Patents
Literature
601 results about "Fluid infusion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intravenous infusion administration of fluids into a vein by means of a steel needle or plastic catheter. This method of fluid replacement is used most often to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance, or to correct fluid volume deficits after excessive loss of body fluids, in patients unable to take sufficient volumes orally.
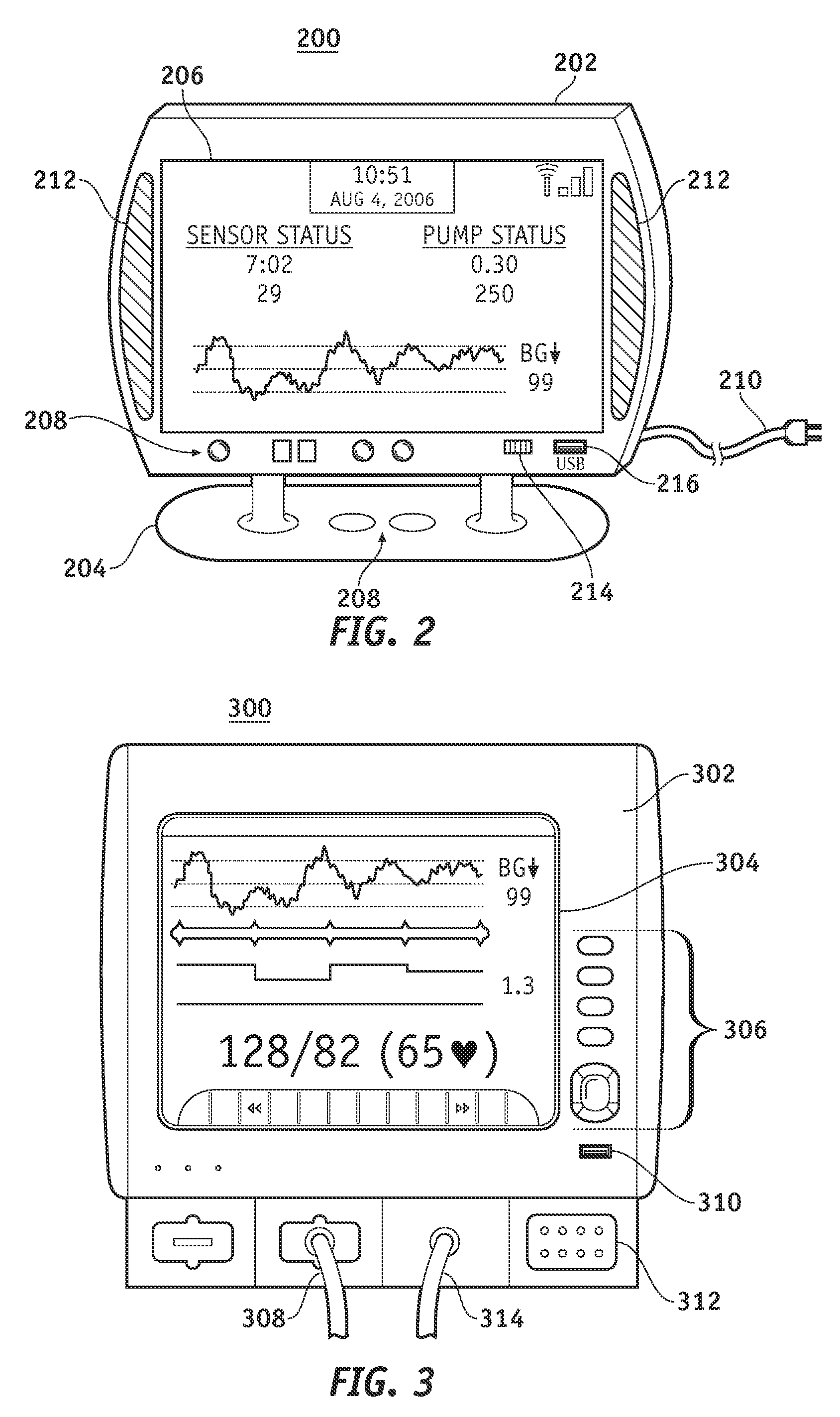
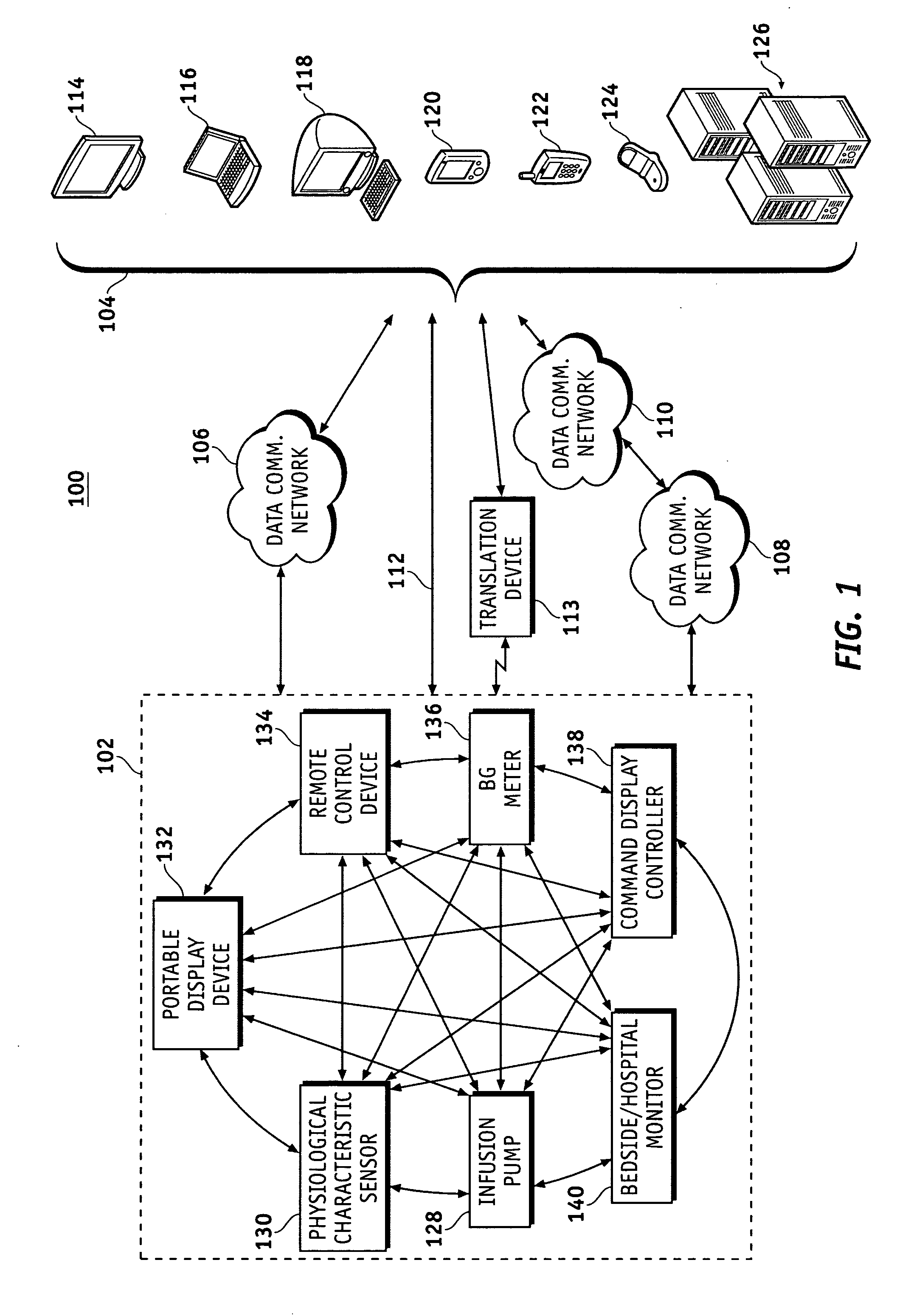
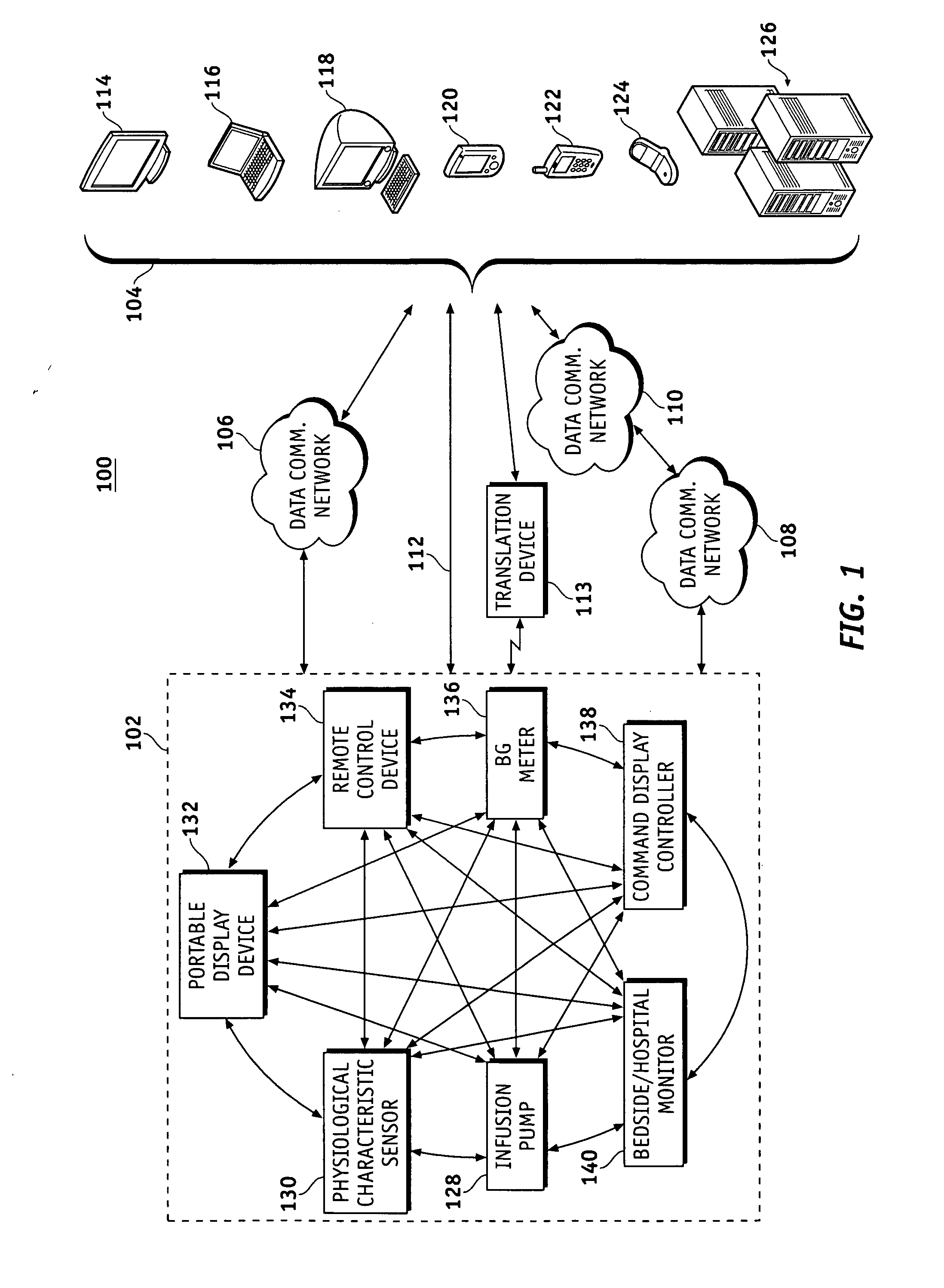
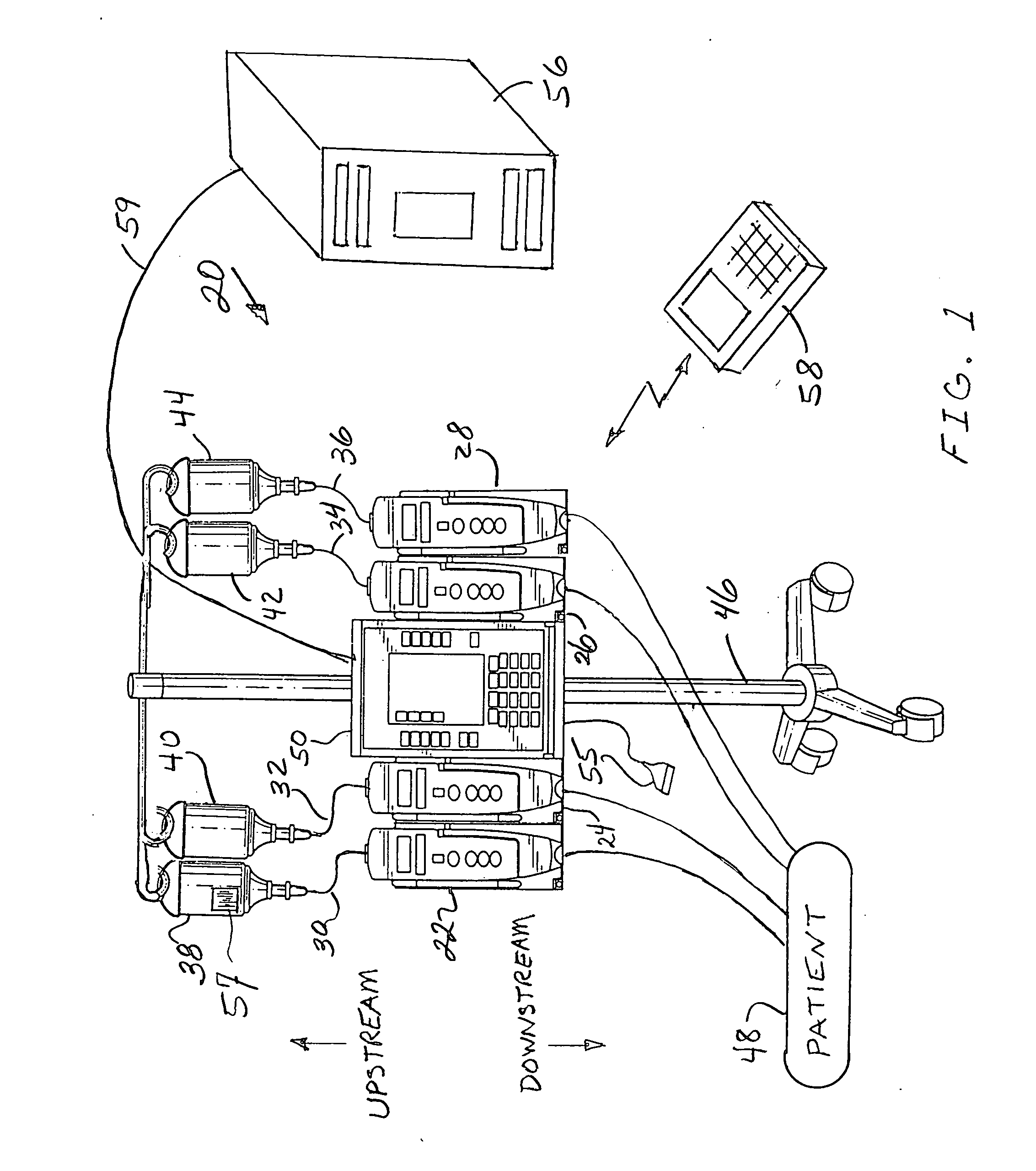
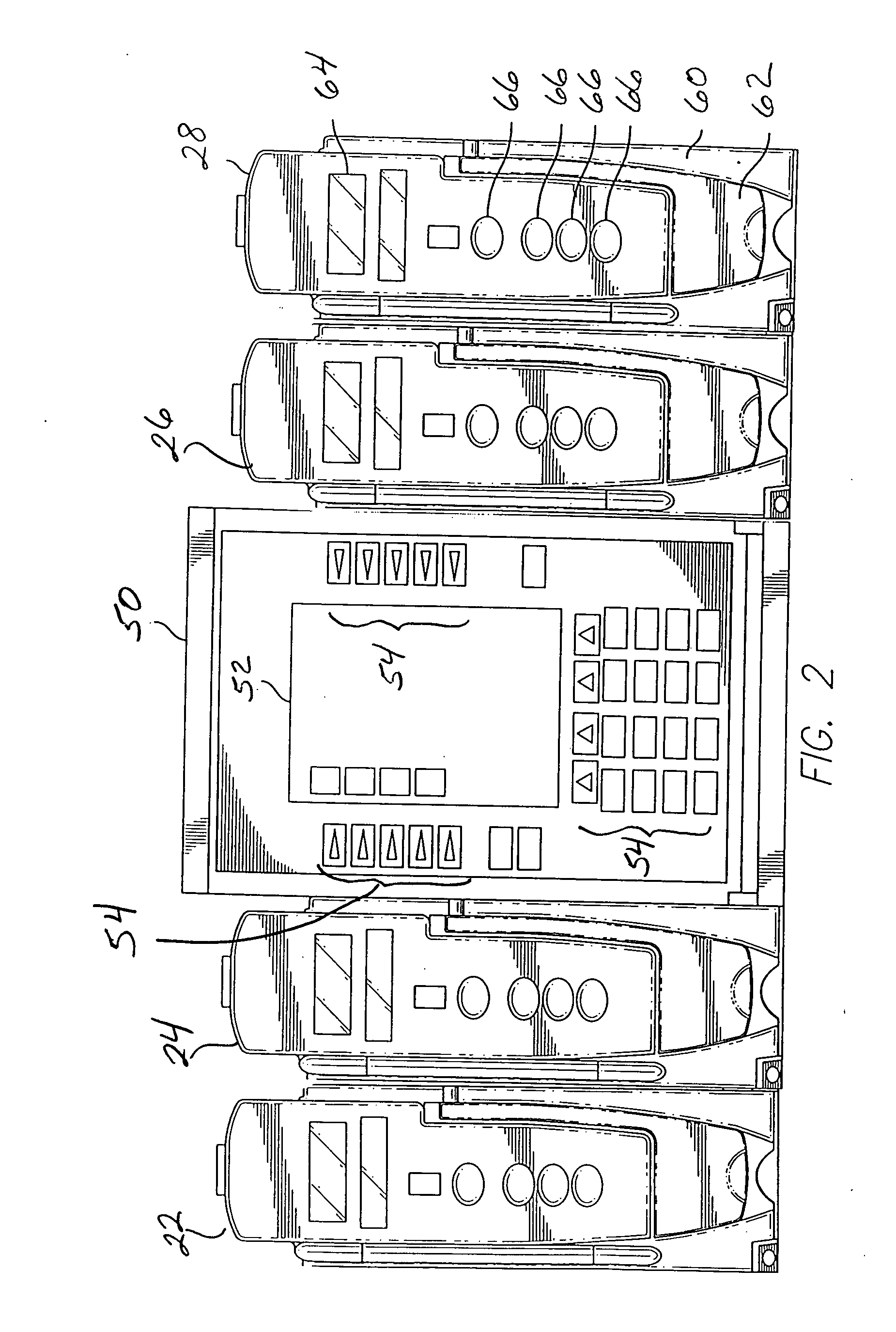
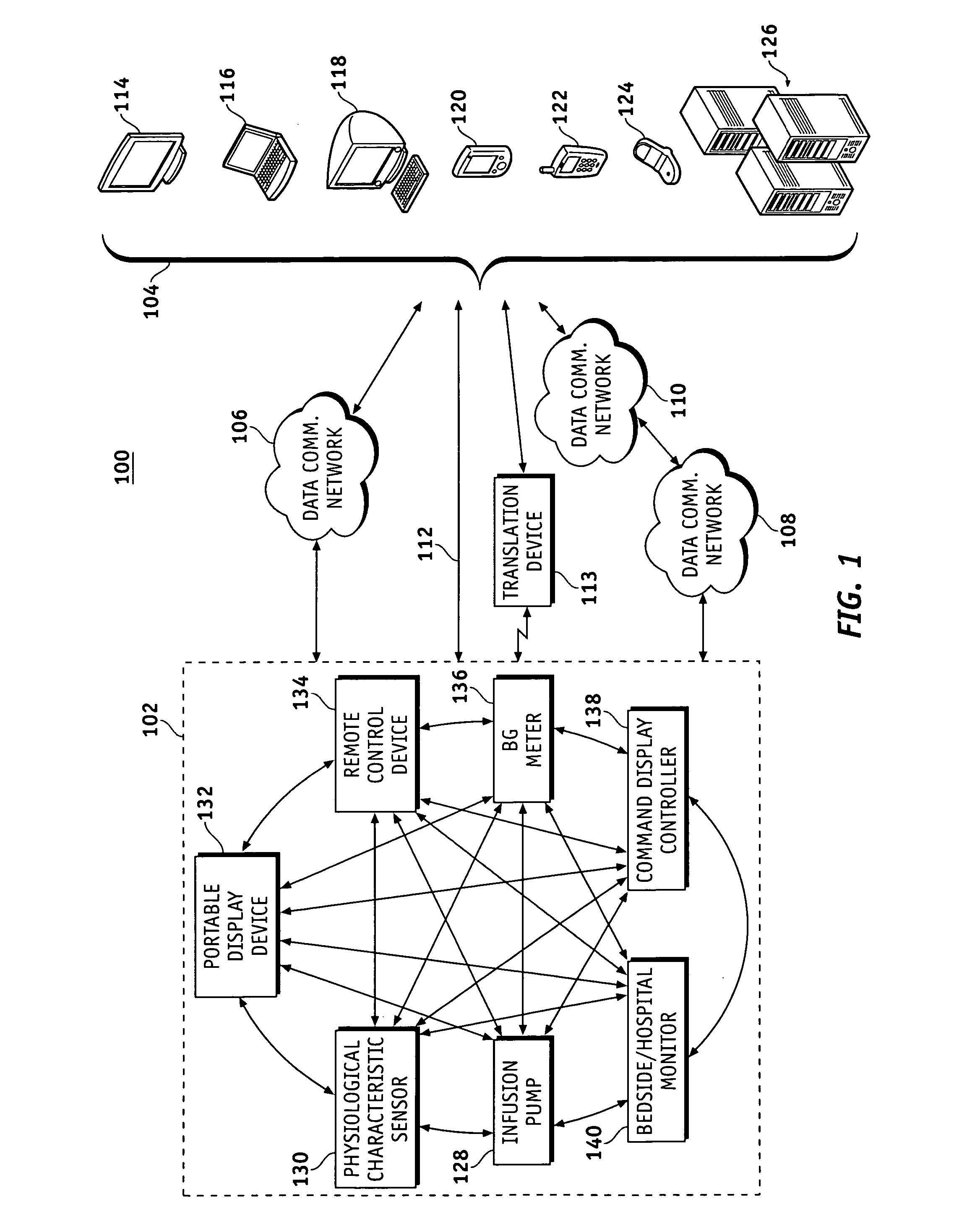
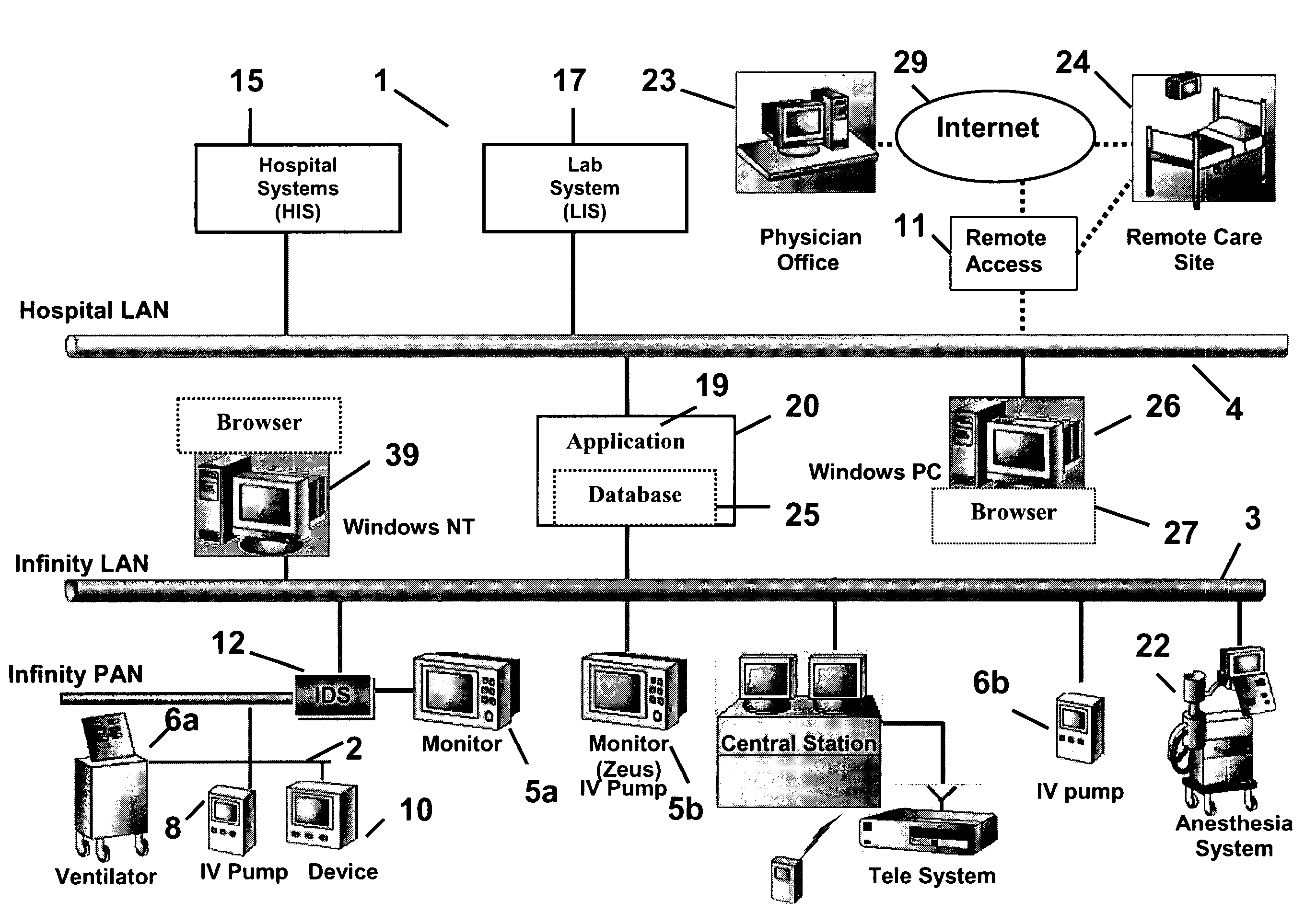
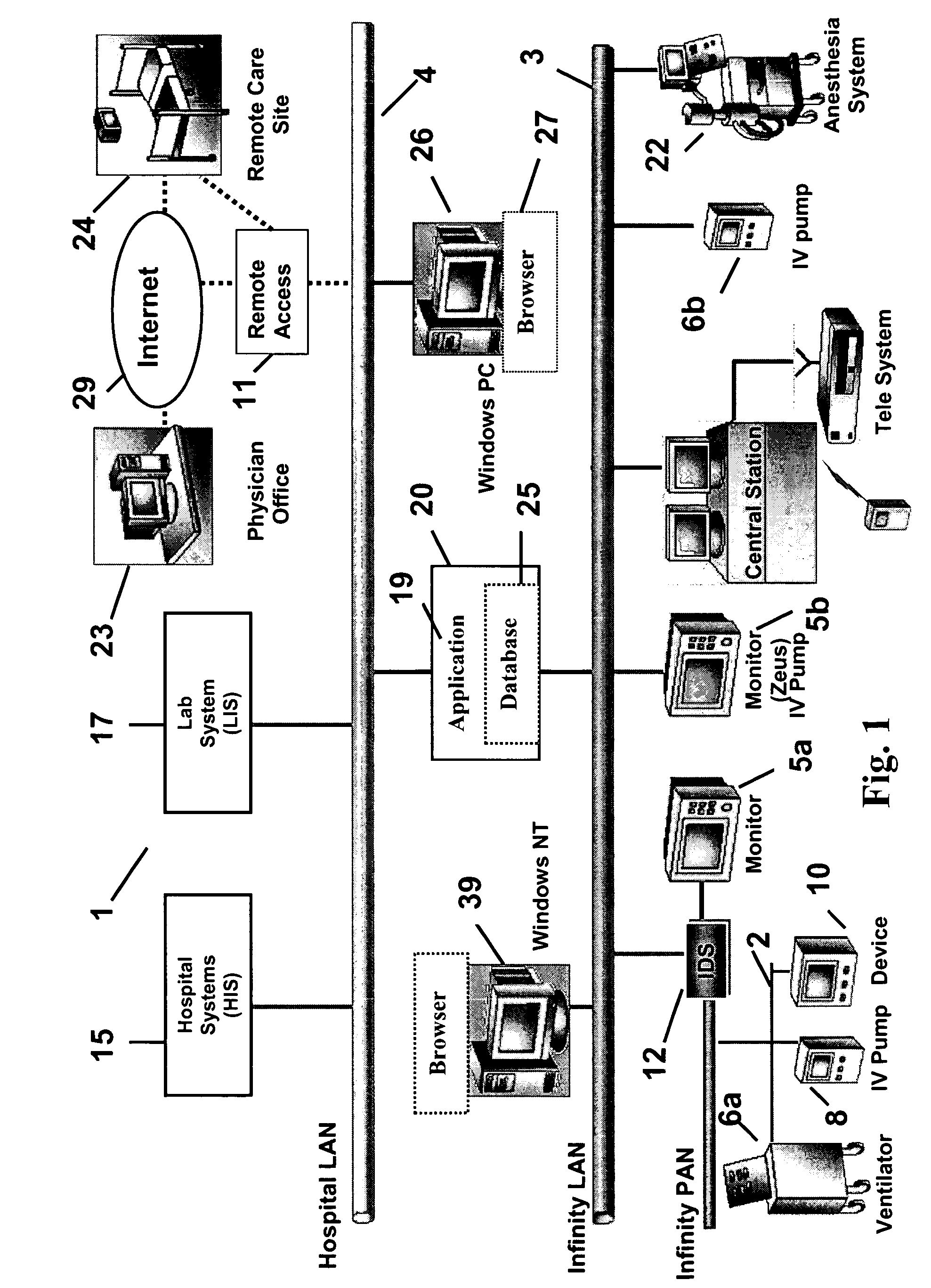
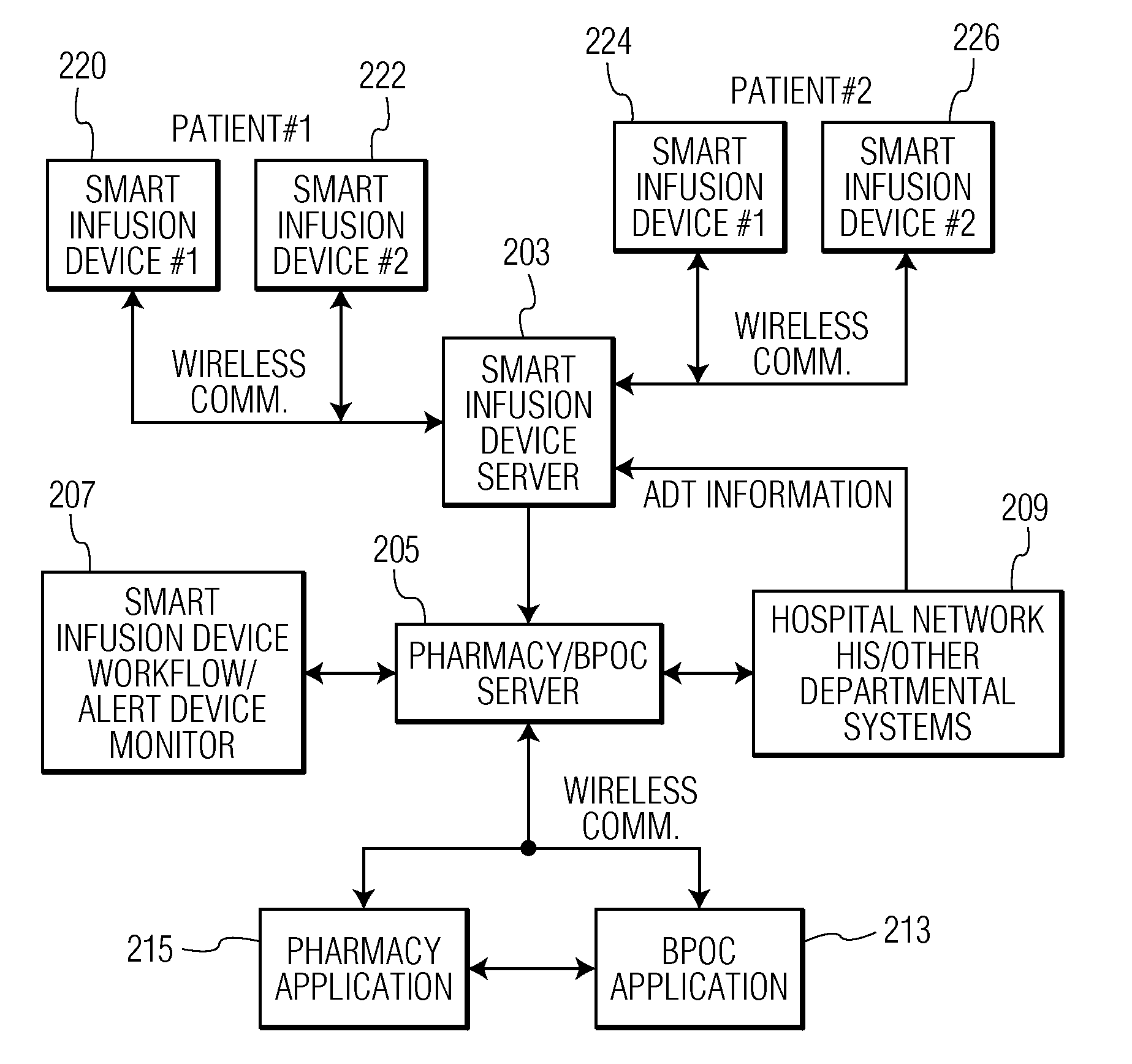
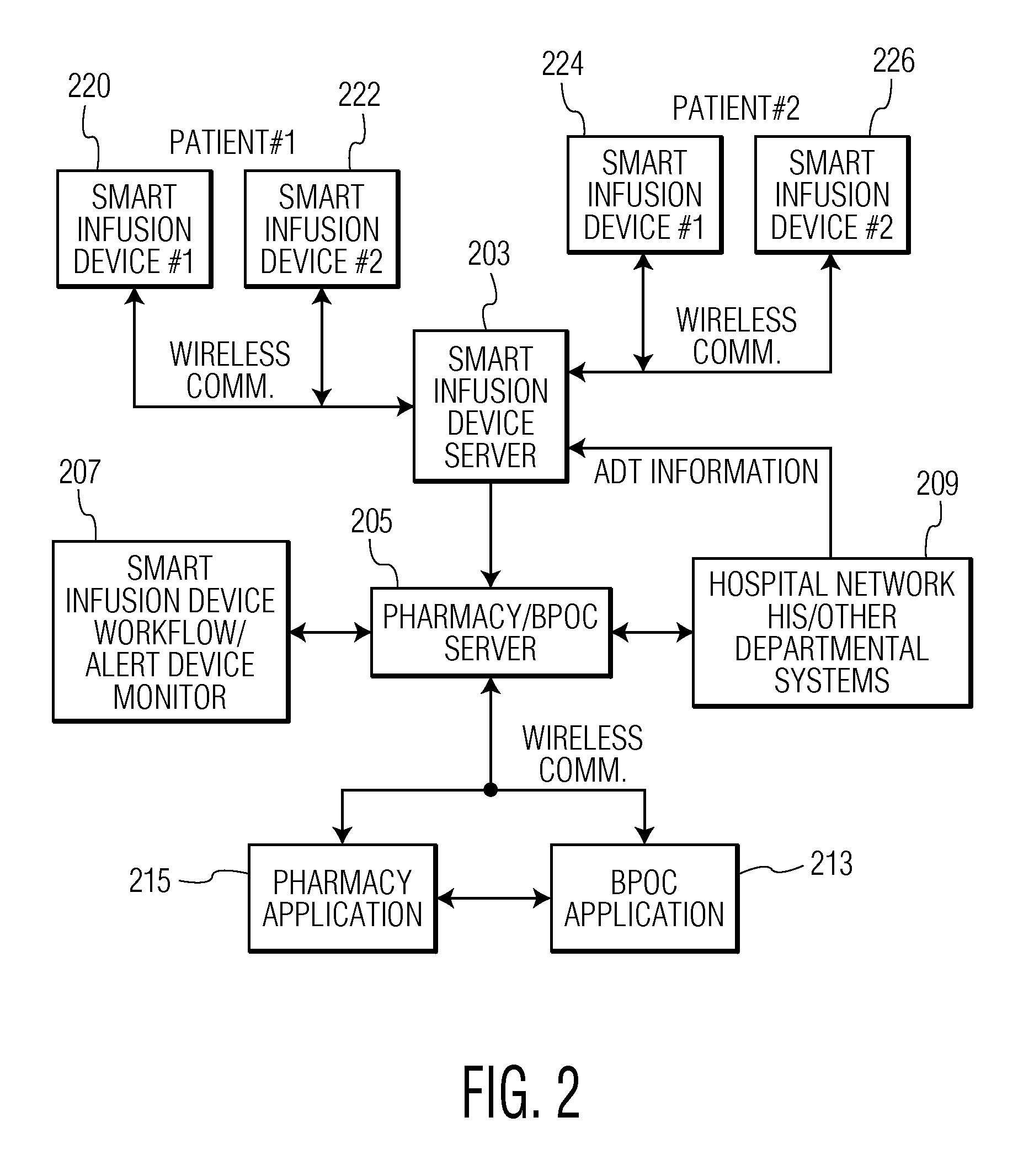
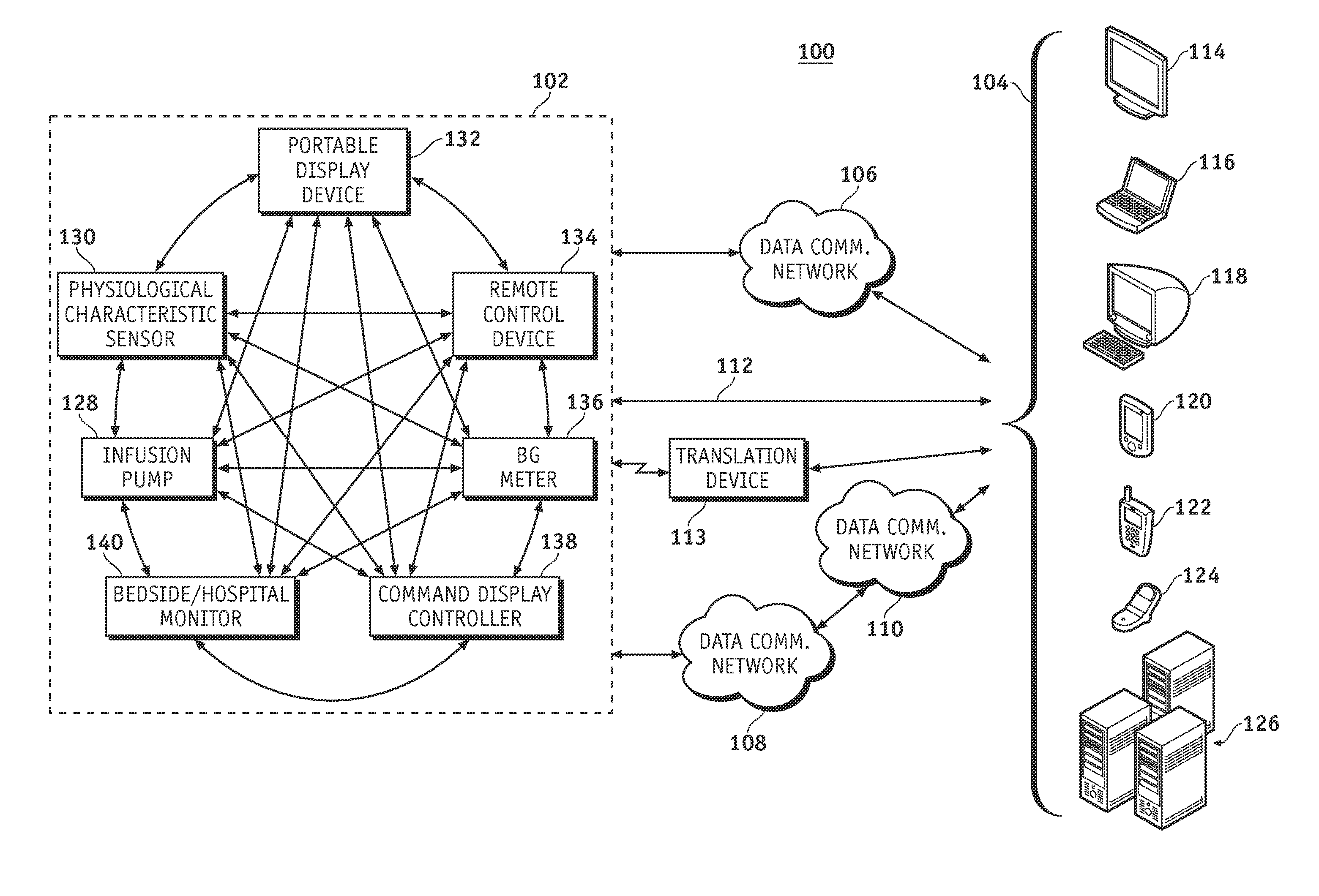
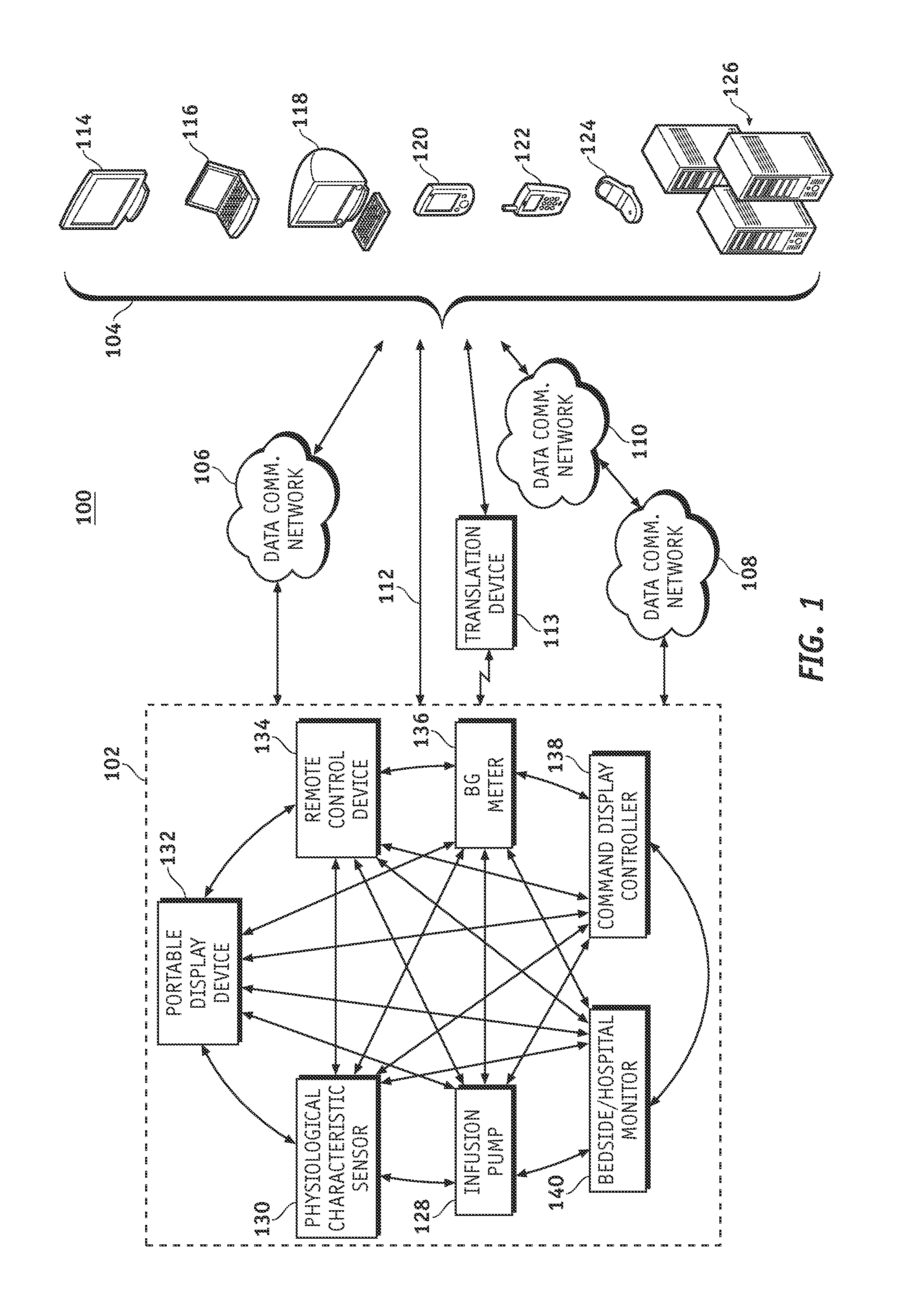
Wireless data communication protocols for a medical device network
InactiveUS20070258395A1Efficient routingDrug and medicationsBroadcast transmission systemsWireless Application ProtocolFluid infusion
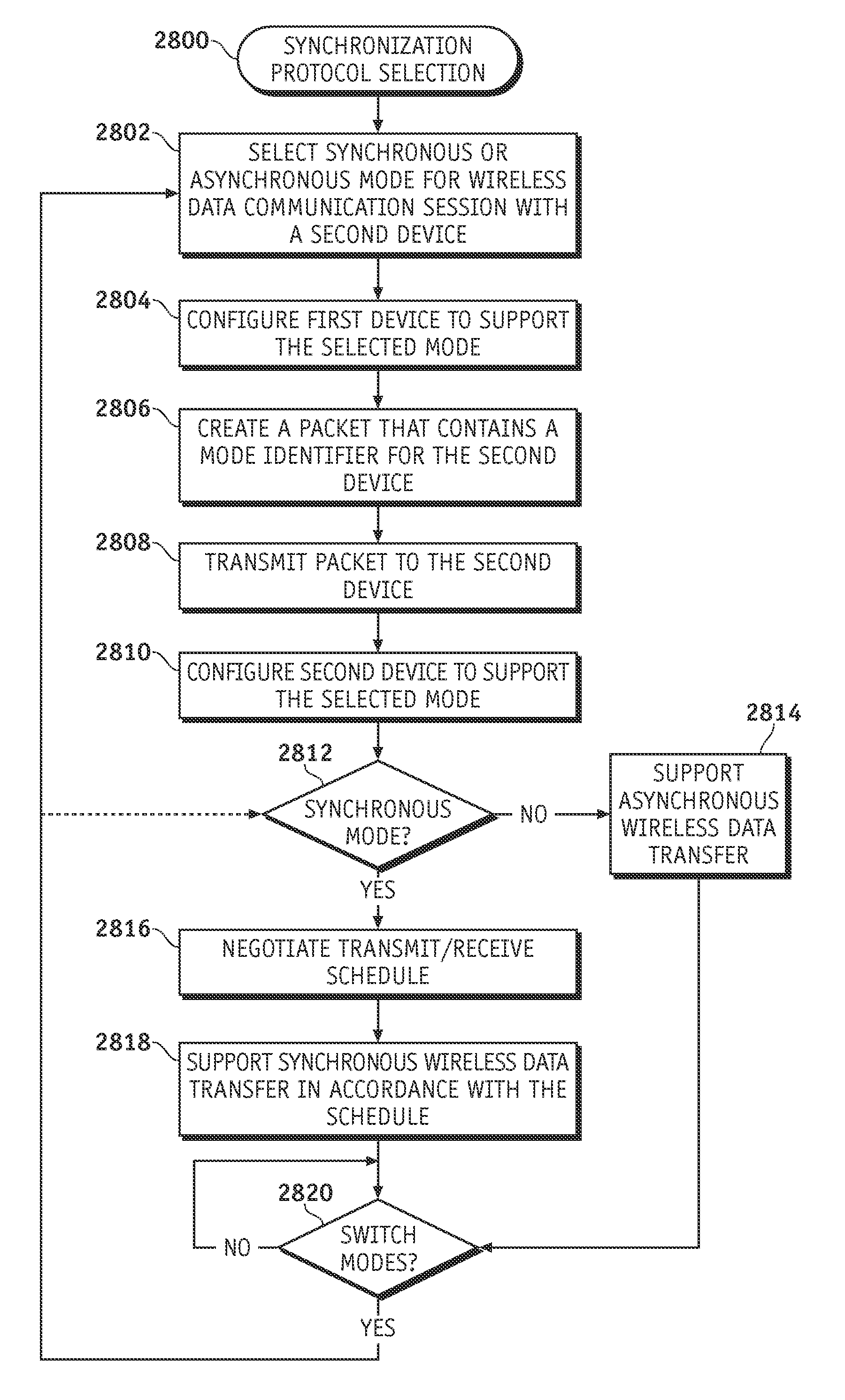
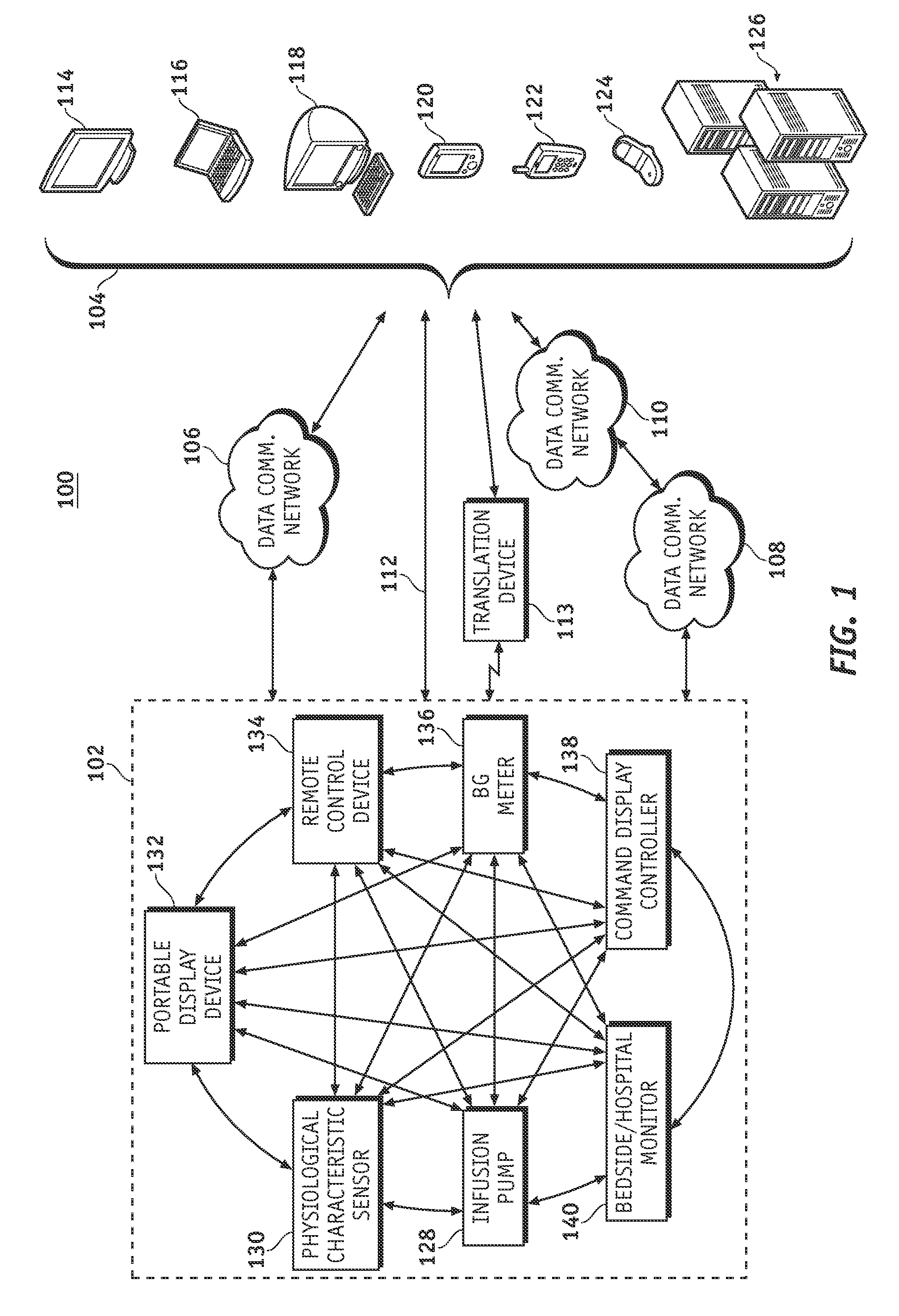
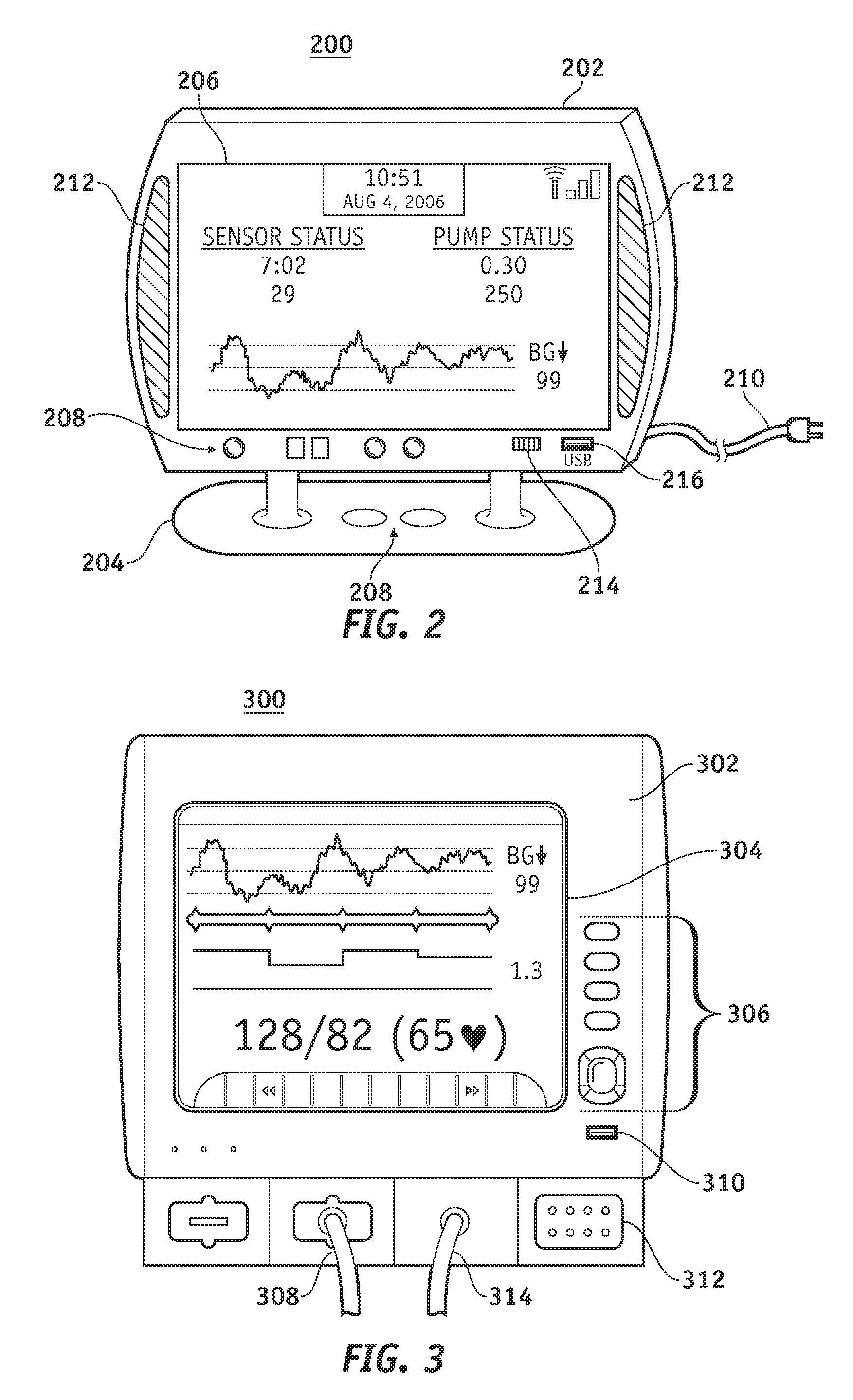
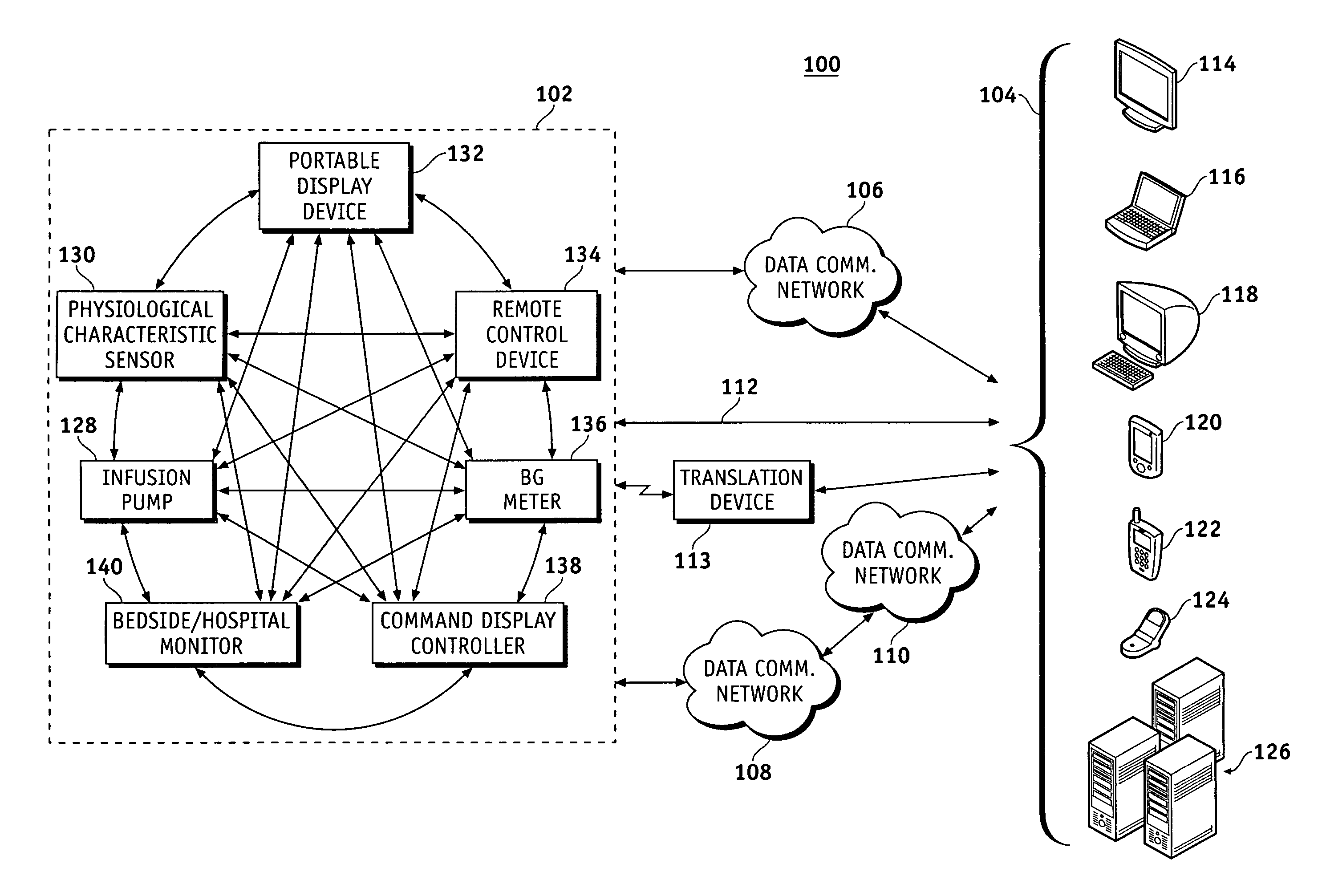
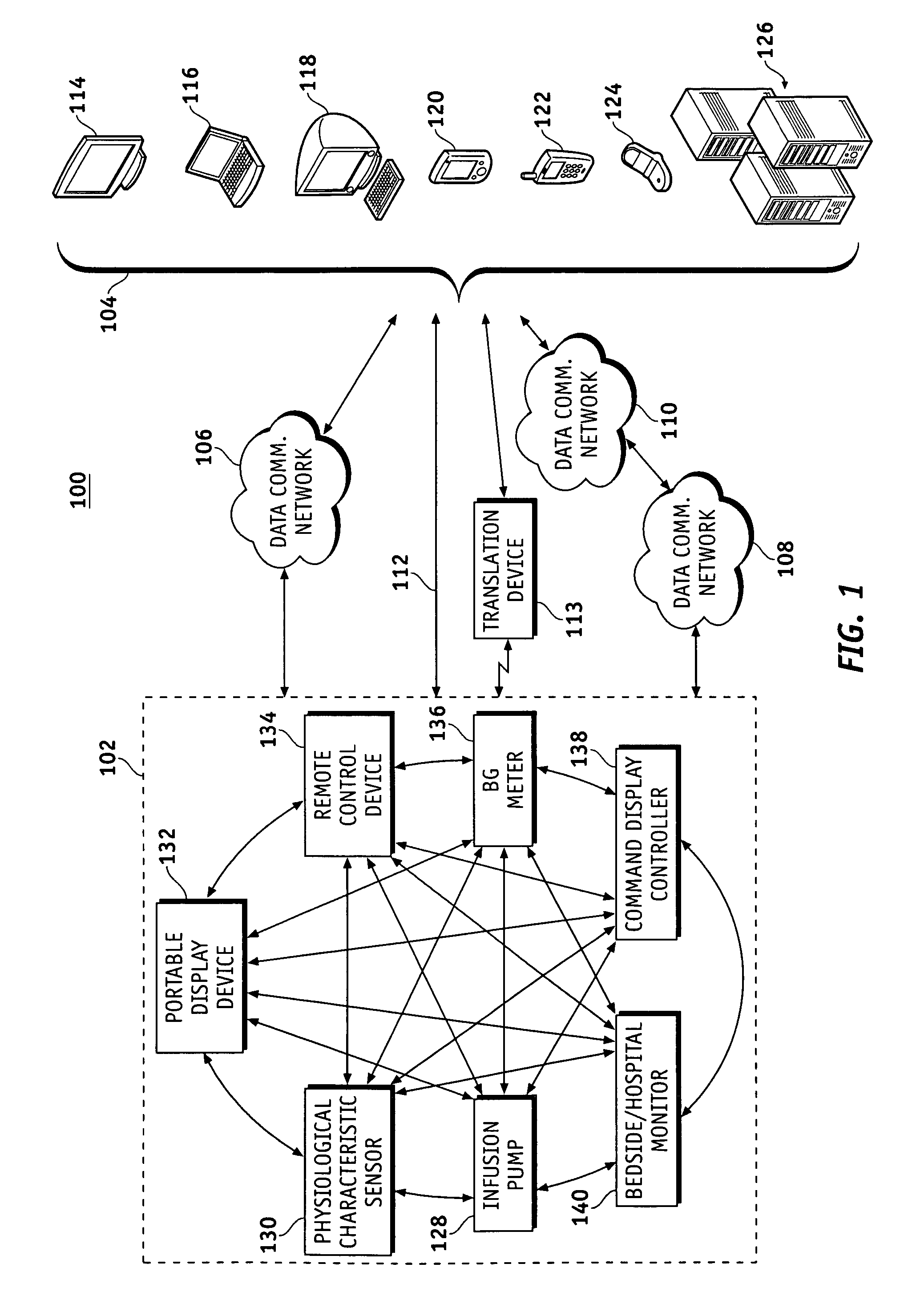
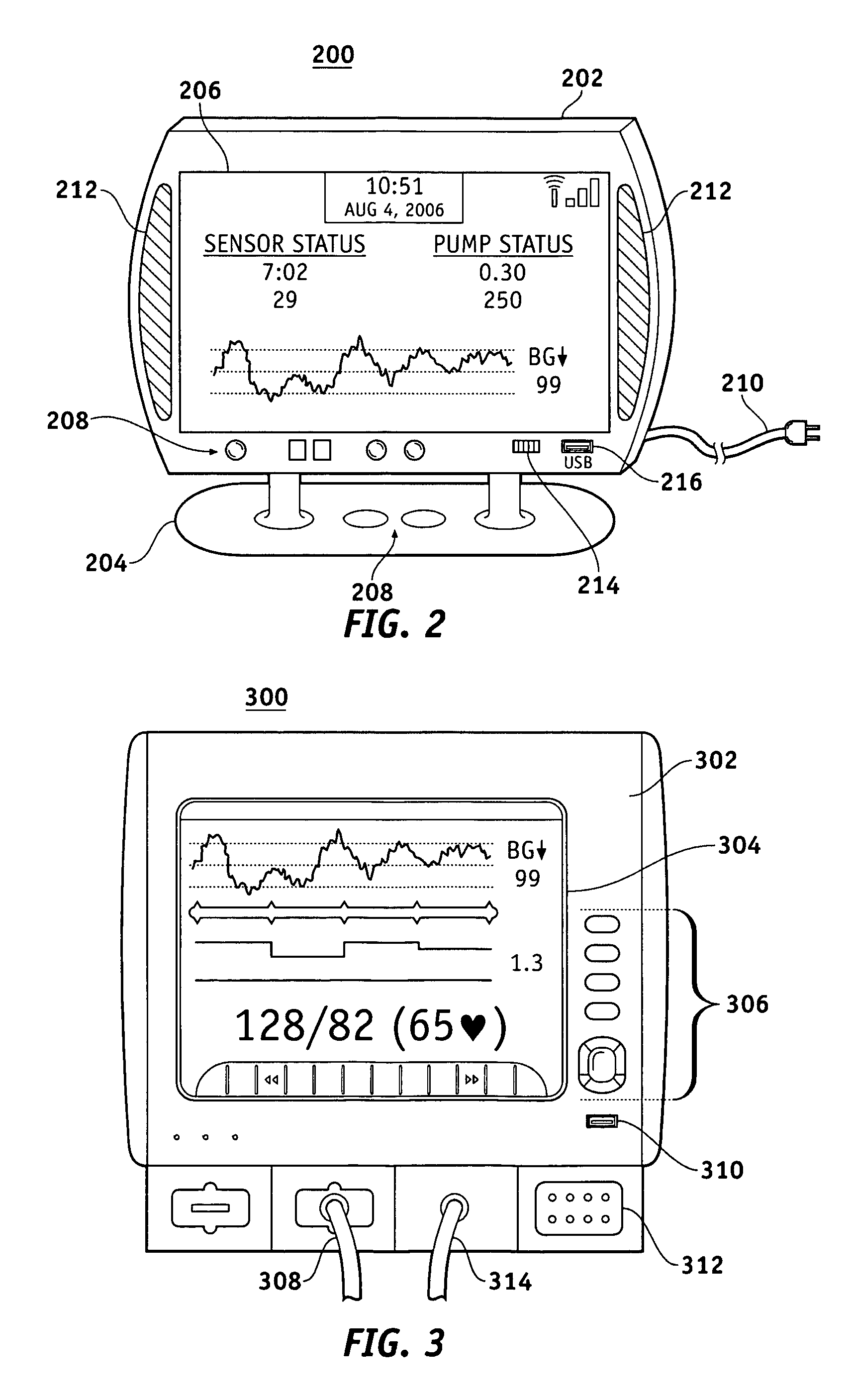
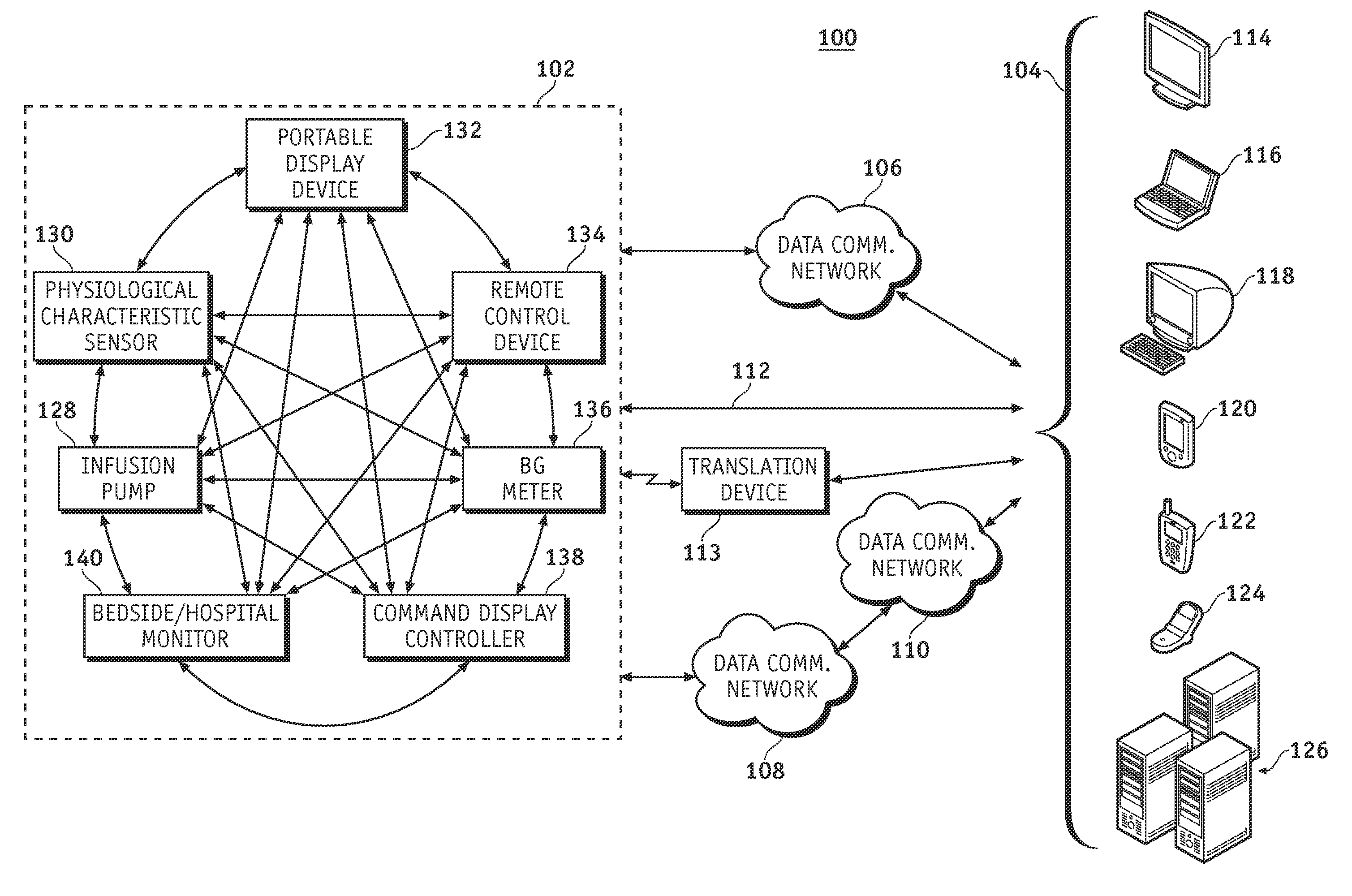
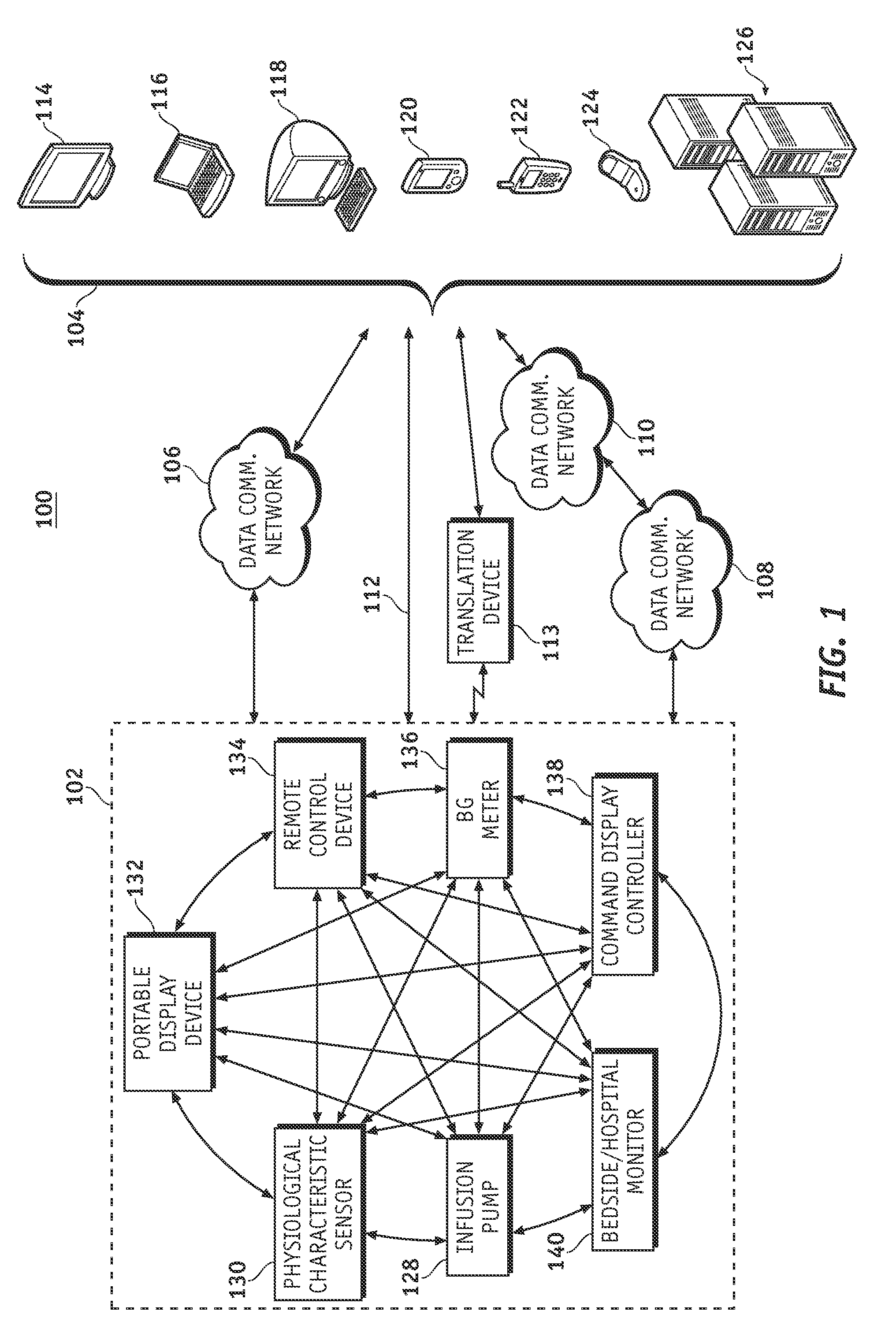
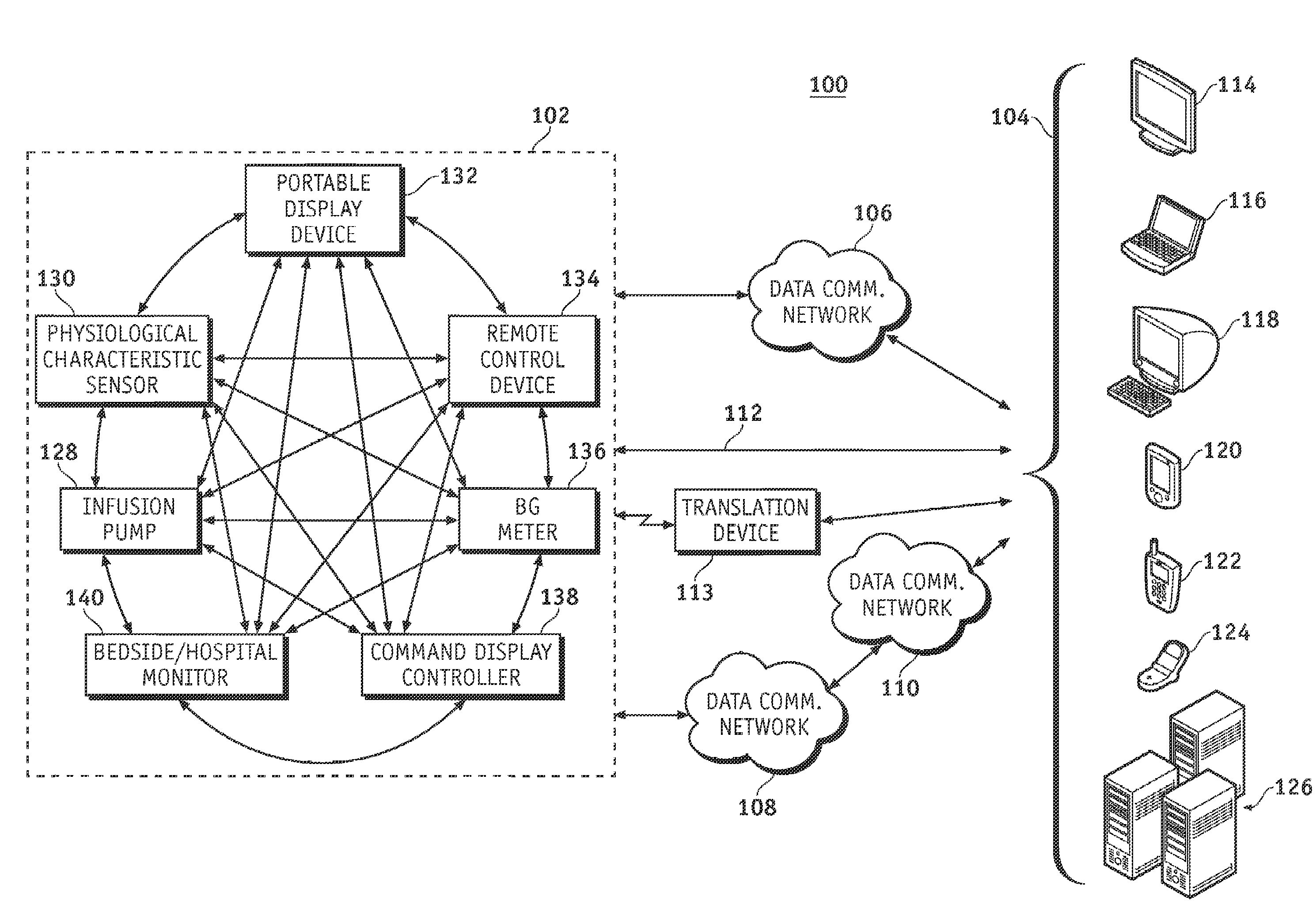
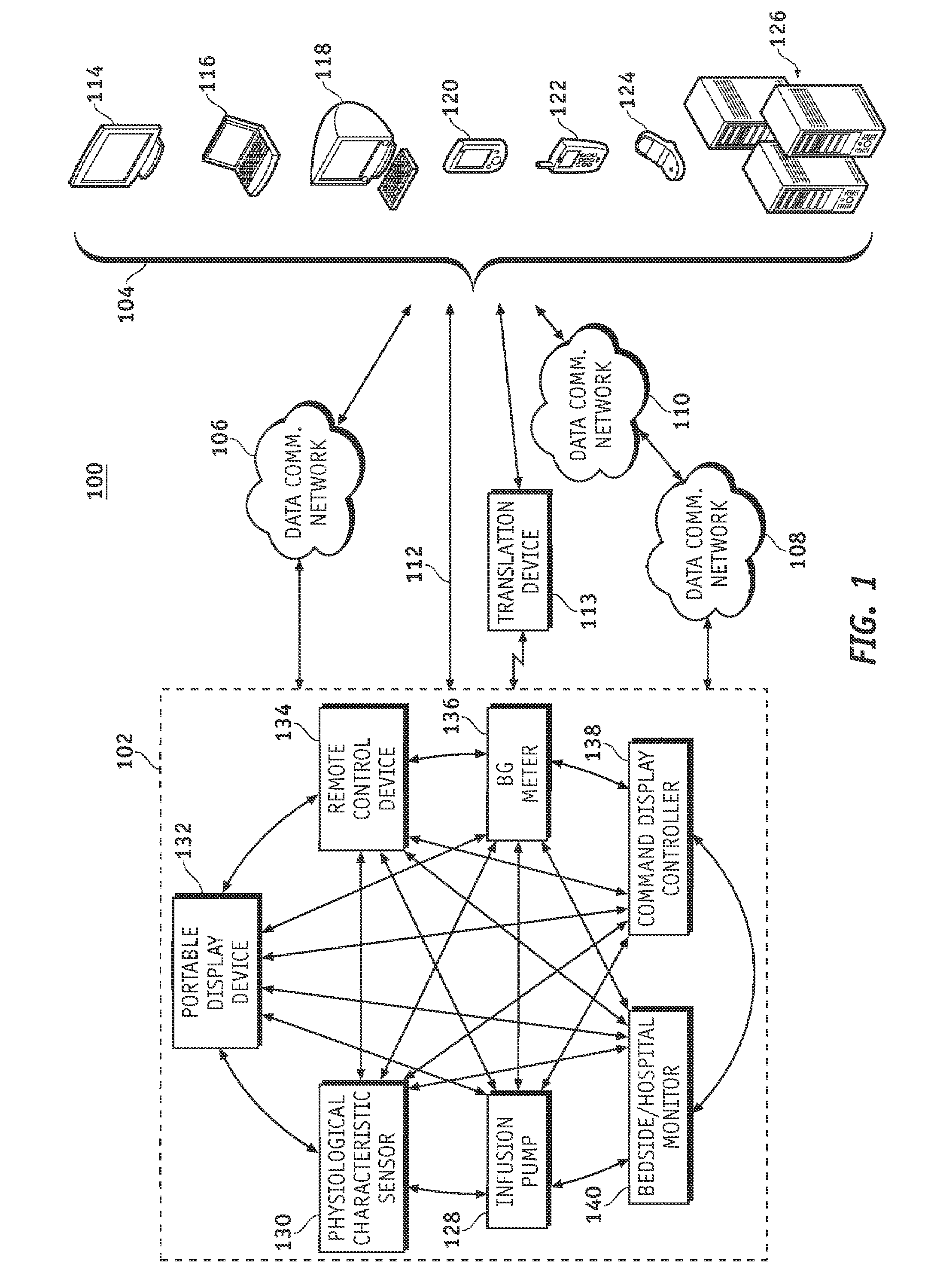
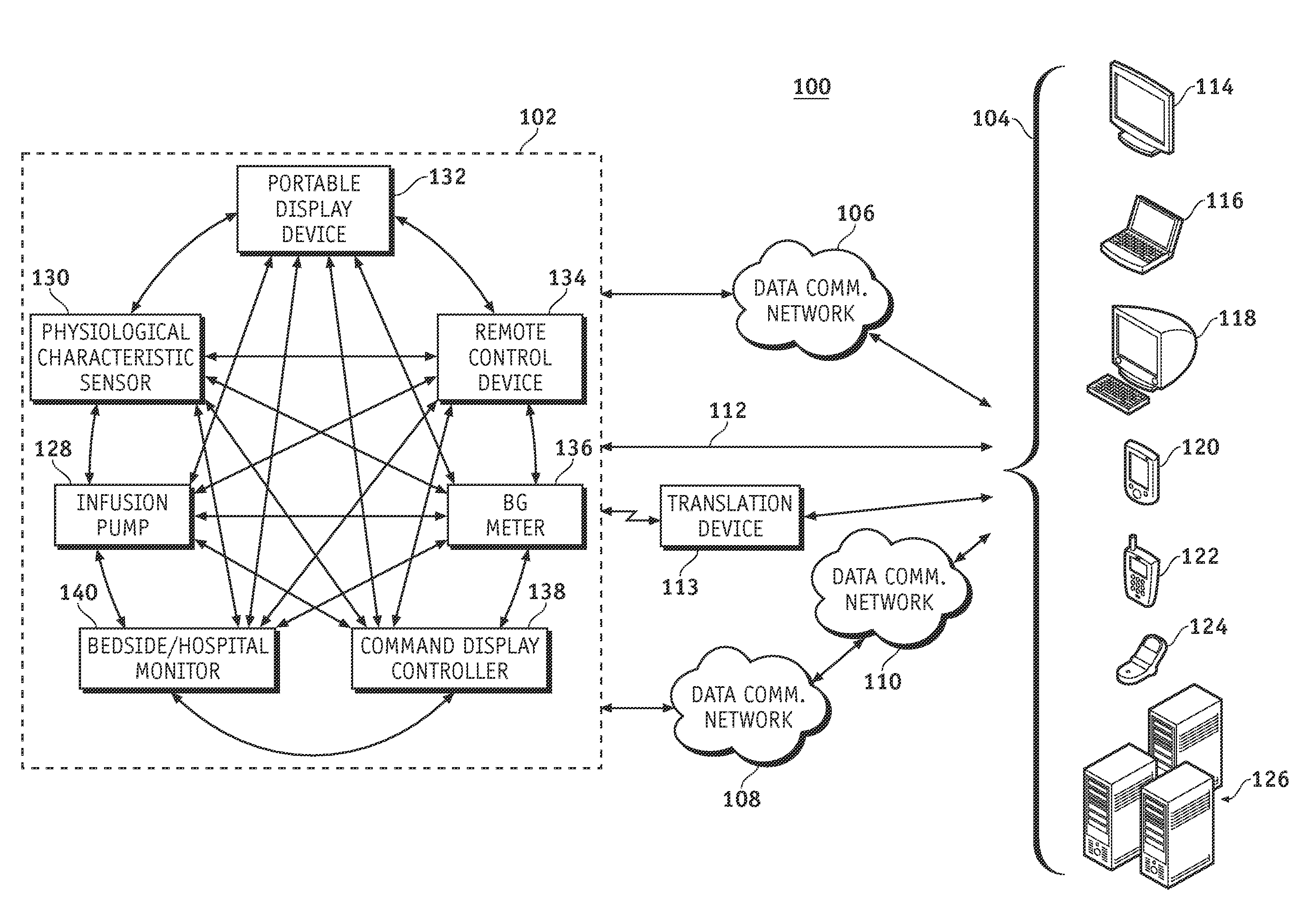
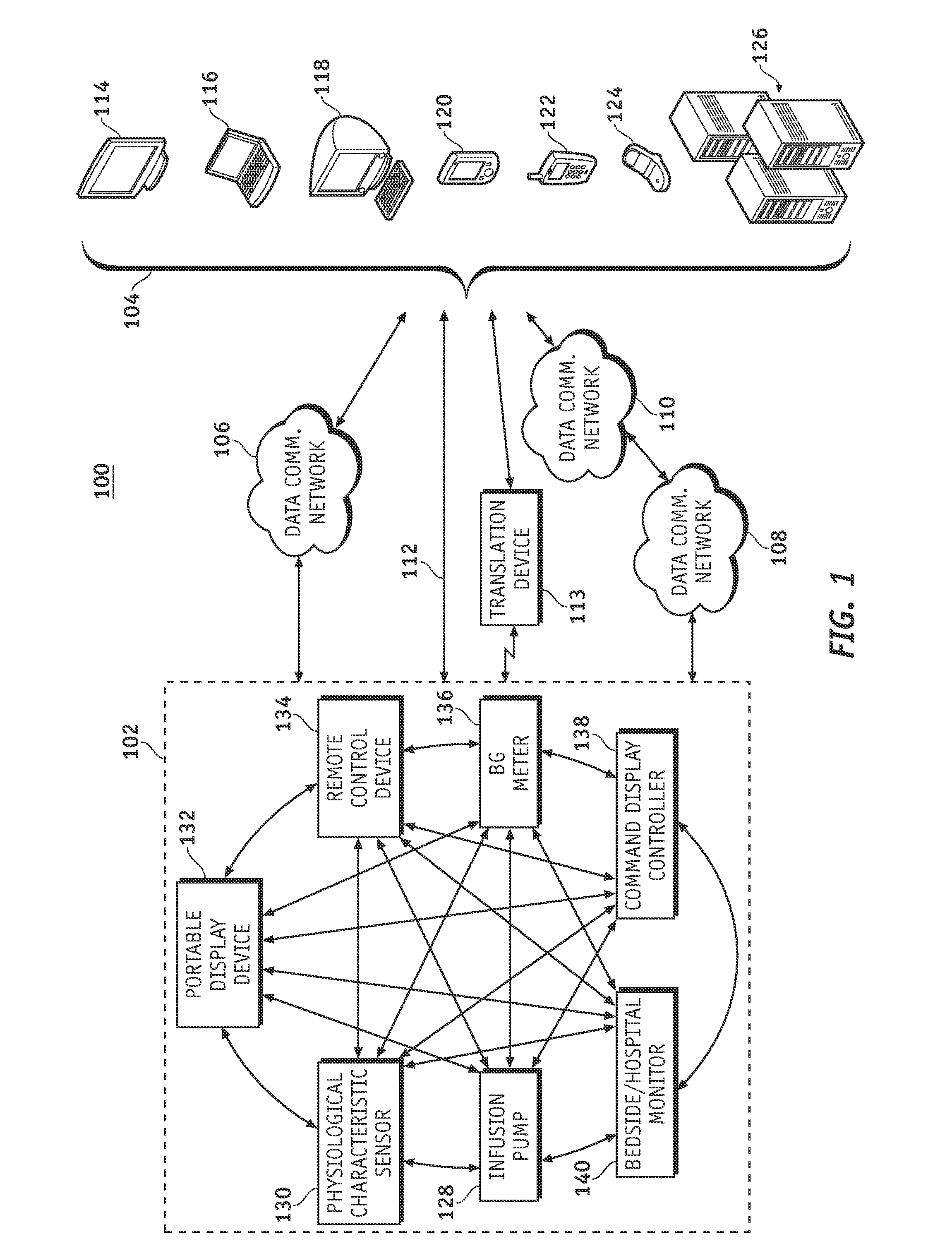
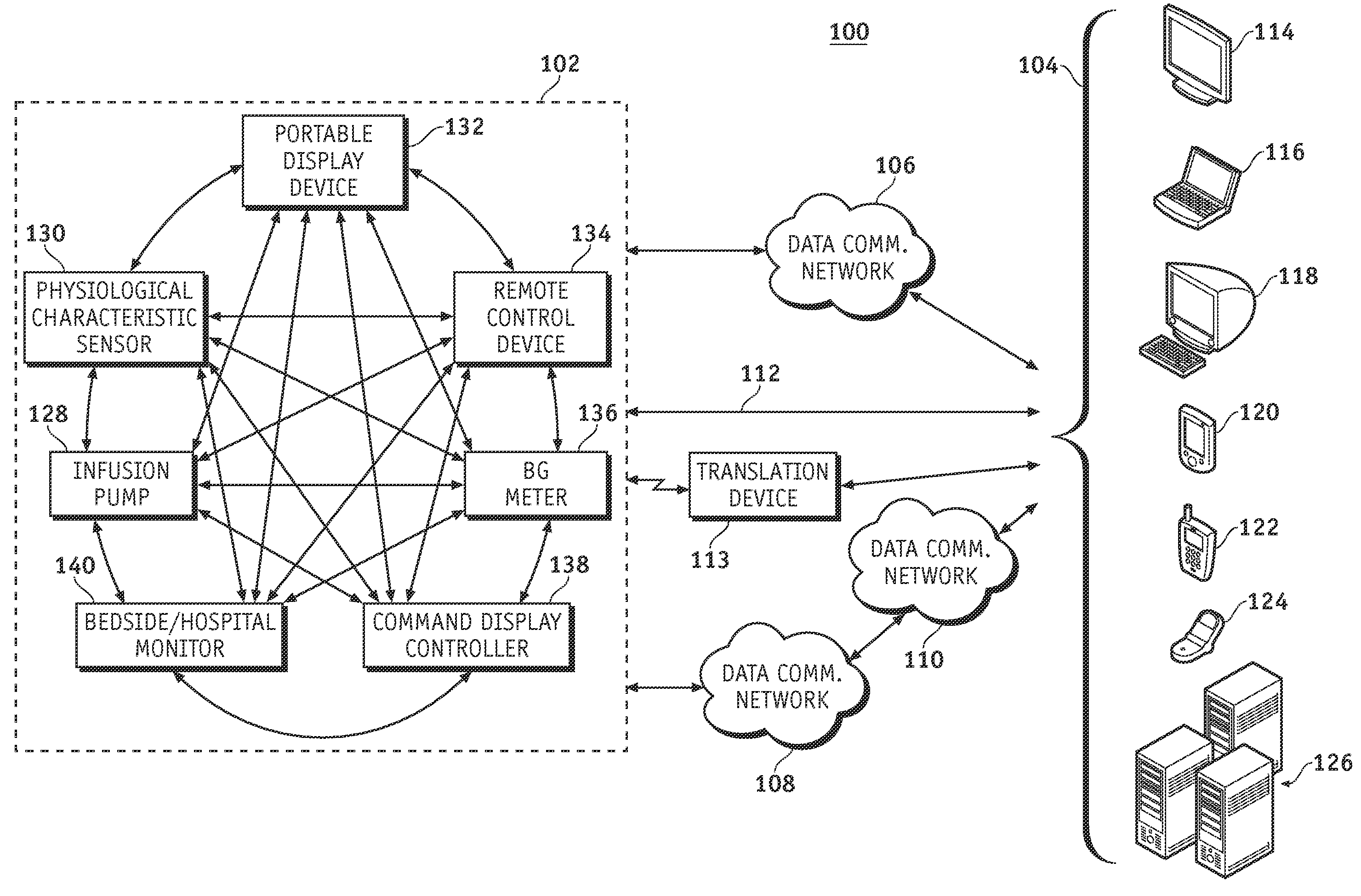
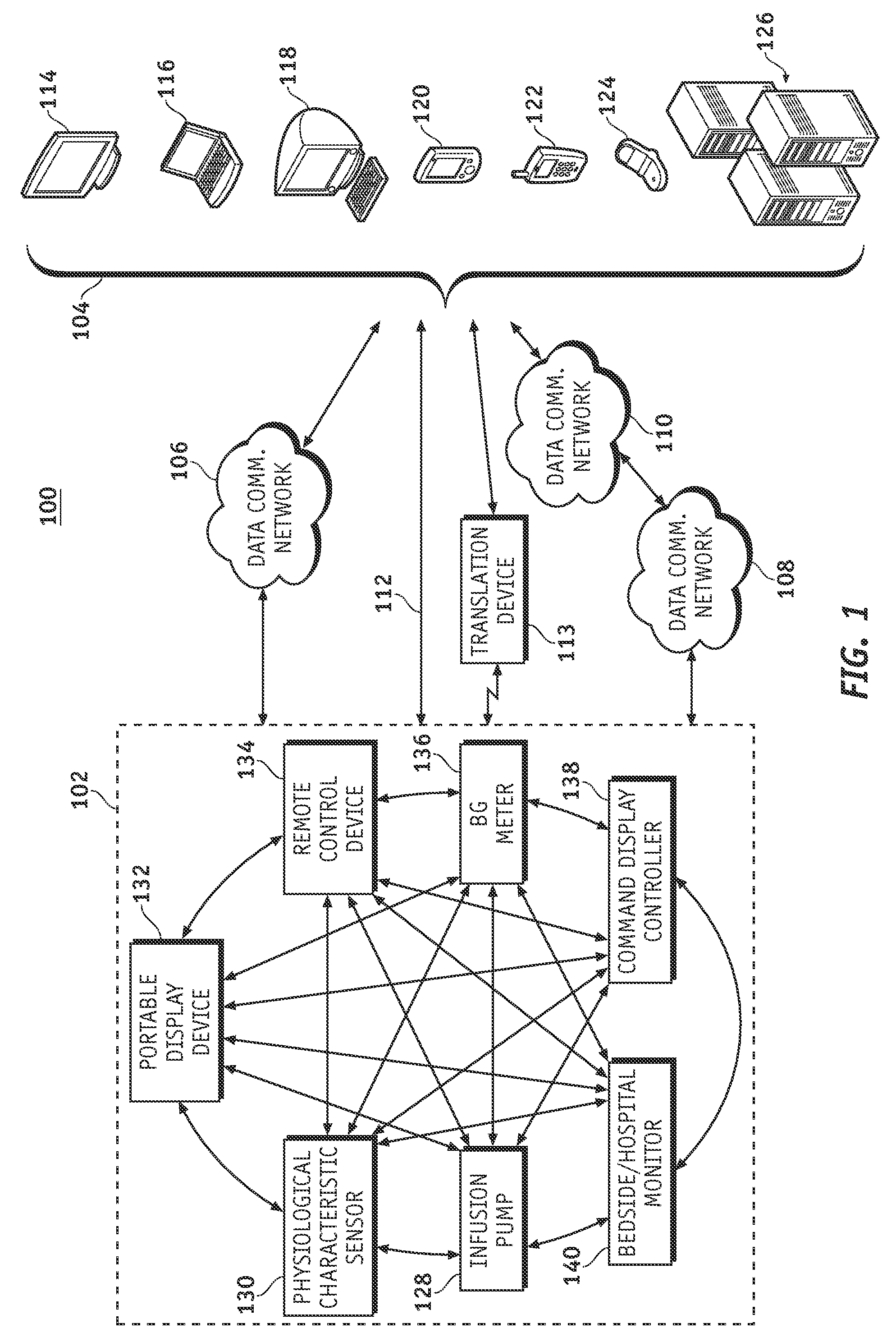
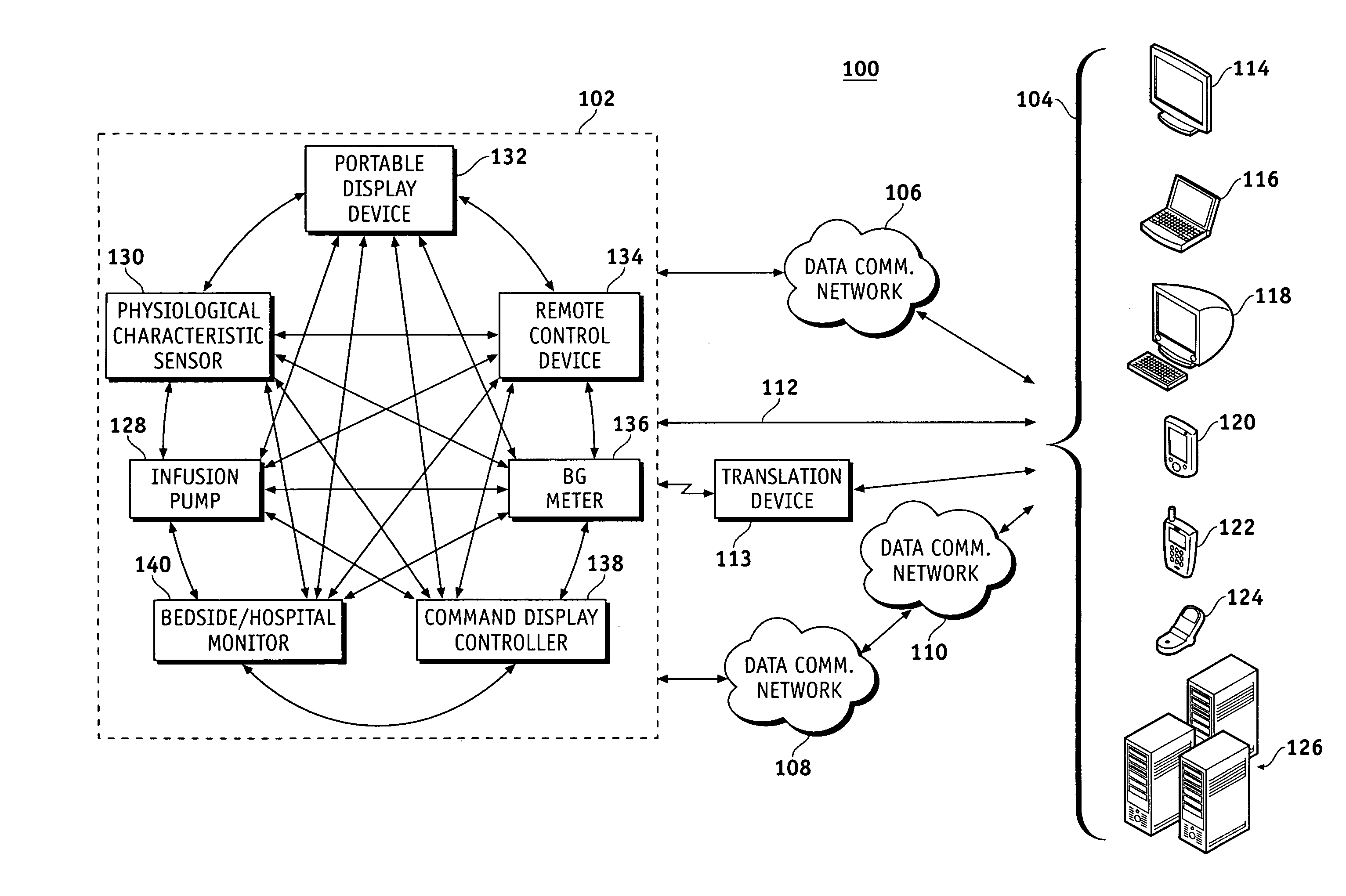
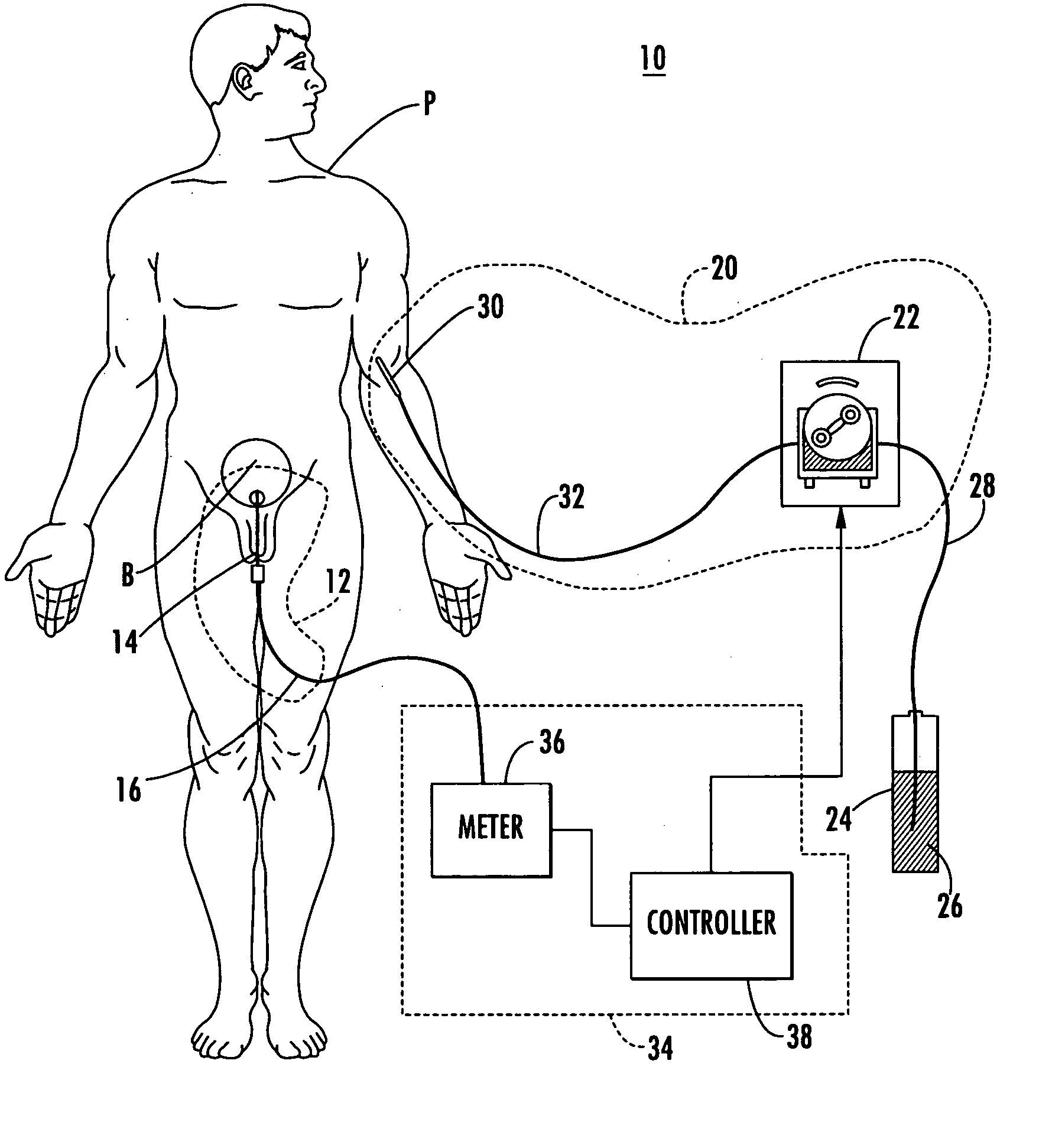
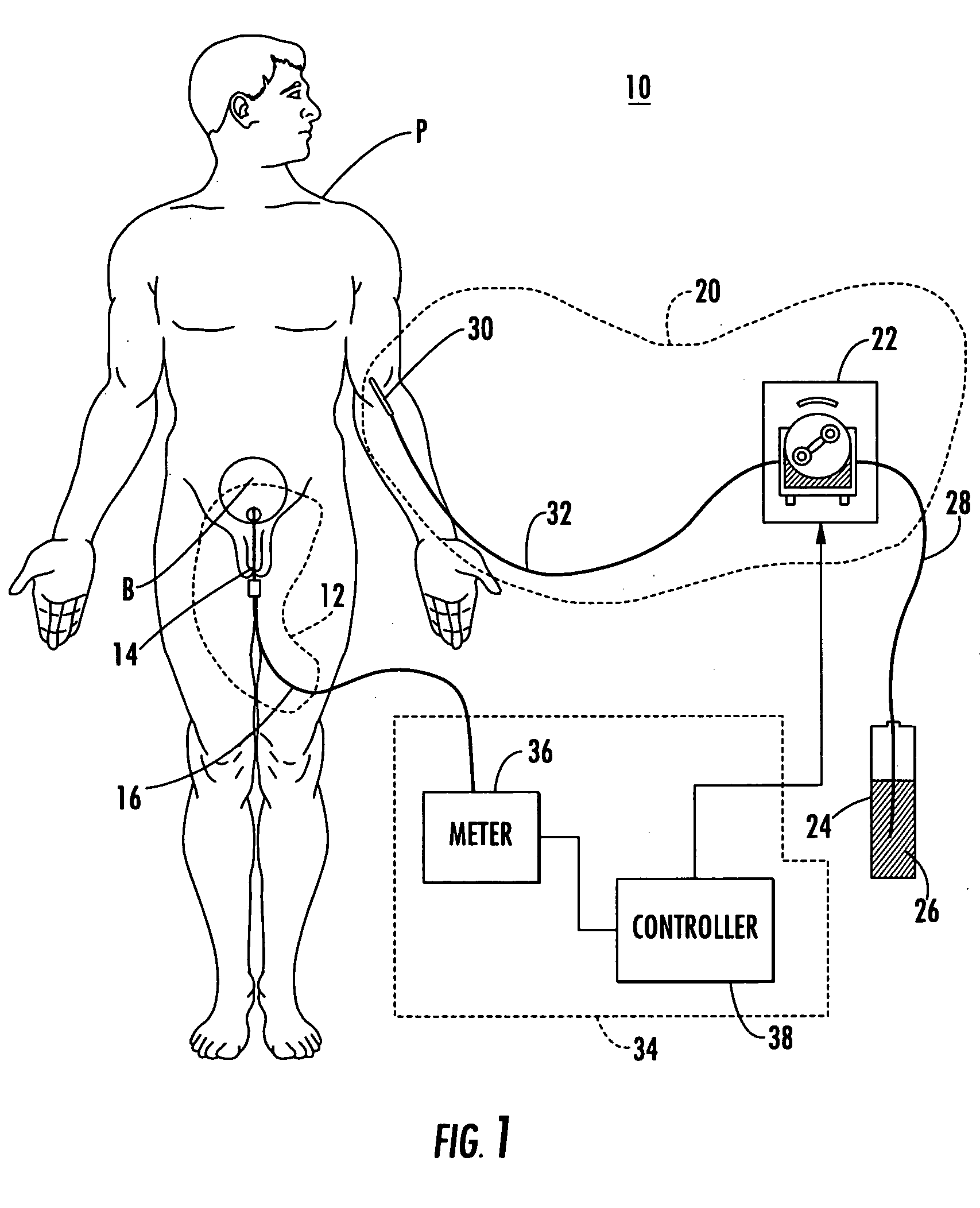
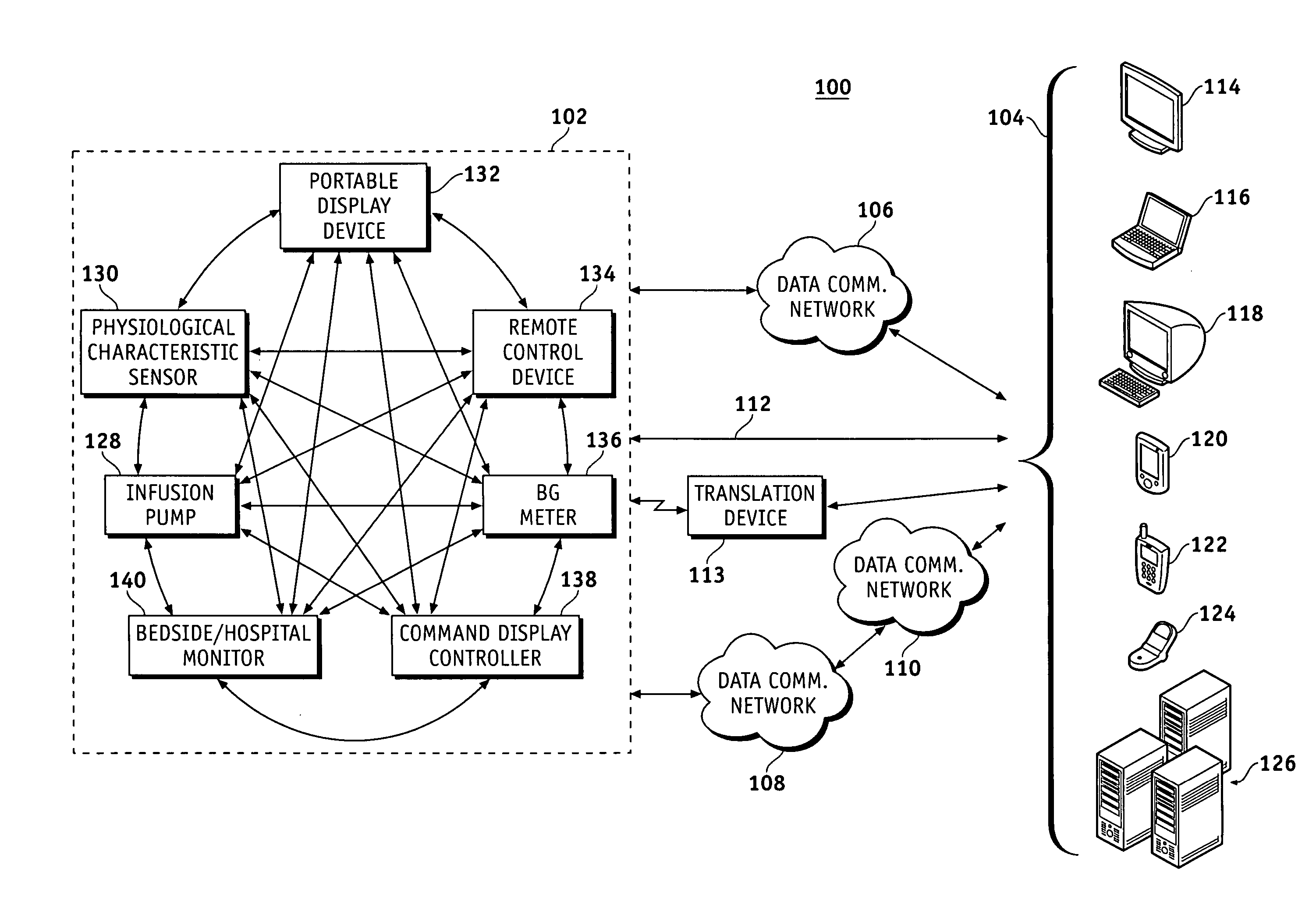
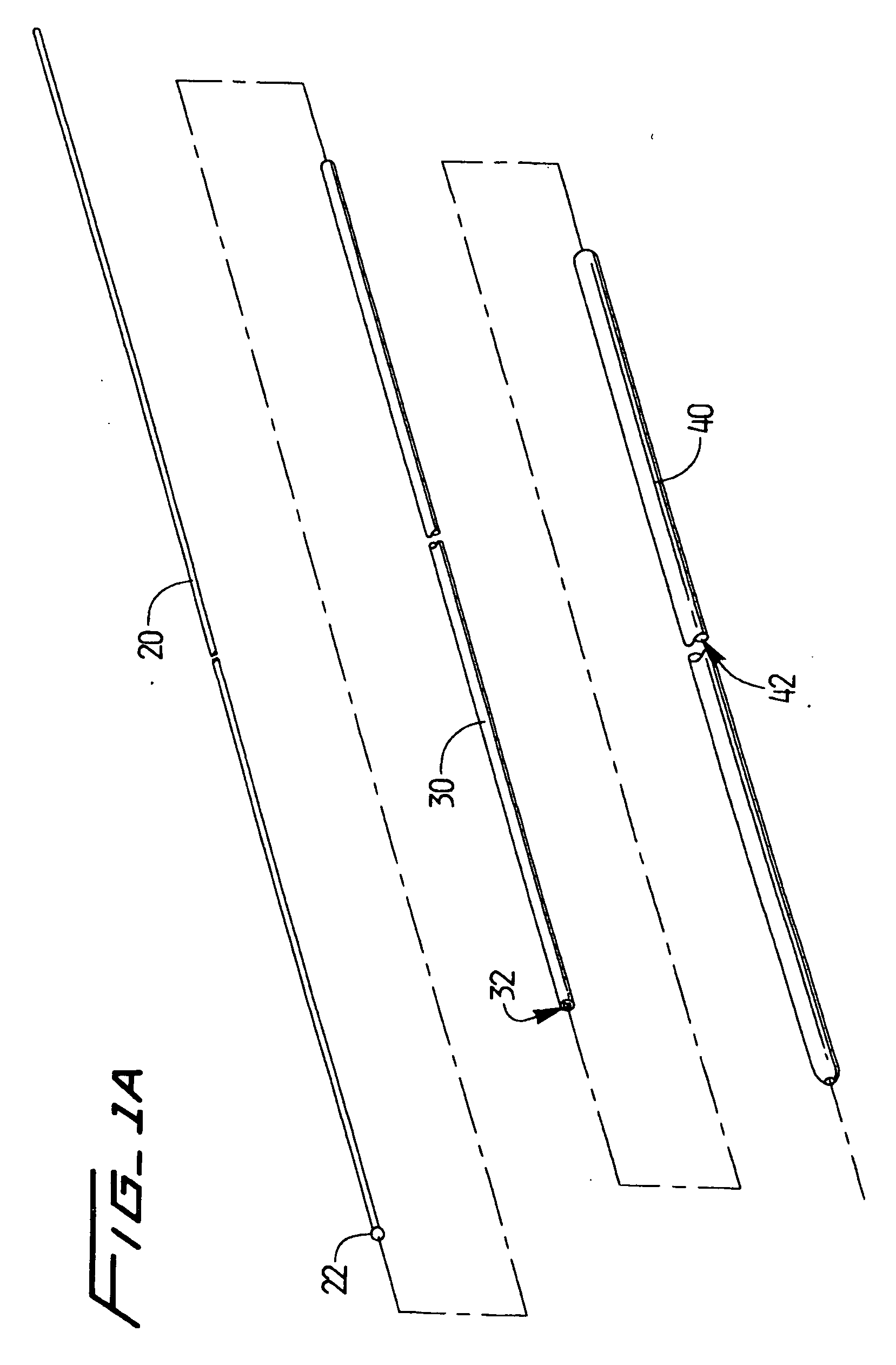
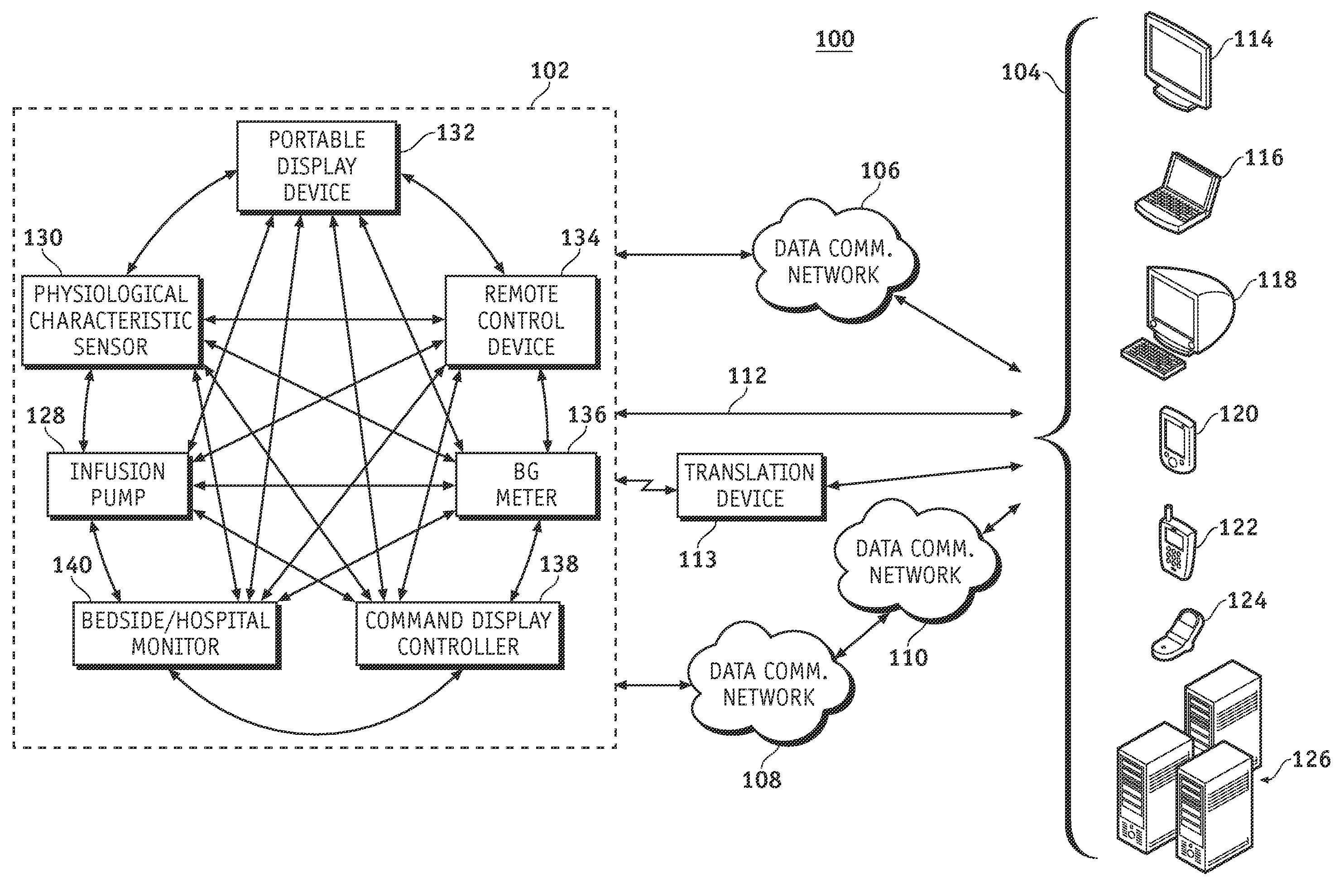
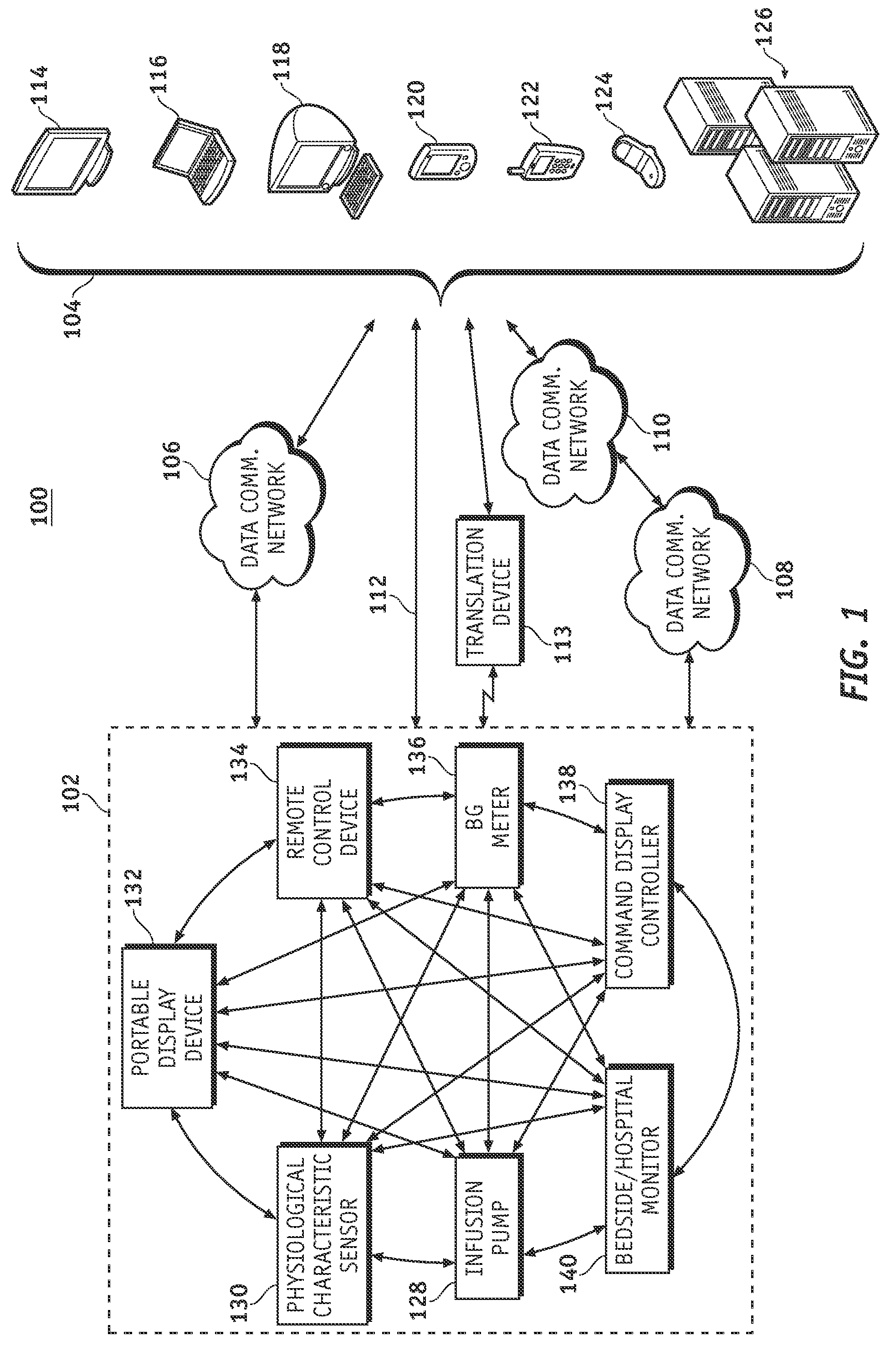
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. The networked medical devices are configured to support a variety of wireless data communication protocols for efficient communication of data within the medical device network. In addition, the wireless medical devices may be configured to support a number of dynamically adjustable wireless data communication modes to react to current operating conditions, application-specific data content, or other criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Remote monitoring for networked fluid infusion systems
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. Such external communication allows the infusion system to be extended beyond the traditional short-range user environment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
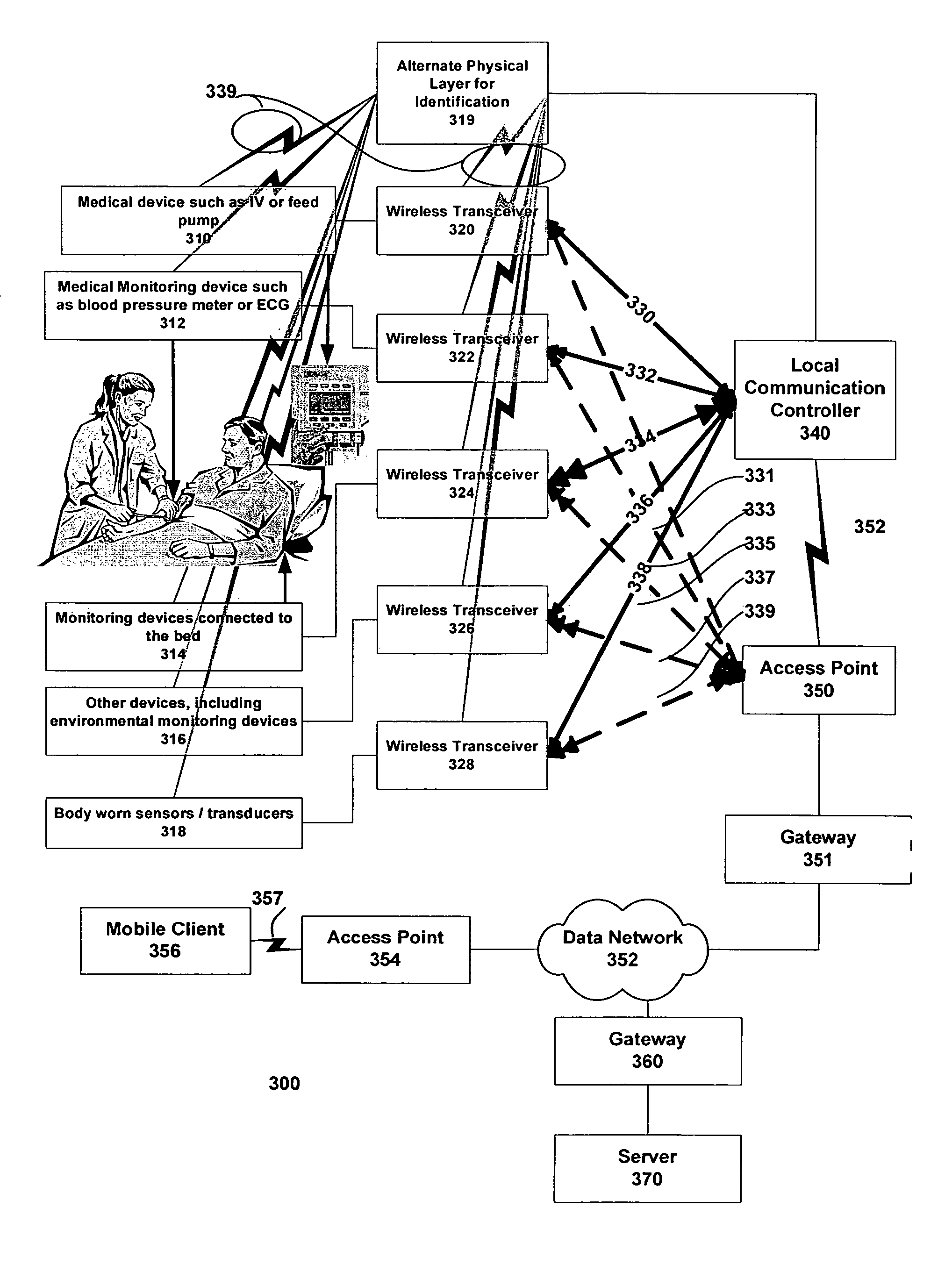
Identification of devices in a medical device network and wireless data communication techniques utilizing device identifiers
InactiveUS20070253021A1Efficient routingDrug and medicationsMultiplex communicationControl signalFluid infusion
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. The networked medical devices are configured to support a variety of wireless data communication protocols for efficient communication of data within the medical device network. In addition, the wireless medical devices may be configured to support a number of dynamically adjustable wireless data communication modes to react to current operating conditions, application-specific data content, or other criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
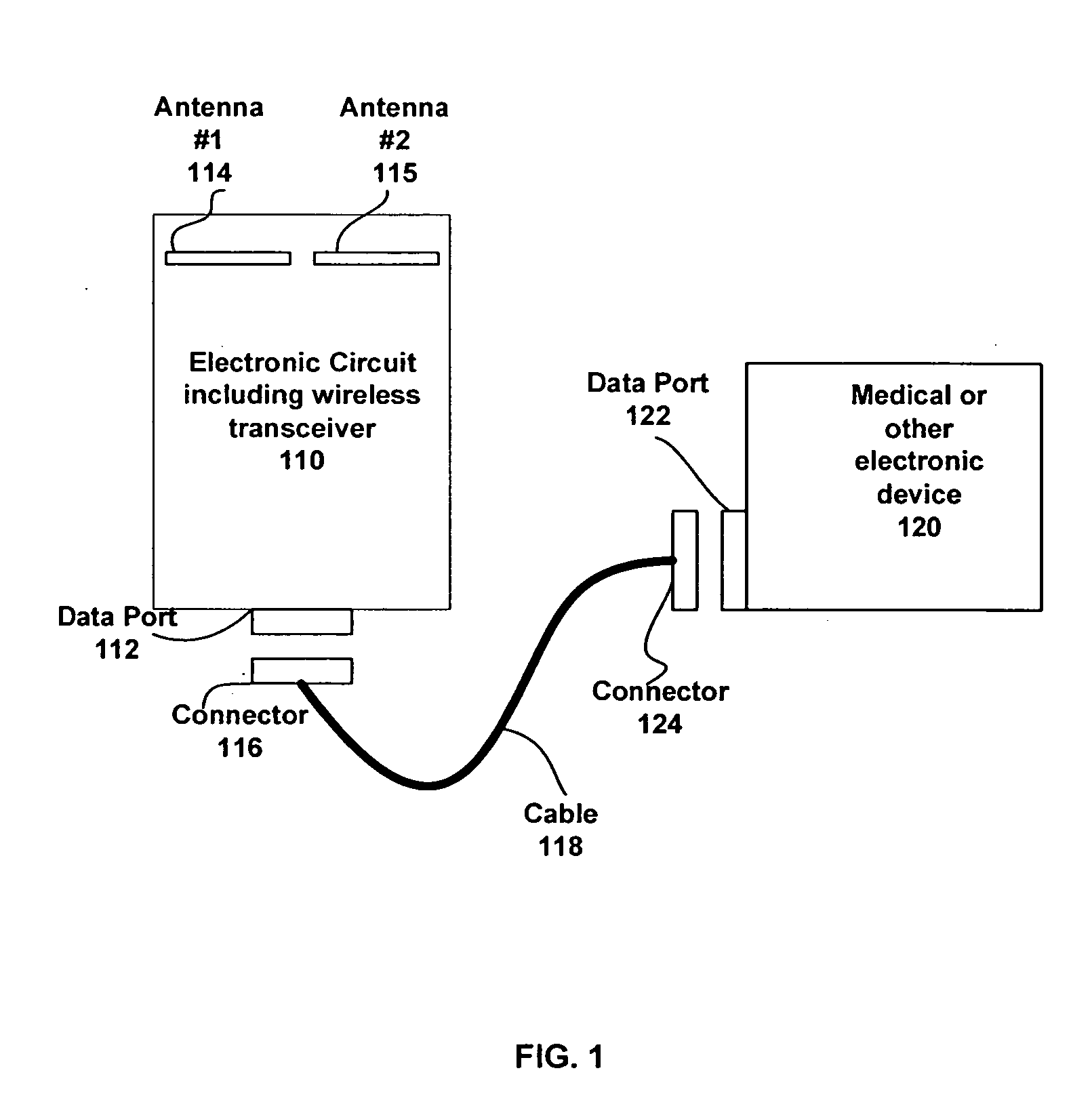
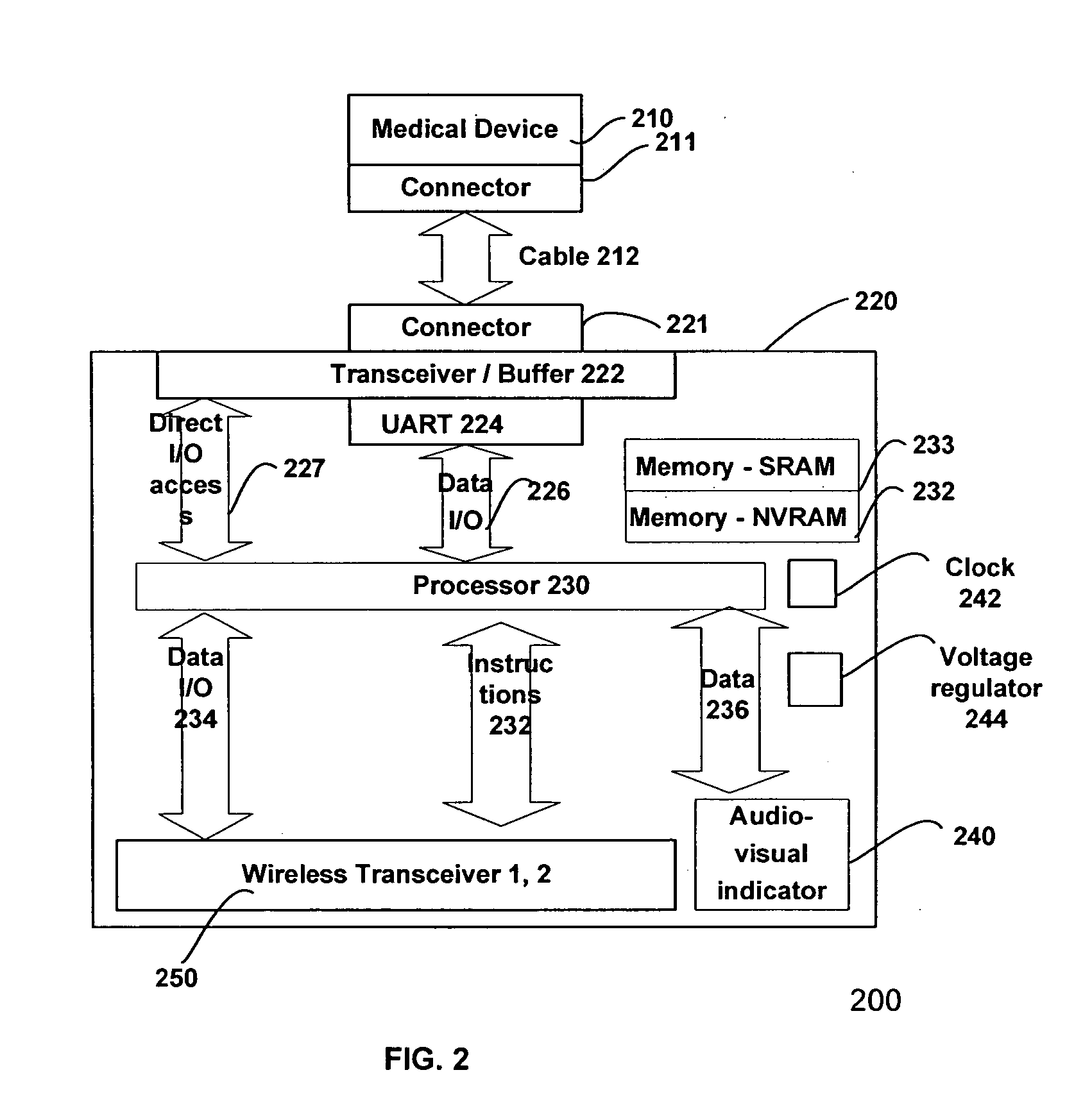
Provisioning and controlling medical instruments using wireless data communication
This invention teaches a method of automating some of the tasks requiring continuous data collection at the patient bedside in a hospital in a manner which significantly reduces the chances of error in providing treatment. These tasks include provisioning of the IV pumps or other fluid infusion pumps, feed pumps, oxygen delivery systems, gathering, recording, storing, and analyzing signals from ECG machine or pulse oxymeter or any other medical device. This invention teaches the use of wireless transceiver modules which are connected to the data ports on the medical instrument to gather the data and transmit the data to a wireless access point. Protocols to identify the patient, care provider, medicine, equipment, and treatment are described. Use of an external means for verifying the identity of the medical device and the medicine is also described.
Owner:CARETRENDS
Broadcast data transmission and data packet repeating techniques for a wireless medical device network
InactiveUS20070255116A1Efficient routingDrug and medicationsMedical devicesComputer networkControl signal
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. The networked medical devices are configured to support a variety of wireless data communication protocols for efficient communication of data within the medical device network. In addition, the wireless medical devices may be configured to support a number of dynamically adjustable wireless data communication modes to react to current operating conditions, application-specific data content, or other criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Router device for centralized management of medical device data
InactiveUS20070255348A1Facilitates centralized gatheringEasy to processElectrotherapyDrug and medicationsControl signalFluid infusion
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. Such external communication allows the infusion system to be extended beyond the traditional short-range user environment. One particular system embodiment includes a network router device that functions as a centralized storage, processing, and routing unit for data received from the body network devices. The network router device is configured to generate HTML documents (web pages) to facilitate Internet-based setup, management, and control.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
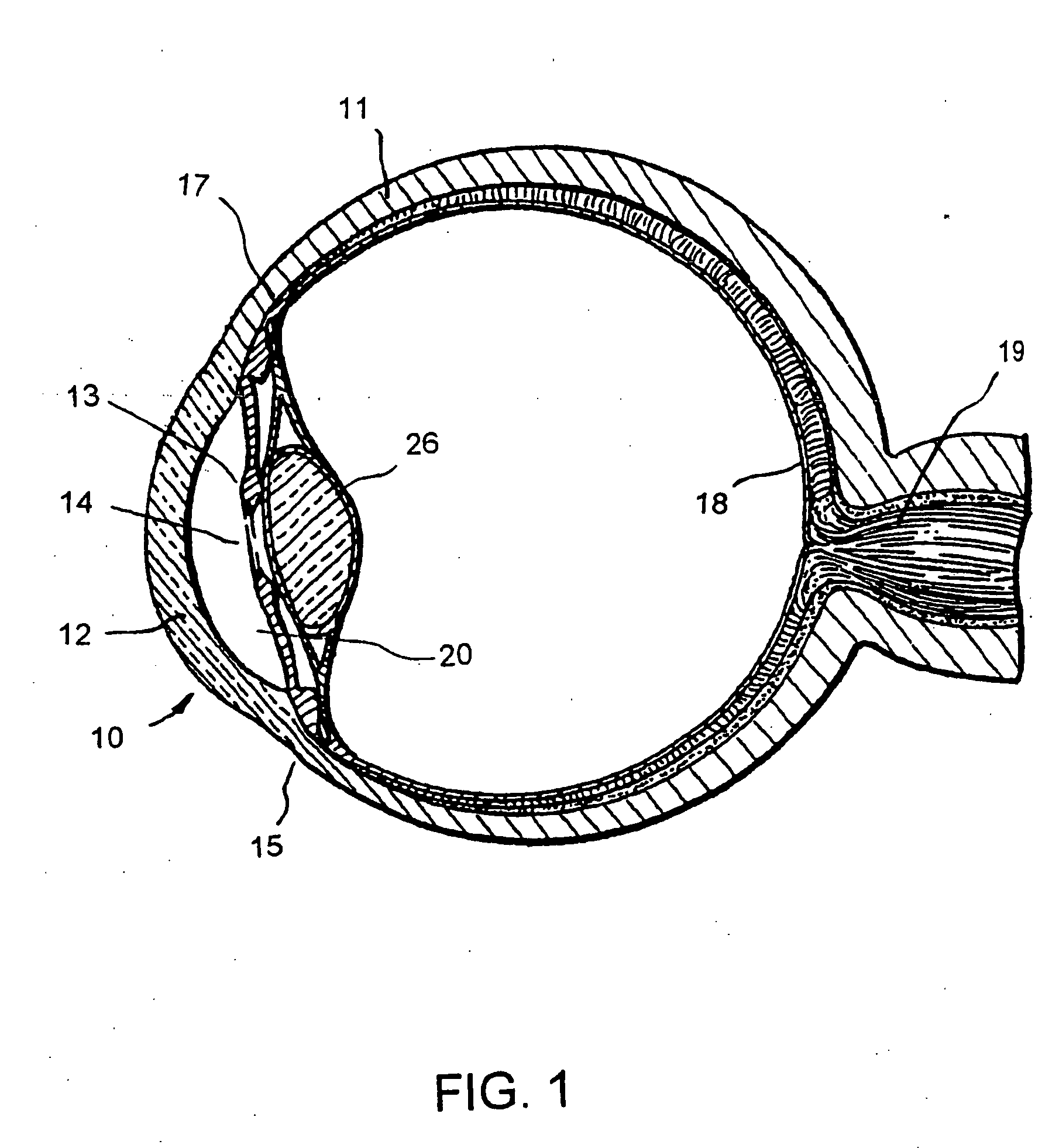
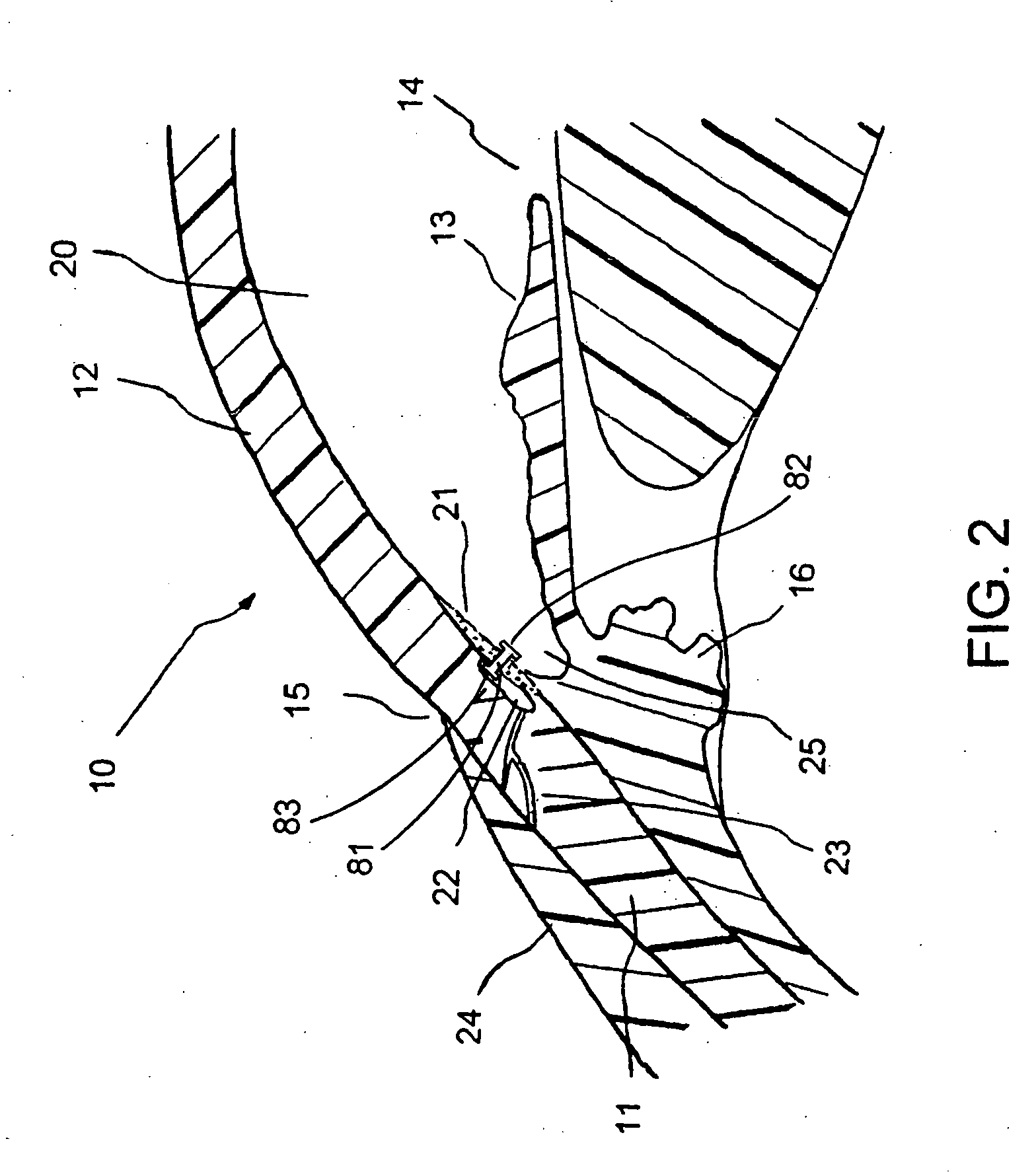
Fluid infusion methods for glaucoma treatment
The invention relates to methods of treating glaucoma, such as a method that includes inserting a stent through an incision in an eye; the stent having an inflow portion that is in fluid communication with an outflow portion of the stent; transporting the stent from the incision through the anterior chamber of the eye to an aqueous cavity of the eye, such that the inflow portion of the stent is positioned in the anterior chamber and the outflow portion of the stent is positioned at the aqueous cavity; and infusing fluid from the inflow portion to the outflow portion of the stent.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Wireless data communication for a medical device network that supports a plurality of data communication modes
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. The networked medical devices are configured to support a variety of wireless data communication protocols for efficient communication of data within the medical device network. In addition, the wireless medical devices may be configured to support a number of dynamically adjustable wireless data communication modes to react to current operating conditions, application-specific data content, or other criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Subnetwork synchronization and variable transmit synchronization techniques for a wireless medical device network
ActiveUS20070251835A1Efficient routingWeather/light/corrosion resistanceDrug and medicationsWireless Application ProtocolFluid infusion
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. The networked medical devices are configured to support a variety of wireless data communication protocols for efficient communication of data within the medical device network. In addition, the wireless medical devices may be configured to support a number of dynamically adjustable wireless data communication modes to react to current operating conditions, application-specific data content, or other criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Data communication in networked fluid infusion systems
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. Such external communication allows the infusion system to be extended beyond the traditional short-range user environment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Intervertebral disc augmentation and rehydration with superabsorbent polymers
ActiveUS20070150061A1Simple and fast and easy methodEasily reversibleSpinal implantsTissue regenerationMedicineFluid infusion
The embodiments provide a method for treating an intervertebral disc having a nucleus pulposus and an annulus fibrosis, using one or more superabsorbent polymers. Additionally, the embodiments provide a method for bulking up an intervertebral disc having a nucleus pulposus and an annulus fibrosis, using one or more superabsorbent polymers. The methods comprise introducing an amount of the superabsorbent polymers into the intervertebral disc space without removing nucleus pulposus or annulus fibrosis material.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Resectoscopic Device And Method
InactiveUS20070244353A1Reduce traumaShorten the timeEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFluid infusionViewing instrument
A surgical instrument has a channel dimensioned to receive a viewing instrument and enable the viewing instrument to be moved to or from a position near an optically transparent portion of a blunt, enclosed distal end of a shaft to provide unobstructed viewing through the distal end, and a position to the proximal side of an enclosed working area to provide viewing of the enclosed working area. A surgical instrument also or alternatively has a fluid routing switch within a shaft which can selectively connect a fluid infusion channel to at least one fluid export pore or a return channel. A method involves moving a viewing instrument to or from a position near an optically transparent portion of a blunt, enclosed distal shaft end and a proximal side of an enclosed working area. A method also or alternatively involves changing a position of a fluid routing switch within the shaft.
Owner:LARSEN DANE M
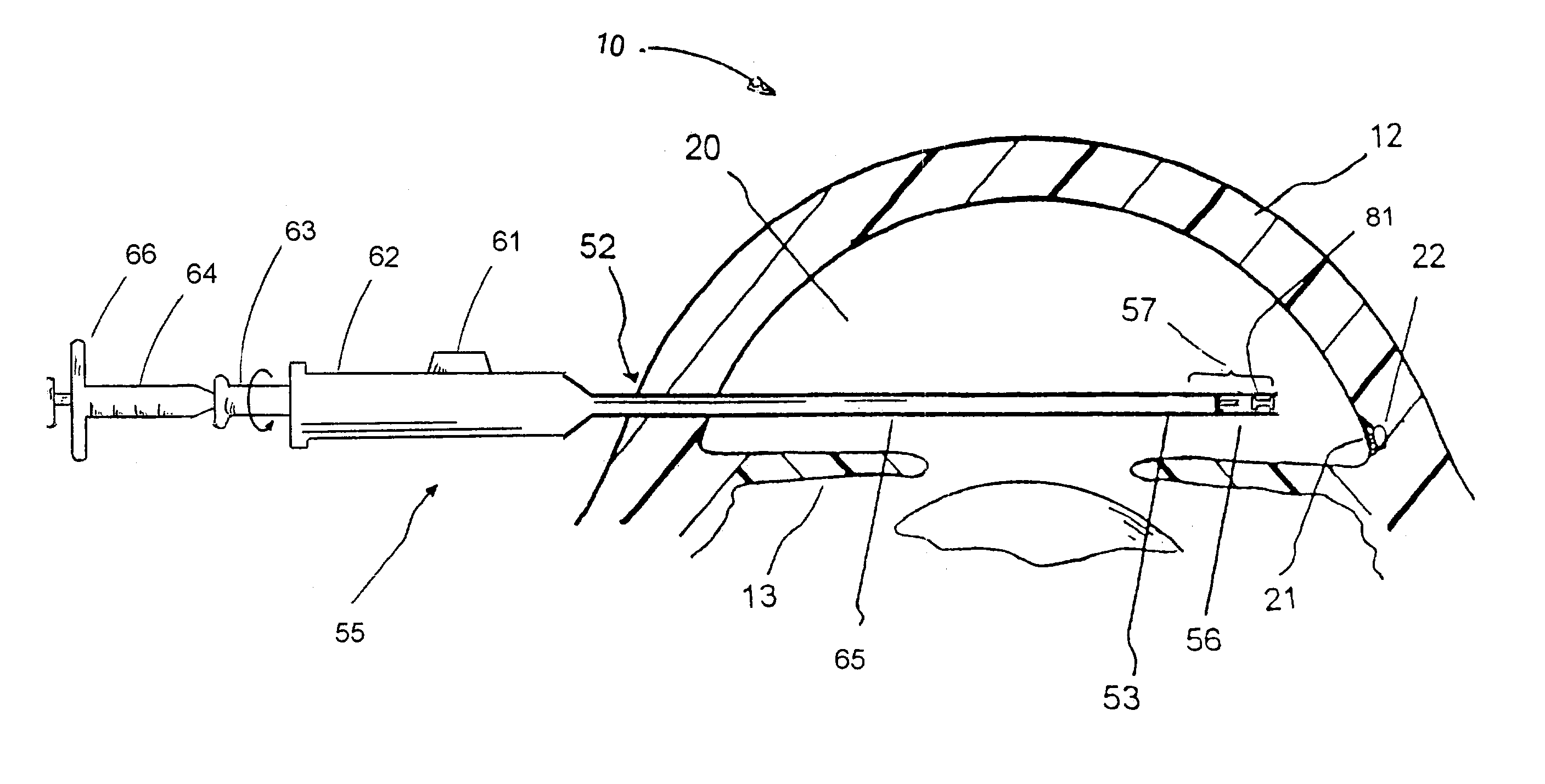
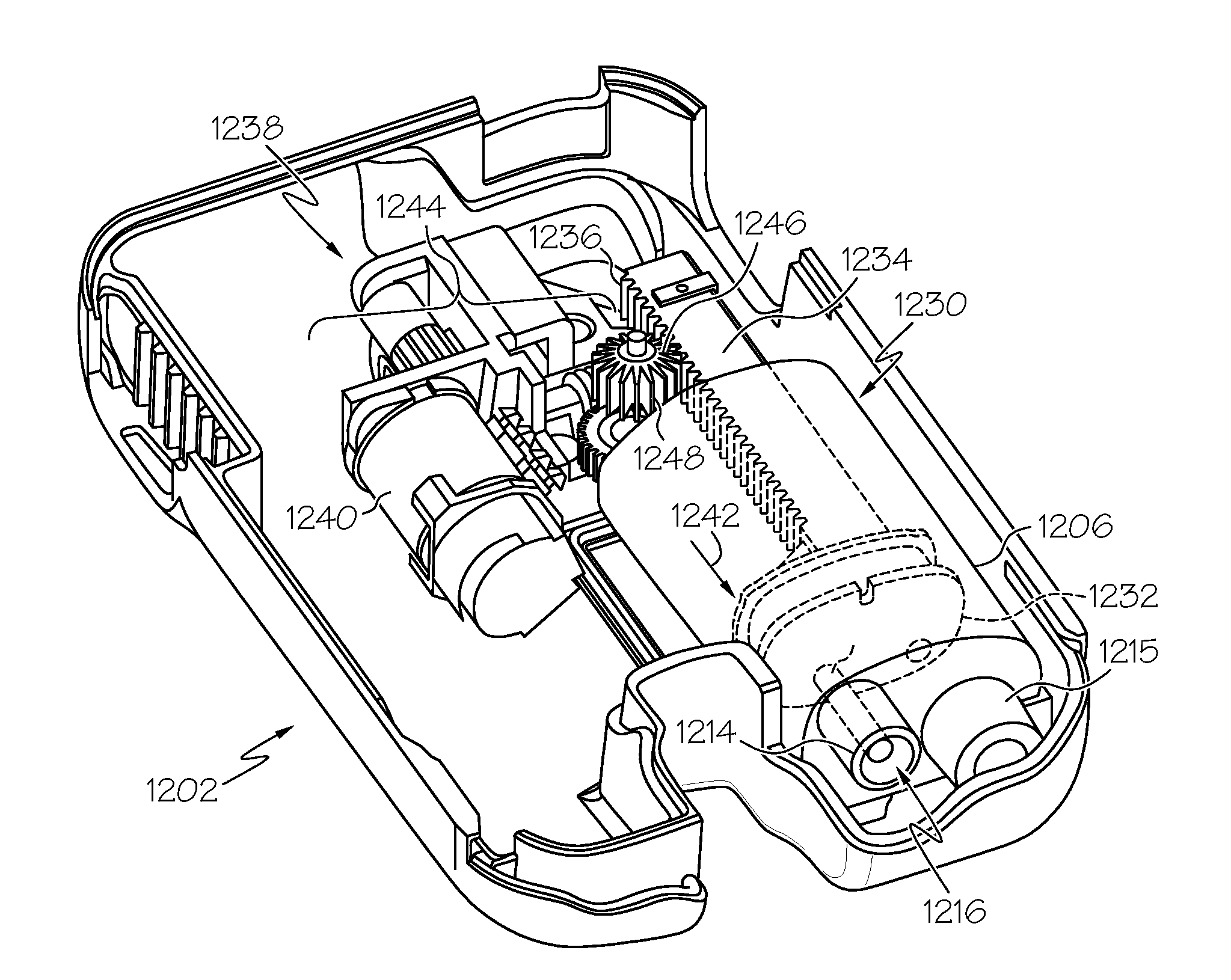
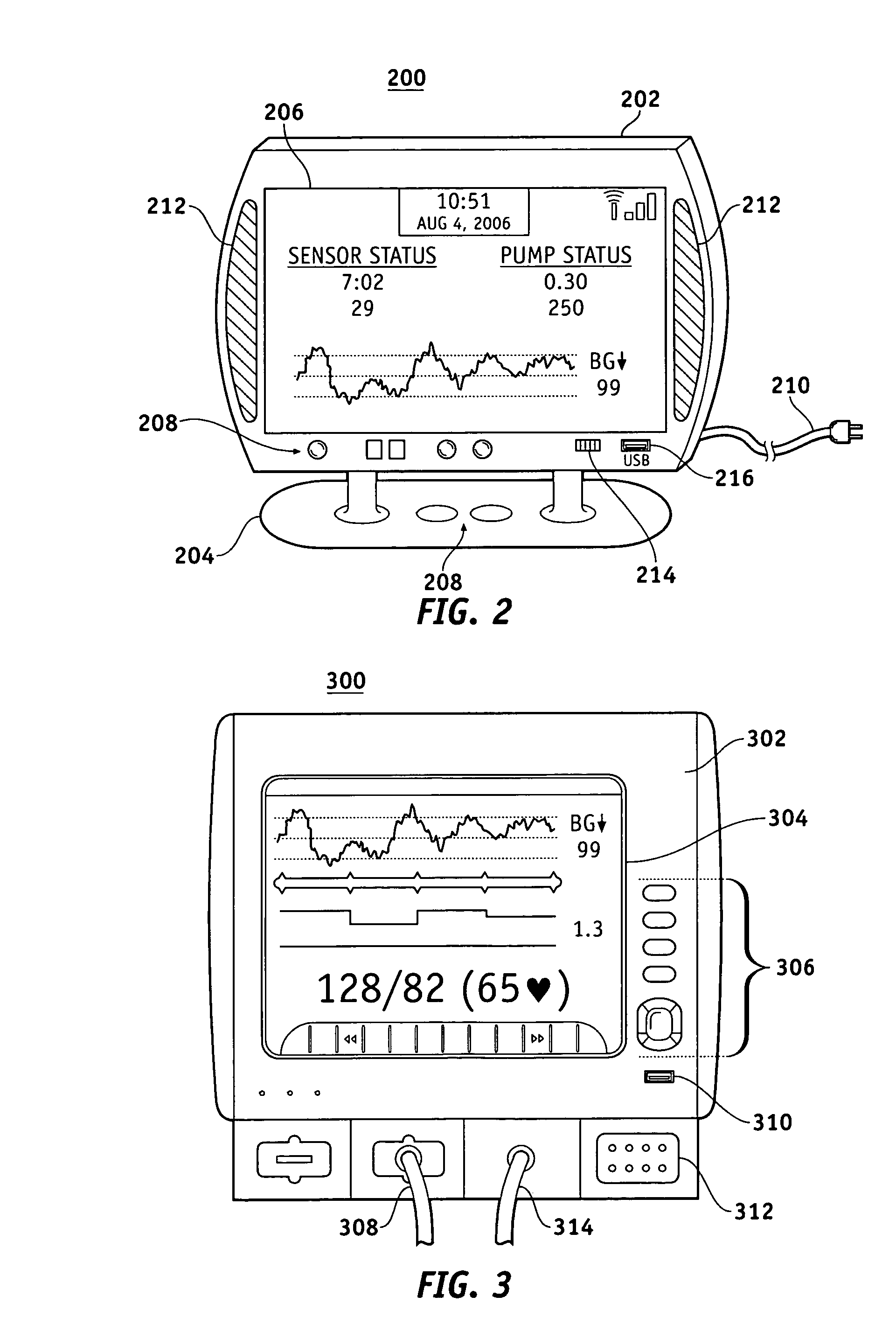
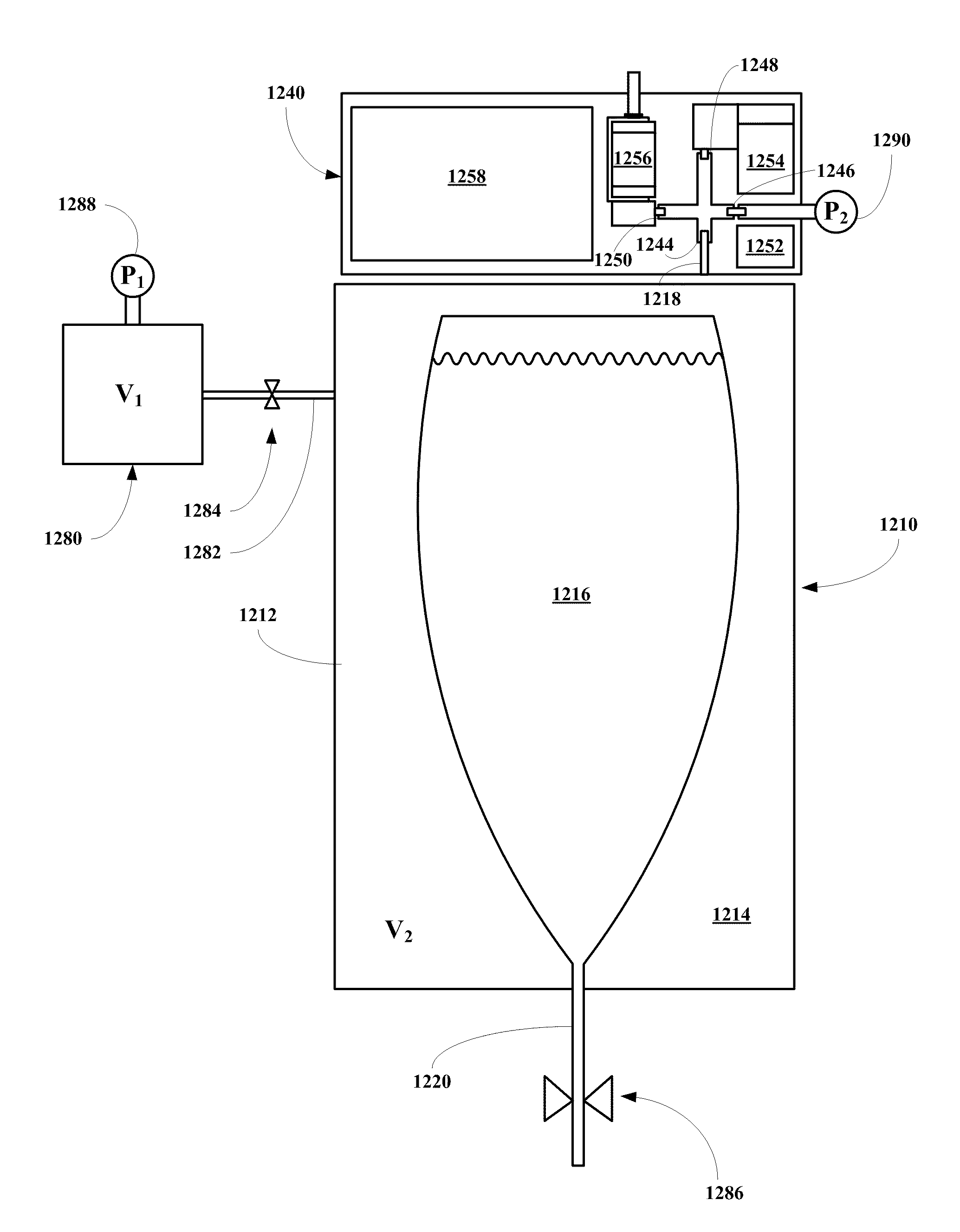
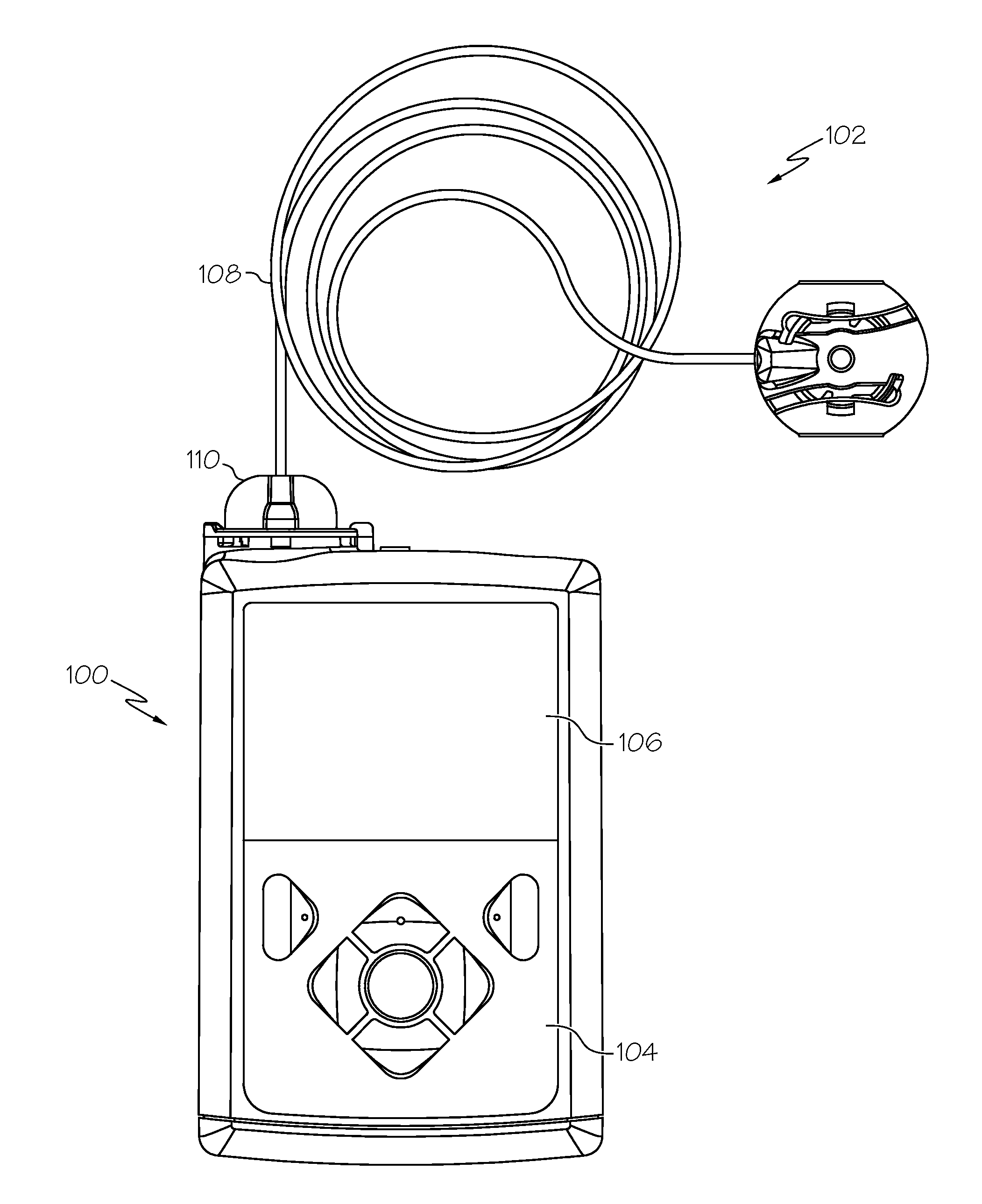
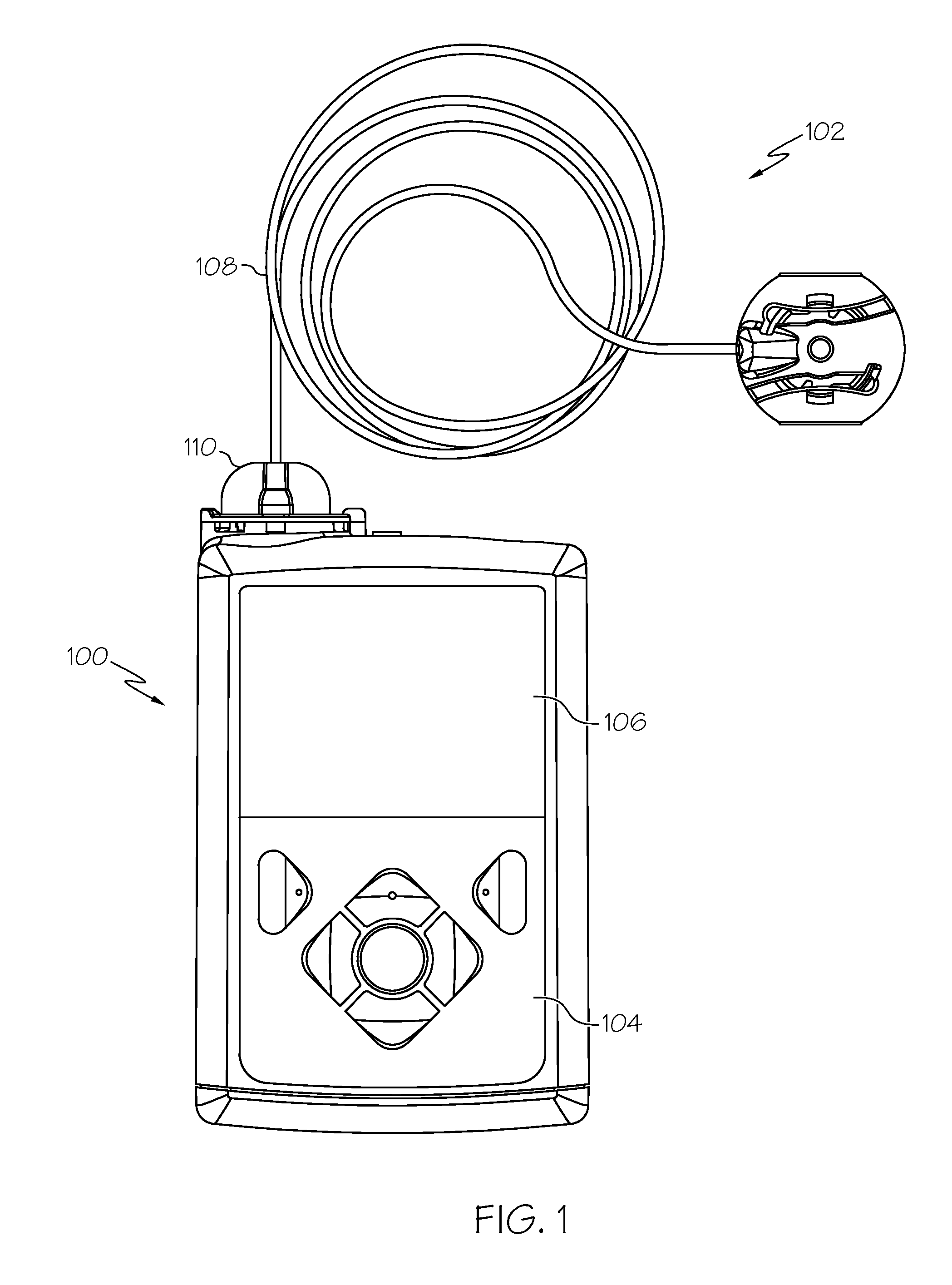
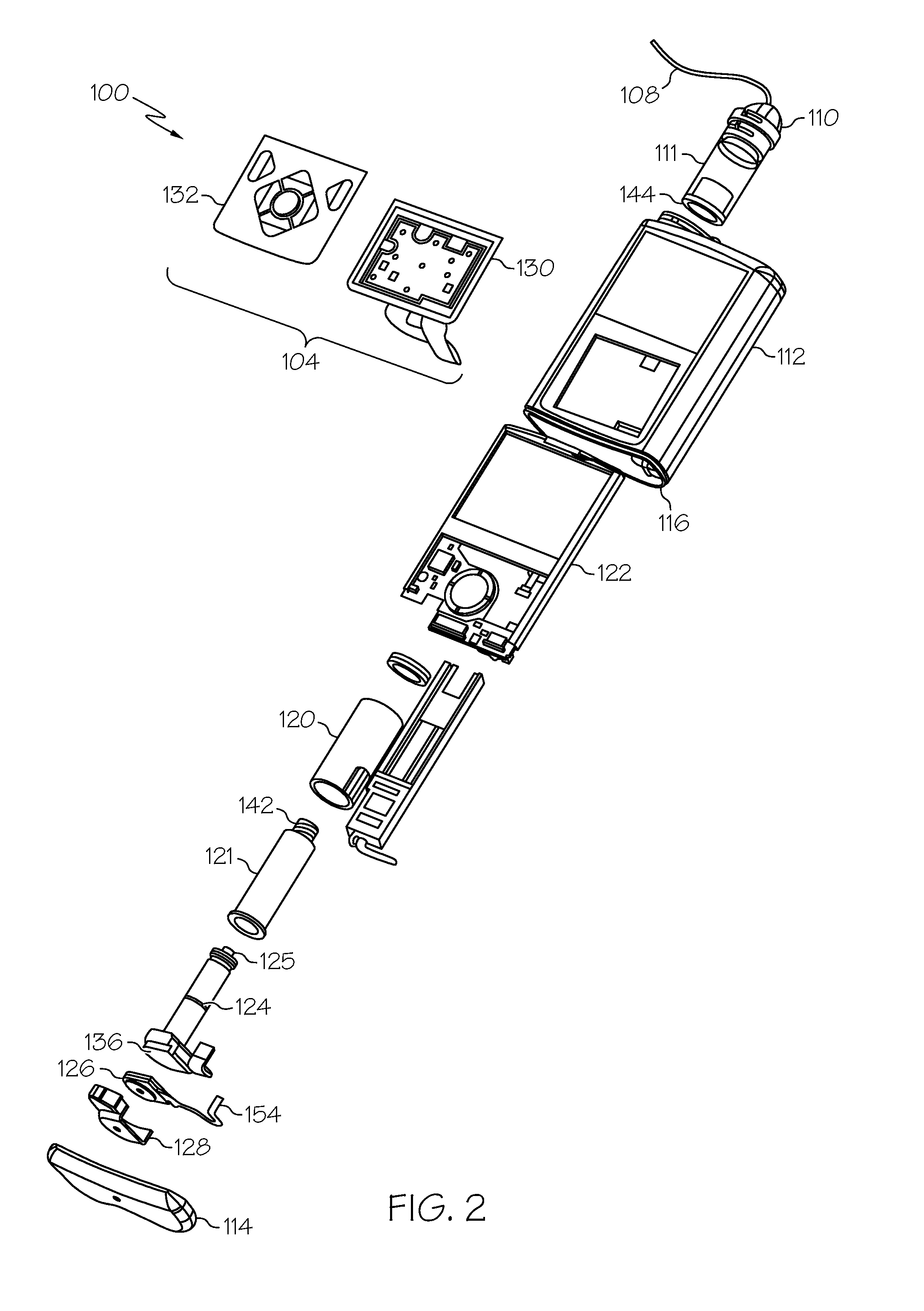
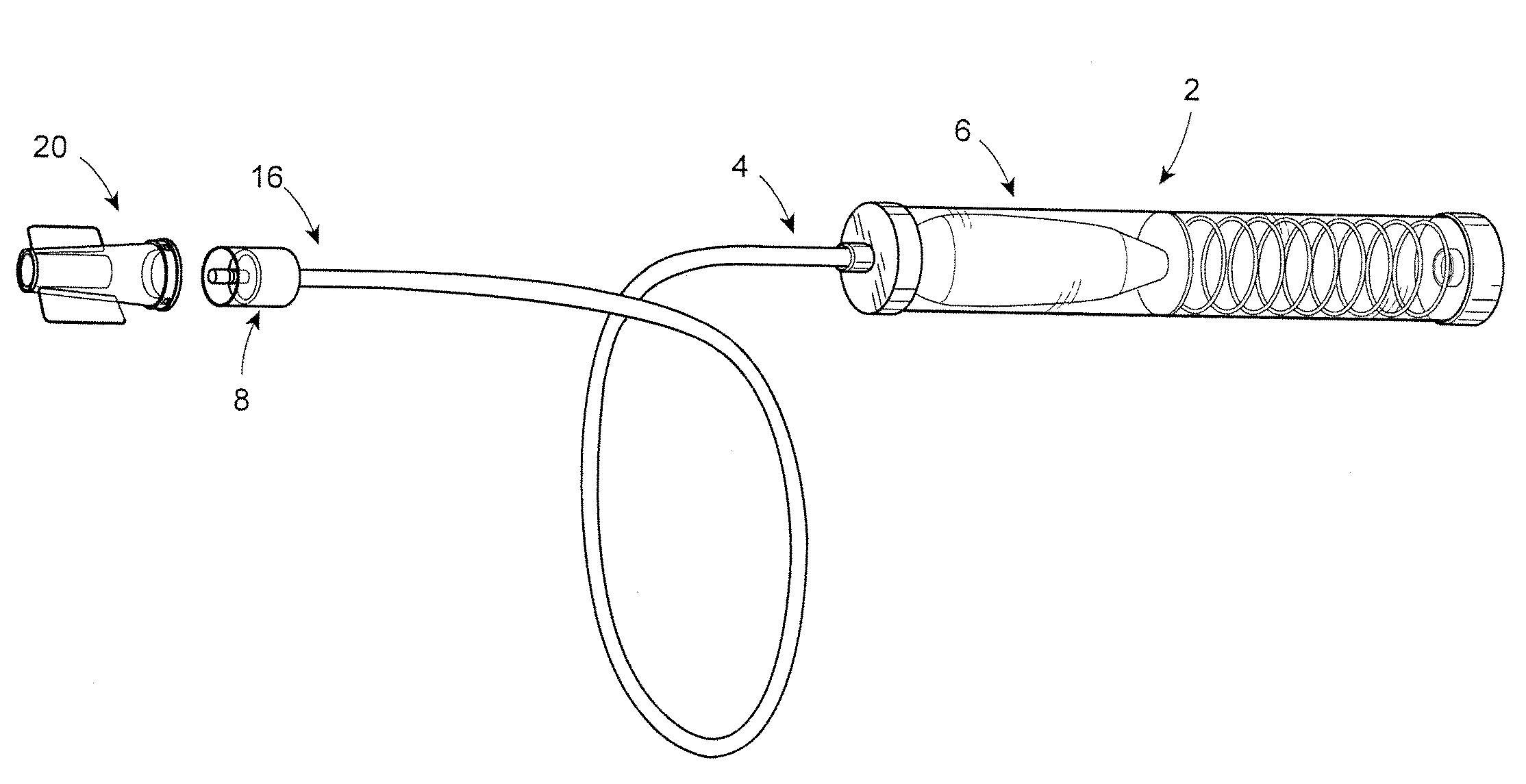
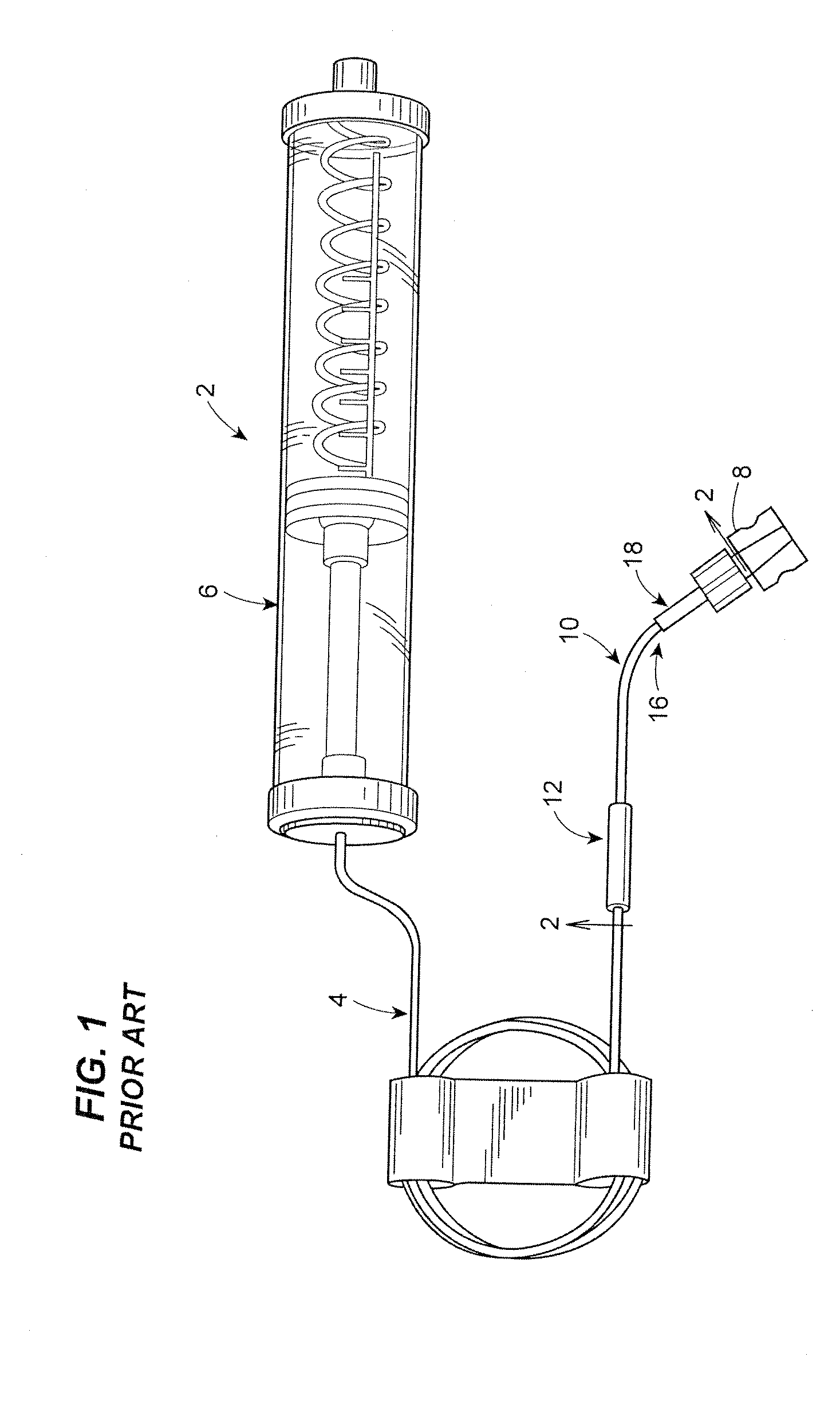
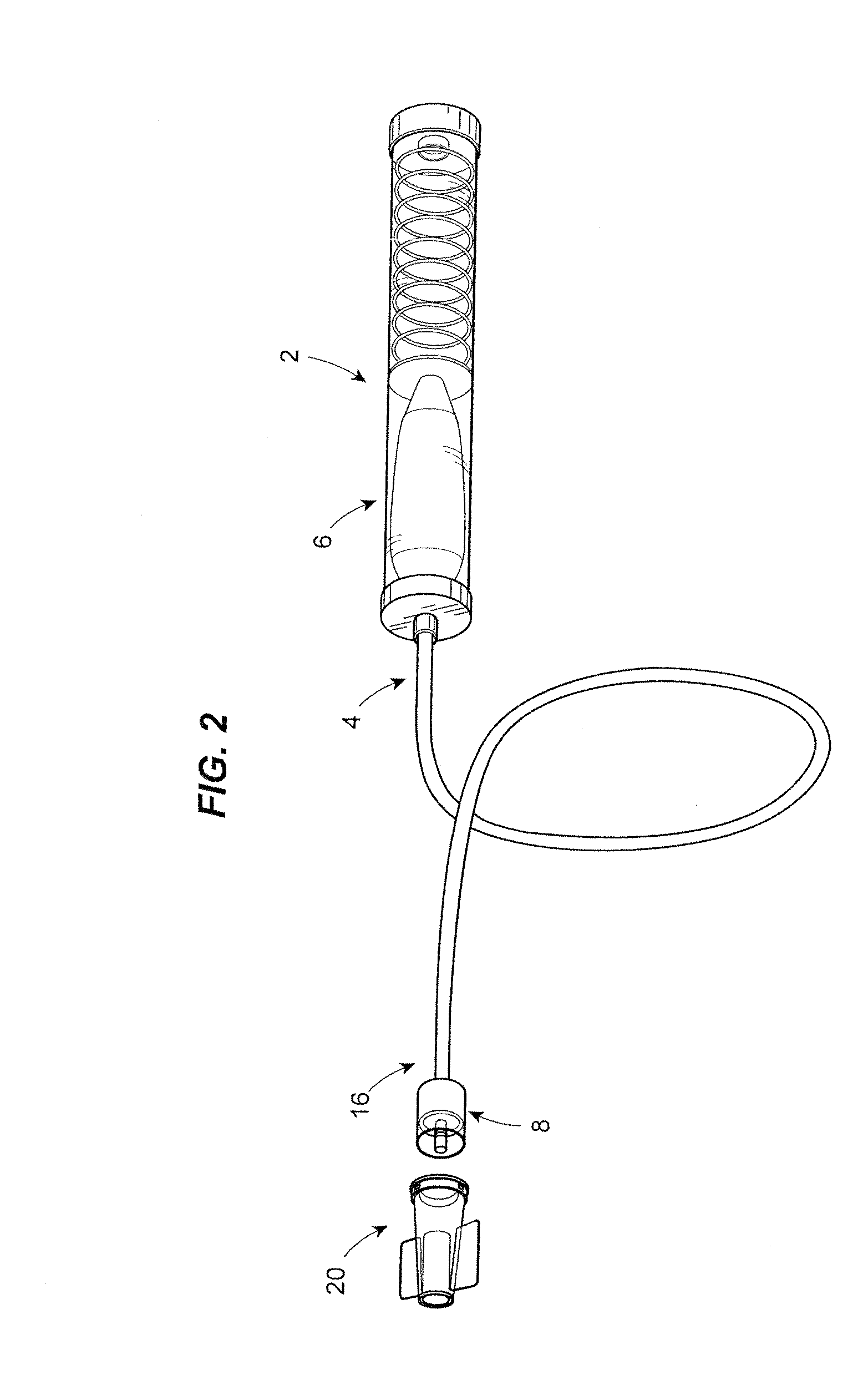
Fluid reservoir seating procedure for a fluid infusion device
A method of seating a fluid reservoir in a housing of a fluid infusion device is presented here. The method is performed prior to establishing an outgoing fluid flow path from the fluid reservoir. The method begins by detecting insertion of the fluid reservoir into the housing of the fluid infusion device. In response to detecting the insertion, the method determines whether the fluid reservoir is in need of depressurization. When the fluid reservoir is in need of depressurization, the drive motor assembly of the fluid infusion device is rewound to depressurize the fluid reservoir. After depressurizing the fluid reservoir, an equalization state for the fluid reservoir is achieved. After achieving the equilibrium state, the drive motor assembly is advanced to obtain an initial seated state for the fluid reservoir.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Fluid infusion methods for glaucoma treatment
InactiveUS20060116626A1Convenient treatmentReduce and inhibit and slow effectLaser surgeryEye implantsFluid infusionInsertion stent
Methods of treating glaucoma are disclosed, such as a method that includes inserting a stent through an incision in an eye; the stent having an inflow portion that is in fluid communication with an outflow portion of the stent; transporting the stent from the incision through the anterior chamber of the eye to an aqueous cavity of the eye, such that the inflow portion of the stent is positioned in the anterior chamber and the outflow portion of the stent is positioned at the aqueous cavity; and infusing fluid from the inflow portion to the outflow portion of the stent.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
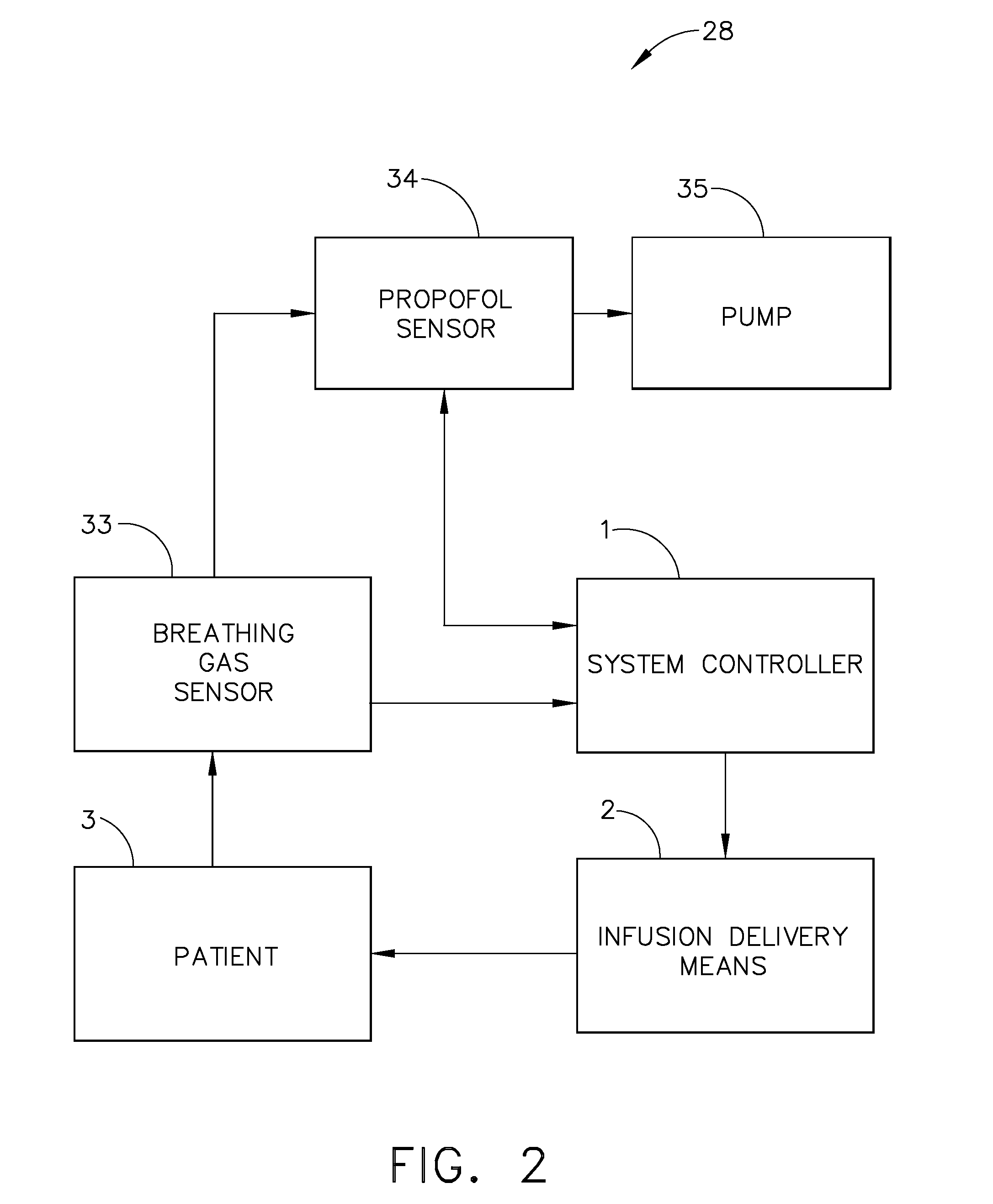
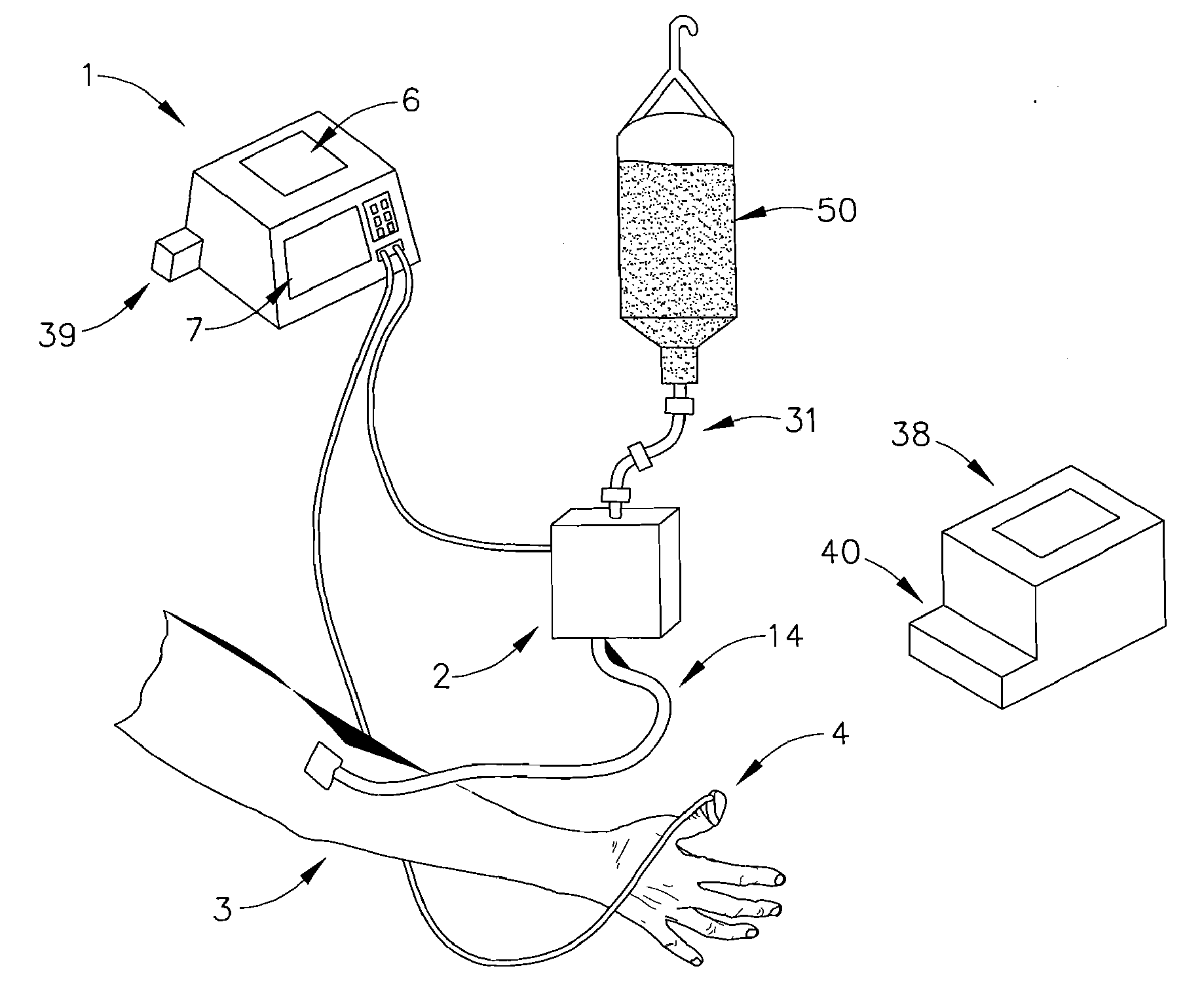
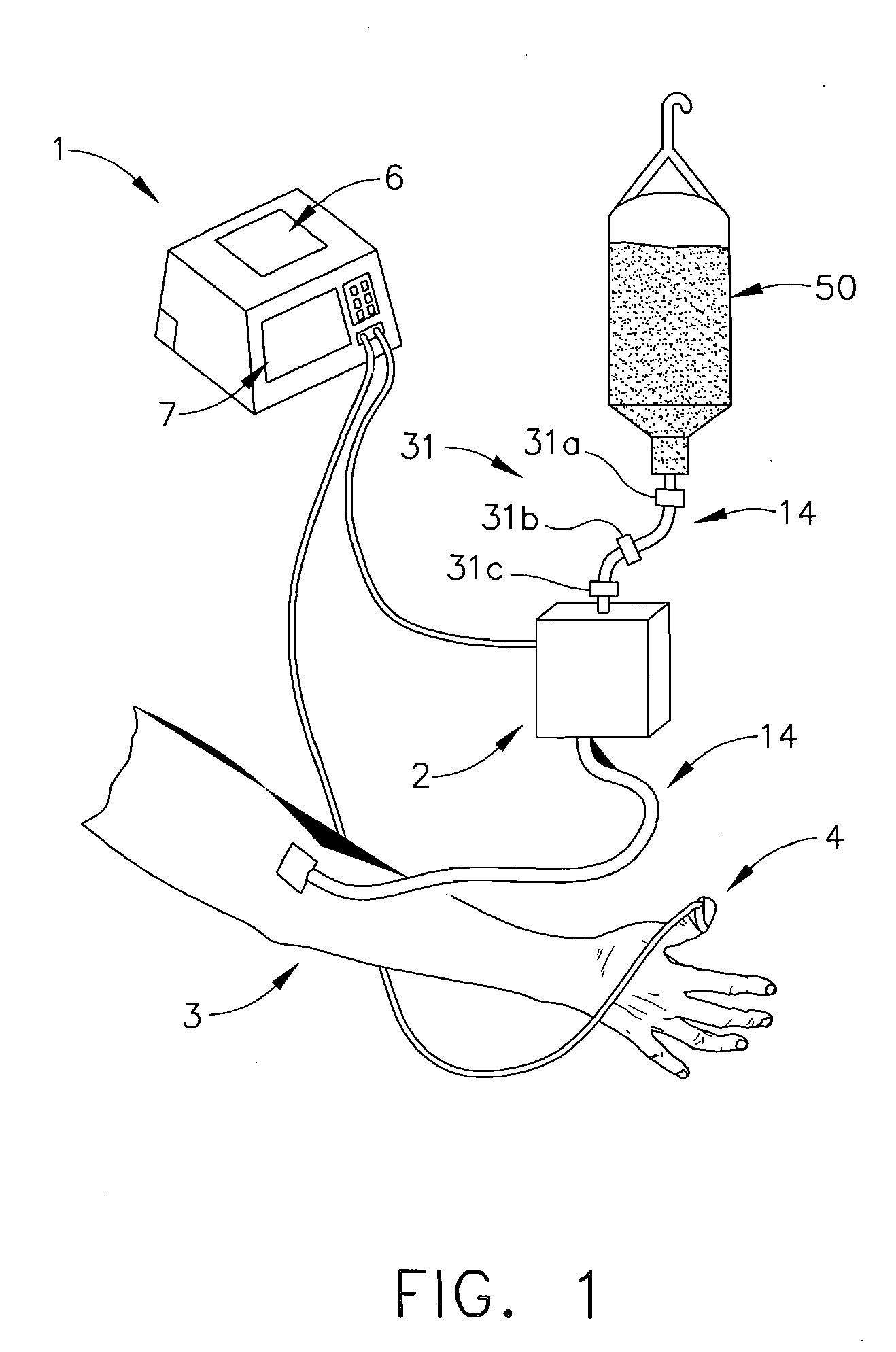
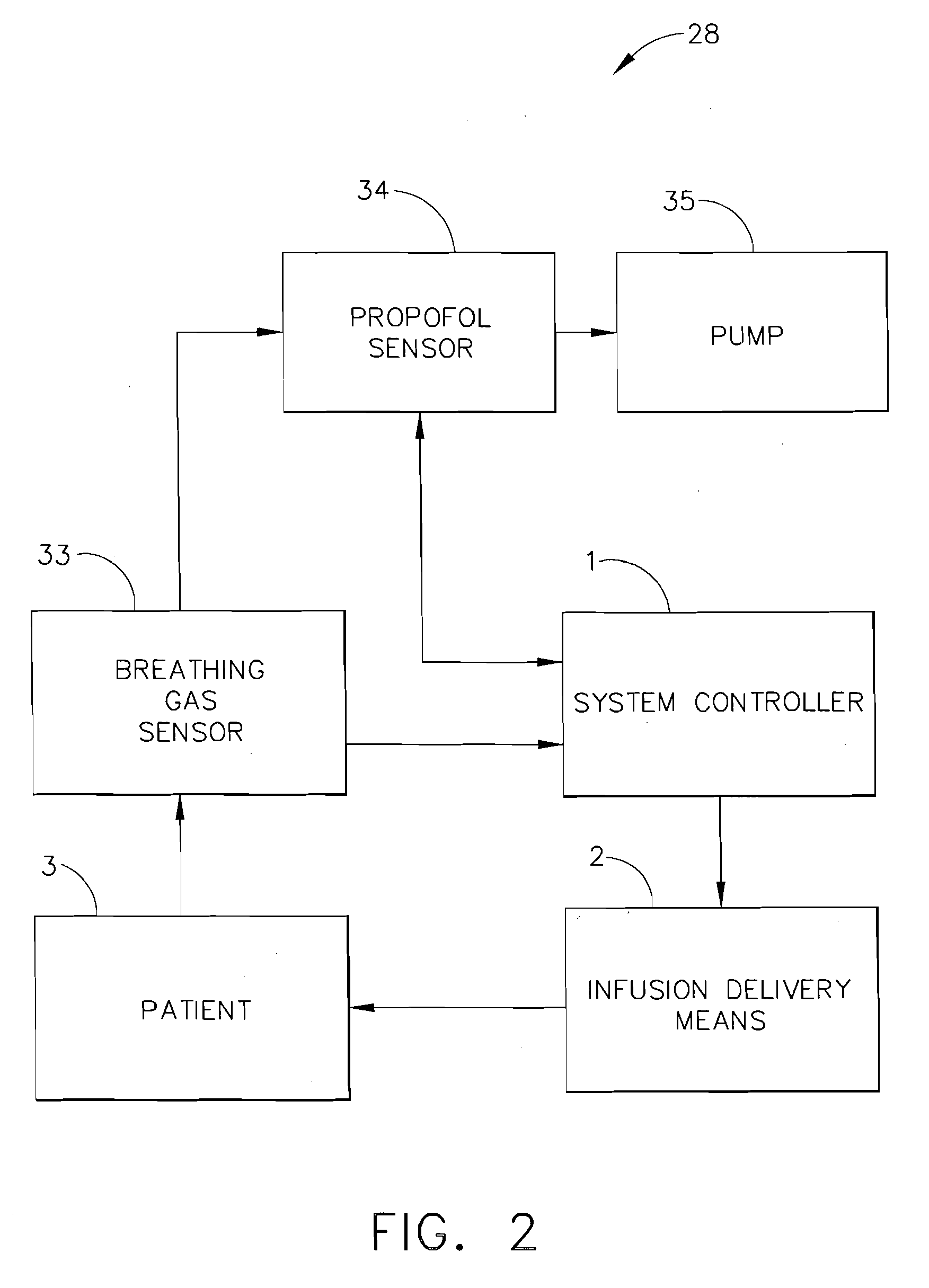
Apparatus and methods for controlling and automating fluid infusion activities
The present invention provides apparatuses and methods to safely and economically deliver infusion fluid to a patient during a medical procedure. The infusion fluid may be a sedative, analgesic, amnestic or other pharmaceutical agent (drug) for alleviating a patient's pain and anxiety before, during and / or after a medical or surgical procedure. In general the apparatus comprises a microprocessor-based controller that receives inputs from a plurality of physiological monitors attached to a patient. The system controller processes the data from the physiological monitors and based upon a fluid infusion algorithm delivers infusion fluid to a patient. The physiological monitors monitor the patient throughout the course of the procedure and depending upon the health of the patient, drug delivery may be adjusted to optimize the procedure while ensuring the patient's health is maintained. Functionality detectors such as an occlusion sensor, air-in-line sensor and a fluid detection sensor alert a clinician to such hazards as a pressure build up in the infusion line, air-bubbles in the infusion line, and the absence of fluid in the infusion line.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
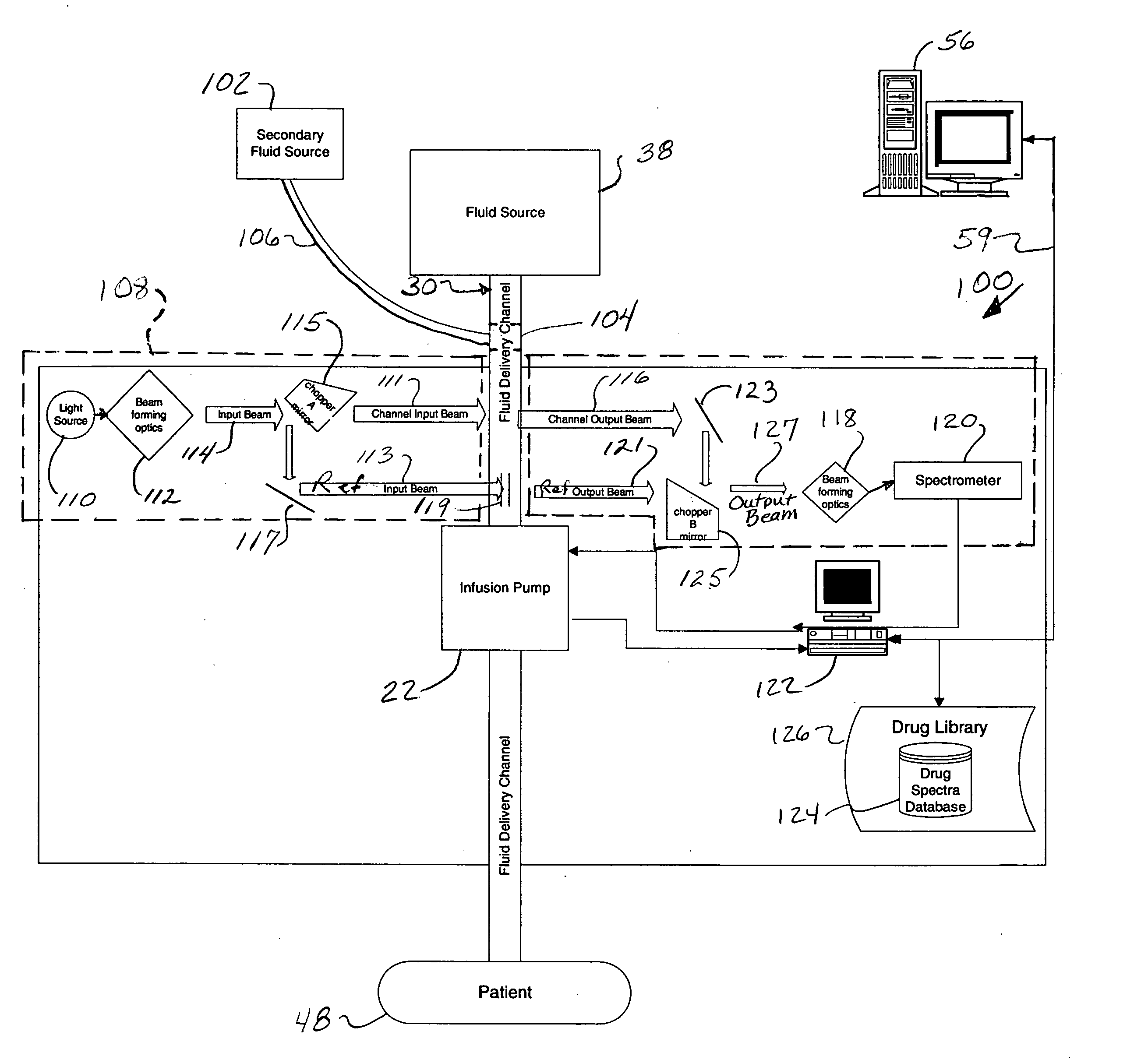
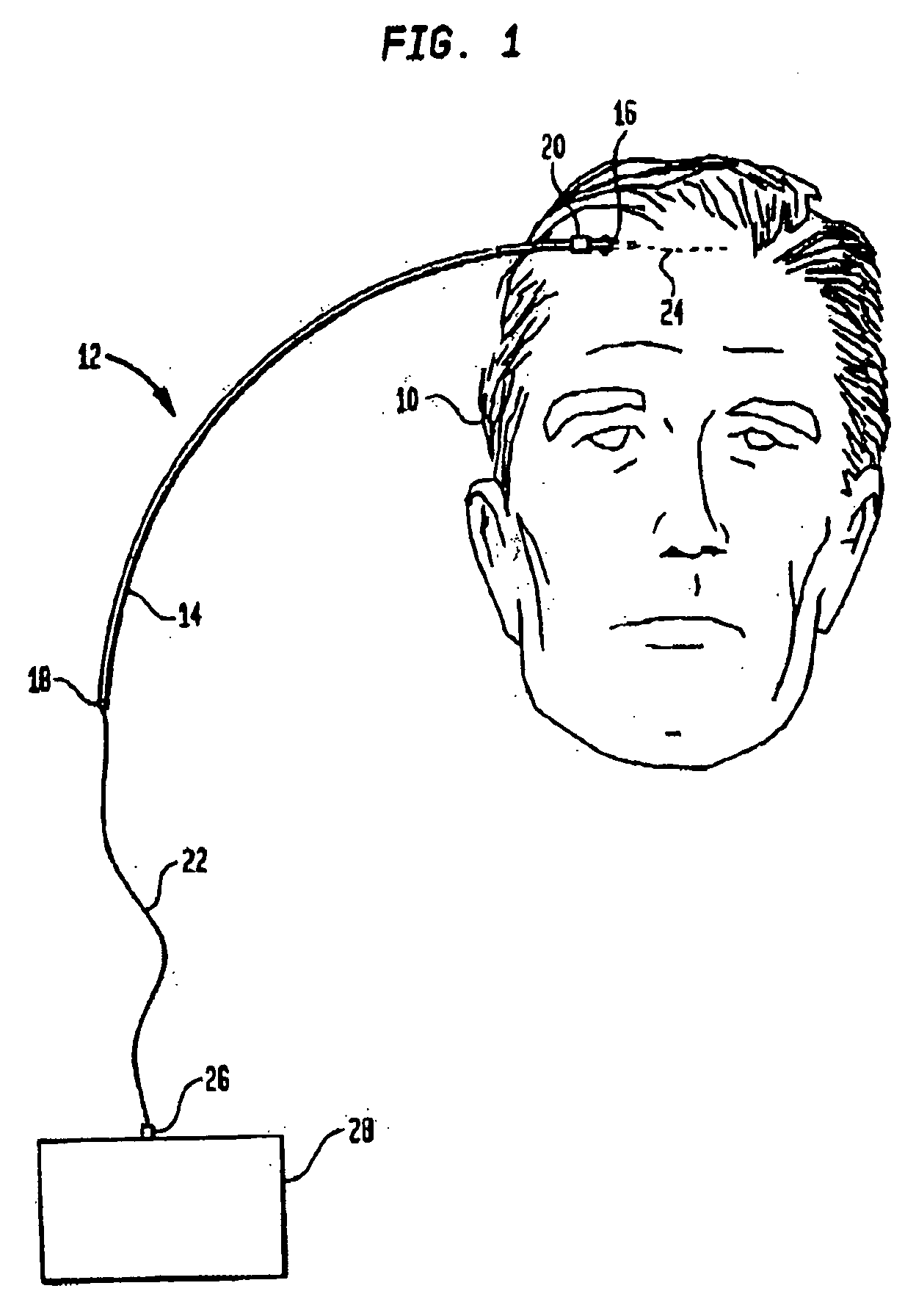
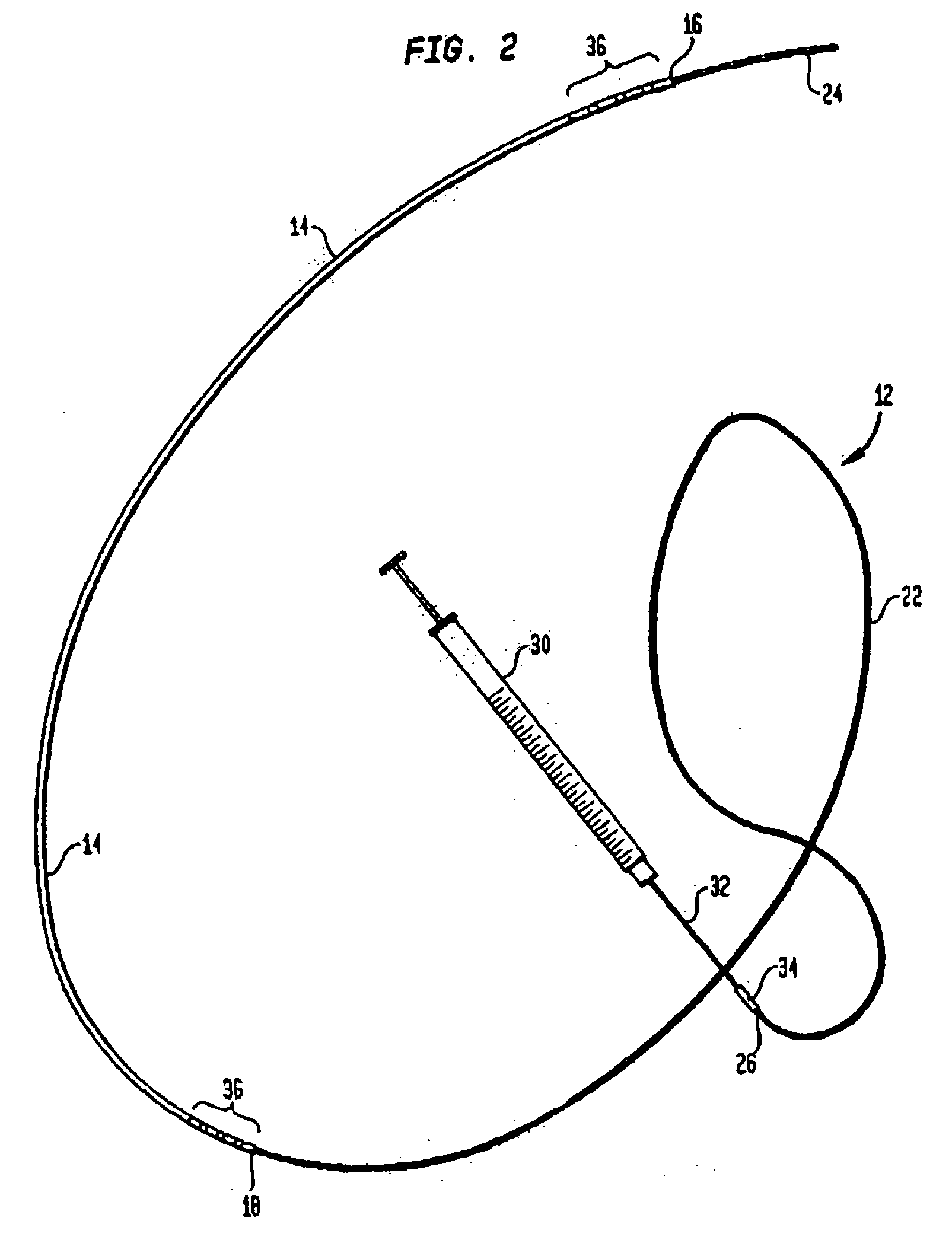
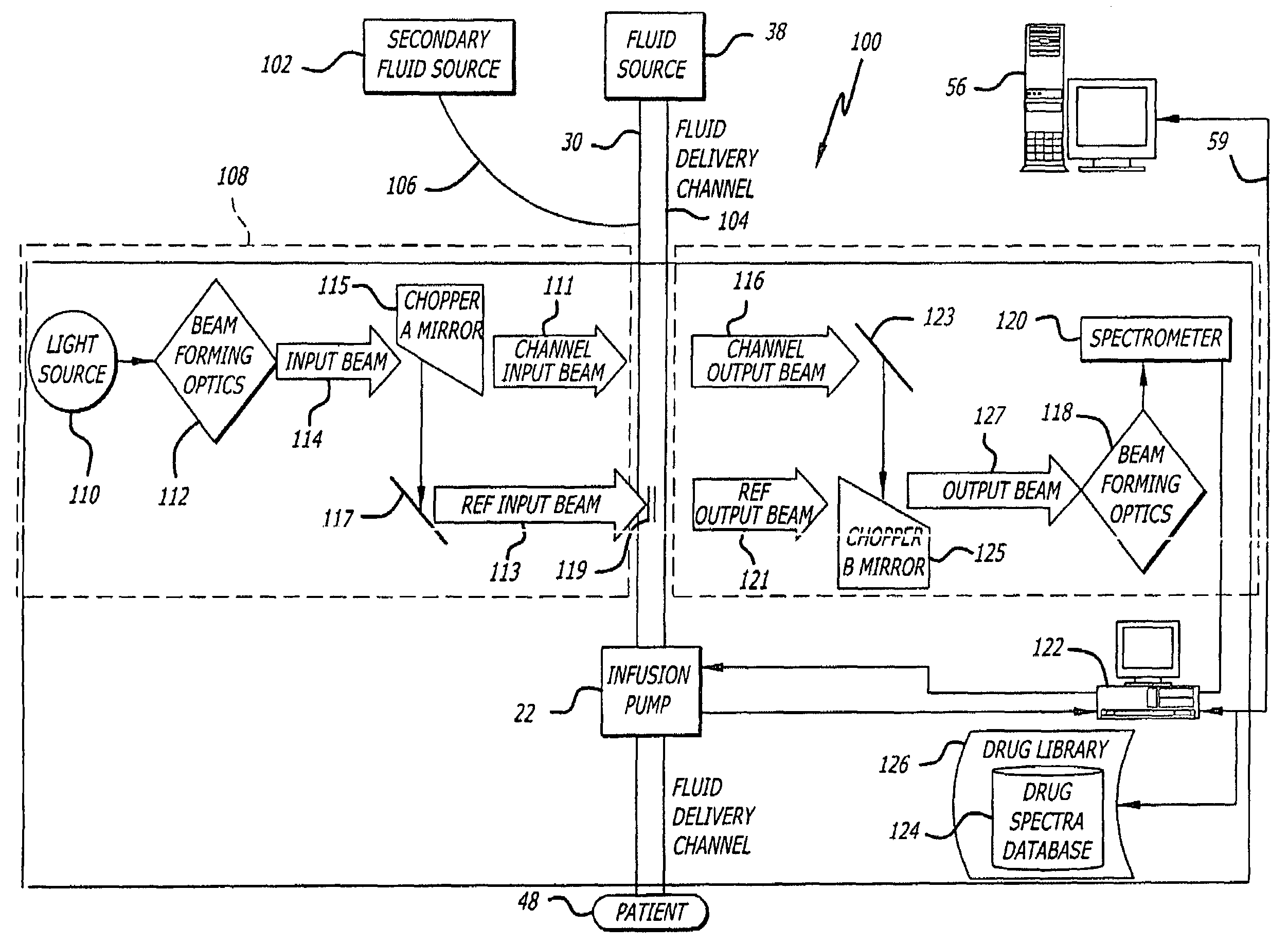
Fluid verification system and method for infusions
An apparatus and method are provided to verify the composition of a medical fluid in a fluid infusion channel by comparison with clinician-entered input. Light is transmitted through the channel and detected by a sensor that generates signals representative of the spectral data of the light detected. A processor compares the spectral data of the light detected to the spectral data associated with the expected contents of the channel to verify that the correct fluid is being infused.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
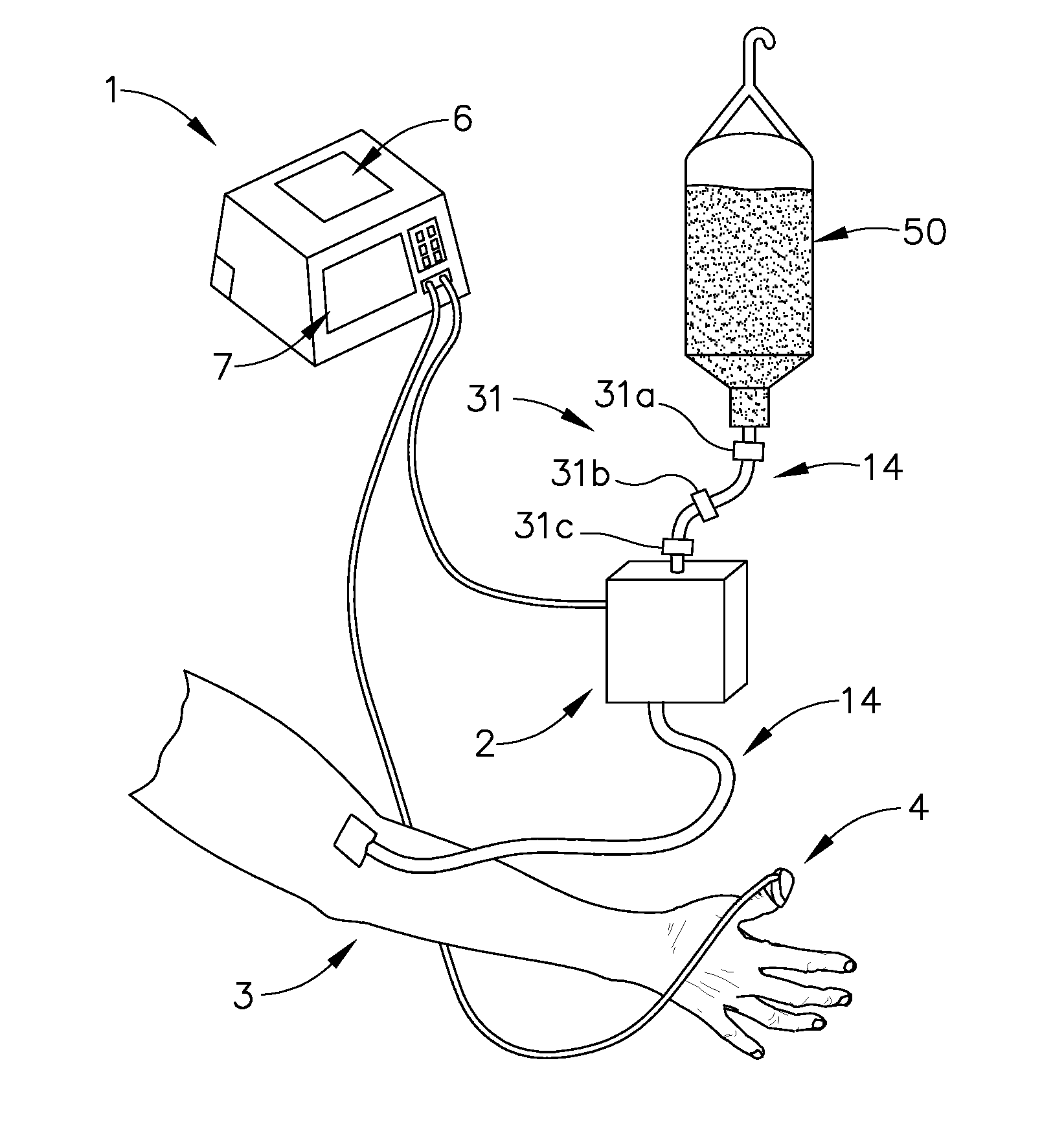
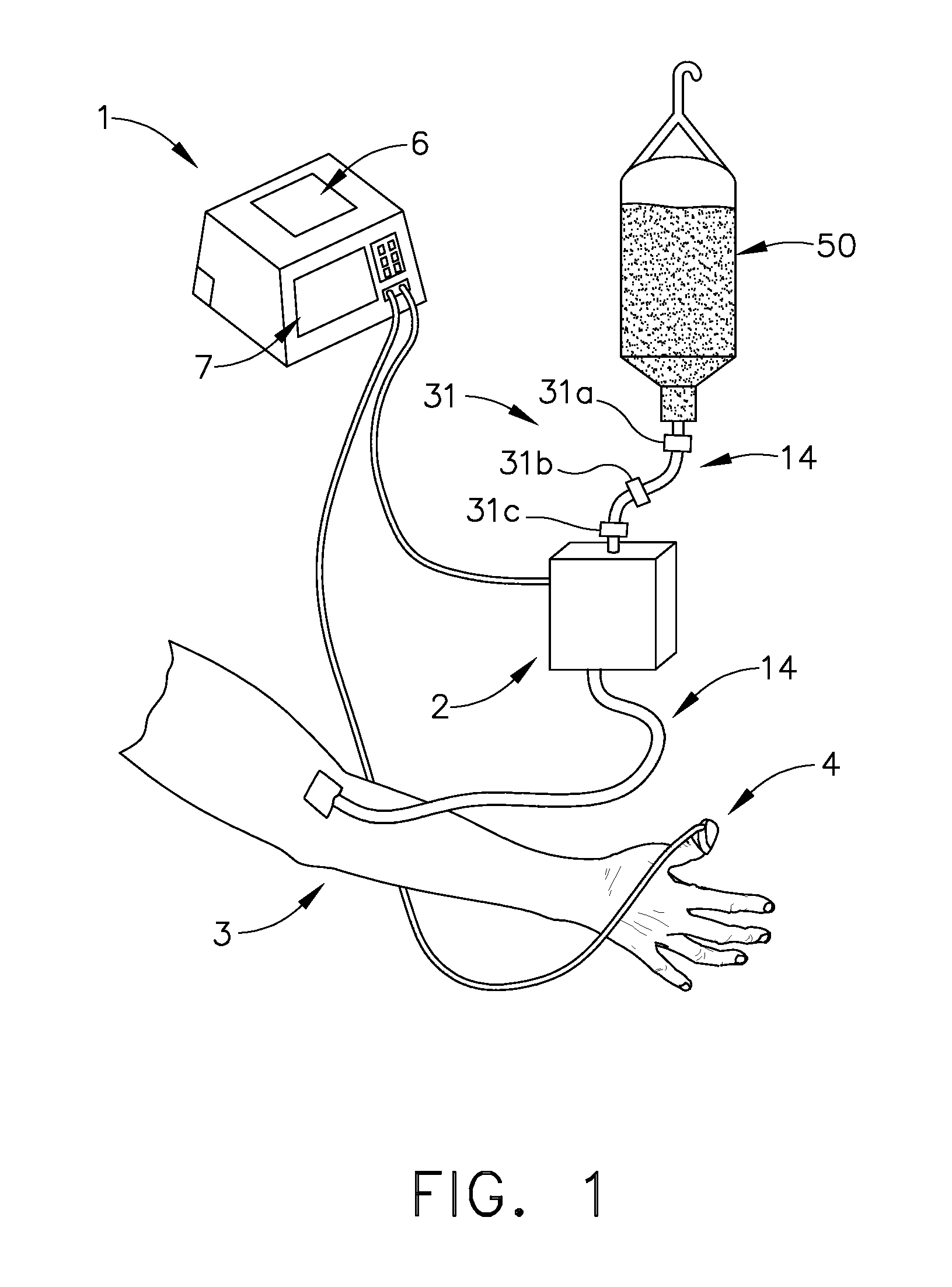
Patient hydration system with a redundant monitoring of hydration fluid infusion
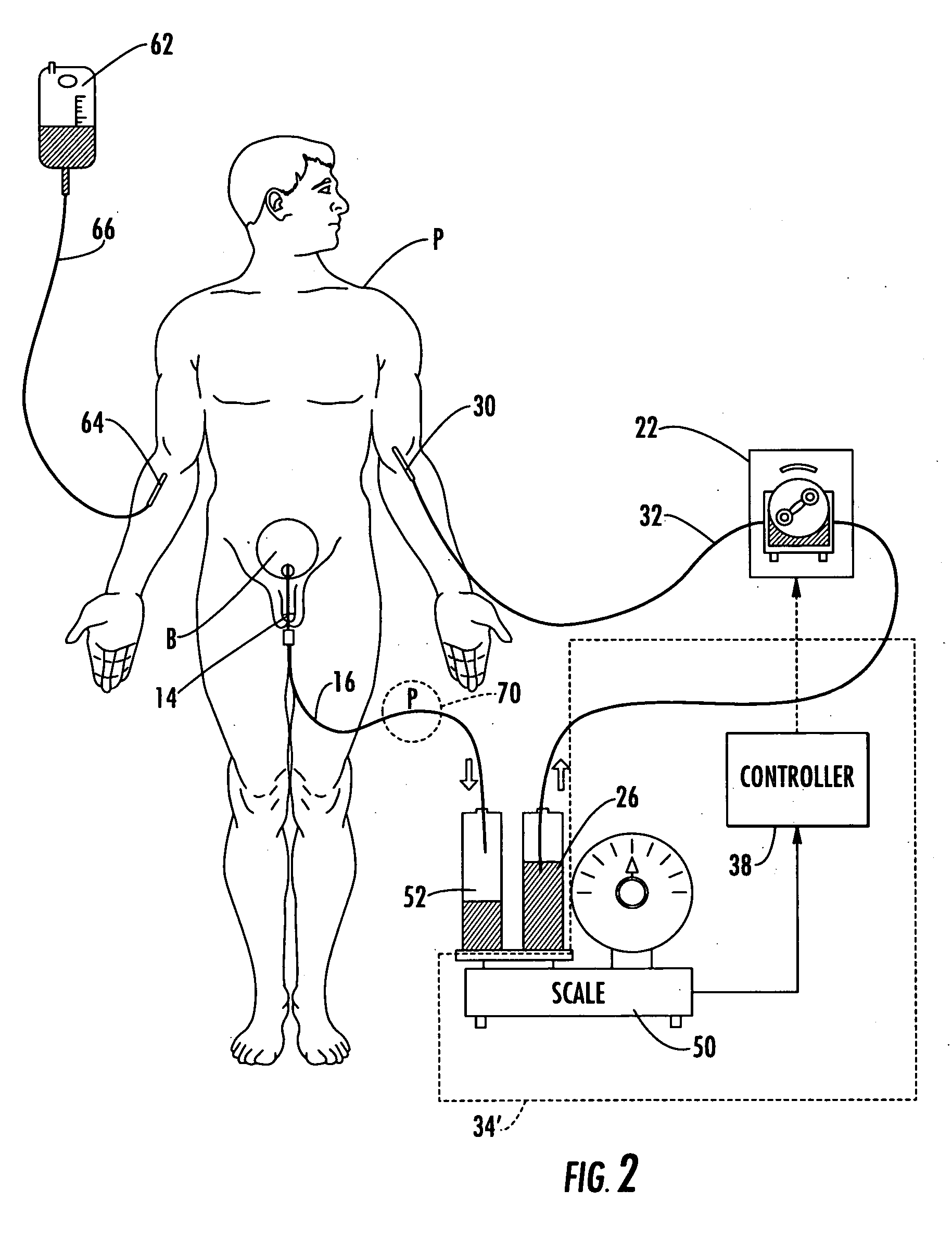
ActiveUS20060270971A1Prevent kidney damagePrevent dehydrationMedical devicesPressure infusionMeasurement deviceFluid infusion
A patient hydration system including an infusion device for administering hydration fluid to a patient, and a hydration fluid measurement device responsive to a source of hydration fluid, a patient urine output measurement device. A controller is responsive to the hydration fluid measurement device and the patient urine output measurement device. The controller operates the infusion device, in response to the patient urine output measurement device and the hydration fluid measurement device, to hydrate the patient based on the patient's urine output. The controller also monitors the operation history of the infusion device thereby providing redundancy in the measurement of the amount of hydration fluid administered to the patient.
Owner:MEDICAL SYST
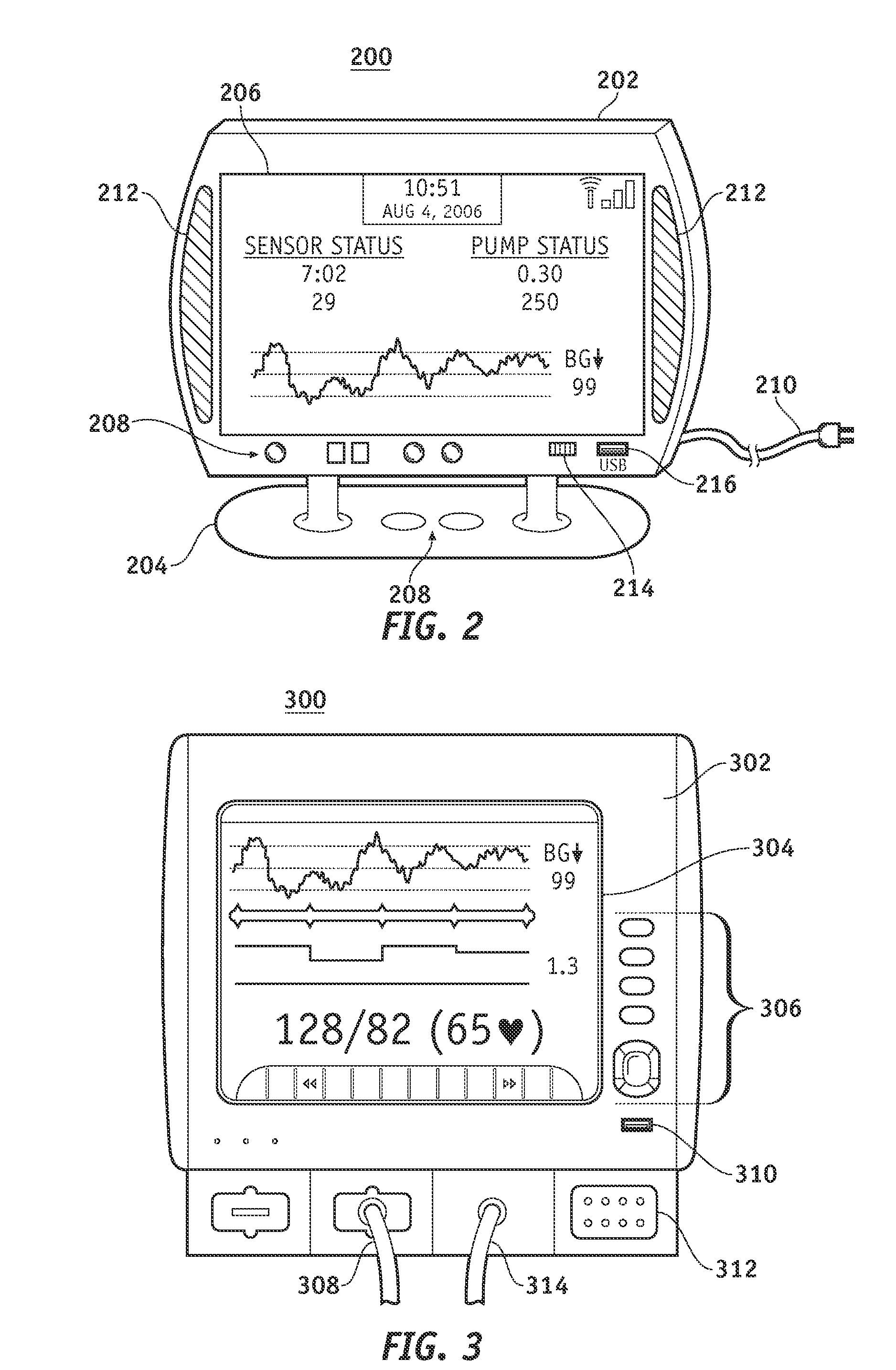
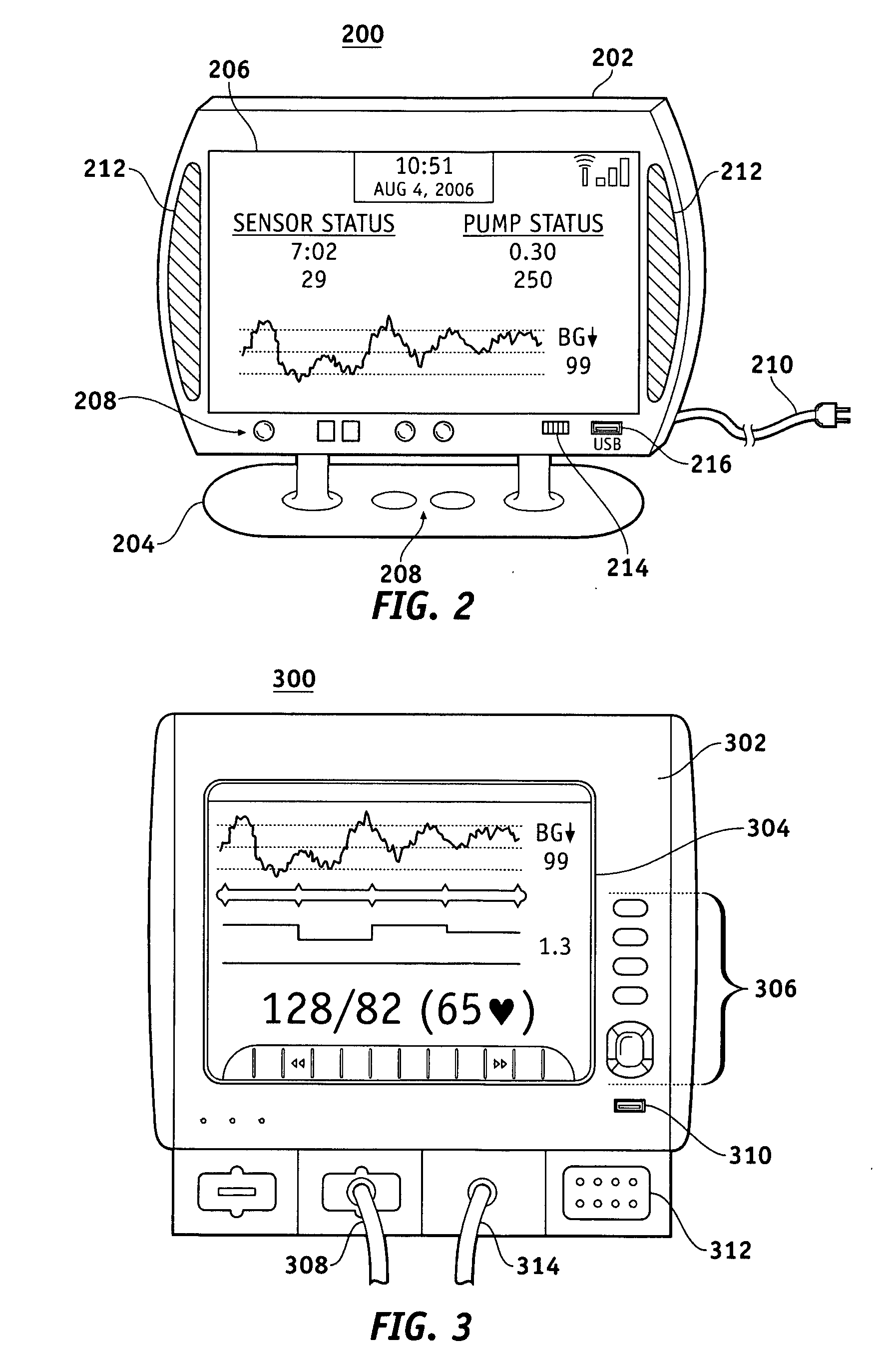
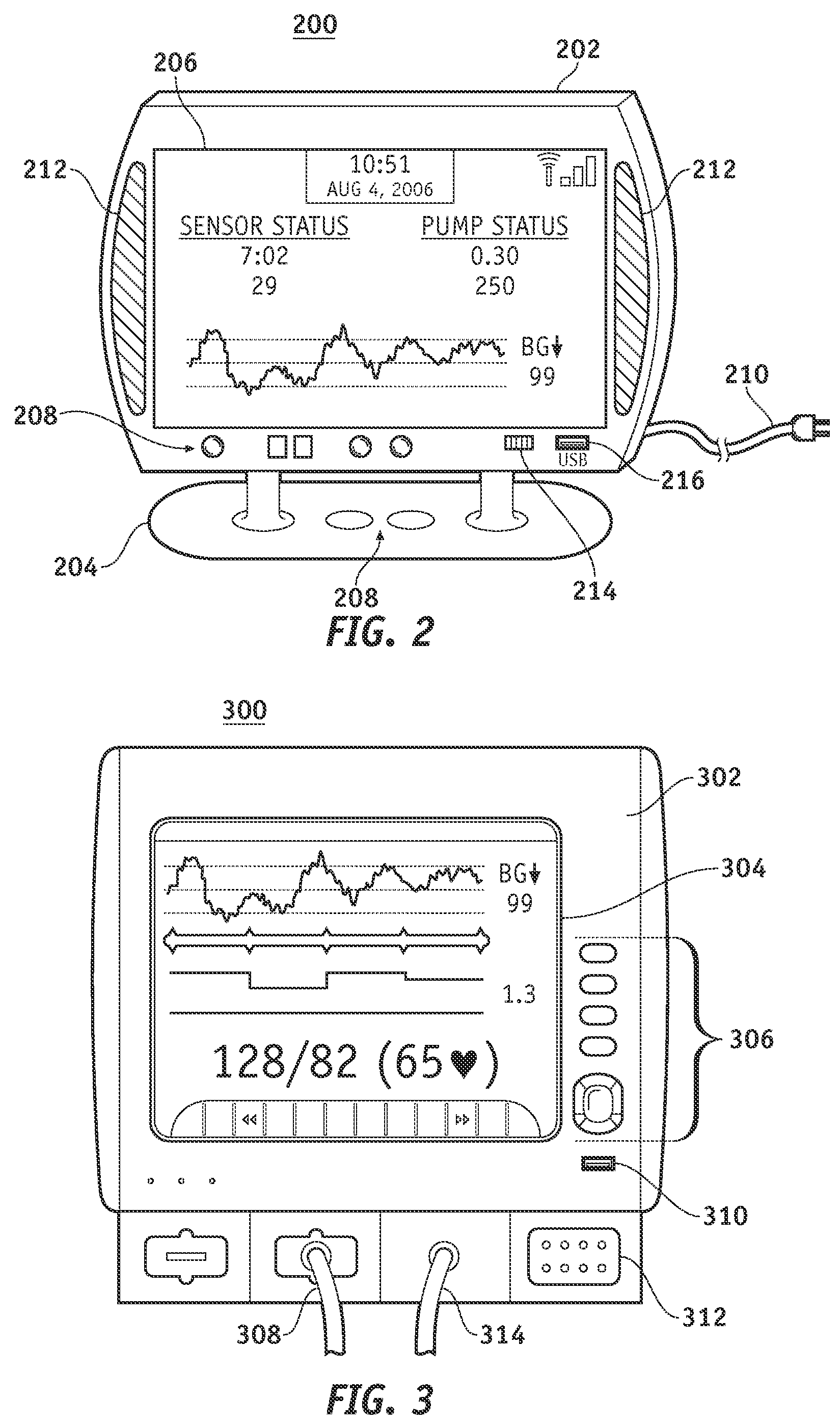
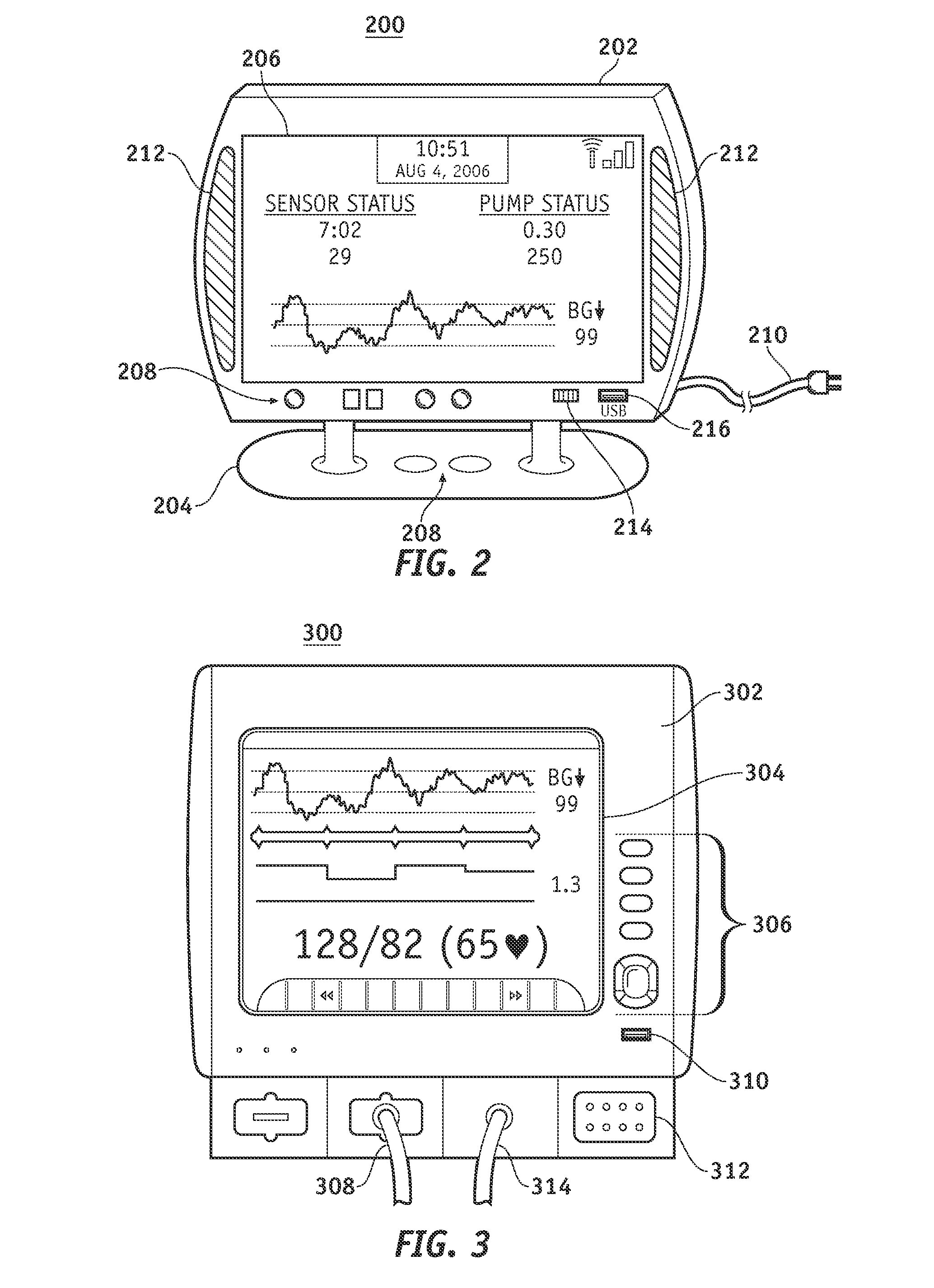
Monitor devices for networked fluid infusion systems
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. Such external communication allows the infusion system to be extended beyond the traditional short-range user environment.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Guidewire with adjustable stiffness
ActiveUS20100305475A1Significant transitionIncrease flexibilityGuide wiresIntravenous devicesDistal portionAdjustable stiffness
A medical guidewire system including an inner member having an outer diameter and an outer member having an inner diameter, the inner diameter being larger than the outer diameter. The inner and outer members are relatively slidable to adjust a stiffness of the guidewire system. The lumen of the outer member forms a gap for fluid flow therethrough. A connector has a first end portion connected to the outer member, a second end portion connected to the inner member and a fluid infusion channel communicating with the gap for injection of fluid through the gap to exit a distal portion of the outer member.
Owner:CARDIOGUIDANCE BIOMEDICAL
Subnetwork synchronization and variable transmit synchronization techniques for a wireless medical device network
ActiveUS8073008B2Weather/light/corrosion resistanceDrug and medicationsWireless Application ProtocolBody area network
A fluid infusion system as described herein includes a number of local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices can be configured to support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices can be configured to support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. The networked medical devices are configured to support a variety of wireless data communication protocols for efficient communication of data within the medical device network. In addition, the wireless medical devices may be configured to support a number of dynamically adjustable wireless data communication modes to react to current operating conditions, application-specific data content, or other criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Fluid Balance Monitoring System with Fluid Infusion Pump for Medical Treatment
ActiveUS20110196304A1Control flowEasy to controlAutomatic syringesMedical devicesFluid infusionFluid balance monitoring
Owner:ATHENA GTX +1
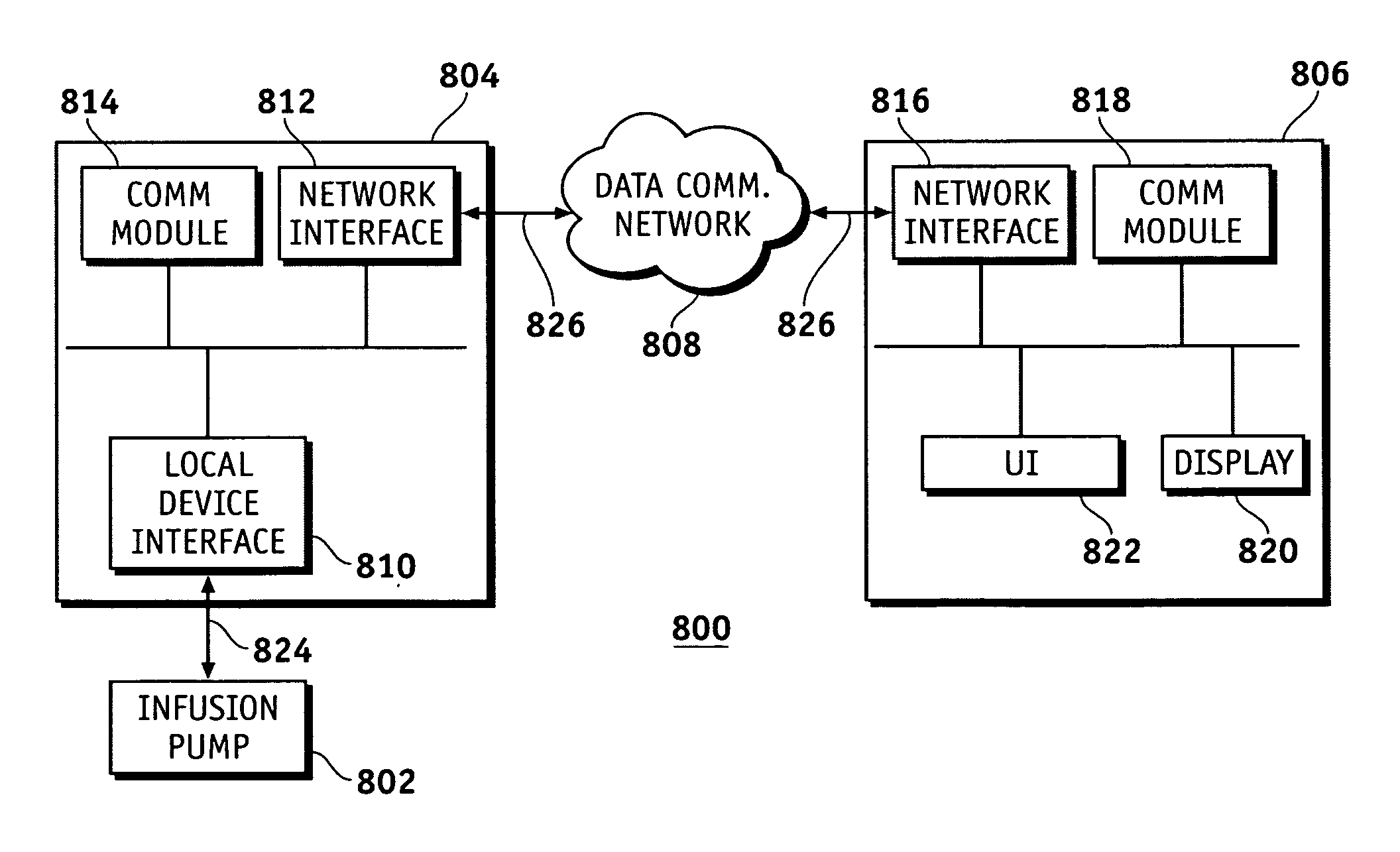
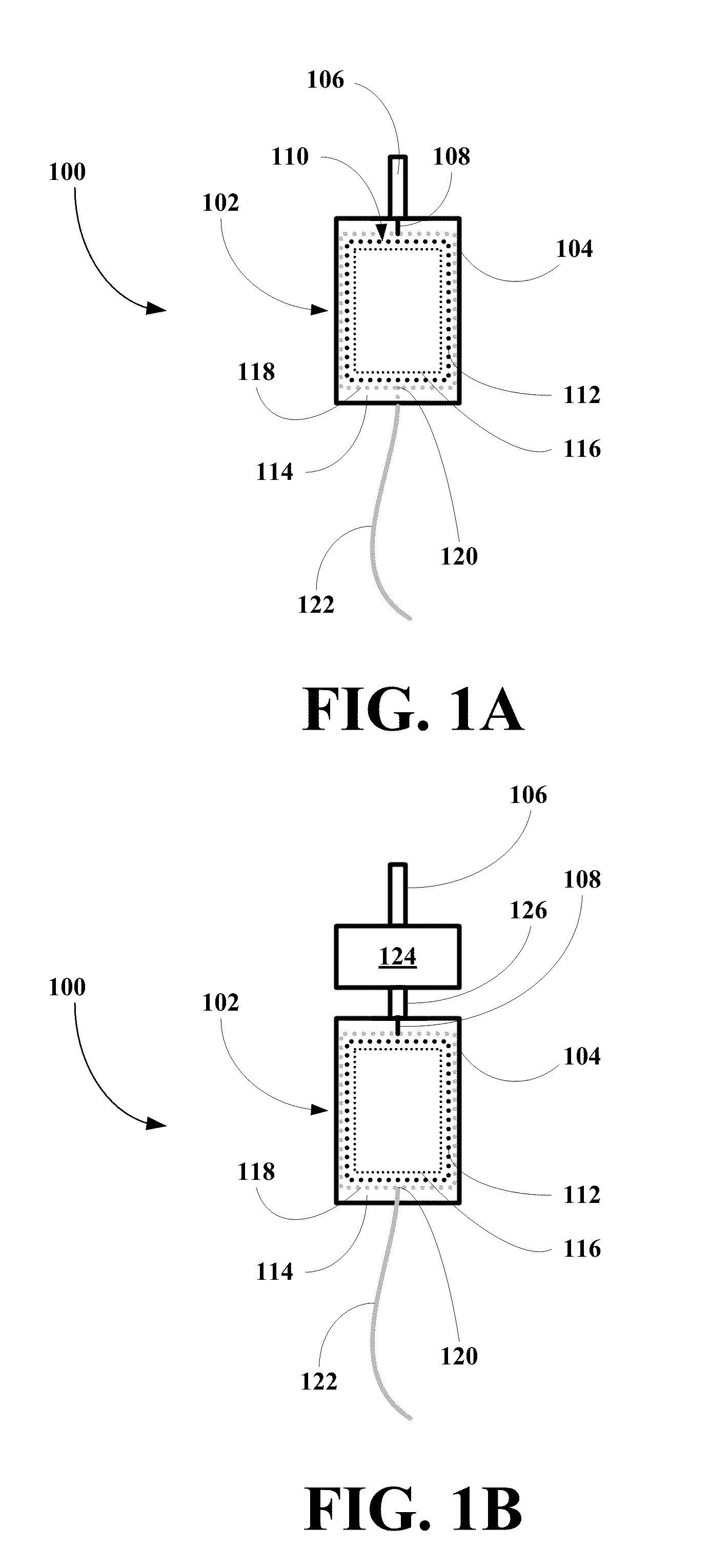
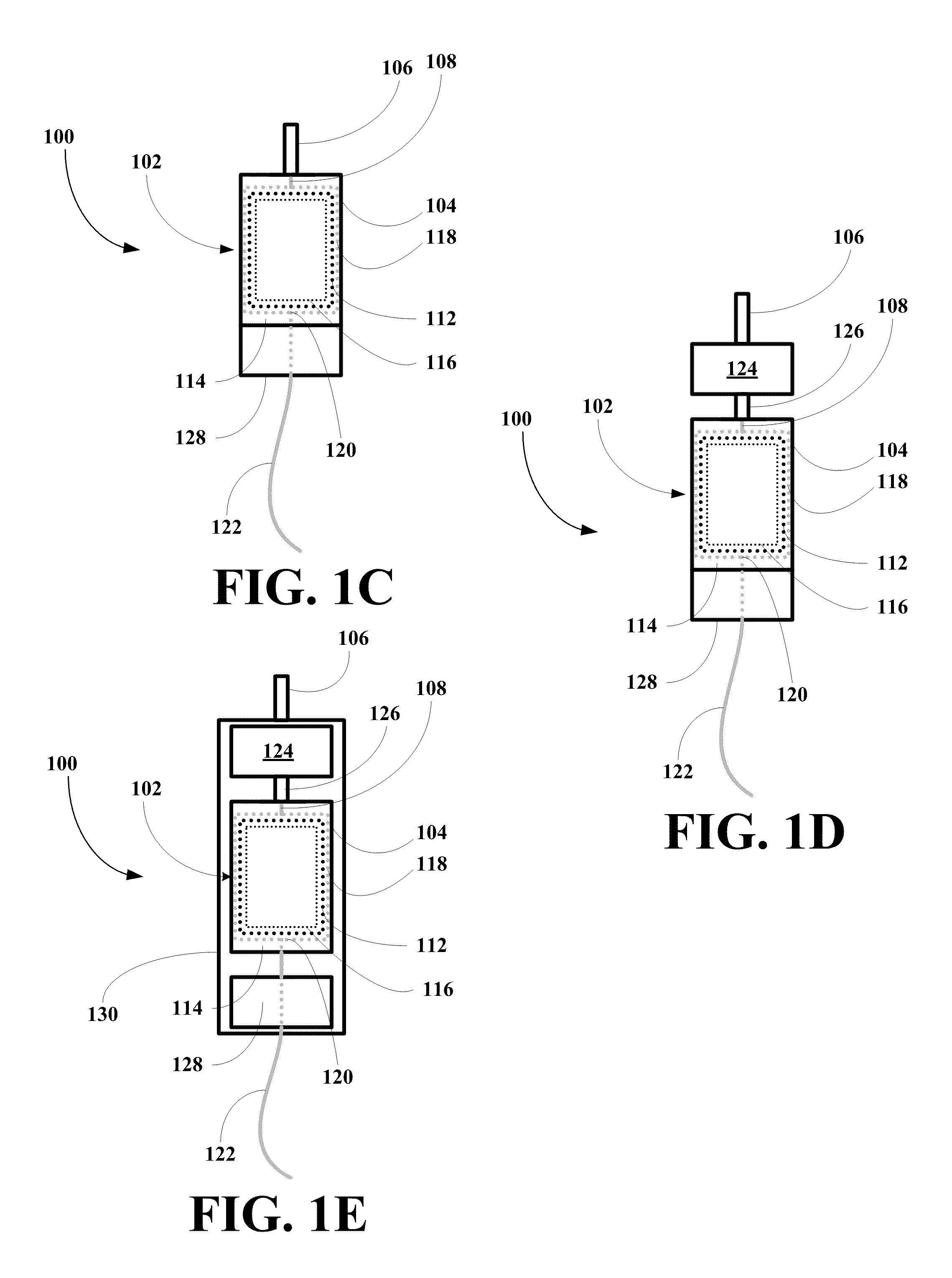
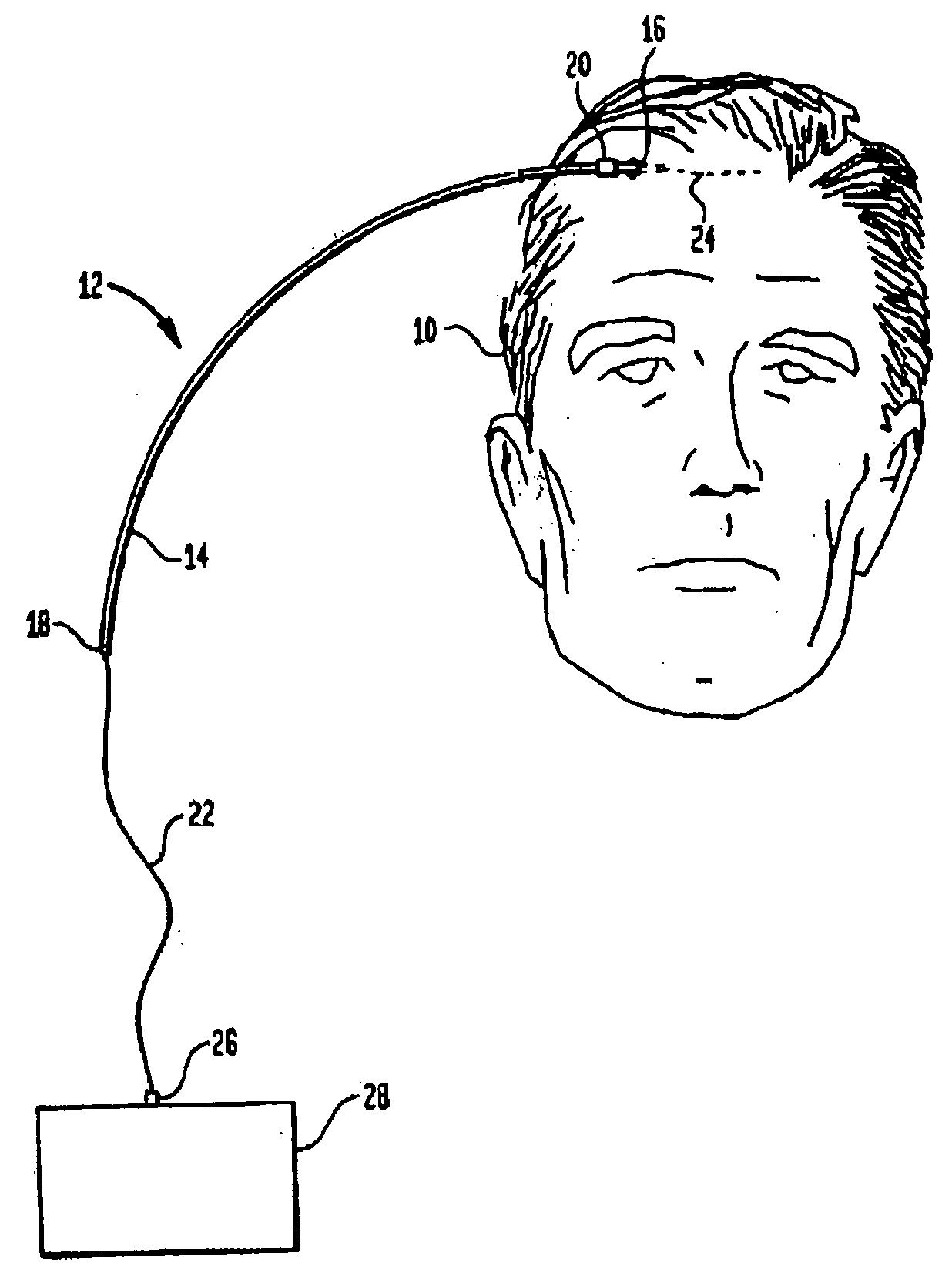
Infusion device and method for infusing material into the brain of a patient
InactiveUS20060129126A1Utilized effectively and accuratelyReduce flow rateGuide needlesMulti-lumen catheterFluid infusionGuide tube
A fluid infusion device and a method of using the same. The device includes an outer, flexible guide catheter having a distal end for introduction beneath the skull of a patient and a proximal end remaining external of the patient. A flexible infusion fiber is located within the guide catheter and has a distal end extending outwardly from the guide catheter to be located in a target area within the patient's brain. The infusion fiber can be fixed or axially movable within the guide catheter. In the latter embodiment, the proximal end of the infusion fiber extending outwardly from the guide catheter can be manipulated to locate the distal end of the infusion fiber in the target area. An infusion pump is connected to the proximal end of the infusion fiber to infuse a minute quantity of fluid at an extremely low flow rate into the brain of the patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Fluid verification system and method for infusions
An apparatus and method are provided to verify the composition of a medical fluid in a fluid infusion channel by comparison with clinician-entered input. Light is transmitted through the channel and detected by a sensor that generates signals representative of the spectral data of the light detected. A processor compares the spectral data of the light detected to the spectral data associated with the expected contents of the channel to verify that the correct fluid is being infused.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
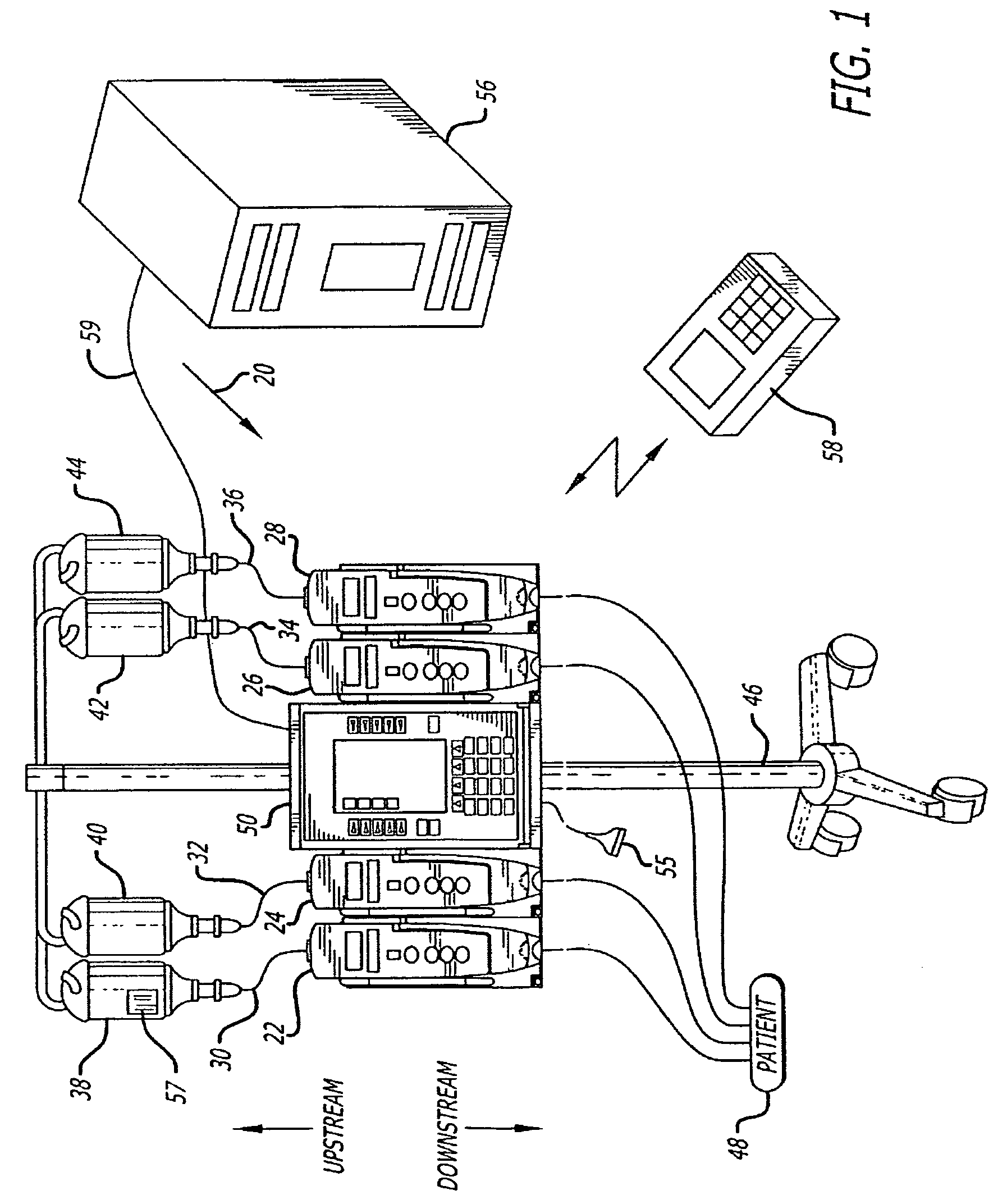
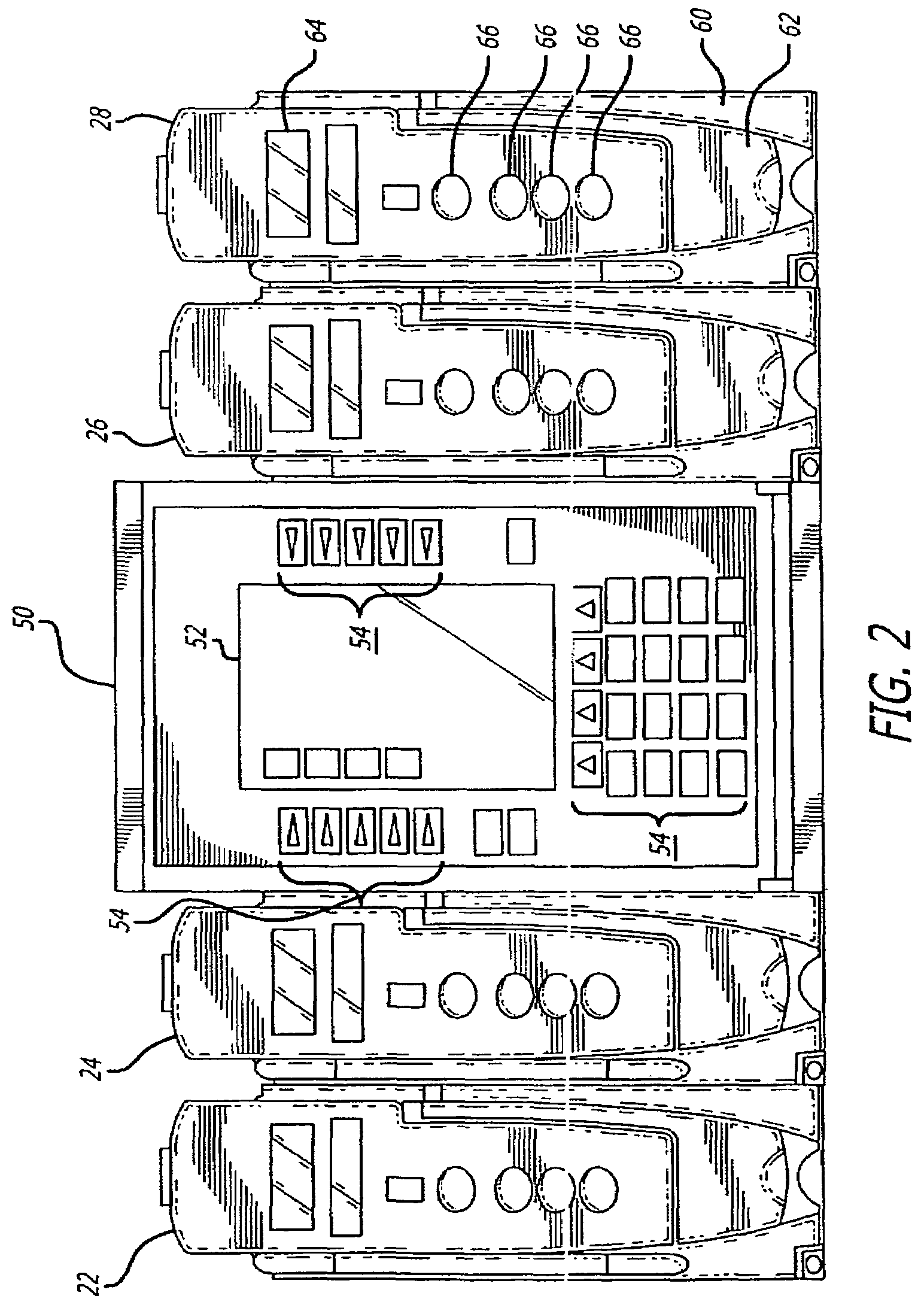
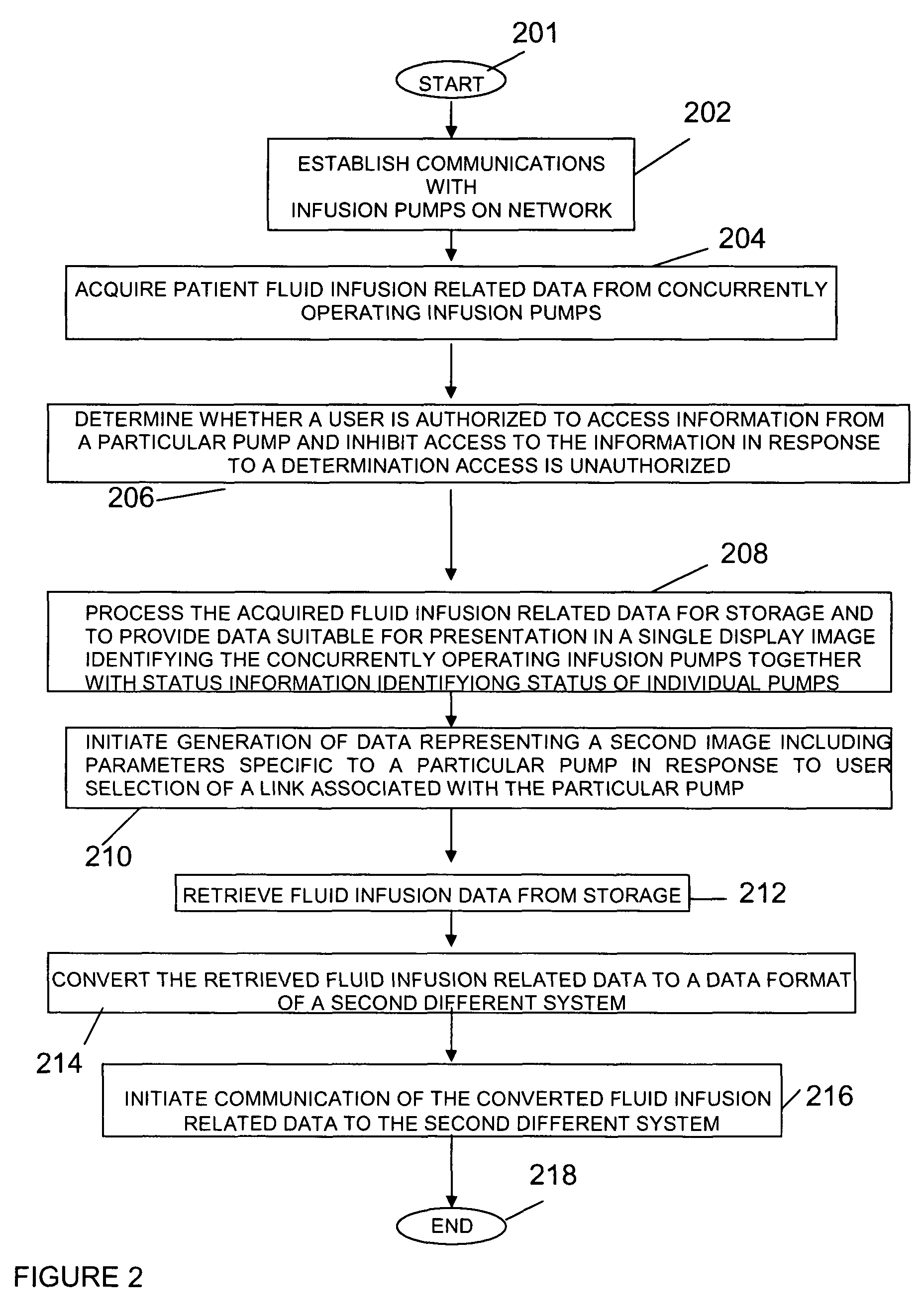
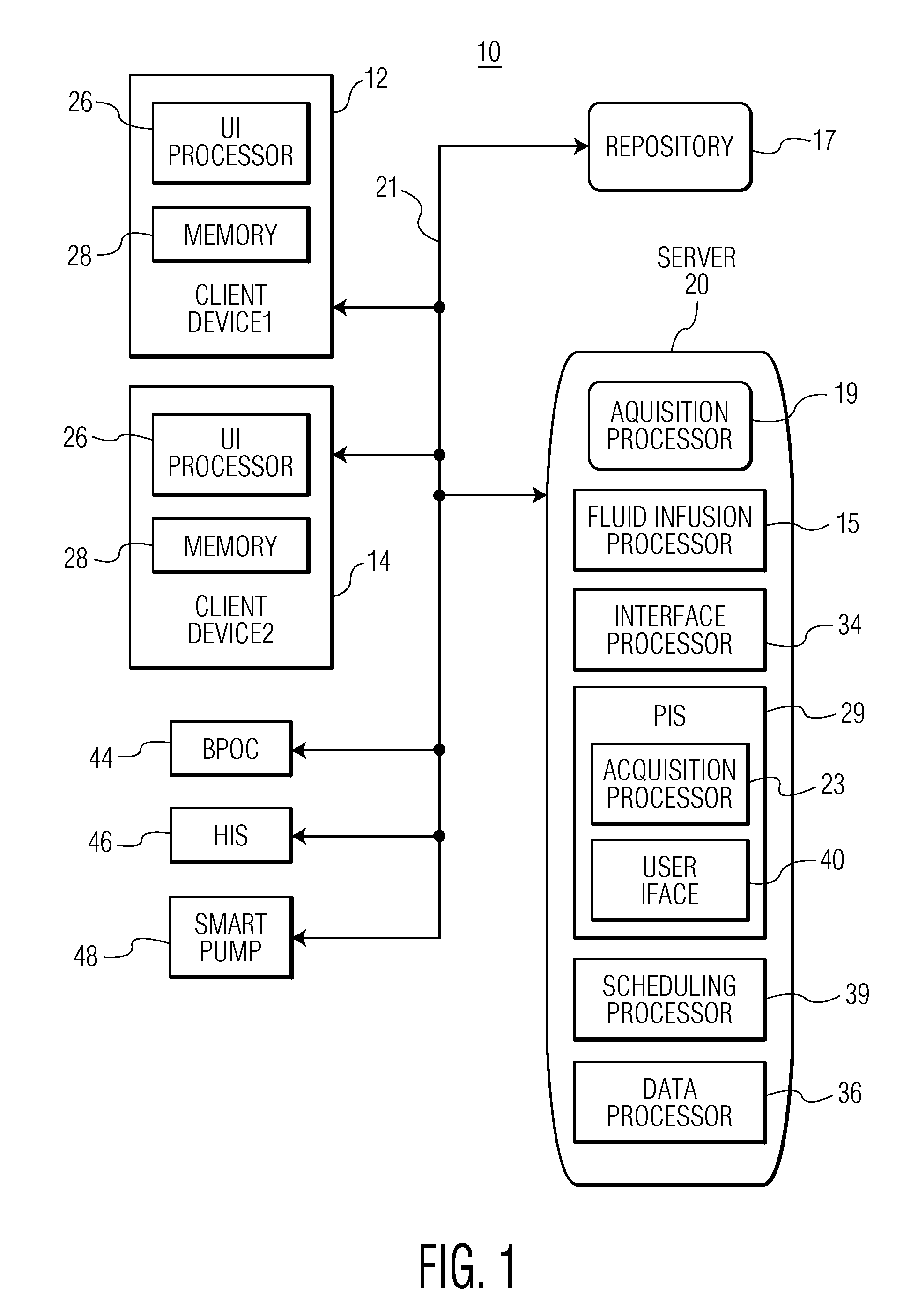
Healthcare system supporting multiple network connected fluid administration pumps
A system and user interface according to invention principles supports concurrently managing and maintaining multiple medical devices (e.g., infusion pumps) and processing and displaying the data produced by the medical devices within a Healthcare enterprise. An information system supports a plurality of network connected infusion pumps. The system includes an acquisition processor for acquiring fluid infusion related data from a plurality of concurrently operating infusion pumps. A data processor processes the acquired fluid infusion related data to provide data suitable for presentation in a single display image identifying the plurality of concurrently operating infusion pumps together with status information identifying status of individual pumps of the plurality of concurrently operating infusion pumps.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
Integrated Medication and Infusion Monitoring System
ActiveUS20100121654A1Data processing applicationsDrug and medicationsMedical recordInformation repository
A System manages IV pumps so that clinicians automatically receive alerts, decisions, and actions required to maintain a patient IV medication therapy according to a prescribed treatment protocol. An infusion pump monitoring system, includes an acquisition processor for acquiring fluid infusion parameters comprising a patient identifier, infusion fluid identifier and a rate of fluid infusion, for administration of an infusion fluid to a patient at a point of care using an infusion pump. The system also includes a repository of patient medical record information. A fluid infusion monitor uses acquired fluid infusion parameters for automatically searching a patient medical record in the repository for information concerning rate of fluid infusion of a particular infusion fluid and determining if a rate of a previously administered dose of the particular infusion fluid was lower than a rate indicated in the fluid infusion parameters. An interface processor automatically initiates generation of a message indicating a potential adverse reaction to the particular infusion fluid in response to a determination of a lower rate being employed for previously administering the particular infusion fluid.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
Wireless data communication protocols for a medical device network
InactiveUS20120016305A1Drug and medicationsTime-division multiplexWireless Application ProtocolComputer network
A fluid infusion system includes local “body network” devices, such as an infusion pump, a handheld monitor or controller, a physiological sensor, and a bedside or hospital monitor. The body network devices support communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between one another. In addition, the body network devices support networked communication of status data, physiological information, alerts, control signals, and other information between the body network devices and “external” devices, systems, or communication networks. The networked medical devices support a variety of wireless data communication protocols. In addition, the wireless medical devices support a number of dynamically adjustable wireless data communication modes to react to current operating conditions, application-specific data content, or other criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Apparatus and methods for controlling and automating fluid infusion activities
InactiveUS20090177146A1Reduce riskMedical devicesPressure infusionFluid infusionTranquilizing Agents
The present invention provides apparatuses and methods to safely and economically deliver infusion fluid to a patient during a medical procedure. The infusion fluid may be a sedative, analgesic, amnestic or other pharmaceutical agent (drug) for alleviating a patient's pain and anxiety before, during and / or after a medical or surgical procedure. In general the apparatus comprises a microprocessor-based controller that receives inputs from a plurality of physiological monitors attached to a patient. The system controller processes the data from the physiological monitors and based upon a fluid infusion algorithm delivers infusion fluid to a patient. The physiological monitors monitor the patient throughout the course of the procedure and depending upon the health of the patient, drug delivery may be adjusted to optimize the procedure while ensuring the patient's health and pain level are maintained.
Owner:NESBITT MATTHEW T +5
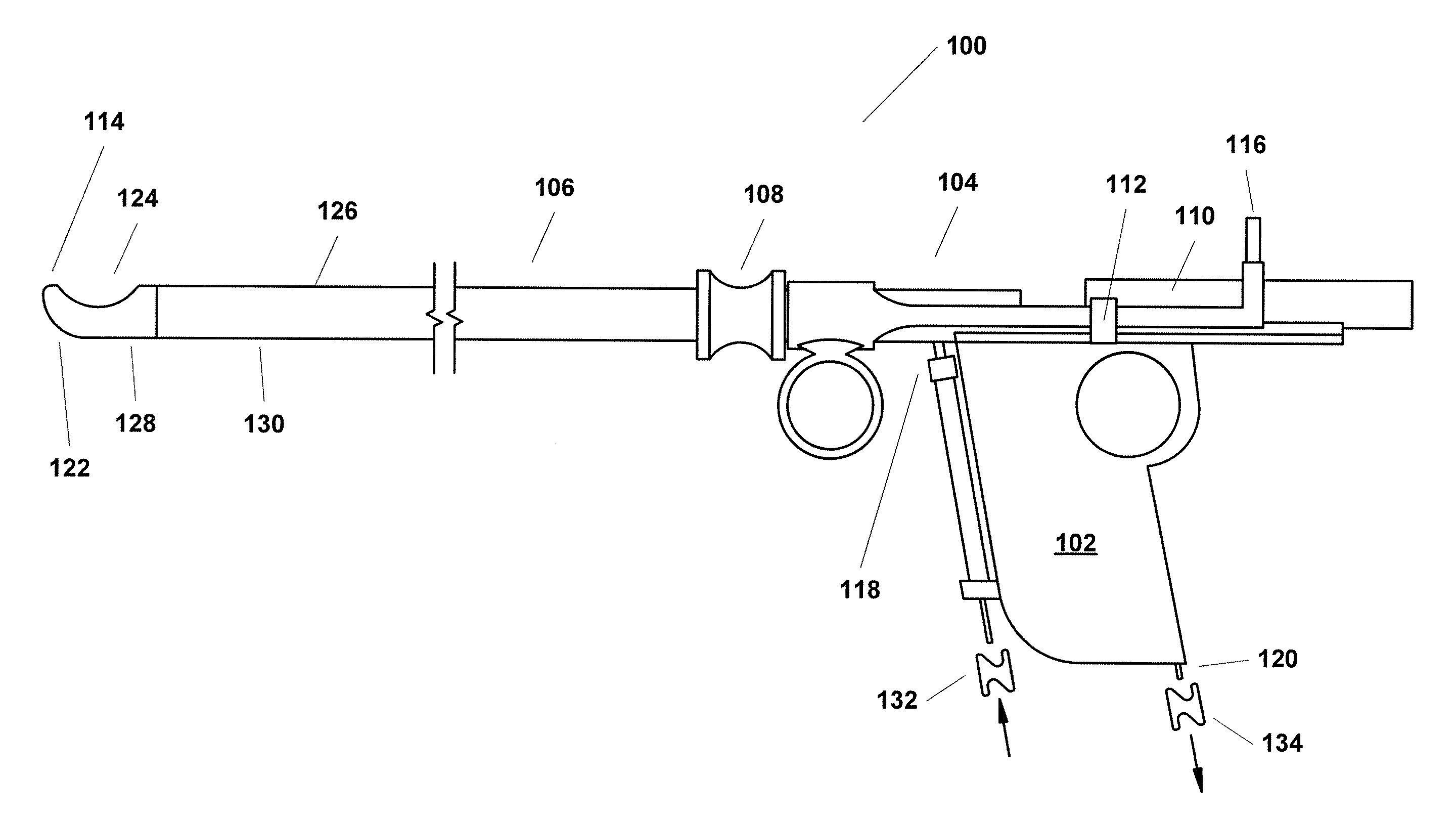
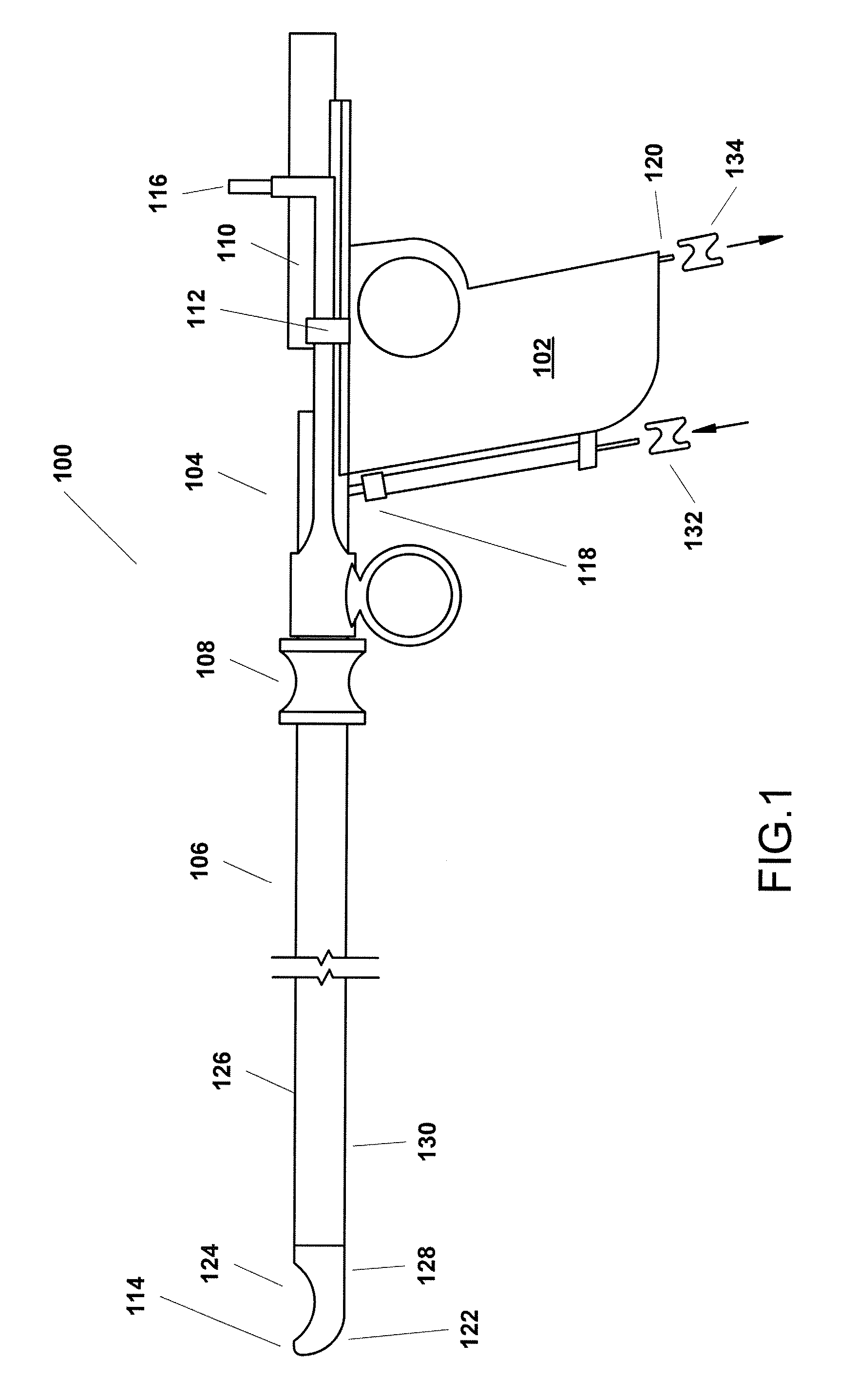
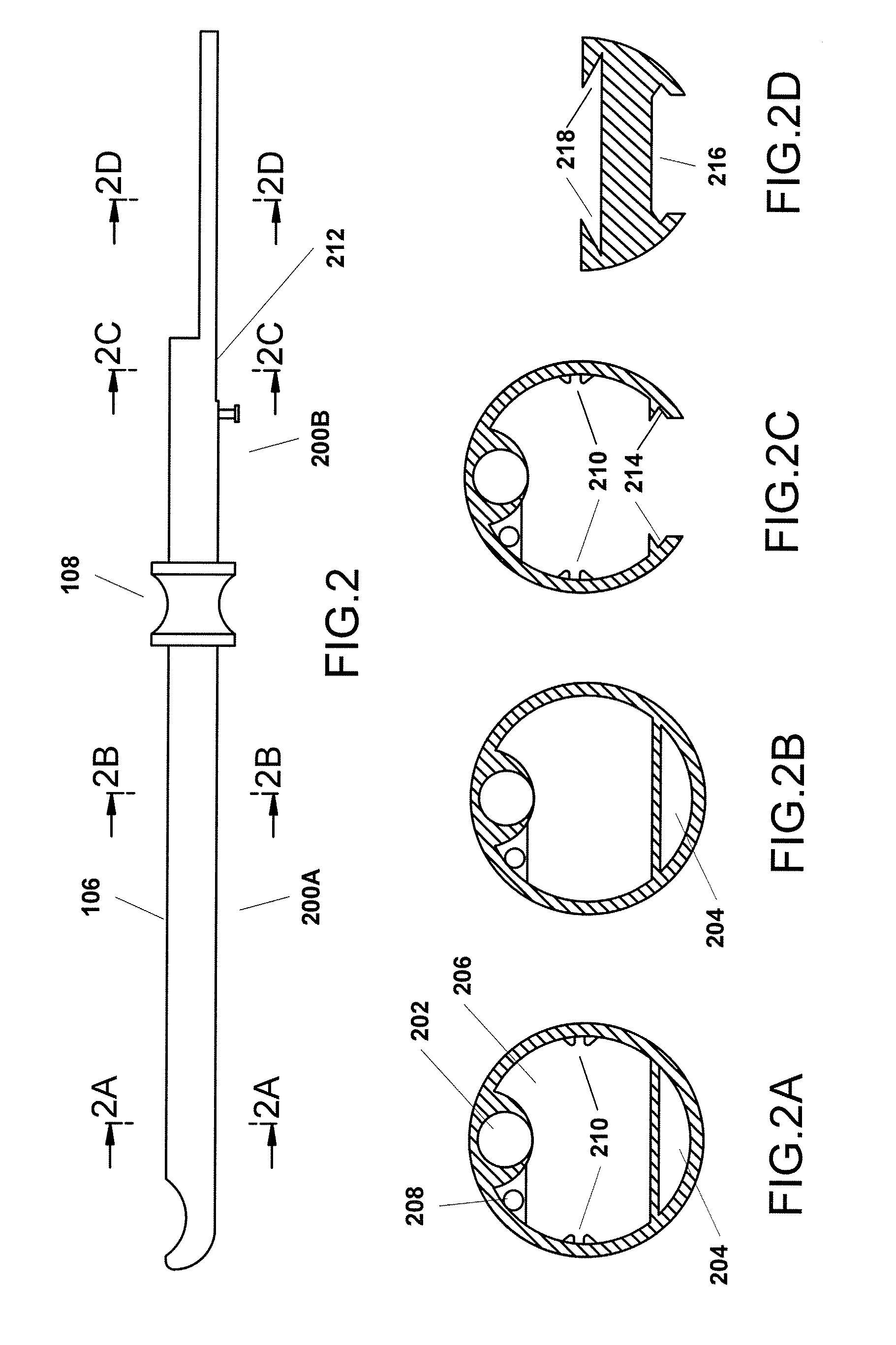
Monitoring the seating status of a fluid reservoir in a fluid infusion device
A device for delivering fluid to a user includes a housing, a drive motor assembly in the housing, a force sensor, and an electronics module. The drive motor assembly regulates delivery of fluid by actuating a piston of a fluid reservoir, and the force sensor generates output levels in response to force imparted thereto during, for example, fluid delivery operations. The electronics module processes the output levels of the force sensor to assess the operating health of the force sensor, to check for occlusions in the fluid delivery path, and to monitor the seating status of the fluid reservoir.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Device to Indicate Priming of an Infusion Line
InactiveUS20100063445A1Measured value indication by color changeInfusion syringesFluid infusionInfusion set
A priming indicator for a fluid infusion system includes a luer cap or other component of the infusion system having an indicator surface covered by a membrane. The membrane exhibits a first visual characteristic, such as being opaque, when dry and exhibits a second characteristic, such as becoming less opaque, when wet. Once the membrane becomes wet, indicia on the surface, which may be provided on a rod at least partially covered by the membrane, becomes visible, thereby indicating an intravenous tube to which the luer cap is secured has been primed or is nearly primed. The indicator may alternately be employed at an upstream end of an infusion set, such as at the port of a medical bag providing a supply of fluid, to indicate a low level of fluid in the medical bag.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
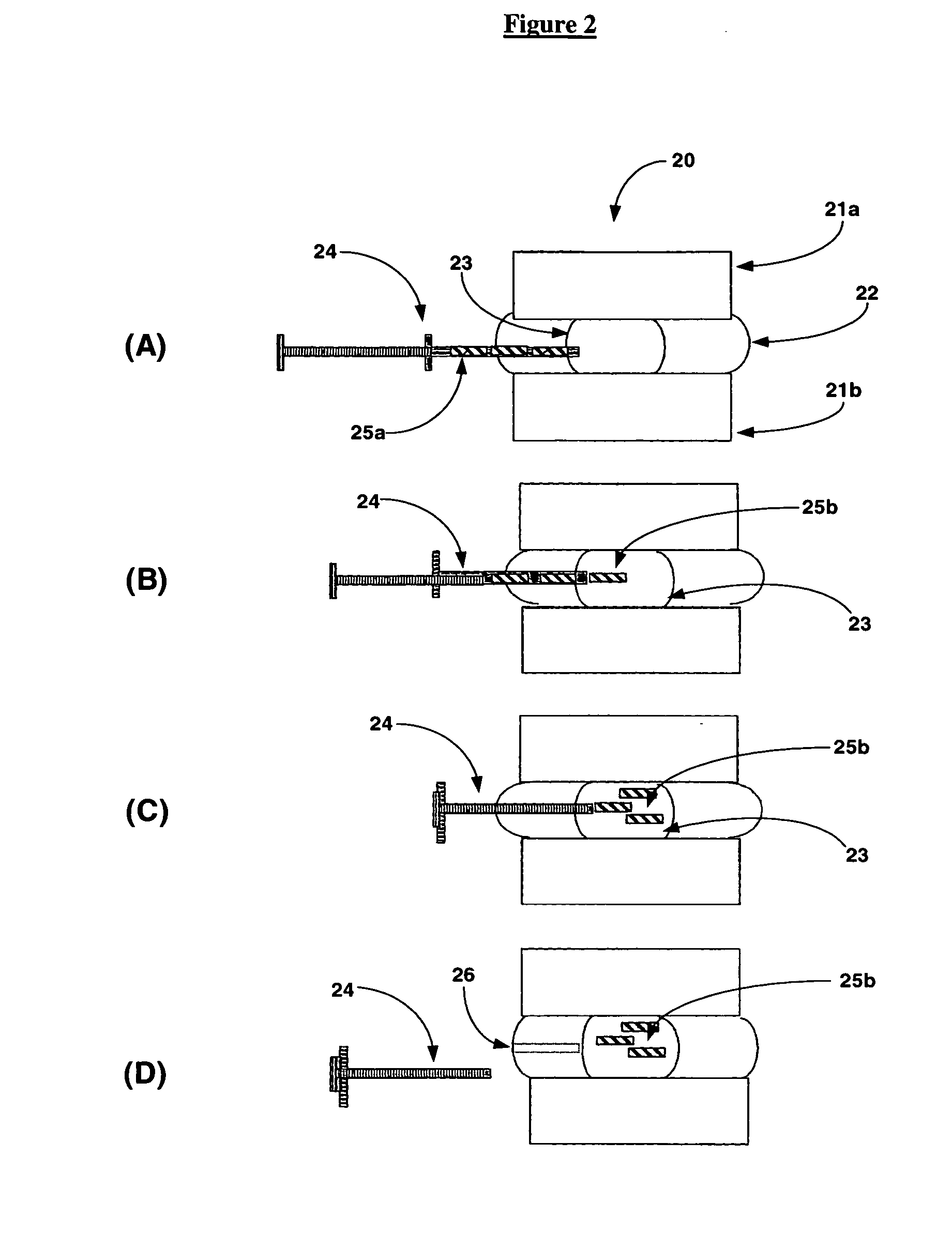
Fluid Delivery and Treatment Device and Method of Use
ActiveUS20120059309A1Facilitate formation of newPromote disseminationStentsBalloon catheterFluid infusionMedical device
A medical device system is provided herein which has an elongated, flexible hollow member with an expandable infusion segment attached at the most distal end of the device. The device has a plurality of fluid infusion ports on the expandable infusion segment for delivering an intended fluid to a target site in a body lumen. Additionally, a method is provided herein for infusing an intended fluid to a target site within a body lumen.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com