Patents
Literature
1342 results about "Skull" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
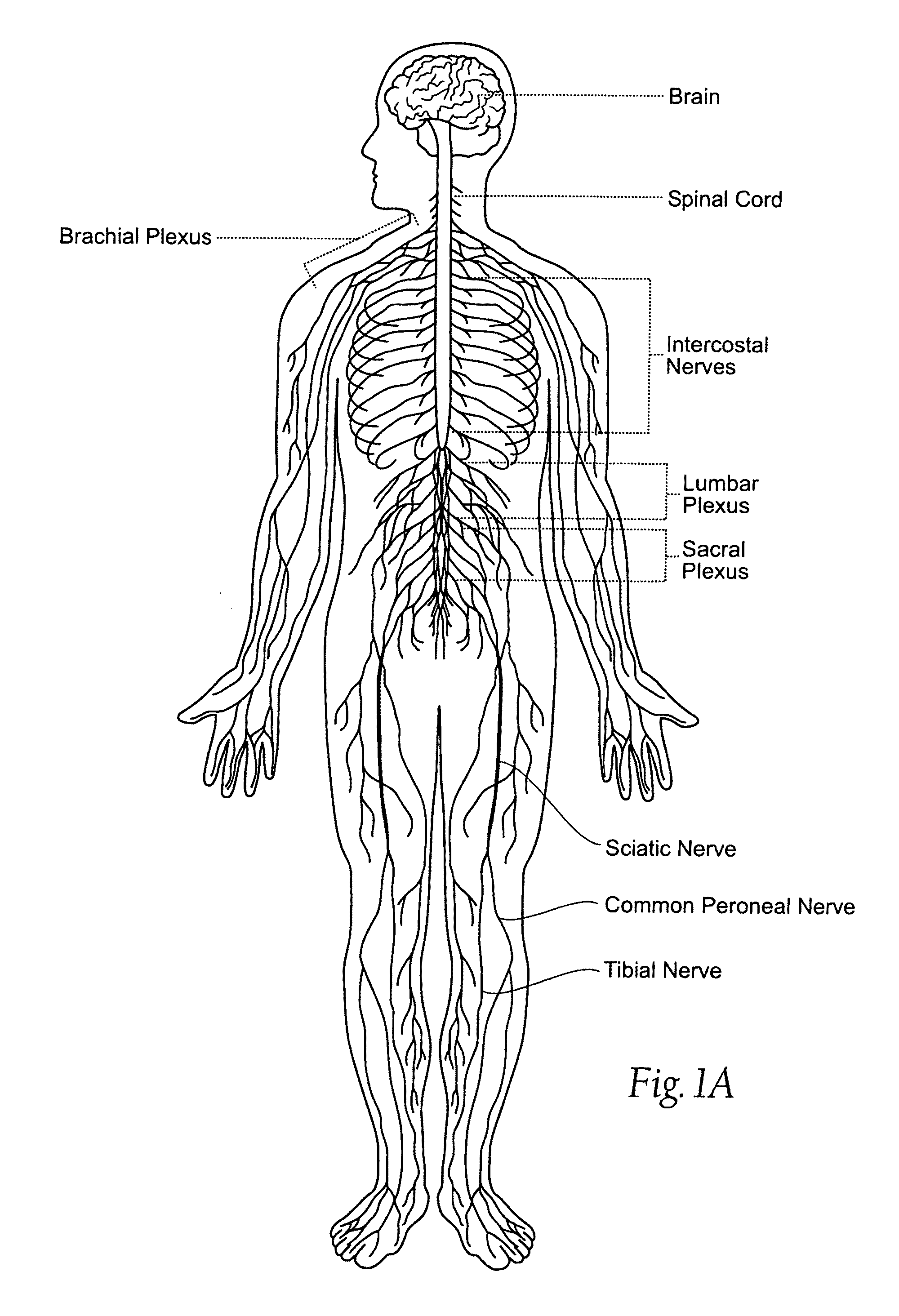
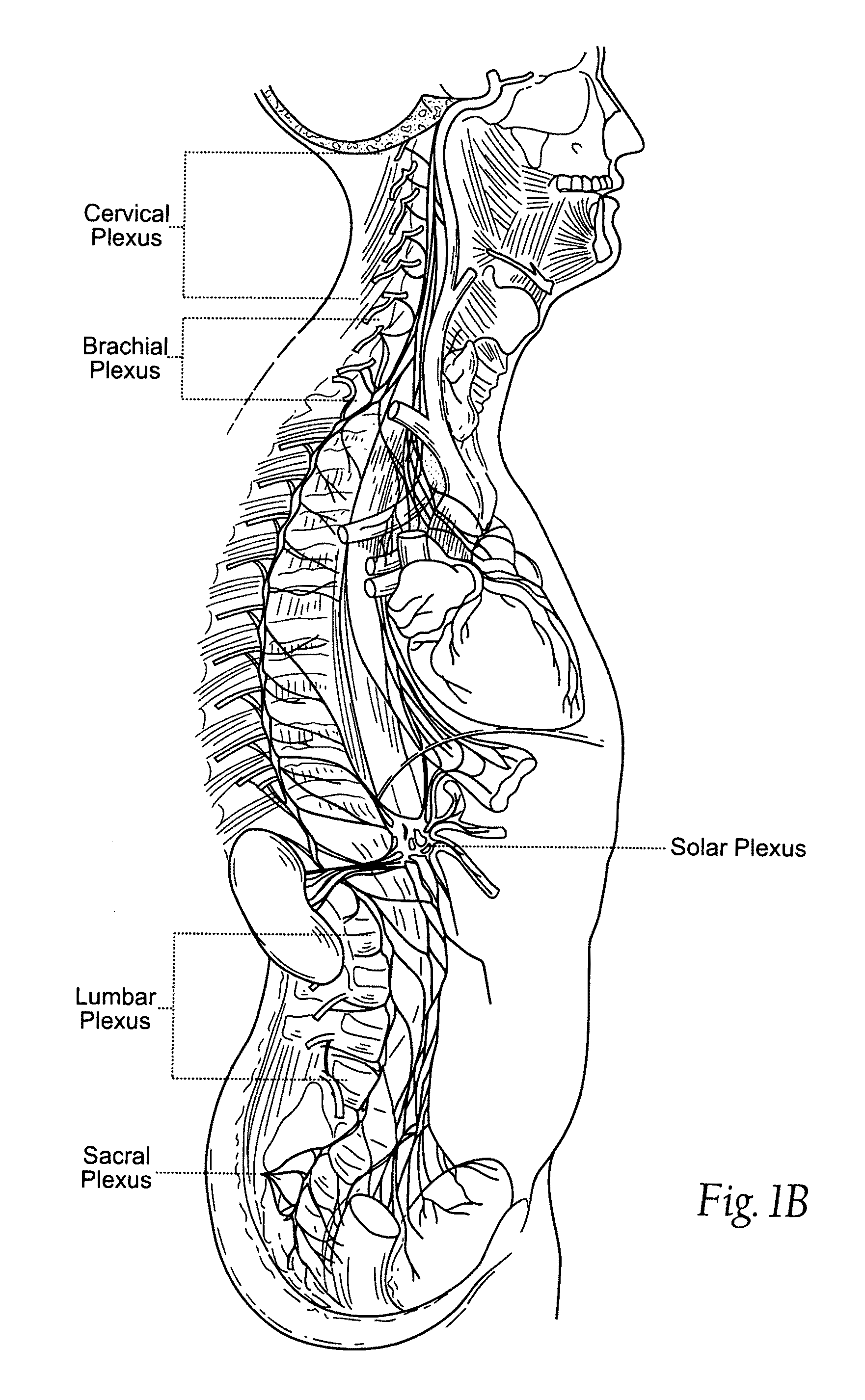
The skull is a bony structure that forms the head in vertebrates. It supports the structures of the face and provides a protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium or facial skeleton that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton.
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
InactiveUS20060106381A1Effective treatmentPermit flexionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnDevice form
Surgical implants are configured for placement posteriorly to a spinal canal between vertebral bodies to distract the spine and enlarge the spinal canal. In the preferred embodiments the device permits spinal flexion while limiting spinal extension, thereby providing an effective treatment for treating spinal stenosis without the need for laminectomy. The invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. Numerous embodiments are disclosed, including elongated, length-adjustable components coupled to adjacent vertebral bodies using pedicle screws. The preferred embodiments, however, teach a device configured for placement between adjacent vertebral bodies and adapted to fuse to the lamina, facet, spinous process or other posterior elements of a single vertebra. Various mechanisms, including shape, porosity, tethers, and bone-growth promoting substances may be used to enhance fusion. The tether may be a wire, cable, suture, or other single or multi-filament member. Preferably, the device forms a pseudo-joint in conjunction with the non-fused vertebra. Alternatively, the device could be fused to the caudal vertebra or both the cranial and caudal vertebrae.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Technique for using heat flow management to treat brain disorders
InactiveUS6248126B1Prevent and reduce occurrenceModulates seizureImplantable neurostimulatorsSurgical instruments for heatingDiseaseBrain section
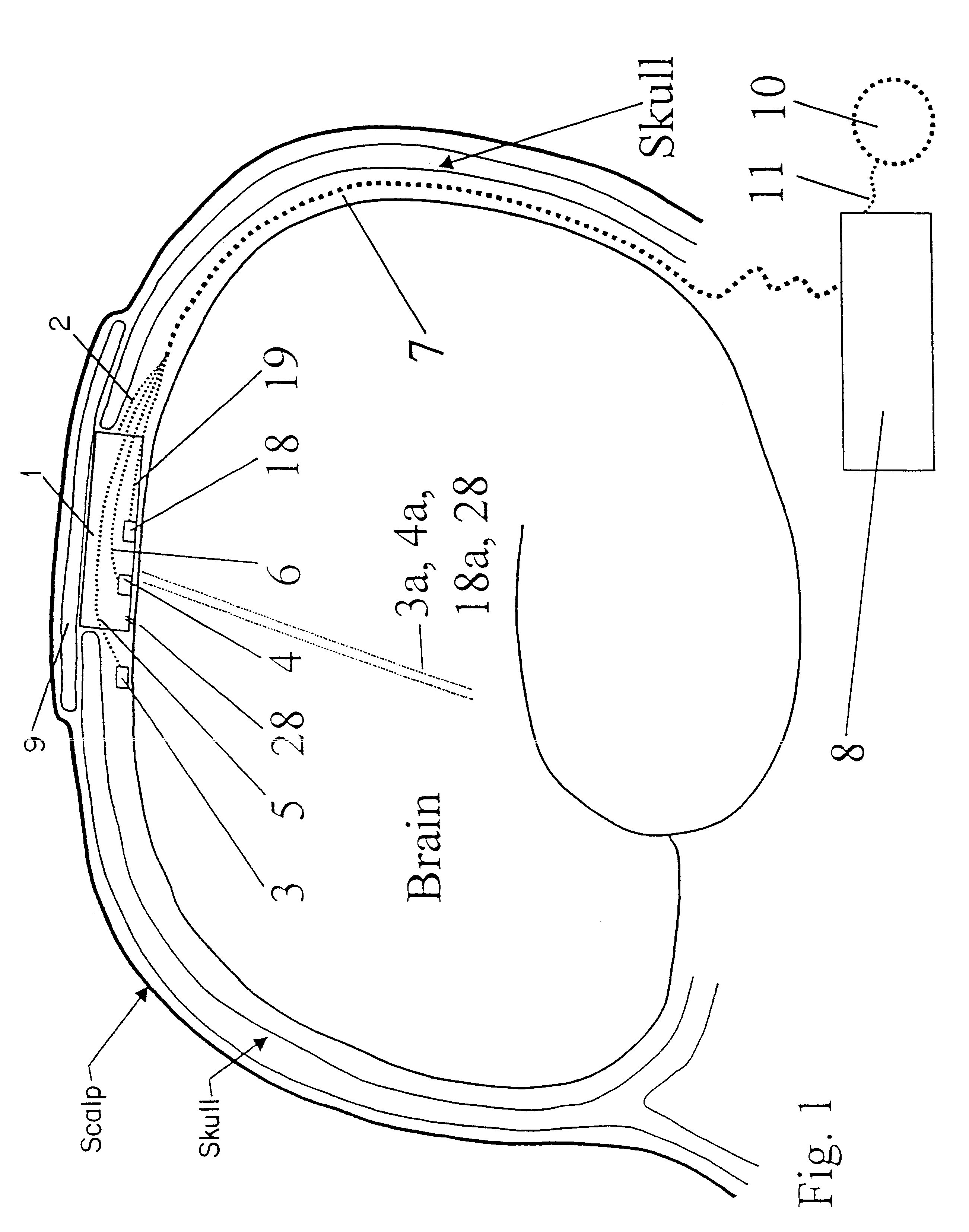
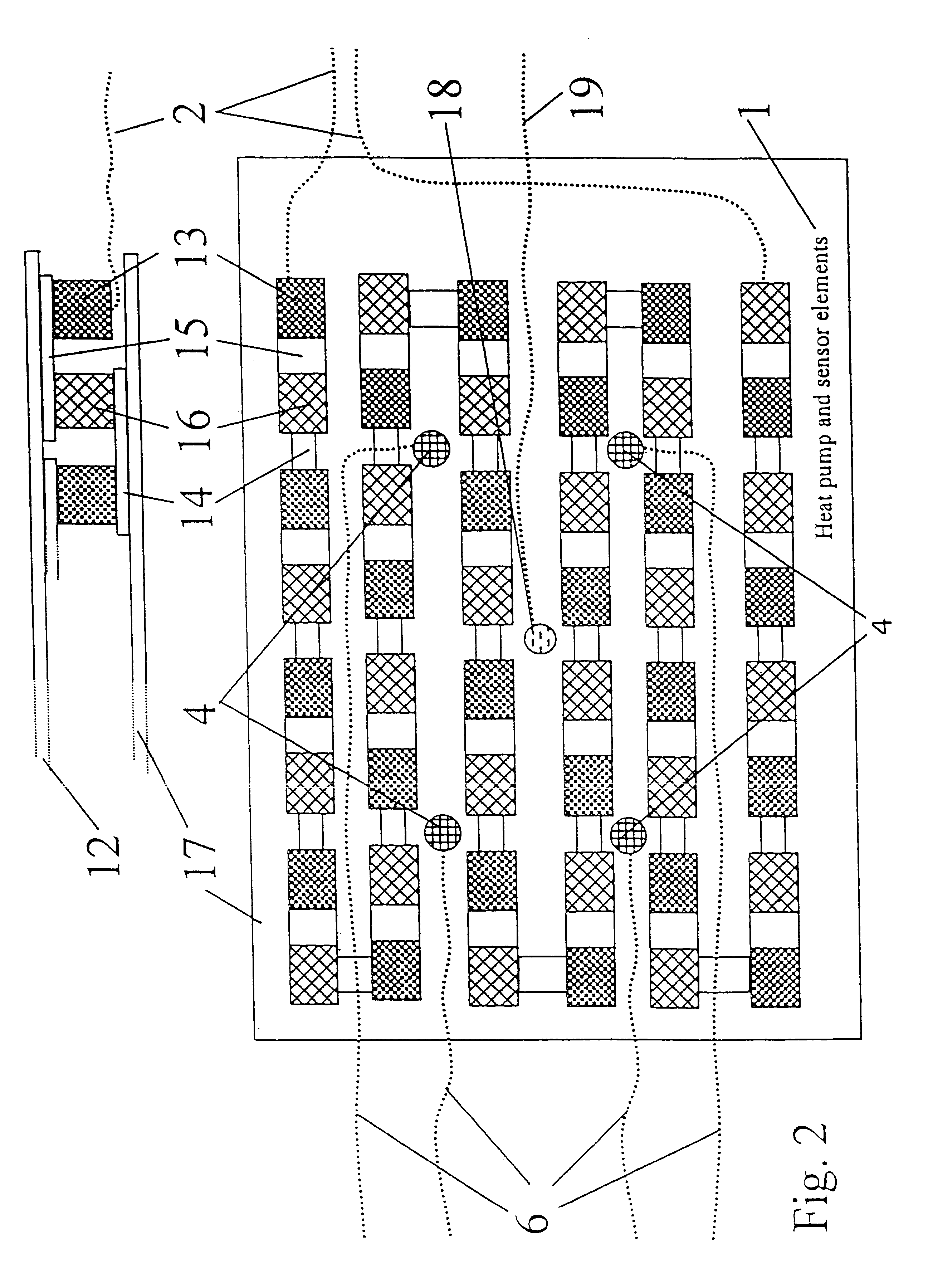
A method of treating a brain disorder by heat transfer from brain tissue comprising the steps of surgically cutting a heat transfer aperture into a patient's skull, thereby exposing a predetermined portion of patient's brain; surgically implanting into said heat transfer aperture a heat pump having one or more electrical sensor elements and one or more temperature sensor elements; surgically implanting a heat transfer management unit in a body cavity of said patient such that a micro controller of the heat transfer management unit is connected to one or more activity sensor elements and one or more temperature sensor elements contacting brain tissue and connecting the heat transfer management unit to said heat pump via a lead bundle. Optionally, the heat transfer unit may be located external to the patient's body. Responsive to signals from one or more activity or temperature sensor elements, mathematical algorithms of the heat transfer management unit determine abnormal brain activity, causing the heat pump to remove heat from the brain tissue into a heat sink, thereby cooling the predetermined portion of the patient's brain. This technique utilizes acute hypothermia by means of a Peltier cooler or similar device to cool the brain temperature to reduce or prevent seizure initiation and / or propagation. The method may be used in association with brain stimulation and / or drug application to acutely avoid the occurrence of a seizure episode.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Treatment of epilepsy by brain stimulation
InactiveUS7003352B1Small sizeInhibition amountElectrotherapyPressure infusionMedicineElectrical stimulations
Introducing one or more stimulating drugs to the brain and / or applying electrical stimulation to the brain is used to treat epilepsy. At least one implantable system control unit (SCU) produces electrical pulses delivered via electrodes implanted in the brain and / or drug infusion pulses delivered via a catheter implanted in the brain. The stimulation is delivered to targeted brain structures to adjust the activity of those structures. The small size of the SCUs of the invention allow SCU implantation directly and entirely within the skull and / or brain. Simplicity of the preferred systems and methods and compactness of the preferred system are enabled by the modest control parameter set of these SCU, which do not require or include a sensing feature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Devices and methods using an implantable pulse generator for brain stimulation
A device for brain stimulation includes a lead having a longitudinal surface; at least one stimulation electrode disposed along the longitudinal surface of the lead; at least one recording electrode, separate from the at least one stimulation electrode, disposed on the lead; and an implantable pulse generator coupled to the at least one stimulation electrode. In some instances, the implantable pulse generator can be implanted into a burr hole in the skull made for insertion of the lead into the brain.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
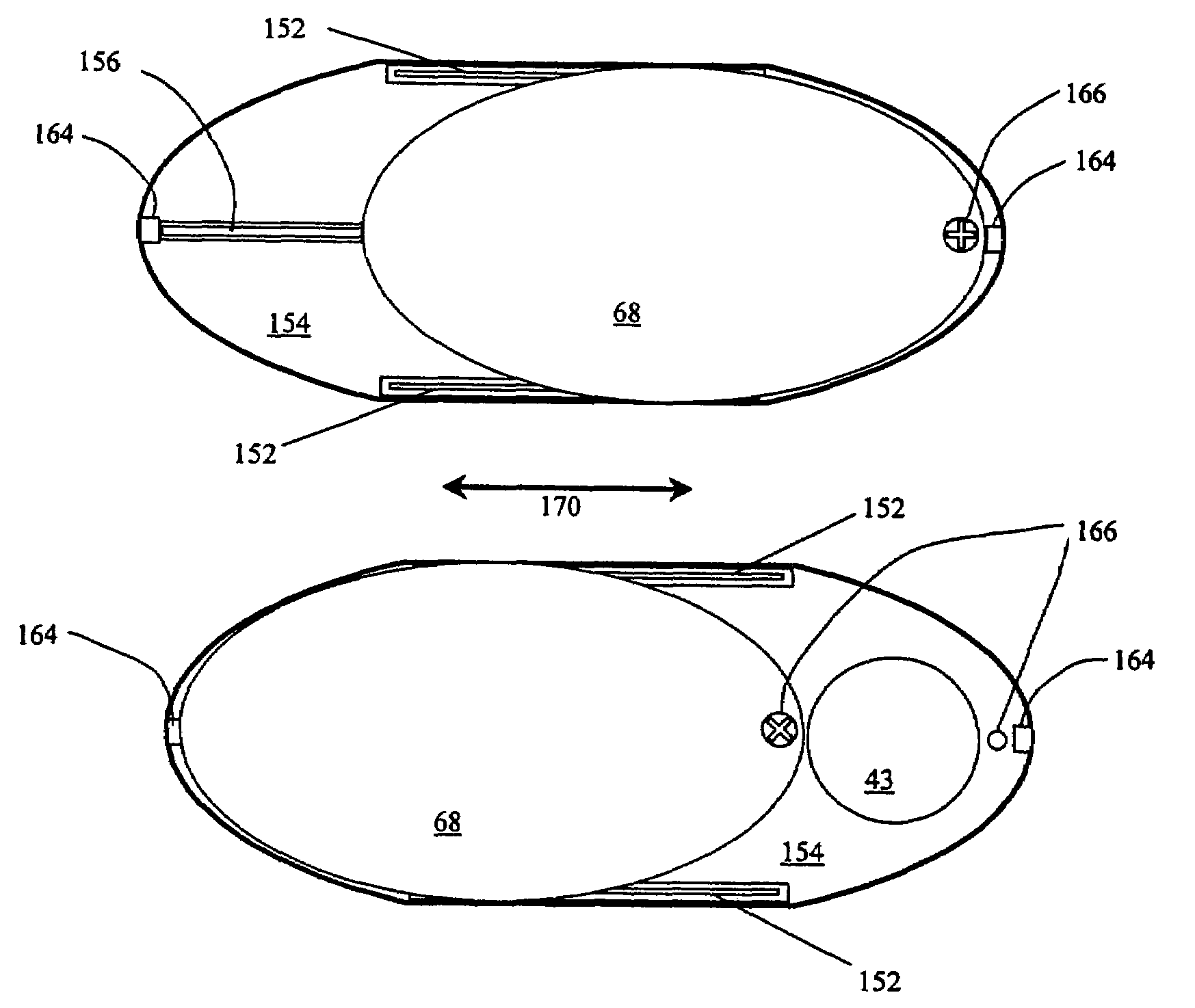
Skull-mounted electrical stimulation system and method for treating patients
ActiveUS20060293723A1Extension of timeMinimal discomfortHead electrodesMedical devicesDrugs infusionClosed loop
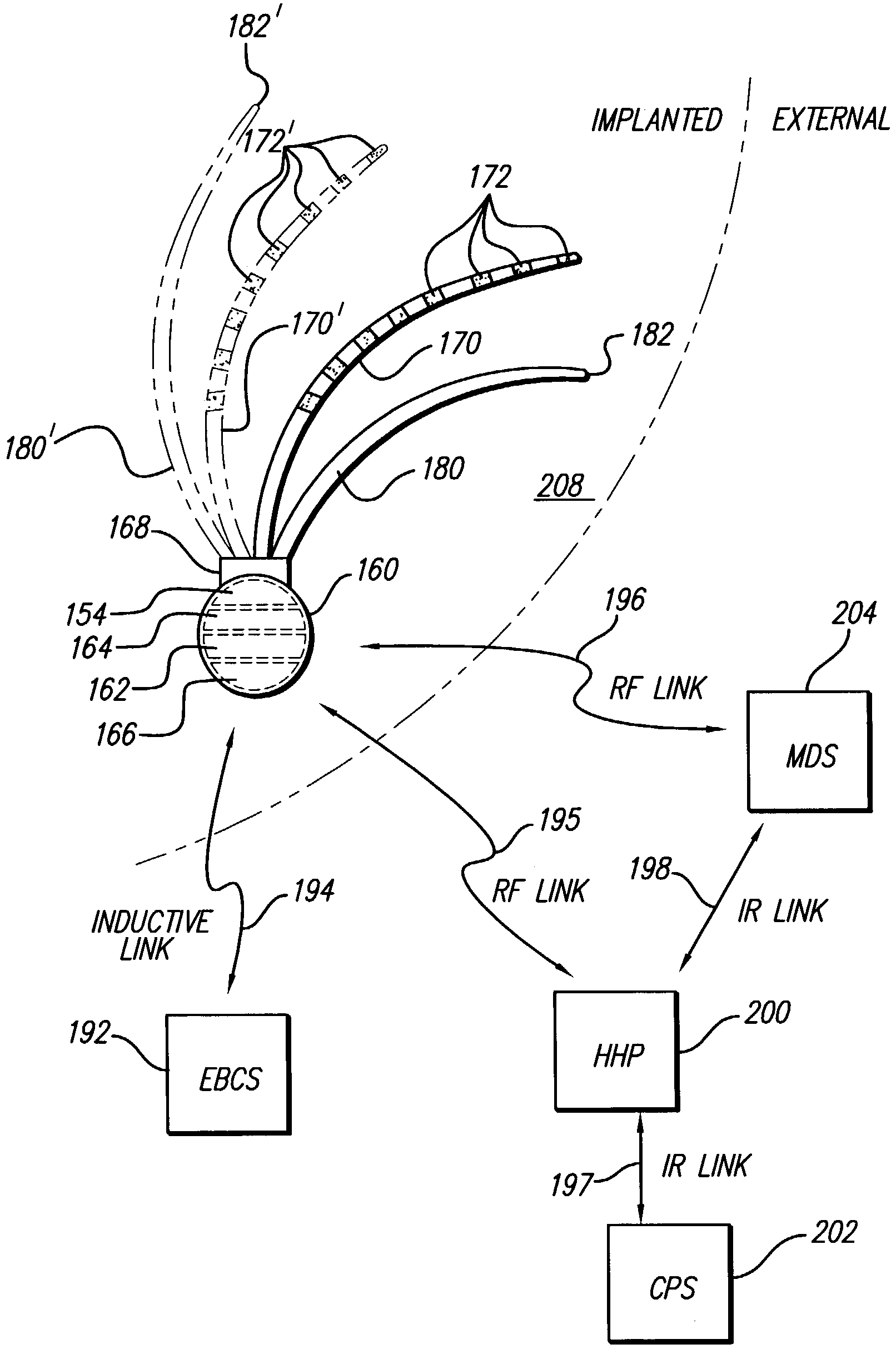
A system and method for applying electrical stimulation or drug infusion to nervous tissue of a patient to treat epilepsy, movement disorders, and other indications uses at least one implantable system control unit (SCU) (110), including an implantable signal / pulse generator (IPG) and one or more electrodes (152, 152′). The IPG is implanted in the mastoid area (143) of the skull (140) and communicates with at least one external appliance (230), such as a Behind-the-Ear (BTE) unit (100). In a preferred embodiment, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one SCU includes a sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method for modelling customised earpieces
InactiveUS20040107080A1Easy to placeAdditive manufacturing apparatusHearing aid design aspectsSpeech identificationHeadphones
The present invention relates to a method for computer-controlled modelling of customised earpieces. These earpieces include housings for hearing aids, wireless or connected communication devices (headsets, mobile phones, personal agents), loud speakers, tinnitus masking devices, devices recording vibrations in the skull and transforming these into audio signals, voice recognition devices, earplugs, noise blockers with selective frequencies or sound levels, Man Machine Interface (MMI) products that enable clear communication even in the noisiest environments, or products related to wireless Internet applications. All these earpieces may be worn in the user's meatus and / or auditory canal. The invention also relates to a computerised system for manufacturing such customised earpieces. In particular, the invention is directed to a computerised system that models an earpiece based on a three-dimensional replica of the user's meatus and / or auditory canal.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
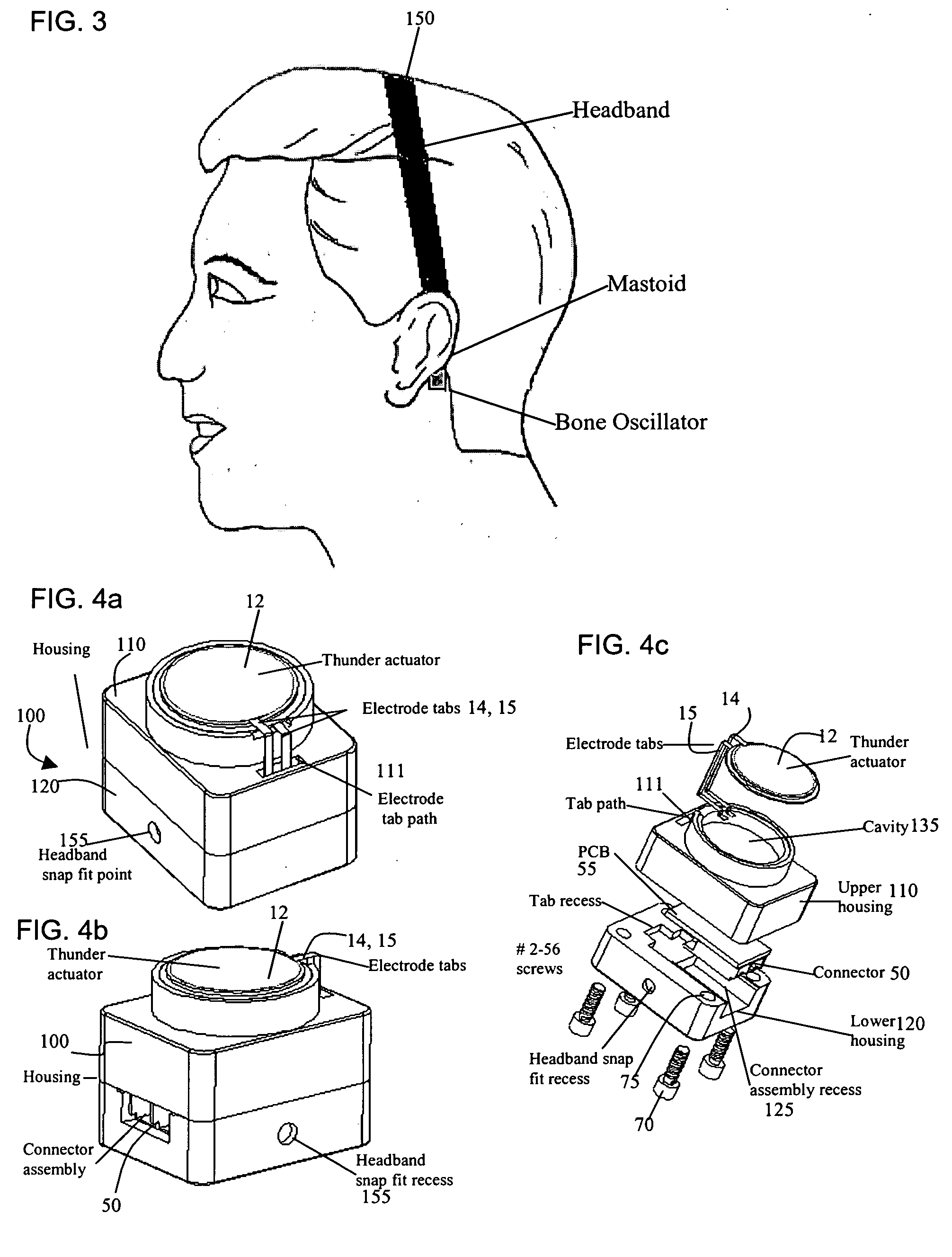
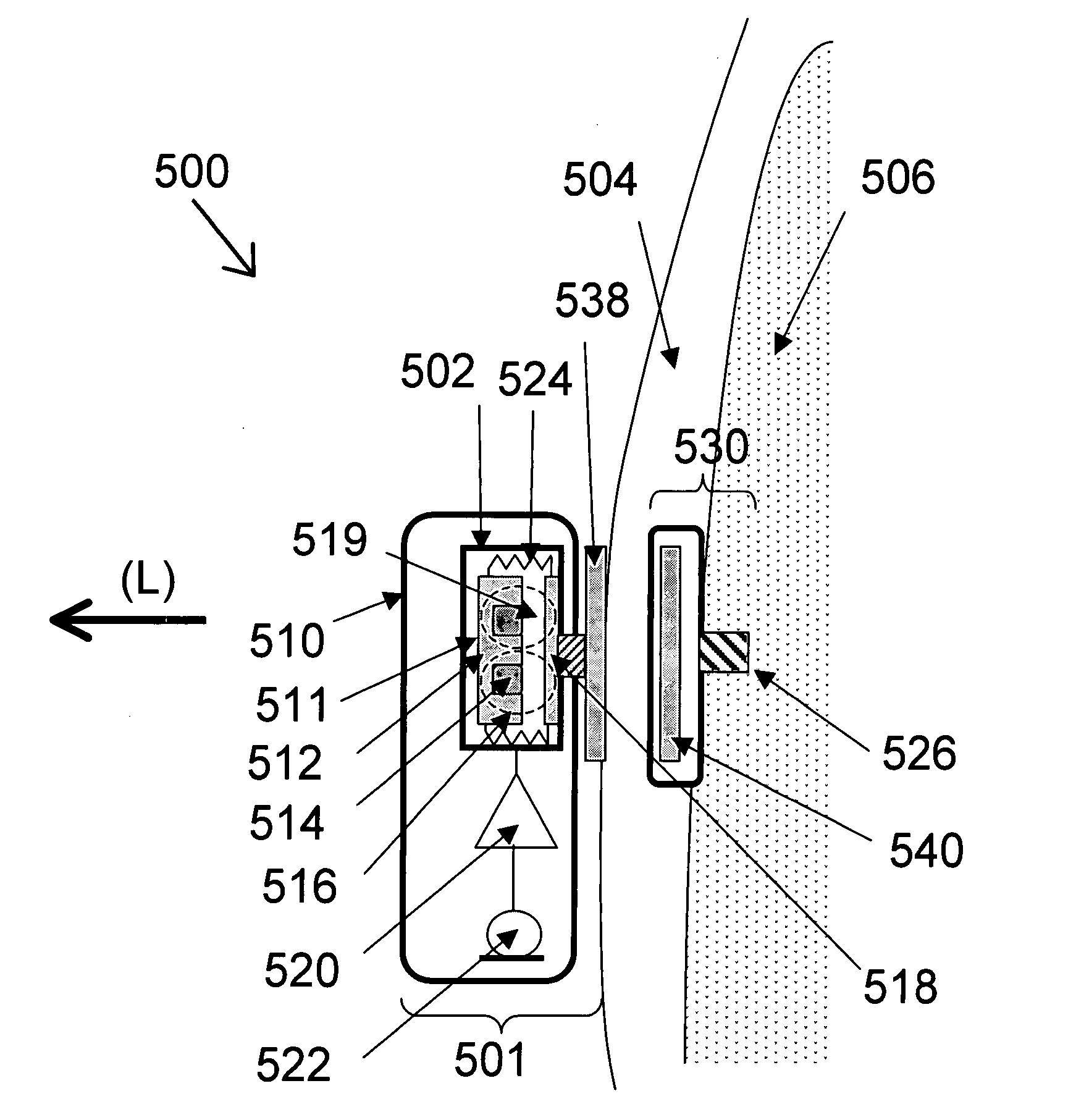
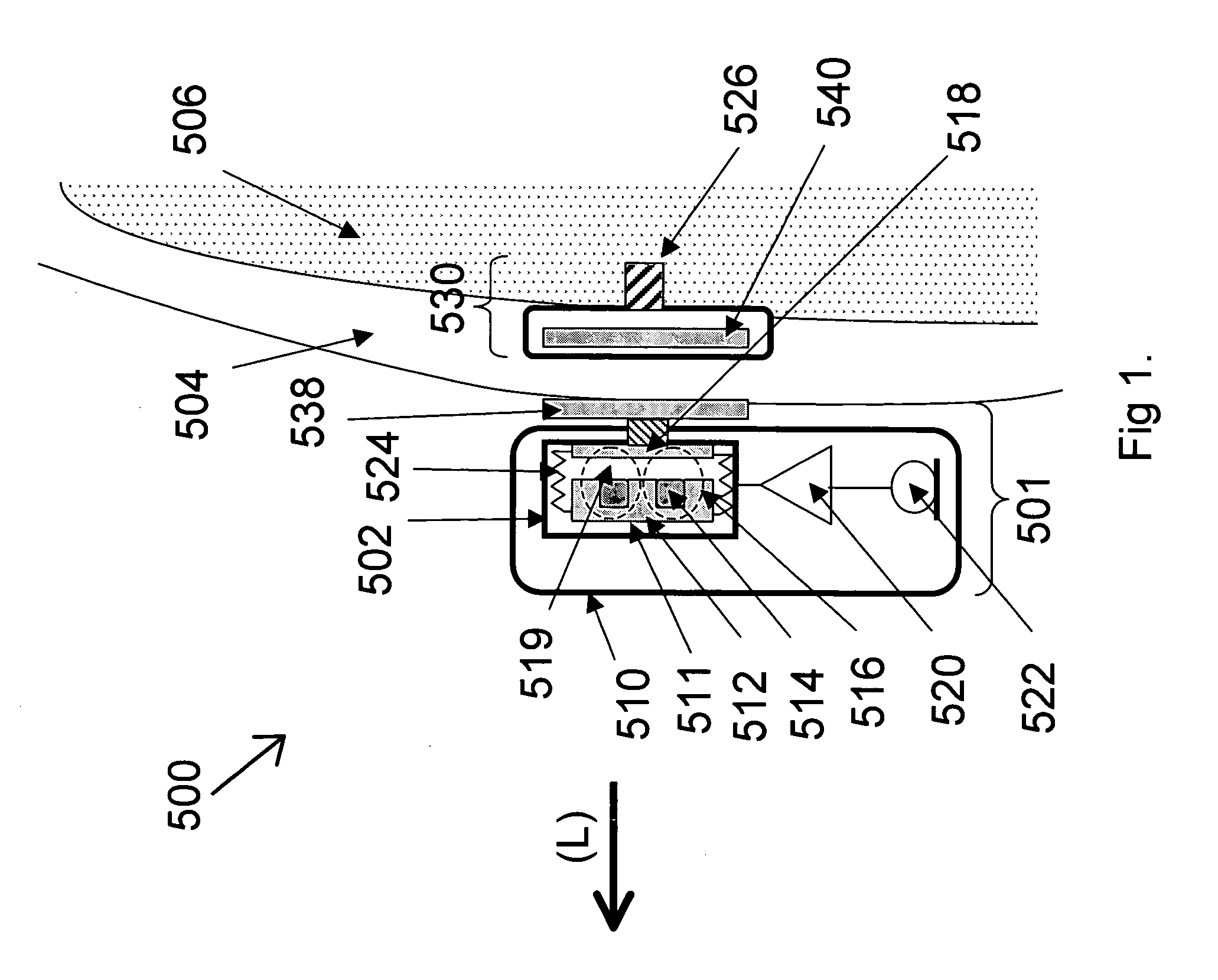
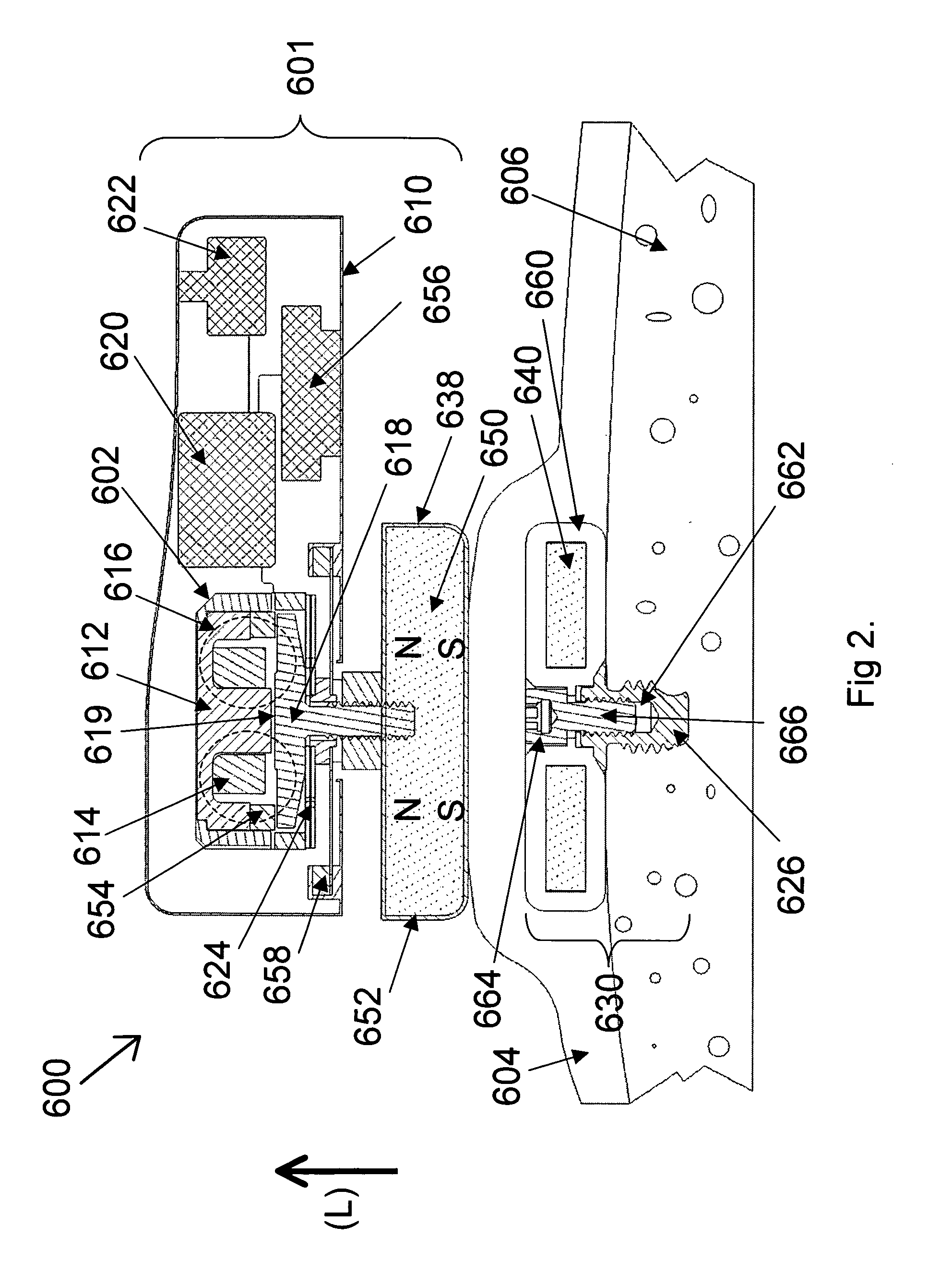
Bone-conduction hearing-aid transducer having improved frequency response
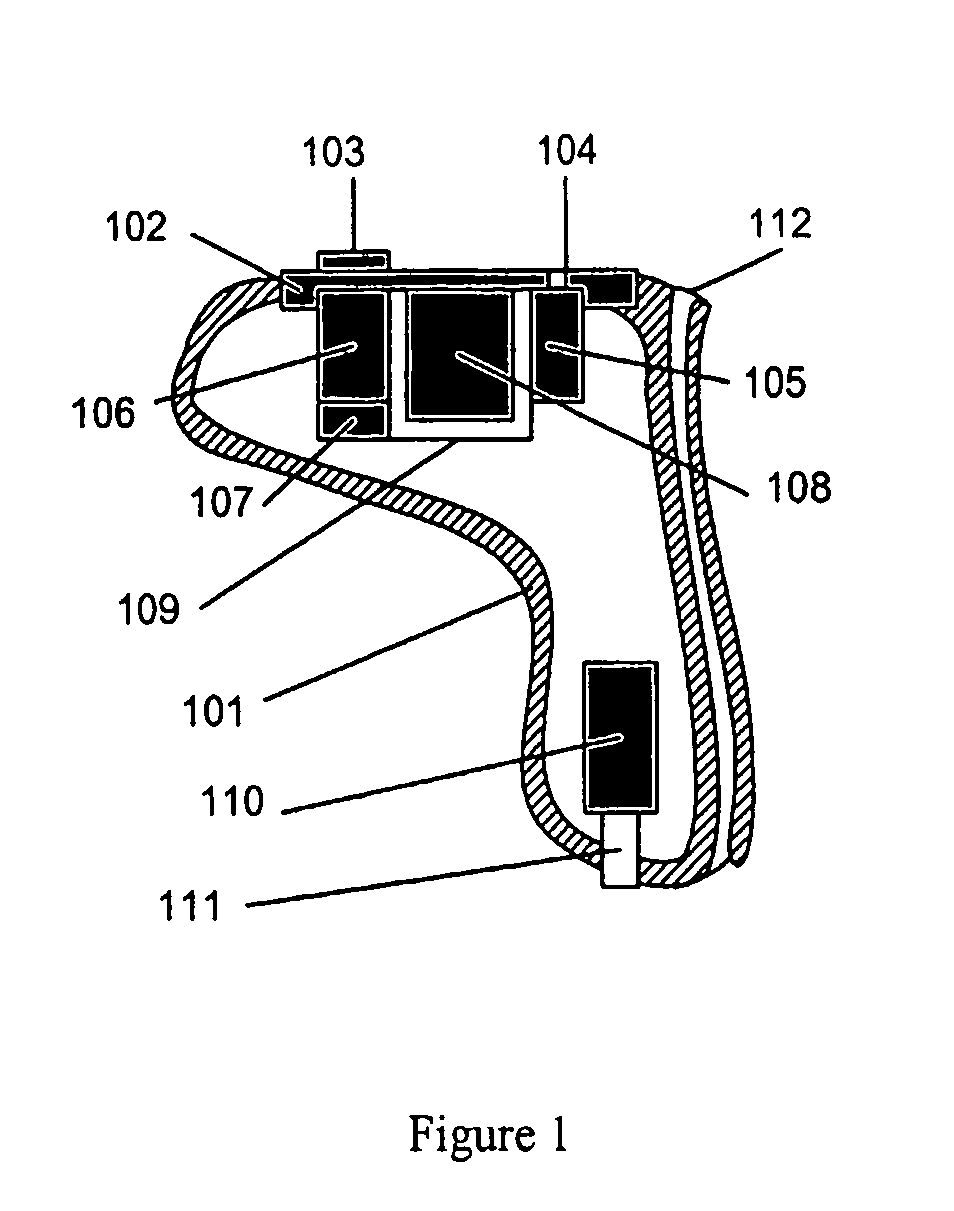
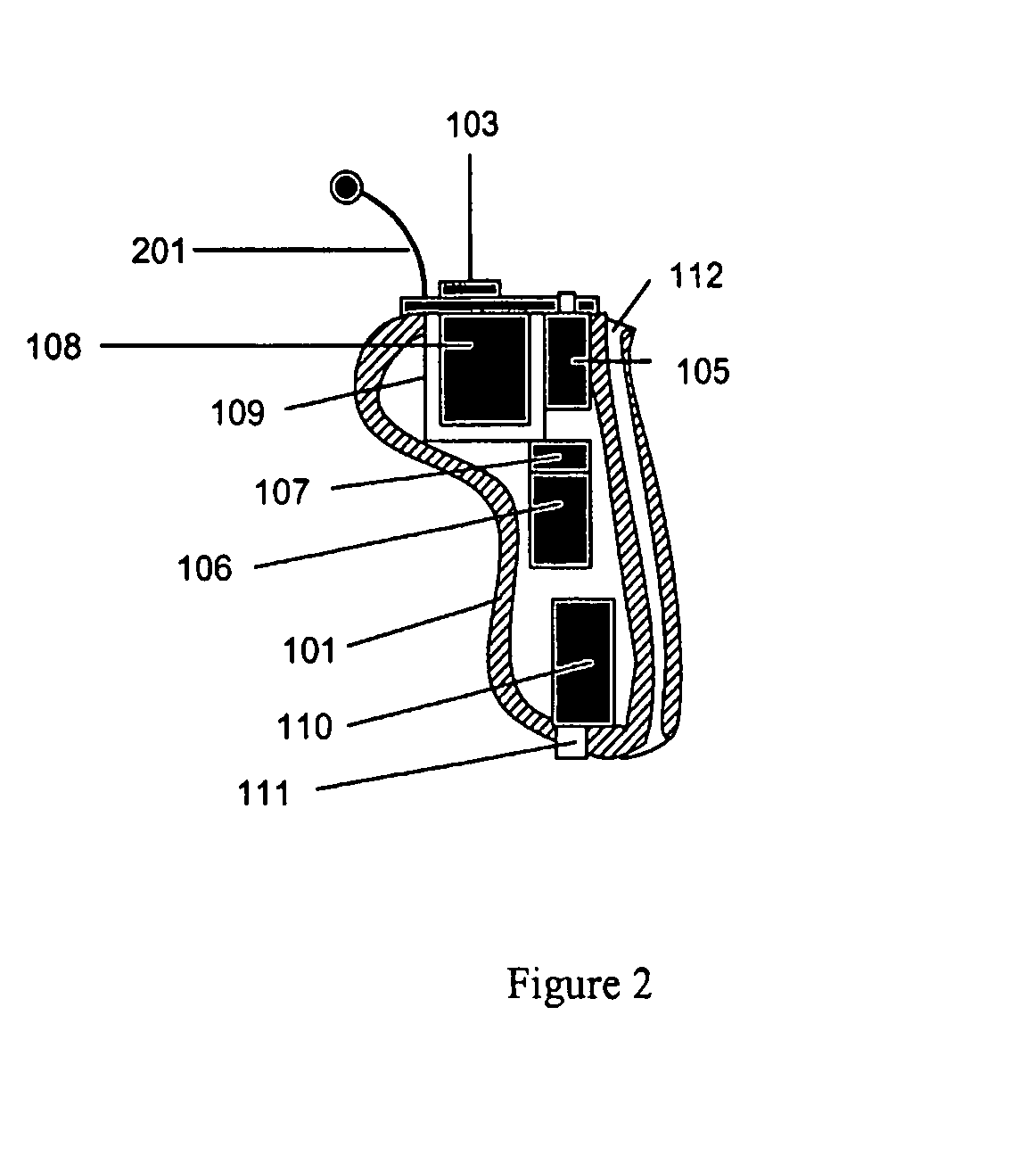
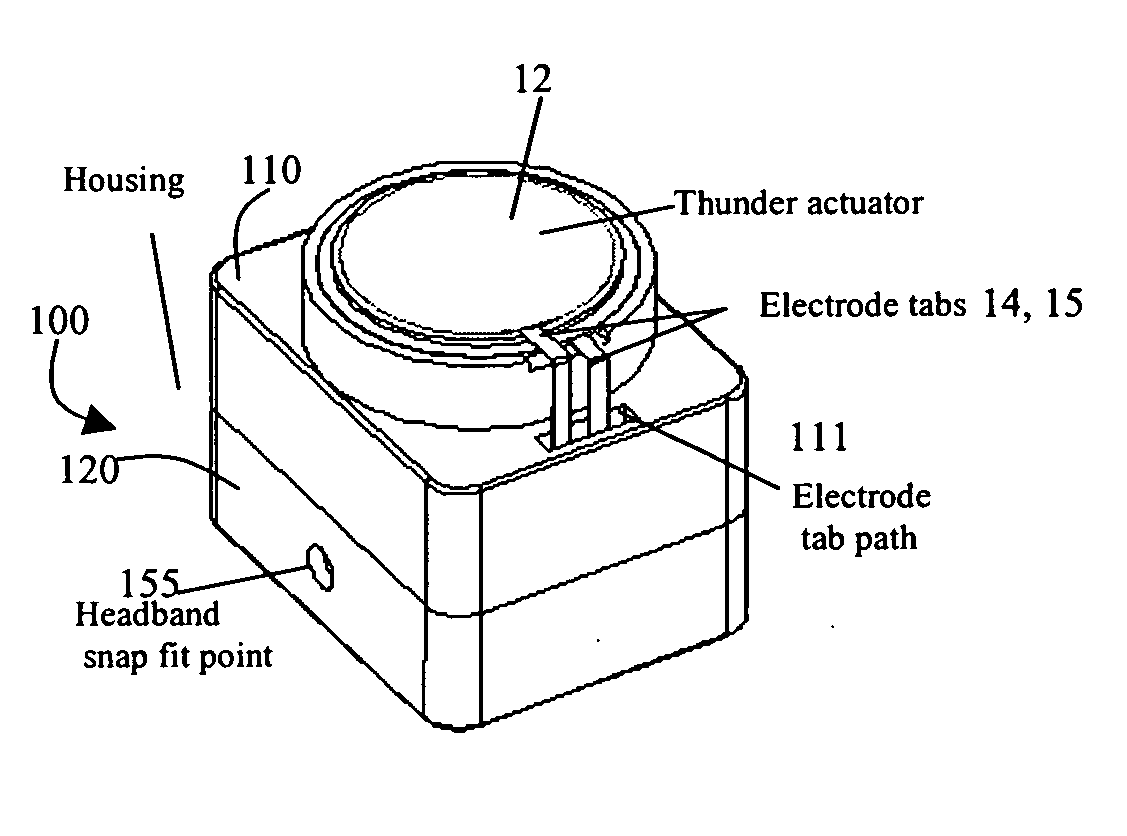
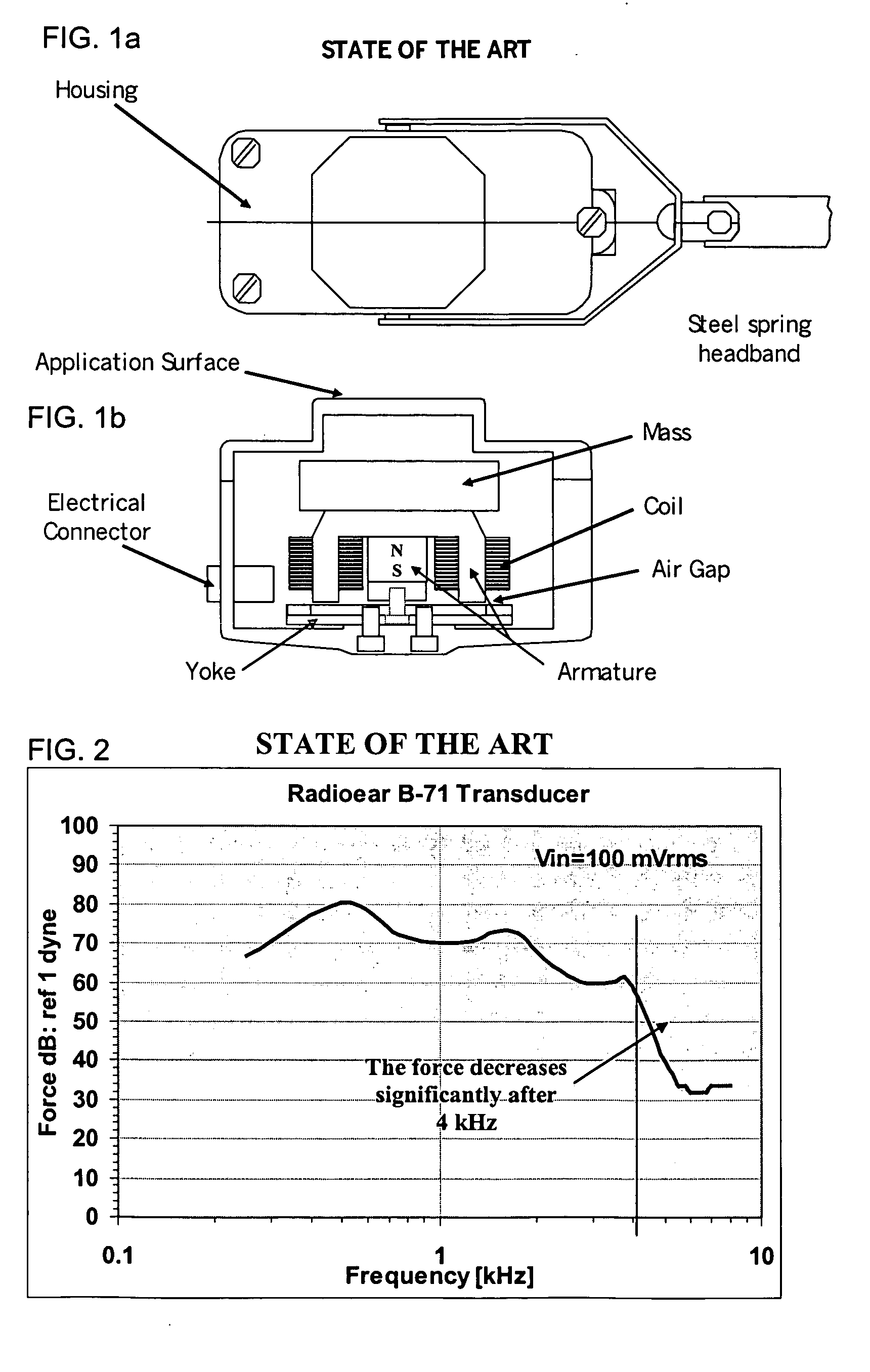
InactiveUS20070041595A1Eliminates soldering wireEliminate useRecord carriersPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersFrequency spectrumBone structure
A hearing-aid device and a method for transmitting sound through bone conduction are disclosed. The hearing-aid device comprises a piezoelectric-type actuator, housing and connector. The piezoelectric actuator is preferably a circular flextensional-type actuator mounted along its peripheral edge in a specifically designed circular structure of the housing. During operation, the bone-conduction transducer is placed against the mastoid area behind the ear of the patient. When the device is energized with an alternating electrical voltage, it flexes back and forth like a circular membrane sustained along its periphery and thus, vibrates as a consequence of the inverse piezoelectric effect. Due to the specific and unique designs proposed, these vibrations are directly transferred trough the human skin to the bone structure (the skull) and provide a means for the sound to be transmitted for patients with hearing malfunctions. The housing acts as a holder for the actuators, as a pre-stress application platform, and as a mass which tailors the frequency spectrum of the device. The apparatus exhibits a performance with a very flat response in the frequency spectrum 200 Hz to 10 kHz, which is a greater spectrum range than any other prior art devices disclosed for bone-conduction transduction which are typically limited to less than 4 kHz.
Owner:FACE INT
Hearing aid system
InactiveUS20070053536A1Easy to changeLittle strengthBone conduction transducer hearing devicesDeaf-aid setsSkin contactEngineering
A bone conduction hearing aid system for generating bone conduction vibrations is disclosed. The bone conduction hearing aid system has an external hearing aid unit with a vibrator and a skin contact pressure plate. The skin contact pressure plate is placed on an outside of the external hearing aid unit and the skin contact pressure plate is magnetically attached to an implanted unit anchored to the skull under the skin. The vibrator transforms an electrical signal into mechanical vibrations and the skin contact pressure plate allows transmission of the vibrations from the vibrator to the implanted unit when the external hearing aid unit is magnetically fixed to the implanted unit.
Owner:OTICON
Device for multicentric brain modulation, repair and interface
InactiveUS20080154331A1Implanted easily and effectivelyShorten the timeHead electrodesExternal electrodesSurgical operationMedicine
A brain stimulation device, including: a cranial chip that is configured to be surgically implanted between a patient's scalp and skull; at least three stimulation leads connected to the cranial chip, wherein each lead has a plurality of stimulation electrodes thereon; control circuitry in the cranial chip for controlling the operation of the stimulation leads and stimulation electrodes; and a power source in the cranial chip for powering the simulation leads and the stimulation electrodes and the control circuitry.
Owner:E SOC +1
Biological interface systems with wireless connection and related methods
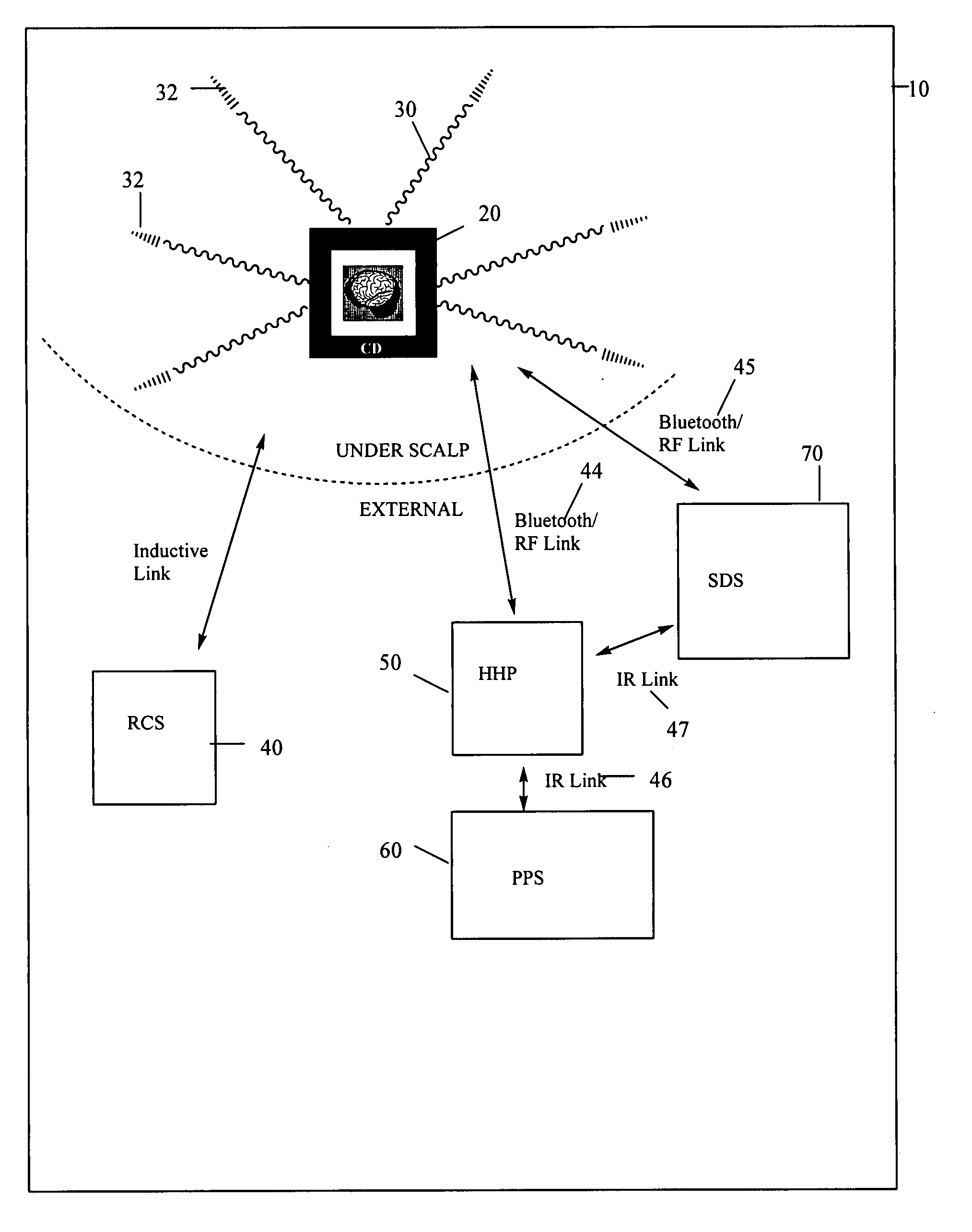
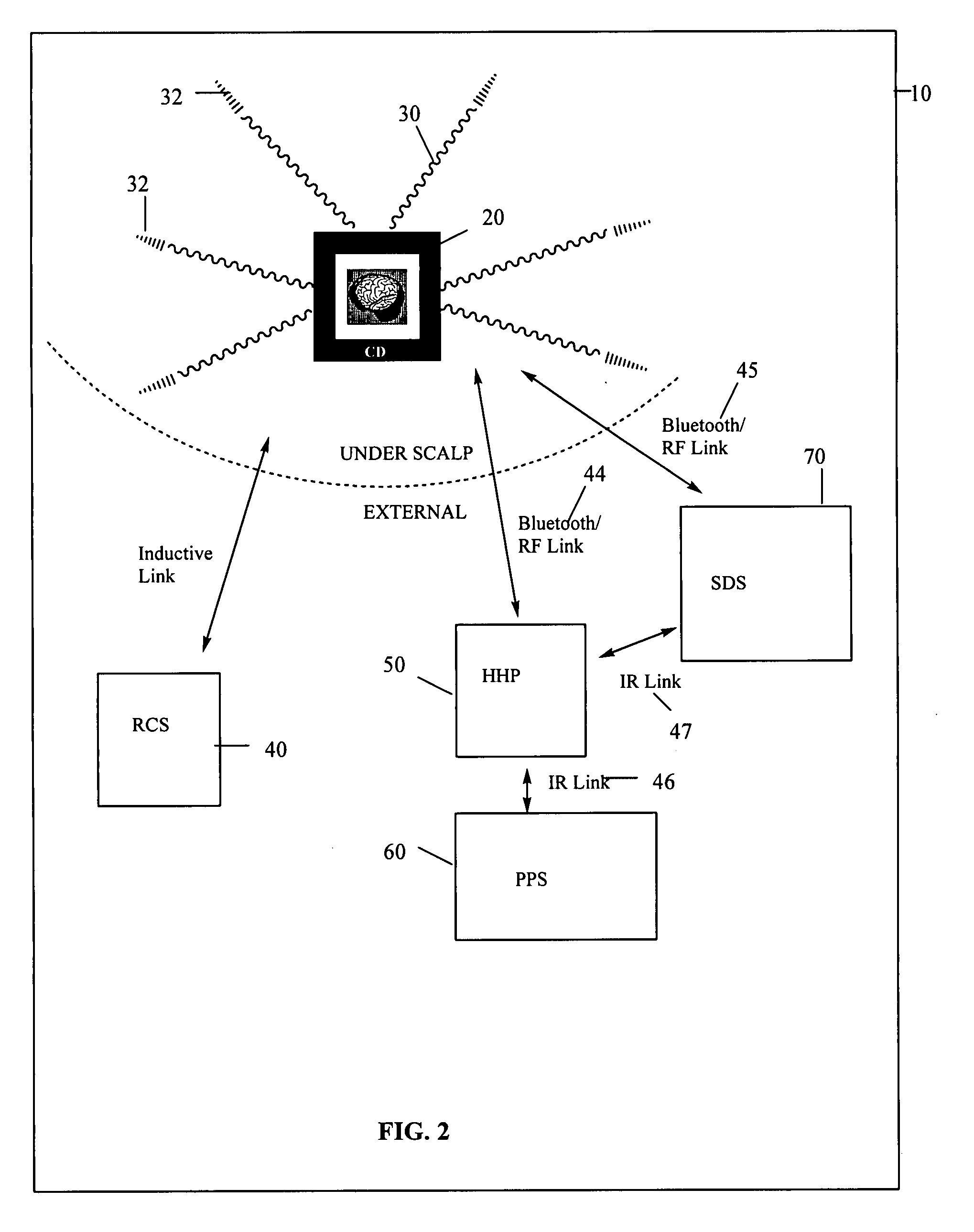
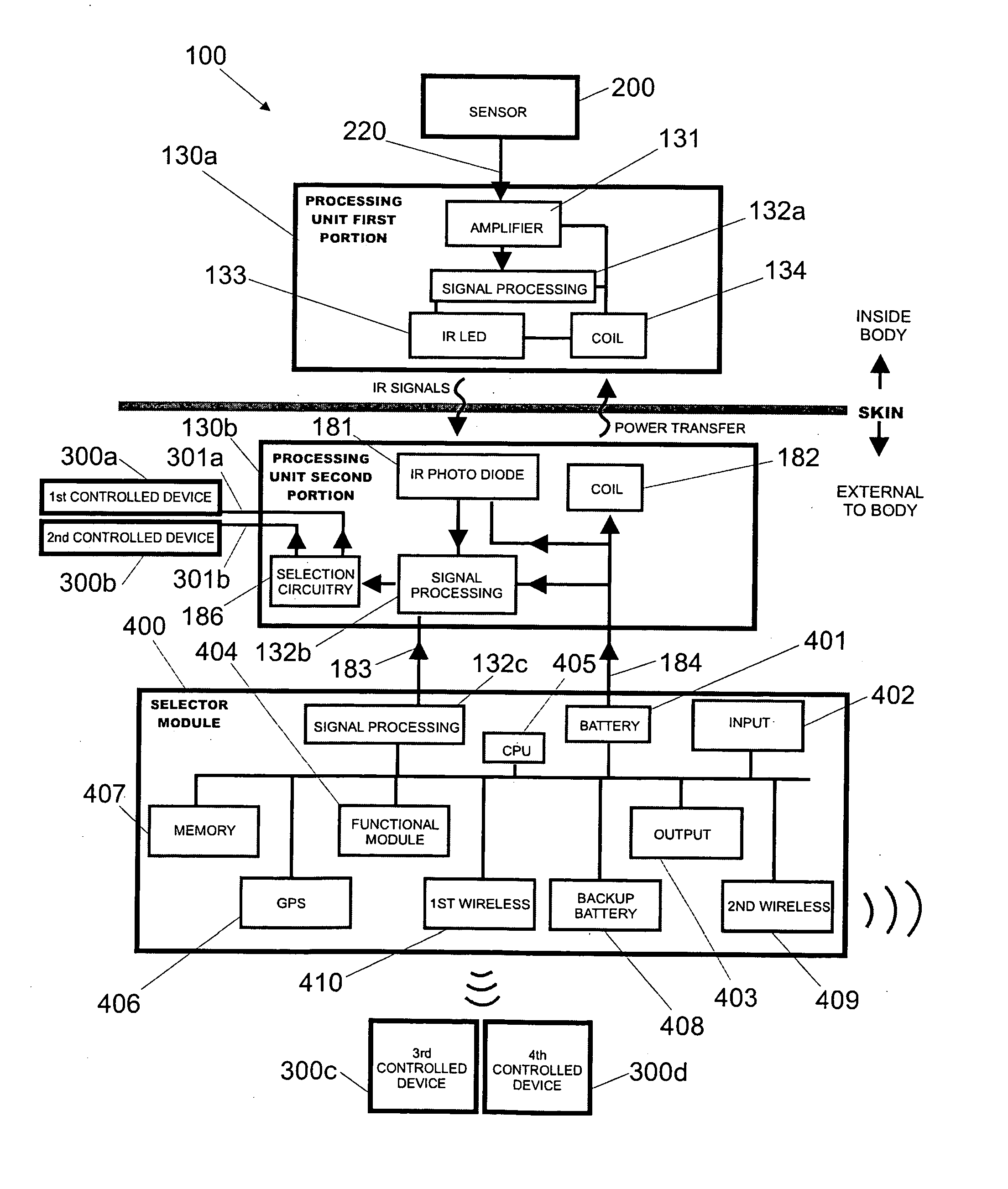
InactiveUS20060058627A1Facilitate communicationImprove the quality of lifeElectroencephalographyElectro-oculographyHead scalpEngineering
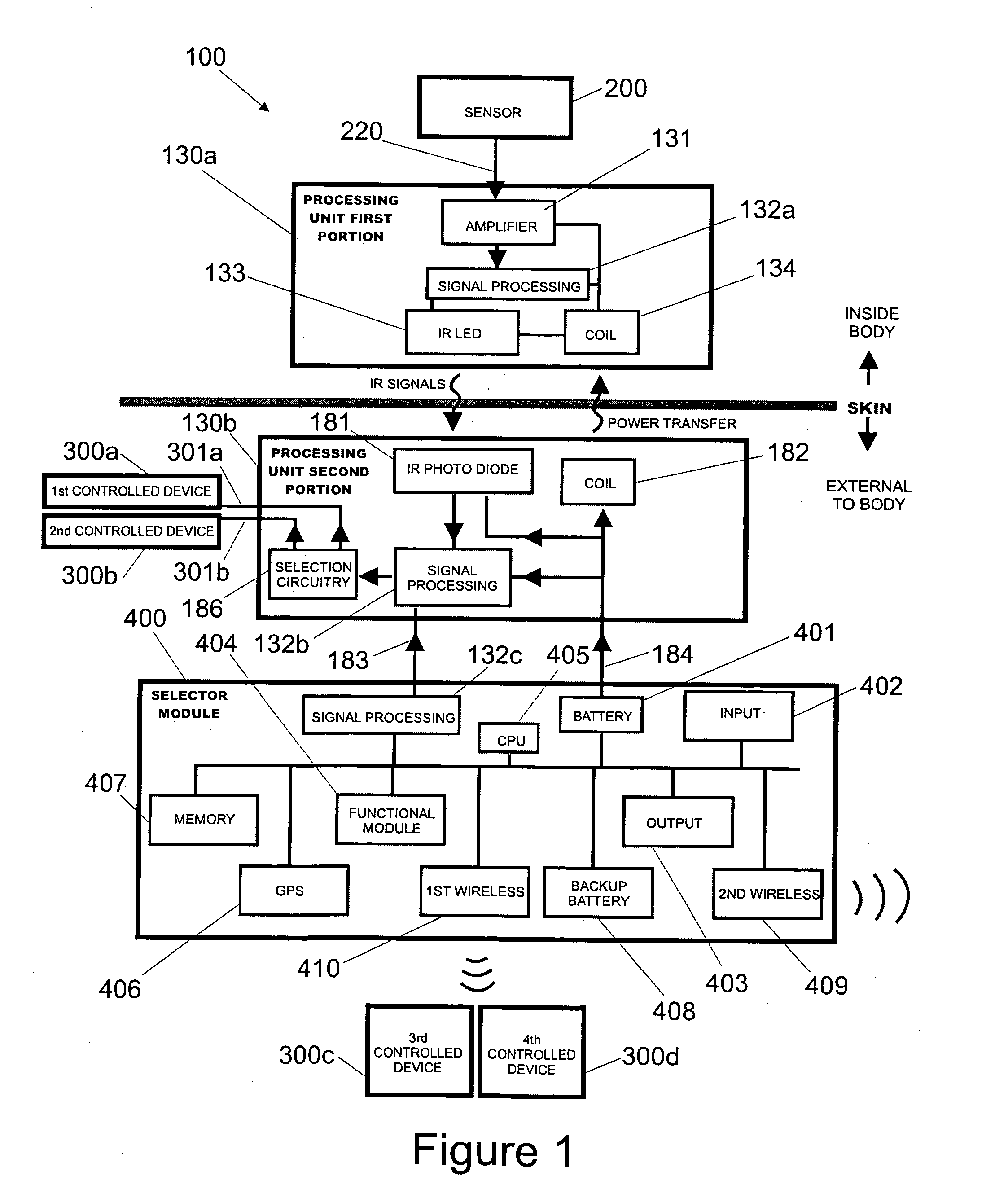
Various embodiments of a biological interface system and their related methods are disclosed. A biological interface system may include a sensor including a plurality of electrodes configured to detect multicellular signals emanating from one or more living cells of a patient and a processing unit configured to receive the multicellular signals from the sensor, to process the multicellular signals to produce processed signals, and to transmit the processed signals. The system may also include a controlled device configured to receive the processed signals from the processing unit. The processing unit may include a processing unit first portion and a processing unit second portion, where the processing unit first portion is implanted under the scalp on the skull of the patient, and the processing unit second portion is placed above the scalp of the patient at a location proximal to the processing unit first portion.
Owner:CYBERKINETICS NEUROTECH SYST
Bone conductive devices for improving hearing
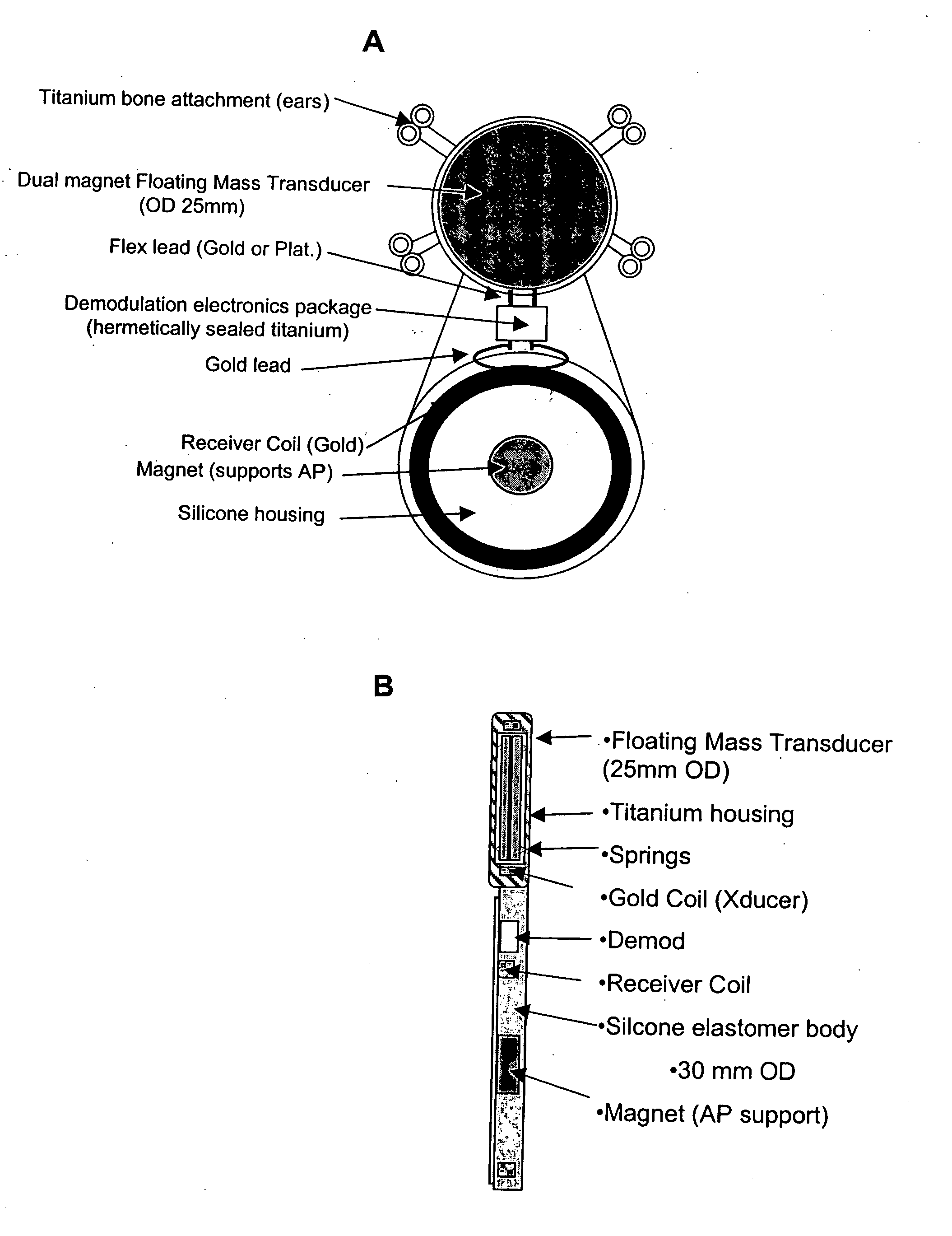
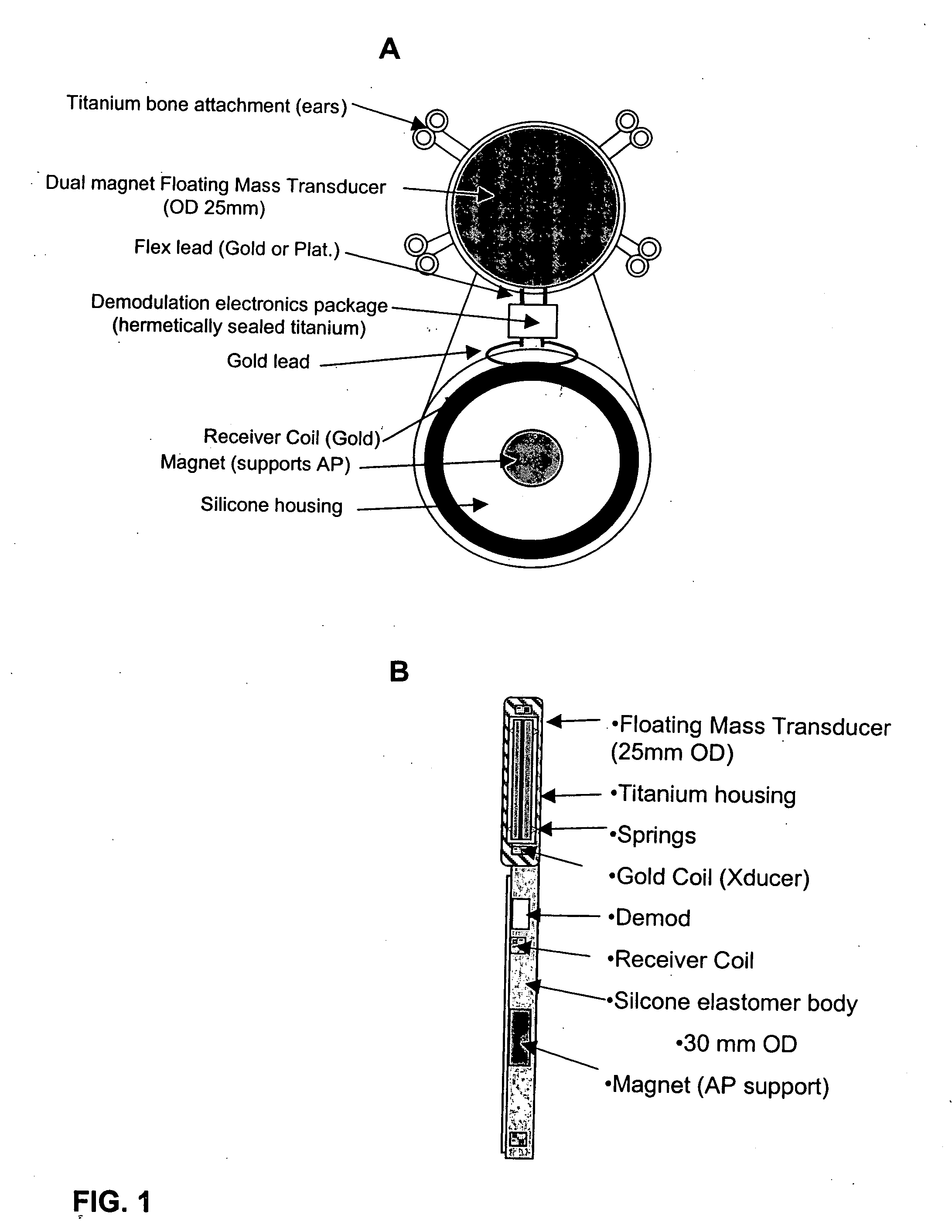
The present invention relates to implantable medical devices for improving sound perception by subjects with conductive or mixed conductive / sensorineural hearing loss. In particular, the present invention provides methods and devices for vibrating the skull of a hearing impaired subject.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
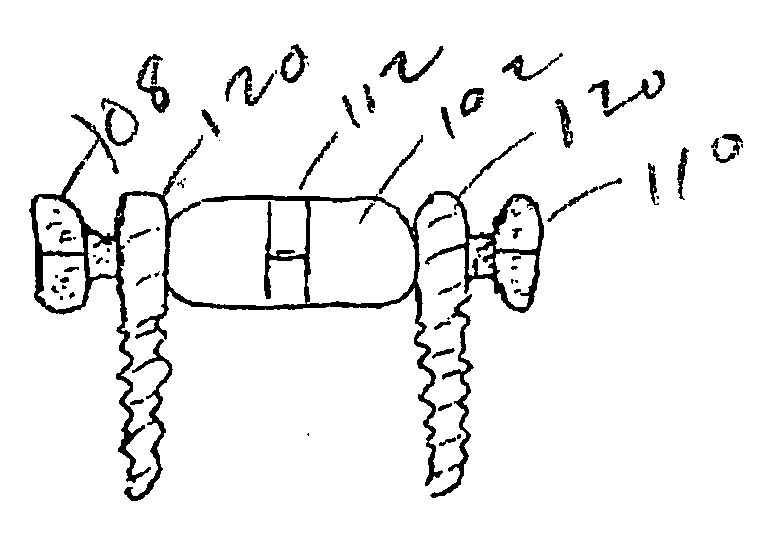
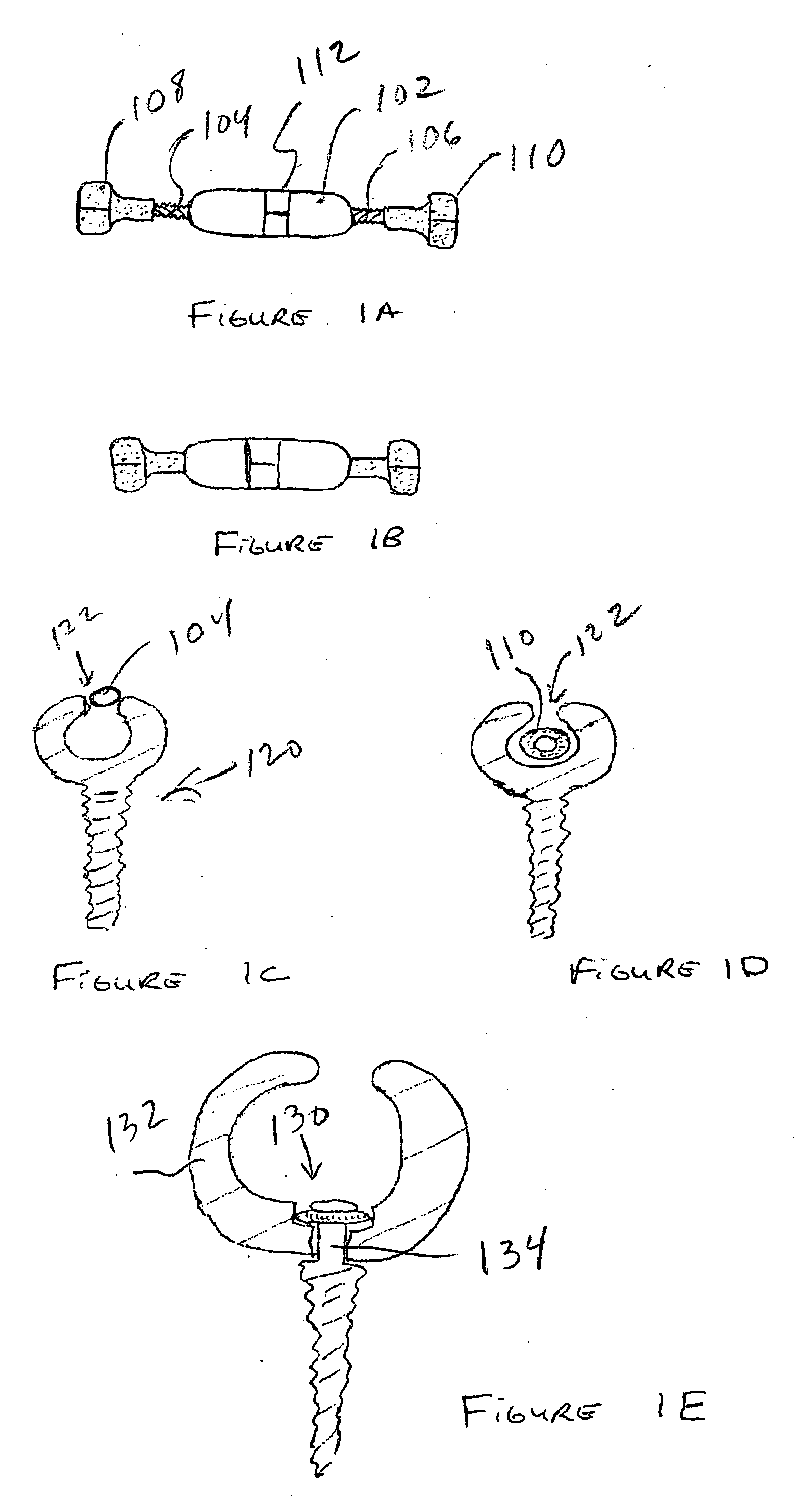
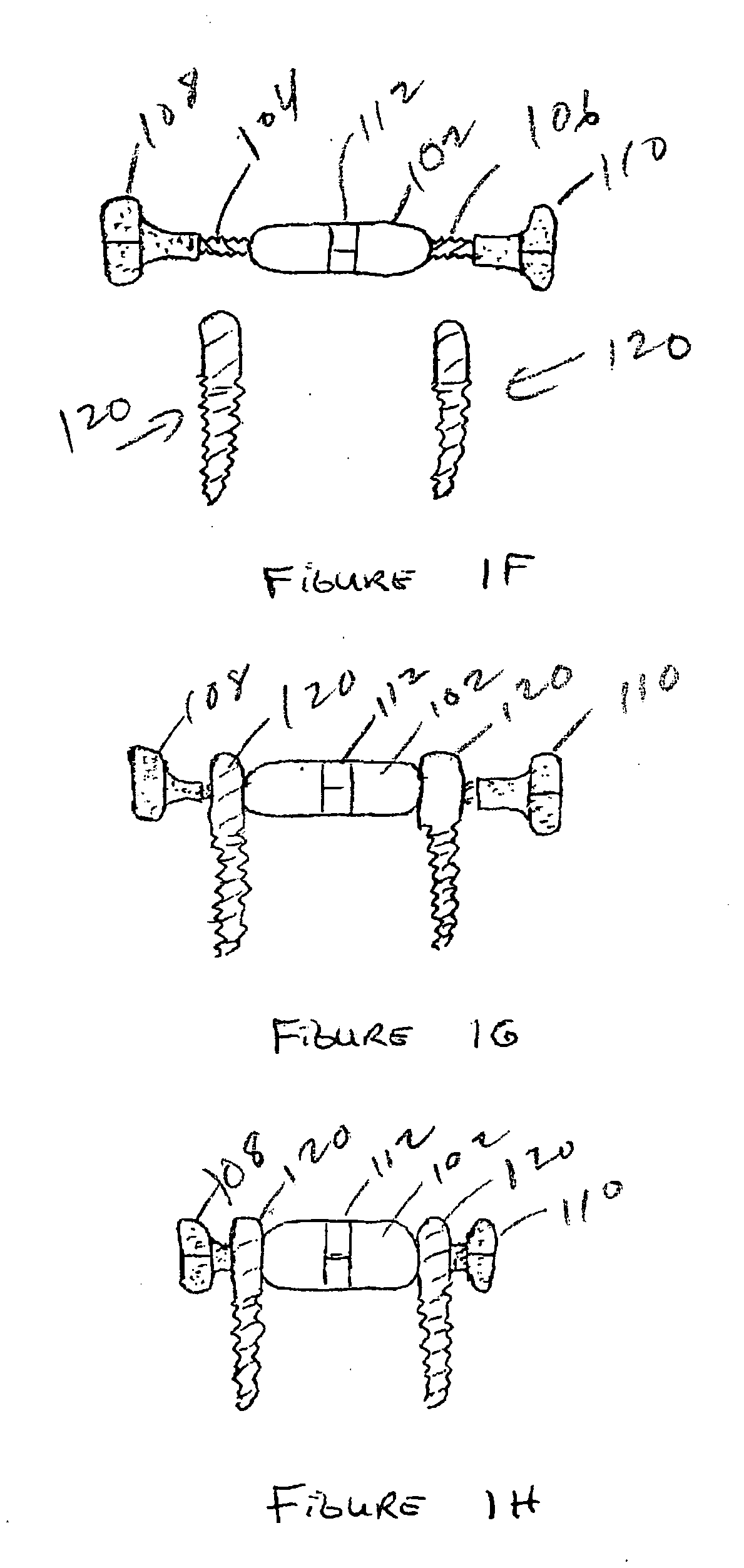
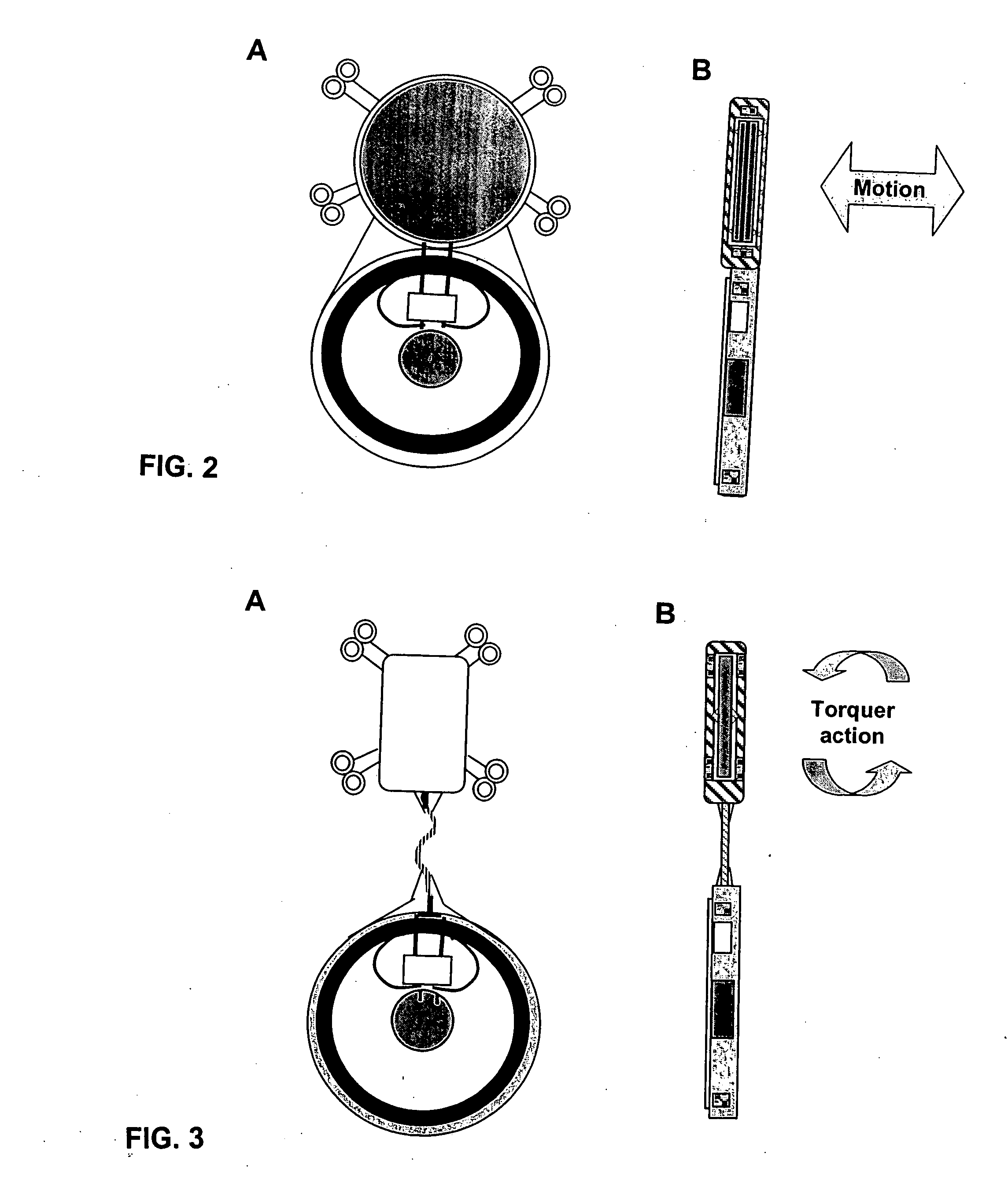
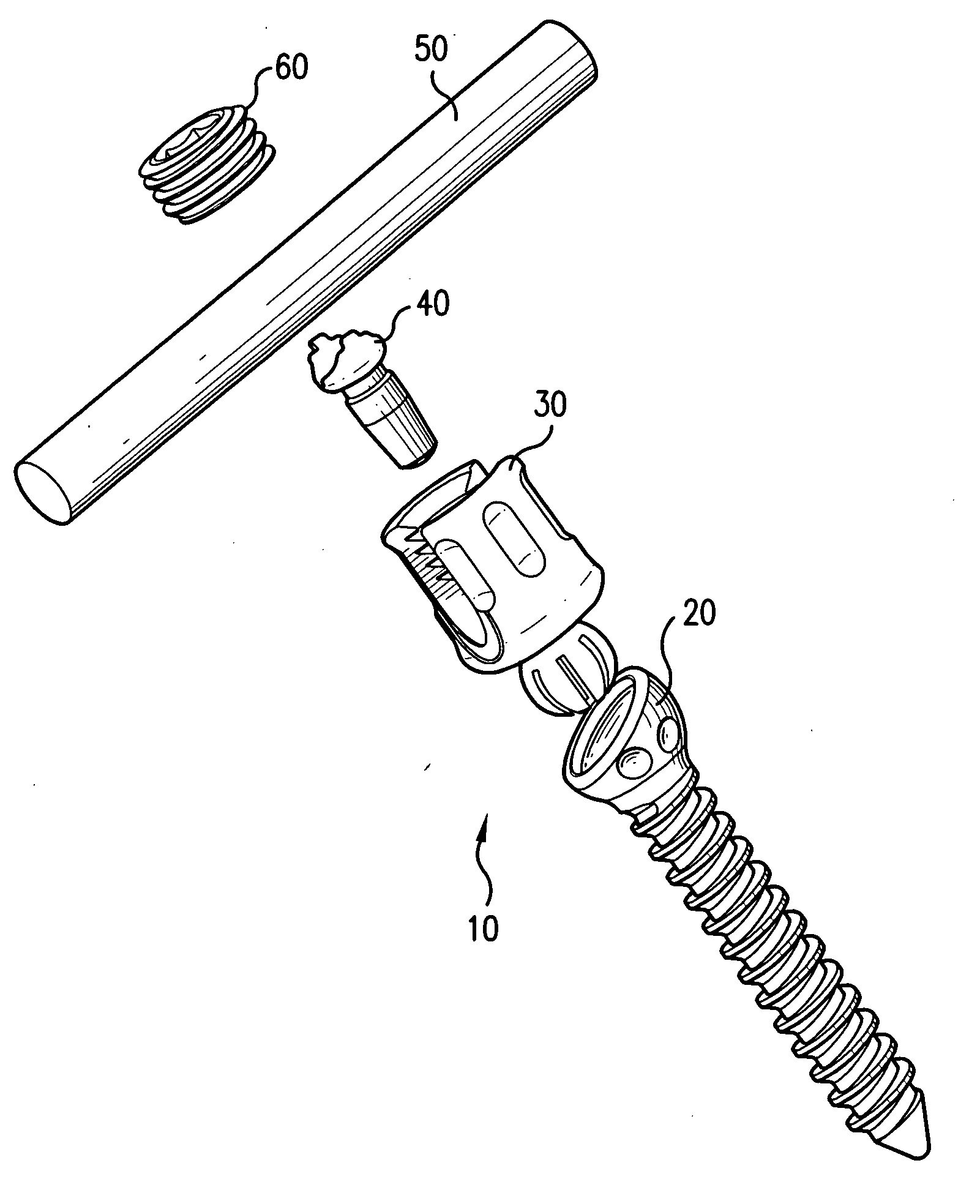
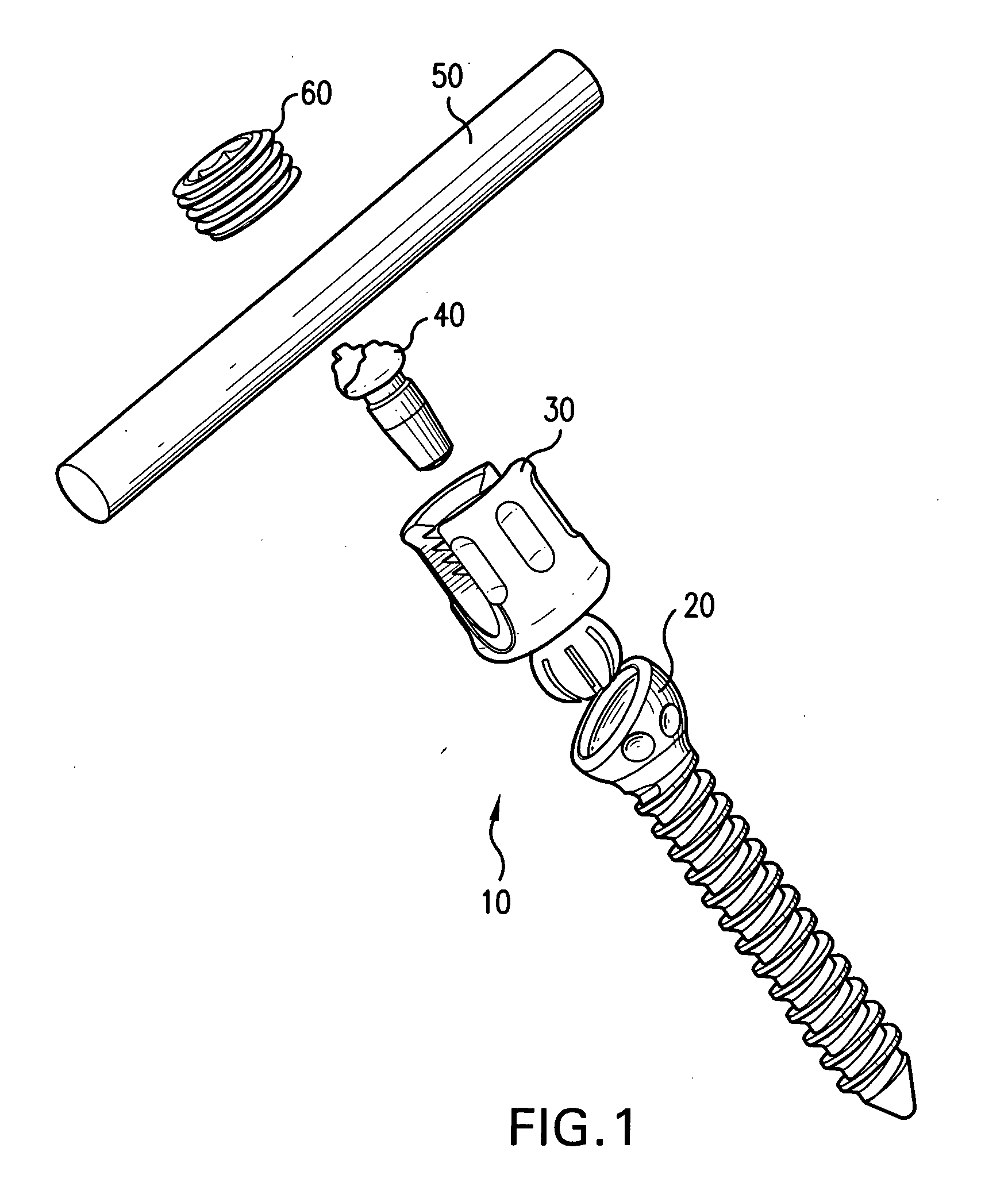
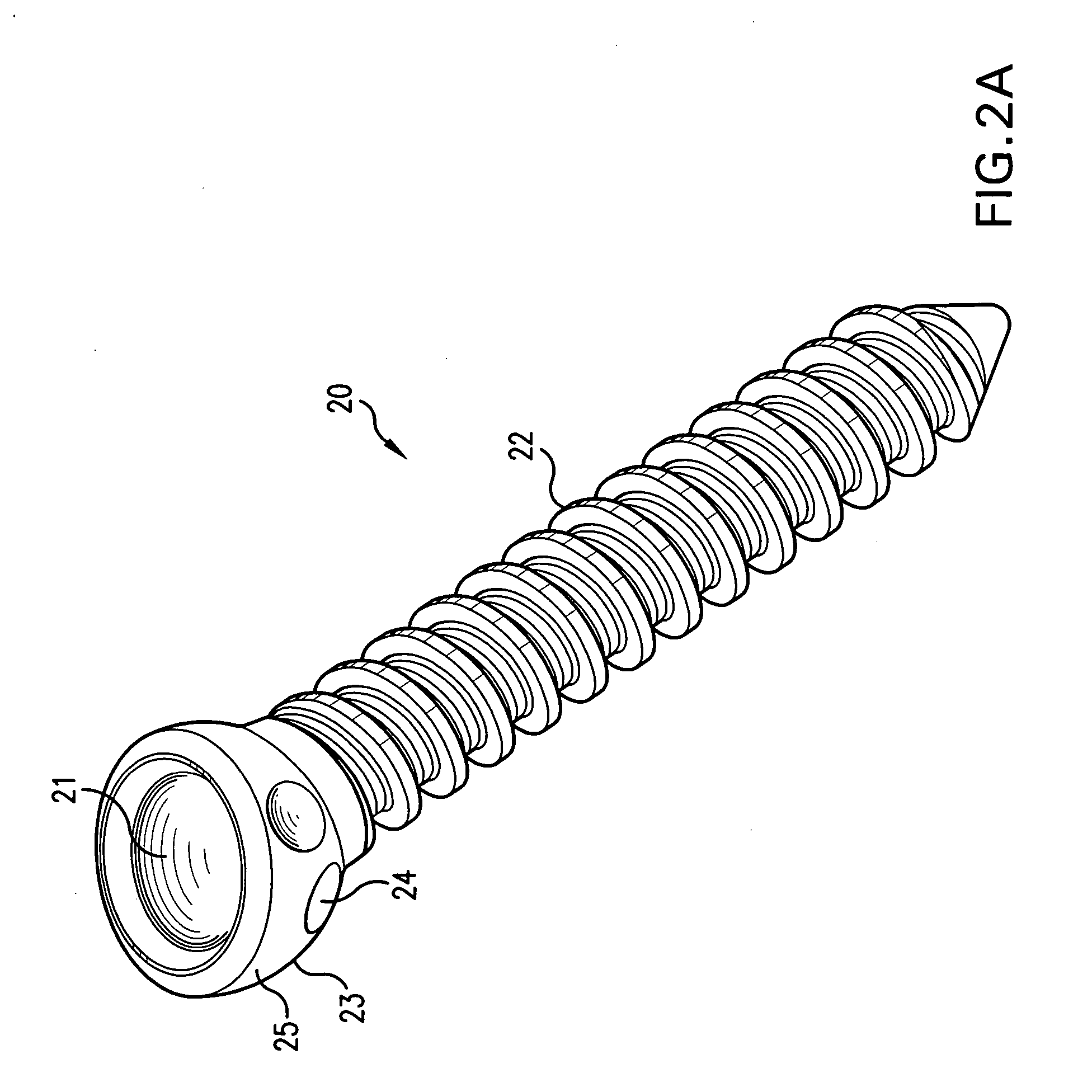
Biased angle polyaxial pedicle screw assembly
ActiveUS20050192573A1Accurate distanceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringPedicle screw
A pedicle screw assembly and method of assembly comprises a longitudinal member; a screw head comprising a bulbous end, wherein the screw head has a slot adapted to receive the longitudinal member; a bone fixator component comprising a concave socket having a biased angled top and a rounded bottom adapted to receive the screw head; a locking pin adapted to engage the screw head, the bone fixator component, and the longitudinal member; and a blocker adapted to engage the screw head and to secure the longitudinal member. Additionally, the bone fixator component may be configured as any of a bone screw and a hook.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
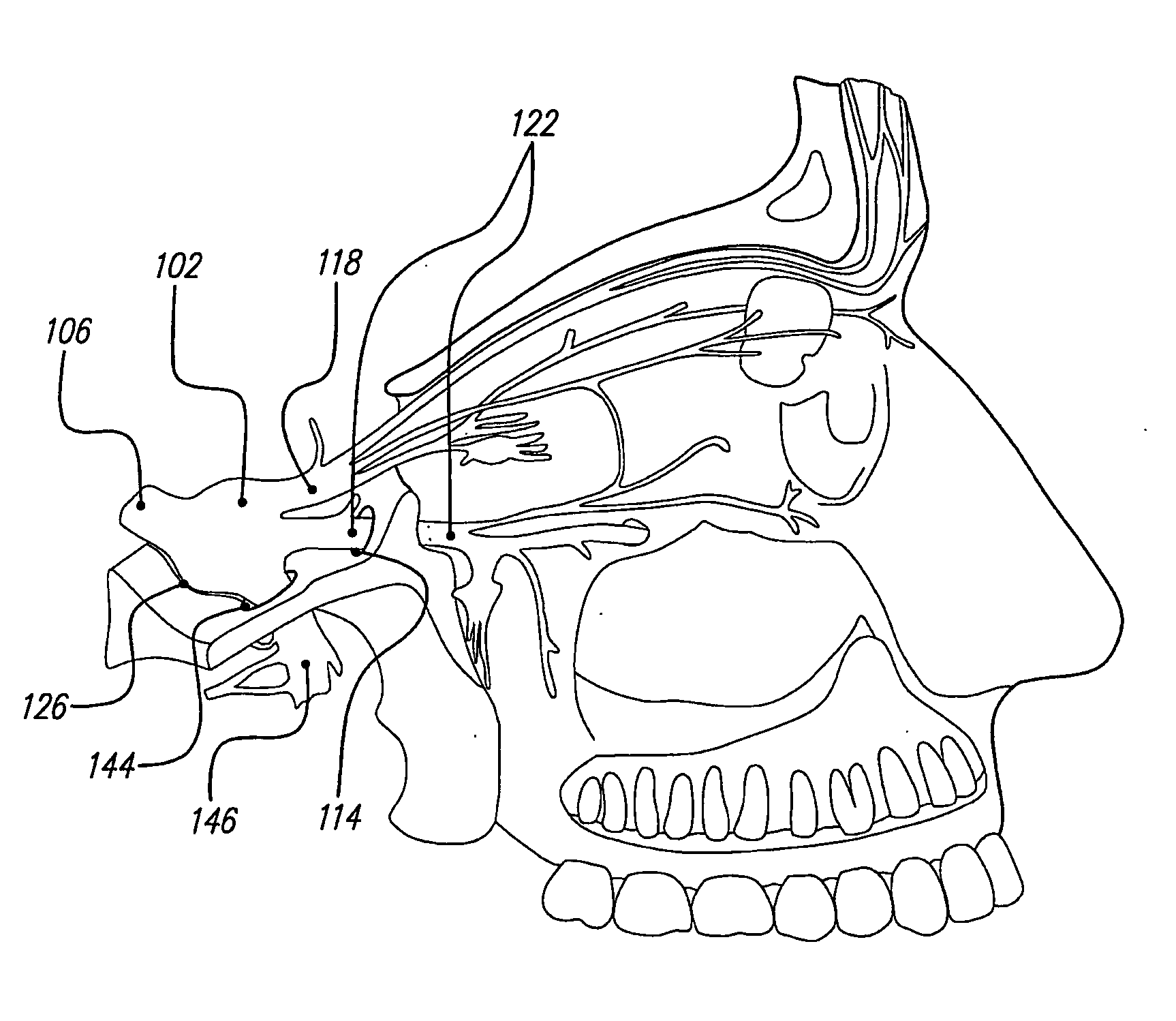
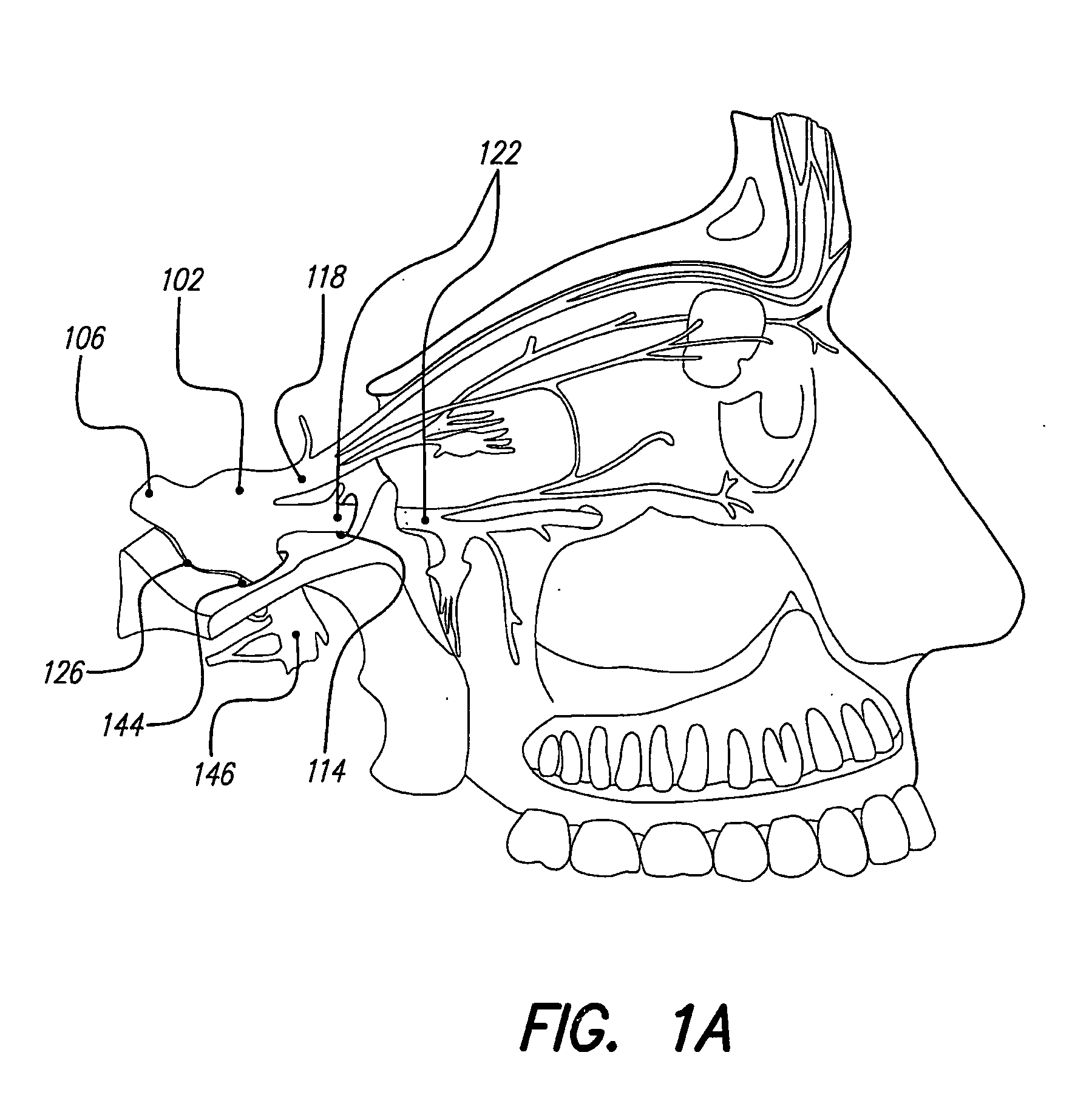
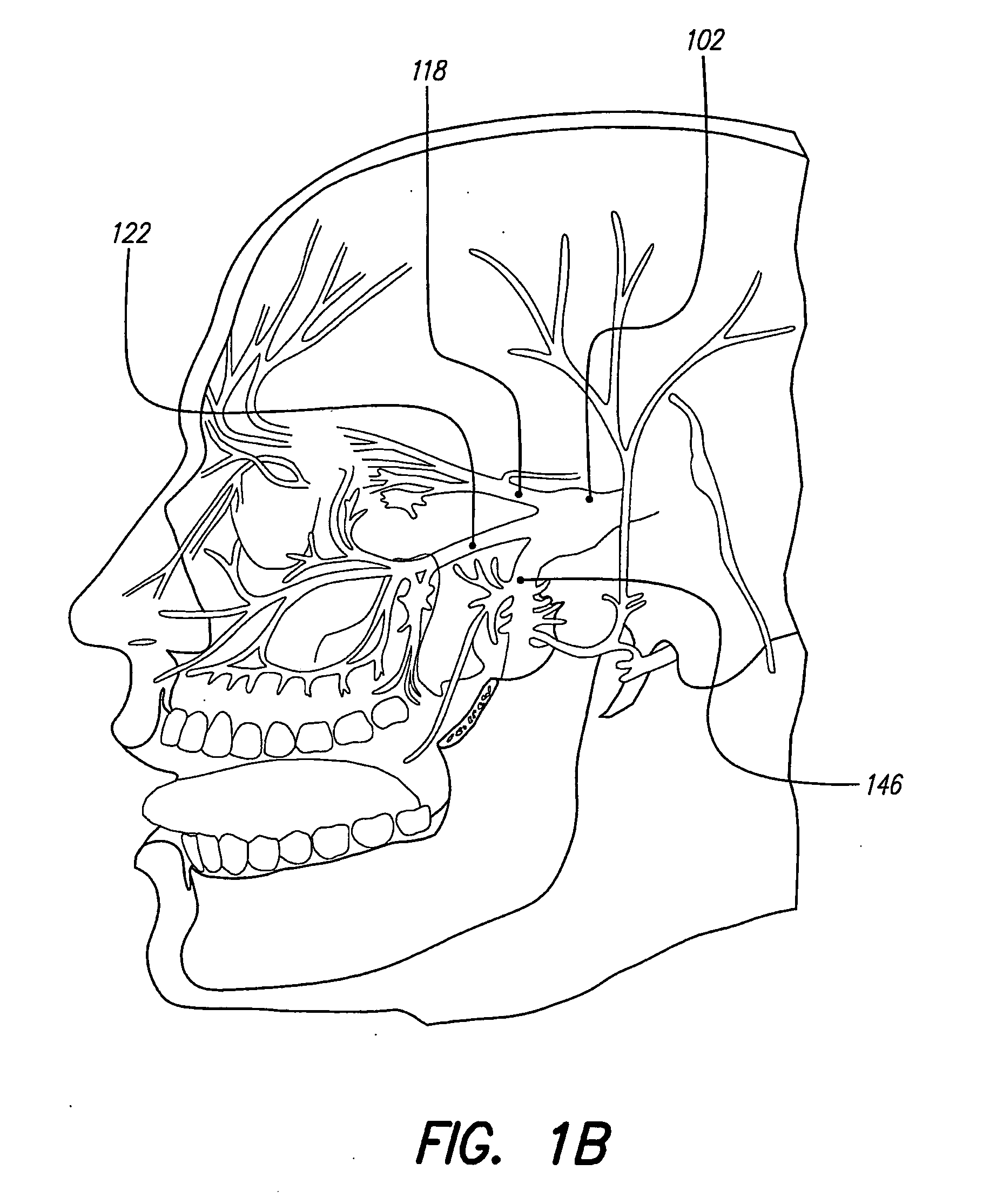
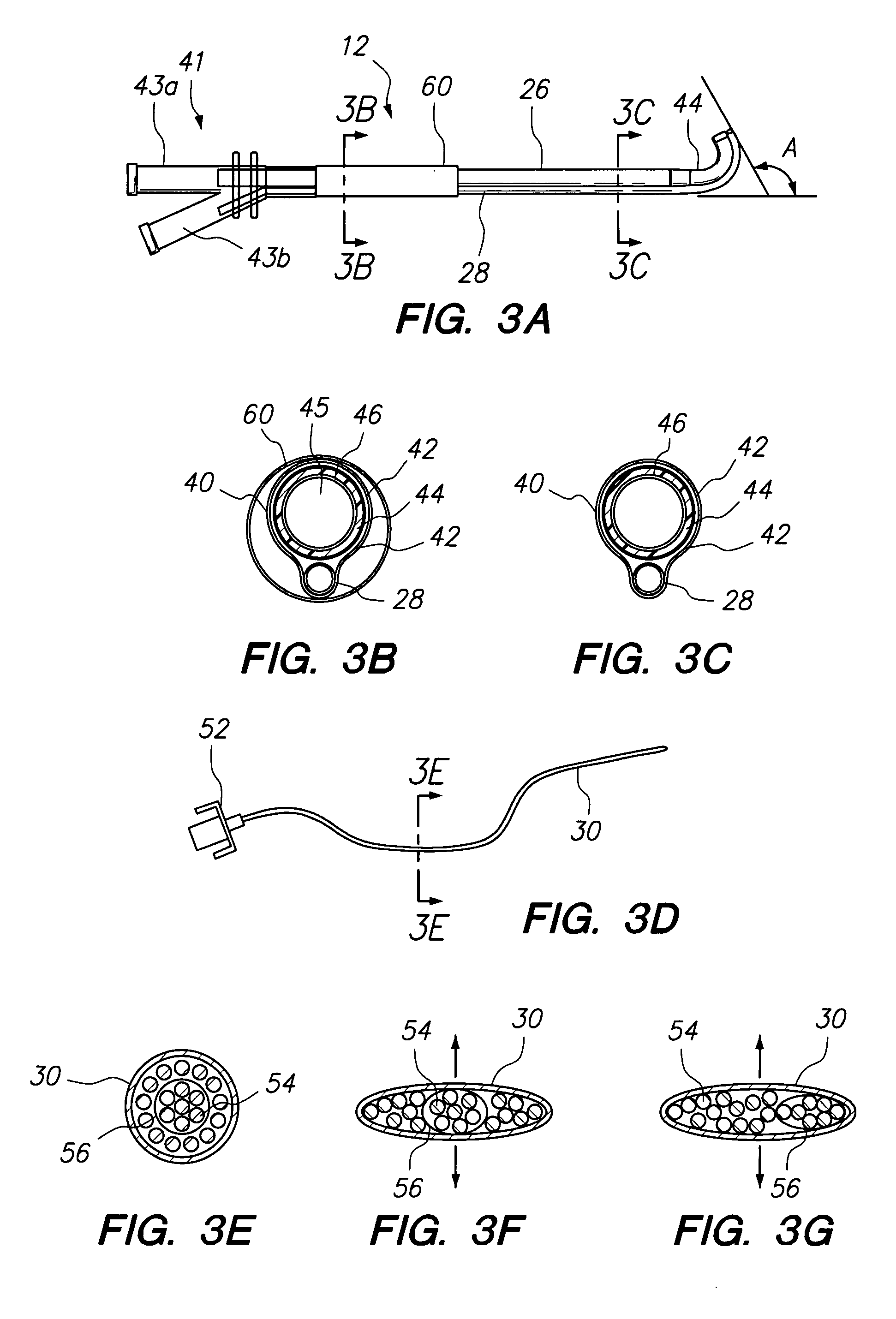
Endoscopic Methods and Devices for Transnasal Procedures
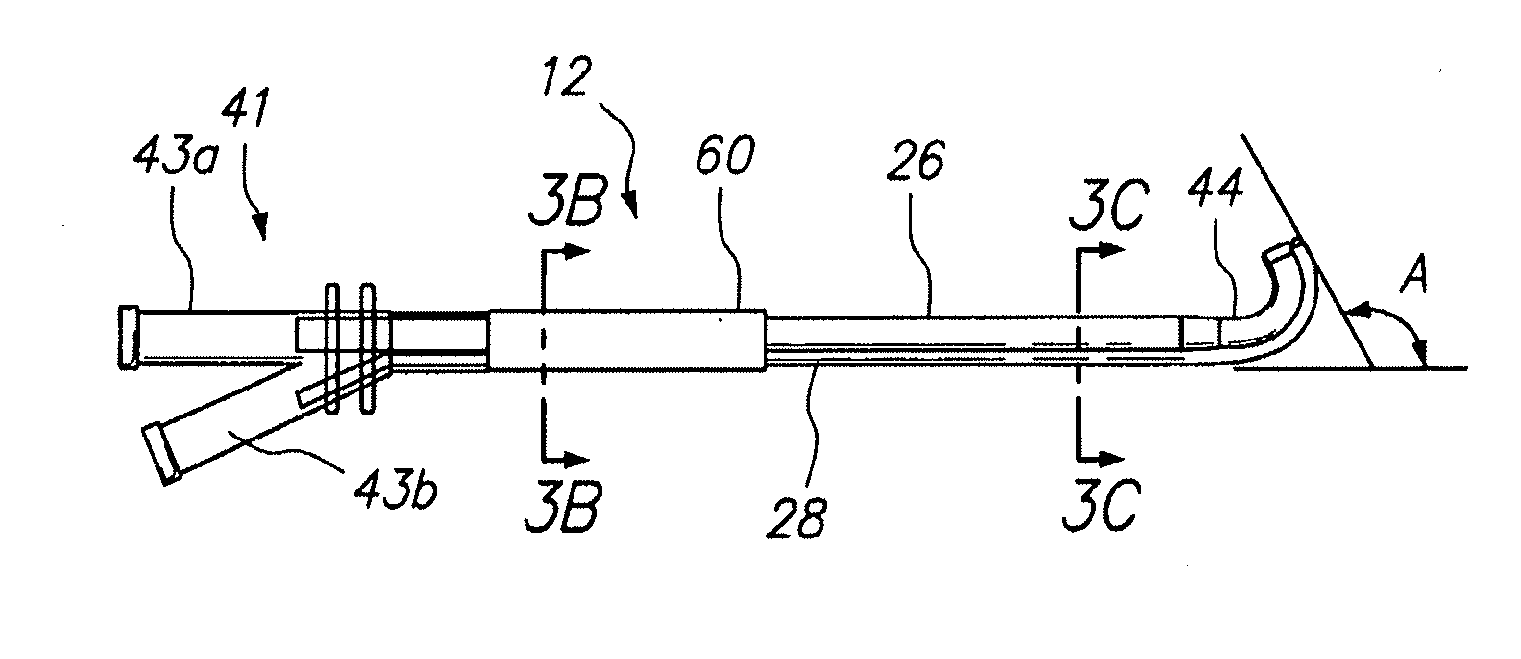
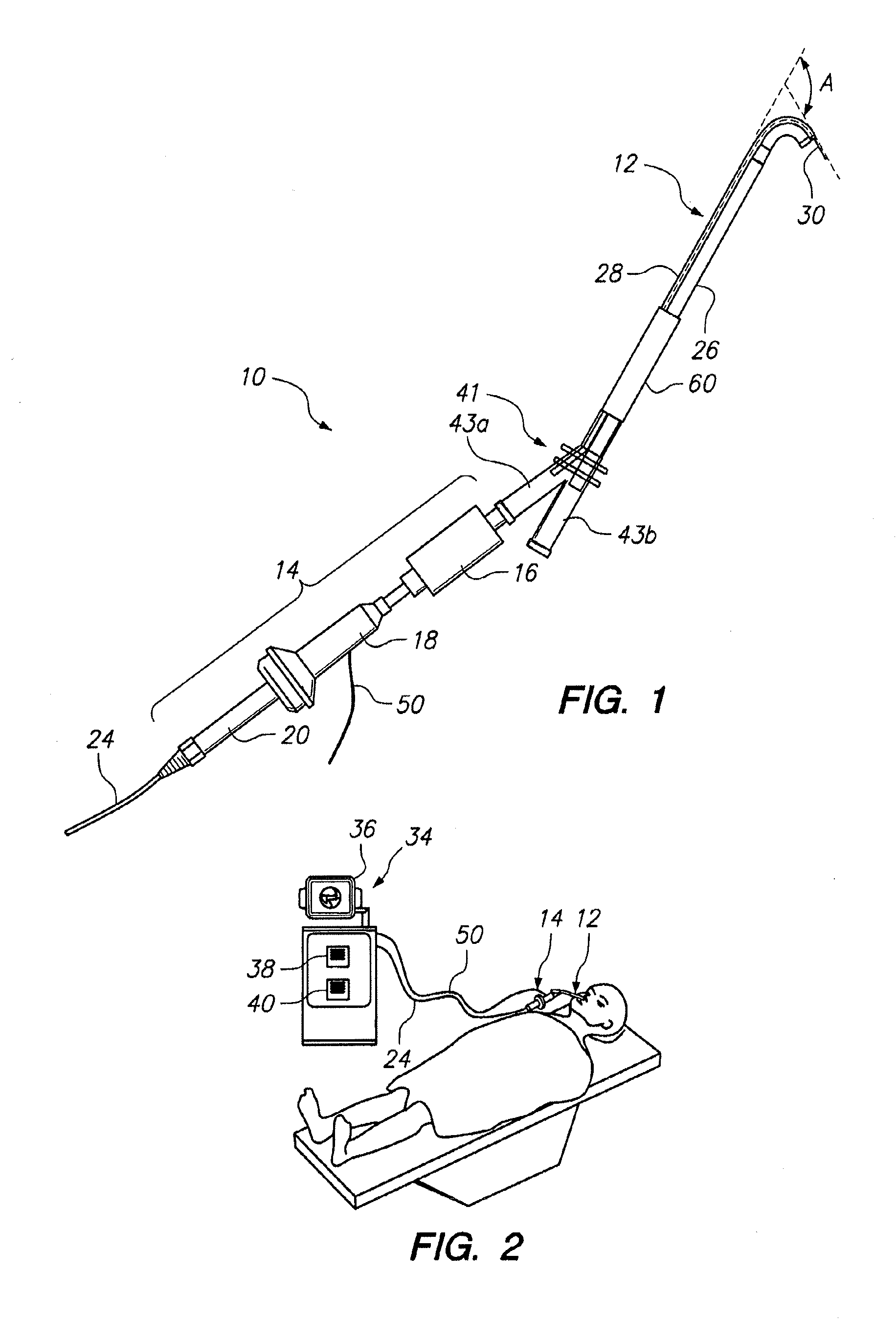
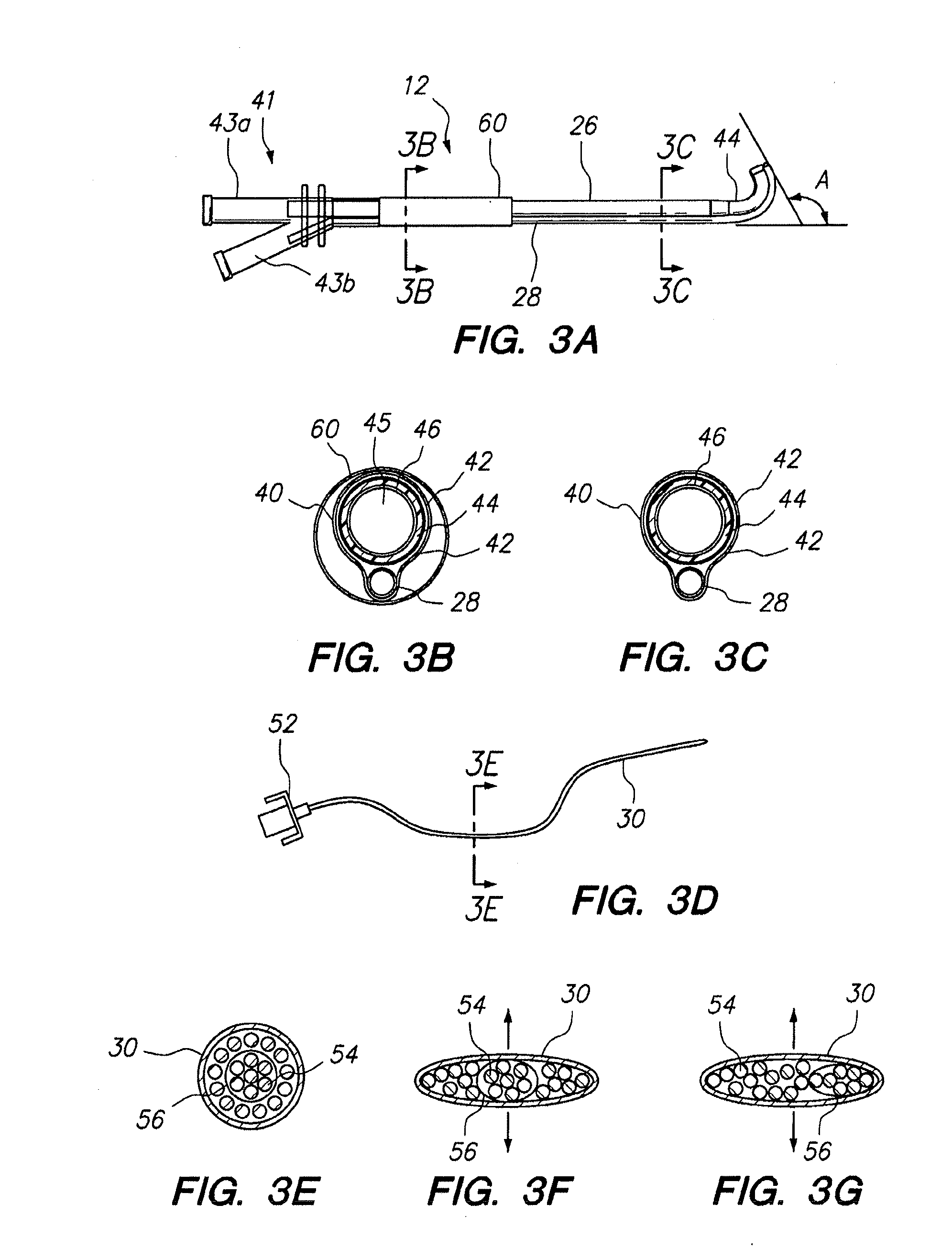
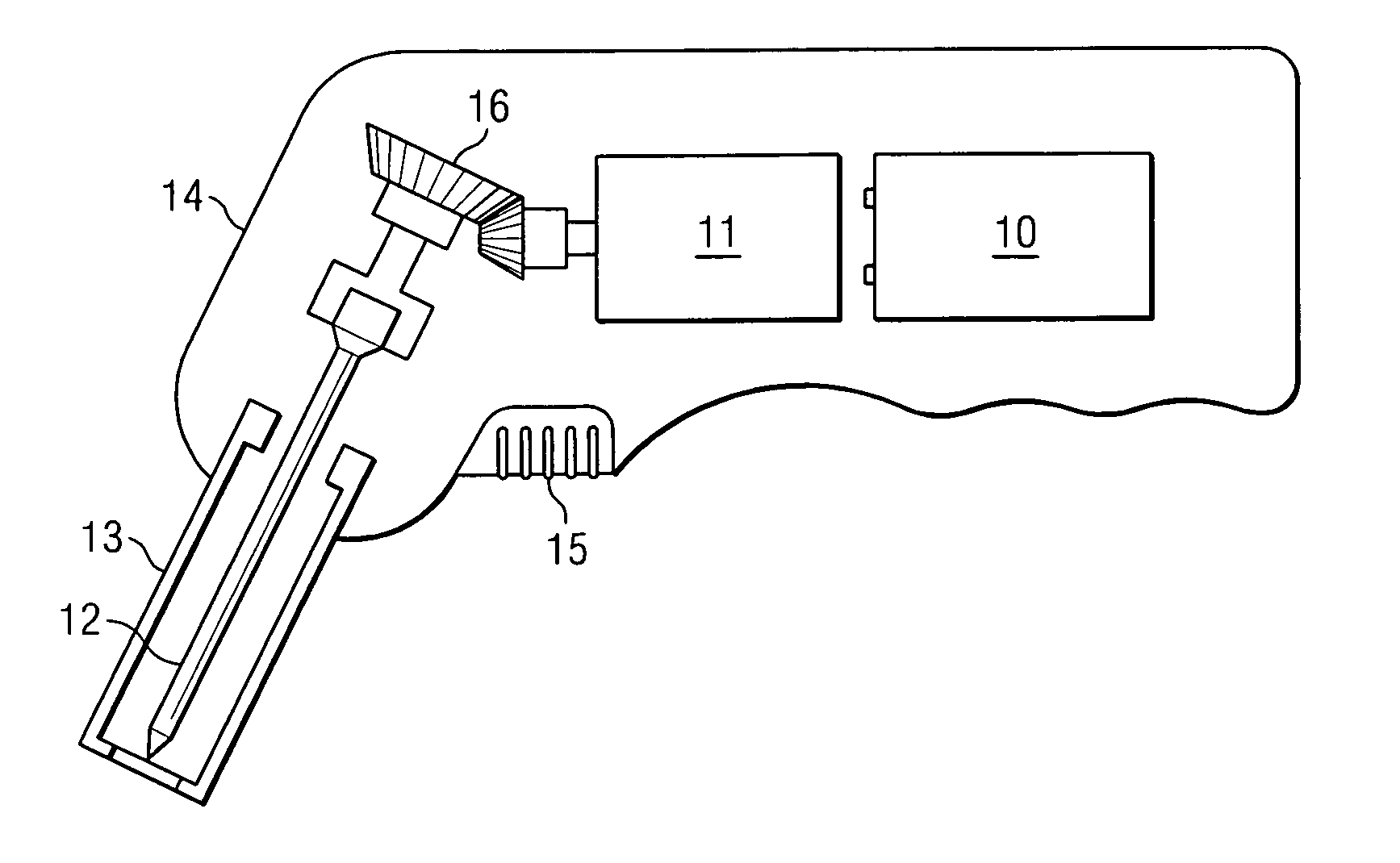
ActiveUS20120265094A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce exposureSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsThroatNose
Medical devices, systems and methods that are useable to facilitate transnasal insertion and positioning of guidewires and various other devices and instruments at desired locations within the ear, nose, throat, paranasal sinuses or cranium. Direct viewing of such placements via an endoscope.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
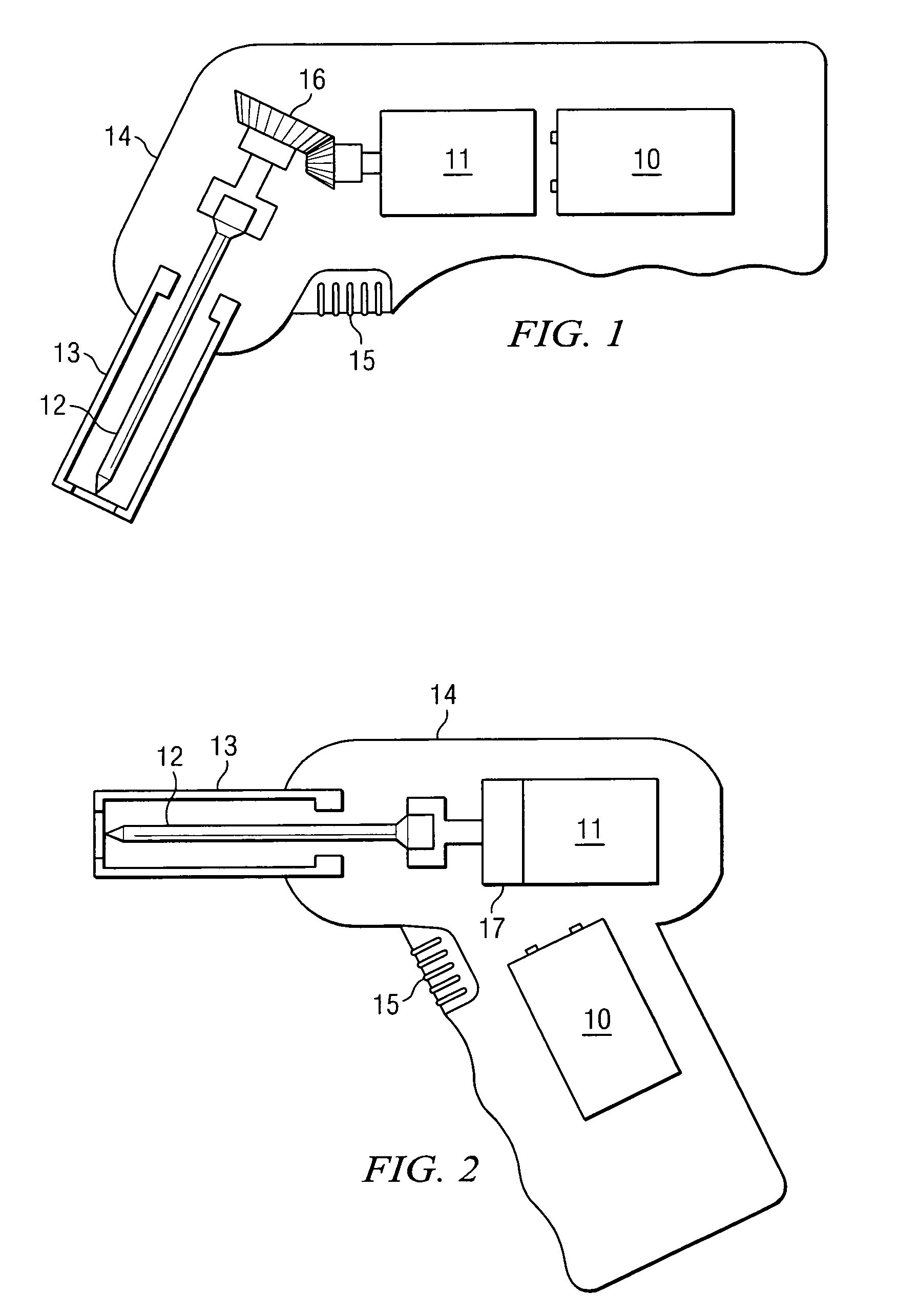
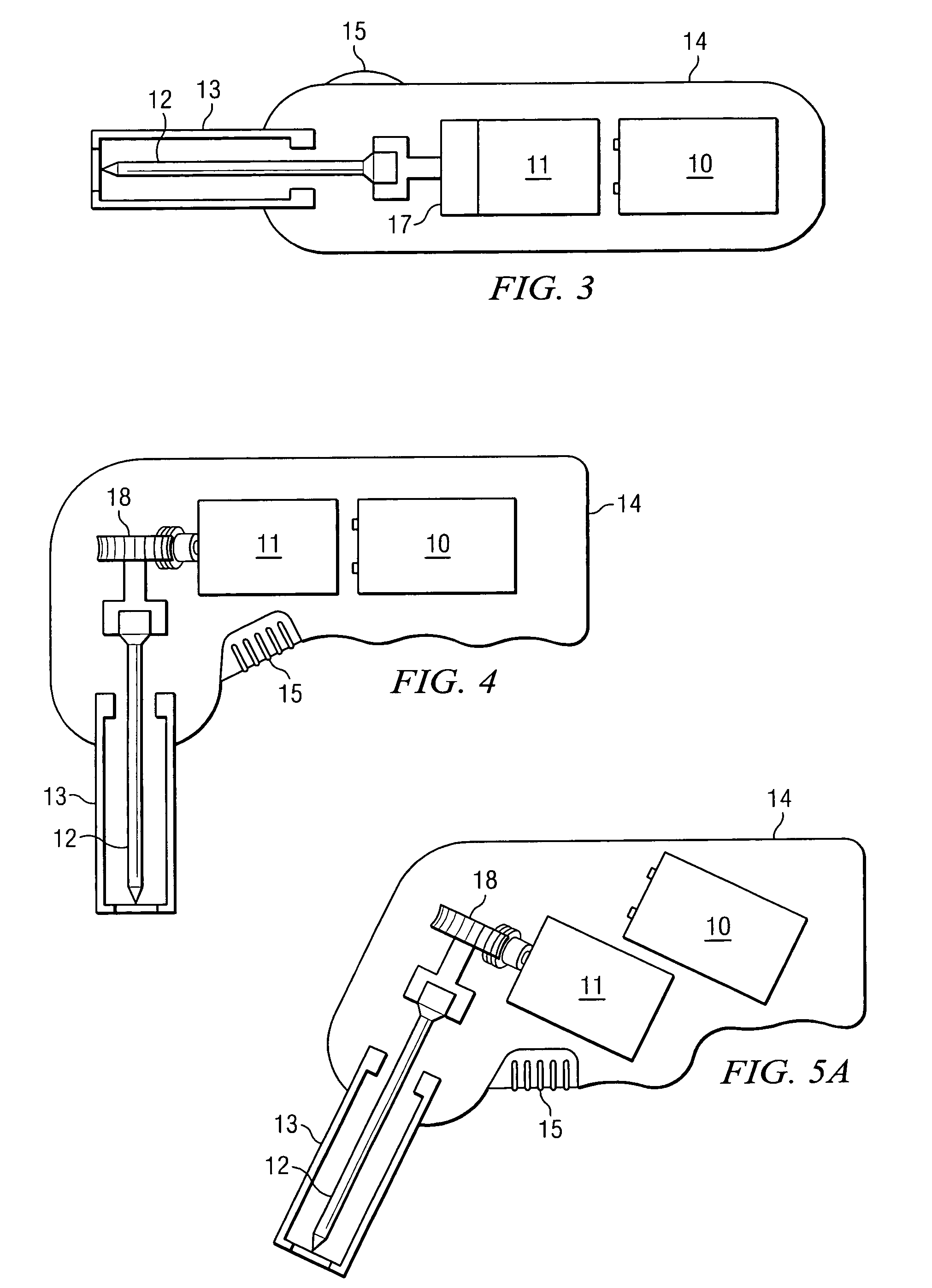
Apparatus and method to provide emergency access to bone marrow
An apparatus and method for penetrating the bone marrow is provided. The apparatus includes a housing, a penetrator assembly, operable to penetrate the bone marrow, a connector operable to releasably attach the penetrator assembly to a drill shaft, the drill shaft operable to connect the penetrator assembly to a gear assembly, a gear assembly operable to engage and rotate the drill shaft, a motor operable to engage the reduction gear assembly and drive the penetrator into the bone marrow by rotation of the drill shaft, and a power supply and associated circuitry operable to power the motor. The apparatus and method may be adapted to insert a probe through the skull and into the brain.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
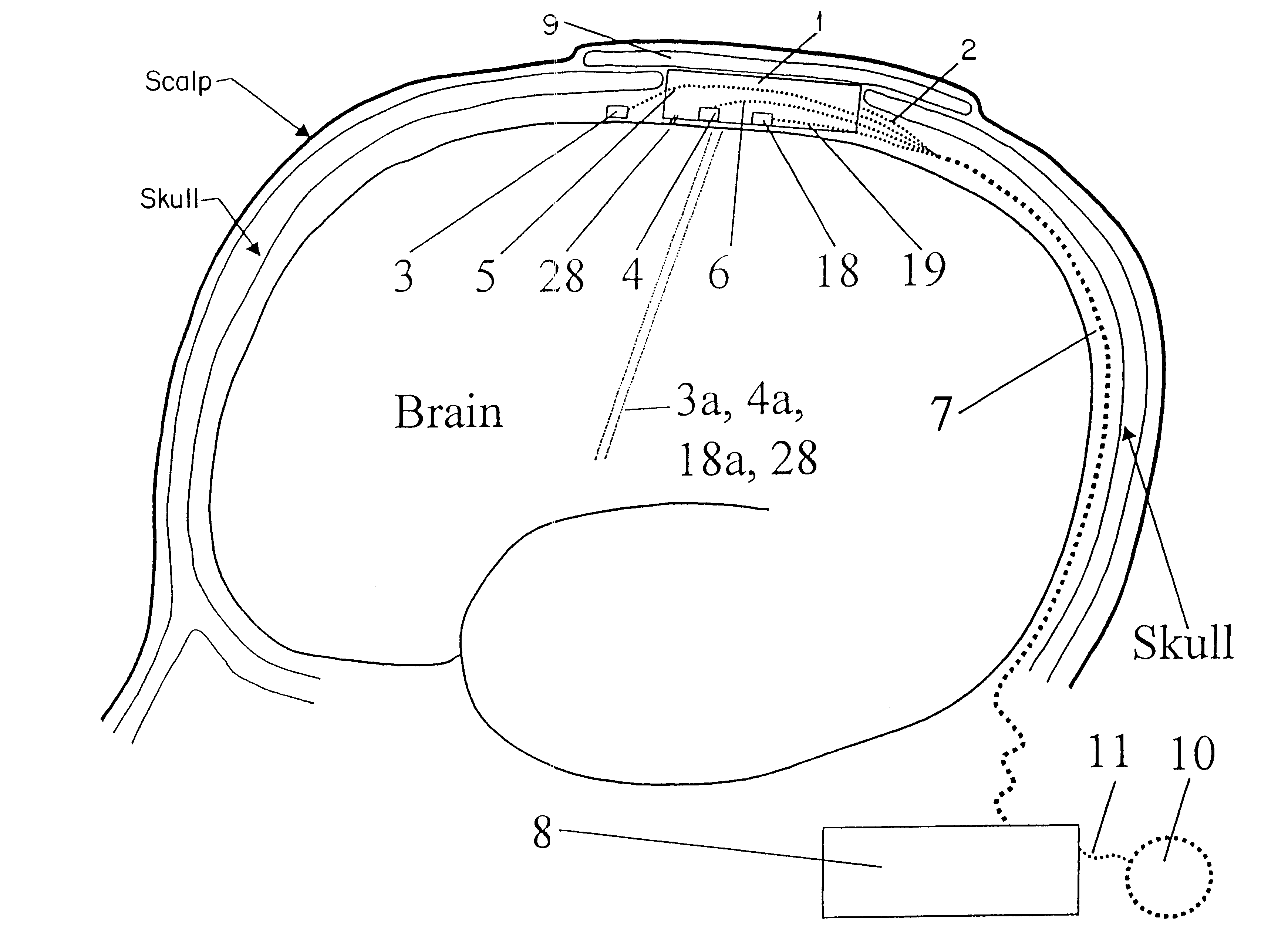
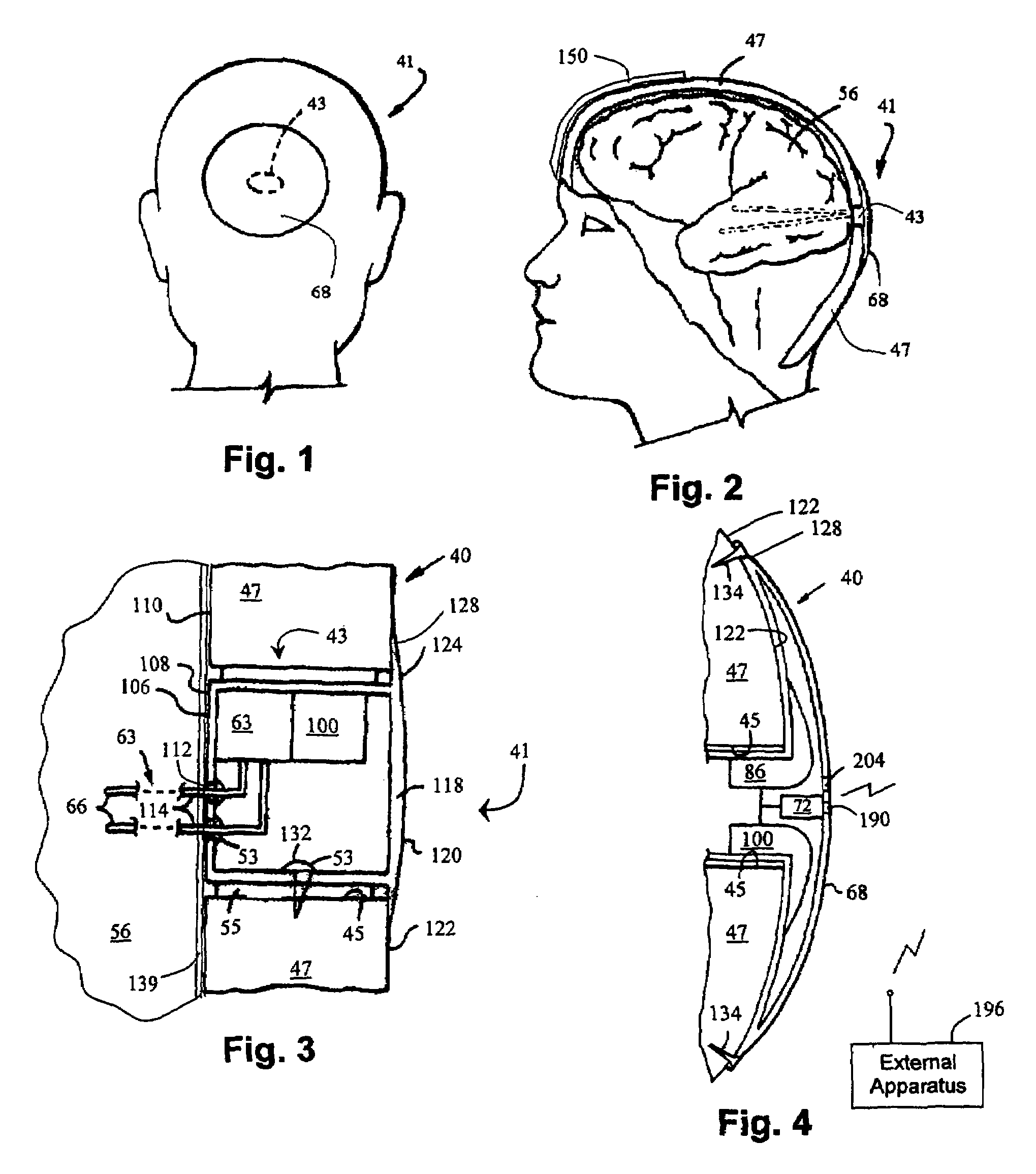
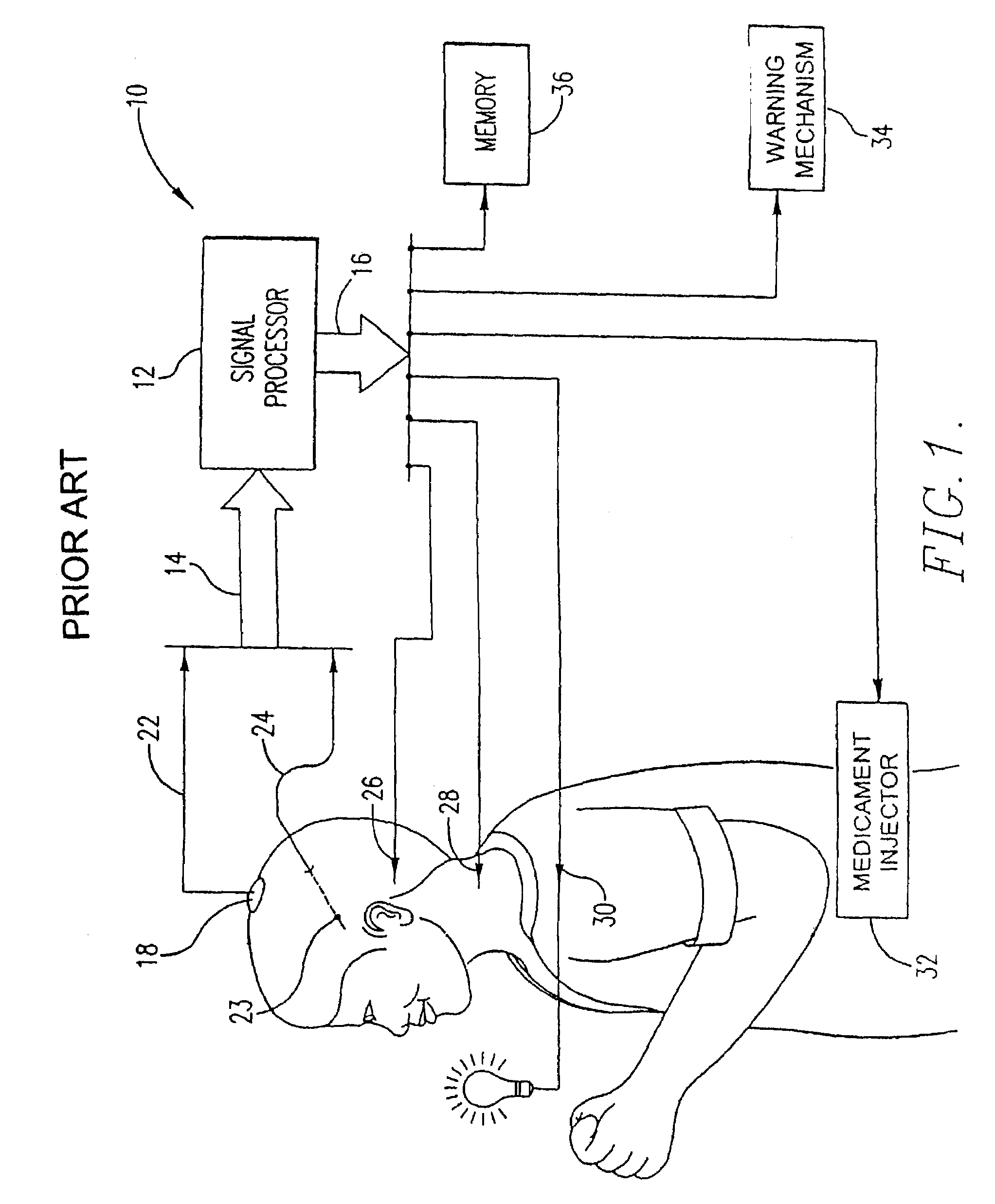
Cerebral or organ interface system
InactiveUS7346391B1Good conditionEnergy efficient and cost-effectiveElectroencephalographyHead electrodesEngineeringCerebrum
A cerebral and / or interface system has a housing mechanism configured to be at least partially spaced in a cavity formed in the subject's skull; an attaching mechanism for attaching the housing mechanism to the subject's skull; a sealing mechanism for providing a fluid-tight seal between the housing mechanism and the subject's skull; a control mechanism spaced within the housing mechanism; a communication mechanism with one or more sensors embedded in the subject's brain connecting the control mechanism to the subject's brain; and a power source spaced within the housing mechanism. Optional embodiments include a treatment portion for cooling or heating adjacent tissue, a medicament portion for administering medicament to adjacent tissue, a separate auxiliary compartment with a removable lid secured to or spaced apart from the housing mechanism, contacts extending outwardly from housing mechanism, and / or a supporting mechanism for precisely displacing the housing mechanism angularly or along x-, y-, and z-axes.
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
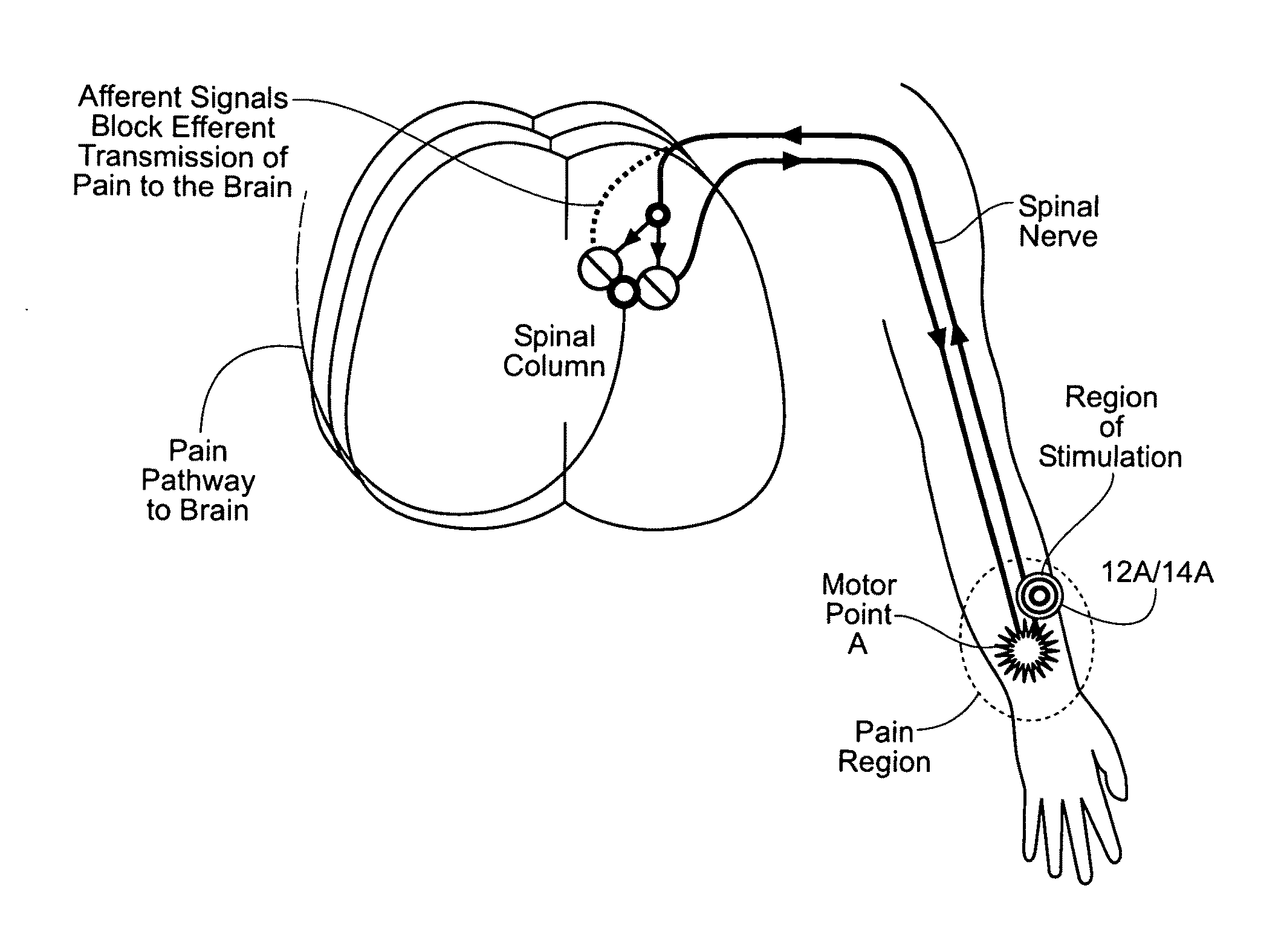
Systems and methods to place one or more leads in tissue to electrically stimulate nerves of passage to treat pain
It has been discovered that pain felt in a given region of the body can be treated, not by motor point stimulation of muscle in the local region where pain is felt, but by stimulating muscle close to a “nerve of passage” in a region that is superior (i.e., cranial or upstream toward the spinal column) to the region where pain is felt. Spinal nerves such as the intercostal nerves or nerves passing through a nerve plexus, which comprise trunks that divide by divisions and / or cords into branches, comprise “nerves of passage.”
Owner:NDI MEDICAL
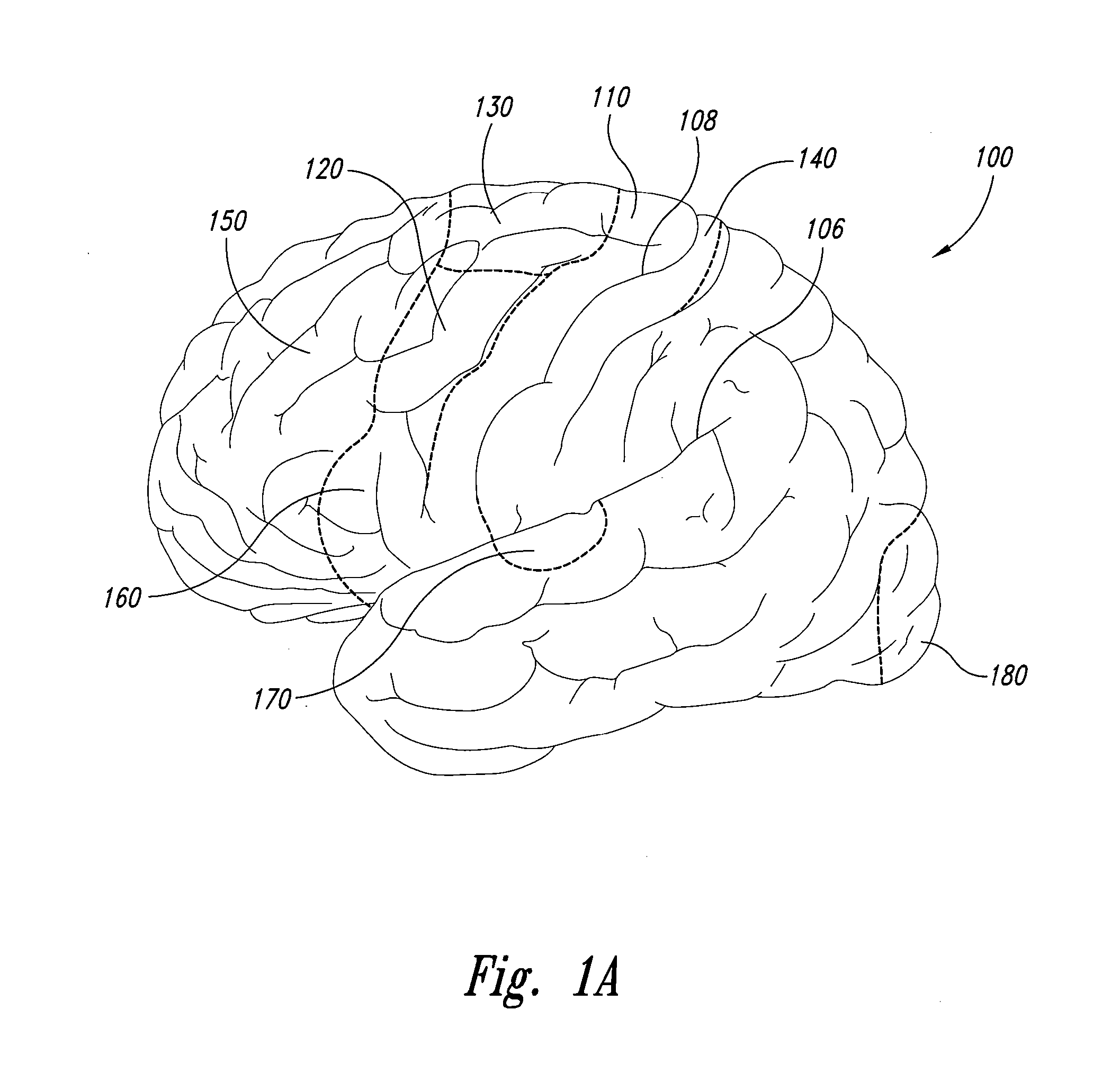
Implantable cortical neural lead and method
A neural lead and method of treating neurological disorders by stimulation of the cerebral cortex of the brain is provided. The lead is designed for reduction of strain between the lead body and the lead paddle caused by the position of the lead body above the cranium and the lead paddle beneath the cranium. The lead is also designed to include a two dimensional chronic electrode array for better stimulation coverage of the target area of the cerebral cortex. A method of treating a neurological disorder by stimulating the cerebral cortex is also presented.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
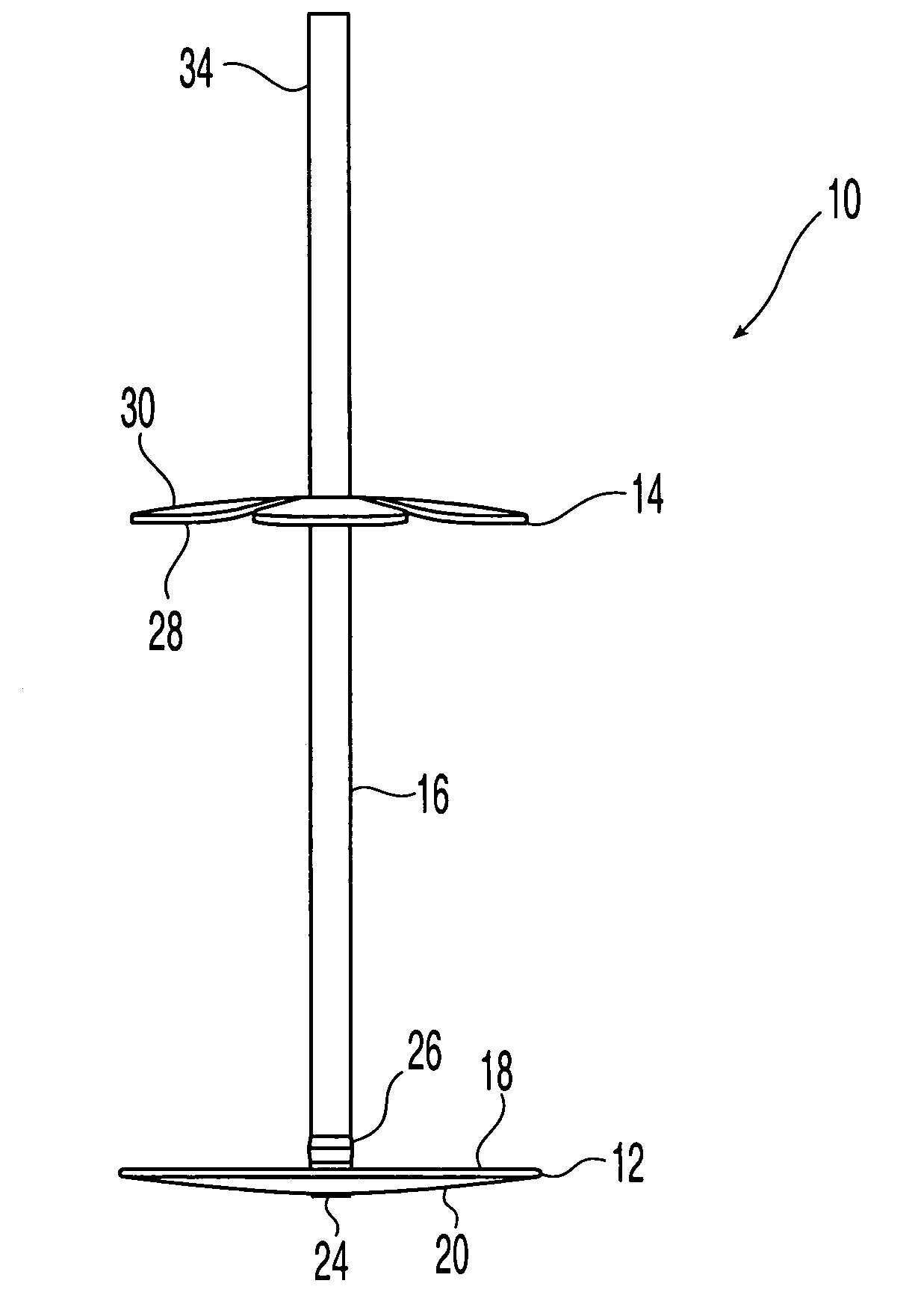
Cranial flap clamp and instrument for use therewith
InactiveUS7361178B2Reduce riskPrevent movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMechanical engineeringSkull
The disclosed cranial flap clamp includes first and second clamping members and an extension member. A portion of the first member is positionable against inferior surfaces of a bone flap and skull and a portion of the second member is positionable against superior surfaces of the flap and skull. The extension member extends from the first member and fits between the flap and skull. The second member has a through opening for receiving the extension member. Movement of either of the clamping members urges the inner surface of the first member against the inferior surfaces of the flap and skull and urges the inner surface of the second member against the superior surfaces of the flap and skull. A stop provided by mechanical deformation of the extension member at any location along its length secures the clamp.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Endoscopic methods and devices for transnasal procedures
Medical devices, systems and methods that are useable to facilitate transnasal insertion and positioning of guidewires and various other devices and instruments at desired locations within the ear, nose, throat, paranasal sinuses or cranium. Direct viewing of such placements via an endoscope.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Electrode System For Neural Applications
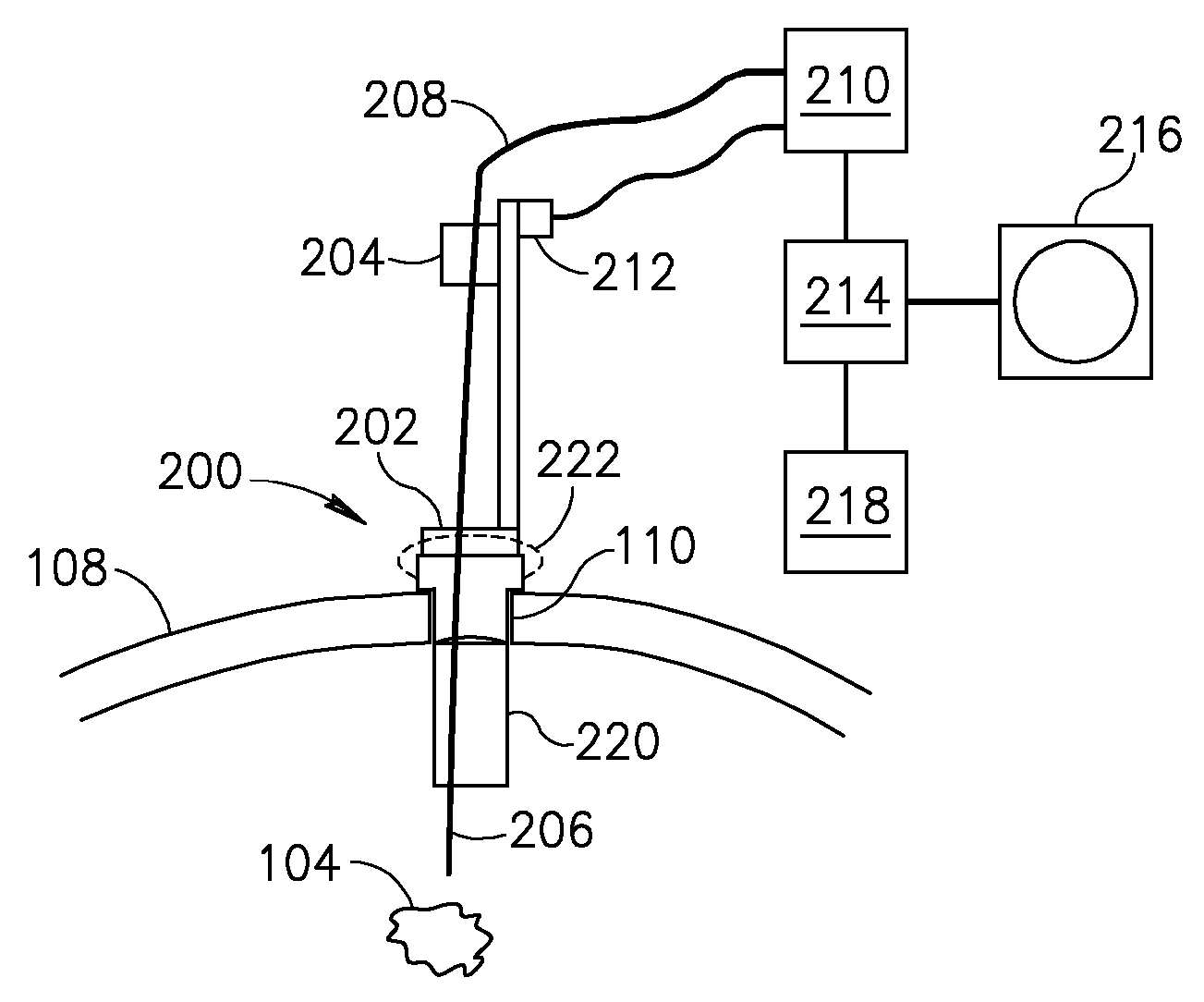
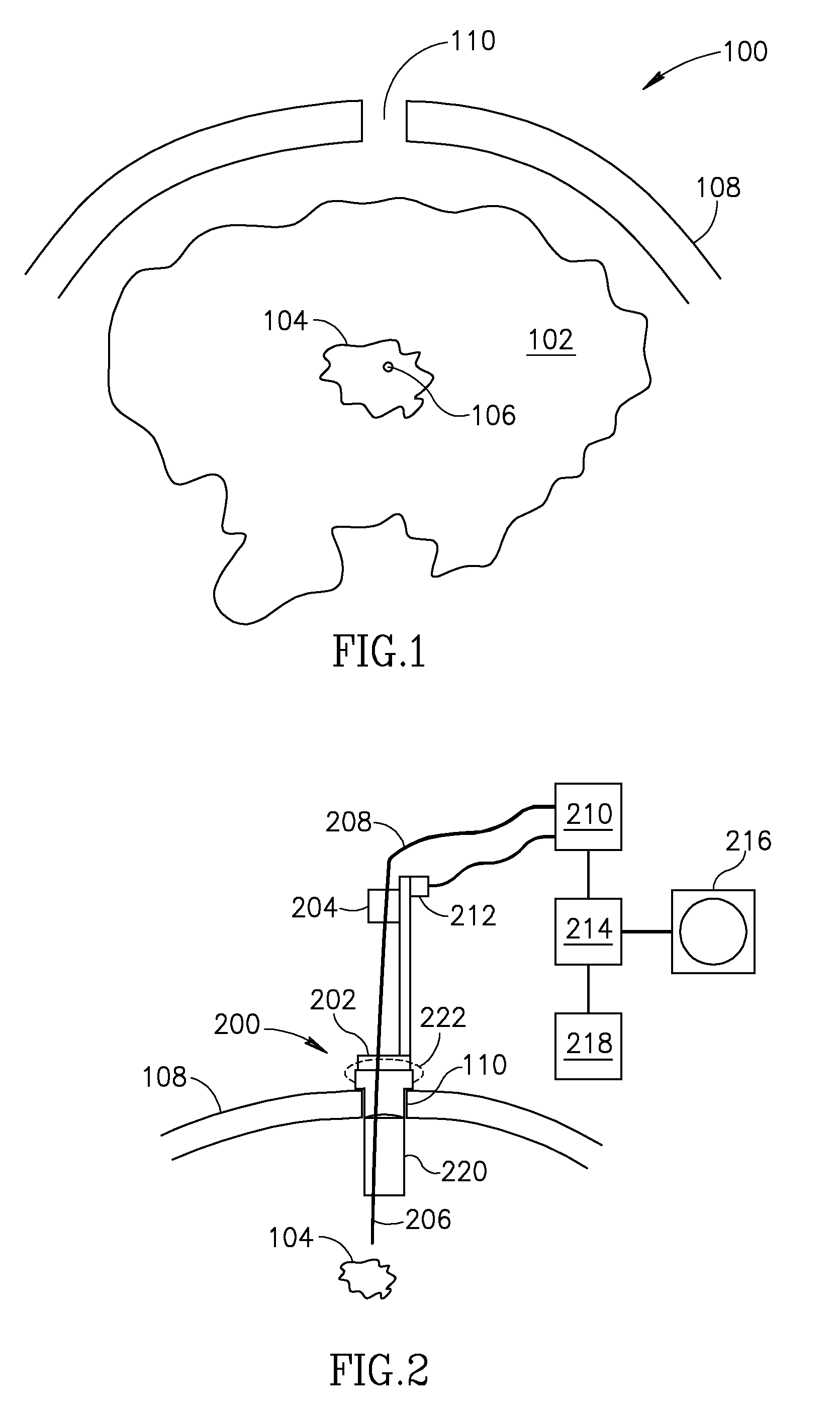
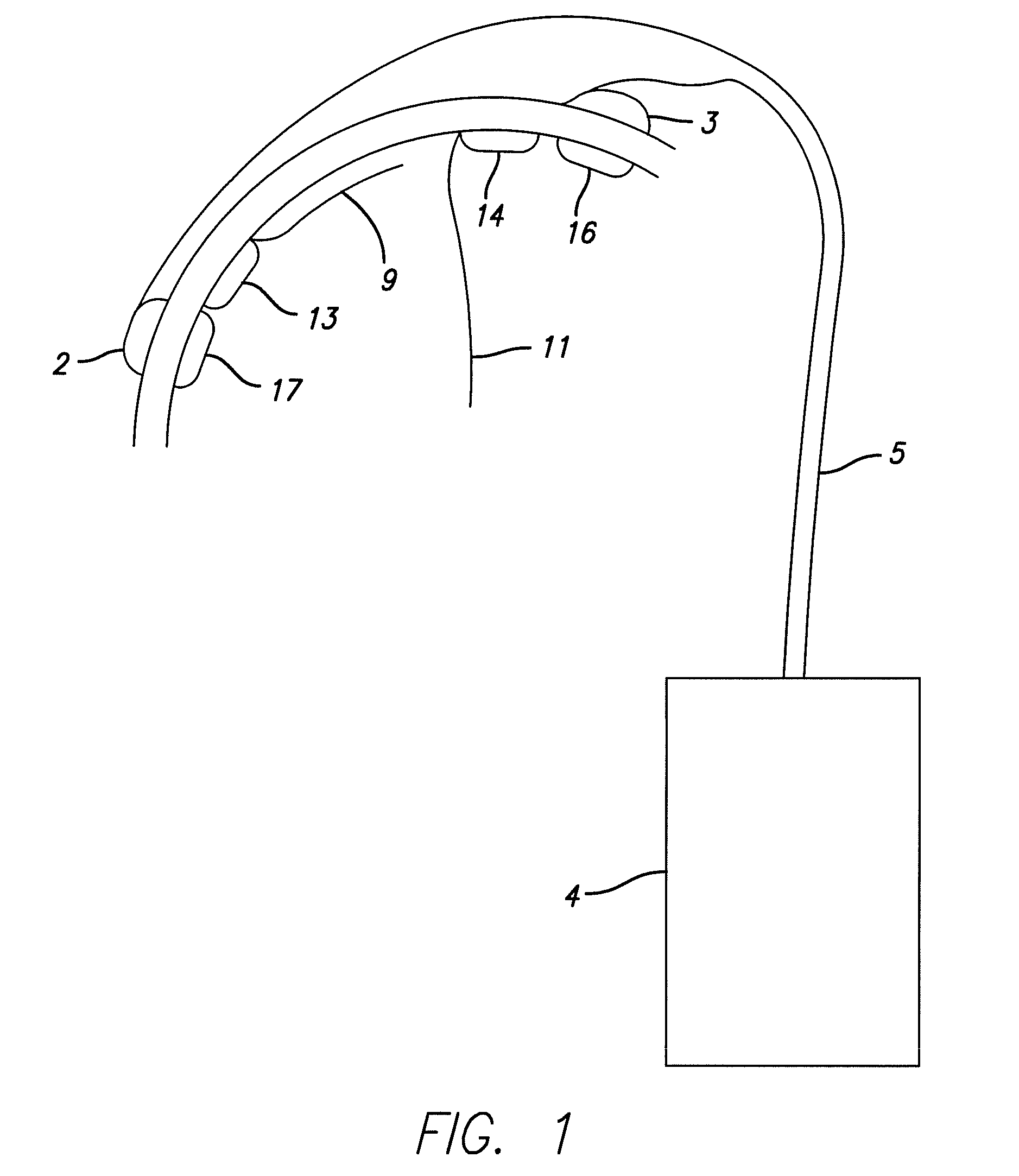
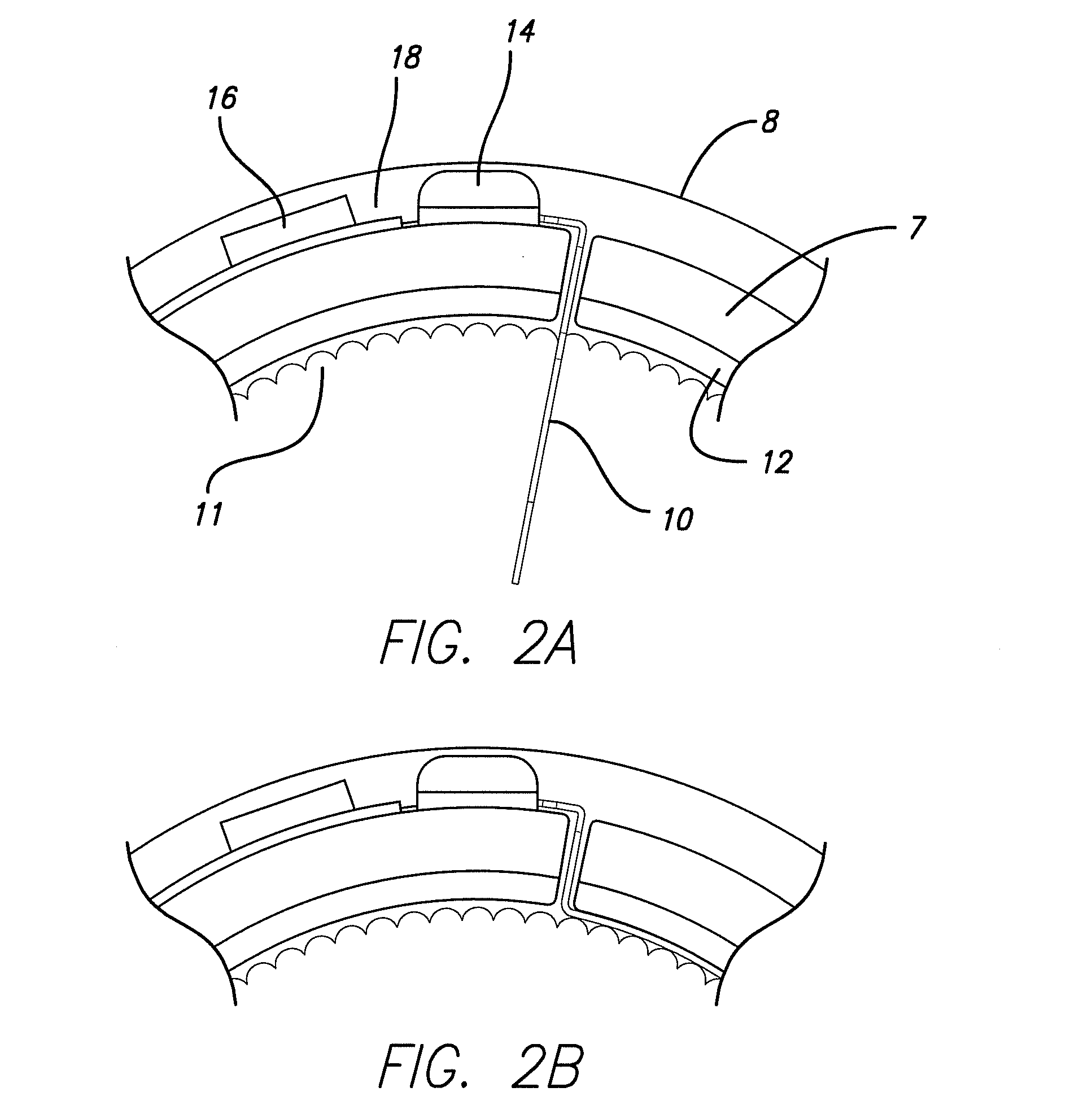
InactiveUS20070129770A1Prevents inference of drive mechanismFast and accurate determinationHead electrodesExternal electrodesSkullEnvironmental geology
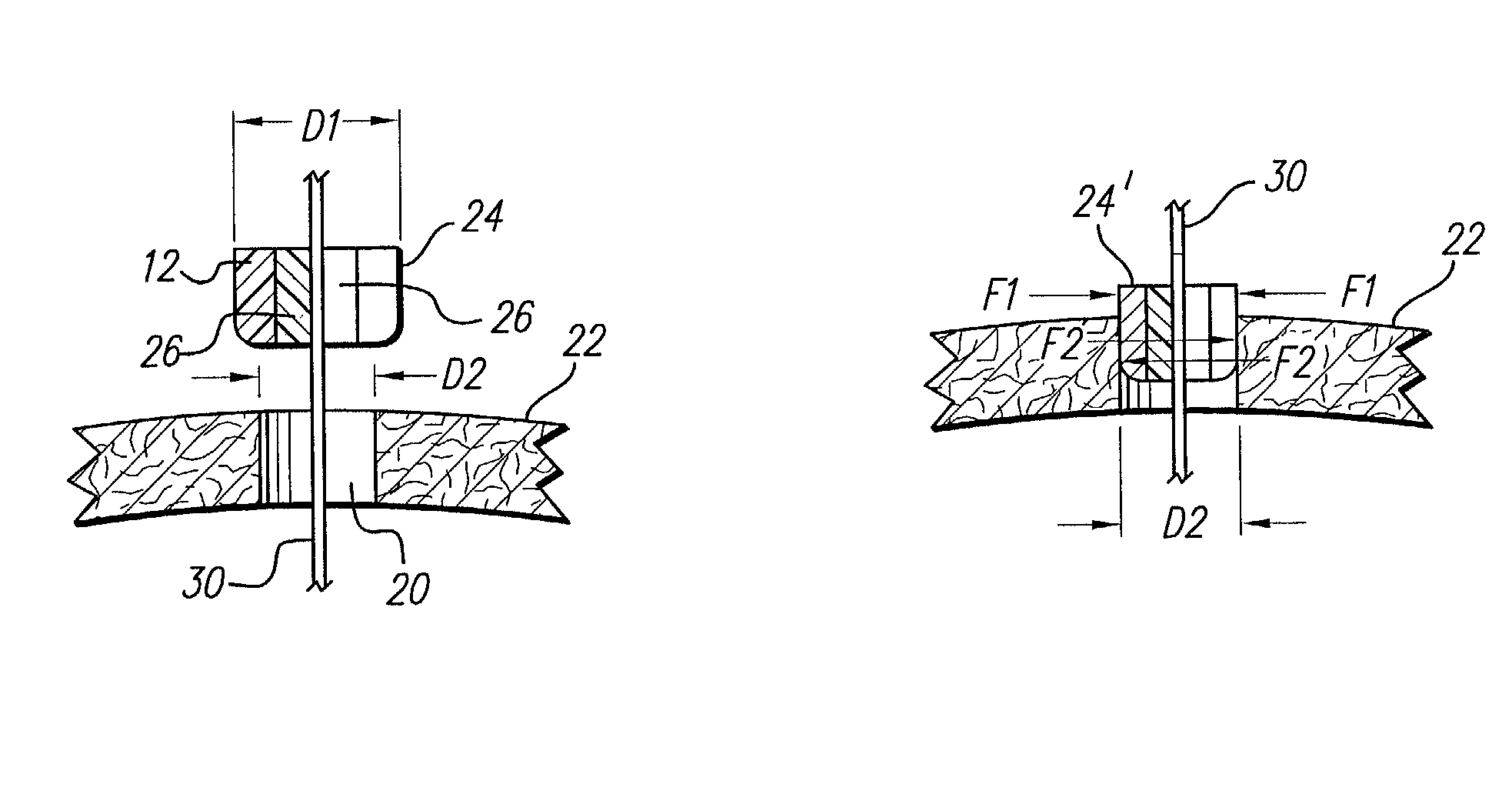
Methods and apparatus for positioning electrodes in a skull. In some embodiments of the invention multiple measurements are made and a desired location is determined or estimated from the results of the measurements.
Owner:YOUNIS IMAD
Cranial sealing plug
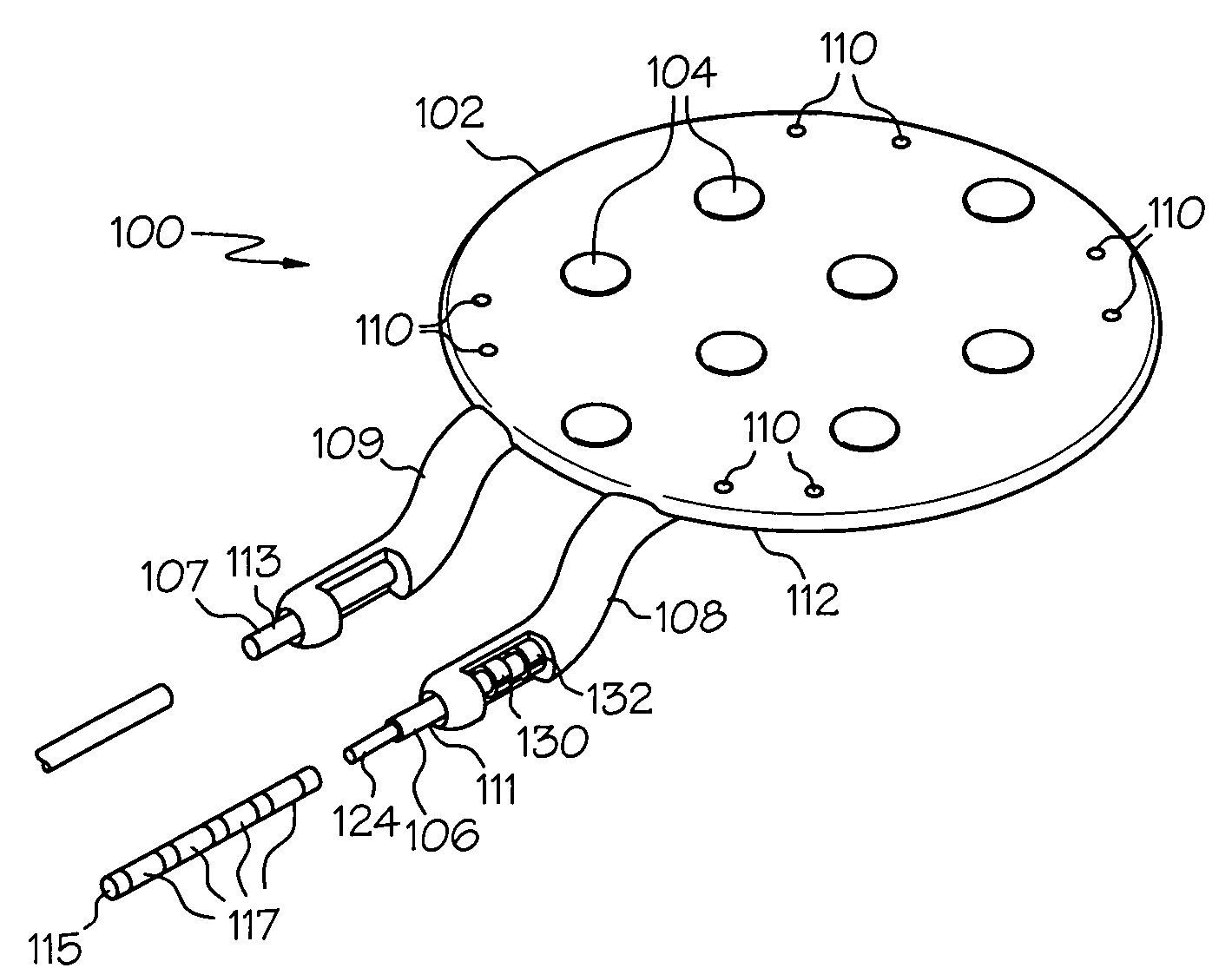
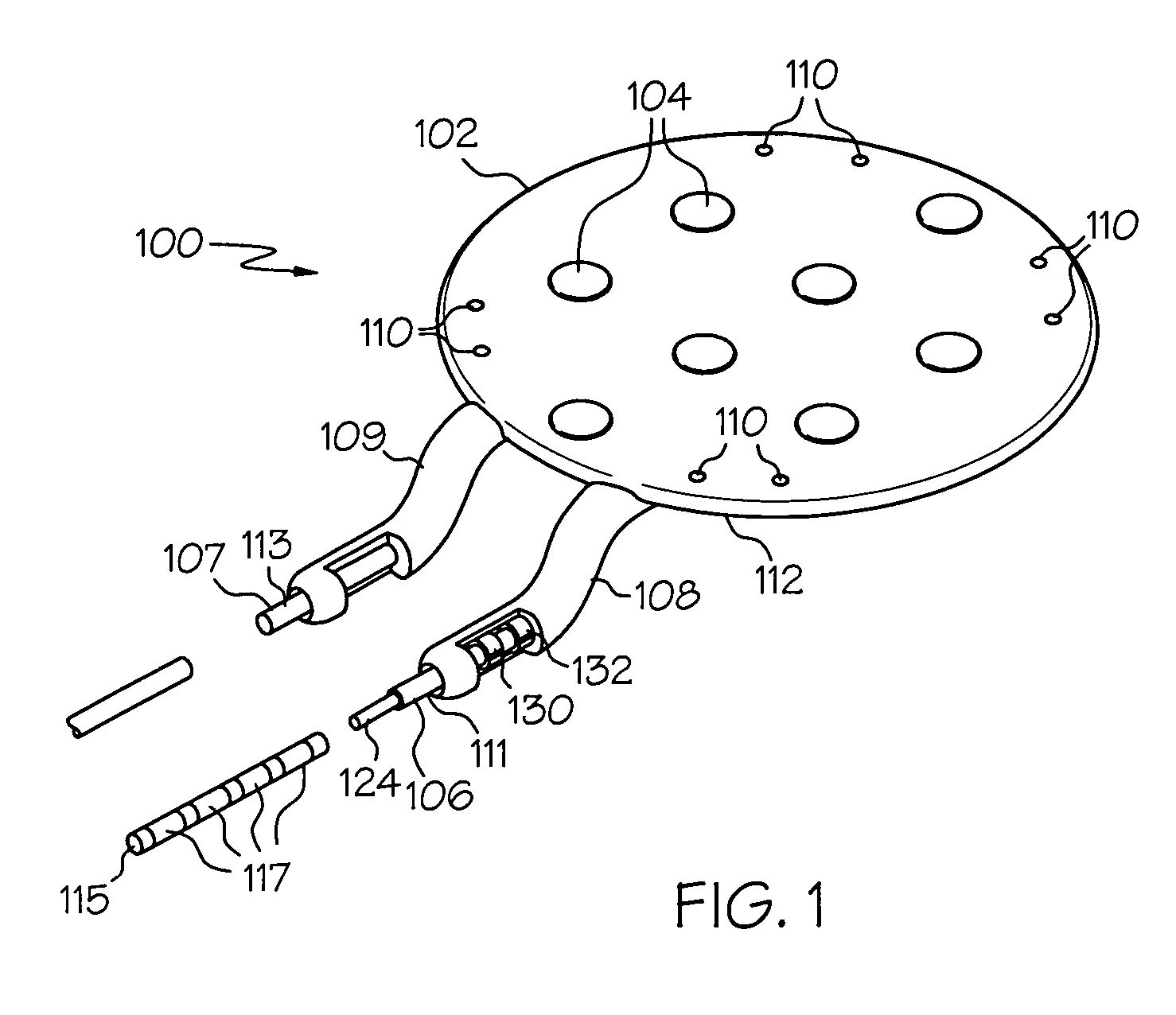
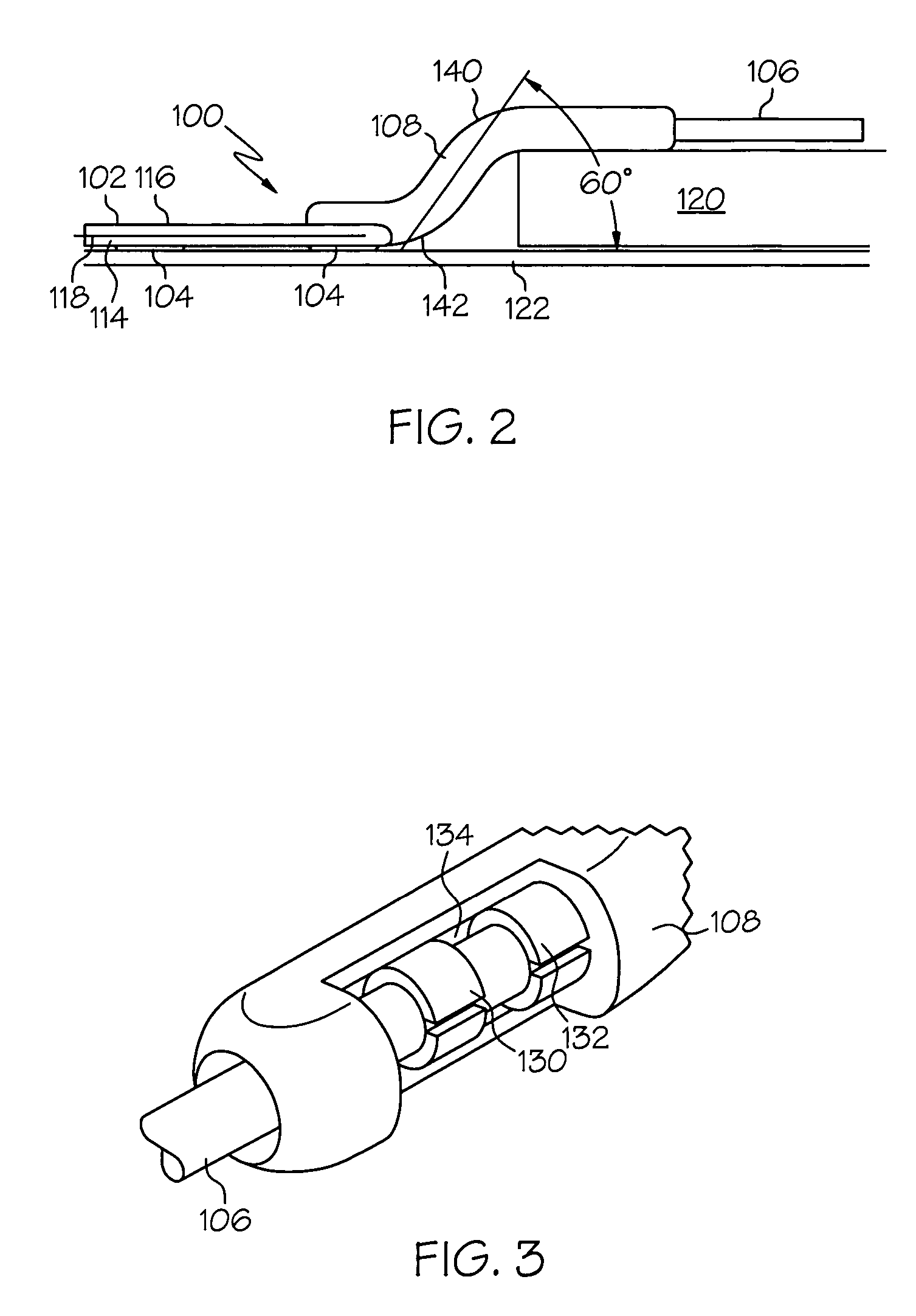
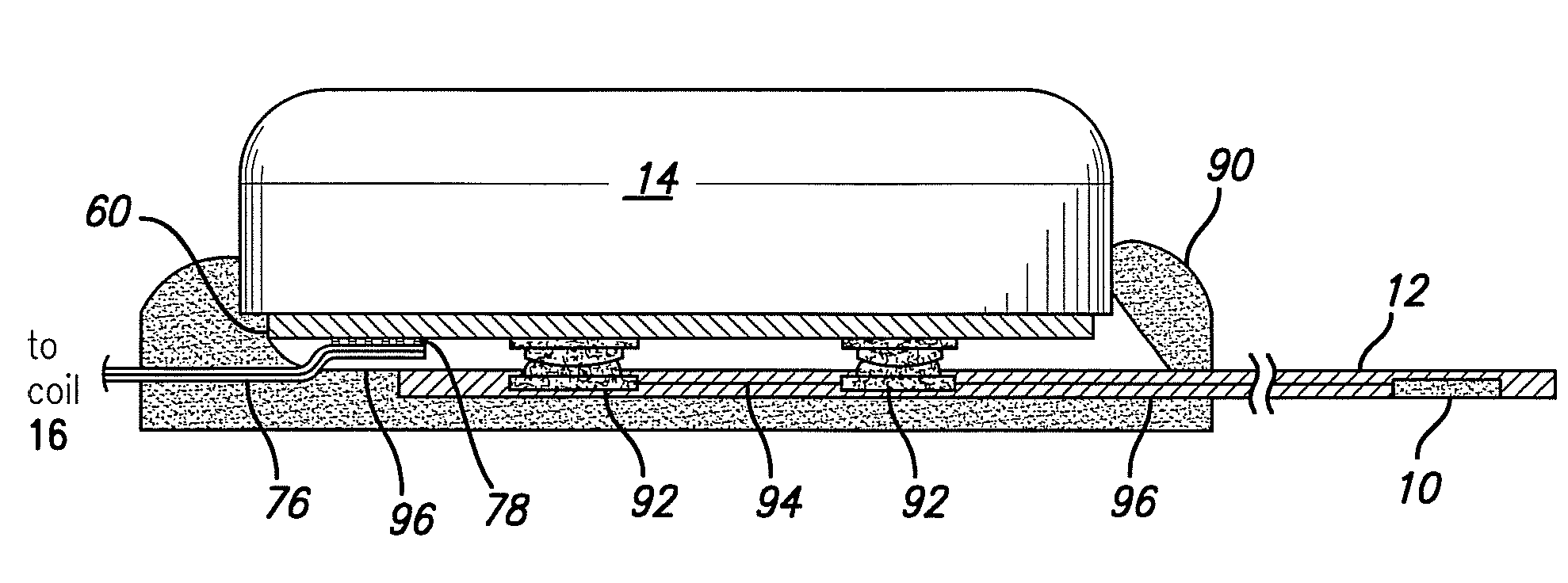
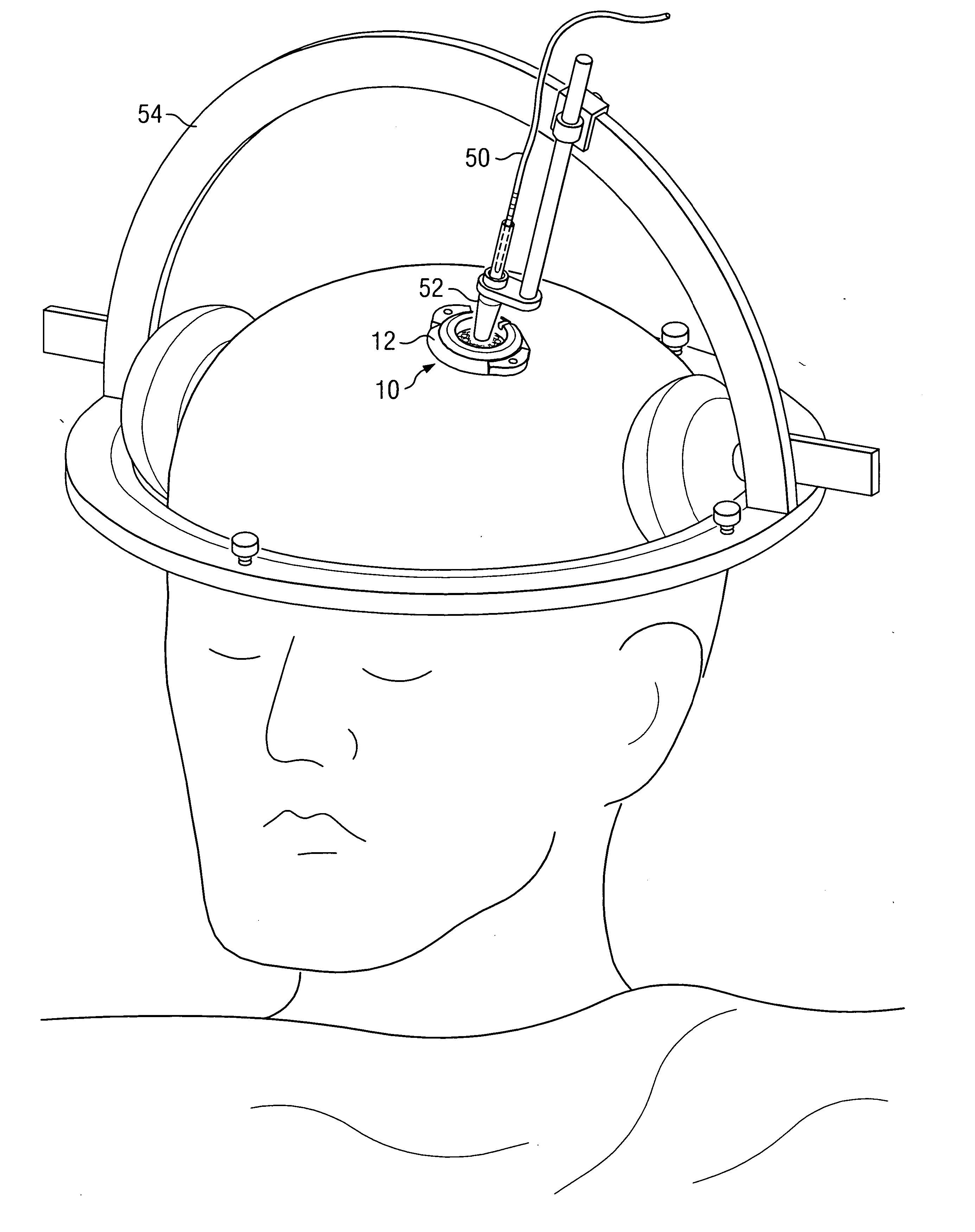
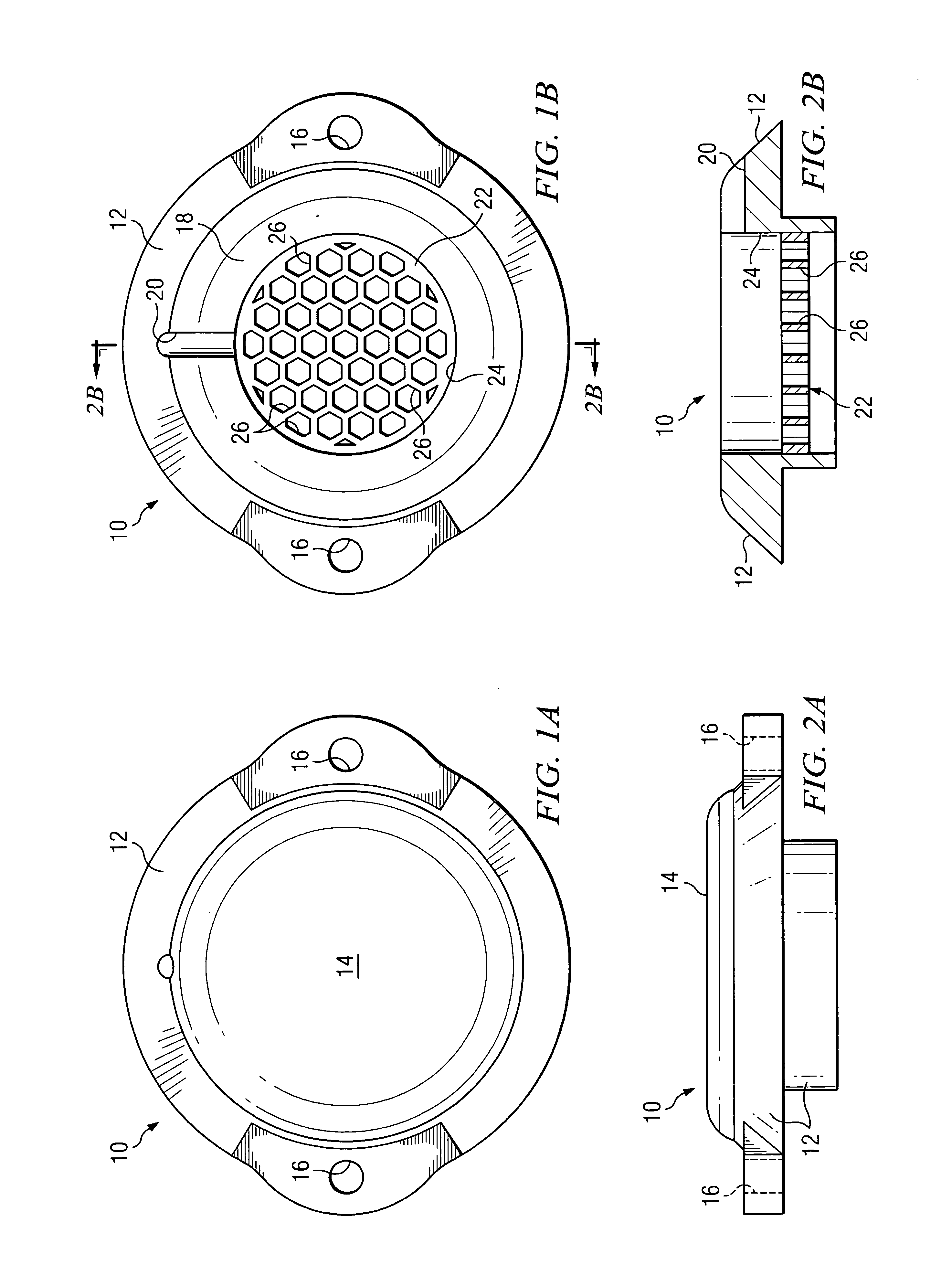
Various embodiments of a burr hole plug assembly offer significant improvements for allowing lead and / or cannula access through a burr hole drilled through a patient's skull in connection with a Deep Brain Stimulation system, and subsequent sealing of such burr hole. The various burr hole plug assemblies described: (a) accommodate various burr hole sizes and provide a secure fit in the burr hole; (b) accommodate various locations for lead positioning and adjustment; (c) allow the lead to remain in a static position when the burr hole plug assembly is placed; (d) protect the lead from fracture at the exit location of the plug; (e) remain flush with the skull to avoid skin erosion and to eliminate unsightly flange protrusion from the patients' skull; (f) adequately hold the lead in place over time; and (g) provide a selection of various types of burr hole plug assemblies and sizes for use by the implanting surgeon, thereby eliminating the need for surgeons to resort to custom plugs and plug assemblies made in the operating room specifically to fit a given patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
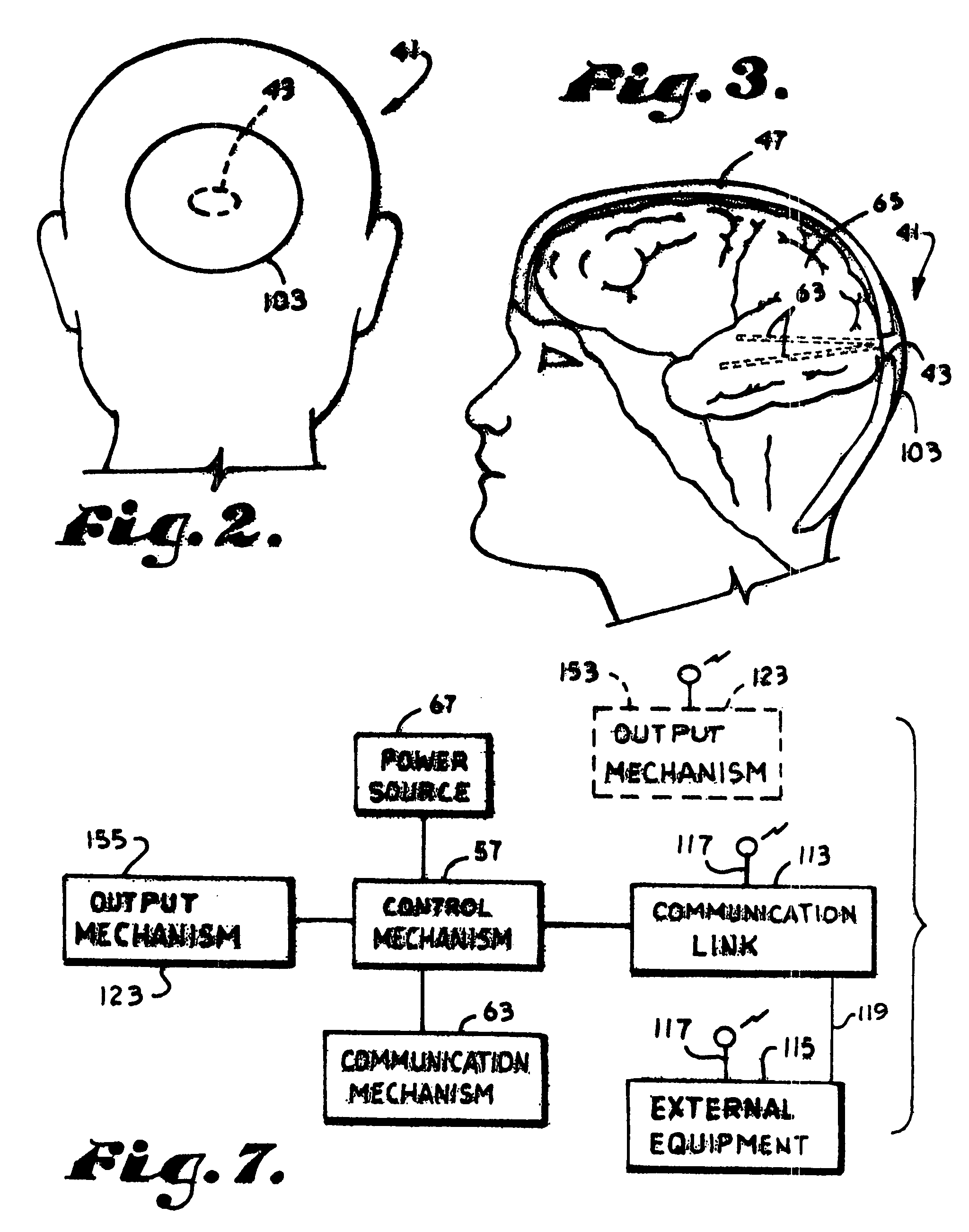
Bi-directional cerebral interface system
InactiveUS7177678B1Good conditionCost-effectiveElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyTelecommunications linkEngineering
A cerebral interface system including a housing mechanism spaced at least partially in a cavity formed in the subject's skull; an attaching mechanism; a fluid-tight sealing mechanism; a control mechanism; a communication mechanism with one or more sensors embedded in the subject's brain connecting the control mechanism to the subject's brain; a power source; an inner wall substantially aligned with an inner surface of the subject's skull; an outer wall which may include an auxiliary portion extending tangentially outwardly from the cavity formed in the subject's skull; a communication link connecting the control mechanism to external apparatus for transmitting or receiving information related to detecting, predicting, controlling, or aborting abnormal brain activity of the subject; and an output mechanism which is activatable by the control mechanism.
Owner:OSORIO IVAN +1
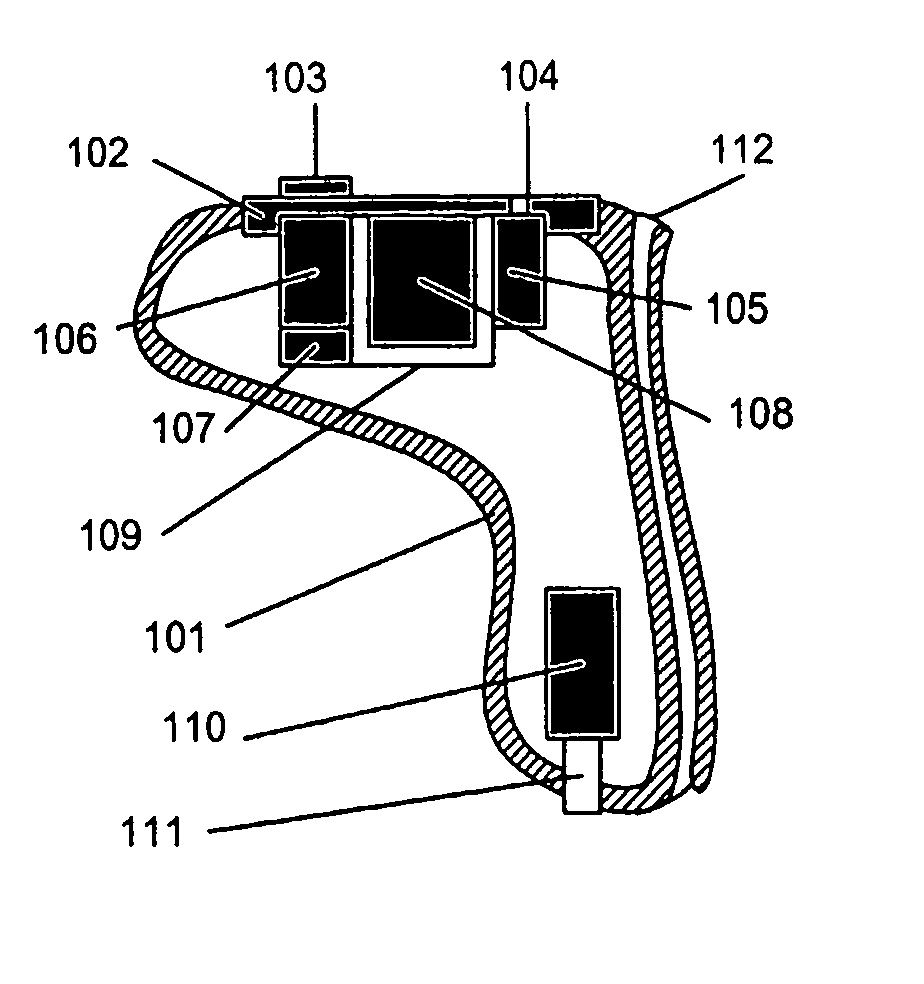
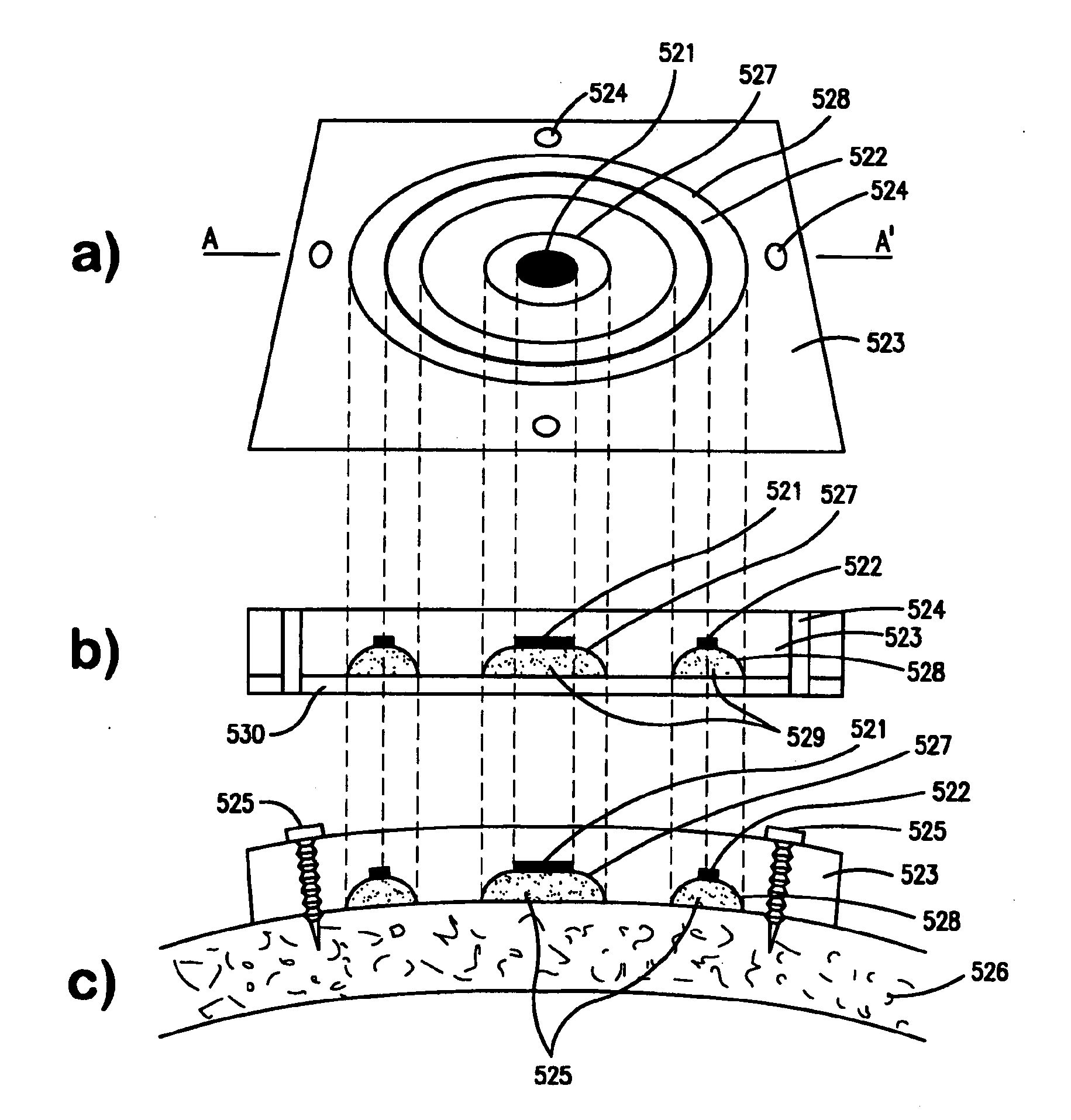
Therapeutic Cranial Wrap for a Contrast Therapy System
The present invention relates to a therapeutic cranial wrap for use with a thermal contrast therapy systems and methods for providing a temperature regulated fluid. The cranial wrap includes an active thermal exchange bladder and an active compression bladder, adapted to fit the cranial therapy site. The thermal exchange bladder may be coupled to the thermal contrast therapy system. The compression bladder may compress the therapy site. In some embodiments, the compressive bladder may be integrated into the thermal exchange bladder, or may be omitted. The cranial wrap also includes a contoured shell, known as a hood shaped therapy pad, which is adapted to snugly fit the cranial therapy site and provide neck support. Adjustable straps, including at least one strap that circumvents the cranium, secure the cranial wrap in a fitted position adjacent the therapy site. The cranial wrap couples to the thermal contrast therapy system which includes a hot and cold fluid reservoir, a mixing valve, and a fluid pump.
Owner:VITALWEAR
Infusion device and method for infusing material into the brain of a patient
InactiveUS20060129126A1Utilized effectively and accuratelyReduce flow rateGuide needlesMulti-lumen catheterFluid infusionGuide tube
A fluid infusion device and a method of using the same. The device includes an outer, flexible guide catheter having a distal end for introduction beneath the skull of a patient and a proximal end remaining external of the patient. A flexible infusion fiber is located within the guide catheter and has a distal end extending outwardly from the guide catheter to be located in a target area within the patient's brain. The infusion fiber can be fixed or axially movable within the guide catheter. In the latter embodiment, the proximal end of the infusion fiber extending outwardly from the guide catheter can be manipulated to locate the distal end of the infusion fiber in the target area. An infusion pump is connected to the proximal end of the infusion fiber to infuse a minute quantity of fluid at an extremely low flow rate into the brain of the patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Cortical Implant System for Brain Stimulation and Recording
ActiveUS20150157862A1Shorter electrode arraysLess distortionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLaminating printed circuit boardsDiseaseEngineering
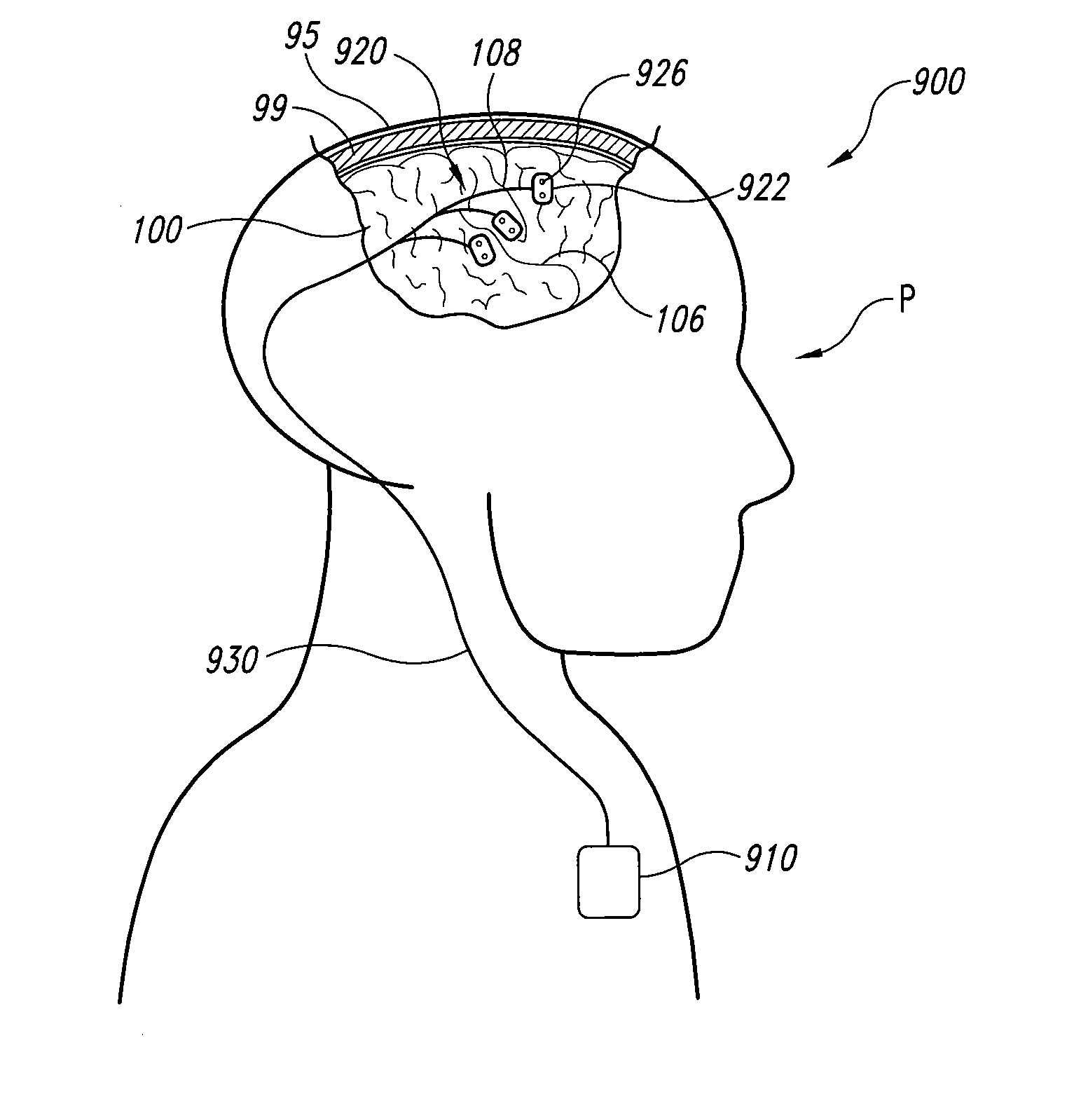
The present invention consists of an implantable device with at least one package that houses electronics that sends and receives data or signals, and optionally power, from an external system through at least one coil attached to at least one package and processes the data, including recordings of neural activity, and delivers electrical pulses to neural tissue through at least one array of multiple electrodes that are attached to the at least one package. The device is adapted to electrocorticographic (ECoG) and local field potential (LFP) signals. A brain stimulator, preferably a deep brain stimulator, stimulates the brain in response to neural recordings in a closed feedback loop. The device is advantageous in providing neuromodulation therapies for neurological disorders such as chronic pain, post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), major depression, or similar disorders. The invention and components thereof are intended to be installed in the head, or on or in the cranium or on the dura, or on or in the brain.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC
Apparatus and method for neural-signal capture to drive neuroprostheses or control bodily function
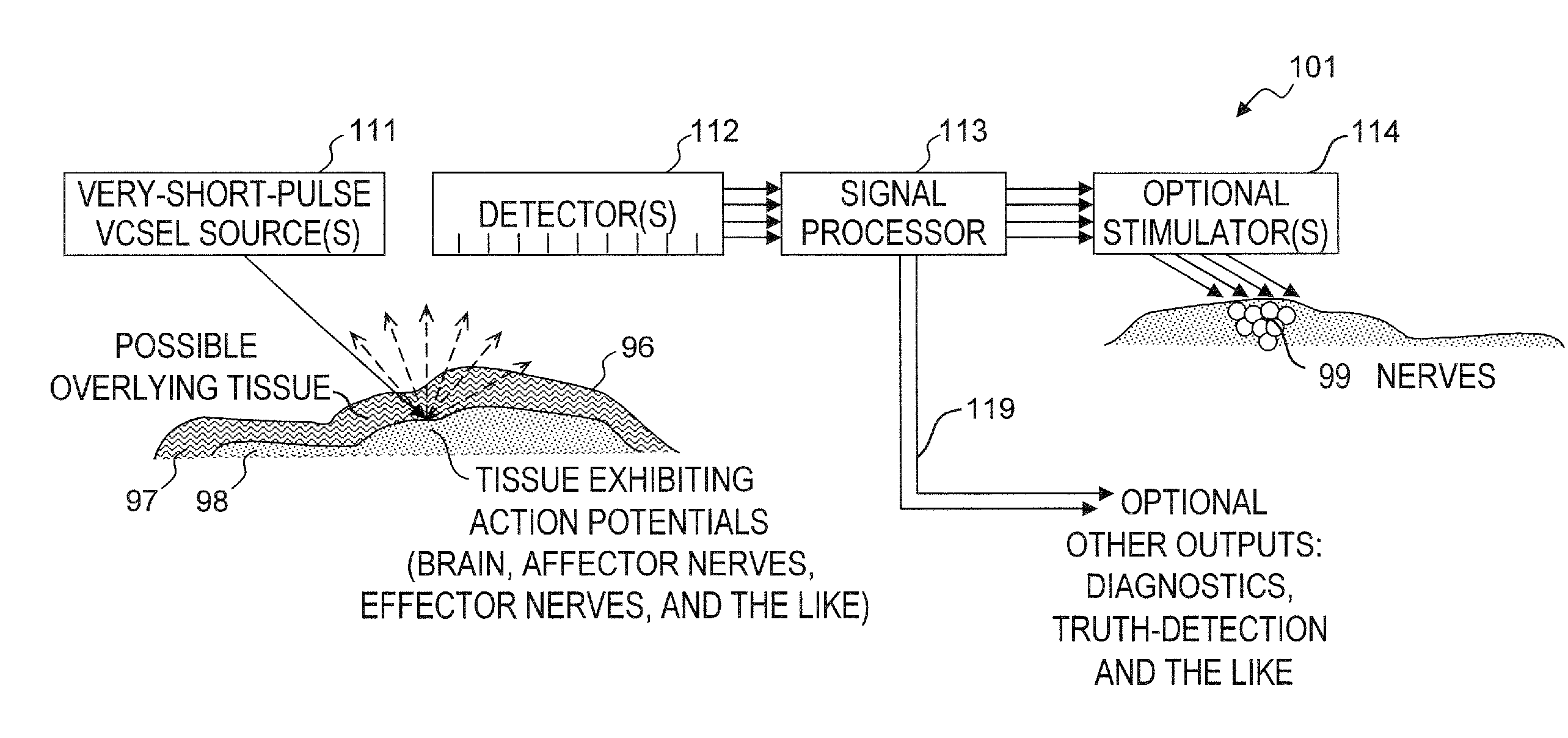
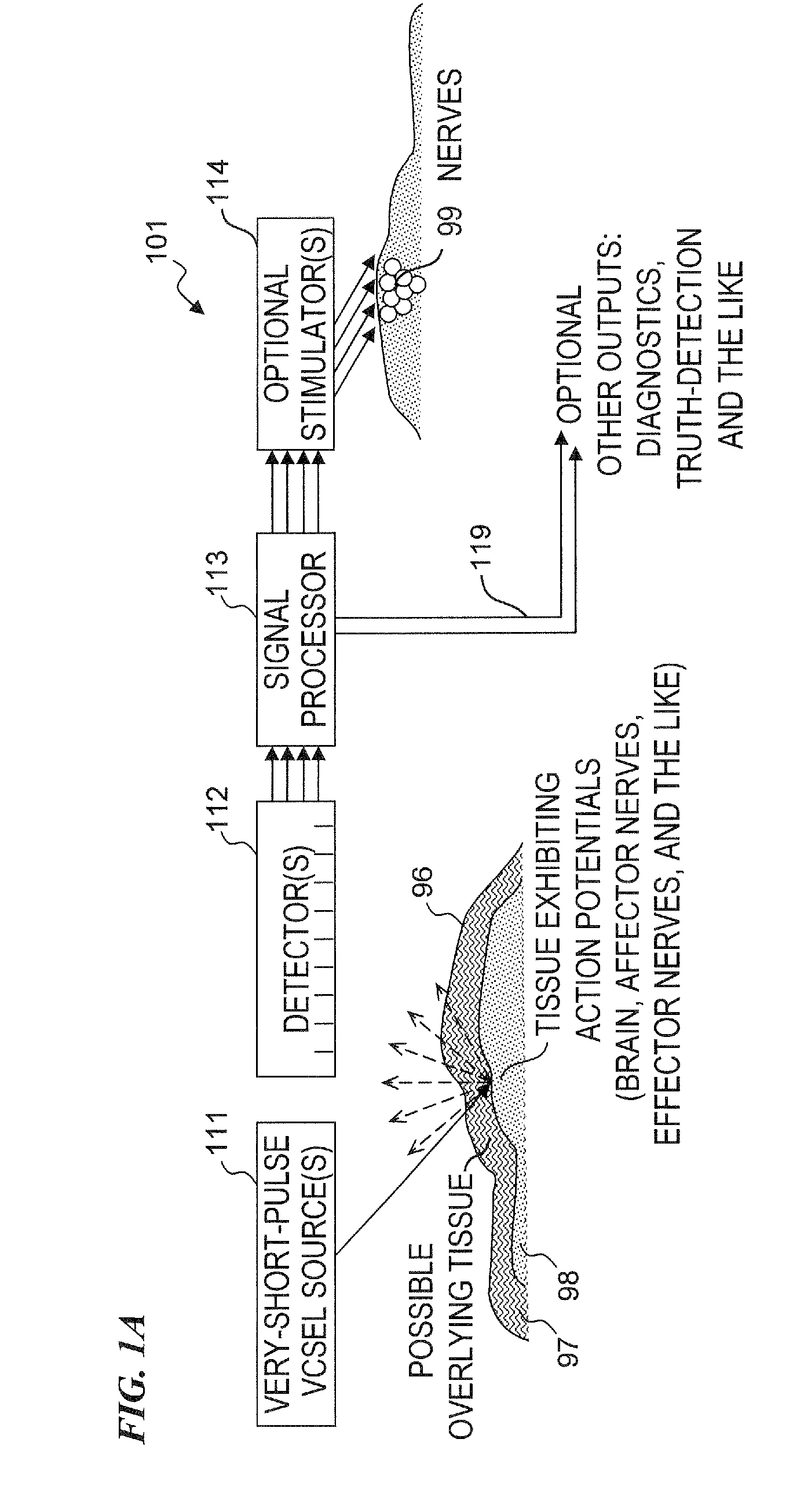
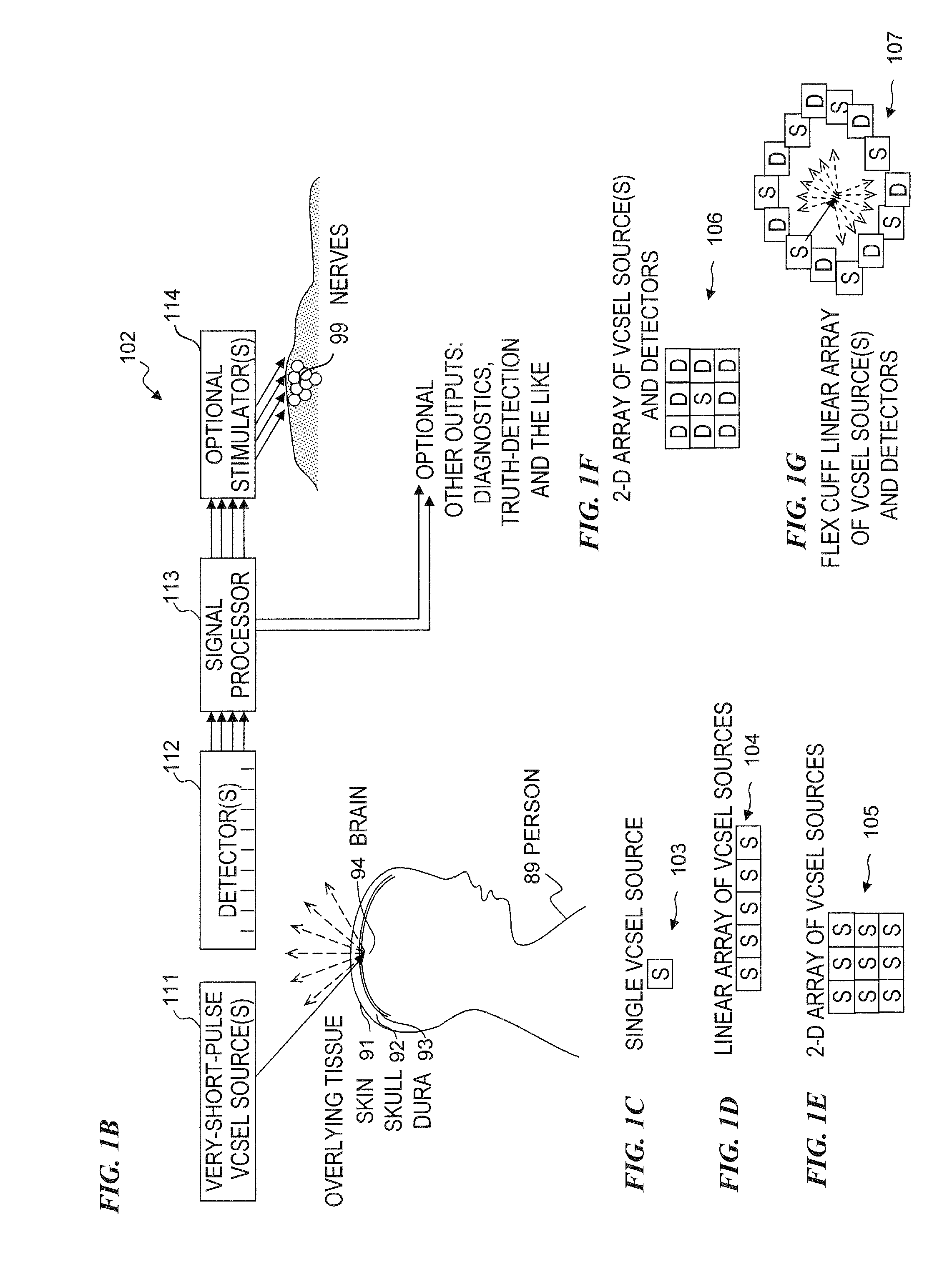
Method and apparatus for detecting nerve activity of an animal. Some embodiments include outputting a light pulse having a wavelength onto a volume of animal tissue such that the light pulse interacts with active nerves of the tissue; measuring a light signal resulting from the interaction of the light pulse with the tissue; transmitting an electrical signal based on the measured light signal; signal-processing the electrical signal; and outputting a response signal, which can optionally be used to control a prosthetic device, stimulate another nerve, or display / diagnose a condition. Some embodiments output a plurality of light wavelengths and / or pulses, which are optionally high-frequency intensity modulated. Some embodiments analyze DC, AC, and phase components of signals to spatially resolve locations of neural activity. Some embodiments output light pulse(s) and detect the resultant light from outside a human skull to detect neural activity of human brain tissue inside the skull.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Electrode configurations for reducing invasiveness and/or enhancing neural stimulation efficacy, and associated methods
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Electrical stimulation system and associated apparatus for securing an electrical stimulation lead in position in a person's brain
InactiveUS20050143800A1Stable positionPrevent movementHead electrodesDiagnosticsElectricityBurr holes
In one aspect, an apparatus is provided for securing an electrical stimulation lead in position in a person's brain. The apparatus includes a flexible disc comprising a substantially radial slot adapted to secure the lead in position within the brain after implantation. The slot is adapted to elastically expand as the lead is inserted into the slot and is also adapted to elastically contract on the lead to secure the lead in position within the brain after implantation. The apparatus further includes a ring adapted to seat within a burr hole formed in the person's skull. The ring comprises a channel adapted to receive and secure the flexible disc.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Treatment of neurological disorders via electrical stimulation, and methods related thereto
ActiveUS20110137381A1Prevent seizure activityImprove responseHead electrodesNon invasiveElectrical stimulations
Disclosed are medical devices for the prevention and / or treatment of neurological disorders via electrical stimulation, and methods related thereto. The devices may also be utilized to detect disorders before the prevention or treatment of a neurological disorder. These devices are minimally or non-invasive. The present medical devices comprise various components, which include electrodes and control electronics. The electrodes are targeting electrodes constructed from ring type structures or virtually connected disc type arrays. The electrodes are located entirely outside the skull. The present medical devices also comprise one or more subsystems, a control system, a battery unit, and wires connecting the one or more subsystems. These devices may also be used for acute seizure control.
Owner:BRAINVITAL CORP
Electrical stimulation system and associated apparatus for securing an electrical stimulation lead in position in a person's brain
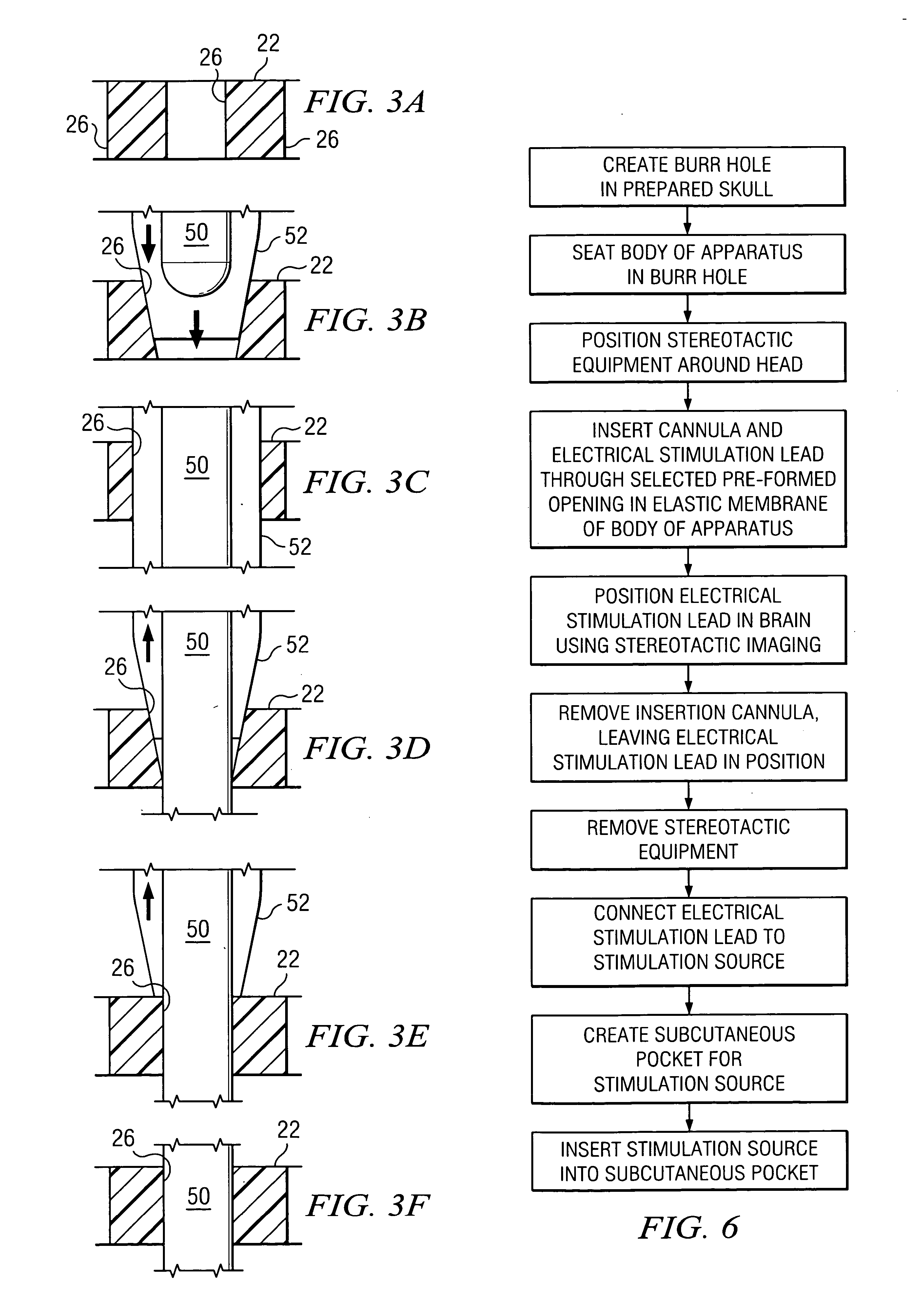
InactiveUS20050143799A1Simply and easily insertedReduce riskHead electrodesIntracranial pressure measurementElectricityBurr holes
In one aspect, an apparatus is provided for securing an electrical stimulation lead in position in a person's brain. The apparatus includes a body configured to seat within a burr hole formed in the person's skull. The apparatus also includes a central elastic membrane coupled to the body and extending across a central aperture of the body. The elastic membrane includes a number of pre-formed openings provided for purposes of securing the lead in position within the brain after implantation. Each pre-formed opening may penetrate through an entire thickness of the elastic membrane. Each pre-formed opening may be selected for insertion of the lead into the brain. Each pre-formed opening is adapted to elastically expand as the lead is inserted through the pre-formed opening and positioned in the brain and is adapted to elastically contract on the lead to secure the lead in position within the brain after implantation.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com