Patents
Literature
342results about "Carburetting by solid carbonaceous material pyrolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
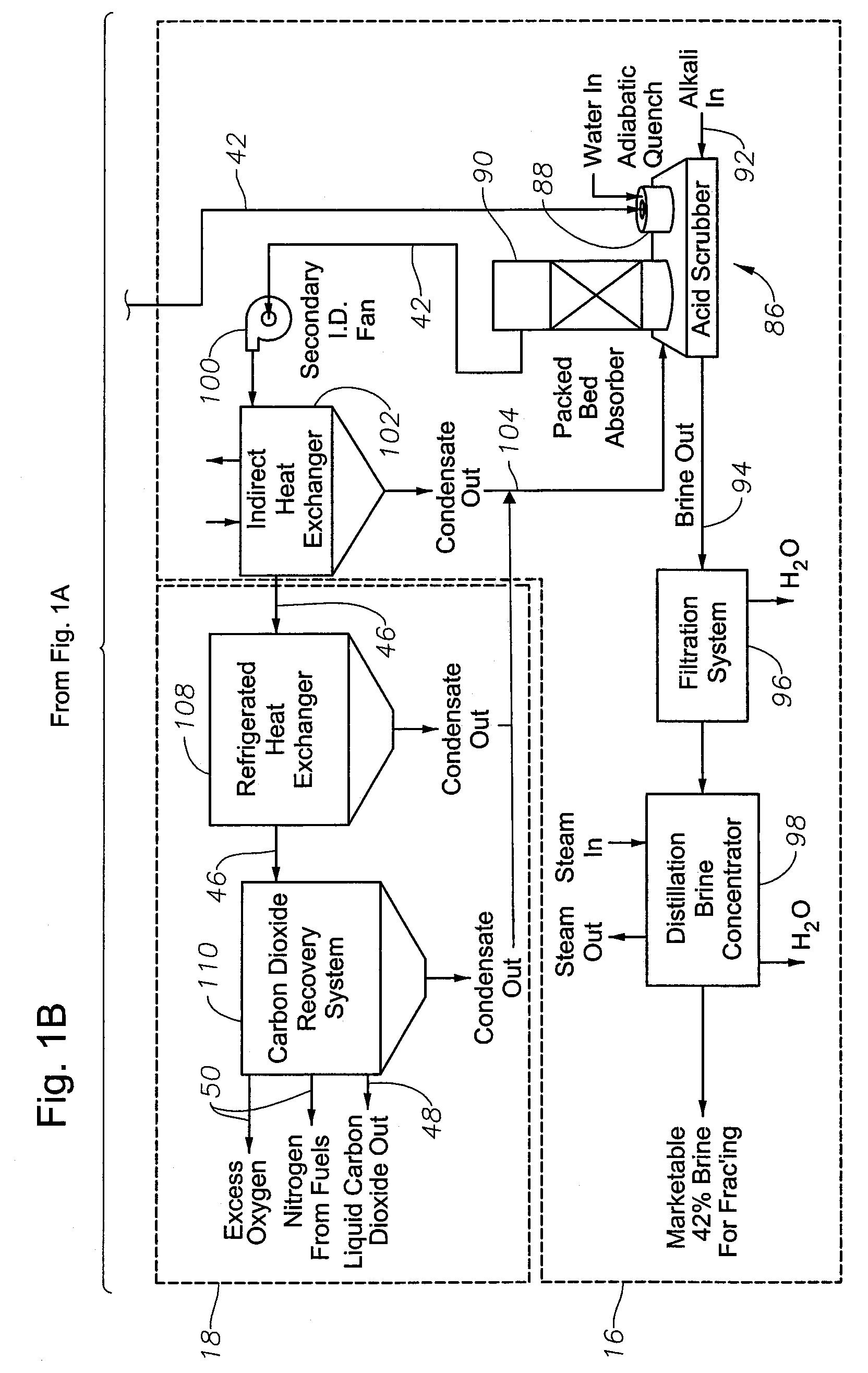
Method and apparatus for producing methane from carbonaceous material
InactiveUS20060265953A1Efficient productionEfficient deliveryHydrogen separationGaseous fuelsHydrogenReaction zone
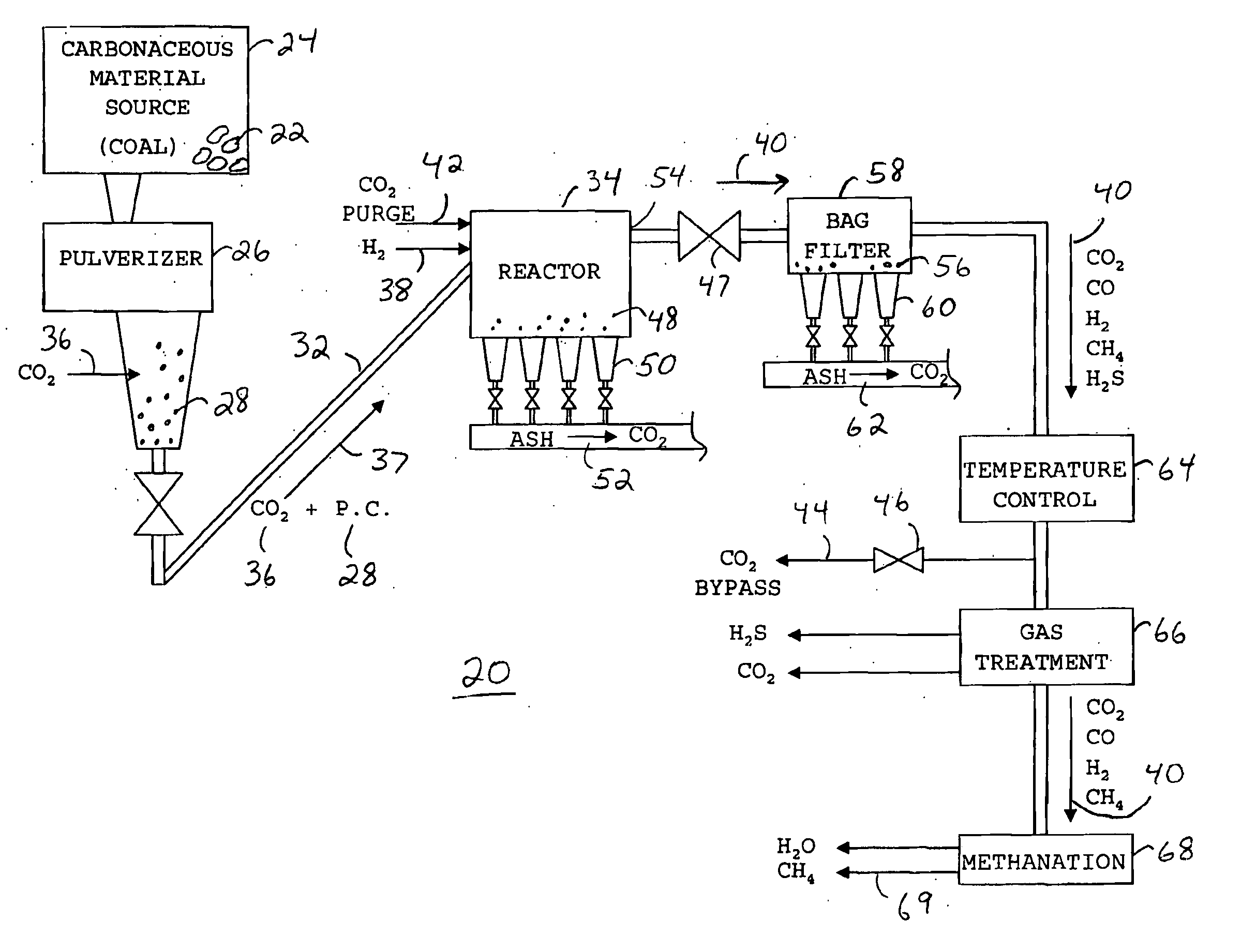
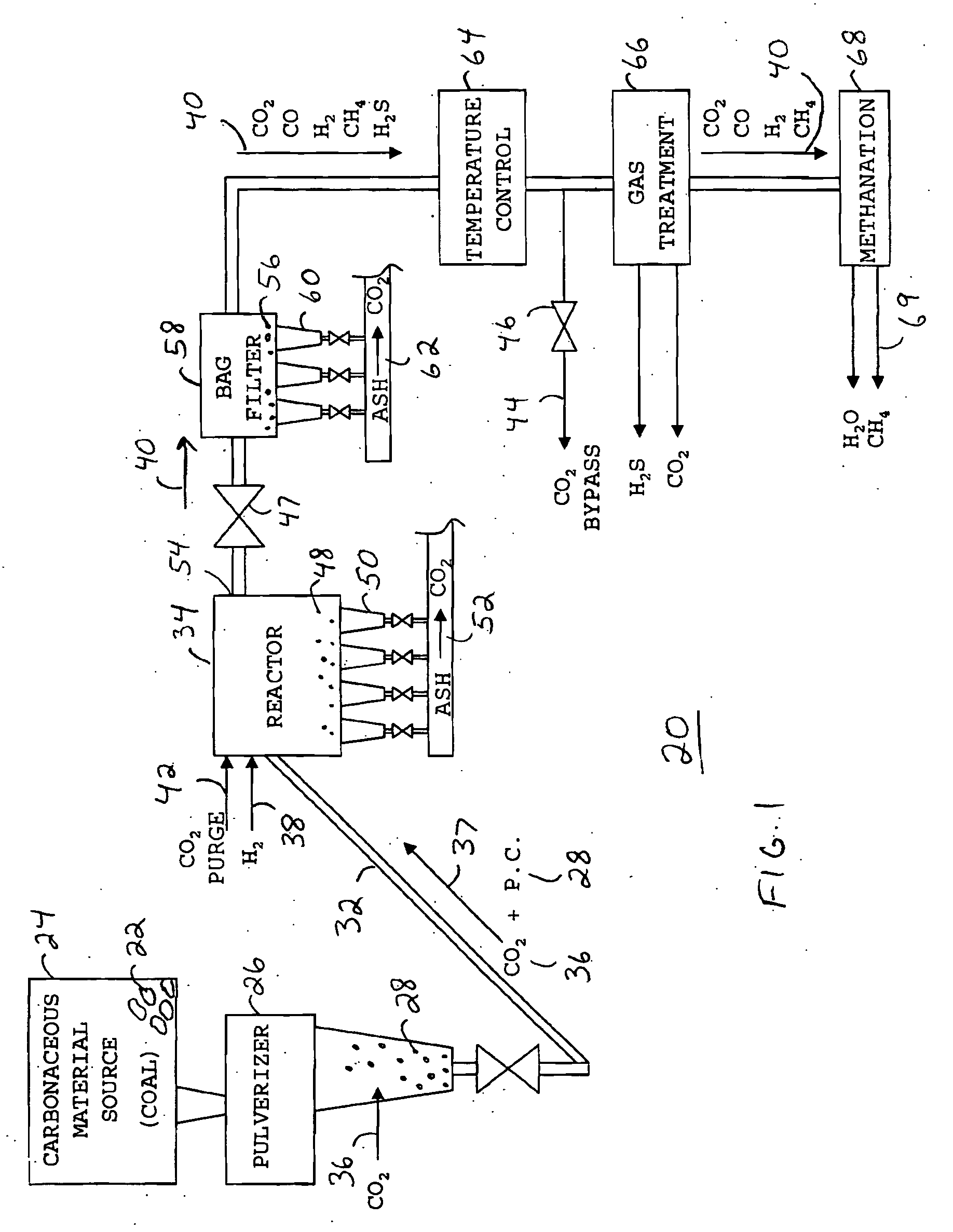
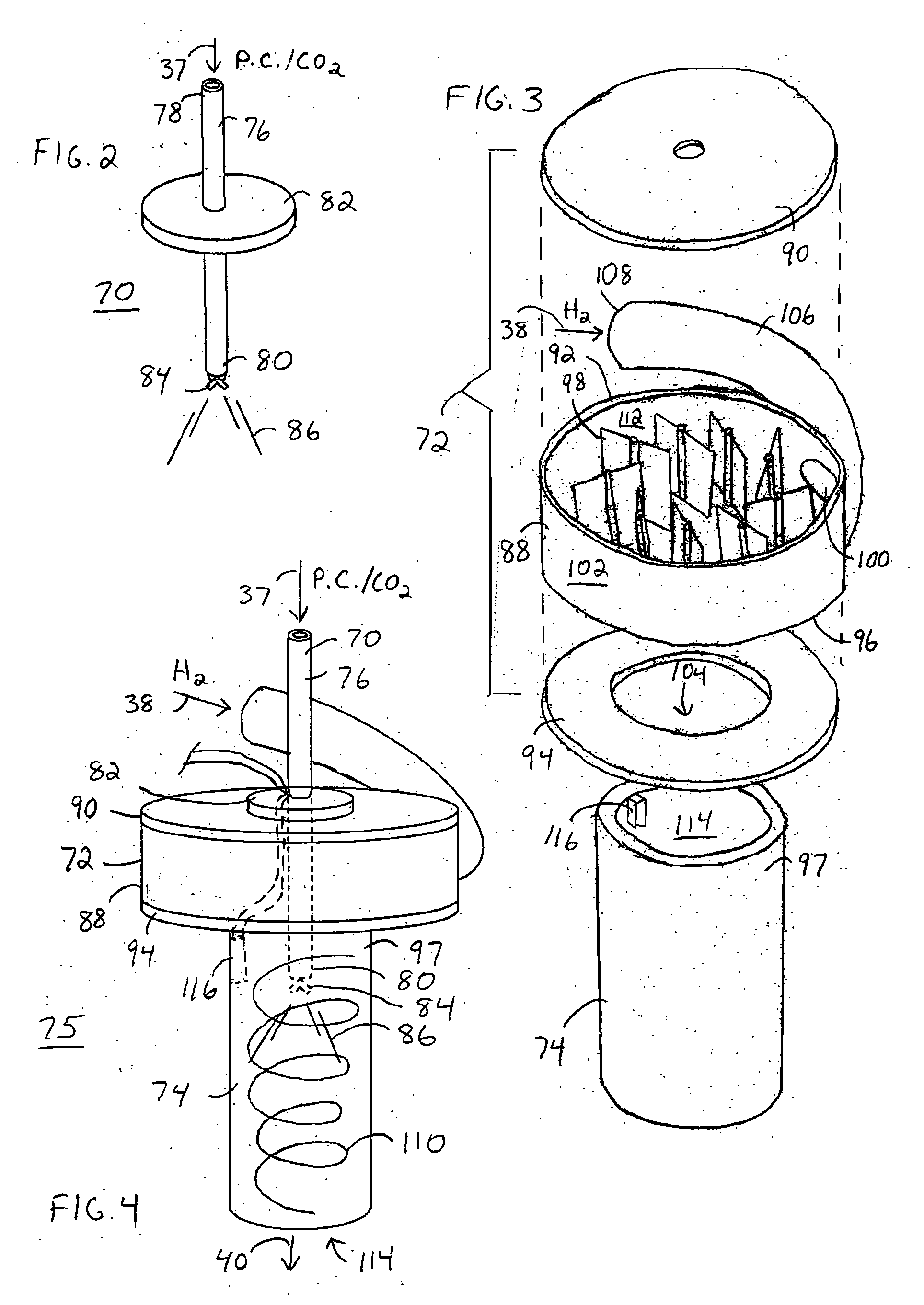
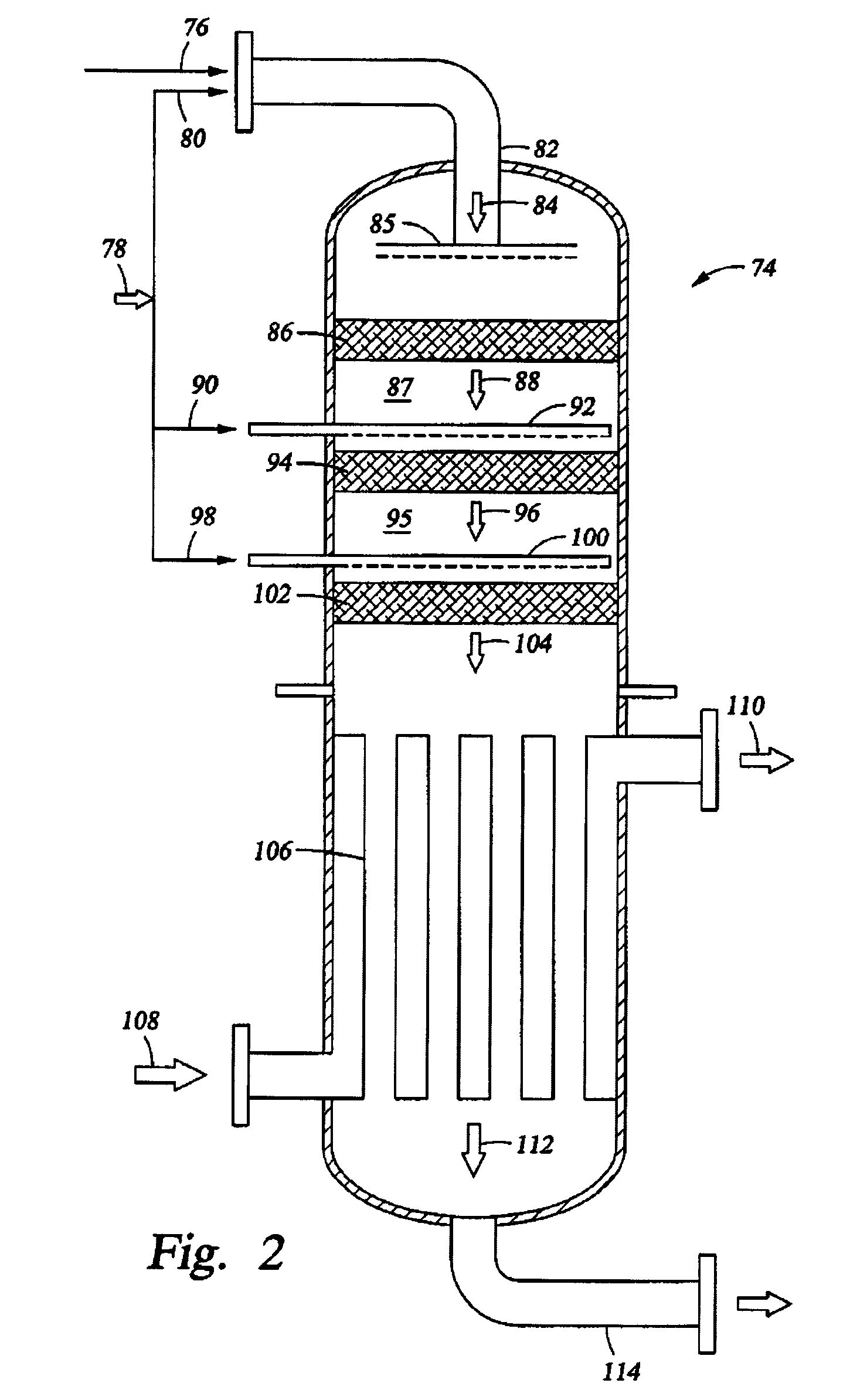
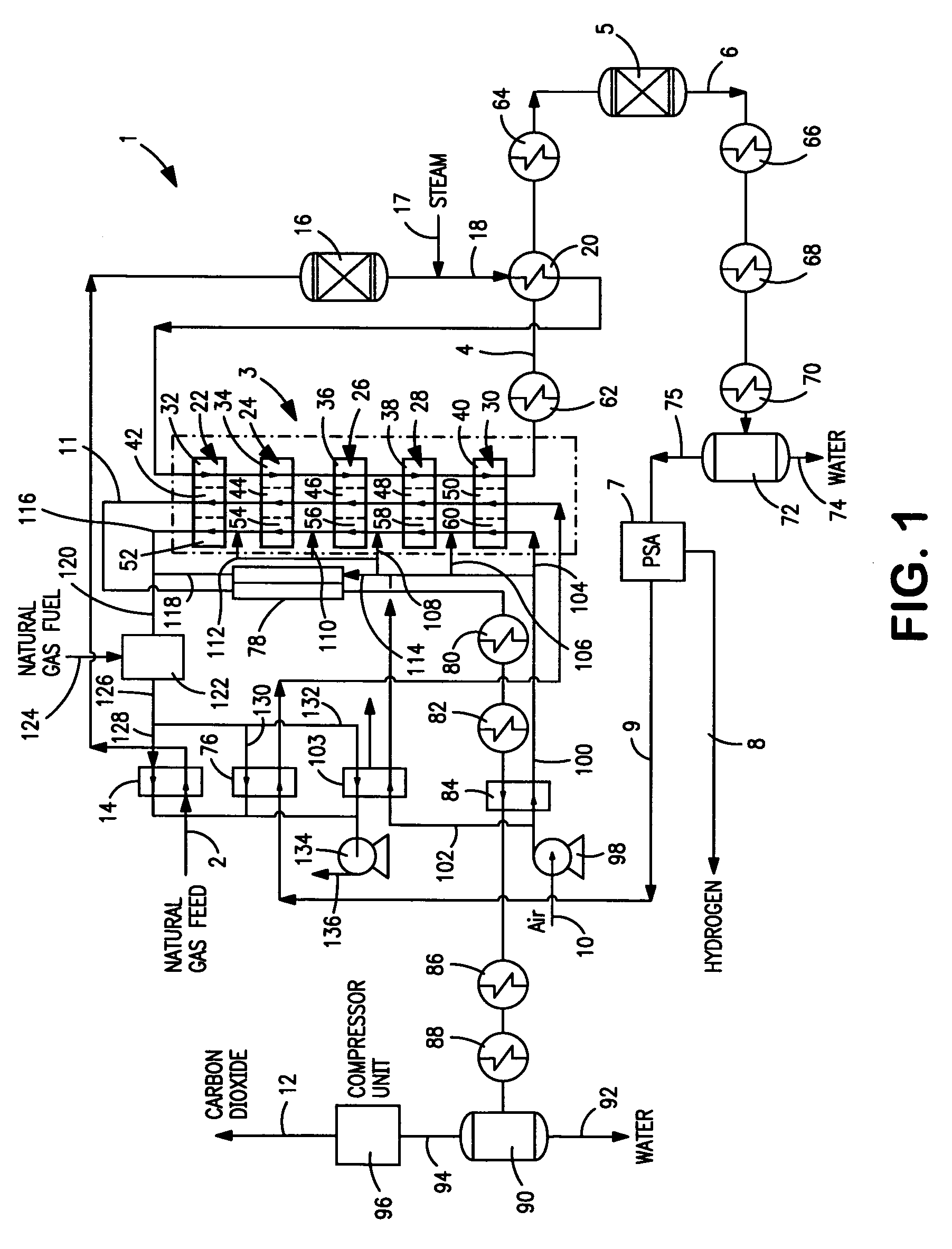
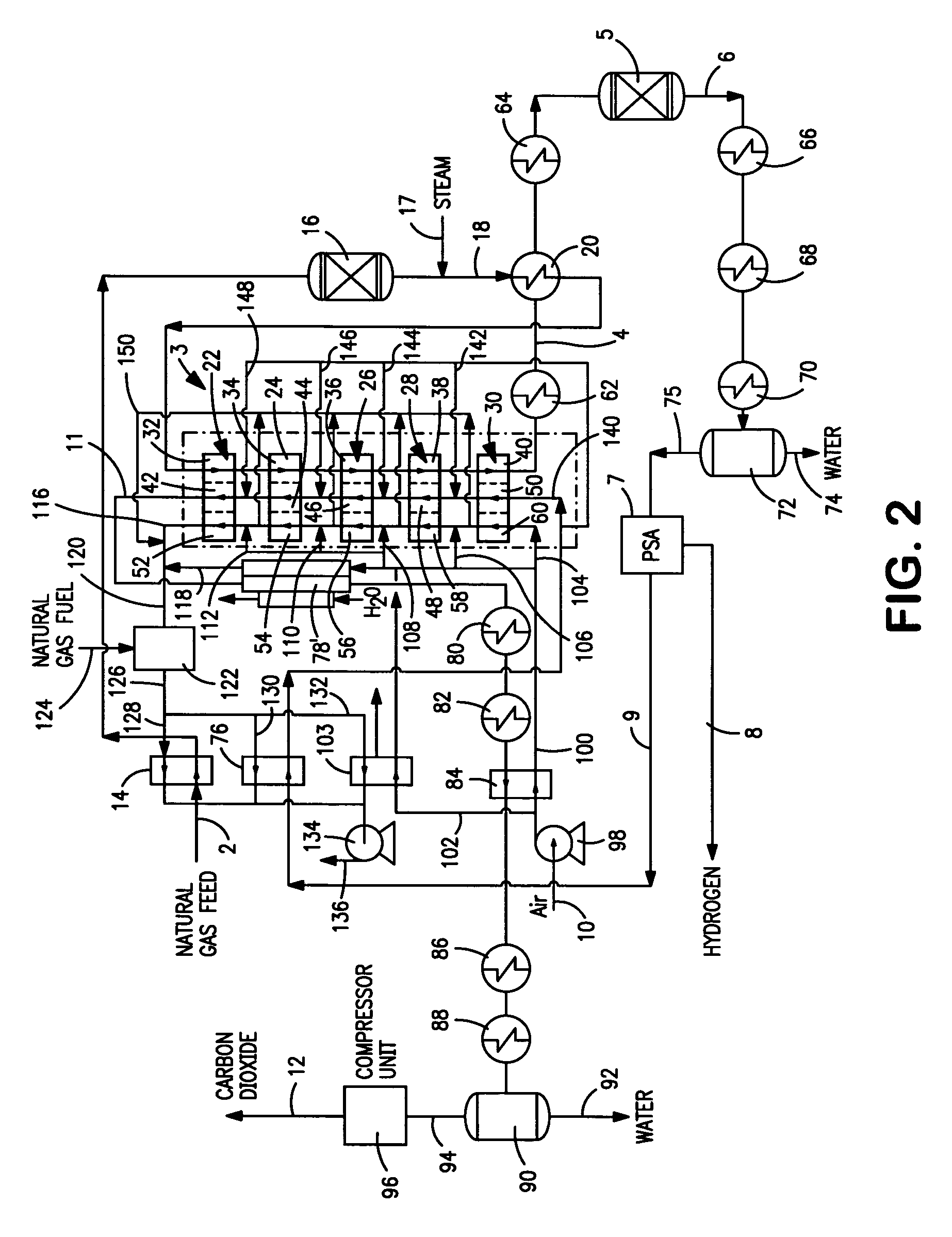
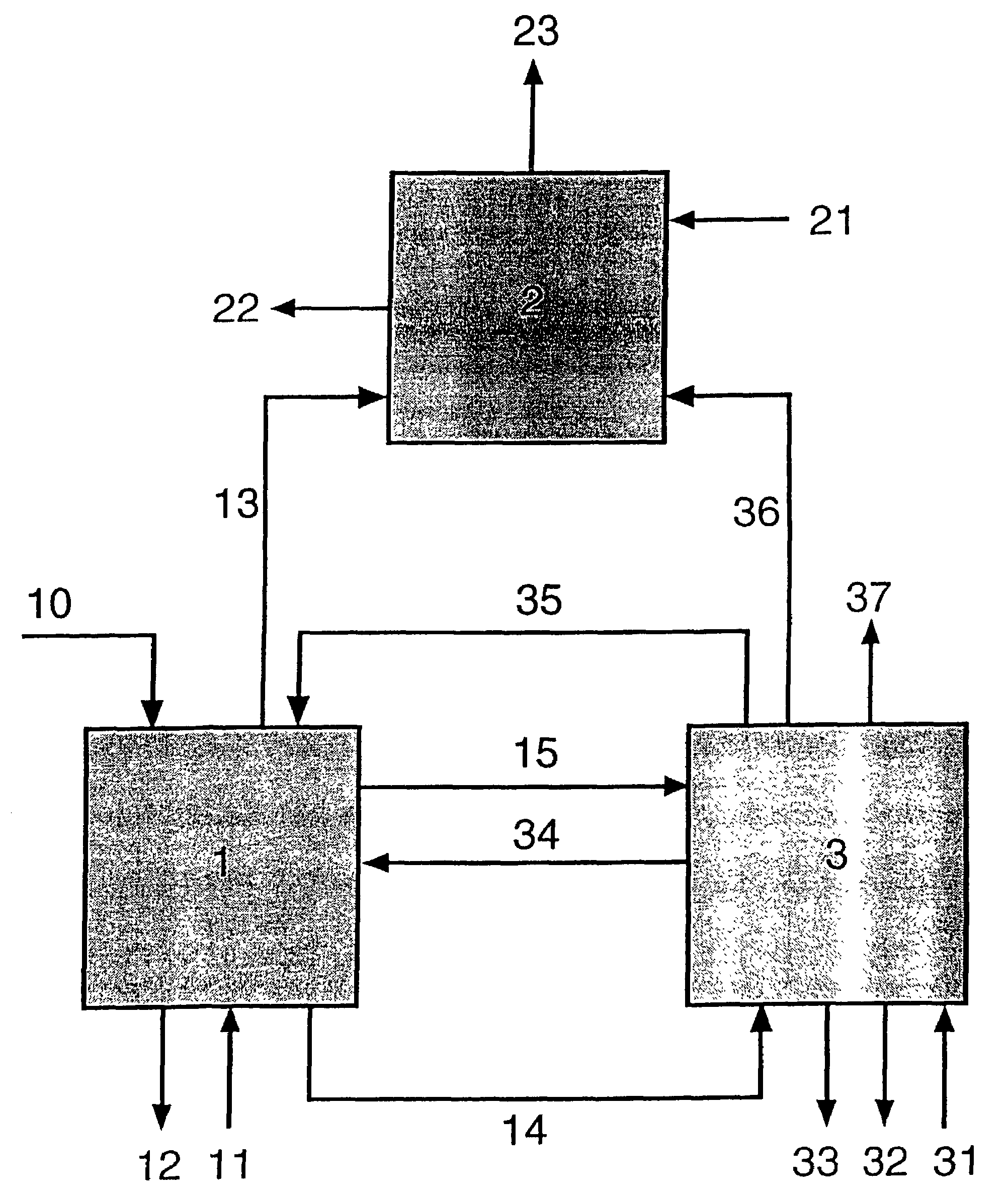
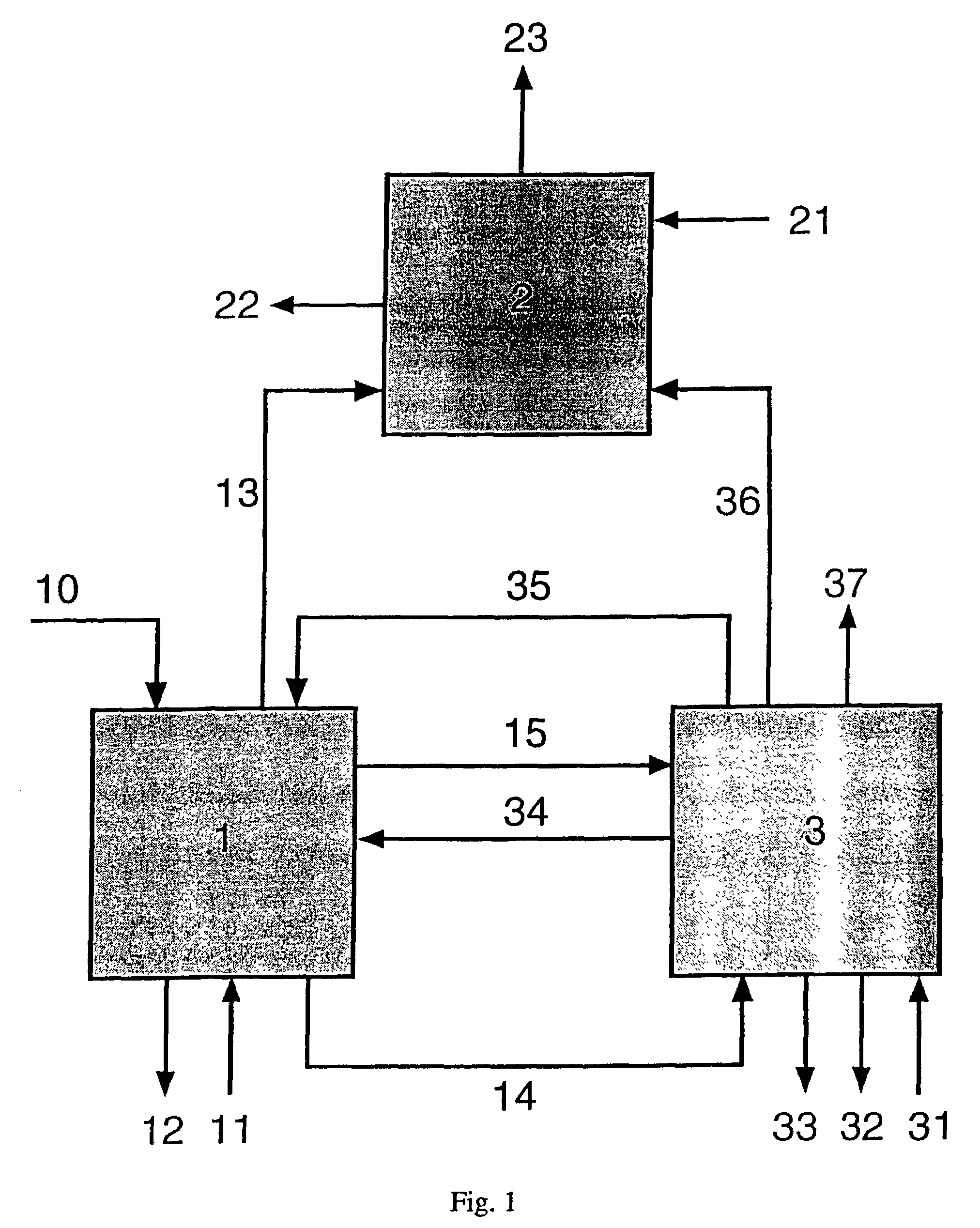
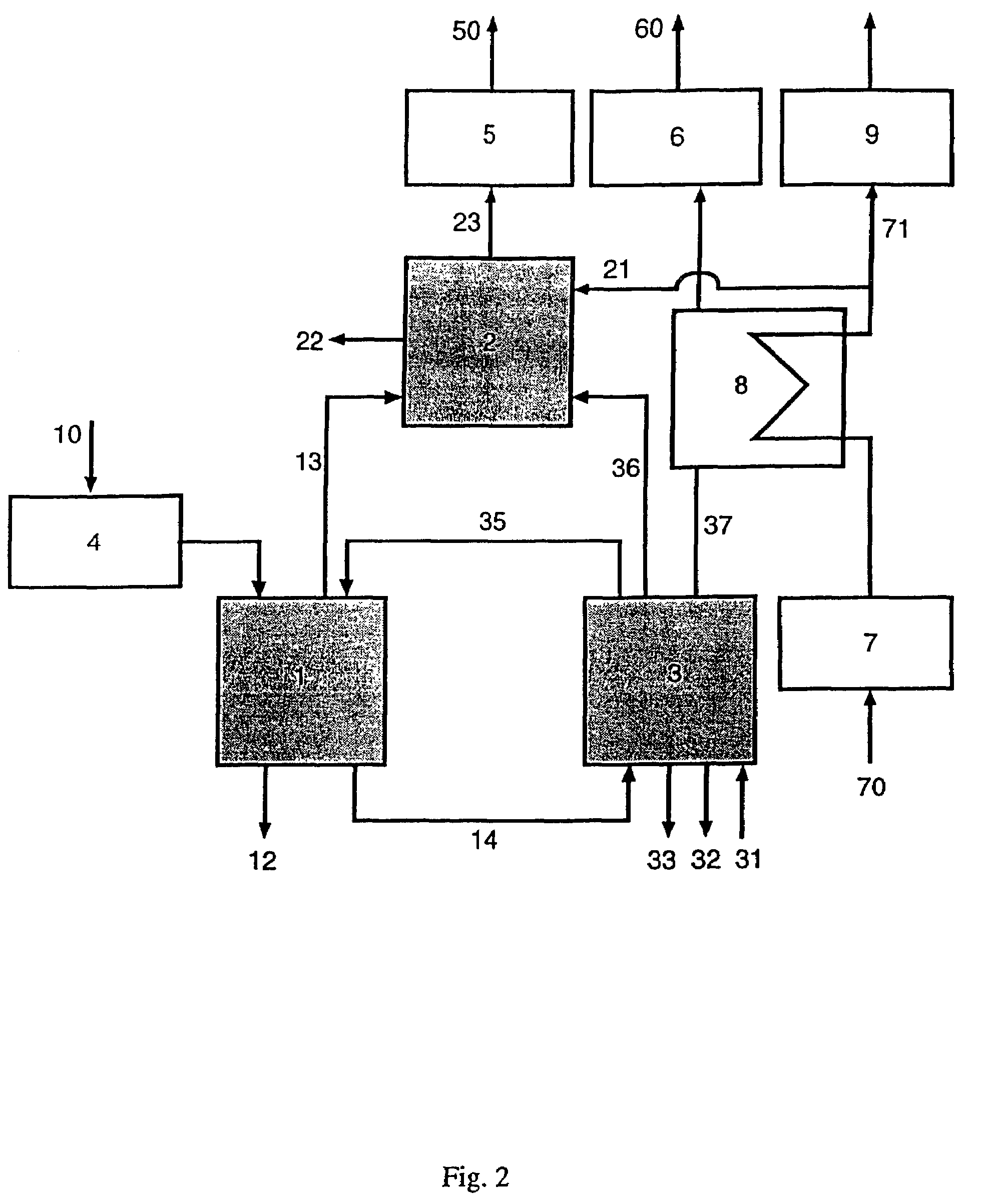
A method for producing methane (69) from a carbonaceous (22) material includes conveying pulverized carbonaceous material (28) entrained in an inert carrier fluid, such as carbon dioxide (36), into a reactor (34). The reactor (34) includes a vortex region (72) for receiving hydrogen gas (38) and imparting a swirling motion to the hydrogen gas (38). The pulverized carbonaceous material (28) is exposed to the swirling stream of hydrogen gas (38) in a first reaction zone (114) within the reactor (34) to form an exit gas (40) that includes methane (69). Remaining unreacted carbonaceous material (28) is further exposed to the hydrogen gas (38) in a second, low velocity, reaction zone (120). The methane rich exit gas (40) is subsequently extracted from the reactor (34) for further processing.
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
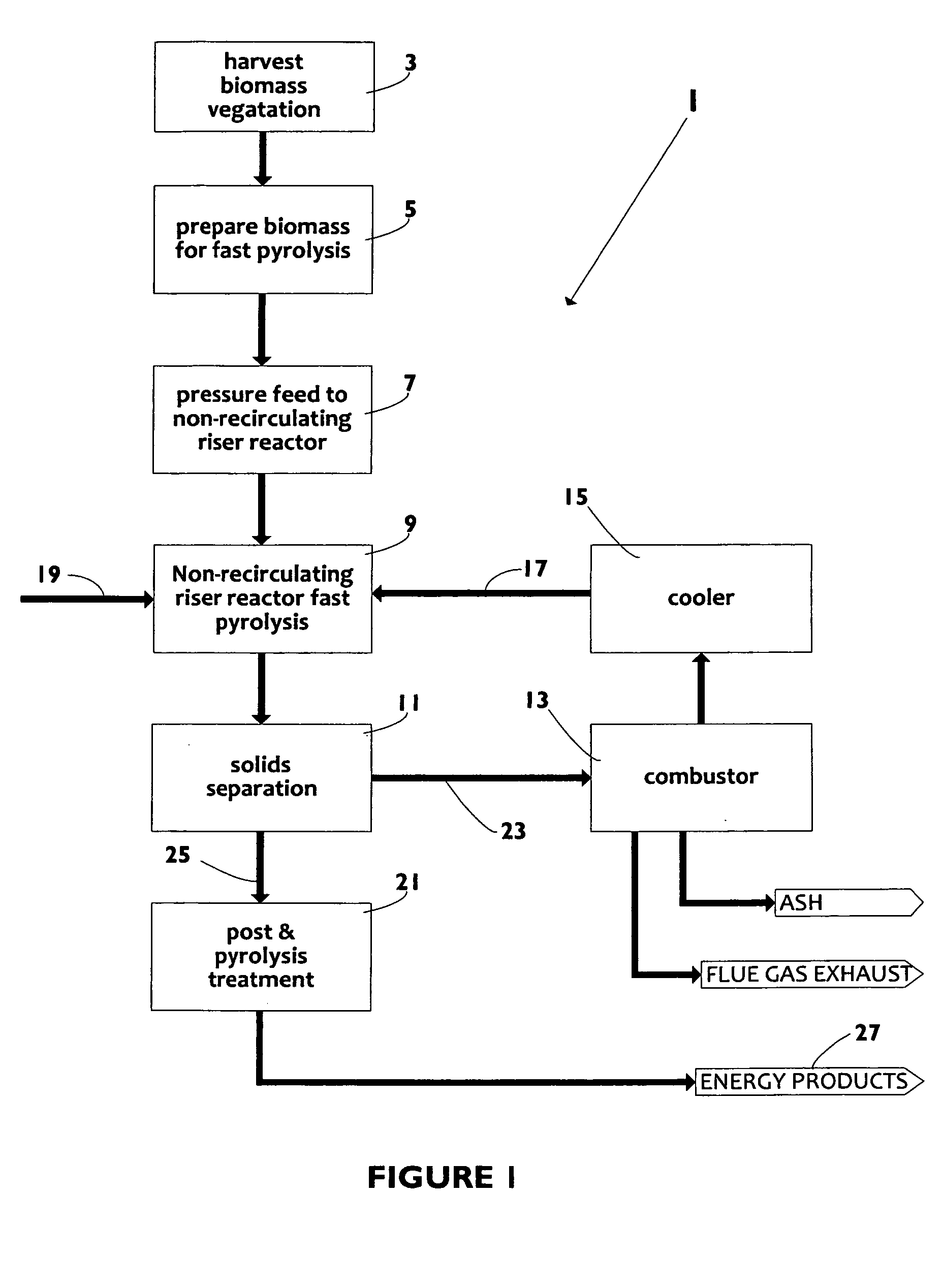
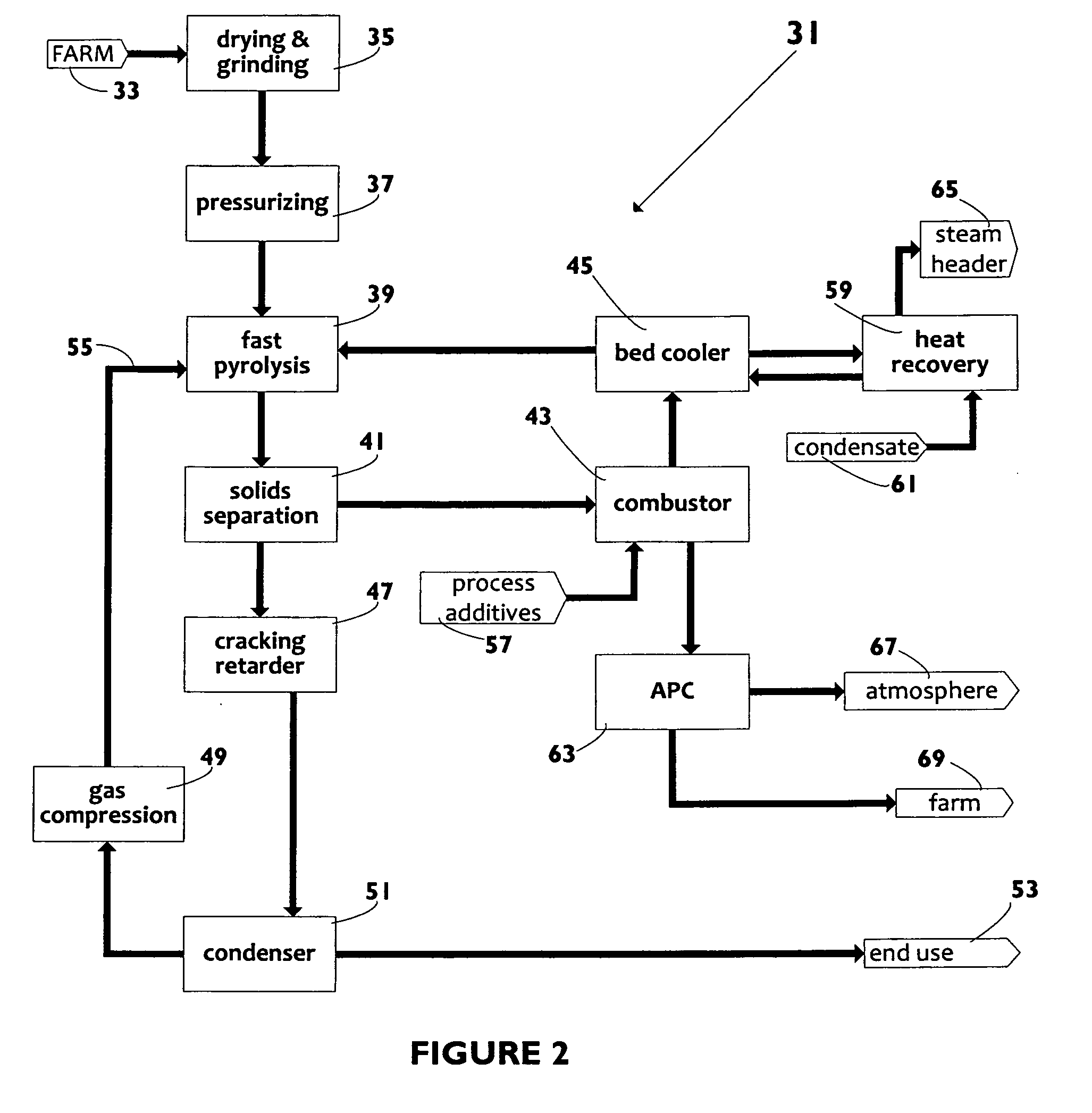
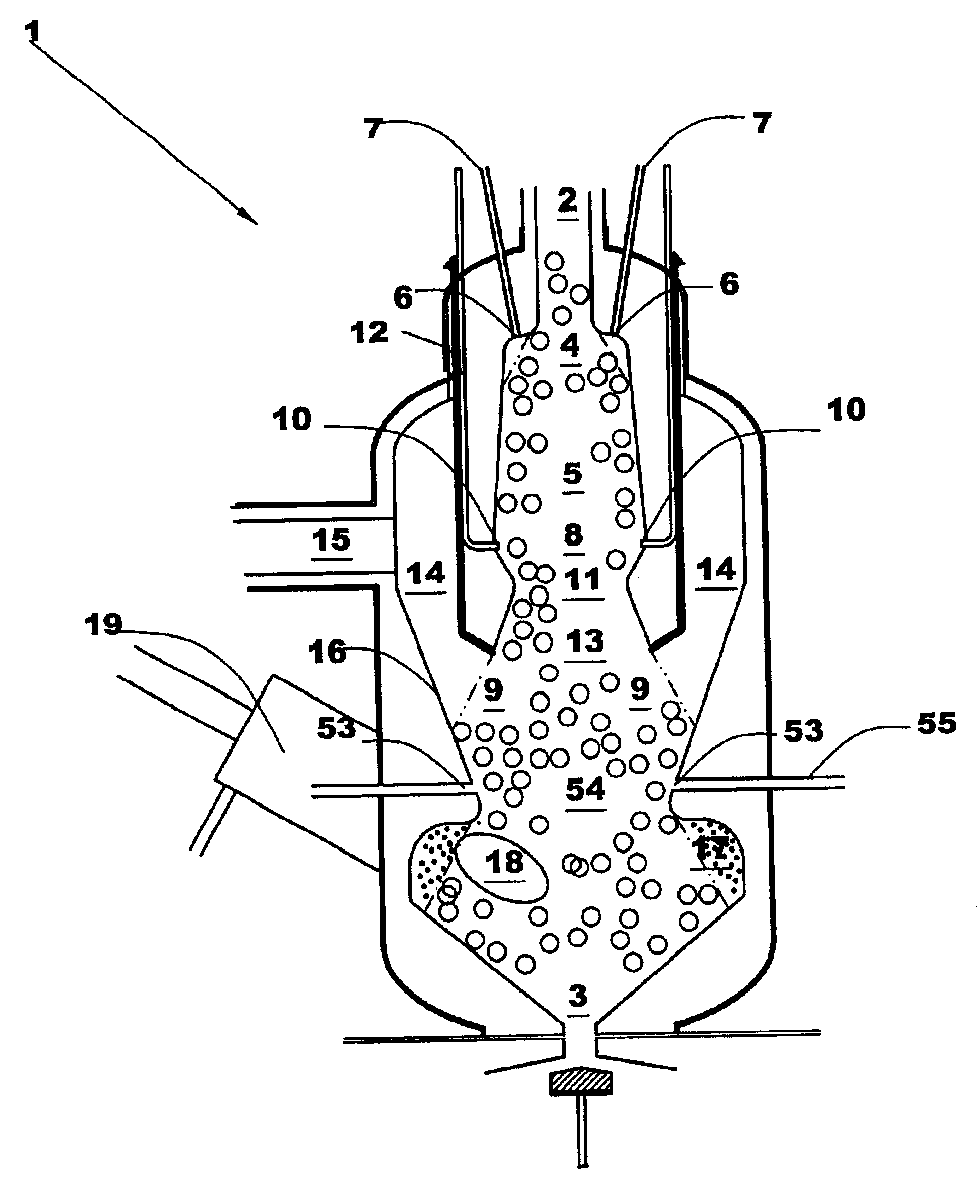
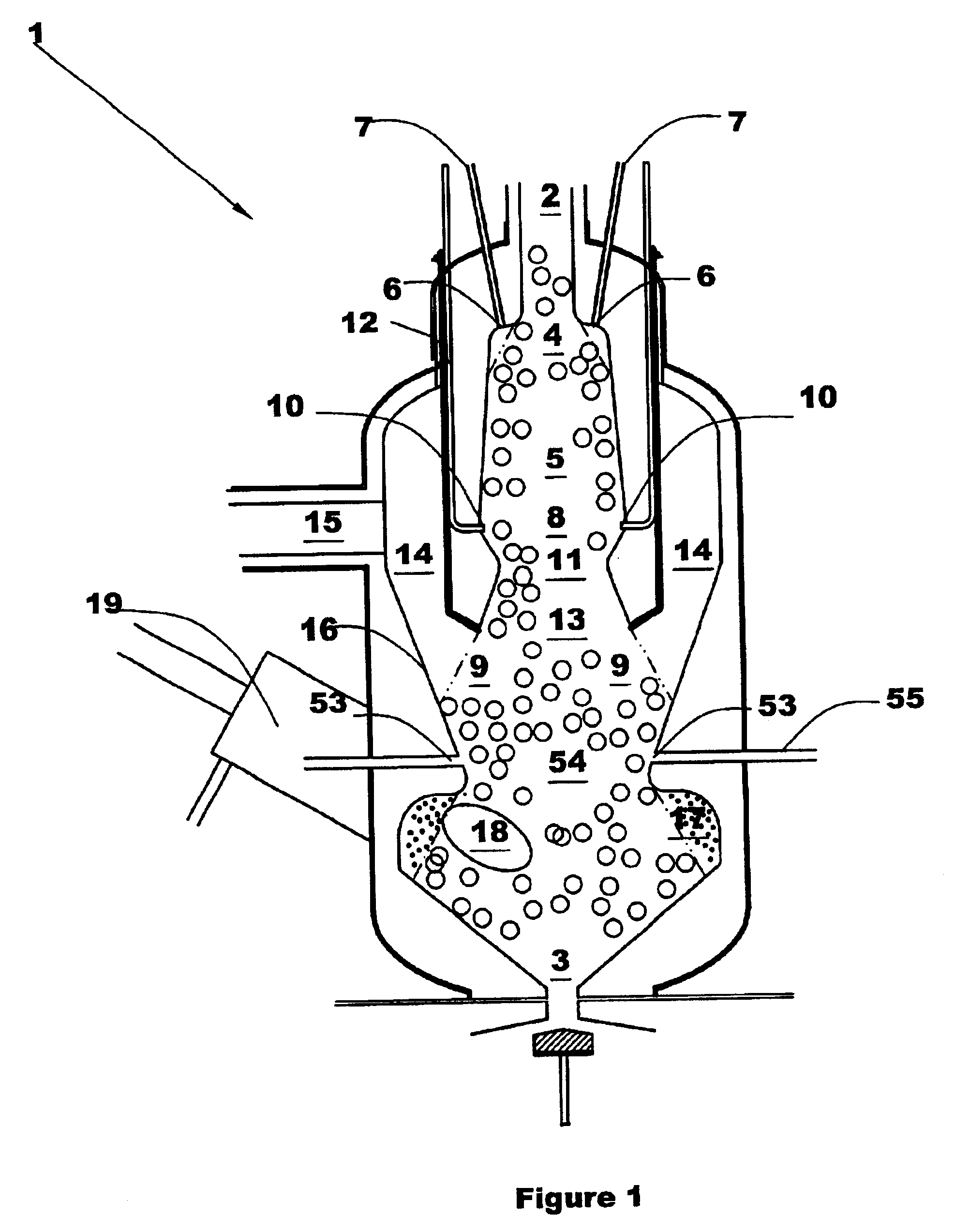
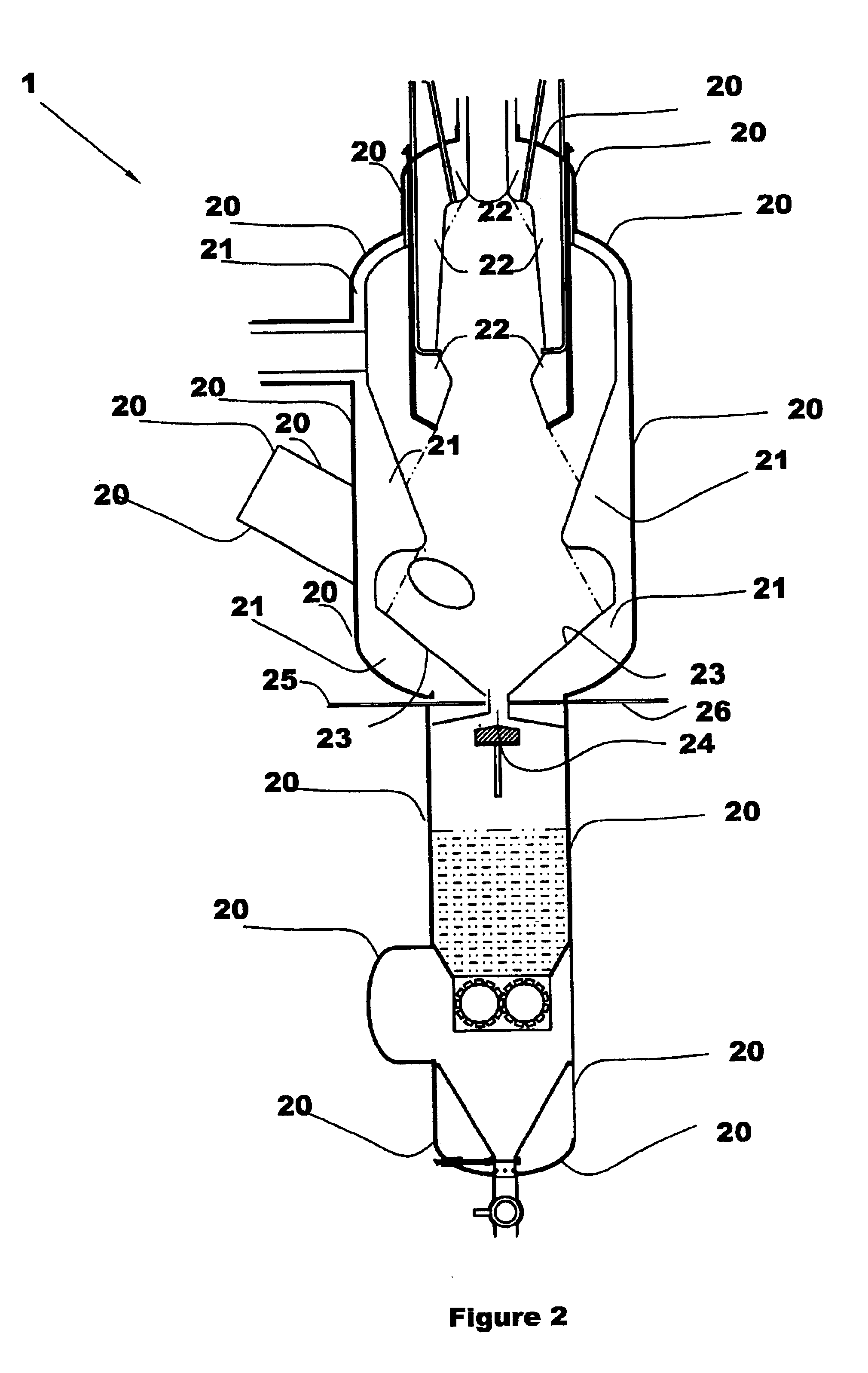
Biomass fast pyrolysis system utilizing non-circulating riser reactor
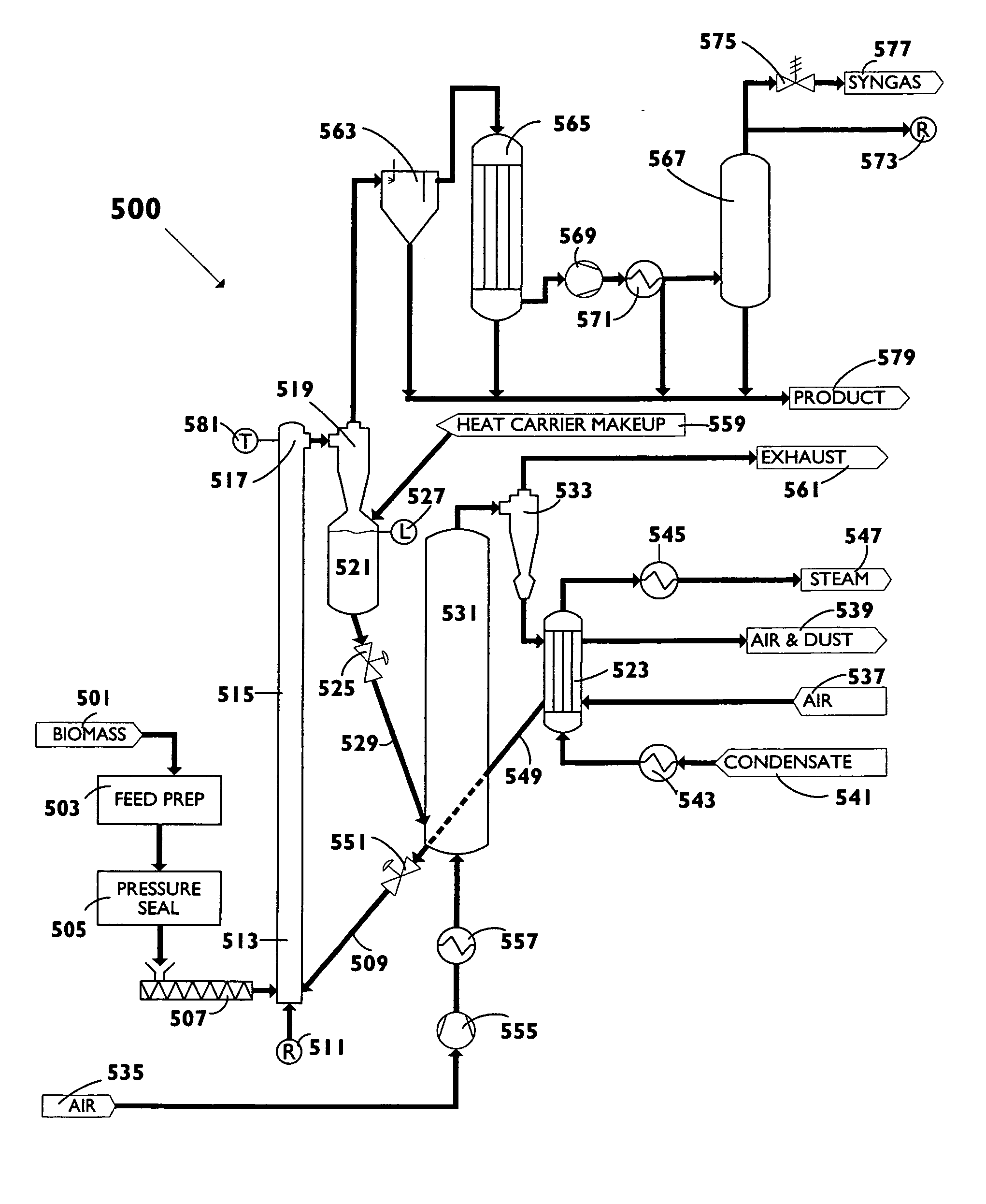
A biomass fast pyrolysis system for conversion of biomass vegetation to synthetic gas and liquid fuels includes: a) a non-circulating riser reactor for pyrolysis of biomass vegetation feedstock utilizing a heat carrier, the non-circulating riser reactor being physically structured and adapted to have a rate of reaction of at least 8,000 biomass vegetation feedstock lbs / hr / ft2, utilizing a ratio of heat carrier to biomass vegetation feedstock of about 7:1 to about 11.5:1, the riser reactor having a base input region at its bottom, a central reaction region and an output region at its top, the riser reactor including a cyclone disengager at its output region for separation of pyrolysis resulting char and heat carrier from the pyrolysis product gases, the cyclone disengager having an output downcomer and an output upcomer, the cyclone disengager output downcomer being connected to and feeding into a side combustor unit, the riser reactor being a non-circulating riser reactor in that the heat carrier is not returned directly to the riser reactor from the cyclone disengager and travels first down the cyclone disengager output downcomer to the side combustor unit; and, b) the side combustor unit for combusting pyrolysis resultant char and reheating the heat carrier the side combustor having a heat carrier downcomer connected to the base input region of the riser reactor.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENERGY GLOBAL
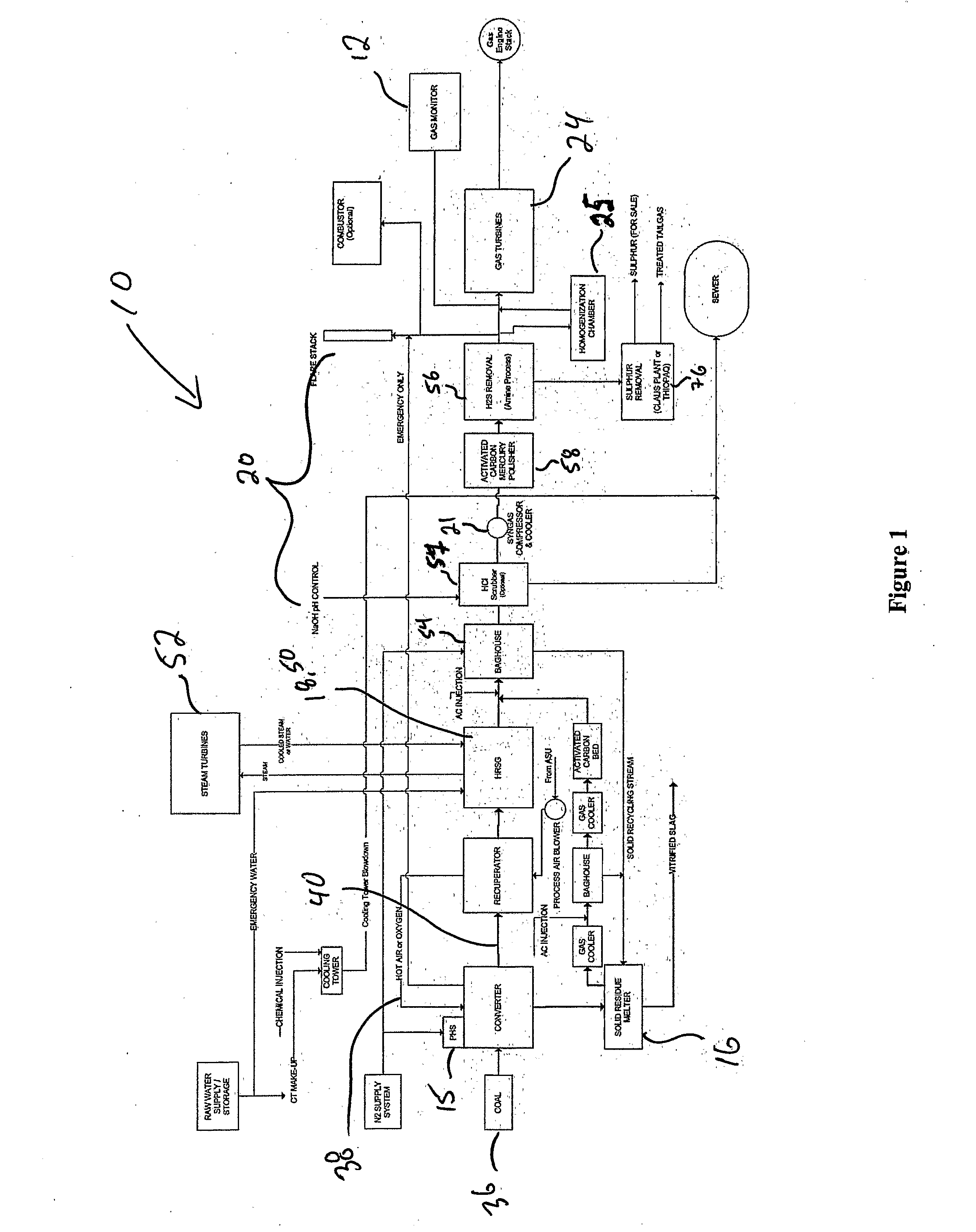
System for the Conversion of Coal to a Gas of Specified Composition
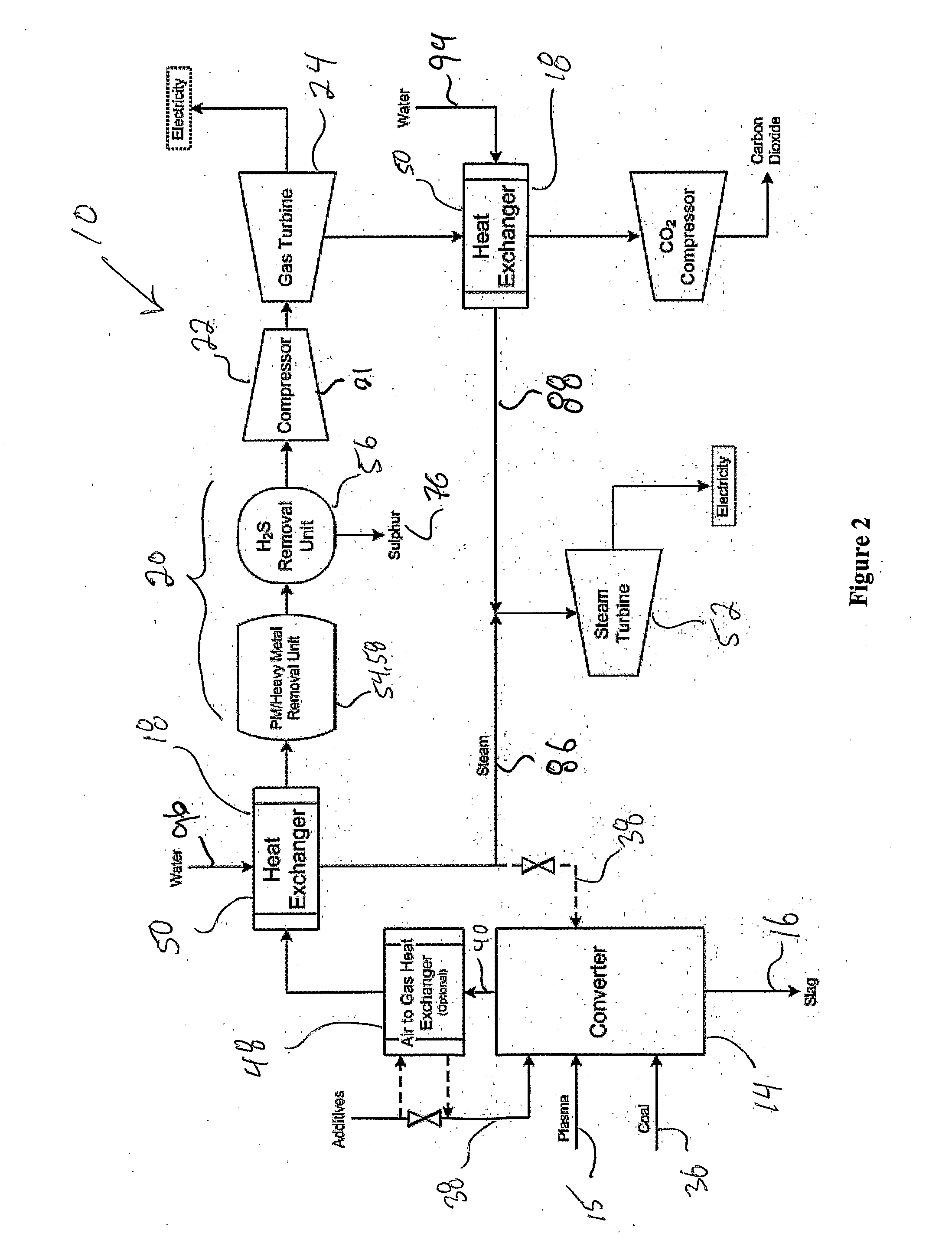
InactiveUS20080222956A1Energy inputCarburetting by solid carbonaceous material pyrolysisEnergeticsProduct gas
The present invention provides a coal gasification system with an integrated control subsystem. The system generally comprises, in various combinations, a gasification reactor vessel (or converter) having one or more processing zones and one or more plasma heat sources, a solid residue handling subsystem, a gas quality conditioning subsystem, as well as an integrated control subsystem for managing the overall energetics of the conversion of coal to energy and maintaining all aspects of the gasification processes at an optimal set point The gasification system may also optionally comprise a heat recovery subsystem and / or a product gas regulating subsystem.
Owner:PLASCO ENERGY GROUP INC
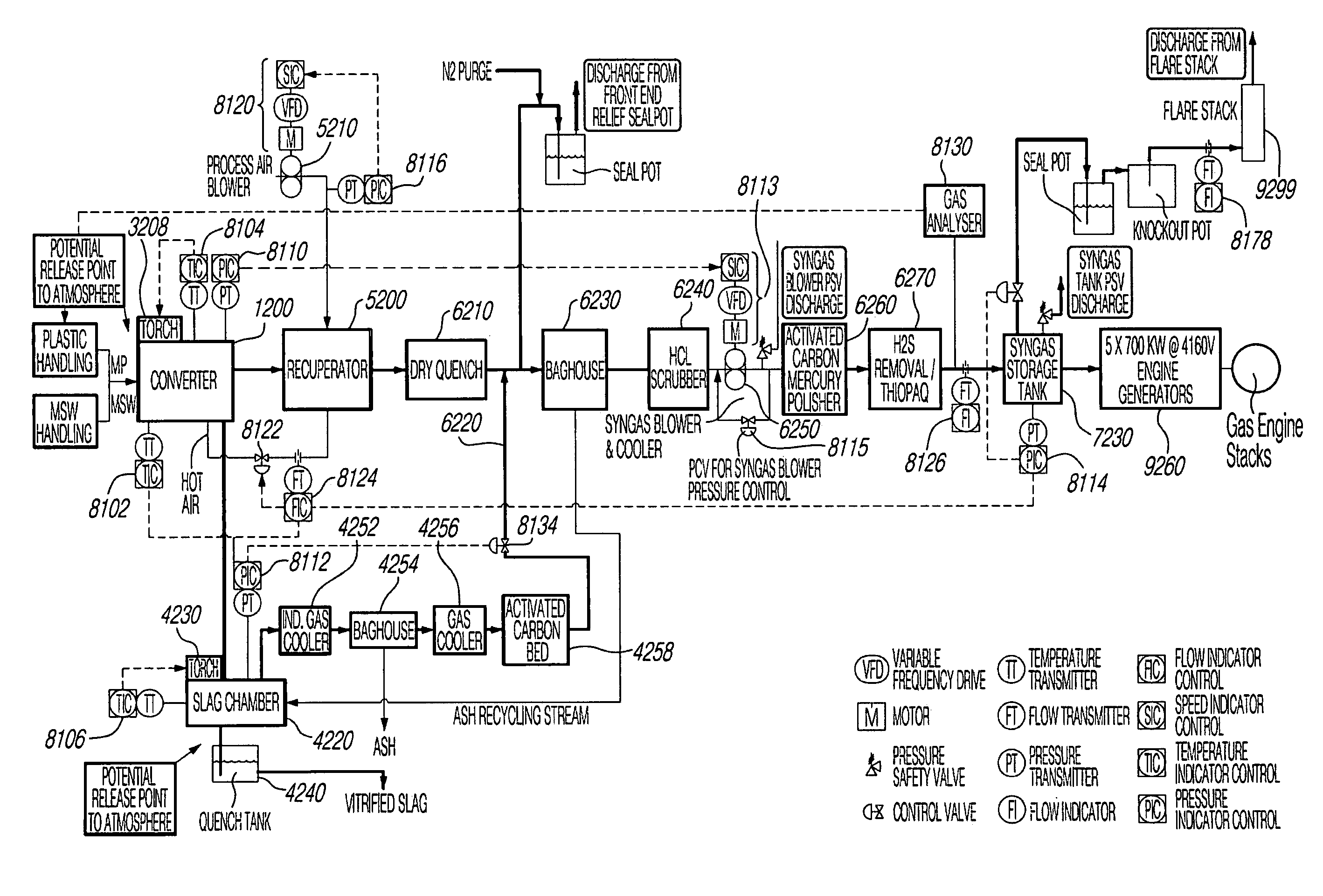
Low Temperature Gasification Facility with a Horizontally Oriented Gasifier
A low-temperature gasification system comprising a horizontally oriented gasifier is provided that optimizes the extraction of gaseous molecules from carbonaceous feedstock while minimizing waste heat. The system comprises a plurality of integrated subsystems that work together to convert municipal solid waste (MSW) into electricity. The subsystems comprised by the low-temperature gasification system are: a Municipal Solid Waste Handling System; a Plastics Handling System; a Horizontally Oriented Gasifier with Lateral Transfer Units System; a Gas Reformulating System; a Heat Recycling System; a Gas Conditioning System; a Residue Conditioning System; a Gas Homogenization System and a Control System.
Owner:PLASCO CONVERSION TECH INC
Production of hydrogen and removal and sequestration of carbon dioxide from coal-fired furnaces and boilers
InactiveUS7282189B2Increase ratingsValue maximizationOrganic chemistryNitrogen compoundsHydrogenProcess engineering
Methods for reducing and eliminating carbon dioxide from the emissions of solid fuel fired power plants, particularly coal fired power plants, and to sequester the carbon dioxide, typically by using existing equipment. In some embodiments, the methods involve pyrolyzing the solid fuel to remove volatile matter and using the volatile matter to produce hydrogen. Additionally, the methods may involve burning the solid fuel or pyrolized solid fuel at very fuel rich stoichiometric conditions. Sequestration may include the production of a carbon dioxide-containing solution and the pumping of the solution into the ground, particularly in areas high in limestone.
Owner:ZAUDERER BERT
Gas conditioning system
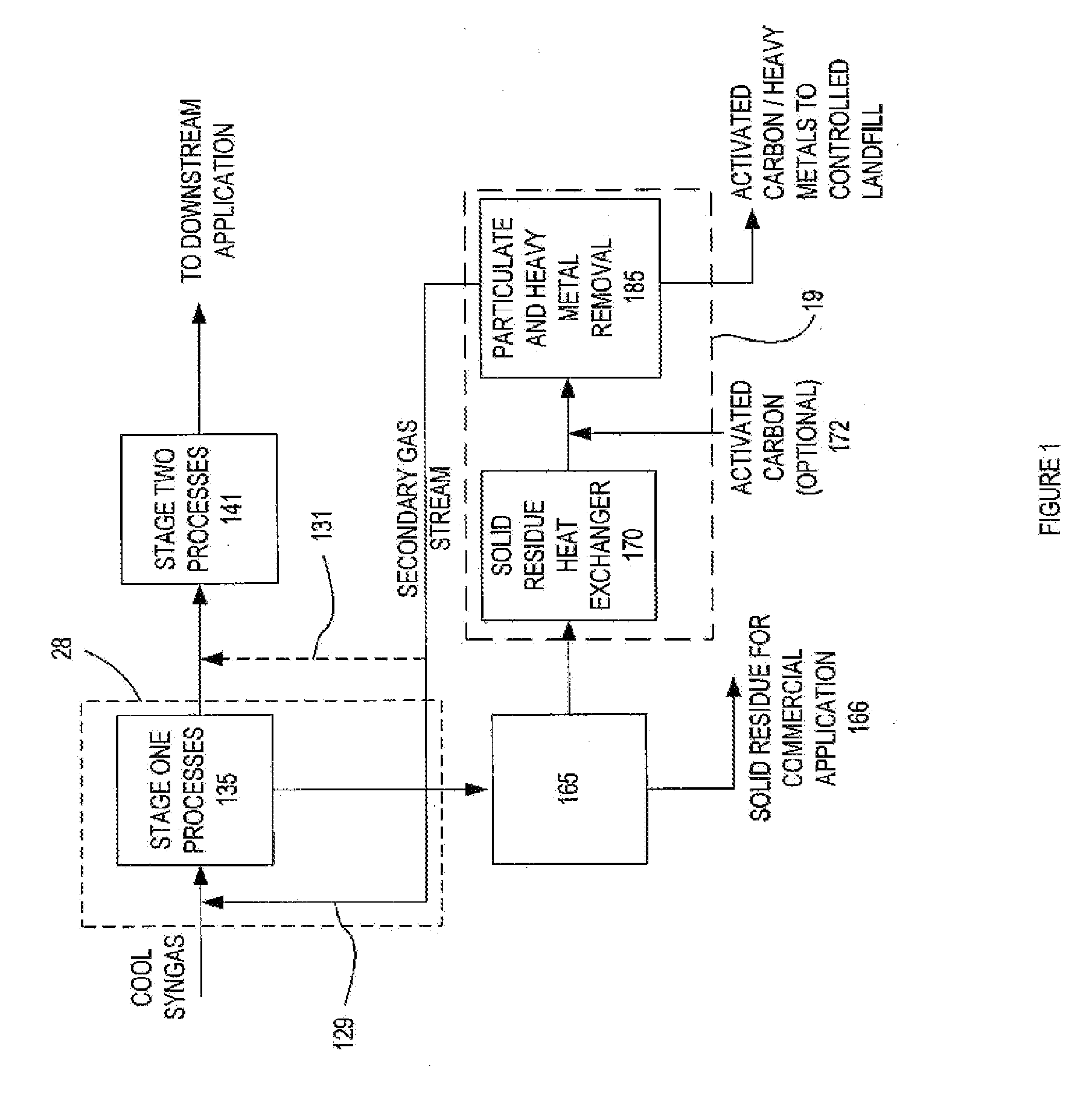
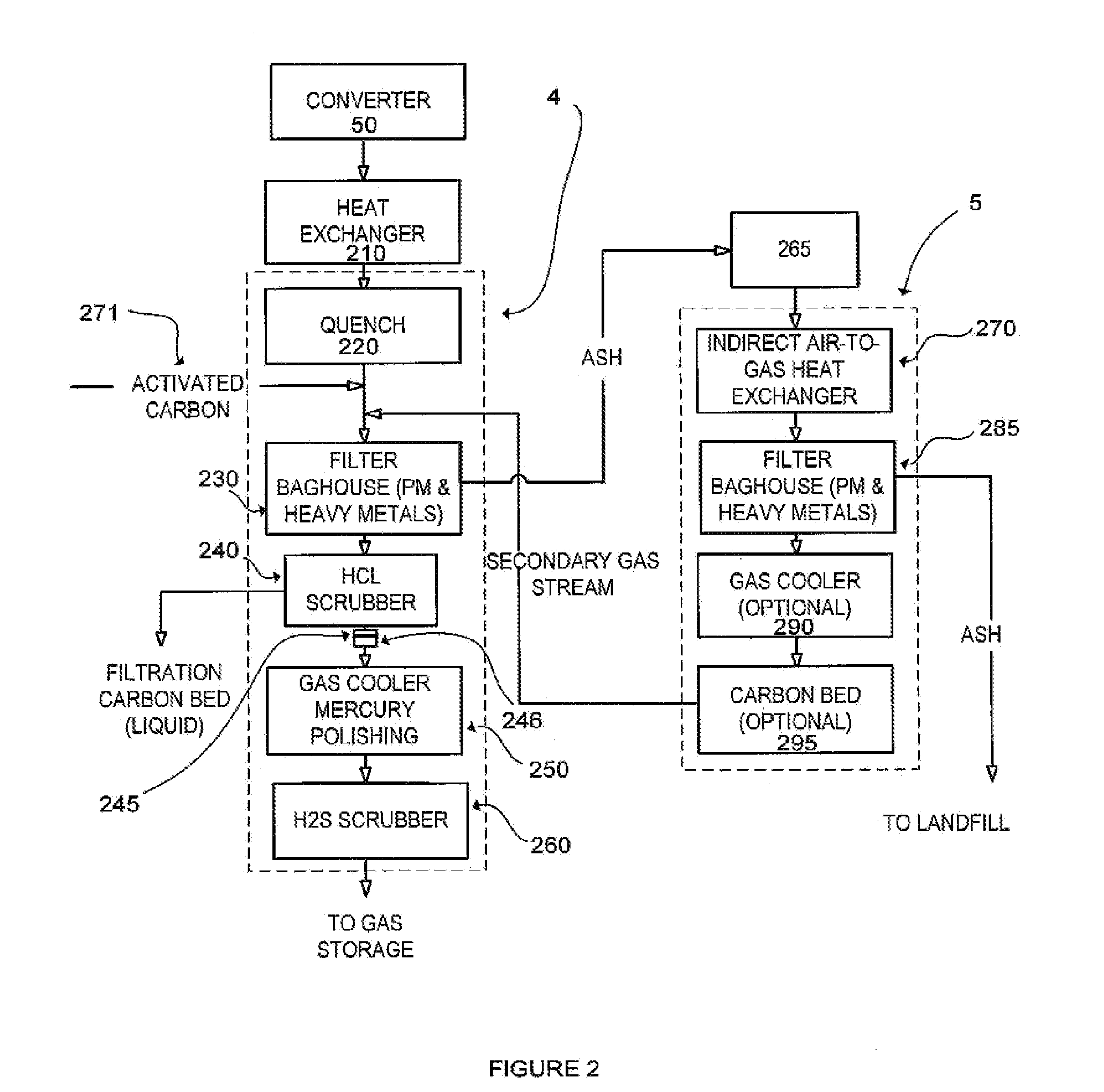
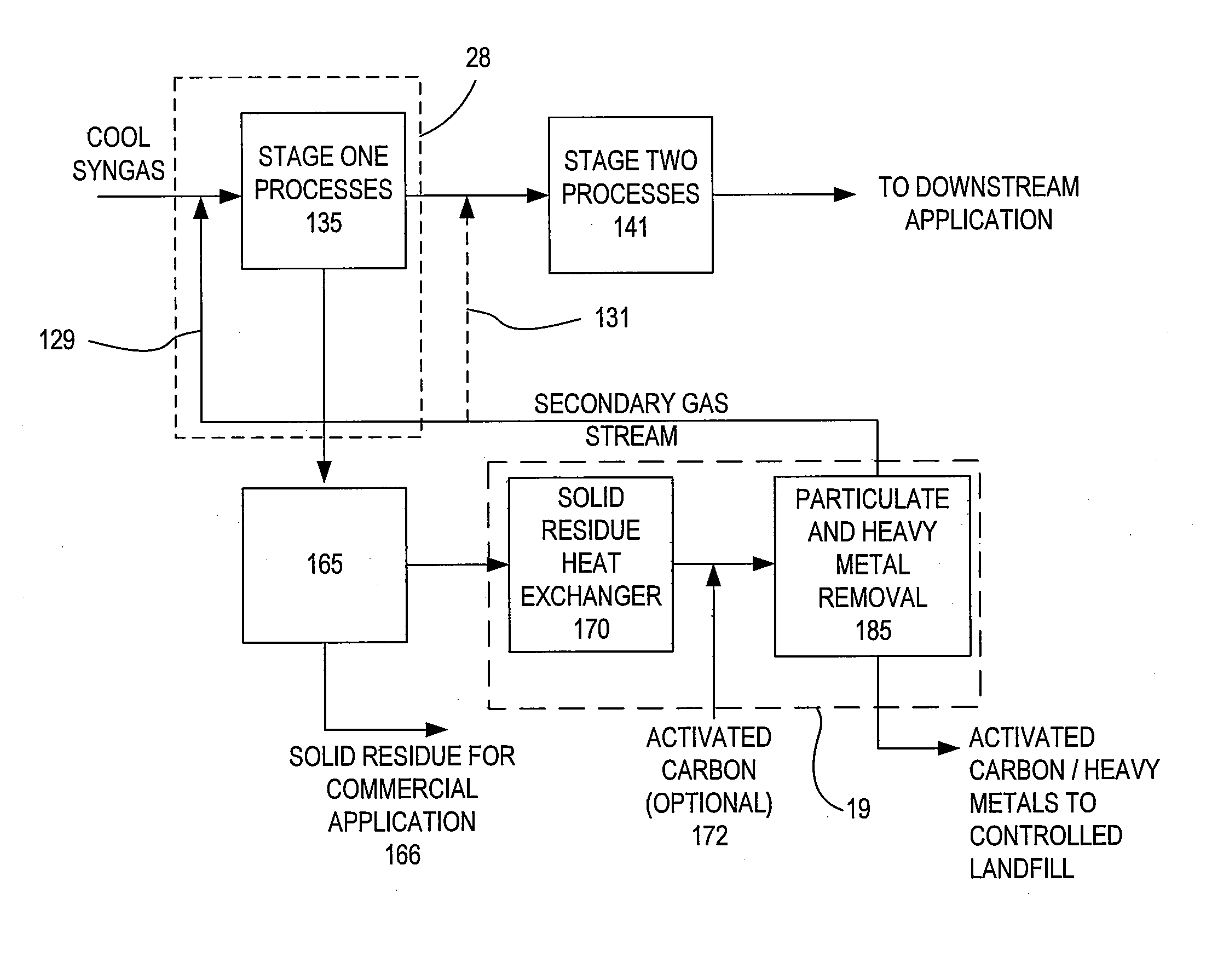
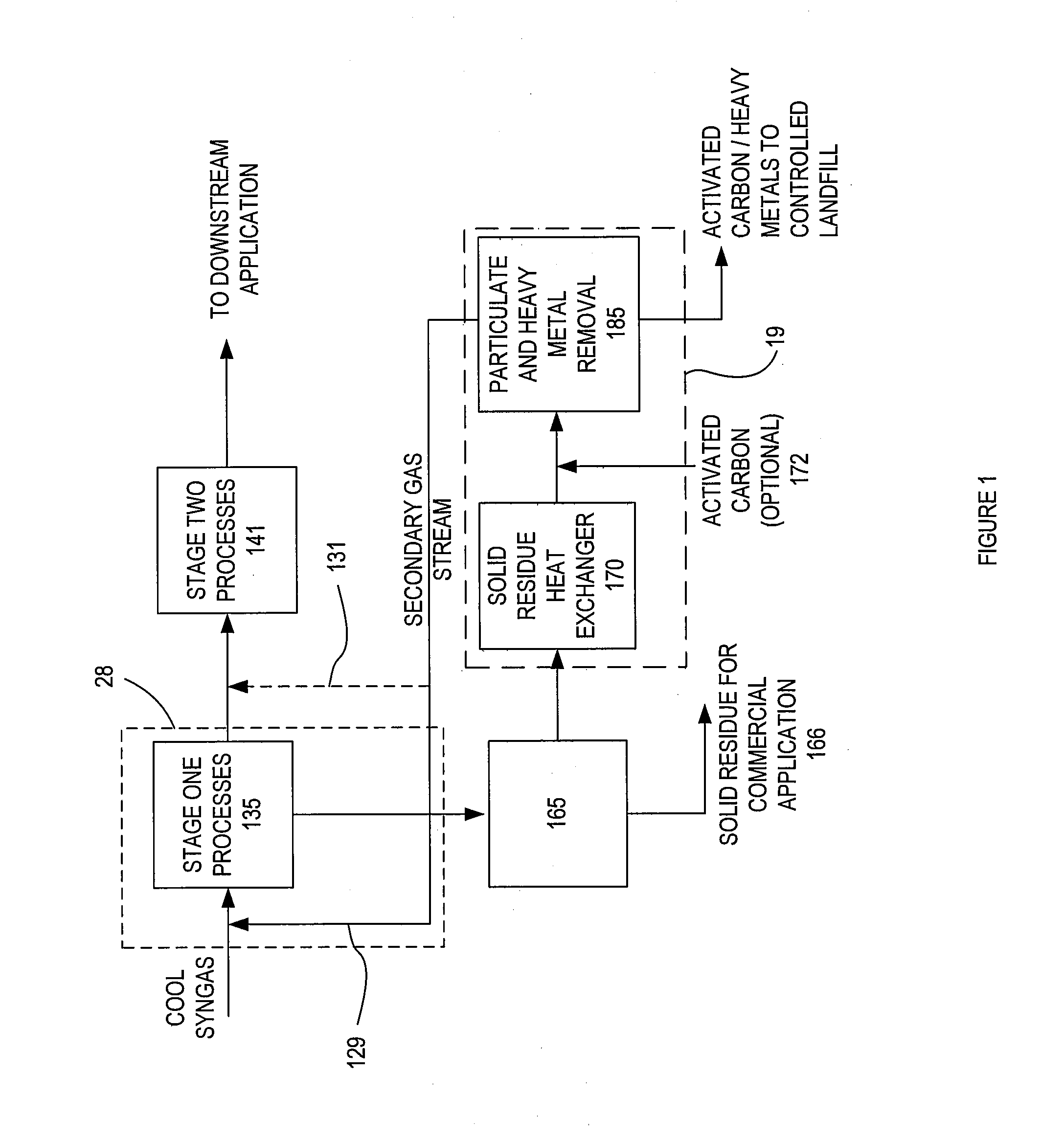
The present invention provides a gas conditioning system for processing an input gas from a low temperature gasification system to an output gas of desired characteristics. The system comprises a two-stage process, the first stage separating heavy metals and particulate matter in a dry phase, and the second stage including further processing steps of removing acid gases, and / or other contaminants. Optional processes include adjusting the humidity and temperature of the input gas as it passes through the gas conditioning system. The presence and sequence of processing steps is determined by the composition of the input gas, the desired composition of output gas for downstream applications, and by efficiency and waste minimization.
Owner:PLASCO ENERGY GROUP INC
Gas Conditioning System
The present invention provides a gas conditioning system for processing an input gas from a low temperature gasification system to an output gas of desired characteristics. The system comprises a two-stage process, the first stage separating heavy metals and particulate matter in a dry phase, and the second stage including further processing steps of removing acid gases, and / or other contaminants. Optional processes include adjusting the humidity and temperature of the input gas as it passes through the gas conditioning system. The presence and sequence of processing steps is determined by the composition of the input gas, the desired composition of output gas for downstream applications, and by efficiency and waste minimization.
Owner:PLASCO ENERGY GROUP INC
Method using solar energy, microwaves and plasmas to produce a liquid fuel and hydrogen from biomass or fossil coal
ActiveUS20100258429A1Promote gasificationImproving thermal inertiaElectrical coke oven heatingSolar heating energySludgeFractionating column
A system uses thermal solar energy coupled with microwaves and plasma for producing carbon monoxide (CO) and dihydrogen (H2) from carbonated compounds (biomass, domestic waste, sludge from waste water, fossil coal), wherein the obtained gaseous mixture yields, amongst others, hydrocarbon fuels (olefins, paraffin), esters, and alcohols via a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis. In a first step the carbonated compounds are roasted and pyrolized to produce char and dry coal, and a mixture of superheated gases containing CO2, steam, tars and non-condensable volatile materials. The method includes in a second step, and from the pyrolyis products (char or coal, gas mixture), generating a syngas substantially containing a mixture of carbon monoxide and dihydrogen, the mixture being used in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis units. After the Fischer-Tropsch step, the synthesis products are separated in a distillation column after heating in solar furnaces of mixed furnaces (solar / microwave).
Owner:UGOLIN NICOLAS
Portable hydrogen generator
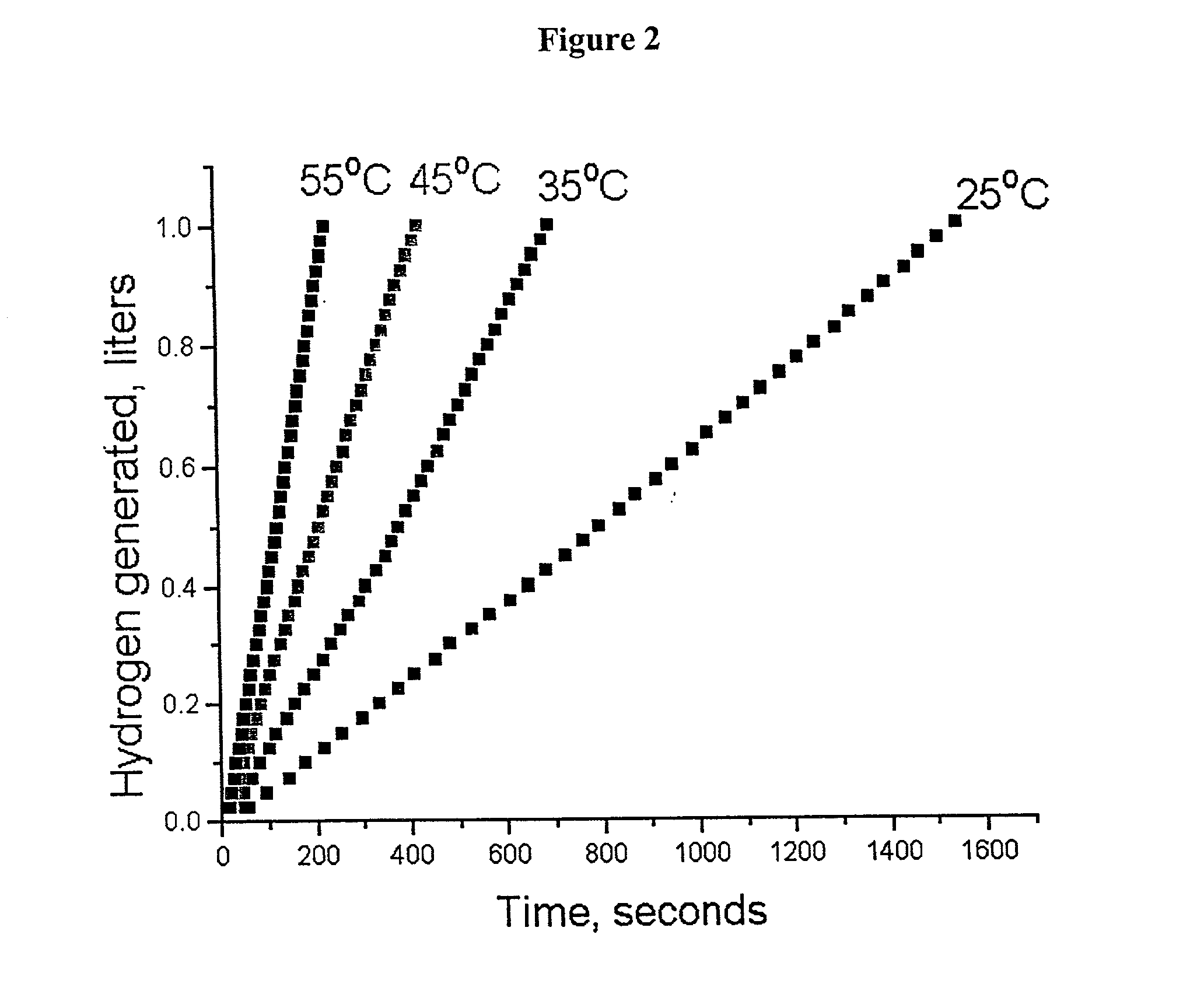
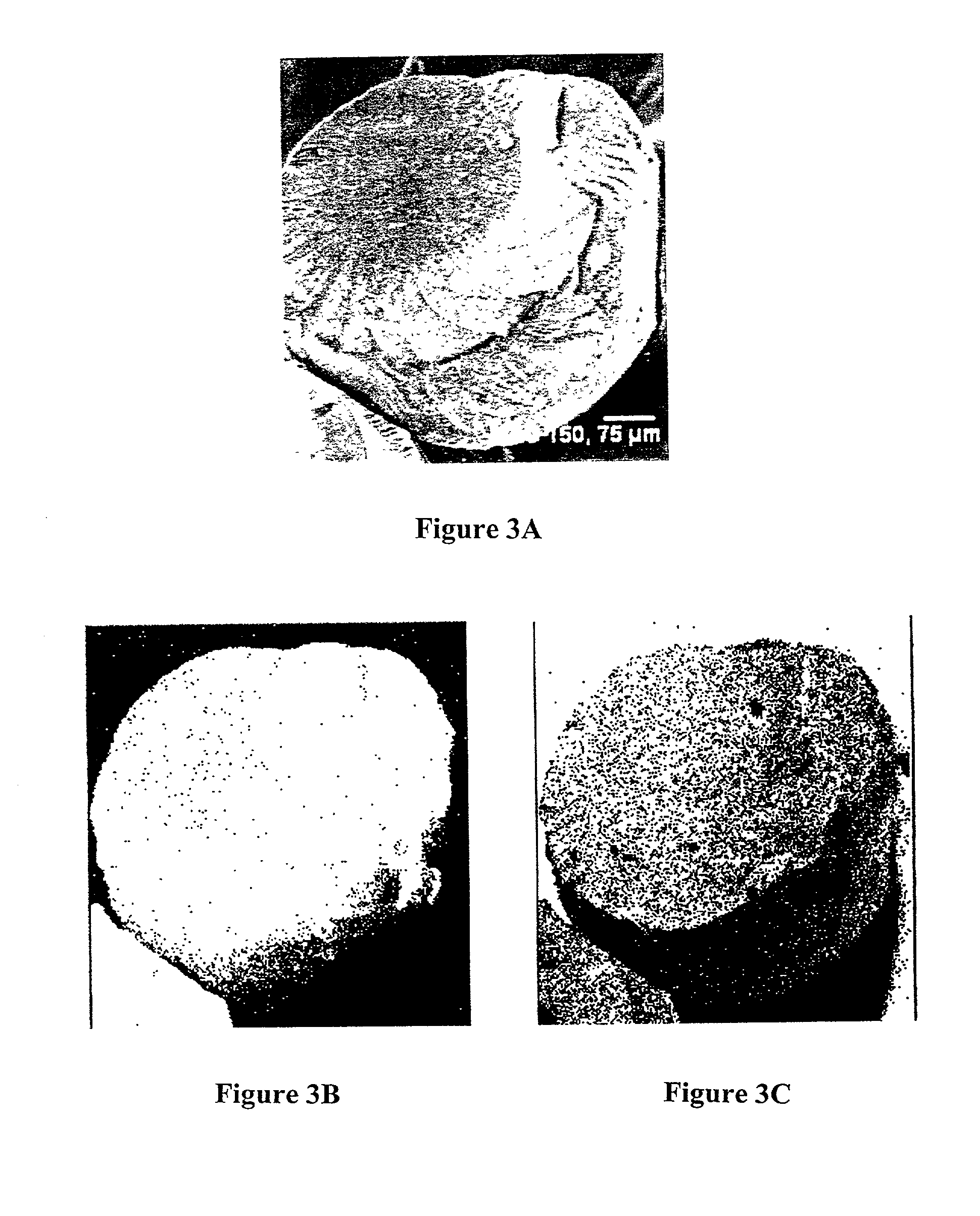
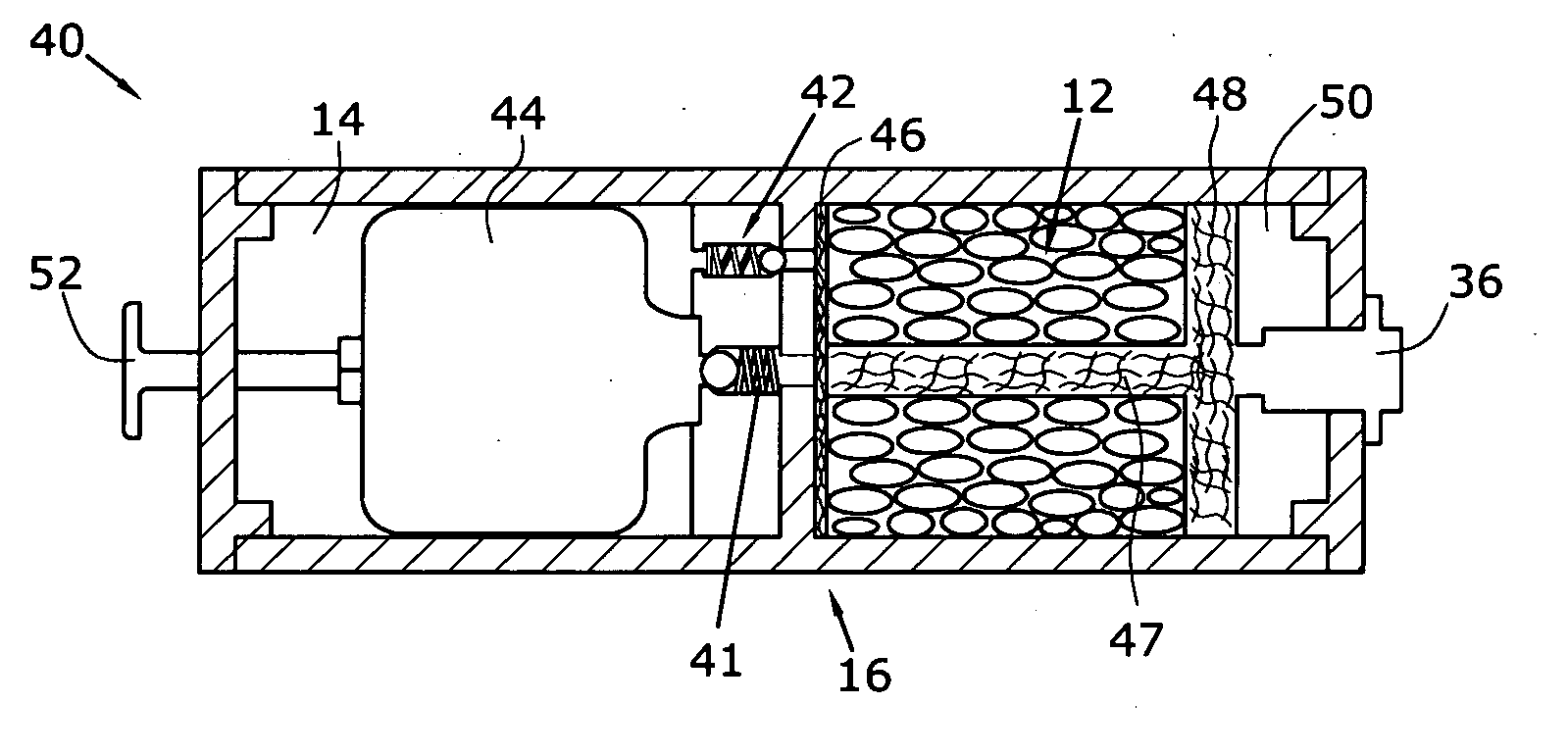
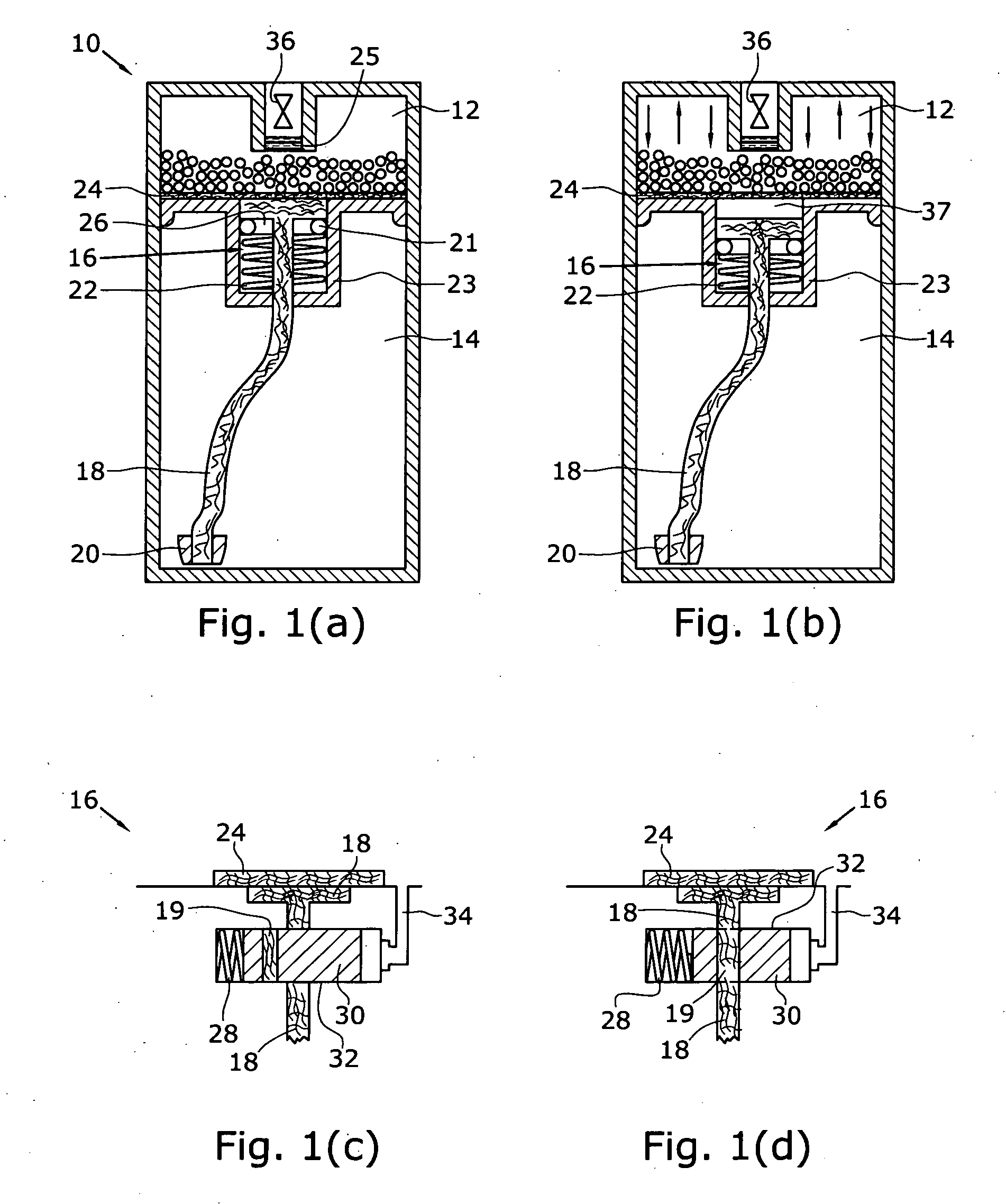
A hydrogen generation system includes a fuel container, a spent fuel container, a catalyst system and a control system for generating hydrogen in a manner which provides for a compact and efficient construction while producing hydrogen from a reaction involving a hydride solution such as sodium borohydride.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
Synthesis gas process comprising partial oxidation using controlled and optimized temperature profile
ActiveUS7261751B2Low selectivityRisk of explosion can be minimizedHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCarburetting by solid carbonaceous material pyrolysisPartial oxidationFixed bed
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Synthesis gas process comprising partial oxidation using controlled and optimized temperature profile
ActiveUS20060029539A1Risk of explosion can be minimizedIncrease the molar ratioHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCarburetting by solid carbonaceous material pyrolysisForming gasPartial oxidation
This invention relates to methods for reacting a hydrocarbon, molecular oxygen, and optionally water and / or carbon dioxide, to form synthesis gas. The preferred embodiments are characterized by delivering a substochiometric amount of oxygen to each of a multitude of reaction zones, which allows for optimum design of the catalytic packed bed and the gas distribution system, and for the optimization and control of the temperature profile of the reaction zones. The multitude of reaction zones may include a series of successive fixed beds, or a continuous zone housed within an internal structure having porous, or perforated, walls, through which an oxygen-containing stream can permeate. By controlling the oxygen supply, the temperatures, conversion, and product selectivity of the reaction can be in turn controlled and optimized. Furthermore the potential risks of explosion associated with mixing hydrocarbon and molecular oxygen is minimized with increased feed carbon-to-oxygen molar ratios.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Synthesis gas production and power generation with zero emissions
InactiveUS6333015B1Avoid water pollutionEliminate needElectrical coke oven heatingGasifier electrodesClosed loopProduct gas
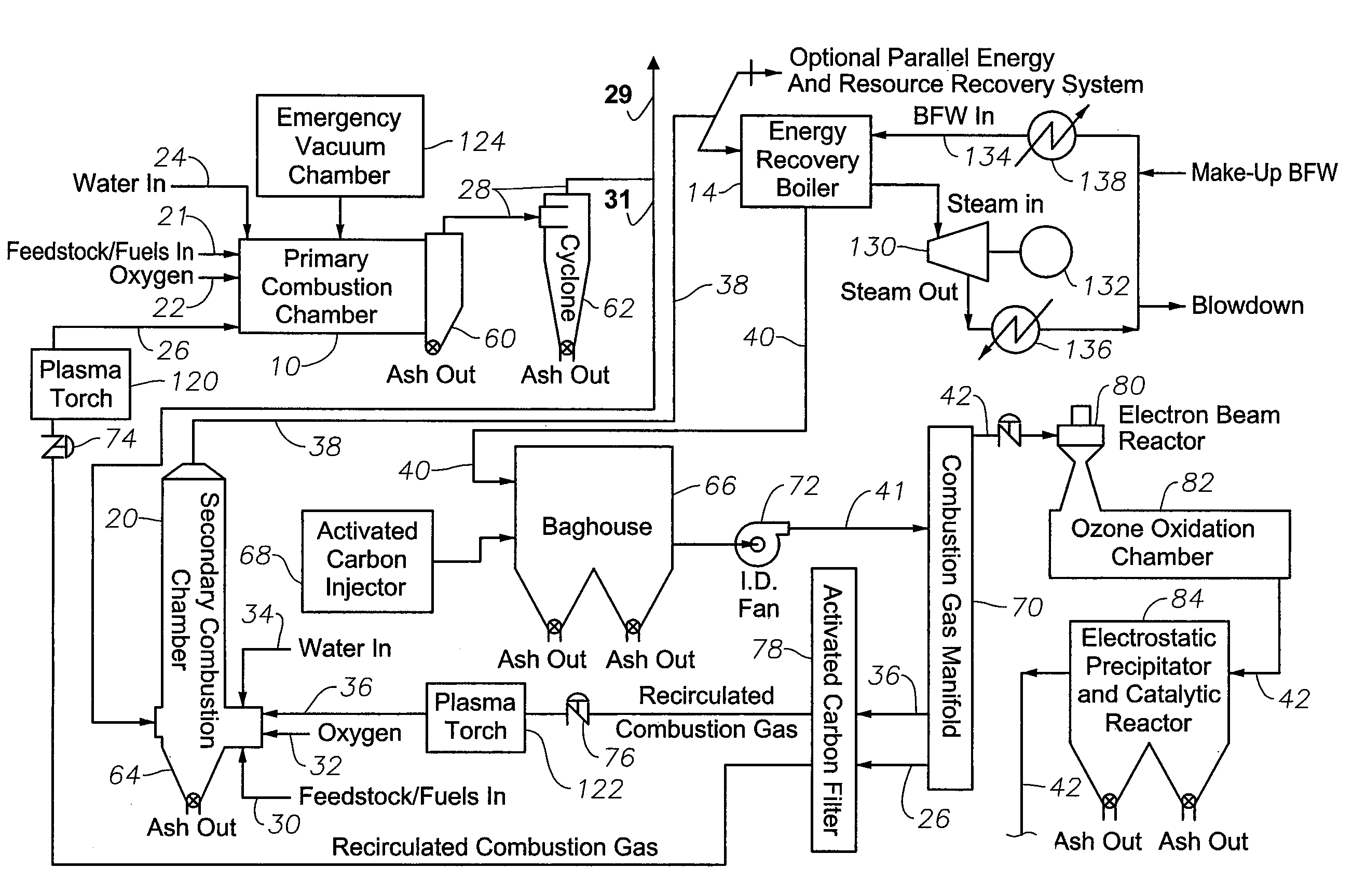
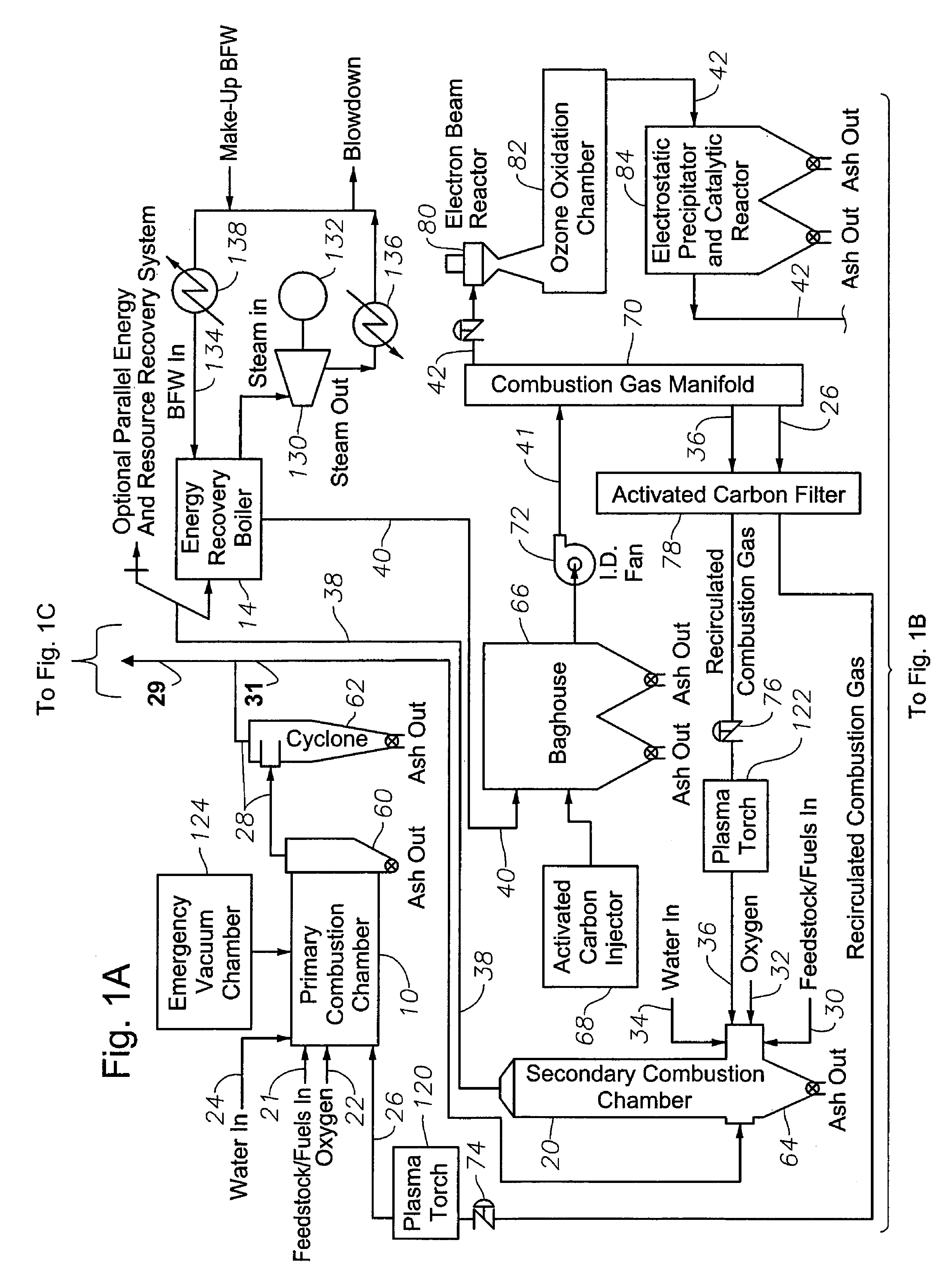
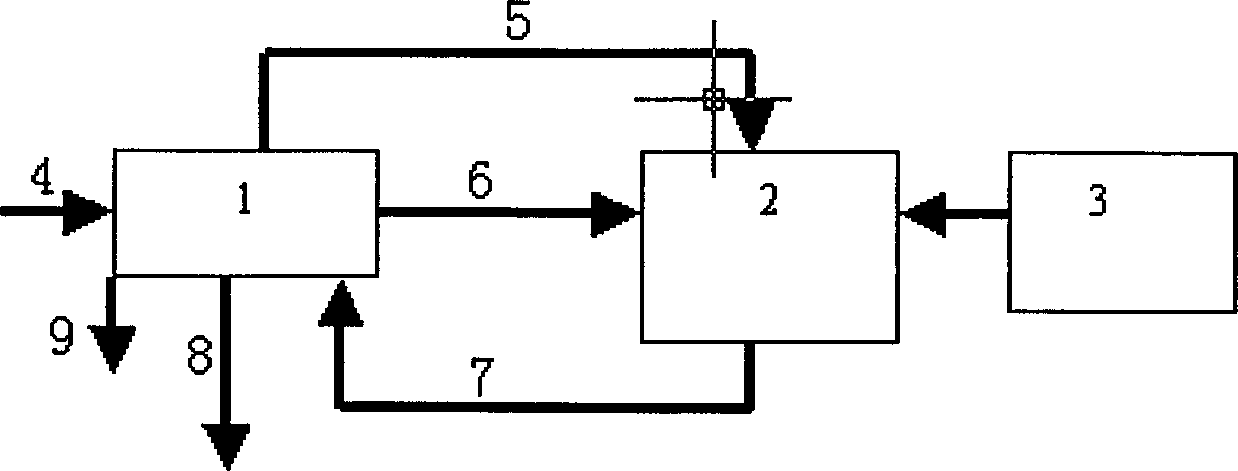
A process and apparatus for producing and burning synthesis gas. Carbonaceous waste material is pyrolytically decomposed in a primary reactor in the presence of steam to produce raw product gas containing H2 and CO. The raw product gas and CO2 is then introduced into a coke containing secondary reactor under pyrolyzing conditions, so that the CO2 and coke react to produce combustible gas having an increased CO content. The combustible gas is mixed with oxygen and CO2 to produce a combustible mixture which is burned as a fuel to produce heat, CO2 and H2O. A portion of the produced CO2 is recovered and used as the source of CO2 gas in the combustible mixture and as a source of CO2 gas for the secondary reactor. Preferably filters and scrubbers are used in a closed loop system to avoid undesirable emissions into the environment.
Owner:LEWIS GLORIA B
Process for pyrolytic heat recovery enhanced with gasification of organic material
InactiveUS7452392B2Improve throughputInhibition formationGas modification by gas mixingWaste based fuelThermal energyForming gas
This invention is a reactor and a process for the conversion of organic waste material such as municipal trash, sewage, post-consumer refuse, and biomass to commercially salable materials.The invention produces the following:1. Maximum energy conversion from the organic material2. High volume consumption of the organic feed material3. Less pollution of gaseous products than prior art systems4. Solid residuals for disposal are minimal and non-hazardous.The conversion is accomplished by combining anaerobic gasification and pyrolysis of the feed organic material and making it into synthetic gas. The synthetic gas is a mixture of hydrocarbons (CxHy), hydrogen, and carbon monoxide with small amounts of carbon dioxide and nitrogen. An essential feature of the invention is a hot driver gas, devoid of free oxygen and rich in water, which supplies the entire thermal and chemical energy needed for the reactions. This hot driver gas is produced by complete sub-stoichiometric combustion of the fuel (CxHy) before it enters the reactor.
Owner:NICK PETER A +4
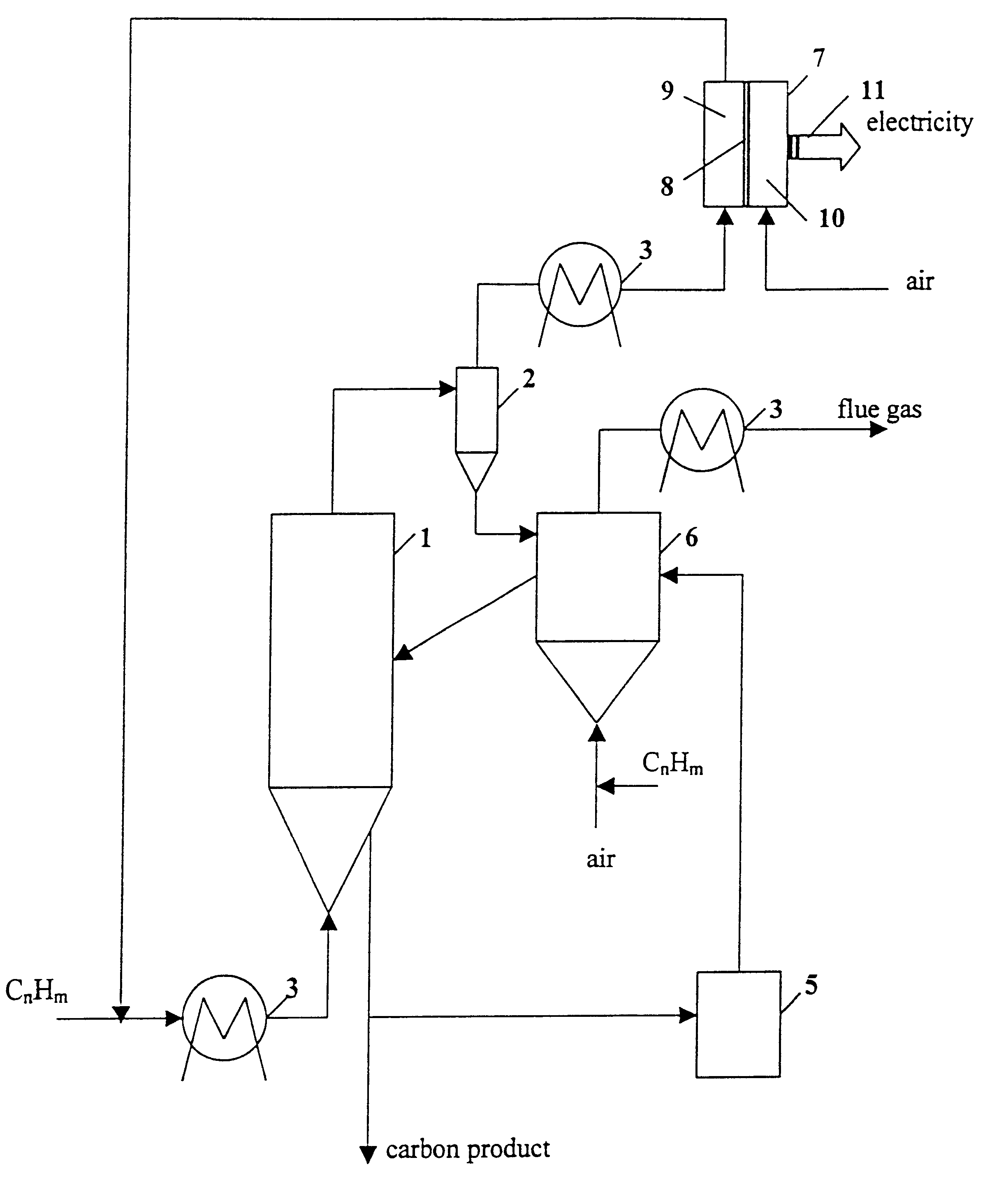
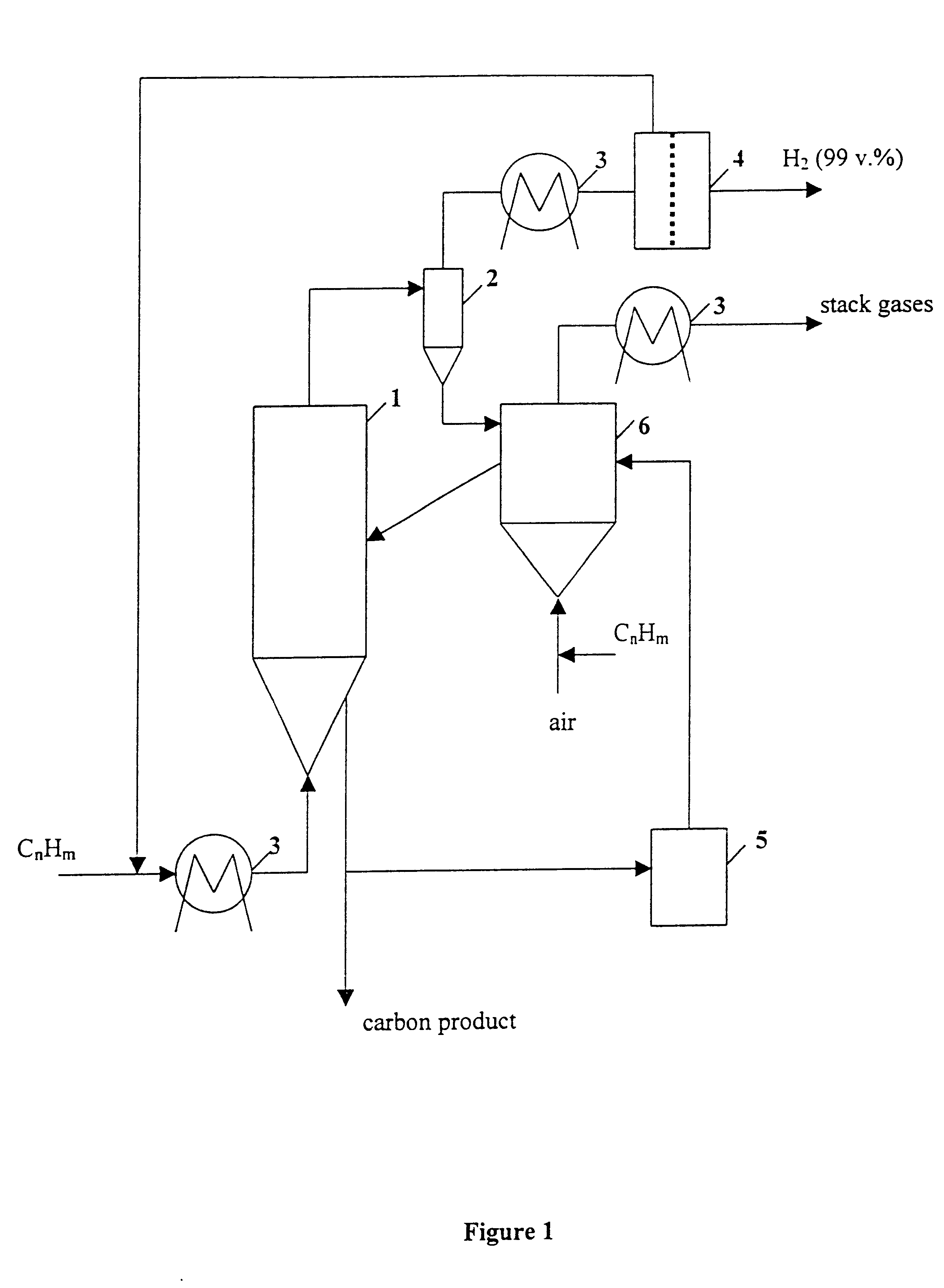
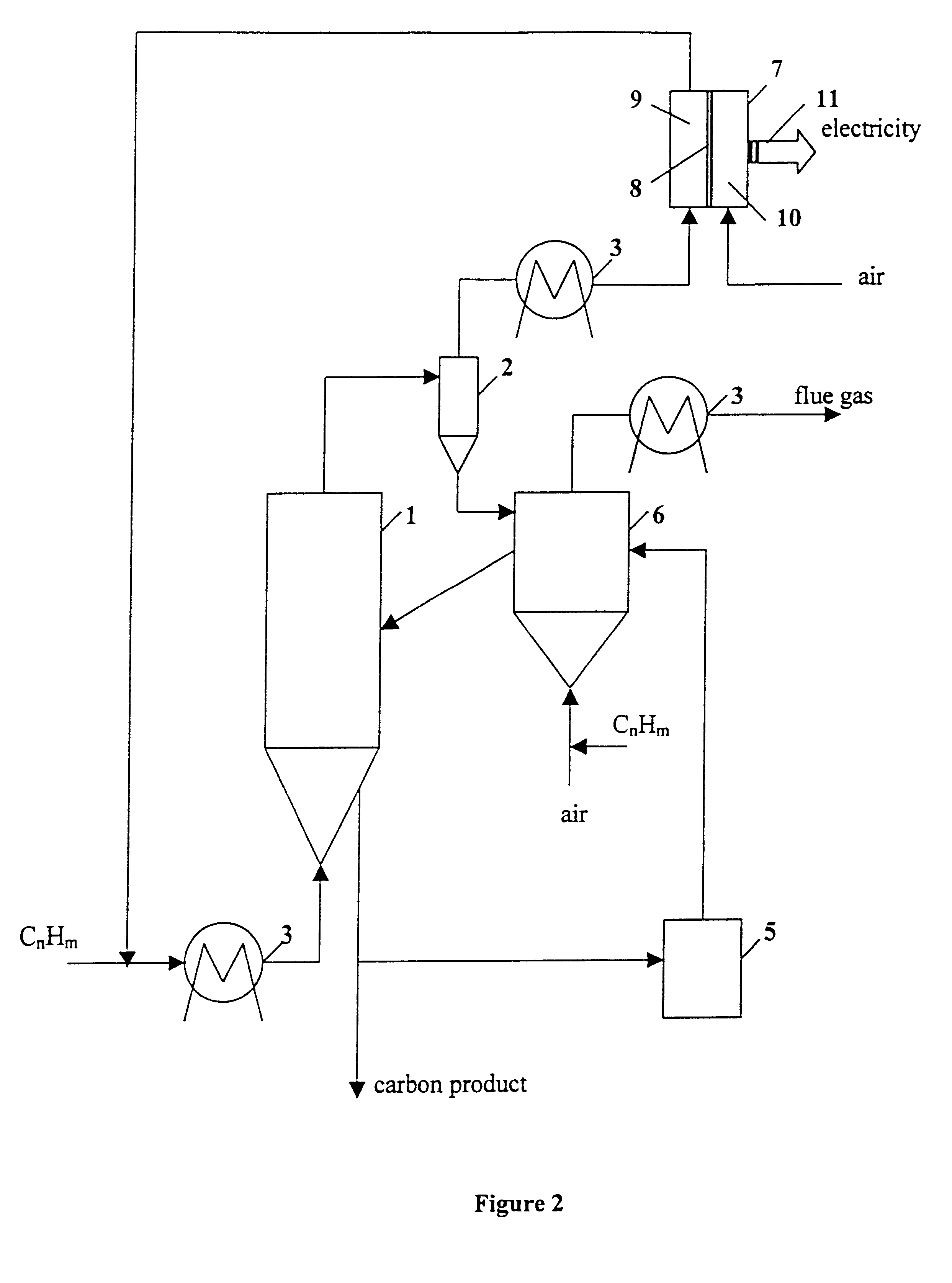
Thermocatalytic process for CO2-free production of hydrogen and carbon from hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20020007594A1Pigmenting treatmentPressurized chemical processDecompositionBiological activation
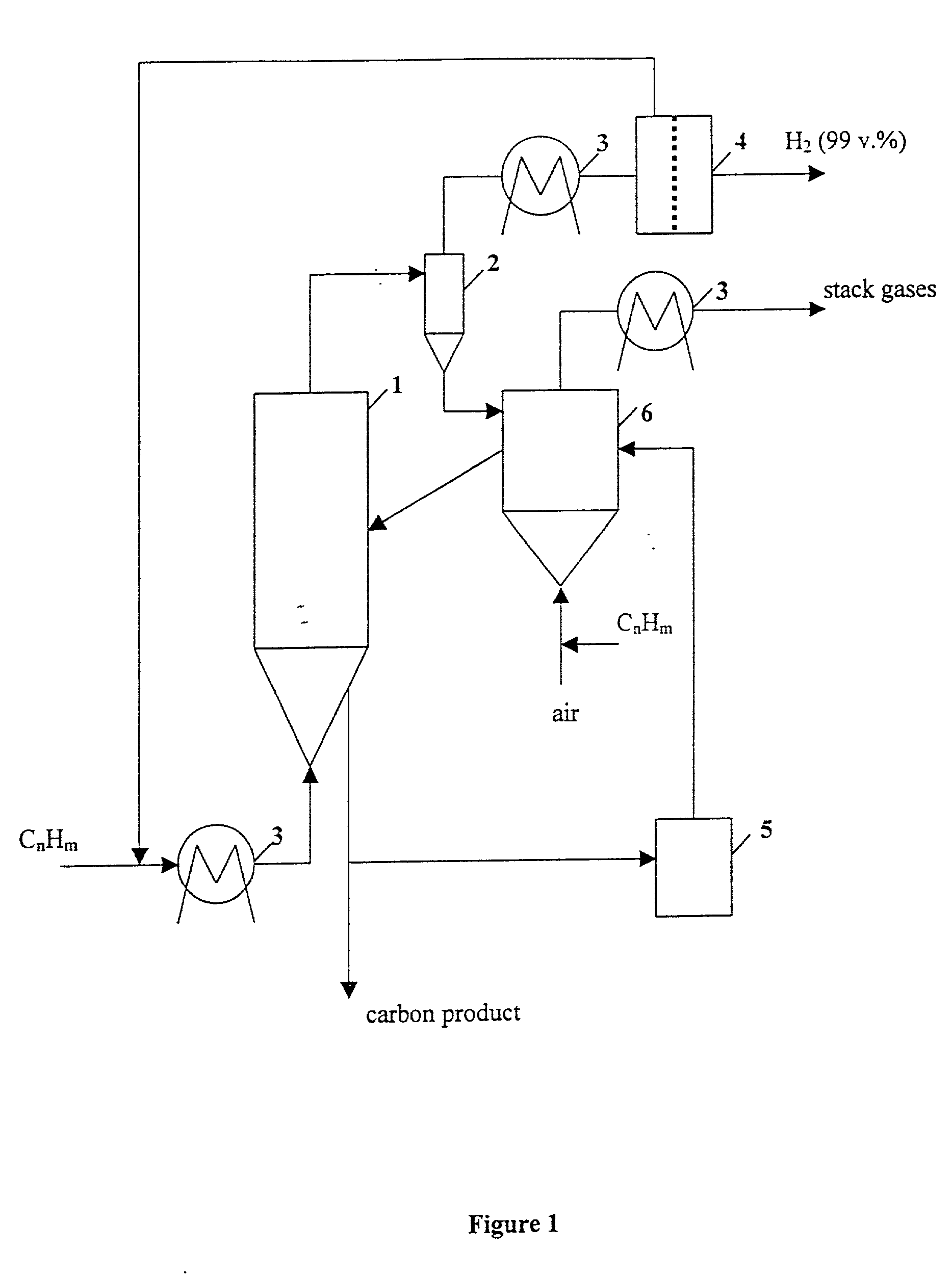
This invention relates to a novel process for sustainable CO2-free production of hydrogen and carbon by thermocatalytic decomposition (or dissociation, pyrolysis, cracking) of hydrocarbon fuels over carbon-based catalysts in the absence of air and / or water. The process is applicable to any hydrocarbon fuel, including sulfurous fuels. Combination of a catalytic reactor with a gas separation unit allows to produce high purity hydrogen (at least, 99.0 v %) completely free of carbon oxides. In a preferred embodiment, sustainable continuous production of hydrogen and carbon is achieved by both internal and external activation of carbon catalysts. Internal activation of carbon catalyst is accomplished by recycling of hydrogen-depleted gas containing unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons back to the reactor. External activation can be achieved via surface gasification of carbon catalysts by hot combustion gases during catalyst heating. The process can conveniently be integrated with any type of fuel cell.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Method and apparatus to protect synthesis gas via flash pyrolysis and gasification in a molten liquid
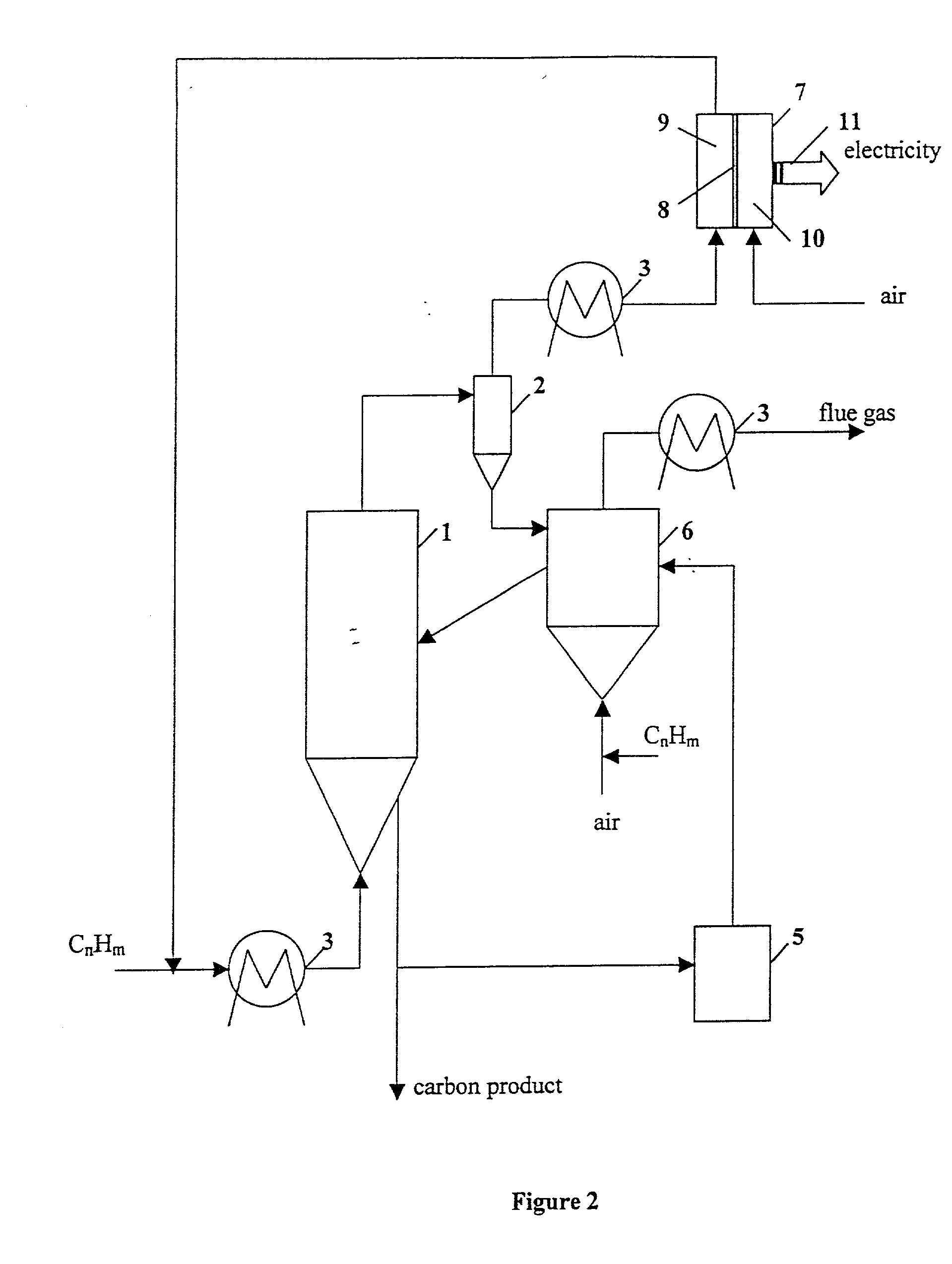
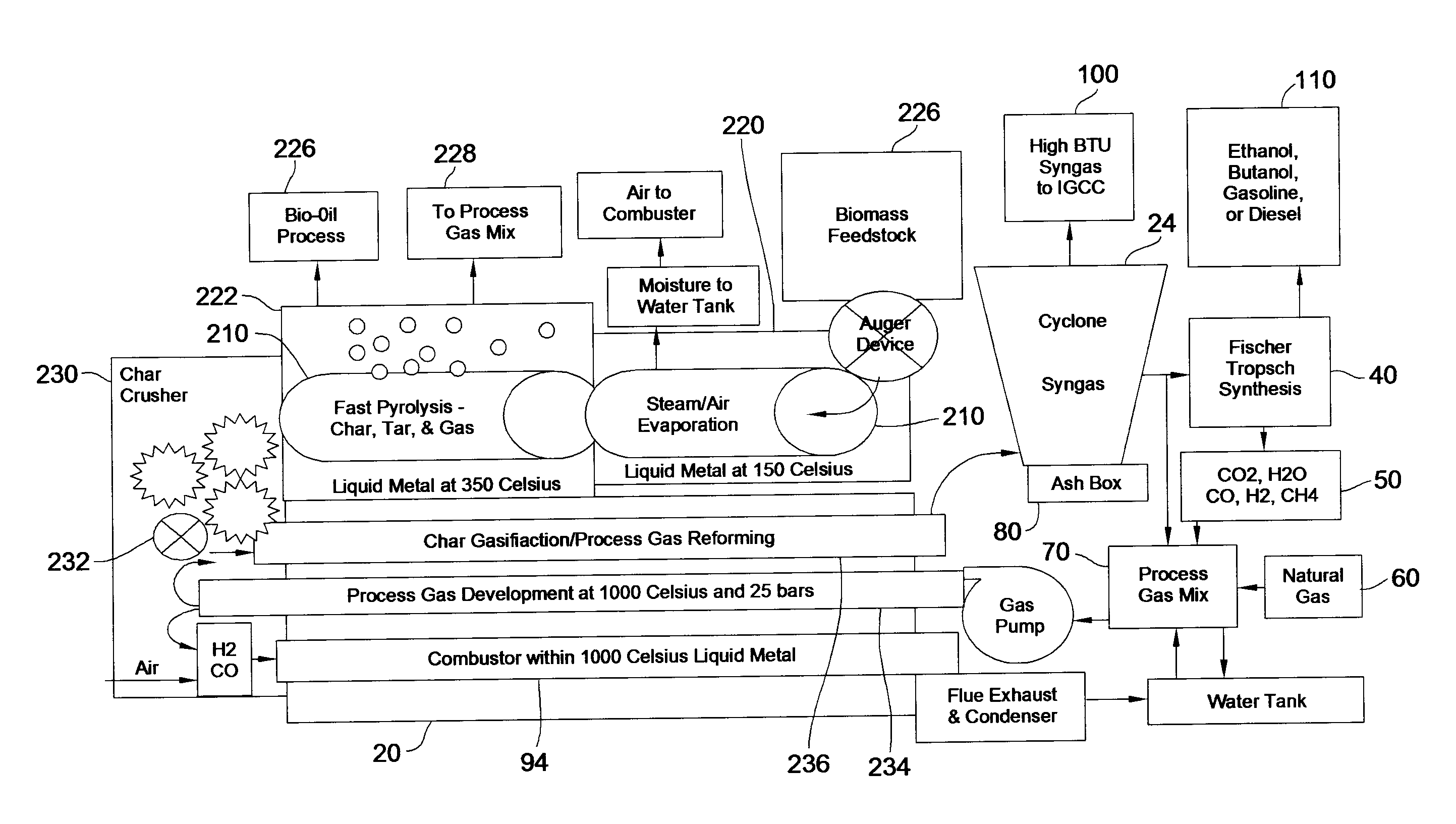
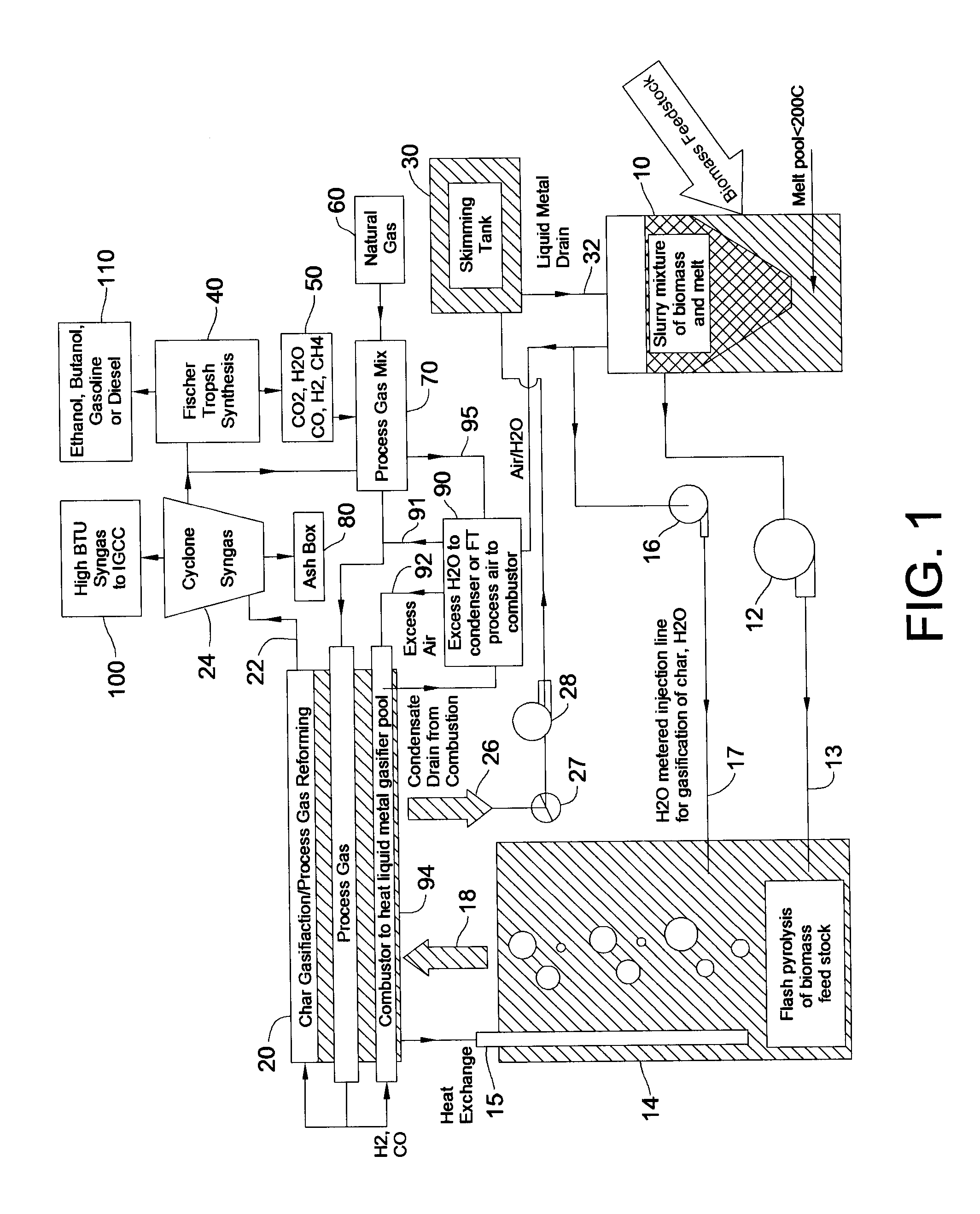
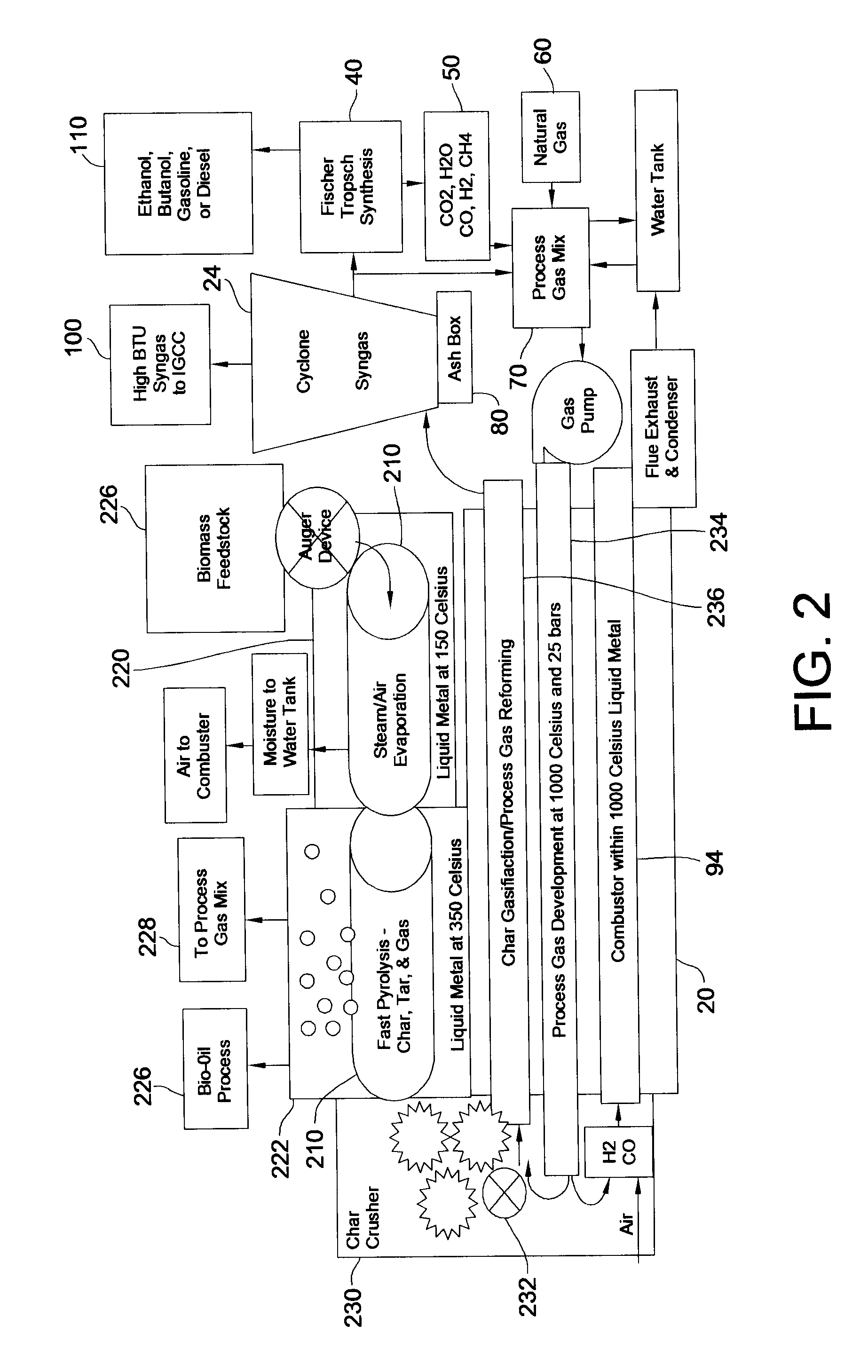
InactiveUS20080307703A1Improve efficiencyLittle heating lossWaste based fuelRetortsSyngasThermodynamics
Disclosed are a method and a corresponding apparatus for converting a biomass reactant into synthesis gas. The method includes the steps of (1) heating biomass in a first molten liquid bath at a first temperature, wherein the first temperature is at least about 100° C., but less than the decomposition temperature of the biomass, wherein gas comprising water is evaporated and air is pressed from the biomass, thereby yielding dried biomass with minimal air content. (2) Recapturing the moisture evaporated from the biomass in step 1 for use in the process gas. (3) Heating the dried biomass in a second molten liquid bath at a second temperature, wherein the second temperature is sufficiently high to cause flash pyrolysis of the dried biomass, thereby yielding product gases, tar, and char. (4) Inserting recaptured steam into the process gas, which may optionally include external natural gas or hydrogen gas or recycled syngas for mixing and reforming with tar and non-condensable gases. (5) Further reacting the product gases, tar, and char with the process gas within a third molten liquid bath at a third temperature which is equal to or greater than the second temperature within the second molten liquid bath, thereby yielding high quality and relatively clean synthesis gas after a relatively long residence time needed for char gasification. A portion of the synthesis gas so formed is combusted to heat the first, second, and third molten liquid baths, unless external natural or hydrogen gas is available for this use.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Integrated coal gasification combined cycle power generator
Embodiments of the invention provide an IGCC which achieves improved plant thermal efficiency by using a cooling steam supply system that cools the high-temperature sections of the gas turbine 34. Embodiments of the invention further provide and IGCC in which the cooling steam recovery system recovers steam after cooling the gas-turbine high-temperature section and makes practical re-use of the energy and substances within the system. Therefore, embodiments of the invention can reduce or eliminate the degradation of certain equipment by cooling the high-temperature sections. Methods are provided for increasing the thermal efficiency o an IGCC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Hydrogen generation catalyst
InactiveUS20020083643A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationControlled releaseBorohydride
The present invention relates to a composition and method for storage and controlled release of hydrogen. In particular, the present invention relates to the use of borohydride based solutions as a hydrogen storage source and a catalyst system to release hydrogen therefrom.
Owner:PROTONEX TECH CORP
Hydrogen generating fuel cell cartridges
InactiveUS20060191199A1Extended shelf lifeEfficient productionThermal non-catalytic crackingReactant parameters controlFuel cellsHydrogen
A gas-generating apparatus includes a reaction chamber having a first reactant, a reservoir having an optional second reactant, and a self-regulated flow control device. The self-regulated flow control device stops the flow of reactant from the reservoir to the reaction chamber when the pressure of the reaction chamber reaches a predetermined level. Methods of operating the gas-generated apparatus and the self-regulated flow control device, including the cycling of a shut-off valve of the gas-generated apparatus and the cycling of the self-regulated flow control device are also described.
Owner:INTELLIGENT ENERGY LTD
System for hot solids combustion and gasification
ActiveUS8110012B2Enhanced overall recoveryEliminate needGas modification by gas mixingCombustion enginesCombustionReducer
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC +1
Thermocatalytic process for CO2-free production of hydrogen and carbon from hydrocarbons
This invention relates to a novel process for sustainable CO2-free production of hydrogen and carbon by thermocatalytic decomposition (or dissociation, pyrolysis, cracking) of hydrocarbon fuels over carbon-based catalysts in the absence of air and / or water. The process is applicable to any hydrocarbon fuel, including sulfurous fuels. Combination of a catalytic reactor with a gas separation unit allows to produce high purity hydrogen (at least, 99.0 v %) completely free of carbon oxides. In a preferred embodiment, sustainable continuous production of hydrogen and carbon is achieved by both internal and external activation of carbon catalysts. Internal activation of carbon catalyst is accomplished by recycling of hydrogen-depleted gas containing unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons back to the reactor. External activation can be achieved via surface gasification of carbon catalysts by hot combustion gases during catalyst heating. The process can conveniently be integrated with any type of fuel cell.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
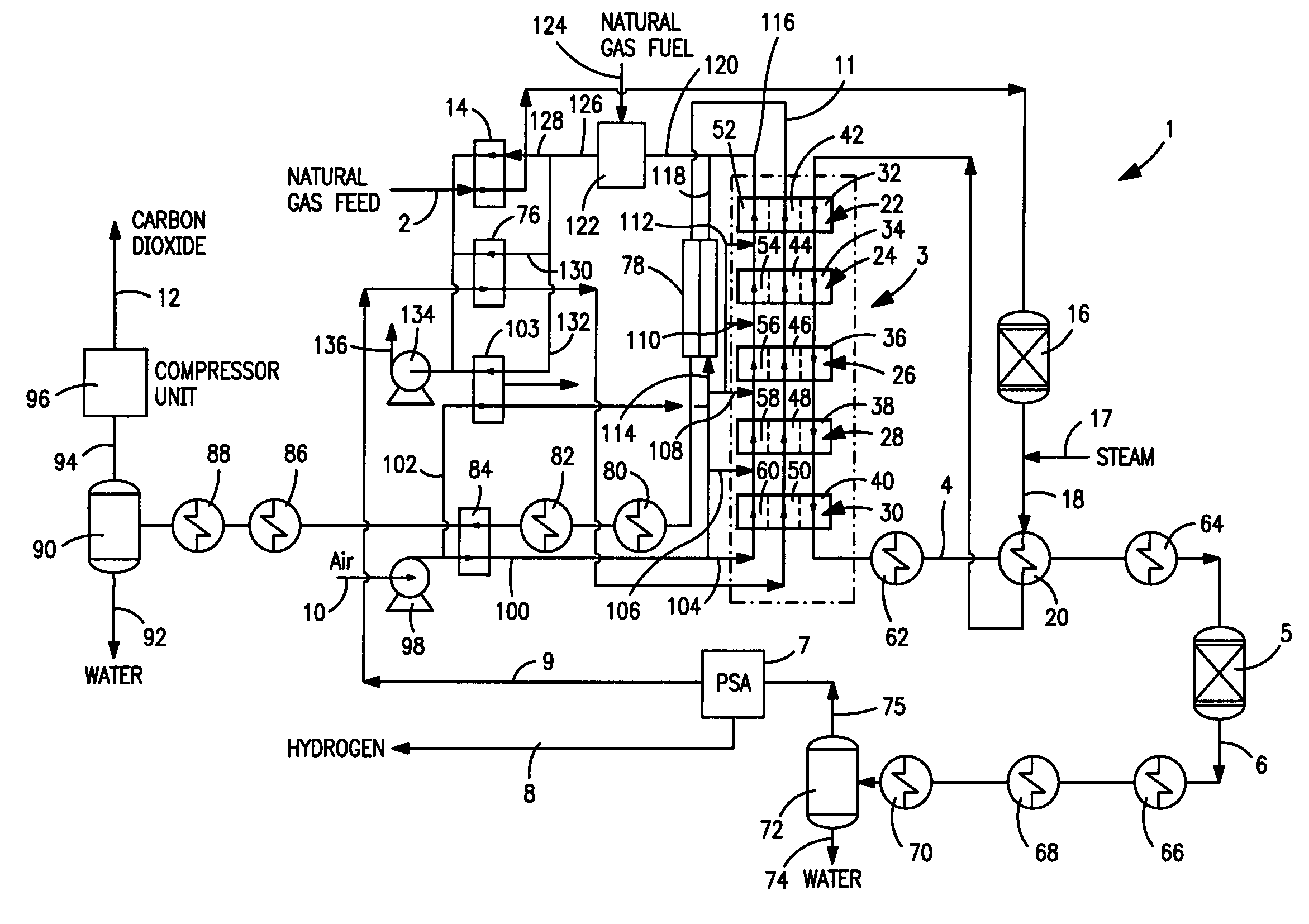
Method and apparatus for producing synthesis gas
InactiveUS20070289215A1Increase the number ofCatalytic gas-gas reactionOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideSyngasCombustion
A method and apparatus for reacting a hydrocarbon containing feed stream by steam methane reforming reactions to form a synthesis gas. The hydrocarbon containing feed is reacted within a reactor having stages in which the final stage from which a synthesis gas is discharged incorporates expensive high temperature materials such as oxide dispersed strengthened metals while upstream stages operate at a lower temperature allowing the use of more conventional high temperature alloys. Each of the reactor stages incorporate reactor elements having one or more separation zones to separate oxygen from an oxygen containing feed to support combustion of a fuel within adjacent combustion zones, thereby to generate heat to support the endothermic steam methane reforming reactions.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC +1
Reduced-emission gasification and oxidation of hydrocarbon materials for liquid fuel production
InactiveUS8038746B2Reduce system sizeHigh heat transfer rateHydrogenGas modification by gas mixingLiquid hydrocarbonsLiquid fuel
Owner:CLARK STEVE L
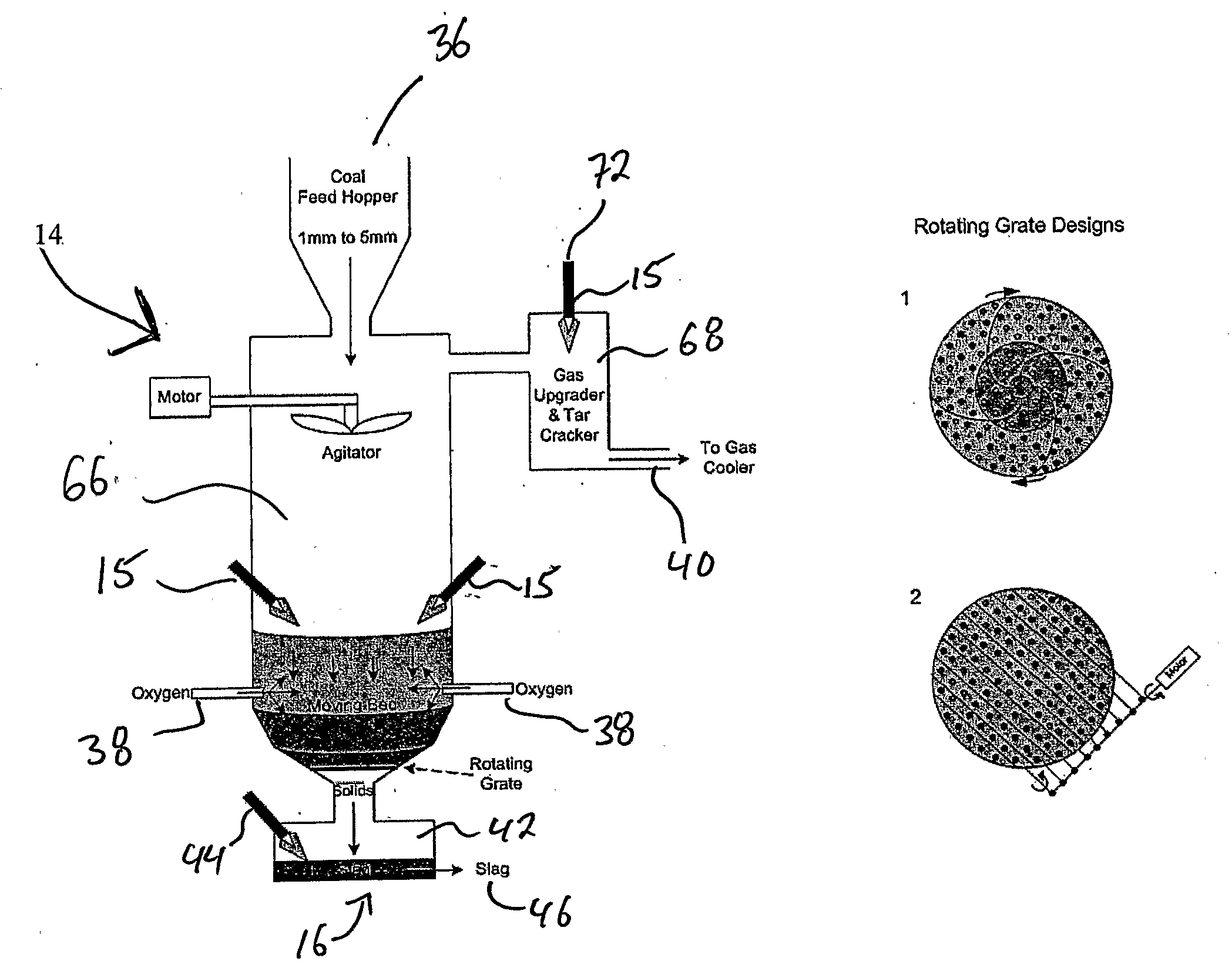
Multi-faceted gasifier and related methods
InactiveUS6960234B2Increased hydrogen productionImprove overall plant economicsLiquid degasificationCoke ovensActivated carbonInjection port
A gasifier is disclosed combining a fixed bed gasification section where coarse fuel is gasified and an entrained flow gasification section where fine fuel is gasified. The fixed bed section includes upper and lower sections. Coarse fuel is devolatilized in the upper fixed bed section and subjected to elevated temperatures sufficient to crack and destroy tars and oils in the effluent gases. The entrained flow gasification section is disposed in a lower plenum adjacent the lower fixed bed section. A plurality of injection ports are configured to introduce oxygen, steam, or air into different sections of the gasifier to control temperature and operating conditions. Activated carbon may be formed in the upper fixed bed section and in the entrained flow section. The activated carbon may be used as a sorbent to remove pollutants from the effluent gases. The gasifier may be used with various coarse and fine fuel feedstocks.
Owner:EMERY ENERGY
Method and apparatus for generating combustible synthesis gas
InactiveUS20070012229A1Maximizing conversionExtensive interactionProductsGasifier feeding meansCombustionProcess engineering
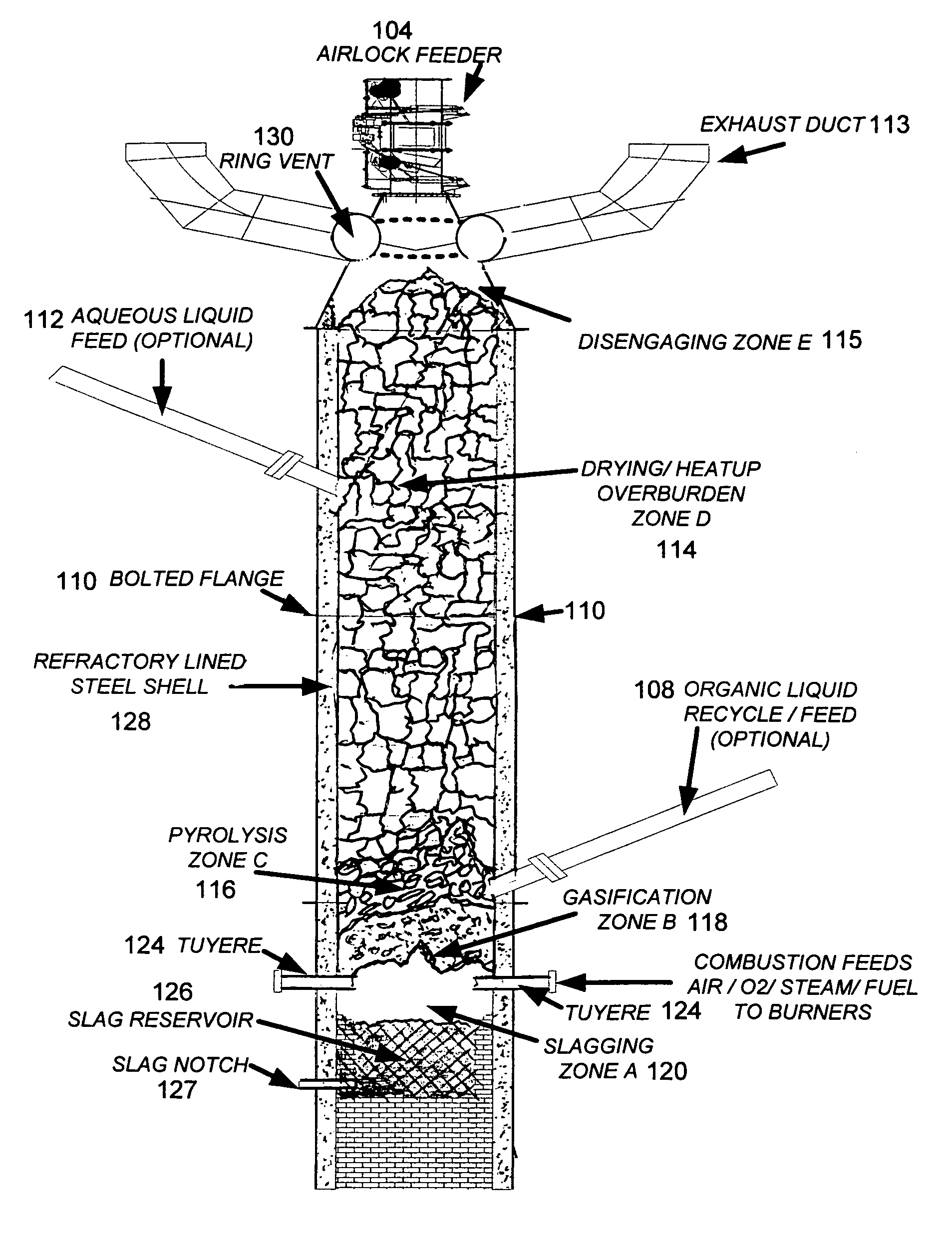
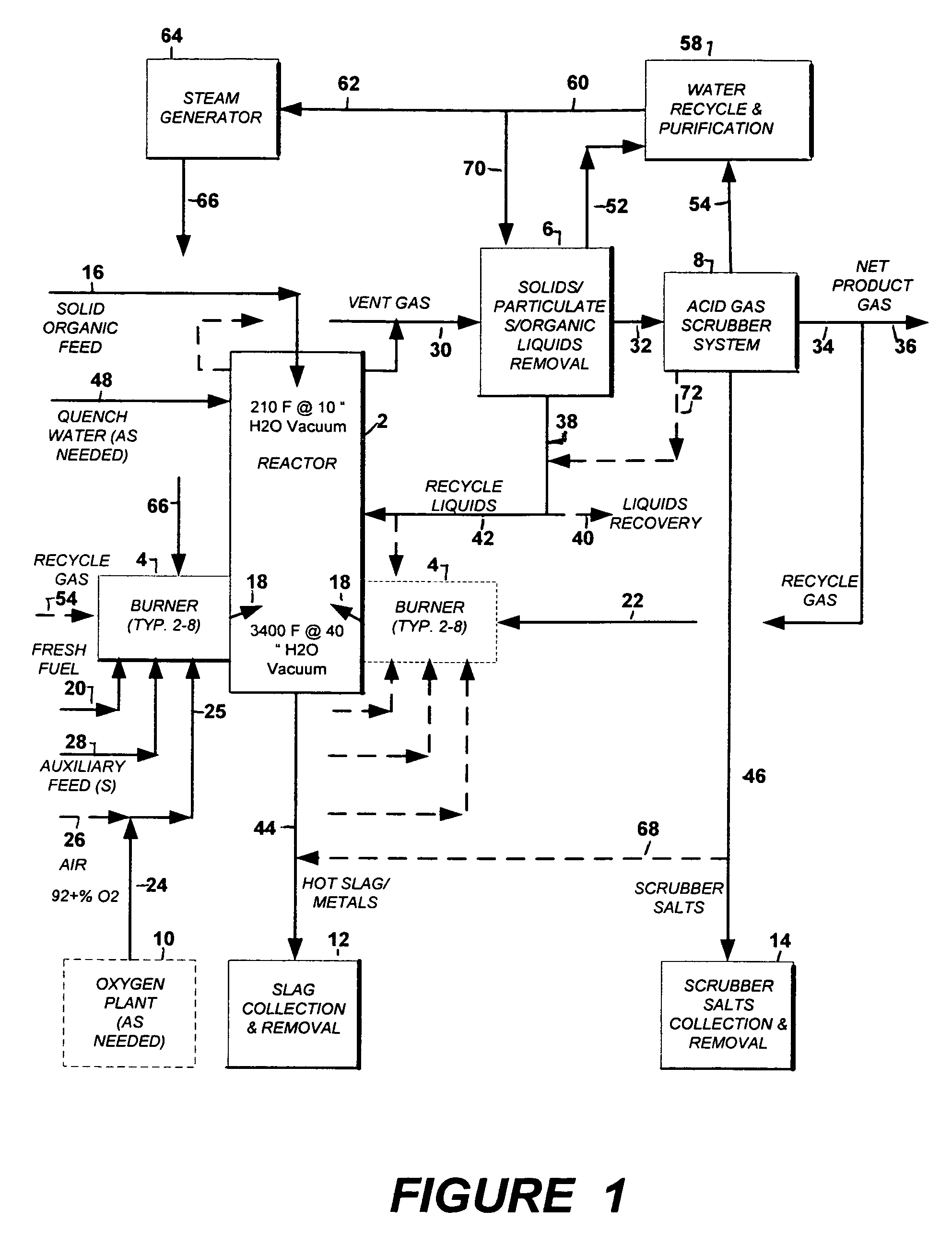
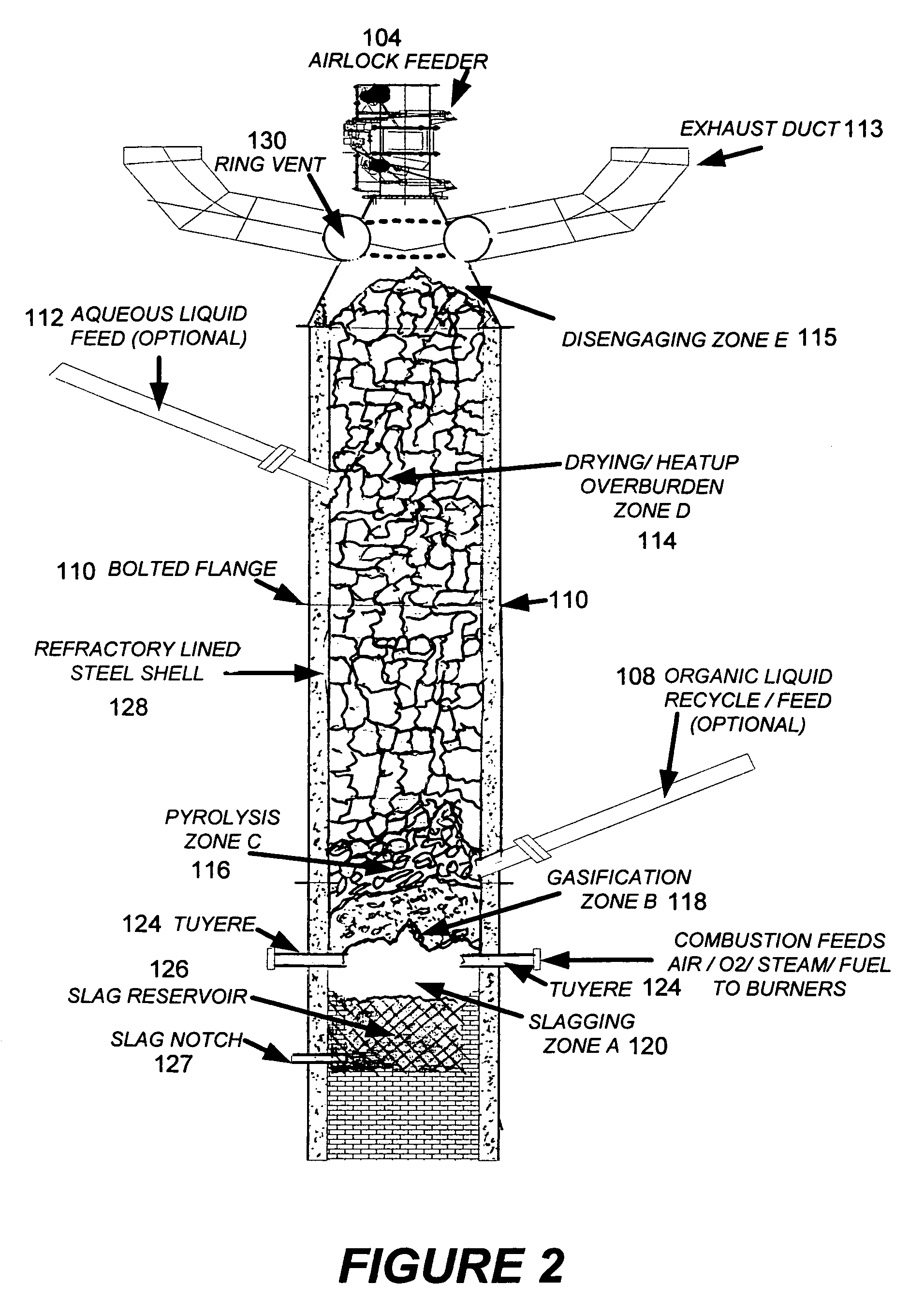
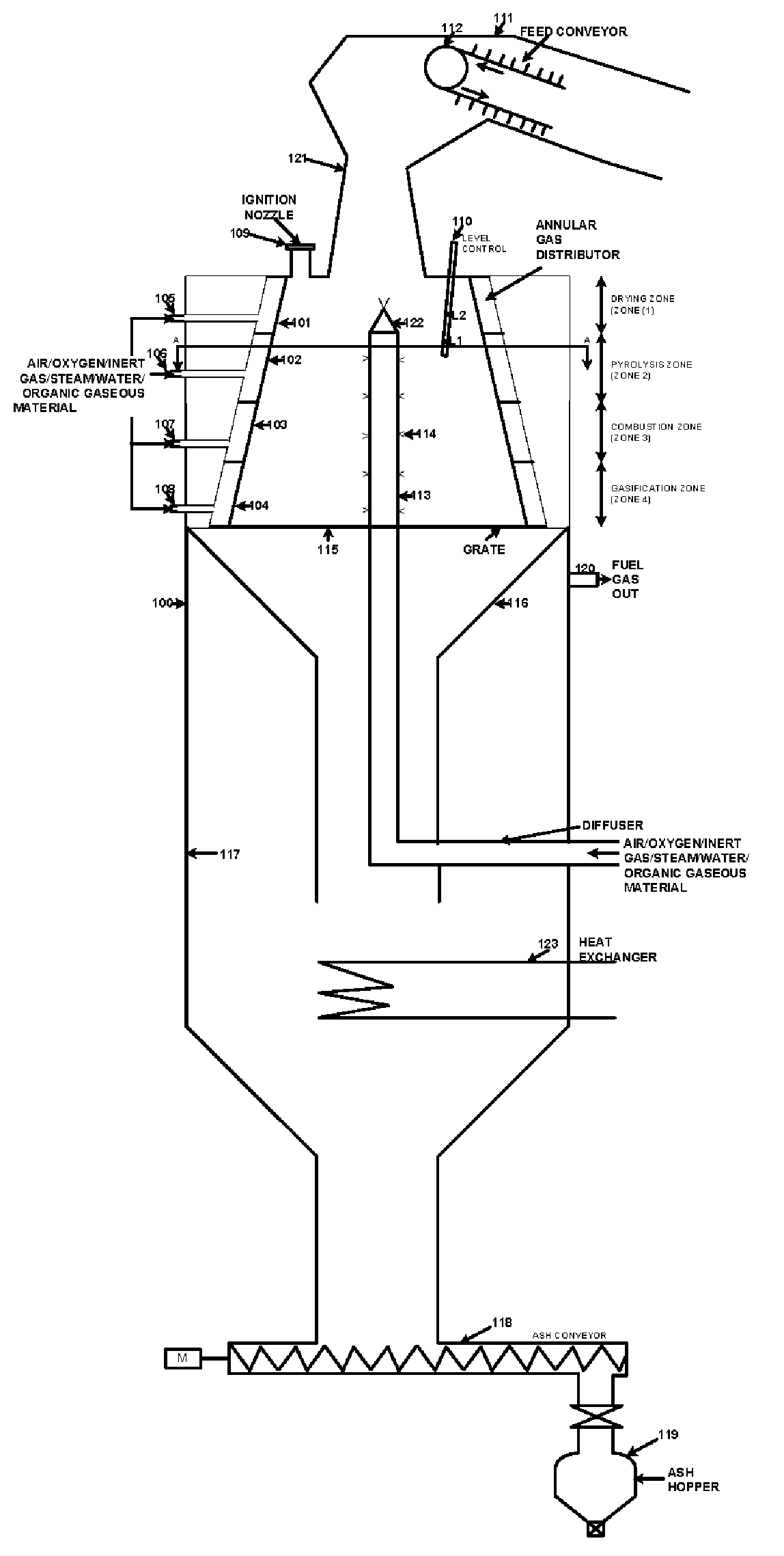
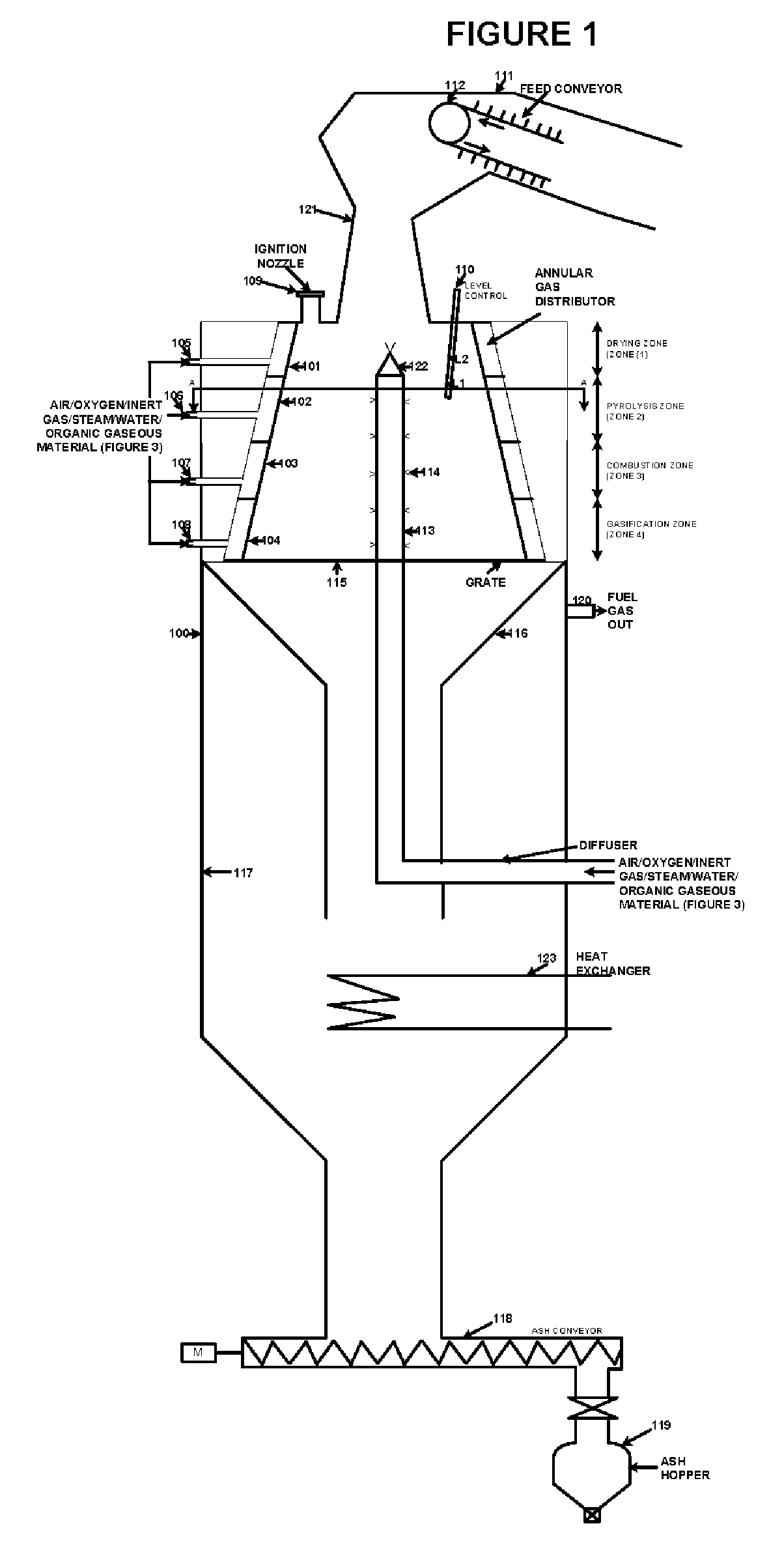
The present application discloses an apparatus for gasification of solid, liquid and gaseous organic feed materials having a fuel value into synthesis gas. The apparatus comprises: a gasification reactor vessel having a tapered interior with a minimum of four zones for introducing reaction gas mixtures, a central perforated diffuser pipe, a solid and liquid material inlet at the upper end of the uppermost zone, a solid and gas discharge outlet at the lower end of the bottom zone, wherein the reactor vessel defining a sequence of reaction zones from the material inlet to the material outlet including drying, pyrolysis, combustion and gasification zones, and confining downwardly moving the column of the feed materials within the zones, gas feed inlet pipes for introducing reaction gas into the zones, a synthesis gas discharge pipe below the zones, and a heat exchanger below the zones.
Owner:JC ENVIRO ENTERPRISES CORP
Compact fuel gas reformer assemblage
InactiveUS6773684B2Speed up heat exchangeSuitable for useHydrogenCarburetting by solid carbonaceous material pyrolysisCombustorFuel cells
Owner:INT FUEL CELLS
System for hot solids combustion and gasification
ActiveUS20100050654A1Small modificationEnhanced overall recoveryGas modification by gas mixingCombustion enginesCombustionEngineering
In a retrofit system for hot solids combustion and gasification, a chemical looping system includes an endothermic reducer reactor 12 having at least one materials inlet 22 for introducing carbonaceous fuel and CaCO3 therein and a CaS / gas outlet 26. A first CaS inlet 40 and a first CaSO4 inlet 64 are also defined by the reducer reactor 12. An oxidizer reactor 14 is provided and includes an air inlet 68, a CaSO4 / gas outlet 46, a second CaS inlet 44, and a second CaSO4 inlet 66. A first separator 30 is in fluid communication with the CaS / gas outlet 26 and includes a product gas and a CaS / gas outlet 32 and 34 from which CaS is introduced into said first and second CaS inlets. A second separator 50 is in fluid communication with the CaSO4 / gas outlet 46 and has an outlet 52 for discharging gas therefrom, and a CaSO4 outlet from which CaSO4 is introduced into the first and second CaSO4 inlets 62, 66. The chemical looping system is in fluid communication with at least a portion of an existing power generation system.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC +1
Reduced-Emission Gasification and Oxidation of Hydrocarbon Materials for Liquid Fuel Production
InactiveUS20080275278A1Reduce system sizeRaise the combustion temperatureGas modification by gas mixingLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionThermal energyLiquid hydrocarbons
A system and process are disclosed for the controlled combustion of a wide variety of hydrocarbon feedstocks to produce thermal energy, liquid fuels, and other valuable products with little or no emissions. The hydrocarbon feeds, such as coal and biomass, are first gasified and then oxidized in a two-chamber system / process using pure oxygen rather than ambient air. A portion of the intermediate gases generated in the system / process are sent to a Fischer-Tropsch synthesis process for conversion into diesel fuel and other desired liquid hydrocarbons. The remaining intermediate gases are circulated and recycled through each of the gasification / oxidation chambers in order to maximize energy production. The energy produced through the system / process is used to generate steam and produce power through conventional steam turbine technology. In addition to the release of heat energy, the hydrocarbon fuels are oxidized to the pure product compounds of water and carbon dioxide, which are subsequently purified and marketed. The system / process minimizes environmental emissions.
Owner:CLARK STEVE L
Method and device for pyrolyzing and gasifying organic substances or substance mixtures
InactiveUS7214252B1Small particle sizeAllow useFluidized bed combustionSolid waste disposalReaction zoneAmount of substance
An apparatus for pyrolysis and gasification of organic substances and mixtures thereof is provided with a pyrolysis reactor (1), a fluidized-bed firing (3) for pyrolysis residue, a reaction zone (2) for the pyrolysis gases (13) and circulating fluidized-bed material (35). The pyrolysis reactor (1) has a sluice for introducing application material (10) thereinto. An inlet for the fluidized-bed material (35) is disposed next to the combustion fluidized bed (3). Transport apparatus (14) for mixture of solid pyrolysis residue and circulating fluidized bed material (35) is disposed at or near a bottom of the fluidized bed (3) and lower end of the pyrolysis reactor (1). An overflow is situated at or near the top of the fluidized bed (3) while a heat transfer member is positioned within the reaction zone (2).
Owner:HERHOF UMWELTTECHN
Device and method for suppressing refuse end gas injurant using pyrolysis and aerification technology
InactiveCN1769397ANo emissionsPrevent gasificationThermal non-catalytic crackingSolid waste disposalThermal dissociationVaporization
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for starting a fast light-off catalytic fuel reformer
InactiveUS6869456B2Optimize reformate yieldStart fastCombination devicesHydrogenCatalytic reformingControl system
A method for starting a fast light-off catalytic reformer for producing hydrogen-rich reformate fuel from hydrocarbon fuel and air, the reformer having means for receiving flows of fuel and air, a reforming catalyst for reforming the fuel and air mixture, and an ignition device. A control system selects fuel and air flow rates to form a lean fuel / air mixture and operates the ignition device to ignite the lean mixture to produce hot exhaust gases that flow over and heat the reforming catalyst for a first length of time. Fuel flow is then stopped temporarily for a second length of time, and further ignition is terminated. Fuel flow is then restarted and adjusted to provide a rich fuel / air mixture which is directed to the heated catalyst for reforming into reformate fuel. Air flow may also be adjusted in setting the lean and / or rich fuel / air mixtures.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Popular searches
Gasification processes details Hydrogen production Pulverulent fuel combustion burners Chemical/physical/physico-chemical nozzle-type rreactors Hydrogen/synthetic gas production Gas contaminants removal Combustible gas production Bio-feedstock Chemical/physical/physico-chemical processes Gas purification by non-gaseous materials condensation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com