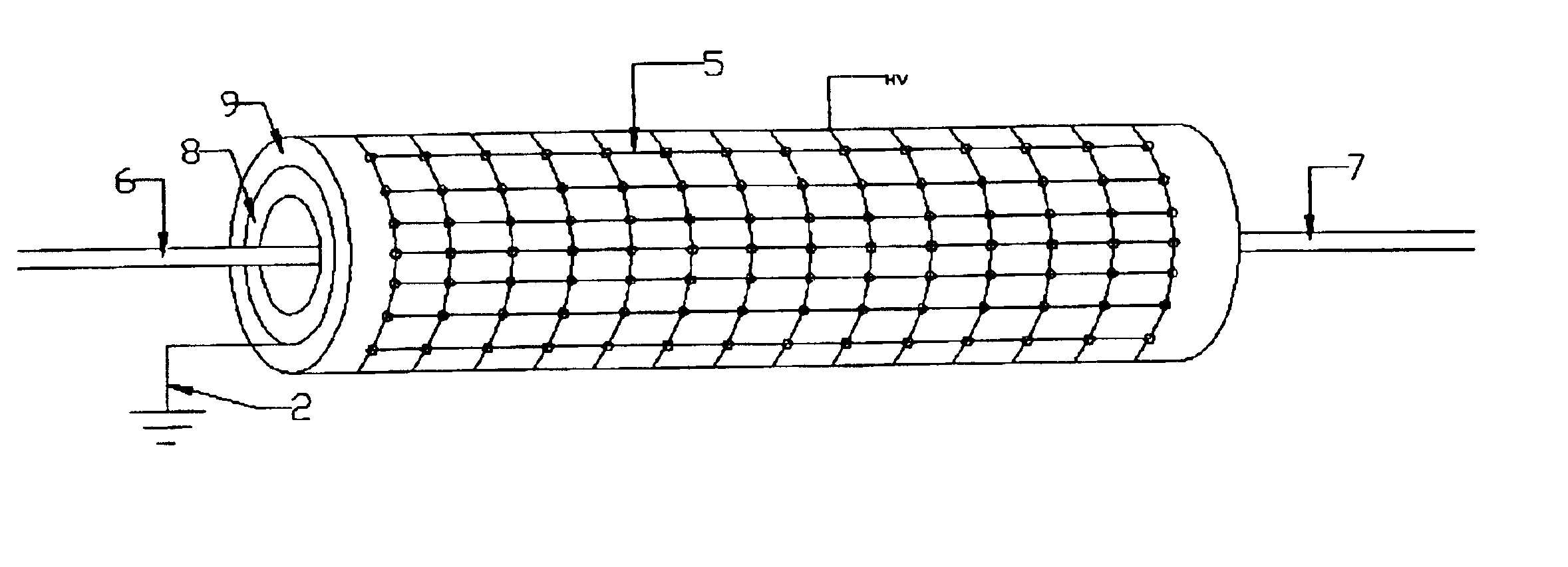
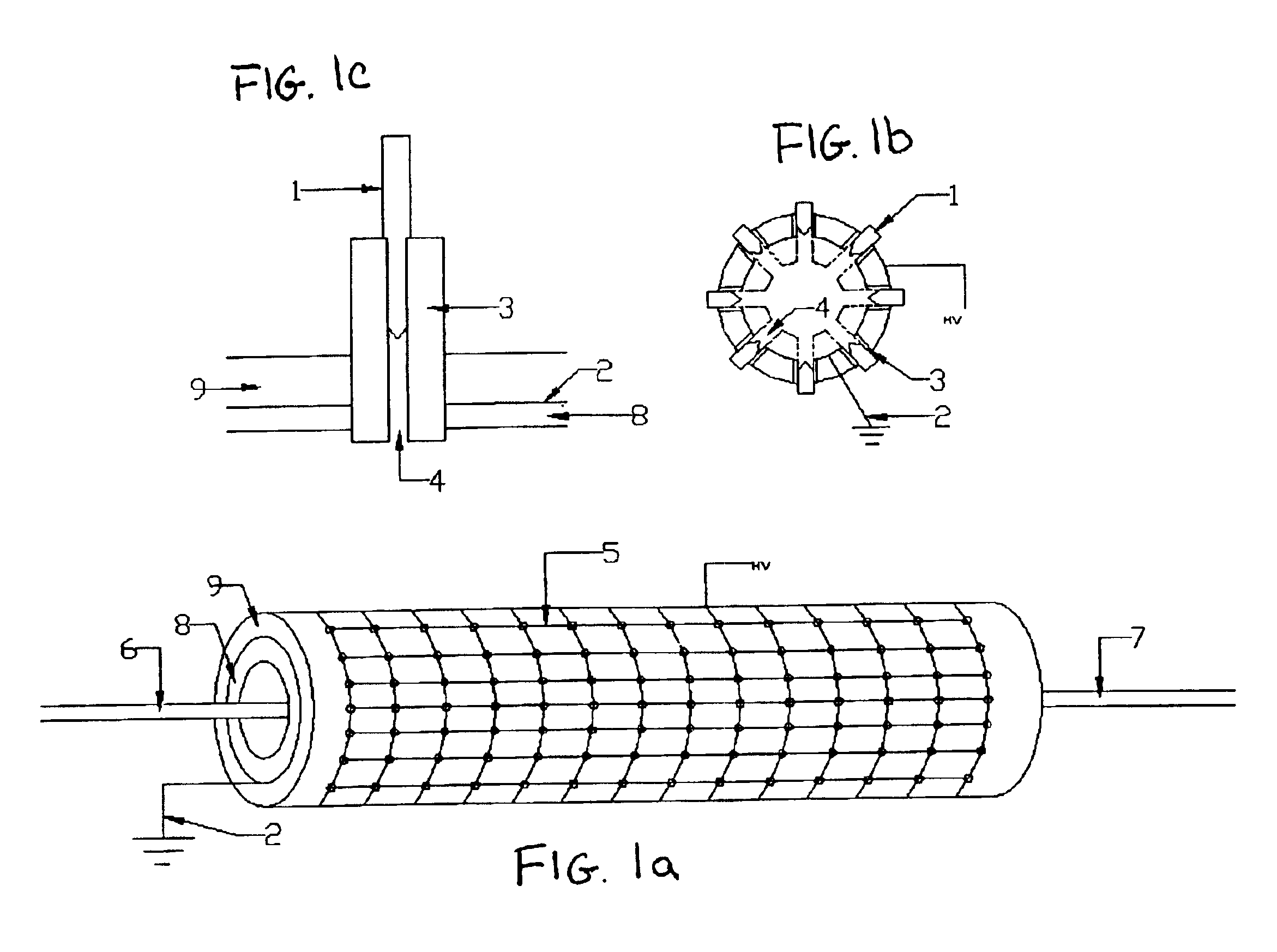
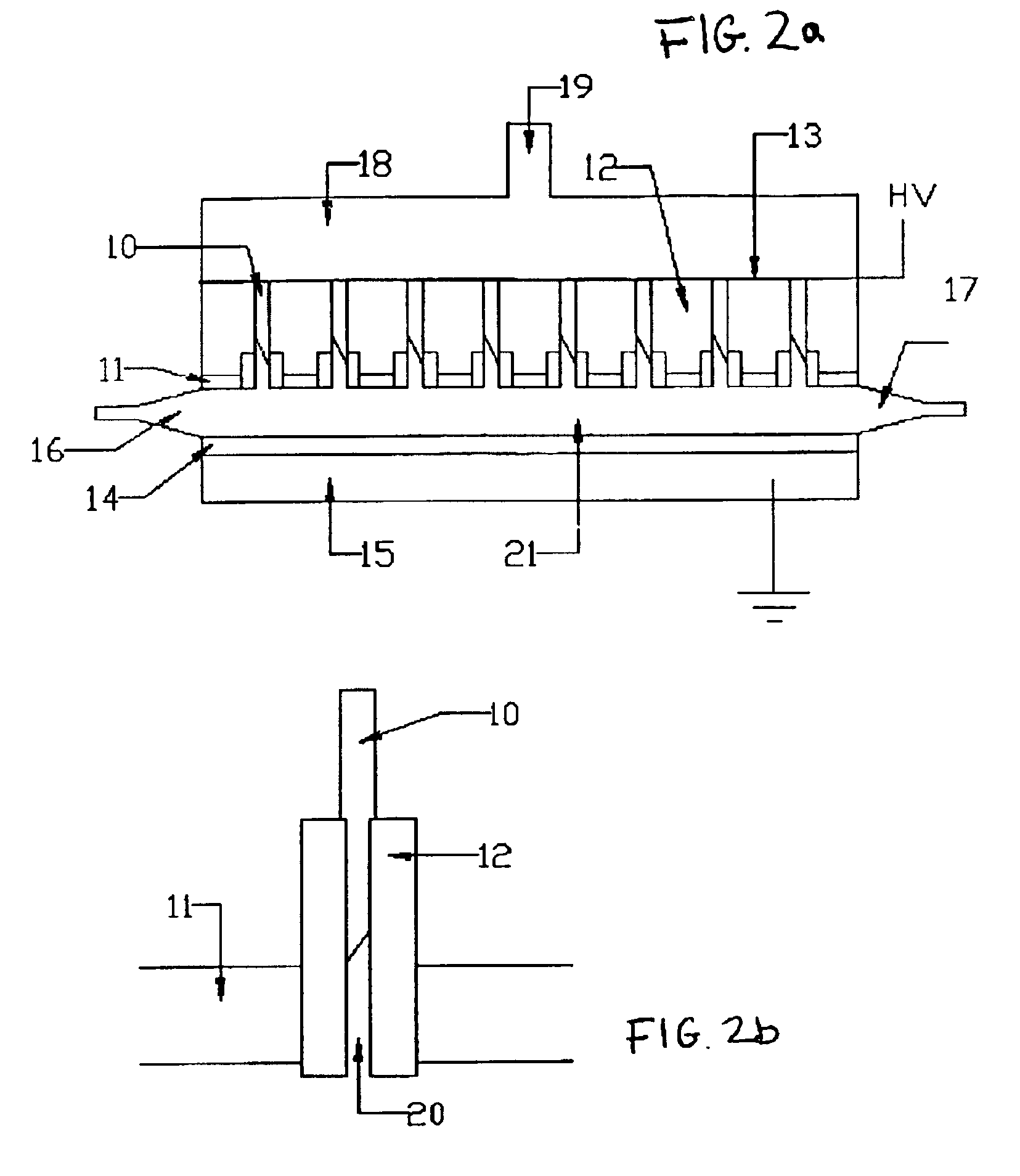
Patents
Literature
3722 results about "Reducing atmosphere" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A reducing atmosphere is an atmospheric condition in which oxidation is prevented by removal of oxygen and other oxidizing gases or vapours, and which may contain actively reducing gases such as hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and gases such as hydrogen sulphide that would be oxidized by any present oxygen.
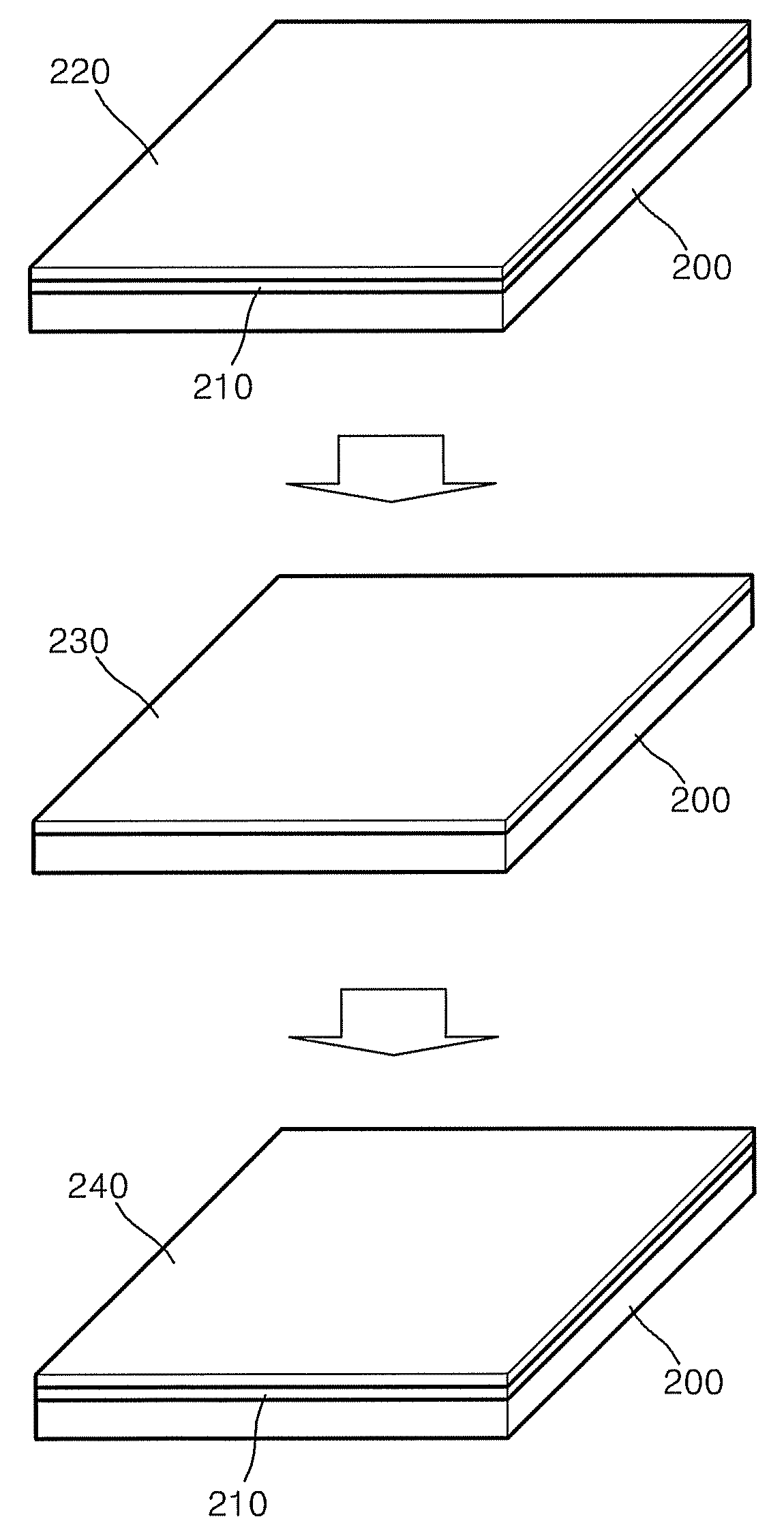
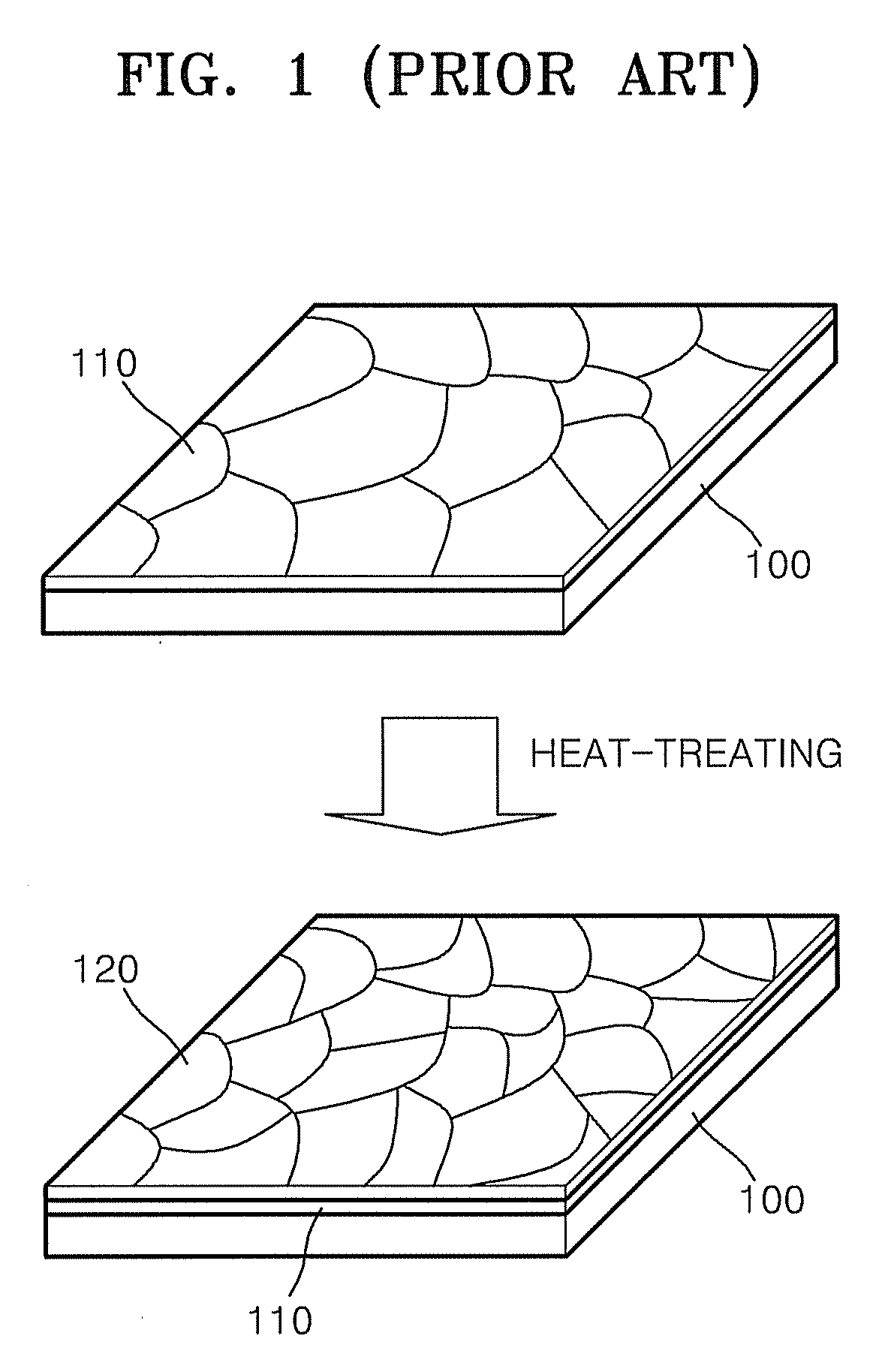
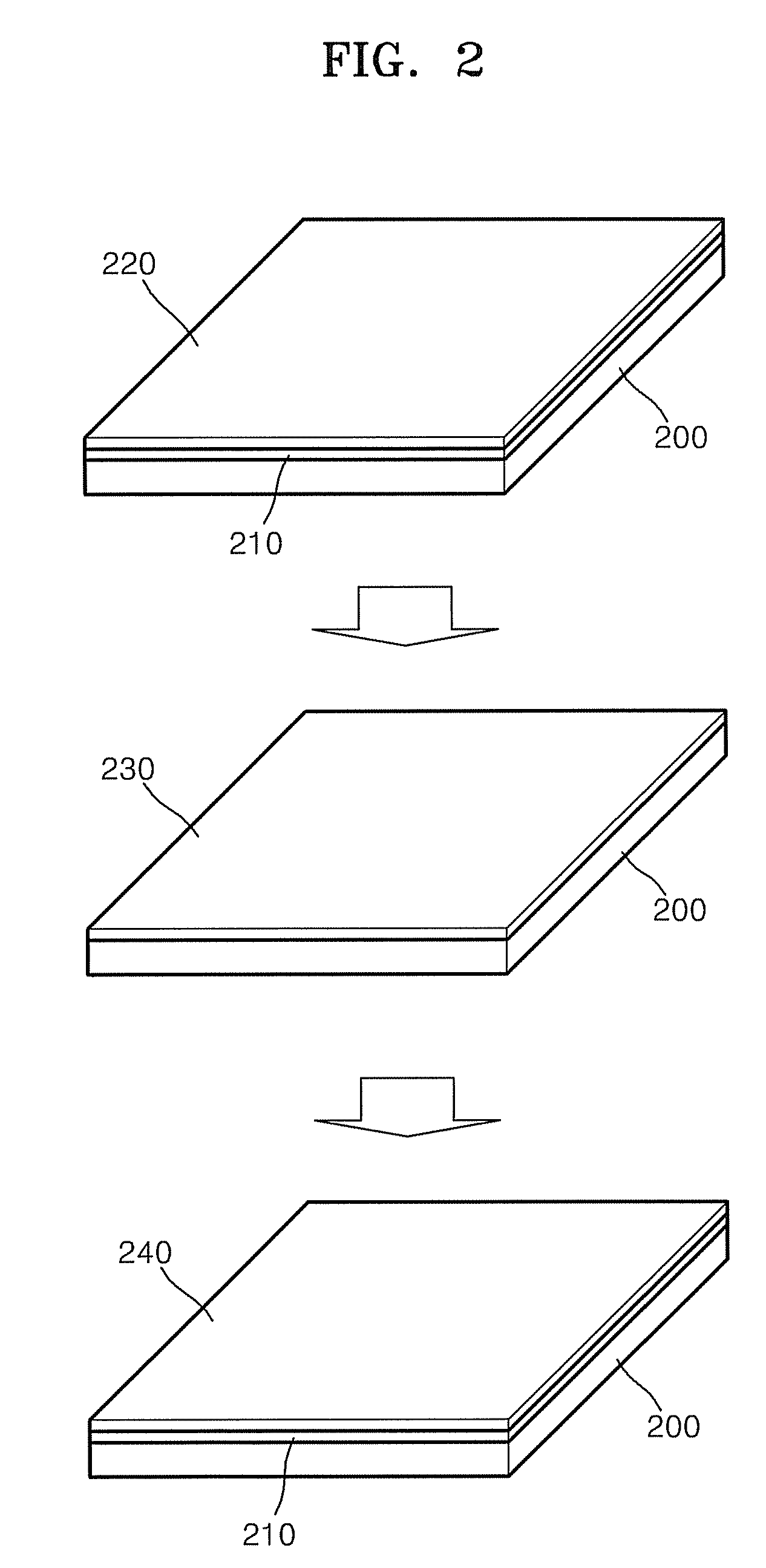
Single crystalline graphene sheet and process of preparing the same
A single-crystal graphene sheet includes a polycyclic aromatic molecule wherein a plurality of carbon atoms are covalently bound to each other, the single-crystal graphene sheet comprising between about 1 layer to about 300 layers; and wherein a peak ratio of a Raman D band intensity to a Raman G band intensity is equal to or less than 0.2. Also described is a method for preparing a single-crystal graphene sheet, the method includes forming a catalyst layer, which includes a single-crystal graphitizing metal catalyst sheet; disposing a carbonaceous material on the catalyst layer; and heat-treating the catalyst layer and the carbonaceous material in at least one of an inert atmosphere and a reducing atmosphere. Also described is a transparent electrode including a single-crystal graphene sheet.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
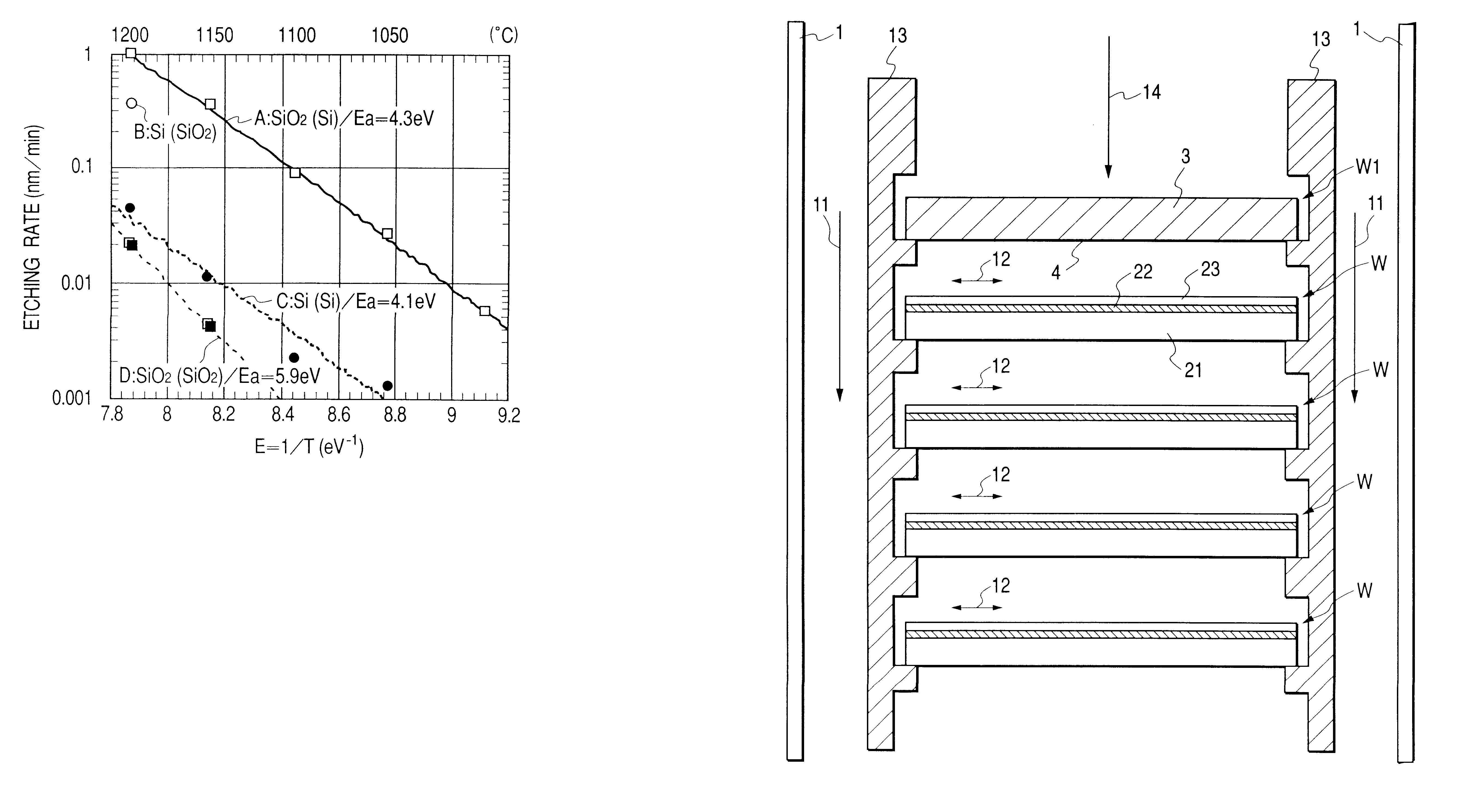
Method and apparatus for heat-treating an SOI substrate and method of preparing an SOI substrate by using the same
InactiveUS6171982B1Reduce the presence of impuritiesMaintain consistencyMuffle furnacesSolid-state devicesWaferingHydrogen
An SOI substrate having on the surface thereof a single crystal silicon film formed on an insulator is heat-treated in a hydrogen-containing reducing atmosphere in order to smooth the surface and reduce the boron concentration without damaging the film thickness uniformity in a single wafer and among different wafers. The method is characterized in that the single crystal silicon film is arranged opposite to a member of non-oxidized silicon for heat treatment.
Owner:CANON KK
High temperature, conductive thin film diffusion barrier for ceramic/metal systems
A multilayer ceramic substrate having a thin film structure containing capacitor connected thereto is provided as an interposer capacitor, the capacitor employing platinum as the bottom electrode of the capacitor. In a preferred capacitor, a dielectric material such as barium titanate is used as the dielectric material between the capacitor electrodes. The fabrication of the interposer capacitor requires an in-situ or post deposition high temperature anneal and the use of such dielectrics requires heating of the capacitor structure in a non-reducing atmosphere. A layer of a high temperature, thin film diffusion barrier such as TaSiN on the lower platinum electrode between the electrode and underlying multilayer ceramic substrate prevents or minimizes oxidization of the metallization of the multilayer ceramic substrate to which the thin film structure is connected during the fabrication process. A method is also provided for fabricating an interposer capacitor with a multilayer ceramic substrate base and a thin film multilayer structure having at least one capacitor comprising at least one bottom platinum electrode.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of recycling a delaminated wafer and a silicon wafer used for the recycling
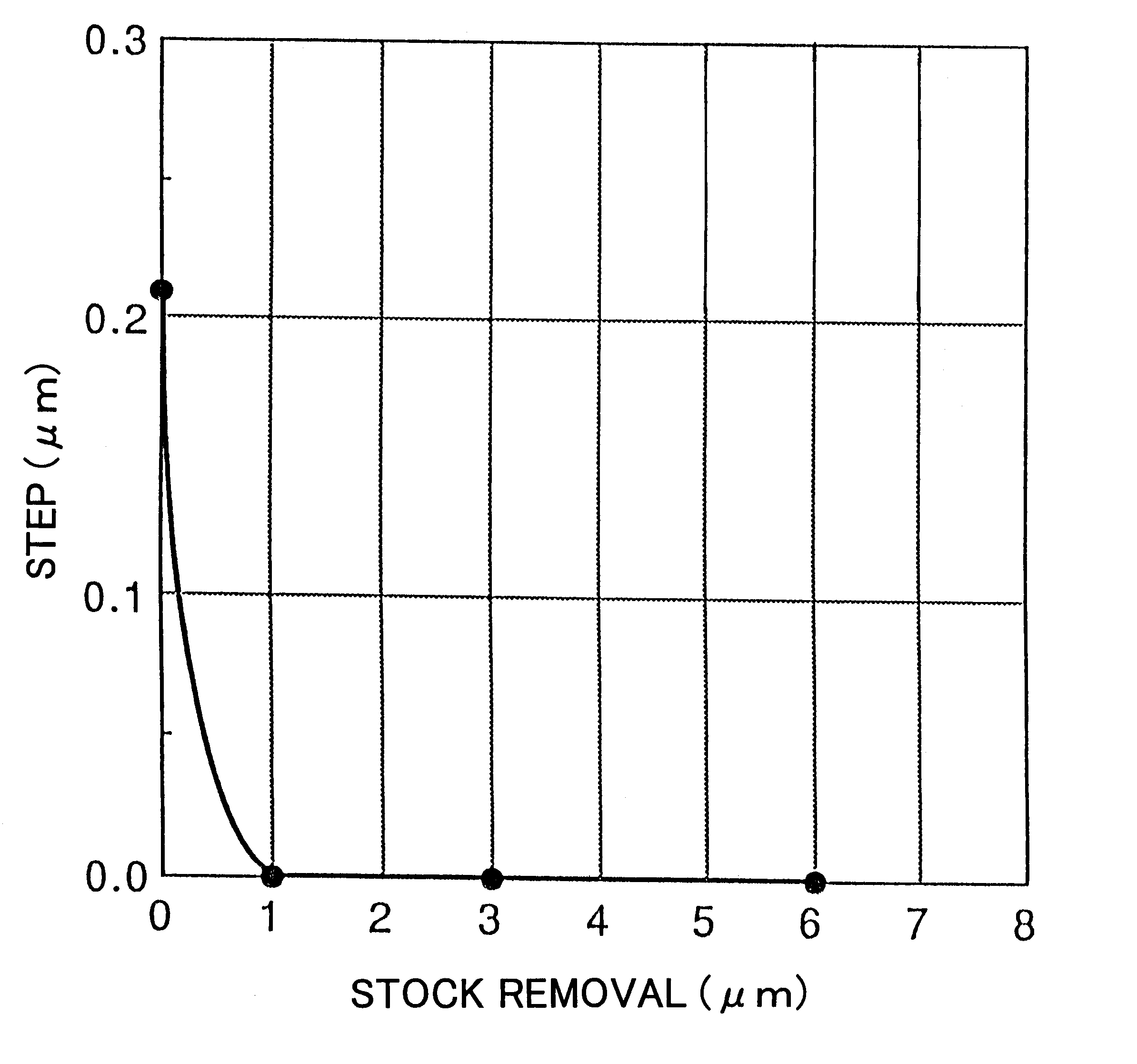
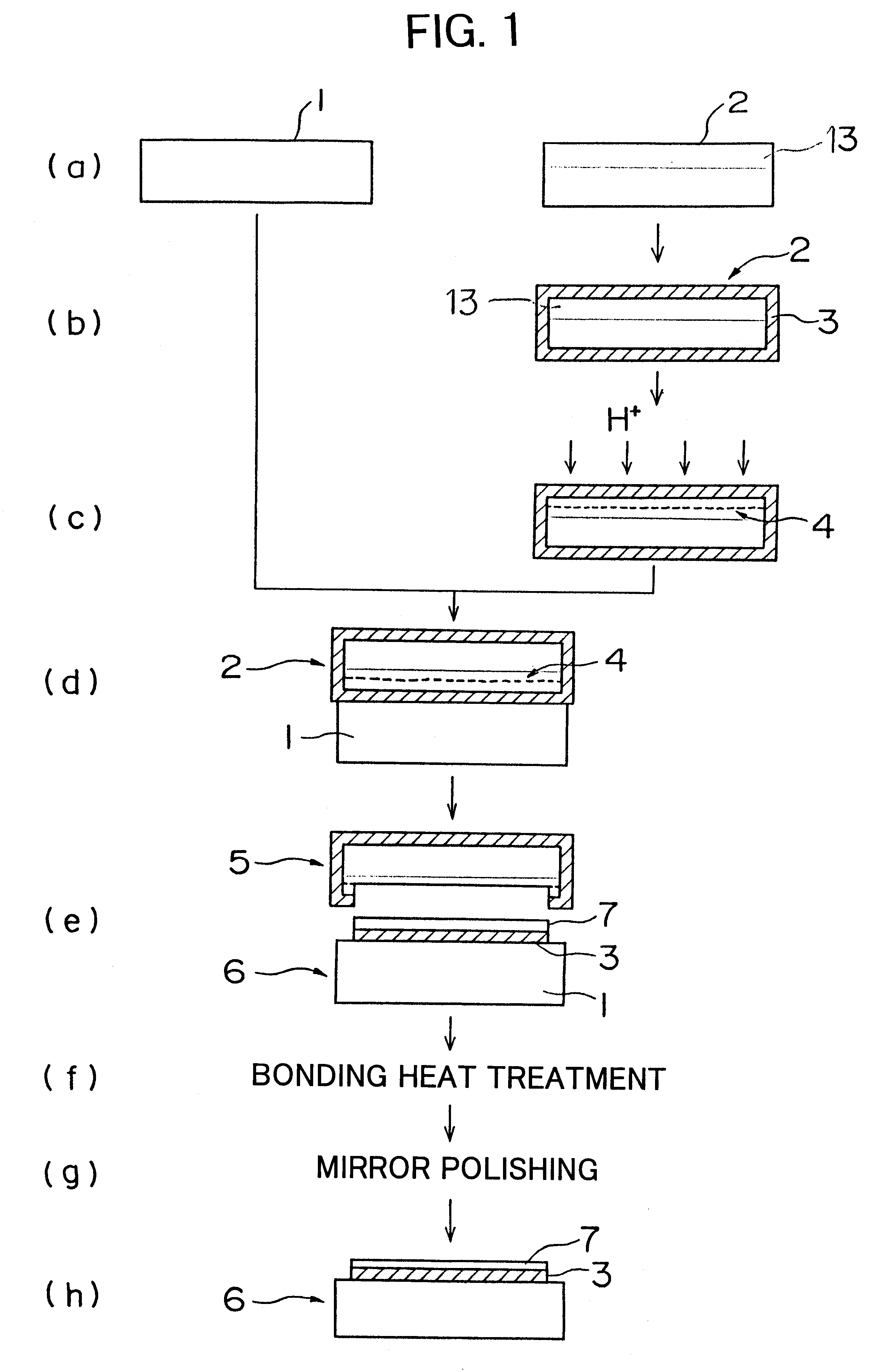
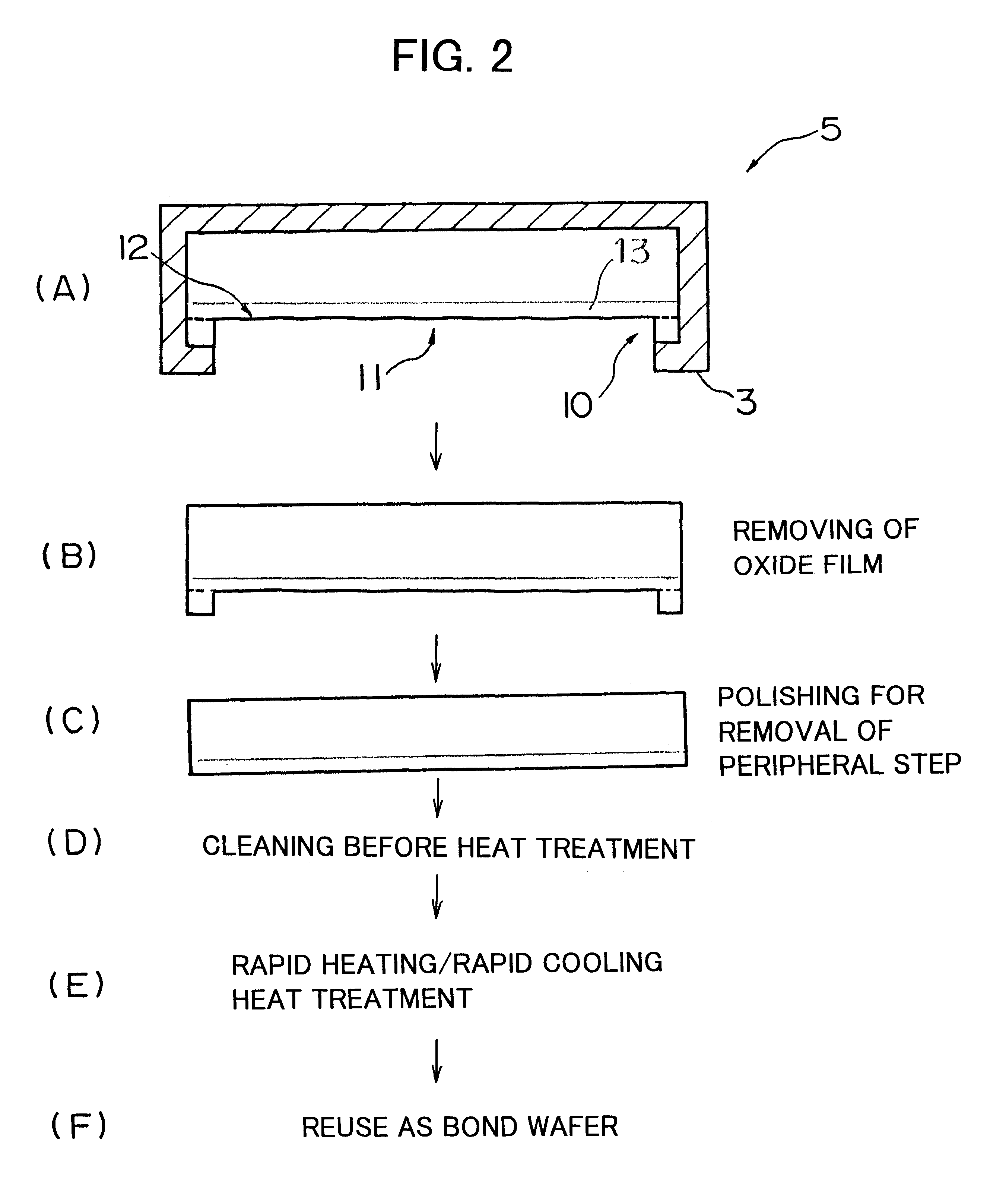
InactiveUS6284628B1Easy to disassembleImprove surface roughnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateWafering
There is disclosed a method of recycling a delaminated wafer produced as a by-product in producing an SOI wafer according to a hydrogen ion delaminating method by reprocessing it for reuse as a silicon wafer, wherein at least polishing of the delaminated wafer for removing of a step in the peripheral part of the delaminated wafer and heat treatment in a reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen are conducted as the reprocessing. There are provided a method of appropriately reprocessing a delaminated wafer produced as a by-product in a hydrogen ion delaminating method to reuse it as a silicon wafer actually, and particularly, a method of reprocessing an expensive wafer such as an epitaxial wafer many times for reuse, to improve productivity of SOI wafer having a high quality SOI layer, and to reduce producing cost.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Magnetic particle and method of preparing the same, and magnetic recording medium
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic particle obtained by heat-treating a hexagonal ferrite magnetic material in reducing atmosphere containing hydrocarbon gas.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
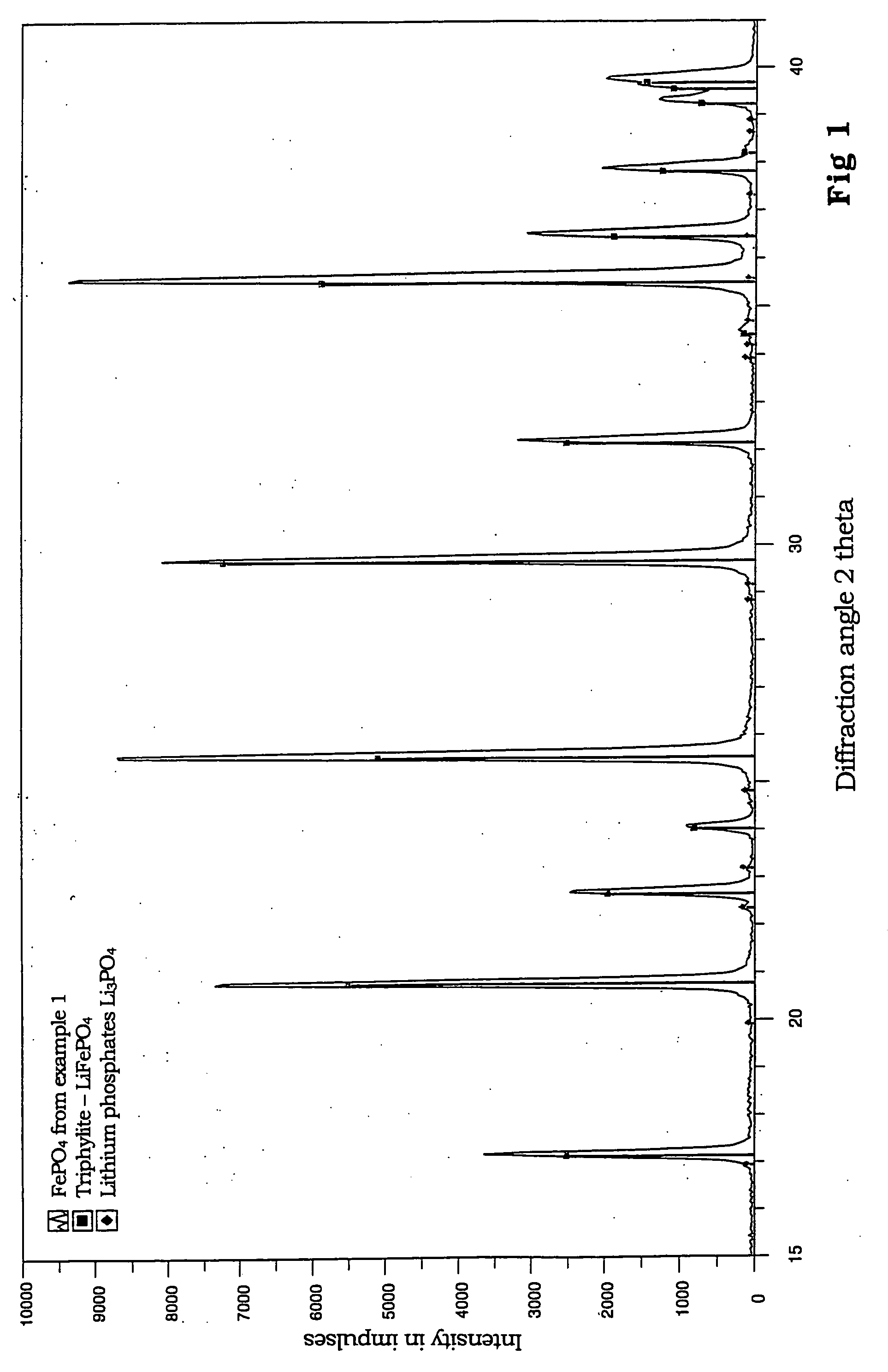
Binary, ternary and quaternary lithium phosphates, method for the production thereof and use of the same
ActiveUS20040151649A1High specific capacitySimple and inexpensivePhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesRoom temperatureReducing atmosphere
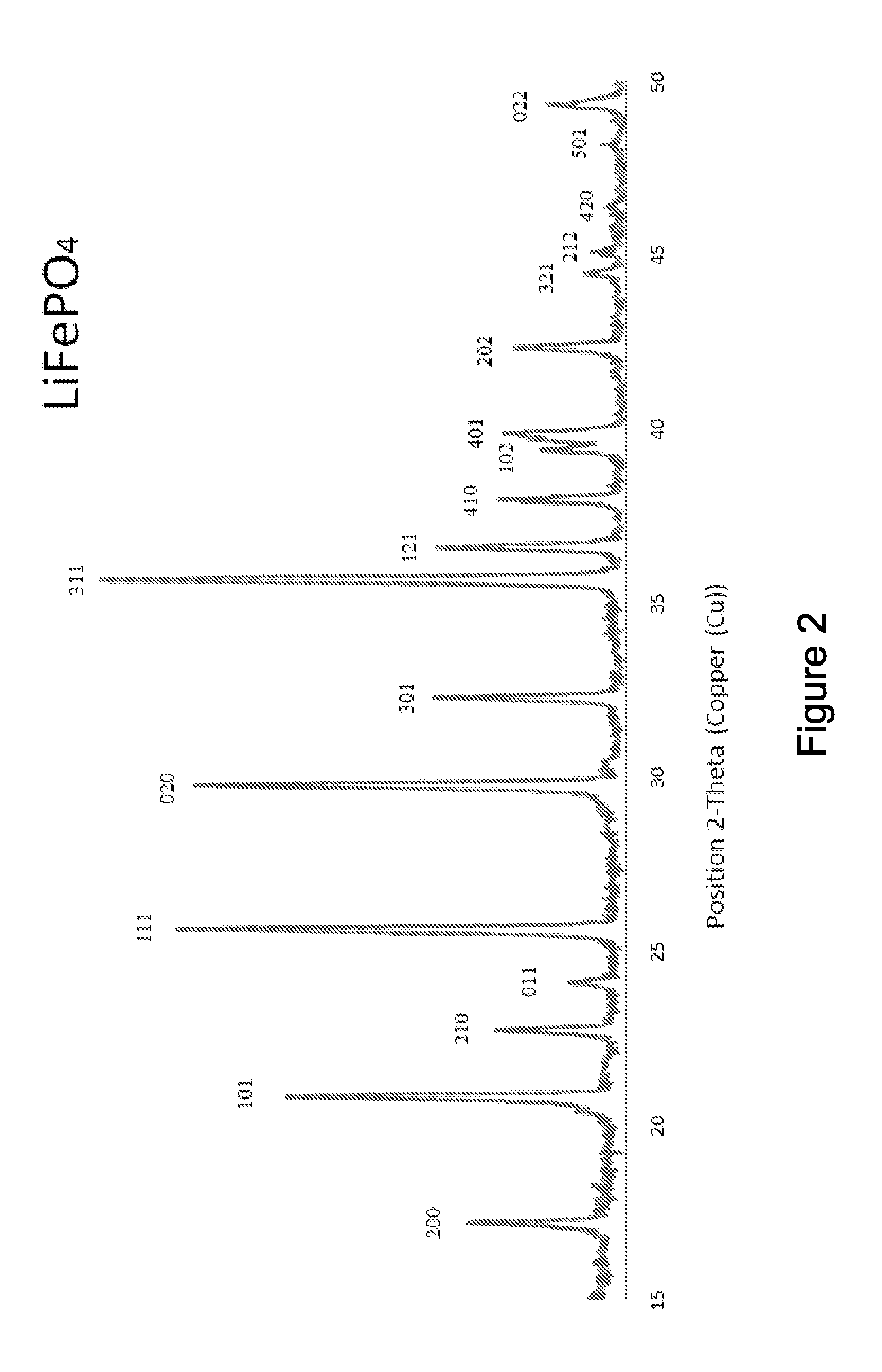
The invention relates to binary, ternary and quaternary lithium phosphates of general formula Li(FexM<1>yM<2>z)PO4 wherein M<1 >represents at least one element of the group comprising Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Al, Zr, and La; M<2 >represents at least one element of the group comprising Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Al, Zr, and La; x=between 0.5 and 1, y=between 0 and 0.5, z=between 0 and 0.5, provided that x+y+z=1, or x=0, y =1 and z=0. The said lithium phosphates can be obtained according to a method whereby precursor compounds of elements Li, Fe, M<1 >and / or M<2 >are precipitated from aqueous solutions and the precipitation product is dried in an inert gas atmosphere or a reducing atmosphere at a temperature which is between room temperature and approximately 200° C. and tempered at a temperature of between 300° C. and 1000° C. The inventive lithium phosphates have a very high capacity when used as cathode material in lithium accumulators.
Owner:ZENT FUR SONNENENERGIE & WASSERSTOFF FORSCHUNG BADEN WURTTEMBERG GEMEINNUTZIGE STIFTUNG
Manufacturing methods of catalysts for carbon fiber composition and carbon material compound, manufacturing methods of carbon fiber and catalyst material for fuel cell, and catalyst material for fuel cell
The carbon fibers of this invention is characterized in that irreducible inorganic material particles in a mean primary particle size below 500 nm and reducible inorganic material particles in a mean primary particle size below 500 nm were mixed by pulverizing and then, the mixture was heat treated under the reducing atmosphere and metal particles in a mean particle size below 1 μm were obtained, and the mixed powder of the thus obtained metal particles with the irreducible inorganic material particles are included in the carbon fibers.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
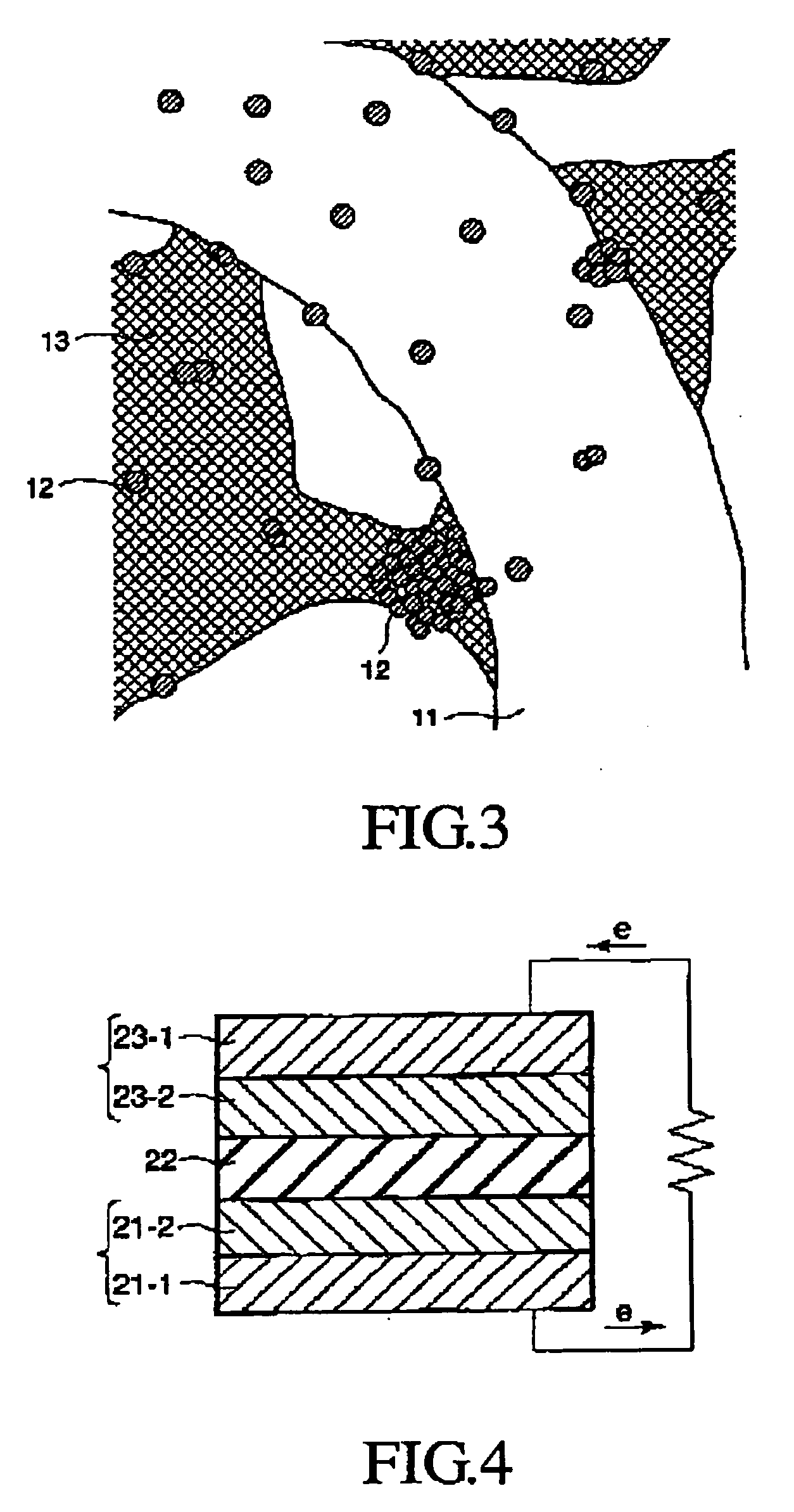
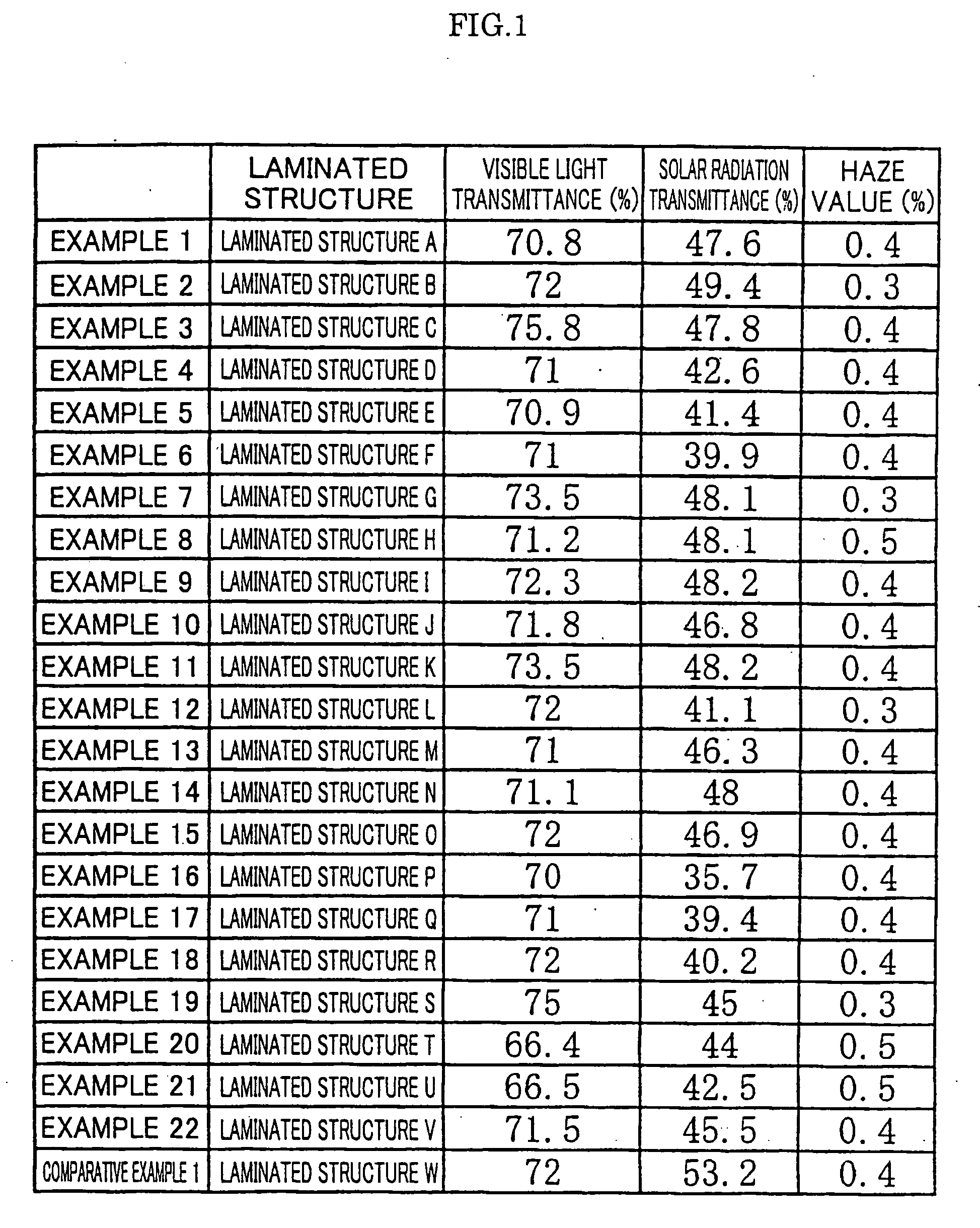
Laminated structure for shielding against solar radiation
ActiveUS20060008640A1Thin thicknessEasy to addTungsten oxides/hydroxidesSynthetic resin layered productsOptoelectronicsReducing atmosphere
To provide a laminated structure for shielding against solar radiation having high solar radiation blocking characteristics with low manufacturing costs. Fine particles 11 functioning to block solar radiation are obtained by firing tungstic acid under a reductive atmosphere, a liquid dispersion to form a solar radiation blocking material is prepared by crashing and dispersing treatment of the fine particles, a polymer base dispersing agent, and solvent, and thus prepared liquid dispersion to form a solar radiation blocking material is added to vinyl resin, which is molded into a sheet shape to obtain an intermediate film 12. Thus obtained intermediate film 12 is sandwiched between two sheets to be laminated selected from sheet-glass or plastic to obtain an intermediate layer 2, which is heated and bonded each other to prepare a laminated structure for shielding against solar radiation.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Non-oxidizing polymeric medical implant
InactiveUS20050059750A1Improve antioxidant capacityPrevent further oxidationSurgeryPharmaceutical containersCross-linkNitrogen gas
A medical implant made of polymeric material having an increased oxidation resistance is formed by a method including the steps of placing a resin powder in a sealed container. A substantial portion of the oxygen is removed from the sealed contained by either a vacuum, an oxygen absorbent or by flushing with inert gas. The container is then repressurized with a gas such as nitrogen, argon, helium or neon so that long term storage may be possible. On use, the resin in transferred to a forming device which both melts and forms the resin in an oxygen reduced atmosphere to produce a polymeric raw material such as a rod or bar stock. The medical implant is then formed from this raw material annealed and sealed in an airtight package in an oxygen reduced atmosphere. The implant is then radiation sterilized and thereafter annealed in the package for a predetermined time and temperature sufficient to form cross-links between any free radicals in neighboring polymeric chains.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Method for preparing high-density spherical ferric lithium phosphate as anode material of lithium-ion battery
InactiveCN1635648AHigh bulk densityIncrease volume capacityElectrode manufacturing processesLithium compoundsPhosphateLithium-ion battery
This invention discloses the method for preparing high-density spherical lithium ferric phosphate used as the positive material of lithium ion cell, which contains synthesizing the ferric iron salt aqueous solution, phosphorus source aqueous solution and alkali aqueous solution to form spherical or spheroid ferric phosphate precursor, uniformly mixed with lithium source, carbon source and doped metal compound after being washed and dried, high temperature heat treating at 600-900 degree centigrade for 8-48 hr under inertia or reducing atmosphere protection to obtain lithium ferric phosphate with mean grain size of 7-12 micrometer,2.0-2.2g / cm3 of tap density, high buck density of 140-155mAh / g first discharge ratio capacity at normal temperature, and high volume ratio capacity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
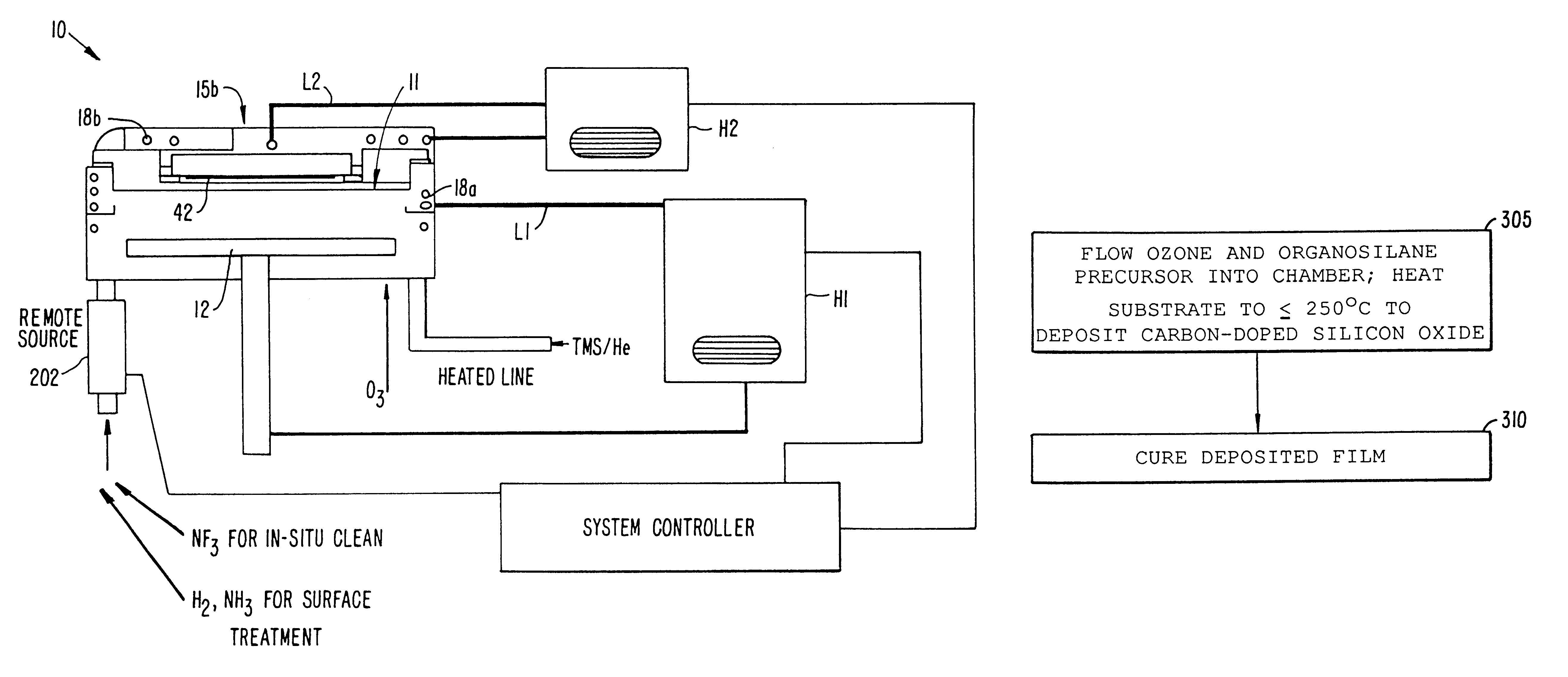
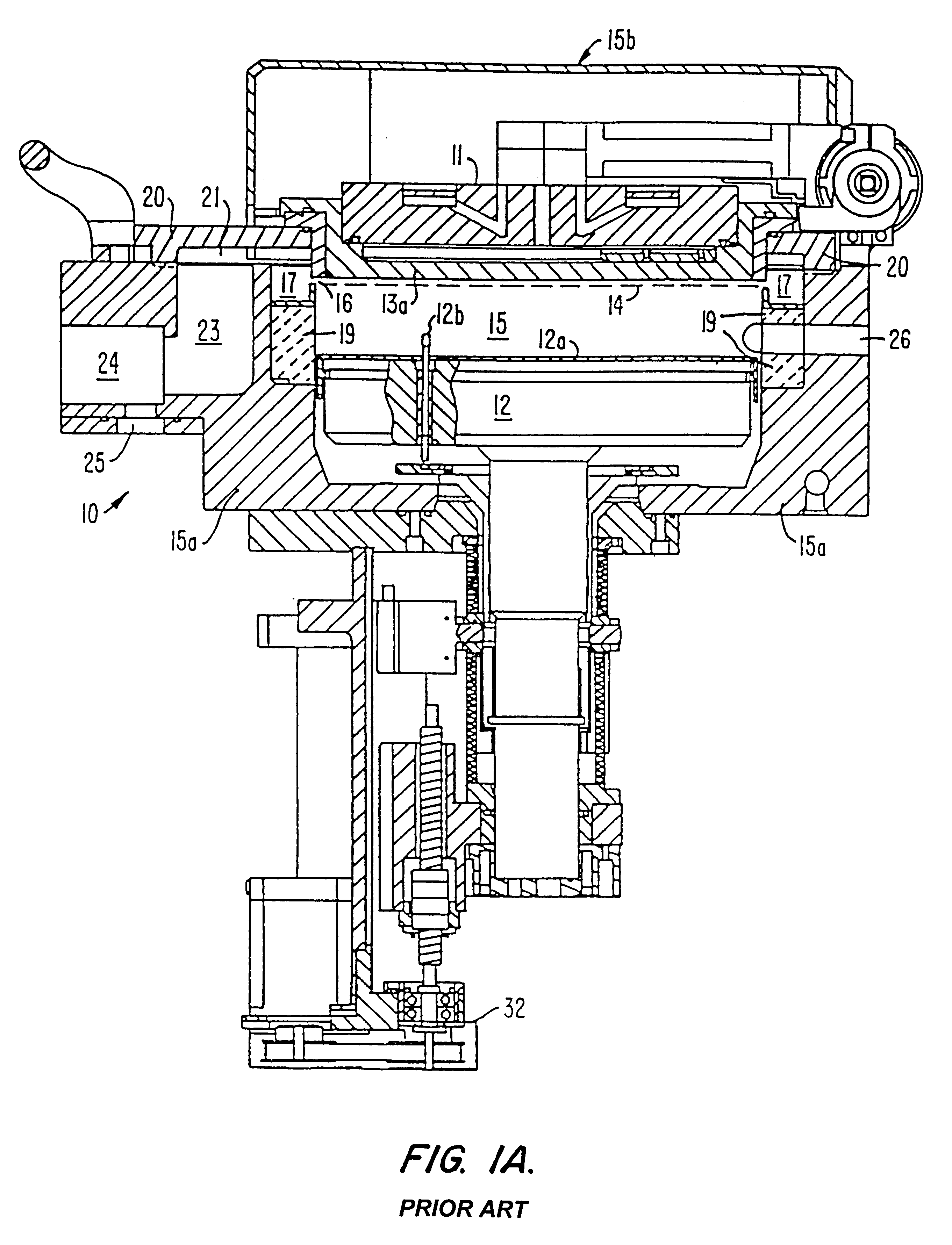
Post-deposition treatment to enhance properties of Si-O-C low K films
InactiveUS6486061B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSilicon oxygenReducing atmosphere
A method for providing a dielectric film having enhanced adhesion and stability. The method includes a post deposition treatment that densifies the film in a reducing atmosphere to enhance stability if the film is to be cured ex-situ. The densification generally takes place in a reducing environment while heating the substrate. The densification treatment is particularly suitable for silicon-oxygen-carbon low dielectric constant films that have been deposited at low temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Silicon thin film anode for lithium secondary battery and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS20090061319A1Increase capacityExcellent characteristicsElectrode carriers/collectorsVacuum evaporation coatingCarbon coatingReducing atmosphere
Disclosed are a silicon thin film anode for a lithium secondary battery having enhanced cycle characteristics and capacity and a preparation method thereof. A preparation method for a silicon thin film anode for a lithium secondary battery, comprises: preparing a collector including a metal; forming an anode active material layer including a silicon on the collector; forming one or more interface stabilizing layer, by annealing the collector and the anode active material layer under one of an inert atmosphere, a reduced atmosphere, and a vacuum atmosphere to react a metallic component of at least one of the collector and the anode active material layer with a silicon component of the anode active material layer at an interface therebetween; and forming a carbon coating layer on the anode active material layer by performing an annealing process in a hydrocarbon atmosphere.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing fuel oil by biomass hydrothermal liquefaction
InactiveCN101805629AImprove conversion ratePotential for industrial applicationsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionMass ratioReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for producing fuel oil by biomass hydrothermal liquefaction. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: fully mixing a biomass raw material and solvent water (or adding catalyst water solution) to prepare seriflux, wherein a mass ratio of a catalyst to the raw material is 1:10 to 1:50, and the mass ratio of the raw material to water is 1:2 to 1:8; performing a reaction in a slurry bed reactor under a reducing atmosphere; controlling a liquefaction reaction temperature between 300 and 450 DEG C, a reaction pressure between 5 and 30 MPa and reaction time between 5 and 40 minutes; after the reaction, separating a product to obtain the fuel oil, solid residue, water, gas and the like. The method has the advantages of achieving complete biomass conversion, high oil product productivity, obtaining an oil product with a heat value equal to that of standard oil, relieving dependence on fossil energy, contributing to environment protection, lowering production cost and achieving good social and economic benefits.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electrode active composite materials and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS20100279117A1PhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesNanoparticleLithium metal
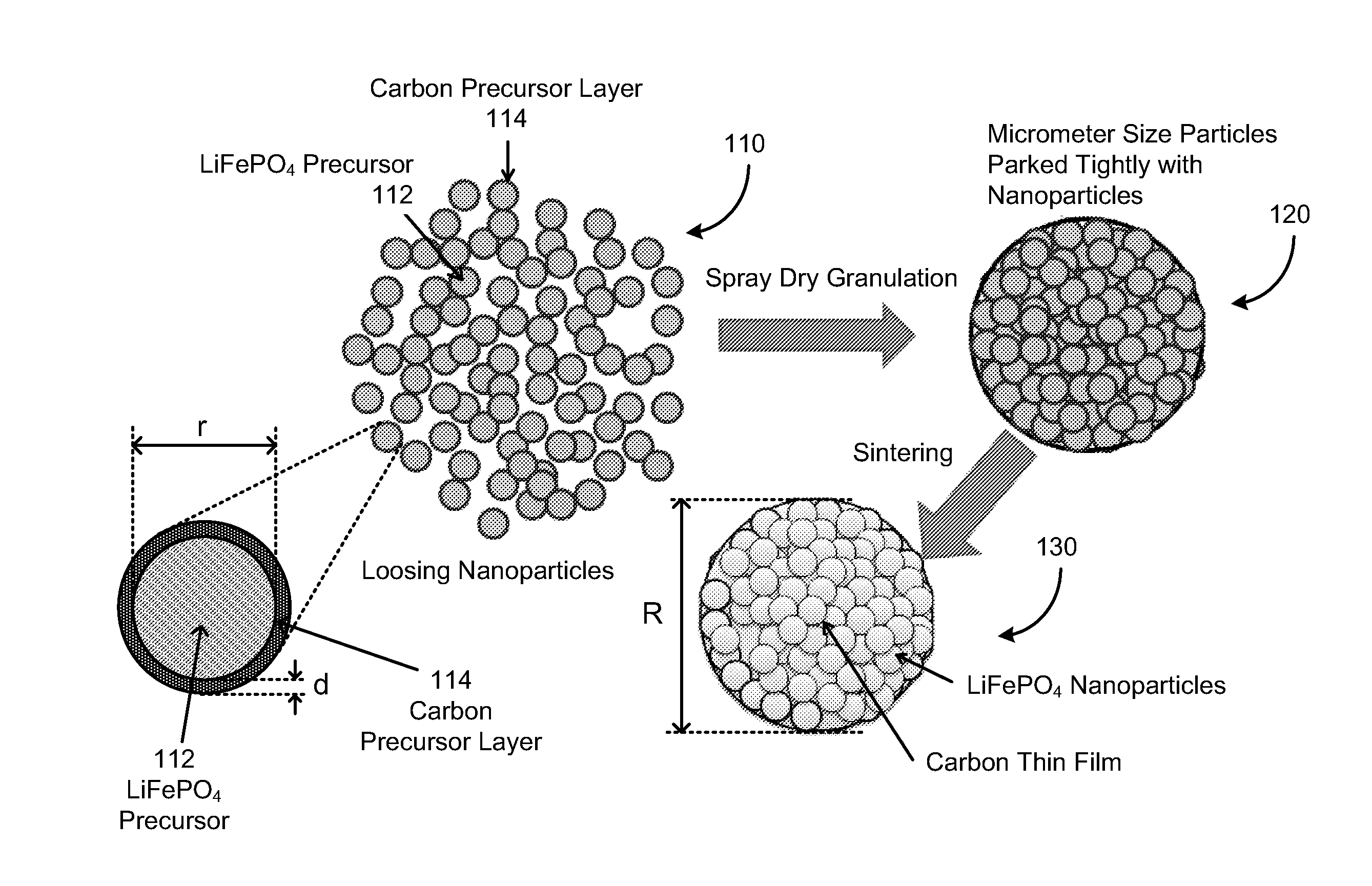
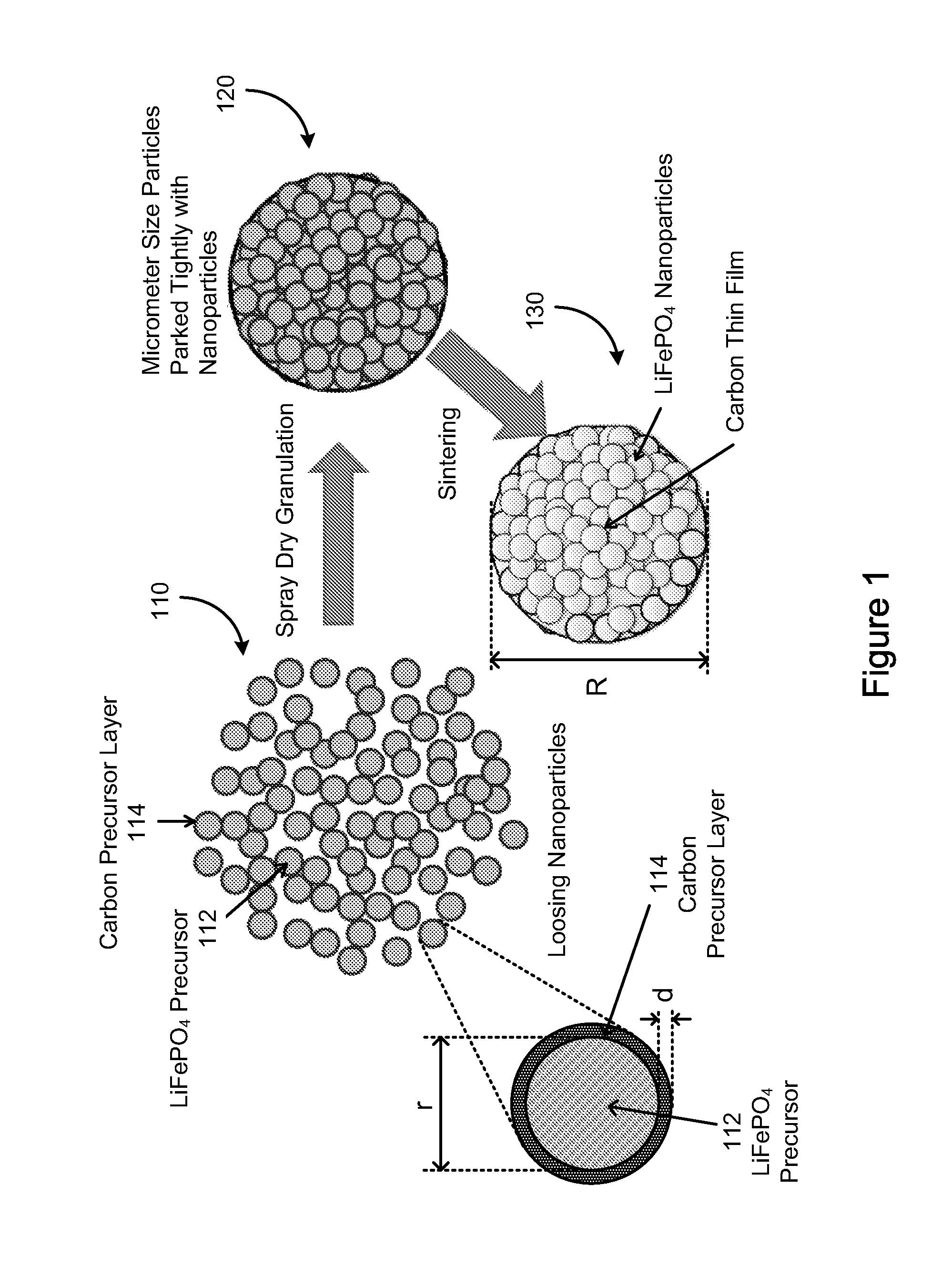
In one aspect of the invention, a method of synthesizing a lithium metal phosphate composite usable for a lithium secondary battery includes the steps of forming a nanometer-size precursor comprising lithium source and metal phosphate nanoparticles having each nanoparticle at least partially coated a layer of carbon precursor, spray drying the nanometer-size precursor at a first desired temperature to form micron-size particles packed with the lithium metal phosphate precursor nanoparticles, and sintering the micron-size particles at a second desired temperature under an inert and / or reduction atmosphere to form a micron-size lithium metal phosphate composite.
Owner:MEECOTECH
Sintered quartz glass products and methods for making same
InactiveUS6012304AReduce sinteringLonger sintering timeGlass shaping apparatusCeramic shaping apparatusSilica particleDevitrification
A number of unique processes are disclosed for manufacture of sintered high-purity quartz glass products in which a shaped silica body or preform is made from an aqueous slurry of micronized silica particles by gel casting, slip casting or electrophoretic deposition. The silica particles may comprise a major portion by weight of crystalline silica. In one embodiment of the invention the sintered quartz glass is transparent, substantially bubble-free and suitable for scientific or optical uses. In another embodiment the porous silica preform is fired in steam to increase the hydroxyl content and then nitrided in a nitrogen-hydrogen reducing atmosphere. A minute amount of chemically-combined nitrogen in the high-purity quartz glass is sufficient to provide a tremendous improvement in physical properties and an incredible increase in the resistance to devitrification.
Owner:LOXLEY TED A +2
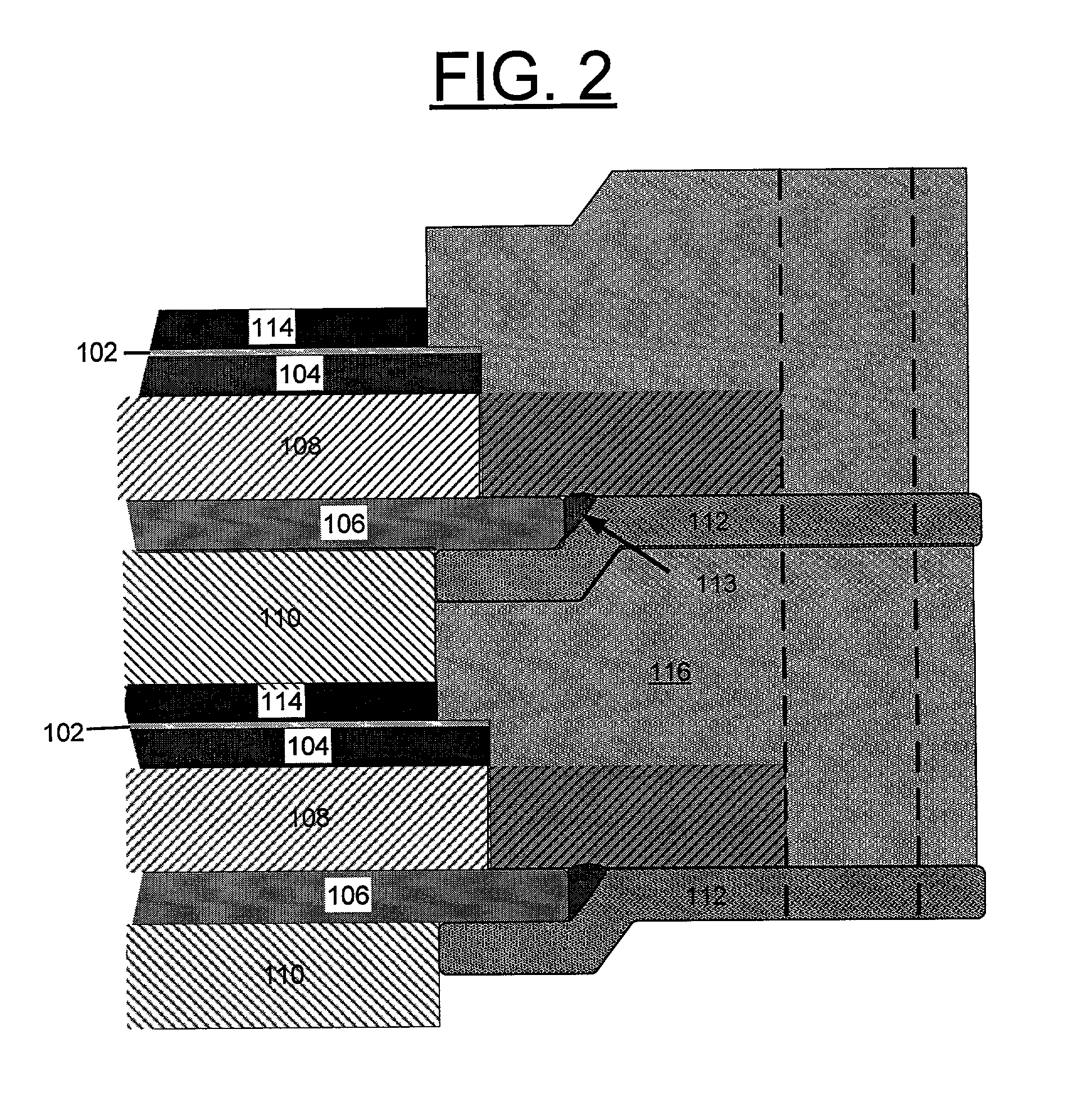
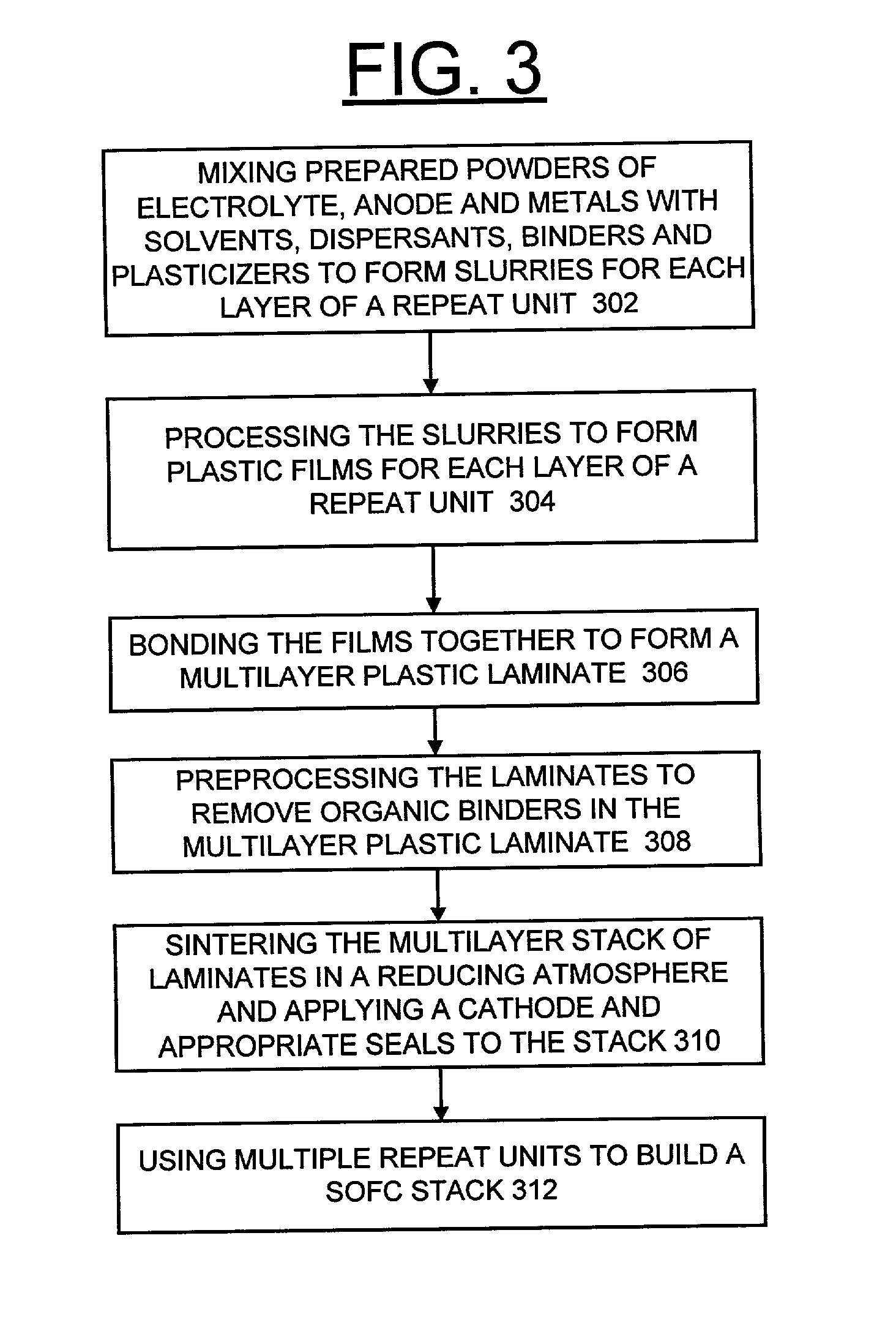
Solid oxide fuel cell with enhanced mechanical and electrical properties
InactiveUS20030232230A1Improve mechanical propertiesGood electrical propertiesFuel cells groupingCeramic shaping apparatusMechanical propertyContact resistance
A solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) repeat unit includes an oxide electrolyte, an anode, a metallic fuel flow field, a metallic interconnect, and a metallic air flow field. The multilayer laminate is made by casting tapes of the different functional layers, laminating the tapes together and sintering the laminate in a reducing atmosphere. Solid oxide fuel cell stacks are made by applying a cathode layer, bonding the unit into a gas manifold plate, and then stacking the cells together. This process leads to superior mechanical properties in the SOFC due to the toughness of the supporting metallic layers. It also reduces contact resistances in stacking the cells since there is only one physical contact plane for each repeat unit.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
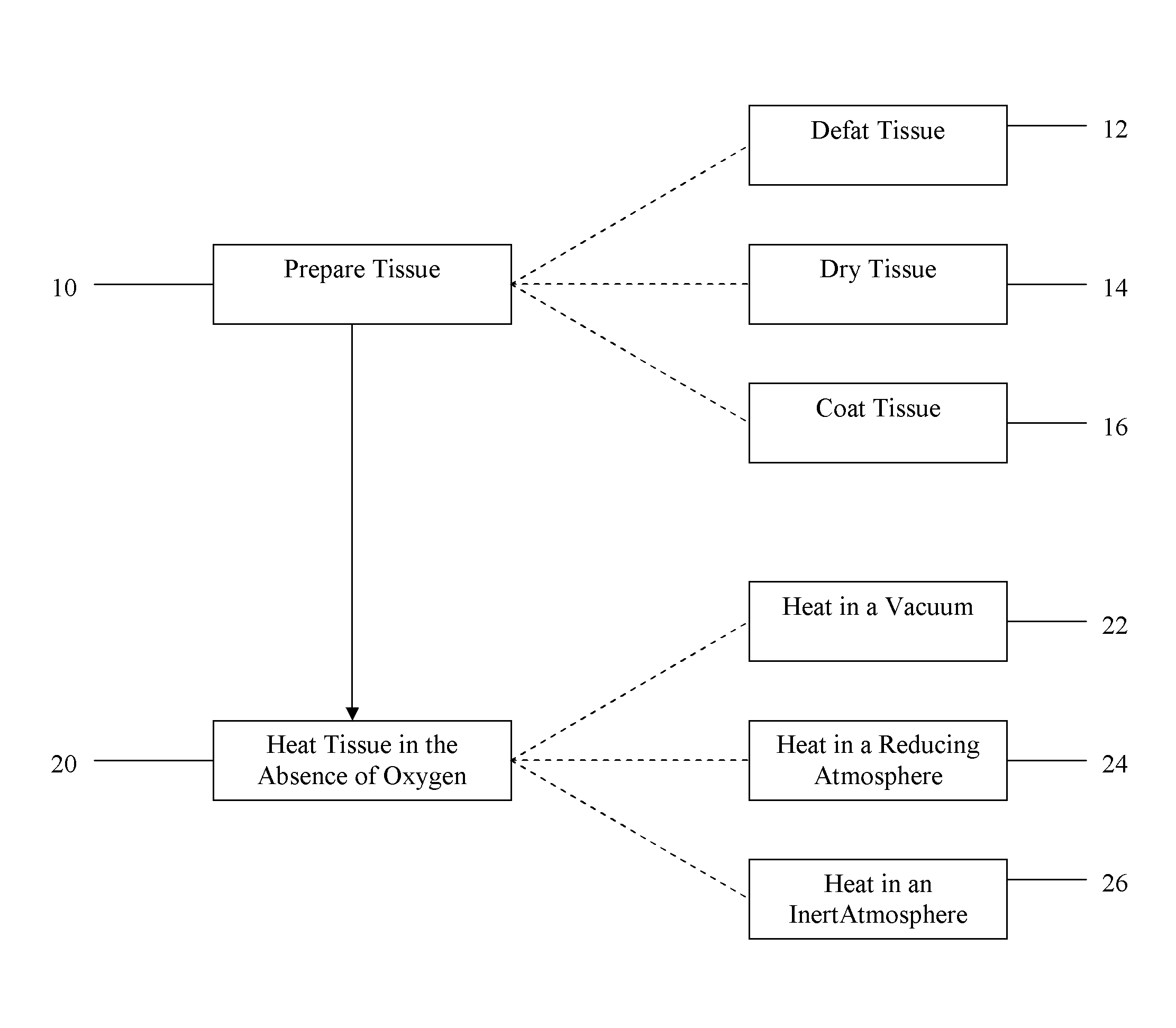
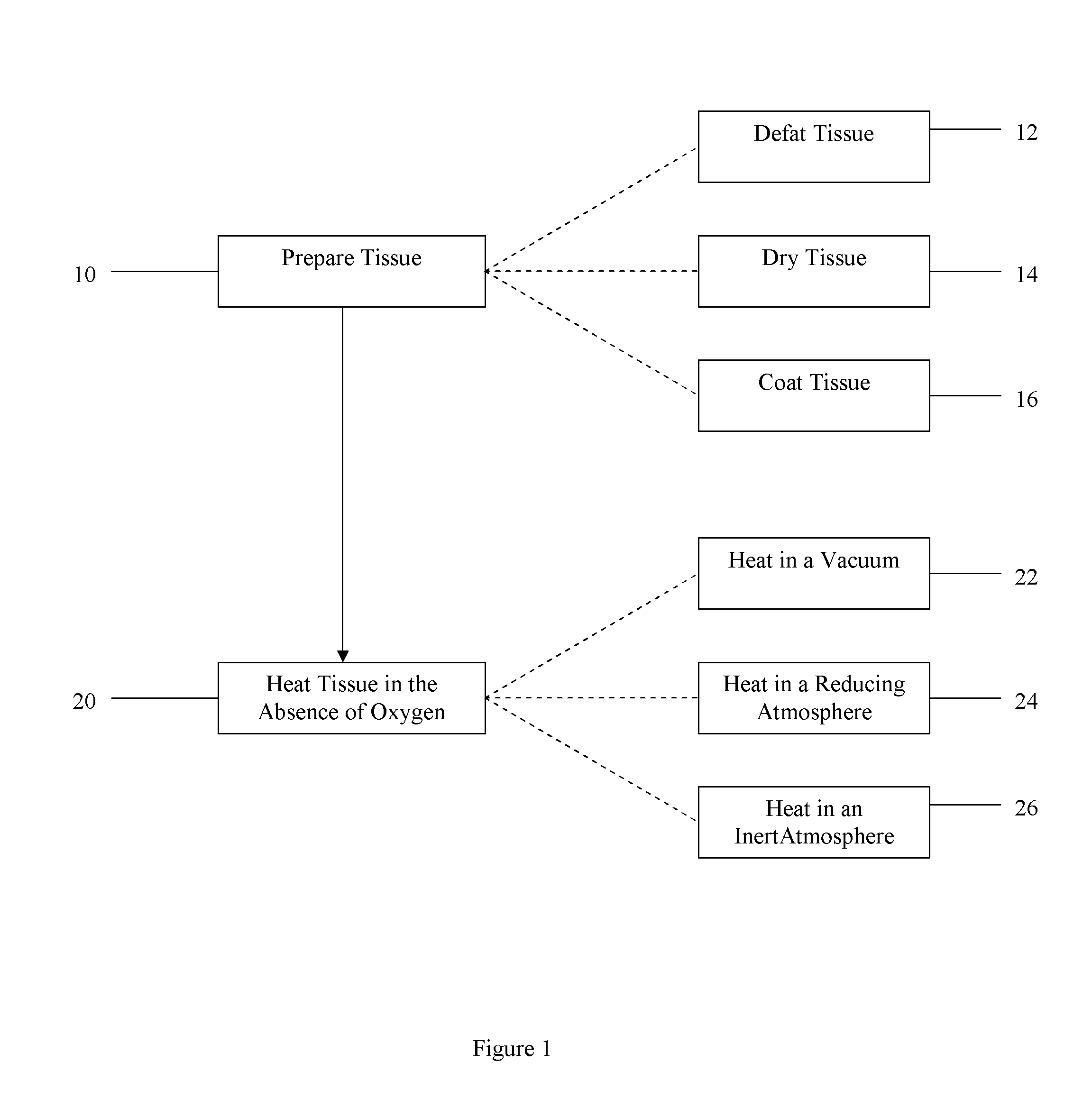
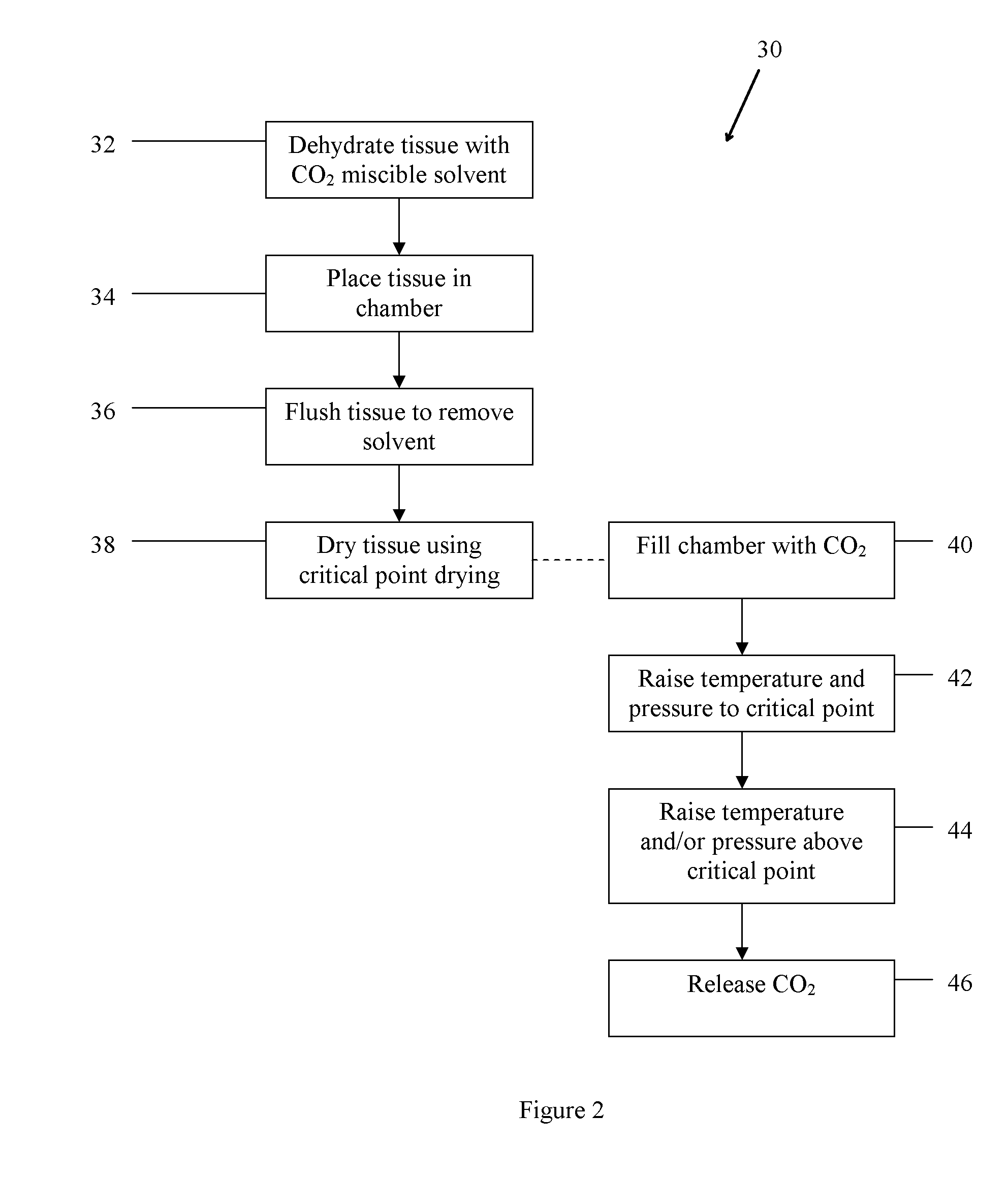
Method of treating tissue
ActiveUS20090087471A1Promotes remodelingEasy to replaceBone implantSkeletal disorderBone CortexReducing atmosphere
In one embodiment, the method comprises providing tissue, preparing the tissue, and treating the tissue to improve remodeling characteristics of the tissue. The tissue may be, for example, cortical bone. Treating the tissue to improve remodeling characteristics may comprise heating the tissue, treating the tissue with a chemical, or other. Heating the tissue may be done in the absence of oxygen and may comprise heating the tissue in a vacuum, heating the tissue in an inert atmosphere, heating the tissue in a reducing atmosphere, coating the tissue with a protective coating and heating the tissue, or other. Further embodiments comprise treating the tissue in supercritical fluids, for example, to dry or virally inactivate the tissue.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
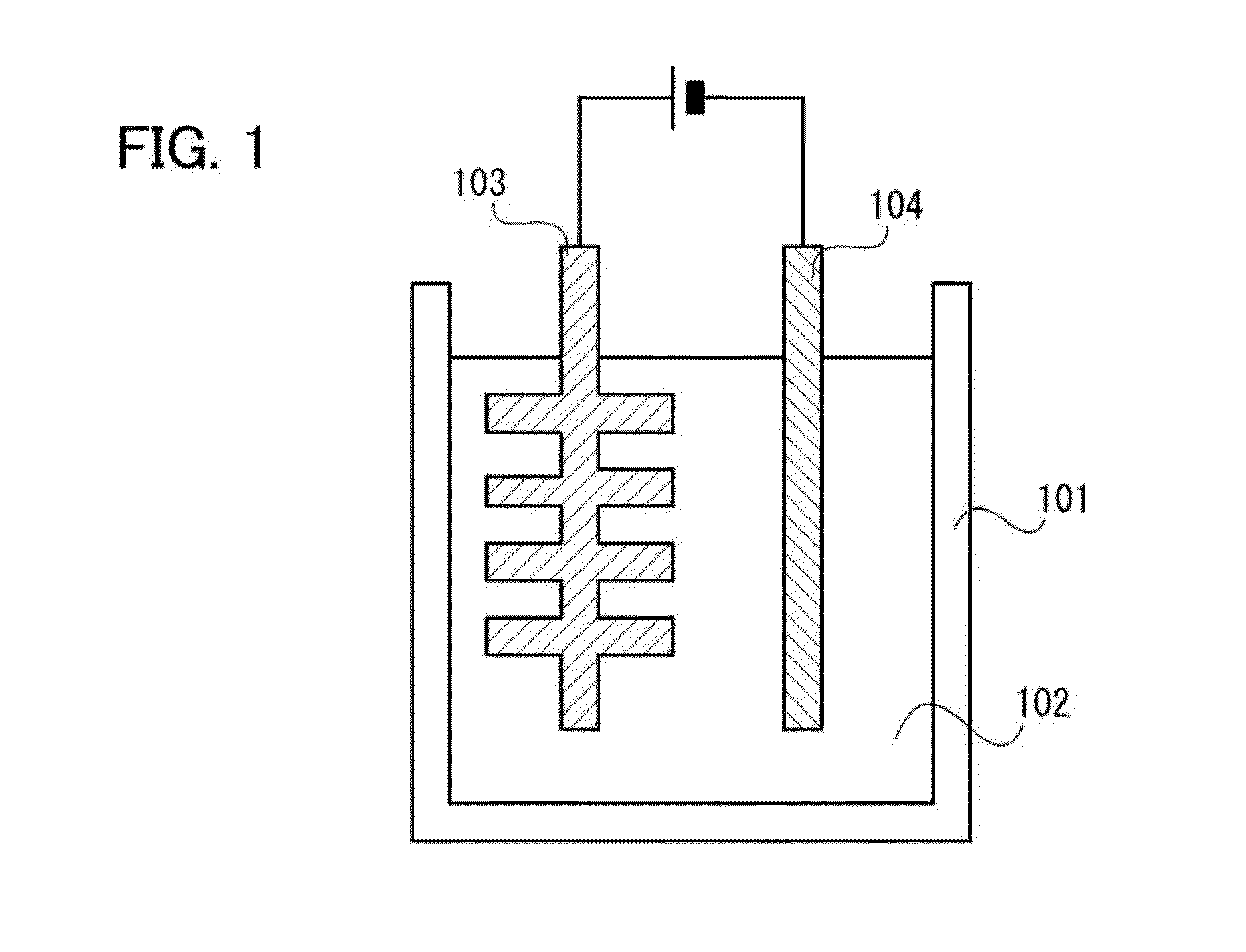
Single-layer and multilayer graphene, method of manufacturing the same, object including the same, and electric device including the same
ActiveUS20120308884A1High densityImprove discharge capacityElectrolysis componentsCarbon compoundsReducing atmosphereCvd graphene
Graphene is formed with a practically uniform thickness on an uneven object. The object is immersed in a graphene oxide solution, and then taken out of the solution and dried; alternatively, the object and an electrode are immersed therein and voltage is applied between the electrode and the object used as an anode. Graphene oxide is negatively charged, and thus is drawn to and deposited on a surface of the object, with a practically uniform thickness. After that, the object is heated in vacuum or a reducing atmosphere, so that the graphene oxide is reduced to be graphene. In this manner, a graphene layer with a practically uniform thickness can be formed even on a surface of the uneven object.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
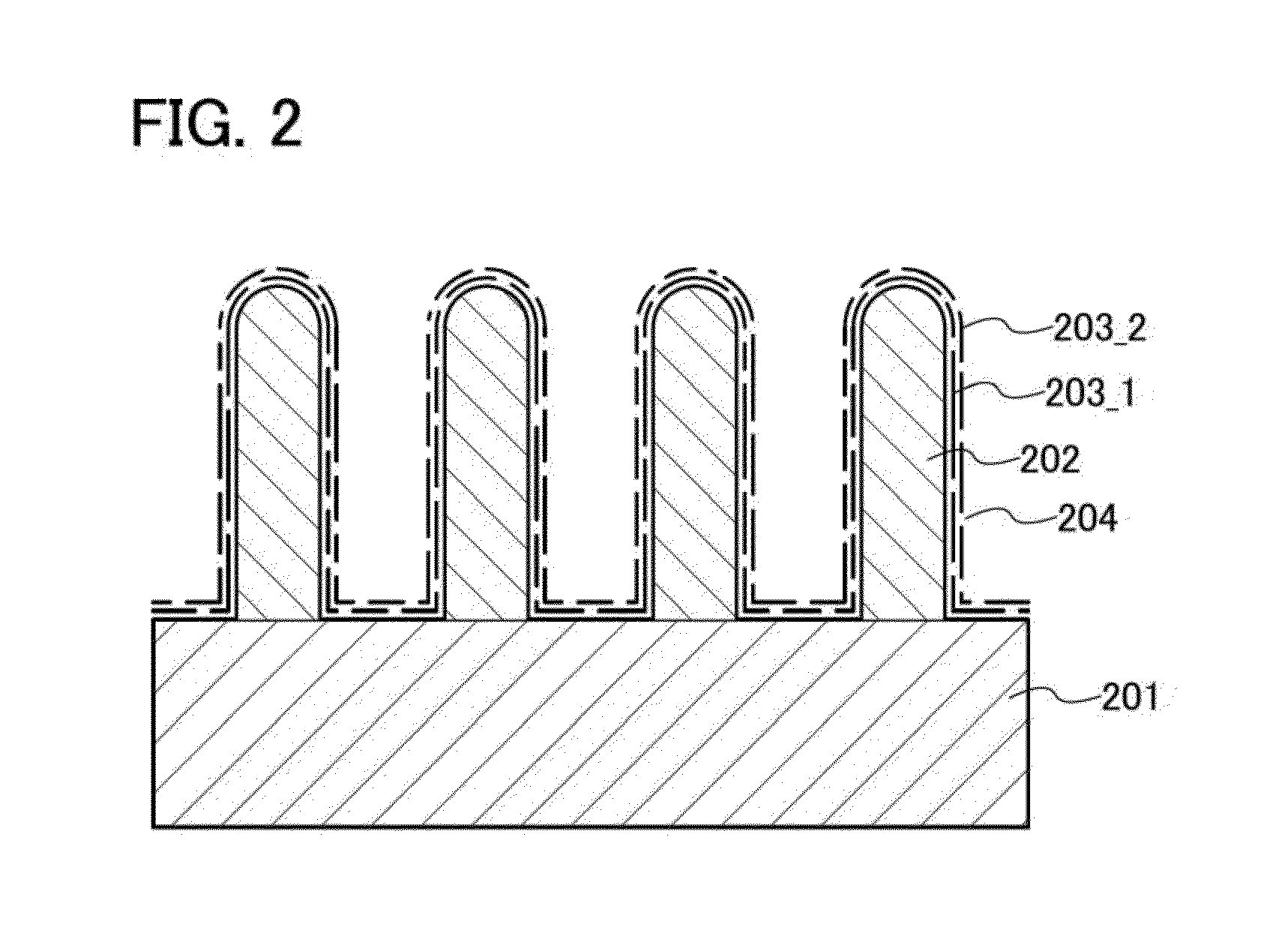
Method of manufacturing electrode
ActiveUS20120308891A1Large electric capacityExcellent electrical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode thermal treatmentElectric capacityReducing atmosphere
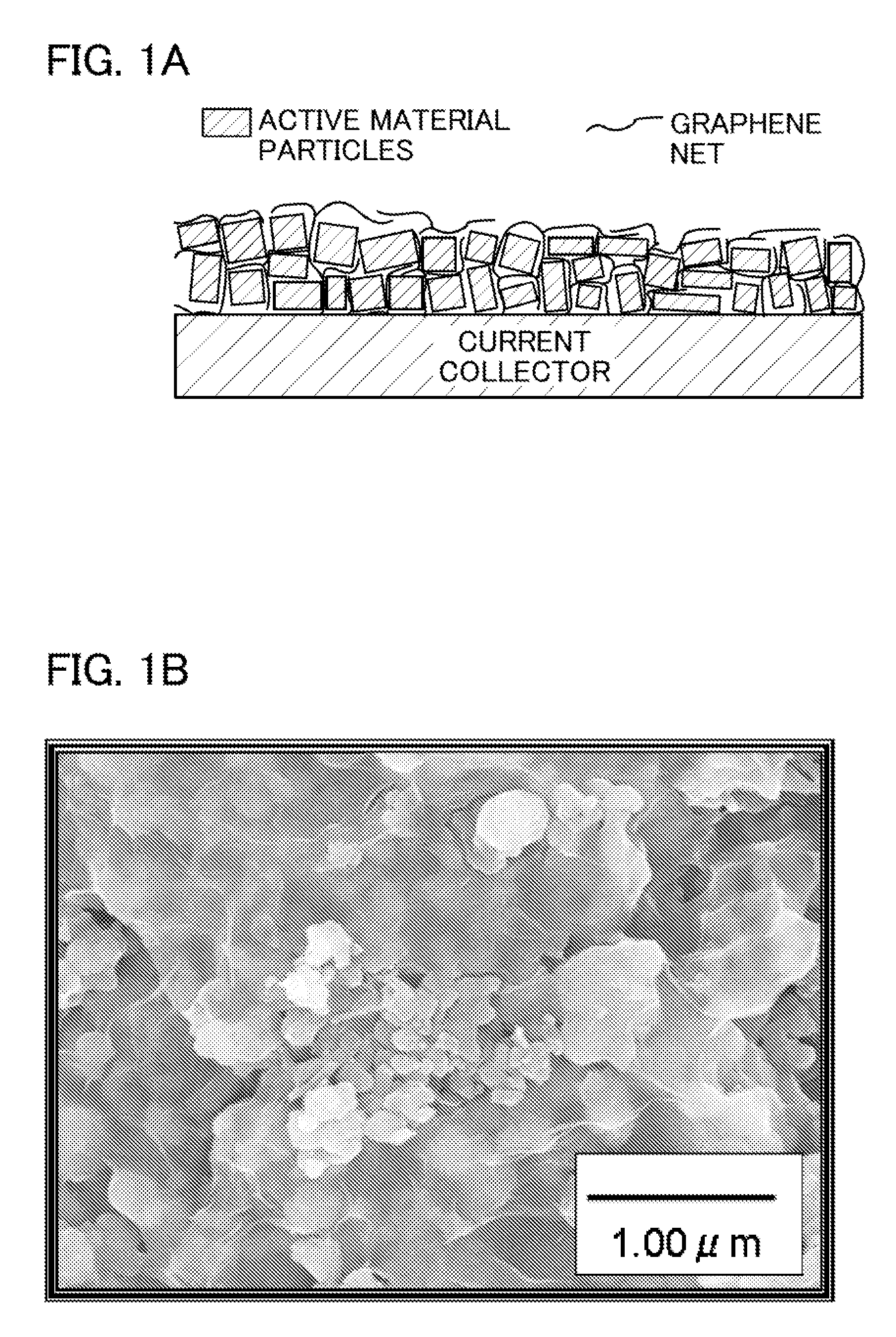
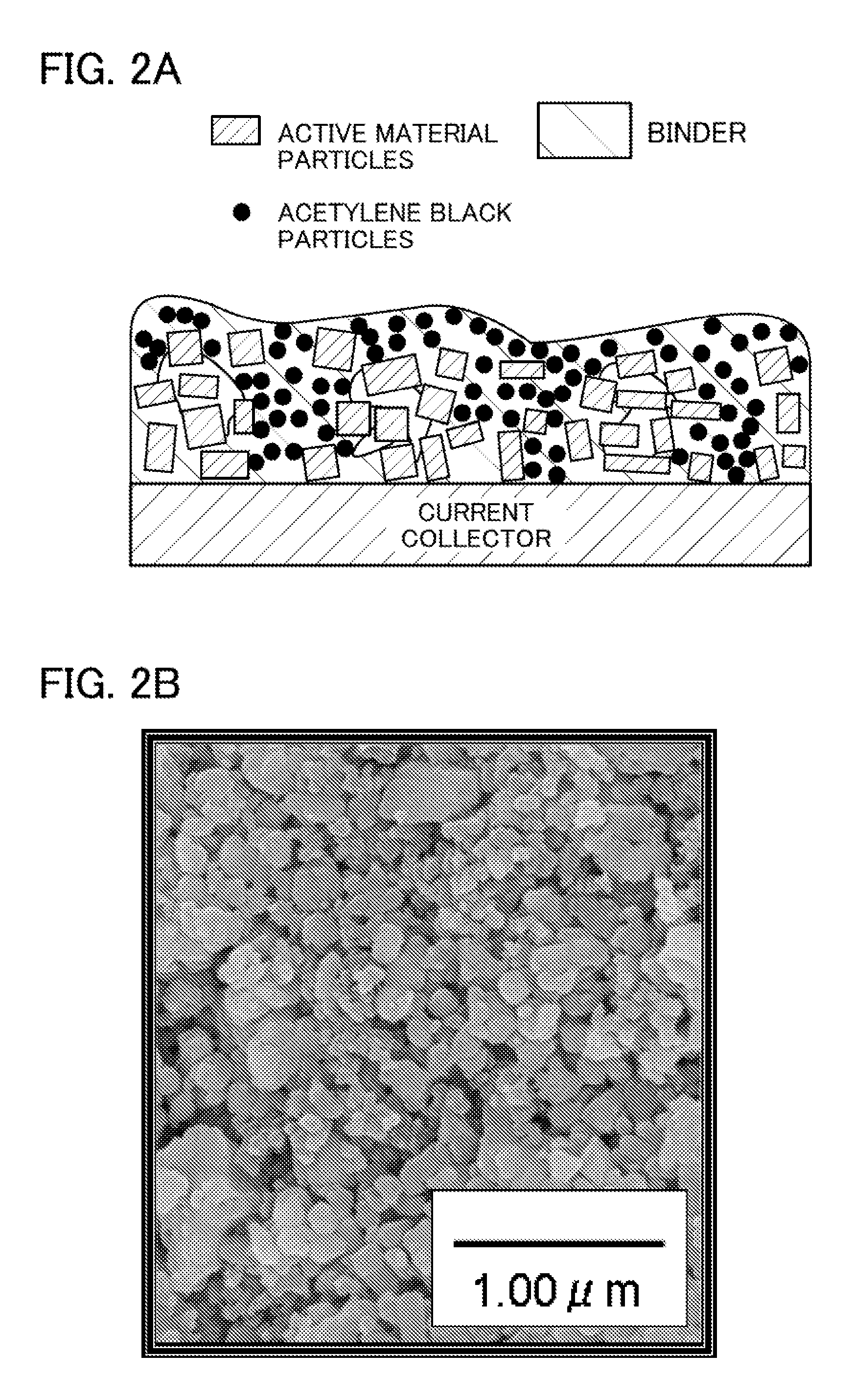
To increase the conductivity and electric capacity of an electrode which includes active material particles and the like and is used in a battery, a graphene net including 1 to 100 graphene sheets is used instead of a conventionally used conduction auxiliary agent add binder. The graphene net which has a two-dimensional expansion and a three-dimensional structure is more likely to touch active material particles or another conduction auxiliary agent, thereby increasing the conductivity and the bonding strength between active material particles. This graphene net is obtained by mixing graphene oxide and active material particles and then heating the mixture in a vacuum or a reducing atmosphere.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Nano carbon doped electrocatalyst for fuel cell, and application of nano carbon doped electrocatalyst
InactiveCN103050714AChange the microstructureChange Edge Face DefectsPhysical/chemical process catalystsCell electrodesMicrowave radiometryHigh heat
The invention relates to a nano carbon doped electrocatalyst for a fuel cell, and application of the nano carbon doped electrocatalyst. The electrocatalyst is prepared by adopting the steps of: complexing a nitrogen-containing and / or boron-containing organic precursor and a transition metal salt to form a composite; adding nano carbon as a carrier, and heating and reacting a mixture by adopting a microwave radiation method; and after the reaction is complete, filtering and drying, placing a product obtained after the reaction in an inert atmosphere and / or reducing atmosphere, and treating at a high temperature of 500-1500 DEG C to obtain the nano carbon doped electrocatalyst. The nano carbon doped electrocatalyst is very low in cost, high in activity and stability and excellent in anti-poisoning capacity.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Single-layer and multi-layer hollow carbon nanosphere and preparation method and application thereof
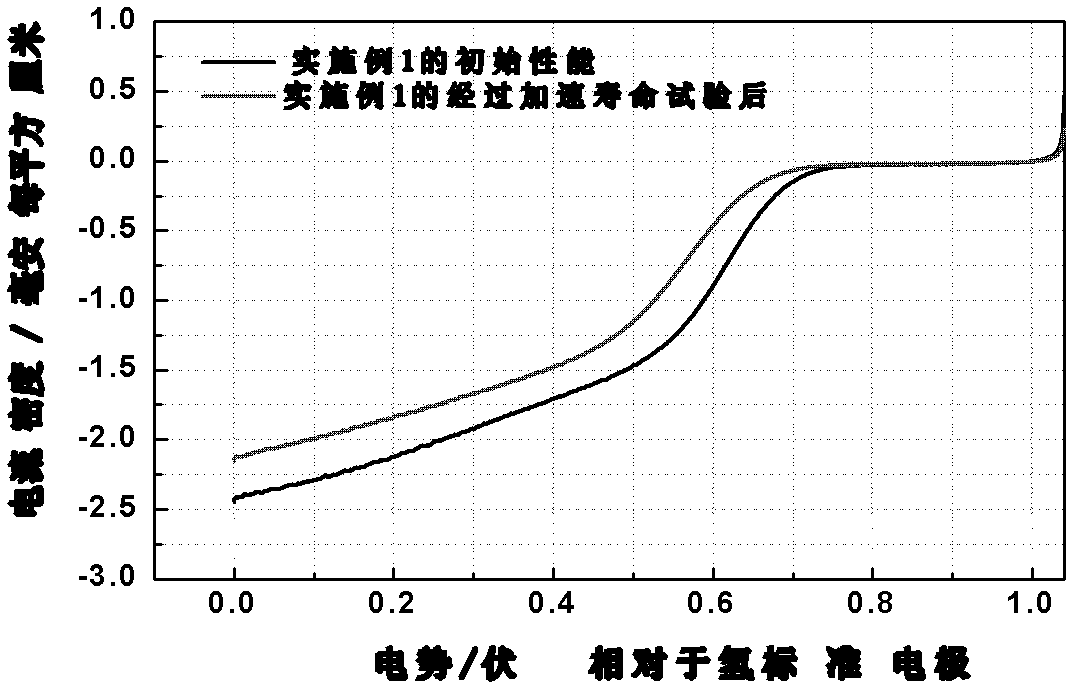
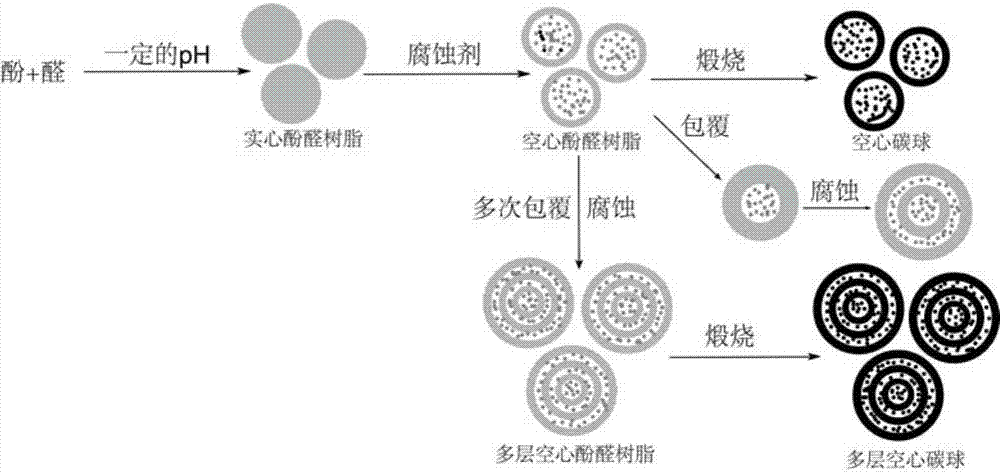
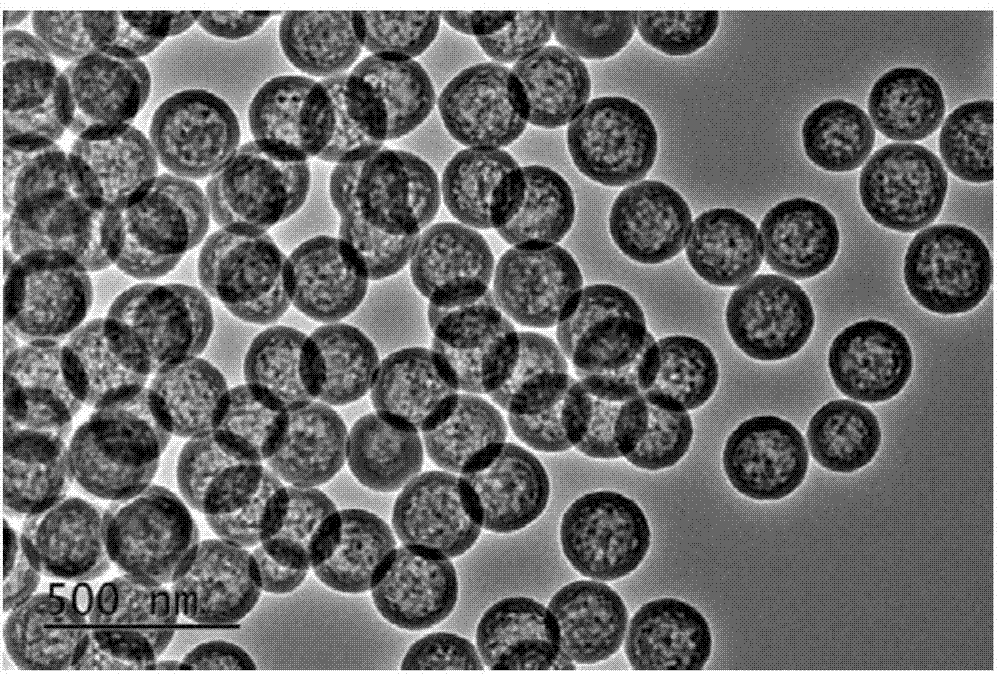
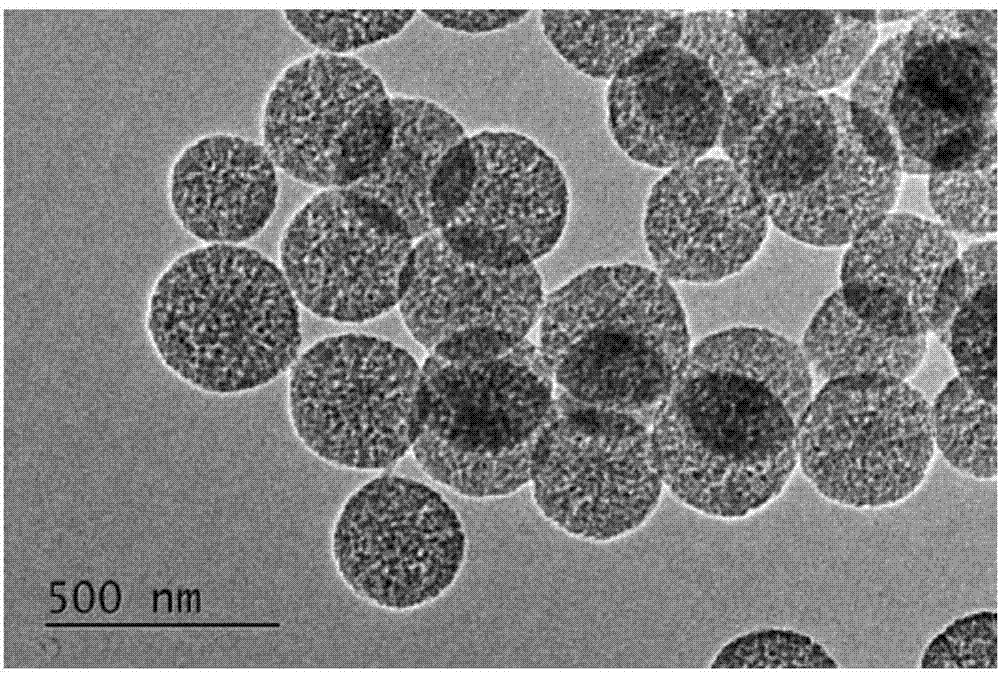
ActiveCN104843665AEasy to operateMild reaction conditionsMaterial nanotechnologySolubilityIn situ polymerization
The invention discovers and proposes a characteristic that interior species of phenolic resin are nonuniform in distribution in a polymerization process, and discloses a method for preparing a hollow carbon sphere by utilizing the characteristic of phenolic resin. The method comprises: (1) putting phenol into water or a solvent, adjusting the pH, then adding aldehyde and stirring at a certain temperature for a period of time; (2) adding a corrosive agent in a reaction system, stirring at a certain temperature, and selectively removing a part with a relatively low polymerization degree inside a polymer by utilizing a solubility difference of interior species for different solvents, to obtain an intermediate product, that is, a hollow sphere of phenolic resin polymer; and (3) calcining the intermediate product that is obtained in step (2) in an inertia or reducing atmosphere, naturally cooling to room temperature, and thus completing preparation of the hollow carbon sphere. The method is simple and practicable, and the prepared hollow carbon sphere is uniform in shape and controllable in dimension. Moreover, by utilizing a characteristic that the phenolic resin can be in-situ polymerized on surfaces of different nanometer particles, on one hand, a multi-layer hollow structure can be prepared in a multi-cladding and layer-by-layer corrosion manner, and on the other hand, the different nanometer particles can also be packaged in a cavity in an in-situ mode, so as to prepare a nuclear shell or egg yolk-nuclear structure. The prepared hollow carbon sphere has a potential application value in aspects of silicon-carbon negative electrode material, Li-S battery, supercapacitor, heavy metal ion adsorption, and the like.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
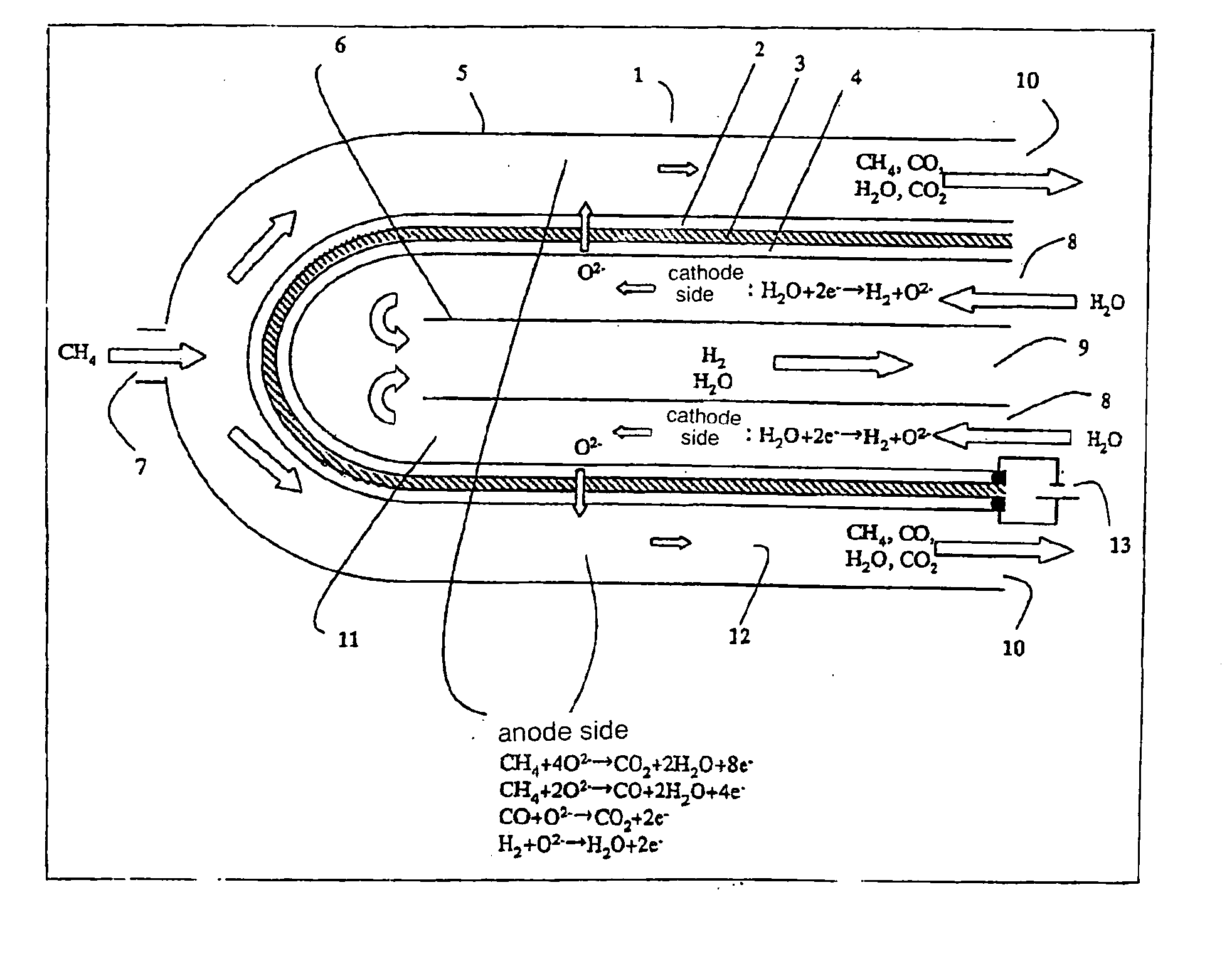
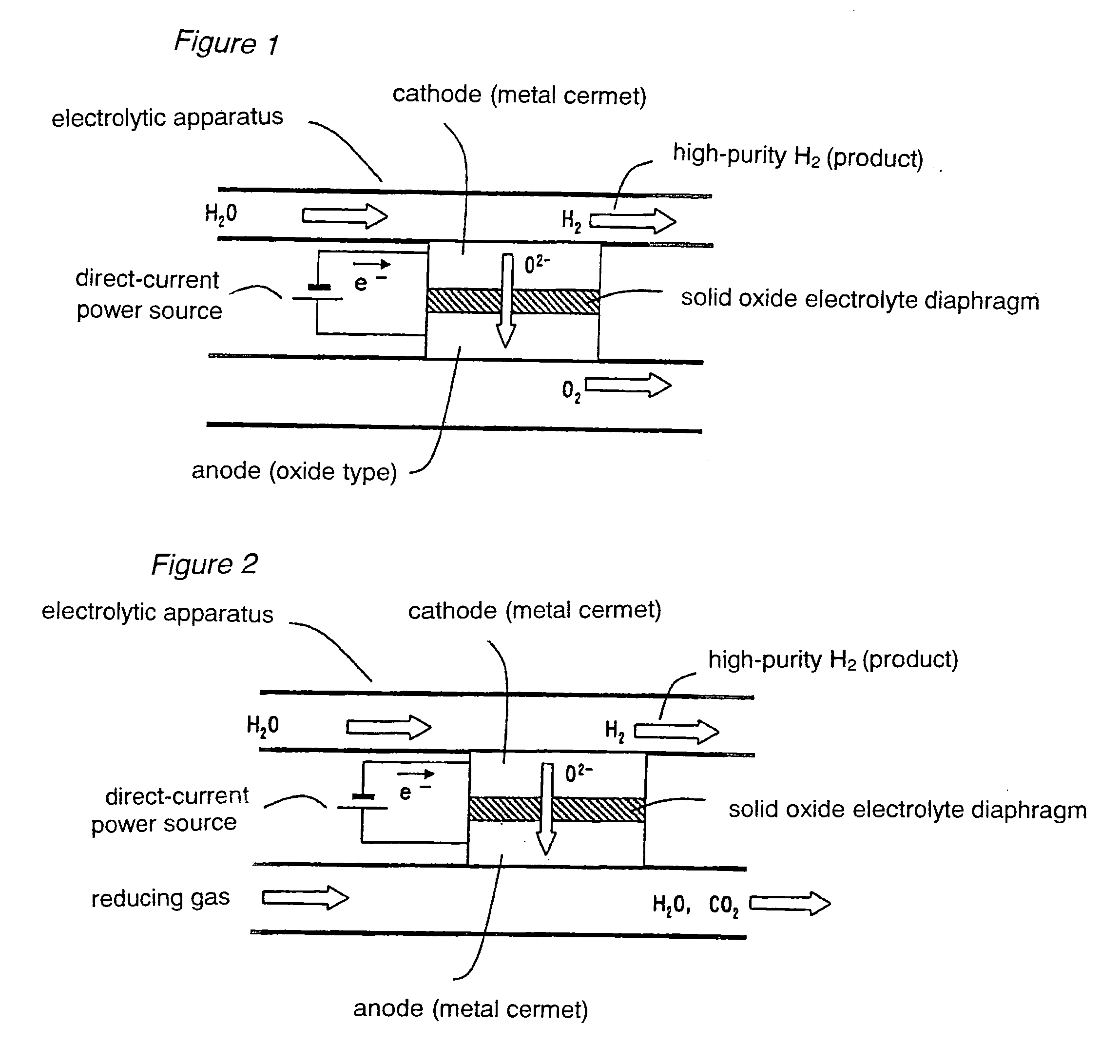
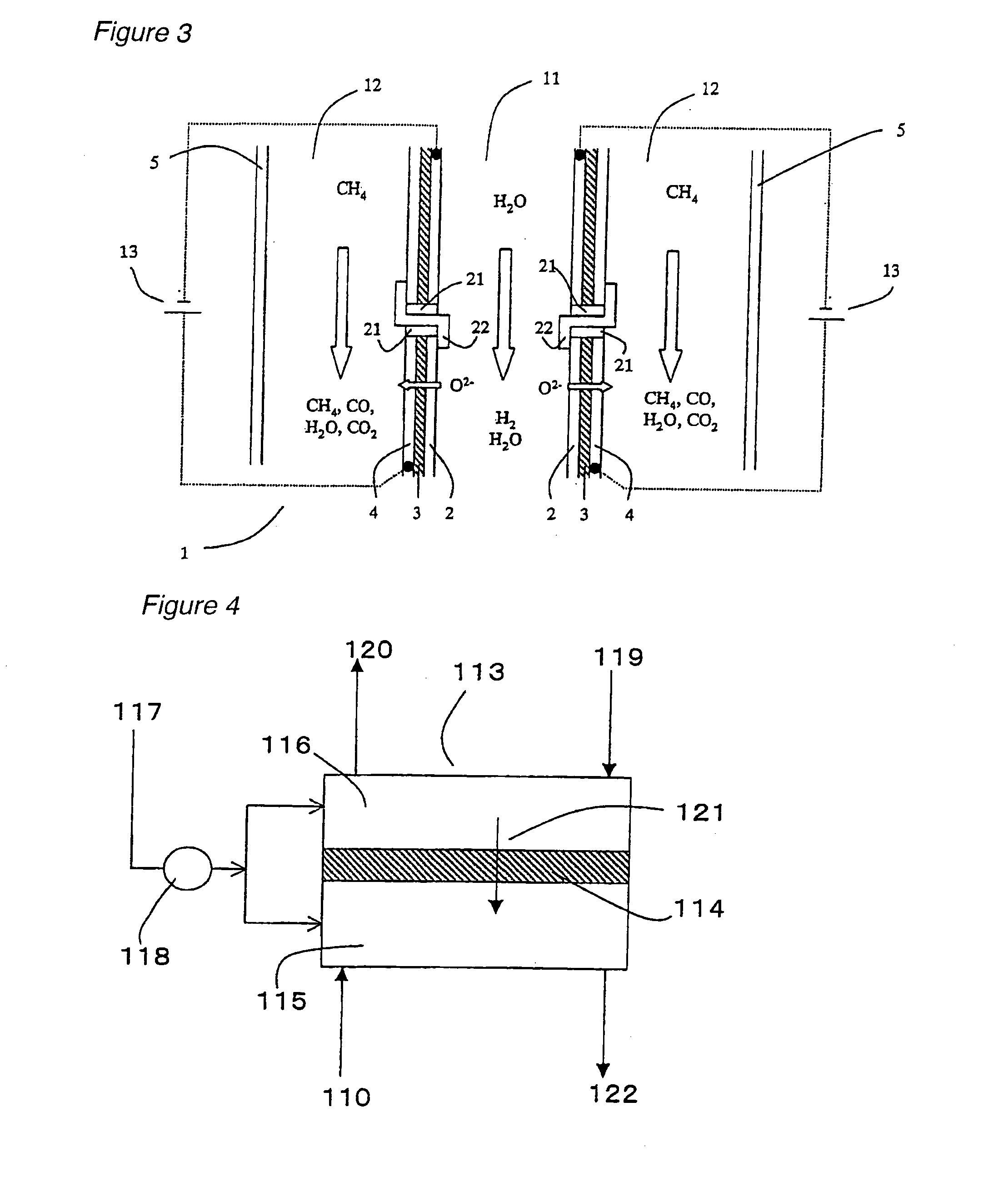
Method and apparatus for producing hydrogen
An electrolyzer structure is provided that is suitable for use in a method that produces hydrogen by steam electrolysis by feeding reducing gas to an anode side and feeding steam to a cathode side of an electrolyzer that is partitioned into the anode side and the cathode side by a diaphragm of solid oxide electrolyte, and feeding power to the anode and cathode of the electrolyzer. One embodiment of the present invention relates to an apparatus that produces hydrogen by high temperature steam electrolysis and that comprises an electrolyzer partitioned into an anode side and a cathode side by a solid oxide electrolyte diaphragm, a conduit that feeds reducing gas to the anode side of the electrolyzer, and a conduit that feeds steam to the cathode of the electrolyzer, in which a metal cermet stable in a reducing atmosphere is used as the material of the anode and the cathode. Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a method of producing hydrogen by high temperature steam electrolysis for reducing electrolysis voltage by feeding steam to a cathode side and feeding hydrocarbon-containing gas to an anode side for reaction with oxygen ion, the cathode side and the anode side being provided in a high temperature steam electrolytic apparatus in which an electrolyzer is partitioned into the anode side and the cathode side using a solid oxide electrolyte as the diaphragm, wherein offgas discharged from the anode side of the electrolytic apparatus is admixed into the hydrocarbon-containing gas that is fed to the anode side of the electrolytic apparatus.
Owner:EBARA CORP +1
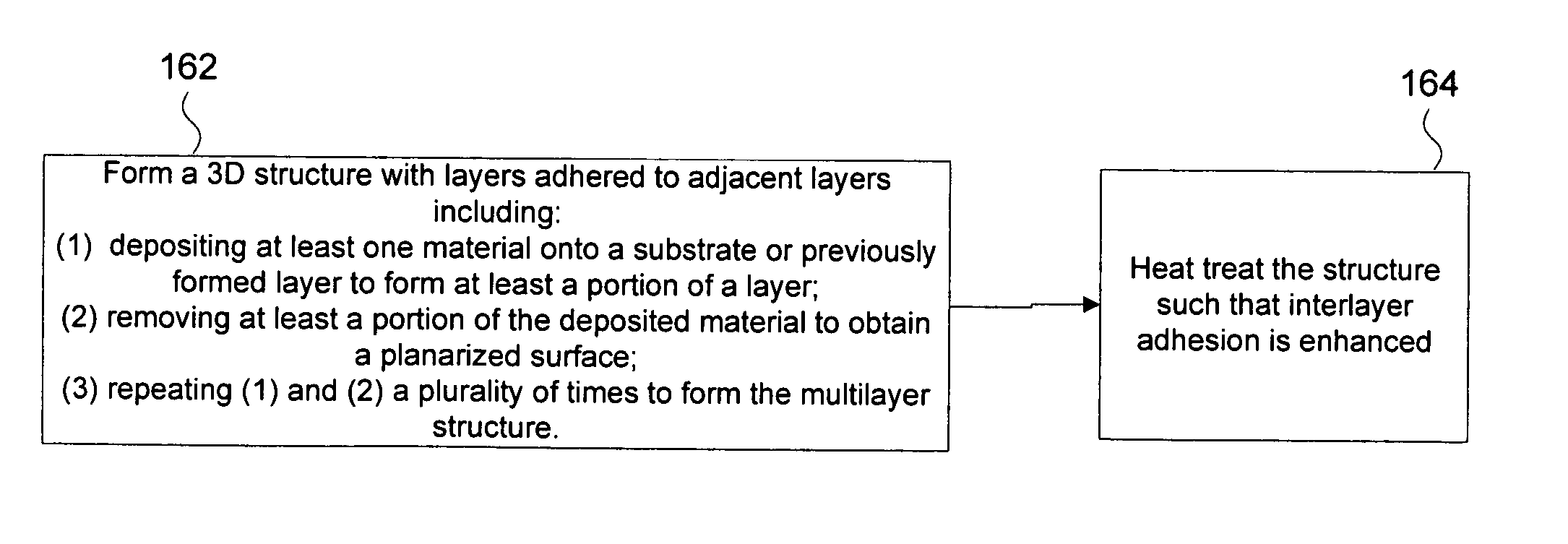
Method of electrochemically fabricating multilayer structures having improved interlayer adhesion
InactiveUS20050029109A1Improve propertiesImprove interlayer adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConductive pattern reinforcementReducing atmosphereHeat treating
Multi-layer microscale or mesoscale structures are fabricated with adhered layers (e.g. layers that are bonded together upon deposition of successive layers to previous layers) and are then subjected to a heat treatment operation that enhances the interlayer adhesion significantly. The heat treatment operation is believed to result in diffusion of material across the layer boundaries and associated enhancement in adhesion (i.e. diffusion bonding). Interlayer adhesion and maybe intra-layer cohesion may be enhanced by heat treating in the presence of a reducing atmosphere that may help remove weaker oxides from surfaces or even from internal portions of layers.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
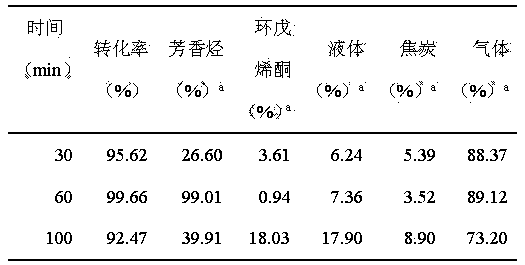
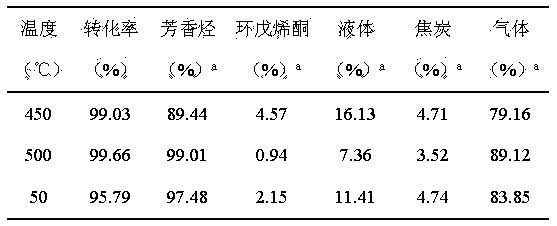
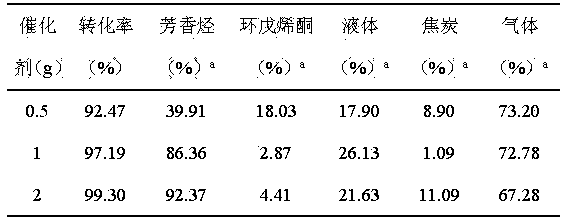
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon and cyclopentenone from biomass derivative gamma-valerolactone by catalytic conversion
InactiveCN104230615AGood dehydrogenation performanceInhibition of partial polymerizationHydrocarbonsPreparation from heterocyclic compoundsLiquid productReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon and cyclopentenone from biomass derivative gamma-valerolactone by catalytic conversion, which comprises the following steps: (1) using biomass derivative gamma-valerolactone as a raw material, which is prepared by carrying out hydrogenation reaction on levulinic acid; (2) introducing one or more transition metals into a zeolite molecular sieve, and preparing a reaction catalyst at the reaction temperature of 350-550 DEG C by using a fixed bed or fluid bed as a reactor; (3) in an inert or reducing atmosphere, carrying out contact reaction on the raw material gamma-valerolactone and catalyst under the reaction pressure of 0-10 MPa; and (4) after the pyrolysis gas is condensed, collecting the liquid product in the condensation receiver, thereby obtaining the aromatic hydrocarbon product (of benzene, toluene and xylene) and the cyclopentenone product. By using the renewable biomass derivative gamma-valerolactone as the raw material, the method has the advantage of milder reaction conditions, and the catalyst is simple to prepare and easy to recover and reuse.
Owner:湖南清欣绿色环保有限公司
Coal bed gas deoxidation catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101664679AExtend your lifeElimination of active oscillationsGas purification by catalytic conversionCatalyst activation/preparationRare-earth elementAlkaline earth metal
The invention relates to a coal bed gas deoxidation catalyst as well as a preparation method and the application thereof. The coal bed gas deoxidation catalyst takes one or the combination of severalplatinum group noble metals, i.e. Pd, Pt, Ru, Rh and Ir, as main catalyzing active components and takes one or the combination of several alkali metal / alkaline-earth metal oxides, i.e. Na2O, K2O, MgO,CaO, SrO and BaO, and multi-element compound oxides of CeO2, lanthanide series rare earth elements, i.e. Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, and the like, or / and transition elements, i.e. Y, Zr, La, and the like, or / and gamma-Al2O3 as auxiliary catalysts, and the catalyzing components are loaded on an inert carrier in a coating way so as to prepare an integral catalyst. The coal bed gas deoxidation catalyst hasthe advantages of low igniting temperature, stable combustion process, high activity, long service life, and the like, is suitable for the methane catalyzing and combustion process taking coal bed gasdeoxidation purification as a purpose and can also be extensively applied to the catalyzing and combustion process of CO and low-carbon hydrocarbon under fuel-rich and oxygen-poor reducing atmosphere.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chemical processing using non-thermal discharge plasma
InactiveUS6923890B2Simple processEnhanced water gas shiftingHydrogenMolecular sieve catalystsChemical treatmentFiber
A method for activating chemical reactions using a non-thermal capillary discharge plasma (NT-CDP) unit or a non-thermal slot discharge plasma (NT-SDP) unit (collectively referred to as “NT-CDP / SDP”). The NT-CDP / SDP unit includes a first electrode disposed between two dielectric layers, wherein the first electrode and dielectric layers having at least one opening (e.g., capillary or a slot) defined therethrough. A dielectric sleeve inserted into the opening, and at least one second electrode (e.g., in the shape of a pin, ring, metal wire, or tapered metal blade) is disposed in fluid communication with an associated opening. A non-thermal plasma discharge is emitted from the opening when a voltage differential is applied between the first and second electrodes. Chemical feedstock to be treated is then exposed to the non-thermal plasma. This processing is suited for the following exemplary chemical reactions as (i) partial oxidation of hydrocarbon feedstock to produce functionalized organic compounds; (ii) chemical stabilization of a polymer fiber (e.g., PAN fiber precursor in carbon fiber production; (iii) pre-reforming of higher chain length petroleum hydrocarbons to generate a feedstock suitable for reforming; (iv) natural gas reforming in a chemically reducing atmosphere (e.g., ammonia or urea) to produce carbon monoxide and Hydrogen gas; or (v) plasma enhanced water gas shifting.
Owner:PLASMASOL CORP
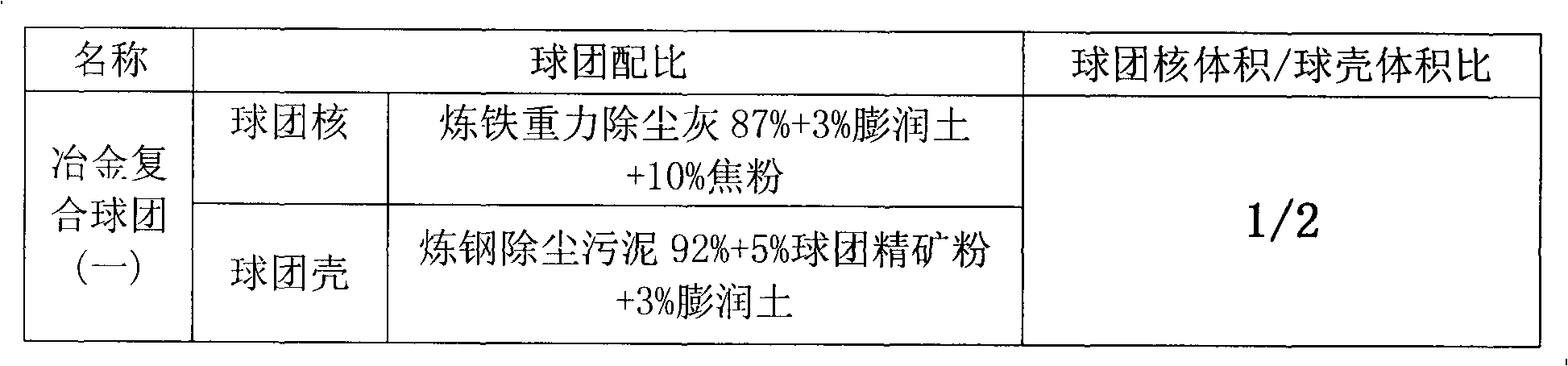
Metallurgical composite pelletizing prepared through twice pelletizing method, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101613800AImprove iron gradeIncrease valueBlast furnace detailsManufacturing convertersSocial benefitsAdhesive
The invention provides a metallurgical composite pelletizing prepared through a twice pelletizing method, as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The pelletizing is provided with a pelletizing shell formed by a central pelletizing core and a pellet material coating the outside of the pelletizing core. The internal pelletizing core of the formed pelletizing is in a reducing atmosphere, the outside of the formed pelletizing is in an oxidizing atmosphere, and the metallurgical composite pelletizing undergoing twice pelletizing satisfies the metallurgical requirements. The pelletizing core takes an iron-containing material and reducing coal dust or coke powder as raw materials in which adhesive and waste fly dust are added, and is obtained by means of disk pelletization or pressure pelletization. The pelletizing shell takes the iron-containing material and the pelletizing core as raw materials in which the adhesive is added, and is obtained by means of disk pelletization and taking the pelletizing core as the center of the sphere. Various metallurgical performance indexes of the composite pelletizing are highly better than normal pellets. The composite pelletizing not only realizes the harmlessness and the recycling of the waste fly ash, but also can greatly improve the technical and economic indexes of iron making blast furnaces. In addition, the composite pelletizing not only achieves such social benefits as energy conservation, emission reduction, environment protection and environment pollution treatment, but also can create considerable economic benefits.
Owner:CHONGQING ANGRUIYUE SCI & TECH
Nanostructured titanium oxide material and its synthesis procedure
ActiveUS20060078726A1Stable nanotubular structureLarge specific surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsFiberNanowire
Nanomaterials of the JT phase of the titanium oxide TiO2-x, where 0≦x≦1 having as a building block a crystalline structure with an orthorhombic symmetry and described by at least one of the space groups 59 Pmmn, 63 Amma, 71 Immm or 63 Bmmb. These nanomaterials are in the form of nanofibers, nanowires, nanorods, nanoscrolls and / or nanotubes. The nanomaterials are obtained from a hydrogen titanate and / or a mixed sodium and hydrogen titanate precursor compound that is isostructural to the JT crystalline structure. The titanates are the hydrogenated, the protonated, the hydrated and / or the alkalinized phases of the JT crystalline phase that are obtained from titanium compounds such as titanium oxide with an anatase crystalline structure, amorphous titanium oxide, and titanium oxide with a rutile crystalline structure, and / or directly from the rutile mineral and / or from ilmenite. The titanates are submitted to dynamic thermal treatment in an inert, oxidizing or reducing atmosphere to produce the JT phase of the TiO2-x, where 0≦x≦1 with an orthorhombic structure.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Ethylene polymers and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6646069B2Improve impact resistanceImprove balanceOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationChromium CompoundsCrack resistance
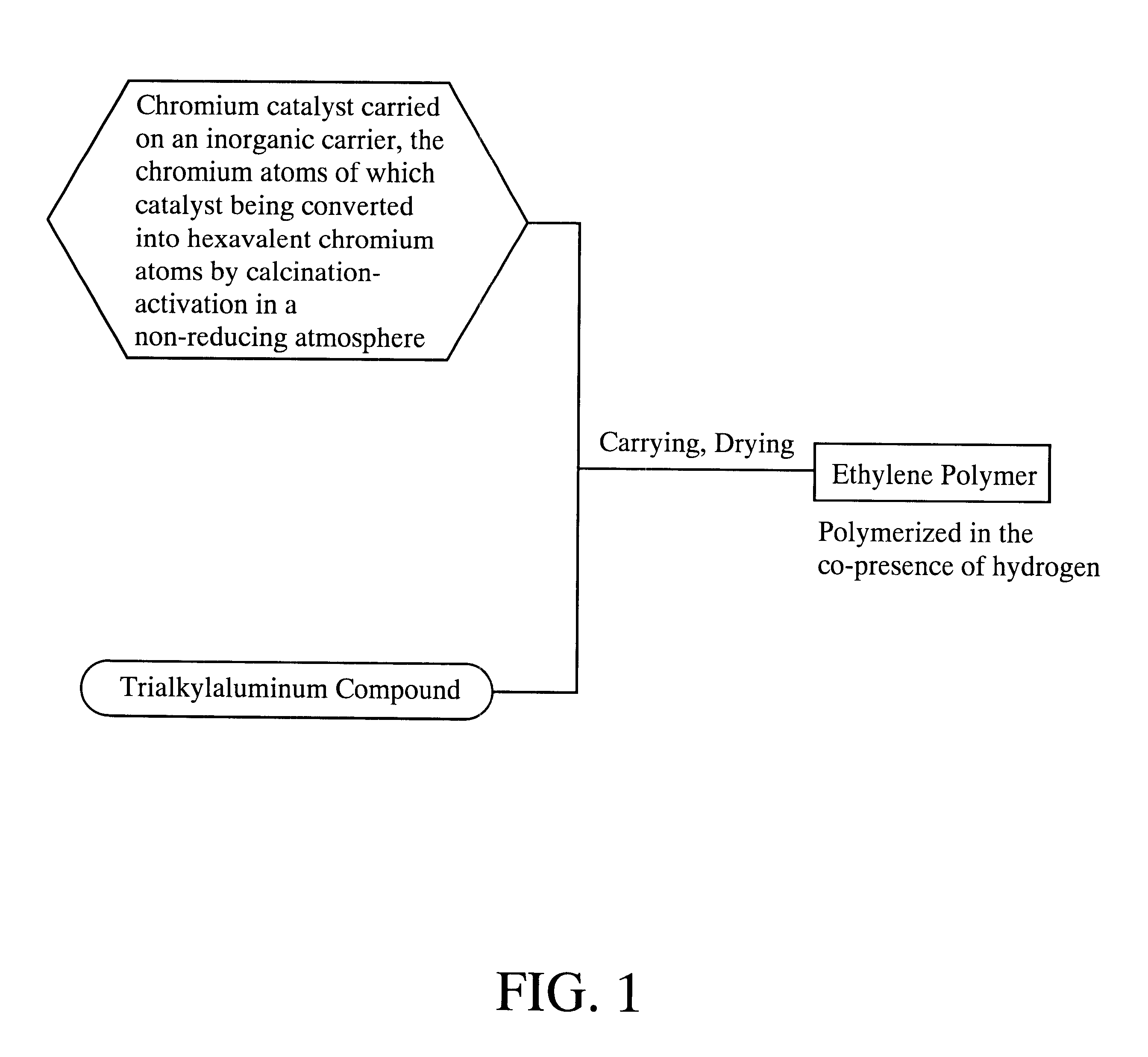
The invention relates to a method for producing an ethylene polymer, comprising performing polymerization of ethylene in co-presence of hydrogen using a trialkylaluminum compound-carried chromium catalyst, wherein the chromium catalyst is obtained by calcination-activating a chromium compound that is carried on an inorganic oxide carrier in a non-reducing atmosphere to convert chromium atoms in the chromium compound into hexavalent chromium atoms for at least a portion thereof, and treating with a trialkylaluminum compound in an inert hydrocarbon solvent to carry thereon and removing to dry the solvent so that the chromium atoms are not over-reduced by the trialkylaluminum compound, and to an ethylene polymer suitable for blow molded articles obtained by the production method. The ethylene polymer of the invention have improved environment stress crack resistance (ESCR) and impact resistance in a good balance and are suitable for molded blow articles, in particular large size blow molded articles.
Owner:JAPAN POLYOLEFINS CO LTD
Preparation method of porous carbon nanofiber
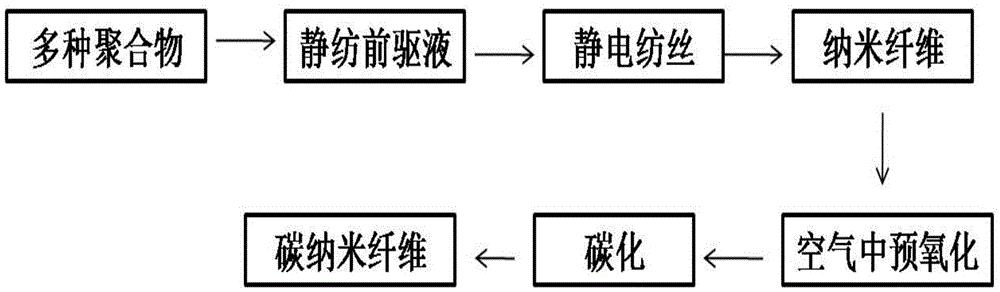
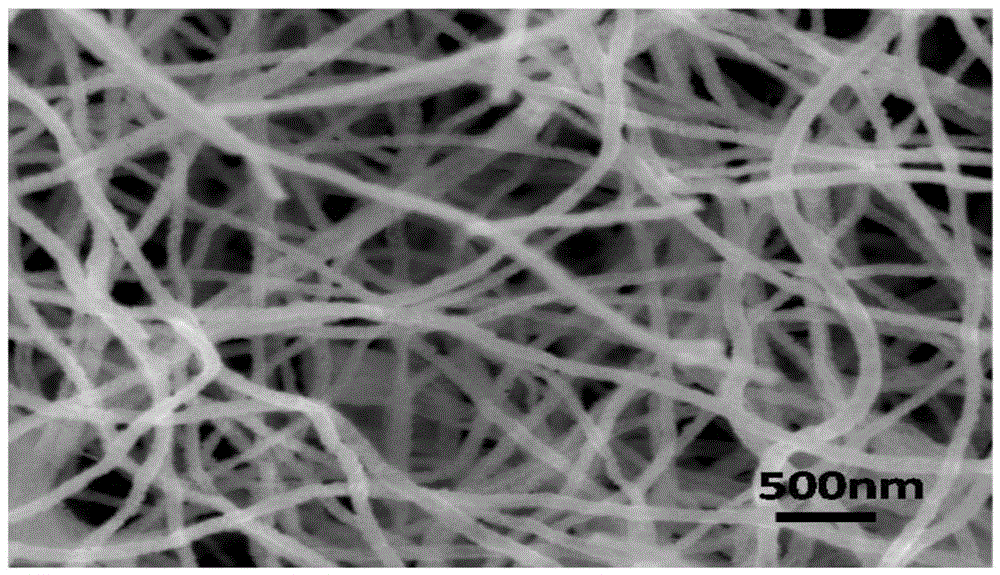
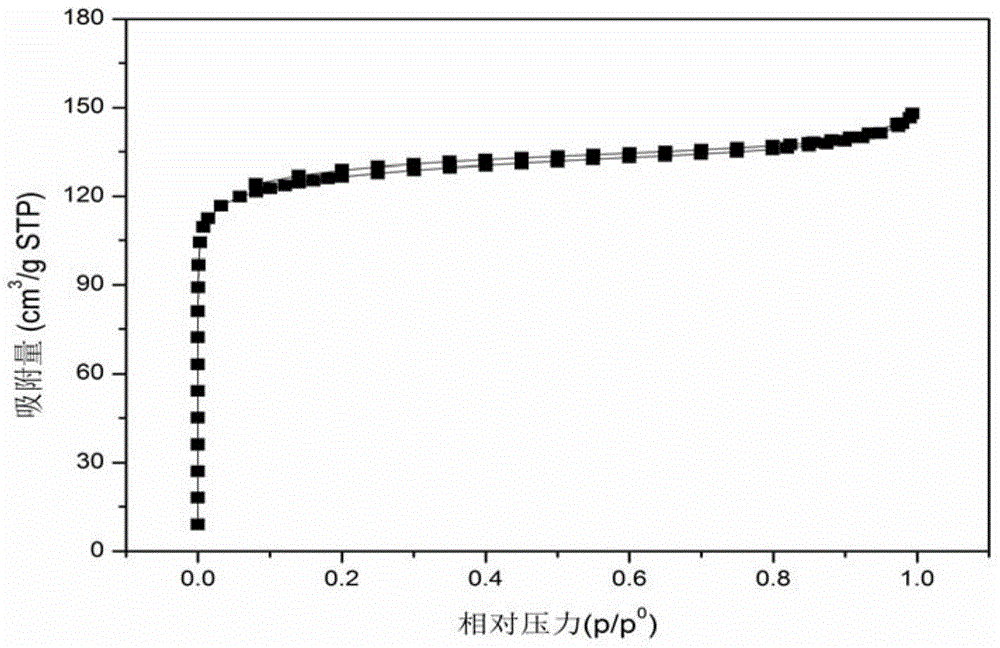
The invention belongs to the field of functional materials and discloses a preparation method of porous carbon nanofiber. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: a polymer is added to a solvent and stirred, and a spinning precursor solution is obtained; parameters are set, the spinning precursor solution is subjected to electrostatic spinning, and nanofiber is obtained; at the temperature rise speed of 1 DEG C / min-5DEG C / min, the nanofiber is preoxidized in air for 2-5 hours at the temperature of 100 DEG C-300 DEG C, and the preoxidized nanofiber is obtained; finally, at the temperature rise rate of 3DEG C / min-10DEG C / min, the preoxidized nanofiber is carbonized for 2-5 hours at the temperature of 600 DEG C-1,400 DEG C in an inert or reducing atmosphere, and the carbon nanofiber is obtained. The method is simple in technology, low in cost, high in yield, environment-friendly and beneficial to industrial production; meanwhile, pore diameter distribution and the specific surface area of the prepared carbon nanofiber are controllable; the carbon nanofiber can be applied to the fields of supercapacitors, batteries, catalysts, catalyst carriers, adsorption and filtration materials and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com