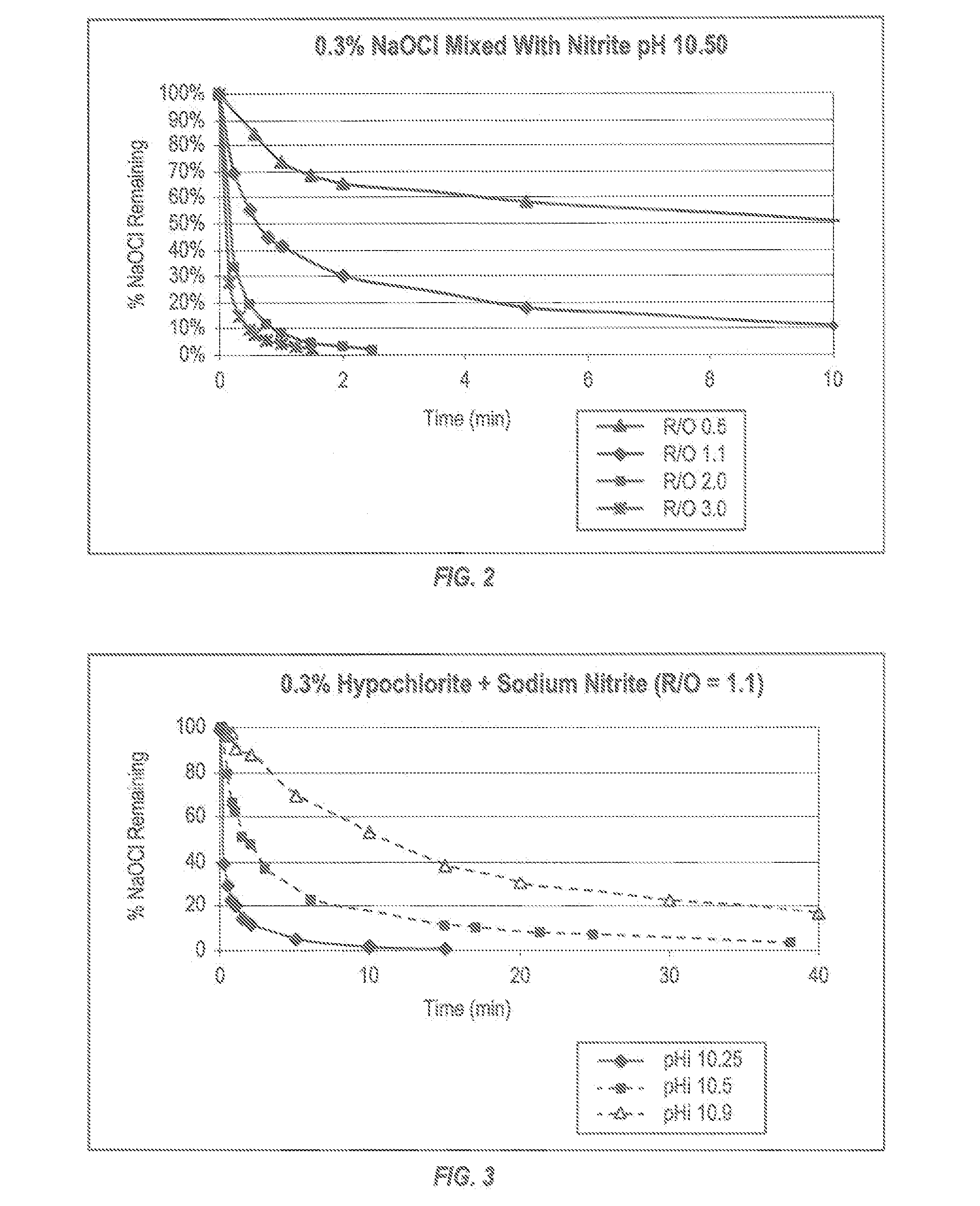
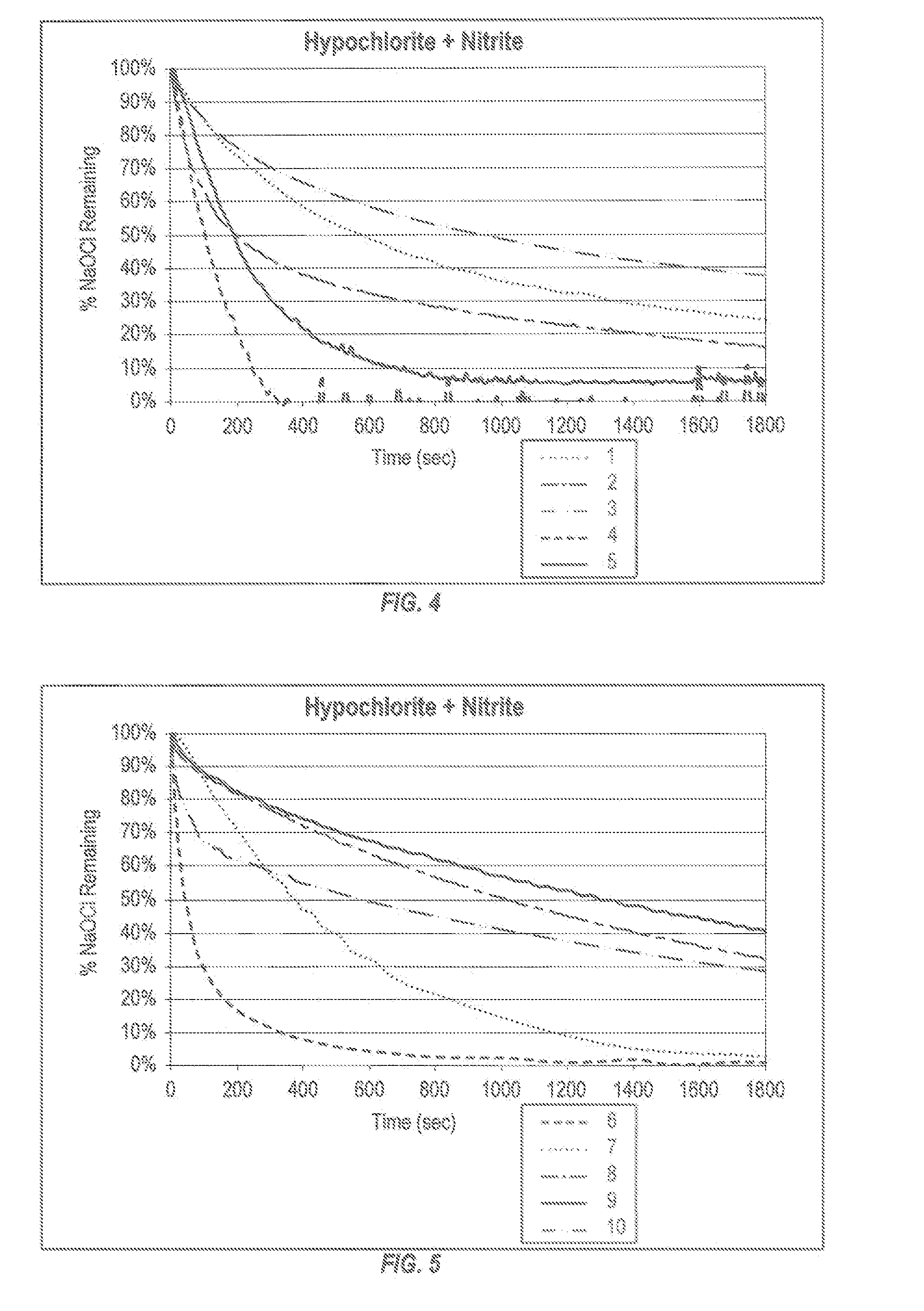
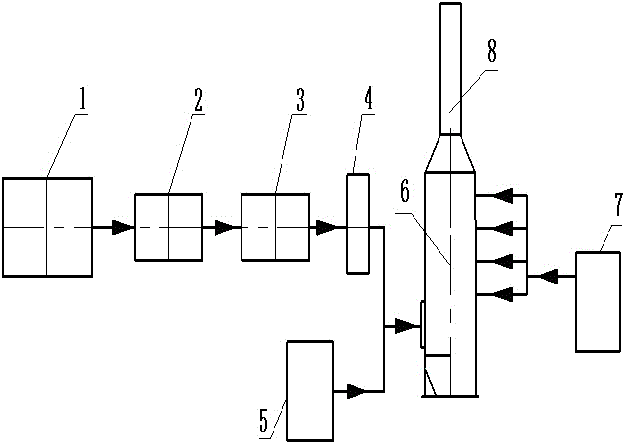
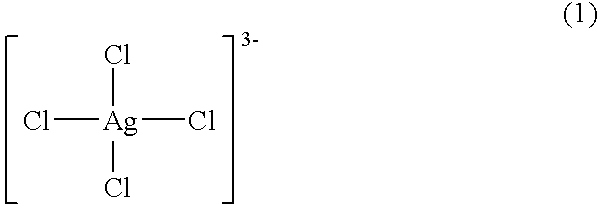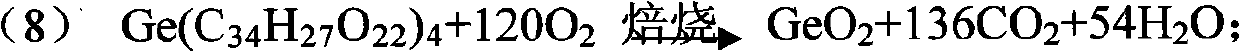Patents
Literature
1827 results about "Sodium chlorate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sodium chlorate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaClO₃. It is a white crystalline powder that is readily soluble in water. It is hygroscopic. It decomposes above 300 °C to release oxygen and leave sodium chloride. Several hundred million tons are produced annually, mainly for applications in bleaching paper.
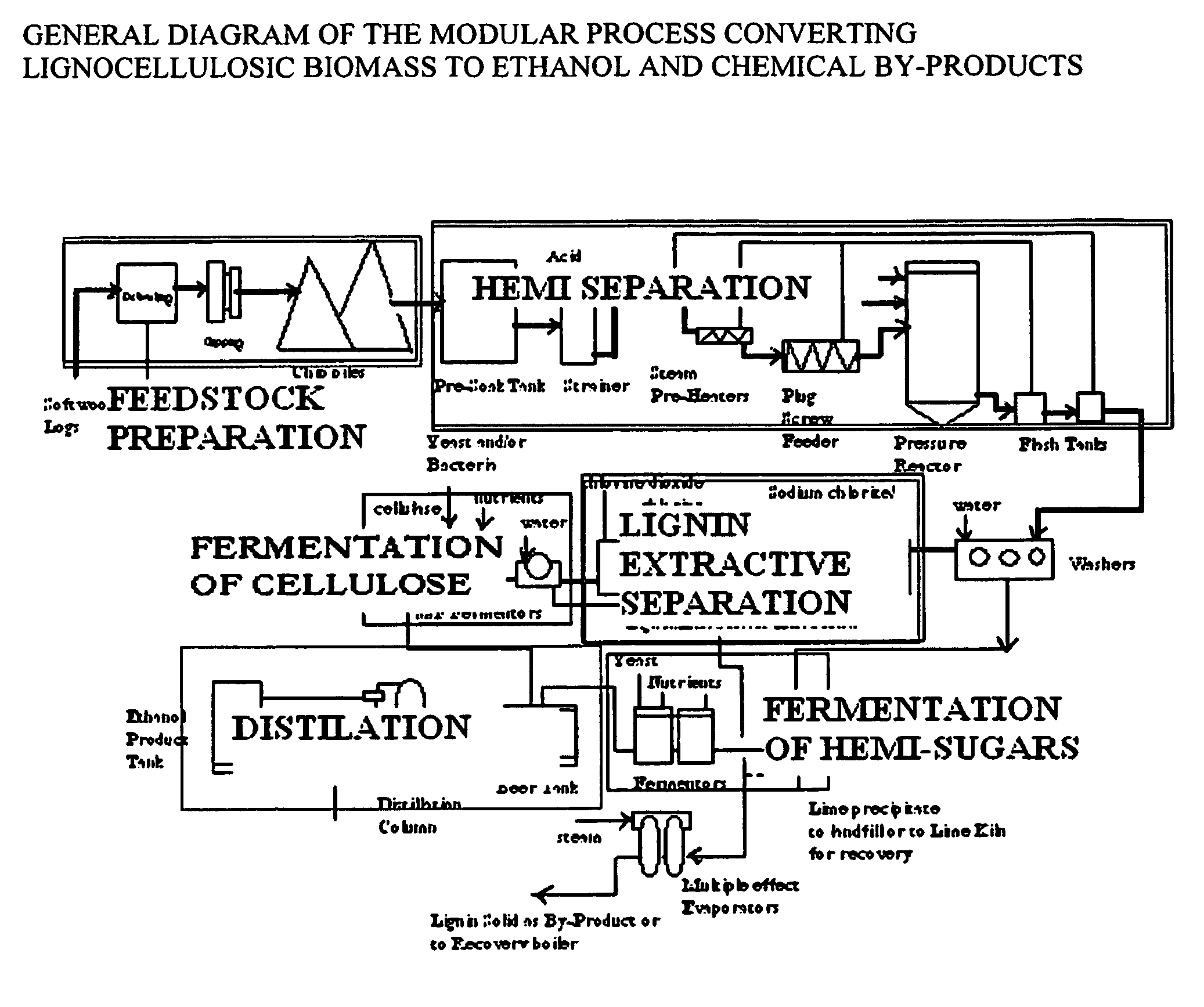
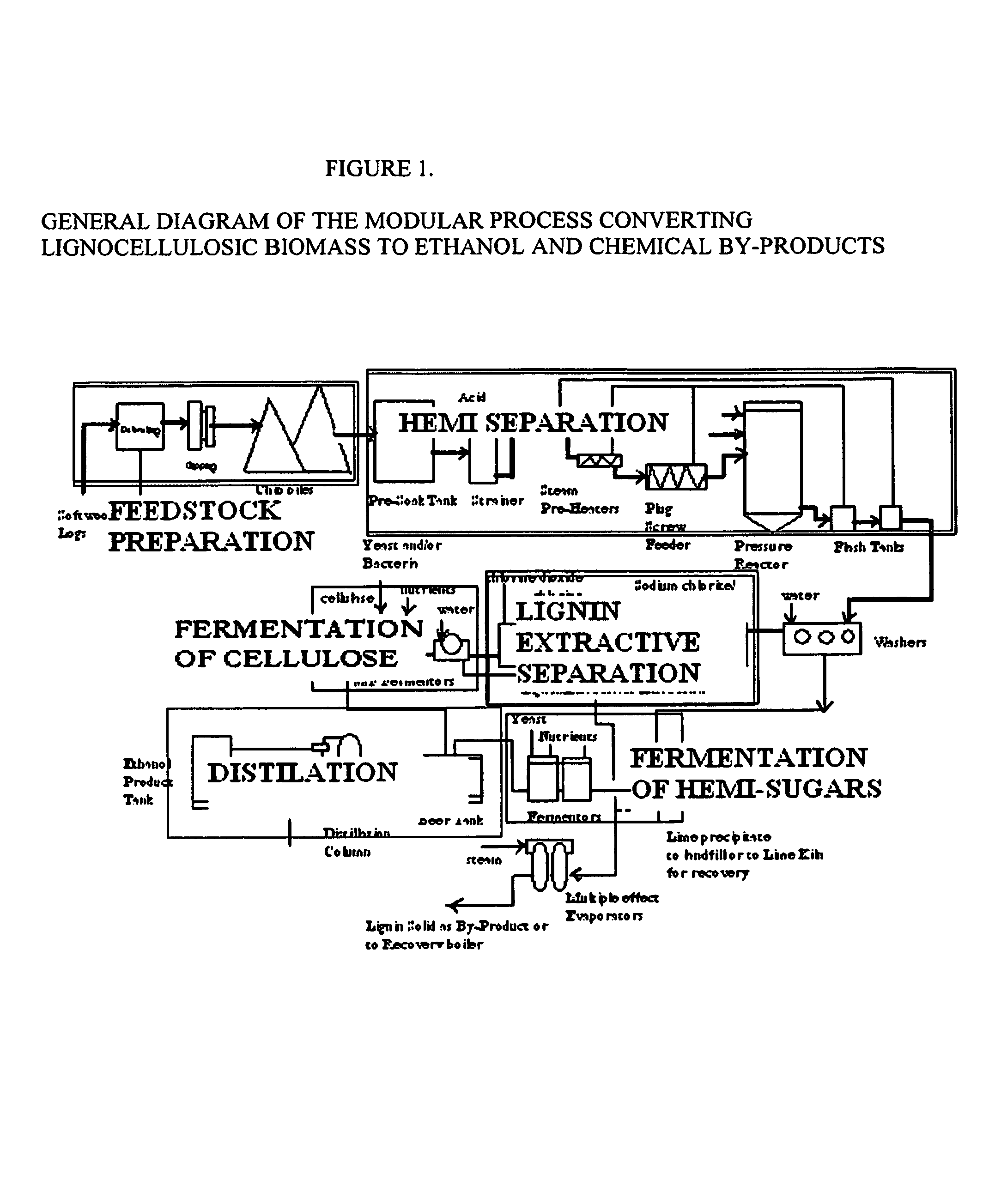
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS20080057555A1Robust and cost-effectiveImprove responseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentButanediol
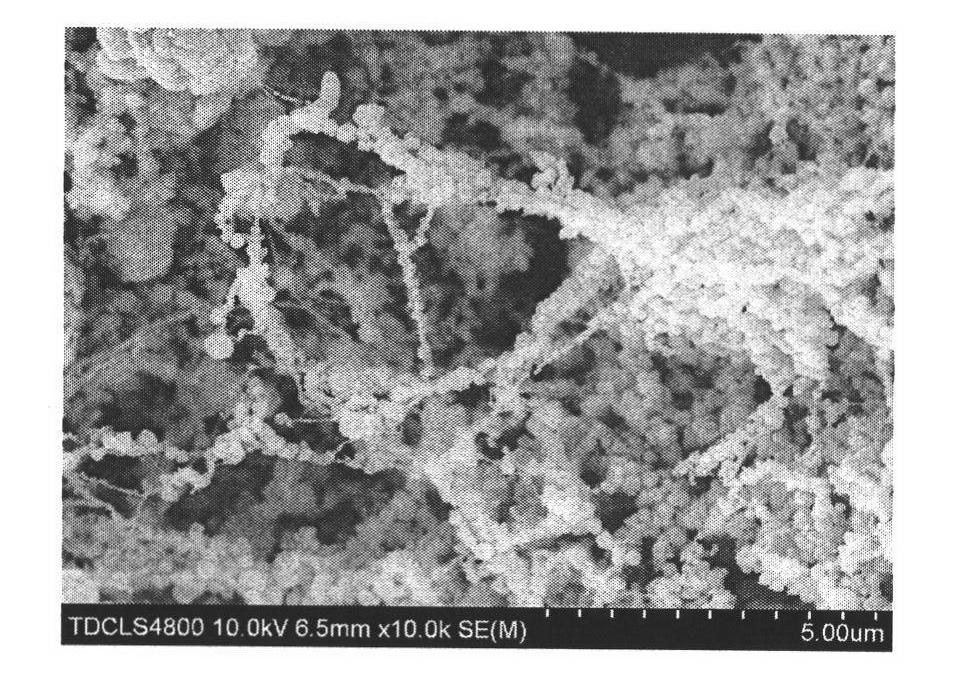
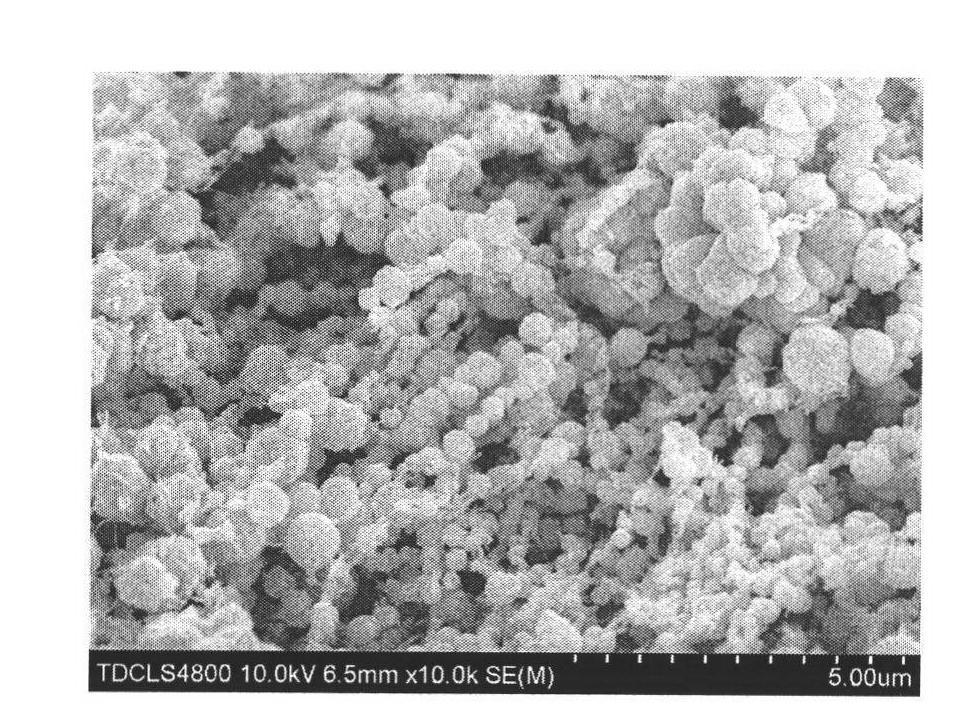
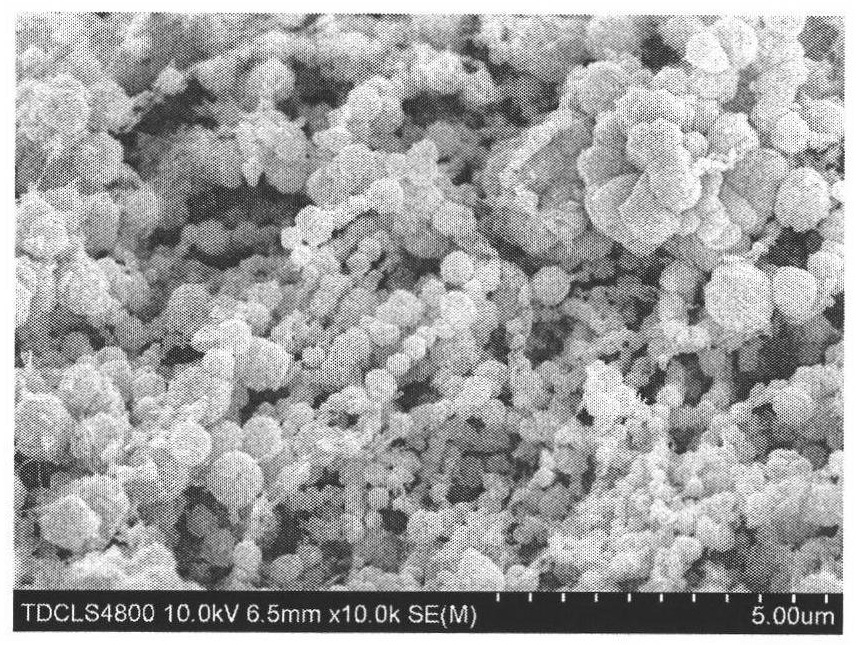
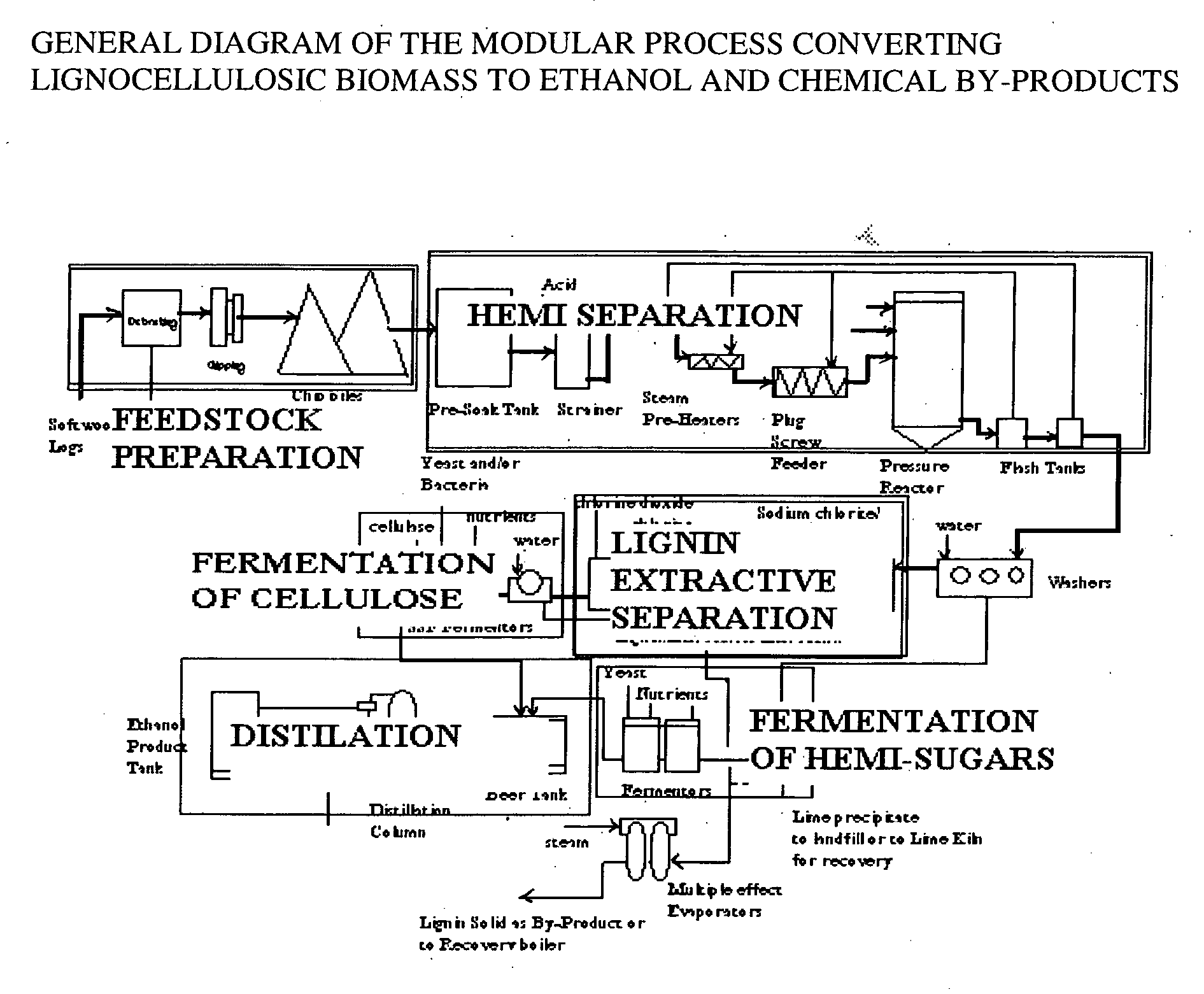
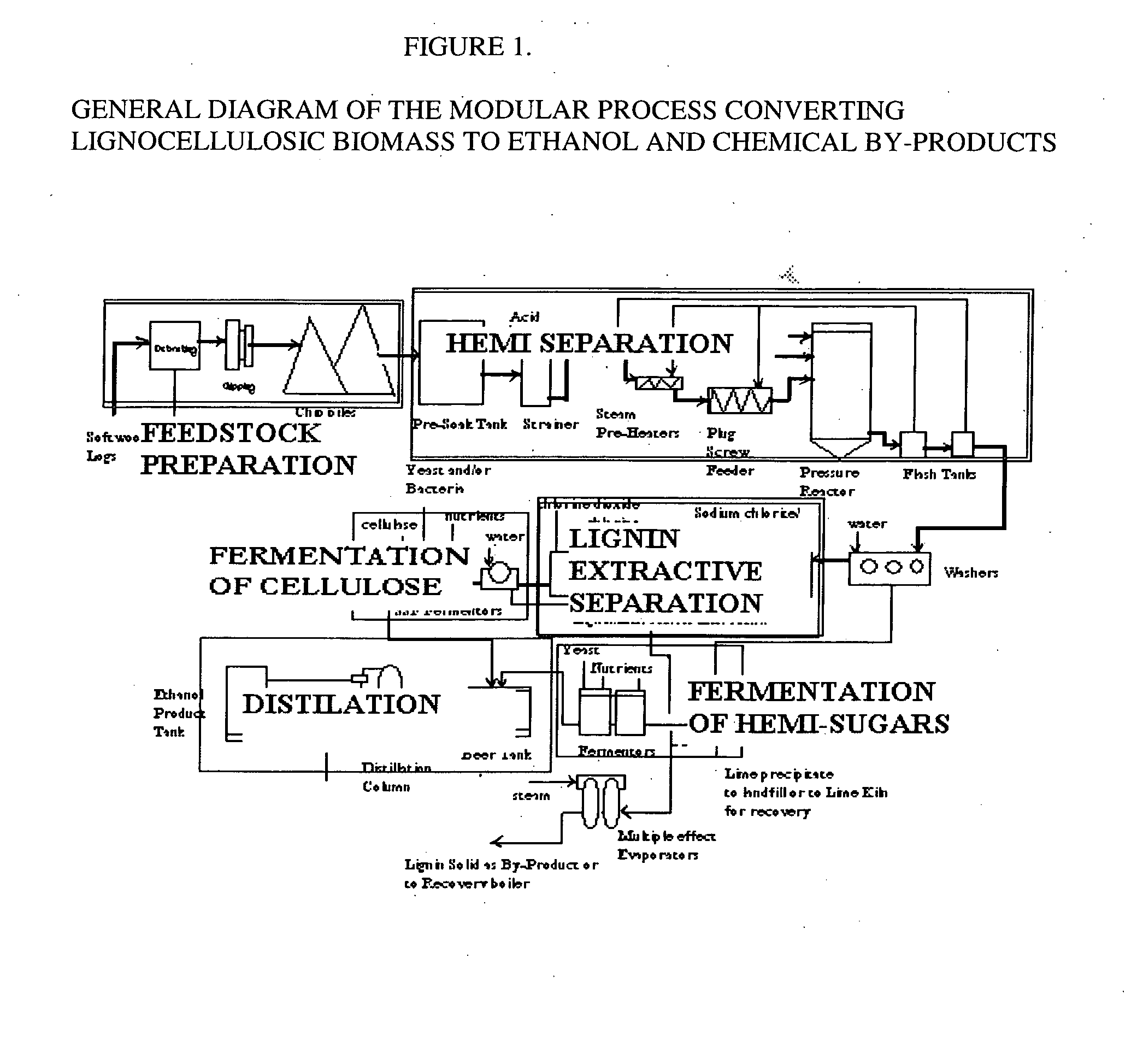
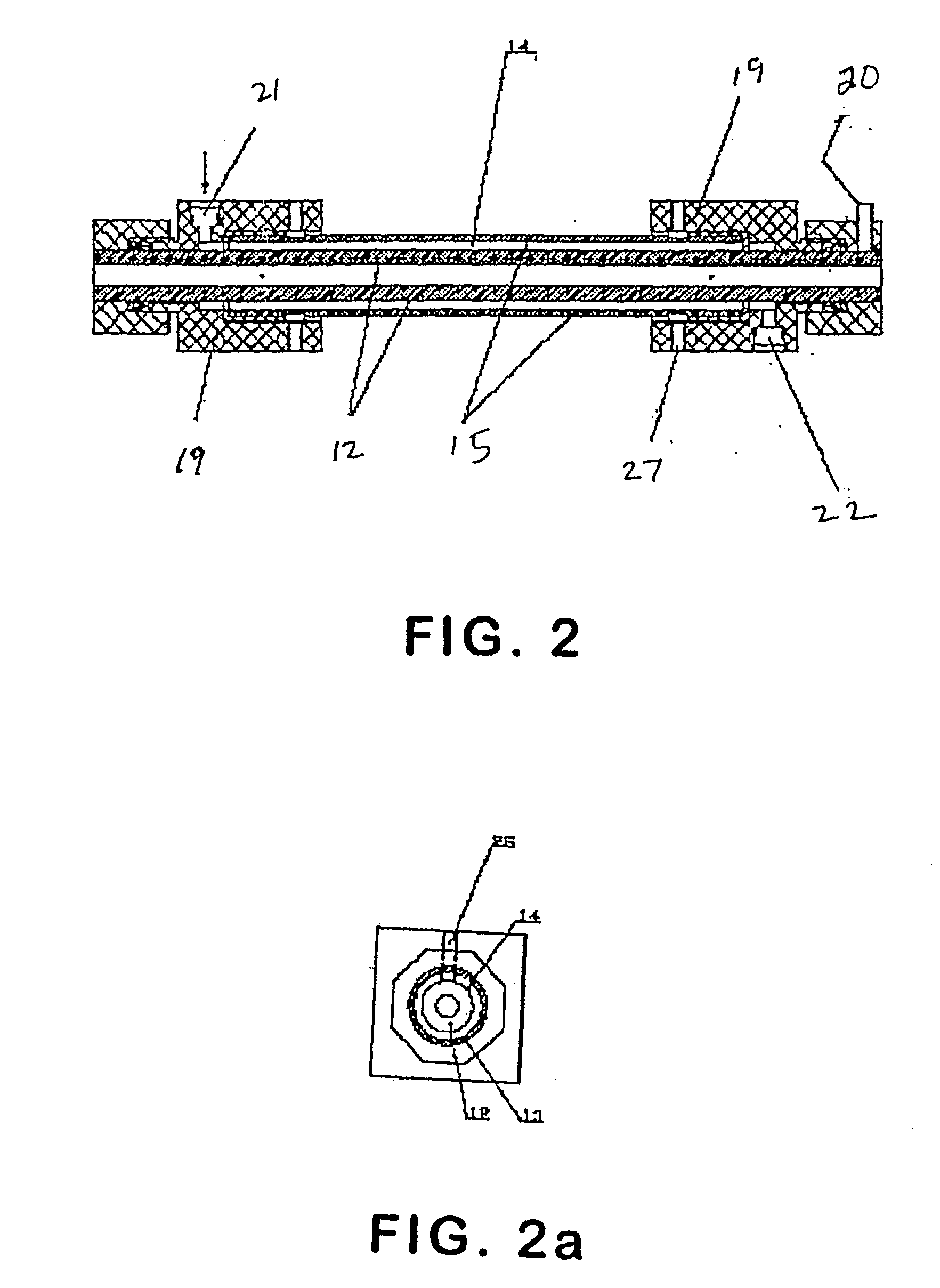
A continuous and modular process converts lignocellulosic materials for the production of ethanol principally and / or chemicals such as methanol, butanediol, propanediol, hydrocarbon fuel, etc. Renewable lignocellulosic biomass such as but not all inclusive hardwoods (gum, beech, oak, sweet gum, poplar, eucalyptus, etc.), soft woods (pines, firs, spruce, etc.), corn stovers, straws, grasses, recycled papers, waste products from pulp and paper mills, etc can be used as feedstock. The process is designed to be modular and the feed entry point can be selected to adapt to different biomass feedstock. Lignocellulosic biomass such as hardwood and softwood are subjected to chemical / pressure treatment stages using potent and selective chemicals such as sodium chlorite / acetic acid (anhydrous) and chlorine / chlorine dioxide to separate the main components—lignin, cellulose (glucose) and hemicelluloses (xylose, arabinose, galactose)—into three process streams. The separated carbohydrates are further subjected to washing, cleaning, neutralization, and / or mild hydrolysis and subsequently fermented to produce ethanol. Residual lignin and extractives remained with the cellulose are removed by chemical treatment steps to enhance the fermentations of cellulose. Pre-hydrolysate after neutralization to neutralize and remove toxic components such as acetic acid, furfural, phenolics, etc. containing (xylose, arabinose, galactose) and hexoses (glucose) can be either separately or together with the purified cellulosic fraction fermented to produce ethanol. Approximately 100 gallons of ethanol, suitable to be used as a fuel, can be produced from one dried ton of wood. Significant amount of lignin are separated as a by-product and can be converted to hydrocarbon fuel, surfactant, drilling aid, or can be incinerated for generation of power and steam.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
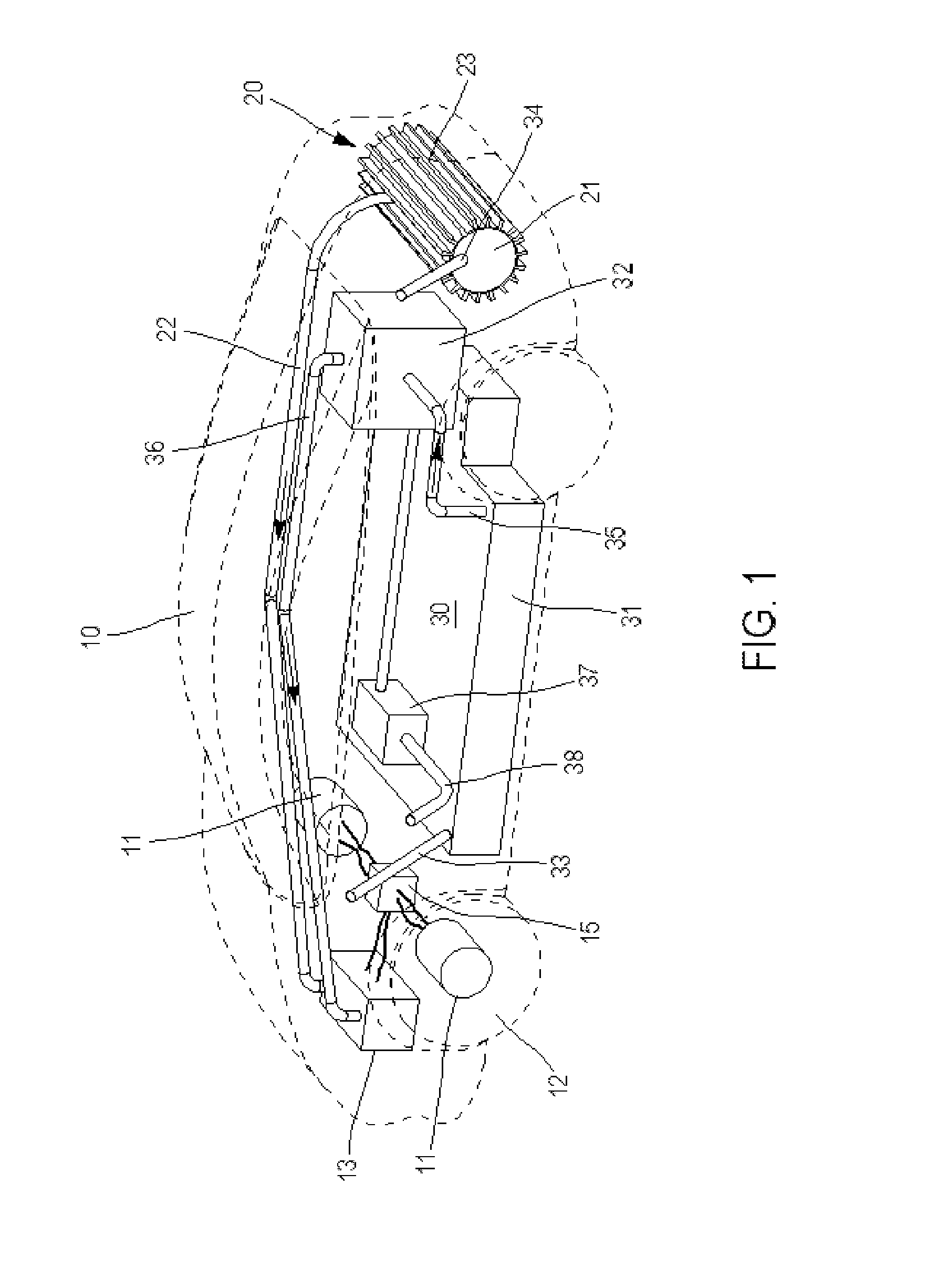
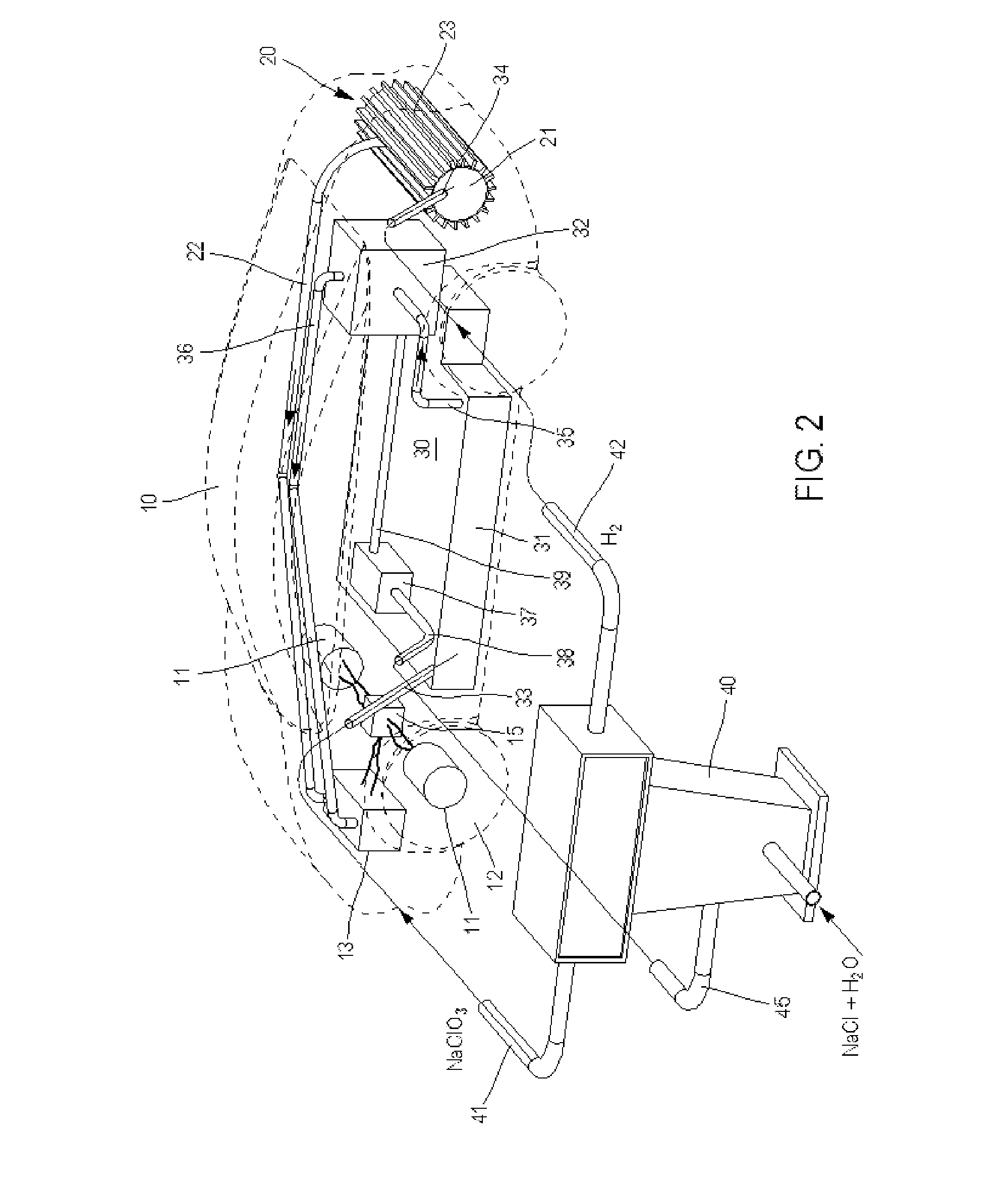
System for Producing and Supplying Hydrogen and Sodium Chlorate, Comprising a Sodium Chloride Electrolyser for Producing Sodium Chlorate
InactiveUS20130115535A1Increase supplyIncrease productionCellsReactant parameters controlElectrolysisSodium chlorate
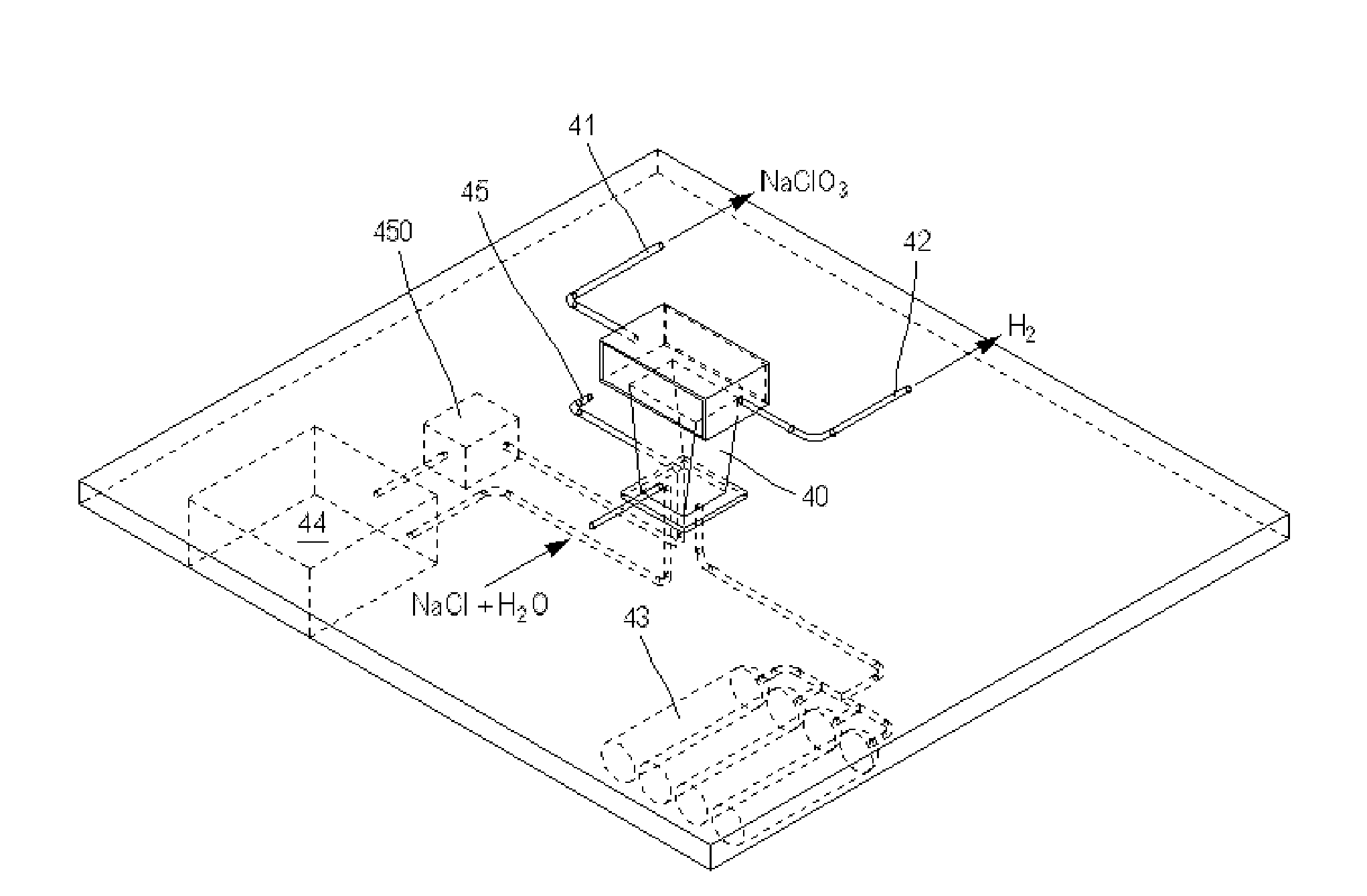
A system is provided for producing hydrogen and oxygen based on decomposition of sodium chlorate (NaClO3). In a service station, NaClO3 is produced by a sodium chloride (NaCl) electrolyser. The service station is supplied with water (H2O), NaCl, and energy in order to carry out an electrolysis reaction in the electroyser, to produce NaClO3 and gaseous hydrogen (H2). The NaClO3 and H2 are supplied to vehicles. Each vehicle includes a reactor for decomposing the NaClO3 and producing reaction products of NaCl and oxygen, with the oxygen being supplied to a fuel cell.
Owner:MICHELIN & CO CIE GEN DES ESTAB MICHELIN
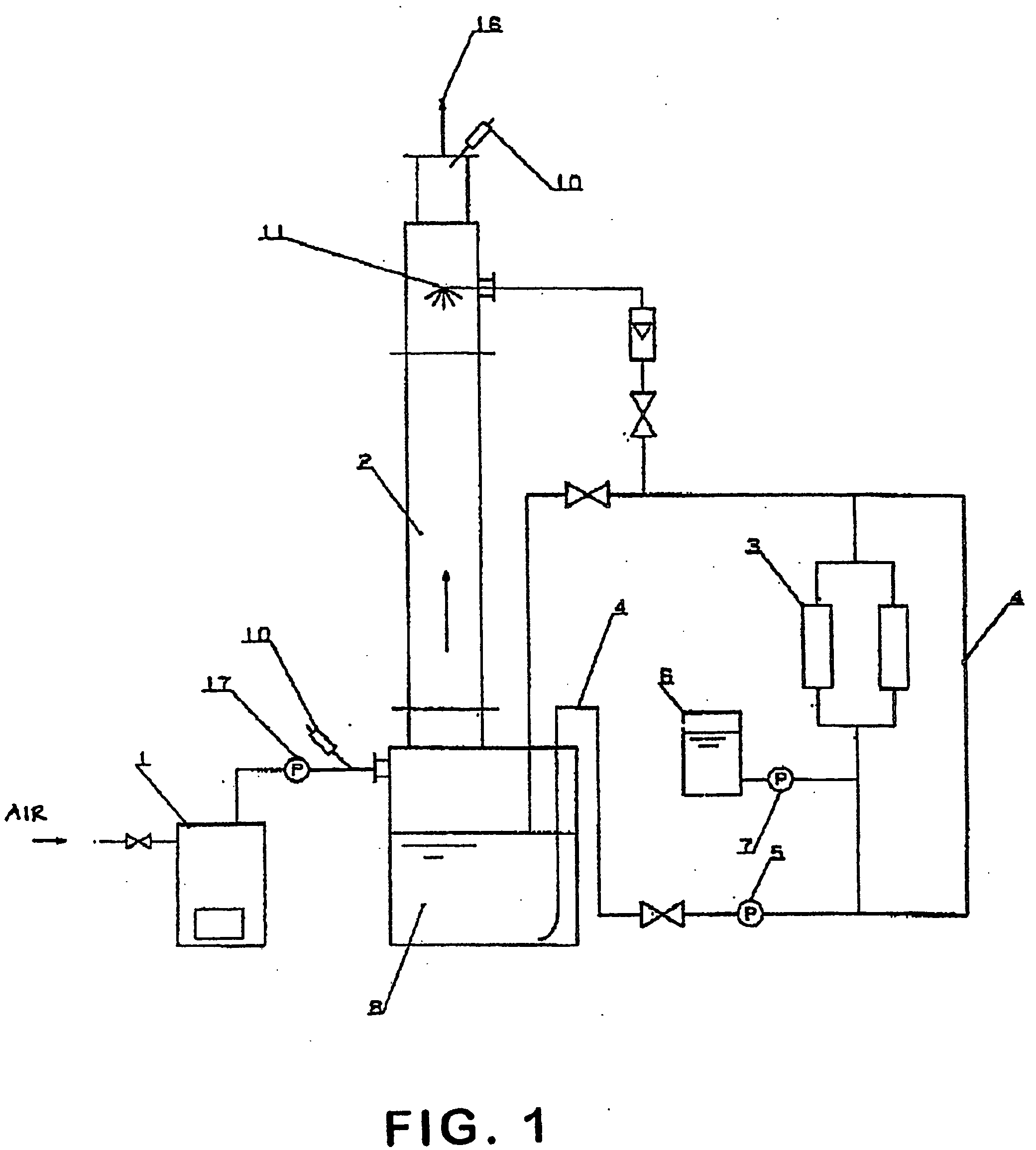
Method and device for deodorization and purification of exhaust gas or flue gas
InactiveUS20030164309A1Easy can be electrolyzedHigh densityCyanogen compoundsLighting and heating apparatusHazardous substancePotassium hydroxide
A method and device for removing, deodorizing and purifying odor, smoke and harmful substances from exhaust gas or flue gas employs a water solution containing hypohalogen acid such as hypochlorous acid soda, an alkaline electrolyte such as potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide and a saline electrolyte such as sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium bromide or potassium bromide which is electrolyzed to produce an electrolytic water solution which is fed to a deodorizing tower and brought into contact with exhaust gas or flue gas to remove odor, smoke and harmful substances in the exhaust gas or flue gas.
Owner:OMEGA CO LTD
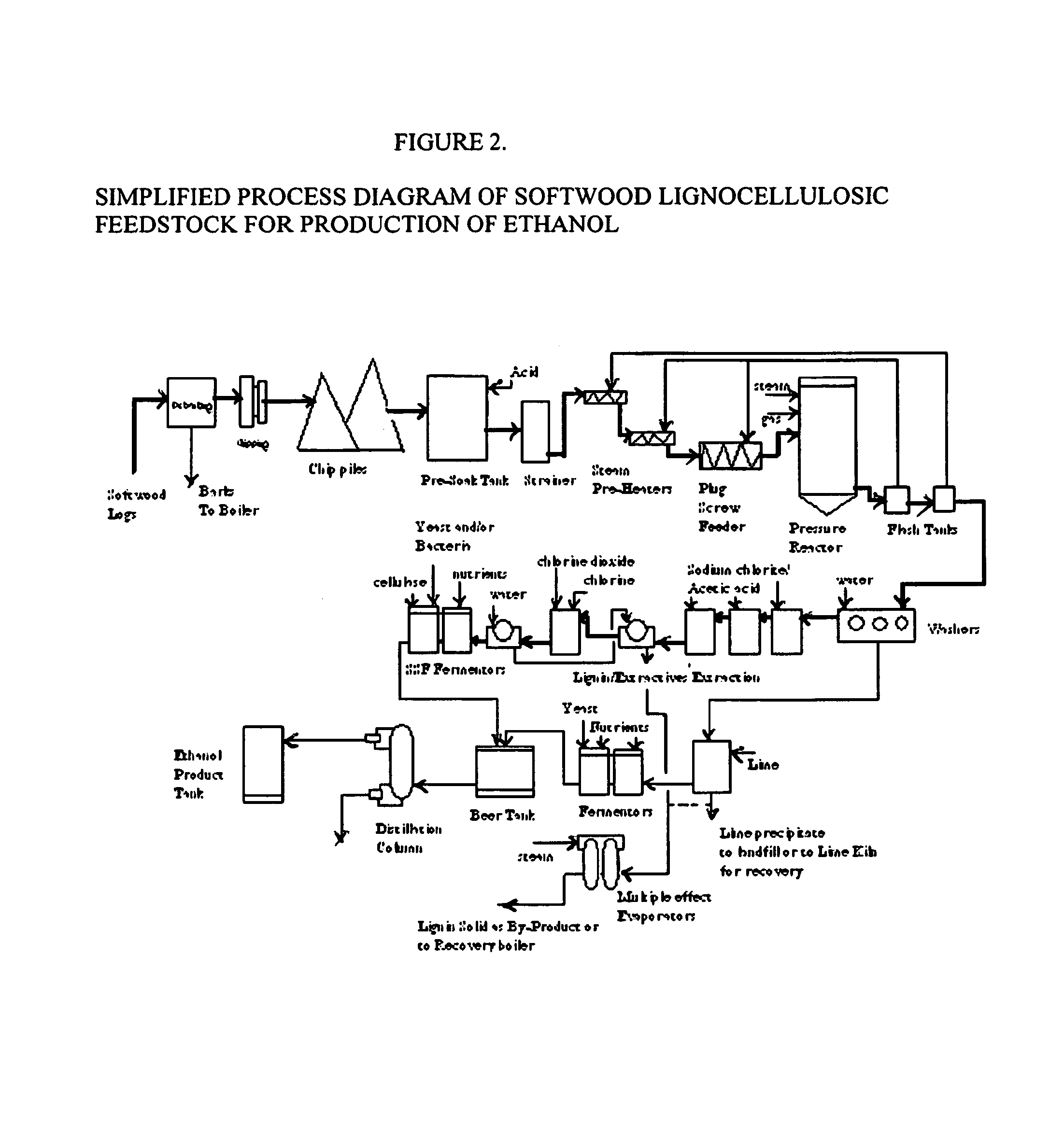
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS7666637B2Robust and cost-effectiveImproving biological reactivity of celluloseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentHydrolysate
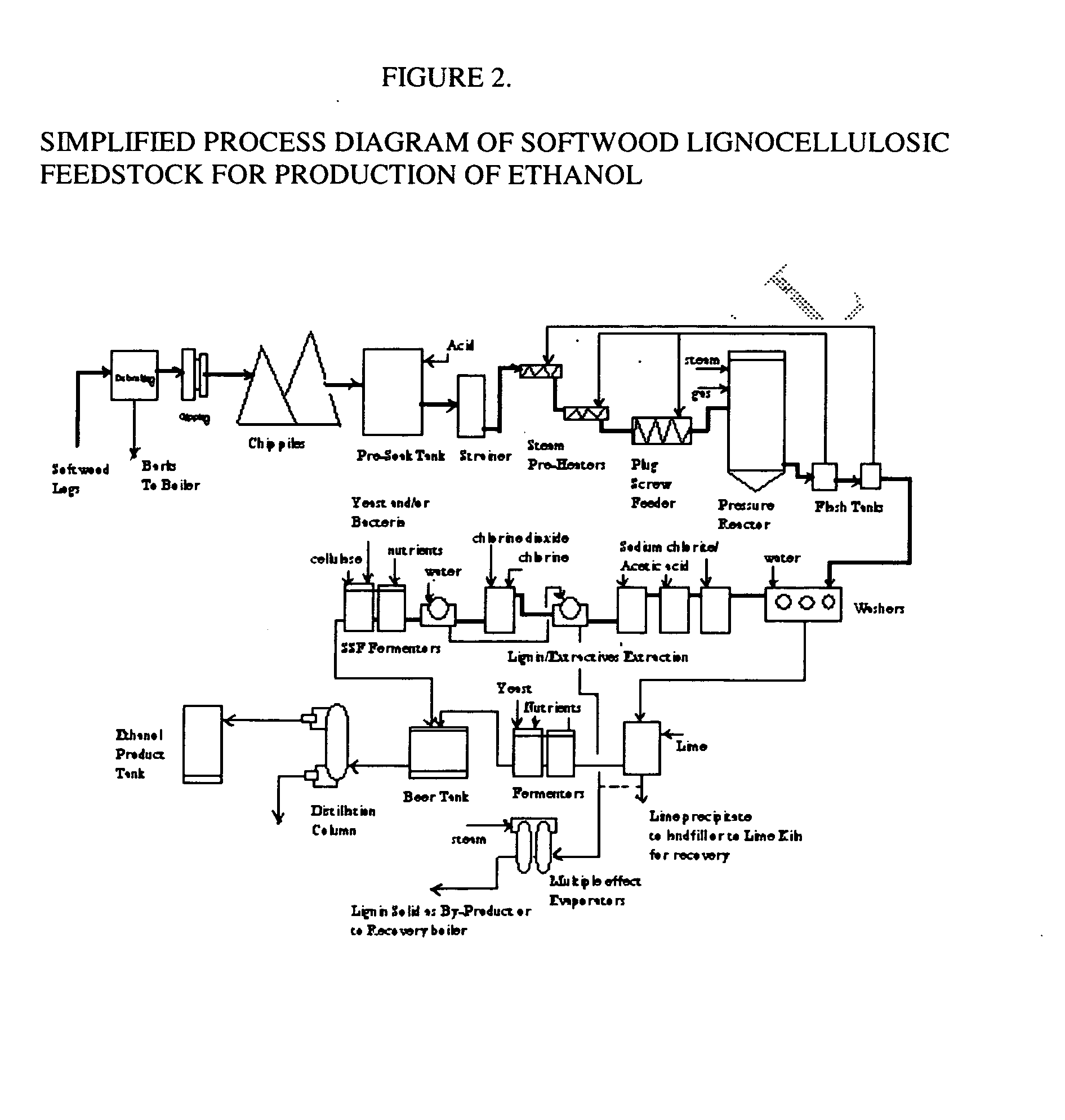
The invented process separates main components in lignocellulosic biomass, specifically hardwoods, softwoods into lignin and fractions of high purity sugars which are used for ethanol production. The invented process comprises of treatment stages at high temperature and high pressure with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. Residual lignin and extractives in the cellulosic solid fraction are selectively removed by chemical treatments of sodium chlorite, anhydrous acetic acid, chlorine and chlorine dioxide to enhance the purity and biological conversion of cellulose to ethanol. The pre-hydrolysate generated from the acid treatment stage, containing xylose, arabinose, galactose, glucose and the purified cellulosic fraction are enzymatically hydrolyzed and fermented to produce ethanol. Significant amount of lignin from the process is recovered as a by-product.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
Method for quickly and efficiently removing heavy metals in water body
ActiveCN104276646AImprove cleanlinessGood chromaWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPotassium permanganatePrecipitation
The invention relates to a method for removing heavy metals in a water body, which is characterized in that common oxidizers for water treatment, such as hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, potassium permanganate and the like, are utilized for oxidization to activate the zero-valent iron surface and continuously generate fresh iron (III) / (II) (hydro)oxide and other active components, thereby quickly and efficiently removing heavy metals in the water body, including As, Hg, Cd, Pb, Cr, Se, Sb, Cu, Zn and the like, in a mode of adsorption, precipitation, redox or the like.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method and device for deodorization and purification of exhaust gas or flue gas
InactiveUS20060124444A1Reduce needRemove films of protein oil and fatsLighting and heating apparatusExhaust apparatusElectrolysisHazardous substance
A method and device for removing, deodorizing and purifying odor, smoke and harmful substances from exhaust gas or flue gas employs a water solution containing hypohalogenous acid compounds such as sodium hypochlorite, an alkaline electrolyte such as potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide and a saline electrolyte such as sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium bromide or potassium bromide which is electrolyzed to produce an electrolytic water solution which is fed to a deodorizing tower and brought into contact with exhaust gas or flue gas to remove odor, smoke and harmful substances in the exhaust gas or flue gas.
Owner:NAKAMURA SHINICHI +2
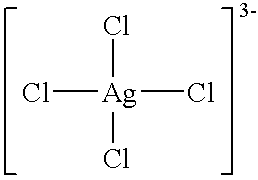
Antimicrobial agents
InactiveUS6726936B1Wide disinfecting spectrumAvoid problemsInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideMicrobial agentSolvent
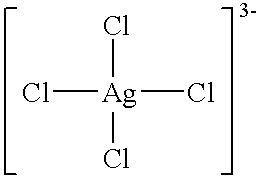
An antimicrobial agent includes silver-chloro complex salts and chloride, and further oxidizing agents such as sodium hypochlorite or sodium chlorite. As a result, it is possible to provide the antimicrobial agent having immediate and residual disinfecting and antimicrobial effects on bacteria and molds of a wide variety of species and capable of demonstrating instantaneous deodorizing effect. The antimicrobial agent includes the silver-chloro complex salts and chloride, and further a compound, for example, such as alcohols or surfactants, which has compatibility with a solvent such as water which dissolves the chloride. As a result, it is possible to provide the antimicrobial agent which can be used conveniently at the stored concentration, and which has immediate effect and cleansing ability without causing rust or deposition of salts in use. Further, the antimicrobial agent includes the silver-chloro complex salts, and chloride, for example, such as polyaluminium chloride or benzalkonium chloride, which has at least (I) a property capable of existing as a supersaturated aqueous solution in the presence of a crystal nucleus at least at room temperature for 24 hours or longer and (II) a property capable of being decomposed when dissolved in water.
Owner:YOKOSAWA METAL
Tuberculocidal synergistic disinfectant compositions and methods of disinfecting
InactiveUS6245361B1Remain stable and effectiveMore tolerableBiocideDead animal preservationAmmonium compoundsSodium chlorate
An aqueous cleaning and disinfecting composition is disclosed that is a synergistic combination of (a) a sufficient amount of a chlorine-containing bleach compound such as sodium hypochlorite or sodium dichloroisocyanurate to provide from about 1,100 parts per million by weight of available chlorine level with (b) from about 600 to 800 parts per million by weight of bactericidal quaternary ammonium compounds such as mixtures of didecyldimethylammonium chloride and (C12-C16 alkyl)dimethylbenzylammonium chlorides. Such compositions are tuberculocidal at unexpectedly low concentrations. Also disclosed are two component compositions and methods of disinfecting surfaces containing tubercule bacilli and other pathogenic micro-organisms such as bacteria and viruses.
Owner:JOHNSONDIVERSEY INC
Preparation method for coal combustion improver
The invention relates to a preparation method for a coal combustion improver. After common coal is added with coal additives for combustion, the effect of energy saving and emission reduction is obvious and effective. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: 1. high-stability sodium chlorate and potassium chloride react with each other to produce potassium chlorate when water is added and the sodium chlorate and the potassium chloride are dissolved; 2. leavening agent sodium acetate is introduced to conduct base exchange with humate in coal, low ignition point humate is produced and the ignition performance of the coal is reduced; and 3. ferric oxide required by the formula is compound insoluble in water. Thereby, ferric chloride and calcium oxide are used to react with each other to produce ferric oxide when water is added and the ferric chloride and the calcium oxide are dissolved. Other products in the market do not at all have the preparation and application characteristics of the three compounds.
Owner:GUANGHUA SCI & TECH SHANGHAI +1
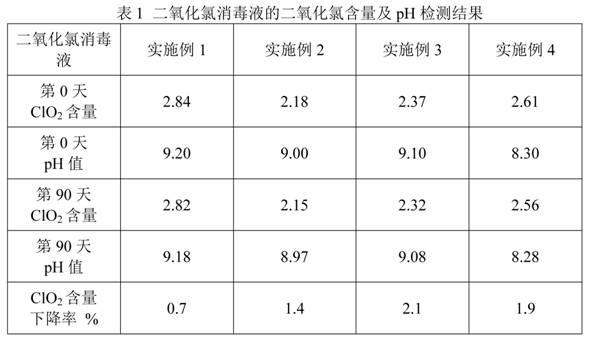
Stabilized chlorine dioxide disinfection solution and its preparation method
The invention discloses a stabilized chlorine dioxide disinfection solution and its preparation method. The disinfection solution is composed of component A and component B, wherein component A is stabilized sodium chlorite solution consisting of chlorite, a stabilizing agent, a complexing agent, a pH stabilizing agent, and the balance a pH conditioning agent and water; component B is an activating agent, which can be at least one of citric acid and hydrochloric acid. The product of the invention has the advantages of stability, long shelf-life, and a validity period up to 2 years, and can be used as a disinfectant. The disinfection solution of the invention has simple process and convenient usage. In the invention, the original mode of pH value adjusting by acid is changed, and zinc chloride and zinc acetate are employed to remove sodium hydroxide in raw materials and reach the purpose of pH value adjusting. Simultaneously, zinc acetate and sodium hydroxide generate no amphoteric substance, and the actual operation is easier.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
Catalyst for air sterilization, disinfection and purification and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105536825AImprove removal efficiencyNo secondary pollutionBiocideGas treatmentWave bandEnvironmental chemistry
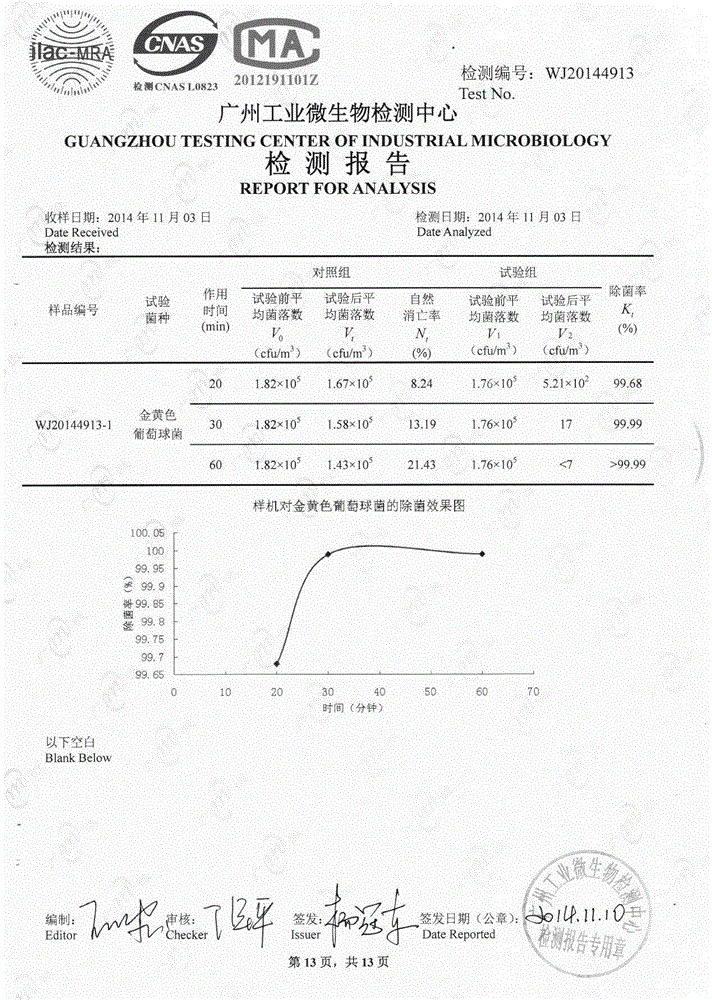
The invention provides a catalyst for indoor air sterilization, disinfection and purification. A carrier of the catalyst is formed by adopting silicon dioxide, zeolite, kieselguhr, sepiolite, montmorillonite, aluminum oxide and other inorganic porous materials or cordierite and mullite honeycomb ceramic as a carrier, immersing the carrier in a sodium chlorite stabilizing solution or a chlorine dioxide stabilizing solution and drying the mixture. The material is irradiated by an ultraviolet lamp (an A wave band, a B wave band and a C wave band are all effective), gas phase free radicals .OH, .CIO2, .HO2, .O and other active particles are generated, a chain reaction is induced, viruses, bacteria, mould and other microbial pollutants are rapidly killed, and formaldehyde and other chemical pollutants are removed. Compared with the prior art, purification efficiency is high, no secondary pollution is generated, the service life is long, simplicity and reliability are achieved, and the catalyst can coexist with the man and machine. An air disinfection purifier made of the catalyst as a filtering material is detected by a third party mechanism accepted by CNAS and CMA, in a test cabin of 30M<3>, the bacterial eliminating rate in 15 min is 99.68%, the bacterial eliminating rate in 30 min is 99.99%, and the formaldehyde removal rate reaches 99.1% in 1 h.
Owner:SHENZHEN KFAIR ENVIRONMENTAL TECH DEV CO LTD
Electrolytic cell and system for treating water
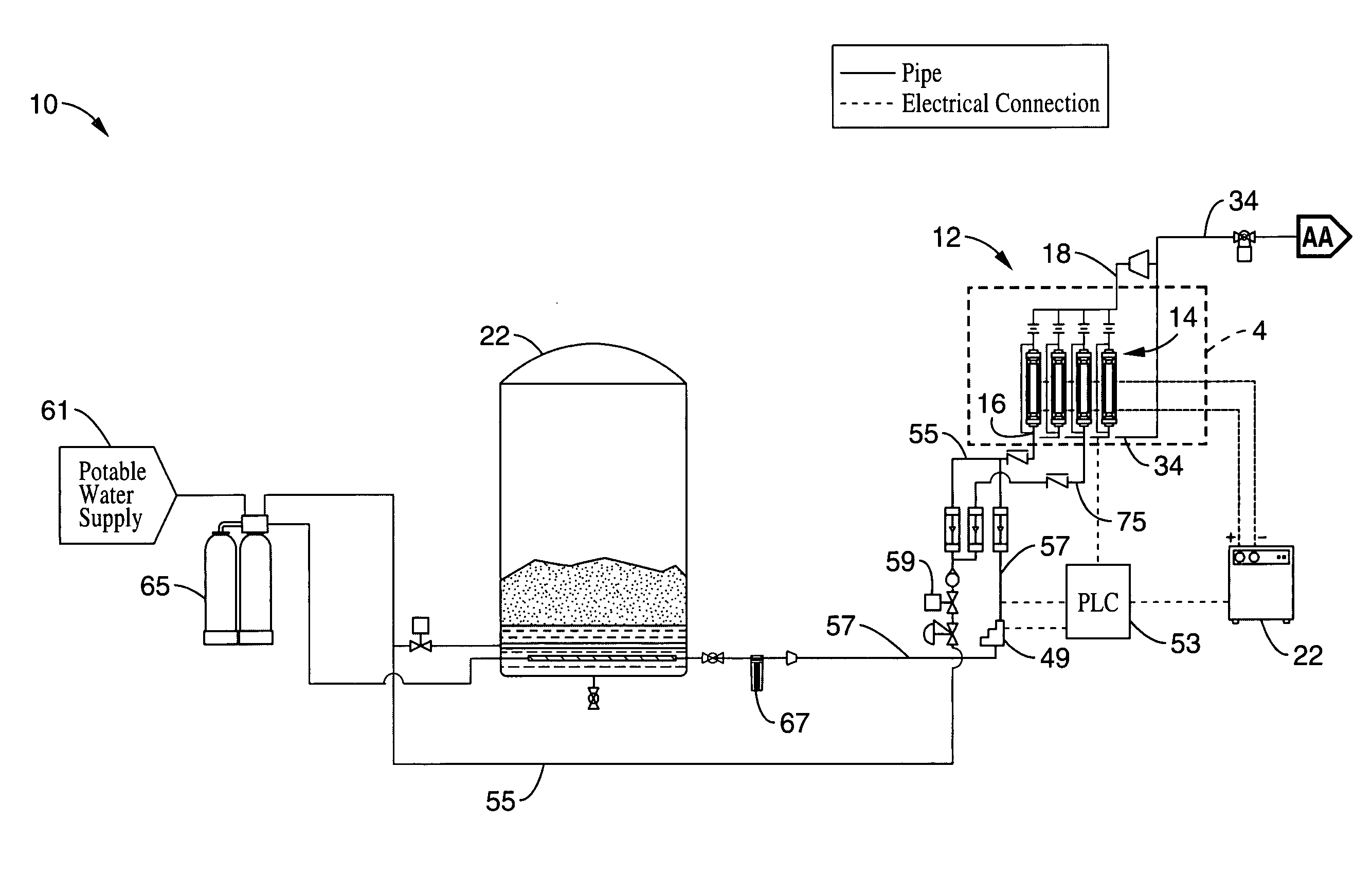
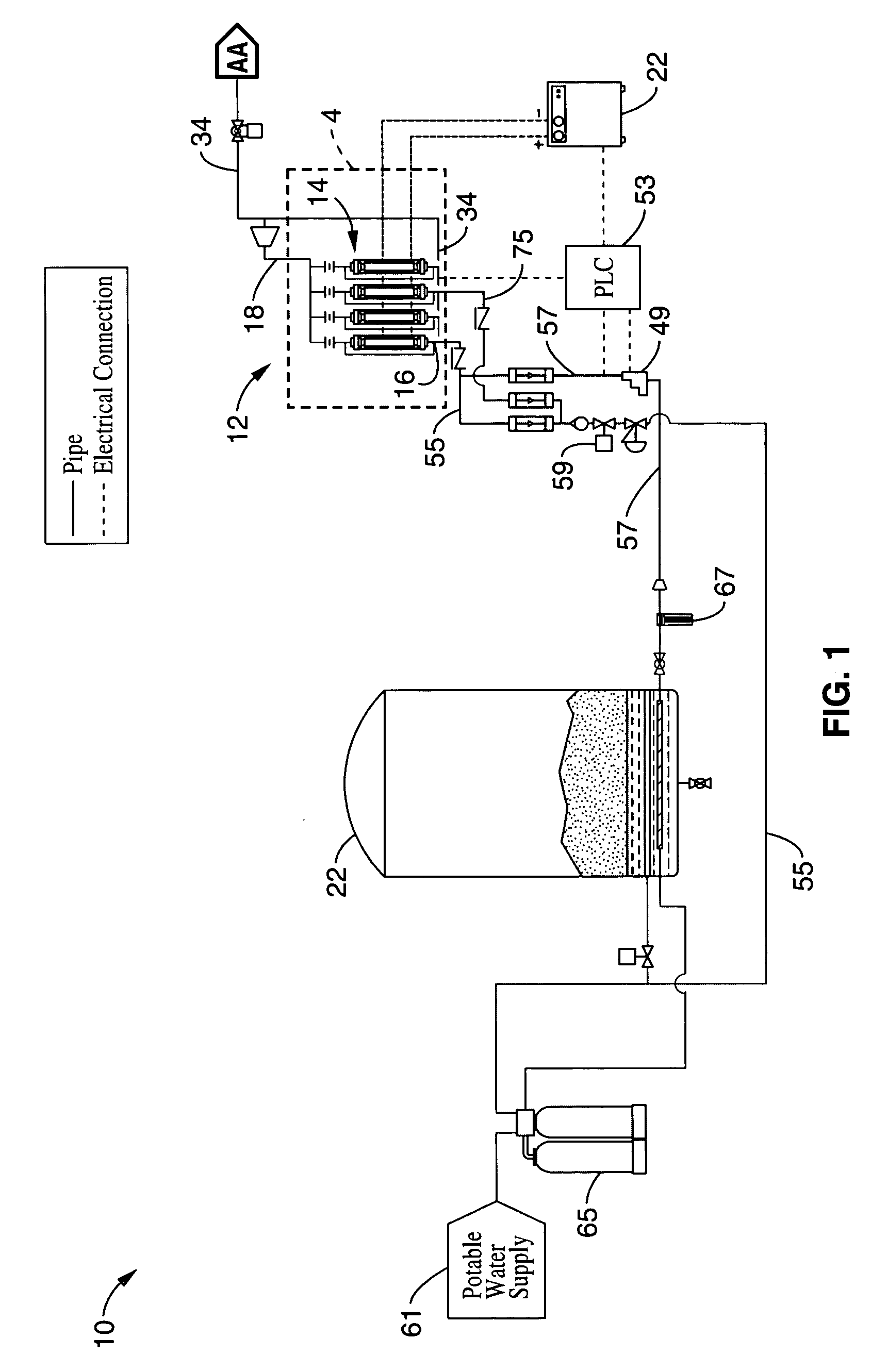
A water treatment system is disclosed having electrolytic cell for liberating hydrogen from a base solution. The base solution may be a solution of brine for generating sodium hypochlorite, or potable water to be oxidized. The cell has first and second opposing electrode endplates held apart from each other by a pair of supports such that the supports enclose opposing sides of the endplates to form a cell chamber. One or more inner electrode plates are spaced apart from each other in the cell chamber in between the first and second electrode plates. The supports are configured to electrically isolate the first and second electrode plates and the inner electrode plates from each other. The first and second electrode plates are configured to receive opposite polarity charges that passively charge the inner electrode plates via conduction from the base solution to form a chemical reaction in the base solution as the base solution passes through the cell chamber.
Owner:UGSI SOLUTIONS INC
Ordinary temp. parkerizing liquid
InactiveCN1401820AFast phosphatingFast combinationMetallic material coating processesSoftened waterManganese
An ordinary-temp phosphating liquid for the phosphate treatment of surface of iron and steel contains phosphoric acid (2-4 wt.%), zinc oxide (0.4-0.6 wt.%), zinc nitrate (0.5-1.5 wt.%), nickel nitrate (3-5 wt.%), manganese nitrate (2-4 wt.%), sodium borofluorate (0.2-1 wt.%), sodium chlorate (2-3 wt.%), citric acid (0.5-2 wt.%), and softened water (the rest). Its advantages are high stability, long film-forming time, and high film strength and resistance to corrosion.
Owner:CHINA NATIONAL HEAVY DUTY TRUCK GROUP
Method for extracting platinum-palladium out of copper anode mud
ActiveCN103305699ASimple configurationEasy to operateProcess efficiency improvementPlatinumProcess equipment
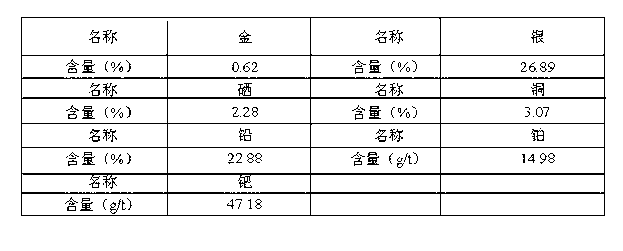
The invention discloses a method for extracting platinum-palladium out of copper anode mud. The method is characterized in that the platinum-palladium is extracted by employing a secondary gold dust chlorination gold leaching liquid, and the method comprises the following process steps of: firstly, carrying out sulfation roasting on the copper anode mud, carrying out primary chlorination gold leaching, carrying out sulfur dioxide gas reduction so as to obtain a primary reduction liquid, and subsequently carrying out zinc powder replacement so as to enrich gold, silver, platinum and palladium into secondary gold powder; secondly, dissolving the secondary gold powder, removing the impurities, filtering the obtained filtered residue, carrying out secondary chlorination gold leaching, adding ammonium chloride and a reduction inhibitor sodium chlorate into the filtered liquid, and reacting so as to obtain platinum and palladium precipitate; and finally reducing the filtered liquid by using a liquid sulfur dioxide to leach the gold. The method is simple in process equipment arrangement and convenient to operate; the recycling rate of the gold in the copper anode mud is increased; and meanwhile the platinum-palladium is effectively enriched in platinum-palladium concentrate.
Owner:SHANDONG HUMON SMELTING
Method for preparing cuprous oxide/ bacterial cellulose nano composite material
InactiveCN102121038AMaintain nanostructureOvercoming the disadvantages of difficult recyclingMaterial nanotechnologyCopper oxides/halidesGas detectorHydroquinone Compound
The invention relates to a method for preparing a cuprous oxide / bacterial cellulose nano composite material. The preparing method comprises the following steps of: obliquely inoculating acetobacter xylinum strains into culture solution, and culturing the strains to obtain a bacterial cellulose gel film; performing surface activation treatment on the bacterial cellulose gel film in sulfuric acid solution and sodium hypochlorite solution respectively; and sequentially soaking the surface activated bacterial cellulose gel film into Cu(NO3)2 solution and hydroquinone solution to perform reduction reaction to obtain the cuprous oxide / bacterial cellulose nano composite material. The method has the advantages that: the preparation process is simple; and the prepared composite material keeps the nano structure of cuprous oxide particles, simultaneously has good strength performance, and has wide application prospect on the aspects of electrode devices, catalysts, gas sensitive sensors and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method of oxidative cationic modified starch slurry
The invention provides a preparation method of oxidative cationic modified starch slurry, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, dissolving starch into water to prepare starch milk; secondly, using an oxidant namely sodium hypochlorite to perform oxidation reaction with the starch to obtain oxidized starch; thirdly, removing chlorine; fourthly, adopting a cationic etherifying agent to perform etherification reaction; and finally, performing dehydration and drying. When the modified starch prepared from the starch serves as the slurry, the slurry not only has the characteristics of high fluidity, low viscosity and high concentration usage of oxidative starch slurry, but also solves the problem that the oxidative starch has poor thermal stability through quaternary ammonium etherification, and simultaneously, the slurry additionally obtains the following advantages that: the adhesiveness to a warp is significantly improved; the serous membrane forming capacity is strong, and the slurry is difficult to break and burst; the paste viscosity is stable, and the fluidity is good; the slurry has certain hygroscopicity, and has high co-solvency with a synthetic slurry; a membrane is easy to be dissolved in water, and is easy to desize; and paste solution has high thermal stability, is not influenced by high heat fusing, and the like.
Owner:内蒙古奈伦农业科技股份有限公司
Method for recovering germanium from flyash by wet process
InactiveCN101906542ATake advantage ofReduce pollutionProcess efficiency improvementSodium chlorateHydrometallurgy
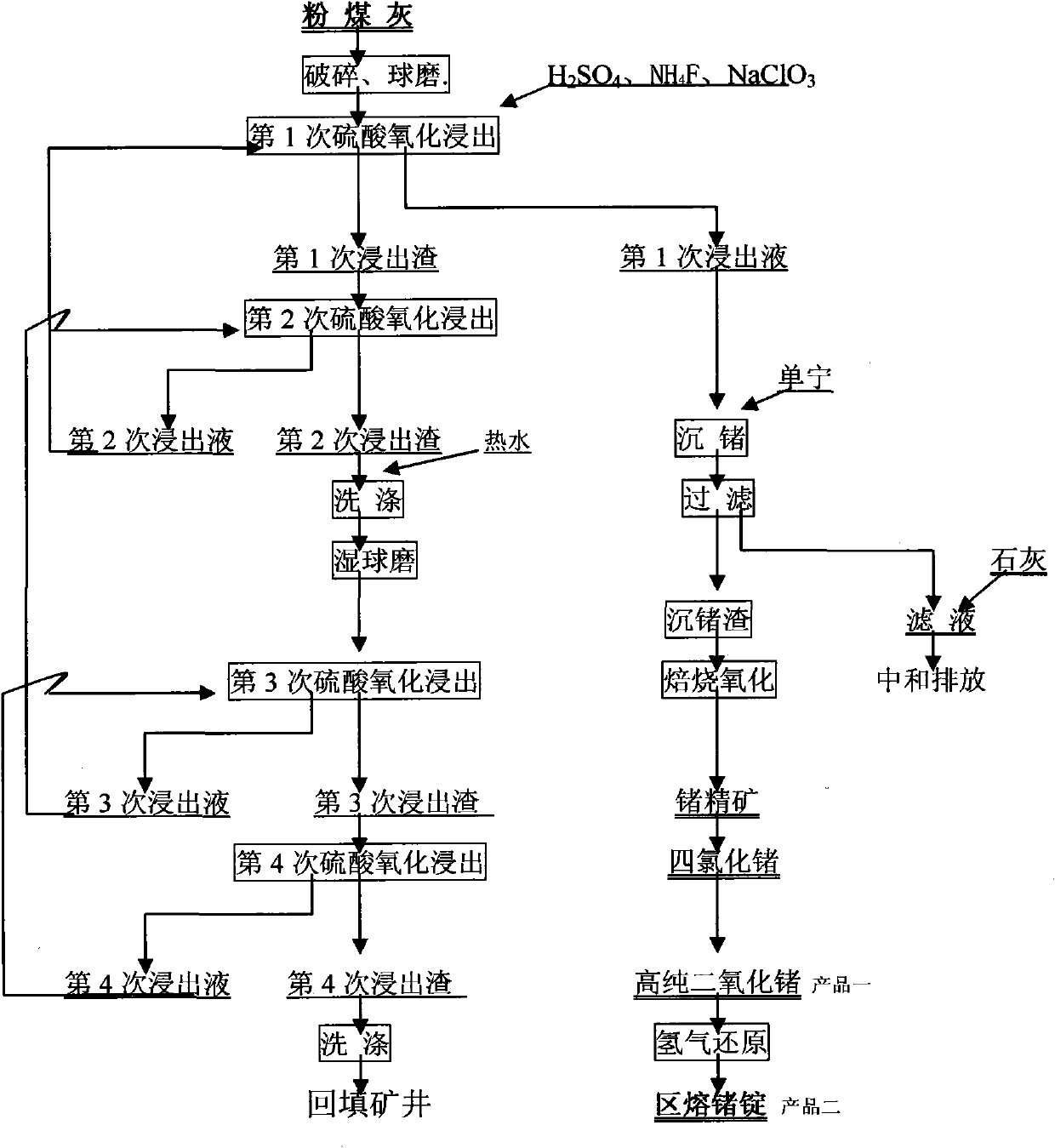
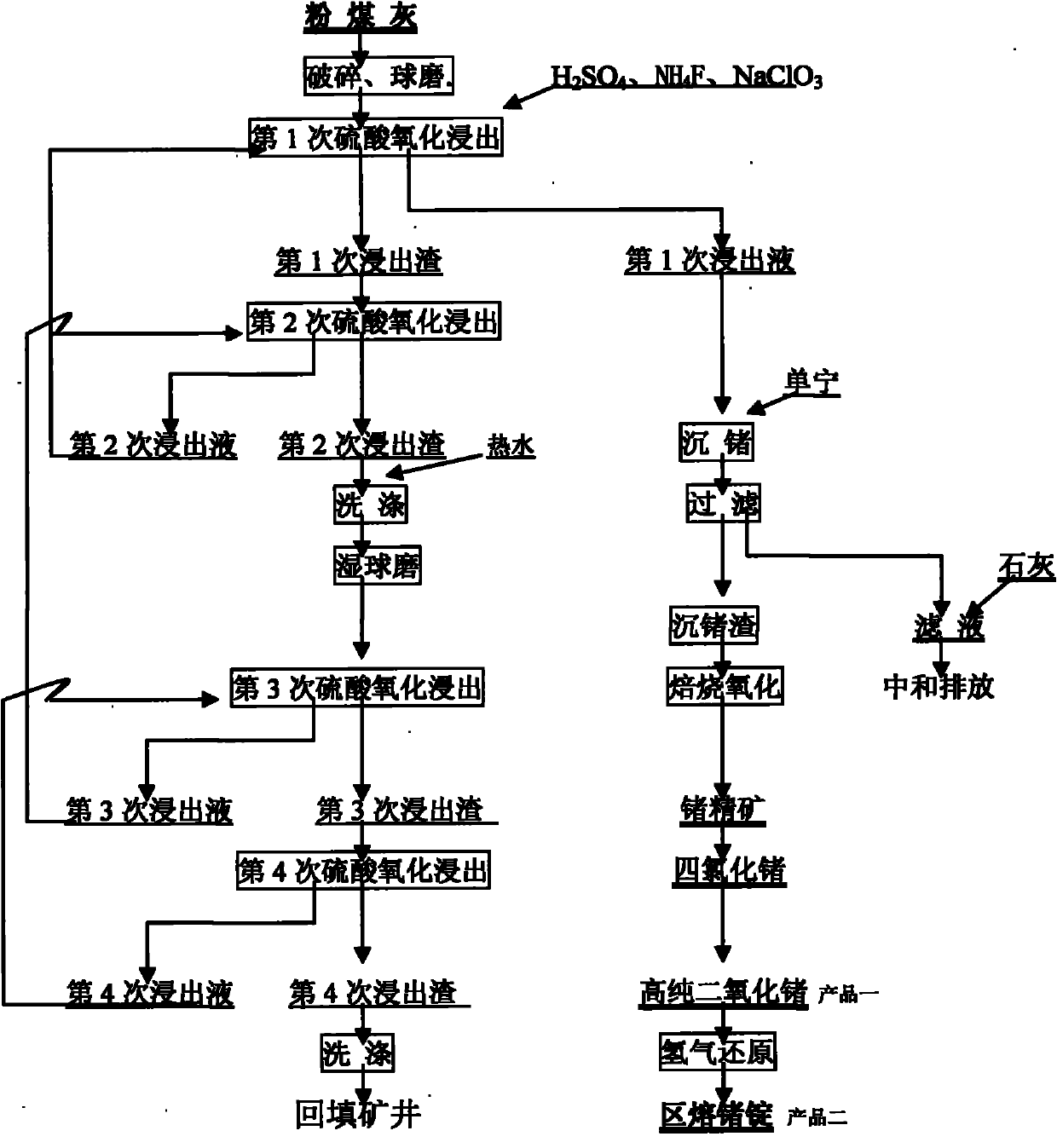
The invention relates to a method for recovering germanium from flyash by a wet process, belonging to the technical field of wet-process metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) crushing flyash to more than 200 meshes by a wet process; (2) carrying out oxidizing leaching twice on wet flyash by using a sulfuric acid solution, sodium chlorate and ammonium fluoride; (3) crushing the flyash to 200-400 meshes for a second time; (4) leaching 3 or 4 times by using the same condition as that of the first leaching; (5) regulating the pH value of the first leached liquid to 2-2.5 by using ammonia water, and then precipitating and leaching out germanium in the liquid by using tannin with a weight percentage content of 80-99 percent; (6) drying and roasting the germanium precipitate to prepare a germanium concentrate; distilling the germanium concentrate with hydrochloric acid by using a conventional method to obtain germanium tetrachloride; and redistilling, rectifying, purifying and hydrolyzing to obtain high-purity germanium dioxide. The invention is used for flyash after recovering germanium by a fire process, sufficiently utilizes rare germanium metal, reduces the pollution of tailings to the environment, and has the advantages of low cost and high recovery rate.
Owner:JIUJIANG BAIDUN VANADIUM TECH TRADING
Method for selective solvent extraction of heterogenite with full-wet-process
InactiveCN101509069ATake advantage ofProcess efficiency improvementFerric hydroxideReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for selectively leaching heterogenite, which is based on the whole wet method and characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: ball-milling and pulping heterogenite minerals until the requirement that the particle size is smaller than 150 meshes is met; putting the heterogenite minerals into concentrated sulfuric acid, concentrated hydrochloric acid or a mixed solution of both the concentrated sulfuric acid and the concentrated hydrochloric acid; adding a reducing agent containing ferrous ions to carry out reduction reaction for 5 to 9 hours under the conditions that the pH value of the solution is 1.0 to 2.0 and the reaction temperature is 60 to 90 DEG C; sampling and detecting, and stopping adding the reducing agent when the content of Cobalt in the residue is lower than 0.5% and the content of the ferrous ions in the solution is lower than 2.0g / L; adding sodium chlorate or hydrogen peroxide as an oxidizing agent, or pumping air into the solution, to oxidize the residue ferrous iron into ferric iron; adding sodium carbonate to the solution to adjust the pH value of the solution to 2.5 to 4.5; reacting for 2 to 3 hours, to precipitate the ferric iron in the form of ferric hydroxide; and leaching the waste residue after the reaction. The invention has the advantages of low production cost and low environmental pollution level.
Owner:南通新玮镍钴科技发展有限公司
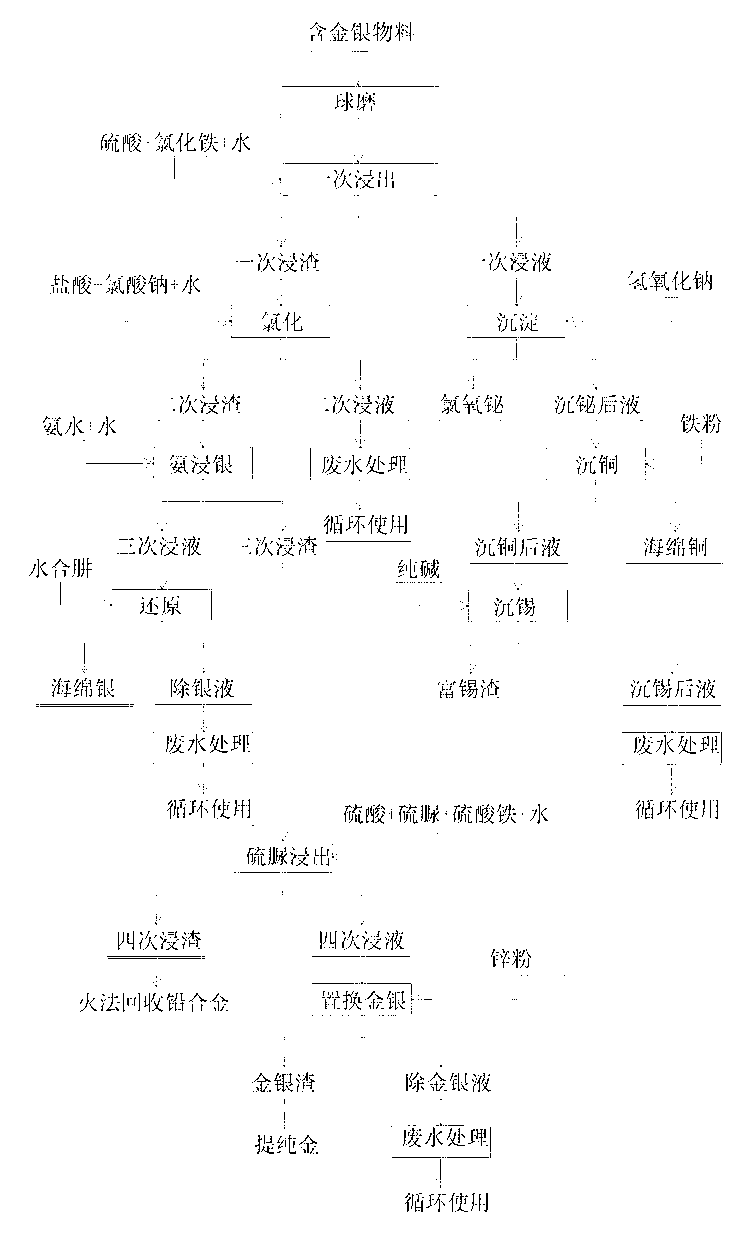
Comprehensive recycling process for polymetallic material containing gold and silver
ActiveCN103276217AImprove leaching rateImprove protectionProcess efficiency improvementBall millMaterials science
The invention discloses a comprehensive recycling process for polymetallic material containing gold and silver, belongs to the field of non-ferrous metal comprehensive recovery, and mainly comprises the following steps: ball-milling polymetallic material containing gold and silver, leaching bismuth, copper and tin from the polymetallic material by sulfuric acid leaching agent and ferric chloride, recovering the bismuth, copper and tin; retaining lead, gold and silver in the first leaching residue; and recovering the lead, gold and silver. According to the comprehensive recycling process provided by the invention, bismuth, copper and tin are leached from the polymetallic material by sulfuric acid leaching agent and ferric chloride, the oxidation of the ferric in the ferric chloride, and the chloride solution function of the chloride ion to bismuth and tin are creatively utilized, the addition of sulfuric acid and ferric chloride has the effect of changing silver oxide and silver sulfide into silver chloride, so as to reduce the chlorination step cost, and further reduce the dosage of sodium chlorate and hydrochloric acid, and the leaching rate of gold and silver is greatly improved accordingly. The comprehensive recycling process provided by the invention has the advantages that the technology is simple and practicable, the process is short, the device is simple, and the operation is convenient; and the adopted raw material is common, cheap and pollution free.
Owner:CHENZHOU YANGTAO CHEM
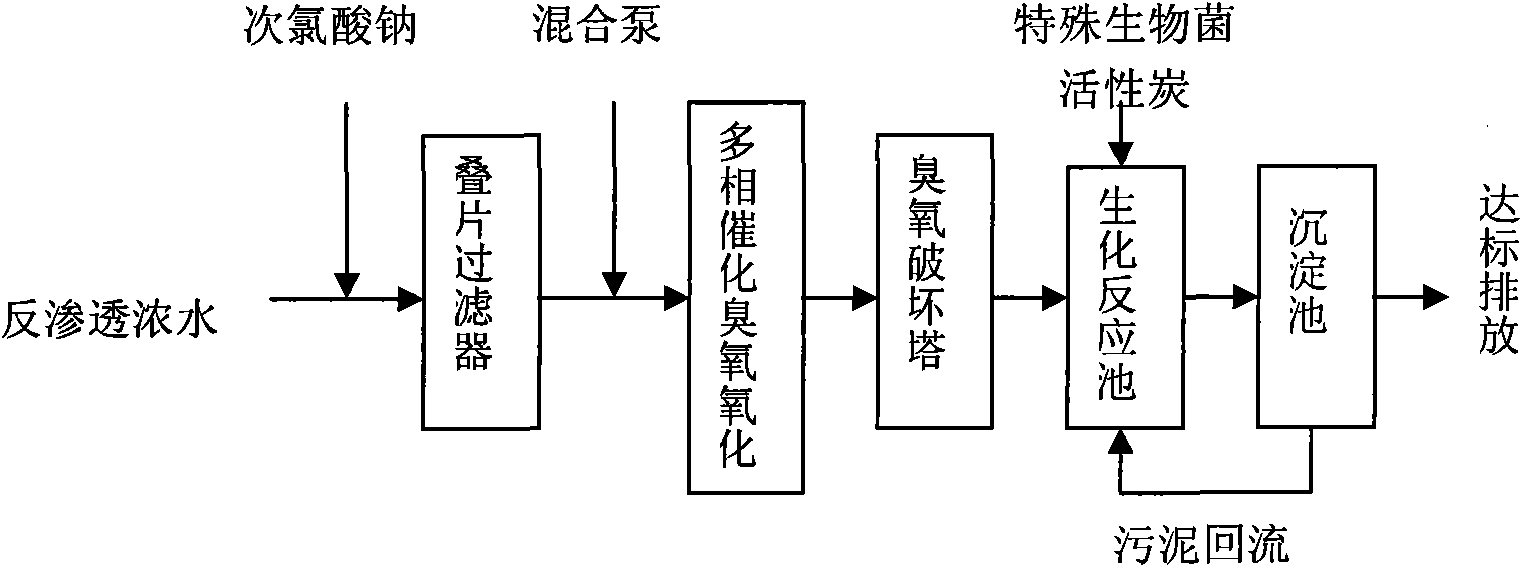
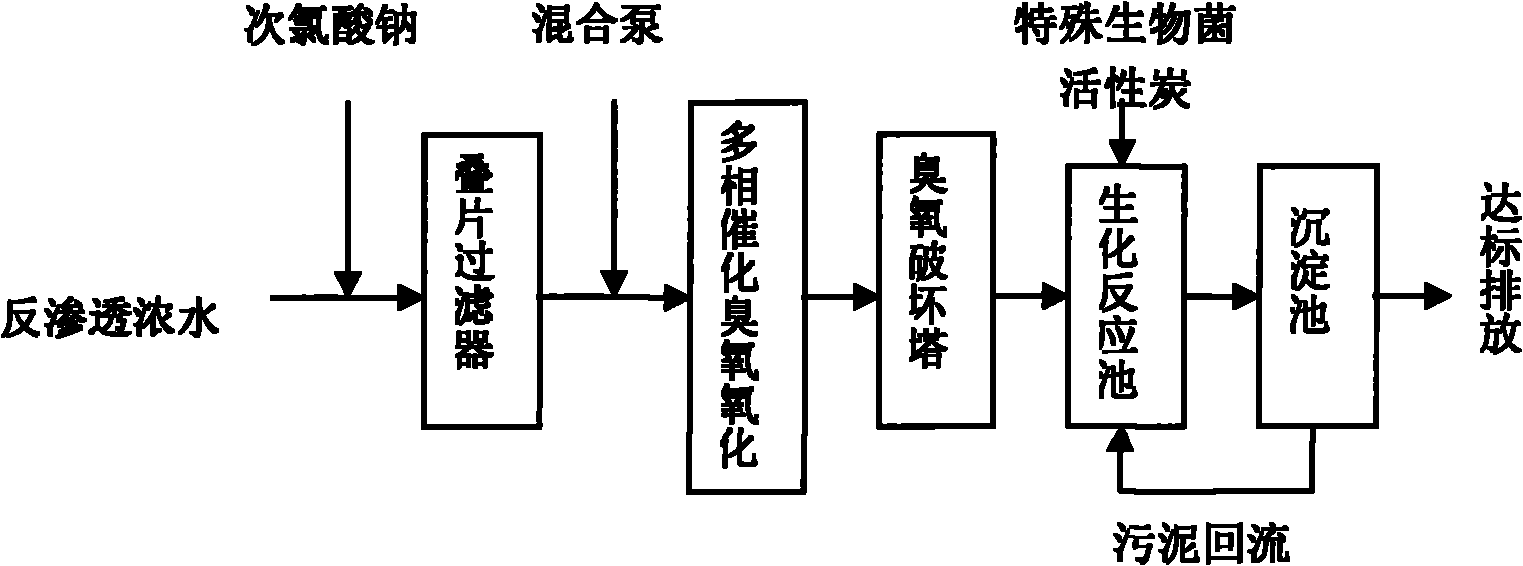
Method for treating reverse osmosis concentrated water
ActiveCN102040312AImprove biodegradabilityMultistage water/sewage treatmentSodium chlorateChemical oxygen demand
The invention provides a method for treating reverse osmosis concentrated water. In the method, the process flows of a laminated filter, heterogeneous catalytic ozone oxidation reaction, an ozone destruction tower and a biochemical reaction tank are adopted. The method comprises the following steps of: adding sodium hypochlorite into the reverse osmosis concentrated water produced in the recycling process of oil refining production wastewater subjected to biochemical treatment and membrane process treatment, sterilizing, filtering by using the laminated filter, fully mixing with ozone, adding into a reactor filled with a zirconium titanate catalyst and performing ozone oxidation; and performing biochemical treatment by using a biochemical reactor with special biological bacteria, wherein the chemical oxygen demand (COD) of effluent after the reverse osmosis concentrated water is treated is below 60mg / L.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Microbial and odor control using amorphous calcium silicate impregnated with sodium chlorite
InactiveUS20030021819A1Long time-rangeIncrease time scaleHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCalcium silicateDisinfectant
The present invention is directed to the a composition and method for microbial and odor control. In one embodiment, the method includes mixing amorphous calcium silicate impregnated with a chlorite salt to form a reactant, combining the reactant with an activator to form the composition, and applying the composition to the treatment area. The present invention also includes the preparation of a product usable as a disinfectant and deodorizer, wherein the product includes a mixture of an amorphous and a chlorite salt and wherein the product is packaged as a tablet, permeable sachet, or a permeable patch attachable to a plastic bag. The present invention may also be applied using several methods to reduce the spoilage of produce. The present invention further includes a method for producing chlorine dioxide in accordance with a step-function release profile.
Owner:BIO CIDE INT
Composition of hypochlorous acid and its applications
InactiveUS7323118B2Inexpensive as processAntibacterial agentsBiocideChemical compositionChloride sodium
Composition of Hypochlorous acid characterized because it has the following chemical compositionHypochlorous acid 6.5-7.3%Hydrochloric acid 27.6-28.5%Sodium chloride 13.6-14.2%Sodium hypochlorite 34.8-35.4%Chlorine in solution 7-6.5%Dissolved oxygen 10.5-8.1%The composition of hypochlorous acid has medical application in humans and in veterinary practice, both prophylactic and therapeutic. It can also be applied in antisepsis and sterilization of foods and in the treatment of water and water supply systems. In flower growing is can be used for the disinfection of crops and the elimination of fusarium and sigatoka negra.
Owner:AQUILABS
Composition for generating chlorine dioxide
InactiveUS6602442B1Transportation safetyMade preciselyBiocidePeroxide active ingredientsLithium hypochloriteSodium bisulfate
A dry disinfectant composition for the production of aqueous solutions of chlorine dioxide of predetermined concentration is formulated of a mixture of lithium hypochlorite, sodium bisulfate and sodium chlorite. Special liquid and dry formulations are also contemplated for convenience of use, for quality assurance and for safety.
Owner:OCCIDENTAL CHEM CORP
Method adopting combined technology of pre-oxidation and coagulating sedimentation to process wastewater containing thallium and ammonia-nitrogen
InactiveCN105293775AShort operating timeLess investmentWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentNitrogen gasHydrolysis
The invention discloses a method adopting a combined technology of pre-oxidation and coagulating sedimentation to process wastewater containing thallium and ammonia-nitrogen. According to the method, a sodium hypochlorite oxidizing agent is added into a wastewater collecting tank so as to oxidize metal ions in wastewater, the monovalent thallium is fully oxidized into trivalent thallium, monovalent thallium is converted into complex under the effect of strong oxidant, and at the same time, the nitrogen in ammonia-nitrogen is degraded and removed in the form of nitrogen gas. After pre-oxidation, the wastewater is lifted to an integral processing facility through a self-sucking pump; ferrous sulfate and poly aluminum chloride (PAC) are added to form alumen ustum flocculus in a precipitation unit, the precipitate is wrapped, the thallium complex is adsorbed, then quicklime is added to adjust the solution to an alkaline environment; in the alkaline environment, Fe<3+>, Al<3+>, and prepolymer products thereof carry out hydrolysis quickly to form Fe(OH)3 flocculus and Al(OH)3 flocculus; before the flocculus becomes big, the adsorption sites on the surface of flocculus form covalent bonds with Ti<3+>, the flocculus becomes bigger and bigger very quickly and goes on absorbing Ti<3+> in water; at the same time, Ti<3+>, Fe<3+>, Al<3+>, Zn<2+>, lead, and cadmium carry out co-precipitation reactions, and thus the heavy metal ions in water are removed.
Owner:HUNAN LIHONG NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Targeted performance of hypohalite compositions thereof
InactiveUS20130216631A1Prevent and minimize negative side effectReduce oxidant concentrationInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideSodium chlorateHypochlorite
This invention relates to extend the benefits of using hypochlorite compounds such as sodium hypochlorite to clean and disinfect articles while reducing or eliminating the side effects of treating an article with a strong oxidant material. The invention relates to a single step process involving mixing of precursor compositions of a suitable hypohalite or hypohalous acid with a solution of a reducing agent. Optionally a buffer may be present in either or both precursor compositions, such that at time of use such active hypohalous acid concentration in the resulting aqueous mixture remains at a sufficient activity level to effect one or more desired benefits against a target substrate for a desired period of time. The oxidant is substantially consumed by reaction with the reducing agent after the time needed for achieving the desired benefit has passed.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
Method for comprehensively recovering mercury and selenium from metallurgical slag
InactiveCN104498722ALow costNo emissionsProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumMetallurgical slagHydroxylamine
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering mercury and selenium from metallurgical slag and belongs to the field of metallurgy. The method comprises following steps: grinding the metallurgical slag to the range of 130-150 microns, blending the metallurgical slag with quick lime accounting for 10-30% of the metallurgical slag and roasting at a temperature ranging from 750 to 900 DEG C for 6-8 hours; collecting dust from mercury-containing vapor firstly by use of a cloth bag and then by virtue of cyclone, condensing the mercury vapor by use of a two-stage condensation apparatus to recovery the mercury, and returning mercurial soot and a tail gas adsorption filler to the metallurgical slag for reutilization, wherein no pollutant is emitted in the process; next, leaching selenium-containing slag by use of an oxidation solution prepared from hydrochloric acid and sodium chlorate in the ratio of 2:1, analyzing the contents of Hg<2+>, Fe<2+>, Ca<2+> and Mg<2+> in the leachate in the liquid-solid ratio of 2:1, respectively, precipitating the ions by use of sodium sulfide in the ratio of 1:1 to the total content of the ions and then filtering to remove the irons, and reducing for 2 hours by use of hydroxylamine hydrochloride, thereby obtaining the elemental selenium after washing the precipitate. The method for comprehensively recovering mercury and selenium from the metallurgical slag is high in extraction rate and prone to industrial production.
Owner:贵州重力科技环保股份有限公司
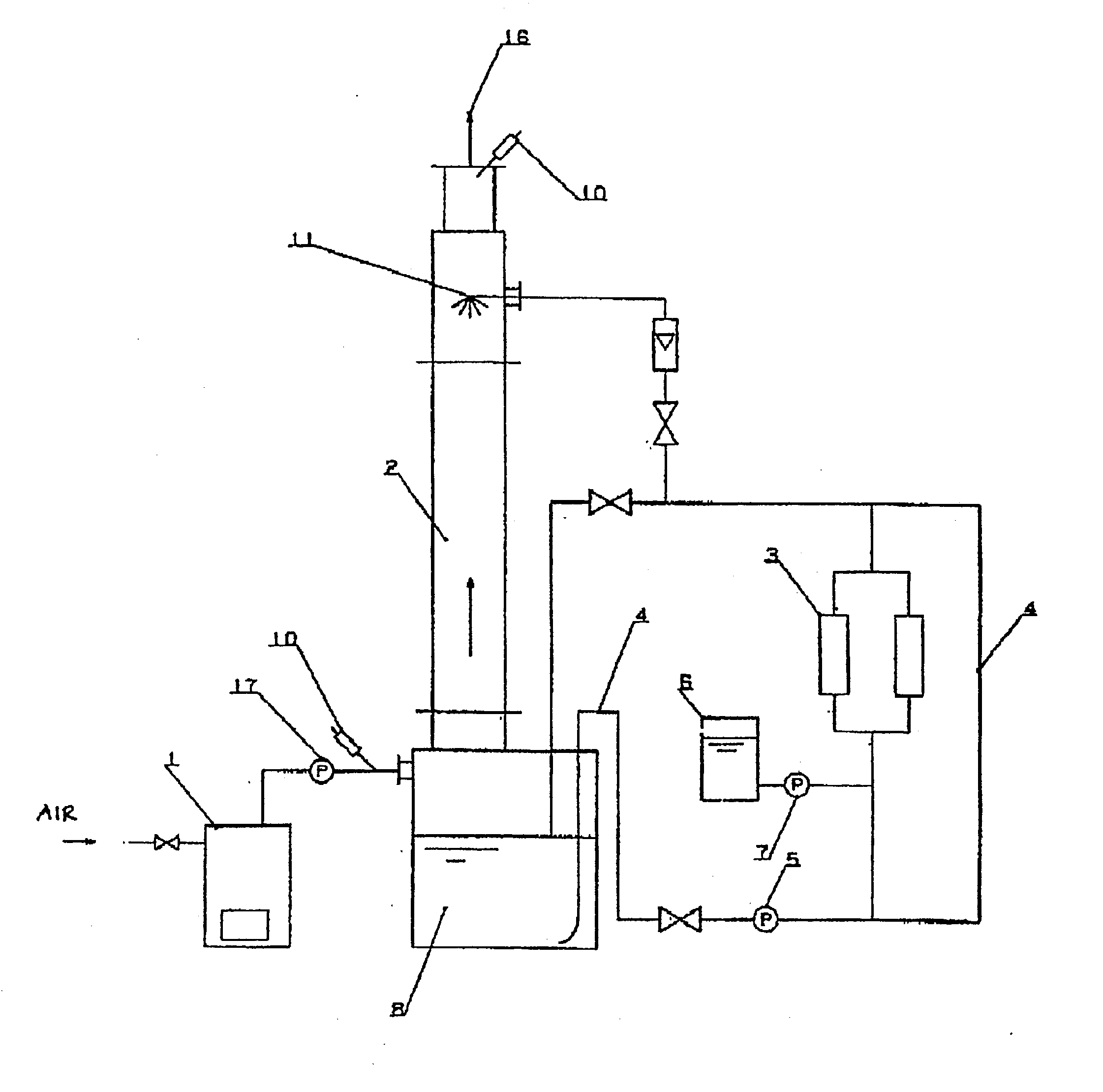
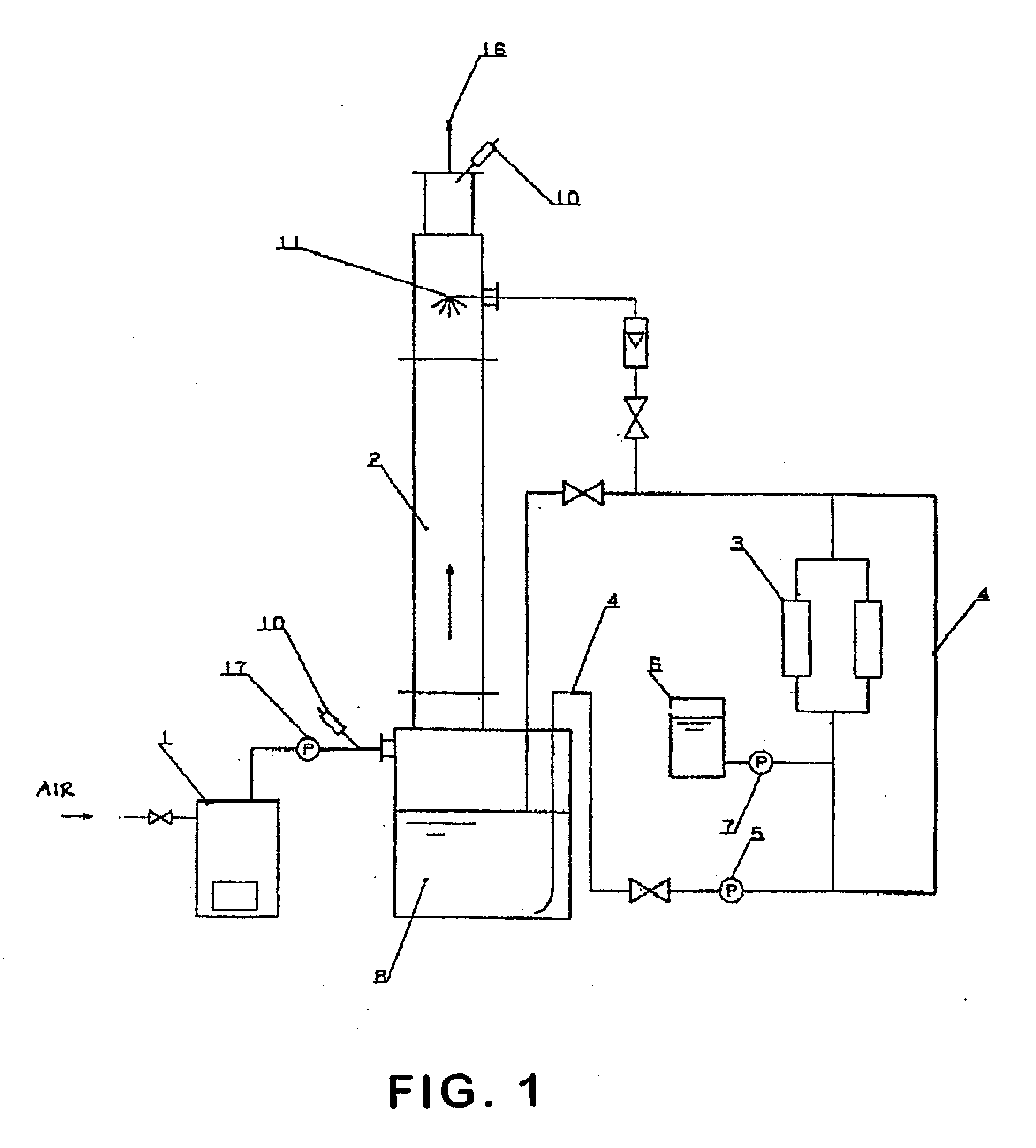
Formulation Of Electrolyte Solutions For Electrochemical Chlorine Dioxide Generators
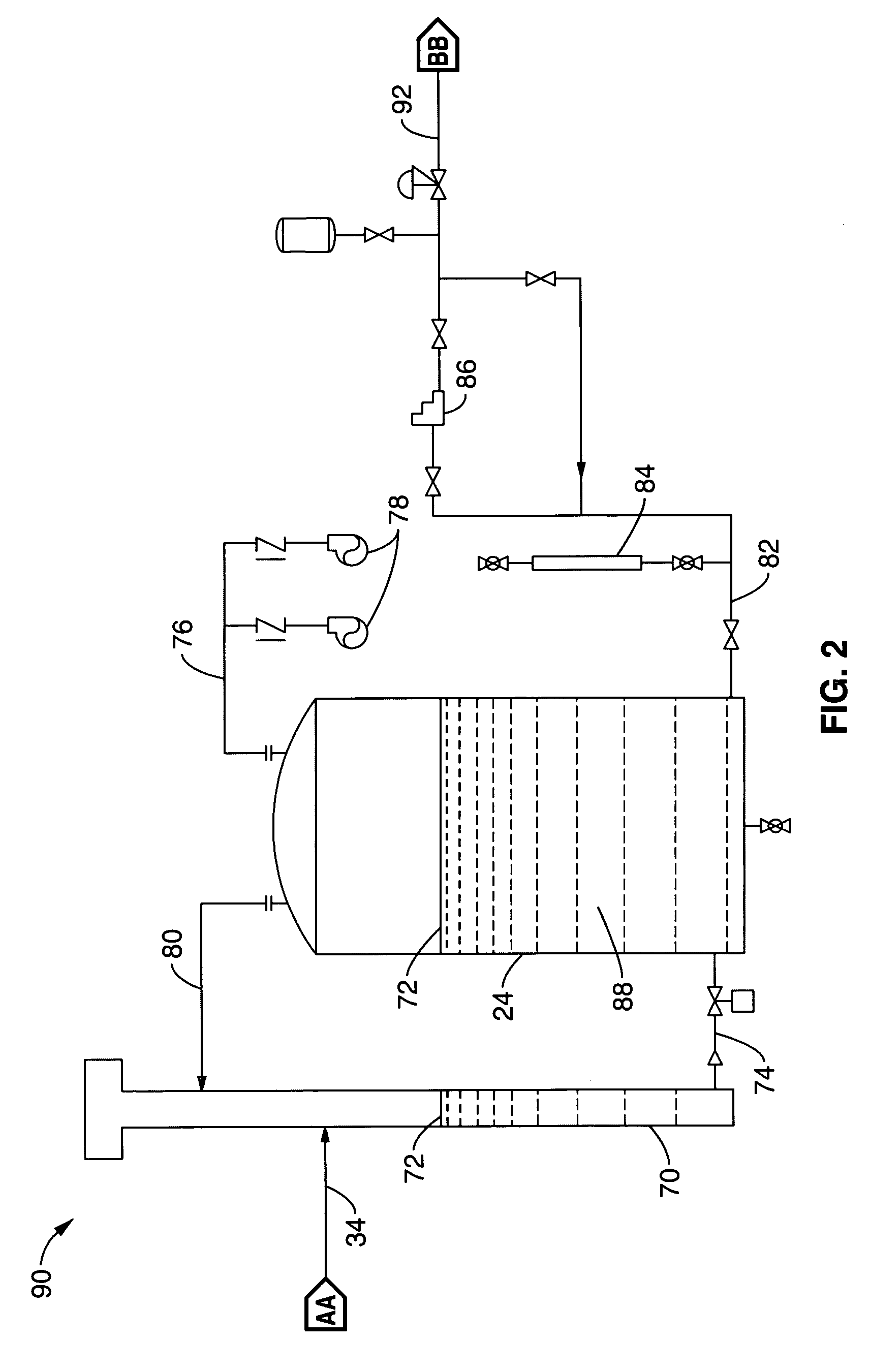
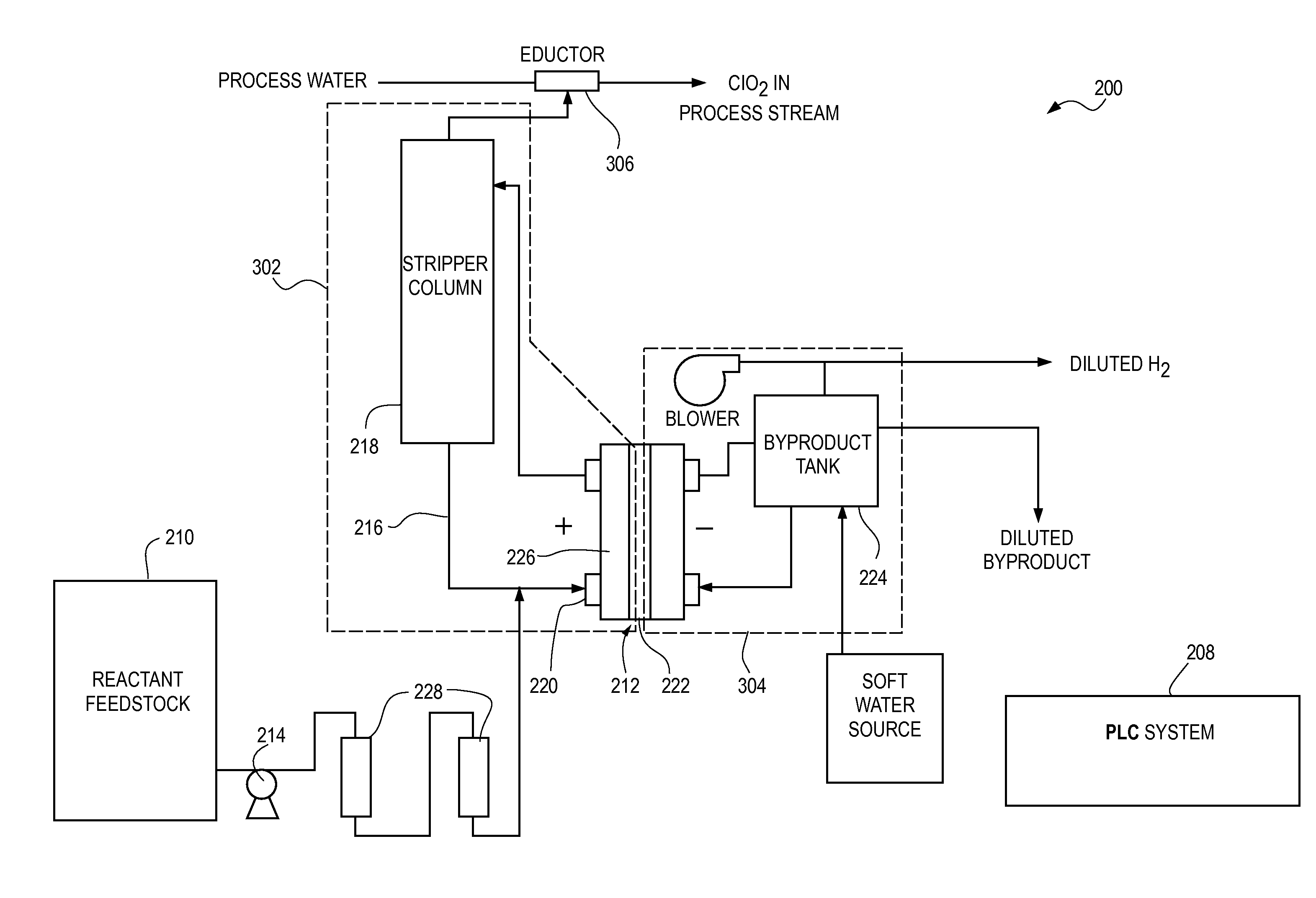
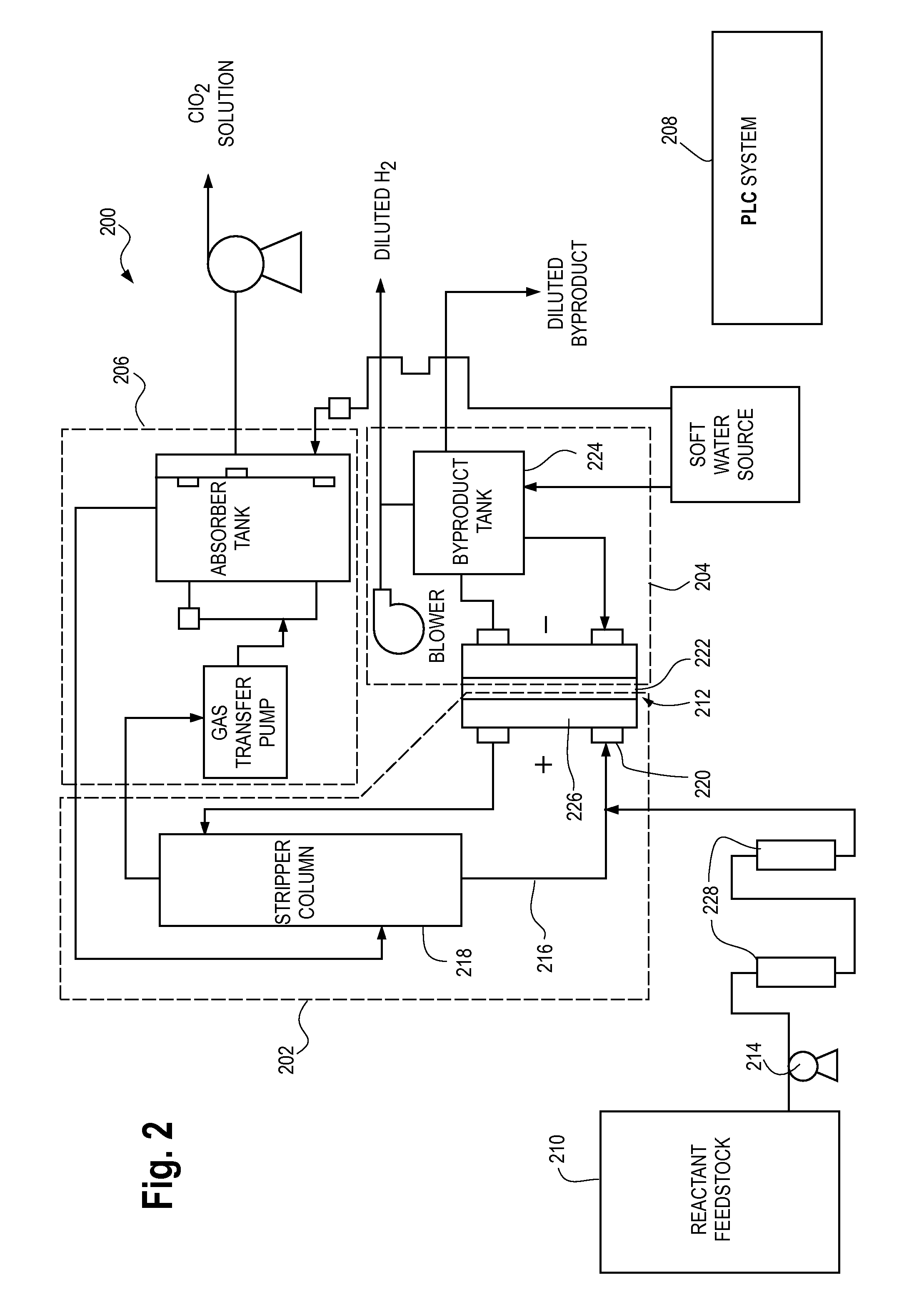
The current disclosure relates to a feed solution for an electrochemical generator, the feed solution comprising at least one of a chlorite solution and / or a chlorate solution, wherein hardness-causing ion concentration in at least one of the chlorite solution and / or the chlorate solution is reduced to less than 1 part per million using at least one of an ion exchange method and / or a precipitation method. The current disclosure additionally relates to an electrochemical chlorine dioxide generator wherein the reactant feedstock is an electrolyte solution passed through an ion exchange column, the ion exchange column capable of substantially removing hardness-causing ions in the electrolyte solution. The current disclosure further relates to a method for assessing acceptable concentrations of hardness-causing impurities in an electrolyte solution. Additionally, the current disclosure relates to methods for reducing impurities in a sodium chlorite reactant feedstock.
Owner:PURELINE TREATMENT SYST
Poly ferrosilicium coagulant and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101386435AReduce turbidityReduce CODWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSodium chlorateSulfate
The invention discloses a poly silicon iron coagulating agent and a preparation method thereof, relates to an inorganic polymer coagulating agent and a preparation method thereof and solves the disadvantages of poor adaptability to low temperature and low turbidity water quality, high production cost, complex preparation technique and secondary pollution to the environment in the existing preparation process of poly silicon iron coagulating agent. The poly silicon iron coagulating agent of the invention is made from soluble glass, soluzione leggermente acida, ferrous sulfate and sodium chlorate. The preparation method of the poly silicon iron is as follows: step 1. raw materials are weighted; step 2. the soluble glass is added into the soluzione leggermente acida and activated silicic acid is prepared after the reaction; 3. the ferrous sulfate and the sodium chlorate are added into the rest soluzione leggermente acida and then the activated silicic acid obtained in step 2 is added, thus obtaining the poly silicon iron coagulating agent. The poly silicon iron coagulating agent is applicable to low temperature and low turbidity water quality and has the advantages of low preparation cost, simple preparation method and no pollution during the preparation process.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Targeted performance of hypohalite methods thereof
ActiveUS20130217610A1Reduce concentrationPrevent and minimize side effectInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideSide effectSodium chlorate
This invention relates to extend the benefits of using hypochlorite compounds such as sodium hypochlorite to clean and disinfect articles while reducing or eliminating the side effects of treating an article with a strong oxidant material. The invention relates to a single step process involving mixing of precursor compositions of a suitable hypohalite or hypohalous acid with a solution of a reducing agent. Optionally a buffer may be present in either or both precursor compositions, such that at time of use such active hypohalous acid concentration in the resulting aqueous mixture remains at a sufficient activity level to effect one or more desired benefits against a target substrate for a desired period of time. The oxidant is substantially consumed by reaction with the reducing agent after the time needed for achieving the desired benefit has passed.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
Gas phase oxidization-liquid phase oxidization-absorption three-section type dry-wet-process flue gas denitration process
InactiveCN104971594AEfficient removalReduce equipment costsDispersed particle separationAir quality improvementPotassium manganateSlurry
The invention discloses a gas phase oxidization-liquid phase oxidization-absorption three-section type dry-wet-process flue gas denitration process. According to the process, ozone is used as a gas-phase oxidant to oxidize one part of nitric oxide in flue gas into high-valence-state nitric oxide capable of being absorbed by slurry; any one or a mixture solution of more of hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, sodium chlorite, sodium chlorate, sodium persulfate, potassium chlorate, potassium hypermanganate and potassium dichromate is sprayed to be used as a liquid-phase oxidant to oxidize the residual high-valence-state nitric oxide in the flue gas into the high-valence-state nitric oxide; and the flue gas enters an absorption tower and a magnesium hydroxide solution is sprayed to absorb the high-valence-state nitric oxide. Compared with the prior art, the process firstly adopts two times of oxidization of a gas phase and a liquid phase and a magnesium oxide wet process is used for absorbing so that a target of efficiently removing the nitric oxide is realized; and by virtue of the technical scheme, the use amount of the ozone is reduced, the equipment cost and operation cost are reduced and the denitration efficiency is improved and can reach more than or equal to 93%.
Owner:SHANGHAI SANQING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com