Patents
Literature
680 results about "Levulinic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
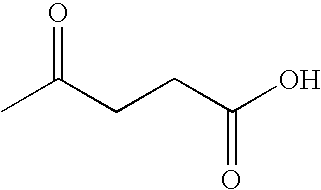
Levulinic acid, or 4-oxopentanoic acid, is an organic compound with the formula CH₃C(O)CH₂CH₂CO₂H. It is classified as a keto acid. This white crystalline solid is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is derived from degradation of cellulose and is a potential precursor to biofuels, such as ethyl levulinate.
Methods for conversion of carbohydrates in ionic liquids to value-added chemicals
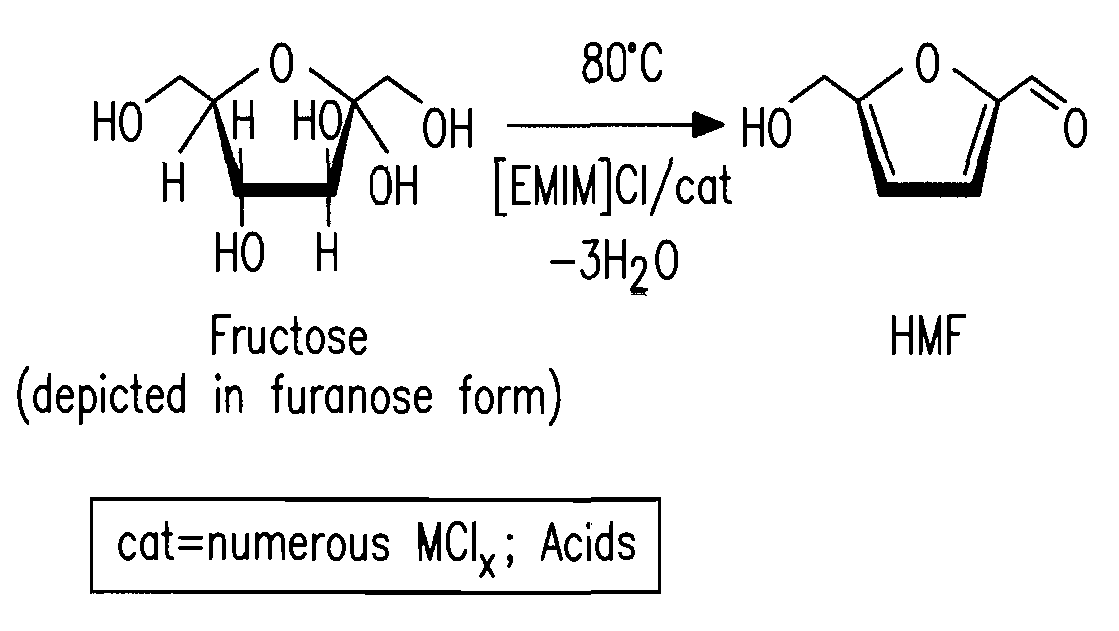
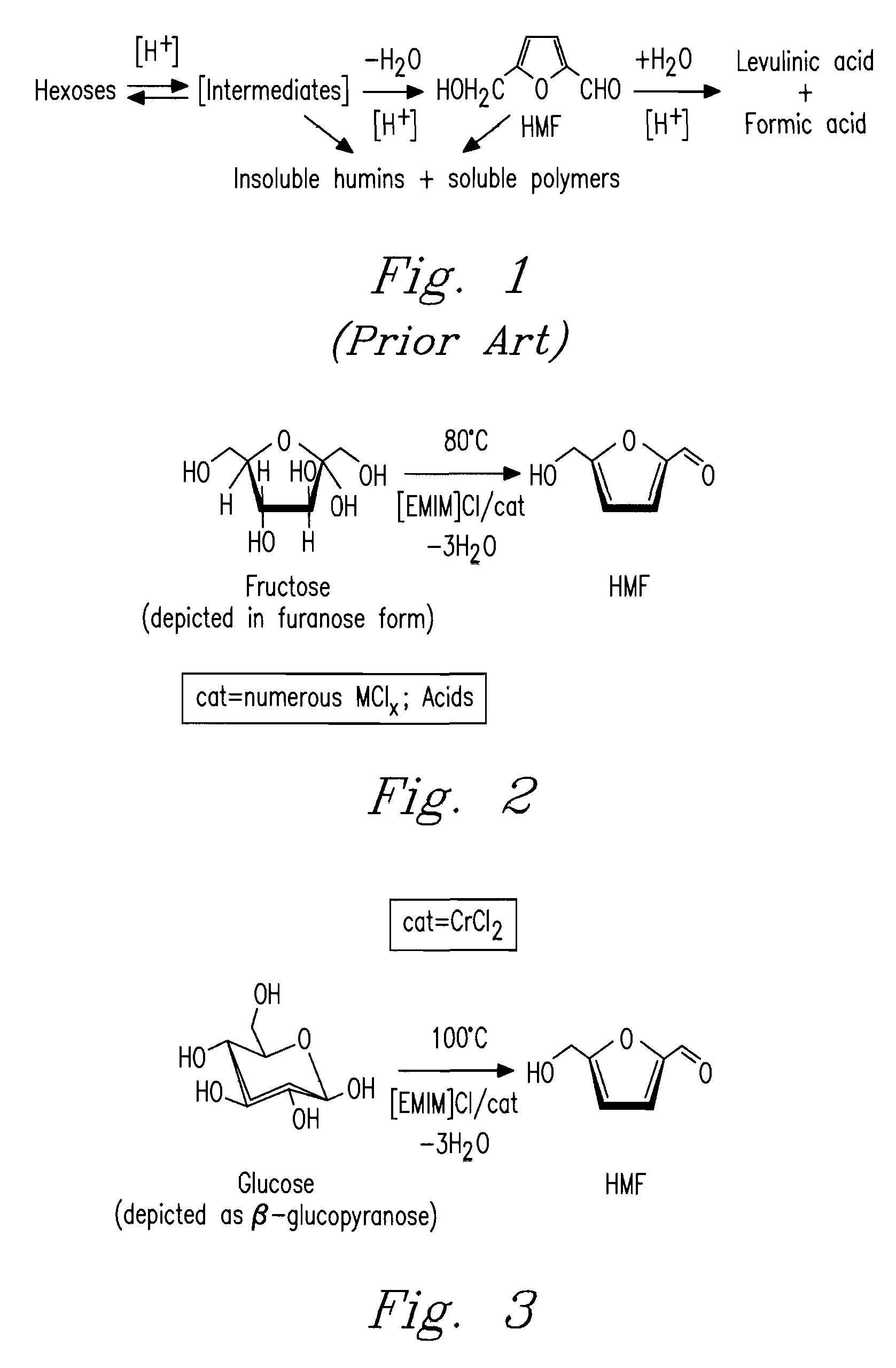
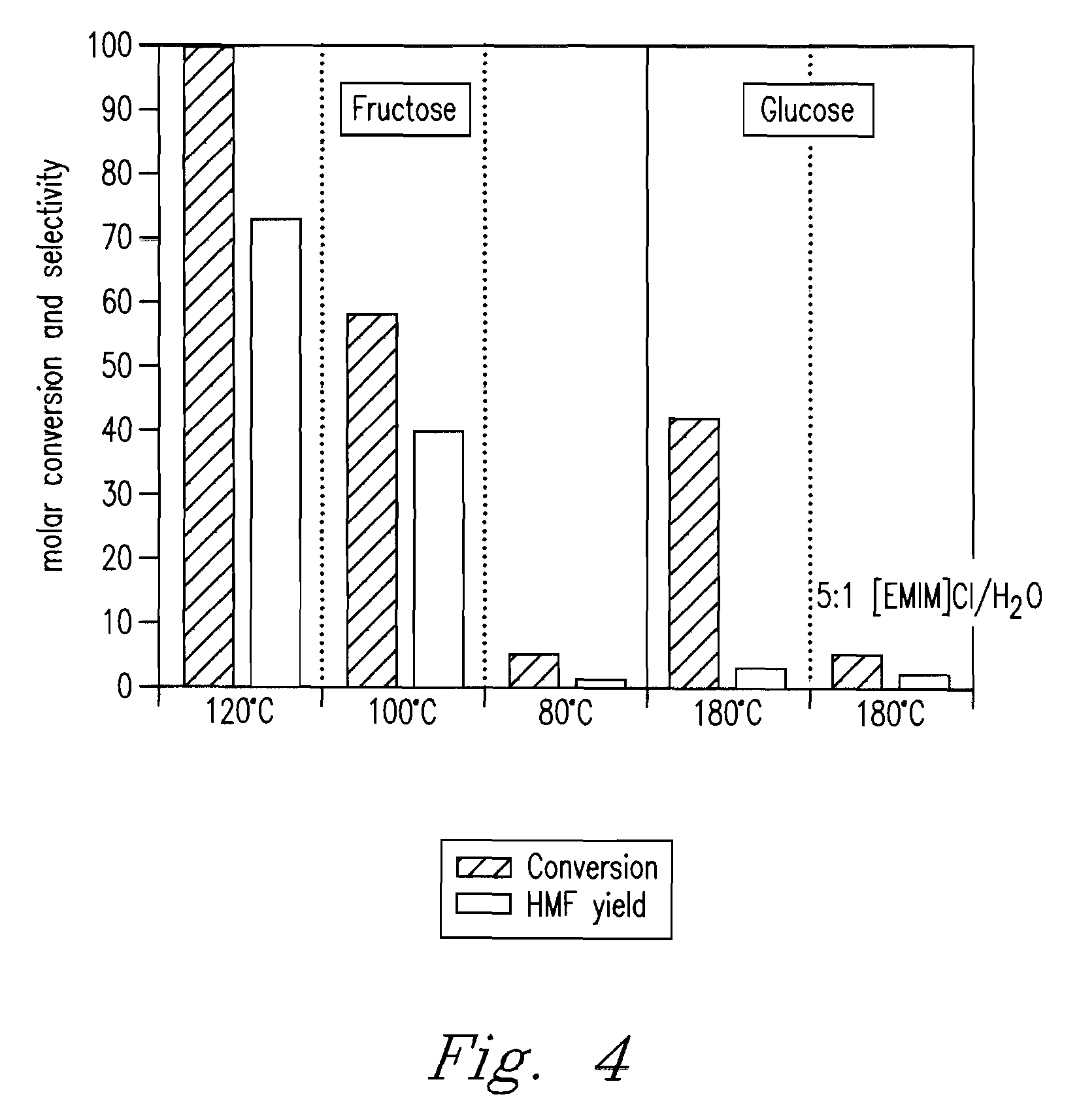
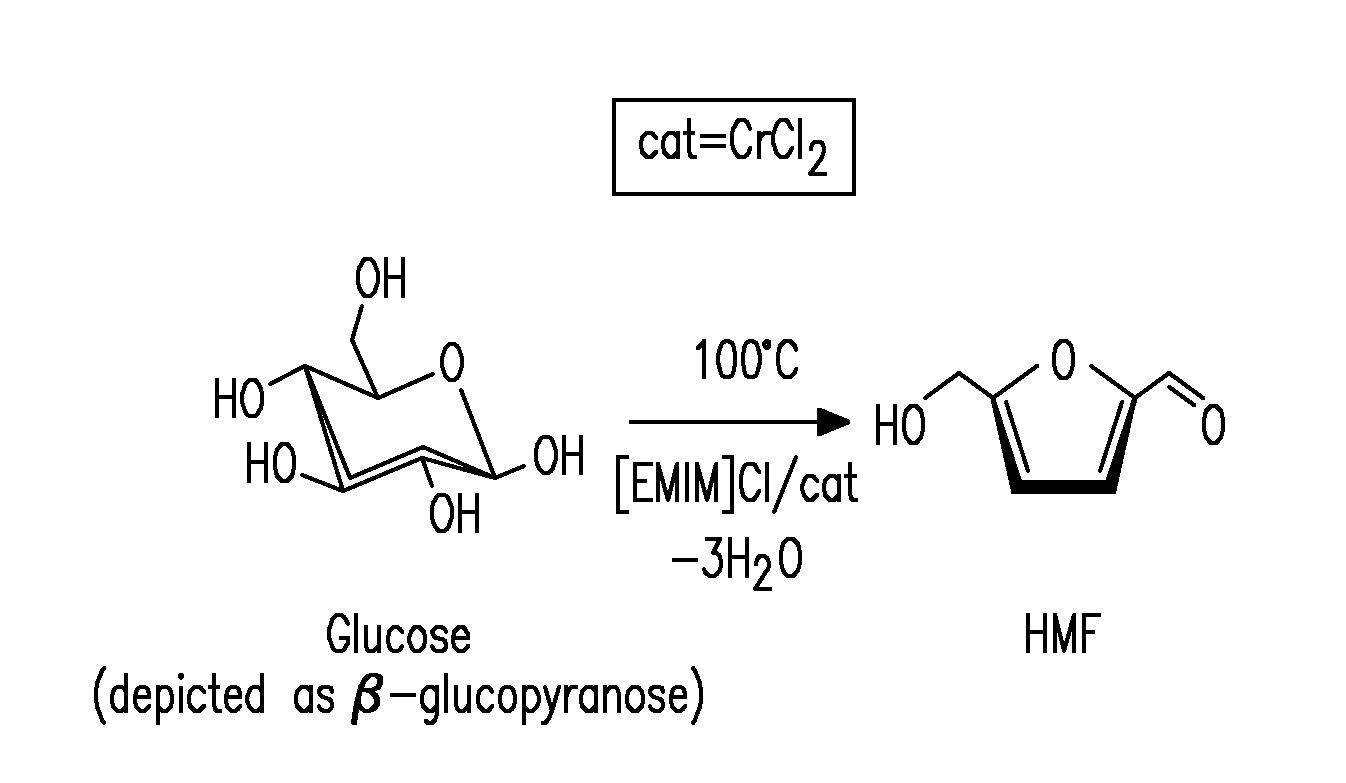
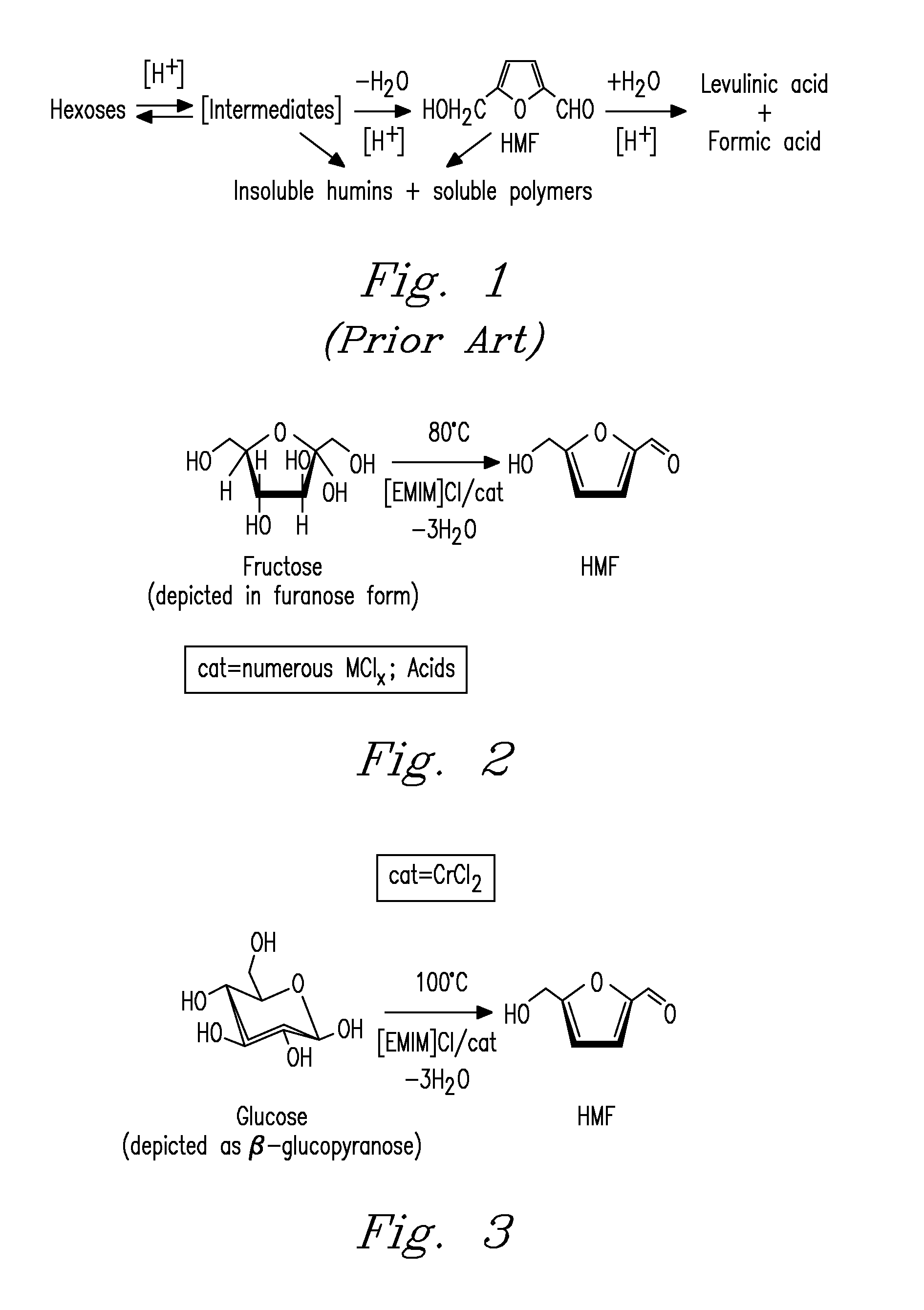
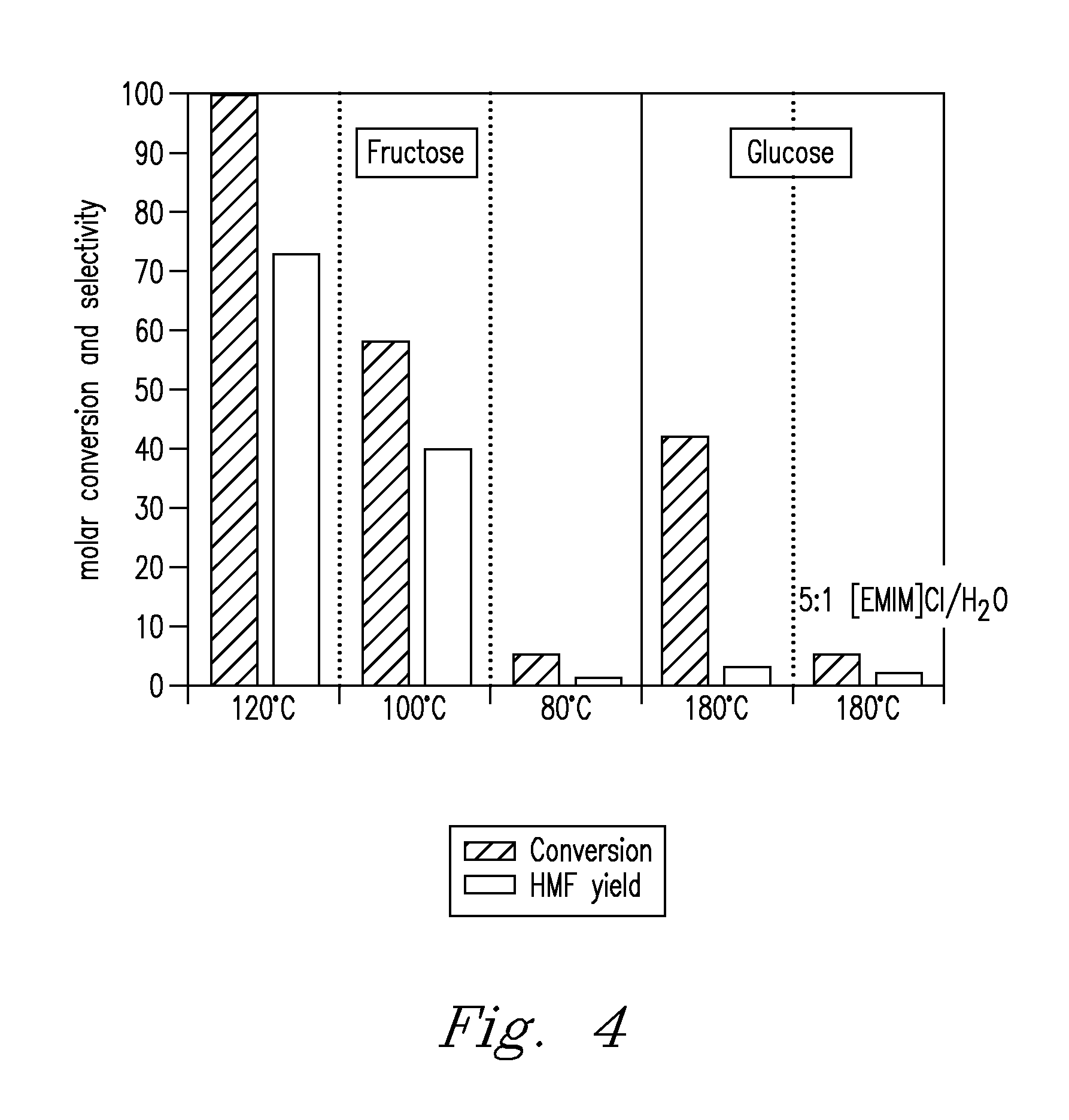
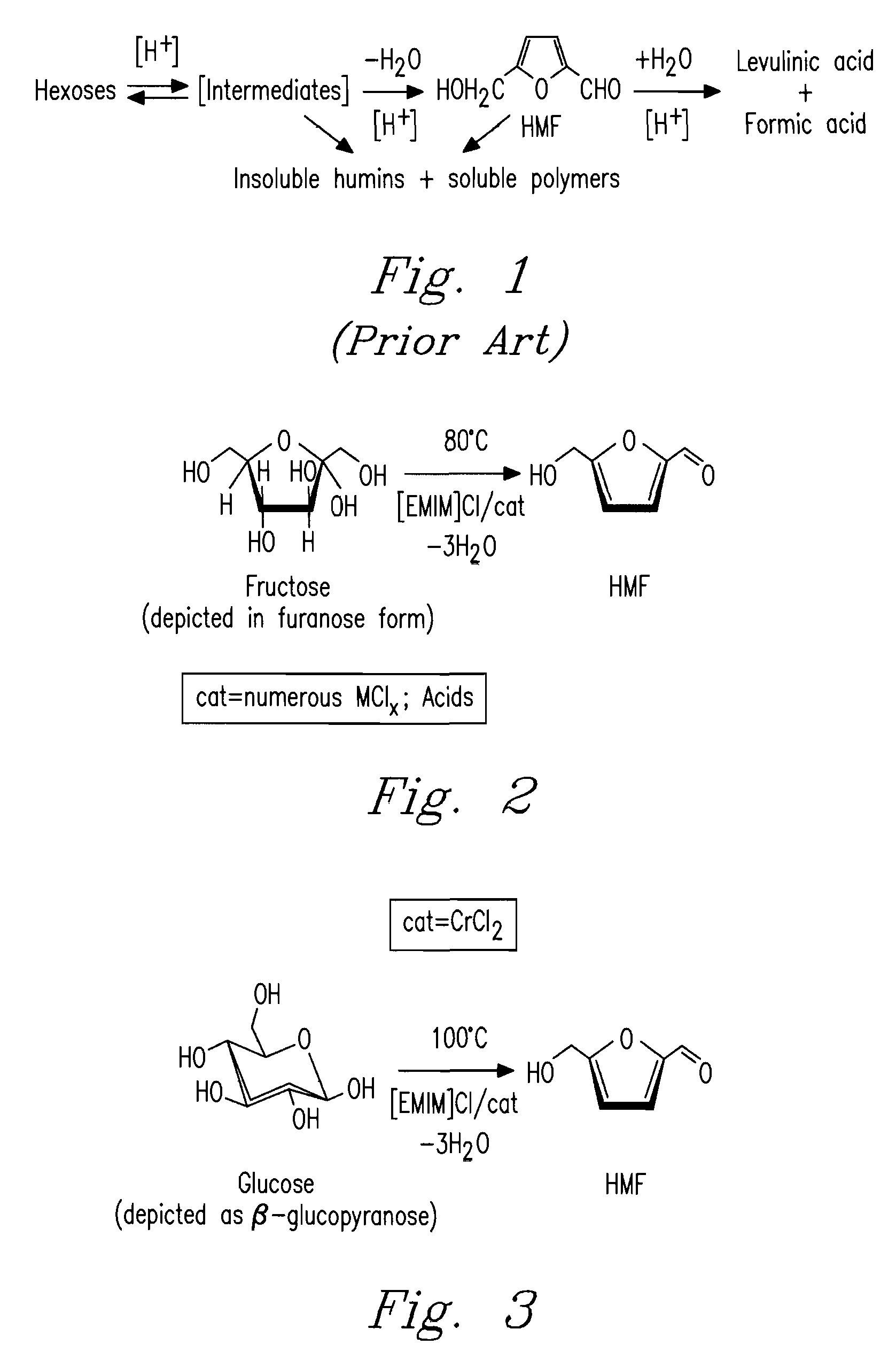
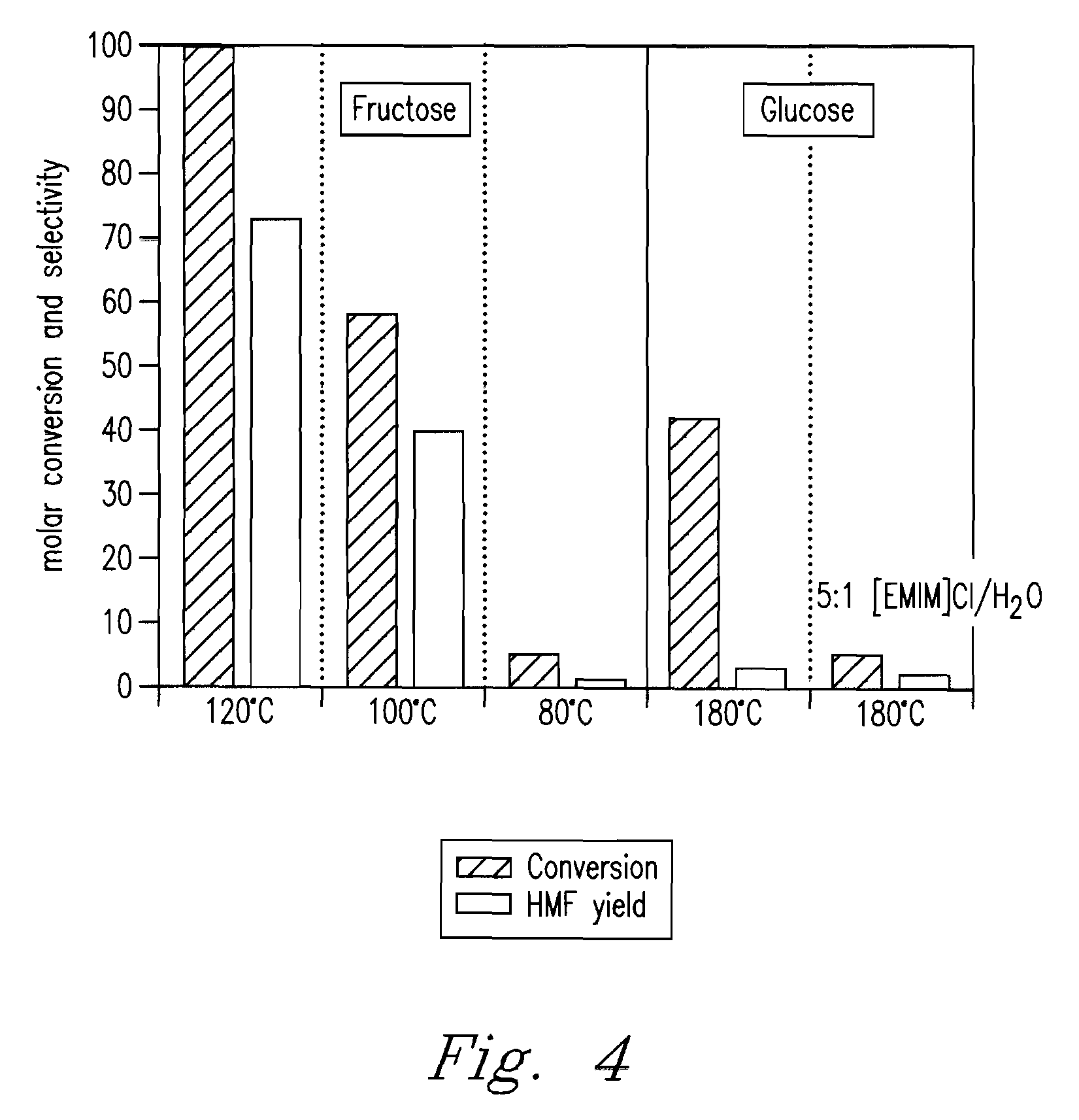
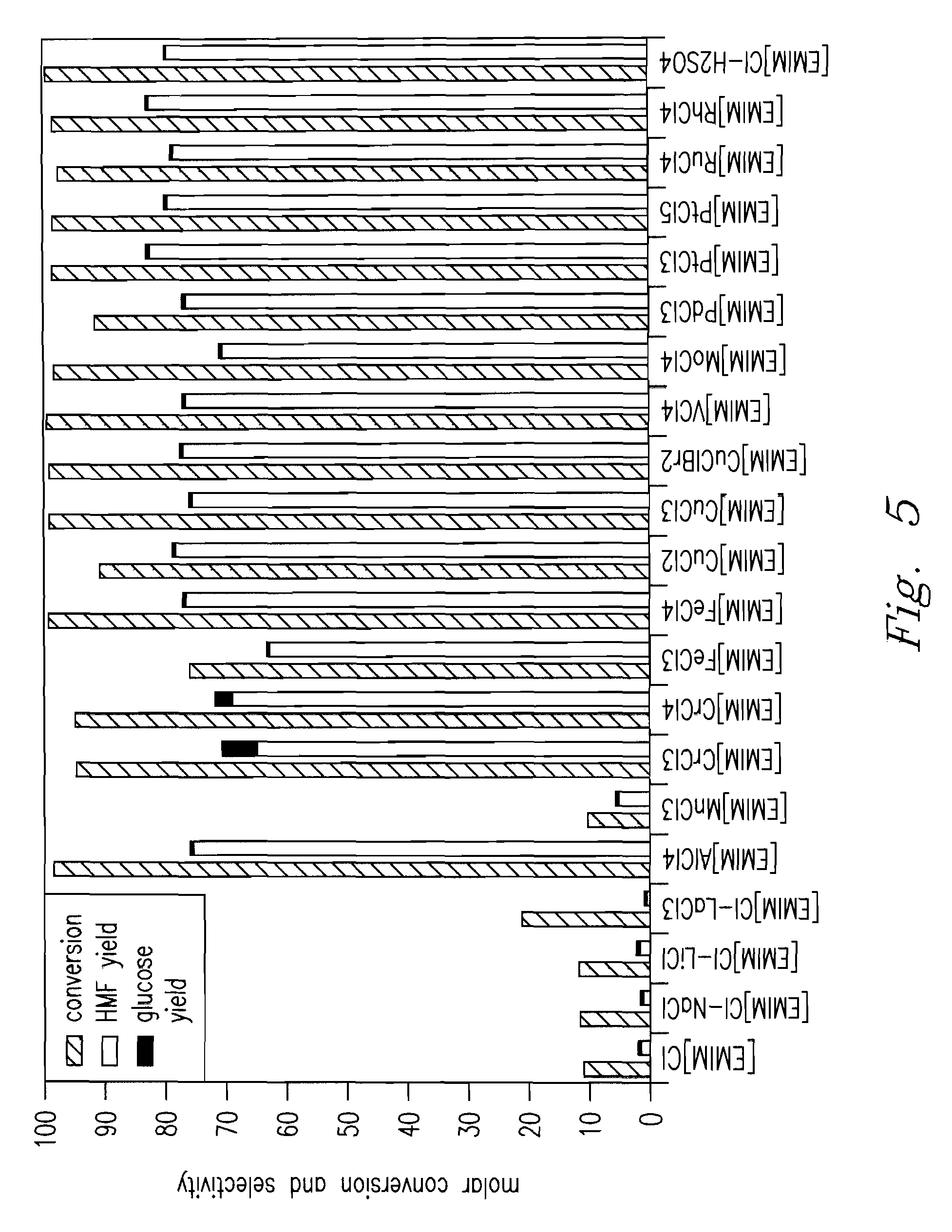
Methods are described for converting carbohydrates including, e.g., monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides in ionic liquids to value-added chemicals including furans, useful as chemical intermediates and / or feedstocks. Fructose is converted to 5-hydroxylmethylfurfural (HMF) in the presence of metal halide and acid catalysts. Glucose is effectively converted to HMF in the presence of chromium chloride catalysts. Yields of up to about 70% are achieved with low levels of impurities such as levulinic acid.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Topical aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy for the treatment of acne vulgaris
InactiveUS6897238B2Reduce sebum productionSmall sizeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesDisease
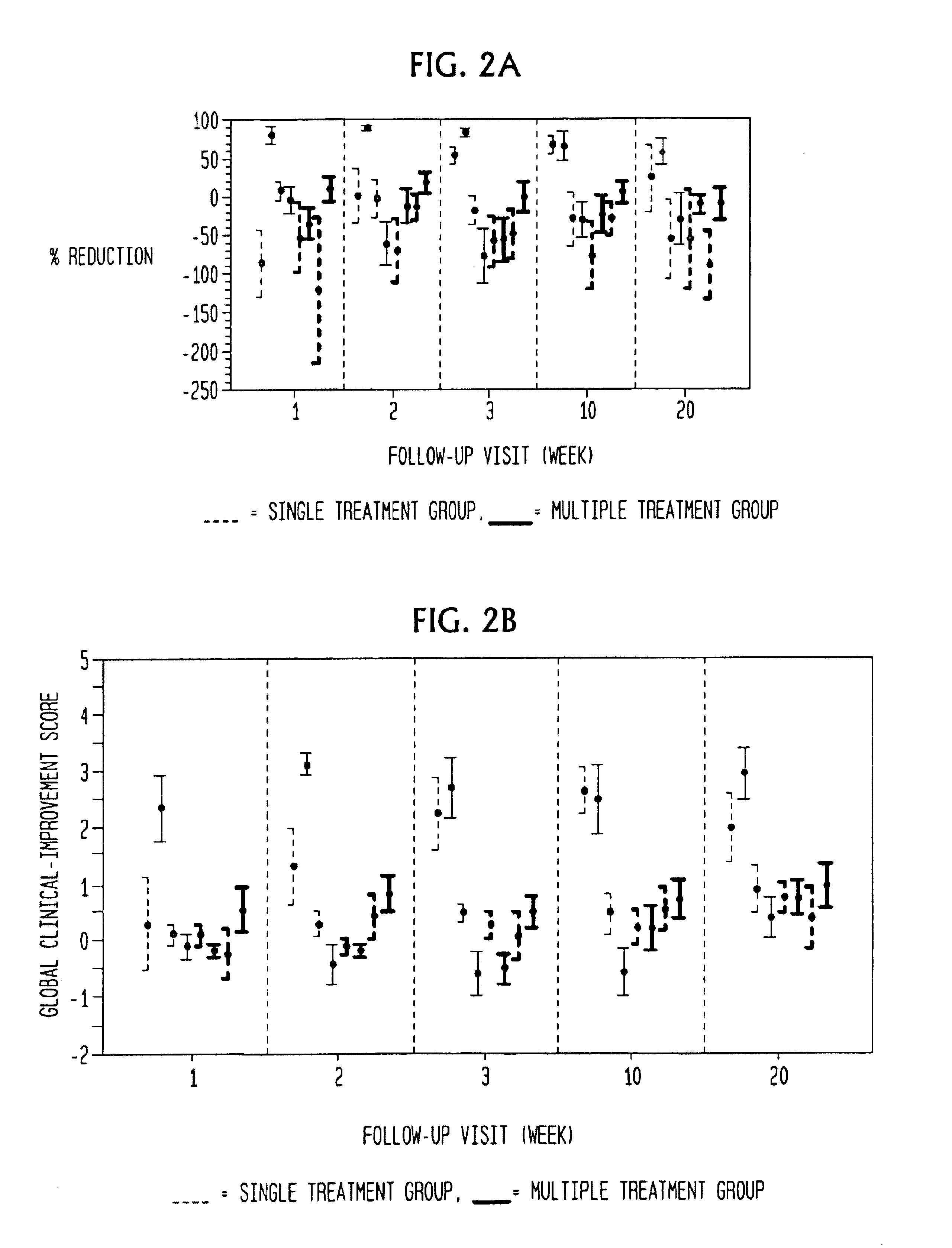
Light treatments of sebaceous gland disorders with 5-aminolevulinic acid and photodynamic therapy are disclosed. A preferred treatment includes topical application of 5-aminolevulinic acid to the skin followed by light exposures with repeated treatment at various intervals. At low doses of ALA and photodynamic therapy (PDT) in single or multiple treatments, improvement in the sebaceous gland disorder, e.g., acne, provides the discovery that diminishment in sebum secretion and the eradication of bacteria occurs. At high doses of ALA and a single high energy PDT treatment, permanent changes to the sebaceous gland and sebum secretion have been discovered.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Preparation of levulinic acid esters and formic acid esters from biomass and olefins
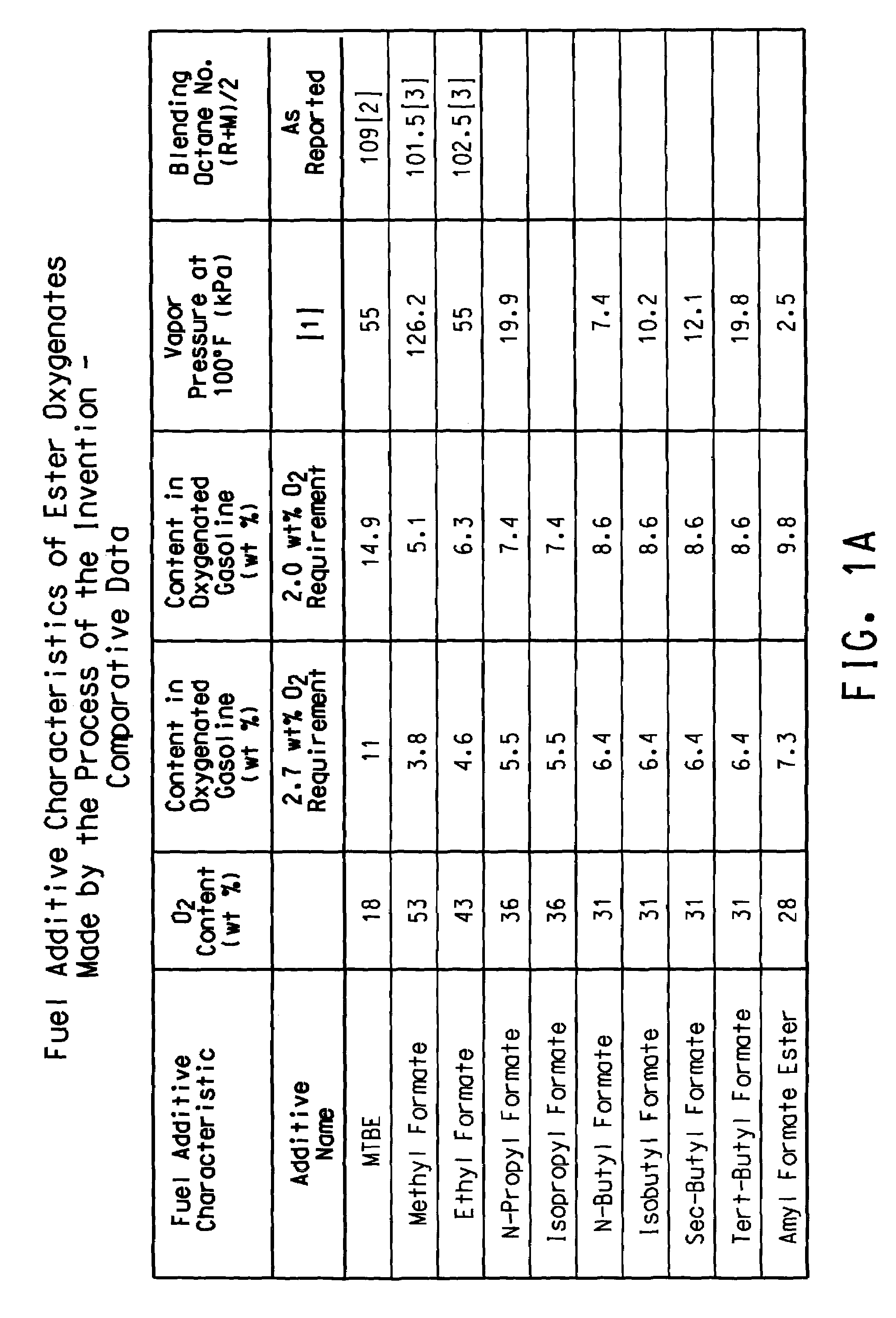
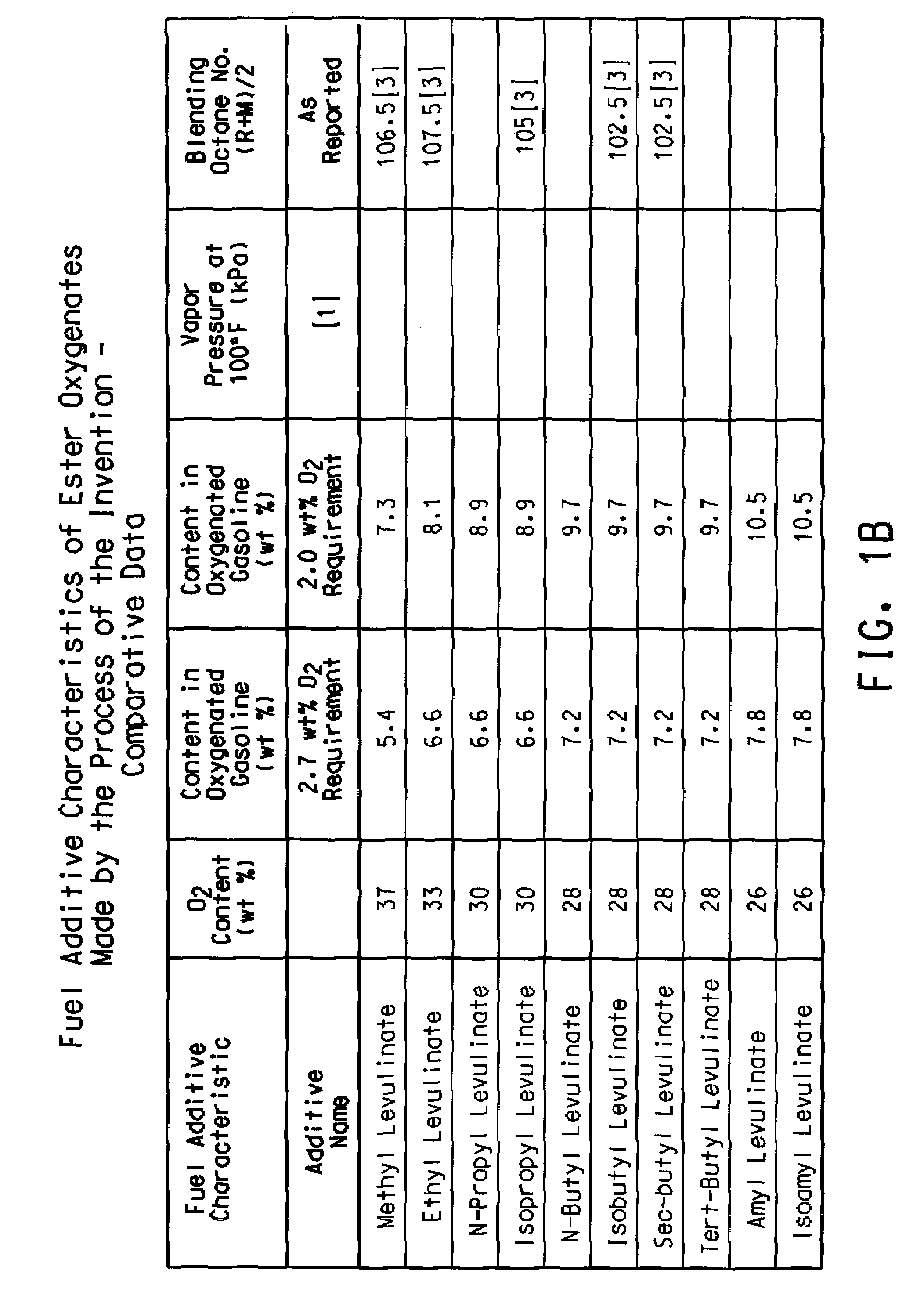
This invention relates to a process for producing a mixture of levulinic acid esters and formic acid esters from biomass and olefins, and the composition prepared therefrom. This invention also relates to usage of the mixture of these esters as fuel and as fuel additives for gasoline fuel, diesel fuel, and biofuel.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Production of levulinic acid and levulinate esters from biomass
InactiveUS20100312006A1Improve production yieldHigh purityPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic compound preparationPropanoic acidFurfural
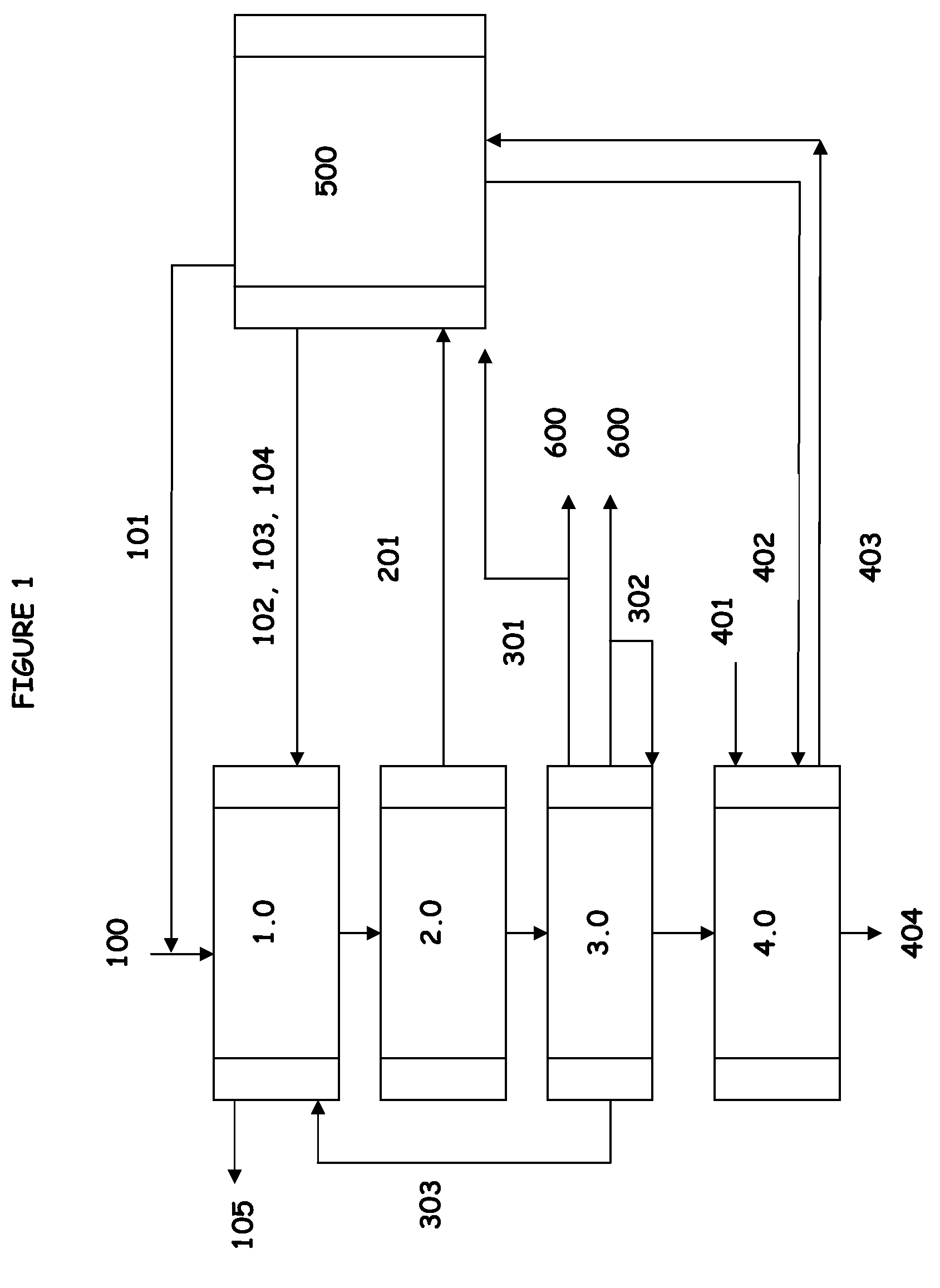
A process for producing levulinic acid and its esters from biomass is disclosed comprising: (i) feed preparation module characterized by subjecting biomass to a high-temperature refining treatment; (ii) hydrolysis reaction module that facilitates the hydrolysis of biomass to its respective sugars and their subsequent transformation to levulinic acid, formic acid, furfural, and char as well as facilitates the separation of lignin-based char by-product; (iii) product separation and recovery module utilizing a solvent extraction technique such as using furfural by-product as extracting solvent; and (iv) optionally, conversion of levulinic acid to levulinate ester. When desired, the disclosed process may be integrated into existing pulp mills.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
Biomass refining by selective chemical reactions
InactiveUS20110071306A1High substrate loadingShort reaction timeSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChemical reactionPropanoic acid
A method is disclosed for the acid hydrolysis of carbohydrates in or from biomass, using a solvent system including an aqueous ether, where the ether form a majority of the system, which affords high yields to the platform chemicals such as 2-furfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF). The later can also undergo a domino reaction to chemicals including levulinic acid, particularly with oxygenated anions and greater water content. A total dissolution and reaction of biomass occurs under a range of relatively mild conditions (combined Severity range ˜2.2-2.6). Lignin and lignin derived products can be easily separated by precipitation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for cogeneration of 5-hydroxymethyl-furfural, acetylpropionic acid and formic acid by high temperature catalytic dehydration of glucose in formic acid
The invention discloses a method for coproduction of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural, an acetylpropionic acid and a formic acid through high-temperature catalysis and dehydration of the formic acid of glucose. The method specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, establishment of a formic acid reaction system, namely the glucose is added into the formic acid solution, and the weight ratio of the glucose to the formic acid in the reaction system is 0.05-0.2 to 1; and the mixture is reacted for 2 to 6 hours in the presence of the catalyst at a temperature of between 120 and 220 DEG C which is higher than the boiling temperature of the formic acid, and the reaction system is single-phase reaction or biphase reaction; and secondly, separation of products after reaction by a fractionating tower device, namely graded separation of 5-HMF, LA and the formic acid. The method can convert the glucose into the products, namely the 5-HMF, the LA and the formic acid with high added values through effective acid catalysis and dehydration, and has high conversion of reactant during the reaction process and obvious economic benefit; and the 5-HMF, the LA and the formic acid can be directly taken as chemical products to be further converted, and are good raw materials for synthesizing other chemical products.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Process for permeation enhanced reactive extraction of levulinic acid
InactiveUS20060201879A1Minimize formationSpeed up the extraction processSemi-permeable membranesOrganic compound preparationLevulinic acidAlcohol
A process for permeation enhanced reactive extraction of levulinic acid from a liquid aqueous phase comprising levulinic acid, wherein the levulinic acid from the aqueous phase is brought into contact with a liquid alcohol phase at esterification conditions in the presence of a catalyst at a temperature in the range of from 50 to 250° C., the aqueous phase and the alcohol phase being separated from each other by a membrane, and an aqueous stream depleted in levulinic acid and an alcohol stream comprising ester of levulinic acid are formed.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
New Flux Composition and Process For Use Thereof
ActiveUS20100175790A1Minimizing and eliminating fluxEliminate residueWelding/cutting media/materialsThin material handlingLevulinic acidSoldering
The invention relates to a composition of matter comprising a soldering flux, wherein the flux consists essentially of a combination of a fluxing agent and a solvent, and wherein the fluxing agent comprises a keto acid such as levulinic acid or acetylbutyric acid. The flux may also comprises an ester acid, or comprises a mixture of the keto acid with the ester acid. The solvent comprises a mixture of a tacky solvent with a non-tacky solvent. The invention also relates to a process comprising soldering at least two surfaces together, each of which comprises a metal area to which solder can adhere by employing the following steps in any order: applying solder to at least one of the metal areas, aligning the metal areas so that they are superimposed over one another, heating at least one of the areas to a temperature that comprises at least the melting temperature of the solder. The last step comprises joining the superimposed areas to one another. The process employs the flux composition operatively associated with the solder, and in one embodiment the invention comprises a mixture of the flux composition with powdered solder. In another embodiment, the process comprises IMS, C4 and C4NP processes and the solder comprises a lead free solder. The invention also comprises a product produced by the foregoing process or processes.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Methods of making alkyl lactates and alkyl levulinates from saccharides
InactiveUS20150045576A1Organic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionLevulinic acidAlcohol
Unique methods have been developed to convert saccharides into value-added products such as alkyl lactates, lactic acid, alkyl levulinates, levulinic acid, and optionally alkyl formate esters and / or hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). Useful catalysts include Lewis acid catalysts and Brønsted acid catalysts including mineral acids, metal halides, immobilized heterogeneous catalysts functionalized with a Brønsted acid group or a Lewis acid group, or combinations thereof. The saccharides are contacted with the catalyst in the presence of various alcohols.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Process for the liquefaction of lignocellulosic material
InactiveUS20070100162A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationCelluloseHydrogen atom
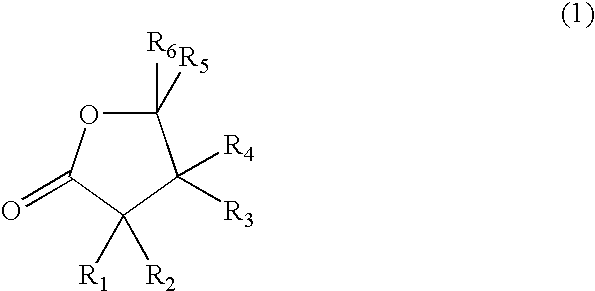
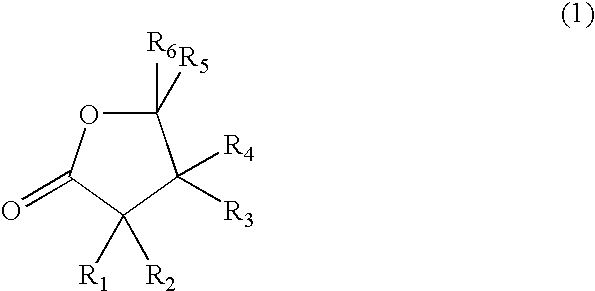
A process for the liquefaction of lignocellulosic or cellulosic material, wherein solid lignocellulosic or cellulosic material is heated at a temperature in the range of from 100 to 300° C. in the presence of an acid catalyst and a solvent, wherein the solvent-to-solid material weight ratio is at most 50, the acid catalyst is present in a concentration of at most 50% by weight of acid based on the weight of solvent and acid, and the solvent comprises a compound having a gamma lactone group of the general molecular formula (1) wherein R1 to R6 each represent, independently, a hydrogen atom or an organic group connected with a carbon atom to the lactone group or the solvent comprises furfural, levulinic acid or a compound obtainable from furfural or levulinic acid by hydrogenation, dehydration, aldolcondensation, dimerisation or oligomerisation, esterification with an alcohol, or a combination of two or more of these reactions.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method for purifying, reclaiming and condensing sugar in lignocellulose prehydrolysis liquid
ActiveCN101787398AEasy to operateEasy for industrialized continuous productionGlucose productionCelluloseFiltration membrane
The invention relates to a method for reclaiming and condensing sugar and removing toxicity inhibitors in lignocellulose prehydrolysis liquid by the applied nanofiltration technology. The method is realized by the following scheme: the pH value of the lignocellulose prehydrolysis liquid is firstly adjusted to 2.0-5.0, and the filtration pretreatment is carried out to remove suspended impurities; and then a filtration membrane is used for condensing sugar and remove inhibitors, the sugar of glucose, xylose and the like is trapped by the nanofiltration membrane, the weakly acidic inhibitors (formic acid, acetic acid, levulinic acid and the like) and the furfural inhibitors (furfural, 5-hydroxymethyl furfural and the like) continually penetrate through the nanofiltration membrane, the various inhibitors in the prehydrolysis liquid are removed, and the sugar in the prehydrolysis liquid is condensed to realize the purification, reclaiming and condensation of the sugar in the prehydrolysis liquid, so that the fermentability of the sugar is improved. The invention has the advantages of simple and safe operation, high efficiency and energy saving, and facilitates the continuous production; the nanofiltration has effects of purification, reclaiming and condensation; and the method can realize the industrial production.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Viricidal and microbicidal compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20120121679A1Reduced viabilityEfficient reductionAntibacterial agentsBiocideLevulinic acidActive agent
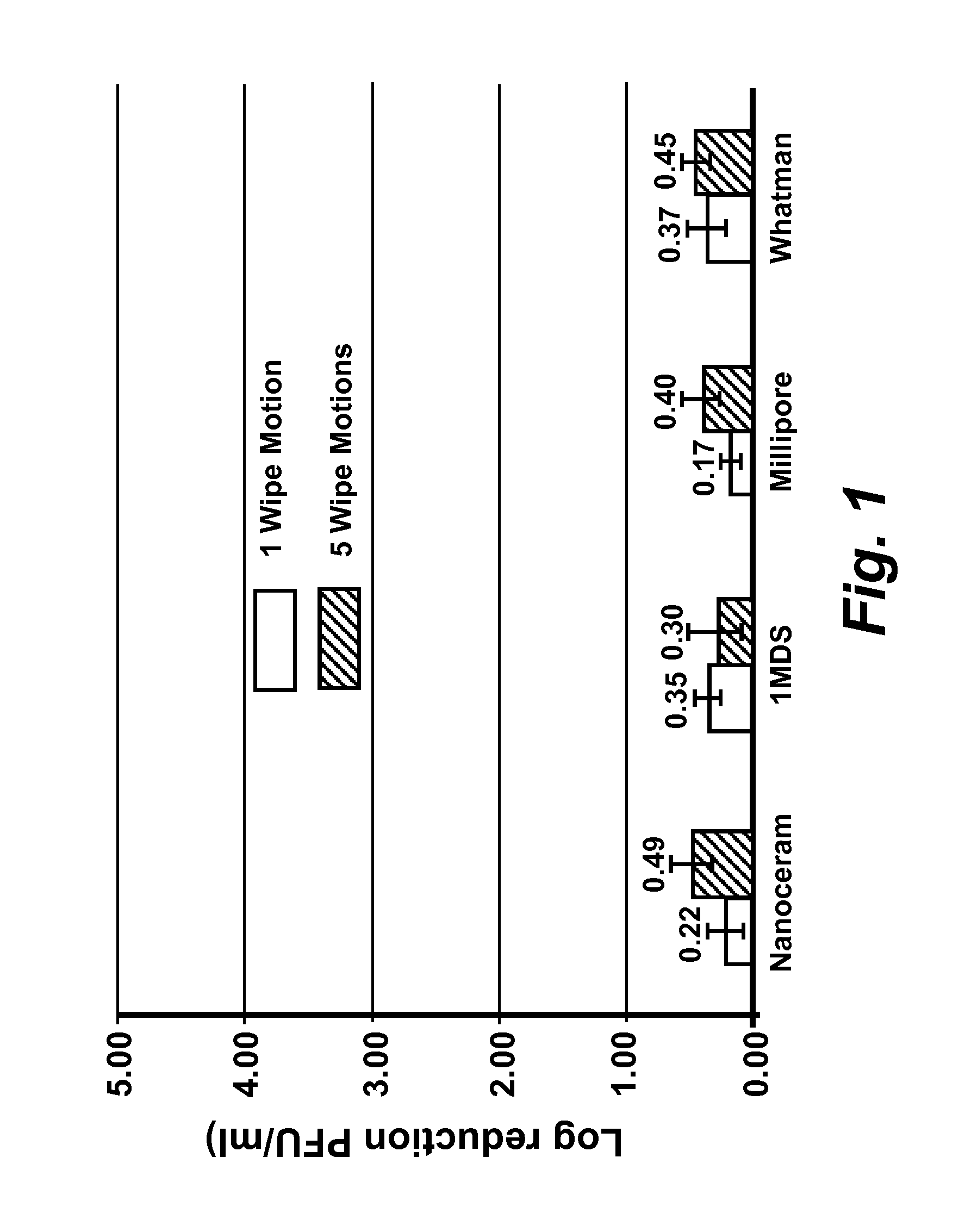
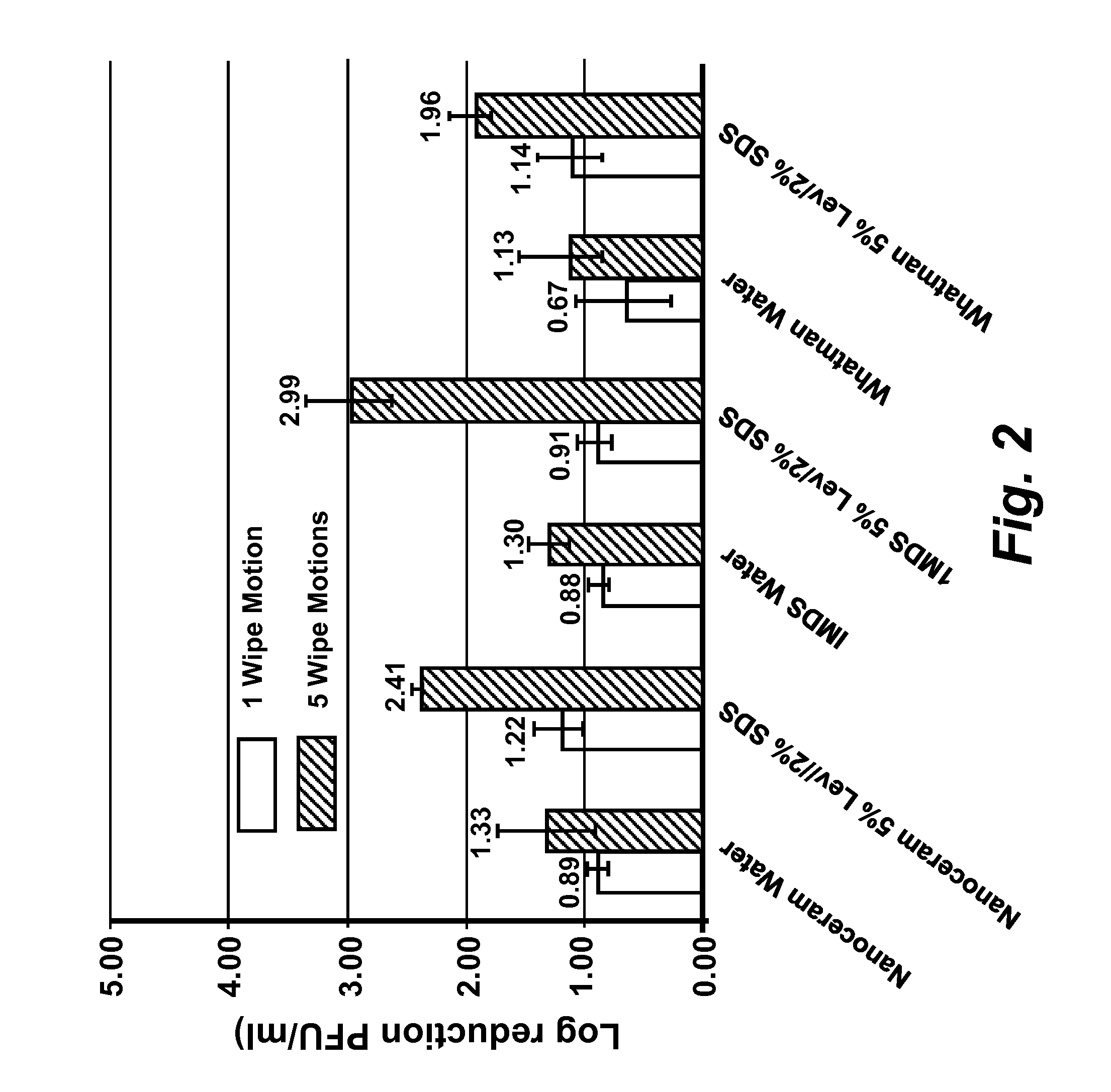
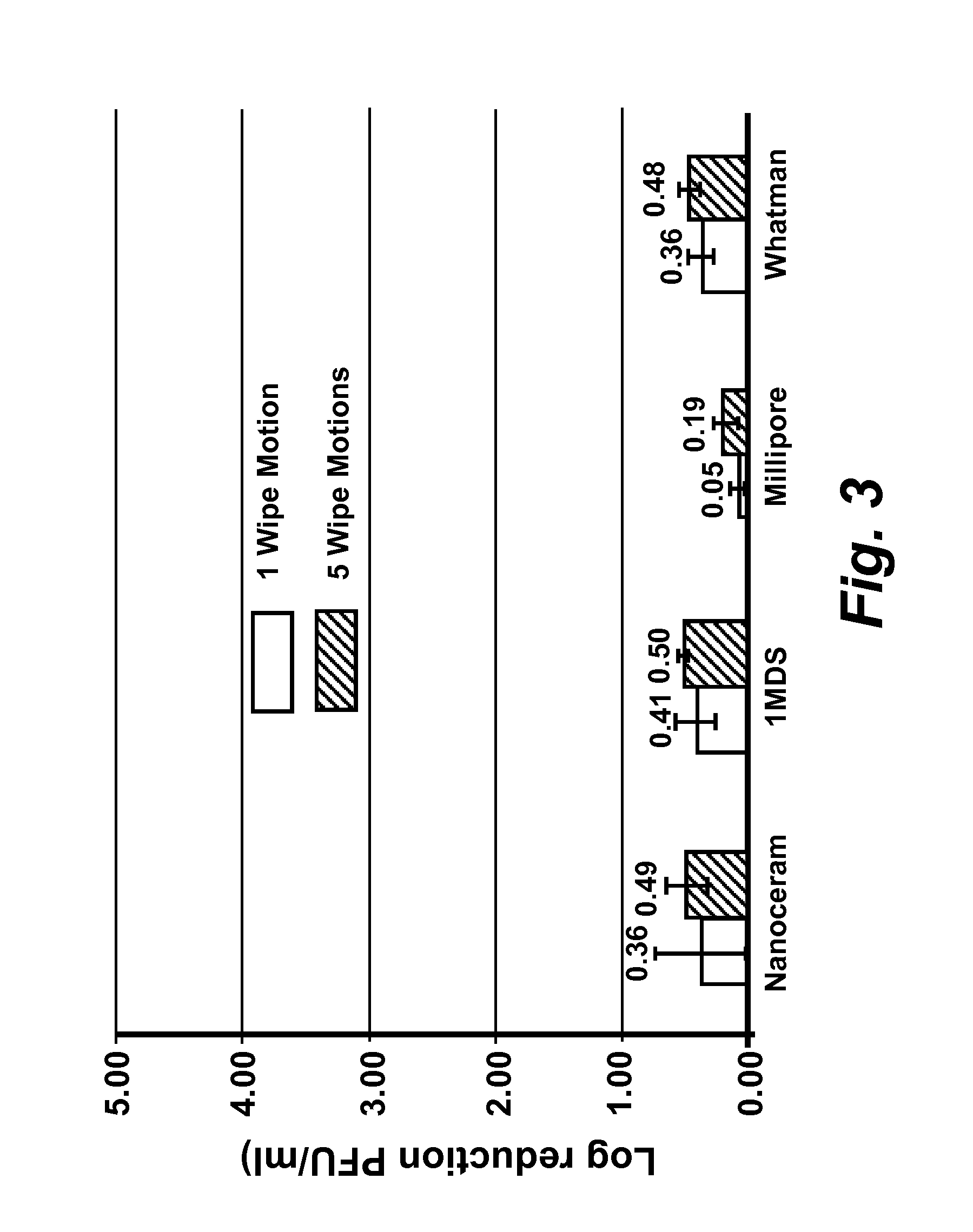
The present disclosure encompasses compositions comprising a surfactant, and an acid such as, but not limited to, levulinic acid, that together have a synergistic effect in reducing the viability of a virus population compared to the efficacy of the individual compounds. This synergy allows the formulation of compositions where the active agents (including an acid and a surfactant) are present at concentrations effective to inactivate viruses on surfaces, including human skin. The viricidal compositions disclosed herein are efficacious without damaging the surface to which they may be applied, or even altering the organoleptic properties of a treated food substance. The viricidal compositions and wipes containing such compositions are suitable for sanitizing any surface suspected of having a viral load thereon, or where it is desirable to ensure that a viral load is as low as possible.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
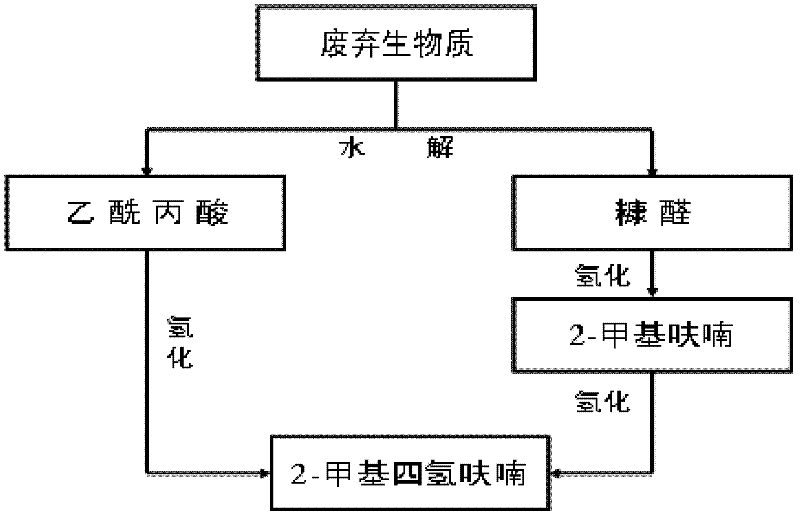
Method for preparing 2-methyltetrahydrofuran from waste biomass
ActiveCN102558106AReduce pollutionReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryLevulinic acidPropanoic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing 2-methyltetrahydrofuran from waste biomass, which comprises the following steps: carrying out acid hydrolysis reaction on the waste biomass to obtain furfural and levulinic acid; sequentially carrying out first hydrogenation reaction and second hydrogenation reaction on the furfural to obtain the 2-methyltetrahydrofuran; and carrying out hydrogenation reaction on the levulinic acid to obtain the 2-methyltetrahydrofuran. The method provided by the invention more sufficiently utilizes the waste biomass, and adopts non-noble metal catalysts, thereby lowering the production cost.
Owner:北京雷恩新材料科技有限公司
Aqueous Polymer Compositions Obtained From Epoxidized Natural Oils
ActiveUS20100330375A1Quickly self-crosslinkImproved color stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyurethane dispersionCarbamate
Aqueous polyurethane dispersions are made from urethane prepolymers comprising one or more polyhydroxy compounds from ketone functional molecules derived from an epoxidized natural oil. Addition of a hydrazine functional moiety to the prepolymer dispersion can further provide a crosslinking mechanism resulting in the formation of azomethine linkages in the resulting polyurethane during drying. When the ketone functional molecule is derived from levulinic acid and epoxidized vegetable oil, the resulting urethane dispersion can also be converted into a hybrid polyurethane-vinyl dispersion by adding and polymerizing one or more vinyl monomers in the polyurethane prepolymer or polyurethane dispersion.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
New flux composition and process for use thereof
InactiveUS20080124568A1Minimize and substantially eliminate flux residueProcess can be minimizedWelding/cutting media/materialsThin material handlingLevulinic acidSoldering
The invention relates to a composition of matter comprising a soldering flux, wherein the flux consists essentially of a combination of a fluxing agent and a solvent, and wherein the fluxing agent comprises a keto acid such as levulinic acid or acetylbutyric acid. The flux may also comprises an ester acid, or comprises a mixture of the keto acid with the ester acid. The solvent comprises a mixture of a tacky solvent with a non-tacky solvent. The invention also relates to a process comprising soldering at least two surfaces together, each of which comprises a metal area to which solder can adhere by employing the following steps in any order: applying solder to at least one of the metal areas, aligning the metal areas so that they are superimposed over one another, heating at least one of the areas to a temperature that comprises at least the melting temperature of the solder. The last step comprises joining the superimposed areas to one another. The process employs the flux composition operatively associated with the solder, and in one embodiment the invention comprises a mixture of the flux composition with powdered solder. In another embodiment, the process comprises IMS, C4 and C4NP processes and the solder comprises a lead free solder. The invention also comprises a product produced by the foregoing process or processes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
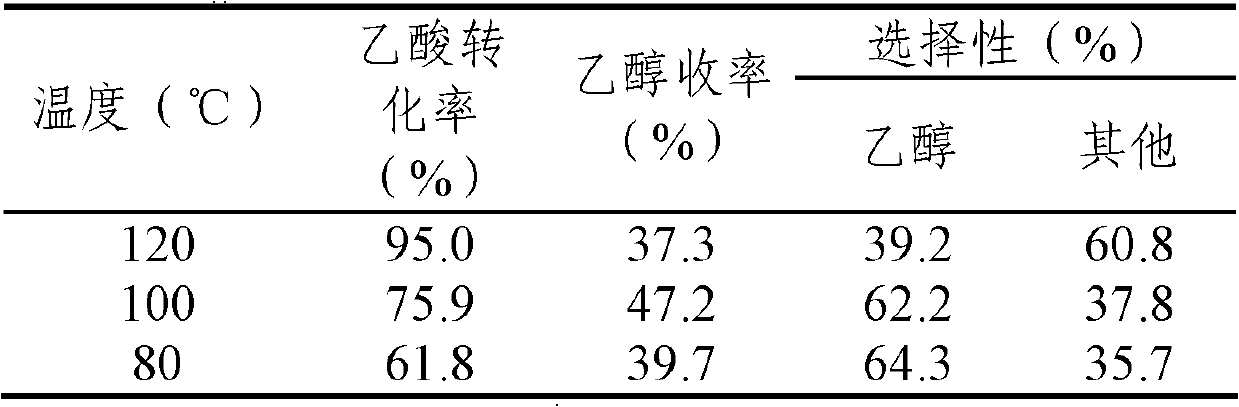
Method for preparing monohydric alcohol or dihydric alcohol through organic acid hydrogenation
ActiveCN103288596AOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparation3-Hydroxypropionic acidPropanoic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing monohydric alcohol or dihydric alcohol through organic acid hydrogenation. According to the method, any one of acetic acid, propionic acid, valeric acid, stearic acid, oleic acid, palmitic acid, levulinic acid, lactic acid, succinic acid, 3-hydracrylic acid and other organic acids is taken as a reactant, and an A-B / X supported catalyst is adopted, wherein the component A is any one or more than two from Ir, Pt, Pd, Rh and Ru, the assistant B is any one or more than two from Mo, Re and W, the carrier X is any one in SiO2, activated carbon, titanium oxide, zirconium oxide, SiO2-Al2O3 (the mass content of Al2O3 accounts for 17 percent) and molecular sieves, the mass load amount of A in the catalyst is 0.5-10 percent, the molar ratio of the assistant B to A is 0.01-1.0, the reaction pressure is 2-20 MPa, and the reaction temperature is 40-180 DEG C. The catalyst has the characteristics of mild reaction conditions, high reaction activity and good selectivity, and a novel effective way for preparing monohydric alcohol or dihydric alcohol from biomass is provided.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for the production of furfural and levulinic acid from lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20140018555A1Enough timeOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationCelluloseOrganic solvent
A process for producing furfural and levulinic acid from lignocellulose-comprising biomass is disclosed. The biomass is slurried using water and optionally an acid, subjected to hydrolysis, and then subjected to a solid / liquid separation to yield at least an aqueous fraction comprising C5 and C6 sugars and a solid fraction comprising cellulose and lignin. Furfural is obtained by adding an organic solvent to the aqueous fraction, heating at 120-220° C. for a sufficient time to form furfural, cooling, and separating an organic phase comprising at least part of the furfural from an aqueous phase. Levulinic acid is obtained by suspending the solid fraction in water and optionally an acid, heating the suspension to 140-220° C., and separating an aqueous fraction comprising the levulinic acid from a solid fraction.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
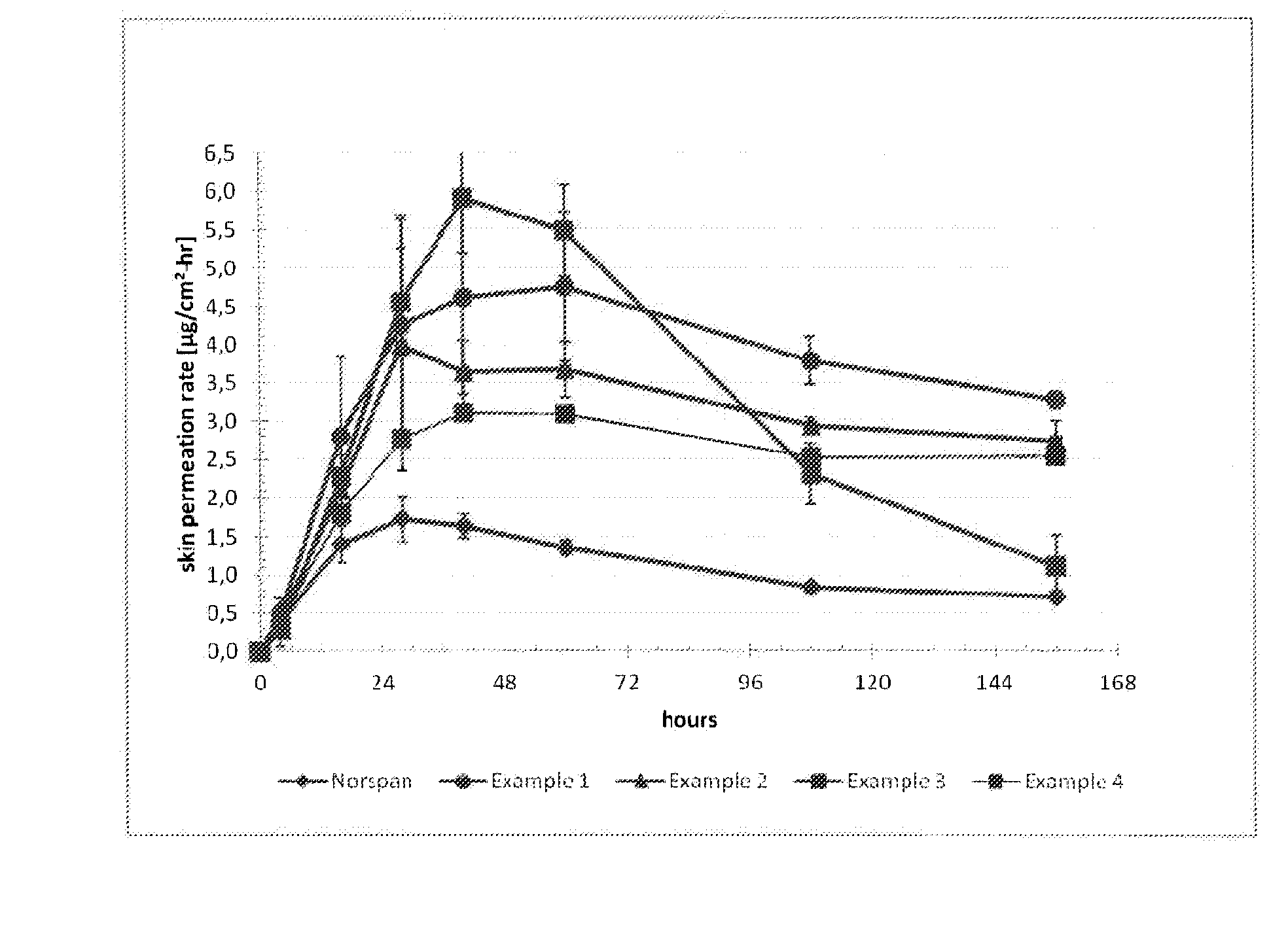
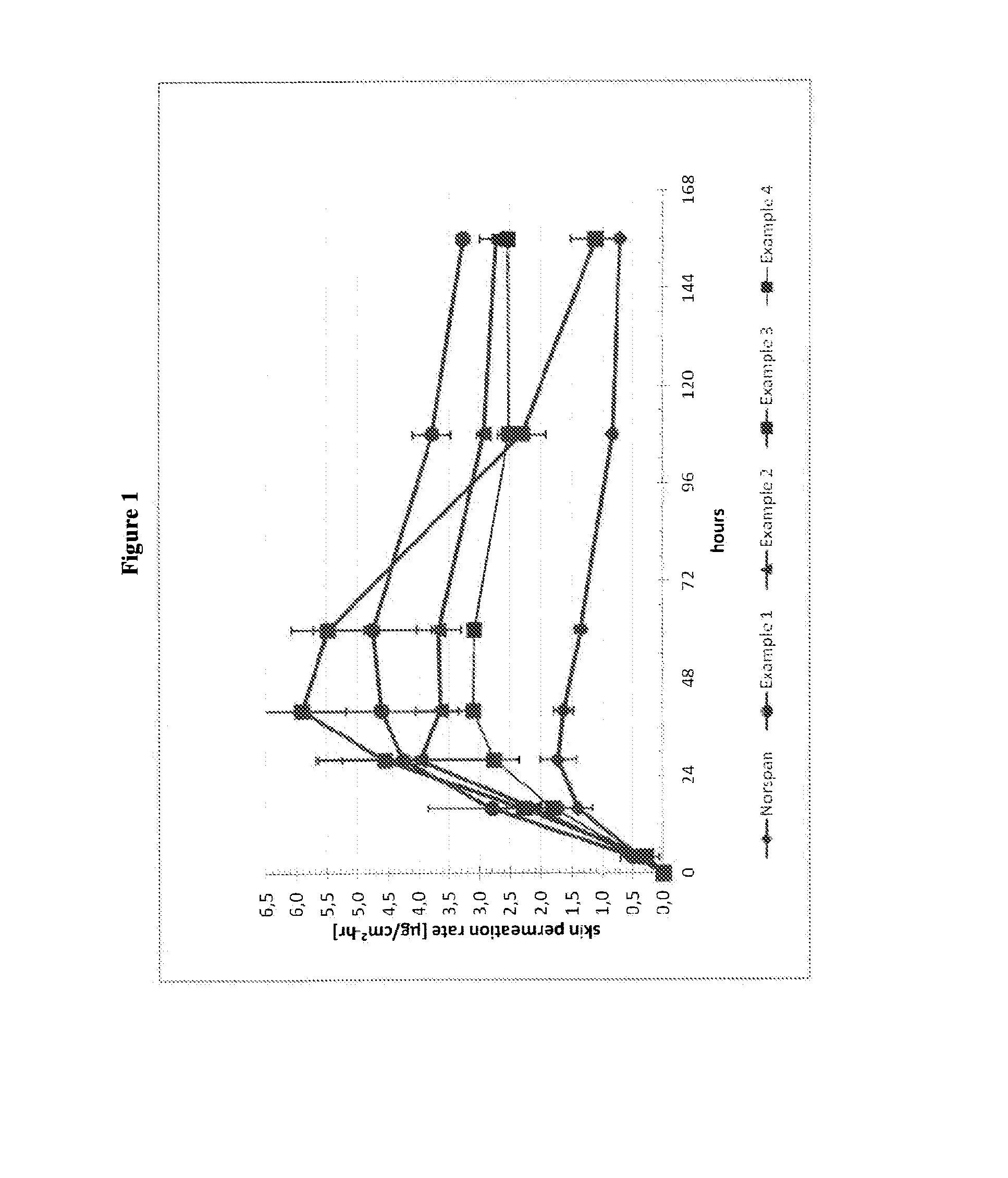
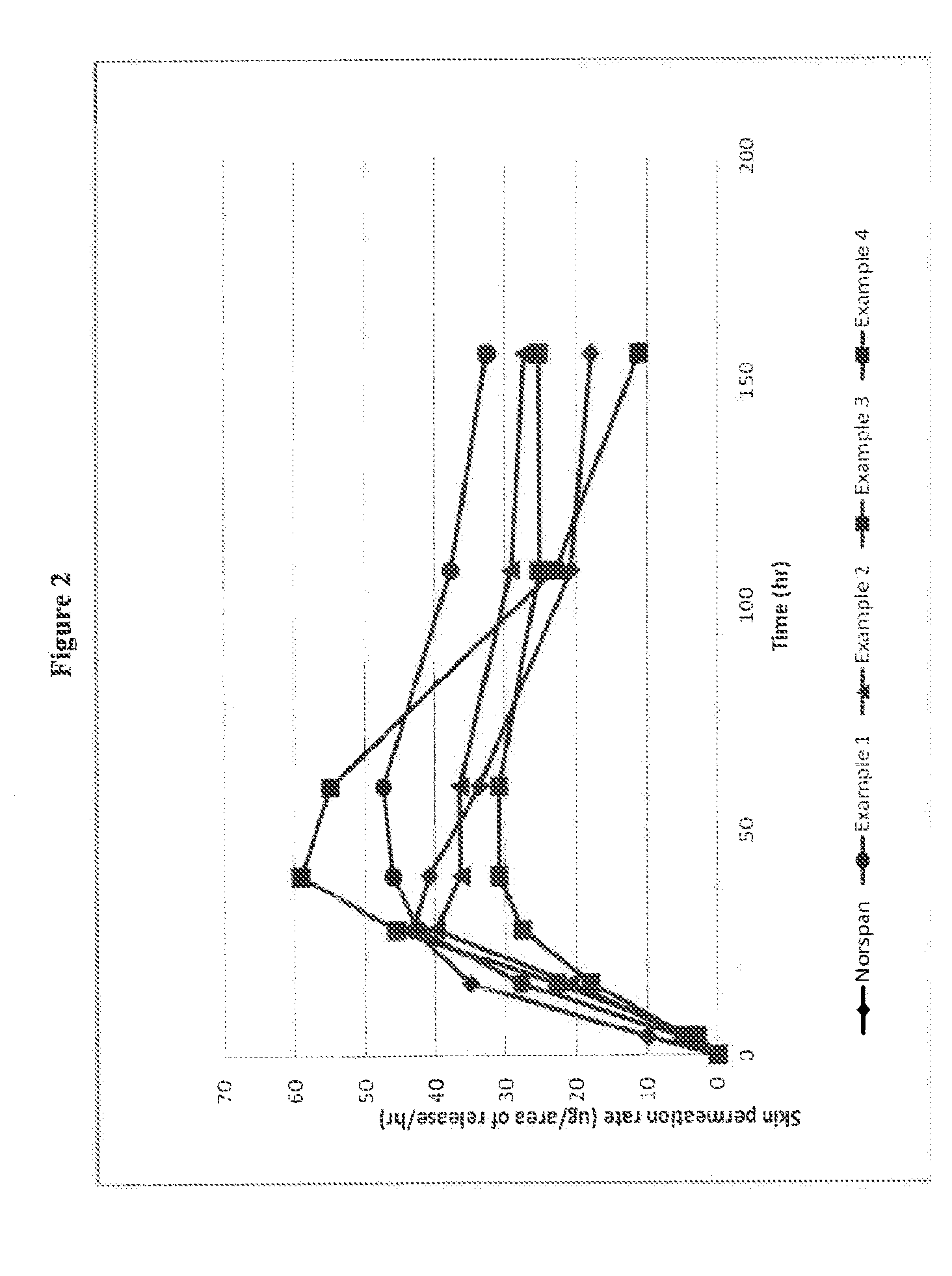
Transdermal delivery system comprising buprenorphine
InactiveUS20140363487A1Small area of releaseImprove adhesionBiocideNervous disorderLevulinic acidSkin contact
The invention relates to transdermal therapeutic system for the transdermal administration of buprenorphine, comprising a buprenorphine-containing self-adhesive layer structure comprising A) a buprenoφhine-impermeable backing layer, and B) a buprenorphine-containing pressure-sensitive adhesive layer on said buprenorphine-impermeable backing layer, the adhesive layer comprising a) at least one polymer-based pressure-sensitive adhesive, b) an analgesically effective amount of buprenorphine base or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and c) a carboxylic acid selected from the group consisting of oleic acid, linoleic acid and linolenic acid, levulinic acid and mixtures thereof, in an amount sufficient so that said analgesically effective amount of buprenorphine is solubilized therein to form a mixture, and the carboxylic acid buprenorphine mixture forms dispersed deposits in the said pressure-sensitive adhesive, wherein said buprenorphine-containing pressure-sensitive adhesive layer is the skin contact layer.
Owner:LTS LOHMANN THERAPIE-SYST AG
Levulinic acid ester derivatives as reactive plasticizers and coalescent solvents
The present invention is directed to ester derivatives of levulinic acid that are useful as plasticizers and / or coalescent solvents in polymer compositions, compositions comprising the ester derivatives, methods of making the derivatives and the compositions, and the use of the derivatives as additives in polymer compositions.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Methods for conversion of carbohydrates in ionic liquids to value-added chemicals
Methods are described for converting carbohydrates including, e.g., monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides in ionic liquids to value-added chemicals including furans, useful as chemical intermediates and / or feedstocks. Fructose is converted to 5-hydroxylmethylfurfural (HMF) in the presence of metal halide and acid catalysts. Glucose is effectively converted to HMF in the presence of chromium chloride catalysts. Yields of up to about 70% are achieved with low levels of impurities such as levulinic acid.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Cogeneration method for sugar and acetylpropionic acid by utilizing lignocellulose-like biomass
The present invention is process of co-producing sugar and levulic acid solution with lignocellulose material, and belongs to the field of biomass resource utilizing technology. Agricultural and forestry waste as reaction material is dilute acid hydrolyzed in a two-step process at certain temperature and in the presence of 0.01-0.2 mol concentration hydrochloric acid solution, hydroiodic acid solution, sulfuric acid solution or other inorganic acid solution as catalyst to produce both sugar solution and levulic acid solution in the total conversion rate over 20 wt%. The present invention provides one new way for utilizing lignocellulose comprehensively.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
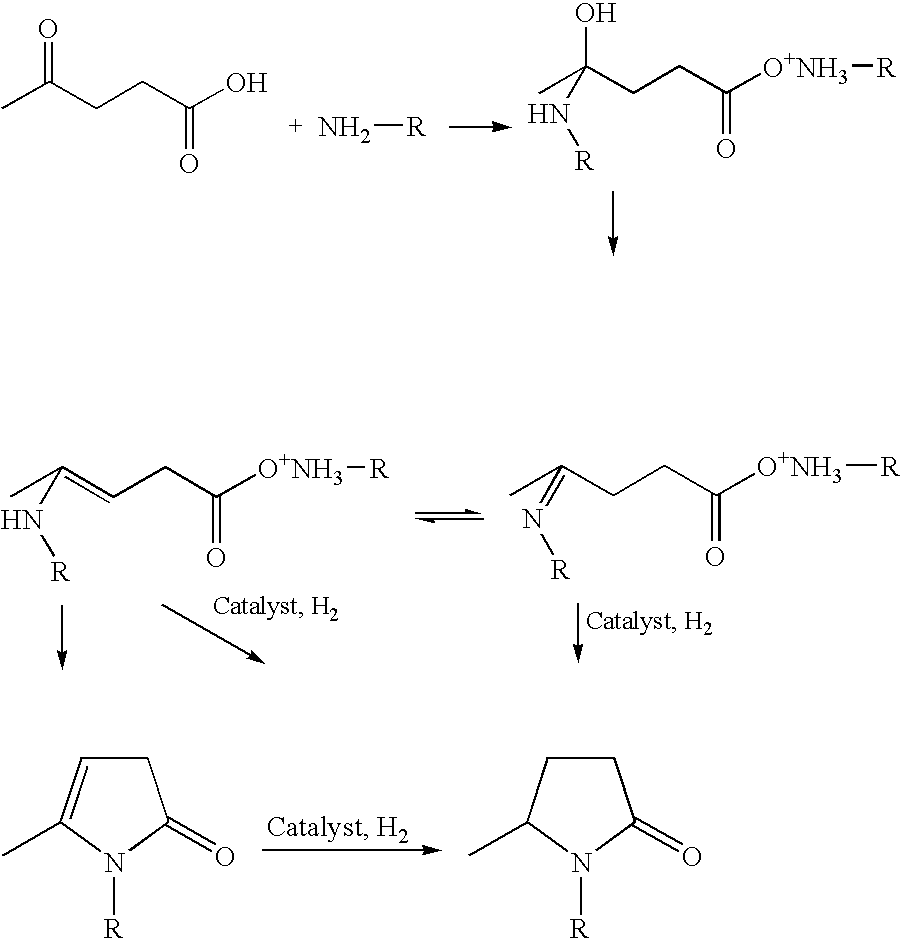
Process for making 5-methyl-N-alkyl-2-pyrrolidone from alkyl amine(s) and levulinic acid
This invention relates to a process for producing a reaction product comprising 5-methyl-N-alkyl-2-pyrrolidone by (a) reacting levulinic acid with alkyl amine(s) and (b) hydrogenating the products of step (a) in the presence of a metal catalyst, which is optionally supported.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for improving fruit color
A method for promoting the colouring on fruit (apple, pear, peach, grape, etc) features that the 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA), or levulinic acid (LA)1 or glutamic acid (Glu) is applied to the fruit.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
5-amino levulinic acid (ALA) high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
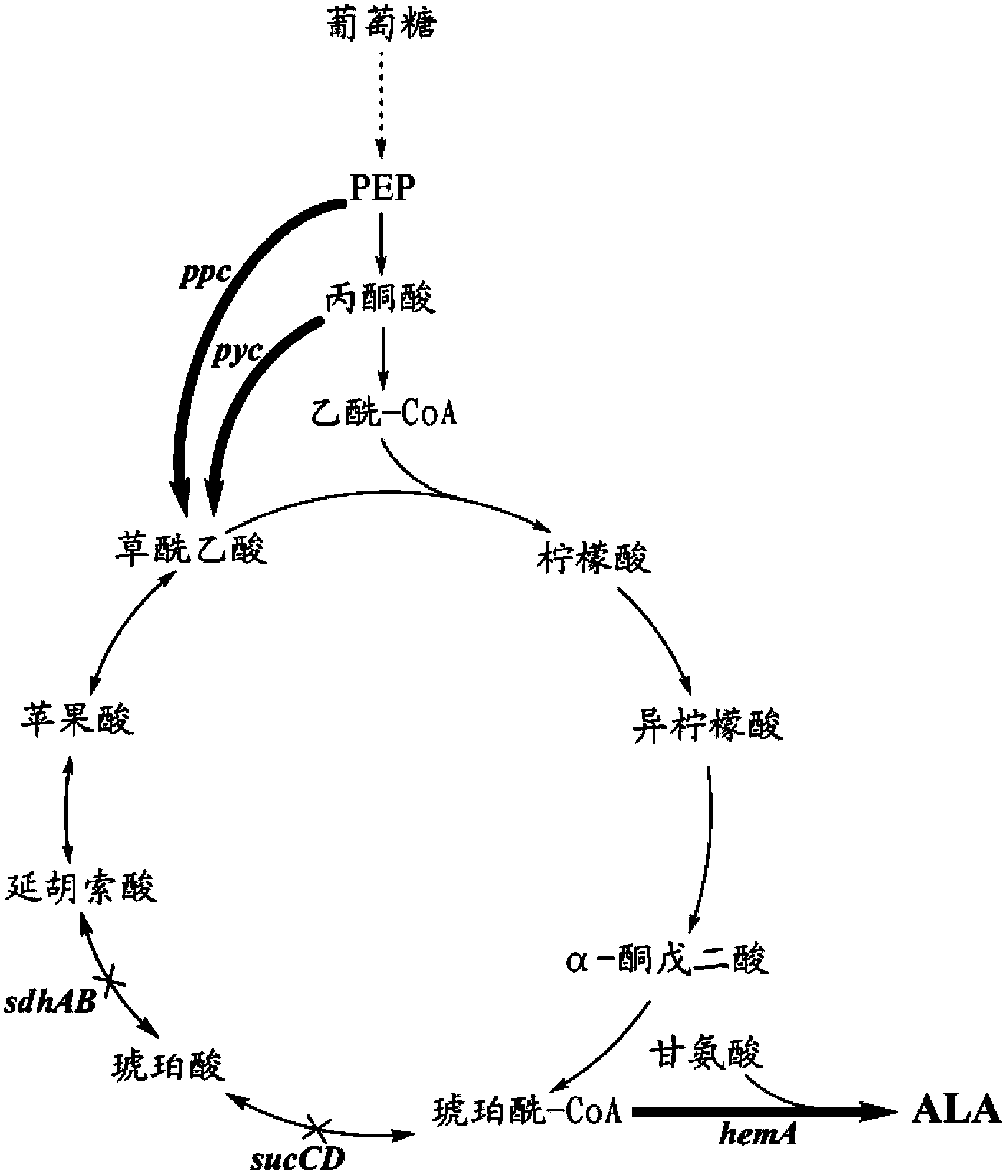
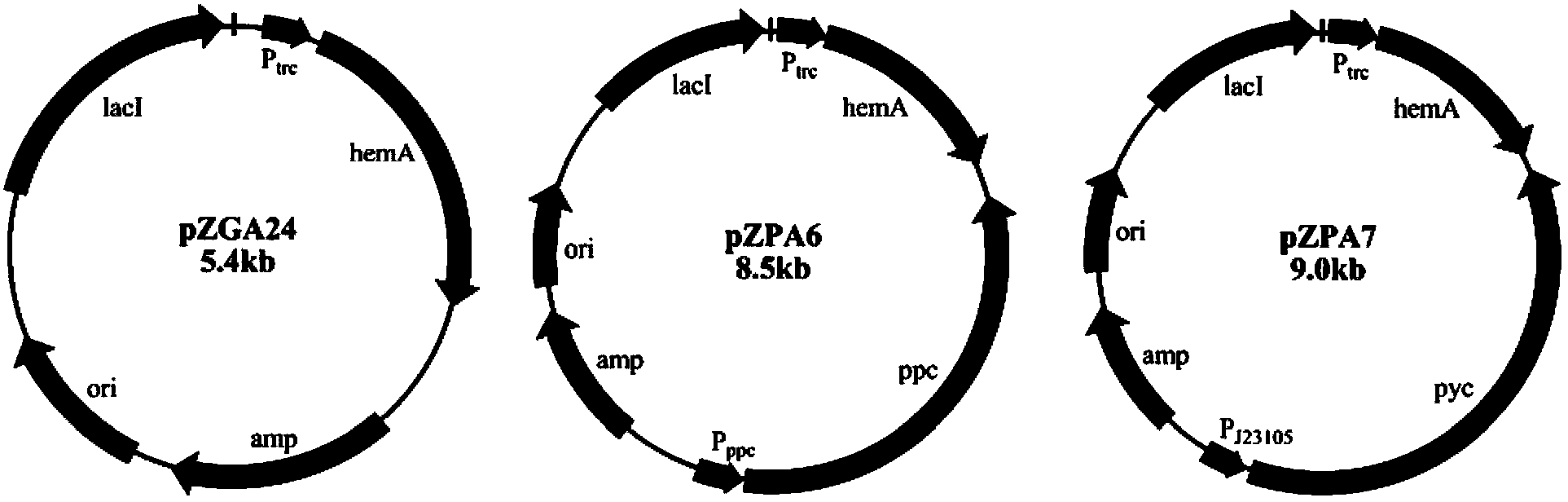
A method for constructing an ALA production bacterial strain, the method enhances the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate and in the 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) production bacterial strain, or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate, such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or reducing the activity of related enzymes in the downstream metabolic pathway of succinyl coenzyme A in the bacterial strain, such as succinyl coenzyme A synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase, and / or reducing the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylated kinase and / or malic enzyme. An ALA high-yield bacterial strain constructed by utilizing the method, and method for utilizing the bacterial strain to prepare ALA.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Controlled Drug Delivery Using a Zein Layer Modified with Levulinic Acid
The disclosure relates to medical devices coated with zein admixed with levulinic acid. The medical device may further include a therapeutic agent in contact with zein admixed with levulinic acid. Zein admixed with levulinic acid allows the therapeutic agent to be retained on the device during delivery and also controls the elution rate of the therapeutic agent following implantation. The disclosure further relates to methods of delivering a therapeutic agent on said medical devices as well as their use especially in the form of stents for prevention of restenosis.
Owner:MED INST INC +1
Additives derived from biomass extracted by biodiesel fuel oil
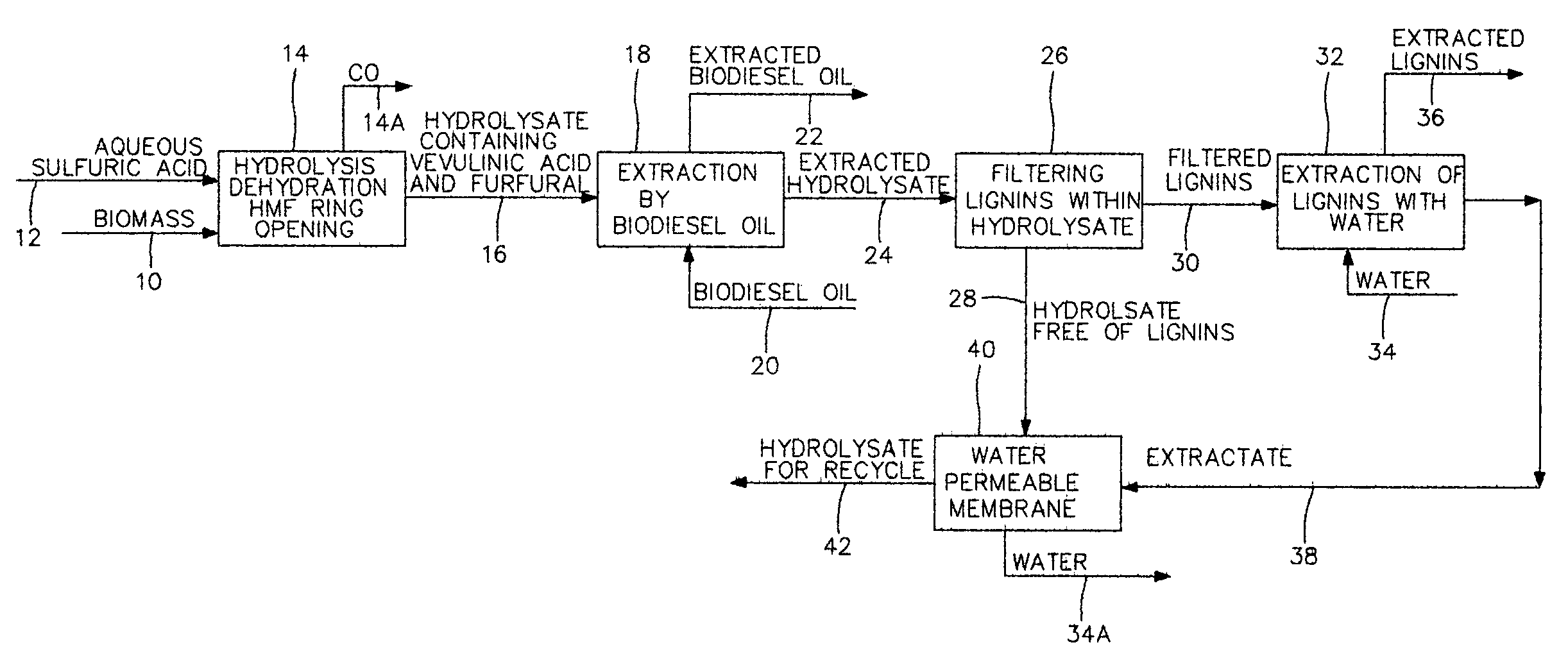
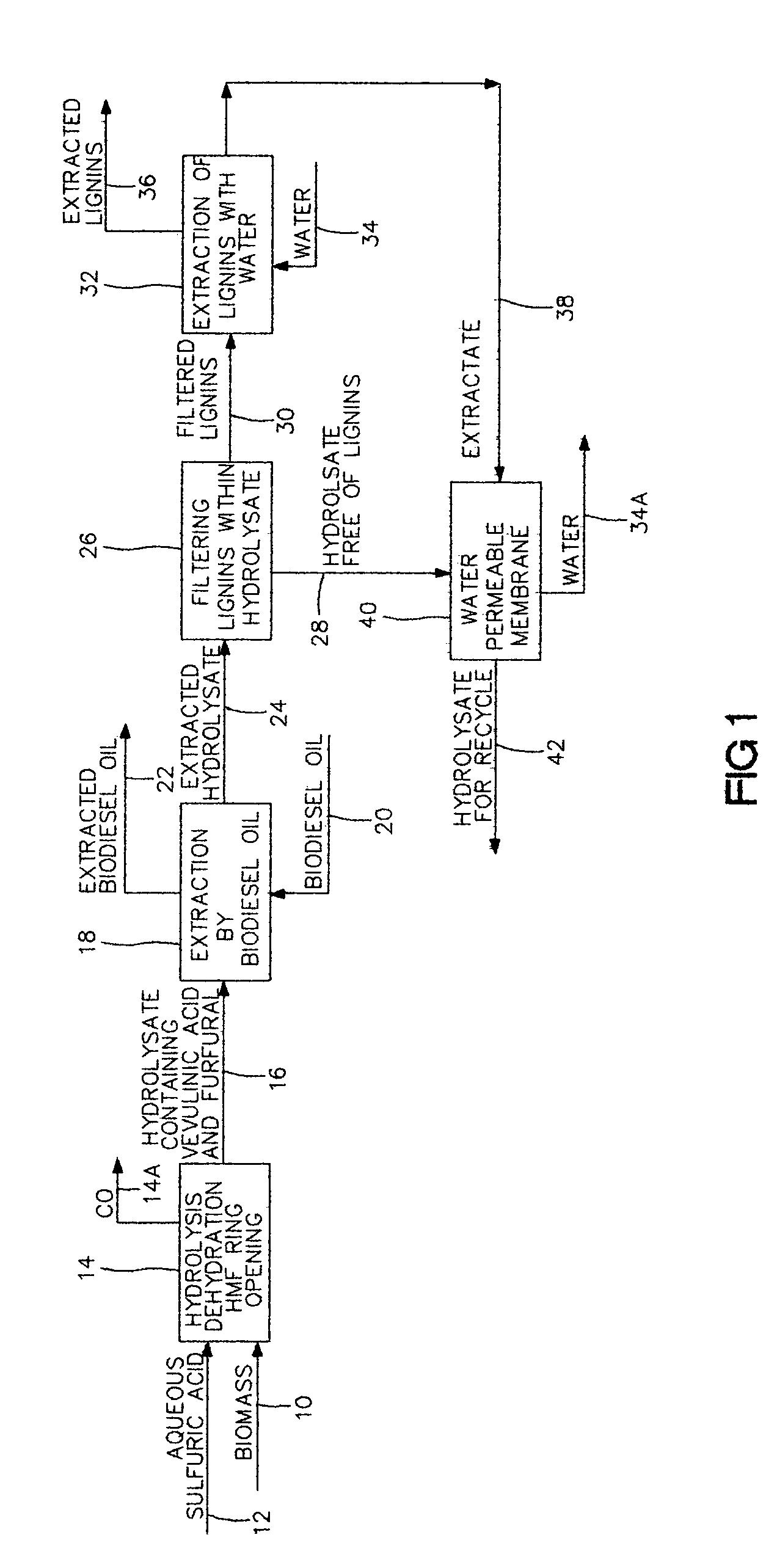
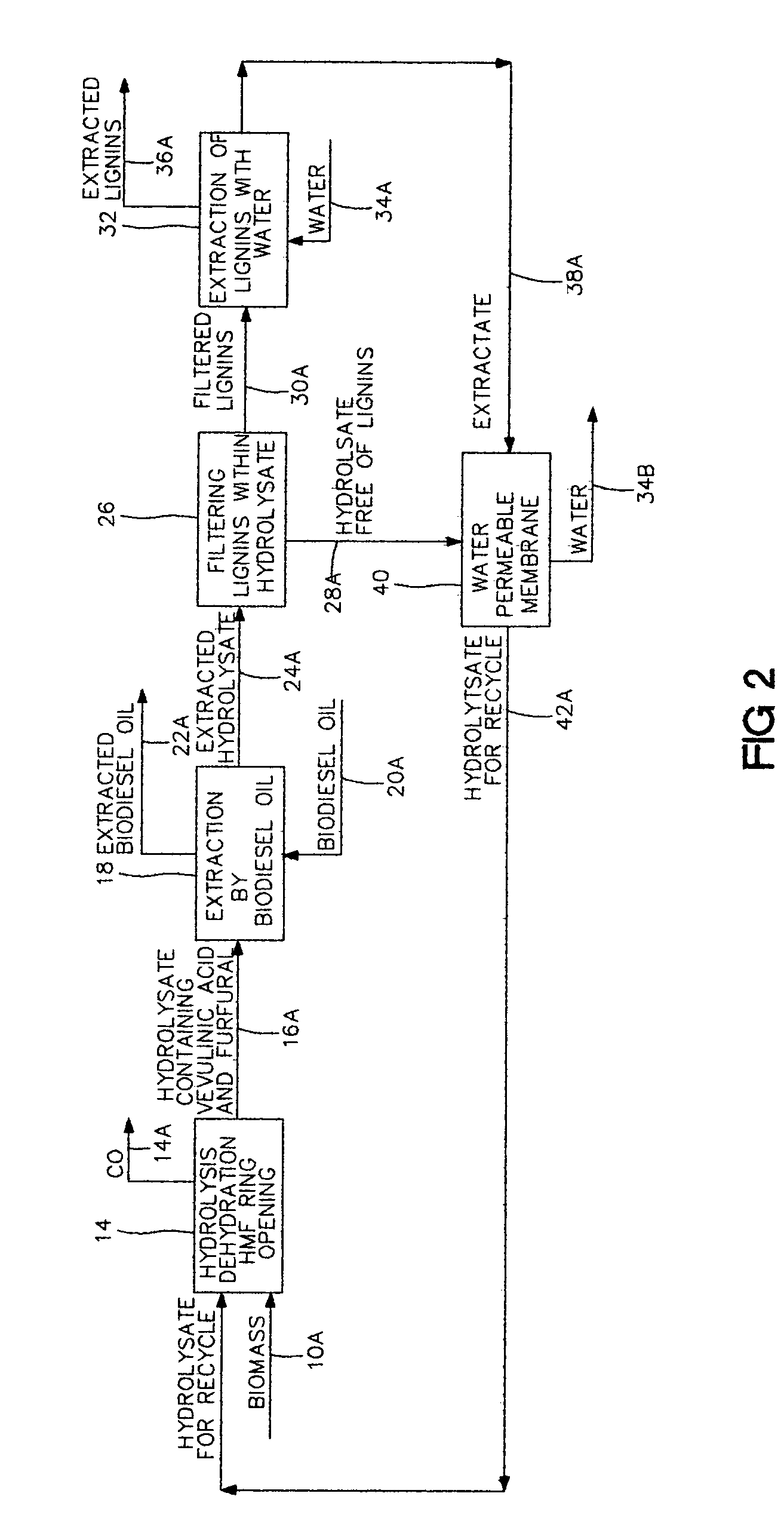
Aqueous sulfuric acid is used for hydrolysis of a biomass, constituting a hydrolysate, to produce organic compounds. Organic compounds such as furfural and hyroxymethylfurfural are formed within the hydrolysate. Heterocyclic ring opening within hyroxymethylfurfural forms levulinic acid within the hydrolysate. Furfural and levulinic acid are extracted by a biodiesel fuel oil to increase content of biodiesel fuel oil. Biodiesel fuel oil generally consists of vegetable oils, insoluble in aqueous sulfuric acid, and affords access to, extraction of furfural and levulinic acid. Extracted hydrolysate is recycled for further hydrolysis of biomass.
Owner:LIGHTNER GENE E
Method for separating acetylpropionic acid from mono saccharide hydrolyzate
InactiveCN1775731AHigh yieldSimple processCarboxylic compound separation/purificationLevulinic acidPropanoic acid
The invention relates to the resin absorbing separation and purification technique, relating to a method for separating acetyl propionic acid from monosaccharide hydrolyzate, passing the acetyl propionic acid hydrolyzate containing residual sugar and other impurities such as neutral matter and formic acid through weakly basic anion exchange resin column, firstly washing off unabsorbable impurities such as sugar with the deionized water, then eluting acetyl propionic acid and formic acid from the resin with acid water solution, and the acetyl propionic acid eluting solution is concentrated at normal pressure and vacuum-distilled to be able to obtain high-content acetyl propionic acid whose purity is up to 98.5% and whose total yield can be above 85%. The method has the advantages of simple processing flow, low production cost and being easy to industrialize.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation of levulinate from glucose by molecular screen catalytic hydrolysis
InactiveCN1680257AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationMolecular sieveLevulinic acid
Production of acetylpropionic acid by molecular sieve catalytic hydrolyzing glucose is carried out by: 1) calcining molecular sieve catalyst at 500-900deg.C; 2) adding calcined molecular sieve catalyst and glucose solution with concentration 5-100g / L into closed high-pressure reactor with weight ratio of glucose and catalyst 6-0.5; 3) inducing nitrogen into reactor, discharging air from reactor, raising temperature to 120-220deg.C, and reacting for 2-20hrs at 0.1-2Mpa. Its advantages include moderate reaction, high catalyst activity, no corrosion, and easy separation of catalyst, material and product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods for conversion of carbohydrates in ionic liquids to value-added chemicals
Methods are described for converting carbohydrates including, e.g., monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides in ionic liquids to value-added chemicals including furans, useful as chemical intermediates and / or feedstocks. Fructose is converted to 5-hydroxylmethylfurfural (HMF) in the presence of metal halide and acid catalysts. Glucose is effectively converted to HMF in the presence of chromium chloride catalysts. Yields of up to about 70% are achieved with low levels of impurities such as levulinic acid.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Method for the preparation of alkyl levulinates
InactiveCN102405205AAvoid formingLow costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPropionateLevulinic acid
Provided is a process for the conversion of furfuryl alcohol into levulinate esters in a single step reaction comprising addition of the product levulinate ester to the reaction mixture of an alkanol and furfuryl alcohol in the presence of a strong protic acid catalyst, wherein high yield of the levulinate ester is accompanied by low amounts of tarry residue that do not precipitate or solidify in the reaction mixture.
Owner:SEGETIS
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com