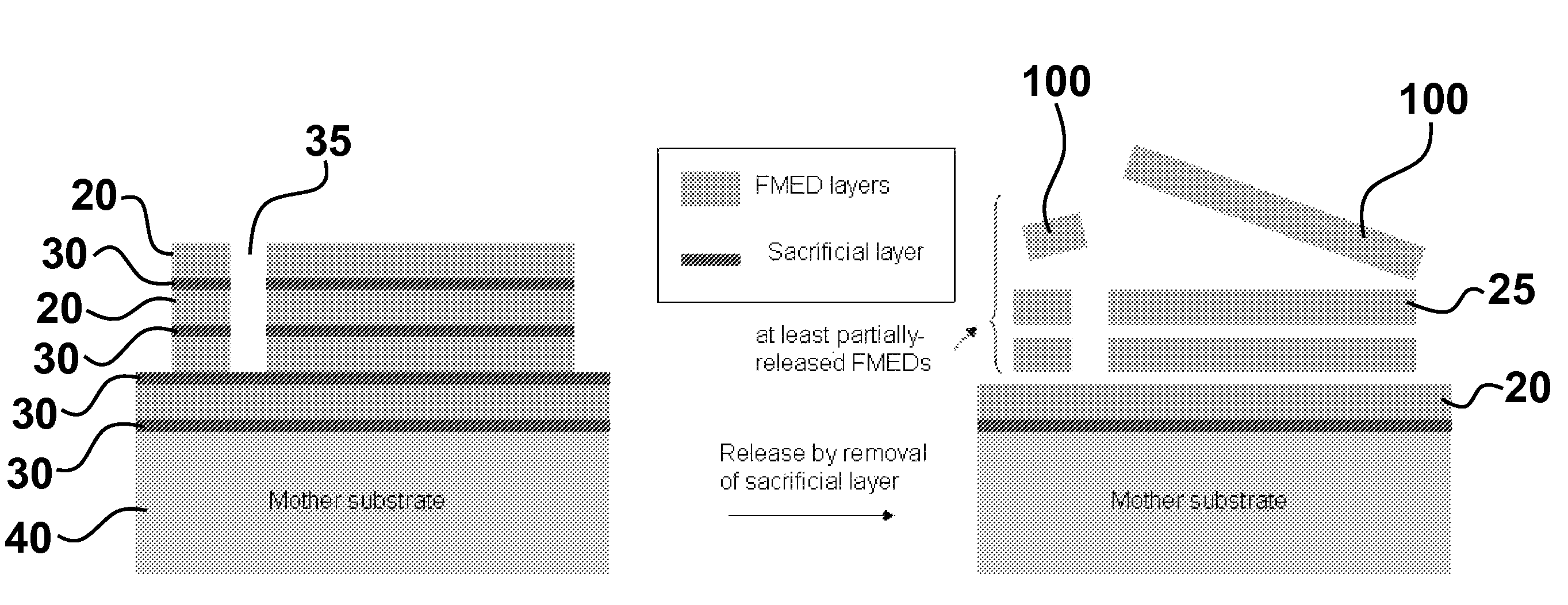Patents
Literature
23490results about "Adhesives" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
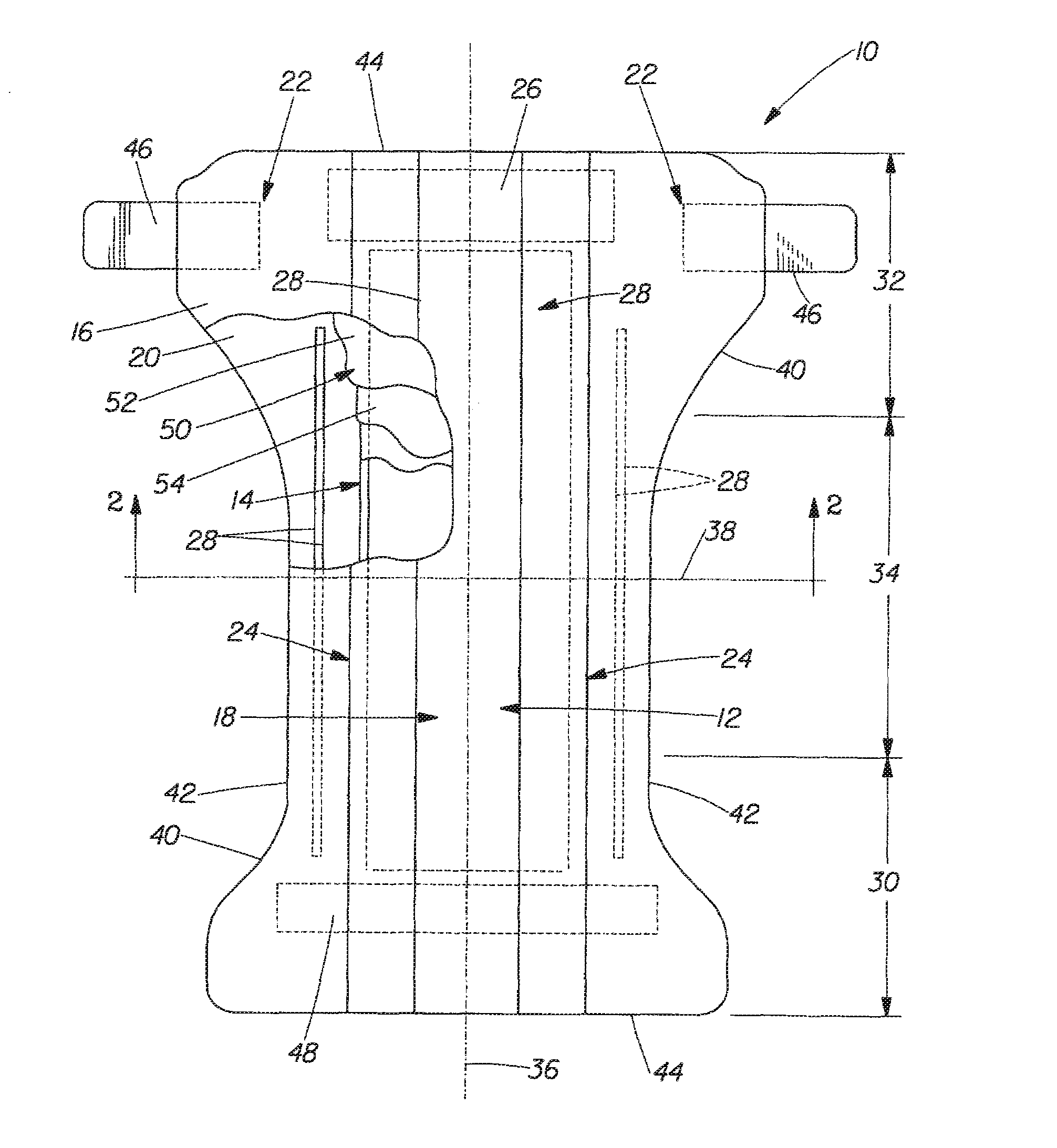
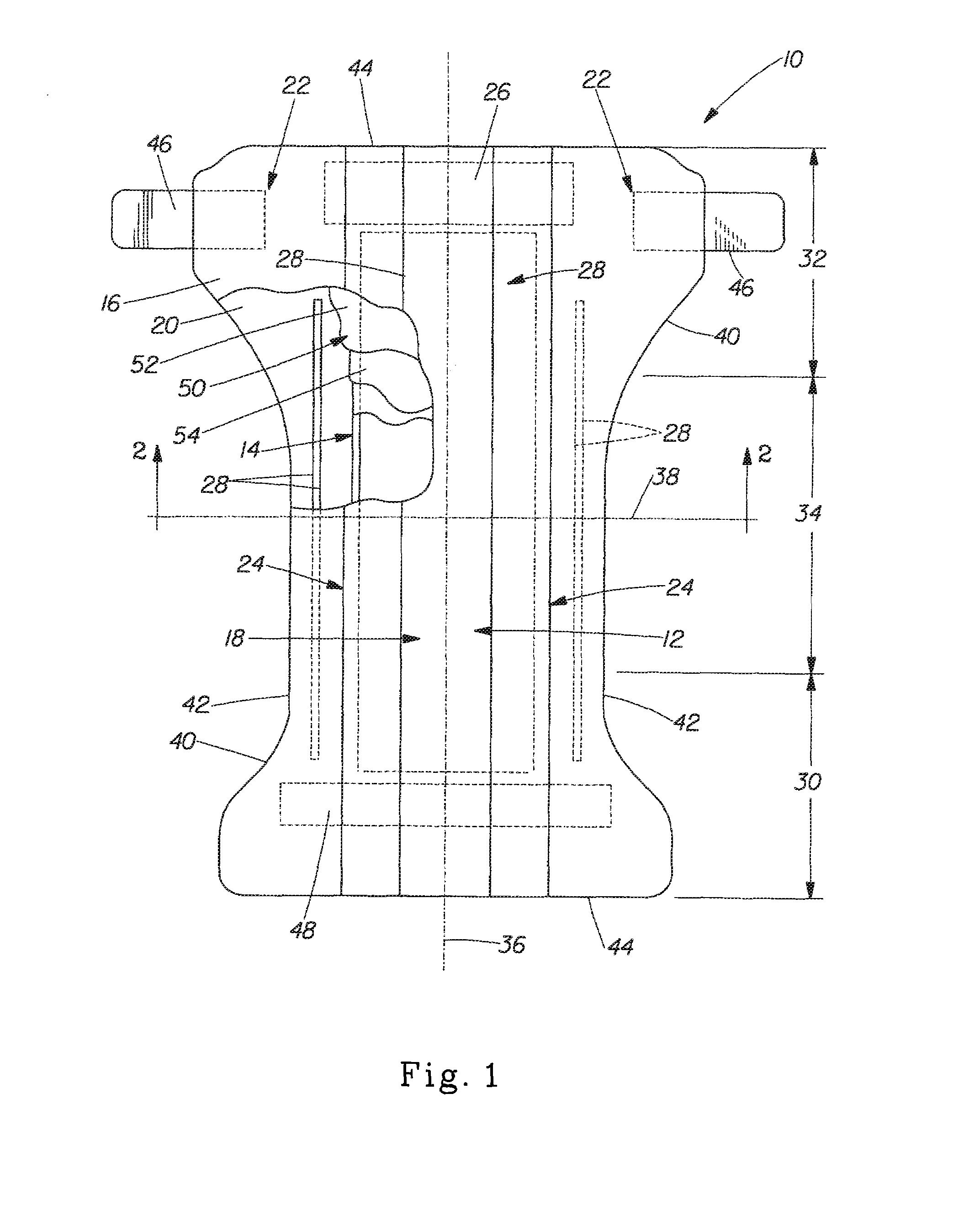
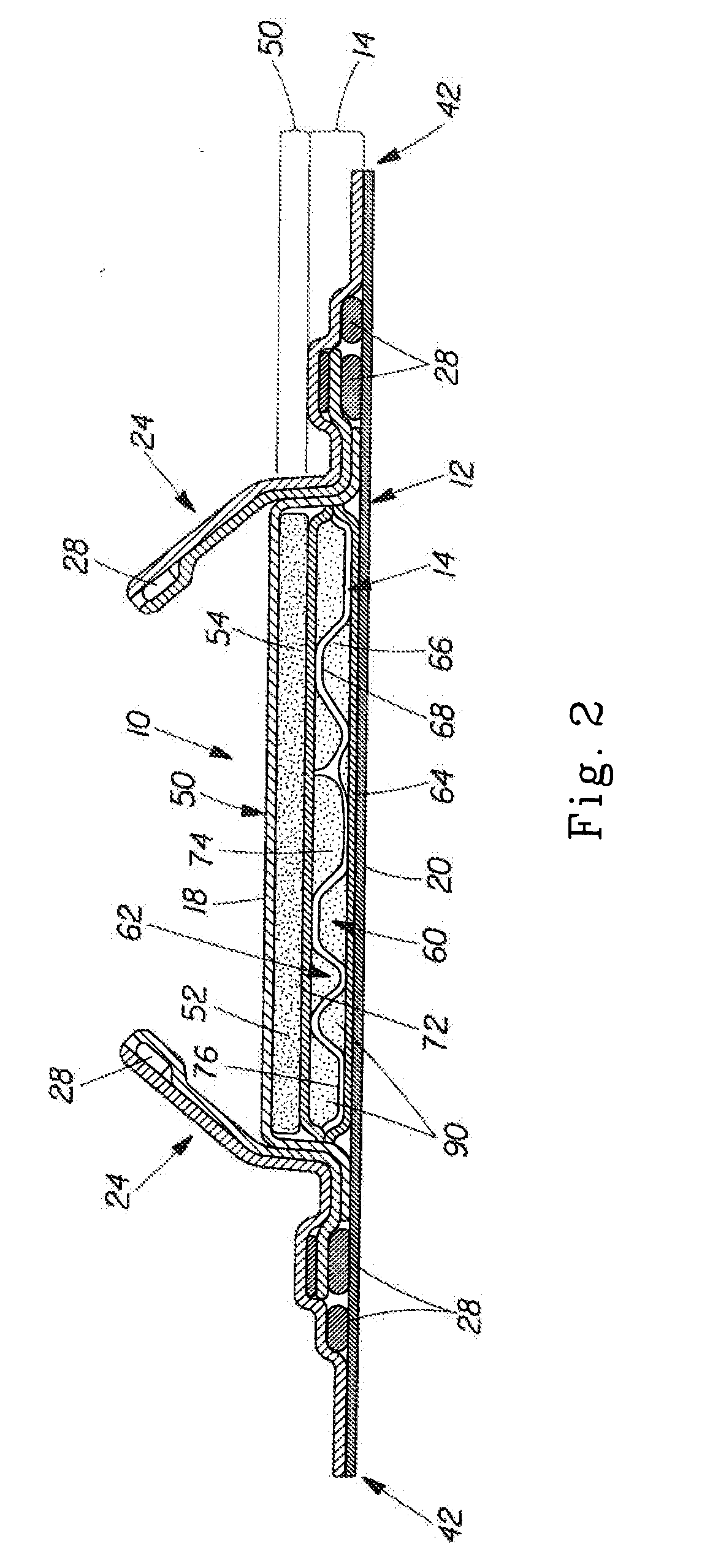
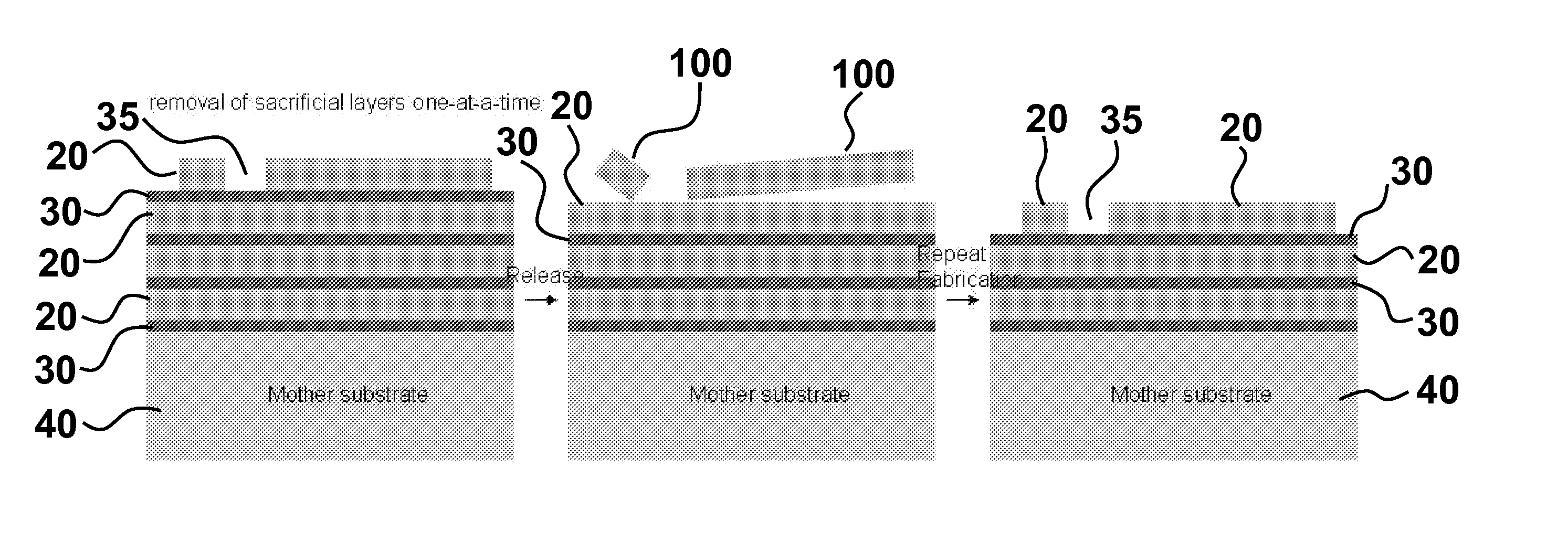
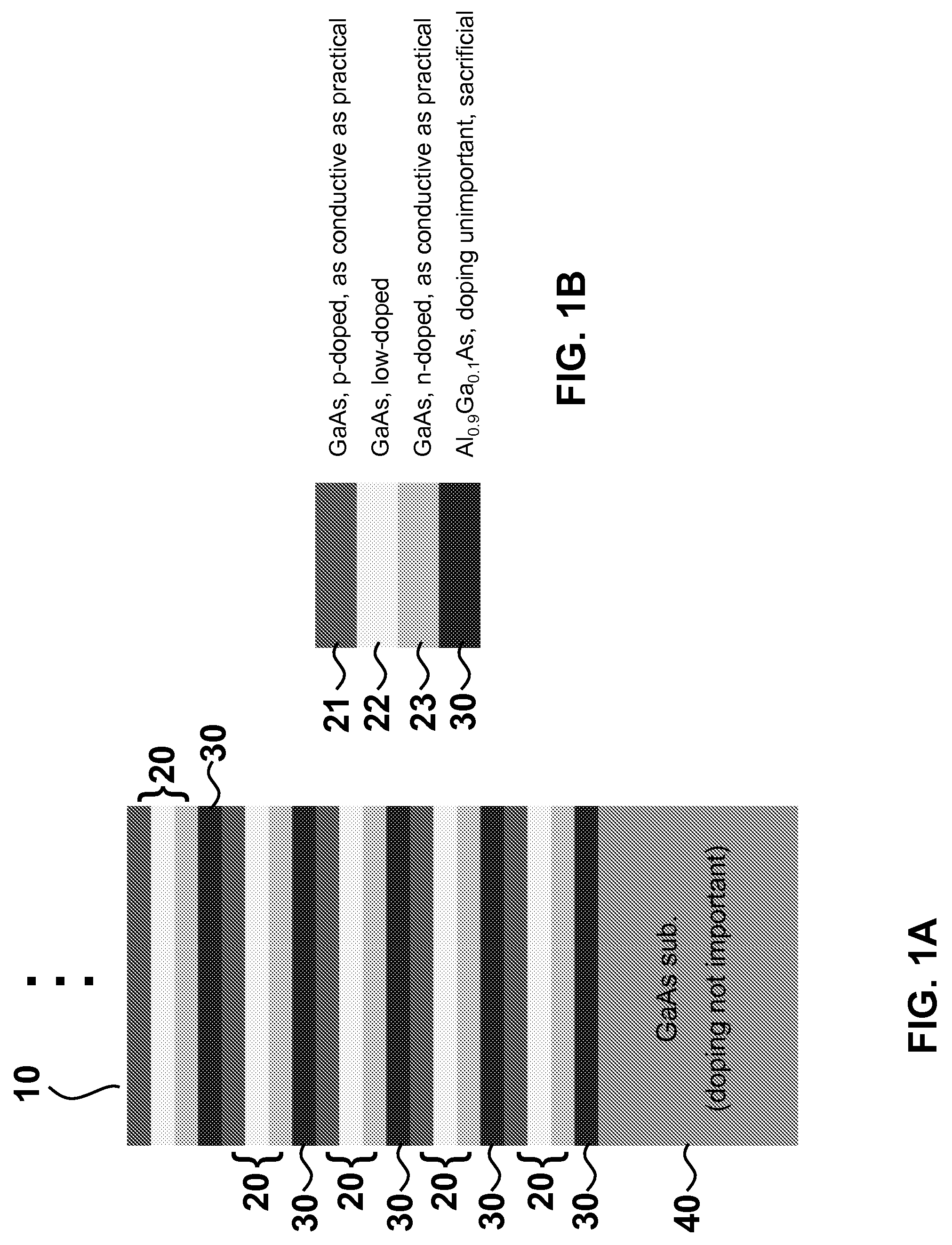
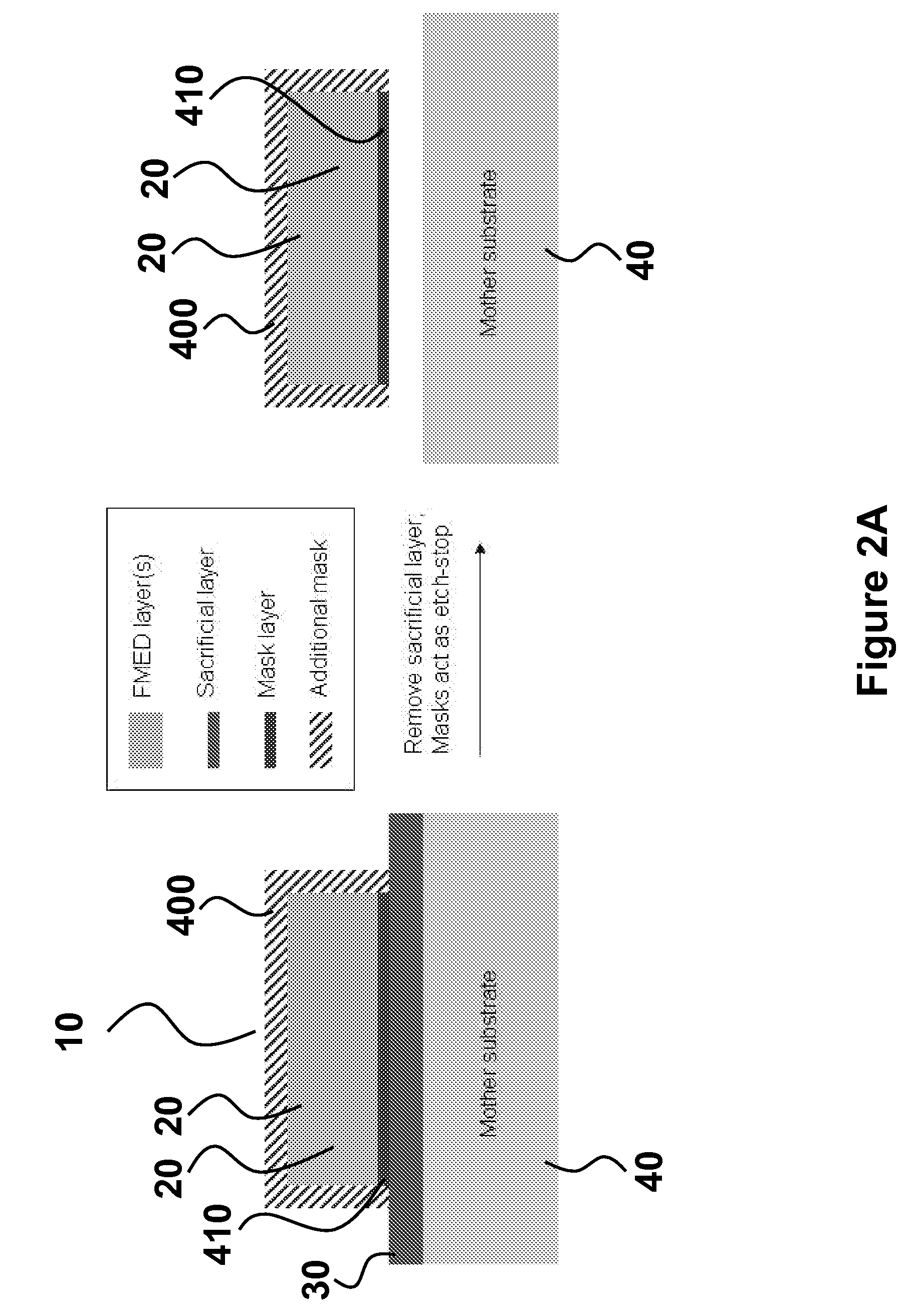
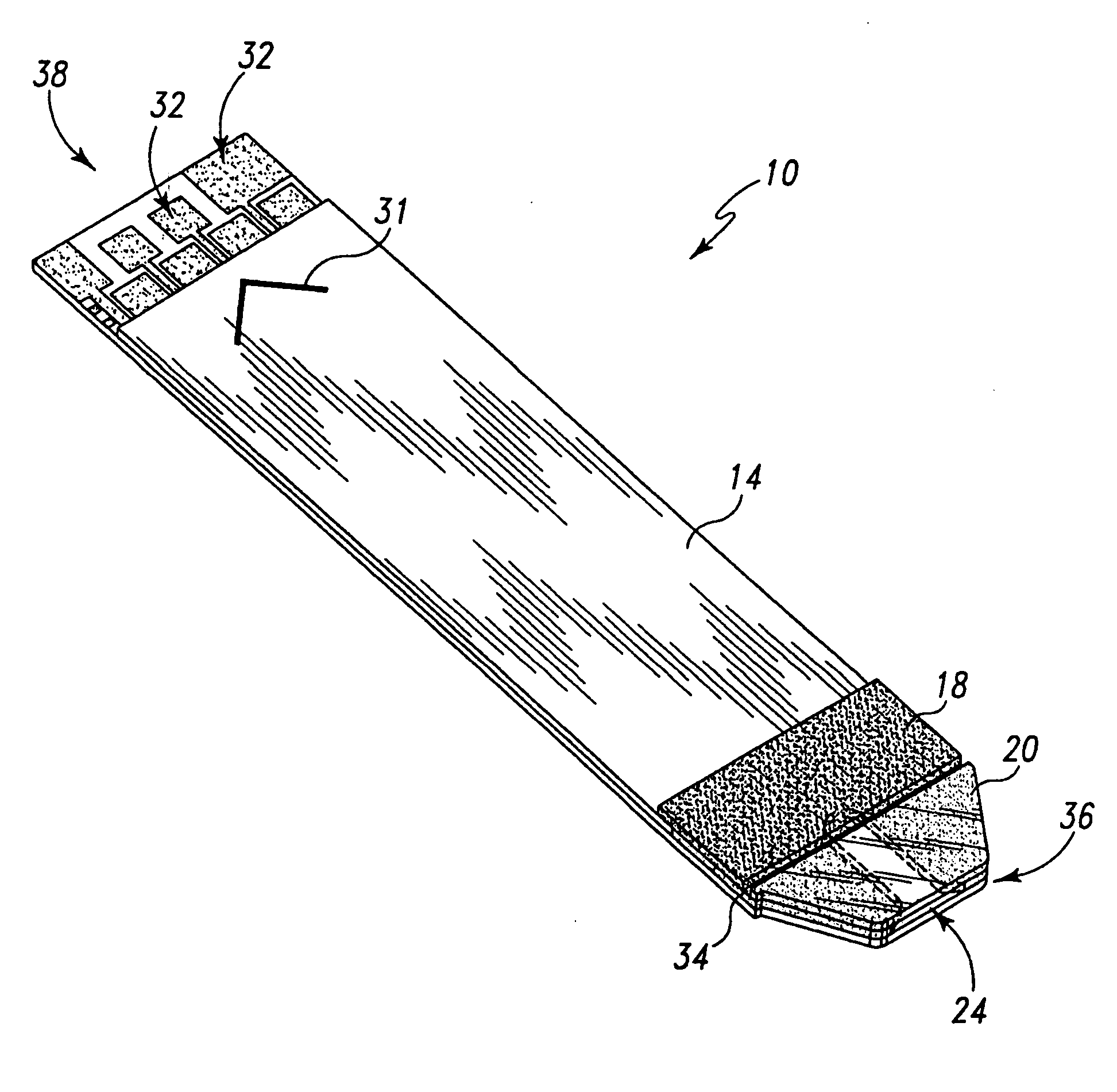
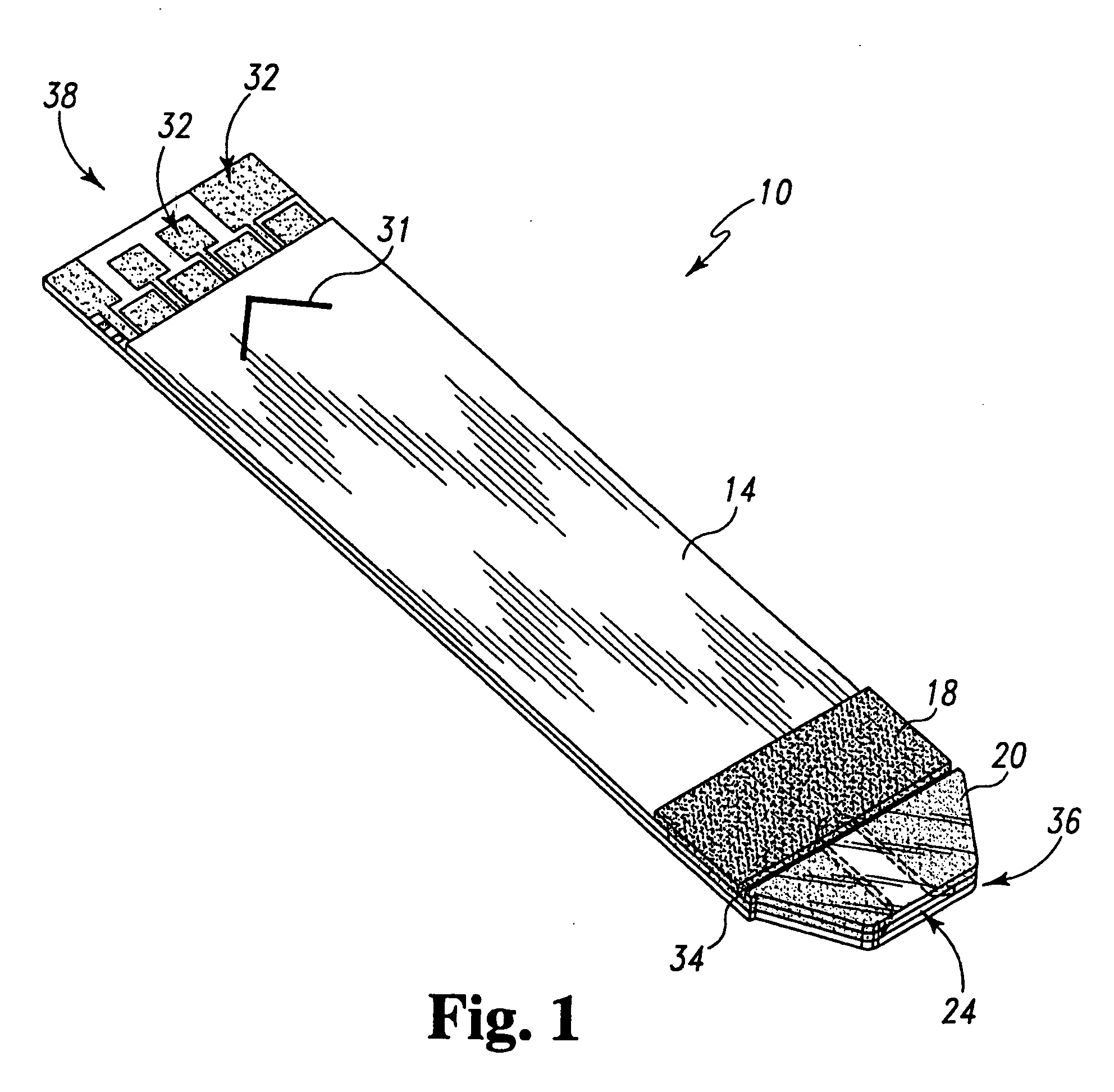
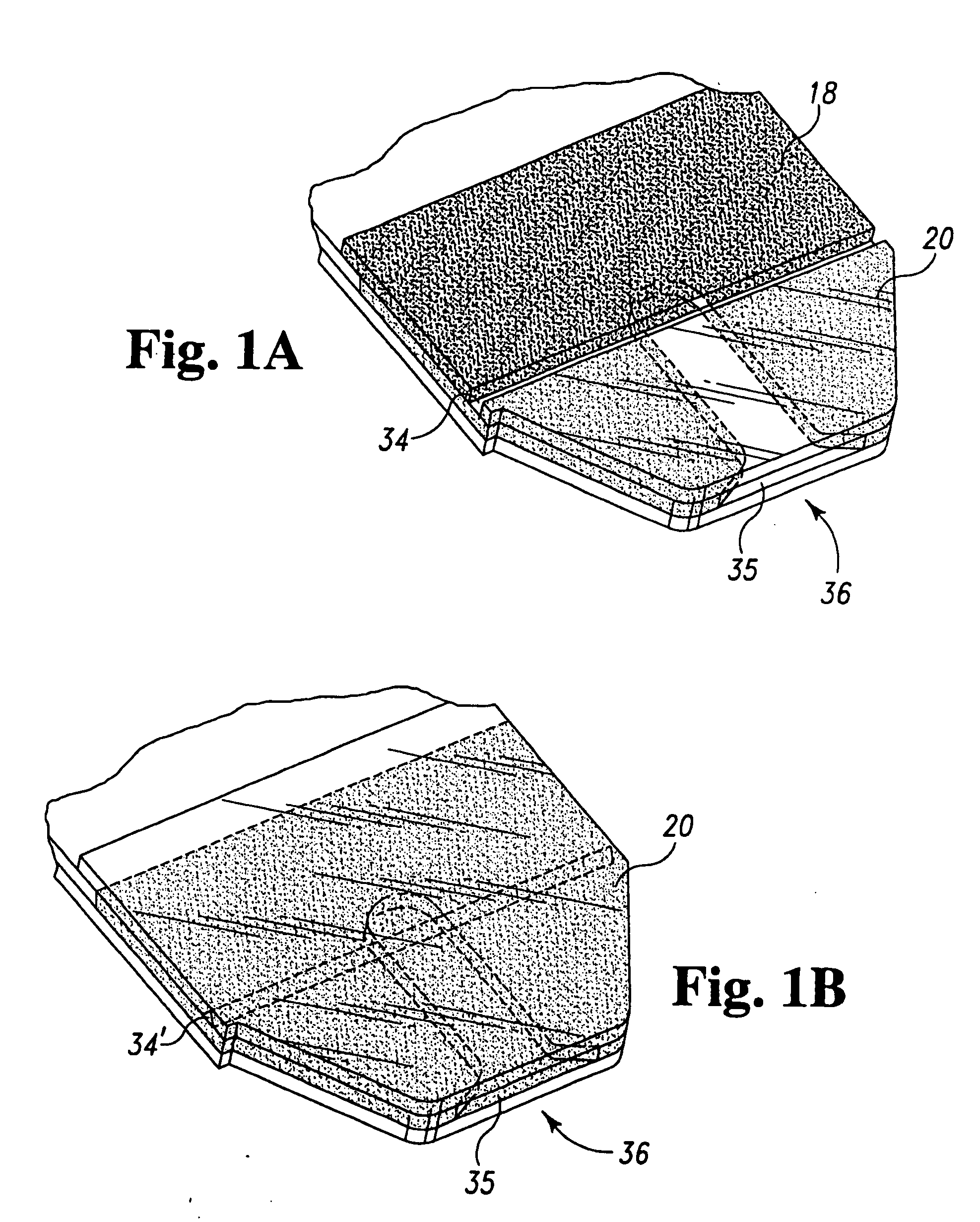
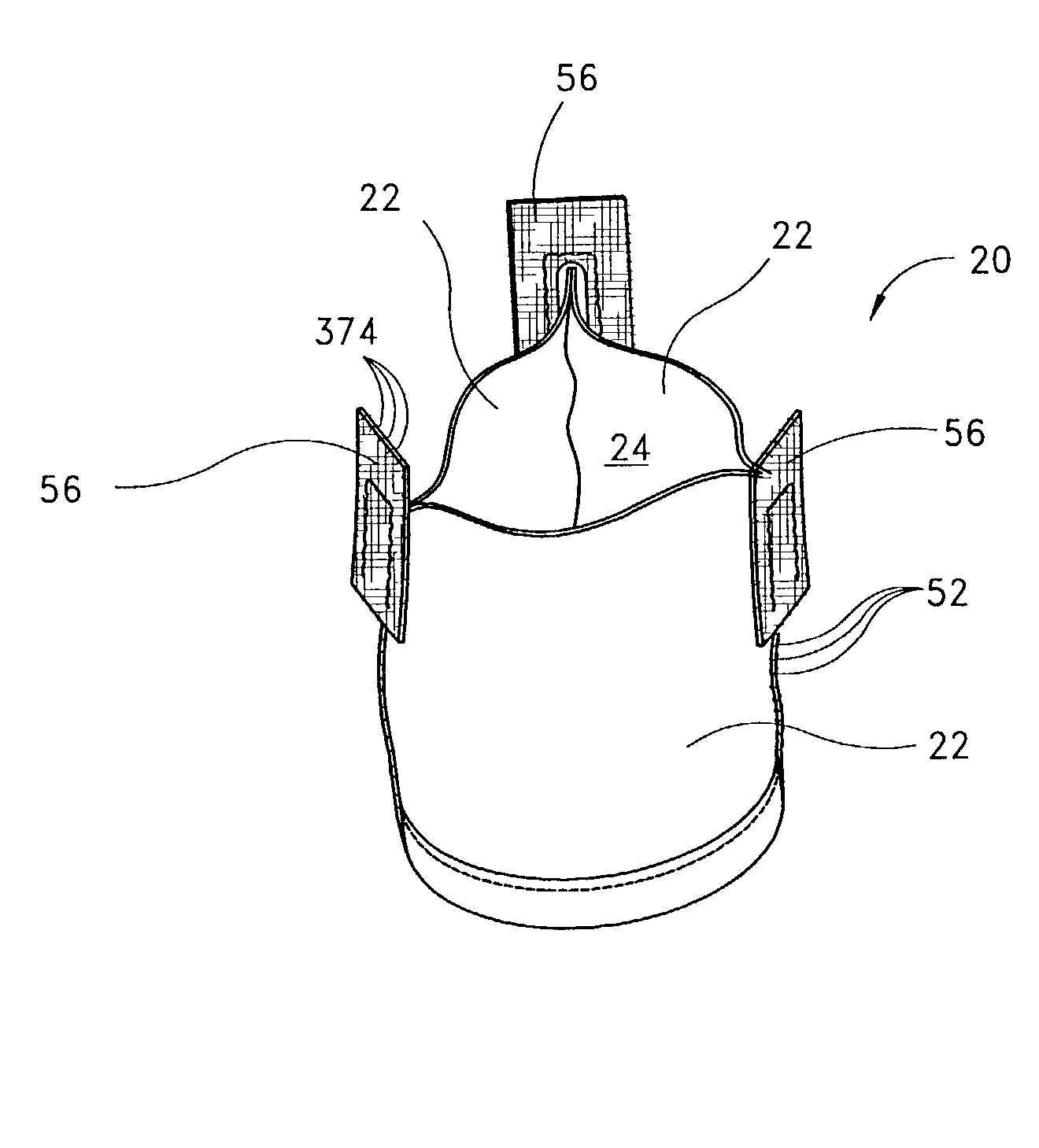
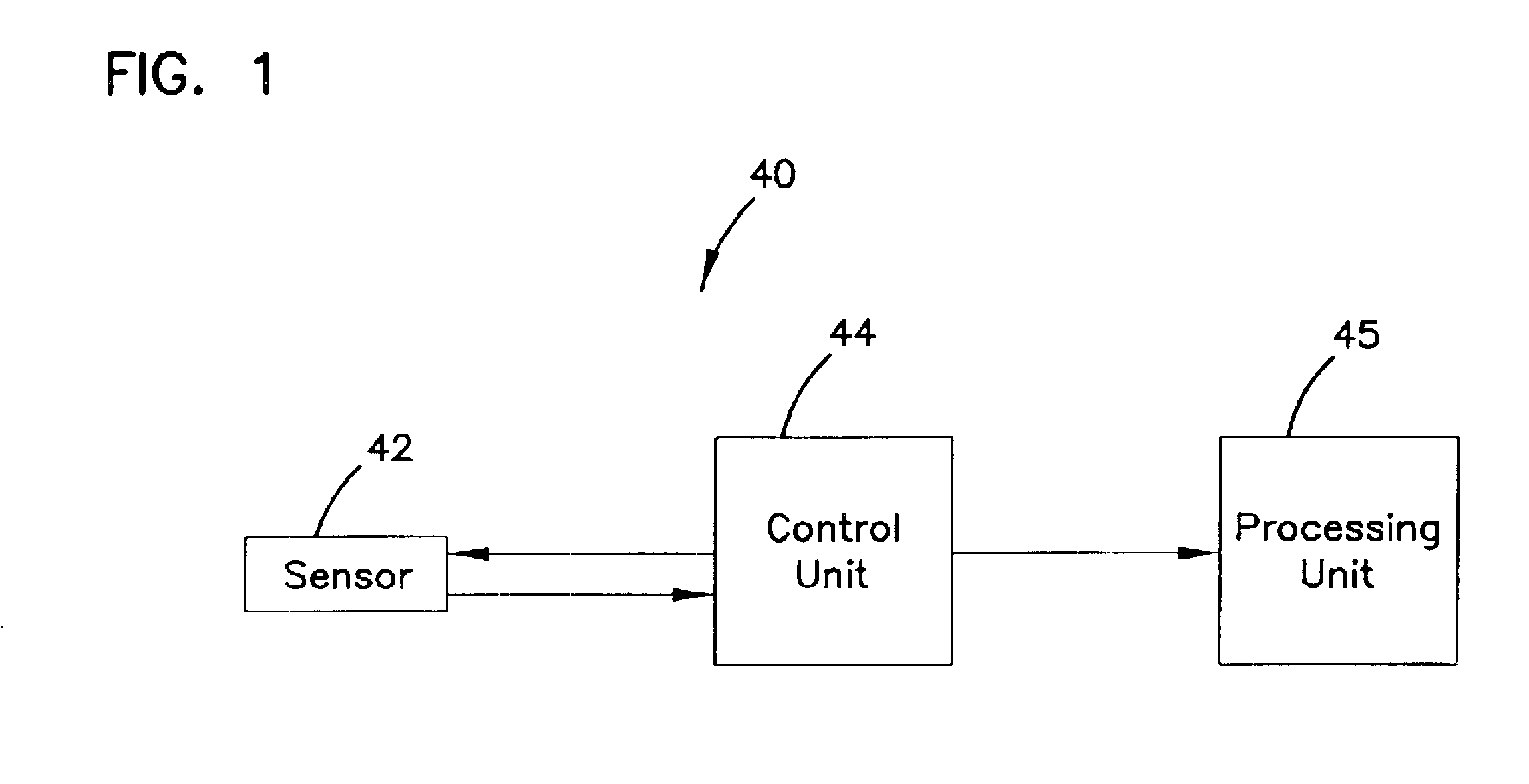
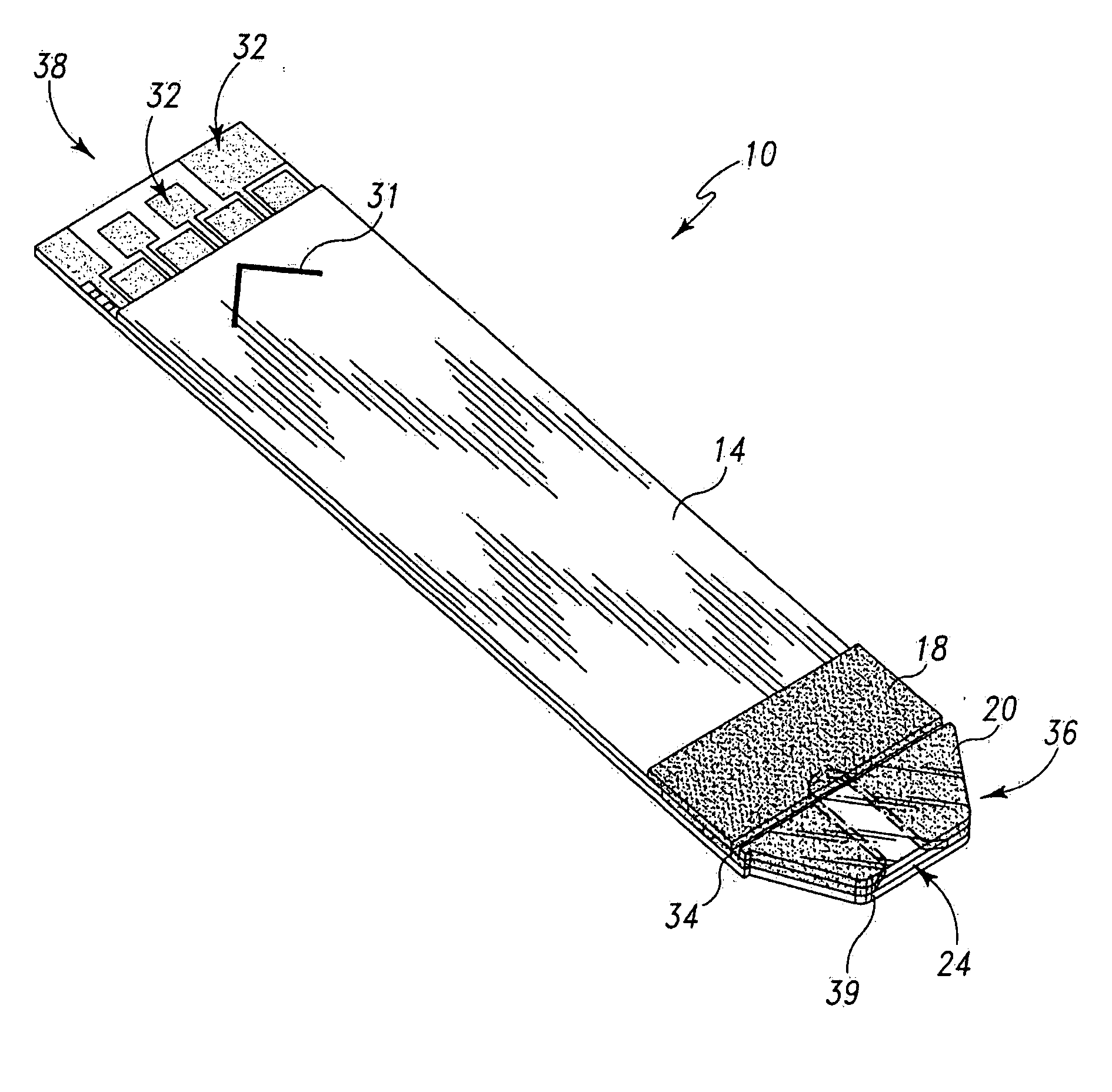
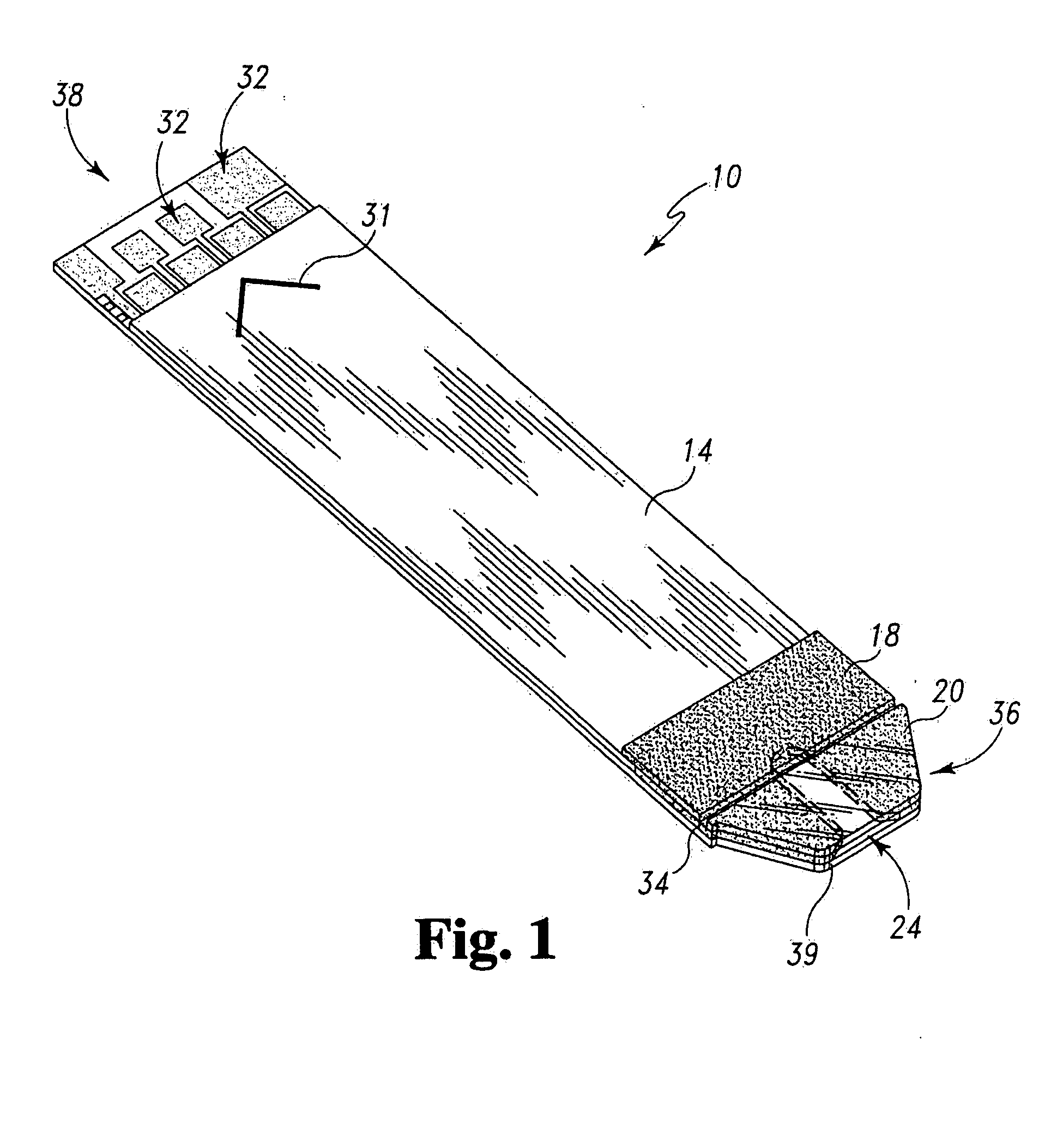
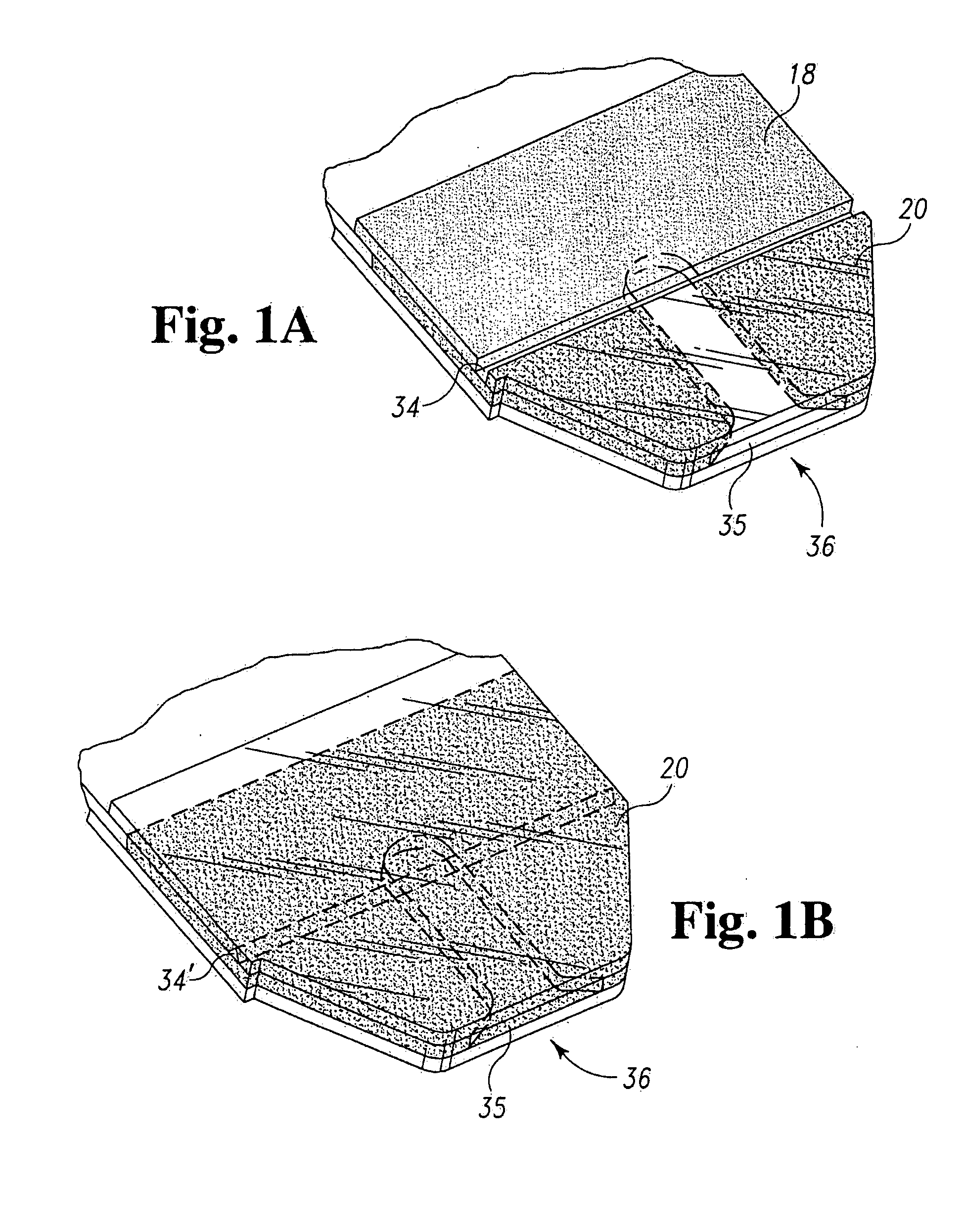
Systems and methods for manufacture of an analyte-measuring device including a membrane system
InactiveUS20060015020A1Minimized in sizeMaximize adhesionLaminationLamination apparatusAnalyteBiomedical engineering
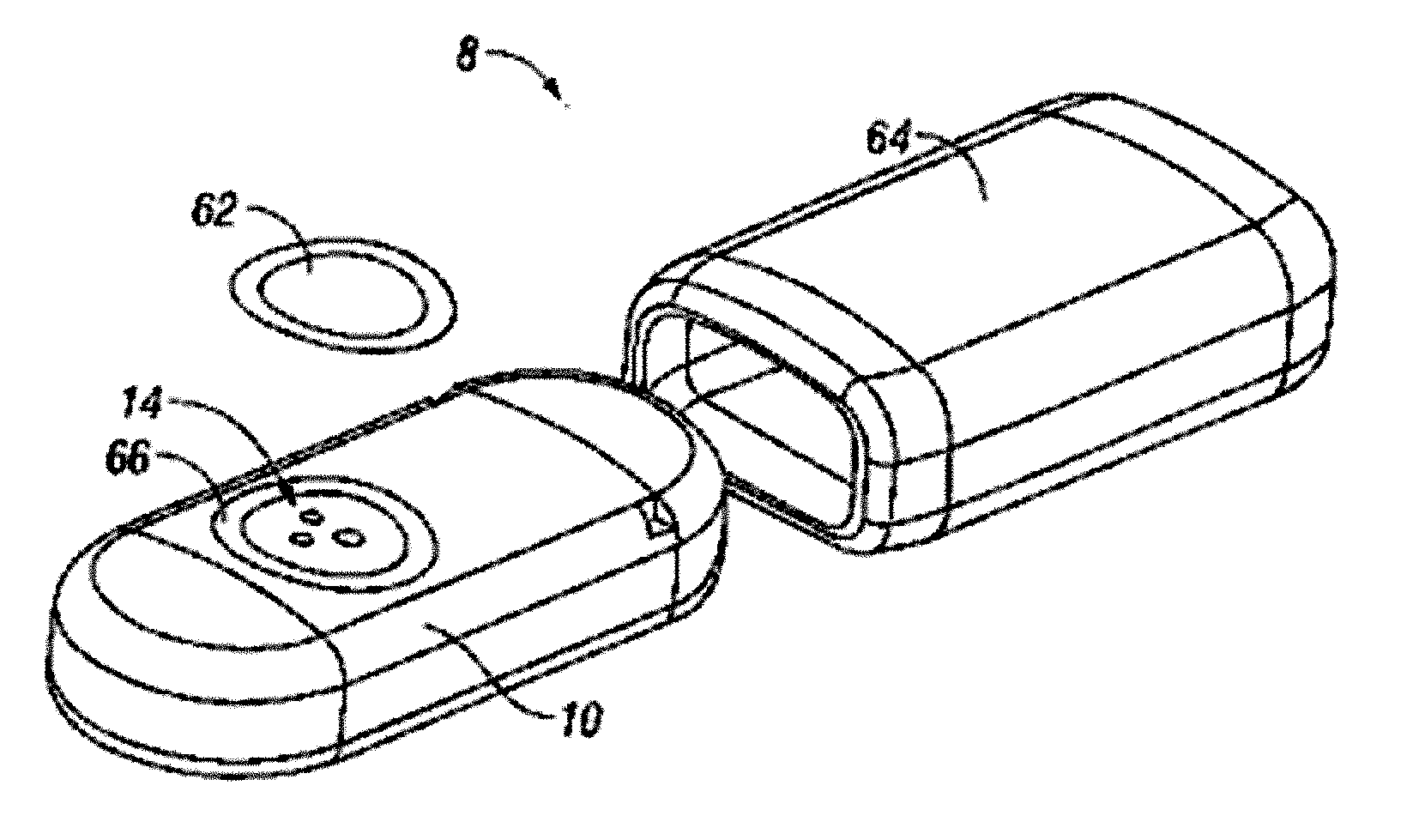
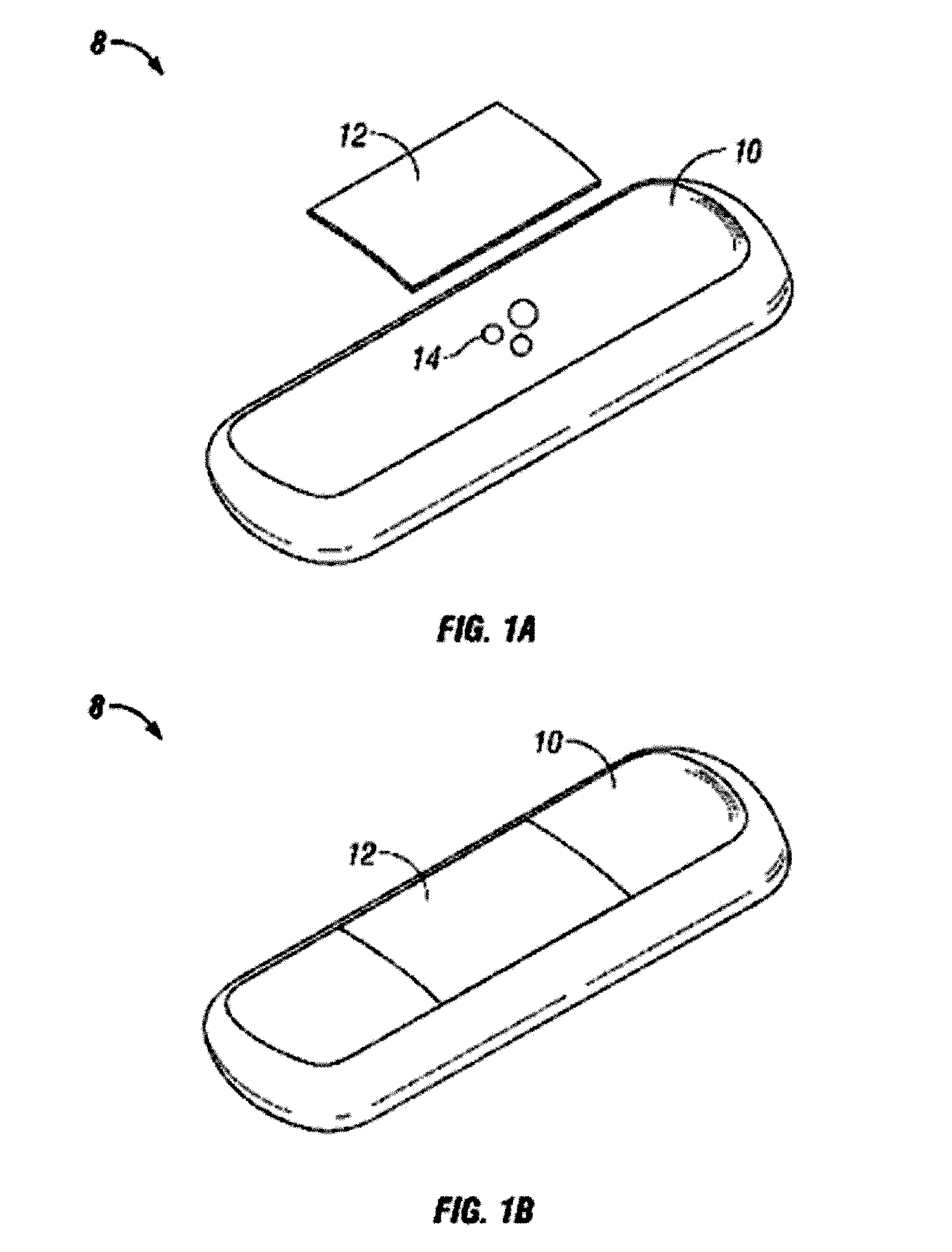
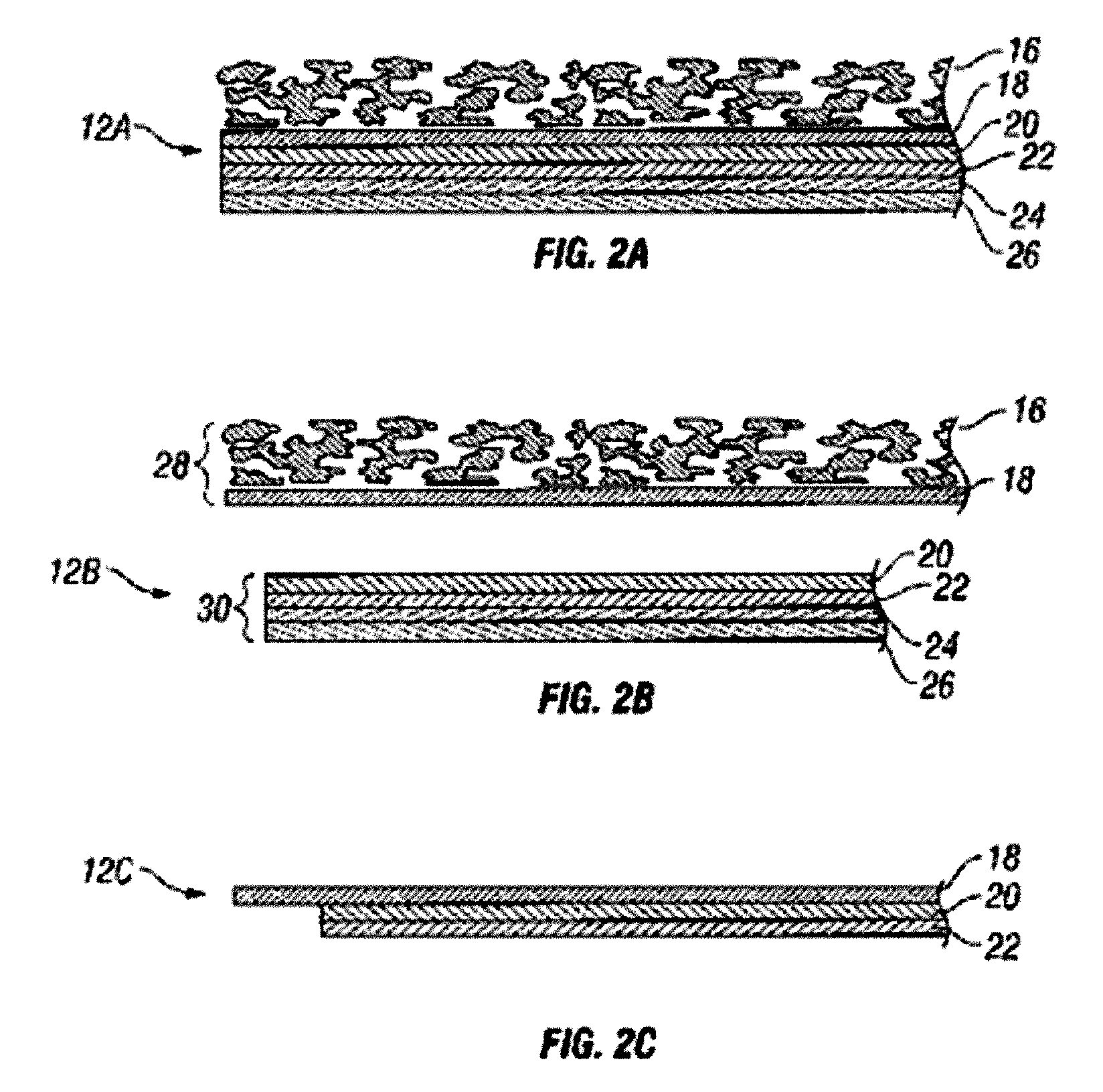
Abstract of the DisclosureSystems and methods for manufacture of an analyte-measuring device, including adhering a membrane system that allows the passage of the analyte therethrough to a sensing mechanism. The implantable analyte-measuring device includes a body formed from a material that is substantially similar to the membrane system so as to enable sufficiently strong adhesion therebetween, which enables a sufficiently strong adhesive joint capable of withstanding in vivo cellular forces. In some embodiments, the device body includes an insert to which the membrane system is adhered, wherein the insert is formed from a material substantially similar to the membrane system to enable strong adhesion therebetween. The analyte-measuring device is designed with optimized device sizing and maximum membrane adhesion and longevity to enable controlled transport of analytes through the membrane system in vivo with improved device performance.
Owner:DEXCOM
Carbon nano-tube thin film structure and preparation method thereof
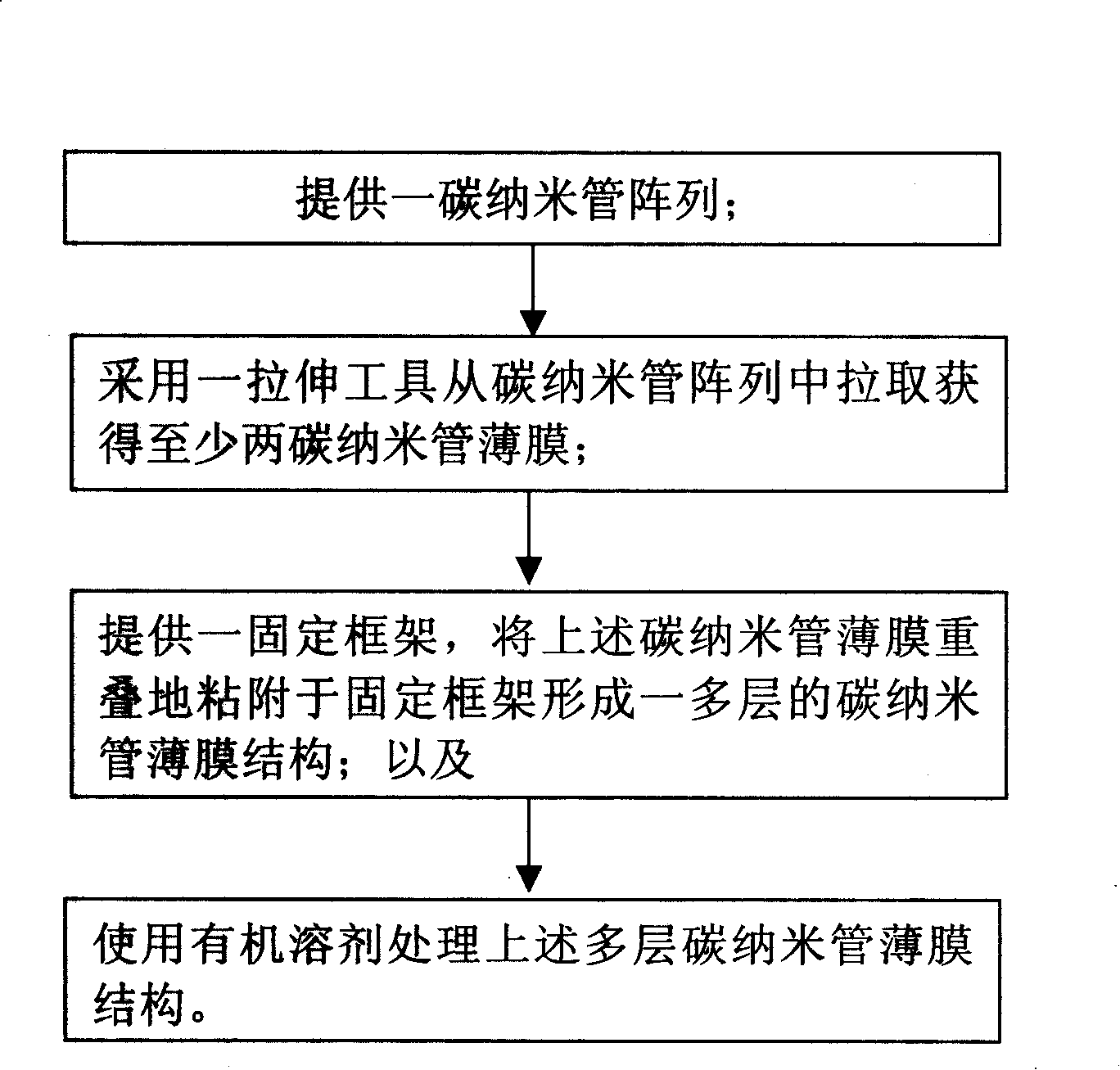
ActiveCN101239712ASmall surface to volume ratioNon stickyMaterial nanotechnologyLamination ancillary operationsOrganic solventFixed frame
The present invention provides a preparing method of carbon nanotube film structure, including following steps: providing a carbon nanotube array; adopting a pulling tool to acquire at least two carbon nanotube films from the carbon nanotube array; providing a fixed frame, forming a multiple-layer carbon nanotube film structure by overlap adhereing the carbon nanotube film in the fixed frame; and treating the multiple-layer carbon nanotube film by an organic solvent. The carbon nanotube film structure prepared by the method includes at least two layers overlapped and cross-over installed carbon nanotube film, which includes multiple carbon nanotube bundle end to end and arranged in the direction, the multiple-layer carbon nanotube film further includes millipore crosswise formed by multiple carbon nanotube bundles.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
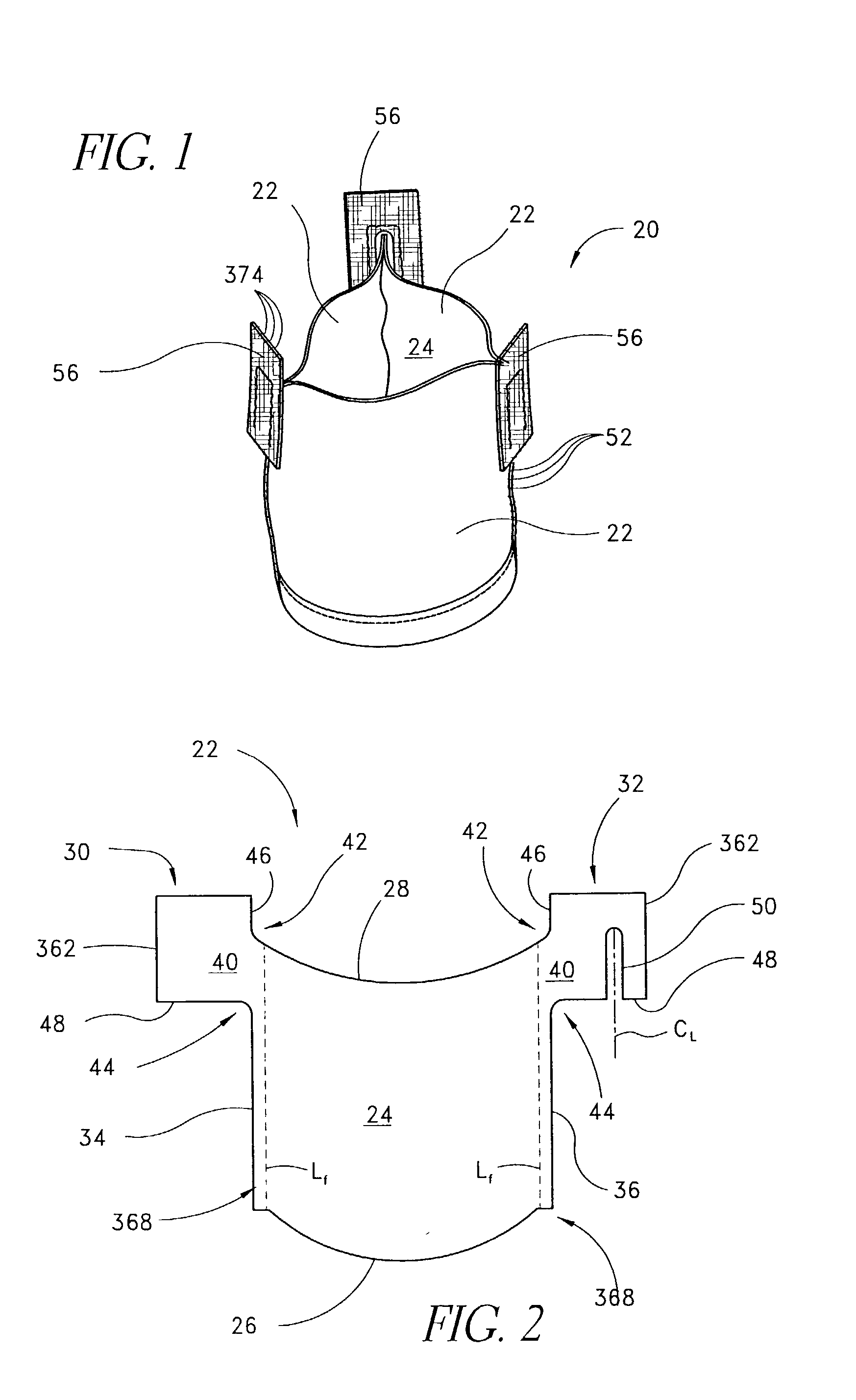
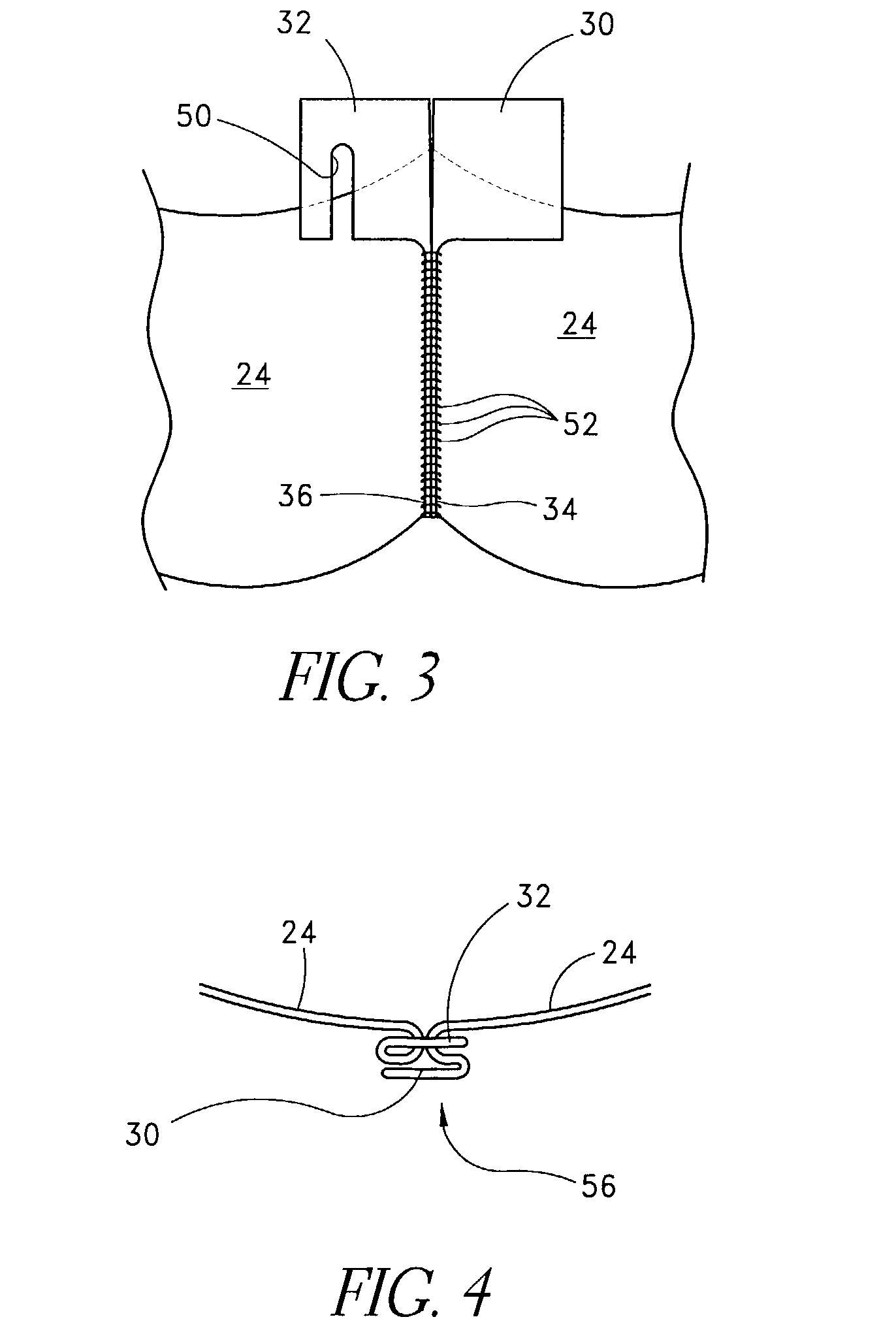
Disposable Absorbent Article With Substantially Continuously Distributed Absorbent Particulate Polymer Material And Method
A disposable absorbent core comprises first and second absorbent layers each comprising an absorbent particulate polymer material such that the absorbent particulate polymer material is substantially continuously distributed across an absorbent particulate polymer material area. A disposable absorbent article and method for making the absorbent core are also disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
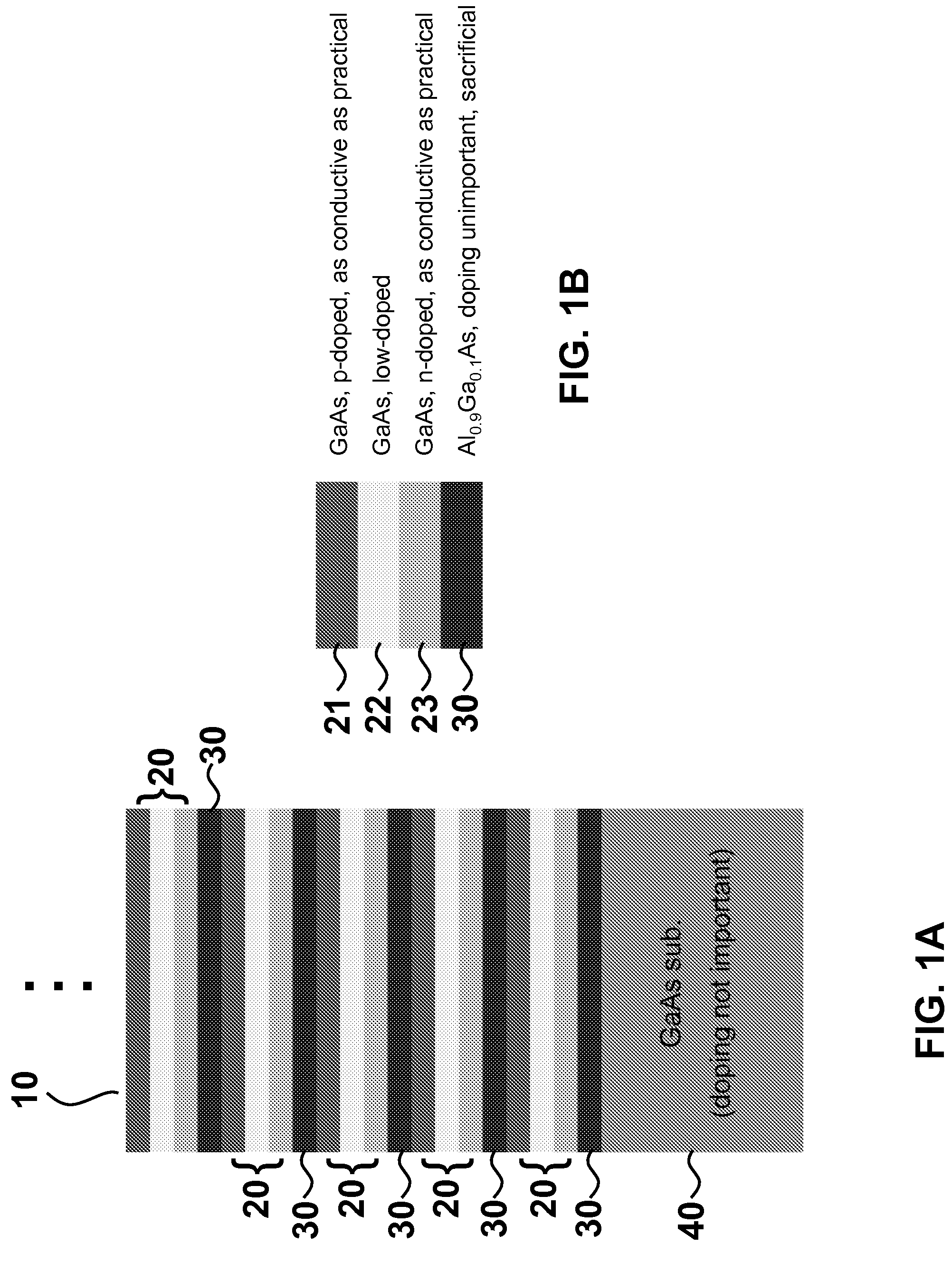
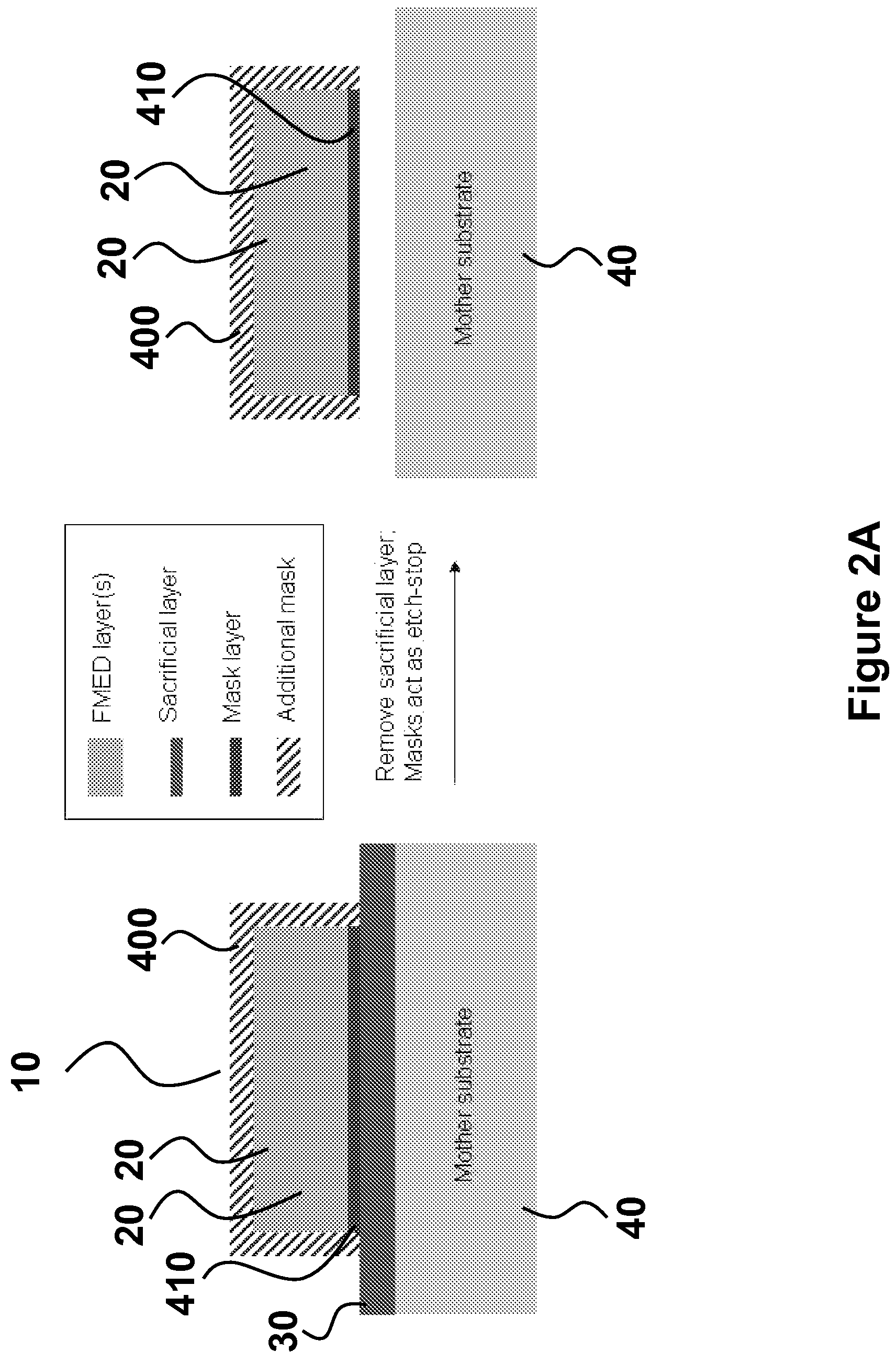
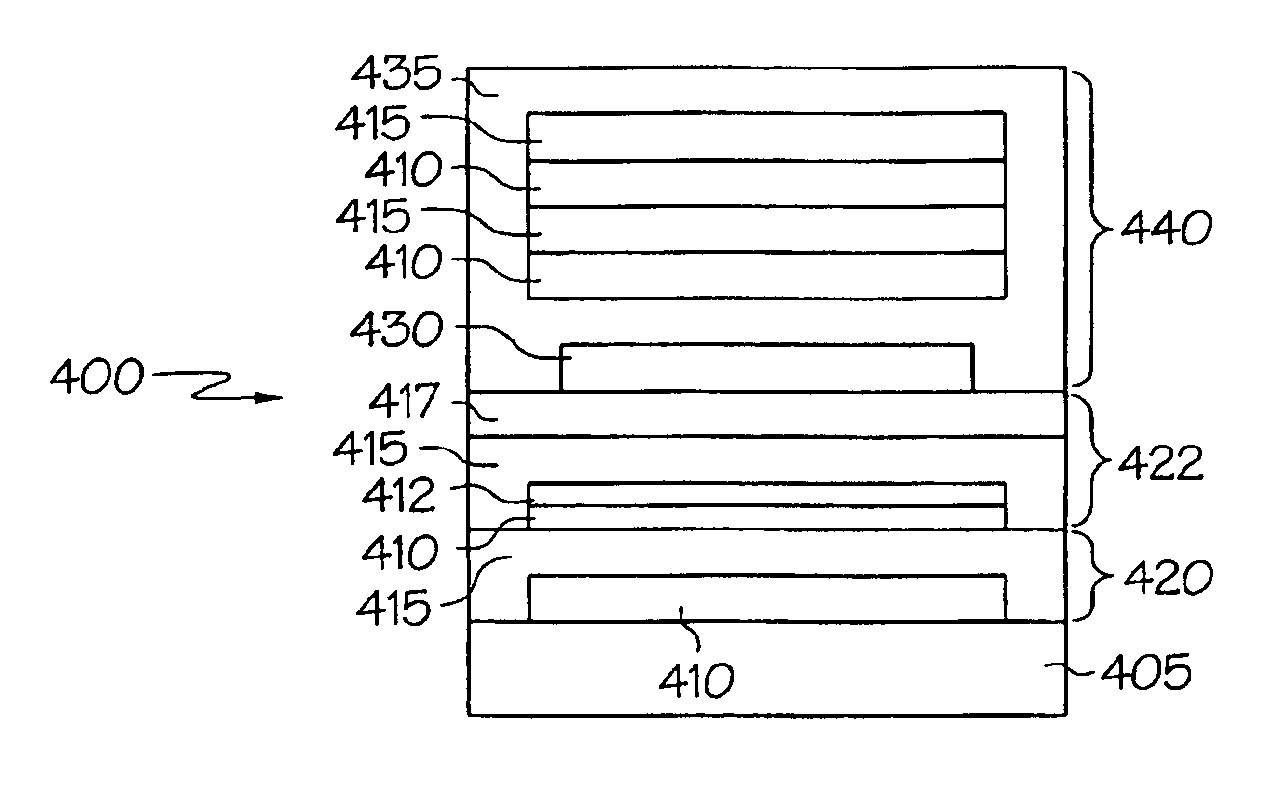
Release strategies for making transferable semiconductor structures, devices and device components
ActiveUS20080108171A1Low cost structureLow costFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsSemiconductor structureDevice Subassembly
Provided are methods for making a device or device component by providing a multilayer structure having a plurality of functional layers and a plurality of release layers and releasing the functional layers from the multilayer structure by separating one or more of the release layers to generate a plurality of transferable structures. The transferable structures are printed onto a device substrate or device component supported by a device substrate. The methods and systems provide means for making high-quality and low-cost photovoltaic devices, transferable semiconductor structures, (opto-)electronic devices and device components.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
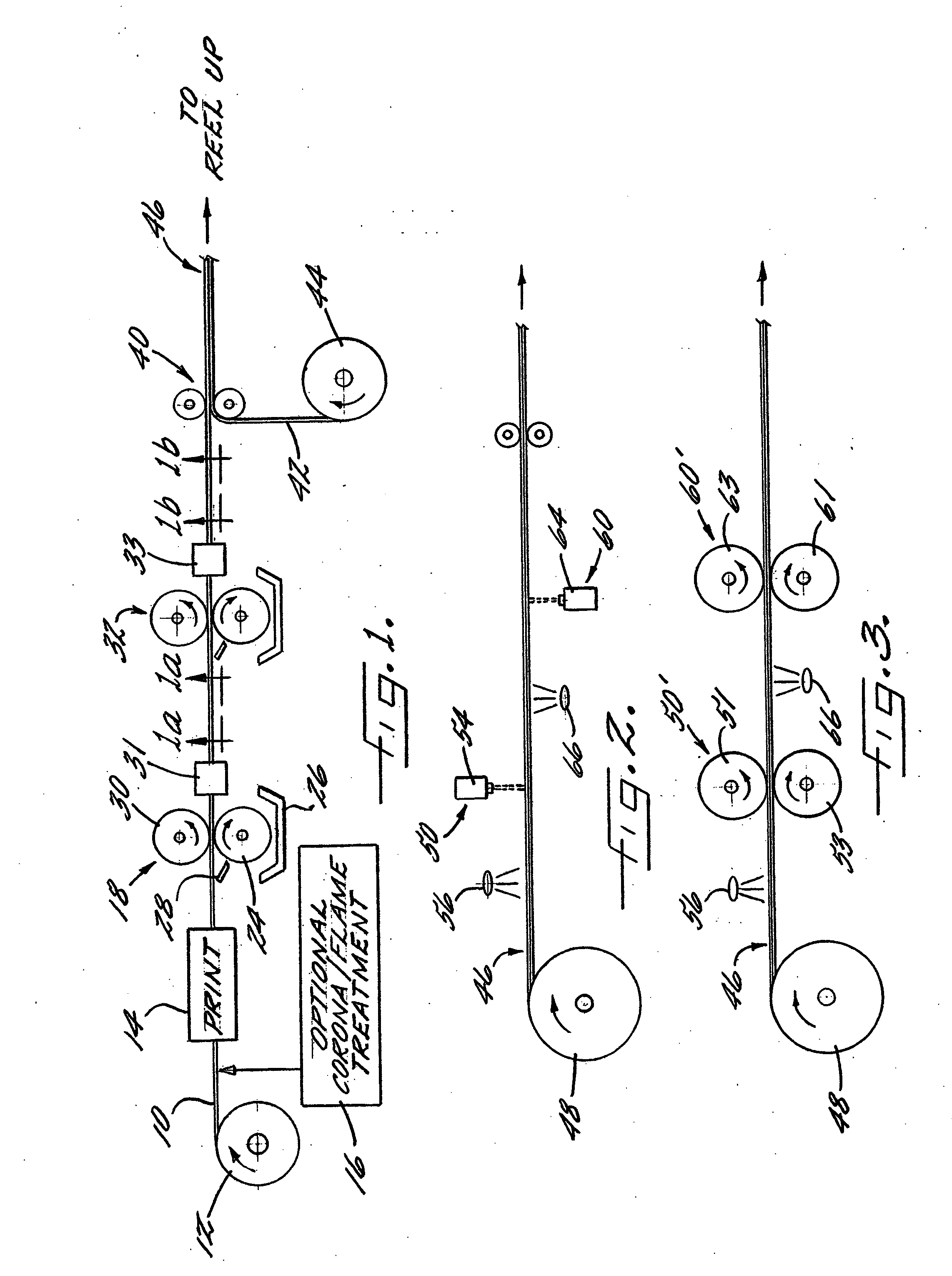
Method of Making Prefastened Refastenable Disposable Absorbent Articles
The present disclosure relates to methods for manufacturing absorbent articles, and in particular, methods for making pre-fastened refastenable pant diapers. Aspects of the methods according to the present disclosure relate to the fabrication of refastenable pant diapers wherein discrete chassis are advanced in a machine direction such that the lateral axis is parallel with the machine direction. First side panels are then refastenably connected with the first waist region, and second side panels are permanently connected the second waist regions of the discrete chassis. The chassis are connected with discrete lengths of side panel material and / or connection zone material. The chassis are then folded, and the first and second side panels are subsequently bonded together. The article is then subjected to knife cut at or adjacent the bonded regions to create discrete, pre-fastened refastenable pant diapers.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method of Making Prefastened Refastenable Disposable Absorbent Articles
InactiveUS20120061015A1Lamination ancillary operationsLaminationKnife cutsElectrical and Electronics engineering
Aspects of the methods according to the present disclosure relate to the fabrication of refastenable pant diapers wherein discrete chassis are advanced in a machine direction such that the lateral axis is parallel with the machine direction. First side panels are then refastenably connected with the first waist region, and second side panels are permanently connected the second waist regions of the discrete chassis. The methods disclosed herein connect chassis with discrete lengths of side panel material and / or connection zone material, and forms a continuous web of articles formed by intermittently spaced chassis and intermittently spaced side panels bridging the gap between the intermittently spaced chassis. The chassis are then folded in the cross direction parallel to a lateral centerline and the first and second side panels are subsequently bonded together. The article is then subjected to knife cut adjacent the bonded regions to create discrete, pre-fastened refastenable pant diapers.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
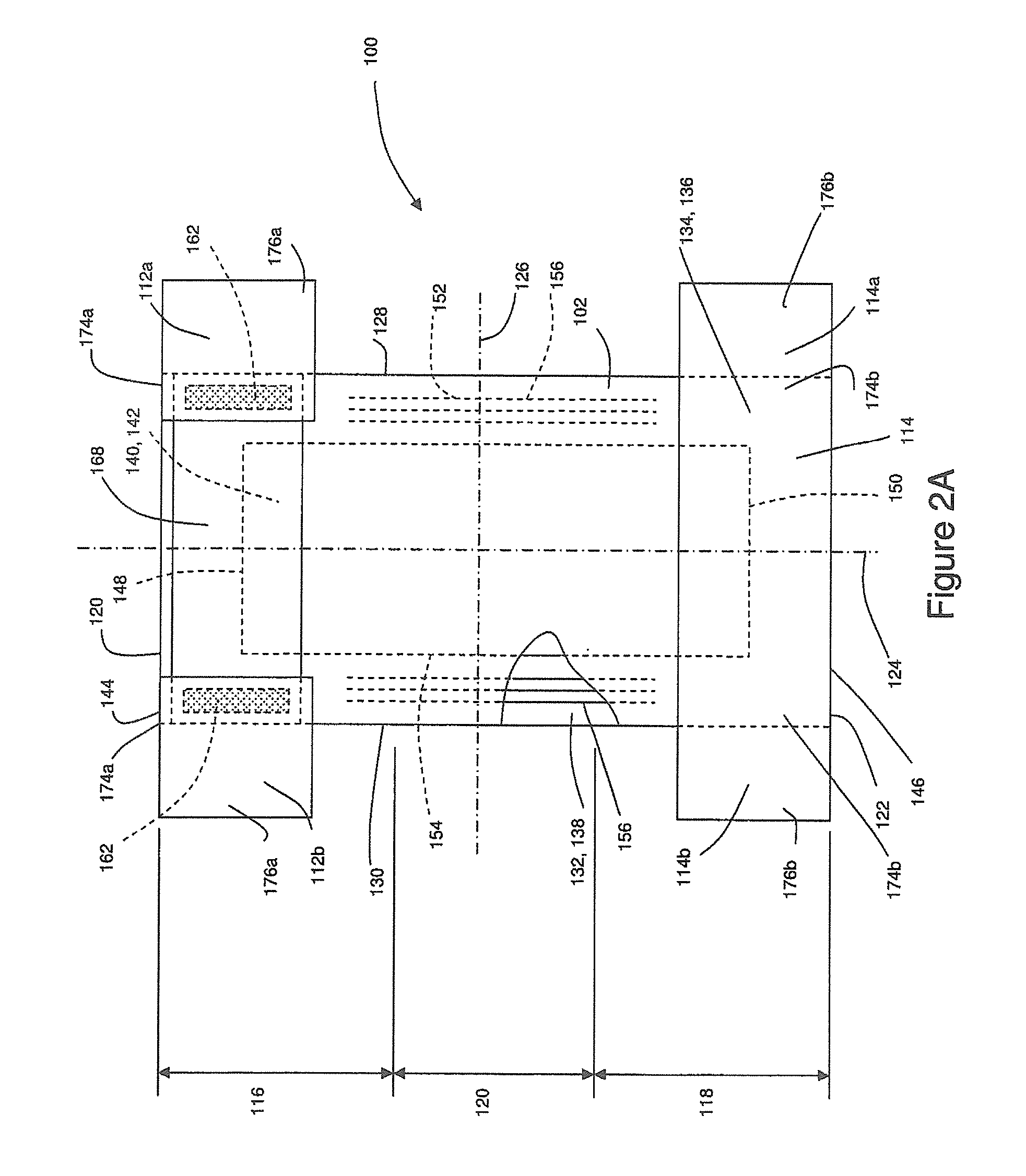
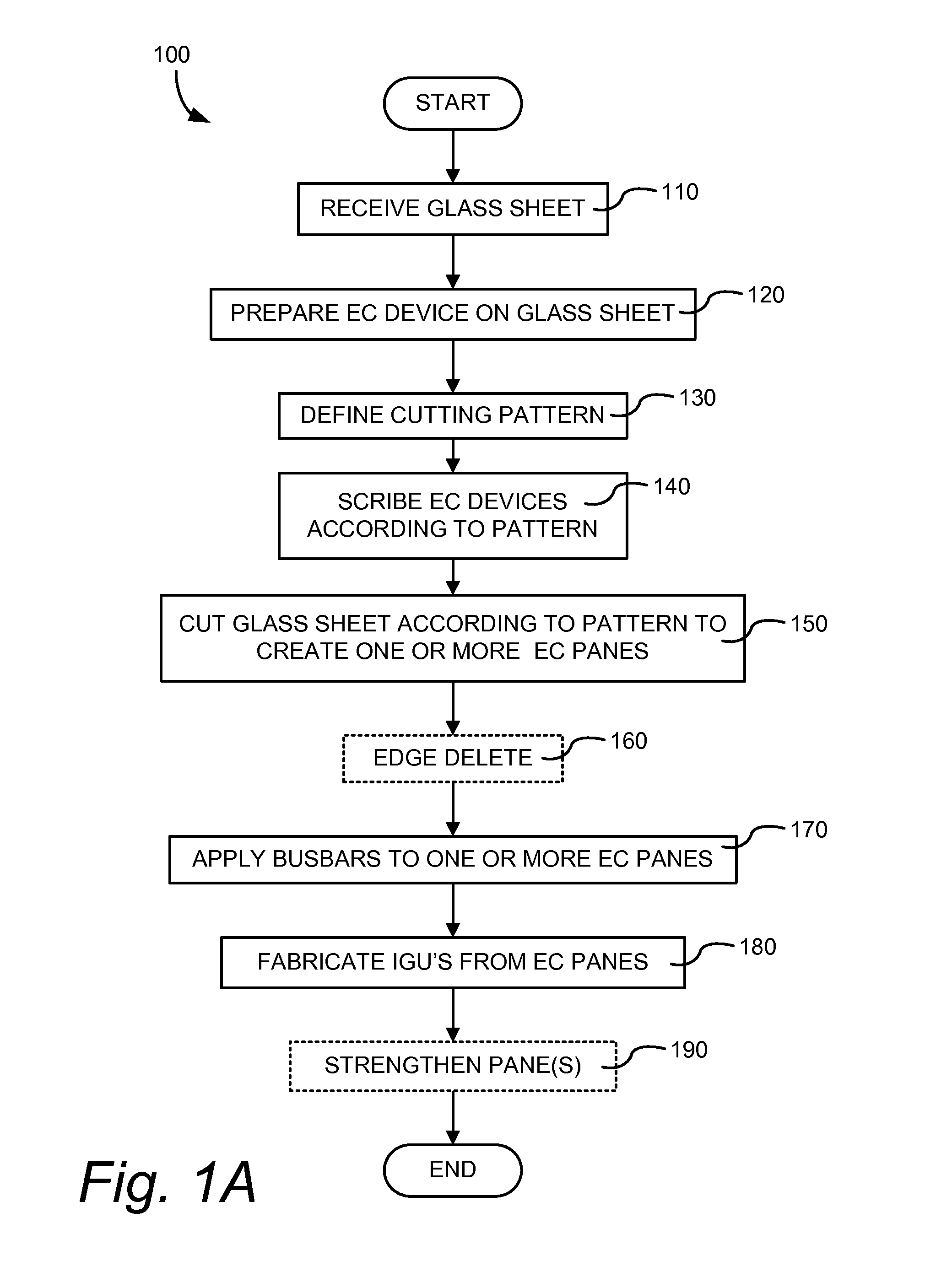
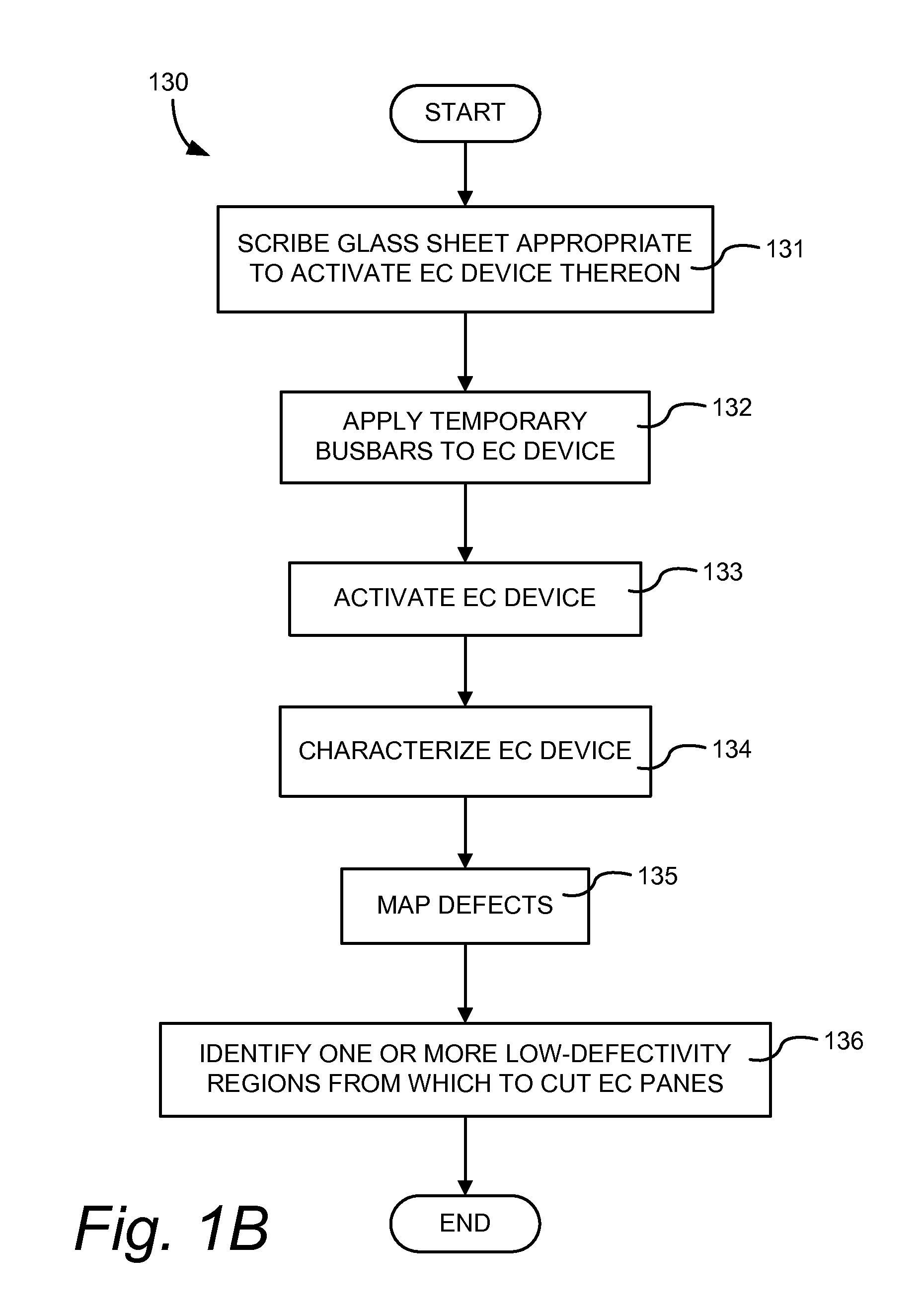
Electrochromic window fabrication methods
ActiveUS20120026573A1Maximize effective useLamination ancillary operationsLaminationEngineeringElectrochromism
Methods of manufacturing electrochromic windows are described. An electrochromic device is fabricated to substantially cover a glass sheet, for example float glass, and a cutting pattern is defined based on one or more low-defectivity areas in the device from which one or more electrochromic panes are cut. Laser scribes and / or bus bars may be added prior to cutting the panes or after. Edge deletion can also be performed prior to or after cutting the electrochromic panes from the glass sheet. Insulated glass units (IGUs) are fabricated from the electrochromic panes and optionally one or more of the panes of the IGU are strengthened.
Owner:VIEW INC
Method and apparatus for making an apertured web
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method of cutting material for use in implantable medical device
A method of cutting material for use in an implantable medical device employs a plotted laser cutting system. The laser cutting system is computer controlled and includes a laser combined with a motion system. The laser precisely cuts segments out of source material according to a predetermined pattern as designated by the computer. The segments are used in constructing implantable medical devices. The cutting energy of the laser is selected so that the cut edges of the segments are melted to discourage delamination or fraying, but communication of thermal energy into the segment beyond the edge is minimized to avoid damaging the segment adjacent the edge.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
Prismatic multiple waveguide for near-eye display
ActiveUS20120062998A1Compensation effectConvenient and accurateOptical articlesLaminationDisplay devicePupil
A near-eye display includes a compound waveguide for presenting viewers with virtual images visible within an eyebox at a limited relief distance from the compound waveguide. The compound waveguide is assembled from a plurality of waveguides that are at least partially optically isolated for conveying different portions of the virtual image. An input couple injects the different portions of the virtual image into predetermined combinations of the waveguides, and an output coupling ejects the different portions of the virtual image from the waveguides toward the eyebox in a form that at least partially constructs a pupil within the eyebox.
Owner:VUZIX
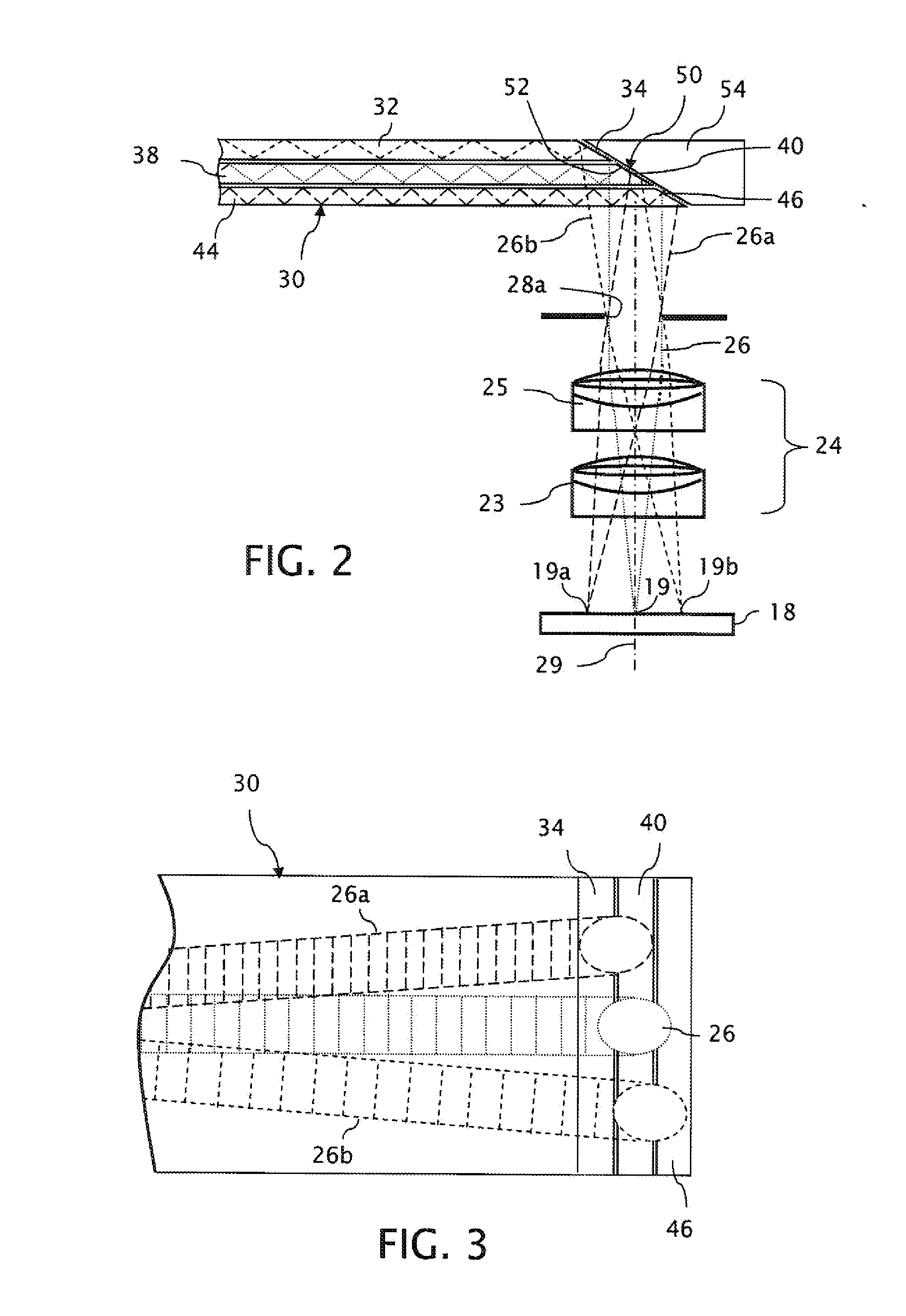
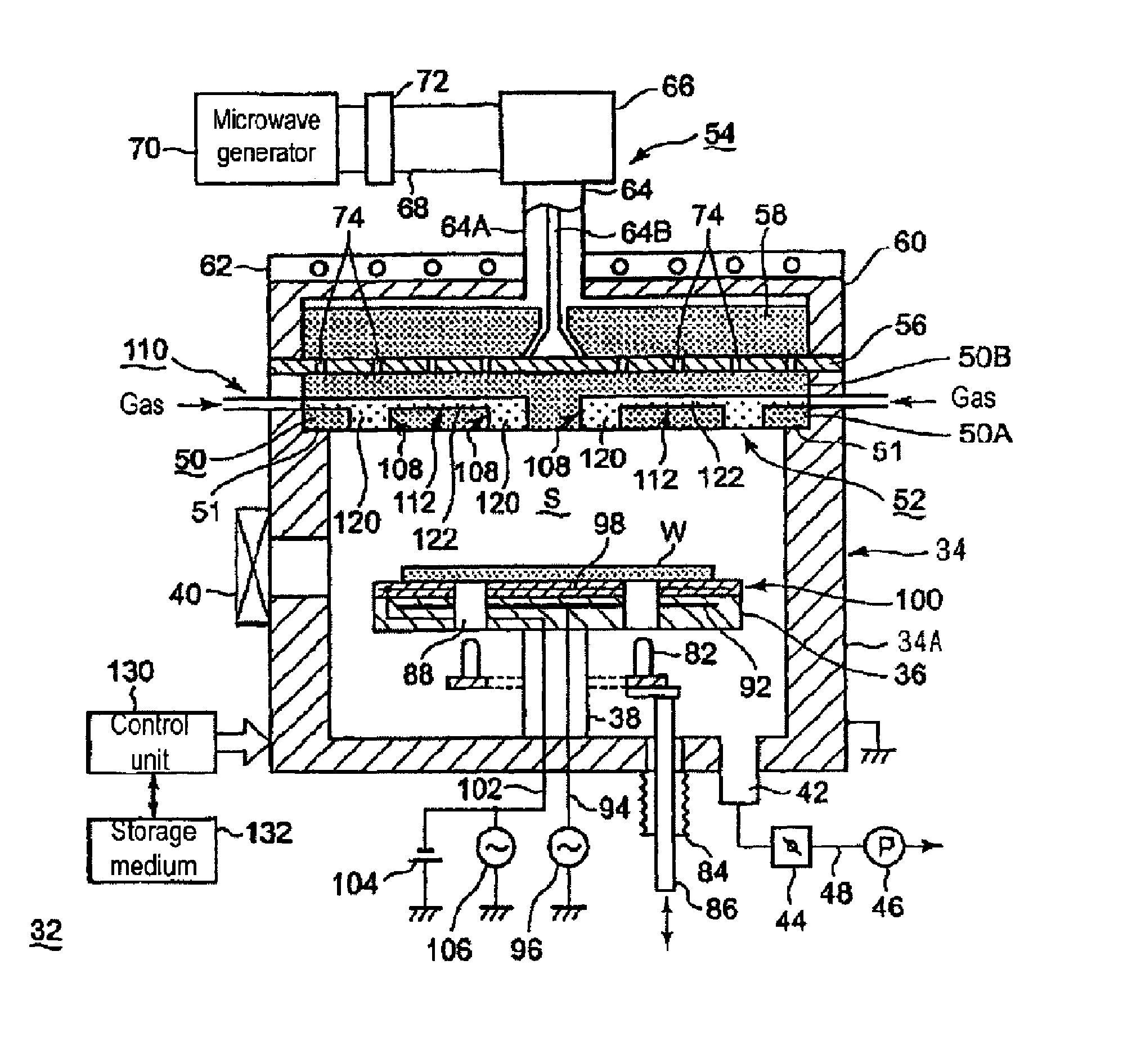
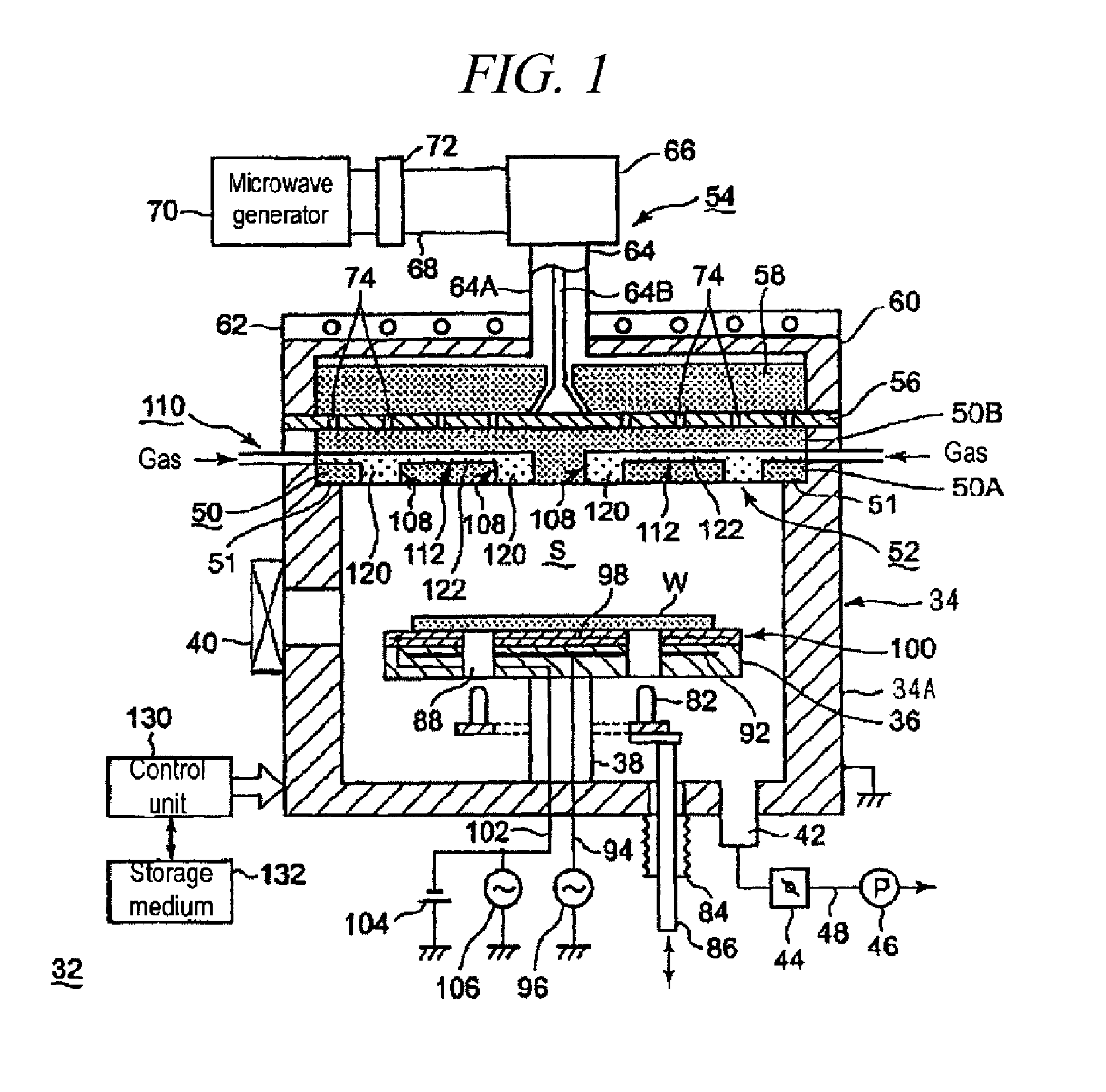
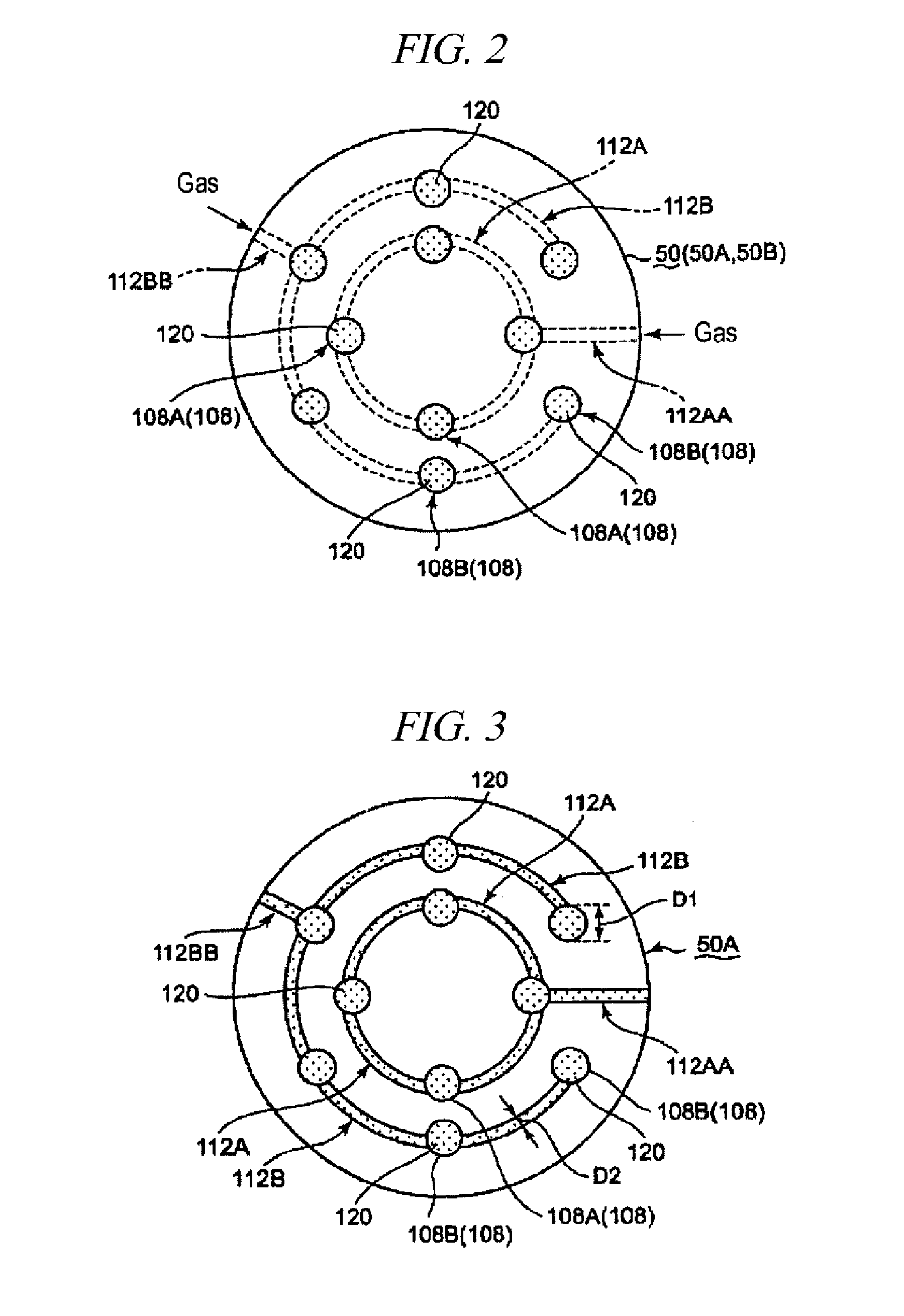
Manufacturing method of top plate of plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20130292047A1Efficient solutionKeep in circulationElectric discharge tubesSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A manufacturing method of a top plate hermetically attached to an upper opening of a tubular shaped container body for forming a processing container of a plasma processing apparatus is provided. The manufacturing method includes the steps of; preparing a top plate body comprised of a dielectric body for transmitting an electromagnetic wave, and having a gas ejection hole for ejecting a gas into the processing container; forming a discharge prevention member having a discharge prevention member body comprised of a dielectric body having a permeability, and a dense member comprised of a dielectric body without a permeability covering at least a side face of the discharge prevention member body; and attaching the discharge prevention member in the gas ejection hole of the top plate body.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Frag shield
Fabric laminates having superior resistance to penetration of fragments, such as shrapnel. The fabrics are formed of high-strength fibers consolidated with from about 7% to about 15% by weight of an elastomeric matrix composition, and in combination with protective layers of a polymer film on each surface of the fabric. The fabrics achieve a significant improvement in fragment resistance compared to fabrics of the prior art, while also maintaining excellent ballistic resistant properties.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Test strip with slot vent opening
ActiveUS20050013731A1Easy doseRobust manufacturing processAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionMechanical engineeringTest strips
A test strip with a covering layer having a novel slot. The slot divides the inventive covering layer into two parts and provides a vent opening that allows air to escape as fluid enters a cavity or sample receiving chamber formed in the test strip. In preferred embodiments, the covering layer is clear such that the user can see through it and the slot doubles as a “fill line.” The user can thus watch the fluid sample enter the test strip, progress through the capillary cavity, and then stop at the slot or fill-line. This provides positive assurance to the user that the sample size is sufficient and the test strip has been filled properly. The present invention also provides an advantageous method of mass-producing the inventive test strips without having to align the slot or vent opening laterally with respect to the test strips and without having to punch a vent opening. The method is also well suited to mass production by roll processing techniques.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
Method of cutting material for use in implantable medical device
A method of cutting material for use in an implantable medical device employs a plotted laser cutting system. The laser cutting system is computer controlled and includes a laser combined with a motion system. The laser precisely cuts segments out of source material according to a predetermined pattern as designated by the computer. The segments are used in constructing implantable medical devices. The cutting energy of the laser is selected so that the cut edges of the segments are melted to discourage delamination or fraying, but communication of thermal energy into the segment beyond the edge is minimized to avoid damaging the segment adjacent the edge.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
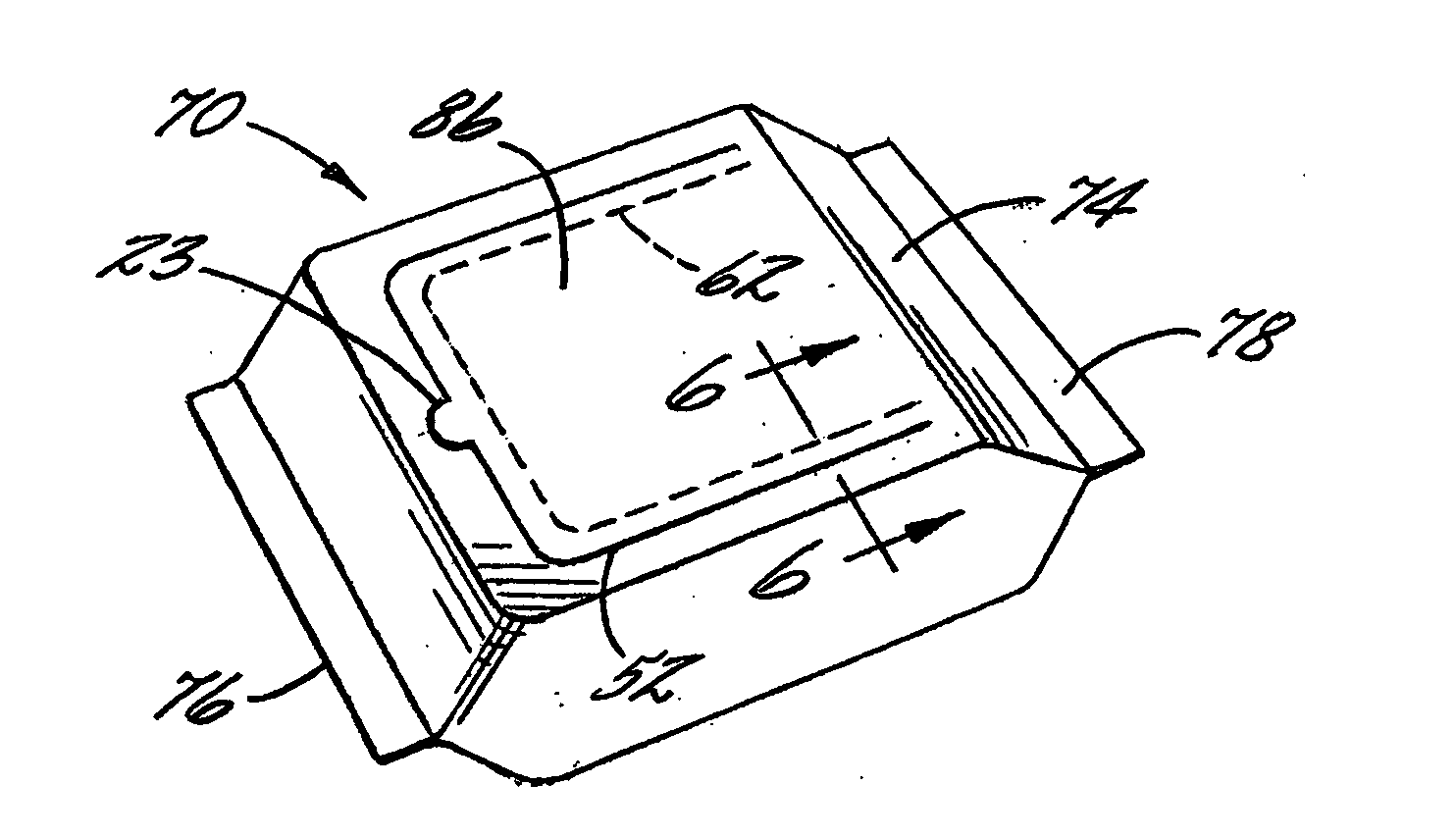
Flexible packaging structure with a built-in opening and reclose feature, and method for making same
ActiveUS20050276525A1Envelopes/bags making machineryWrappersMechanical engineeringPressure sensitive
A flexible packaging laminate is formed to have a built-in opening and reclose feature by forming the laminate as a two-part structure having an outer structure joined in face-to-face relation with an inner structure. Score lines are formed in both structures to enable an opening to be formed through the laminate by lifting an opening portion (e.g., a flap or the like) of the two structures out of the plane of the laminate. The score line through the outer structure defines a larger opening than the score line through the inner structure, such that a marginal region of the outer structure extends beyond the edge of the opening portion of the inner structure. A pressure-sensitive adhesive is used to re-adhere the marginal region to an underlying surface of the inner structure adjacent the opening through the laminate.
Owner:SONOCO DEV INC
Components and methods for use in electro-optic displays
ActiveUS20040027327A1Avoid problemsLiquid surface applicatorsStatic indicating devicesElectricityDisplay device
A front plane laminate useful in the manufacture of electro-optic displays comprises, in order, a light-transmissive electrically-conductive layer, a layer of an electro-optic medium in electrical contact with the electrically-conductive layer, an adhesive layer and a release sheet. This front plane laminate can be prepared as a continuous web, cut to size, the release sheet removed and the laminate laminated to a backplane to form a display. Methods for providing conductive vias through the electro-optic medium and for testing the front plane laminate are also described.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Indirect printing of AGM
ActiveUS20060024433A1High accuracy of distributionHigh accuracy of and patternBaby linensCoatingsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
The present invention relates to a method of applying absorbent gelling material (AGM) granules by indirect printing onto an carrier layer for use in an absorbent article, particularly diaper for babies or adults, training pants, pull-up diapers (diaper pants), sanitary napkins, panty liners or the like. These articles typically comprise the carrier layer with the AGM particles together with further layers, making up the complete article.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
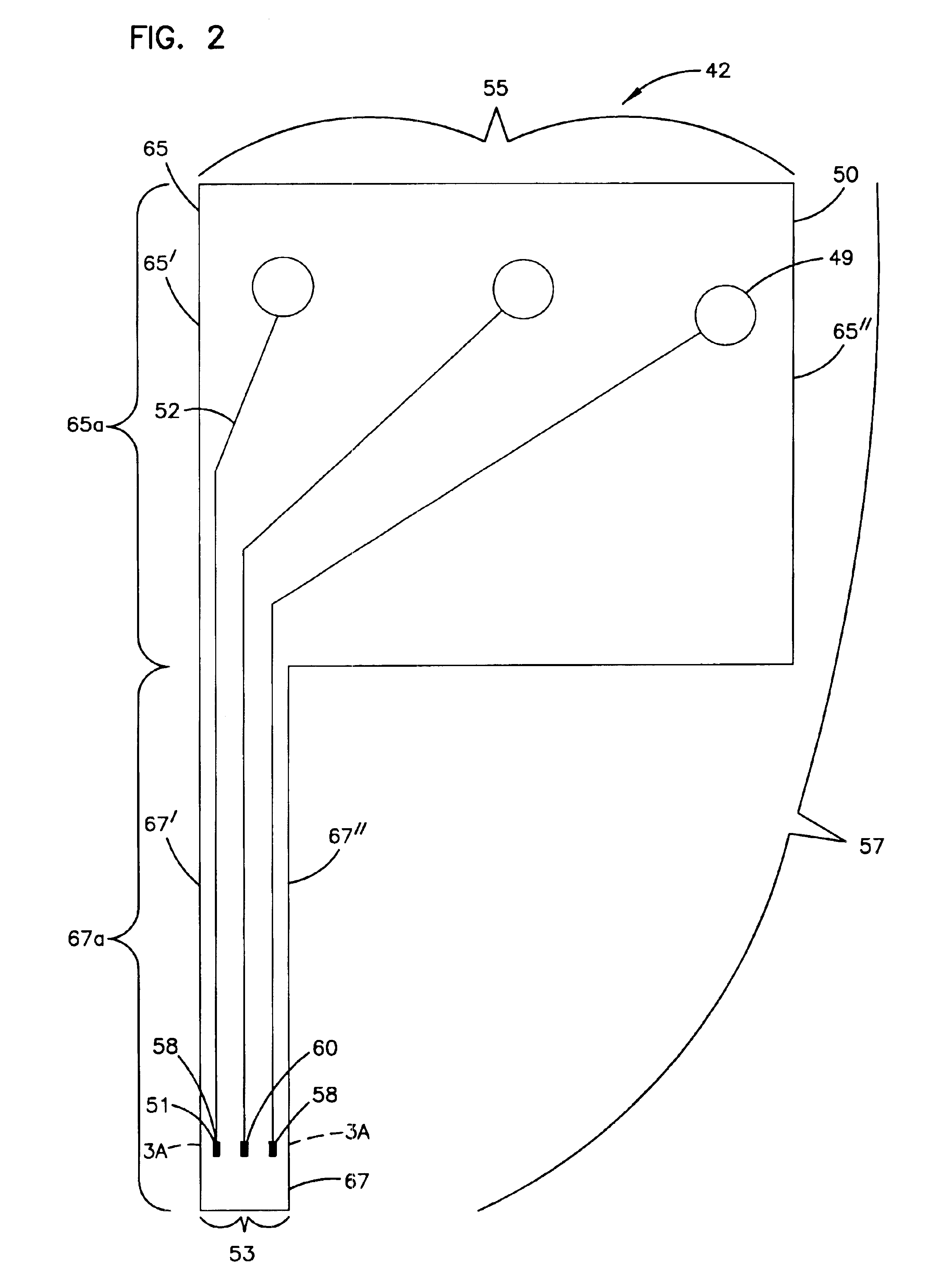
Method of making a transcutaneous electrochemical sensor
InactiveUS6973706B2Efficient productionWave amplification devicesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringConductive materials
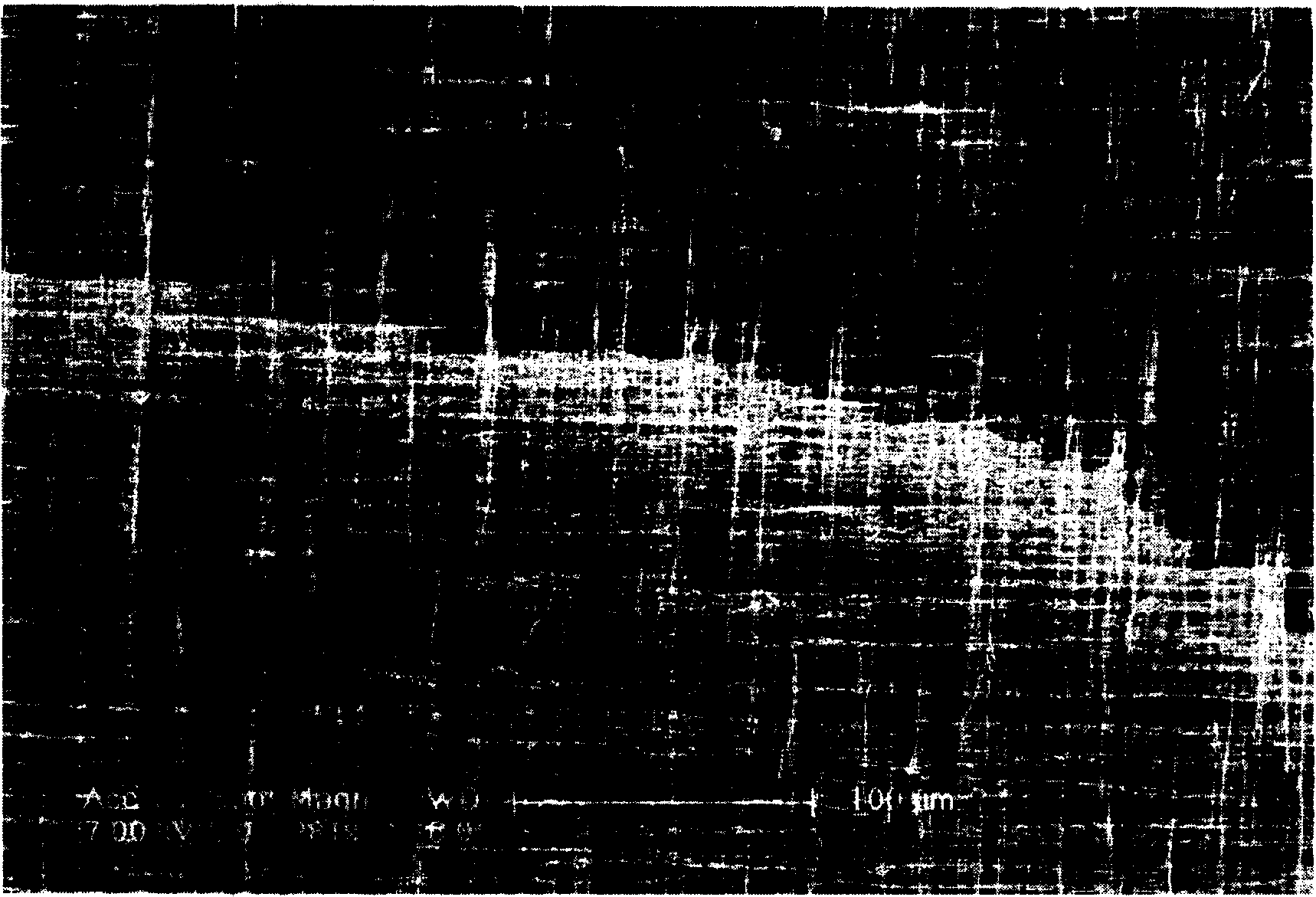
A process for the manufacture of small sensors with reproducible surfaces, including electrochemical sensors. One process includes fanning channels in the surface of a substrate and disposing a conductive material in the channels to form an electrode. The conductive material can also be formed on the substrate by other impact and non-impact methods. In a preferred embodiment, the method includes cutting the substrate to form a sensor having a connector portion and a transcutaneous portion, the two portions having edges that define one continuous straight line.
Owner:THERASENSE
Apparatuses and Methods for Making Absorbent Articles
The present disclosure relates to methods and apparatuses for assembling diapers, each including a chassis connected with front and back elastic belts. As discussed in more detail below, opposing end regions of the chassis are connected with regions of the elastic belts where the elasticity of the elastic belts has been removed or deactivated. An elastic laminate may be formed by continuously bonding elastic strands between a first continuous substrate layer and a second continuous substrate layer such that the elastic strands are bonded to both the first substrate layer and the second substrate layer in heavy-bond regions. And the elastic strands are bonded to the first substrate layer and / or the second substrate layer with in light-bond regions. The elastic strands are then intermittently deactivated by cutting the strands into one or more discrete pieces in the light-bond regions. The discrete pieces retract and remain in the light-bond regions.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Apparatuses and Methods for Making Absorbent Articles
ActiveUS20130255864A1Slow and controlled rateLamination ancillary operationsLaminationChassisLight Bond
The present disclosure relates to methods and apparatuses for assembling absorbent articles, and more particularly, diaper pants, each including a chassis connected with front and back elastic belts. As discussed in more detail below, opposing end regions of the chassis are connected with regions of the elastic belts where the elasticity of the elastic belts has been removed or deactivated. As discussed in more detail below, an elastic laminate may be formed by continuously bonding elastic strands between a first continuous substrate layer and a second continuous substrate layer. The elastic strands are then intermittently severed in light-bond regions of the elastic laminate. Adhesive on the laminate causes the severed elastic ends to retract or snap back from the light-bond regions at a relatively slower and / or controlled rate.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Release strategies for making transferable semiconductor structures, devices and device components
ActiveUS7932123B2Low costReduce layeringFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsSemiconductor structureElectron
Provided are methods for making a device or device component by providing a multilayer structure having a plurality of functional layers and a plurality of release layers and releasing the functional layers from the multilayer structure by separating one or more of the release layers to generate a plurality of transferable structures. The transferable structures are printed onto a device substrate or device component supported by a device substrate. The methods and systems provide means for making high-quality and low-cost photovoltaic devices, transferable semiconductor structures, (opto-)electronic devices and device components.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method for edge sealing barrier films
An edge-sealed barrier film composite. The composite includes a substrate and at least one initial barrier stack adjacent to the substrate. The at least one initial barrier stack includes at least one decoupling layer and at least one barrier layer. One of the barrier layers has an area greater than the area of one of the decoupling layers. The decoupling layer is sealed by the first barrier layer within the area of barrier material. An edge-sealed, encapsulated environmentally sensitive device is provided. A method of making the edge-sealed barrier film composite is also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Composition and process for the sealing of microcups in roll-to-roll display manufacturing
InactiveUS7144942B2Improve adhesionQuality improvementLamination ancillary operationsLaminationCrystallographyElectrophoresis
Owner:E INK CALIFORNIA
Method of transferring a micro device
A micro device transfer head and head array are disclosed. In an embodiment, the micro device transfer head includes a base substrate, a mesa structure with sidewalls, an electrode formed over the mesa structure, and a dielectric layer covering the electrode. A voltage can be applied to the micro device transfer head and head array to pick up a micro device from a carrier substrate and release the micro device onto a receiving substrate.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method of thermoforming a bladder structure
InactiveUS6837951B2Increase awarenessImprove efficiencySolesOrnamental textile articlesBladder structureThermal contact
A method for thermoforming a resilient, fluid-filled bladder structure with thermal contact molding is disclosed. The bladder includes two sheets of thermoplastic material that are separated by at least one core formed of two spaced outer layers connected together by a plurality of connecting members. The bladder is formed by bonding the sheets to the core, bonding the sheets to each other around the periphery of the core and forming a sidewall between the sheets in a single mold. A fluid is then inserted into the space bounded by the peripheral bond and the two sheets such that the connecting members are extended.
Owner:NIKE INC
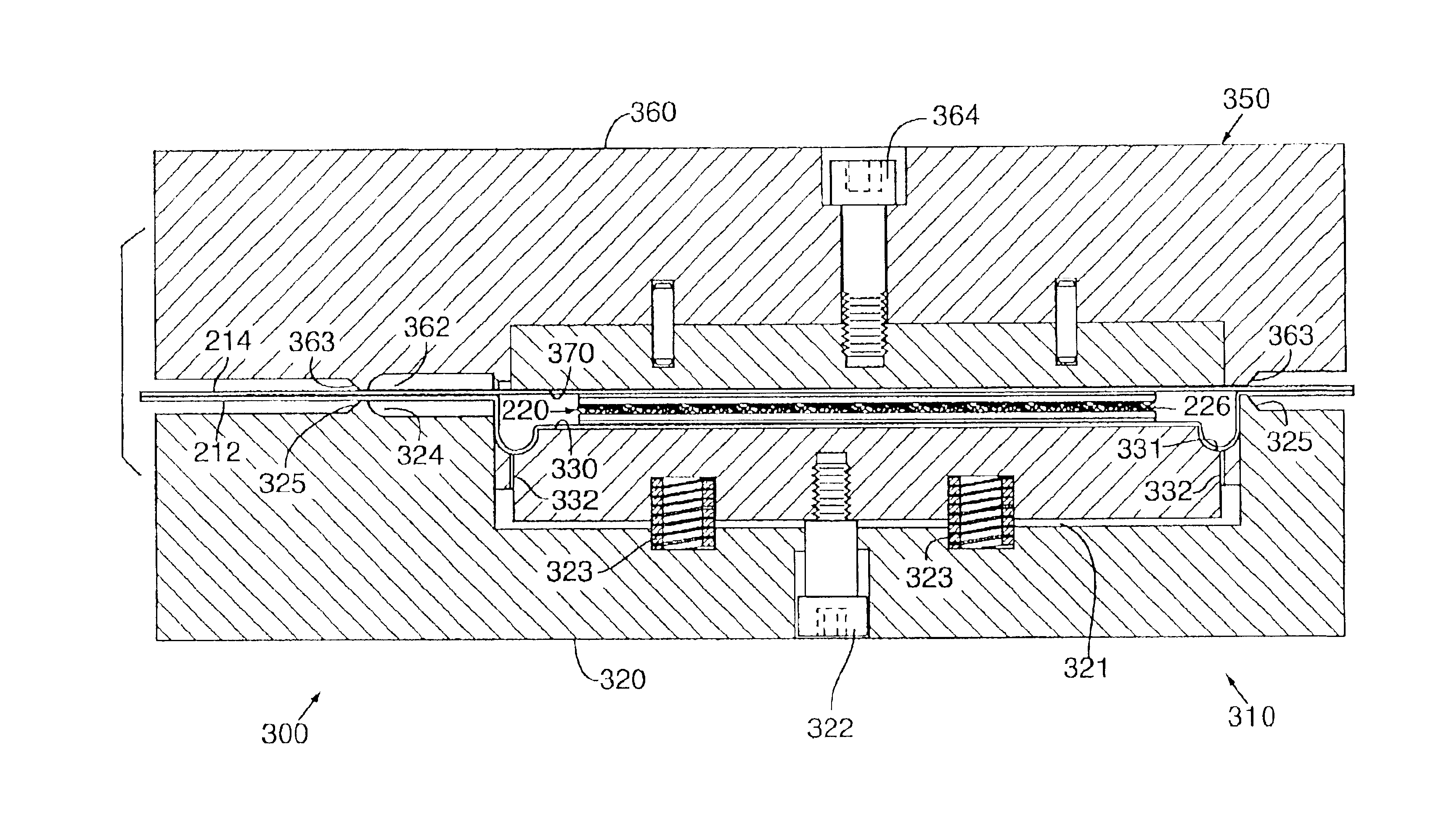
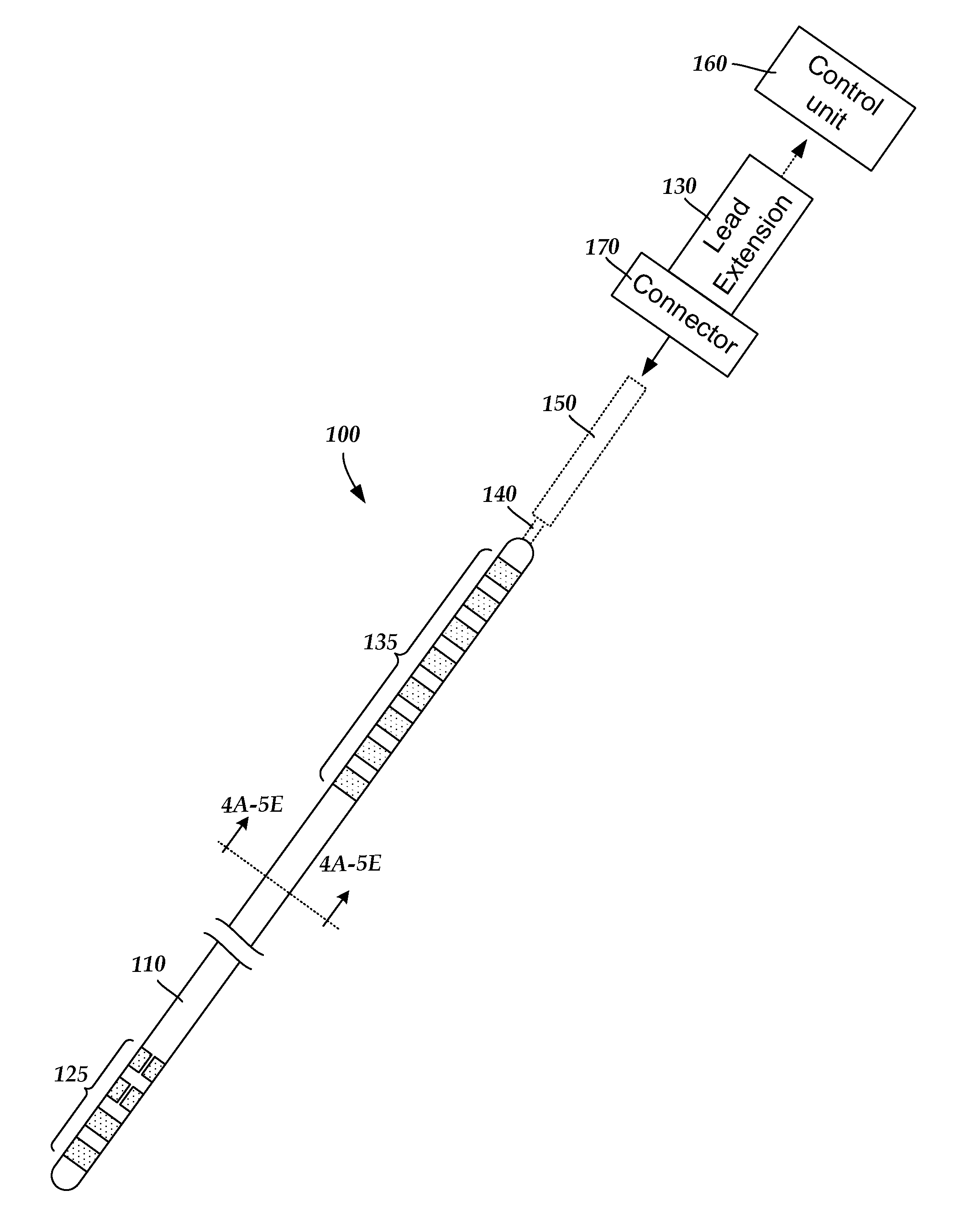
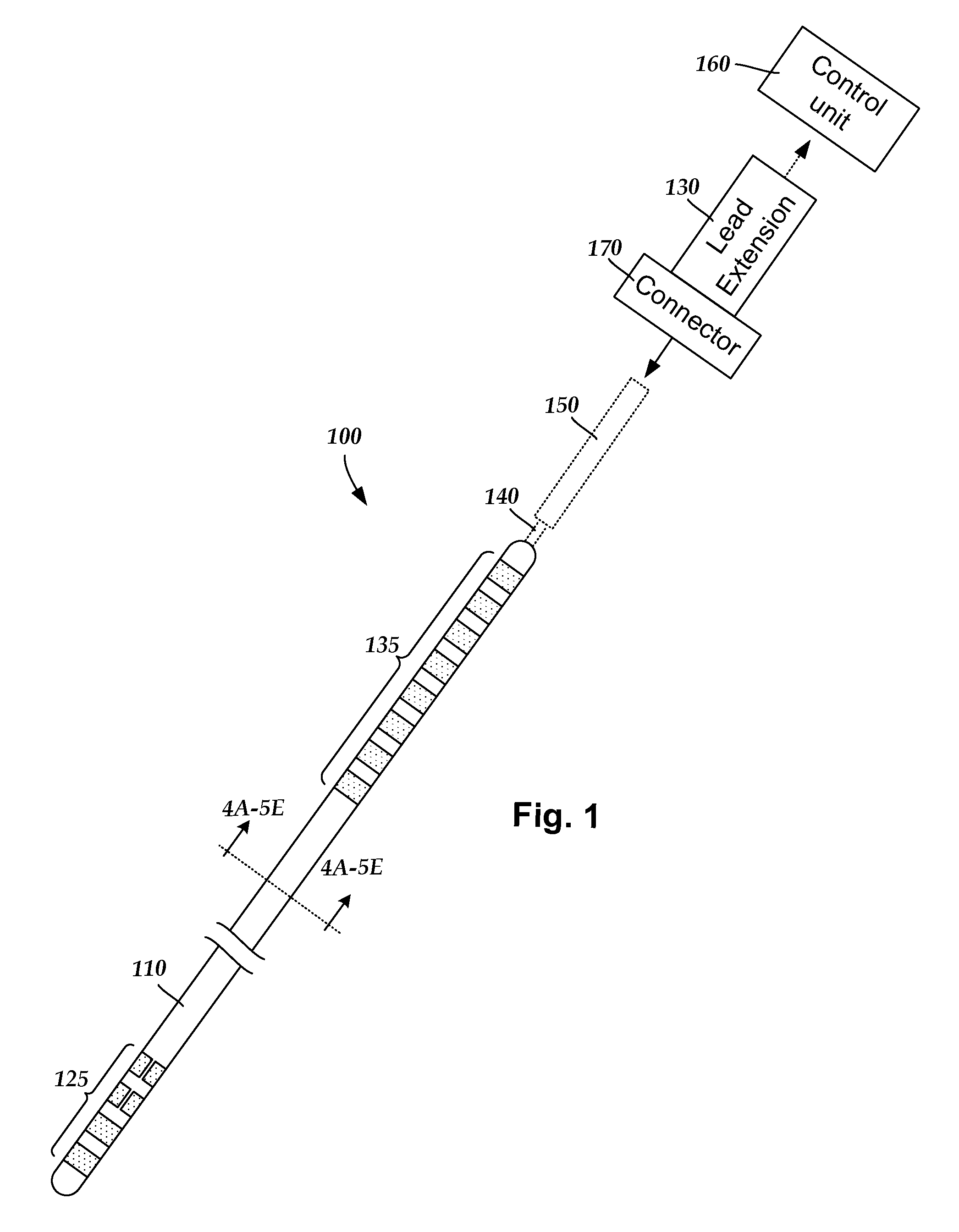
Systems and methods for making and using improved leads for electrical stimulation systems
ActiveUS20130105071A1Reduce gapLine/current collector detailsHead electrodesElectricityElectrical conductor
A method for manufacturing a lead includes pre-forming at least one relief section along a length of an elongated conductor having a first end and an opposing second end. The conductor with the pre-formed relief section is inserted into a conductor lumen defined along a length of an elongated lead body. The lead body has a first end and an opposing second end. An electrode is disposed at the first end of the lead body. The first end of the conductor is electrically coupled to the electrode. A terminal is disposed at the second end of the lead body. The second end of the conductor is electrically coupled to the terminal.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Pedestal with a thermally controlled platen
InactiveUS20010004880A1Liquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringThermal transmittance
A workpiece support having dichotomy of thermal paths therethrough is provided for controlling the temperature of a workpiece support thereon. In one embodiment, a workpiece support includes a platen body having a plug centrally disposed in a workpiece support surface of the platen body. A lower surface of the plug defines a void between the plug and a bottom of the bore. The void creates a dichotomy of thermal paths through the platen body thus controlling the temperature of a wafer support surface. Alternatively, the plug and platen body may be fabricated from materials having different rates of thermal conductivity to created the dichotomy of thermal paths in addition to or in absence of the void.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Curable aqueous composition and use as fiberglass nonwoven binder
This invention relates to a formaldehyde-free curable aqueous composition containing a polyacid, a polyol and a phosphorous-containing accelerator. The composition may be used as a binder for heat resistant nonwovens such as nonwovens composed of fiberglass.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Method of room temperature covalent bonding
InactiveUS7109092B2High densityLow densityLayered productsDecorative surface effectsRoom temperatureFluorine containing
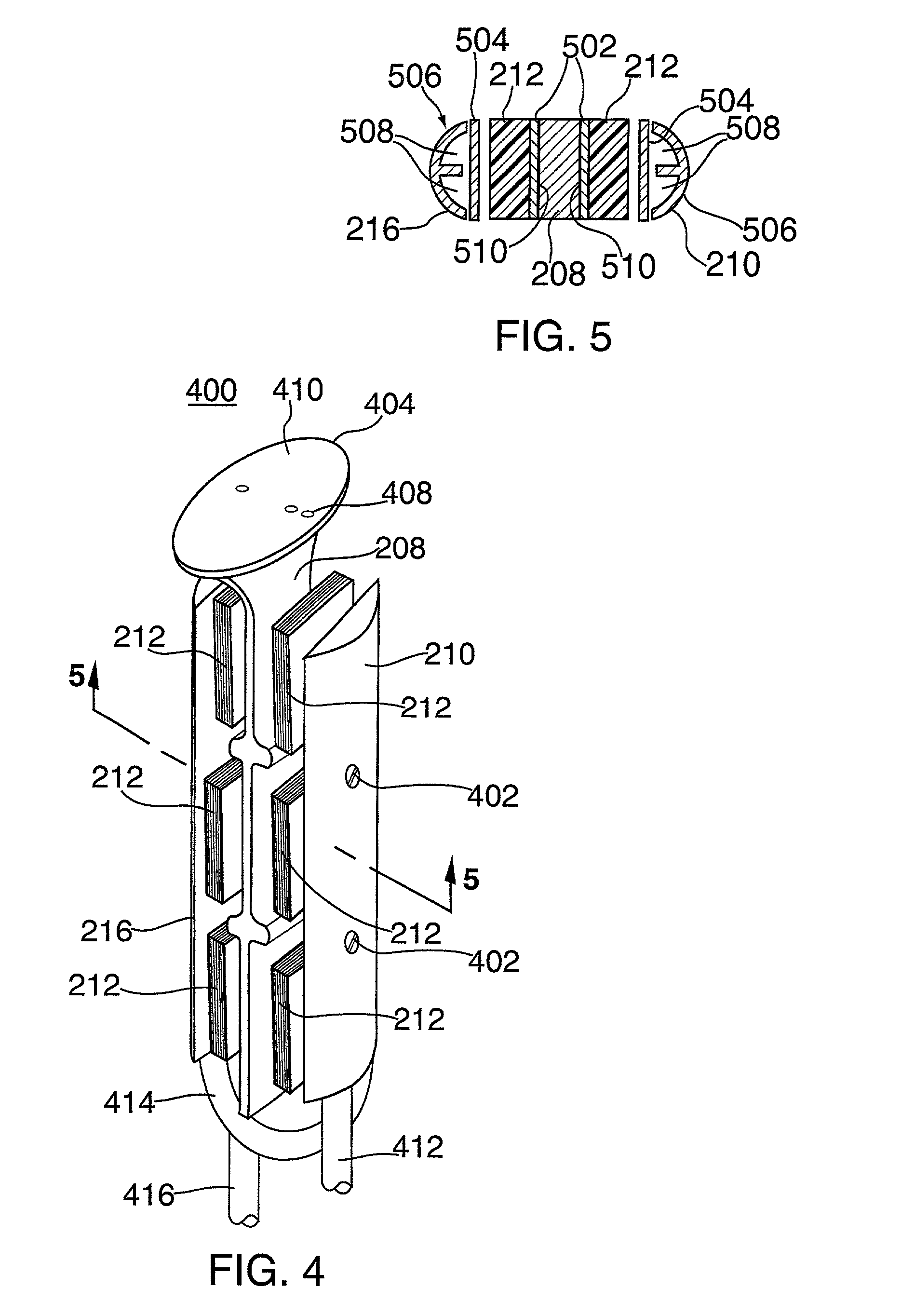
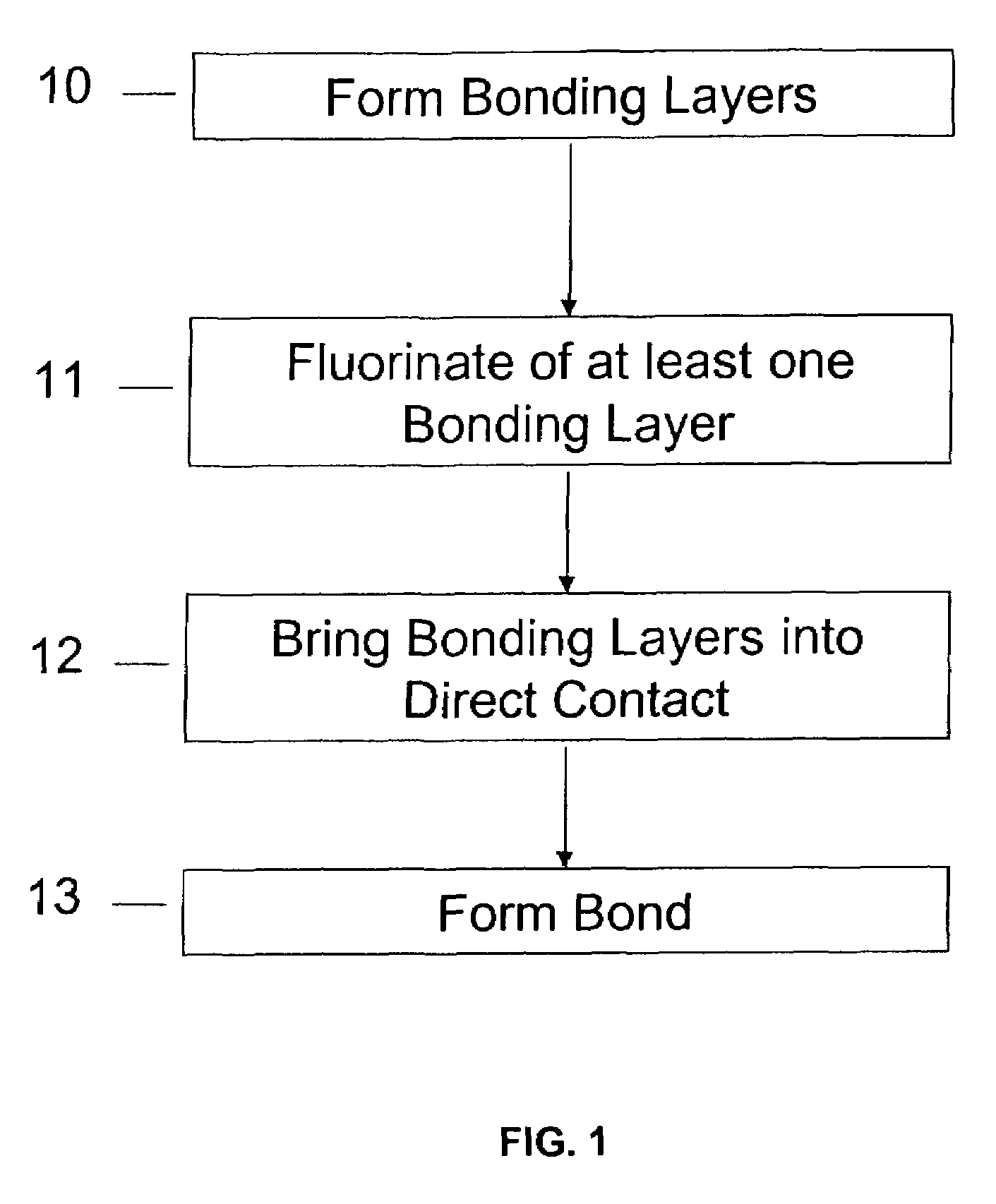
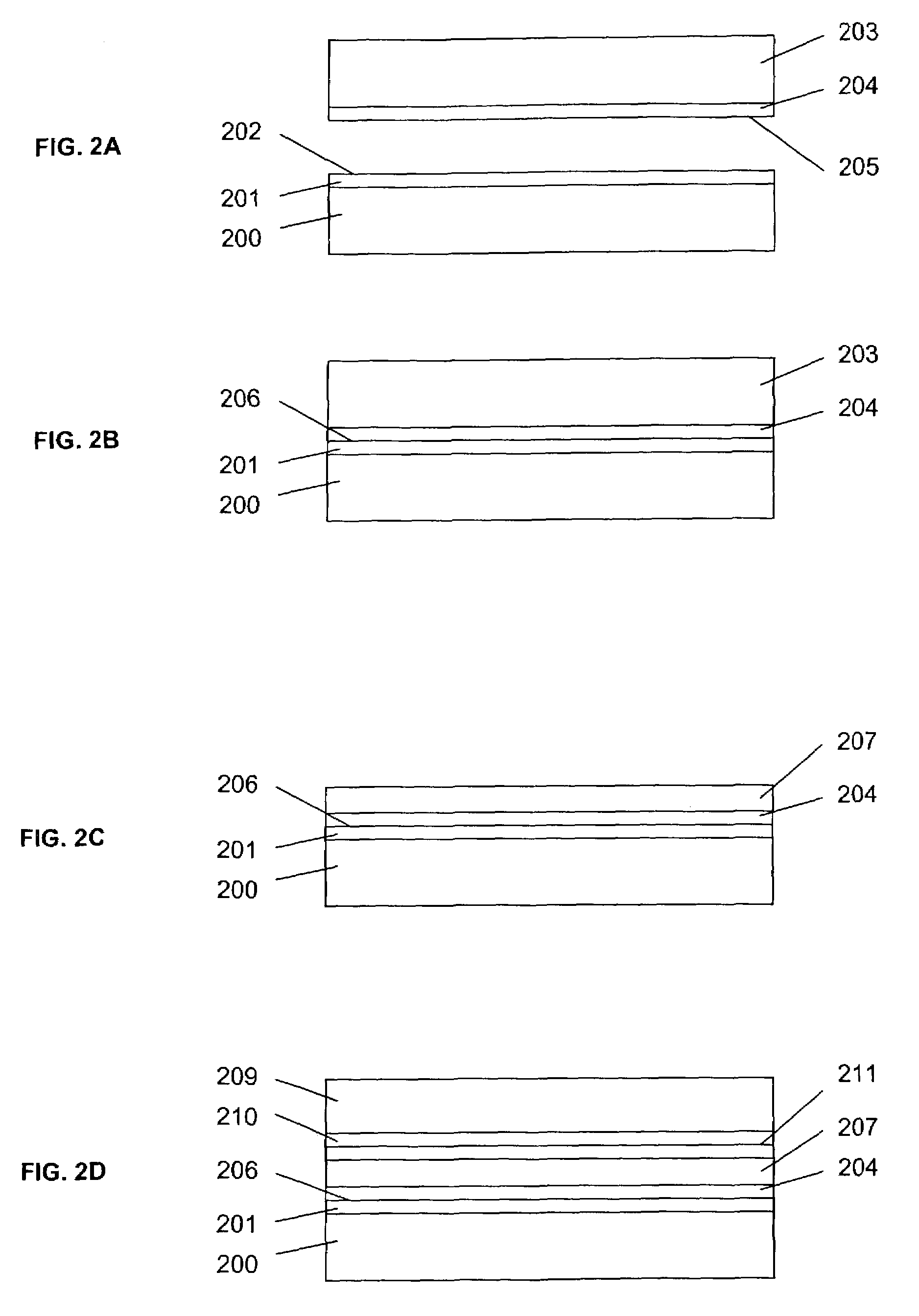
A method of bonding includes using a bonding layer having a fluorinated oxide. Fluorine may be introduced into the bonding layer by exposure to a fluorine-containing solution, vapor or gas or by implantation. The bonding layer may also be formed using a method where fluorine is introduced into the layer during its formation. The surface of the bonding layer is terminated with a desired species, preferably an NH2 species. This may be accomplished by exposing the bonding layer to an NH4OH solution. High bonding strength is obtained at room temperature. The method may also include bonding two bonding layers together and creating a fluorine distribution having a peak in the vicinity of the interface between the bonding layers. One of the bonding layers may include two oxide layers formed on each other. The fluorine concentration may also have a second peak at the interface between the two oxide layers.
Owner:INVENSAS BONDING TECH INC
Test strip with flared sample receiving chamber
ActiveUS20050019212A1Promotes wickingReduce doseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReduced doseTest strips
A test strip with a sample receiving chamber having a novel flared portion that terminates in a sample receiving opening. The flared portion provides a reservoir from which sample fluid can be drawn into the capillary or sample receiving chamber. The wider opening provided by the present invention is easier to “target” with a sample fluid. In preferred embodiments, the hydrophilic reagent layer extends to the dosing end or side of the test strip and further promotes wicking of the sample into the sample receiving chamber and thus reduces dose hesitation. In other preferred embodiments, a tapered dosing end is provided on the test strip in combination with the flared portion, and this combination create a test strip that will draw sample fluid into the sample receiving chamber regardless of where along the dosing edge of the test strip the fluid sample makes contact.
Owner:ROCHE OPERATIONS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com