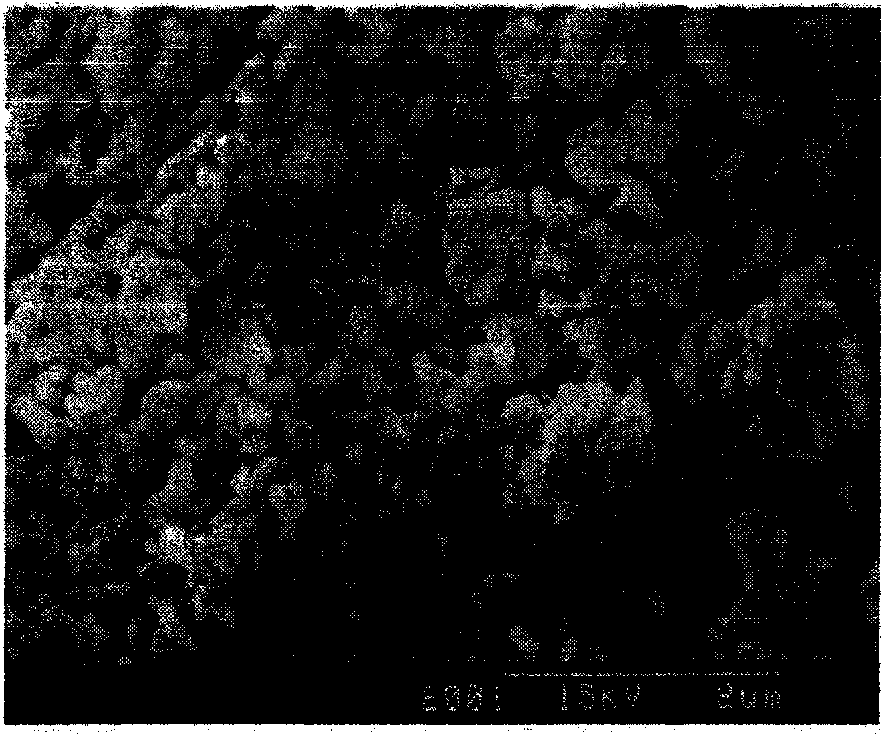Patents
Literature
679 results about "High magnesium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In hypermagnesemia, the level of magnesium in blood is too high. Magnesium is one of the body's electrolytes, which are minerals that carry an electric charge when dissolved in body fluids such as blood, but the majority of magnesium in the body is uncharged and bound to proteins or stored in bone.
Method for preparing lithium adsorbent resin
ActiveCN102631897AGood choiceImprove efficiencyOther chemical processesLithium compoundsLithiumHigh magnesium
The invention discloses a method for preparing lithium adsorbent resin. The method includes steps of 1, preparing a precursor of the lithium adsorbent resin; 2, uniformly mixing the prepared precursor with adhesives and porogen to prepare disperse phase; 3, preparing continuous phase incompatible with the disperse phase; 4, adding the disperse phase into the continuous phase, stirring, leading the disperse phase to be scattered into beads with suitable granularity, and solidifying the beads into spherical particles under certain conditions; and (5) removing substances such as a dispersing agent, the porogen and the like in the spherical particles, and obtaining the lithium adsorbent resin capable of being used for extracting lithium from high-magnesium and low-lithium brine after activating treatment. The preparation method is simple, and the prepared lithium adsorbent resin has the advantages of zero pollution, high efficiency and adsorbent capacity, long service period, recyclability and the like.
Owner:SUNRESIN NEW METERIALS CO LTD XIAN
Method for producing low phosphorus steel by smelting semisteel
InactiveCN101696462APrevent rephosphorizationEasy to operateManufacturing convertersSteelmakingHigh magnesium
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy, and relates to a method for producing low phosphorus steel by smelting semisteel, which solves the technical problem of controlling the steelmaking end point of a converter within 0.006 percent. The method is mainly realized by adjusting slag-making parameters of the converter smelting by adopting a single slag method, which comprises that: the slag-making materials added in the converter slag-making process consist of 40-50kg of active lime, 20-30kg of high-magnesium lime and 15-25kg of composite slag former based on per ton of tapping molten steel; and the slag-making materials are added in twice. In addition, by controlling an oxygen supply system and an end point control system, the dephosphorization rate of the converter can reach over 92 percent; molten steel containing less than 0.006 percent of phosphorus is obtained; steel ladle slag de-P and alloy re-P are controlled within 0.002 percent. The method can stably produce finished low phosphorus steel containing less than 0.010 percent of phosphorus, and is characterized by simple operation method, small investment on equipment and low production cost.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +3
Ion sieve for selectively extracting lithium and application thereof
The invention relates to an ion sieve for selectively extracting lithium and the application thereof. The ion sieve adopts one or the compound of more than one of the following components: Li4Ti5O12, LixMeyTi5O12, and Li4MemTinO12, wherein Me is one or the compound of more than one of the following components: V, Fe, Co, Mn, Al, Ba, Ag, Zr, and Nb, x is greater than 3 and smaller than 4, y is greater than 0 and smaller than 1, m is greater than 0 and smaller than 1, and n is greater than 4 and smaller than 5. The ion sieve is particularly applicable to magnesium and lithium separation in brine with a high magnesium / lithium ratio, and has favorable intercalation and deintercalation performances to Li ions. The material for the titanic acid lithium ion sieve provided by the invention is easy to get and low in cost, the ion sieve has high selectivity and higher adsorptive capacity to the Li ions, as well as long circulating life. The process adopting the titanic acid lithium ion sieve to perform magnesium and lithium separation has the advantages of short procedure, simplicity in operation, low manufacturing cost, and easiness in industrial application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing lithium carbonate by using salt lake brine with high magnesium-to-lithium ratio
InactiveCN101698488AReduce energy consumptionNo way outLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesEvaporationCalcination
The invention provides a method for preparing industrial lithium carbonate by using salt lake brine with a high magnesium-to-lithium ratio. In the method, a TBP-CON-KS+FeCl3 is used as an extraction system to extract and back-extract impurity-free salt lake brine with a high magnesium-to-lithium ratio, the residual liquid obtained after back-extraction is converted by alkaline liquor for precipitation, the precipitate is washed to form an industrial lithium carbonate product and the lithium carbonate content is more than or equal to 99.0 percent and is in accordance with the requirements of GB / T 11 075-2003 standards. The method has the advantages that: liquid-liquid extraction with an organic solvent is adopted to realize the separation of lithium from magnesium, the lithium carbonate is precipitated by inorganic slats, the lithium carbonate is extracted from the salt lake brine with a high magnesium-to-lithium ratio, the process is simple, the control is easy, the operational reliability is high and the application range is wide; a process of calcination and diluted lithium solution evaporation and concentration is saved, the energy consumption is only 30 to 50 percent of that of the conventional process for producing lithium carbonate by using lithium-containing brine; initial raw material consumption comparison show that the production cost of the method is only about 8 percent of that of the prior art; and the raw material brine can return to a storage pool after the extraction of the lithium carbonate, so no by production disposal problem is involved, environmental pollution is relatively low and lithium yield in the whole process is more than or equal to 70 percent.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
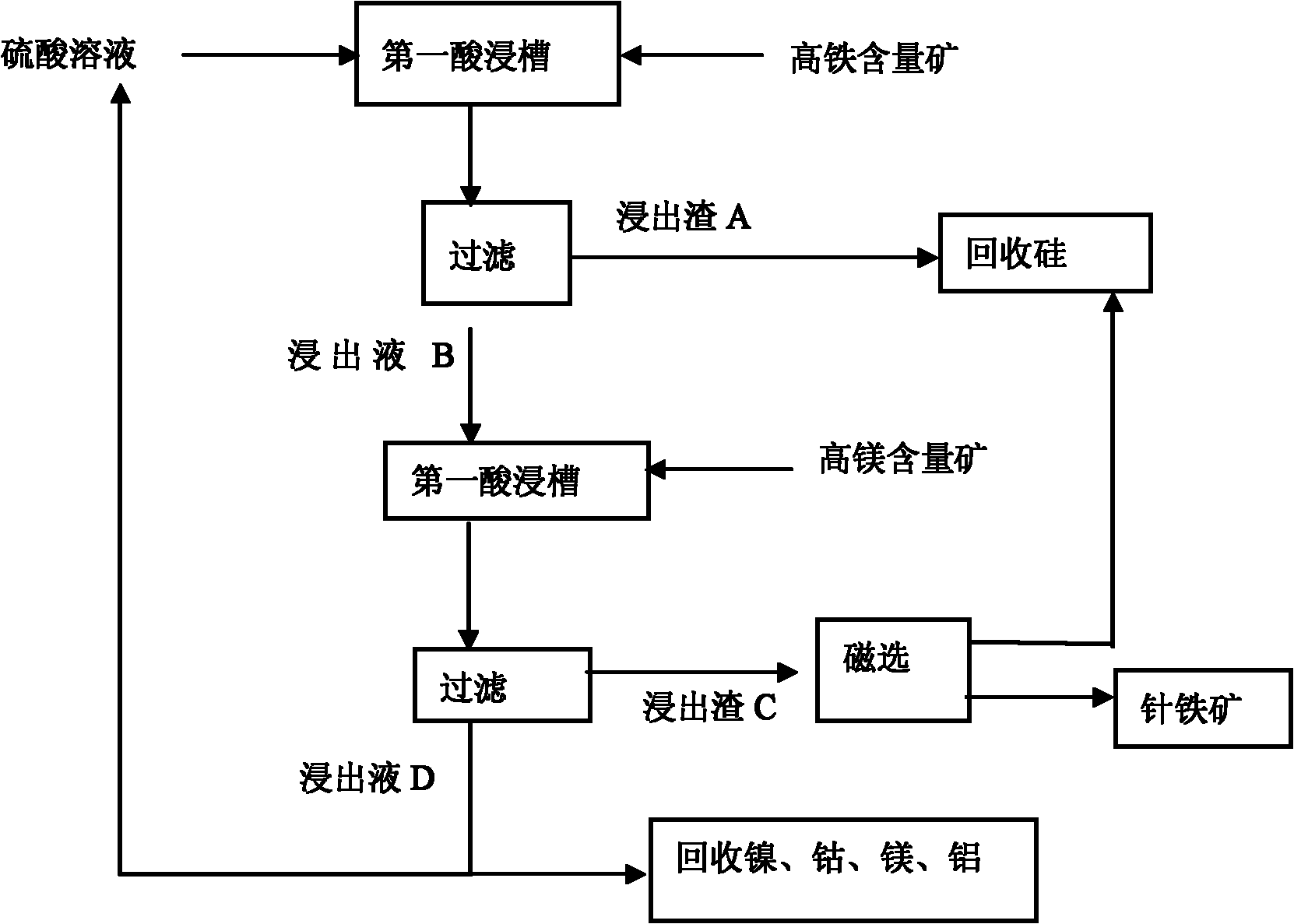
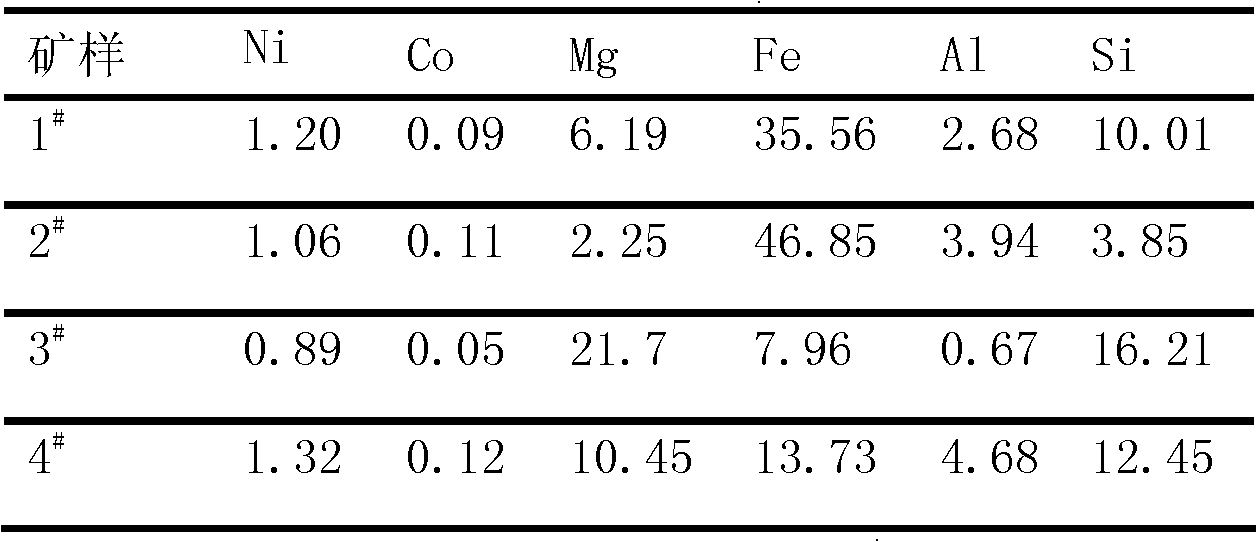
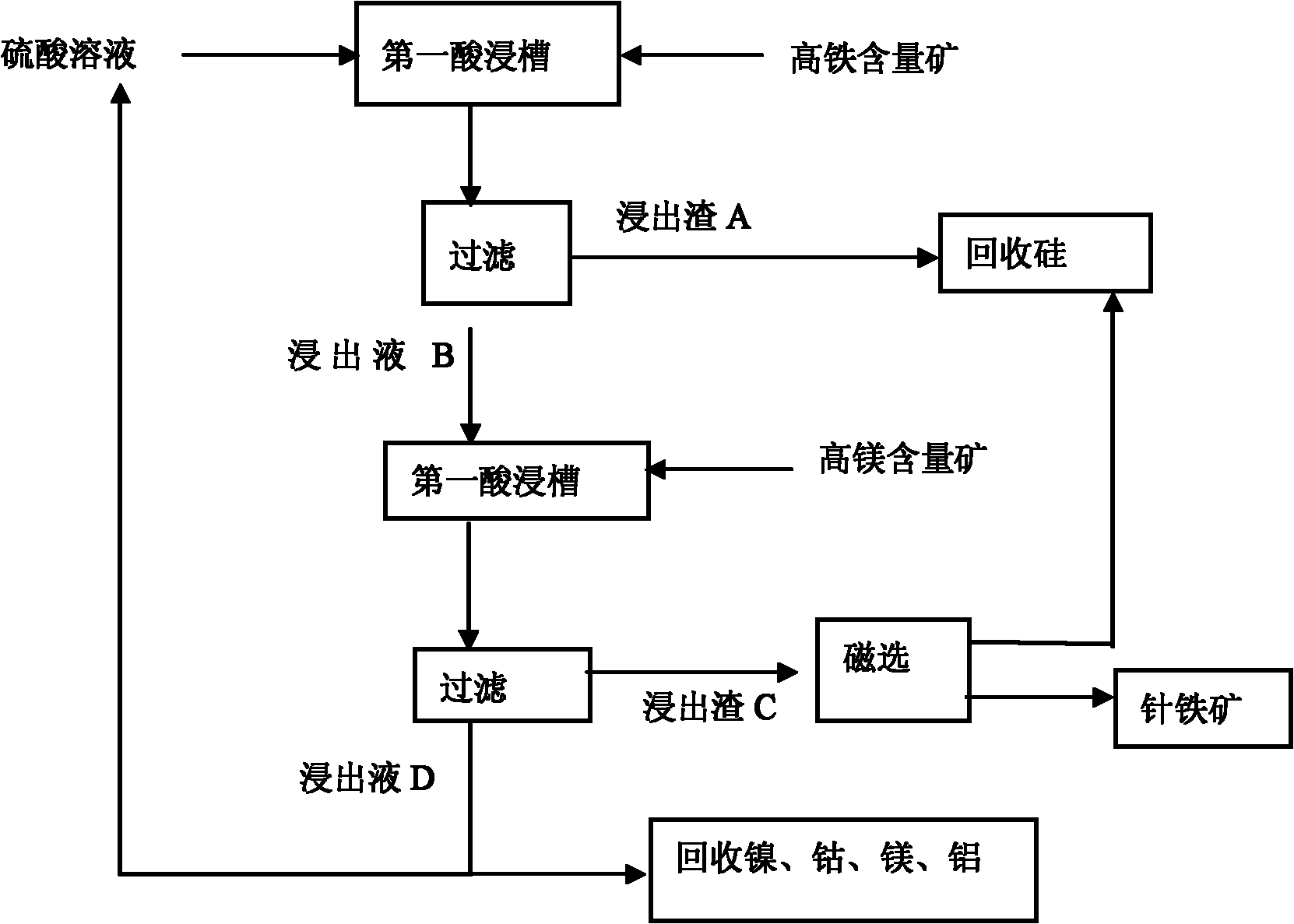
Normal-pressure leaching method for simultaneously processing laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content
InactiveCN102206749AOvercoming the disadvantage of requiring autoclave leachingOvercome the drawbacks of leachingIron oxides/hydroxidesProcess efficiency improvementLateriteNon magnetic
The invention discloses a normal-pressure leaching method simultaneously processing laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content, comprising the following steps of: screening the laterites with high iron content and high magnesium content; adding sulfuric acid to the laterite with high iron content for leaching so as to obtain leaching residue A and a leaching solution B; adding the laterite with high magnesium content to the leaching solution B, leaching to obtain leaching residue C and a leaching solution D; carrying out magnetic separation on the leaching residue C, wherein a magnetic part E is recovered as an iron product, and a non-magnetic part F and the leaching residue A are mixed to be used for recovering silicon products; delivering a part of the leaching solutionD into a purifying and recovering process, and returning the other part of the leaching solution D into the leaching process of the laterite with high iron content, and carrying out a next leaching period; repeating the leaching period for 4-5 times, and completely delivering a leaching solution I obtained from a last leaching period into the recovering processes of nickel, cobalt, aluminum and magnesium. The normal-pressure leaching method has the advantages of low cost and acid consumption and high leaching efficiency of the nickel and the cobalt and realizes the efficient separation and the recycling of iron, silicon, the nickel and the cobalt and the discharge without acid liquor.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
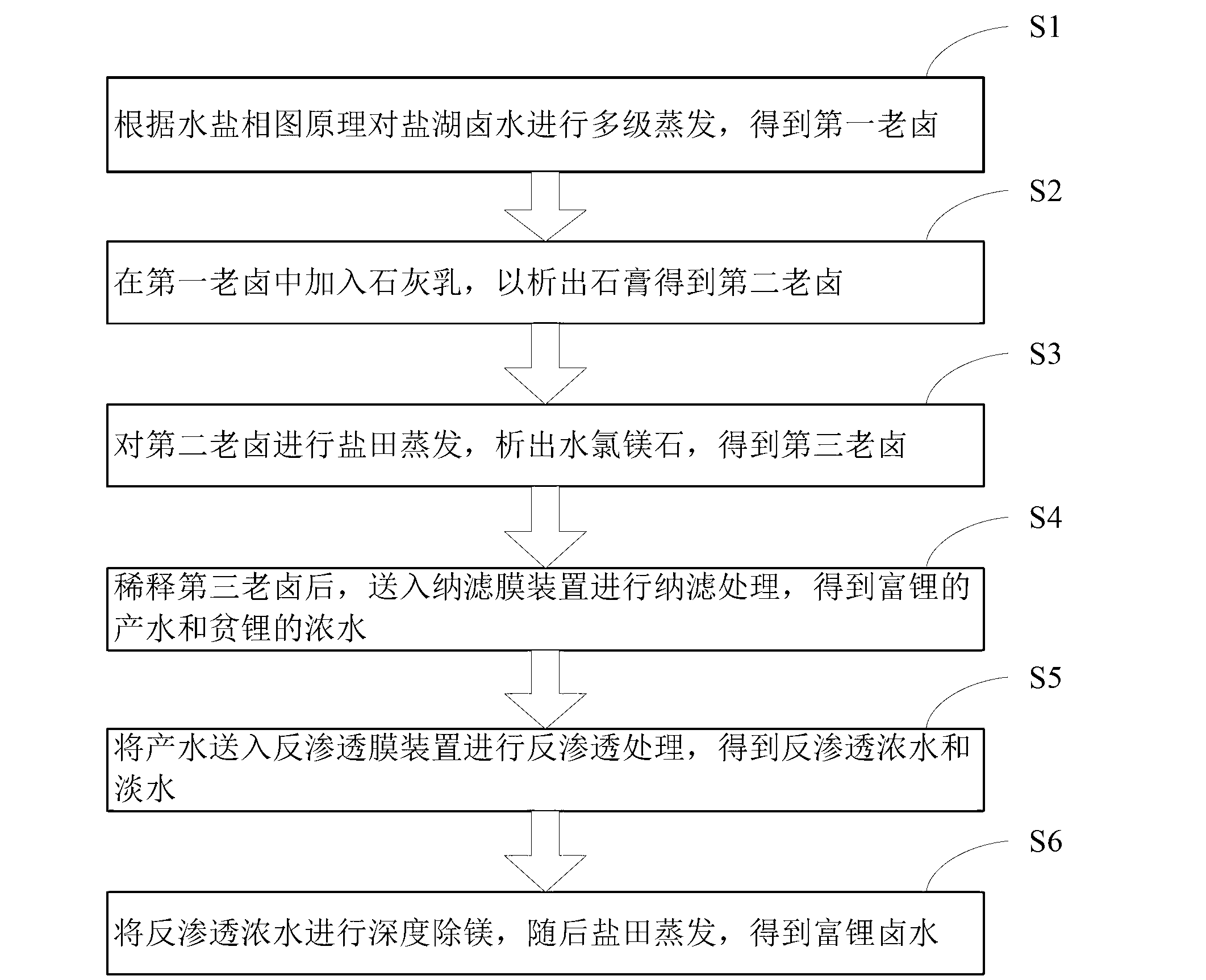
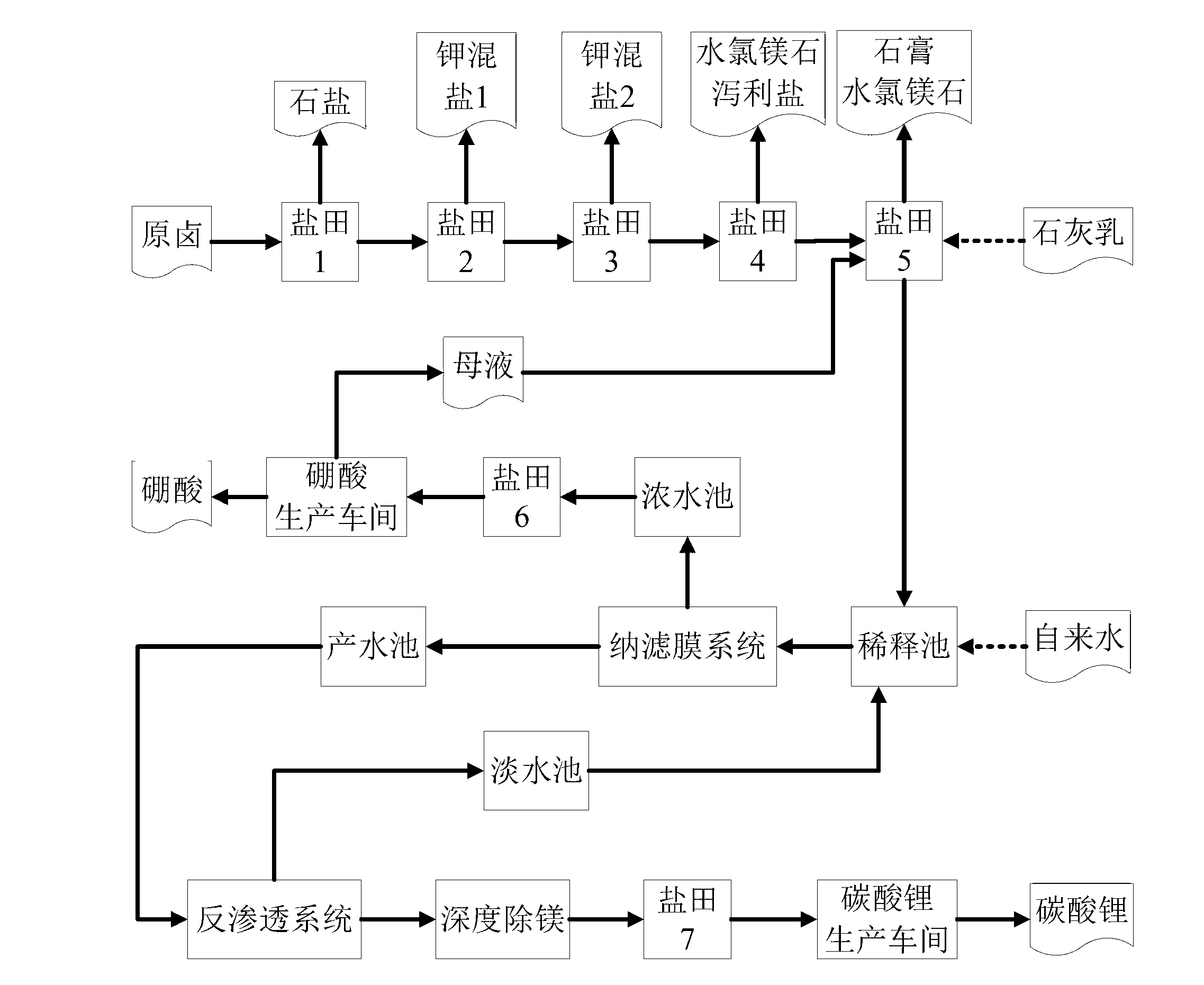
Salt lake brine treatment method for separating lithium from high-magnesium-lithium-ratio salt lake brine
ActiveCN103074502ATake advantage ofHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementReverse osmosisEvaporation
The invention discloses a salt lake brine treatment method for separating lithium from high-magnesium-lithium-ratio salt lake brine. The treatment method comprises the steps that S1, the salt lake brine is subjected to multistage salt pan evaporation to form first old brine; S2, sulphur removal is conducted: lime milk is added to the first old brine for separating out gypsum, and second old brine is obtained; S3, the second old brine is subjected to salt pan evaporation, bischofite is separated out, and third old brine is obtained; S4, the third old brine is diluted, and sent to a nanofiltration membrane device for nanofiltration treatment, and contributing water rich in lithium and thick water poor in lithium are obtained; and S5, the contributing water in Step S4 is sent to a reverse osmosis membrane device for reverse osmosis treatment, and reverse osmosis thick water and fresh water are obtained. The method combines a salt pan technology with a membrane system, makes full use of solar energy, and reduces energy consumption; a technological process is simple; equipment is easy to configure, mount and transfer; popularization and an application are very easy.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
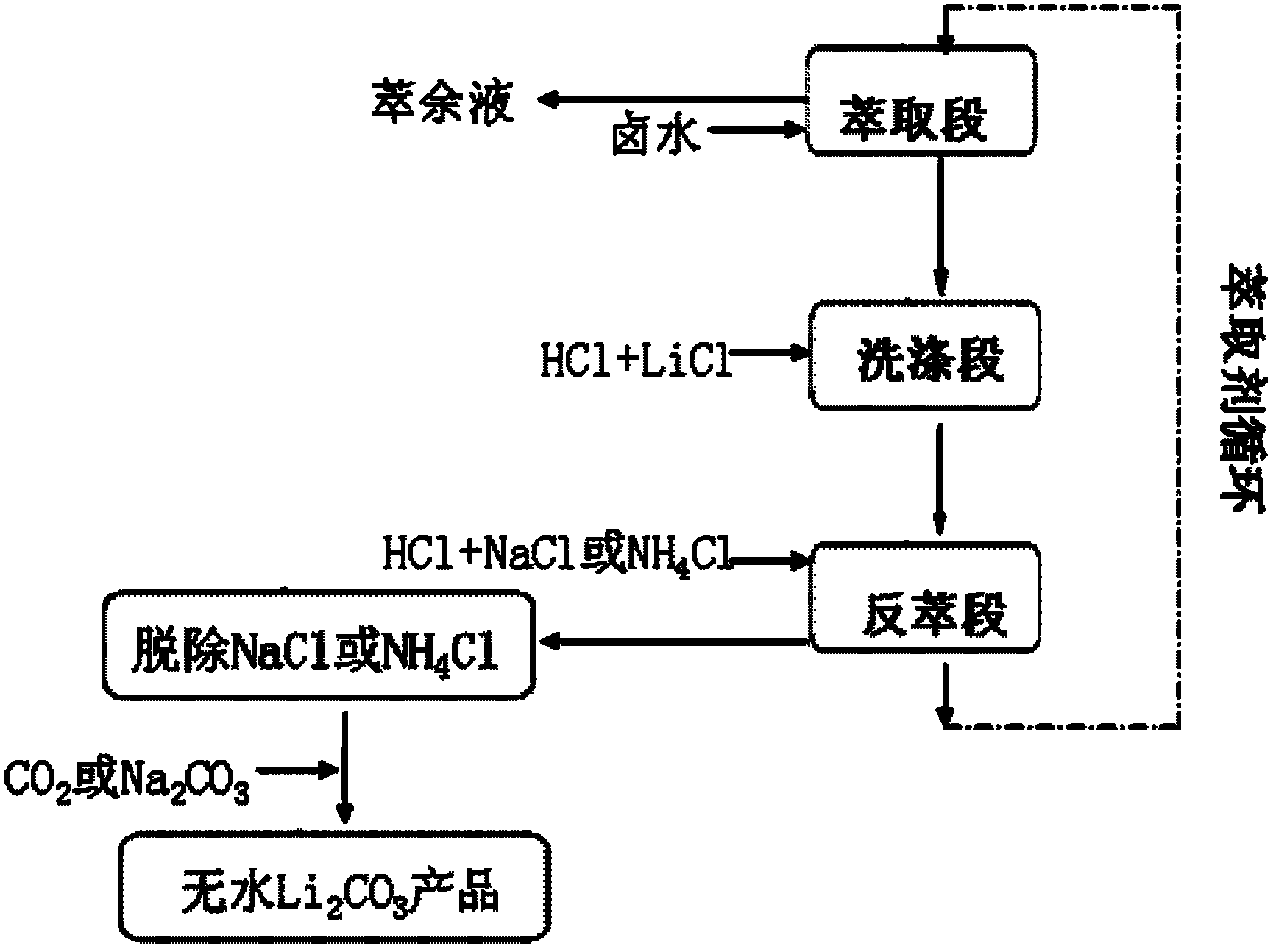
A method for extracting lithium carbonate from high magnesium-lithium ratio salt lake brine
InactiveCN102275956AReduce lossesNo decrease in recycling efficiencyNanotechnologyLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesHigh magnesiumInorganic salts
The invention discloses a method for extracting lithium carbonate from salt lake brine with high magnesium / lithium ratio, belonging to the technical filed of inorganic salt extraction. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out extraction, washing and stripping steps to obtain a stripping solution composed of NaCl and LiCl or NH4Cl and LiCl, then introducing CO2 or adding Na2CO3, and controlling the pH value and dynamic conditions to obtain a nanoscale or microscale Li2CO3 product. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple steps, low equipment requirement and wide sources of raw materials, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for smelting high-carbon steel from semi-steel
InactiveCN102766722ARealize the purpose of simultaneous dephosphorization and carbon conservationShorten the formation timeManufacturing convertersMelting tankSilicon alloy
The invention provides a method for smelting high-carbon steel from semi-steel. The method adopts the semi-steel after extraction of vanadium as a raw material, and comprises the following steps of: adopting a low vanadium extraction process during smelting of a vanadium extraction converter to ensure that the carbon content of the semi-steel after the extraction of vanadium is not smaller than 3.70 weight percent, and the temperature of the semi-steel is not lower than 1,290 DEG C; adding active lime into the converter according to a standard of 10 to 15 kg in a ton of steel, adding high-magnesium lime into the converter according to a standard of 7 to 10 kg in a ton of steel, shaking the converter back and forth to ensure that the active lime and the high-magnesium lime are uniformly mixed with steel slag in the converter, then adding the semi-steel into the converter, and adding a ferro-silicon alloy into the converter, wherein the added amount of the ferro-silicon alloy can ensure that the initial alkalinity of furnace slag is 2 to 3; performing converting, and pouring out the furnace slag when the temperature of a molten pool is raised to be 1,400 to 1,500 DEG C; adding active lime into the converter according to a standard of 12 to 18 kg in a ton of steel and adding high-magnesium lime into the converter according to a standard of 9 to 12 kg in a ton of steel to perform secondary slagging; performing converting, and adding manganiferous iron ore into the converter to ensure that the alkalinity of the furnace slag is 4 to 5 and a CaO-SiO2-FeO-MnO low-melting-point slag system is formed; adding a cooling agent into the converter after converting for 3 to 5 minutes, and continuously converting until target molten steel and terminal furnace slag are obtained; and tapping. According to the method, dephophorization and carbon maintenance can be realized at the same time.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD +2
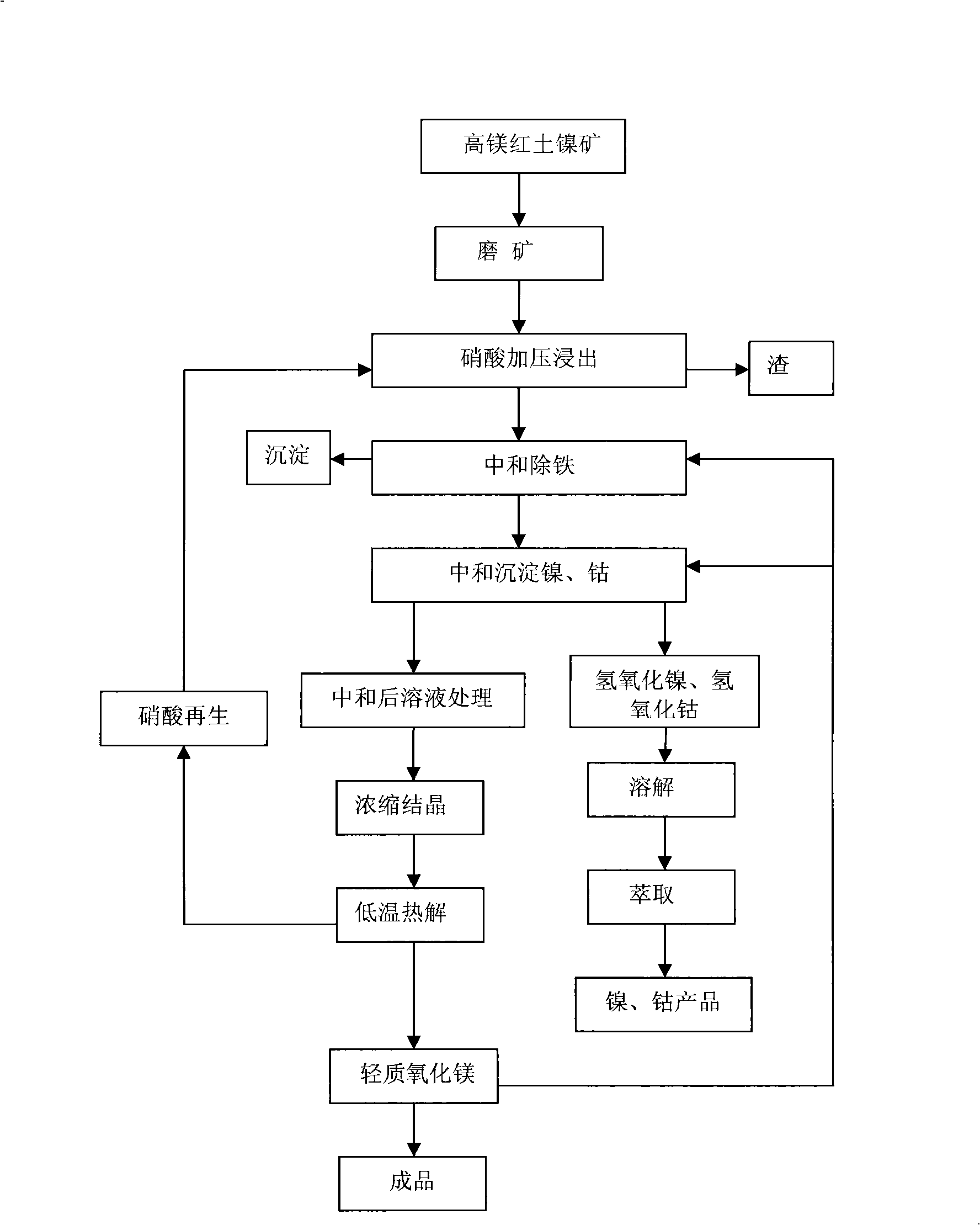
Treating method for high magnesium laterite nickel mine
InactiveCN101289704AEfficient extractionEfficient leachingProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionHigh magnesium
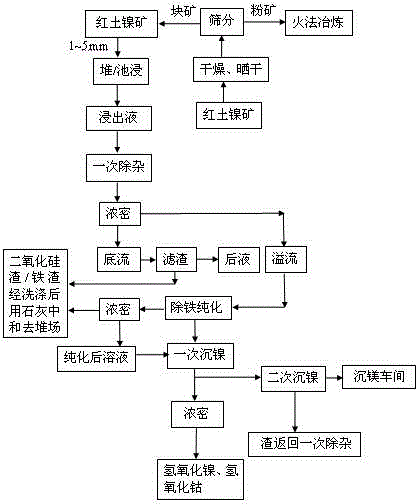
The invention discloses a method for treating high magnesium laterite-nickel ores. The method comprises the following steps of preliminary treatment of ore, pressurized leaching, iron purification of leach solution, deposition of nickel and cobalt, condensation and crystallization, production of light magnesium oxide by low-temperature thermal decomposition of crystals and regeneration of nitric acid. Under mild conditions of low temperature and pressure, leaching ratios of nickel and cobalt both reach 95 percent, the leaching ratio of magnesium reaches 98 percent, the iron content in the leach solution is less than 1g / L, and no silicon dioxide is leached out. The method can fully recover nickel, cobalt and magnesium, and the magnesium is generated in the form of light magnesium oxide, and the leaching agent-nitric acid can be recovered and regenerated for n, thereby better resolving the problems of highly efficient leaching-out of nickel and cobalt and reasonable utilization of magnesium; moreover, the technical flow is simple and has low requirements on equipment, and in the process of leaching out, the scab phenomenon does not occur in a high-pressure pan, so that the method is applied to the large-scale industrial production.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Method for separating magnesium from lithium and extracting lithium from brine
InactiveCN101538057ASolve the difficult technical problems of filtrationSimple technical processMultistage water/sewage treatmentSolution crystallizationFiltrationHigh energy
The invention provides a method for separating magnesium from lithium and extracting the lithium from high magnesium-lithium ratio brine (brine from a saline lake, from underground and from an oil-gas field). The method comprises: sodium salt and potassium and magnesium mixed salt are separated from the brine by evaporation of a saltpan; after boron extraction, sodium hydroxide is used for precipitating Mg<2+> from obtained old brine, and crystallized Mg(OH)2 is obtained by modification and precipitation condition control; filtration and separation are carried out to remove the Mg(OH)2 to realize separation of magnesium and lithium; after filtered mother solution is vaporized and concentrated for 2-4 times, Na2SO4 and NaCl are separated by crystallization, and pure caustic soda can be added to form lithium carbonate from lithium; or the operation of further evaporation is carried out until Na2SO4 and NaCl are separated by multiple times of natural evaporation or forced evaporation concentration and multiple times of cooling crystallization; the operations of evaporation and concentration are carried out until LiCl saturation, and LiCl products can be prepared after the operation of cooling crystallization is carried out. Compared with the prior art for separating the magnesium from the lithium and extracting the lithium from the brine, the method obtains the crystallized Mg(OH)2 by modification and precipitation condition control, solves the existing technical problem of hard filtration of Mg(OH)2, solves the defects of high energy consumption, complex process and high cost of the existing calcination method, and solves the fundamental defects of low Li<2+> recovery ratio and complex technical process of the traditional precipitation method. The Li<2+> recovery ratio ranges from 85-93%, Mg<2+> removal ratio is more than 99.5%, and the method solves the problem of extracting Li<+> and Mg<2+> from high-magnesium and low-lithium brine with Mg<2+> / Li<+>>=20 mass ratio.
Owner:钟辉
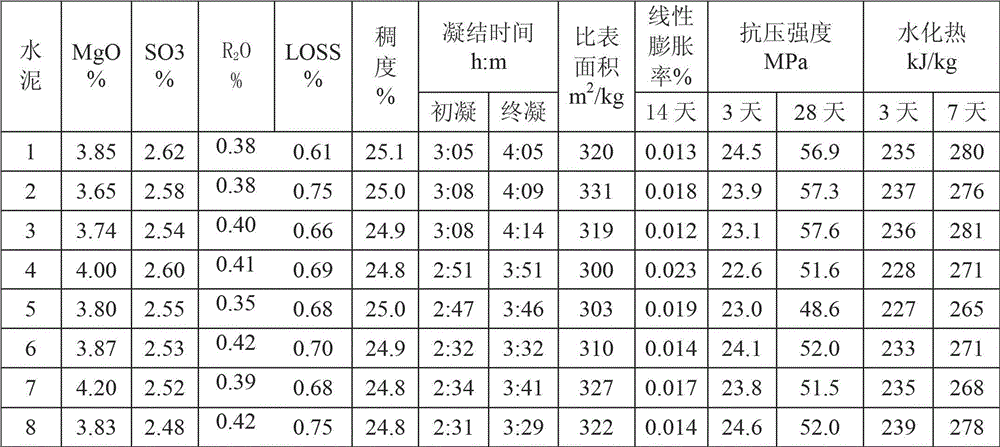
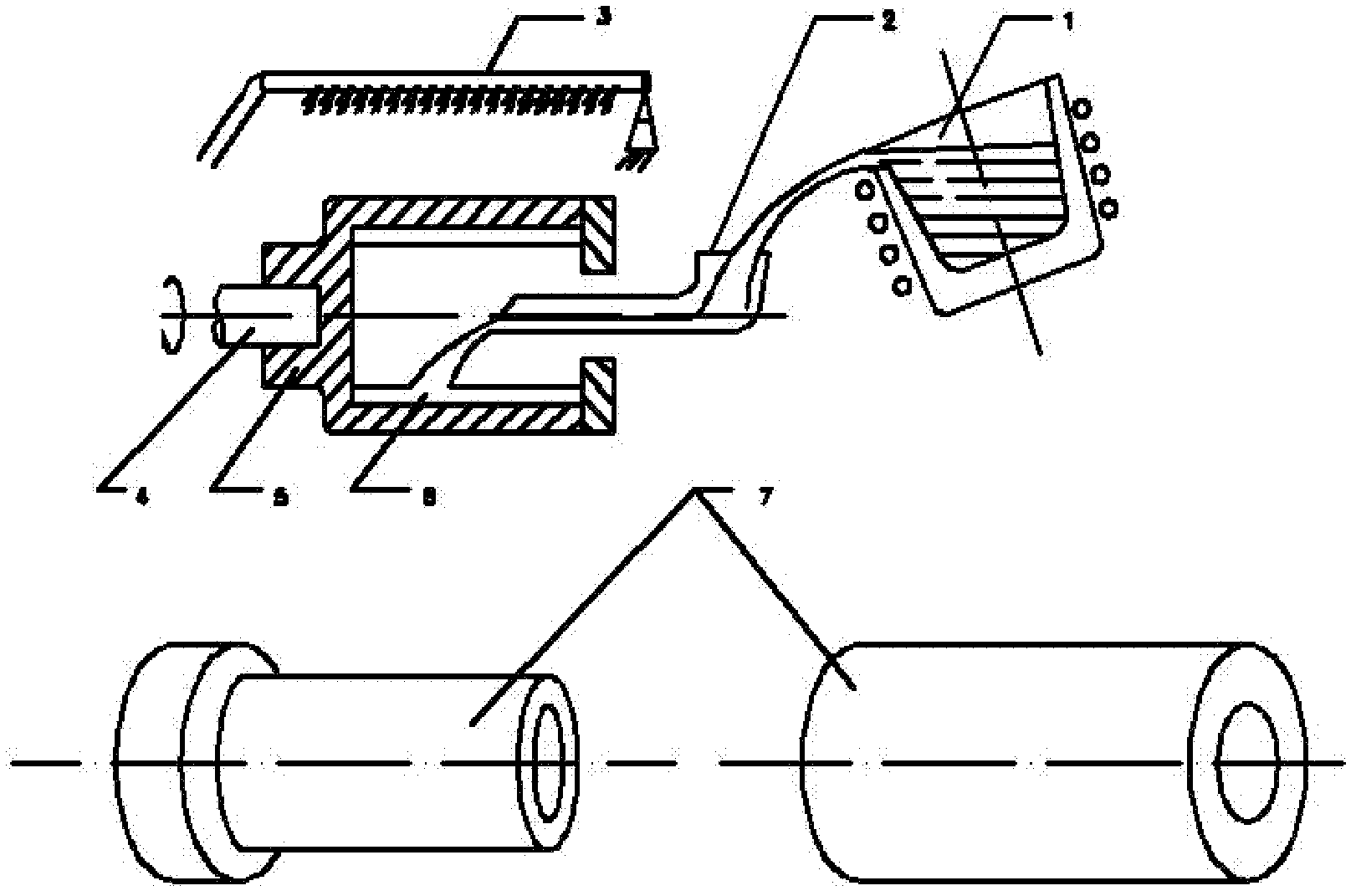
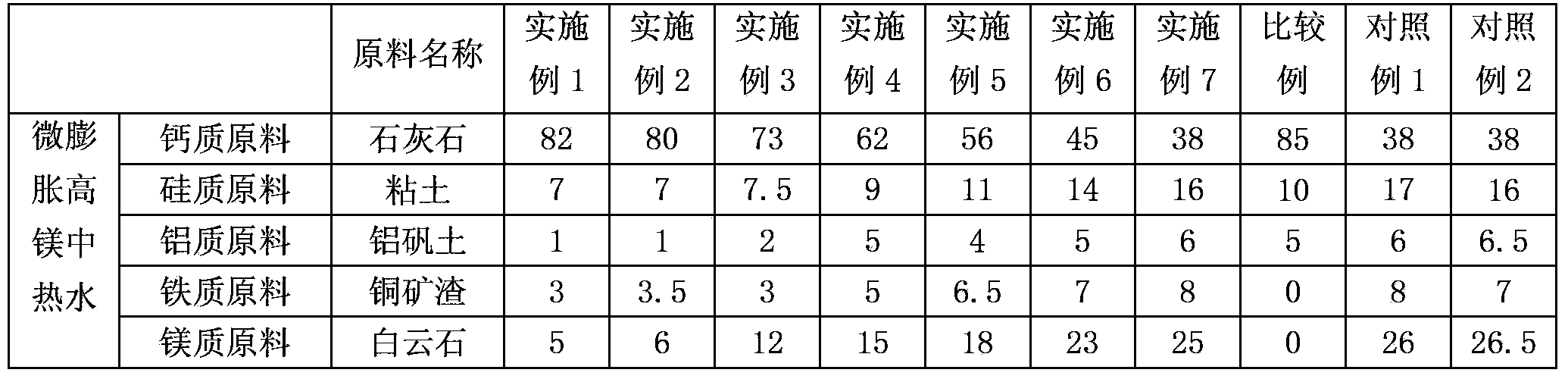
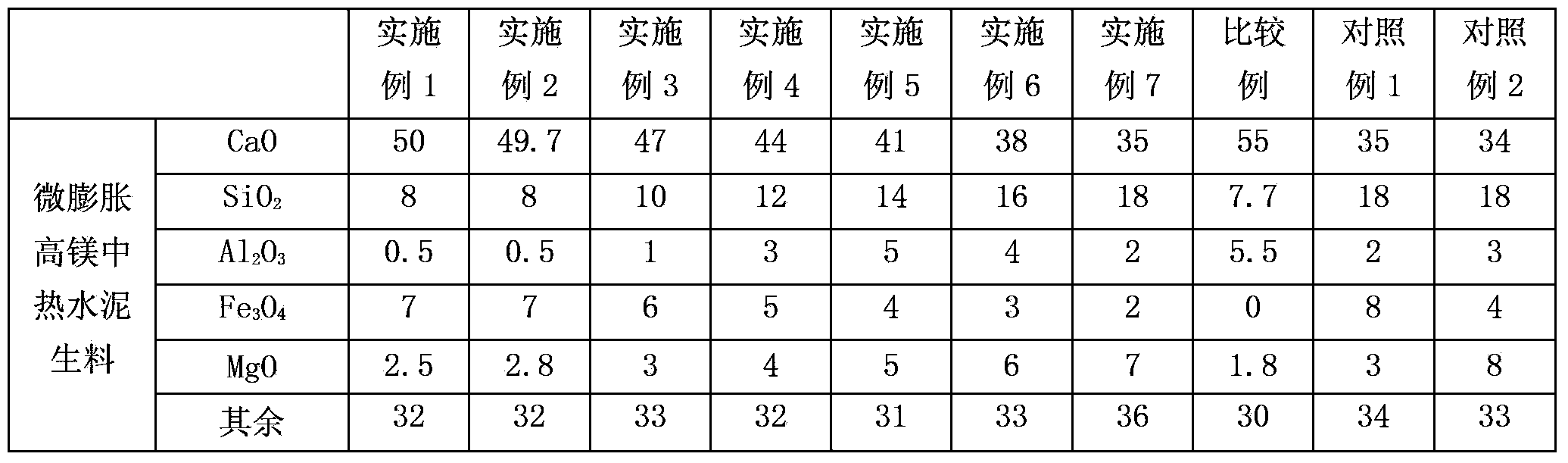
High-magnesium low-heat portland cement clinker aggregate and preparation method thereof
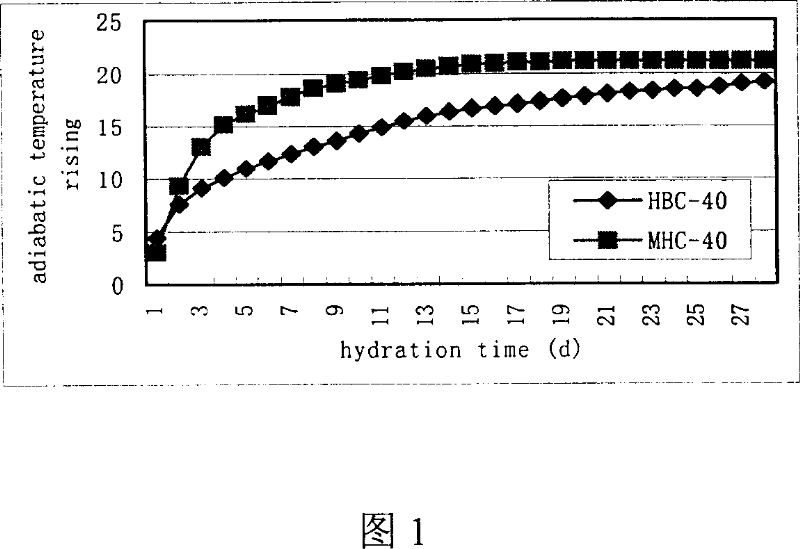
InactiveCN101041560AImprove crack resistanceLow heat of hydrationClinker productionHigh magnesiumPortland cement
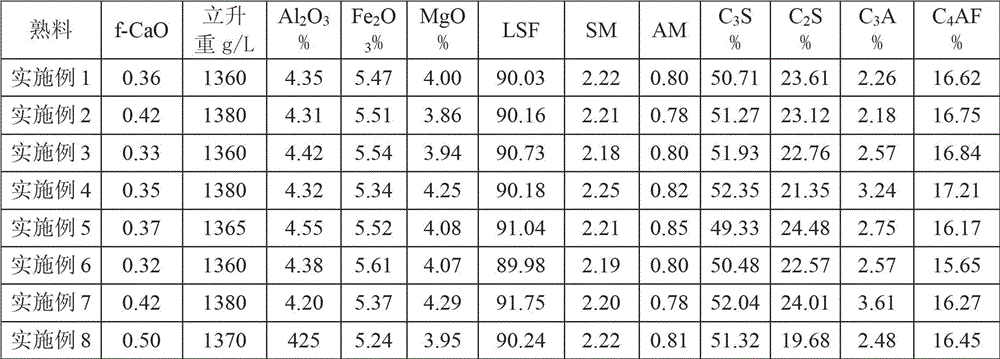
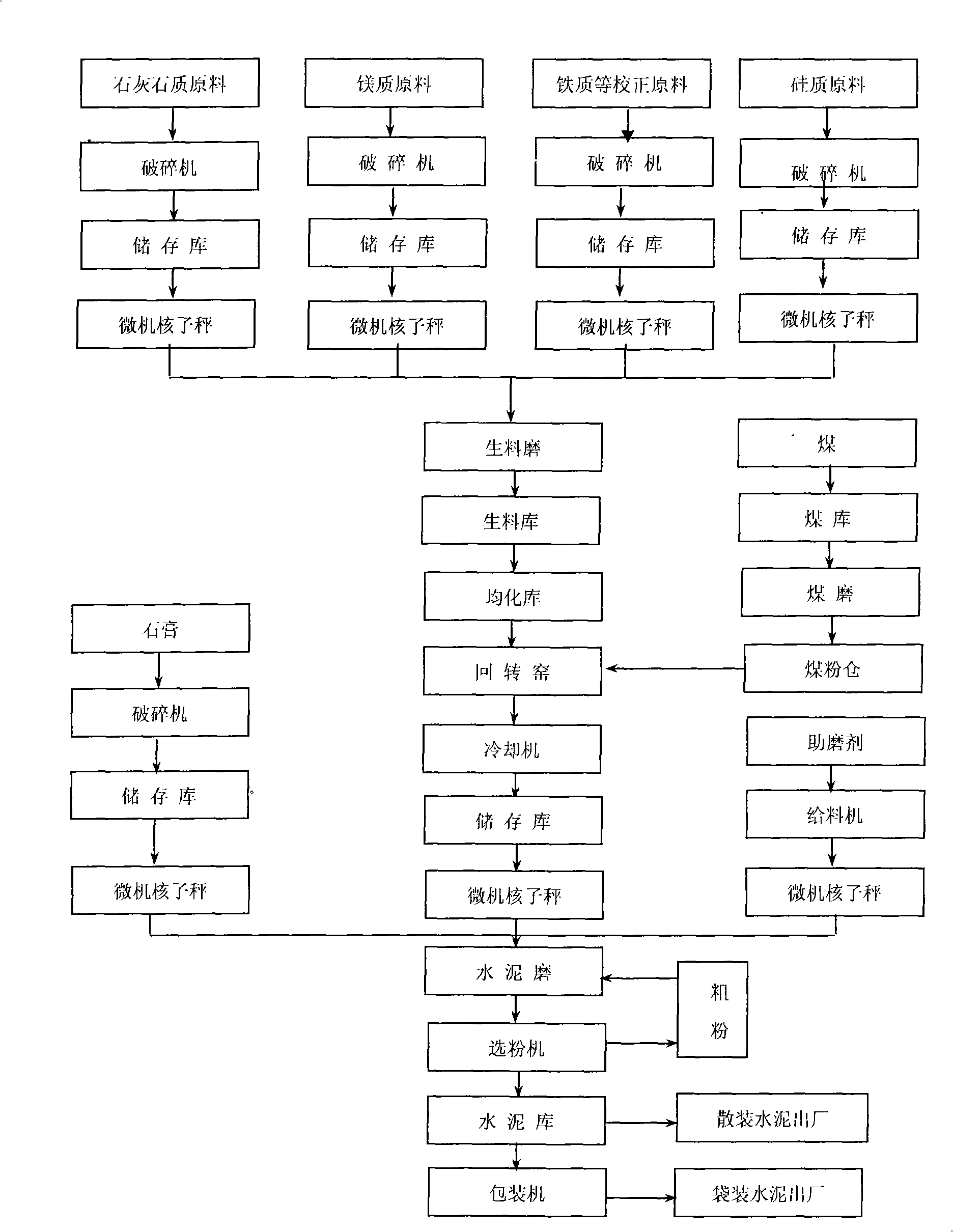
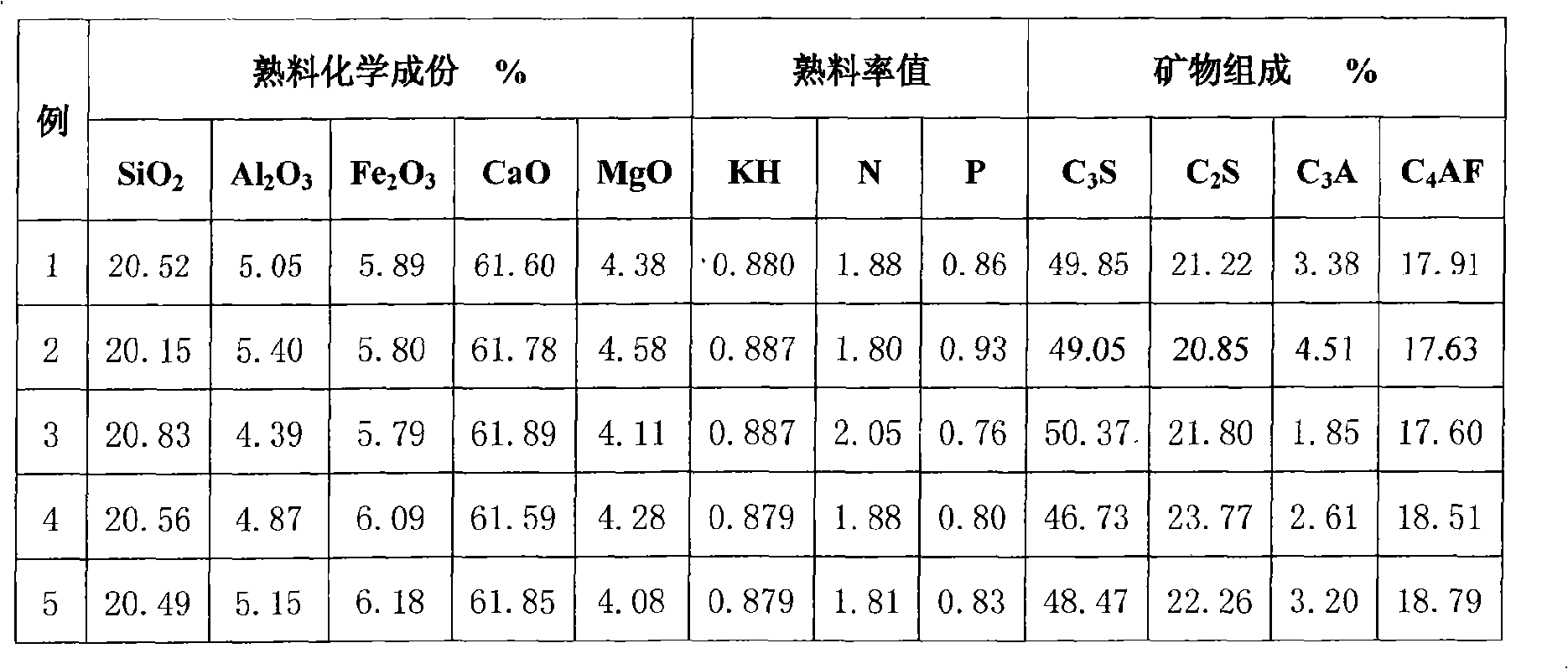
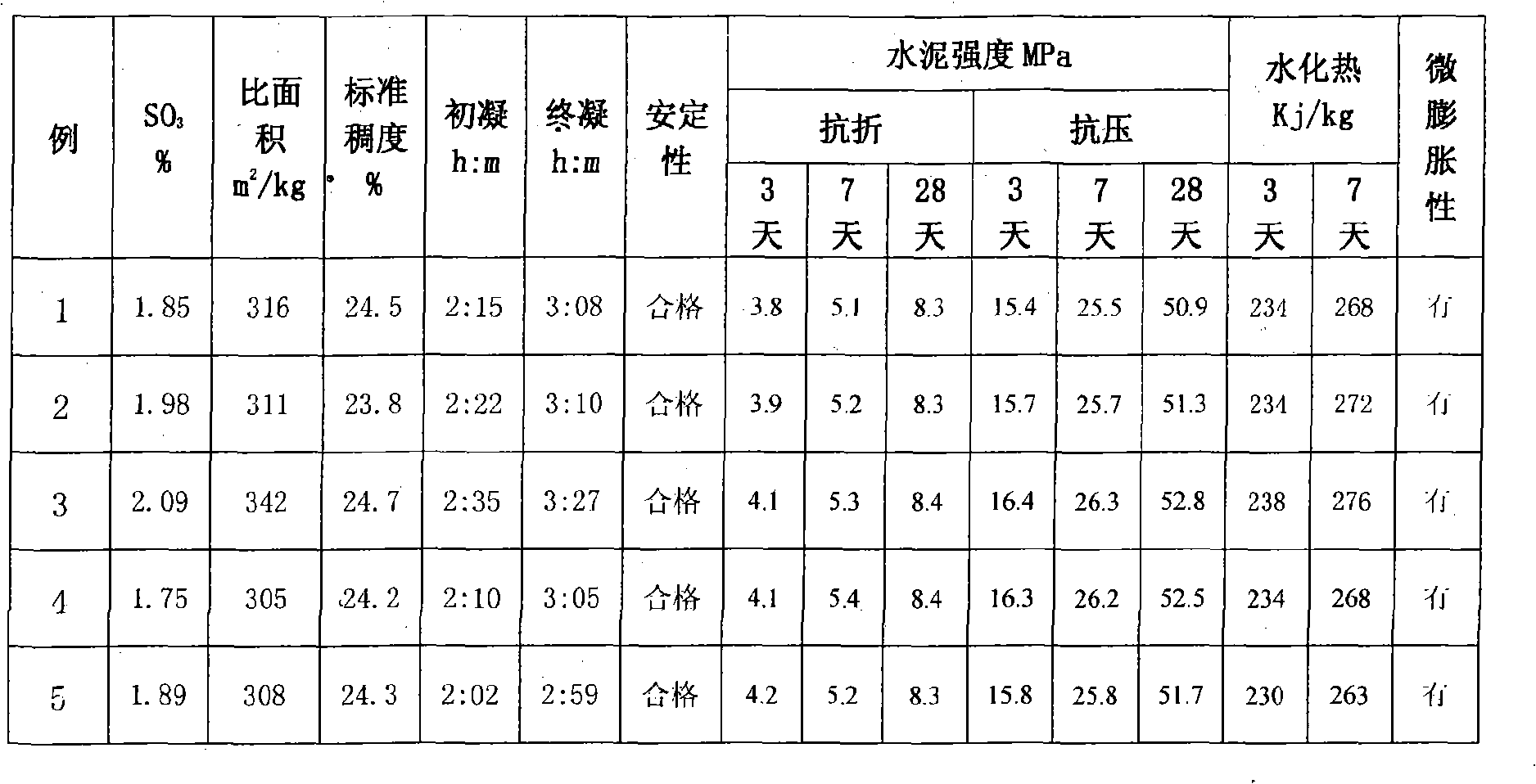
The invention discloses a high-magnesium lower thermal silicate cement clinker, making mineralogical composition at (mass percent): 40 -65% C2S, 15-40% C3S, 1-8% C3A, 10-25% C4AF and content of MgO at 2.0-6.0%. The invention also discloses a preparing method of high-magnesium lower thermal silicate cement clinker, including indispensable steps of producing cement clinker with raw materials and controlling content of MgO of cement clinker at 2.0-6.0%.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Converter dephosphorizing and steelmaking method
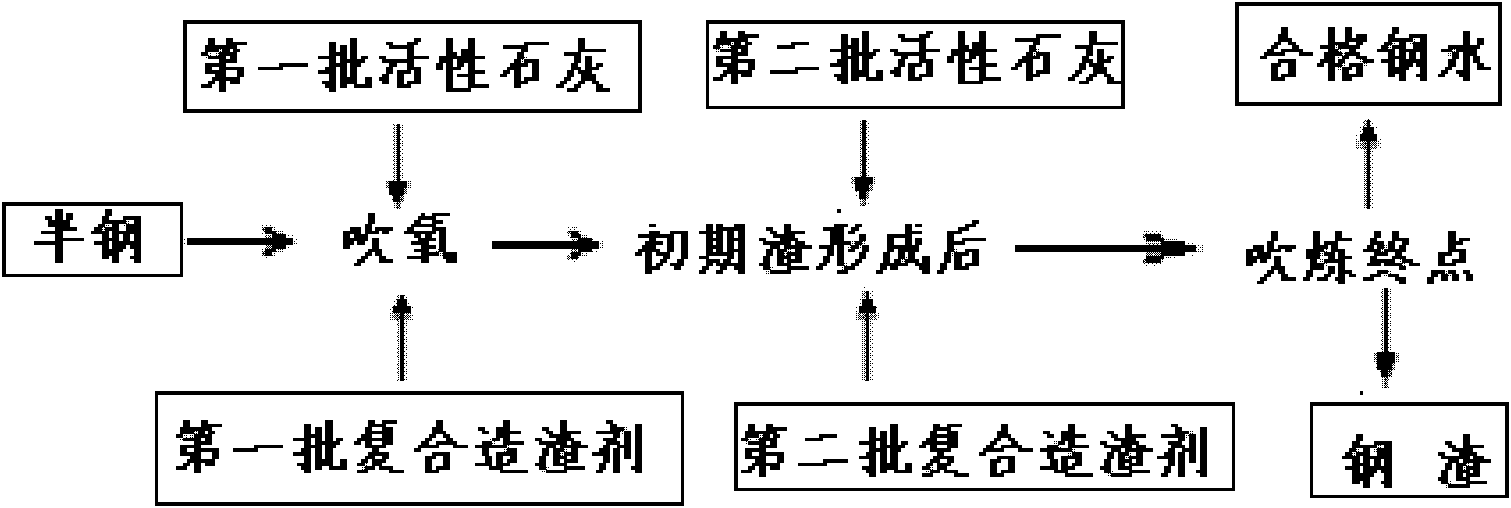
The invention provides a converter dephosphorizing and steelmaking method. The method comprises the following steps of: a, adding slag making materials which consist of active lime, high-magnesium lime and a composite slagging agent into a converter molten pool; blowing and slagging by a dephosphorizing oxygen lance oxygen blowing process and an inert gas bottom blowing process to remove phosphorus in molten steel; and pouring 60 to 80 percent of slag out when the molten pool temperature in a converter is between 1,420 and 1,450 DEG C, the alkalinity of the slag is between 2.0 and 2.5 and the total iron content in the slag is between 10 and 15 weight percent; and b, adding the slag making materials into the converter molten pool; blowing and slagging by a normal oxygen lance oxygen blowing process and the inert gas bottom blowing process to further remove the phosphorus in the molten steel; pouring the slag out when the molten pool temperature in the converter is between 1,680 and 1,700 DEG C, the alkalinity of the slag is between 3.2 and 4.2 and the total iron content in the slag is between 16 and 23 weight percent to obtain the molten steel with the phosphorus element content of not more than 0.009 weight percent. By the method, the dephosphorizing efficiency and the dephosphorizing effect of the converter are improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +2
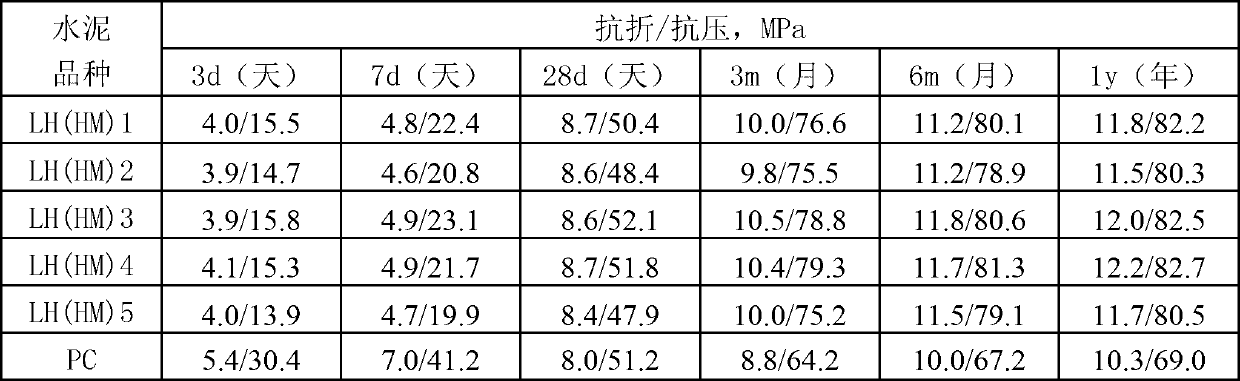
Micro-expansive moderate-heat Portland cement and production method thereof
InactiveCN102976641AHigh strengthHeat of hydration controlClinker productionHigh magnesiumPortland cement
The invention discloses a micro-expansive moderate-heat Portland cement and a production method thereof. The cement contains micro-expansive moderate-heat Portland cement clinker and gypsum in a weight ratio of 92:8-98:2, and also comprises grinding aid which accounts for 0-0.1 wt% of the sum of micro-expansive moderate-heat Portland cement clinker and gypsum. The raw meal of the micro-expansive moderate-heat Portland cement clinker is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 65-80% of calcium raw material, 5-20% of silicon correction raw material, 5-15% of iron correction raw material and 3-10% of magnesium correction raw material. The micro-expansive moderate-heat Portland cement clinker is prepared by the following steps: grinding the raw meal, dehydrating the slurry, drying and crushing the filter cake, and firing to obtain the clinker. By adopting the low-aluminum high-iron high-magnesium low-saturation-ratio formula, the invention effectively controls the hydration heat of cement, displays the micro-expansive property, and can compensate the volume shrinkage in the concrete cooling process, thereby reducing or avoiding cracks.
Owner:GUANGXI YUFENG CEMENT
High-magnesium minimum-inflation low-heat cement and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102898050AWide variety of sourcesTake advantage ofCement productionHigh magnesiumPortland cement
The invention discloses high-magnesium minimum-inflation low-heat cement and a preparation method thereof. A high-magnesium minimum-inflation low-heat cement clinker comprises the following mineral compositions in percentage by weight: 10-35% of C3S, 40-65% of C2S, 1-5% of C3A, 10-20% of C4AF and 6.0-8.0% of MgO. The concrete prepared by the cement has the characteristics of good liquidity, low water requirement amount, low hydration heat, high long-term strength, good durability and minimum inflation performance, and can be used for compensating the contraction of big-volume concrete and hydraulic concrete and reducing a concrete crack. Compared with the traditional portland cement and the low-heat portland cement, the high-magnesium minimum-inflation low-heat cement is more favorable for realizing the volume stability and the safety of the concrete, and is an ideal cementing material for the major projects, especially the big-volume concrete and hydraulic concrete engineering.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Steelmaking and slagging method
The invention provides a steelmaking and slagging method. The method comprises the following steps of: adding semisteel from which vanadium is extracted into a steel refining furnace; blowing oxygen into the steel refining furnace and blowing; in two minutes after the blowing is started, adding 9 to 11kg of lime, 9 to 11kg of high-magnesium lime, 3 to 8kg of fluxing agent, and 11 to 14kg of acid composite slag into the steel refining furnace based on one ton of semisteel from which vanadium is extracted; and in 9 minutes after the first slag is formed and blowing is started, adding 9 to 11kg of lime and 9 to 11kg of high-magnesium lime into the steel refining furnace based on one ton of semisteel from which vanadium is extracted, and continuously blowing to obtain molten steel and final slag. The fluxing agent is refined steel slag. Slagging is performed by the method, the slag can be formed quickly, the consumption of an iron and steel material is reduced, smelting time is shortened and steelmaking cost is saved.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +3
Method for refining lithium from salt lake brine with high magnesium-lithium ratio
InactiveCN103570048AVerify feasibilityTake advantage ofLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesSulfate radicalsReverse osmosis
The invention discloses a method for refining lithium from salt lake brine with a high magnesium-lithium ratio. The method comprises the following steps: 1) removing sulfate radicals from brine from which sodium and potassium are extracted, evaporating the brine to obtain lithium-rich and boron-rich brine; 2) extracting boron from the lithium-rich and boron-rich brine to obtain boric acid and lithium-rich brine; 3) separating the lithium-rich brine by using a nanofiltration membrane to obtain primary concentrated water and primary produced water; 4) through reverse osmosis, separating the primary produced water to obtain secondary produced water and fresh water; 5) removing magnesium from the secondary produced water, and evaporating the secondary produced water to obtain refined lithium-rich brine. The method is simple in technological process; by the method, the energy consumption is greatly reduced, salt lake brine resources are fully used, and the recycling rate of the lithium ions is greatly improved; influence of the boron on lithium carbonate or other lithium salt products is avoided, thus the quality and the competitiveness of products are greatly improved.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for leaching nickel and cobalt form low-iron and high-magnesium and high-iron and low-magnesium laterite-nickel ore by using waste dilute sulphuric acid
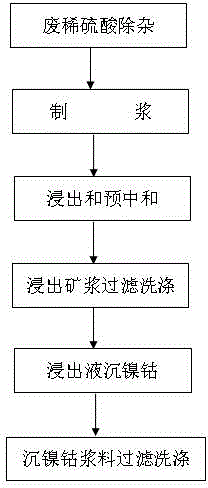
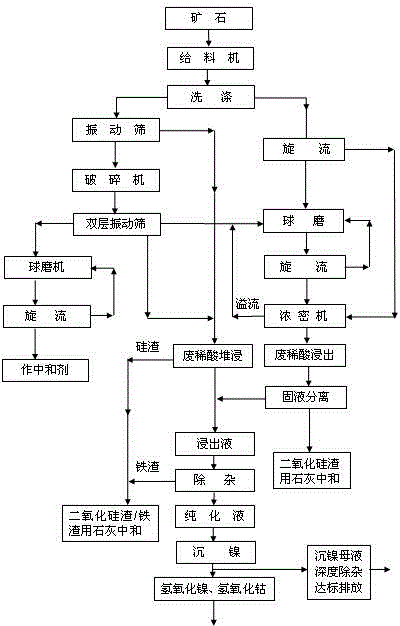
The invention provides a method for leaching nickel and cobalt from low-iron and high-magnesium and high-iron and low-magnesium laterite-nickel ore by using waste dilute sulphuric acid. Nickelous hydroxide, cobaltous hydroxide and the like are directly extracted by leaching the laterite-nickel ore with non-concentrated decolored and desalinated waste dilute sulphuric acid. The method specially comprises the steps of: removing impurities out of the waste dilute sulphuric acid, slurrying, leaching and pre-neutralizing, filtering and washing leached ore pulp, settling nickel and cobalt from leachate, filtering and washing nickel and cobalt settled slurry, electrically depositing nickel, and post-treating and recycling iron, magnesium, manganese and the like. The method provided by the invention overcomes the technical difficulty, ensures that a technology of a direct dilute sulphuric acid atmospheric pressure leaching process route operates stably, is greatly lowered in cost, is high in production efficiency, and is high in recycling rate of nickel, cobalt, iron, magnesium, manganese and other metals. The waste dilute sulphuric acid which is an byproduct in industries such as dye industry and is difficult to treat is effectively recycled, the method is environmental-friendly, any harmful gas is not emitted, waste slag is solid materials, trees can be planted on the waste slag for greening, the waste slag can be recycled, and waste water can completely reach the standard for emission.
Owner:杭州蓝普水务有限公司
High-magnesium moderate-heat portland cement and production method thereof
InactiveCN101353231AReduce water demandThe micro-expansion property hasClinker productionHigh magnesiumPortland cement
The invention relates to a high-magnesium moderate heat portland cement, which is characterized in that (1) the contents of MgO and SO3 in the cement are 3.0-6.5% and 1.4-2.2% respectively; (2) the weight percentages of the mineral composition for grinding cement clinker are 35-55% of C3S, 15-35% of C2S, 1-6% of C3A and 10-25% of C4AF; and the content of MgO in the cement clinker is 3.0-6.5%; (3) in the raw materials for calcining the clinker, the contents of MgO, CaO and Fe2O3 are respectively controlled at a certain value within the ranges of 2.5-3.8%, 38.0-42.0% and 3.5-4.5%, and the variation ranges thereof are respectively controlled within plus or minus 0.10%, plus or minus 0.20% and plus or minus 0.15%. The production method of the cement mainly comprises three procedures of raw material milling, clinker calcining and cement grinding, namely, 'two grinding and one calcining'. The concrete made from the cement is characterized by good fluidity, low water requirement, moderate cement heat, high later strength, good durability, microdilatancy performance, and the like; compared with the conventional portland cement and moderate heat portland cement, the high-magnesium moderate heat portland cement is more favorable for realizing high performance of the concrete.
Owner:湖南石门特种水泥有限公司
Composite slagging agent for making semisteel, and preparation method and using method thereof
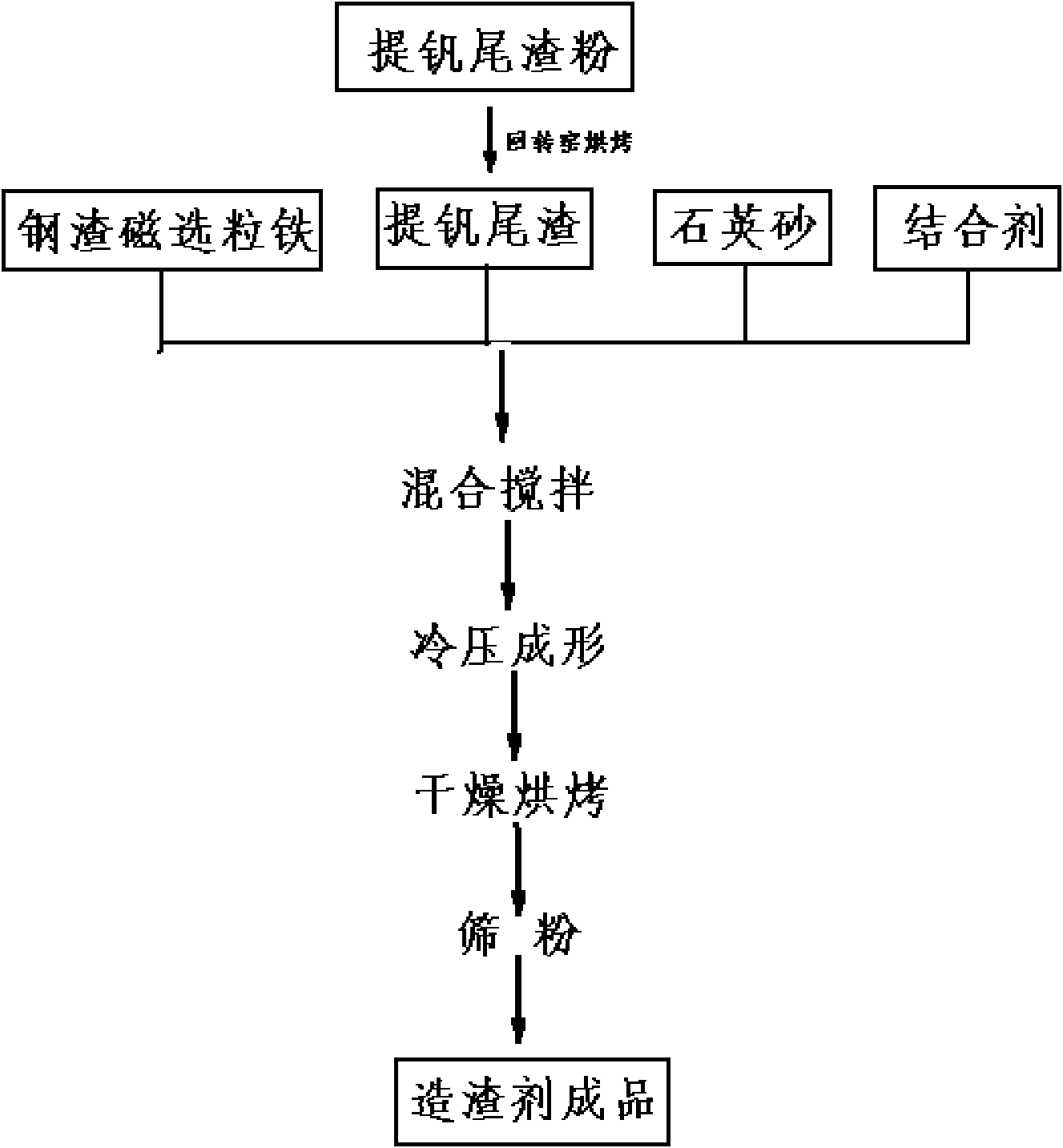
InactiveCN102181610AGood effect of removing PSteelmaking process runs smoothlyRecovering materialsManufacturing convertersHigh magnesiumSlag
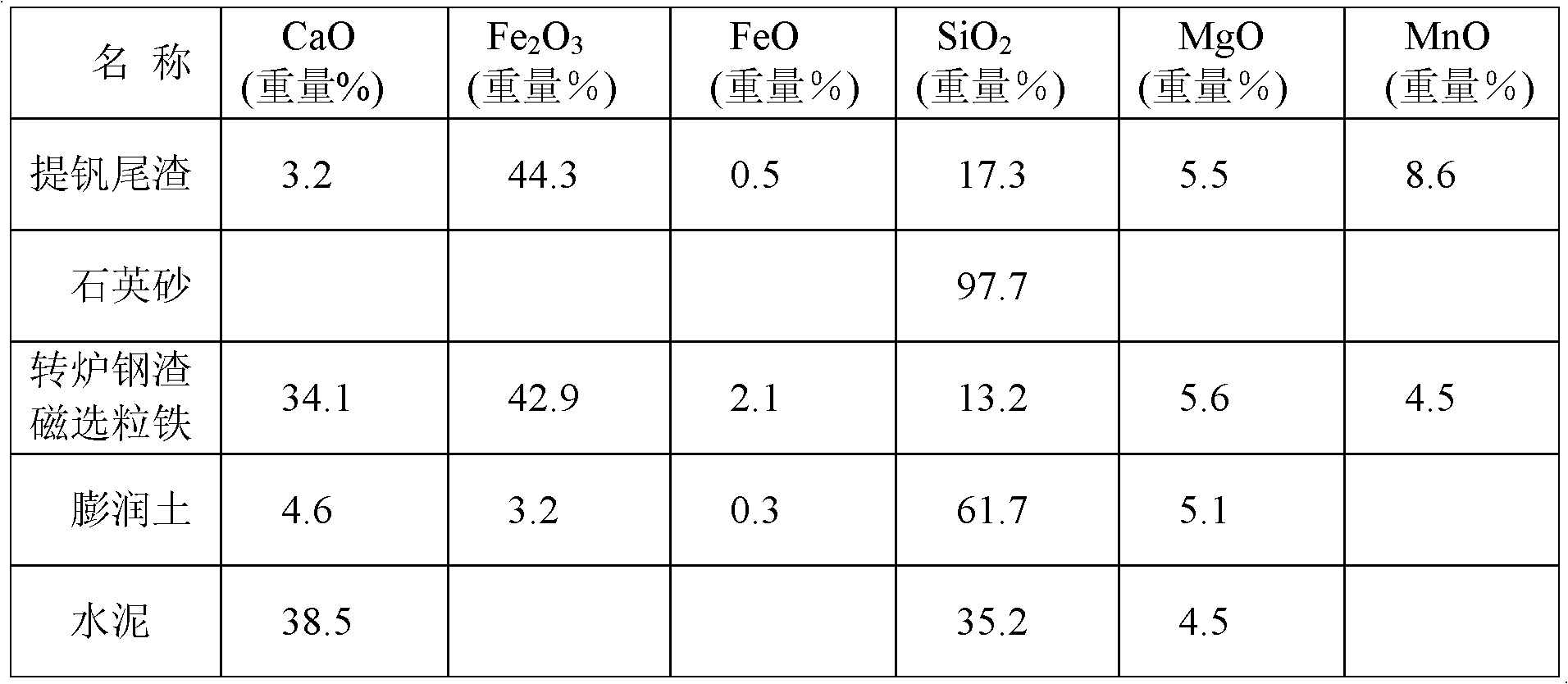
The invention discloses a composite slagging agent for making semisteel, and a preparation method and a using method thereof. The slagging agent comprises the following components in part by weight: 26 to 36 parts of iron-containing oxide, 27 to 35 parts of SiO2, 7 to 13 parts of CaO, 4 to 7 parts of MnO and 4 to 8 parts of MgO, wherein the iron-containing oxide comprises Fe2O3 and FeO in the weight ratio of (50-60):1. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing vanadium-extracted tailings, quartz sand, converter steel slag magnetic ball iron and a binding agent according to a certain mass ratio and uniformly stirring; pressing into pellets; and drying to obtain the slagging agent. The slagging agent prepared by the preparation method can be used for making the semisteel together with active lime and high-magnesium lime. By the composite slagging agent prepared by the method, the defects that the slag is easy to splash and dry, has a poor dephosphorization effect, is extremely difficult to operate and the like are overcome in the semisteel making and using process.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +3
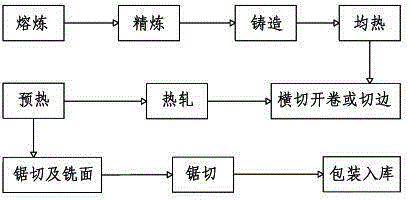
Preparation method for high-magnesium aluminum alloy O-state plate of 5XXX series
InactiveCN105177327AReduce the production process of annealingReduce production processHigh magnesiumAlloy
The invention relates to a preparation method for a high-magnesium aluminum alloy O-state plate of 5XXX series. The method comprises the steps of smelting, refining, casting, soaking, saw cutting, surface milling, preheating, hot rolling, cross-cutting and uncoiling or edge trimming, saw cutting, packaging and warehousing and the like. According to the preparation method, the high-magnesium aluminum alloy O-state plate of the 5XXX series is prepared through a new production process, under the condition that the performance and structure stability of high-magnesium aluminum alloy are maintained, the production procedures can be reduced, and surface quality defects of the high-magnesium aluminum alloy can be reduced; products can be directly produced after the aluminum alloy plate with the thickness being equal to or larger than 3 mm is subjected to hot rolling, the product yield can be substantially increased, and production efficiency can be improved sufficiently.
Owner:广西南南铝加工有限公司
Method for synchronously dephosphorization and vanadium extraction of vanadium-containing molten iron
The invention discloses a method for synchronously dephosphorization and vanadium extraction of vanadium-containing molten iron. The method comprises the following steps of: controlling temperature of vanadium-containing molten iron at 1230-1250 DEG C; carrying out oxygen-injection blowing, wherein oxygen flow is constantly controlled at 17000-25000Nm<3> / h, and the blowing process sequentially comprises three stages; the first stage starts from blowing to 1-2min of blowing, gun position is 1.6-1.8m, and lime for controlling alkalinity of slag to be 2-4 lime and 15-20kg / tFe of iron scale are added simultaneously; the second stage starts after 1-2min of blowing, gun position is 1.8-2.1m, and 5-18kg / tFe of iron scale is added in the process that oxygen-injection time is not greater than 3min; and the third stage starts from blowing to 2min of the end, 0.5-2kg / tFe of high-magnesium lime is added, and gun position is reduced to 1.6-1.8m; and blowing to end, and discharging semi-steel and vanadium slag. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that corrosion to lining of a vanadium extraction converter is effectively avoided, and dephosphorization and vanadium extraction are synchronously implemented; and TFe content in the vanadium slag is reduced.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Method for preenriching and separating lithium and boron from salt lake brine by liquid-liquid-liquid three-phase extraction
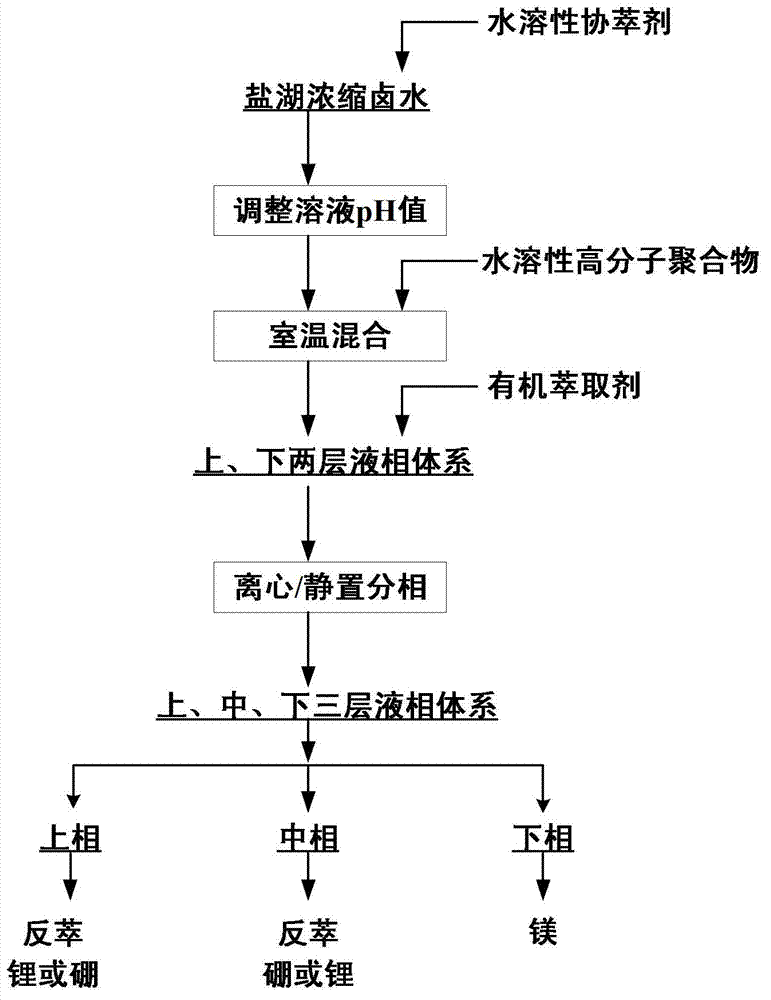
InactiveCN103031448AAchieve primary separationWide range of pH adaptationLithium compoundsBoron compoundsImpurityPolymer
The invention relates to a method for preenriching and separating lithium and boron from salt lake brine by liquid-liquid-liquid three-phase extraction, which comprises the following steps: adding water-soluble auxiliary extractant into a salt lake concentrated brine solution, regulating the pH value of the brine, adding water-soluble high molecular polymer, and thoroughly mixing at room temperature to obtain an upper / lower two-layer liquid-phase system; adding organic extractant, and mixing to obtain an upper / middle / lower three-layer liquid-phase system; and taking the upper and middle phases from the three-liquid-phase system, and respectively recovering lithium and boron in the upper and middle phases by back washing. The invention can simultaneously enrich and extract lithium and boron by one-step extraction from high-magnesium / lithium-ratio salt lake brine, and can separate the lithium and boron from abundant coexistent ions of magnesium, calcium and other impurity metals in the brine. The lithium and boron are respectively selectively enriched from the upper and middle phases in the three-liquid-phase system to implement primary separation, thereby facilitating the subsequent purification and refinement. The three-liquid-phase extraction can be carried out under neutral or weakly-acidic conditions, and has strong adaptability.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
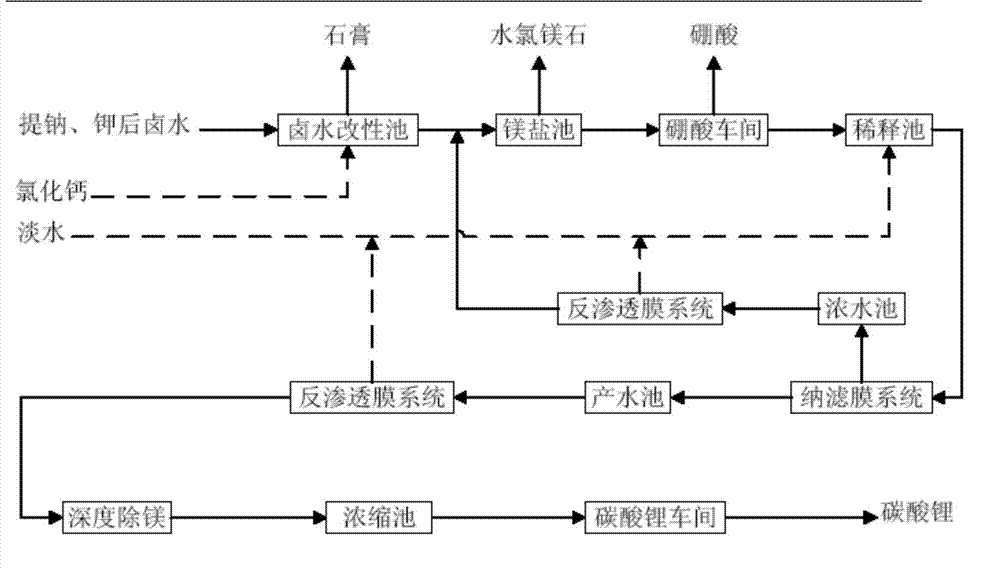
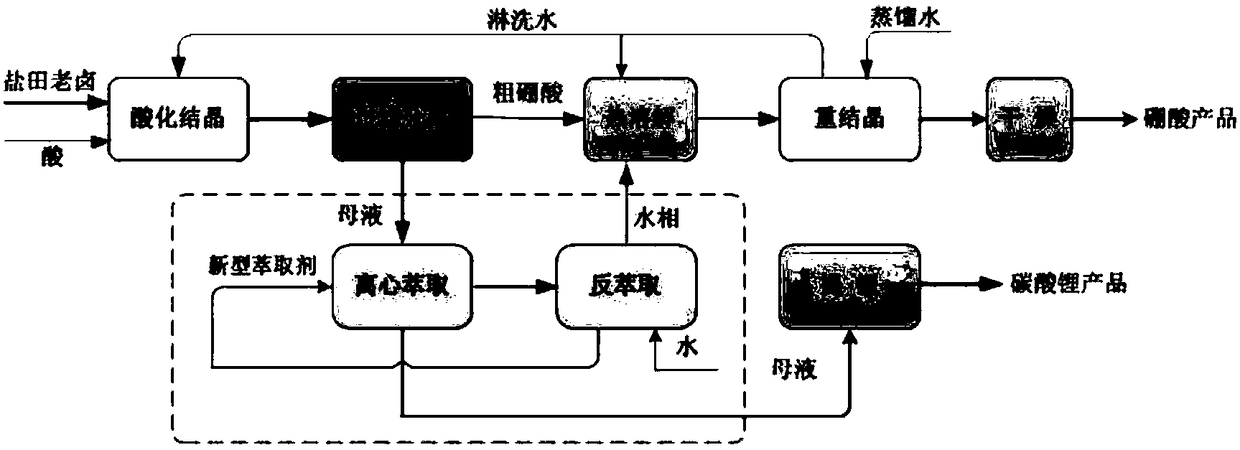
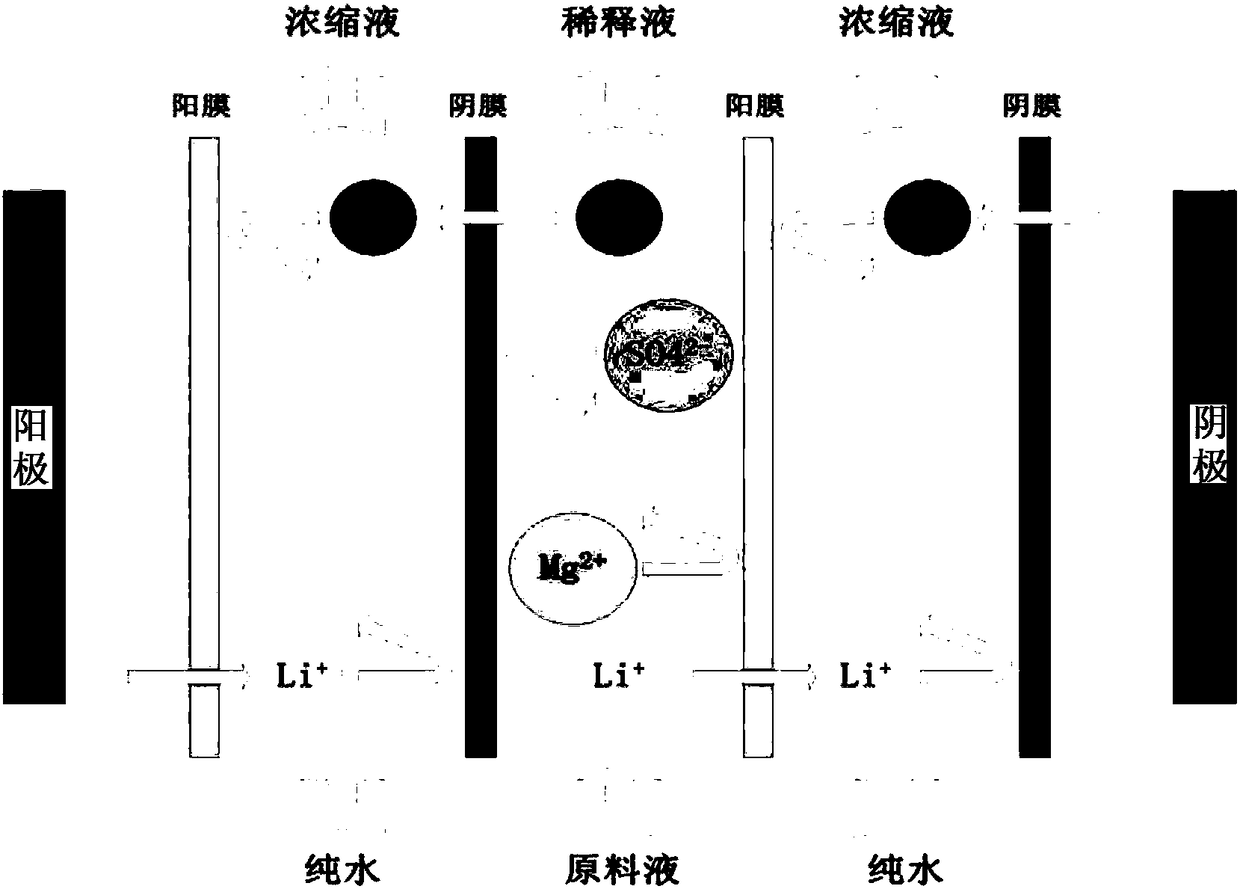
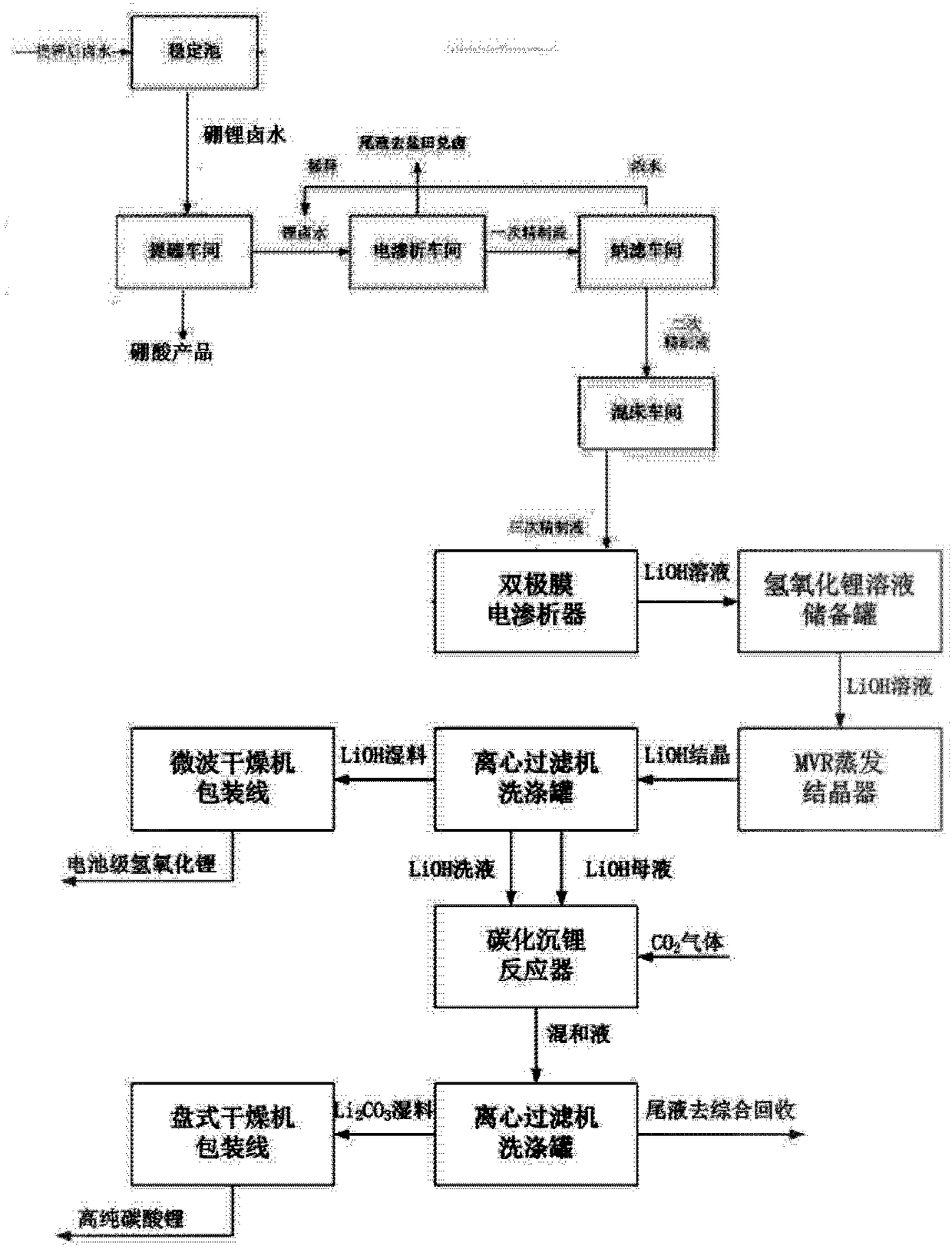
Method for directly preparing lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate from salt lake brine with high magnesium-to-lithium ratio
ActiveCN108341420AEasy to operateEfficient extractionBoron oxyacidsLithium oxides/hydroxidesPotassiumEvaporation
The invention discloses a method for directly preparing lithium hydroxide and lithium carbonate from salt lake brine with a high magnesium-to-lithium ratio. The method comprises the following steps: 1, further stabilizing brine obtained after potassium extraction of a salt pan in a stabilization pond to form boron and lithium brine with low potassium and sodium content; 2, carrying out boron extraction treatment on the boron and lithium brine to form a boric acid product and lithium brine; 3, 4 and 5, allowing the lithium brine to go through three times of refining to obtain a thirdly refinedsolution; 6, allowing the thirdly refined solution to go through a bipolar membrane electrodialyzer to form a lithium hydroxide solution; 7, allowing the lithium hydroxide solution to go through an evaporation crystallizer to obtain a lithium hydroxide monohydrate solid and evaporation mother liquor; 8, washing the lithium hydroxide monohydrate solid for recrystallization to form battery grade lithium hydroxide and a washing solution; and 9, allowing the evaporation mother liquor and the washing solution to go through a gas-liquid reactor to react with carbon dioxide gas to form the lithium carbonate. The method has the advantages of good maneuverability, and great increase of the recovery rate of lithium ions.
Owner:马培华
Graded aluminium alloy cylinder liner material and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103160715AImprove tribological performanceSmall expansion coefficientHigh magnesiumCentrifugal force
The invention relates to a graded aluminium alloy cylinder liner material and a preparing method thereof. The graded aluminium alloy cylinder liner material is characterized by containing following component, by weight, 15.0%-25.0% of Si, 3.0%-7% of Ni, 0.8%-1.8% of Mg, 0.5%-2.5% of Cu, 0.3%-0.7% of Mn, 0.04%-0.10% of RE, 0.01%-0.10% of P, and the balance aluminium. The preparing steps comprise burdening according to alloy components; smelting, covering, refining, purifying, and modifying; centrifugal force field forming; heat treating; and obtaining required end products after machining and honing. According to the graded aluminium alloy cylinder liner material and the preparing method thereof, by means of the alloy formula containing high content of Si, Mg and Ni, structural texture containing the high content of Si, Mg2Si and Ni is formed beneficially, and the prepared graded cylinder liner material has the advantages of being resistant to high temperature, resistant to abrasion, and low in dilatation coefficient. Meanwhile, the P-RE double compound modification process technique and a centrifugal force field controlled by a variable frequency motor are utilized, primary silicon and eutectic silicon phase texture are strongly refined, and tribology performance of the cylinder liner is greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA WEAPON SCI ACADEMY NINGBO BRANCH +1
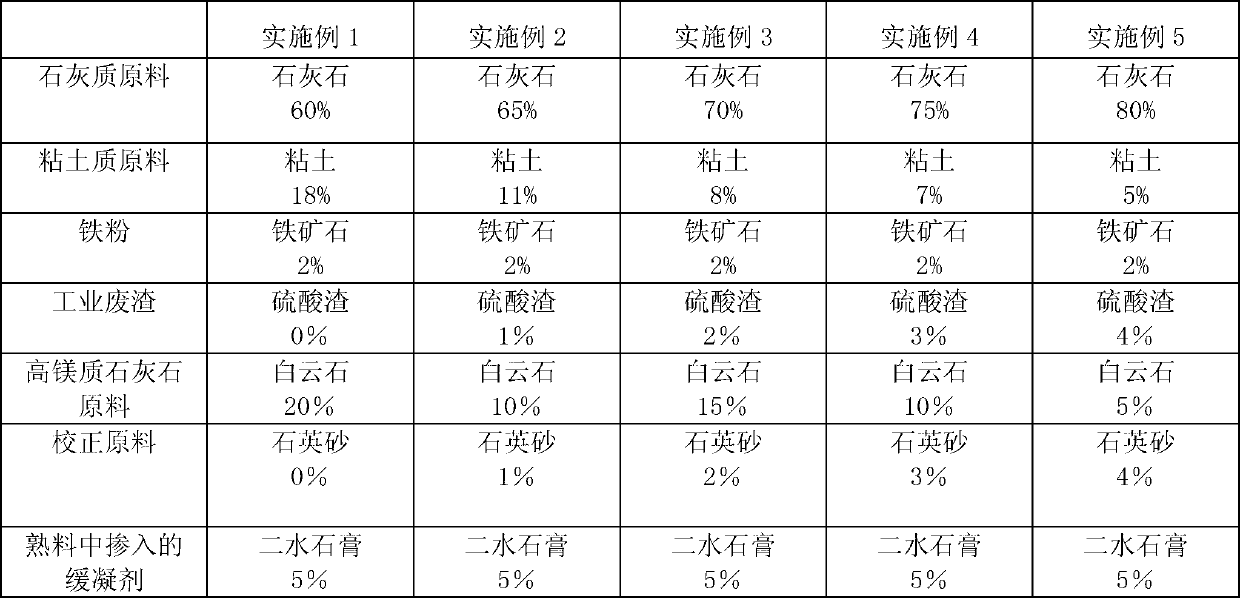
Minimum inflation high magnesium moderate heat cement, production method therefor and applications thereof
The invention discloses a kind of minimum inflation high magnesium moderate heat cement, a production method therefor and applications thereof. The cement is prepared from calcium raw materials, silicon materials, aluminum raw materials, iron raw materials, magnesium raw materials, correction raw materials and clinker activating agents through two-grinding and one-burning process. The content of MgO in the clinkers is raised to 6-9%, the content of periclase is controlled to 2-8%, the minimum inflation performance of periclase can be used fully, the contraction of mass concrete can be compensated, concrete cracks can be decreased, and therefore the volume stability and safety of concrete are raised.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Preparation process of medium-strength anti-corrosion high-magnesium aluminum alloy plate
The invention discloses a preparation process of a medium-strength anti-corrosion high-magnesium aluminum alloy plate and belongs to the technical field of aluminum alloy machining. The preparation process of the medium-strength anti-corrosion high-magnesium aluminum alloy plate comprises batching, smelting, degassing and filtering, casting, homogenizing annealing, saw cutting and milling, preheating, hot rolling, edge-cutting or cross-cutting uncoiling, drawing and saw cutting, wherein the drawing refers to performing edge-cutting processing on the plate after natural cooling and then drawing the plate on a drawing machine by the drawing amount of 3-7%. Compared with a high-magnesium aluminum alloy plate prepared by use of a traditional cold rolling method, the preparation process is capable of breaking through the limitation of the opening degree of a cold-rolling mill and producing a thick plate; the obtained plate is high in straightness, low in internal stress, even in cold deformation and excellent in corrosion property.
Owner:广西南南铝加工有限公司
Method for extracting lithium salt from salt lake bittern with low-magnesium-lithium ratio with calcium circulation solid phase conversion method
ActiveCN101508450AReduce lossesPrecipitation crystal form is goodCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesProcess efficiency improvementSolid phasesRaw material
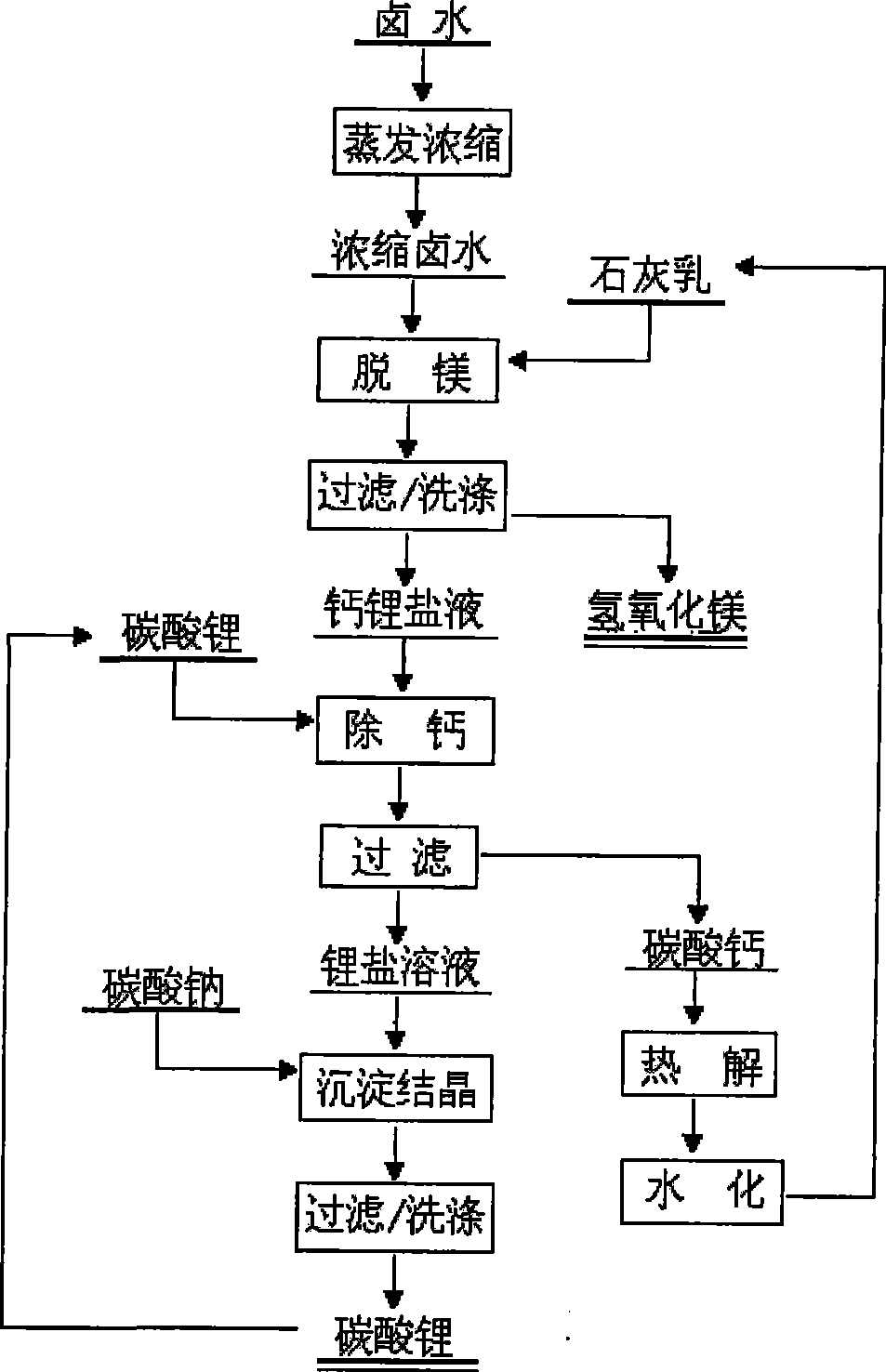
The invention relates to a method for extracting lithium salts from saline salt brine with a low magnesium-lithium ratio through a calcium cycling solid-phase conversion method. The method is to take the saline salt brine with the low magnesium-lithium ratio as a raw material and adopt the technological flows of brine concentration, magnesium and sulfur removal through lime cream, calcium separation through lithium carbonate, lithium extraction through sodium carbonate, thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate, hydration of quicklime into cream, and the like to extract lithium carbonate products. The main technical points of the method comprises that: the method is based on a solid-phase conversion principle of anions (OH, CO3) and realizes magnesium and calcium removal of the brine, purification of the lithium salts and closed cycle of calcium through solid-phase conversion of Ca(OH)2, Mg(OH)2, Li2CO3, Ca(OH)2, CaCO3, CaO, Ca(OH)2. The method comprehensively utilizes magnesium resources and lithium resources of saline lakes, has the characteristics of high magnesium removal efficiency, good purification effect of the lithium salts, high recovery rate of lithium and magnesium, low energy consumption, low cost, closed cycle of the calcium, small project investment, and the like, and is particularly suitable for industrial production on a large scale. In addition, the whole process is simple, clean and environment-friendly.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Acidolysis method of magnesium-containing phosphate rock
ActiveCN102417169AAchieving Theoretical UtilizationEasy to processCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesAmmonium sulfatesHigh magnesiumPhosphor
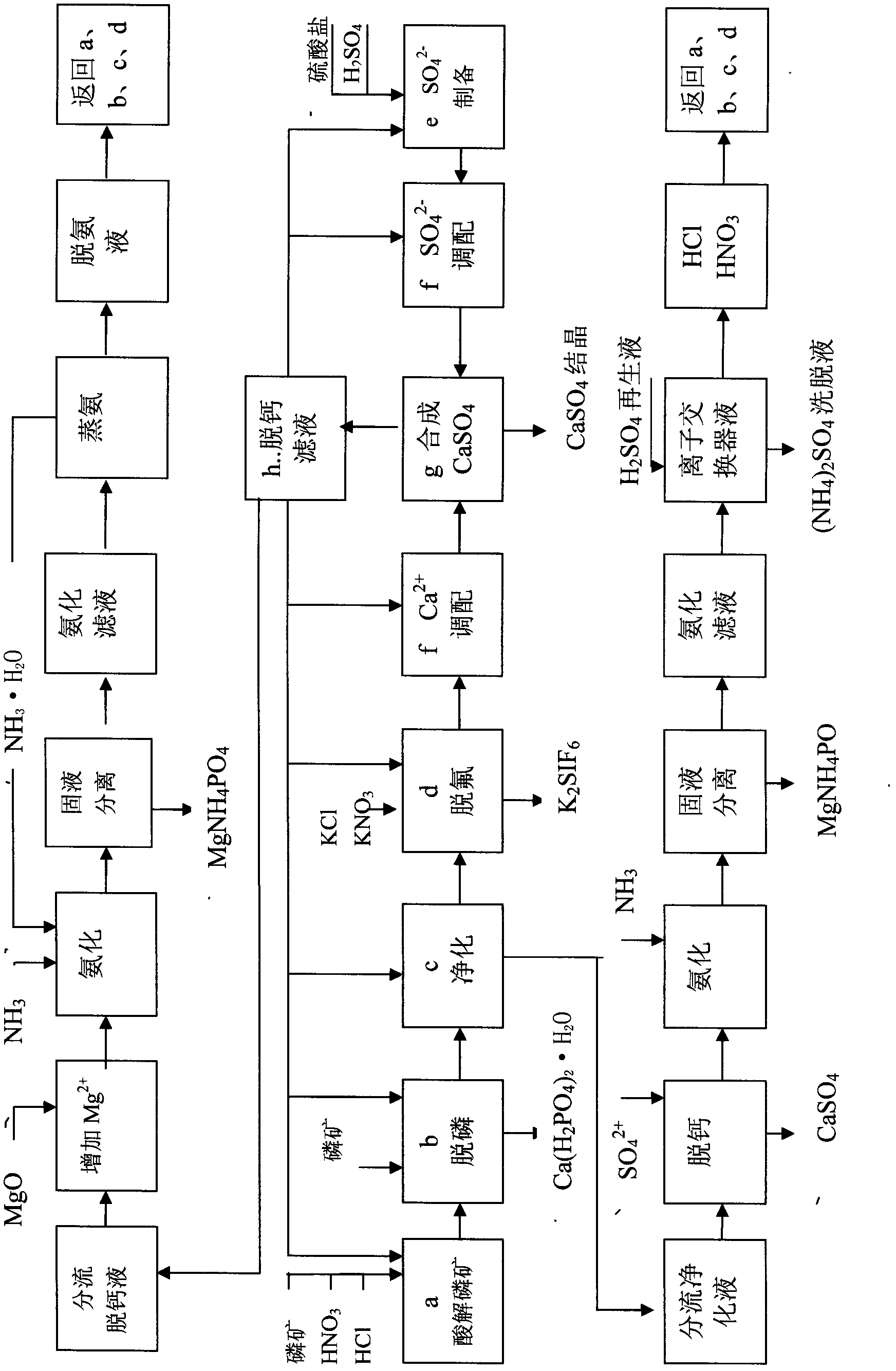
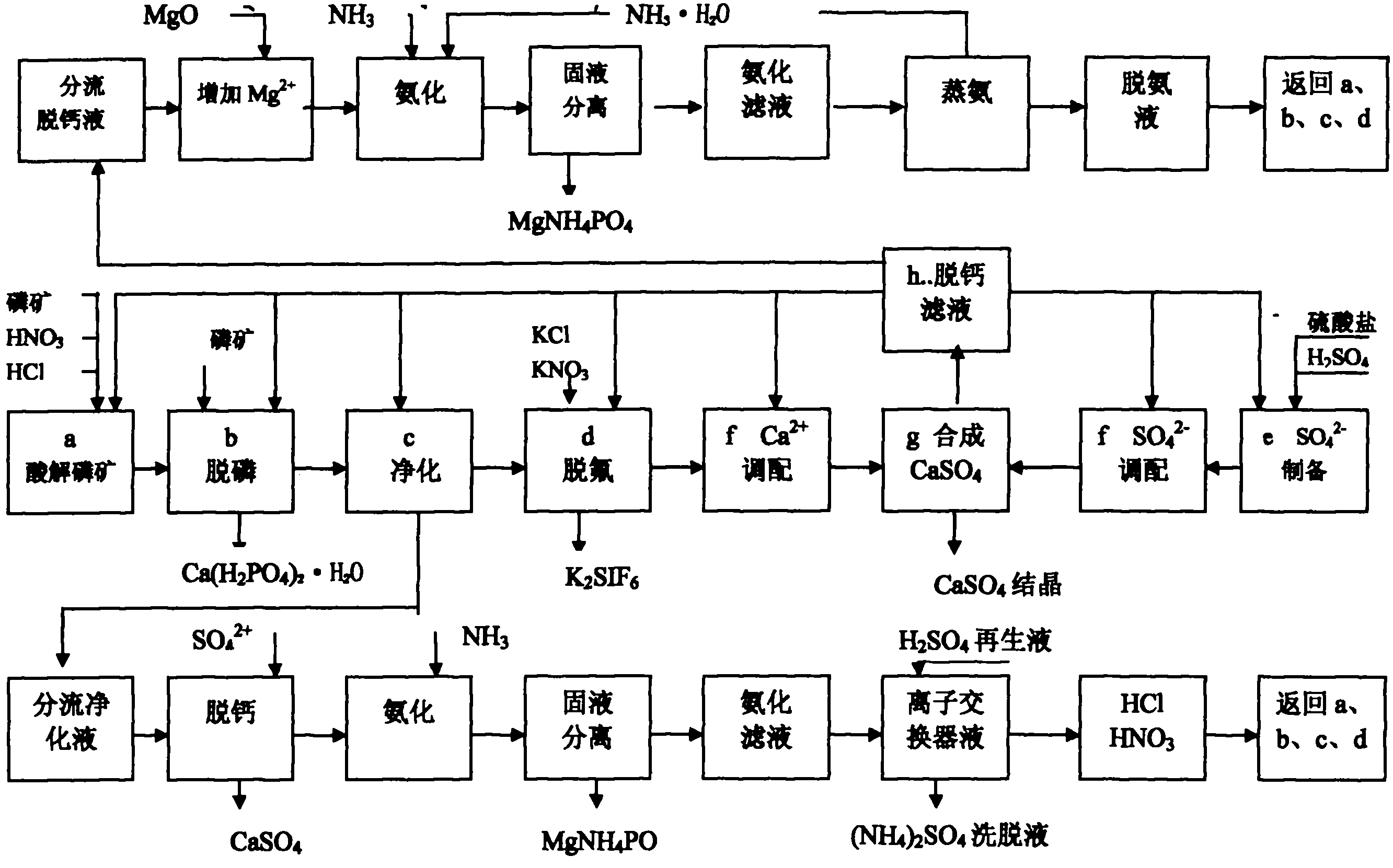
The invention discloses an acidolysis method of magnesium-containing phosphate rock. The method provided by the invention is characterized by comprising the following steps of: carrying out acidolysis on the magnesium-containing phosphate rock to obtain a water-soluble calcium, magnesium and phosphoric acid containing acidolysis solution, carrying out acidolysis on the phosphate rock by using the generated phosphoric acid to generate Ca(H2PO4)2.H2O solid, performing a reaction between H2SO4 and water-soluble calcium to generate high-pureness calcium sulfate whisker, and performing a reaction between water-soluble magnesium and phosphor in the acidolysis solution and NH3 to generate character separation magnesium ions of a MgNH4PO4 solid so as to realize complete high-efficiency comprehensive utilization of the acidolyzed magnesium-containing phosphate rock. The focus of the invention is to change magnesium ions into controllable parameters which are beneficial to circulation of the acidolysis solution. The magnesium-containing phosphate rock can be efficiently utilized, and also the compound magnesium ammonium phosphate can be used to realize the separation of phosphor magnesium from a circulation medium HCl or HNO3 or CaCL, Ca(NO3)2, thus realizing the combination and combined production with a present ammonium phosphate and phosphor product processing technology. The method provided by the invention has advantages of concise technology, less investment, low energy consumption, low cost, high benefit and no discharge of ''three wastes (waste gas, wastewater and industrial residue)'', and fully presents great business value and great resource value of the high magnesium-containing phosphate rock.
Owner:武善东 +1
Ionic liquid modified positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110026091AImprove interception effectReduce retentionMembranesSemi-permeable membranesHigh magnesiumPolyamide
The invention discloses an ionic liquid modified positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: on a supporting bottom film, firstly, carrying out interfacial polymerization on polyamine and polyacyl chloride to form a primary polyamide layer, and then carrying out an amidation reaction on acyl chloride groups remaining on the surface of the primary polyamide layer and amino functionalized ionic liquid to prepare the composite film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing apolyamine aqueous phase solution and a polyacyl chloride organic phase solution; (2) carrying out interfacial polymerization on the surface of the bottom film to prepare a primary polyamide nanofiltration membrane; and (3) reacting the amino-functionalized ionic liquid solution with acyl chloride groups on the surface of the primary polyamide layer, and carrying out heat treatment to obtain the positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane. By changing the charge property of the composite membrane, lithium resources in the salt lake brine with a high magnesium-lithium ratio can be effectively extracted, the magnesium-lithium separation factor of the composite membrane is lower than 0.15, and the flux is 40-50L / m<2>h. The method has the advantages that the preparation method is simple, and the method has a good industrial application prospect in the aspect of salt lake lithium extraction.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
High-magnesium phosphorite de-magging method with by-product magnesium ammonium phosphate
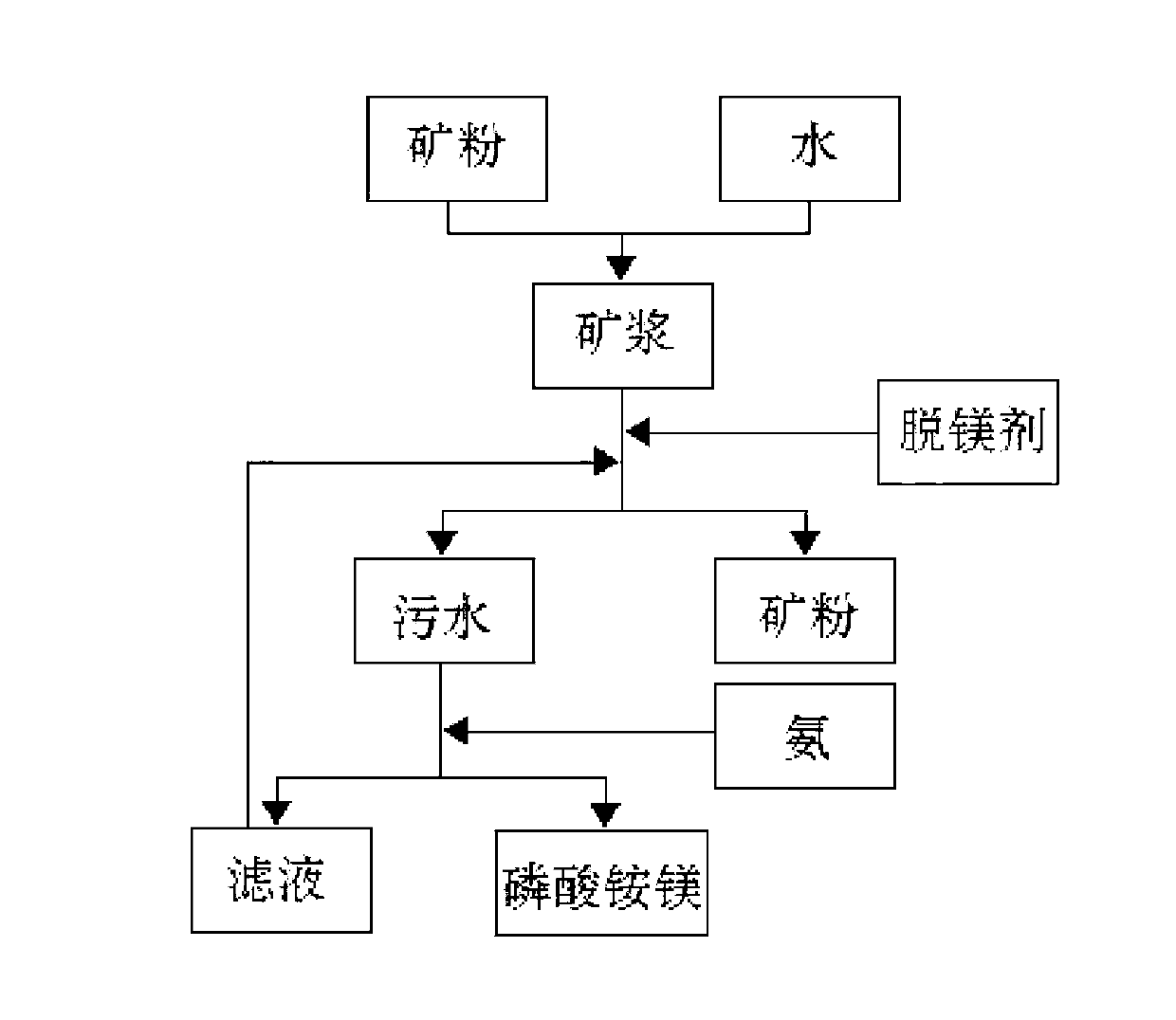
InactiveCN102992284AHigh removal rateReduce contentRaw phosphate material treatmentPhosphoric acidMagnesium ammonium phosphate
The invention discloses a high-magnesium phosphorite de-magging method with a by-product magnesium ammonium phosphate. The method is as below: mixing a mineral powder and water to obtain a pulp; then adding a magnesium removal agent into the pulp for reaction; then separating wastewater and mineral powder after magnesium removal; adding ammonia into the wastewater to generate magnesium ammonium phosphate; filtering to obtain a magnesium ammonium phosphate product; and adding a recycled filtrate from filter into the pulp. The invention has advantages of economical equipment investment and good operating environment; sulfuric acid and / or phosphoric acid is used as a magnesium removal agent, has high removal rate of magnesium, significantly reduces magnesium content in the phosphate, and especially has obvious effect on phosphate with high magnesium content, so as to reduce loss of phosphorus pentoxide in the phosphate; the wastewater can be recycled to save water resource, and causes no impact on the environment; the treated concentrate in a wet production significantly improves bubble phenomenon and filtering performance, so as to improve production capacity and labor productivity of the whole device, and reduce the production cost; and magnesium in the phosphate can be used for production of a magnesium ammonium phosphate slow release fertilizer, and generates good economic benefit.
Owner:GUIZHOU KAILIN GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com