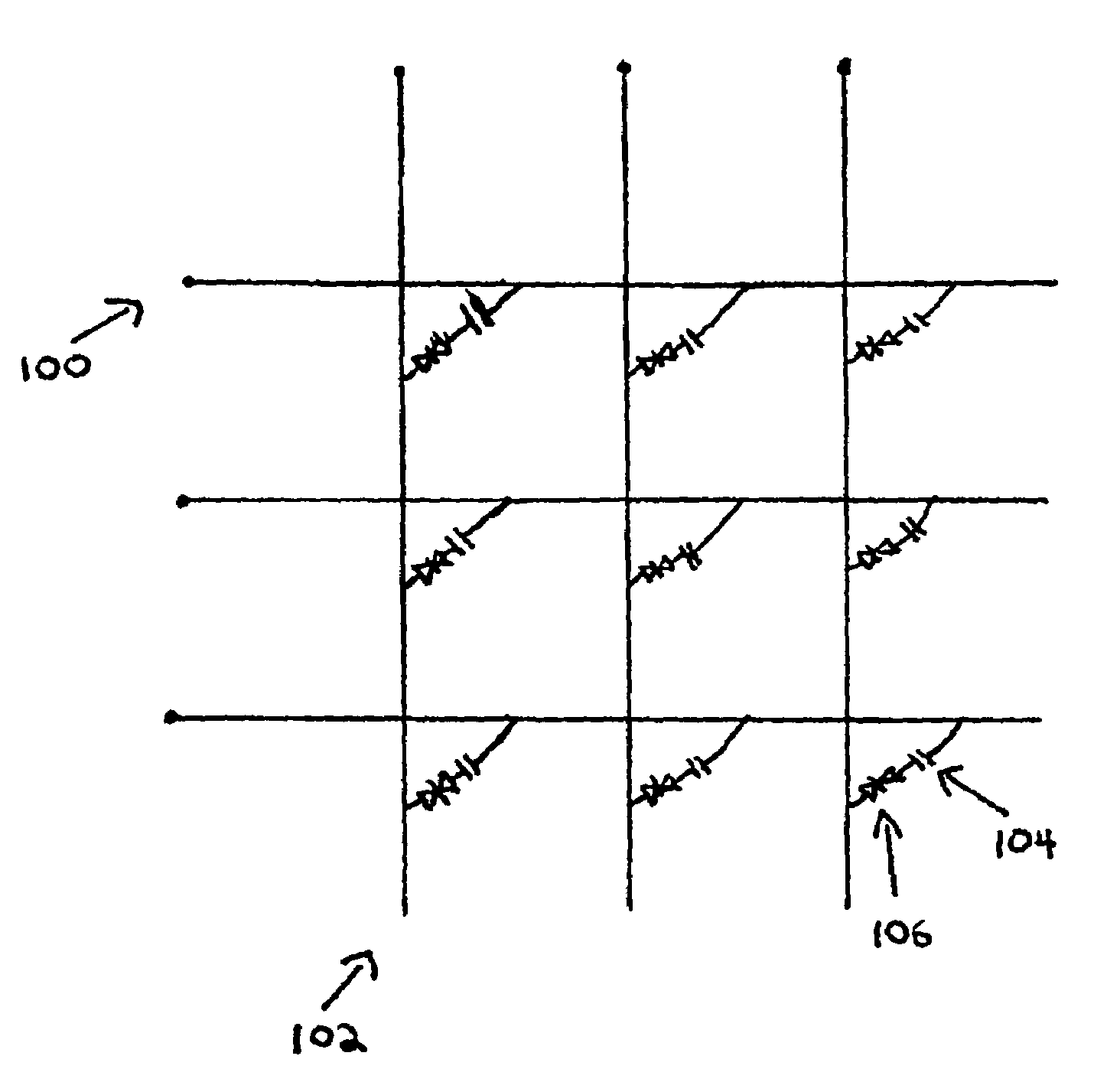
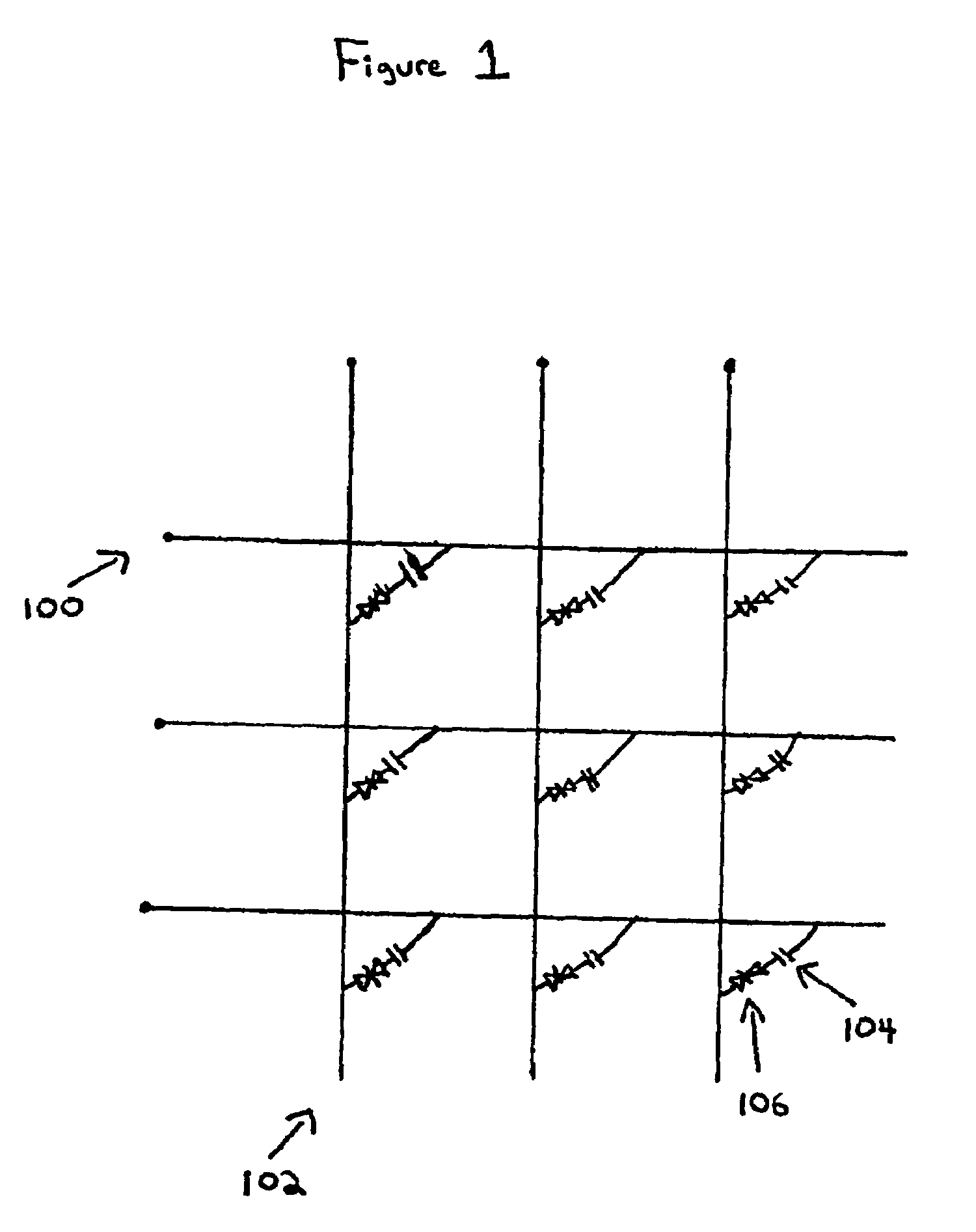
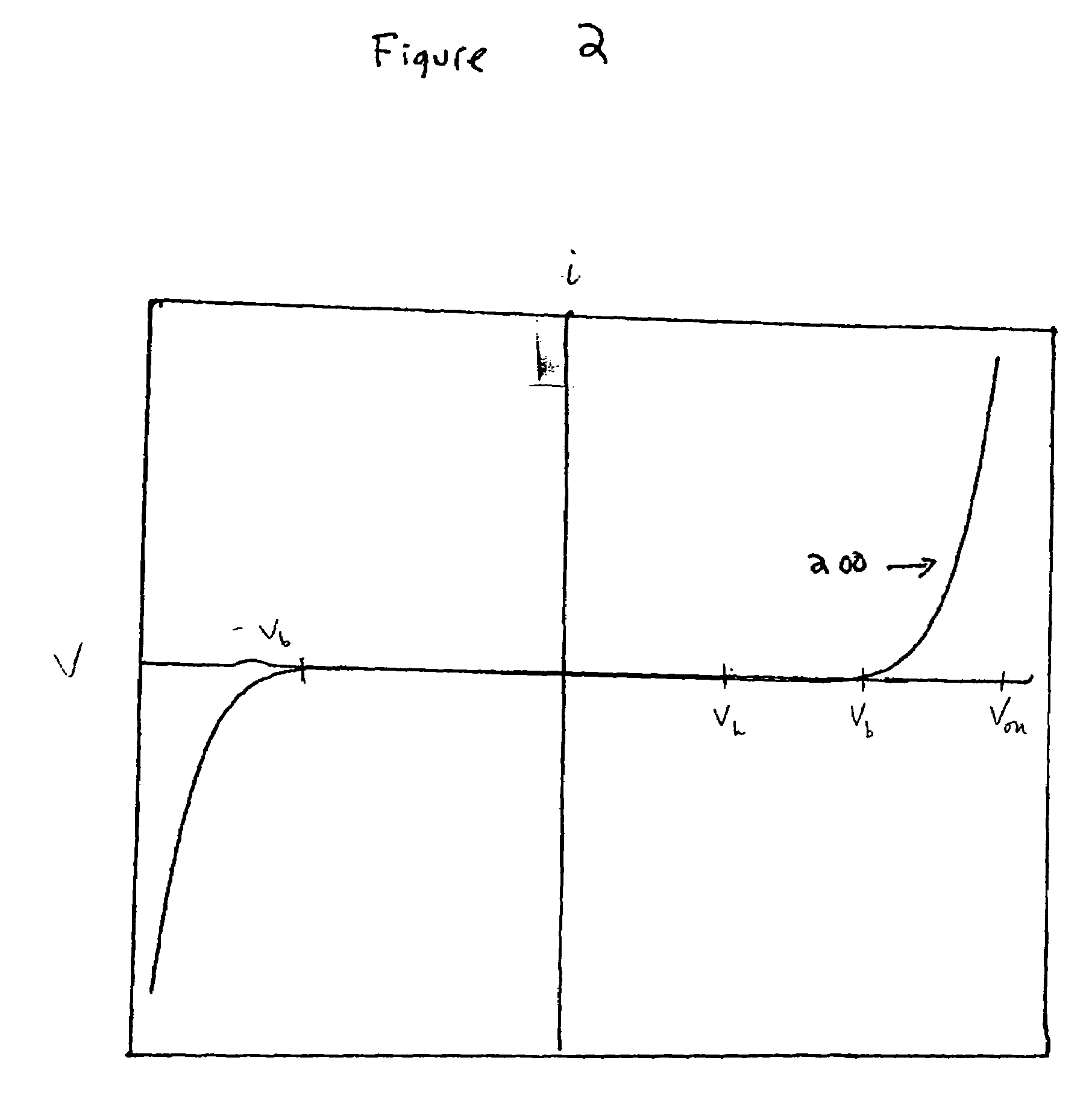
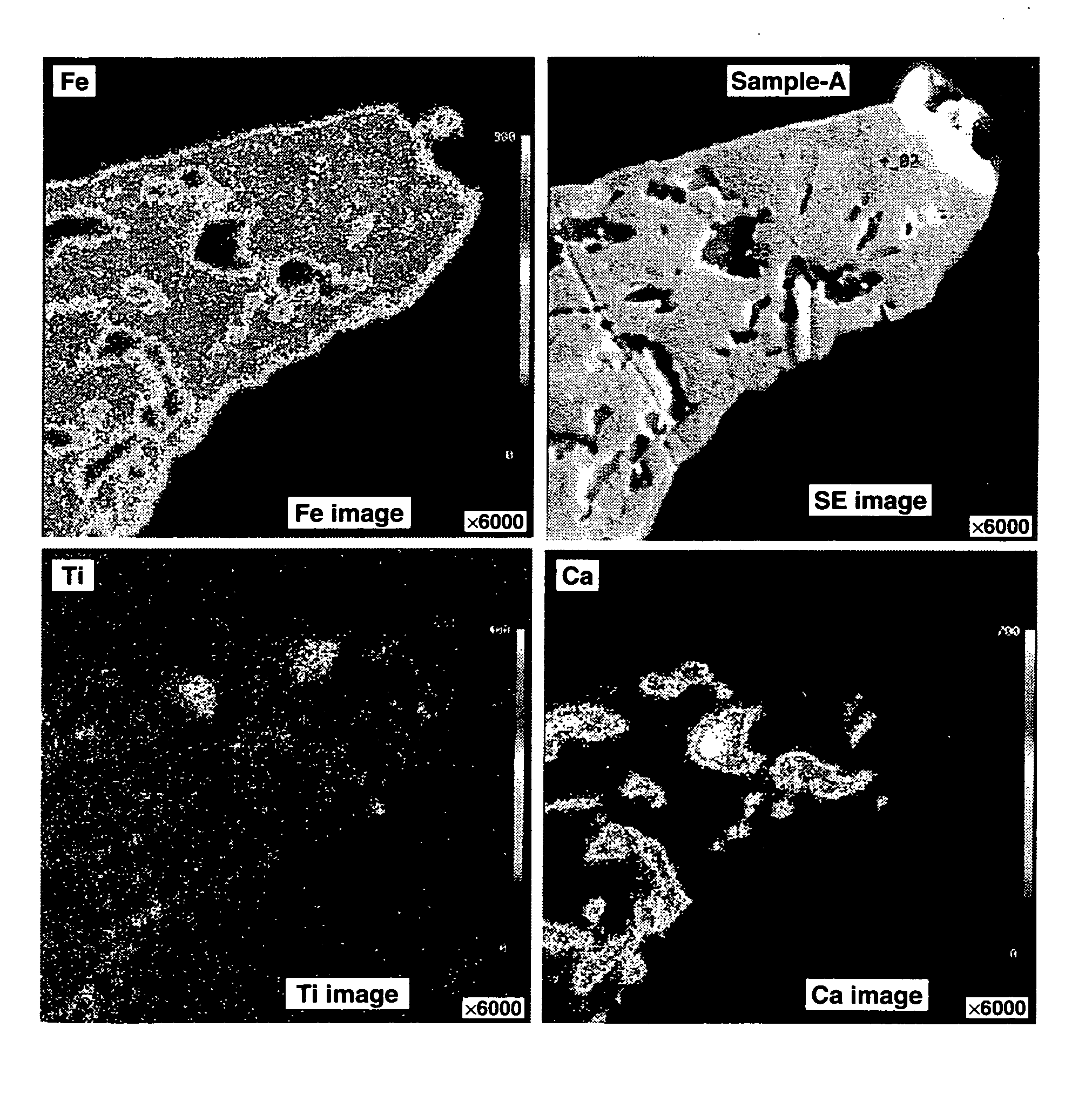
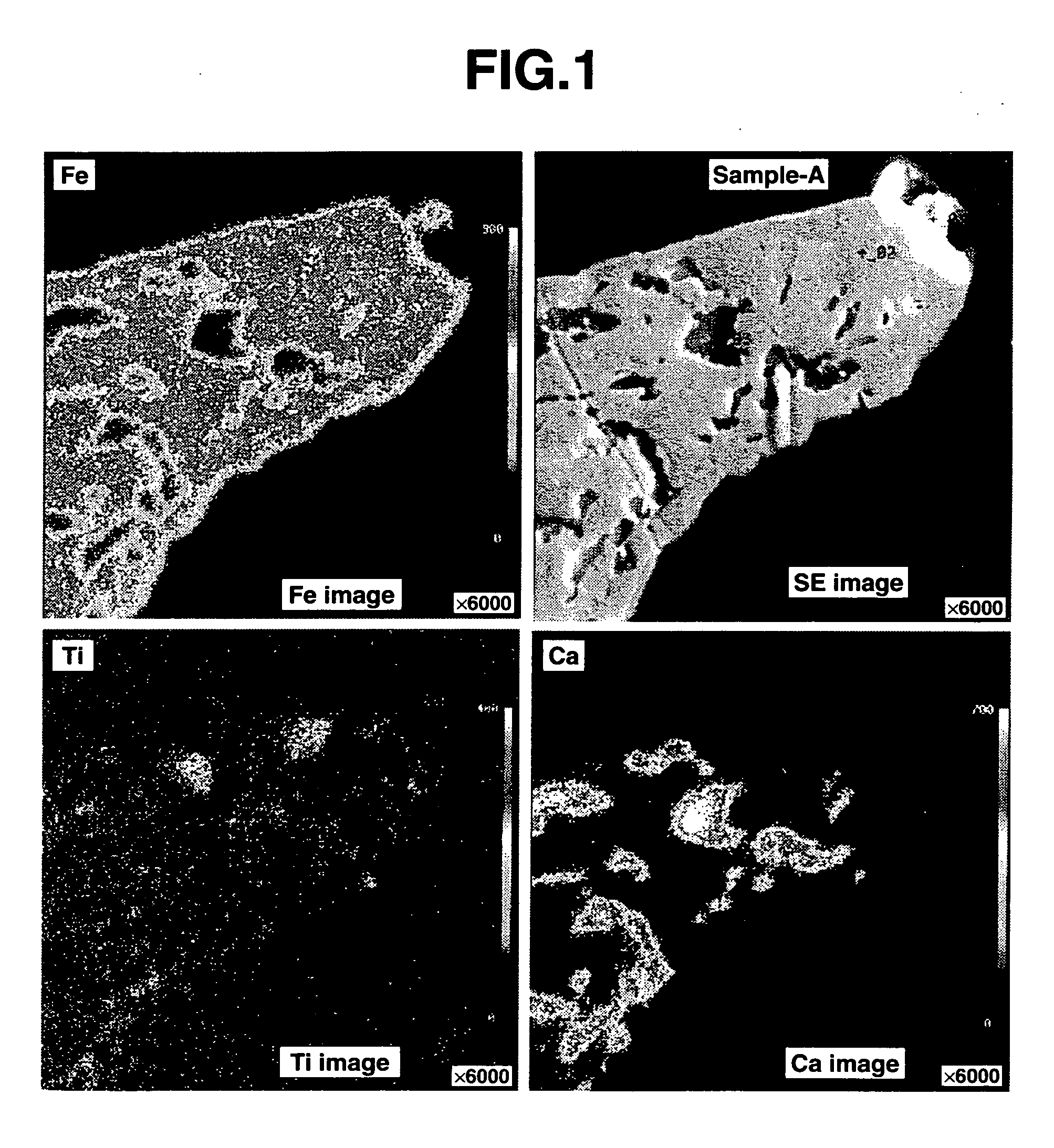
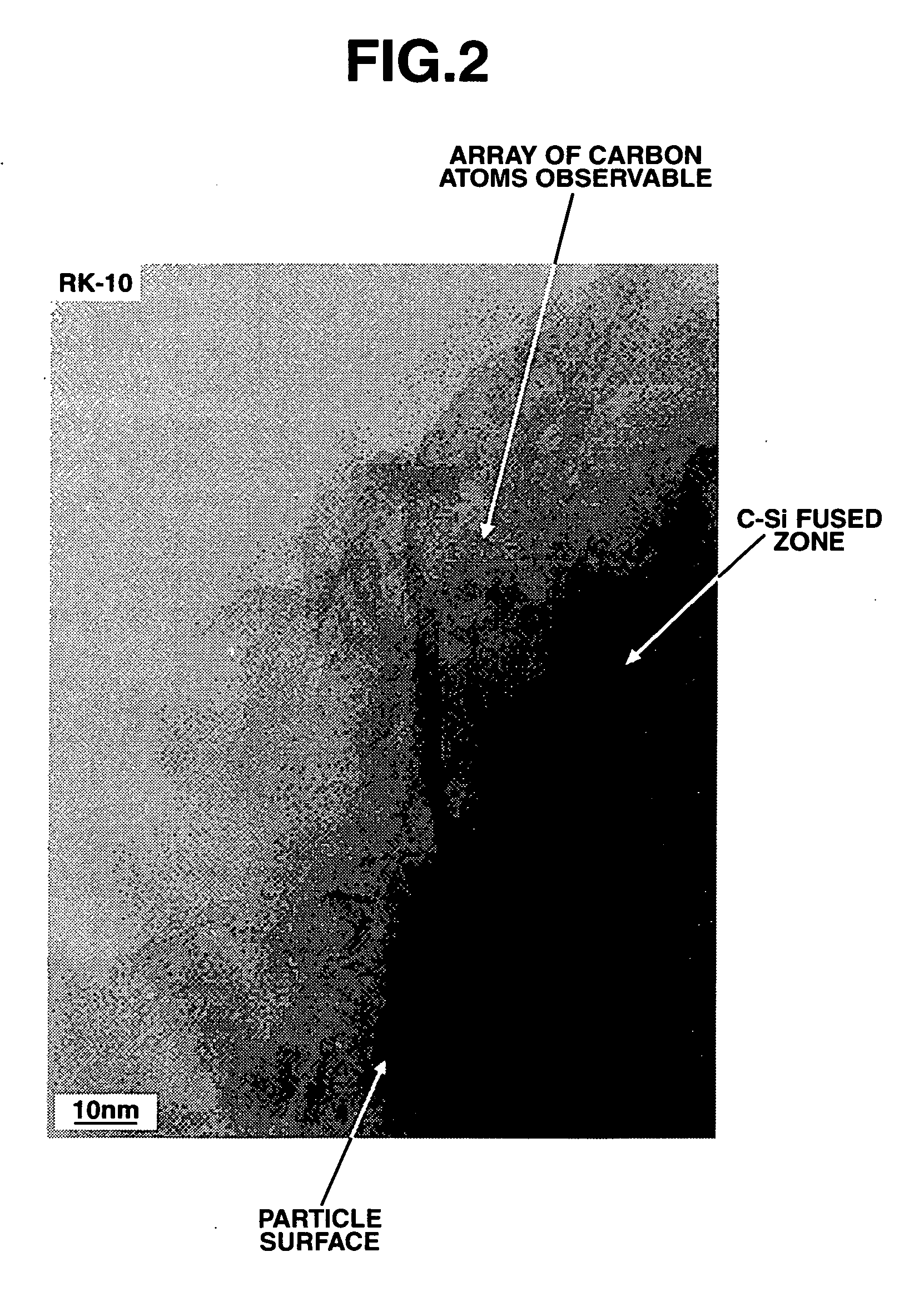
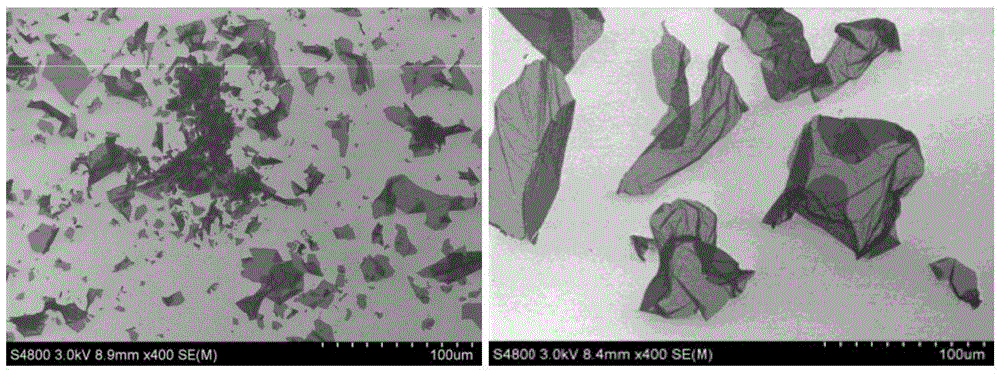
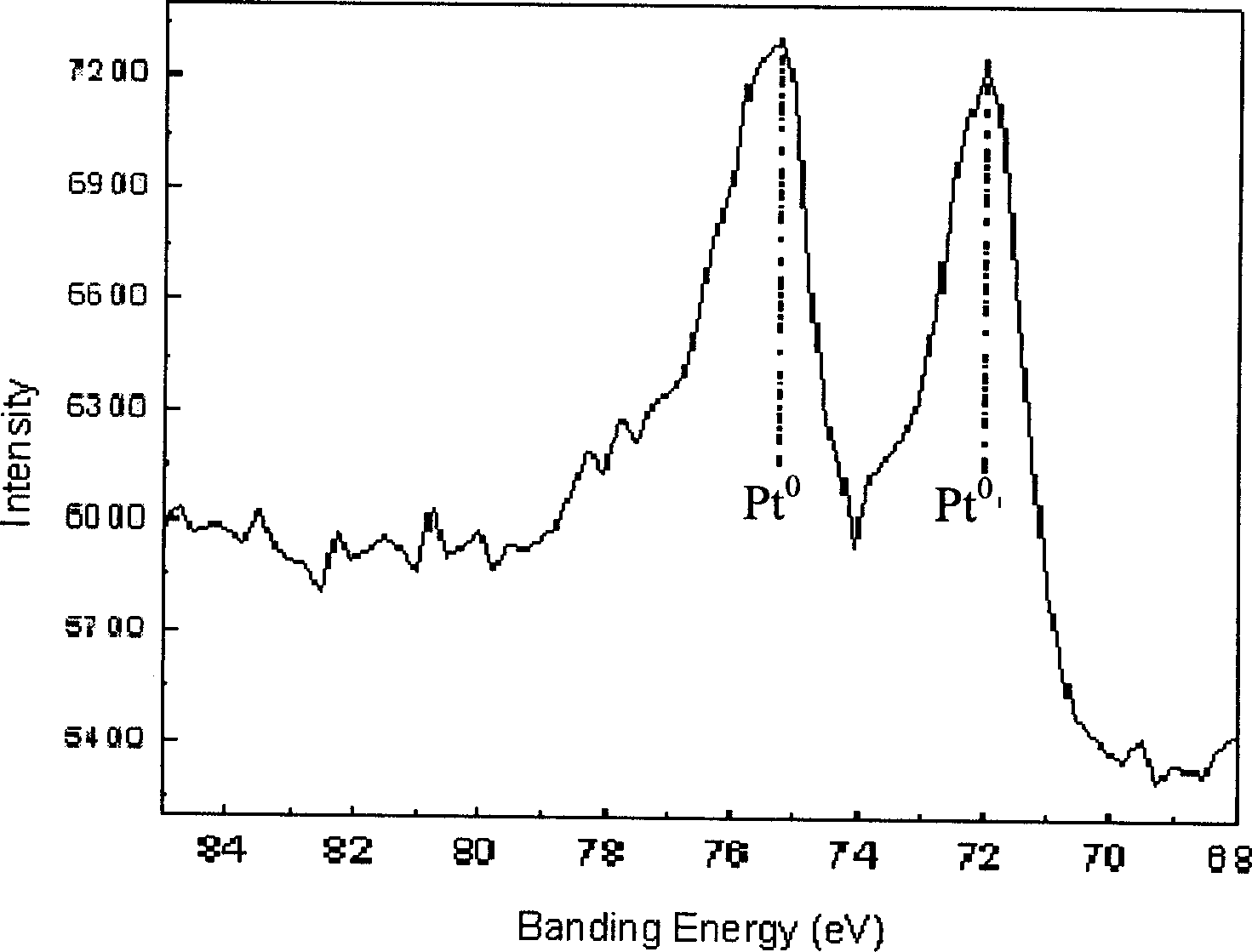
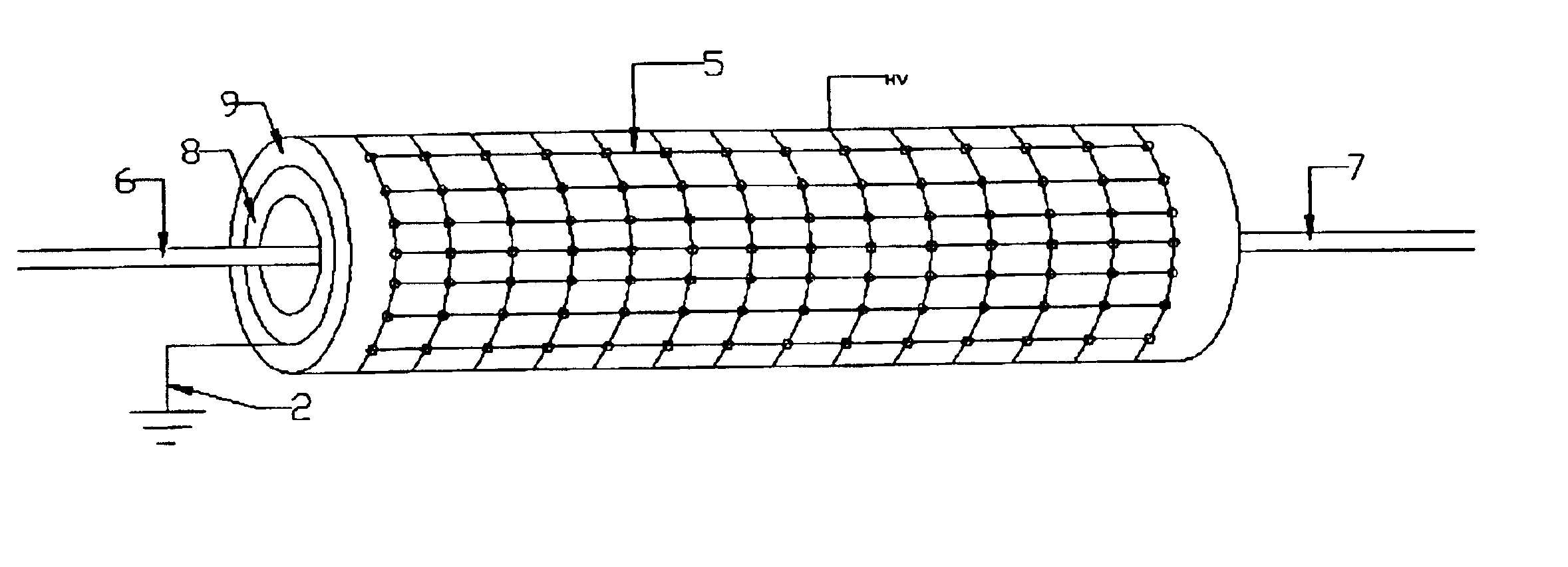
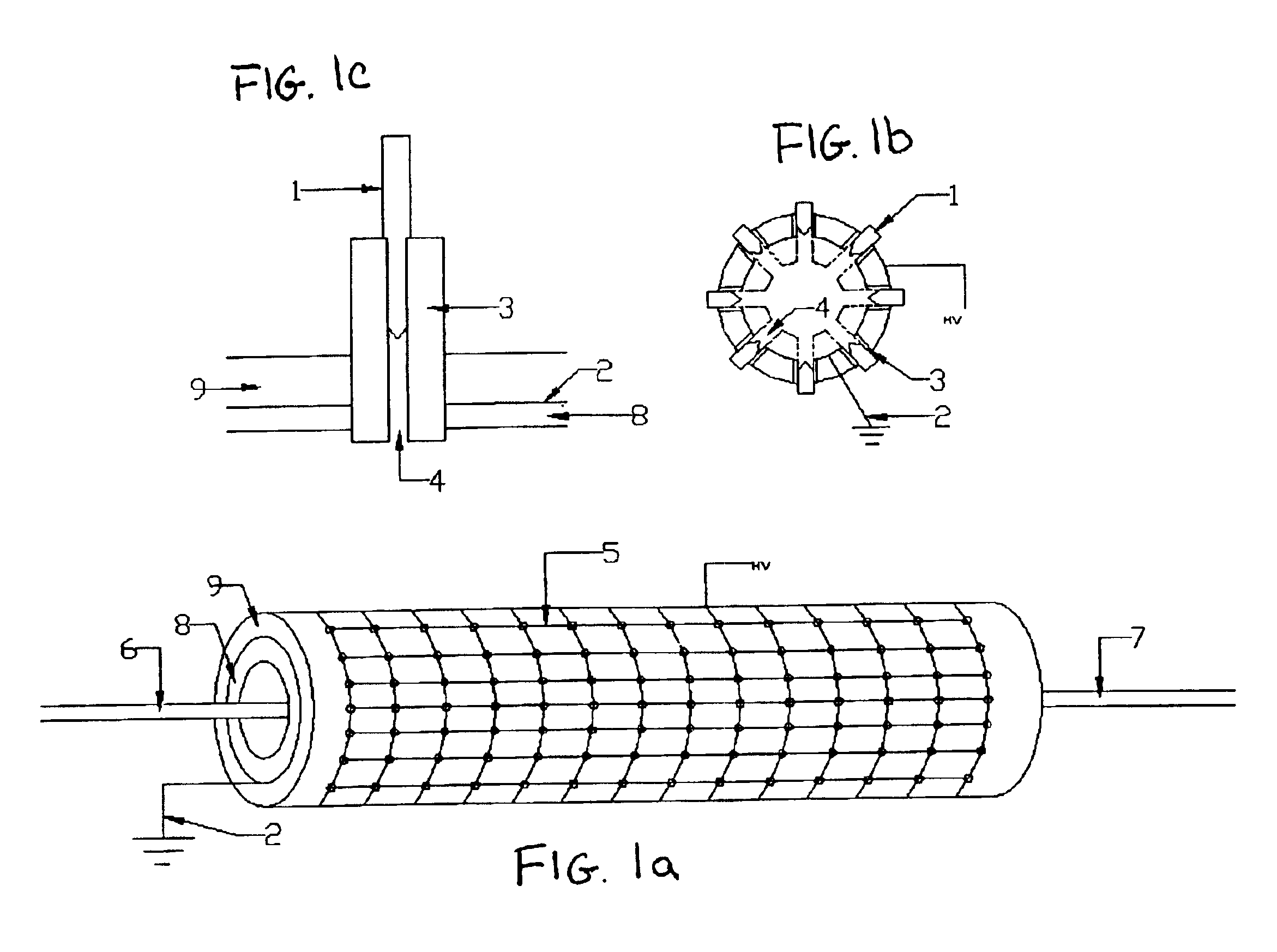
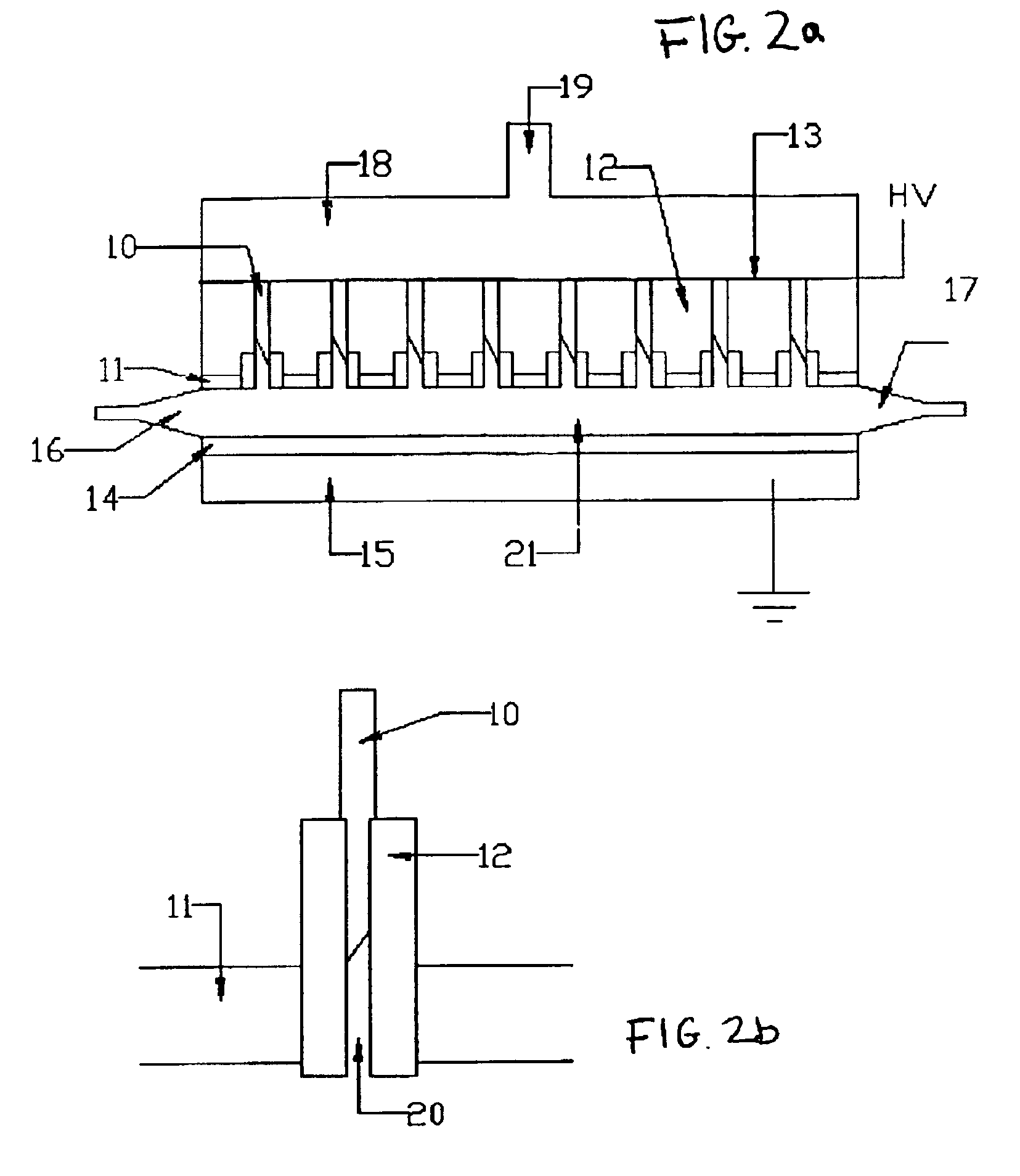
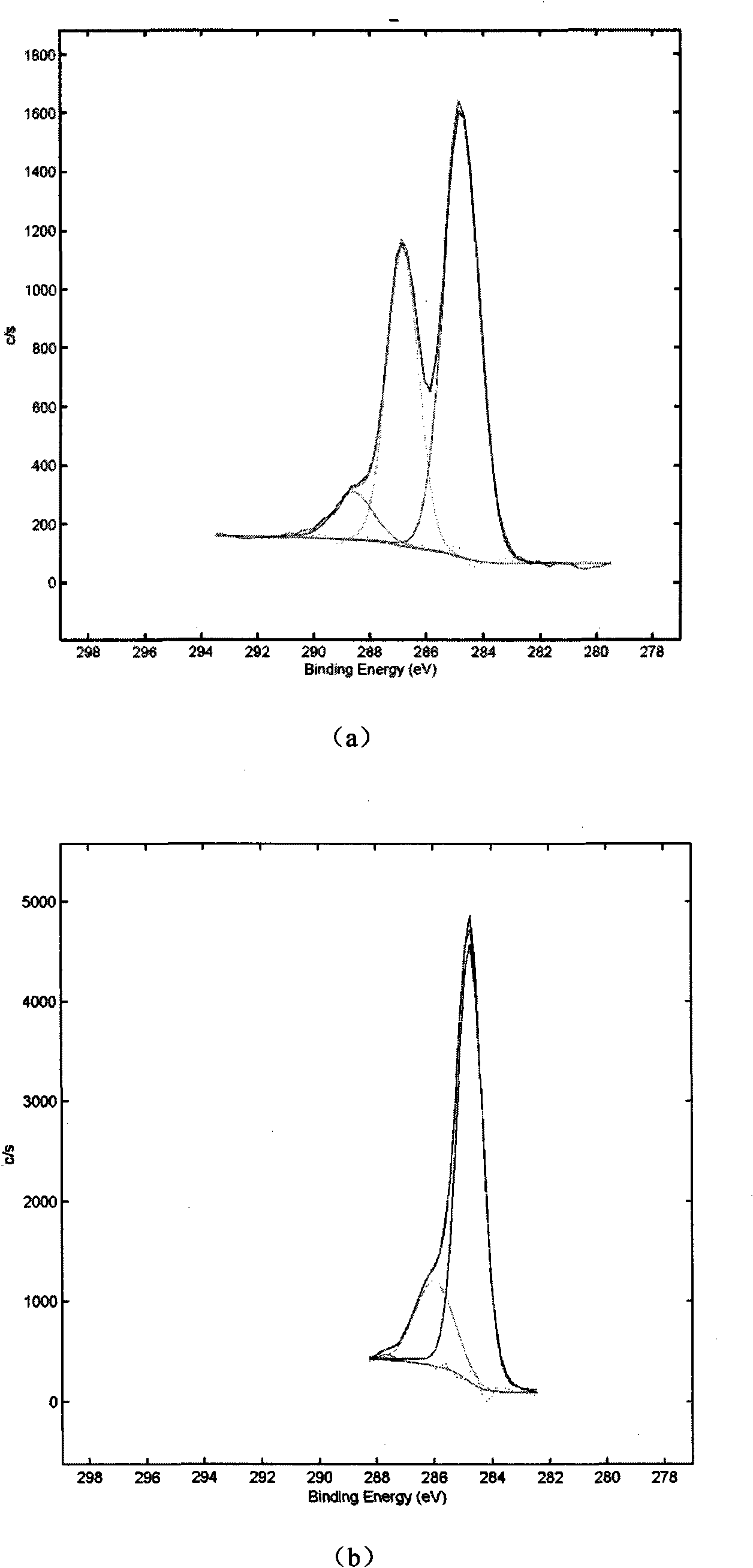
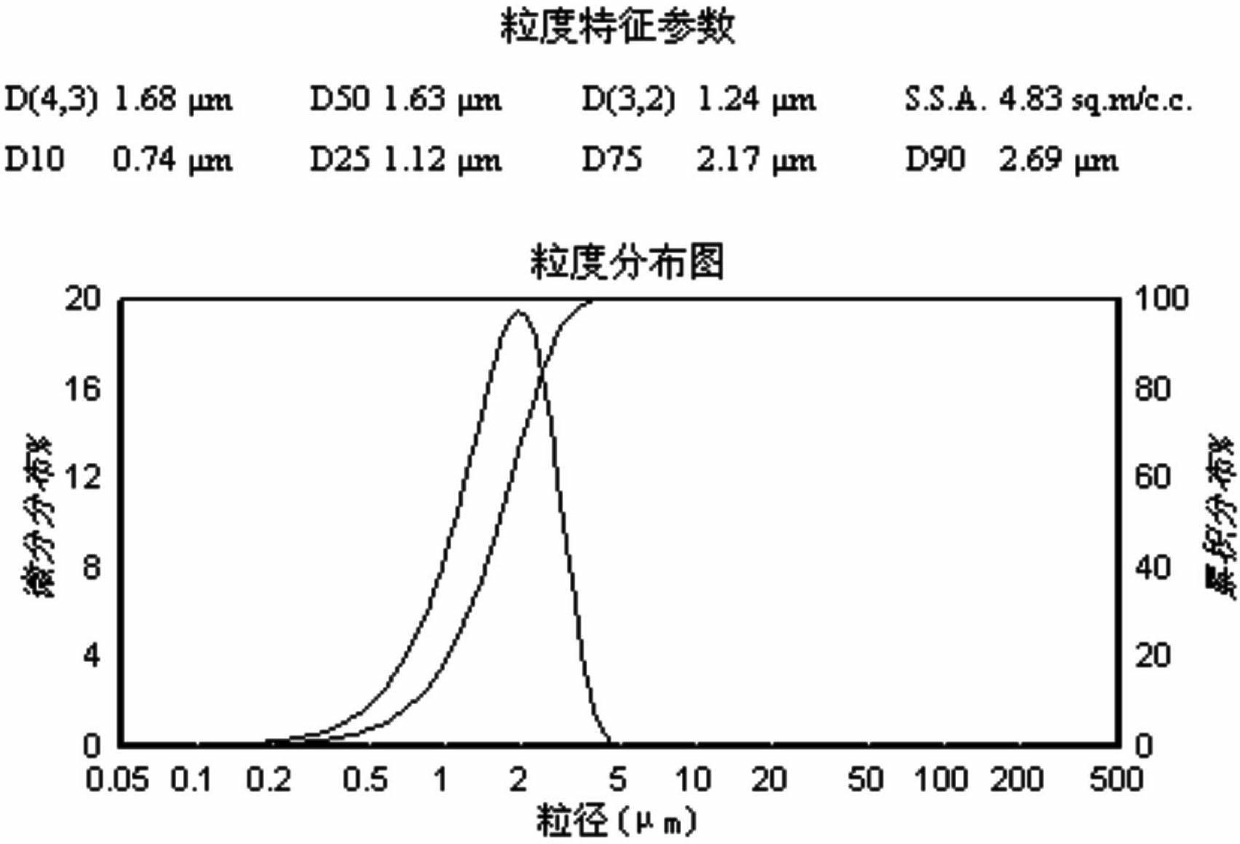
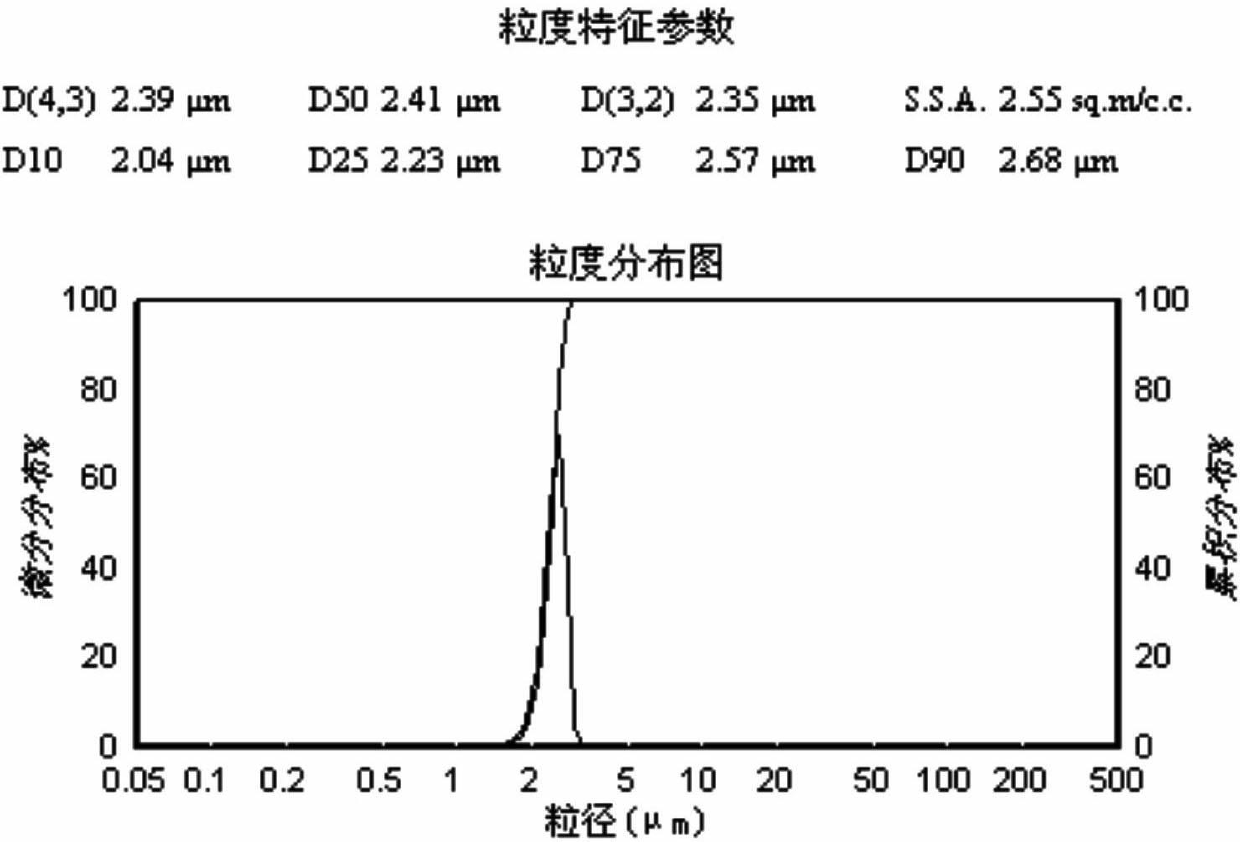
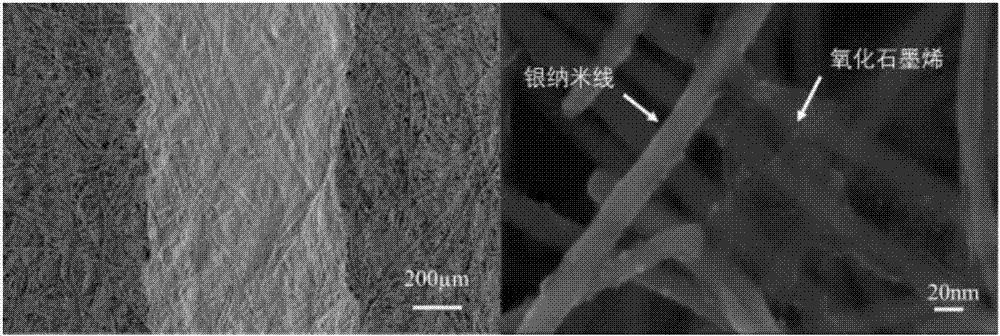
Patents
Literature
1265 results about "Chemical reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reduction (chemistry) Reduction is a chemical reaction that involves the gaining of electrons by one of the atoms involved in the reaction between two elements. The term refers to the element that accepts electrons, as the oxidation state of the element that gains electrons is lowered.
Purification of biologically-produced 1,3-propanediol
InactiveUS20050069997A1Reduce the amount of waterFermented solutions distillation/rectificationMembranesEscherichia coliDistillation
A process for purifying 1,3-propanediol from the fermentation broth of a cultured E. coli that has been bioengineered to synthesize 1,3-propanediol from sugar is provided. The basic process entails filtration, ion exchange and distillation of the fermentation broth product stream, preferably including chemical reduction of the product during the distillation procedure. Also provided are highly purified compositions of 1,3-propanediol.
Owner:DUPONT IND BIOSCIENCES USA LLC +1
Printable electronic display
InactiveUS6980196B1Easy to manufactureLow costElectromagnetic wave systemStatic indicating devicesMicroparticleNonlinear element
A display system includes a substrate upon which the display system is fabricated; a printable electrooptic display material, such as a microencapsulated electrophoretic suspension; electrodes (typically based on a transparent, conductive ink) arranged in an intersecting pattern to allow specific elements or regions of the display material to be addressed; insulating layers, as necessary, deposited by printing; and an array of nonlinear elements that facilitate matrix addressing. The nonlinear devices may include printed, particulate Schottky diodes, particulate PN diodes, particulate varistor material, silicon films formed by chemical reduction, or polymer semiconductor films. All elements of the display system may be deposited using a printing process.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cell negative electrode material and metallic silicon power therefor
InactiveUS20060051670A1Improve cycle performanceLow costSiliconSynthetic resin layered productsImpuritySilicon
A metallic silicon powder is prepared by effecting chemical reduction on silica stone, metallurgical refinement, and metallurgical and / or chemical purification to reduce the content of impurities. The powder is best suited as a negative electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte secondary cells, affording better cycle performance.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
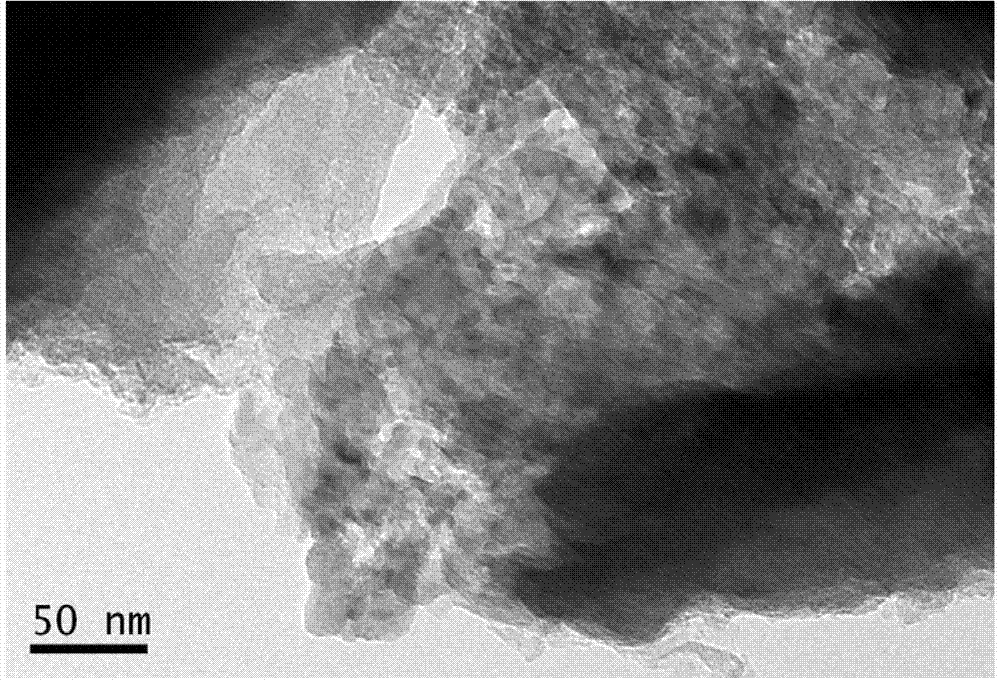
Graphene film with ultrahigh flexibility and high thermal conductivity and preparation method of graphene film
ActiveCN105523547AGuarantee unimpededGood electrical and thermal conductivityGrapheneHigh pressureCvd graphene
The invention discloses a graphene film with ultrahigh flexibility and high thermal conductivity and a preparation method of the graphene film. The graphene film is prepared from an ultralarge uniform graphene oxide sheet through steps of solution film-formation, chemical reduction, high-temperature reduction, high-pressure compression and the like. The graphene film is formed through physical crosslinking of macroscopic multi-layer folded graphene with microscale folds, and inter-lamella slippage can be realized, so that the graphene film has ultrahigh flexibility. The graphene lamellar structure of the graphene film is perfect, the lamellas have ultralarge crystalline areas which are about 100 mu m and contain few defects, the structure is compact after high-pressure compression, and the graphene film has ultrahigh electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity. The graphene film with ultrahigh flexibility and high thermal conductivity can be bent repeatedly more than 1,200 times, the elongation at break is 12%-18%, the electrical conductivity is 8,000-10,600 S / cm, the thermal conductivity is 1,800-2,600 W / mK, and the graphene film can be used as a high-flexibility, thermal-conducting and electric-conducting device.
Owner:杭州德烯科技集团有限公司
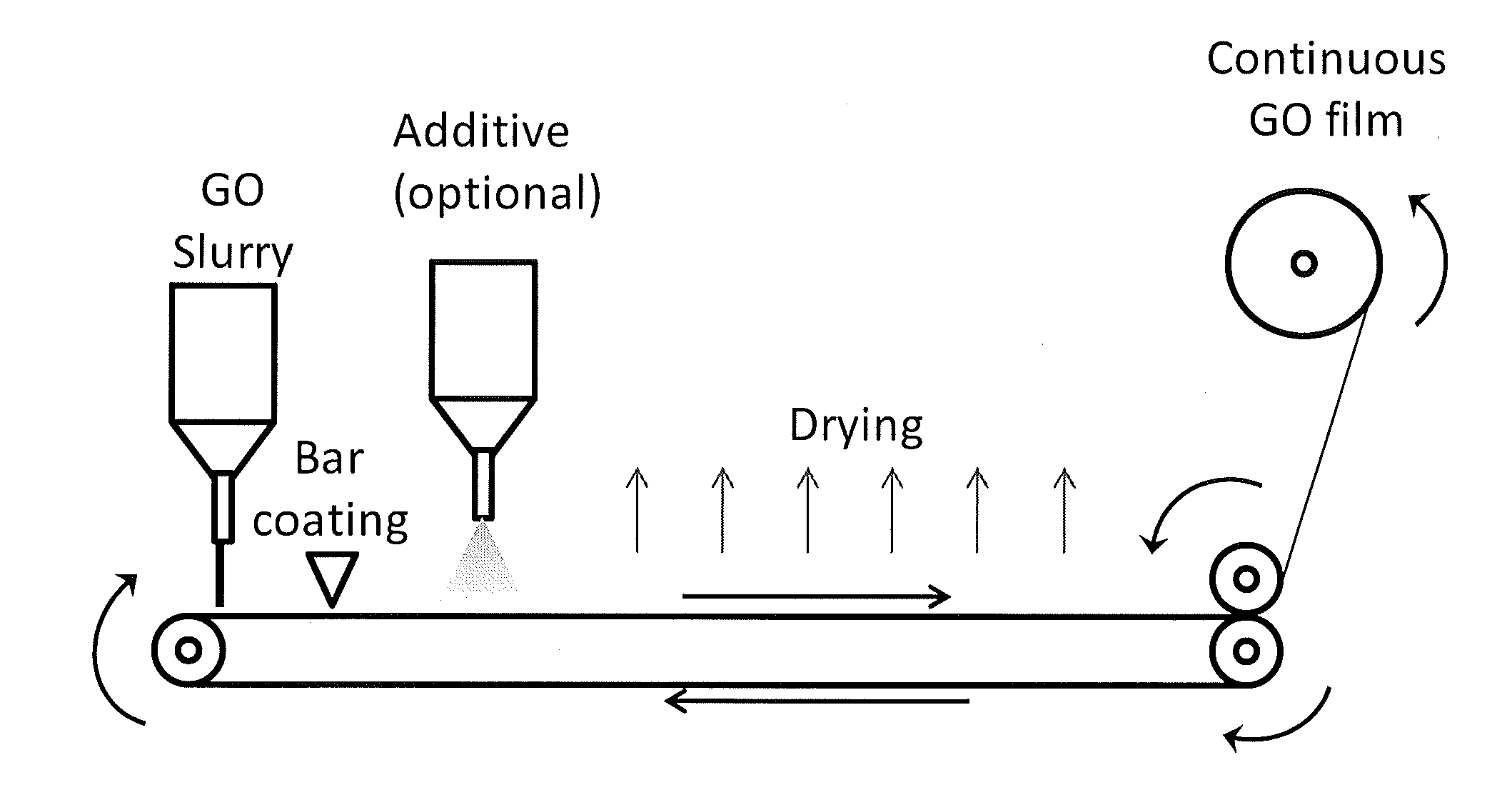
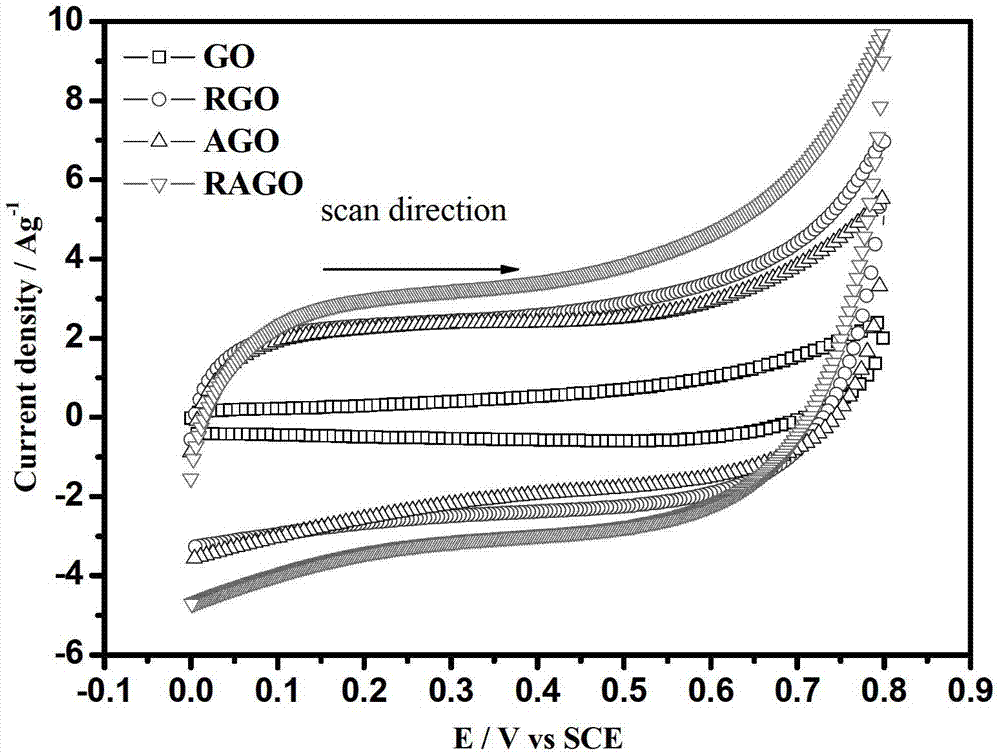
Method for preparing graphene oxide films and fibers
ActiveUS20150111449A1Improve conductivityHigh densityCarbon compoundsFilament/thread formingFiberSolid content
We report a method of preparation of highly elastic graphene oxide films, and their transformation into graphene oxide fibers and electrically conductive graphene fibers by spinning. Methods typically include: 1) oxidation of graphite to graphene oxide, 2) preparation of graphene oxide slurry with high solid contents and residues of sulfuric acid impurities. 3) preparation of large area films by bar-coating or dropcasting the graphene oxide dispersion and drying at low temperature. 4) spinning the graphene oxide film into a fiber, and 5) thermal or chemical reduction of the graphene oxide fiber into an electrically conductive graphene fiber. The resulting films and fiber have excellent mechanical properties, improved morphology as compared with current graphene oxide fibers, high electrical conductivity upon thermal reduction, and improved field emission properties.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
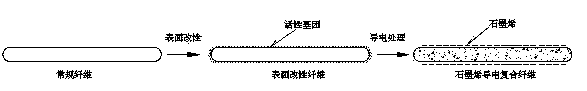
Preparation method of graphene electroconductive composite fiber
The invention provides a preparation method of a graphene electroconductive composite fiber. The method is characterized by comprising the following procedures: in a textile fiber surface modification procedure, a textile fiber is soaked into a silane coupling agent KH560 solution with the concentration of 1-30 percent for 2-3 hours and then is put into an oven of 50-65 DEG C to be dried to prepare the surfactant modified textile fiber; in a graphene dispersion system preparation procedure, graphene is prepared from an oxidized graphene aqueous solution prepared by means of a Hummer's method in a chemical reduction method, and a uniform and stable graphene dispersion system with the concentration of 0.1-5 percent is prepared under the function of a dispersing agent; in a graphene composite fiber preparation procedure, the modified textile fiber is soaked in the graphene dispersion system for 2-3 hours and then put into the oven of 50-65 DEG C to be dried to obtain the graphene electroconductive composite fiber. The preparation method is simple and reasonable in process, easy to operate, high in yield, high in reduction degree and high in conductivity and anti-radiation performance; the using amount of graphene is less and the dispersion system is uniform and stable.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Preparation method for three-dimensional porous graphene for supercapacitor
InactiveCN102923698AReduce the degree of reunionChange surface structureGrapheneHybrid/EDL manufacturePorous grapheneAdhesive
The invention provides a preparation method for three-dimensional porous graphene for a supercapacitor. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: ultrasonically dispersing graphene oxide; fully mixing with a strong alkali solution; pre-drying until a surface is humidified; then activating at a vacuum environment at 120 to 180 DEG C or in protective gas atmosphere at 180 to 1200 DEG C under a high temperature; and etching the surface of the graphene to obtain a three-dimensional porous structure through high-temperature strong alkali and stream, so as to improve a specific surface area of a graphene material. According to the preparation method, activated graphene oxide is reduced through chemical reduction and high-temperature reduction methods, so as to improve a performance of activated graphene. The activated graphene and an adhesive are mixed to prepare into electrode paste based on a certain mass ratio, and the electrode paste is loaded on a conductive current collector to prepare into a supercapacitor electrode, so that a degree of agglomeration of the graphene on a pole piece can be further reduced, and a high electrochemical performance can be obtained.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Catalyst system for reducing nitrogen oxide emissions
InactiveUS20070149385A1Molecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationChemical reactionNitrogen oxide
A multi-functional catalyst composition is provided. The multi-functional catalyst composition comprises a cracking catalyst material capable of enabling the conversion of the primary hydrocarbon into at least one secondary hydrocarbon having a lower molecular weight than the primary hydrocarbon, and a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) material capable of enabling the chemical reduction of NOx species. Further embodiments presented include a catalyst system comprising the catalyst, an apparatus for reducing NOx emissions comprising the catalyst system, and a method for making the catalyst material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for preparing antibacterial nanometer silver colloid
ActiveCN101731272ASmall particle sizeUniform size distributionBiocideDisinfectantsHigh concentrationBiological materials
The invention discloses a method for preparing antibacterial nanometer silver colloid, belonging to the technical field of nanometer biological materials. The method uses a chemical reduction method, comprising the following steps: dissolving water-soluble protective agent in silver nitrate water solution with the concentration of 0.001-0.1mol / L, wherein the mass ratio of protective agent to silver nitrate is 0.5-10.0:1; carrying out ice bath on sodium borohydride water solution with the concentration of 0.001-0.2mol / L for 10-30min; and dropwise adding the silver nitrate water solution containing protective agent in the sodium borohydride water solution with the speed of 30-60 drop / min, stirring by a magnetic stirrer, stirring for 20-40min after dropwise adding to prepare the nanometer silver colloid with the grain size of 5-80nm, wherein the mol ratio of the sodium borohydride to the silver nitrate is 1.0-30.0:1. The nanometer silver colloid prepared by the invention has the advantages of high concentration, high stability, high dispensability, and obviously-enhanced antibacterial property.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
High-performance aqueous graphene paint and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses high-performance aqueous graphene paint and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the high-performance aqueous graphene paint comprises the following steps of: oxidizing natural graphite in an oxidant, adopting a two-step chemical reduction method to obtain organic molecule-modified graphene aqueous solution; and adding polyester, a neutralizing agent, a flatting agent, an antifoaming agent, a cross-linking agent and a catalyst by adopting a solution co-mixing method to obtain aqueous graphene paint. A conductive coating with high conductive performance and mechanical performance is obtained by carrying out spray-coating, ink-jet printing and printing on the obtained paint, the conductive coating can be applied to the field such as electromagnetic shielding, static electricity preventing, corrosion preventing, radiating, wear-resisting and electronic circuits, and therefore, the application value is extensive.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for reducing loaded metal catalyst using low temperature plasma
InactiveCN1647858ARestore quickly and efficientlyGood dispersionCatalyst activation/preparationOxygenLow temperature plasma
The method of reducing loaded metal catalyst with low temperature plasma includes the steps of: 1) dissolving active metal salt component in deionized water or distilled water to form solution with metal component content of 0.01-20 wt%, filling solution into catalyst carrier, letting stand at room temperature for 8-24 hr and drying at 40-110 deg.c for 2-10 hr; and 2) setting the catalyst between two electrodes of plasma apparatus, introducing inert gas, air or oxygen as plasma discharge gas into discharge tube of pressure of 50-10000 Pa, and applying DC or AC voltage of 100-20000 V across the electrodes to process for 5-200 min. The low temperature plasma contains great amount of electrons, has powerful reducing capacity to reduce metal ion into metal simple substance and has no negative reaction appearing at high temperature. The process is simple, short in reduction time, without need of chemical reductant and environment friendly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Chemical processing using non-thermal discharge plasma
InactiveUS6923890B2Simple processEnhanced water gas shiftingHydrogenMolecular sieve catalystsChemical treatmentFiber
A method for activating chemical reactions using a non-thermal capillary discharge plasma (NT-CDP) unit or a non-thermal slot discharge plasma (NT-SDP) unit (collectively referred to as “NT-CDP / SDP”). The NT-CDP / SDP unit includes a first electrode disposed between two dielectric layers, wherein the first electrode and dielectric layers having at least one opening (e.g., capillary or a slot) defined therethrough. A dielectric sleeve inserted into the opening, and at least one second electrode (e.g., in the shape of a pin, ring, metal wire, or tapered metal blade) is disposed in fluid communication with an associated opening. A non-thermal plasma discharge is emitted from the opening when a voltage differential is applied between the first and second electrodes. Chemical feedstock to be treated is then exposed to the non-thermal plasma. This processing is suited for the following exemplary chemical reactions as (i) partial oxidation of hydrocarbon feedstock to produce functionalized organic compounds; (ii) chemical stabilization of a polymer fiber (e.g., PAN fiber precursor in carbon fiber production; (iii) pre-reforming of higher chain length petroleum hydrocarbons to generate a feedstock suitable for reforming; (iv) natural gas reforming in a chemically reducing atmosphere (e.g., ammonia or urea) to produce carbon monoxide and Hydrogen gas; or (v) plasma enhanced water gas shifting.
Owner:PLASMASOL CORP
Nitrogen-doped transparent graphene film and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20120161192A1Increase flexibilityGood electrical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsHydrogenWork function
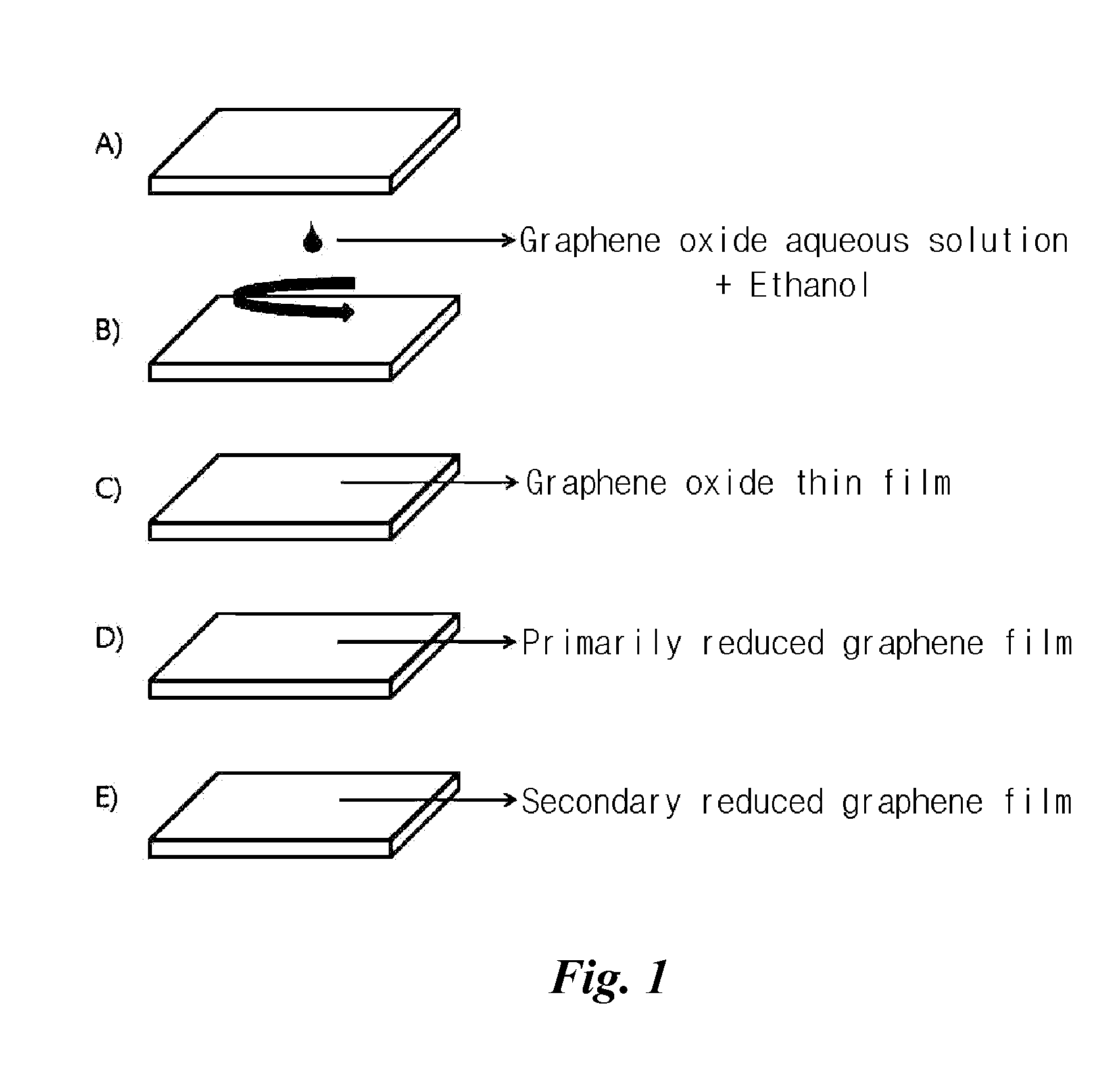
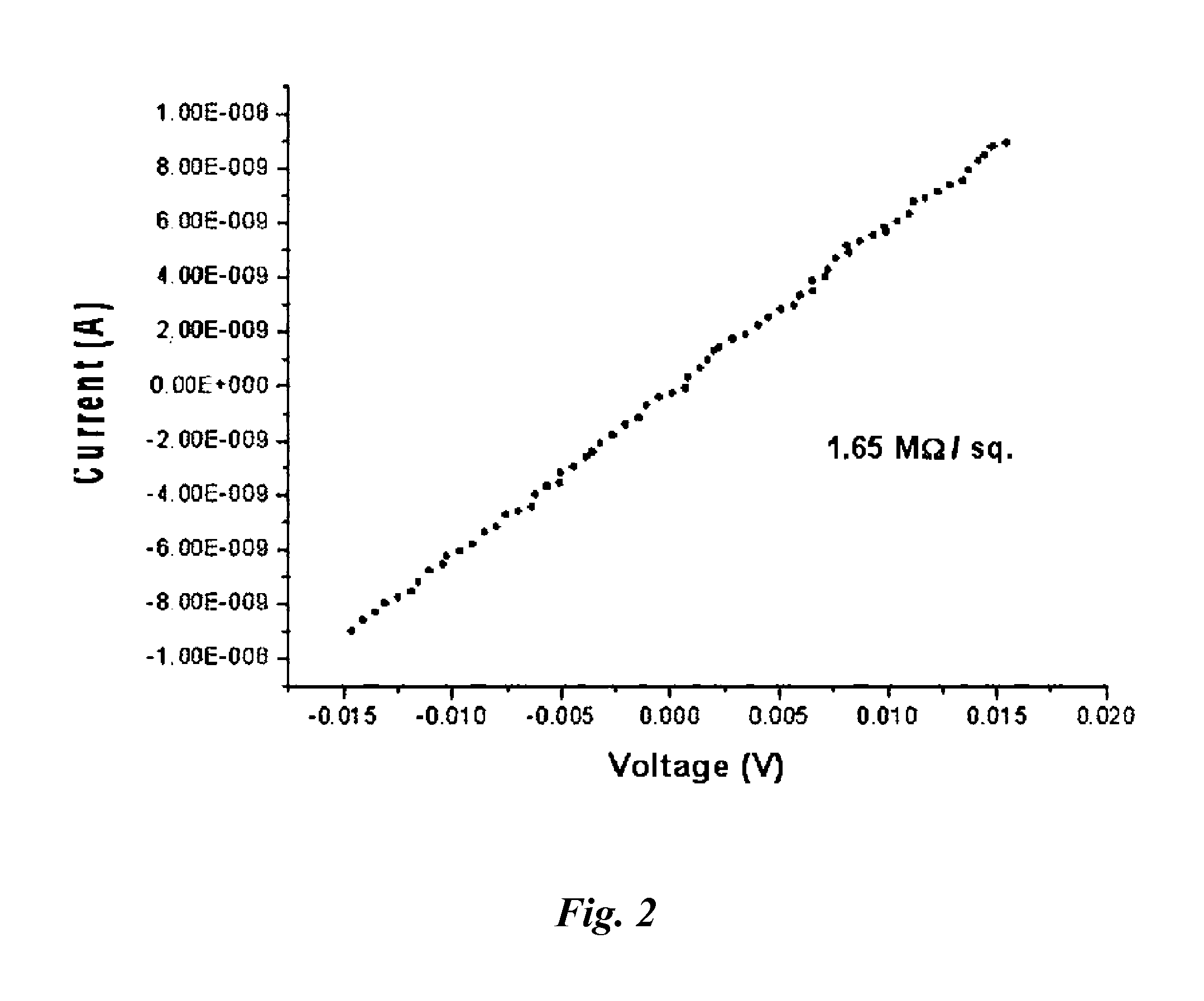
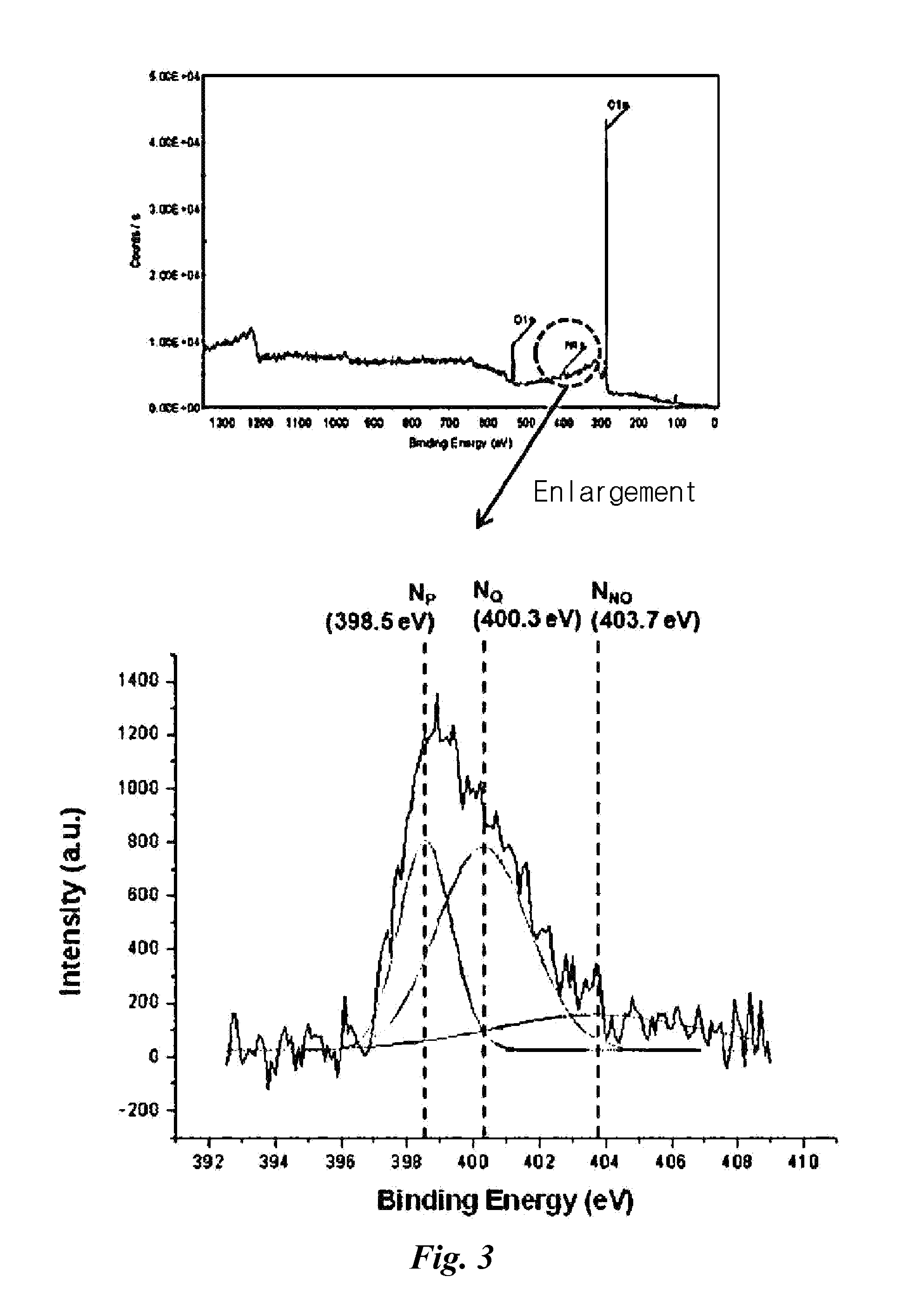
Provided is a transparent graphene film which is prepared by maintaining the primary reduced state of a graphene oxide thin film via chemical reduction, reducing the graphene oxide thin film with chemical vapor deposition, and doping nitrogen, thereby enhancing the conductivity and enabling the control of work function and a manufacturing method thereof. According to the present disclosure, a flexible, transparent, electrical conductivity-enhanced, and work function controllable graphene film can be large area processed and produced in large quantities so that can be applied in real industrial processes by forming a graphene oxide thin film on a substrate, performing the primary chemical reduction using a reducing agent, and performing further the secondary thermal reduction and nitrogen doping by injecting hydrogen and ammonia gas through chemical vapor deposition equipment.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of active radical with surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect
InactiveCN102759520AQuick checkIncrease surface areaRaman scatteringChemical vapor depositionCadmium Cation
The invention provides a preparation method of an active radical with a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect, belongs to the technical field of spectrum detection, and relates to the preparation technology of the SERS active radical, which is rapid, has high sensitivity and performs a low trace detection function. The preparation method is characterized in that firstly, a nano porous silicon columnar array with a large specific surface area is prepared by utilizing a hydrothermal etching technology; afterwards, a nanowire structure of an II-VI group compound semiconductor (such as zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, cadmium sulfide, cadmium selenide, cadmium telluride, and the like) by utilizing a chemical vapor deposition method; and finally, nano particles of precious metal (such as gold, silver, copper and the like) are finally prepared on the nanowire structure by using a chemical reduction method, so as to obtain an active radical material. The preparation method has a wide application prospect in the aspects of clinical biomolecular fast recognition, trace chemical substance detection, biological sample analysis, and the like. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation process of each material is simple, the condition is mild and the repetition rate reaches 100 percent.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Hybrid in-situ dry cleaning of oxidized surface layers
ActiveUS20110212274A1Increased resistivity film resistivityIncreased sheet resistivity resistivityVacuum evaporation coatingPretreated surfacesSurface layerHydrogen
According to one embodiment, the method includes providing a substrate containing a metal-containing barrier layer having an oxidized surface layer, exposing the oxidized surface layer to a flow of a first process gas containing plasma-excited argon gas to activate the oxidized surface layer and applying substrate bias power during the exposing of the oxidized surface layer to the flow of the first process gas. The method further includes exposing the activated oxidized surface layer to a second process gas containing non-plasma-excited hydrogen gas, wherein the exposure to the first process gas, in addition to activating the oxidized surface layer, facilitates chemical reduction of the activated oxidized surface layer by the second process gas containing the hydrogen gas. A thickness of the metal-containing barrier layer is not substantially changed by the hybrid in-situ dry cleaning process.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Transparent graphene conductive thin film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102750998AGood light permeabilityImprove conductivityNon-insulated conductorsCarbon-silicon compound conductorsTransmittanceIndium tin oxide
The invention discloses a transparent graphene conductive thin film and a preparation method of the film, aiming at improving the acid and alkali resistance of a transparent conductive thin film. The transparent graphene conductive thin film is a graphene thin film with the thickness of 1-50nm and the electrical conductivity of 300-800S / cm, and has the light transmittance of 70-85% for light with the wavelength within the range of 200-1100nm. The preparation method of the transparent graphene conductive thin film comprises the steps of: oxidizing graphite, preparing a graphene oxide water mixed liquid, preparing a graphene oxide thin film, and reducing to obtain the transparent graphene conductive thin film. Compared with the prior art, the transparent graphene conductive thin film which is prepared by a high-temperature reduction or chemical reduction method has the advantages of being good in light transmittance and electrical conductivity, large in preparation area, simple in preparation method and low in cost; and the transparent graphene conductive thin film can be used for replacing the traditional inorganic oxide electrode material indium tin oxide (ITO), thus providing infinite space for the transparent conductive thin film and the related fields.
Owner:BTR NEW MATERIAL GRP CO LTD
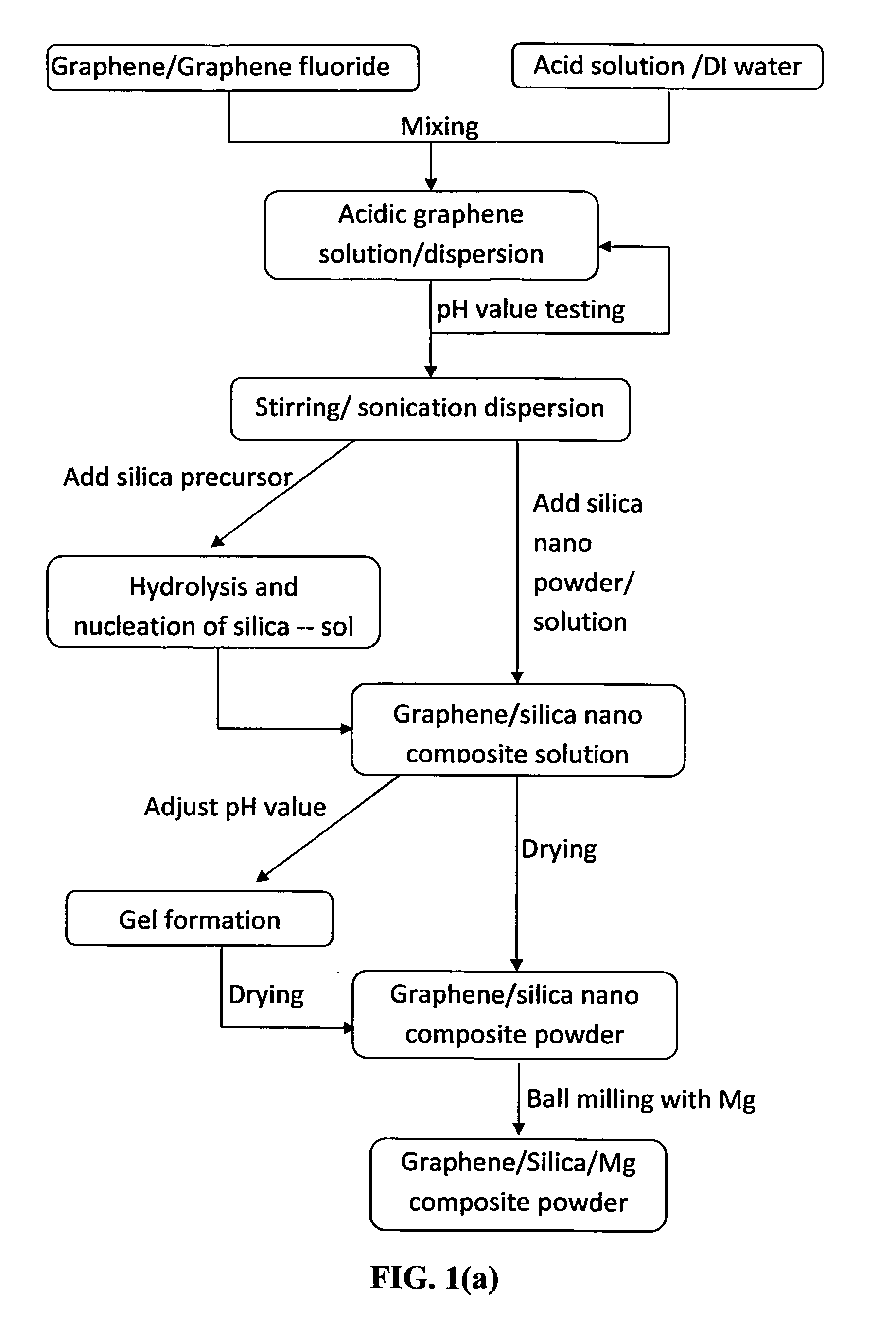
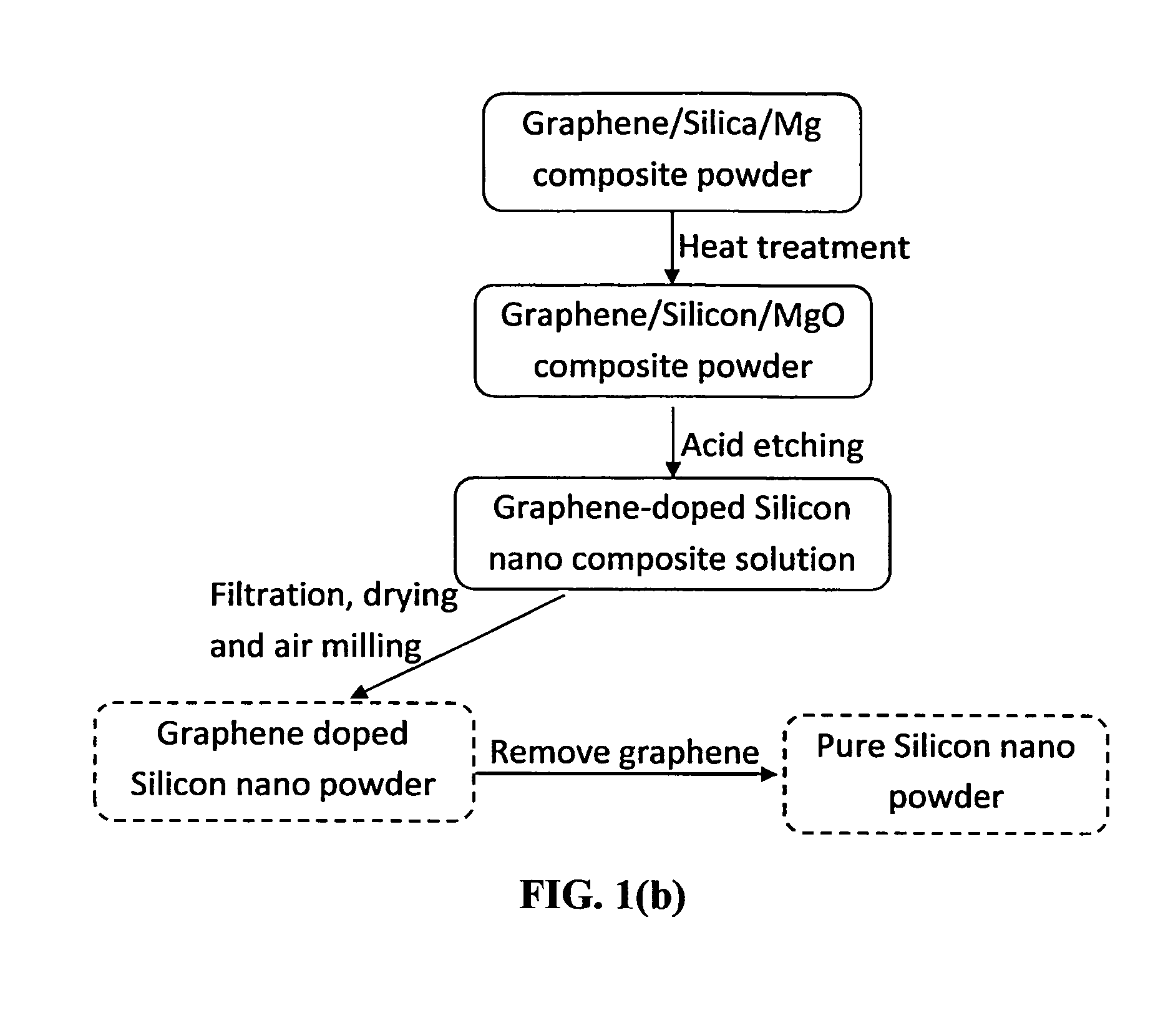
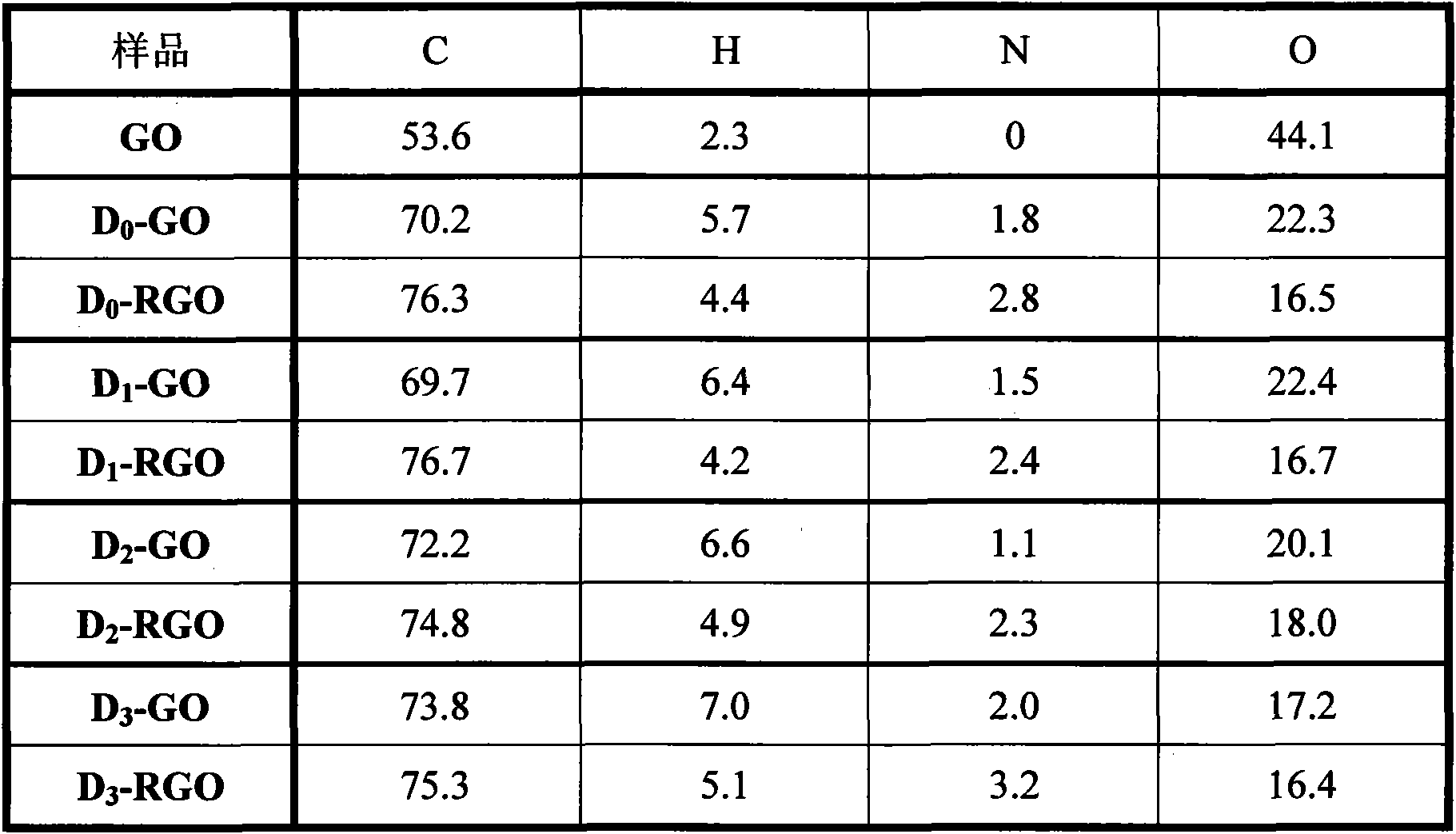
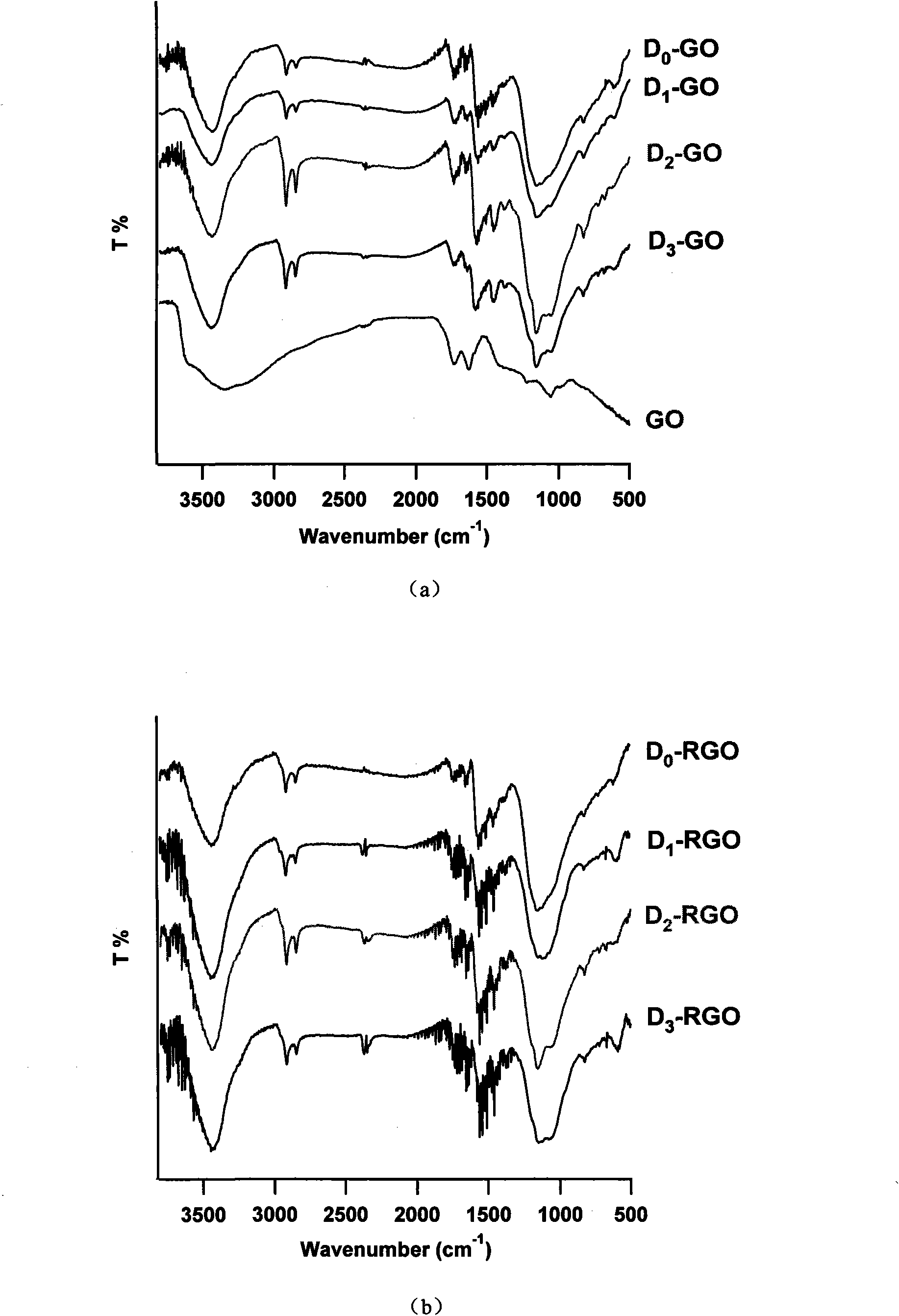
Methods for mass-producing silicon nano powder and graphene-doped silicon nano powder
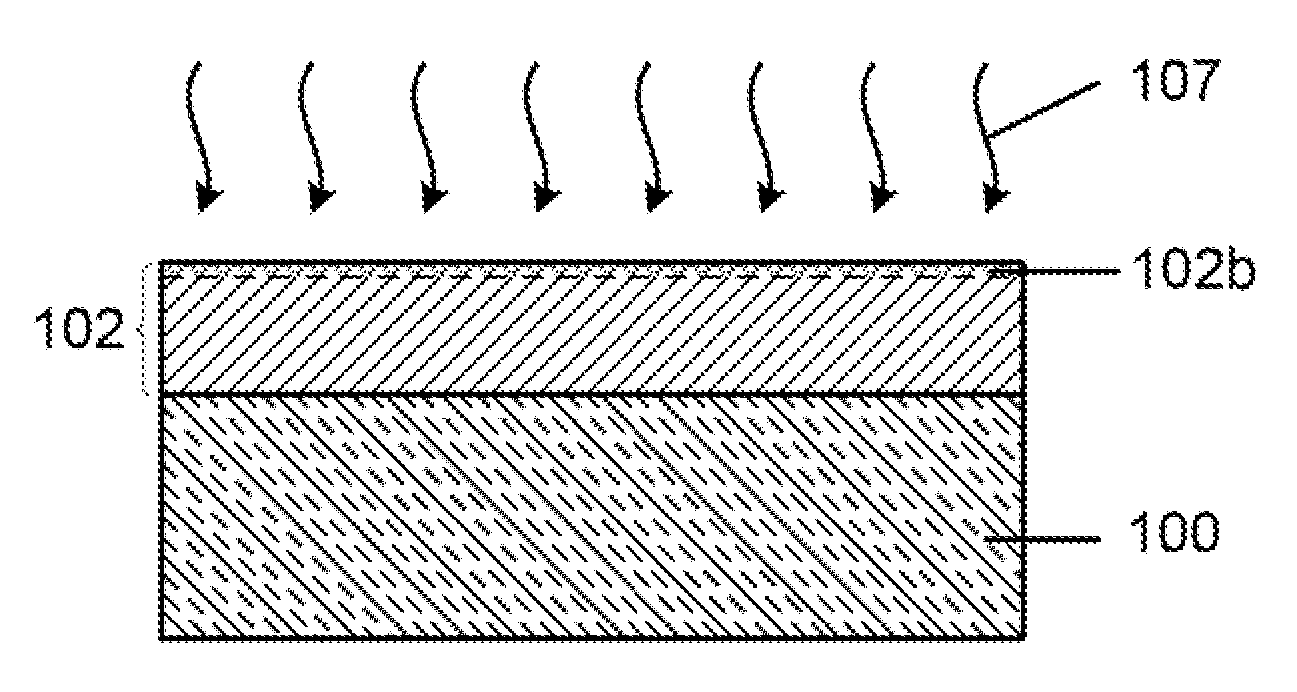
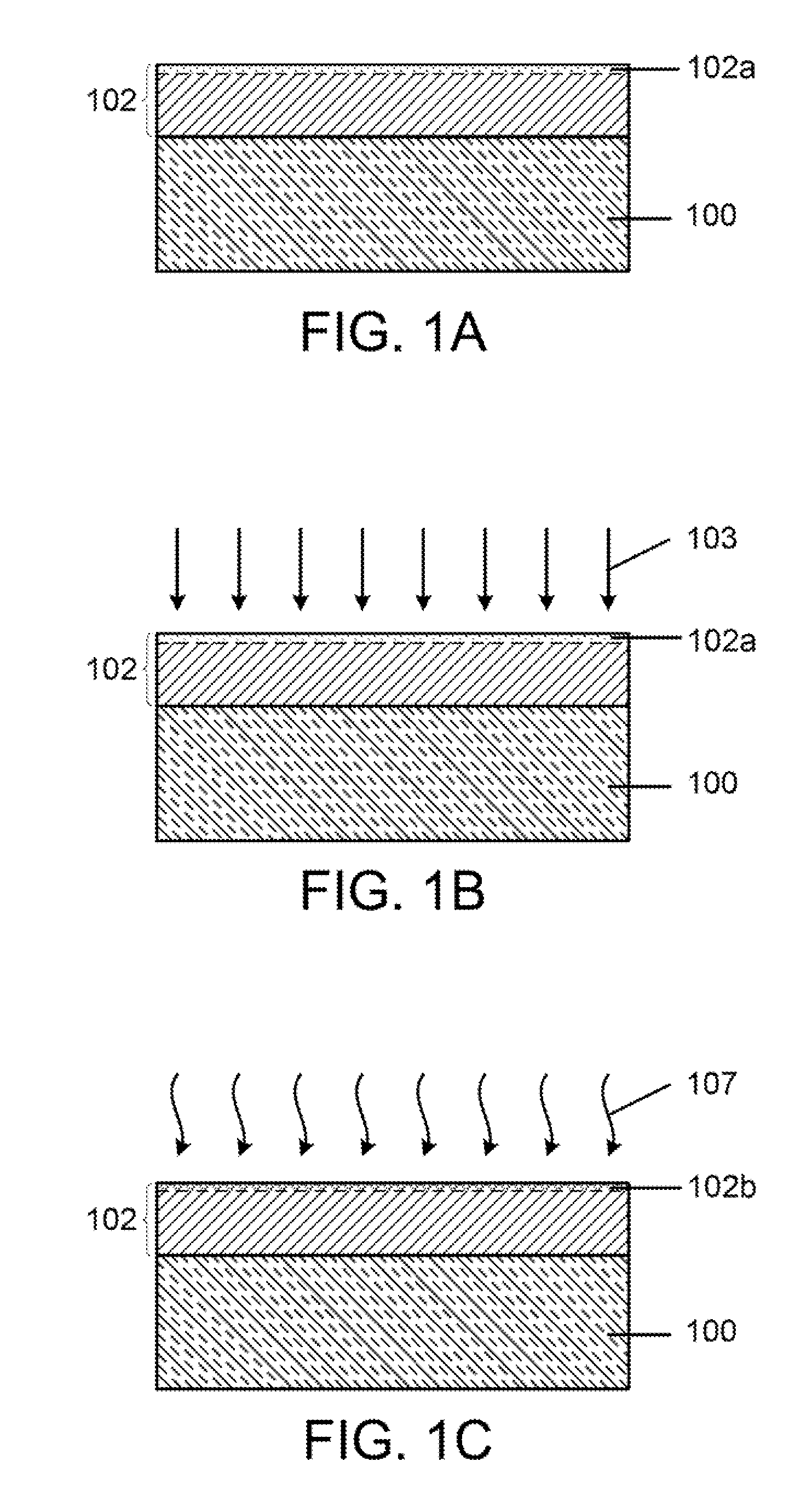
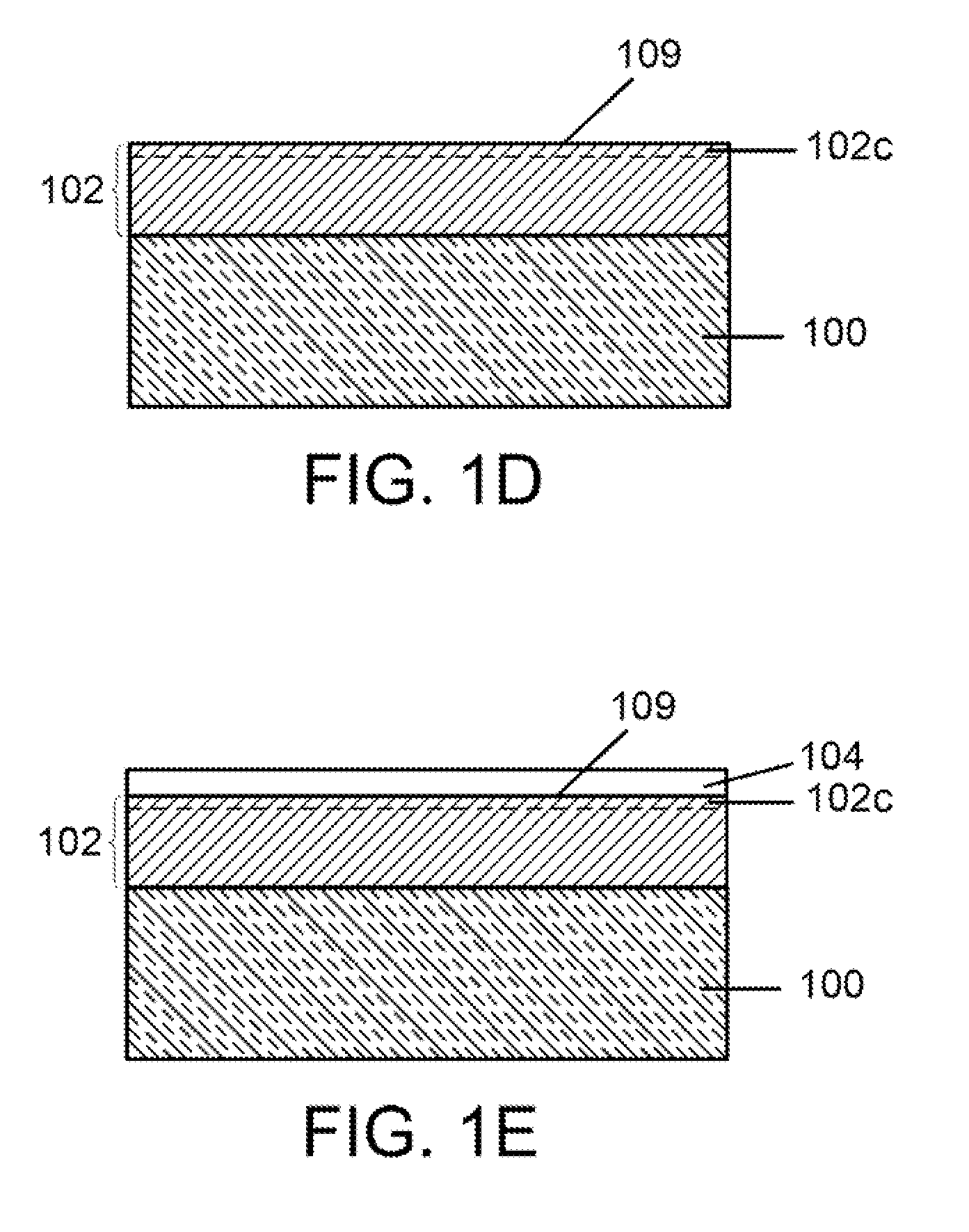
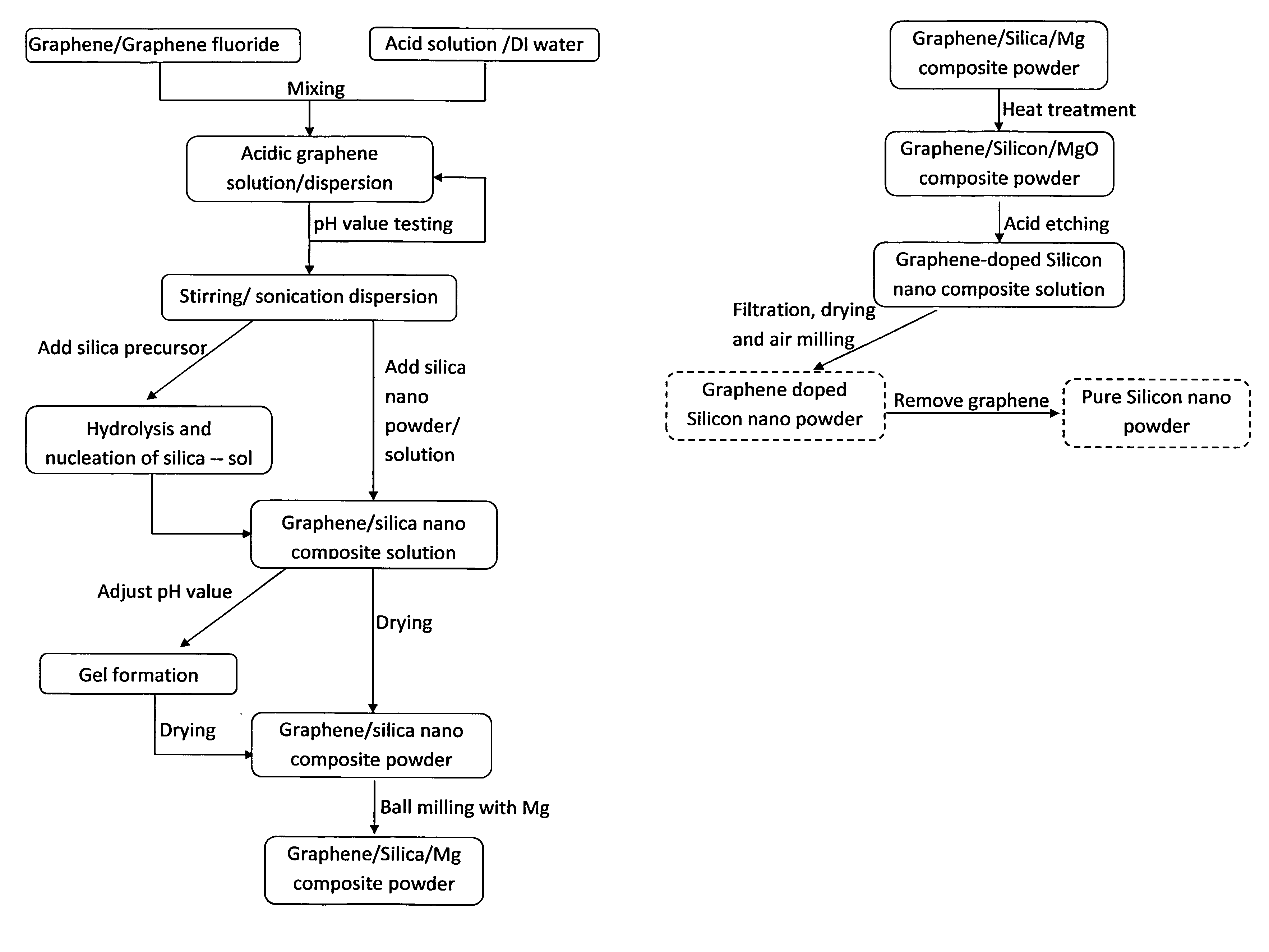
Disclosed is a facile and cost effective method of producing nano silicon powder or graphene-doped silicon nano powder having a particle size smaller than 100 nm. The method comprises: (a) preparing a silicon precursor / graphene nano composite; (b) mixing the silicon precursor / graphene nano composite with a desired quantity of magnesium; (c) converting the silicon precursor to form a mixture of graphene-doped silicon and a reaction by-product through a thermal and / or chemical reduction reaction; and (d) removing the reaction by-product from the mixture to obtain graphene-doped silicon nano powder.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Preparation method of grapheme capable of dispersing in organic solvent
ActiveCN101863465AExcellent solvent dispersion performanceEasy to synthesizeOrganic solventHydrazine compound
The invention relates to a preparation method of grapheme capable of dispersing in an organic solvent, comprising chemical reduction of a graphene oxide stem grafting arborization substituent group and graphene oxide. In the invention, the arborization substituent group with huge volume is utilized to functionalize graphene oxide, thereby the obtained graphene oxide can be dispersed in a majority of organic solvents, and after the graphene oxide is reduced by hydrazine hydrate, the obtained graphene still keeps excellent organic solvent dispersibility. In the invention, excess reactants, impurities and solvent in the preparation process of a solution method are removed by utilizing means of filtering and washing so that a purified graphene product is obtained, and the graphene product is powdery, is convenient to store and transport, and meets the requirement of preparation in macroscopic quantity. The graphene prepared by utilizing the invention has excellent solvent dispersibility, therefore, a powdery graphene sample can be dispersed in a specific organic solvent again as required to obtain required graphene sol for large-scale application.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spherical silver powder and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102632248ANarrow particle size distributionSimple preparation processPyrrolidinonesDisplay device
The invention discloses a spherical silver powder, wherein the particle size distribution range of the spherical silver powder is 0.1-5 mum, and the D50 particle size is 1.0-3.5 mum; the tap density of the spherical silver powder is greater than 3.6 g / cm<3>; and the specific surface area of the spherical silver powder is less than 1.0 m<2> / g. The preparation method for the spherical silver powder comprises the following step of: with L-ascorbic acid as a reductive agent and polyvinylpyrrolidone as a protective agent, reducing silver out of a reaction material, namely silver nitrate solution, by a chemical reduction method, wherein the pH value of the reaction system is controlled to be constant between 3 to 6 during the whole reaction process of the chemical reduction method, so as to keep the speed of the reduction reaction for silver nitrate stable. The spherical silver powder disclosed by the invention is narrow in particle size distribution range, excellent in dispersity, high in tap density, small in specific surface area, and especially suitable for preparing a silver paste for the electrode of a solar cell and the electrode of a plasma displayer.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH +1
Synthesis of metallic nanoparticle dispersions capable of sintering at low temperatures
A process is described for the synthesis of metallic nanoparticles by chemical reduction of metal salts in the presence of organic ligands capable of binding to the metal particle surfaces and stabilizing them against agglomeration. The resultant nanoparticles or dispersions of the particles can be sintered into highly conductive films or traces at temperatures as low as 80° C. in 10 minutes or less.
Owner:NCC NANO LLC
Benzene hydrogenation catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102600888AExcellent benzene hydrogenation catalytic performanceHigh catalytic activityMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationBenzeneAdjuvant
The invention relates to a benzene hydrogenation catalyst as well as a preparation method and application of the benzene hydrogenation catalyst. The catalyst consists of an active component Ru and adjuvants, wherein the active component Ru is loaded on the catalyst by a carrier; the adjuvants are one or two of La, Ce, Fe, Zn, Cu and B, and the carrier is a mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41 modified by one or two of ZrO2, ZnO and CuO. The invention also provides a method for preparing cyclohexene and cyclohexane by benzene hydrogenation catalyzed by the catalyst. The catalyst provided by the invention can be prepared by a dipping sedimentation method or a chemical reduction method and has a higher catalytic activity and cyclohexene selectivity.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Preparation method and application of conductive ink based on metal nanowire and graphene oxide
ActiveCN106867315AEasy to prepareEasy to operateInksMetallic pattern materialsSurface-active agentsFlashlight
The invention provides a preparation method and application of conductive ink based on metal nanowire and graphene oxide. The graphene oxide is simultaneously used as a dispersing agent, a thickening agent and a stabilizing agent. The metal nanowire, the graphene oxide, the deionized water, the alcohol solvent, the dispersing agent, the surface active agent, the flatting agent and the de-foaming agent are uniformly mixed at a certain mass ratio, so as to acquire the conductive ink product. The acquired ink can be directly written or printed on various substrate materials so as to construct a conductive circuit with high conductivity, stability, flexibility and high adhesion; the constructed conductive circuit is dried for 3-10 minutes under room temperature, so that ultrahigh conductivity is achieved; furthermore, the graphene oxide is reduced and the metal nanowire is sintered according to the methods, such as, selecting sintering temperature at 50-200 DEG C or performing chemical reduction under room temperature or utilizing an xenon flashlight to sinter, so that the conductivity of the conductive circuit is further increased.
Owner:XUZHOU LANOXENE INST CO LTD
Method for preparing low-temperature nitrogen-doped graphene supported nano Pd hydrogenation catalyst
InactiveCN104028293AHigh catalytic activityImprove reusabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationDispersityDoped graphene
The invention relates to a method for preparing a low-temperature nitrogen-doped graphene supported nano Pd hydrogenation catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: ultrasonically stripping graphite oxide, thereby obtaining an aqueous solution of highly dispersed graphite oxide; selecting different nitrogen sources, and synthesizing nitrogen-doped graphene at low temperature through a hydrothermal method; and performing ultrasonic treatment on the nitrogen-doped graphene, adding a certain amount of PdCl2 solution, and adding a reducing agent, thereby preparing the highly dispersed supported nano Pd hydrogenation catalyst by a chemical reduction method. Because nitrogen atoms, which contain lots of lone pair electrons and can achieve a coordination effect with metal nanoparticles, are mixed into a carbon skeleton of graphene, runoff and conglomeration of the metal nanoparticles are effectively avoided, and the dispersity of the metal nanoparticles on the surface of graphene is improved. The catalyst is used for a hydrogenation reaction of olefins and has extremely high catalytic activity and high reusability. The catalyst is simple in preparation method and low in cost, the nitrogen content is high, doped nitrogen is controllable, and industrial production is easily realized.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of inorganic/organic hybridization antibacterial film
The invention relates to a preparation method of an inorganic / organic hybridization antibacterial film. The preparation method mainly comprises the steps of: (1) preparing a nano-silver-loaded molecular sieve germicide with stronger stability by ion exchange and a chemical reduction method; and preparing a molecular sieve / polymer hybridization antibacterial film loaded with nano-silver particles by a phase transformation film preparation process; and (2) taking N,N-dimethylformamide as a solvent and a reducing agent simultaneously, reducing silver ions to nano-silver serving as an antibacterial function body in a film casting liquid system in situ, and firmly loading the nano-silver in a polymer porous matrix material by a dispersion action and a coupling action of a coupling agent so as to form a nano-silver-loaded polymer porous film. The hybridization antibacterial film, provided by the invention, keeps excellent water flux, high retention rate and tough mechanical intensity, and has excellent antibacterial function, and can effectively solve the problems of loss of the silver ions of the silver-ion-loaded molecular sieve in the membrane filtration, loss of the nanometer inorganic particles in the polymer porous matrix, easy pollution of a separation film by microorganisms, and the like.
Owner:天津鼎芯膜科技有限公司
Method for preparing loading type nano Pd/C catalyst from colloidal solution
InactiveCN1966144AAvoid organic pollutionReduce manufacturing costCatalyst carriersNanostructure manufacturePalladium catalystChemical reduction
The invention relates to a method for using colloid solution to prepare carrier nanometer Pd / C catalyst, wherein said method comprises that using chemical reduction to process palladium salt to prepare the nanometer palladium colloid solution with stable surface activity, then using some carrier to absorb it to obtain the palladium colloid, to obtain the nanometer palladium catalyst with different loaded amounts. The inventive catalyst can be used in hydrogenation.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
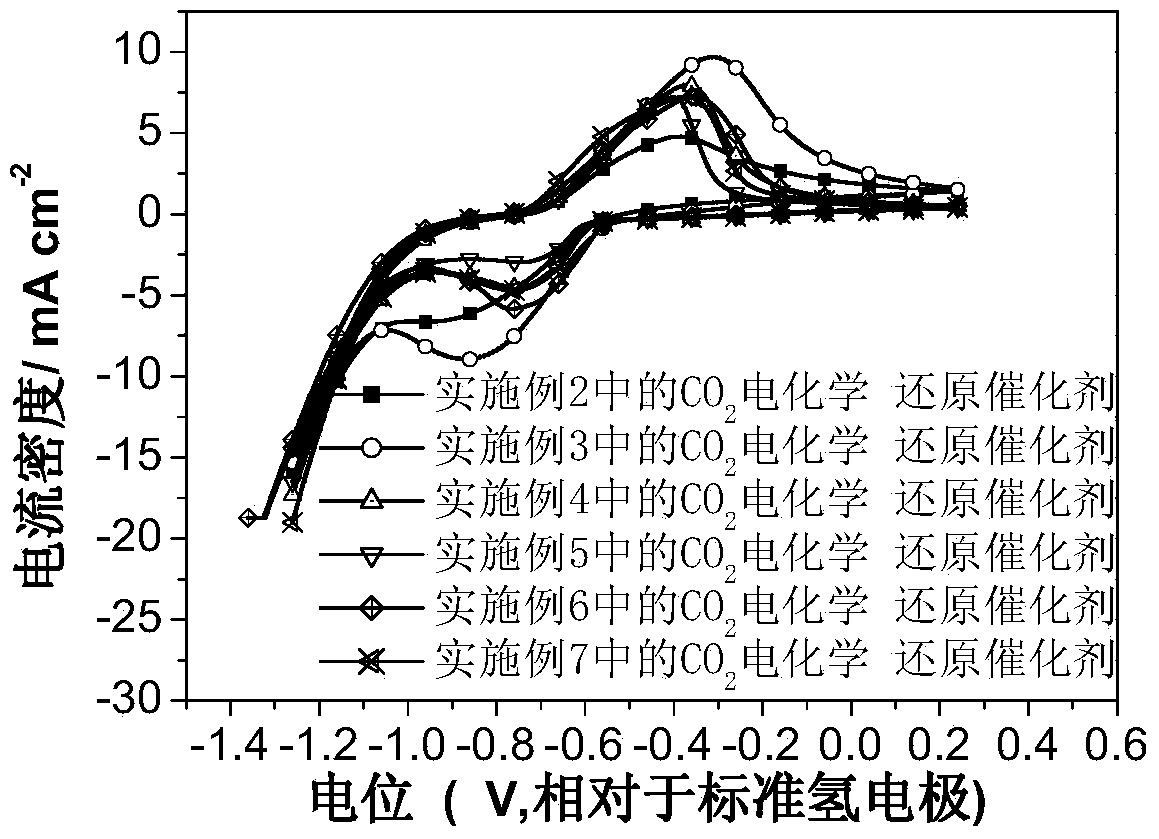
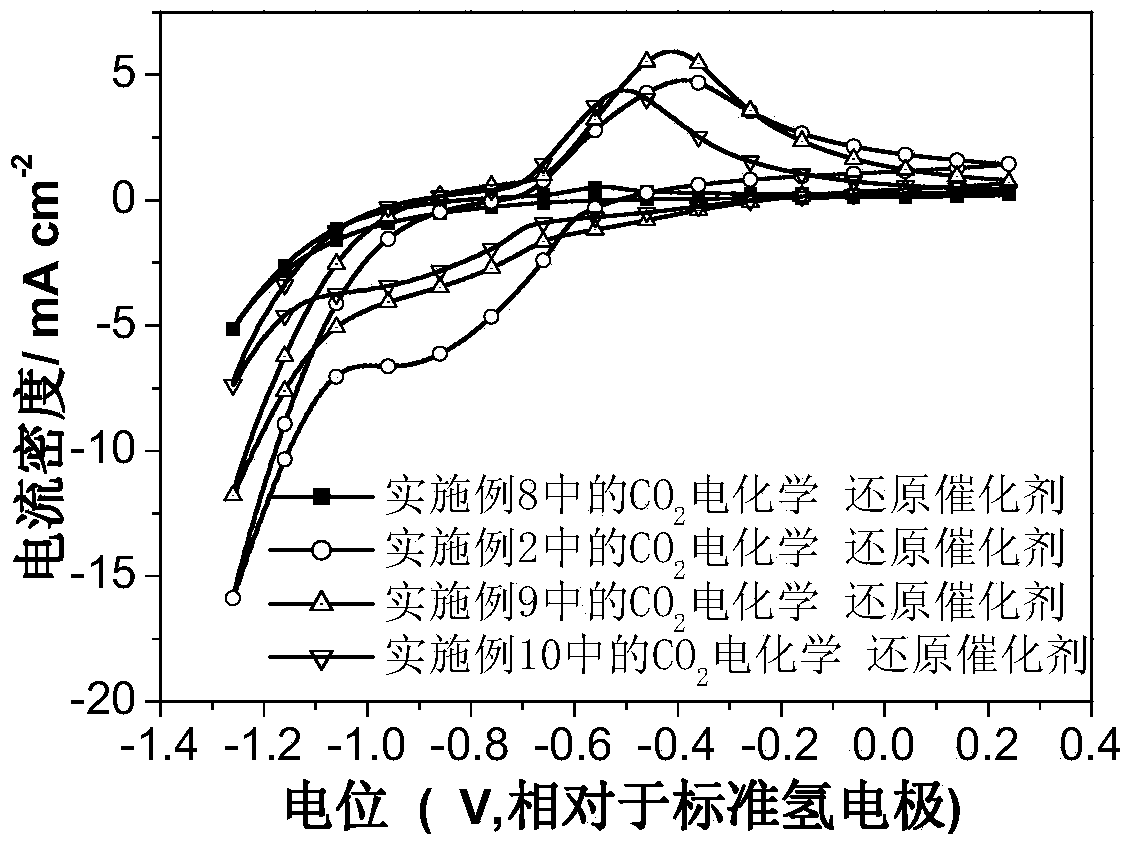
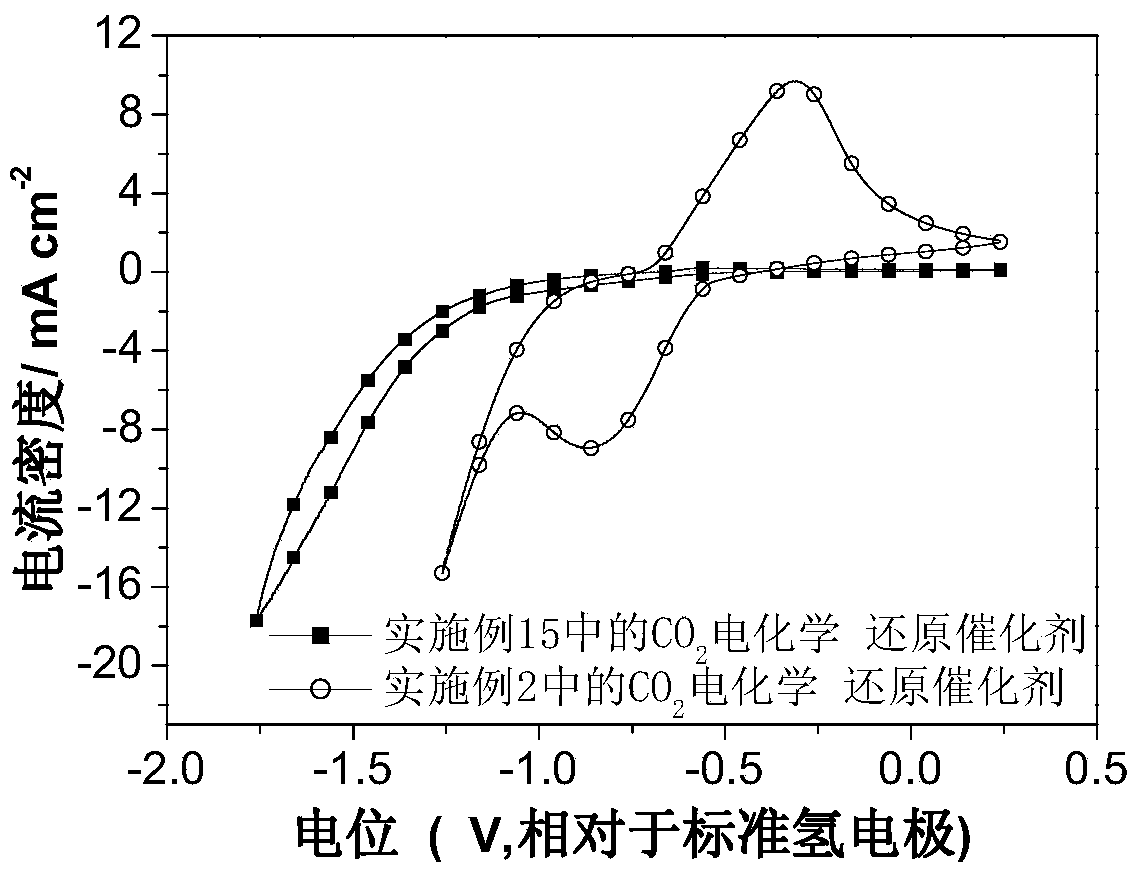
Carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103715436AIncrease the number of active sitesThe synthesis method is simpleMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesTin dioxideTrisodium citrate
The invention relates to a carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst comprises tin dioxide nanoflower, wherein the tin dioxide nanoflower is synthesized through hydrothermal reaction and comprises the synthesis raw materials including 0.1-0.5M of tin dioxide, 1-5M of trisodium citrate mixed solution and 0.1-0.5M of sodium hydroxide. The carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst is applied to a carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst gas diffusion electrode. The carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst has the advantages that the specific surface area of the catalyst is enlarged, the electrochemical reduction catalytic activity of the catalyst for carbon dioxide reduction is improved, the hydrogen evolution reaction is effectively inhibited, and the selectivity of formic acid in a product is improved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Graphene composite porous counter electrode, preparation method and application thereof
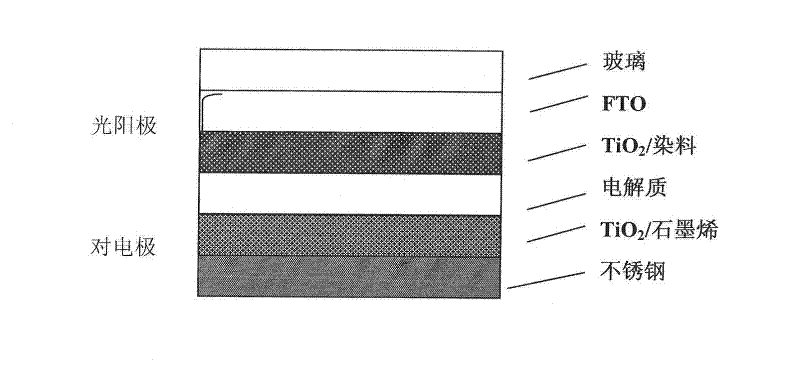
ActiveCN102347143AGuaranteed normal transmissionLarge active surface areaLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufacturePorosityFluid electrolytes
The invention discloses a graphene composite porous counter electrode, a preparation method and application thereof. The composite porous counter electrode is a mixture of grapheme and inorganic nanometer particles coated on a conductive substrate. The preparation method concretely comprises the following steps of: mixing the grapheme prepared through chemical reduction with the inorganic nanometer particles; adding a small amount of organic binder; coating the organic binder on a substrate material, such as metal, conductive glass or conductive plastic and the like; and obtaining the graphene composite porous counter electrode through thermal treatment. The porosity of the composite counter electrode ensures that the composite counter electrode and a liquid electrolyte have larger effective contact area; and the composite counter electrode has the photoelectric conversion efficiency equivalent to a magnetron sputtering Pt electrode when being applied to a dye sensitized solar cell. The composite electrode has the advantages of low cost, favorable stability and mechanical property and the like and has important significant on the wide application of the dye sensitized solar cell.
Owner:中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所苏州研究院
Method for treating chlorinated organic pollutants in underground water by using slow-release compound repair material
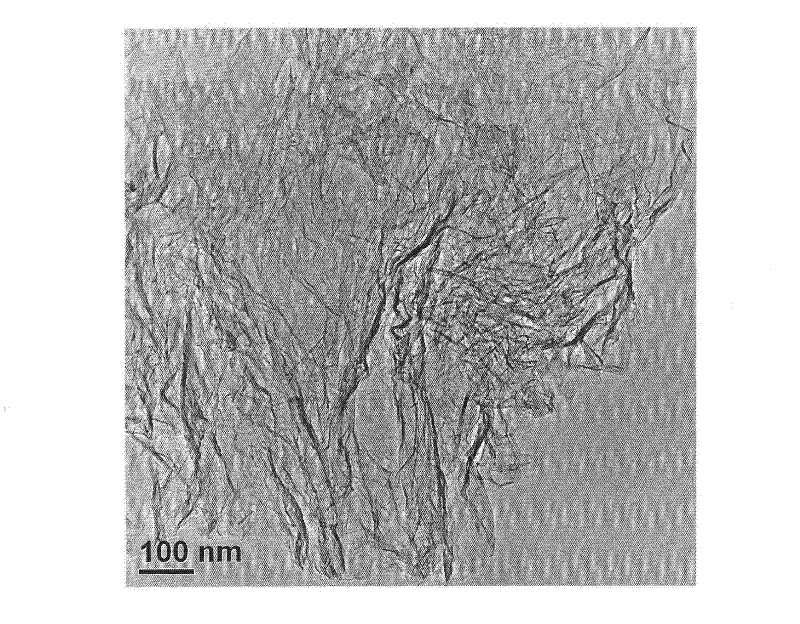
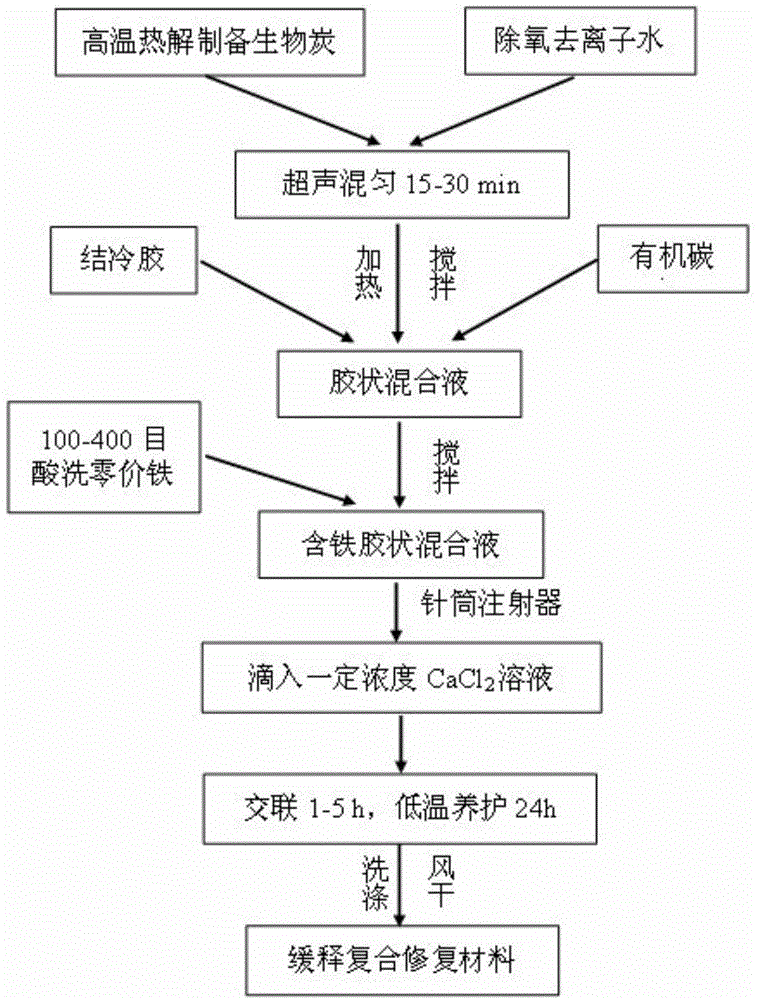
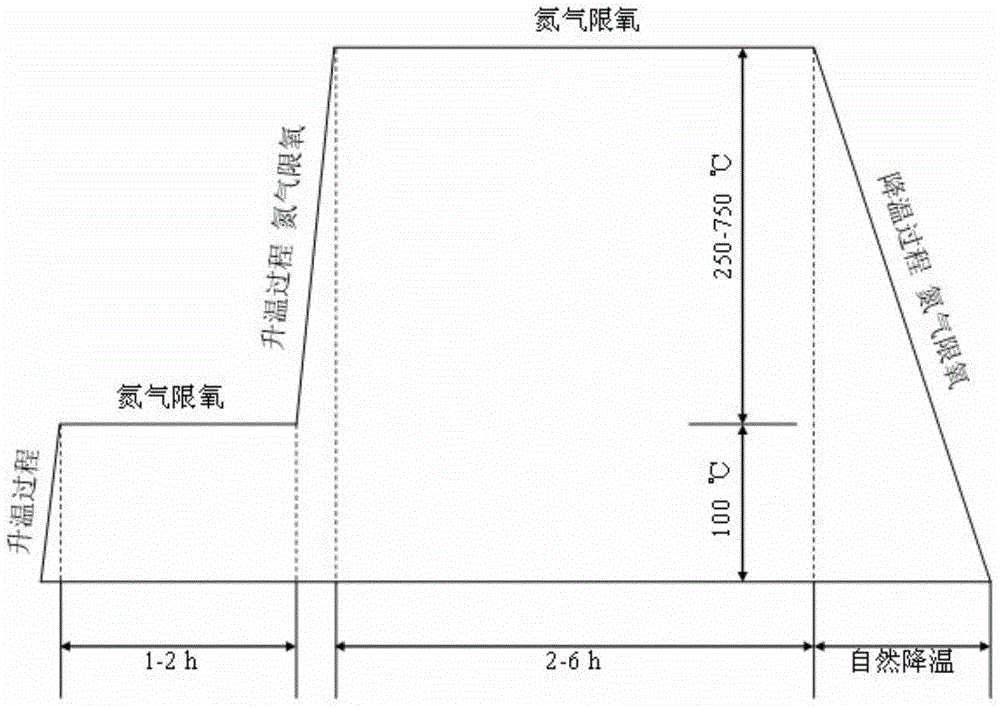
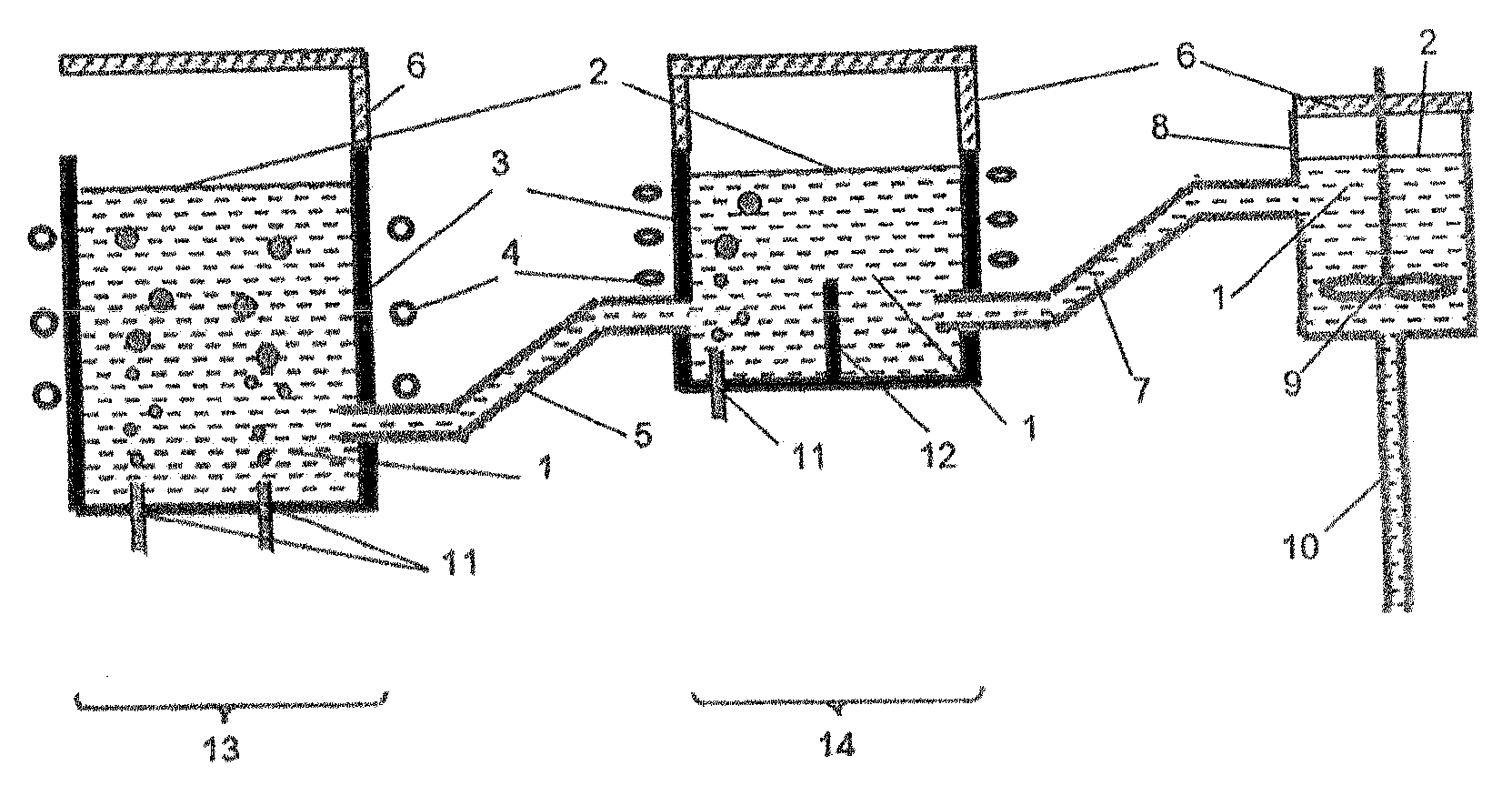
ActiveCN104876321AAchieving Synergistic Enhanced RestorationEfficient removalOther chemical processesBiological water/sewage treatmentMicrosphereSorbent
The invention discloses a method for treating chlorinated organic pollutants in underground water by using a slow-release compound repair material. The method comprises the following steps: (1), preparing charcoal through high temperature pyrolysis; (2), pre-treating zero-valent iron through acid pickling; (3), adding water into the charcoal, then adding xanthan gum and an organic carbon source, and finally, adding zero-valent iron, and through steps of treating, obtaining the slow-release compound repair material; then treating chlorinated organic pollutants in underground water by adopting an in situ injection repairing method or an in situ PRB repairing method. According to the method provided by the invention, the xanthan gum with high mechanical strength and strong mass transfer performance is used as a novel slow release embedding medium, the physical adsorbent charcoal, the chemical reductant zero-valent iron and the bioreductive drug organic carbon source are taken as effective components for composite embedding, so that gel microspheres with stable structures are formed, and the method provided by the invention has the advantages of sustained release, simple and convenient operation, low cost, environment friendliness and the like, can effectively achieve physically, chemically and biologically collaborated and enhanced remediation, and can effectively remove target pollutants.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
Method and system for producing glass, in which chemical reduction of glass components is avoided
InactiveUS20100242543A1High refractive indexReduce componentsGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusOxygenOxidizing agent
In the apparatus for producing glass reduction of reduction-sensitive components in the glass melt is reduced or preferably is prevented during the melting and / or fining processes by introducing an oxidizing agent into the glass melt. The apparatus has a melt crucible, a fining vessel, and a device for conducting oxygen and / or ozone into the glass melt in the melt crucible and / or fining vessel, in order to suppress reduction of reduction-sensitive components of the glass melt. A preferred embodiment of the apparatus has a metallic skull crucible, which includes the melt crucible and / or the fining vessel. The apparatus preferably includes a homogenization unit connected to the fining vessel to receive glass melt from the fining vessel in order to further process the glass melt after refining.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Platinum-based selective hydrogenation catalyst as well as preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN101502797AHigh activityGood dispersionOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationActivated carbonActive component
The invention relates to a platinum-based selective hydrogenation catalyst. The catalyst uses active carbon as a carrier; and based on the total mass of the catalyst, in terms of mass content, the content of active component platinum metal is 0.5 to 5 percent, and the grain diameter of the platinum metal is less than 30 nanometers. The invention also relates to a preparation method for the catalyst: after the active carbon is subjected to ultrasonic treatment by nitric acid solution with a certain concentration, the active carbon is repeatedly washed by deionized water to be neutral and then added into PtCl2 aqueous solution with a certain pH value to carry out ultrasonic immersion, the solution is filtered, a filer cake is pulped and then reduced by using a chemical reduction method and filtered and washed until no chloride ion exist, and the filter cake is transferred into an oven to be dried to form a nano Pt / active carbon catalyst. The invention further relates to application of the catalyst. The catalytic hydrogenation activity of the catalyst is good, the selectivity is high, the catalyst can effectively inhibit dechlorination without adding dehalogenation inhibitor, the preparation process is simple to operate, and the platinum metal is easy to recover.
Owner:XIAN CATALYST NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com