Patents
Literature
2066 results about "Raffinate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
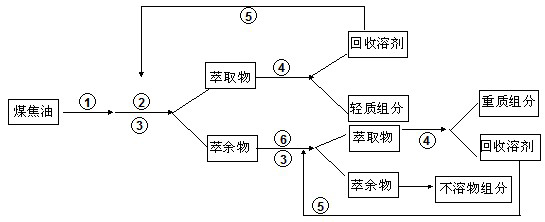
In chemical separation terminology, the raffinate (from French raffiner, to refine) is a product which has had a component or components removed. The product having the removed materials is referred to as the extract. For example, in solvent extraction, the raffinate is the liquid stream which remains after solutes from the original liquid are removed through contact with an immiscible liquid. In metallurgy, raffinating refers to a process in which impurities are removed from liquid material.
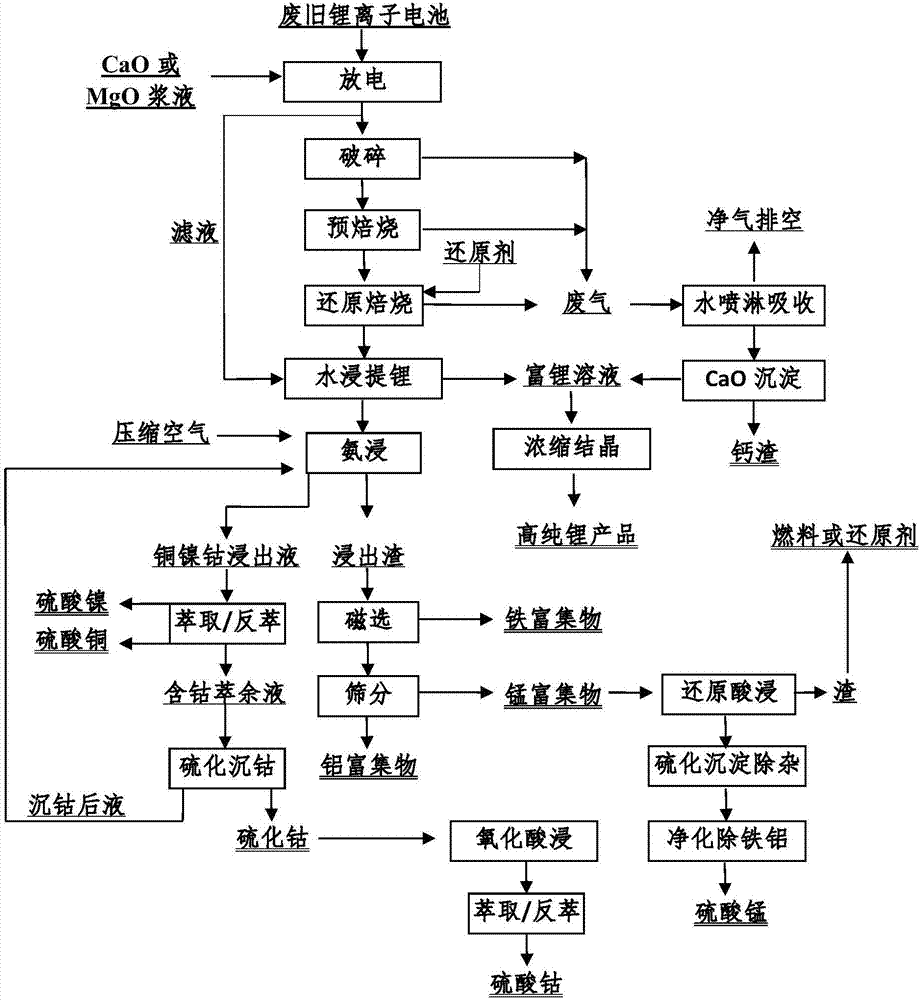
Method for comprehensively recycling valuable metals from spent lithium ion battery
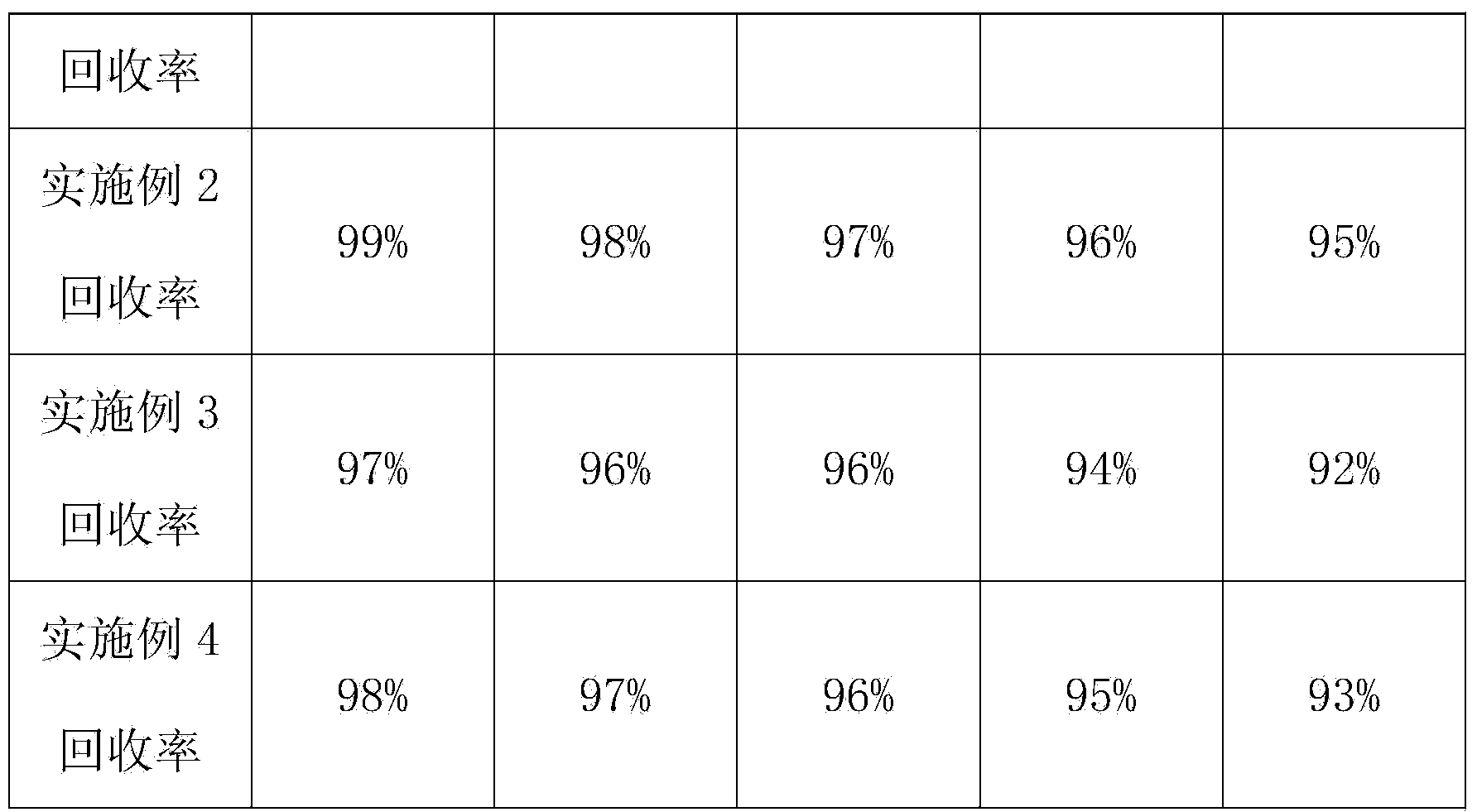
ActiveCN107017443AThe pre-processing process is simpleHigh recovery rateWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementVulcanizationSlag
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recycling valuable metals from a spent lithium ion battery. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out electric discharge treatment on a spent battery, crushing, pre-roasting at 300-400 DEG C, adding a reducing agent, and carrying out reduction roasting at 450-700 DEG C; carrying out water extraction and evaporative crystallization on fine aggregates obtained through the reduction roasting, so as to obtain a high-purity lithium product, leaching copper, nickel and cobalt from leached slag and roasted lump materials by virtue of ammonia oxide, carrying out magnetic separation and sieving on ammonia leaching slag so as to obtain iron and aluminum enriched products, and carrying out reduction acid leaching, purification and edulcoration on sieved products, so as to obtain a high-purity manganese sulfate solution; and carrying out extraction and selective reverse extraction on ammonia leaching liquid, so as to obtain a high-purity nickel sulfate solution and a high-purity copper sulfate solution, and carrying out vulcanization cobalt precipitation, oxidation acid leaching and extraction purification on raffinate, so as to obtain a high-purity cobalt sulfate solution. The method is high in extraction rate of valuable metals and applicable to the treatment of multiple waste lithium ion battery raw materials and efficient utilization of multiple elements, and sorting is not required.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUANGHUA SCI TECH
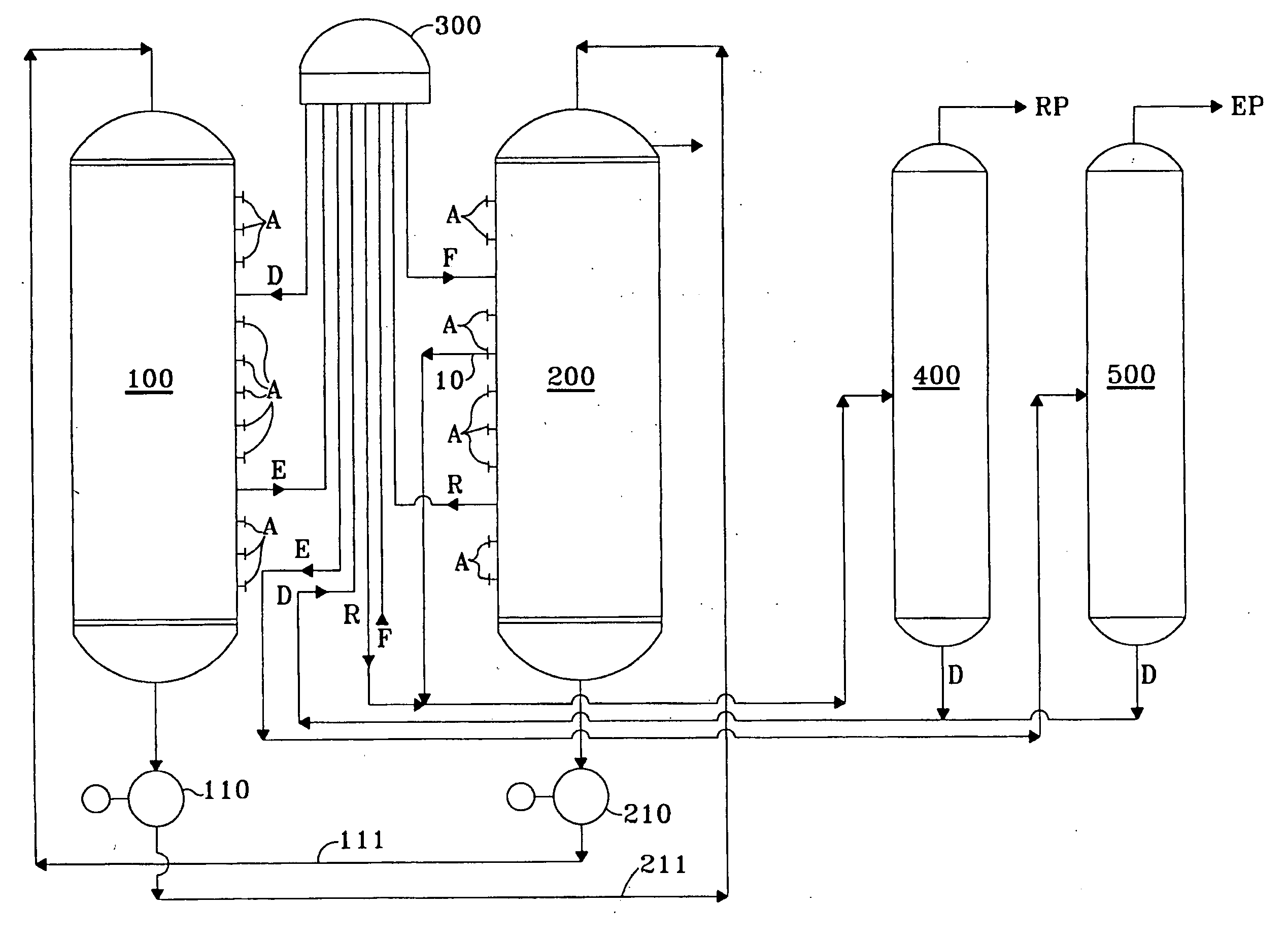
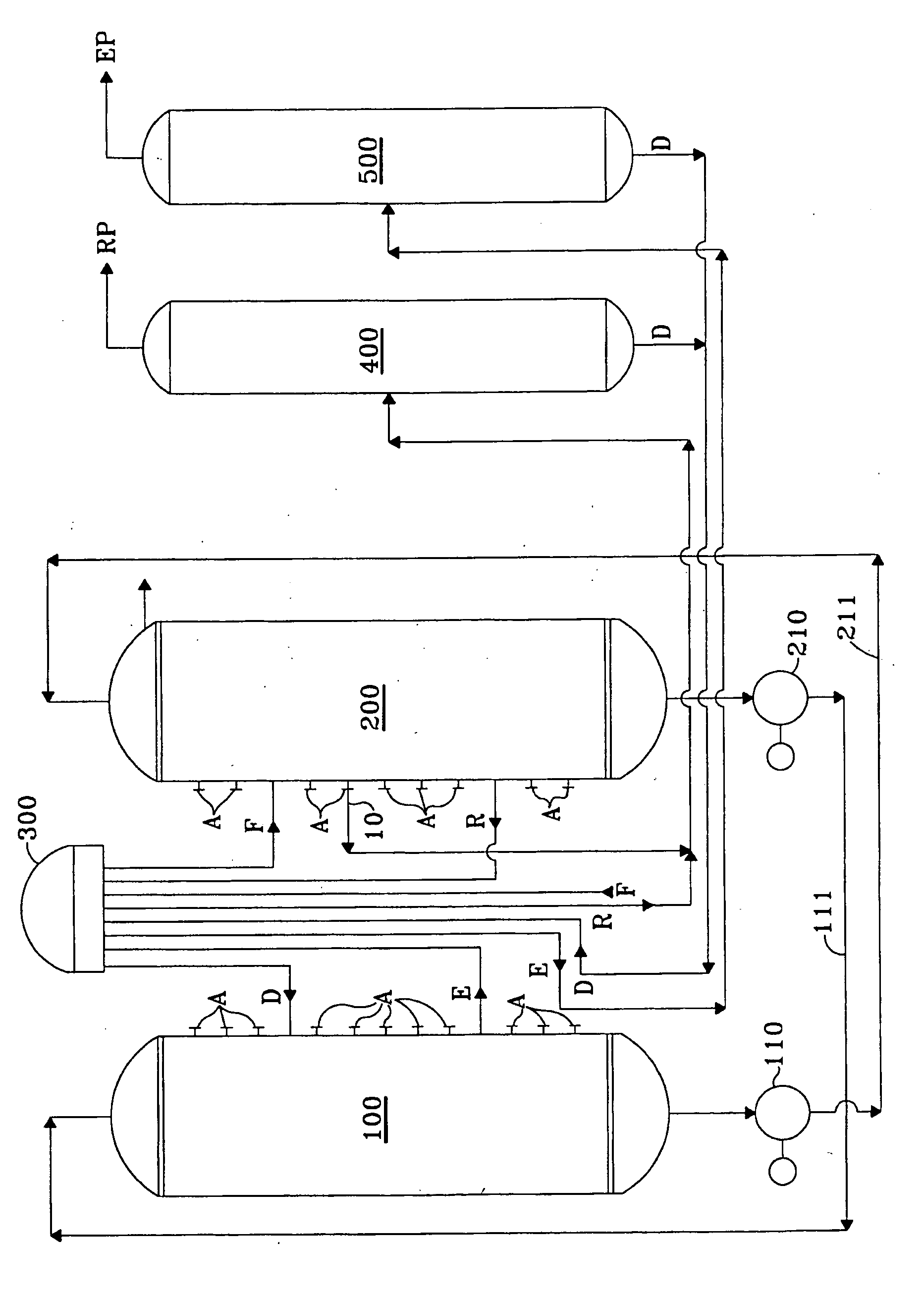
Product recovery from simulated-moving-bed adsorption
Product purity from or capacity of a simulated-moving-bed adsorptive separation process is increased by flushing the contents of the transfer line previously used to remove the raffinate stream away from the adsorbent chamber, preferably into the raffinate column used to separate desorbent from raffinate product. Preferably a stream from the adsorbent chamber at an intermediate point between the feed entry point and raffinate withdrawal is used as the flushing liquid. This flush step eliminates the passage of a quantity of the raffinate material into the adsorbent chamber in the transfer-line flush period or when the process conduit is subsequently used to charge the feed stream to the adsorbent chamber.
Owner:UOP LLC
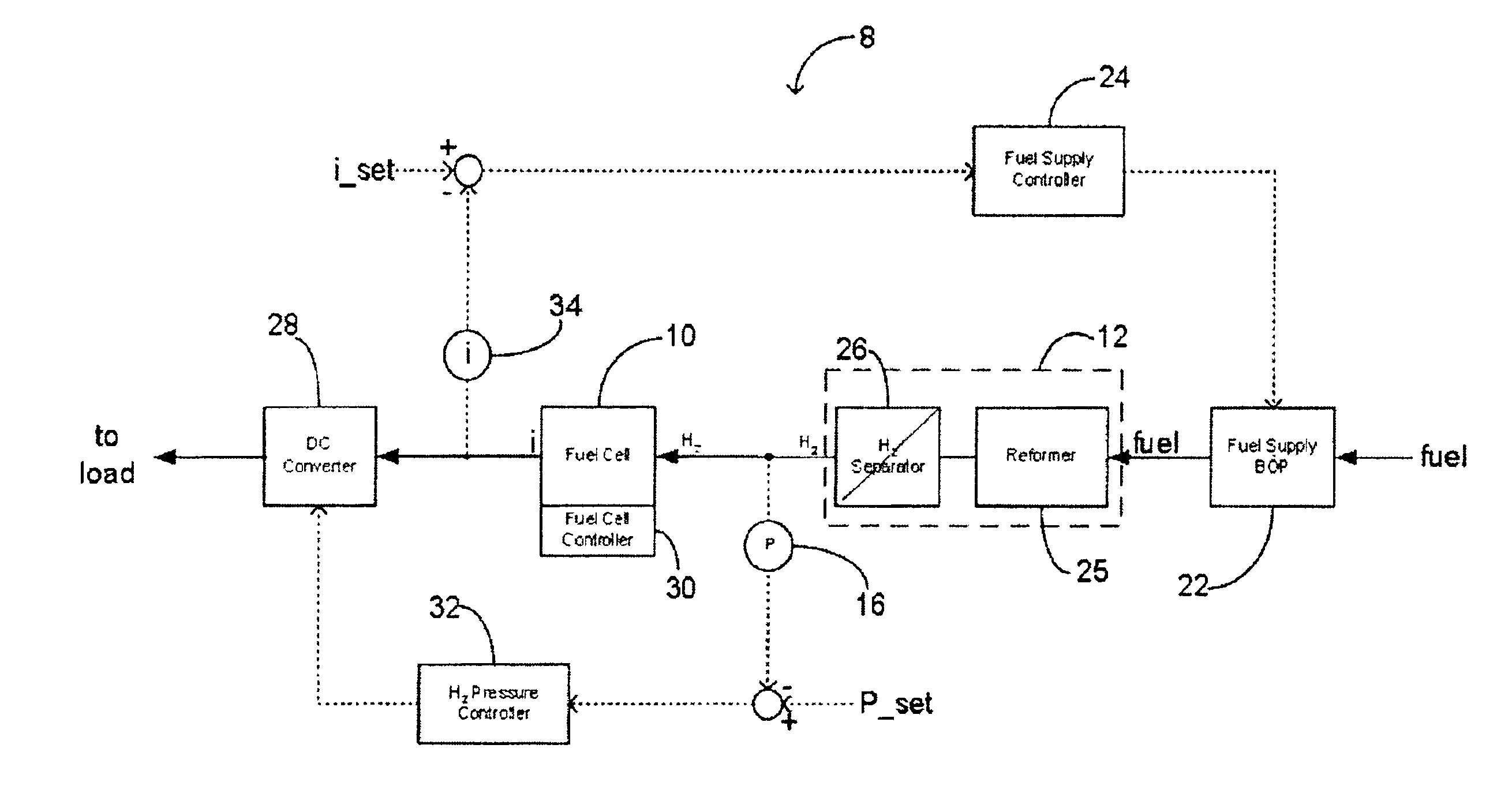
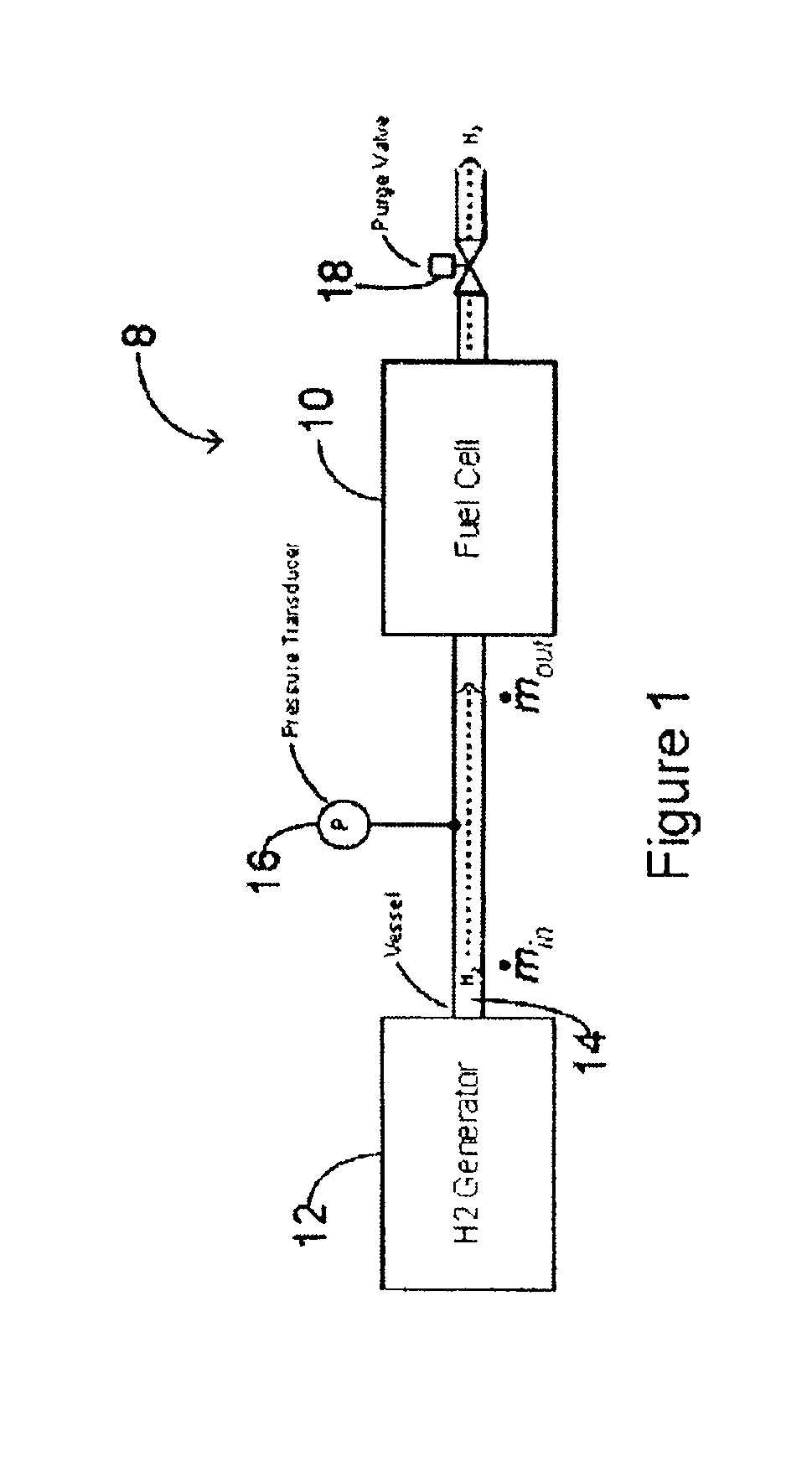
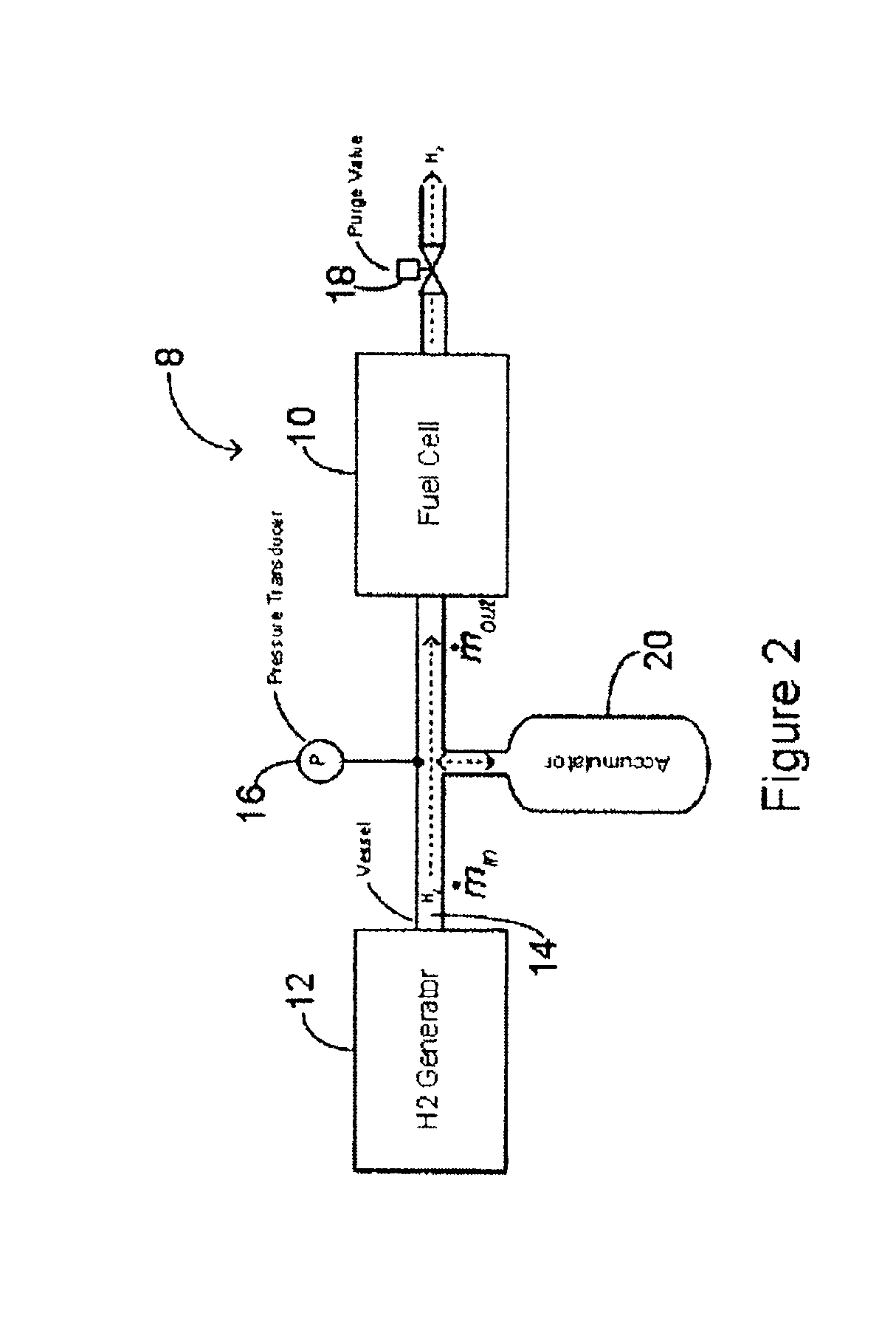
Method and system for controlling the operation of a hydrogen generator and a fuel cell
InactiveUS6893755B2Batteries circuit arrangementsReactant parameters controlThermodynamicsHydrogen pressure
This application relates to a method and system for controlling the supply of fuel to a dead-ended hydrogen fuel cell. The invention may be utilized, for example, to more efficiently integrate the operation of a hydrogen fuel cell and a hydrogen generator, such as a reformer coupled with a hydrogen separation unit. The invention ensures that the production and consumption of hydrogen are effectively balanced to avoid negative feed line pressure fluctuations. The fuel supply control subsystem and hydrogen consumption control subsystems are, however, “decoupled” and hence independently operable. The invention may include an accumulator disposed in a flow path between the hydrogen generator and the fuel cell for storing hydrogen under pressure. The accumulator is sufficiently large in volume such that the pressure of hydrogen in the flow path does not deviate substantially from a target pressure, even during the waste purging sessions. The system enables the use of low-cost pressure transducers in place of mass flow meters. In one aspect of the invention raffinate flow from the hydrogen separator can be controllably adjusted to regulate the temperature or other operating parameters of the reformer.
Owner:CELLEX POWER PRODS
SCR denitration catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101185886AImprove structural stabilityImprove mechanical stabilityCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSilanesAmmonium paratungstate
The invention relates to a preparation method of an SCR denitration catalyst, which comprises the following steps: (1) Al2O3 sol is prepared, which comprises the steps that hot ammonia, the Al2O3 is added in drops into the ammonia and then HCI is added and the mixture is stirred; (2) Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2 composite sol is prepared, which comprises the steps that tetratethoxy-silane, butyl titanate, deionized water are sequentially put into ethanol to be aging and then the sol prepared by step (1) is adding to be stirred and aging; (3) vector is coated, which comprises the steps that cordierite honeycomb immersed into the sol of step (2) and the raffinate in a channel is cleaned, dried and roasted after being taken out; (4) active component impregnating solution is prepared, which comprises the steps that lanthanum nitrate, ammonium metavanadate and ammonium paratungstate are dissolved into the deionized water after being mixed together and oxalate acid is added to be aging; (5) the active component is loaded, which comprises the steps that the vector of the step (3) is immersed into the impregnating solution of the step (4) and then the raffinate in the channel is cleaned to be dried and roasted. The invention also relates to the denitration catalyst which is prepared by the method.
Owner:山西蒲洲博奇环保科技有限公司
Catalytic conversion method for preparing lower olefins and aromatics
The invention relates to a catalytic conversion method for preparing lower olefins and aromatics. Raw oil with different cracking performances enters different reaction zones of a first riser reactor to contact with a catalytic cracking catalyst for cracking reaction to separate a spent catalyst from reaction oil gas, wherein the reaction oil gas is separated to obtain a product containing lower olefins, gasoline, distillates with distillation range of 180-250 DEG C and catalytic wax oil, wherein the gasoline is extracted by light aromatics to obtain light aromatics and gasoline raffinate; the raw materials are cracked to be sent into a second riser reactor to contract with a hot regenerated catalyst for catalytic conversion; and the spent catalysts of the two riser reactors are burned and regenerated in the same one regenerator and then returns to the two riser reactors. The method uses heavy raw materials to furthest produce the lower olefins, such as propylene, ethylene, and the like, particularly the propylene, the production rate can exceed 40 wt%, and at the same time the method can coproduce the aromatics, such as toluene, xylene, and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
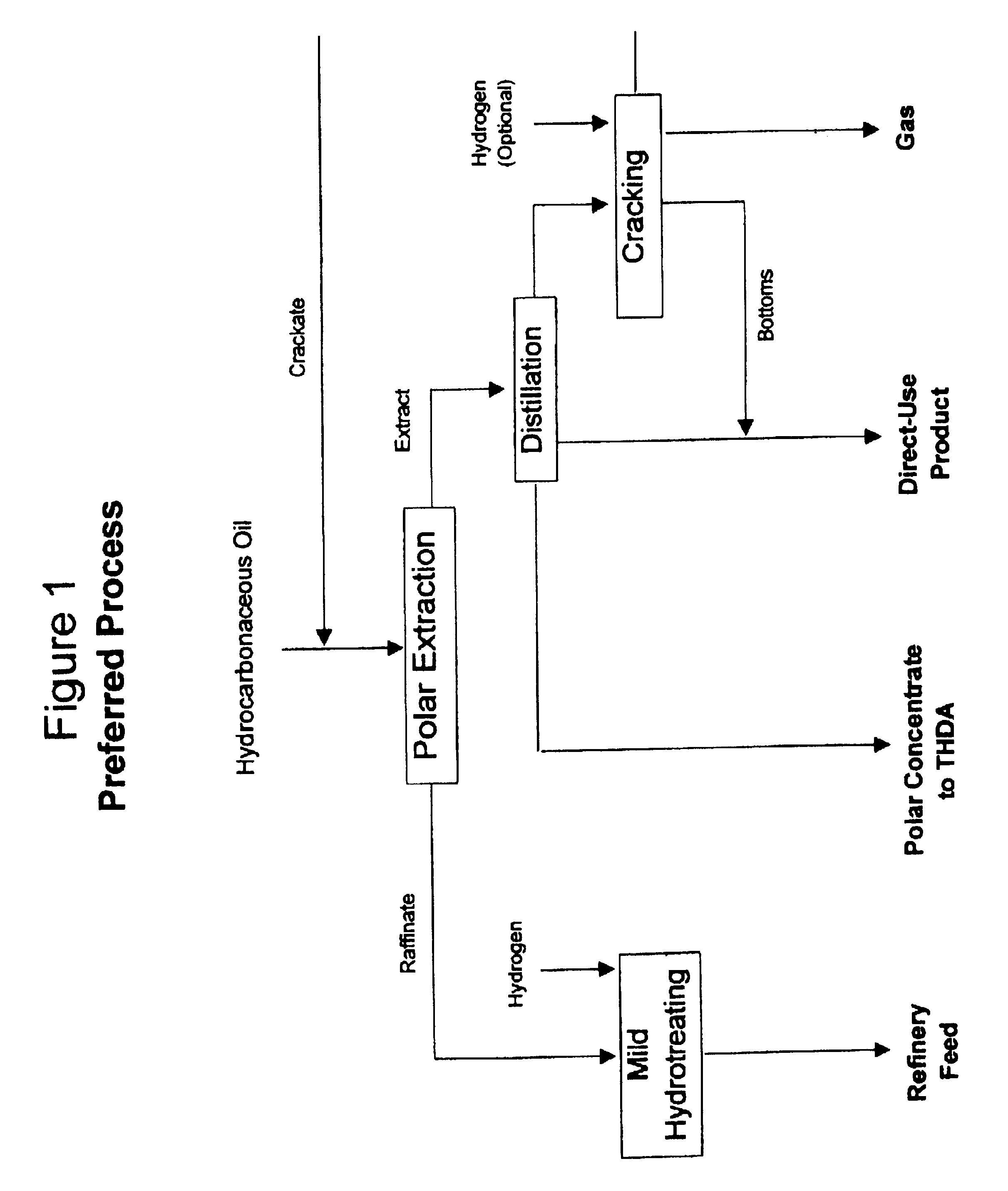
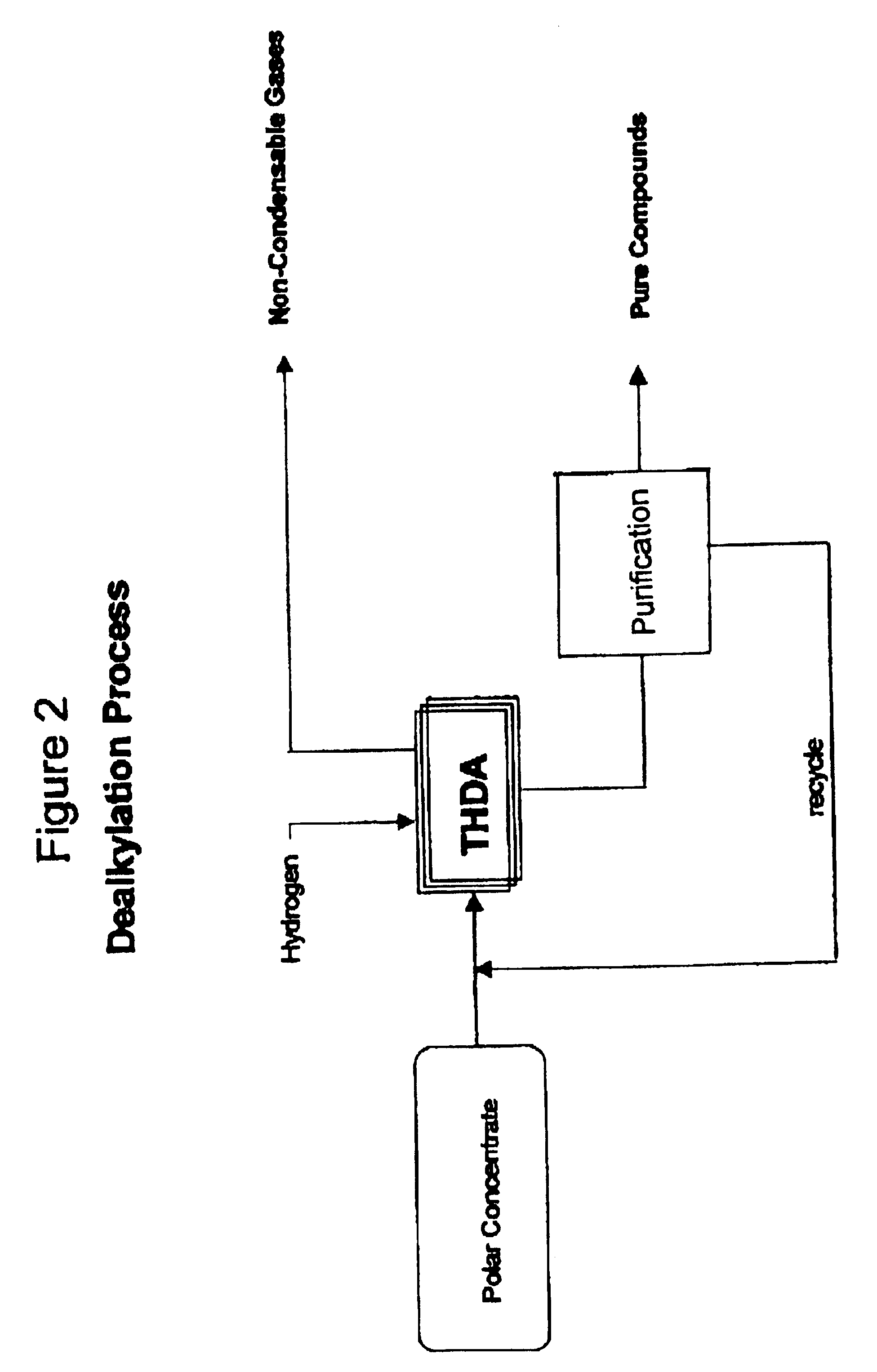
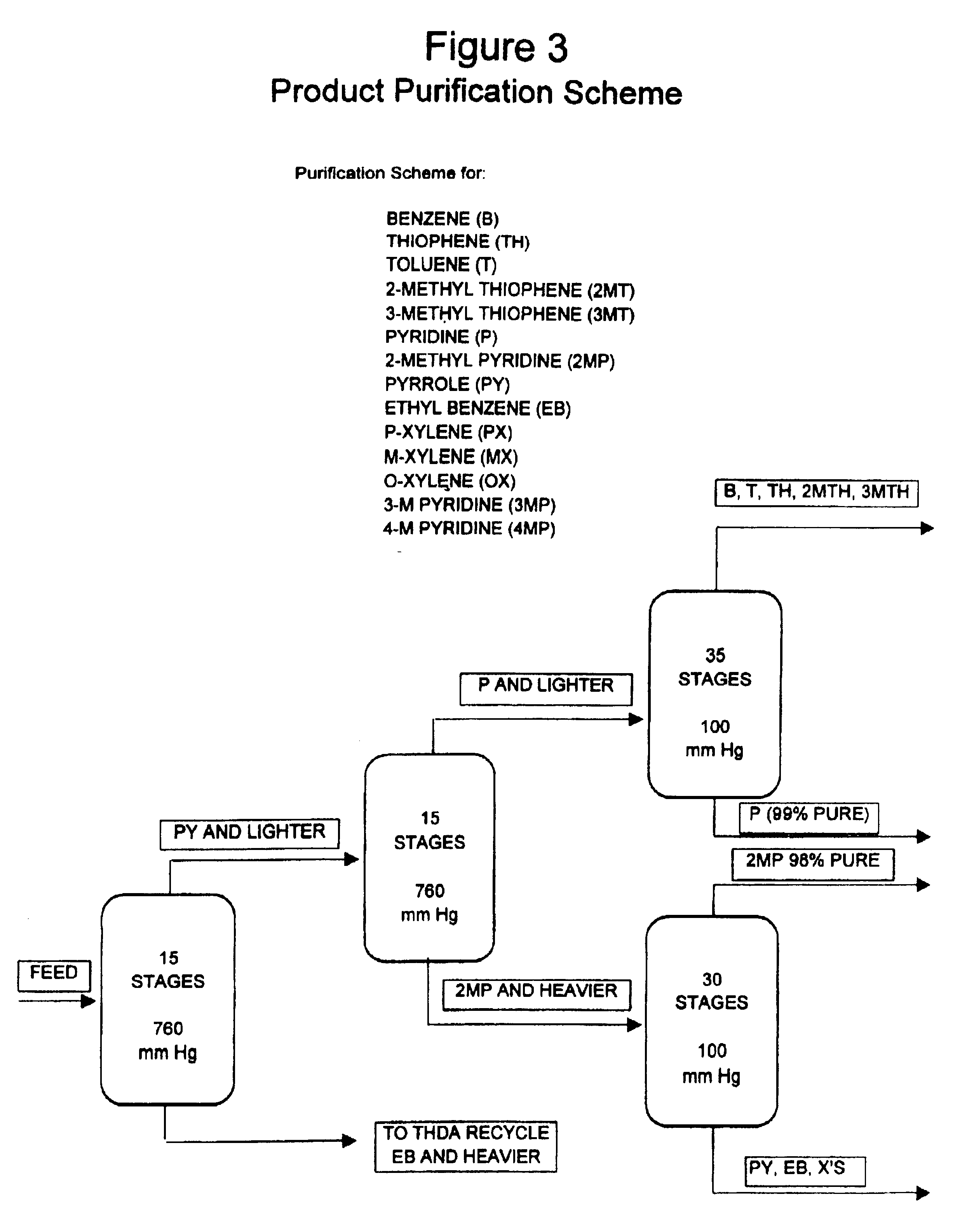
Process for enhancing the value of hydrocarbonaceous natural resources
InactiveUS20050167337A1Little and wasteLittle and valueHydrocarbon distillationTreatment with hydrotreatment processesSolubilityNatural resource
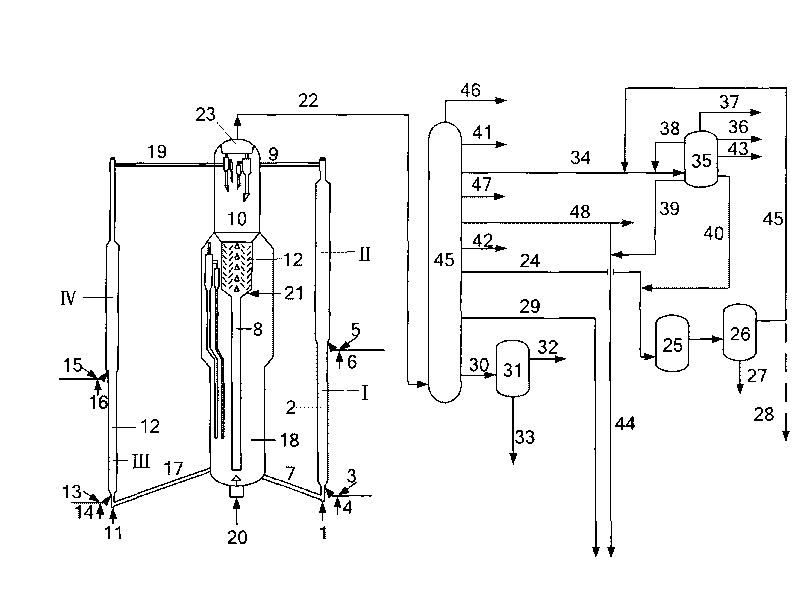
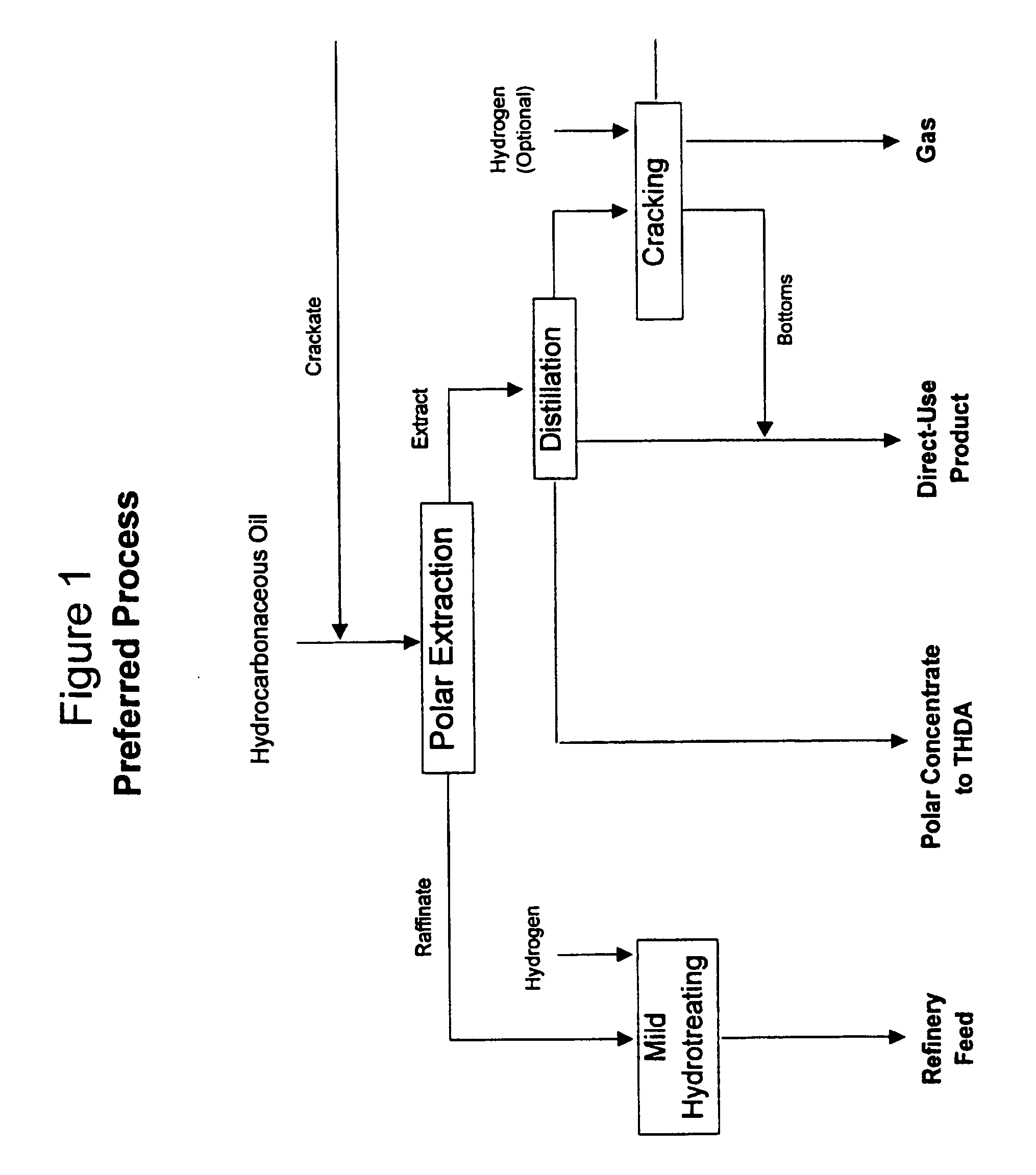
A process for upgrading hydrocarbonaceous oil containing heteroatom-containing compounds where the hydrocarbonaceous oil is contacted with a solvent system that is a mixture of a major portion of a polar solvent having a dipole moment greater than about 1 debye and a minor portion of water to selectively separate the constituents of the carbonaceous oil into a heteroatom-depleted raffinate fraction and heteroatom-enriched extract fraction. The polar solvent and the water-in-solvent system are formulated at a ratio where the water is an antisolvent in an amount to inhibit solubility of heteroatom-containing compounds and the polar solvent in the raffinate, and to inhibit solubility of non-heteroatom-containing compounds in the extract. The ratio of the hydrocarbonaceous oil to the solvent system is such that a coefficient of separation is at least 50%. The coefficient of separation is the mole percent of heteroatom-containing compounds from the carbonaceous oil that are recovered in the extract fraction minus the mole percent of non-heteroatom-containing compounds from the carbonaceous oil that are recovered in the extract fraction. The solvent-free extract and the raffinate concentrates may be used directly or processed to make valuable petroleum, chemical or industrial products.
Owner:JAMES W BUNGER & ASSOC
Process for enhancing the value of hydrocabonaceous natural recources
InactiveUS6875341B1Little and valueReduce total process throughputRefining with acid-containing liquidsHydrocarbonsSolubilitySolvent free
Owner:JWBA
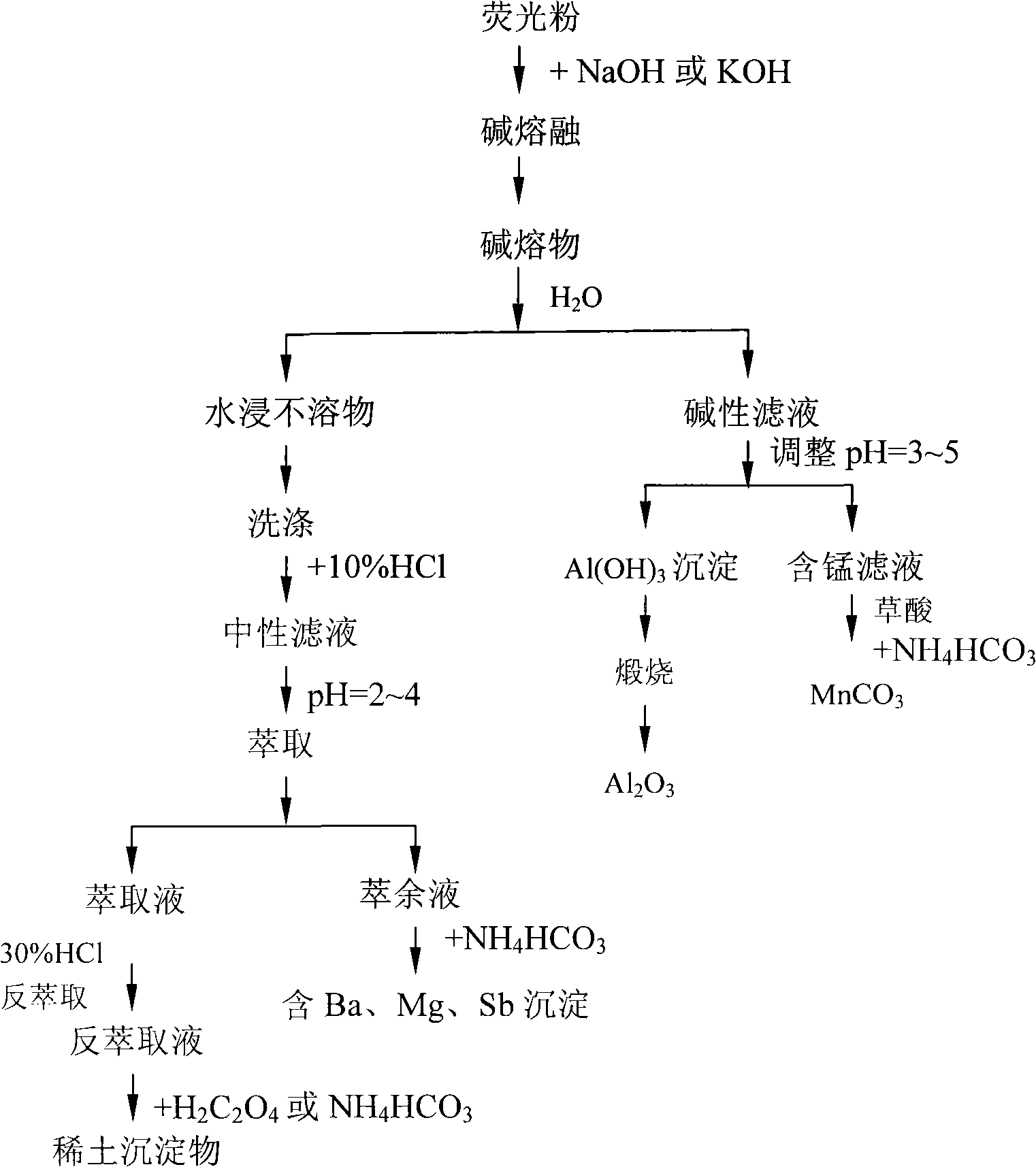
Process for recovering rare earth element in waste florescent lamps
InactiveCN101307391AReasonable processProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementAlkaline earth metal
The invention provides a method for reclaiming a rare earth element from abandoned fluorescent lamp. The invention is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of: melting fluorescent powder by NaOH or KOH and adding water into an alkali melted substance to produce water insoluble substances and alkaline filtrate; dissolving the water insoluble substances into hydrochloric acid to produce neutral filtrate; extracting the neutral filtrate by P204 or P507 to produce extraction liquid and raffinate; back extracting the extraction liquid by HCl to produce back-extraction liquid, and precipitating the back-extraction liquid by H2C2O4 or NH4HCO3 to produce rare earth precipitate containing mixed Y, Ce, Tb and Eu; precipitating the raffinate by the NH4HCO3 to produce precipitate containing Mg, Ba and Sb; adjusting the pH value of the alkaline filtrate to between 3 and 5 to produce Al(OH)3 precipitate and manganiferous filtrate; washing, filtering and calcining the Al(OH) precipitate to produce alumina; and adding oxalic acid into the manganiferous filtrate to produce manganous carbonate. The method realizes that the rare earth element, Eu, Tb, Ce and Y are separated from Mg, Ba, Ca and other alkaline-earth metals, ensures that resources are comprehensively reclaimed and used, and has the advantages of reasonable process flow, economy and practicality.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RES INST OF NON FERROUS METALS
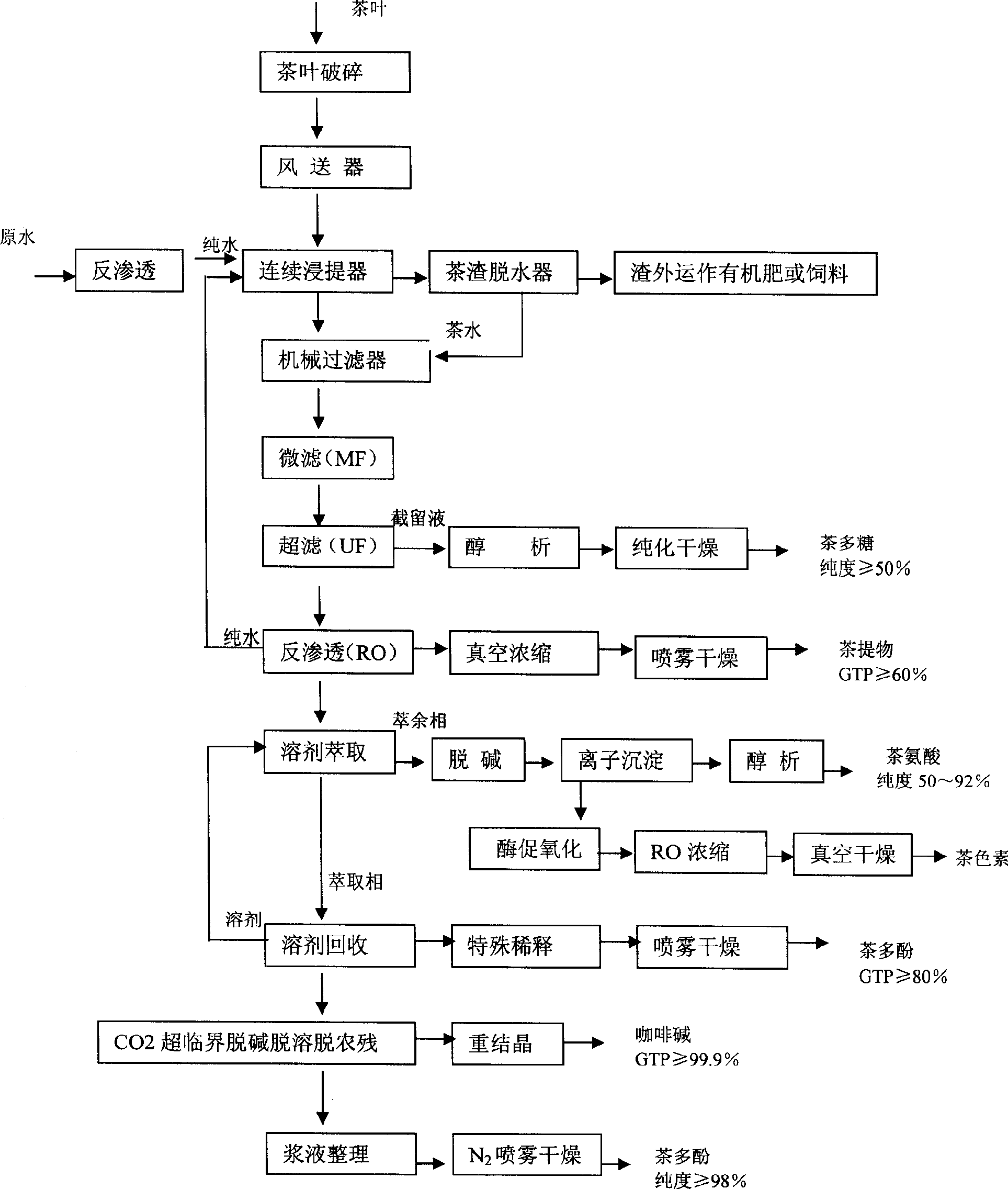
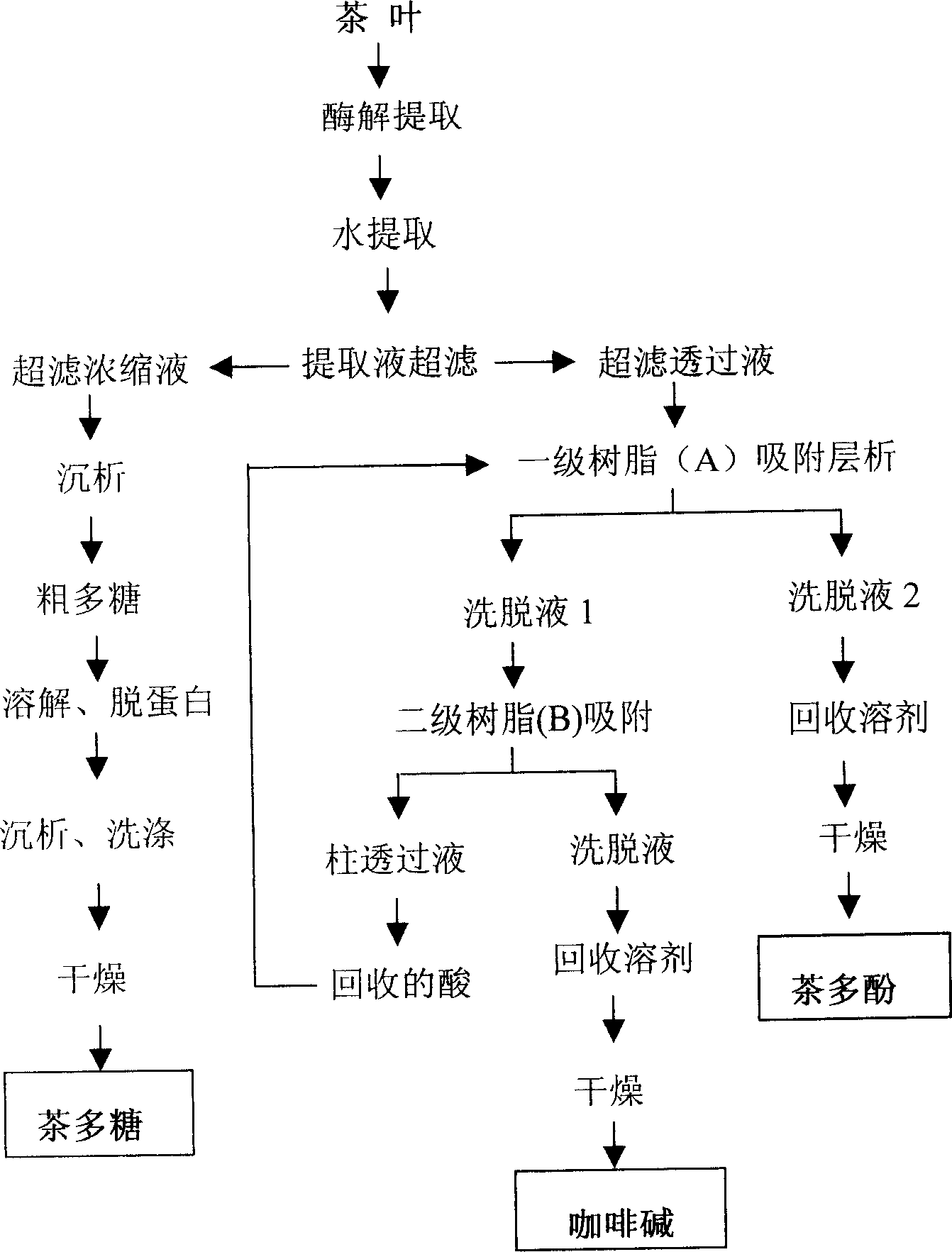
Process for extracting tea polyphenol, theanine, tea polysaccharide and tea pigment from tea
InactiveCN1837201AHigh purityReduce labor intensityCarboxylic acid amide separation/purificationBulk chemical productionForeign matterPhenolic content in tea
The invention discloses an extracting polyphenol, theanine, tea polysaccharide and tea pigment method from tea, which is characterized by the following: using deionized water for lixiviating tea at constant temperature with continuous flow upstream at multi-speed; adopting microstrainer to dislodge the foreign matter of raffinate; using hyperfiltration for putting-off pectin and protein; concentrating by hyperfiltration and dehydration; extracting tea polyphenol by acetic acid ethyl ester and recovering dissolvant; stripping caffeine of extracting extract phase, pesticide residue and dissolvant by CO2 supercritical fluid; getting tea polyphenol by low-temperature nitrogen spray-drying; using alcohol separation and low temperation vacuum drying by hyperfiltration trapped fluid to prepare tea polysaccharide; separating alcohol recrystallization by basic copper carbonate and hydrogen sulfide to get theanine; using enzymatic oxidation and alkaline air to oxygenate remain polyphenols substance of liquid phantom; getting tea pigment by hyperfiltration dehydration compression and vacuum drying; merging caffeine form carbon dioxide above-critical fluid and caffeine from carrene; recovering dissolvent; using deionized water for washing; obtaining caffeine by recrystallization vacuum drying.
Owner:张守政
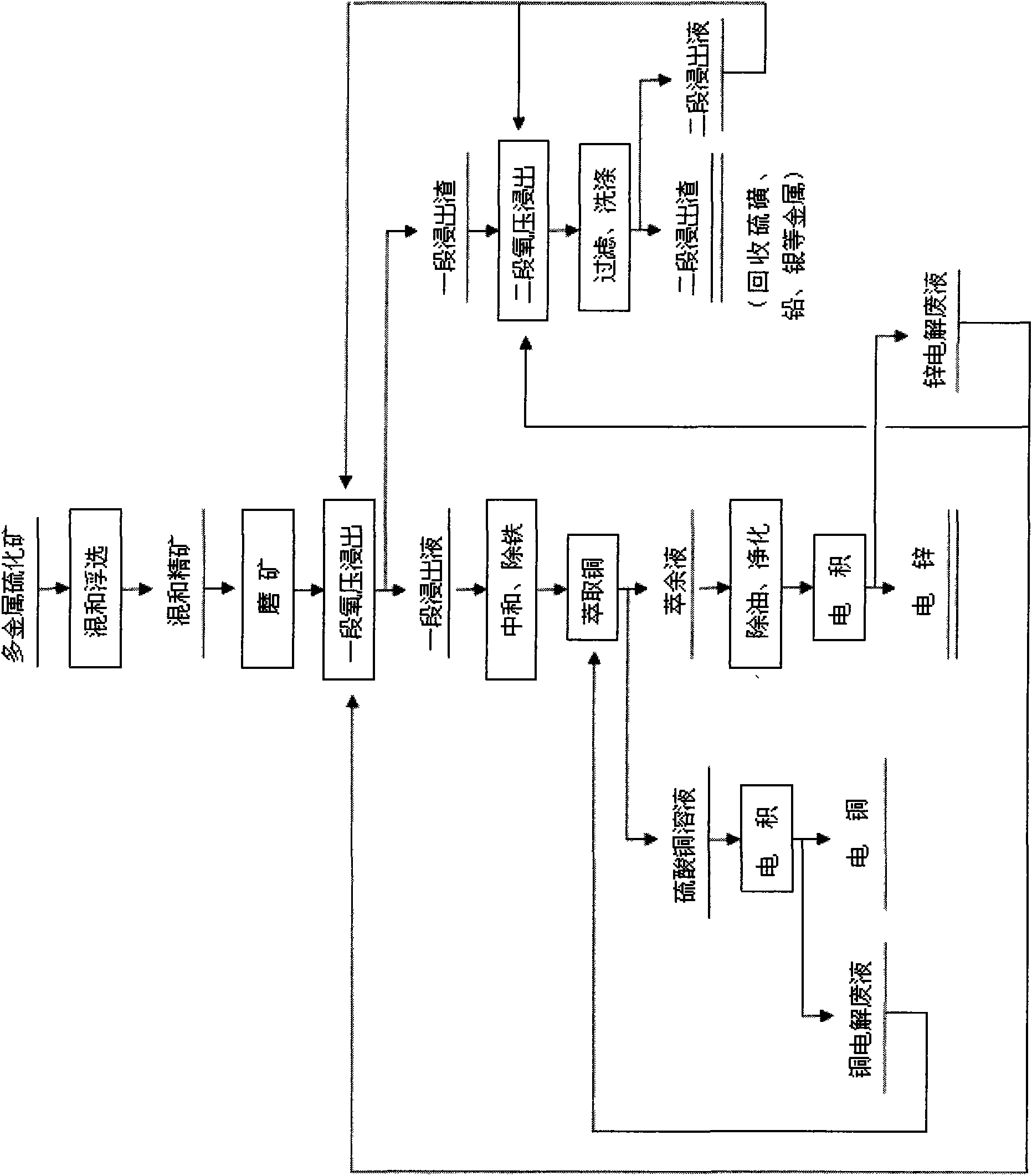
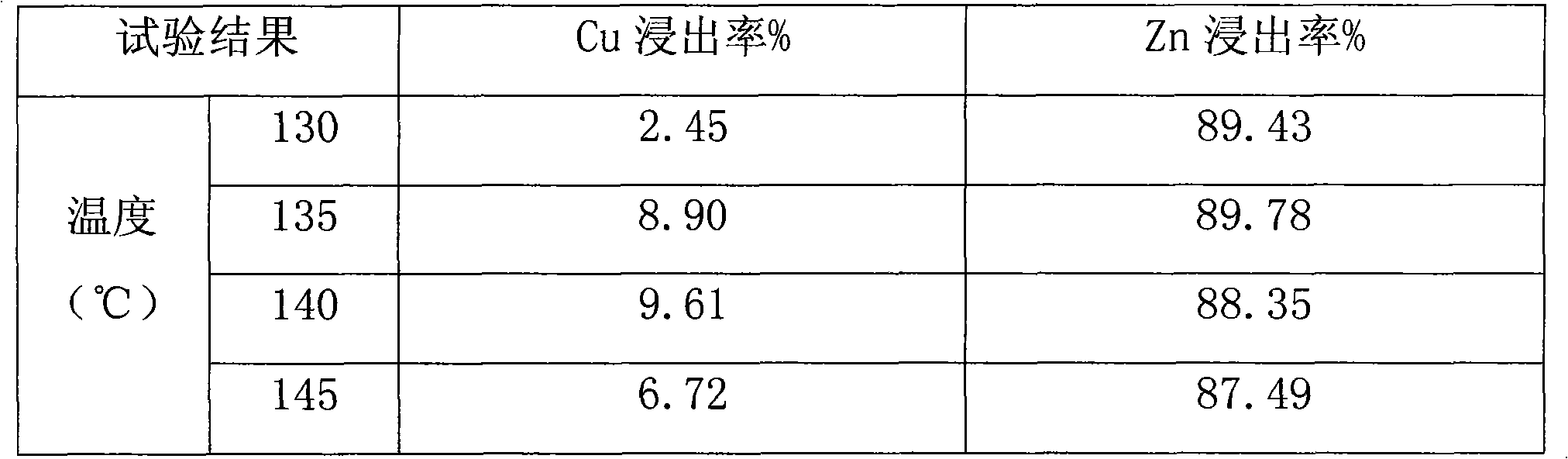
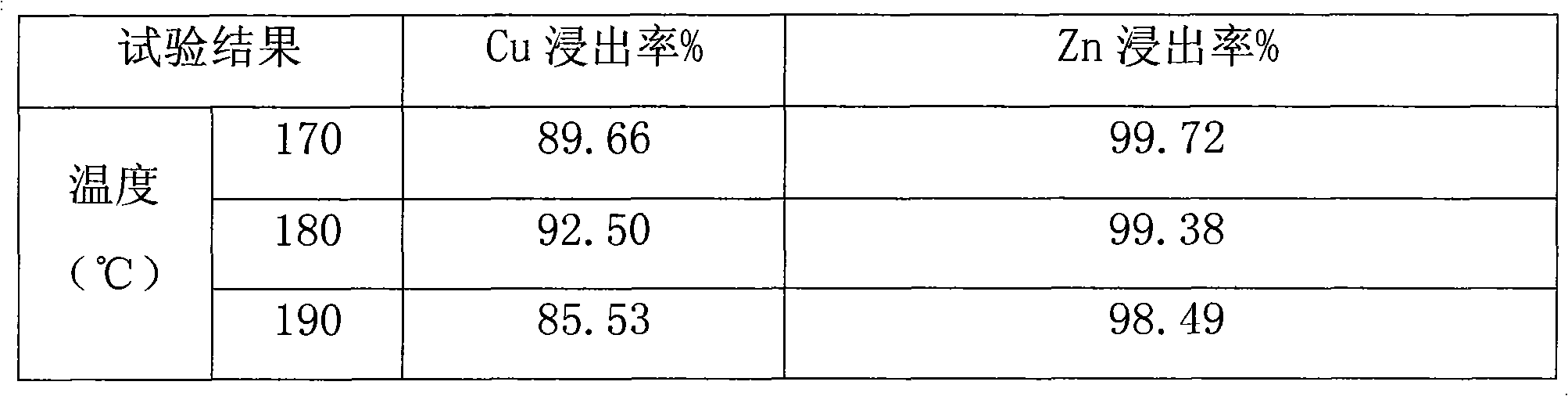
Comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc
InactiveCN101643857AHigh recovery rateSimple processSulfur preparation/purificationFlotationRecovery methodLead smelting
The invention discloses a comprehensive recovery method of complex polymetal sulphide ore containing copper, lead and zinc and adopts dressing-metallurgy combination method and hydrometallurgy-pyrometallurgy combination method to recover metals. The recovery method comprises the following steps: first performing bulk flotation to the complex polymetal sulphide ore, fine grinding the obtained concentrate, leaching by using two-step counter flow oxygen pressure leaching process, extracting and separating copper and zinc from the obtained leachate, electrodepositing the strip liquor of copper-loaded organic phase to obtain cathode copper, cleaning the obtained raffinate and electrodepositing to obtain cathode zinc; pressurizing leaching residue to perform flotation separation and obtain sulfur concentrate and lead silver residue, distilling sulfur concentrate to obtain sulfur; performing lead smelting process to lead silver residue to obtain electrolytic lead product and lead anodic slime; and comprehensively recovering noble metals such as gold, silver and the like from lead anodic slime. The method can greatly improve the metal recovery rate, resource utilization and the economic efficiency of mines and generate a lot of sulfur so as to obviously reduce the sulfur dioxide pollution to the atmosphere.
Owner:WESTERN MINING CO LTD
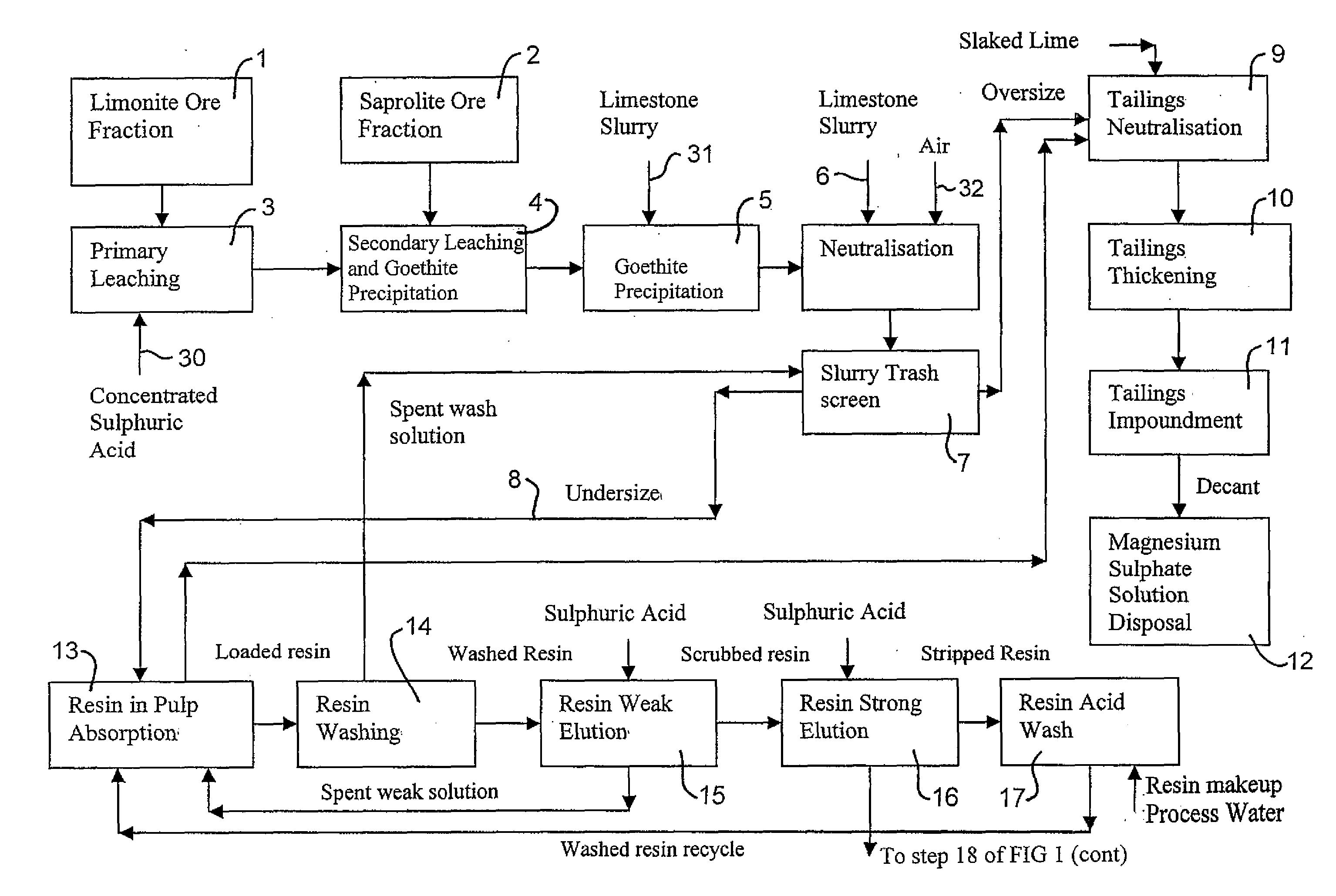
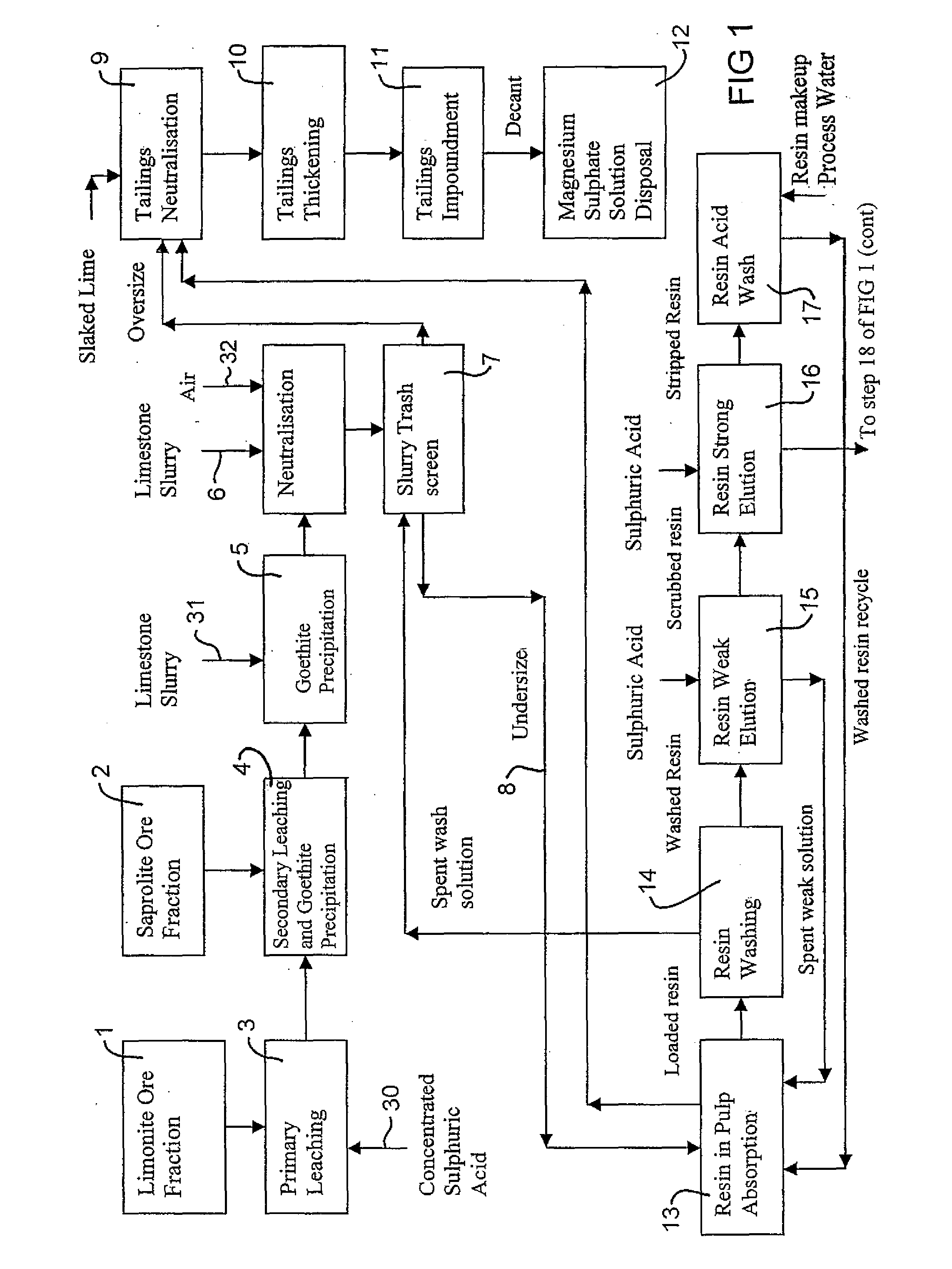
Process for recovery of nickel and cobalt from laterite ore
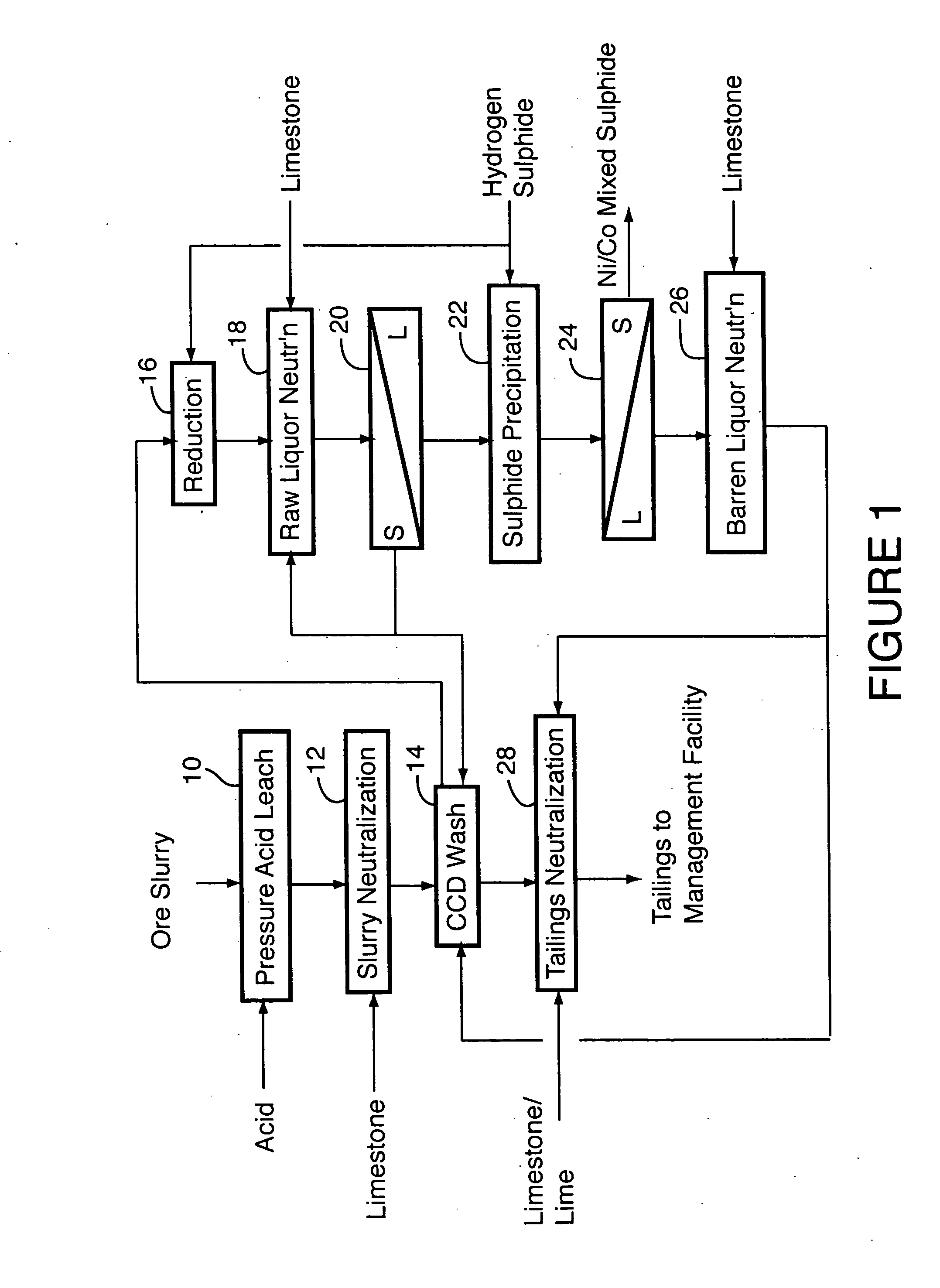
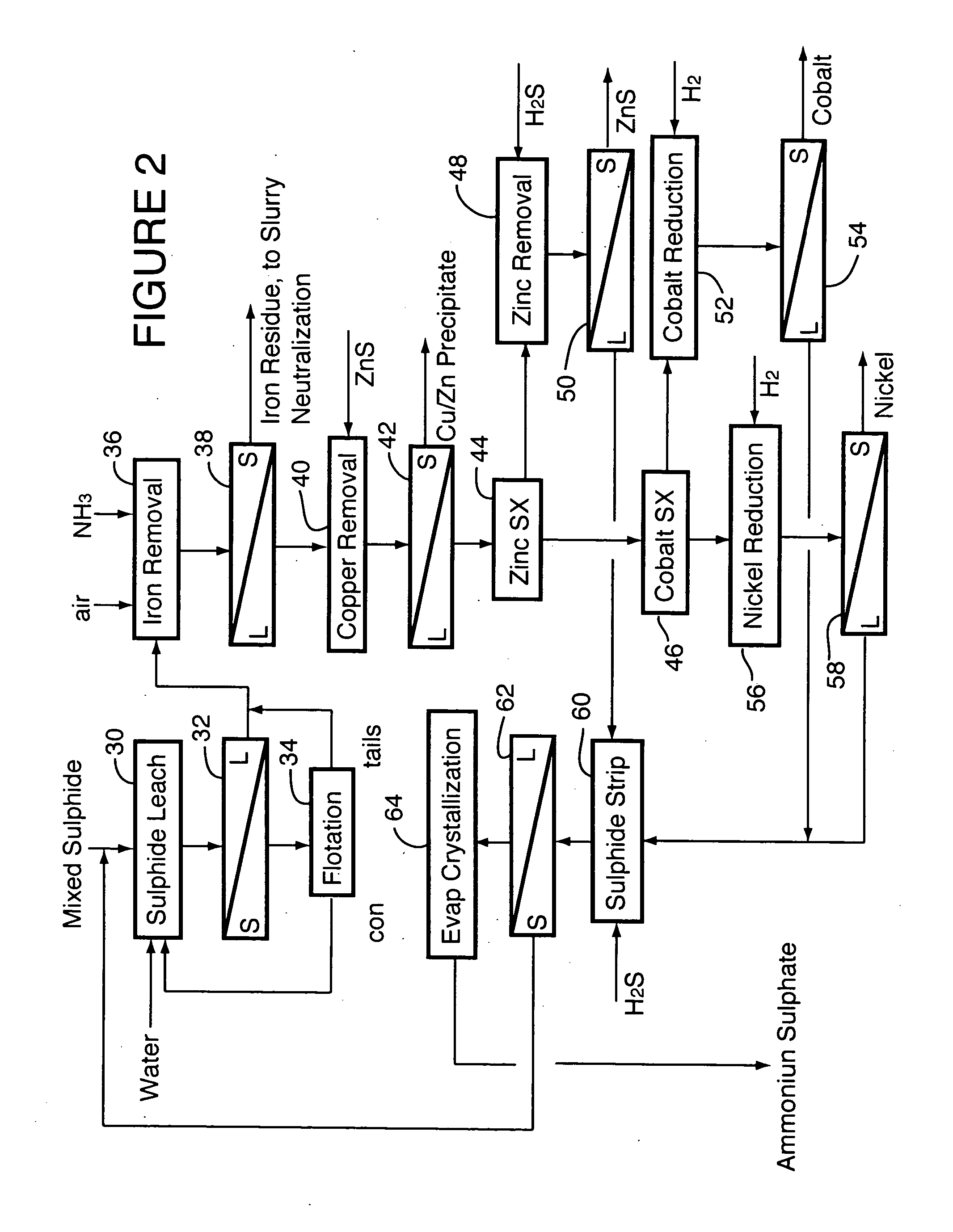
ActiveUS20060228279A1Efficient separation and recoveryHigh purityCobalt sulfidesSolvent extractionFree solutionSlurry
A process for recovering nickel and cobalt values from nickel- and cobalt-containing laterite ores as an enriched mixed nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate and for producing nickel and cobalt metal from the nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate. The laterite ore is leached as a slurry in a pressure acid leach containing an excess of aqueous sulphuric acid at high pressure and temperature, excess free acid in the leach slurry is partially neutralized to a range of 5 to 10 g / L residual free H2SO4 and washed to yield a nickel- and cobalt-containing product liquor, the product liquor is subjected to a reductant to reduce any Cr(VI) in solution to Cr(III), the reduced product liquor is neutralized to precipitate ferric iron and silicon at a pH of about 3.5 to 4.0, and the neutralized and reduced product liquor is contacted with hydrogen sulphide gas to precipitate nickel and cobalt sulphides. The precipitated nickel and cobalt sulphides can be leached in a water slurry in a pressure oxidation leach, the leach solution subjected to iron hydrolysis and precipitation, the iron-free solution contacted with zinc sulphide to precipitate copper, the iron- and copper-free solution subjected to zinc and cobalt extraction by solvent extraction to produce a nickel raffinate, the nickel raffinate contacted with hydrogen gas to produce nickel powder and the cobalt strip solution from the solvent extraction step contacted with hydrogen gas to produce cobalt powder.
Owner:SHERRITT INTERNATIONAL
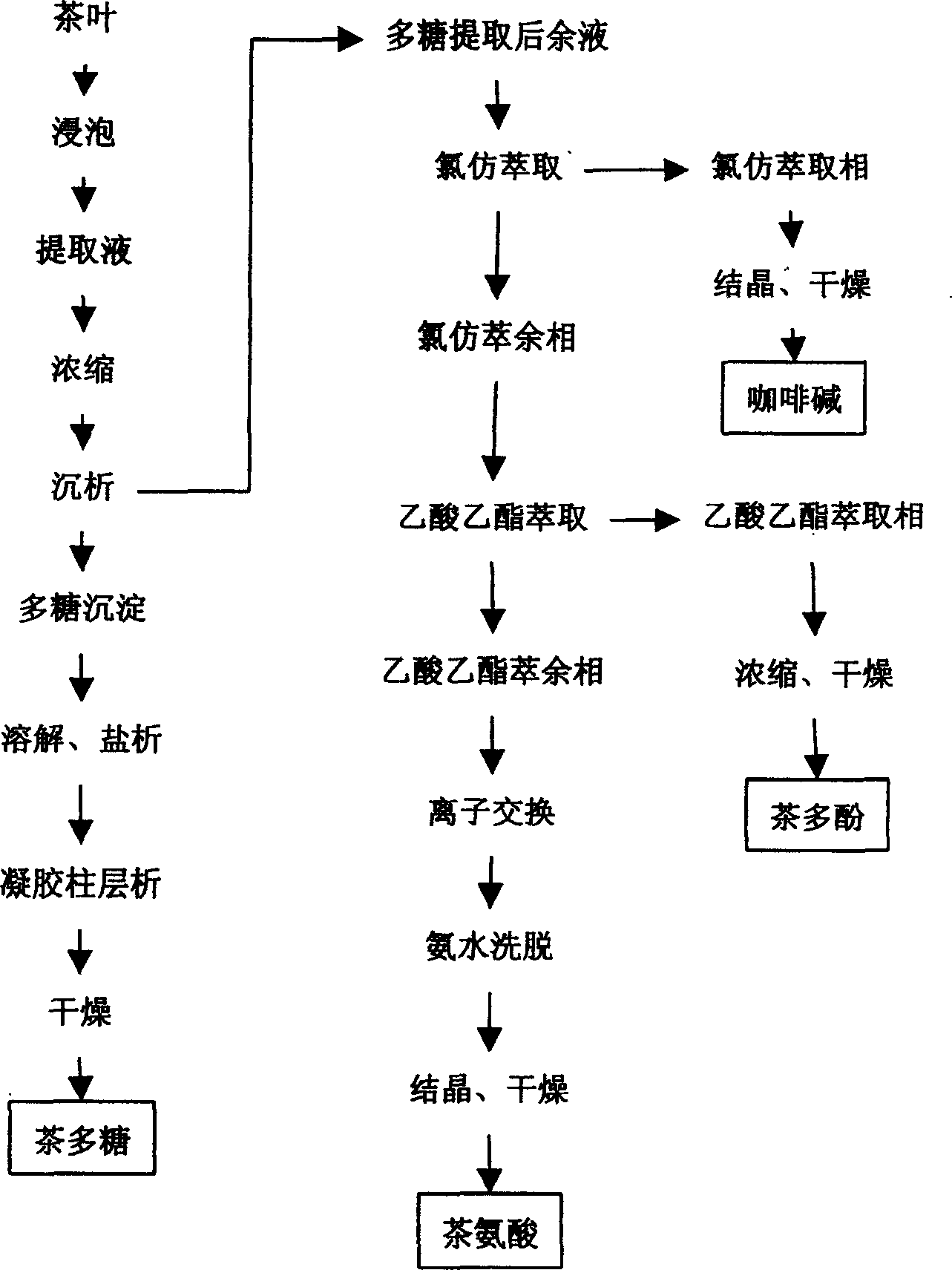
Process for synthetic extraction of polysaccharides, tea-polyphenol, theanine, caffeine from tea
InactiveCN1557841AReduce lossesNo structural damageOrganic chemistrySolid solvent extractionTheanineEthyl acetate
The comprehensive process of extracting tea polysaccharide, tea polyphenol, theanine and coffine from tea includes the following steps: water or organic solvent extraction of tea powder under the action of microwave, concentration, precipitation and water dissolving the extract liquid, salt separating to eliminate protein and separation in gel column and drying to obtain tea polysaccharide; chloroform extraction of the raffinate, ethyl acetate extraction of the chloroform raffinate and drying to obtain tea polyphenol; No. 732 cationic exchange resin extraction of the ethyl acetate raffinate, concentration, crystallization and drying to obtain theanine; and crystallizing and drying the chloroform extract liquid to obtain coffine. The present invention has the advantages of short extraction time, high extraction rate, less loss of active matter, etc.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
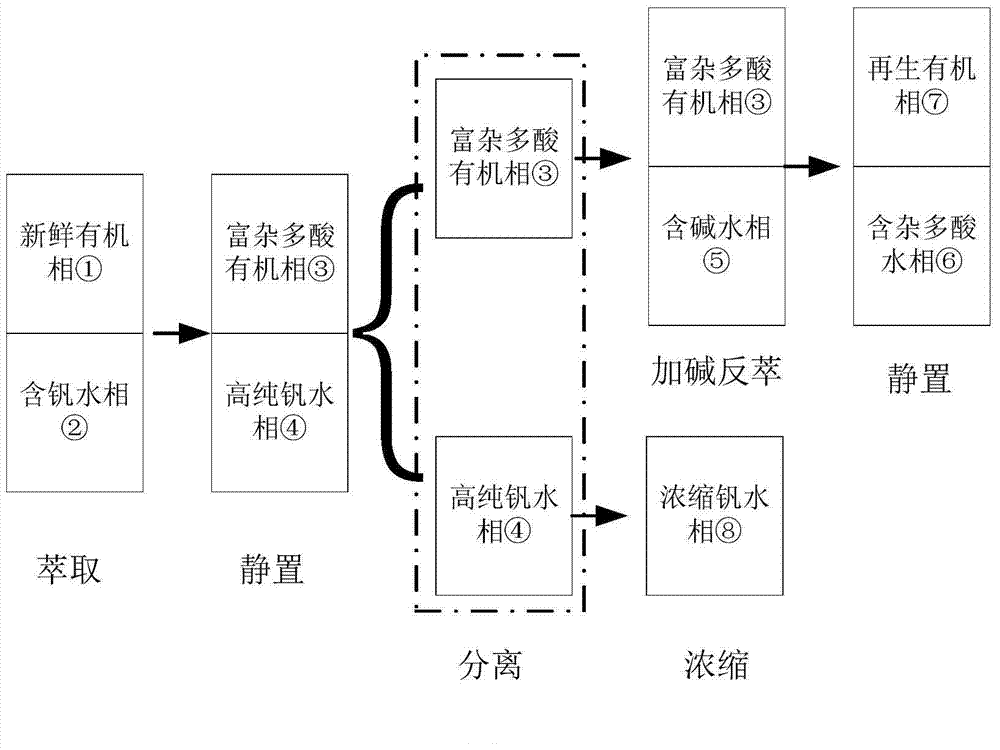
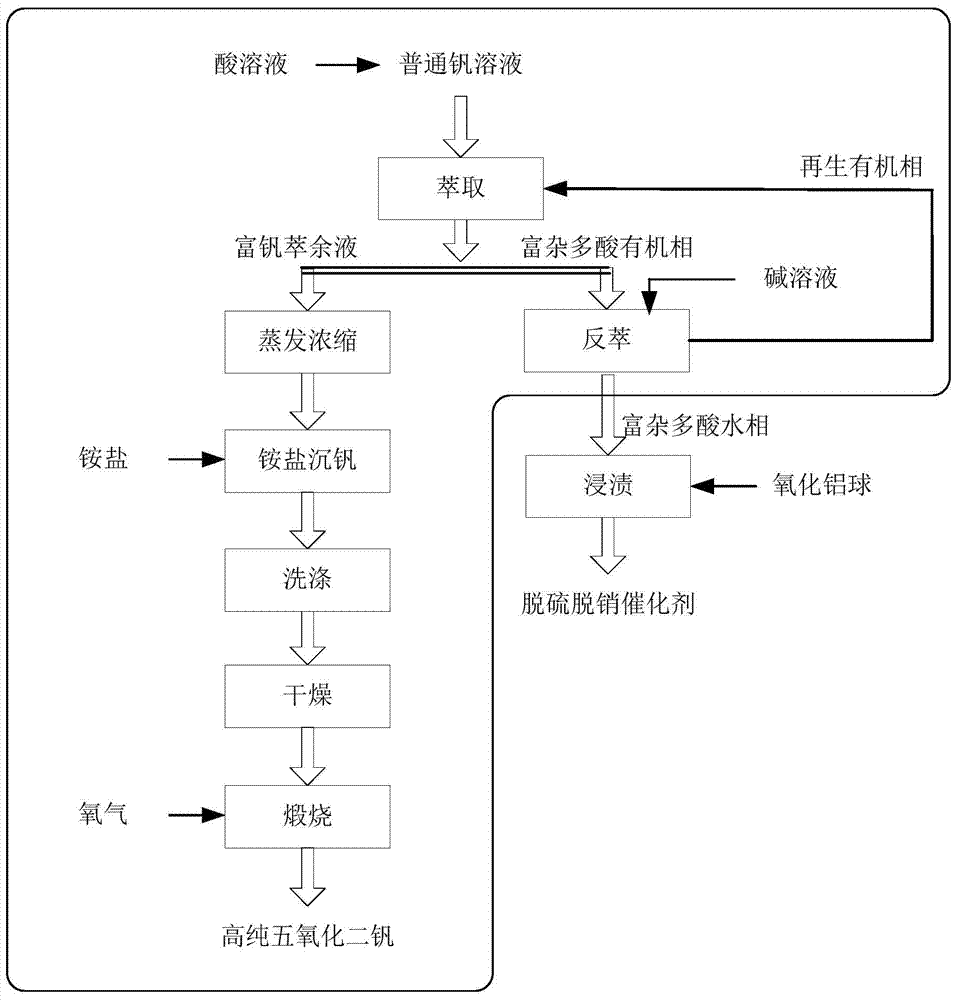
Method for preparing high-purity vanadium from heteropolyacid impurity in amine extraction mode
ActiveCN103540745AIncrease added valueImprove thermal stabilityProcess efficiency improvementAmmonium metavanadateRaffinate
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-purity vanadium from heteropolyacid impurities in an amine extraction mode. Generally an ordinary vanadium solution is doped with impurities such as chromium, silicon, phosphorus, tungsten, molybdenum and arsenic, if acid is added into the solution, heteropolyacids such as phosphorus tungsten, phosphorus vanadium tungsten, silicon tungsten, phosphorus molybdenum tungsten, silicon molybdenum tungsten, molybdenum vanadium arsenic and tungsten arsenic can be formed, the impurities in the solution are removed by carrying out compounding synergic extraction on the heteropolyacids in the ordinary vanadium solution by using amines and a synergist so as to obtain a purified vanadium-containing raffinate, subsequently the vanadium-containing raffinate is evaporated and concentrated to be the concentration that each liter of the solution contains 40g vanadium, ammonium salt is further added into the concentrated liquid to obtain ammonium metavanadate solid, vanadium pentoxide with the purity greater than 99.9% is obtained through washing in pure water, drying and calcining in an oxygen atmosphere, the organic phase after the heteropolyacid is extracted is subjected to reverse extraction by using an alkali solution so as to form a heteropolyacid water phase, and the organic phase is recycled and circulated. The method has low requirement on equipment, and is simple to operate, key extraction agents are good in thermal stability and not sensitive in acid and alkali, and a recycling and circulating method is simple and easy to be industrialized.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
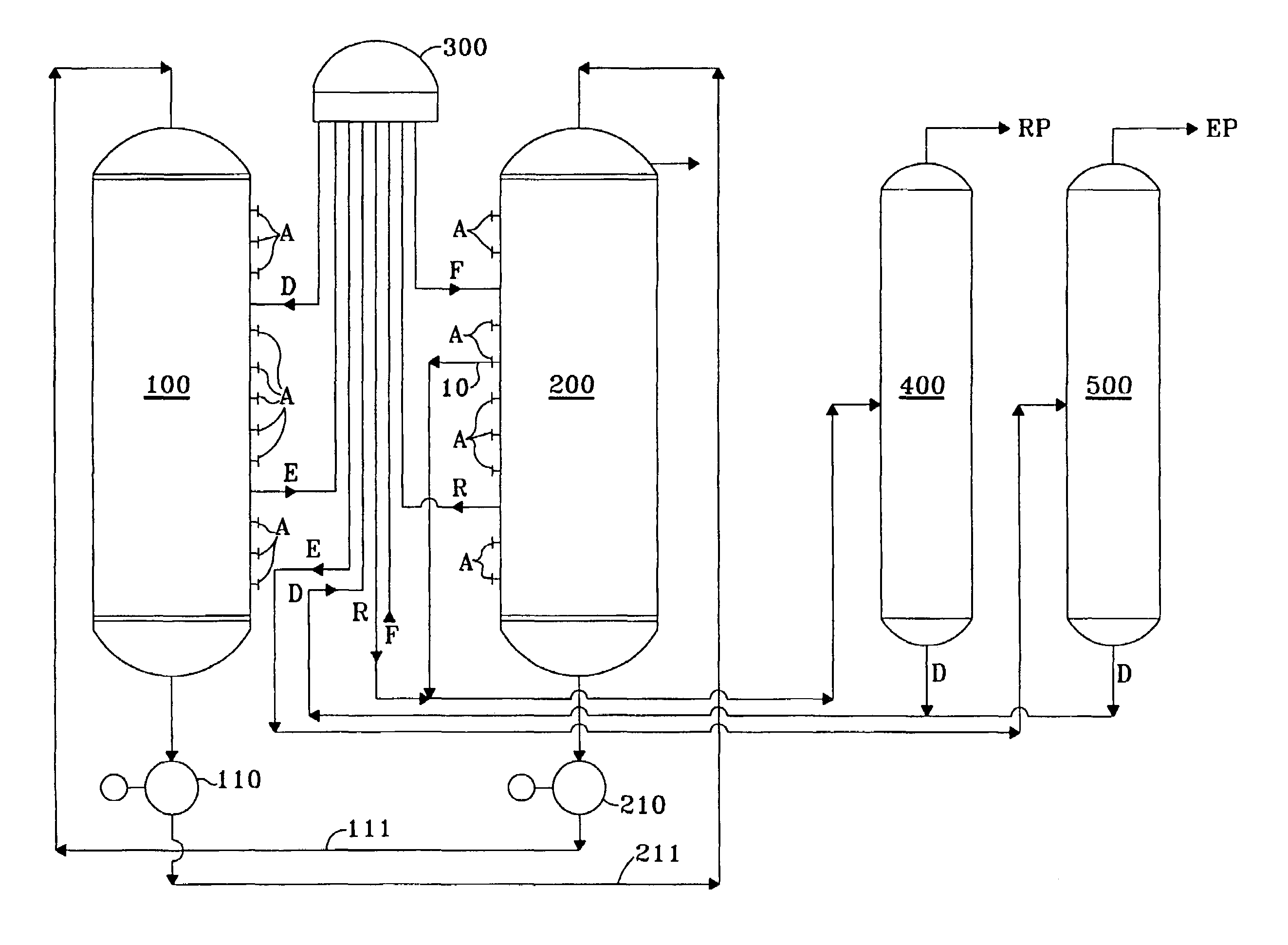
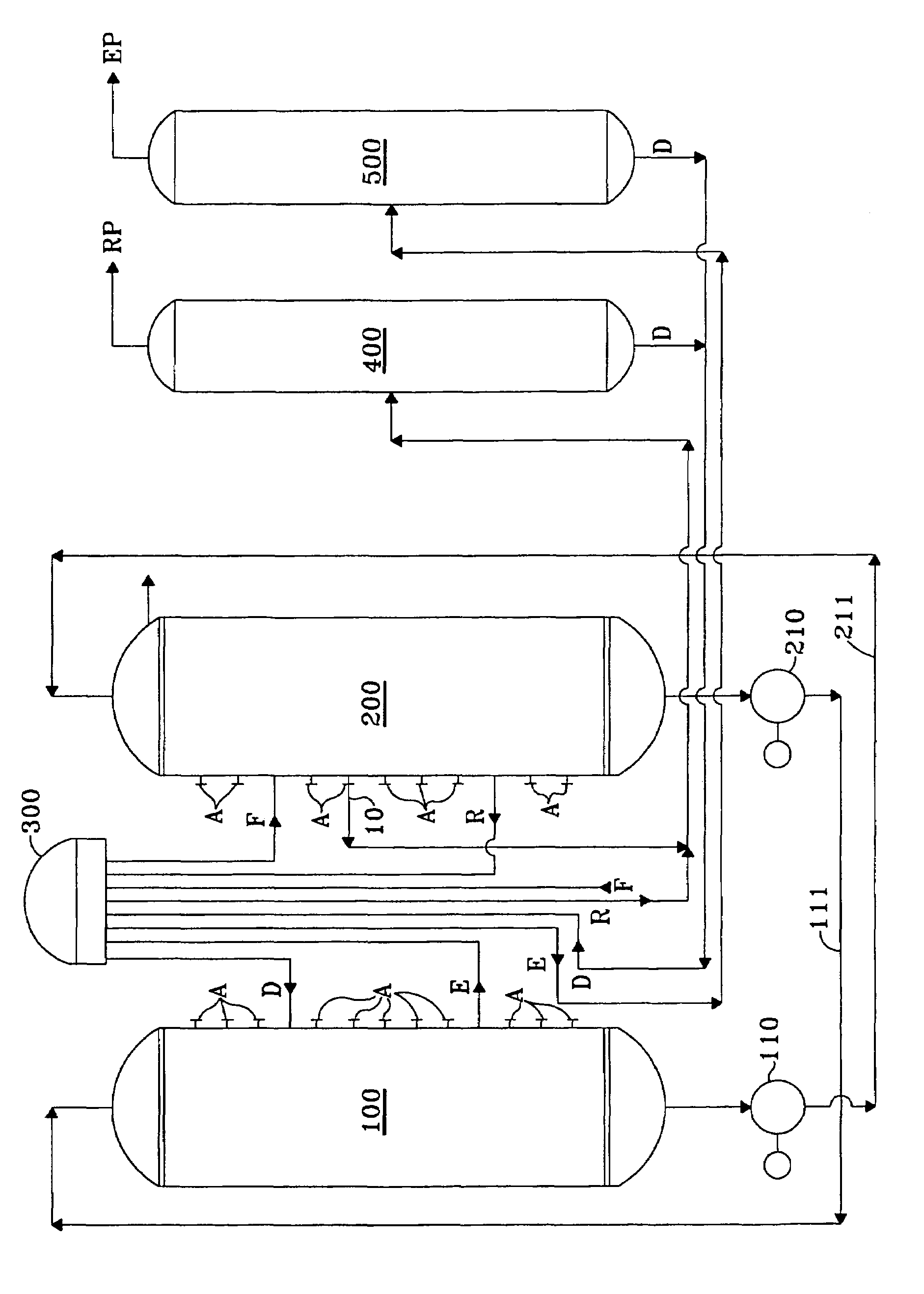
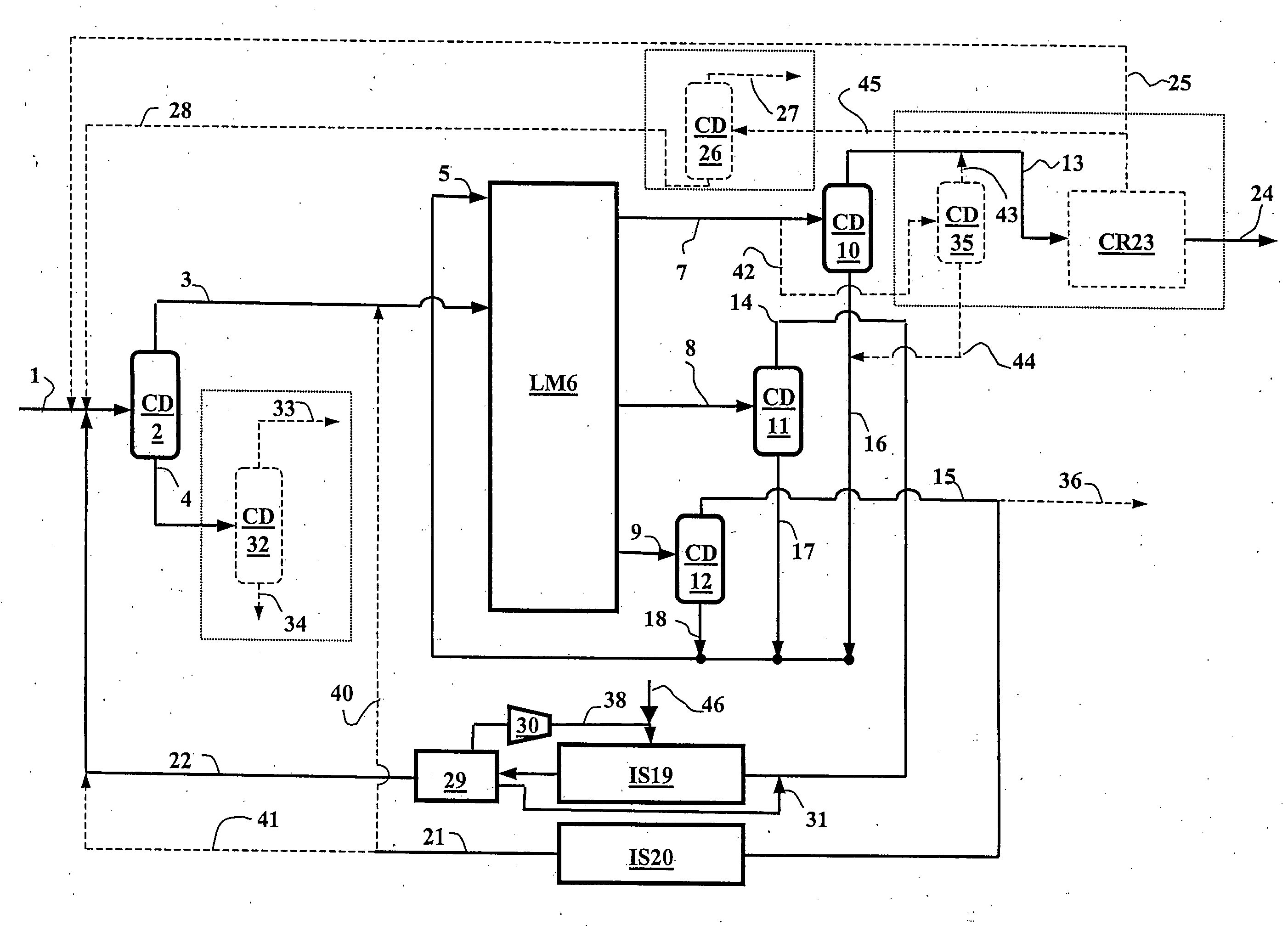
Method for producing paraxylene comprising an adsortion step and two isomerization steps
ActiveUS7915471B2Overcome disadvantagesHydrocarbon by isomerisationSolid sorbent liquid separationIsomerizationSimulated moving bed
A process for producing para-xylene from a hydrocarbon feed is described in which an adsorption column operating as a simulated moving bed with at least five zones delivers an extract, a 2-raffinate and an intermediate raffinate.The extract is distilled and the distillate is optionally re-crystallized to recover para-xylene with a purity of at least 99.7%. The 2-raffinate is distilled then isomerized in a reactor preferably operating in the liquid phase and at a low temperature. The intermediate raffinate with an enriched ethylbenzene content is distilled then isomerized in the vapour phase.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Process for extracting tea polyphenol, caffeine as a byproduct thereof and tea polysaccharide from tea
InactiveCN1699586AHigh extraction rateLess pectinaseOrganic chemistryFermentationPhenolic content in teaAdditive ingredient
Disclosed is a process for extracting tea polyphenol, caffeine as a byproduct thereof and tea polysaccharide from tea, which comprises, (1) extracting active ingredients including tea polyphenol, caffeine and tea polysaccharide from the tea through composite enzymolysis abstraction and water abstraction, (2) filtering the raffinate with hyperfiltration membrane, (3) subjecting the membrane compression liquid to ethanol deposition so as to obtain crude polysaccharides, removing protein and carrying out ethanol deposition, drying to obtain the tea polysaccharides, (4) separating and purifying through second level resin adsorption chromatography, thus obtaining tea polyphenol as well as caffeine as by-product.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Recovery method of copper indium gallium selenide thin-film solar panel
ActiveCN103184338ASimple processEasy to operatePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodElectrolysis
The invention provides a recovery method of a copper indium gallium selenide thin-film solar panel. The method comprises the steps that: the copper indium gallium selenide thin-film solar panel is crushed into pieces; the pieces are soaked by using a H2SO4+H2O2 system, such that a soaking liquid is obtained; the soaking liquid is filtered, such that a first leachate is obtained; with a first phase ratio of 1, the first leachate is extracted by using an extraction agent; separation is carried out, such that a first extraction liquid and a first raffinate are obtained; the extraction agent is composed of 30% of P2O4 and 70% of kerosene by volume percentage, the extraction and balance time is 5-20min; an HCl solution is adopted as a stripping agent, and the first extraction liquid is striped by using a second phase ratio, such that In and stripping residual liquid are obtained; a reducing agent is added into the first raffinate; when a reduction reaction is finished, crude Se and a second leachate are obtained by filtering; alkali is added into the second leachate, and a pH value is regulated such that the pH value is constantly higher than 14; when a reaction is finished, filtering is carried out, such that a filtering slag comprising a hydroxide of Cu and a water solution comprising Ga are obtained; the alkali is NaOH, the pH value adjustment process is to add the NaOH in the reaction process after pH=14 so that the pH is always kept more than 14 during the reaction process, and the reaction time is kept for 0.5-2h; and the water solution is electrolyzed.
Owner:FIRST SEMICON MATERIALS
Process for mutual separation of platinum group metals
ActiveUS20050066774A1Avoid high levels of impuritiesReduce impurityRuthenium/rhodium/palladium/osmium/iridium/platinum compoundsLiquid solutions solvent extractionIridiumDecomposition
A process for mutual separation of platinum group metals (PGM), wherein highly stable compounds and steps are used to efficiently remove impurity elements while preventing increase of impurity content relative to that of the PGM in the mother liquor and also preventing decomposition of a chloro complex, and palladium, platinum, iridium, ruthenium and rhodium are separated mutually in such a way that each of the separated PGM has a sufficient purity to be a commercial product. A process for mutual separation of PGM, comprising the first step for leaching a raw material containing PGM and impurity elements, second step for removing the impurity elements from the leach liquor by solvent extraction, third step for recovering palladium from the raffinate, fourth step for removing cationic impurity elements from the raffinate by solvent extraction, fifth step for recovering platinum from the raffinate by hydrolysis, sixth step for recovering ruthenium from the precipitate by leaching, and seventh step for recovering iridium by solvent extraction to prepare the stripping liquor containing iridium and raffinate containing rhodium.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
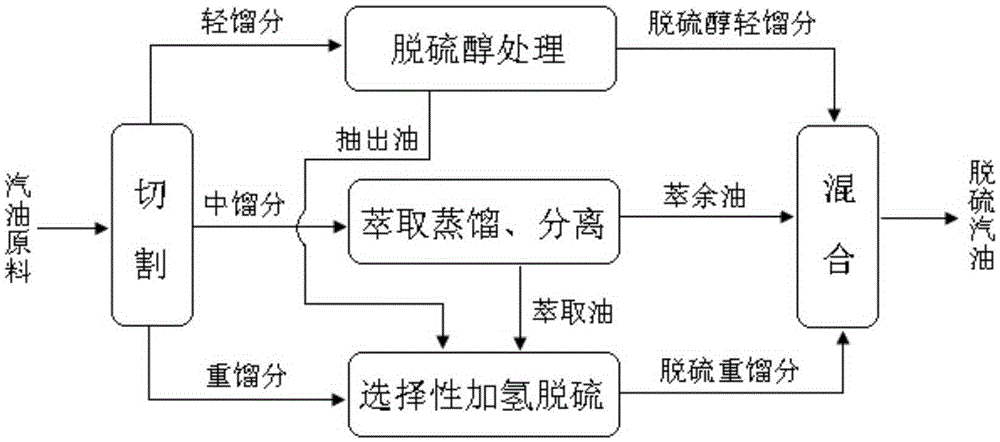
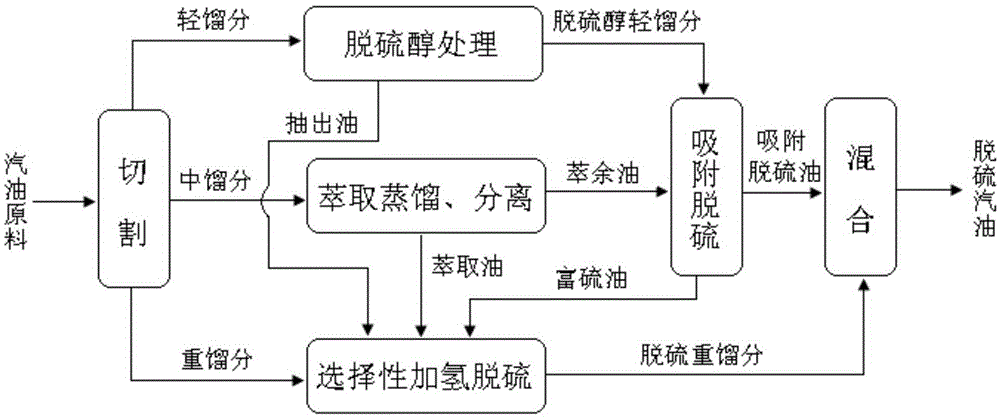
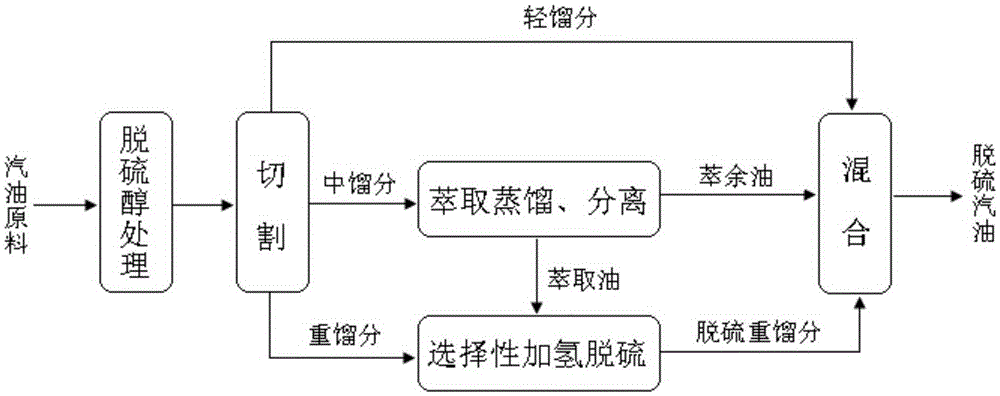
Coupling method of catalytic cracking gasoline desulfurization
ActiveCN105296000AEasy to removeRemoval is not easy to achieveTreatment with hydrotreatment processesOrganic solventExtractive distillation
The invention provides a coupling method of catalytic cracking gasoline desulfurization. The coupling method comprises the following steps: cutting gasoline raw materials into light fractions, medium fractions and heavy fractions; carrying out extractive distillation on the medium fractions by an organic solvent to obtain olefin-contained raffinate and extracts which contain sulfide and arene; separating the organic solvent in the extracts to obtain extraction oil; carrying out selective hydrodesulfurization on the extraction oil and the heavy fractions to obtain the desulfurization heavy fractions; mixing the light fractions, the raffinate and the desulfurization heavy fractions to obtain desulfurization gasoline, wherein the cutting temperature of the light fractions and the medium fractions is 35 to 60DEG C, and the cutting temperature of the medium fractions and the heavy fractions is 140 to 160DEG C. According to the coupling method of the gasoline desulfurization, the octane value loss of a gasoline product can be obviously reduced, and desulfurization load is drastically lowered while deep desulfurization is realized. The yield of the product is greater than 95%.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
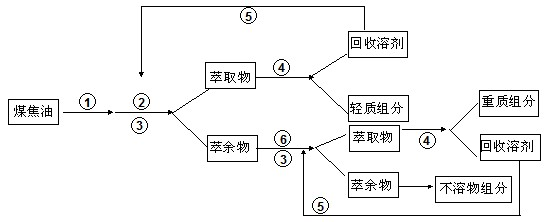
Extracting and separating method of high-temperature coal tar
InactiveCN102492451AHigh purityEfficient separationTar working-up by solvent extractionTime rangeDistillation
An extracting and separating method of high-temperature coal tar belongs to a coal tar separation method. The extracting and separating method includes the step of adding No.1 or No.2 solvent into the coal tar at the ordinary pressure for secondary extraction and separation. Extraction processes are carried out under the pretreatment condition of sufficiently mixing and heating, heating temperature is lower than 150 DEG C, raw materials of the coal tar are respectively mixed with the No.1 or No.2 solvent according to the volume proportion of 1:2 to 4, extraction time ranges from 1 to four hours, extracts and raffinate are obtained after the No.1 solvent and the coal tar are filtered and separated when the system is balanced, and the No.1 solvent is recovered by distillation and recycled. The extracting and separating method has the advantages that energy saving effect of equipment is evident, process is simple and convenient, operation conditions are moderate, manufacturing cost and investment of the equipment are low and benefits are evident. Adding quantity of the solvent and extraction operation parameters are changed, separation depth and process capacity of the coal tar can be flexibly mastered and selectively controlled.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Product recovery from simulated-moving-bed adsorption
Product purity from or capacity of a simulated-moving-bed adsorptive separation process is increased by flushing the contents of the transfer line previously used to remove the raffinate stream away from the adsorbent chamber, preferably into the raffinate column used to separate desorbent from raffinate product. Preferably a stream from the adsorbent chamber at an intermediate point between the feed entry point and raffinate withdrawal is used as the flushing liquid. This flush step eliminates the passage of a quantity of the raffinate material into the adsorbent chamber in the transfer-line flush period or when the process conduit is subsequently used to charge the feed stream to the adsorbent chamber.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for extraction and separation of tungsten and molybdenum from tungsten and molybdenum mixed solution
ActiveCN102876906AOvercoming Difficult Phase Splitting ProblemsOvercoming the problem of large loss in tungsten co-extractionProcess efficiency improvementTungstateDiluent
The invention provides a method for extraction and separation of tungsten and molybdenum. Hydrogen peroxide is filled in the tungsten and molybdenum mixed solution, the pH value is regulated to be acidic, and the acid tungsten mixed solution is taken as a water phase feed liquid to carry out extraction and separation with an organic phase. The organic phase comprises trialkylphosphine oxide, tributyl phosphate and a diluting agent; the organic phase conducts the multi-stage extraction with the water phase feed liquid, molybdenum is extracted into the organic phase, and tungsten is left in a raffinate, so that the separation of tungsten and molybdenum is achieved. The load-bearing organic phase adopts an alkaline back-extraction agent to carry out back-extraction to obtain a molybdenum-contained solution, and the organic phase subjected to the back-extraction returns to the extraction process. Tungsten and molybdenum are extracted and separated in the tungsten and molybdenum mixed solution containing H2O2 by adopting a novel binary mixture extracting agent, the method has the advantages that extraction and the back-extraction are high in split-phase speed, the separation effect of tungsten and molybdenum is good, the tungsten co-extraction loss is low, the loss of the organic phase as well as the environmental pollution is low, the industrialization is easy to realize, and the method is especially suitable for separating tungsten and molybdenum in the tungstate solution with high molybdenum content.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Process for extracting rare-earth from sulfuric acid treating phosphorite process
ActiveCN101824536AEasy extractionHigh yield of rare earth extractionProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementPhosphorite
The invention provides a process for extracting rare earth from a sulfuric acid treating phosphorite process. In the process, a sulfuric acid refining process and a rare earth extracting process are combined, and the rare earth is reclaimed from low-concentrate sulfuric acid raffinate generated in a crude phosphoric acid extracting and refining process so as to realize reclamation of a rare-earth element. The process comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting the rare-earth element from the raffinate by adopting acidic or neutral extractant to obtain rare earth loaded organic phase and secondary raffinate; (2) washing the rare earth loaded organic phase and performing back extracting on the rare earth-loading organic phase by using acid to obtain rare earth strip liquor and blank organic phase; and (3) precipitating the rare earth strip liquor to obtain solid rare earth salt after pH value of the obtained rare earth strip liquor is adjusted, and calcining the strip liquor to obtain rare earth oxide. The process has the advantages of realizing reclamation of the rare-earth element, relatively easily extracting the rare earth, along with high rare earth extraction yield.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for Producing Paraxylene Comprising an Adsortion Step and Two Isomerization Steps
ActiveUS20080262282A1Overcome disadvantagesHydrocarbon by isomerisationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationXylyleneIsomerization
A process for producing para-xylene from a hydrocarbon feed is described in which an adsorption column operating as a simulated moving bed with at least five zones delivers an extract, a 2-raffinate and an intermediate raffinate.The extract is distilled and the distillate is optionally re-crystallized to recover para-xylene with a purity of at least 99.7%. The 2-raffmate is distilled then isomerized in a reactor preferably operating in the liquid phase and at a low temperature. The intermediate raffinate with an enriched ethylbenzene content is distilled then isomerized in the vapour phase.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
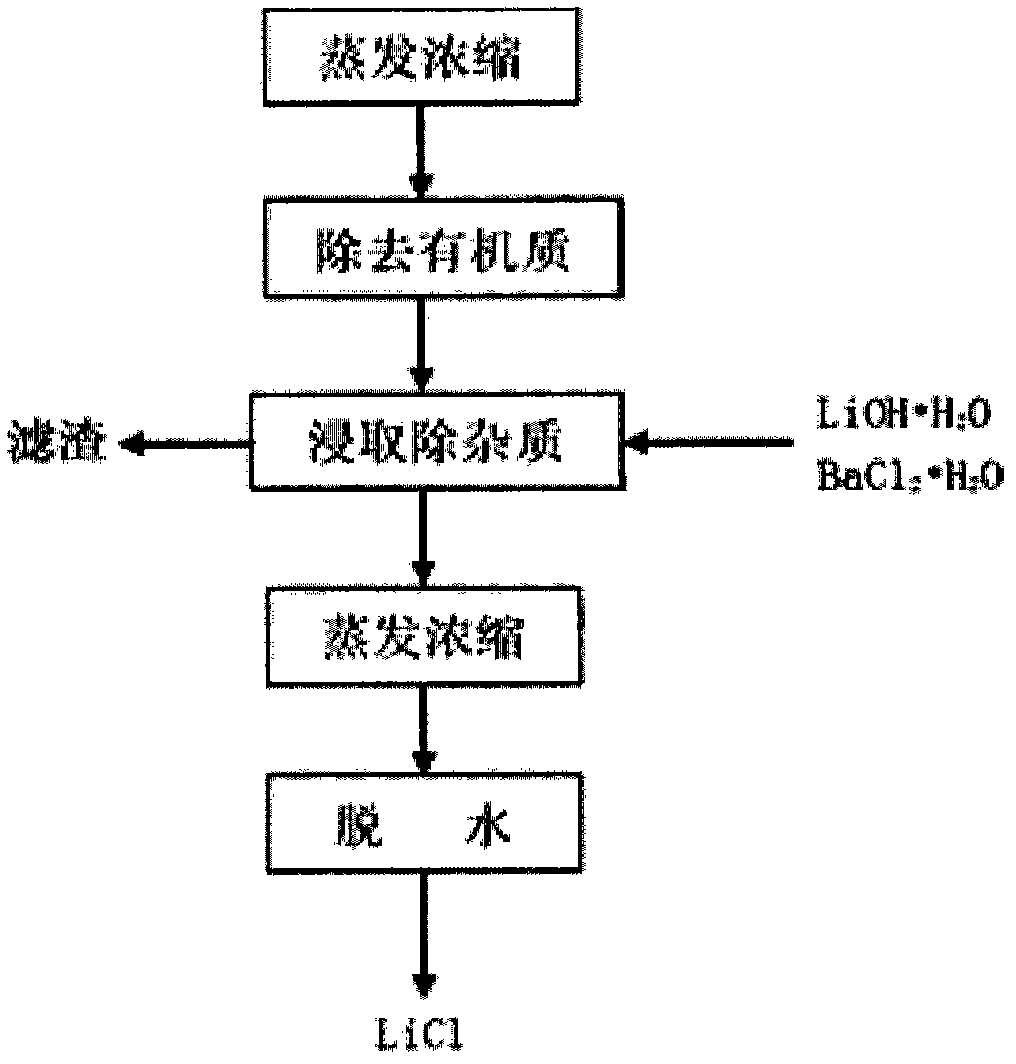
Method for extracting lithium salt from lithium brine
InactiveCN102992358AIncrease profitAvoid hydrolysisLithium halidesLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesLithiumAlkaline earth metal
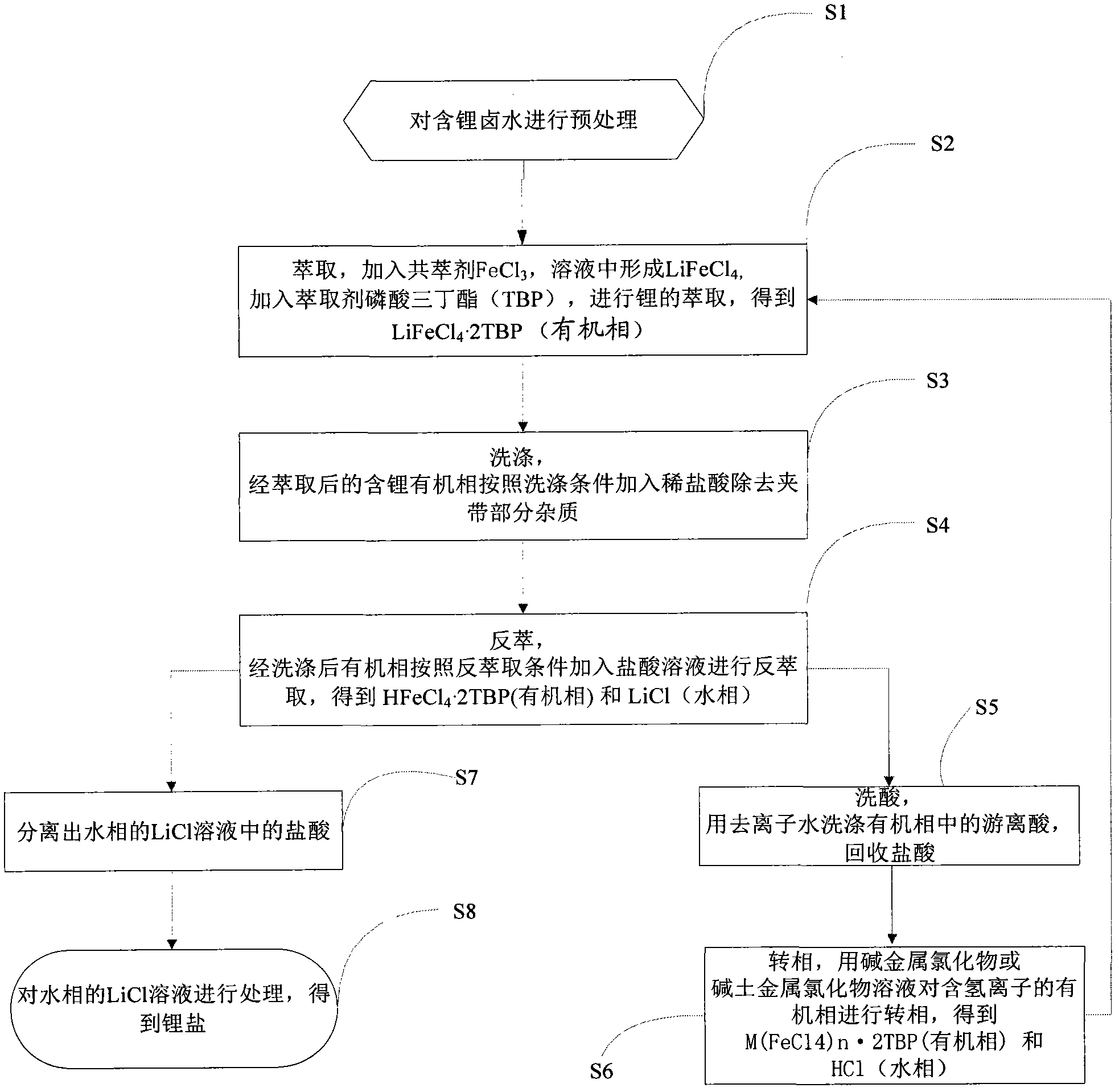
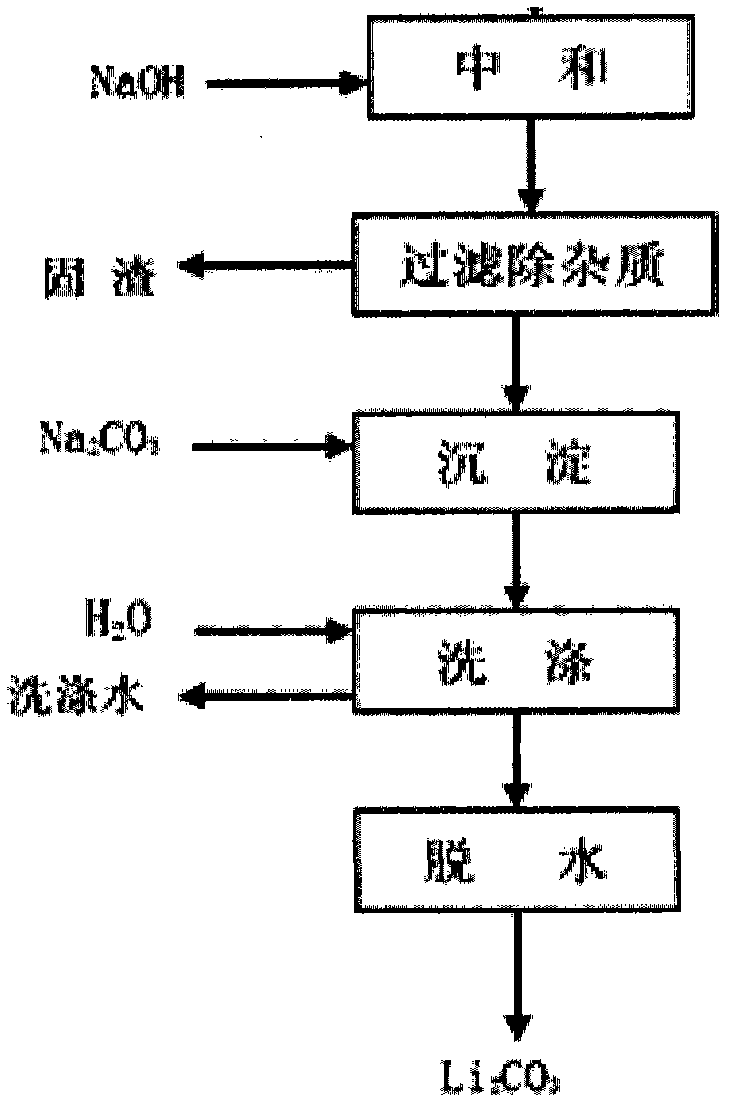
The invention provides a method for extracting lithium salt from lithium brine. The method comprises the following steps: extraction step: adding a co-extracting agent FeCl3 and an extraction agent tributyl phosphate (TBP) to lithium brine to extract lithium so as to obtain an organic phase LiFeCl4.2TBP and a water phase raffinate; reverse extraction step: adding a hydrochloric acid liquor to the organic phase LiFeCl4.2TBP for reverse extraction to obtain organic phase LiFeCl4.2TBP and water phase LiCl; and phase inversion step: inversing phase for the organic phase LiFeCl4.2TBP containing hydrogen ions by a liquor of alkali chloride, alkaline earth chloride or a mixture MCln (n is greater than or equal to 1) as a phase inversion agent to obtain an organic phase M(FeCl4)n.2TBP. According to the method for extracting lithium salt from lithium brine provided by the invention, the production cost of extracting lithium salt can be lowered.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
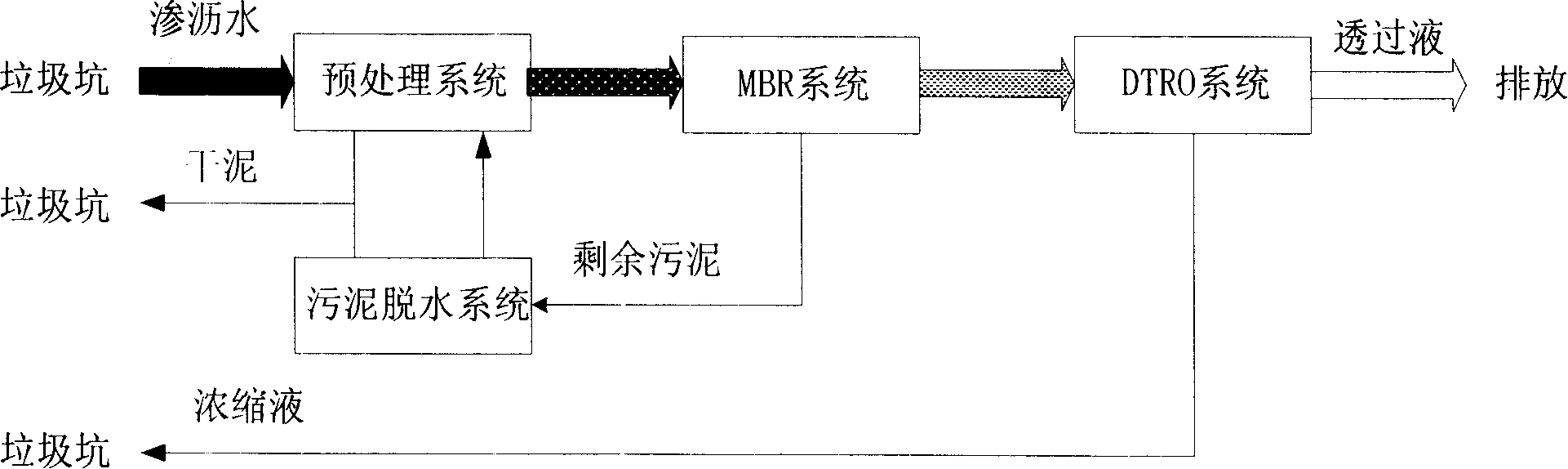
Method and system for processing leachate of garbage burning factory
ActiveCN101209881AImprove water qualityLow investment costTreatment using aerobic processesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisHigh concentrationForeign technology
The invention relates to a treatment method and a system of leachate of a garbage incineration plant. The method comprises that: a coagulant is added into the leachate to carry out coagulative precipitation pretreatment and to remove suspended matter; after the pretreatment, evaporation and concentration treatment are carried out on the leachate to obtain condensate water, and residue and raffinate of contaminants are removed; ammonia stripping treatment is carried out on the condensate water to remove ammonia and nitrogen; after ammonia stripping treatment, after-treatment is carried out on the condensate water to meet the environmental discharge standard. The system comprises a pretreatment system, an evaporation and concentration system, an ammonia stripping system and an after-treatment system which are connected in sequence. The invention is applicable to treating various garbage leachates with high concentration, including leachate with low content of biochemical contaminant, and can reach national primary discharge standard; heat energy of garbage incineration is used for treating leachate, thus realizing the purpose of treating waste with waste without secondary pollution; the invention has the advantages of low cost of investment and operation, energy saving, and long-term operational feasibility and load and impact resistance which are superior to prior art; the performance and operation of the invention are not restricted by foreign technology.
Owner:SHENZHEN ENERGY ENVIRONMENT ENG
Catalytic conversion method for preparing lower olefins and aromatics
The invention relates to a catalytic conversion method for preparing lower olefins and aromatics. Raw oil with different cracking performances enters different reaction zones of a first riser reactor to contact with a catalytic cracking catalyst for cracking reaction to separate a spent catalyst from reaction oil gas, wherein the spent catalyst after stripping enters a first regenerator and returns to a first riser after scorching regeneration, the reaction oil gas is separated to obtain a product containing lower olefins, gasoline, distillates with distillation range of 180-250 DEG C and catalytic wax oil, wherein the gasoline is extracted by light aromatics to obtain light aromatics and gasoline raffinate; the raw materials are cracked to be sent into a second riser reactor to contract with a hot regenerated catalyst for catalytic conversion; and the spent catalyst is burned and regenerated in a second regenerator and then returns to a second riser reactor. The method uses heavy rawmaterials to furthest produce the lower olefins, such as propylene, ethylene, and the like, particularly the propylene, the production rate can exceed 40 wt%, and at the same time the method can coproduce the aromatics, such as toluene, xylene, and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for recovering valuable metal from waste power battery cathode waste material
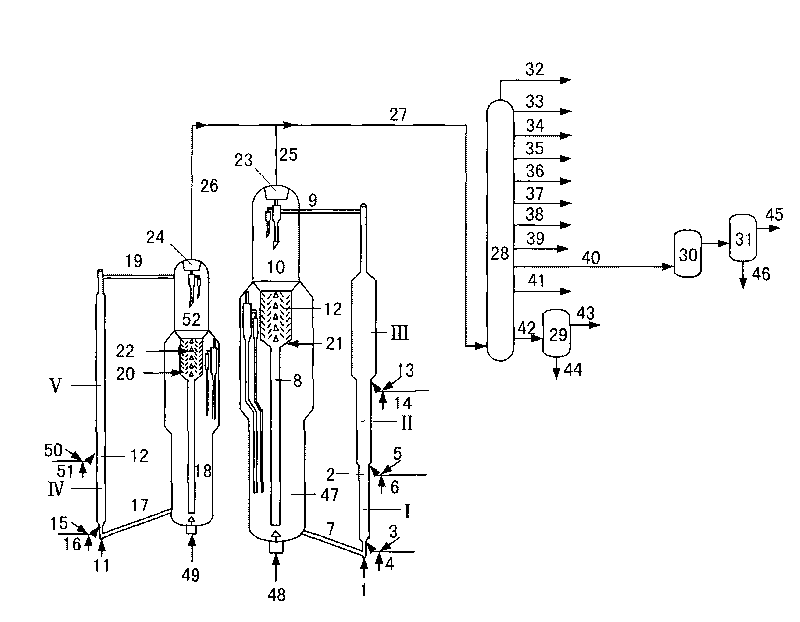
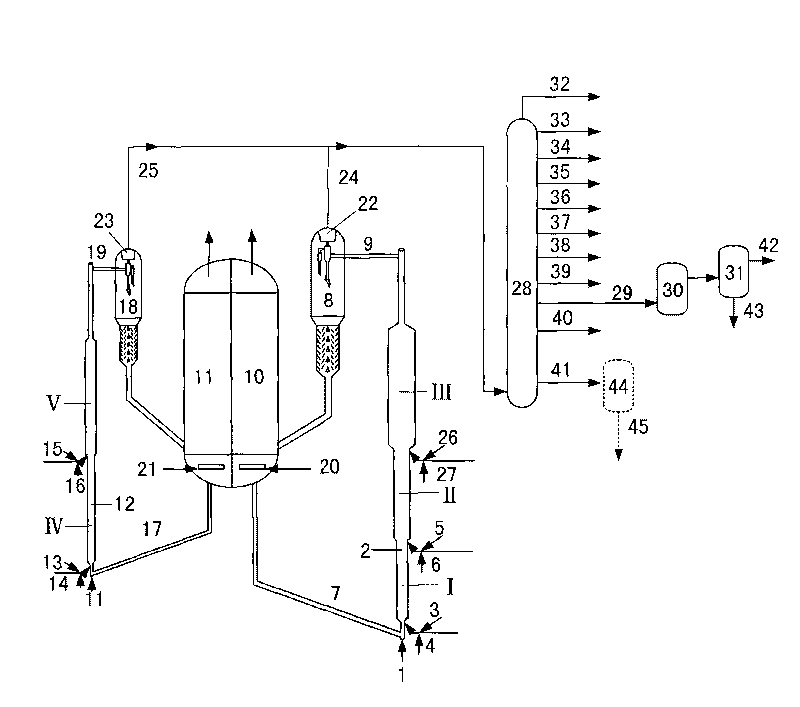
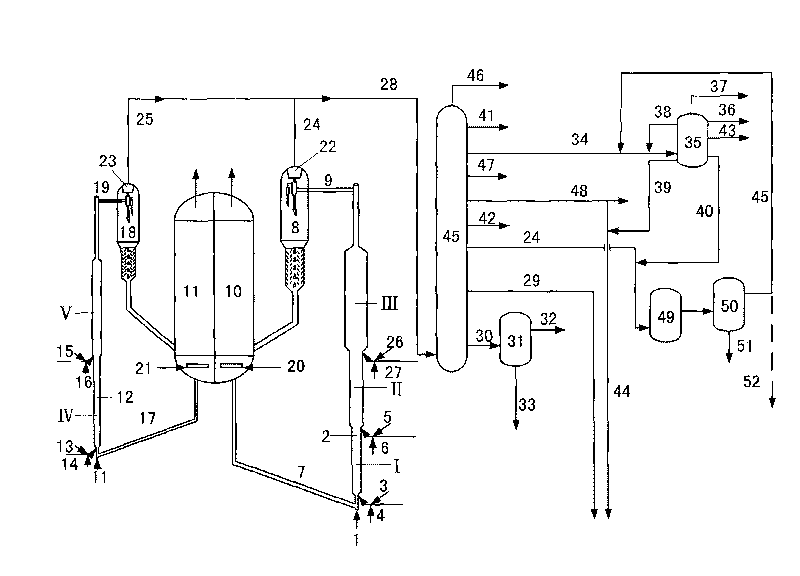
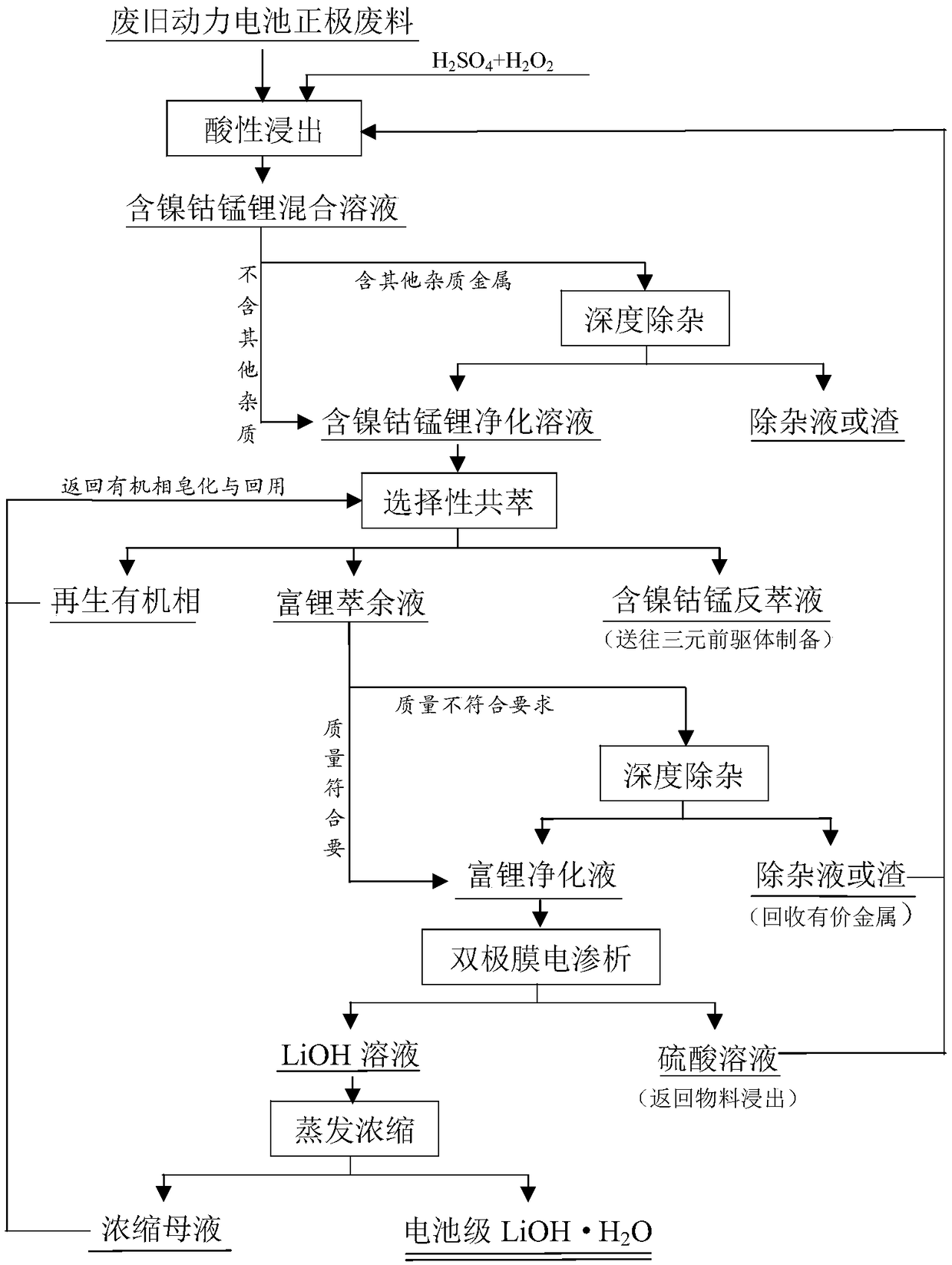
ActiveCN108517409AAvoid high alkali consumptionAvoid conversionWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementManganeseRaffinate
The invention discloses a method for recovering valuable metal from a waste power battery cathode waste material. The method comprises the following steps that (1) the waste power battery cathode waste material is subjected to acid dipping treatment, and a nickel cobalt manganese and lithium containing mixed solution is obtained; (2) the nickel cobalt manganese and lithium containing mixed solution is subjected to impurity removal, nickel cobalt manganese and lithium containing purified liquid and impurity removed liquid or impurity removed residue are obtained; (3) nickel cobalt and manganeseare separated from the nickel cobalt manganese and lithium containing purified liquid through a selective co-extraction method, and nickel cobalt and manganese containing strip liquid and lithium-rich extraction raffinate are obtained; (4) lithium-rich extraction raffinate is subjected to deep impurity removal treatment, and lithium-rich purified liquid and impurity removal liquid or impurity removal residue are obtained; (5) the lithium-rich purified liquid is treated by adopting a bipolar membrane electrodialysis method after being subjected to deep degreasing treatment, and a lithium hydroxide solution and a sulfuric acid solution are generated; and (6) the lithium hydroxide solution is evaporated and concentrated, and a battery-level lithium hydroxide monohydrate and concentrated mother liquid are obtained. The recovery rate of nickel cobalt manganese and lithium is higher than 98%, and appreciation of metal products is achieved while the valuable metal is efficiently recovered.
Owner:CHANGSHA RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
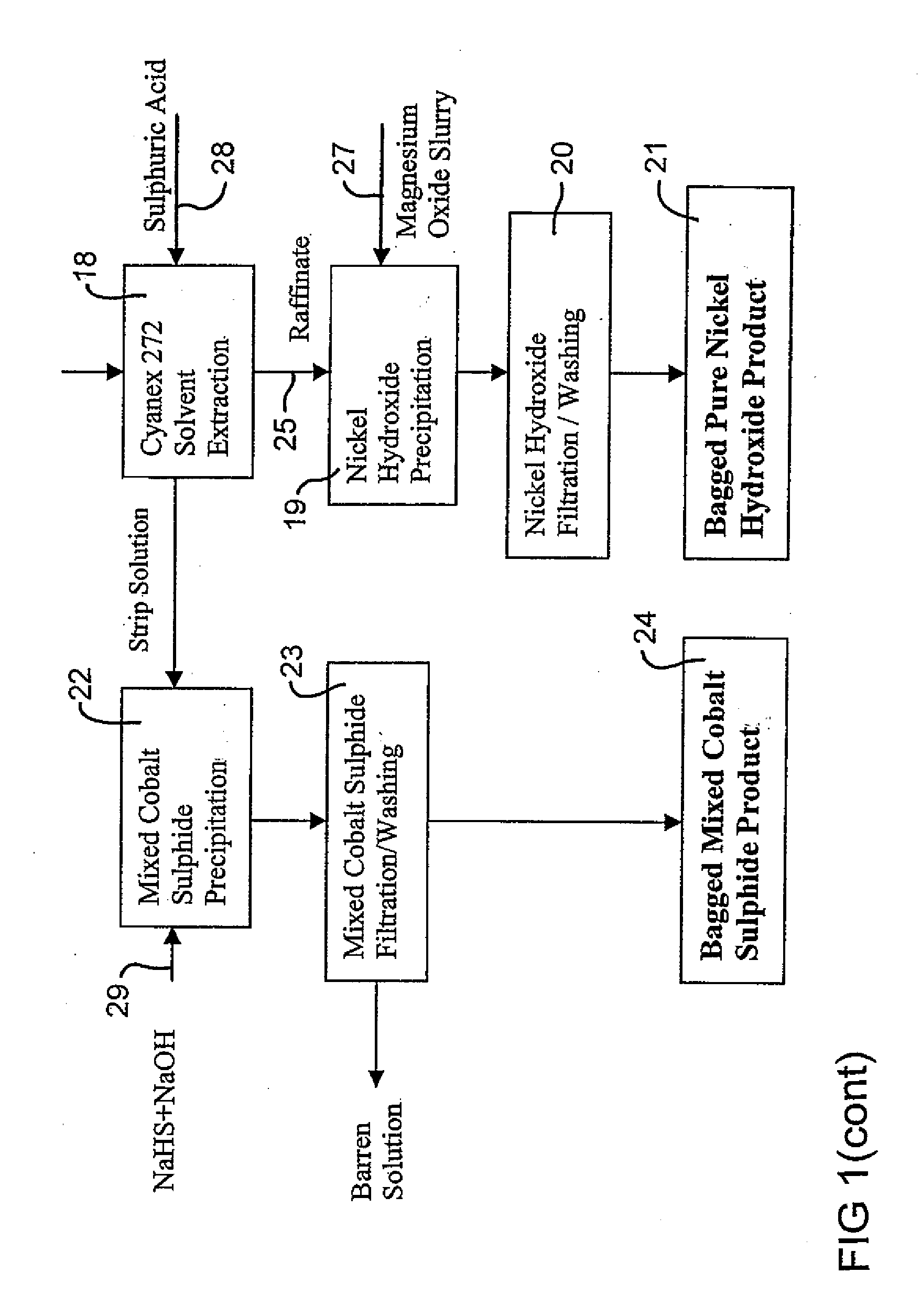
Extraction of Nickel and Cobalt from a Resin Eluate Stream
InactiveUS20070297960A1Easy to transportEasy to disassembleNickel compounds preparationIron compoundsManganeseCopper
A process for the recovery of nickel and cobalt from an acidic resin eluate containing at least nickel and cobalt, said process including the steps of: (a) treating the eluate with an immiscible organic reagent (18) to selectively absorb the majority of the cobalt, and a portion of any copper, zinc and manganese present in the eluate, leaving a raffinate containing the nickel and minor impurities; (b) neutralising the raffinate to precipitate the nickel as nickel hydroxide (19); (c) stripping the cobalt from the organic reagent (22); and (d) recovering the cobalt (23).
Owner:BHP BILLITON SSM TECH PTY LTD
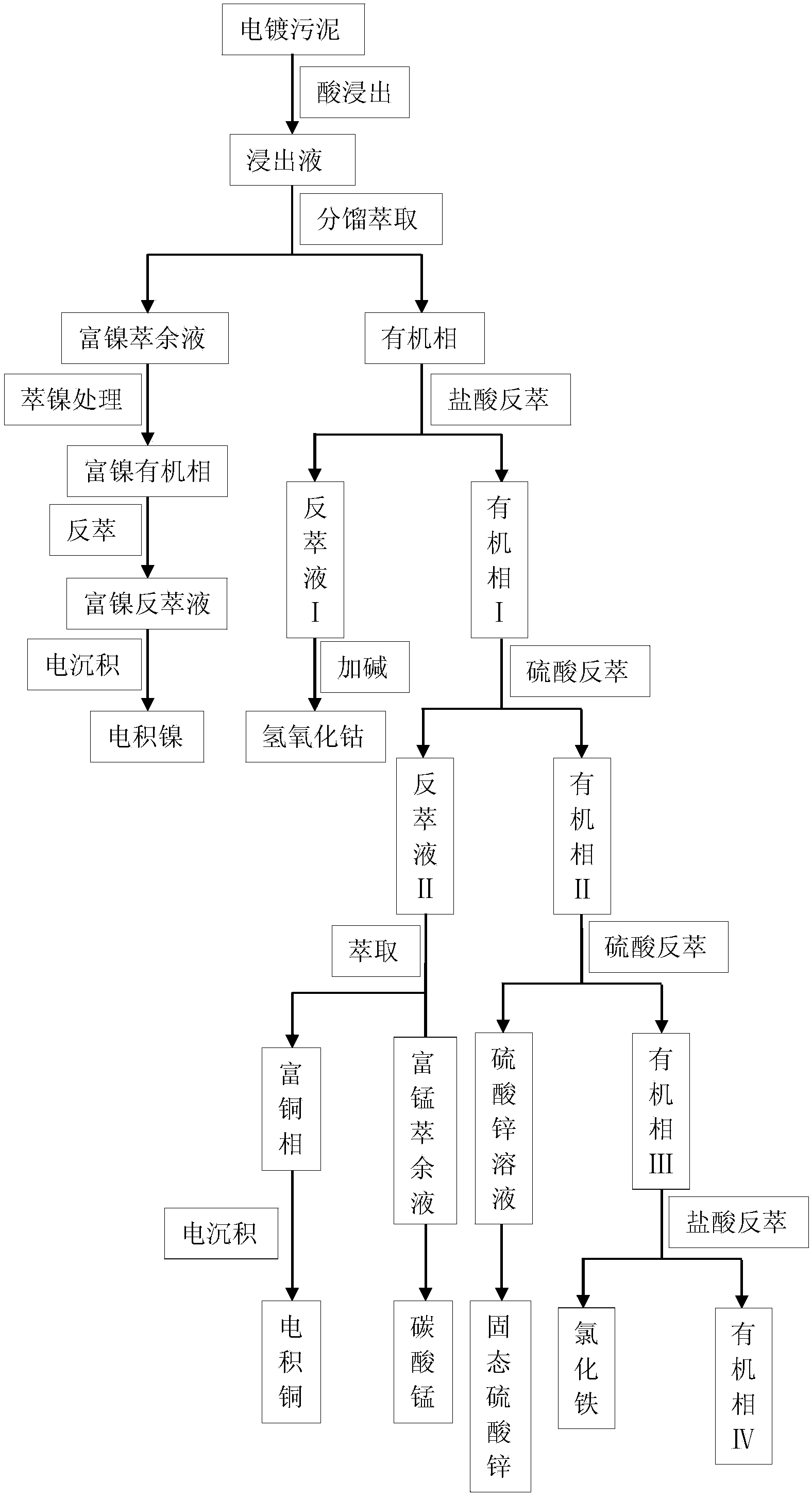
Separating and recycling method of nickel, cobalt, copper manganese and zinc in electroplating sludge
The invention provides a separating and recycling method of nickel, cobalt, copper manganese and zinc in electroplating sludge. The method comprises the steps that acid leaching is performed on the electroplating sludge to obtain leaching agents for fractional extraction, organic phases and nickel-rich raffinate are obtained, four steps of reverse extraction are performed on the organic phases by sequentially adapting hydrochloric acid, vitriol, the vitriol and the hydrochloric acid, and four kinds of corresponding strip liquor are achieved; then follow-up recycle is performed on the nickel-rich raffinate and the four kinds of strip liquor, and separation and recycle of the nickel, the cobalt, the copper manganese and the zinc are completed. According to the method, the complete extraction mode is adopted, the nickel, the cobal, calcium, magnesium, the copper, manganese and the zinc are sequentially extracted step by step and then recycled respectively, a technology procedure is short, production efficiency is high, the equipment investment is small, operation cost is low, the environment is protected, recycling of the nonferrous metal is achieved, and good social benefits and economical benefits are obtained.
Owner:JIANGXI GUANGDE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Extracting and purifying technology of high purity nickel
The invention relates to an extracting and purifying technology of high purity nickel, mainly comprising the following steps of firstly, adding oxidant of hydrogen peroxide in nickel sulfate, adding sodium carbonate after complete reaction, producing and precipitating complex compound, and deironing by filtering; secondly, using P204 after clarifying mother solution, carrying out homogeneous saponification by using sodium hydroxide, carrying out countercurrent extraction, obtaining Cu hydrochloric acid by carrying out backextraction on an organic phase by using sulfuric acid segmentation by segmentation, and obtaining metals such as Co, Mn, Ca, Zn and the like by treating the Cu hydrochloric acid by backextraction; and thirdly, using P507 as raffinate, carrying out homogeneous saponification on the raffinate by using the sodium hydroxide, carrying out countercurrent extraction, obtaining magnesium by treating an organic phase of dilute sulfuric acid by backextraction, recovering magnesium sulfate by an aqueous phase, obtaining nickel by carrying out backextraction on the residual organic phase plus anolyte or the dilute sulfuric acid, and obtaining electronic grade nickel sulfate from the aqueous phase. The technology has the advantages of simple process, low cost and high metal yield without solid waste calcium and magnesium slag, fluoride reagent consumption and environmental pollution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LANBO METAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com