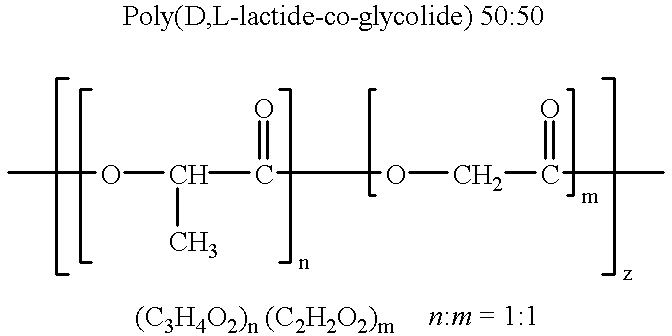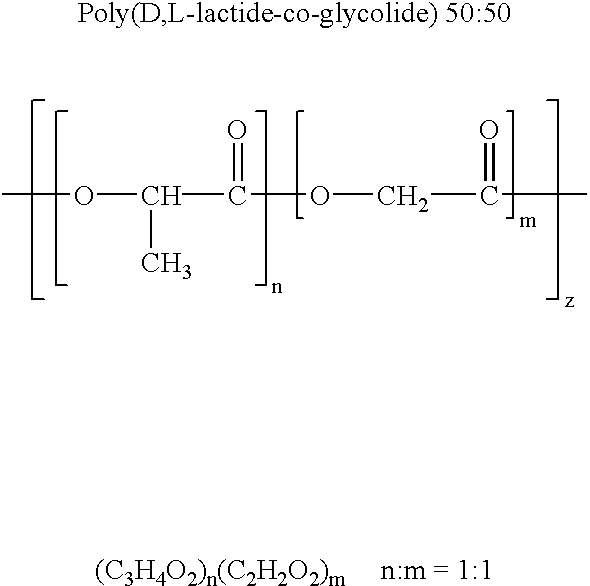Patents
Literature
24958results about How to "Extended shelf life" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Therapeutic treatment and prevention of infections with a bioactive materials encapsulated within a biodegradable-biocompatible polymeric matrix
InactiveUS6309669B1Sustained release of active agent over timeEfficient and effective usePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAdjuvantEnd-group
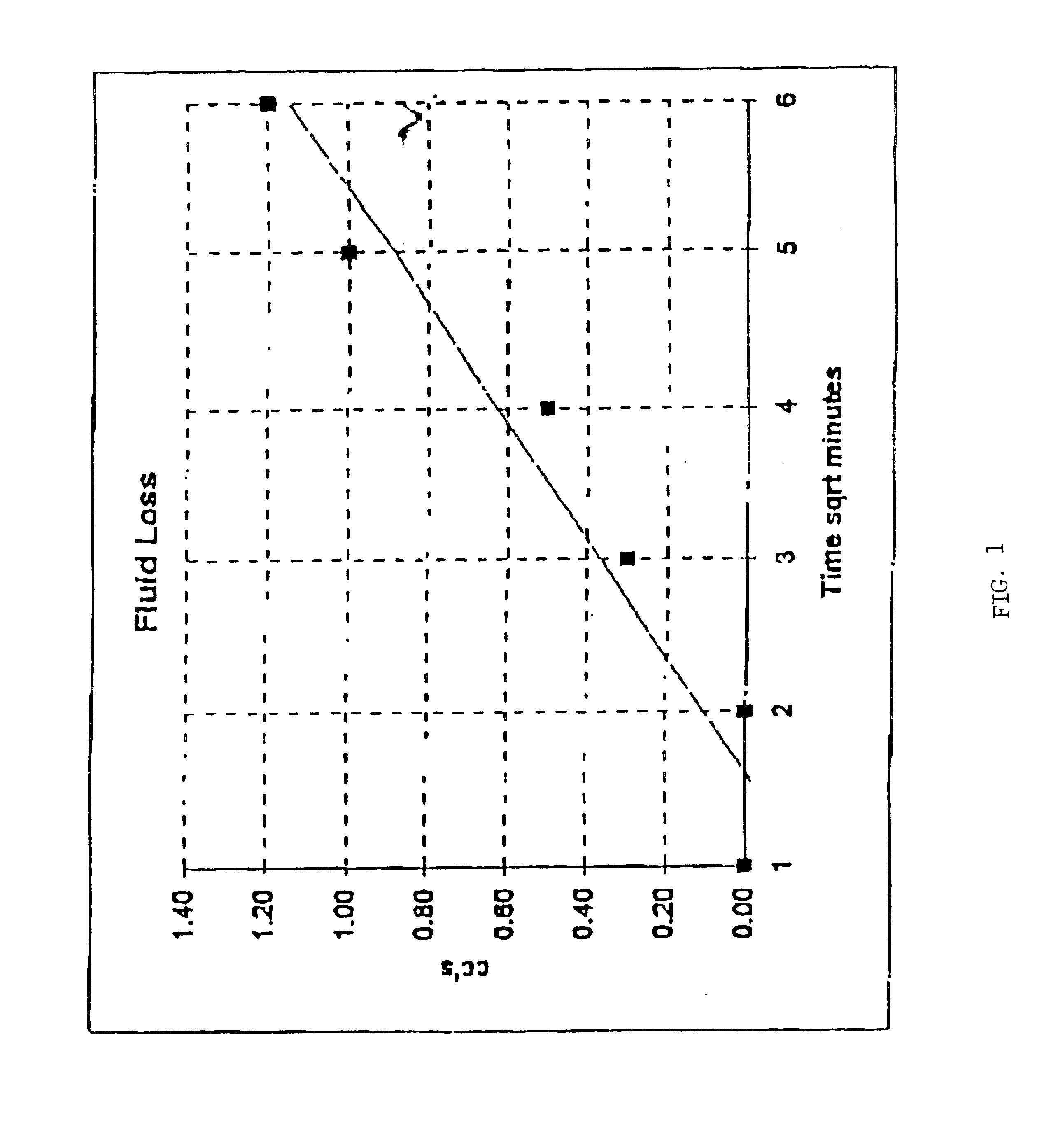
Novel burst-free, sustained release biocompatible and biodegrable microcapsules which can be programmed to release their active core for variable durations ranging from 1-100 days in an aqueous physiological environment. The microcapsules are comprised of a core of polypeptide or other biologically active agent encapsulated in a matrix of poly(lactide / glycolide) copolymer, which may contain a pharmaceutically-acceptable adjuvant, as a blend of upcapped free carboxyl end group and end-capped forms ranging in ratios from 100 / 0 to 1 / 99.
Owner:ARMY GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Moist snuff non-tobacco composition and a method for producing thereof
InactiveUS20090065013A1Extended shelf lifeReduced activityTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentMoist snuffFood science
Owner:SWEDISH MATCH NORTH EURO
Antimicrobial silver compositions
The present invention comprises methods and compositions for antimicrobial silver compositions comprising silver nanoparticles. The present invention further comprises compositions for preparing silver nanoparticles comprising at least one stabilizing agent, one or more silver compounds, at least one reducing agent and a solvent. In one aspect, the stabilizing agent comprises a surfactant or a polymer. The polymer may comprise polymers such as polyacrylamides, polyurethanes, and polyamides. In one aspect, the silver compound comprises a salt comprising a silver cation and an anion. The anion may comprise saccharinate derivatives, long chain fatty acids, and alkyl dicarboxylates. The methods of the present invention comprise treating devices with the silver nanoparticle compositions, including, but not limited to, such devices as woven wound care materials, catheters, patient care devices, and collagen matrices. The present invention further comprises treatment of humans and animals wacr6ith the antimicrobial devices described herein.
Owner:AVENT INC
Heparin barrier coating for controlled drug release
ActiveUS20050004663A1Reduce frictional forceReduce forceSuture equipmentsStentsCompound (substance)Antioxidant
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. These therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may also further reduce a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. In addition, these therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds may be utilized to promote healing, including the formation of blood clots. The drugs, agents, and / or compounds may also be utilized to treat specific diseases, including vulnerable plaque. Therapeutic agents may also be delivered to the region of a disease site. In regional delivery, liquid formulations may be desirable to increase the efficacy and deliverability of the particular drug. Also, the devices may be modified to promote endothelialization. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned. In addition, the devices utilized to deliver the implantable medical devices may be modified to reduce the potential for damaging the implantable medical device during deployment. Medical devices include stents, grafts, anastomotic devices, perivascular wraps, sutures and staples. In addition, various polymer combinations as well as other therapeutic agents may be utilized to control the elution rates of the therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds from the implantable medical devices. In each of these instances, antioxidants are utilized to prolong product integrity.
Owner:WYETH
Negative Working, Heat-Sensitive, Lithographic Printing Plate Precursor
ActiveUS20080213696A1Number of defectSize of defectPhotosensitive materialsDuplicating/marking methodsSimple Organic CompoundsPhosphoric acid
A heat-sensitive negative-working lithographic printing plate precursor includes on a grained and anodized aluminum support a coating including hydrophobic thermoplastic polymer particles, a hydrophilic binder, and an organic compound, wherein the organic compound includes at least one phosphonic acid group or at least one phosphoric acid group or a salt thereof.
Owner:AGFA OFFSET BV
Methods and compositions for metal nanoparticle treated surfaces
ActiveUS20070207335A1Extended shelf lifeConvenient coatingMaterial nanotechnologyBiocidePolyamideSolvent
The present invention comprises methods and compositions comprising metal nanoparticles. The invention comprises metal nanoparticles and surfaces treated with a metal nanoparticle coating. The present invention further comprises compositions for preparing nanoparticles comprising at least one stabilizing agent, one or more metal compounds, at least one reducing agent and a solvent. In one aspect, the stabilizing agent comprises a surfactant or a polymer. The polymer may comprise polymers such as polyacrylamides, polyurethanes, and polyamides. In one aspect, the metal compound comprises a salt comprising a metal cation and an anion. The anion may comprise saccharinate derivatives, long chain fatty acids, and alkyl dicarboxylates.
Owner:AVENT INC
Calcium-supplemented beverages and method of making same
InactiveUS7052725B2Effective sweetnessClean tasteAnimal feeding stuffFood ingredientsCalcium supplementCalcium salts
Owner:PEPSICO INC
Albumin fusion proteins
InactiveUS20070048282A1Extended shelf lifeImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAlbumin
The present invention encompasses albumin fusion proteins. Nucleic acid molecules encoding the albumin fusion proteins of the invention are also encompassed by the invention, as are vectors containing these nucleic acids, host cells transformed with these nucleic acids vectors, and methods of making the albumin fusion proteins of the invention and using these nucleic acids, vectors, and / or host cells. Additionally the present invention encompasses pharmaceutical compositions comprising albumin fusion proteins and methods of treating, preventing, or ameliorating diseases, disorders or conditions using albumin fusion proteins of the invention.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Liquid phase chip for joint detection of multiple tumor markers and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a liquid phase chip for joint detection of multiple tumor markers and a preparation method thereof. The liquid phase chip comprises micro-balloons of a coupled antibody (at least two of the followings: AFP, CEA, CA125, CA153, CA19-9, CA242, CA72-4, PSA, HGH, Beta-HCG), corresponding biotin-labeled detection antibodies, streptavidin phycoerythrin and vegetable hydrosol or polysaccharide hydrosol which has a solute content of 1-10 wt per thousand and does not contain protein. The preparation of the liquid phase chip comprises refining and purification of hydrosol, coupling between captured antibodies and micro-balloons, preparation of biotin-labeled antibodies, dispersing the coupled micro-balloons into the vegetable hydrosol or the polysaccharide hydrosol, and the like. The liquid phase chip has the advantages of stable performance, good micro-balloon dispersivity, long preservation time, fast and convenient use and operation, small amount of samples in use, high detection sensitivity, wide linear scope and low detection cost, can detect ten tumor markers at most at one time, and requires a cost which is a quarter of the total fee of conventional methods.
Owner:HENAN YUKANG BIOTECH
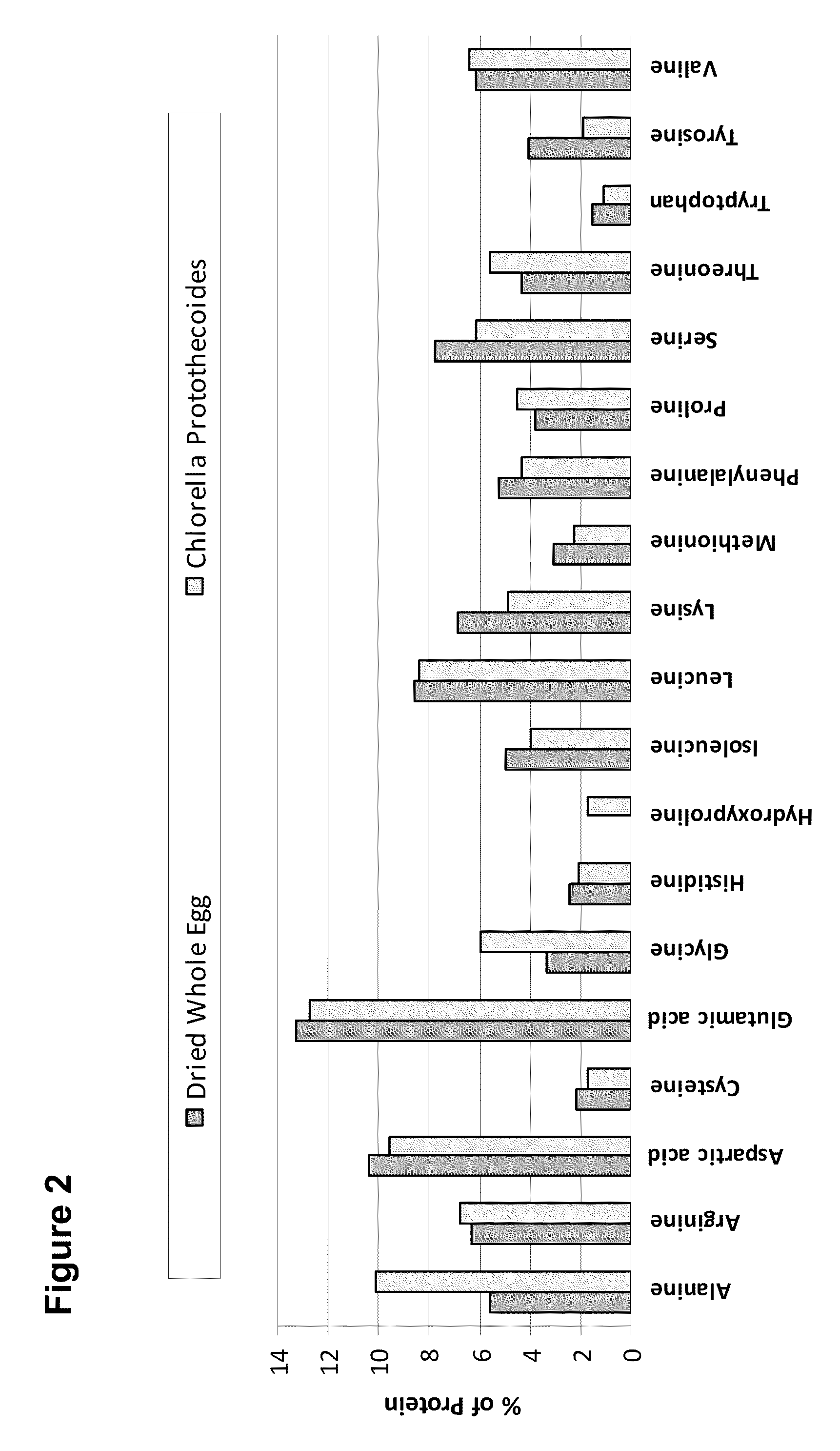
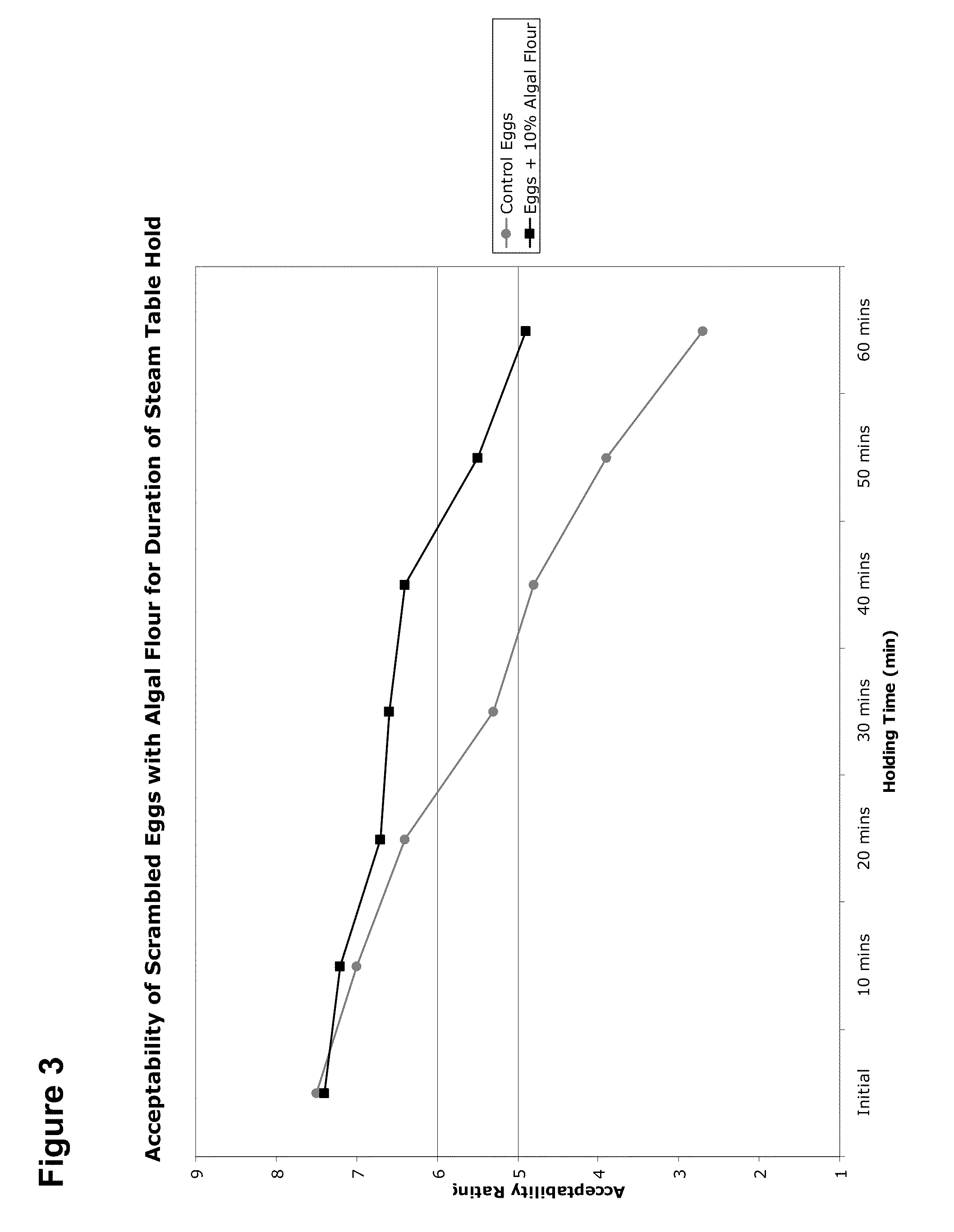
Food Compositions of Microalgal Biomass
InactiveUS20100239712A1Cheaply and efficiently scaleReduce the amount requiredMilk preparationDough treatmentDry weightAdditive ingredient
The invention provides algal biomass, algal oil, food compositions comprising microalgal biomass, whole microalgal cells, and / or microalgal oil in combination with one or more other edible ingredients, and methods of making such compositions by combining algal biomass or algal oil with other edible ingredients. In preferred embodiments, the microalgal components are derived from microalgal cultures grown and propagated heterotrophically in which the algal cells comprise at least 10% algal oil by dry weight.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
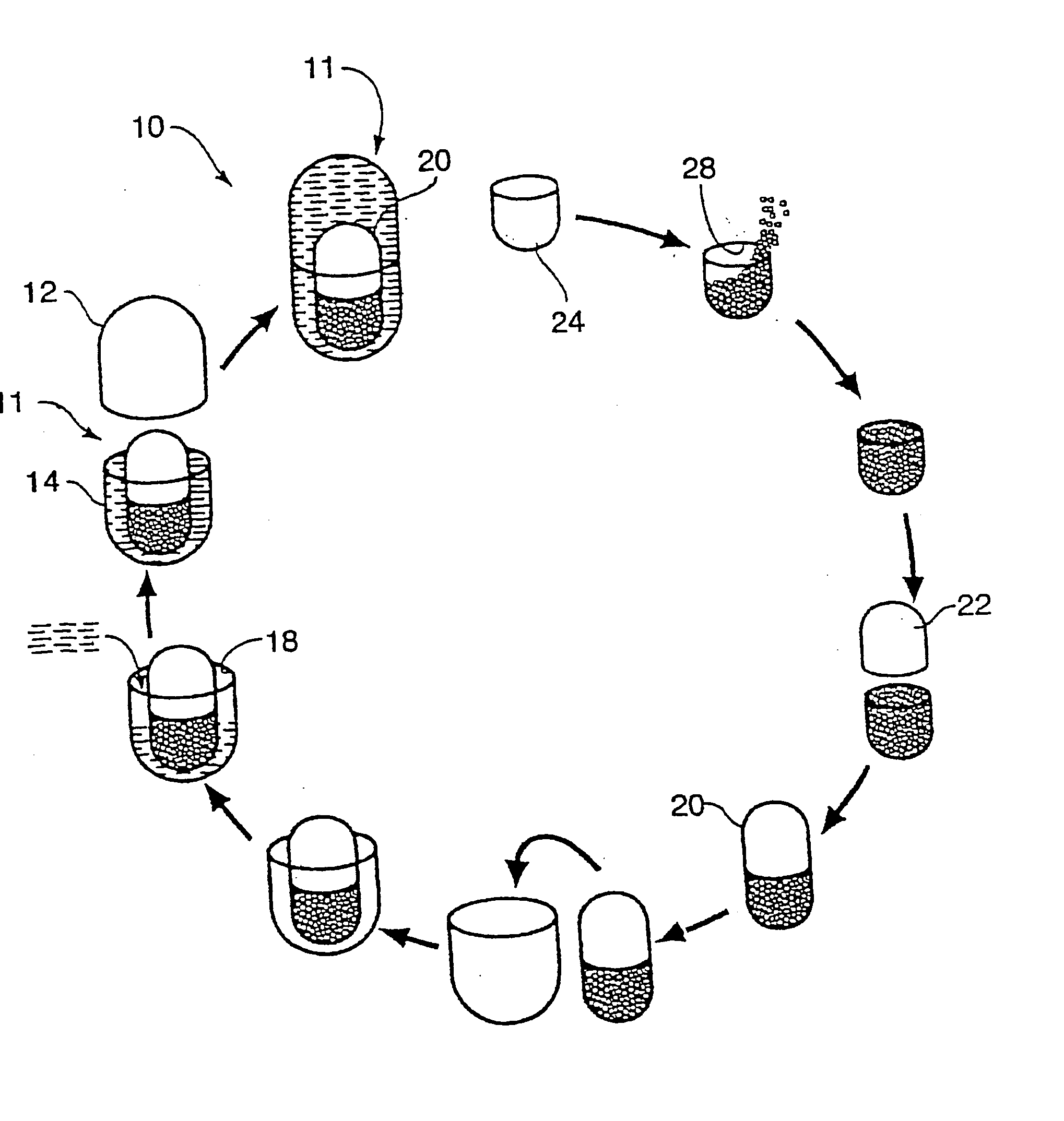
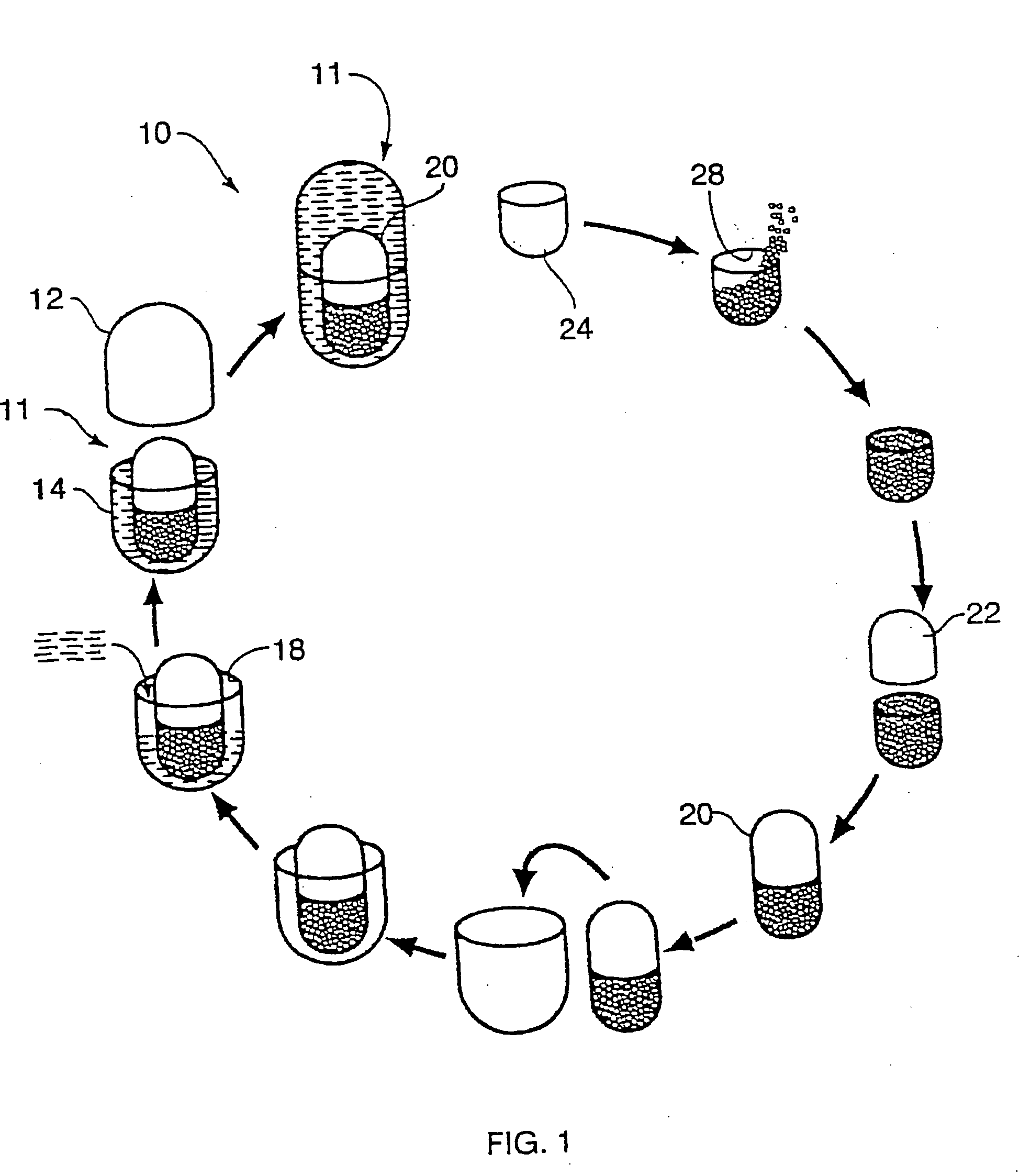
Multi-phase, multi-compartment capsular delivery apparatus and methods for using same
ActiveUS20050008690A1Extended shelf lifeFacilitate desirable propertyPowder deliveryCapsule deliveryDietary supplementAdditive ingredient
A multi-compartment capsule, comprising, a first receiving chamber comprising at least one ingredient having a first physical state, wherein said ingredient is selected from the group consisting of a nutraceutical, a vitamin, a dietary supplement and a mineral; and a second receiving chamber comprising at least one ingredient having a second physical state, wherein said ingredient is selected from the group consisting of a nutraccutical, a vitamin, a dietary supplement and a mineral; wherein said first physical state of said ingredient of said first receiving chamber being different from said second physical state of said ingredient of said second receiving chamber; and said ingredient of said first receiving chamber being different from said ingredient of said second receiving chamber.
Owner:INNERCAP TECH
Smart tray for dispensing medicaments
ActiveUS7080755B2Less-proneMinimal amountElectrotherapyDrug and medicationsEngineeringBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a method and system that utilizes one or more cassettes or trays, which hold one or more types of medicaments, the cassettes or trays being configured for secure and intelligent dispensing of the medicaments. In one embodiment, a smart tray for dispensing medicaments includes: a housing; a chamber within the housing to store the medicament units; an outlet defined in the housing to dispense the medicament units; and a rotatable disk within the housing and defining at least one radial groove configured to hold at least one medicament unit, the rotatable disk being positioned between the storage chamber and the outlet whereby when the rotatable disk rotates, the at least one radial groove carries the at least one medicament unit from the chamber to the outlet. In a further embodiment, the smart tray includes a memory device within the housing to store information pertaining to the medicament units stored in the tray and / or information pertaining to the status or operation of the tray.
Owner:HANDFIELD MICHAEL +1
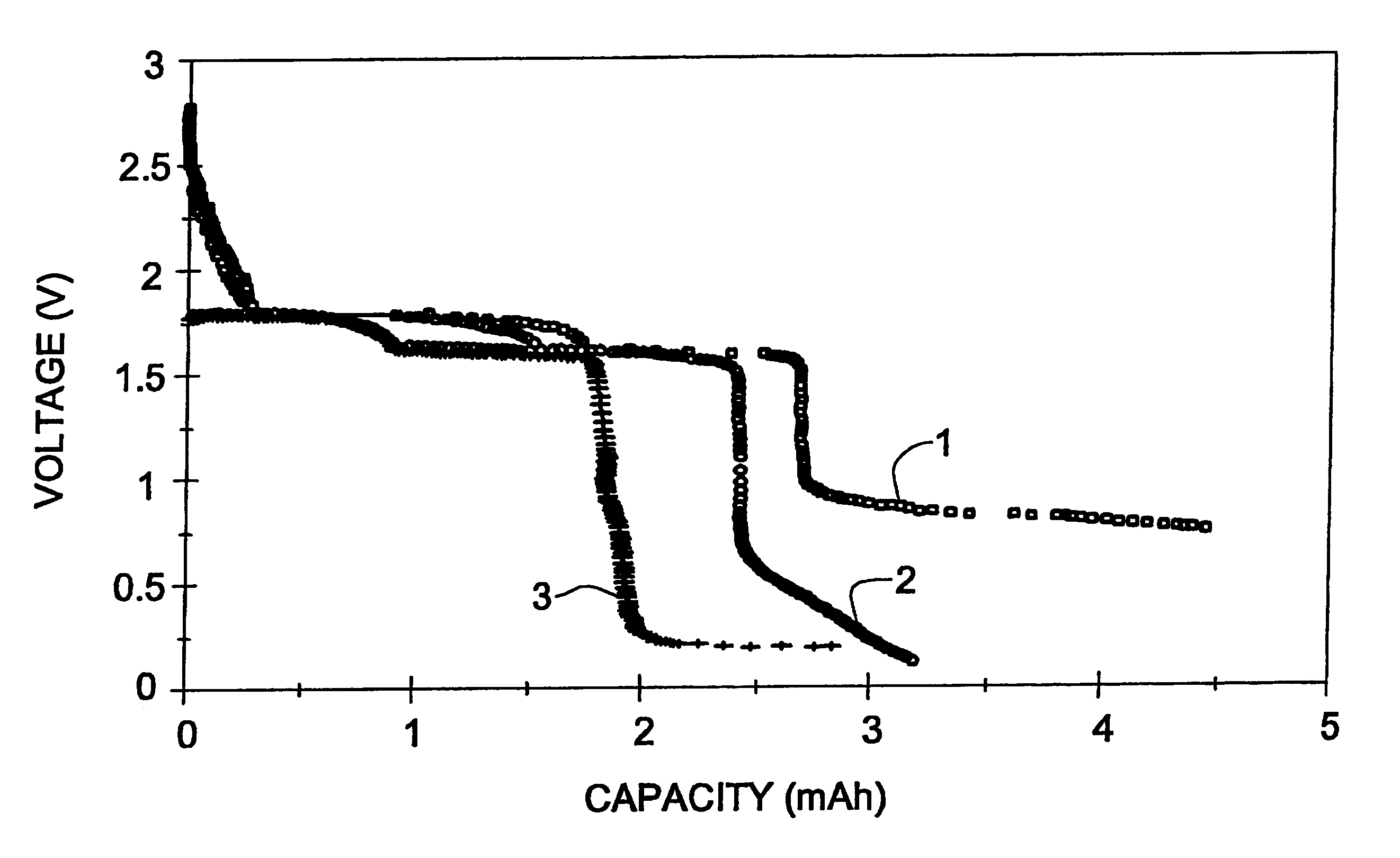
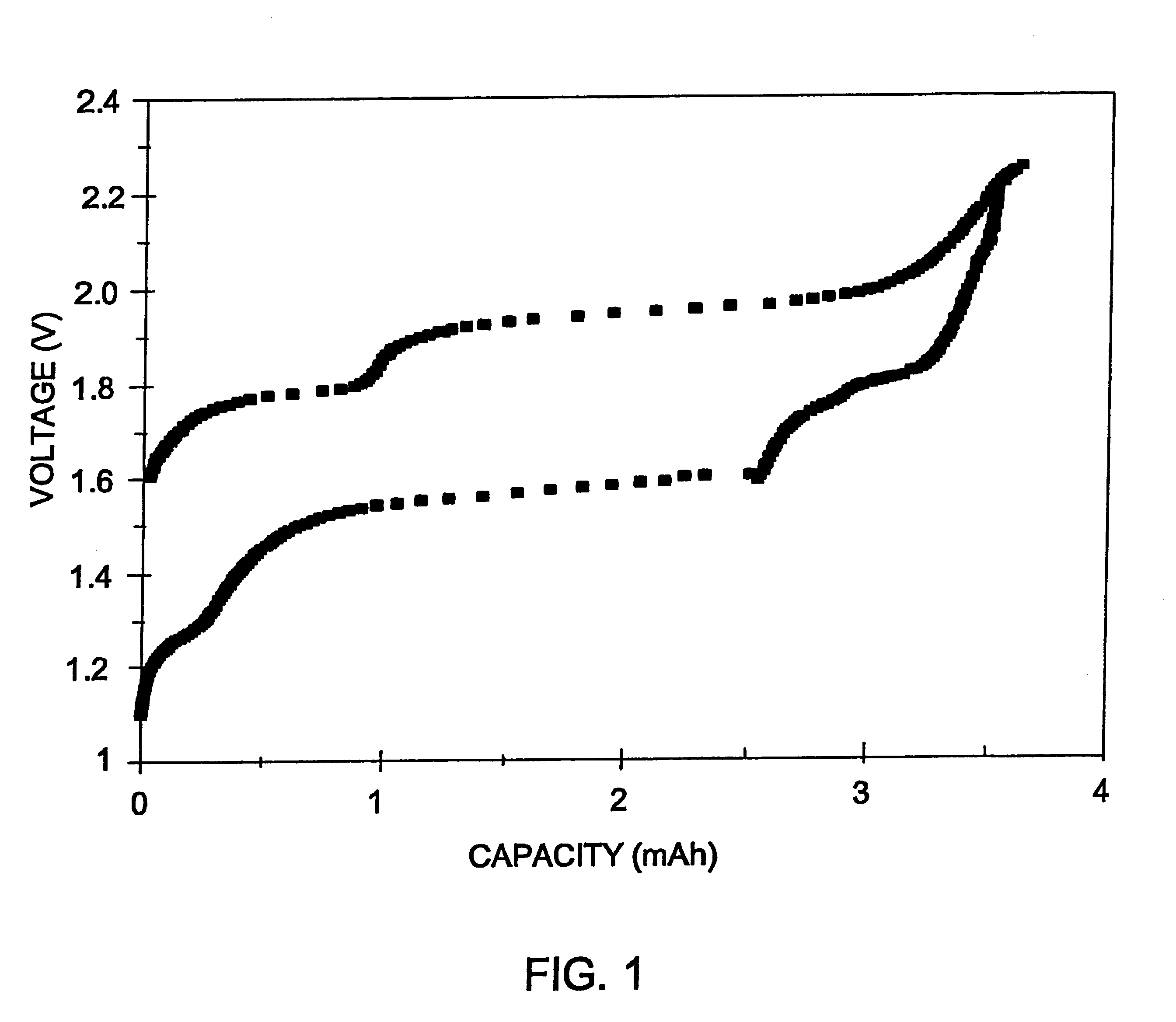
Long cycle-life alkali metal battery
InactiveUS6203947B1Improve cycle lifeFast charging rateElectrochemical processing of electrodesElectrode carriers/collectorsHigh pressureElectrochemical cell
The present invention provides a cathode for use in a secondary electrochemical cell, such cathode being coated with a very thin, protective film, permeable to ions. The protective film of the cathode usually has a thickness of up to about 0.1 mum and it provides protection against high voltage charging and overdiscbarging. The present invention further provides a secondary electrochemical cell comprising such a cathode.
Owner:RAMOT UNIV AUTHORITY FOR APPLIED RES & INDAL DEVMENT
Power having nutrition of paddy, bean, fruit, vegetables and tea with the functions of equalizing the nutrition, losing weight and reducing blood sugar
ActiveCN101116510ABalanced nutritionHave weight lossPre-extraction tea treatmentMetabolism disorderFiberGlucose polymers
The present invention provides a low-lipid, high-fiber, balanced-nutritional, instant-taking and instant-resolving powder made from all natural components including corn, bean, flower, vegetable, fruit, tea and bi-usage plants for both food and medication. The nutritional powder provided by the present invention has not only the functions to balance the nutrition, but also the effect to decrease the body weight, lower the blood glucose, and effectively prevent and treat the diabetes.
Owner:湖南湘泉药业股份有限公司
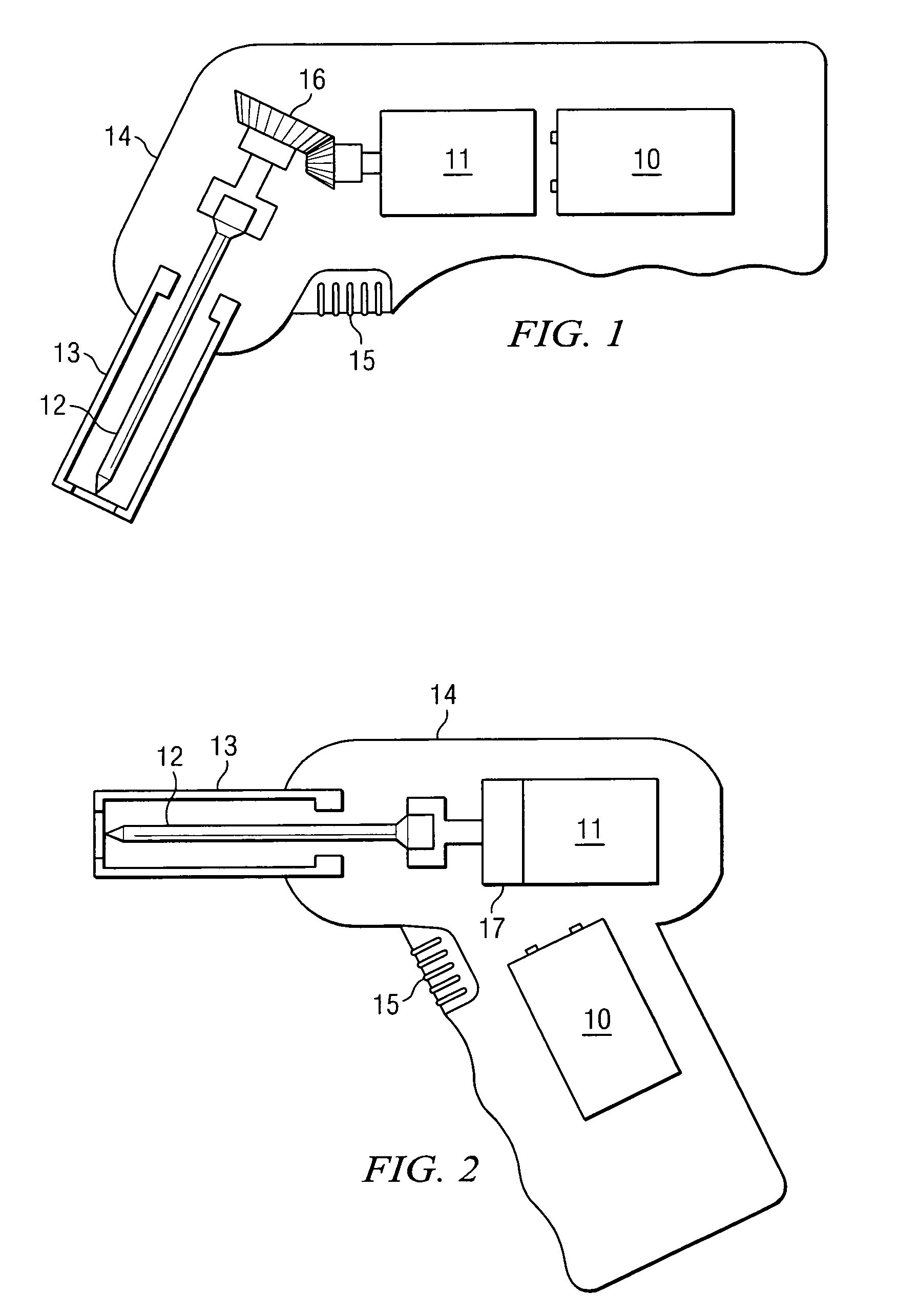
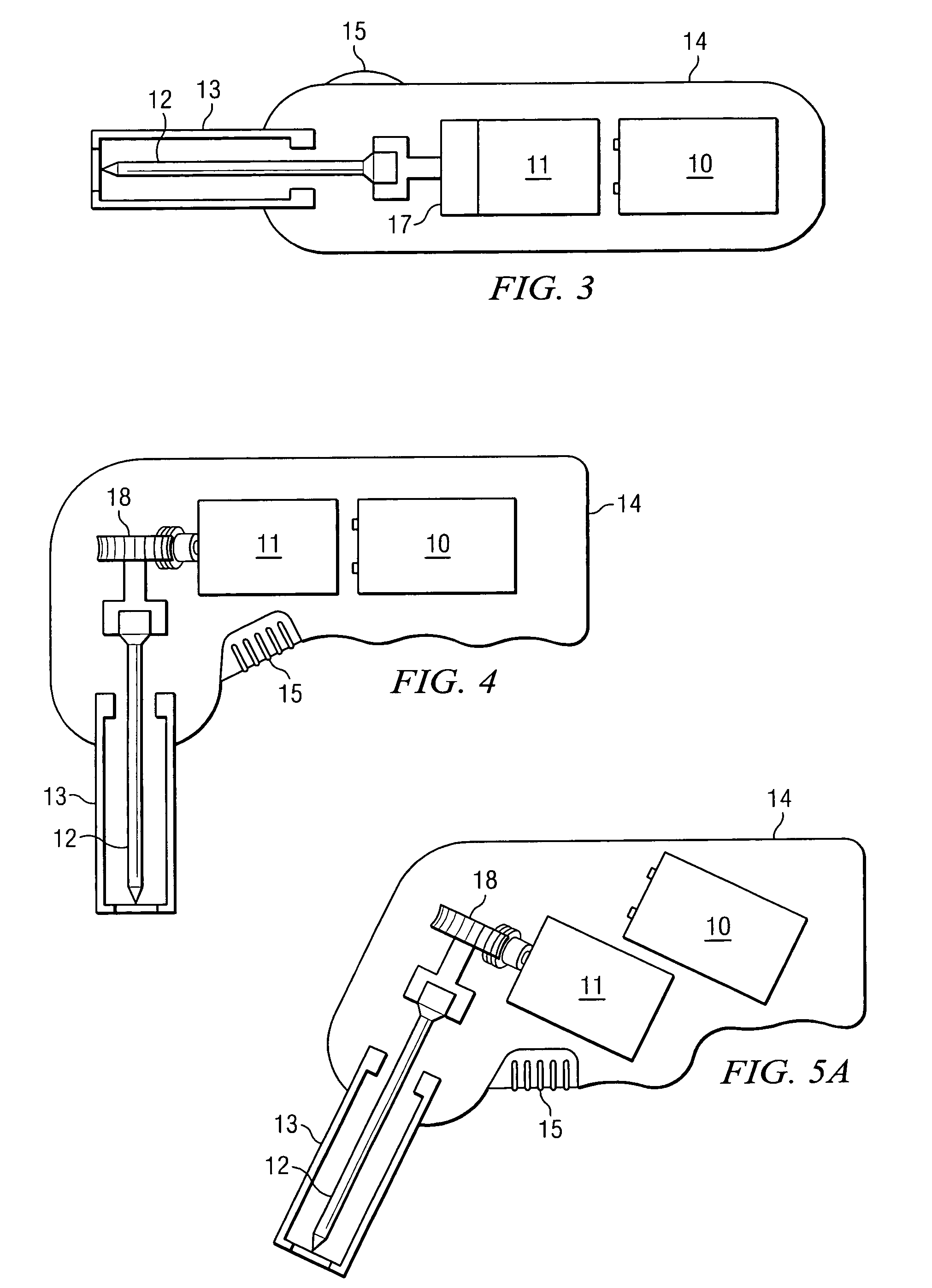
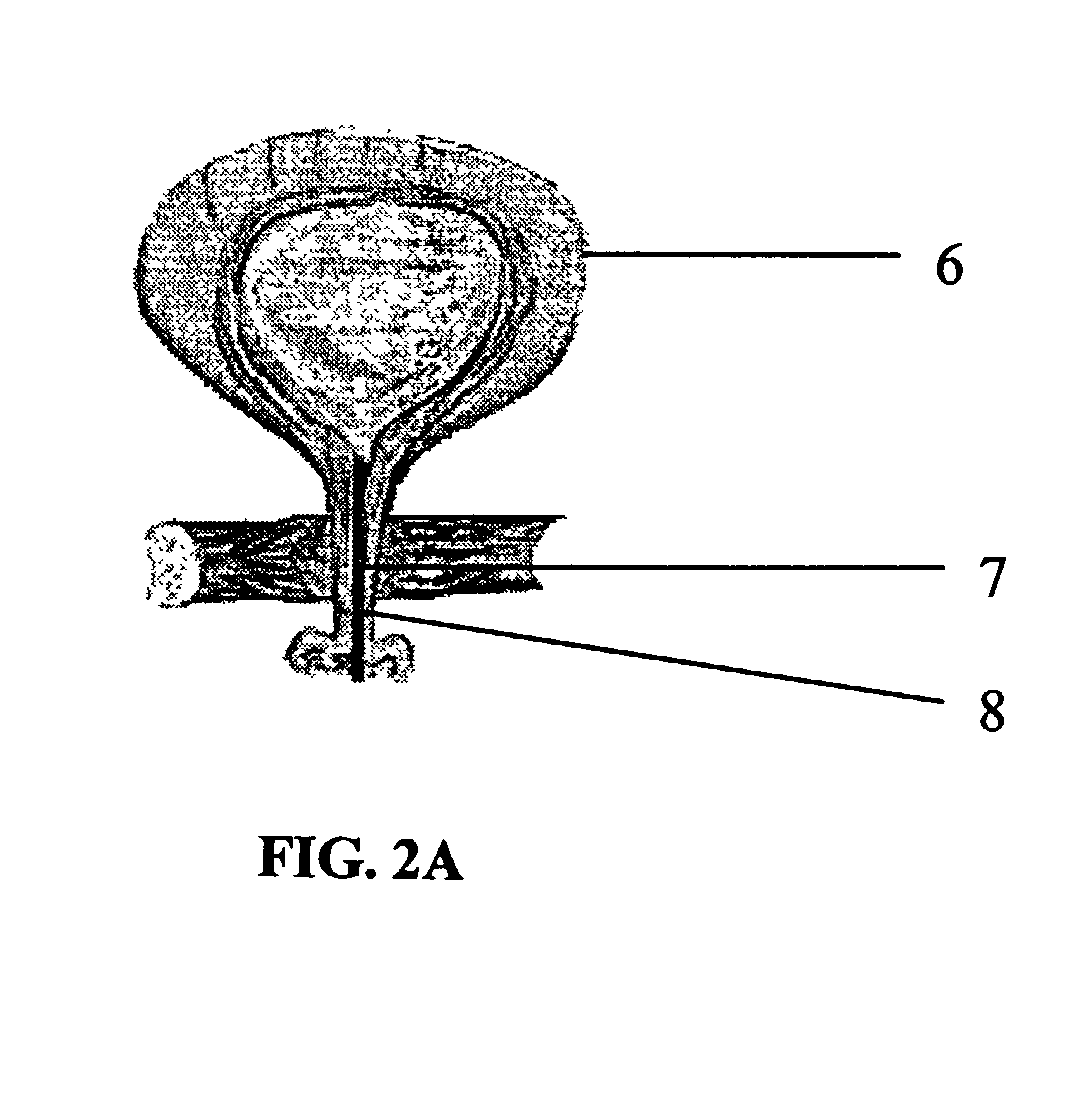
Apparatus and method to provide emergency access to bone marrow
An apparatus and method for penetrating the bone marrow is provided. The apparatus includes a housing, a penetrator assembly, operable to penetrate the bone marrow, a connector operable to releasably attach the penetrator assembly to a drill shaft, the drill shaft operable to connect the penetrator assembly to a gear assembly, a gear assembly operable to engage and rotate the drill shaft, a motor operable to engage the reduction gear assembly and drive the penetrator into the bone marrow by rotation of the drill shaft, and a power supply and associated circuitry operable to power the motor. The apparatus and method may be adapted to insert a probe through the skull and into the brain.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Biodegradable injectable implants containing glycolic acid
InactiveUS7314636B2Non-migratoryEasy to moveSolution deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsionGlycolic acid
Owner:MEDGRAFT MICROTECH
Therapeutic treatment and prevention of infections with a bioactive material(s) encapuslated within a biodegradable-bio-compatable polymeric matrix
InactiveUS6902743B1Induce productionSustained release of active agent over timePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic treatmentActive agent
Novel burst-free, sustained release biocompatible and biodegrable microcapsules which can be programmed to release their active core for variable durations ranging from 1-100 days in an aqueous physiological environment. The microcapsules are comprised of a core of polypeptide or other biologically active agent encapsulated in a matrix of poly(lactide / glycolide) copolymer having a molar composition of lactide / glycolide from 90 / 10 to 40 / 60, which may contain a pharmaceutically-acceptable adjuvant, as a blend of uncapped free carboxyl end group and end-capped forms ranging to ratios from 100 / 0 to 1 / 99.
Owner:ARMY UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Albumin fusion proteins
The present invention encompasses albumin fusion proteins. Nucleic acid molecules encoding the albumin fusion proteins of the invention are also encompassed by the invention, as are vectors containing these nucleic acids, host cells transformed with these nucleic acids vectors, and methods of making the albumin fusion proteins of the invention and using these nucleic acids, vectors, and / or host cells. Additionally the present invention encompasses pharmaceutical compositions comprising albumin fusion proteins and methods of treating, preventing, or ameliorating diseases, disordrs or conditions using albumin fusion proteins of the invention.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC
Immunoconjugate formulations
ActiveUS20070031402A1Great stabilityLong shelf lifePharmaceutical delivery mechanismAntiviralsSucroseGlycerol
The present invention provides an immunoconjugate formulation that is substantially free of particles, the immunoconjugate formulation comprising: an immunoconjugate and one or more excipients selected from the group consisting of: sucrose, polysorbate 20, polysorbate 80, cyclodextrin, dextrose, glycerol, polyethylene glycol, mannitol, sodium chloride, and an amino acid, wherein the formulation is a buffered aqueous solution having a pH of 4.5 to 7.6. The present invention also provides an immunoconjugate formulation that is substantially free of aggregates, the immunoconjugate formulation comprising: an immunoconjugate and one or more excipients selected from the group consisting of histidine, sucrose, glycine and sodium chloride, wherein the formulation is a buffered aqueous solution having a pH of 4.5 to 7.6. The present invention further provides an immunoconjugate formulation that is substantially free of both particles and aggregates.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Combination of proton pump inhibitor, buffering agent, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
InactiveUS20050249806A1Preventing gastric acid related disorderReduce riskBiocideSenses disorderNonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs/NSAIDsBuffering agent
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising a proton pump inhibitor, one or more buffering agent and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug are described. Methods are described for treating gastric acid related disorders and treating inflammatory disorders, using pharmaceutical compositions comprising a proton pump inhibitor, a buffering agent, and a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Owner:SANTARUS
Composition exhibiting enhanced formulation stability and delivery of topical active ingredients
InactiveUS7758888B2Improve stabilityExtended shelf lifeAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBenzoyl peroxideMedicine
A therapeutic, cosmetic or cosmeceutic composition for topical application, capable of stabilizing an active ingredient and delivering the active ingredient, comprising a plurality of microcapsules having a core-shell structure. The microcapsules have a diameter of approximately 0.1 to 100 micron. The core of each microcapsule includes at least one active ingredient and is encapsulated within a microcapsular shell. The shell is comprised of at least one inorganic polymer obtained by a sol-gel process, and the shell protects the active ingredient before topical application and is designed to release the active ingredient from the microcapsules following application. The composition is useful in encapsulating active ingredients, such as benzoyl peroxide, that are unstable in other formulation, or are irritating to the skin.
Owner:SOL GEL TECH
Implantable drug delivery device
Implantable devices for controlled delivery of a drug are provided which include a substrate; at least two reservoirs in the substrate, each reservoir having an opening; at least one therapeutic agent in each of the reservoirs; a reservoir cap sealing each opening; a mechanical rupturing mechanism which moves into contact with and ruptures the reservoir cap to permit release the therapeutic agent from the reservoir through the opening; and a mixing chamber adjacent the reservoirs, wherein upon release of the therapeutic agent from at least one of the reservoirs, the therapeutic agent is combined with a carrier fluid in the mixing chamber and then transported to a delivery site in a human or animal.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
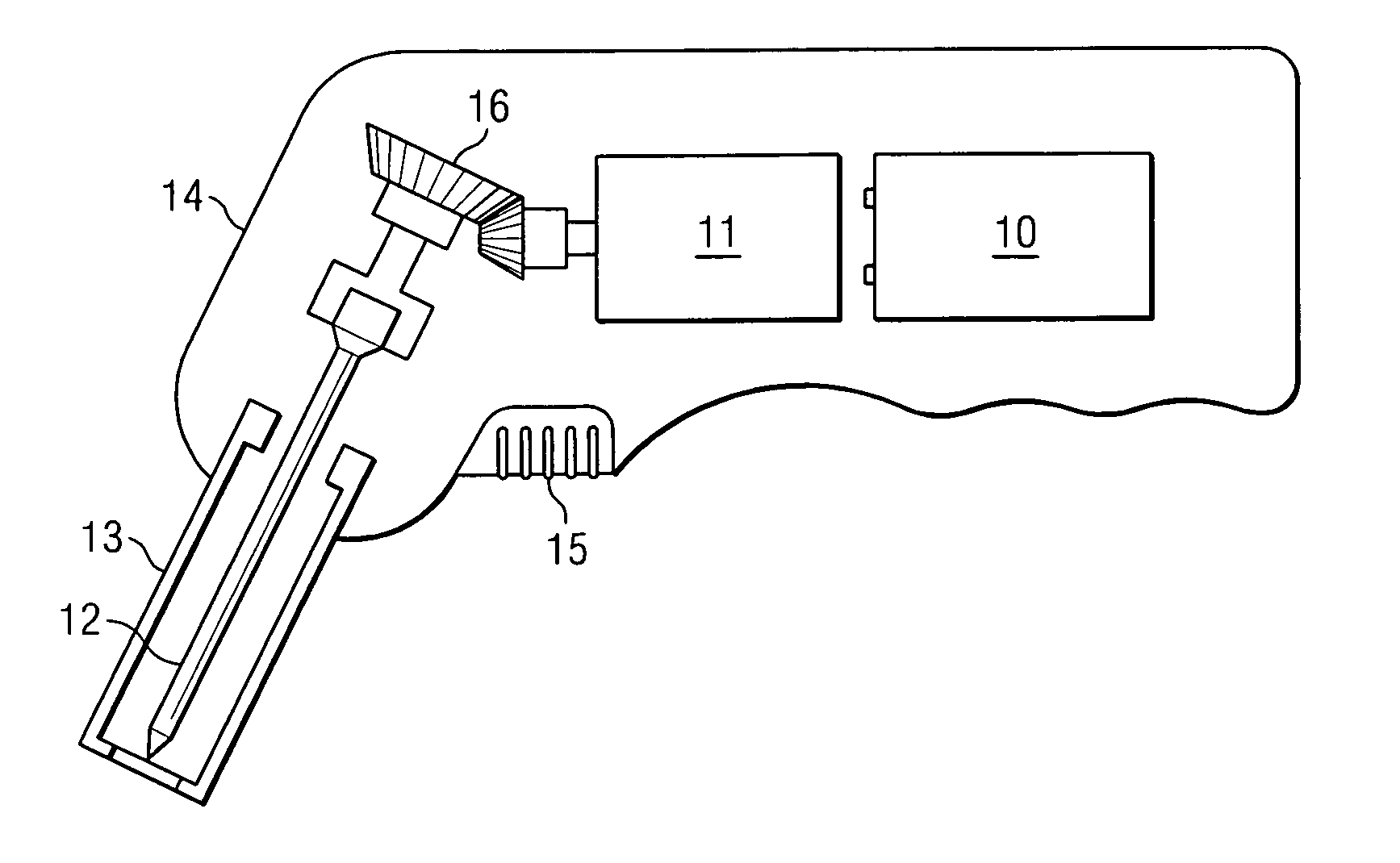
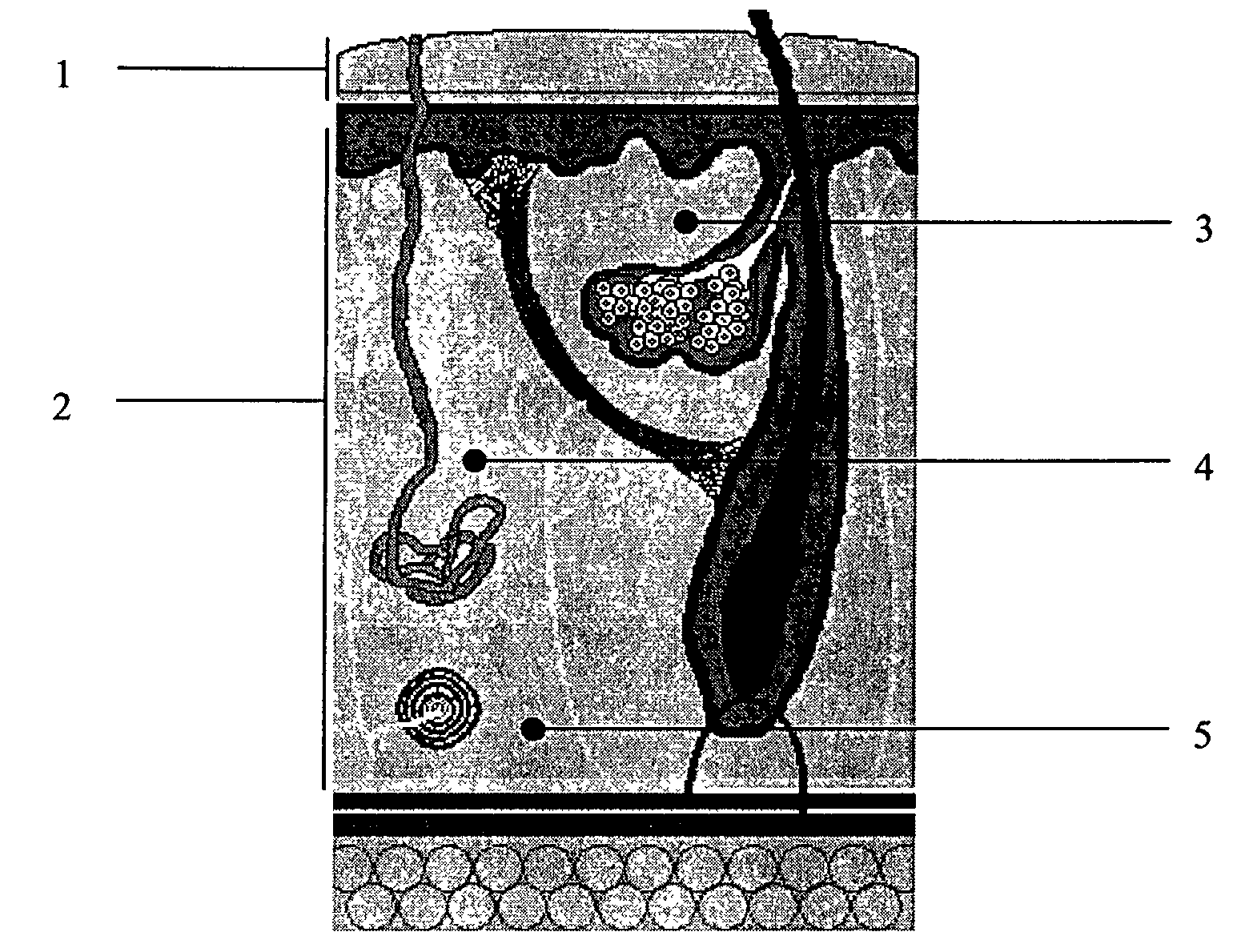
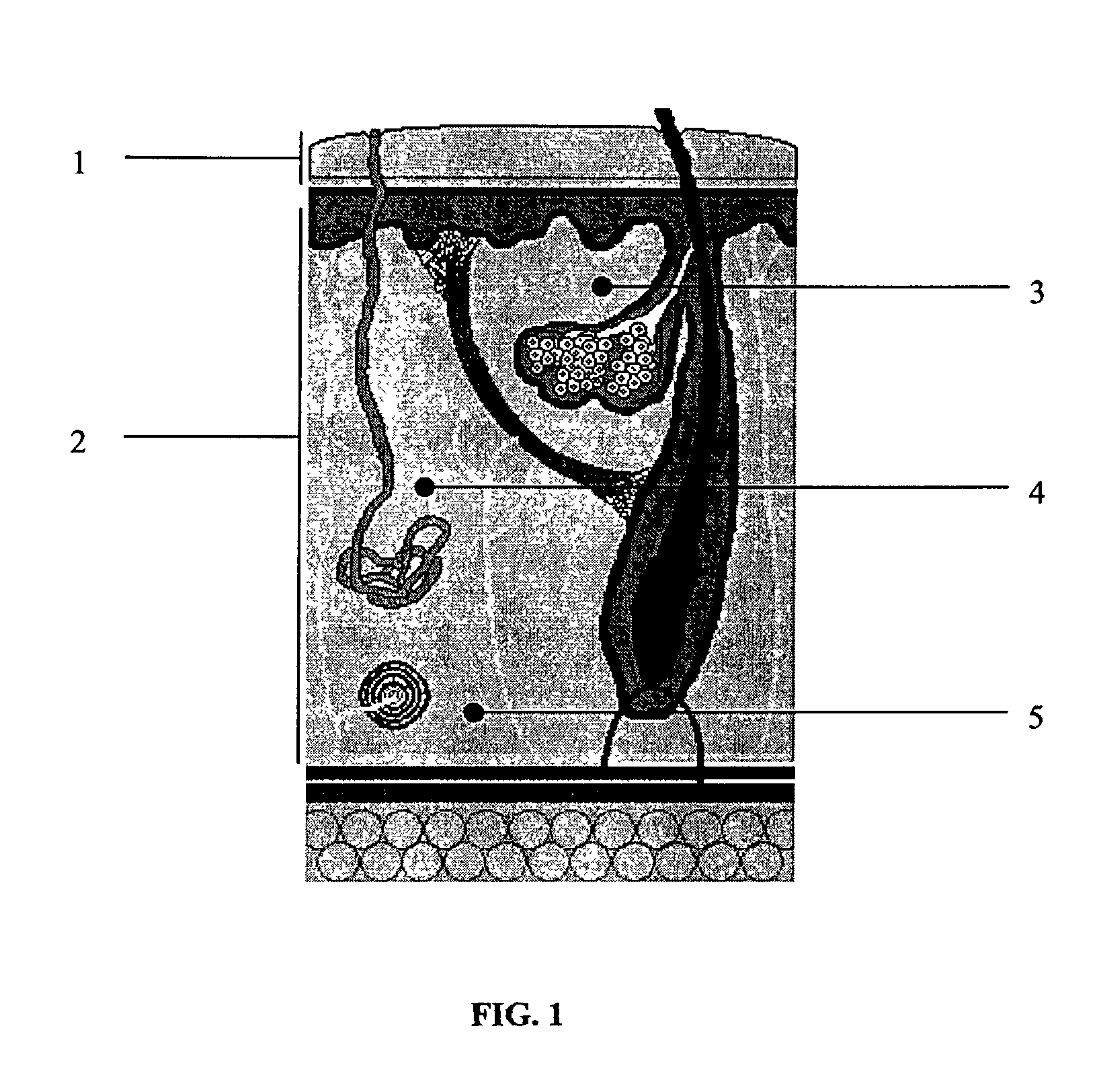
Skin penetrating device and method for subcutaneous solid drug delivery
ActiveUS8353863B2Easy to keepHigh hardnessMedical devicesIntravenous devicesTherapeutic effectBody tissue
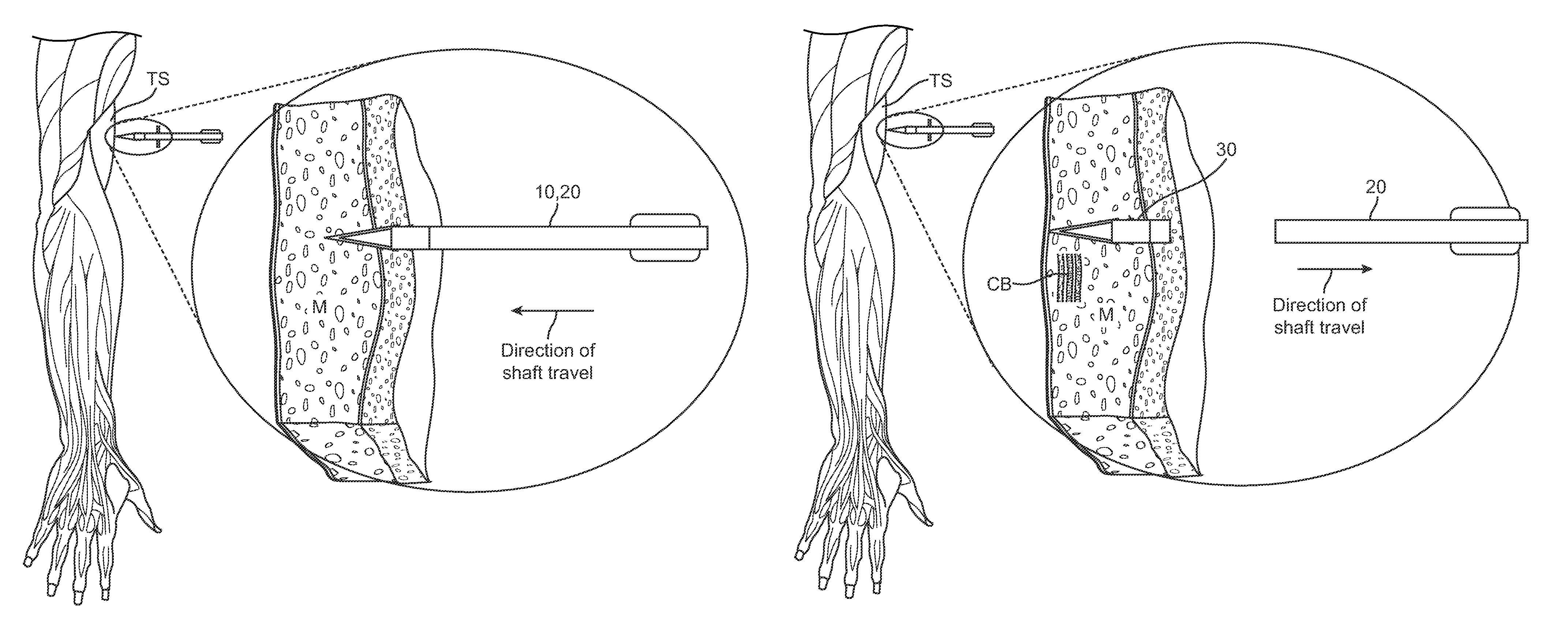
Embodiments described herein provide a skin penetrating device and method for the subcutaneous delivery of therapeutic agents in solid form. One embodiment provides such a device comprising an elongated shaft having proximal and distal ends and a skin penetrating element detachably coupled to the shaft. At least a portion of the penetrating element is fabricated from a solid form therapeutic agent composition that dissolves in body tissue and is absorbed into the blood stream so as to produce a therapeutic effect. The penetrating element has shape for penetrating and lodging beneath the skin when inserted through the skin by force applied from the shaft. The penetrating element is configured to detach from the shaft when the shaft is pulled away from the skin so as to leave the element in place beneath the skin where it is absorbed by body tissue and the therapeutic agent is released.
Owner:INCUBE LABS
Multi component controlled release system for oral care, food products, nutraceutical, and beverages
InactiveUS6887493B2Improve bioavailabilityImprove stabilityCosmetic preparationsPowder deliveryActive agentMicrosphere
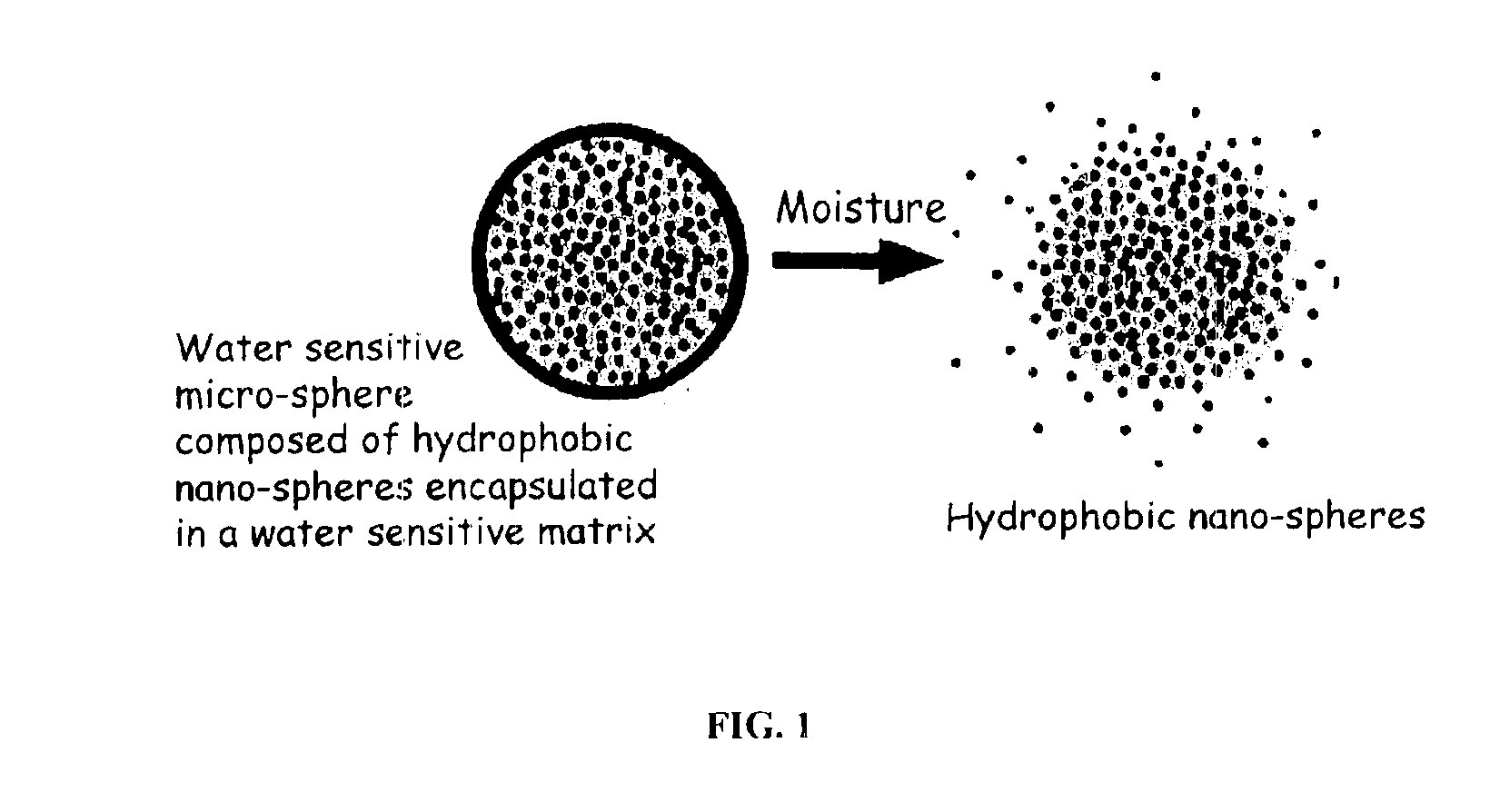
The present invention relates to an improved controlled release system that can encapsulate different flavors, sensory markers, and active ingredients, or combinations of flavors, sensory markers and various active ingredients and release multiple active ingredients in a consecutive manner, one after the other. The controlled delivery system of the present invention is substantially free-flowing powder formed of solid hydrophobic nanospheres that are encapsulated in a moisture sensitive microspheres. The flavors, and active ingredients encapsulated in the hydrophobic nanospheres, in the water sensitive microsphere, or in both the nano and the microsphere. The flavors and active ingredients encapsulated in the nanospheres can be the same or different from those encapsulated in the microspheres. The encapsulation of different flavors or active agents in the various components of the system, such as nanospheres and microspheres, provides flavor transition (change in flavor character) during the use of the products. The controlled release system of the present invention enhances the stability and bioavailability of wide range of flavors, sensory markers, and other active ingredients, prolong their residence time in the oral cavity, control their release characteristics, and prolong the sensation of flavors and other sensory markers in the mouth to provide long lasting organoleptic perception or long lasting mouthfeel. The invention further relates oral care, food products, and beverages comprising the controlled release system of the present invention.
Owner:SHEFER ADI +1
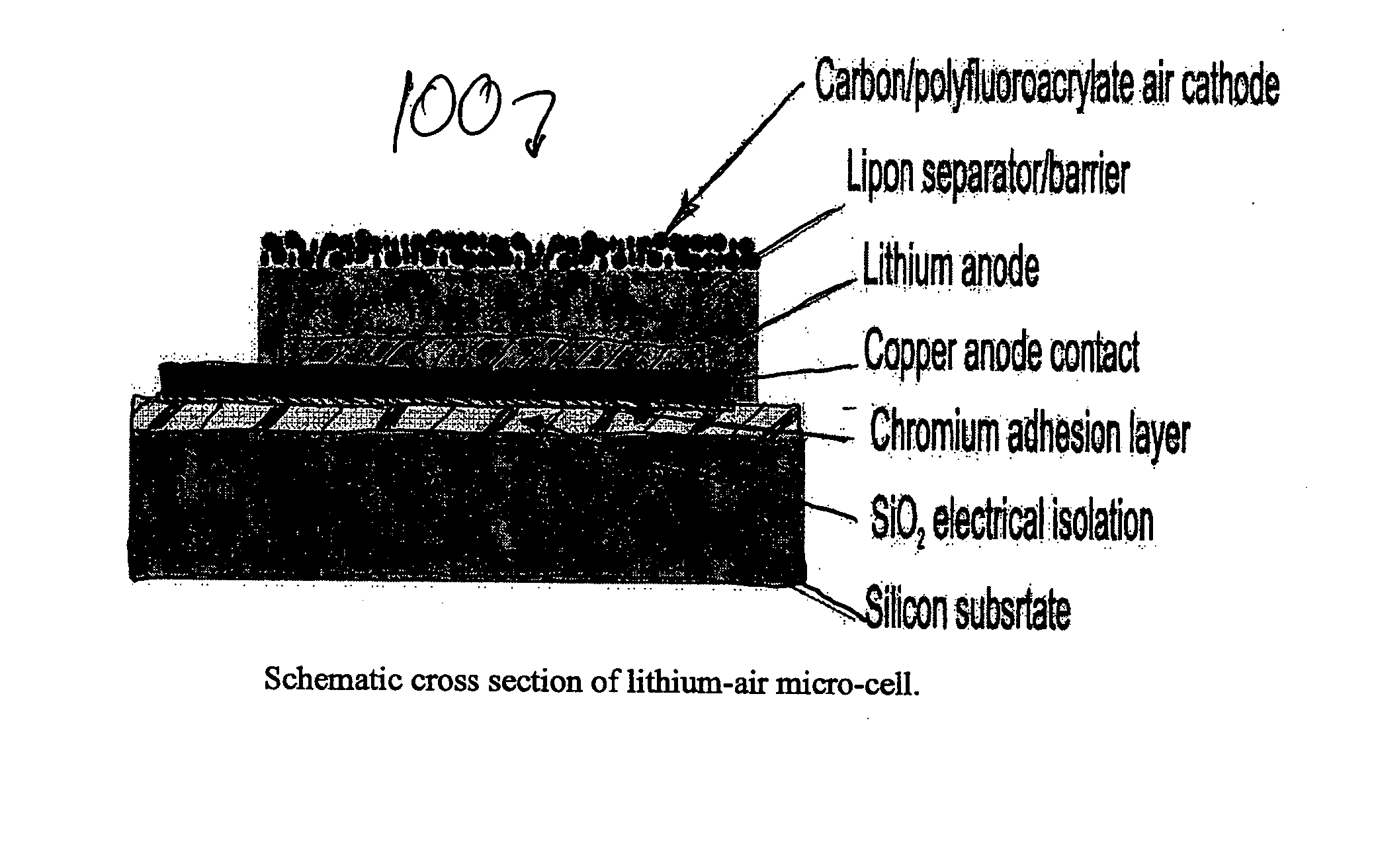
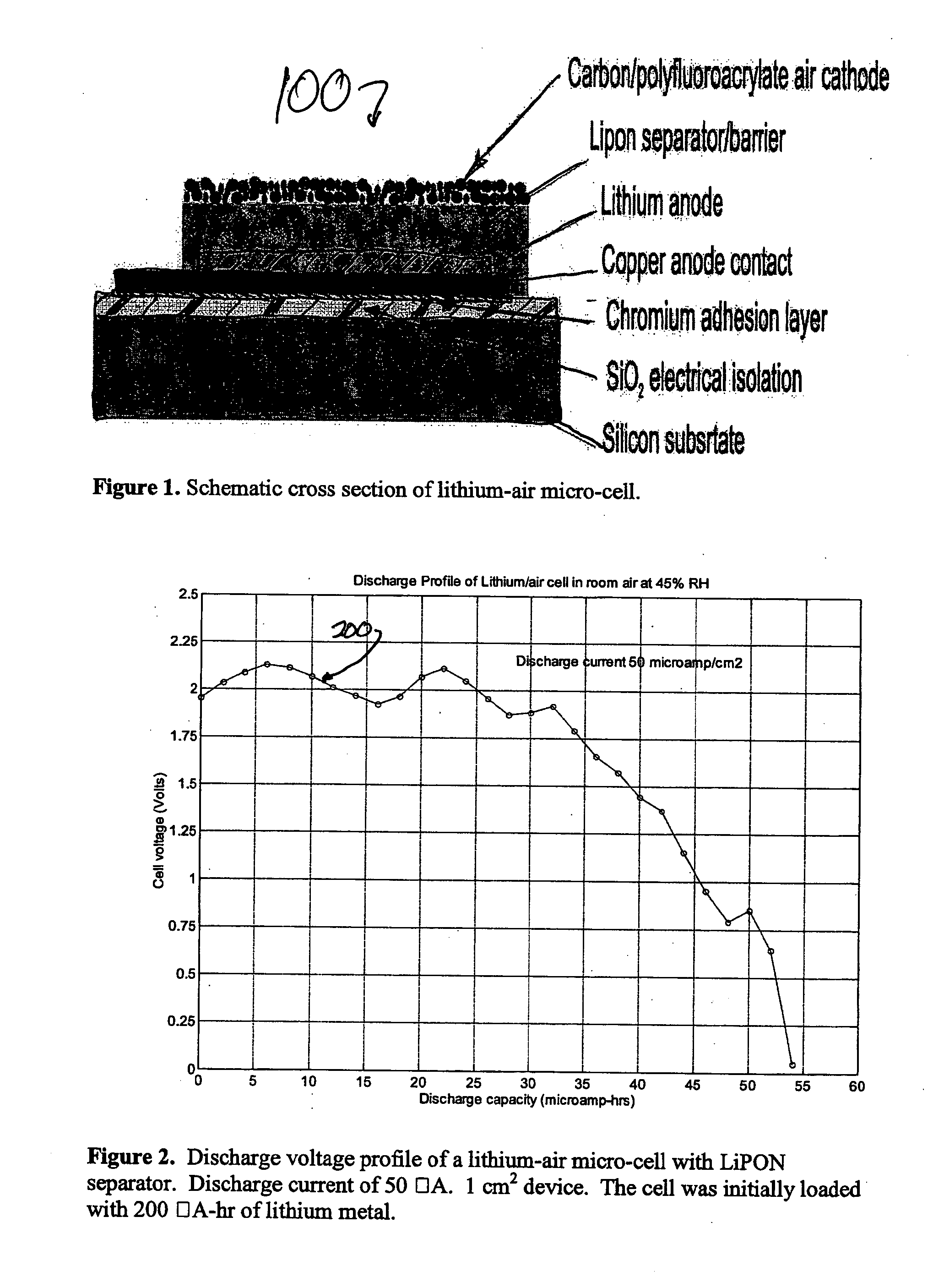
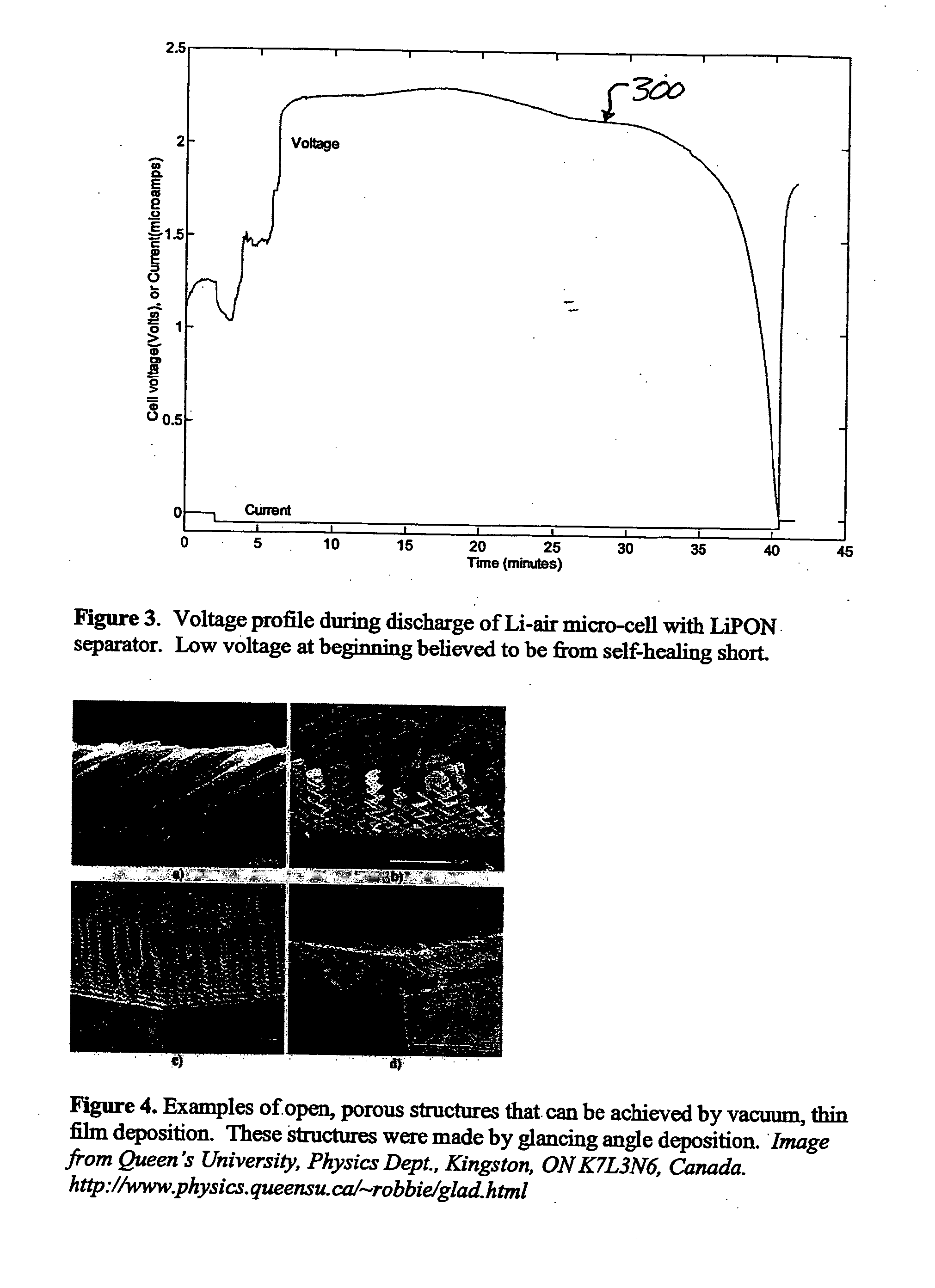
Lithium/air batteries with LiPON as separator and protective barrier and method
InactiveUS20050095506A1Extended shelf lifeProvide protectionFuel and primary cellsElectrode carriers/collectorsProtective barrierLithium–air battery
A method and apparatus for making lithium / air batteries with LiPON as separator and protective barrier, and the resulting cell(s) and / or battery(s). Some embodiments include an apparatus that includes a lithium anode; a polymer-air cathode; and a LiPON separator between the anode and cathode. In some embodiments, the polymer-air cathode includes a carbon-polyfluoroacrylate material. In some embodiments, the anode overlays a copper anode contact.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
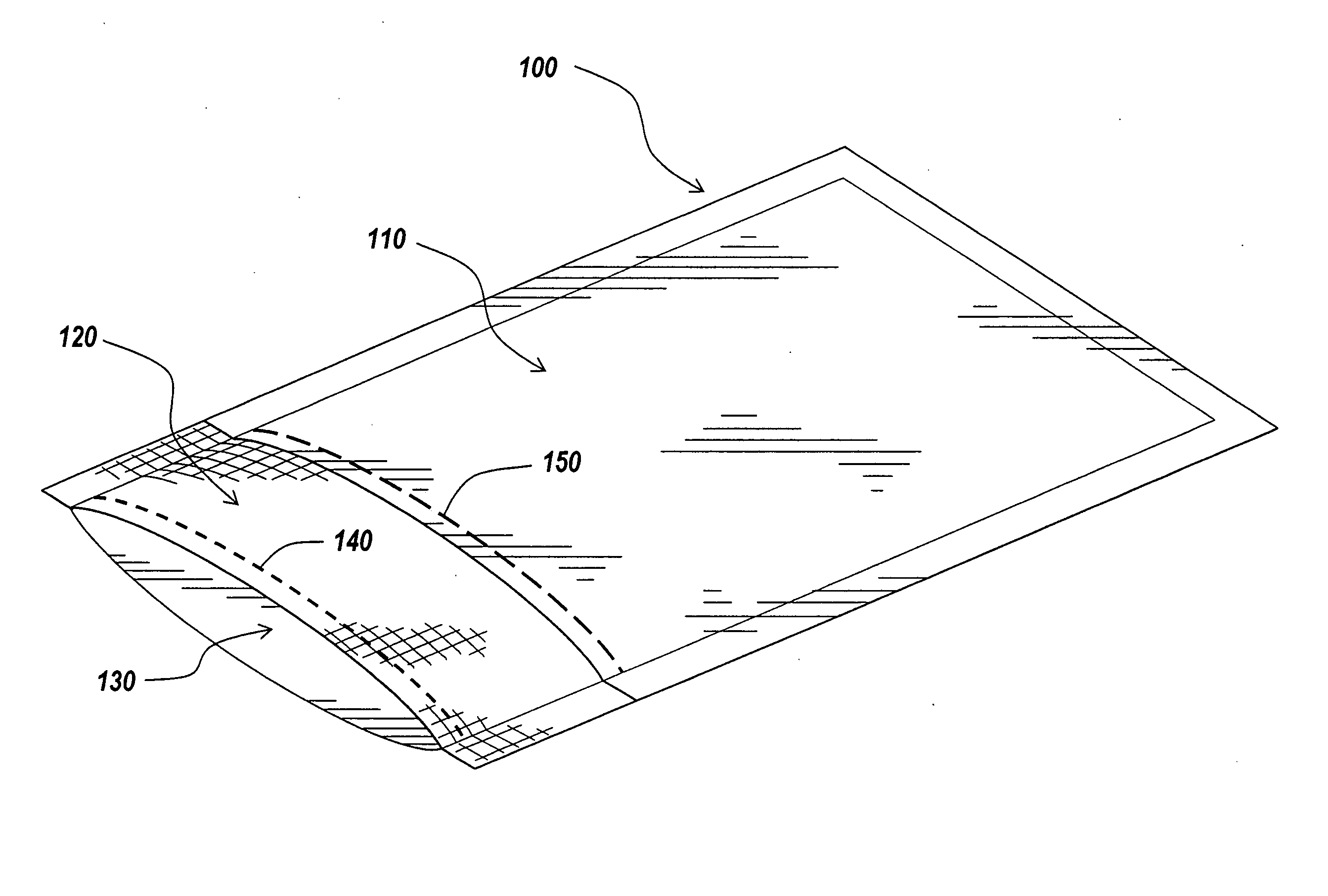
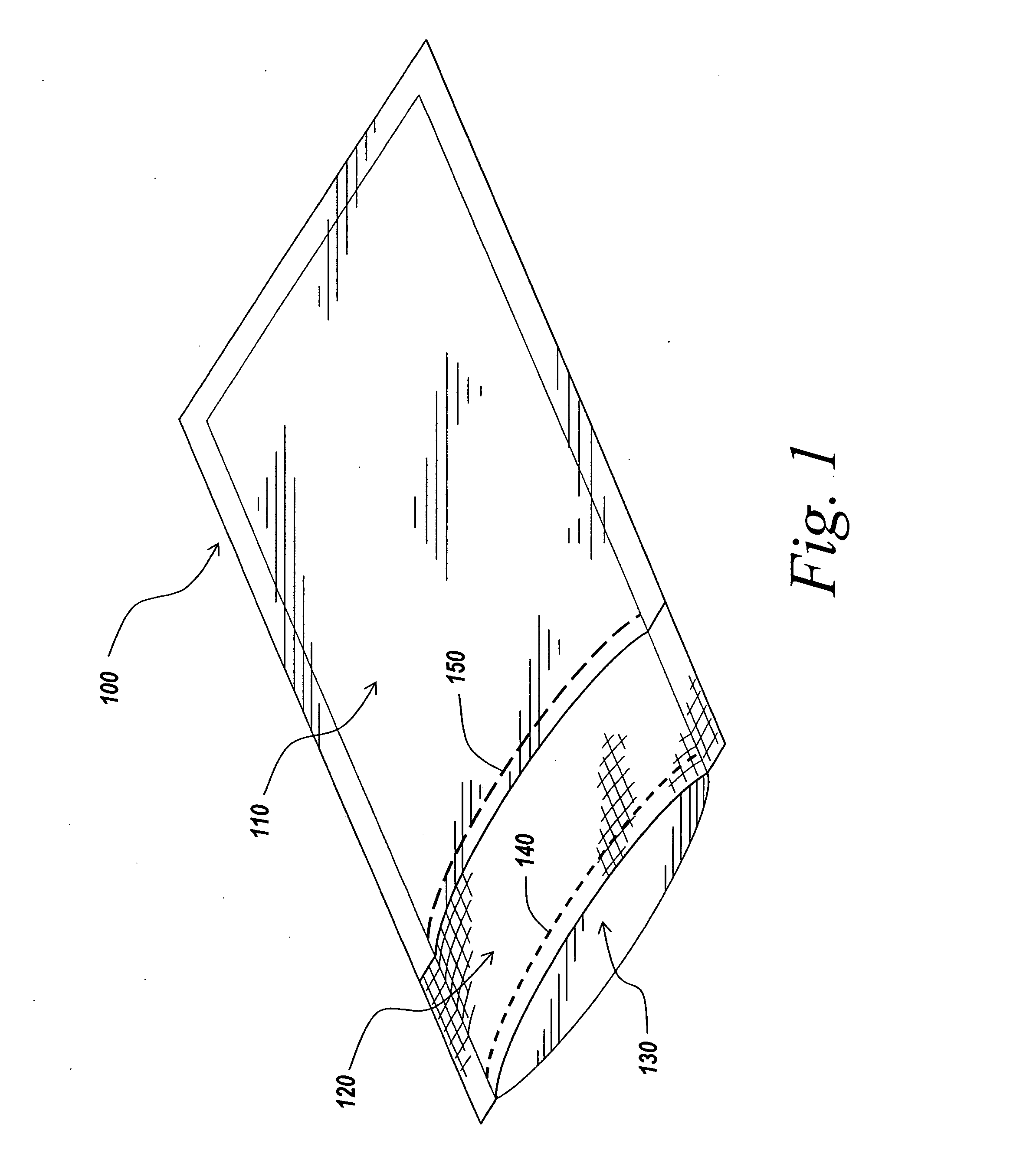
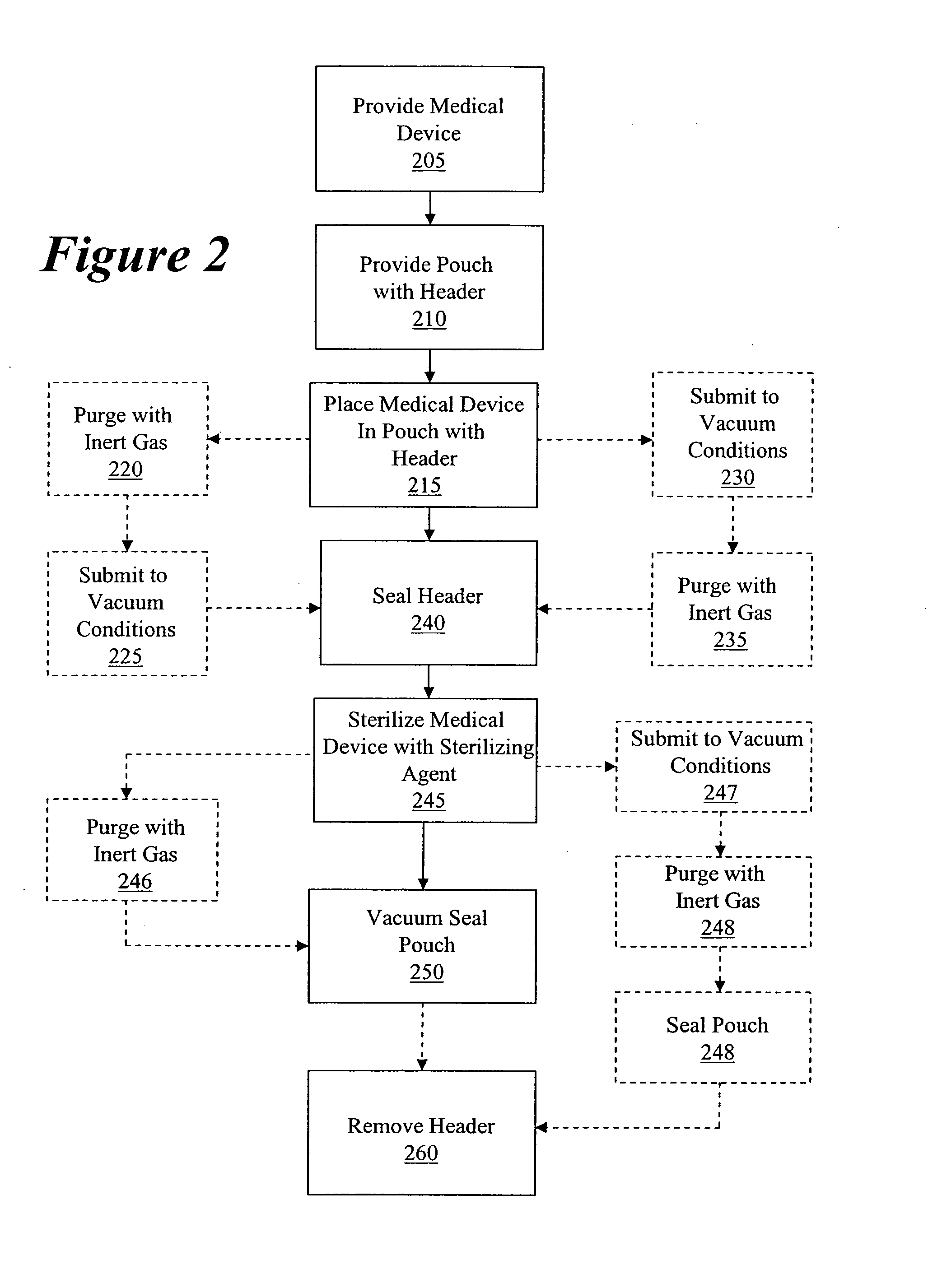
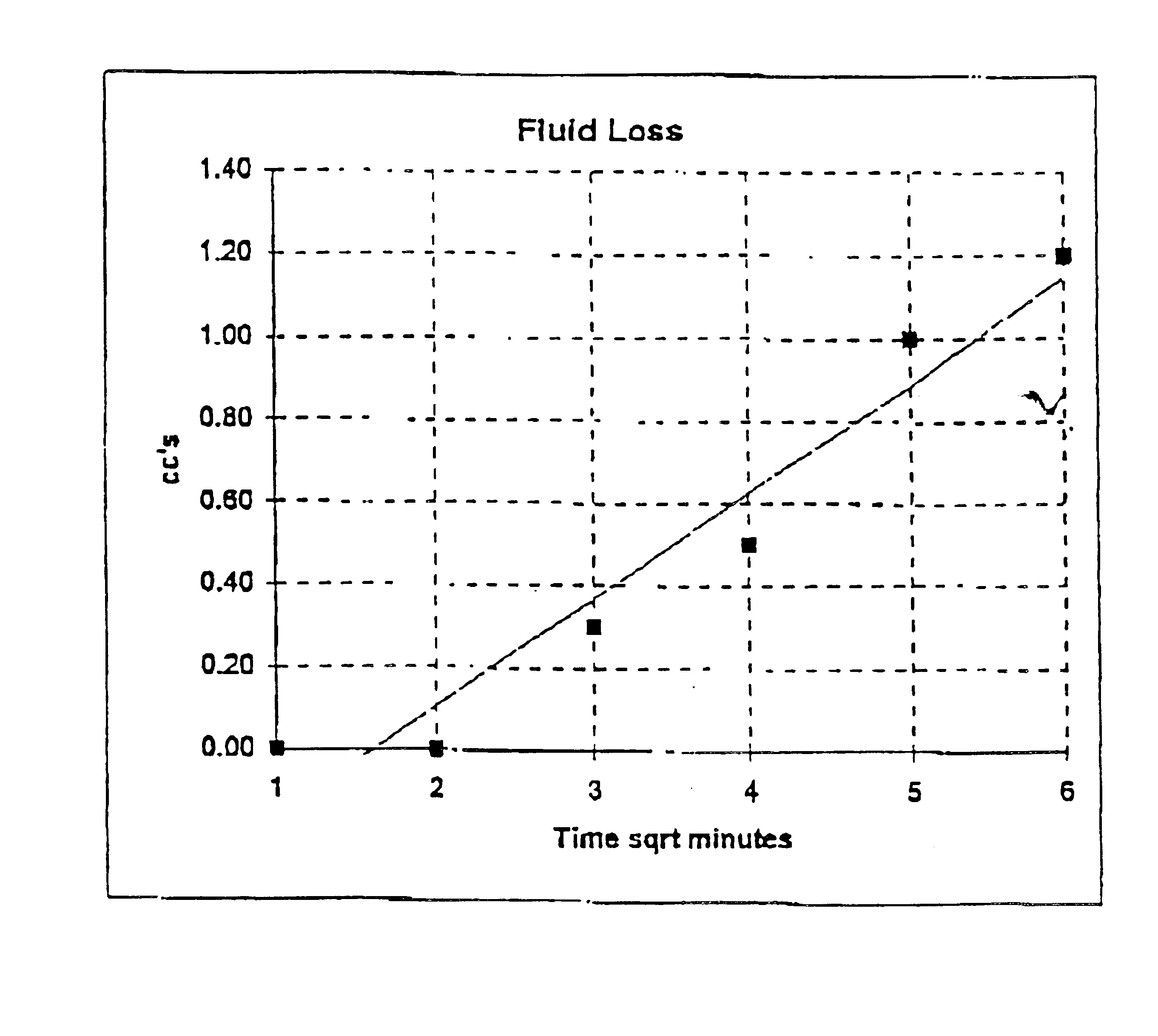
Packaging and sterilization of medical devices
InactiveUS20070084144A1Minimize timeExtended shelf lifeStentsSurgical furnitureCompound (substance)Fish oil
A method for the sterilization and packaging of a chemically sensitive medical device is provided. The chemically sensitive medical device has a coating derived from fish oil, a vitamin E compound or a combination thereof. The packaging pouch for the chemically sensitive medical device comprises a non-permeable chamber and a gas-permeable header. The sterilizing agent is administered to the packaged chemically sensitive medical device at a temperature of between about 20° C. and 40° C.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
Gelled hydrocarbon compositions and methods for use thereof
InactiveUS6849581B1Improve stabilityAvoid stabilityOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsOrganic baseOrganic fluid
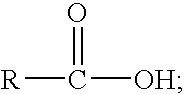
Gelled organic compositions and methods for using same. The gelled compositions may be liquid organic fluids, such as gelled liquid hydrocarbons, formed from a mixture of an organic-base fluid, a carboxylic acid, and one or more metal source compounds, such as a metal salt of carboxylic acid. The gelled compositions may be used in variety of applications including, but not limited to, oil field, pipeline and processing facility applications.
Owner:BJ SERVICES LLC +1
Reactive oligomers for isocyanate coatings
InactiveUS6221494B1Extended shelf lifeHigh glossAluminium compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsEpoxyOligomer
The invention is directed to a two-pack solvent-based ambient curable coating composition comprising a binder of a hydroxyl and crosslinking components. The hydroxyl component includes a linear or branched cycloaliphatic moiety-containing reactive oligomer or blend of oligomers with a weight average molecular weight not exceeding 3,000, a polydispersity not exceeding about 1.7 with at least 2 hydroxyl groups, at least 1, on average, being a primary hydroxyl group. The reactive oligomer is formed by the reaction of an oligomeric acid with monofunctional epoxy. The crosslinking component includes one or more of an oligomeric crosslinker containing at least 2 isocyanate groups. The coating composition of the invention is particularly suited in automotive refinish coatings.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Foodstuff
InactiveUS20050079244A1Promoting growth and activityImprove balanceMilk preparationDigestive systemBiologyGastrointestinal tract
The present invention relates to a foodstuff which comprises colostrum, a probiotic and a prebiotic. The triple combination of colostrum, a probiotic and a prebiotic is particularly beneficial for the gastrointestinal tract and health of animals.
Owner:MARS INC
Bag-in-container with prepressurized space between inner bag and outer container
InactiveUS20110248035A1Extended shelf lifeLarge containersLinings/internal coatingsEngineeringControl space
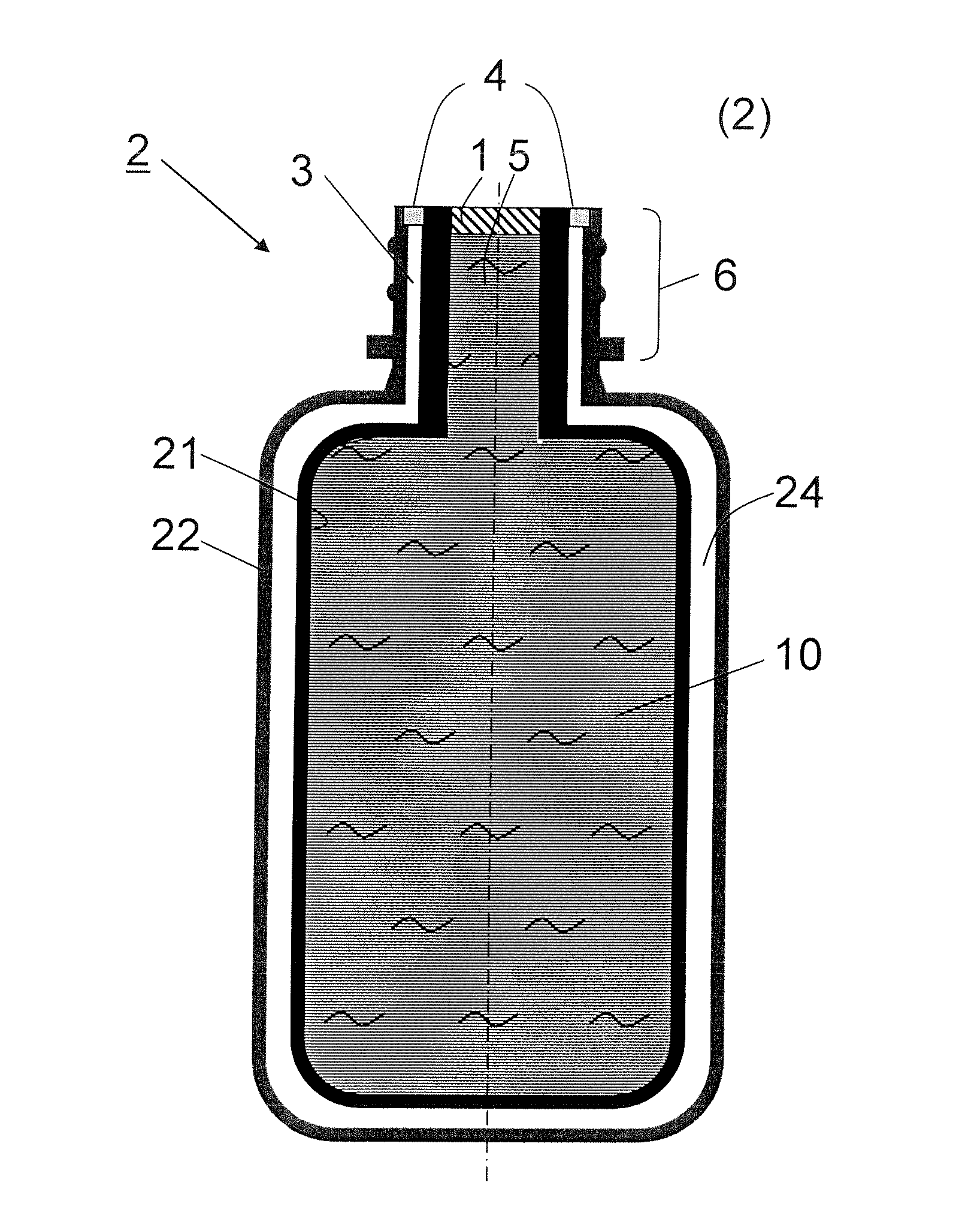
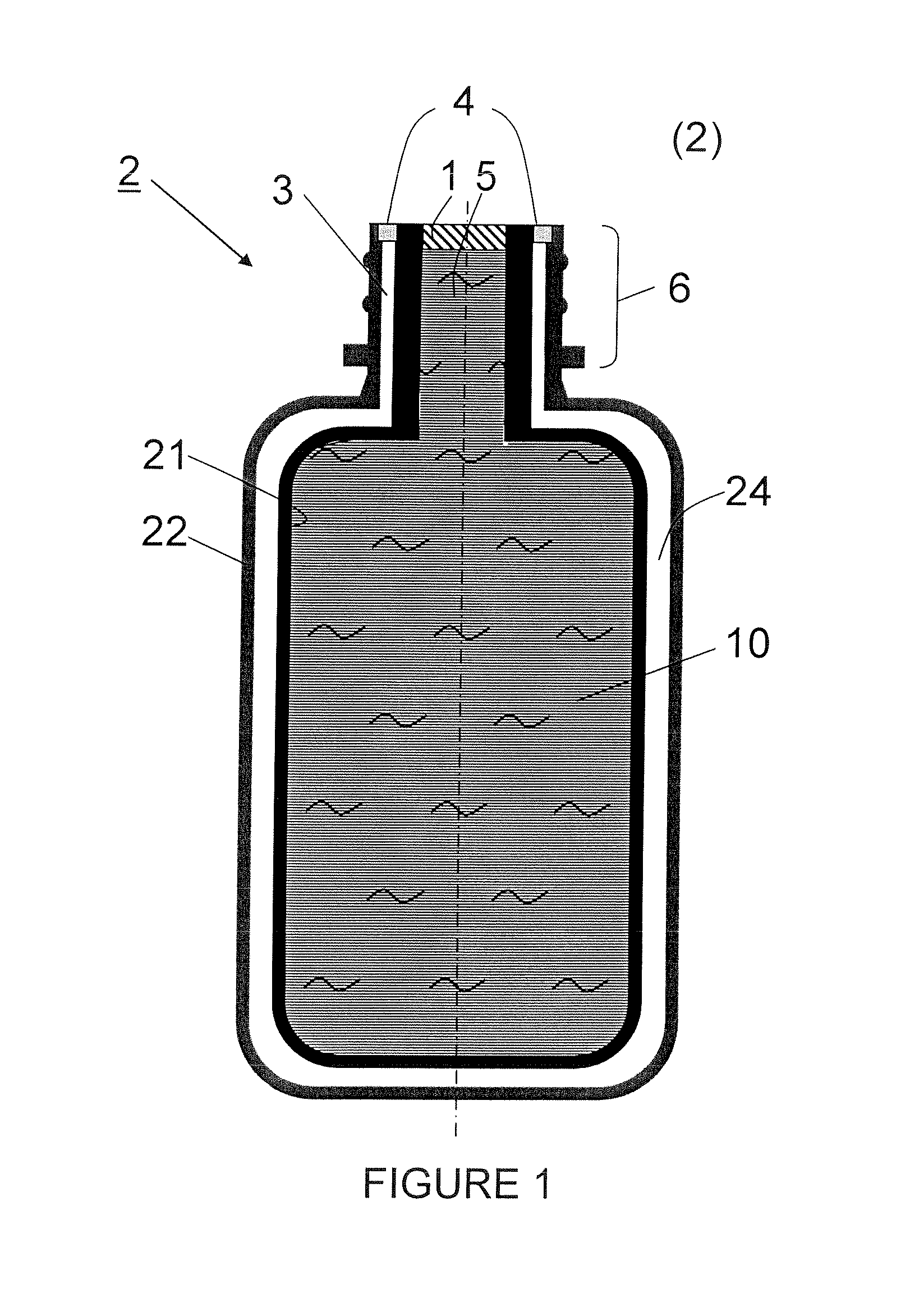
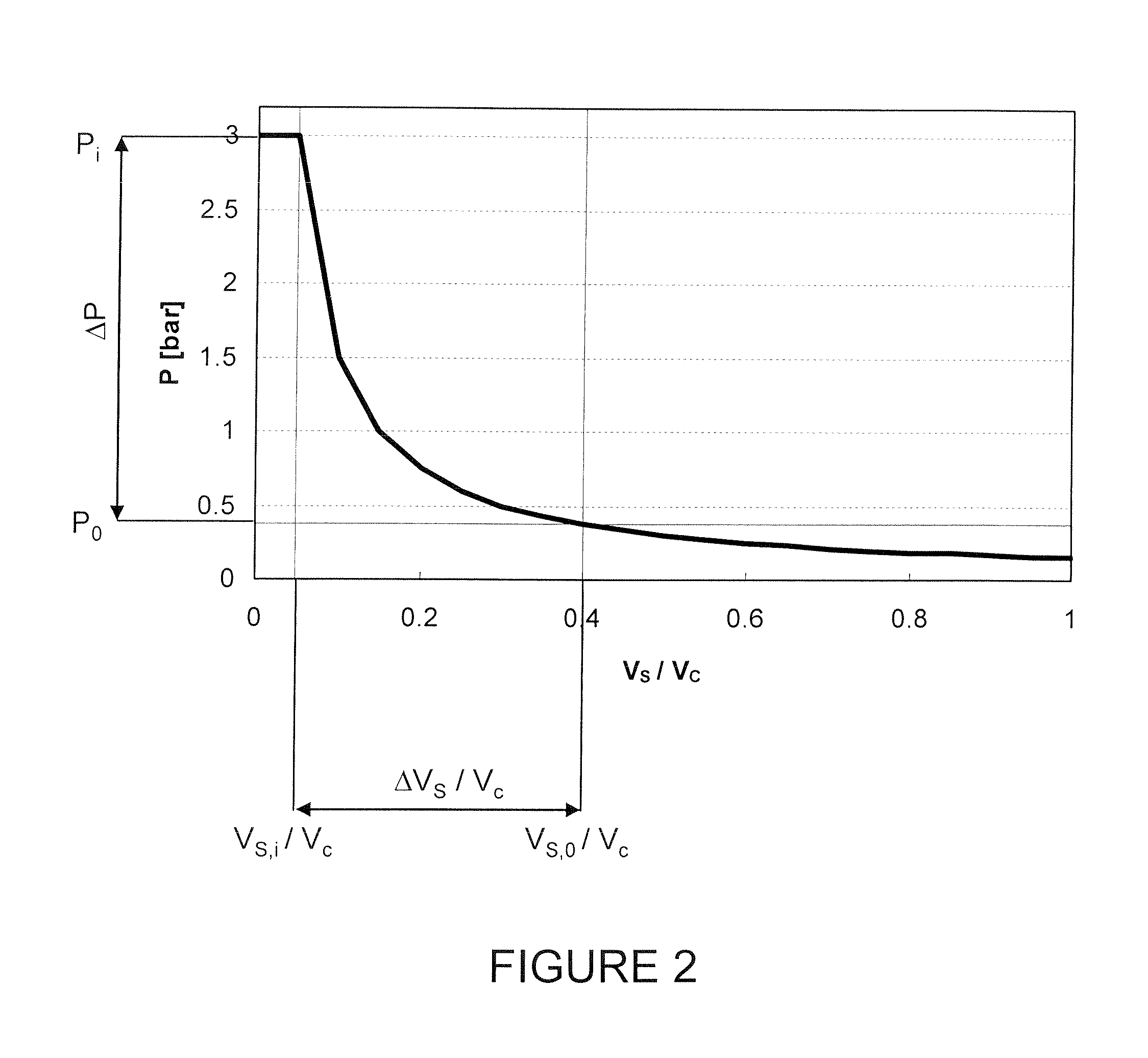
Bag-in-container having an inner layer forming a bag filled with a fluid, the bag being separatable from an outer layer forming the container. The bag-in-container has a mouth fluidly connecting the volume defined by the bag to the atmosphere and separated therefrom by a seal. The container further having at least one space vent fluidly connecting the space between inner and outer layers and to the atmosphere. A vent provides a closure to control the gas flow between the space and the atmosphere. The space contains an amount of gas (Vs,i) at a pressure (Pi) insufficient to compress the bag to drive out more than 80% of the fluid contained therein. The present invention also concerns a kit of parts including a bag-in-container and a dispensing appliance.
Owner:ANHEUSER BUSCH INBEV SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com