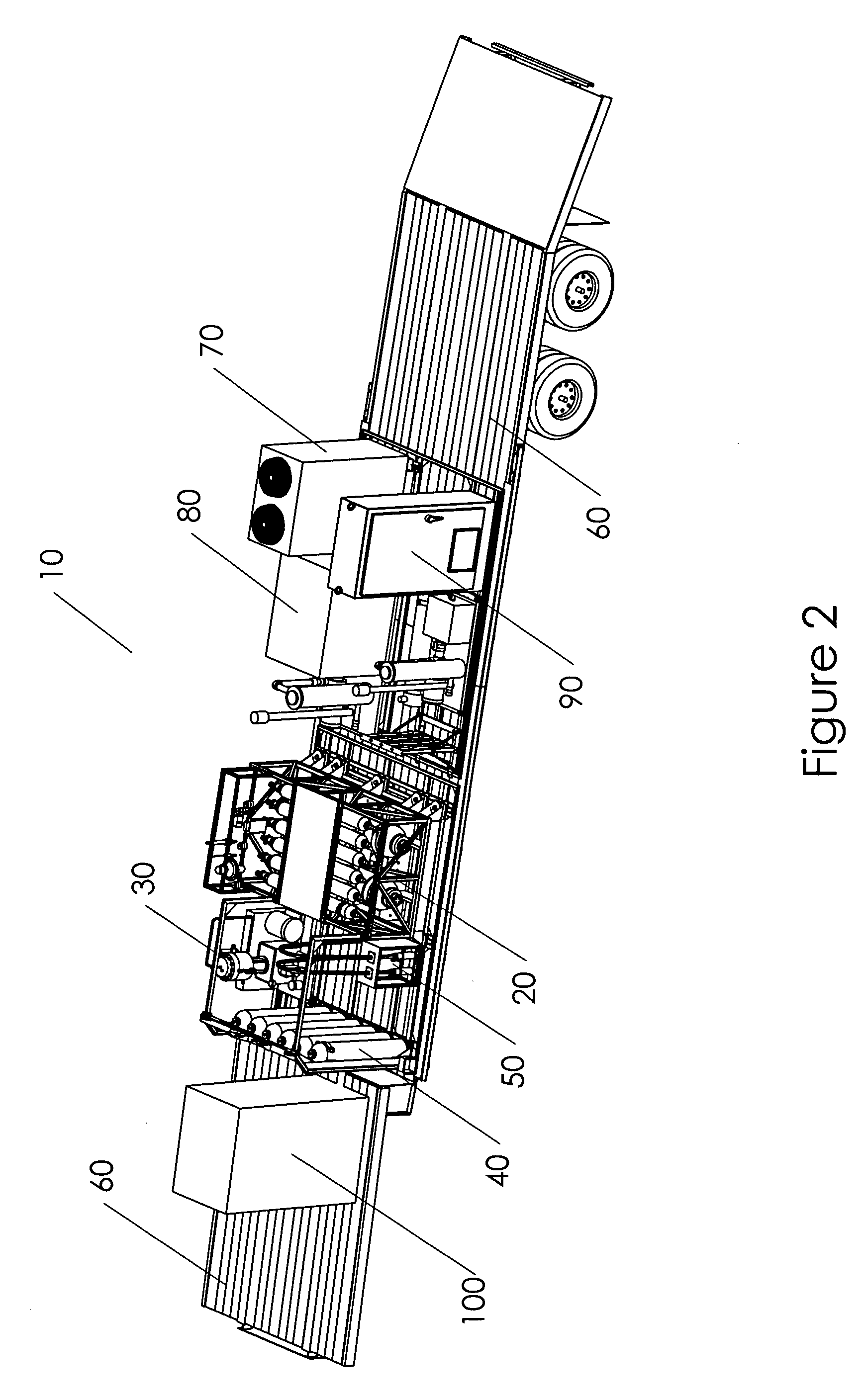
Mobile hydrogen delivery system
A mobile hydrogen delivery system for delivering a compressed stream of hydrogen at pressures up to 15000 psig. The mobile hydrogen delivery system includes a hydrogen compression system, a gaseous hydrogen storage system, and a delivery system for supplying hydrogen to end users. A mobile platform supports the hydrogen compression system, the gaseous hydrogen storage system, and the dispensing system. The mobile platform may be any platform, such as a trailer, capable of being pulled, pushed, or supported by any type of vehicle, such a truck, train, boat, tractor, etc.
Owner:HARNYSS IP LLC +1
Duplex coated steel composite products and method of manufacturing them
InactiveUS6110571AEasy to useElevation is easyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCarbidePlasma nitridation
Duplex coated steel composite products comprising a first layer of a nitrided layer formed by applying glow discharge at a current density from 0.001 to 2.0 mA / cm2 to the surface of metal parts by using gaseous ammonia and gaseous hydrogen while maintaining the temperature of the metal parts at 300 to 650 DEG C., thereby applying plasma nitriding and a second layer comprising a hard film comprising a nitride, carbide and / or carbonitride of one or more of elements selected from Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta and Cr coated on the first layer by the PVD method of a laminate film or a gradient laminate film of such hard film. The treated products are excellent in adhesion with the substrate and durability and have both oxidation resistance and wear resistance.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Porous silica granule, method for producing the same, and method for producing synthetic quartz glass powder using the porous silica granule
InactiveUS6849242B1Minimizes pore diameterHigh bulk densitySilicaGlass blowing apparatusMean diameterSlurry
The granule consists of individual granules approximately spherical in shape, having a pore volume of 0.5 cm3, a mean diameter of pores of 50 nm or less, a specific surface area of 100 m2 / g or less, and a bulk density of 0.7 g / cm3 or higher. It is produced by dispersing a fumed silica obtained by hydrolysis of a silicon compound into pure water to obtain a slurry, and drying the slurry. The granule is used for producing high purity synthetic quartz glass powder. The method further comprises: a first heat treatment under an oxygen-containing atmosphere, a second heat treatment in a temperature range of from 600 to 1100° C., and a third heat treatment in a temperature range of from 1100 to 1300° C. under an atmosphere containing hydrogen chloride; and a step of densification comprising calcining the product at a temperature not higher than 1500° C. under vacuum or in an atmosphere of gaseous hydrogen or gaseous helium. To calcine the powder without causing fusion adhesion of the particles, bubbling fluidization of said porous silica granule is conducted by supplying gaseous helium and calcining thereof in a temperature range of from 1000 to 1600° C.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS +1
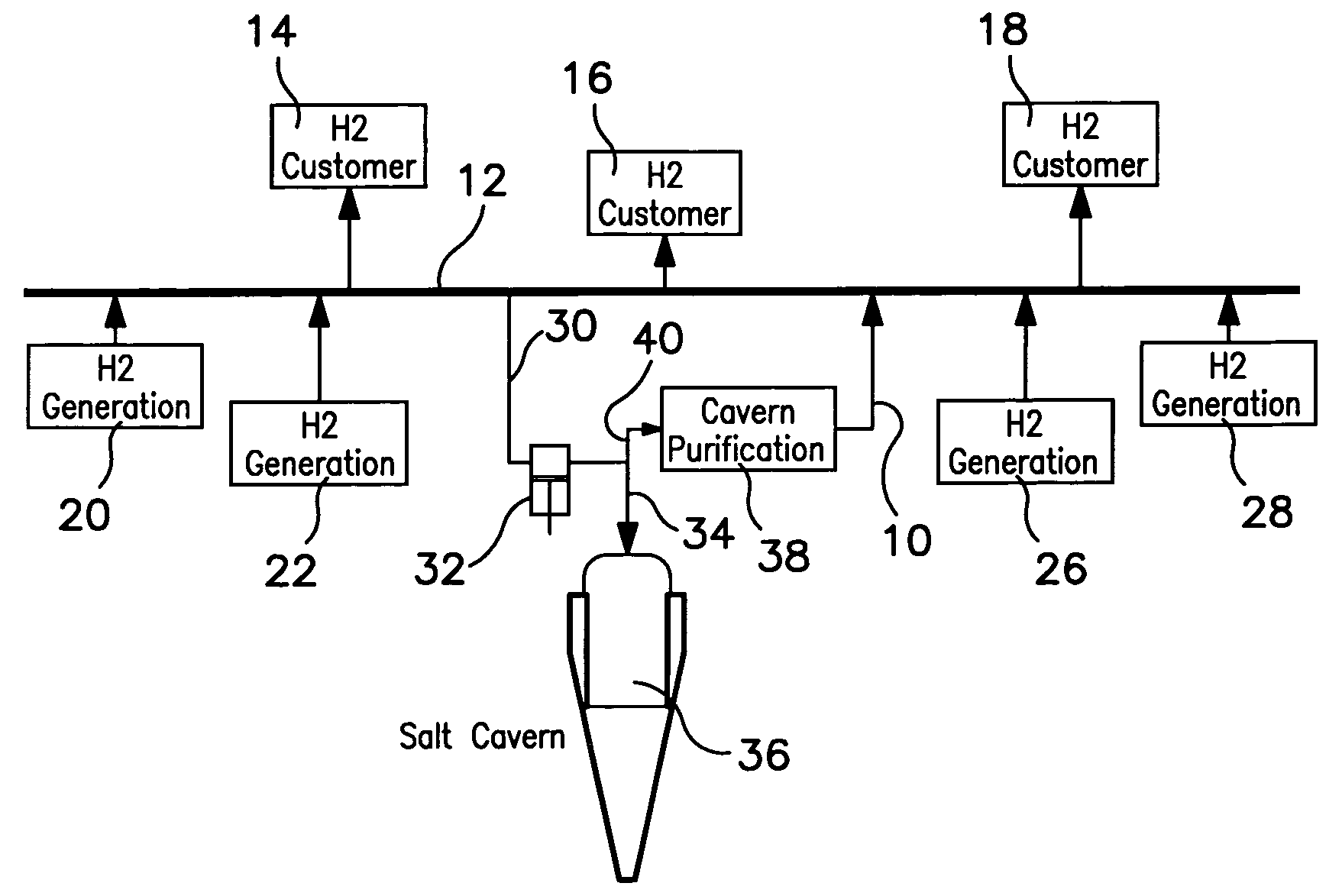
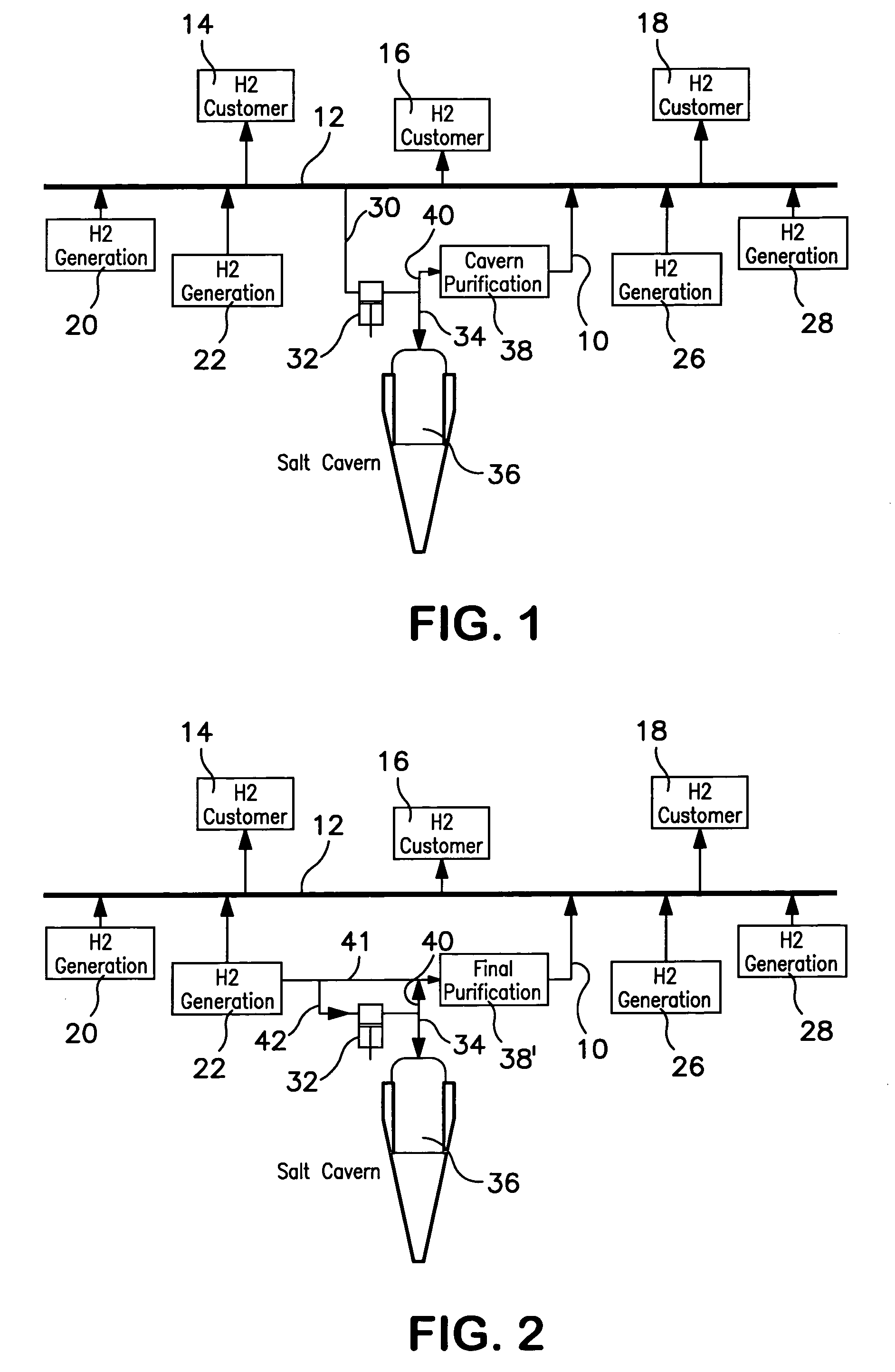
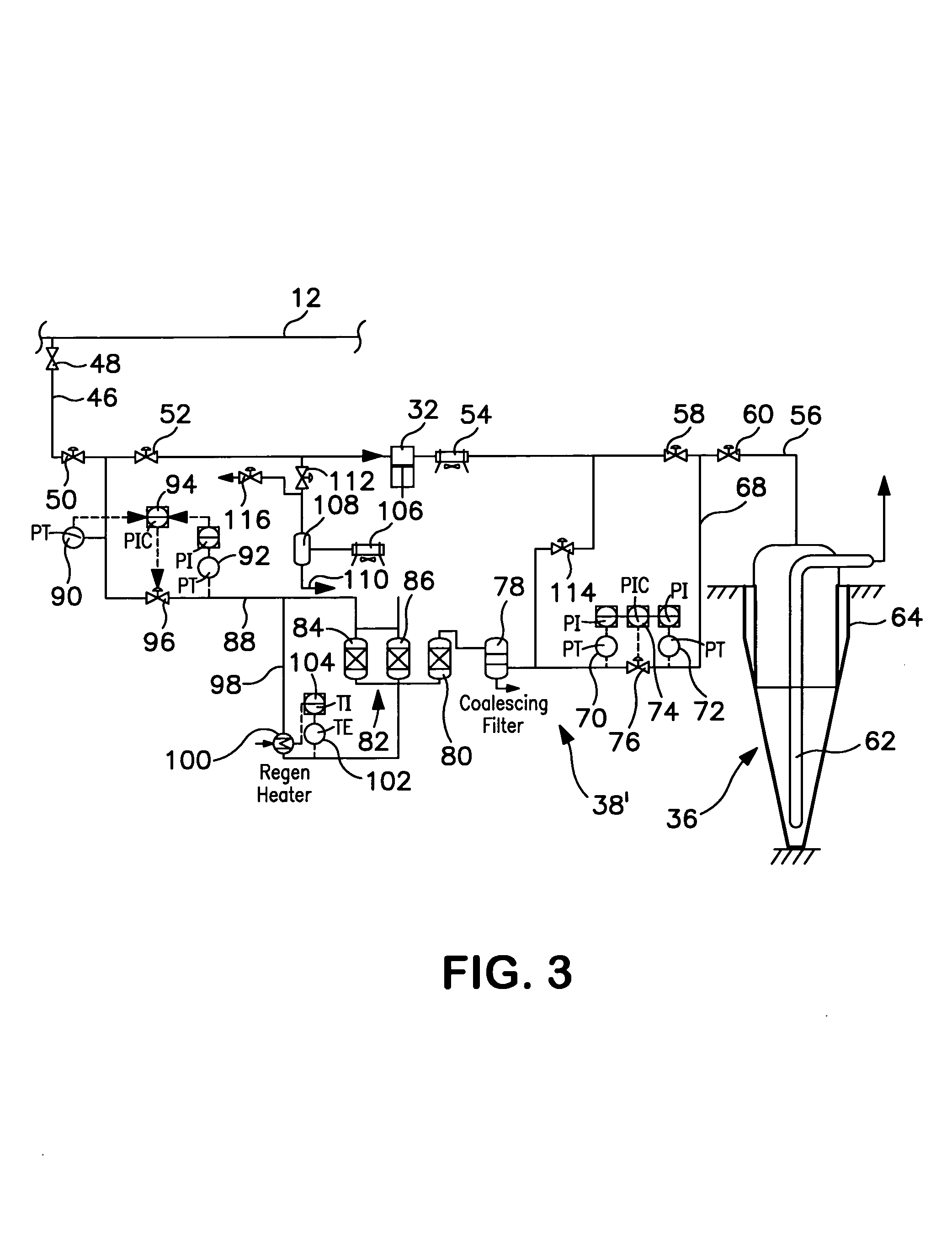
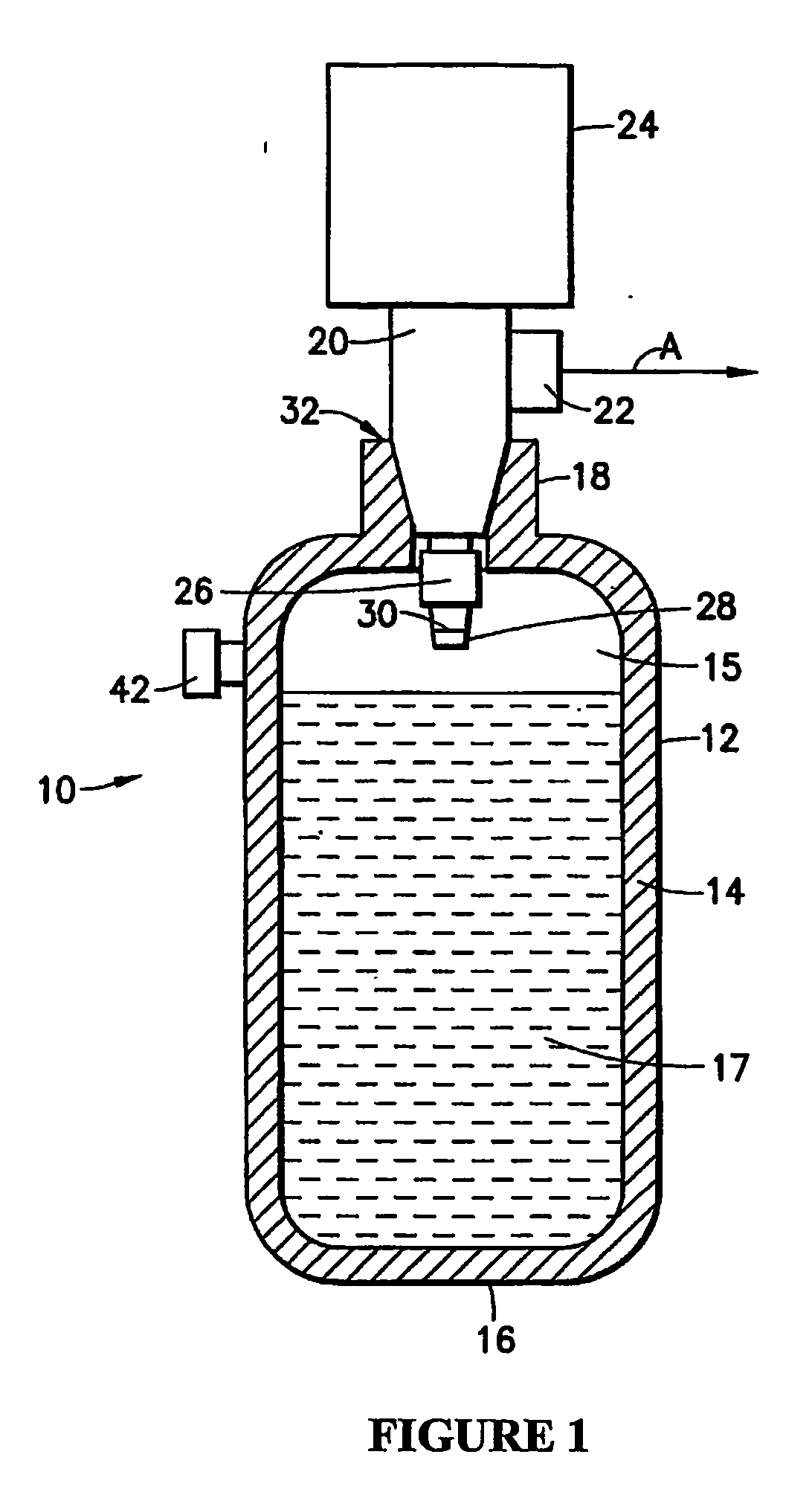
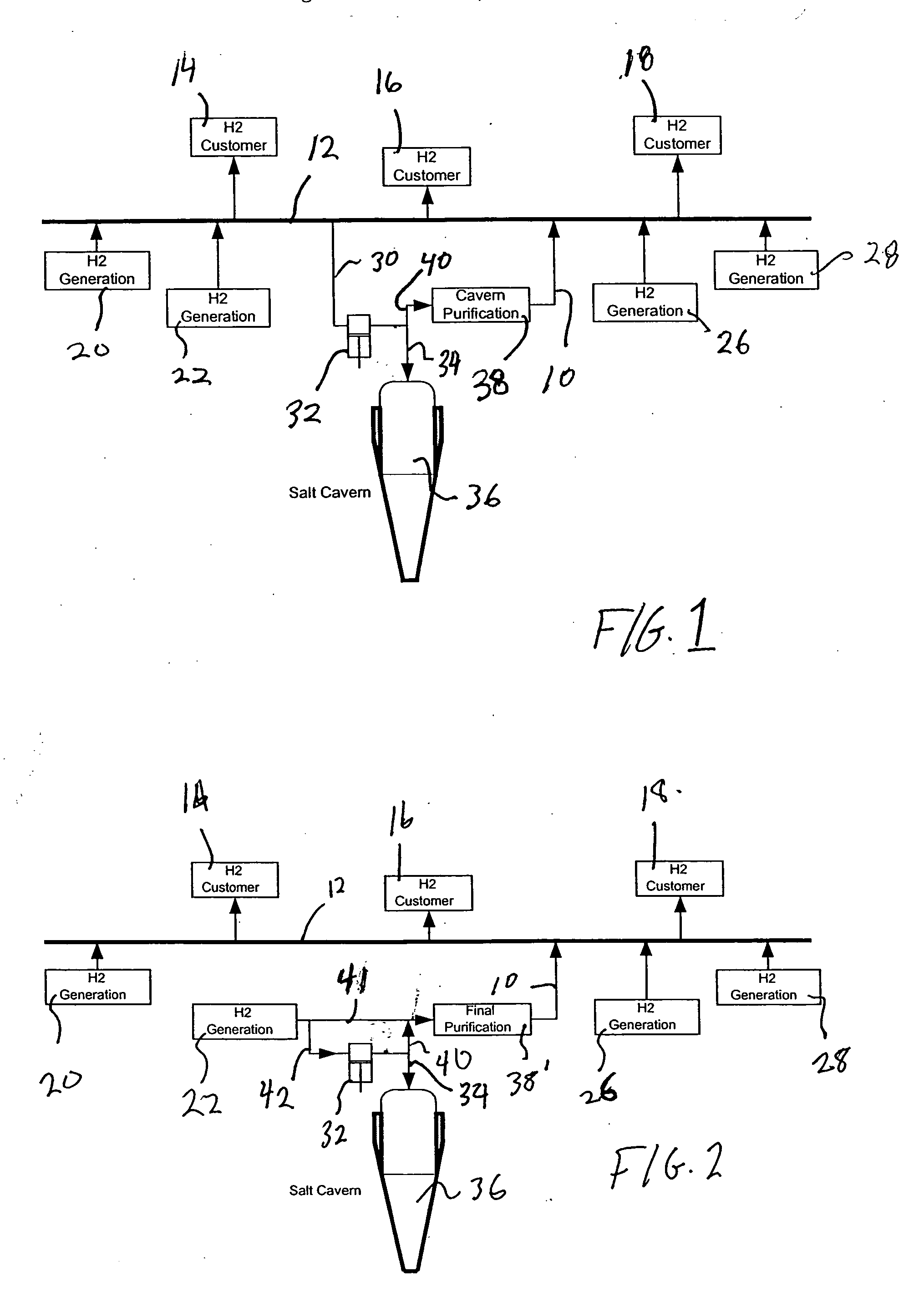
Method of storing and supplying hydrogen to a pipeline
A method of storing and supplying a gaseous hydrogen product to a pipeline under a product purity specification in which a hydrogen stream made up of gaseous hydrogen is compressed to form a compressed hydrogen stream and introduced into a salt cavern for storage. A crude hydrogen stream, contaminated from storage in the salt cavern is recovered and purified by sufficiently removing at least carbon dioxide and water vapor to produce a hydrogen product stream having an impurity level at or below the product purity specification. The hydrogen product stream is supplied back to the pipeline. Alternatively, during periods of low demand, hydrogen produced by a production facility is both purified and supplied to the pipeline and stored in the salt cavern. During high demand period, both the output of the production facility and hydrogen retrieved from the salt cavern are purified and supplied to the pipeline.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
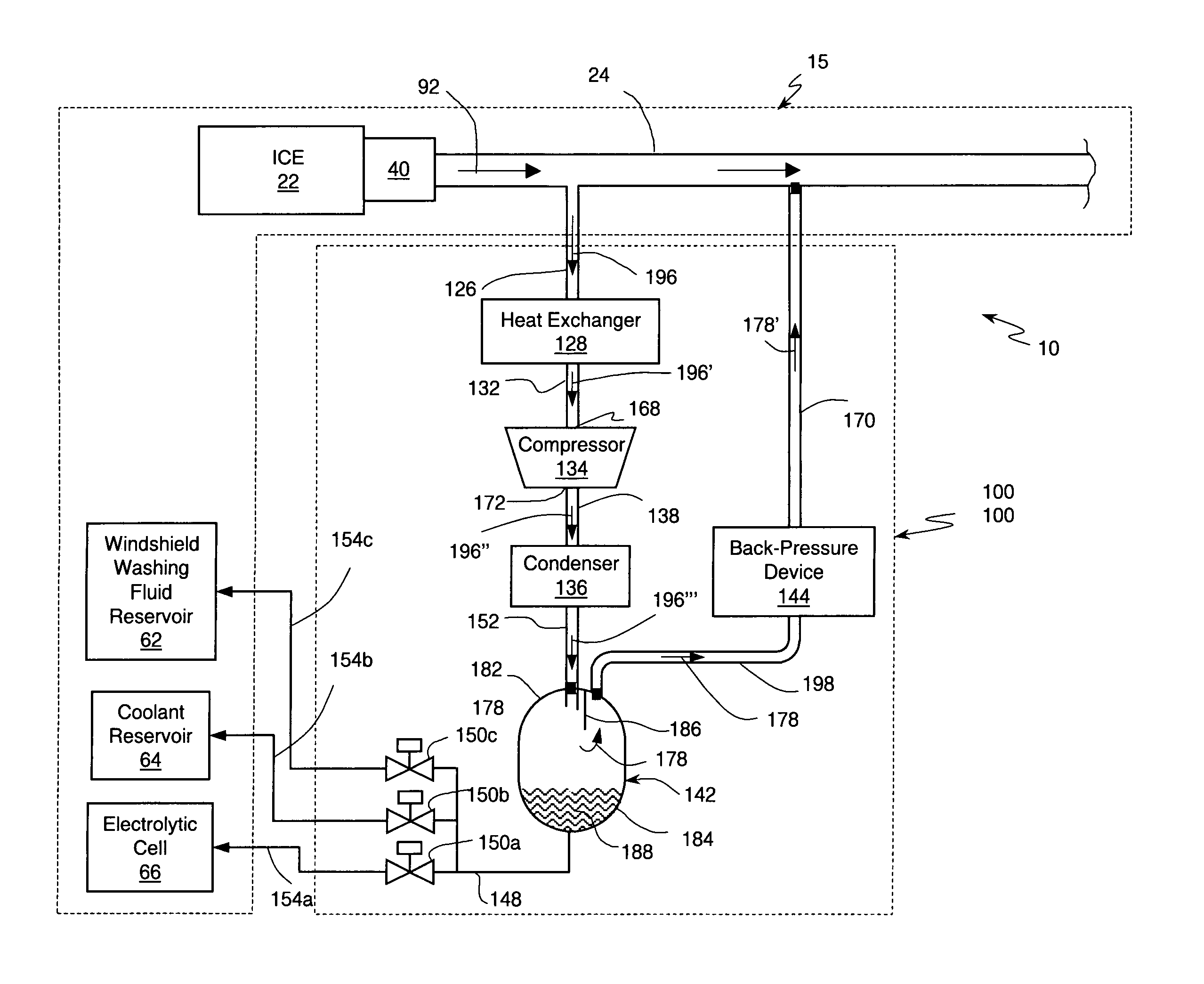
Internal combustion engine/water source system
InactiveUS7302795B2Increase pointsSimple and reliable processNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineWater source
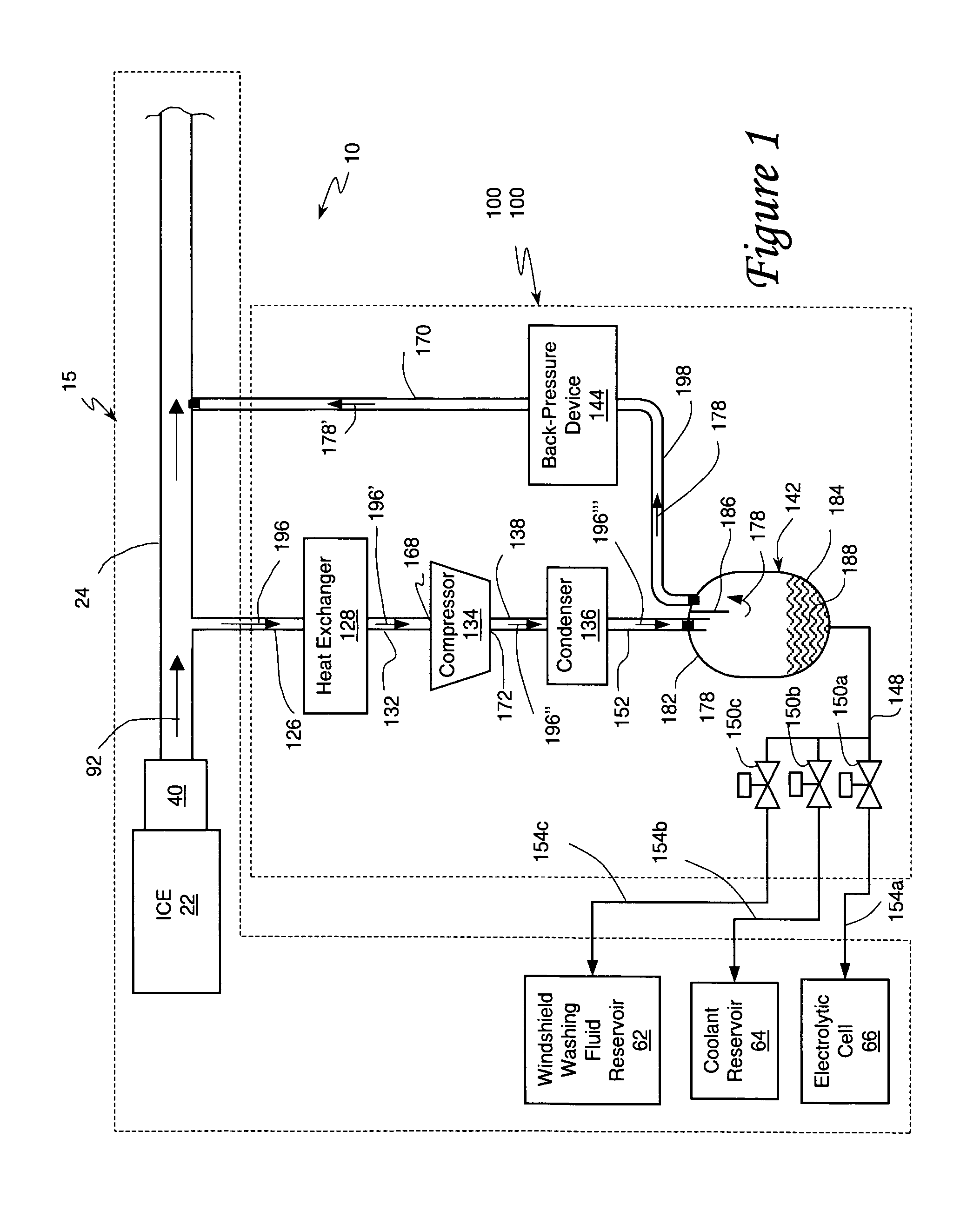
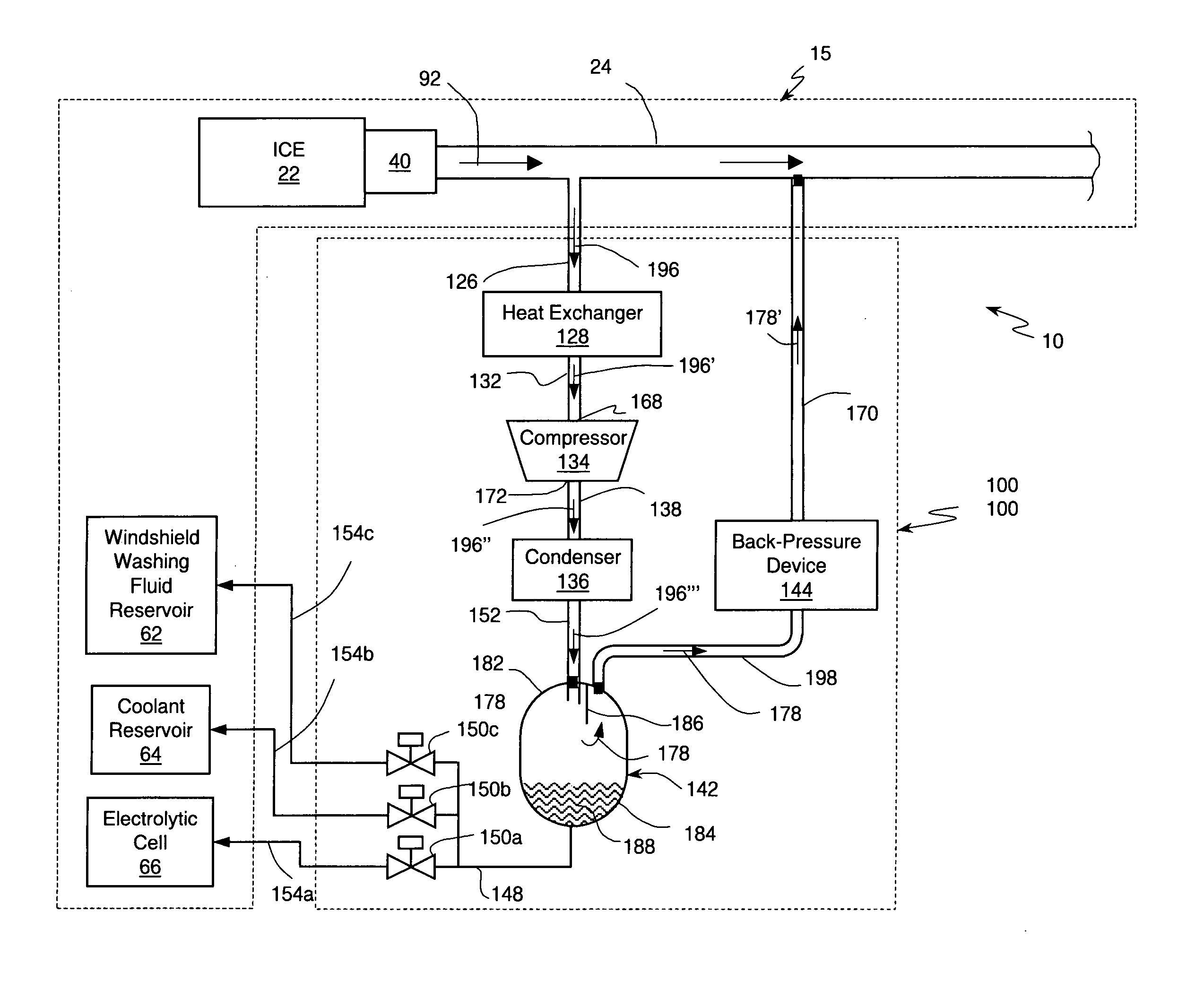
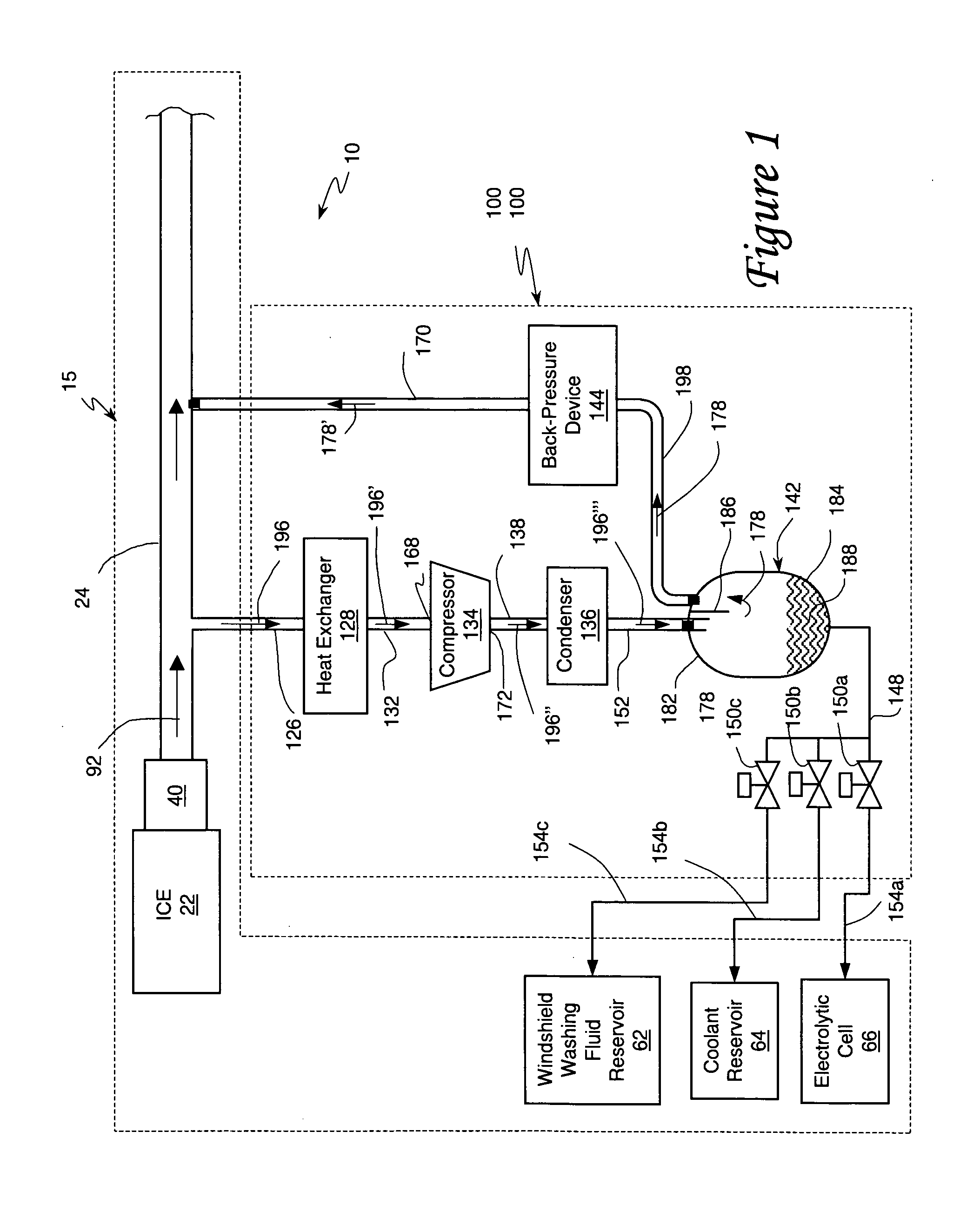
An internal combustion engine system for automotive vehicle wherein liquid water is produced by cooling a portion of exhaust gases at elevated pressure to induce condensation. The use of elevated pressure allows condensation to occur at a higher dew point which is easier to realize with cooling by ambient air. Liquid water condensate is collected and provided to an electrolytic cell for electrolysis into gaseous hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen gas generated by the cell is used by the internal combustion engine to reduce internal combustion engine wear and to reduce exhaust pollutants especially during start-up. Alternate uses of the liquid water include a replenishment of engine coolant and window washing fluid.
Owner:VETROVEC JAN
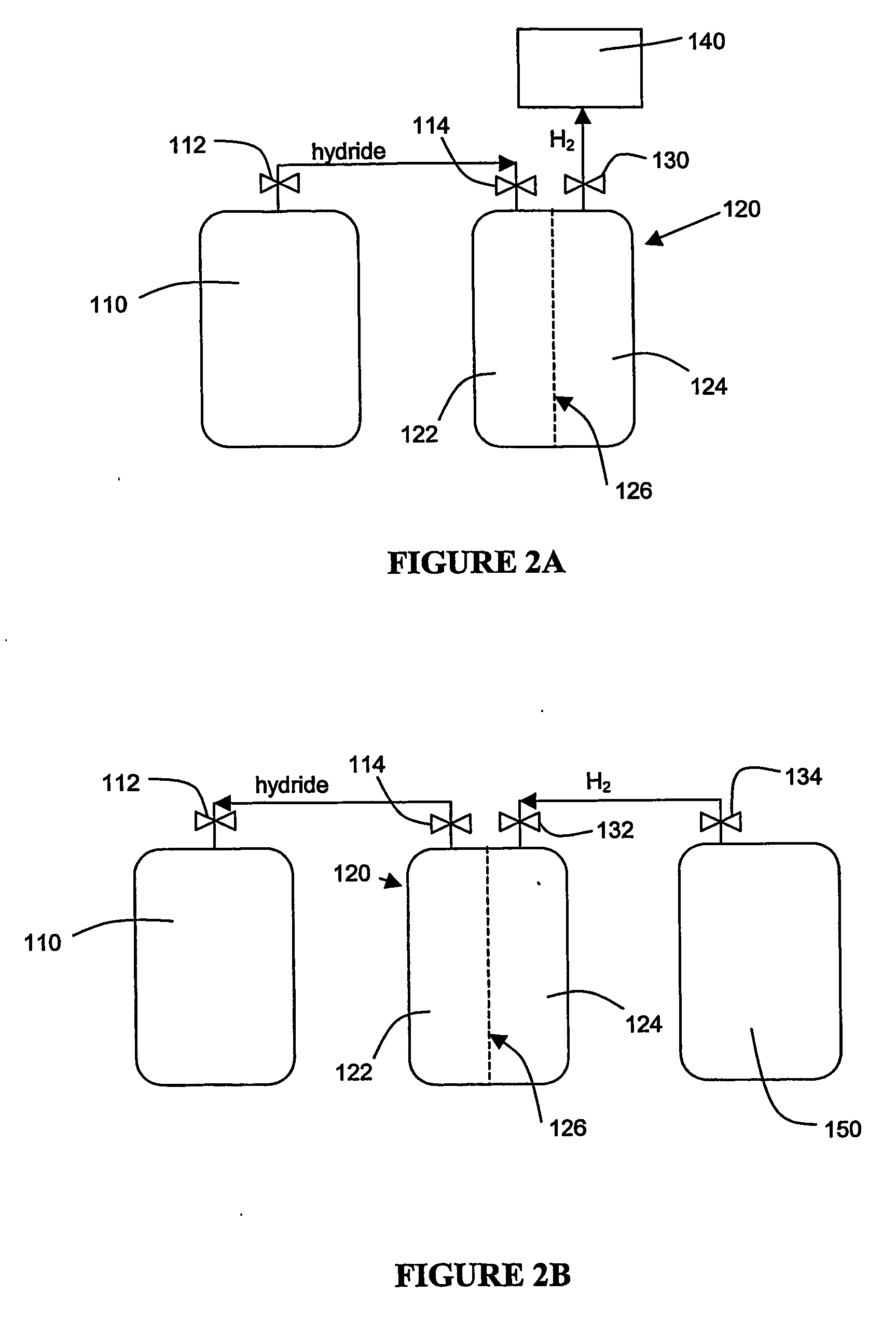
Method for managing storage of gaseous hydrogen
InactiveUS20090250138A1Increase profitImprove hydrogen utilizationLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsHydrogen vehicleGaseous hydrogen
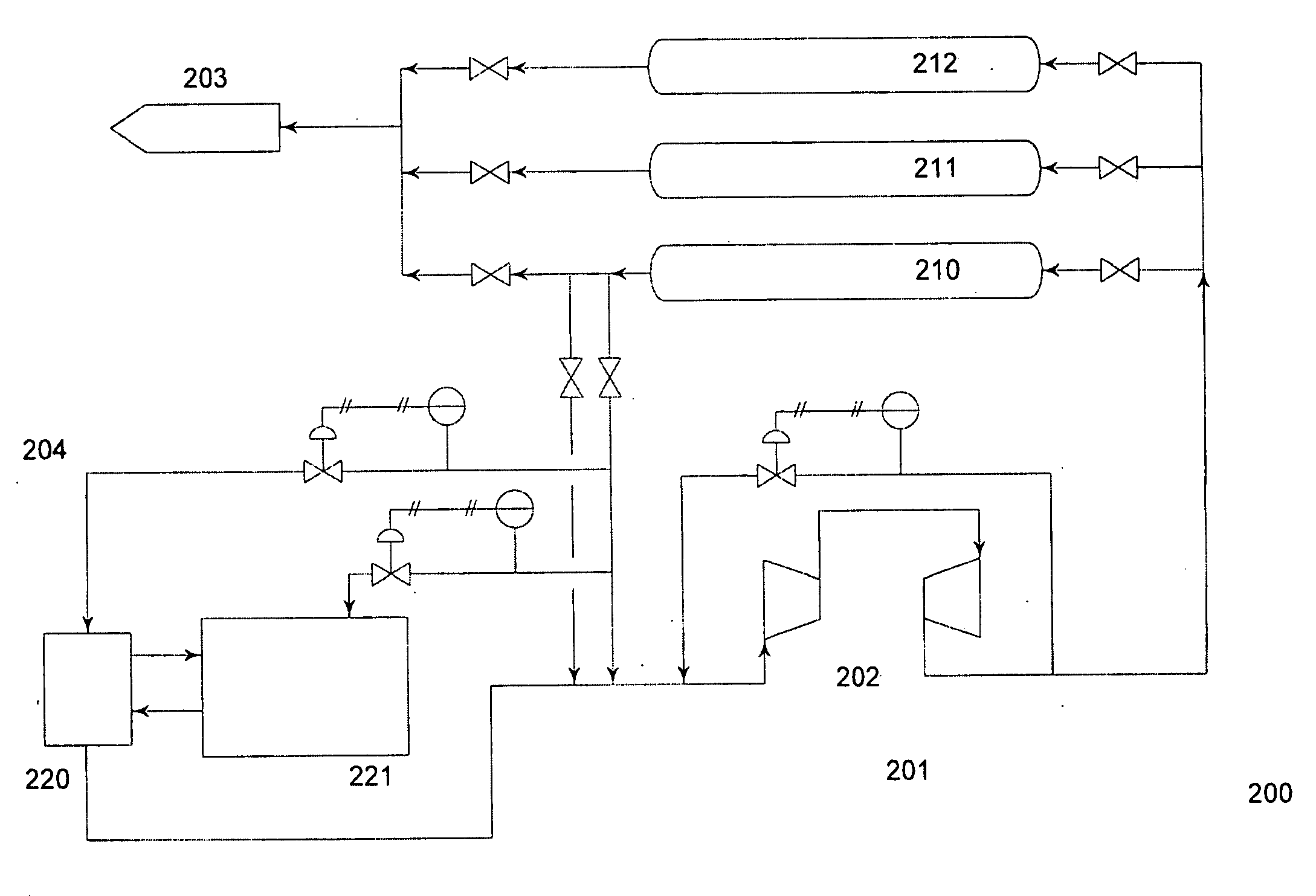
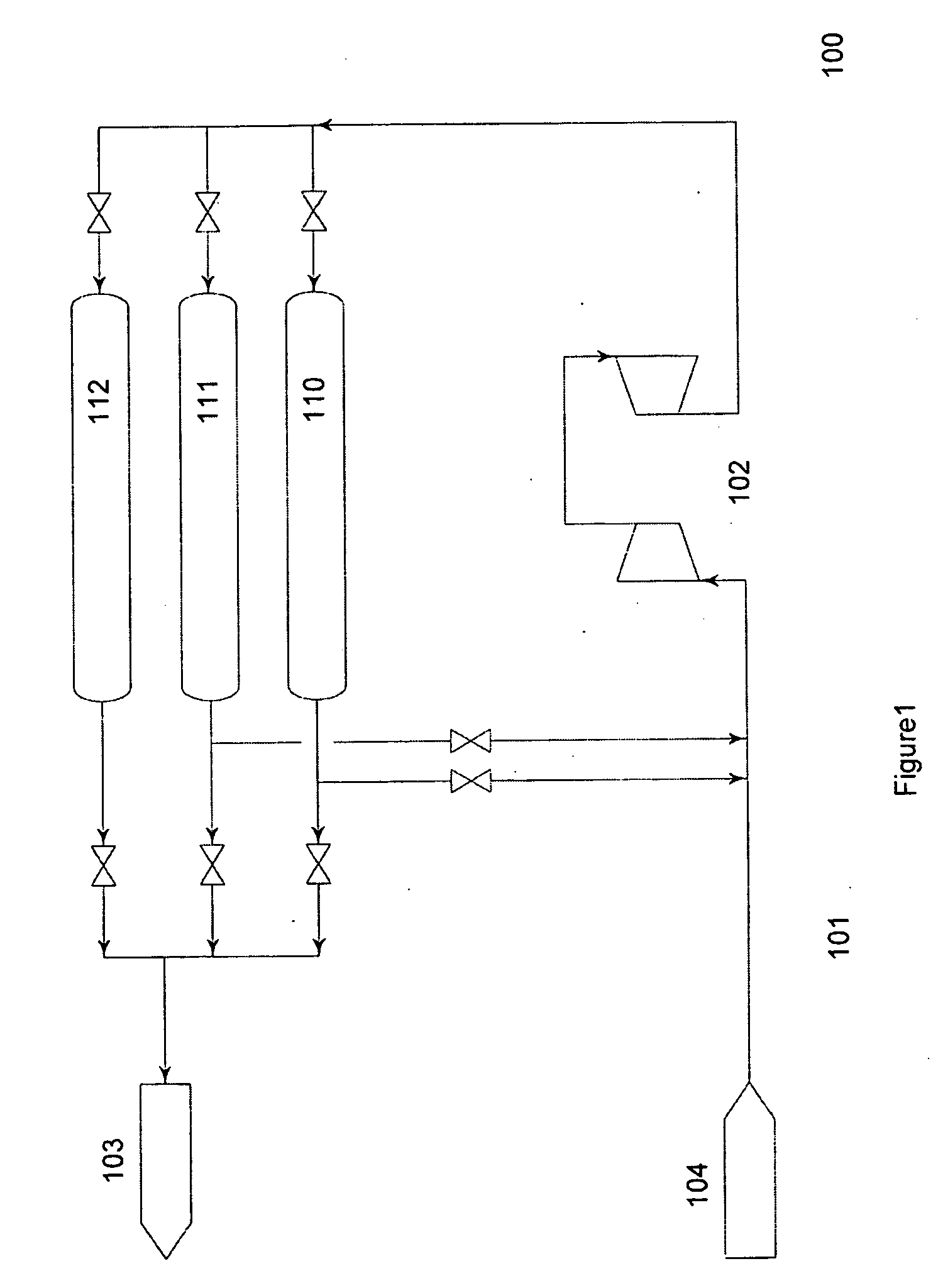
The present invention discloses methods for managing the storage of gaseous hydrogen and increasing the utilization rate of gaseous hydrogen stored in a cascade storage system. In order to increase the hydrogen utilization rate of the cascade storage system, after dispensing gaseous hydrogen to a hydrogen vehicle, gaseous hydrogen is transferred via a compressor from at least one storage vessel at a lower pressure to at least one storage vessel at a higher, dispensable pressure. The methods of the present invention economically and efficiently increase the utilization rate of gaseous hydrogen stored in a cascade storage system.
Owner:TEXACO INC
Internal combustion engine/water source system
InactiveUS20070137590A1Easy to operateReduce pollutantsElectrolysis componentsInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineWater source
An internal combustion engine / water source system for a vehicle powered by a internal combustion engine wherein liquid water is produced by cooling a portion of engine exhaust gases in a vortex tube to induce condensation. In one embodiment, engine exhaust gases are pumped into the vortex tube by a compressor. After removing a portion of water vapor, cooled exhaust gases may be re-introduced to engine's combustion chamber thereby providing an exhaust gas recirculation. In an automotive vehicle, liquid water generated by the invention may be collected and provided to an electrolytic cell for electrolysis into gaseous hydrogen to reduce exhaust pollutants during cold engine start. Alternatively, water generated by the invention may be injected into engine combustion chamber to increase power and to reduce production of nitrogen oxides.
Owner:VETROVEC JAN
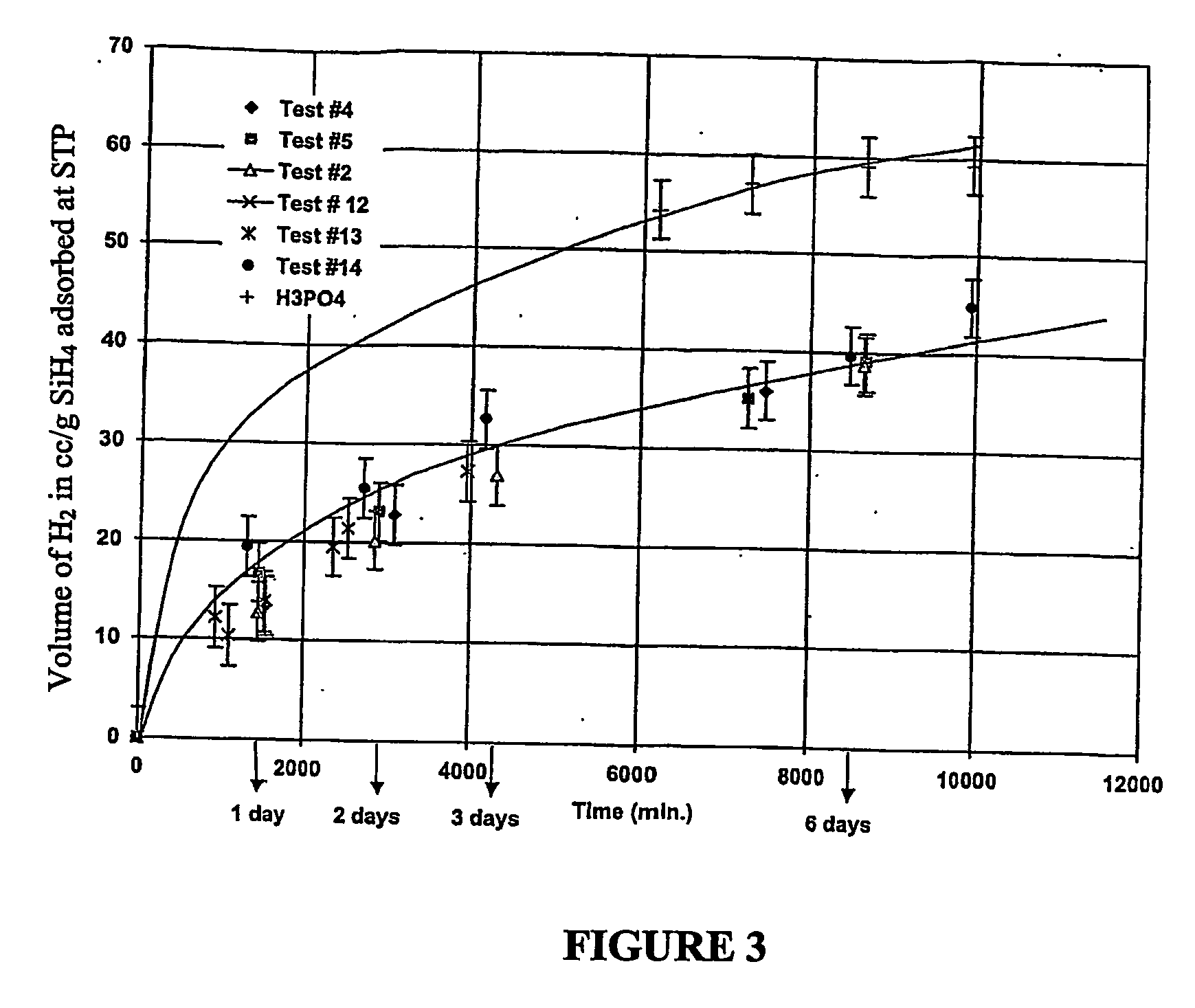
Hydrogen generation
An apparatus and method including storage and dispensing vessels to safely store and dispense gaseous hydrides, where the storage and dispensing vessels contain a solid-phase physical sorbent medium having a physically sorptive affinity for gaseous hydrides, and wherein the gaseous hydride is decomposed in the apparatus to generate hydrogen gas. The gaseous hydrides include, but are not limited to, silane, germane, stibine and diborane. The gaseous hydrides decompose spontaneously and / or decomposition is enhanced using surface modified adsorbents. The hydrogen generated by the apparatus may be used in a fuel cell or other hydrogen gas consuming unit.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Method of storing and supplying hydrogen to a pipeline
A method of storing and supplying a gaseous hydrogen product to a pipeline under a product purity specification in which a hydrogen stream made up of gaseous hydrogen is compressed to form a compressed hydrogen stream and introduced into a salt cavern for storage. A crude hydrogen stream, contaminated from storage in the salt cavern is recovered and purified by sufficiently removing at least carbon dioxide and water vapor to produce a hydrogen product stream having an impurity level at or below the product purity specification. The hydrogen product stream is supplied back to the pipeline. Alternatively, during periods of low demand, hydrogen produced by a production facility is both purified and supplied to the pipeline and stored in the salt cavern. During high demand period, both the output of the production facility and hydrogen retrieved from the salt cavern are purified and supplied to the pipeline.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Method for filling gaseous hydrogen storage tanks
InactiveUS20090151809A1Efficient refilling of the gaseous hydrogen storage tanksEfficient dispensing of gaseous hydrogenVessel mounting detailsGas handling applicationsHydrogen vehicleGaseous hydrogen
The present invention discloses methods for filling gaseous hydrogen storage tanks. The methods of the present invention include methods for refilling gaseous hydrogen storage tanks utilizing a cascade fill. The methods of the present invention provide for the efficient refilling of the gaseous hydrogen storage tanks and the efficient dispensing of gaseous hydrogen to hydrogen vehicles.
Owner:TEXACO INC
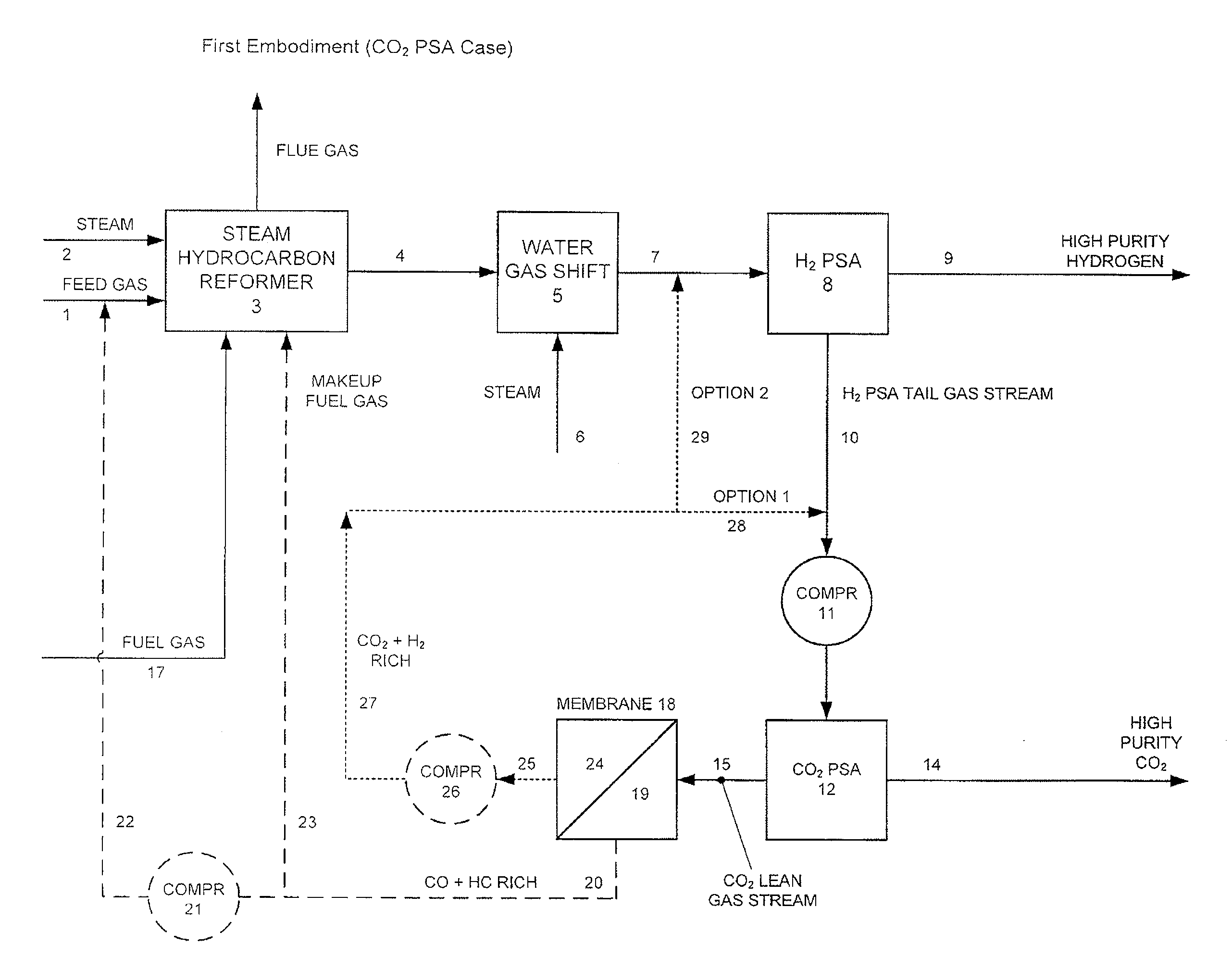
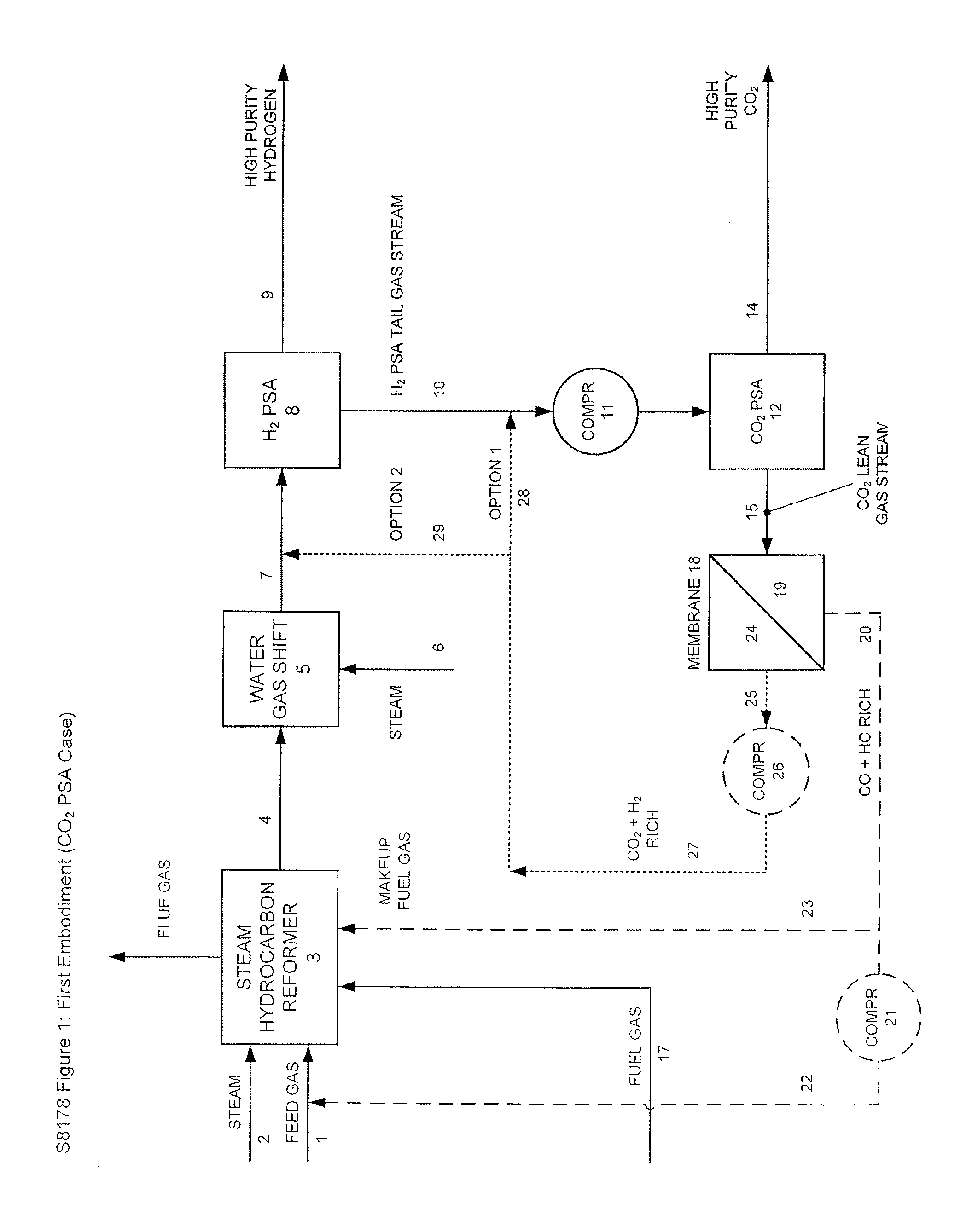
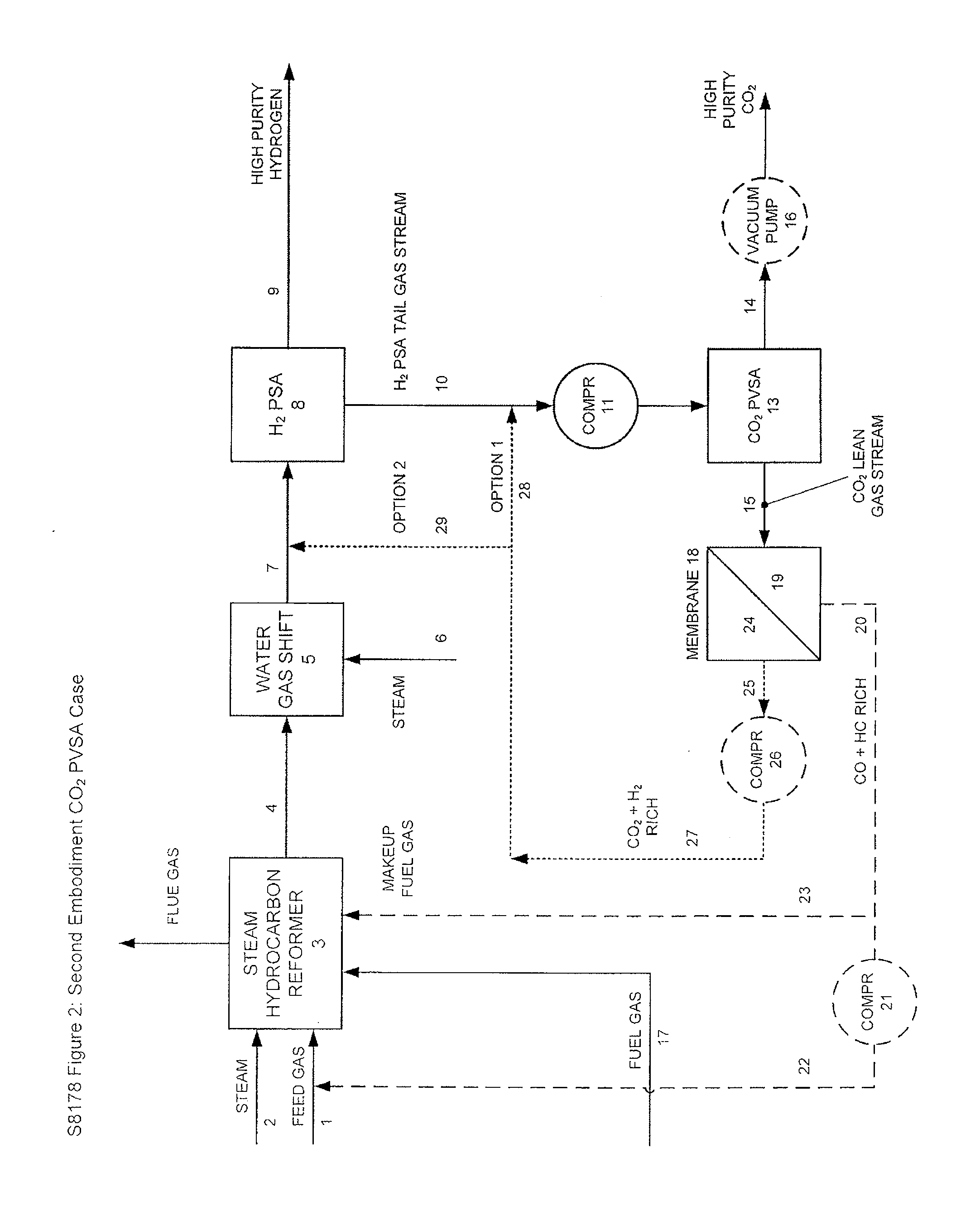
Processes For The Recovery Of High Purity Hydrogen And High Purity Carbon Dioxide
The present invention provides for various processes for recovering high purity gaseous hydrogen and high purity gaseous carbon dioxide from the gas stream produced using steam hydrocarbon reforming, especially steam methane reforming, utilizing a H2 pressure swing adsorption unit in combination with either a CO2 pressure swing adsorption unit in combination with a membrane separation unit or a CO2 pressure vacuum swing adsorption unit in combination with a membrane separation unit. The present invention further relates to a process for optimizing the recovery of carbon dioxide from waste gas streams produced during the hydrogen purification step of a steam hydrocarbon reforming / water gas shift reactor / H2 pressure swing adsorption unit utilizing either a CO2 pressure swing adsorption unit in combination with a membrane separation unit or a CO2 pressure vacuum swing adsorption unit in combination with a membrane separation unit. The present invention even further relates to the apparatus necessary to carry out the various processes of the present invention.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE IND US LP +1
Transportable hydrogen refueling station
InactiveUS20060180240A1Reduce riskEasy to monitorTank vehiclesGas handling applicationsHigh pressureGaseous hydrogen
A portable hydrogen refueling stations which can dispense gaseous hydrogen from one or more internal high pressure tanks. The refueling station can be refilled with a lower pressure hydrogen gas feed and then compressed for storage within a refueling station.
Owner:QUANTUM FUEL SYST TECH WORLDWIDE INC
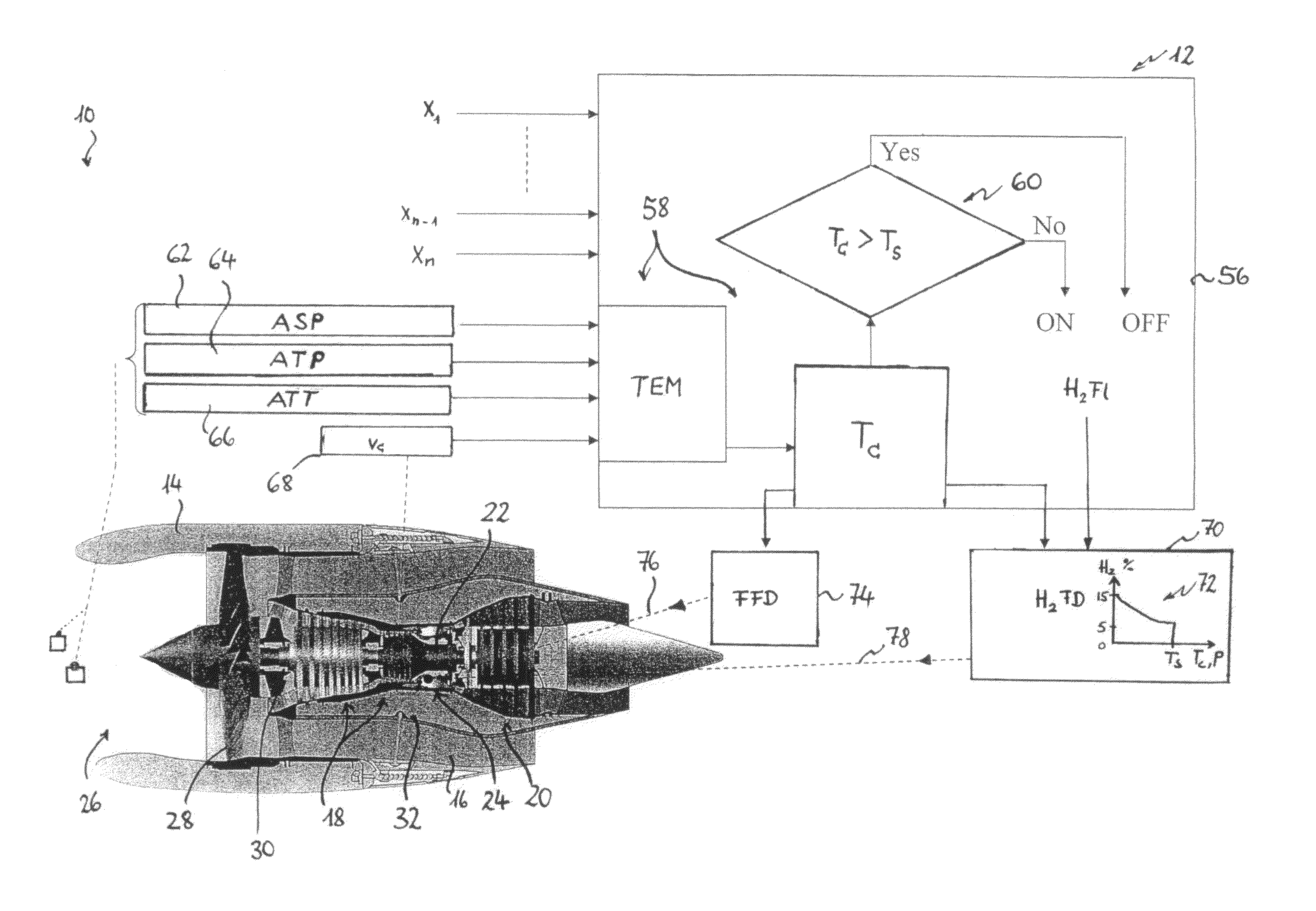
Method for calculating hydrogen temperature during vehicle fueling
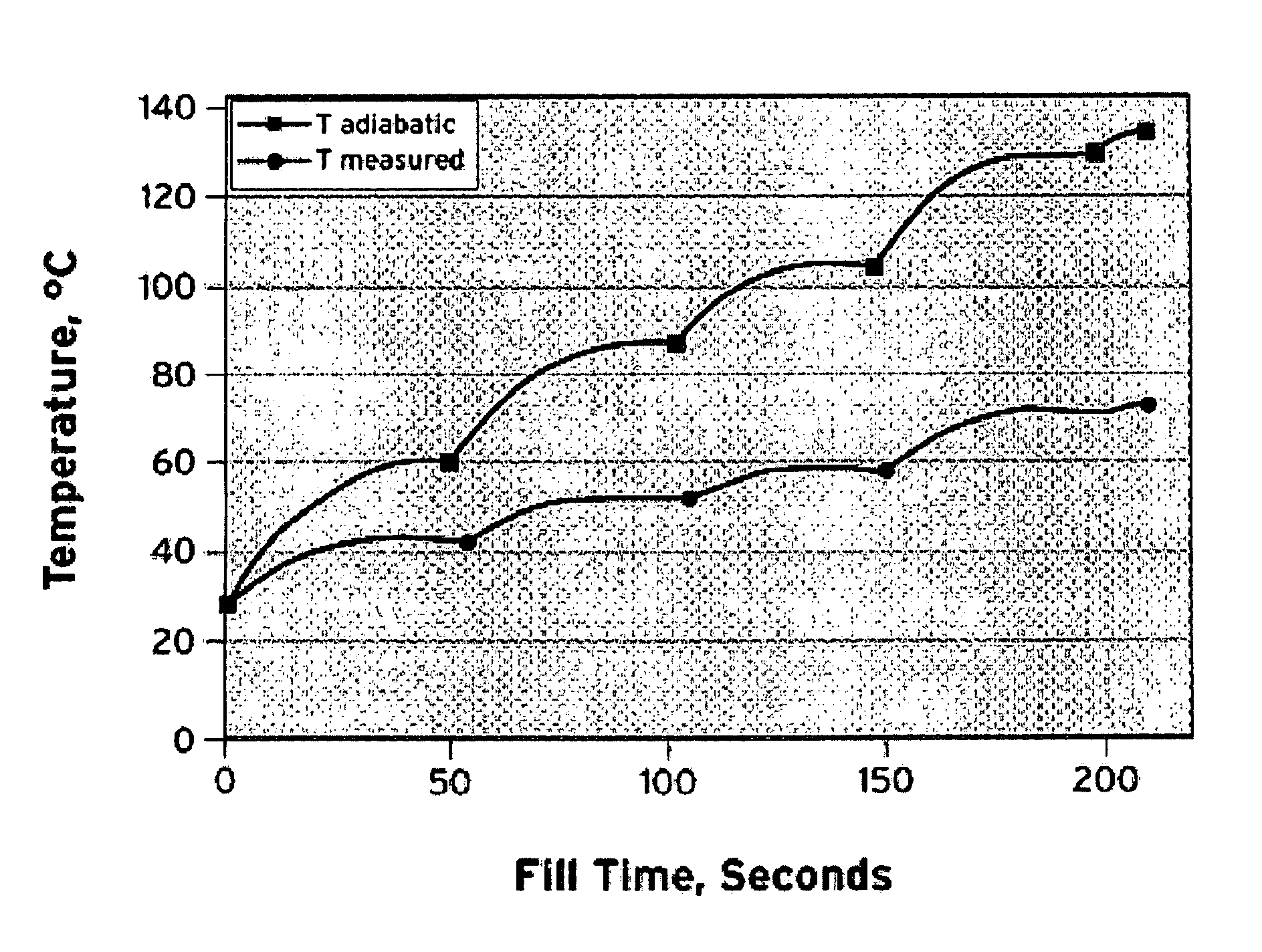
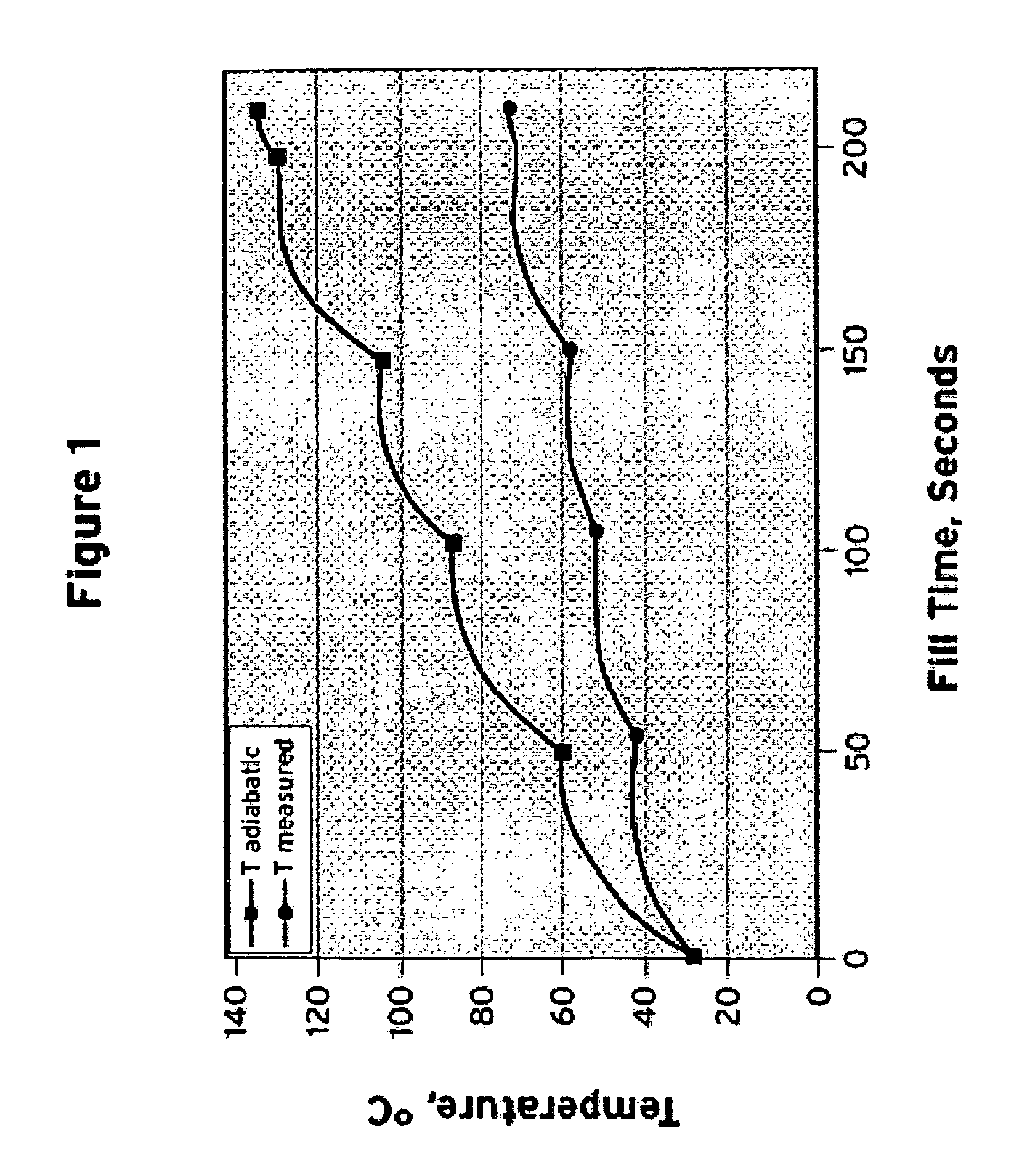
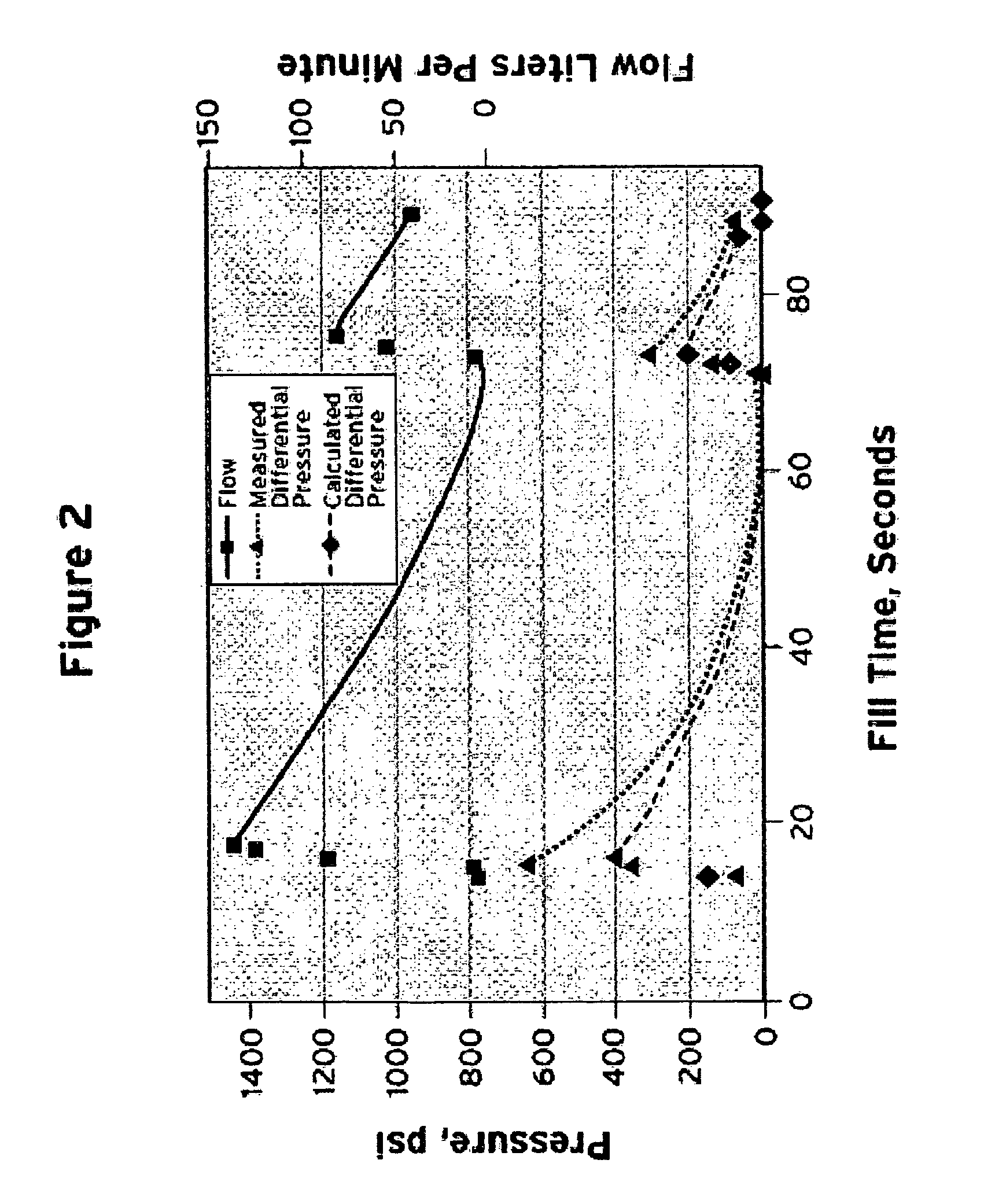
InactiveUS7647194B1Convenient and accurate calculationSafe fueling experienceThermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionOn boardFilling rate
Methods for accurately and conveniently calculating the temperature of gaseous hydrogen during vehicle fueling are disclosed. The metered amount of hydrogen added to the on-board storage tank, the ambient conditions, The pressure measured at the dispenser, and a correlation to account for heat transfer are the inputs to the methods of the present invention. These inputs eliminate the need for obtaining temperature and pressure information from the vehicle which is out of the control of the dispenser and / or energy provider. In addition, the use of the equation of the present invention does not require the fill rate to be limited and the corresponding fill time to be extended.
Owner:TEXACO INC
Hydrogen and oxygen production and accumulating apparatus including an internal combustion engine and method
An apparatus, including an internal combustion engine, produces hydrogen fuel from water to power the engine, comprises water supply means, fuel storage means, controlling means, a collector receiving combustion products output from engine's operation, a transformer utilizing thermo-impact of the combustion products and decomposing supplied water into hydrogen and oxygen, an ion divider electrically separating hydrogen and oxygen ions into gaseous hydrogen, further directed into the fuel storage means and controllably fed substantially into engine's cylinders, and gaseous oxygen. It also includes exhaust means outputting exhaust products from the collector into the atmosphere, on their way out heating water in the water supply means. The fuel storage means contain initial hydrogen or another predetermined fuel. Electrolyzer means are provided to supplement hydrogen and oxygen ions production. Recommended temperature and parts size ranges for six-and eight-cylinder engines are disclosed. A truck engine usable embodiment is also illustrated and described.
Owner:YATSENKO YURIY
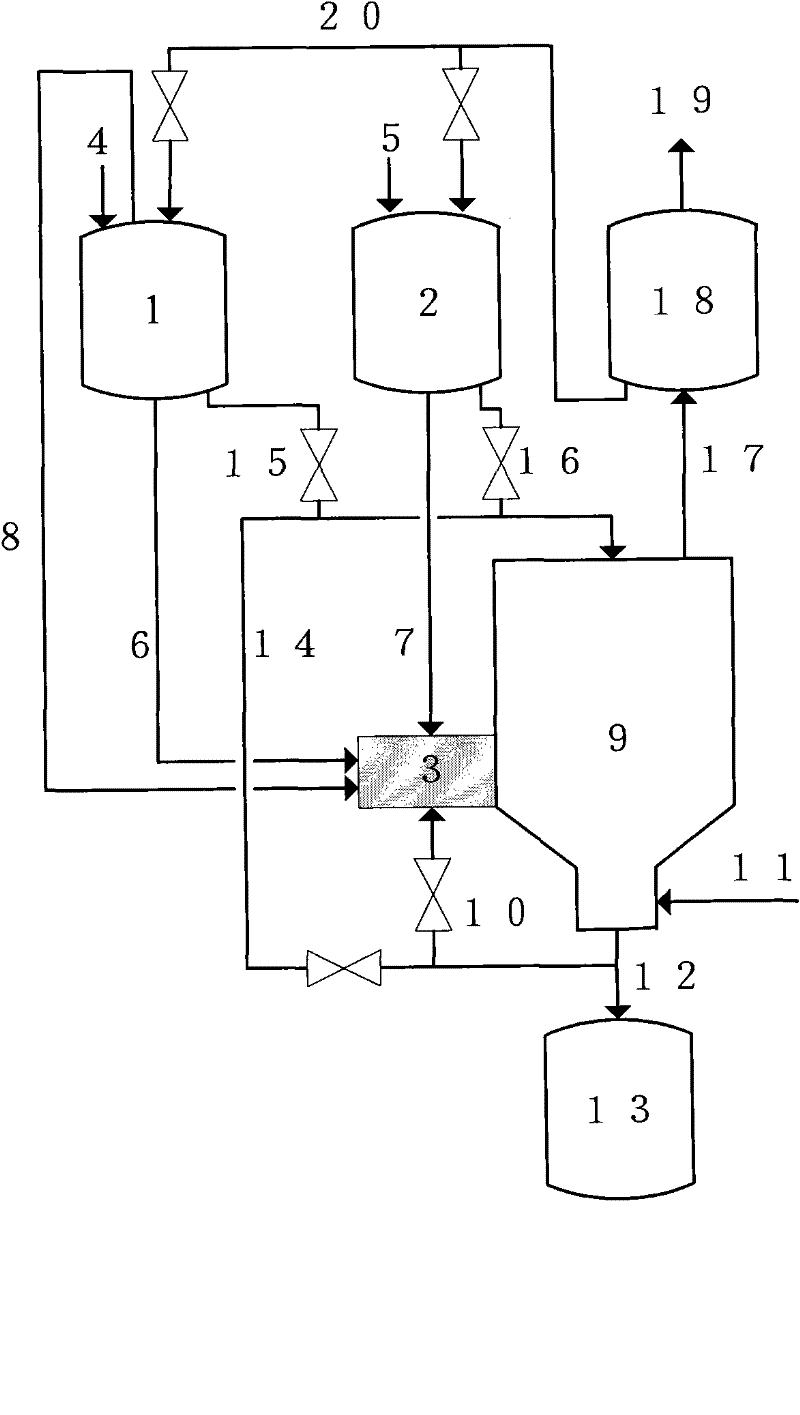
Hydrolysis method for material containing hydrolysable halogen atom
ActiveCN102234117AAvoids problems with clogging gaseous product channelsRelieve stressSilicaPreparation from chloridesHalogenGaseous hydrogen
The invention discloses a short-procedure, less-investment and simple-operation hydrolysis method for a material containing hydrolysable halogen atom. The method is characterized in that: a material containing hydrolysable halogen atom and a material containing water are subjected to mixing and reacting in a mixing and reaction unit; at least one reactant reacts as completely as possible through controlling reaction conditions, in particular, a key point is that the resulting reaction products are dried solid oxide and gaseous hydrogen halide, then the solid oxide is removed from a gas-solid separation and purification unit, and the gaseous hydrogen halide is processed through a gas product cleaning unit. The solid oxide and the gaseous hydrogen halide prepared through the method are valuable commodities, and the gaseous hydrogen halide further can be applicable for a synthesis process of halide. In addition, the method can be applicable for processing industrial waste containing the hydrolysable halogen atom, and producing solid oxides and hydrogen halide through adopting compounds containing the hydrolysable halogen atom.
Owner:刘基扬
Mobile hydrogen delivery system
A mobile hydrogen delivery system for delivering a compressed stream of hydrogen at pressures up to 15000 psig. The mobile hydrogen delivery system includes a hydrogen compression system, a gaseous hydrogen storage system, and a delivery system for supplying hydrogen to end users. A mobile platform supports the hydrogen compression system, the gaseous hydrogen storage system, and the dispensing system. The mobile platform may be any platform, such as a trailer, capable of being pulled, pushed, or supported by any type of vehicle, such a truck, train, boat, tractor, etc.
Owner:HARNYSS IP LLC +1
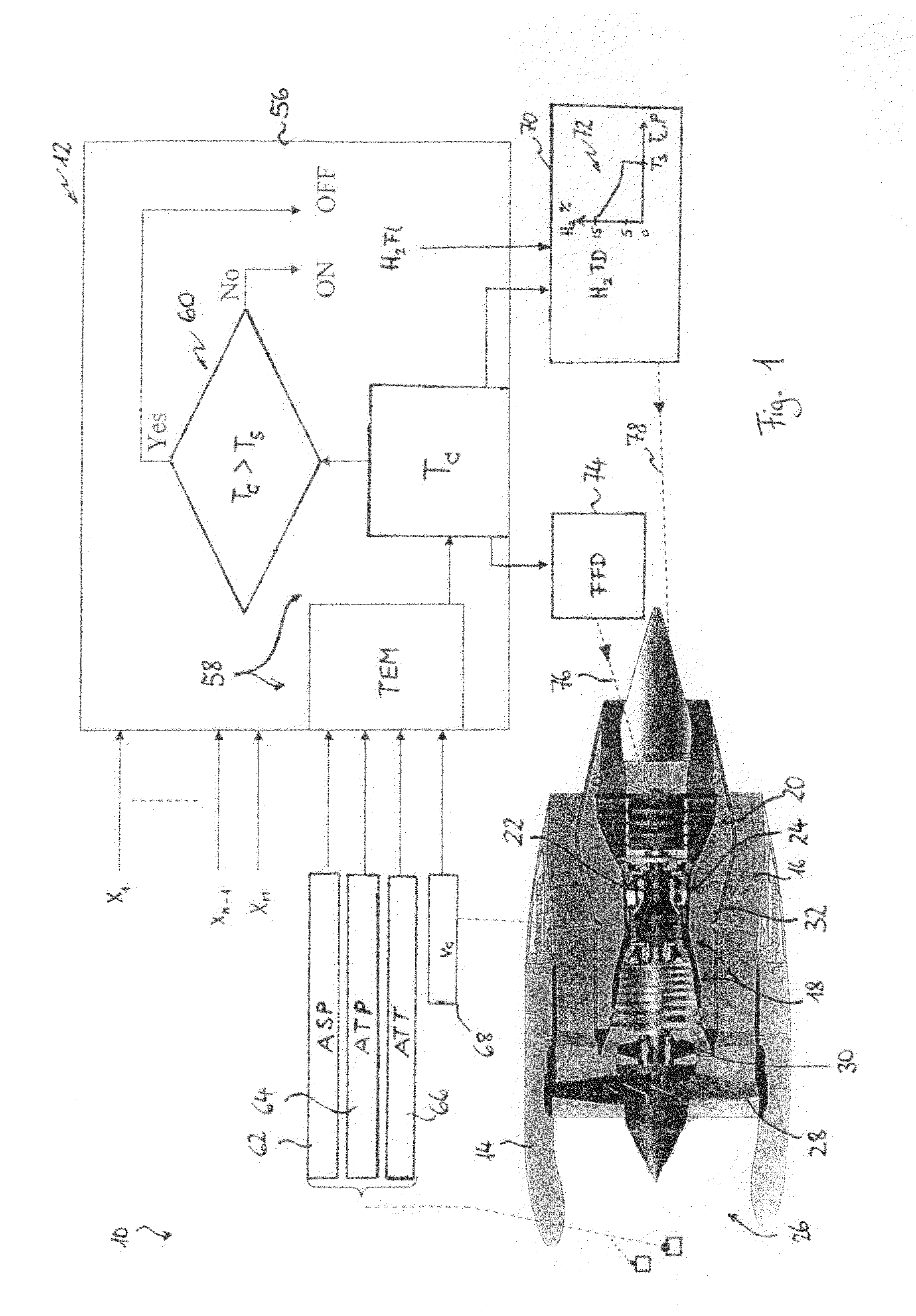
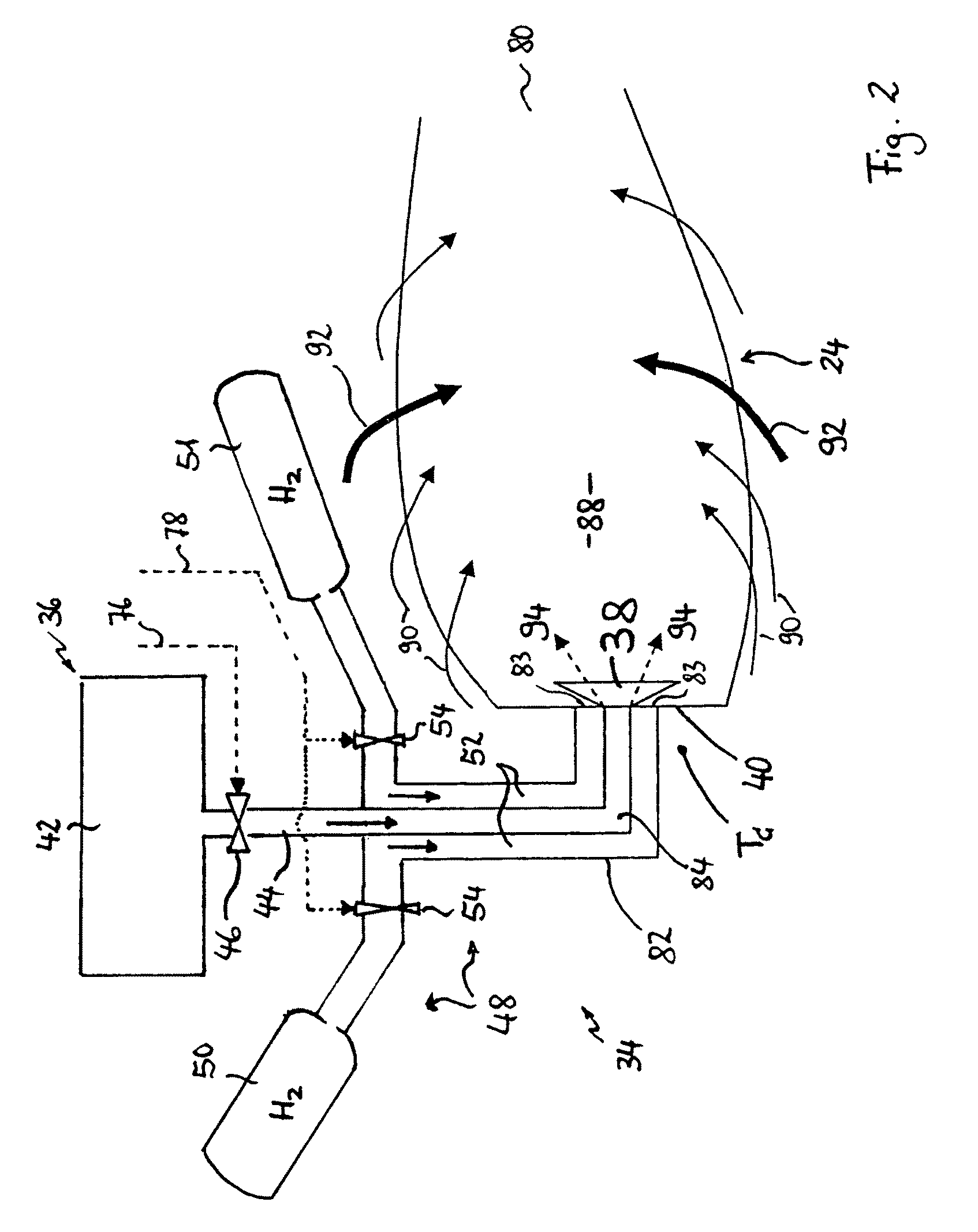
Gas turbine engine and method for reducing turbine engine combustor gaseous emission
ActiveUS8056344B2Reduce hydrogen consumptionSmall sizeAnalogue computers for vehiclesFuel supply regulationCombustorGaseous hydrogen
Owner:AIRBUS SAS
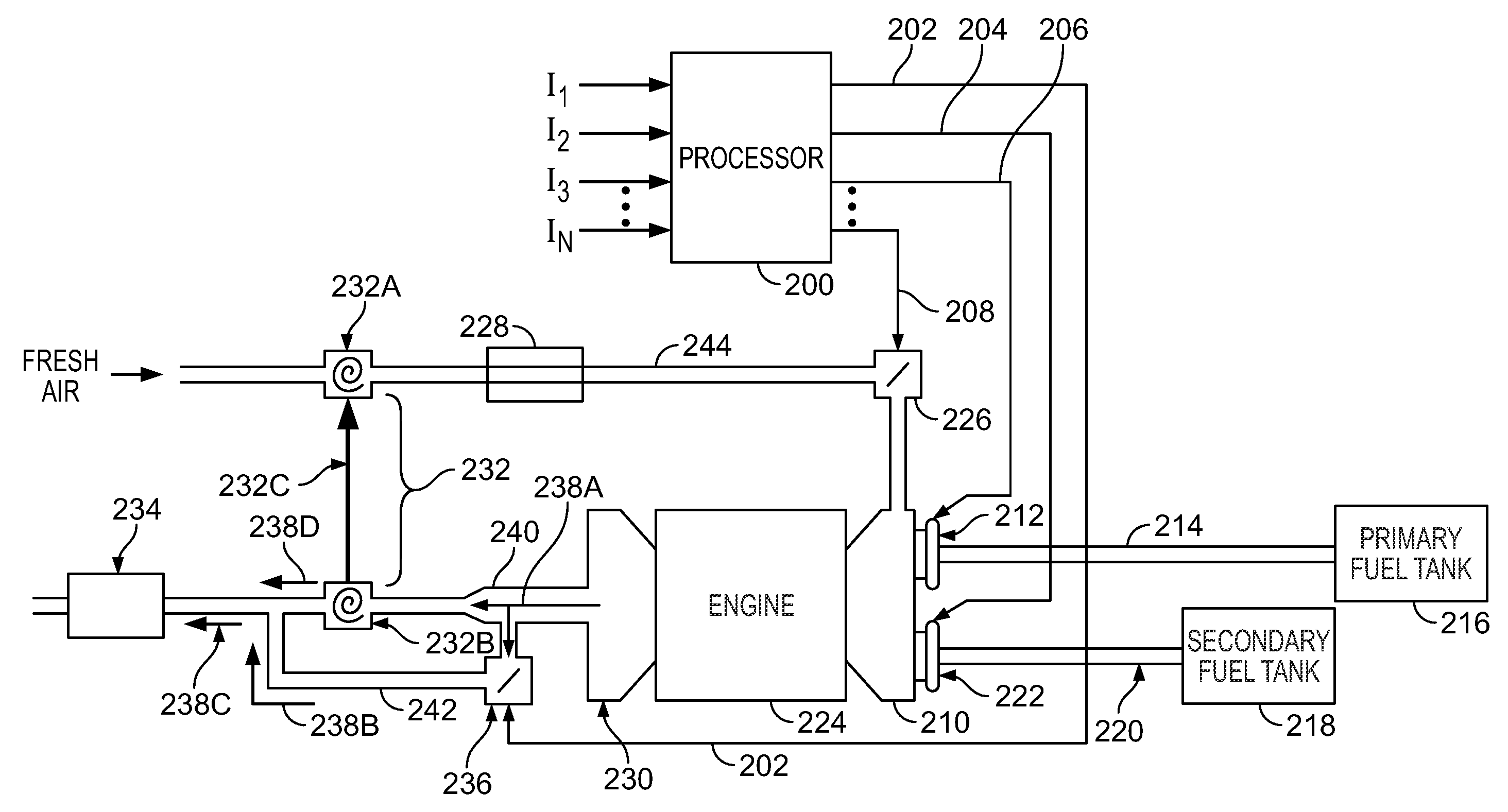
Bi-fuel engine with variable air fuel ratio
ActiveUS20110301826A1Reduce the temperatureReduction tendencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesGasoline fuelHydrogen fuel
A conventional gasoline engine is retrofitted to operate as a bi-fuel engine calibrated to burn Hydrogen gas as a primary fuel and gasoline as a secondary fuel at various acceptable air fuel ratios while avoiding forbidden air fuel ratios. The engine is preferably operated to burn Hydrogen fuel in a charged mode and in a lean mode at certain acceptable air fuel ratios where relatively very little NOx emissions occur. When additional power or acceleration is requested, processor controlled fuel injectors are operated to inject relatively small amounts of gasoline into the engine resulting in a fuel mixture that prevents increases in NOx emissions as the processor controls the engine to operate at a stoichiometric air fuel ratio where a catalytic converter is best able to reduce harmful emissions into the environment. The injection of the secondary liquid gasoline fuel to the gaseous Hydrogen fuel the temperature of the fuels significantly reduces or eliminates backfiring tendency of the engine. The engine has a safety feature in that the Hydrogen fuel is shut off if a leakage of Hydrogen is detected. The engine then operates with gasoline fuel used as a backup fuel.
Owner:H2 IP INVESTMENTS LTD
Subterranean hydrogen storage process
A method for the storage of hydrogen within a subterranean solid carbonaceous formation such as a coal seam. At least one well extends from the surface of the earth into the formation and a pressure gradient extends from the formation to the well to desorb methane within the formation and flow the methane into the well. Subsequent to recovery of the methane from the formation, gaseous hydrogen is injected into the well and into the formation. The injection of hydrogen is carried out under a pressure sufficient to cause the injected hydrogen to become absorbed within the matrix of the carbonaceous formation. Subsequent to storage of the hydrogen, a pressure gradient is established from the formation to the surface to withdraw previously introduced hydrogen to the surface. At least one common well is used for recovery of methane from the formation and introduction of hydrogen into the formation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Internal combustion engine/water source system
InactiveUS20070006571A1Reliable generationSuitable for mass productionNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesWater sourceLiquid water
An internal combustion engine system for automotive vehicle wherein liquid water is produced by cooling a portion of exhaust gases at elevated pressure to induce condensation. The use of elevated pressure allows condensation to occur at a higher dew point which is easier to realize with cooling by ambient air. Liquid water condensate is collected and provided to an electrolytic cell for electrolysis into gaseous hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen gas generated by the cell is used by the internal combustion engine to reduce internal combustion engine wear and to reduce exhaust pollutants especially during start-up. Alternate uses of the liquid water include a replenishment of engine coolant and window washing fluid.
Owner:VETROVEC JAN
Hydrogen/oxygen generating system with temperature control
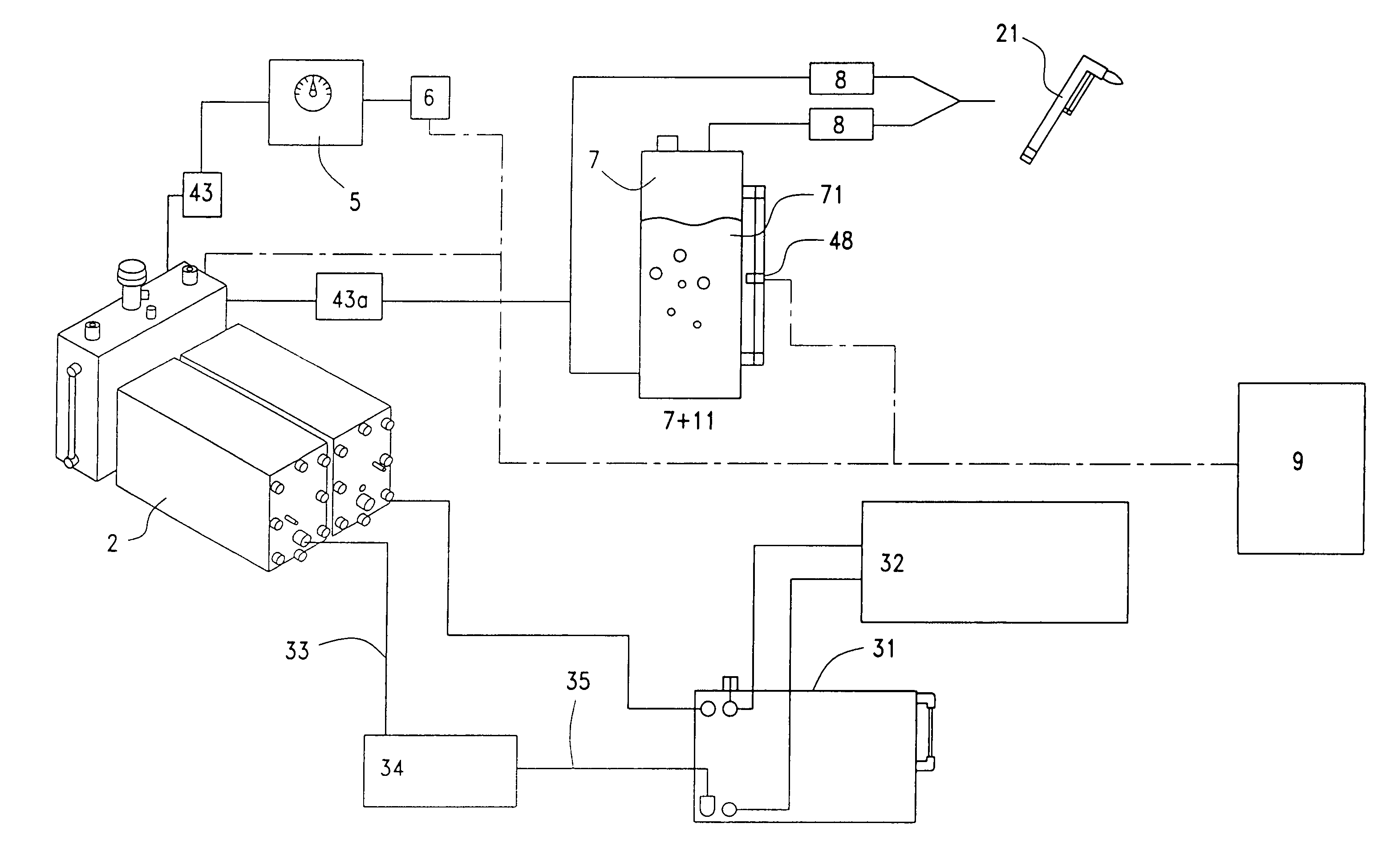
InactiveUS6977120B2Reduce usageIncrease volumeCellsPhotography auxillary processesWater useEngineering
A mixed hydrogen-oxygen fuel generator system uses an electrolytic solution to generate gaseous hydrogen-oxygen fuel through the electrolysis of water. This generator system includes: at least one electrolytic cell with multiple metallic plates used as an internal isolation system in which two of the plates separately connect to both the positive and negative terminal of a DC circuit. These plates are used for the electrolysis of the electrolytic solution in the cell(s) to produce, under pressure, mixed hydrogen-oxygen fuel. The apparatus also includes a cooling system containing a water cooling tank in which there are two zones: one is the electrolytic solution circulation coil and the another is a water circulation zone. The cooler provides the circulating, cooling water used to adjust the temperature of the operating cell and of the electrolyte solution to within a given temperature range in order to ensure that the cell is not affected by excessively elevated temperatures that can stop operations due to cell overheating. Another effect of this cooling system is to precipitate moisture out of the generated gas products. The ignition flame temperature of the gaseous fuel produced can be adjusted for specific applications by passage of the hydrogen / oxygen gas stream through a temperature-control fluid. Thus, continuous 24 hours operation can be achieved along with better gas production efficiency and fuel cell energy generation.
Owner:CHOU NAI SUNG
Etch process for etching microstructures
InactiveUS6936183B2Limited amountAvoid static frictionDecorative surface effectsCoupling light guidesHydrogen fluoridePhysical chemistry
A two-step method of releasing microelectromechanical devices from a substrate is disclosed. The first step comprises isotropically etching a silicon oxide layer sandwiched between two silicon-containing layers with a gaseous hydrogen fluoride-water mixture, the overlying silicon layer to be separated from the underlying silicon layer or substrate for a time sufficient to form an opening but not to release the overlying layer, and the second step comprises adding a drying agent to substitute for moisture remaining in the opening and to dissolve away any residues in the opening that can cause stiction.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electrical Apparatus Oil Sampler and Conditioner for Solid State Sensors
ActiveUS20130247647A1Accurate and reliable monitoringShort response timeMaterial testing goodsAnalysis dataElectrical devices
A gas monitoring apparatus and system that provides for reliable and accurate monitoring of gaseous hydrogen and other compounds in dielectric oil. The apparatus provides an environment for and is used in conjunction with metal oxide semiconductor sensors. Thermal conditioning zones for oil provide an environment in which variations in oil temperature and ambient temperature are eliminated to insure that analytical data are not affected by these environmental conditions.
Owner:SERVERON CORP
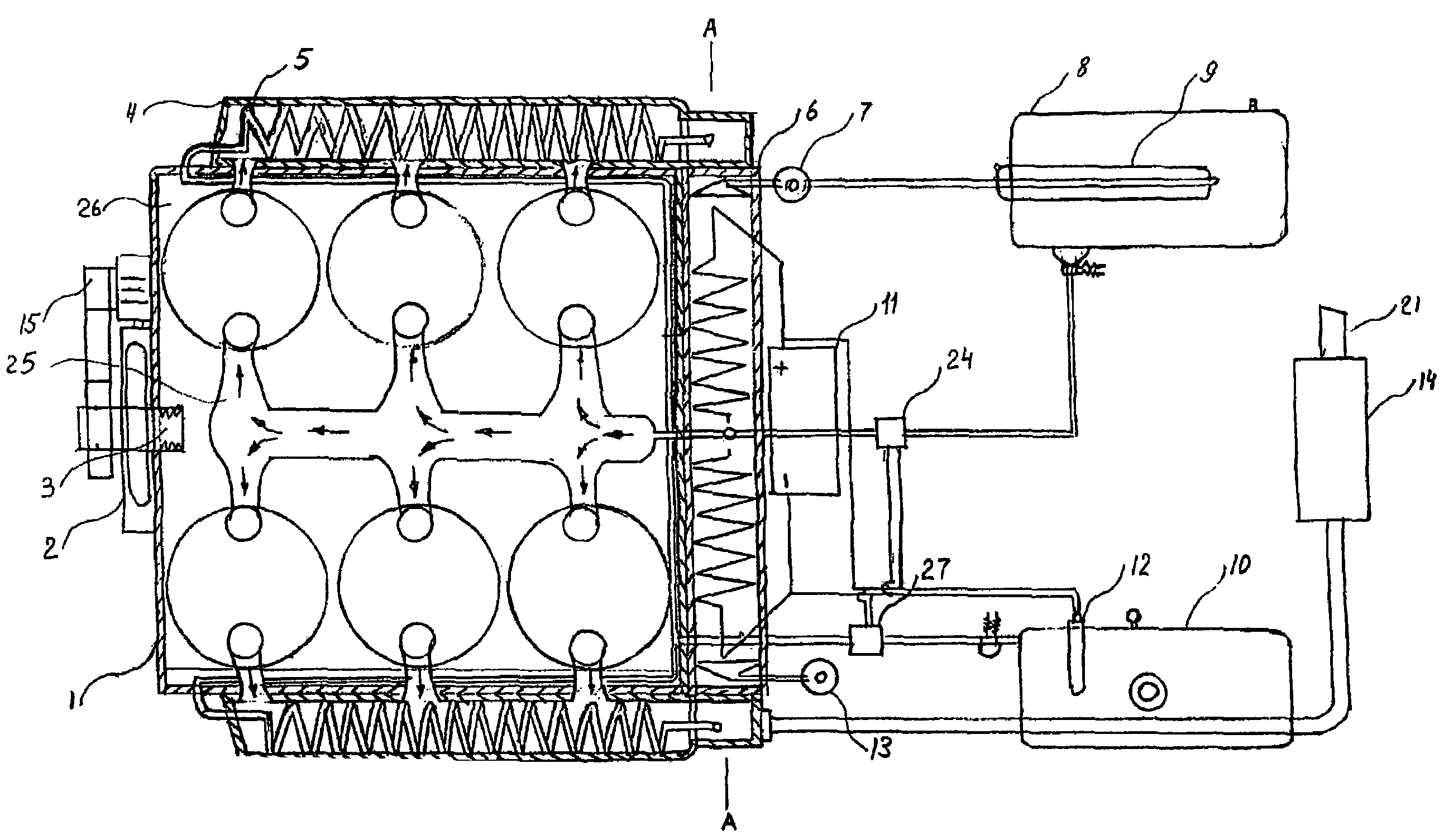
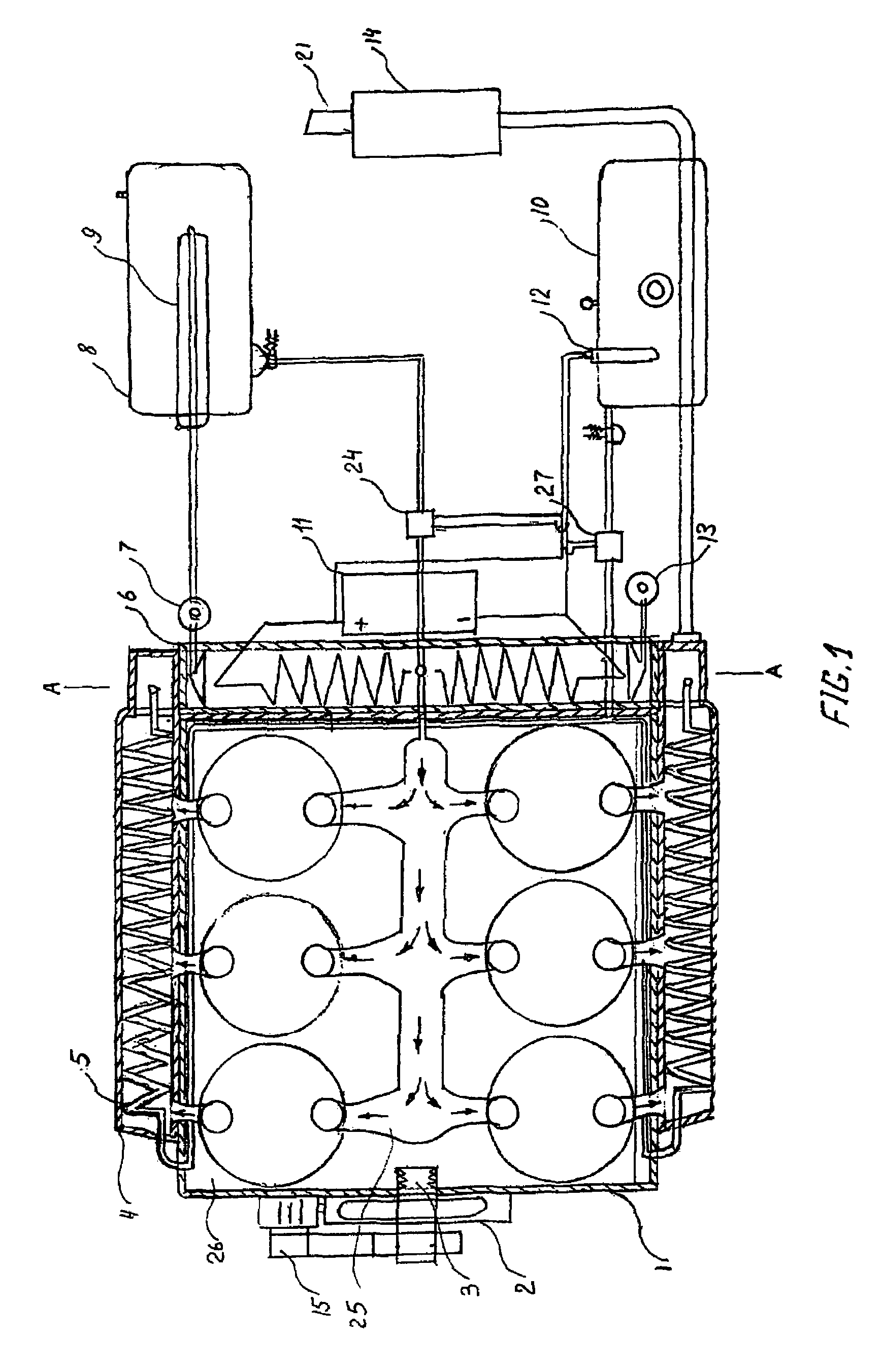
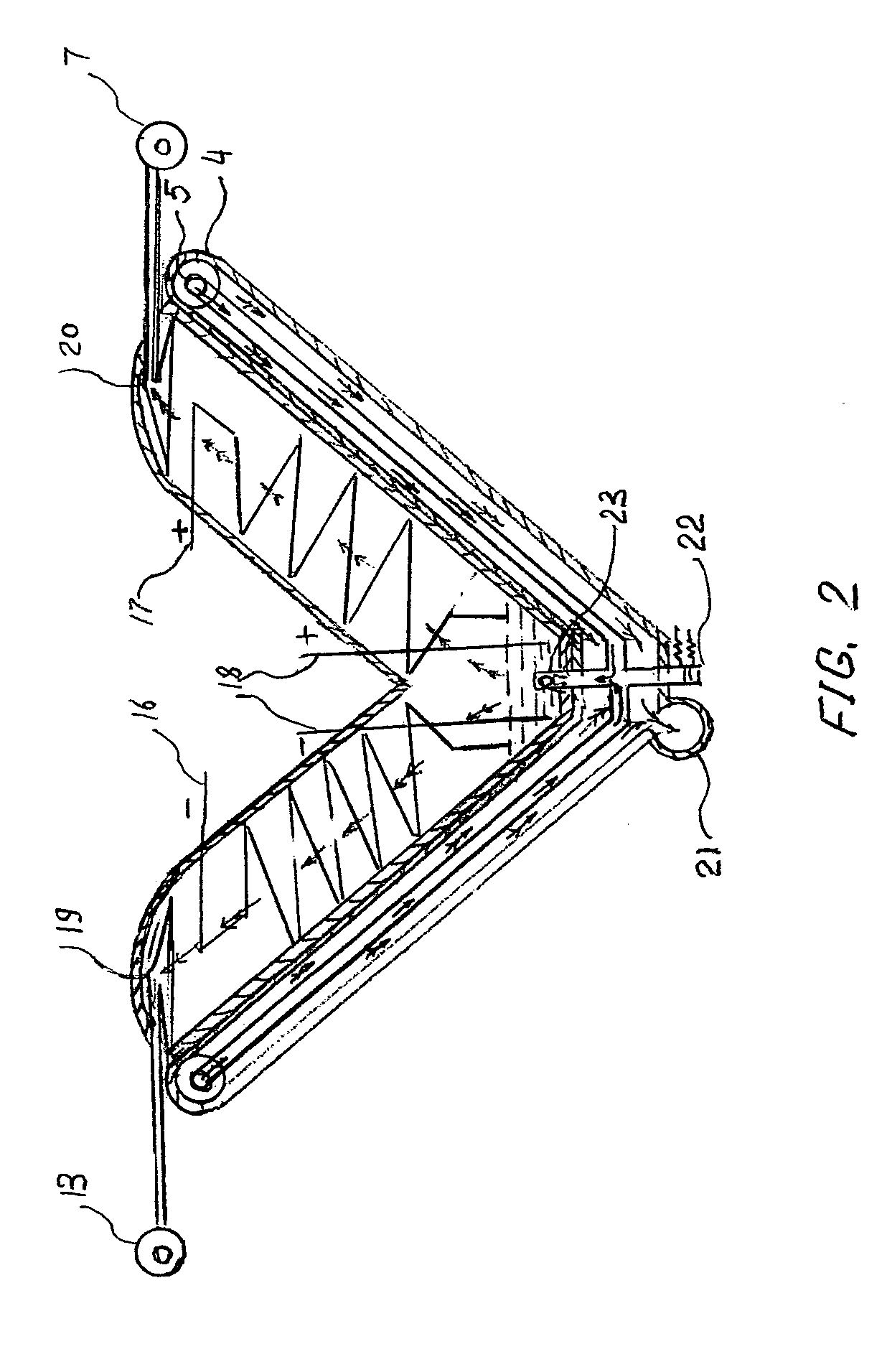
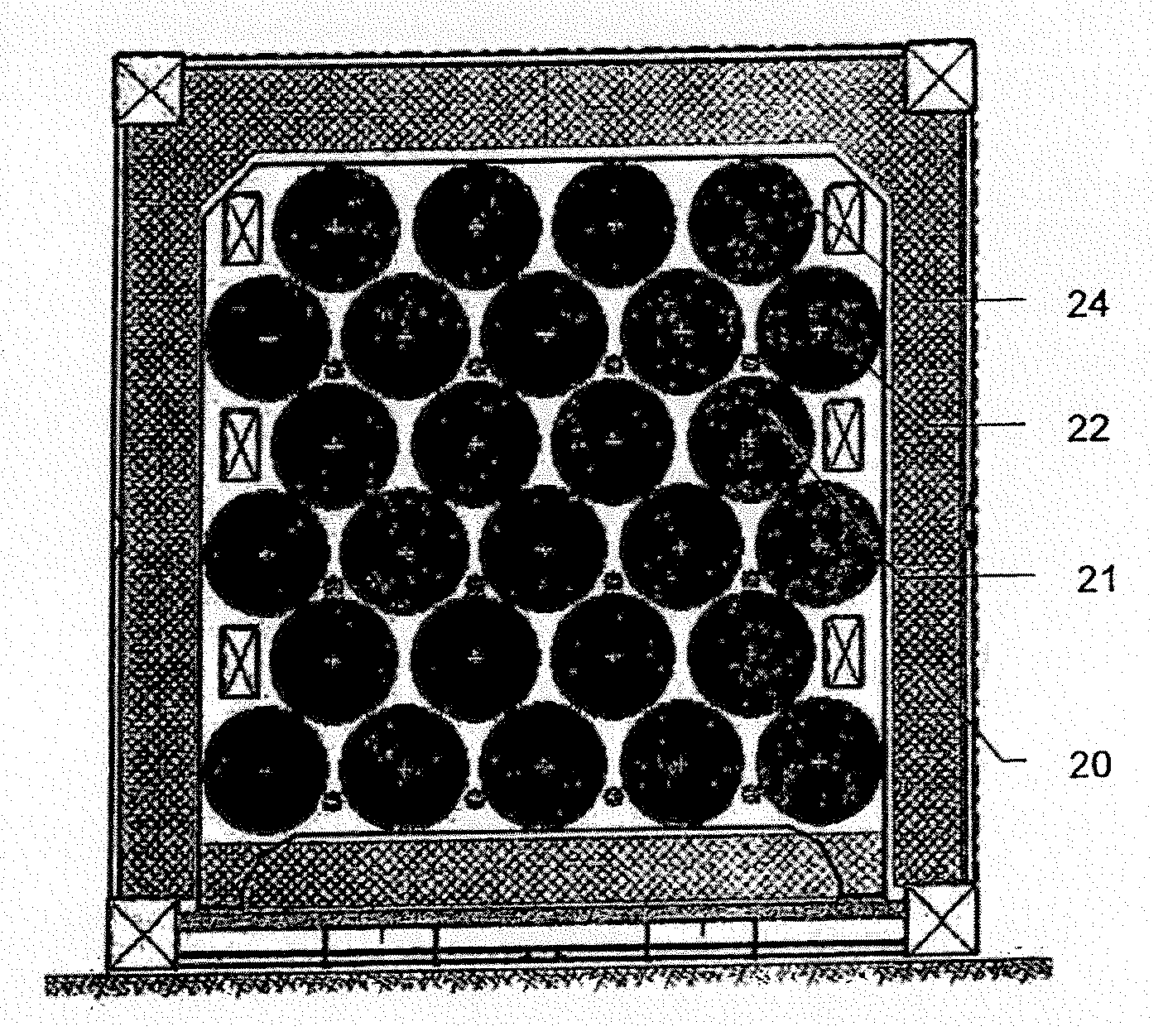
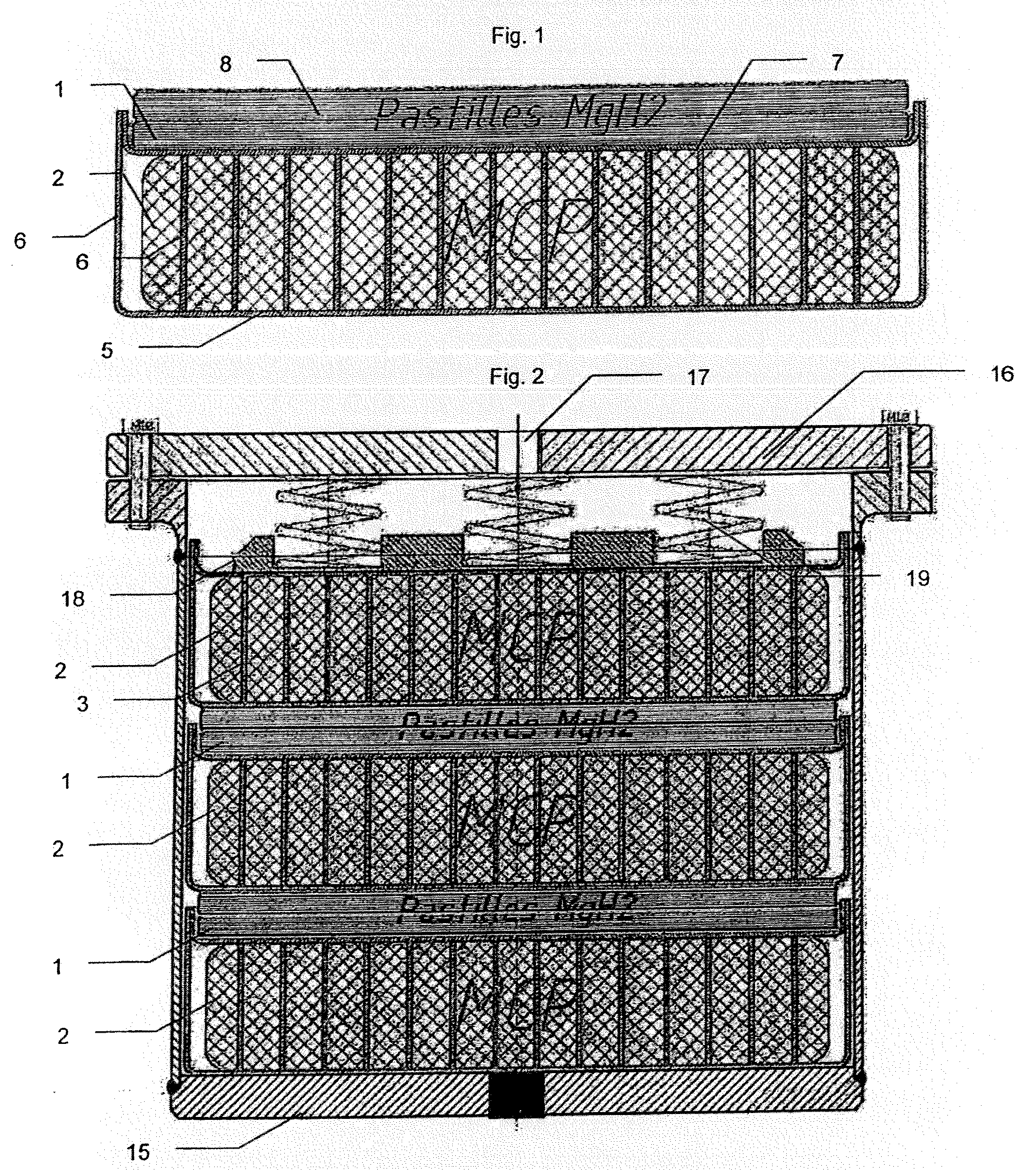
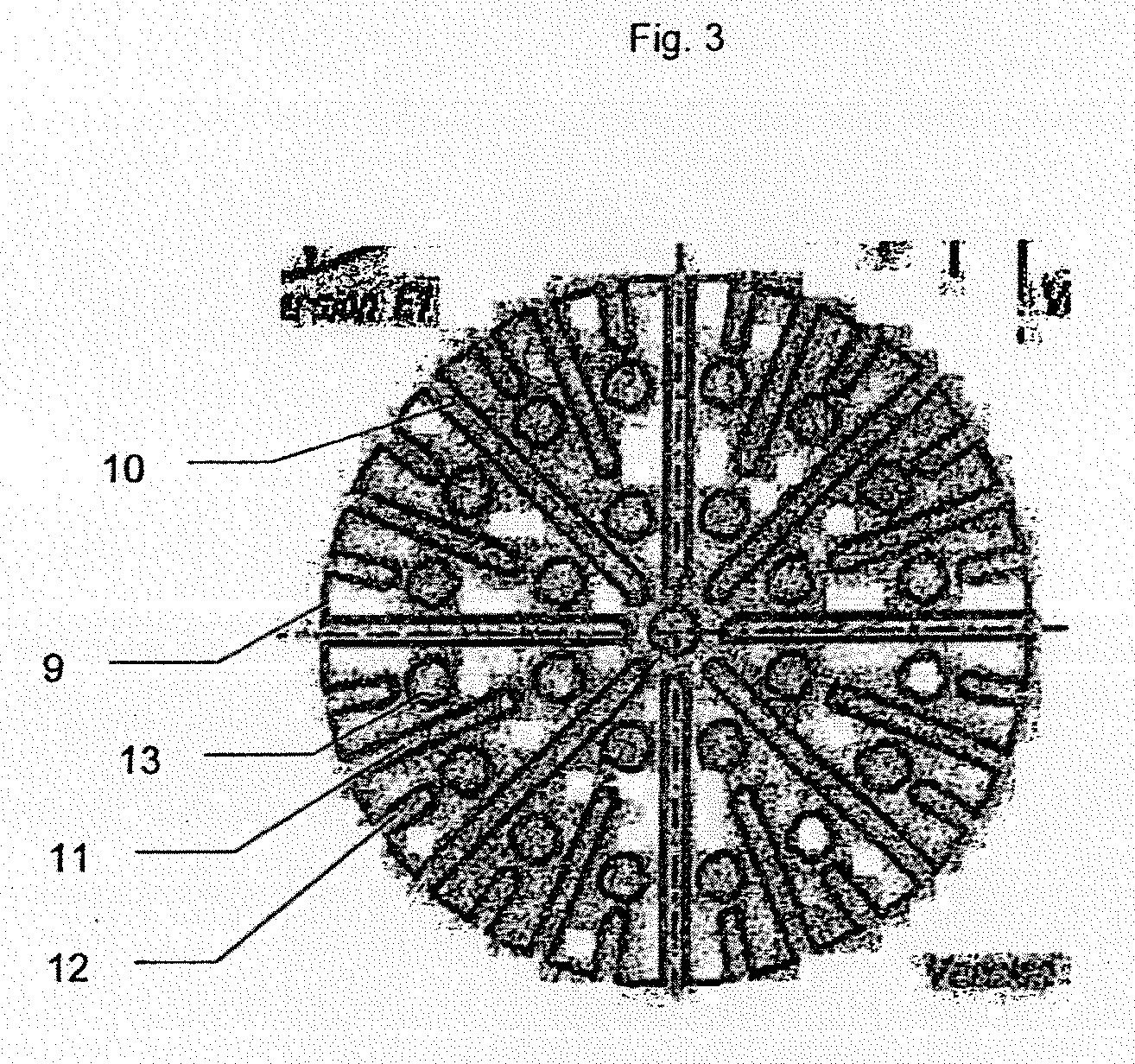
Tank for storing and withdrawing hydrogen and/or heat
InactiveUS20120201719A1Safe handlingSpeed up heat exchangeReversible hydrogen uptakeChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsProcess engineeringGaseous hydrogen
The present invention relates to a tank for storing and withdrawing hydrogen by means of a reversible hydriding / dehydriding reaction, said tank consisting of a thermally insulated chamber that includes a plurality of elements (2) for storing hydrogen in the form of hydrides, each element having at least one surface for exchange with the gaseous hydrogen and at least one heat exchange surface, characterized in that it further comprises a plurality of heat storage elements (3) for preserving and releasing the heat that is associated with the reversible hydriding / dehydriding reaction.
Owner:MCPHY ENERGY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com