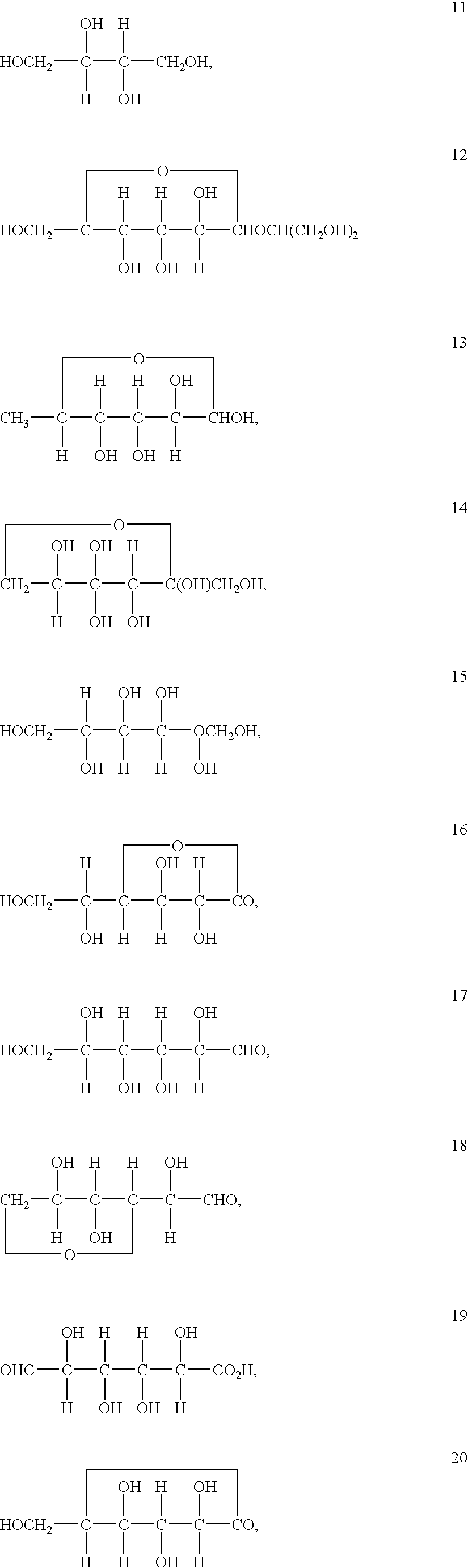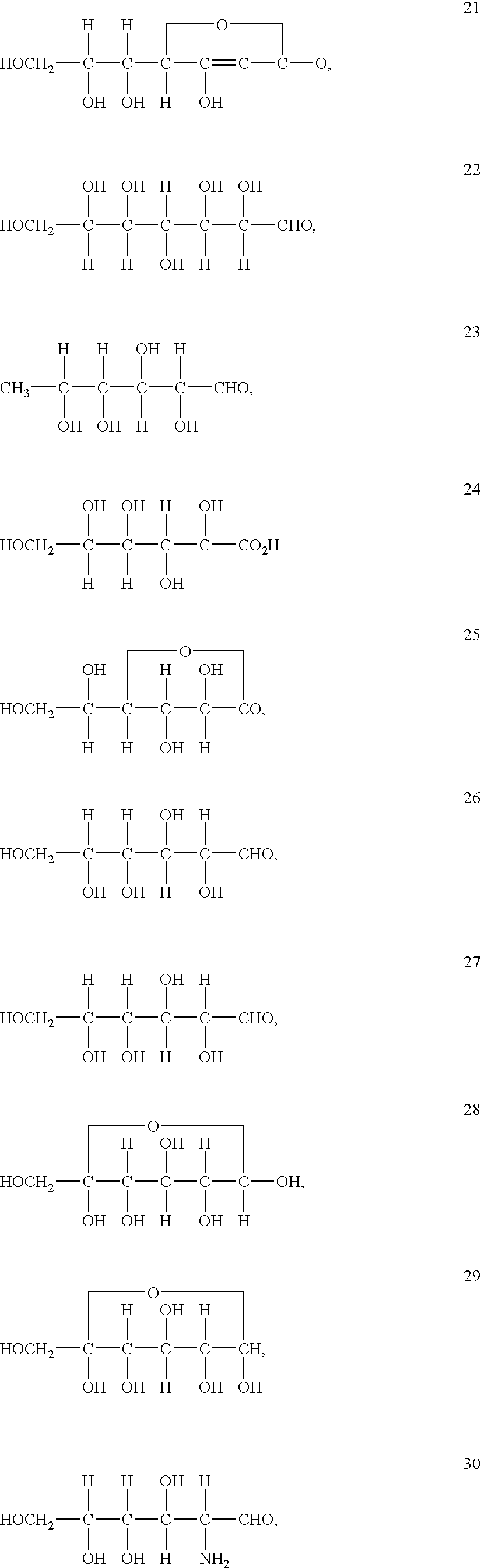Patents
Literature
2423 results about "Vanadium atom" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
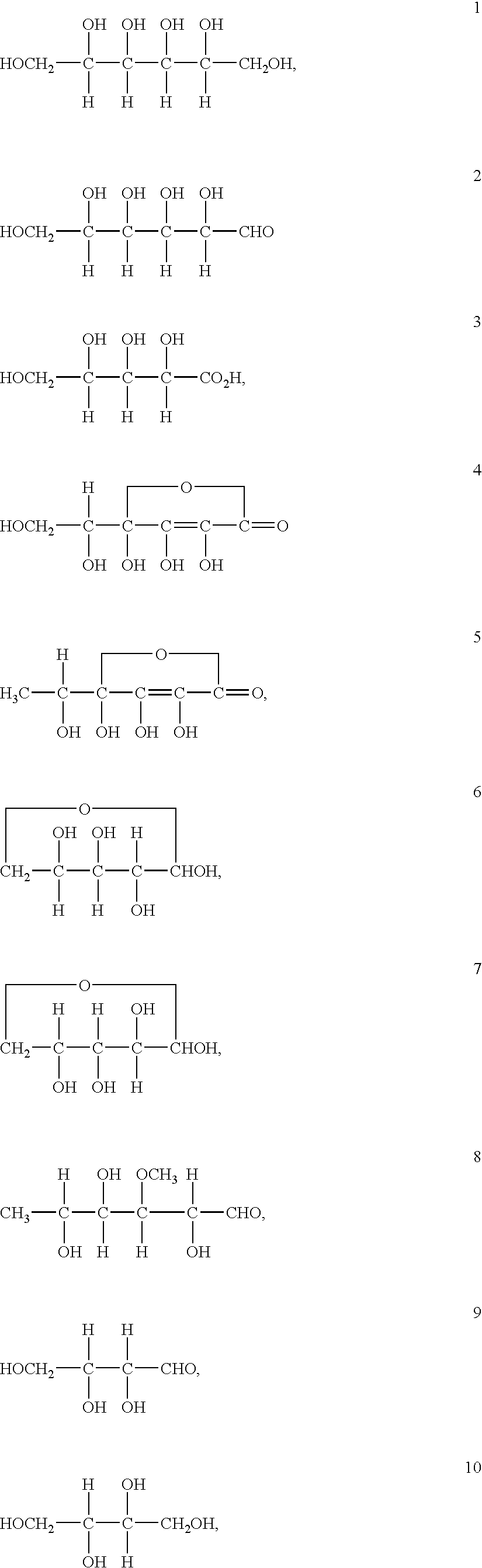
Vanadium is a chemical element with atomic number 23 which means there are 23 protons and 23 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Vanadium is V. Vanadium is a hard, silvery grey, ductile, and malleable transition metal.
Stabilized vanadium electrolyte solutions for all-vanadium redox cells and batteries
InactiveUS6562514B1Effective amountEasy to modifyFinal product manufactureRegenerative fuel cellsRedoxPhysical chemistry
Owner:JD HLDG INC
Metallurgical V-N microalloying and compound deoxidation cored wire
A metallurgical V-N microalloying and compound deoxidation cored wire contains a core wire and a cladding steel belt. The technical key point of the cored wire is as follows: the core wire of the cored wire consists of a vanadium-increasing agent, a nitrogen-increasing agent and a deoxidizing nitrogen-fixing agent of which particle sizes are less than 6mm, wherein the vanadium-increasing agent is ferrovanadium, nitrided ferrovanadium or vanadium pentoxide; the nitrogen-increasing agent is ferrosilicon nitride, silicomanganese nitride, ferromanganese nitride, ferrochromium nitride, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride or calcium cyanamide; and the deoxidizing nitrogen-fixing agent contains one or more of aluminum, calcium, magnesium and barium, and can also contain one or more of titanium, zirconium, niobium, manganese, chromium, silicon, carbon and iron. By adopting the cored wire, the V / N ratio of steel can get closer to the optimal proportion, the enhancing function of vanadium can be utilized furthest, vanadium resources can be saved, the recovery rate of nitrogen is high, the nitrogen content is stable, the compound deoxidation function can also be realized, the V-N microalloying cost can be reduced and the quality of steel can be increased.
Owner:侯巍 +2
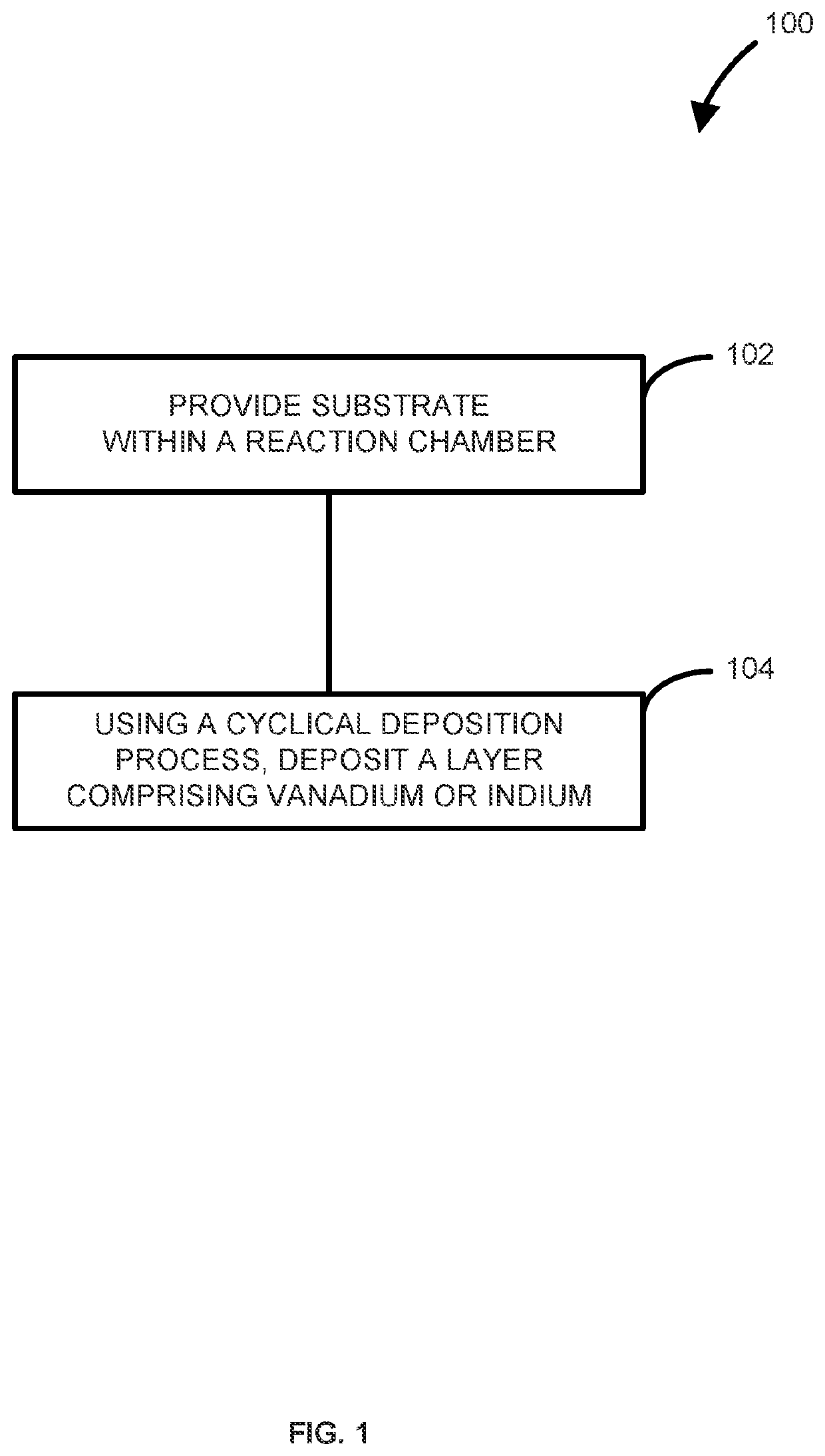
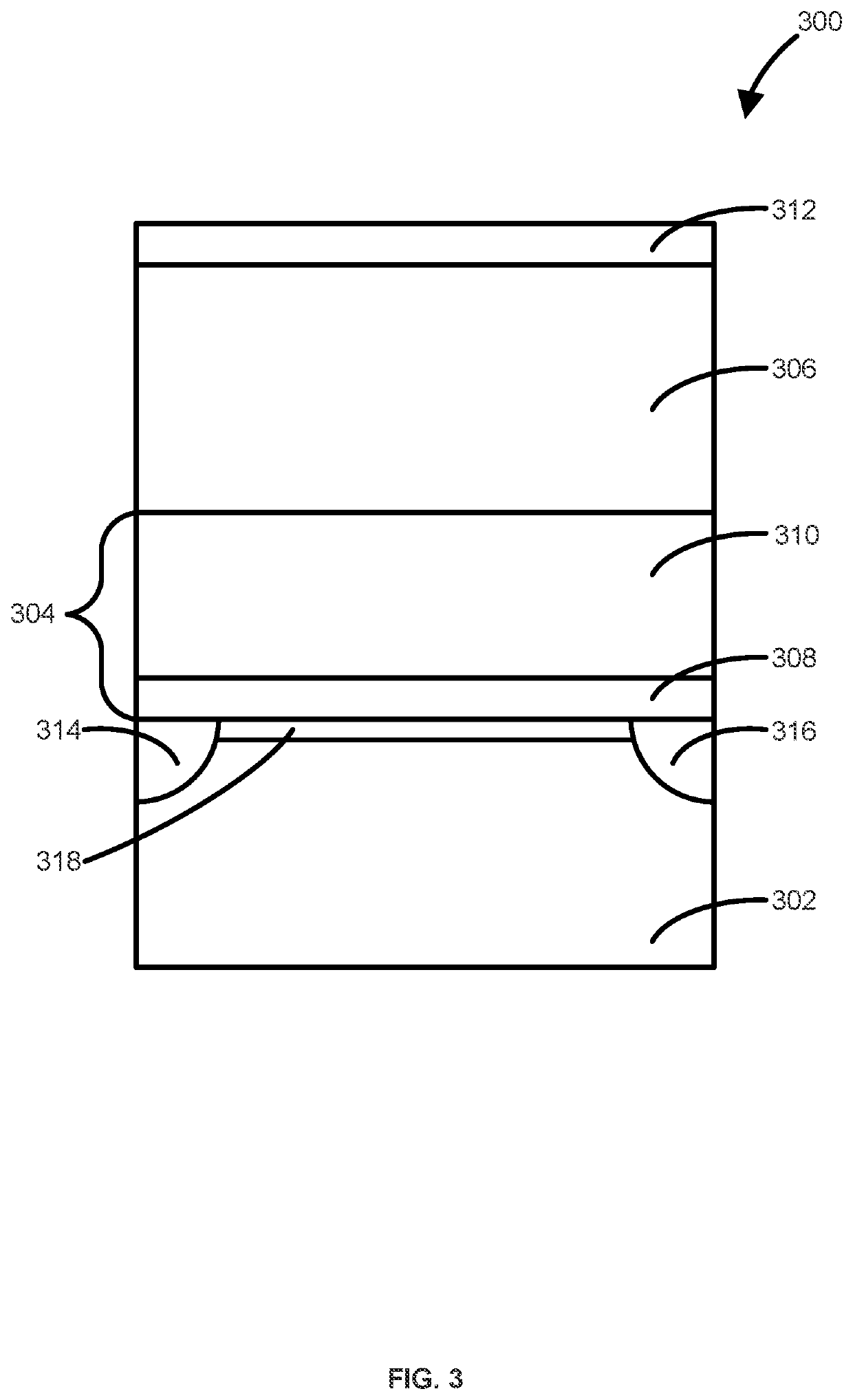
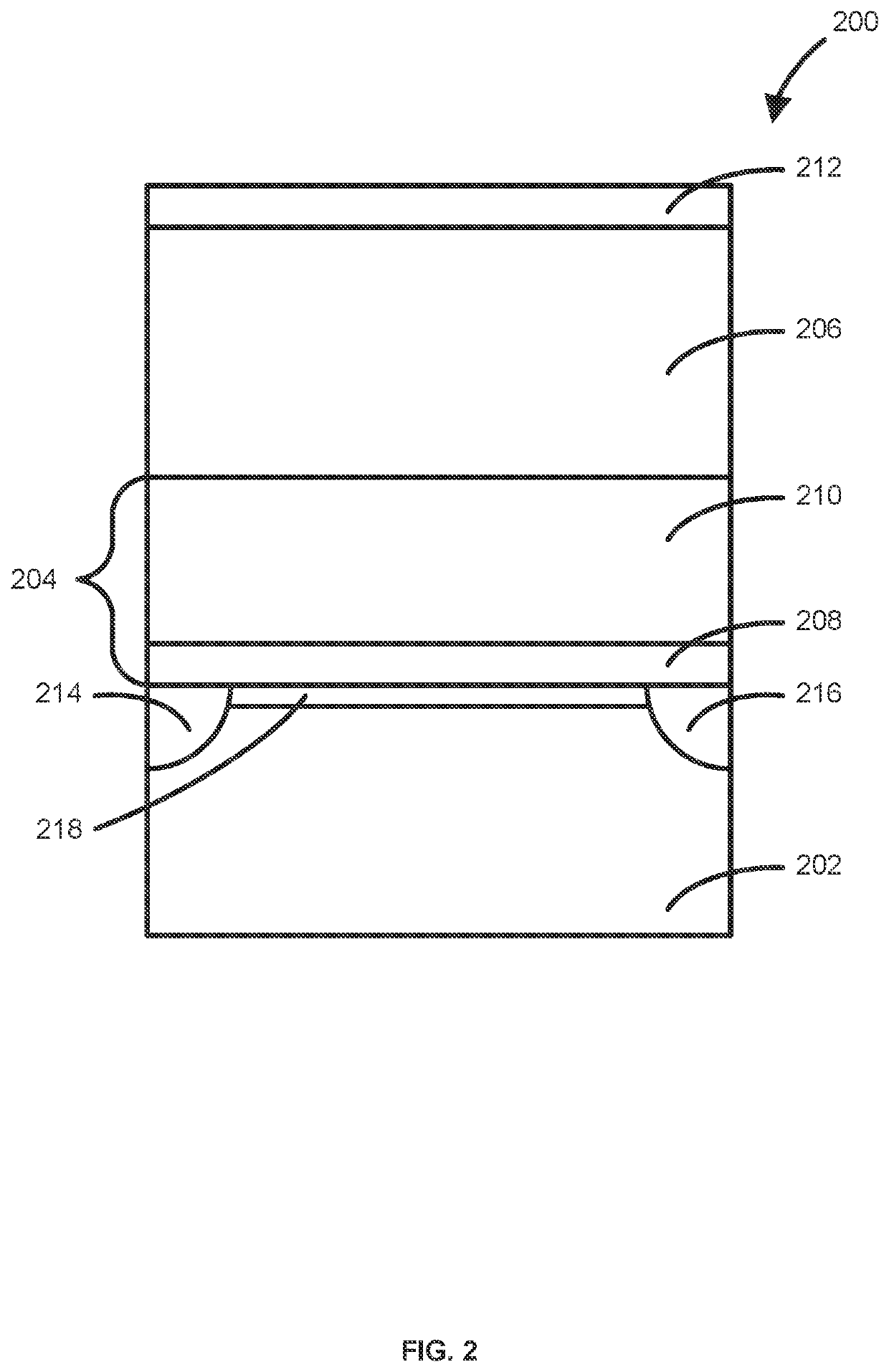
Method of forming structures including a vanadium or indium layer
ActiveUS20210242011A1Readily apparentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumChemical physics
Methods and systems for depositing vanadium and / or indium layers onto a surface of a substrate and structures and devices formed using the methods are disclosed. An exemplary method includes using a cyclical deposition process, depositing a vanadium and / or indium layer onto the surface of the substrate. The cyclical deposition process can include providing a vanadium and / or indium precursor to the reaction chamber and separately providing a reactant to the reaction chamber. The cyclical deposition process may desirably be a thermal cyclical deposition process. Exemplary structures can include field effect transistor structures, such as gate all around structures. The vanadium and / or indium layers can be used, for example, as barrier layers or liners, as work function layers, as dipole shifter layers, or the like.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
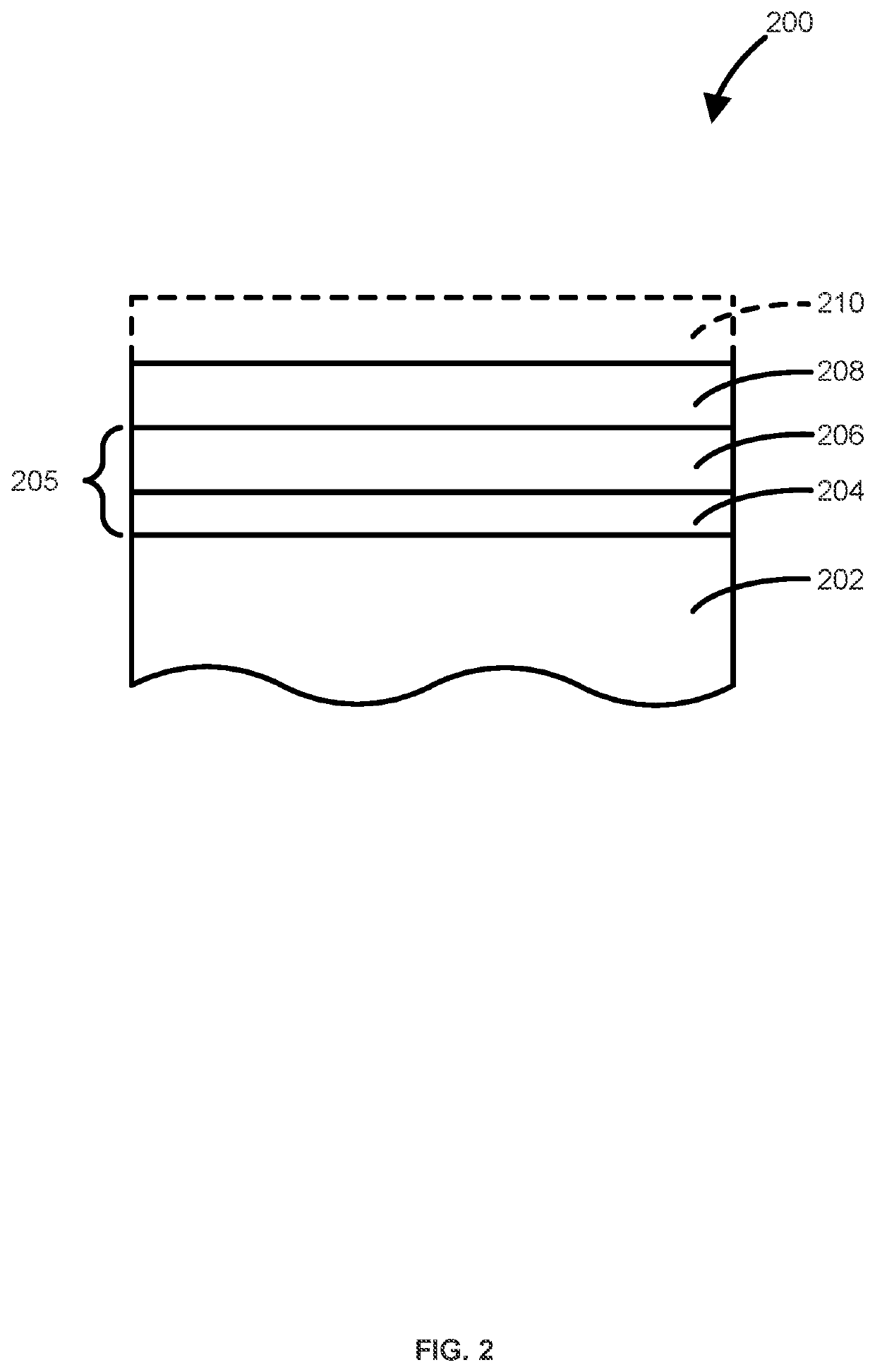
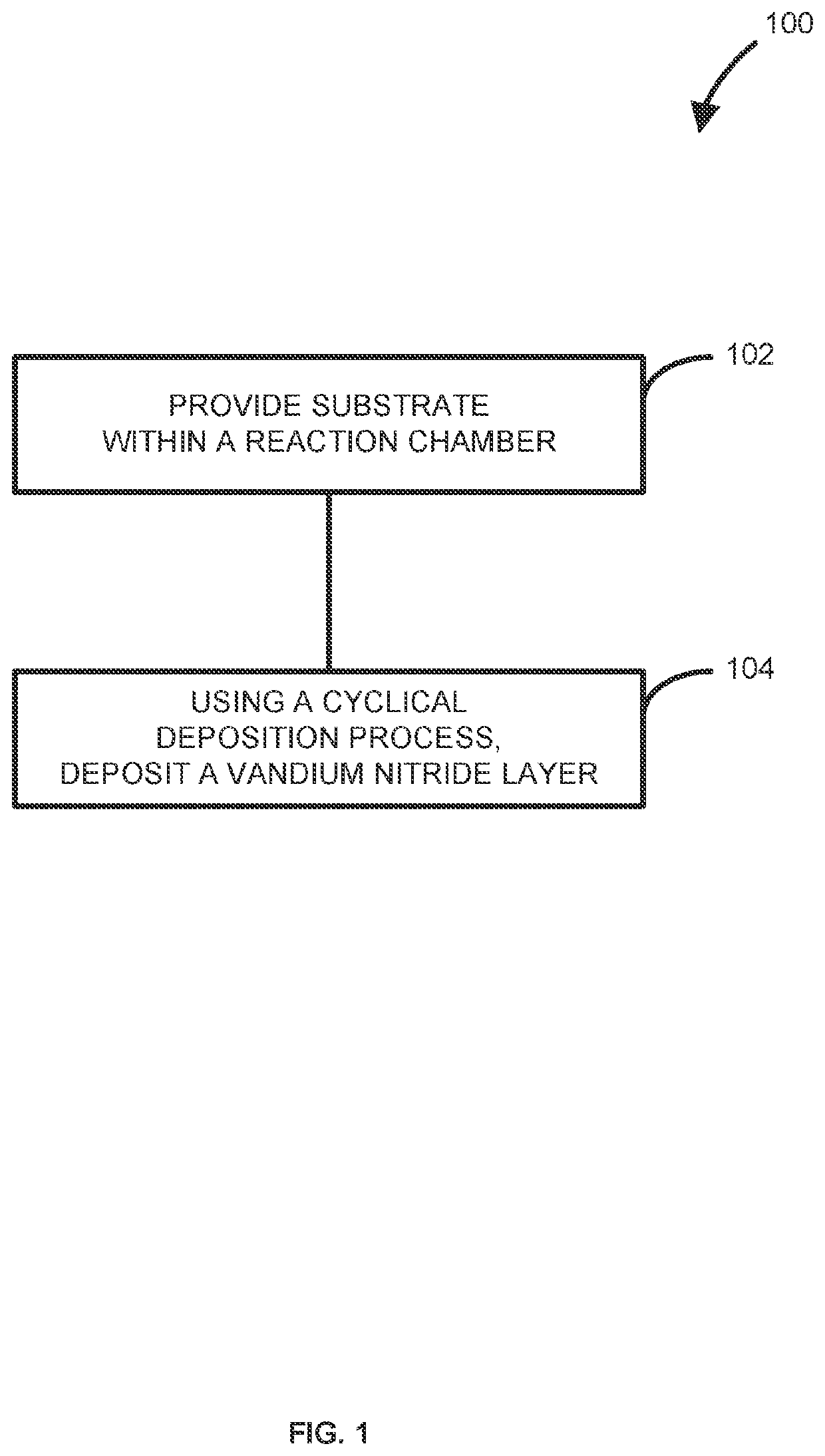
Method of forming vanadium nitride layer and structure including the vanadium nitride layer
PendingUS20210180184A1Readily apparentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingVanadium nitrideVanadium atom
Methods and systems for depositing vanadium nitride layers onto a surface of the substrate and structures and devices formed using the methods are disclosed. An exemplary method includes using a cyclical deposition process, depositing a vanadium nitride layer onto a surface of the substrate. The cyclical deposition process can include providing a vanadium halide precursor to the reaction chamber and separately providing a nitrogen reactant to the reaction chamber. The cyclical deposition process may desirably be a thermal cyclical deposition process.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Glazing coated with at least one layer having thermochromic properties
InactiveUS20050147825A1Other chemical processesSynthetic resin layered productsOptical propertyVanadium oxide
A glazing coated with at least one layer having thermochromic properties comprising vanadium oxide, and also with at least one other layer having thermal properties, such as an infrared reflecting layer, and / or at least one other layer having optical properties, such as antireflection in the visible, and / or electrical conduction properties; and having a particular application for making solar control glazing.
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
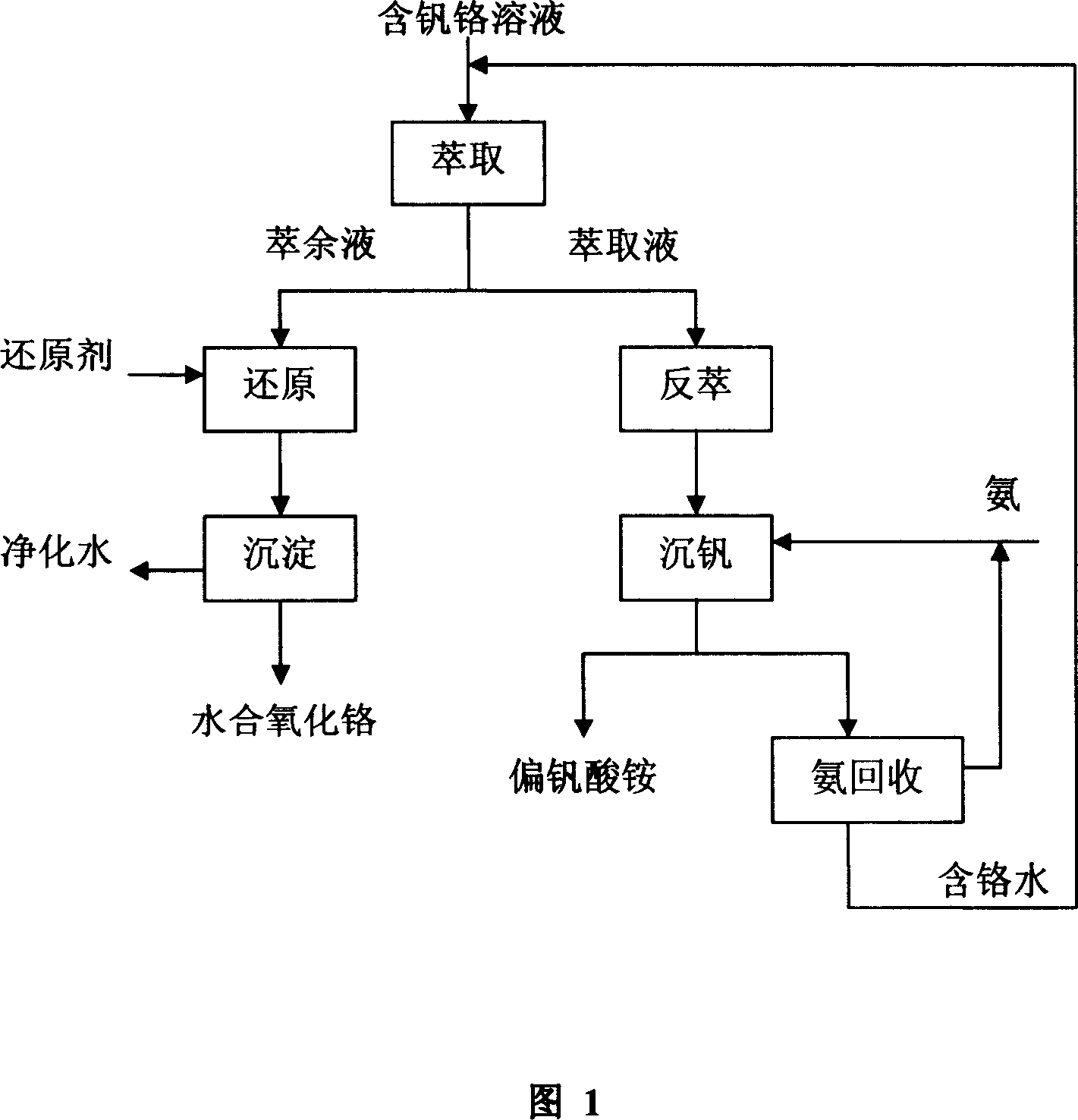
Method for separating and reclaiming vanadium and chromium from solution containing vanadium and chromium
ActiveCN101121962ALow costSimple processProcess efficiency improvementHydration reactionDistillation
This invention relates to an entirely new technology of completely recovering chromium and vanadium from vanadium-chromium miscible liquid. The main procedures include: first a primary-secondary compound amine extracting agent contacts the vanadium-chromium miscible liquid by means of countercurrent contact and extract, so as to extract most of vanadium and a small amount of chromium into a organic phase while most of chromium stays into a aqueous phase; and a reduction reaction is conducted with pH of acid adjustable faffinate (aqueous phase) and a certain amount of a reducing agent; the sodium hydroxide is used for adjusting pH value of the solution and filter, and finally the product is hydrous chromium oxide; at that time, the lye is used as a stripping agent; the vanadium is stripped from the vanadium-rich organic phase into water in the manner of countercurrent contact; and the vanadium is separated from the solution witthe method of ammonium precipitation and in the form of ammonium metavanadate; and finally the supernatant clear solution of the one is processed with deposited vanadium with a high-efficient distillation technology, and the strong aqua ammonia is left in the tower top and deamidization solution is left in the tower bottom until the extraction process is reached. The invention uses the primary-secondary compound amine as the extracting agent, extracts and separates vanadium and chromium selectively at a low temperature. The invention not only has a simple process flow, but also is low-cost, quite applicable in large-scale industrial production. In addition, the invention also provides high-purity ammonium metavanadate and 16 percentage strong aqua ammonia, and makes sure the vanadium and chromium can be completely recovered through re-use of the solution.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting vanadium from vanadium slag clinker leached by ammonium carbonate
ActiveCN102560086ALow costImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionMetallurgy
The invention discloses a method for extracting vanadium from vanadium slag clinker leached by ammonium carbonate. The method comprises the following steps of: calcifying and roasting vanadium slag of which the molar ratio of CaO to V2O5 is (2-3):1 at the temperature of between 700 and 900 DEG C, grinding the vanadium slag clinker, sieving, and leaching by an ammonium carbonate solution at the leaching temperature of between 60 and 98 DEG C for 30 to 120 minutes, filtering to obtain vanadium-containing leachate, performing vanadium deposition on the vanadium-containing leachate to obtain a vanadium finished product, wherein when the ammonium carbonate solution is leached, the concentration of the ammonium carbonate solution is between 200 and 800 g / L, and a liquid / solid ratio of the ammonium carbonate solution to the vanadium slag clinker is (5-30):1. According to the method, a leaching process is easy to operate and low in cost, and has low requirement on the equipment; and a leaching agent is low in cost and can be recycled, so that the production cost is reduced. By the method, the leaching rate of the vanadium is high, namely is over 90 percent, impurity elements and particularly a phosphorus element in the leachate are reduced, and the leaching rate of phosphorus is less than 10 percent.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Microbolometer for infrared detector or Terahertz detector and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20110315981A1Improve business performanceLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPyrometry using electric radation detectorsComposite filmMicrobolometer
A microbolometer includes a micro-bridge structure for uncooling infrared or terahertz detectors. The thermistor and light absorbing materials of the micro-bridge structure are the vanadium oxide-carbon nanotube composite film formed by one-dimensional carbon nanotubes and two-dimensional vanadium oxide film. The micro-bridge is a three-layer sandwich structure consisting of a layer of amorphous silicon nitride base film as the supporting and insulating layer of the micro-bridge, a layer or multi-layer of vanadium oxide-carbon nanotube composite film in the middle of the micro-bridge as the heat sensitive and light absorbing layer of the microbolometer, and a layer of amorphous silicon nitride top film as the stress control layer and passivation of the heat sensitive film. The microbolometer and method for manufacturing the same can overcome the shortcomings of the prior art, improve the performance of the device, reduce the cost of raw materials and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method of carbon coated vanadium sodium phosphate positive electrode material
InactiveCN105336924AEasy diffusion distanceImprove electrochemical performanceNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsCell electrodesSodium phosphatesElectrical battery
A preparation method of a carbon coated vanadium sodium phosphate positive electrode material comprises the steps: with glucose as a reducing agent and a carbon source and water as a dispersant, carrying out ball milling of NH4VO3, NaH2PO4.2H2O and glucose in water, carrying out spray drying, calcining, and thus obtaining the carbon coated vanadium sodium phosphate positive electrode material. The method has the advantages of low synthesis temperature, simple steps, easily obtained raw materials, and advantageous industrialization; the obtained carbon coated vanadium sodium phosphate positive electrode material has a structure with uniform primary particles, has the particle size of 100-200 nm, and has the characteristics of short sodium ion diffusion distance, fast transmission speed, high specific surface area, high electrical conductivity and fast ion transmission and the like. The obtained carbon coated vanadium sodium phosphate positive electrode material is assembled into a battery; in a voltage scope of 2.0-3.75 V and under 1 C multiplying power, the highest first charge and discharge capacity per gram can reach 93.5 mAh*g<-1>, the capacity retention rate can be up to 97.7% after cycling for 50 circles with the 1C multiplying power, and excellent electrochemical performance is showed.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Phase-transition intelligent materials with adjustable phase-transition temperature and process for preparing same
InactiveCN1837061AReduce infrared transmittanceIt has the function of intelligent temperature controlOther chemical processesVanadium oxidesVanadium dioxideMaterials science
The invention relates to an intelligent phase-change material with adjustable phase-change temperature and its preparing process, which comprises making doped vanadium dioxide precursor through liquid phase precipitation method, carrying out filtering, scouring, drying, heating and crystallizing. The crystal grain dimension of the obtained phase-change material is less than 100 nanometers, thus can be applied into intelligent window coating material and temperature measurement resistors.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for extracting vanadium and chromium from converter vanadium chromium slag
ActiveCN103614566AIncrease concentrationReduce concentrationProcess efficiency improvementSlagPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for extracting vanadium and chromium from converter vanadium chromium slag. The method comprises the following steps: 1) adding Na2CO3 into the vanadium chromium slag, mixing uniformly and carrying out oxidizing roast on the mixture, wherein the addition of Na2CO3 is controlled according to a molar ratio of V2O3 / Na2CO3 in the vanadium chromium slag being 0.1-0.4; grinding the roasted clinker, and leaching with water to obtain a primary roasted leaching solution and residue; 2) drying and grinding the residue to serve as a raw material from which vanadium and chromium can be extracted in the second step, adding Na2CO3 in the residue, mixing uniformly and carrying out oxidizing roast on the mixture, wherein the addition of Na2CO3 is controlled according to a molar ratio of (V2O3+Cr2O3) / Na2CO3 in the residue being 0.1-0.4; grinding the roasted clinker, and leaching with water to obtain a secondary roasted leaching solution; and 3) separately separating and extracting the vanadium and chromium from the primary roasted leaching solution and the secondary roasted leaching solution. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process and high in vanadium and chromium immersion ratio and brings convenience for separating vanadium from chromium subsequently.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
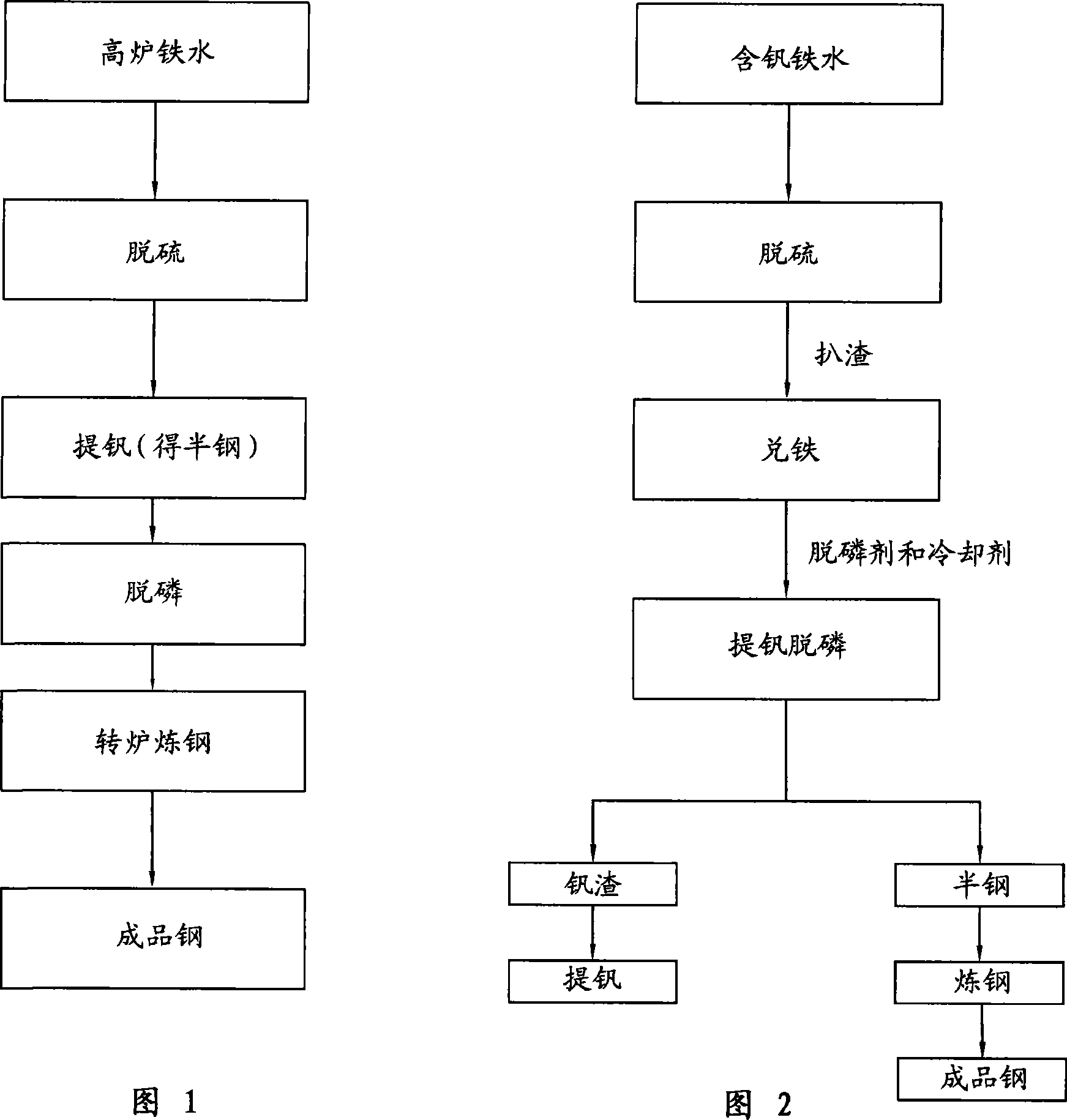
Method for extracting vanadium and removing phosphorus from vanadium-containing molten iron and steel-smelting technique using the same method
The invention provides a vanadium extraction dephosphorization process from vanadium melted iron and a steel-smelting technology which uses the process. The vanadium extraction dephosphorization process from vanadium melted iron comprises adding vanadium extraction dephosphorization agent and cooling agent in melted iron in the process of oxygen supply blowing for vanadium melted iron, and obtaining vanadium slag and low phosphorus semi-steel. The process can extract vanadium at the same time of dephosphorization, thereby not only guaranteeing the effective extraction of vanadium, but also effectively removing phosphorus in melted iron.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Full vanadium ion fluid cell electrolyte and preparing process thereof
InactiveCN1719655ASimple production processLow costConductive materialRegenerative fuel cellsIonChemistry
This invention relates to an electrolyte of a full-vanadium ionic fluid-flow battery composed of V salt sulfate, H2So4, water, alcohol and additives, which are Na2SO4, Na pyrophosphate, salufer and hydrogen peroxide. This invention also provides a preparation method: pumping qualified V liquid from a V-plant into a reaction tank, regulating the PH value of the solution and inletting liquid SO2 into it to be recovered, then the PH value of the solution is regulated with Na2SO4 to deposit VO2 to be dissolved in the solution containing H2SO4, water and alcohol to be added with the additives to be electrolyzed in the tank to get the V electrolyte with 50% of 3valence and 4 valence V separately and density of 1.0mol / L~4.2mol / L .
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Production method for a bulk SiC single crystal with a large facet and monocrystalline SiC substrate with homogeneous resistance distribution
ActiveUS8865324B2Improve adaptabilityPolycrystalline material growthGlass/slag layered productsDopantSource material
A method is used to produce a bulk SiC single crystal. A seed crystal is arranged in a crystal growth region of a growing crucible. An SiC growth gas phase is produced in the crystal growth region. The bulk SiC single crystal having a central longitudinal mid-axis grows by deposition from the SiC growth gas phase, the deposition taking place on a growth interface of the growing bulk SiC single crystal. The SiC growth gas phase is at least partially fed from an SiC source material and contains at least one dopant from the group of nitrogen, aluminum, vanadium and boron. At least in a central main growth region of the growth interface arranged about the longitudinal mid-axis, a lateral temperature gradient of at most 2 K / cm measured perpendicular to the longitudinal mid-axis is adjusted and maintained in this range. The bulk SiC single crystal has a large facet region.
Owner:SICRYSTAL GMBH
Metallic catalyst for synthesizing dimethoxym ethane and methyl formate and production method thereof and use
InactiveCN101327444ALarge specific surface areaSmall particlesMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationFormate EstersTitanium
The present invention relates to a metal catalyst synthesizing methylal and methyl formate. In weight percentage of the metal catalyst, the content of vanadium is calculated by the weight of V2O5; the content of titanium is calculated by the weight of TiO2; the weight proportion of the V2O5 and the TiO2 in the catalyst is 5 to 70 to 30 to 95; the V2O5 and the TiO2 take 20 percent to 100 percent of the catalyst in weight percentage; the content of accessory ingredient is calculated by the content of the oxide of the accessory ingredient and takes 0wt percent to 2.0wt percent of the catalyst in weight percentage; support takes 0wt percent to 78wt percent of catalyst in weight percentage. The catalyst has the advantages of high methanol conversion rate, the high selectivity of the methylal and the methyl formate, the good stability of the catalyst and long life.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
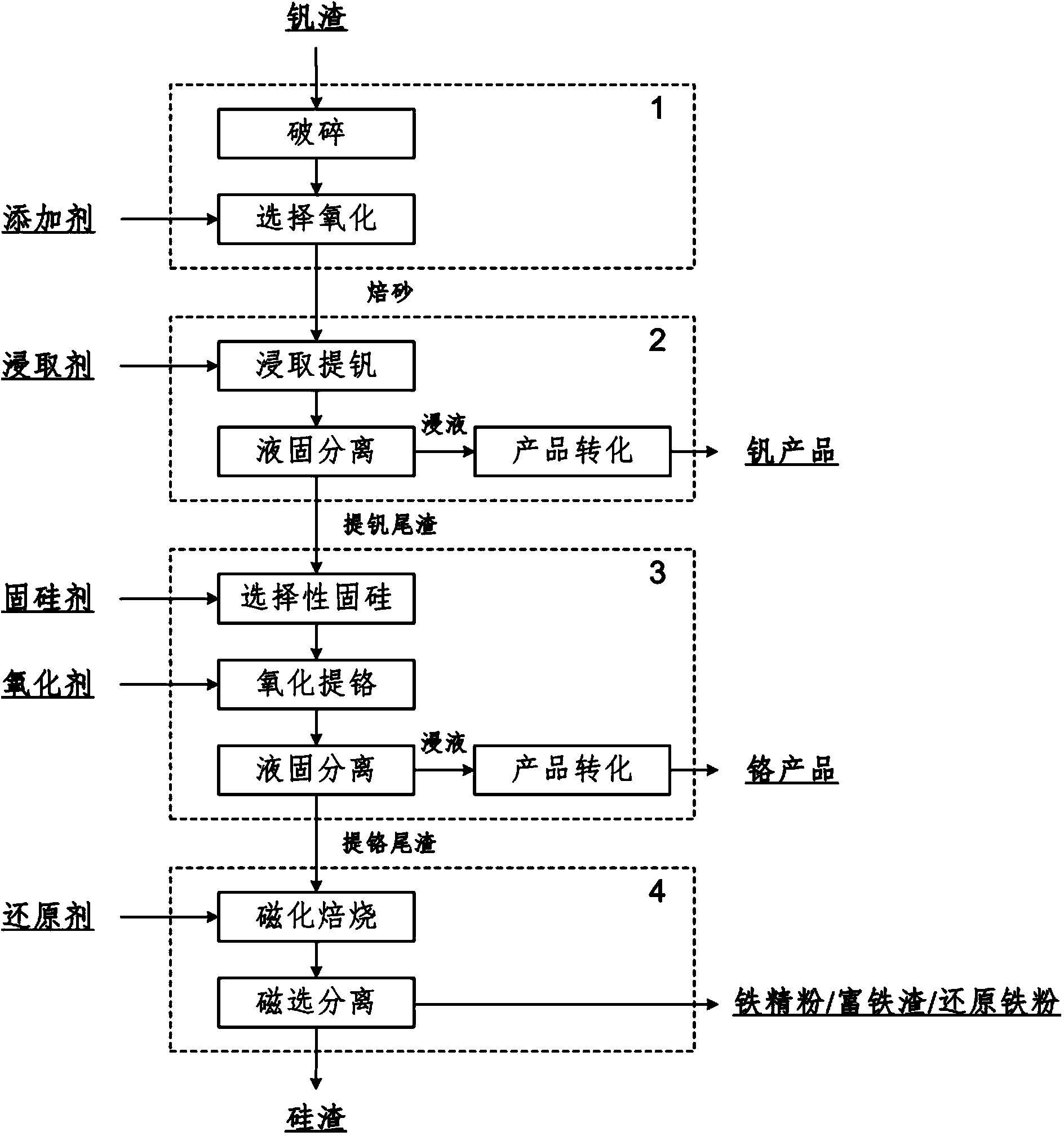
Clean process method for extracting vanadium, chromium and iron from vanadium slag step by step
The invention relates to a clean process method for extracting vanadium, chromium and iron from vanadium slag step by step. The clean process method comprises the following steps of: selectively oxidizing the vanadium slag to obtain a roasted product; leaching the obtained roasted product by using a leaching agent to extract vanadium, carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain vanadium-containing leach liquor and vanadium-extracted tailings, and carrying out product transformation on the vanadium-containing leach liquor to prepare vanadium series products; adding the obtained vanadium-extracted tailings and a silicon fixing agent to a sodium hydroxide solution, selectively fixing silicon, then oxidizing to extract chromium, then carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain chromium-containing leach liquor and chromium-extracted tailings, and carrying out product transformation on the chromium-containing leach liquor to prepare chromium series products; mixing the chromium-extracted tailings with a reducing agent, and carrying out magnetizing roasting and magnetic separation to obtain silicon slag and ion concentrate powder / iron-enriched slag / reduced iron powder. The clean process method disclosed by the invention realizes the step-by-step extraction and high-efficiency separation of valuable components such as vanadium, chromium and iron which are contained in the vanadium slag, prevents the mutual entrainment of vanadium, chromium and iron products; in addition, the clean process method disclosed by the invention realizes the near zero discharge of waste water and the recycling of final slag and is clean and pollution-free.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
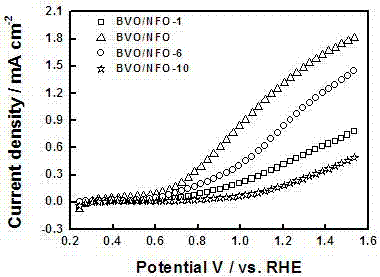
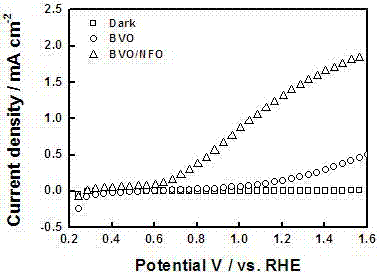
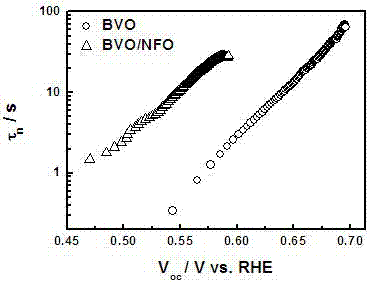
Ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide-modified bismuth vanadate photoelectrode and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107324441AInhibitory complexPromote oxygen evolution reactionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationBismuth vanadateDecomposition
The invention discloses a ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide-modified bismuth vanadate photoelectrode and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, depositing bismuth oxyiodide on the surface of conductive glass, then coating the surface with the deposited bismuth oxyiodide with a dimethyl sulfoxide solution of vanadyl acetylacetonate, annealing, performing alkali soaking and rinsing with water to remove excessive vanadium pentoxide, and then drying to obtain a bismuth vanadate photoelectrode, and modifying ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide on the surface of the bismuth vanadate photoelectrode by adopting a cyclic voltammetry method in a three-electrode system, thus obtaining the ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide-modified bismuth vanadate photoelectrode. The invention further discloses applications of the ferro-nickel oxyhydroxide-modified bismuth vanadate photoelectrode in photoelectrocatalytic decomposition water. The prepared photoelectrode is used for producing hydrogen from photoelectrocatalytic decomposition water, can inhibit the compounding of photon-generated carriers, the service life of carriers generated by a BiVO4 photoelectrode can be effectively prolonged, and the oxygen evolution reaction on the surface of the photoelectrode can be promoted, so that the solar optic hydrogen conversion efficiency of a semiconductor photoelectrode can be improved.
Owner:HUANGHE S & T COLLEGE
Surface treated steel plate excellent in corrosion resitance electroconductivity and appearance of coating film
ActiveUS20060177685A1Hot-dipping/immersion processesRecord information storageO-Phosphoric AcidPhosphate
The present invention provides a surface-treated steel sheet including a steel sheet; a plating layer provided on at least one of the surfaces of the steel sheet, the plating layer containing at least one metal selected from the group consisting of zinc and aluminum; a first layer film provided on the surface of the plating layer and containing (α) 1 to 2000 mg / m2 of silica in terms of SiO2, (β) a total of 1 to 1000 mg / m2 of phosphoric acid groups in terms of P, (γ) a total of 0.5 to 800 mg / m2 of at least one metal selected from the group consisting of Mg, Mn, and Al in terms of a metal element, and (δ) 0.1 to 50 mg / m2 of a tetravalent vanadium compound in terms of V; and a second layer film formed to a thickness of 0.1 to 5 μm on the first layer film and containing a resin (A) having at least one type of functional group selected from the group consisting of OH and COOH groups, and at least one rust-proofing additive (B) selected from the group consisting of (a) a phosphate, (b) Ca ion-exchanged silica, (c) a molybdate, (d) silicon oxide, and (e) at least one organic compound selected from the group consisting of triazoles, thiols, thiadiazoles, thiazoles, and thiurams. The surface-treated steel sheet has excellent corrosion resistance without containing hexavalent chromium in a coating, and also has excellent conductivity and coating appearance.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
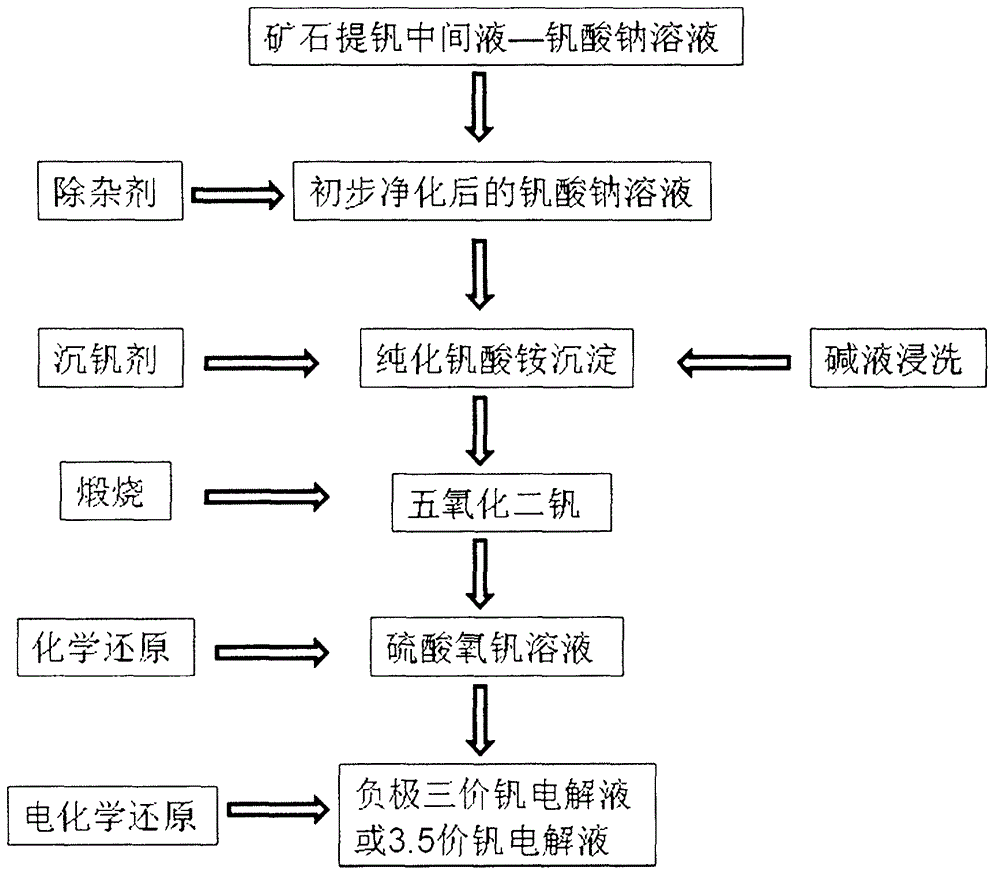
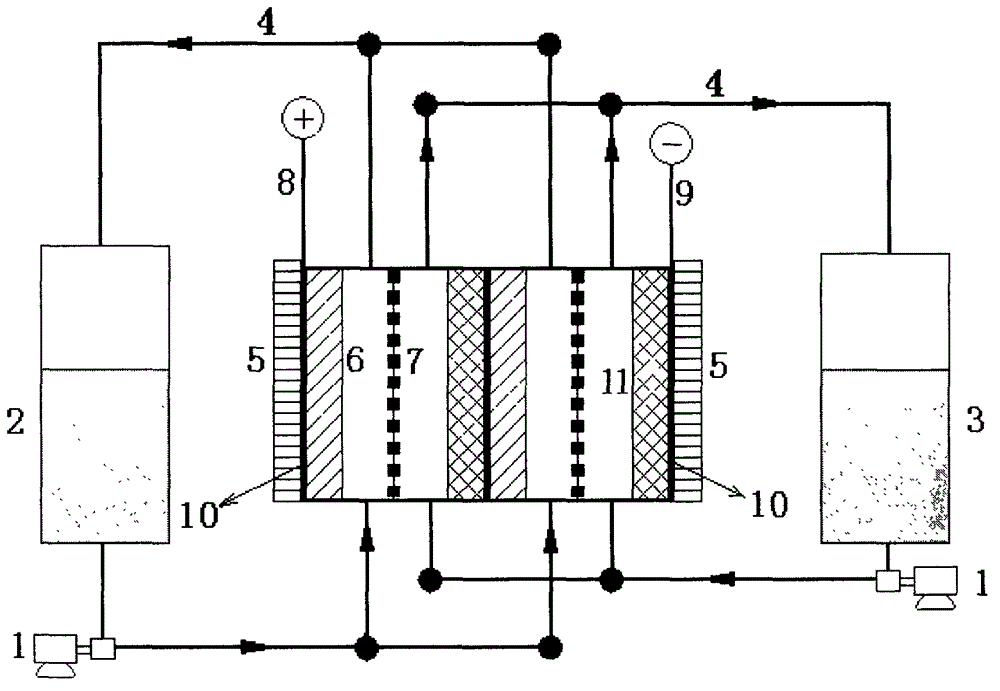
Combined chemical-electrochemical method for preparing vanadium redox flow battery electrolyte
InactiveCN104037439AEasy to operateHigh purityRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium compoundsHigh concentrationElectrolysis
The invention relates to a combined chemical-electrochemical method for preparing an all-vanadium redox flow battery electrolyte. The method adopts a solid or solution containing soluble vanadate, especially vanadium slag leachate obtained after steel-making with vanadic titano-magnetite, for production of a high-purity high-concentration vanadium electrolyte. The method is characterized in that a vanadyl sulfate electrolyte with a sulfuric acid concentration of 1 to 6 mol / L and a vanadium concentration of 1 to 5 mol / L can be prepared through impurity removal, acidic vanadium precipitation, multiple alkaline leaching and vanadium precipitation, calcination and reduction, an electrochemical process is cooperatively used so as to prepare a 3.5-valent or 3-valent vanadium electrolyte, and after electrolysis, the vanadium electrolyte of a positive electrode can be repeatedly used through chemical reduction. The method provided by the invention can treat the vanadium slag leachate and the solid or solution containing soluble vanadate and has the advantages of simple process flow, mild reaction conditions, substantially reduced cost, etc.; and the prepared high-purity high-concentration vanadium electrolyte is especially applicable to an all-vanadium redox flow battery.
Owner:NO 63971 TROOPS PLA +1
Loaded V-P-O catalyst and its prepn and use
InactiveCN1453071ASmall particlesHigh catalytic activityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDecompositionOxide
The catalyst consists of loaded vanadium and phosphor oxide and SiO2 carrier formed via pyrogenic decomposition with the loaded amount being 15-58 wt%. It has a V / P atom ratio of 1.2, specific area 117-210 sq m / g, and the main phase being vanadyl pyrophosphate phase. It is used as the catalyst for air oxidizing n-butane to prepare cis-butenedioic anhydride and has one single-path conversion rate of 33-51 % and cis-butenedioic anhydride selectivity of 61-87 % in the typical temperature range of 380-400 deg.c.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Activated carbon supported cobalt based catalyst for directly converting of synthesis gas to mixed linear alpha-alcohols and paraffins
ActiveUS7670985B2High activityHigh selectivityPigmenting treatmentOrganic compound preparationAlkaneActivated carbon
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Deironing method for vanadium-bearing stone coal lixivium
ActiveCN105695738AReduce loss rateReduce the impact of vanadium enrichmentOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid salt preparationPregnant leach solutionIron powder
The invention relates to a deironing method for vanadium-bearing stone coal lixivium. According to the technical scheme, the deironing method comprises the steps that vanadium-bearing stone coal is firstly subjected to crushing, roasting and ore grinding to obtain vanadium-bearing stone coal roasted ore, the vanadium-bearing stone coal roasted ore and water are stirred to obtain vanadium-bearing stone coal ore pulp, then a leaching agent is added, heating and stirring are carried out, and solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain the vanadium-bearing stone coal lixivium and leaching residues; reduced iron powder is added into the vanadium-bearing stone coal lixivium, and the adding amount of the reduced iron power is 2-4 times the stoichiometric number of the chemical reaction for reducing Fe3+ in the vanadium-bearing stone coal lixivium into Fe2+; heating and stirring are carried out, the pH value is adjusted to range from 1.5 to 5, heating and stirring are carried out, solid-liquid separation is carried out, and deironed lixivium and a filter cake are obtained; and the deironed lixivium is used for the vanadium enrichment technology, and a ferrous oxalate dehydrate byproduct is obtained after the filter cake is dried. Vanadium and iron in the vanadium-bearing stone coal lixivium can be effectively separated, the iron in the vanadium-bearing stone coal lixivium can be recycled, the vanadium loss rate in the deironing process is low, the iron content of the deironed lixivium is low, and the influence of the iron on the subsequent vanadium enrichment technology is reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
All-vanadium redox flow battery state-of-charge online monitoring method and system
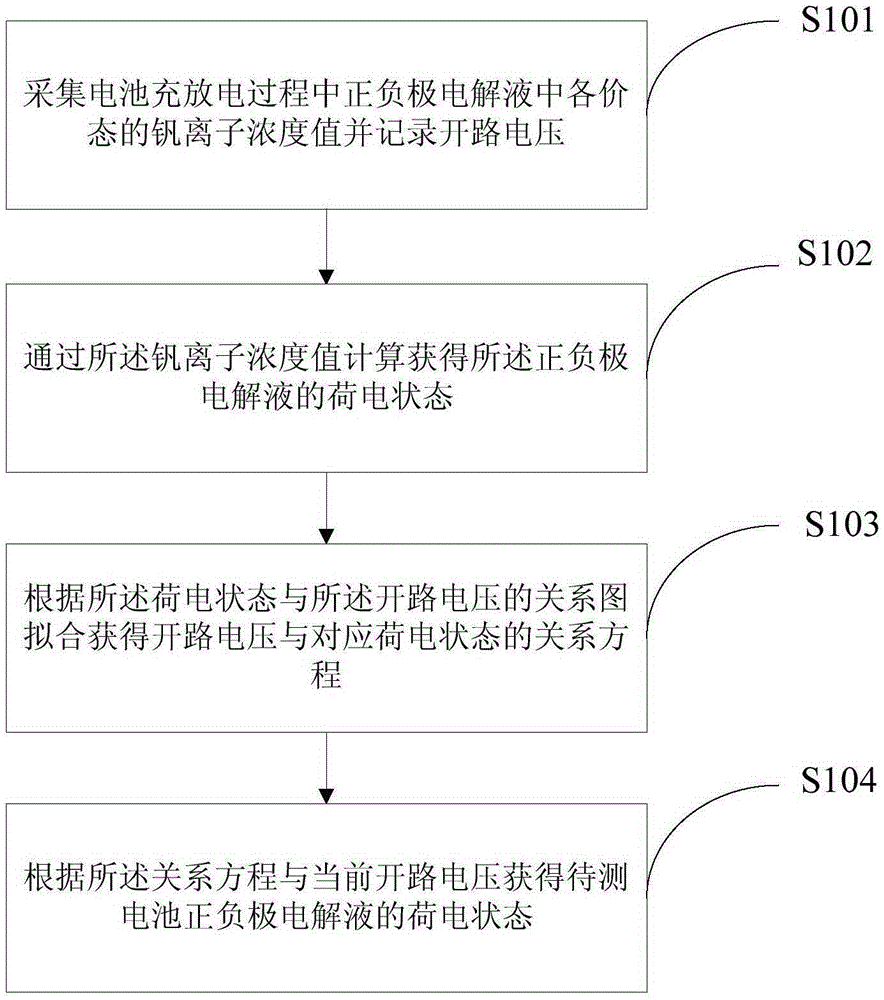
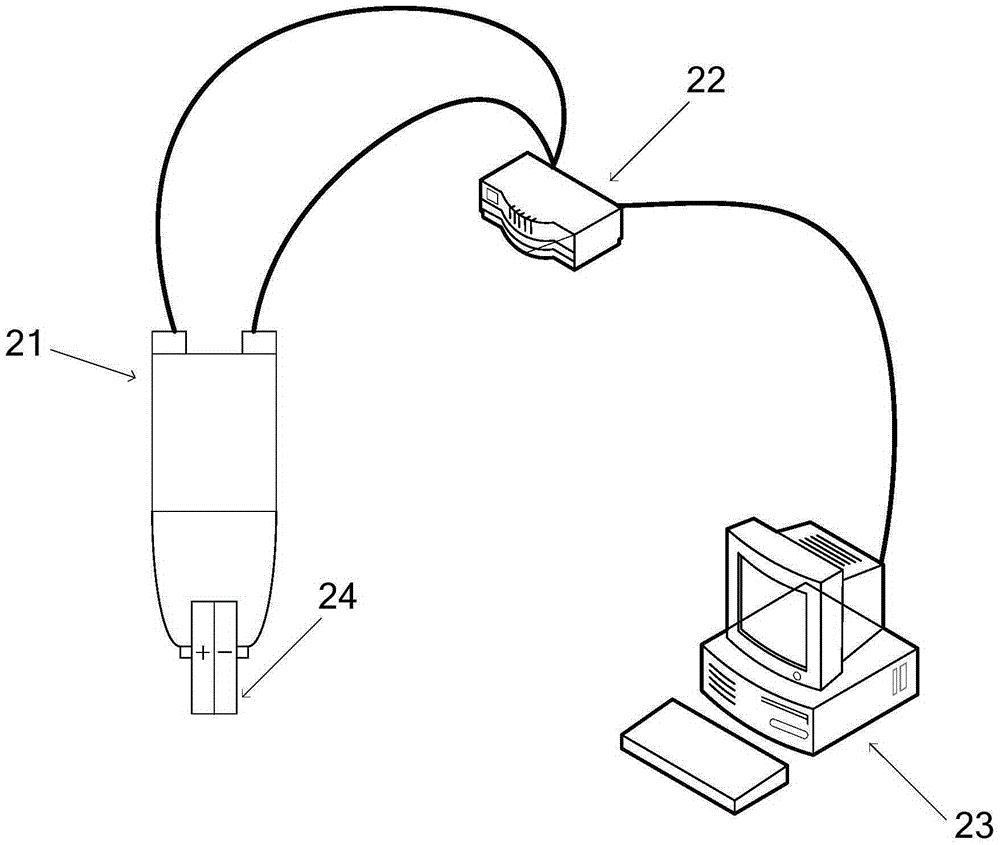
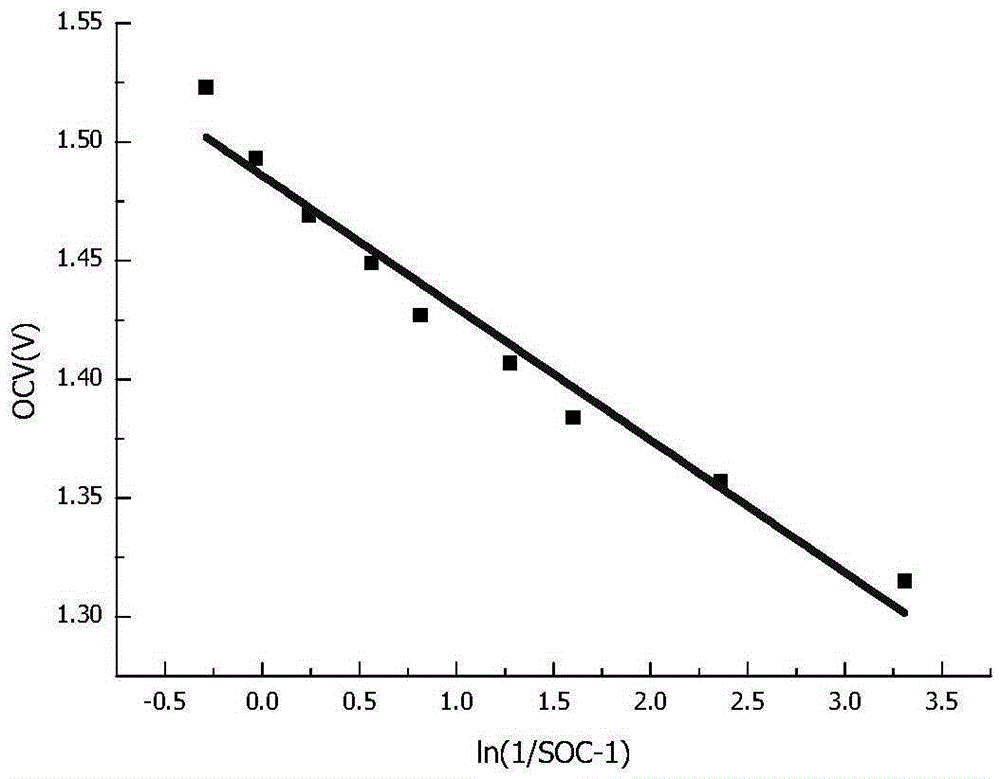
The invention provides an all-vanadium redox flow battery state-of-charge online monitoring method and system. The monitoring method comprises the steps that the vanadium ion concentration value of each valence state in positive and negative electrode electrolyte in the battery charging and discharging process is acquired and open-circuit voltage is recorded; the state-of-charge of the positive and negative electrode electrolyte is calculated via the vanadium ion concentration value; a relation equation of open-circuit voltage and the corresponding state-of-charge is obtained according to the relational graph of the state-of-charge and open-circuit voltage through fitting; and the state-of-charge of the positive and negative electrode electrolyte of a battery to be measured is obtained according to the relation equation and current open-circuit voltage. The relevant parameters of the positive and negative electrode electrolyte are acquired so that unnecessary error in the calculation process of the battery state-of-charge can be weakened and finally the state-of-charge of the battery electrolyte can be obtained through measurement. According to the method, an existing open-circuit voltage method equation is corrected, and fitting of a negative electrode relation equation and a positive electrode relation equation is respectively performed so that the accurate state-of-charge of the positive and negative electrode electrolyte can be calculated.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRICAL POWER RES INST +1
Vanadium selenide/carbon-based composite material, preparation method of material, and negative electrode of lithium ion battery
ActiveCN104051733AUniform particle distributionSmall particle sizeSecondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesHexagonal crystal systemHigh rate
The invention provides a vanadium selenide / carbon-based composite material, a preparation method of the material, and a negative electrode of a lithium ion battery. Vanadium selenide in the vanadium selenide / carbon-based composite material is of a hexagonal crystal system and is deposited on the surface of a carbon-based material, or the surfaces of vanadium selenide particles are at least partially coated with the carbon-based material to form vanadium selenide / carbon particles of a core shell-like structure; the vanadium selenide / carbon particles are connected through carbon nets to obtain the high conductivity. In the negative electrode of the power lithium ion battery, prepared from the vanadium selenide / carbon-based composite material provided by the invention, since selenide with the relatively large specific capacity is combined with the carbon-based material, the negative electrode has the characteristics of large capacity, high rate and high cyclic stability. Therefore, the negative electrode made of the composite material has the relatively large capacity, relatively long service life and relatively low price when applied to the lithium ion battery.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method of nano-structure WC-Co composite powder
InactiveCN102350506AWell mixedOvercoming coarse compound salt crystallizationChromium CompoundsVanadium oxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano-structure WC-Co composite powder, and belongs to the field of an alloy preparation method. The method comprises the following steps in sequence: adding a carbonic powder material which is excessive to tungsten, vanadium and chromium carbides into water-soluble saturated mixed aqueous solution of tungsten-containing compound, cobalt-containing compound, chromium-containing compound and vanadium-containing compound to adsorb the saturated composite salt solution; dehydrating and drying to form a nano-scale composite salt thin layer on the surface of the carbonic powder material; removing crystal water out of the composite salt at the temperature below 500 DEG C under a condition of isolating air, and decomposing the composite salt into composite oxide of tungsten oxide, chromium hemitrioxide, vanadium oxide and cobalt oxide, further heating, and reducing and carbonizing the composite oxide on the surface of the carbonic powder material to generate the WC-Co nano-structure composite powder at the temperature below 850 DEG C. The preparation is a simpler and more reliable novel preparation method of the nano WC-Co composite powder by a direct carbonization method.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Converter vanadium extraction process adopting top blowing oxygen lance to blow cooling agents
The invention relates to a converter vanadium extraction process adopting a top blowing oxygen lance to blow cooling agents, belongs to the technical field of ferrous metallurgy, and is used for solving the problems that the temperature of a molten pool is difficult to control in the vanadium extraction course, the dynamic condition is poor and the like and increasing the oxidation conversion rate of vanadium and the quality of vanadium slag. The converter vanadium extraction process comprises a powder supply system and an oxygen supply system; and the cooling agents are blown through using a supersonic oxygen jet of the top blowing oxygen lance, and the aims of controlling the temperature of the molten pool in the vanadium extraction course and improving the stirring ability of the molten pool are achieved by utilizing a principle that powder rapidly reacts with hot iron to absorb heat, thereby achieving the technical effect of efficient vanadium extraction. The cooling agents enters the oxygen lance via a powder supply pipe in the powder blowing process; an outlet of the powder supply pipe can be positioned between the upper part of a lance body and an Raoult outlet of a blowing head; and the inner diameter of the powder supply pipeline is in the range of 15 to 180mm, the powder blowing flow rate is in the range of 20 to 800kg / min, the carrier gas flow rate is in the range of 100 to 4000Nm3 / h, and the carrier gas pressure is in the range of 0.5 to 1.6Mpa. The converter vanadium extraction process is suitable for vanadium extraction converters of 200 to 300t; and by adopting the converter vanadium extraction process, the semi-steel vanadium content can be reduced to below 0.03 percent, and the quality of vanadium slag (V2O5) is increased by more than 1 percent, so that the recovery rate of vanadium resources is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Lithium iron vanadium manganese phosphate nano oxide compound anode material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102891316AHigh crystallinityImprove conductivityCell electrodesCrystallinityLithium-ion battery
The invention relates to a lithium iron vanadium manganese phosphate nano oxide compound anode material and a preparation method thereof. The lithium iron vanadium manganese phosphate nano oxide compound anode material comprises a component A and a compound B carbon source, wherein the component A comprises 95-99.9wt% of lithium iron vanadium manganese phosphate compound Lix+3y+zFexV2yMnz(PO4)x+3y+z and 0.1-5wt% of nano oxide; and the component B carbon source accounts for 0.5-35wt% by mass of the lithium iron vanadium manganese phosphate compound Lix+3y+zFexV2yMnz(PO4)x+3y+z in the component A. The preparation method of the compound anode material comprises the steps of: firstly weighing a lithium source, an iron source, a vanadium source, a manganese source and a phosphorus source according to proportions, uniformly ball-grinding and mixing, pre-sintering after tabletting, crushing, adding the nano oxide and the component B carbon source, ball-grinding, calcining, crushing and refining. The lithium iron vanadium manganese phosphate nano oxide compound anode material provided by the invention has better crystallinity and conductivity as well as high specific capacity, and has wide application prospects in the field of lithium ion batteries.
Owner:中科(马鞍山)新材料科创园有限公司
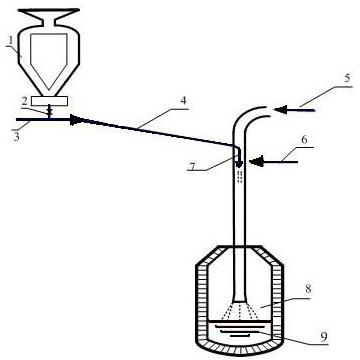
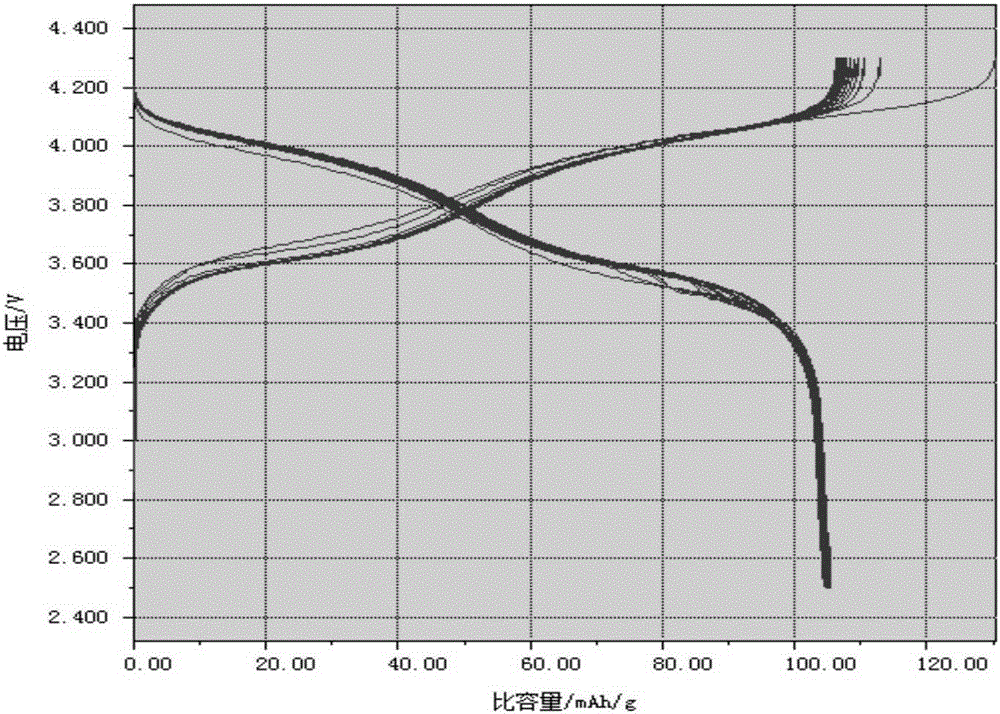
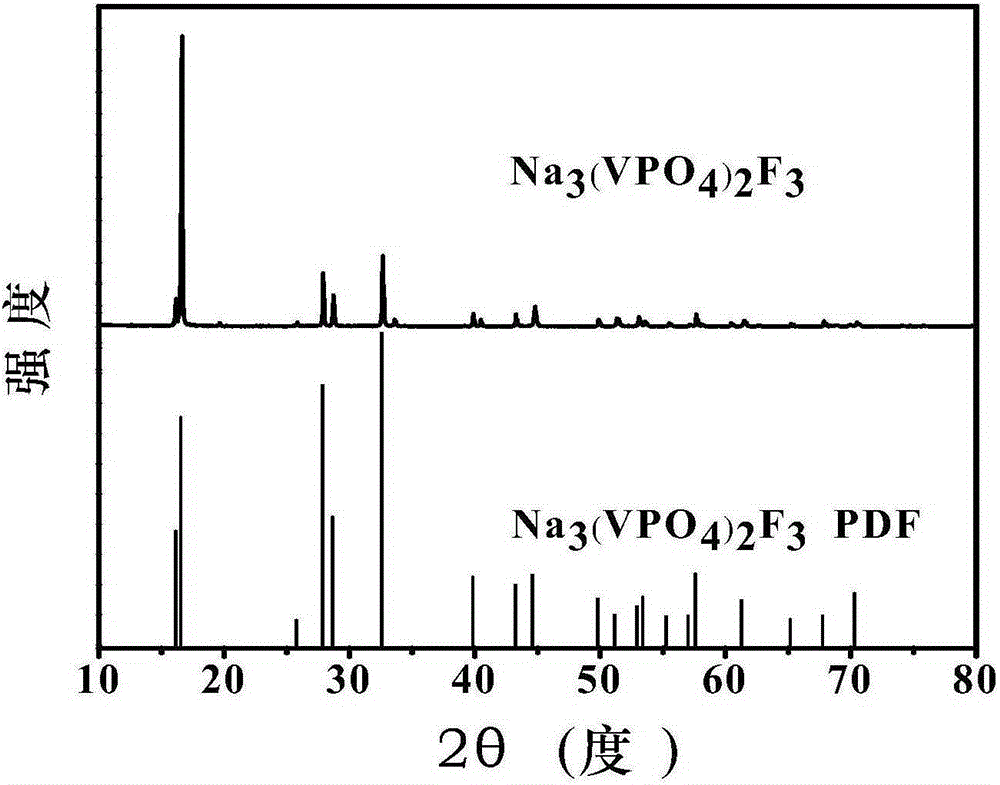
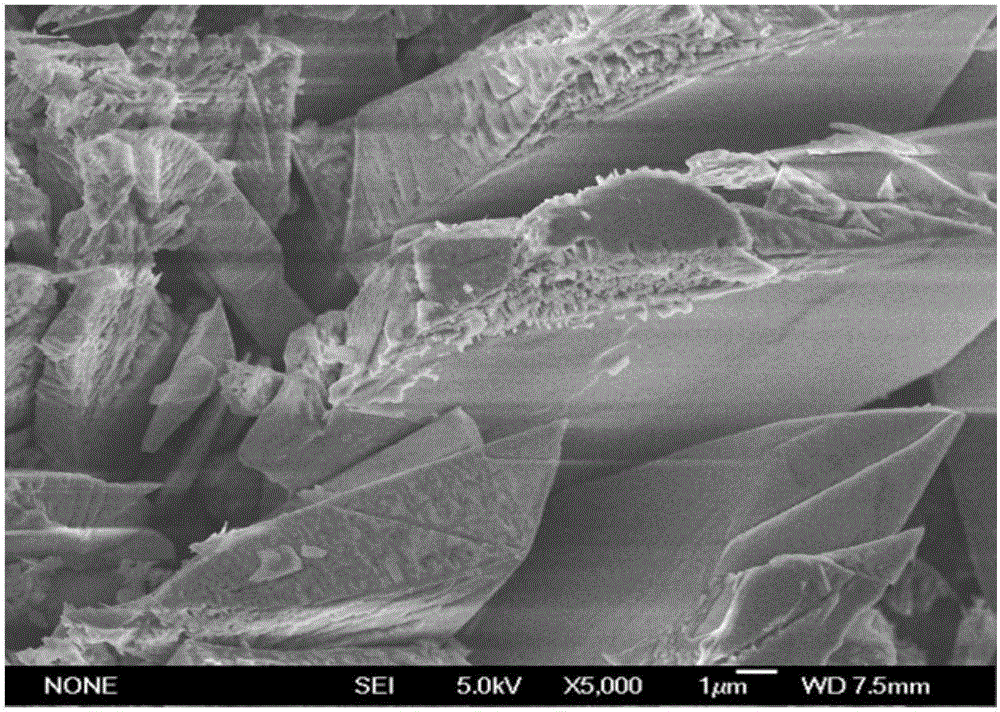
Sodium vanadium fluorophosphate as well as low-temperature environment-friendly preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN106495124AImprove electrochemical performanceSynthesis temperature is lowCell electrodesPhosphorus compoundsAqueous solutionSpecific discharge
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrode materials and relates to sodium vanadium fluorophosphate as well as a low-temperature environment-friendly preparation method and use thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing a mixed water solution of a sodium source, a vanadium source, a phosphorus source and a fluorine source, reacting by virtue of the mixed water solution at 20-180 DEG C to obtain sodium vanadium fluorophosphate, wherein the vanadium source is a trivalent vanadium source and / or a tetravalent vanadium source; the chemical constitution of sodium vanadium fluorophosphate is Na3(VOxPO4)2F3-2x, and x is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1. According to the low-temperature environment-friendly preparation method, the mixed water solution of the sodium source, thephosphorus source, the fluorine source and the trivalent vanadium source and / or a tetravalent vanadium source can generate spontaneous reaction at 20-35 DEG C, the reaction can be accelerated at a temperature high than 35 DEG C and lower than 180 DEG C, and well-crystallized sodium vanadium fluorophosphate can be obtained. Sodium vanadium fluorophosphate can be used as an anode to be assembled into a battery, the specific discharge capacity is not lower than 100mAh / g, and the cycling stability is good.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalyst for producing epoxy compound and process for producing epoxy compounds with the same
InactiveUS20030171604A1High yieldImprove utilization efficiencyOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesIndiumHafnium
The present invention provides a catalyst capable of producing an epoxy compound in high yield and improving the utilization efficiency of the oxidizing agent as well as a method of producing an epoxy compound using that catalyst. A catalyst for producing an epoxy compound by oxidizing a compound having at least one ethylenic double bond with an oxidizing agent, comprising a polyatom-containing heteropolyoxometalate anion (A1) having two defective and / or three defective structure sites and containing silicon as the heteroatom, and an element (E1) being at least one element selected from the group consisting of vanadium, tantalum, niobium, antimony, bismuth, chromium, molybdenum, selenium, tellurium, rhenium, cobalt, nickel, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, platinum, iridium, silver, gold, zinc, aluminum, gallium, indium, scandium, yttrium, titanium, zirconium, hafnium, germanium, tin and lanthanoids, and being different from the polyatom.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Aqueous zinc ion battery vanadium-based positive electrode material and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111573731AHighlight substantiveImprove cycle stabilitySecondary cellsPositive electrodesElectrical batteryCoin cell
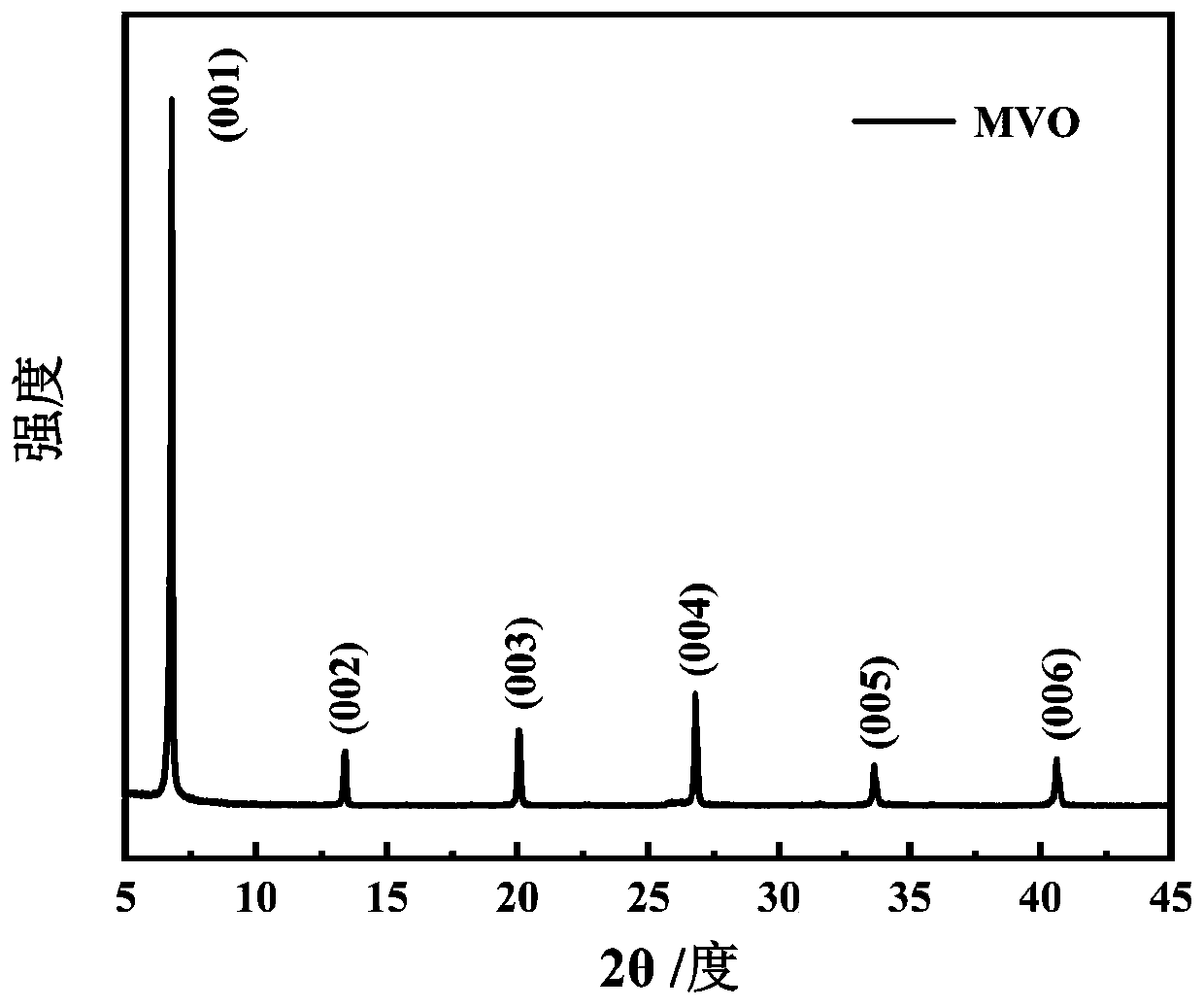
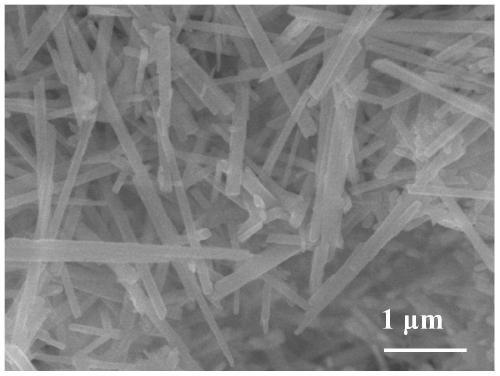
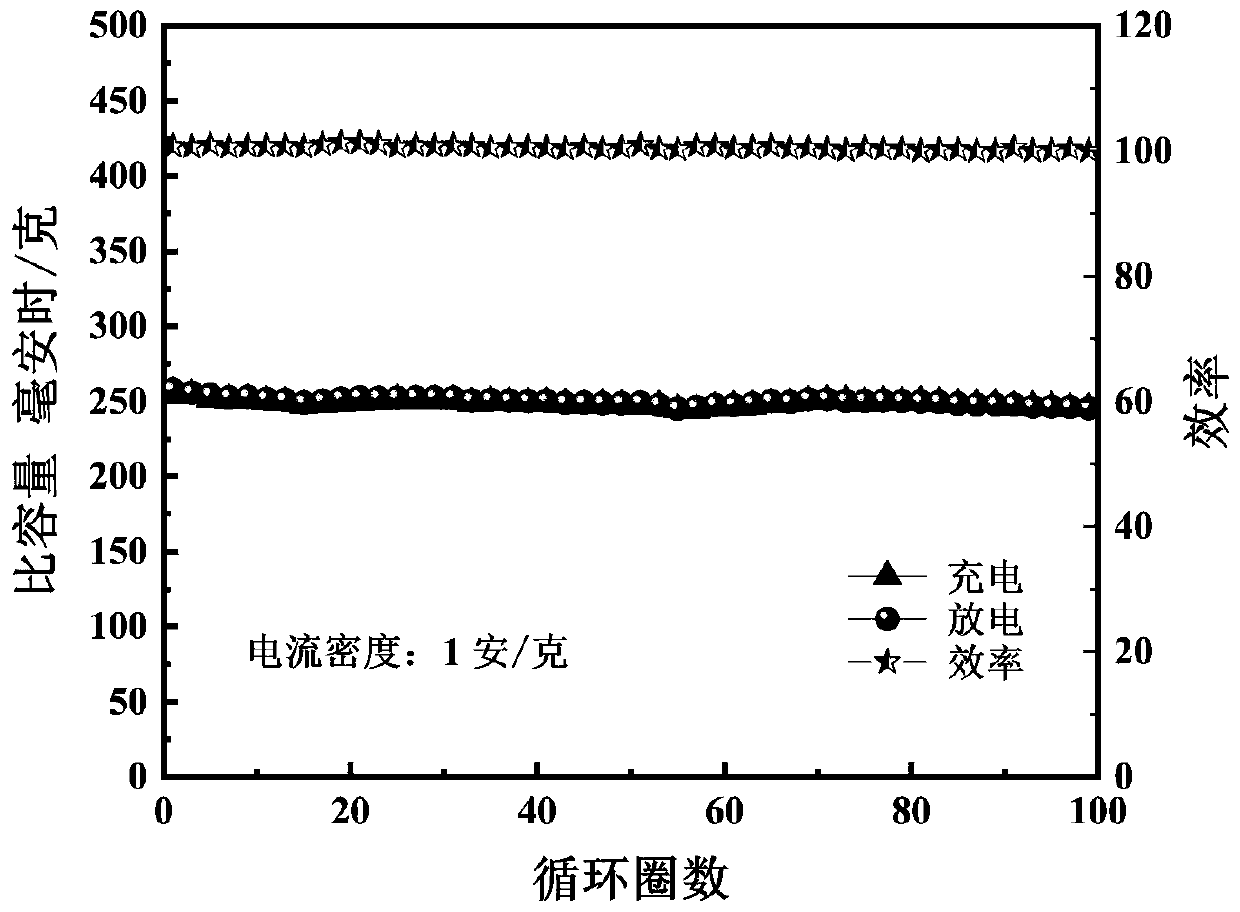
The invention discloses an aqueous zinc ion battery vanadium-based positive electrode material which has the following chemical composition: MxV2O5.nH2O, M is Mg or Sn; 0 < x < = 2; 0 < n < = 2. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving vanadium pentoxide in deionized water, dropwise adding an acidic solution after stirring, stirring in a water bath until the reaction is complete, dissolving M salt in deionized water, dropwise adding the solution after complete dissolution, and carrying out hydrothermal reaction after complete reaction. After the obtained positive electrode material is assembled into a button cell, an electrochemical performance test is carried out, and during the test, the current density range is 0.1-10A g <-1 >, and the voltage range is 0.1-1.8 V.The preparation method is simple and convenient, and has low requirements on experimental conditions. The microstructure of the synthetic material is a nanobelt, and the synthetic material has largerinterlayer spacing so that the layered structure is more stable, deintercalation and intercalation of zinc ions are further facilitated, and the assembled zinc ion battery shows excellent cycling stability and rate capability.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com