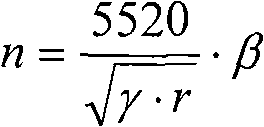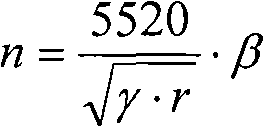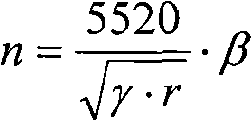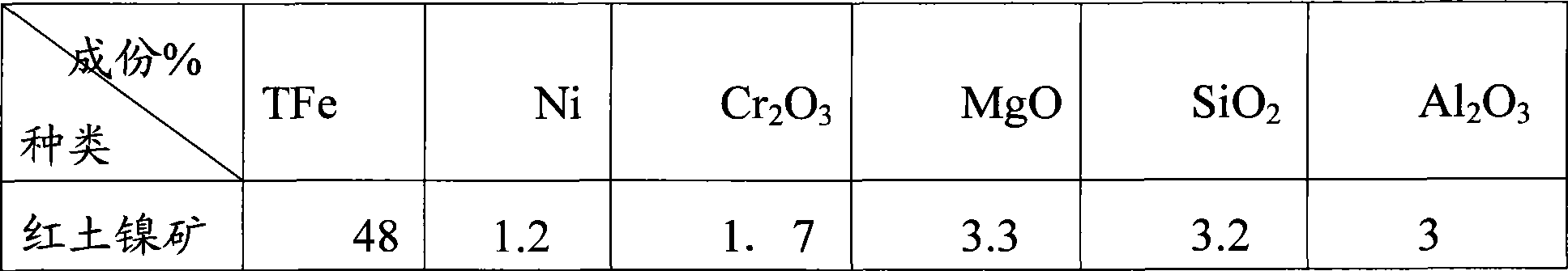Patents
Literature
1537 results about "Ferrochrome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ferrochrome, or Ferrochromium (FeCr) is a type of ferroalloy, that is, an alloy between chromium and iron, generally containing 50% to 70% chromium by weight. Ferrochrome is produced by electric arc carbothermic reduction of chromite. Most of the world's ferrochrome is produced in South Africa, Kazakhstan and India, which have large domestic chromite resources. Increasing amounts are coming from Russia and China. The production of steel is the largest consumer of ferrochrome, especially the production of stainless steel with chromium content of 10 to 20% is the main application of ferrochrome.
Metallurgical V-N microalloying and compound deoxidation cored wire
A metallurgical V-N microalloying and compound deoxidation cored wire contains a core wire and a cladding steel belt. The technical key point of the cored wire is as follows: the core wire of the cored wire consists of a vanadium-increasing agent, a nitrogen-increasing agent and a deoxidizing nitrogen-fixing agent of which particle sizes are less than 6mm, wherein the vanadium-increasing agent is ferrovanadium, nitrided ferrovanadium or vanadium pentoxide; the nitrogen-increasing agent is ferrosilicon nitride, silicomanganese nitride, ferromanganese nitride, ferrochromium nitride, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride or calcium cyanamide; and the deoxidizing nitrogen-fixing agent contains one or more of aluminum, calcium, magnesium and barium, and can also contain one or more of titanium, zirconium, niobium, manganese, chromium, silicon, carbon and iron. By adopting the cored wire, the V / N ratio of steel can get closer to the optimal proportion, the enhancing function of vanadium can be utilized furthest, vanadium resources can be saved, the recovery rate of nitrogen is high, the nitrogen content is stable, the compound deoxidation function can also be realized, the V-N microalloying cost can be reduced and the quality of steel can be increased.
Owner:侯巍 +2
High-carbon high-chromium high-niobium cast iron self-protecting flux-cored wire
InactiveCN101406994AHigh hardnessLow viscosityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaHigh carbonNiobium
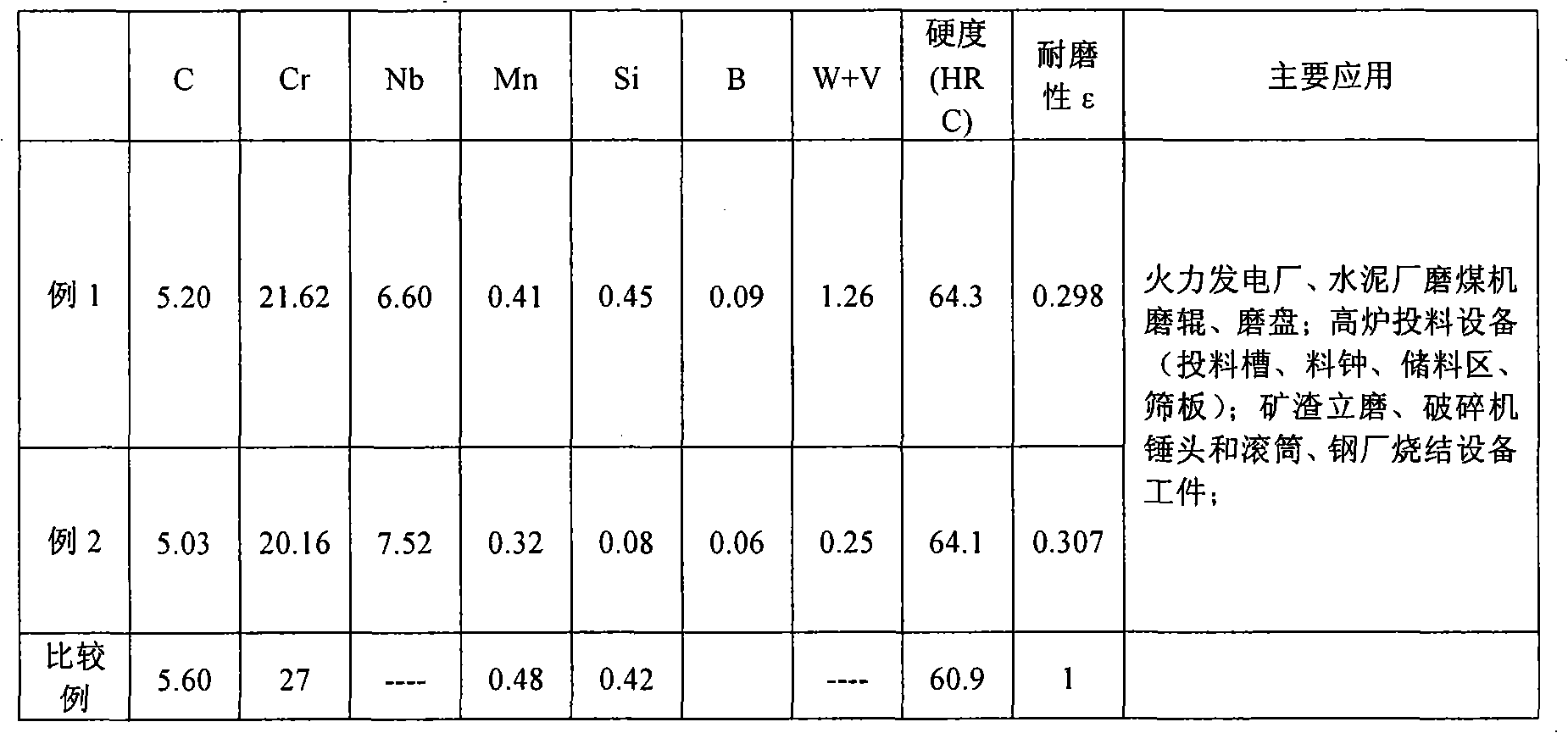
The invention provides a high-carbon high-chromium high-niobium cast iron self-protection flux-cored wire. The flux-cored wire has a steel belt as an outer skin. The flux core comprises the following components in weight percentage: 10 to 30 percent of ferroniobium, 20 to 30 percent of high carbon ferrochrome, 0.1 to 3 percent of V, 0.2 to 3 percent of W, 0.6 to 0.8 percent of ferromanganese, 0.2 to 0.8 percent of 75 ferrosilicon, 20 to 30 percent of chromium carbide, 5 to 12 percent of graphite, 1 to 10 percent of aluminum-magnesium alloy, 1 to 5 percent of silicon carbide and 1 to 3 percent of ferroboron; and the percentage of a counter weight is between 46 and 54 percent. The high-carbon high-chromium high-niobium cast iron self-protection flux-cored wire has the advantages of high hardness, good wear resistance, good oxidation resistance and strong shock resistance, and is widely applied to grinding rolls and grinding disks of coal grinding machines in thermal power plants and cement plants, material charging equipment in blast furnaces(material charging slots, receiving cones, material storage areas and sieve plates), slag vertical mills, hammer heads and rollers of crushers and sintering equipment workpieces in steel plants.
Owner:CENT RES INST OF BUILDING & CONSTR CO LTD MCC GRP
Iron alloy fusing sample preparation method for X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis
InactiveCN101832891AReduce sample preparation timeAnalytical results are reliableMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationX-rayFerrosilicon
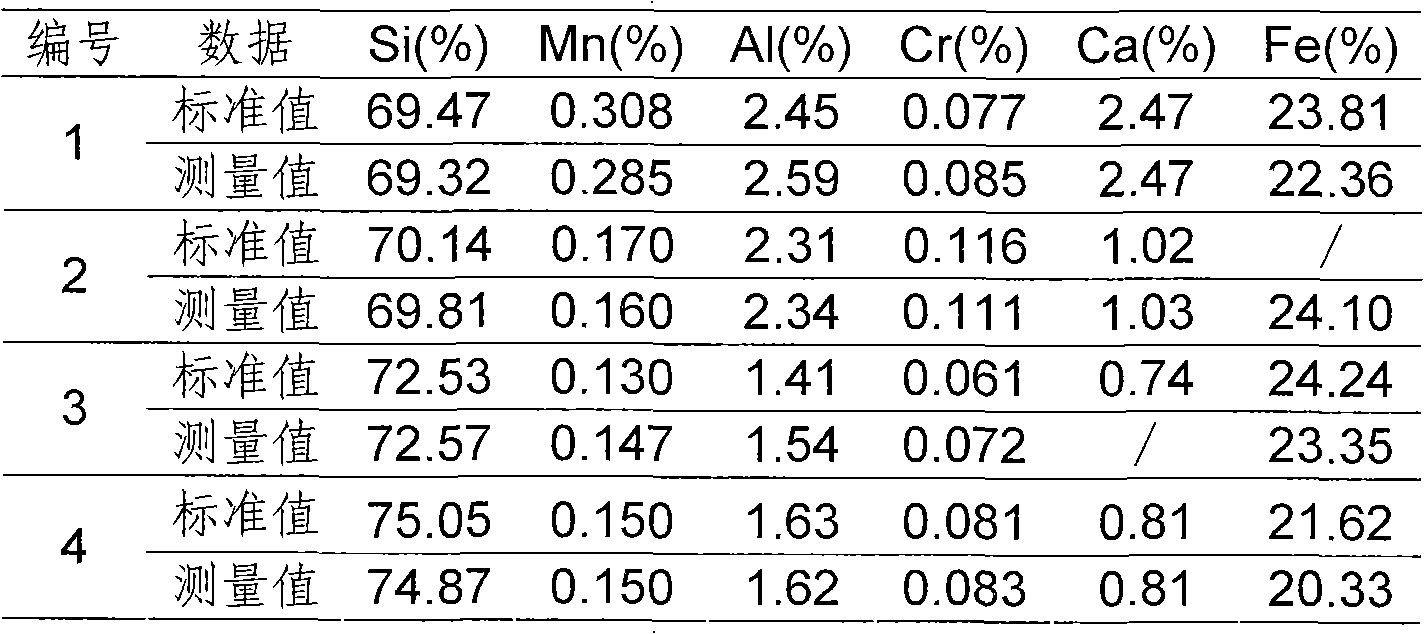
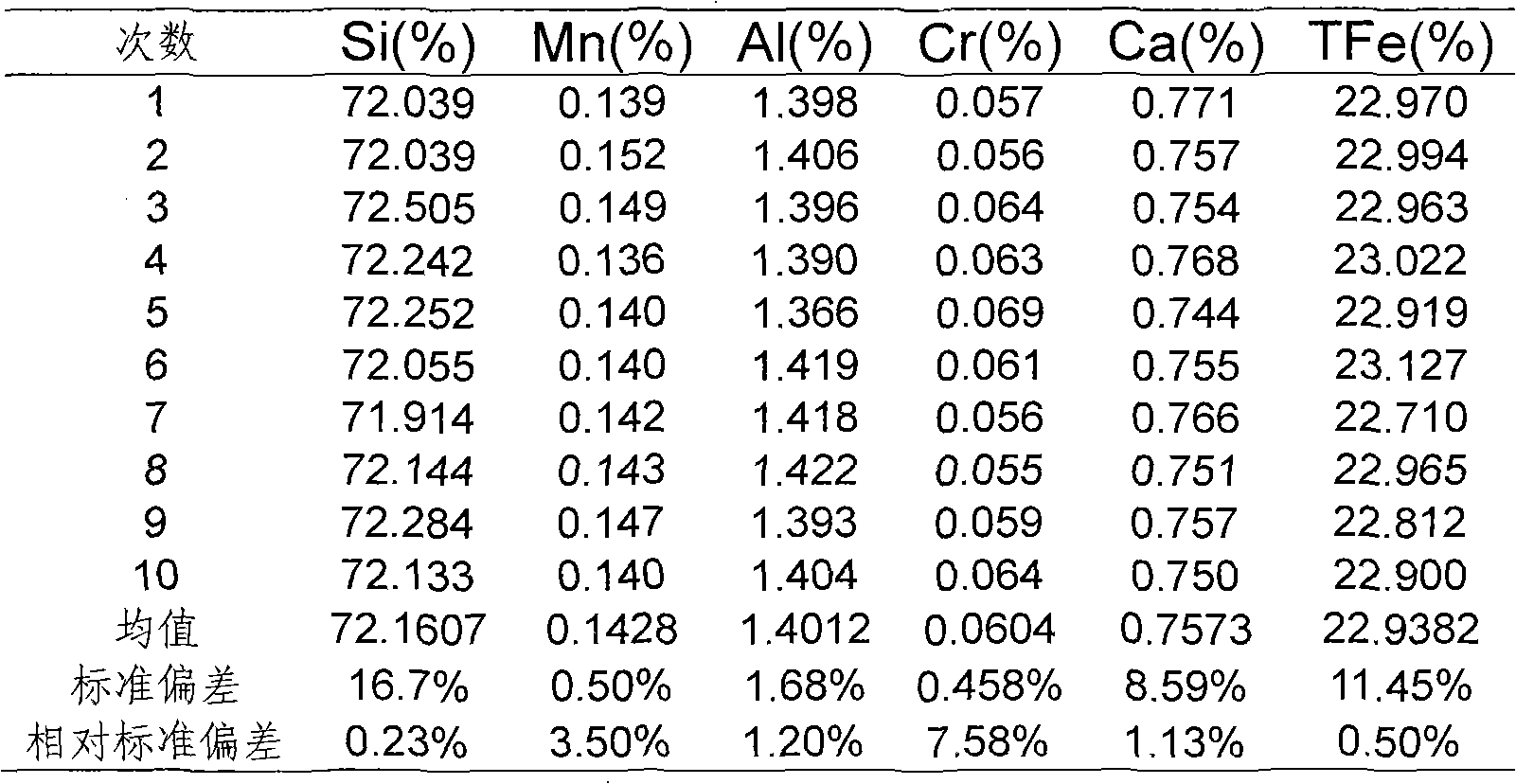
The invention relates to an iron alloy fusing sample preparation method for X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis, belonging to the technical field of materialization detection and aiming to solve the problem that fusing a film production alloy sample can erode a platinum crucible. The method comprises the steps of building up wall of the platinum crucible, preparing an oxidizing agent, pre-oxidizing an iron alloy sample and fusing and preparing sample from the iron alloy sample. The invention provides the fusing sample preparation method suitable for various iron alloys such as ferromanganese, silicomanganese, calcium silicon, ferrosilicon, ferromolybdenum, ferrotitanium, cymrite, ferrochrome, ferrocolumbium, ferrovanadium, silicon silicomanganese and the like. By adopting the method, a glass fusing piece can be manufactured without eroding the valuable platinum crucible, the sample can be completely oxidized in the sample preparation process, the sample preparation time is short, the prepared glass fusing piece is uniform and perfect, and the mineral effect and the granularity effect can be completely eliminated. The invention has safe and reliable method, simple and convenient operation and good repeatability, is suitable for various iron alloy samples and widens the application range of the fluorescence analysis.
Owner:HBIS COMPANY LIMITED HANDAN BRANCH COMPANY
High hardness ferritic stainless steel wearable surfacing flux-cored wire
InactiveCN101224527AOvercome the disadvantage of poor wear resistanceHigh hardnessWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaHigh carbonBoron carbide
The invention provides a high hardness ferrite stainless steel wearable flux-cored wire, which takes a low carbon steel H08A cold rolling thin steel strip as an external wrapper; furthermore, the wrapper is internally provided with a powder core which is composed of graphite, metal and alloy powder; the weight percentages of all ingredients of the powder core are 50-75% of high carbon ferrochrome, 10-16% of ferrovanadium, 6-10% of ferrotitanium, 2-10% of tungsten carbide, 2-3% of nickel powder, 1.5-2.5% of silver graphite, 1-3.5% of boron carbide, 1-2% of aluminium magnesium powder, 0-10% of metallic chromium, and the residual quantity of reduced iron powder; the filling proportion of the powder core is 46-50%; the invention adopts the technical proposal that high-content ferrovanadium and adequate alloy powders such as tungsten carbide and boron carbide, etc. are added into the flux-cored wire, changes the microstructure of the existing ferrite stainless steel flux-cored wire surfacing alloy, overcomes the shortages of poor wearability and ductility, and can be applied to submerged arc bead weld manufacture or repair of the parts which has high requirement of abrasion and the corrosion resistance of the wearable grain.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
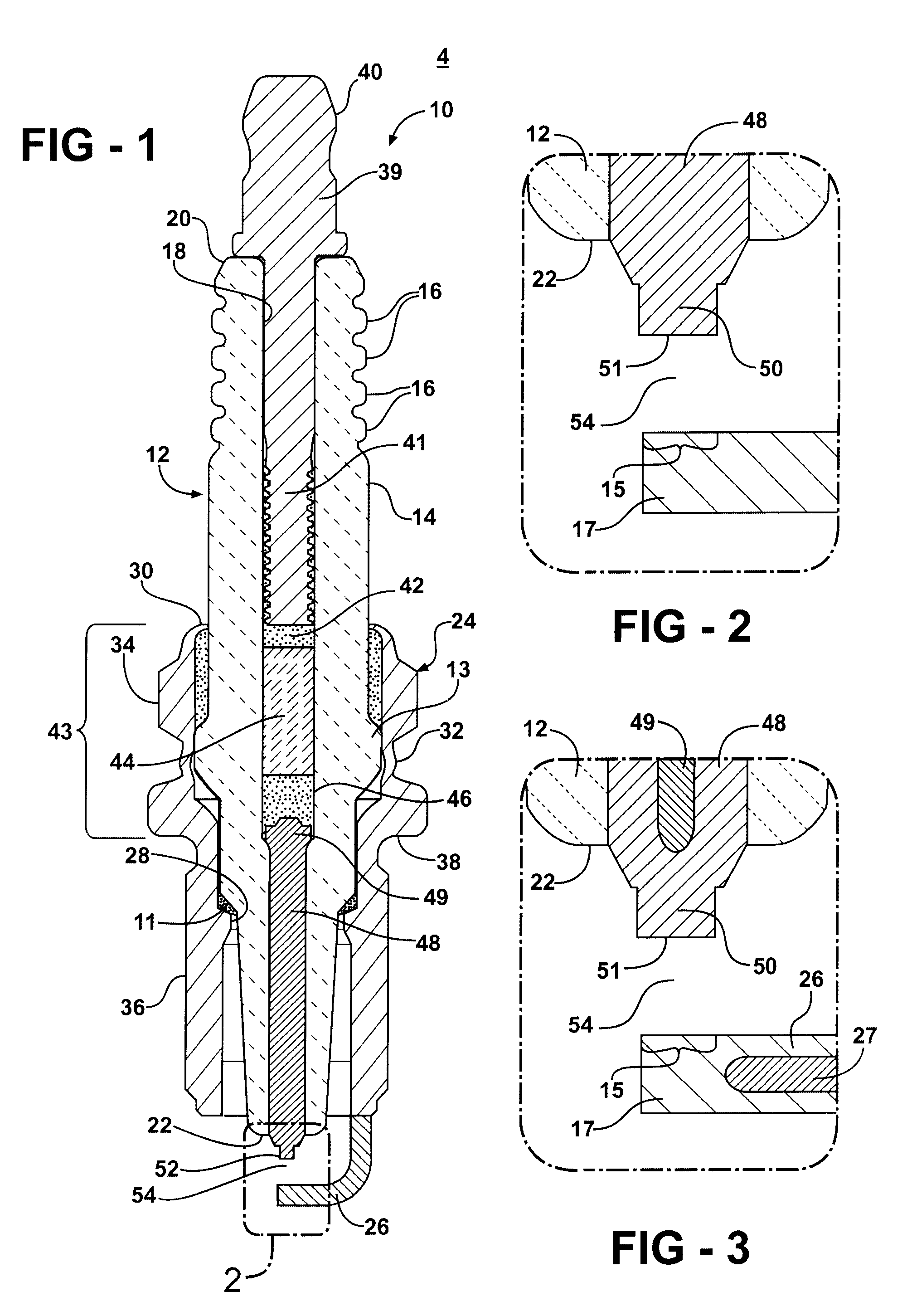
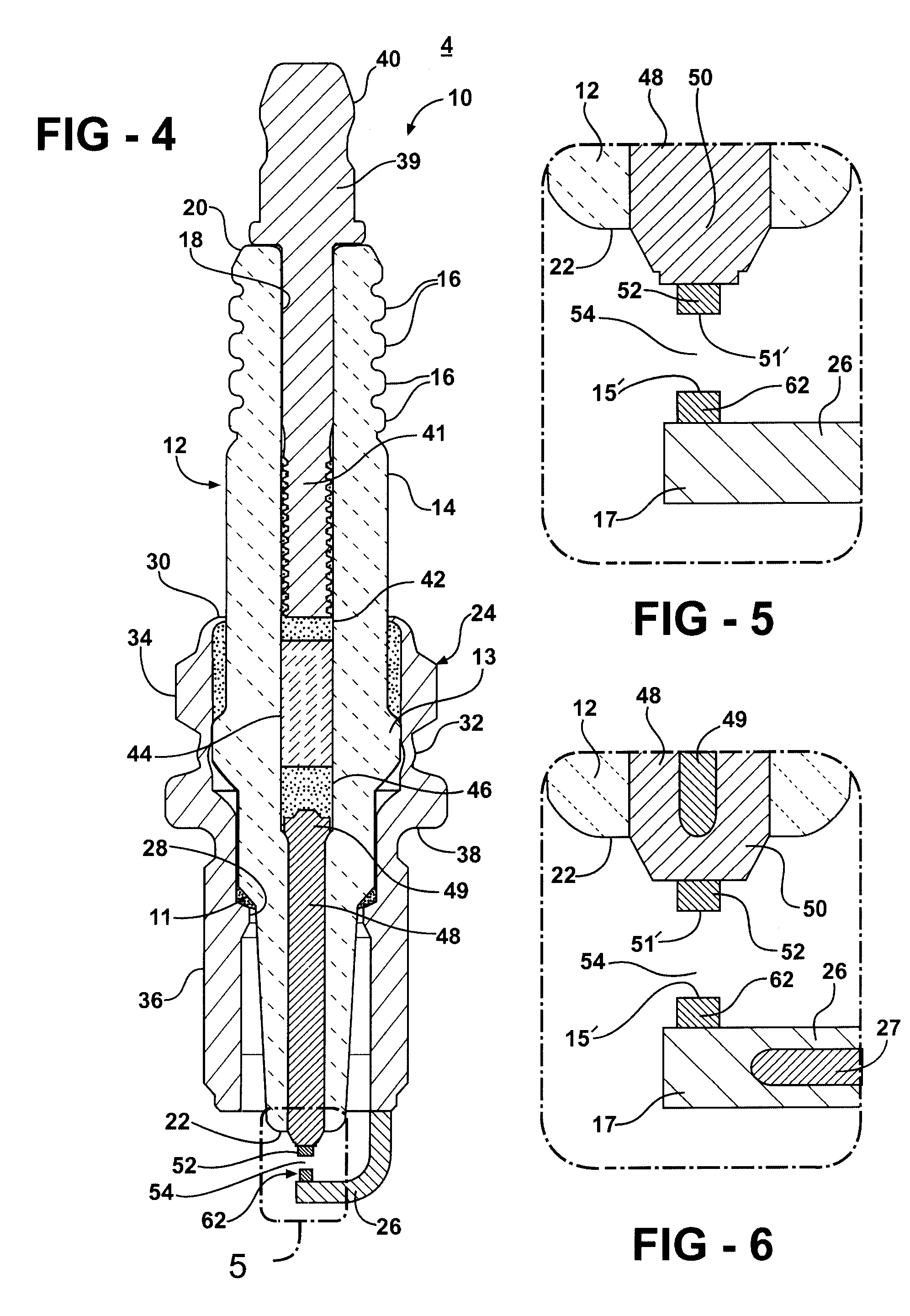
Electrode for an Ignition Device
An electrode for an ignition device is made from a Ni-based nickel-chromium-iron alloy which has improved resistance to high temperature oxidation, sulfidation, corrosive wear, deformation and fracture includes, by weight of the alloy: 14.5-25% chromium; 7-22% iron; 0.2-0.5% manganese; 0.2-0.5% silicon; 0.1-2.5% aluminum; 0.05-0.15% titanium; 0.01-0.1% total of calcium and magnesium; 0.005-0.5% zirconium; 0.001-0.01% boron, and the balance substantially Ni. It may also include at least one rare earth element selected from the group consisting of: yttrium, hafnium, lanthanum, cerium and neodymium in amounts ranging from 0.01-0.15% by weight, and incidental impurities, including cobalt, niobium, molybdenum, copper, carbon, lead, phosphorus or sulfur. These total of these impurities will typically be controlled to limits of 0.1% cobalt, 0.05% niobium, 0.05% molybdenum, 0.01% copper, 0.01% carbon, 0.005% lead, 0.005% phosphorus and 0.005% sulfur. The ignition device may be a spark plug which includes a ceramic insulator, a conductive shell, a center electrode disposed in the ceramic insulator having a terminal end and a sparking end with a center electrode sparking surface, and a ground electrode operatively attached to said shell having a ground electrode sparking surface, the center electrode sparking surface and the ground electrode sparking surface defining a spark gap therebetween. At least one of the center electrode or the ground electrode includes the solution-strengthened Ni-based nickel-chromium-iron alloy. The Ni-based nickel-chromium-iron alloy electrodes of the invention may also include a core with thermal conductivity greater than that of the Ni-based nickel-chromium-iron alloy, such as copper or silver or their alloys.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE LLC
6063 aluminium alloy with high strength and elongation coefficient an dproduction thereof
The invention opened a high strength and high extensibility 6063 Al alloy which contain the Cu, Mn, chrome, Fe, Zn, Ti, Al. The process is: a, founding: adding the material to the furnace melting stir ring and skimming coving refining skimming and refining thermal retardation casting ingot. b extruding and heat processing: isotroping air cooling, heating extruding quenching cutting cooling stretching straightening aging treatment product. The process has improved the mechanics of the alloy, also the elongation percentage (60%) and the intensity (40%). The tensile strength has been improved to 280-300 MPa, the elongation percentage is improved to 13%. So it satisfy the windows and the curtain wall's need.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Preparation method of wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron
The invention discloses a preparation method of wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron and belongs to the technical field of metal materials. According to the preparation method, common scrap steel, carburant, ferrochromium, ferromolybdenum, copper plates, ferrochromium nitride, ferrosilicon, ferromanganese, ferroboron and aluminum are smelted in an electric furnace so as to form the wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron. The molten wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 3.0-3.5% of C, 18-25% of Cr, 0.3-0.5% of Mn, 0.3-0.5% of Si, 0.18-0.25% of N, 0.5-0.8% of Mo, 0.2-0.4% of B, 0.08-0.12% of Al, 0.5-1.0% of Cu, less than 0.05% of S, less than 0.05% P and the balance of Fe. Molten iron is treated with an inoculator when taken out from the electric furnace, and is treated with a suspending agent when poured, so as to obtain fine solidification structures. Therefore, the wear-resistant high-chromium cast iron has excellent properties.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Titanium Base Alloy
The invention refers to the non-ferrous metallurgy, i.e. to the creation of the modern titanium alloys, having the high genericity. Titanium-base alloy contains aluminum, vanadium, molybdenum, chromium, iron, zirconium, oxygen and nitrogen. Herewith the components of the alloy have the following ratio by weight %; aluminun—4.0-6.0; vanadium—4.5-6.0; molybdenum—4.5-6.0; chromium—2.0-3.6; iron—0.2-0.5; zirconium—0.1-less than 0.7; oxygen—0.2 max; nitrogen—0.05 max; titanium—balance. Technical result—creation of the titanium alloy with the required strength and plastic properties. The alloy may be used to produce the wide range of the products including the large-size forgings and die-forgings as well as semiproducts of small section, such as bars and plates up to 75 mm thick.
Owner:VSMPO AVISMA CORP
Series flux cord welding rod used for pile-up welding reparing and remanufacturing large type medium high carbon steel parts
InactiveCN100999041AImprove crack resistanceHigh carbon contentArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsHigh carbonRare earth
The present invention discloses a series flux-cored wire for reparation and refabrication of large-size medium-high carbon steel components and parts. Its chemical composition includes (wt%) 5-10 of fluorite, 25-45% of high-carbon ferrochrome, 2-10% of high-carbon manganese iron, 5-8% of tantiron, 10-15% of ferro-molybdenum, 8-14% of rare earth oxide, 5-15% of metal nickel, 2-5% of ferrovanadium, 0.5-2% of graphite, 2-4% of chloride and 1-2.5% of aluminium-magnesium alloy. Its external covering adopts low-carbon steel tape.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO WEIERDE SPECIAL WELDING IND
High chromium cast iron self protective build-up welding cored welding wire and its usage
InactiveCN1714986ARealize direct surfacingOverlay welding wear-resistant and corrosion-resistantArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsHigh carbonManganese
The self-protective high chromium cast iron cored build-up welding wire has metal powder core comprising nickel powder 6-8 wt%, middle carbon manganese iron 8-10 wt%, No. 45 ferrosilicon 9-12 wt%, high carbon ferrochromium 65-75 wt%, metal Cr powder 18-21 wt%, ferromolybdenum 5-7 wt% and Al-Mg powder 1.5-2.5 wt%, and with one welding wire filling amount of 0.49-0.53. The present invention makes it possible to use the welding wire in submerged arc welding without needing added flux and protecting gas, results in raised comprehensive welding performance and raised welding quality, and may be applied widely in build-up welding field requiring high antiwear, anticorrosive and anticracking performance.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
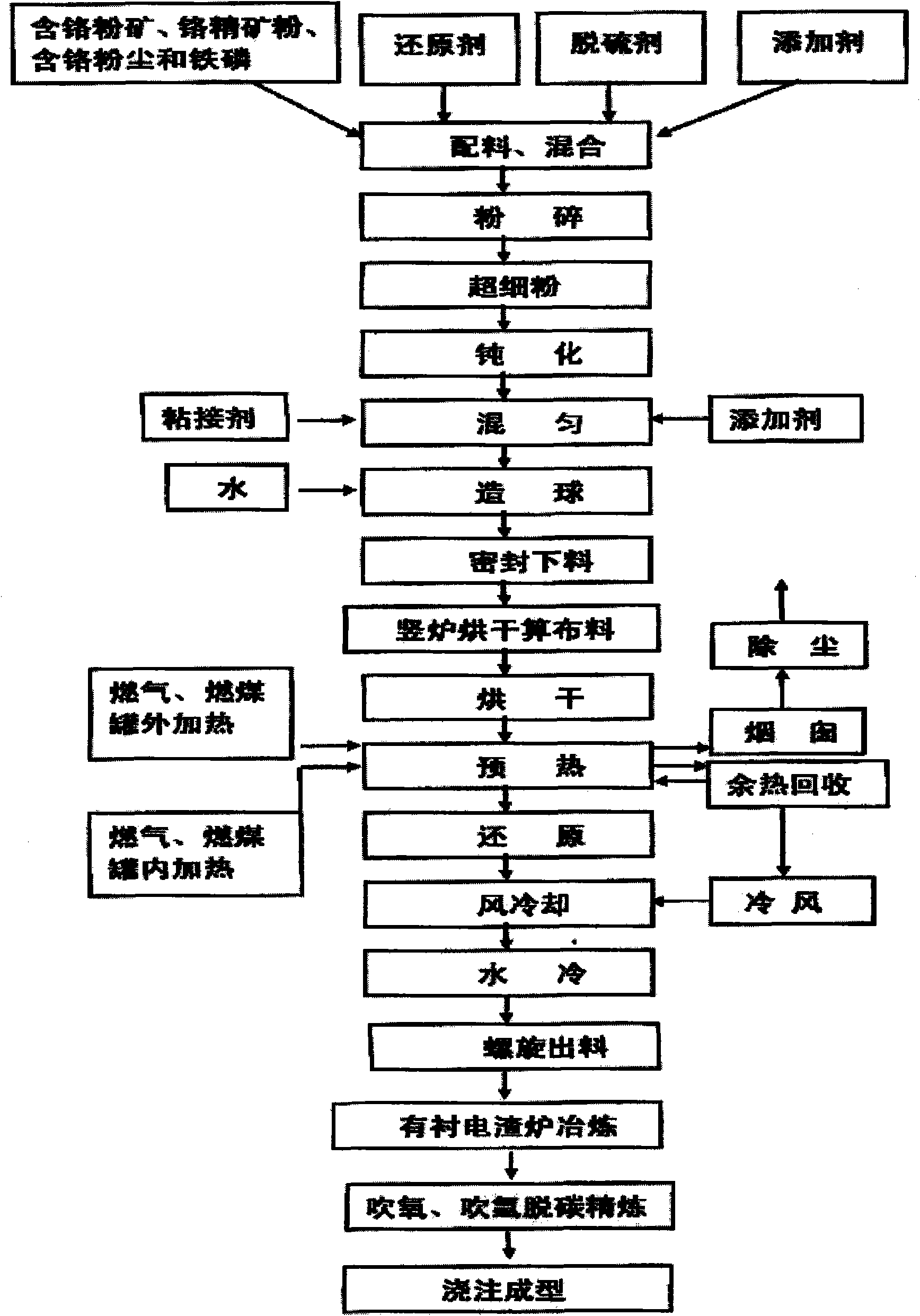
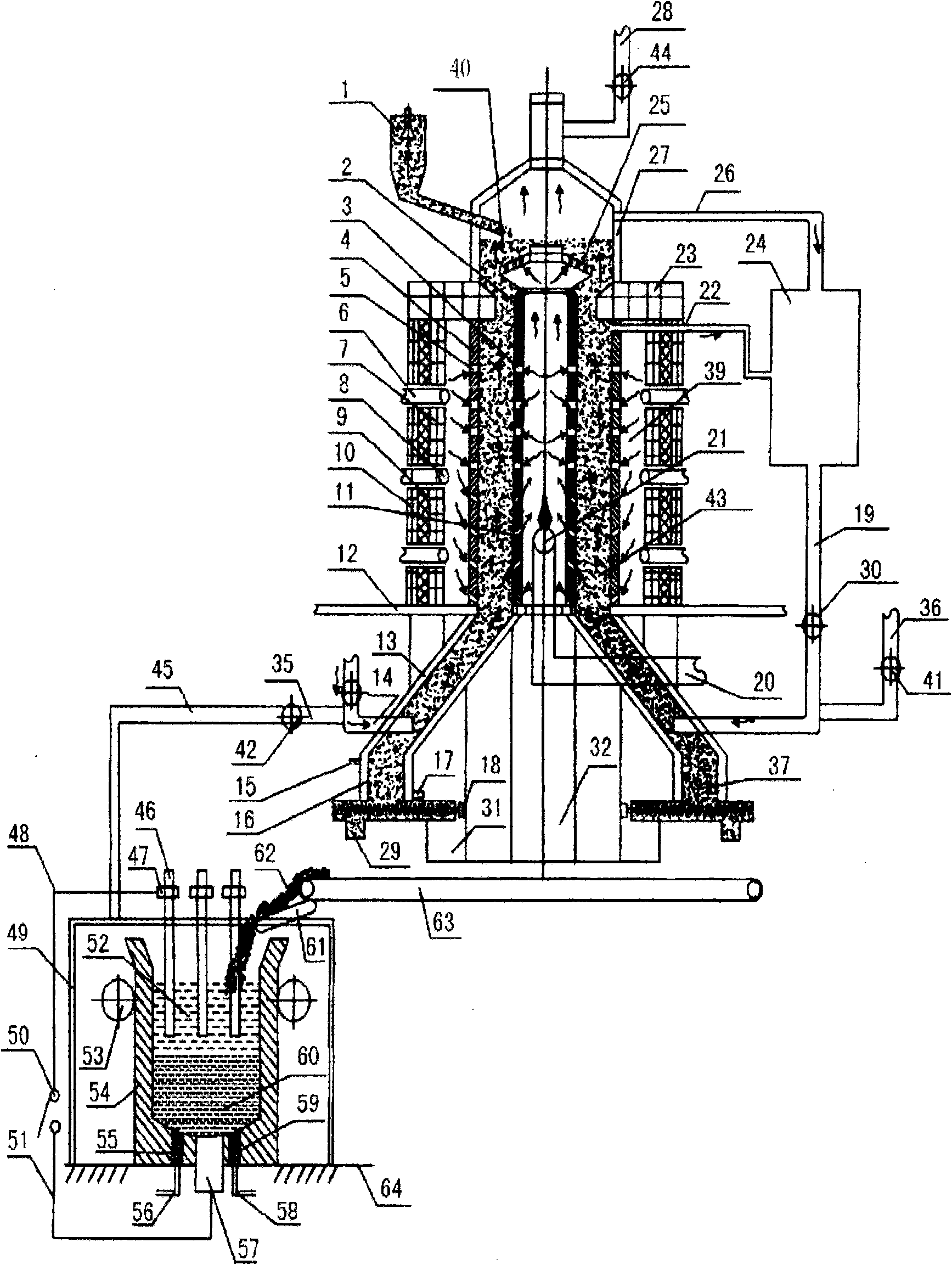
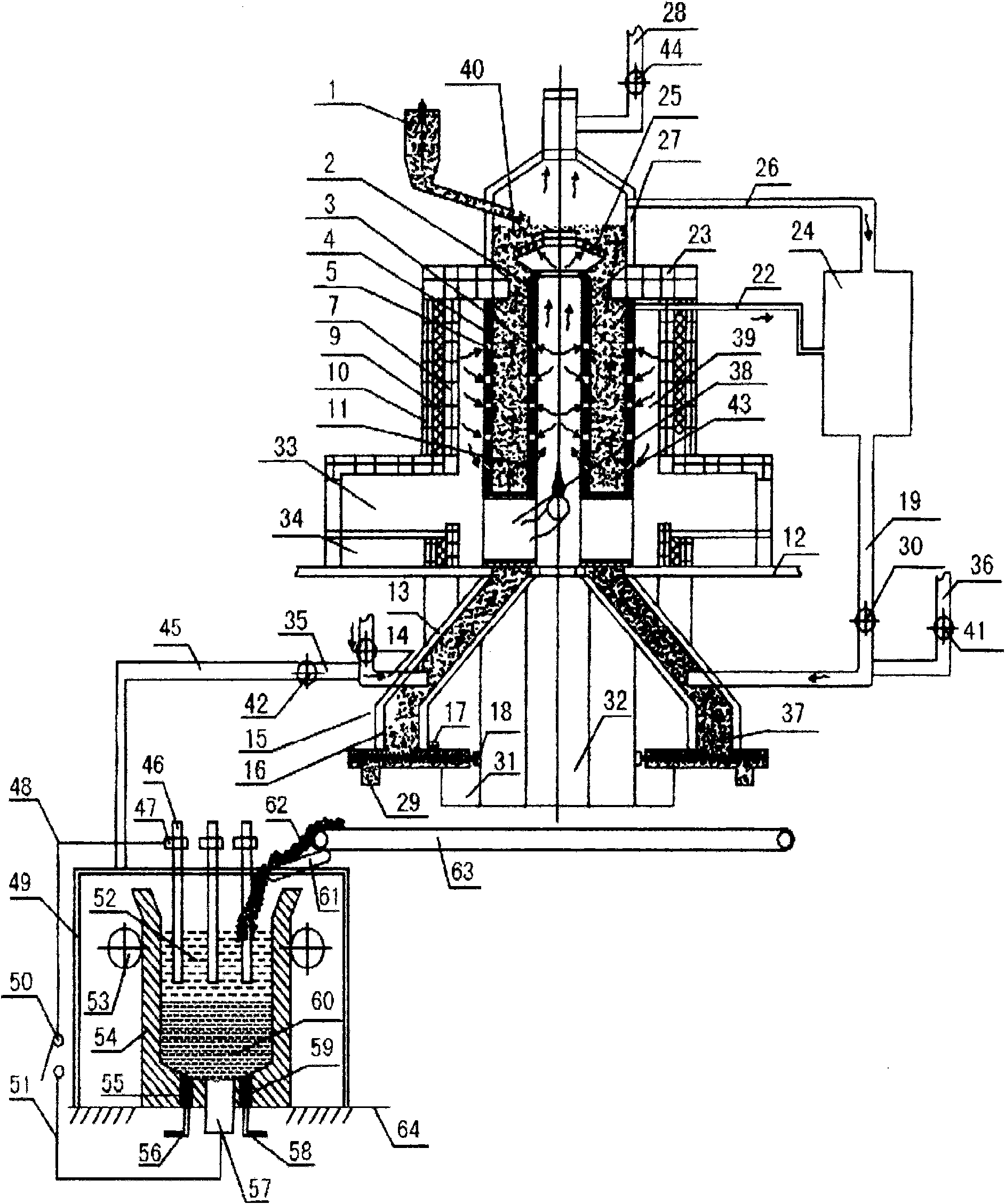
Process and device for smelting chromium irons and chromium-containing molten iron by using chromium ore powder
InactiveCN101538629AImprove applicabilityHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementShaft furnaceUltra fineSolvent
The invention relates to a process and a device for smelting chromium irons and chromium-containing molten iron by using chromium ore powder, which belongs to metallurgical industry steel-making raw material. The process comprises the following steps: mixing chromium iron containing raw materials with reducing agent, solvent and catalyst to prepare ultra fine powder, mixing to make pelletizing materials, sending the pelletizing materials into a reducing furnace, obtaining chromium irons pellets after the reduction reaction, and directly adding reduced pellets into a lining electroslag furnace for being smelted into the chromium-iron alloy or the chromium-containing molten iron. The device comprises an internal-external heating vertical reducing furnace, a lining electroslag furnace and a residual heat recovery system. The invention has the advantages that: firstly, the reduction temperature is low, the speed is high, the energy consumption is reduced, the production cost is lowered, the production efficiency is high, and the uniformity of the quality is good; secondly, the degree of mechanization is high, the procedure is simple, the yield is large, the mass production can be performed; thirdly, the waste of raw materials is reduced, the environment pollution is lowered; fourthly, the source of raw materials adopting the chromium ore powder and chromium-containing waste, the cost is low; fifthly, the waste resource can be recycled so as to save the resource consumption; and sixthly, the high-temperature pellets are directly smelted by adopting the lining electroslag furnace, the heat efficiency is high, the energy consumption is low, the material purity is high and the quality is good, and the device is simple with less investment.
Owner:丁家伟
Ni-Cr-Fe alloy and its production process
InactiveCN1847440ASave resourcesOptimize the smelting processBlast furnace detailsRecycling and recovery technologiesGranularityManganese
The present invention is Ni-Cr-Fe alloy and its production process. The Ni-Cr-Fe alloy contains Ni 1.5-6.0 wt%, Cr 3.0-21.0 wt%, Si 0.6-2.0 wt% and Mn 0.3-0.8 wt%, except Fe, and can meet the requirement for use as material smelting stainless steel. The production process includes the following steps: producing Ni-Cr agglomerate with industrial Ni-Cr waste, Ni-Cr ore powder of granularity smaller than 10 mm, flux, coke and water and through pelletizing, sintering and sieving; and smelting with the Ni-Cr agglomerate, Ni-Cr ore of granularity greater than 10 mm, flux and coke in a blast furnace. The present invention has sang in resource and environment friendship.
Owner:DONGDA CASTING WUJIANG
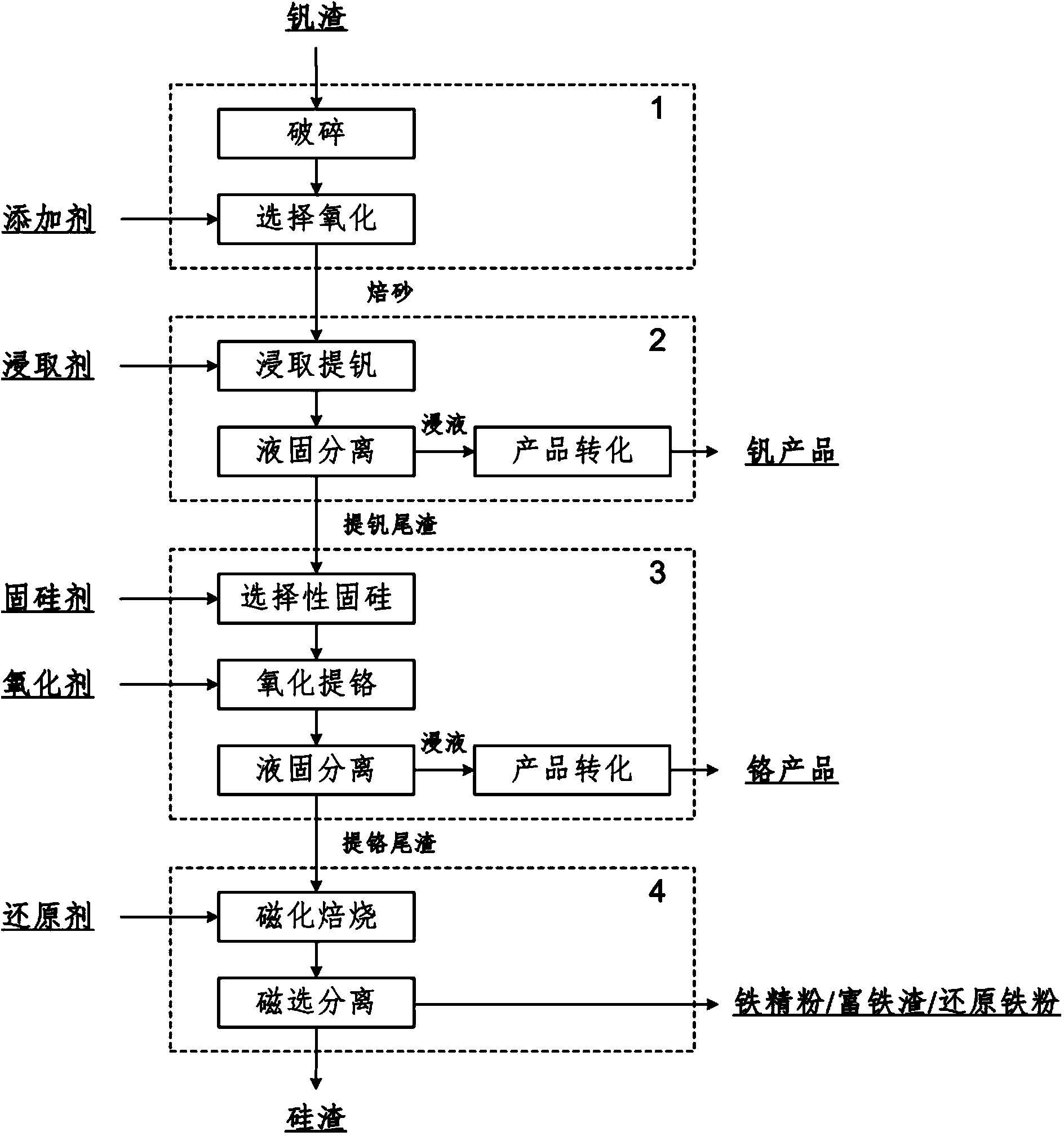
Clean process method for extracting vanadium, chromium and iron from vanadium slag step by step
The invention relates to a clean process method for extracting vanadium, chromium and iron from vanadium slag step by step. The clean process method comprises the following steps of: selectively oxidizing the vanadium slag to obtain a roasted product; leaching the obtained roasted product by using a leaching agent to extract vanadium, carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain vanadium-containing leach liquor and vanadium-extracted tailings, and carrying out product transformation on the vanadium-containing leach liquor to prepare vanadium series products; adding the obtained vanadium-extracted tailings and a silicon fixing agent to a sodium hydroxide solution, selectively fixing silicon, then oxidizing to extract chromium, then carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain chromium-containing leach liquor and chromium-extracted tailings, and carrying out product transformation on the chromium-containing leach liquor to prepare chromium series products; mixing the chromium-extracted tailings with a reducing agent, and carrying out magnetizing roasting and magnetic separation to obtain silicon slag and ion concentrate powder / iron-enriched slag / reduced iron powder. The clean process method disclosed by the invention realizes the step-by-step extraction and high-efficiency separation of valuable components such as vanadium, chromium and iron which are contained in the vanadium slag, prevents the mutual entrainment of vanadium, chromium and iron products; in addition, the clean process method disclosed by the invention realizes the near zero discharge of waste water and the recycling of final slag and is clean and pollution-free.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-strength casted air-colled bainite wear-resisting steel and preparing method
InactiveCN1775983AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove toughnessMolten metal pouring equipmentsFoundryWear resistant
The invention relates to a high strength foundry air cooling bainite wear resistant steel that the chemical constituents is 0.32-0.65 C, 0.8-3.0 Si, 1.2-3.0 Mn, 0.5-0.8 Cr, 0.3-0.8 Cu, 0.001-0.008 B, 0.18-0.35 Al, 0.05-0.15 Y, 0.05-0.20 Ti, 0-0.12 Mg, 0-0.12 Ca, 0-0.15 Zn, and 0.10<Mg+Ca+Zn<0.25, the else is Fe and trace impurities. The process includes the following steps: smelting waste steel, pig iron, ferrochrome iron and copper board, adding ferrosilicon and ferromanganese preliminary deoxidation into melting down and alloying; heating to 1600-1660 degree centigrade after adjusting the constituents adding aluminum deoxidatioin and alloying and blast furnace tapping; putting the compounding modification particle of Yt, boron, titanium, magnesium, calcium, and zinc on the bottom of pouring ladle, taking modification process to the molten steel; molding the molten steel after modification process into normal matrix for casting. The invention could prolong the useful life of antifriction component, improve working efficiency, and have good economic benefit.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
High-boron cast steel containing granular boride and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a preparing method of granular boride high-boron cast steel, which comprises the following steps: allocating 0.15%-0.45% C,0.75%-2.70% B, 0.34 %-1.50% Ti, 0.80%-1.20% Cr, 0.50%-1.50% Si, 0.50%-1.50% Mn, 0.04%-0.12% Ce, 0.08%-0.20% Al, 0.03%-0.10% Ca, 0.01%-0.06 N, P<0.05%, S<0.05% and Fe; setting B / C=5.0-6.0, B / Ti=1.8-2.2; adopting electric stove to melt; mixing common scrap steel, pig iron and chromium iron; heating to melt; adding into silicon iron and manganese iron; adding into ferroboron and ferrotitanium before tapping; adjusting furnace-front element to be quality; heating-up; adding into silicon-calcium alloy; pre-deoxidizing; end-deoxidizing with aluminum; micro-alloying; proceeding composite deteriorating process outside of the furnace with cerium and nitrogen; keeping the temperature; proceeding oil-cooling quenching; tempering under the low temperature; getting the product. This invention possesses merits of high hardness and strength and good tenacity and resistance, which can increase the durability of wear resisting part.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Composite roll for centrifugally casting high-chromium cast iron and a preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a composite roll for centrifugally casting high-chromium cast iron and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of the steel rolling. The composite roll comprises a roll external layer and a roll core. The chemical components of the materials of the roll external layer in terms of the percentage by weight are as below: 25-28 of alloy scrap iron of a high-nickel-chromium infinite chilled iron roll, 28-30 of carbon ferrochrome, 1.5-2.5 of mid-carbon ferromanganese, 2.5-3.5 of ferroboron, 0.5-0.8 of silicon-calcium-barium alloy, 0.2-0.4 of aluminum, 0.3-0.5 of ferrotitanium, 0.2-0.4 of rare earth ferrosilicon, 0.10-0.15 of zinc, 0.15-0.18 of magnesium and the balance of low-carbon waste steel sheet. The roll core is high-strength alloy cast iron or low-alloy ductile cast iron. The roll external layer and the roll core are formed through centrifugal composite casting. The roll has low production cost, contains a small number of impurities and has high degree of purity; the hardenability, the mechanical performance and the thermal fatigue of the roll can be improved; and the roll has long service life and low production cost.
Owner:江苏环立板带轧辊有限公司
Hypoeutectic high-chromium white cast iron and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a hypoeutectic high-chromium white cast iron, which comprises the following components calculated according to mass fraction: 1.9-2.4 of C, 16-22 of Cr, less than or equal to 0.8 of Si, less than or equal to 0.7 of Mn, 0.5-1.0 of Ni, 1.0-1.7 of Mo, less than 0.04 of S, less than 0.06 of P, 0.05-0.4 of RE, 0.5-1.0 of Cu, 0.05-0.15 of Zn, 0.1-0.3 of V and the balance of Fe. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: defining the mixture ratio according to the requirement of mass fraction and mixing; mixing scrap steel and pig iron in an intermediate-frequency induction furnace and heating the mixture to be melt; after molten iron is smelt, sequentially adding high carbon ferro-chrome, manganese iron, nickel and molybdenum and smelting again; feeding a zinc ingot with small granularity and rare earth or vanadium at the bottom of a casting ladle, covering a steel sheet or scrap iron and compacting; pouring the molten iron into the casting ladle and carrying out metamorphism and deslagging treatment; casting the molten iron and forming to obtain a hypoeutectic high-chromium white cast iron piece; then placing the hypoeutectic high-chromium white cast iron piece into a heat treatment furnace for thermally treating; and quenching and tempering to obtain a hypoeutectic high-chromium white cast iron material with the hardness of 60-66HRC (Hardness Rockwell) and the impact ductility of 10-14J / cm<2>. The hypoeutectic high-chromium white cast iron has the advantages of low cost, high wear resistance and reliable use safety. In addition, the preparation method of the hypoeutectic high-chromium white cast iron is simpler, and is easy in operation and strong in practicability.
Owner:云南化铸科技有限责任公司
High-boron high-speed steel roller material and smelting process thereof
ActiveCN102994692AHigh yieldEasy to useProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceMetallic aluminumSilicon alloy
The invention provides a high-boron high-speed steel roller material and a smelting process thereof. The smelting process of the high-boron high-speed steel roller material comprises the following steps: firstly, adopting Q235 waste steel, ferrotungsten, ferromolybdenum, ferrovanadium, high carbon ferro-chrome, metal copper, metal aluminum, calcium-silicon alloy, rare earth ferrosilicon magnesium alloy, ferrocolumbium, ferroboron, ferrosilicon, vanadium-nitrogen alloy, zirconium ferrosilicon and ferrotitanium as materials for smelting low-alloy high-speed molten steel in an electric furnace; then, adding the ferrovanadium and part of ferroboron to carry out alloying in a discharging process; finally, adding part of ferroboron and composite modificator in a casting ladle, adding the vanadium-nitrogen alloy, the zirconium ferrosilicon, the ferrosilicon and part of ferroboron in the casting process. The obtained casting piece has a little alloy elements, excellent abrasive resistance and good thermal fatigue resistance. When the high-boron high-speed steel roller material is used as a roller, the service life is prolonged by more than six times relative to a high nickel-chrome infinite cast-iron roller, and prolonged by 20% relative to a high-vanadium high-speed steel roller. Moreover, the roller is safe to use and reliable.
Owner:YUNNAN HEAVY EQUIP MFG GRP
Copper base particle reinforced friction material
InactiveCN1995436AHigh degree of alloyingHigh strengthFriction liningManufacturing cost reductionGraphite
The invention discloses a reinforced friction material of copper-based particle in the friction material making domain, which comprises the following parts: 30-70% Cu, 4-11% Sn, 1-15% Al, 5-18% Fe, 2-15% Al2O3, 2-15% SiO2, 0-15% ferrochrome and 5-20% graphite.
Owner:大连远通制动制品有限公司
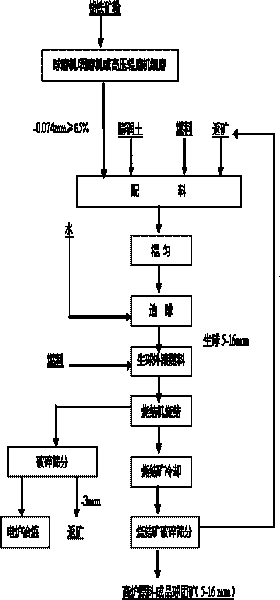
Sintering technology of ferrochrome mineral powder
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-toughness high-boron medium-chrome low-carbon wear-resisting alloy steel and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-toughness high-boron medium-chrome low-carbon wear-resisting alloy steel and a preparation method thereof. The high-toughness high-boron medium-chrome low-carbon wear-resisting alloy steel comprises the following chemical components by weight percentage: 0.20-0.5% of C, 5-12% of Cr, 0.5-1.2% of Si, 3.5-5.5% of Mn, 0.3-2.8% of B, 0.3-2.1% of Cu, 0.2-0.5% of Ti, 0.05-0.25% of Ca, 0.03-0.3% of Ce, 0.02-0.18% of N, 0.05-0.3% of Nb, 0.04-0.09% of Al, 0.1-0.5% of SiMgRe, 0.04-0.13% of K, less than 0.03% of S, less than 0.04% of P and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurity elements. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding a copper plate, silicon iron and ferromanganese iron after steel scrap and chromium iron are melted; after the component adjustment before furnace is qualified, increasing the temperature of the melt to 1560-1620 DEG C, adding a calcium-silicon alloy and aluminum for deoxidation, and orderly adding ferrotitanium and ferroboron, melting, and then discharging; putting a composite inoculant composed of granular rare-earth magnesium alloy with granule size being less than 12mm, metal cerium, Si3N4, VN, Nb and K at the bottom of a steel ladle after baking, and performing inoculation treatment on the molten steel by a rush-into-ladle method, wherein the casting temperature of the molten steel ranges from 1400 DEG C to 1450 DEG C; preserving the heat of castings for 4-6 hours at 700-780 DEG C, and then carrying out subcritical air quenching to obtain the alloy steel.
Owner:丁家伟
Ultra supercritical heat-resistant steel welding rod and production method thereof
InactiveCN103737199AGood workmanshipGood mechanicalWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaFerrosiliconManganese
The invention discloses an ultra supercritical heat-resistant steel welding rod which is composed of an H08A core wire and coating wrapping the surface of the core wire, wherein contents of sulfur, phosphorus, arsenic, aluminum and the like in the H08A core wire are low, and the coating comprises components of 30%-39% of marbles, 22%-30% of fluorites, 6%-9% of rutiles, 7.5%-8.6% of ferromolybdenum, 29%-31% of chromium metal, 5%-9% of silica powder, 2%-5% of ferrosilicon, 1%-1.8% of ferrovanadium, 0.4%-0.8% of ferroniobium, 1.8%-2.8% of nickel powder, 0.4%-0.8% of sodium carbonate, 0.4%-0.8% of carboxyl methyl cellulose (CMC), 0.2%-0.6% of amorphous graphite, 0.6%-1.5% of nitrogen-bearing ferrochromium, 1.6%-3% of electrolytic manganese, 3%-3.8% of cobalt powder and 4%-5% of ferroboron.
Owner:ATLANTIC CHINA WELDING CONSUMABLES
Special flux-cored wire for surfacing repair of BD roller
InactiveCN101804530AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaHigh carbonManganese
The invention discloses a special flux-cored wire for surfacing repair of a BD roller, which consists of a tube skin and a flux core, wherein the tube skin is an H08A steel strip, and the flux core comprises the following components by weight percent: 15-25% of high-carbon ferrochrome, 2-10% of micro-carbon ferrochrome, 5-7% of metal manganese, 6-12% of ferromolybdenum, 3-10% of ferrotungsten, 5-10% of ferrovanadium, 0.5-6% of ferrotitanium, 0.3-5% of yttrium-based rare-earth, 1-3% of ferrocolumbium, 4-10% of cryolite and 10-50% of ferrous powder, wherein the filling coefficient is 30-45%. The special flux-cored wire selects a Cr-Mo-W-V alloy system with optimal alloy matching and carries out Ti-Nb-Re micro-alloy grain refinement, thereby leading a surfacing repair layer to have the advantages of high hardness, high wear resistance, high toughness and high anti-cold and hot alternating thermal fatigue performance, and exponentially prolonging the service life of the BD roller after surfacing repair in comparison with the BD roller after the ordinary roller flux-cored wire repair.
Owner:邯郸市永固冶金备件有限公司
Wear-resistant overlaying flux-cored wire
InactiveCN104325232ASimple welding processA large amountWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaElectrolysisFerrosilicon
The invention relates to a wear-resistant overlaying flux-cored wire. The wear-resistant overlaying flux-cored wire comprises a low-carbon steel outer layer and a flux core inner layer, wherein the filling coefficient of a flux core is 45-55 percent, and the overlaying flux-cored wire is characterized in that the flux core comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1-6 parts of microcrystalline graphite, 1-4 parts of aluminum-magnesium alloy, 1-2 parts of fluoride, 1-2 parts of silicate, 1-3 parts of titanate, 1-2 parts of carbonate, 30-80 parts of high carbon ferro-chrome, 15-45 parts of metal chromium carbide, 5-10 parts of electrolytic chromium powder, 3-6 parts of high carbon ferromanganese, 1-4 parts of rare earth ferrosilicon, 2-6 parts of ferrosilicon, 4-10 parts of ferromolybdenum, 5-10 parts of ferrotungsten, 5-10 parts of ferrovanadium, 4-10 parts of ferrocolumbium, 4-10 parts of ferrotitanium and 1-4 parts of ferroboron. The wear-resistant overlaying flux-cored wire has the advantages of good hardness, wear resistance and anti-cracking performance.
Owner:李永锋
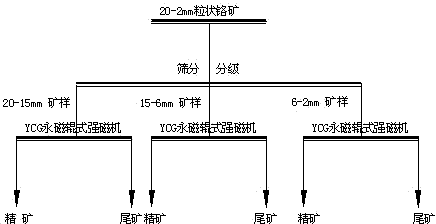
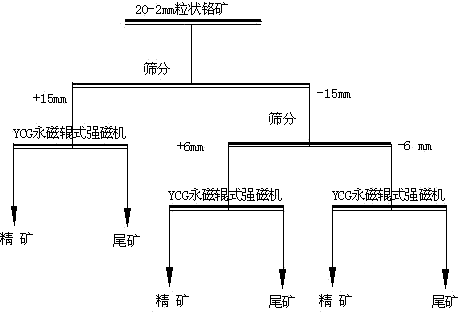
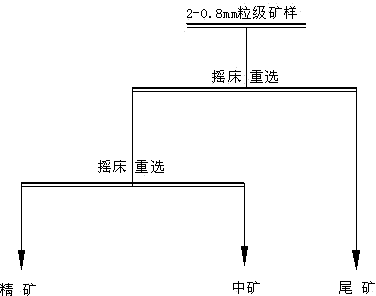
Novel beneficiation technology of high-grade ferrochrome ore
The invention discloses a novel beneficiation technology of high-grade ferrochrome ore. The novel beneficiation technology includes the following technological processes that ferrochrome ore is broken and is screened and classified into the ore of +20 mm fraction and the ore of -20 mm fraction. The ore of the +20 mm fraction receives manual back picking or hotching, large waste ore is thrown, and block concentrate is obtained. The narrow grade of the -20 mm fraction is screened and classified into four fractions, namely the 20-15 mm fraction, the 15-6 mm fraction, the 6-2 mm fraction and the 2-0 mm fraction. For the 20-15 mm fraction, the 15-6 mm fraction and the 6-2 mm fraction, a permanent magnet roller type intensity magnetic separator is used for performing dry intense magnetic separation. The 2-0 mm fraction is further screened and classified into the 2-0.8 mm fraction and the 0.8-0 mm fraction. For the 2-0.8 fraction, a shaker is selected again to obtain shaker gravity concentrate, and for the 0.8-0 mm fraction, a spiral chute and the shaker are used and a united procedure is selected again to obtain the thin-particle gravity concentrate. The novel beneficiation technology can be used for obtaining the concentrate and removing tailings in advance and has the advantage of being lower in energy consumption compared with other technologies. The technology can be used for grading chrome ore and can also be used for grading other weak magnetic iron minerals such as manganese ore, goethite, siderite and limonite.
Owner:SINOSTEEL MAANSHAN INST OF MINING RES
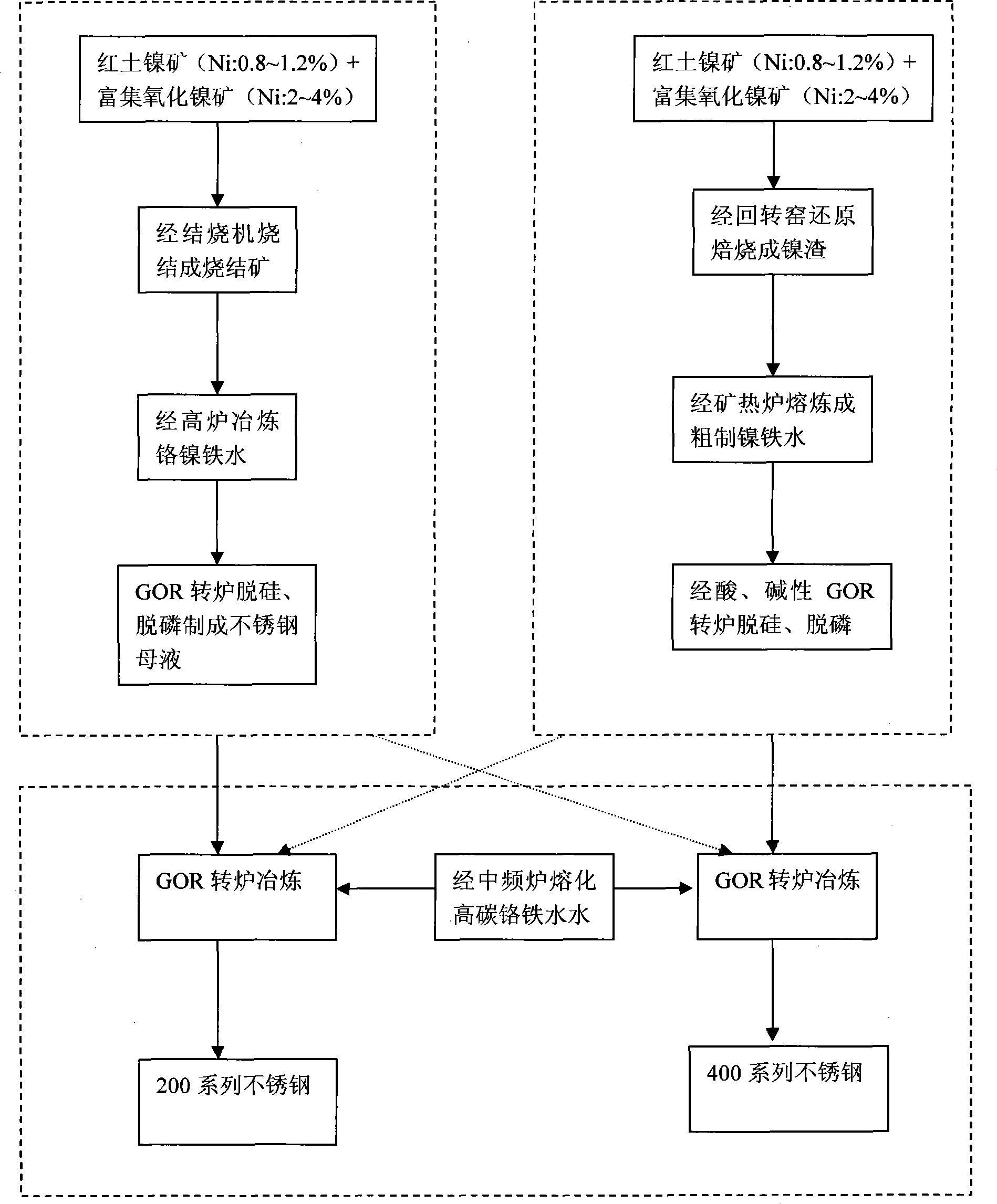
Process for directly producing austenitic stainless steel by utilizing oxide nickel
ActiveCN101445845AImprove dephosphorization efficiencyHigh yieldBlast furnace detailsElectric arc furnaceFerrochrome
The invention relates to a technological process for stainless steel smelting, in particular to a process for directly producing austenitic stainless by utilizing oxide nickel. The process has the following advantages: oxide nickel of various grades is adopted to obtain different ingredients of molten nickel iron by smelting in a blast furnace and a submerged arc furnace, an electric arc furnace is cancelled as a melting unit, the chemical heat of the molten iron is utilized to melt all or part of chromium and manganese alloy, and a bottom-blowing argon-oxygen converter is utilized to dephosphorize so as to improve the dephosphorization efficiency of molten chromium iron and the obtainment yield of chromium, thereby the following series and trademarks of products, i.e. 200 series of 201, 202, J4, and the like, 300 series of 304,304L, 316,321,329, and the like, are produced; and meanwhile, all links in the whole production flows are organically combined, and various energy sources, such as coal gas, steam, afterheat, and the like are fully utilized and recycled, thereby the energy consumption is low, the secondary waste gas discharge amount not great, the production cost and the raw material cost are low, and the investment and the occupied area are not great.
Owner:陈法官 +1
Soldering wire material containing nitrogen alloyed alloy core in form of hard surface
InactiveCN1562552AGuaranteed performanceIncrease productivityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaHigh carbonNitrogen
A nitrogen alloyed welding wire with hard surface and alloy core for repairing on manufacturing rolling roller, mine machinery and large digger features that its core powder is prepared from alloy powder and mineral powder through mixing, and contains rutile, high-carbon ferrochromium, low-carbon ferrochromium, Si Al-Mg alloy, Mn, ferromolybdenum, ferrovanadium, ferrotictanium, Ni, chromium nitride and Fe. The nitrogen is used to replace part of carbon for alloying, so improving anticracking performance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Pile up welding flux cored wire used for remanufacturing compound bimetal large special wear resistant parts
InactiveCN100999042ASimple manufacturing methodReduce consumptionArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsWear resistantHigh carbon
The present invention discloses a surfacing flux-cored wire for refabrication of composite bimetal large-size special wear-resistant component. Its chemical composition includes (by wt%) 45-55% of high-carbon ferrochrome, 1-4% of high-carbon manganese iron, 4-6% of tantiron, 1-4% of ferrovanadium, 1-4% of ferromolybdenum, 2-5% of rare earth oxide, 10-20% of graphite, 1-4% of ferroniobim, 5-8% of chrome powder, 1-2% of ferroboron, 4-6% of fluorite and 2-5% of aluminium-magnesium powder. Its external covering adopts low-carbon steel tape. Besides, said invention also provides its application method.
Owner:QINHUANGDAO WEIERDE SPECIAL WELDING IND
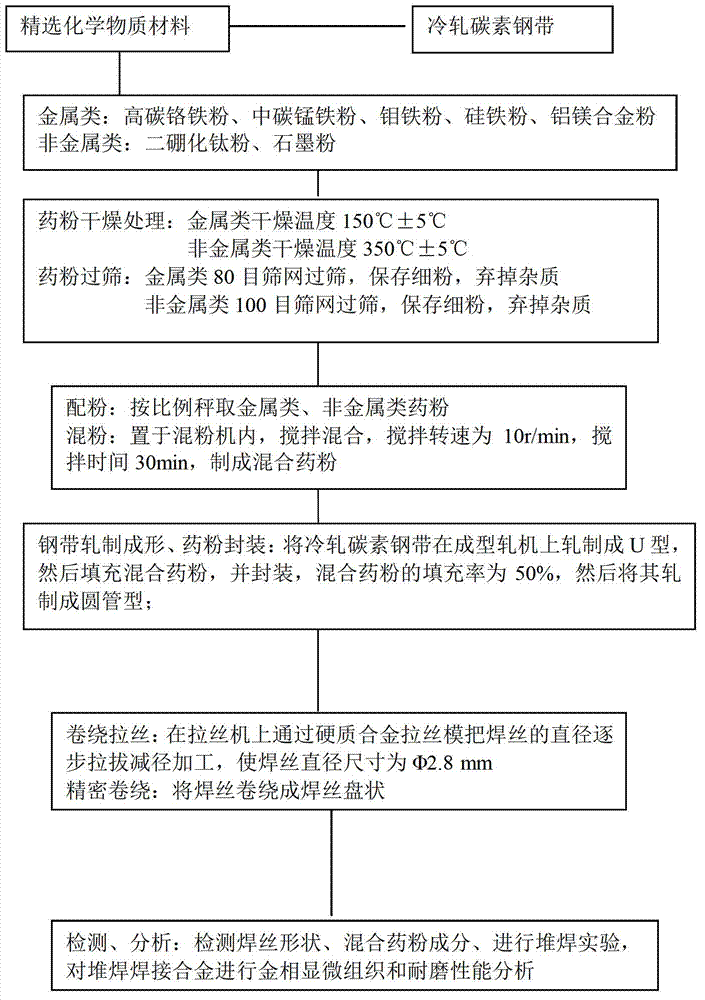
Method for manufacturing TiB<2> ceramic-reinforced wear-resistant surfacing flux-cored welding wire
InactiveCN103240547AImprove welding strengthImprove wear resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaFerrosiliconManganese
The invention relate to a method for manufacturing a TiB<2> ceramic-reinforced wear-resistant surfacing flux-cored welding wire. The method aims to overcome shortcomings of existing flux-cored welding wires for wear-resistant surfacing. The method includes mixing metal powder with nonmetal powder; manufacturing a steel strip of the welding wire; adding the powder into the steel strip; and winding the steel strip to form a reel and packaging the reel to obtain the titanium diboride ceramic-reinforced wear-resistant surfacing flux-cored welding wire. The metal powder includes high-carbon ferrochrome powder, medium-carbon ferromanganese powder, ferromolybdenum powder, ferrosilicon powder and aluminum magnesium alloy powder, the nonmetal powder includes titanium diboride powder and graphite powder. The method has the advantages that the proportion of chemical compositions of a powder core of the flux-cored welding wire is reasonable and advanced, data are accurate, the TiB<2> ceramic-reinforced wear-resistant surfacing flux-cored welding wire is good in welding effect and high in quality, a welded joint is high in strength and good in wear-resistant performance, the hardness of a welded layer reaches HRC68.4, the wear-resistant performance is improved by 20%, and the titanium diboride ceramic-reinforced wear-resistant surfacing flux-cored welding wire is perfect.
Owner:太原理工技术转移有限公司
Flux-cored steel belt for build-up welding and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101306493AIncrease varietyIncrease weld widthWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaHigh carbonFerrosilicon
The invention discloses a resurfacing welding used drug cored steel strap and the preparation method. The steel strap is prepared from a mild steel strap and drug powder enwrapped therein, the shape of the steel strap is a tube with the longitudinal cross-section to be in a long and flat shape or in a similar rectangle shape, the longitudinal length can be determined randomly, and the transverse sides of the steel strap are connected in a seam manner or a related joint manner; the drug powder is uniformly filled in the tube rolled from the steel strap, wherein the particle diameter of the drug powder is smaller than 120 Mum, the components include (by weight) 45-70 parts of high carbon ferrochrome, 5-35 parts of ferrovanadium, 1-8 parts of No.75 ferrosilicon, 1-10 parts of high carbon ferromanganese, 2-16 parts of ferroboron, 1-8 parts of ferrotitanium, 0-5 parts of ferroniobium, 2-8 parts of ferromolybdenum, 0-10 parts of graphite, 0-5 parts of fluorite and 0-6 parts of potassium titanate. The drug cored steel strap adopting the invention can efficiently improve the abrasion resistance of the metal on the resurfacing welding layer and the stability of the electric arc, and can be coiled into coils, thereby being suitable for continuous automatic resurfacing welding.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com