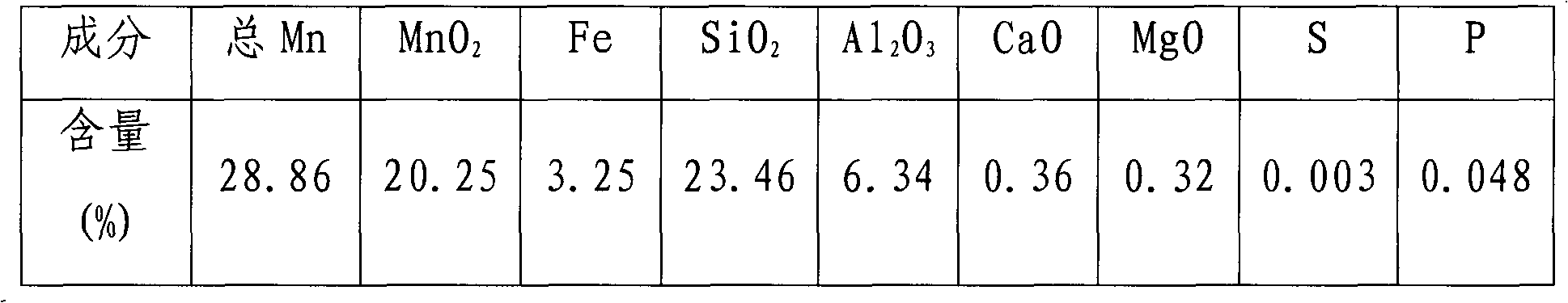
Patents
Literature
2076 results about "Leaching rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
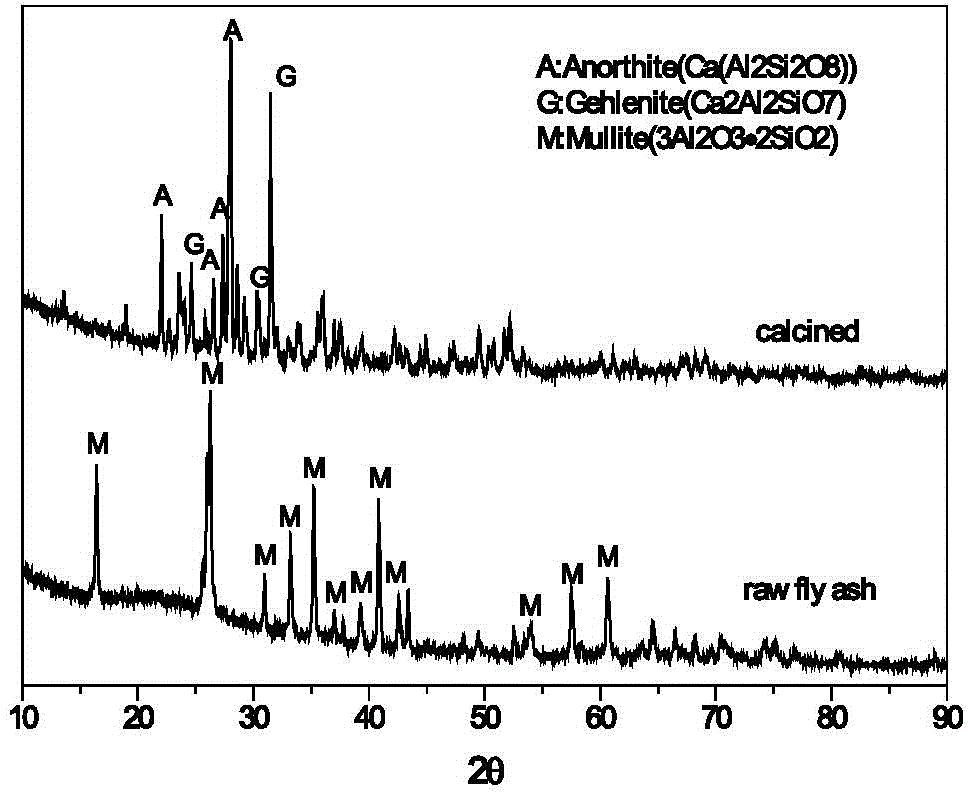
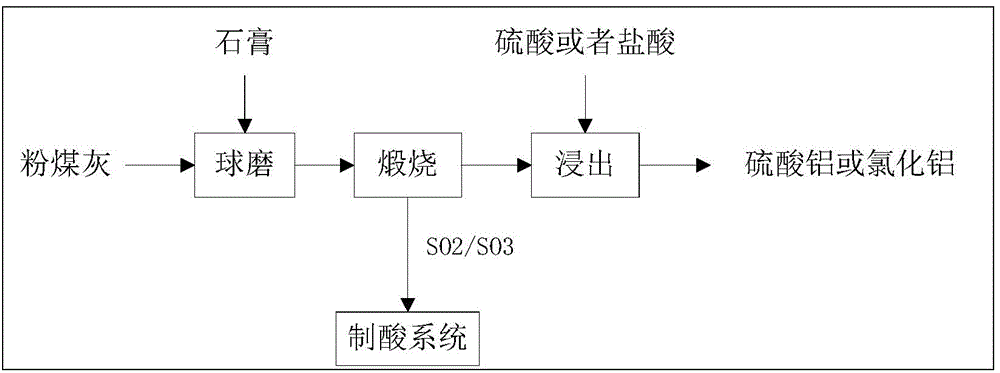
Method for cooperative activation of fly ash and decomposition of gypsum for recovery of sulfur resource
The invention provides a method for cooperative activation of fly ash and decomposition of gypsum for recovery of a sulfur resource. According to the method, solid waste, i.e., fly ash, discharged by a coal-fired power plant or coal-fired boiler is used as a raw material, a certain proportion of desulfurized gypsum discharged by the coal-fired power plant or waste phosphogypsum produced in the phosphorus chemical industry is added and mixed with the fly ash, then the obtained mixture is subjected to ball milling, and activation and calcination at a temperature of 950 to 1450 DEG C are carried out for 5 to 180 min; calcium sulfate in the gypsum are almost totally decomposed after calcination, and produced gas contains sulfur dioxide or sulfur trioxide which can be used as feed gas for preparation of sulfuric acid; and calcination enables solid fly ash to be activated, leaching with a sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid solution is carried out at a temperature of 50 to 100 DEG C, and the leaching rate of alumina is greater than 80%. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that since all the raw materials are solid waste, the purpose of treating the waste by using the waste is achieved; elemental sulphur in the gypsum can be recovered; and the fly ash can be activated and activity of the fly ash can be improved, so a high alumina recovery rate at a low temperature can be realized. With the method, high-efficiency extraction of alumina in the fly ash is realized; the sulfur resource in the gypsum is recovered; shortage in industrial sulphur in the sulfuric acid industry in China is compensated; and the method has good economic benefits and wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Penetration of copper-ethanolamine complex in wood
InactiveUS20060078686A1Reduce premature precipitationPretreated surfacesCoatingsPhosphatePreservative
Addition of base improves the homogeneity of aqueous copper amine complex preservatives injected into wood. The base includes at least a portion of alkali metal hydroxides, alkali metal carbonates, alkali metal phosphates, alkali metal borates, and / or alkali metal pyrophosphates, the corrosivity of the composition to steel and galvanized steel is reduced, and the leach rate of the copper from the wood is also reduced.
Owner:OSMOSE
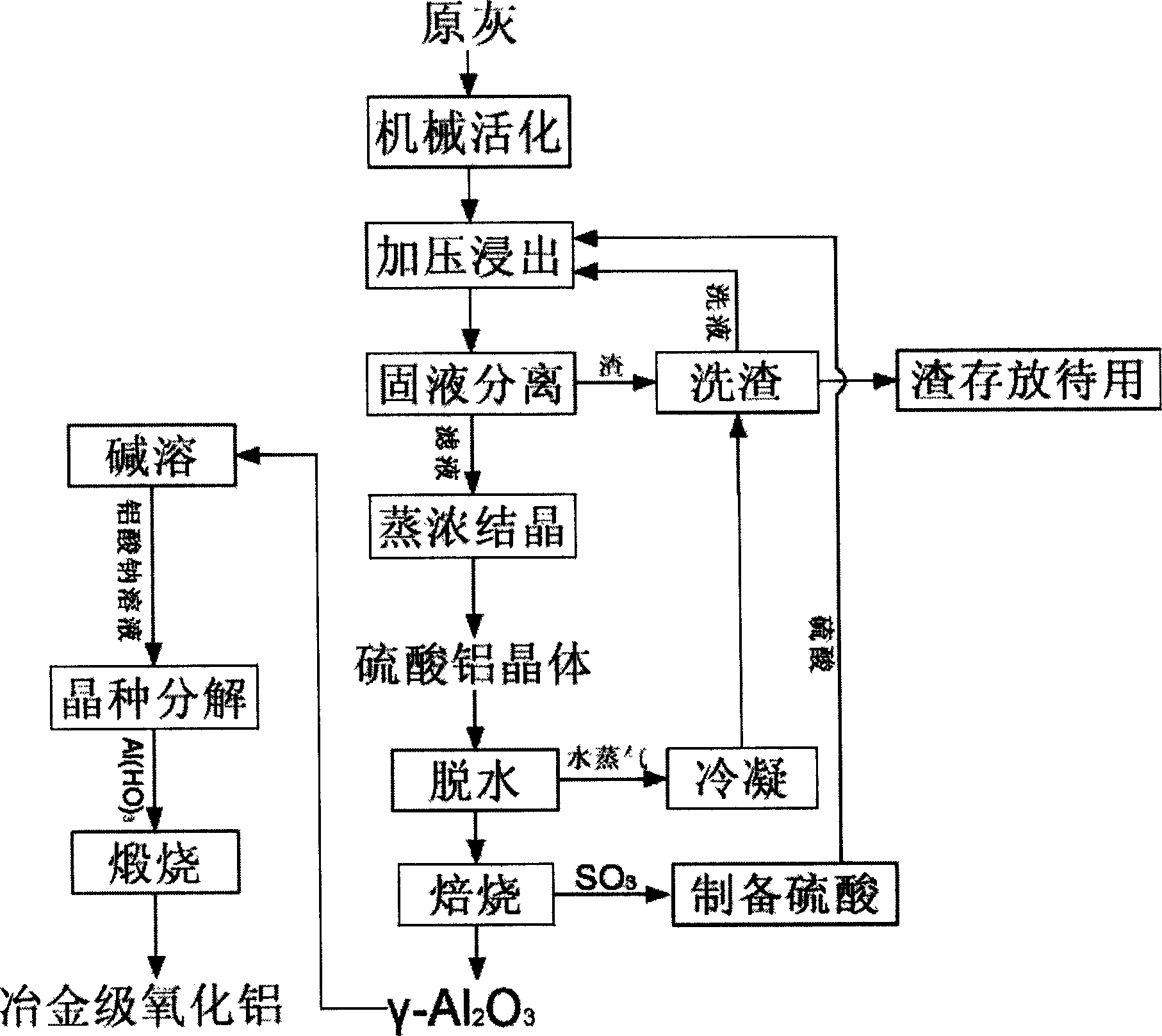
Method for preparing alumina by using fly ash
InactiveCN101397146AEffective leachingPromote leachingAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAluminium hydroxideSodium aluminate
The invention discloses a method for producing alumina by disposing and utilizing industrial solid wastes, in particular to a method for preparing alumina by fly ash, comprising the steps as follows: the fly ash is mechanically activated; the activated fly ash, water and concentrated sulfuric acid react in a reaction kettle under the conditions of heating and pressurizing; the solid is separated from the liquid after the temperature of the reaction is reduced so as to gain aluminium sulfate liquid; the aluminium sulfate liquid is evaporated, concentrated and cooled so as to precipitate aluminium sulphate crystals; the aluminium sulphate crystals are dehydrated and decomposed to gain gama-Al2O3 and SO3; coarse gama-Al2O3 is dissolved in alkaline solution; after the solid is separated from the liquid, the pure sodium aluminate solution is gained; aluminum hydroxide crystal seed is added to the sodium aluminate solution so as to precipitate the aluminum hydroxide; the coarse gama-Al2O3 can be prepared by circularly dissolving the seed-precipitated alkaline solution after vaporization-concentration; the metallurgical alumina can be gained by baking the prepared aluminum hydroxide. The method adds no additive, can lead the alumina in the fly ash to be effectively leached out with the leaching rate more than 90% and saves the energy resource.
Owner:SHENYANG ALUMINIUM MAGNESIUM INSTITUTE
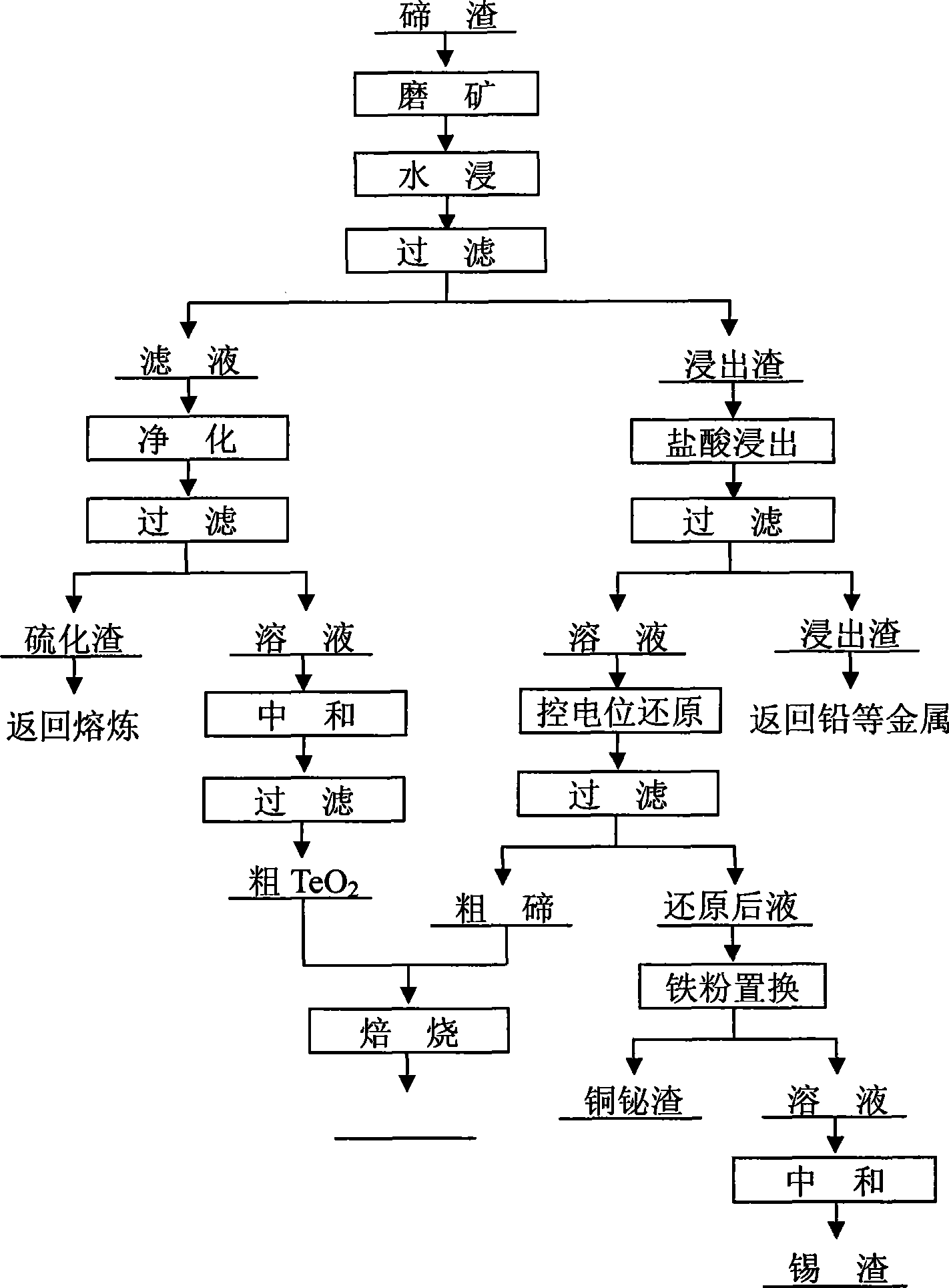
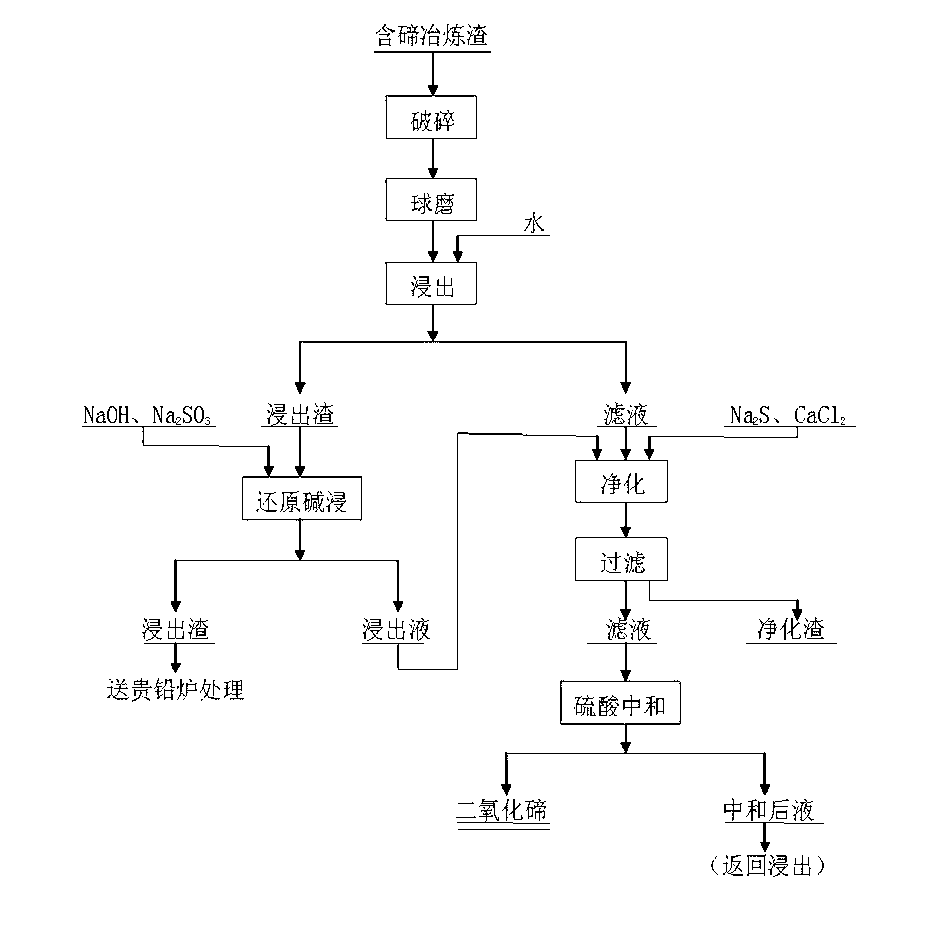
Method for separating tellurium from tellurium slag
InactiveCN101508426APrecisely control the amount addedImprove solubilityElemental selenium/telluriumSludgeSlag
The invention relates to a method for separating tellurium from tellurium slag, which comprises the following steps: firstly, grinding the tellurium slag, leaching out the obtained product in an aqueous solution, purifying and neutralizing a water leaching solution, and producing tellurium dioxide; secondly, performing hydrochloric acid leaching on water leaching residue in a hydrochloric acid system, cooling and filtering an acid leaching solution, and returning acid leaching residue to an anode sludge treatment process; thirdly, performing controlled potential reduction on the acid leaching solution to produce coarse tellurium, and performing roasting and impurity removal on the coarse tellurium and the tellurium dioxide produced by neutralization to obtain pure tellurium dioxide; and fourthly, using the conventional method to reclaim valuable metals such as copper, bismuth, tin, and the like from a reduced solution respectively. The total tellurium leaching rate of the method is as high as more than 98 percent, and the produced coarse tellurium has the advantages of low content of impurity elements, small amount of return slag, small modification amplitude of equipment, short treatment time, and low treatment cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
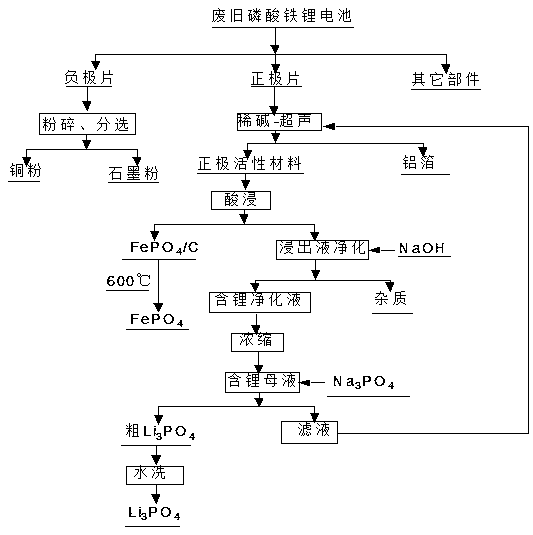
Recovery method for cathode material of waste lithium iron phosphate battery
InactiveCN107739830AEasy to separate naturallyLow costWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodPhosphate
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
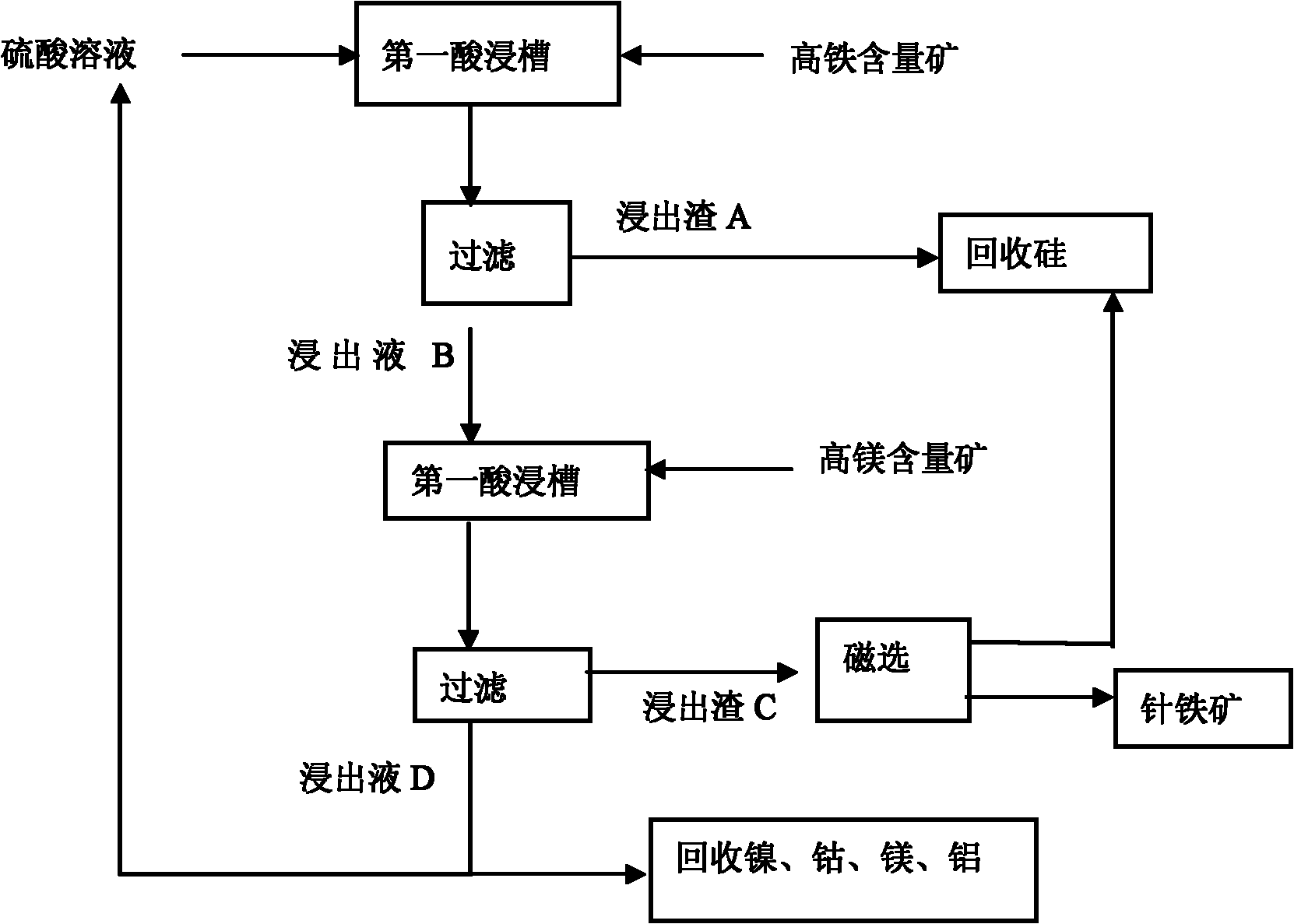
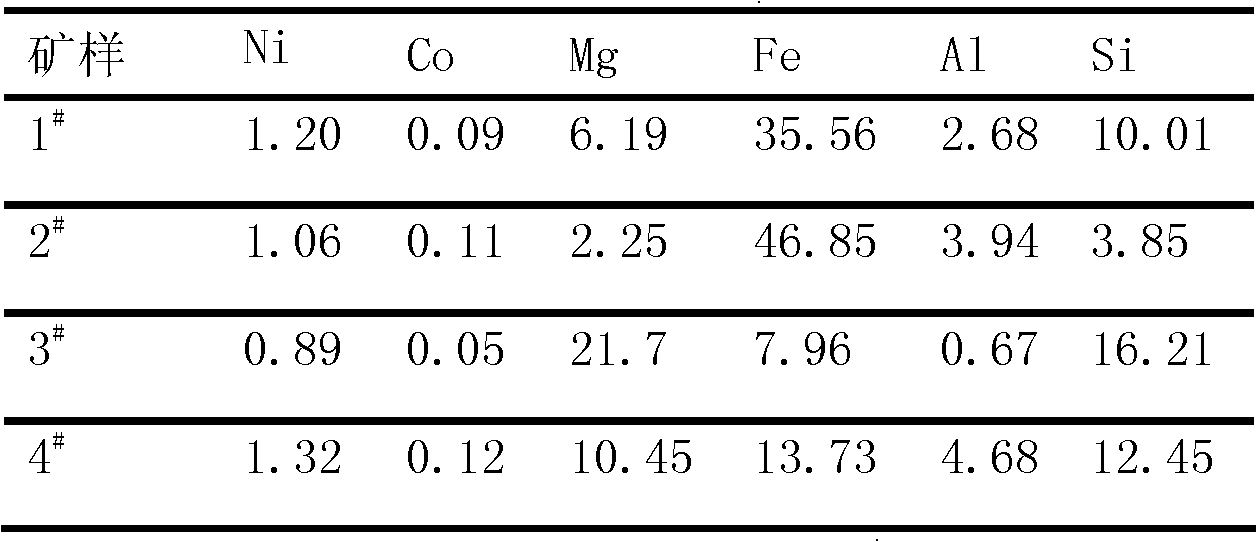
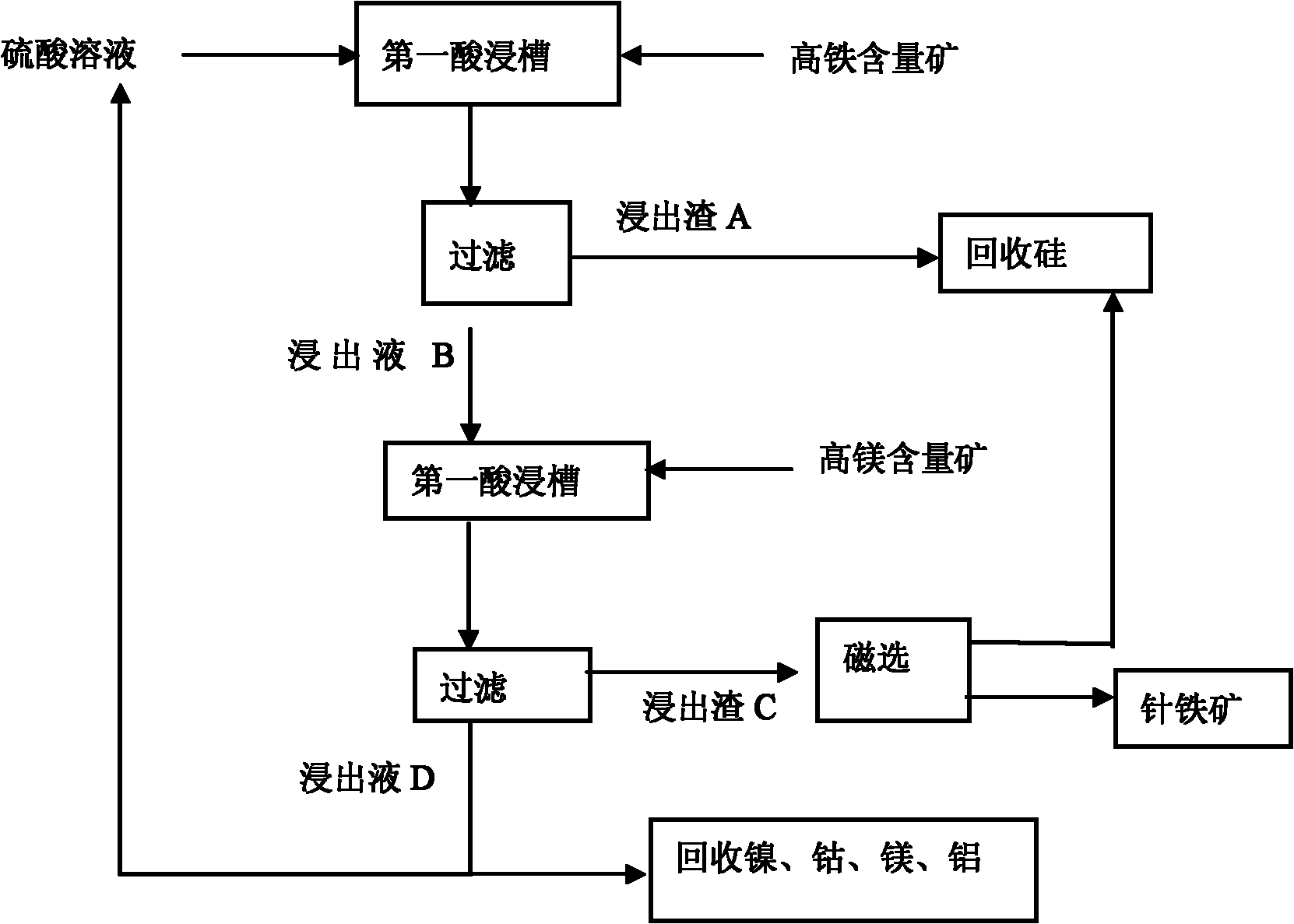
Normal-pressure leaching method for simultaneously processing laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content
InactiveCN102206749AOvercoming the disadvantage of requiring autoclave leachingOvercome the drawbacks of leachingIron oxides/hydroxidesProcess efficiency improvementLateriteNon magnetic
The invention discloses a normal-pressure leaching method simultaneously processing laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content, comprising the following steps of: screening the laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content; adding sulfuric acid to the laterite with high iron content for leaching so as to obtain leaching residue A and a leaching solution B; adding the laterite with high magnesium content to the leaching solution B, leaching to obtain leaching residue C and a leaching solution D; carrying out magnetic separation on the leaching residue C, wherein a magnetic part E is recovered as an iron product, and a non-magnetic part F and the leaching residue A are mixed to be used for recovering silicon products; delivering a part of the leaching solutionD into a purifying and recovering process, and returning the other part of the leaching solution D into the leaching process of the laterite with high iron content, and carrying out a next leaching period; repeating the leaching period for 4-5 times, and completely delivering a leaching solution I obtained from a last leaching period into the recovering processes of nickel, cobalt, aluminum and magnesium. The normal-pressure leaching method has the advantages of low cost and acid consumption and high leaching efficiency of the nickel and the cobalt and realizes the efficient separation and the recycling of iron, silicon, the nickel and the cobalt and the discharge without acid liquor.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
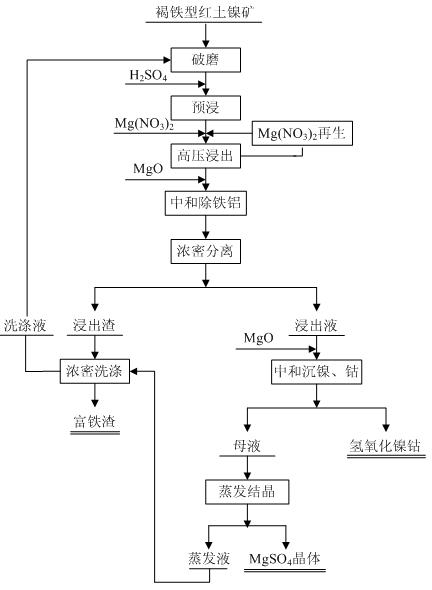
Method for leaching limonitic laterite nickel ore
InactiveCN102534206AReduce consumptionEasy to operate and controlProcess efficiency improvementSlagSlurry
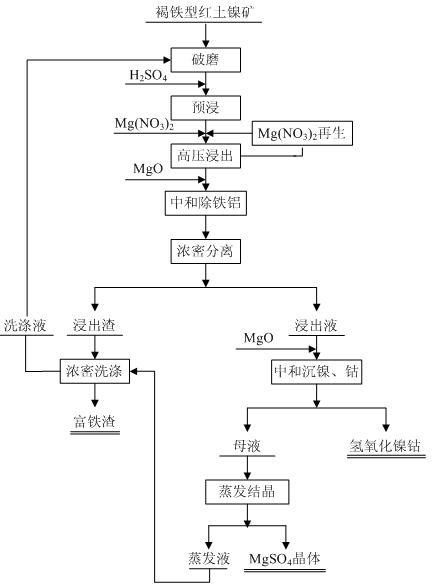
The invention discloses a method for leaching limonitic laterite nickel ore and relates to a process method for recovering nickel, cobalt and iron through treatment of laterite nickel ore by wet process. The method is characterized in that the technical process comprises: (1) grinding raw limonitic laterite nickel ore into fine powder, making slurry, adding sulfuric acid, heating the slurry and leaching the slurry; (2) adding Mg(NO3)2 into the pre-leached slurry, heating with stirring, pressurizing the slurry and leaching the slurry; 3) at the end of leaching, neutralizing the slurry, removing iron and aluminum from the slurry, and separating to obtain a leaching solution and a leaching residue; and 4) washing the leaching residue to obtain washing liquid and iron-enriched slag, neutralizing the leaching solution, precipitating nickel and cobalt, obtaining nickel and cobalt hydroxides, evaporating a mother solution from which nickel and cobalt are separated to crystallize magnesium sulfate and comprehensively recovering magnesium sulfate. The method realizes the high-efficiency selective leaching of nickel and cobalt, the leaching rate reaches over 90 percent, the iron leaching rate is lower than 0.8 percent and iron-enriched slag with an iron content of over 55 percent is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Method for separating tombarthite from phosphorus ore
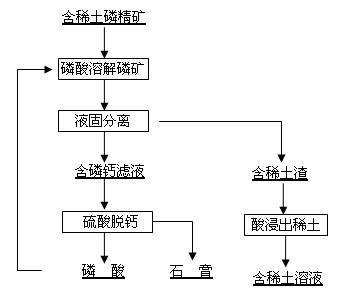
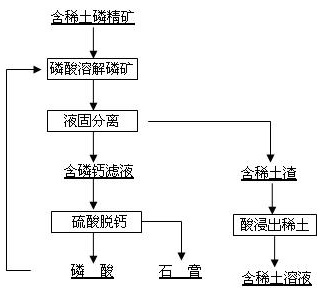
The invention discloses a method for separating tombarthite from phosphorus ore and relates to the method for separating the tombarthite from the phosphorus ore containing the tombarthite. The method is characterized in that the process steps are as follows: (1) mixing phosphate concentrate containing the tombarthite with a phosphoric acid solution for performing reaction; (2) filtering for getting a reaction solution and slag containing the tombarthite; (3) adding acid into the slag containing the tombarthite for leaching for getting leachate containing the tombarthite, and further recycling the tombarthite through one or more of an extraction method, an ion exchange adsorption method, a precipitation method and a crystallization method; and (4) performing decalcification on the reaction solution obtained by filtration and then returning to the step (1). By adopting the method, the precipitation rate of the tombarthite in the phosphorus ore is greater than 85%, the slag rate is small, the grade of the tombarthite in the slag is high, the leaching rate of the tombarthite in the slag is high, no additives are added during the process and the product quality of the phosphoric acid is not affected; and furthermore, the phosphoric acid used during the process can be self-produced and can also be circulating dilute phosphoric acid, dilute phosphoric acid and the like generated during the production process of the phosphoric acid, thereby being tightly linked with the production process of the phosphoric acid through the sulfuric acid method.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
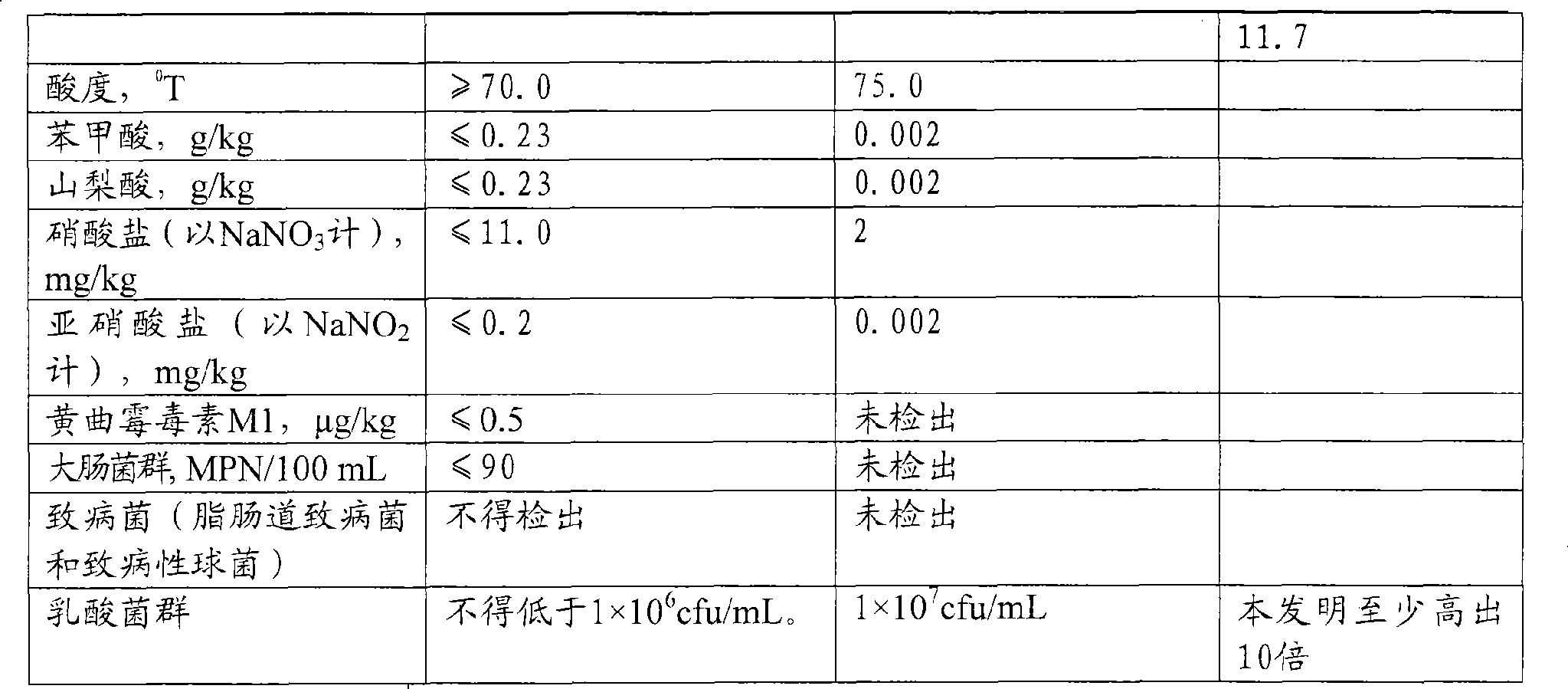
Stirring type corn yoghourt and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101455236ARetain nutritionImprove exudation rateMilk preparationFood preparationAbsorption rateBiology
The invention relates to a stirring type cereal sour milk and a method of preparing the same. The cereal sour milk is made through lactobacillus and probiotics ferment by using raw materials with the following weight components: raw fresh milk of 700-875 parts, cereal powder 1-30 parts; additive agent for dairy food of 5-44 parts; lactobacillus strain / functionality probiotics strain of 0.2-0.8 parts; corrective of 48-82 parts; stabilizing thickening agent of 3-10 parts; homogeneous pourable dense quasi-fluid which is the external appearance showing the color of added cereal powder with suspended corresponding cereal powder; the tissue is fine, smooth and uniform and a few whey is allowed to be precipitated; organoleptic attribute, nutritive index, health indicator and content of lactobacillus series of the cereal sour milk are all better than that in the GB2746 cultured milk quality index. The present invention is characterized in that the cereal powder that is formed by pulverizing and swelling processes reserves the nutrient of cereal to the utmost extent and improves the hot water leaching rate and absorption rate of its nutrient components; the technique is more compact and the operation is easy; the production efficiency is high and the consumption human populations of the products are widened; the cereal sour milk is easy to digested and absorbed, and the taste is better.
Owner:SHANDONG DEYI DAIRY IND
Waste lithium ion battery recycling method completing stripping and leaching through one step
ActiveCN107326181ASimple processShort processWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodFiltration
The invention discloses a waste lithium ion battery recycling method completing stripping and leaching through one step and belongs to the technical field of electrode material recycling. According to the method, waste lithium ion batteries serve as raw materials; after discharging and manual or mechanical cracking are conducted, the waste lithium ion batteries are immersed into pure water or a sulfuric acid solution with certain concentration; then, acidity of the solution is adjusted, and a reducing agent is added for stripping and leaching; and finally, filtration is conducted, so that valuable metal, namely nickel, cobalt, manganese and lithium, enter filtrate, and copper foil, aluminum foil and graphite enter filter residues to be recycled. The method is simple in process, short in flow and high in operability; the copper foil and the aluminum foil are thoroughly separated from active materials, and the purposes that the copper foil and the aluminum foil in the waste lithium ion batteries are stripped, and the valuable metal, namely nickel, cobalt, manganese and lithium, are leached out of the active materials through one step are achieved; the leaching rate of each type of the valuable metal, namely nickel, cobalt, manganese and lithium is higher than 99%, and the concentration of copper, the concentration of aluminum and the concentration of iron in a leaching solution are each less than 1 g / L; and industrial application value is remarkable.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
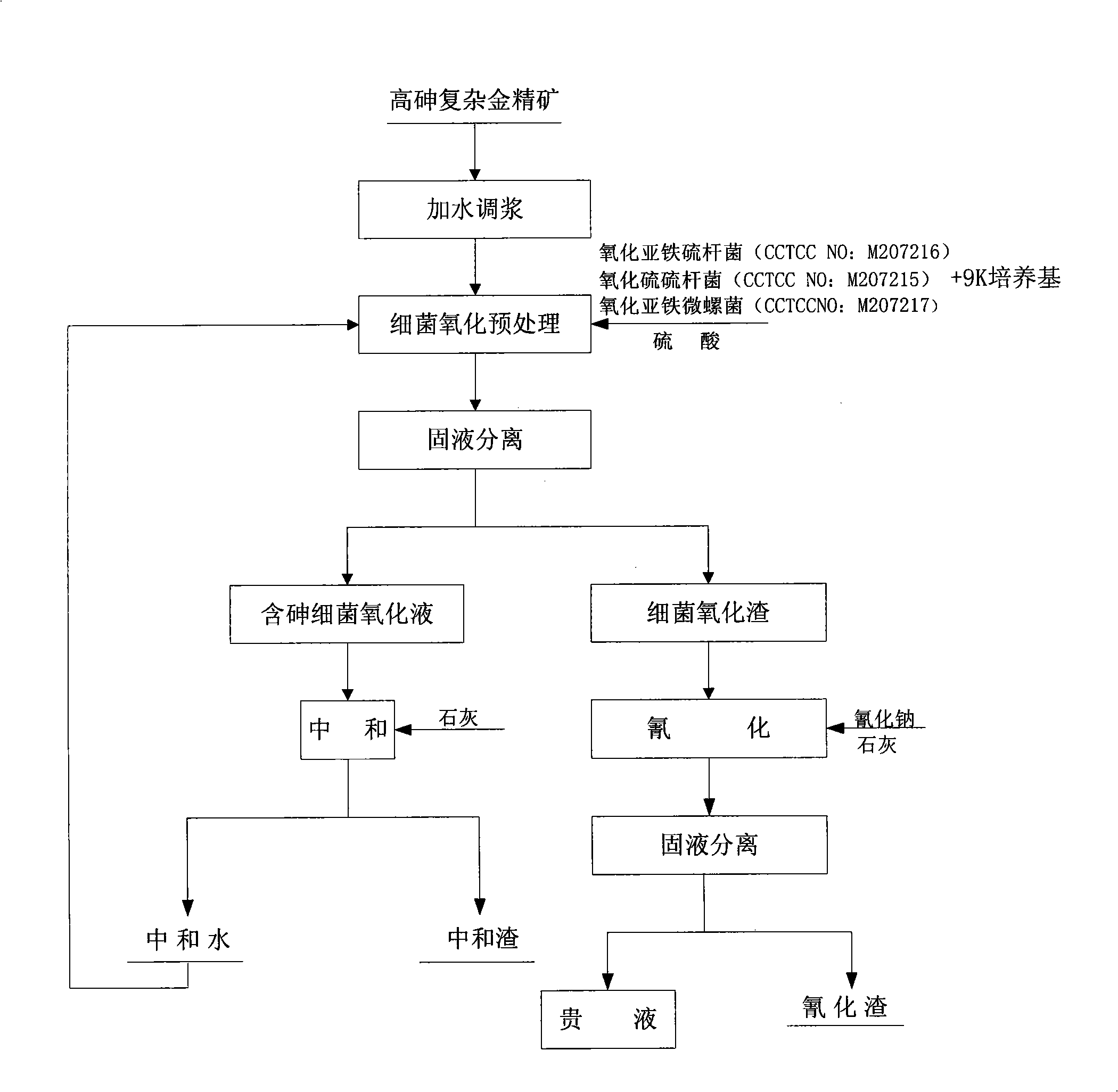
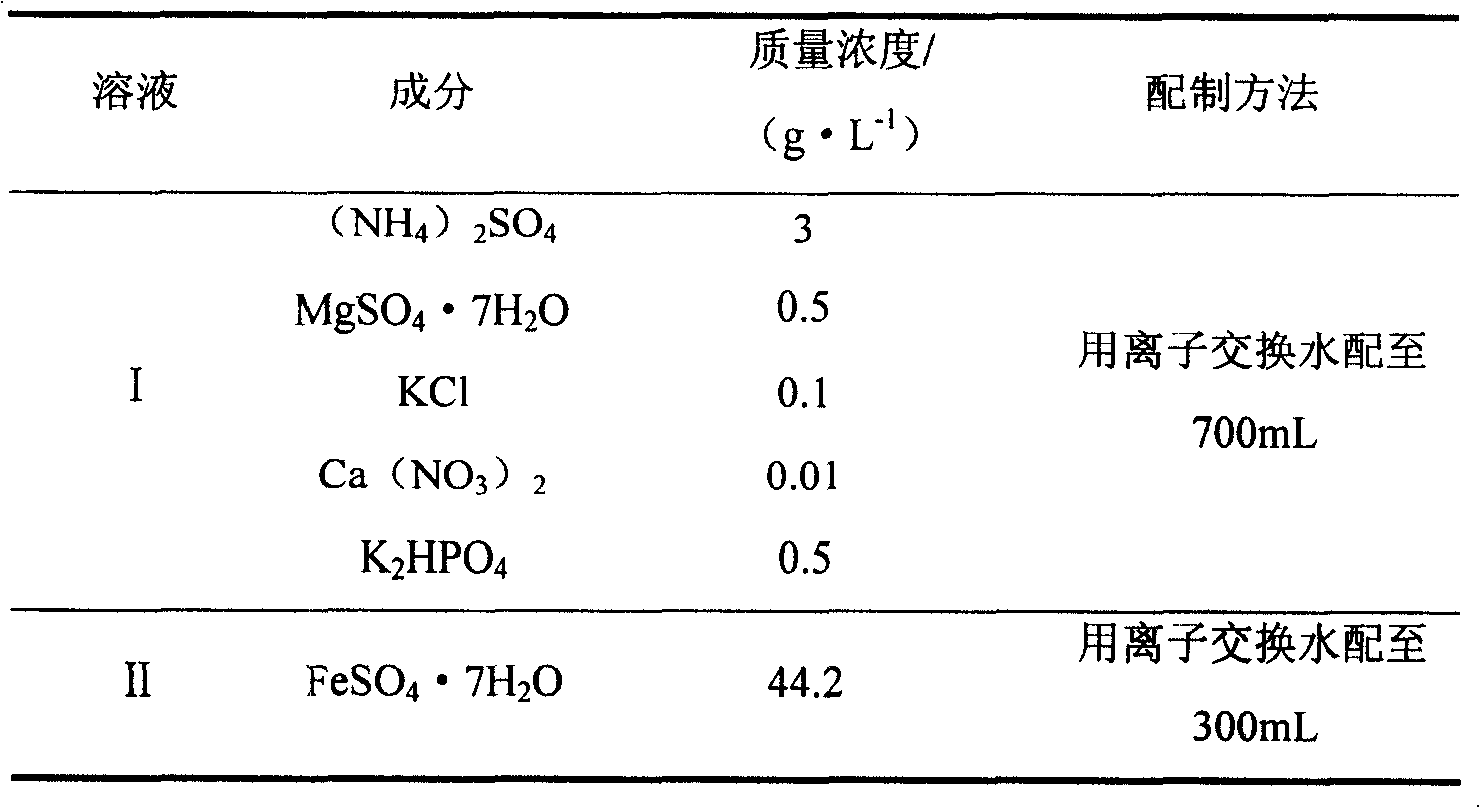
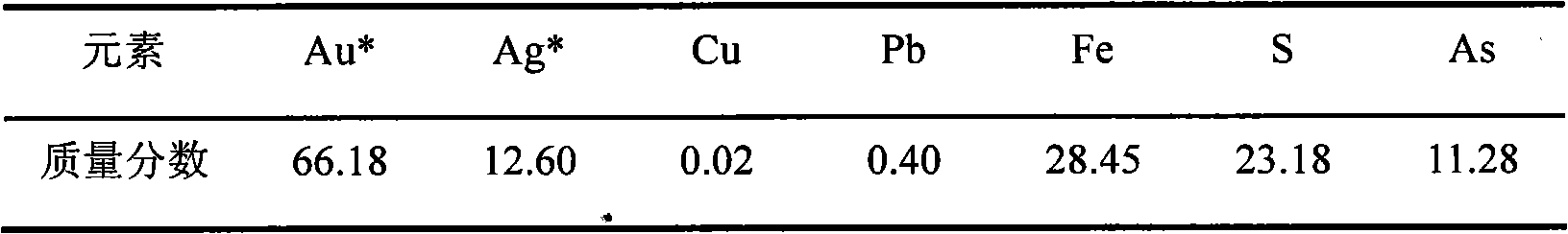
Cyanidation aurum-extracting method for preprocessing high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by oxidation with arsenic resistant strains
InactiveCN101333599AIncrease growth temperatureStable temperatureProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansResistant strain
Disclosed is a cyaniding gold extraction method for pre-treating high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore by arsenic-resistant bacteria oxidation, comprising five steps of arsenic-resistant bacteria culture, flotation concentrate mixing, bacterial oxidation of flotation concentrates, solid-liquid separation and cyaniding gold extraction. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts specific arsenic-resistant bacteria which are prepared by mixing Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Thiobacillus thiooxidans and Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and conducts oxidation pretreatment of high-arsenic complex refractory gold ore. The high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic can be pretreated, and the arsenic removal rate is 85 to 98 percent. The leaching rate of gold is up to 90 to 95 percent after cyaniding leaching. The cyaniding gold extraction method adopts unique bacteria for leaching ores, greatly saves cooling cost, conducts direct oxidation of high-arsenic complex gold ore containing 8 to 20 percent of arsenic, and has advantages of being widely adaptable, simple in operation, environmentally friendly and remarkably beneficial.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for preparing electrolytic manganese metal with low-grade pyrolusite wet leaching
InactiveCN102094119AReduce pollutionWide variety of sourcesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisPyrolusite
The invention discloses a method for preparing electrolytic manganese metal with low-grade pyrolusite wet leaching, which comprises the following steps of: after low-grade pyrolusite is crushed and screened, mixing slurry with electrolytic manganese anolyte, adding sulfuric acid to control acidity, and reducing high-valent manganese insoluble in water into low-valent manganese readily soluble in water through a redox reaction by using reduced iron powder or waste iron scraps as a reducing agent; controlling certain acidity, reaction temperature and time, stirring and leaching, and then precipitating and filtering; purifying, decontaminating and separating a filter liquor to obtain a pure manganese sulfate solution; and electrolyzing the manganese sulfate solution to obtain an electrolytic manganese product, wherein the leaching rate of manganese is higher than 98%, the recovery rate of manganese is higher than 90%, and the purity of electrolytic manganese metal is higher than 99.8%. The method has the advantages that the raw materials of the reducing agent have wide sources and low price, the reaction time is short, the conditions of the leaching process are mild, the leaching rate of manganese is high, the purification process is simple, and the process route of the present carbonic acid manganese ore for preparing electrolytic manganese metal is not changed.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY +1
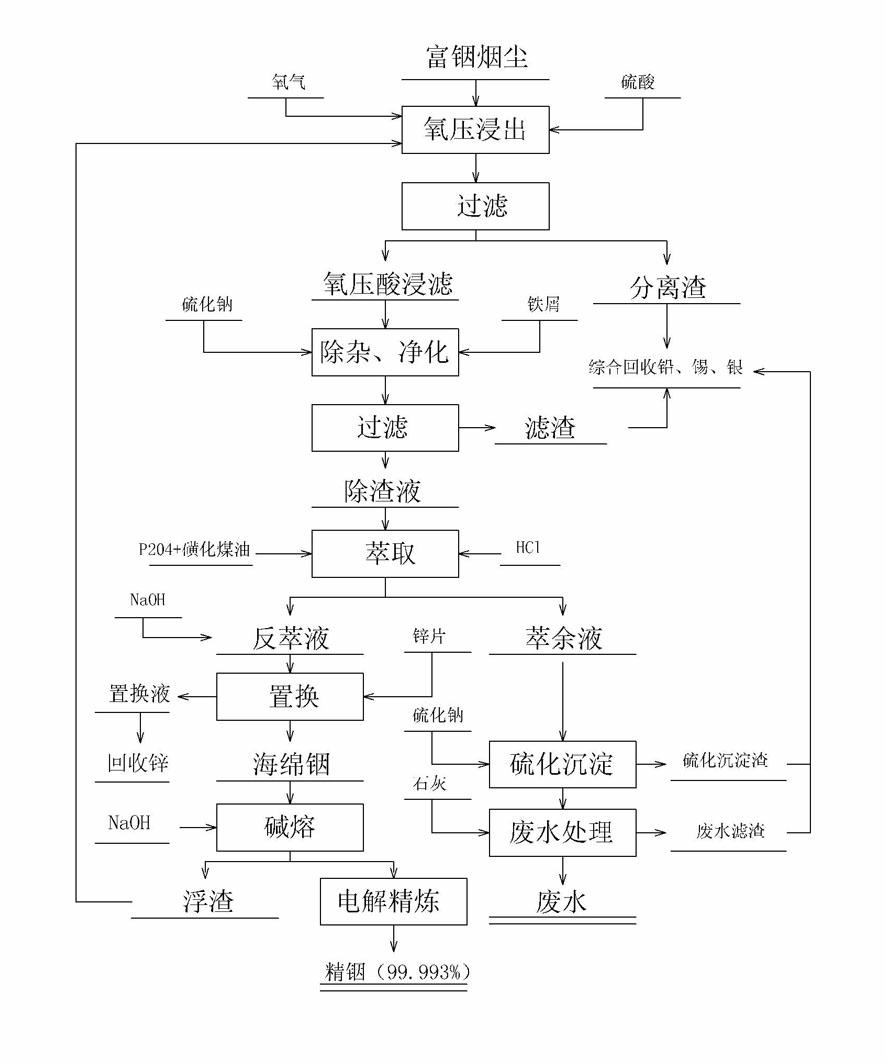
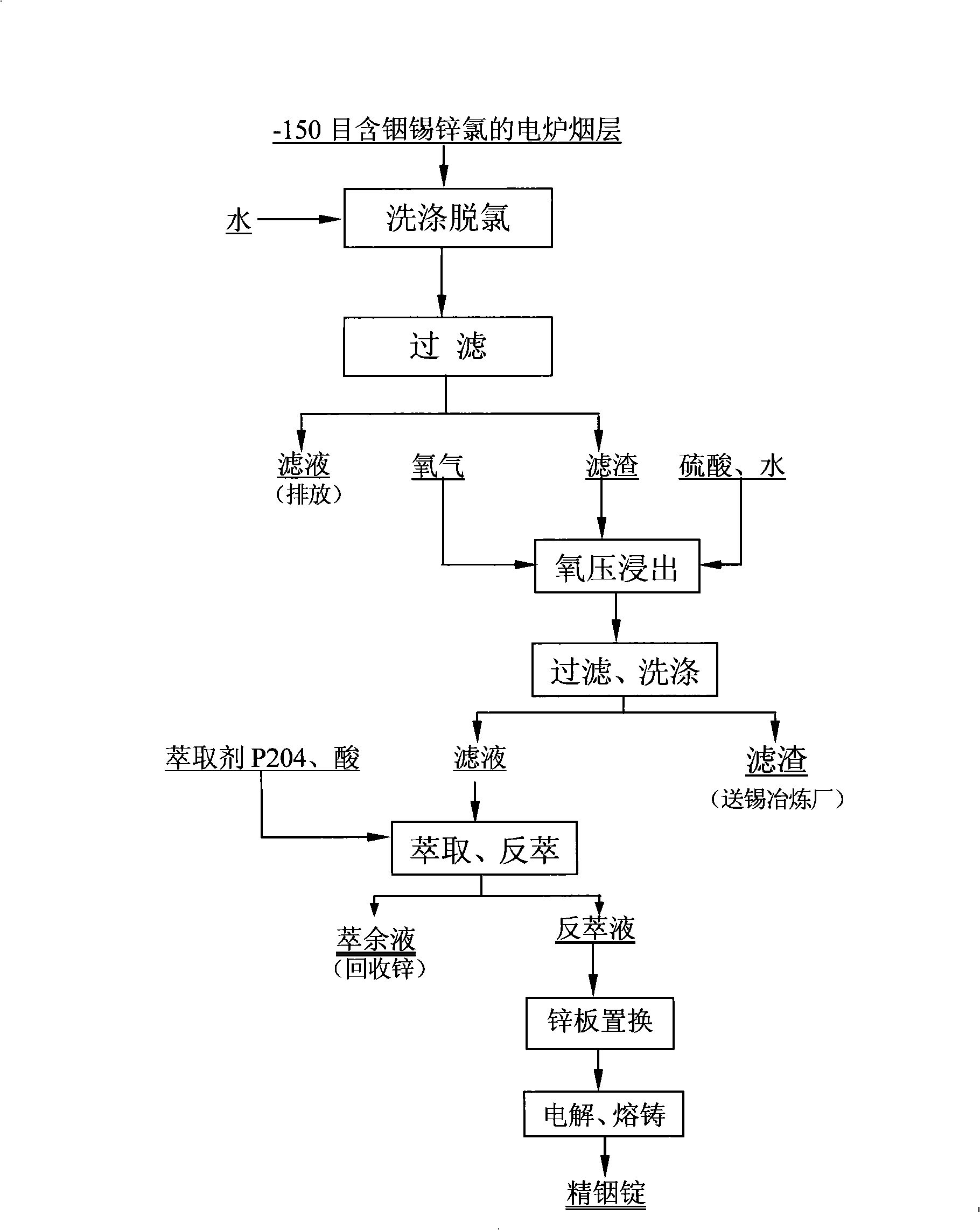
Method for extracting indium from indium-rich smoke dust by using oxygen pressure technology
The invention provides a method for extracting indium from indium-rich smoke dust by using an oxygen pressure technology. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: carrying out leaching indium extraction of the difficult-to-handle indium-rich smoke dust of a Pb-Sn reverberatory furnace by adopting a wet-process metallurgical oxygen pressure acid leaching technology, and highly enriching and recycling valuable metals in the raw material; and purifying to remove impurities of leachate, and carrying out extraction, replacement and electrolytic refining, thereby obtaining greater than 99.995% of electrical indium products. The technology method has the advantages that the indium leaching rate of the indium-rich smoke dust of the Pb-Sb reverberatory furnace and the enrichment rate of the valuable metals can be obviously increased, and the comprehensive recycling effect can be achieved, thereby waster water of indium smelting can be discharged up to the standard after being processed with low cost, the environmental pollution in the indium extraction process is eliminated. In the process, the leaching rate of the indium is more than 97%, leaching residues containless than 0.01% of indium, the enrichment rate of plumbum, tin, bismuth and zinc is more than 98%, the quality of refined indium products is more than 99.995%, and plumbum enriching slag containing greater than 60% of Pd is obtained. The technical scheme can independently form a system, can also be used for improving and perfecting old technologies and has higher popularization and application value.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
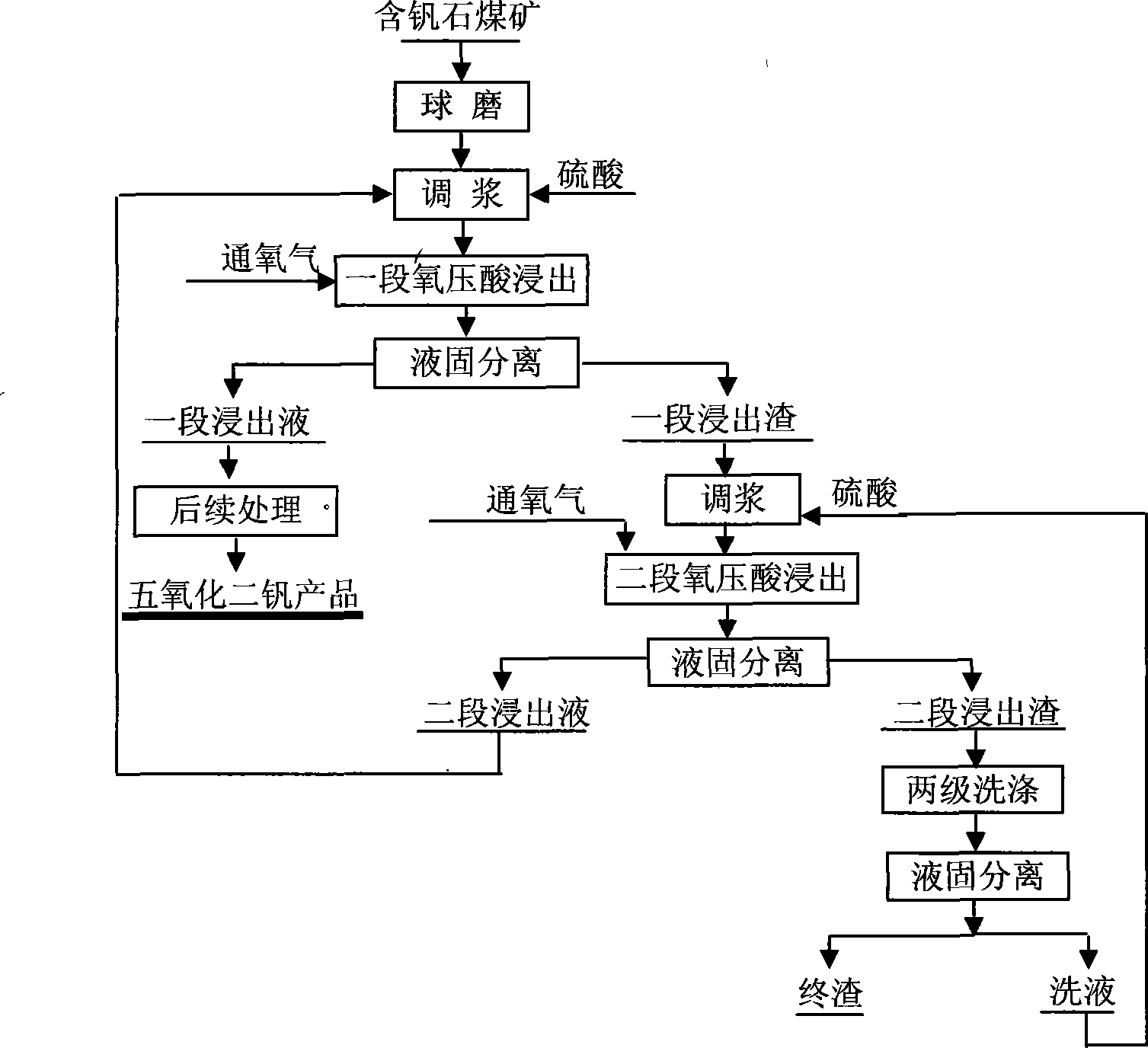
Method for leaching vanadium from vanadium-containing coal mine
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
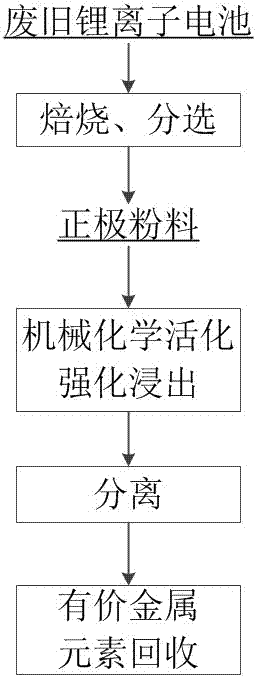
Method for enhancing metal recovery of waste lithium ion battery
PendingCN107083483AReduce acid consumptionHigh cost of solutionWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementLeaching rateMechanical force
The invention provides a method for enhancing metal recovery of a waste lithium ion battery. The method for enhancing the metal recovery of the waste lithium ion battery comprises the steps that firstly, the waste lithium ion battery is calcinated, smashed and sorted so that positive electrode powder materials can be obtained; and then, wet leaching is conducted on the positive electrode powder materials, and mechanical and chemical activation is achieved through a high-energy ball mill in the leaching process, wherein mechanical and chemical activation is executed during leaching, so that the obtained leach liquor can be further used for recovery of valuable metal elements. By the adoption of the method for enhancing the metal recovery of the waste lithium ion battery, the procedure is simple, the operability is high, under the cooperative action of mechanical force and chemical activation, the leaching time of the positive electrode powder material can be greatly shortened, the leaching rate of the metal elements is improved, cost is reduced, and the market prospect is good.
Owner:SINO SCI PROCESS BEIJING SCI&TECH CO LTD
Technology for extracting tellurium dioxide from tellurium-containing smelting slag
ActiveCN102992280AImprove leaching rateReduce dosageWaste processingSolid waste disposalSlagMaterials science
The invention relates to a technology for extracting tellurium dioxide from tellurium-containing smelting slag. The technology comprises the following steps: ball-milling tellurium slag, leaching by water, carrying out reduction alkali leaching, vulcanizing, carrying out silicon removal purification, and neutralizing to precipitate tellurium. The method has the advantages of tellurium leaching rate improvement, reduction of the alkali application amount in the leaching operation, and production cost reduction. The method is characterized in that sodium hydrosulphite is adopted as a transition agent to transit insoluble high-valence tellurium to low-valence tellurium, so the leaching rate leaching rate is increased. The total tellurium leaching rate can reach above 90% under a suitable technological condition; and after recovering tellurium through neutralizing, the TeO2 grade of the smelting slag can reach above 50%, and the content of tellurium in the waste liquid obtained after the neutralizing is 0.1-0.3g / L. The method also has the advantages of further enrichment of copper, lead, bismuth, antimony and precious metals in the leaching slag, realization of the resource reuse, production cost reduction, and energy saving, and is of great importance to the resource recovery and the environmental protection.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
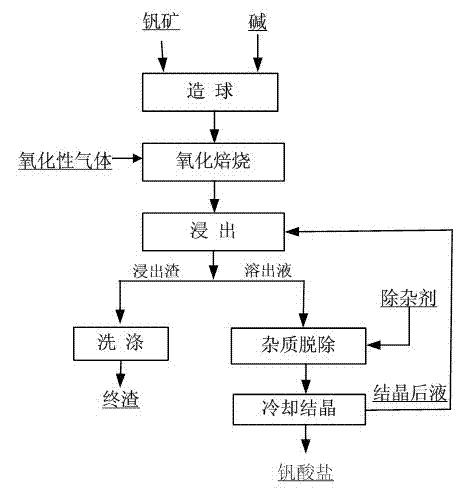
Efficient vanadium extraction method by performing alkali roasting on vanadium mineral
ActiveCN103088207ABreak the barrierEfficient DissolutionProcess efficiency improvementPotassium hydroxideDissolution
The invention discloses an efficient vanadium extraction method by performing alkali roasting on vanadium mineral. The method comprises the following processing steps of: (1) mixing the vanadium mineral with sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide for pellet fabrication, and oxidizing and roasting pellets at the temperature of 300-700 DEG C to obtain roasted clinker; (2) leaching the roasted clinker using water or aqueous alkali corresponding to the step 1, and then carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain leaching residue and a vanadium dissolution solution; and (3) cooling and crystallizing silicon-removed vanadium digestion solution to obtain vanadate. The alkali roasting is used by the method provided by the invention, because alkali can function as a caking agent in the aggregating process, the caking agent can be saved; not only is the roasting temperature reduced largely and process flow largely shortened, but also no waste gas, ammonia-nitrogen wastewater and the like are discharged, as well as a leachate can be recycled; and a silicate phase can be directly destroyed to promote the destroy and the oxidization of a vanadium phase, and the oxidative enveloping and the leaching hindering of the silicate phase to the vanadium can be prevented so that the efficient vanadium leaching can be realized and the leaching rate can reach more than 95%.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
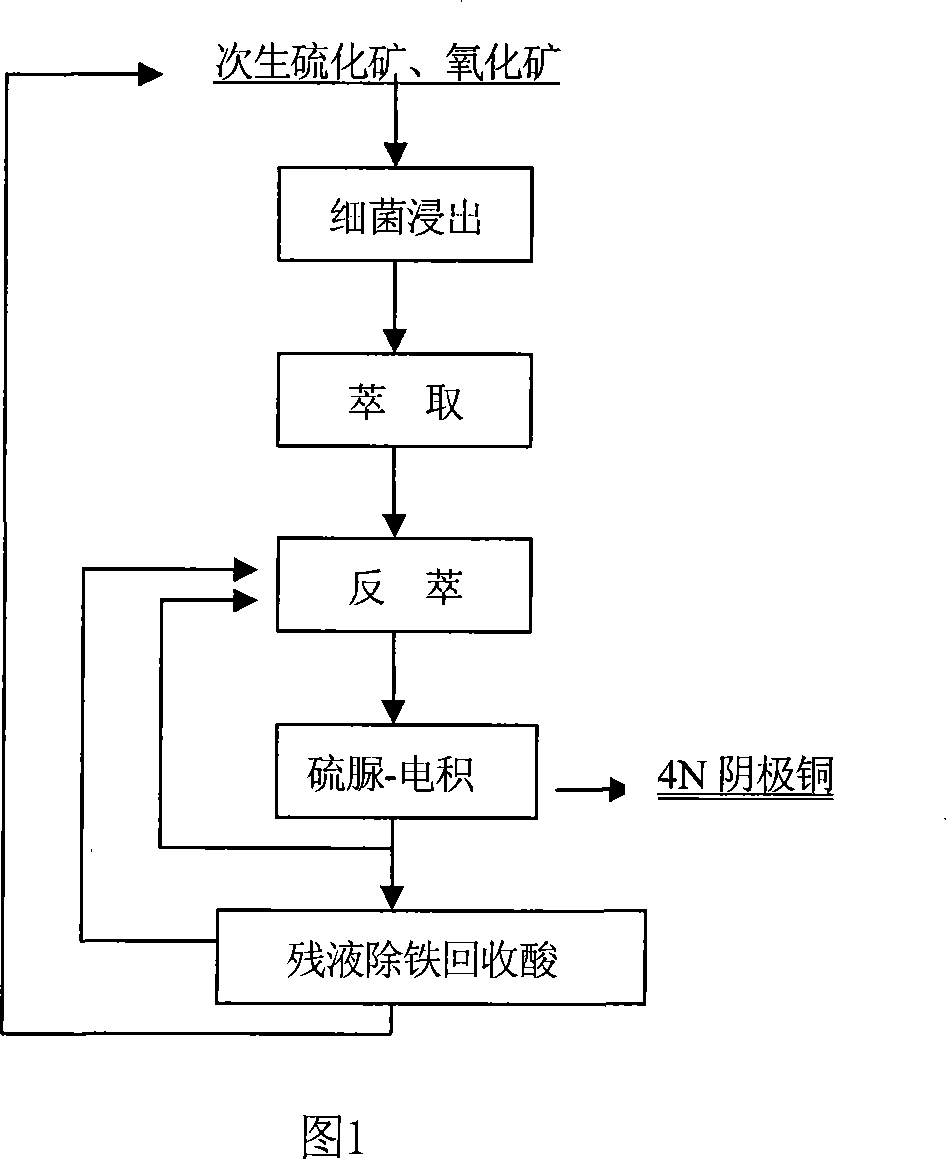
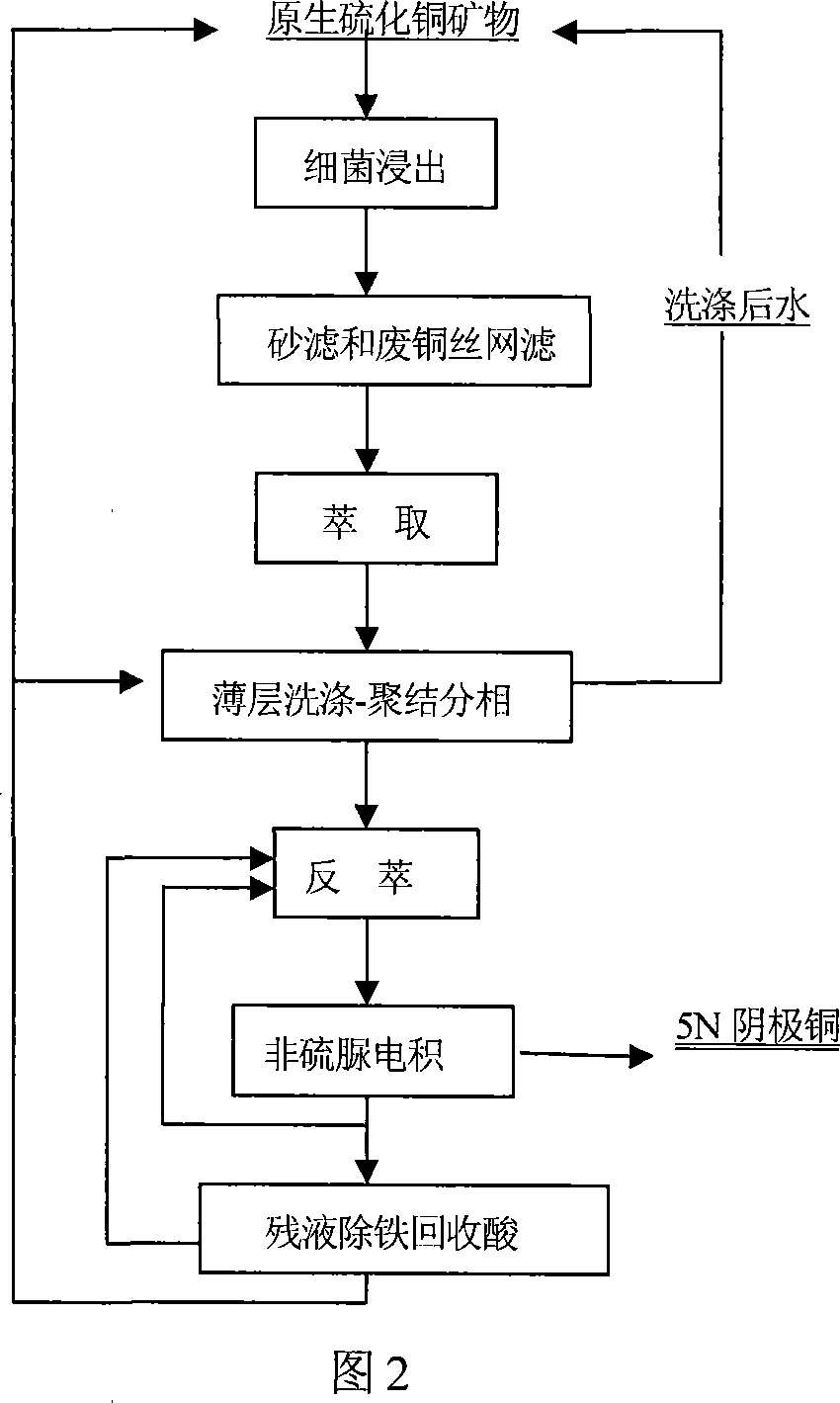
Method of preparing high purity copper by bacteria leaching primary sulfide ore
InactiveCN101033508AEnhanced synergistic leachingIncrease leaching ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSulfurThin layer
The invention relates to a method of preparing high pure copper from the leachate of primary sulfide ore bacteria, including: it leaches the primary sulfide ores and its mixture by using the mixture of middle and mesophilic bacterias. It filters and extracts the bacterial leaching solution, and conducts thin-layer wash-condensate, coalescence phase, and back-extraction electrowinning for the organic phase load. The invention uses hybrid strains of bacteria and sub-culture techniques to enhance the synergy of the bacterial leaching role and the minerals leaching rate, uses gelatin and other additives without sulfur element to reduce the sulfur impurities.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for treating indium stannum smoke raw material
InactiveCN101307385AEasy to settleEasy to settle into slagProcess efficiency improvementIndiumResource utilization
The invention relates to a treatment method for raw materials containing indium, tin, zinc and chlorine, in particular to a method for reclaiming valuable metal aiming at producing smoke dust containing the indium and the chloride during the smelting of the zinc, lead, and the tin. The method uses water to wash and remove the chloride in smoke dust raw material, then a dechlorination material is added into a pressure titanium kettle, is added with sulphuric acid and is aerated with oxygen to perform oxygen pressure heating leaching so that the indium and the zinc are leached and enter solution, the tin is leached out and transformed into metastannic acid to sink into residue, and the filtered tin-containing filter residue is reclaimed and reused; the indium and the zinc enter the solution, extracting agent P204 is adopted to extract the indium to realize the indium-zinc separation, extraction liquid is subject to the back extraction and the zinc plate replacement to produce sponge indium, the sponge indium is electrolyzed, purified, and melted and cast to produce an indium ingot product; and remaining liquid is extracted to reclaim the zinc. The method solves the corrosion resistant problem of the prior equipment, namely the pressure titanium kettle, improves the leaching rate of the indium, deposits the tin at the same time, solves the problem of indium-tin separation, and has the characteristics of reducing energy consumption and production cost, high resource utilization rate, and environmental protection.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN GROUP HLDG
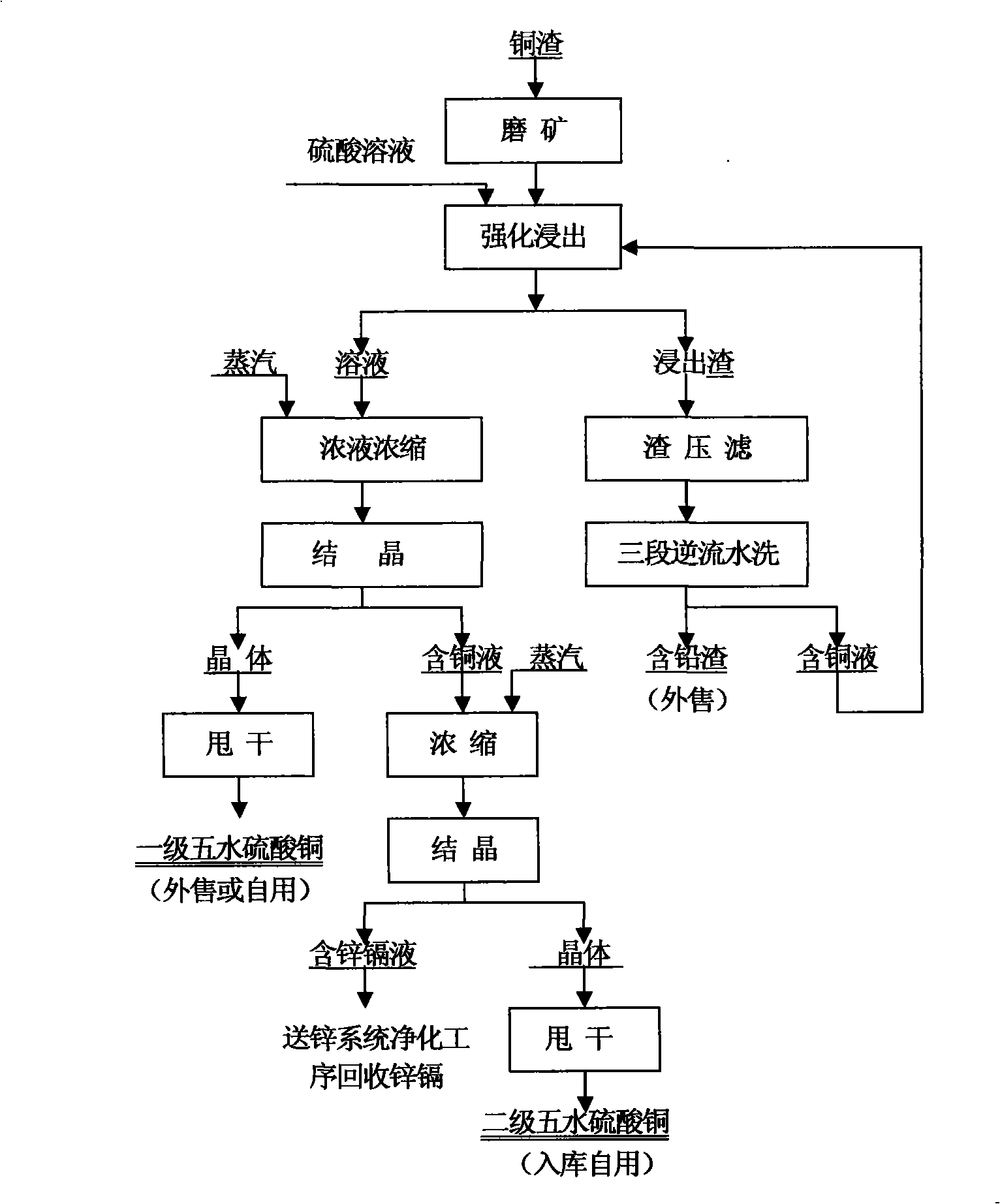
Process method for producing copper sulfate by intensified leaching of copper-containing materials
InactiveCN101538646AImprove leaching rateImprove product qualityProcess efficiency improvementHigh energyNon-ferrous extractive metallurgy
The invention relates to a process method for producing copper sulfate by intensified leaching of copper-containing materials, which has short production flow, low energy consumption, good environment and high metal recovery rate and belongs to the technical field of integrated recovery and utilization of nonferrous metal smelting slag. The process method is mainly characterized in that the copper slag is directly intensifiedly leached, and the oxidation roasting process of the copper slag is replaced by intensified leaching, thereby solving the problems of high energy consumption, great environmental pollution and long process flow of the copper slag during the oxidation roasting process. As the process method intensifies the leaching conditions, the leaching rate of copper is improved to be more than 94 percent, and the leaching time is reduced to 2 hours from the conventional 24 hours, thereby greatly improving the production efficiency of the copper sulfate, effectively reducing the production cost, reducing the production flow of the copper sulfate by one third, and greatly improving the metal recovery rate.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
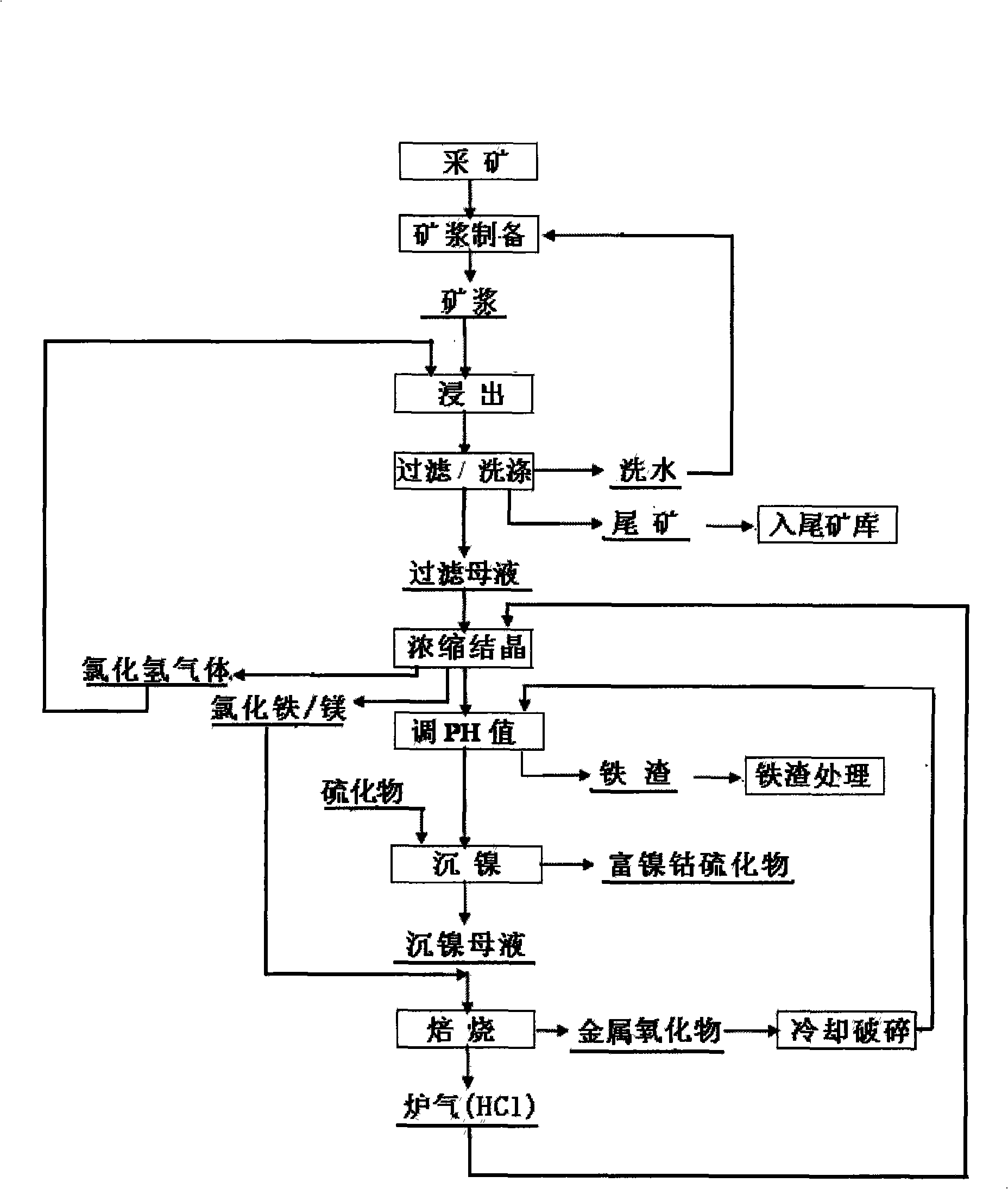
Process for abstracting nickel and cobalt by using wet method to chloridize laterite-nickel ore
InactiveCN101285127AImprove leaching efficiencyIncrease profitProcess efficiency improvementMetallic sulfideLaterite
The invention relates to a method for extracting nickel and cobalt from a laterite-nickel ore, comprising the following steps of mineral preparation, chloride leaching, solid-liquid separation, leaching liquid concentration, sulfide precipitation, solid-liquid separation and hydrochloric acid recovery of the laterite-nickel ore. A chloride leaching agent is mixing solution of metal chloride and hydrochloric acid; the leaching liquid is concentrated by heating; ferric chloride and magnesium chloride are crystallized and separated out so that Fe / Ni ratio is reduced below 1 / 5 of Fe / Ni ratio before the concentration; the magnesium oxide or the ferric oxide generated in the hydrochloric acid recovery process is used as neutralizer; polysulfide, just precipitated metal sulfide and metal sulfide are used as sulfuration precipitator; mother liquor with precipitated nickel is roasted with the ferric chloride and the magnesium chloride which are obtained by concentrating the leaching liquid; the metal chloride in the mother liquor and the metal chloride obtained from the concentration are hydrolyzed into chlorine hydride and metal oxide; and the obtained acid is recycled to use. The method for extracting nickel and cobalt from the laterite-nickel ore improves the leaching rate of valuable metals such as nickel, cobalt and so on in the leaching process of the laterite-nickel ore, reduces the energy consumption and is environment friendly.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
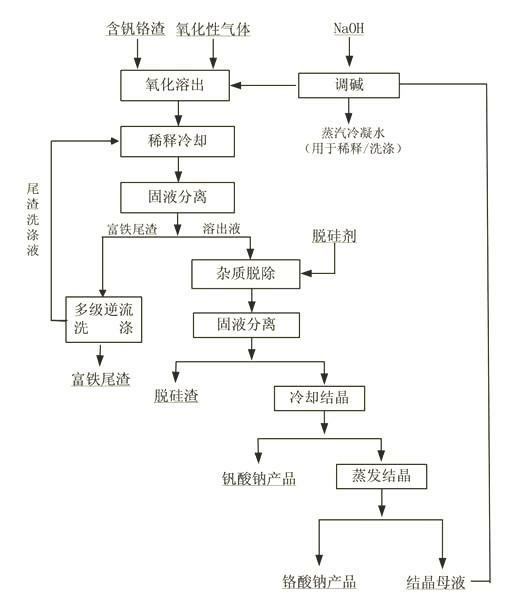
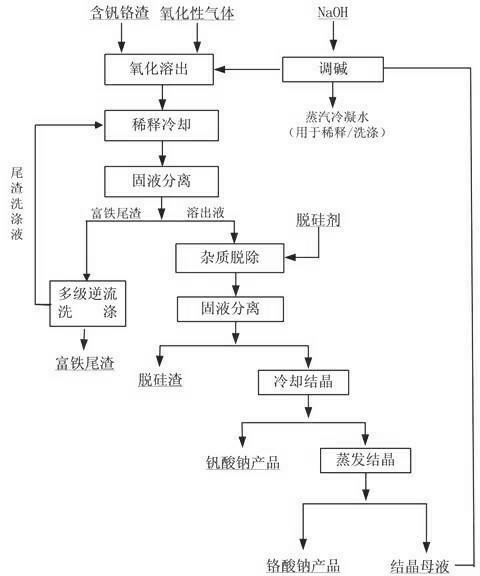
Method for recovering vanadium and chromium from vanadium and chromium-containing slag
The invention discloses a method for recovering vanadium and chromium from vanadium and chromium-containing slag, which comprises the following processing steps of: (1) reaction: enabling the vanadium and chromium-containing slag to have a heating oxidation reaction with oxidizing gas in NaOH solution with the mass concentration of 10-60%, and obtaining reactant slurry; (2) dilution: using diluent to dilute the reactant slurry until the concentration of sodium hydroxide of the slurry is 100-350g / L, and obtaining mixed slurry; (3) filtering separation: carrying out filtering separation on the mixed slurry at the temperature of 80-130 DEG C, and obtaining iron-rich tailings and eluate; (4) impurity removal: adding desiliconization agent into the eluate for removing impurities, then carrying out solid-liquid separation, and obtaining liquid subjected to impurity removal and silicon-containing residue; (5) sodium vanadate crystallization: cooling and crystallizing the liquid subjected to impurity removal, and obtaining sodium vanadate and crystallized liquid; and (6) sodium chromate crystallization: evaporating and crystallizing the crystallized liquid, and obtaining sodium chromate. According to the method, the leaching rate of vanadium and chromium reaches 99%, and the final slag contains less than 0.1wt% of vanadium and chromium, so that the method has the characteristics of being low in vanadium and chromium content of the tailings and high in extraction efficiency of vanadium and chromium.
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Moderate thermophilic enriched substance used for mineral leaching of copper pyrites
InactiveCN101560485APromote leachingReduce inhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationFerroplasma thermophilum
The invention discloses a moderate thermophilic enriched substance used for mineral leaching of copper pyrites, comprising five mineral leaching microorganisms: acidithiobacillus caldus S2, leptospirillum ferriphilum YSK, sulfobacillus acidophilus ZW-1, sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans YN22 and ferroplasma thermophilum L1; the pH value and the temperature which are most suitable for the growth of the enriched substance are respectively 1.4-2.0 and 45-48 DEG C. Compared with the existing microorganisms used for brass bio-heap leaching, the enriched substance not only improves the leaching reaction kinetics and shortens the leaching period, but also reduces the passivation inhibition phenomenon and increases the bioleaching speed and the leaching rate of the copper pyrites; furthermore, the enriched substance can endure high concentration metallic ion at the late stage of bioleaching.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Ore leaching method for ion-adsorbing type rare earth ore
ActiveCN105112692AImprove leaching rateFacilitate desorptionProcess efficiency improvementAmmoniacal nitrogenPregnant leach solution
The invention discloses an ore leaching method for ion-adsorbing type rare earth ore. According to the method, a leaching agent solution is adopted for first leaching of the ion-adsorbing type rare earth ore, most of hydrated rare earth ions easy to desorb and positive ions in the leaching agent solution perform exchangeable desorption, and the rare earth ions enter a first rare earth leaching solution; then an auxiliary leaching agent solution or a mixed solution of an auxiliary leaching agent and a leaching agent is adopted for second leaching of the ion-adsorbing type rare earth ore, the auxiliary leaching agent and hydrated rare earth ions difficult to desorb in the ion-adsorbing type rare earth ore perform complexing, desorption of rare earth difficult to leach is promoted, and a second rare earth leaching solution is obtained. The ore leaching method is simple and easy to control, the leaching rate of the rare earth is increased, the consumption of the leaching agent and the auxiliary leaching agent is reduced, production costs are reduced, and the ammonia-nitrogen pollution is reduced.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
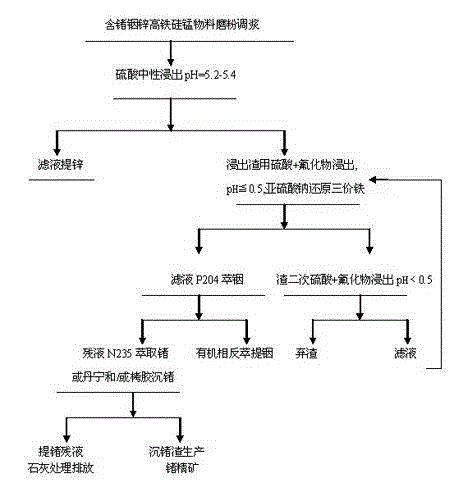
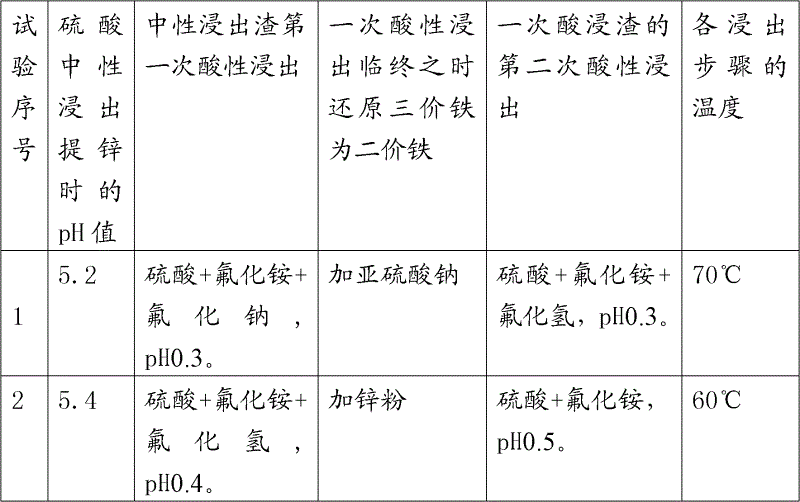
Method for extracting germanium, indium and zinc from high iron, silicon and manganese materials containing germanium, indium and zinc
A method for extracting germanium, indium and zinc from high iron, silicon and manganese materials containing germanium, indium and zinc belongs to the technology of hydrometallurgy. Sulfuric acid and fluoride are adopted for acid leaching for two times, leaching rate of germanium can reach 90% above, and secondary acid leaching slag contains germanium equal to and less than 0.005%. The total leaching rate of indium reaches 95% above, and tailings contain indium equal to and less than 0.003%. Germanium concentrate obtained by germanium extraction through an extraction method contains fluorine less than 1%. Low temperature leaching is performed at 70+-10 DEG C, the structure of iron vitriol slag is damaged as little as possible, and the concentration of ferric iron in leaching liquid is reduced. Ammonium iron hexafluoride produced in the leaching process shields the ferric iron, P204 indium extraction, N235 germanium or tannin extraction and tannin extract germanium deposit are improved, and the poisoning phenomenon in ferric iron of P204 and N235 is reduced. Comprehensive recovery utilization rate of germanium, indium and zinc in high iron, silicon and manganese materials is greatly improved.
Owner:YUNNAN WUXIN IND
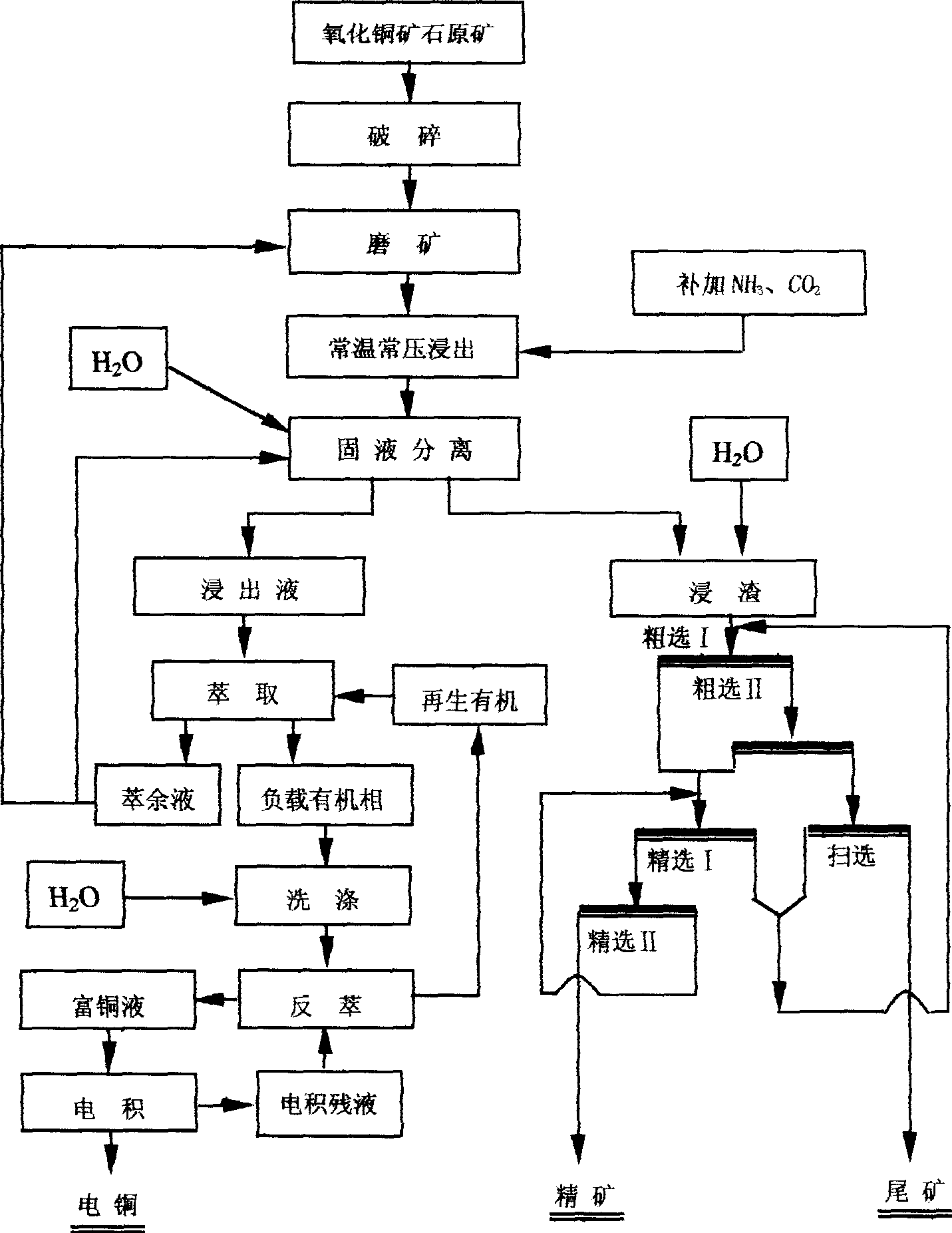
Normal temperature normal pressure ammonia infusion-extraction-electrodeposition-slag infusion flotation of copper oxide green ore
InactiveCN1718786AEasy to recycleReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementSlagLower grade
A process for extracting copper from copper oxide ore includes such steps as immersing in ammonia water in ordinary temp and ordinary pressure condition, extracting electrodeposition, and floatation. Its advantages are low consumption of energy and low cost. It is especially suitable for the low-grade copper oxide ore with high content of Ca and Mg.
Owner:方建军 +2
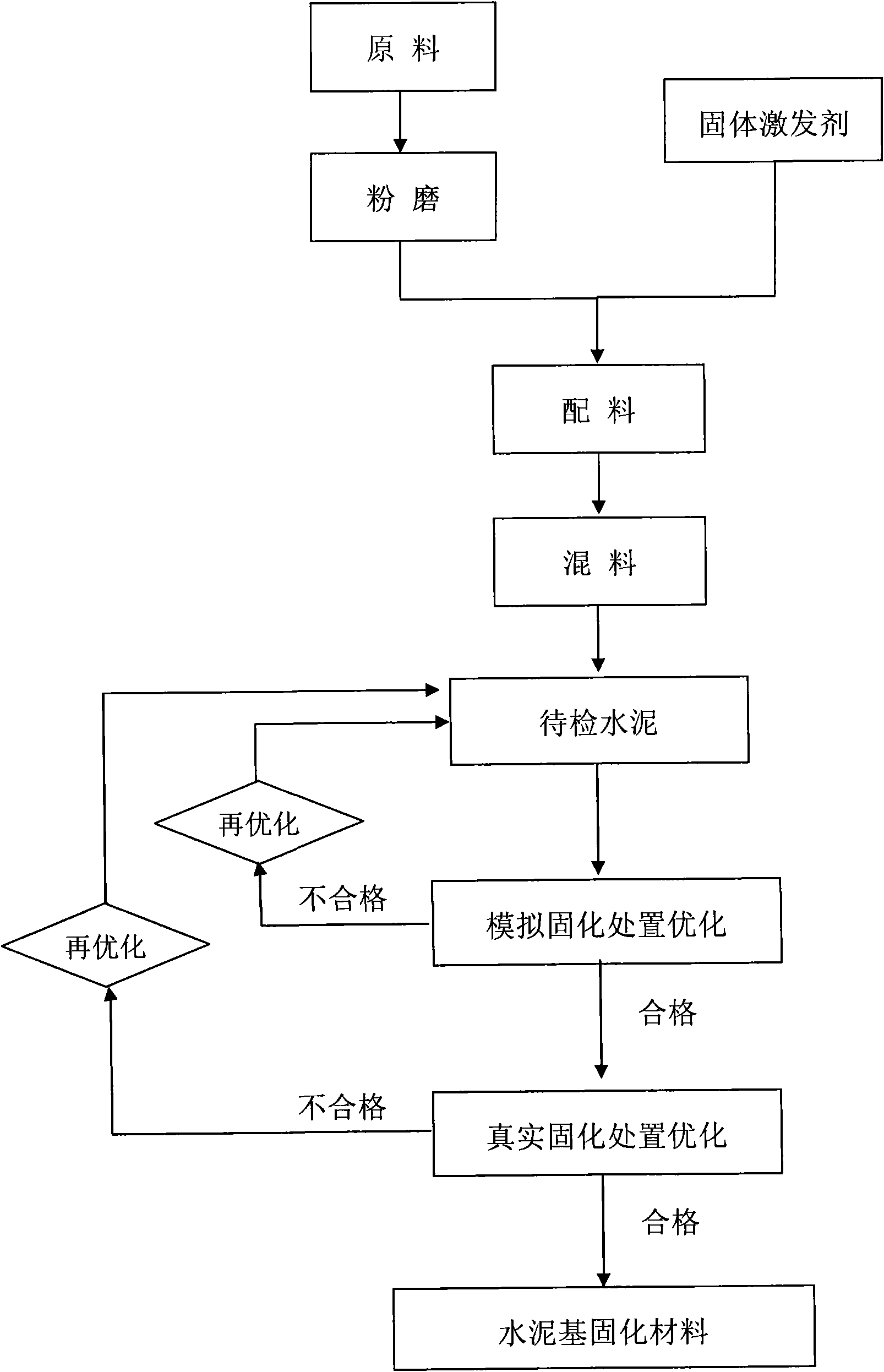
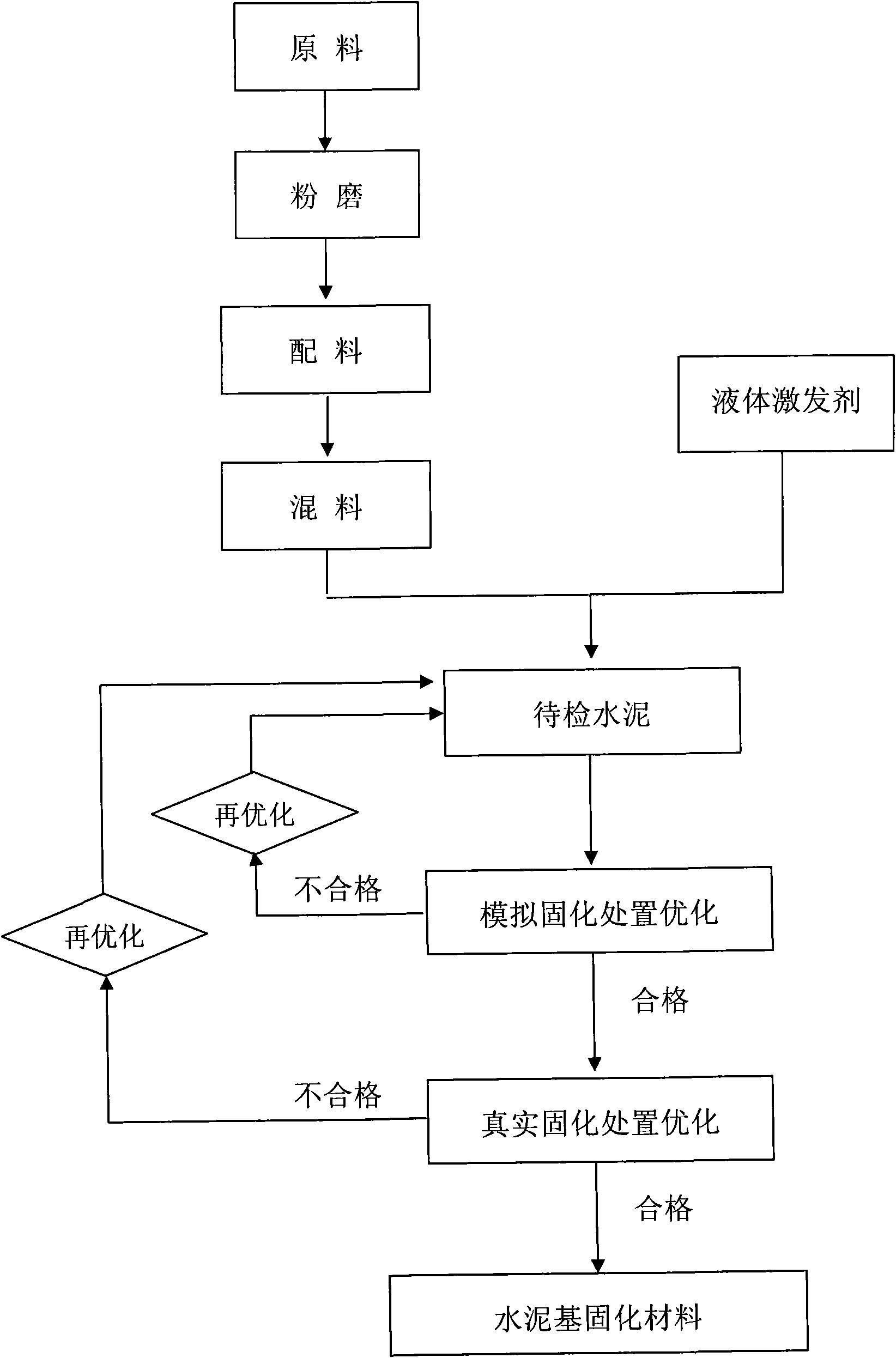
A cement-based solidified material for processing middle and low radioactive incineration ash and a method for processing middle and low radioactive incineration ash
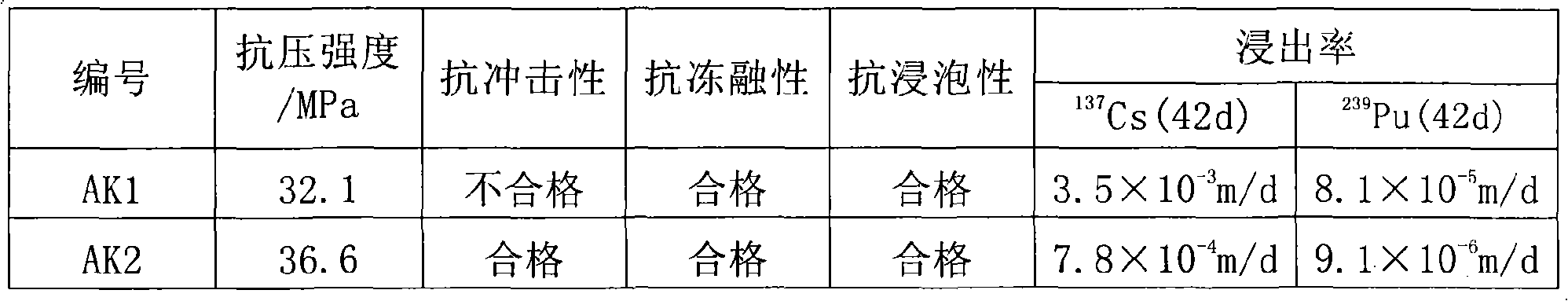
The invention discloses a cement-based solidified material for processing middle and low radioactive incineration ash and a method for processing middle and low radioactive incineration ash. The solidified material, using the slag, fly ash, zeolite, metakaolin, cement clinker as the material to be excited, is obtained through the even mixture with activator after grinding. The liquid activator or combined solid activator can be used as the activator. Mix the material to be excited and activator together, according to the package content of 30-40%, mix with the incineration ash, stir, and maintain to solidification in light of the solidification operation. The cement-based solidified material of the invention can prepare the nuclear waste solidified body with the incineration ash package content greater than 30%, stable mechanical performance, and low leaching rate of radionuclide ion. Especially when solidifying the plutonium-containing waste, the 42-day Pu leaching rate is 10 cm / d. The invention will play an important role in the middle and low radioactive incineration ash processing with good application prospect.
Owner:浙江合力海科新材料股份有限公司
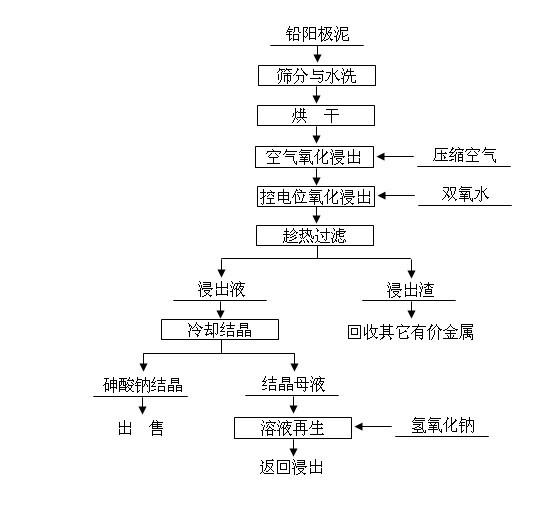
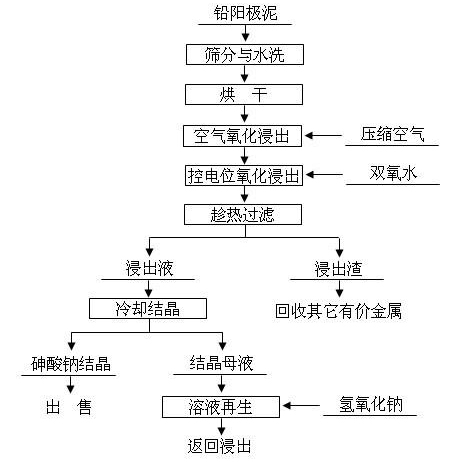
Method for removing and recovering arsenic from lead anode slime
ActiveCN101928838AHigh removal rateAvoid secondary pollutionProcess efficiency improvementArsenic pollutionSodium hydroxide
The invention discloses a method for removing and recovering arsenic from lead anode slime, which comprises the following steps of: performing screening, hot water washing and baking on the lead anode slime, performing oxidation leaching by controlling potential in sodium hydroxide solution, oxidizing the arsenic by using compressed air and hydrogen peroxide as oxidants respectively, adding the oxidized arsenic into alkaline leachate, and ensuring metals such as bismuth, lead, stibium and copper are oxidized and then enter alkaline leaching residue together with noble metals; and after alkaline oxidization leaching process is finished, filtering while hot, performing cooling crystallization on the leachate to generate sodium arsenate crystals, supplementing certain sodium hydroxide to crystallization mother liquor, returning the crystallization mother liquor to the leaching process, and separating and recovering the arsenic and other valuable metals from the lead anode slime. The arsenic leaching rate is over 98.0 percent and the secondary arsenic pollution is free; and the method has the advantages of low requirement on equipment materials, safe operation, low labor intensity, short treatment time and good operating environment.
Owner:YONGZHOU FUJIA NON FERROUS METALS
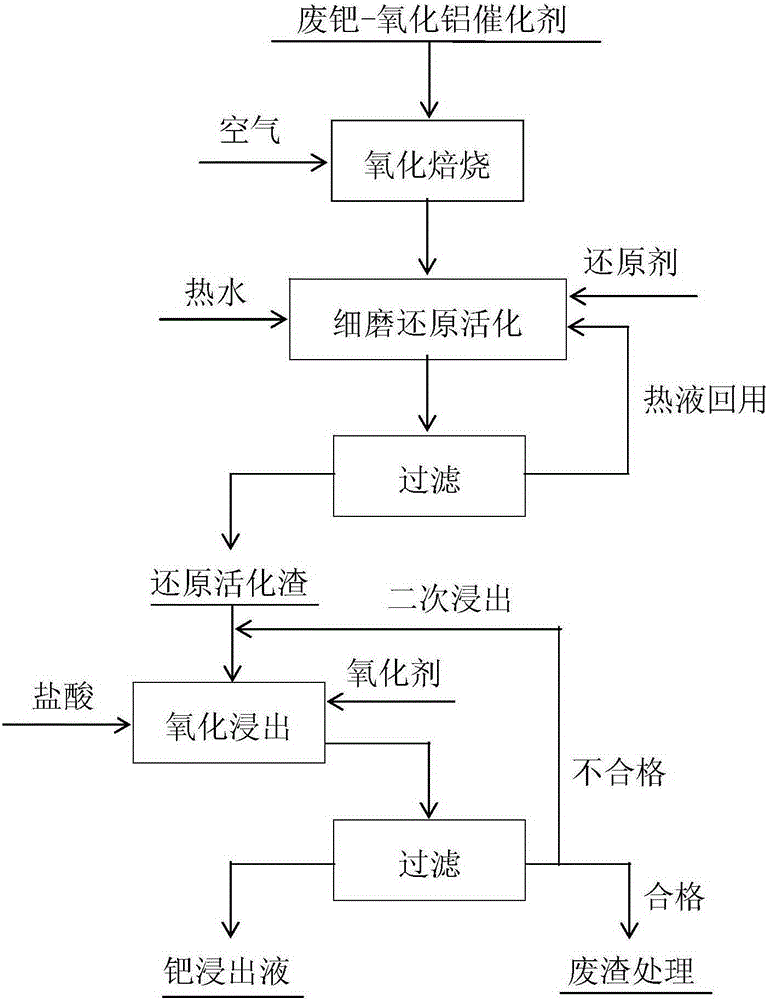
Method for recycling metal palladium from waste palladium-aluminum oxide catalysts
ActiveCN105256146AImprove matchHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementChemical industryAir atmosphere
The invention belongs to the technical field of recovery of noble metals from waste catalysts through wet process and particularly relates to a method for recycling metal palladium from waste palladium-aluminum oxide catalysts. The process of the method mainly comprises the following steps: fluidizing, oxidizing and roasting; pre-grinding, reducing and activating; and oxidizing and leaching. The method specifically comprises the following steps: quickly roasting and decarbonizing waste catalysts at 550-650 DEG C in the air atmosphere; cooling the waste catalysts and then finely grinding, reducing and pre-treating the waste catalysts in a reducer-containing hydrothermal solution system; and oxidizing reduction slag in a hydrochloric acid and oxidant system to leach palladium. Through the method for recycling the metal palladium from the waste palladium-aluminum oxide catalysts, the problem of low leaching rate of palladium from palladium-aluminum oxide based catalysts of the petroleum chemical industry in the prior art can be solved. The method is short in process, simple to operate and low in production cost; and the leaching and recycling rate of palladium reaches over 99%.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
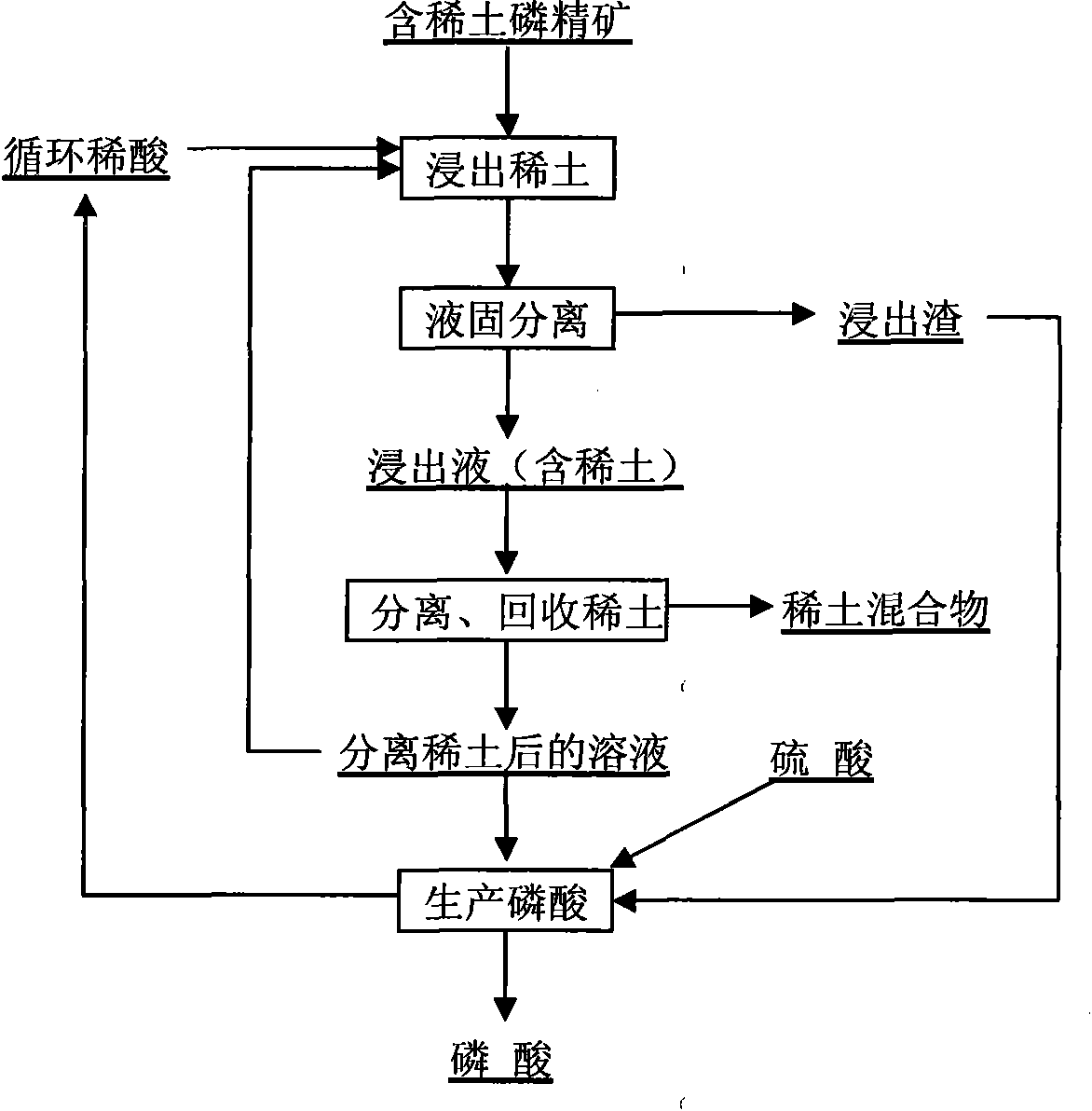
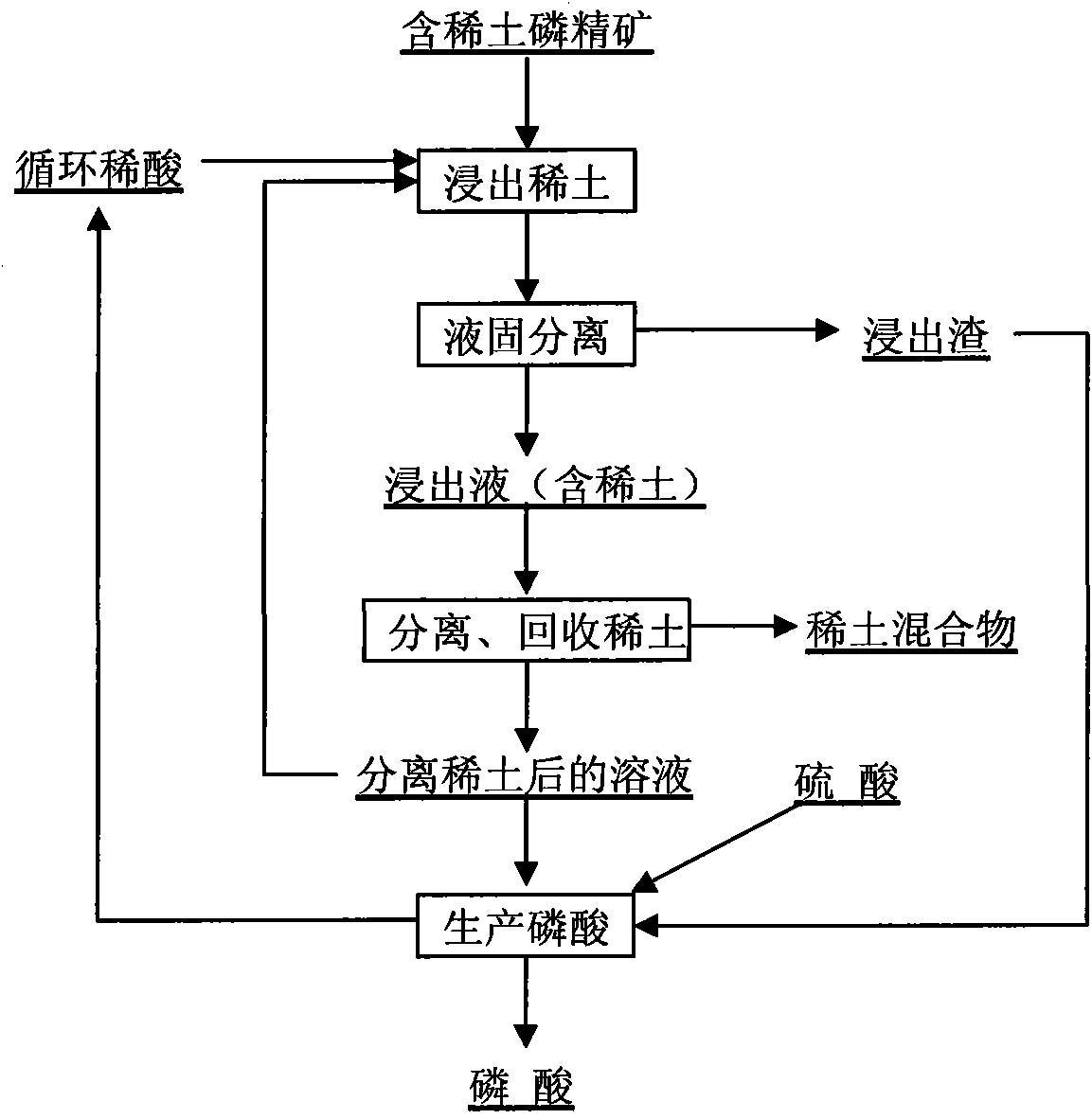
Method for recovering rare earth from rare-earth-contained phosphorite
The invention discloses a method for recovering rare earth from rare-earth-contained phosphorite, which relates to the method for recovering the rare earth from phosphorite and is characterized by comprising the following steps: mixing a rare-earth-contained phosphate concentrate with a phosphoric acid solution for stirring reaction; immersing the rare earth into the solution; carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a rare-earth-contained phosphoric acid solution; then, separating and recovering the rare earth from the rare-earth-contained phosphoric acid solution through uniting one or several of an extraction method, an ion exchange adsorption method, a precipitation method and a crystallization method; and enabling the phosphoric acid solution after slag is leached and the rare earth is separated and recovered to enter a wet-process phosphoric acid production system to produce a phosphoric acid. In the method for recovering the rare earth from the rare-earth-contained phosphorite, by taking the phosphoric acid solution as a leaching agent, the rare earth is extracted from the rare-earth-contained phosphorite without adding a surface active agent, thereby, the quality of a phosphoric acid product is not influenced, and the rare-earth leaching rate is about as high as 90 percent, and moreover, the leaching agent for leaching the rare earth is the phosphoric acid generated in the phosphoric acid production course, and can also be circular dilute phosphoric acid, diluted phosphoric acid and the like generated in the phosphoric acid production course. The method for recovering the rare earth from the rare-earth-contained phosphorite is tightly linked with a sulfuric acid-method phosphoric acid production process.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com