Method for extracting lithium salt from salt lake bittern with low-magnesium-lithium ratio with calcium circulation solid phase conversion method
A phase inversion method and technology of salt lake brine, applied in the direction of lithium carbonate; Fine particle size of the product, etc., to achieve the effects of easy filtration and washing, improved recovery, and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
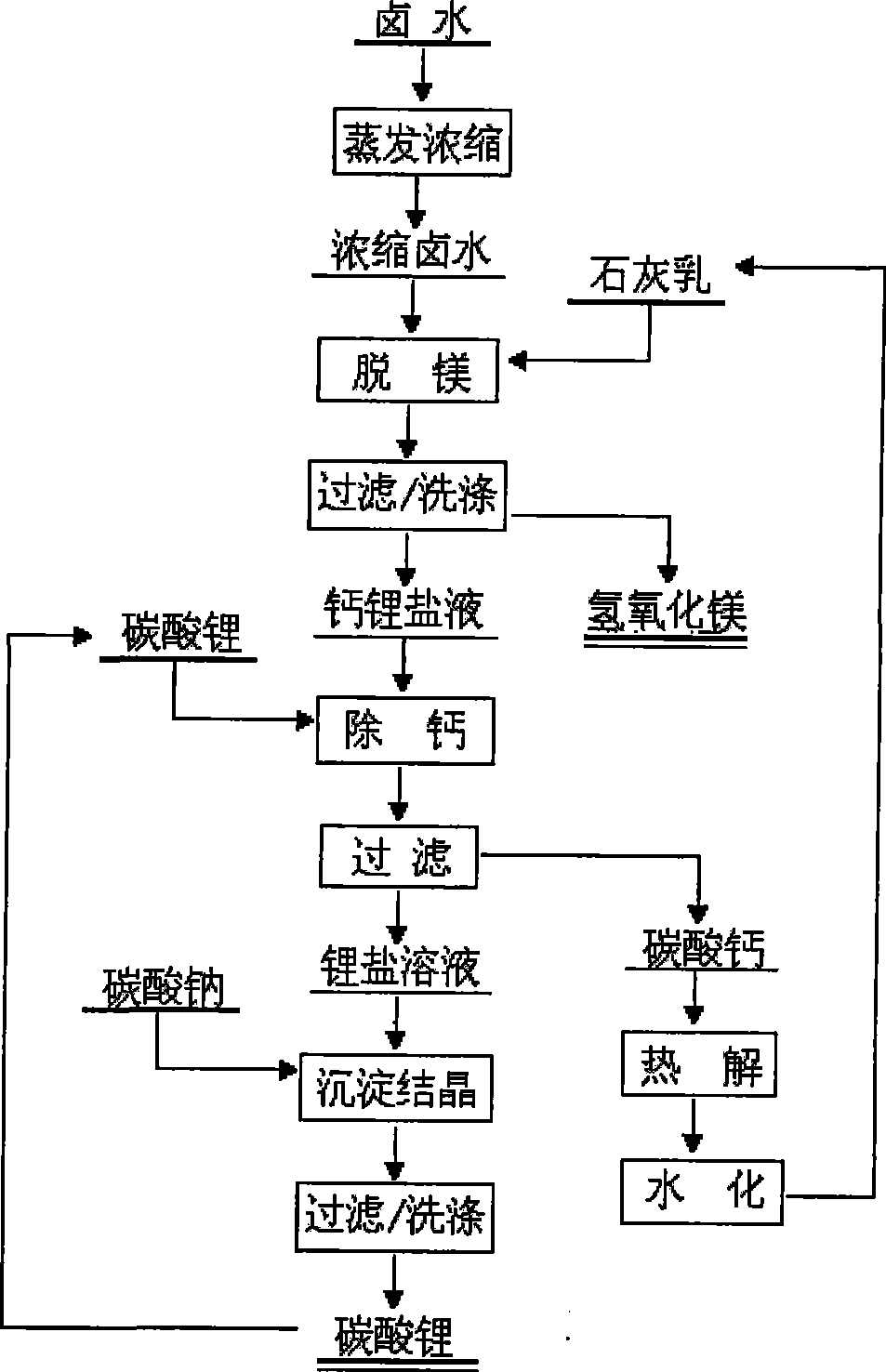
[0046] A. Take low-magnesium-lithium-ratio salt lake brine and dehydrate and concentrate it. The contents of lithium and magnesium in the concentrated brine are 7.4g / L and 20.8g / L respectively; the temperature of the brine is 94°C.
[0047] B. Add water to the reactor (demagnesizing device) according to the liquid-solid ratio of 3:1, and stir; take quicklime (CaO) according to the CaO / Mg (mass ratio) of 2.8 and add it to the water in the demagnesizing reactor to form milk of lime.
[0048] C. The reactor is constantly stirred, and the hot concentrated brine is slowly added into the reactor; the reaction time of feeding is 180min.
[0049] D. Filtrate and wash while it is hot; the washing liquid is returned to prepare milk of lime; the temperature of the filtered solution (removed magnesium solution) is 62°C, and the main components (g / L) are: lithium 6.3, magnesium <0.1, calcium 29.5.
[0050] E. Add water to the reactor (decalcifier) according to the liquid-solid ratio of 3...
Embodiment 2
[0055] A. Take low-magnesium-lithium-ratio salt lake brine and dehydrate and concentrate it. The contents of lithium and magnesium in the concentrated brine are 11.5g / L and 27.6g / L respectively; the temperature of the brine is 97°C.
[0056] B. Add water into the reactor (demagnesizing device) according to the liquid-solid ratio of 3:1, and stir; take quicklime (CaO) according to the CaO / Mg (mass ratio) of 2.5 and add it to the water in the demagnesizing reactor to form milk of lime.
[0057] C. The reactor is constantly stirred, and the hot concentrated brine is slowly added into the reactor; the reaction time of feeding is 120min.
[0058] D. Filtrate and wash while it is hot; the washing liquid is returned to prepare milk of lime; the temperature of the filtered solution (removed magnesium solution) is 68 ° C, and the main components (g / L) are: lithium 9.5, magnesium <0.1, calcium 38.0.
[0059] E. Add water to the reactor (decalcifier) according to the liquid-solid ratio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com