Method for extracting germanium, indium and zinc from high iron, silicon and manganese materials containing germanium, indium and zinc
A technology of high iron and indium zinc, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of frequent alkaline washing of organic phases, difficult extraction and production, and complex components.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
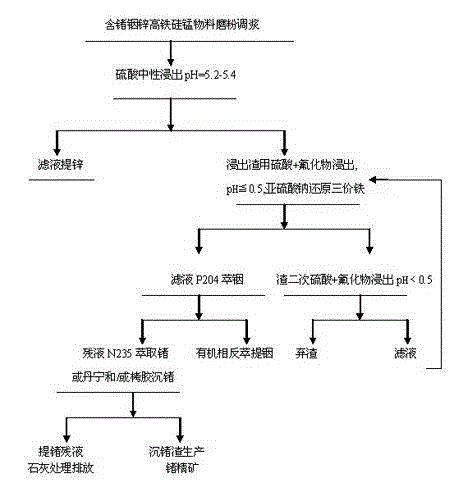
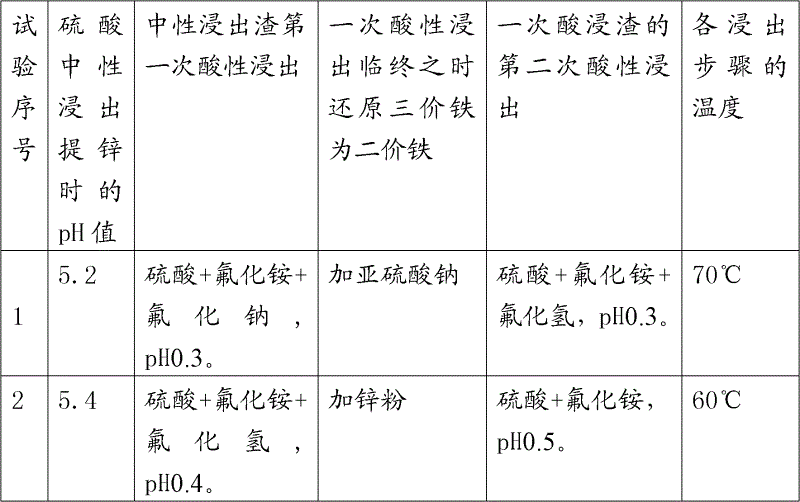
[0012] Embodiment 1. The raw material containing 0.0294% of germanium, 0.069% of indium, 8.9% of ferric iron, 12.7% of zinc, 24.5% of calcium, and 4.8% of silicon dioxide is first carried out neutral leaching with sulfuric acid, and the pH5.2 infiltration solution contains Germanium 0.28mg / l, indium 0 zinc 34.6g / l, medium leaching residue was acid leached twice with sulfuric acid according to the conventional method (sulfuric acid 100g / l, temperature 95-100 ℃) two leaching total leaching rate germanium 21.5%, indium 98.2%, leaching 0.0245% germanium, micro-indium, and 0.57% iron from tailings. The tailings were acid leached with sulfuric acid and 20g / l sodium chloride, 20% hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid and 20g / l ammonium fluoride , PH≤0.5, temperature above 80°C, time 2-3 hours, liquid / solid=3. The leaching results of the sulfuric acid and sodium chloride group contained germanium 18.1mg / l, the slag contained germanium 0.0235%, and the leaching solution of the 20% hydrochlor...
Embodiment 2
[0013] Embodiment 2. Raw material composition contains germanium 0.0245%, indium 0.08%, ferric iron 8, % zinc 11.2%, silicon dioxide 5.2%, manganese 1.5%, after middle dipping dezincification, slag is treated with sulfuric acid and ammonium fluoride (fluorine ion 20g / l) to carry out acid leaching once, the leaching solution contains germanium 65.2mg / l, indium 241mg / l, iron 22.7g / l, the leaching residue is carried out the second acid leaching with sulfuric acid and ammonium fluoride (fluoride ion 10g / l) For leaching, the immersion solution contains germanium 10.75mg / l, indium 38mg / l, iron 4.78g / l, the secondary leaching tailing slag contains 0.0011% germanium, and the leaching rate of slag is 98.3%.
Embodiment 3
[0014] Example 3. The raw material contains 0.0219% germanium and 0.08% indium. After intermediate leaching, the leaching residue is acid-leached twice with hydrogen fluoride (fluoride ion 20g / l) and sulfuric acid. The leaching tailings contain 0.0048% germanium, and the leaching rate is 88.2%. After intermediate leaching with this raw material, acid leaching was carried out twice with sodium fluoride (fluoride ion 20g / l), leaching 0.0069% of tailing germanium, and the leaching rate was 87.9%.
[0015] Embodiment 4. Carry out the P204 kerosene system extraction indium with the one-time pickling solution of example 2, three-stage extraction rate 98%, ferric iron 5.2%. Raffinate is precipitated germanium with tannin / germanium=30, precipitation rate 98.6%, With tannin extract / germanium=90, the precipitated germanium precipitation rate is 94.5%, and with N235 kerosene system, under the condition of adding 5 times of germanium complexing agent, the three-stage extraction rate is 89....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com