Patents
Literature
96 results about "Viewing instrument" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A viewing instrument is a device used for viewing or examining an object or scene, or some electrical property or signal. In some cases the thing viewed is mathematical. The names of many viewing instruments is derived from the English suffix -scope, meaning "see", which derives from the scientific Latin suffix -scopium, meaning a viewing instrument, which in turn originates from the ancient Greek verb skopein, meaning "to examine".
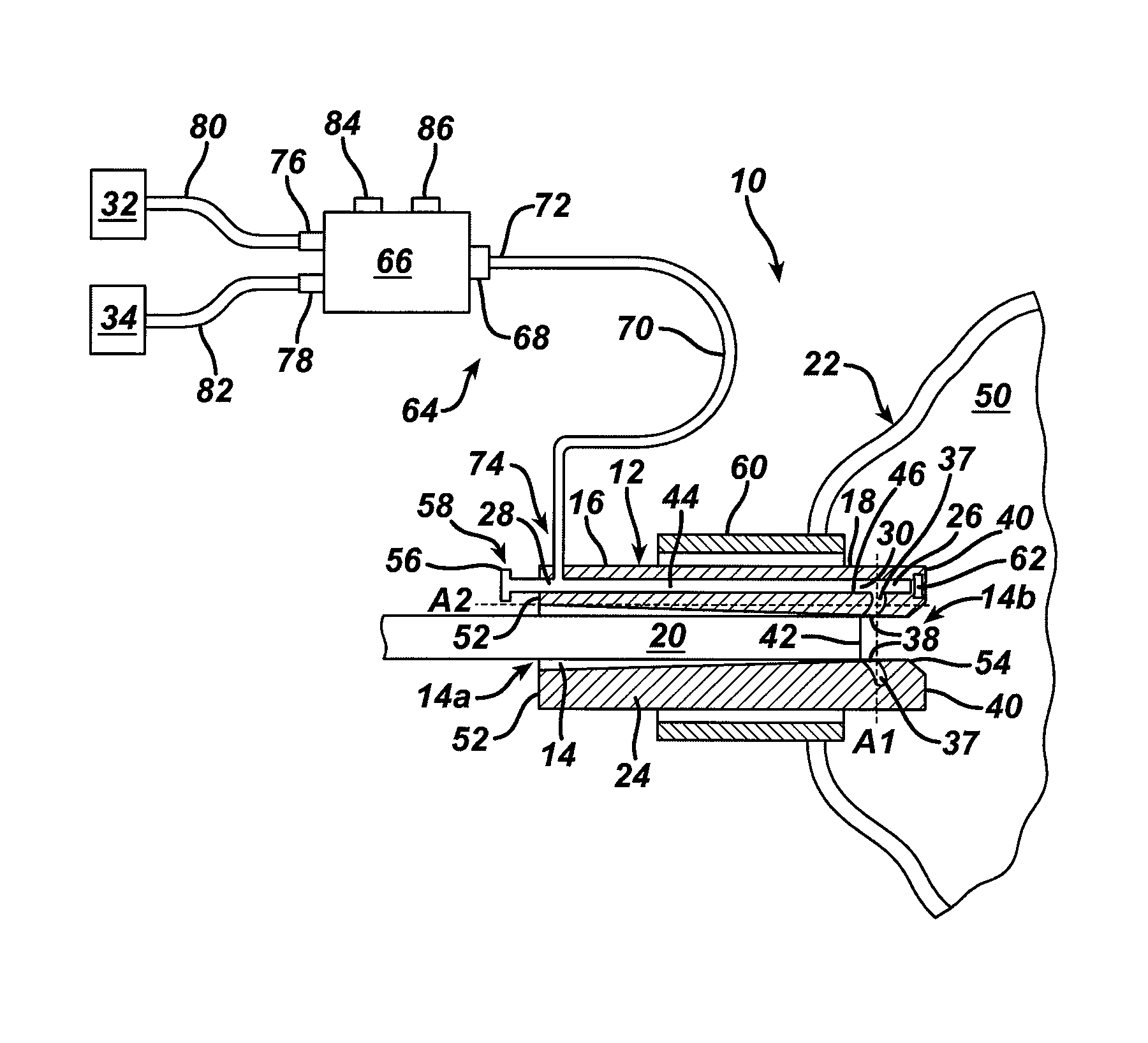
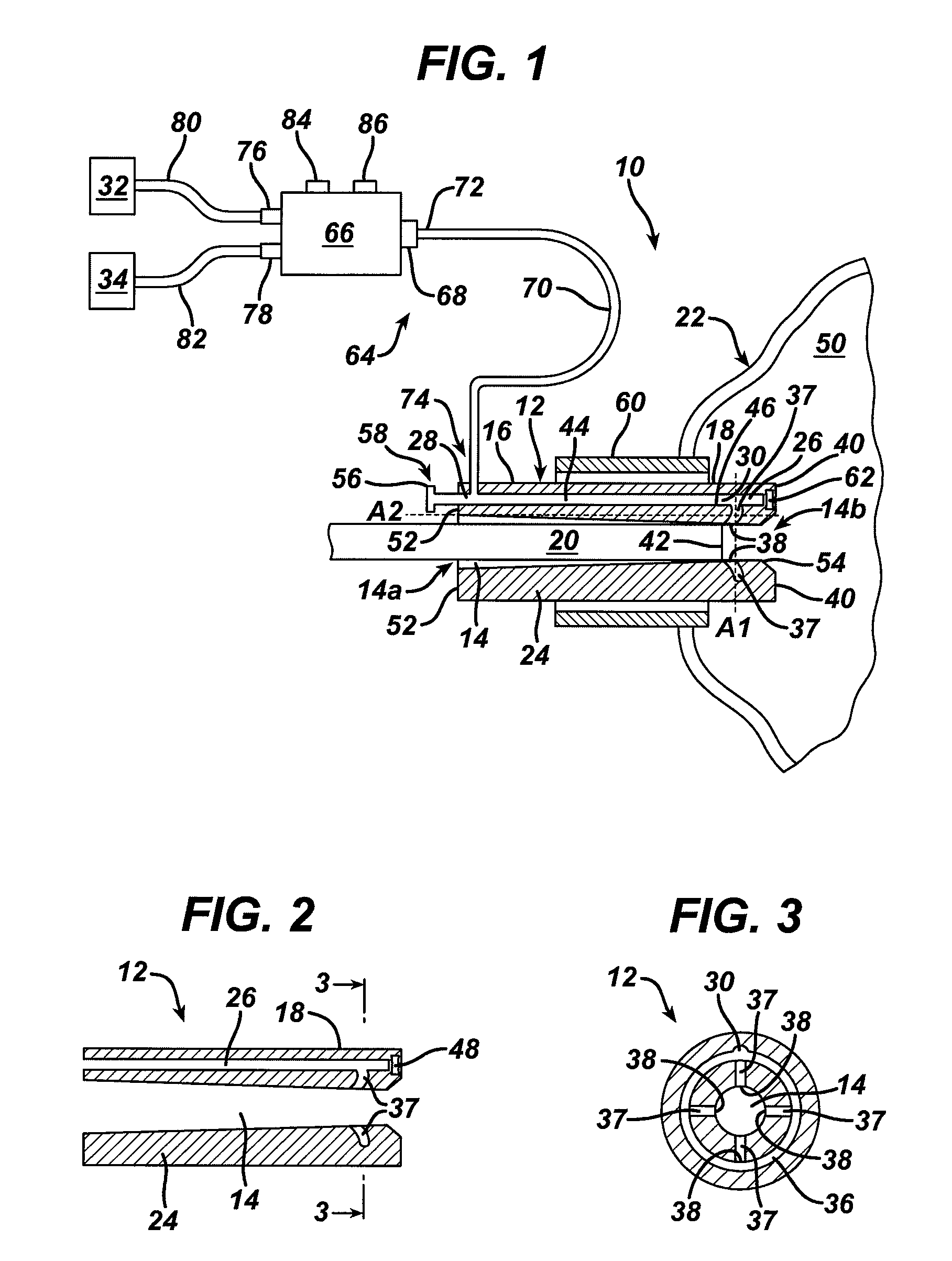
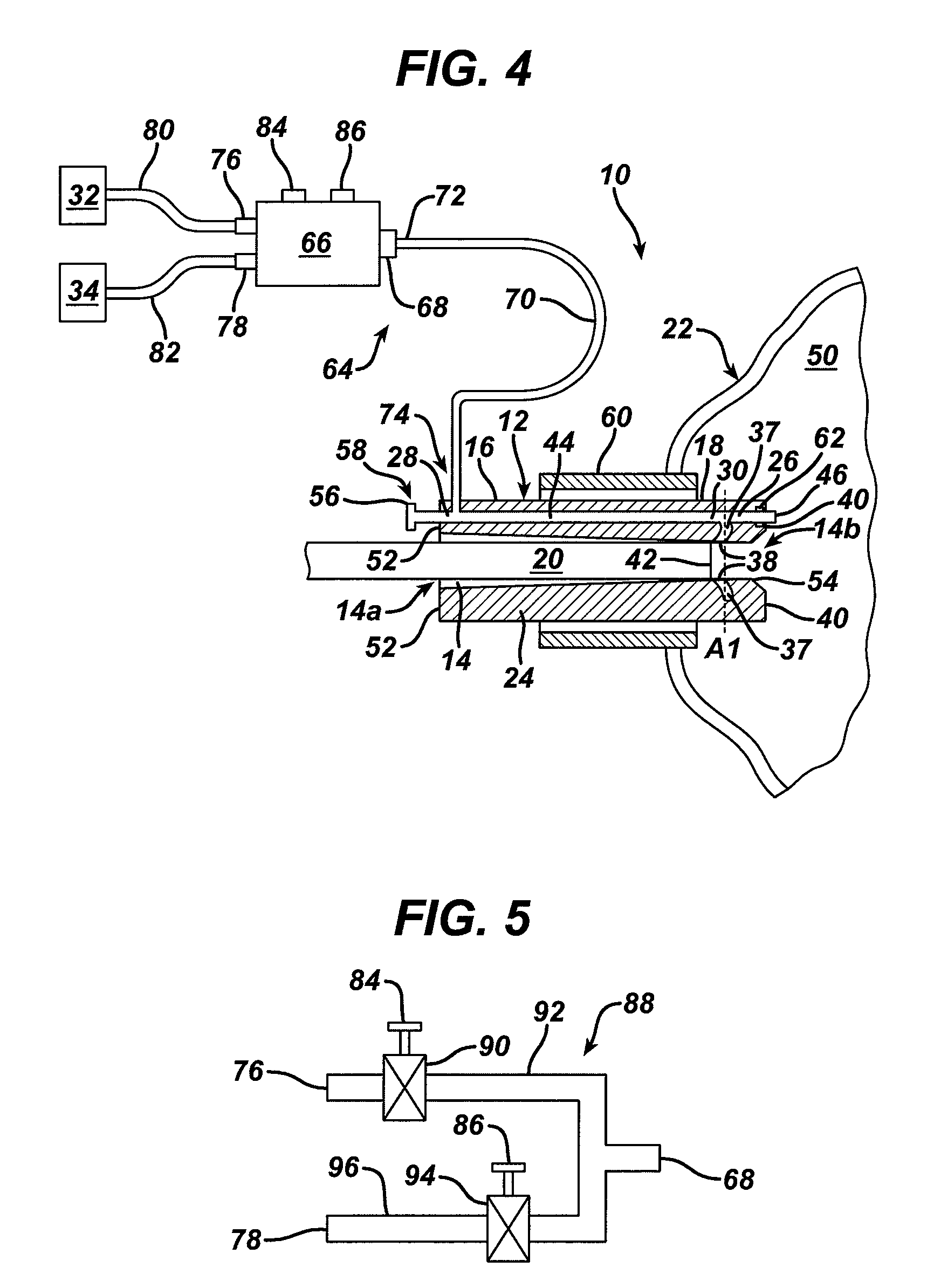
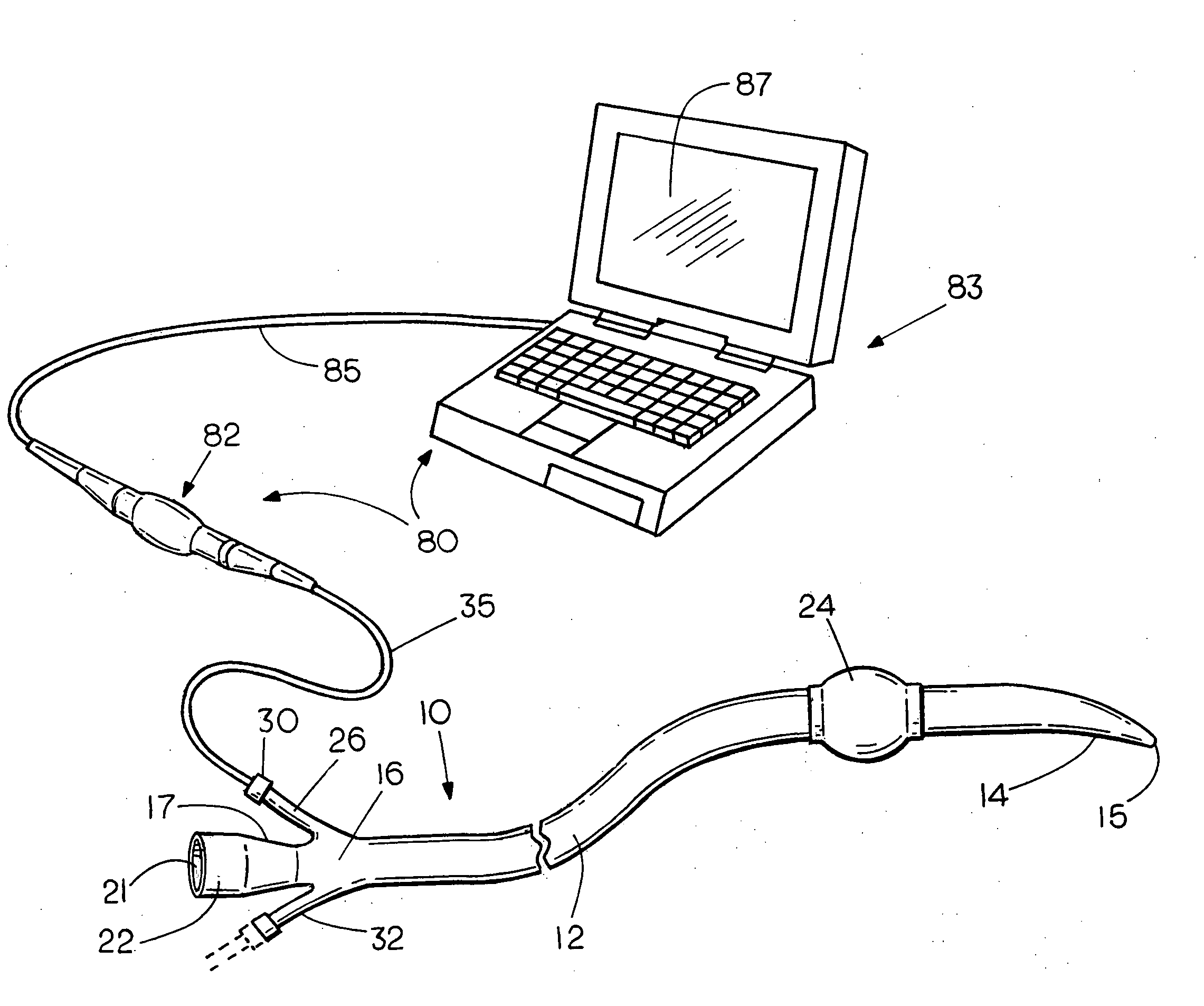
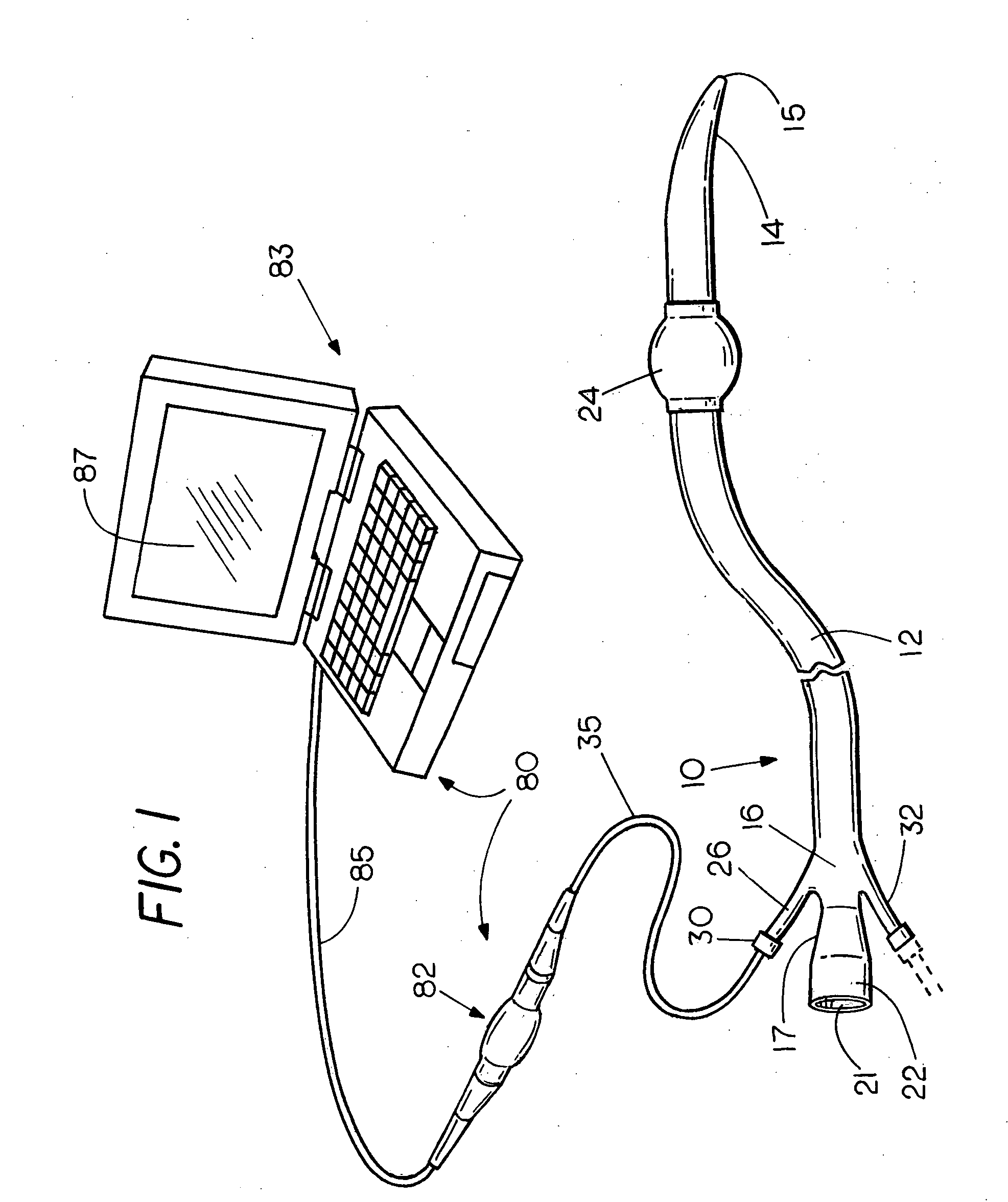
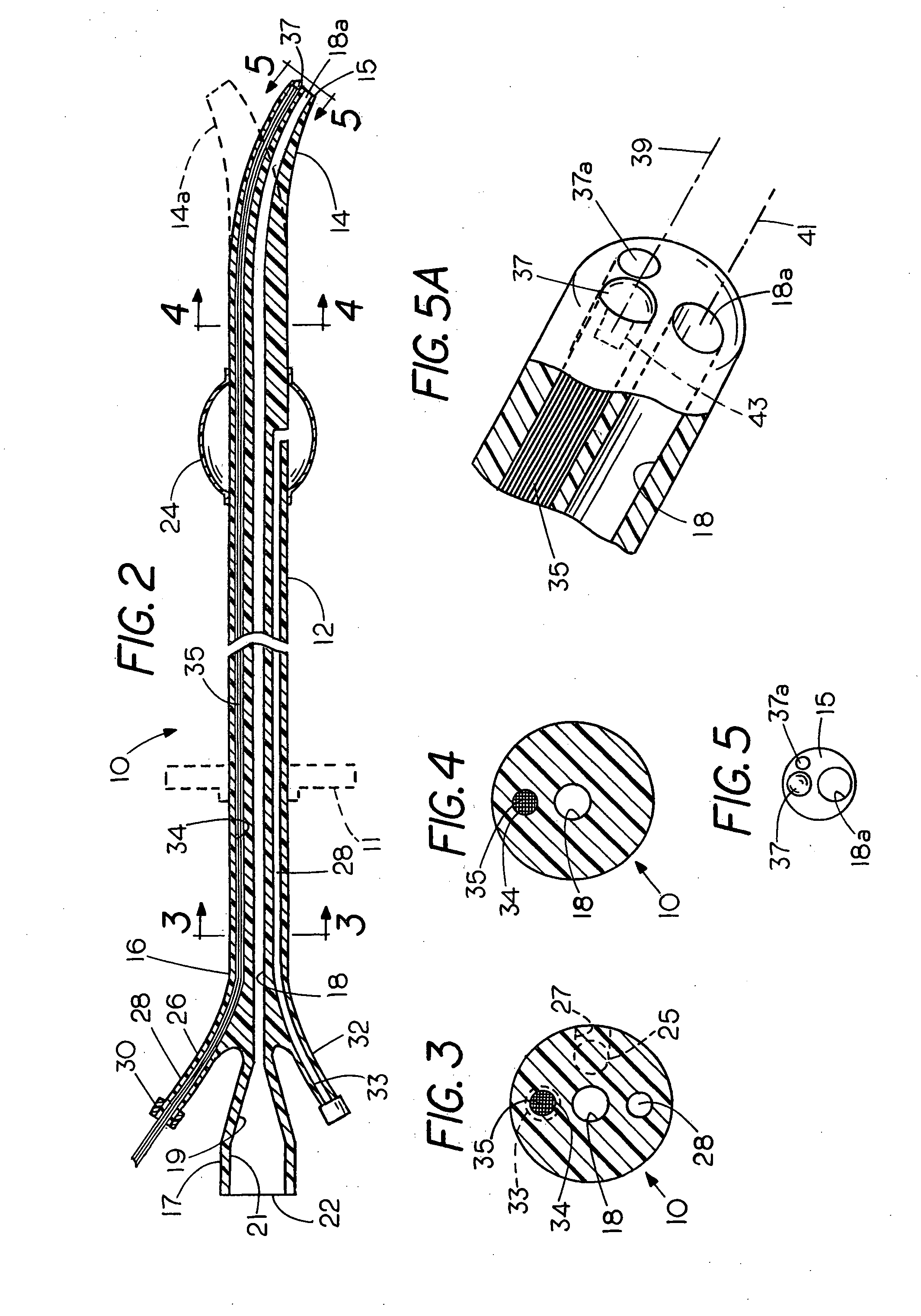
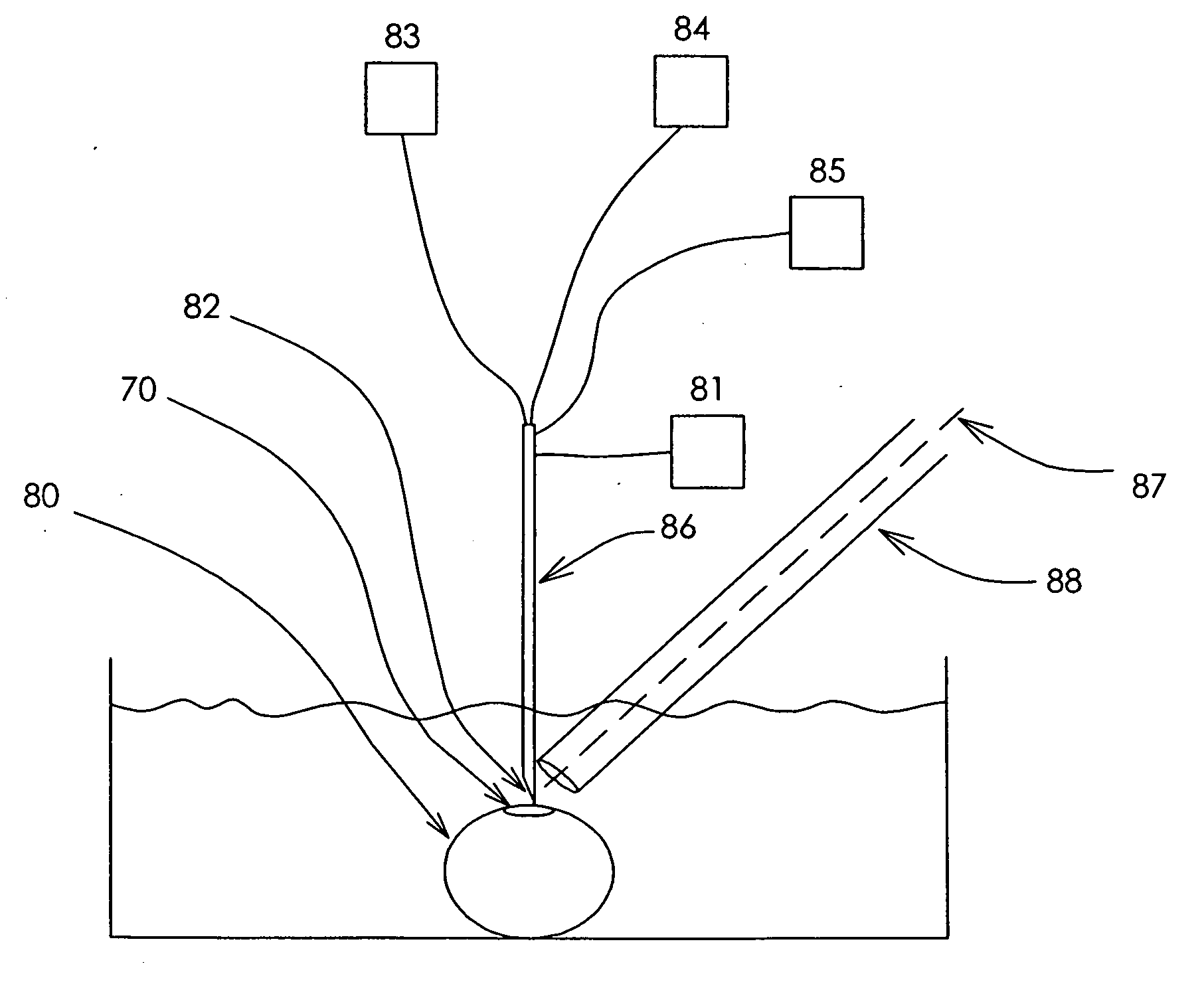
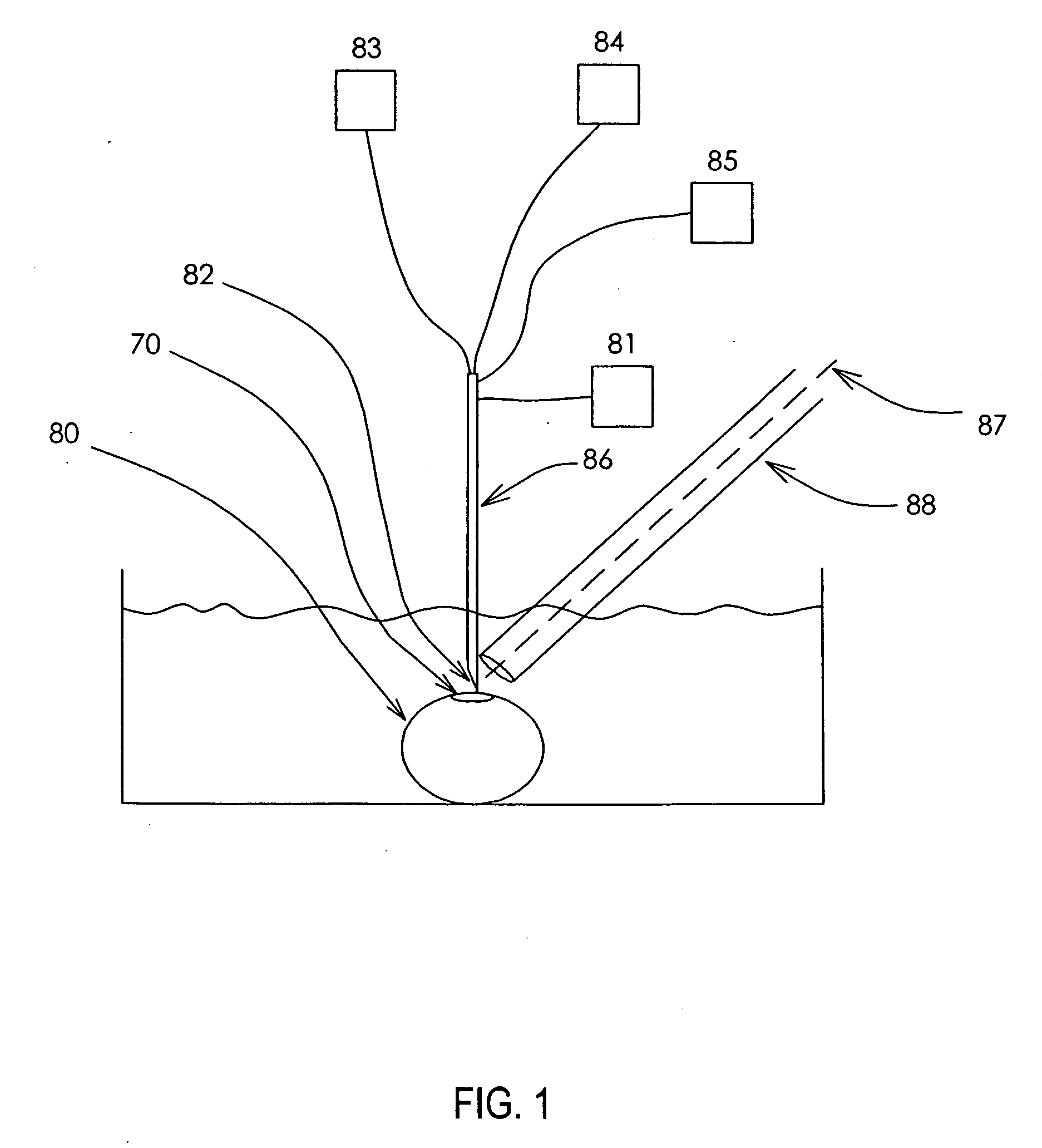
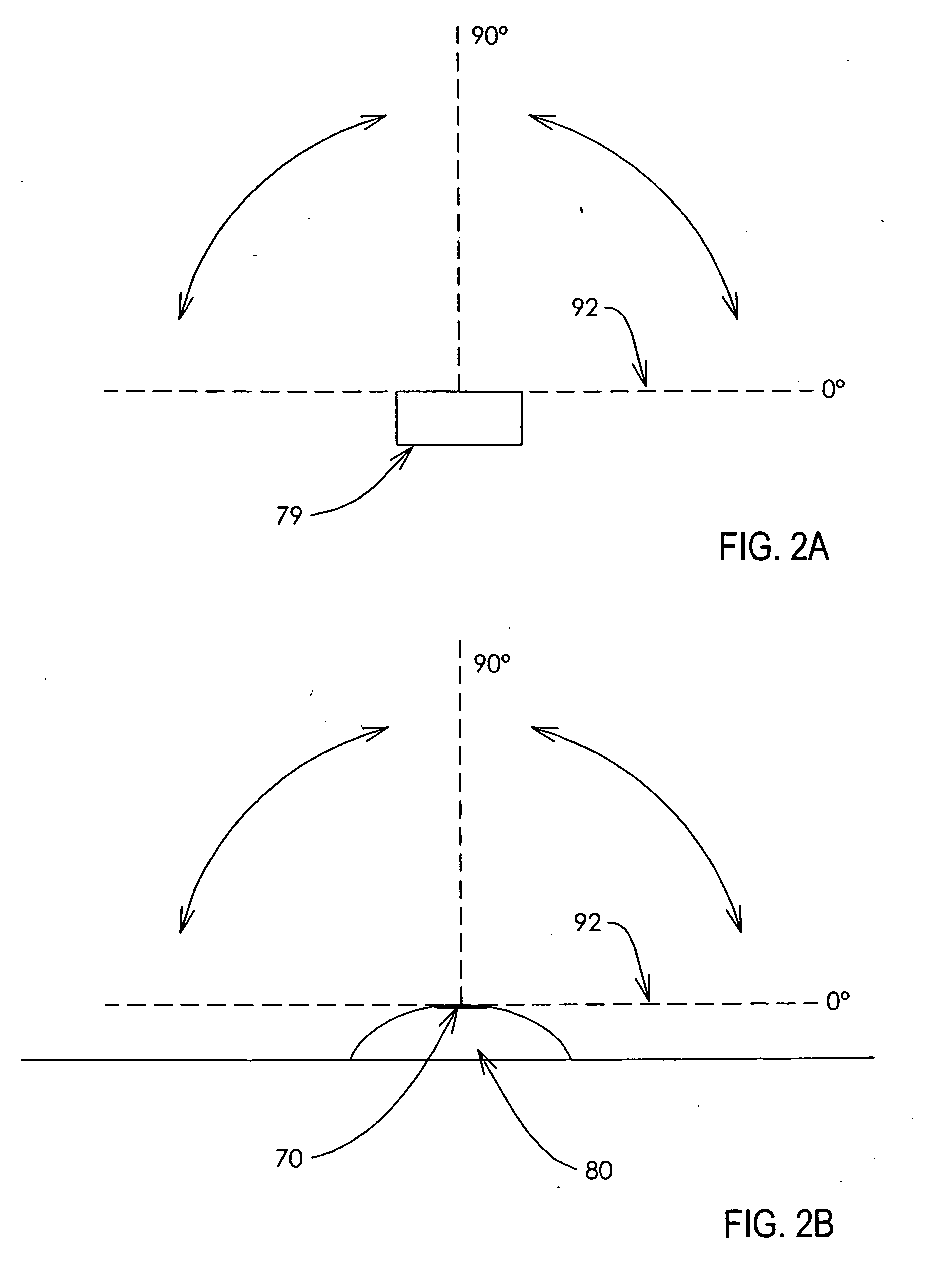
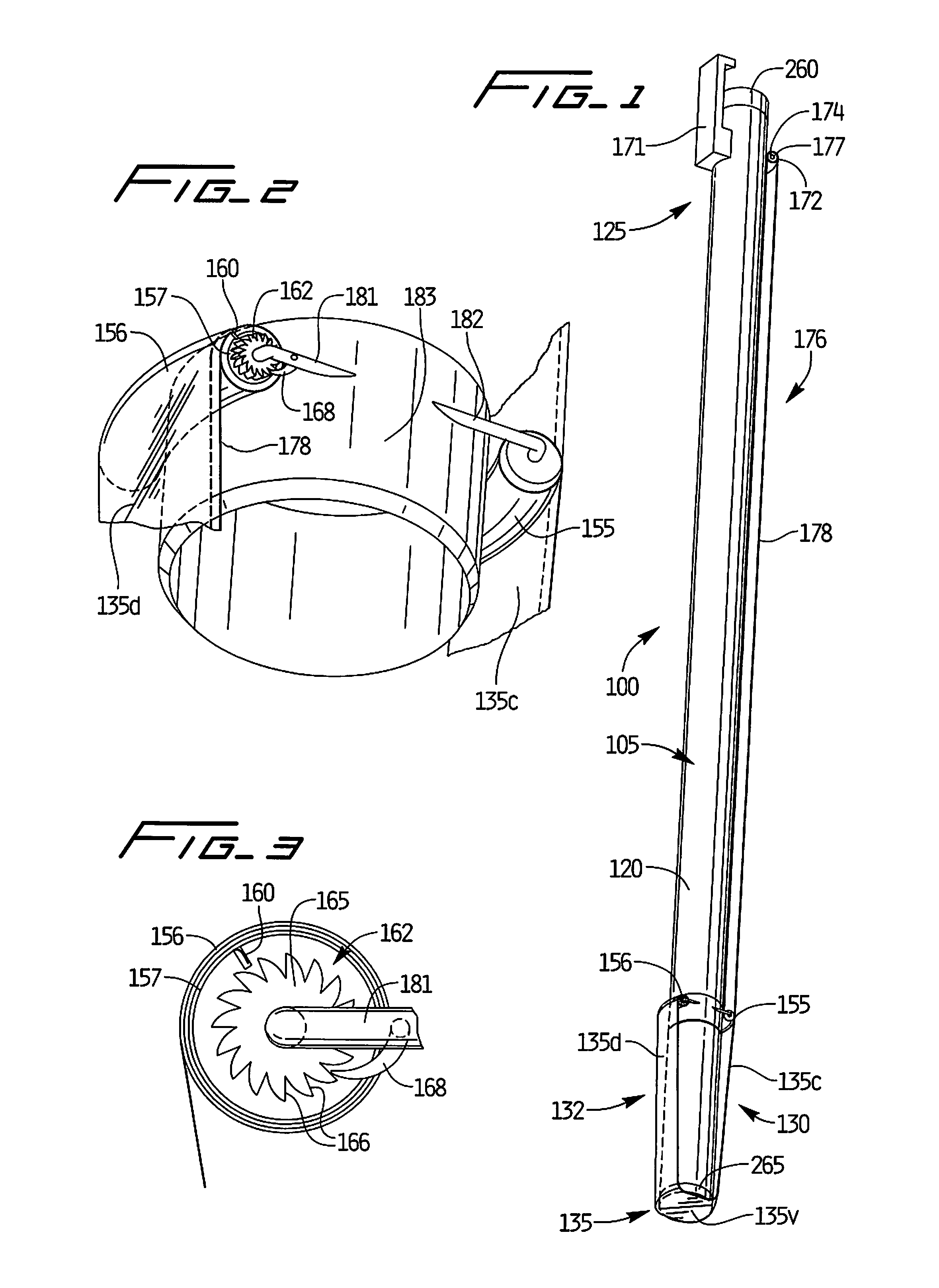
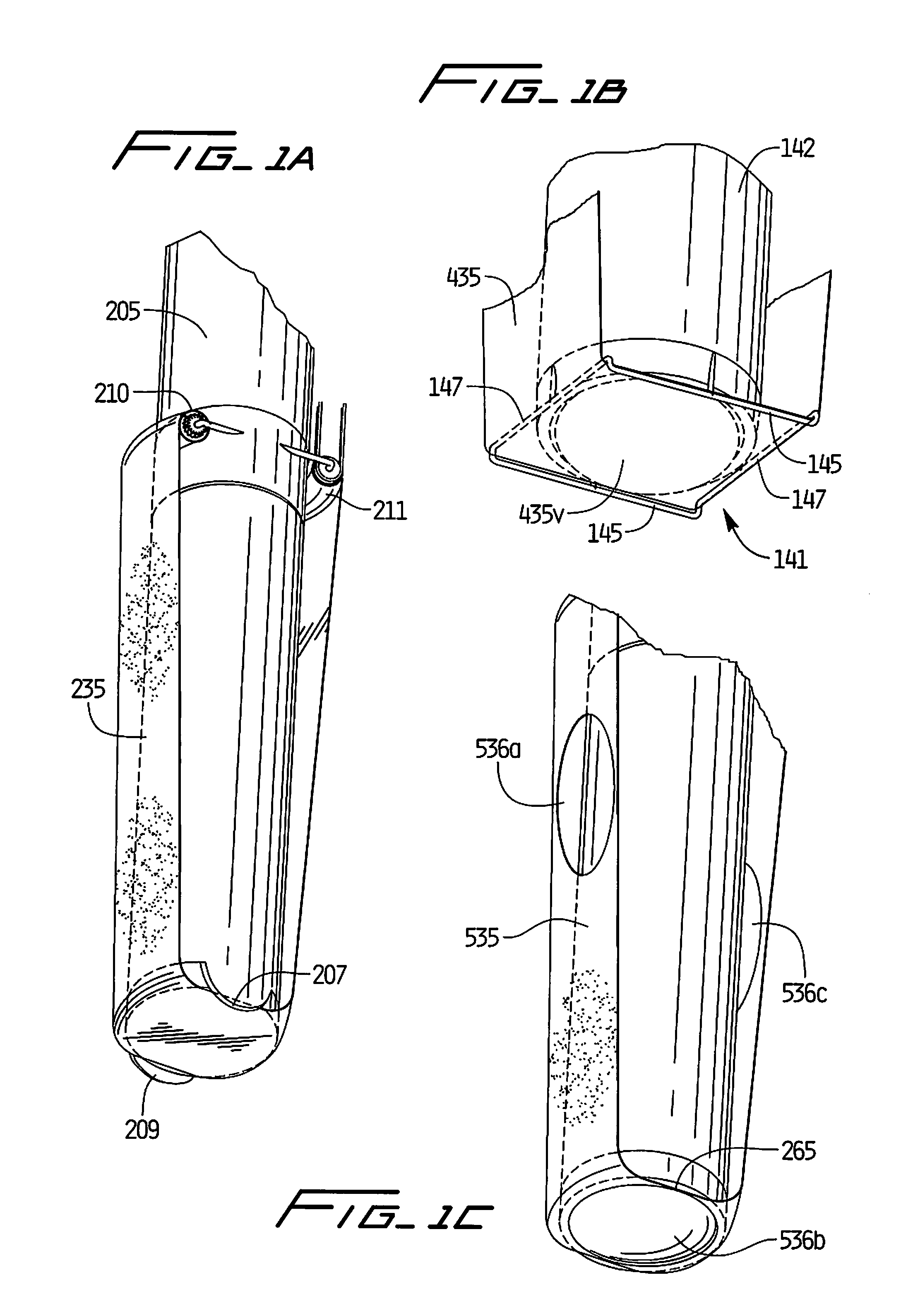
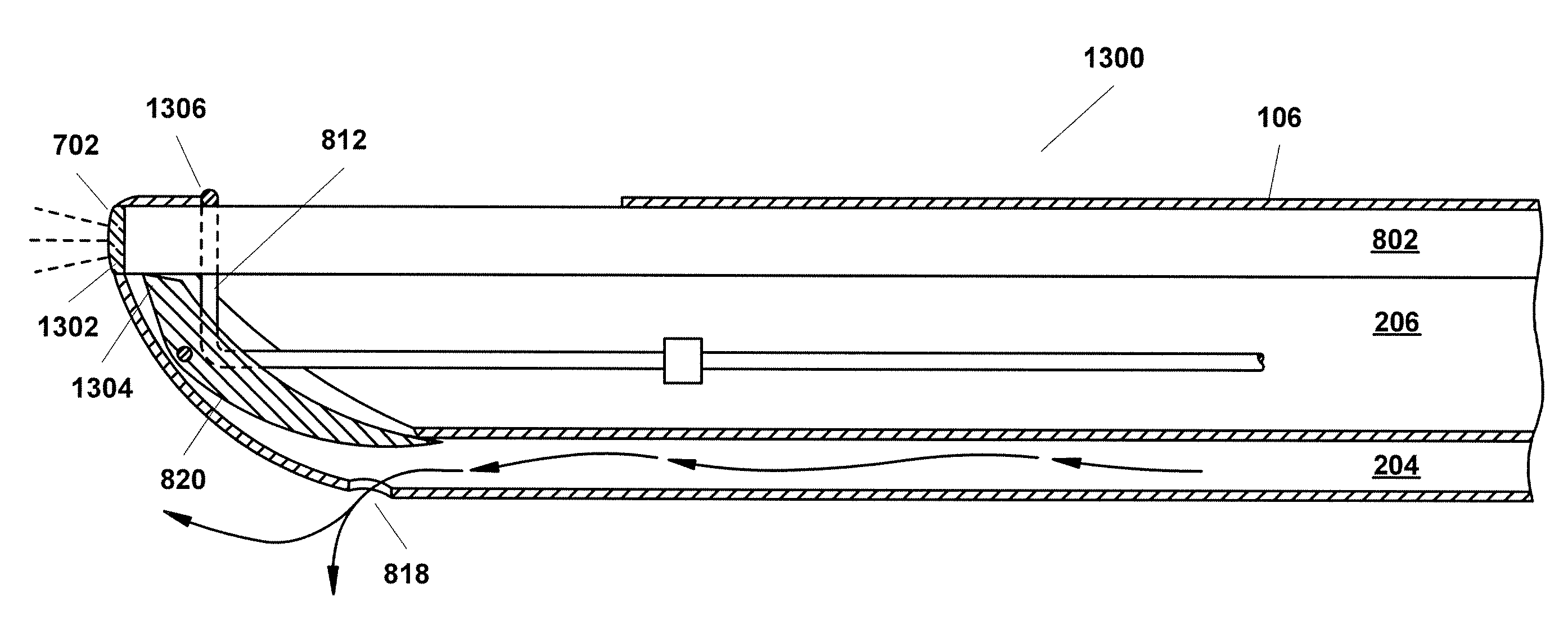
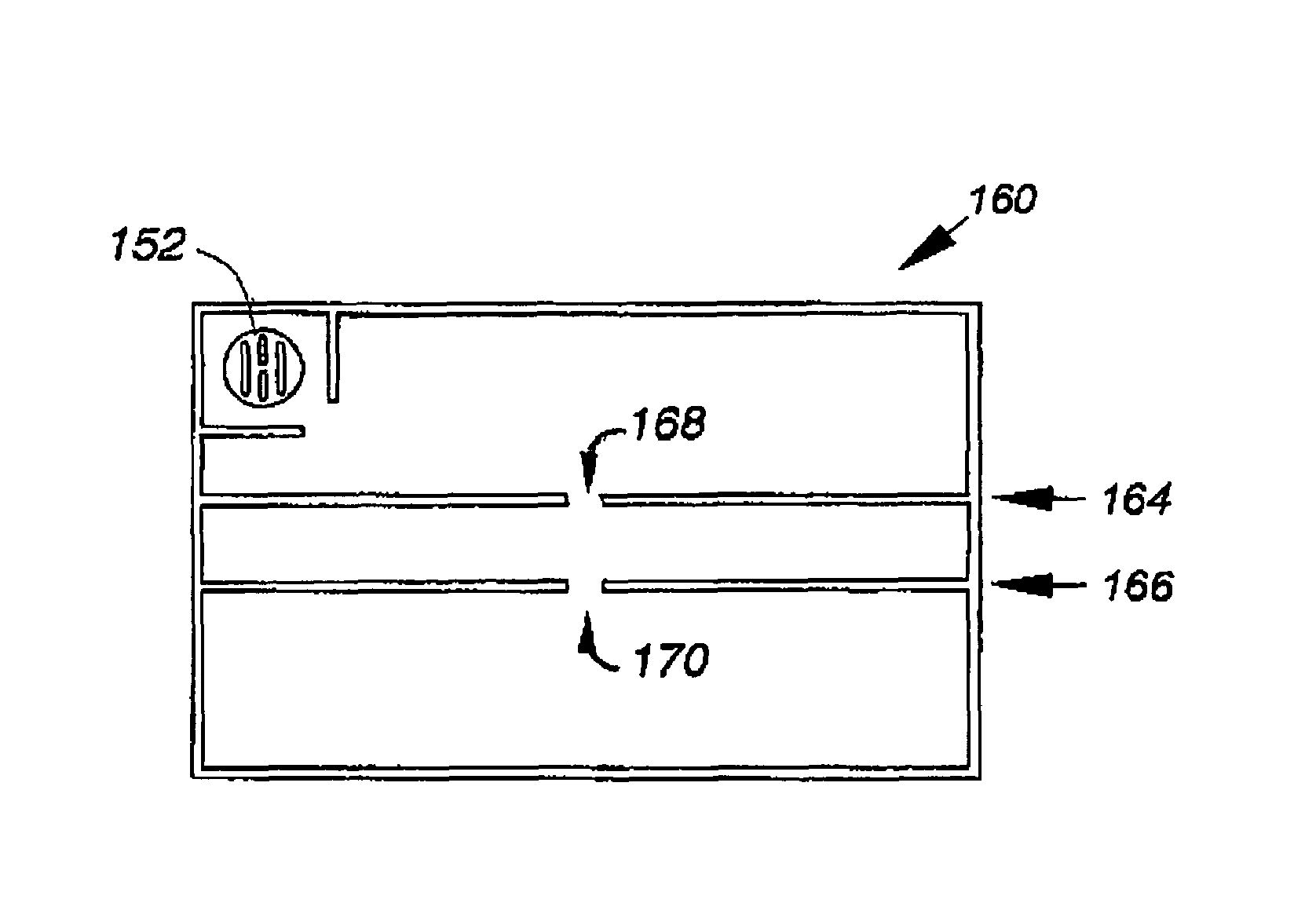
Methods and devices for maintaining visibility and providing irrigation and/or suction during surgical procedures
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Smart-phone adapter for ophthalmoscope
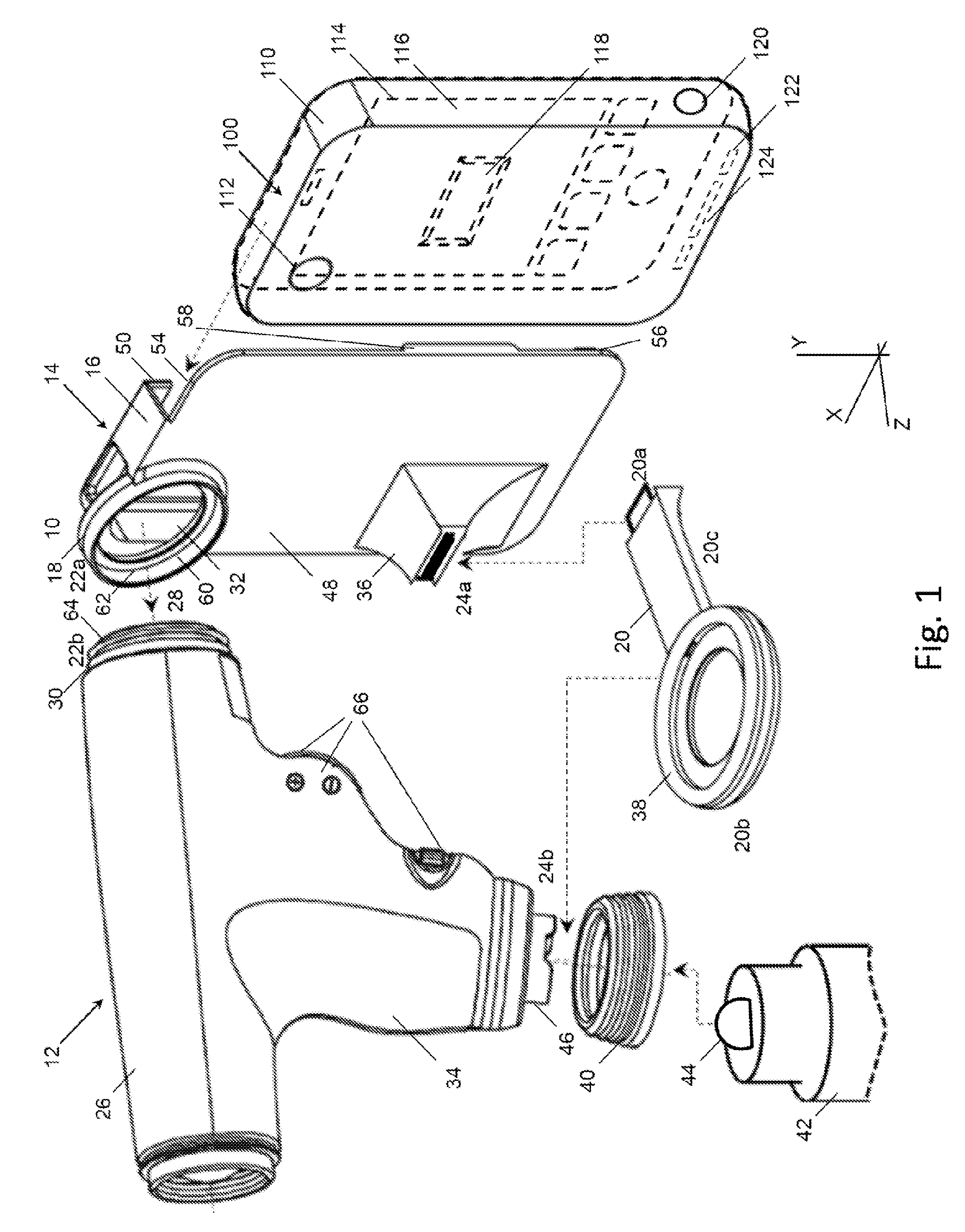
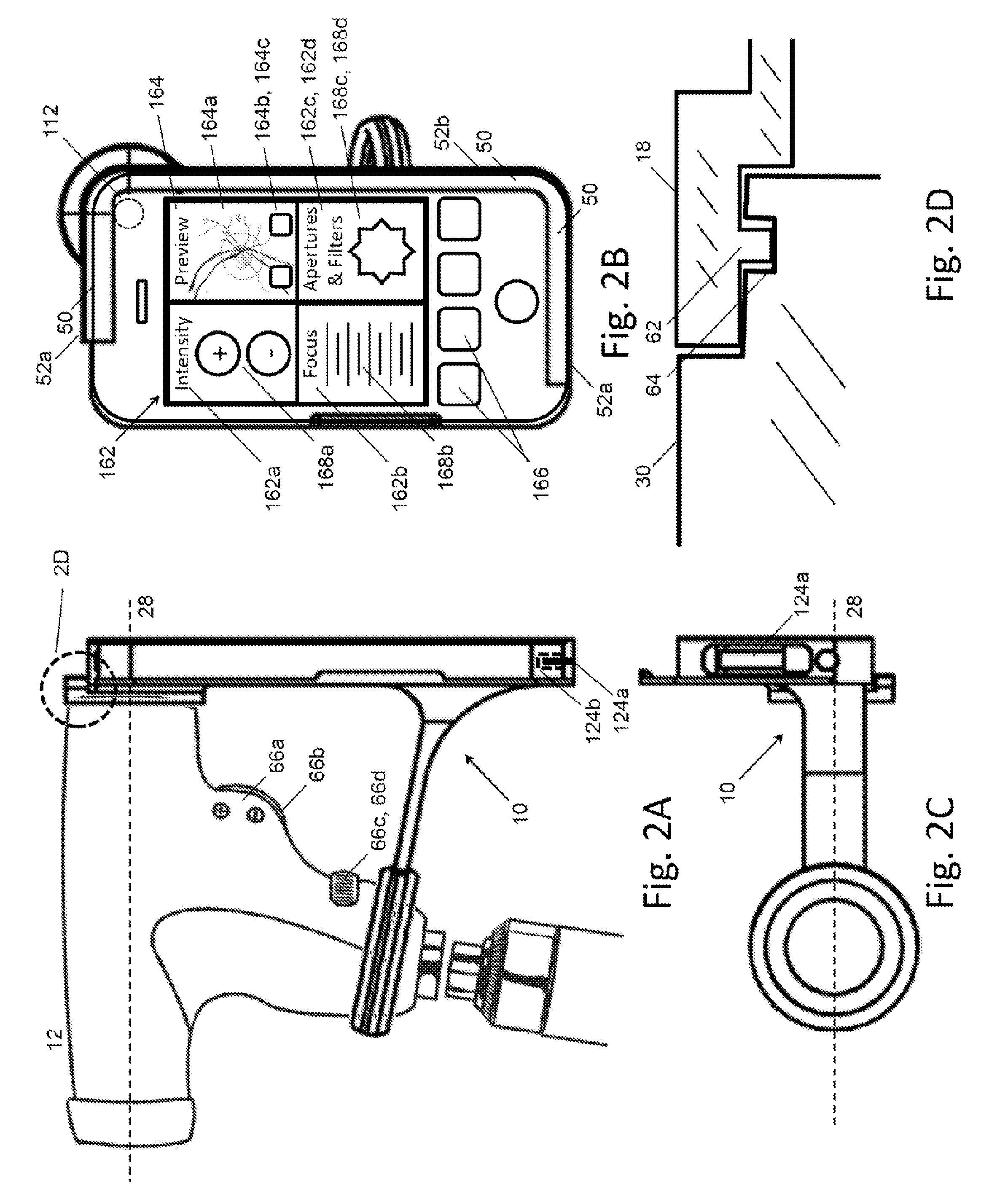
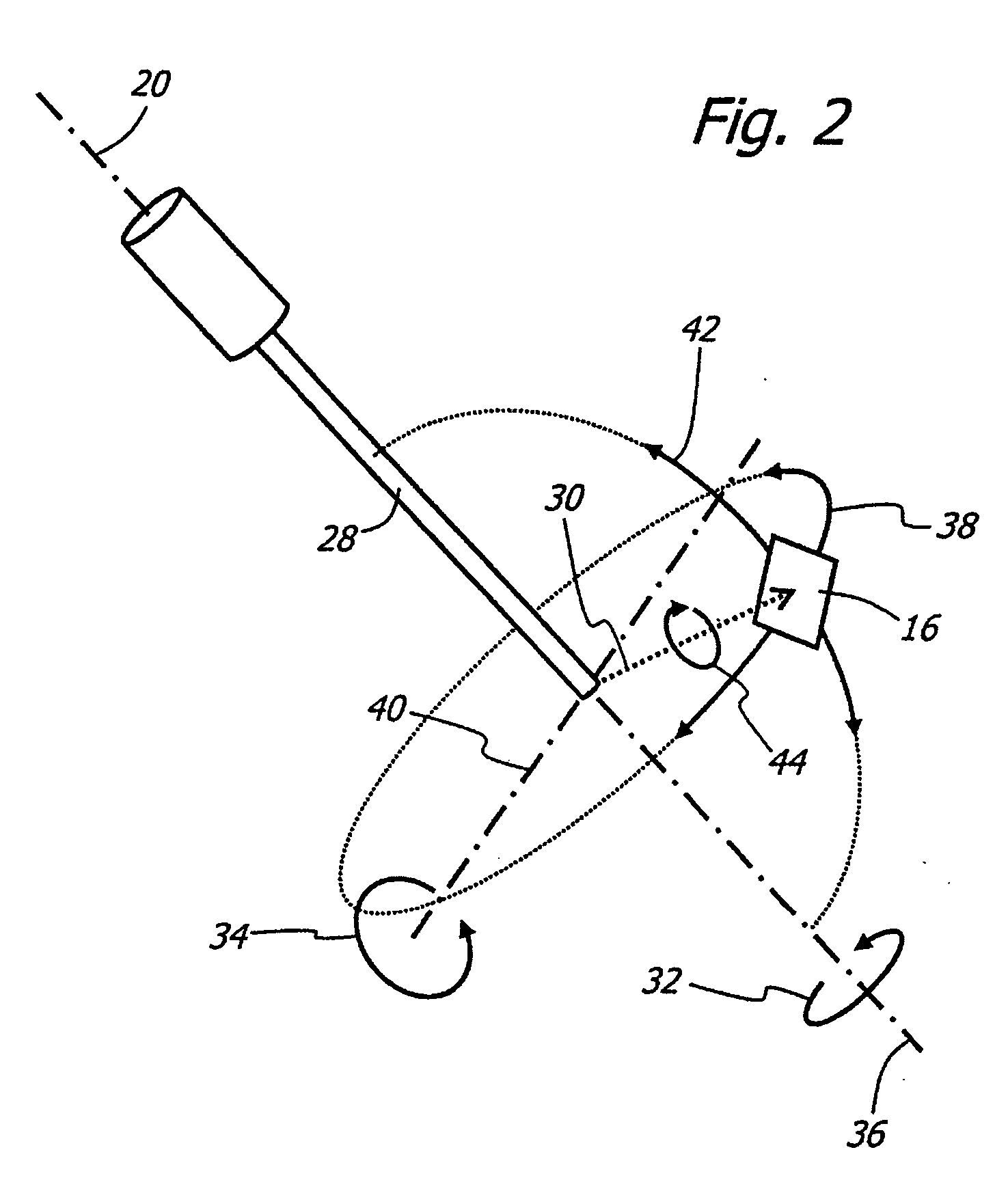
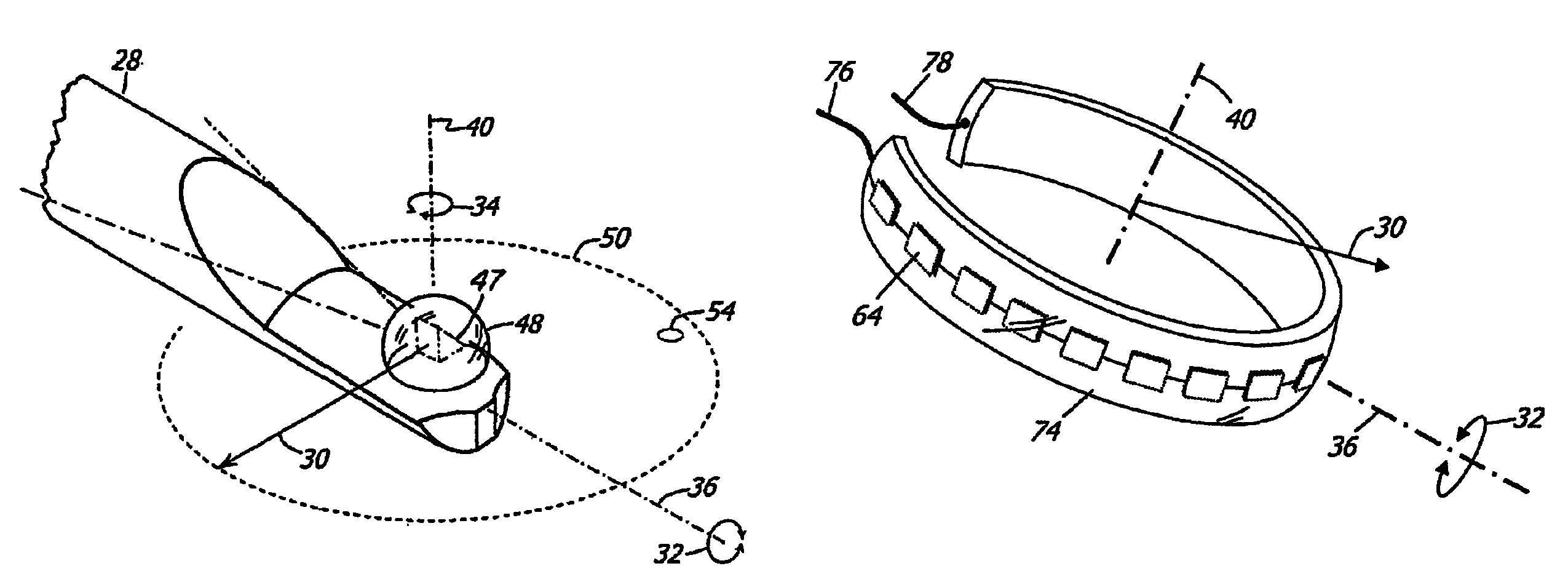
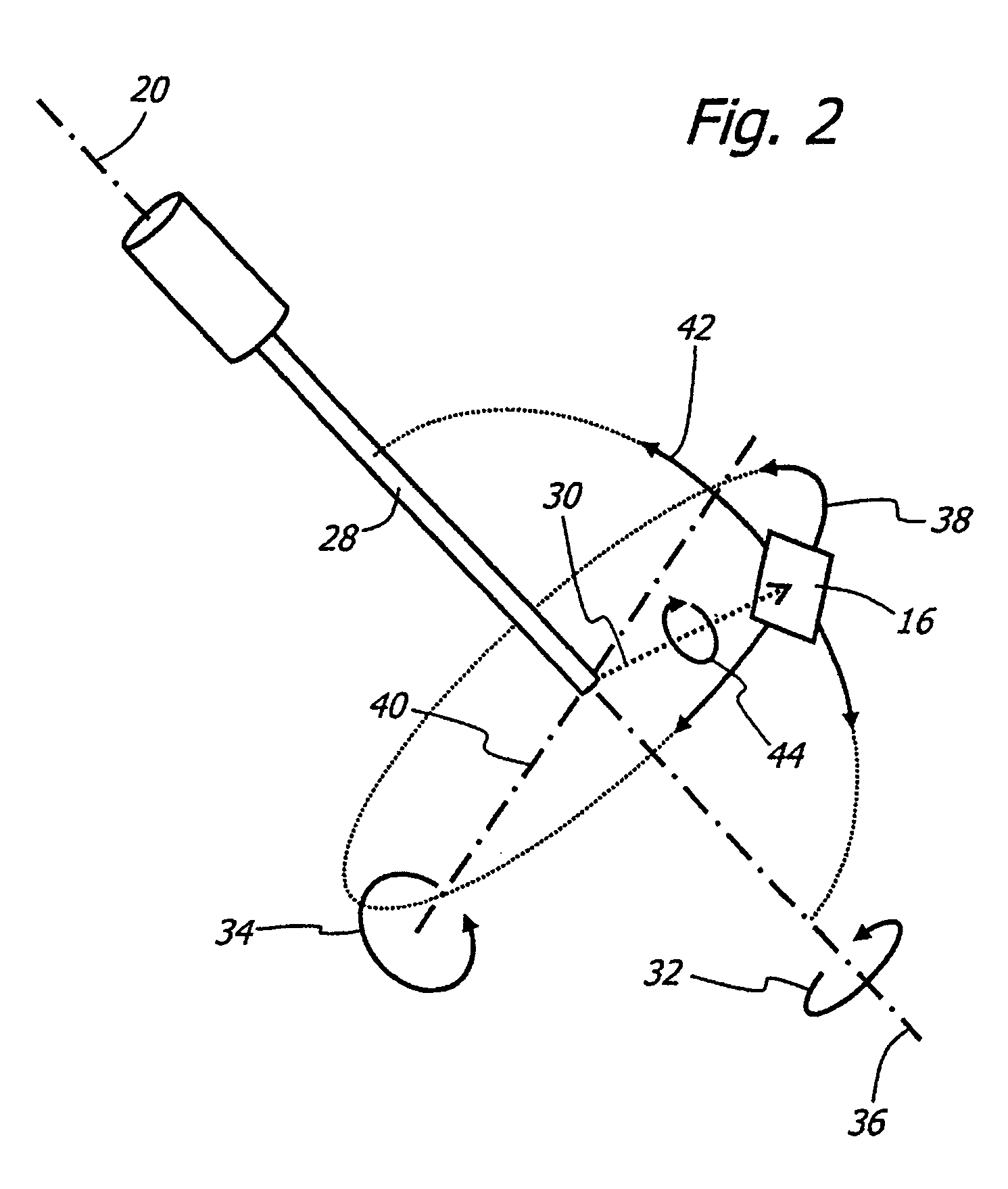
An adapter system connects a smart-phone or other camera to an ophthalmoscope or other viewing instrument at multiple locations with a single bracket. A fitting attached to the bracket connects the adapter to the viewing instrument in the region near its view port, close to the optical axis. A brace attached to the bracket connects the adapter to the viewing instrument in the region of the instrument's handle or other support structure, located away from the optical axis. The brace has a frame that holds the camera in place and aligns the camera lens with the optical axis of the instrument. The processor of the smart-phone or other mobile communications device can provide specific information related to the particular viewing instrument and can also be used in the operation and control of smart-scope instruments through a communications link.
Owner:INTUITIVE MEDICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for ultrasound imaging with biplane instrument guidance
InactiveUS6261234B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasound imagingViewing instrument
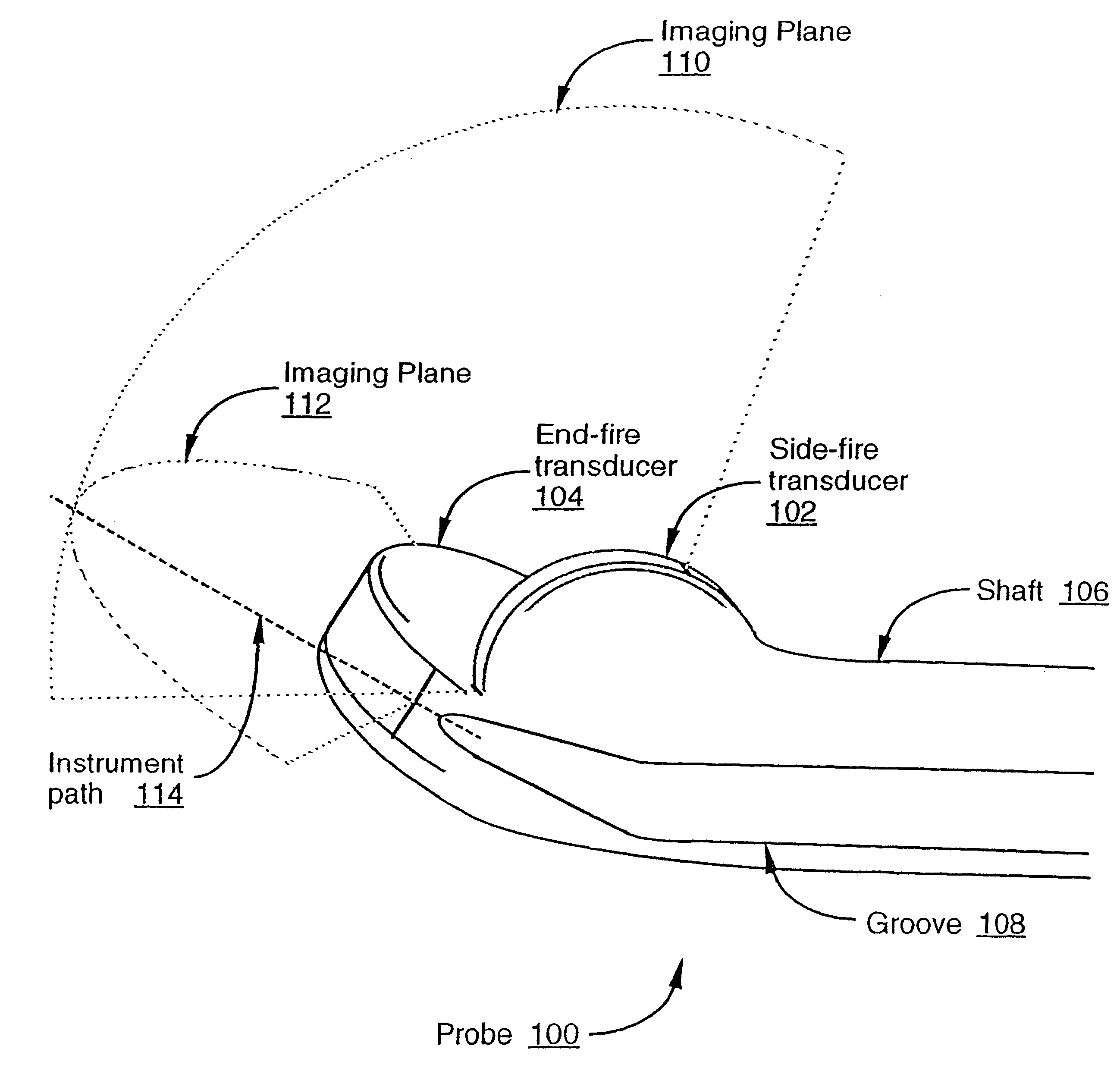
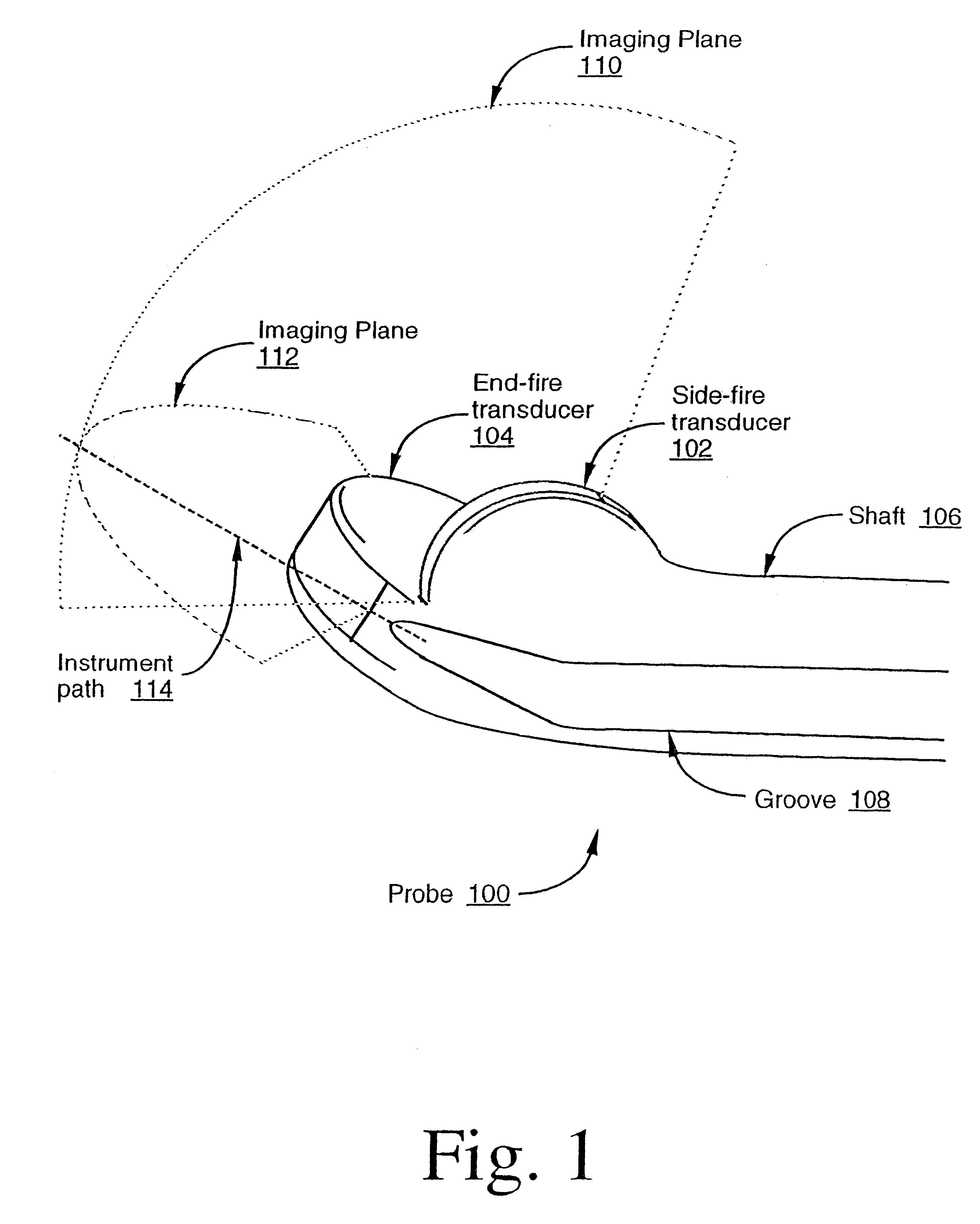
Methods and apparatuses for providing simultaneous viewing of an instrument in two ultrasound imaging planes. An ultrasound imaging probe is provided which can generate at least two ultrasound imaging planes. In one embodiment, the two imaging planes are not parallel (i.e., the planes intersect). An instrument path is positioned with respect to the planes such that an instrument may be simultaneously viewed in both imaging planes. In one embodiment, the instrument path is provided at an intersection that, at least partially, defines the intersection of the two imaging planes.
Owner:DIASONICS ULTRASOUND
Resectoscopic Device And Method
InactiveUS20070244353A1Reduce traumaShorten the timeEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFluid infusionViewing instrument
A surgical instrument has a channel dimensioned to receive a viewing instrument and enable the viewing instrument to be moved to or from a position near an optically transparent portion of a blunt, enclosed distal end of a shaft to provide unobstructed viewing through the distal end, and a position to the proximal side of an enclosed working area to provide viewing of the enclosed working area. A surgical instrument also or alternatively has a fluid routing switch within a shaft which can selectively connect a fluid infusion channel to at least one fluid export pore or a return channel. A method involves moving a viewing instrument to or from a position near an optically transparent portion of a blunt, enclosed distal shaft end and a proximal side of an enclosed working area. A method also or alternatively involves changing a position of a fluid routing switch within the shaft.
Owner:LARSEN DANE M
Flexible visually directed medical intubation instrument and method
Owner:PERCUVISION
Stereoscopic endoscope system and TV imaging system for endoscope
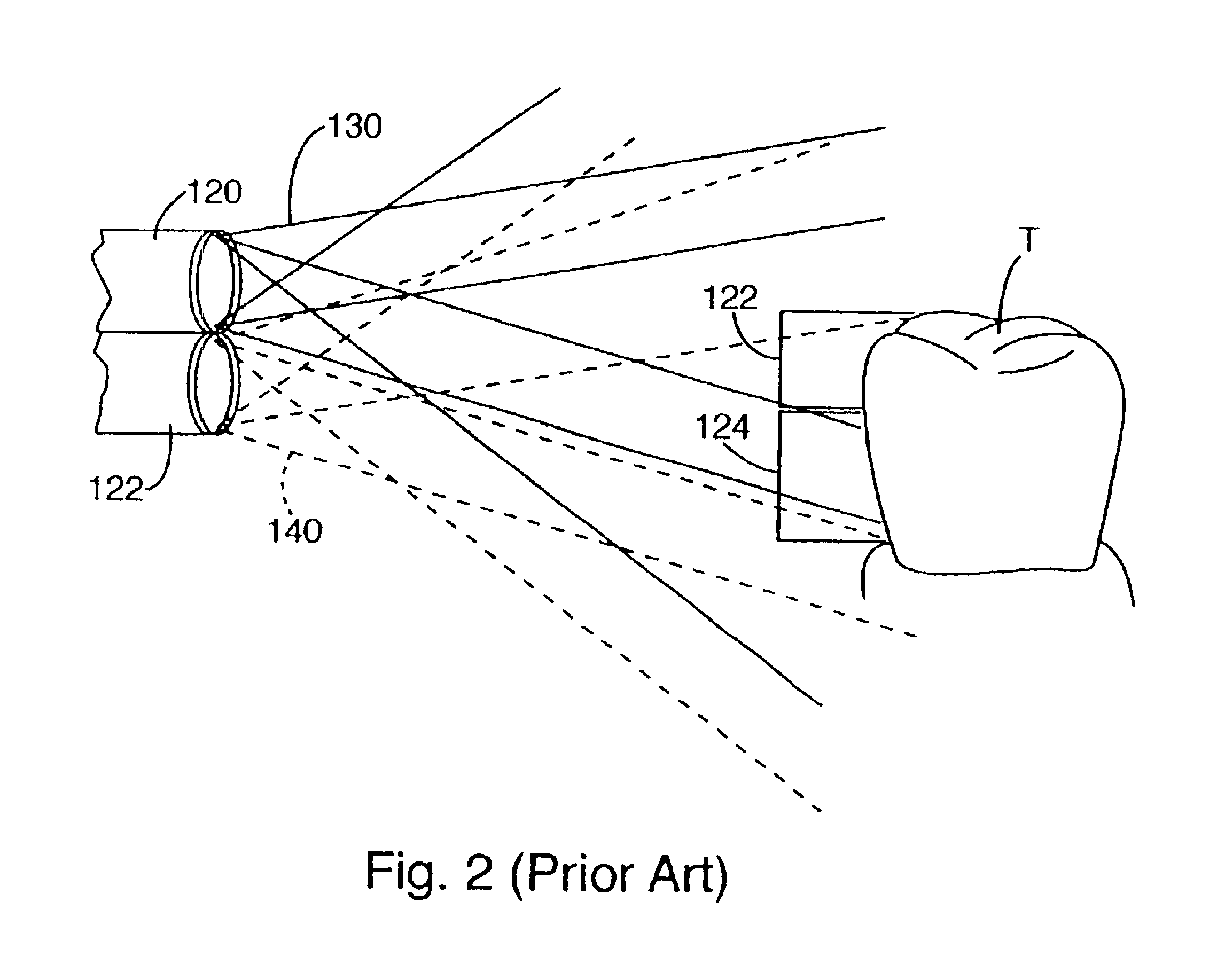
An armor (111a) of a scope unit (131) and a diaphragm (123) are arranged to be mutually freely turnable. The shape of an outer section (123c) of the diaphragm (123) and the shape of the inside of a scope joint (130a) of a TV camera unit (130) substantially agree with each other, and the outer section (123c) of the diaphragm (123) and the inside of the scope joint (130a) engage with each other. In a state in which the outer section (123c) of the diaphragm (123) and the inside of the scope joint (130a) are engaged with each other, a ring screw (133) is meshed with a thread (130b) so that the scope unit (131) and TV camera unit (130) will unitedly be joined with each other. At this time, since the outer section (123c) of the diaphragm (123) is engaged with the scope joint (130a), the diaphragm and TV camera unit can be turned relative to an objective optical system (119) and relay optical system (121) with the optical axis of the relay optical system (121) as an axis of turning. Moreover, a liquid-crystal shutter 124 in the TV camera unit (130) has two interceptive areas (124a, 124b) which can be switched temporally alternately. The interceptive areas (124a, 124b) intercept one of two light beams passing through either of aperture stops (123a, 123b).
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
Resectoscopic device and method
InactiveUS20100312053A1Reduce traumaShorten the timeEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsMedicineViewing instrument
A surgical instrument has a channel dimensioned to receive a viewing instrument and enable the viewing instrument to be moved to or from a position near an optically transparent portion of a blunt, enclosed distal end of a shaft to provide unobstructed viewing through the distal end, and a position to the proximal side of an enclosed working area to provide viewing of the enclosed working area. A surgical instrument also or alternatively has a fluid routing switch within a shaft which can selectively connect a fluid infusion channel to at least one fluid export pore or a return channel. A method involves moving a viewing instrument to or from a position near an optically transparent portion of a blunt, enclosed distal shaft end and a proximal side of an enclosed working area. A method also or alternatively involves changing a position of a fluid routing switch within the shaft.
Owner:LARSEN DANE M
Microinjection devices and methods of use
InactiveUS20050246783A1Easy injectionReduce pressureMedical devicesIntravenous devicesViewing instrumentComputer science
The present invention provides for microinjection devices comprising a needle and a viewing instrument wherein the viewing instrument provides magnified viewing of an object to an operator from an angle other than a right angle to the object.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Microinjection devices and methods of use
InactiveUS20080124787A1Easy injectionReduce pressureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsViewing instrumentComputer science
The present invention provides for microinjection devices comprising a needle and a viewing instrument wherein the viewing instrument provides viewing of an object to an operator from an angle other than a right angle to the object.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
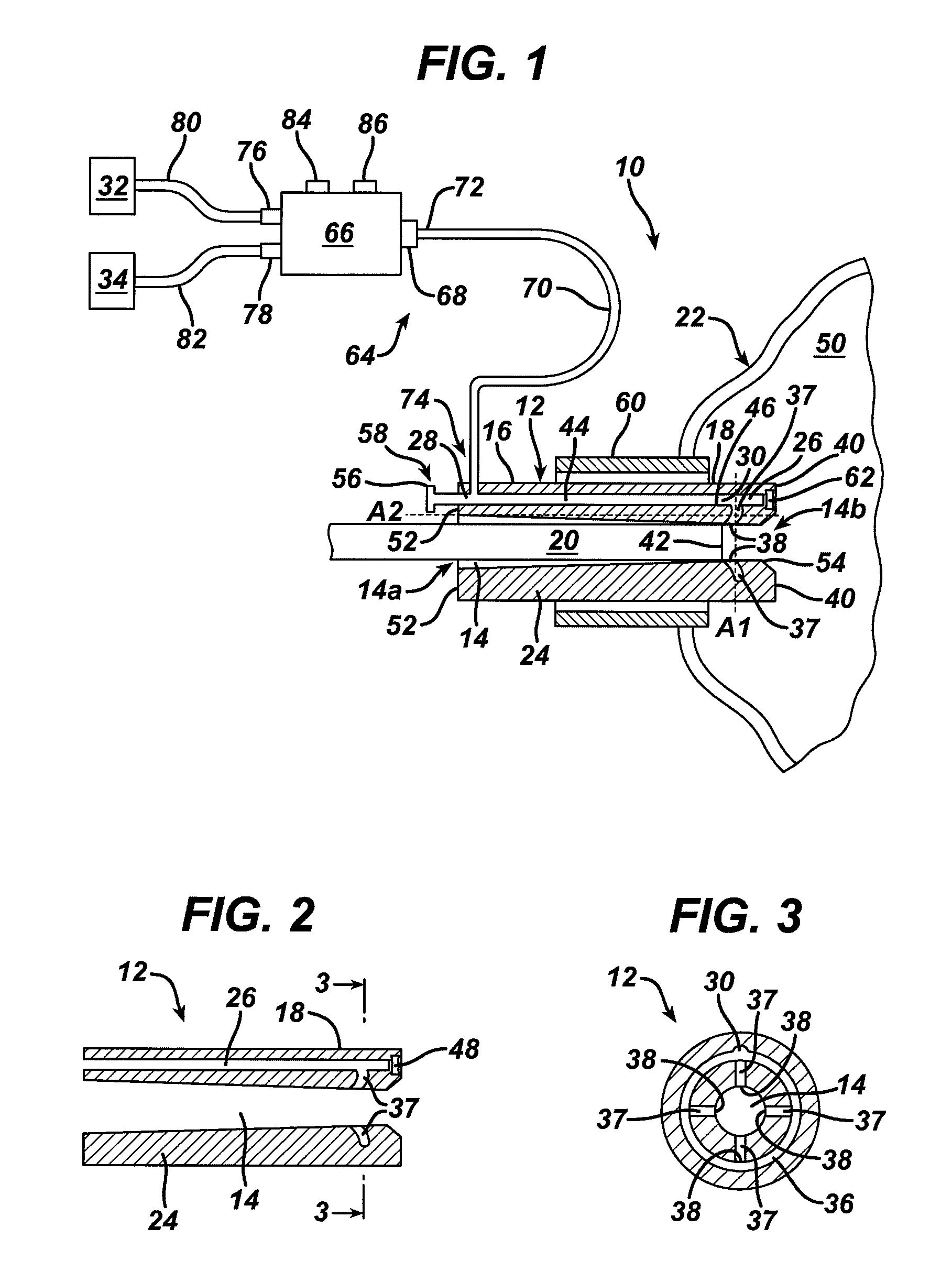
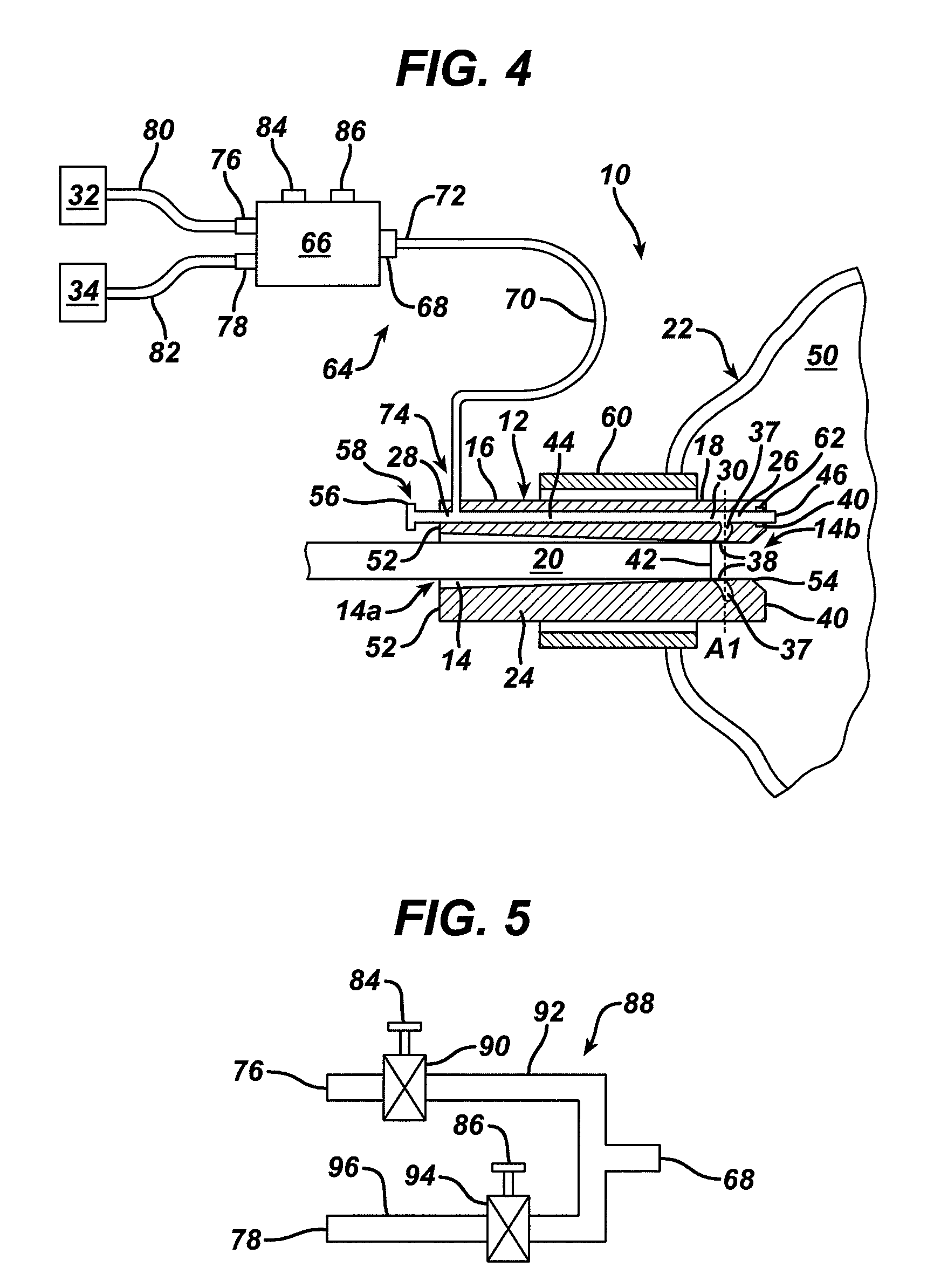
Methods and devices for maintaining visibility and providing irrigation and/or suction during surgical procedures
Methods and devices are provided for providing irrigation and / or suction to a surgical site and maintaining clear visibility through a lens of a scoping device during a surgical procedure. In general, the methods and devices can allow for a surgical instrument to maintain visibility during a surgical procedure using a fluid conduit coupled to the surgical instrument. A surgical device can include a sheath having at least one lumen extending therethrough configured to allow a surgical viewing instrument to be disposed therein. The sheath can also have a passageway extending therethrough configured to allow fluid to flow therethrough. The fluid conduit can be configured to be movable between positions that can allow alternative directions of fluid toward and / or away from a viewing element on the surgical instrument and fluid away from the viewing element and toward a surgical field in a body cavity.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
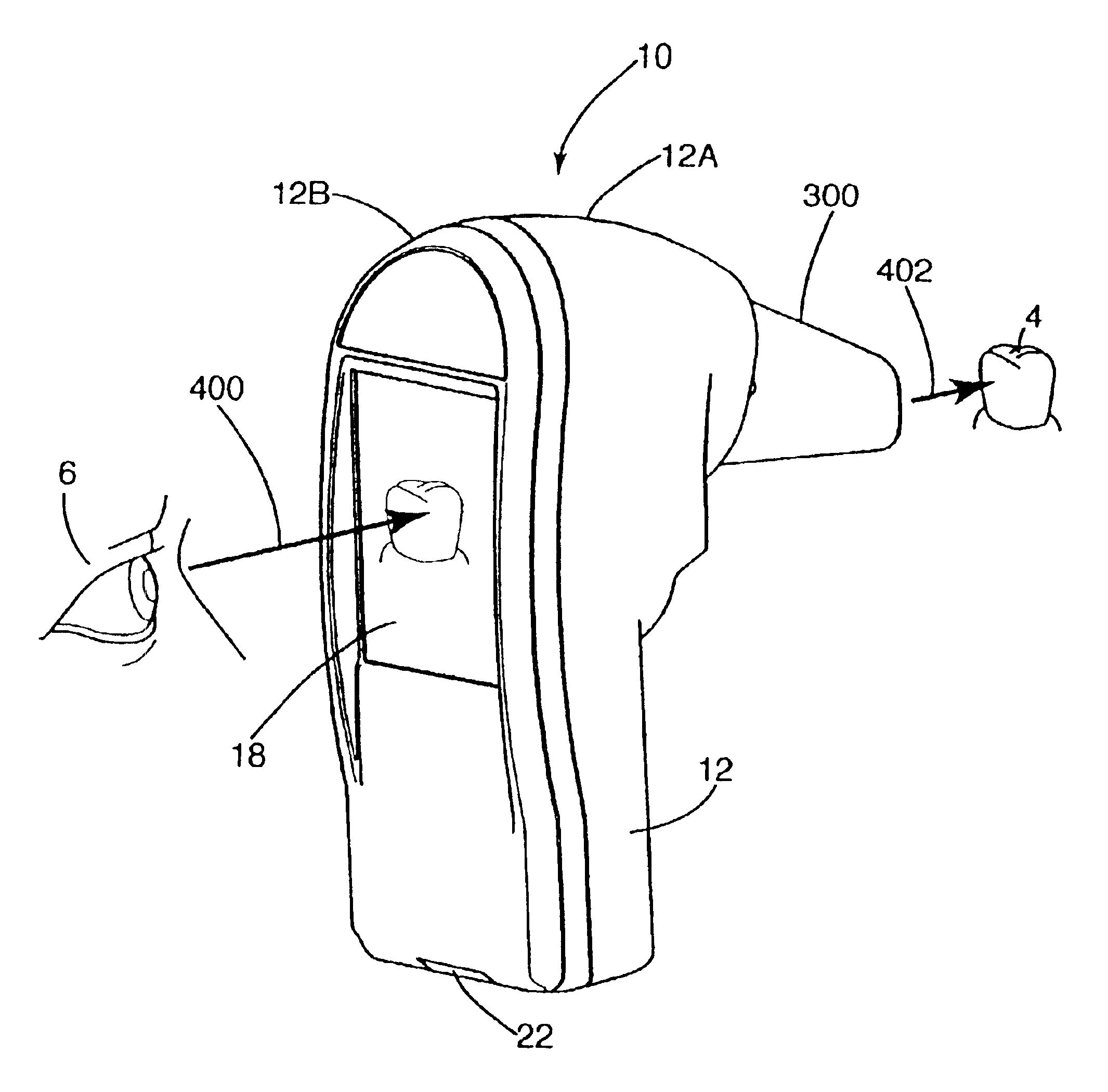
Optical measurement device and related process
InactiveUS6867864B2Accurate representationPoor color fidelityRadiation pyrometrySurgeryColor imageOptical property
An instrument and related process for measuring color, shade, gloss, shape and / or translucence of a tooth. First, the instrument uses searchlight illumination to illuminate a tooth with constant irradiance. Second, the instrument uses colorimetric imaging to collect time-separated frames of different wavelengths of light reflected from a tooth and to combine those frames into a color image. Third, the instrument includes a sanitary shield to establish a reference color and a predetermined distance to a target tooth. Fourth, the instrument provides line-of-sight viewing so an operator may simultaneously view a display of the image on the instrument and the object being measured. Fifth, the instrument is impervious to pollutants because it incorporates a sealed measurement window. Sixth, optical measurements of a tooth taken by a dentist are compared to optical measurements of a prosthetic restoration for that tooth to confirm satisfactory matching of optical characteristics of the tooth and restoration.
Owner:X RITE INC
Endoscope wiper blade cleaner
A minimally invasive surgical instrument including a viewing instrument and a wiper mechanism configured and adapted to clean a lens of the viewing instrument. The wiper mechanism includes a wiper that is configured and adapted to contact and translate across a surface of the lens. An actuator moves the wiper across the lens to clean the lens.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Use of pearlescent and other pigments to create a security document
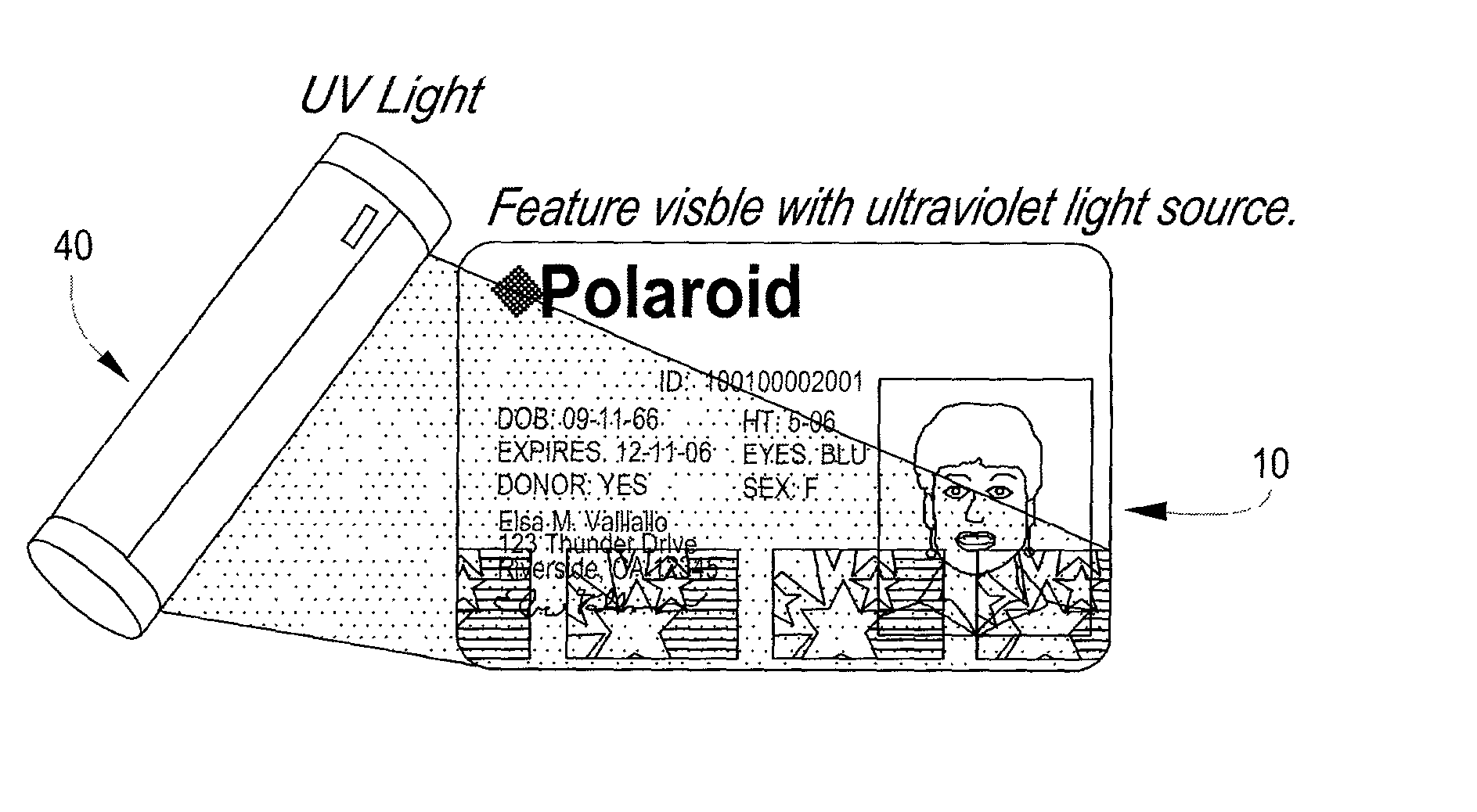
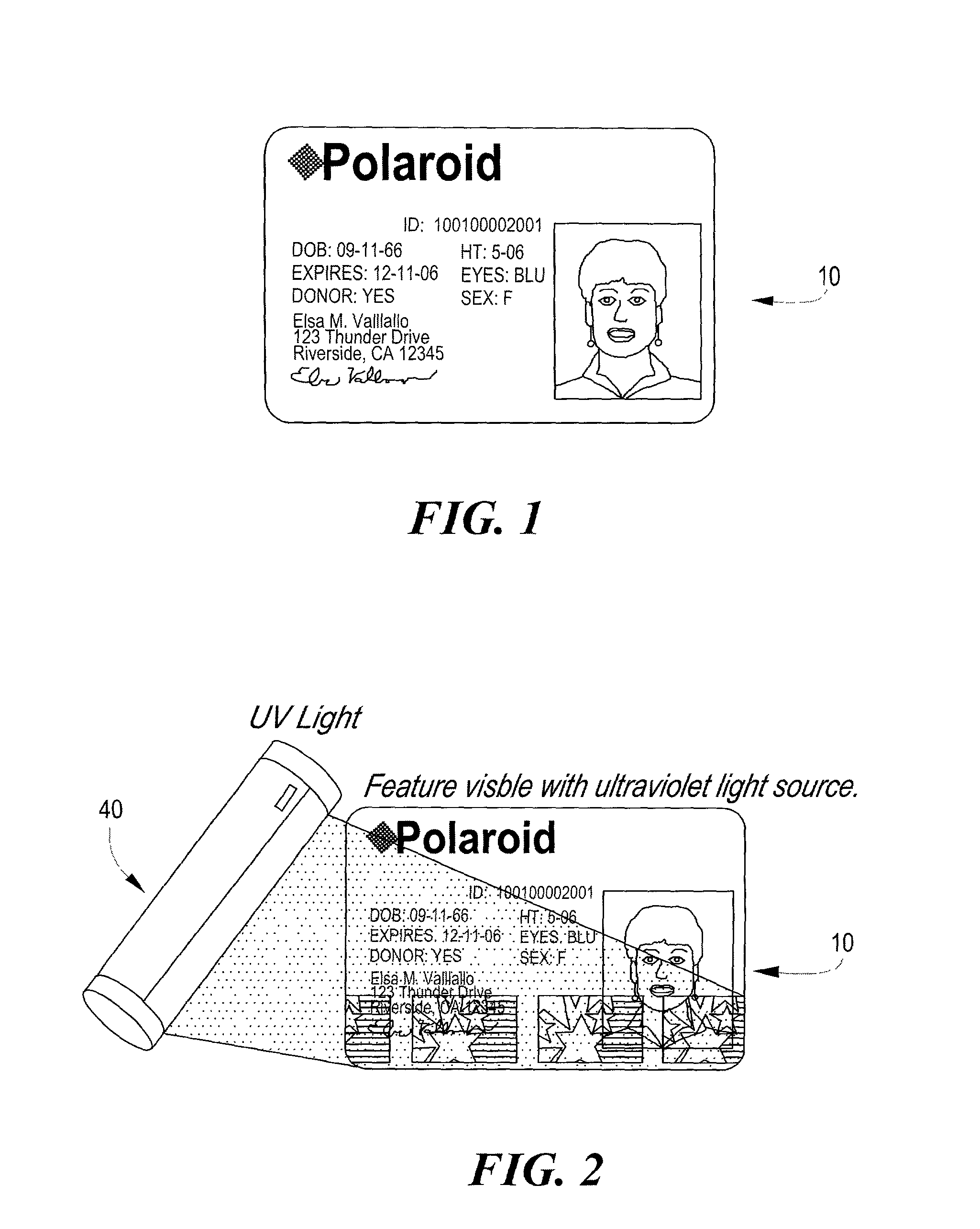
InactiveUS20030062421A1Improve security levelOther printing matterRecord carriers used with machinesEngineeringPaper document
A security instrument and method of forming the same, in which the instrument is comprised of a series of layers which overlay one another, and in which at least one of the layers has a pattern imprinted thereon in a predetermined location, with pearlescent materials of varying colors and hues. When the layers are bonded together on a base member, a design emerges at the surface that provides optical variations, depending on the attitude and lighting at which the instrument is viewed.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
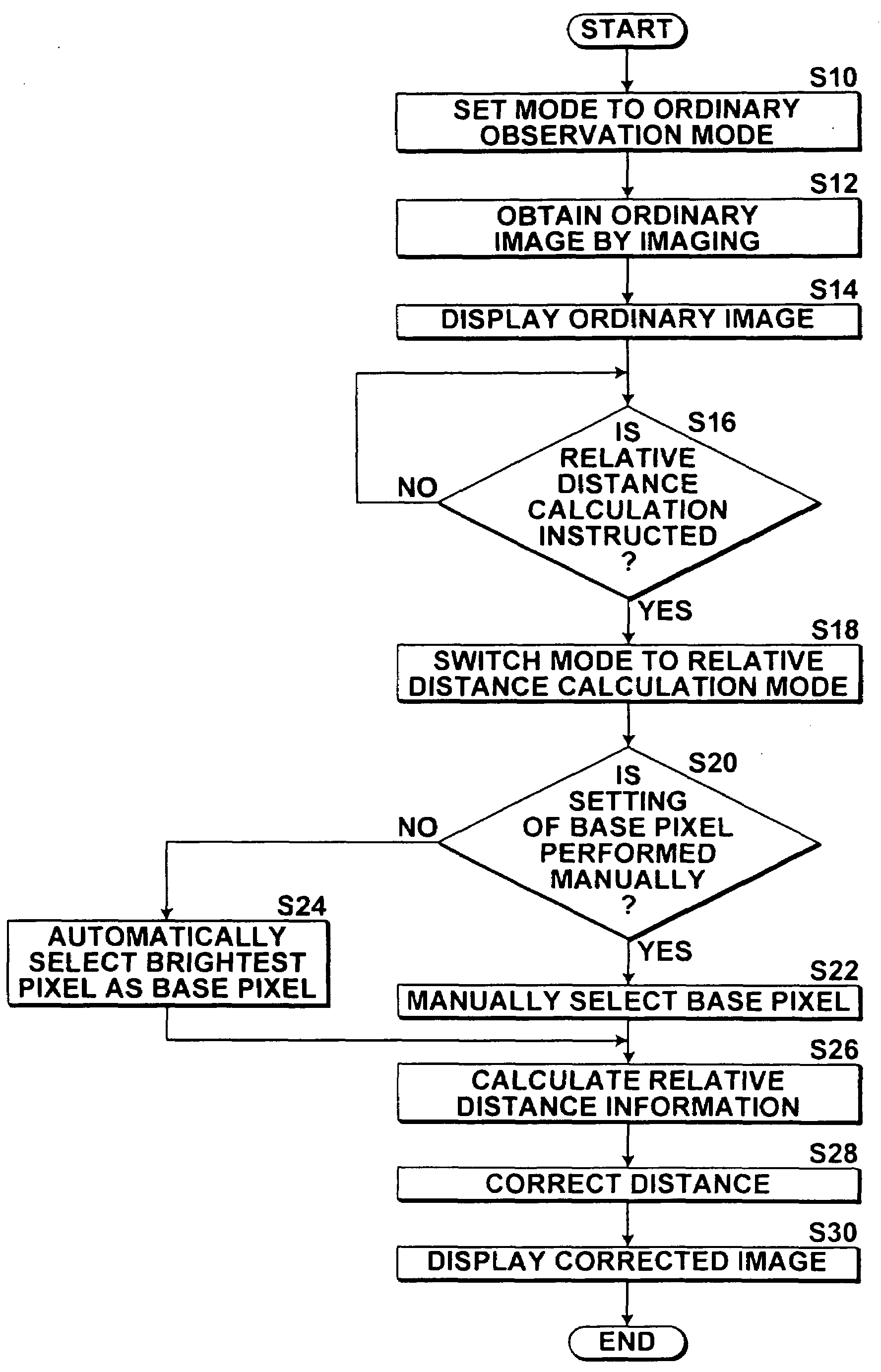
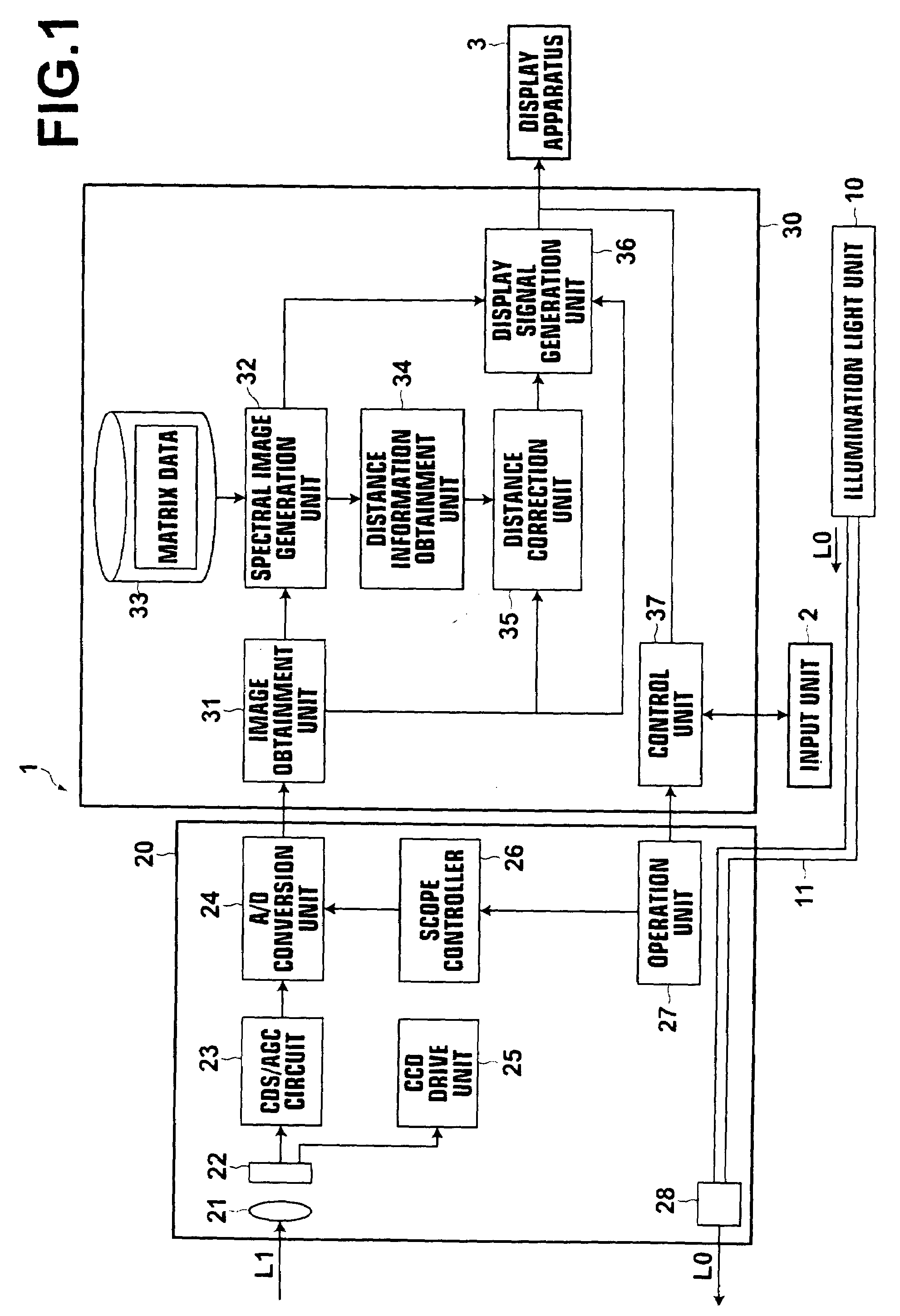
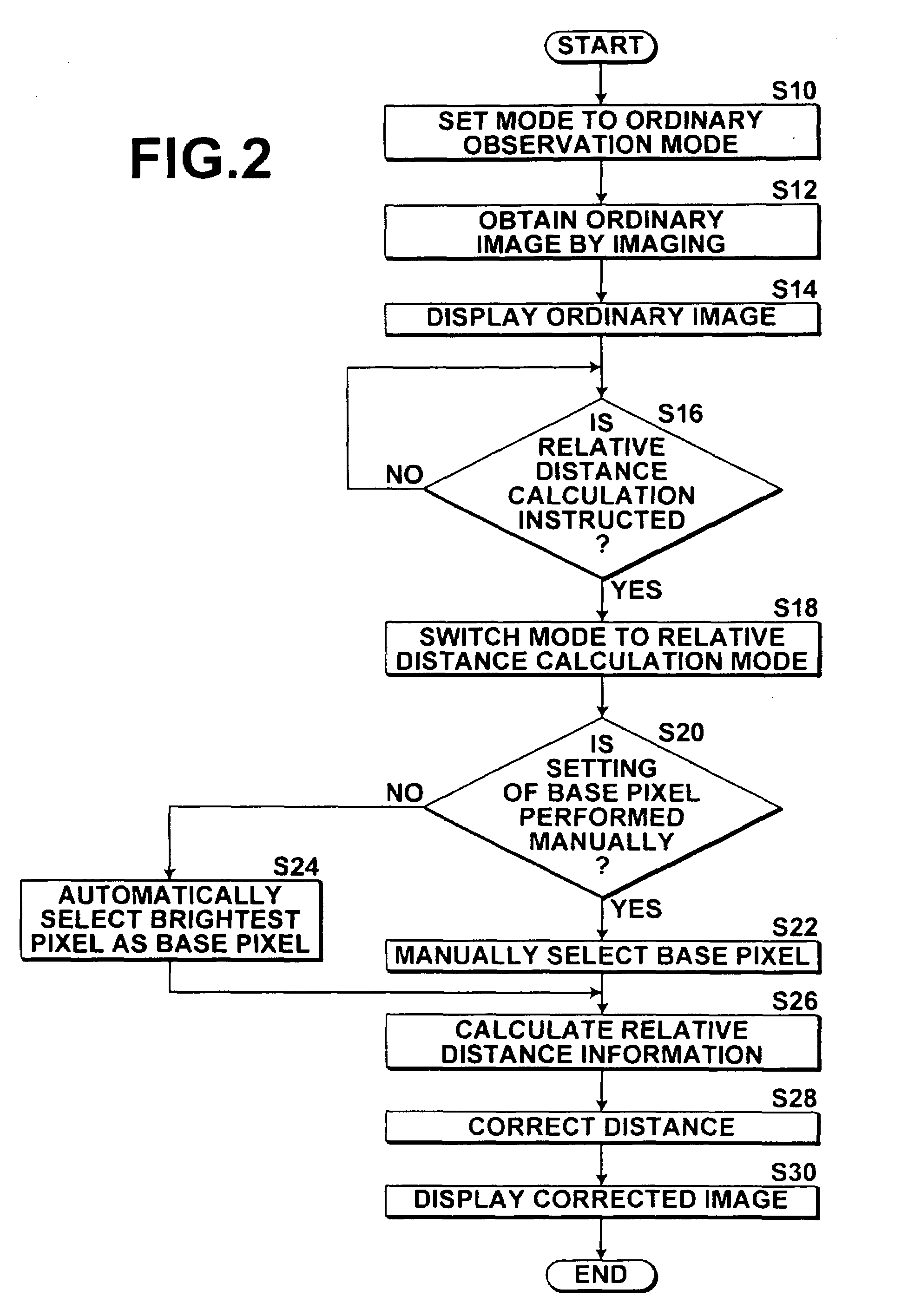
Distance information obtainment method in endoscope apparatus and endoscope apparatus
InactiveUS20090322863A1Low costIncrease the burdenImage enhancementImage analysisViewing instrumentLength wave
Distance information between an observation-target and each pixel of an imaging device is obtained in an endoscope apparatus. The endoscope apparatus includes a scope unit having an illumination-light illuminating unit and an imaging device, and a spectral image processing unit that generates a spectral estimation image signal of a predetermined wavelength by performing spectral image processing on an image signal output from the imaging device. The illumination-light illuminating unit illuminates the observation-target with illumination-light, and the imaging device images the observation-target by receiving light reflected from the observation-target illuminated with the illumination-light. The spectral image processing unit generates the spectral estimation image signal of the predetermined wavelength greater than or equal to 650 nm, as a spectral estimation image signal for obtaining distance information. Distance information representing a distance between the observation-target and each of the pixels is obtained based on the spectral estimation image signal for obtaining distance information.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
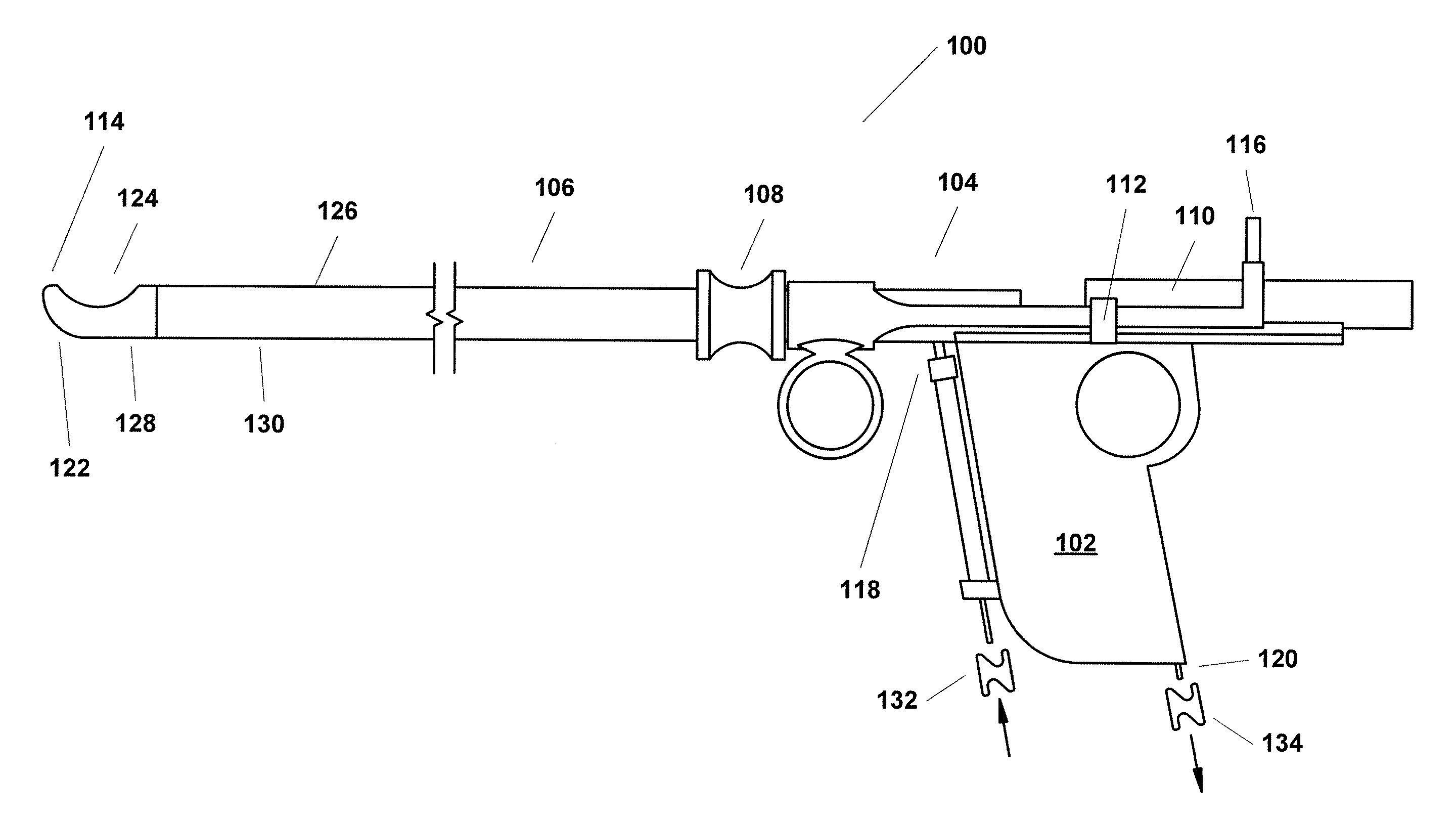
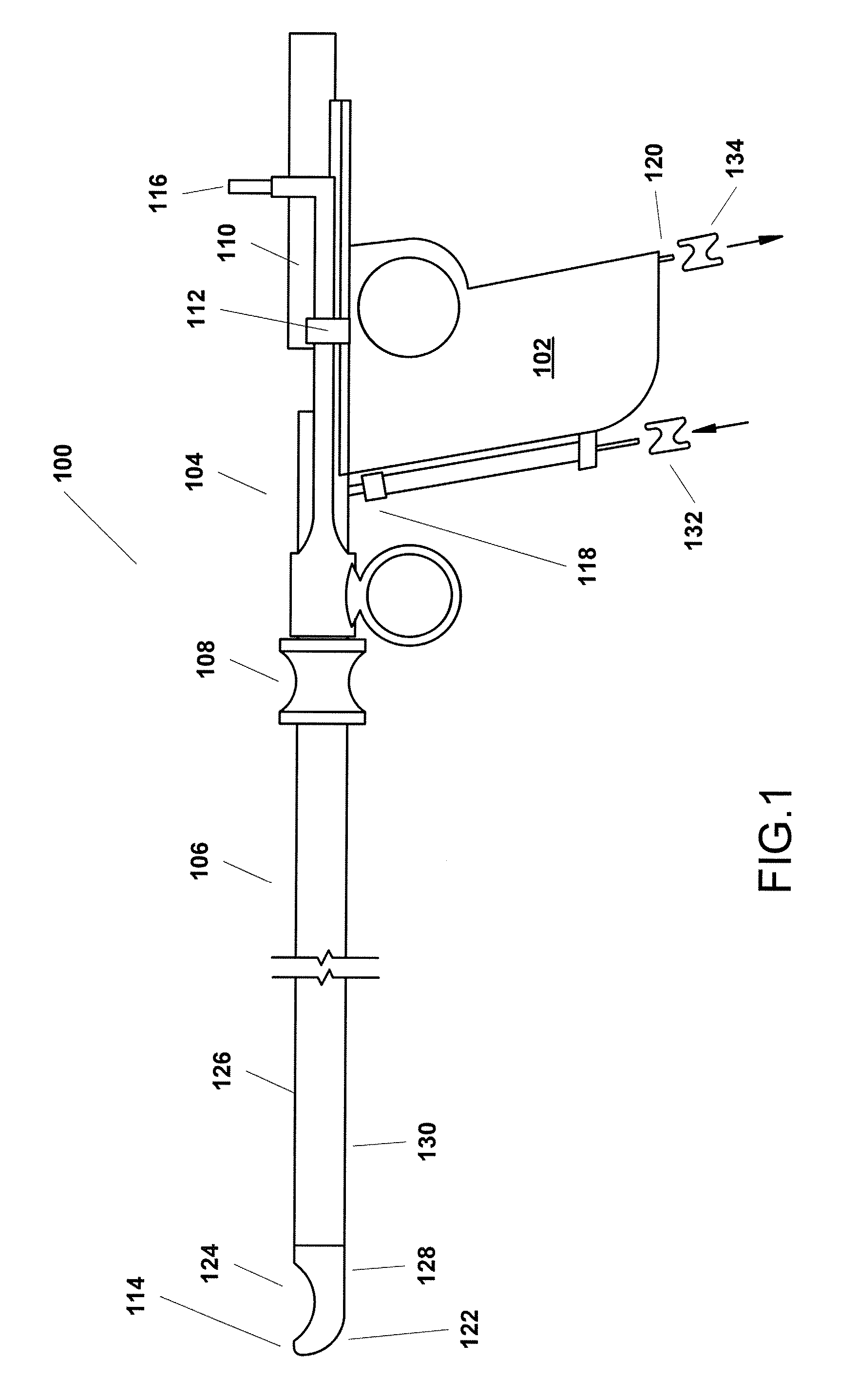
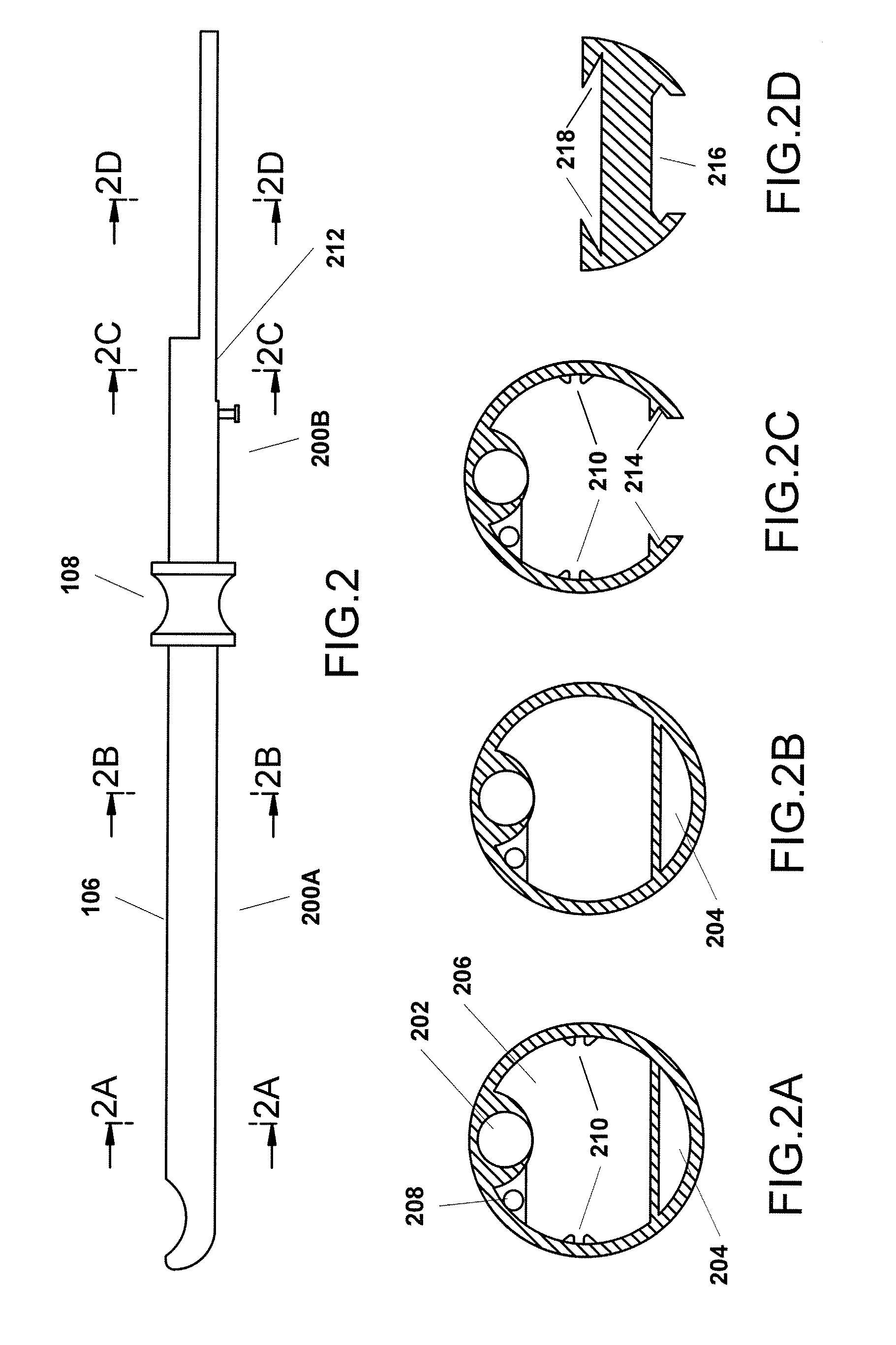
Triangulation mechanism for a minimally invasive surgical device
InactiveUS8845517B2Facilitates triangulationEasy transitionCannulasSurgical needlesLess invasive surgeryTriangulation
A surgical device including a seal anchor that includes leading and trailing portions. A plurality of ports longitudinally extends between the leading and trailing portions. The ports are adapted and configured to receive surgical objects therein. At least one of the surgical objects is a viewing instrument including a viewing portion. During a surgical procedure, surgical objects inserted in the other ports are selectively positionable with respect to the viewing instrument.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
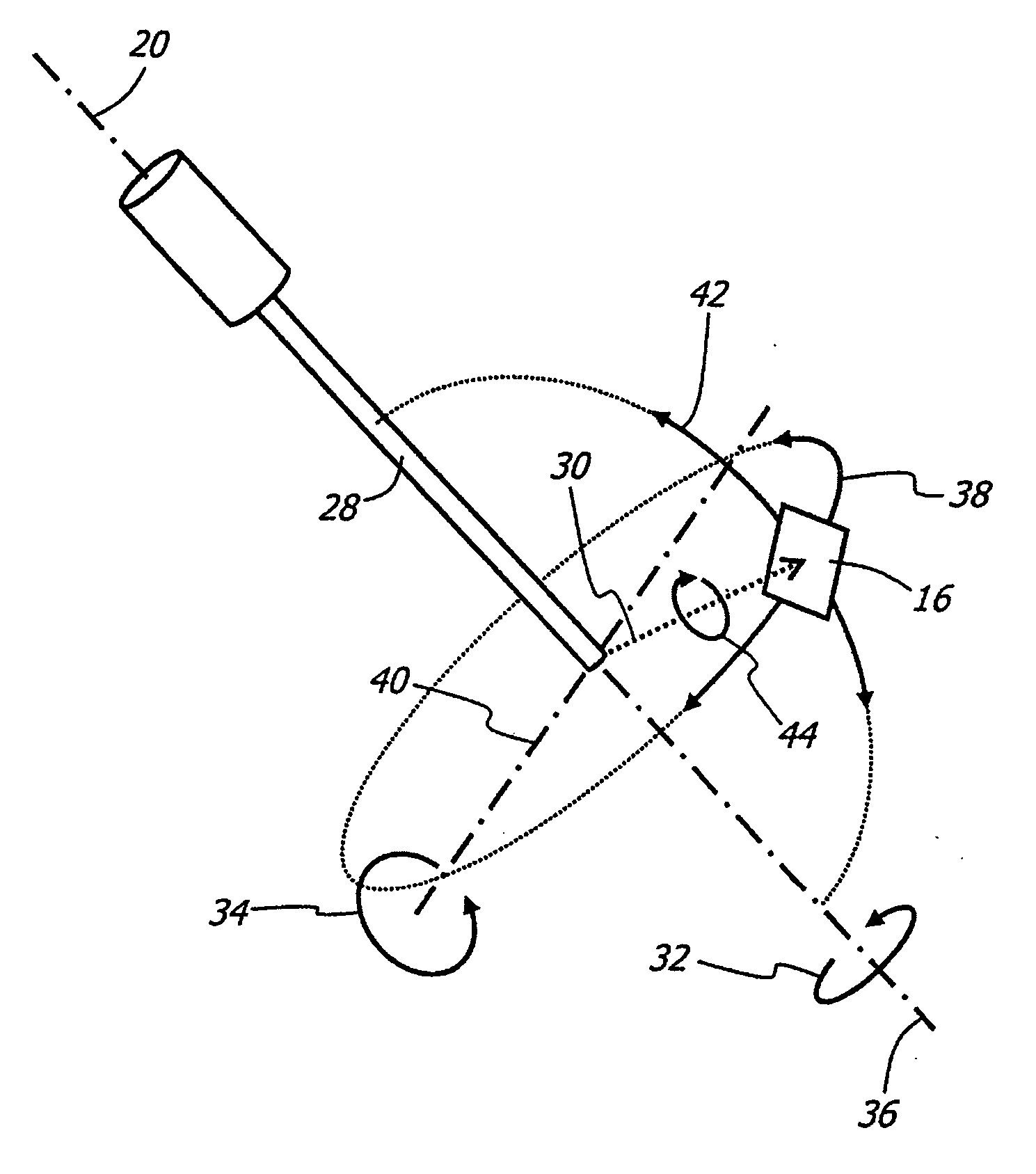
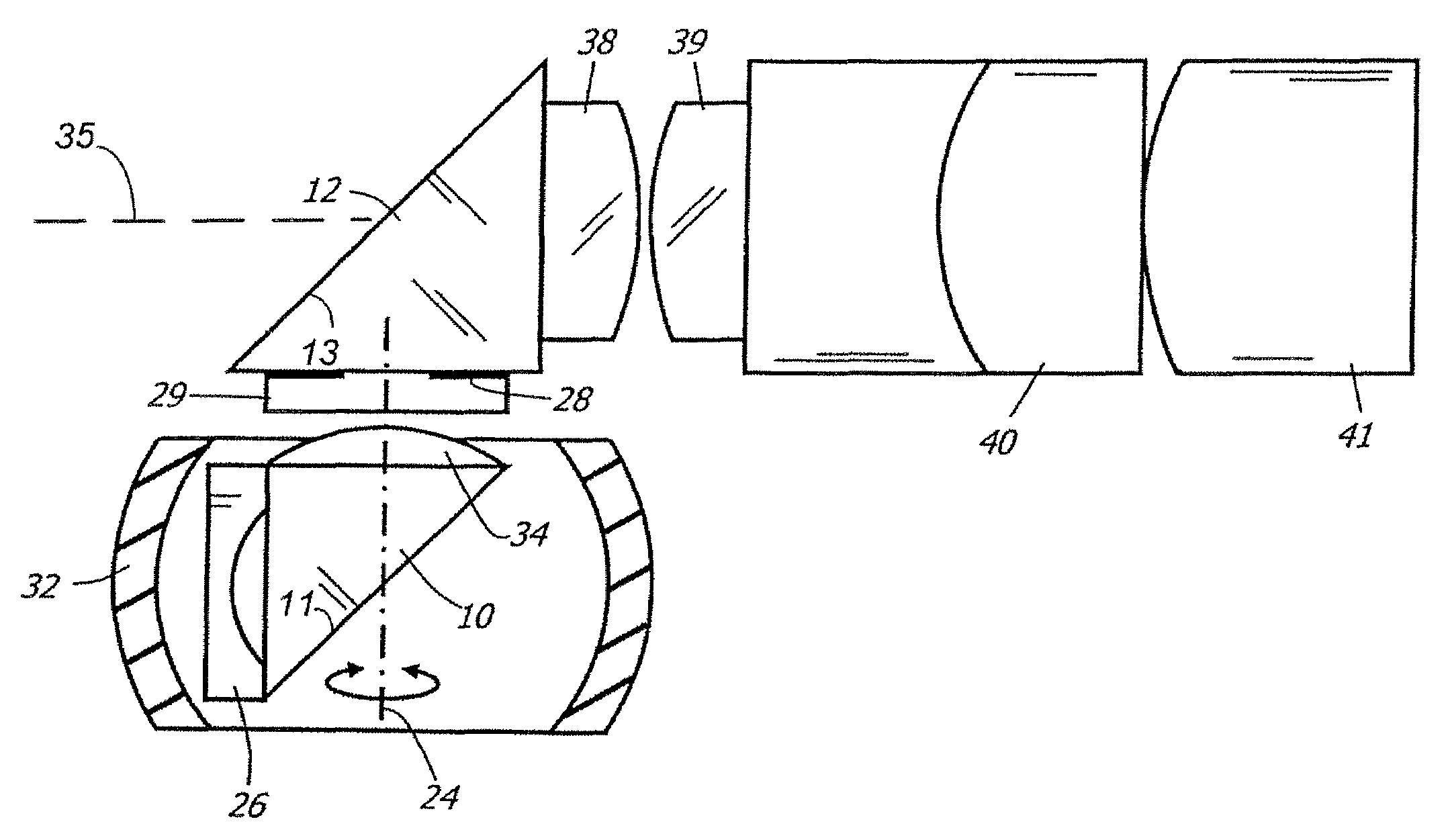
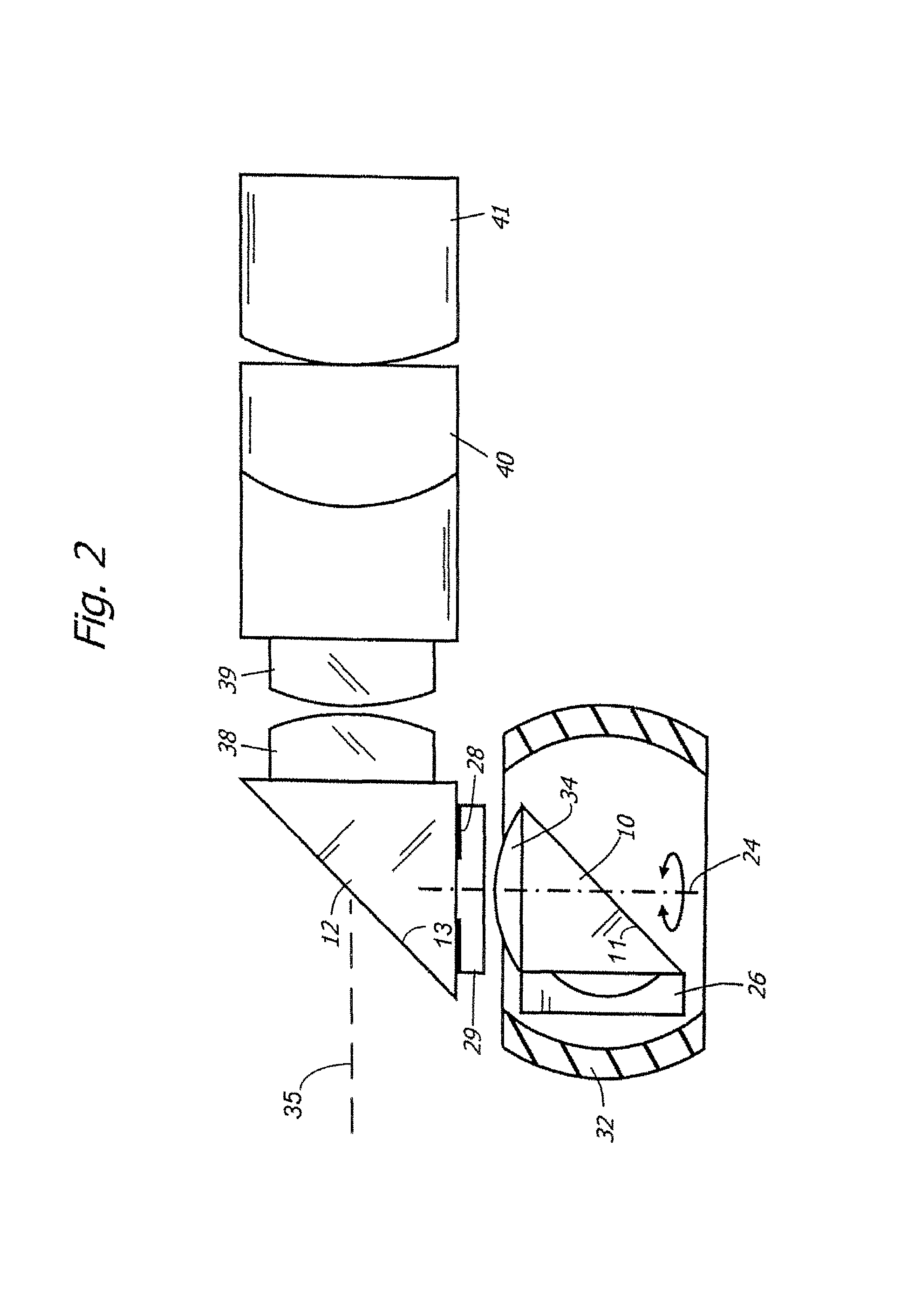
Variable direction of view instrument with distal image sensor
A viewing instrument having a variable direction of view is disclosed generally comprising a shaft, a sensor mounted in the distal end of the shaft such that the image plane of the sensor is substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the shaft, and a reflecting element that rotates about an axis substantially perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the shaft. In some embodiments, a negative lens is mounted adjacent the reflecting element, and in certain embodiments, a positive lens is positioned adjacent the image sensor.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
Optical system for variable direction of view instrument
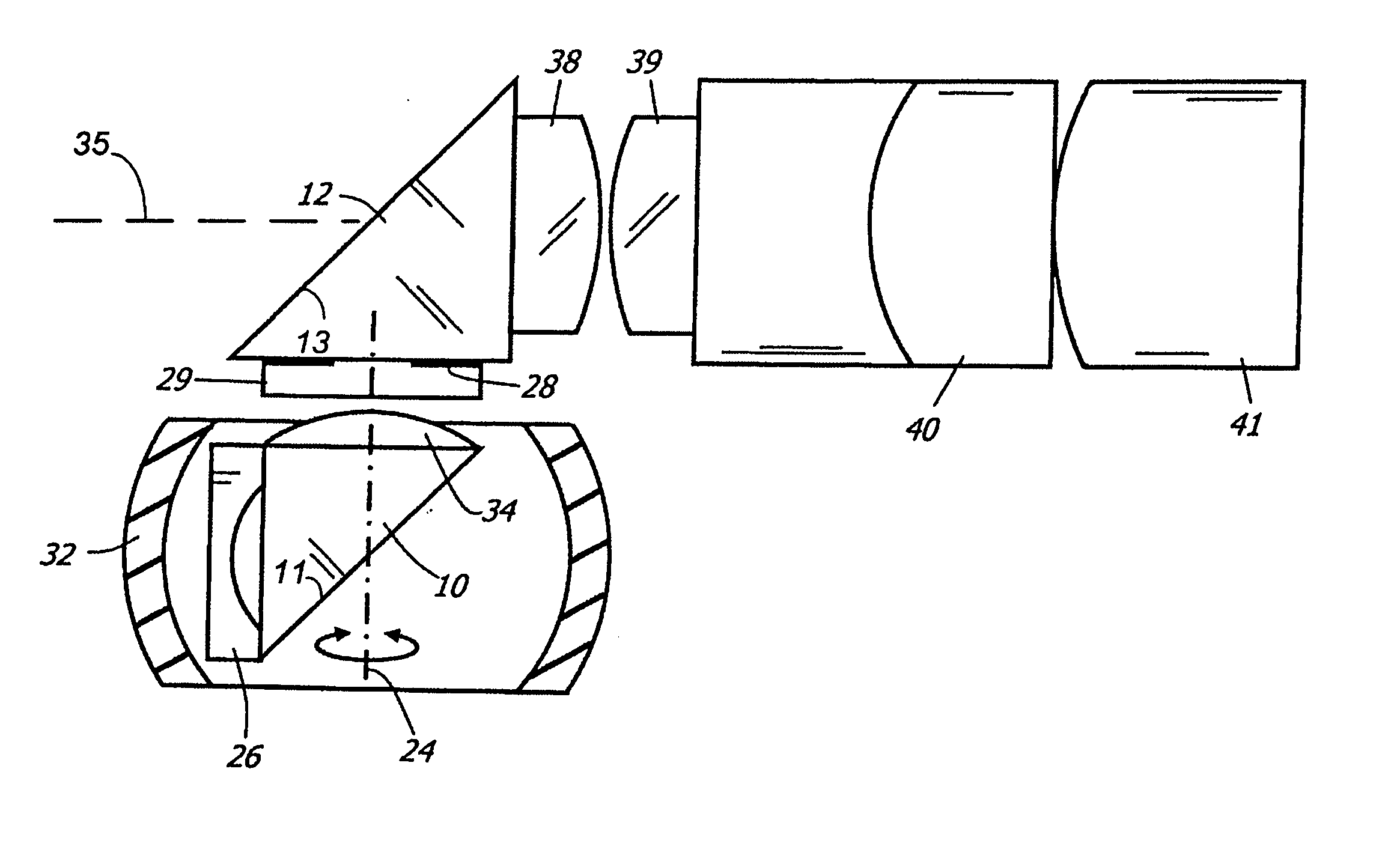
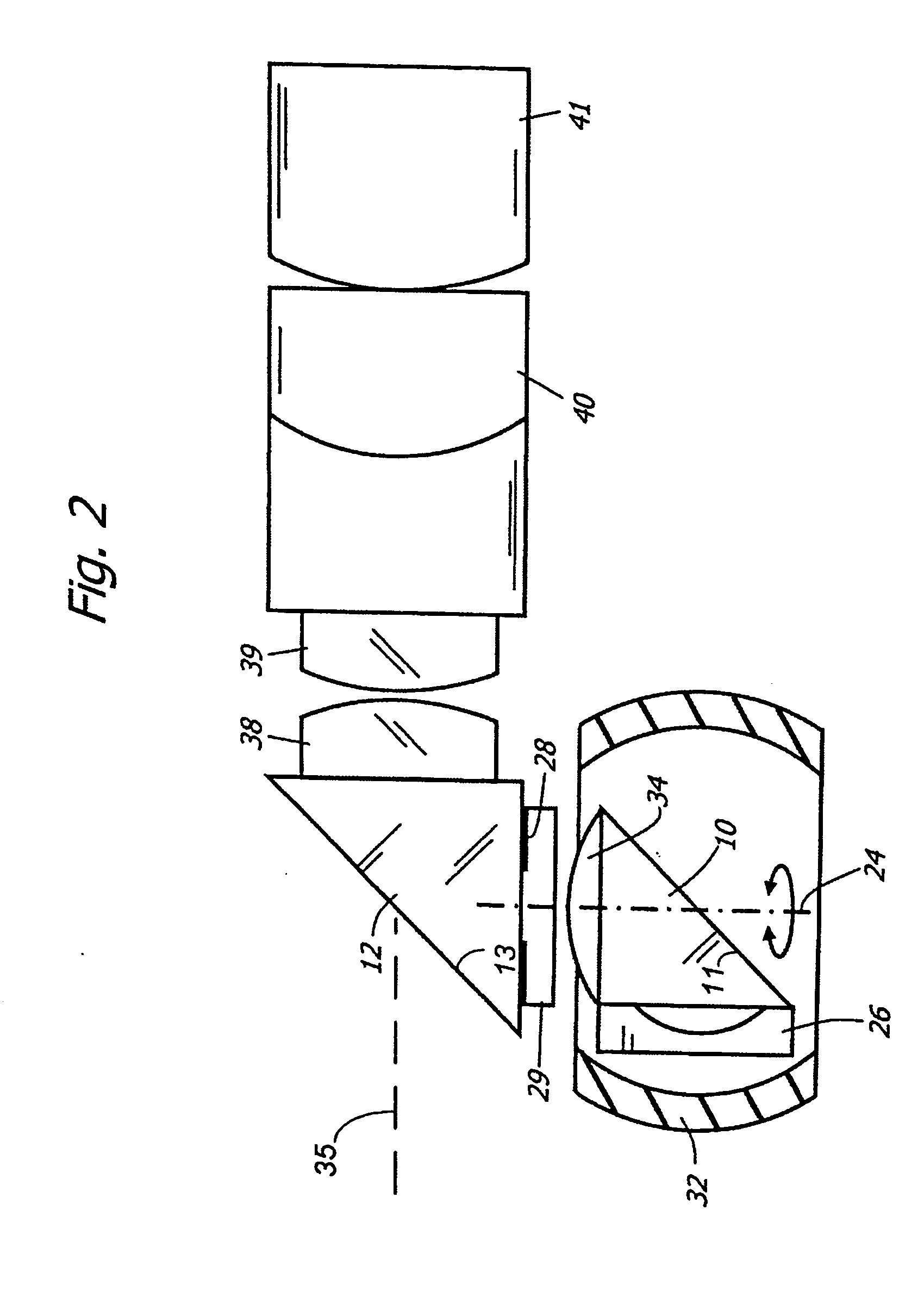
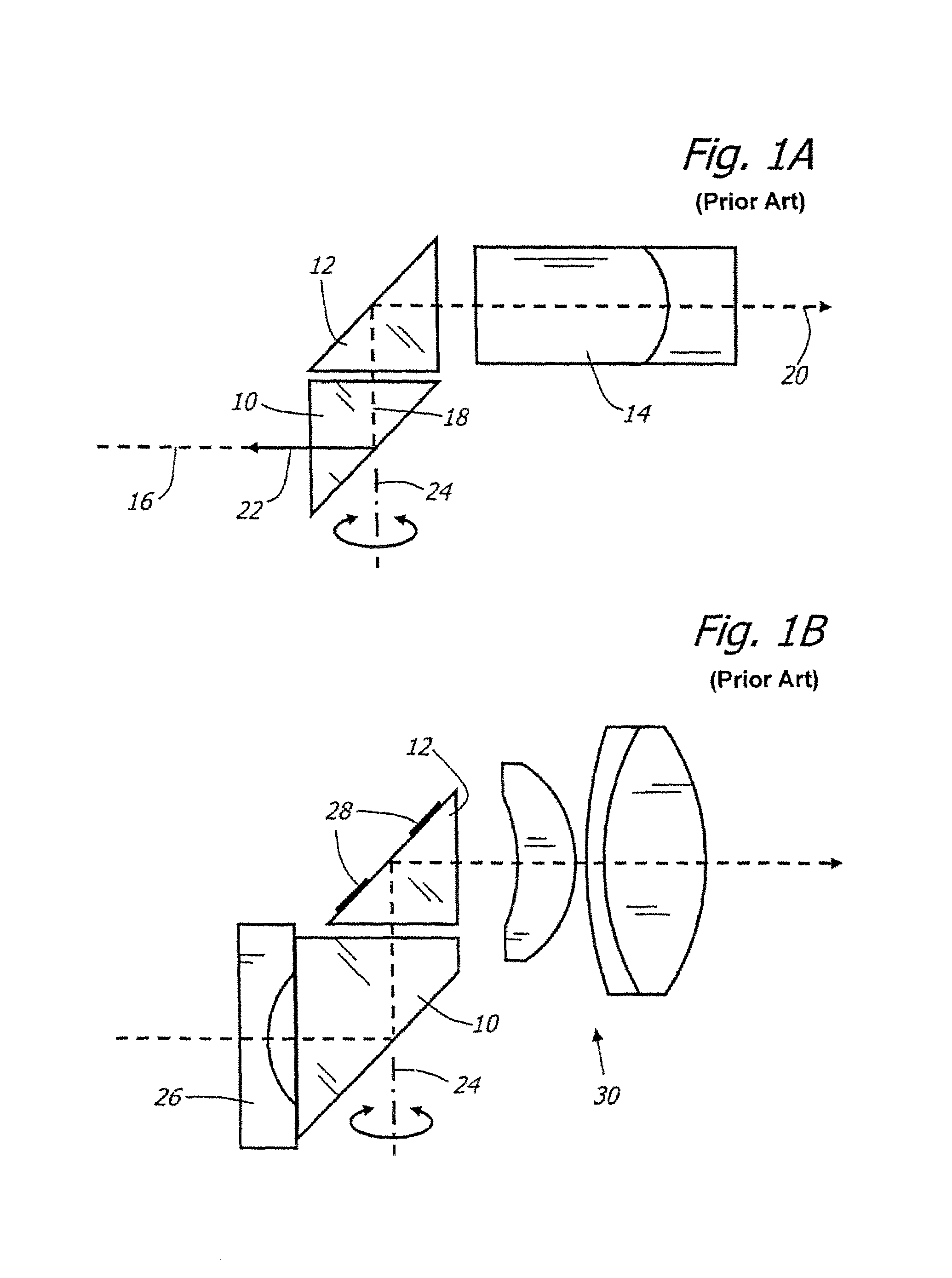
ActiveUS20060256450A1Large scanning rangeLarge scanning range and field of viewPrismsEndoscopesViewing instrumentOptic system
A optical system for a viewing instrument with a variable direction of view is disclosed generally comprising shaft, first and second reflectors located at the distal end of the shaft, where the first reflector rotates about an axis angularly offset from the longitudinal axis of the shaft, and an entrance pupil positioned in the optical path created by the reflectors and preceding the reflecting surface of the second reflector. In certain embodiments, the entrance pupil comprises an aperture stop positioned between the first and second reflectors. In some embodiments, the system includes negative and positive lenses located adjacent the entrance and exit faces of the first reflector.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
Covering Apparatus For An Endoscope Lens
InactiveUS20120238818A1Increase awarenessEasy to cleanEndoscopesSurgical drapesCamera lensViewing instrument
A covering apparatus for a surgical viewing instrument. The apparatus includes a tape having a first length overlying the viewing portion of the surgical viewing instrument, the tape movable across the viewing portion to move the first length away from the viewing portion and advance a second cleaner length of tape to a position overlying the viewing portion.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Microinjection devices and methods of use
InactiveUS7339090B2Easy injectionReduce pressureMedical devicesIntravenous devicesViewing instrumentComputer science
The present invention provides for microinjection devices comprising a needle and a viewing instrument wherein the viewing instrument provides magnified viewing of an object to an operator from an angle other than a right angle to the object.
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Resectoscopic device and method
InactiveUS7794393B2Reduce traumaShorten the timeEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFluid infusionMedicine
A surgical instrument has a channel dimensioned to receive a viewing instrument and enable the viewing instrument to be moved to or from a position near an optically transparent portion of a blunt, enclosed distal end of a shaft to provide unobstructed viewing through the distal end, and a position to the proximal side of an enclosed working area to provide viewing of the enclosed working area. A surgical instrument also or alternatively has a fluid routing switch within a shaft which can selectively connect a fluid infusion channel to at least one fluid export pore or a return channel. A method involves moving a viewing instrument to or from a position near an optically transparent portion of a blunt, enclosed distal shaft end and a proximal side of an enclosed working area. A method also or alternatively involves changing a position of a fluid routing switch within the shaft.
Owner:LARSEN DANE M
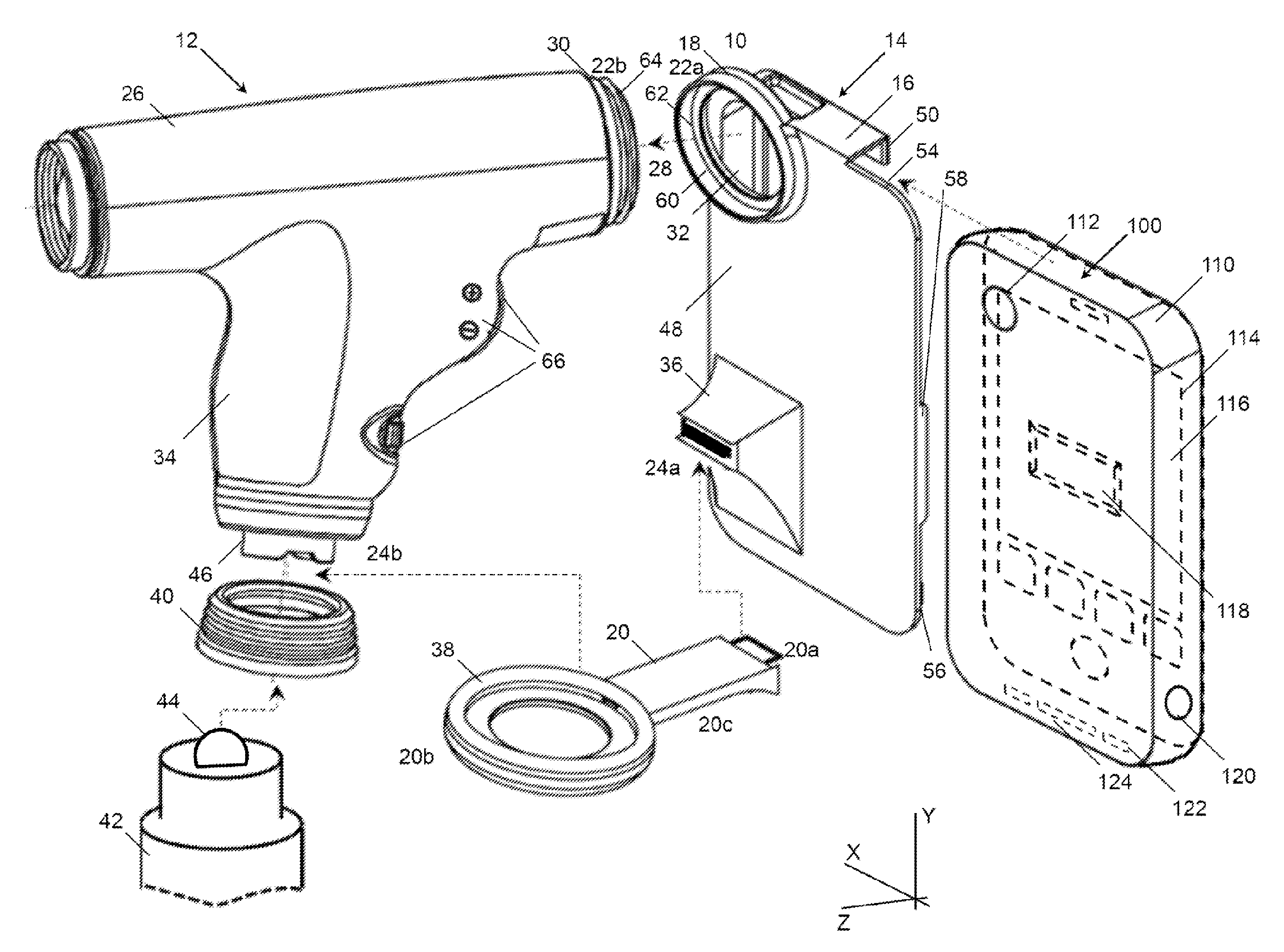
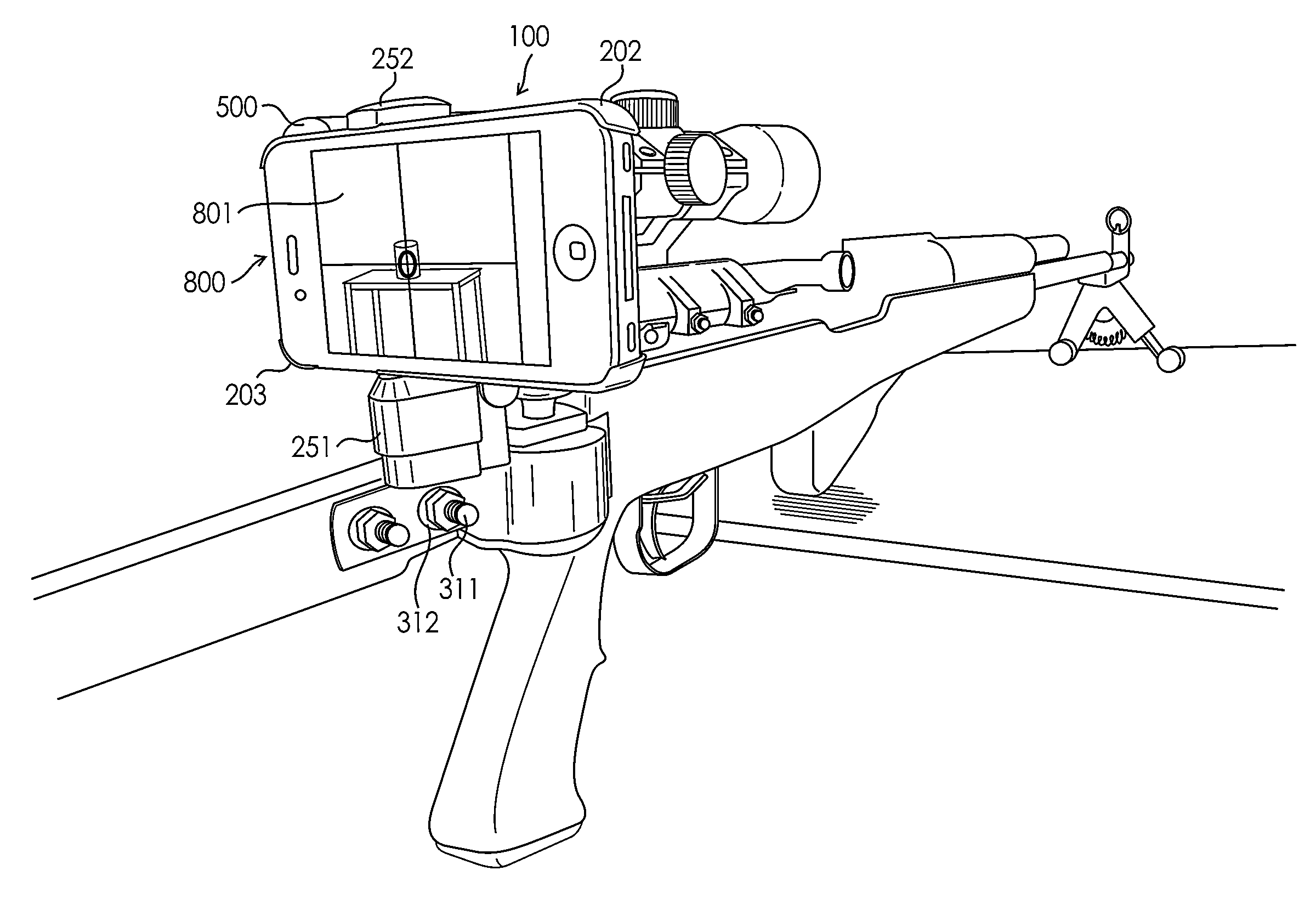
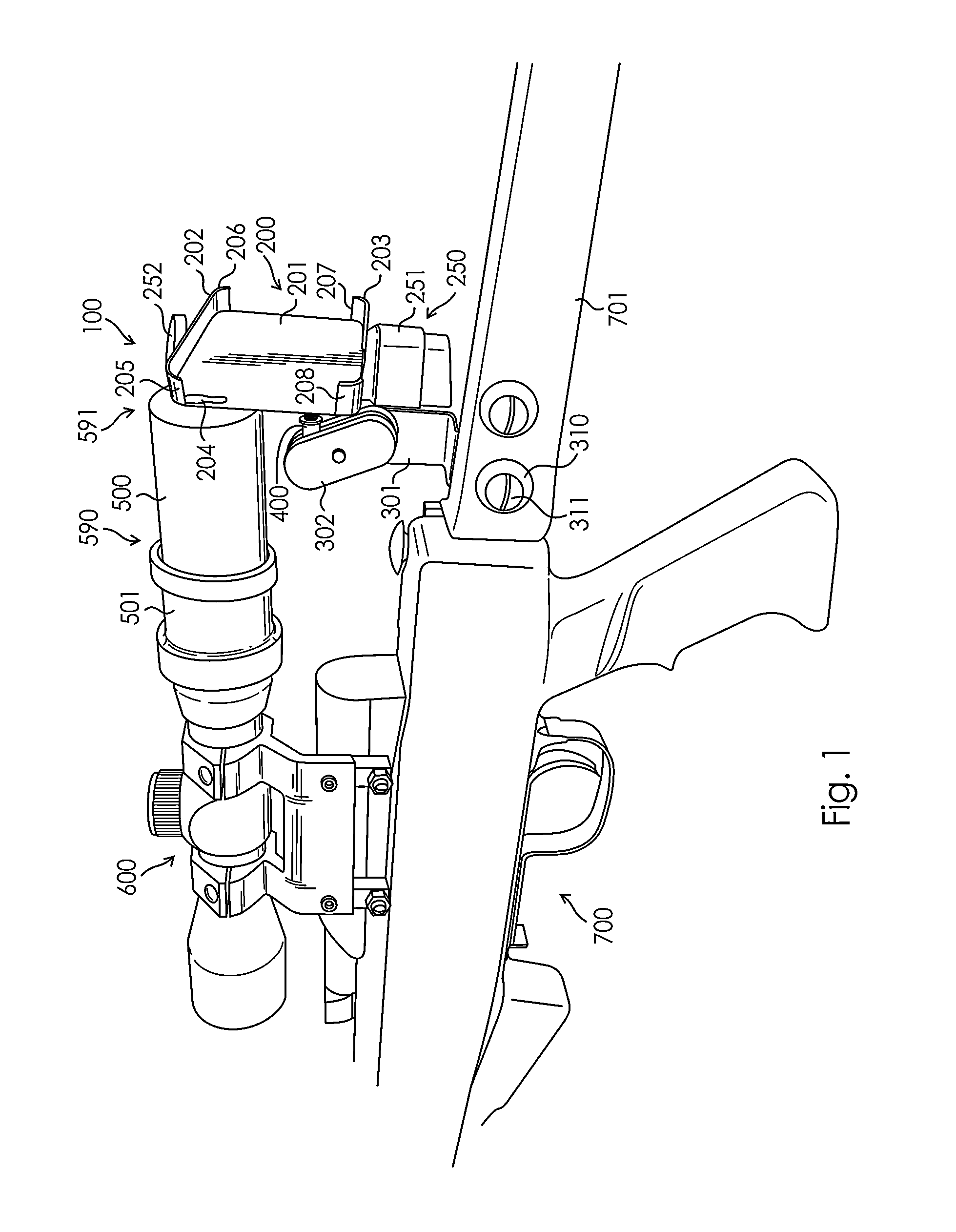
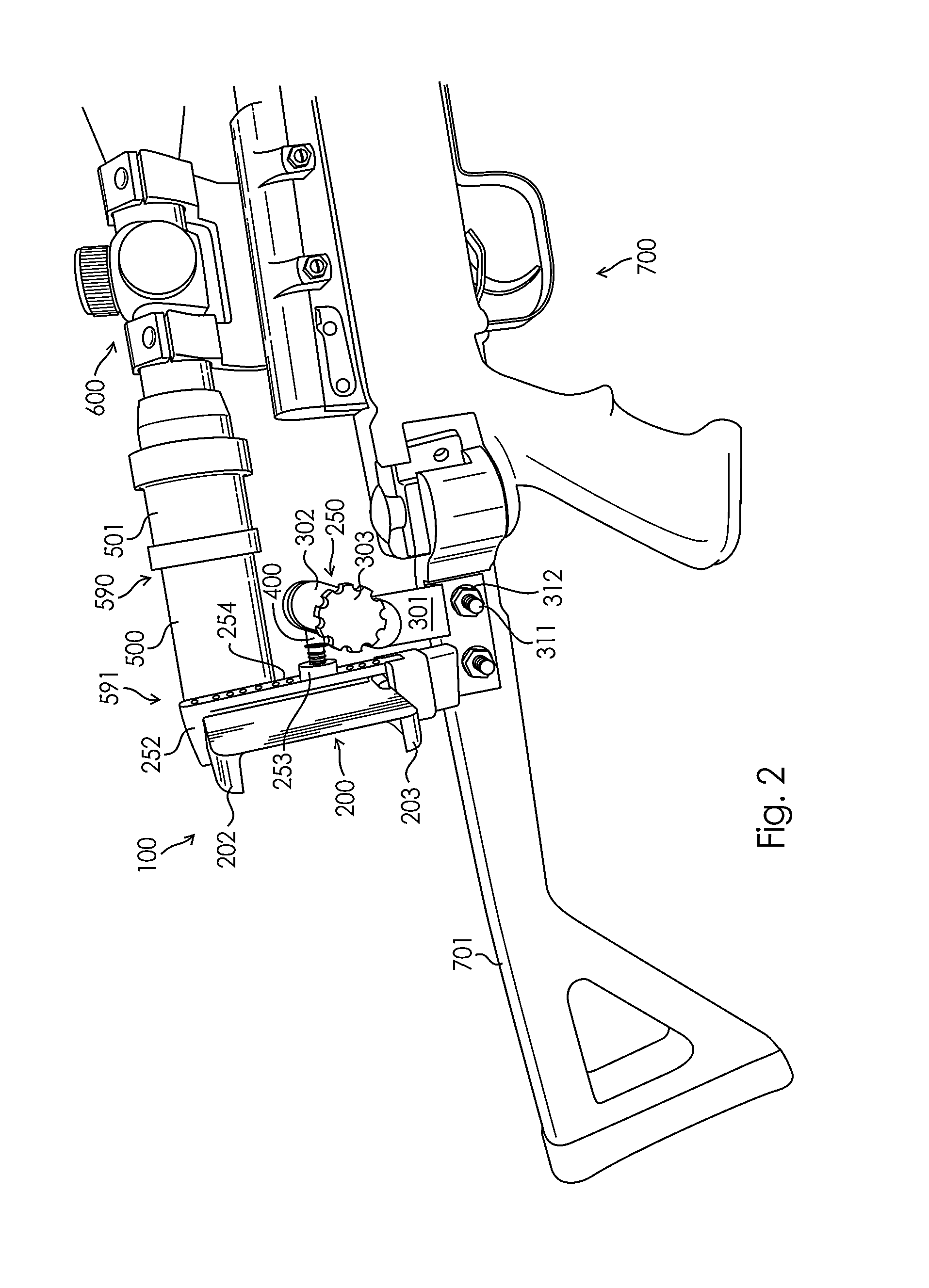
Camera Mount Apparatus and System for a Scope
This disclosure relates to an apparatus for mounting a camera onto a firearm and an associated device for capturing images and recordings of a firearm target. The apparatus allows for easy attachment of cameras of varying sizes onto the scope of a firearm and along the same longitudinal axis of the scope. The apparatus comprises a sleeve connected to a scope of a firearm, the sleeve being hallow and having a longitudinal axis longitudinal axis forming an unobstructed axial bore and generally coaxial with a longitudinal axis of the scope; a base member with a hole and adapted to receive a camera with the hole of the base member positioned adjacent to the lens of the camera and the longitudinal axis of the camera lens is generally coaxial with the longitudinal axis of the scope.
Owner:ISCOPE OPTICS LLC
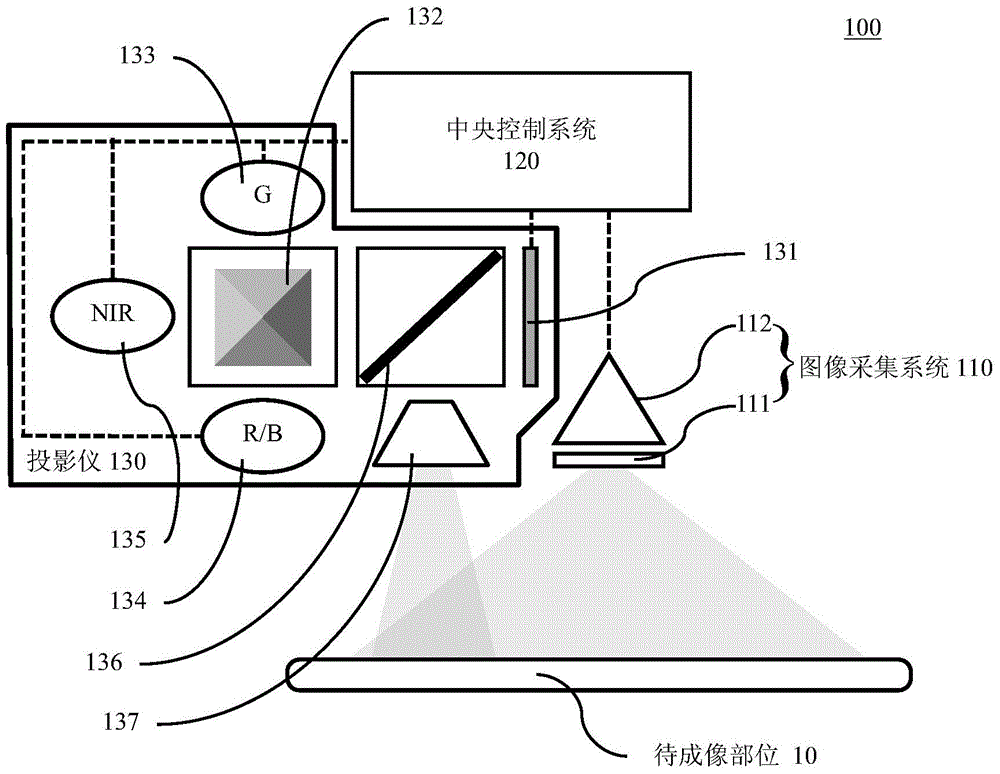
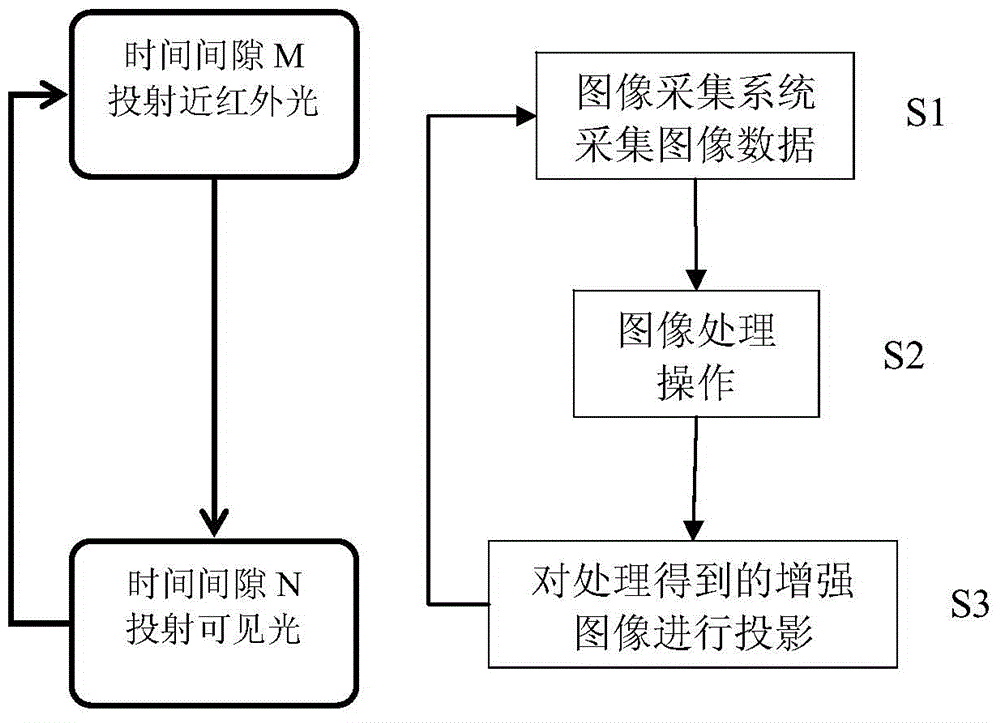
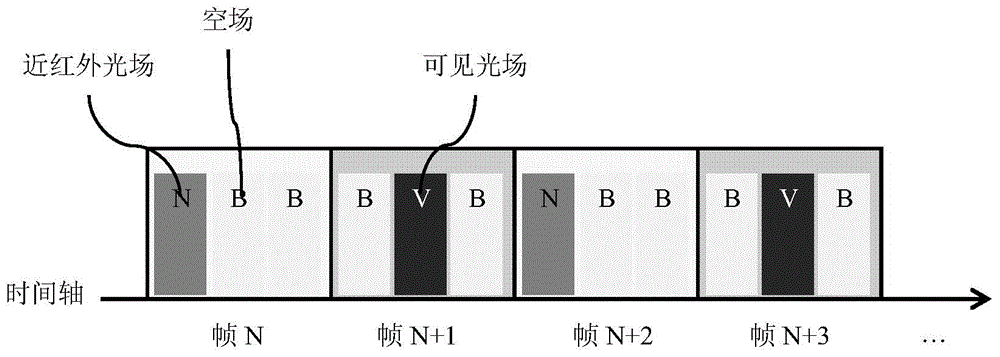
Vein viewing instrument and imaging method thereof
InactiveCN104146683AReduce volumeGood consistency of illuminationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsVeinIlluminance
The invention relates to a vein viewing instrument and an imaging method of the vein viewing instrument. The vein viewing instrument comprises an image collection system, a central control system and a projector. The image collection system and the projector are respectively electrically connected with the central control system. According to the vein viewing instrument, based on the time division multiplexing principle, a near infrared source is arranged in the projector, and the projector has both the light source function and the projection function, so that the size of the vein viewing instrument is reduced; light homogenizing systems such as a color splitting prism are further arranged in the projector, so that illuminance uniformity of projected near infrared light is good, the projected near infrared light can not exceed a preset projection light range, the use rate is improved, disturbance of the environment caused by leaking light is reduced, and power consumption is reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Illumination system for variable direction of view instruments
A illumination system for variable direction of view instruments is disclosed generally comprising an endoscope having a longitudinal axis and a variable view vector that pivots about a pivot axis angularly offset from the longitudinal axis. The view vector has an attendant viewing field that travels along a path as the view vector pivots, defining a viewing range. A source of illumination is arranged in a plane offset from the plane in which the view vector pivots and provides an annular, solid angle of illumination that covers the viewing range. In certain embodiments, the pivot axis is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis and the illumination plane is parallel to the pivot plane. In some embodiments, the source of illumination is a plurality of light emitting diodes arranged around the pivot axis.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
Illumination system for variable direction of view instruments
A illumination system for variable direction of view instruments is disclosed generally comprising an endoscope having a longitudinal axis and a variable view vector that pivots about a pivot axis angularly offset from the longitudinal axis. The view vector has an attendant viewing field that travels along a path as the view vector pivots, defining a viewing range. A source of illumination is arranged in a plane offset from the plane in which the view vector pivots and provides an annular, solid angle of illumination that covers the viewing range. In certain embodiments, the pivot axis is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis and the illumination plane is parallel to the pivot plane. In some embodiments, the source of illumination is a plurality of light emitting diodes arranged around the pivot axis.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
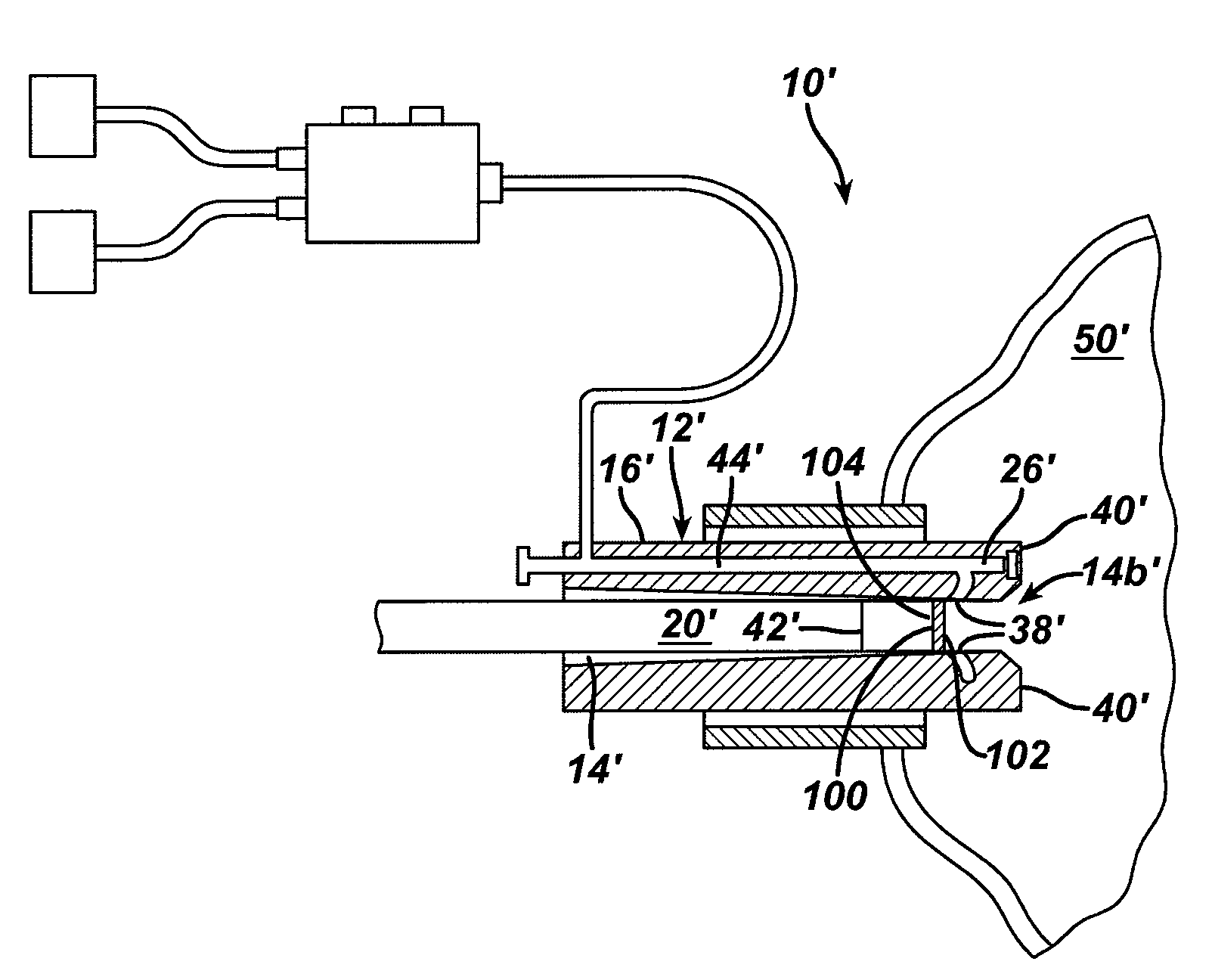
Heater for surgical viewing instruments
ActiveUS7537563B2Minimized foggingConvenient user accessExothermal chemical reaction heat productionOther heat production devicesCircular discSodium acetate
A system and associated method is used for warming an endoscope, laparoscope, or other such instrument to minimize fogging. The preferred embodiment comprises a pad for wrapping around an instrument, including a one or more substances operative to generate heat through an exothermic reaction; and an activation disc located around the periphery of the pad to provide for convenient user access. In the preferred embodiment, the activator is a mixture of water and sodium acetate, and the disc is made of perforated stainless steel. A housing contains the pad in sleeve form and an optional heat-conductive tube to receive the instrument around which the pad is wrapped. The pad may be partitioned.
Owner:JOSNOE MEDICAL INC
Optical system for variable direction of view instrument
ActiveUS7221522B2Large scanning range and field of viewIncrease the diameterPrismsEndoscopesViewing instrumentOptic system
A optical system for a viewing instrument with a variable direction of view is disclosed generally comprising shaft, first and second reflectors located at the distal end of the shaft, where the first reflector rotates about an axis angularly offset from the longitudinal axis of the shaft, and an entrance pupil positioned in the optical path created by the reflectors and preceding the reflecting surface of the second reflector. In certain embodiments, the entrance pupil comprises an aperture stop positioned between the first and second reflectors. In some embodiments, the system includes negative and positive lenses located adjacent the entrance and exit faces of the first reflector.
Owner:KARL STORZ IMAGING INC
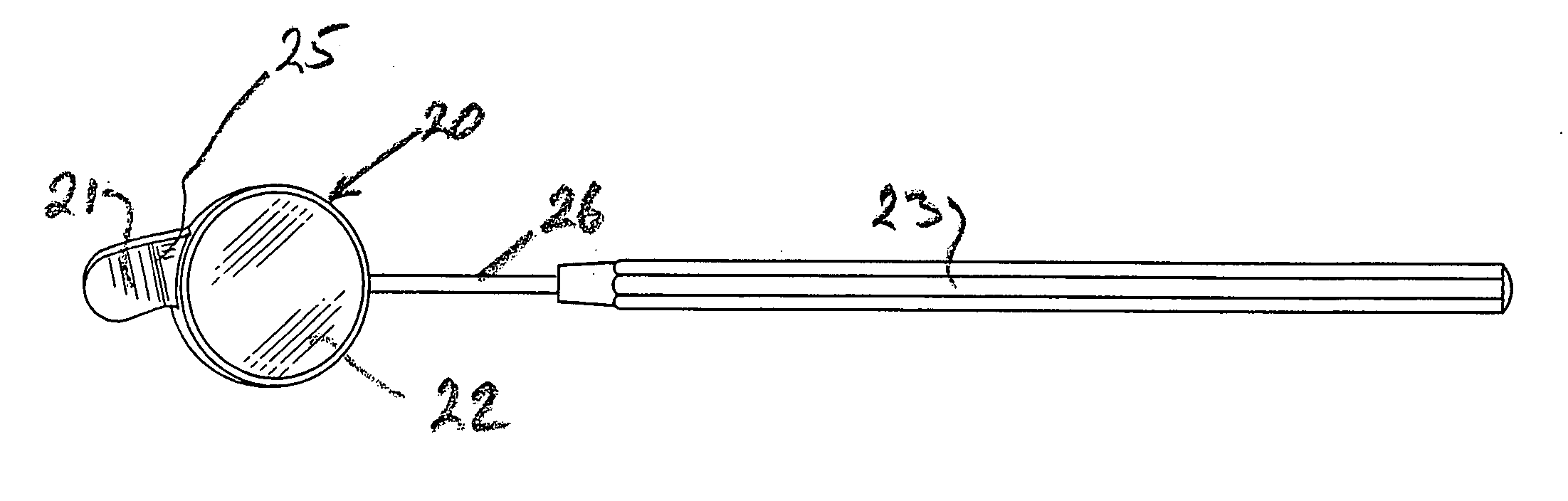
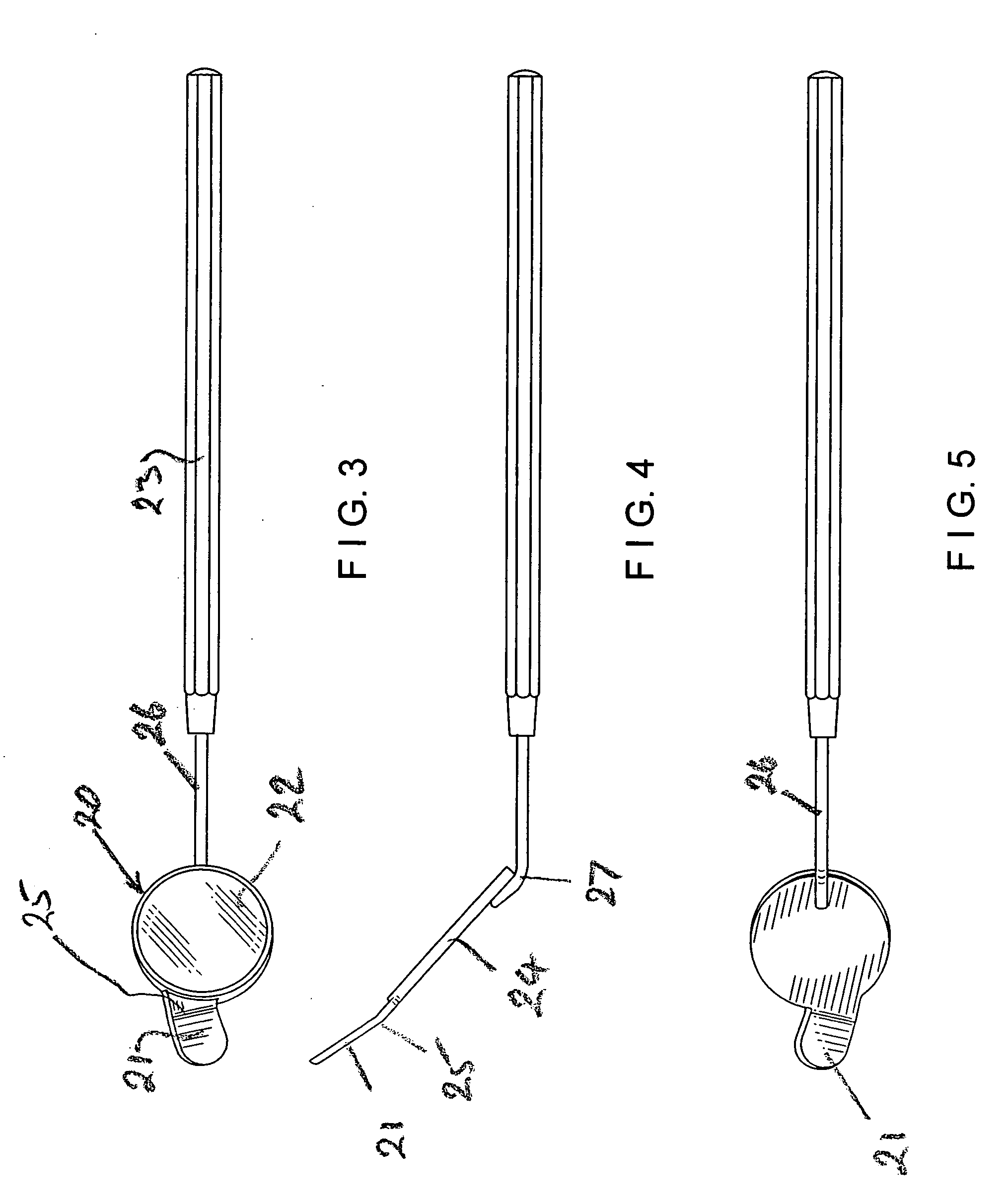
Viewing instrument
A viewing instrument, particularly for use in dentistry, in which a finger or like element is attachable to or integral with a mirror to hold material out of the sight-line when viewing the mirror. In the case of a dental implement, the element is a retractor attached or attachable to a dentists inspection mirror.
Owner:COLETON STUART
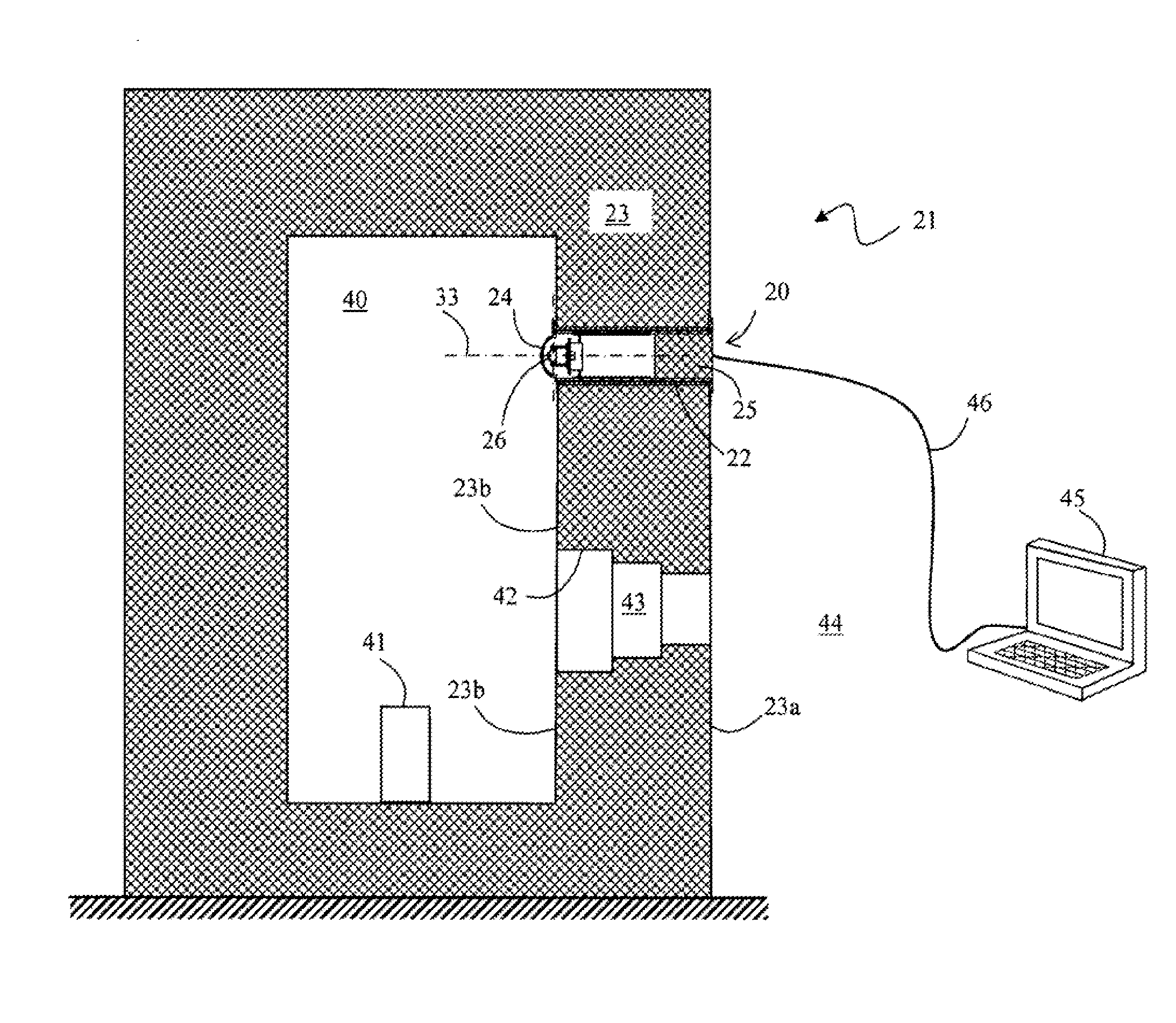
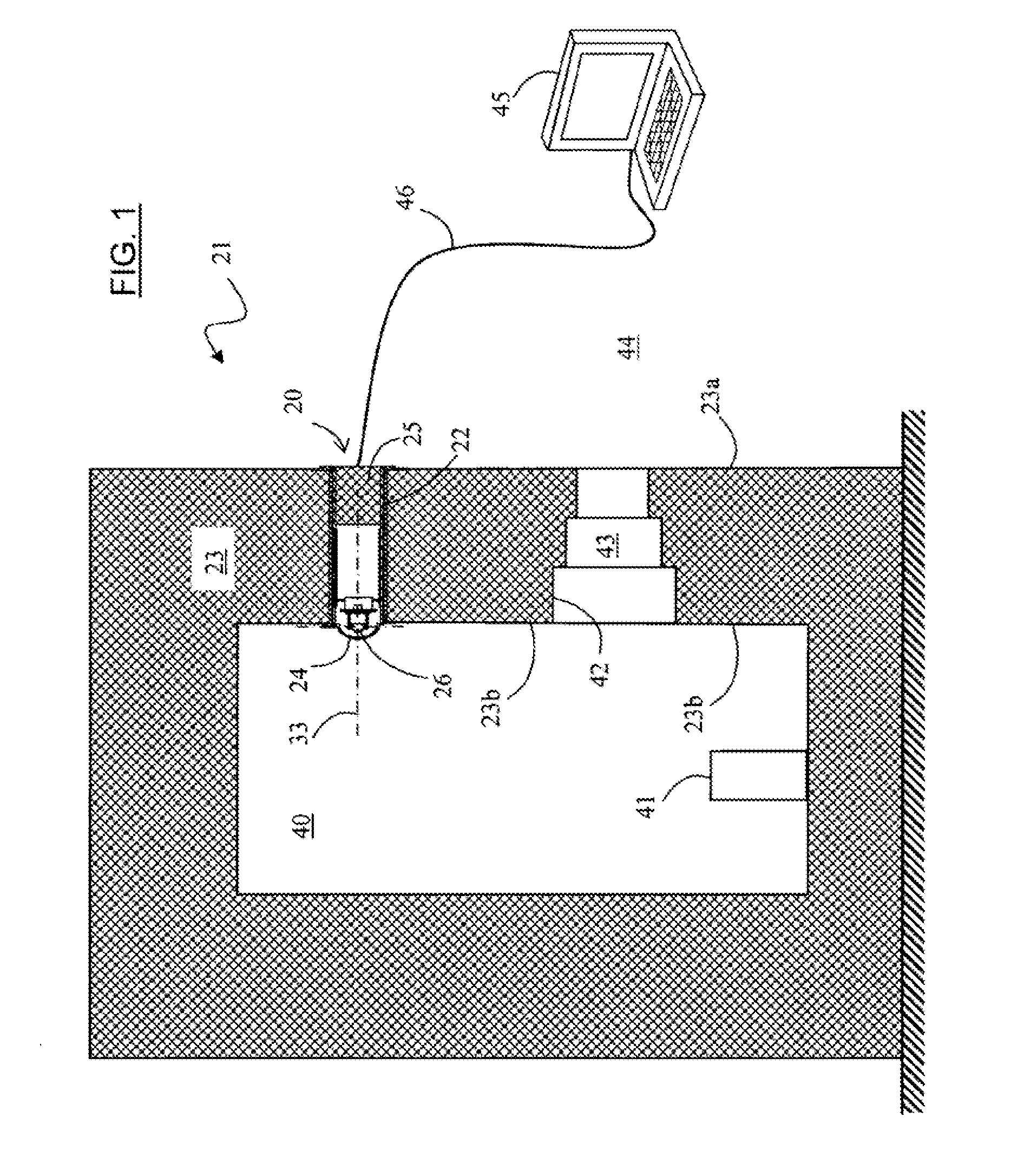
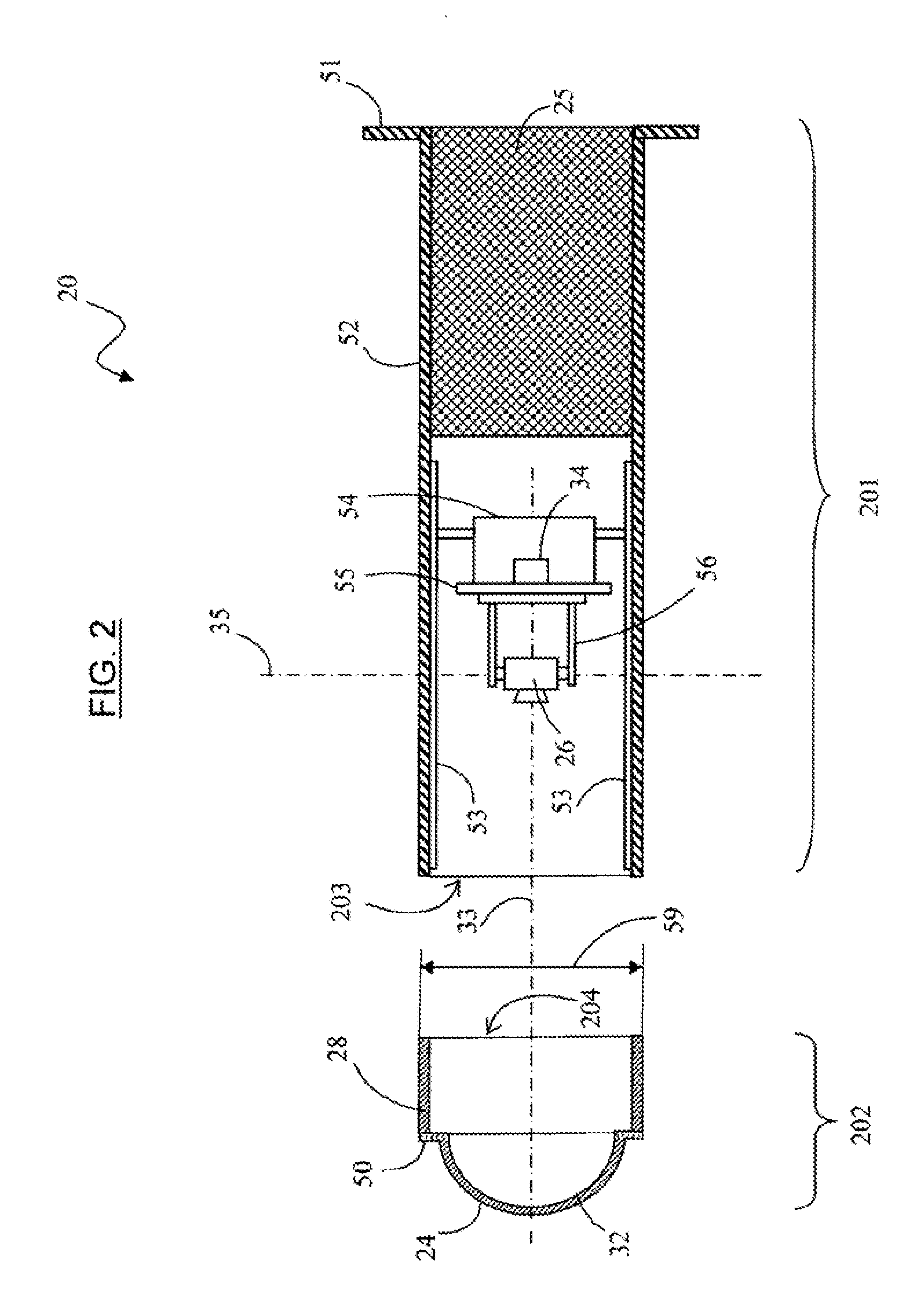
Device for observing the inside of a hot cell, hot cell provided with said device, and method for maintaining said device
ActiveUS20120113245A1Reduce manufacturing costExtended service lifePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansViewing instrumentHot cell
The invention provides a method of maintaining a cell including a wall pierced by a cavity fitted with a monitoring or observation instrument, the instrument comprising a dome projecting into the inside of the cell, a protection shield, an observation sensor arranged between the dome and the shield, and a travel mechanism for moving the sensor between a position retracted inside the cavity and a deployed position. The method comprises the following operations:extracting the protection shield, the observation sensor, and the sensor travel mechanism out from the cavity, to the outside of the cell;where appropriate, replacing the observation sensor;inserting a replacement dome into the cavity and sliding it into the proximity of the dome that has remained in position in the cavity;inserting the protection shield, the observation sensor and the sensor travel mechanism into the cavity and sliding them into contact with the replacement dome; andmoving the dome that has remained in position in the cavity until it is expelled into the inside of the cell, by pressing the replacement dome against the dome that has remained in position.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Observation apparatus
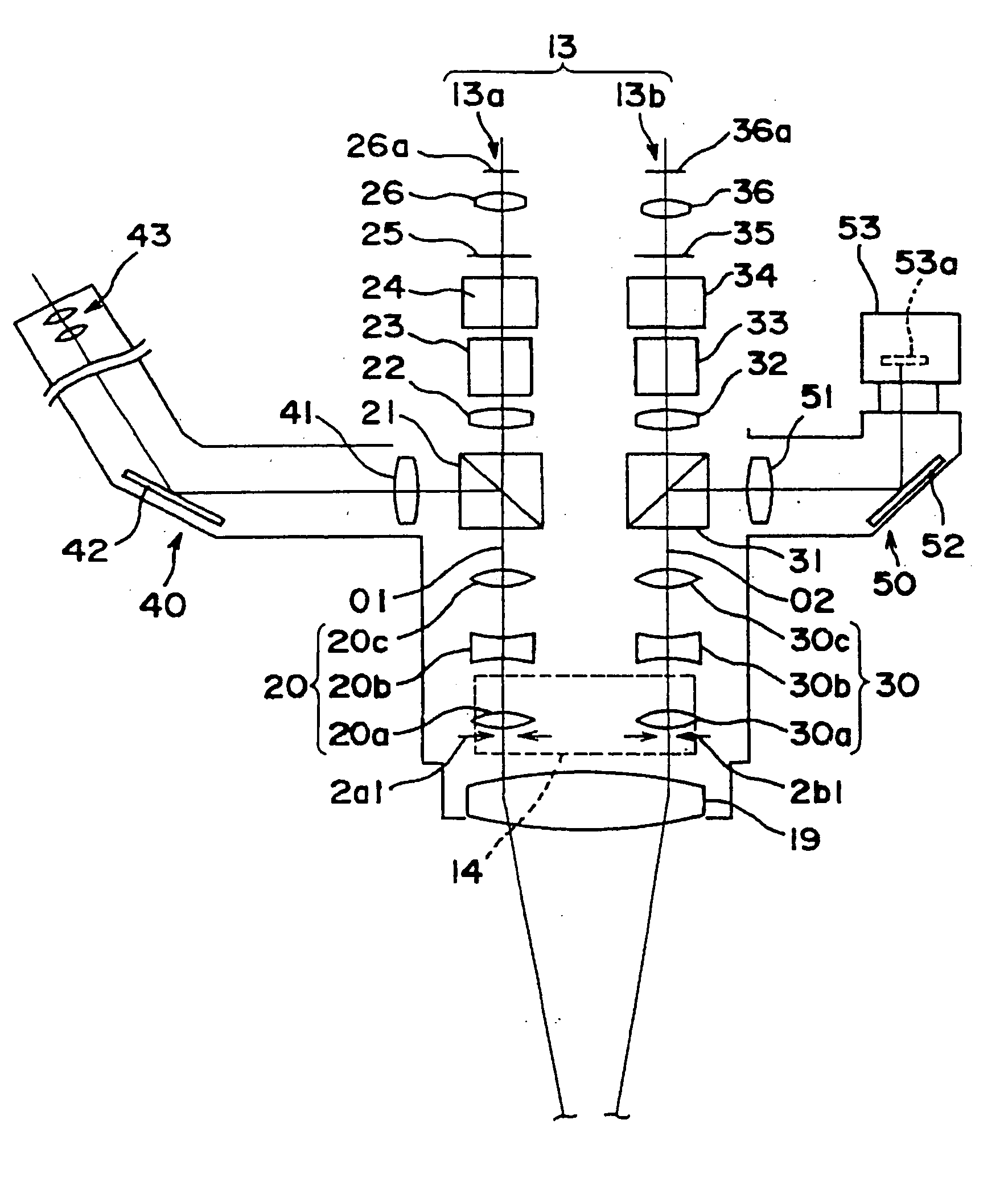
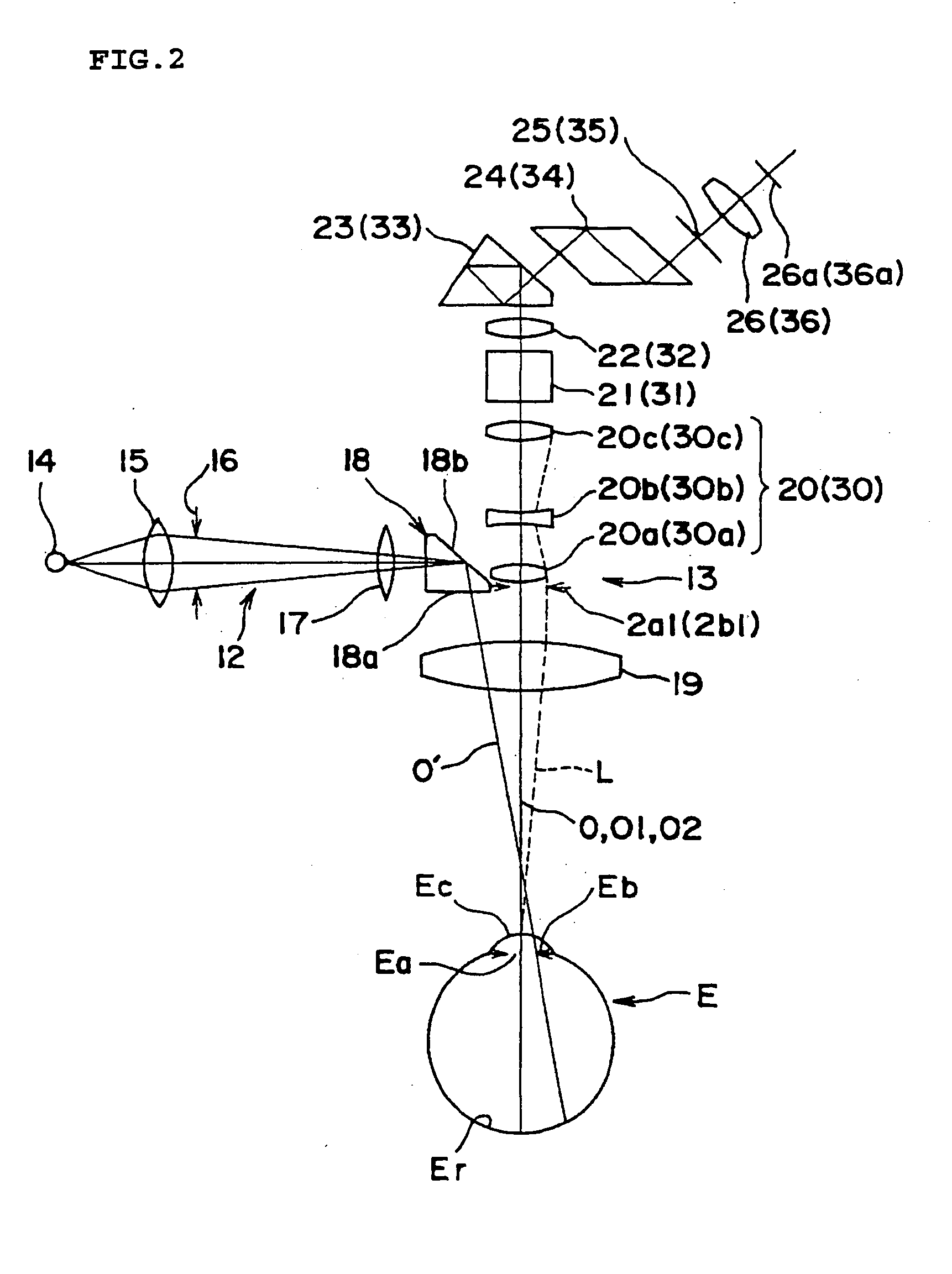
InactiveUS20050018134A1Eliminate astigmatismEliminate chromatic aberrationSurgeryMicroscopesAxis–angle representationViewing instrument
An observation apparatus capable of preferably removing an astigmatism and chromatic aberration which occur in an observation image is provided. An apex angle of a contact prism is inputted by operating an apex angle setting knob of a control panel. A fitting angle of the contact prism is inputted by operating a fitting angle setting knob. A control unit determines the amount of correction for astigmatism of a left observation optical system and the amount of correction for astigmatism of a right observation optical system based on a recognized observation magnification and the inputted apex angle. An axial angle for the astigmatism of the left observation optical system and an axial angle for the astigmatism of the right observation optical system are determined based on the inputted fitting angle. Variable cross cylinder lens rotating drive units are controlled to rotate cylinder lenses of each of the right and left observation optical systems, thereby obtaining the determined axial angle and the determined amount of correction.
Owner:KK TOPCON
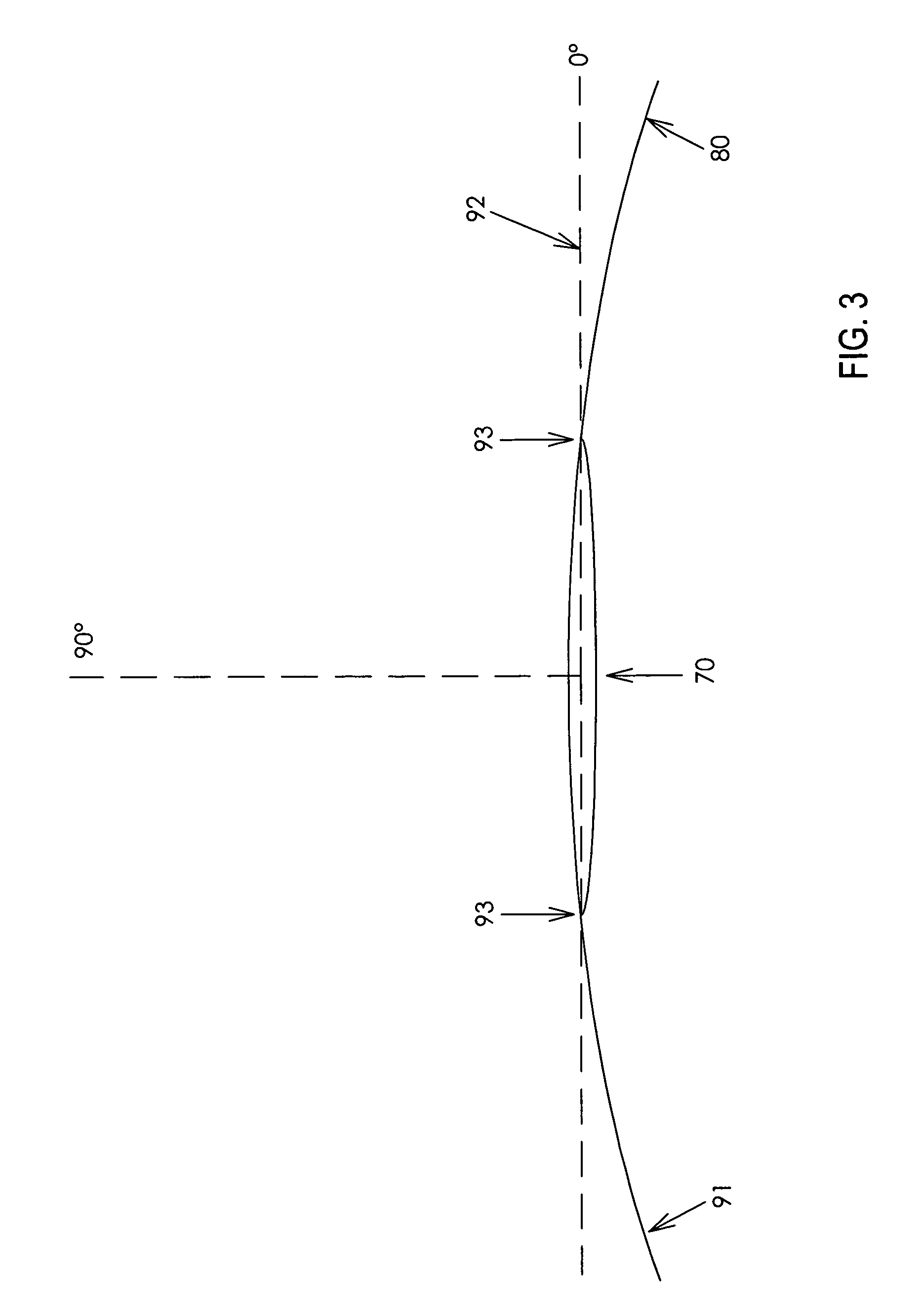
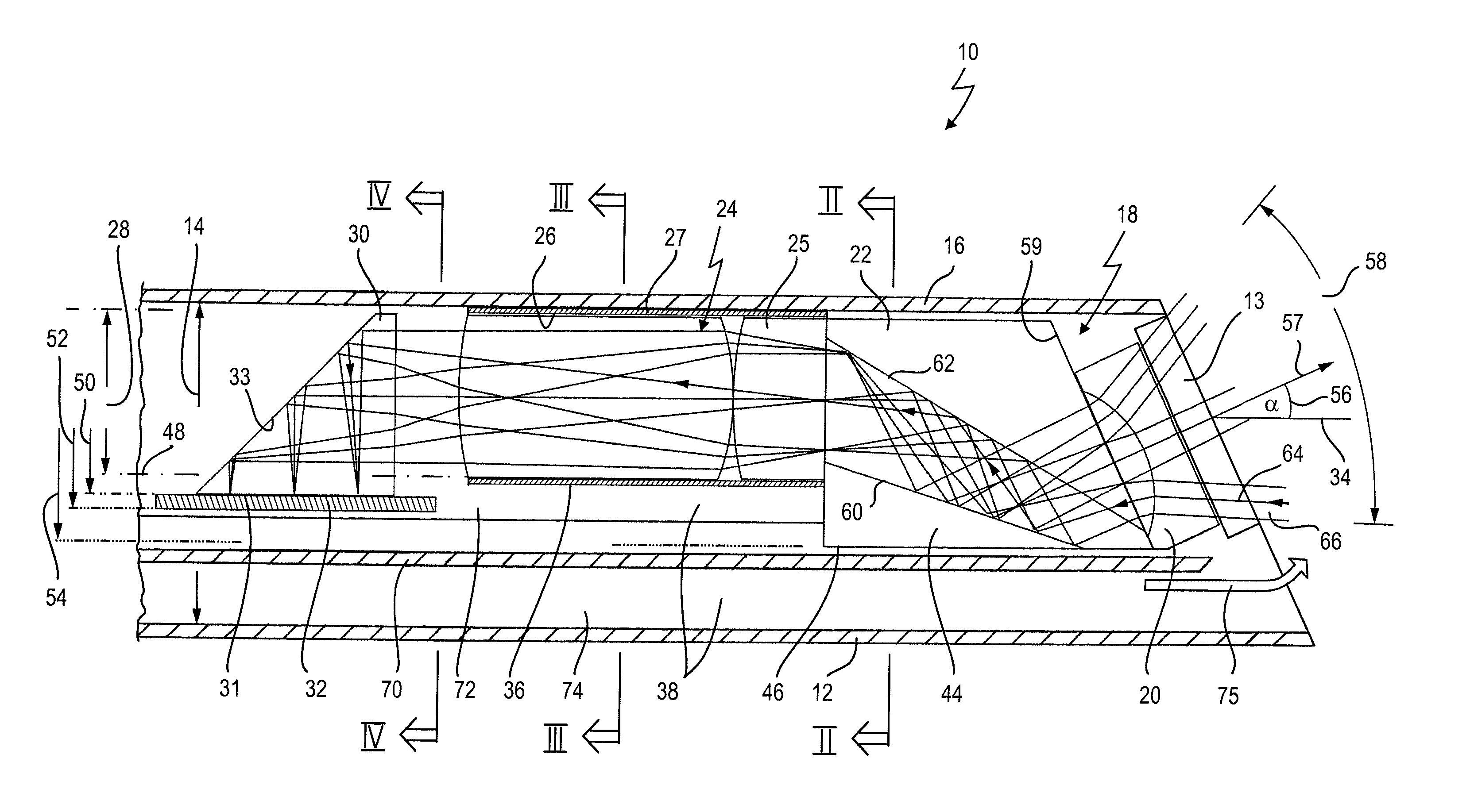
Observation Instrument Comprising A High-Resolution Image Recorder
ActiveUS20140135577A1Improve overall utilizationConvenient ArrangementPrismsSurgeryViewing instrumentMedicine
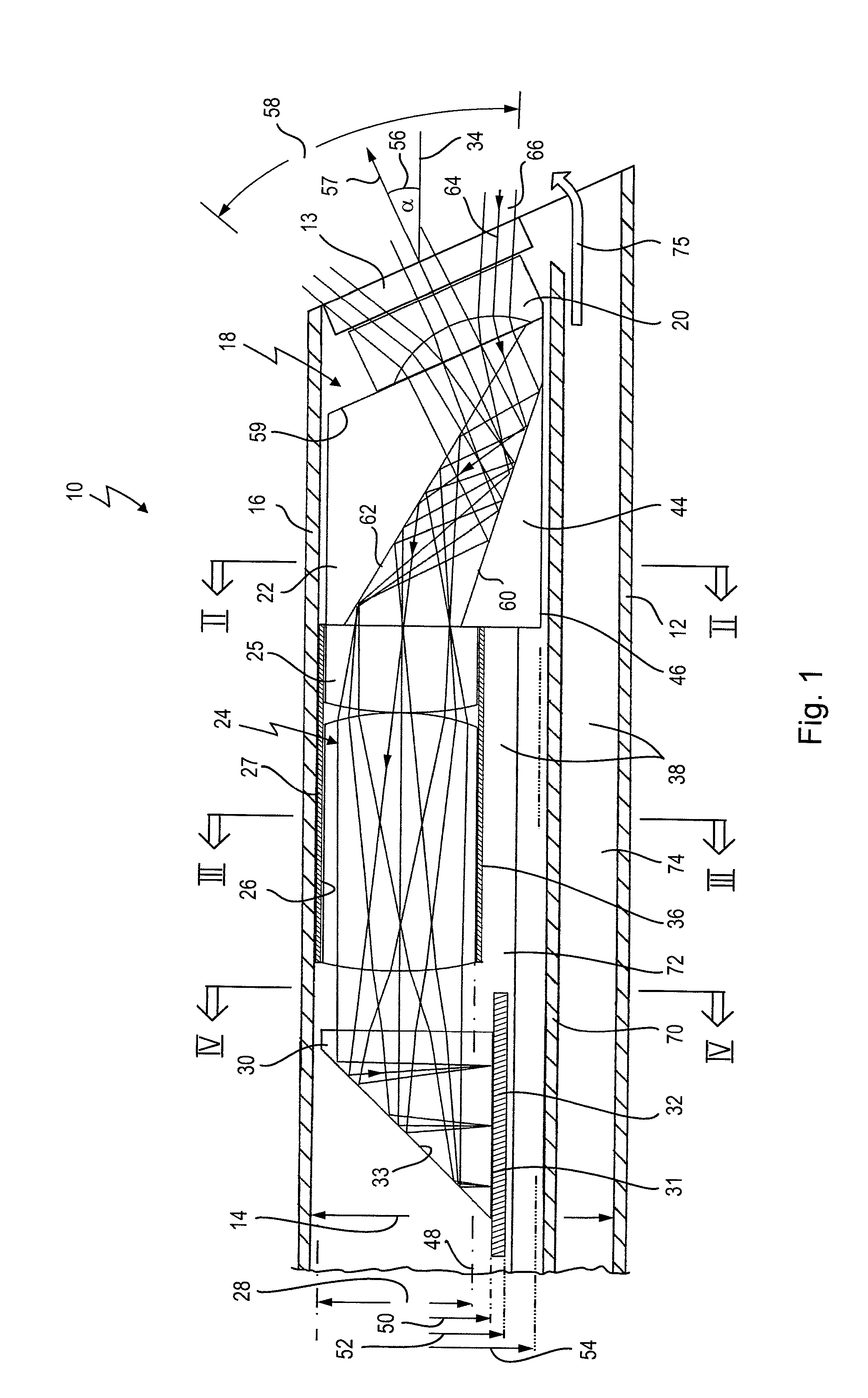
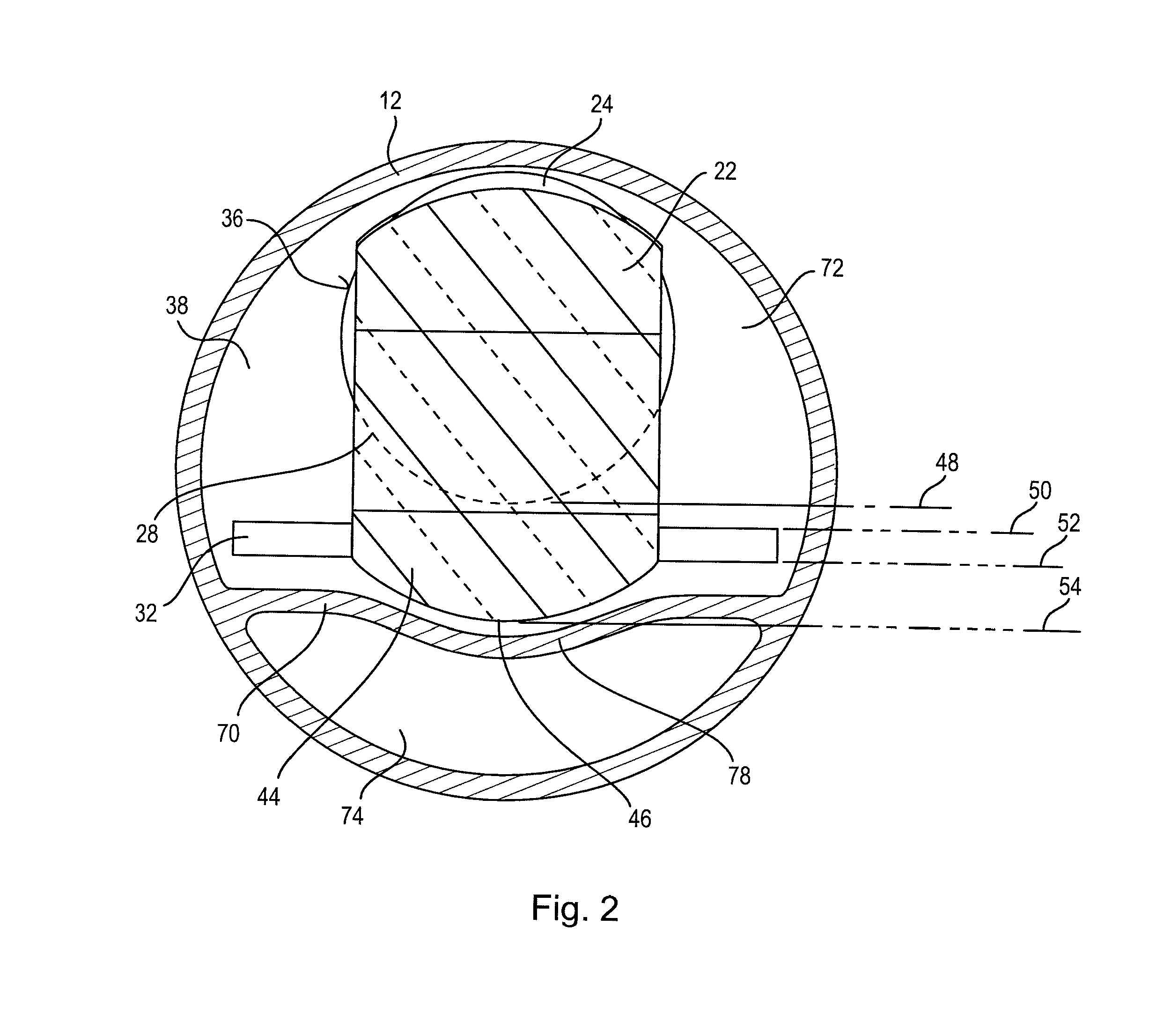
An instrument includes a hollow body with an internal diameter and an optoelectronic image recording system, which is arranged in an end region of the body and has a lens system on an image entrance side. The lens system has a cylindrical section and an image sensor. An external diameter of the cylindrical section is less than the internal diameter of the body, such that an interspace remains between an inner side of the body and an outer side of the lens system, providing access in the body for components. With a viewing direction of 0° to 90° from the optical axis of the lens system, a deflection prism is arranged on the image entrance side at the lens system, and has a section extending laterally beyond the external diameter of the cylindrical section. An image entrance plane of the image sensor runs approximately parallel to the optical axis.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com