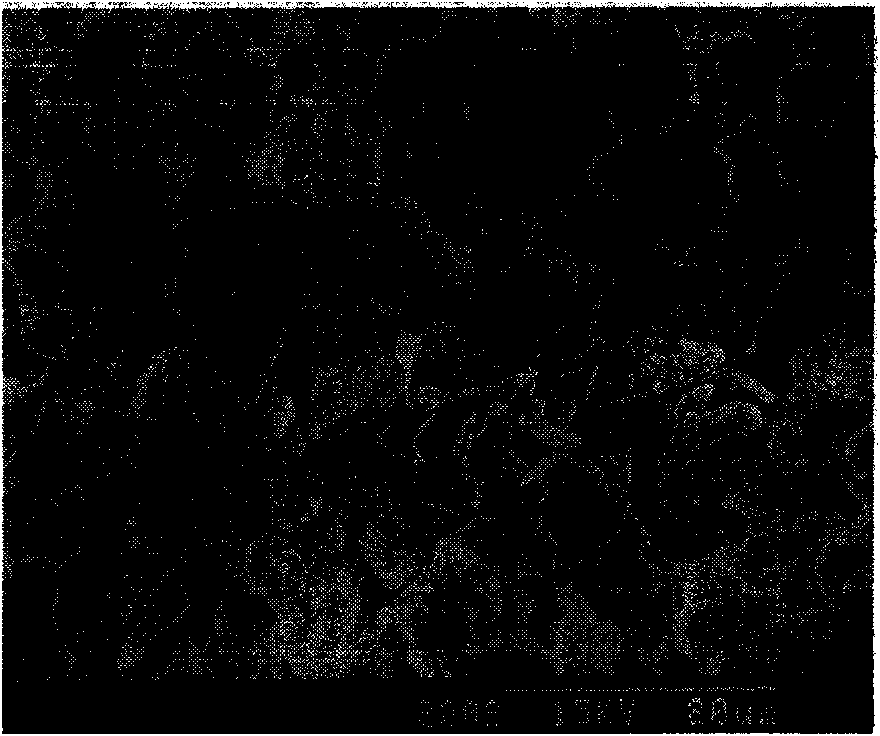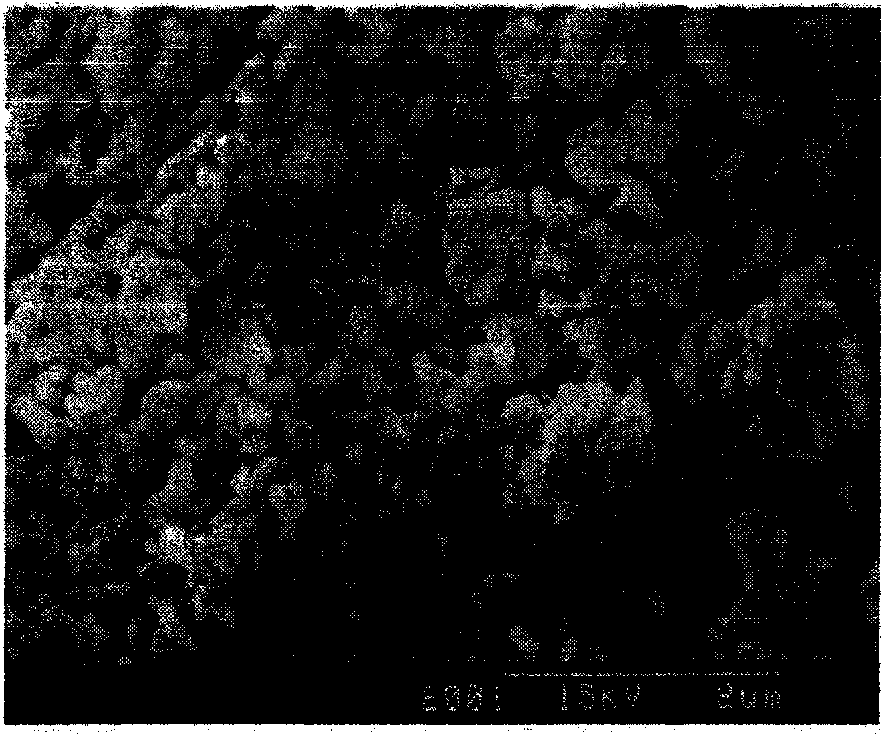Method for separating magnesium from lithium and extracting lithium from brine
A technology of brine magnesium and brine, applied in the field of brine magnesium lithium separation and preparation of inorganic lithium salt products, can solve the problems of difficult filtration, large quantity, large loss, etc., achieve simple technical process, overcome low recovery rate, and low production cost Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Table 1 embodiment brine composition (unit: g / L)
[0019] brine name
[0020] Get 2 liters of old bittern (see Table 1 for composition) after natural evaporation and precipitation of sodium chloride, potassium and magnesium mixed salts from the brine of Jinaier Salt Lake in Xitai, Qinghai; 300 mL of magnesium hydroxide slurry with a concentration of 15% (mass ratio) As the bottom liquid, add it into a 5000mL beaker (reactor), take 700mL of analytically pure sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 16mol / L, add the old brine and sodium hydroxide solution into the reactor continuously in parallel, and add the old brine at a rate of 40mL / min, the sodium hydroxide solution was added at a rate of 13mL / min, and the reaction temperature was controlled and kept at 85°C with a constant temperature water bath; at the same time, 3 grams of analytically pure polyacrylamide was added at one time, and 54 grams of analytically pure octadecylamine hydrochloride was a...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Get 2.0L of old bittern that Table 1 forms; Get concentration and be that 600mL of magnesium hydroxide slurry of 3.5% (mass ratio) is bottom liquid, join in the 5000mL beaker (reactor), get concentration and be 50% (mass ratio percentage) Industrial grade liquid caustic soda 700mL, old brine and liquid caustic soda are continuously added to the reactor in parallel flow, the old brine is added at a rate of 40mL / min, the liquid caustic soda is added at a rate of 13mL / min, and the reaction temperature is controlled and maintained at 85°C by a constant temperature water bath; At the same time, add 5 grams of industrial first-grade polyferric sulfate at one time, and add industrial first-grade ammonium bicarbonate in 2 times. For the first time, 20 grams of ammonium bicarbonate was added at the beginning of the reaction, and for the second time, ammonium bicarbonate was added when the reaction was halfway through. 22 grams, after adding the reaction materials, use the above-m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com