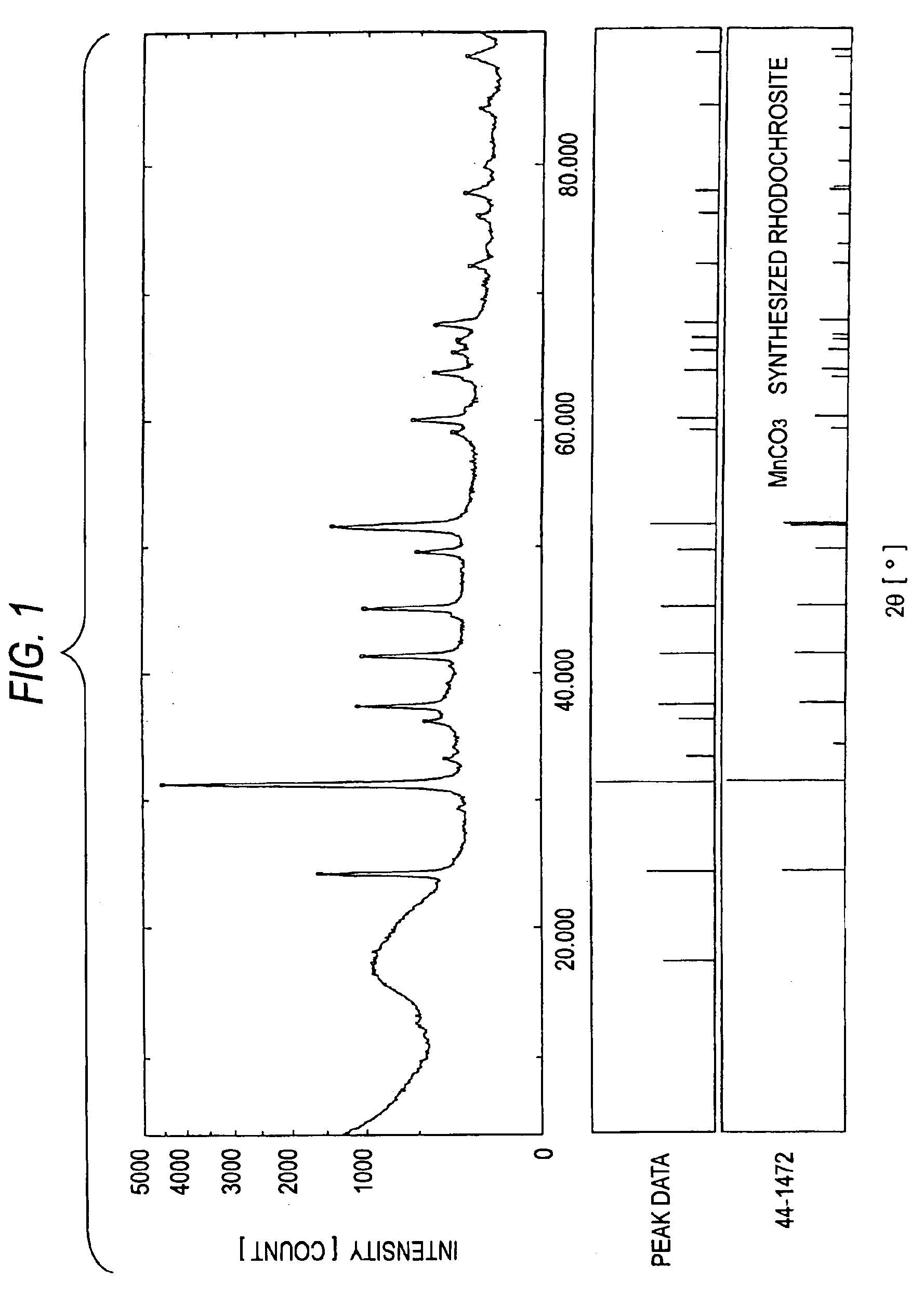
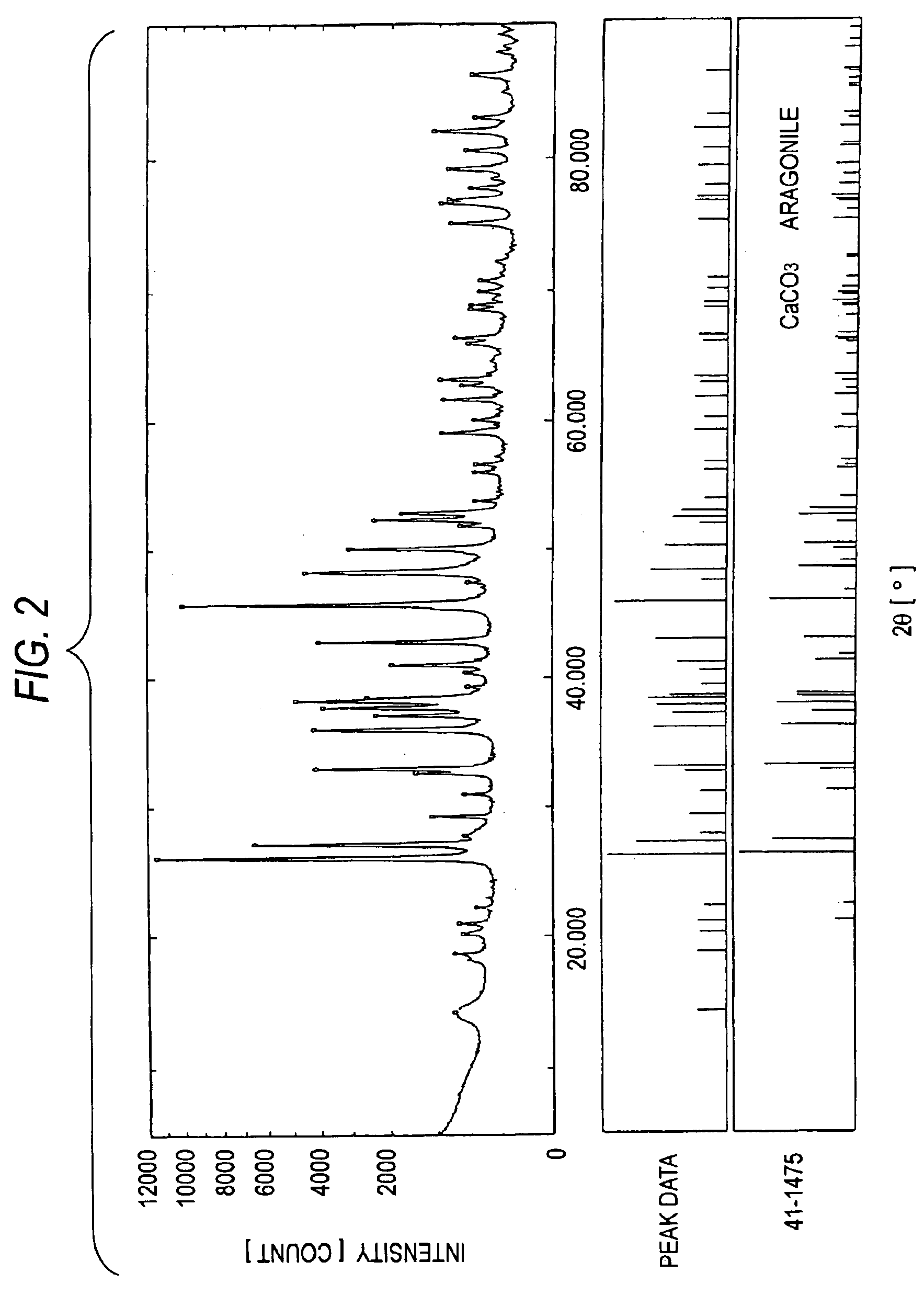
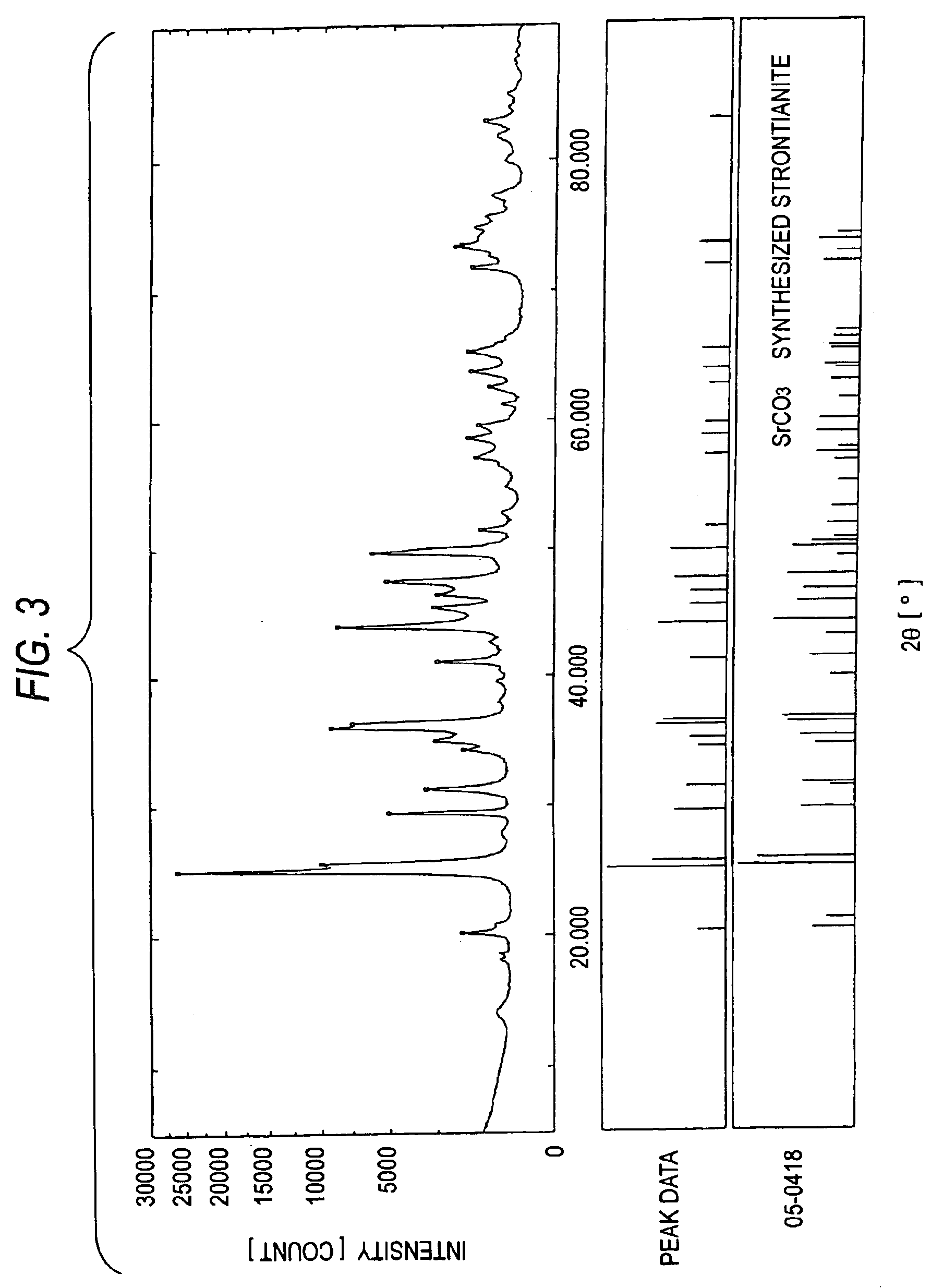
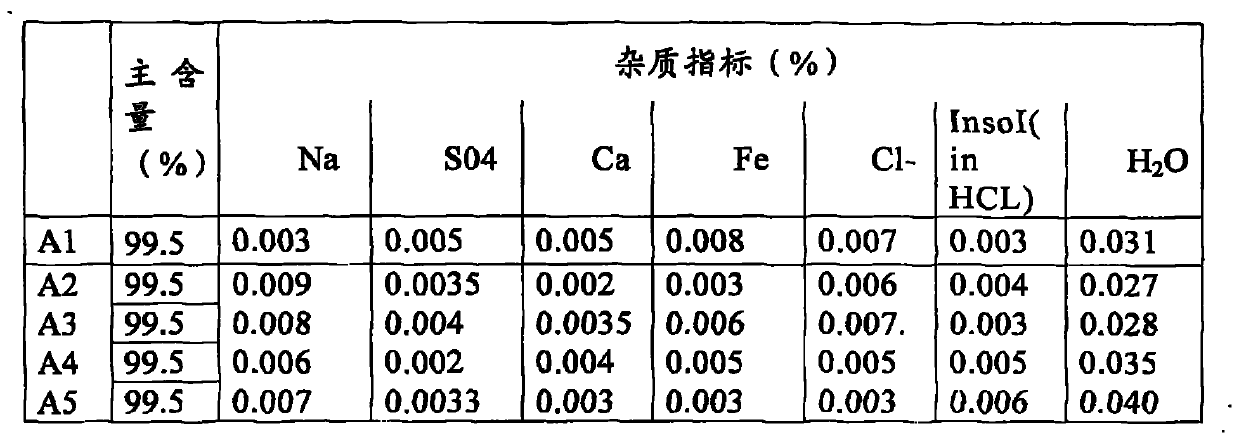
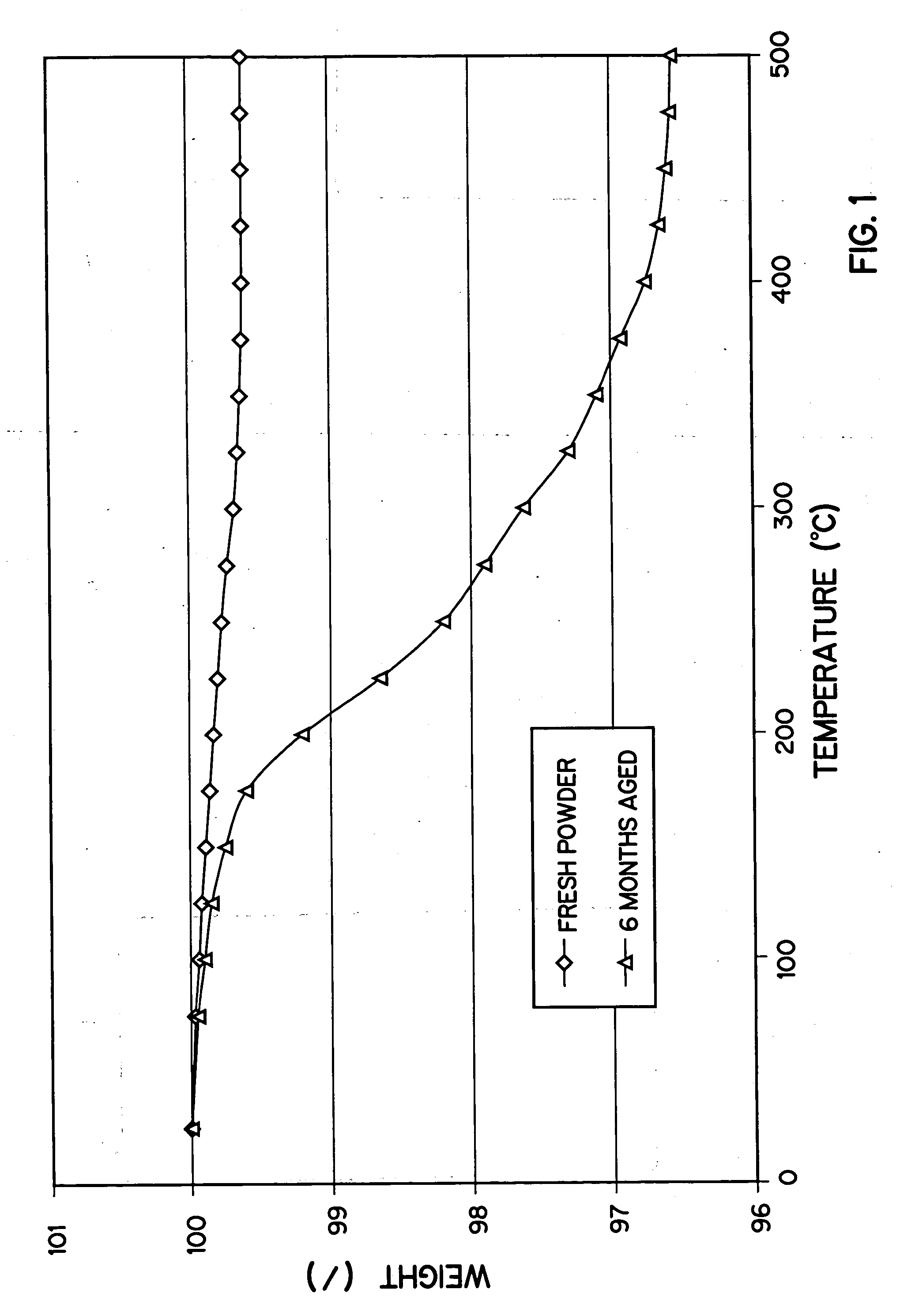
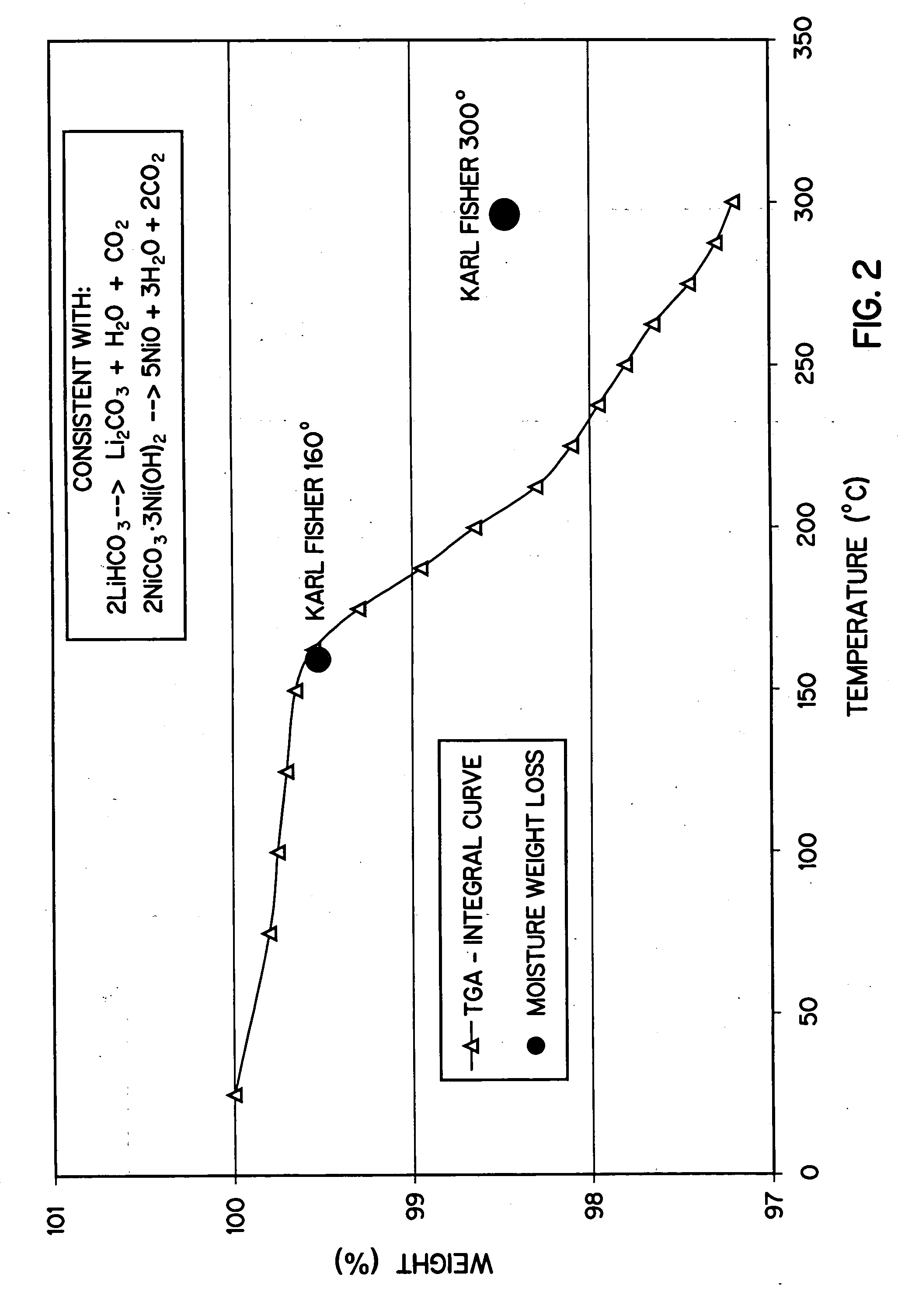
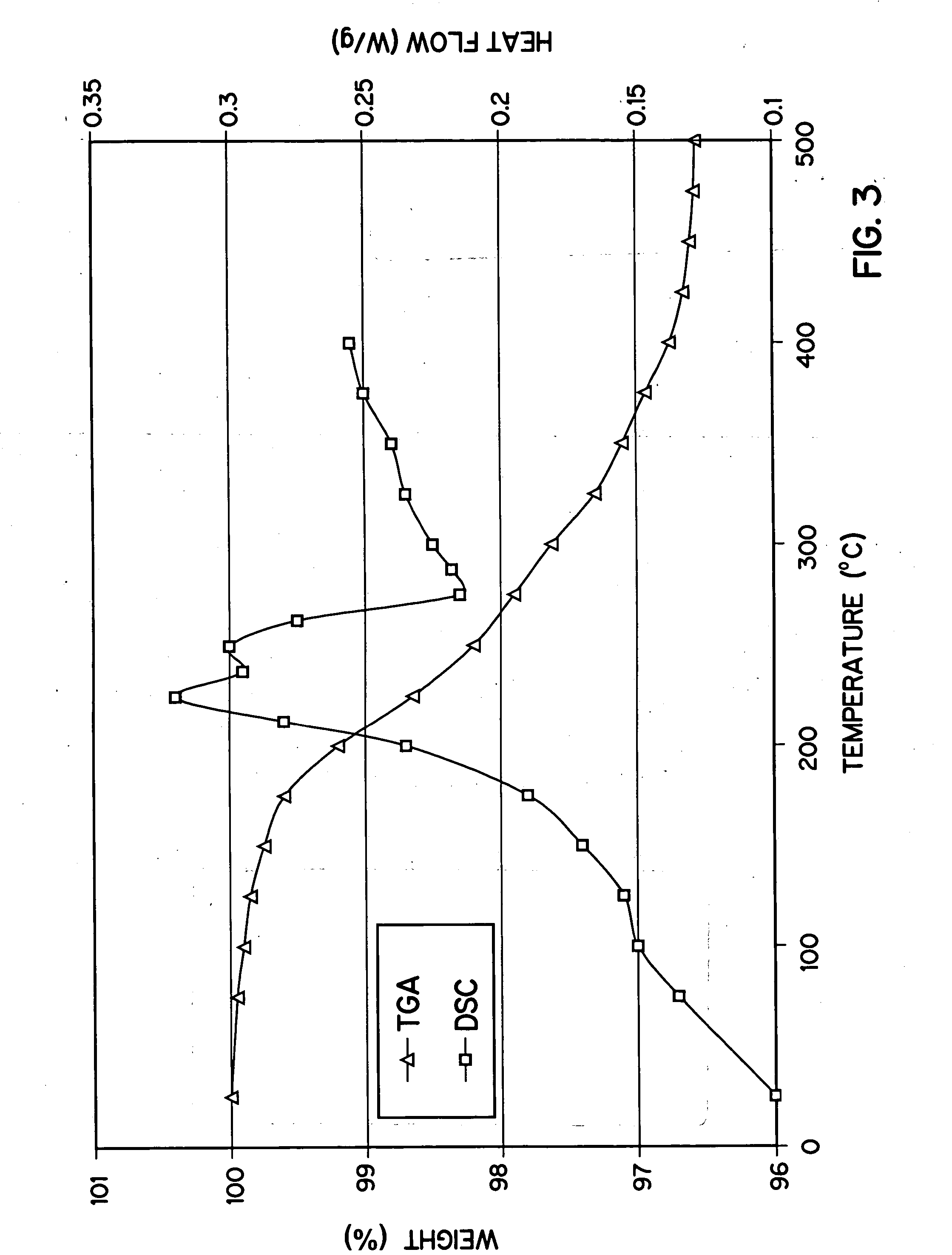
Patents
Literature
1397results about "Lithium carbonates/bicarbonates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for extracting and sequestering carbon dioxide
InactiveUS6890497B2Reduce CO burdenWithout significant expenditureCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCombination devicesDicarbonateAlkaline earth metal
A method and apparatus to extract and sequester carbon dioxide (CO2) from a stream or volume of gas wherein said method and apparatus hydrates CO2, and reacts the resulting carbonic acid with carbonate. Suitable carbonates include, but are not limited to, carbonates of alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, preferably carbonates of calcium and magnesium. Waste products are metal cations and bicarbonate in solution or dehydrated metal salts, which when disposed of in a large body of water provide an effective way of sequestering CO2 from a gaseous environment.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Removing carbon dioxide from waste streams through co-generation of carbonate and/or bicarbonate minerals
ActiveUS20060185985A1Improve ecologic efficiency of processEcologic efficiencyCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisWaste stream
Apparatuses and methods for removing carbon dioxide and other pollutants from a gas stream are provided. The methods include obtaining hydroxide in an aqueous mixture, and mixing the hydroxide with the gas stream to produce carbonate and / or bicarbonate. Some of the apparatuses of the present invention comprise an electrolysis chamber for providing hydroxide and mixing equipment for mixing the hydroxide with a gas stream including carbon dioxide to form an admixture including carbonate and / or bicarbonate.
Owner:CARBONFREE CHEM HLDG LLC
Layer-layer lithium rich complex metal oxides with high specific capacity and excellent cycling
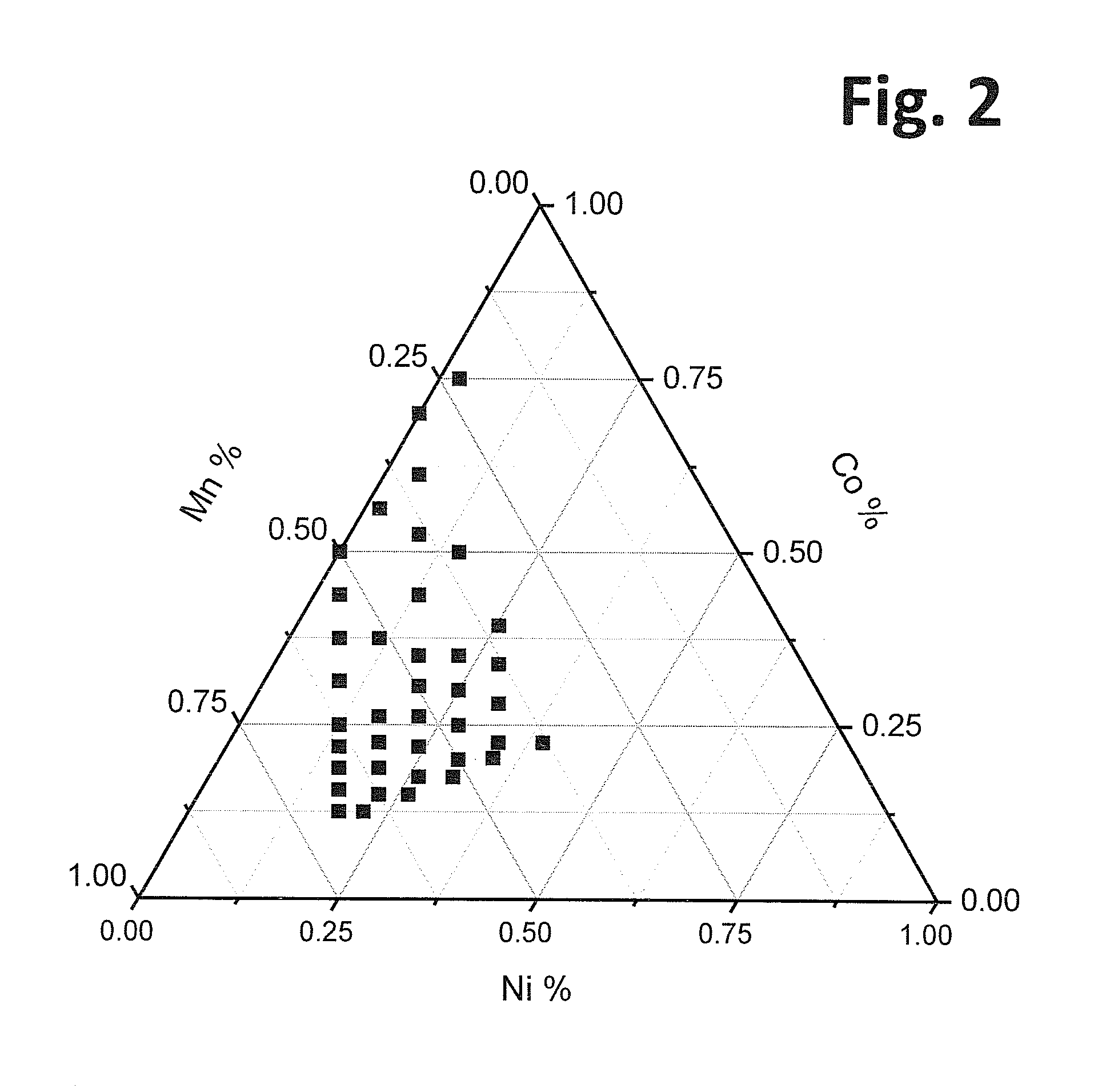
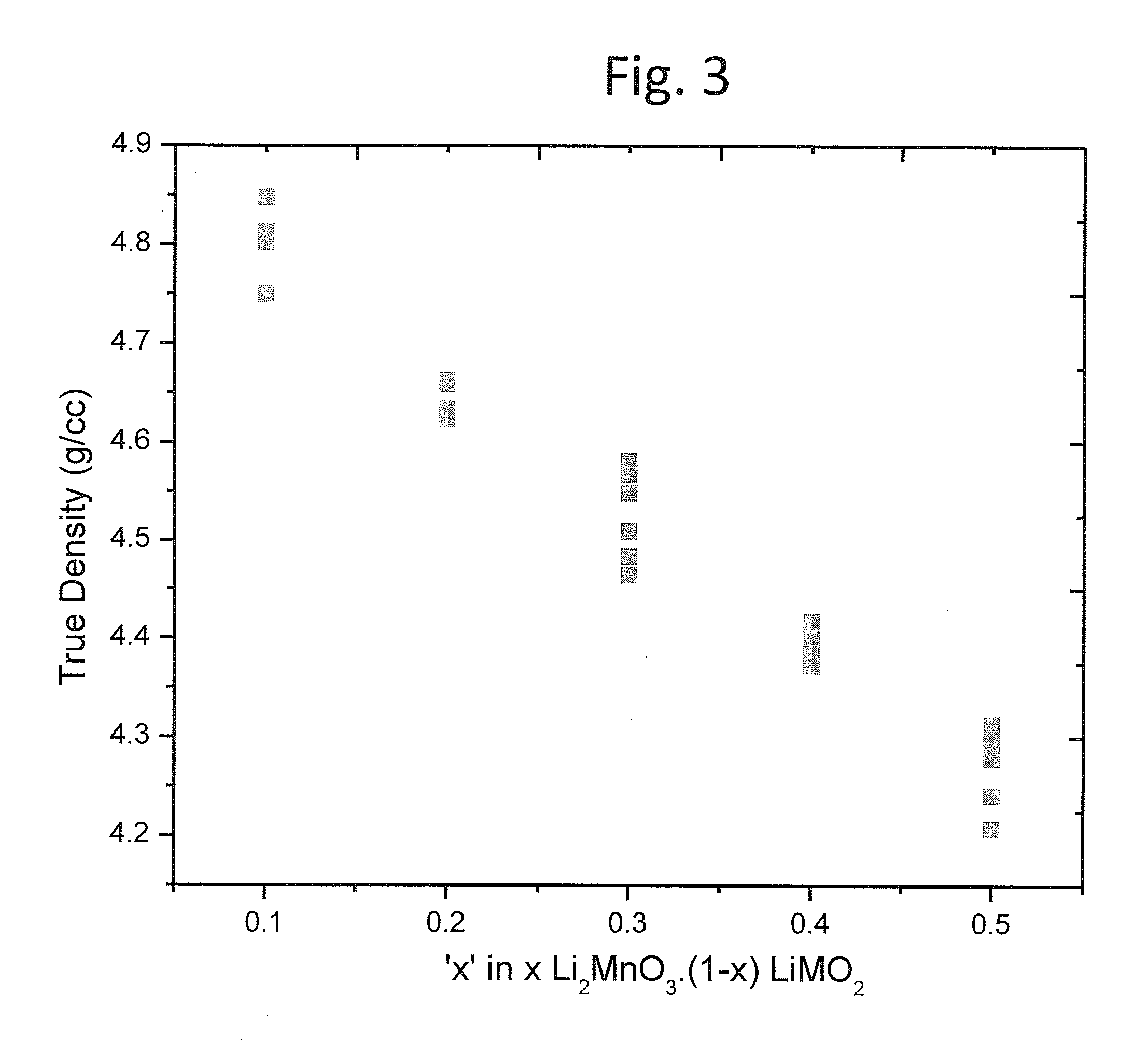
Lithium rich and manganese rich lithium metal oxides are described that provide for excellent performance in lithium-based batteries. The specific compositions can be engineered within a specified range of compositions to provide desired performance characteristics. Selected compositions can provide high values of specific capacity with a reasonably high average voltage. Compositions of particular interest can be represented by the formula, xLi2MnO3.(1−x)LiNiu+ΔMnu−ΔCowAyO2. The compositions undergo significant first cycle irreversible changes, but the compositions cycle stably after the first cycle.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Barriers for polymer-coated implantable medical devices and methods for making the same
InactiveUS6953560B1Reduce and prevent and inflammationReduce and prevent proliferationStentsSurgeryHafniumPt element
An implantable medical device and methods for making the implantable medical device are disclosed. The implantable medical device includes a substrate. At least a portion of the substrate is coated with a first layer including a polymer containing a drug. A barrier overlies the first layer. The barrier significantly reduces the rate of release of the drug from the polymer, thereby sustaining release of the drug from the medical device for a longer time.The barrier may be a homogeneous layer overlying the first layer, or a number of discrete deposits over the first layer. Alternatively, the barrier may be intermixed with an outer portion of the first layer. The barrier material is biocompatible, and typically has a thickness ranging from about 50 angstroms to about 20,000 microns. Suitable materials for the barrier include, but are not limited to, inorganic compounds, such as inorganic silicides, oxides, nitrides, carbides, as well as pure metals such as aluminum, chromium, gold, hafnium, iridium, niobium, palladium, platinum, tantalum, titanium, tungsten, zirconium, and alloys of these metals. The barriers disclosed may be applied to the first layer by several techniques, depending on the material being applied. Exemplary deposition techniques include physical vapor deposition, alkoxide hydrolysis, and electroless plating.The implantable device may be a stent or a graft, among other possibilities.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Catalyst for fluidized catalytic cracking of heavy hydrocarbon oil and method of fluidized catalytic cracking
InactiveUS6916762B2Efficient inactivationReduce the amount requiredCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesAluminium compoundsHydrogenOxide matrix
An FCC catalyst which not only deactivates catalyst poison metals, such as nickel, vanadium and the like, in feedstock oils, inhibits the generation of hydrogen or coke, has excellent cracking activity and bottom oil-treating ability, and can yield a gasoline and LCO fraction in high yields, but also retains the performances on a high level over long and has an improved catalyst life; and an FCC method using the catalyst. The FCC catalyst has a compound of a bivalent metal or of bivalent and trivalent metals showing an XRD pattern of a carbonate of the bivalent metal; an inorganic oxide matrix and the compound dispersed therein; or an inorganic oxide matrix and the compound dispersed therein together with a crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, and relates to an FCC method in which at least one of the catalysts are used in combination with an FCC catalyst obtained by evenly dispersing a crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite in an inorganic oxide matrix.
Owner:GASOLINEEUM ENERGY CENT FOUND +1
Lithium doped cathode material
Lithium dopant is introduced into lithium rich high capacity positive electrode active materials as a substitution for manganese within the complex metal oxides. In some embodiments, the lithium doped compositions can be written in a two component notation as x.Li2MnO3.(1−x)LiNiu+ΔMnu−Δ−dLidCowO2, where d ranges from about 0.004 to about 0.25 and 2u+w is approximately equal to 1. The materials are believed to form a layer-layer composite crystal structure that has very good cycling properties at high voltages, although the materials exhibit significant first cycle irreversible capacity loss.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
Layer-layer lithium rich complex metal oxides with high specific capacity and excellent cycling
Lithium rich and manganese rich lithium metal oxides are described that provide for excellent performance in lithium-based batteries. The specific compositions can be engineered within a specified range of compositions to provide desired performance characteristics. Selected compositions can provide high values of specific capacity with a reasonably high average voltage. Compositions of particular interest can be represented by the formula, xLi2MnO3.(1−x)LiNiu+ΔMnu−ΔCowAyO2. The compositions undergo significant first cycle irreversible changes, but the compositions cycle stably after the first cycle.
Owner:IONBLOX INC
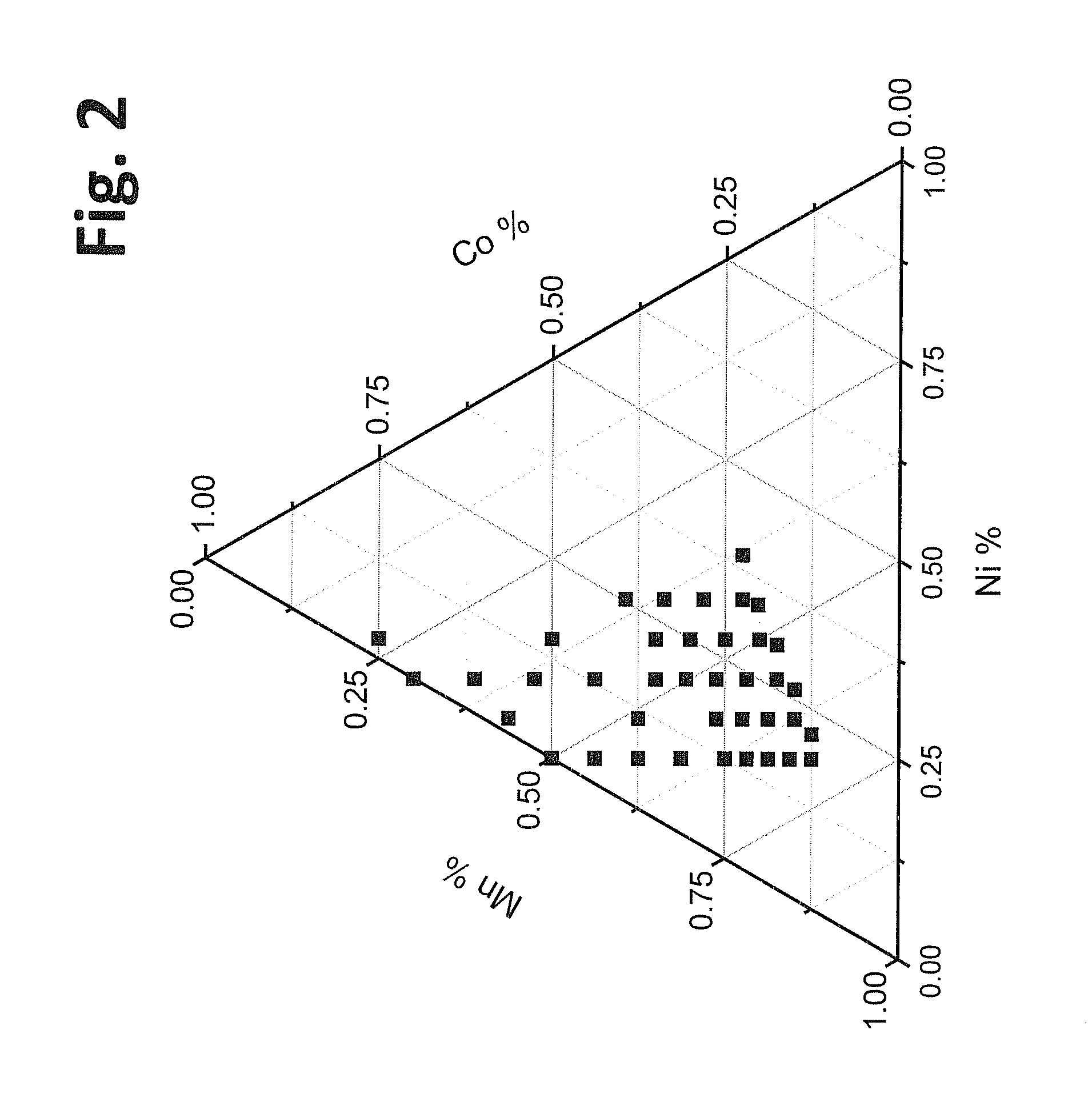
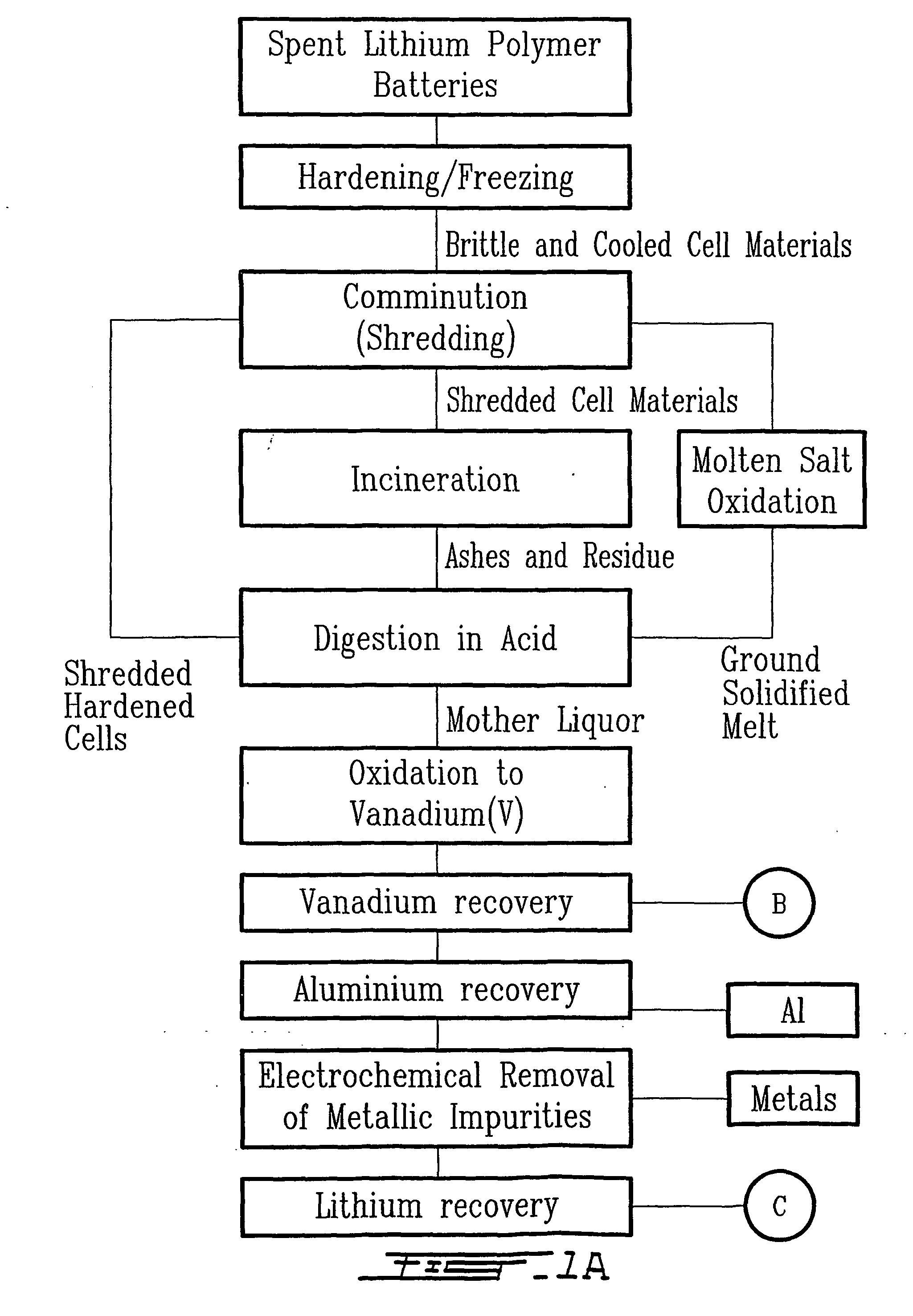
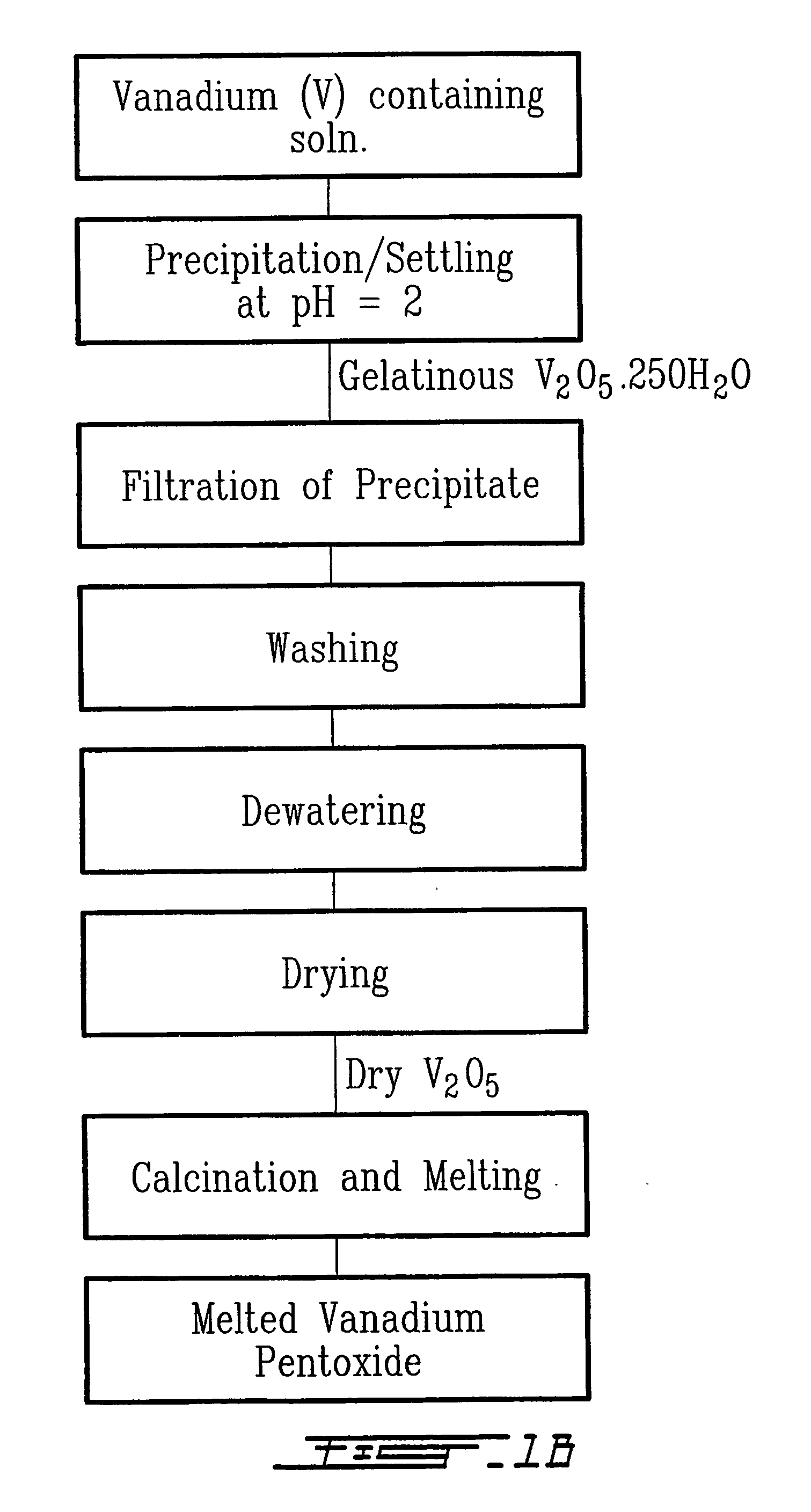
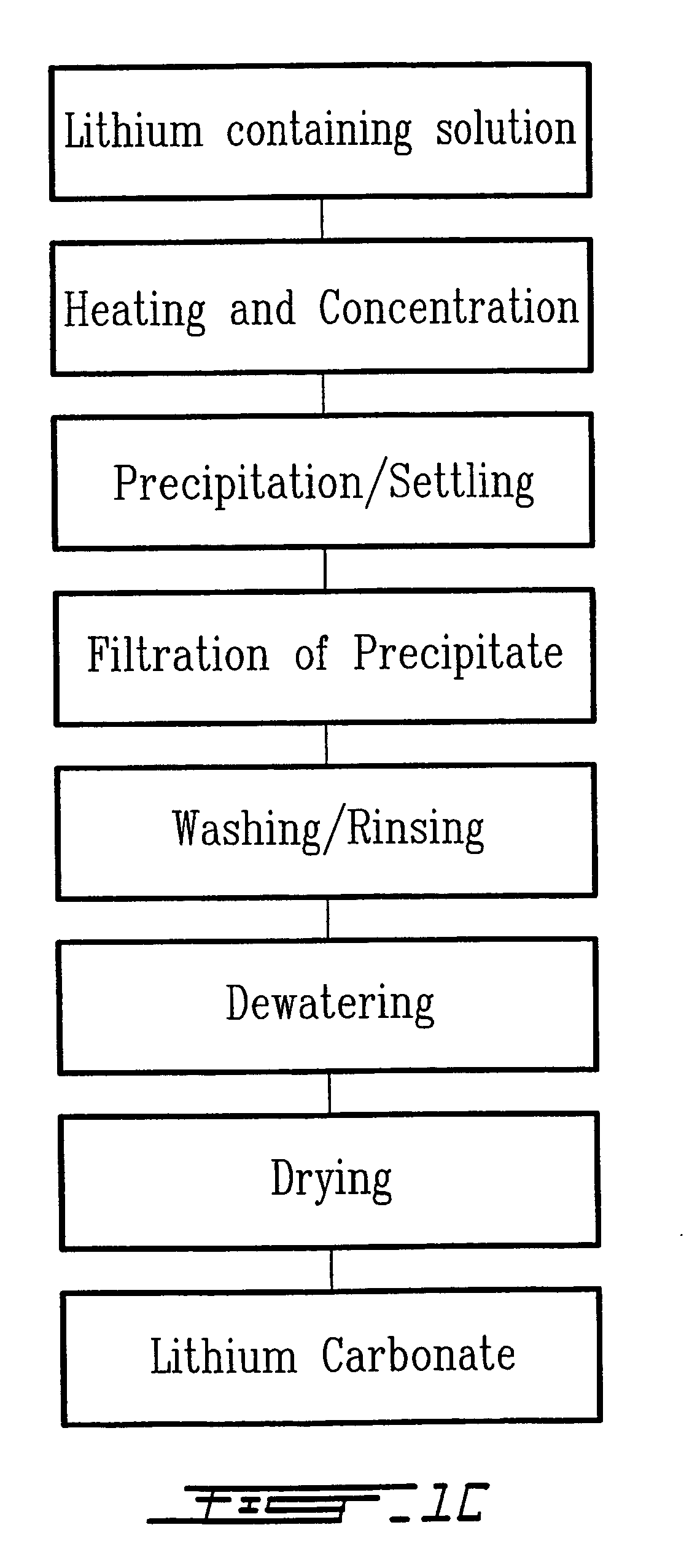
Method for recycling spent lithium metal polymer rechargeable batteries and related materials
The method relates to a pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical process for the recovery and recycling of lithium and vanadium compounds from a material comprising spent rechargeable lithium batteries, particularly lithium metal gel and solid polymer electrolyte rechargeable batteries. The method involves providing a mass of the material, hardening it by cooling at a temperature below room temperature, comminuting the mass of cooled and hardened material, digesting with an acid its ashes obtained by incineration, or its solidified salts obtained by molten salt oxidation, or the comminuted mass itself, to give a mother liquor, extracting vanadium compounds from the mother liquor, separating heavy metals and aluminium therefrom, and precipitating lithium carbonate from the remaining solution.
Owner:AVESTOR
Removing carbon dioxide from waste streams through co-generation of carbonate and/or bicarbonate minerals
ActiveUS7727374B2Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisWaste stream
Apparatuses and methods for removing carbon dioxide and other pollutants from a gas stream are provided. The methods include obtaining hydroxide in an aqueous mixture, and mixing the hydroxide with the gas stream to produce carbonate and / or bicarbonate. Some of the apparatuses of the present invention comprise an electrolysis chamber for providing hydroxide and mixing equipment for mixing the hydroxide with a gas stream including carbon dioxide to form an admixture including carbonate and / or bicarbonate.
Owner:CARBONFREE CHEM HLDG LLC
Process for producing sodium bicarbonate for flue gas desulphurization
InactiveUS20100290967A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementSodium bicarbonateFlue gas
Process for producing sodium bicarbonate for purifying flue gases, according to which an aqueous solution containing sodium sulfate is subjected to electrodialysis to produce a sodium hydroxide solution and a sodium bisulfate solution, the sodium hydroxide solution being carbonated in order to obtain sodium bicarbonate.
Owner:SOLVAY SA
Process and device for extracting battery grade lithium from brine
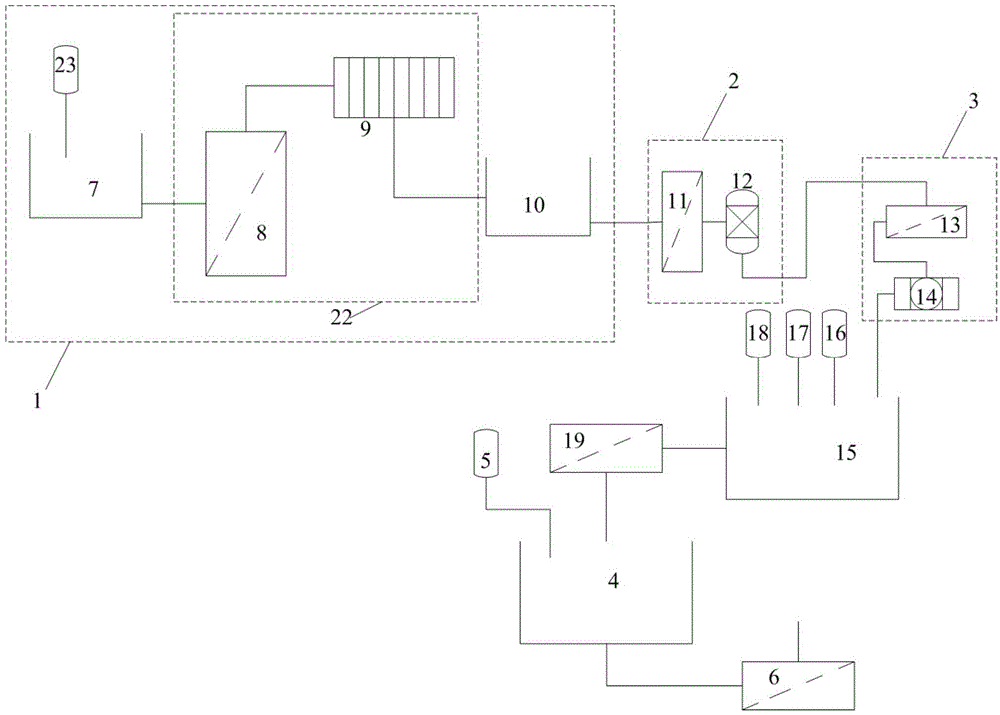
ActiveCN104310446AIncrease the concentration factorHigh yieldLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesPhysical chemistryReverse osmosis
The invention relates to a process and a device for extracting battery grade lithium from brine. The process comprises the following steps: adding an adsorbent into the brine to adsorb lithium ions in the brine, intercepting the adsorbent by using a ceramic membrane filter, performing plate-frame pressure filtration on the ceramic membrane concentrated solution to obtain an adsorbent filter cake, washing and desorbing the adsorbent filter cake so as to obtain a desorption solution; removing magnesium in the desorption solution through a nanofiltration membrane system, entering the nanofiltration membrane permeate into an ion exchange resin tower for performing deep magnesium removal, concentrating through a reverse osmosis membrane, performing deep concentration in a DTRO membrane or electrodialysis equipment, evaporating the concentrated solution, adding BaCl2, Na2CO3 and NaOH into the solution, stirring, filtering in a ceramic membrane filter, performing plate-frame pressure filtration on the ceramic membrane filtrate, adding Na2CO3 into the clear liquid, preparing Li2CO3, washing Li2CO3 through a ceramic membrane, centrifuging, and drying, thereby obtaining the finished battery grade Li2CO3 product.
Owner:JIANGSU JIUWU HITECH
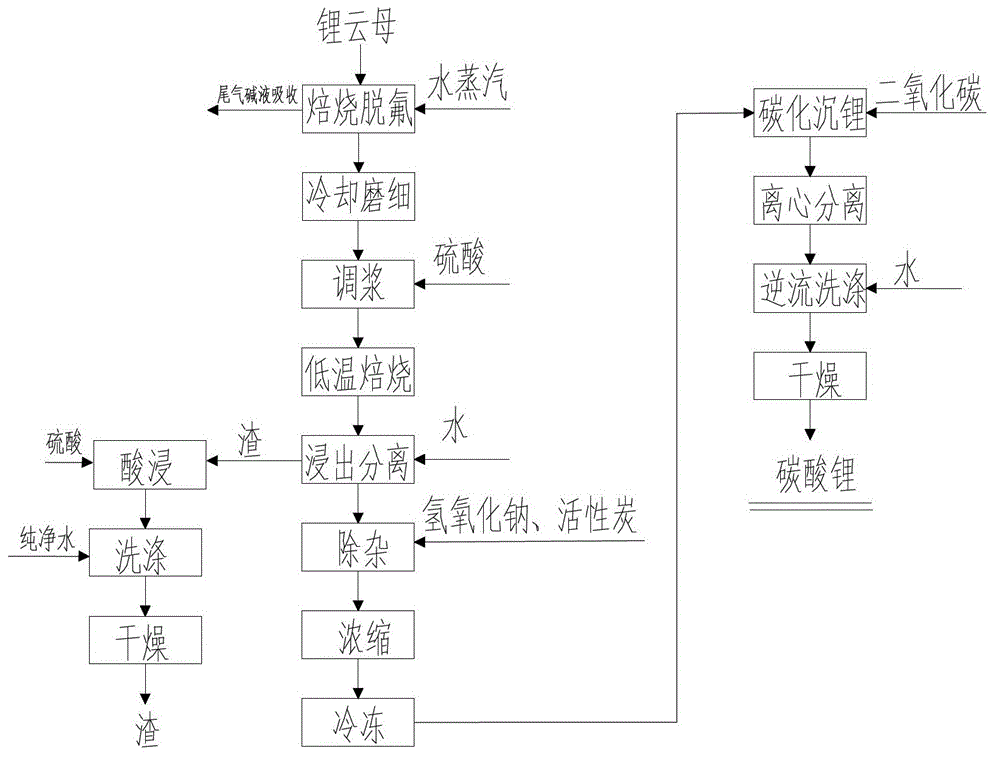
Method for preparing lithium carbonate from lepidolite through sulfuric acid roasting method
ActiveCN103145158AReduce dosageSimple cleaning processLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesResource utilizationLithium carbonate
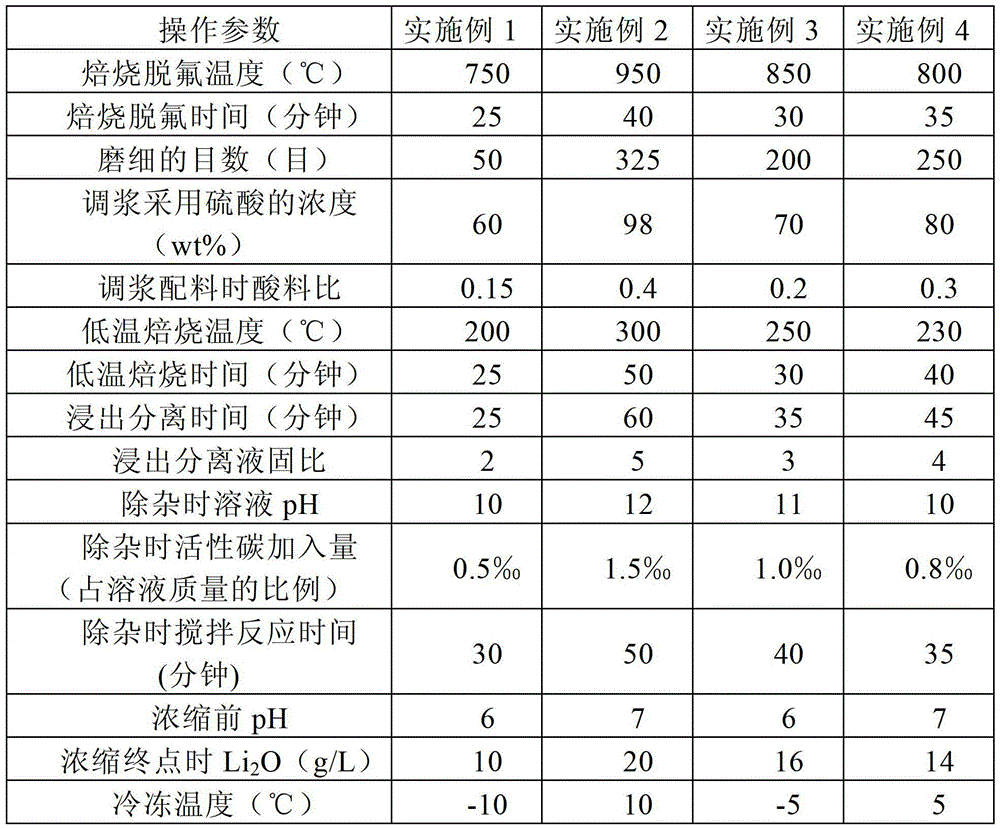
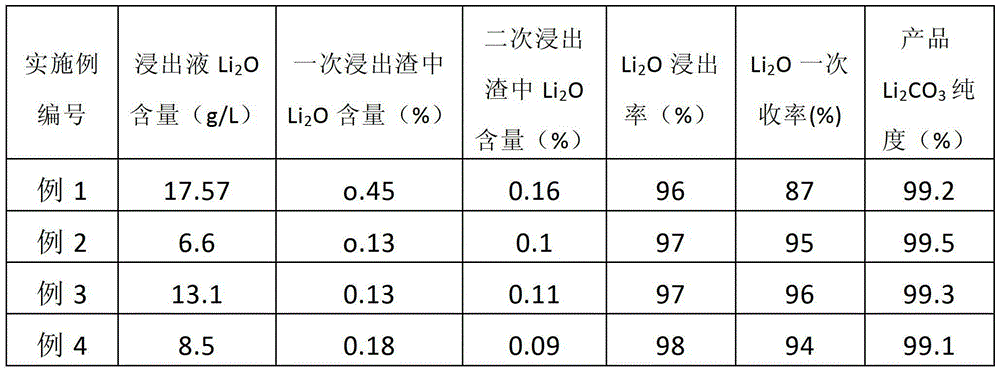
The invention discloses a method for preparing lithium carbonate from lepidolite through a sulfuric acid roasting method, which comprises the following process steps: (1) roasting, and defluorinating; (2) cooling, and grinding; (3) pulping; (4) roasting at low temperature; (5) leaching, and separating; (6) removing impurities; (7) concentrating; (8) freezing; and (9) performing carbonization lithium precipitation to obtain the lithium carbonate product. The method for preparing lithium carbonate from lepidolite through a sulfuric acid roasting method is simple in process, low in sulfuric acid consumption, low in energy consumption and high in resource utilization rate, and causes less environment pollution.
Owner:GANFENG LITHIUM CO LTD
A method for recovering lithium and iron from electric vehicle lithium iron phosphate power battery
ActiveCN102285673ASimple processIron oxides/hydroxidesLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesPower batteryLithium iron phosphate
The invention discloses a method for recovering lithium and iron from a lithium iron phosphate power battery for an electromobile. The method comprises the following steps: 1) disassembling the lithium iron phosphate power battery so as to obtain a positive electrode material, smashing and screening so as to obtain a powder material; 2) adding an alkali solution in the powder material to dissolve aluminum and oxide of aluminum, and filtering so as to obtain filter mud; 3) lixiviating the filter mud with a mixed solution of an acid and a reducing agent so as to obtain lixivium; 4) adding an alkali to regulate the pH value of the lixivium to 1.5-3, precipitating to separate out iron hydroxide, and filtering so as to obtain filtrate; 5) firing iron hydroxide obtained in the step 4) so as to obtain iron oxide; 6) regulating the pH value of the lixivium to 5.0-8.0 with an alkali, precipitating impurities in the lixivium, and filtering so as to obtain filtrate; and 7) adding a solid sodium carbonate in the filtrate, and concentrating and crystallizing the obtained solution so as to obtain lithium carbonate. The recovering method disclosed by the invention has simple process, can be used for simultaneously recovering iron and lithium and can be directly used for production, and the purity of prepared lithium carbonate can reach above 98.5%.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +1
Method for preparing lithium carbonate by extracting lithium from lepidolite
ActiveCN101302018AImprove leaching rateIncrease concentrationLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesCarbonizationIon exchange
Owner:GANFENG LITHIUM CO LTD
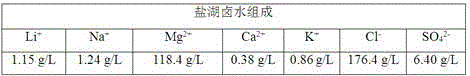
Method for preparing lithium carbonate by using salt lake brine with high magnesium-to-lithium ratio
InactiveCN101698488AReduce energy consumptionNo way outLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesEvaporationCalcination
The invention provides a method for preparing industrial lithium carbonate by using salt lake brine with a high magnesium-to-lithium ratio. In the method, a TBP-CON-KS+FeCl3 is used as an extraction system to extract and back-extract impurity-free salt lake brine with a high magnesium-to-lithium ratio, the residual liquid obtained after back-extraction is converted by alkaline liquor for precipitation, the precipitate is washed to form an industrial lithium carbonate product and the lithium carbonate content is more than or equal to 99.0 percent and is in accordance with the requirements of GB / T 11 075-2003 standards. The method has the advantages that: liquid-liquid extraction with an organic solvent is adopted to realize the separation of lithium from magnesium, the lithium carbonate is precipitated by inorganic slats, the lithium carbonate is extracted from the salt lake brine with a high magnesium-to-lithium ratio, the process is simple, the control is easy, the operational reliability is high and the application range is wide; a process of calcination and diluted lithium solution evaporation and concentration is saved, the energy consumption is only 30 to 50 percent of that of the conventional process for producing lithium carbonate by using lithium-containing brine; initial raw material consumption comparison show that the production cost of the method is only about 8 percent of that of the prior art; and the raw material brine can return to a storage pool after the extraction of the lithium carbonate, so no by production disposal problem is involved, environmental pollution is relatively low and lithium yield in the whole process is more than or equal to 70 percent.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting lithium salt from spodumene
ActiveCN101948124ASimple processReduce manufacturing costProcess efficiency improvementLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesSocial benefitsResource utilization
Owner:GANFENG LITHIUM CO LTD
Method of preparation of positive electrode material
InactiveUS20050069484A1Prolong lifeReduce moisture contentElectrode thermal treatmentOrganic electrolyte cellsElectrical batteryPhysical chemistry
A method for preparing a positive electrode material for a lithium-ion or lithium-ion polymer battery to reduce the moisture content of the positive electrode material. A lithiated transition metal oxide positive electrode material having at least one water-containing compound therein is treated to convert the water-containing compound to a water-free compound. One treatment in the method of the present invention involves exposing the positive electrode material at a temperature of 0-650° C. to a CO2-containing gas. The other treatment in the method of the present invention involves heating the positive electrode material to a temperature greater than 250° C. in the presence of an oxygen-containing gas, such as air and / or O2. The treatments may be, performed sequentially or concurrently.
Owner:ENERDEL
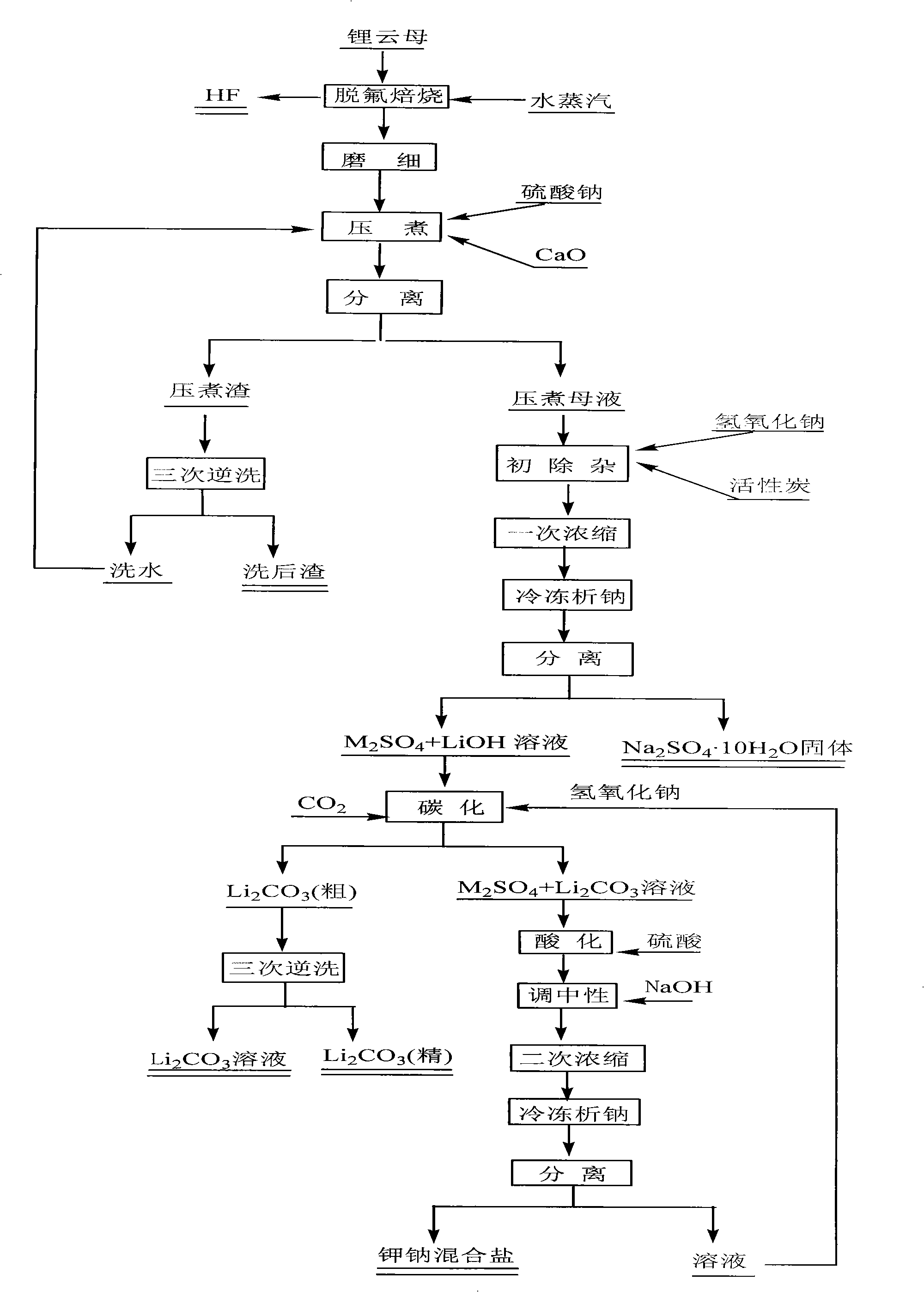
Method for preparing lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate by utilizing soluble lithium-salt solution
ActiveCN107298450AAvoid cumbersomeAvoid pollutionLithium oxides/hydroxidesLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesCalcium hydroxideHigh concentration
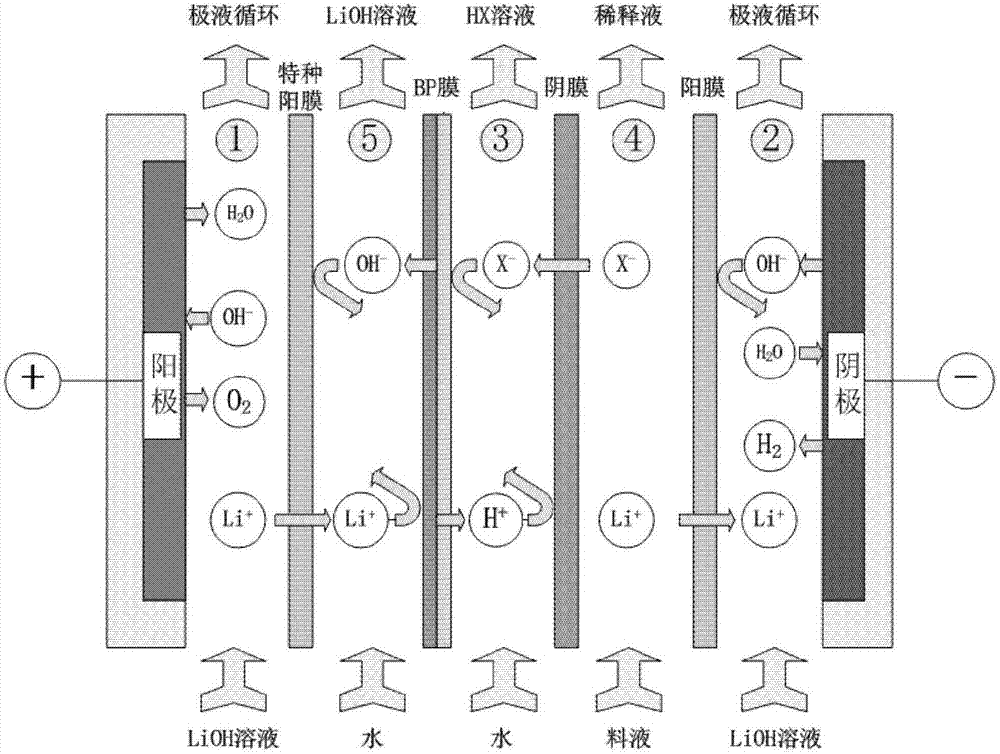
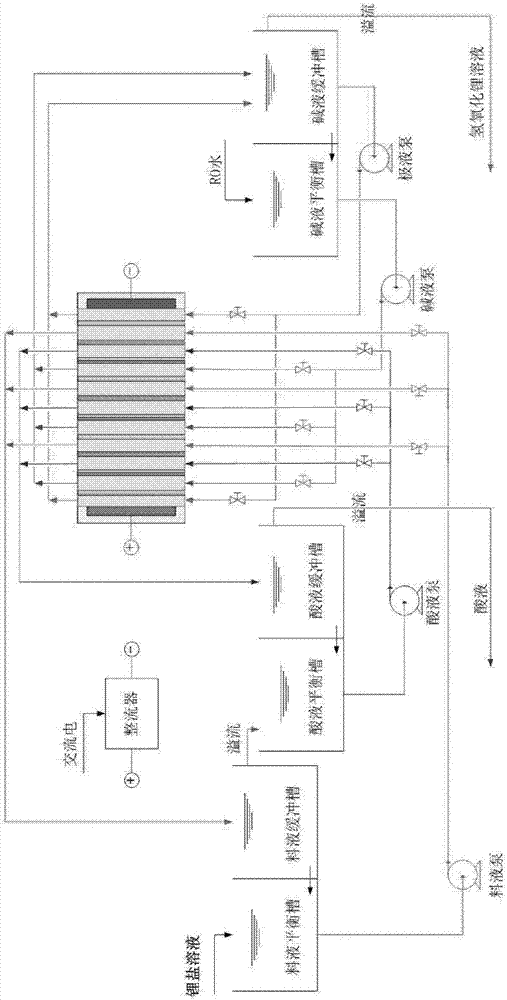
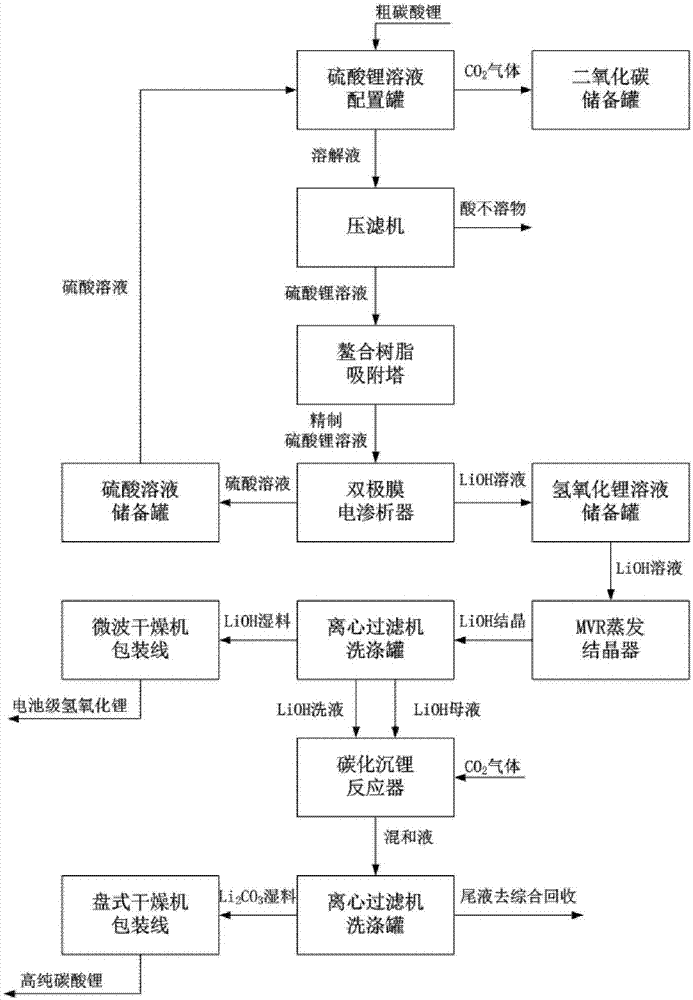
The invention discloses a method for preparing lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate by utilizing a soluble lithium-salt solution. The method comprises the following steps: the soluble lithium-salt solution is used as a raw material to produce the battery-level lithium hydroxide, and a lithium hydroxide solution is utilized to produce the high-purity lithium carbonate. The method is characterized in that various soluble lithium-salt solutions (the lithium solutions are expressed as LiX in the description) can be utilized, and a bipolar membrane electrodialyzer is applied to treat the soluble lithium-salt solutions, so that a higher-concentration LiOH solution and a corresponding HX acidic solution are obtained; the HX acidic solution returns to a previous-stage process for preparing the lithium salt solution; and the LiOH solution is subjected to evaporation concentration and crystallization to obtain the battery-level lithium hydroxide solid, and the produced lithium hydroxide solution can be further reacted with a carbon dioxide gas through a gas-liquid reactor, so that the high-purity lithium carbonate is obtained. The method can realize continuous stable production with low energy consumption, free pollution and large scale, and realize low-cost and high-efficiency manufacture of the battery-level lithium hydroxide and the high-purity lithium carbonate.
Owner:JIANGSU LITHITECH CO LTD
Production of lithium compounds directly from lithium containing brines
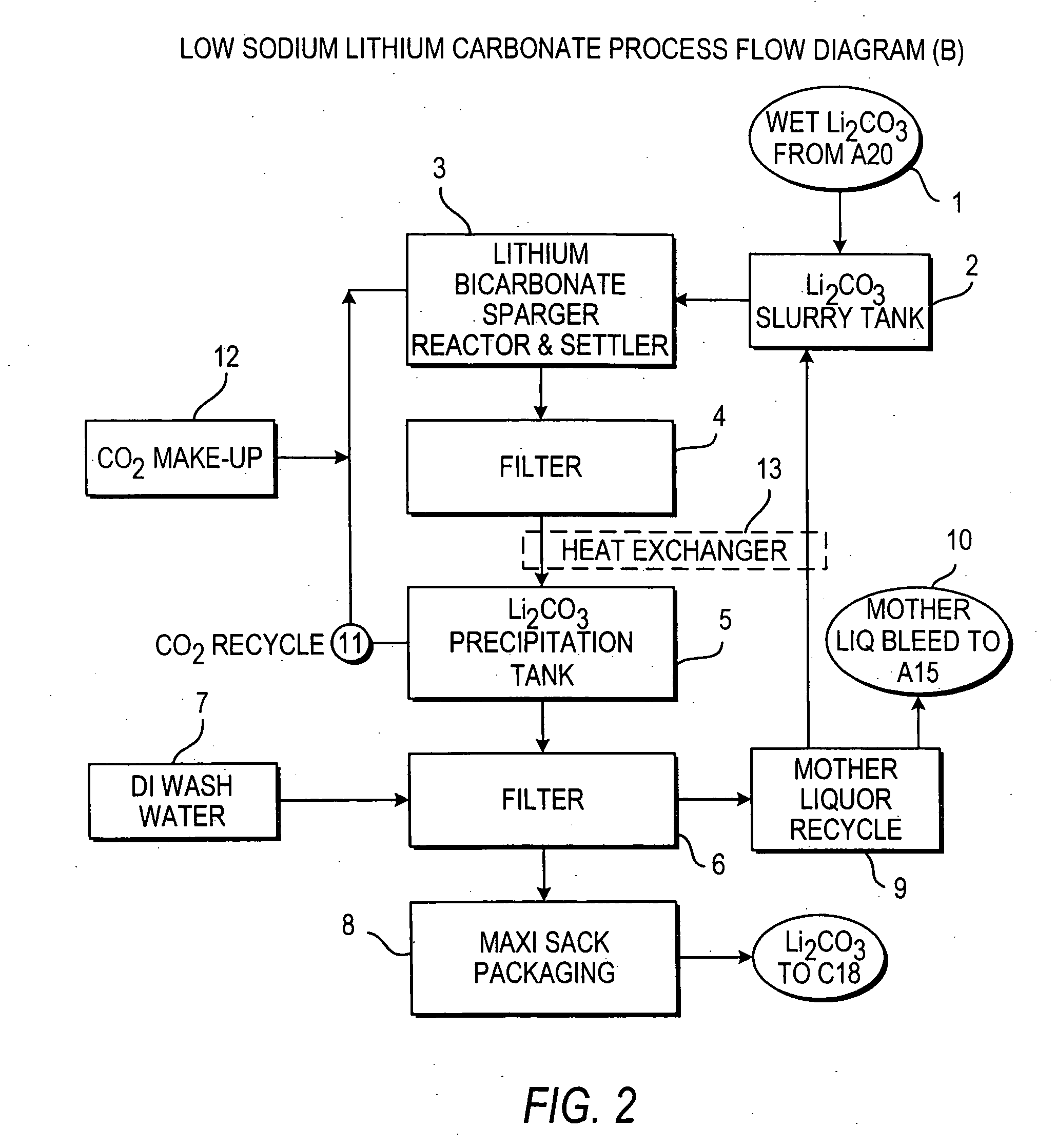
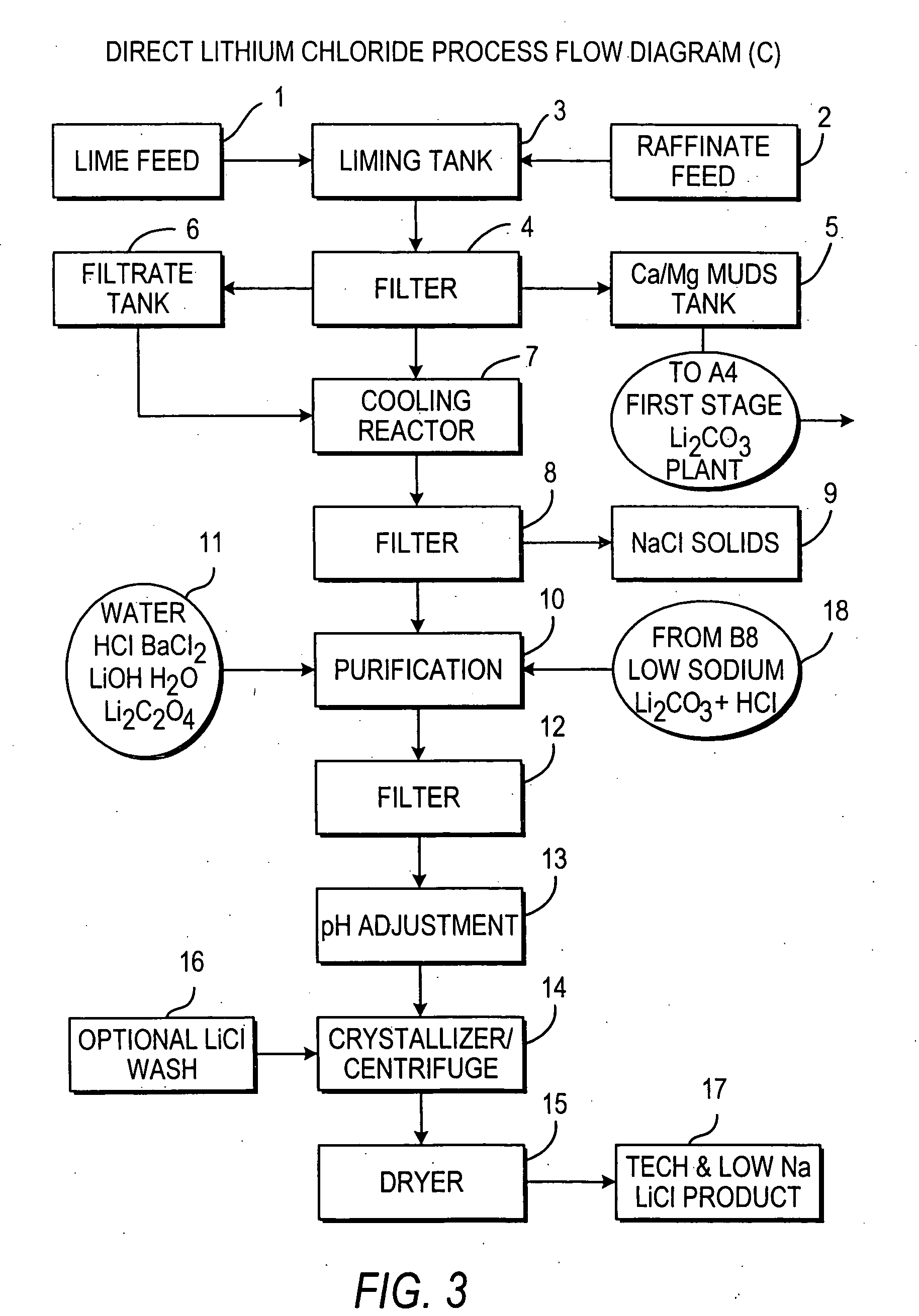
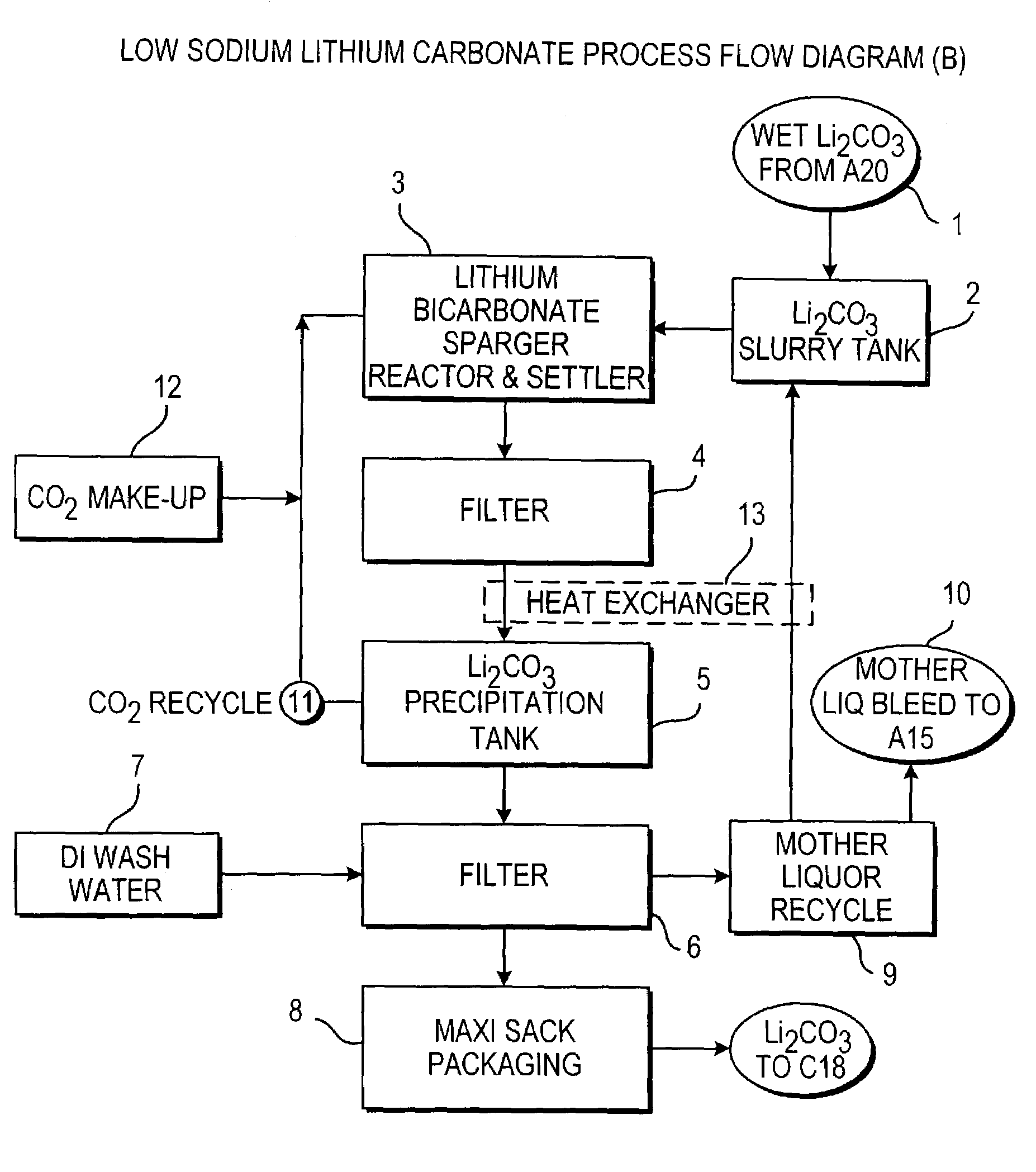
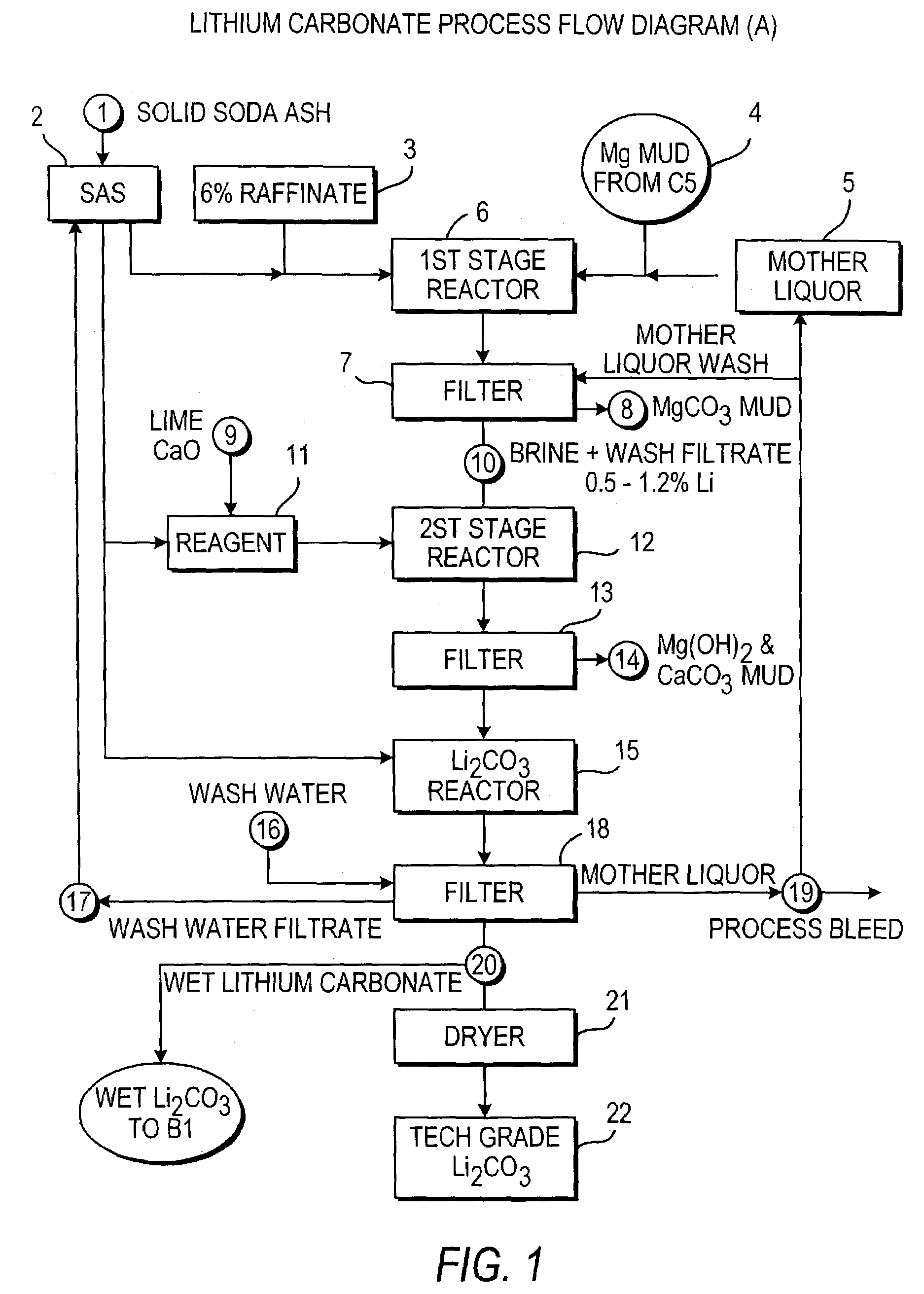
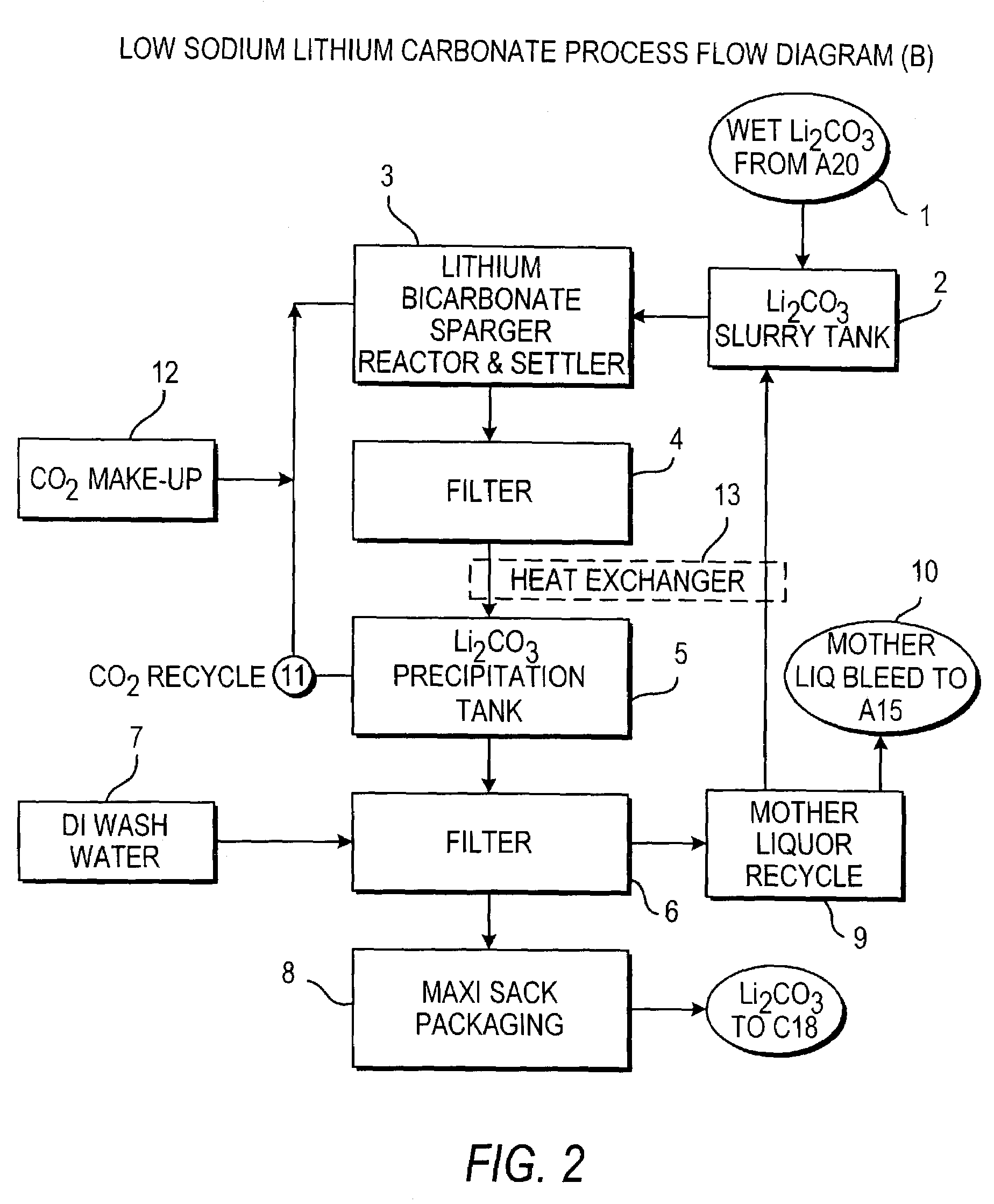
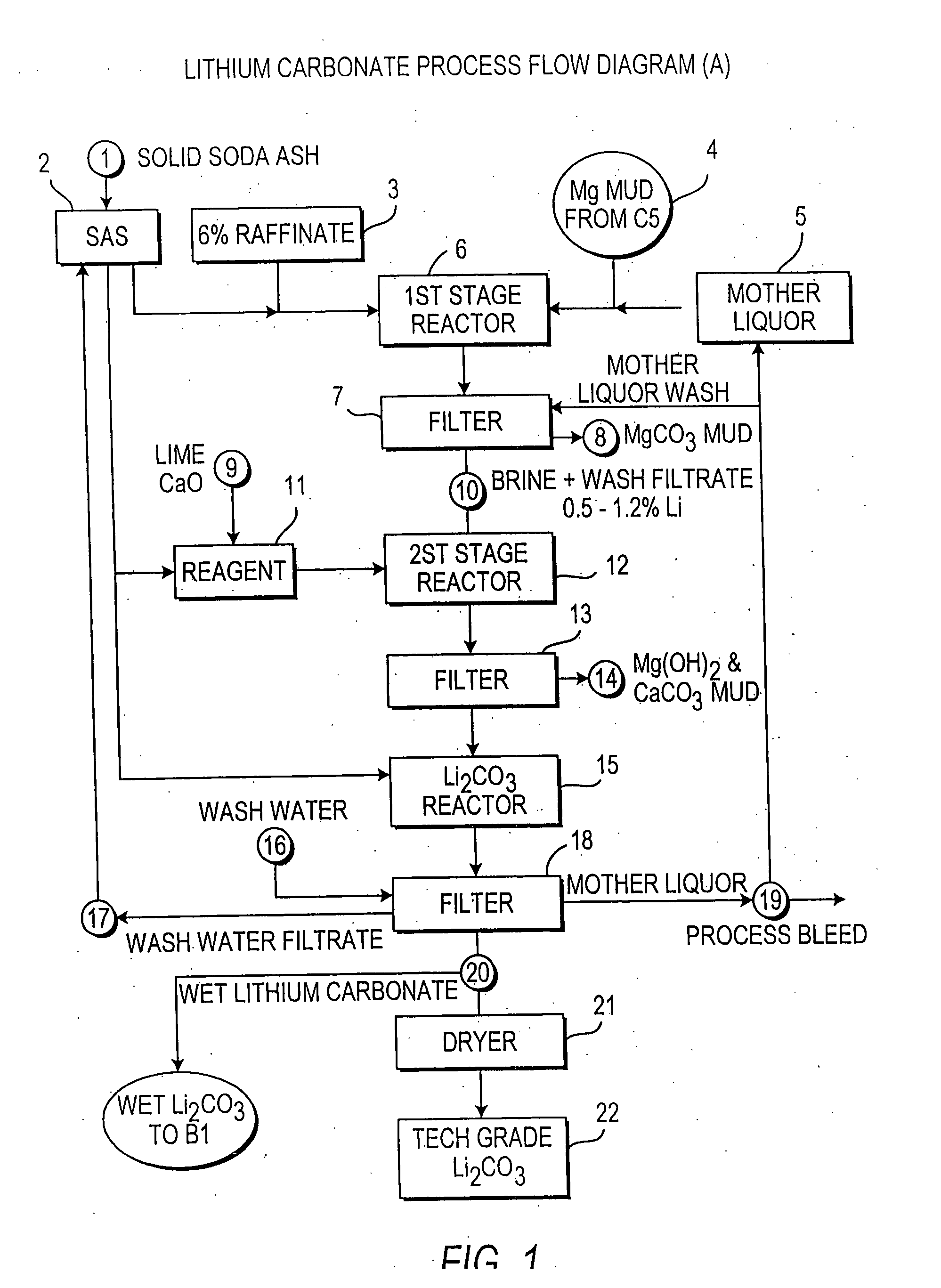
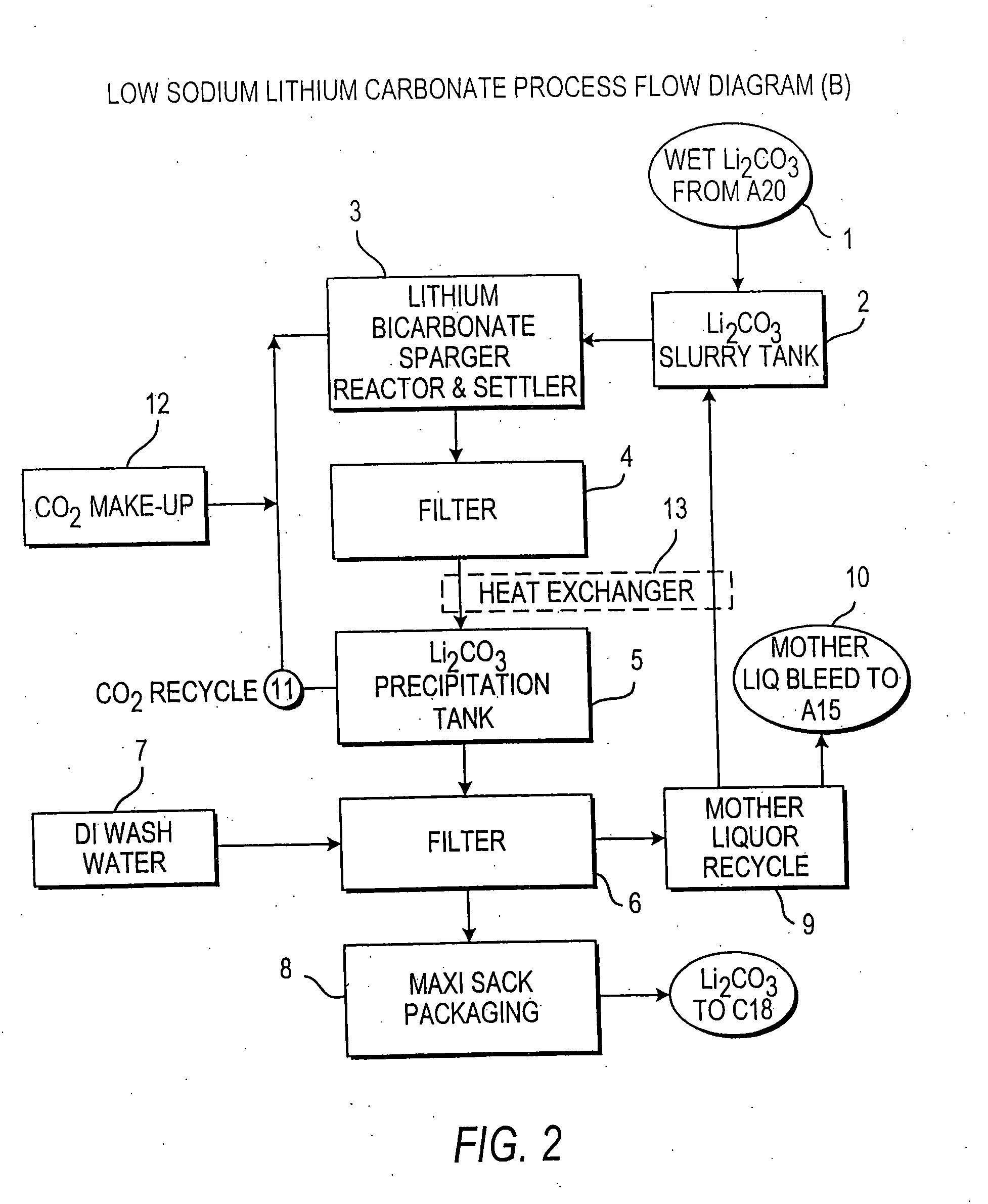
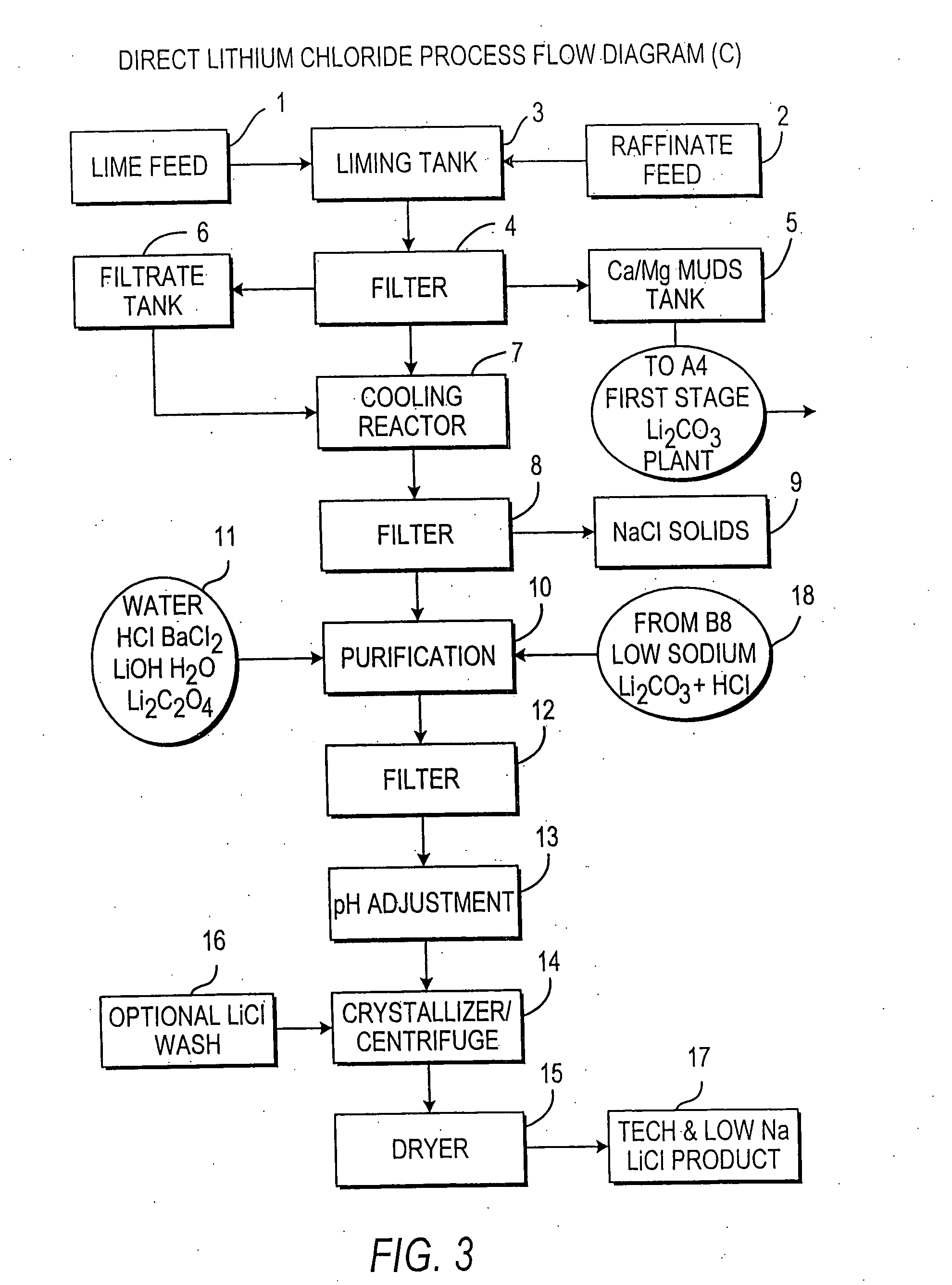
InactiveUS20060115396A1Promote absorptionConstant liquid volumeCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesLithium chlorideLithium carbonate
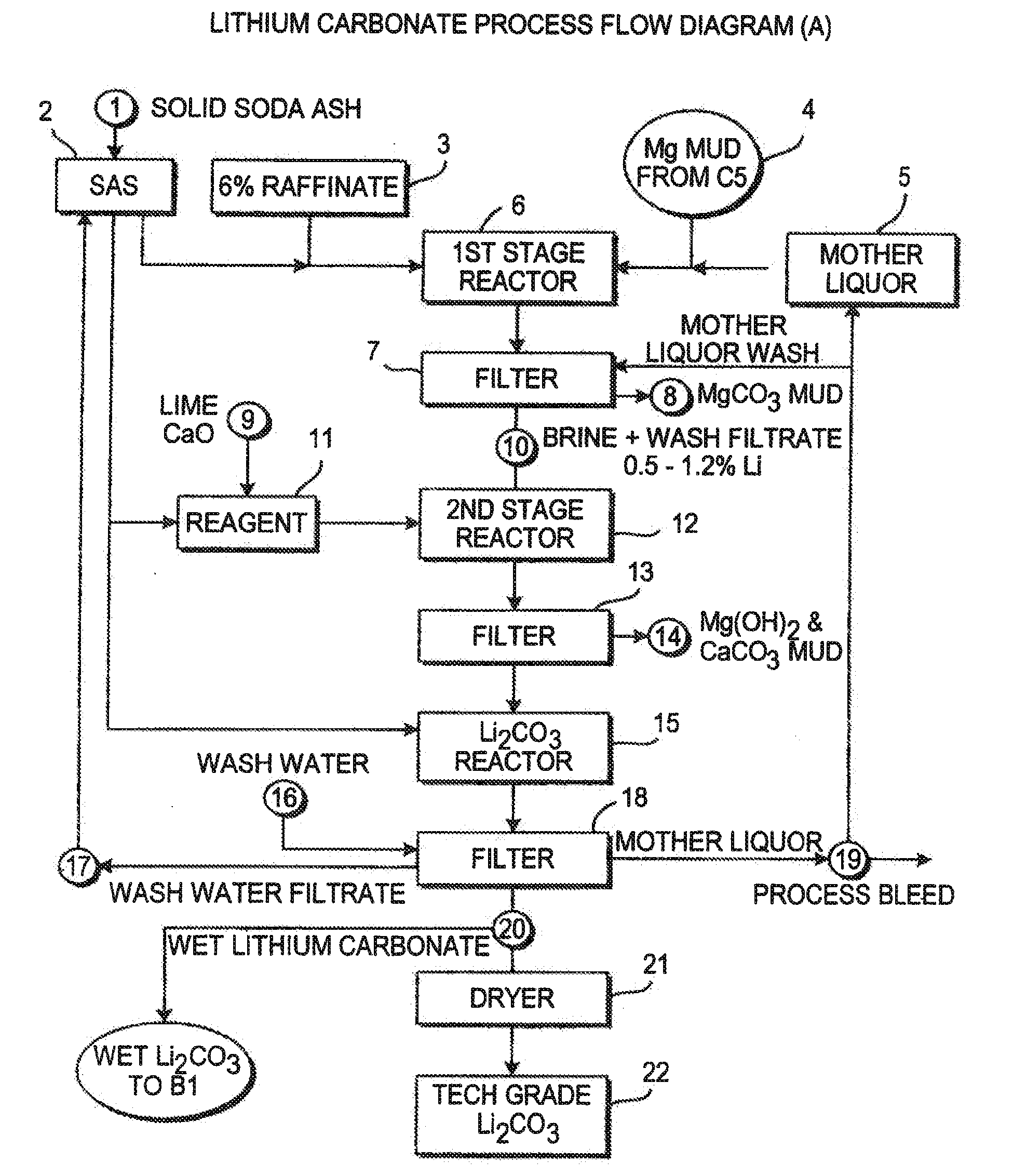
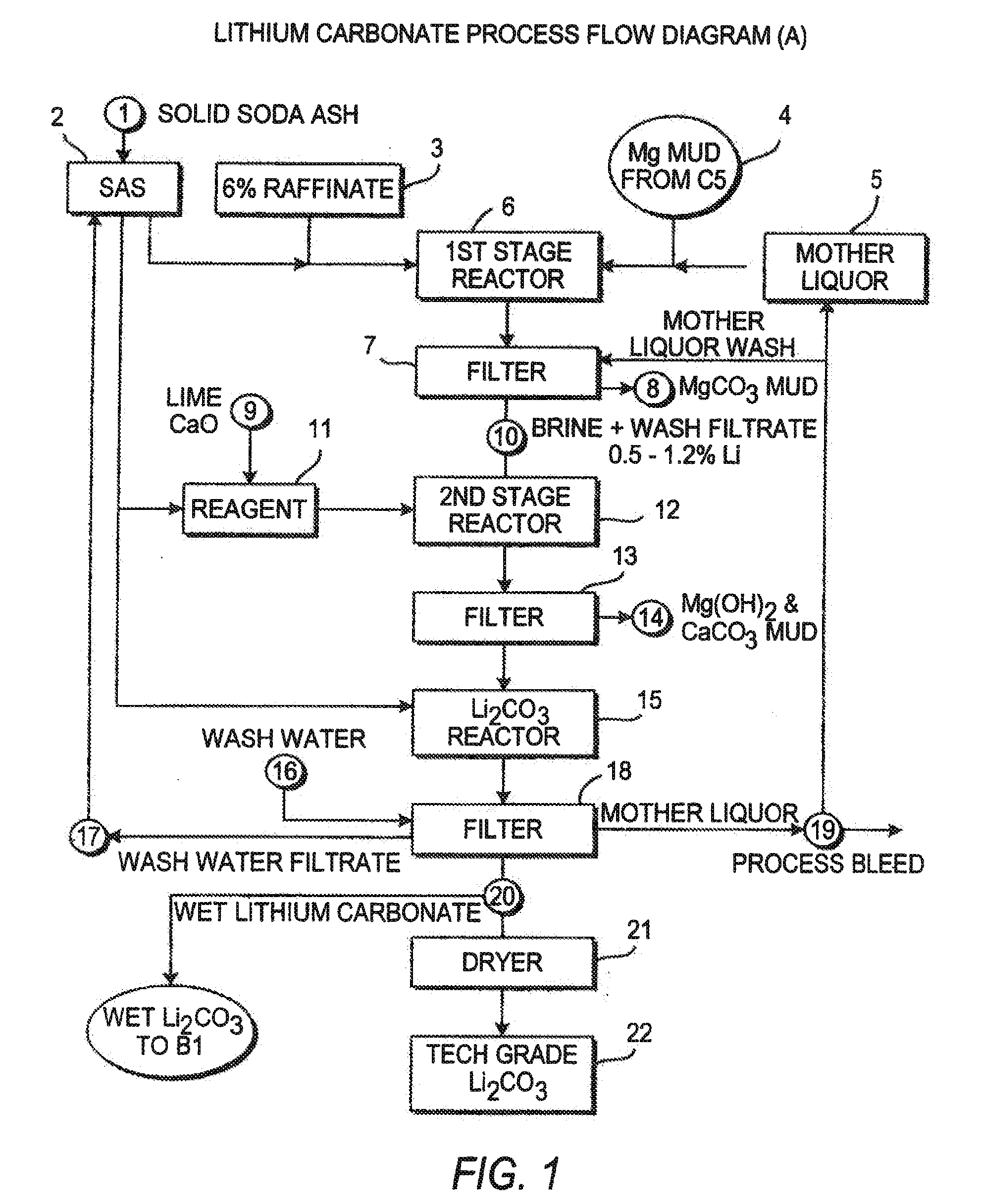
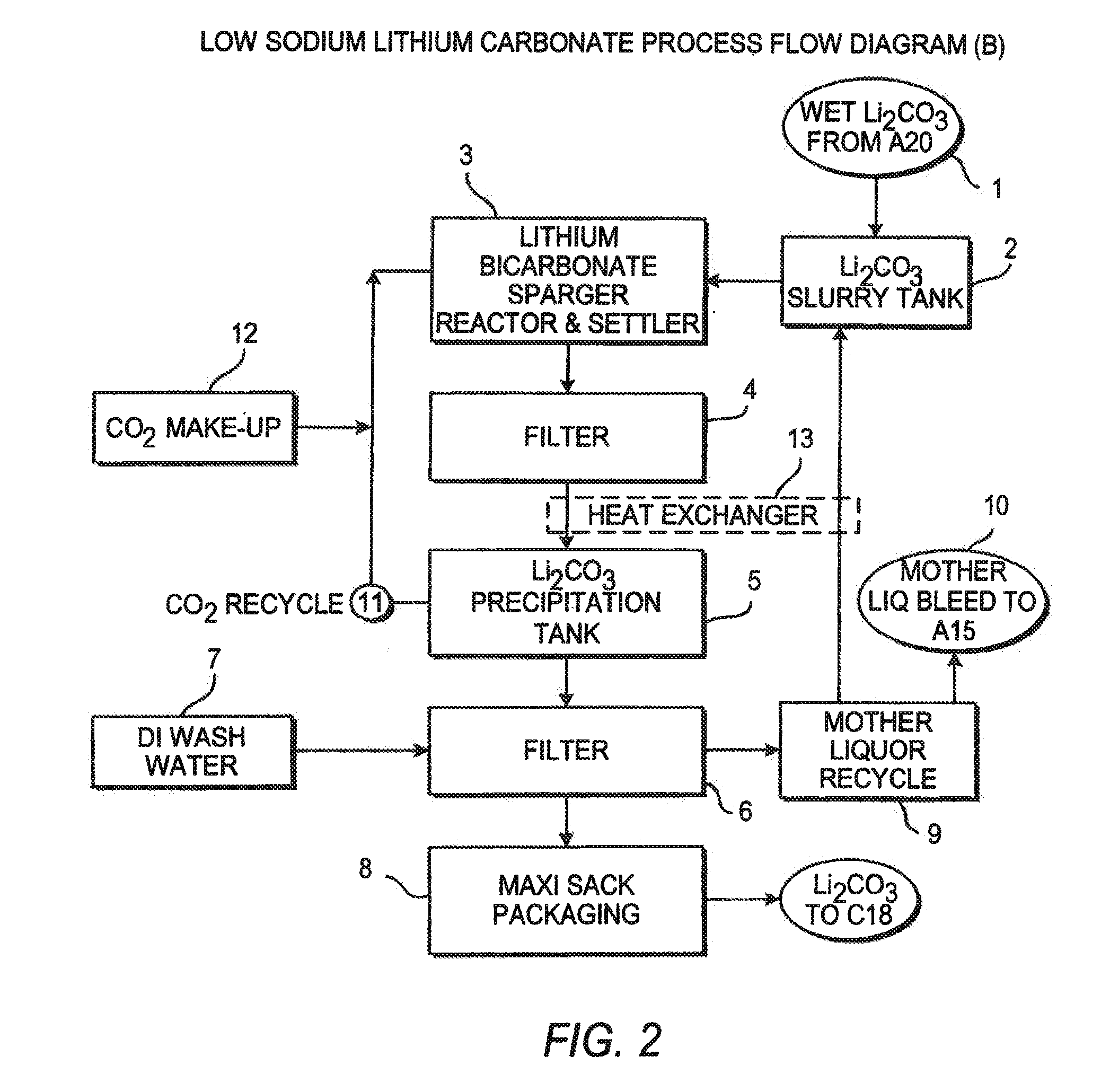
Methods and apparatus for the production of low sodium lithium carbonate and lithium chloride from a brine concentrated to about 6.0 wt % lithium are disclosed. Methods and apparatus for direct recovery of technical grade lithium chloride from the concentrated brine are also disclosed.
Owner:BORYTA DANIEL ALFRED +2
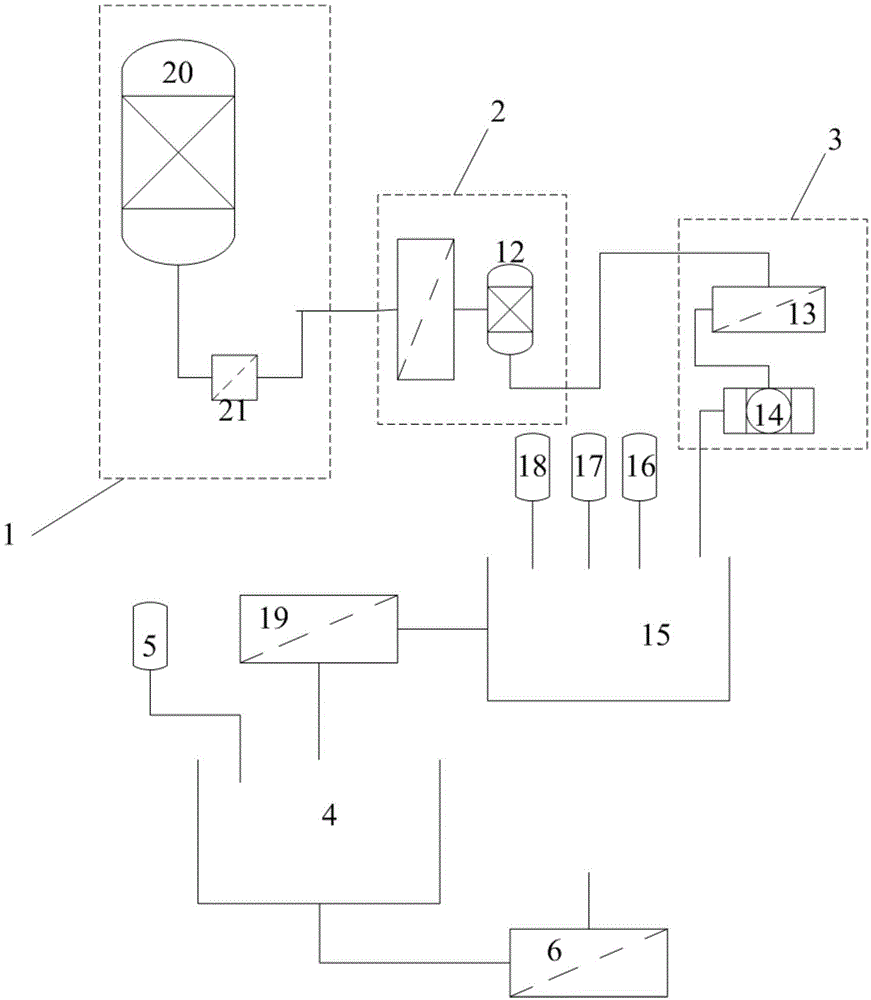
Method for extracting ultrahigh-purity lithium carbonate from salt lake brine with high magnesium-lithium ratio
The invention discloses a method for extracting ultrahigh-purity lithium carbonate from chloride brine with a high magnesium-lithium ratio. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a lithium chloride concentrated solution by an adsorption, desorption and evaporation concentration process; purifying, and precipitating lithium carbonate by using ammonium bicarbonate pulp; and converting into a lithium bicarbonate solution, filtering, and decarburizing. By improving steps and parameters of the conventional process, the purity of a product is more than 99.99 weight percent and the total amount of major impurities is not more than 0.002 weight percent without the introduction of additional high-cost purification steps such as ion exchange resin / membranes; and additional sodium ions are not introduced in the production process, byproducts at all stages can be recycled, and only an extremely small amount of waste solution is generated.
Owner:JIANGSU HAILONG LITHIUM IND TECH
System and method for treating a flue gas stream
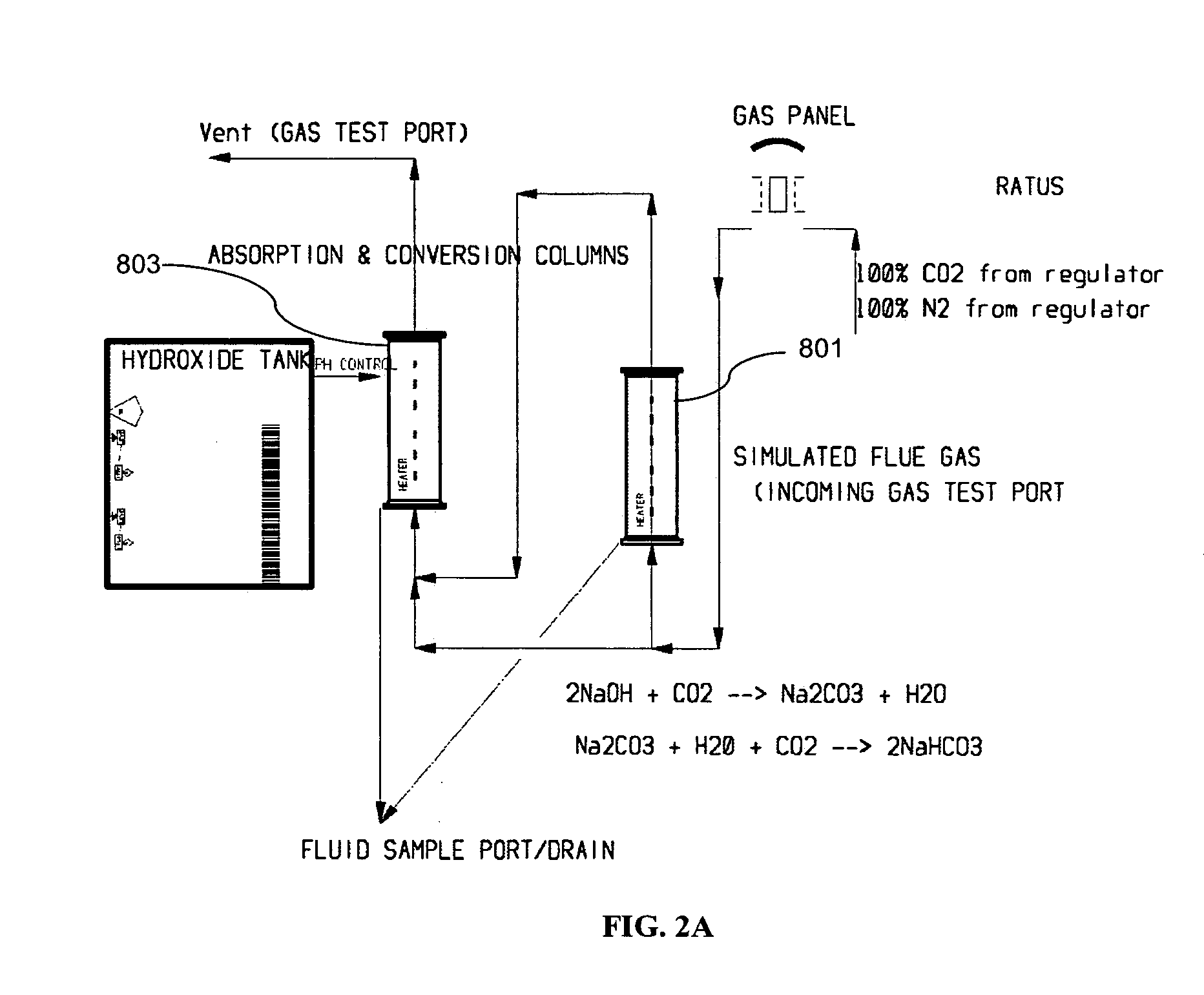
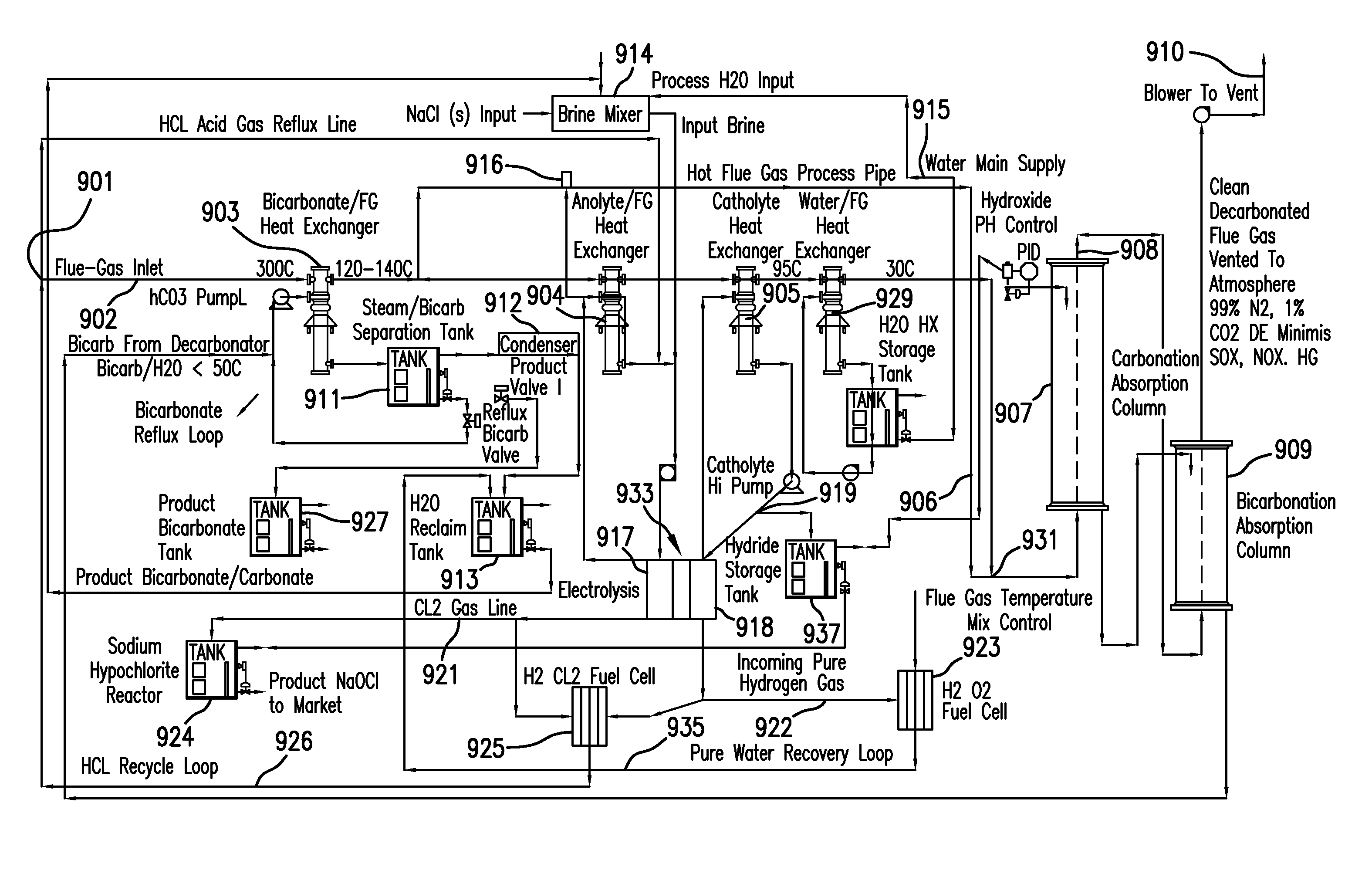
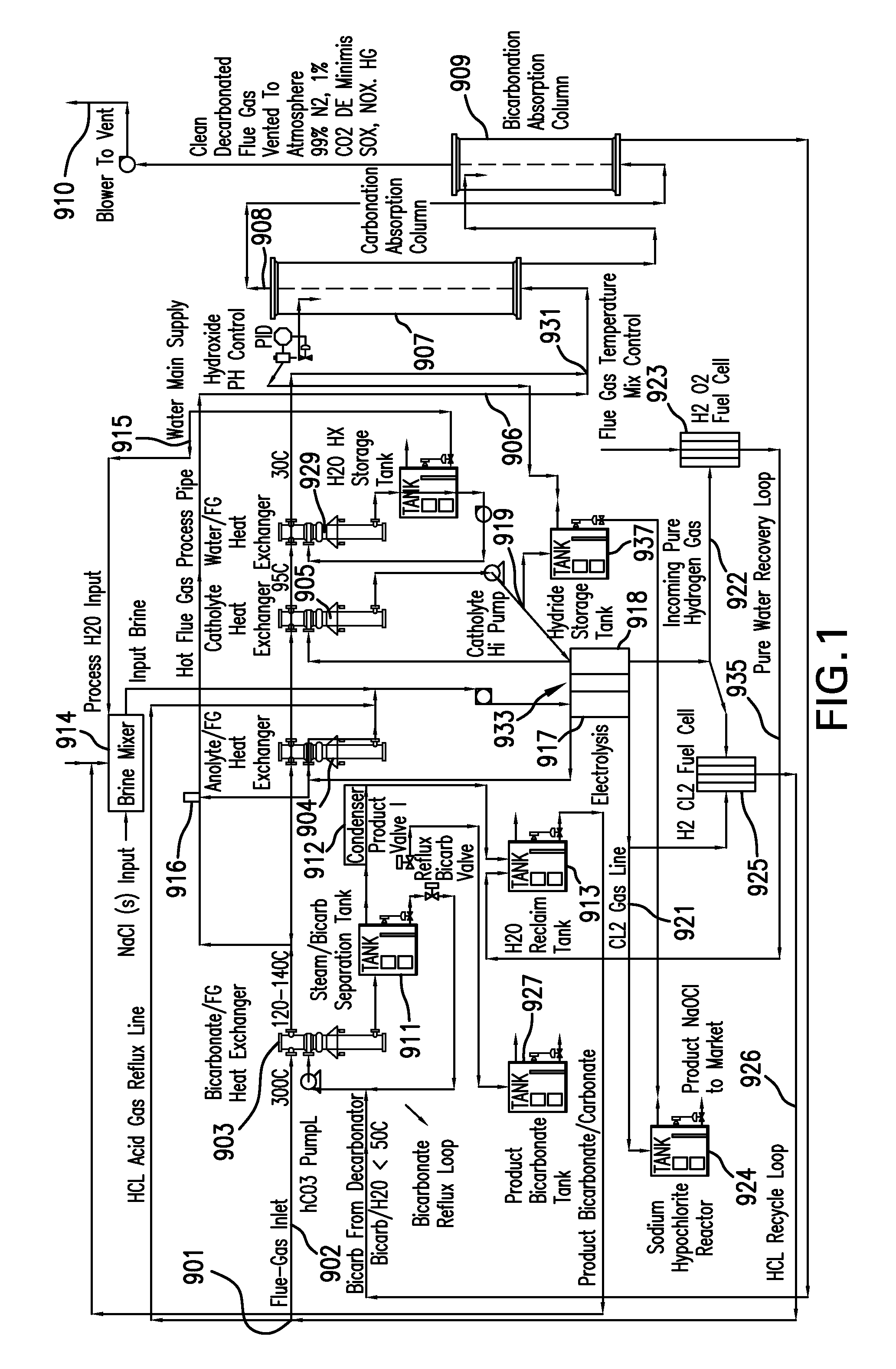
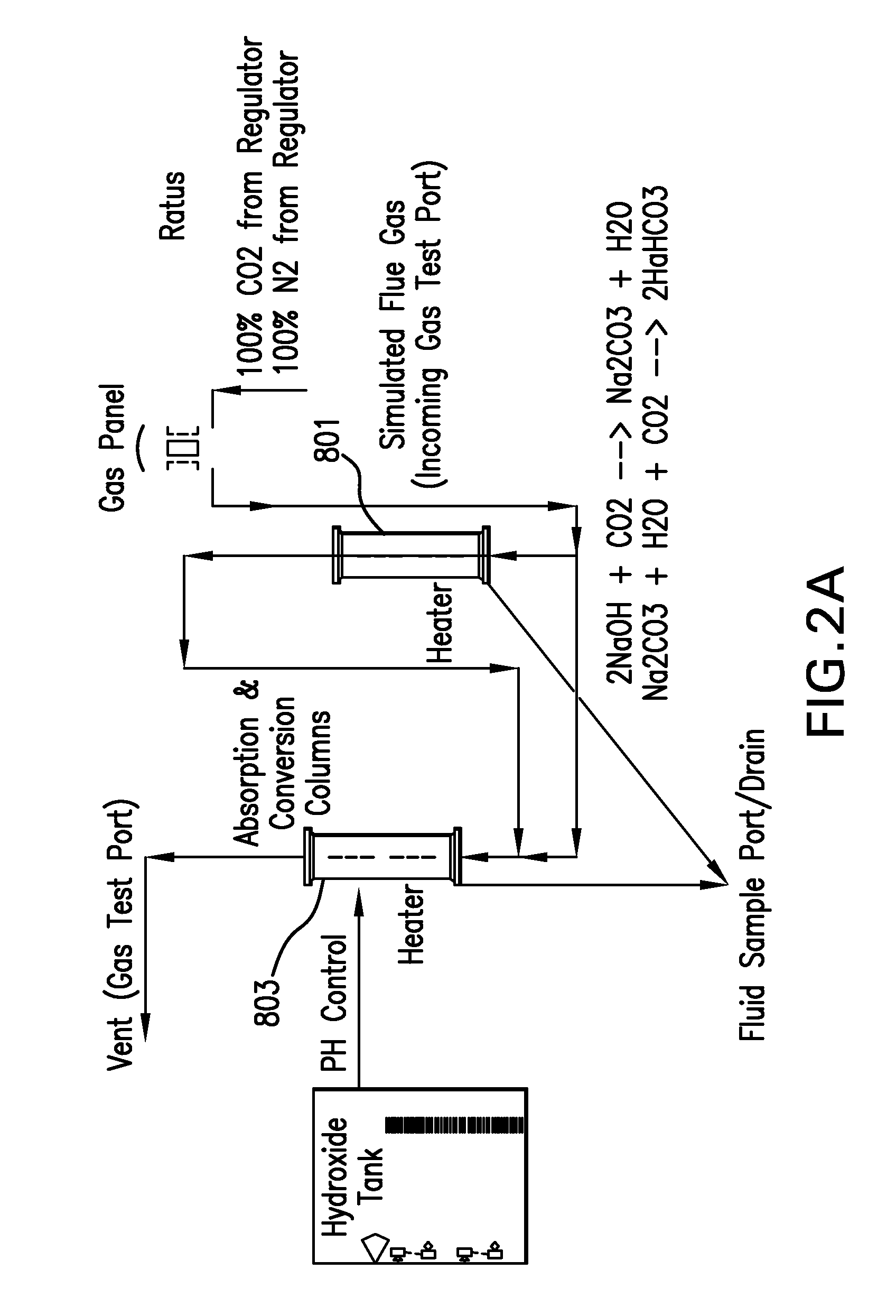
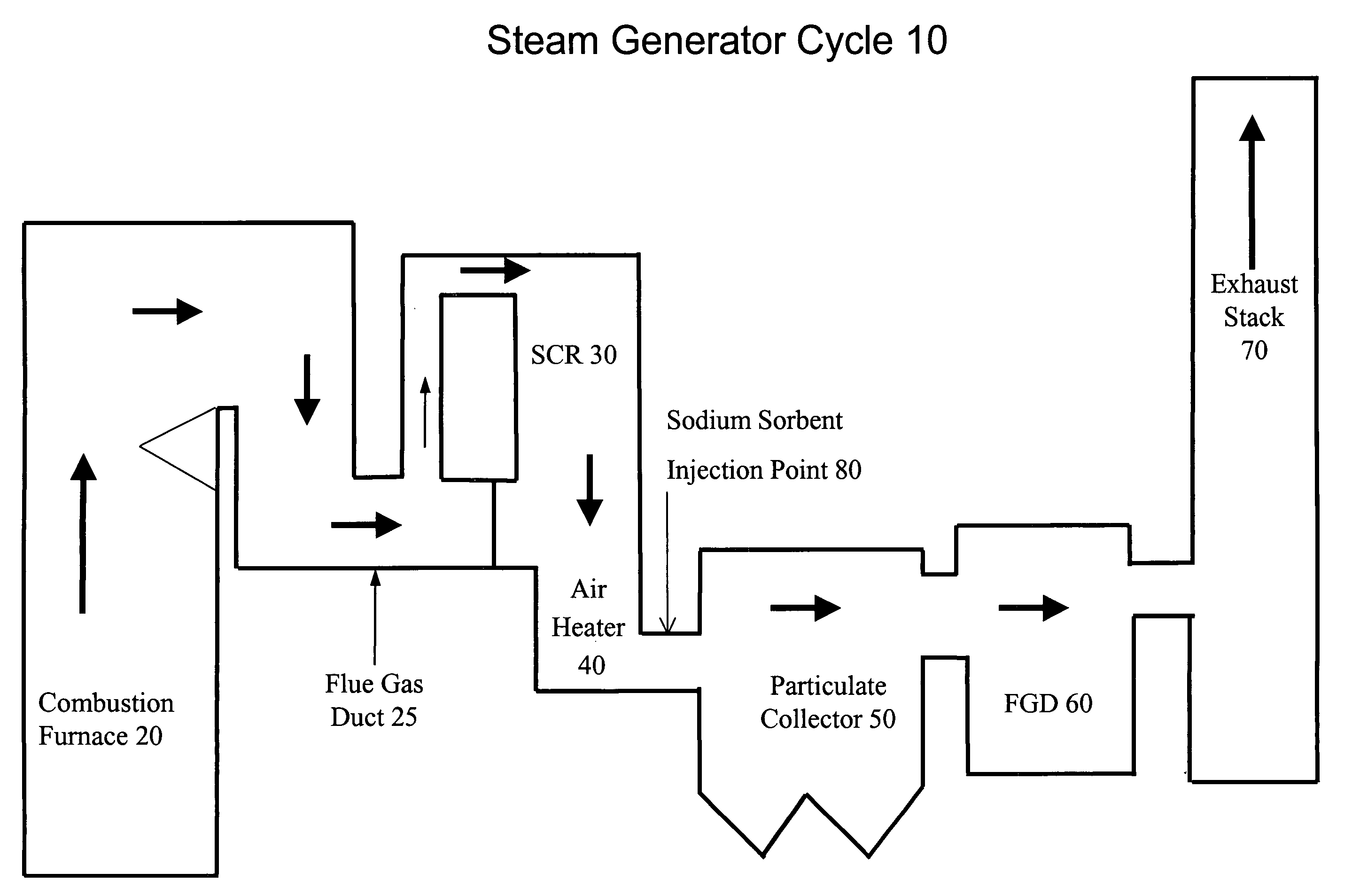
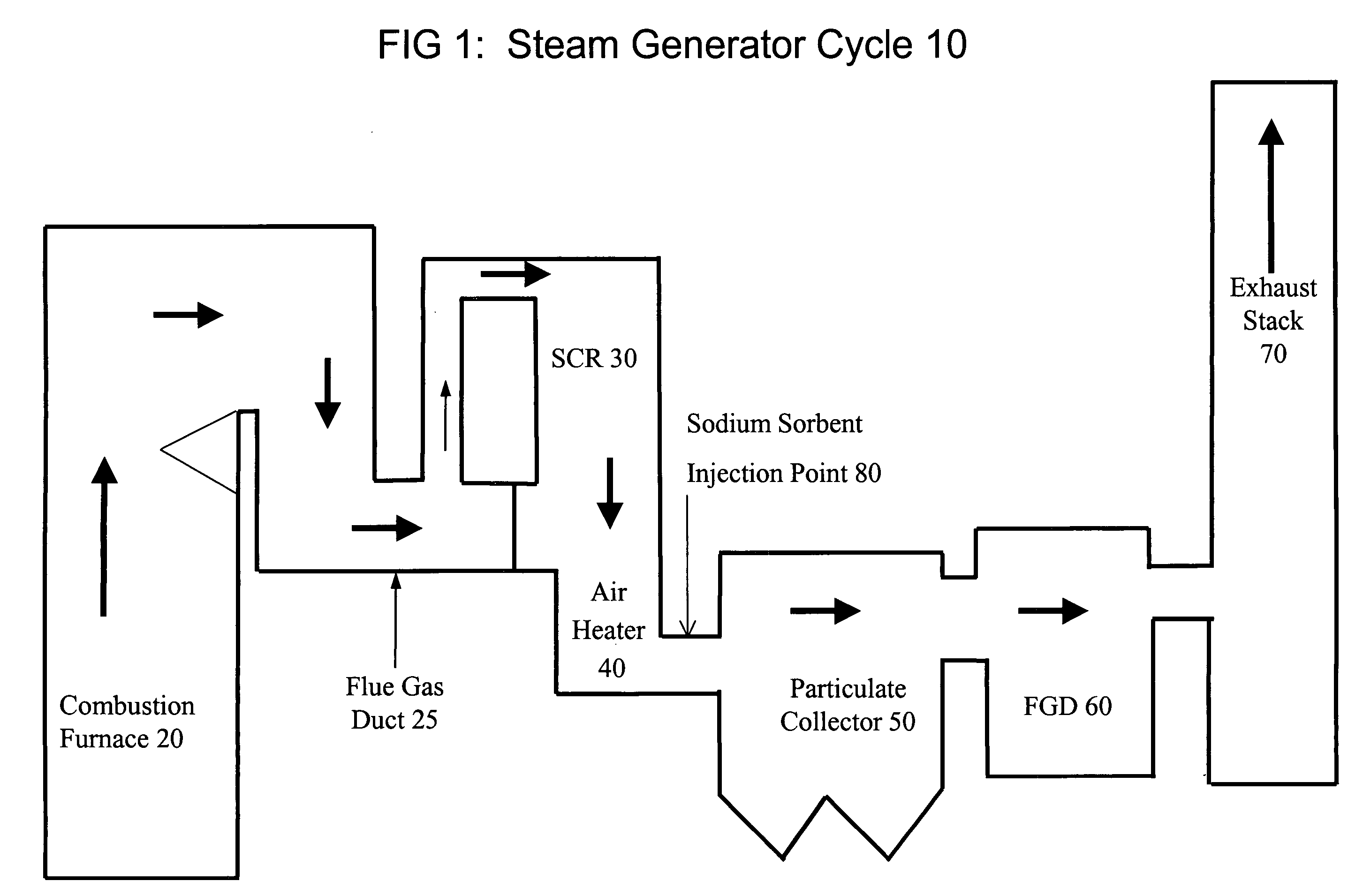
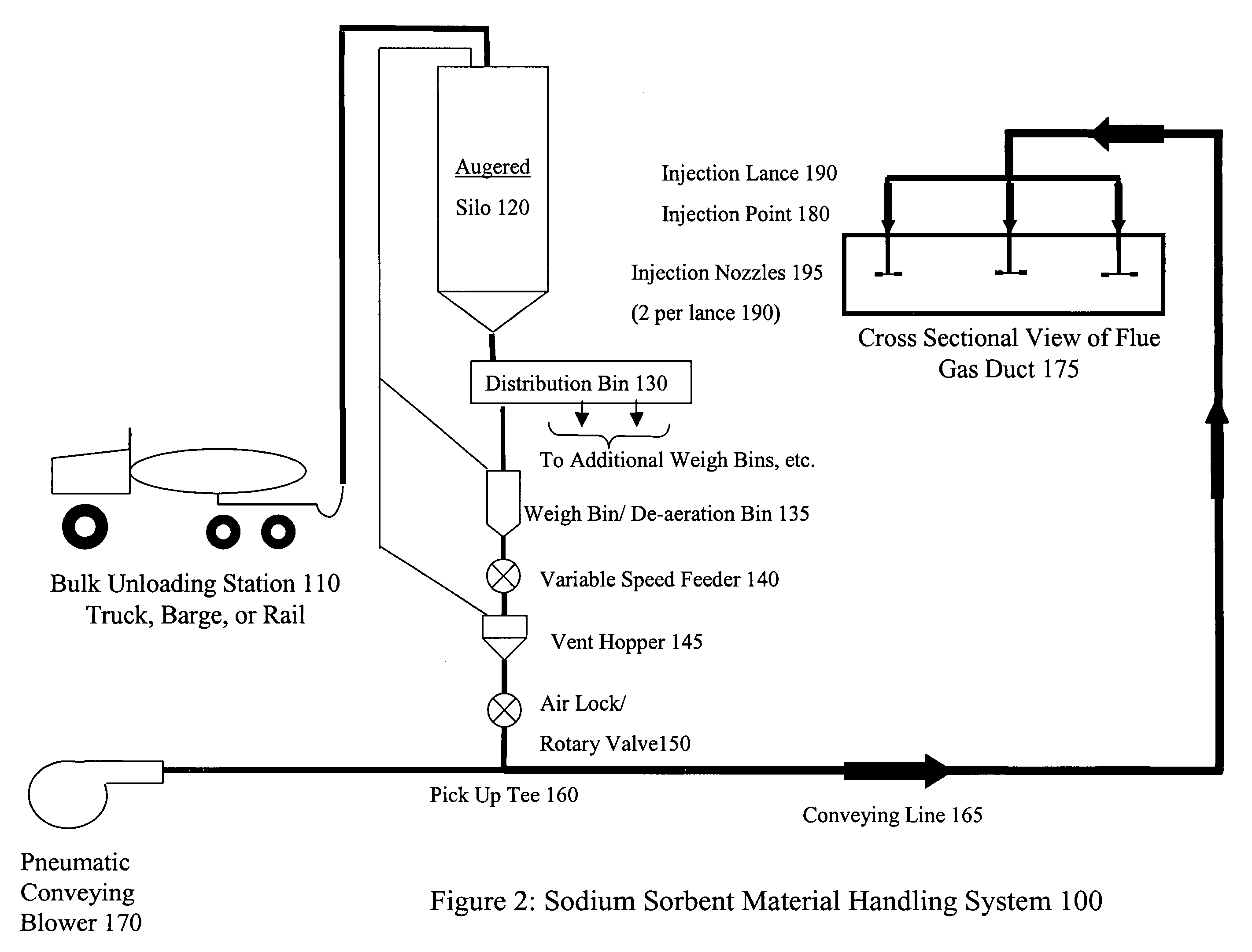
PendingUS20050201914A1Lower volume resistivityEfficient removalCombination devicesGas treatmentParticulatesDicarbonate
The present invention is a system and method for treating a flue gas stream to remove strong acid compounds selected from the group consisting of hydrofluoric acid (HF), hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and sulfur trioxide (SO3) by injecting a sodium sorbent selected from the group consisting of sodium sesquicarbonate, sodium carbonate-bicarbonate, trona ore, mechanically refined trona ore, and trona into the flue gas stream, calcining substantially all of the sodium sorbent in the presence of the flue gas stream to form a soda ash, reducing the concentration of the at least one strong acid compound in the flue gas stream by reacting the at least one strong acid compound with the soda ash to form a sodium based by-product; and changing the chemistry of the flue gas stream to reduce the overall average resistivity of the particulate matter.
Owner:AMERICAN ELECTRIC POWER CO INC
Production of lithium compounds directly from lithium containing brines
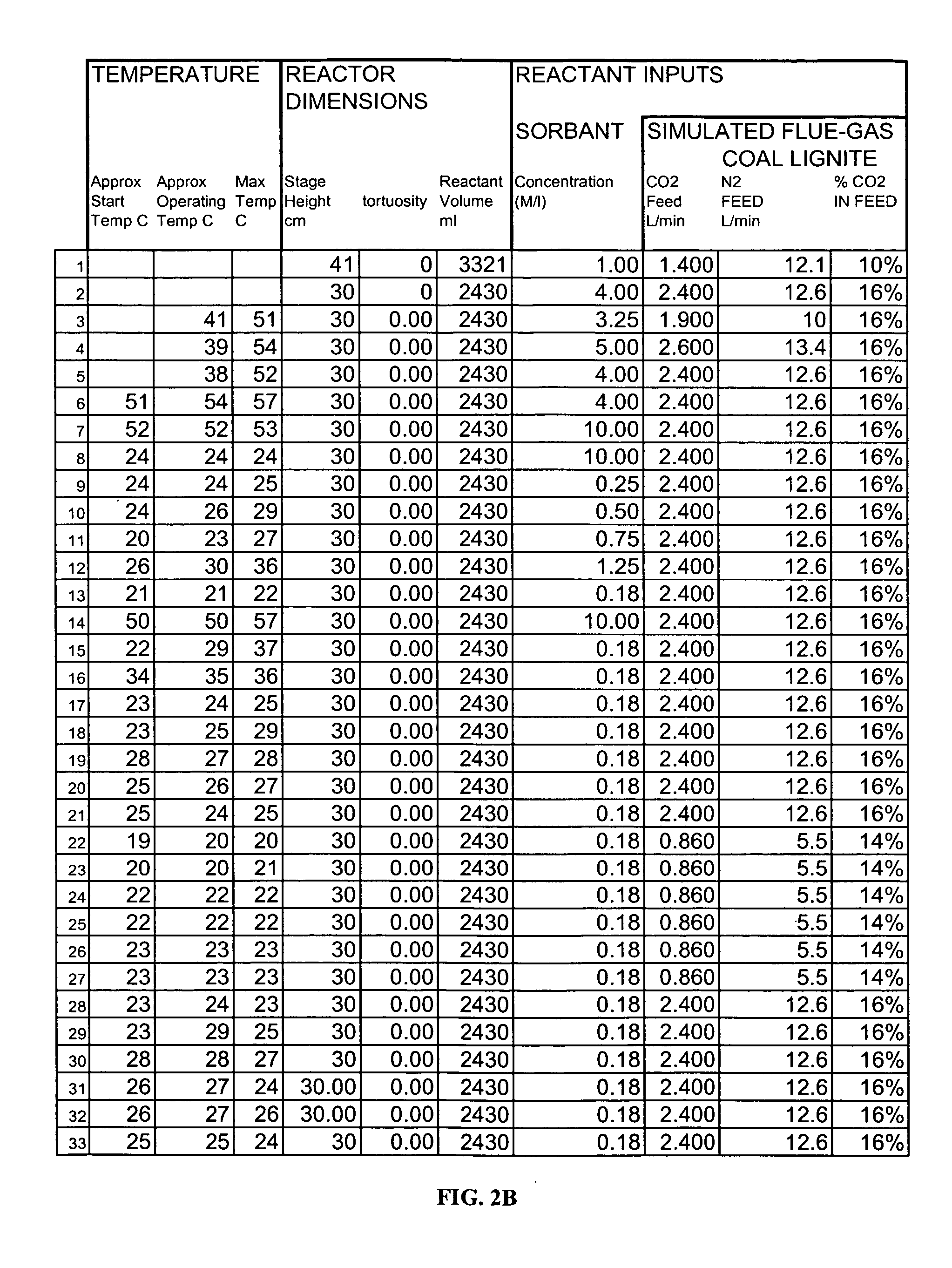
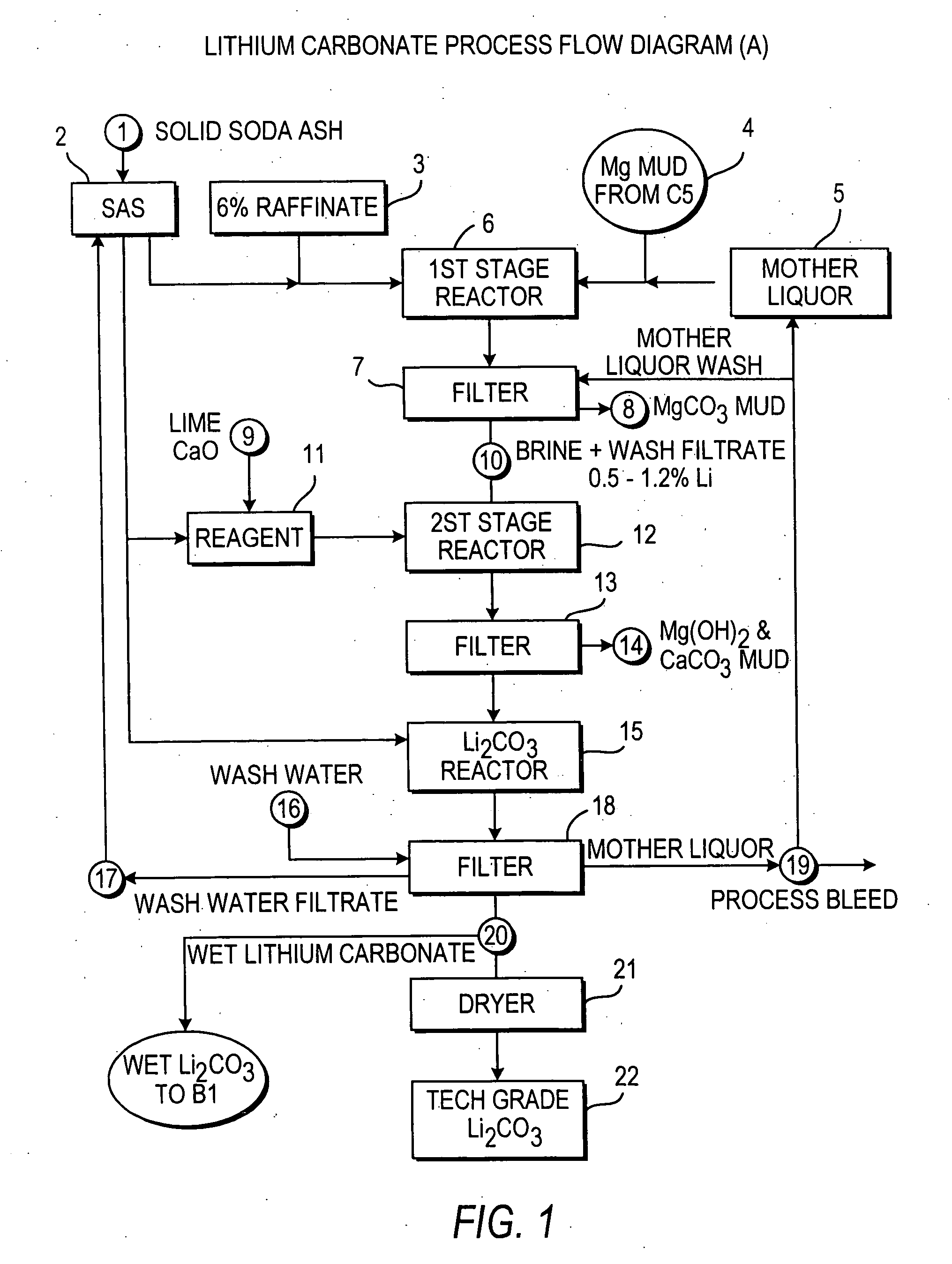
InactiveUS7157065B2Reduce in quantityPromote absorptionCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesSlurryLithium compound
A continuous process for directly preparing high purity lithium carbonate from lithium containing brines by preparing a brine containing about 6.0 wt % lithium and further containing other ions naturally occurring in brines; adding mother liquor containing carbonate to precipitate magnesium; adding a solution of CaO and sodium carbonate to remove calcium and any residual magnesium; precipitating lithium carbonate from the purified brine by adding soda ash solution; filtering to obtain solid lithium carbonate; preparing an aqueous slurry of the lithium carbonate and introducing carbon dioxide gas at a temperature from at least minus 10 to +40° C.; passing the lithium bicarbonate solution through a filter to clarify the solution; introducing said filtered lithium bicarbonate solution into a reactor and adjusting the temperature of the solution to from 60–100° C. to precipitate ultra-pure lithium carbonate.
Owner:ROCKWOOD LITHIUM INC
A method for extracting lithium carbonate from high magnesium-lithium ratio salt lake brine
InactiveCN102275956AReduce lossesNo decrease in recycling efficiencyNanotechnologyLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesHigh magnesiumInorganic salts
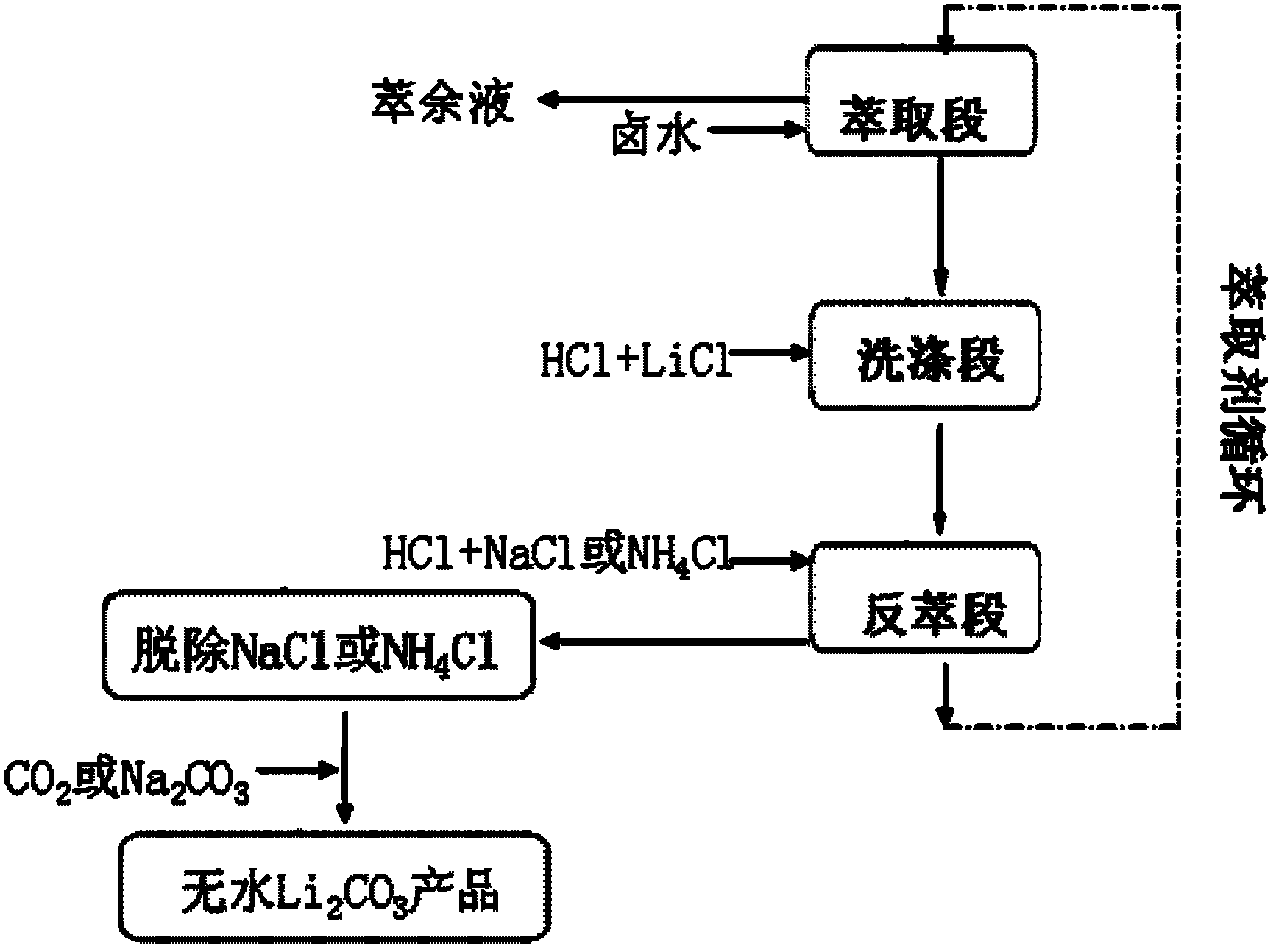
The invention discloses a method for extracting lithium carbonate from salt lake brine with high magnesium / lithium ratio, belonging to the technical filed of inorganic salt extraction. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out extraction, washing and stripping steps to obtain a stripping solution composed of NaCl and LiCl or NH4Cl and LiCl, then introducing CO2 or adding Na2CO3, and controlling the pH value and dynamic conditions to obtain a nanoscale or microscale Li2CO3 product. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple steps, low equipment requirement and wide sources of raw materials, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Production of lithium compounds directly from lithium containing brines
InactiveUS20110123427A1Reduce in quantityPromote absorptionVarying alkali metal carbonate water contentRubidium/caesium/francium compoundsLithium chlorideLithium carbonate
Methods and apparatus for the production of low sodium lithium carbonate and lithium chloride from a brine concentrated to about 6.0 wt % lithium are disclosed. Methods and apparatus for direct recovery of technical grade lithium chloride from the concentrated brine are also disclosed.
Owner:ROCKWOOD LITHIUM INC
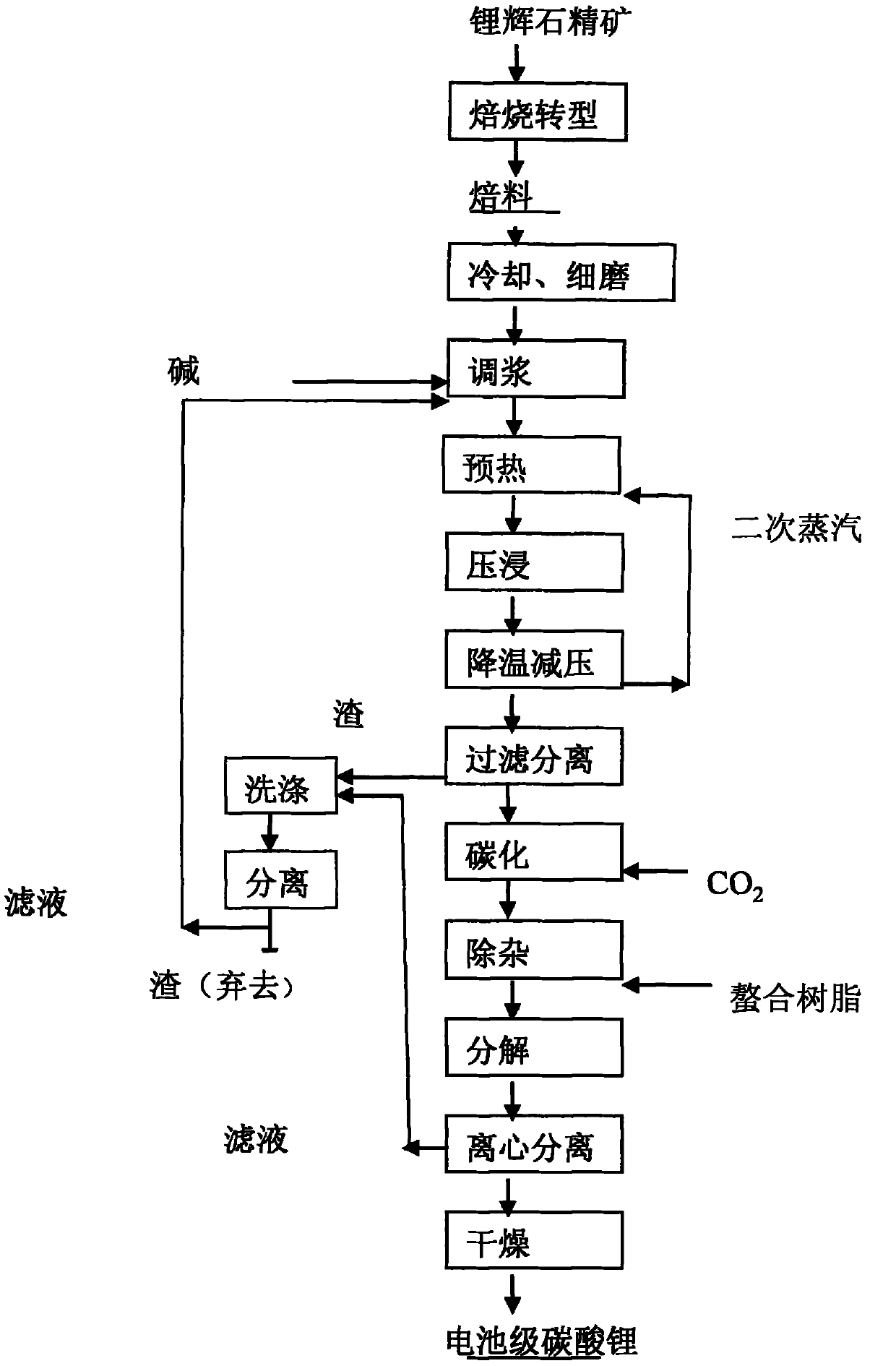
Clean production method of battery level lithium carbonate
The invention belongs to the field of inorganic chemistry and relates to a clean production method of a battery level lithium carbonate. According to the production method of the battery level lithium carbonate, spodumene is adopted as a raw material and the battery level lithium carbonate is obtained through five steps of preparing beta-spodumene lithium concentrate, preparing a lithium sulfate solution, removing ions, preparing lithium carbonate and then preparing the battery level lithium carbonate. According to the production method of the battery level lithium carbonate, a precipitator is directly added into the prepared lithium sulfate to remove metal ions in the lithium sulfate solution without the preparation of industrial lithium carbonate, so that the production cycle and the production cost of the battery level lithium carbonate are greatly reduced; and meanwhile, the production process is simple to operate, safe and environment-friendly. The product prepared by the production method of the battery level lithium carbonate disclosed by the invention is stable in quality and accordant with industrial standards of the battery level lithium carbonate and has important industrial popularization values.
Owner:阿坝中晟锂业有限公司
Production of lithium compounds directly from lithium containing brines
InactiveUS20070160516A1Promote absorptionConstant liquid volumeCrystallization separationCarbonate/bicarbonate preparationLithium chlorideLithium carbonate
Methods and apparatus for the production of low sodium lithium carbonate and lithium chloride from a brine concentrated to about 6.0 wt % lithium are disclosed. Methods and apparatus for direct recovery of technical grade lithium chloride from the concentrated brine are also disclosed.
Owner:ROCKWOOD LITHIUM INC
Process for preparing lithium chlorate by lithium extracted from lepidolite
InactiveCN1827527AReduce energy consumptionReduce investmentLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesLithium carbonateSulfate
The invention relates to a method for preparation of lithium carbonate extracting lithium from lithionite. The invention consists of milling, leaching and filtering after modifying by broasting lithonite ore together with the additive findings such as calcium fluoride, calcium sulfate and sodium sulfate at a certain temperature, adding sodium carbonate into the leachate to deposite lithium ion forming the deposition of lithium carbonate, and washing and drying the solid gained by filtering to get the product of lithium carbonate. The filtered mother liquid returns to the circulation to deposit lithium ion. After secondary circulation, we get the mixed salts of potassium sulfate and sodium sulfate as the educts by washing and drying the aforementioned filtered mother liquid. Some of the mixed salts return as findings roasted with lithonite ore for circulation use, while others can be used as raw material for preparation of potassium sulfate.
Owner:钟辉
Method for separating magnesium from lithium and extracting lithium from brine
InactiveCN101538057ASolve the difficult technical problems of filtrationSimple technical processMultistage water/sewage treatmentSolution crystallizationFiltrationHigh energy
The invention provides a method for separating magnesium from lithium and extracting the lithium from high magnesium-lithium ratio brine (brine from a saline lake, from underground and from an oil-gas field). The method comprises: sodium salt and potassium and magnesium mixed salt are separated from the brine by evaporation of a saltpan; after boron extraction, sodium hydroxide is used for precipitating Mg<2+> from obtained old brine, and crystallized Mg(OH)2 is obtained by modification and precipitation condition control; filtration and separation are carried out to remove the Mg(OH)2 to realize separation of magnesium and lithium; after filtered mother solution is vaporized and concentrated for 2-4 times, Na2SO4 and NaCl are separated by crystallization, and pure caustic soda can be added to form lithium carbonate from lithium; or the operation of further evaporation is carried out until Na2SO4 and NaCl are separated by multiple times of natural evaporation or forced evaporation concentration and multiple times of cooling crystallization; the operations of evaporation and concentration are carried out until LiCl saturation, and LiCl products can be prepared after the operation of cooling crystallization is carried out. Compared with the prior art for separating the magnesium from the lithium and extracting the lithium from the brine, the method obtains the crystallized Mg(OH)2 by modification and precipitation condition control, solves the existing technical problem of hard filtration of Mg(OH)2, solves the defects of high energy consumption, complex process and high cost of the existing calcination method, and solves the fundamental defects of low Li<2+> recovery ratio and complex technical process of the traditional precipitation method. The Li<2+> recovery ratio ranges from 85-93%, Mg<2+> removal ratio is more than 99.5%, and the method solves the problem of extracting Li<+> and Mg<2+> from high-magnesium and low-lithium brine with Mg<2+> / Li<+>>=20 mass ratio.
Owner:钟辉
Method for recovering lithium from waste lithium battery to prepare battery grade lithium carbonate
InactiveCN106505225AHigh recovery rateReduce lossesReclaiming serviceable partsWaste accumulators reclaimingMagnesium saltLithium carbonate
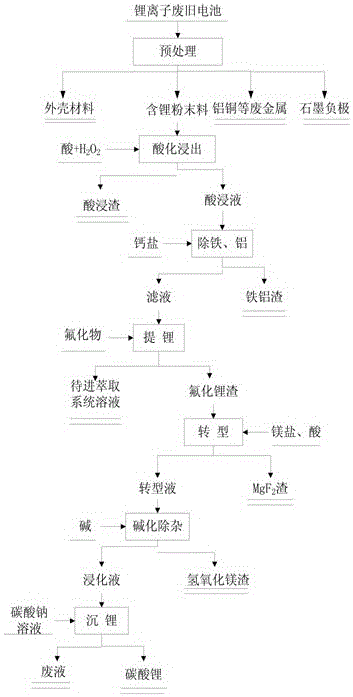
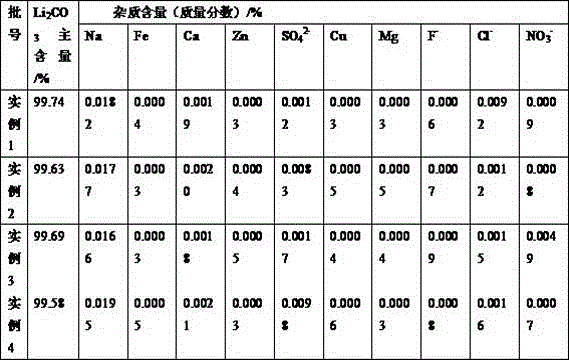
The invention discloses a method for recovering lithium from a waste lithium battery to prepare battery grade lithium carbonate. Lithium is extracted from the waste lithium battery as a raw material to prepare the battery grade lithium carbonate. The method mainly comprises the following steps of (1) battery dismantling; (2) acidifying and leaching; (3) iron and aluminum removal; (4) fluorinating lithium deposition; (5) magnesium salt transformation; (6) alkalifying impurity removal; and (7) lithium deposition employing sodium carbonate. The lithium is recovered from the waste lithium battery to prepare the battery grade lithium carbonate, so that the battery grade lithium carbonate has the advantages of being high in lithium recovery rate, small in losses of other metal elements, friendly to environment and high in product purity; the main content of a product exceeds 99.5%; the requirements of battery grade products are met; and the method is simple in process, low in production cost and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:GANFENG LITHIUM CO LTD
Novel method for producing lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide
InactiveCN102115101ASimple production processLow costLithium oxides/hydroxidesLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesLithium sulphateCalcium hydroxide
The invention relates to a novel method for producing lithium carbonate and lithium hydroxide, which belongs to the technical field of production of lithium salts. The method comprises the following steps of: baking spodumene concentrate; preparing a lithium sulfate solution; preparing lithium carbonate mother liquor; and preparing lithium hydroxide, wherein the lithium hydroxide can also be obtained by adding barium hydroxide into the lithium carbonate mother liquor. The method has the advantages that: lime is added into a lithium carbonate sinker mother liquor to produce the lithium hydroxide by causticizing and transforming, and the production of lithium carbonate is combined with the production of the lithium hydroxide, so that a process flow is simplified, investment and production costs are lowered, a production process is more flexible to regulate and control, and the quality of a lithium carbonate product is more stable. By adopting the method, the mother liquor of lithium carbonate is easier to treat, impurities in the lithium hydroxide mother liquor are easy to treat, and the product quality is not influenced.
Owner:屈俊鸿
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com