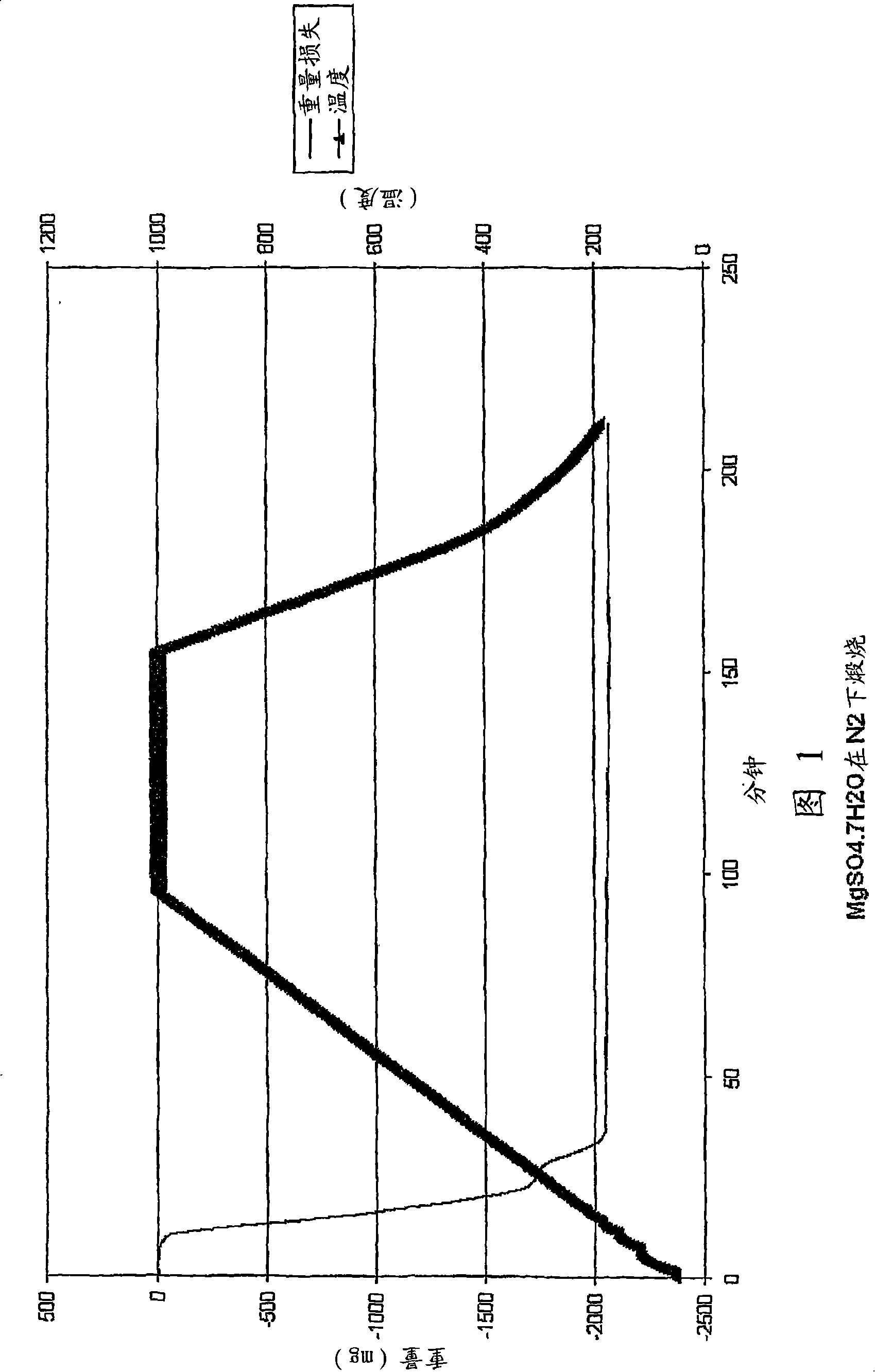
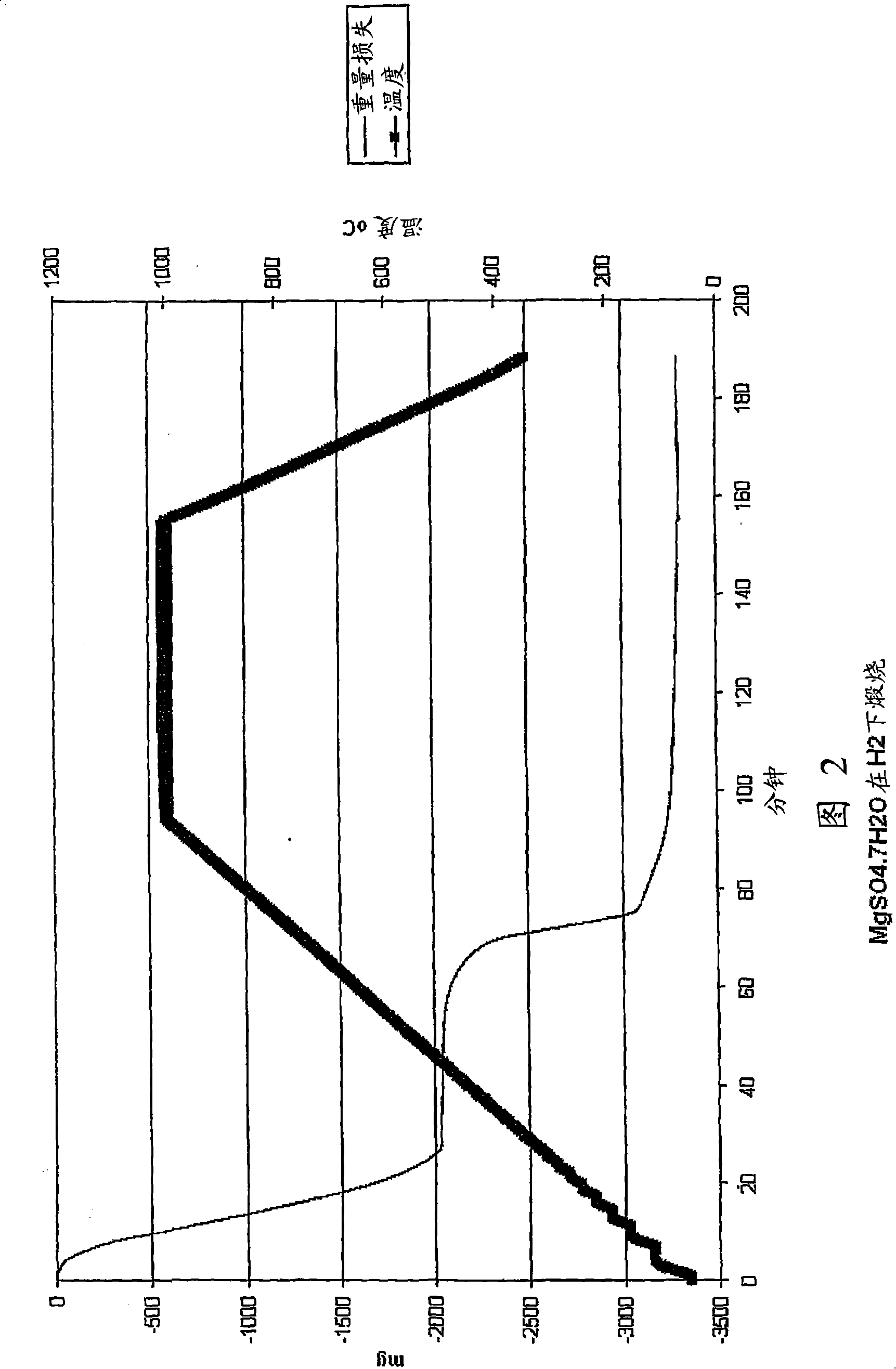
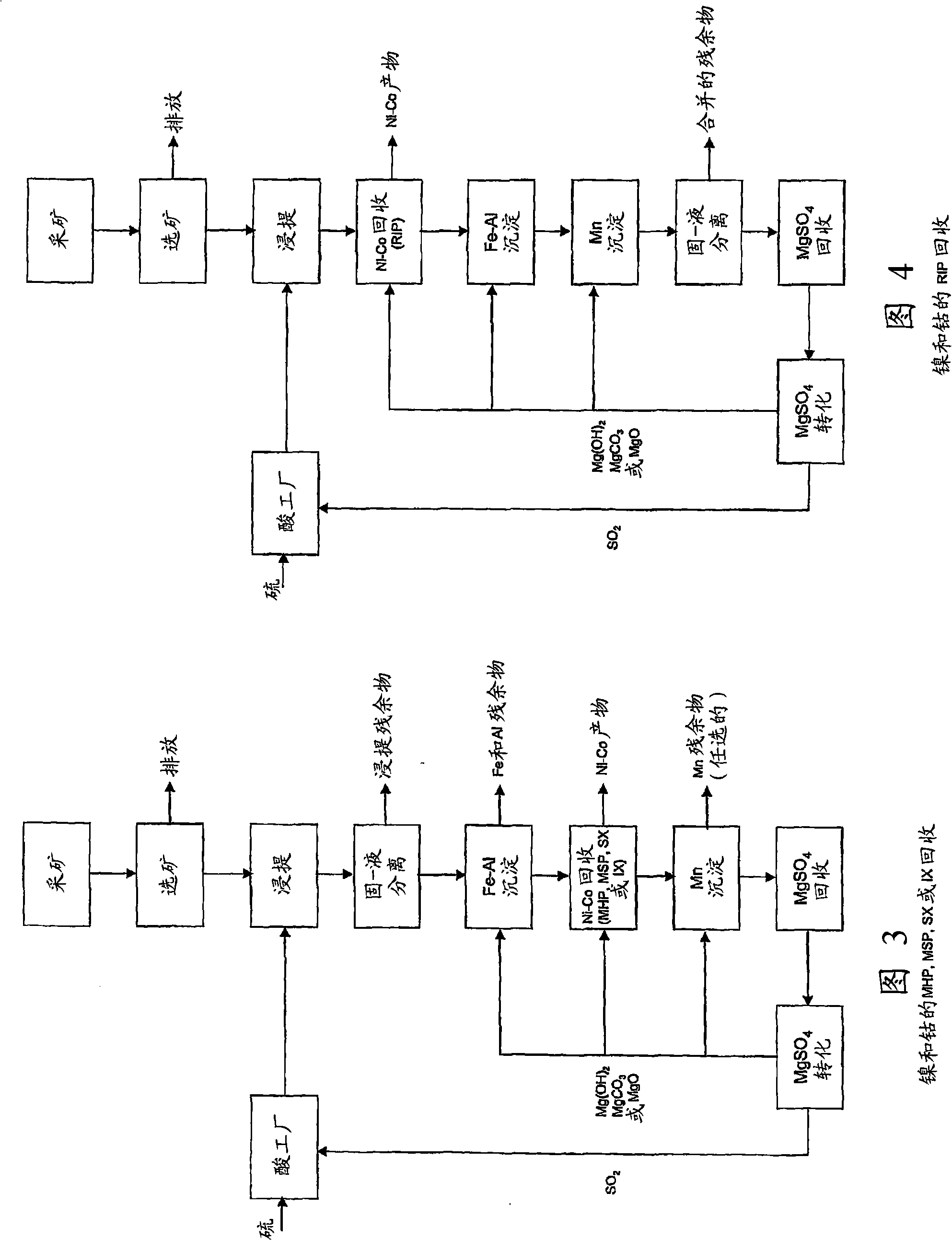
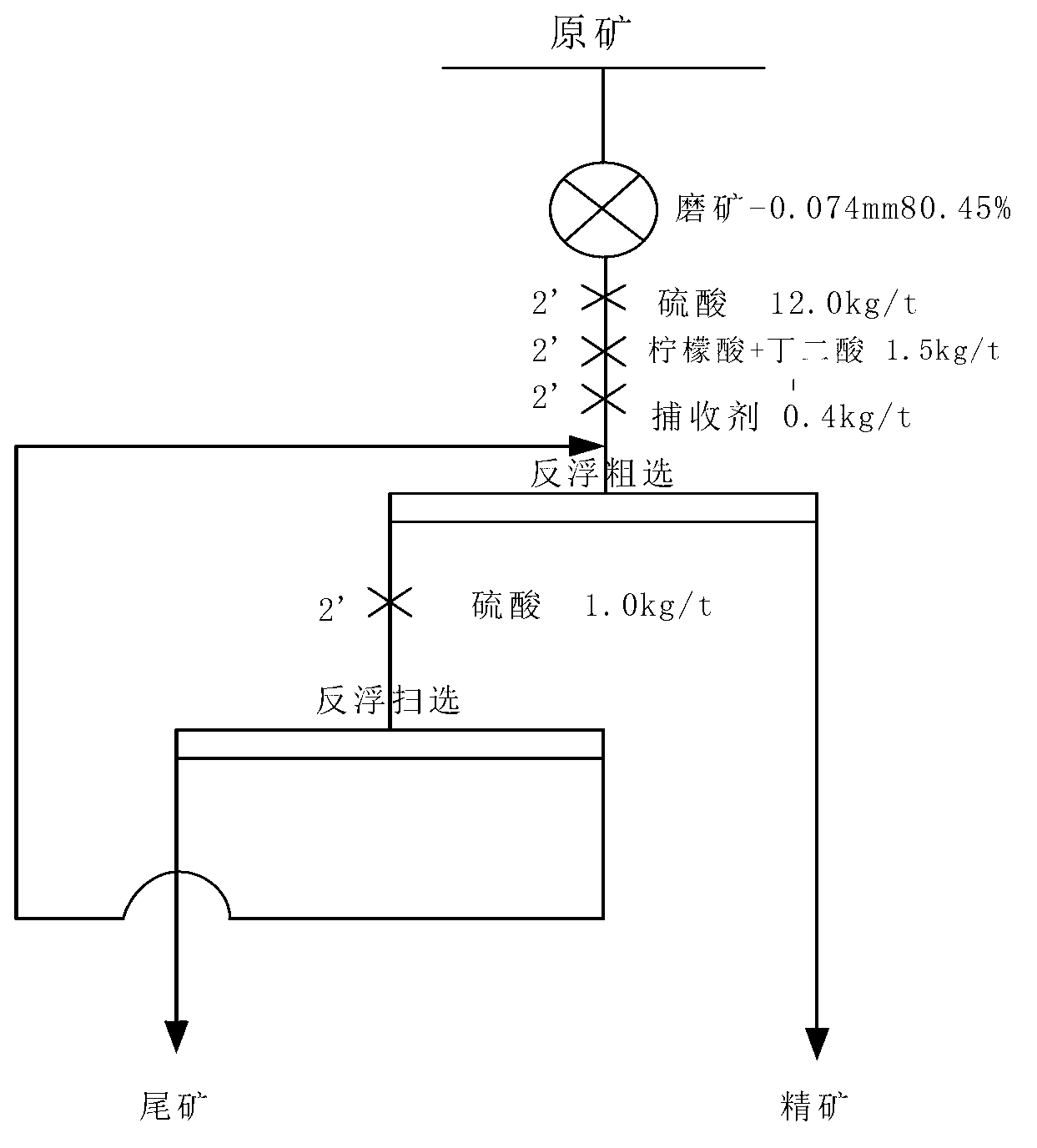
Patents
Literature
138 results about "Low magnesium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low magnesium level is a condition in which the amount of magnesium in the blood is lower than normal. The medical name of this condition is hypomagnesemia. Every organ in the body, especially the heart, muscles, and kidneys, needs the mineral magnesium. It also contributes to the makeup of teeth and bones.
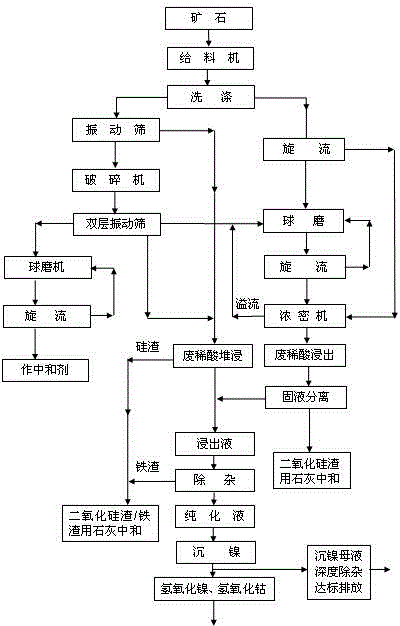
Method for atmospheric digestion of laterite ore
InactiveCN101273146AAvoid it happening againLow costProcess efficiency improvementHigh magnesiumDigestion
An atmospheric leaching process in the recovery of nickel and cobalt from a lateritic ore, said lateritic ore including a low magnesium ore fraction and a high magnesium ore fraction, said process including the steps of: (a) forming an aqueous pulp of said lateritic ore, (b) leaching said aqueous pulp with a concentrated mineral acid at atmospheric pressure to produce a slurry containing a pregnant leach liquor and a leach residue, (c) treating the pregnant leach liquor either separately or as part of said slurry to recover dissolved nickel and cobalt therefrom, leaving a magnesium containing barren solution, (d) treating said magnesium containing solution to recover a magnesium containing salt therefrom.
Owner:BHP比利通创新有限公司
Microbeam tungsten argon arc welding method for magnesium alloy thin-walled tube
InactiveCN102554418AIncrease the difficultyLow yieldArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsArc stabilityManganese
The invention relates to a microbeam tungsten argon arc welding method for a magnesium alloy thin-walled tube. A low-magnesium aluminum alloy welding wire is used as a filling material, and the thin-walled tube is welded by a microbeam tungsten argon arc welding process under inert gas shielding. The low-magnesium aluminum alloy welding wire comprise 9.5%-11.6% of Al (aluminum), 0.6%-1.75% of Zn (zinc), 0.15%-0.35% of Mn (manganese), 0.01%-0.05% of Cu (copper), 0.02%-0.05% of Si (silicon) and the balance Mg (magnesium) in mass percent. The microbeam tungsten argon arc welding method for the magnesium alloy thin-walled tube is high in welding efficiency and convenient and flexible in application, and can be used for obtaining a crack-free welding joint without magnesium-aluminum brittle compounds. Compared with a conventional tungsten argon arc welding method, the microbeam tungsten argon arc welding method has the advantages that arc stability of microbeam argon arc welding for the magnesium alloy thin-walled tube is obviously improved, the tensile strength of the welding joint is 30% higher than that of a conventional tungsten argon arc welding joint, the elongation of the welding joint is increased by 10%, and the use requirements of industrial production on magnesium alloy thin-walled tube welding component can be met.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
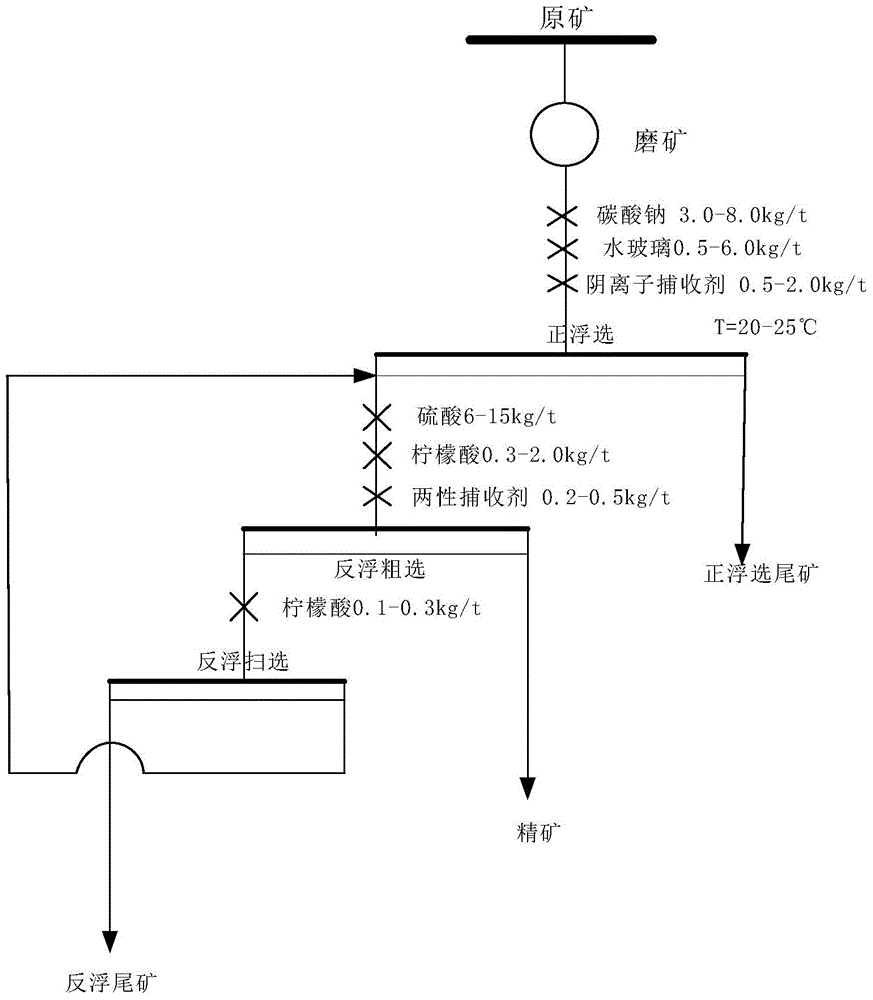
Phosphorite reverse flotation process
ActiveCN103212484ANo pollution in the processEfficient separationFlotationOrganic acidPhosphoric acid
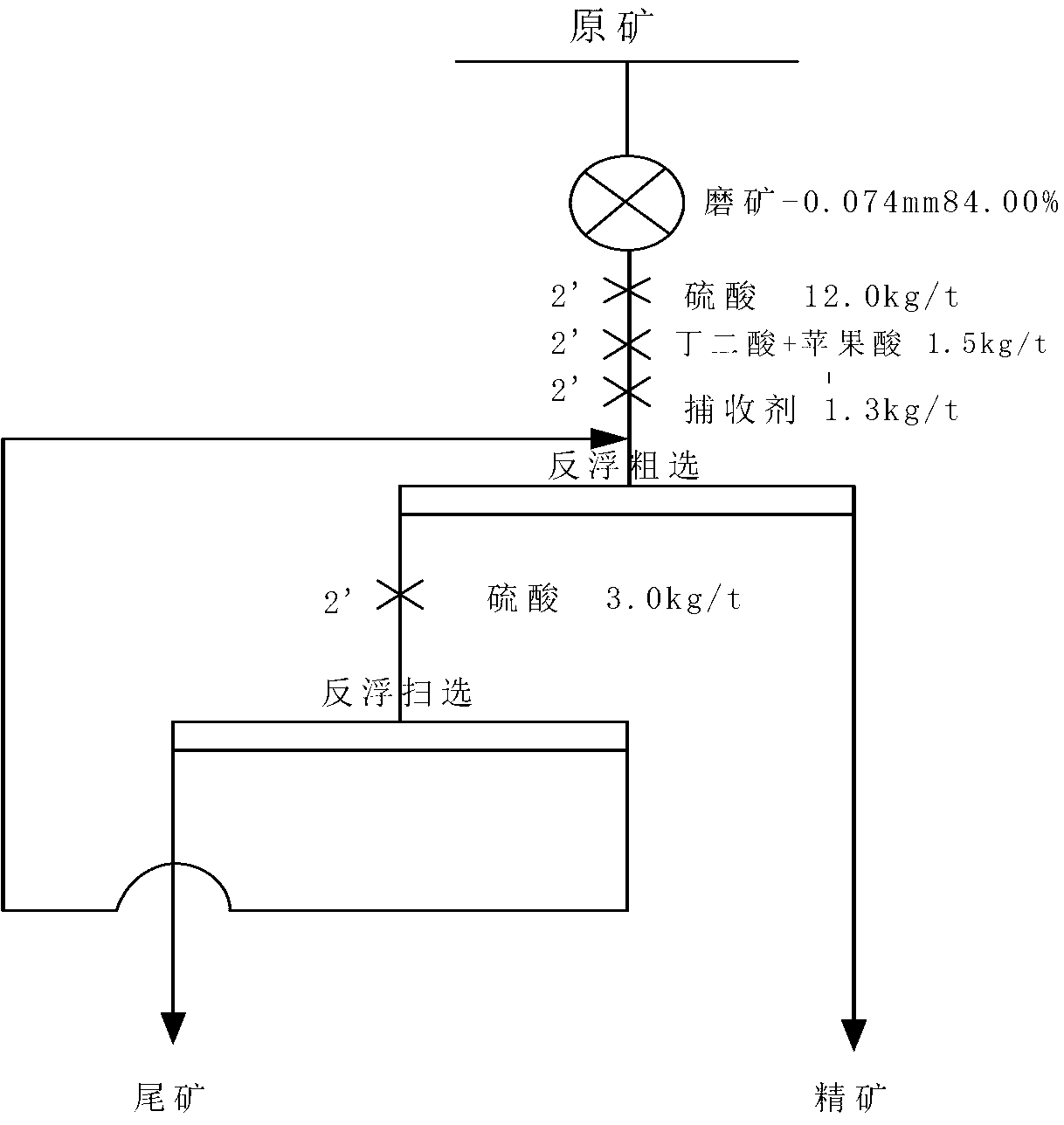
The invention relates to a phosphorite reverse flotation process which comprises the following steps: after carrying out ore crushing, ore grinding and size mixing on phosphorite, enabling the obtained product to enter the reverse flotation process, wherein ore pulp obtained after size mixing is added with sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid to form a regulator and an inhibitor and then is added with micromolecule organic acid to form a combined inhibitor for inhibiting phosphate minerals; carrying out reverse flotation to separate out carbonate minerals by using fatty acids or fatty acid soaps as a collecting agent so as to obtain high-grade low-magnesium phosphate concentrates. The phosphorite reverse flotation process has the following advantage that the micromolecule organic acid inhibitor is adopted to implement effective separation of collophanite and dolomite, so that the grade of the phosphate concentrates is improved, the grade of tailings is reduced and the recovery rate can be improved. Meanwhile, application of phosphoric acid and derivatives thereof to phosphorite reverse flotation is replaced, so that phosphorus resources are saved, service time of phosphate rock resources is prolonged and the defects in the prior art are overcome.
Owner:远安县燎原矿业有限责任公司
Method for leaching nickel and cobalt form low-iron and high-magnesium and high-iron and low-magnesium laterite-nickel ore by using waste dilute sulphuric acid
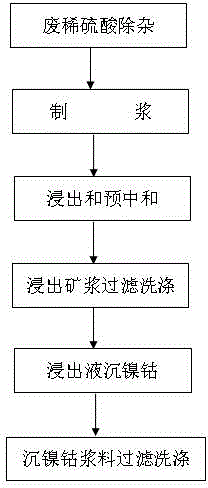
The invention provides a method for leaching nickel and cobalt from low-iron and high-magnesium and high-iron and low-magnesium laterite-nickel ore by using waste dilute sulphuric acid. Nickelous hydroxide, cobaltous hydroxide and the like are directly extracted by leaching the laterite-nickel ore with non-concentrated decolored and desalinated waste dilute sulphuric acid. The method specially comprises the steps of: removing impurities out of the waste dilute sulphuric acid, slurrying, leaching and pre-neutralizing, filtering and washing leached ore pulp, settling nickel and cobalt from leachate, filtering and washing nickel and cobalt settled slurry, electrically depositing nickel, and post-treating and recycling iron, magnesium, manganese and the like. The method provided by the invention overcomes the technical difficulty, ensures that a technology of a direct dilute sulphuric acid atmospheric pressure leaching process route operates stably, is greatly lowered in cost, is high in production efficiency, and is high in recycling rate of nickel, cobalt, iron, magnesium, manganese and other metals. The waste dilute sulphuric acid which is an byproduct in industries such as dye industry and is difficult to treat is effectively recycled, the method is environmental-friendly, any harmful gas is not emitted, waste slag is solid materials, trees can be planted on the waste slag for greening, the waste slag can be recycled, and waste water can completely reach the standard for emission.
Owner:杭州蓝普水务有限公司
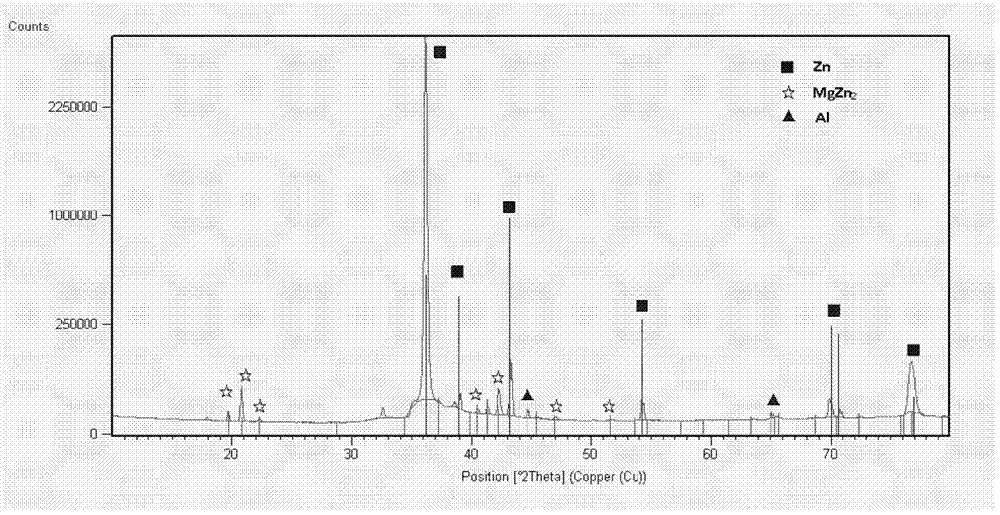
Low-aluminum low-magnesium zinc-aluminum-magnesium plated steel plate and method for producing same
The invention provides a low-aluminum (Al) low-magnesium (Mg) zinc (Zn)-aluminum-magnesium plated steel plate and a method for producing the low-Al low-Mg Zn-Al-Mg plated steel plate. After a steel plate is annealed in nitrogen (N2) containing 0.5-30vol% of hydrogen (H2), the steel plate is impregnated with a plating solution, wherein the temperature of the plating solution is 40-120 DEG C above zero (the melting point of a zinc alloy); before the steel plate is impregnated with the plating solution, the temperature of the plating solution ranges from impregnating temperature to impregnating temperature + 50 DEG C above zero; the steel plate is impregnated with the plating solution for 2-10 seconds, and the steel plate is cooled at the speed of 10-50 DEG C per second after being impregnated with the plating solution; the plating solution comprises the following chemical components: 1.0-2.4% of Al and 1.0-2.0% of Mg, wherein the ratio of the Al to the Mg is more than or equal to 1; the plating comprises the following chemical components: 1.0-2.4% of Al and 1.0-2.0% of Mg, wherein the ratio of the Al to the Mg is more than or equal to 1, and Fe is less than or equal to 1%; the plating is formed by a Zn-rich phase, an Al-rich phase, MgZn2 and eutectic structures thereof; the thickness of an Fe-Al intermetallic compound between the plating and the steel-based interface is not more than 0.5mu m; and the content of Mg in the surface of the plating of every 1mu m is not less than 2%. The Zn-Al-Mg plated steel plate provided by the invention has good corrosion resistance, toughness and weldability, and the process for preparing the Zn-Al-Mg plated steel plate is simple and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Method for reducing magnesium and aluminum impurities in wet-process phosphoric acid
ActiveCN103523764AEasy to operateEase of industrial implementationPhosphorus compoundsPhosphoric acidImpurity ions
The invention discloses a method for reducing magnesium and aluminum impurities in wet-process phosphoric acid. The method comprises the following steps: adding an ammonium fluoride-containing compound into wet-process phosphoric acid, wherein the addition mount of the ammonium fluoride-containing compound is 0.5-5 percent of the mass of wet-process phosphoric acid, the aging temperature is 30-80 DEG C, and the aging time is 5-48 hours; performing free settling, wherein the supernatant liquid is purified wet-process phosphoric acid with low magnesium and aluminum content. The sediment obtained by the method is large in particle and easy to settle, and a removal rate of magnesium and aluminum impurity ions can be 5-40 percent. The method is easy to operate, low in treatment cost and easy for realization of industrial production and has high industrialization popularization value.
Owner:YUNNAN YUNTIANHUA
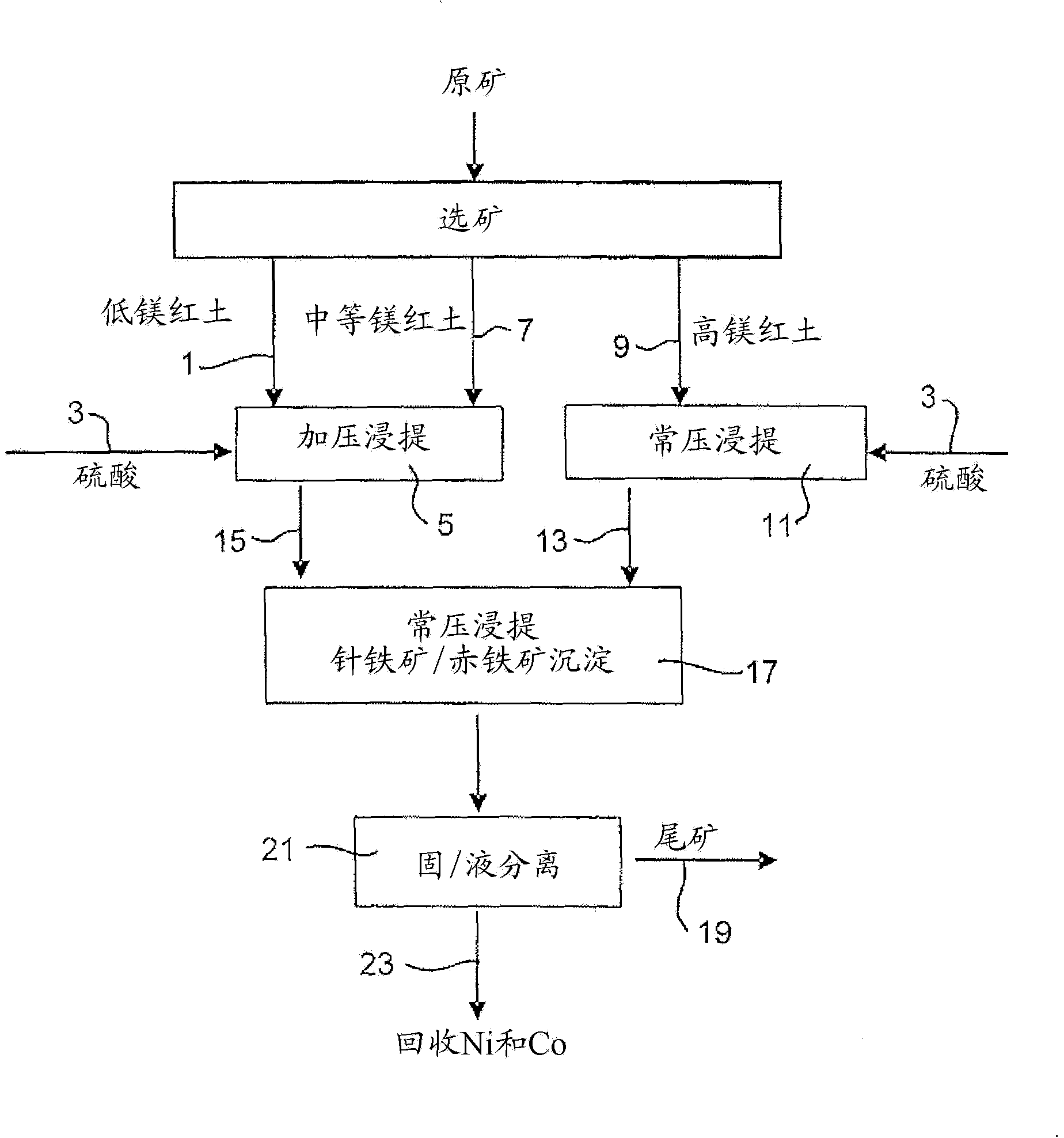
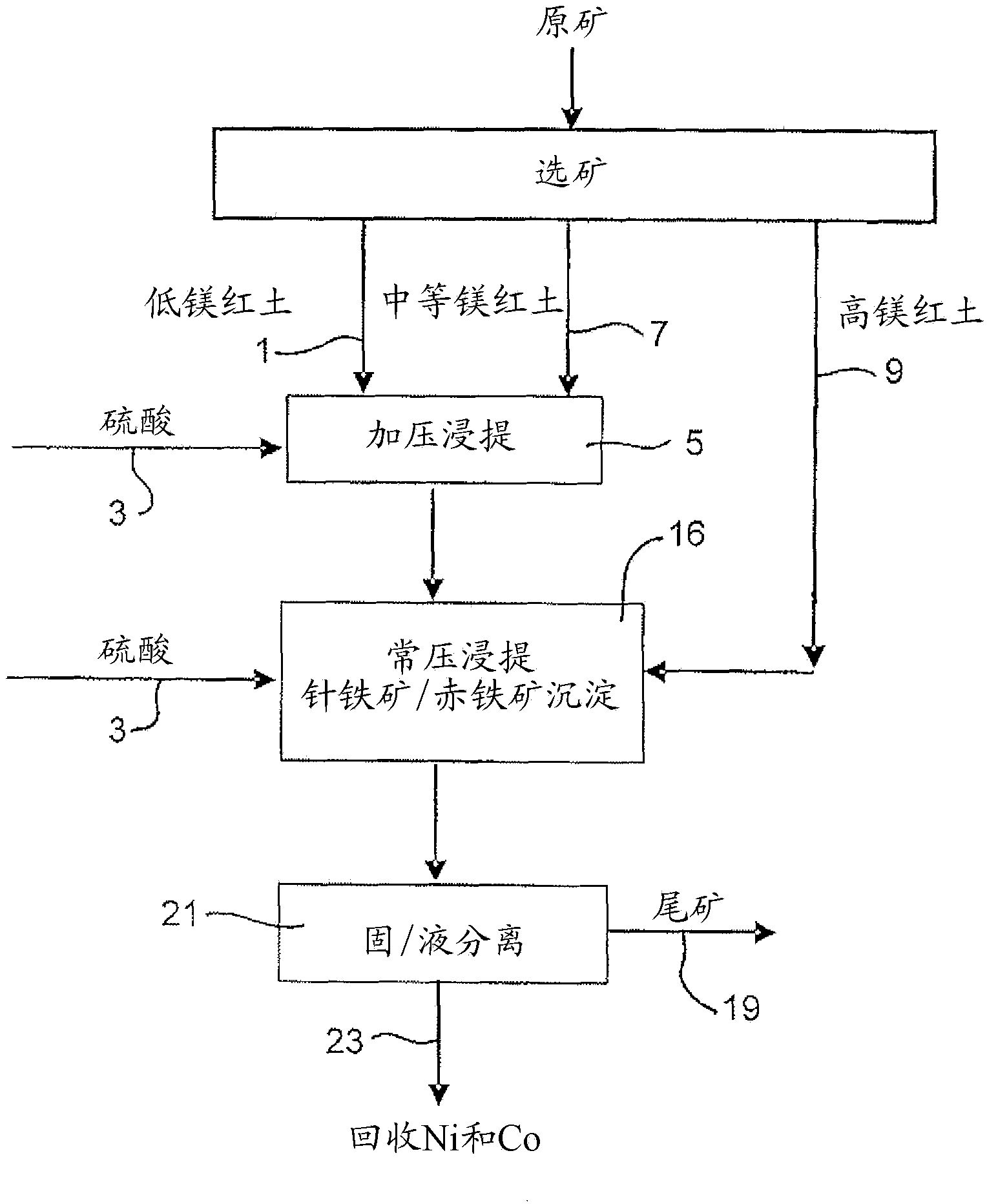
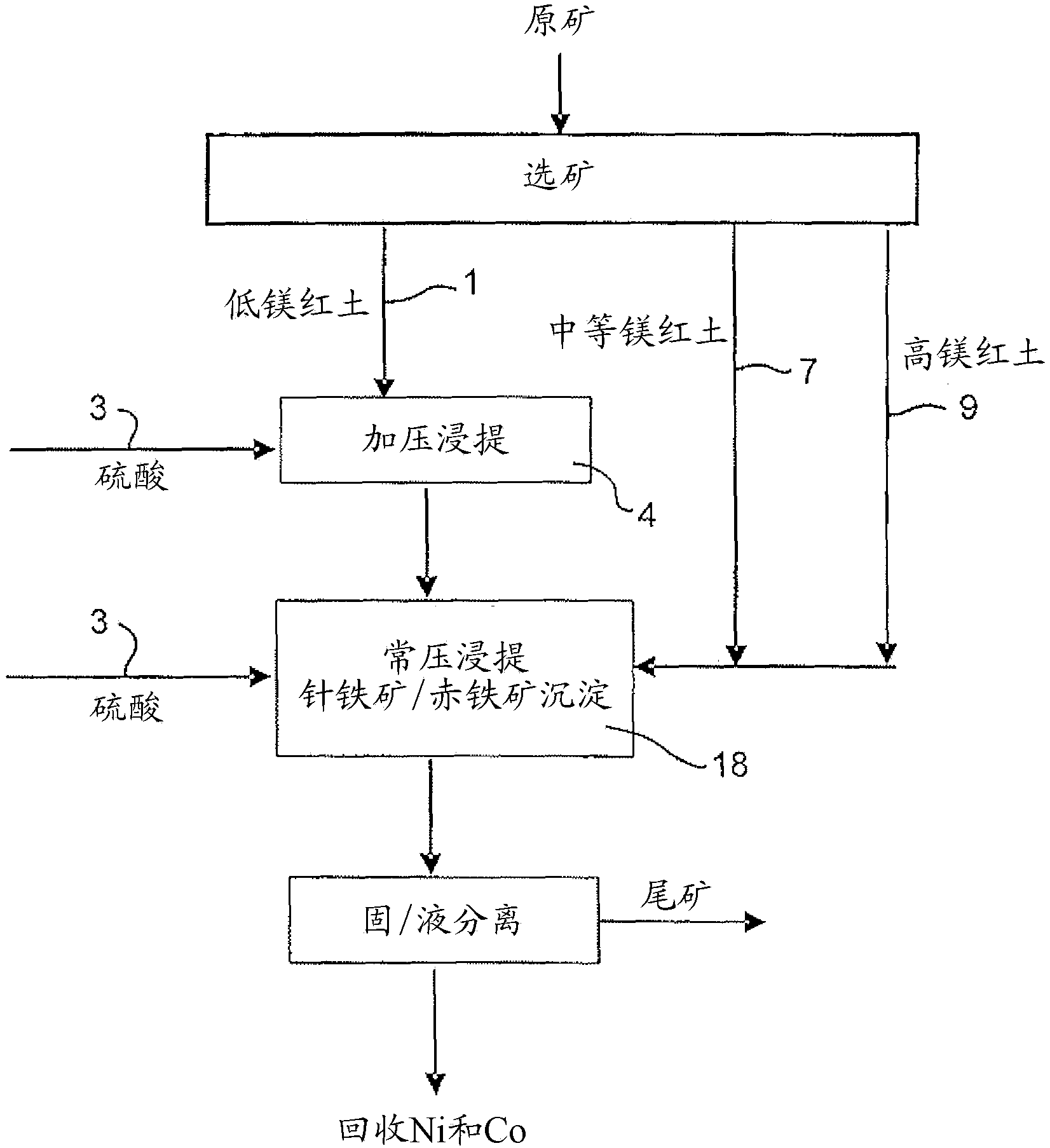
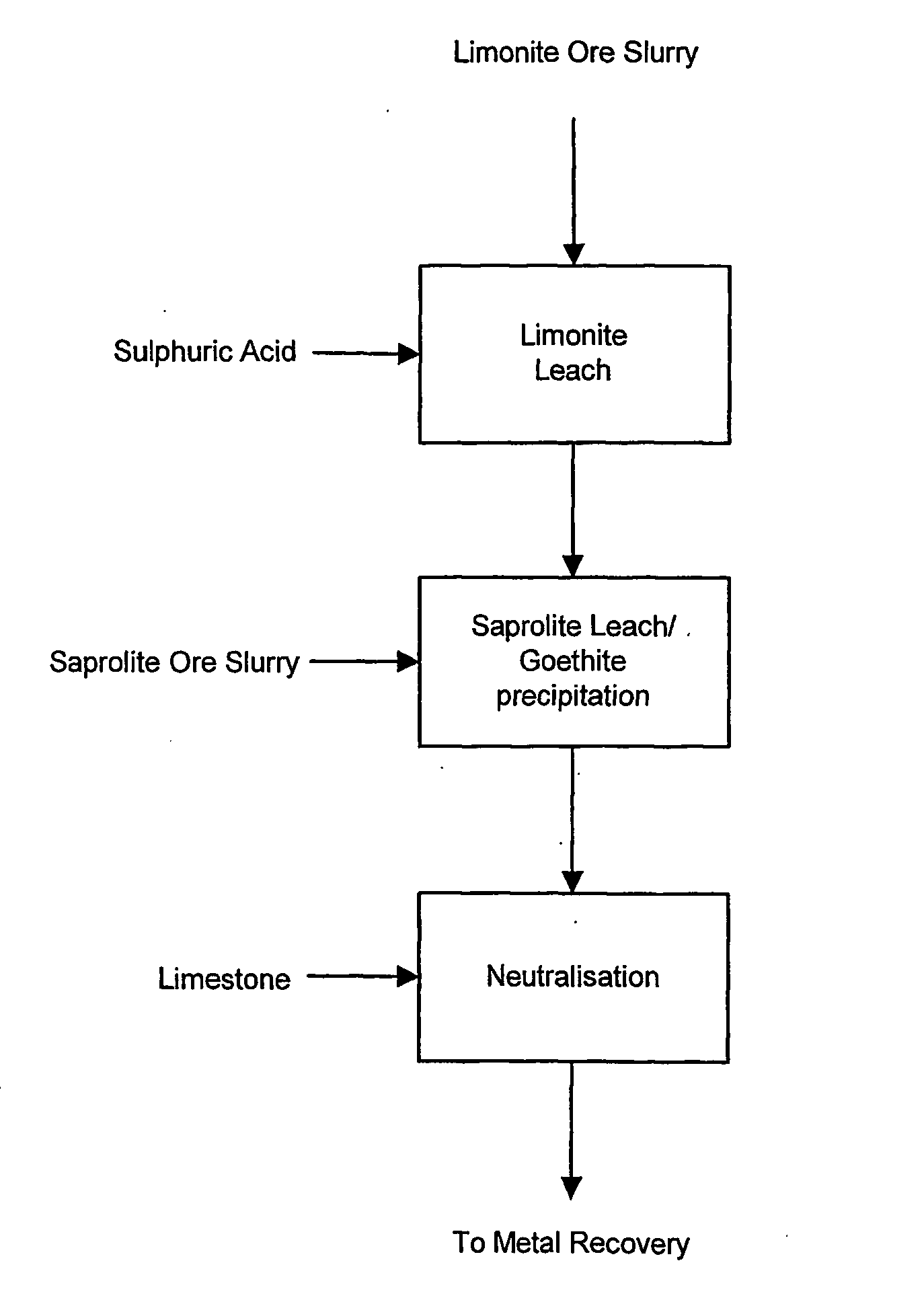
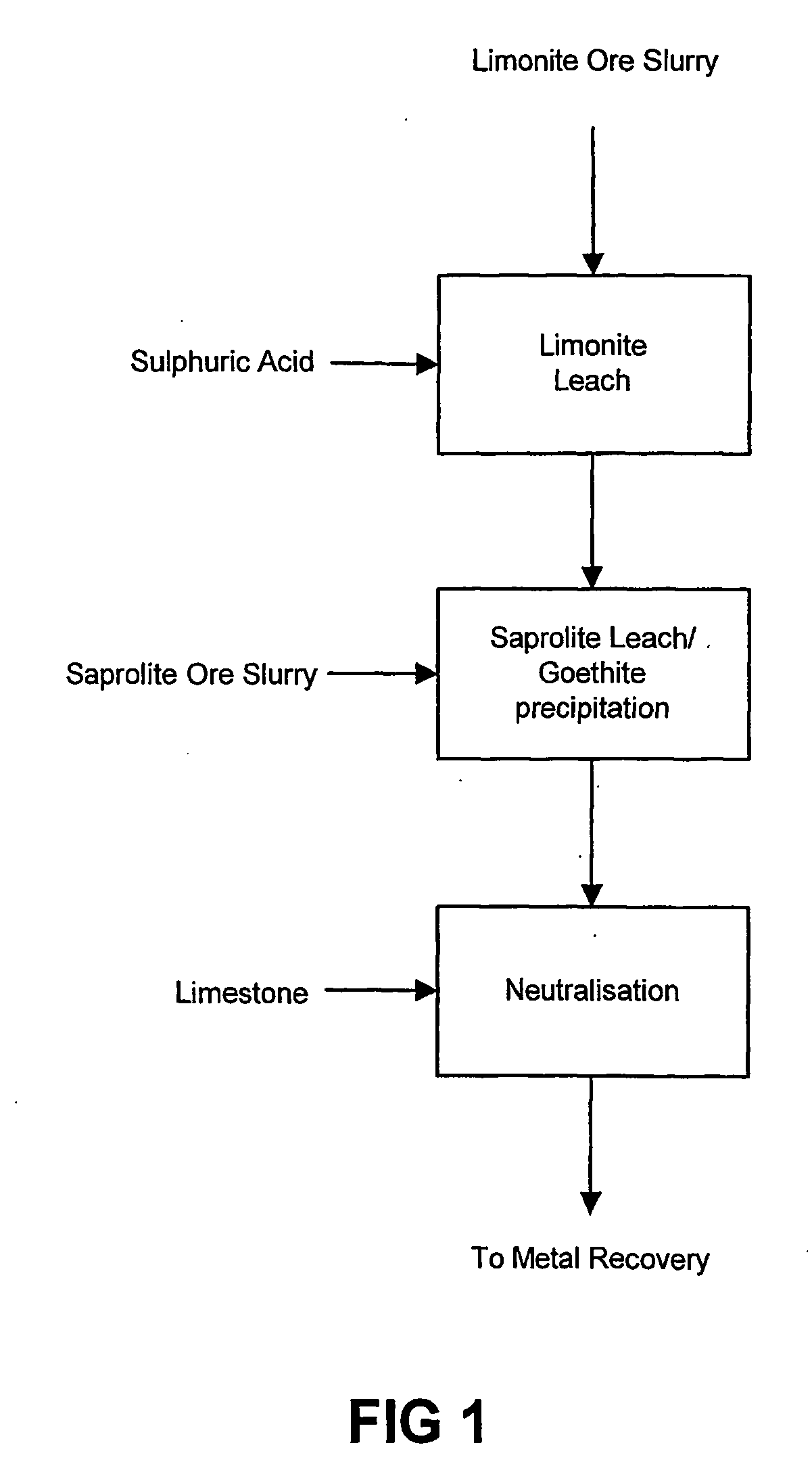
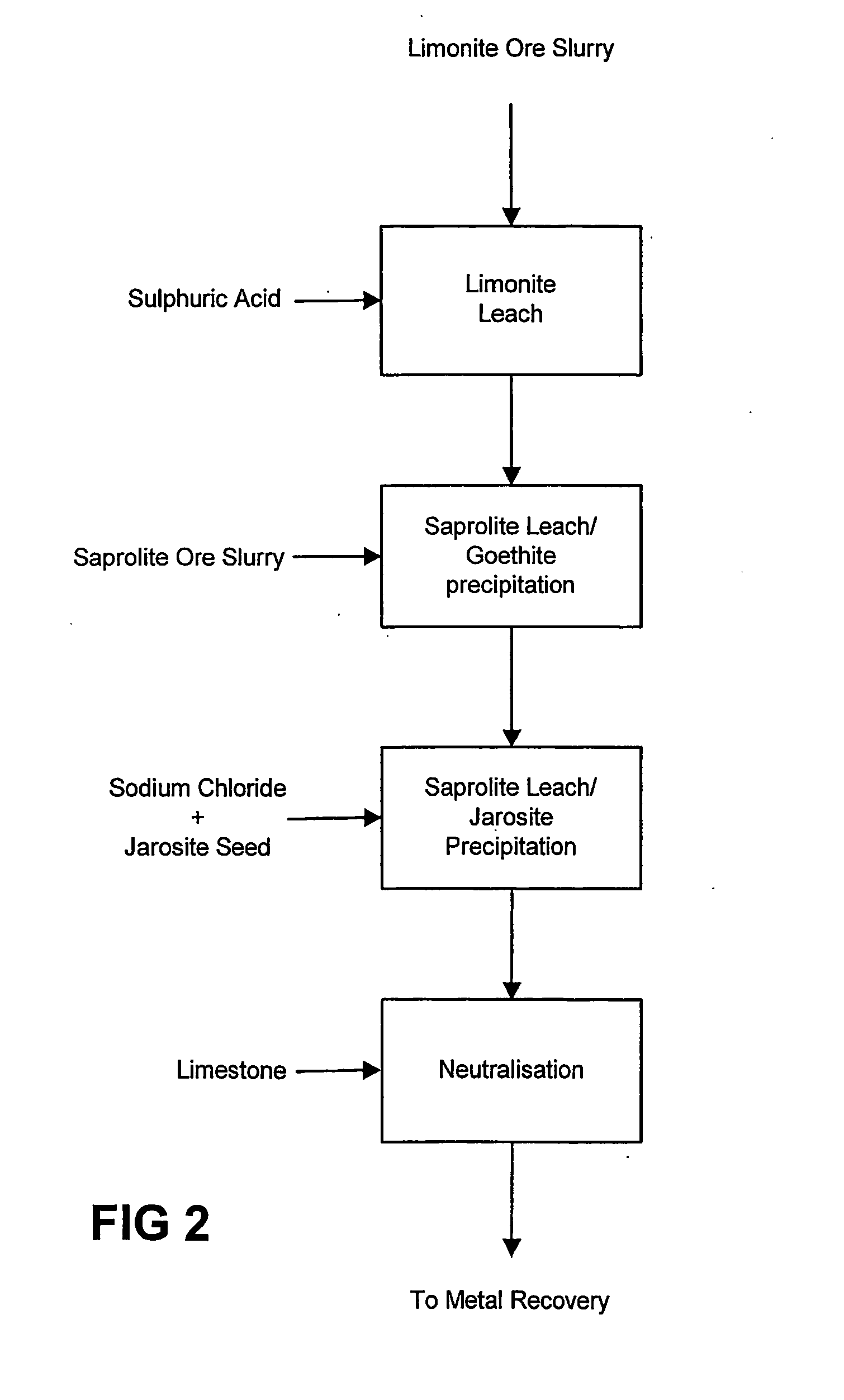
Process for enhanced acid leaching of laterite ores
A process is described for the recovery of nickel and cobalt from a nickeliferous laterite ore including the steps of: a) providing a nickeliferous laterite ore and separating that ore into its low magnesium limonite fraction and high magnesium saprolite fraction; b) treating the limonite fraction in acid solution in a primary high pressure leach step to produce a primary leach slurry; c) adding the saprolite fraction to the primary leach slurry to initiate precipitation of iron as goethite and / or hematite, while simultaneously releasing further acid from the iron precipitation, to effect a secondary atmospheric leach step, producing a secondary leach slurry; wherein all water used to prepare the ore slurries and / or acid solutions has an ionic composition that substantially avoids jarosite formation.
Owner:BHP BILLITON SSM TECH PTY LTD
Silica-calcia low-grade collophanite positive and inverse floatation process
ActiveCN104907183AReduce contentRealize beneficiation and enrichmentFlotationCalcium in biologySesquioxide
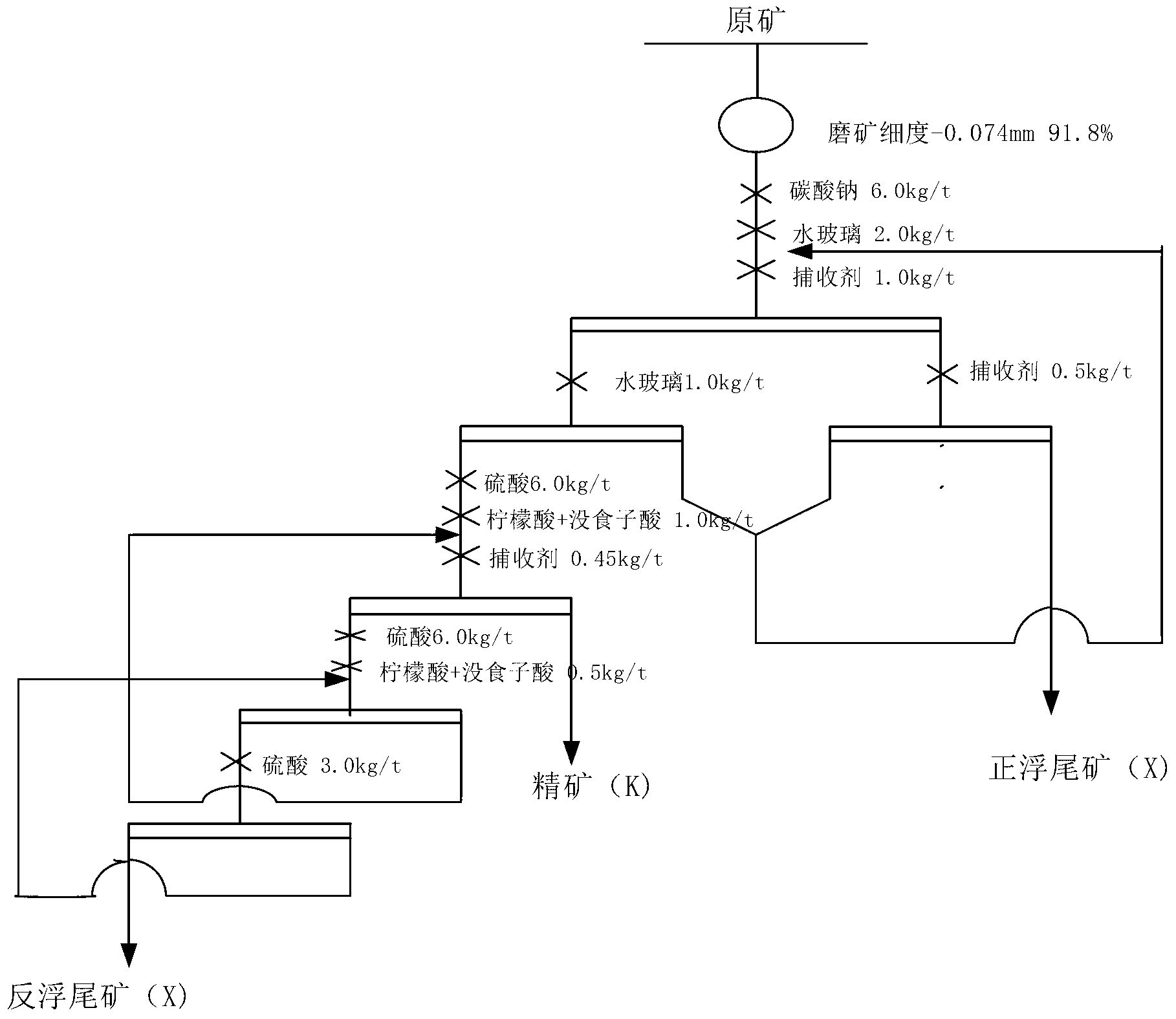
The invention relates to a silica-calcia low-grade collophanite positive and inverse floatation process, which comprises the steps: 1 silica-calcia low-grade collophanite ores are broken up and grinded to enable phosphate minerals and gangue mineral monomers to dissociate, then are added with water to mix size, enter positive and inverse floatation, get rid of impurities in ores, and improve grade of phosphorite. Compared with the prior art, the silica-calcia low-grade collophanite positive and inverse floatation process has the advantages that the content of only one kind of gangue minerals can be reduced by adopting direct floatation and single inverse floatation, can reduce the contents of silicate minerals, carbonate minerals and iron and aluminum silicate minerals, can obtain low magnesium low power half oxide low silicon phosphate concentrate by adopting the silica-calcia low-grade collophanite positive and inverse floatation process, successfully achieves mineral processing enrichment of collophane calcium collophanite, and can improve use rate of phosphorus resource. The silica-calcia low-grade collophanite positive and inverse floatation process overcomes the defects that an existing floatation process can not be applied for mineral processing of silica-calcia collophanite which is high in content of high power half oxides.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
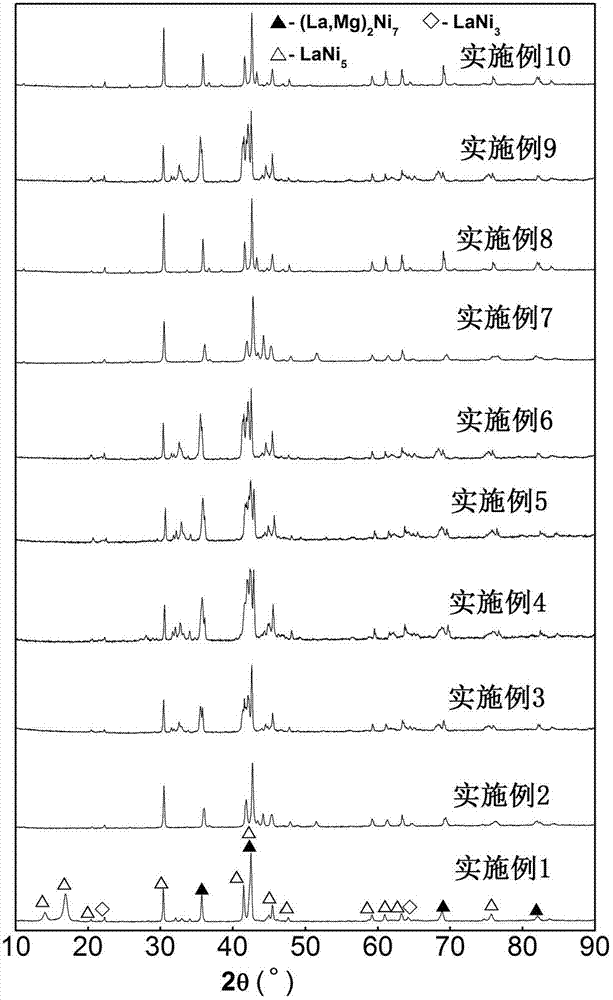
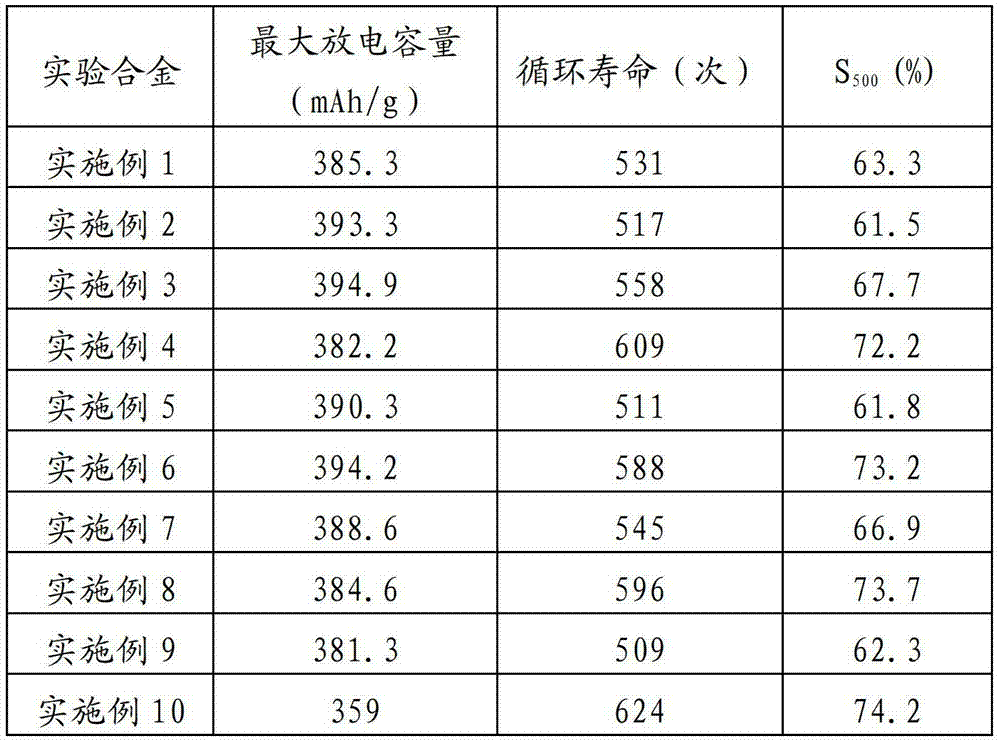
Power battery hydrogen storage electrode alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103165873AImprove electrochemical cycle stabilityStrong anti-powdering abilityAlkaline accumulator electrodesRare-earth elementElectrochemistry
The invention provides a power battery hydrogen storage electrode alloy and a preparation method of the power battery hydrogen storage electrode alloy. The power battery hydrogen storage electrode alloy is formed by low magnesium multi-rare-earth components, the chemical formula is RE1-xMgxNiyAlz, wherein 0.15<=x<=0.2, 3.3<=y<=3.8, and 0.05<=z<=0.15, and the rare earth elements (RE) are at least two elements selected from La, Ce, Sm, Y and Nd. The preparation method is that in inert gas shielding, induction heating smelting is adopted, melting alloy is poured into a tundish and sprayed on the surface of a water-cooling copper roller rotating at a certain speed through a nozzle at the bottom of the tundish to obtain rapid-quenching alloy, and then vacuum annealing is carried out in a vacuum heat treatment furnace. Combined action of the rare earth elements is fully used, the power battery hydrogen storage alloy is prepared by adoption of vacuum melting, the inert gas shielding and the rapid-quenching technology, electrochemical cycling stability of the alloy is improved, and the power battery hydrogen storage electrode alloy and the preparation method of the power battery hydrogen storage electrode alloy have the advantages that the technology is easy to master and suitable for mass production.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Atmospheric pressure leach process for lateritic nickel ore
An atmospheric leach process in the recovery of nickel and cobalt from lateritic ores, said processing including the steps of: a) separating the lateritic ore into a low magnesium containing ore fraction, and a high magnesium containing ore fraction by selective mining or post mining classification; b) separately slurrying the separated ore fractions; c) leaching the low magnesium containing ore fraction with concentrated sulphuric acid as a primary leach step; and d) introducing the high magnesium content ore slurry following substantial completion of the primary leach step and precipitating iron as goethite or another low sulphate containing form of iron oxide or iron hydroxide, wherein sulphuric acid released during iron precipitation is used to leach the high magnesium ore fraction as a secondary leach step.
Owner:CERRO MATOSO
Blast furnace iron-making raw material and blast furnace iron-making method
InactiveCN104531923ASteady and straightLow cost of industrializationBlast furnace detailsLow magnesiumBlast furnace
The invention provides a high-aluminum low-magnesium blast furnace iron-making raw material and a method for high-aluminum low-magnesium blast furnace iron-making by using the high-aluminum low-magnesium blast furnace iron-making raw material. The high-aluminum low-magnesium blast furnace iron-making raw material consists of high-aluminum low-magnesium sintered ore, pellet ore and raw ore; the blast furnace material is free of magnesium-containing ore; the high-aluminum low-magnesium sintered ore is prepared from a mixture of high-aluminum low-magnesium iron ore powder and auxiliary sintering materials in a sintering way; the pellet ore is ordinary pellet ore; the raw ore is high-grade iron ore concentrate. In the blast furnace iron-making process, the high-aluminum low-magnesium sintered ore and the ordinary pellet ore together with reasonably added raw ore are adopted, and appropriate blast furnace operation mechanisms are selected, so that the coal gas flow can be reasonably distributed in the blast furnace iron-making process, the blast furnace slag is good in property, the slag iron can be smoothly discharged, stable and smooth operation of a blast furnace is maintained, and the pig iron making cost is lowered.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Fusion welding method for magnesium and aluminium dissimilar metals
InactiveCN1663727ANo crackMeet the use requirementsArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsImpulse frequencyElectromagnetic pulse
The invention discloses a fusion welding of magnesium and Al heterogeneous metals, which adopts low magnesium Al alloy weld stick as the filling materials, the indifferent gas to protect, the electromagnetic pulse AC tungsten Ar arc to weld magnesium and Al. there into, the mass percentages of the weld stick are: magnesium is 0.5-3.0% with 2.0-3.0mm diameter; the said indifferent gas is Ar gas with purity more than 99.9%; the parameter of the tungsten Ar arc welding is: the basic current is 50-130A, the impulse current is 200-350A, the impulse time is 5-10s, the impulse frequency is 35-75Hz, the welding voltage is 24-26V, the welding speed is 1.0mm / s-1.8mm / s, the Ar gas flux is 10-18L / min, the extension length of the tungsten polar is 5-6mm, the distance between the welding torch jet and the working piece is 6mm-10mm, the thickness of the working piece is 1.5mm-14mm. the invention has high welding efficiency, low cost, convenient operation, and is suitable for the manufacturing of magnesium-Al heterogeneous compound structure.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
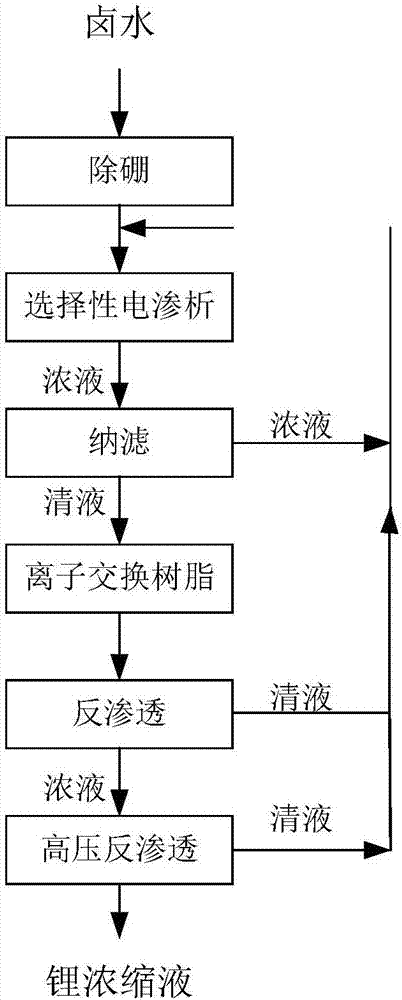
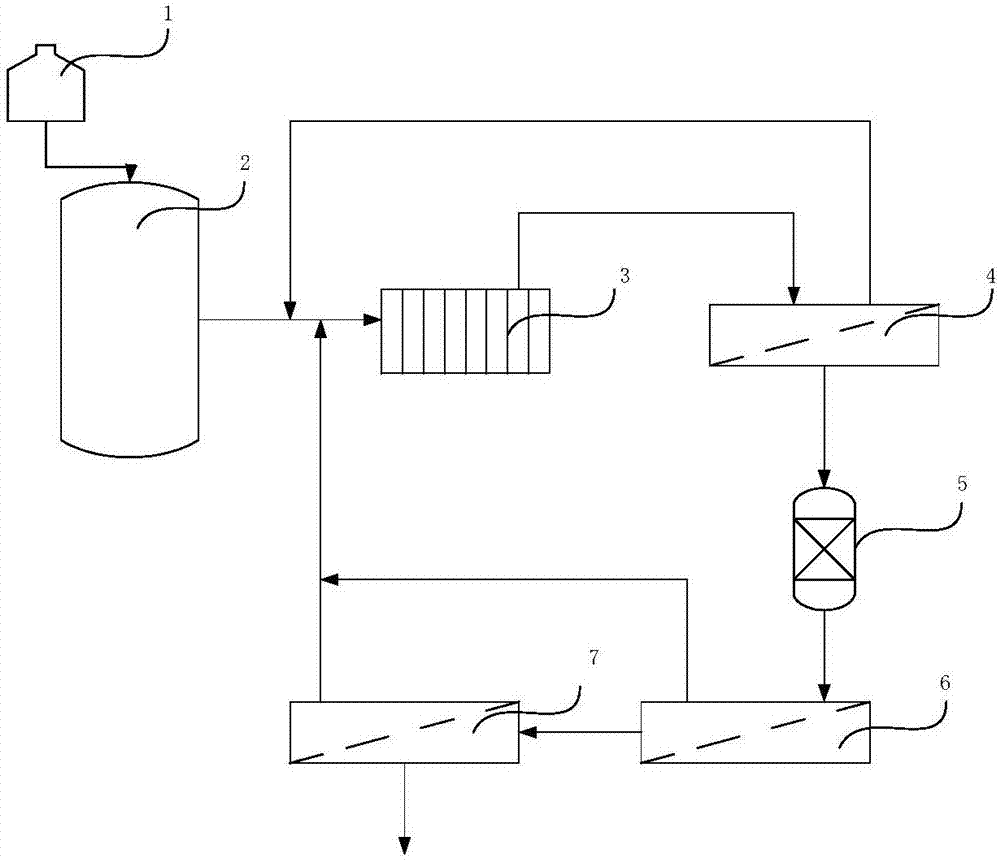
Method and device for extracting lithium from salt lake brine with high magnesium-lithium ratio
PendingCN107399747AAchieve recyclingReduce energy consumptionLithium halidesHigh magnesiumReverse osmosis
The invention provides a method and a device for extracting lithium from salt lake brine with a high magnesium-lithium ratio. The method comprises the following process steps: (1) removing boron from naturally evaporated and concentrated brine; (2) performing selective electrodialysis treatment on the boron-removed brine so as to obtain brine with a low magnesium-lithium ratio; (3) filtering the brine with low magnesium-lithium ratio by using a nanofiltration membrane so as to obtain brine with a low lithium-magnesium ratio; (4) performing deep decontamination on the brine with the low lithium-magnesium ratio by using an ion exchange resin so as to obtain lithium brine; (5) concentrating the lithium brine by using a reverse osmosis membrane so as to obtain a primary concentrated lithium liquid; and (6) filtering the primary concentrated lithium liquid by using a high-pressure osmosis membrane, thereby obtaining a final concentrated lithium liquid. The method is good in operability, the overall energy consumption is reduced, and the lithium extraction efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU JIUWU HITECH
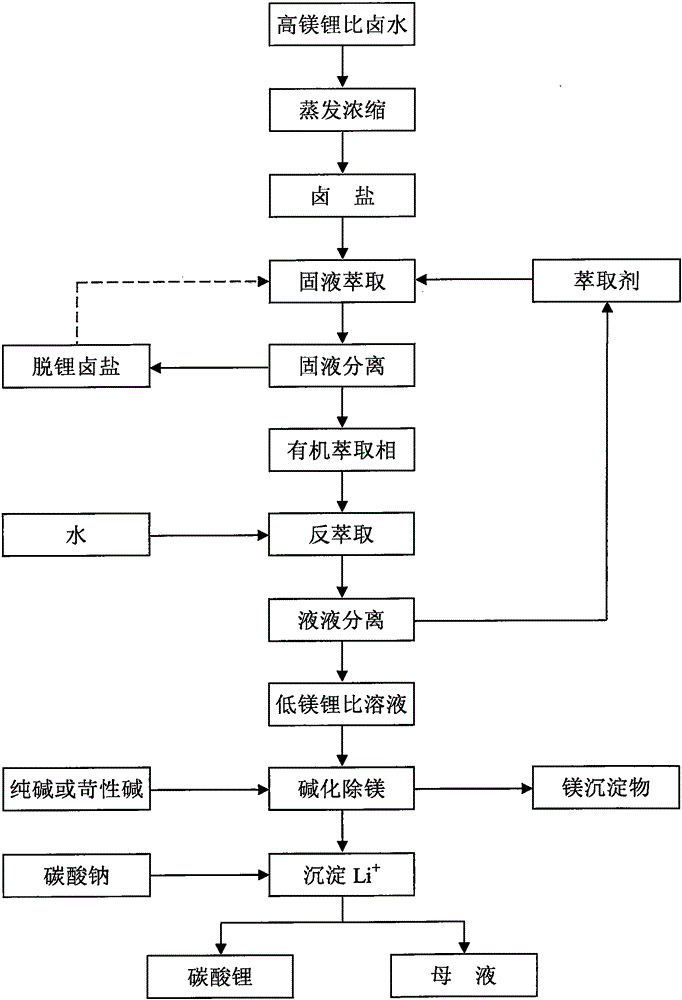
Method for producing lithium carbonate by separating magnesium out of low-lithium bittern and enriching lithium
ActiveCN105152190AEasy to operateThe process is easy to realizeOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationMagnesium carbonatesAlkaneEvaporation
The invention discloses a method for producing lithium carbonate by separating magnesium out of low-lithium bittern and enriching lithium. The method includes the steps of converting salt lake bittern serving as raw materials into halide salt through evaporation dehydration and crystallization separation, directly extracting halide salt through trixylyl phosphate alkane ester or a mixture of trixylyl phosphate alkane ester and monohydric alcohol, obtaining an organic extraction phase and the rest of halide salt after solid-liquid separation, conducting back extraction on the organic extraction phase through water to obtain a low-magnesium-lithium-ratio lithium-rich solution, and obtaining lithium carbonate through condensation and alkalization magnesium removal. The method has the advantages that processes related to the solid-liquid extraction method are simple, co-extraction agents are not needed, the solute distribution drive force is large, and the method is not influenced by bittern extractant two-phase balance; multiple stages of extraction processes are conducted on halide salt, the extraction rate of Li+ is larger than 90%, and the mass ratio of magnesium to lithium in the extraction phase is remarkably decreased; phase splitting is easy due to liquid-liquid back extraction, and the back extraction rates of Li+ and Mg2+ are both larger than 90%; the extraction process is operated under the neutral or weak-acid condition, the production cost is low, and the method is particularly suitable for producing lithium carbonate after separating magnesium out of bittern with the magnesium-lithium mass ratio of 120 or lower.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TINCI MATERIALS TECH
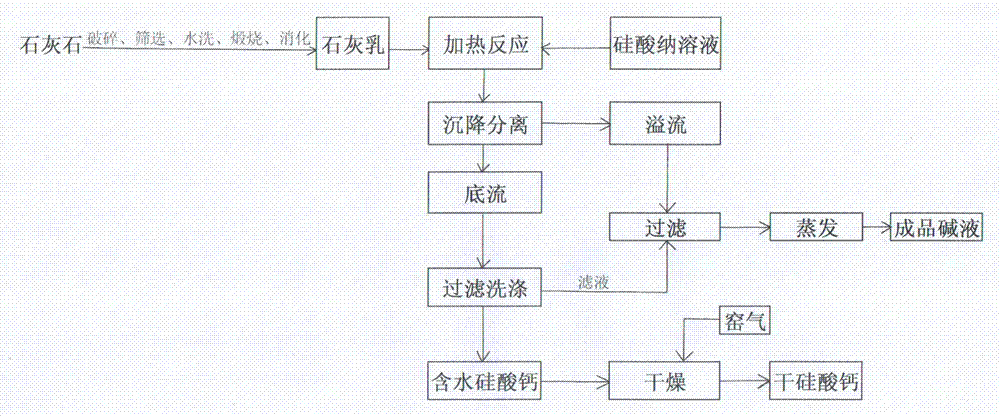
Method for preparing microporus, high-activity and low-density calcium silicate
The invention discloses a method for preparing microporus, high-activity and low-density calcium silicate. Microporus, high-activity and low-density calcium silicate is prepared from raw materials of lime milk and a sodium silicate solution, wherein the molar mass ratio of CaO to SiO2 is 0.95:1.05. The preparation method comprises the following steps: crushing limestone; screening and washing the crushed limestone; calcining the limestone; adding calcined limestone into hot water to generate lime milk; screening the generated lime milk, preparing the effective CaO concentration in the lime milk to be higher than 170 g / L, and performing the heating digestion; preheating the sodium silicate solution, and reacting with the lime milk by heating; after the reaction is finished, performing the settling separation, filtering and washing, wherein overflow is alkaline liquor, and underflow is hydrous calcium silicate; after hydrous calcium silicate is filtered, introducing kiln gas for drying to obtain dry calcium silicate, namely, the finished product; evaporating the reactant obtained by filtering the effusion to obtain finished product alkali liquor. Microporus, high-activity and low-density calcium silicate is prepared from high-calcium low-magnesium CaO and high-purity sodium silicate, so that the problem that active calcium silicate impurities are high in content is solved effectively.
Owner:山西玉竹活性石灰制造有限公司
Welding method capable of eliminating hook defects of magnesium alloy friction stirring overlap joint
ActiveCN104668765AEliminates hook defectsImprove performanceNon-electric welding apparatusJoint heatSpot welding
The invention provides a welding method capable of eliminating hook defects of a magnesium alloy friction stirring overlap joint (including spot welding and wire welding) and belongs to the technical field of magnesium alloy welding. The welding method has the advantages that a low-melting-point metal or alloy interlayer is prearranged between an upper magnesium alloy plate and a lower magnesium alloy plate which are to be welded, pressure and heat generated from shaft shoulder friction are adopted to enable the interlayer and magnesium alloy to react, and a novel combination area is generated in a joint heat affected zone and a thermo-mechanically affected zone, so that formation of the hook defects is avoided, and mechanical properties of the welded joint is improved.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
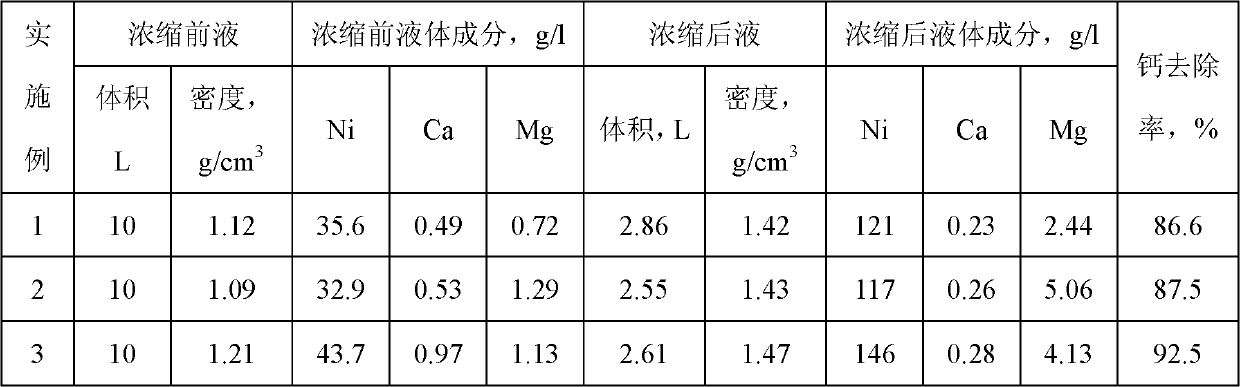
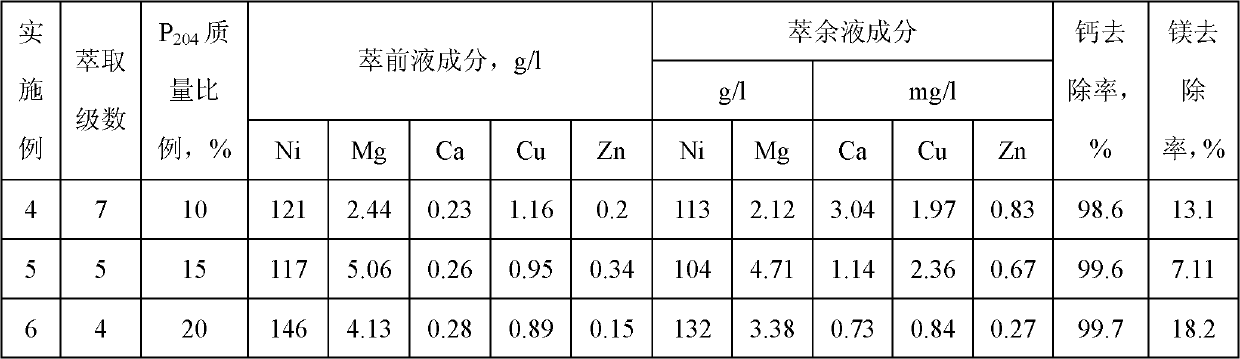
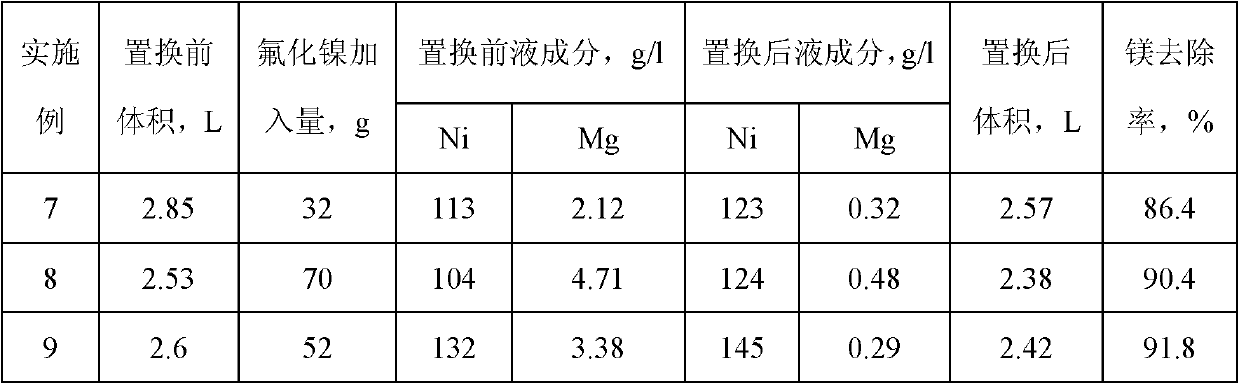
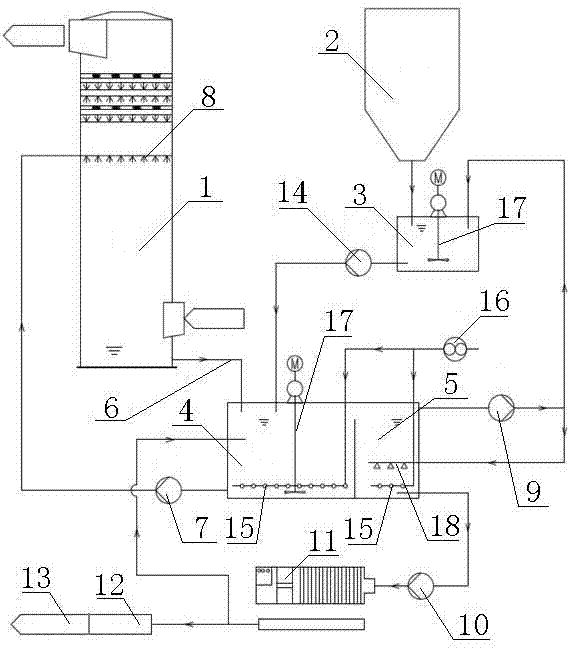
Method for removing calcium-magnesium impurities from nickel sulfate solution
The invention discloses a method for removing calcium-magnesium impurities from a nickel sulfate solution. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) heating a nickel sulfate raw material solution, concentrating, cooling and removing a precipitated solid; (2) extracting a filtrate obtained in the step (1) with a phosphorus-containing extracting agent; and adding nickel fluoride into a raffinate obtained in the step (2), heating to 60-90 DEG C for reacting, cooling and filtering to obtain a needed nickel sulfate solution. Due to the adoption of the method, the using amount of a fluorine salt and the discharge of fluorine-containing waste water are greatly reduced, and new impurity irons are not introduced, the nickel yield is high; and the method is particularly suitable for sulfate systems with high calcium content and low magnesium content.
Owner:SHANGHAI LIGHT IND RES INST
Flue gas desulfurization device and desulfurization method by magnesium oxide process
ActiveCN102886199AEasy to recyclePrevent scalingDispersed particle separationMagnesium sulfatesHigh energyPhysical chemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of atmospheric environment protection, and particularly relates to a flue gas desulfurization device and desulfurization method by a magnesium oxide process. The invention provides a reaction tank using a circulation-oxidization integrated structure in a desulfurization process, and adds clear liquid return, filtrate recovery and other steps, thereby overcoming the defects of complex technique, high investment, low magnesium oxide regeneration rate, high energy consumption, high operating cost and the like in the traditional magnesium oxide laundering-regeneration desulfurization process. The invention is especially suitable for flue gas desulfurization of medium / small machine sets in China, and has active actions on energy source comprehensive utilization and environmental protection in China.
Owner:COAL IND JINAN DESIGN & RES
Method for preparing high-purity magnesium oxalate, lithium carbonate and high-purity nanometer magnesia from salt lake brine of high magnesium-lithium ratio
ActiveCN104803399ANo pollution in the processReduce energy consumptionMaterial nanotechnologyCarboxylic acid salt preparationHigh magnesiumLithium carbonate
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity magnesium oxalate and lithium carbonate from salt lake brine of high magnesium-lithium ratio. The method comprises the following steps: 1) filtering the salt lake brine to remove suspended matters and solid impurities; 2) adding oxalic acid into the filtered salt lake brine; carrying out reaction for 30 to 180 min under the conditions that the temperature is 20 to 60 DEG C, the pH is 3 to 5, and the stirring speed is 150 to 500 rpm, so as to obtain brine of low magnesium-lithium ratio and magnesium oxalate precipitate; washing the magnesium oxalate precipitate with 40 to 60 DEG C hot water for 3 to 5 times; drying the washed magnesium oxalate precipitate at 80 to 102 DEG C for 60 to 120 min to obtain the high-purity magnesium oxalate of which the purity is larger than or equal to 98%; 3) adding an impurity removing agent into the brine of low magnesium-lithium ratio, so as to obtain refined brine; adding sodium carbonate into the refined brine to obtain lithium carbonate crystal; filtering the lithium carbonate crystal; carrying out washing and drying to obtain lithium carbonate. The magnesium oxalate prepared according to the method is high in purity.
Owner:CHANGSHA RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Coarse grain reverse floatation magnesium removal method for phosphorus ore
ActiveCN104801418AImprove discharge rateImprove concentrate qualityFlotationWet separationHigh concentrationSlurry
The invention relates to a coarse grain reverse floatation magnesium removal method for phosphorus ore. The method comprises the following steps of crushing and grinding low-grade phosphorus ore, the floatation feeding granularity constitution satisfies the condition that the granularity of -200 meshes is lower than 50 percent according to the weight, transferring the ground phosphorus ore into a floatation machine stirring trough, mixing the ground phosphorus ore with water to form slurry with concentration more than 50 percent, wherein the temperature of the ore slurry is 10 to 30 DEG C, respectively mixing the ore slurry with an adjusting agent inorganic acid and a reverse floatation mixing capturing agent, carrying out the slurry regulation, replenishing fresh water, carrying out the reverse floatation systematic operation, wherein a foam product is reverse floatation tailings, discharging the reverse floatation tailings to be stacked, a product in the trough is low-magnesium phosphorus ore concentrate. The floatation feed is the coarse-particle high-magnesium phosphorus ore, by optimizing the reverse floatation operation and the chemical system, on the premise of regulating the slurry at the high concentration, the coarse-grain magnesium removal effect can be realized by adopting the reverse floatation mixing trapping agent on the basis of high-concentration slurry, the final magnesium content of the concentrate can be reduced, and the concentrate quality can be improved. The method also has the characteristics of simple flow, good sorting effect and high magnesium discharging rate.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Purification and impurity removal method for lithium chloride mixed solution
InactiveCN106048218AHigh acceptanceReduce calcium and magnesium contentSemi-permeable membranesProcess efficiency improvementLow salinityLithium chloride
The invention belongs to the technical field of lithium production, and particularly relates to a purification and impurity removal method for a lithium chloride mixed solution. The method includes the step that impurity removal is conducted on the high-salinity lithium chloride mixed solution through a nanometer filter to obtain a low-salinity lithium chloride solution, wherein the high-salinity lithium chloride mixed solution is a mixed solution of lithium chloride, magnesium chloride and calcium chloride; in the high-salinity lithium chloride mixed solution, the content of lithium ranges from 0 g / L to 55.0 g / L, and the content of calcium and magnesium ranges from 0 g / L to 30 g / L; in the low-salinity lithium chloride solution, the content of lithium ranges from 0 g / L to 55.0 g / L, and the content of calcium and magnesium is smaller than or equal to 5 mg / L; and a nanometer filter membrane in the nanometer filter is a monovalent ion selective nanometer filter membrane. The content of calcium and magnesium in discharged water subjected to impurity removal through the purification and impurity removal method of a salt chlorine-containing system is extremely low, the content of lithium reaches up to saturation, and possibility is provided for obtaining low-calcium and low-magnesium lithium production intermediate fine products by directly processing lithium production intermediate rough products.
Owner:SICHUAN SIDANENG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Direct and reverse flotation technique for high-magnesium low-grade phosphorus ore coarse grains
The invention relates to a direct and reverse flotation technique for high-magnesium low-grade phosphorus ore coarse grains. The technique comprises the following steps: crushing and grinding high-magnesium low-grade phosphorus ores; transferring into a flotation machine stirring tank and adding water for mixing slurry; keeping the temperature of the ore slurry at 10-30 DEG C, and then respectively adding regulator sodium silicate and inorganic base into the ore slurry; adding a direct flotation collecting agent for mixing the slurry; adding water for performing direct flotation system operation; transferring a direct flotation foam product into a reverse flotation stirring tank, respectively adding the regulator sodium silicate and reverse flotation mixing collecting agent into the reverse flotation stirring tank, and mixing the slurry without adding fresh water; adding fresh water and performing the reverse flotation system operation; discharging and stacking the foam products which are reverse flotation tailings, wherein the products in the tank are low-magnesium phosphorus ore concentrates; concentrating, filtering and drying, thereby acquiring the end products of concentrates. According to the technique, the last magnesium content of the concentrates is reduced and the quality of the concentrates is increased; the process is simple; the energy consumption for ore grinding is low; the dosage of agents is less; the separation effect is good; the discharging rate of magnesium is high; the water quality of concentrate and tailing is improved.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
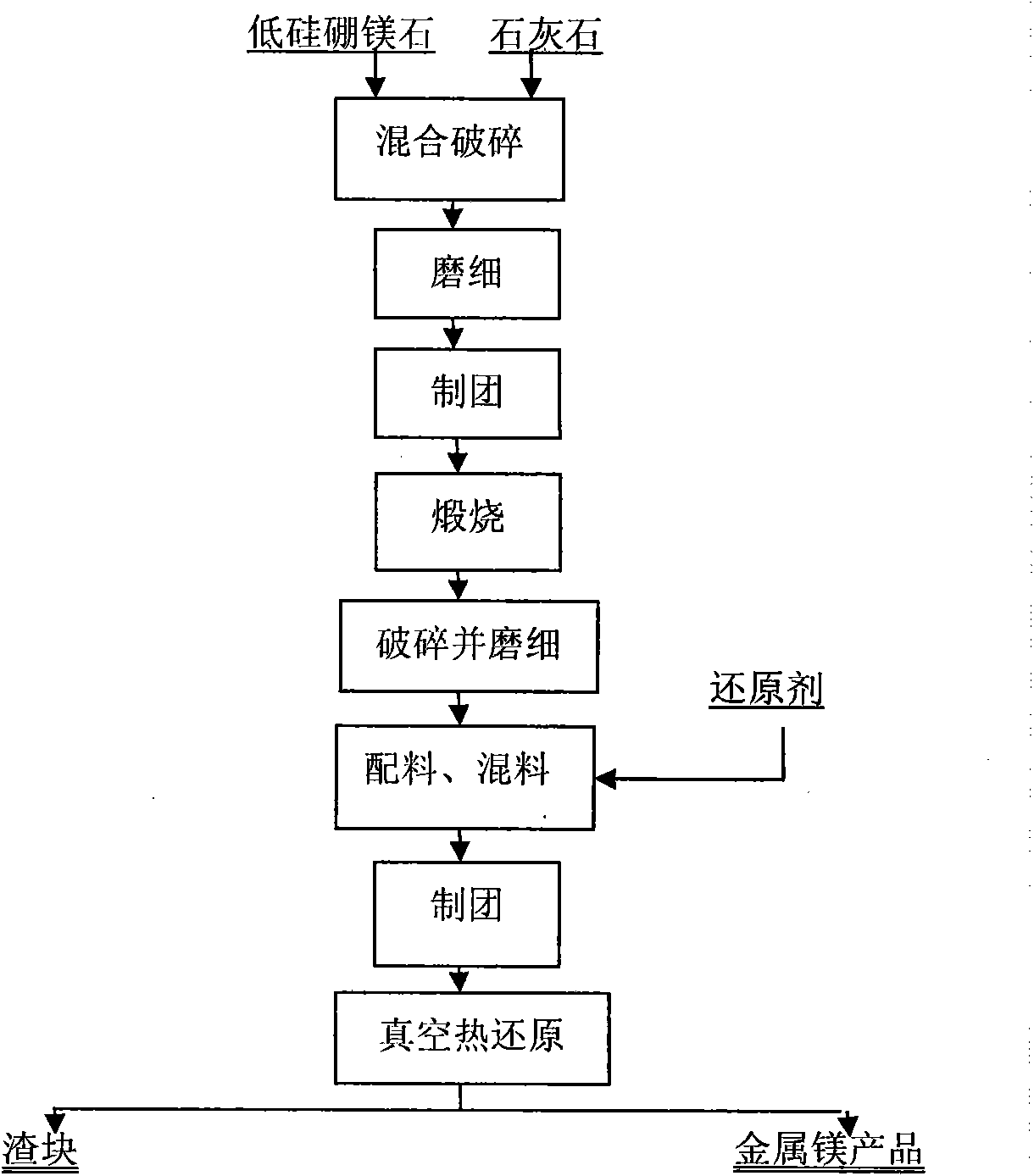
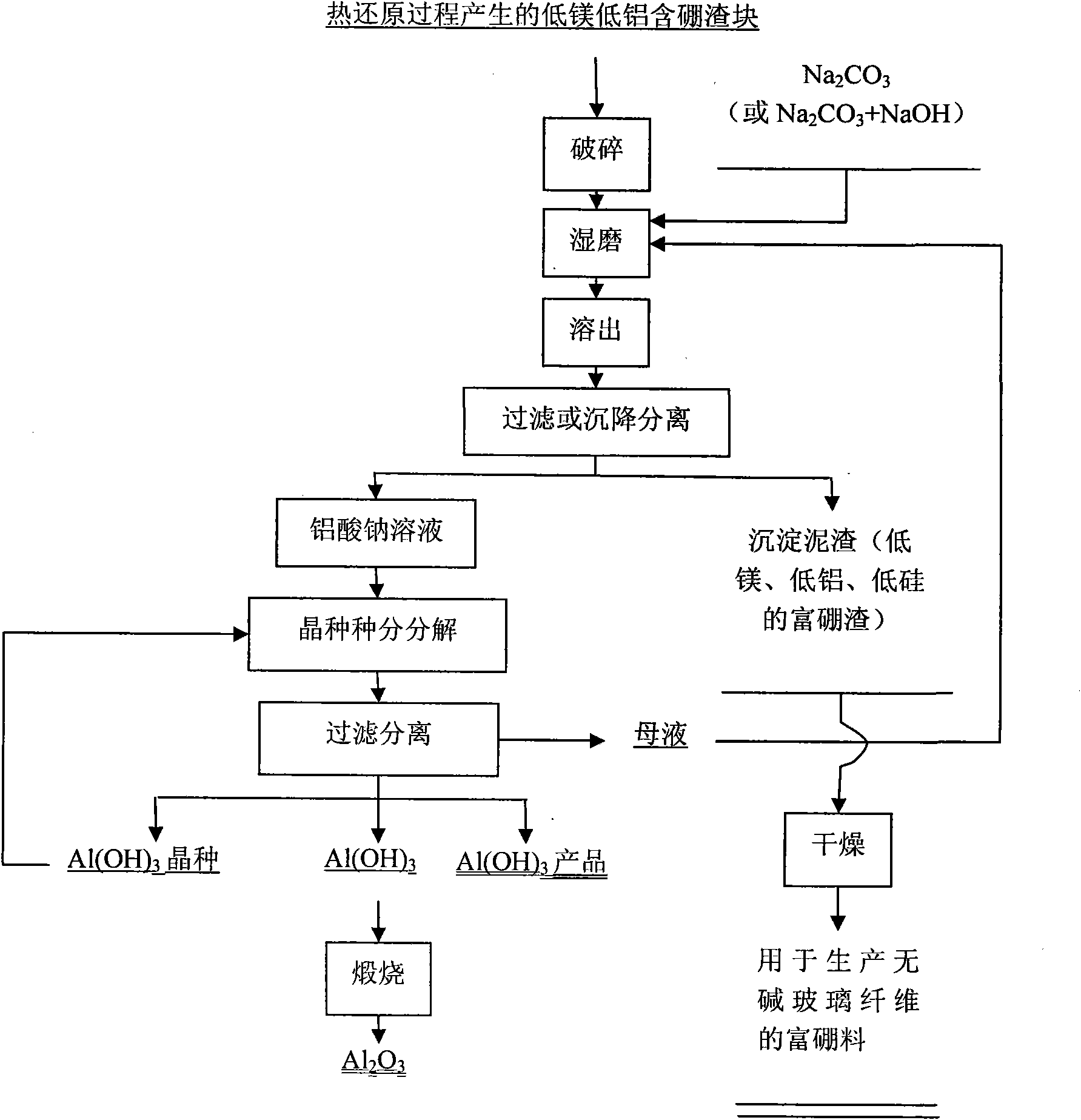
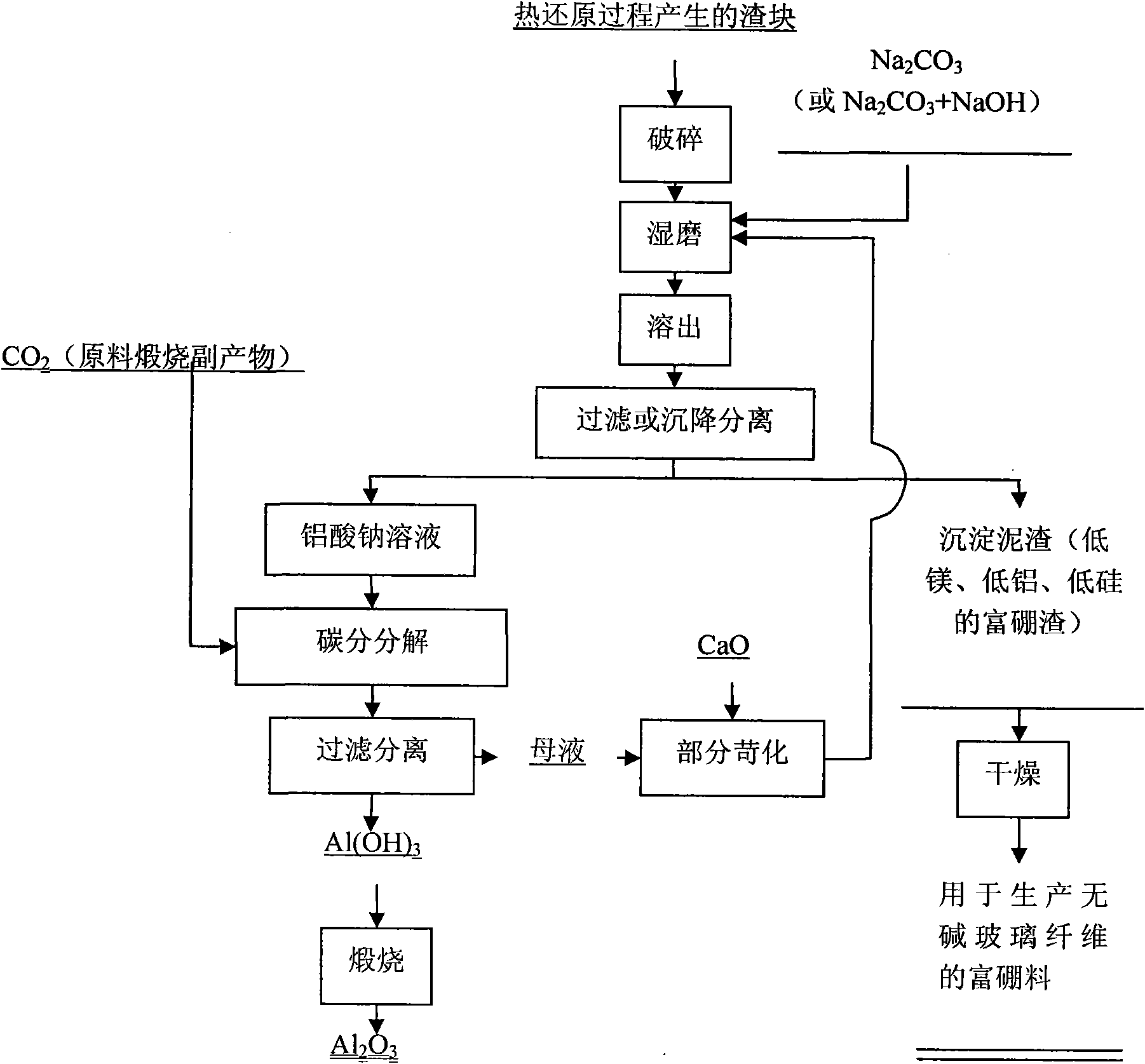
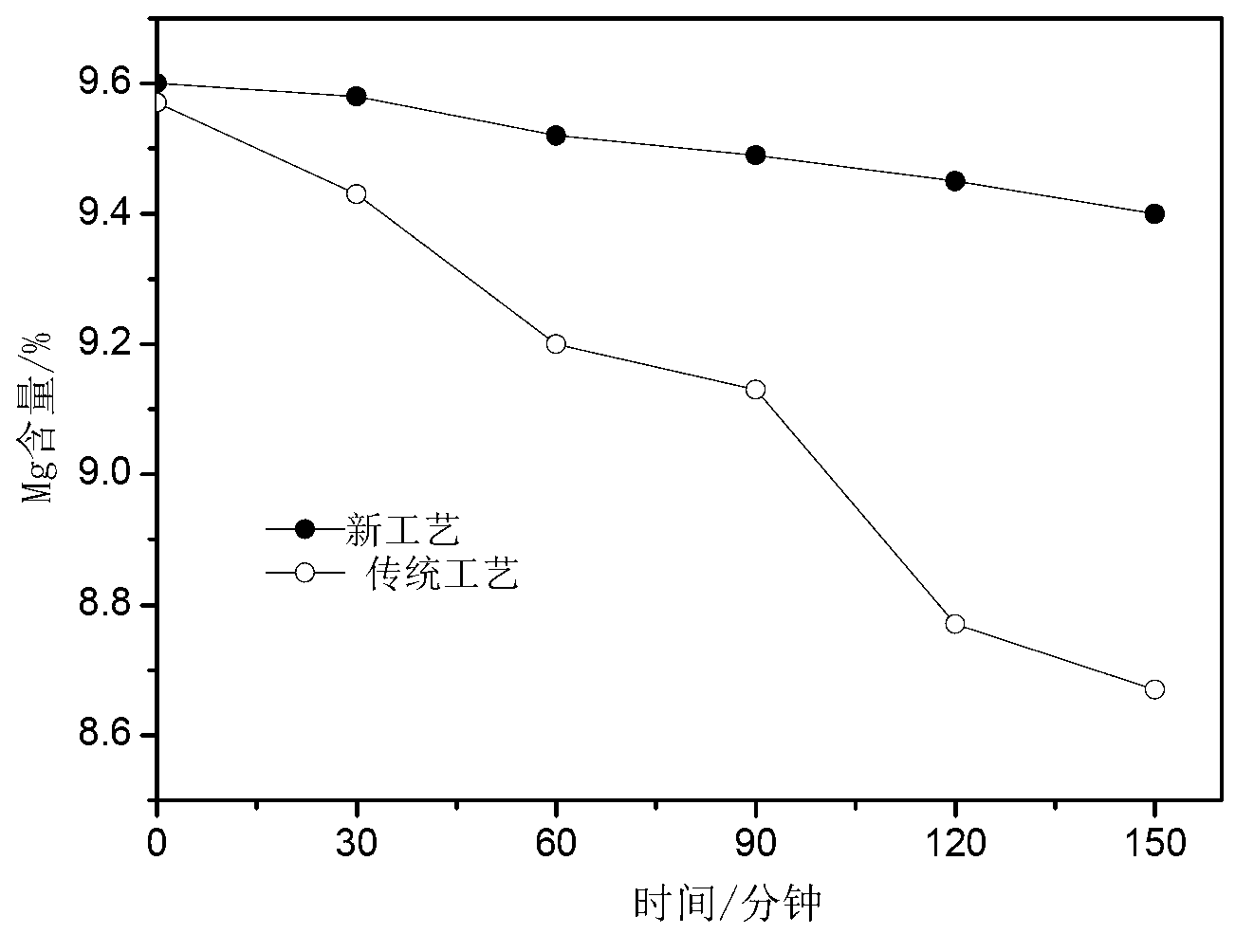
Method for preparing metal magnesium and boron-enriched material from ascharite serving as raw material by vacuum thermal reduction method
The invention discloses a method for preparing a metal magnesium and a boron-enriched material from ascharite serving as a raw material by a vacuum thermal reduction method, and belongs to the technical field of vacuum metal thermal reduction magnesium smelting. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing materials; (2) grinding the materials; (3) calcining; (4) crushing the calcined blocks into the grain diameter of less than 0.2 mm, uniformly mixing the calcined blocks and aluminum powder with the grain diameter of less than 0.2 mm, and pressing into blocks; (5) performing vacuum reduction; (6) leaching slag; (7) filtering and separating; (8) drying; and (9) performing seed decomposition or carbon decomposition, and making the filtered solution of NaAl(OH)4 which contains a small amount of Na2CO3 and NaOH enter a seed decomposition or carbon decomposition container to ensure that the NaAl(OH)4 is decomposed into aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3). The method for extracting the metal magnesium and preparing a low-magnesium boron-enriched material from the ascharite can comprehensively utilize ascharite ore.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Refining method of aluminum-magnesium-series cast aluminum alloy material
The invention relates to a refining method of an aluminum-magnesium-series cast aluminum alloy material. In the method, a novel covering agent is selected for performing surface protection on an aluminum-magnesium-series alloy in a smelting process, a refining agent special for a magnesium-aluminum alloy is prepared simultaneously for refining a melt, and the smelting temperature and the pouring temperature are controlled, so that an aluminum-magnesium-series cast aluminum alloy with higher performance and a low magnesium burnout rate is obtained. According to the method, the novel covering agent and the special refining agent are applied for smelting an Al-Mg-series alloy (the content of Mg is 3-10 percent) under the control of a specific production process, so that the burnout of magnesium is controlled effectively, the production cost is saved, the cleanliness of the alloy is enhanced, and the porosity of the alloy is lowered.
Owner:天津新立中合金集团有限公司
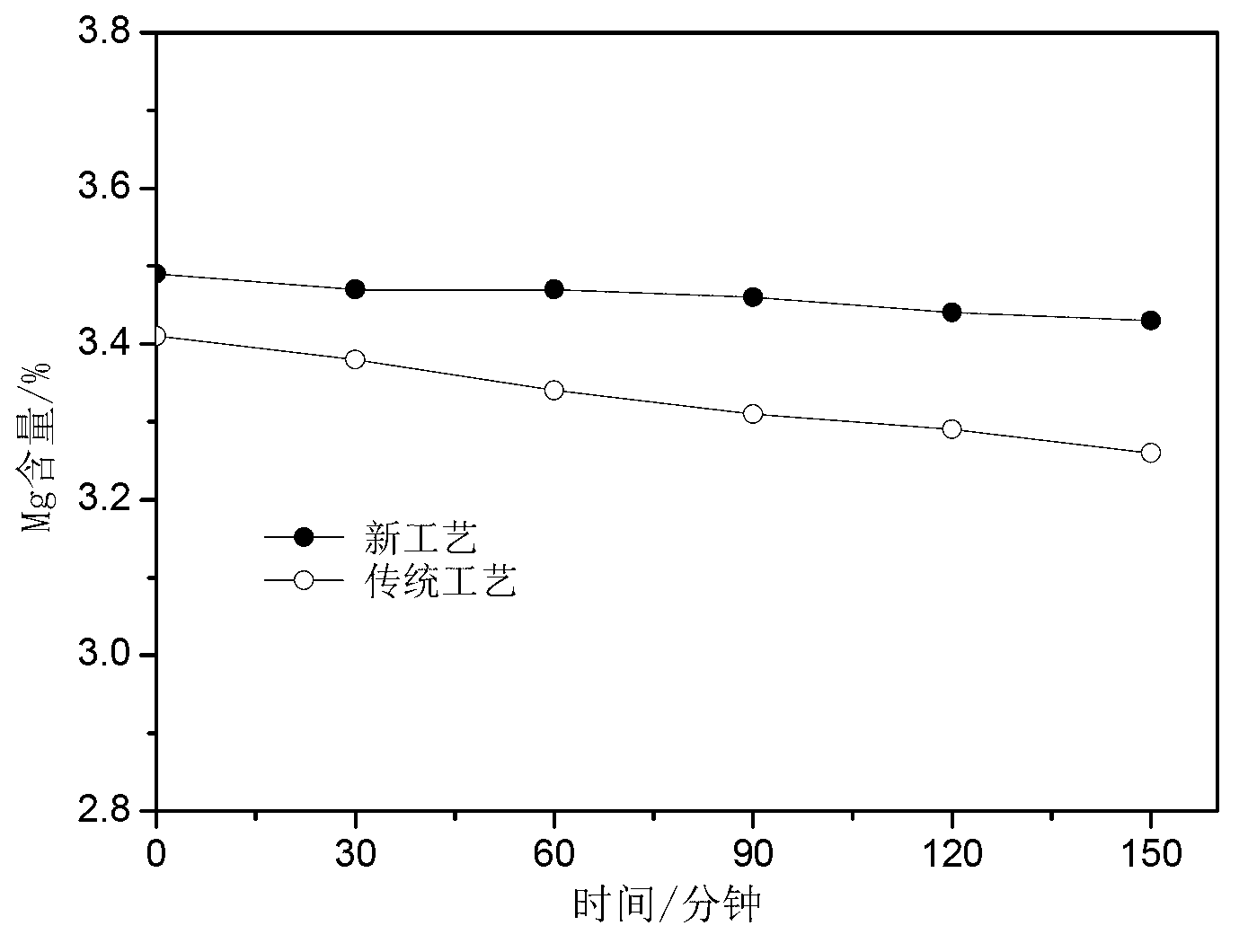
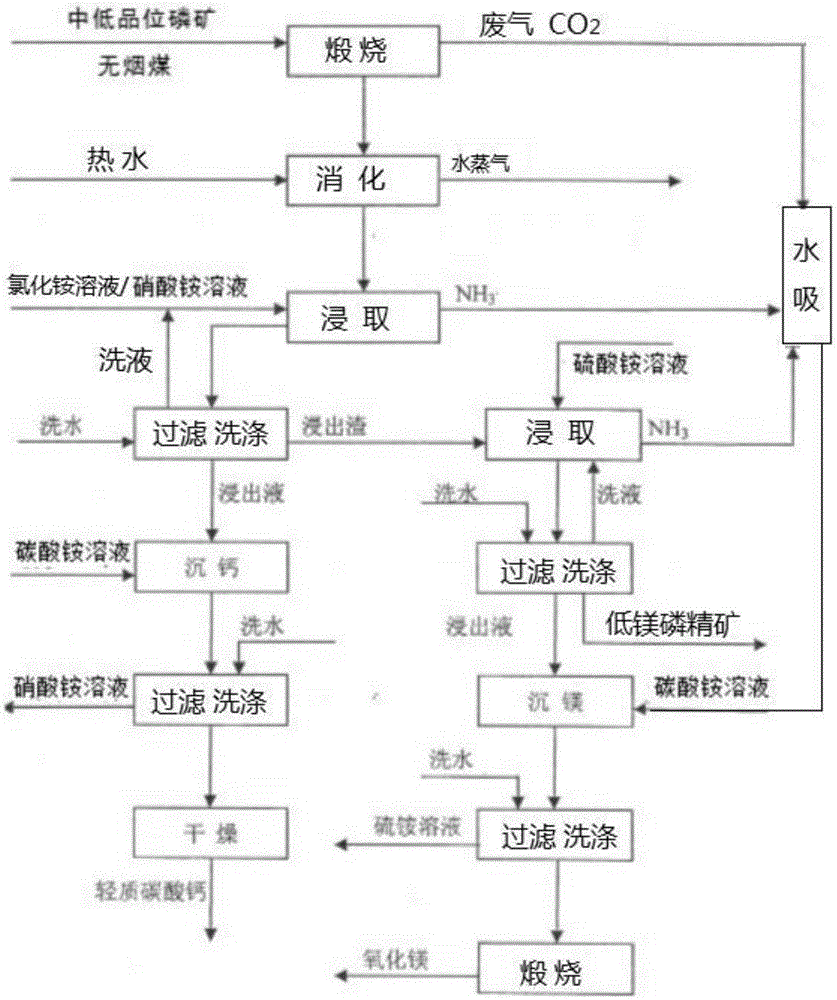
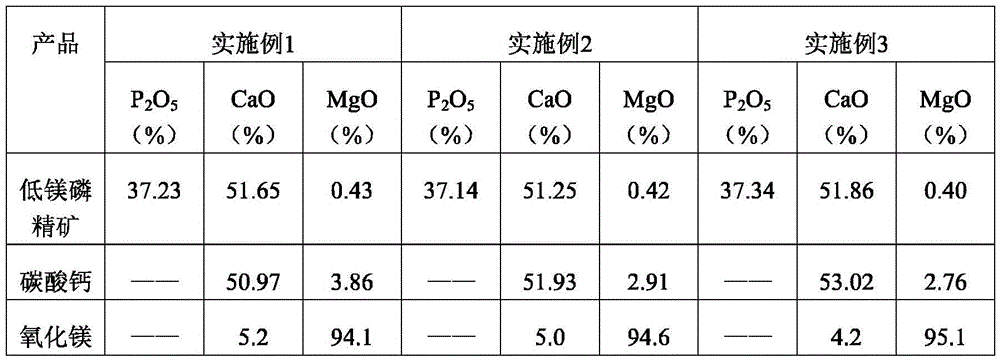
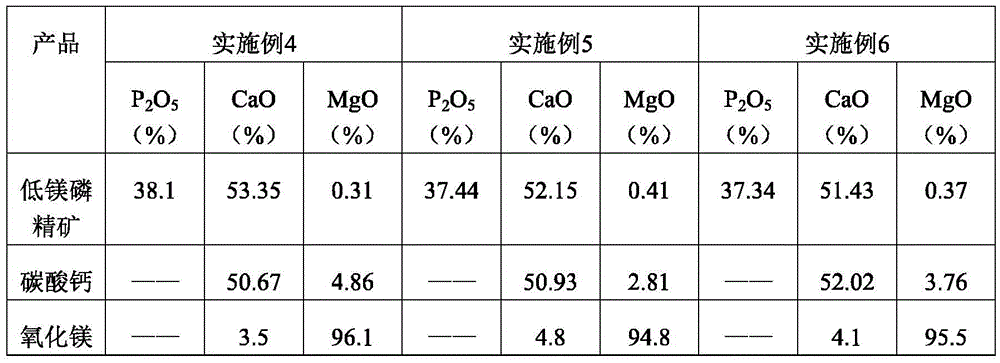
Technology for preparation of low-magnesium phosphate concentrate and byproducts calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from medium and low grade phosphate rock
ActiveCN105540560AEfficient recyclingSolve pollutionCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesRaw phosphate material treatmentInorganic ChemicalPhosphorite
Belonging to the technical field of inorganic chemical industry, the invention provides a technology for preparation of low-magnesium phosphate concentrate and byproducts calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from medium and low grade phosphate rock. The technology includes the steps of: calcining medium and low grade phosphate rock at 900-1100DEG C; and then carrying out slaking, leaching, precipitation and a series of treatment to obtain low-magnesium phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide. The technology maximumly retains phosphorus element in the prepared low-magnesium phosphate concentrate, and produces calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide as the byproducts, so that the calcium, magnesium and phosphorus elements in the medium and low grade phosphate rock can be fully utilized. In the obtained low-magnesium phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide products, the low-magnesium phosphate concentrate has a phosphorus pentoxide content of more than 37% and a magnesium oxide content of less than 0.5%, the calcium carbonate has a calcium oxide content of more than 50%, and the magnesium oxide has purity of over 94%. Therefore, the increase percentage point of phosphorus pentoxide in the low-magnesium phosphate concentrate is over 10.13.
Owner:贵州盛源新材料股份有限公司
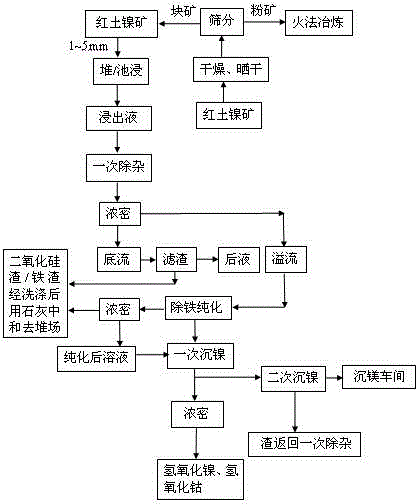
Method for treating low-magnesium limonitic laterite nickel ore
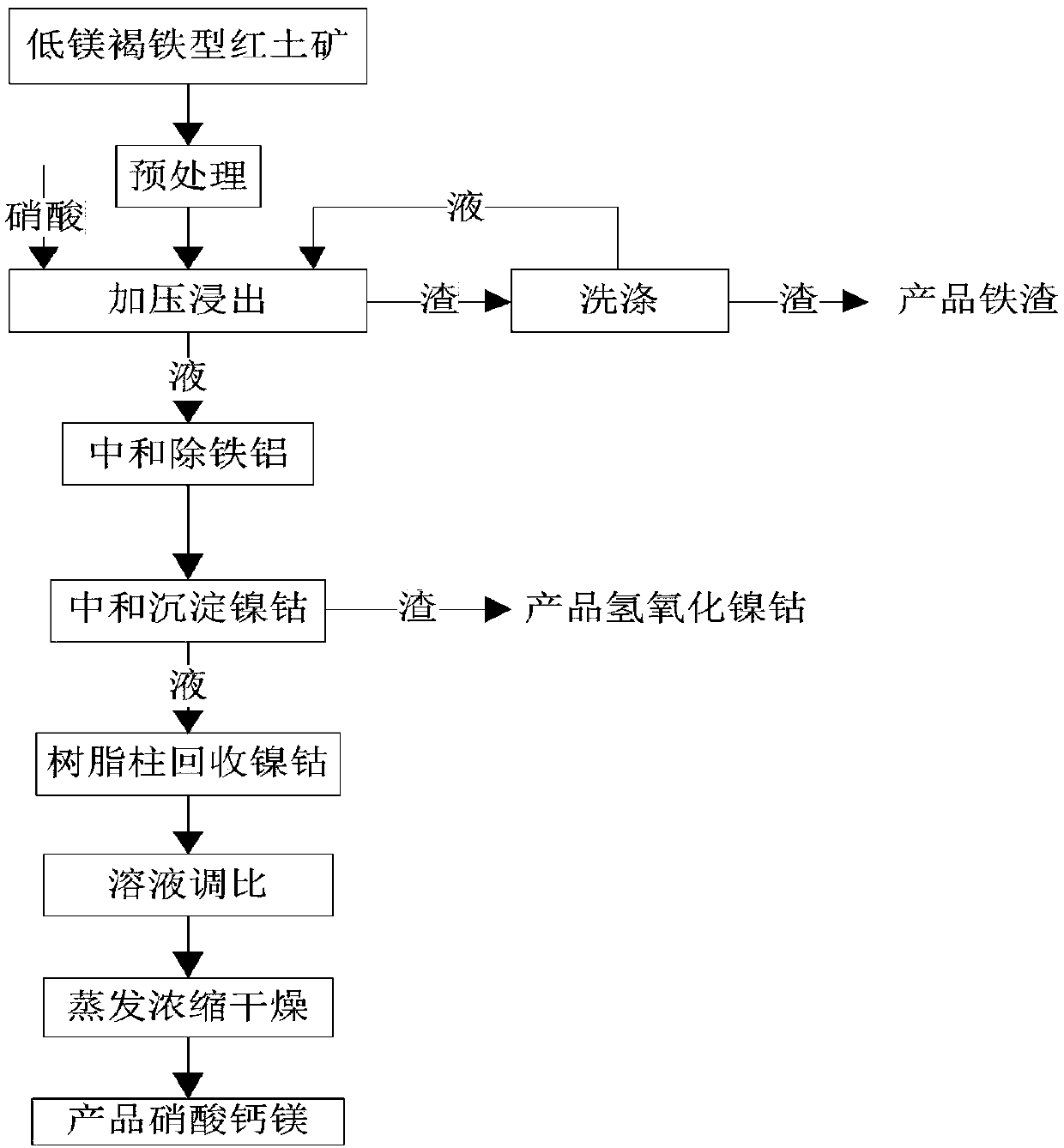
InactiveCN109252056ASolve the problem of comprehensive utilizationAvoid secondary pollutionMagnesium nitratesCalcium/strontium/barium nitratesLateriteCobalt
The invention discloses a method for treating a low-magnesium limonitic laterite nickel ore. The method concretely comprises the following steps: ore grinding pretreatment, nitric acid pressurizationleaching, neutralization for removing iron and aluminum, neutralization for precipitating nickel and cobalt, recovery of the nickel and cobalt through a resin column, solution ratio adjustment, and evaporative concentrating drying. The selective use of a leaching agent and an acid-base regulator in the treatment method makes all steps in the whole method cooperate with each other in order to realize the efficient and sufficient leaching and recovery of cobalt and nickel in the laterite nickel ore, and chemical agents added in the treatment method cooperate with each other to completely convertcalcium and magnesium metals in the laterite nickel ore into a calcium magnesium nitrate mixed fertilizer which can be directly recycled, so completely efficient utilization treatment of resources isachieved, and the problem of comprehensive utilization of the low-magnesium limonitic laterite nickel ore is solved. Substances discharged in the whole treatment process are directly recyclable products, and no wastewater / waste residue / waste gas is discharged, so the method has the advantages of simple and easily-controlled treatment steps, low energy consumption, low cost and high industrial actual values.
Owner:MEISHAN SHUNYING POWER BATTERY MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for joining components made of a high-strength aluminum material and heat exchanger assembled according to the method
InactiveUS20080277455A1Dimension of reducedReduce weightWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesPlate heat exchangerAlloy
The invention relates to a method for joining components made of a high-strength aluminum material, whereby at least two components of high-strength aluminum alloys are joined by soldering, both components separated from each other by at least one aluminum layer with a lower magnesium content compared with the contact surfaces before joining is carried out, and a heat exchanger produced according to this method.
Owner:HANON SYST
Blast furnace smelting raw material and smelting method thereof
InactiveCN109439820AReduce smelting costIncrease production costBlast furnace detailsBlast furnace smeltingBoron
The invention discloses a blast furnace smelting raw material and a smelting method thereof. The invention provides a high-aluminum low-magnesium boron-containing blast furnace smelting raw material and a method for carrying out high-aluminum low-magnesium boron-containing blast furnace smelting by virtue of the furnace material. The furnace material is composed of high-aluminum low-magnesium boron-containing sintered ores, pellet ores and lump ores; magnesium-containing fluxing ores are not added into the blast furnace material in a matching manner; the high-aluminum low-magnesium boron-containing sintered ores are formed by sintering the mixture of high-aluminum iron ore powder, boron-magnesium iron ore powder and sintering auxiliary materials; the pellet ores are common pellet ores; andthe lump ores are high-grade lump ores. According to the blast furnace smelting raw material and the smelting method thereof, the high-aluminum low-magnesium boron-containing sintered ores and the common pellet ores are selected, and the lump ores are reasonably added in a matching manner in a blast furnace smelting process; the slag structure and performance are improved by selecting a reasonable blast furnace operation system; and smooth slag-iron discharge is achieved, so that the stable and smooth running of the blast furnace is kept, and the pig iron smelting cost is lowered.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
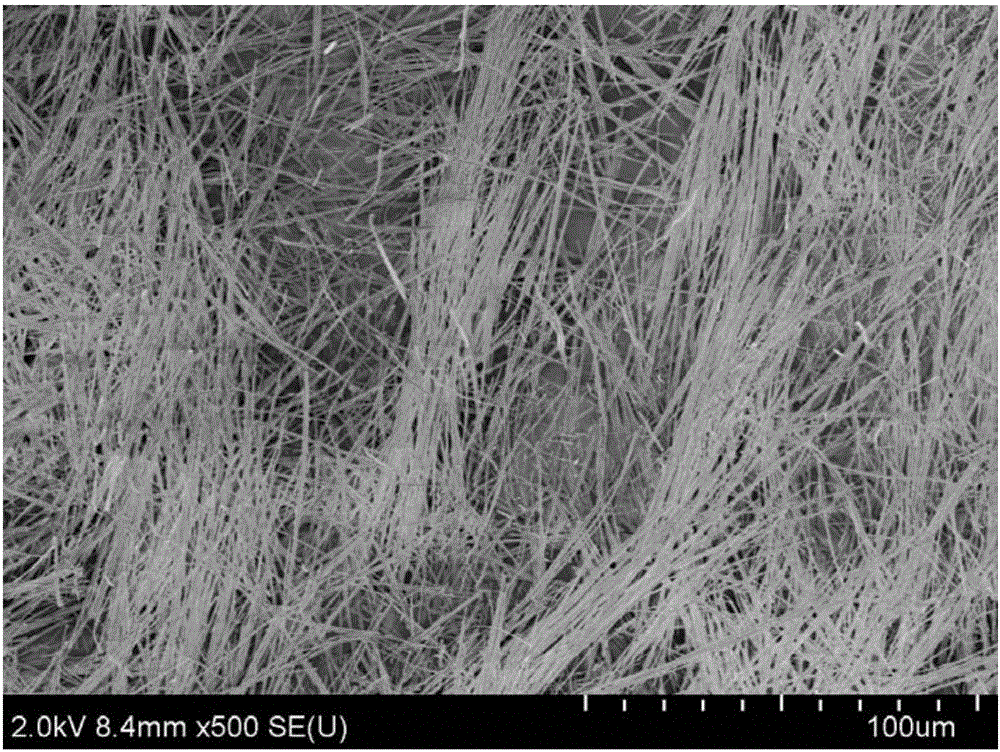
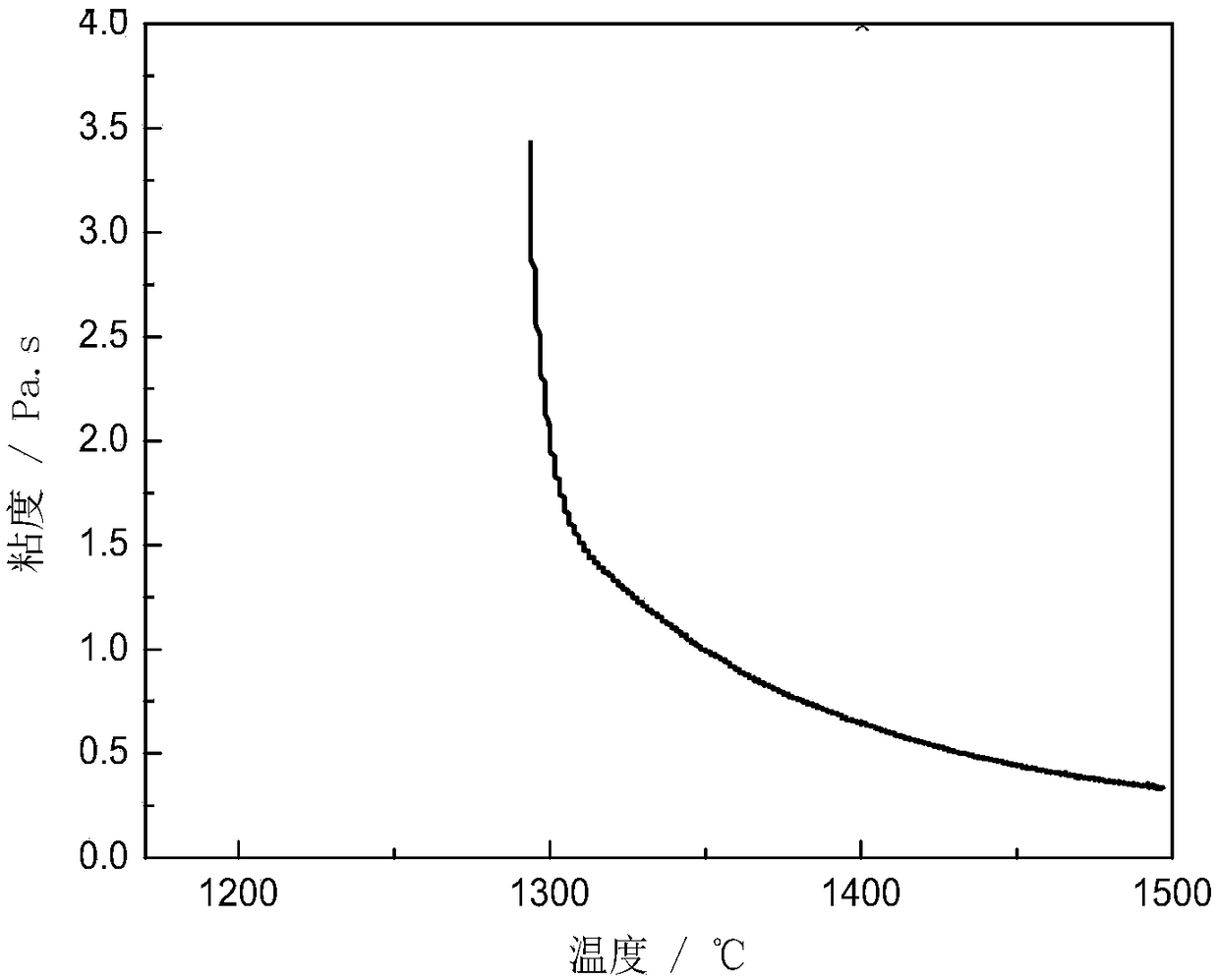
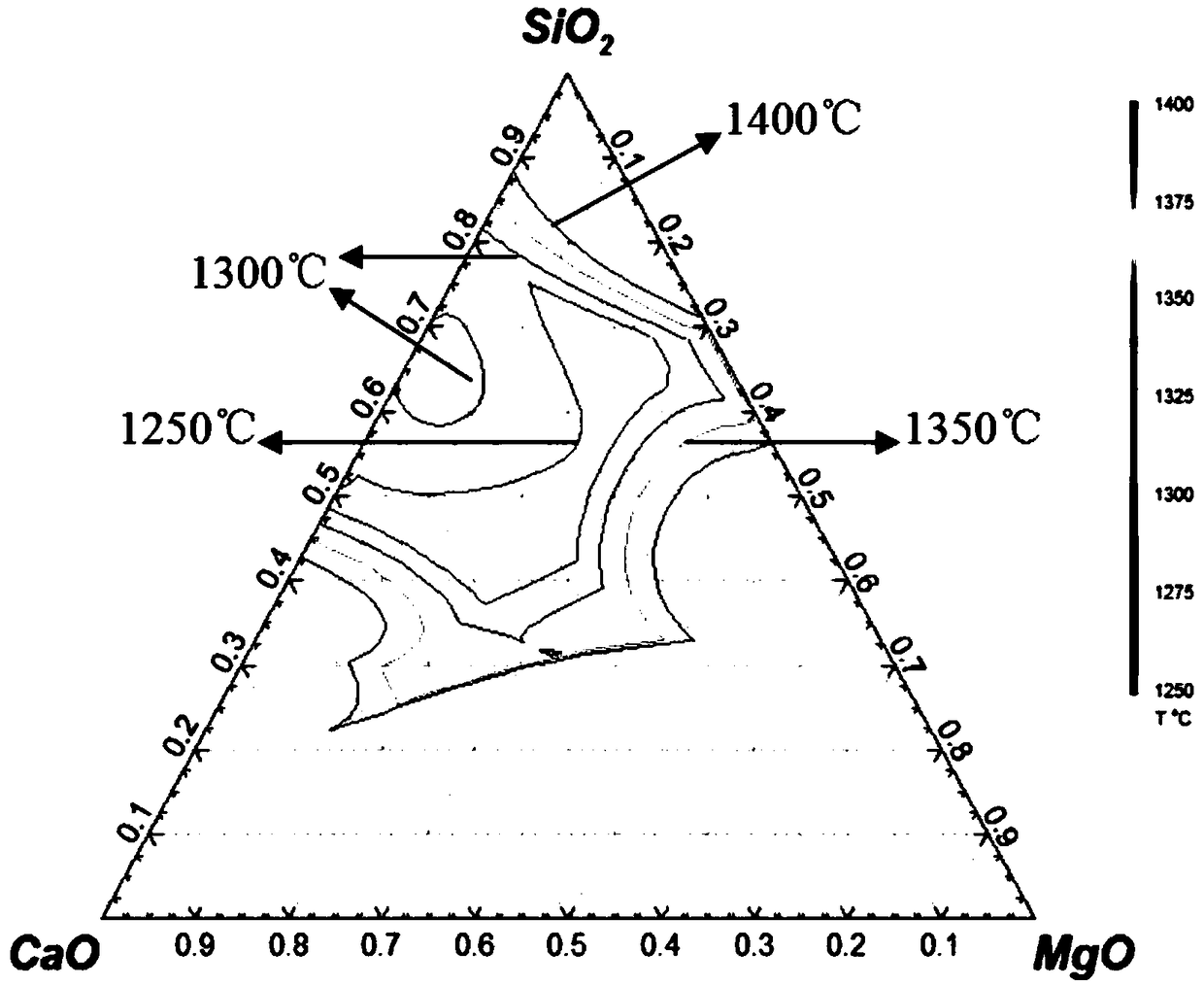
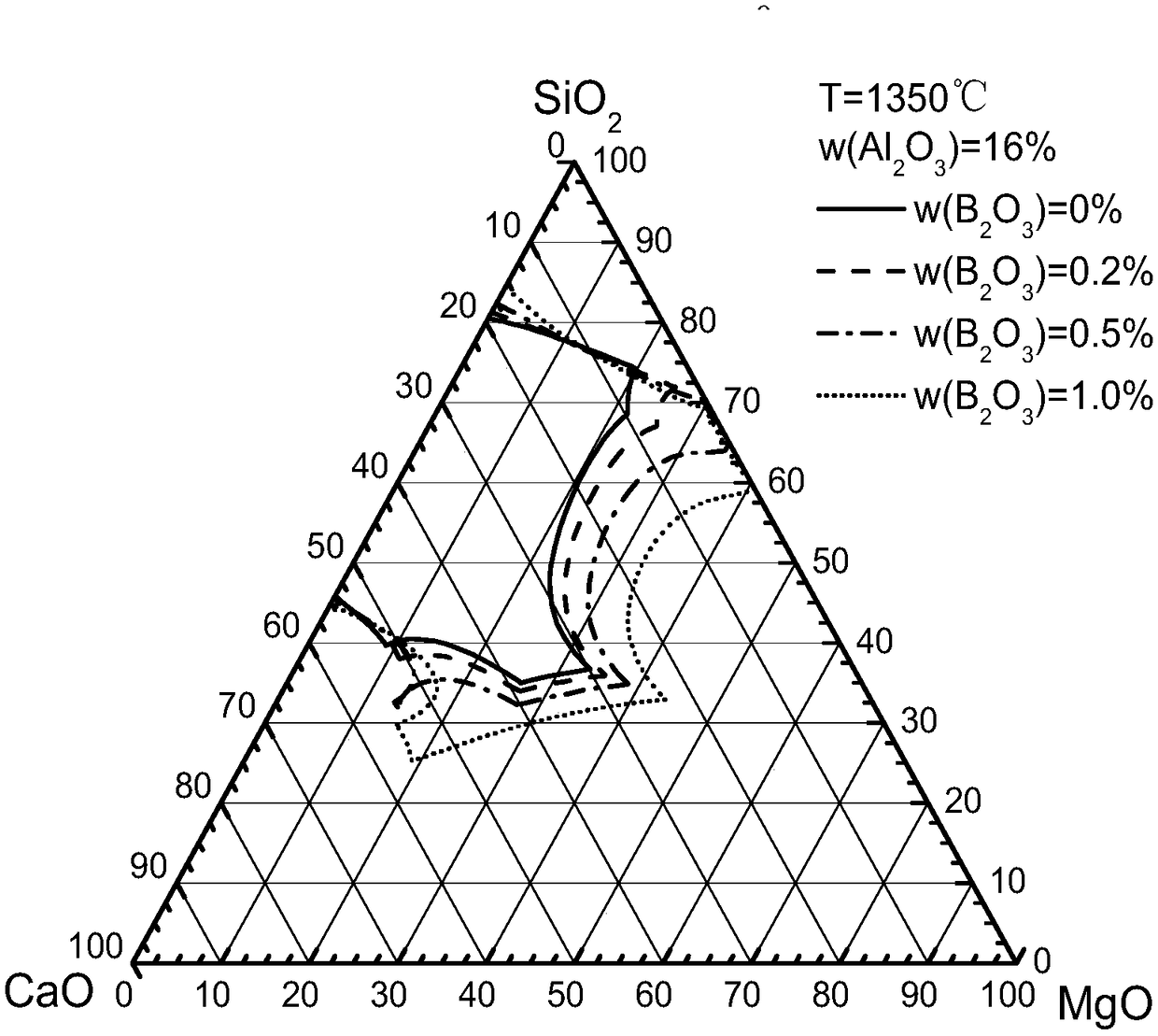
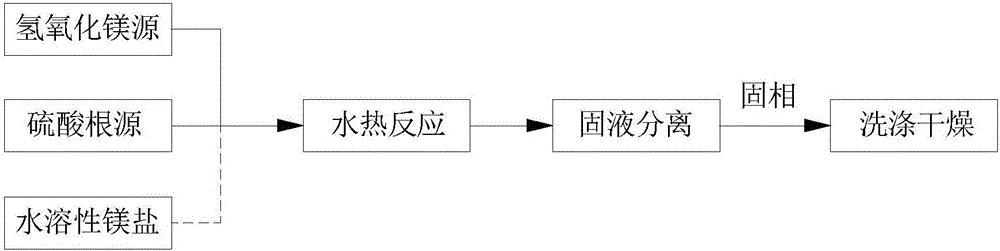
Preparation method of basic magnesium sulfate whiskers
The invention discloses a preparation method of basic magnesium sulfate whiskers. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, mixing a magnesium hydroxide source, a sulfate source and water to obtain a mixture, wherein the mass percent of magnesium hydroxide in the magnesium hydroxide source is not lower than 50%; S2, carrying out hydrothermal reaction on the mixture for 1-40 hours at the temperature of 100-300 DEG C, so as to obtain suspension; and S3, carrying out solid-liquid separation on the suspension, so as to obtain a solid phase and a liquid phase, washing, and drying the solid phase, so as to obtain the basic magnesium sulfate whiskers. According to the preparation method of the basic magnesium sulfate whiskers, the magnesium hydroxide source with relatively low magnesium hydroxide purity is taken as a preparation raw material; on one hand, the pollution and waste of byproduct magnesium hydroxide magnesium slag are reduced, and thus the magnesium harm problem is effectively controlled; and on the other hand, ammonia water, sodium hydroxide and the like are avoided from being used as a base source, and thus the preparation method is reduced. Meanwhile, the preparation method does not need other additives and is simple in technology; and the obtained basic magnesium sulfate product has high purity and good dispersibility.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
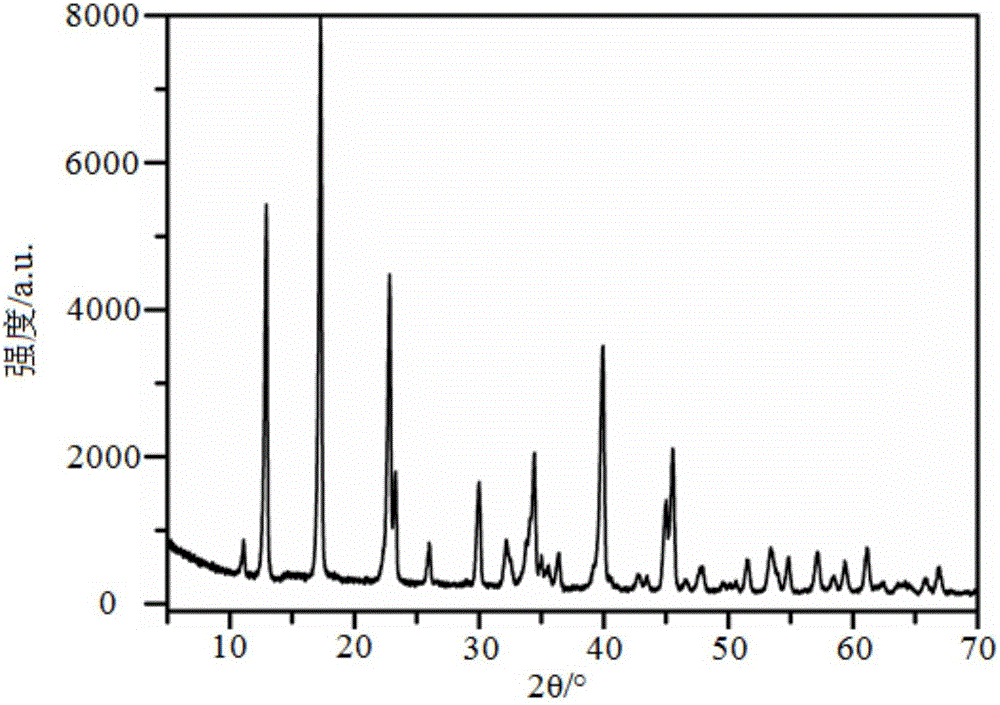
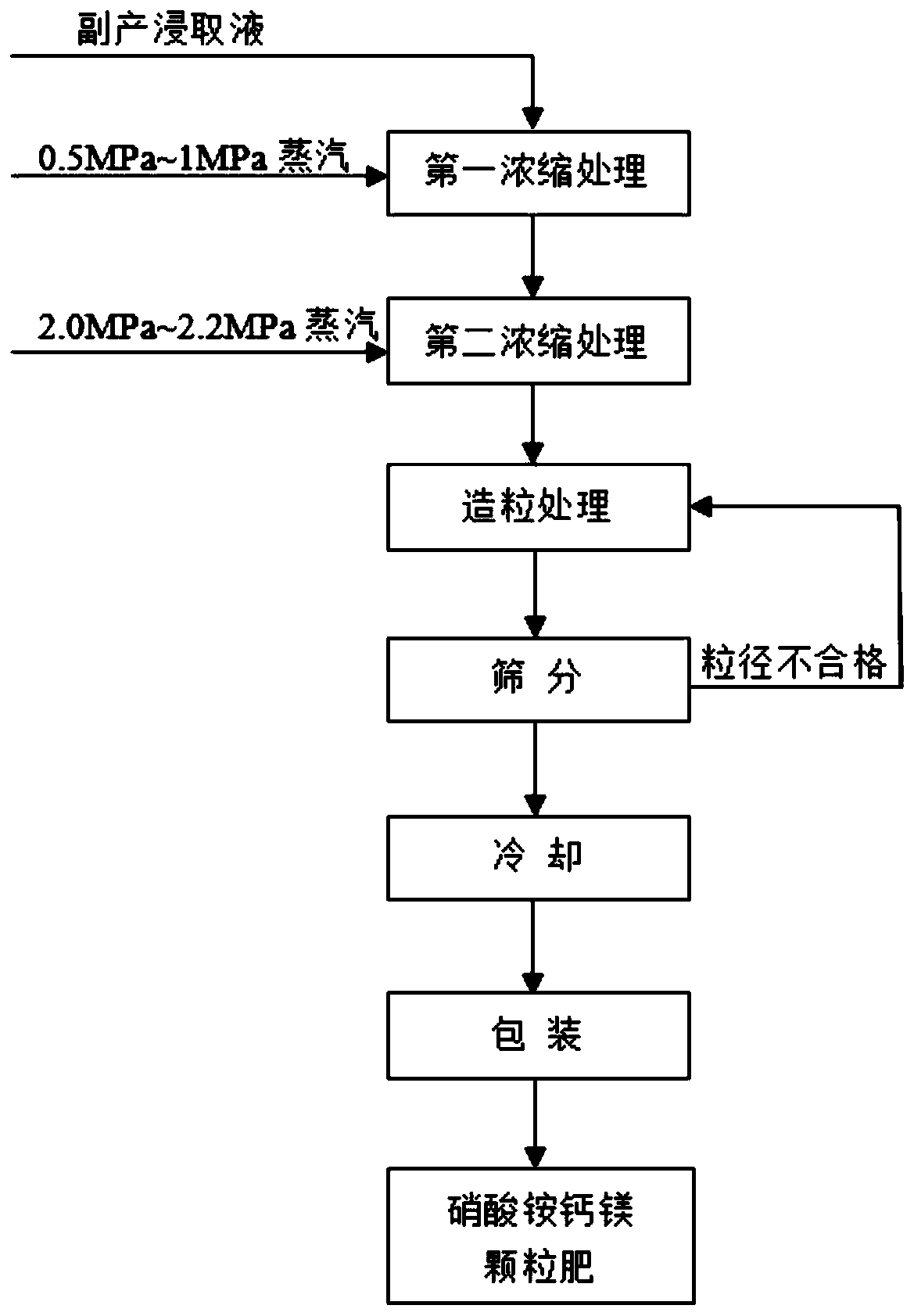
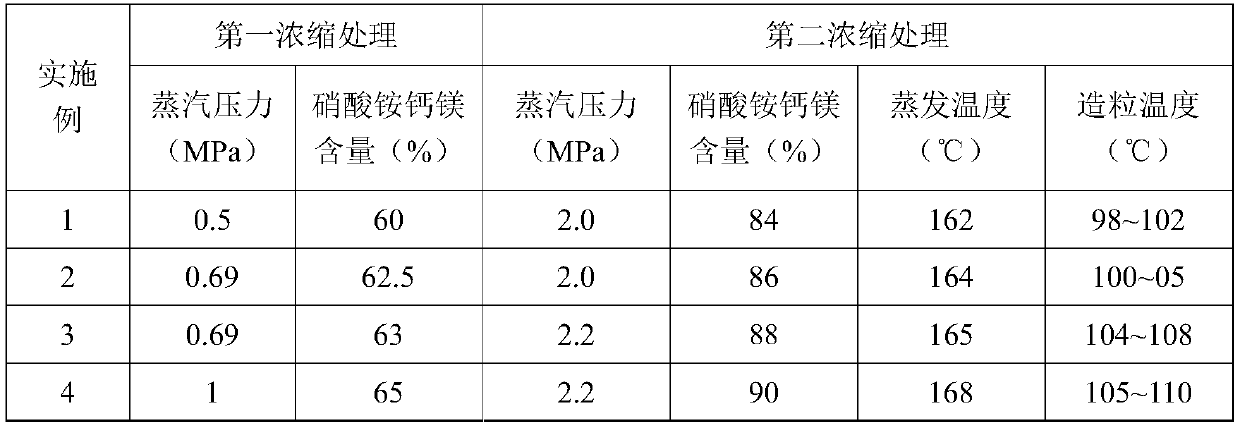
Magnesium calcium ammonium nitrate granular fertilizer and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a magnesium calcium ammonium nitrate granular fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a low-magnesium-phosphorus concentrate by using a medium and low grade phosphate ore as a raw material to obtain a leaching solution; performing concentration treatment on the leaching solution to obtain a concentrate; and performing granulation treatment on the concentrate to obtain the magnesium calcium ammonium nitrate granular fertilizer. The preparation method of the magnesium calcium ammonium nitrate granular fertilizer provided by the invention uses the low-magnesium-phosphorus concentrate by-product leaching solution prepared from the medium and low grade phosphate ore as a raw material to prepare the magnesium calcium ammonium nitrate granular fertilizer, and only needs concentration treatment and granulation treatment in the preparation process without other treatment steps or addition of other raw materials, thereby having a simple process and being easy to operate; no waste liquid and waste residues are generated in the whole production process, so that the method is green and environmentally friendly; and the granular magnesium calcium ammonium nitrate product with a particle pelletizing rate of >=90% and a smooth and round surface is obtained, and has the characteristics of full water solubility, full nutrition, fast fertilizer efficiency, and convenient transportation, storage and application.
Owner:GUIZHOU BATIAN ECOTYPIC ENG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com