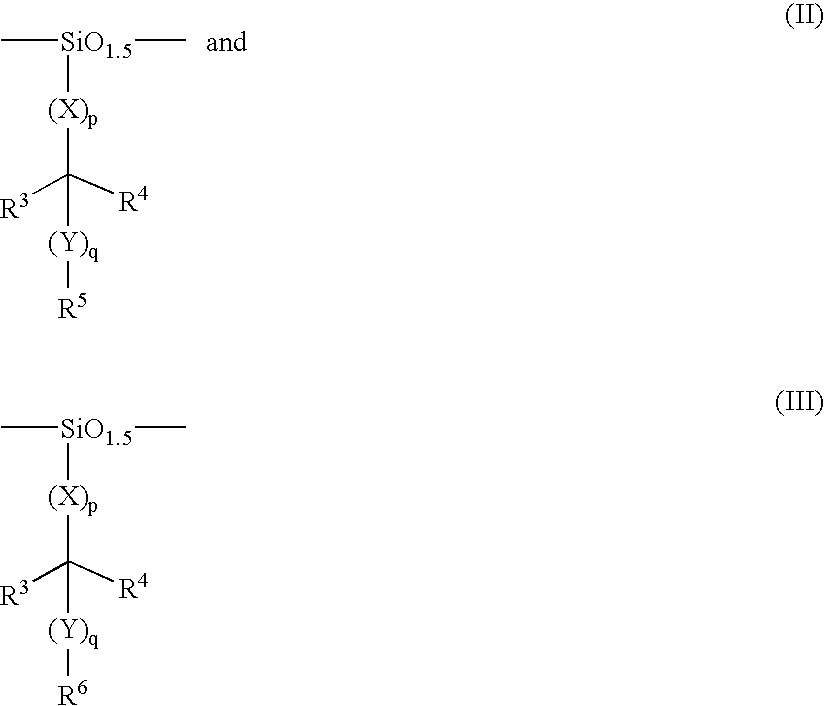
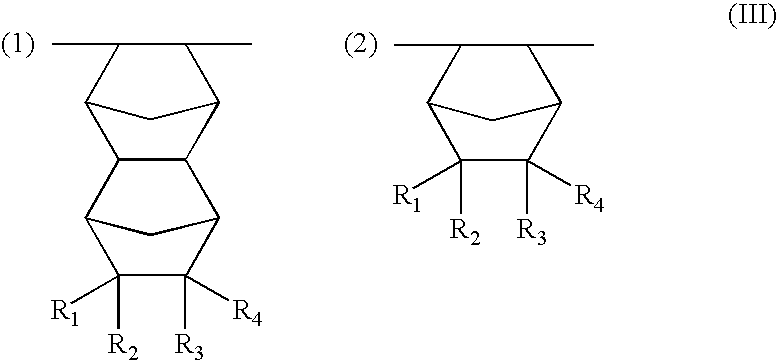
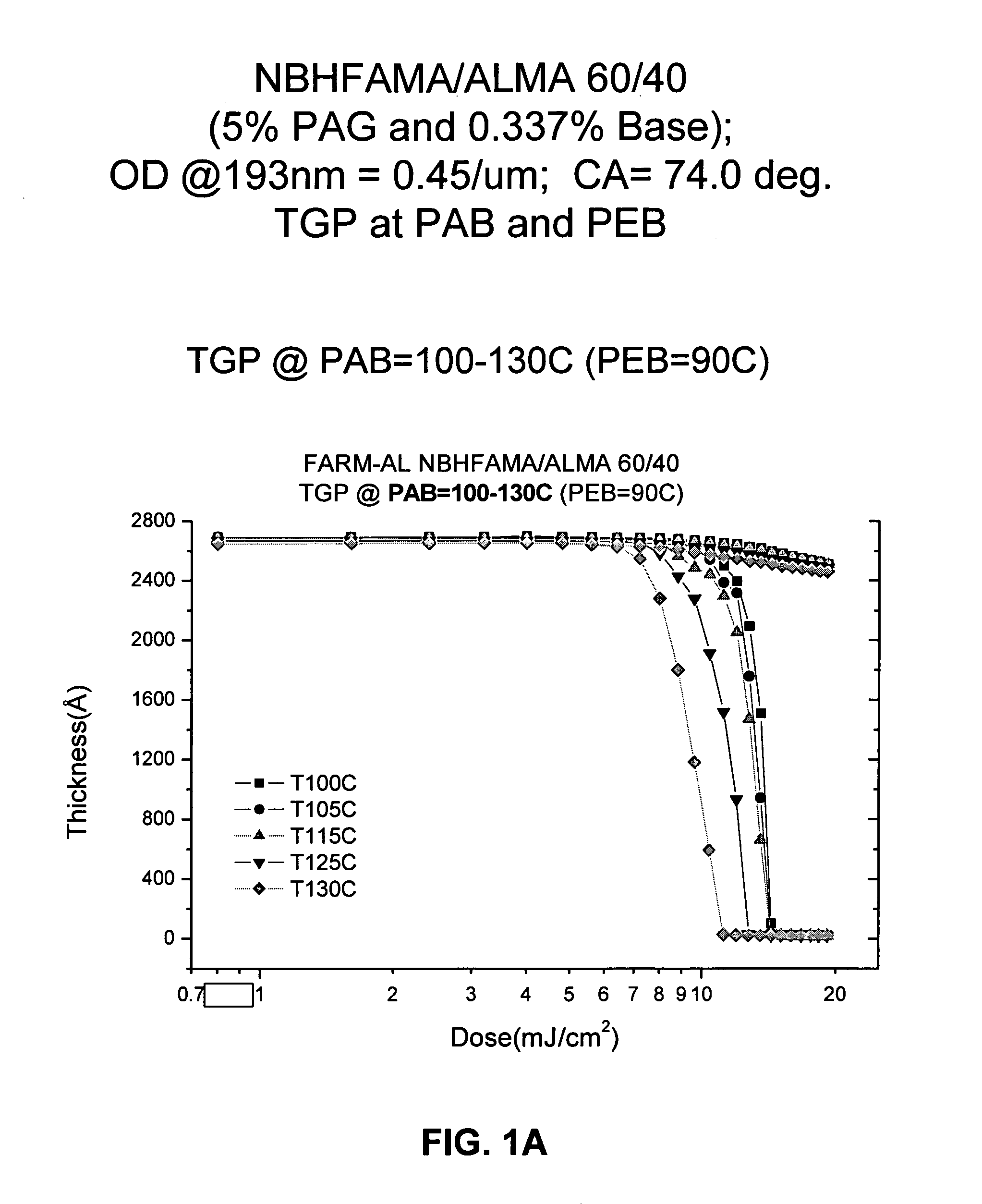
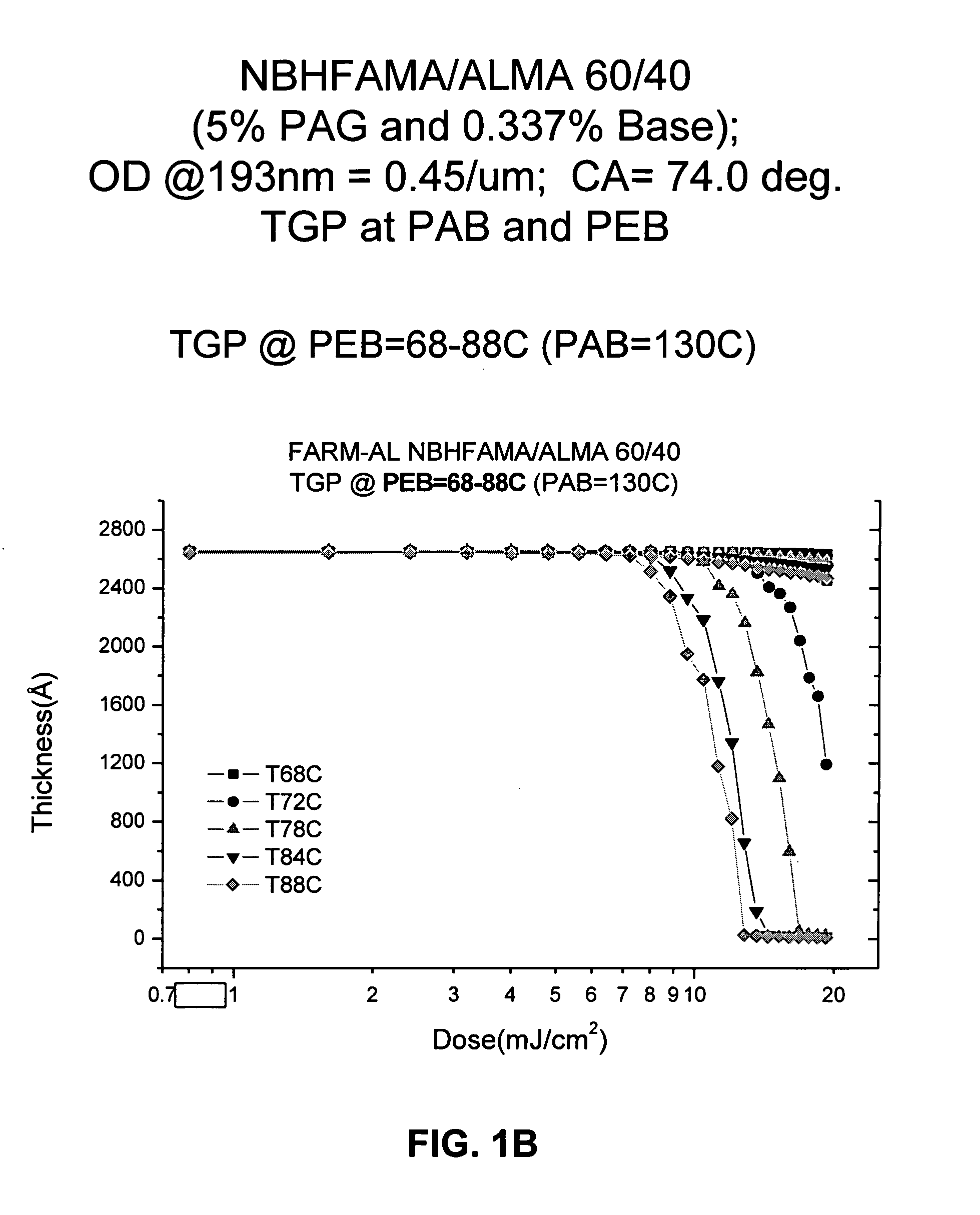
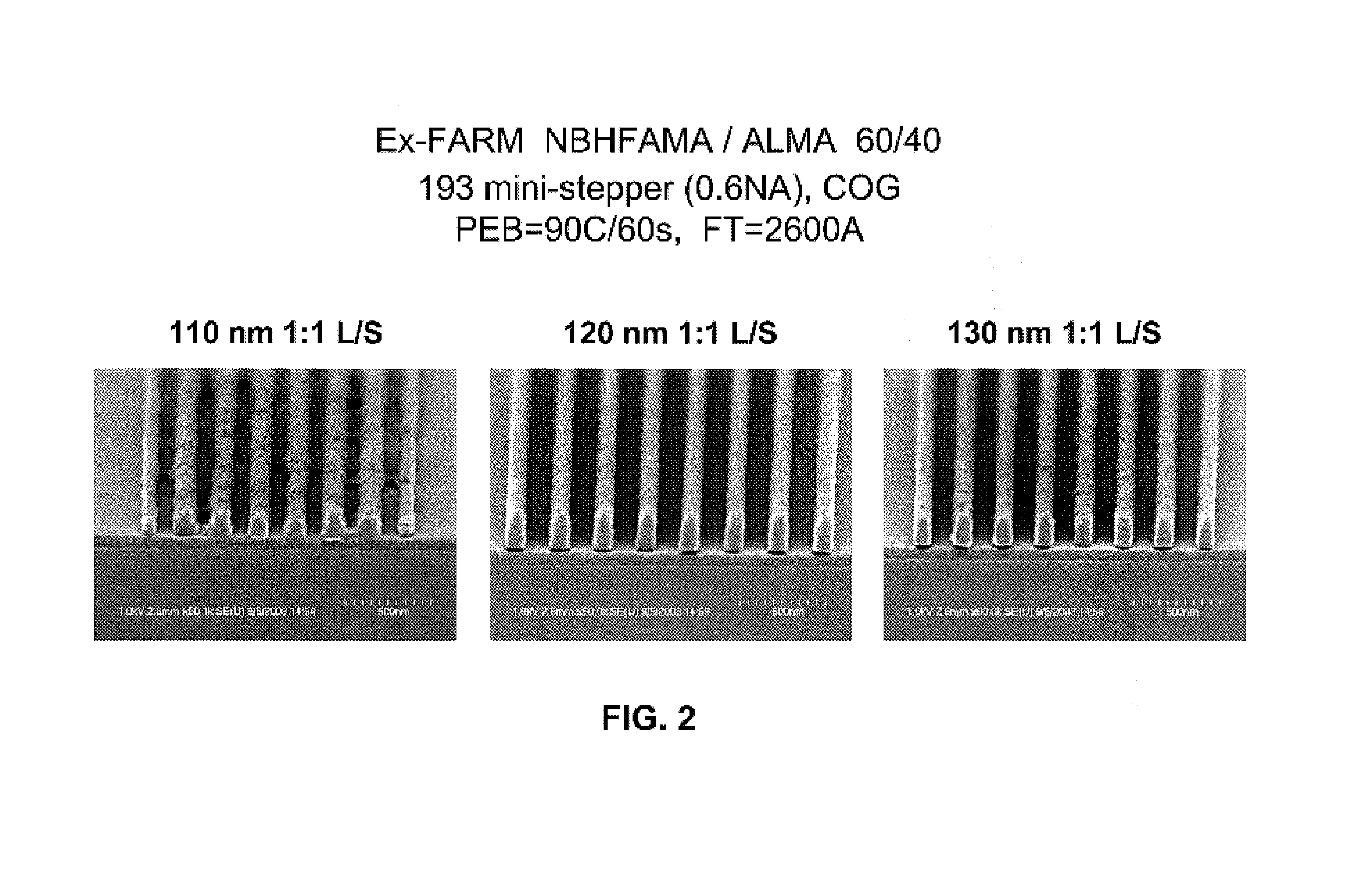
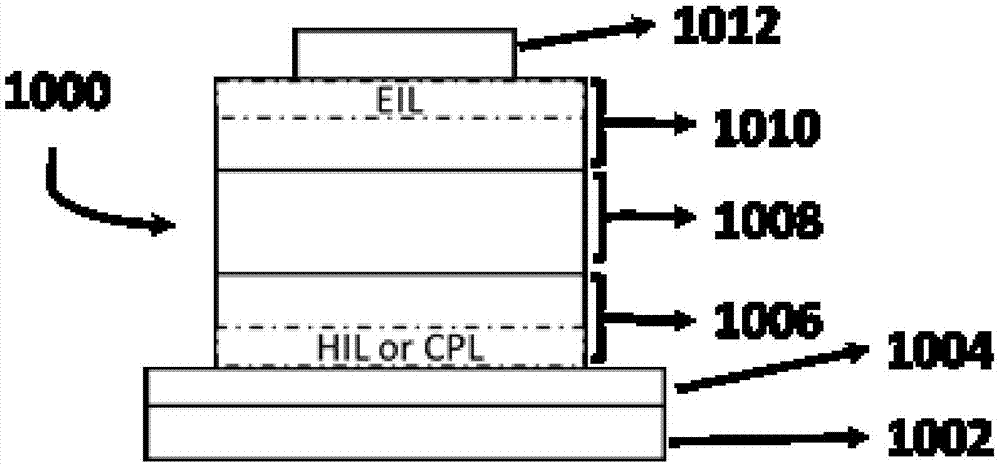
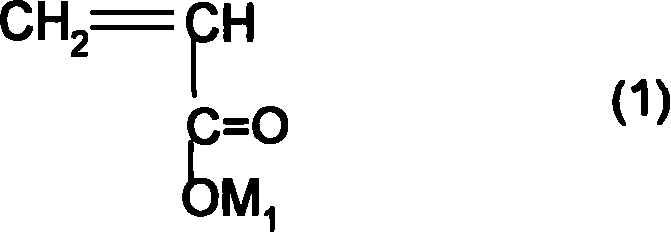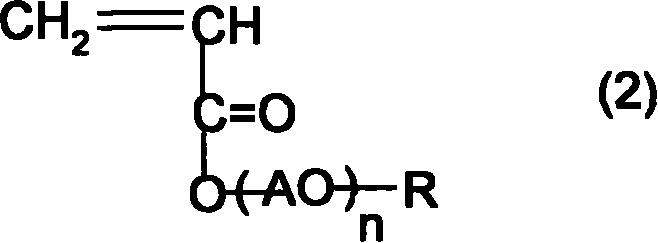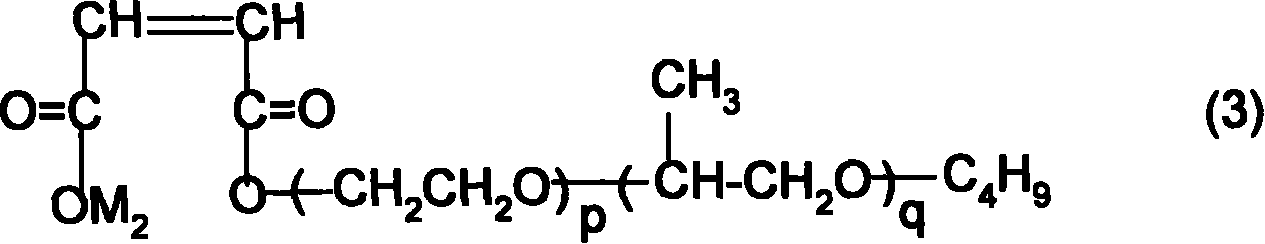Patents
Literature
882 results about "Acid catalysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
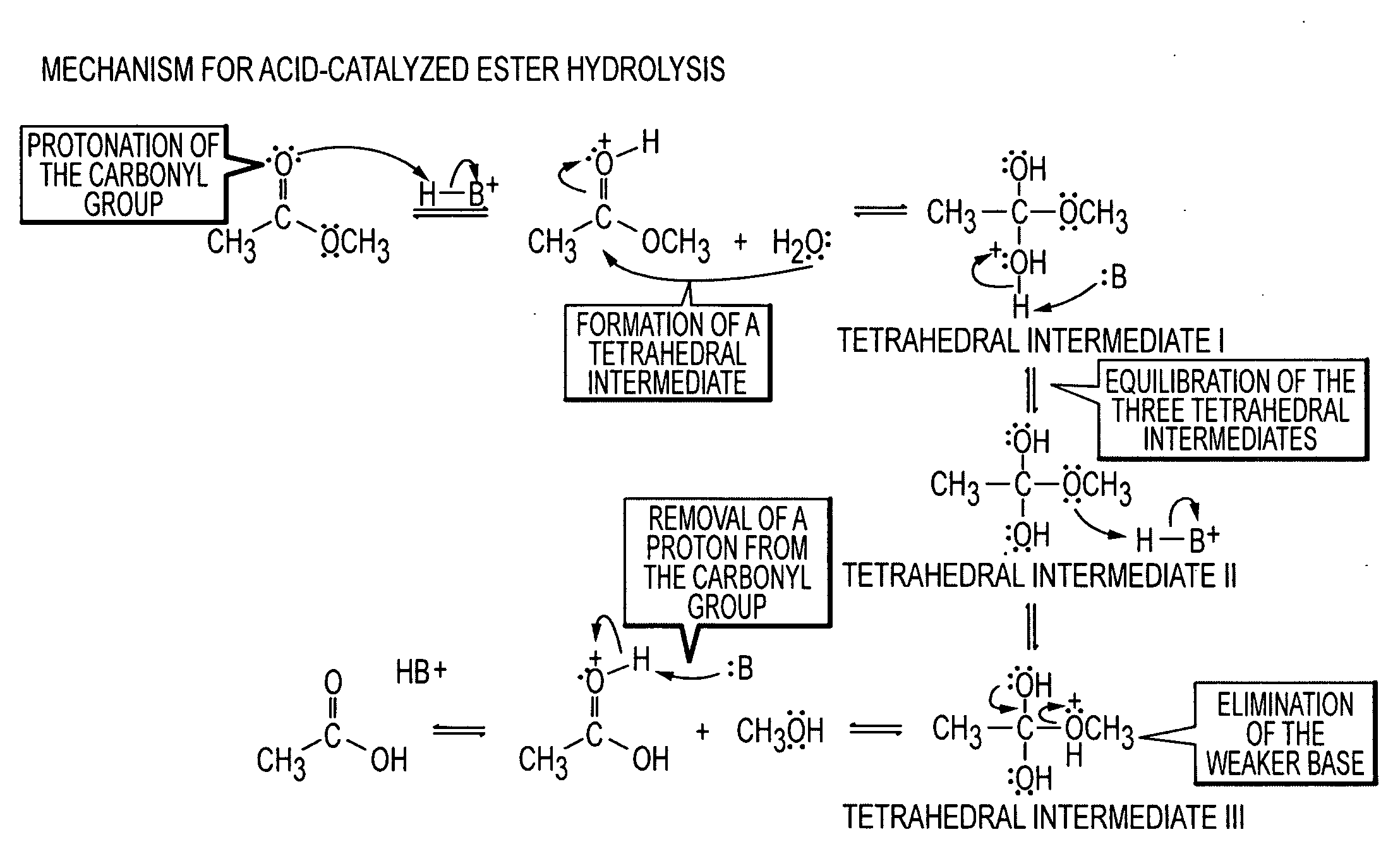
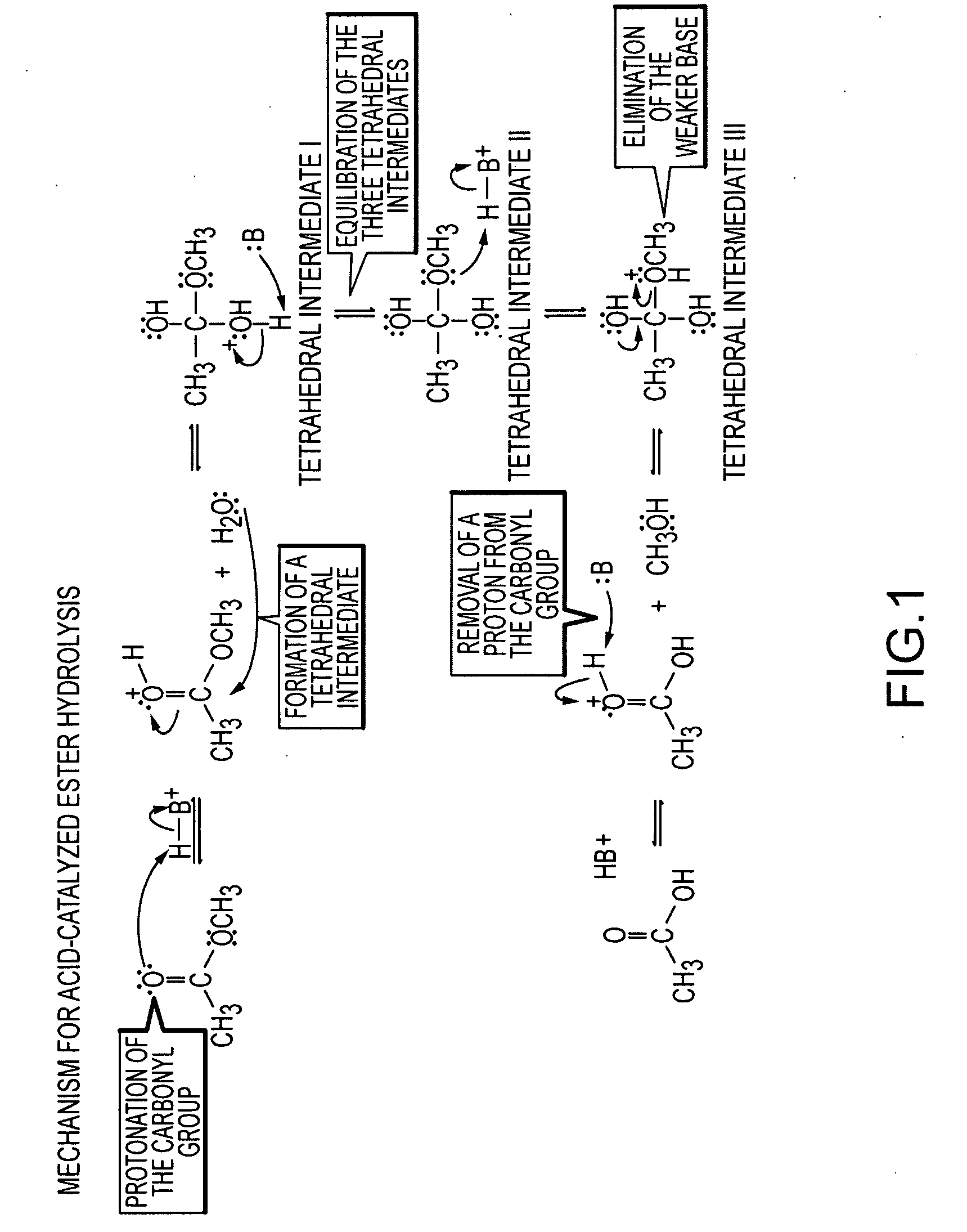
In acid catalysis and base catalysis, a chemical reaction is catalyzed by an acid or a base. By Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, the acid is the proton (hydrogen ion, H⁺) donor and the base is the proton acceptor. Typical reactions catalyzed by proton transfer are esterfications and aldol reactions. In these reactions, the conjugate acid of the carbonyl group is a better electrophile than the neutral carbonyl group itself. Depending on the chemical species that act as the acid or base, catalytic mechanisms can be classified as either specific catalysis and general catalysis. Many enzymes operate by specific catalysis.
Continuous algal biodiesel production facility
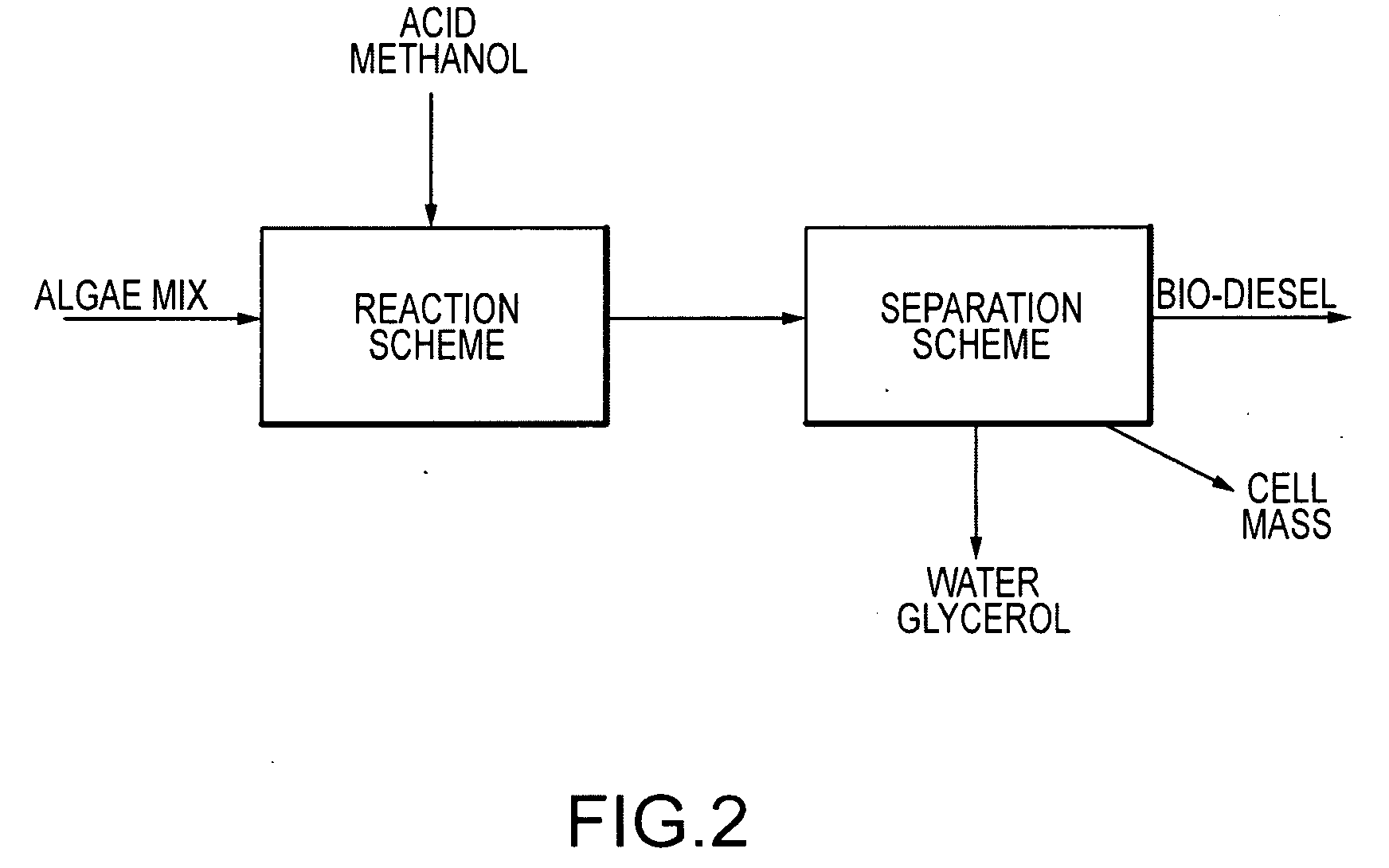
Embodiments of the present invention concern methods, compositions, and apparatus for the continuous conversion of algal lipids into biodiesel. In some embodiments, the biodiesel is formed in a multi-step sequence, the first steps occurring in the presence of water and a strong acid wherein the lipids are released from the algae by means of mechanical and chemical action and are then hydrolyzed to free fatty acids. In a subsequent step, this free fatty acid mixture is reacted with methanol to generate fatty acid methyl esters (also known as biodiesel). Such methods produce biodiesel from algal lipids without the requirement for separate algal cell lysis or lipid extraction or purification prior to the acid catalysis sequence. In other embodiments, the multi-step acid catalysis sequence occurs at 100° C. at two atmospheres of pressure.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Ion exchange composite material based on proton conductive functionalized inorganic support compounds in a polymer matrix
InactiveUS20050053818A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove impermeabilitySemi-permeable membranesSolid electrolytesIon exchangeLiquid fuel
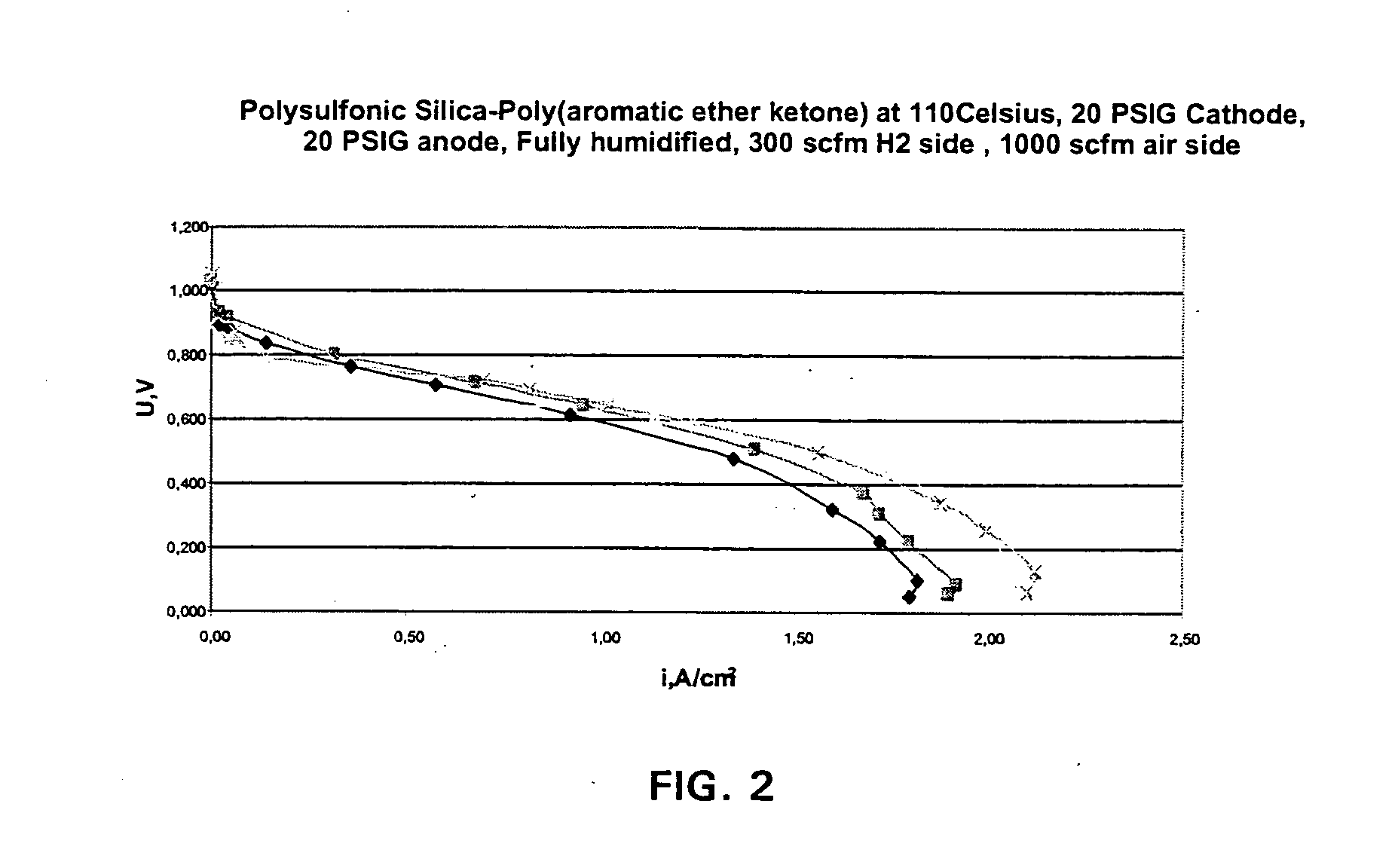
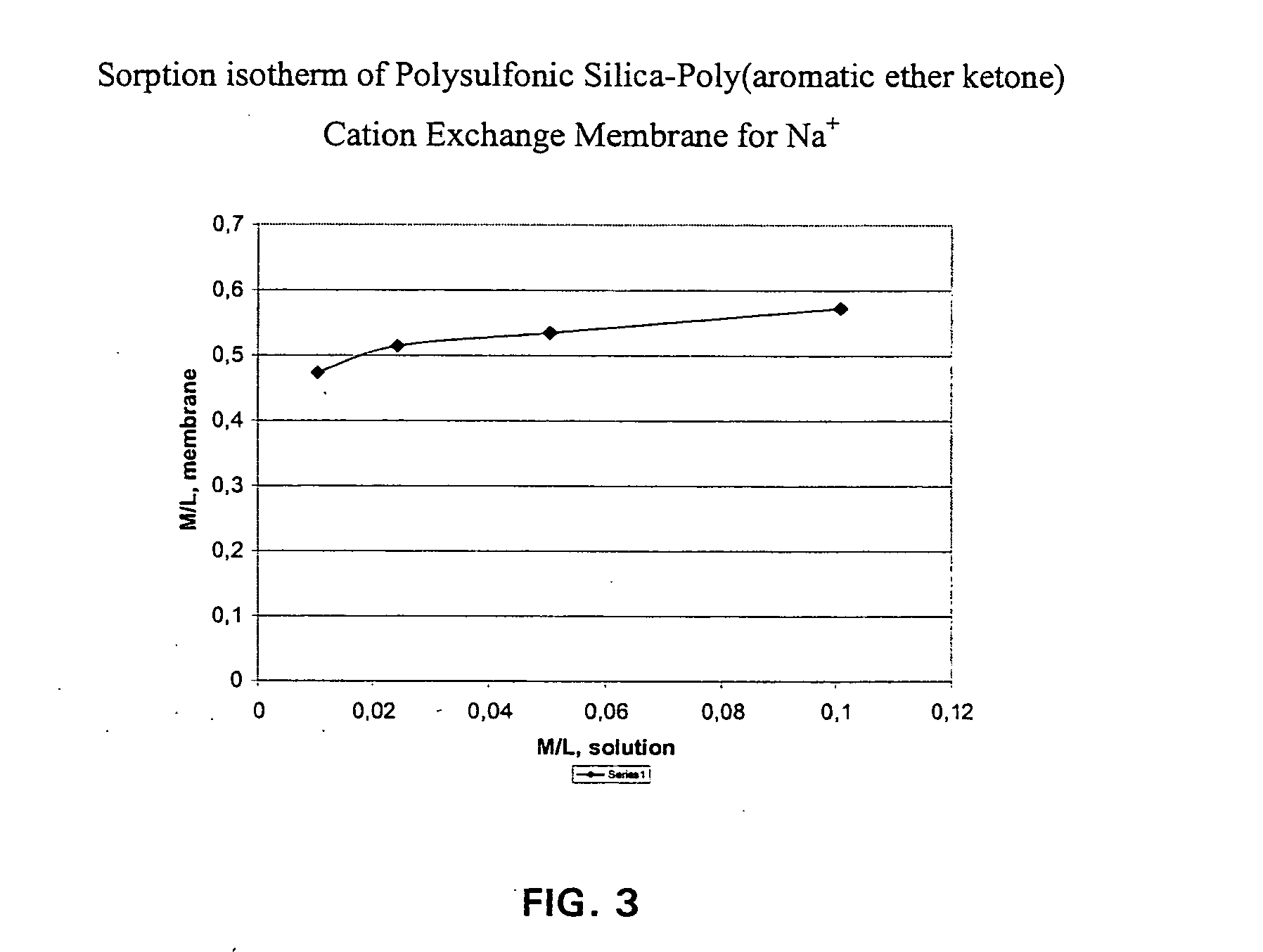
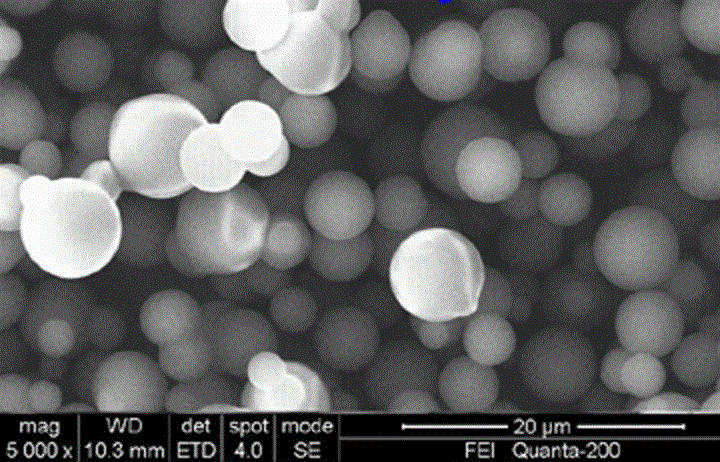
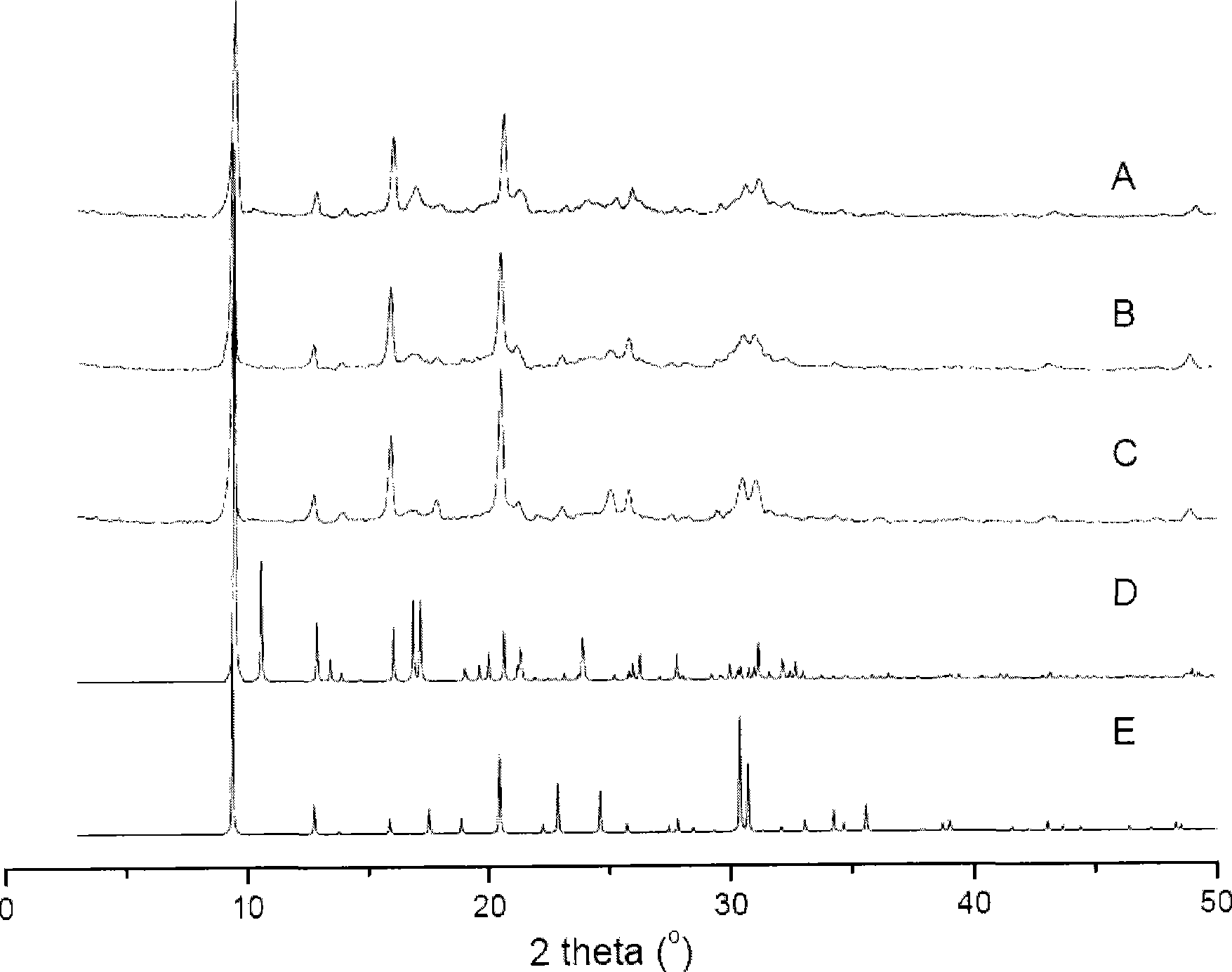
The composite material comprise acid functionalized inorganic supports such as silica dispersed in a functionalized and / or non-functionalized polymer matrix that is based on numerous polymers such as poly(aromatic ether ketones), or poly(benzoyl phenylene), or derivatives thereof. The composite material is characterized by good water retention capabilities due to the acidic functions and the hydrophilicity of the silica particles. Moreover, a good impermeability to gas and liquid fuels commonly used in fuel cell technology, like hydrogen gas or methanol solution, is also obtained due to the presence of silica particles. Good mechanical properties of the composite material let the material to be formed easily in thin film or membrane form. In that form, the composite material is usable for proton exchange membrane for fuel cells, for drying or humidifying membrane for gas or solvent conditioning, or as acid catalytic membrane.
Owner:SIM COMPOSITES INC
Method for cogeneration of 5-hydroxymethyl-furfural, acetylpropionic acid and formic acid by high temperature catalytic dehydration of glucose in formic acid
The invention discloses a method for coproduction of 5-hydroxymethyl furfural, an acetylpropionic acid and a formic acid through high-temperature catalysis and dehydration of the formic acid of glucose. The method specifically comprises the following steps: firstly, establishment of a formic acid reaction system, namely the glucose is added into the formic acid solution, and the weight ratio of the glucose to the formic acid in the reaction system is 0.05-0.2 to 1; and the mixture is reacted for 2 to 6 hours in the presence of the catalyst at a temperature of between 120 and 220 DEG C which is higher than the boiling temperature of the formic acid, and the reaction system is single-phase reaction or biphase reaction; and secondly, separation of products after reaction by a fractionating tower device, namely graded separation of 5-HMF, LA and the formic acid. The method can convert the glucose into the products, namely the 5-HMF, the LA and the formic acid with high added values through effective acid catalysis and dehydration, and has high conversion of reactant during the reaction process and obvious economic benefit; and the 5-HMF, the LA and the formic acid can be directly taken as chemical products to be further converted, and are good raw materials for synthesizing other chemical products.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Low temperature hydrothermal preparation method of biomass carbon microsphere / nanosphere
InactiveCN104649246ALow hydrothermal carbonization temperatureImprove securityMaterial nanotechnologyBiomass carbonPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a low temperature hydrothermal preparation method of alkali catalysis or Lewis acid / proton acid catalysis biomass. The method is as below: adding a certain amount of biomass, deionized water and a proper amount of alkali or Lewis acid / protonic acid into carbide carbon of biomass to a teflon inner liner, stirring to dissolve soluble biomass, filling into a stainless steel reaction kettle, and placing in an oven and reacting for a while at preset temperature, and reacting insoluble biomass in a device equipped with a heating sleeve and a thermostat magnetic stirrer under the preset temperature, wherein the reaction conditions are as below: temperature of 110-160 DEG C (preferably 120-140 DEG C) and reaction time of 6-72 h (preferably 12-36 h); naturally cooling to room temperature, conducting high speed centrifugal separation, and re-dispersing and repeatedly washing the obtained solid with deionized water and 95% ethanol to obtain a colorless supernatant, and drying to obtain carbon microsphere / nanosphere. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of low hydrothermal carbonation temperature and high carbon production rate of the biomass, and is applicable to large-scale industrial production; and the product can be used as a catalyst carrier or adsorbent.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
AEI/CHA eutectic molecular sieve containing triethylamine and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN101450806AMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesMolecular-sieve silicoaluminophosphatesMolecular sieveChemical composition
The invention discloses an AEI / CHA eutectic molecule sieve containing triethylamine. An anhydrous chemical composition of the AEI / CHA eutectic molecule sieve is expressed as mR.(Six.Aly.Pz)O2, wherein x, y and z are molar fractions of Si, Al and P respectively; the x is between 0.001 and 0.98; the y is between 0.01 and 0.6; the z is between 0.01 and 0.6, x+y+z is equal to 1; the R is a template agent, and the m is a mole number of the R; and the value of the m is between 0.02 and 0.6. A preparation method for the AEI / CHA eutectic molecule sieve comprises the following steps: a) according to the mol ratio of oxides of various components, stirring and mixing evenly a silicon source, an aluminum resource, a phosphorus source, the template agent, and water are to obtain an initial gel mixture; and b) transferring the initial gel mixture into a stainless steel synthesis kettle to be sealed, then heating the kettle to a crystallization temperature of between 160 and 250 DEG C, and performing crystallization at constant temperature for 1 to 120 hours under the self-generated pressure, and separating a solid product, washing the solid product to be neutral, and drying the solid product to obtain the AEI / CHA eutectic molecule sieve. The molecule sieve can be used as a catalyst for an acid catalytic reaction after the template agent is removed through the baking.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
SiO2 nanoscale porous material with aerogel property prepared by microwave reaction and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101633505ALarge specific surface areaHigh strengthNanostructure manufactureSilicaSupercritical dryingOrganic solvent
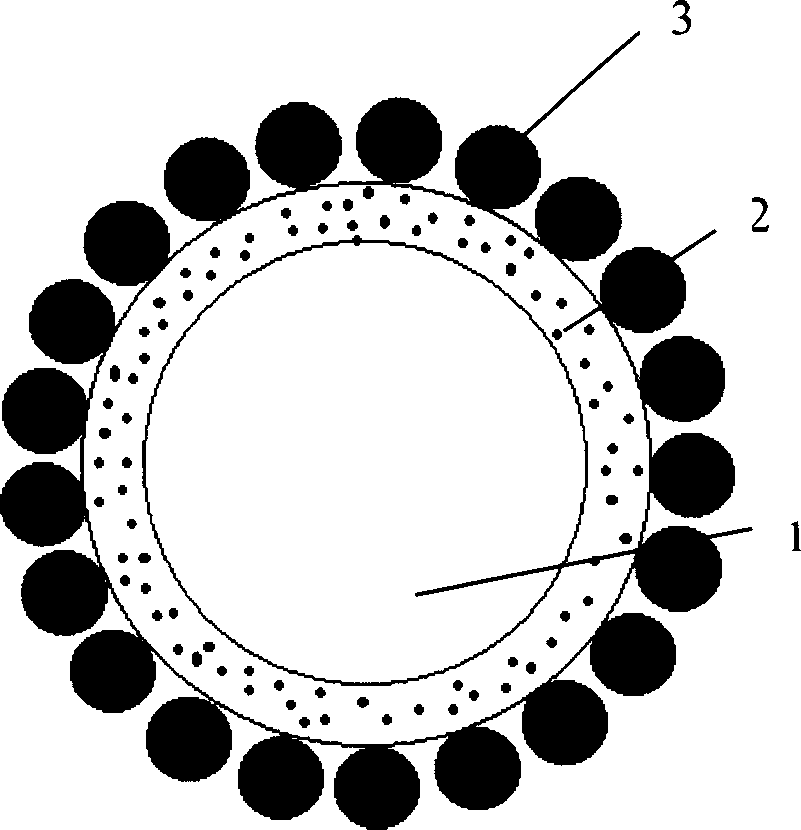
The invention provides a SiO2 nanoscale porous material with aerogel property prepared by microwave reaction and a preparation method thereof; the nanoscale porous material comprises silicon dioxide skeletons (1) and bubble-shaped nanoscale pores (2), wherein the foam-shaped nanoscale pores (2) are arranged among the silicon dioxide skeletons (1). The preparation method comprises four steps, namely preparation of silicon dioxide sol, preparation of wet gel, aging of mother solution and drying at normal pressure and the preparation of silicon dioxide sol comprises the following steps: adopting organosiloxane, organic solvent, water and acid catalysis as raw materials; mixing each components in a defined ratio in a container while adopting microwave radiation to perform hydrolytic polycondensation reaction or adopting microwave radiation to perform hydrolytic polycondensation reaction after mixing the components. Owning to adopting microwave radiation technology, a lot of bubbles are generated in silicon dioxide sol, a large quantity of nanoscale bubble-shaped pores are formed on the silicon dioxide substrate, and meanwhile silicon dioxide space skeletons are retained so that silicon dioxide porous material with extremely large specific area and higher intensity can be obtained. In addition, because carbon dioxide supercritical drying process is not needed, the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:郑文芝 +2
Y/silicate compound molecular sieve and method for preparing same
ActiveCN101618333ALow total acidSuitable for acid catalyzed reactionsMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveAcid catalysis
The invention discloses a Y / silicate compound molecular sieve and a method for preparing the same. The compound material has XRD characteristic diffraction peaks of the Y molecular sieve and a pure silicon molecular sieve. The structure of the compound molecular sieve is a closely combined nucleus-shell type structure taking the Y molecular sieve as the nucleus and the pure silicon molecular sieve as the shell. The compound molecular sieve is prepared by a one-step hydrothermal crystallization method, and the Y molecular sieve is used as the nucleus molecular sieve and buried in the gel of the pure silicon molecular sieve, so that the synthetic process is not related to the complicated preparation steps, and the preparation method is simple. In the compound molecular sieve, the Y molecular sieve used as the nucleus can provide the acid catalysis property, and the pure silicon molecular sieve used as the shell can provide the shape selecting function, so that the Y / silicate compound molecular sieve can be used for all kinds of shape-selective reaction.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
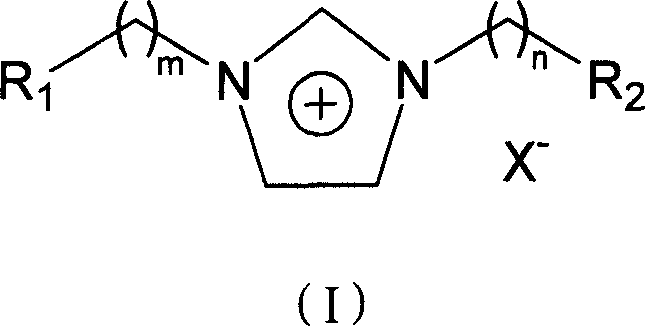
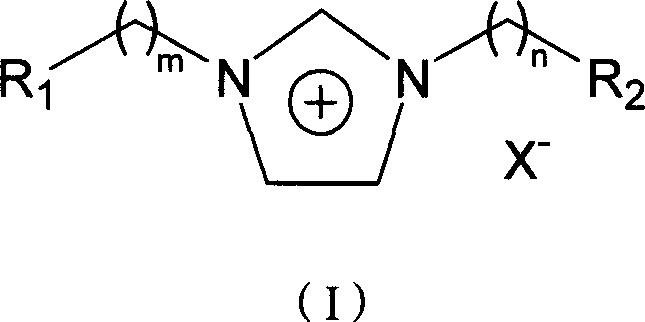
Imidazole two-functionized room temperature inonic liquid and its preparing method
InactiveCN1978433AImprove thermal stabilityExcellent electrochemical propertiesOrganic chemistryHalogenAcid catalysis
This invention relates to a room temperature ionic liquid with dual functional imidazolyl and its preparation. Through reaction of functional imidazole and alkylogen that contains functional group, this ionic liquid first produces dual functional ionic liquid of which anion is halogen anion, then through anion exchange, obtains dual functional ionic liquid that contains different anion. The ionic liquid of this invention has fine heat stability, is stable for water and air, possesses satisfactory electrochemistry character, can be used as electrolyte for electrochemistry research. In orthodox acid catalysis reaction, it not only can be used as catalyst, but also can be used as reaction medium. Meanwhile, it can be used as medium that can separate and extract.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
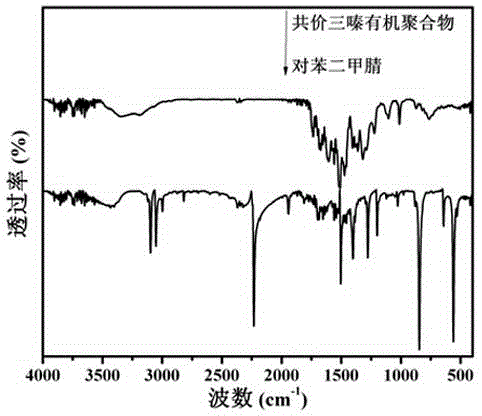
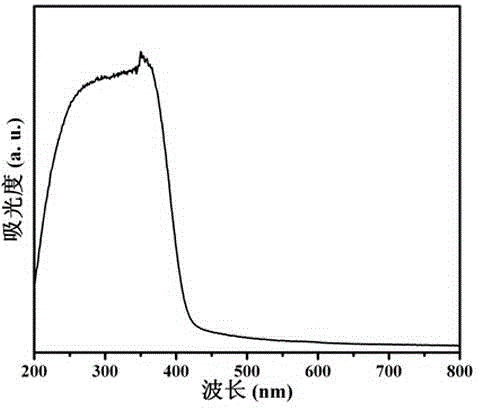
Covalence triazine organic polymer visible-light-driven photocatalyst and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN104525258AImprove stabilityMild preparation conditionsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAcid catalysisTriflic acid
The invention discloses a covalence triazine organic polymer visible-light-driven photocatalyst and the preparing method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of material preparation and photocatalysis. According to the method, normal-temperature liquid-phase polymerization is adopted, para-phthalonitrile serves as the monomer, trimerization is conducted under the catalysis of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, and then the covalence triazine organic polymer visible-light-driven photocatalyst is prepared. By means of the photocatalyst, visible-light reaction is achieved, hydrogen production through water photolysis can be achieved without obvious inactivation, and organic pollutants in waste water can be effectively degraded. The preparing condition is mild, production cost is low, yield is high, actual production requirements are met, and application potential is great.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Quick synthesizing method of triazinyl covalent bond organic framework material with nano pores and application thereof
The invention relates to a quick synthesizing method of a triazinyl organic framework material with nano pores, a triazinyl organic oligomer and a triazinyl organic compound and application thereof. In the presence of a Lewis acid as well as in the presence that an inorganic salt fusing assistant exists or does no exist in at least one single nitrile-based and / or multi-nitrile-based organic compound and under the condition of microwave radiation, the covalent bond organic framework material with a triazinyl structure and nano pores, the triazinyl organic oligomer or the triazinyl organic compound is generated, wherein pores or channels which are positioned in at least one direction in space and have size of over 0.3nm are arranged inside the obtained triazinyl covalent bond organic framework solid. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of short required synthesis time, high production efficiency and low production energy consumption; and the products have wide application range.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Composition of catalyst and solvent and catalysis processes using this composition
ActiveUS7256152B2High selectivityHigh activityHydrocarbon by isomerisationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAlkaneLiquid medium
A composition defined:either as comprising at least one Broensted acid, designated HB, dissolved in a liquid medium with an ionic nature of general formula Q+A−, in which Q+ represents an organic cation and A− represents an anion that is different from B,or as resulting from dissolving at least one Broensted acid, designated HB, in a non-aqueous liquid medium with an ionic nature of general formula Q+A−, in which Q+ represents an organic cation and A− represents an anion that is identical to the anion B, can be used as a catalyst and solvent in acid catalysis processes, in particular in the alkylation of aromatic hydrocarbons, the oligomerization of olefins, the dimerization of isobutene, the alkylation of olefins by isoparaffins, the isomerization of n-paraffins into isoparaffins, the isomerization of n-olefins into iso-olefins, the isomerization of the double bond of an olefin and the purification of an olefin mixture that contains branched alpha olefins as impurities.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Low-activation energy silicon-containing resist system
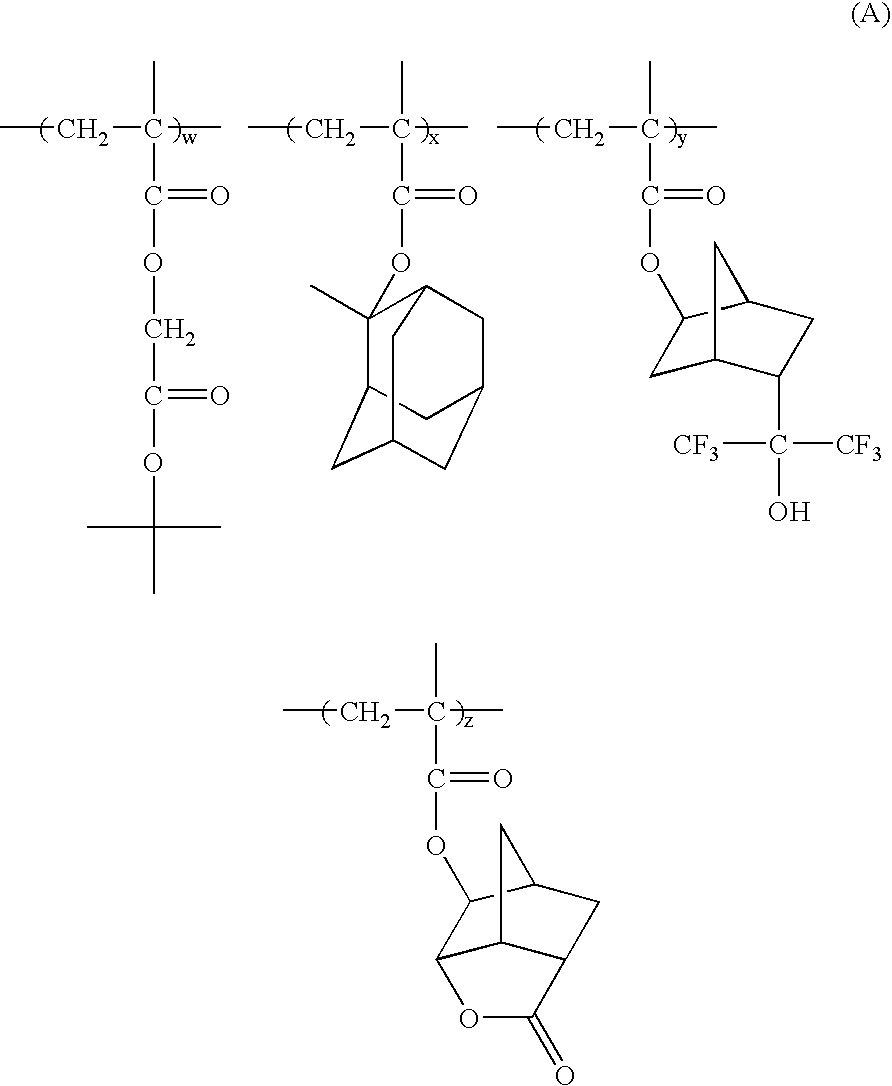
InactiveUS6939664B2Lower activation energyHigh optical densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersPolymer scienceAcid catalysis
Inventive silsesquioxane polymers are provided, and resist compositions that contain such silsesquioxane polymers are provided in which at least a portion of the silsesquioxane polymer contains fluorinated moieties, and at least a portion of the silisesquioxane polymer contains pendant solubility inhibiting acid-labile moieties that have low activation energy for acid-catalyzed cleaving, and the presence of high optical density moieties are minimized or avoided. The inventive polymer also contains pendant polar moieties that promote alkaline solubility of the resist in aqueous alkaline solutions. The inventive polymers are particularly useful in positive resist compositions. The invention encompasses methods of using such resist compositions in forming a patterned structure on a substrate, and particularly multilayer (e.g. bilayer) photolithographic methods, which methods are capable of producing high resolution images at wavelengths such as 193 nm and 157 nm.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
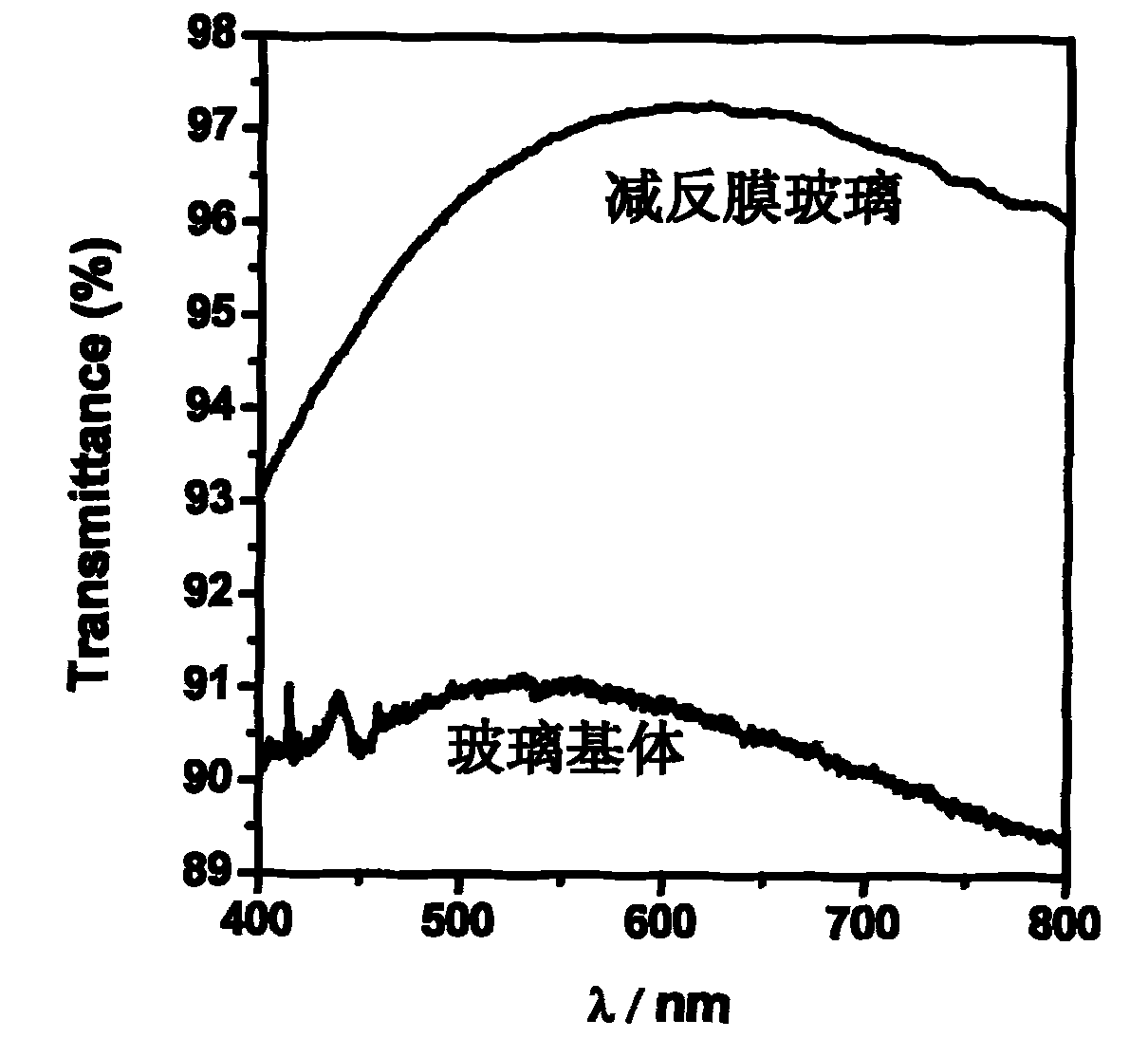
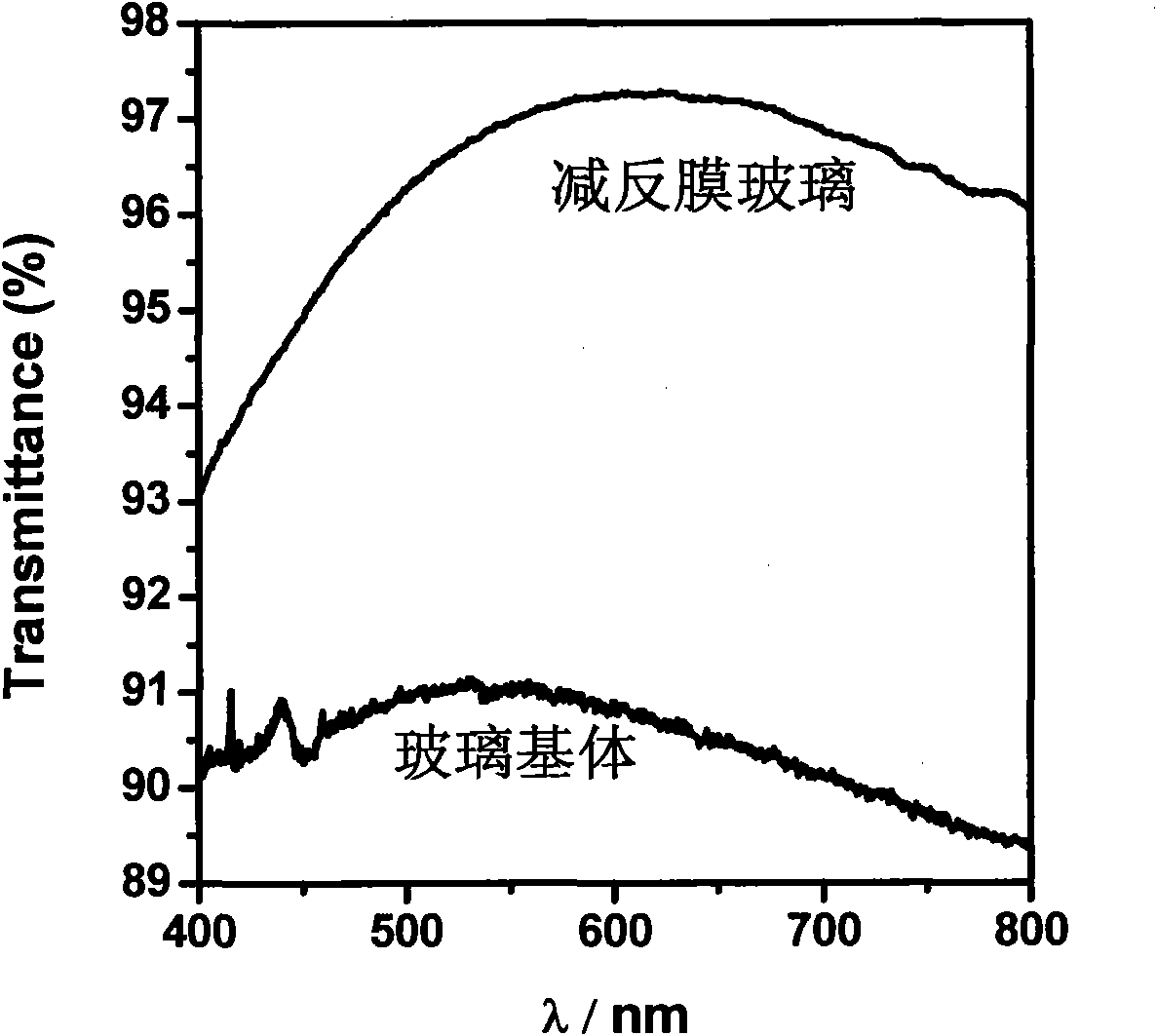
Preparation method of self-cleaning antireflection film with photocatalytic function on surface
The invention discloses a preparation method of a self-cleaning antireflection film with the photocatalytic function on the surface, relating to the field of solar photocatalysis. The method comprises the following steps of: proportionally mixing silica sol obtained through the acid catalysis and the base catalysis of acetate orthosilicate; firstly, coating an antireflection film on a clean glass surface by using a czochralski method; then, coating a layer of titania sol prepared through the hydrolysis of N-butyl titanate; and solidifying at 120 DEG C for 2 h and thermally treating at 500 DEG C for 2 h to obtain the self-cleaning antireflection film with the transmittance over 96 percent and the photocatalytic function on the surface. The antireflection film on the glass surface has higher transmittance while ensuring the firm combination with the glass; and the surface of the antireflection film has the photocatalytic function and the self-cleaning function.
Owner:常州龙腾光热科技股份有限公司
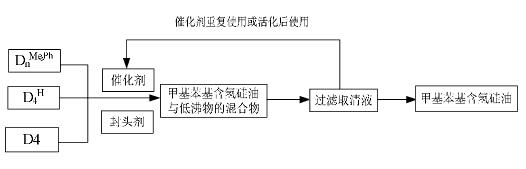
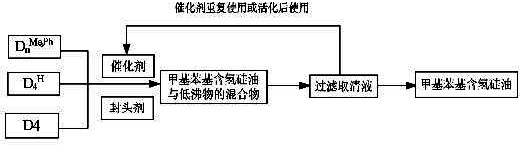
Method for preparing methyl phenyl hydrogen-containing silicone oil by rare earth super acid catalysis
InactiveCN101851333AHigh refractive indexSimple processOther chemical processesAdhesivesPtru catalystMethyl benzene
The invention discloses a method for preparing methyl phenyl hydrogen-containing silicone oil by rare earth super acid catalysis, which comprises the following steps of: taking methyl phenyl cyclosiloxane (DnMe, Ph, wherein n=3, 4, 5, 6), dimethyl cyclosiloxane (Dn, wherein n=3, 4, 5, 6), and methylhydrocyclosiloxane (DnH, wherein n=3, 4, 5, 6) as monomers; adding a blocking agent; and selecting rare earth super acids, controlling the reaction temperature, performing polymerization for a certain period under the protection of N2 gas, gradually raising the temperature to 205 DEG C under -0.9 MPa, and extracting low-boiling substances under reduced pressure to obtain the target product. The method has the advantages that: the catalyst can be separated only by filtering without washing neutralization, and the method has low labor intensity, simple process, simple and convenient operation and no pollution, and is convenient for industrialization. The product prepared by the method has good effects in the LED packaging process.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
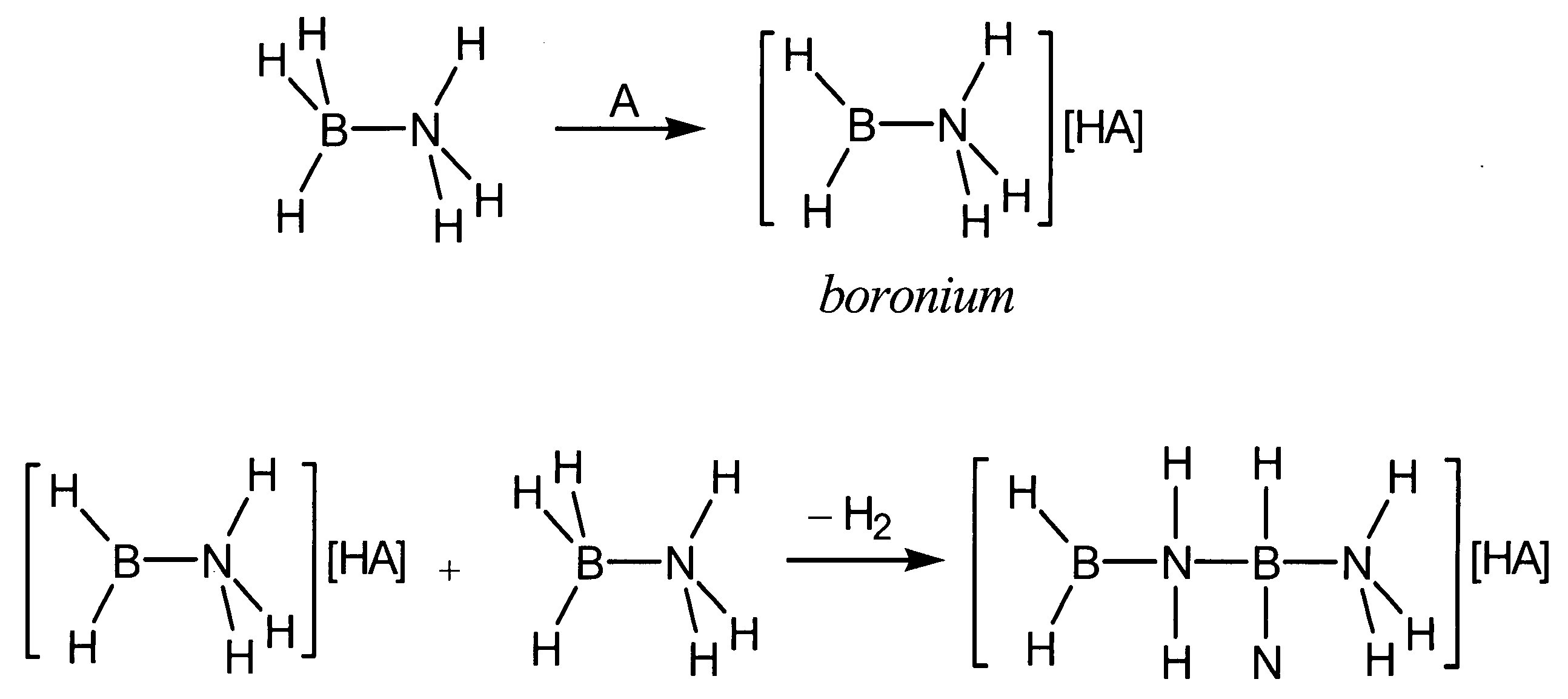
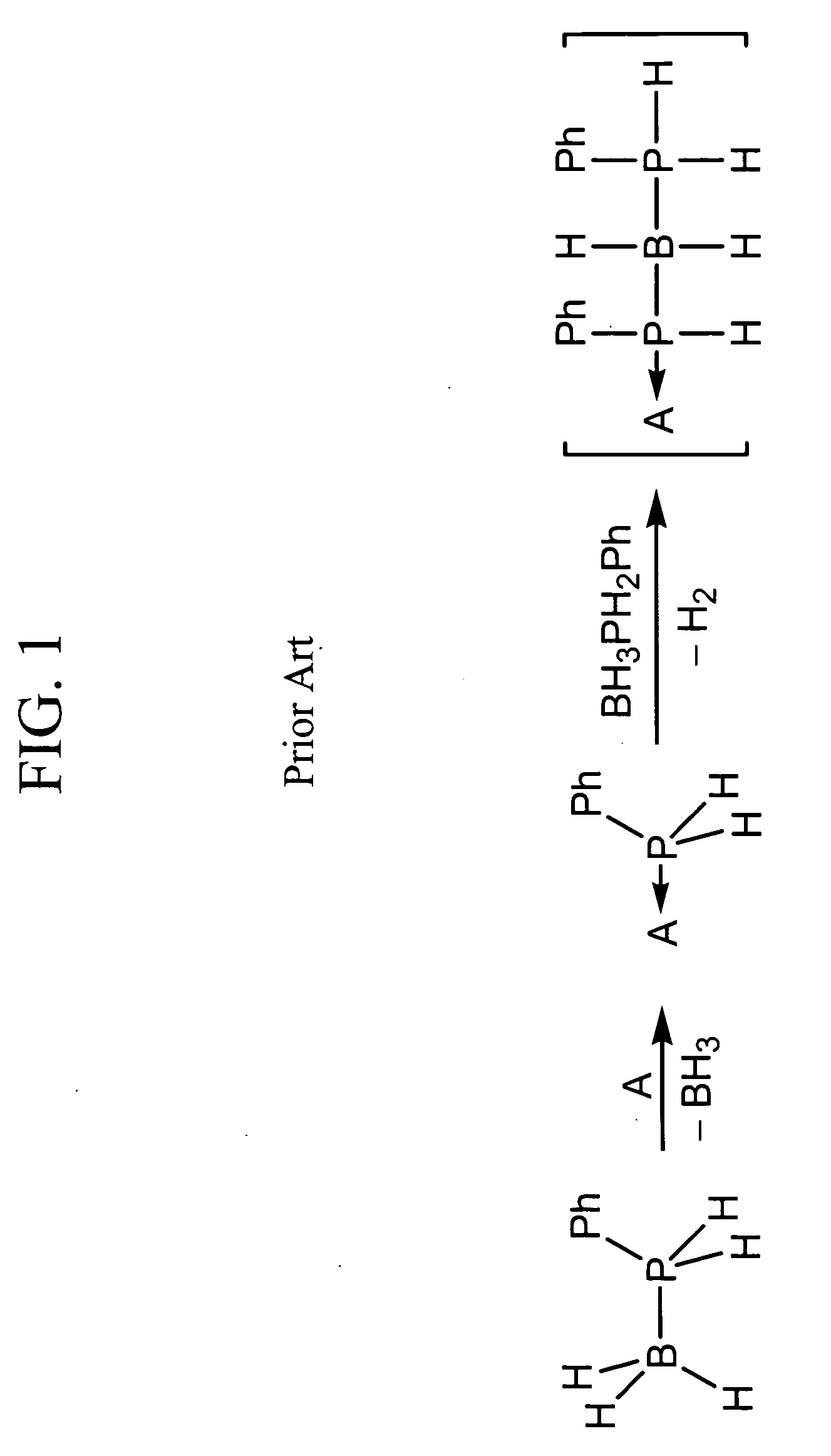
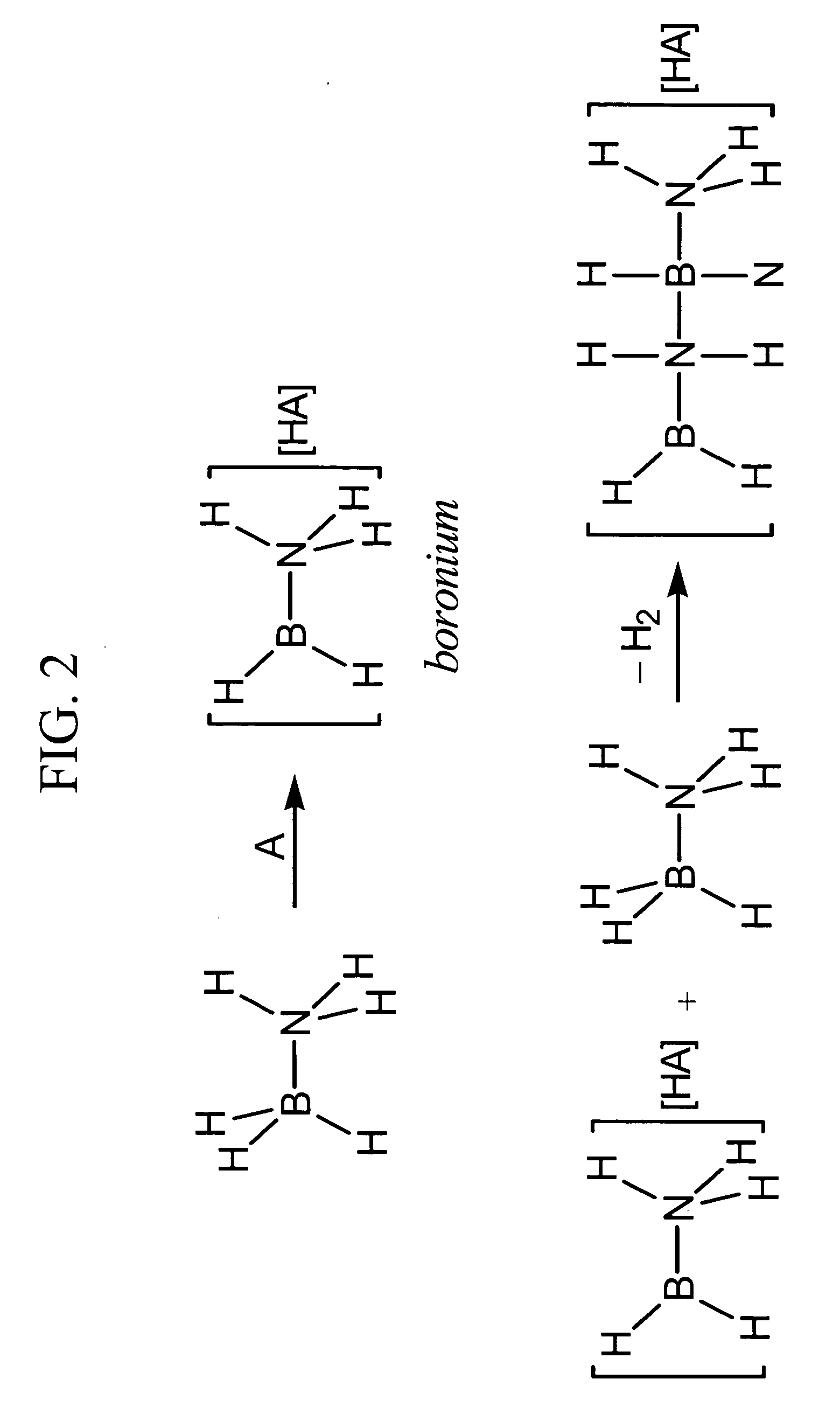
Acid-catalyzed dehydrogenation of amine-boranes
InactiveUS20060292068A1Regenerative fuel cellsCarburetting by solid carbonaceous material pyrolysisHydrogenAcid catalyzed
A method of dehydrogenating an amine-borane using an acid-catalyzed reaction. The method generates hydrogen and produces a solid polymeric [R1R2B—NR3R4]n product. The method of dehydrogenating amine-boranes may be used to generate H2 for portable power sources.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
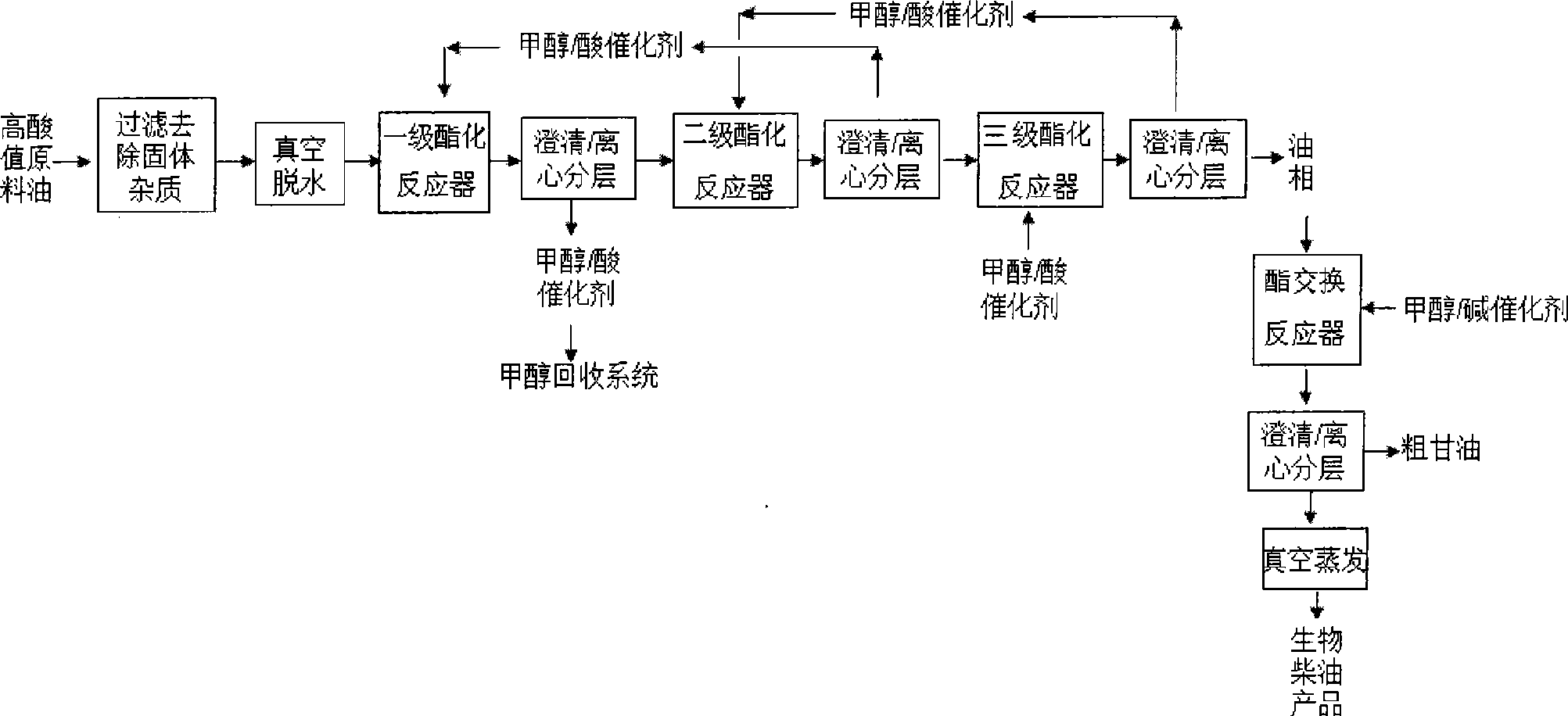
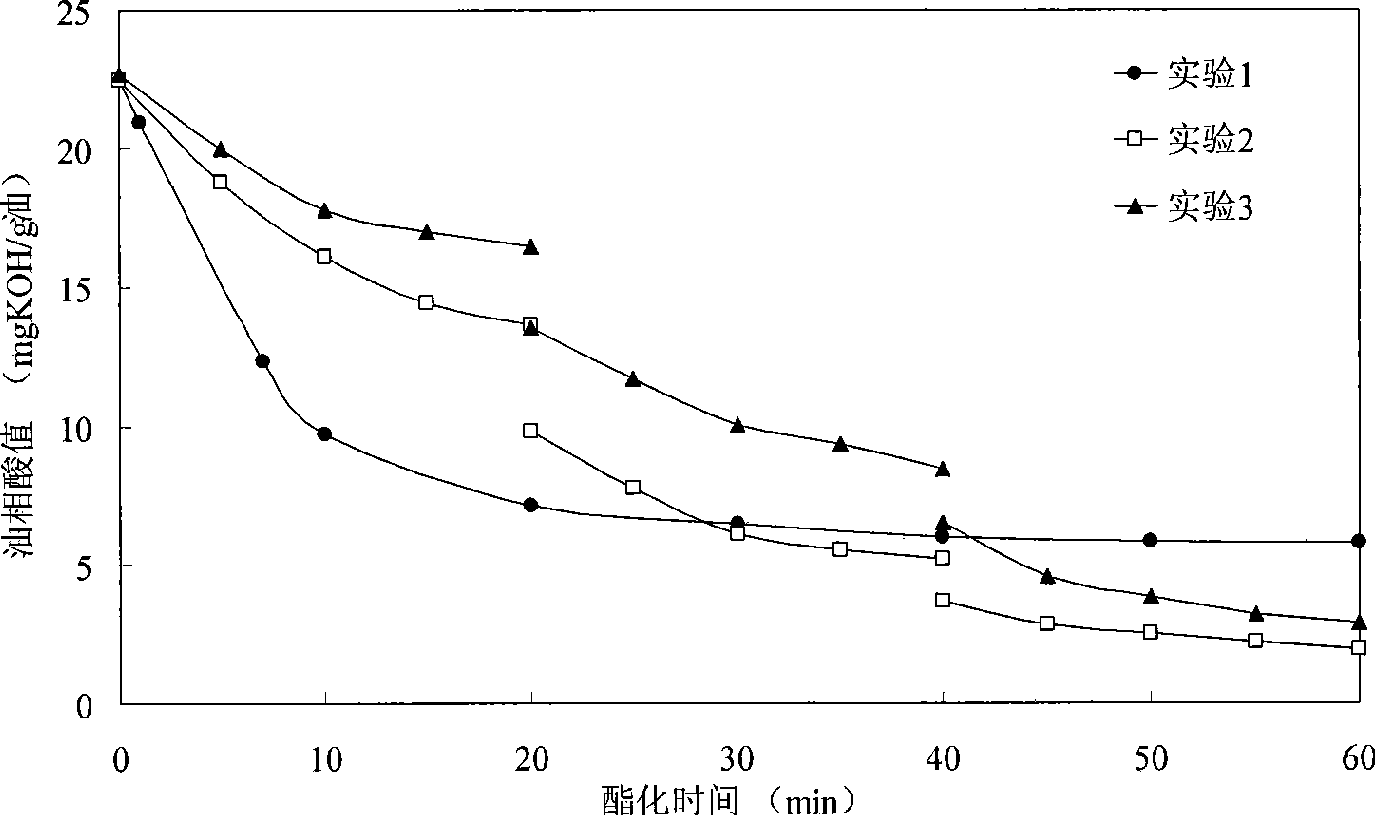
Method for preparing biodiesel by utilizing stratified and graded esterified deacidification of high acid value oil
InactiveCN101445742AHigh reaction conversion rateNot easy to carbonizeBiofuelsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionOil and greaseFiltration
The invention provides a method utilizing high acid value oil as raw material for preparing biodiesel. Various animal and vegetable oil, the acid value of which is larger than 3.0mg KOH / g oil, oilstock, soapstock and acidic oil in a vegetable oil refining process, various food waste oil (restaurant waste oil, hogwash oil, trench waste oil, and the like) and various waste animal oil in industrial processing (waste animal oil in leather processing, waste animal oil in slaughtering process, and the like) are used as raw materials to obtain biodiesel products by filtration for removing solid impurities, vacuum dehydration, stratified graded acid catalytic esterification, alkali catalytic transesterification and vacuum distillation. The method utilizing the high acid value oil as the raw material for preparing the biodiesel has the beneficial effect that the production process can be applied to raw materials with different acid values to produce biodiesel products with high purity by changing the operational series of the stratified graded acid catalytic esterification reaction and has the advantages of simple process, low energy consumption, high conversion rate and small device. And continuous production can be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
193nm resist with improved post-exposure properties
InactiveUS7087356B2High resolution lithographic performanceGood exposure dose latitudePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsResistAcid catalyzed
Acid-catalyzed positive resist compositions which are imageable with 193 nm radiation and / or possibly other radiation and are developable to form resist structures of improved development characteristics and improved etch resistance are enabled by the use of resist compositions containing imaging polymer component comprising an acid-sensitive polymer having a monomeric unit with a pendant group containing a remote acid labile moiety.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Reduction-reducing crack-resisting concrete superplasticizer of graft copolymer and method for preparing the same
Disclosed is a shrinkage-reduction anti-cracking type grafted copolymer concrete superplasticiser, which is prepared from monomer a of acroleic acid or salts, monomer b of alkoxy polyether monoacrylate, monomer c of maleic anhydride hemiester or its salts, monomer d of alpha-propenol omega-methyl polyether and monomer e of phenylethene through free radical copolymerization reaction, wherein the molar ratio of the monomer a, b, c, d and e being 1 : 0.2-0.5 : 0.10-0.25 : 0.10-0.20 : 0-0.10.
Owner:JIANGSU SOBUTE NEW MATERIALS
Synthesis of hydroxylated polyorganosiloxanes by hydrolysis/condensation of halosilanes and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20050288473A1Improve stabilityChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsAcid catalysisSilanes
A method for hydrolyzing / condensing, by acid catalysis, silanes bearing hydrolyzable groups, preferably halogenosilanes and more preferably still chlorosilanes, in a polyphase reaction medium (preferably biphasic), includes contacting the silanes bearing the hydrolyzable groups with water, buffer solution and neutralizing agent, while stirring, then in separating the aqueous phase from the organic phase, which contains the hydrolysis / condensation products, namely hydroxylated polyorganosiloxanes; such method is characterized by (a) employing intensively stirring means producing, in the reaction medium, an agitation at least equivalent to that induced by a shearing corresponding to that provided by a rotor whereof the peripheral speed is not less than 8 m.s−1, preferably not less than 10 m.s1, and more preferably still ranging between 15 and 20 m.s−1, enabling thus organic phase droplets to be formed, of d32 less than 500 μm; and (b) ensuring that the silanes / aqueous phase mass fraction is not less than 0.05, preferably not less than 0.10, and more preferably still ranging from 0.5 to 2.0.
Owner:BLUESTAR SILICONES FRANCE SAS
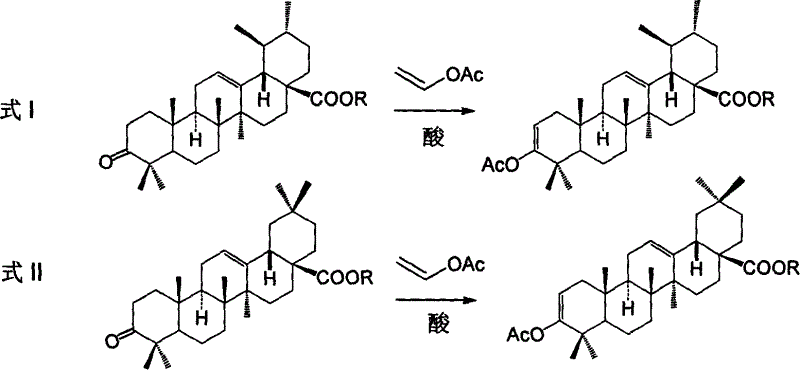
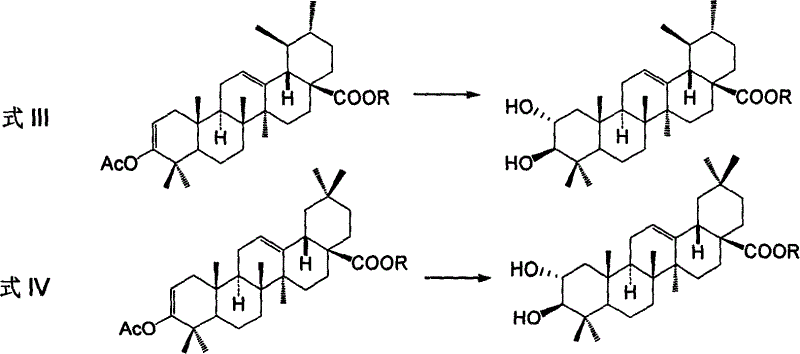
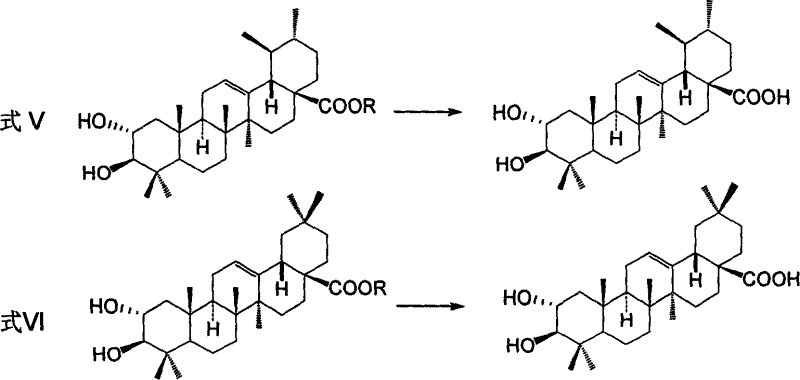
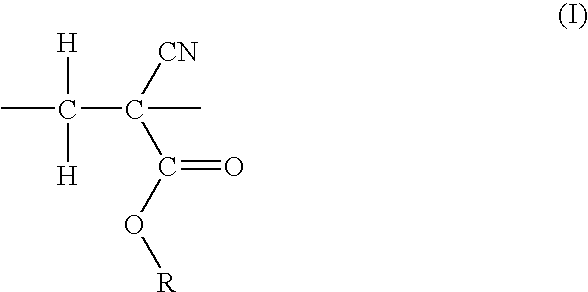
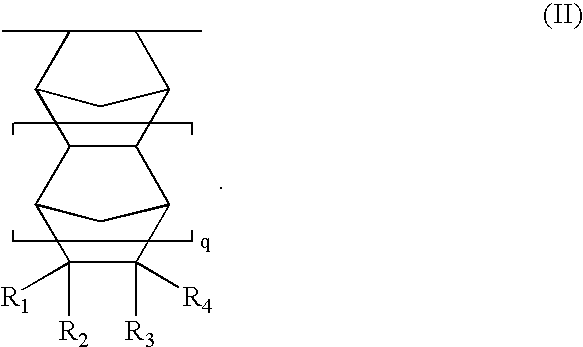
Process for preparing corosolic acid and crataegolic acid
InactiveCN1634971ASimple and efficient synthesisAvoid steric hindranceSteroidsAnti virusCorosolic acid
Disclosed are preparing processes for industrialized application of Corosolic acid with blood sugar lowering, weight reducing, anti-tumor and anti-inflammatory actions and maslinic acid with anti-tumor, anti-virus and cardiovascular diseases resistant actions. The processes include respectively preparing Corosolic acid and maslinic acid using 3-carbonyl ursolic acid ester and 3-carbonyl oleanolic acid ester by acid catalysed enolization esterification reaction, hydroboration oxidation reaction, catalytic hydrogenolysis reaction and haloidlysis reaction.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Resist compositions with polymers having 2-cyano acrylic monomer
InactiveUS6902874B2High resolution lithographic performanceImproved stability/shelf-lifePhoto-taking processesPhotosensitive materialsPolymer scienceAcid catalysis
Acid-catalyzed positive resist compositions which are imageable with 193 nm radiation and / or possibly other radiation and are developable to form resist structures of improved development characteristics and improved etch resistance are enabled by the use of resist compositions containing imaging polymer having a 2-cyano acrylic monomer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Magnetic superfine solid acid catalyst in double-shell structure and its prepn process
InactiveCN1453068APerfect natureHigh catalytic activityCatalyst activation/preparationAcid catalysisSolid acid
The catalyst features that magnetic nucleus is coated with high-specific surface area carrier to form carrier with magnetic nucleus and the carrier with magnetic nucleus is further coated with one layer of strong solid acid. The catalyst is prepared through sol-gel process, in which magnetic nucleus Fe3O4, Co-Fe3O4, Mn-Fe3O4 or Ni-Fe3O4 is coated with high-specific surface area carrier SiO2, ZrO2, Al2O3, TiO2, etc. to form carrier with magnetic nucleus; and subsequent soaking process, in which strong solid acid Zr(SO4)2, SO42--ZrO2, F-ZrO2, etc. is dispersed to the surface of the carrier with magnetic nucleus. This kind of solid acid catalyst in double-shell structure is mainly used in acid catalytic reaction, and features magnetism and high catalytic activity.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Low activation energy photoresists
ActiveUS7193023B2Lower activation energyMinimizing conditionPhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusPolymer scienceCarboxylic acid
Polymers containing an acetal or ketal linkage and their use in lithographic photoresist compositions, particularly in chemical amplification photoresists, are provided. The polymer is prepared from at least one first olefinic monomer containing an acetal or ketal linkage, the acid-catalyzed cleavage of which renders the polymer soluble in aqueous base; and at least one second olefinic monomer selected from (i) an olefinic monomer containing a pendant fluorinated hydroxyalkyl group RH, (ii) an olefinic monomer containing a pendant fluorinated alkylsulfonamide group RS, and (iii) combinations thereof. The acetal or ketal linkage may be contained within an acid-cleavable substituent RCL in the first olefinic monomer. A method for using the photoresist compositions containing these polymers in preparing a patterned substrate is also provided in which the polymer is rendered soluble in aqueous base at a temperature of less than about 100° C. by acid-catalyzed deprotection of pendent acetal- or ketal-protected carboxylic acid groups.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
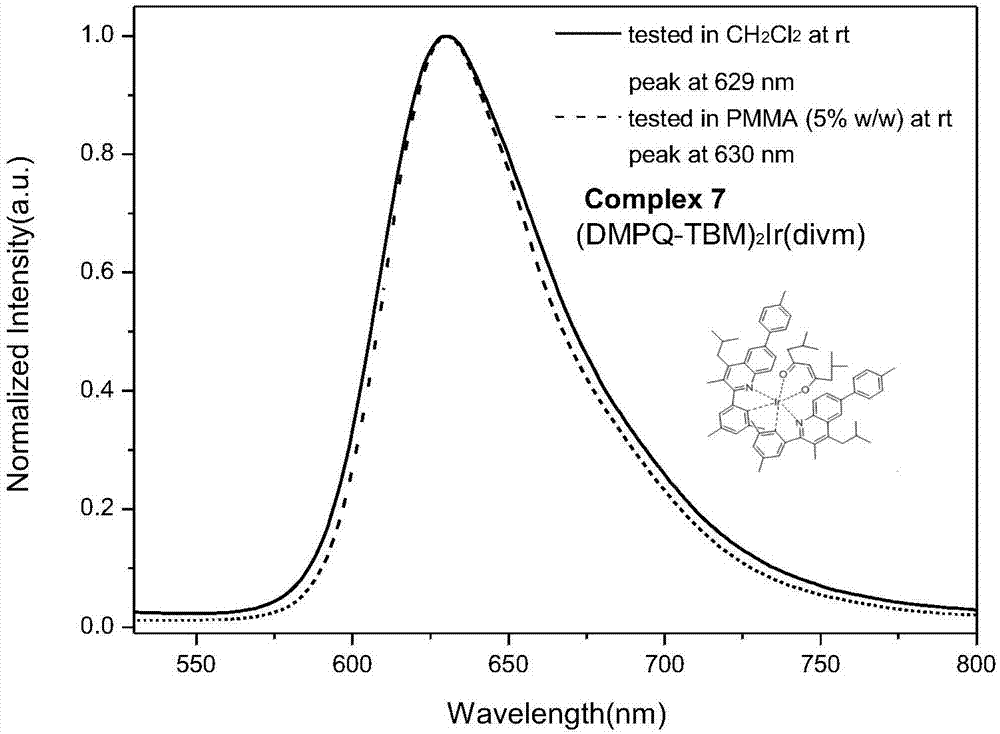
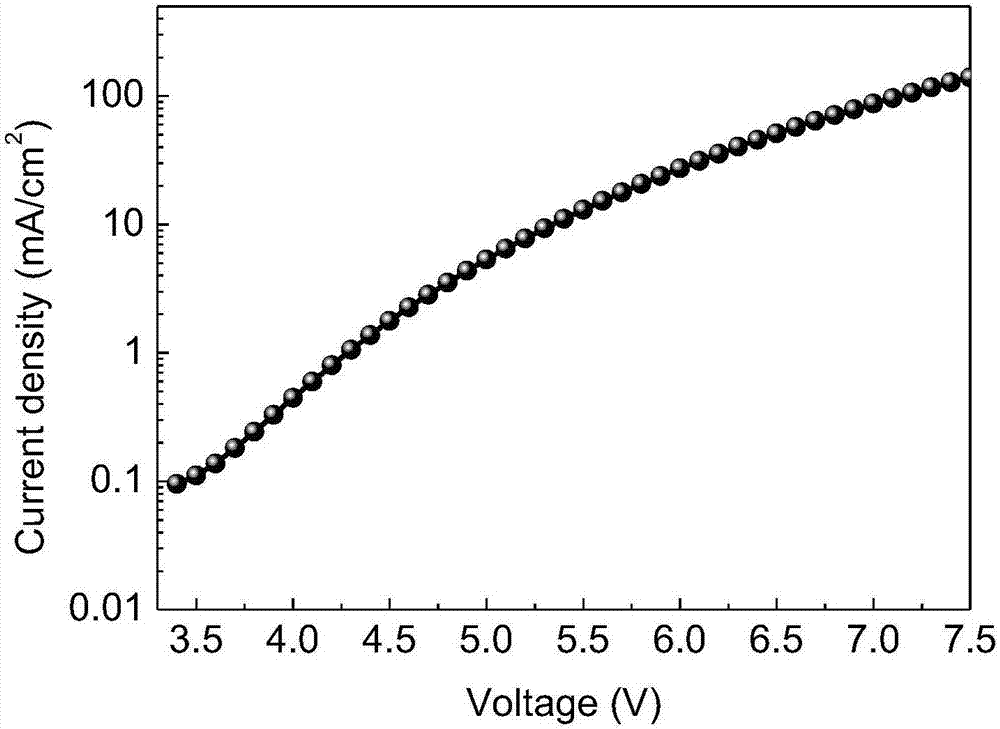
Polysubstituted quinoline-coordinated iridium-hybridized compound as well as preparation method and application of compound
InactiveCN107459535AHigh fluorescence quantum efficiencyQuality improvementIndium organic compoundsSolid-state devicesIridiumAcid catalysis
The invention discloses a polysubstituted quinoline-coordinated iridium-hybridized compound, a preparation method thereof and application of the compound in electroluminescent materials. A modified ligand of the compound comprises 3,5-bis-substituted(R<d> R<d>) in 2-subsittued phenyl, 4-substituted(R<e>) and 3,4,5-tri-substituted(R<d> R<e> R<d>)phenyl. The specific synthesis route of the polysubstituted quinoline-coordinated iridium-hybridized compound comprises the steps of generating substituted quinoline by virtue of amine ester exchange reaction, acid-catalysis Skraup cyclocondensation and hydroxyl halogenating reaction, and preparing ligand by virtue of Suzuki coupling reaction. According to the route, the side reactions of alkyl suzuki coupling reaction and competition of multiple reaction sites are avoided, so that the synthesis efficiency can be improved, and the purifying difficulty can be reduced. According to molecular spectral features and compound modification functions, the iridium-hybridized compound can be clearly used as an electroluminescent material for use in organic photoelectric appliances.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing N doping TiO2
InactiveCN101244382AImprove photocatalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsAcid catalysisNitrogen source
The invention discloses a preparation method of N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst, comprising a plurality of steps as followings: firstly, weighing 0.2 to 2 milliliter HCl solution with a concentration of 37.5%, quickly adding the HCl solution into a mixed solution of tetrabutyl titanate and isopropanol while strenuously agitating the HCl solution, then strenuously agitating for 10 to 20 minutes at a constant temperature of 25 DEG C, then slowly dropping a deionized water solution dissolved with 10% to 60% urea to obtain a yellow transparent sol, standing for 5 to 30 minutes to form a milkiness translucent gel; secondly, hermetically aging the prepared gel for 5 days, drying the wet aged gel for 5 hours at a vacuum condition and a temprature of 65 DEG C to obtain loose tawny dry xerogel powder, then putting the powder into a muffle furnace and calcining for 2 hours to obtain the N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. The invention is characterized in that urea is used as a nitrogen source to prepare nitrogen-doped TiO2 photocatalyst with an acid catalysis sol-gel method. The N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst prepared by the method has the advantages of good photocatalysis activity when excited by a visible light.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Phosphotungstic acid-metal organic skeleton used for catalyzing hydrolysis of cellulose, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105344378AEnsure loading efficiencyEvenly distributedOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGlucose productionCellulosePolymer science
The invention discloses a phosphotungstic acid-metal organic skeleton used for catalyzing hydrolysis of cellulose, and a preparation method and application thereof. According to the invention, organic ligand with strongly electronegative groups and basic groups is screened out and participates in coordination reaction of a metal organic skeletal material so as to realize functionalization, phospho-tungstic acid is directly added into a synthesis system, and immobilization is realized in the process of synthesis. The prepared phosphotungstic acid-metal organic skeleton reduces the frequency of contact with glucose through formation of a hydrogen bond with cellulose so as to reduce side reaction of glucose under the catalysis of acid, high glucose selectivity is obtained, and oriented conversion of cellulose to glucose can be realized; meanwhile, the effect of the hydrogen bond can weaken the effect of a hydrogen bond in cellulose, reduces the crystallization degree of cellulose, enables cellulose to be easier to hydrolyze and improves hydrolysis efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of boron-containing phenolic resin for friction materials
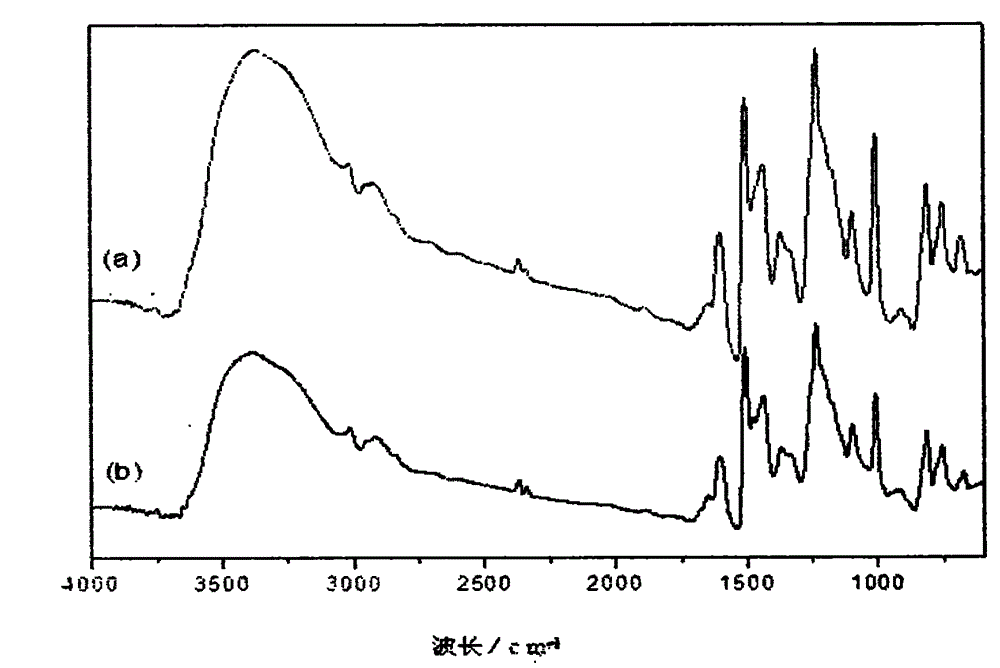
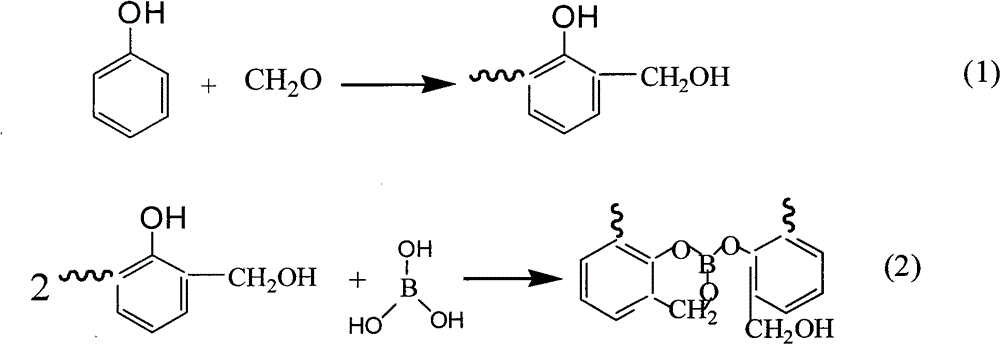
InactiveCN102746479AImprove heat resistanceImprove stabilityOther chemical processesAcid catalysisReaction temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of a boron-containing phenolic resin for friction materials, used for preparing the boron-containing phenolic resin. The method adopts a two-stage process, characterized by firstly reacting phenol with formaldehyde under the effect of acid catalysis to generate a phenolic resin with small molecular weight, and reacting the phenolic resin with small molecular weight with boric acid to generate a boron modified phenolic resin. By adjusting the ratio of raw materials, controlling the reaction temperature, time and other conditions, the boron modified phenolic resin is obtained. Various technical indicators of the boron-containing phenolic resin of the invention all meet the requirements of phenolic resin for friction materials GB / T2441-2009. Compared with the common phenolic resin, the friction materials prepared by using the boron-containing phenolic resin of the invention as a binder of friction materials have better high temperature stability of the friction coefficient and lower wear rate. The preparation method of the invention is similar to the process of the common phenolic resin, and the method is easy to popularize and apply.
Owner:XIANGFAN UNIVERSITY
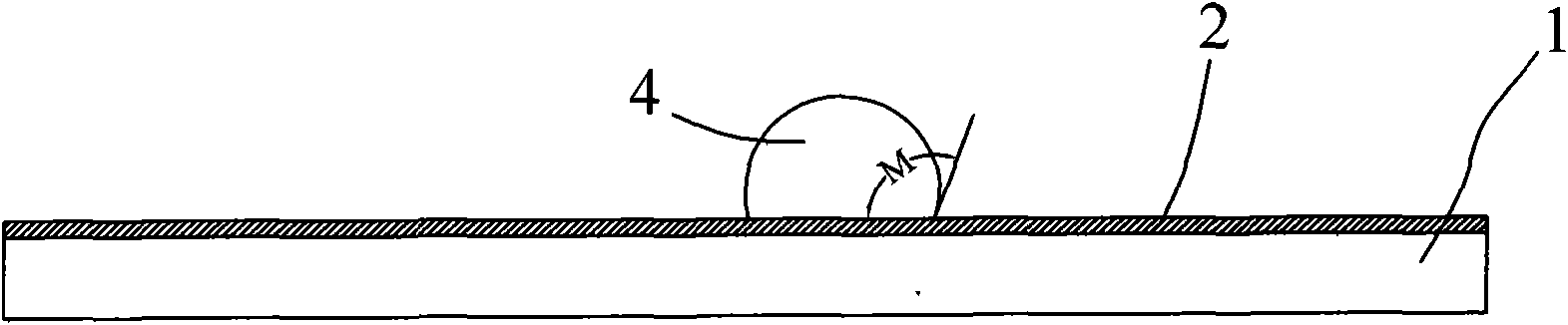
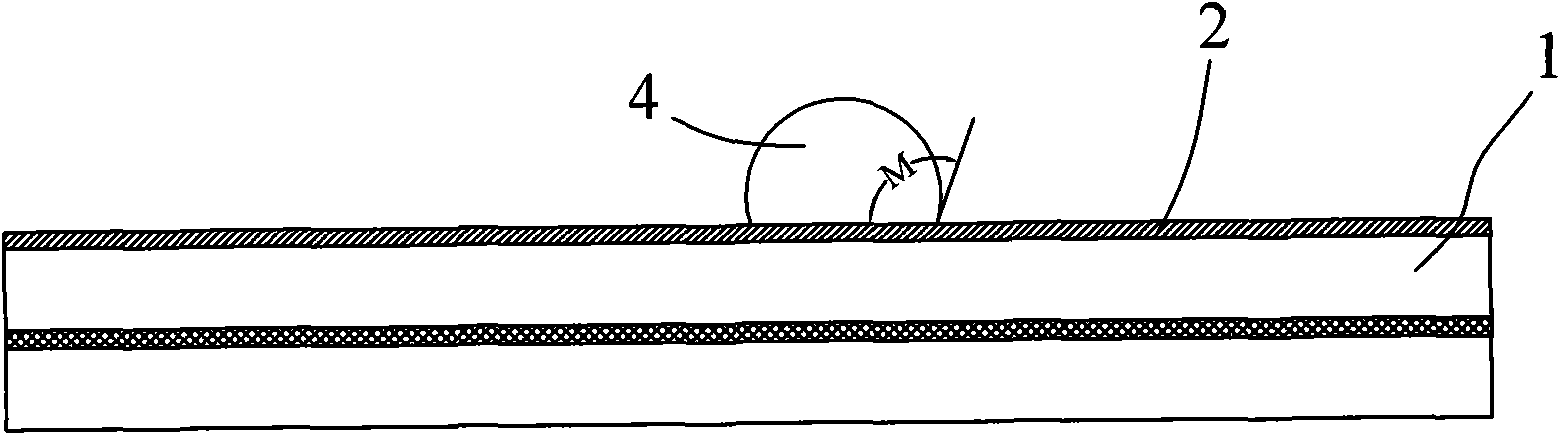
Hydrophobic solution, hydrophobic glass for vehicle and manufacturing method thereof
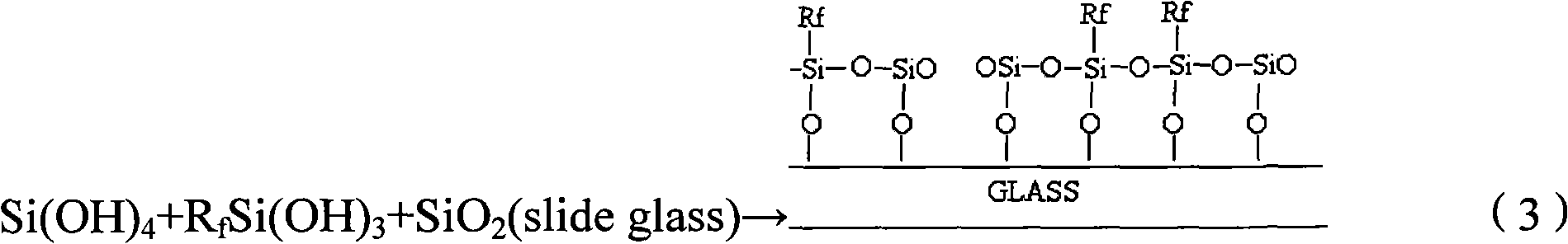
The invention belongs to the surface modification field of vehicle glass, and provides hydrophobic solution, a manufacturing method for hydrophobic glass for a vehicle and the hydrophobic glass for the vehicle. The hydrophobic solution consists of silane, silicate ester, alcohol, acid catalyst and stabilizing agent, wherein the number of carbon atoms of the silane is 10 to 18. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: coating the hydrophobic solution as claim 1 on the surface of a piece of glass to form a hydrophobic film layer, performing physical and chemical reaction on the glass, and thermally treating the glass to obtain the hydrophobic glass. The hydrophobic glass for the vehicle comprises the glass, the hydrophobic film layer formed by the hydrophobic solution is coated on the outer surface of the glass, and the contact angle of the hydrophobic film layer is more than 90 degrees. The silicate ester and the long-chain silane produce hydrolysis reaction under the condition of acid catalysis, and the generated hydrolysis product and a SiOH group on the surface of the fresh glass produce condensation polymerization reaction to form a firm silicon-oxygen chemical bond combination so as to improve the adhesion of the hydrophobic film layer and the glass.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINYI AUTOMOBILE GLASS
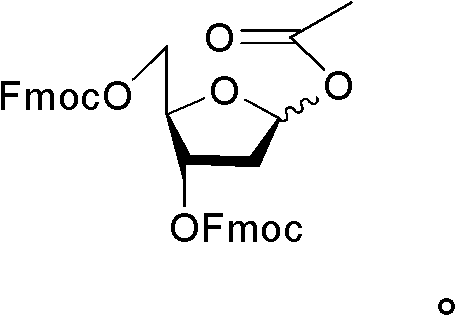
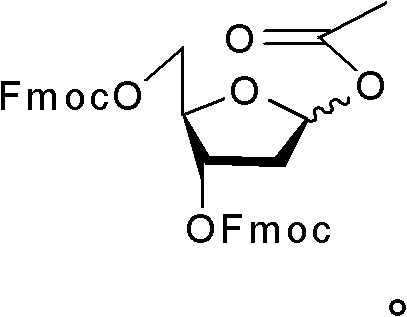
1-acetoxyl-2-deoxy-3, 5-di-O-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl acyl-D-ribofuranose and application
ActiveCN102070679ARaise the ratioHigh synthetic yieldEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesAcetic acidAcetic anhydride
The invention discloses 1-acetoxyl-2-deoxy-3, 5-di-O-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl acyl-D-ribofuranose, which has a following structural formula as the accompanying drawing. A method for preparing the 1-acetoxyl-2-deoxy-3, 5-di-O-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl acyl-D-ribofuranose comprises the following steps: adding 1-methoxyl-2-deoxy-3, 5-di-O-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl acyl-D-ribofuranose and acetic anhydride into solvents; and then, adding catalysts to carry out nucleophilic substitution reaction under the acid catalysis to obtain the 1-acetoxyl-2-deoxy-3, 5-di-O-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl acyl-D-ribofuranose, wherein the solvents are acetic acid and ethyl acetate, the catalysts are sulphuric acid, the reaction temperature is between -30 DEG C and 30 DEG C, and the reaction time t is higher than 0 and lower than or equal to 4 hours. The 1-acetoxyl-2-deoxy-3, 5-di-O-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl acyl-D-ribofuranose disclosed by the invention can be used as a midbody to synthesize 2-deoxy-5-azacytidine.
Owner:QILU PHARMA HAINAN +1
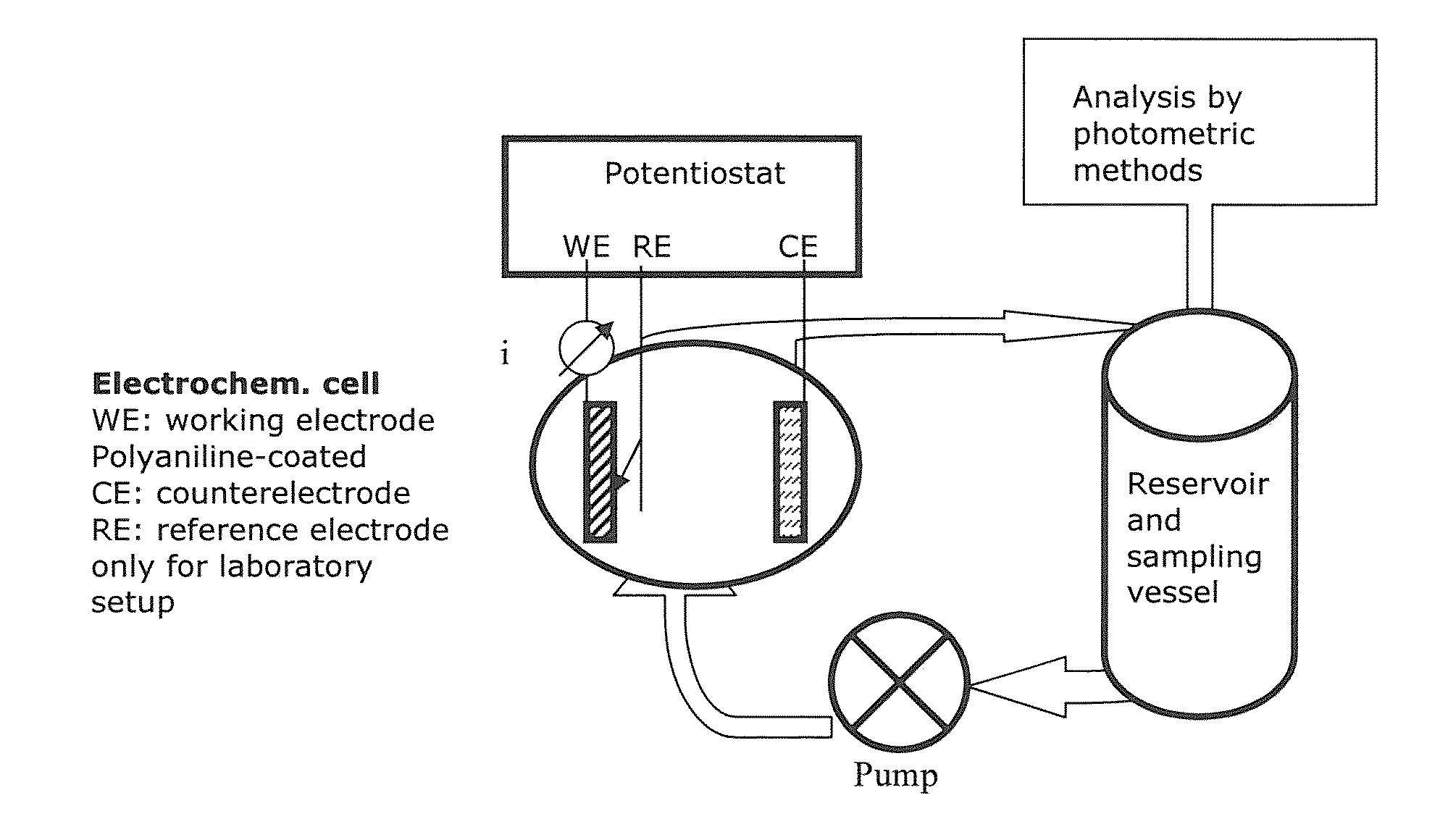
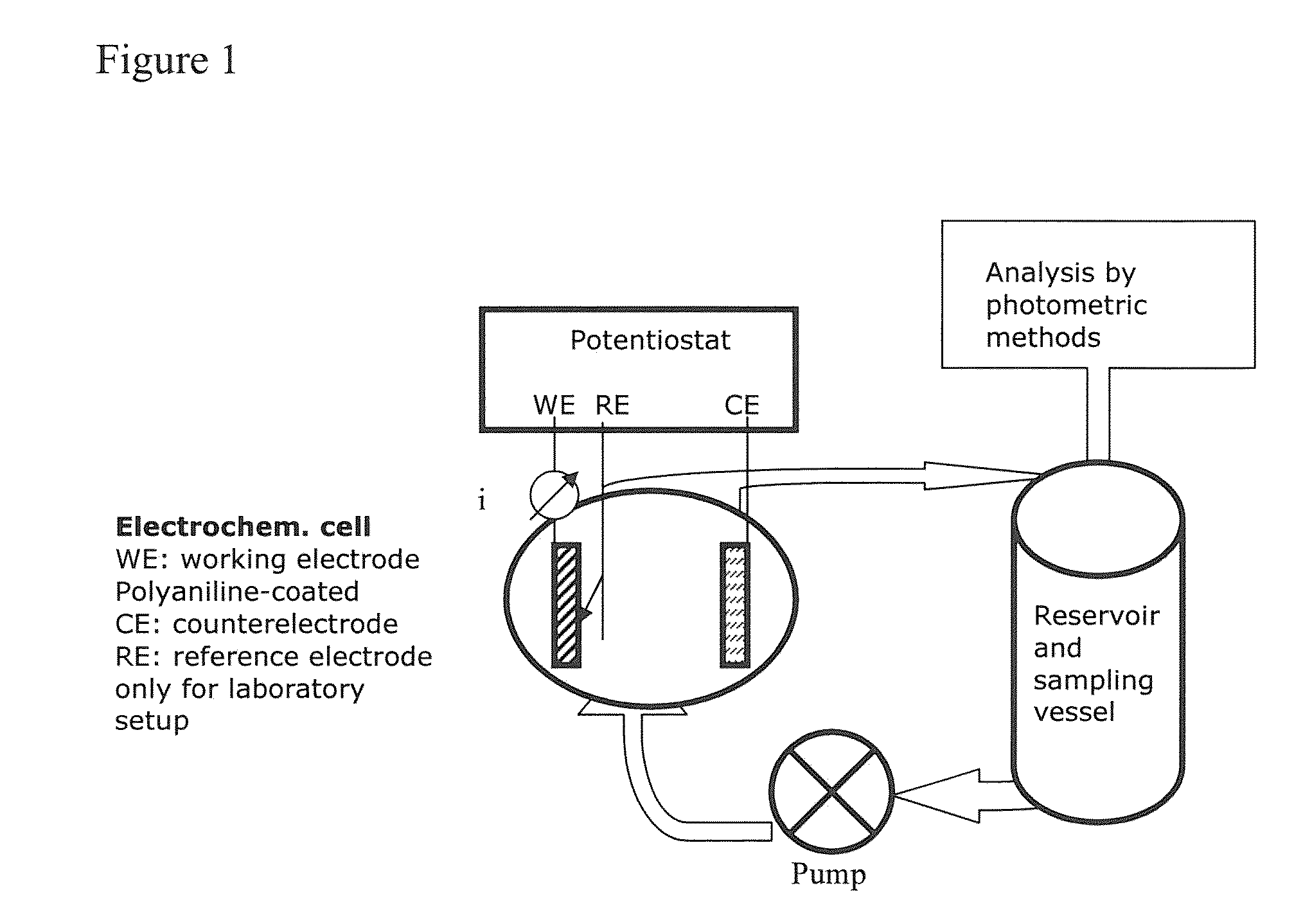
Preparation and use of novel polyanilines for water treatment
InactiveUS20100307974A1Electrostatic separatorsFinal product manufacturePolyaniline derivativesSulfur
The invention relates to a polyaniline, comprising aniline units and organosulphur units, characterized in that the polyaniline is doped and has a number average degree of polymerization of approximately 5 to approximately 50. The scope of the invention also includes a process for the preparation of polyaniline, wherein aniline and at least one organosulphur unit are converted to a polyaniline derivative in an oxidative, acid-catalyzed polymerization reaction. A subject of the invention is also a coated substrate which is coated with the polyaniline according to the invention and also a process for the coating of the substrate. The scope of the invention furthermore also includes a coating composition which is suitable for the coating of the substrate. The invention thus also relates to a process for the preparation of the coating composition. A subject of the invention is also the use of polyaniline which is doped and has sulphur in the main polymer chain for water treatment and / or for the purification of air and also a purification reactor for carrying out the purification process.
Owner:SUD CHEM IP GMBH & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com