Patents
Literature
228 results about "Goethite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
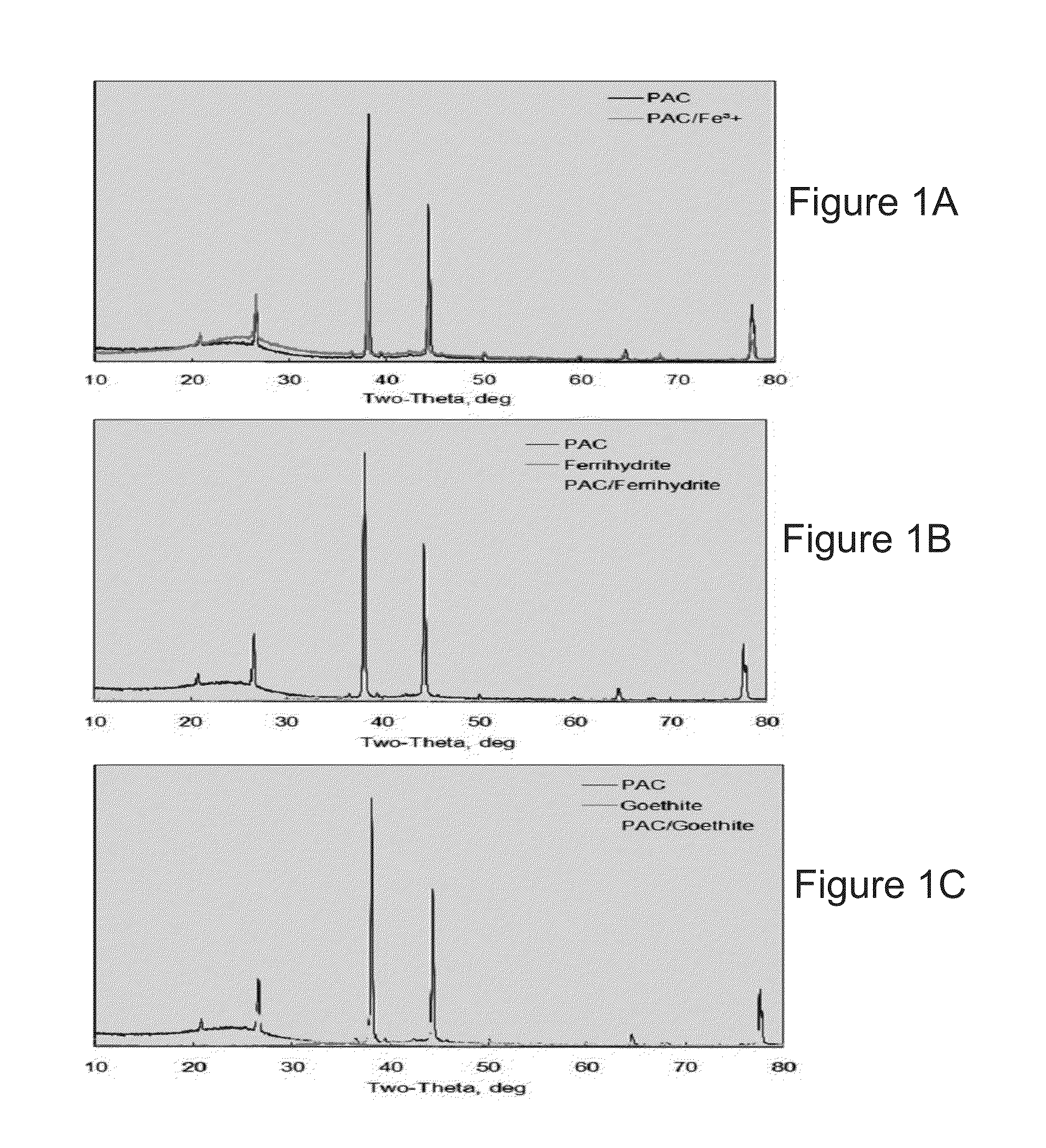
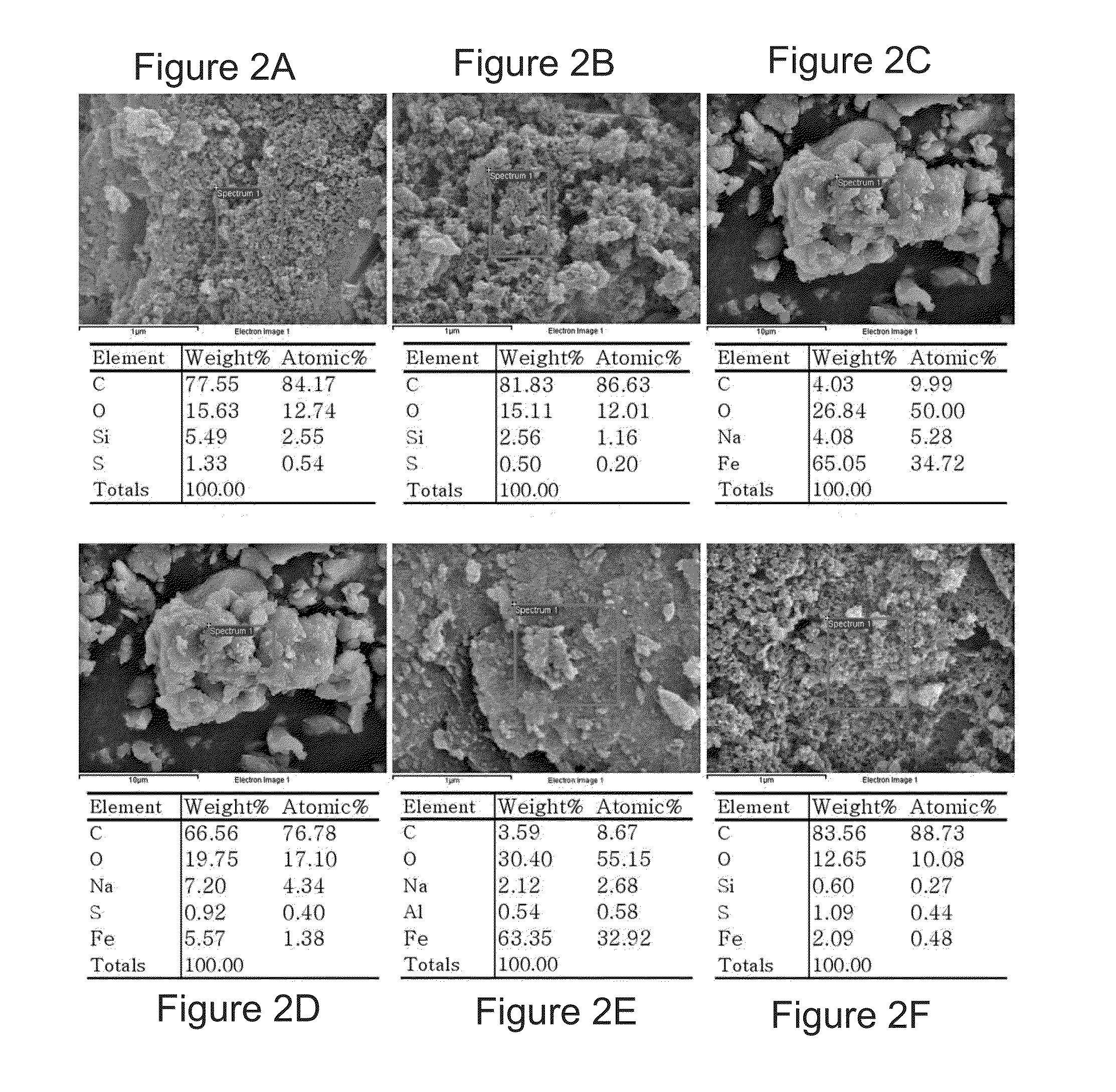
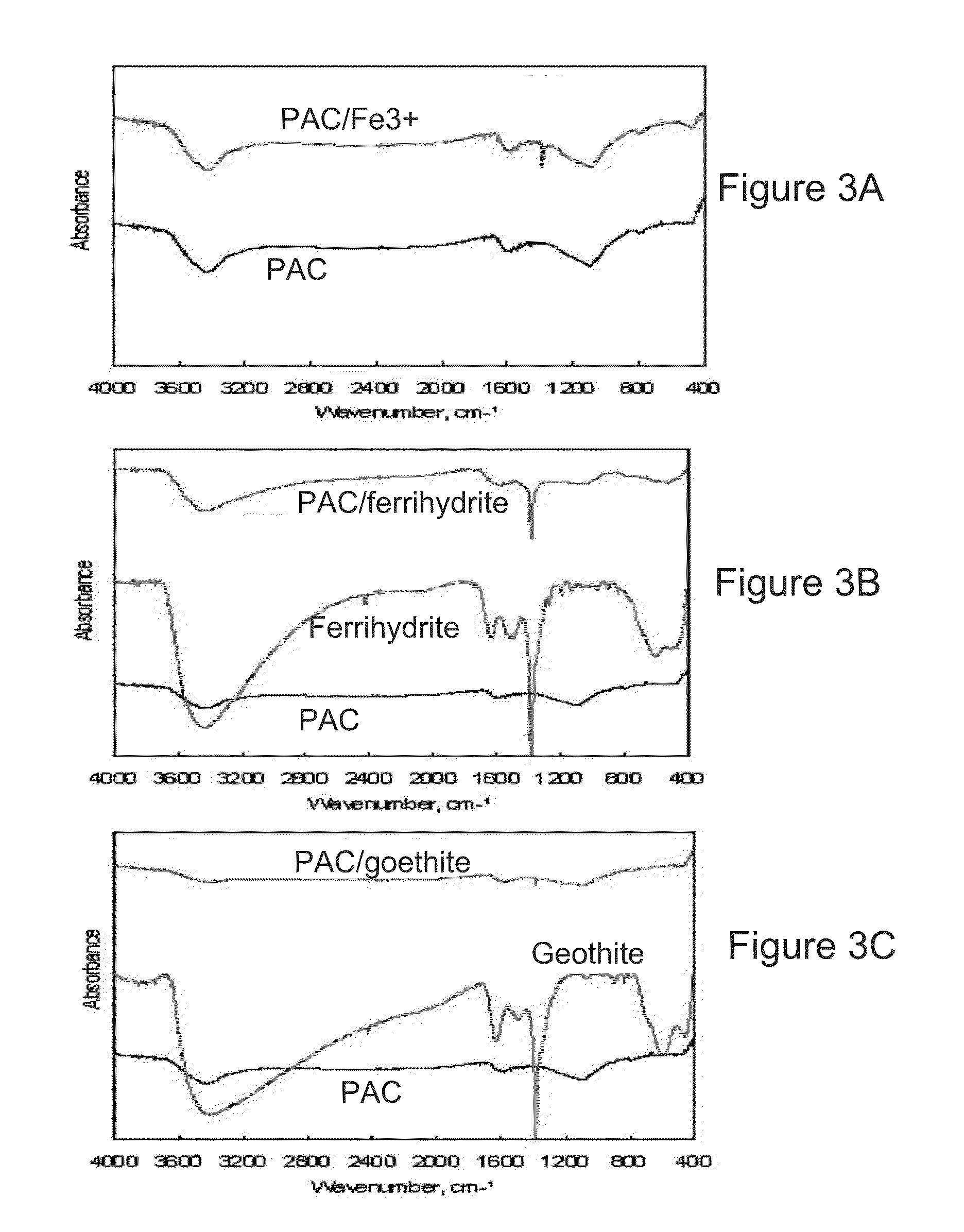
Goethite (FeO(OH); /ˈɡɜːrtaɪt/) is an iron-bearing hydroxide mineral of the diaspore group. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient times for its use as a pigment (brown ochre). Evidence has been found of its use in paint pigment samples taken from the caves of Lascaux in France. It was first described in 1806 based on samples found in the Hollertszug Mine in Herdorf, Germany. The mineral was named after the German polymath and poet Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749–1832).
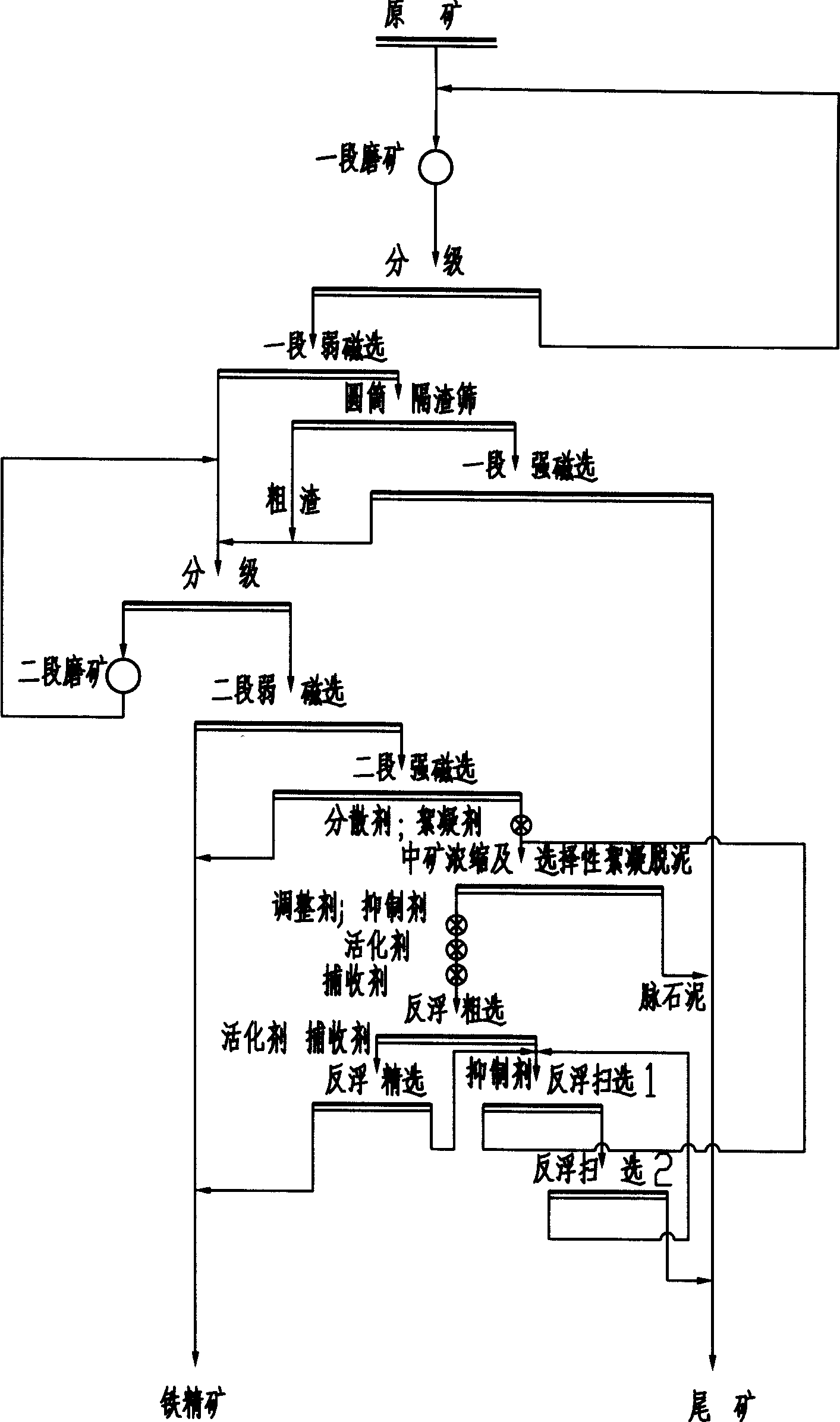
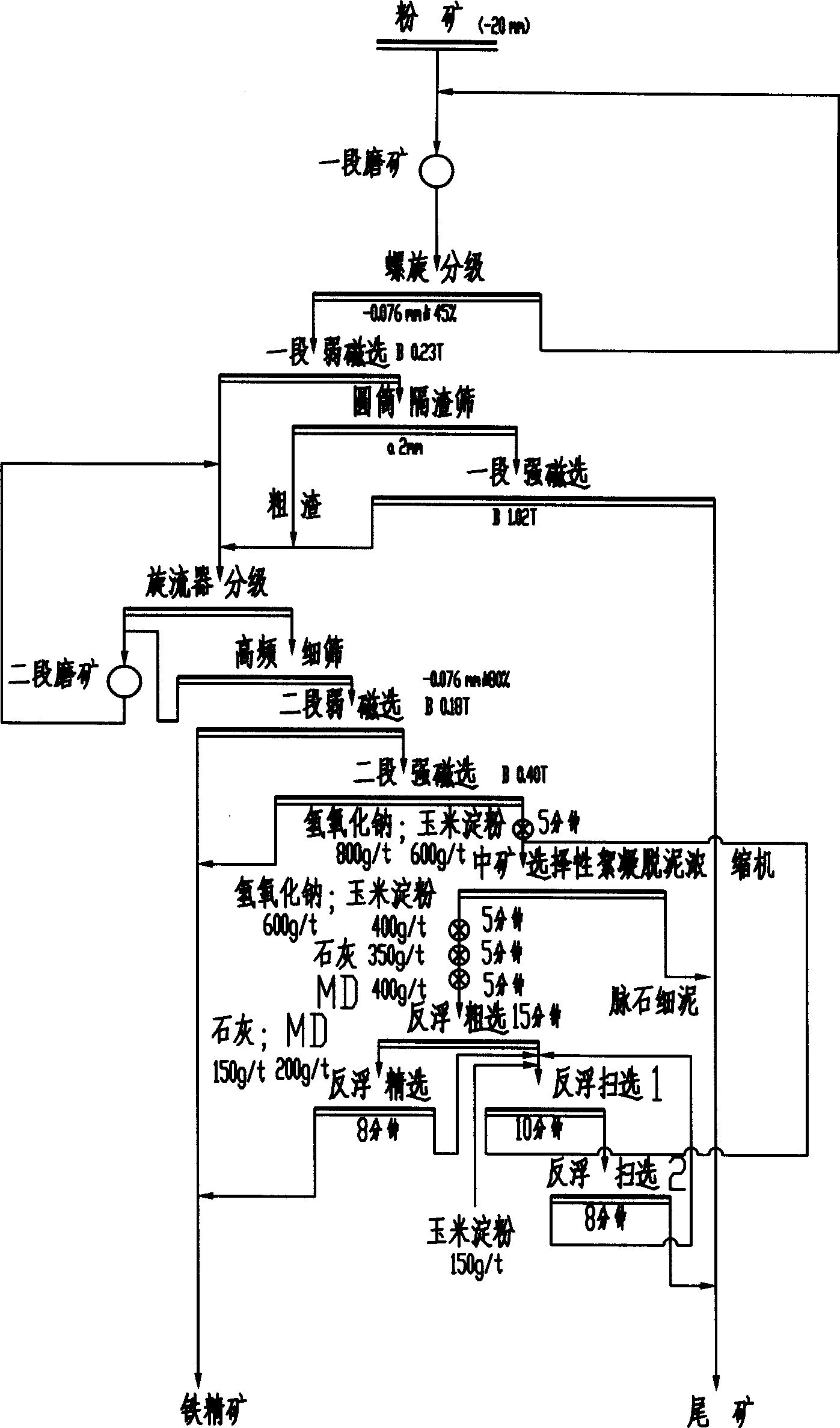
Beneficiation method for recycling specularite
InactiveCN101428248AReduce consumptionReduce the number of equipmentDifferential sedimentationFlotationIronstoneSlag
Owner:SINOSTEEL MAANSHAN INST OF MINING RES
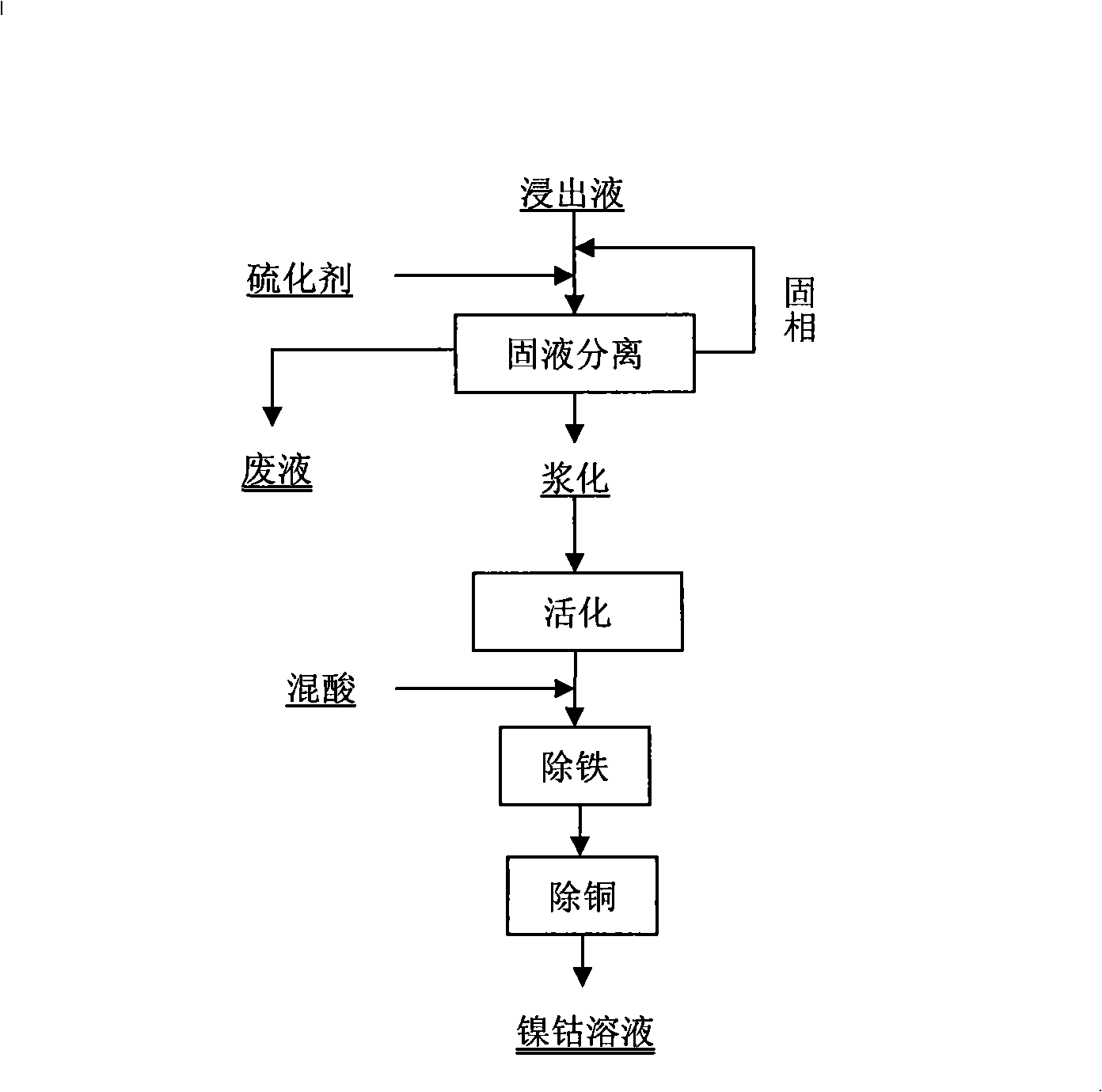
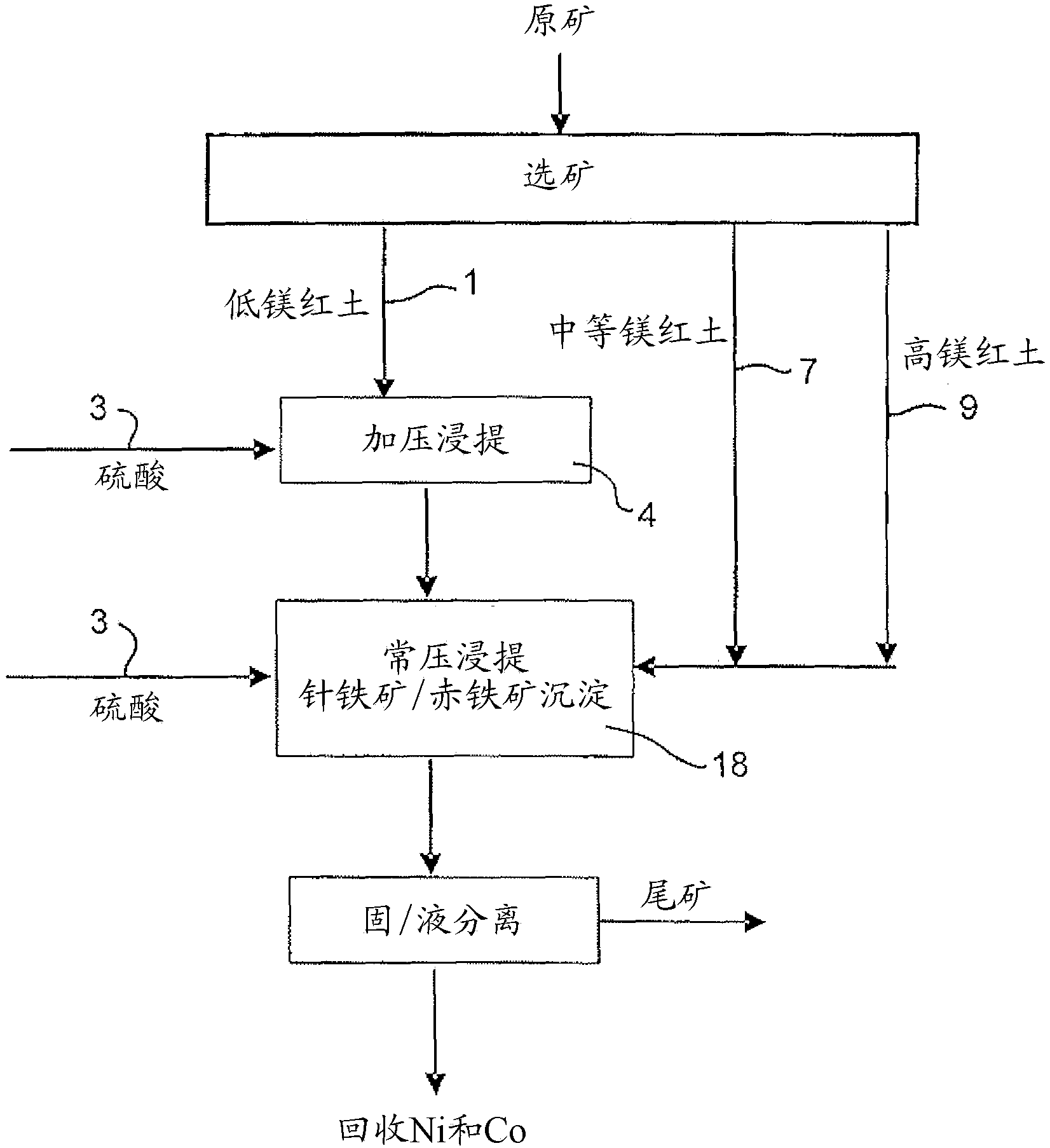
Method for collecting nickel and cobalt from laterite-nickel ore lixivium
ActiveCN101298638AHigh extraction rateReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSlag
The invention discloses a method for separating enriched nickel and cobalt from a laterite nickel ore lixivium, which comprises the following steps: after solid and liquid separation between the laterite nickel ore lixivium and ore slag is implemented, a vulcanizing agent is added into the lixivium, the solid and the liquid are separated after reaction precipitation, and precipitated solid is washed by a new lixivium, thus obtaining sulfide precipitate; after the sulfide precipitate is pulpified, sulphuric acid and solution of nitric acid and mixed acid are added so as to implement oxidizing leaching; the goethite method is adopted for removing iron from a superior pickle liquor; a sodium thiosulfate solution is added so as to implement copper removing; a filtering liquor that is the enriched nickel and cobalt solution is obtained. Compared with the prior art, the method for separating enriched nickel and cobalt from the laterite nickel ore lixivium is implemented at normal temperature and normal pressure, does not need a high-pressure caldron, has less device investment, low running cost, simple technical path, short process and controllable production scale; the vulcanizing agent and acids that are used in the technique can be recycled to the utmost extent and do not have emissions and environment pollution; the extraction yield of nickel and cobalt can achieve over 95 percent, and the method for separating enriched nickel and cobalt from the laterite nickel ore lixivium has low production cost and easy industrialization.
Owner:福建常青新能源科技有限公司
Method for harmless and recycling treatment of stainless steel acid washing waste water neutralization sludge
ActiveCN101982433ASolve the problem of sediment lossImprove water qualitySludge treatmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeAcid washing
The invention discloses a method for harmless and recycling treatment of stainless steel acid washing waste water neutralization sludge, belonging to the field of harmful and valuable heavy metal resource recovery. The stainless steel acid washing waste water neutralization sludge is leached out by sulphuric acid, harmful and poisonous metals manganese, nickel and chromium enter into the leachate, and harmless treatment is carried out on the sludge. Separation, enrichment and recovery of metal resources of iron, manganese, chromium and nickel in the leachate are realized by adopting goethite method, potassium permanganate oxidation method, anion resin exchange method and chelate resin absorption method respectively, and effluent up to the standard is discharged after treatment or is returned to water consuming link in technologic process. The method of the invention has short technological flow, simple operation, management convenience, high recovery rate of valuable metal resources of manganese, nickel and chromium, recycling of multiple valuable metals is realized while the sludge is subject to harmless treatment, and unification of economic benefit, environmental benefit and social benefit is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for directly producing high-purity electronic level cobaltous sulfate by using cobalt-containing waste
ActiveCN102061390AMeet high purity requirementsImprove overall recoveryProcess efficiency improvementTotal recoveryGoethite
The invention provides a method for directly producing high-purity electronic level cobaltous sulfate by using cobalt-containing waste, in particular a process for producing cobaltous sulfate by using cobalt-containing waste. The method comprises the steps of: checking and classifying raw materials, wet-milling and size-mixing, acid-decomposing, filtering, washing, separating, and extracting copper sponge. The method is characterized by also comprising the steps of: removing iron with a goethite process, extracting P2O4 and removing impurities, separating nickel from cobalt, extracting N235, purifying, concentrating and crystallizing. The high purity electron level cobaltous sulfate is directly regenerated by using various kinds of cobalt wastes, the requirement of the modern high-technology industry on high purity of the cobaltous sulfate is met; the total recovery of the cobalt is higher than or equal to 98 percent; various usable elements can be comprehensively recycled, and coppersponge, tungsten carbide, iron hydroxide and nickel carbonate can be regenerated while the electronic level cobaltous sulfate as a main product is regenerated. The invention has the advantages of comprehensively utilizing waste cobalt resources, recycling the wastes, improving the enterprise benefit, and being beneficial to the development of energy conservation, emission reduction, environment protection and circular economy.
Owner:HUNAN JINYUAN NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for recovering gold, silver, tin and copper from industrial wastes
InactiveCN103305698AHigh recovery rateHigh enrichment rateProcess efficiency improvementSlagGoethite
The invention provides a method for recovering gold, silver, tin and copper from industrial wastes. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) adding the industrial wastes in hydrochloric acid solution, adding an oxidant, and performing oxidation acid-leaching treatment to obtain leaching slag, and solution containing tin ions and copper ions; (b) treating the leaching slag to obtain gold and silver; (c) adding iron in the solution containing tin ions and copper ions, and reacting to obtain copper, and a solution containing tin ions and ferrous ions; (d) adding lime in the solution containing tin ions and ferrous ions, and reacting to obtain tin, and solution containing ferrous ions; (e) heating the solution containing ferrous ions, charging air and adding lime, and reacting to obtain goethite and calcium chloride solution; (f) adding concentrated sulphuric acid in the calcium chloride solution to obtain calcium sulphate precipitate and hydrochloric acid solution. The various steps of the method disclosed by the invention are effectively coordinated; zero-discharge in production can be realized; precious metals are efficiently separated, and valent by-products of iron mine and gypsum are obtained; the method has good application prospect.
Owner:NANKANG HENGYUAN CYCLE TECH CO LTD
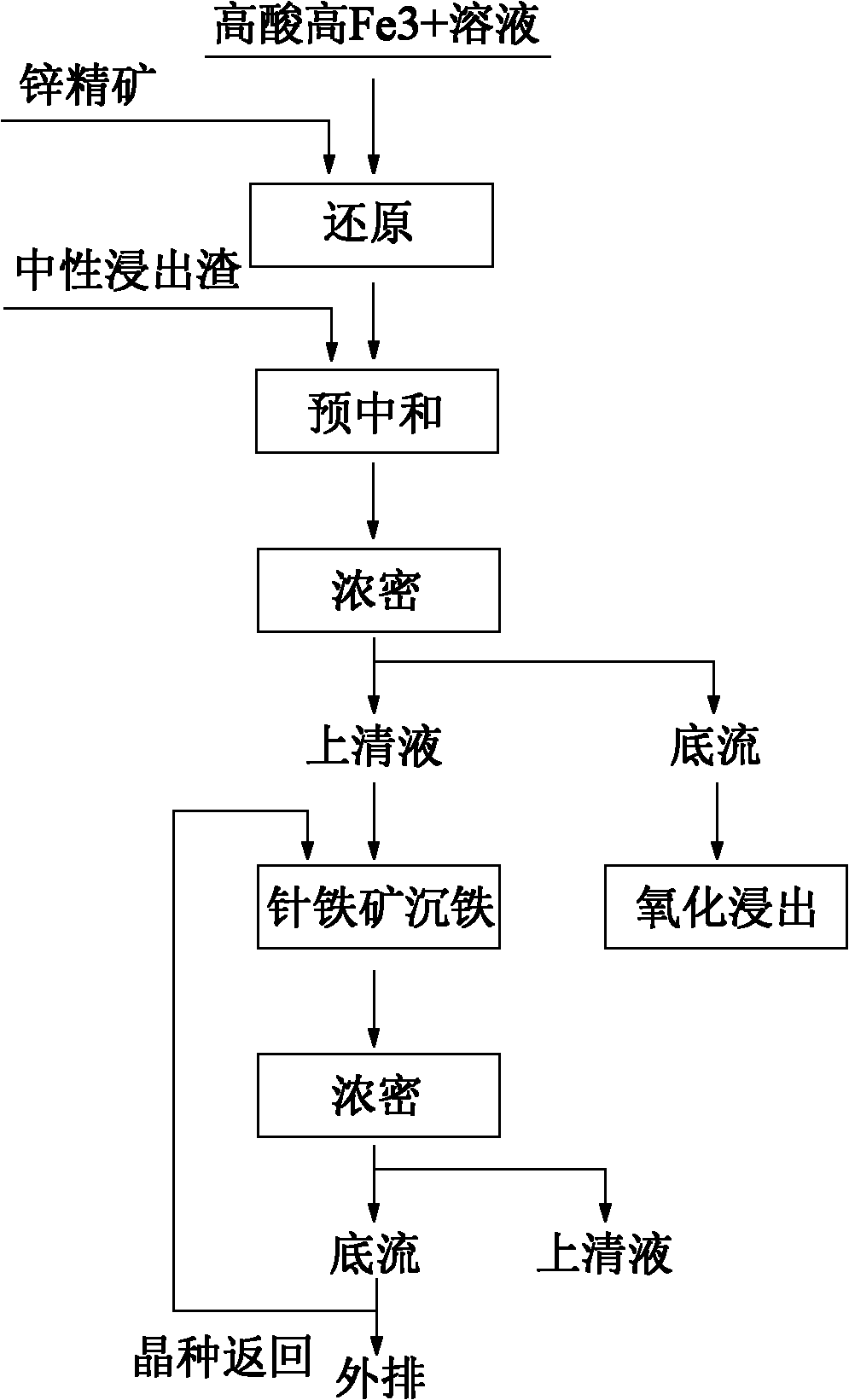
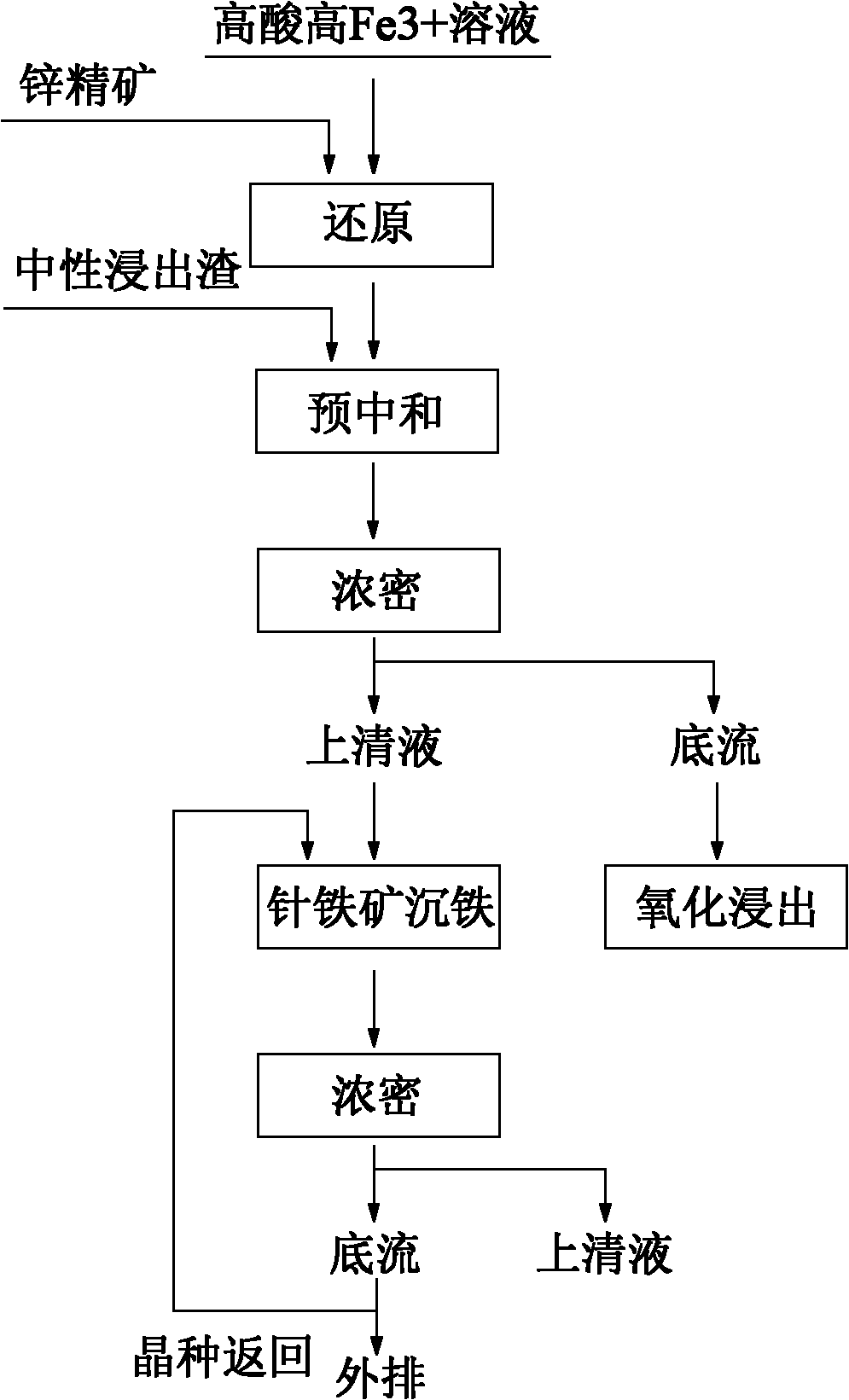
Iron depositing method of high acid and high iron solution goethite during zinc hydrometallurgy
InactiveCN102010994AImprove leaching rateRaise the gradeProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSlag
The present invention provides an iron depositing method of high acid and high iron solution goethite during zinc hydrometallurgy, comprising the following steps: a) carrying through oxidization leaching for zinc concentrate ore by using a sulphuric acid contained solution; b) reducing the leaching liquid by the zinc concentrated ore; c) pre-neutralizing the reduced liquid until pH value is 1.5-2.5, and generating a supernatant and a base flow via solid and liquid separation; d) carrying through goethite iron depositing for the generated supernatant, wherein after iron is deposited, liquid and solid are separated; the overflow is returned into a purification process; a part of the base flow is returned to a first iron depositing reactor as a seed crystal, and the rest base flow is discharged outwardly. The method provided by the present invention, iron is deposited in a form of goethite by using a high acid and high iron solution generated during zinc refining procedure; the grade of iron slag is high; and emissions of waste residues, waste gas and waste water are not increased.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
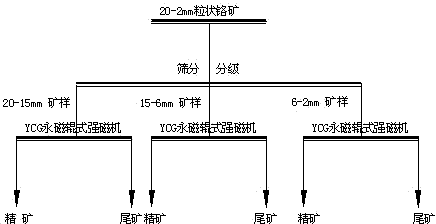
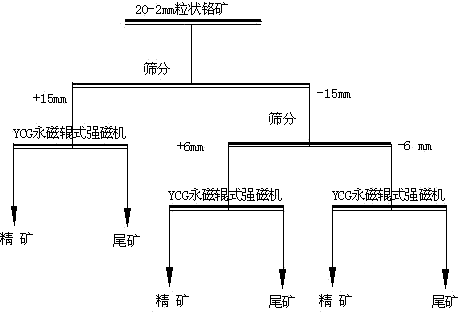
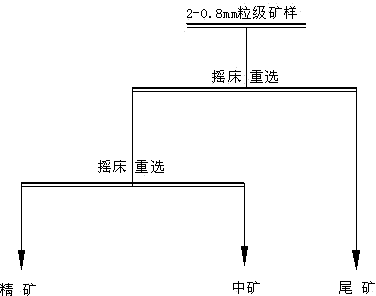
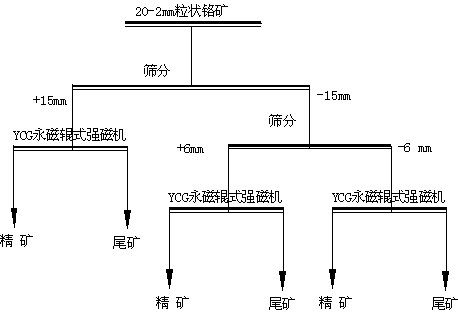
Novel beneficiation technology of high-grade ferrochrome ore
The invention discloses a novel beneficiation technology of high-grade ferrochrome ore. The novel beneficiation technology includes the following technological processes that ferrochrome ore is broken and is screened and classified into the ore of +20 mm fraction and the ore of -20 mm fraction. The ore of the +20 mm fraction receives manual back picking or hotching, large waste ore is thrown, and block concentrate is obtained. The narrow grade of the -20 mm fraction is screened and classified into four fractions, namely the 20-15 mm fraction, the 15-6 mm fraction, the 6-2 mm fraction and the 2-0 mm fraction. For the 20-15 mm fraction, the 15-6 mm fraction and the 6-2 mm fraction, a permanent magnet roller type intensity magnetic separator is used for performing dry intense magnetic separation. The 2-0 mm fraction is further screened and classified into the 2-0.8 mm fraction and the 0.8-0 mm fraction. For the 2-0.8 fraction, a shaker is selected again to obtain shaker gravity concentrate, and for the 0.8-0 mm fraction, a spiral chute and the shaker are used and a united procedure is selected again to obtain the thin-particle gravity concentrate. The novel beneficiation technology can be used for obtaining the concentrate and removing tailings in advance and has the advantage of being lower in energy consumption compared with other technologies. The technology can be used for grading chrome ore and can also be used for grading other weak magnetic iron minerals such as manganese ore, goethite, siderite and limonite.
Owner:SINOSTEEL MAANSHAN INST OF MINING RES
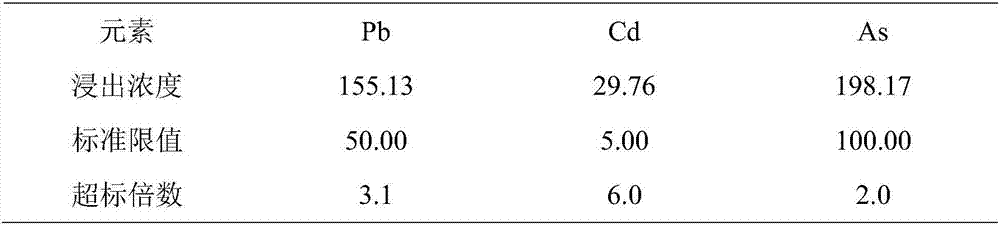
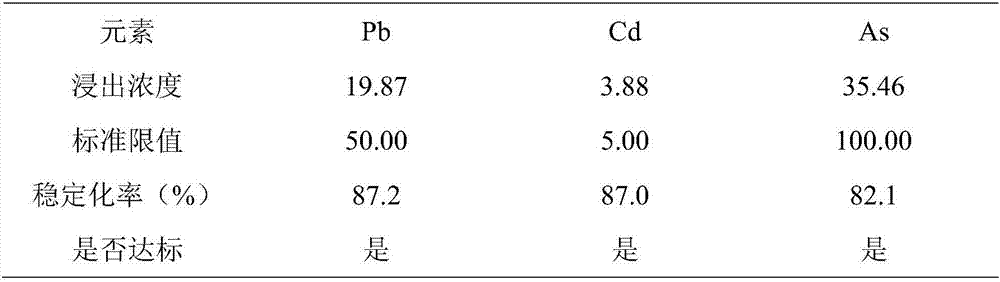
Composite stabilizer for repairing lead, cadmium and arsenic pollution in acid soil
ActiveCN106978191AImprove stabilityThe amount of medicine added is lessOrganic fertilisersSoil conditioning compositionsArsenic pollutionDissolution
The invention discloses a composite stabilizer for repairing lead, cadmium and arsenic pollution in acid soil. The composite stabilizer comprises the following components: calcium superphosphate, goethite, humic acid, quick lime, polyacrylamide and the like. The composite stabilizer is used for repairing heavy metal polluted soil, arsenic, lead and cadmium can be fixed and stabilized simultaneously, the use amount is small, a soil structure is not affected, the soil repairing effect is good, and re-dissolution of heavy metal can be prevented.
Owner:HUNAN XISI ECOLOGY TECH
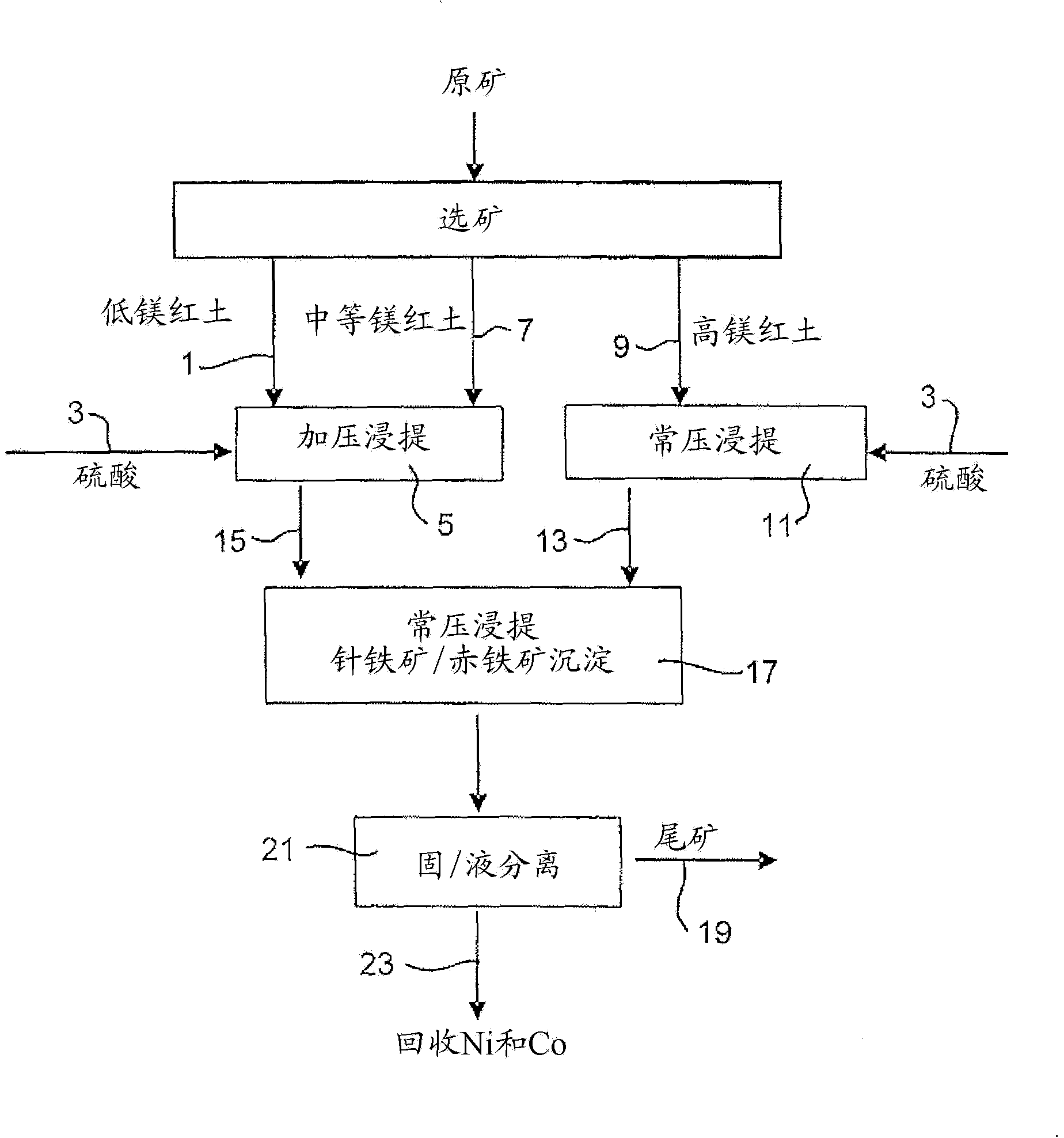
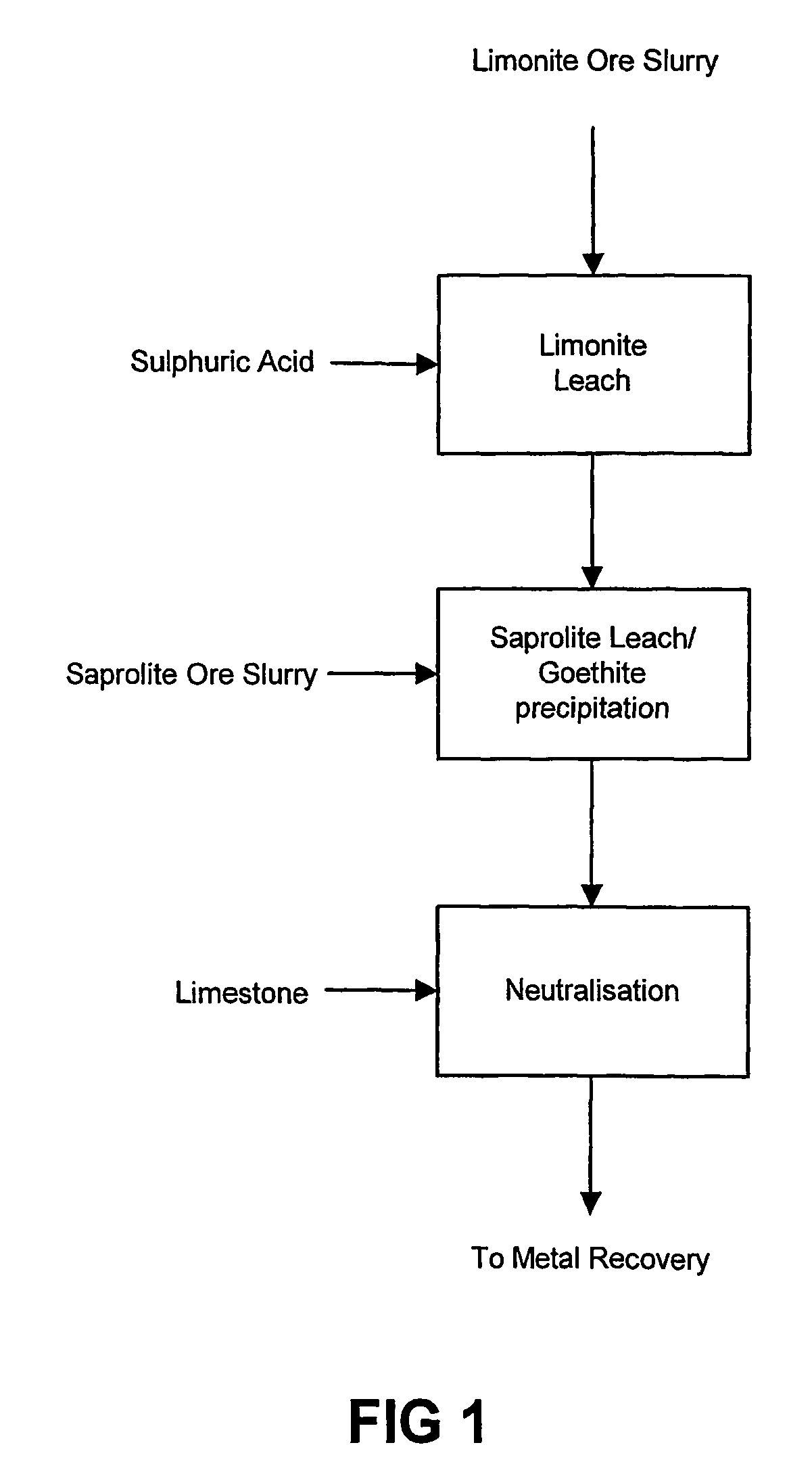
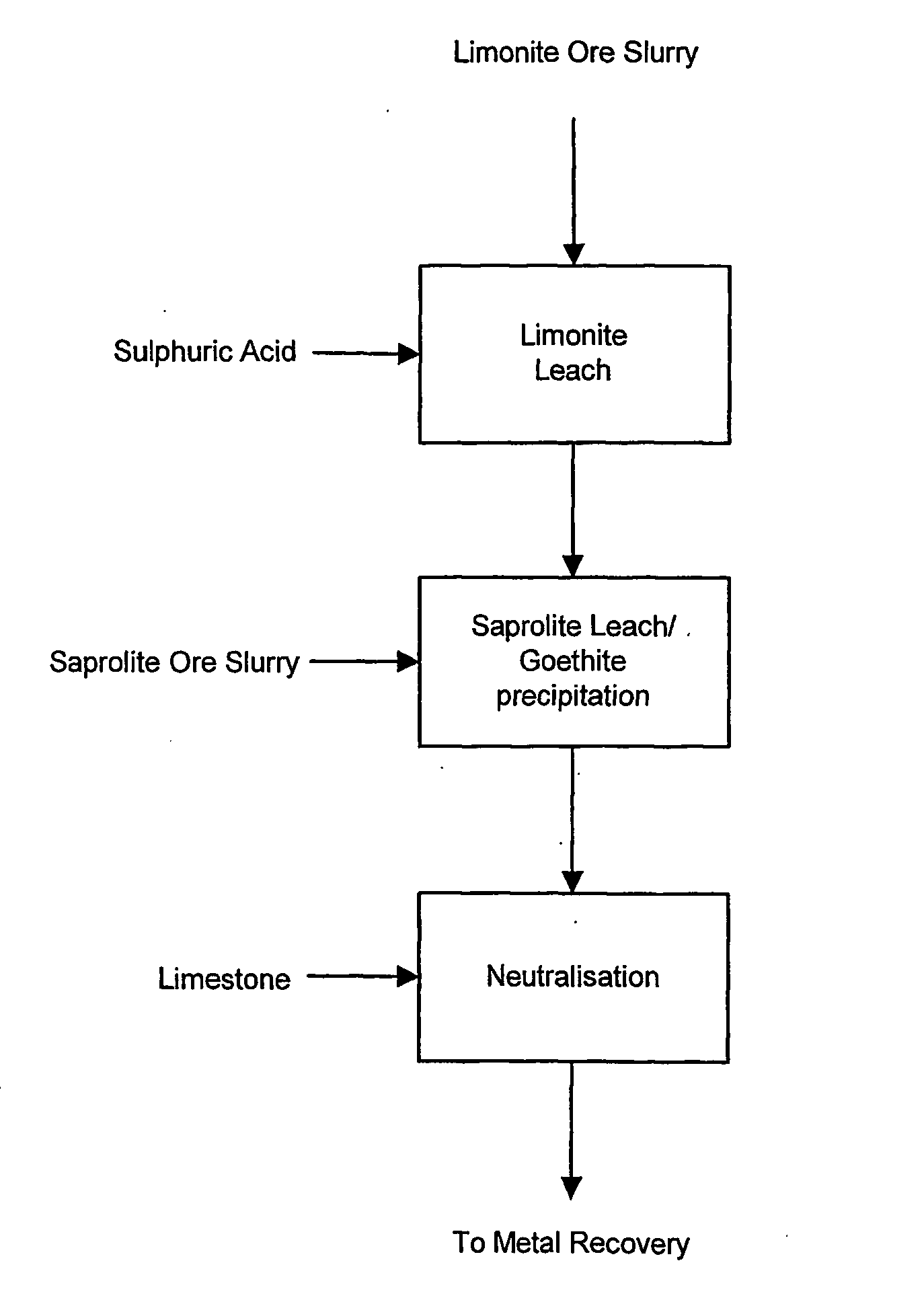
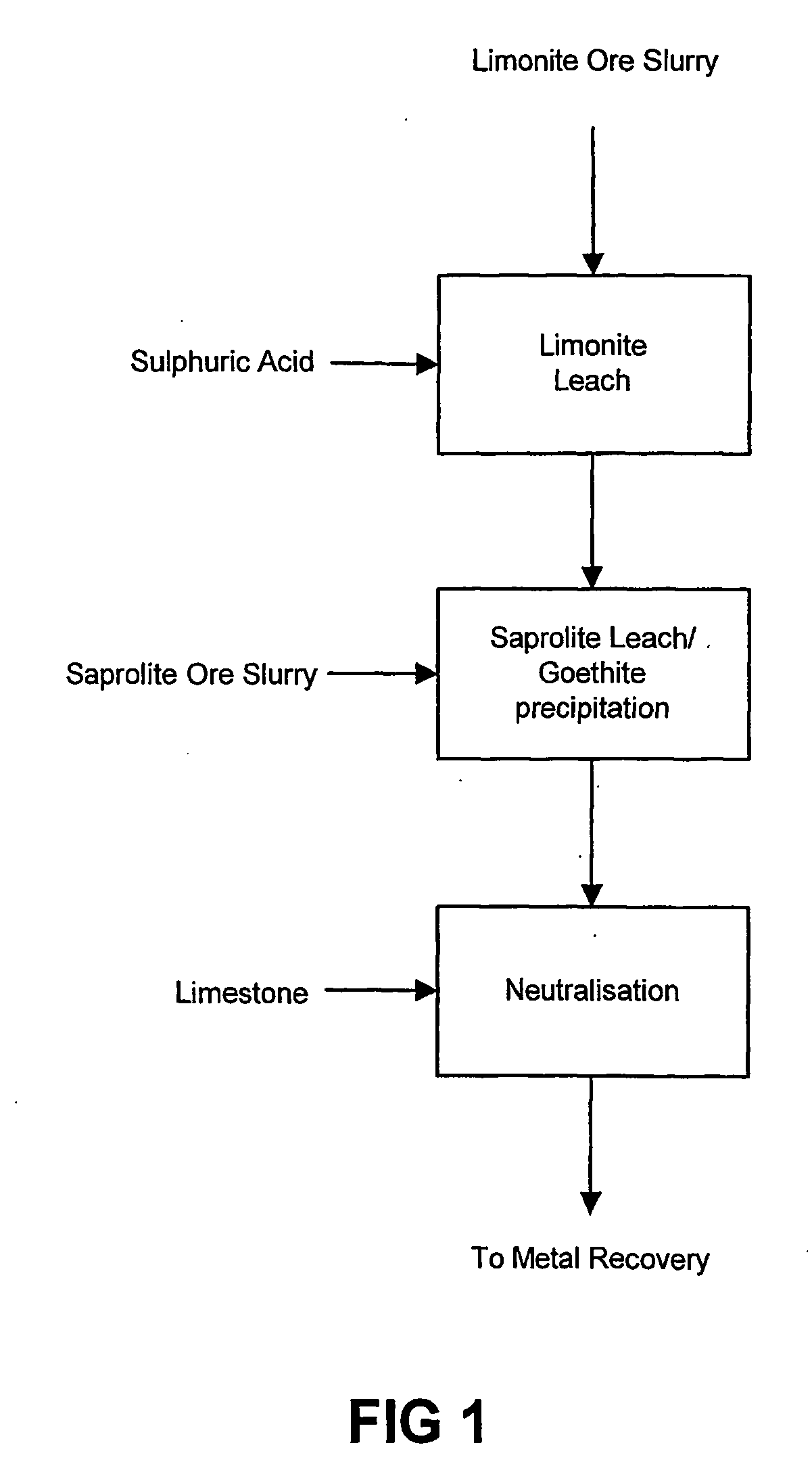
Process for enhanced acid leaching of laterite ores
A process is described for the recovery of nickel and cobalt from a nickeliferous laterite ore including the steps of: a) providing a nickeliferous laterite ore and separating that ore into its low magnesium limonite fraction and high magnesium saprolite fraction; b) treating the limonite fraction in acid solution in a primary high pressure leach step to produce a primary leach slurry; c) adding the saprolite fraction to the primary leach slurry to initiate precipitation of iron as goethite and / or hematite, while simultaneously releasing further acid from the iron precipitation, to effect a secondary atmospheric leach step, producing a secondary leach slurry; wherein all water used to prepare the ore slurries and / or acid solutions has an ionic composition that substantially avoids jarosite formation.
Owner:BHP BILLITON SSM TECH PTY LTD
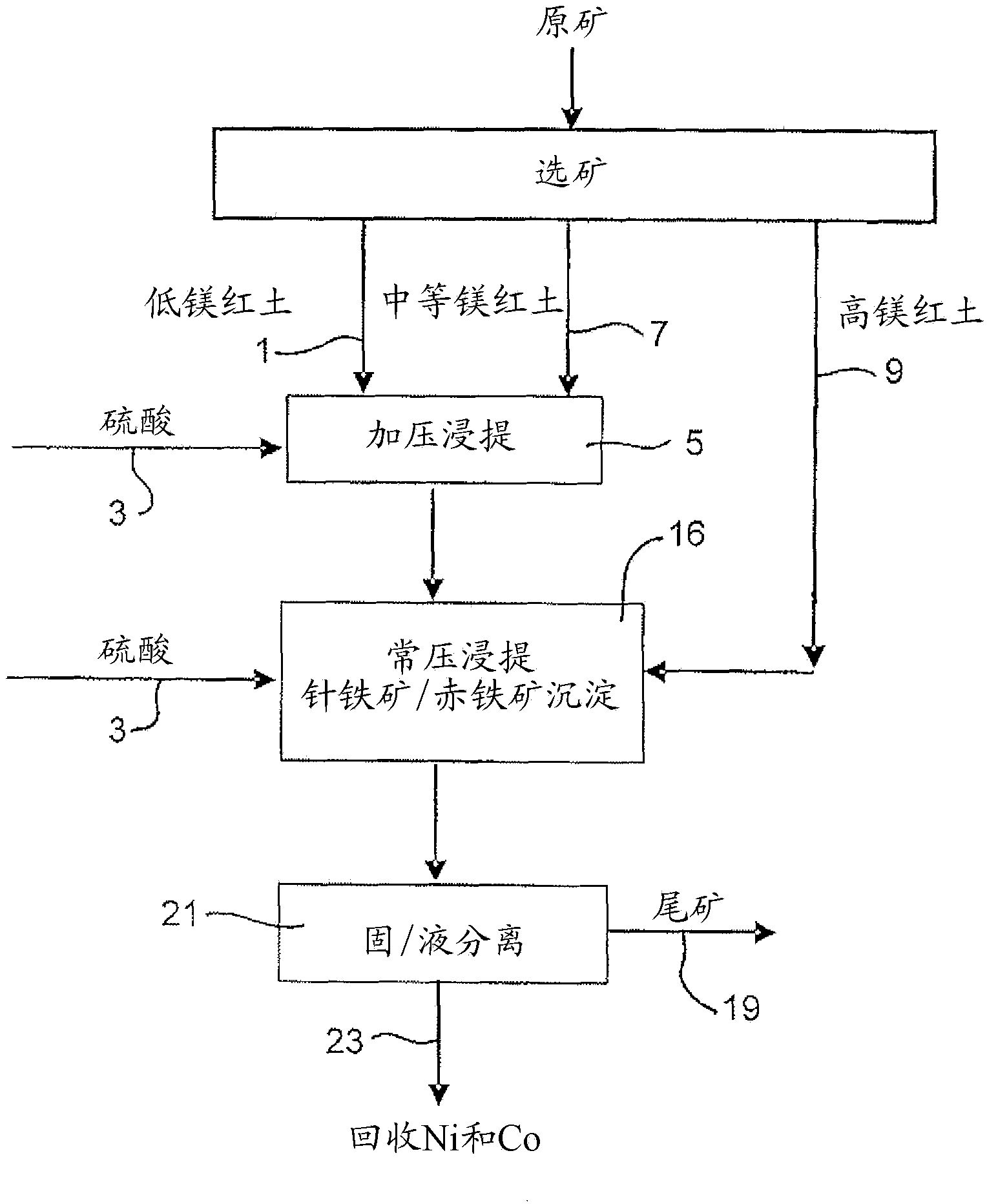
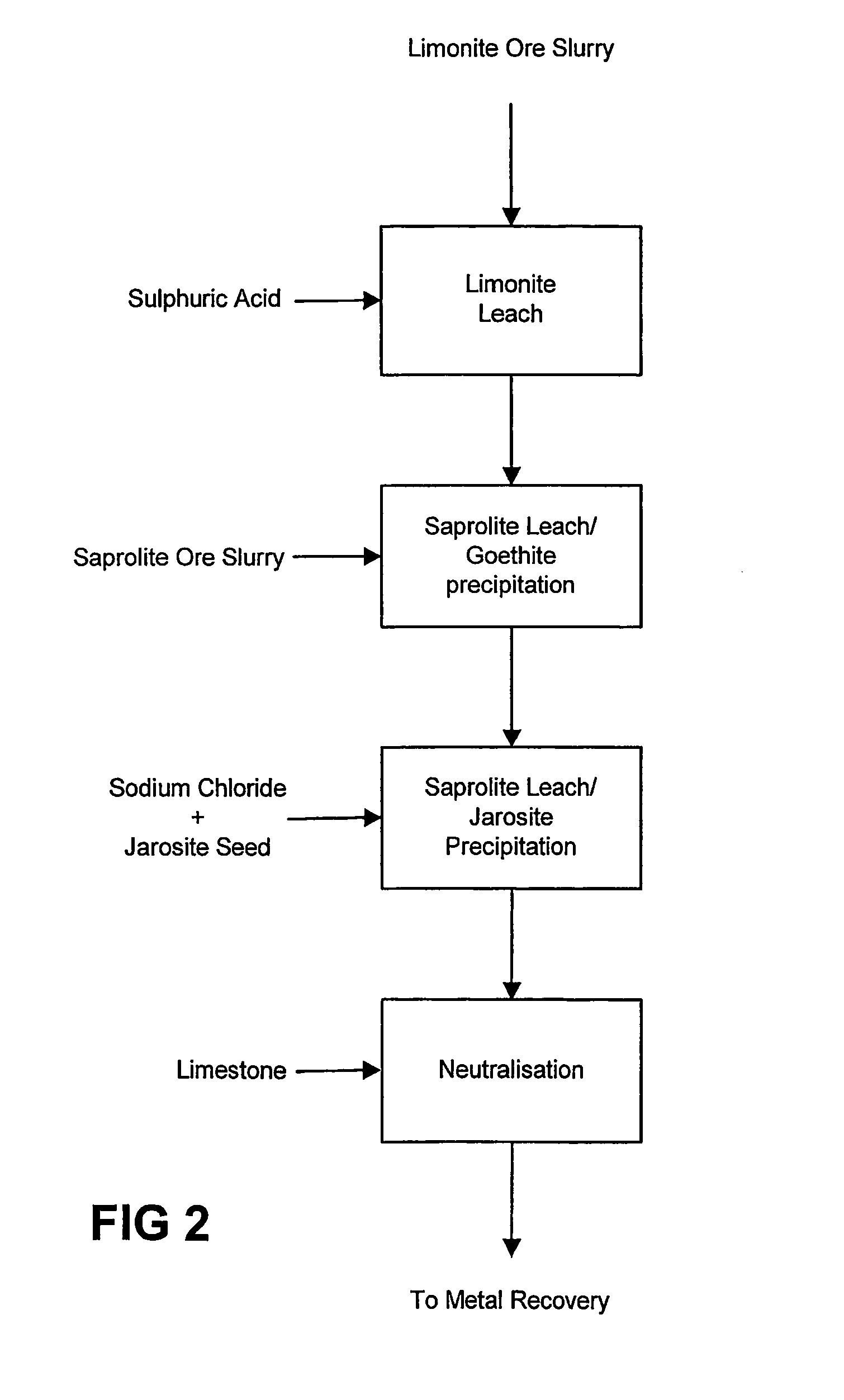
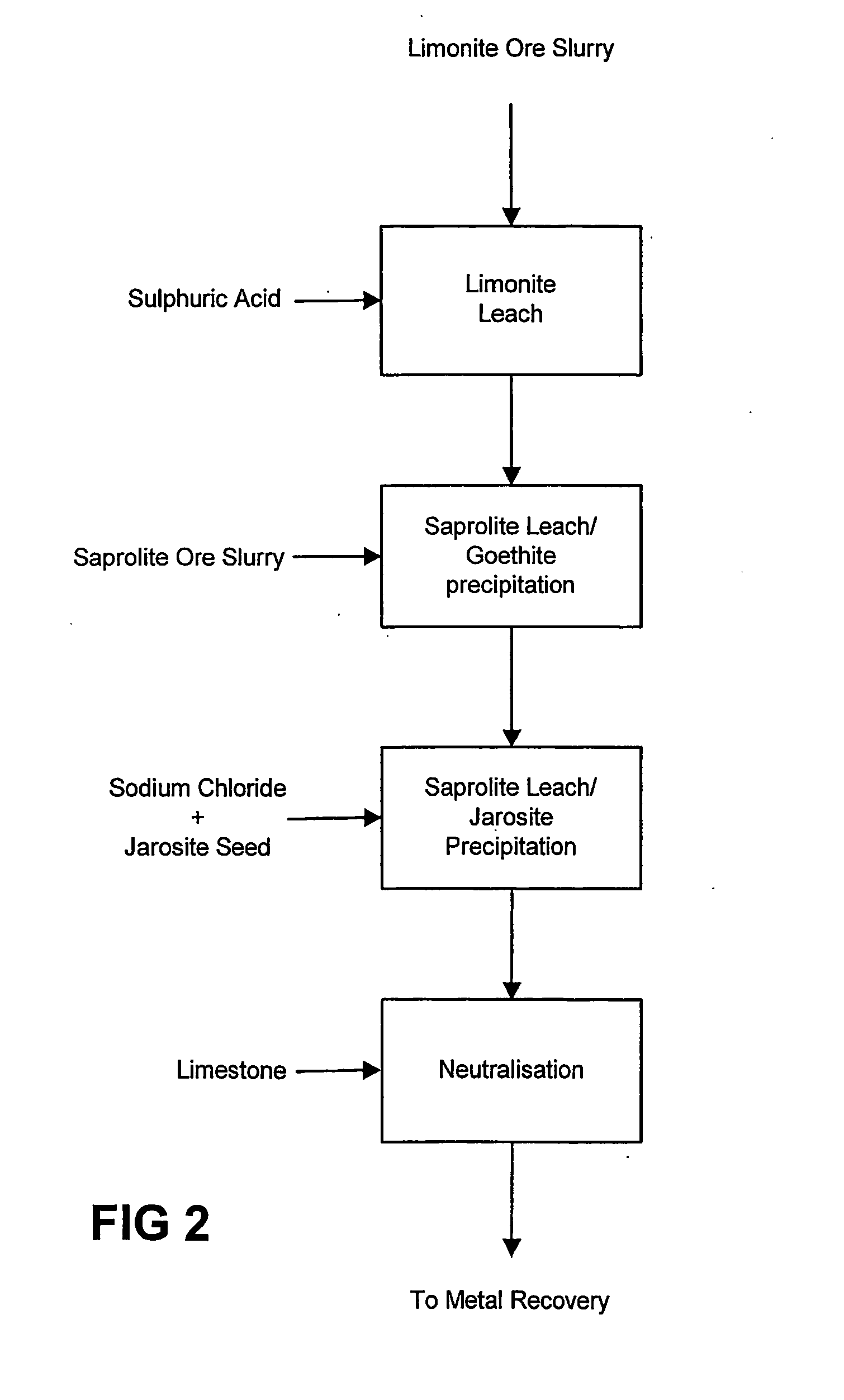
Atmospheric pressure leach process for lateritic nickel ore
An atmospheric leach process in the recovery of nickel and cobalt from lateritic ores, said processing including the steps of: a) separating the lateritic ore into a low magnesium containing ore fraction, and a high magnesium containing ore fraction by selective mining or post mining classification; b) separately slurrying the separated ore fractions; c) leaching the low magnesium containing ore fraction with concentrated sulphuric acid as a primary leach step; and d) introducing the high magnesium content ore slurry following substantial completion of the primary leach step and precipitating iron as goethite or another low sulphate containing form of iron oxide or iron hydroxide, wherein sulphuric acid released during iron precipitation is used to leach the high magnesium ore fraction as a secondary leach step.
Owner:CERRO MATOSO
Method for producing an organic-inorganic hybrid sorbent by impregnating an oxide into nanopores of activated carbone and use thereof in water treatment
ActiveUS20140021139A1Improve adsorption capacityHigh removal rateMolecular sieve catalystsOther chemical processesSorbentMagnetite
This invention relates to a method of manufacturing an organic-inorganic composite hybrid adsorbent by impregnating activated carbon nanopores with an oxide and a water treatment method using the same, and particularly, to an adsorbent including a porous adsorbent and ferrihydrite, goethite, hematite or magnetite incorporated into the porous adsorbent, and a manufacturing method thereof.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
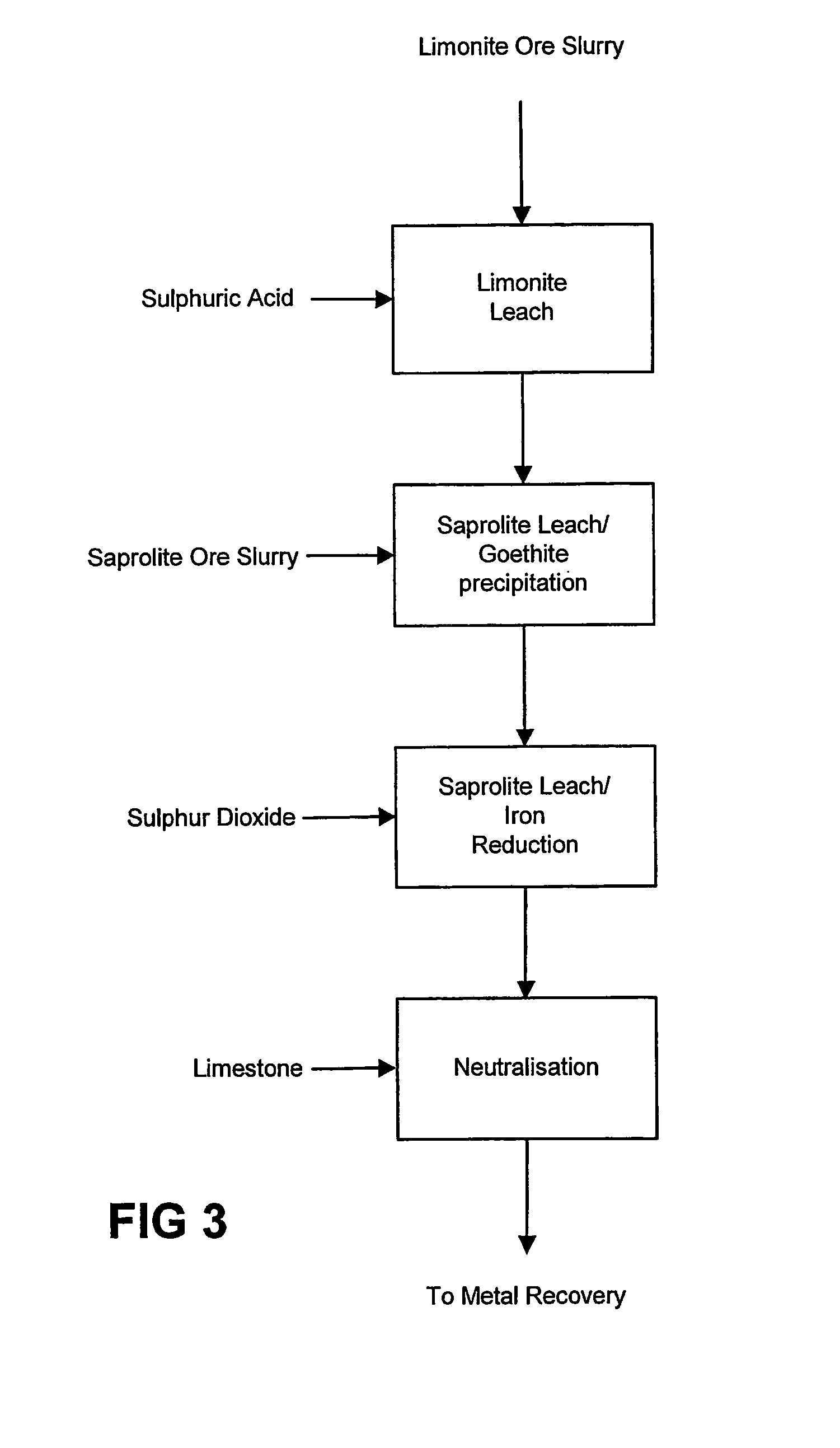
Atmospheric pressure leach process for lateritic nickel ore
An atmospheric leach process in the recovery of nickel and cobalt from lateritic ores, said processing including the steps of: a) separating the lateritic ore into a low magnesium containing ore fraction, and a high magnesium containing ore fraction by selective mining or post mining classification; b) separately slurrying the separated ore fractions; c) leaching the low magnesium containing ore fraction with concentrated sulphuric acid as a primary leach step; and d) introducing the high magnesium content ore slurry following substantial completion of the primary leach step and precipitating iron as goethite or another low sulphate containing form of iron oxide or iron hydroxide, wherein sulphuric acid released during iron precipitation is used to leach the high magnesium ore fraction as a secondary leach step.
Owner:CERRO MATOSO
Phosphorus-removing method based on nano-grade iron
InactiveCN103086460AEasy to disassembleImprove solubilityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionEnvironmental chemistryGoethite
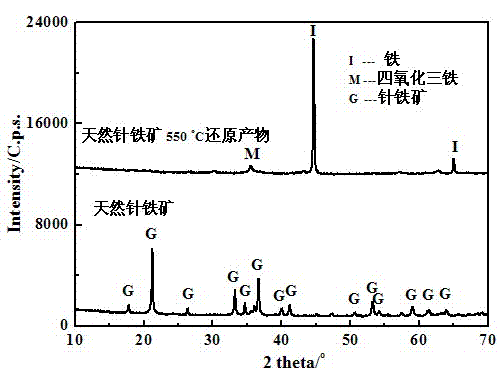
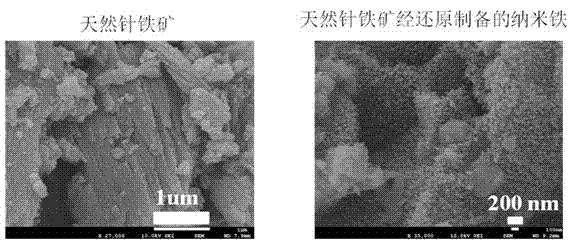
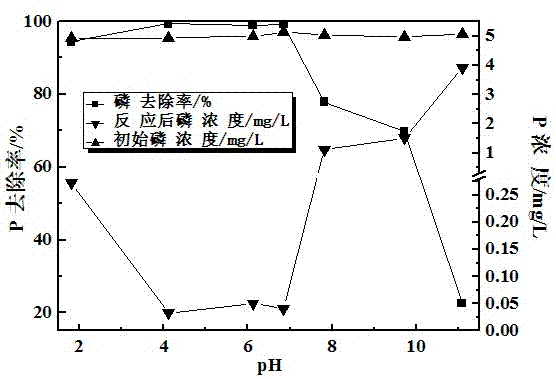
The invention discloses a phosphorus-removing method based on nano-grade iron. The nano-grade iron is prepared by reducing crushed goethite (0.1-5mm) by using hydrogen or carbon monoxide under an environmental temperature of 500-700 DEG C. A phosphorus-removing principle is that: the nano-grade iron obtained by the reduction of goethite releases Fe<3+> under the effects of water and dissolved oxygen; Fe<3+> and PO4<3-> forms FePO4 precipitate; and trace phosphorous in water is removed. With the method provided by the invention, phosphorous-containing wastewater can be effectively purified, and especially a deep phosphorus-removing effect can be provided.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Process for the extractive oxidation of contaminants from raw fuel streams catalyzed by iron oxides
InactiveUS20060131214A1Improve production yieldReduce lossesRefining with metalsRefining with oxygen compoundsOrganic acidHydrogen
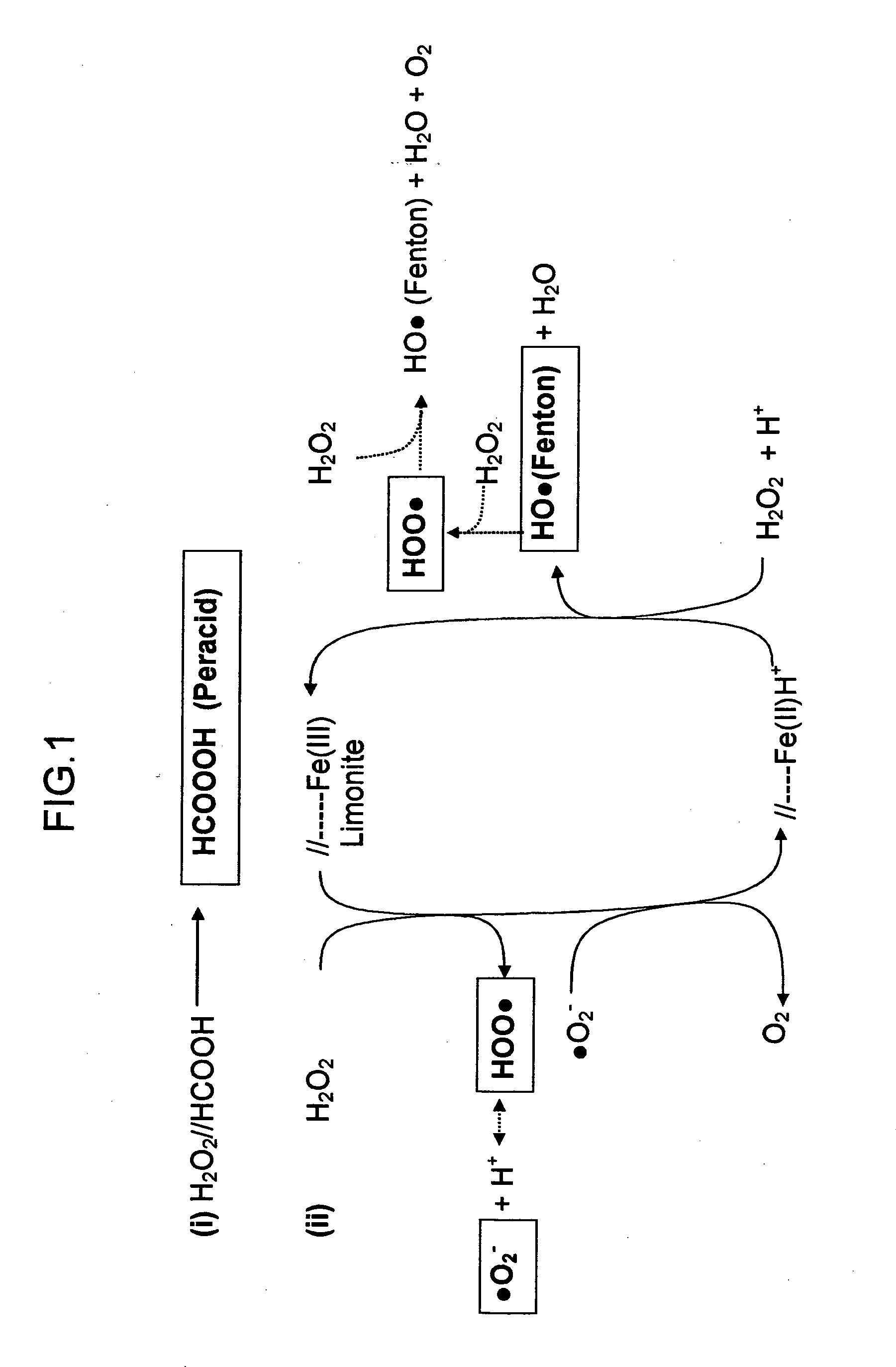
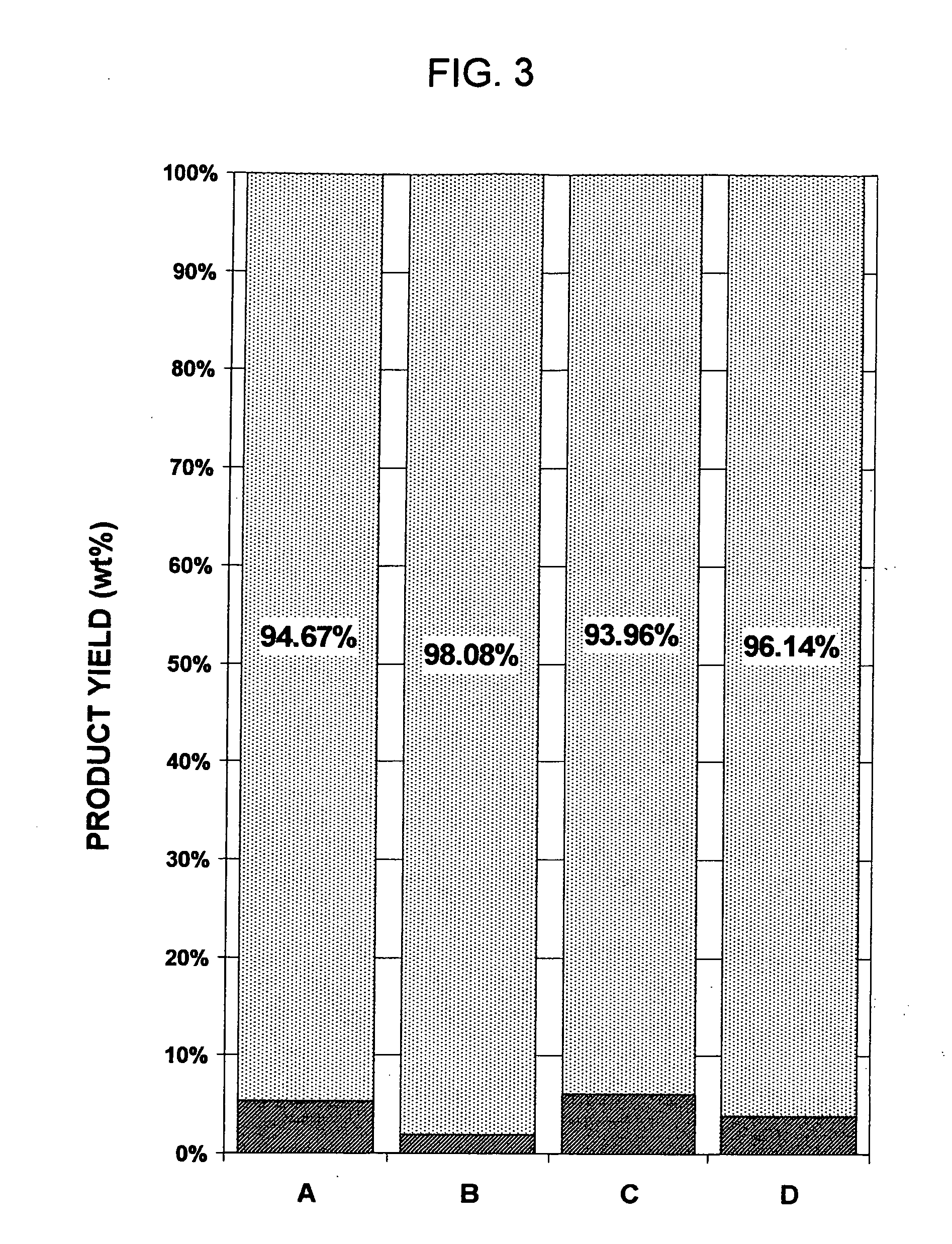
A process is described for the extractive oxidation of contaminants present in raw fuel streams rich in heteroatomic polar compounds and catalyzed by iron oxides contained in natural limonitic goethite, said process comprising contacting said streams with an oxidation pair which is a peroxide in solution / organic acid in amount of at least 3 and an amount between 0.01 and 10 wt % of an iron oxide, both based on the feed, the iron oxide being made up of a reduced natural limonitic goethite. The goethite reduction by a hydrogen stream has the advantage of lowering the migration of non-contaminating polar hydrocarbons from the fuel stream to the aqueous phase, at the same time obtaining higher mass yield of final product fuel while the level of target contaminants to be removed is maintained relative to the state-of-the-art process. Process yields attain 98% weight / weight.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Iron removal process for copper cobalt ore leach liquor
ActiveCN101921914AIncreased Fe contentLow viscosityProcess efficiency improvementSlagMetal impurities
The invention relates to an iron removal process for copper cobalt ore leach liquor, belonging to the cobalt wet smelting industry. At present, the goethite method and the precipitate neutralization iron removal method are combined to remove iron, although the total quantity of iron slag can be reduced, the total quantity of the iron slag is still great because the precipitate neutralization method with high pH value is used for removing iron at a later stage. The process is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, oxidizing the liquor before iron removal to oxidize ferrous iron in the liquor into ferric iron; then, removing most of iron impurities in the oxidized liquor before iron removal by using the goethite method in an iron removal tank, and removing the rest iron and other metal impurities in the liquor by the precipitate neutralization iron removal method; and filter pressing the obtained ore pulp by using a filter press to obtain filter liquor as liquor after iron removal. Under the premise of ensuring the iron removal effect, the iron content in the iron slag is increased by changing the slag form of scrap iron slag, and thus, the total quantity of the iron slag is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUAYOU COBALT
Method for removing trivalent arsenic
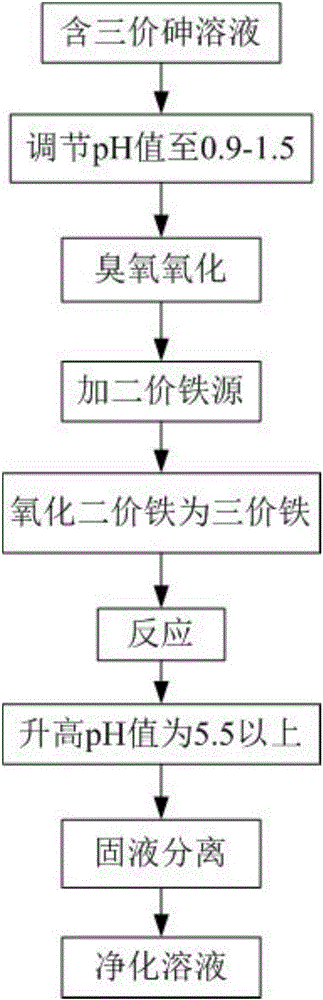
ActiveCN105753218AAvoid removalAvoid formingMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationWastewaterGoethite
The invention provides a method for removing trivalent arsenic, comprising the following steps: (1), oxidizing trivalent arsenic in an arsenic solution into pentavalent arsenic at pH of 0.9-1.5 by using ozone to obtain pentavalent arsenic solution; (2), adding a soluble divalent iron source into the pentavalent arsenic solution, oxidizing divalent iron at a temperature higher than 70 DEG C at pH less than 1.5 into trivalent iron, and reacting the pentavalent arsenic with trivalent iron to obtain a solution containing scorodite crystal precipitate, goethite precipitate and divalent iron; (3), adjusting pH of the solution obtained in step (2), oxidizing the divalent iron in the solution to form iron peroxide gel, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a purified solution.The method enables low-concentration arsenic in waste water to be removed, arsenic content of the purified solution is lower than 0.05 mg / L, the precipitates generated in the arsenic removal process are easy to remove, and the method is simple to perform and is widely applicable to purifying waste water containing low-concentration arsenic.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for simplifying zinc hydrometallurgy process
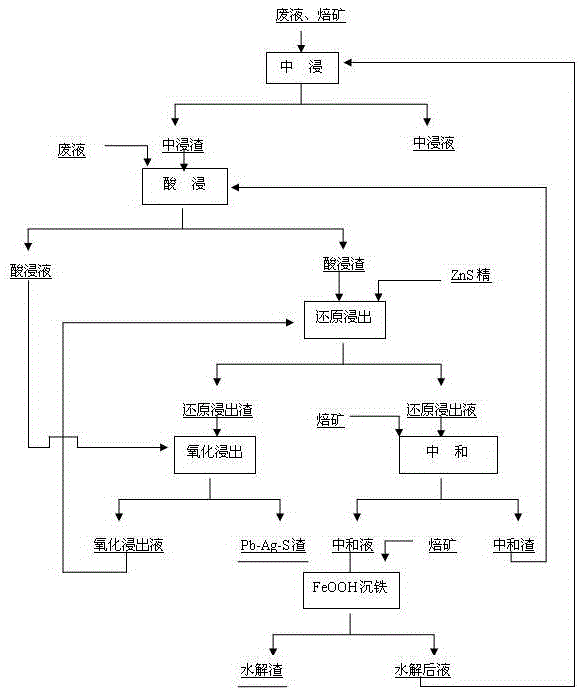
ActiveCN105525093AImprove leaching rateReduce processing costsProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteHydrometallurgy
The invention discloses a method for simplifying a zinc hydrometallurgy process. The method includes the steps that firstly, neutral leaching is conducted on zinc roasted ore so as to obtain neutral leaching liquid and neutral leaching residues; secondly, the neutral leaching residues obtained in the first step are added into acid-containing waste liquid, hot acid leaching is conducted, and acid leaching liquid and acid leaching residues are obtained; thirdly, the acid leaching residues obtained in the second step and ZnS concentrate are added into acid-containing waste liquid, reduction leaching is conducted, and liquid after reduction and reduction residues are obtained; fourthly, zinc roasted ore serving as a neutralizer is added into the liquid after reduction obtained in the third step, neutralizing residues and neutralizing liquid are obtained, and the neutralizing residues are returned to the second step to be subjected to hot acid leaching; fifthly, the reduction residues obtained in the third step are added into the acid leaching liquid obtained in the second step, oxidizing leaching is conducted, oxidizing leaching liquid and lead-silver-sulfide residues are obtained, and the oxidizing leaching liquid is returned to the third step to be subjected to reduction leaching; and sixthly, the neutralizing liquid obtained in the fourth step is added into the zinc roasted ore, iron precipitation with goethite is conducted, and liquid after iron precipitation and goethite residues are obtained.
Owner:云南云铜锌业股份有限公司
Method for recovering copper, zinc and iron from sulphide ore calcine pickle liquor containing gold and silver
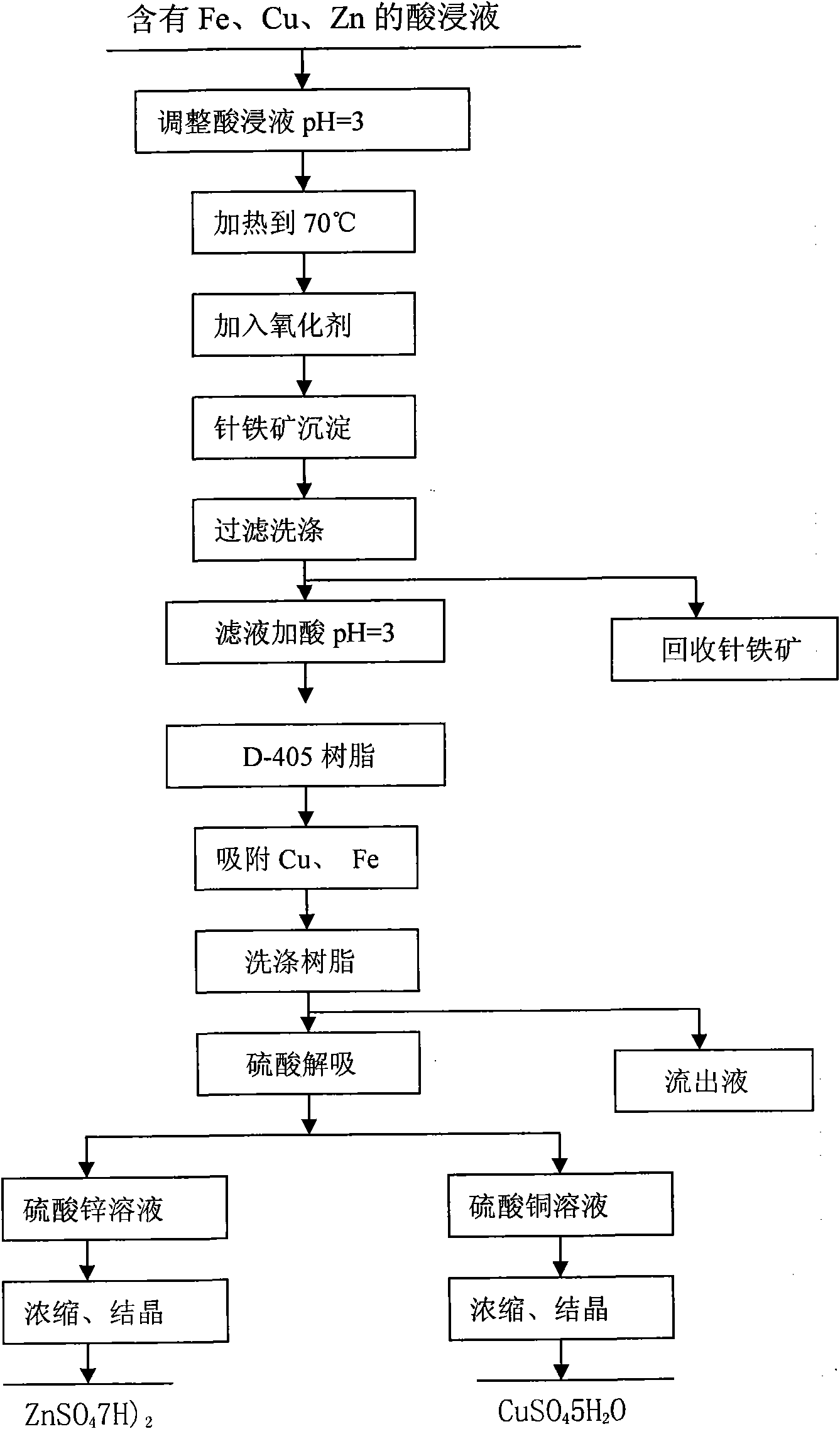
InactiveCN101857923AReduce pollutionReduce recycling costsIron oxides/hydroxidesProcess efficiency improvementSulfateGoethite
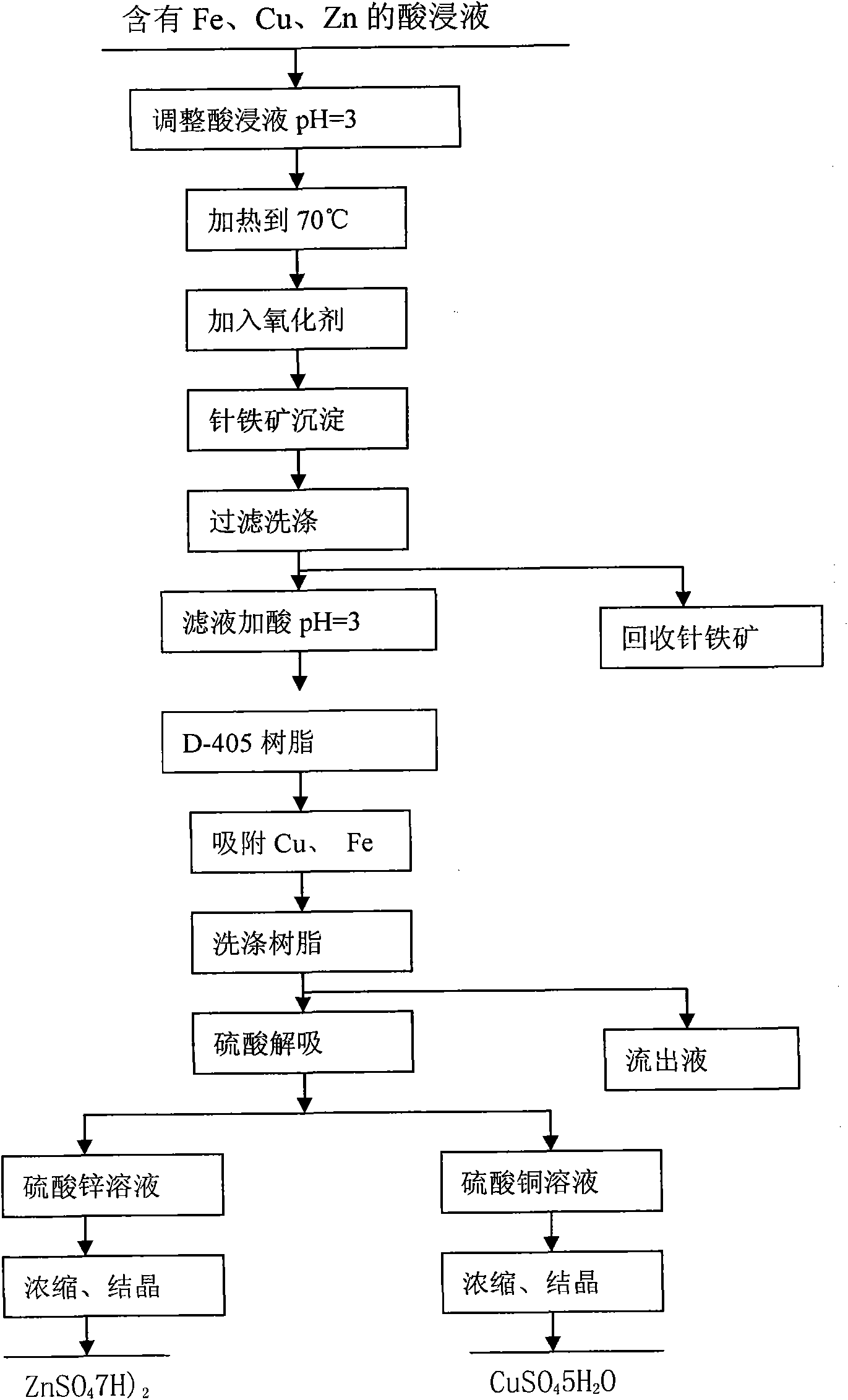
The invention relates to a method for recovering Cu, Zn and Fe from sulphide ore calcine pickle liquor containing Au and Ag. The method comprises the following steps of: adding sulfuric acid to pickle liquor containing Fe, Cu and Zn to regulate the pH value; adding an oxidant in the presence of stirring to ensure that Fe in the solution forms into a goethite precipitate; filtering and washing to recover the goethite and then regulating the pH value; adsorbing Cu and Zn through a resin column; washing off impurities by using water and desorbing Cu and Zn by using a sulfuric acid solution; and heating, evaporating, concentrating and crystallizing a desorbed copper sulfate solution or a zinc sulfate solution to obtain copper sulfate or zinc sulfate. In the method, Fe, Cu and Zn contained in the sulphide ore calcine pickle liquor are comprehensively recovered by adopting a resin method, and the recovery rate of the Fe, Cu or Zn reaches higher than 95 percent. The method has low recovery cost, simple process and small pollution.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Stabilization of Arsenic-Containing Wastes Generated During Treatment of Sulfide Ores
InactiveUS20120164041A1Safe disposalEffective pressureArsenites/arsenatesAntimony compoundsChemical reactionIodide
A method is provided for the efficient stabilization, removal and disposal of arsenic-containing wastes generated in metal recovery processes that employ roasting techniques and the like. The conversion of the mostly trivalent arsenite compounds in the wastes to mostly pentavalent solid arsenate precipitates is accomplished by mixing the wastes with water and a ground iron-containing mineral, such as goethite, to form an aqueous slurry of wastes and ground iron-containing mineral, acidifying the slurry to a pH of less than about 1.0, treating the acidified slurry with oxygen gas in a pressurized vessel at a temperature higher than about 120° C. and providing an oxidation catalyst comprised of a water-soluble nitrate and a water-soluble iodide. The overall efficiency of the controlling chemical reactions is improved by the addition and use of the catalyst. The resulting solid arsenate precipitates, in the form of scorodite, are ideally suited for safe disposal with minimum or no further treatment. Unconverted soluble trivalent arsenic compounds remaining in solution may be converted and precipitated as additional scorodite by mixing and agitating the slurry with soluble iron salts under controlled conditions. The resulting precipitates meet or exceed environmental requirements for impoundment and safe disposal.
Owner:ALTYNALMAS GOLD A CANADA CORP
Process for the manufacture of bio-release iron-manganese fertilizer
InactiveUS7691171B2Improve usabilityBetter bio availabilitySuperphosphatesPhosphatesPyrolusiteWater insoluble
This invention provides a process for the preparation of water insoluble, bio-release iron-manganese fertilizer which comprises, heating phosphoric acid with a mixture of (i) source of iron oxide such as goethite and hematite, (ii) pyrolusite and (iii) one or more basic compound(s) selected from oxide(s) or carbonate(s) of magnesium, calcium, sodium and potassium, (b) neutralisation followed by drying and pulverisation.
Owner:AGTEC INNOVATIONS
Comprehensive recovery process of low-grade matte slag metal resources
ActiveCN105695745AReduce subsequent leaching treatment ore volumeReduce manufacturing costPhotography auxillary processesSulfur preparation/purificationSlagManganese
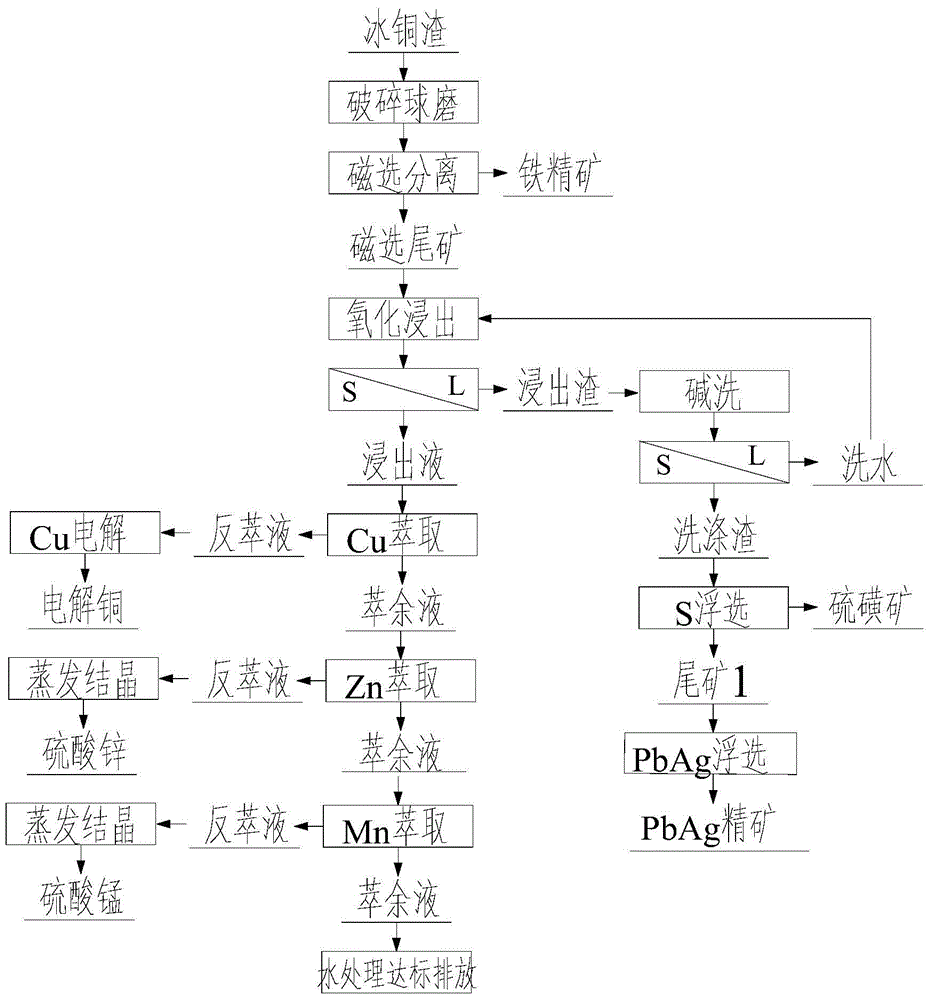
The invention discloses a comprehensive recovery process of low-grade matte slag metal resources. The process comprises the following steps: 1) matte slag performs the crushing and the wet ball milling to reach 100% of particle sizes less than 0.074 mm, and is magnetically separated by a permanent magnetic separator; and magnetically separated tailing is dehydrated for metal leaching and extraction; 2) the magnetically separated tailing performs the oxide leaching to comprehensively leach and extract valuable metal; leaching liquid is extracted to recover Cu; and strip liquor passes through electrodeposition cathode copper plate; 3) copper raffinate removes iron by using a goethite method; after Fe is removed, supernatant is extracted to recover Zn, and the strip liquor is concentrated and crystallized to prepare zinc sulfate; the obtained raffinate is extracted to recover manganese; and the strip liquor is concentrated and crystallized to prepare manganese sulfate; 4) after the raffinate is absorbed by activated carbon to reduce COD, heavy metal is treated by sulfide precipitation; and 5) after leaching slag performs the alkali washing, elemental sulfur and a lead-silver sulfide ore are recovered by flotation. The process solves the difficulty of incomplete recycling of low-grade matte slag, realizes comprehensive recovery of low-grade matte slag resources, and is higher in environmental benefit and economic benefit.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ZHONGKE ZHENGCHUAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
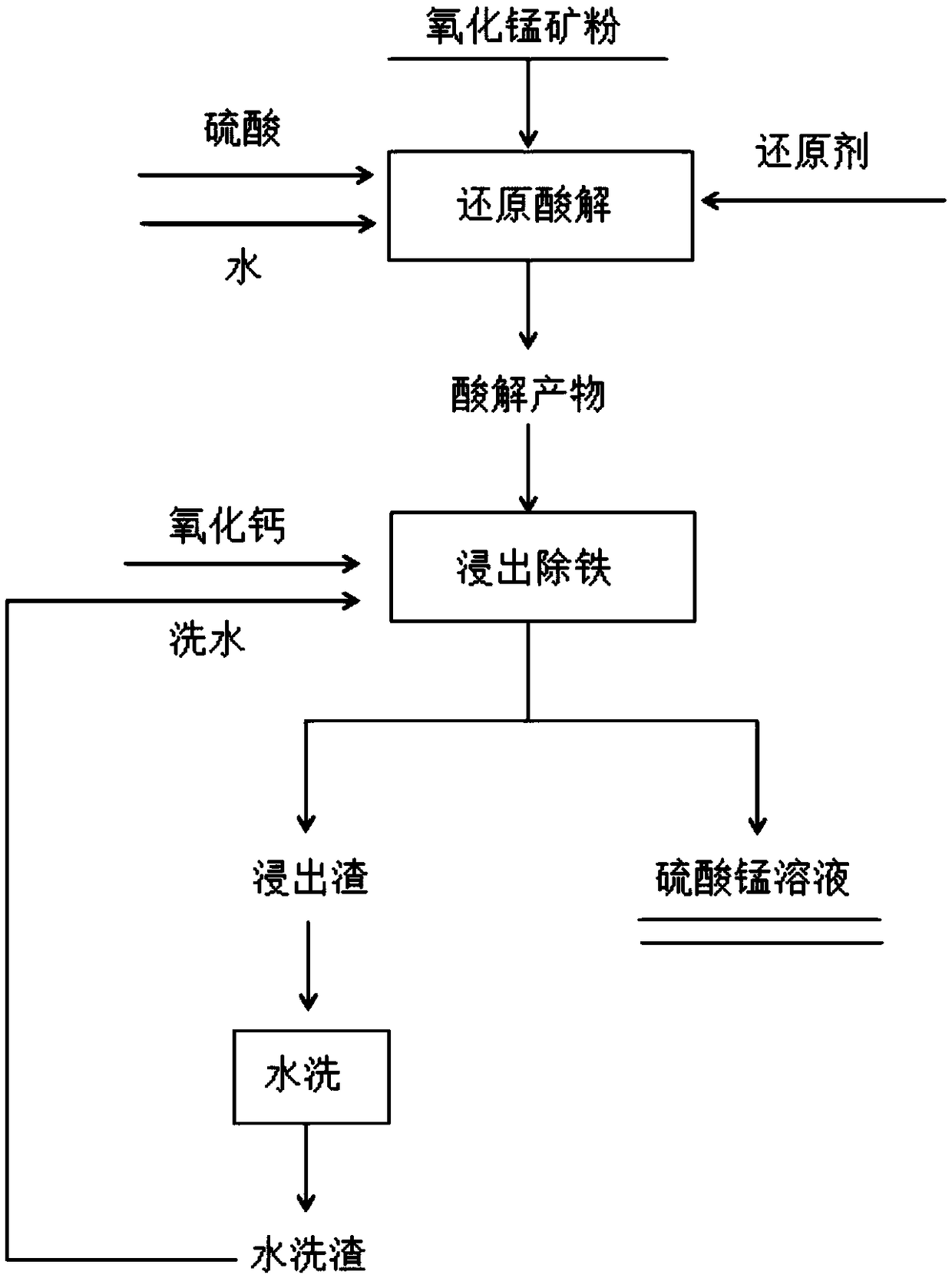
Method for carrying out reduction acidolysis-leaching and simultaneously removing iron to treat oxidized manganese ore
The invention belongs to the technical field of manganese metallurgy and discloses a method for carrying out reduction acidolysis-leaching and simultaneously removing iron to treat oxidized manganeseore. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out reduction acidolysis and leaching, and simultaneously removing the iron. According to the method, biomass waste such as wood dust, straw and the like is used as a reducing agent, so that the environment pollution is reduced, the waste is turned into wealth, and the production cost is reduced. By adopting reduction acidolysis technology,the biomass structure is destroyed by using concentrated sulfuric acid, so that cellulose, hemicelluloses and other substances are hydrolyzed into micromolecular reducing sugar and are used for reducing manganese ore. No heating is needed in the aging process, and the energy consumption is not increased. After aging, the high-valence manganese oxide is reduced to manganese sulfate and can be directly dissolved in water. When the acid solution is leached, the iron ore method is adopted to remove the iron, so that manganese is fed into the solution in the form of manganese sulfate, and the ironis precipitated out by using a goethite-shaped precipitate. The leaching and iron removal are combined together, so that the process flow can be shortened, the operation can be simplified, and the problems that the existing biomass is high in leaching temperature, long in time and the like when the manganese oxide ores are directly leached from the existing biomass are solved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
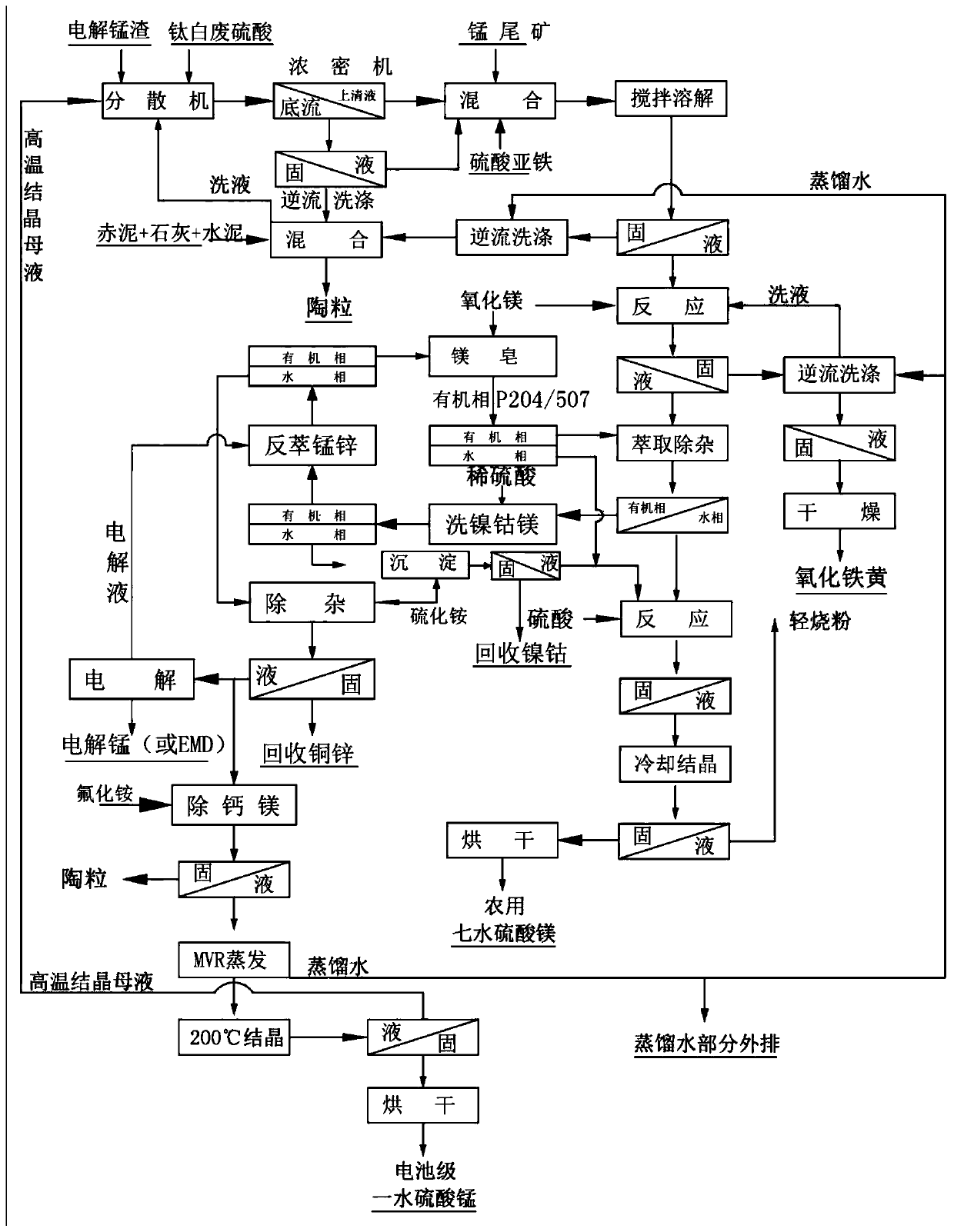
Process for comprehensively recycling electrolytic manganese residues and manganese tailings
InactiveCN110157911ASolve pollutionAddressing Purity IssuesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisManganese
The invention discloses a process for comprehensively recycling electrolytic manganese residues and manganese tailings. The process for comprehensively recycling the electrolytic manganese residues and the manganese tailings specifically comprises the following steps that liquid-phase crushing is performed on the electrolytic manganese residues by adopting a dispersion machine so as to obtain leached residues and leachate; a qualified de-ironed precursor solution without solid particles is obtained through filter pressing, and hydration pulping is performed on the magnesium oxide through the dispersion machine. The process for comprehensively recycling the electrolytic manganese residues and the manganese tailings has the advantages that as long as the manganese content of the electrolyticmanganese residues and the manganese tailings is greater than 1%, the manganese can be enriched and recovered, so that a new profitable industrial way is developed for resource comprehensive recoveryof the manganese tailings, the problems that when electrolytic manganese is produced through a traditional process, pollution is caused due to the fact that sodium jarosite and goethite which are generated through purification iron removal cannot be recovered, the purity of the electrolytic manganese is low due to the fact that the leaching solution is not purely purified and the like are solved,and the process is simple, stable and strong in operability.
Owner:张响 +2
Method for treating nickel-containing laterite by microwave reducing roasting-goethite precipitation conversion method
InactiveCN101392320AFast heatingImprove energy efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementSlurryHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for processing laterite comprising nickel by means of microwave reduction roasting-goethite deposit transformation, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: (1) a carbonaceous reducing agent is added into the laterite, and heated for 5min to 20min under microwave radiation after even blending so as to obtain laterite calcine; and (2) the laterite calcine is blended into slurry and leached, the concentration of the mine slurry is 10wt percent to 30wt percent, the leaching temperature is 80 DEG C to 120 DEG C, the duration for leaching is 2h to 5h, and nickel cobalt in the laterite enters the leached liquid, with iron transformed to goethite deposit. The method consumes less acid which is equal to that of the high-pressure acid leaching method, but the operation temperature and pressure at the leaching stage are greatly lowered by reduction roasting, which is favorable to the decrease in manufacturing cost of leaching equipment.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
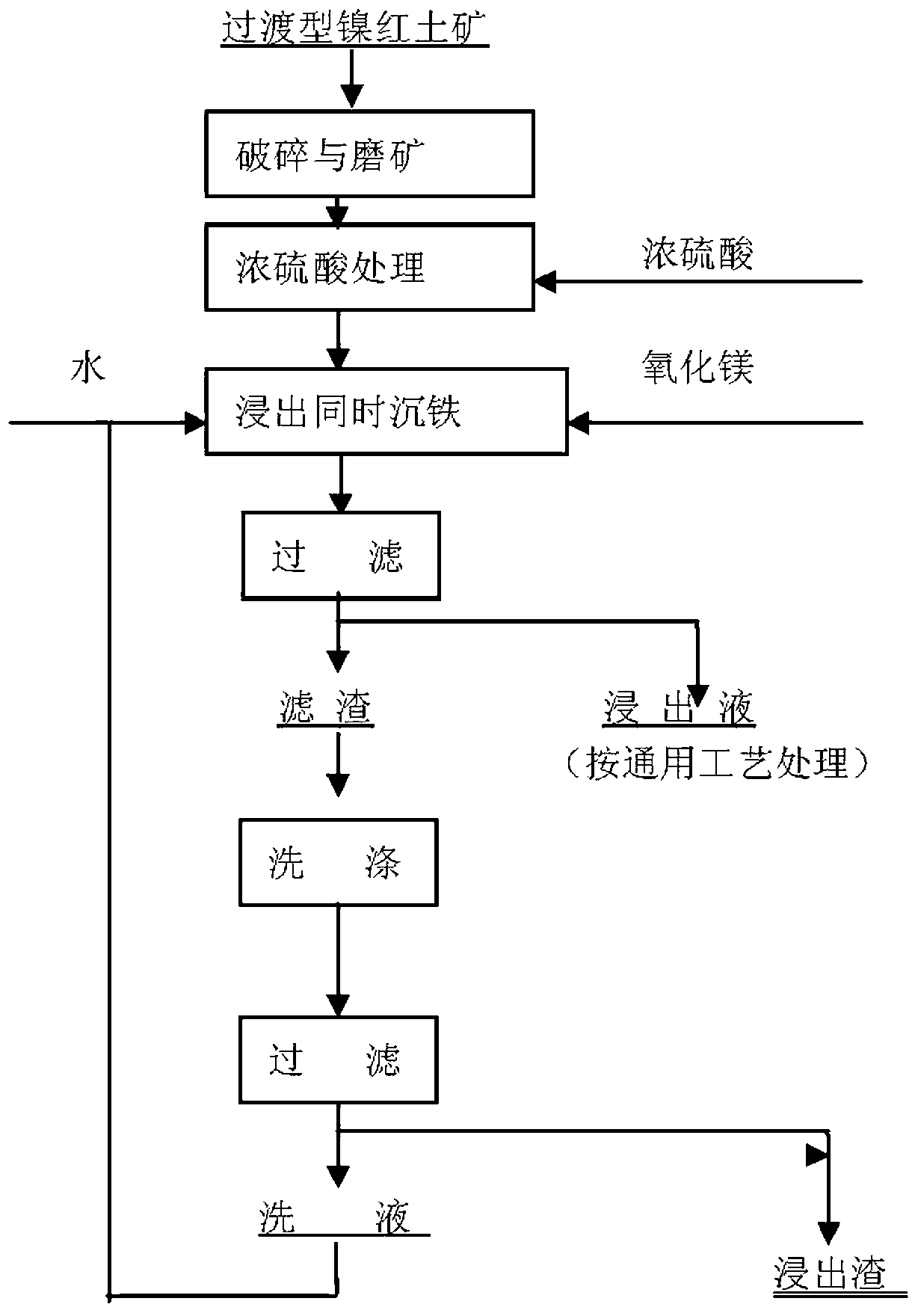
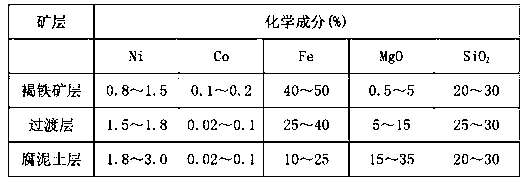
Method for treating normal pressure leaching of transitional nickel laterite ore
A method for treating normal pressure leaching of transitional nickel laterite ore is characterized by comprising two steps which can simultaneously conduct pretreatment and leaching of the nickel laterite ore. The two steps are as follows: (1) pretreatment of the nickel laterite ore and ore grinding: breaking the nickel laterite ore and grinding the ore, adjusting the moisture content, adding concentrated sulfuric acid, and placing the mixed nickel laterite ore for spare after fully being fully stirred; and (2) leaching and deironing: blending magnesium oxide after smashing the block-shaped pretreated materials, adding the blended materials into aqueous solution after being fully and uniformly mixed, conducting the process of Ni-Co leaching and deironing simultaneously, maintaining the liquid-solid ratio, the solution temperature and the solution of the potential hydrogen (pH) value, and conducting liquid-solid separation after being stirred. The normal pressure leaching technology treats the nickel laterite ore which contains 0.8-1.5% of nickel, the leaching rate of nickel can reach above 85%, the leaching rate of cobalt is above 70%, and the liquid-solid separation is easy to carry out. The main phase composition of the leached sunk iron slag after washing is goethite (FeOOH), MgSiO3 and SiO2, no harmful ingredients are contained, and the sunken iron slug can be piled or reutilized.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF NONFERROUS METALS
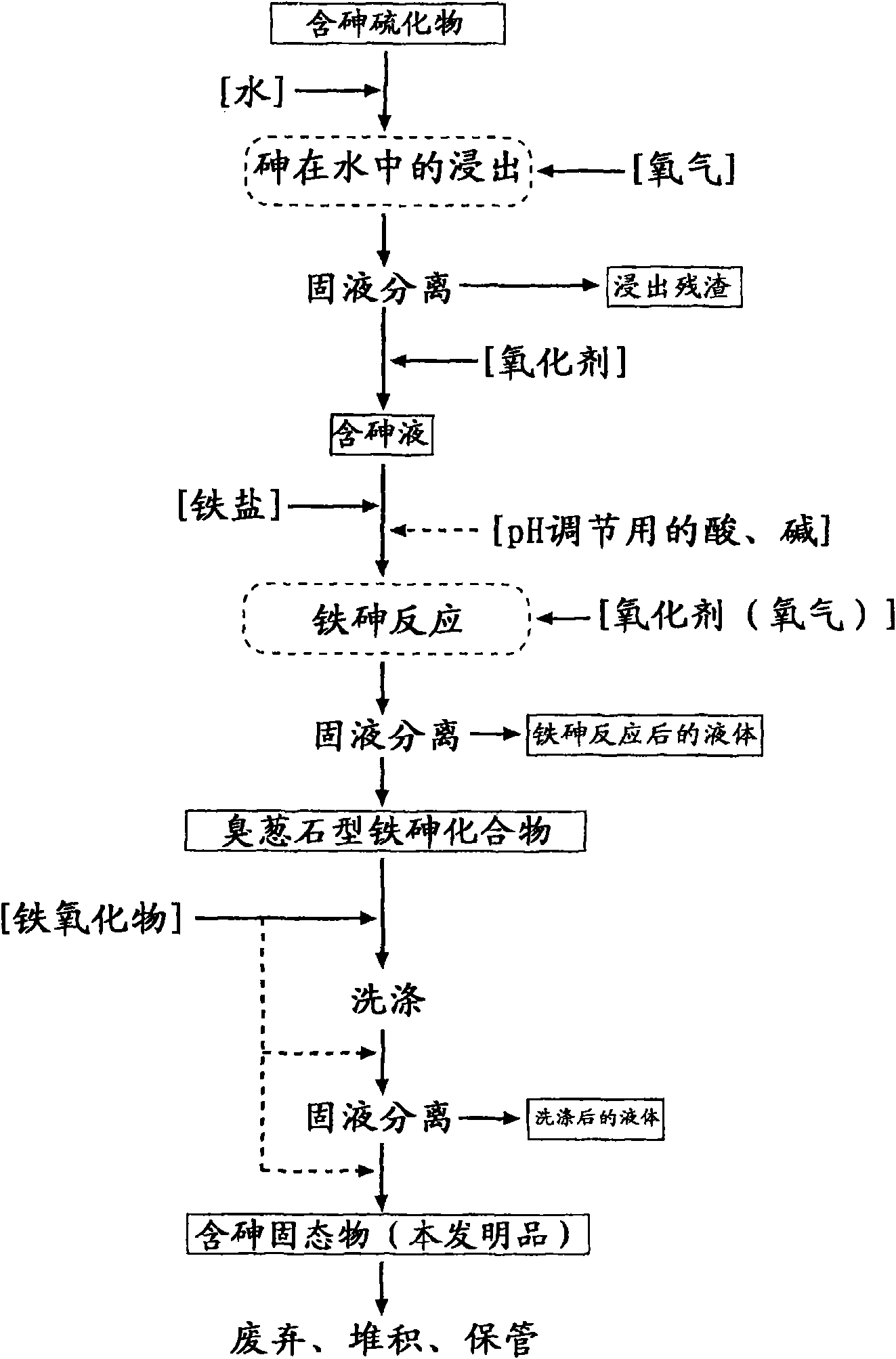
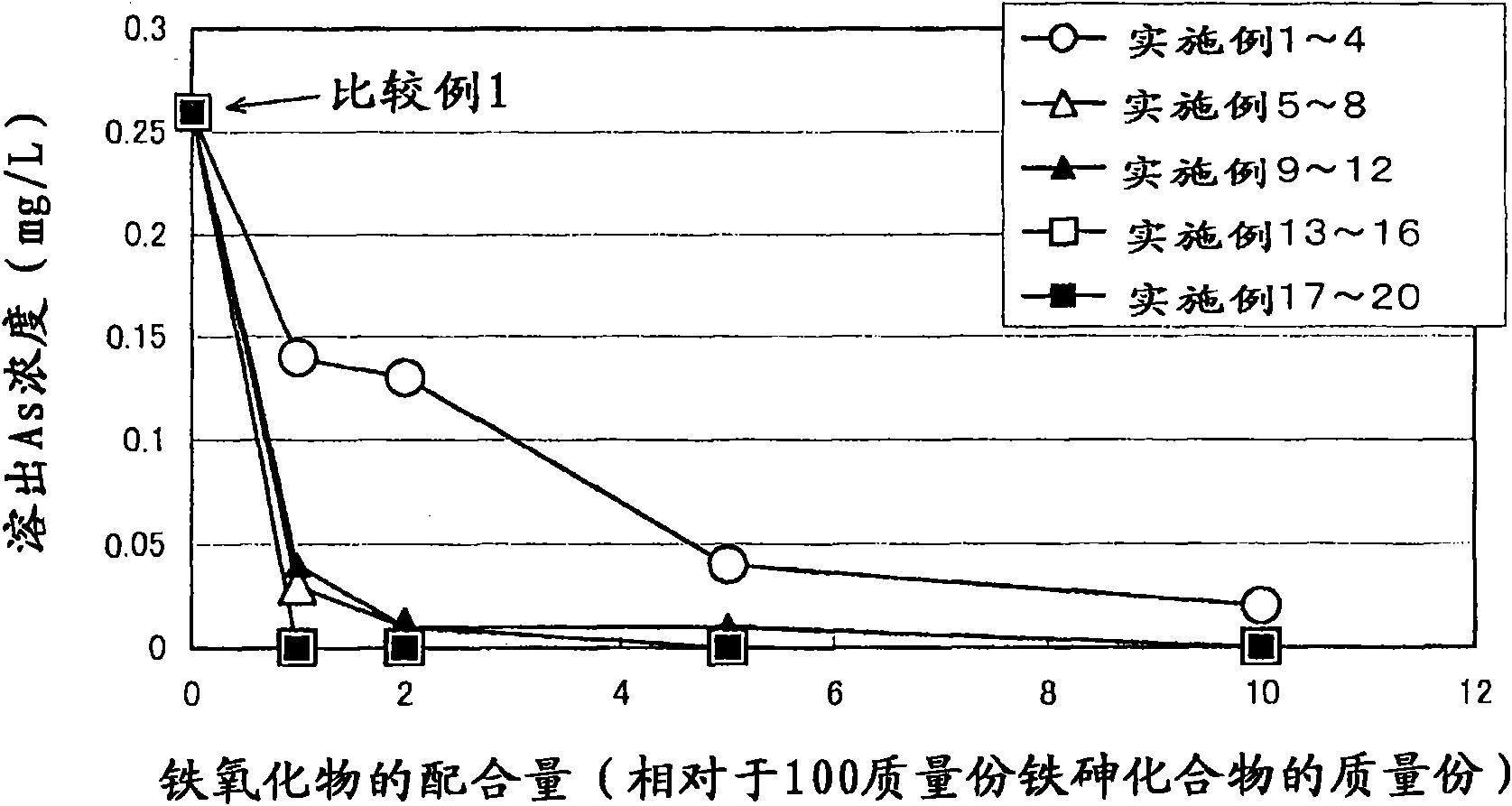
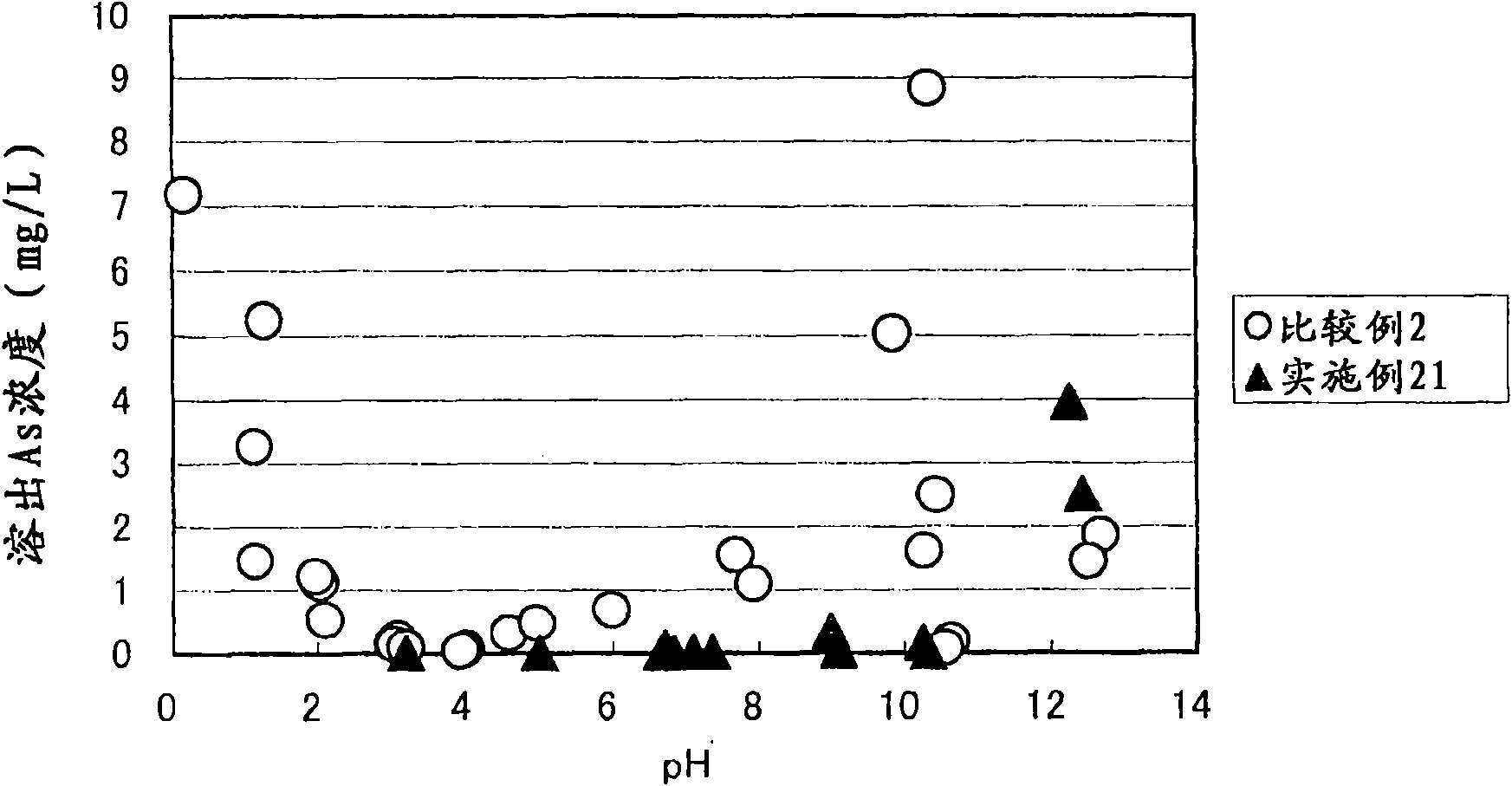
Arsenic-containing solid material and method for production thereof
InactiveCN101636352AStable and excellent dissolution prevention effectShort reaction timeArsenites/arsenatesSolution crystallizationGoethiteAqueous solution
The invention provides an arsenic-containing solid material comprising 100 parts by mass of a scorodite-type iron-arsenic compound and 1 part by mass or more of an iron oxidation compound, wherein the scorodite-type iron-arsenic compound is synthesized by adding an oxidizing agent to an acidic aqueous solution containing a pentavalent arsenic ion and a bivalent arsenic ion to cause the precipitation of the iron-arsenic compound to proceed while agitating the solution, and terminating the precipitation at a pH value of 1.2 or lower. The iron oxidation compound may be goethite, hematite, or a mixture thereof. It is preferred to use an iron oxidation compound having a BET specific surface area of 3 m<2> / g or more, preferably 20 m<2> / g or more.
Owner:DOWA METALS & MINING CO LTD
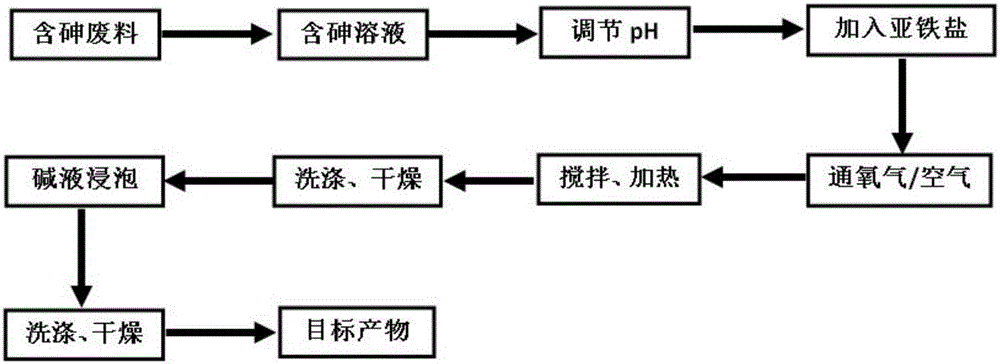
Method for fixing arsenic by preparing ferric arsenate/goethite material of core-shell structure by means of arsenic-containing solution
ActiveCN106075800AAchieve permanent fixationAvoid secondary pollutionChemical protectionArsenatePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for fixing arsenic by preparing a ferric arsenate / goethite material of a core-shell structure by means of an arsenic-containing solution. The method comprises the steps that after the pH value of the arsenic-containing solution is adjusted to be acidic, ferrite is added into the arsenic-containing solution, oxygen-containing gas is led into the arsenic-containing solution, a reaction occurs on the heating condition when the solution is stirred, and ferric arsenate sediment is obtained; and the ferric arsenate sediment is immersed into an alkaline solution for reacting, and then the ferric arsenate / goethite material of the core-shell structure is obtained. According to the method, the ferric arsenate / goethite material of the core-shell structure and with quite good stability can be prepared from arsenic in the arsenic-containing solution by means of a simple and low-cost process, and permanent fixing of the arsenic is achieved.
Owner:湖南知远环保科技有限公司
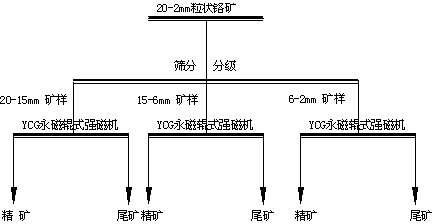
Beneficiation method for recovering chrome lump ore
ActiveCN103894287ARemarkable effect of energy saving and consumption reductionSuitable for deliveryHigh gradient magnetic separatorsManganeseSiderite
The invention discloses a beneficiation method for recovering chrome lump ore. The method comprises the following processing steps: crushing the chrome ore, and classifying three particle size grades including 20-15mm, 15-6mm and 6-2mm by narrow level screening; respectively carrying out dry-type strong magnetic separation on the three classified particle size grades obtained by screening by virtue of a permanent magnet roller type strong magnetic separator; adjusting the speed of a feeding belt of the permanent magnet roller type strong magnetic separator and the distance between the center of a barrel and a separating clapboard to obtain the best grading technical index, wherein the magnetic field intensity of the surface of the belt of the permanent magnet roller type strong magnetic separator is 0.9-1.3T. The method is simple in technological process, the high-quality Cr2O3 ore concentrate can be obtained by screening classification and narrow level screening, and the recovery rate of the Cr2O3 can be increased. The method is short in beneficiation process and is capable of obtaining the ore concentrate and removing tailings in advance; the beneficiation technology has the advantage of being lower in energy consumption compared with other technologies; the method not only can be used for screening the chrome ore, but also can be used for screening other weak magnetic iron minerals such as manganese ore, hematite, goethite, siderite and limonite.
Owner:SINOSTEEL MAANSHAN INST OF MINING RES
Air-stable nano zero-valent iron as well as preparation method and application thereof
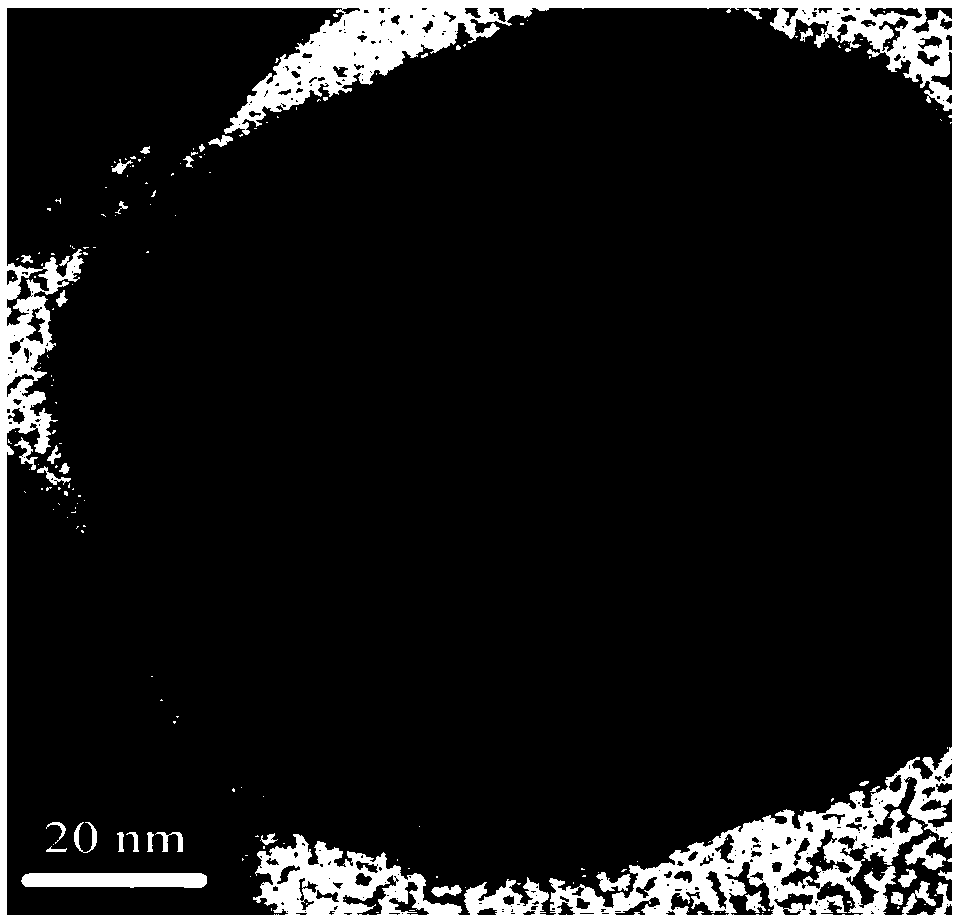
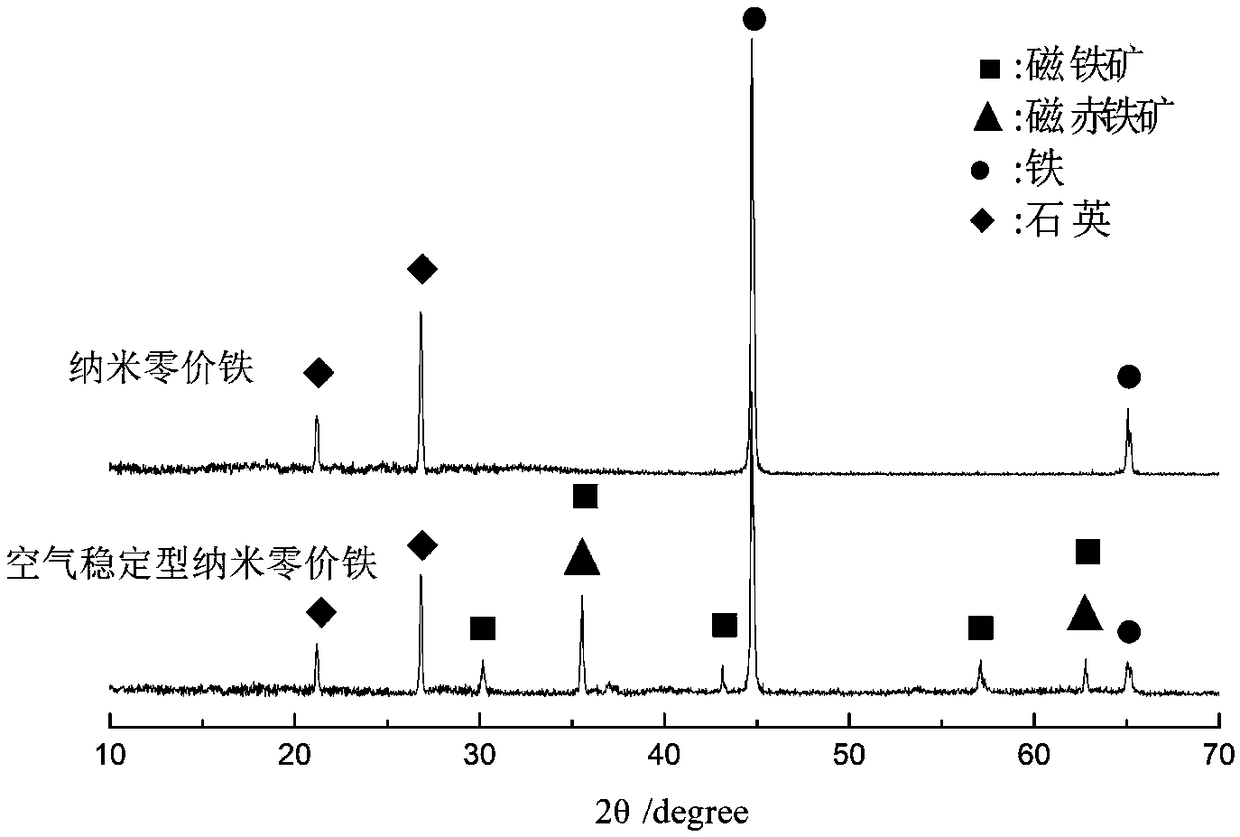
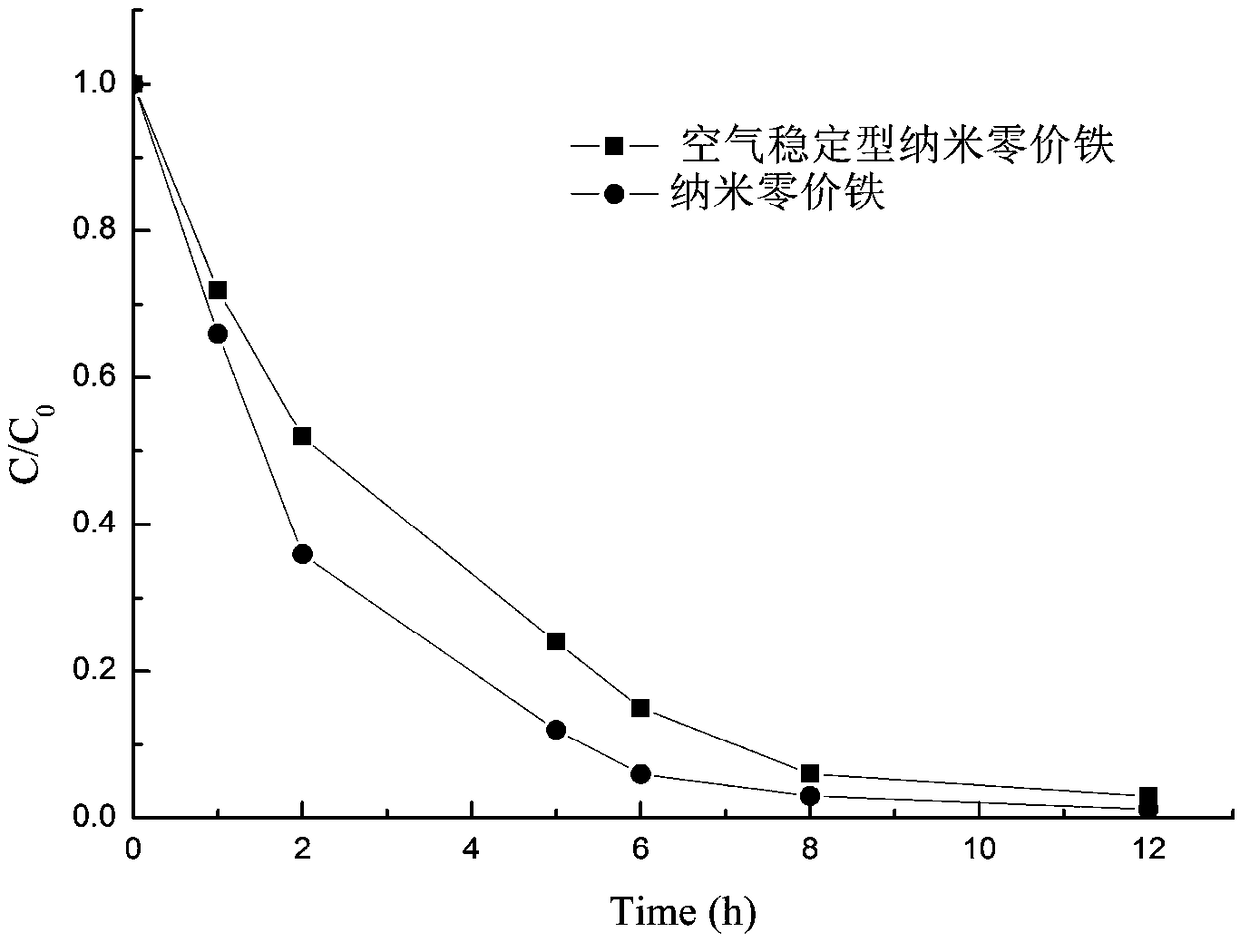
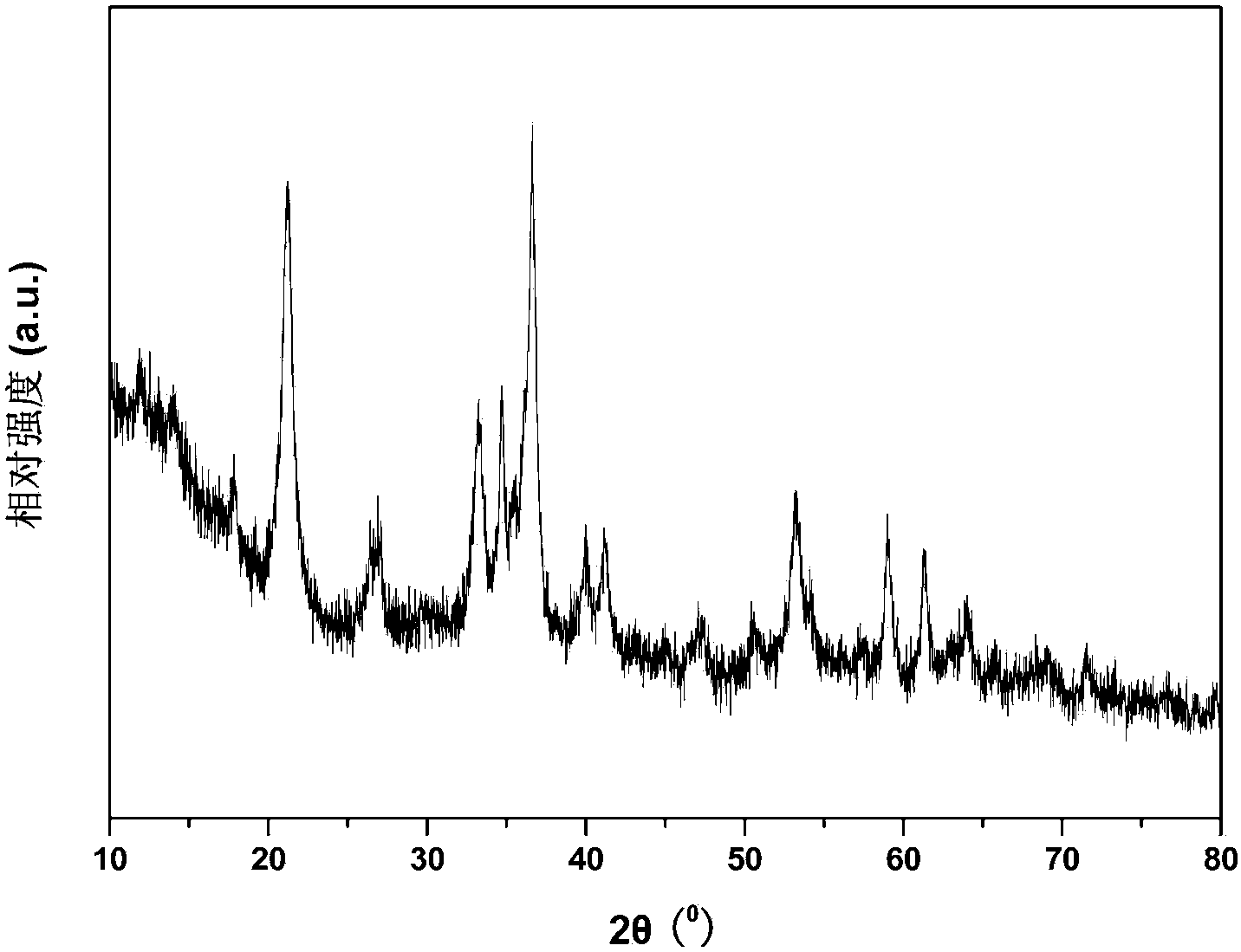
InactiveCN108746604ASimple methodSatisfied with the antioxidant effectMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingGoethiteReducing agent
The invention discloses air-stable nano zero-valent iron as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Natural iron ores of goethite, limonite and hematite and the like are used as precursors, hydrogen is used as a reducing agent for high-temperature reduction to prepare the nanometer zero-valent iron, then the nanometer zero-valent iron is slowly oxidized with air, and the iron oxide layer with 3-5 nm is formed on the surface of the nanometer zero-valent iron. According to the method and the application, used materials are cheap and easily available materials, the preparation method is simple, the cost is low, no additional elements are introduced in the preparation process, and toxic and harmful elements are not contained; and the iron ions released in the water treatment process can further form a flocculating agent to remove phosphate radicals and other pollutants.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV OF TECH
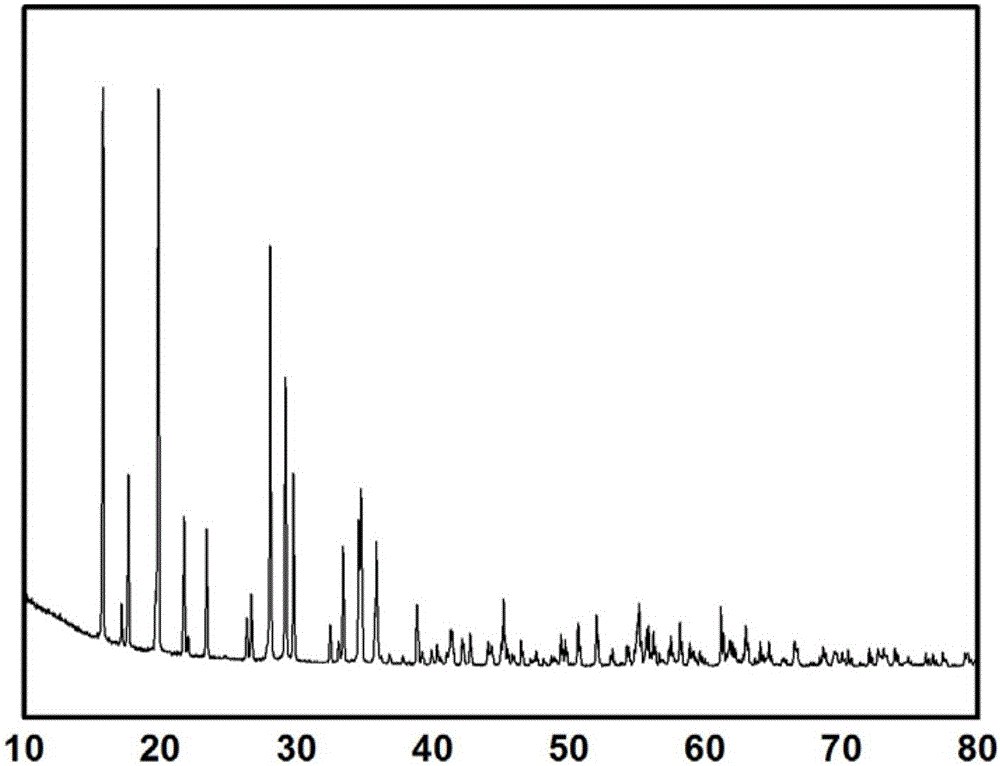
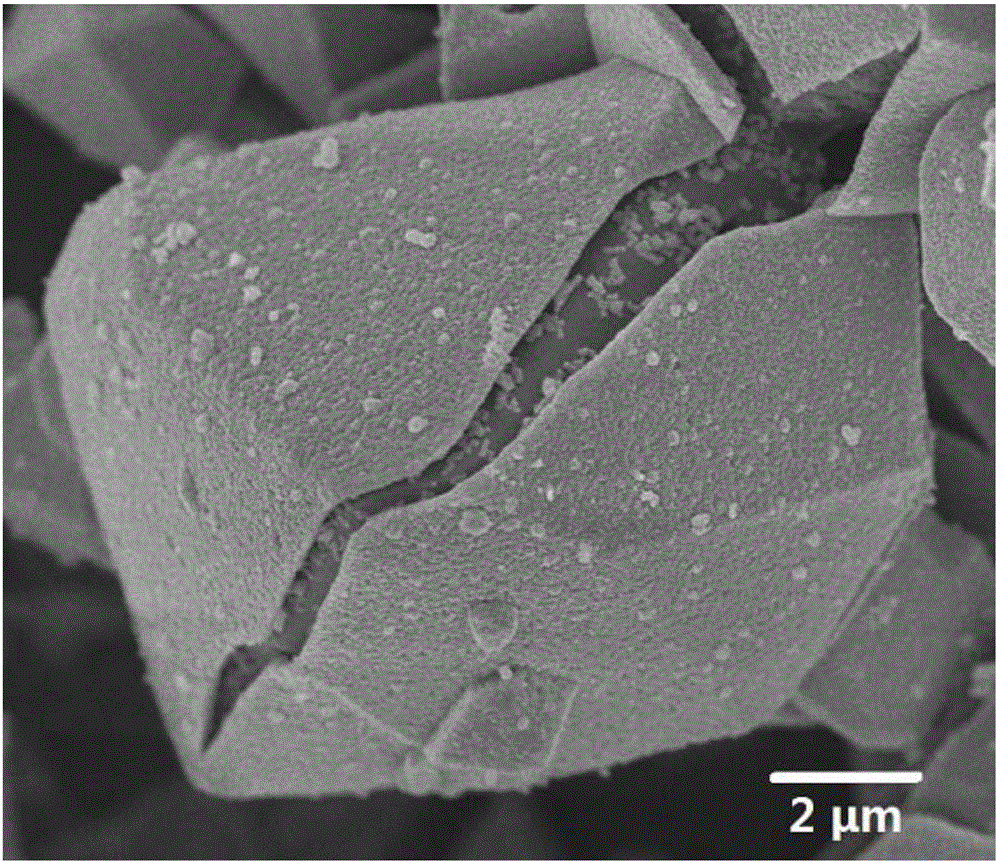
Synthetic method of iron-based magnetic nano goethite
InactiveCN103816903AFacilitate solid-liquid separationEfficient removalMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsWater/sewage treatment by oxidationGeneration rateFerrous salts
The invention discloses a synthetic method of iron-based magnetic nano goethite, relates to a synthetic method of magnetic nano goethite and aims at solving the problem that the current goethite catalyst is difficultly recycled and the secondary pollution is easily generated. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: step one, preparing a ferric salt solution; step two, adding ferrous salt into the ferric salt solution to mix evenly and obtain a mixed solution; step three, dropwise adding an alkaline solution into the mixed solution and stirring, thus obtaining a suspension; step four, adjusting pH value of the suspension, stewing and precipitating, then activating to obtain a reaction mixed solution; step five, filtering and collecting solid-phase matter, washing and drying the solid-phase matter to obtain the iron-based magnetic nano goethite. According to the synthetic method, a ferrous salt solution is prepared firstly, and then the ferric salt is added. The iron-based magnetic nano goethite prepared by the synthetic method is great in specific surface area; solid-liquid separation is carried out by using an additional magnetic field, so that the secondary pollution is avoided; the iron-based magnetic nano goethite is high in catalytic activity and capable of accelerating decomposition of ozone to generate hydroxyl radicals, and increasing the generation rate and the number of the radicals in water.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG ACAD OF SCI INST OF NATURAL RESOURCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com