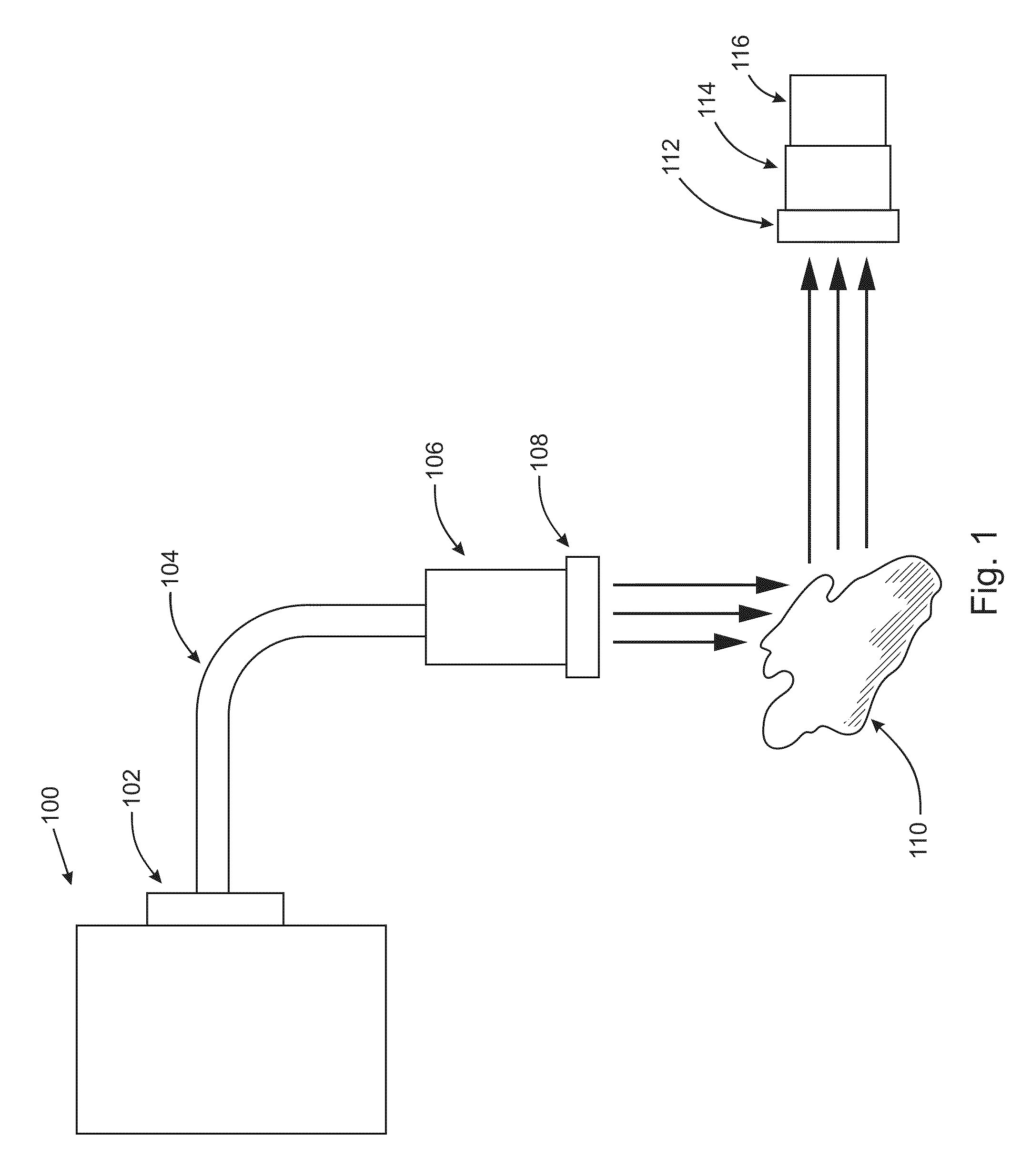
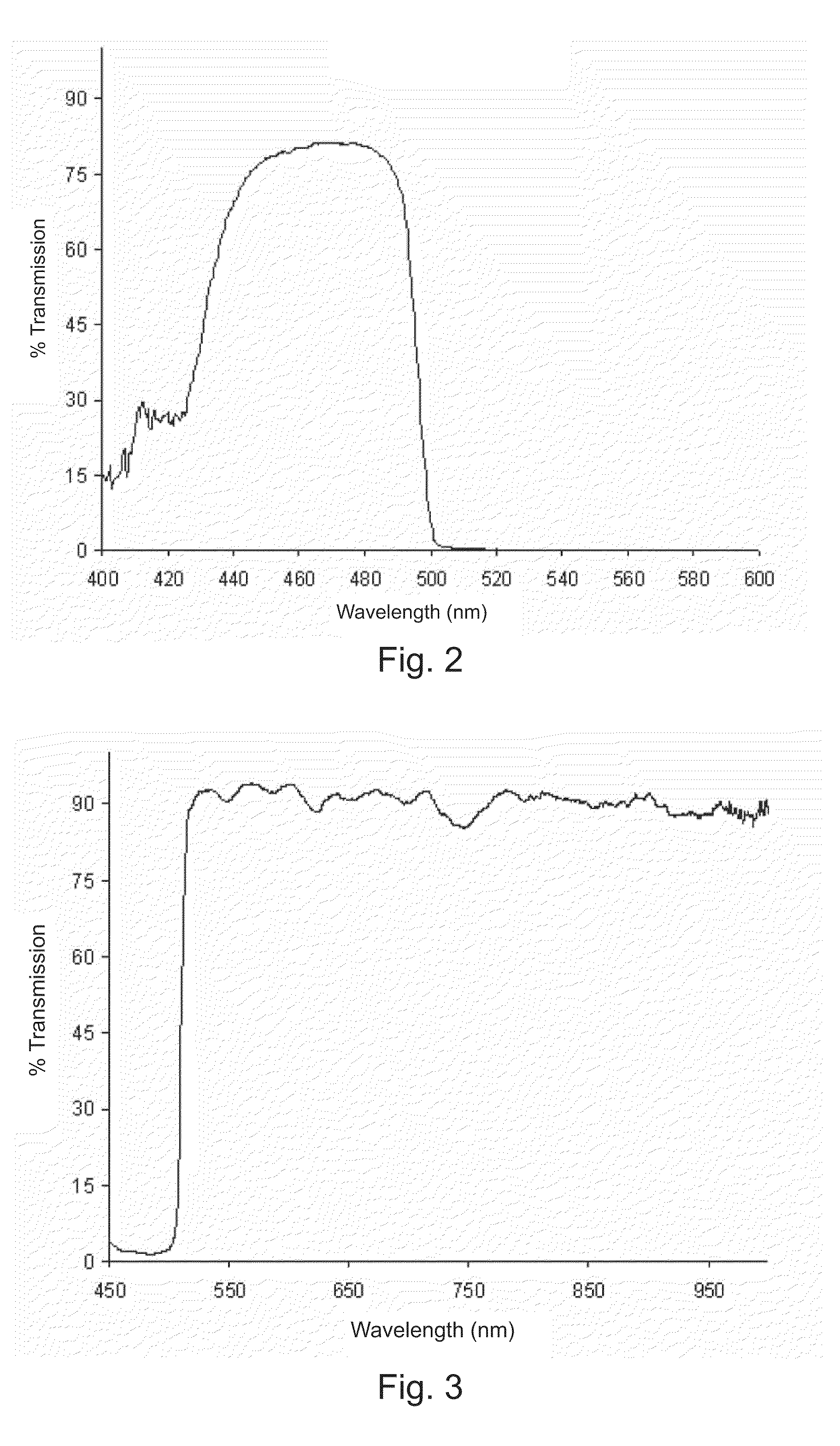
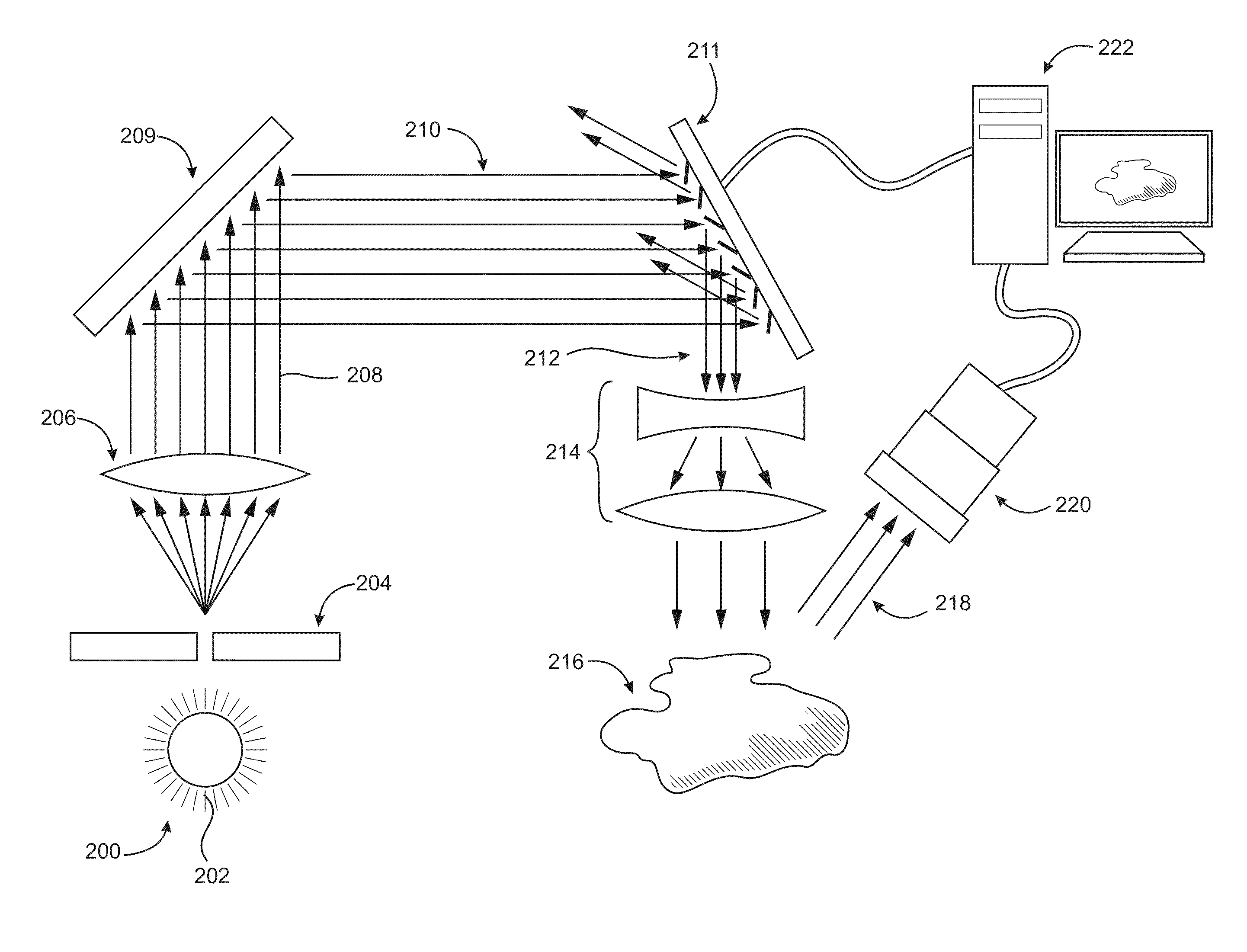
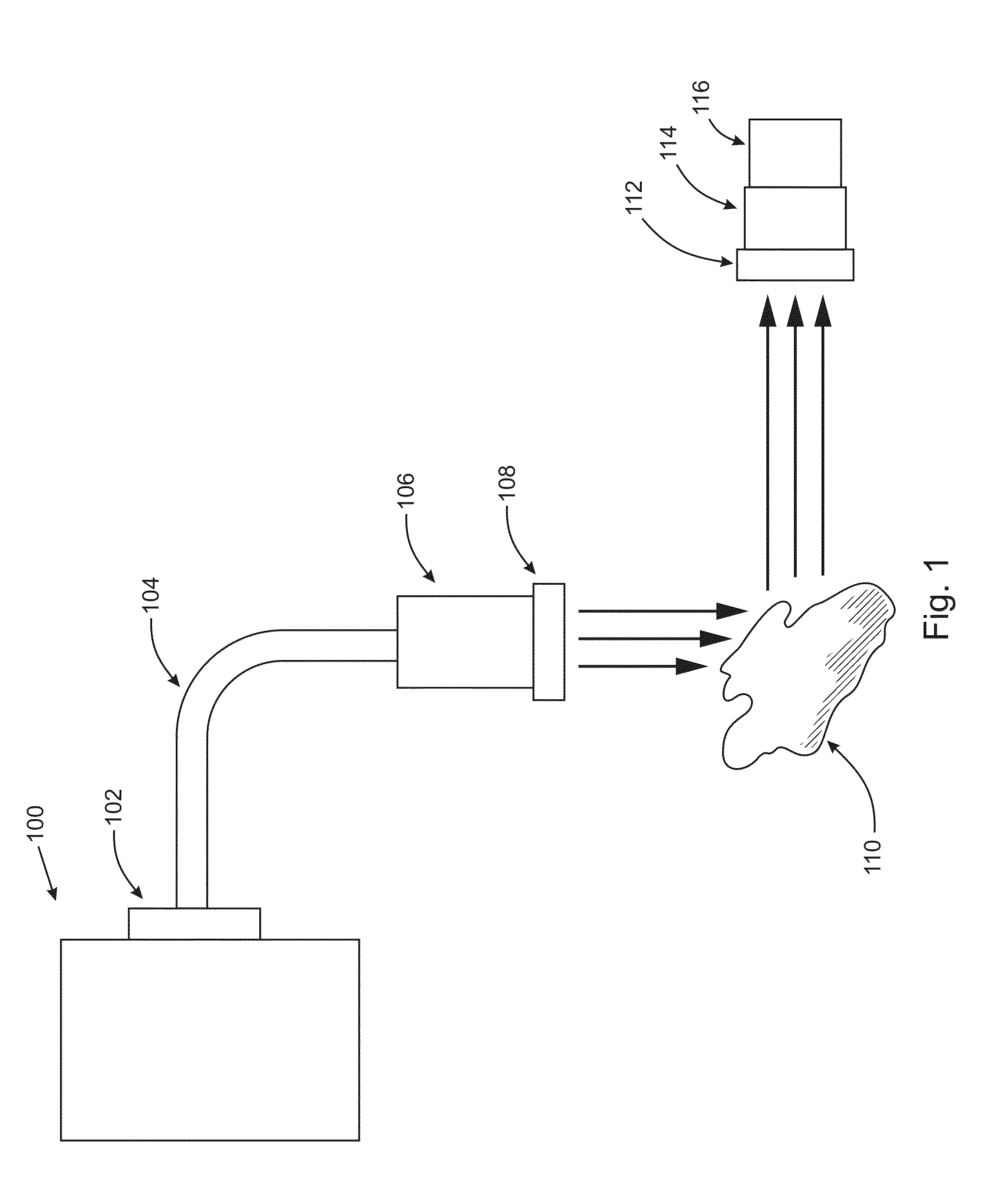
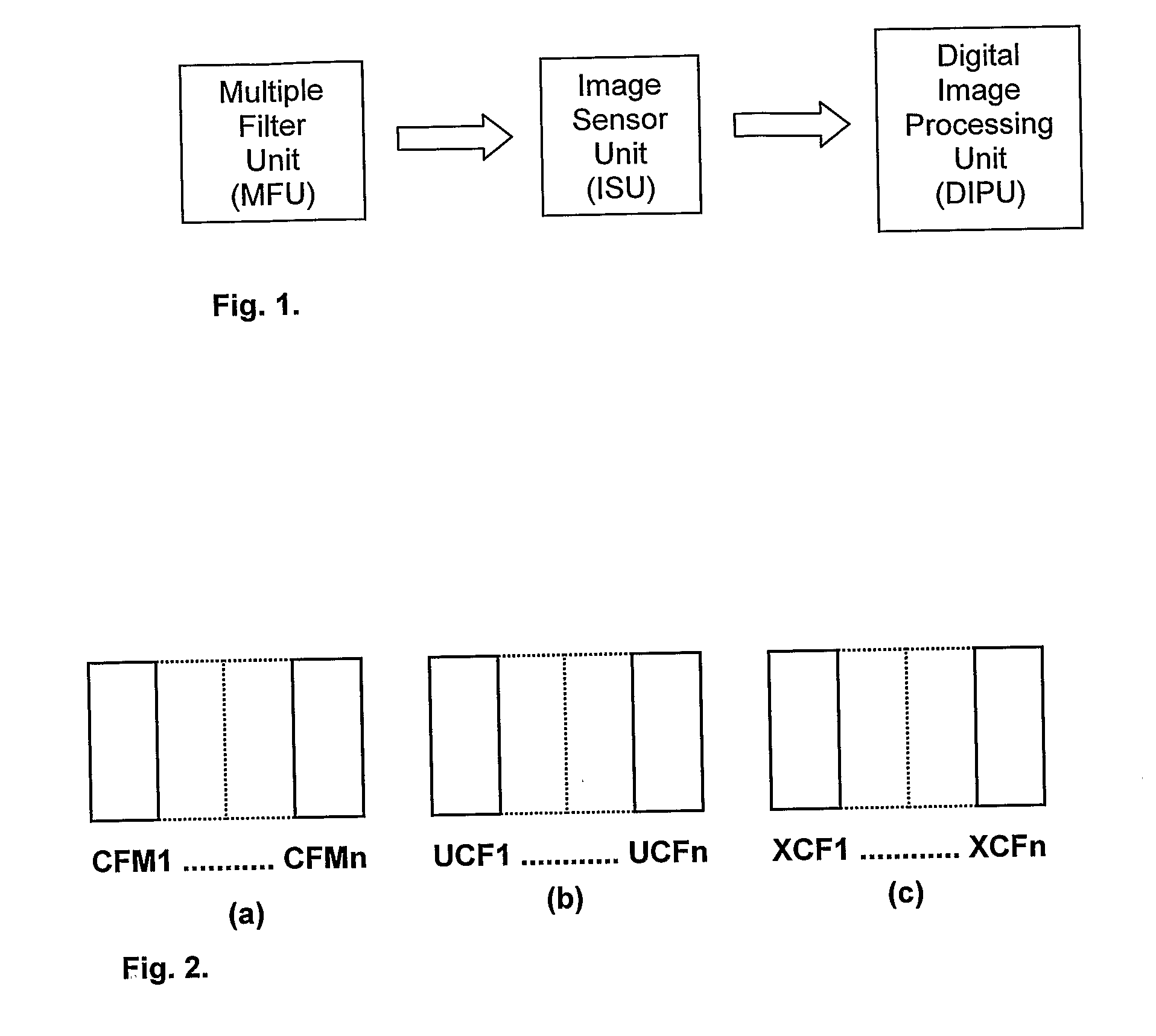
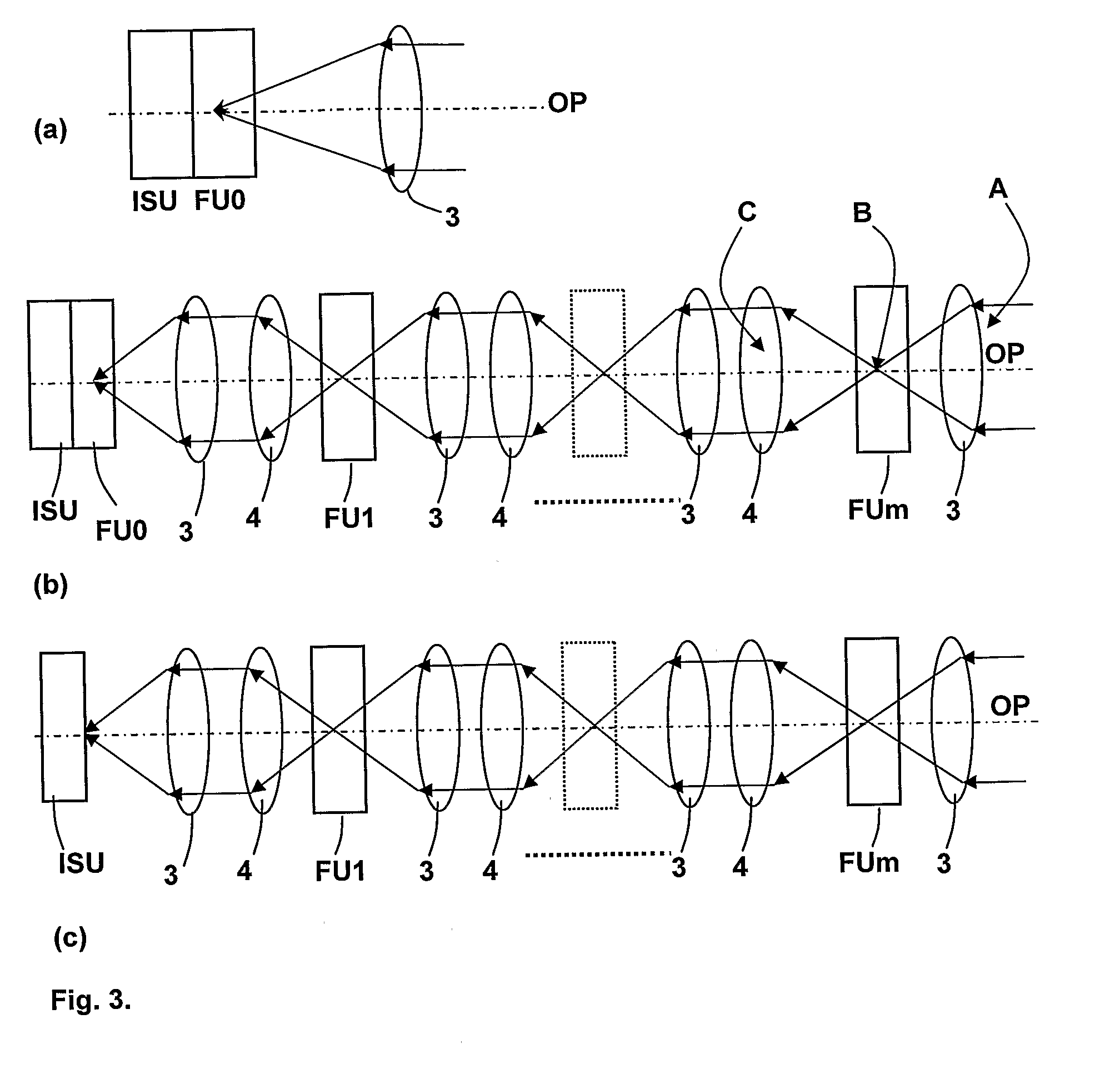
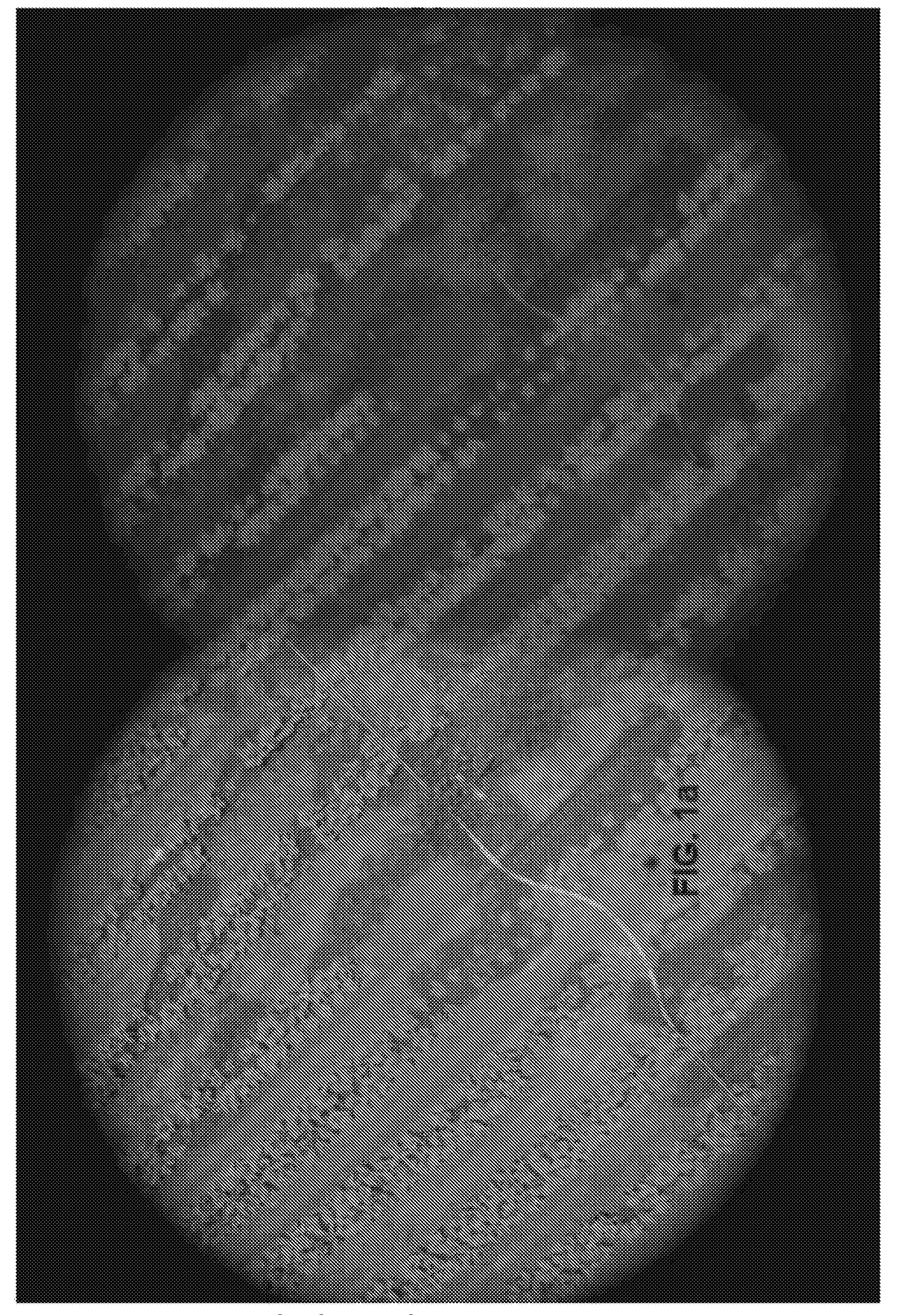
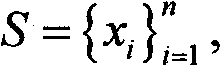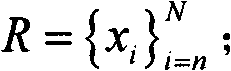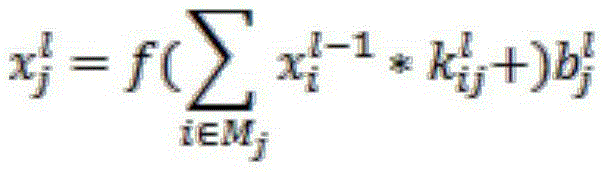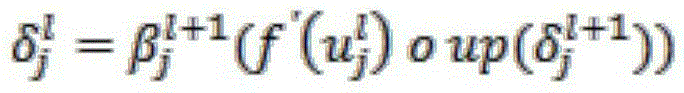Patents
Literature
3616 results about "Spectral image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spectral Image. Spectral Image is a privately held, early stage medical device company focused on the development of imaging technology for biomedical use.
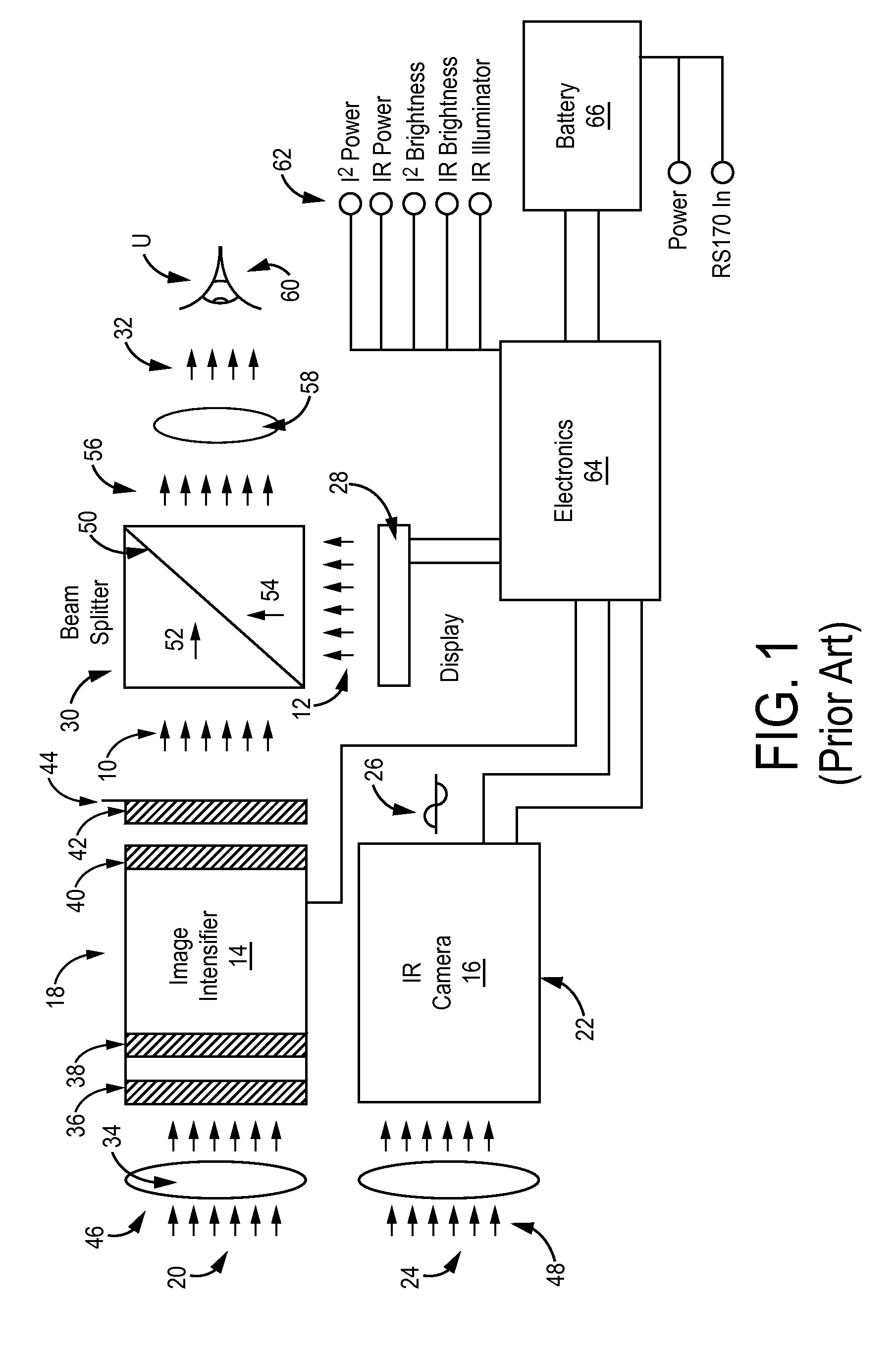
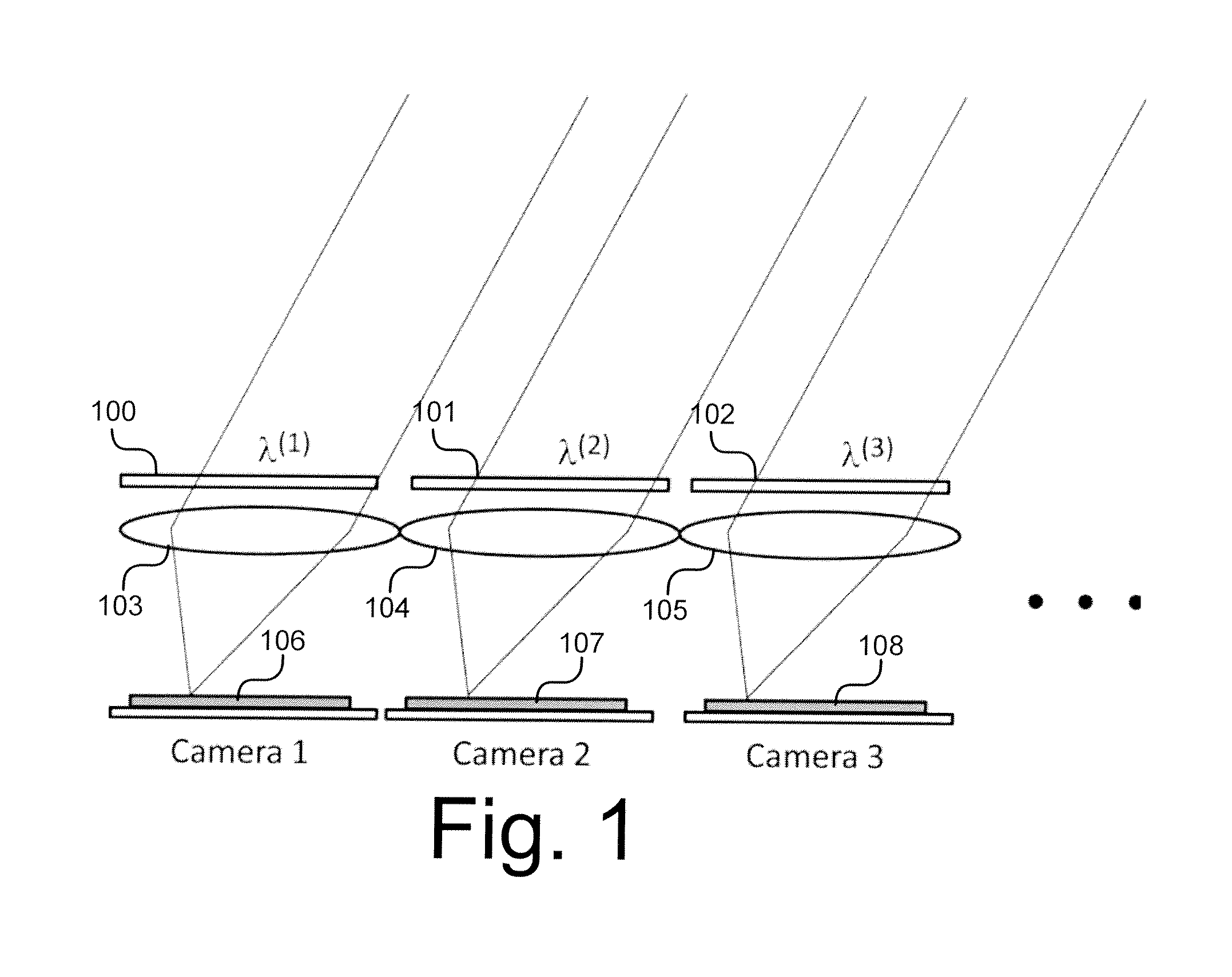
Scanning endoscope
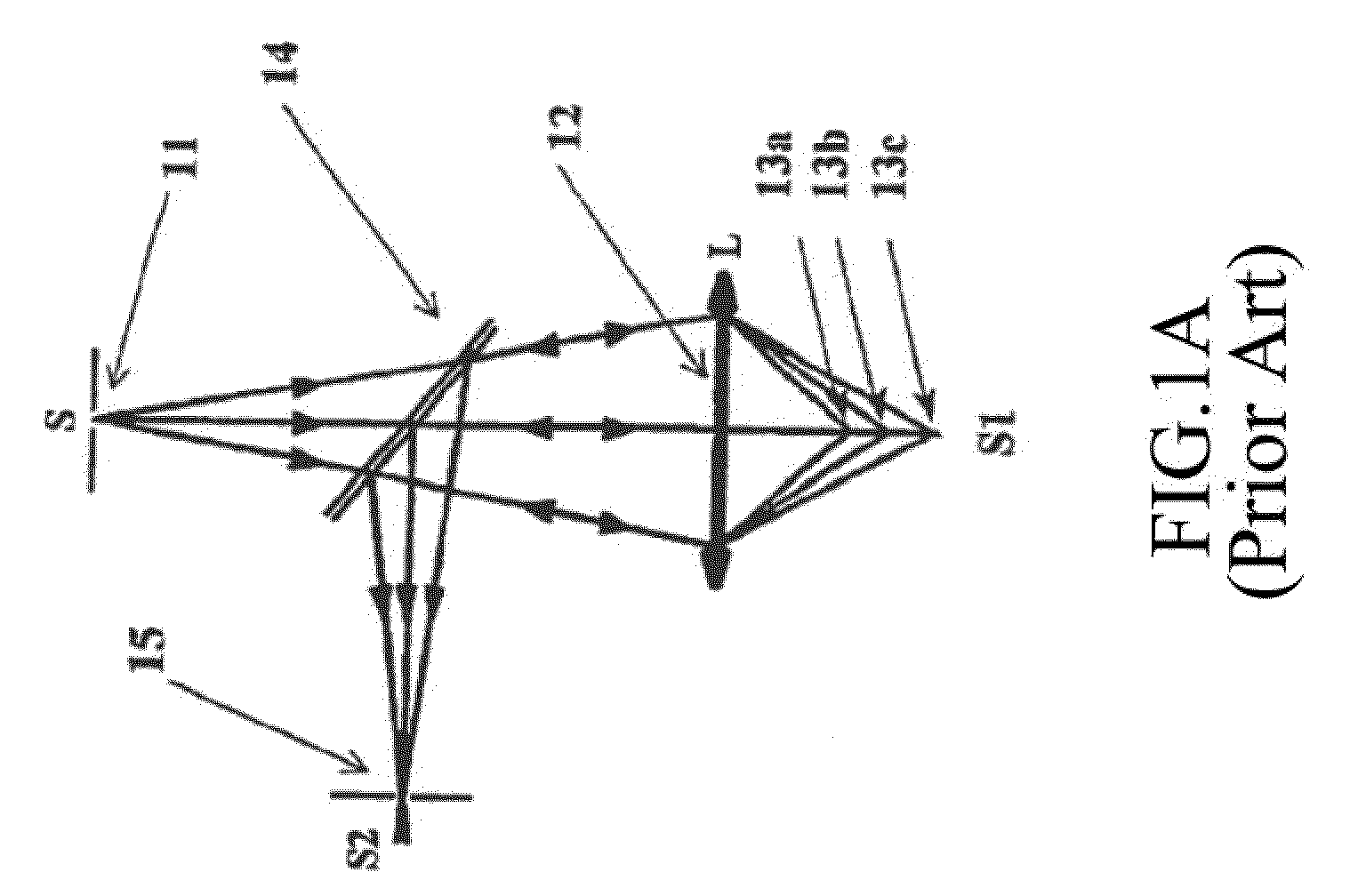
InactiveUS20050020926A1Improve discriminationImprove color gamutTelevision system detailsSurgeryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityLaser transmitter
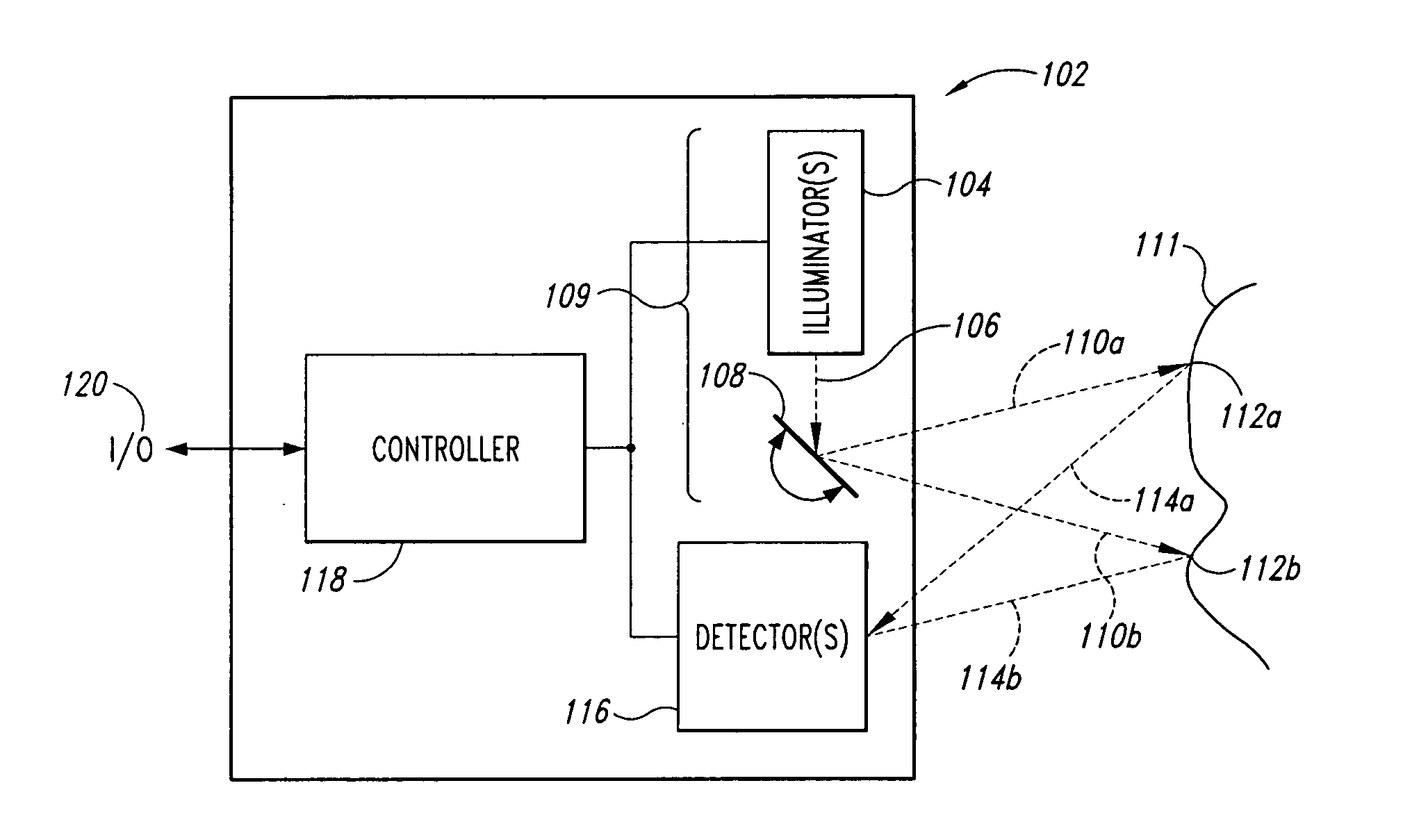
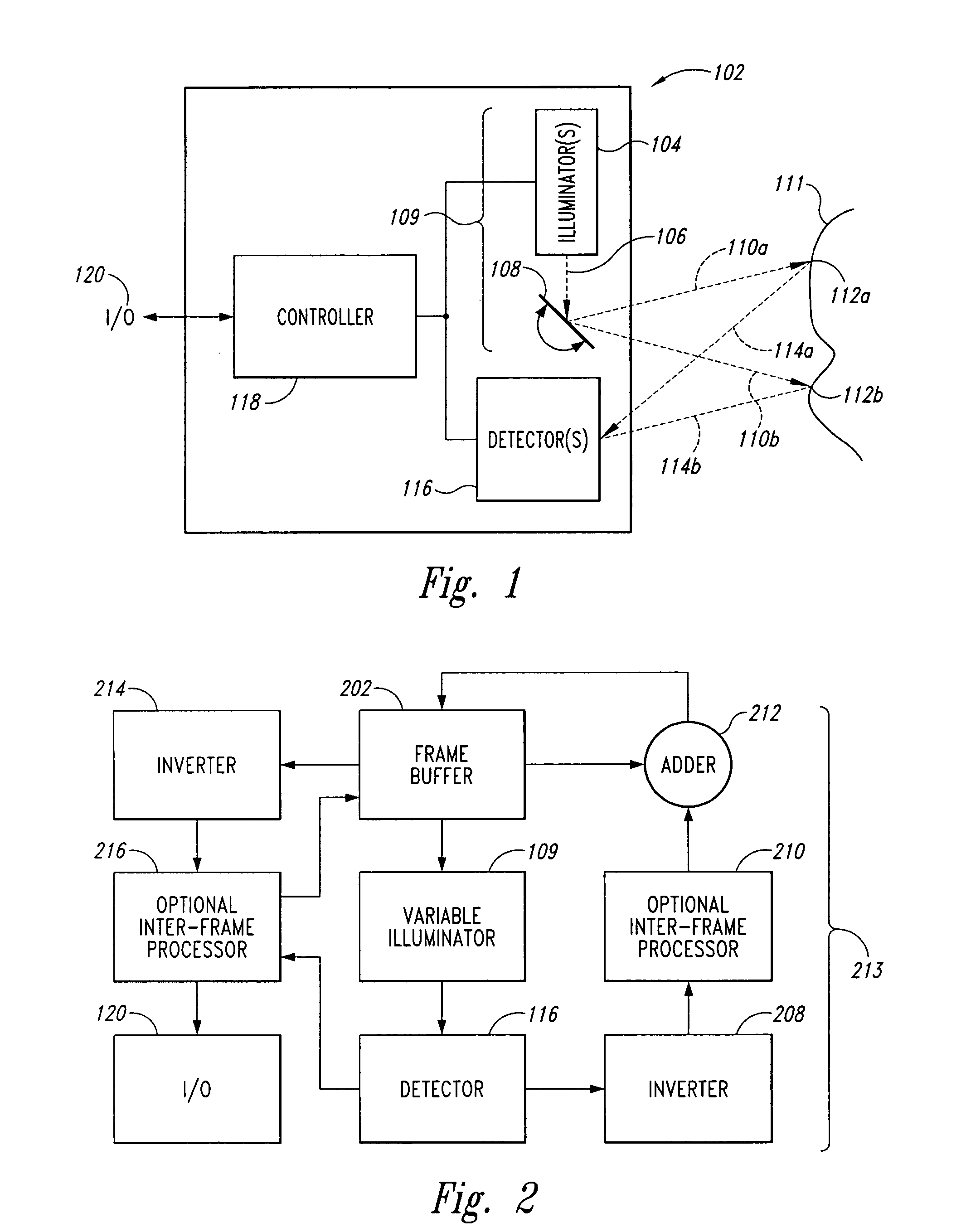
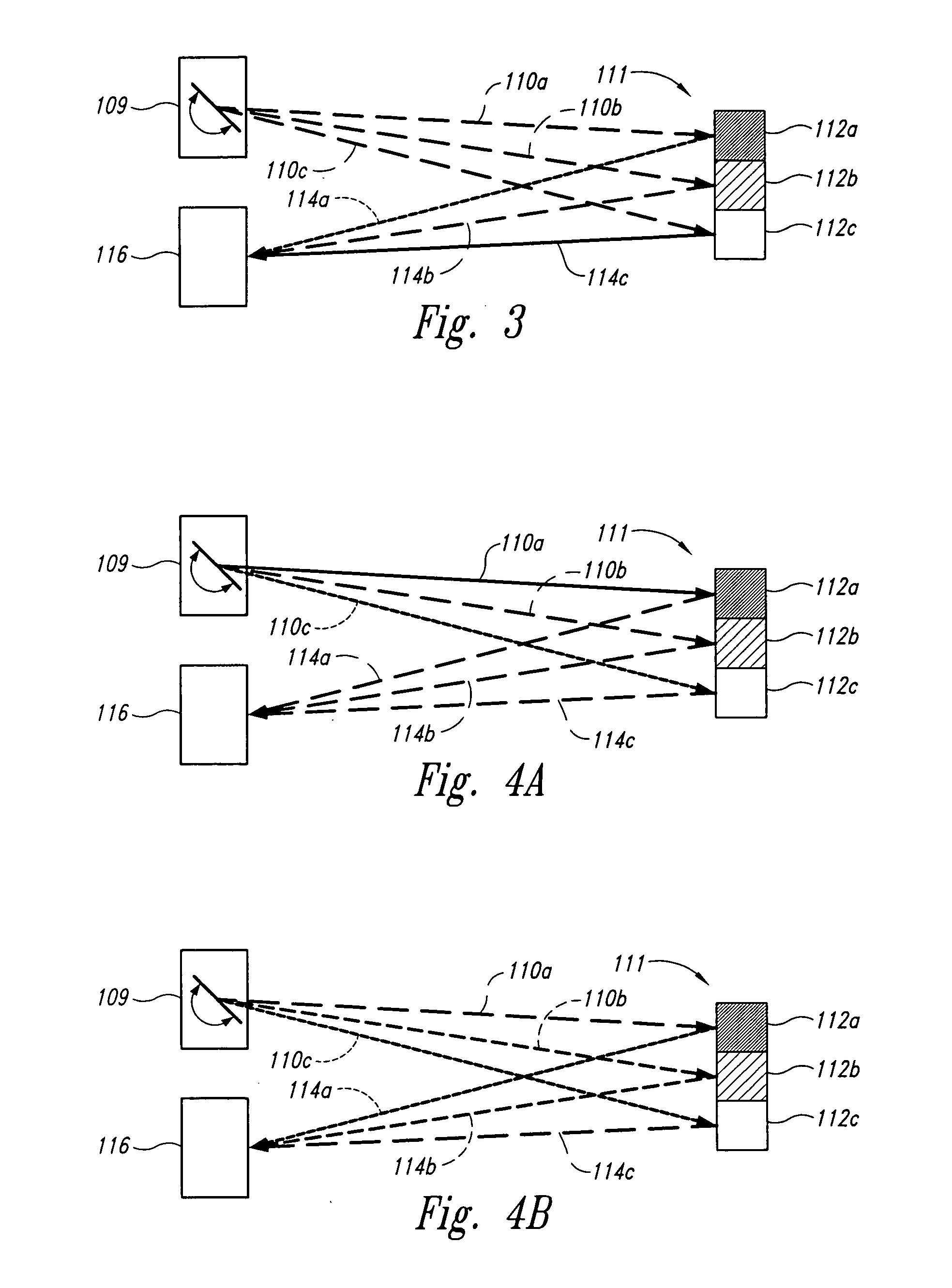
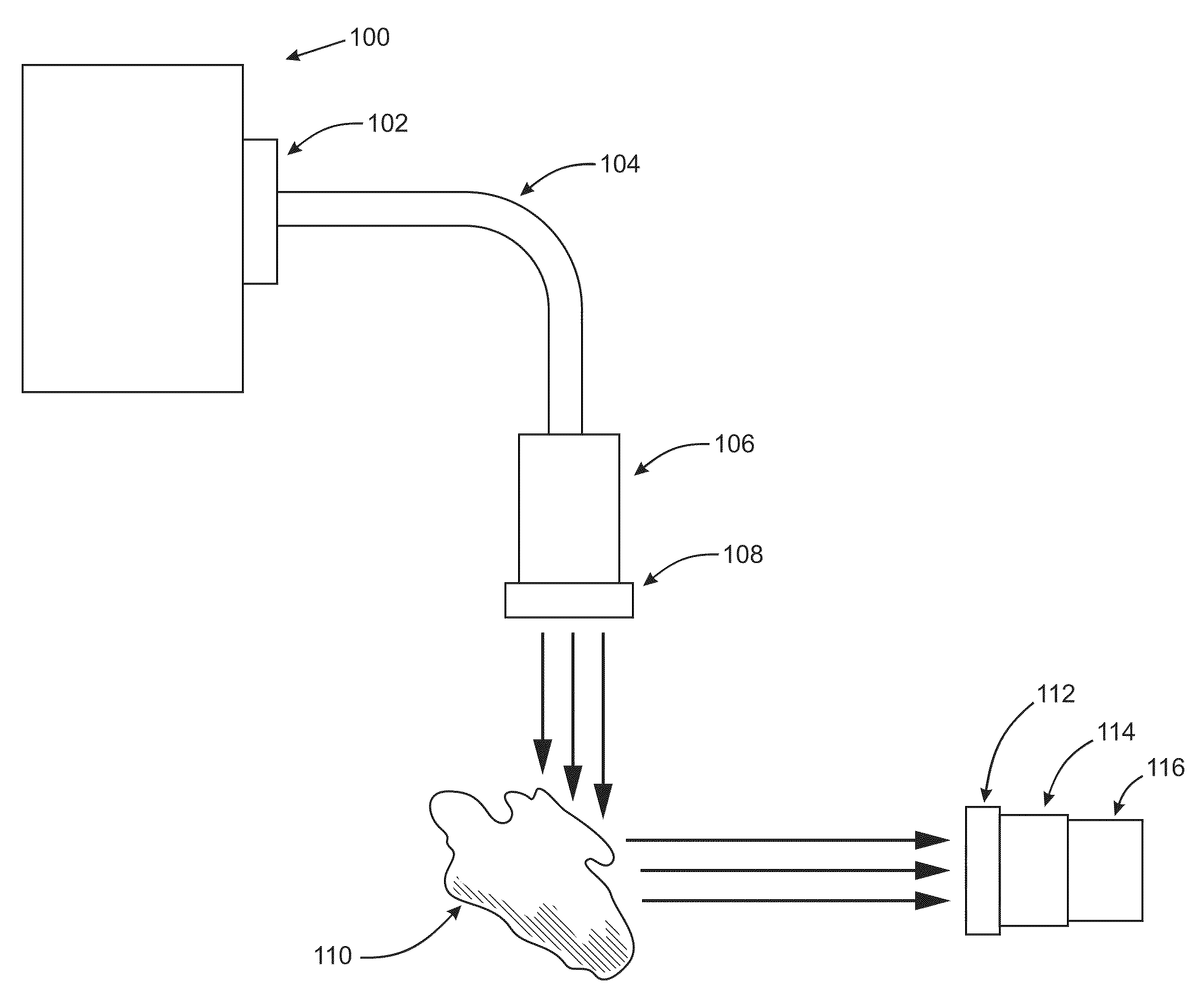
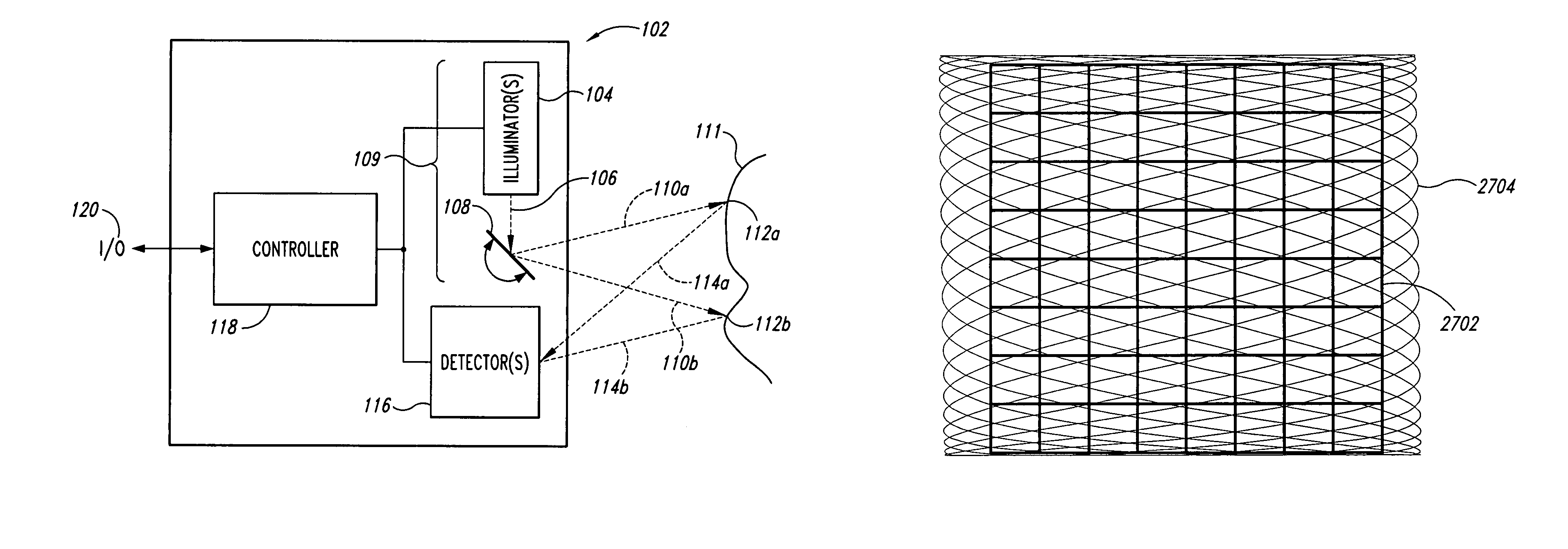
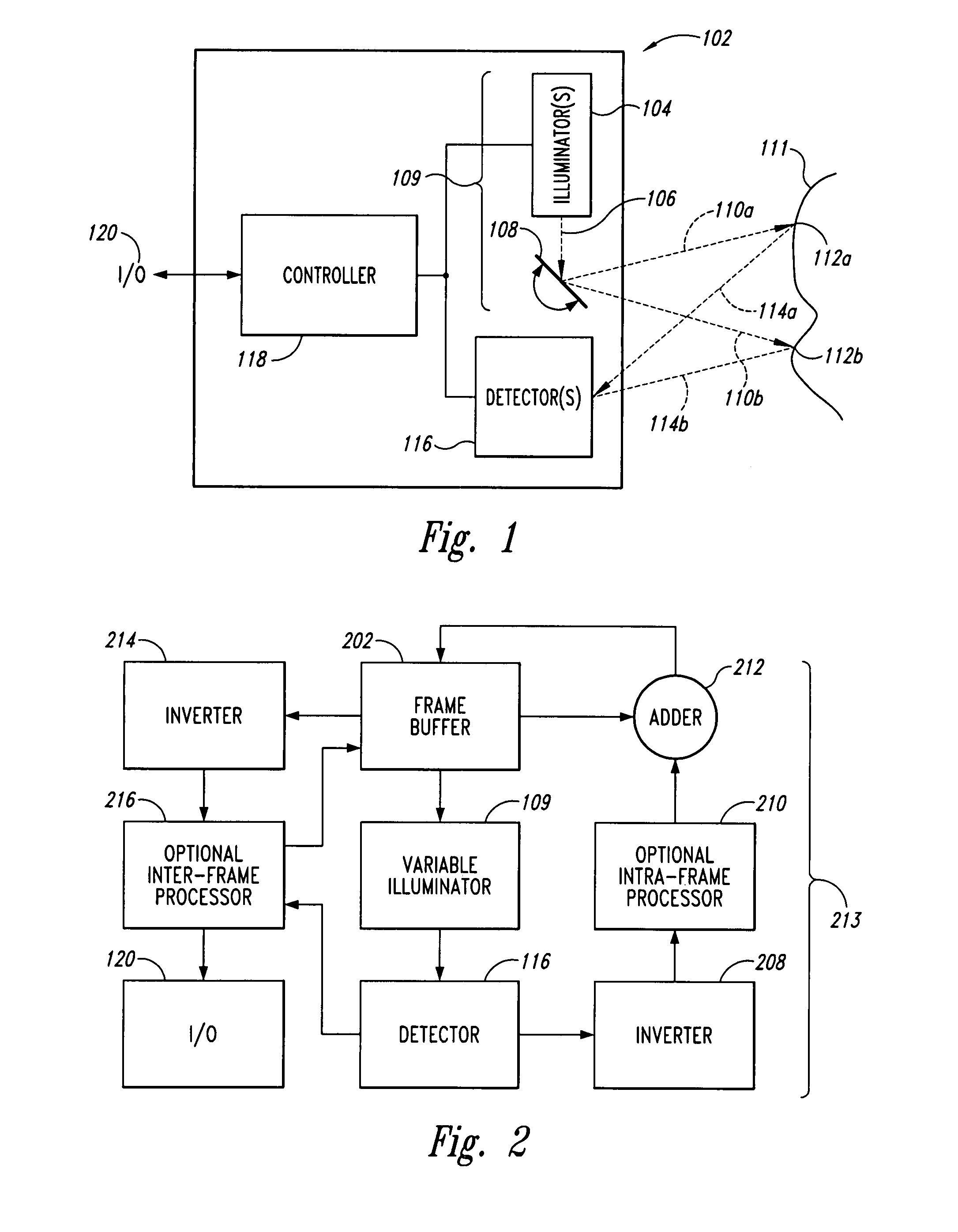
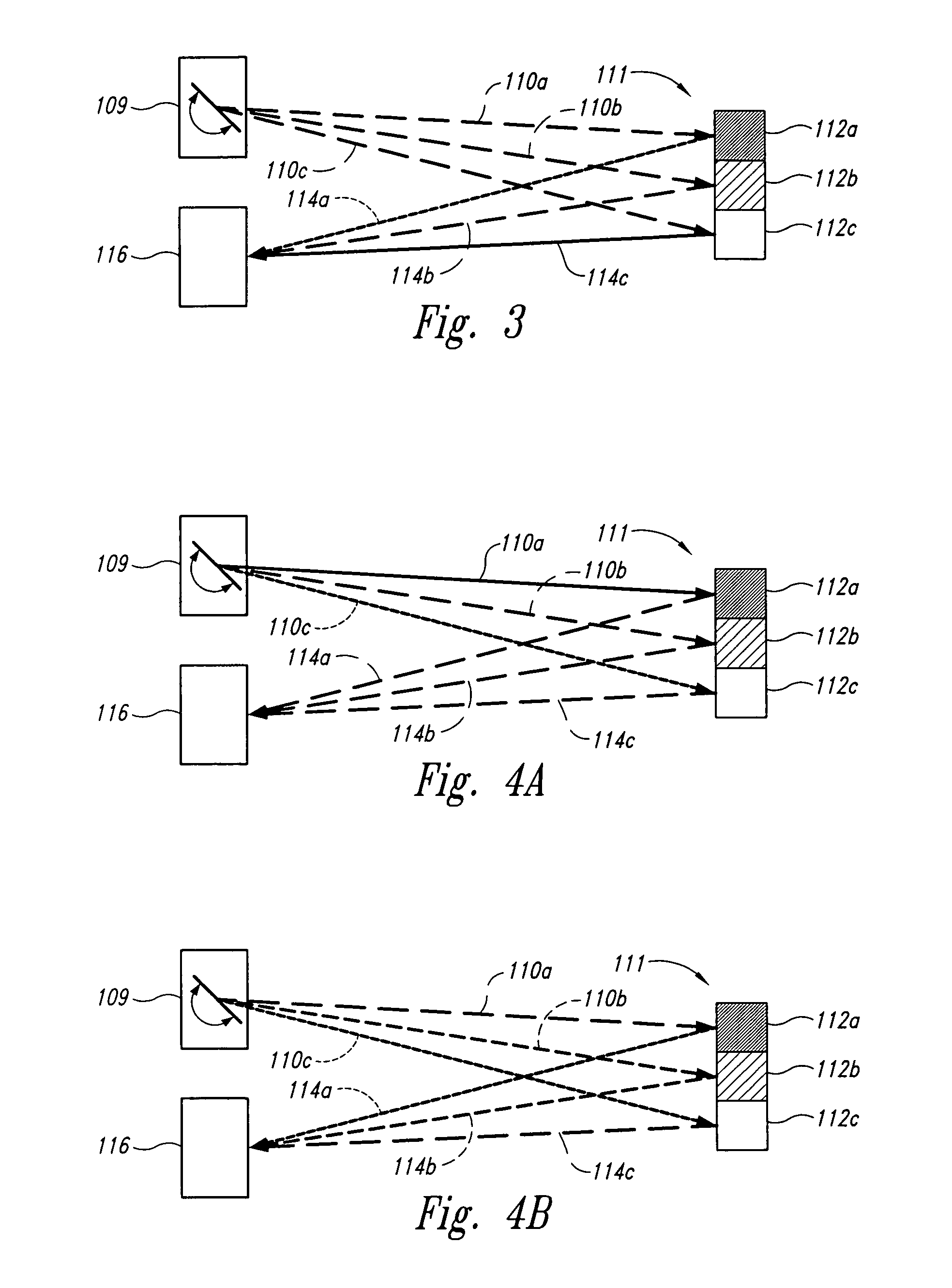
A scanning endoscope, amenable to both rigid and flexible forms, scans a beam of light across a field-of-view, collects light scattered from the scanned beam, detects the scattered light, and produces an image. The endoscope may comprise one or more bodies housing a controller, light sources, and detectors; and a separable tip housing the scanning mechanism. The light sources may include laser emitters that combine their outputs into a polychromatic beam. Light may be emitted in ultraviolet or infrared wavelengths to produce a hyperspectral image. The detectors may be housed distally or at a proximal location with gathered light being transmitted thereto via optical fibers. A plurality of scanning elements may be combined to produce a stereoscopic image or other imaging modalities. The endoscope may include a lubricant delivery system to ease passage through body cavities and reduce trauma to the patient. The imaging components are especially compact, being comprised in some embodiments of a MEMS scanner and optical fibers, lending themselves to interstitial placement between other tip features such as working channels, irrigation ports, etc.
Owner:MICROVISION
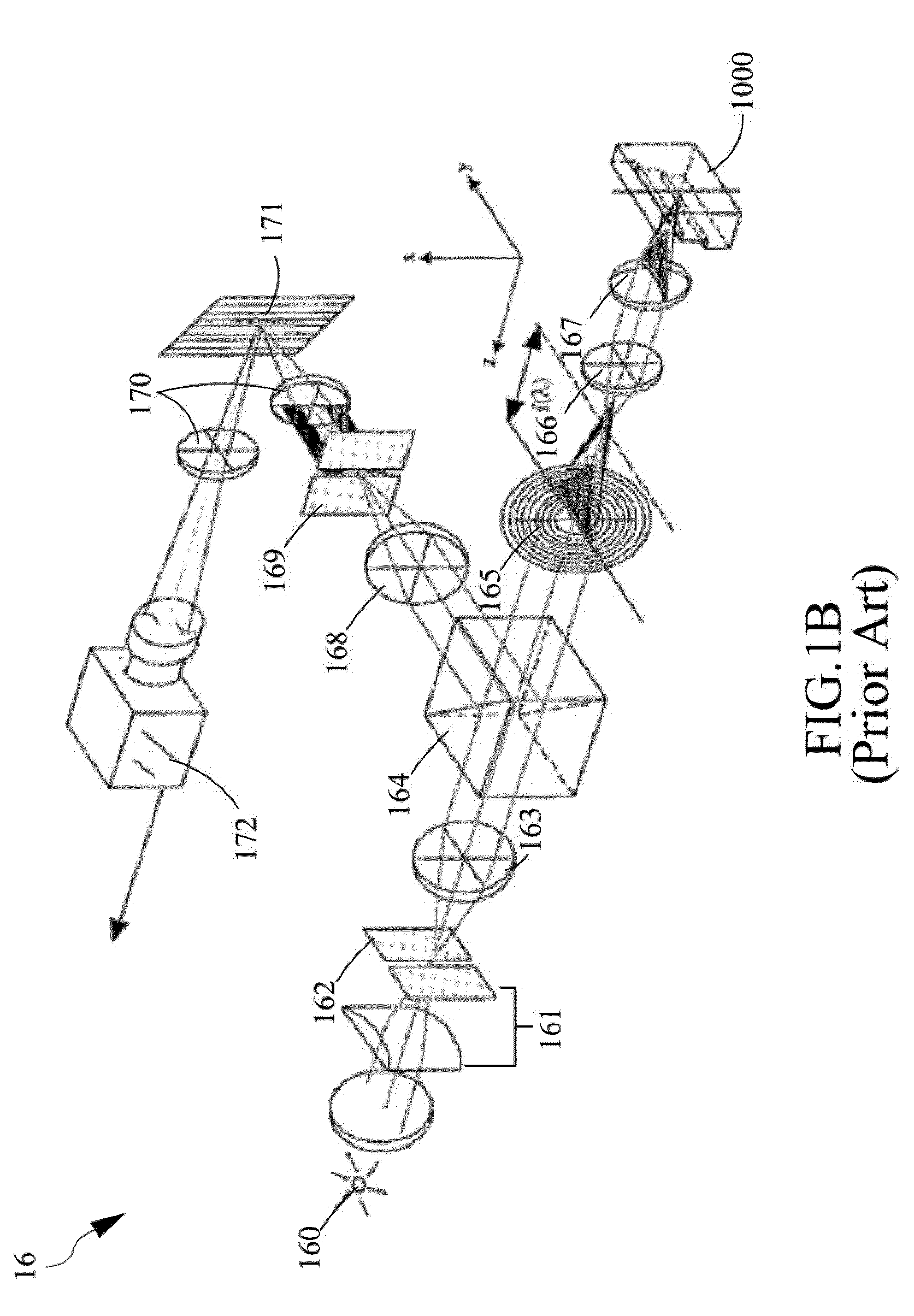
Digital light processing hyperspectral imaging apparatus
A hyperspectral imaging system having an optical path. The system including an illumination source adapted to output a light beam, the light beam illuminating a target, a dispersing element arranged in the optical path and adapted to separate the light beam into a plurality of wavelengths, a digital micromirror array adapted to tune the plurality of wavelengths into a spectrum, an optical device having a detector and adapted to collect the spectrum reflected from the target and arranged in the optical path and a processor operatively connected to and adapted to control at least one of: the illumination source; the dispersing element; the digital micromirror array; the optical device; and, the detector, the processor further adapted to output a hyperspectral image of the target. The dispersing element is arranged between the illumination source and the digital micromirror array, the digital micromirror array is arranged to transmit the spectrum to the target and the optical device is arranged in the optical path after the target.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Digital light processing hyperspectral imaging apparatus
A hyperspectral imaging system having an optical path. The system including an illumination source adapted to output a light beam, the light beam illuminating a target, a dispersing element arranged in the optical path and adapted to separate the light beam into a plurality of wavelengths, a digital micromirror array adapted to tune the plurality of wavelengths into a spectrum, an optical device having a detector and adapted to collect the spectrum reflected from the target and arranged in the optical path and a processor operatively connected to and adapted to control at least one of: the illumination source; the dispersing element; the digital micromirror array; the optical device; and, the detector, the processor further adapted to output a hyperspectral image of the target. The dispersing element is arranged between the illumination source and the digital micromirror array, the digital micromirror array is arranged to transmit the spectrum to the target and the optical device is arranged in the optical path after the target.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
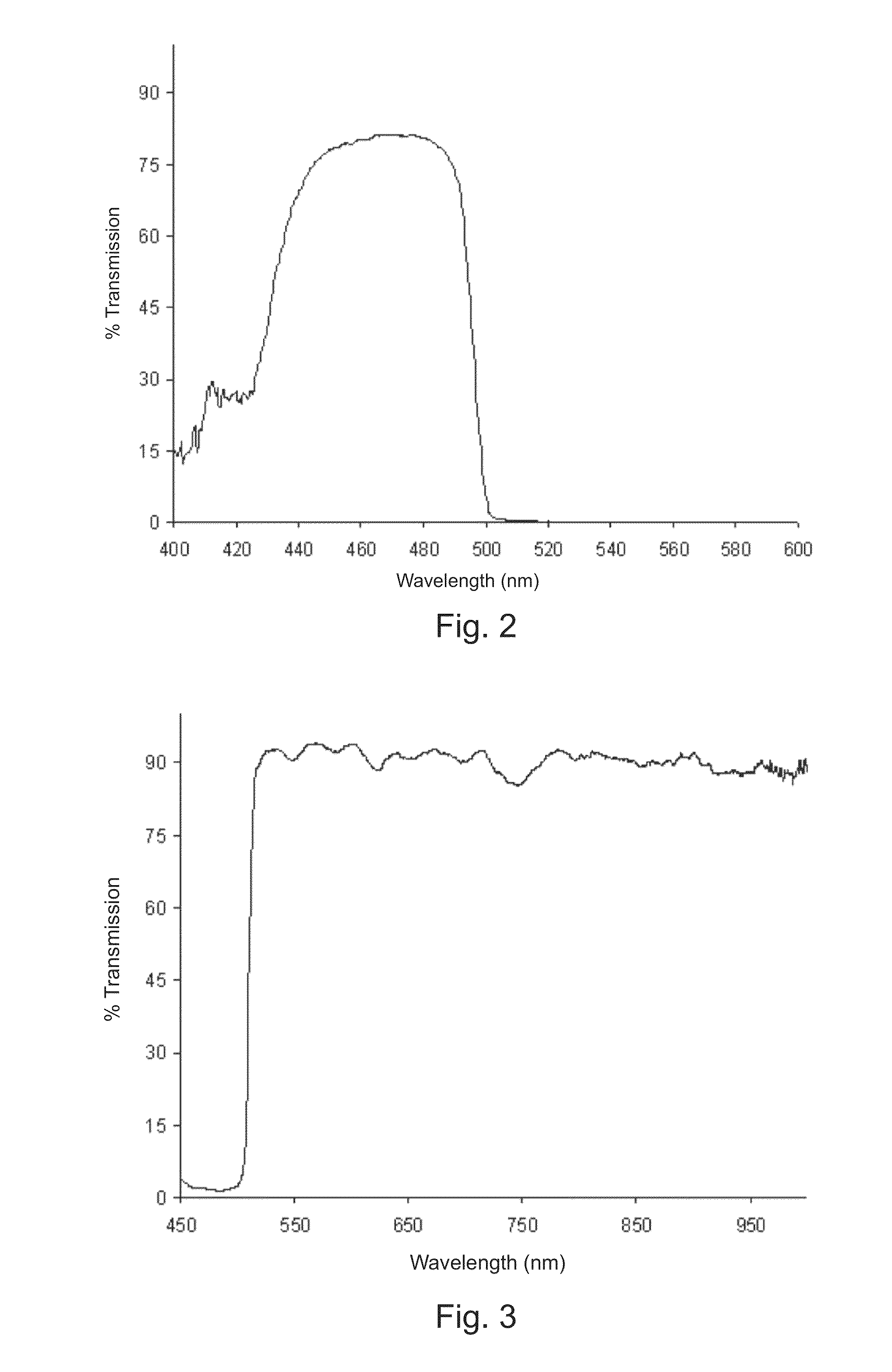
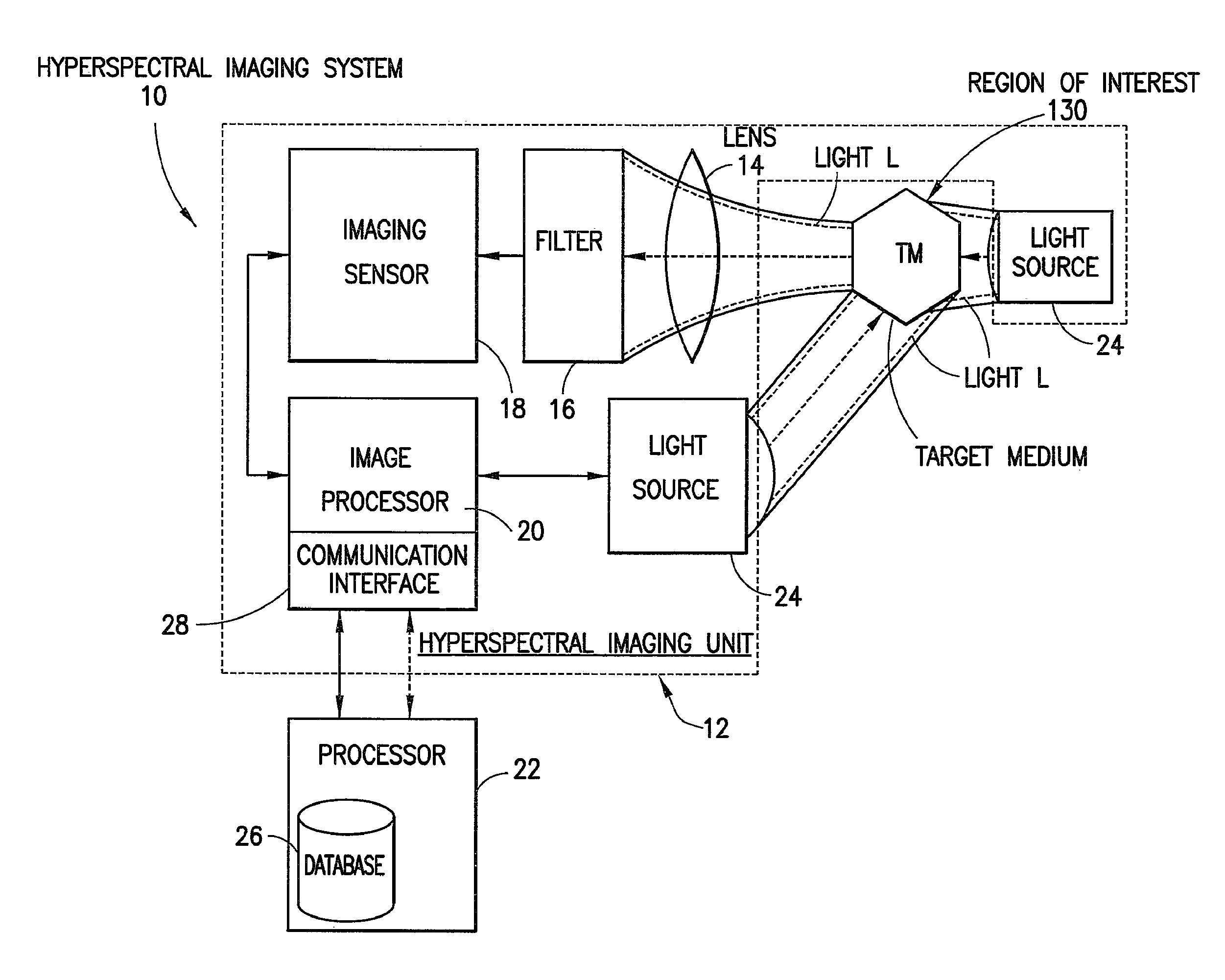
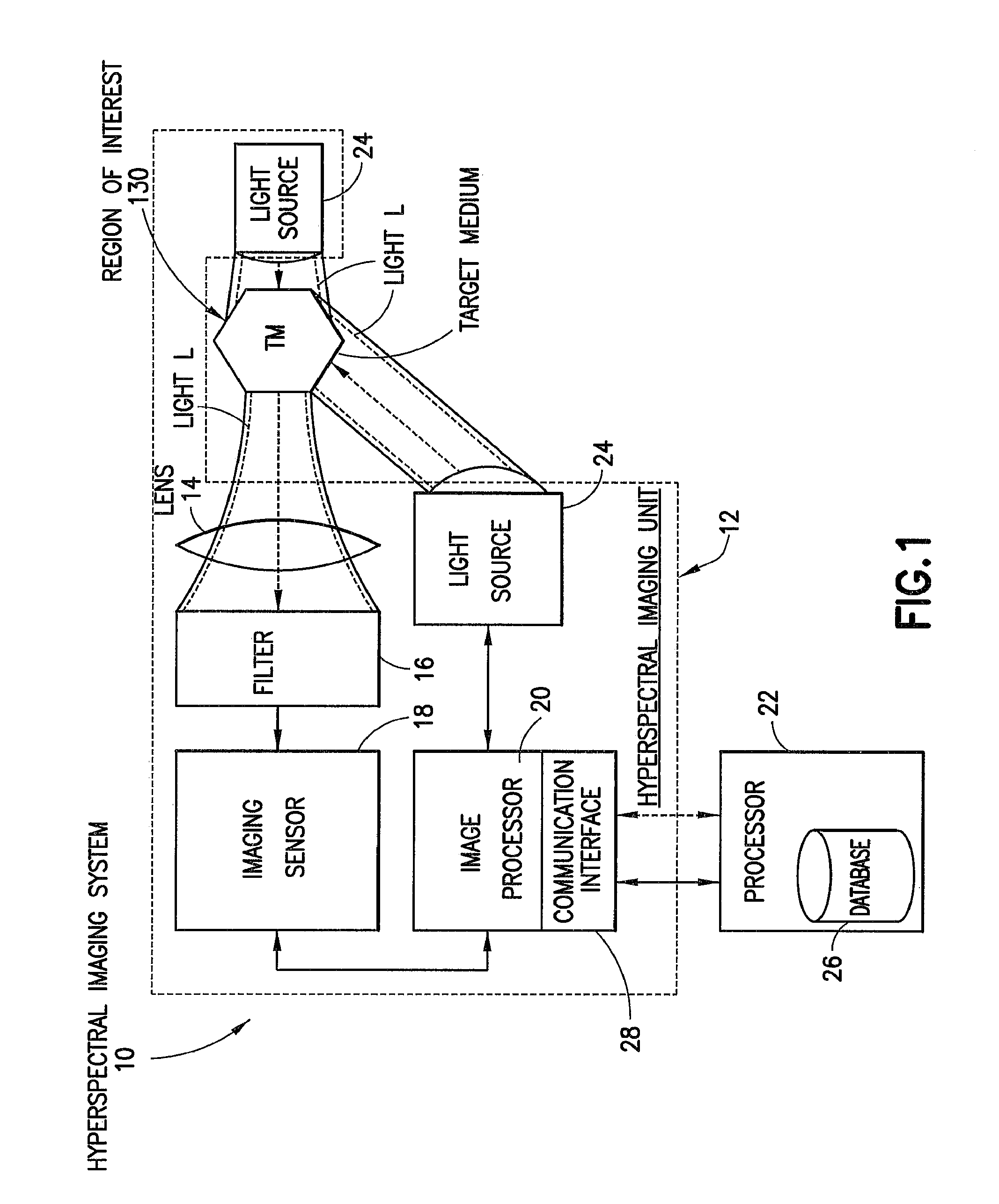
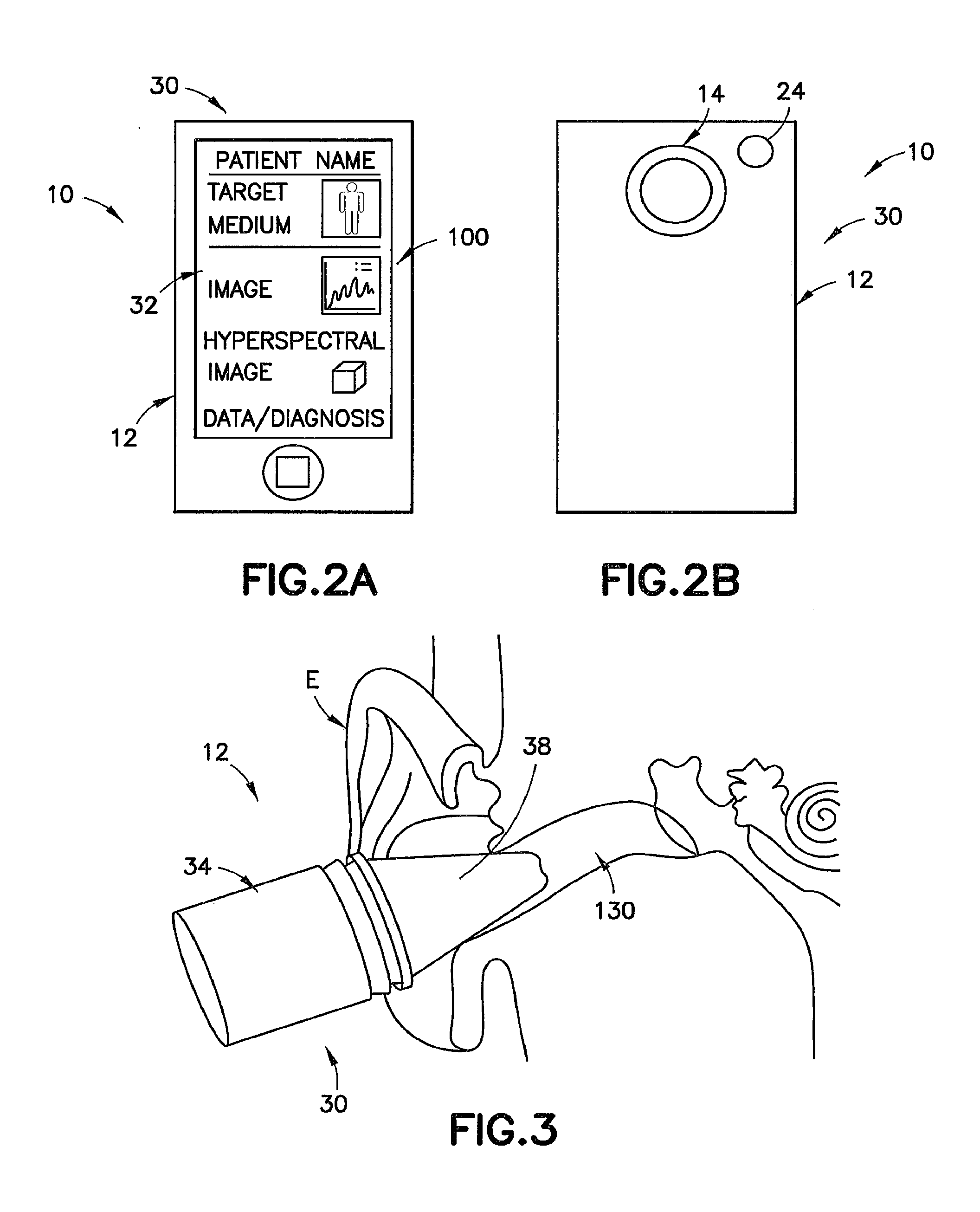
Hyperspectral imaging systems, units, and methods
InactiveUS20150044098A1Superior spectral resolutionImprove data acquisition speedTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometrySpectral bandsImaging data
A hyperspectral imaging system, including: at least one hyperspectral imaging unit, including: at least one lens configured to direct light scattered by, reflected by, or transmitted through a target medium to at least one hyperspectral filter arrangement configured to separate the light into discrete spectral bands; an imaging sensor to: receive the discrete spectral bands from the at least one hyperspectral filter arrangement; detect light by a plurality of pixels for each of the spectral bands; and generate electrical signals based at least in part on at least a portion of the light; and at least one image processor in communication with the at least one imaging sensor and configured to generate hyperspectral image data associated with the target medium; and at least one processor configured to determine biological data based at least partially on at least a portion of the hyperspectral image data.
Owner:SCANADU
Programmable spectral imaging system
InactiveUS7342658B2Improve efficiencyHigh resolutionRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopySpectral transmissionSpatial light modulator
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
High efficiency beam combiner coating
InactiveUS20150213754A1Minimize overlapStatic indicating devicesDiffusing elementsOptical coatingTransmittance
A system having an improved optical coating for use in beam combiner assemblies for an image fusion device using an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display. The system combines multi-spectral images of a scene having superior reflection of the OLED display image while incorporating high transmission of the image fusion device while allowing low power requirements on the system.
Owner:EMAGIN CORP
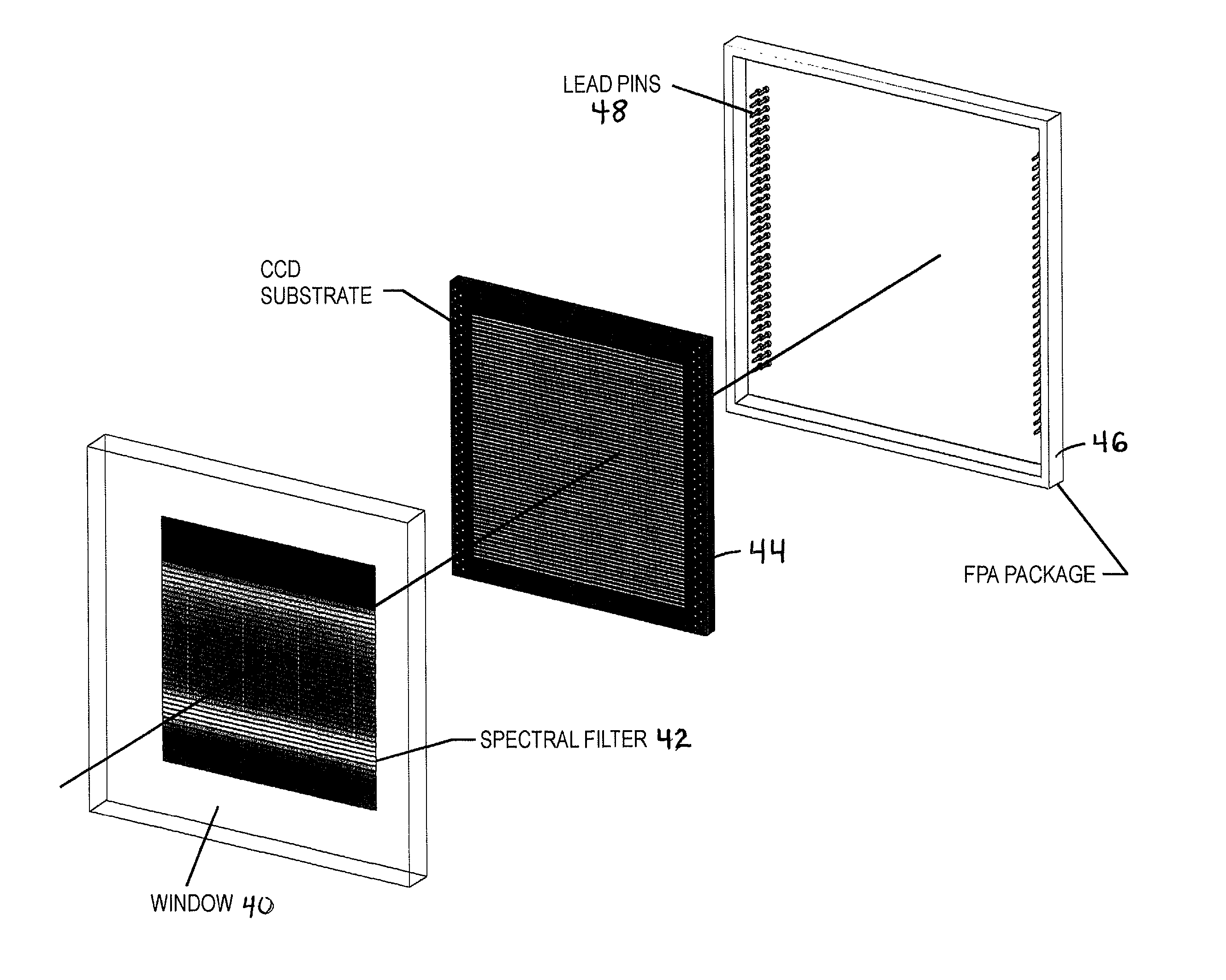
Multispectral or hyperspectral imaging system and method for tactical reconnaissance
A two-dimensional focal plane array (FPA) is divided into sub-arrays of rows and columns of pixels, each sub-array being responsive to light energy from a target object which has been separated by a spectral filter or other spectrum dividing element into a predetermined number of spectral bands. There is preferably one sub-array on the FPA for each predetermined spectral band. Each sub-array has its own read out channel to allow parallel and simultaneous readout of all sub-arrays of the array. The scene is scanned onto the array for simultaneous imaging of the terrain in many spectral bands. Time Delay and Integrate (TDI) techniques are used as a clocking mechanism within the sub-arrays to increase the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the detected image. Additionally, the TDI length (i.e., number of rows of integration during the exposure) within each sub-array is adjustable to optimize and normalize the response of the photosensitive substrate to each spectral band. The array provides for parallel and simultaneous readout of each sub-array to increase the collection rate of the spectral imagery. All of these features serve to provide a substantial improvement in the area coverage of a hyperspectral imaging system while at the same time increasing the SNR of the detected spectral image.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
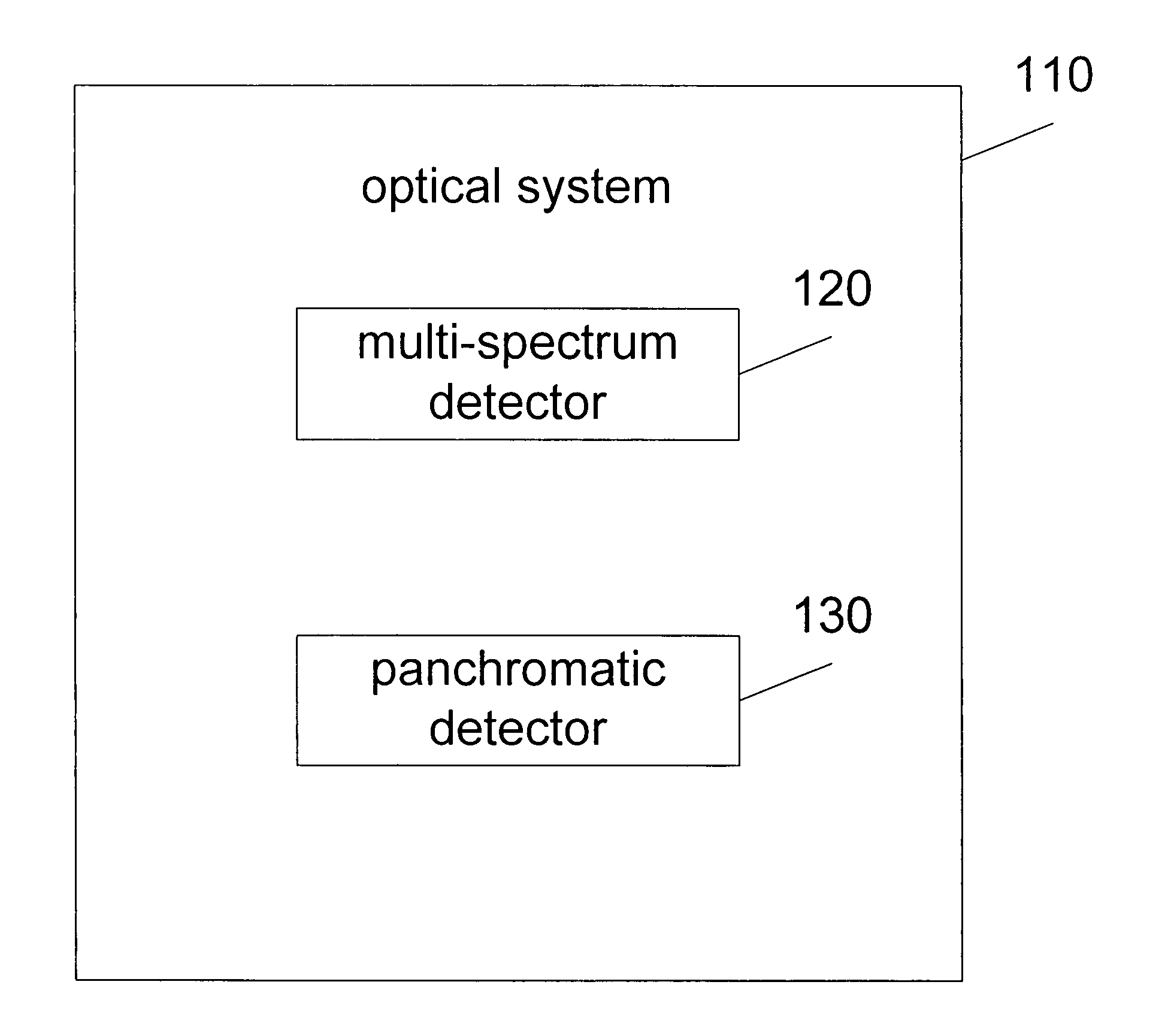
System and method for image fusion
A method of fusing a low resolution multispectral image with a high resolution panchromatic image comprising the step of generating a new synthetic pan image using multispectral bands from the multispectral image.
Owner:NEW BRUNSWICK UNIV OF THE
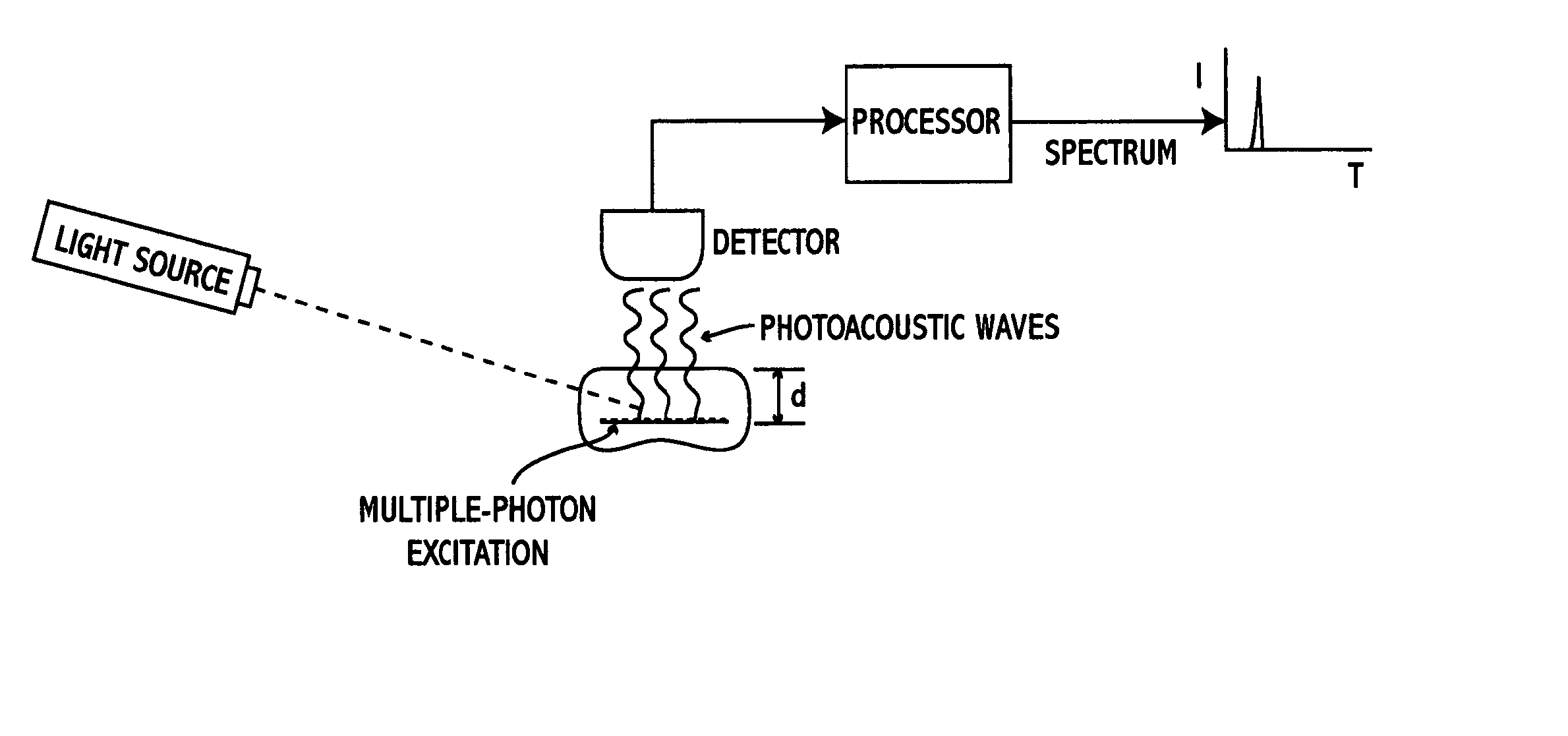
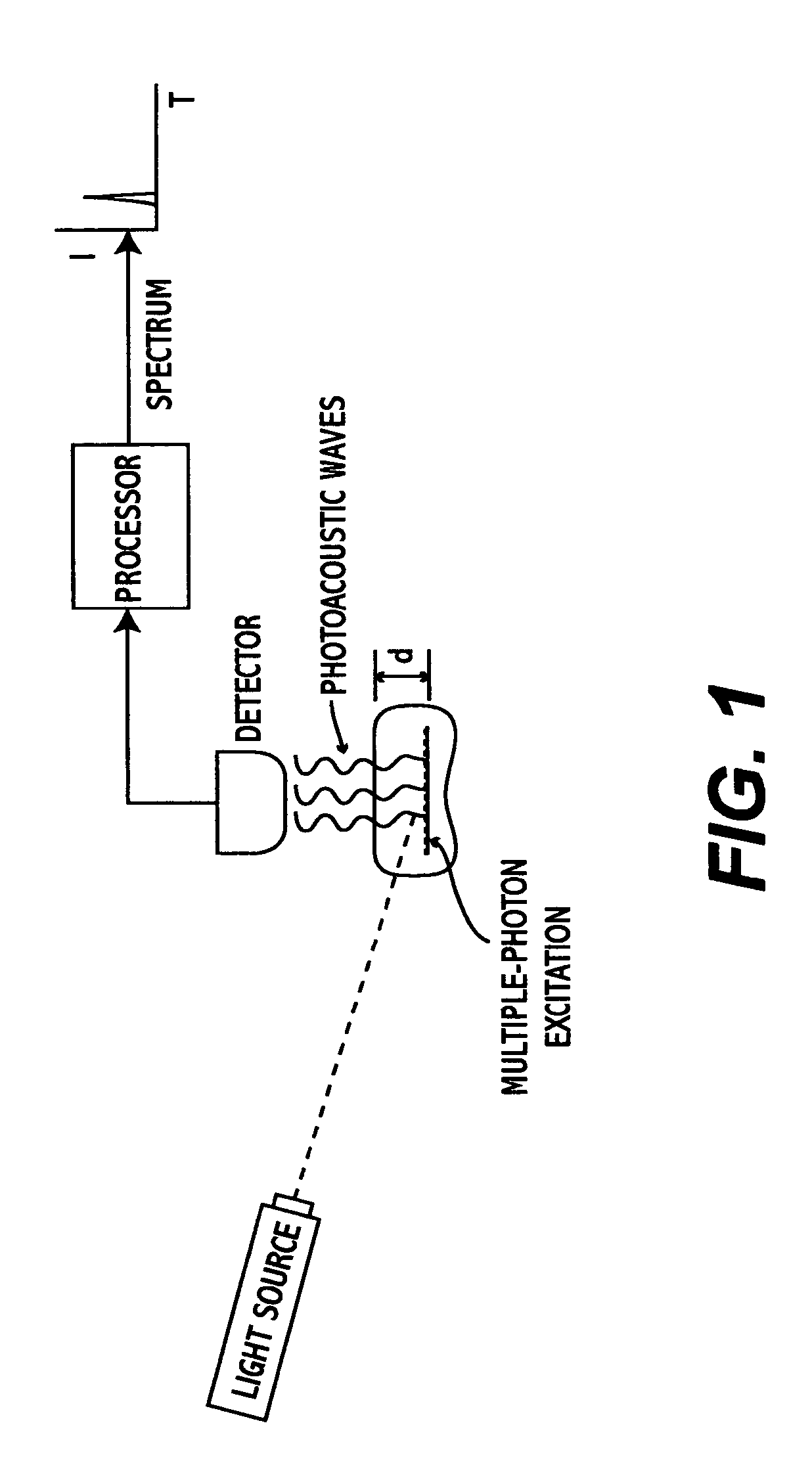
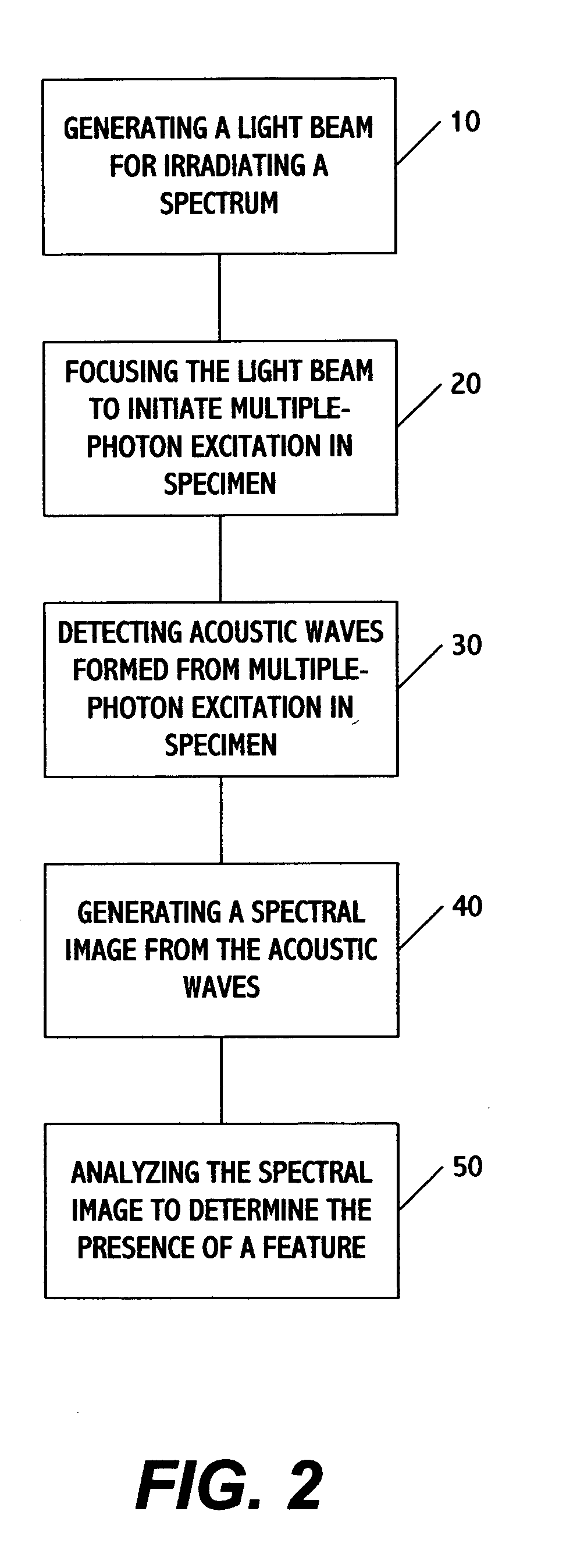
Multiphoton photoacoustic spectroscopy system and method
InactiveUS20050070803A1Non-invasively diagnosingRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightHigh power lasersPhoton
A system and method for performing multispectral imaging locates features of interest in a specimen using a technique known as multiphoton photoacoustic spectroscopy. In this technique, a tunable high-power laser is used to initiate multiphoton excitation events which are then detected as an acoustic signal using a sensor such as an ultrasonic piezoelectric transducer. The transducer signal is processed to form a normalized MPPAS signal intensity which may then be used as a basis for forming a spectral image. Unlike other spectroscopies, MPPAS is able to monitor non-fluorescent species based on non-radiative relaxation of the light-absorbing species in the specimen. In addition, since the majority of energy imparted to the light-absorbing molecules is released through non-radiative pathways, sensitive measurements of even fluorescent molecules can be performed. The system and method may be applied to detect malignant cells in tissue samples although other uses are contemplated.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
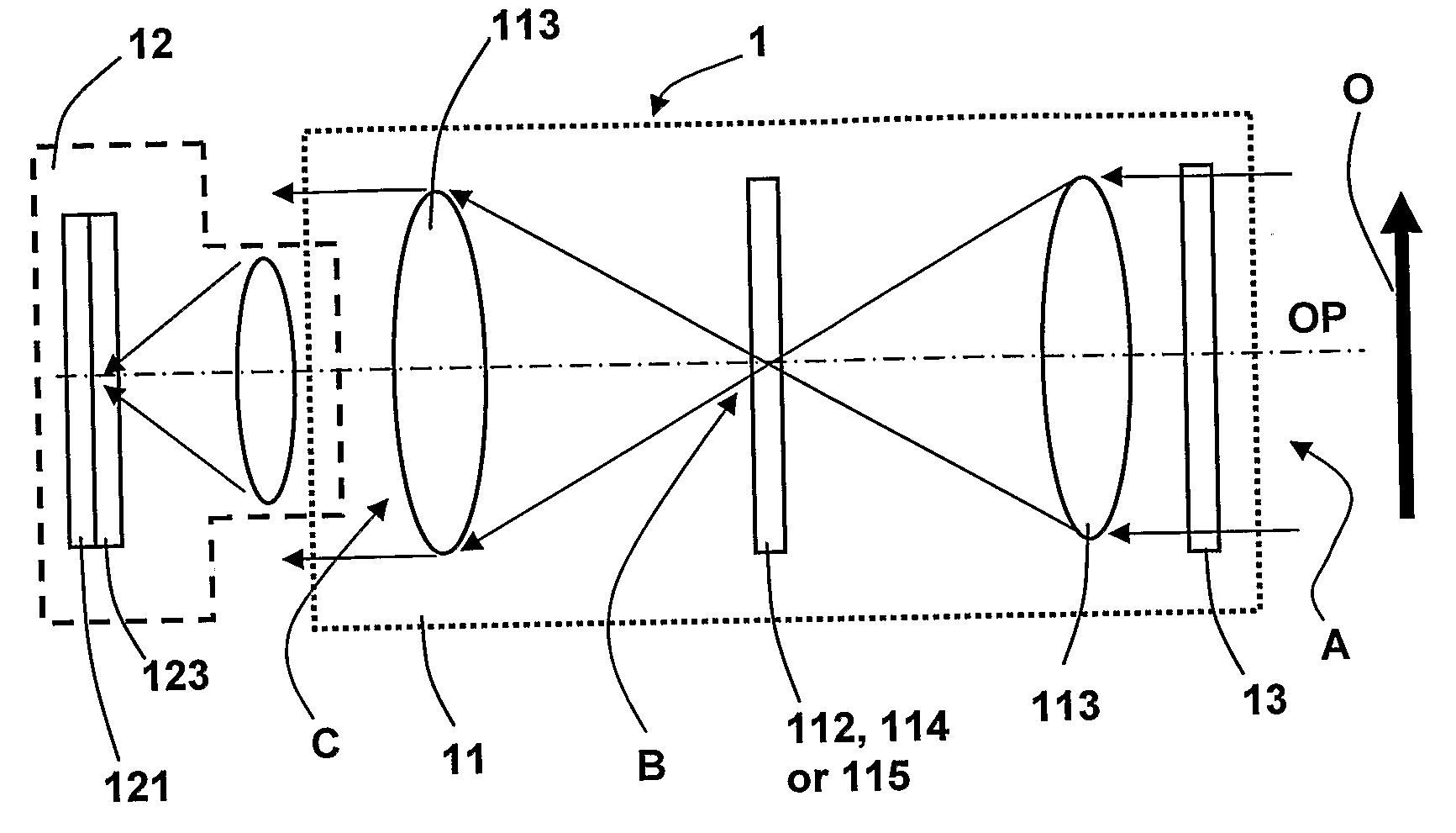
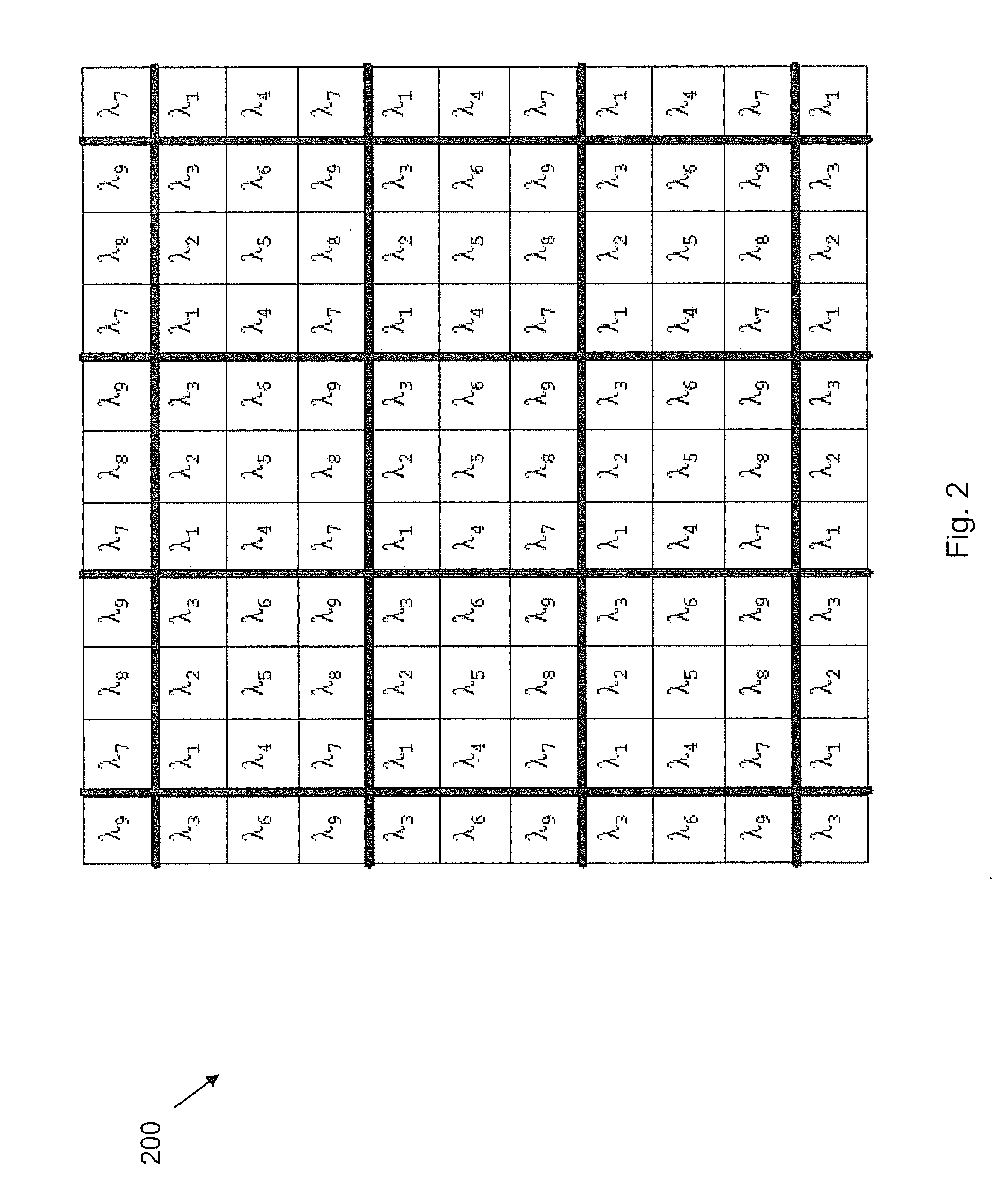
System for Multi- and Hyperspectral Imaging
InactiveUS20080123097A1Improve performanceCost effectiveRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSensor arrayMulti band
The present invention relates to the production of instantaneous or non-instantaneous multi-band images, to be transformed into multi- or hyperspectral images, comprising light collecting means (11), an image sensor (12) with at least one two dimensional sensor array (121), and an instantaneous colour separating means (123), positioned before the image sensor array (121) in the optical path (OP) of the arrangement (1), and first uniform spectral filters (13) in the optical path (OP), with the purpose of restricting imaging to certain parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. The present invention specifically teaches that a filter unit (FU) comprising colour or spectral filter mosaics and / or uniform colour or spectral filters mounted on filter wheels (114) or displayed by transmissive displays (115), is either permanently or interchangeably positioned before the colour separating means (123) in the optical path (OP) in, or close to, converged light (B). Each colour or spectral filter mosaic consists of a multitude of homogeneous filtering regions. The transmission curves (TC) of the filtering regions of a colour or spectral filter mosaic can be partly overlapping, in addition to overlap between these transmission curves and those belonging to the filtering regions of the colour separating means (123). The transmission curves (TC) of the colour or spectral filter mosaics and the colour separating means (123) are suitably spread out in the intervals of a spectrum to be studied. The combination of the colour separating means (123) and the spectral or colour or spectral filter mosaics produces different sets of linearly independent transmission curves (TC). The multiple-filter image captured by the image sensor (12) is demosaicked by identifying and segmenting the image regions that are affected by the regions of the multiple filter mosaic, and after an optional interpolation step, a multi-band image is obtained. The resulting multi-band image is transformed into a multi- or hyperspectral image.
Owner:RP VENTURES TECH OFFICE
Method for aerial imagery acquisition and analysis
A method and system for multi-spectral imagery acquisition and analysis, the method including capturing preliminary multi-spectral aerial images according to pre-defined survey parameters at a pre-selected resolution, automatically performing preliminary analysis on site or location in the field using large scale blob partitioning of the captured images in real or near real time, detecting irregularities within the pre-defined survey parameters and providing an output corresponding thereto, and determining, from the preliminary analysis output, whether to perform a second stage of image acquisition and analysis at a higher resolution than the pre-selected resolution. The invention also includes a method for analysis and object identification including analyzing high resolution multi-spectral images according to pre-defined object parameters, when parameters within the pre-defined object parameters are found, performing blob partitioning on the images containing such parameters to identify blobs, and comparing objects confined to those blobs to pre-defined reference parameters to identify objects having the pre-defined object parameters.
Owner:AGROWING LTD
Spectral imaging for downhole fluid characterization
ActiveUS20070035736A1Reduce pressureConstructionsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsOcean bottomLine tubing
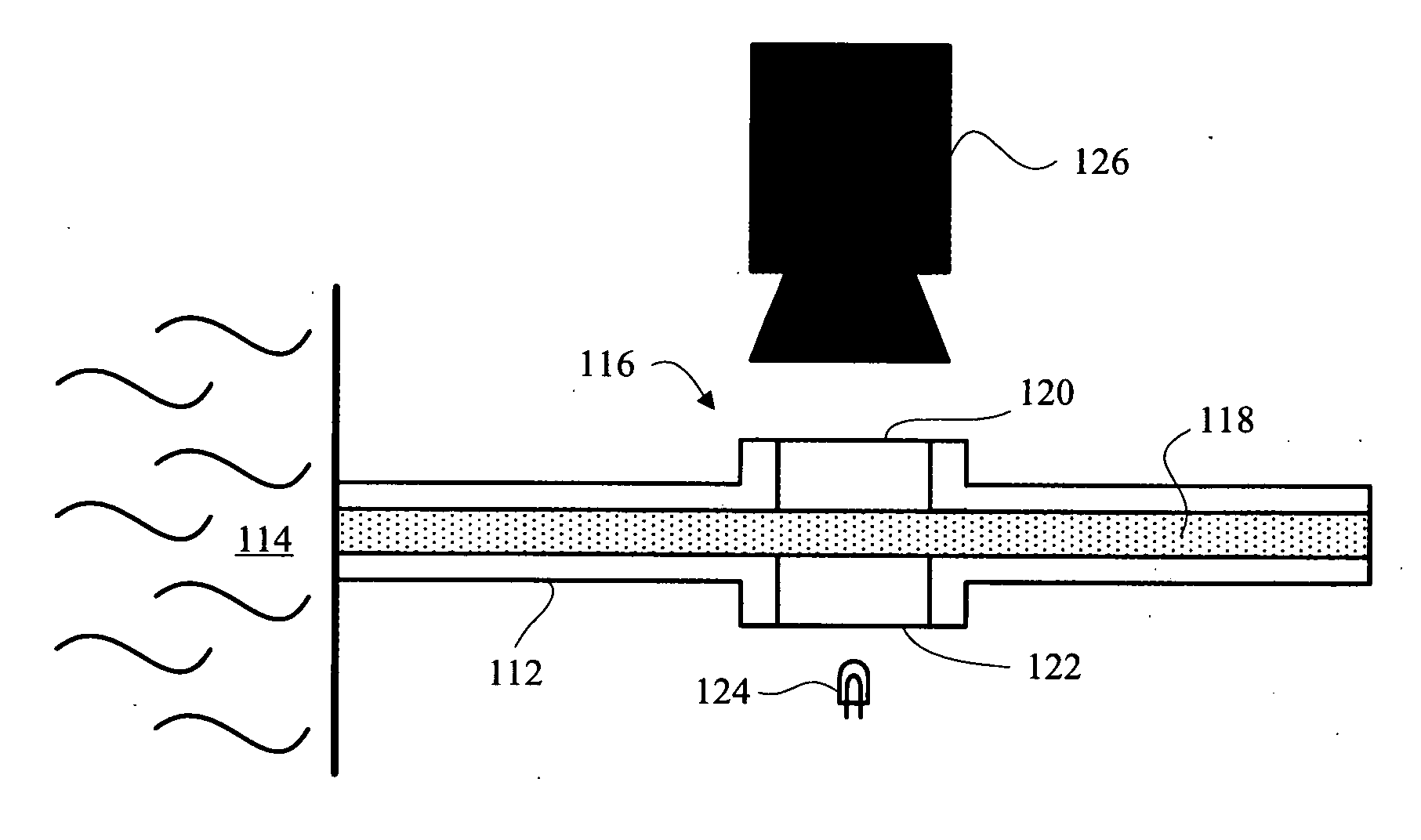
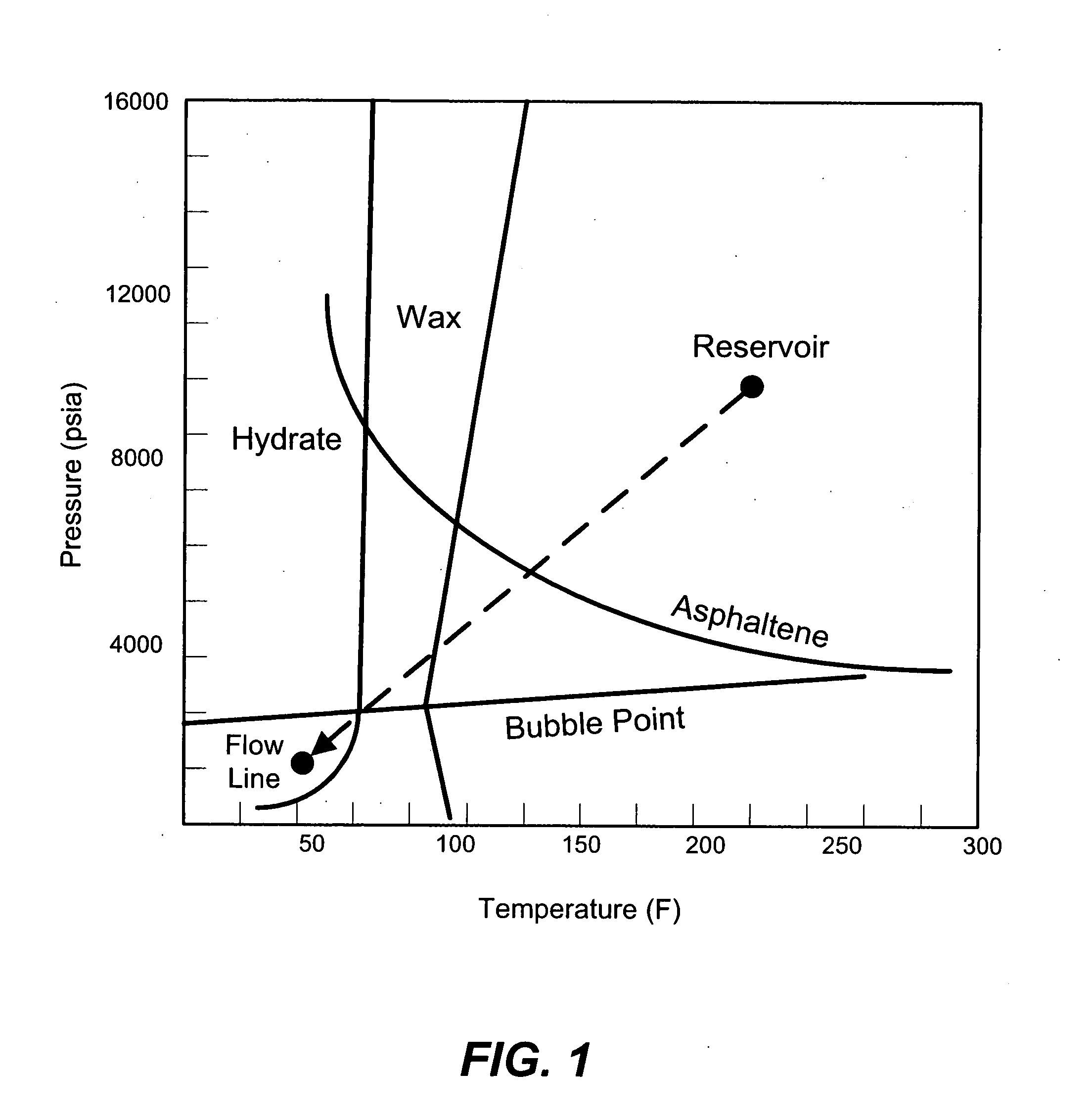
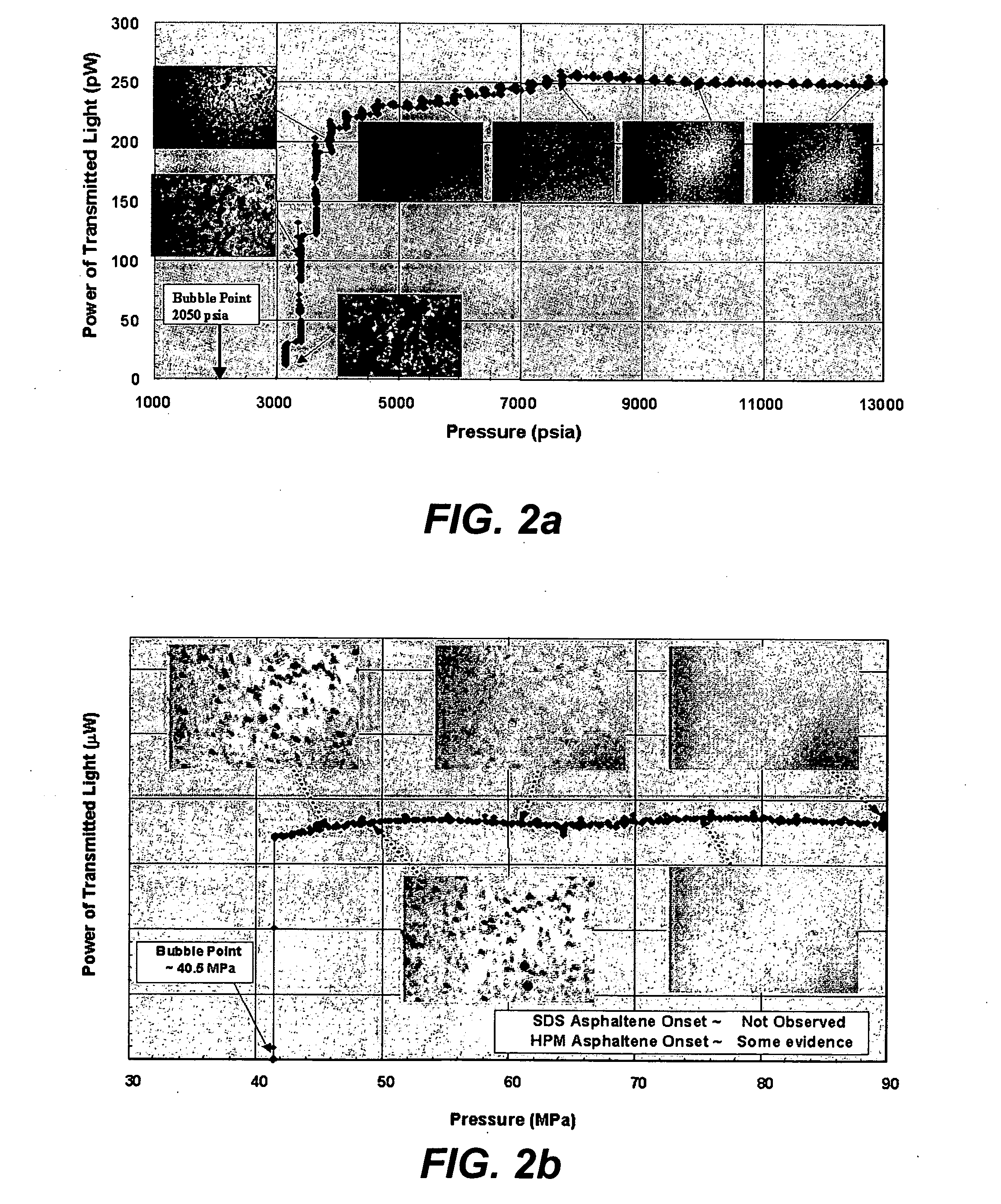
The present invention contemplates implementation of transitory downhole video imaging and / or spectral imaging for the characterization of formation fluid samples in situ, as well as during flow through production tubing, including subsea flow lines, for permanent and / or long term installations. The present invention contemplates various methods and apparatus that facilitate one-time or ongoing downhole fluid characterization by video analysis in real time. The methods and systems may be particularly well suited to permanent and periodic intervention-based operations.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
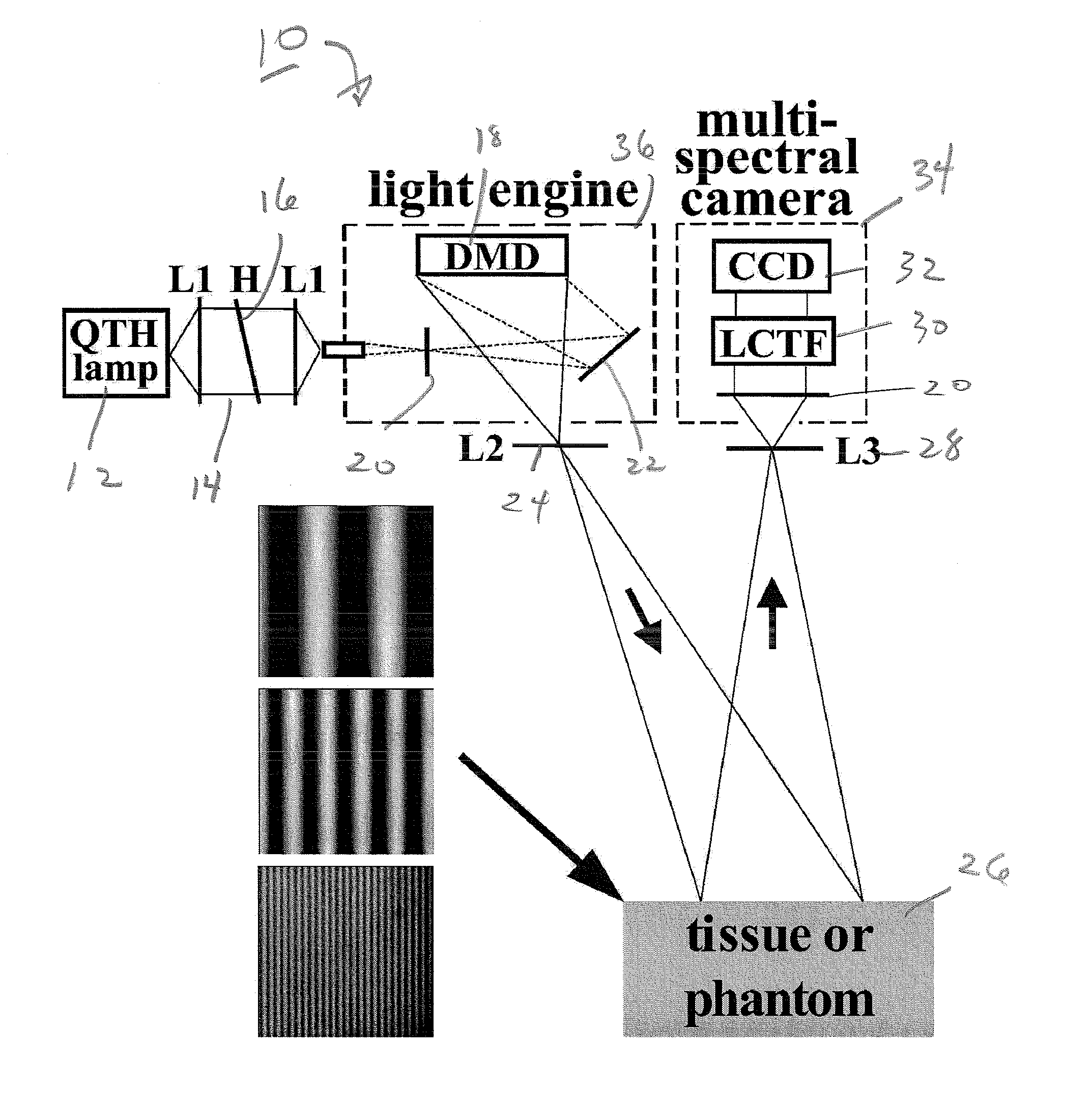
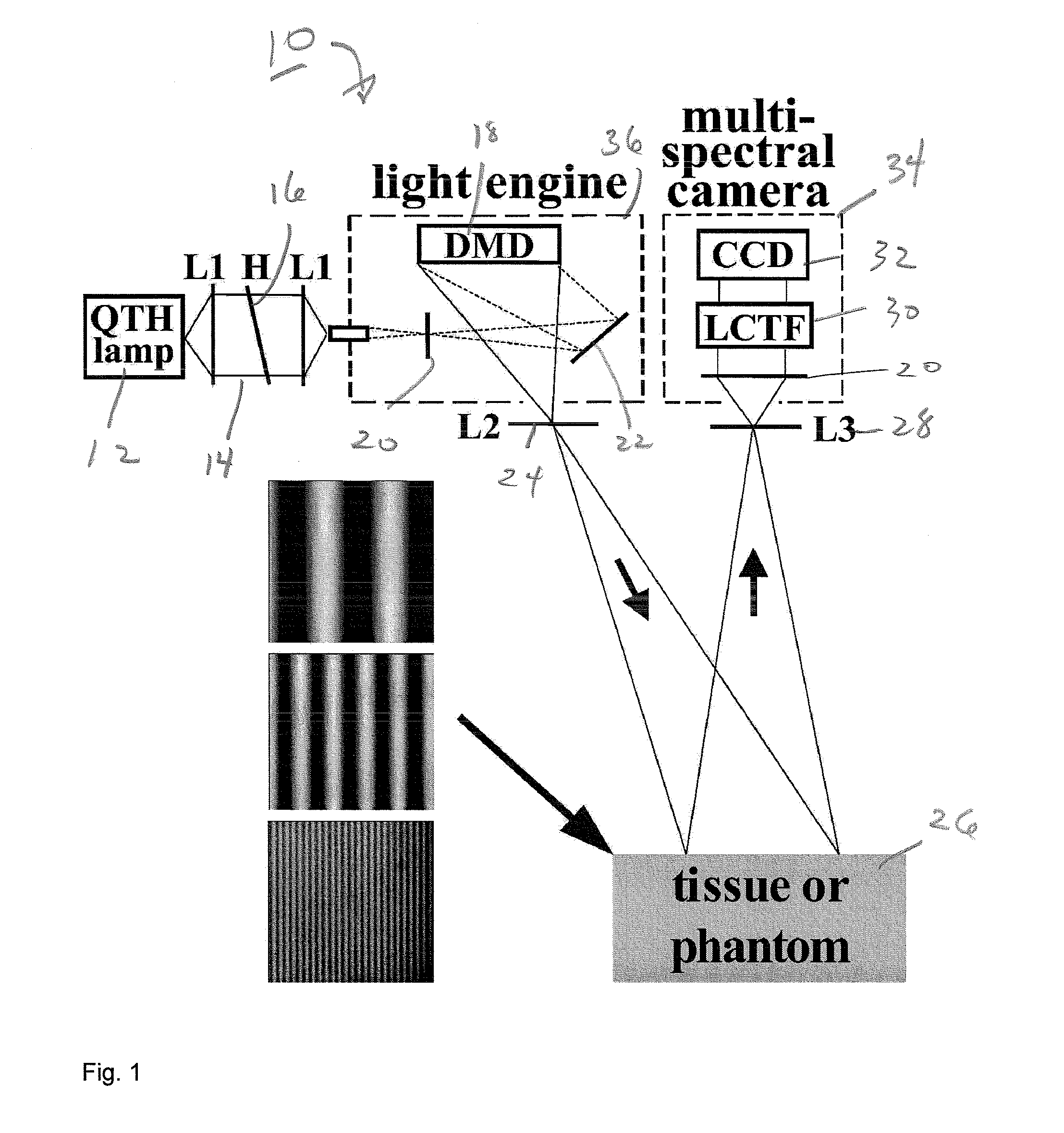
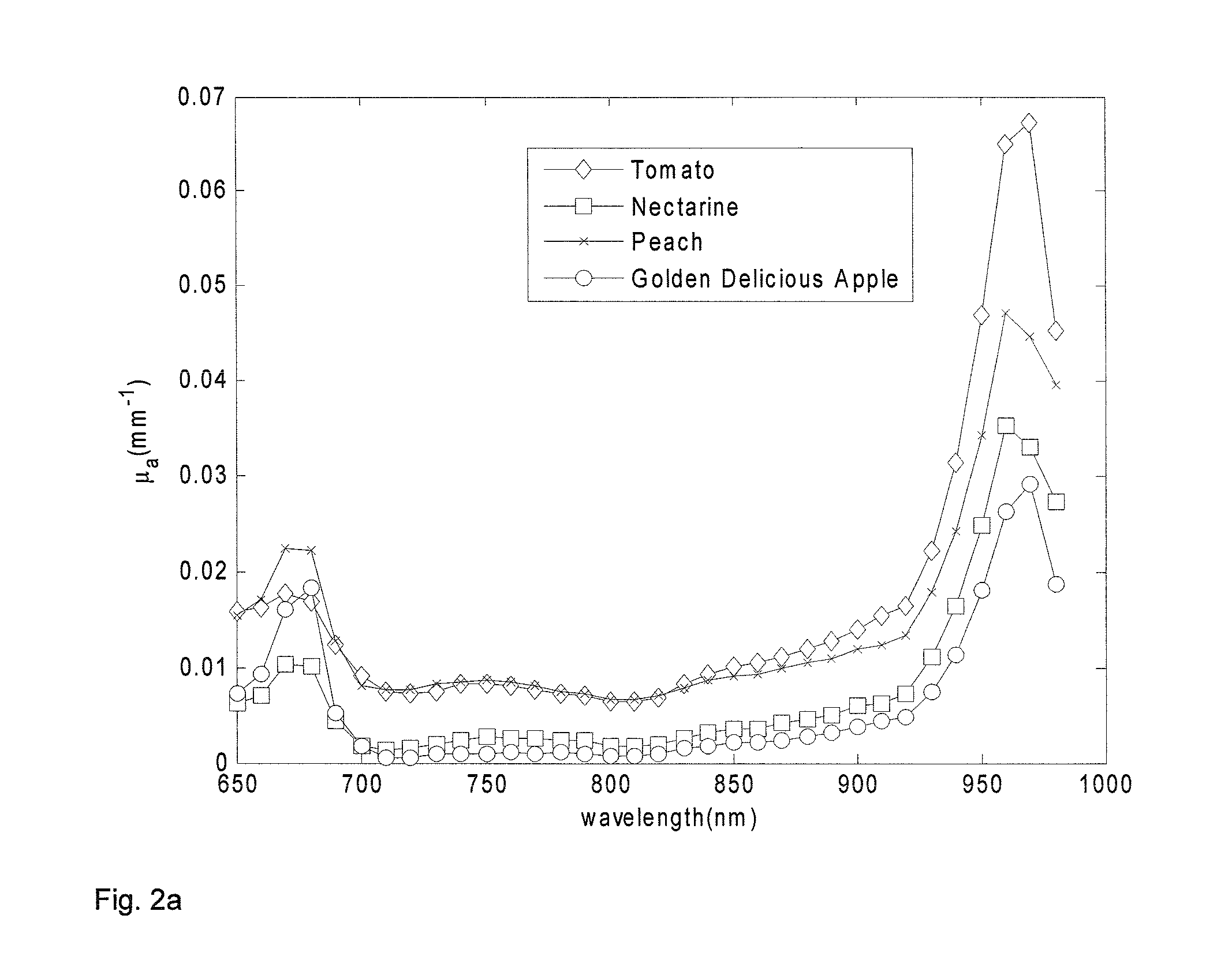
Method and apparatus for performing qualitative and quantitative analysis of produce (fruit, vegetables) using spatially structured illumination
ActiveUS20080101657A1Reduction factorEnhance the imageRaman/scattering spectroscopyCharacter and pattern recognitionDomain imagingSpatial frequency
A method and an apparatus for noninvasively and quantitatively determining spatially resolved absorption and reduced scattering coefficients over a wide field-of-view of a food object, including fruit or produce, uses spatial-frequency-domain imaging (SFDI). A single modulated imaging platform is employed. It includes a broadband light source, a digital micromirror optically coupled to the light source to control a modulated light pattern directed onto the food object at a plurality of selected spatial frequencies, a multispectral camera for taking a spectral image of a reflected modulated light pattern from the food object, a spectrally variable filter optically coupled between the food object and the multispectral camera to select a discrete number of wavelengths for image capture, and a computer coupled to the digital micromirror, camera and variable filter to enable acquisition of the reflected modulated light pattern at the selected spatial frequencies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
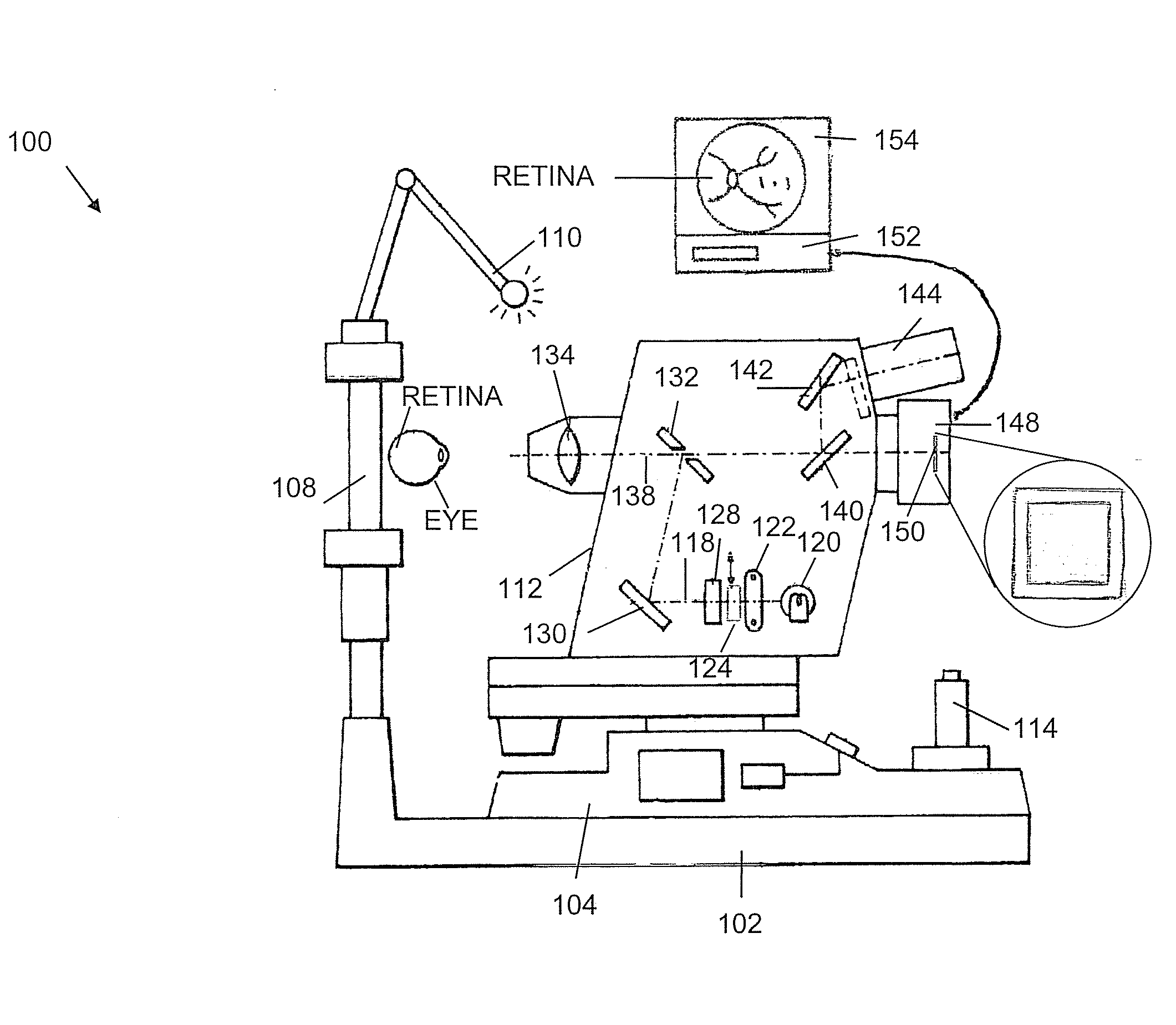
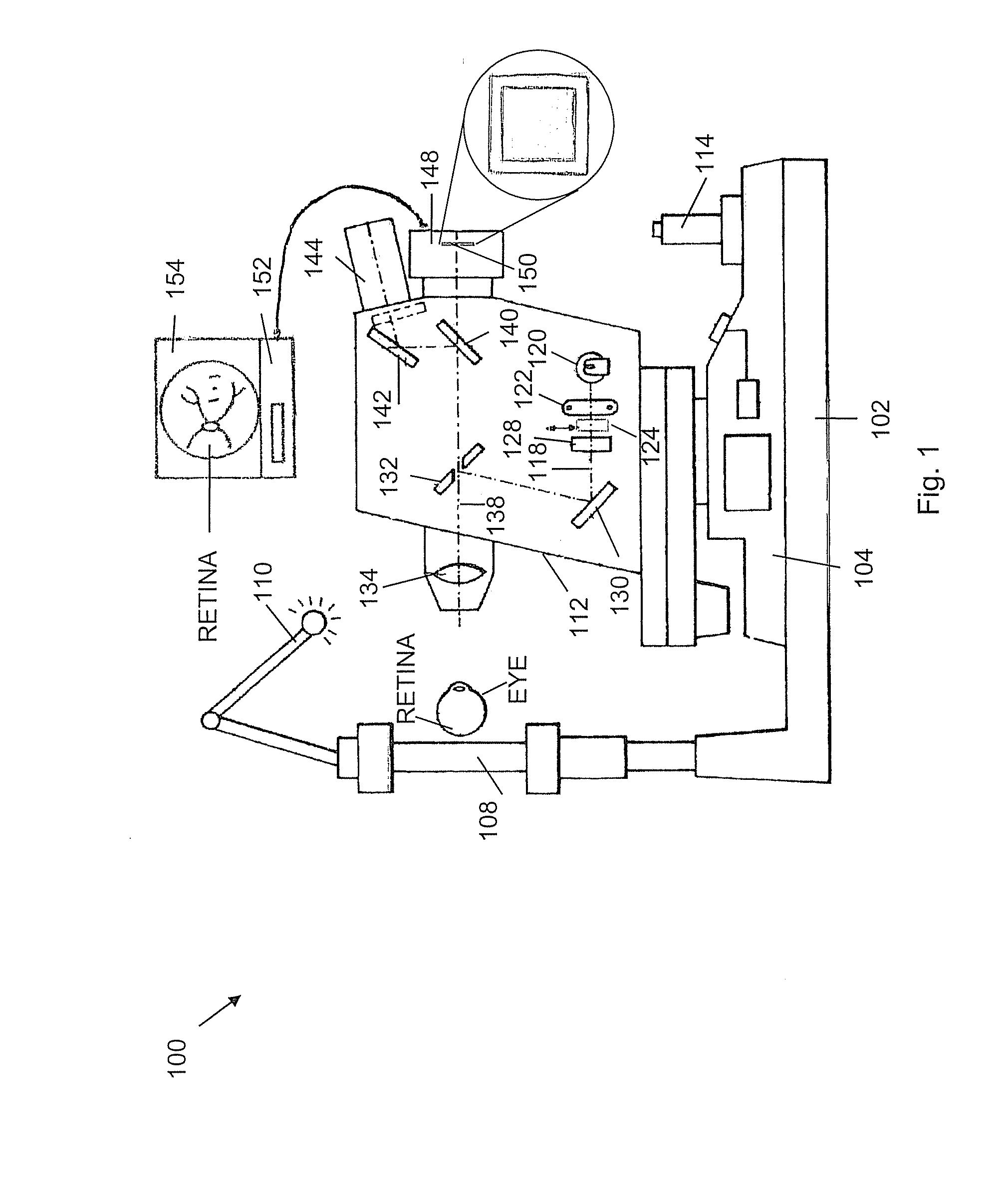
Snapshot Spectral Imaging of the Eye
ActiveUS20090225277A1Minimizes problemStrong robustnessSpectrum investigationDiagnostic recording/measuringFundus cameraPupil
Obtaining spectral images of an eye includes taking an optical system that images eye tissue onto a digital sensor array and optically fitting a multi-spectral filter array and the digital sensor array, wherein the multi-spectral filter array is disposed between the digital sensor array and an optics portion of the optical system. The resulting system facilitates acquisition of a snap-shot image of the eye tissue with the digital sensor array. The snap shot images support estimation of blood oxygen saturation in a retinal tissue. The resulting system can be based on a non-mydriatic fundus camera designed to obtain the retinal images without administration of pupil dilation drops.
Owner:MERGE HEALTHCARE
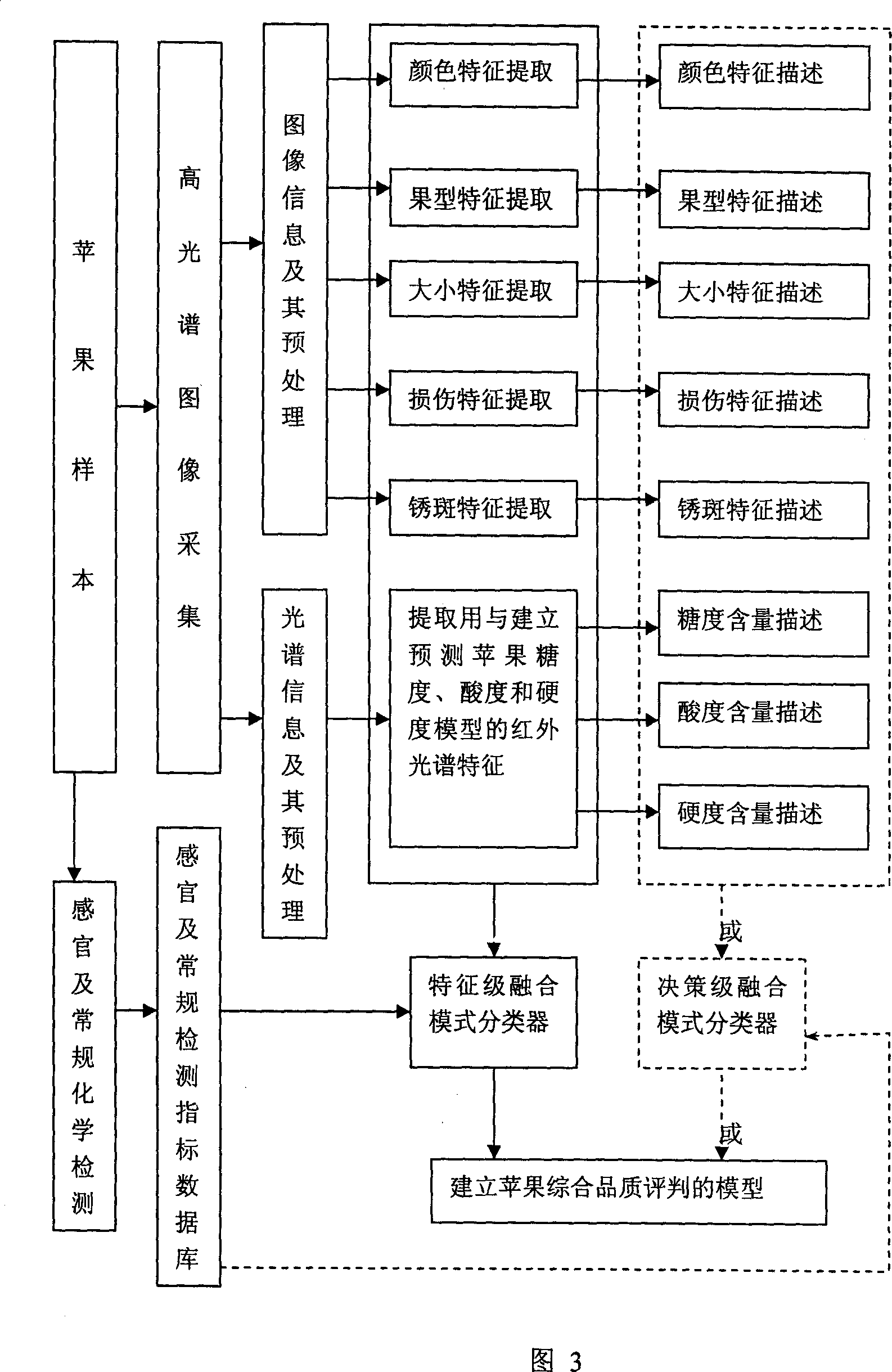
Non-destructive detection method and device for agricultural and animal products based on hyperspectral image technology
InactiveCN1995987AWith artificial intelligenceGuaranteed sampling qualityImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansNon destructiveAnimal product
The invention relates to high optical spectral image technique without harm to agricultural products. It can reflect the appearance of the agriculture products like color, shape, texture, dimension, scar and son on, and internal features like hardness, protein content and connected with knowledge base and experience of experts to make judgment. It can make quick, accurate, timely judgment of products, controlling the overall production with guarantee of the agriculture quality.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
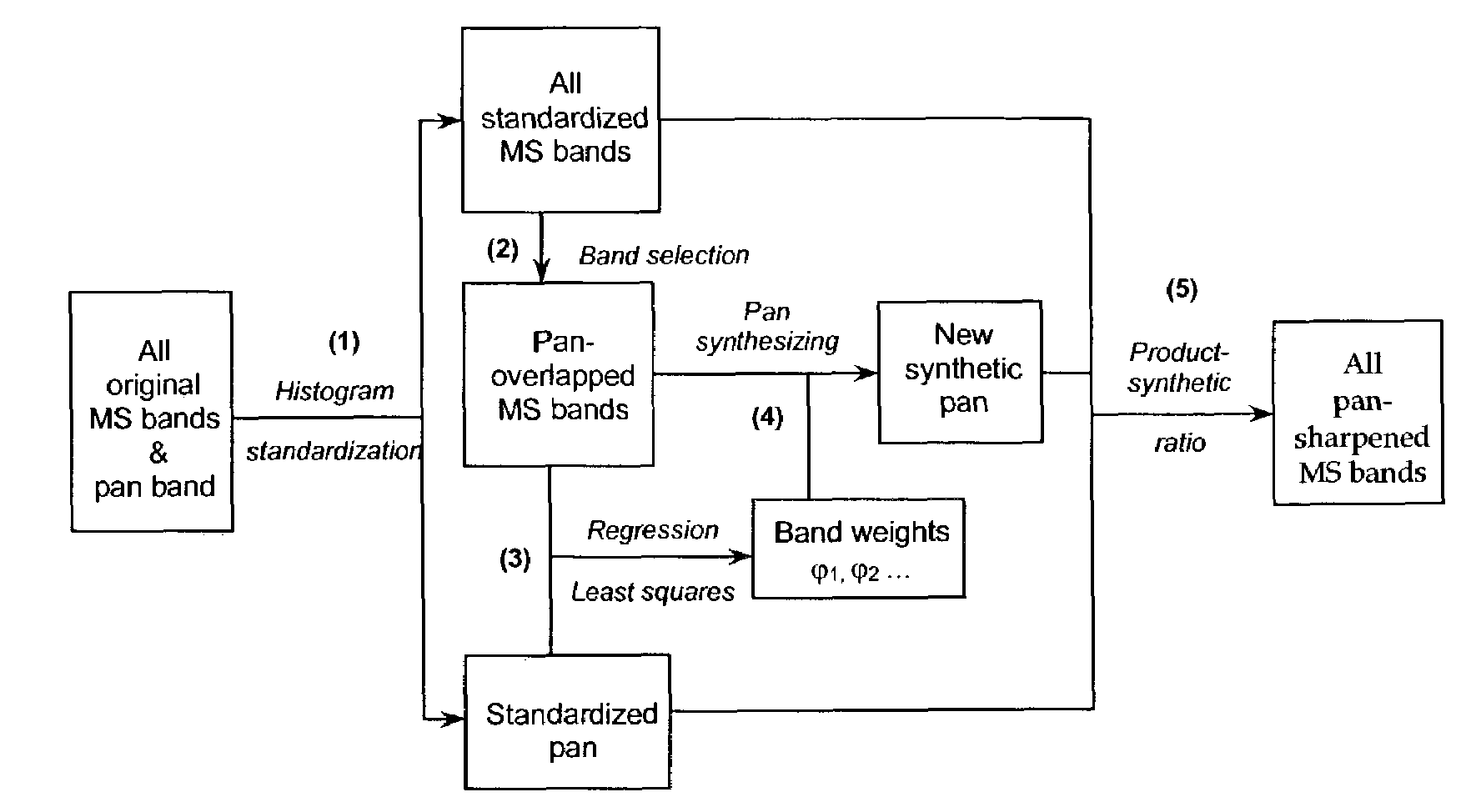
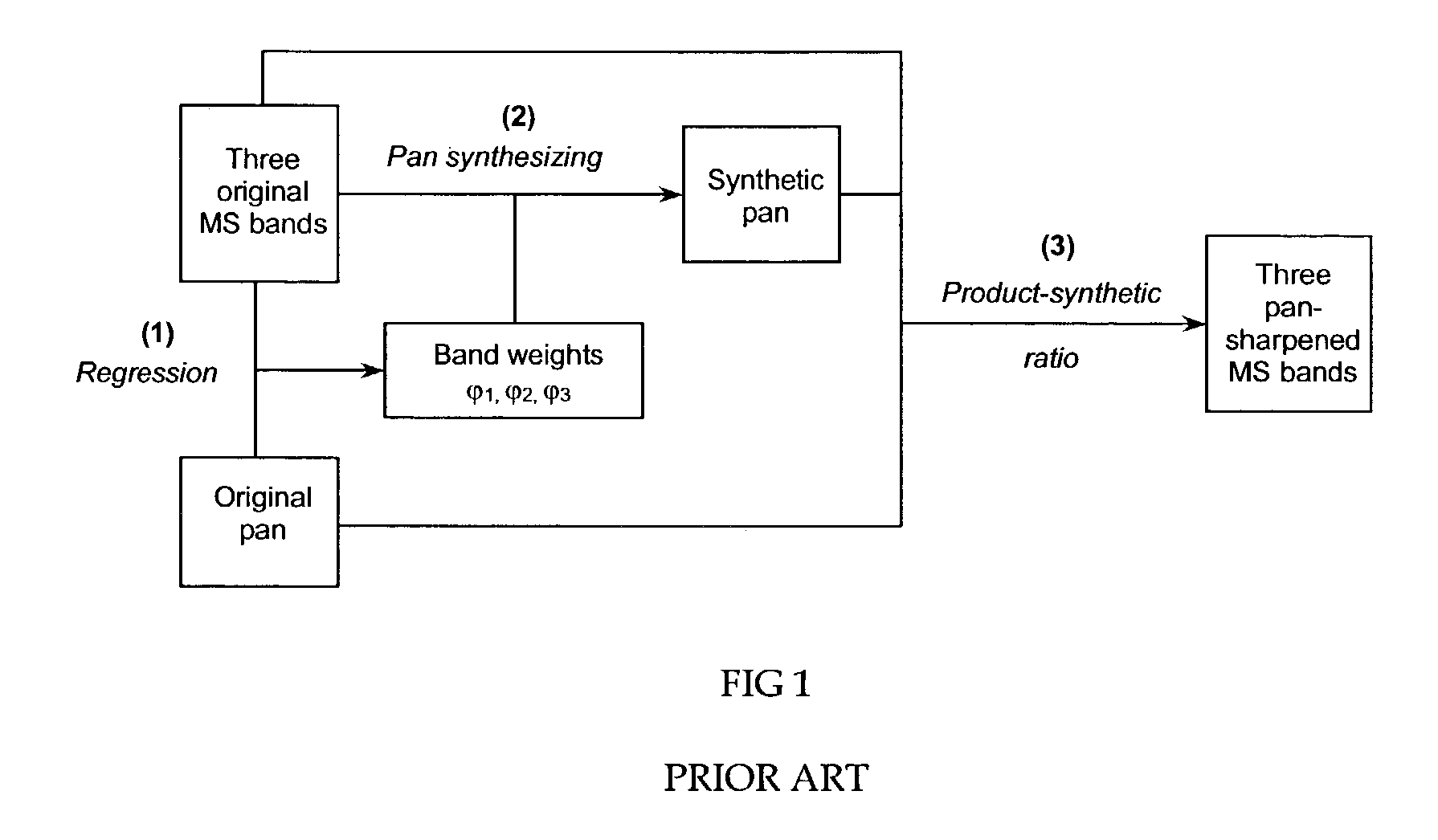
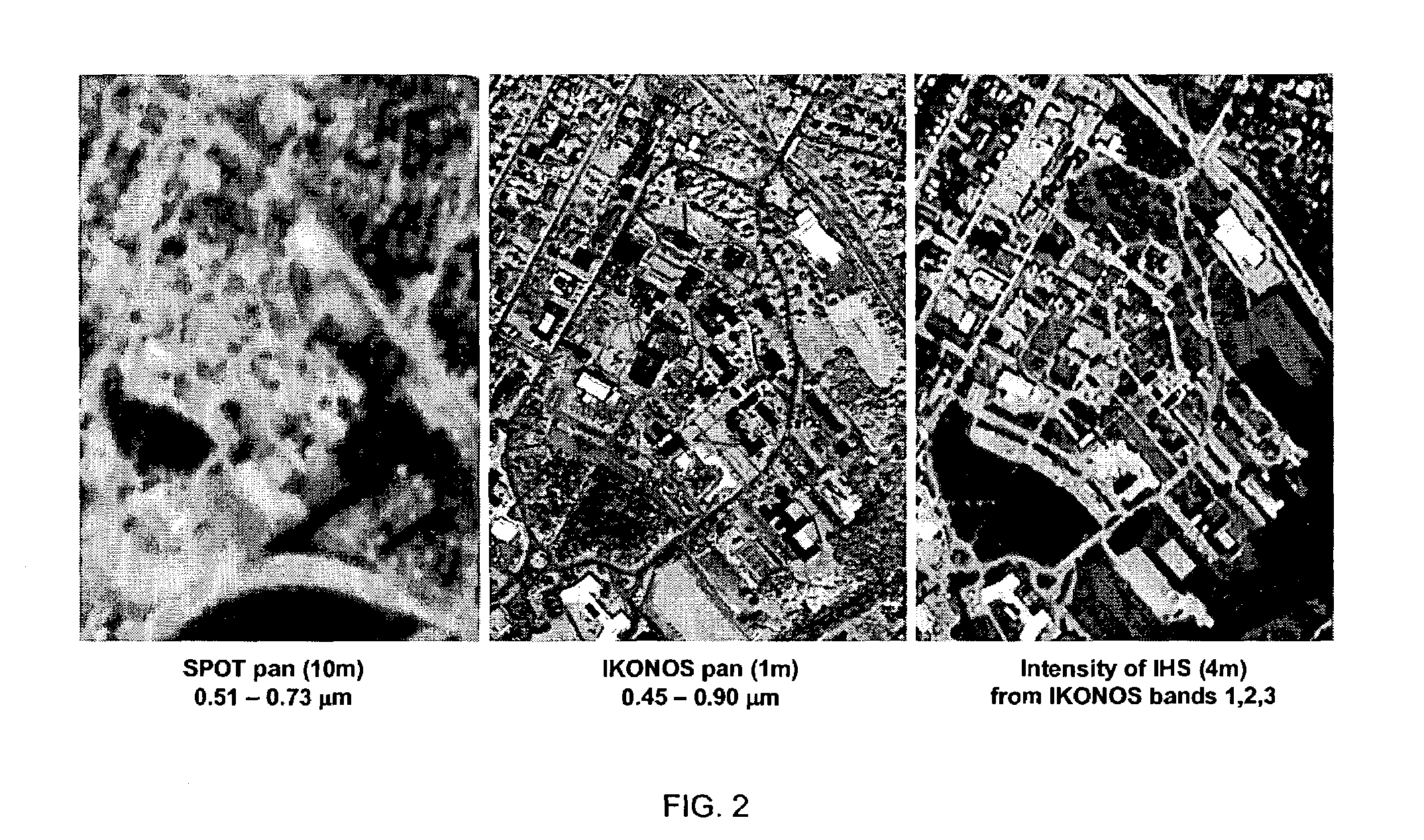
Synthetic panchromatic imagery method and system
ActiveUS7298922B1Quality improvementHigh imagingImage enhancementImage analysisMultispectral imageSpectral weight
Method and system for generating synthetic panchromatic imagery. A method for making a multi-spectral image includes capturing a panchromatic image of an imaging target. Additionally, the method includes capturing at least a first spectral image of the imaging target in a first spectral bandwidth, and capturing at least a second spectral image of the imaging target in a second spectral bandwidth. Also, the method includes determining at least a first spectral weight and a second spectral weight for the first spectral image and the second spectral image respectively. Additionally, the method includes generating a synthetic panchromatic image, determining a registration offset between the synthetic panchromatic image and the captured panchromatic image, warping the first spectral image and the second spectral image, and generating a multi-spectral image.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
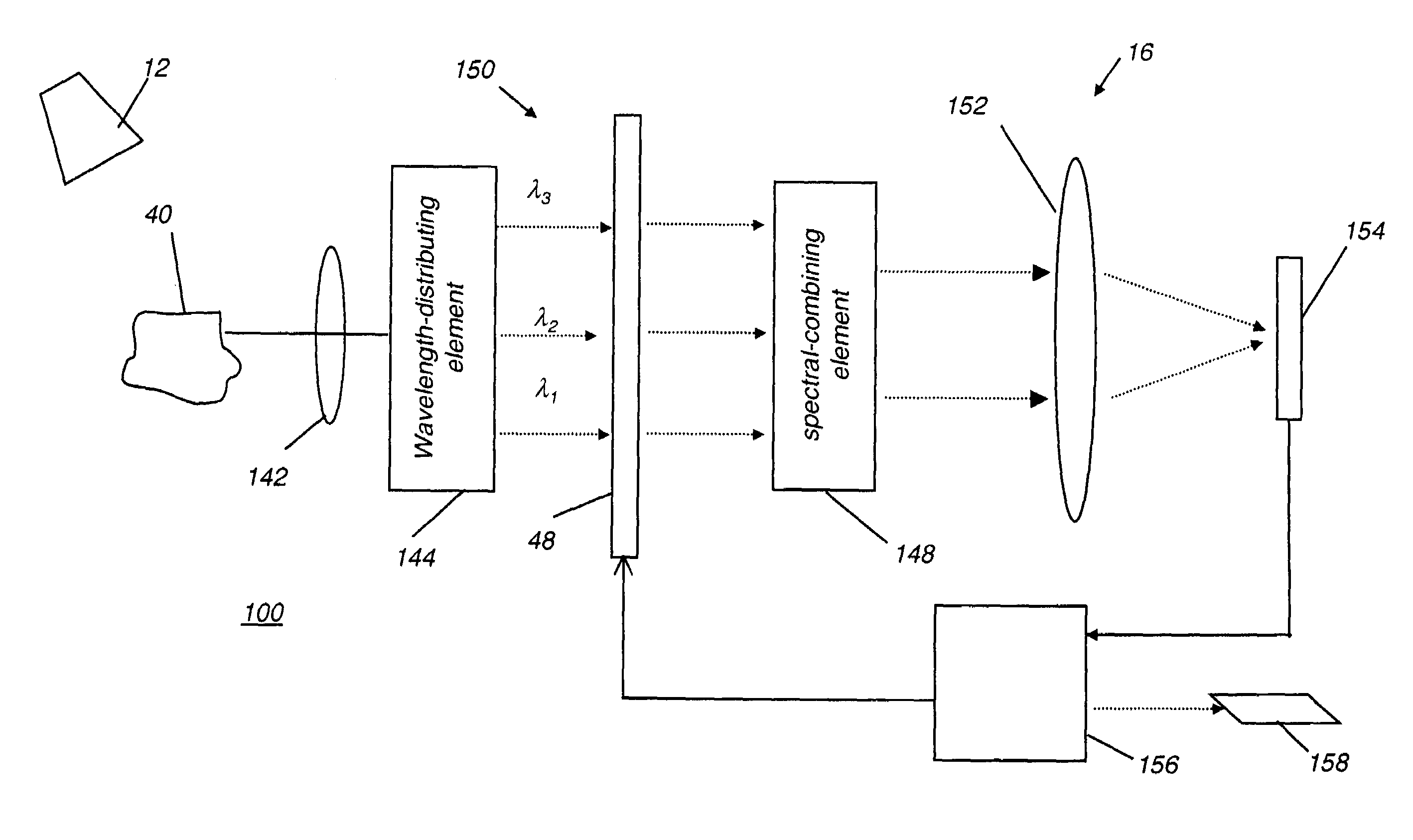
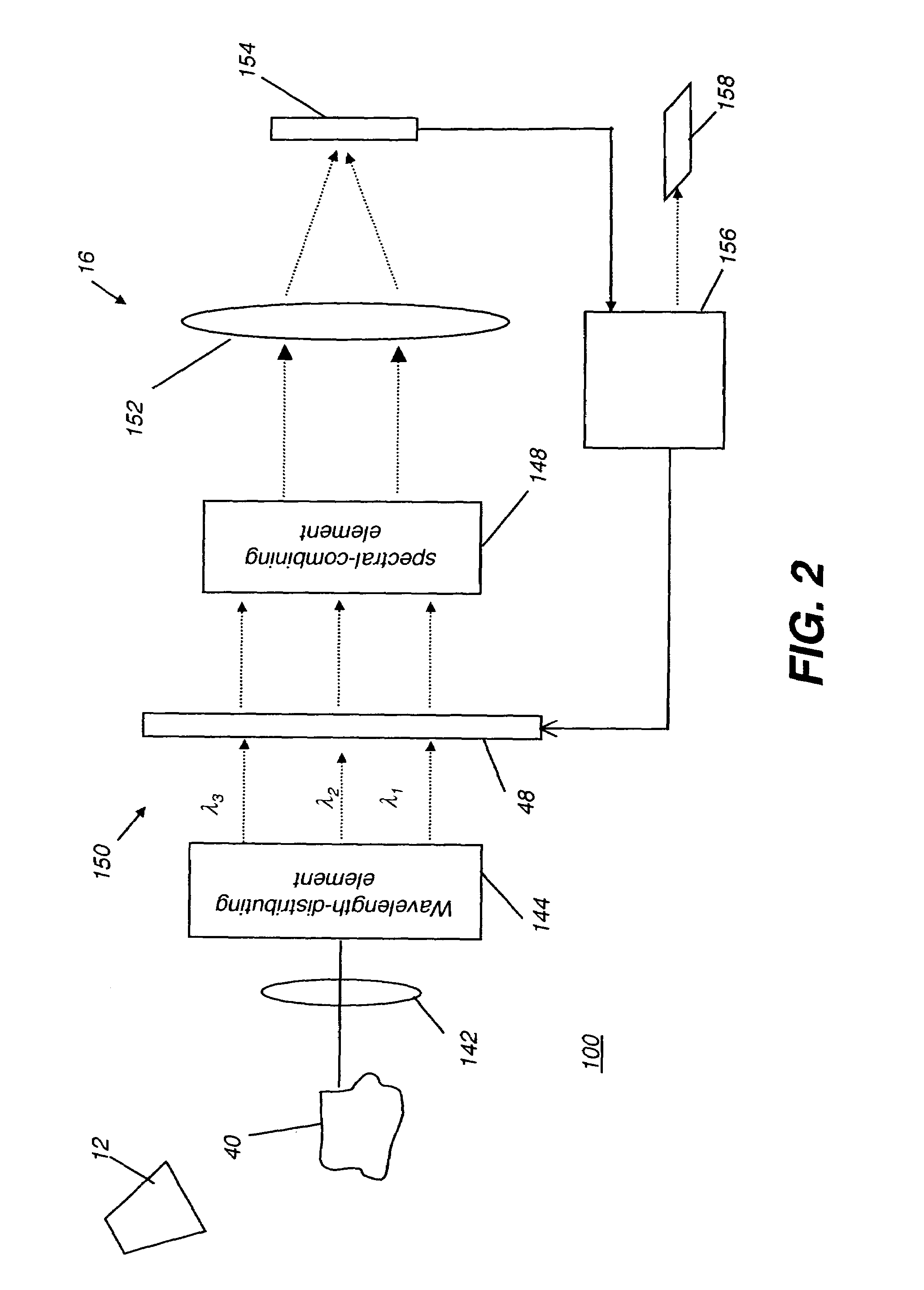
Spectral imaging system
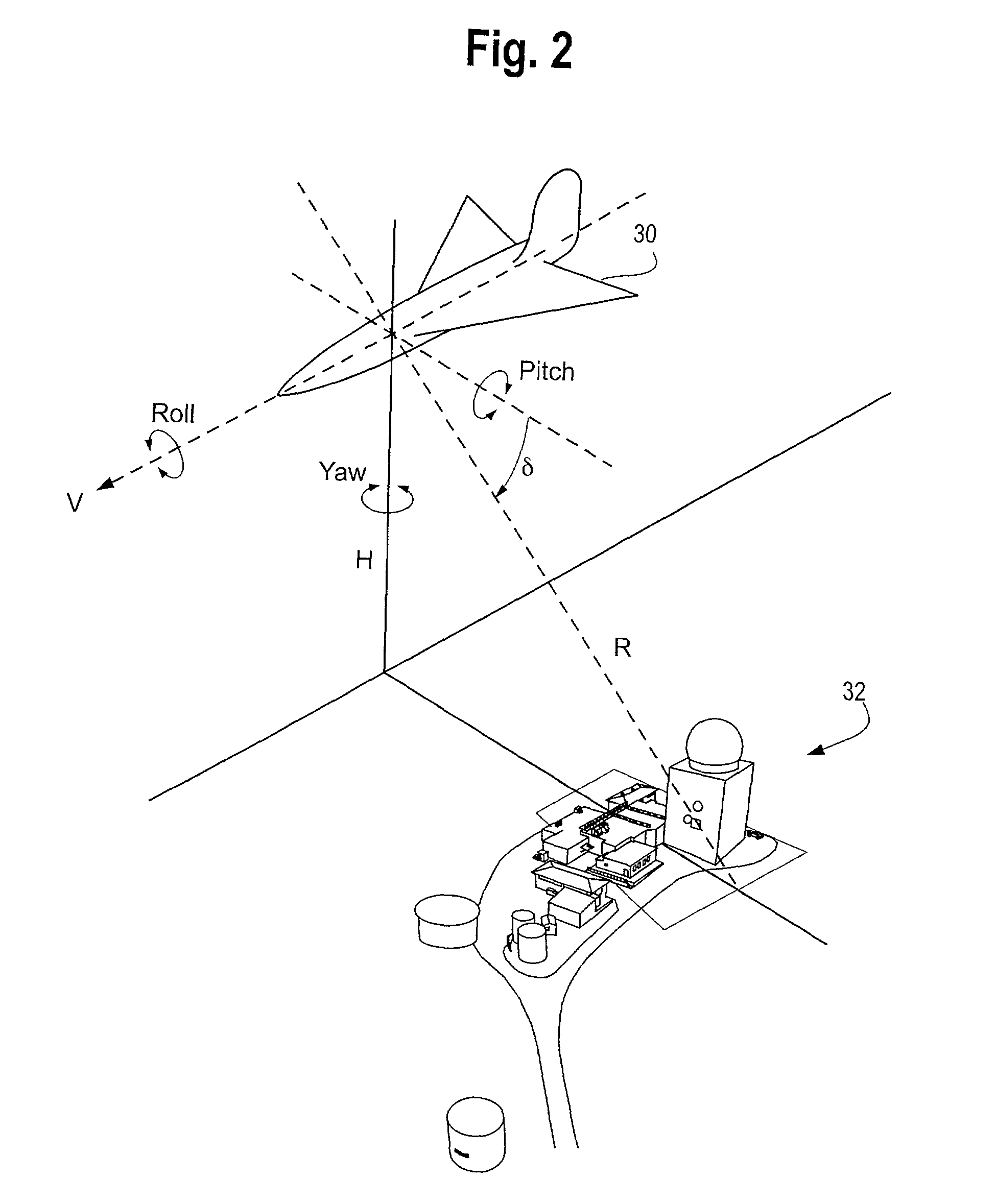
InactiveUS20050151965A1Wide rangeIncrease calibration rangeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationData acquisitionSpectral dimension
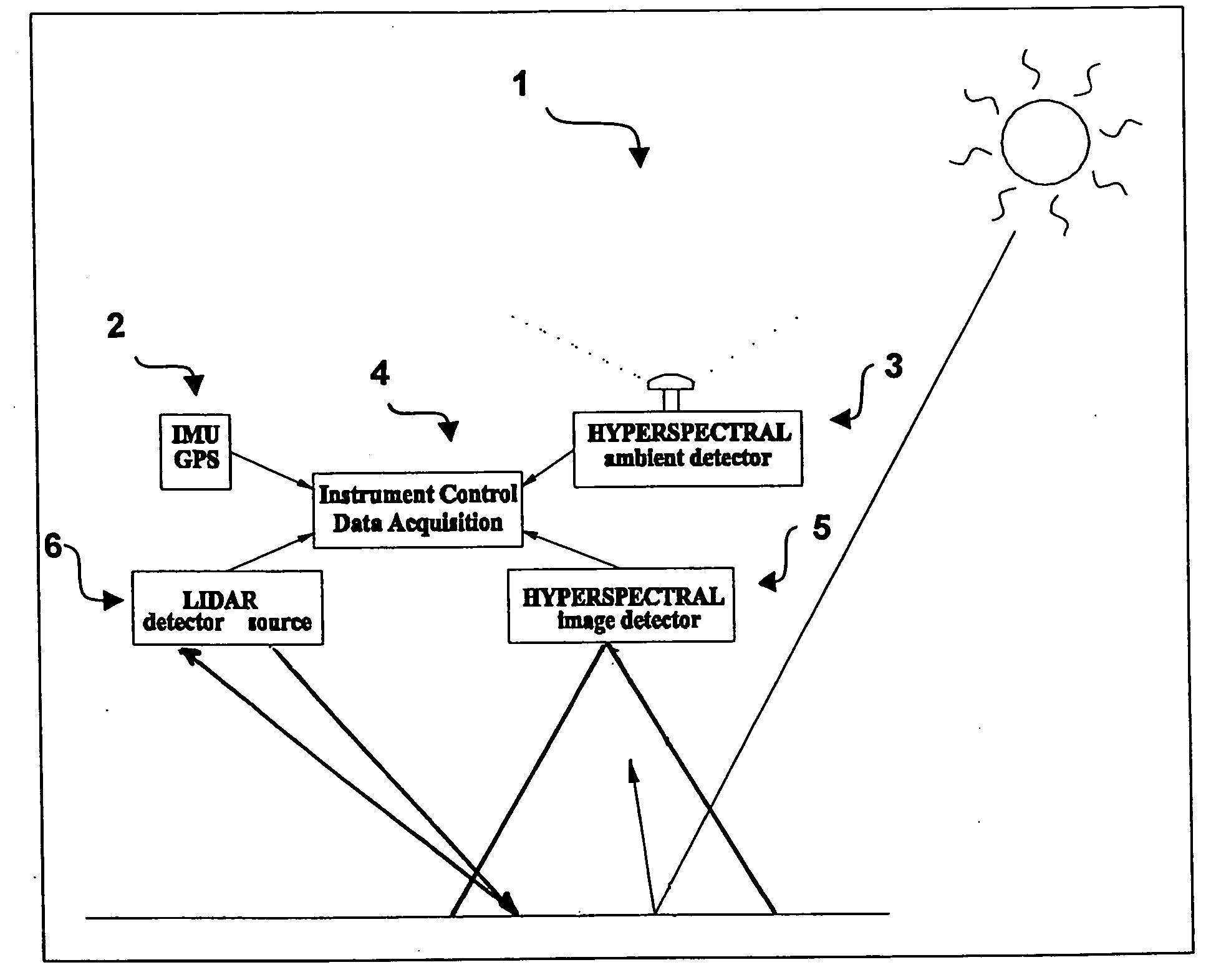
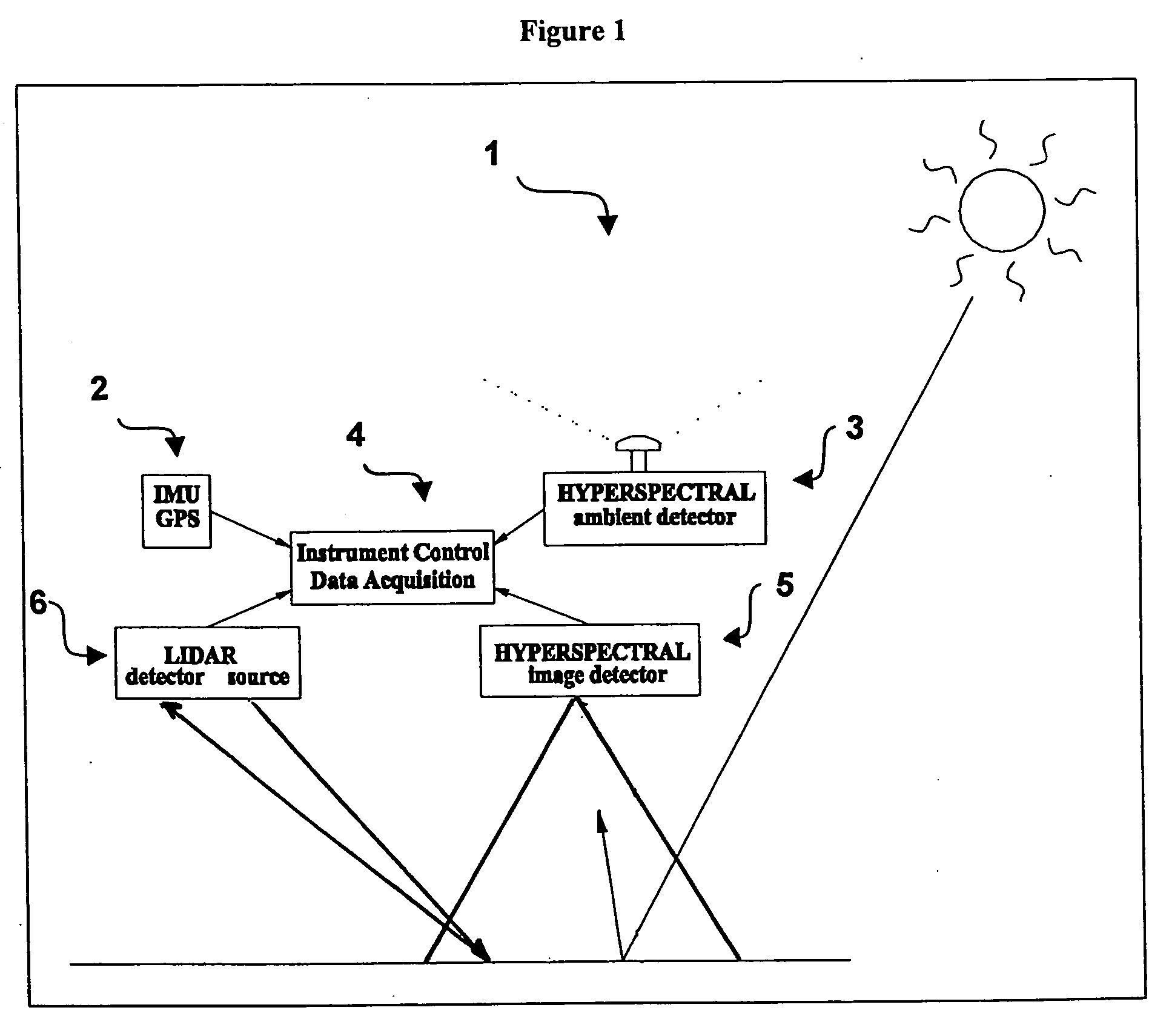
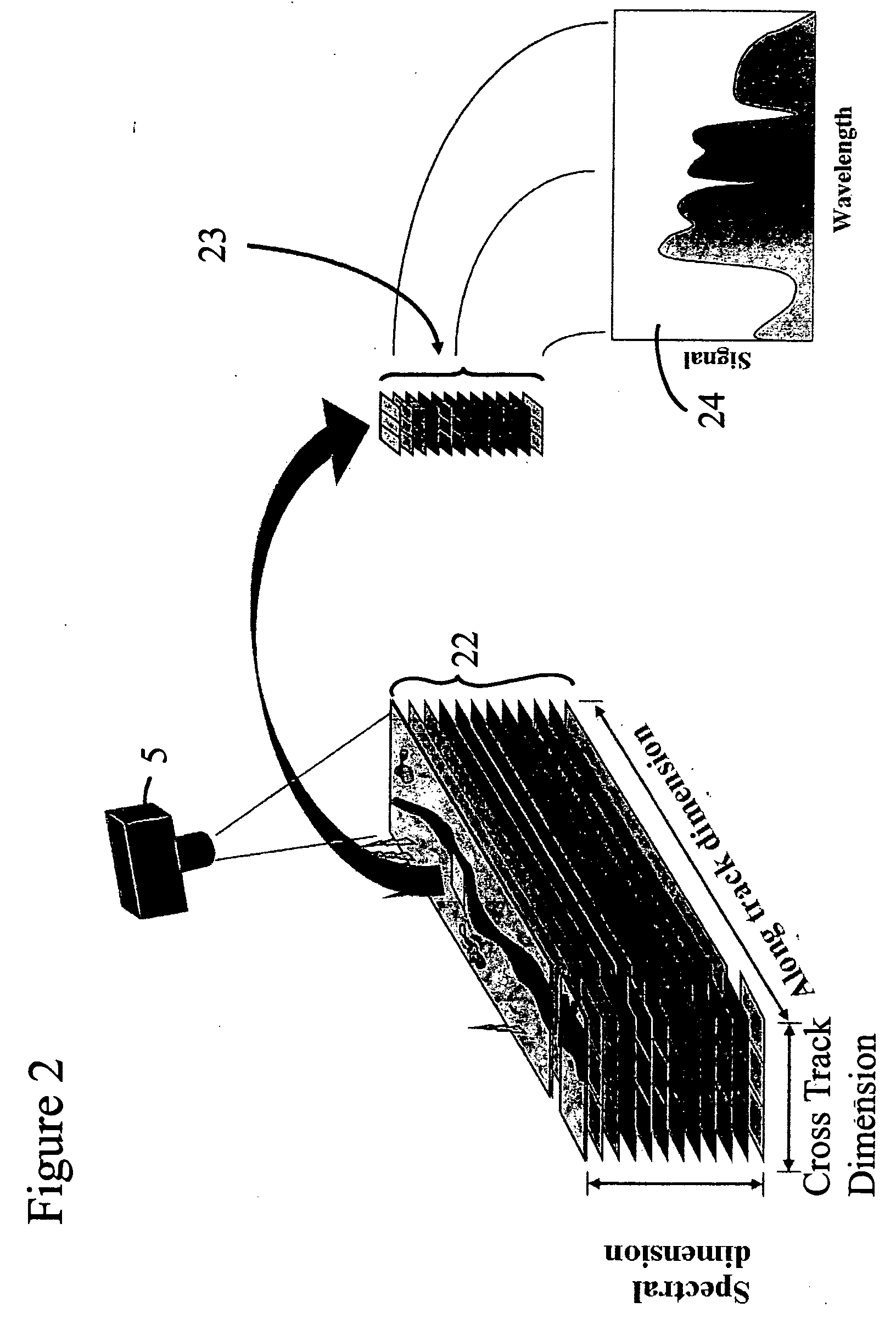
An imaging system and methods for resolving elements of interest through and obscuring environment by removing undesired signals from the intervening, obscuring environment is disclosed. A passive hyperspectral imaging sensor is calibrated and integrated into a system having a positioning and attitude detection system and an instrument control and data acquisition system that records data from sensors in a three-dimensional data cube having two spatial dimensions and a spectral dimension. Either an active detection and ranging system or a look-up-table approach or both are used to remove the noise generated by the intervening, obscuring environment from the data relevant to the elements of interest.
Owner:EATHON INTELLIGENCE
Pseudo-apposition eye spectral imaging system
ActiveUS8665440B1Increase the angle of incidenceRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFiberOptical axis
Owner:MERCURY MISSION SYST LLC
Graph-based semi-supervised high-spectral remote sensing image classification method
ActiveCN102096825AReduce restrictionsReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityPartition of unity
The invention relates to a graph-based semi-supervised high-spectral remote sensing image classification method. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the features of an input image; randomly sampling M points from an unlabeled sample, constructing a set S with L marked points, constructing a set R with the rest of the points; calculating K adjacent points of the points in the sets S and R in the set S by use of a class probability distance; constructing two sparse matrixes WSS and WSR by a linear representation method; using label propagation to obtain a label function F<*><S>, and calculating the label prediction function F<*><R> of the sample points in the set R to determine the labels of all the pixel points of the input image. According to the method, the adjacent points of the sample points can be calculated by use of the class probability distance, and the accurate classification of high-spectral images can be achieved by utilizing semi-supervised conduction, thus the calculation complexity is greatly reduced; in addition, the problem that the graph-based semi-supervised learning algorithm can not be used for large-scale data processing is solved, and the calculation efficiency can be improved by at least 20-50 times within the per unit time when the method provided by the invention is used, and the visual effects of the classified result graphs are good.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Ares method of sub-pixel target detection
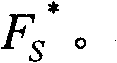
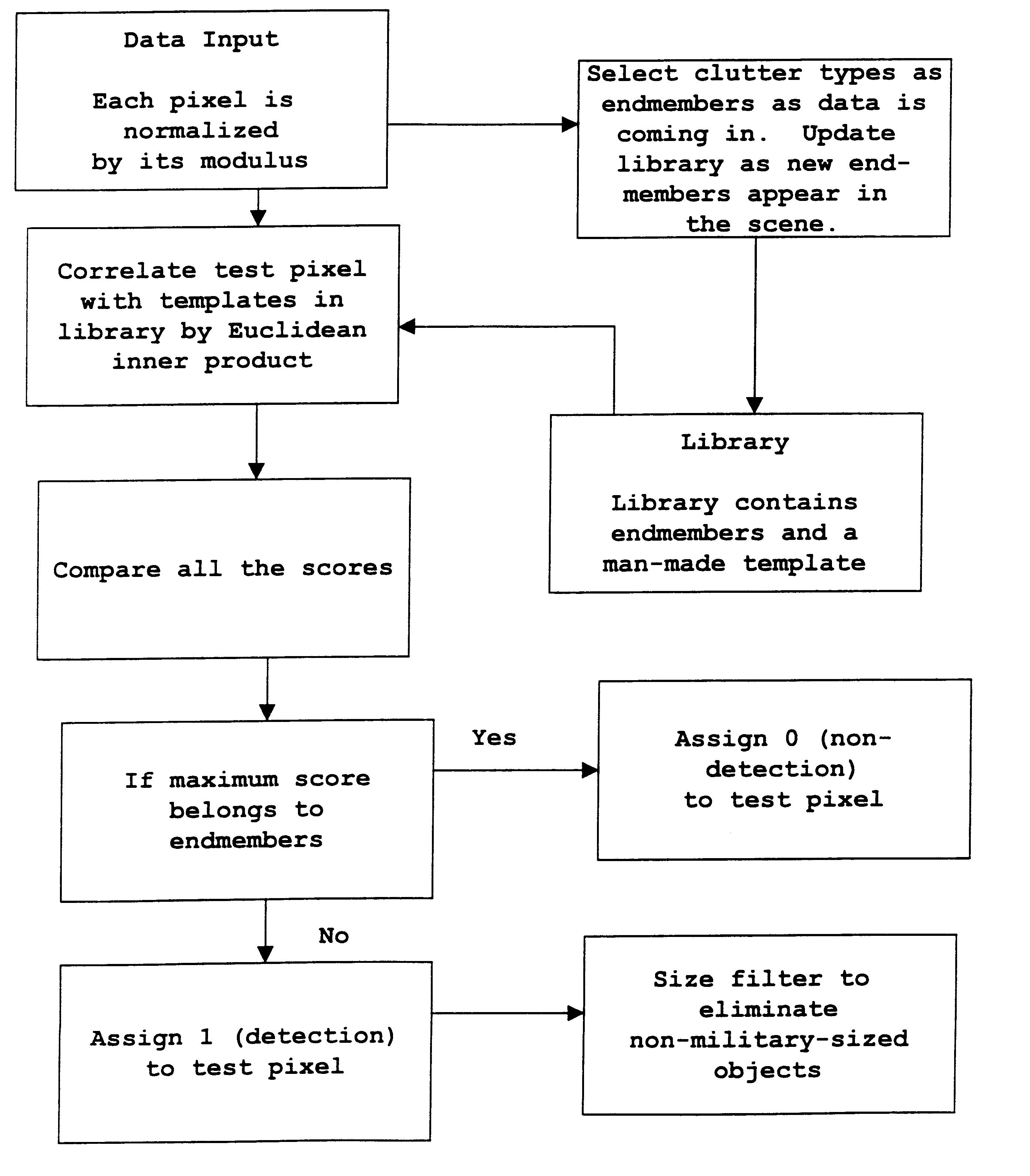
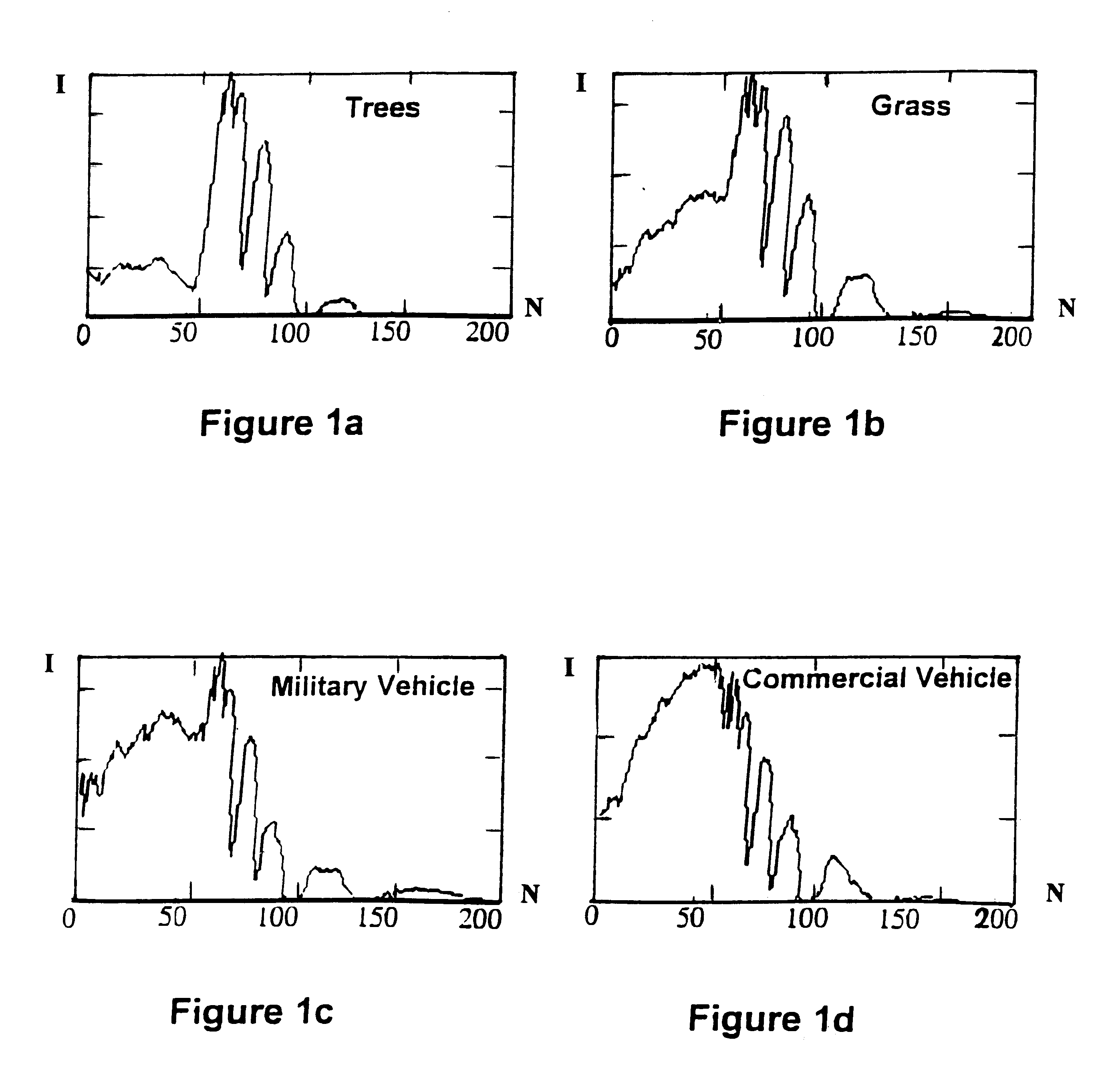
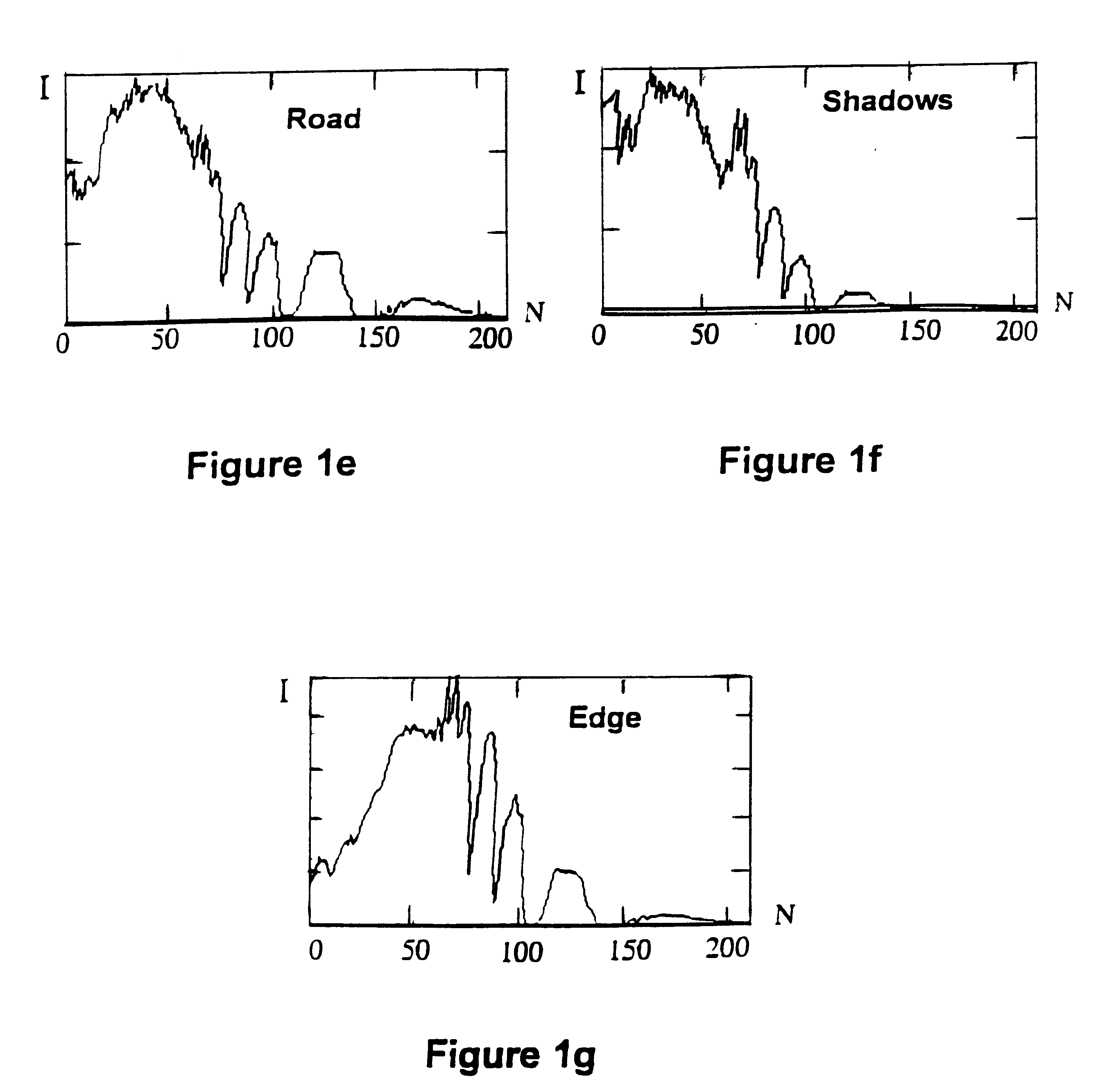
Target detection using algorithms is based on the adaptive real-time endmembers selection from hyperspectral image data. New pixels are correlated with prestored clutter endmembers to obtain subsequently detected target and clutter pixels and then suppressing the latter, leaving about 10% of the image as targets. Targets are then reduced in number by size filtering.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
System and method for assessing a condition of property
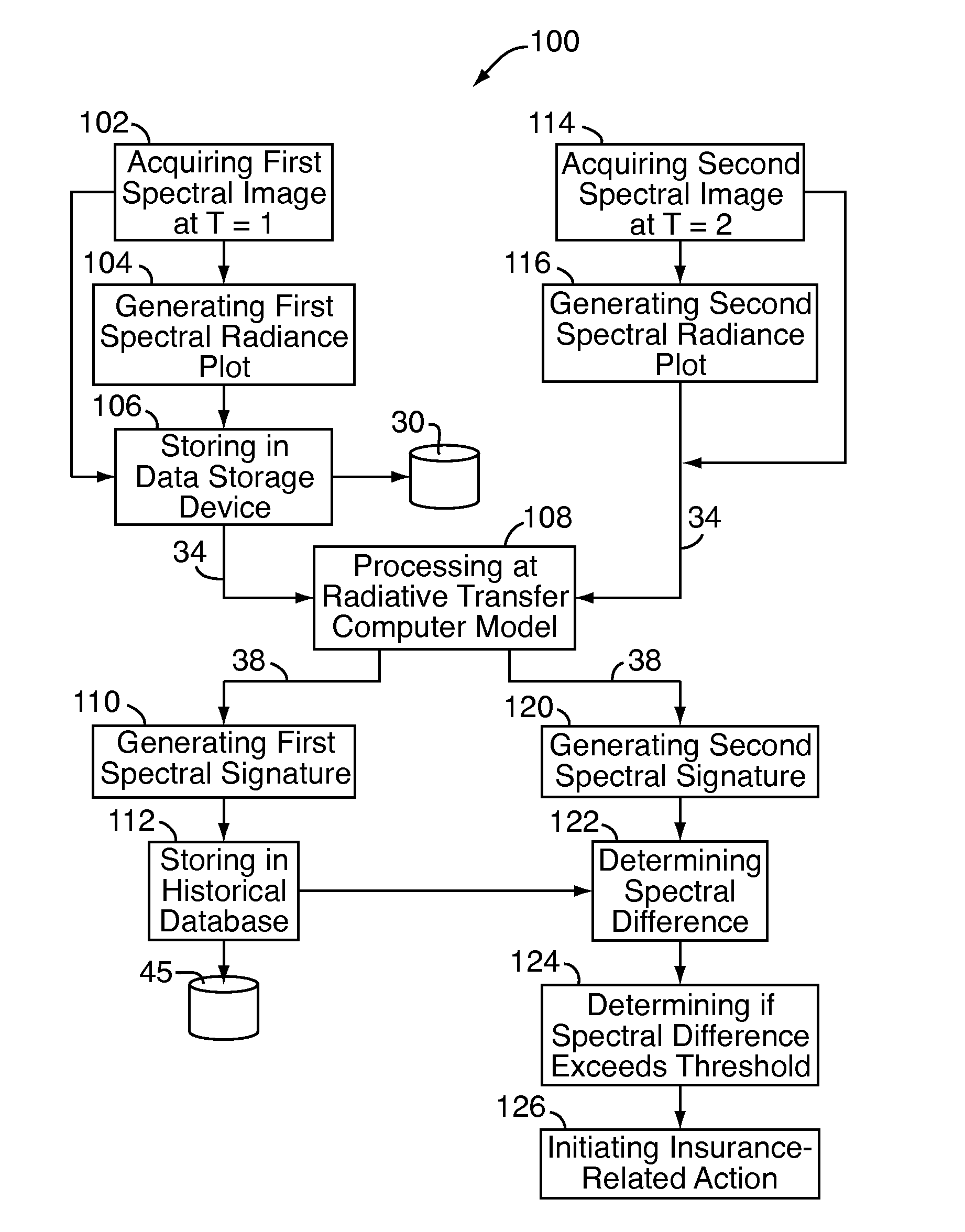
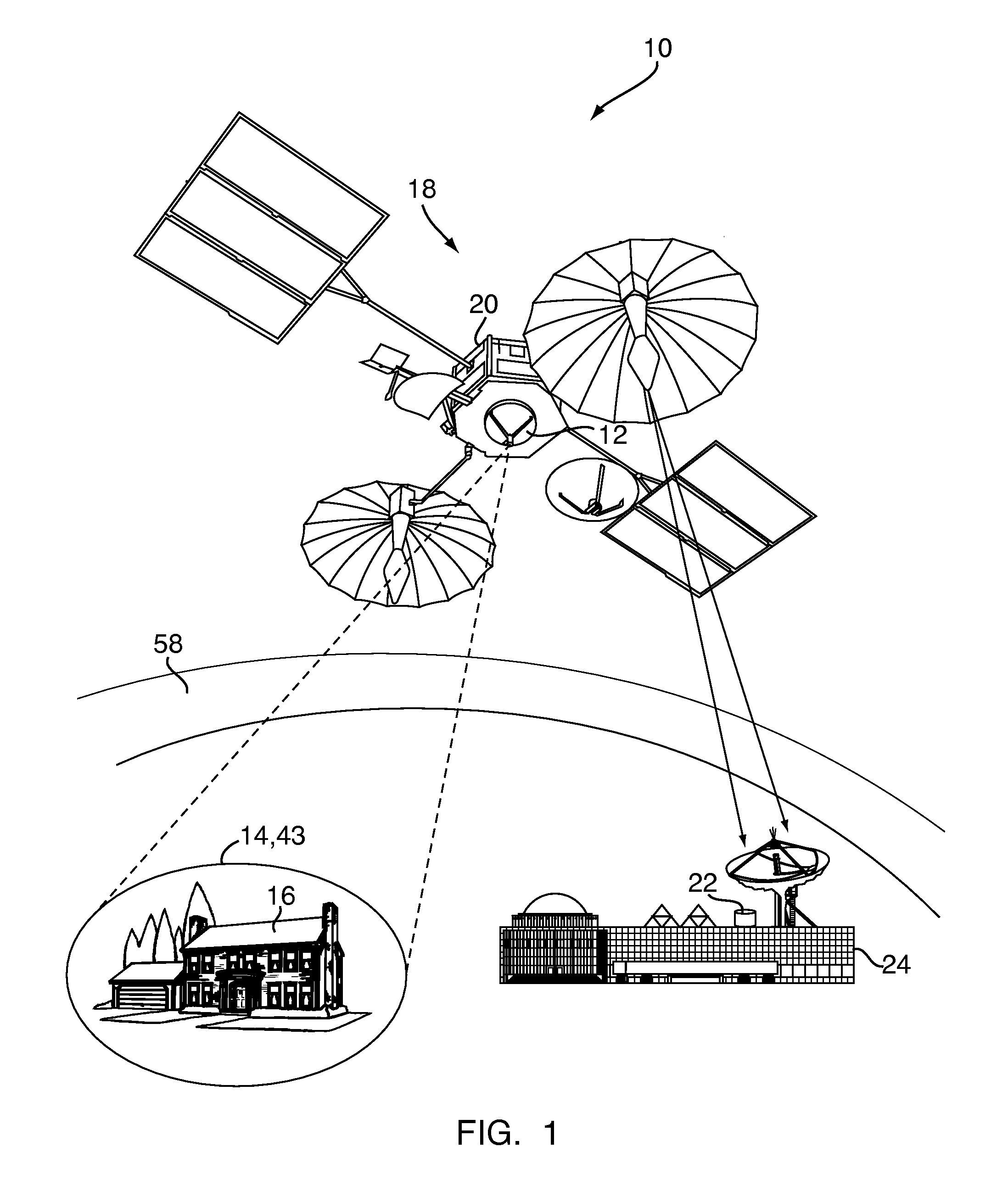
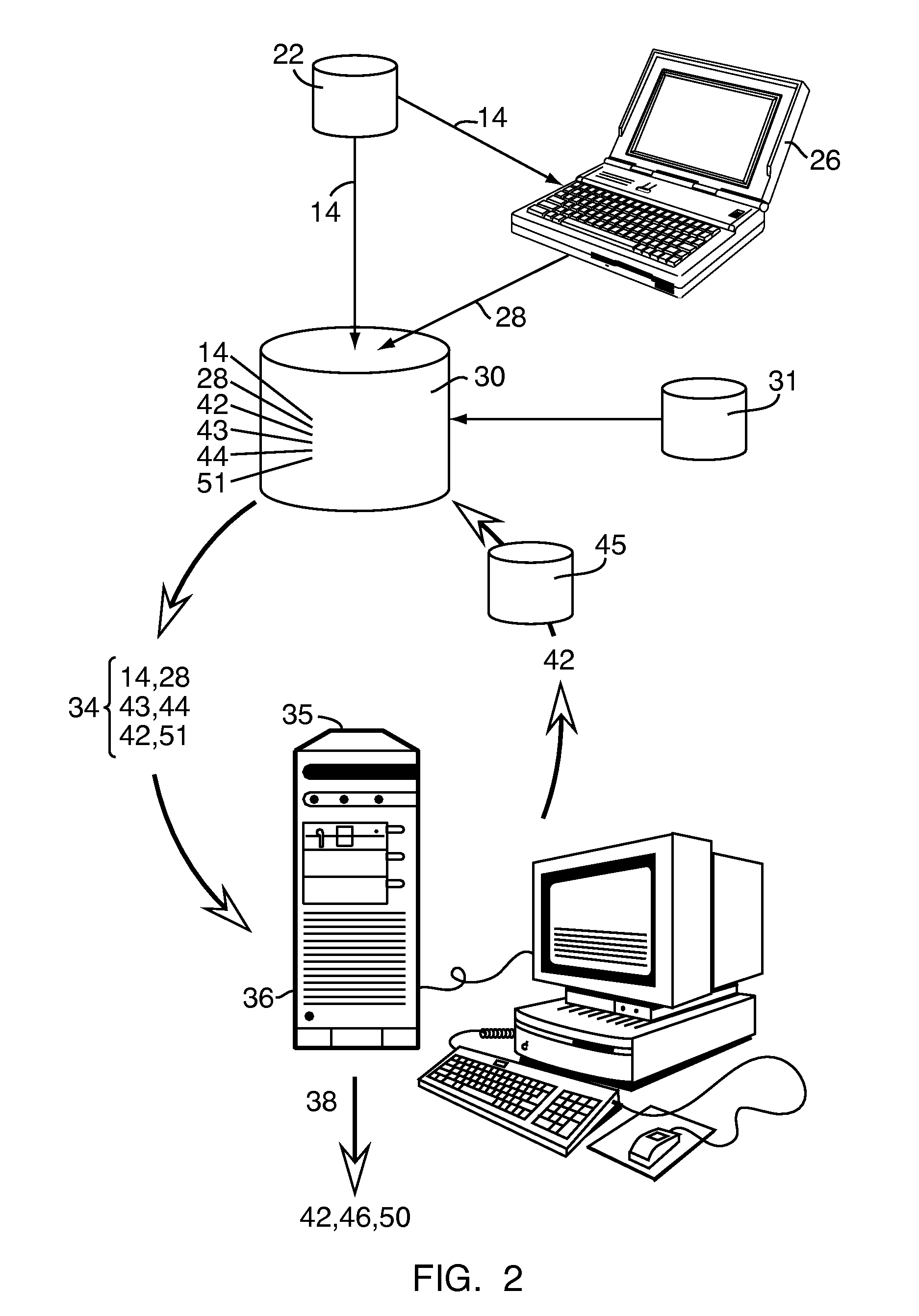
A system and method for assessing a condition of property for insurance purposes includes a sensor for acquiring a spectral image. In a preferred embodiment, the spectral image is post-processed to generate at least one spectral radiance plot, the plot used as input to a radiative transfer computer model. The output of the model establishes a spectral signature for the property. Over a period of time, spectral signatures can be compared to generate a spectral difference, the difference attributed to a change in the condition of the property, such as a fire or flood. In response to the change, an insurance company initiates an insurance-related action such as processing a claim.
Owner:HARTFORD FIRE INSURANCE
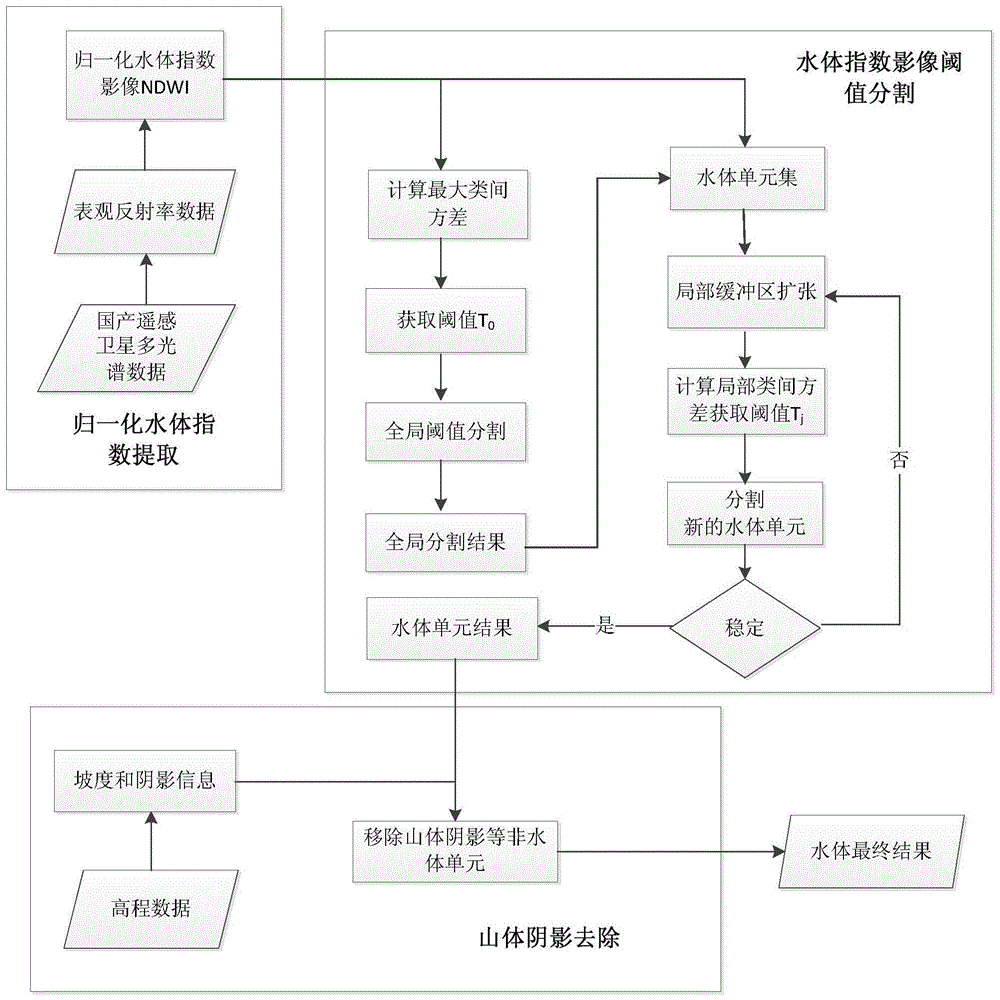
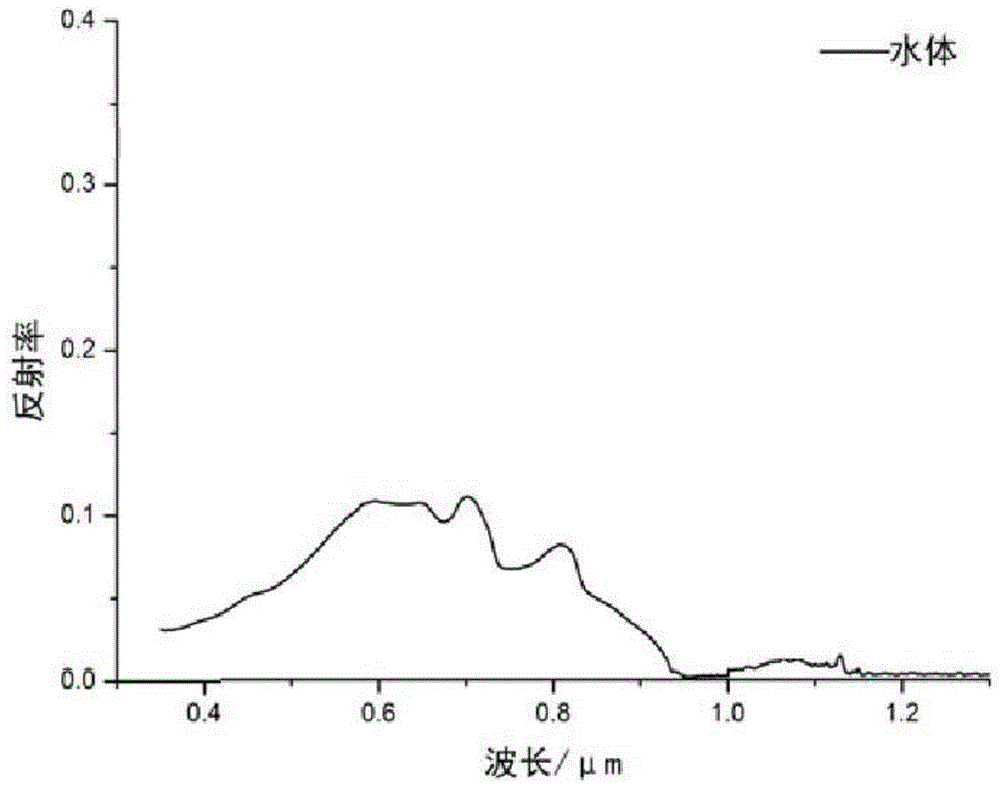
Water body information automatic extraction method for multi-spectral image of remote sensing satellite
ActiveCN105046087AAccurate extractionIncreased maximum brightnessElectromagnetic wave reradiationSpecial data processing applicationsElevation dataInformation extraction
A water body information automatic extraction method for a multi-spectral image of a remote sensing satellite comprises the steps of (1) implementing normalized difference water index (NDWI) extraction on apparent reflectivity data of the multi-spectral image of the domestic remote sensing satellite, and forming an NDWI image; (2) implementing maximum between-cluster variance algorithm based global threshold segmentation initial water body information extraction on the NDWI image; (3) implementing local buffer area expansion and threshold segmentation on the initial water body information, and obtaining a stable water body unit result set; and (4) according to elevation data, obtaining slope and shadow information, removing a shadow from the water body unit result set, and finally finishing the water body information extraction. According to the method, by adopting a computer automatic interpretation method and utilizing a thought of from global segmentation to local iterative segmentation, the NDWI is subjected to water body information extraction in a process manner; and the method is high in extraction precision and easy in engineering.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
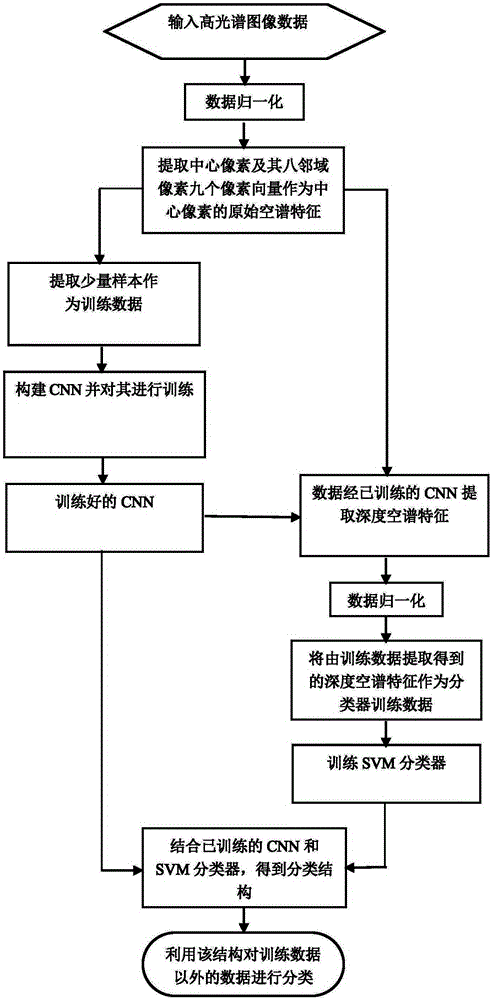
Hyperspectral image classification method based on spectral-spatial cooperation of deep convolutional neural network
ActiveCN105320965ATake advantage ofSolving complex processing problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionDimensionality reductionLabeled data
The present invention relates to a hyperspectral image classification method based on spectral-spatial cooperation of a deep convolutional neural network, which leads the conventional deep convolutional neural network applied to a two-dimensional image into the three-dimensional hyperspectral image classification problem. Firstly, the convolutional neural network is trained by using a small volume of label data, and a spectral-spatial feature of a hyperspectral image is autonomously extracted by using the network without carrying out any compression and dimensionality reduction processing; then, a support vector machine (SVM) classifier is trained by using the extracted spectral-spatial feature so as to classify an image; and finally, the trained neural network is combined with the trained classifier, the neural network extracts a spectral-spatial feature of a to-be-classified target and the classifier determines a specific category of the extracted spectral-spatial feature so as to acquire a structure (DCNN-SVM) that can autonomously extract the spectral-spatial feature of the hyperspectral image and carry out classification to the spectral-spatial feature, thereby forming a set of hyperspectral image classification method.
Owner:陕西令一盾信息技术有限公司
Scanning endoscope
InactiveUS7448995B2Improve discriminationImprove color gamutTelevision system detailsSurgeryLaser transmitterDelivery system
A scanning endoscope, amenable to both rigid and flexible forms, scans a beam of light across a field-of-view, collects light scattered from the scanned beam, detects the scattered light, and produces an image. The endoscope may comprise one or more bodies housing a controller, light sources, and detectors; and a separable tip housing the scanning mechanism. The light sources may include laser emitters that combine their outputs into a polychromatic beam. Light may be emitted in ultraviolet or infrared wavelengths to produce a hyperspectral image. The detectors may be housed distally or at a proximal location with gathered light being transmitted thereto via optical fibers. A plurality of scanning elements may be combined to produce a stereoscopic image or other imaging modalities. The endoscope may include a lubricant delivery system to ease passage through body cavities and reduce trauma to the patient. The imaging components are especially compact, being comprised in some embodiments of a MEMS scanner and optical fibers, lending themselves to interstitial placement between other tip features such as working channels, irrigation ports, etc.
Owner:MICROVISION
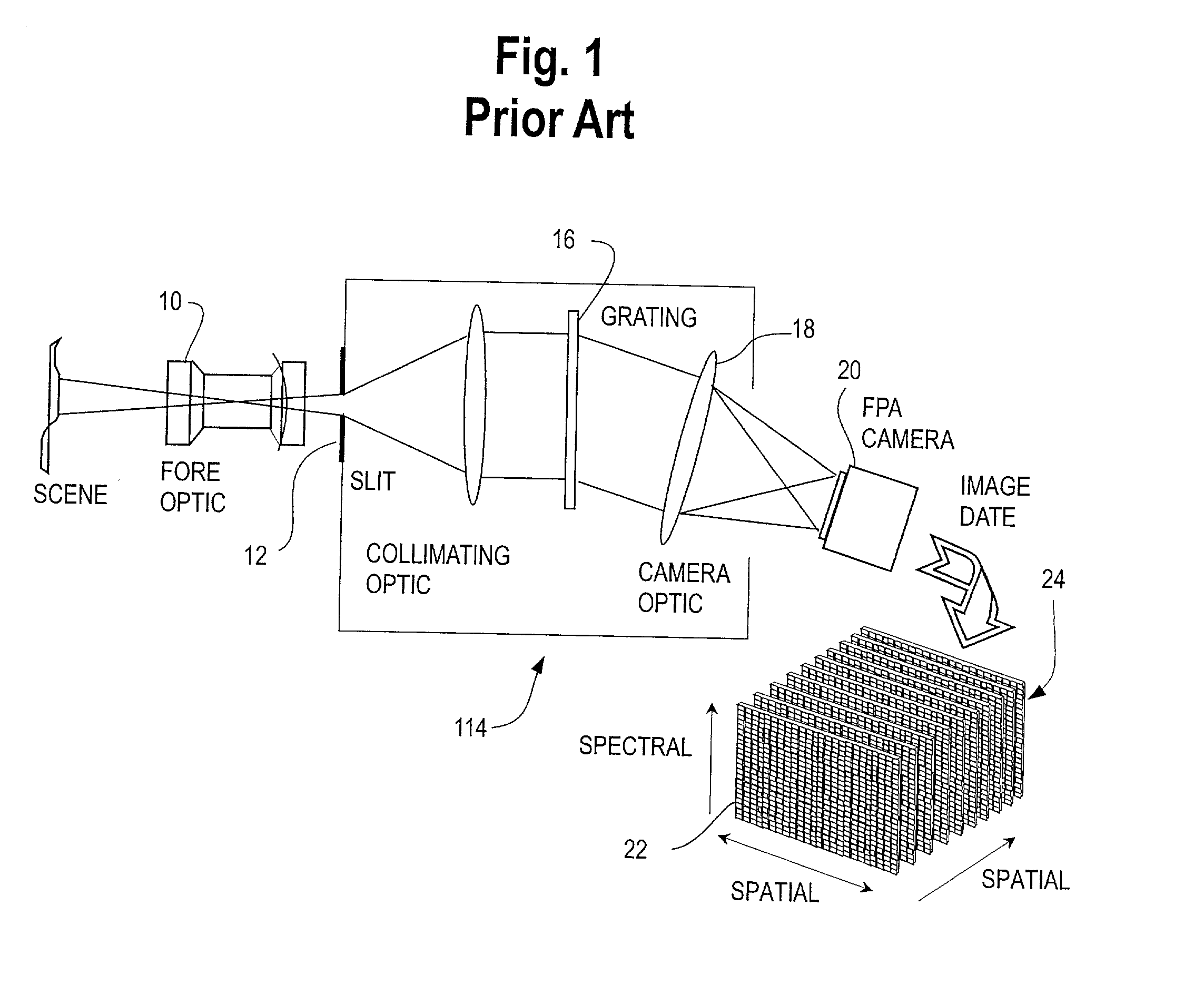
Spectroscopic imaging device employing imaging quality spectral filters
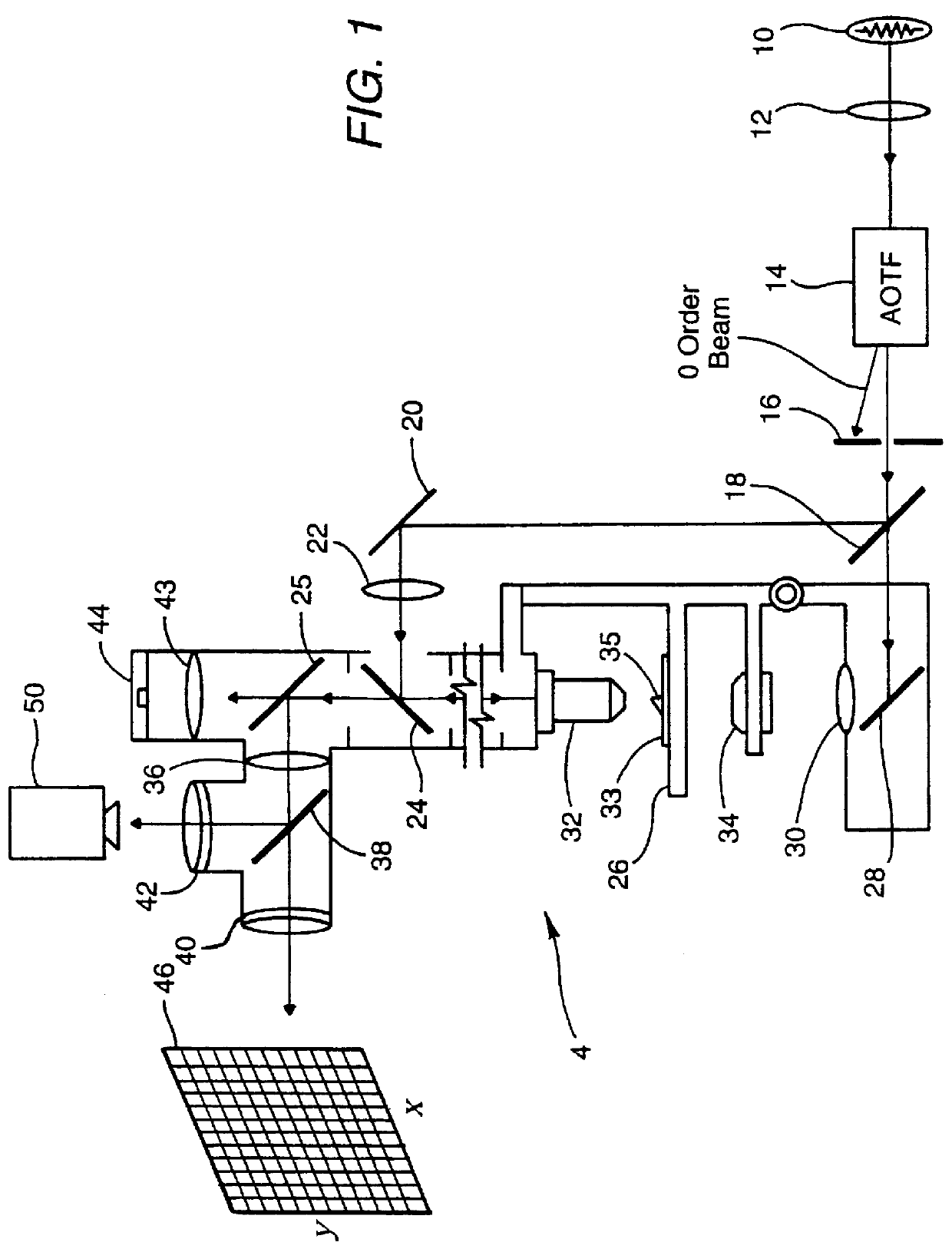
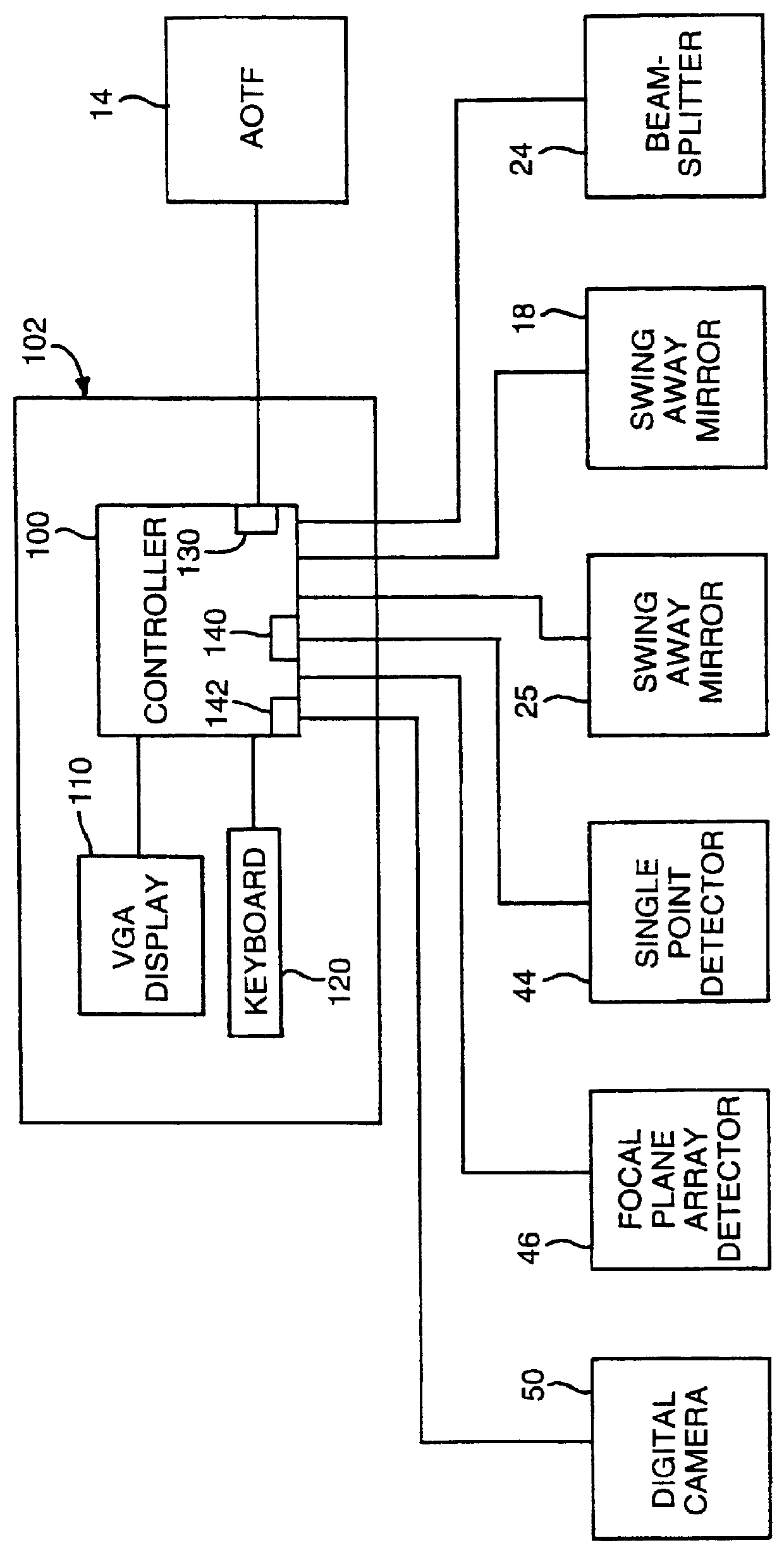
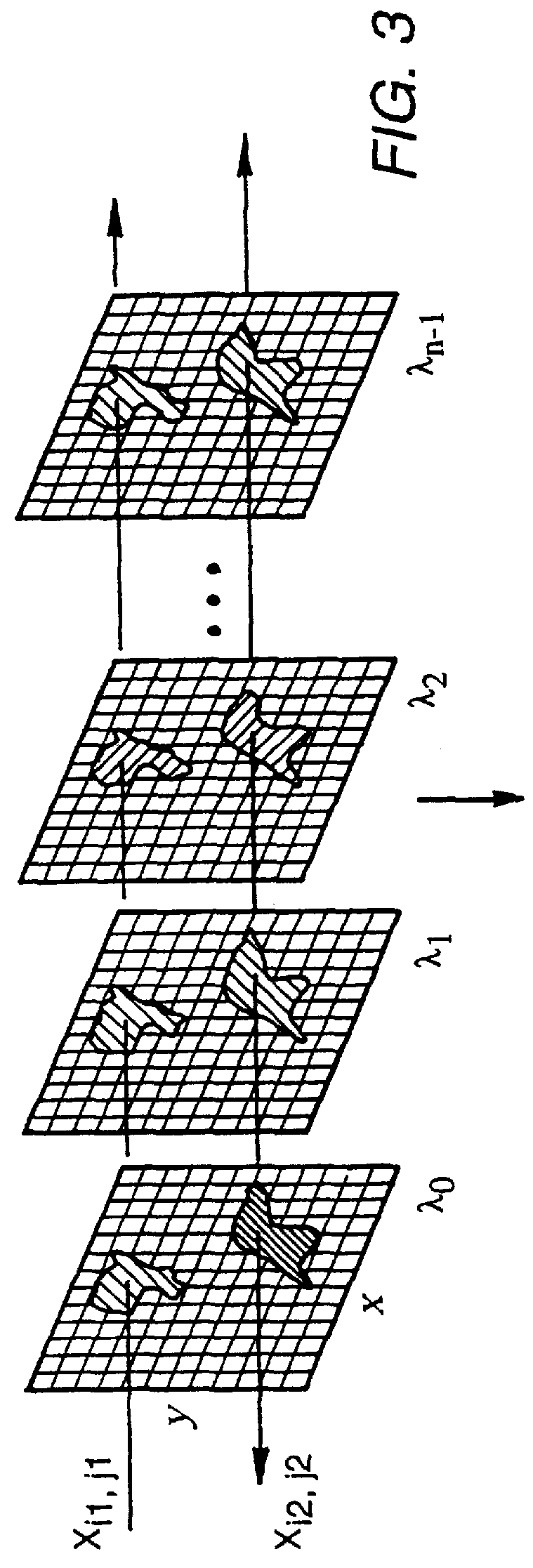
InactiveUSRE36529E1Retaining image fidelityQuick buildRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryLow speedImaging quality
Techniques for providing spectroscopic imaging integrates an acousto-optic tunable filter (AOTF), or an interferometer, and a focal plane array detector. In operation, wavelength selectivity is provided by the AOTF or the interferometer. A focal plane array detector is used as the imaging detector in both cases. Operation within the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared (NIR) spectral regions, and into the infrared spectral region, is achieved. The techniques can be used in absorption spectroscopy and emission spectroscopy. Spectroscopic images with a spectral resolution of a few nanometers and a spatial resolution of about a micron, are collected rapidly using the AOTF. Higher spectral resolution images are recorded at lower speeds using the interferometer. The AOTF technique uses entirely solid-state components and requires no moving parts. Alternatively, the interferometer technique employs either a step-scan interferometer or a continuously modulated interferometer.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
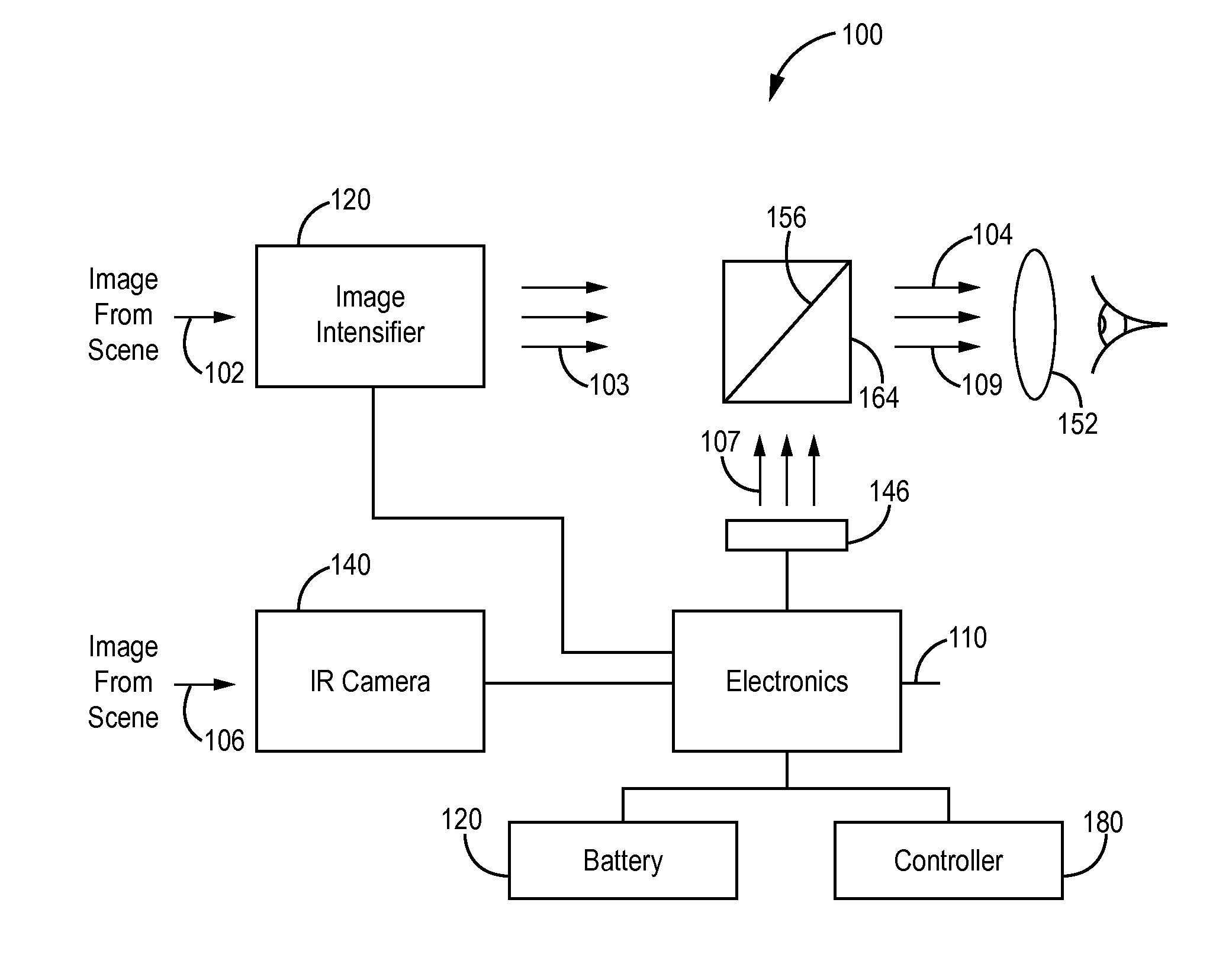
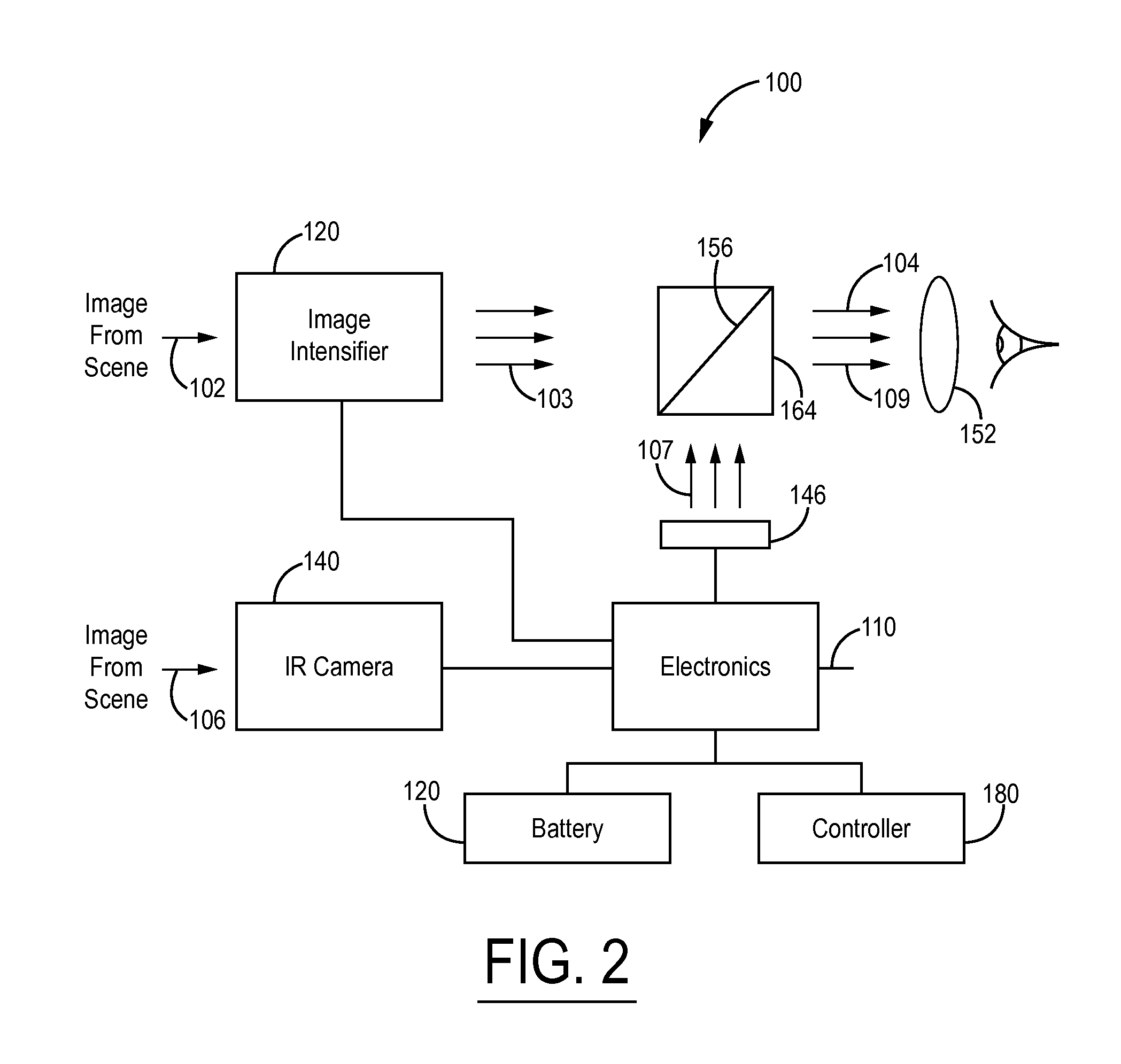
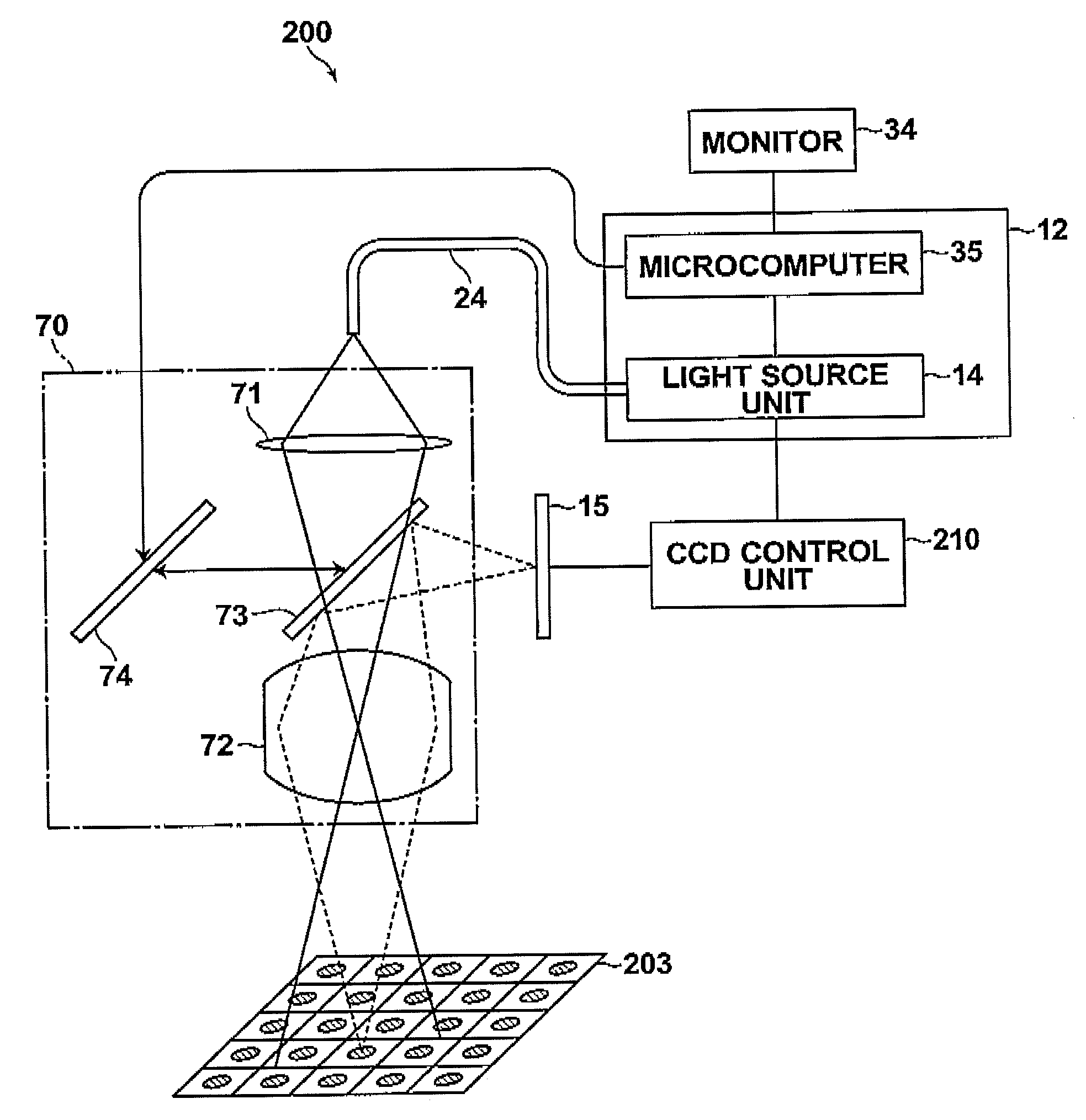
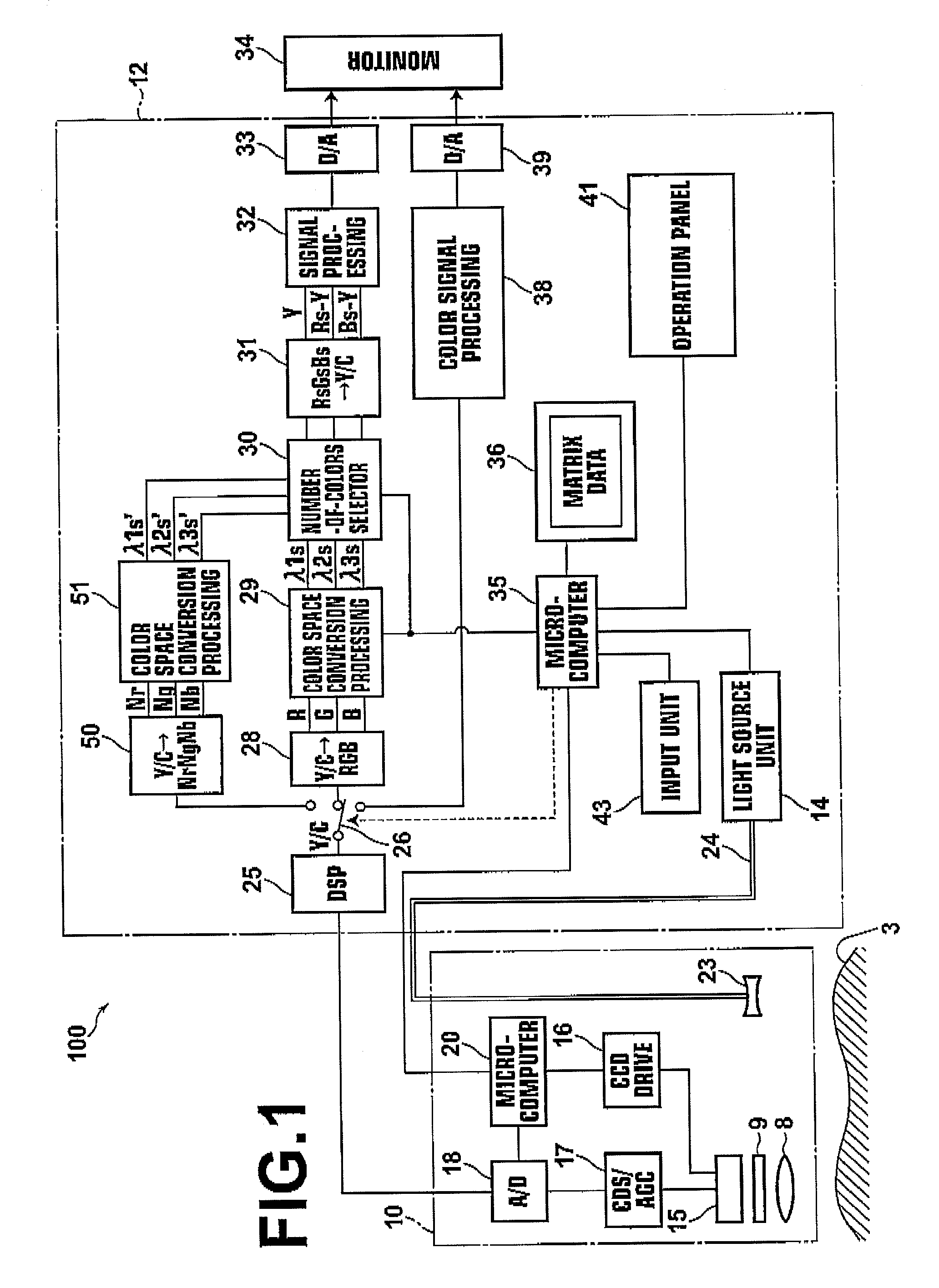
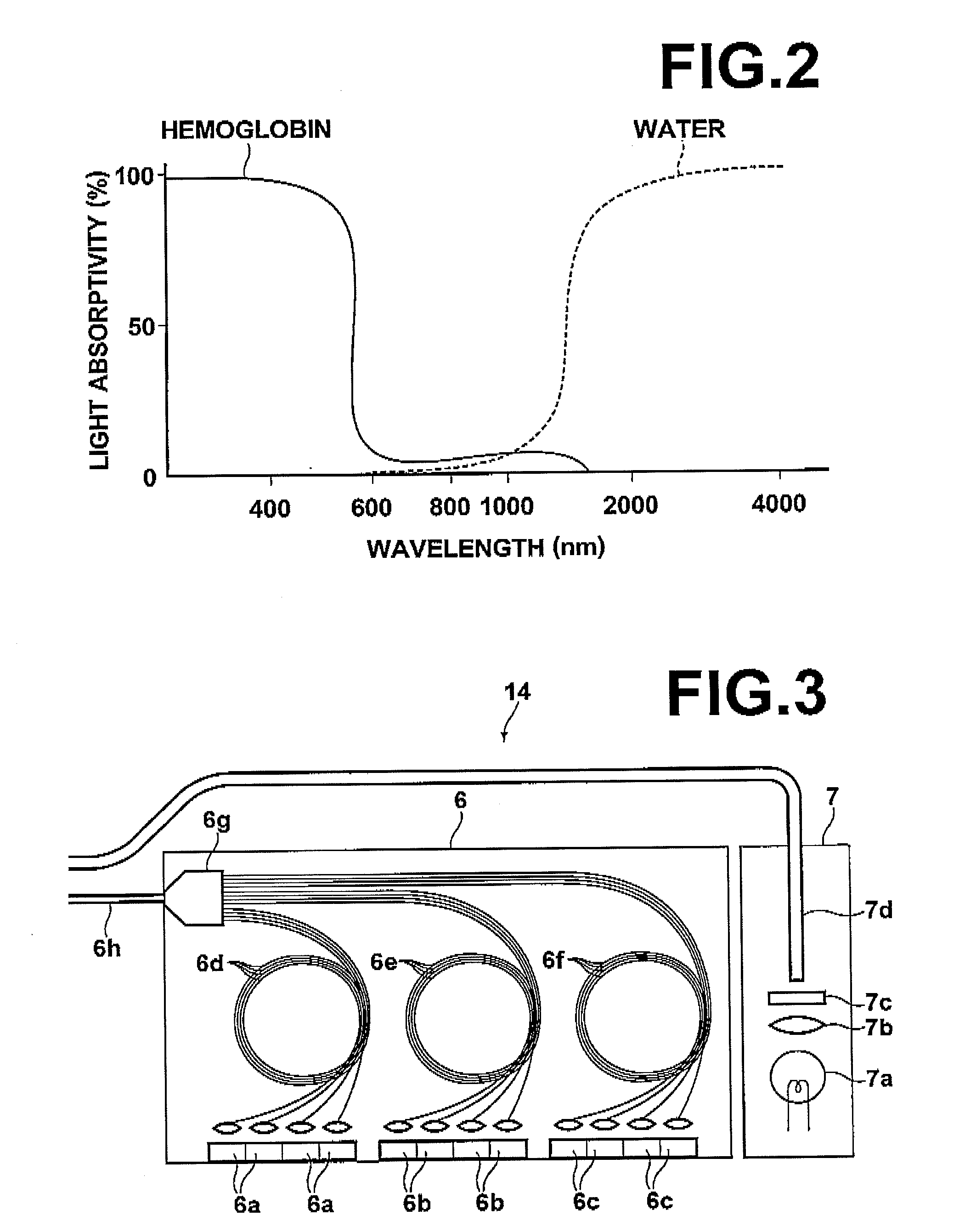
Imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20090021739A1Increasing size of apparatusIncrease in sizeTelevision system detailsSpectrum investigationLength waveImaging equipment
An imaging apparatus includes a light source unit that selectively outputs white light and light in a different wavelength band to an observation target, an imaging unit including an imaging device, and a spectral image formation circuit that generates a spectral image signal for a specified wavelength by an operation using an image signal based on an output from the imaging unit and predetermined matrix data. The imaging unit selectively obtains an image of the observation target for each of first, second and third light components in a visible light region and an image for each of at least fourth and fifth light components in a near-infrared region. Further, the imaging unit includes first spectral devices that make only the first and fourth light components enter first pixels of the imaging device and second spectral devices that make only the second and fifth light components enter second pixels thereof.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
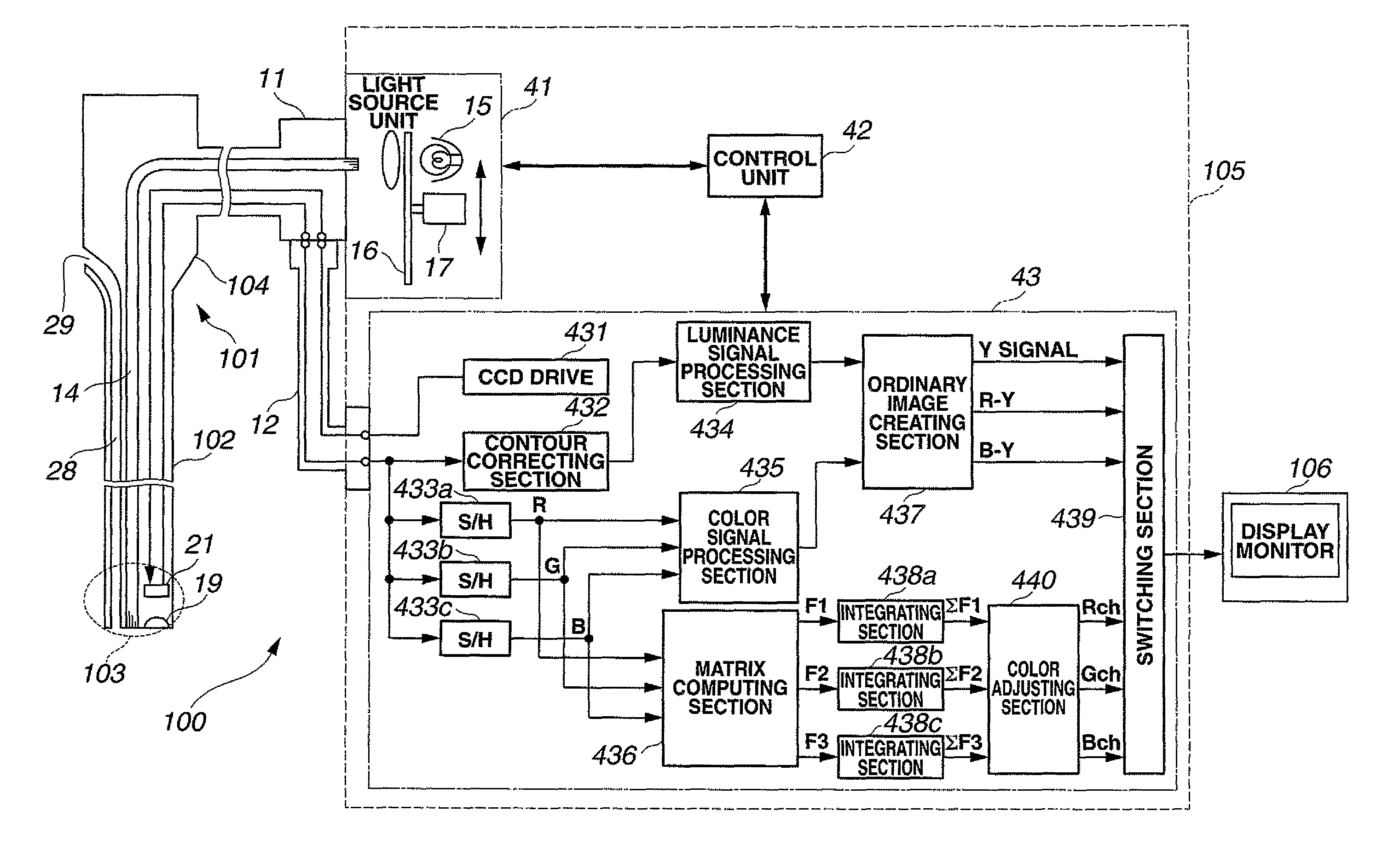
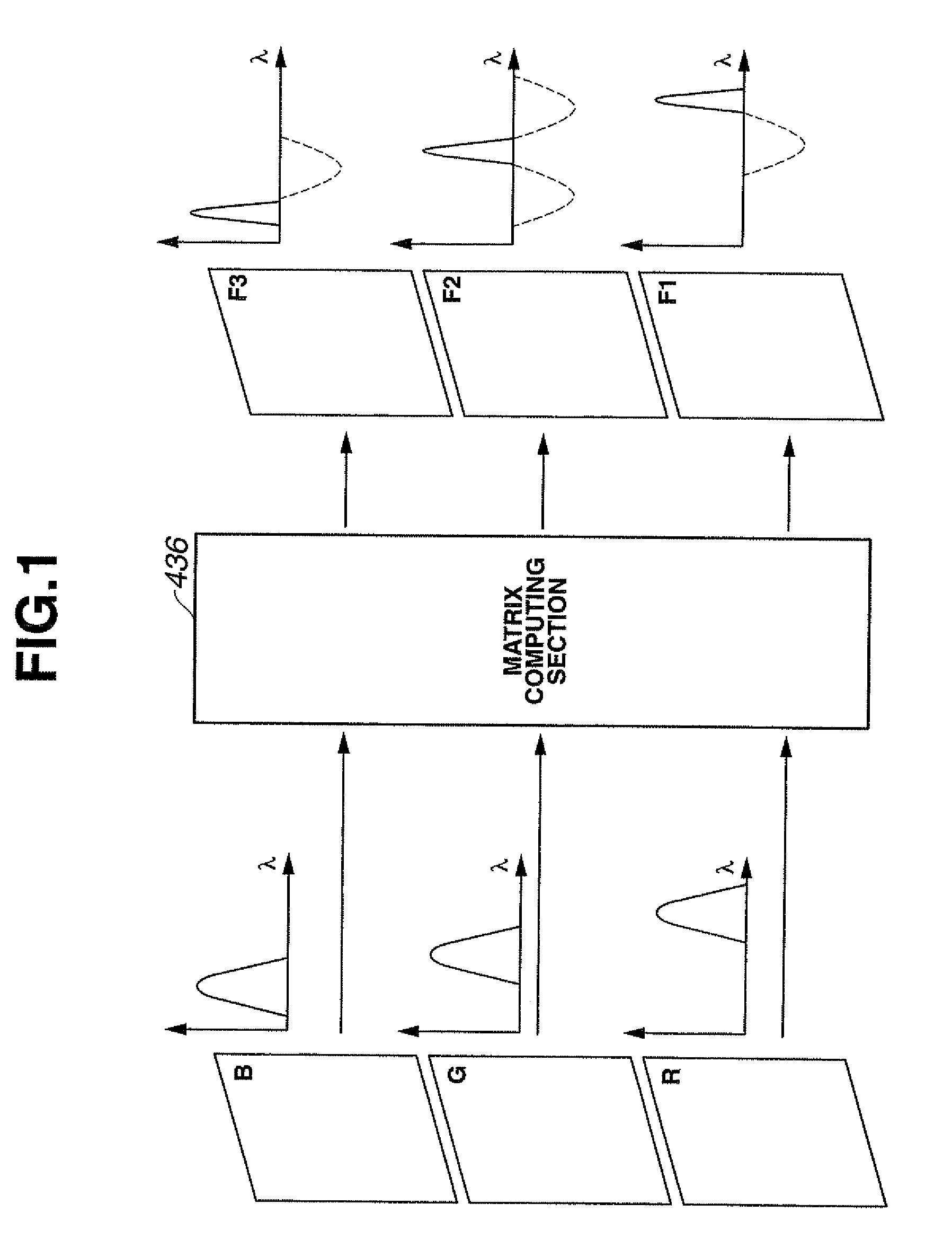
Signal processing device for biological observation apparatus
ActiveUS8279275B2High precisionImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsSpectrum investigationImage signalSignal processing
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Multispectral or hyperspectral imaging system and method for tactical reconnaissance
A two-dimensional focal plane array (FPA) is divided into sub-arrays of rows and columns of pixels, each sub-array being responsive to light energy from a target object which has been separated by a spectral filter or other spectrum dividing element into a predetermined number of spectral bands. There is preferably one sub-array on the FPA for each predetermined spectral band. Each sub-array has its own read out channel to allow parallel and simultaneous readout of all sub-arrays of the array. The scene is scanned onto the array for simultaneous imaging of the terrain in many spectral bands. Time Delay and Integrate (TDI) techniques are used as a clocking mechanism within the sub-arrays to increase the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of the detected image. Additionally, the TDI length (i.e., number of rows of integration during the exposure) within each sub-array is adjustable to optimize and normalize the response of the photosensitive substrate to each spectral band. The array provides for parallel and simultaneous readout of each sub-array to increase the collection rate of the spectral imagery. All of these features serve to provide a substantial improvement in the area coverage of a hyperspectral imaging system while at the same time increasing the SNR of the detected spectral image.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Apparatus for photodynamic therapy and photodetection
ActiveUS20100145416A1Effective therapyRaman/scattering spectroscopyDiagnostics using lightDiseaseFluorescence
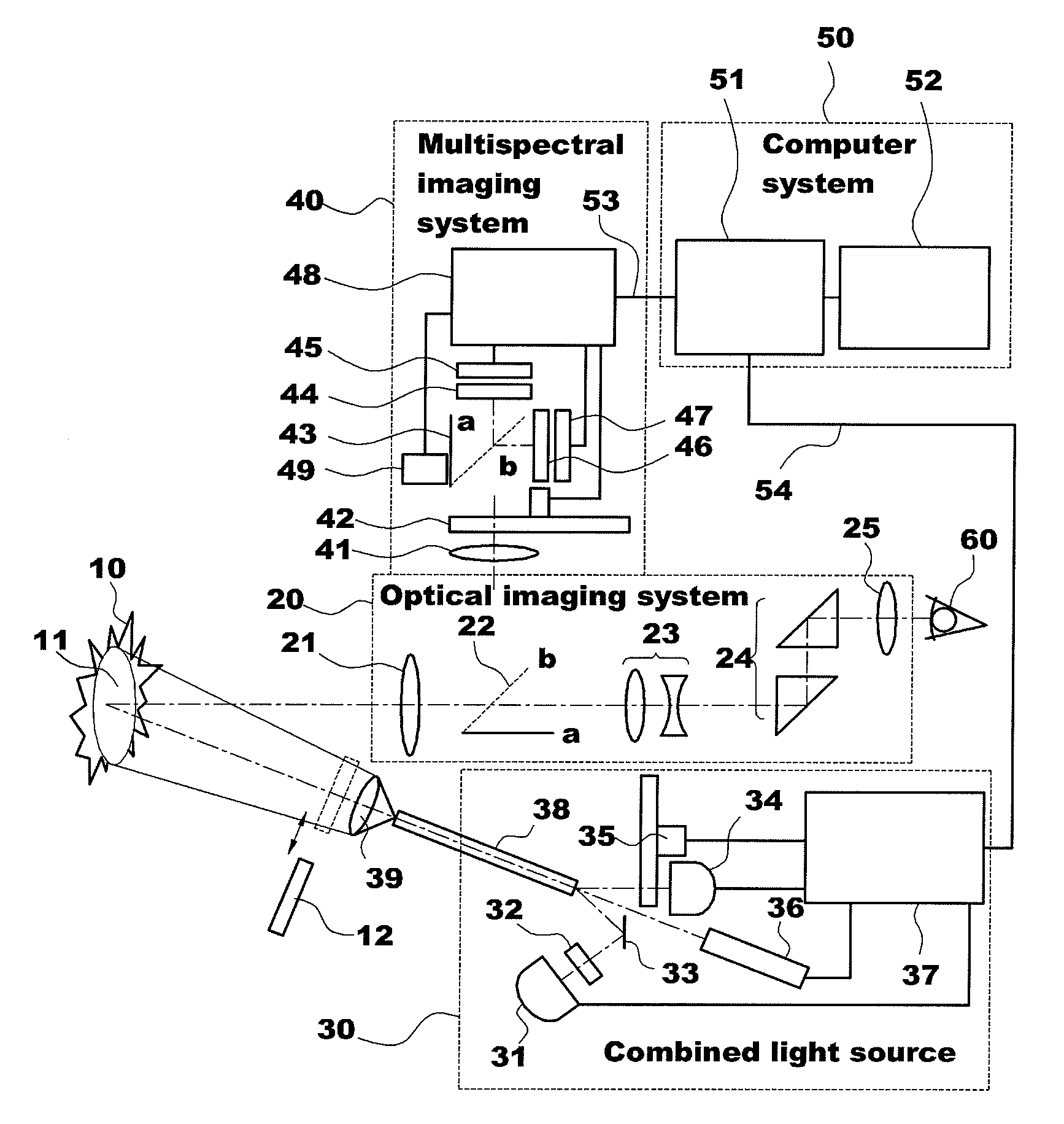
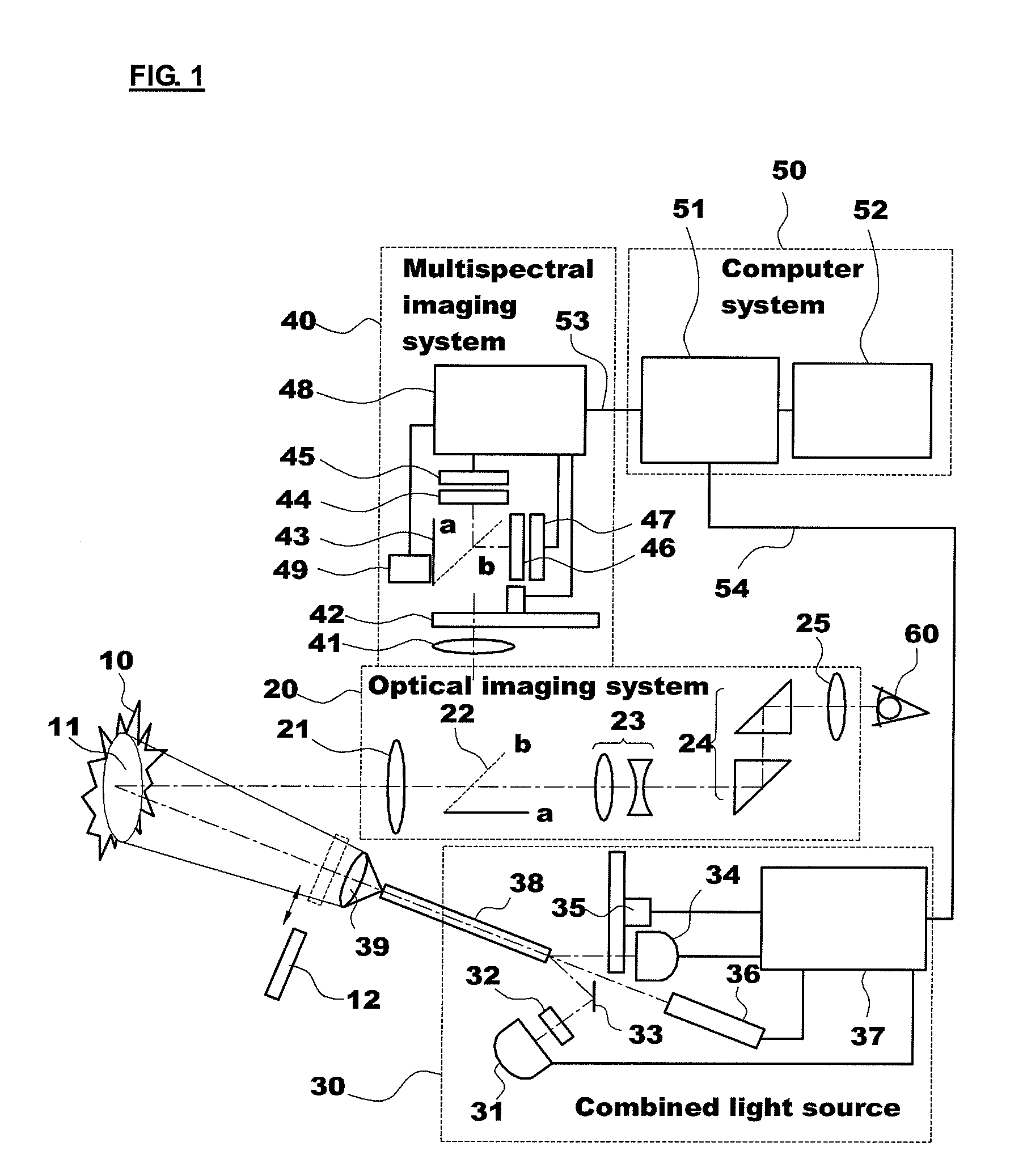
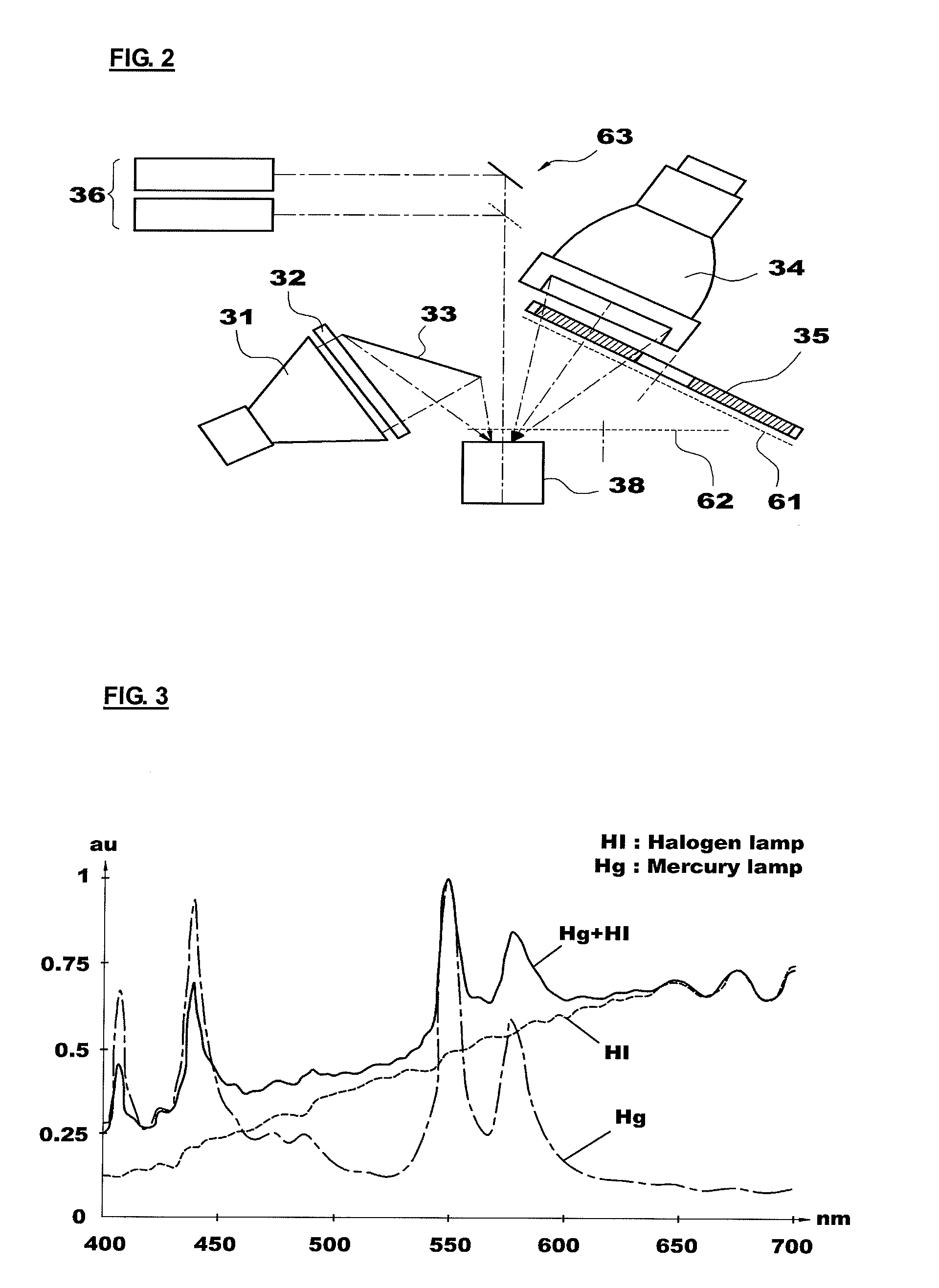
The present invention provides an apparatus for photodynamic therapy and fluorescence detection, in which a combined light source is provided to illuminate an object body and a multispectral fluorescence-reflectance image is provided to reproduce various and complex spectral images for an object tissue, thus performing effective photodynamic therapy for various diseases both outside and inside of the body.For this purpose, the present invention provides an apparatus for photodynamic therapy and photodetection, which provides illumination with light of various wavelengths and multispectral images, the apparatus including: an optical imaging system producing an image of an object tissue and transmitting the image to a naked eye or an imaging device; a combined light source including a plurality of coherent and non-coherent light sources and a light guide guiding incident light emitted from the light sources; a multispectral imaging system including at least one image sensor; and a computer system outputting an image of the object tissue to the outside. Thus, the apparatus for photodynamic therapy and photodetection of the present invention can effectively perform the photodynamic therapy and photodetection by means of the combined light source capable of irradiating light having various spectral components to an object tissue and the multispectral imaging system capable of obtaining images from several spectral portions for these various spectral ranges at the same time, thus improving the accuracy of diagnosis and efficiency of the photodynamic therapy.
Owner:KOREA ELECTROTECH RES INST
Slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module and slit-scan microscopic system and method using the same
ActiveUS20100188742A1Improve performanceMinimized in sizePrismsMicroscopesBroadbandLighting spectrum
The present invention provides a slit-scan multi-wavelength confocal lens module, which utilizes at least two lenses having chromatic aberration for splitting a broadband light into continuously linear spectral lights having different focal length respectively. The present invention utilizes the confocal lens module employing slit-scan confocal principle and chromatic dispersion techniques and the confocal microscopy with optical sectioning ability and high resolution in spectral dispersion to establish a confocal microscopy method and system with long DOF and high resolution, capable of modulating a broadband light to produce the axial chromatic dispersion and focus on different depths toward an object's surface for obtaining the reflected light spectrum from the surface. Thereafter, the spectrum is spatially filtered by a slit and then a peak position with respect to the filtered spectrum along the scanning line is detected by a spectral image sensing unit for generating the sectional profile of the measured surface.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com