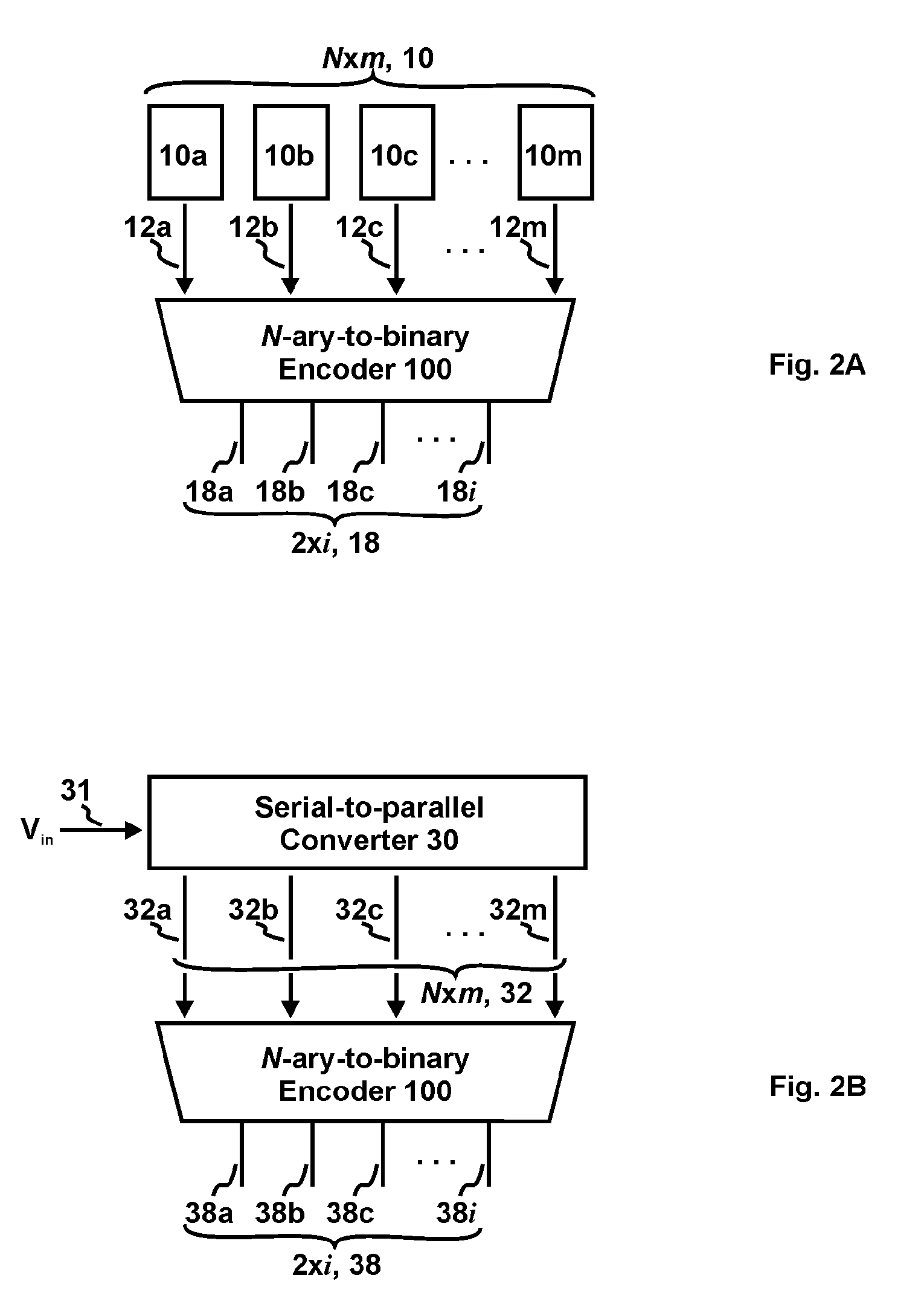
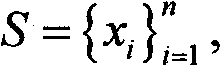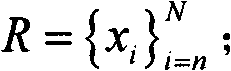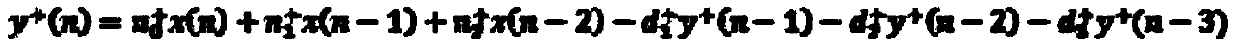Patents
Literature
483 results about "Partition of unity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
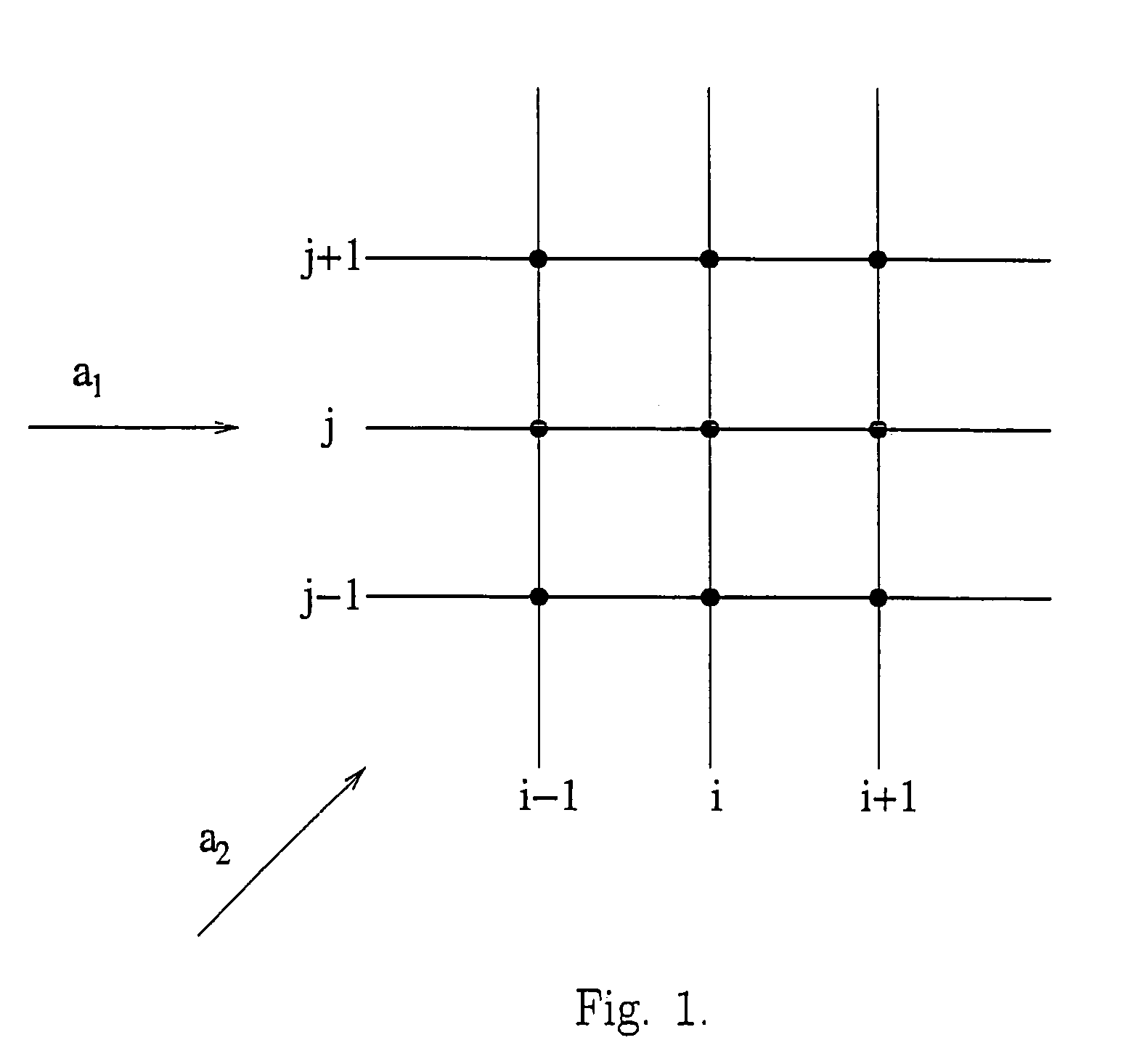
In mathematics, a partition of unity of a topological space X is a set R of continuous functions from X to the unit interval [0,1] such that for every point, x∈X, there is a neighbourhood of x where all but a finite number of the functions of R are 0, and the sum of all the function values at x is 1, i.e., ∑ρ∈Rρ(x)=1. Partitions of unity are useful because they often allow one to extend local constructions to the whole space.
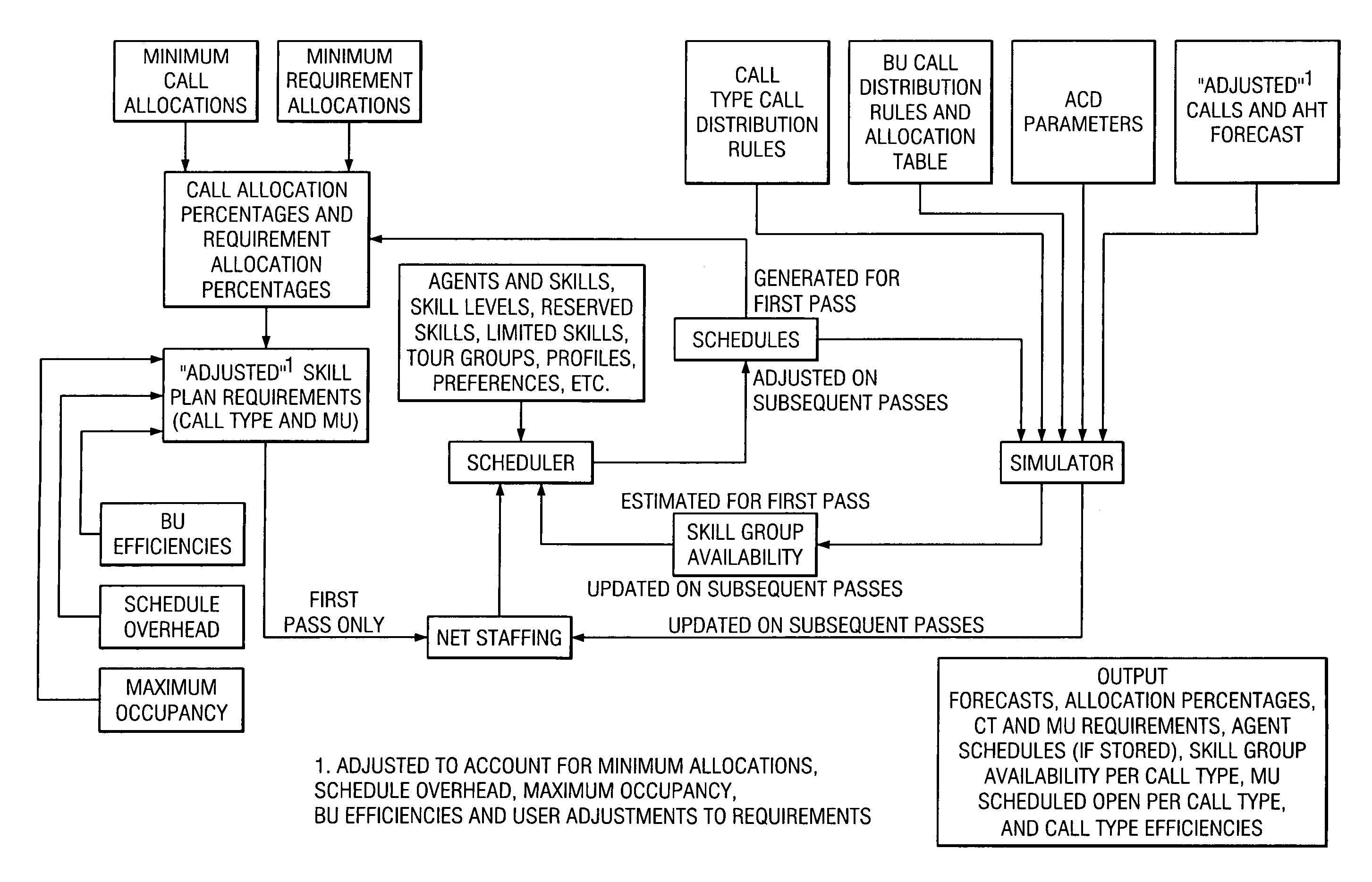
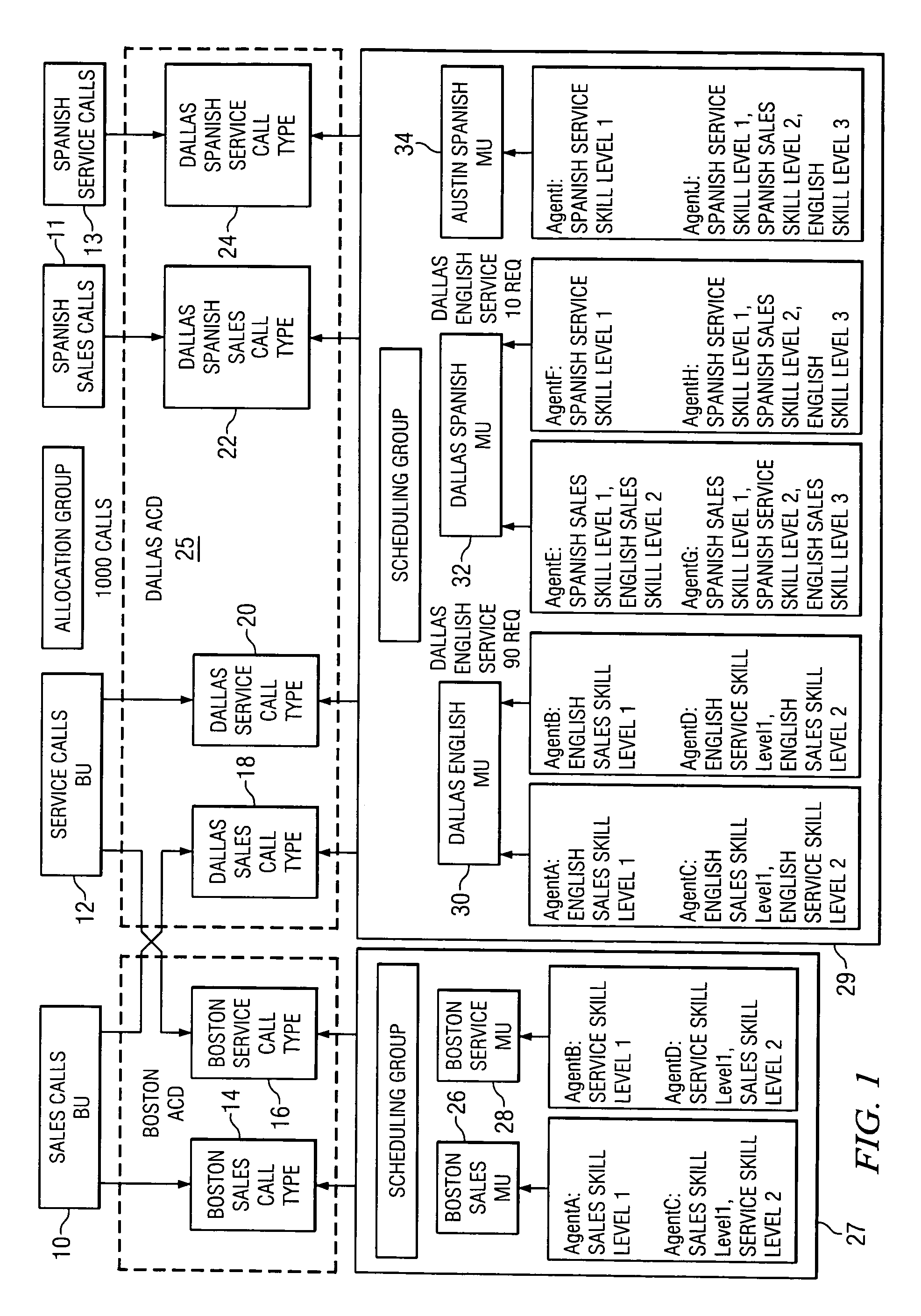
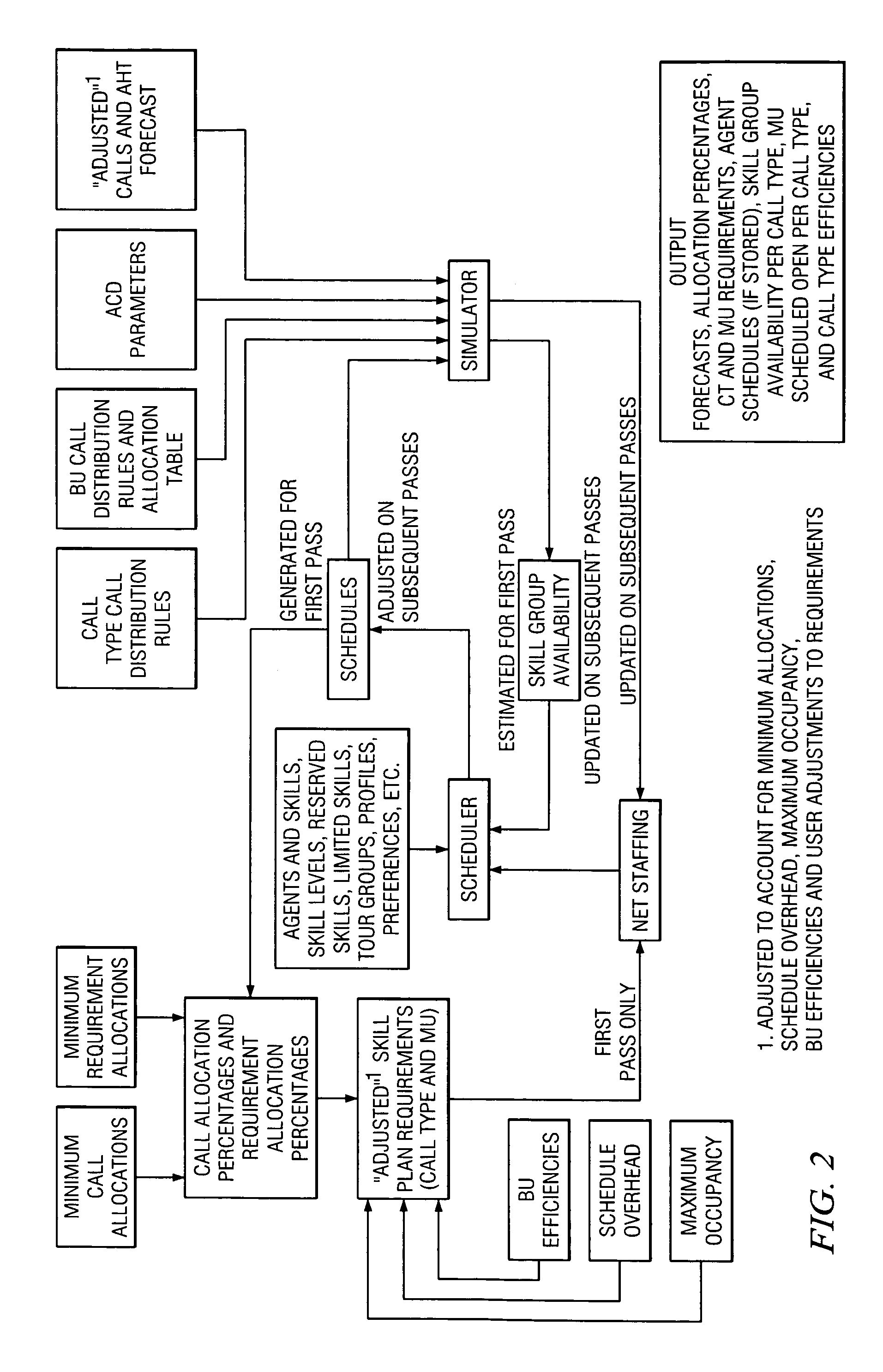
Method and system for skills-based planning and scheduling in a workforce contact center environment
InactiveUS6970829B1Minimum level of skill coverageImprove fitSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsMulti siteManagement unit
A method of forecasting, allocating and scheduling in a single or multi-site skills-based contact or call center environment organized into a hierarchy of zero or more business units at a first, upper level, one or more contact types at a second, intermediate level, and one or more management units at a third, lower level. A user creates (a) a set of given contact allocations that define how contacts are distributed from a given business unit to multiple contact types, and (b) a set of given requirement allocations that define how agent requirements are distributed from a contact type to one or more management units. Agent availability by contact type is then predicted to generate agent availability data. Thereafter, forecasted contacts and forecasted agent requirements are allocated based on the given contact and requirement allocations as well as the agent availability data. Preferably, the agent availability data is predicted using a schedule simulator and is characterized by contact type for agents in the same skill group.
Owner:IEX CORP
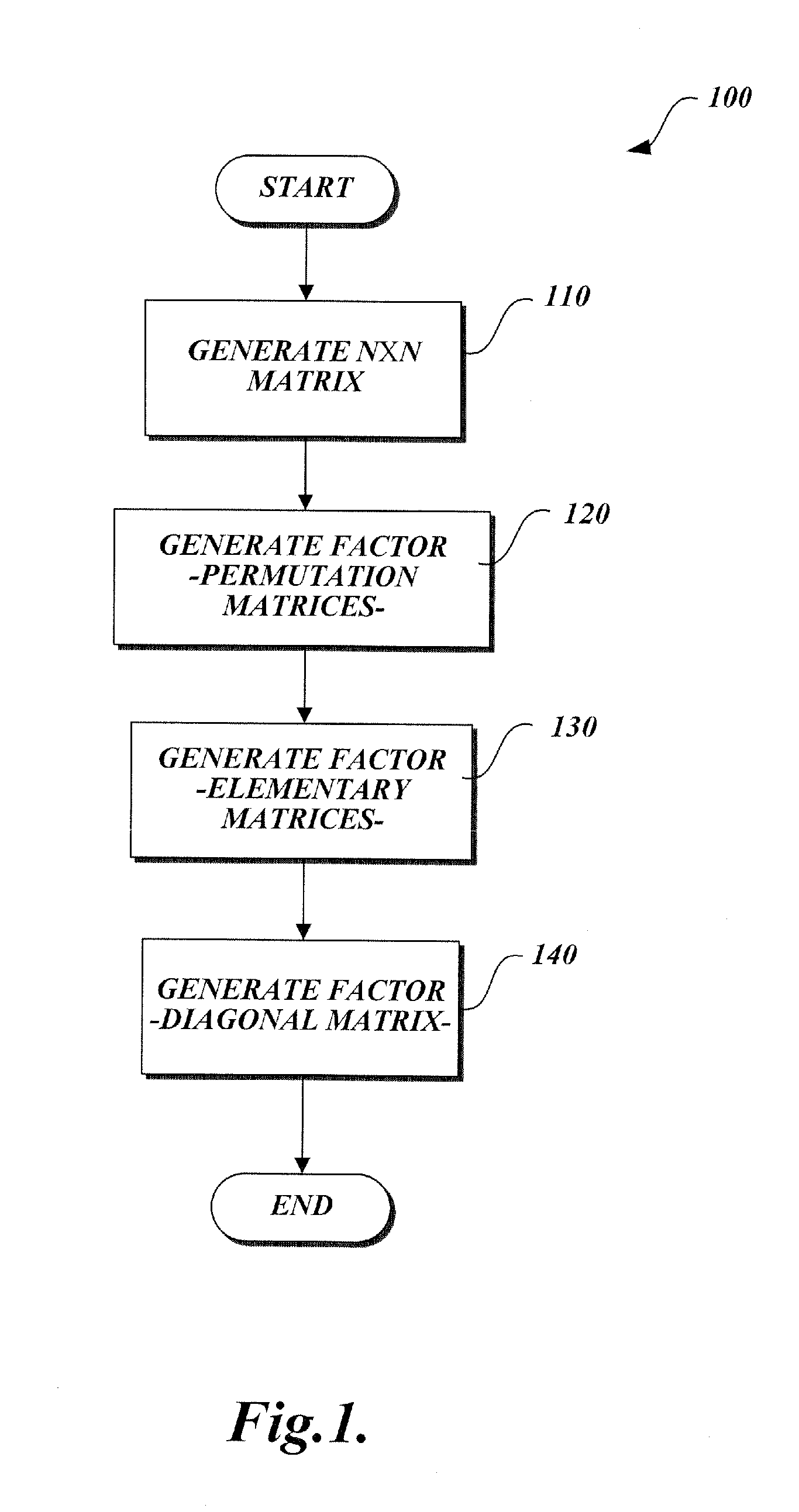
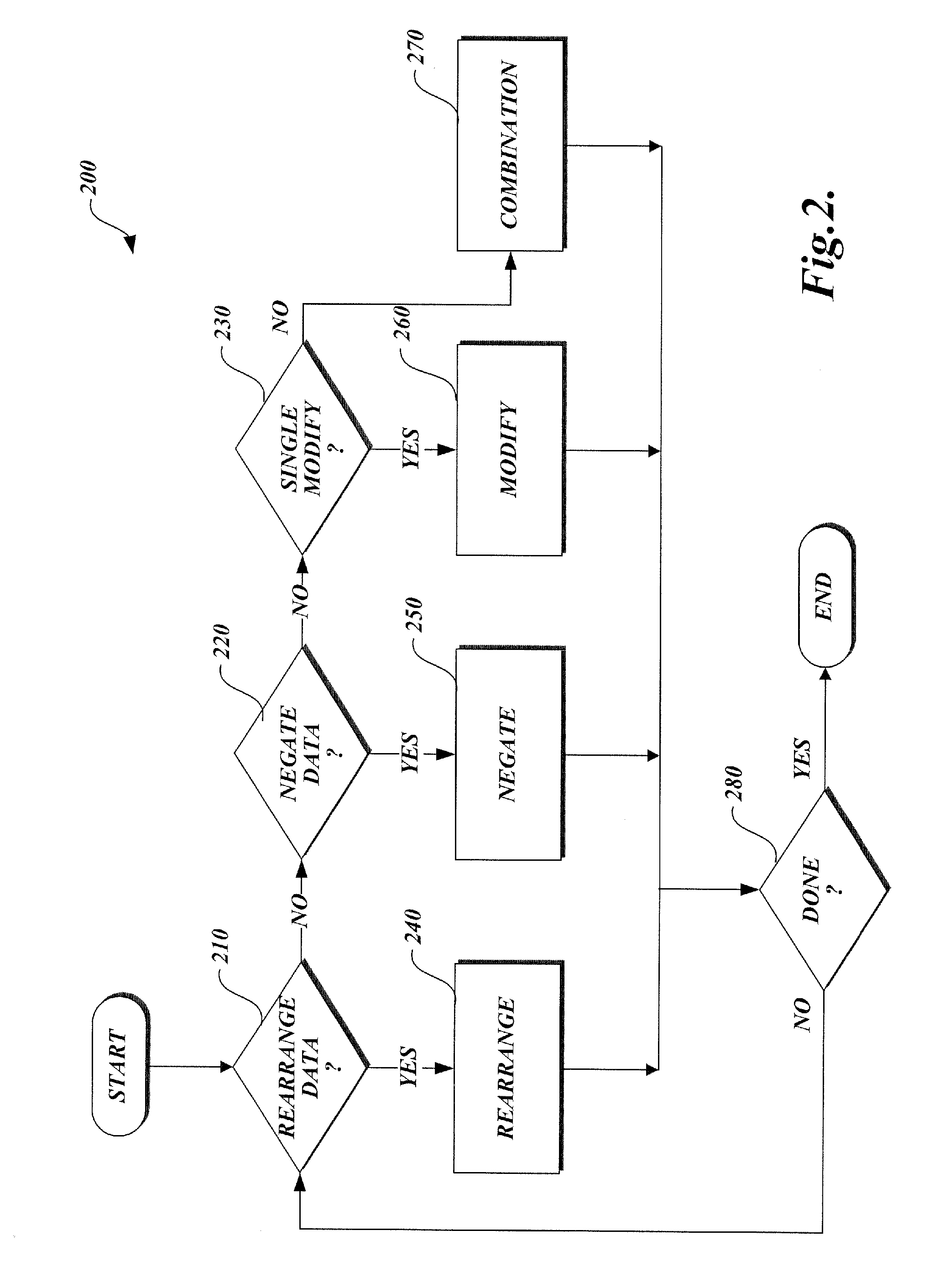
Method of generating matrix factors for a finite-dimensional linear transform
InactiveUS20070211952A1Character and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPartition of unityLU decomposition
A method of generating matrix factors for a finite-dimensional linear transform using a computer. The linear transform is represented by data values stored in a linear transformation matrix having a nonzero determinant. In one aspect, a first LU-decomposition is applied to the linear transformation matrix. Four matrices are generated from the LU-decomposition, including a first permutation matrix, a second permutation matrix, a lower triangular matrix having a unit diagonal, and a first upper triangular matrix. Additional elements include a third matrix Â, a signed permutation matrix Π such that A=ΠÂ, a permuted linear transformation matrix A′, a second upper triangular matrix U1, wherein the second upper triangular matrix satisfies the relationship Â=U1A′. The permuted linear transformation matrix is factored into a product including a lower triangular matrix L and an upper triangular matrix U. The linear transformation matrix is expressed as a product of the matrix factors.
Owner:CELARTEM
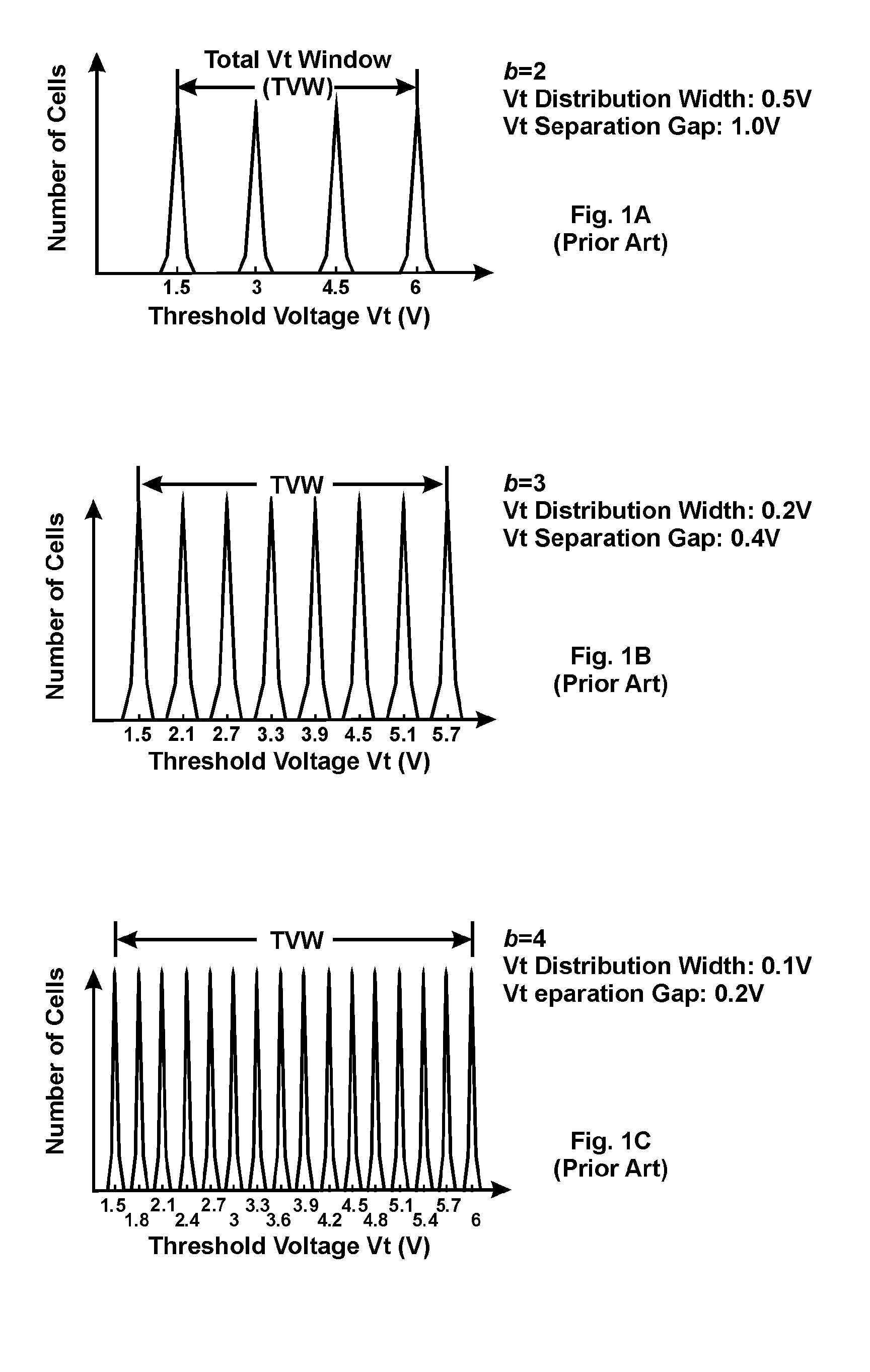
Fractional-Bit Systems
The present invention abandons the conventional approach of incrementing bits-per-cell b by 1, but allows increments of states-per-cell N by as little as 1 between product generations. Because N is no longer an integral power of 2, b takes a fractional value, resulting in a fractional-bit system. In a fractional-bit system, cells are decoded in unit of word. By adjusting the word-width, the system efficiency can be optimized.
Owner:ZHANG GUOBIAO
Graph-based semi-supervised high-spectral remote sensing image classification method
ActiveCN102096825AReduce restrictionsReduce complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation complexityPartition of unity
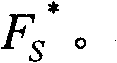
The invention relates to a graph-based semi-supervised high-spectral remote sensing image classification method. The method comprises the following steps: extracting the features of an input image; randomly sampling M points from an unlabeled sample, constructing a set S with L marked points, constructing a set R with the rest of the points; calculating K adjacent points of the points in the sets S and R in the set S by use of a class probability distance; constructing two sparse matrixes WSS and WSR by a linear representation method; using label propagation to obtain a label function F<*><S>, and calculating the label prediction function F<*><R> of the sample points in the set R to determine the labels of all the pixel points of the input image. According to the method, the adjacent points of the sample points can be calculated by use of the class probability distance, and the accurate classification of high-spectral images can be achieved by utilizing semi-supervised conduction, thus the calculation complexity is greatly reduced; in addition, the problem that the graph-based semi-supervised learning algorithm can not be used for large-scale data processing is solved, and the calculation efficiency can be improved by at least 20-50 times within the per unit time when the method provided by the invention is used, and the visual effects of the classified result graphs are good.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
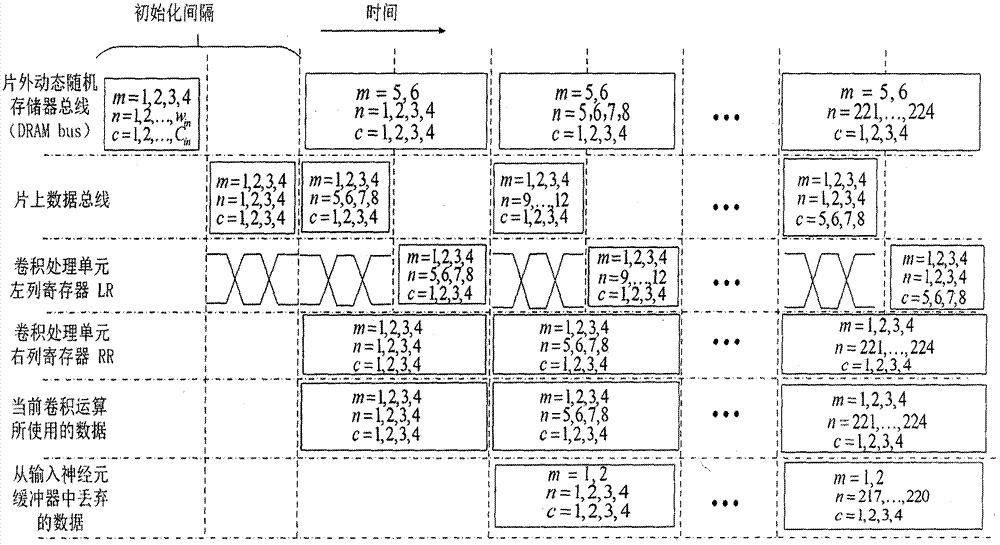
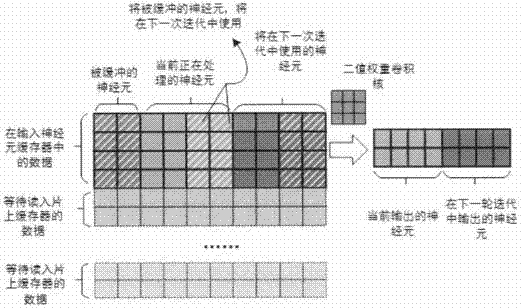
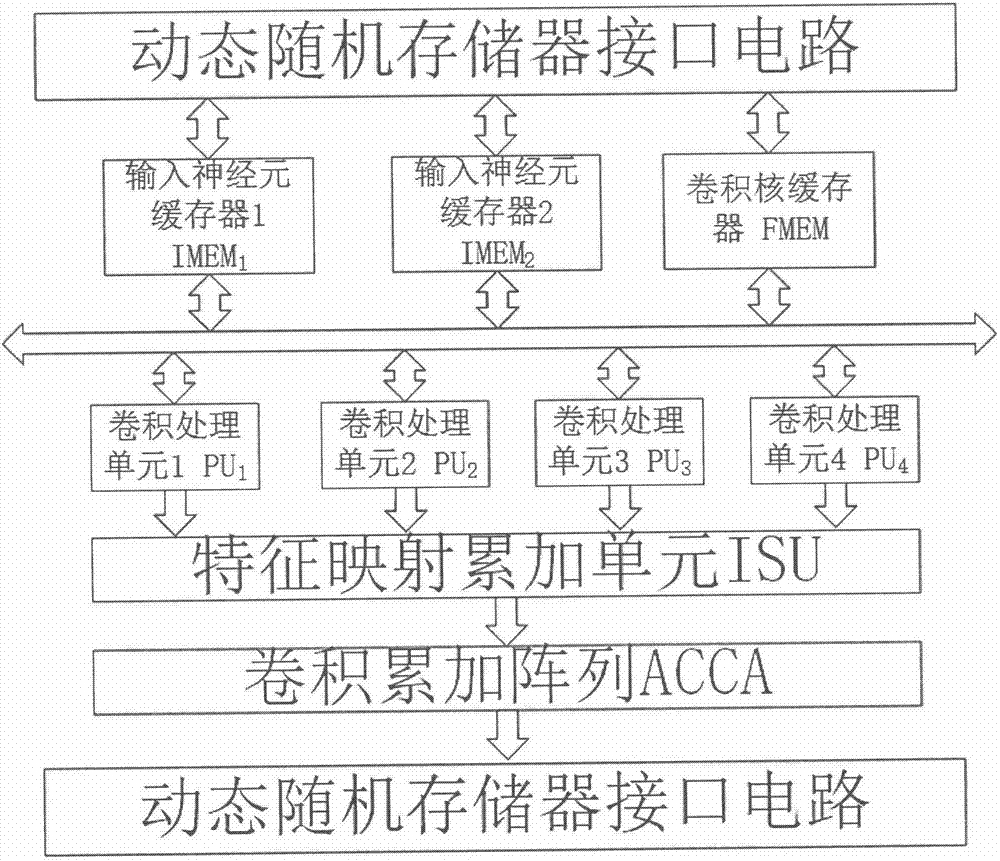
Hardware architecture of binary weight convolution neural network accelerator and calculation process thereof
ActiveCN106875011AReduce accessReduce power consumptionPhysical realisationStatic random-access memoryMemory interface
The invention discloses the hardware architecture of a binary weight convolution neural network accelerator and a calculation process thereof. The hardware architecture comprises three double-ended on-chip static random access memories which are used for buffering the binary weight of input neurons and a convolution layer, four convolution processing units capable of controlling calculation parts to complete major convolution calculation operation according to the calculation process, a feature map accumulation unit and a convolutional accumulation array. The feature map accumulation unit and the convolutional accumulation array are used for further processing the operation result of the convolution processing units to acquire a final correct output neuron value. The entire design exchanges data with an off-chip memory via a dynamic random access memory interface. In addition to the hardware architecture, the invention further provides the detailed calculation process which optimizes the hardware architecture and uses four lines of input feature map as a complete calculation unit. According to the invention, input data are reused to the greatest extent; the access of the off-chip memory is eliminated as much as possible; the power consumption of the deep binary convolution neural network calculation can be effectively reduced; a deep network is supported; and the scheme provided by the invention is a reasonable scheme which can be applied to an embedded system of visual application.
Owner:南京风兴科技有限公司
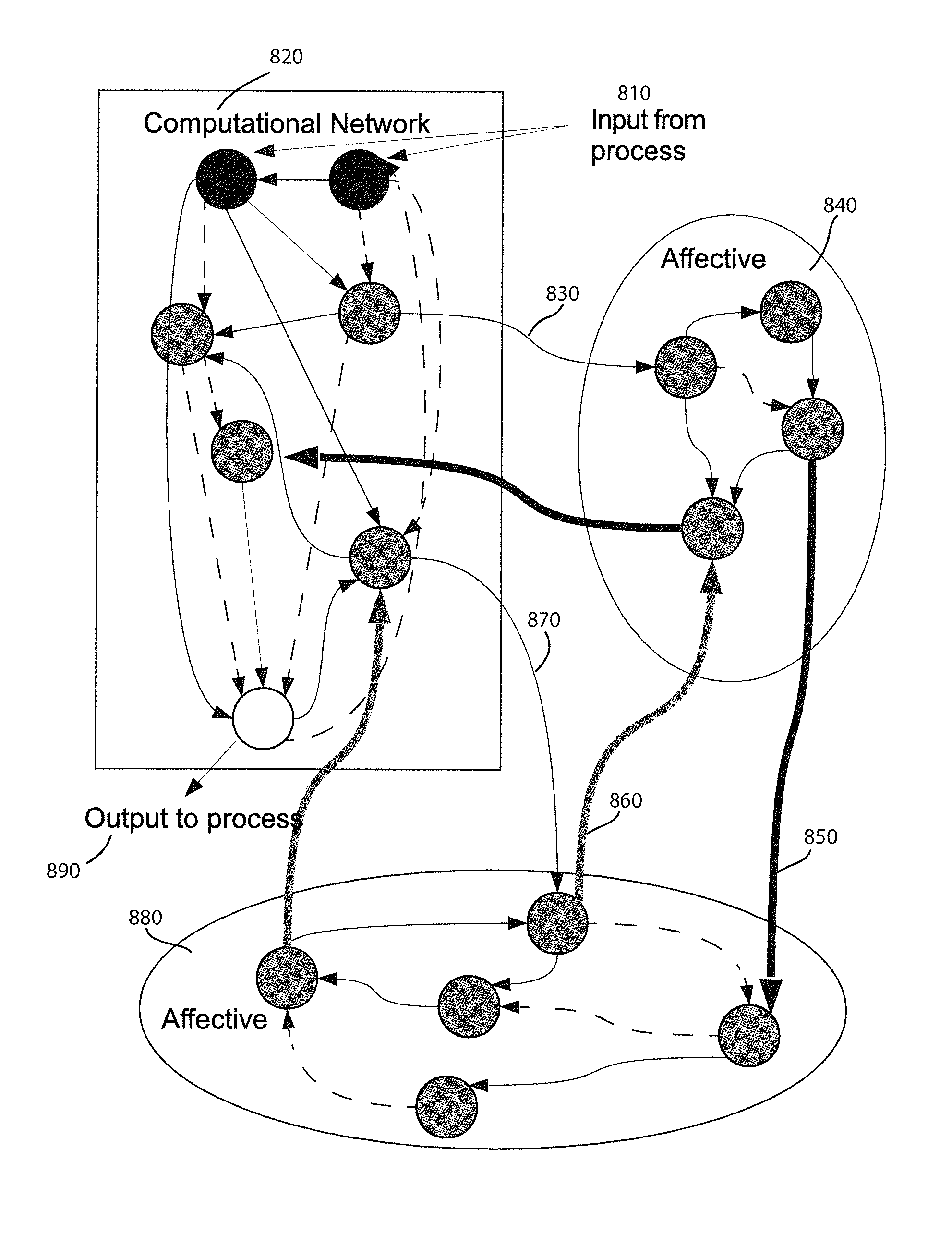
Method and apparatus for constructing a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network with visualization of neural pathways
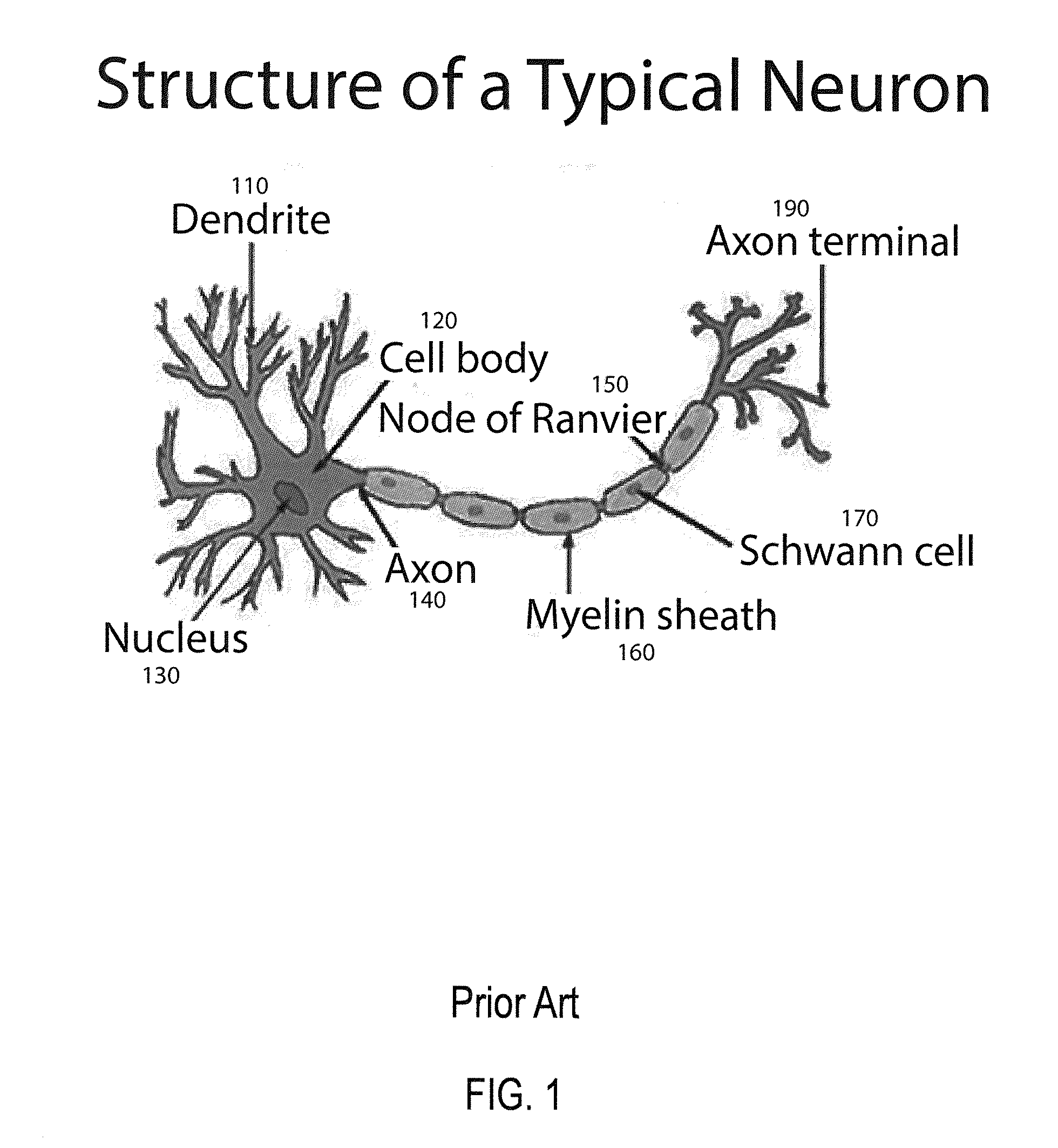
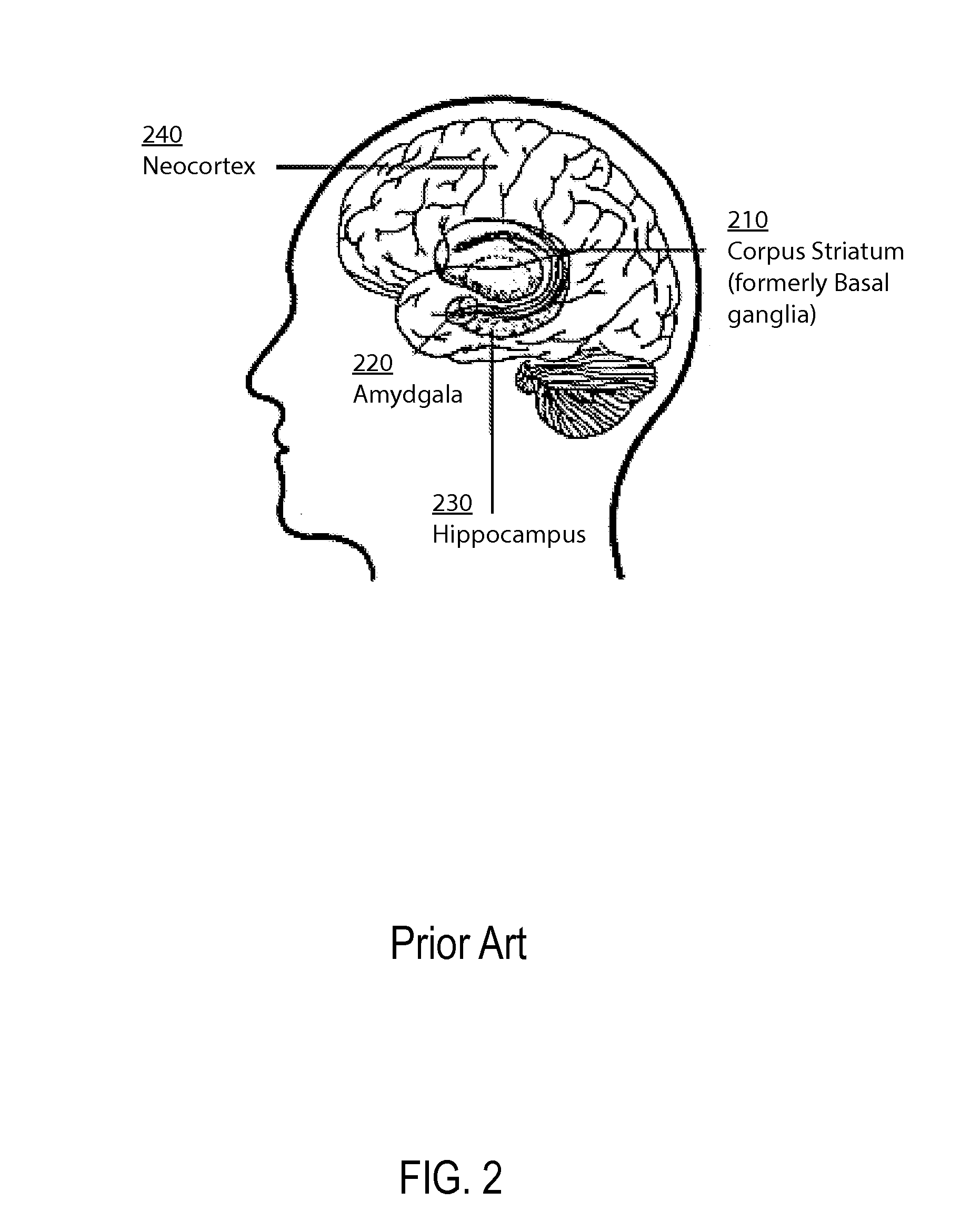
ActiveUS20150106306A1Slow visualizationUnderstand biological neural system behaviorNeural architecturesPhysical realisationNerve networkPartition of unity
A method and apparatus for constructing one of a neuroscience-inspired artificial neural network and a neural network array comprises one of a neuroscience-inspired dynamic architecture, a dynamic artificial neural network array and a neural network array of electrodes associated with neural tissue such as a brain, the method and apparatus having a special purpose display processor. The special purpose display processor outputs a display over a period of selected reference time units to demonstrate a neural pathway from, for example, one or a plurality of input neurons through intermediate destination neurons to an output neuron in three dimensional space. The displayed neural network may comprise neurons and synapses in different colors and may be utilized, for example, to show the behavior of a neural network for classifying hand-written digits between values of 0 and 9 or recognizing vertical / horizontal lines in a grid image of lines.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Systems and methods for the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders
Systems and methods for data compression which facilitate the diagnosis and treatment of neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. The methods comprise performing the following operations by a computing device: generating Normalized Data ("ND") from Original Data ("OD") that defines a Normalized Waveform ("NW") that is unitless and scaled from zero to one; processing ND to extract Micro-Movement Data ("MMD") defining a Micro-Movement Waveform ("MMW") comprising a plurality of MMD points; and generating compressed data comprising a stochastic signature of MMW. Each MMD point determined based on a value of a peak of NW and a value representing an average of all data point values between a first valley of NW immediately preceding the peak and a second valley of NW immediately following the peak. The stochastic signature is defined by empirically estimated values of at least one parameter representing a Probability Distribution Function ("PDF") of a continuous family of PDFs.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
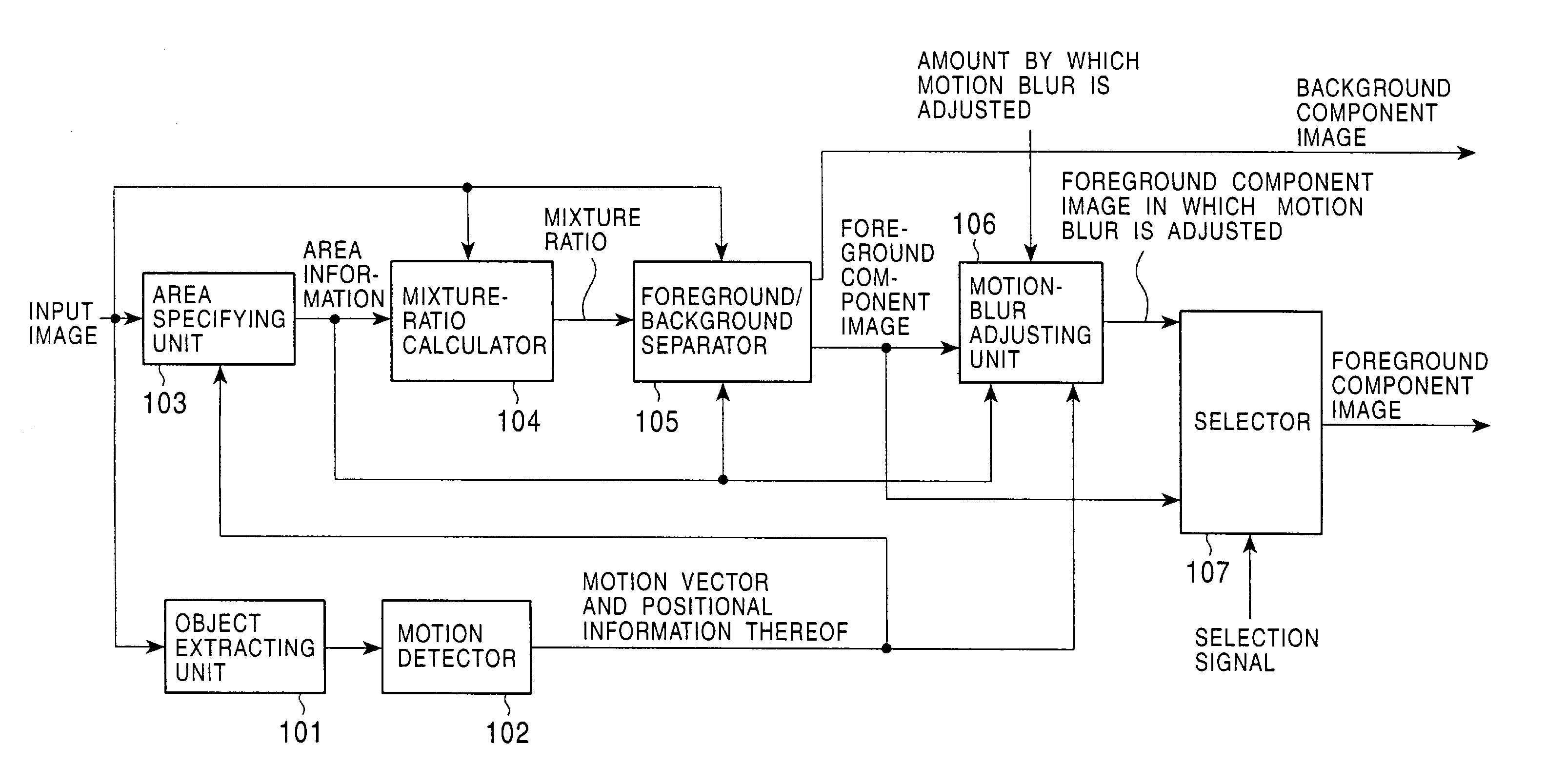
Image processing apparatus
An object of the present invention is to make it possible to adjust the amount of motion blur contained in a blurred image. A unit-of-processing determining portion 901 determines the unit of processing which is formed of pixel data located on a straight line. An equation generator 903 generates simultaneous equations consisting of a plurality of relational expressions based on the unit of processing. A calculator 904 generates foreground object components in which the amount of motion blur is adjusted by solving the simultaneous equations. The present invention can be applied to an image processing apparatus in which a difference between a signal detected by a sensor and the real world is taken into consideration.
Owner:SONY CORP
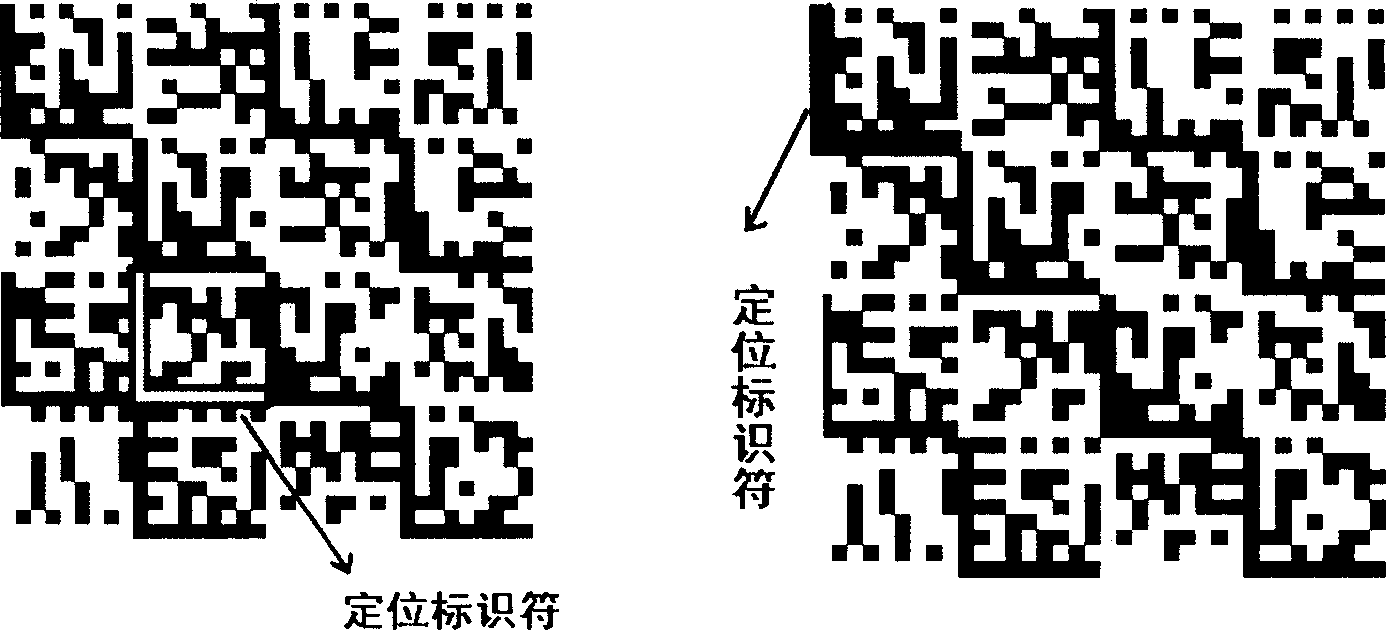
Matrix type two-dimensional bar code and its encoding and decoding method
InactiveCN1801188AImprove securityAny size can be adjustedRecord carriers used with machinesDecoding methodsPartition of unity
The invention discloses a matrix two-dimensional bar code and coding and decoding method, which is characterized by the following: the code graph of bar code is composed of gapless arrangement ní‡m rectangle unit information blocks, wherein m and n is positive integral more than 1; n is different from or the same as m; each rectangle unit information block is composed of gapless arrangements n'í‡m' of different optical characters with two rectangle colorful blocks, wherein n' and m' is positive integral more than 1; n' is different from or the same as m'; each rectangle unit information block contains location ID character and data region; the shape of ID character displays L type or inversed L type along two adjacent edges of rectangle unit information block frame. The bar code contains the following characters: large capacity, high error-correcting rate, high pollution-proof and distortion-proof ability, multiple language editing codes, separating coding and decoding code, random scale adjustment and omnibearing recognizing, which can be applied in multiple domains.
Owner:冯文伦
Digital equalizing method and radio communication receiver implementing said method
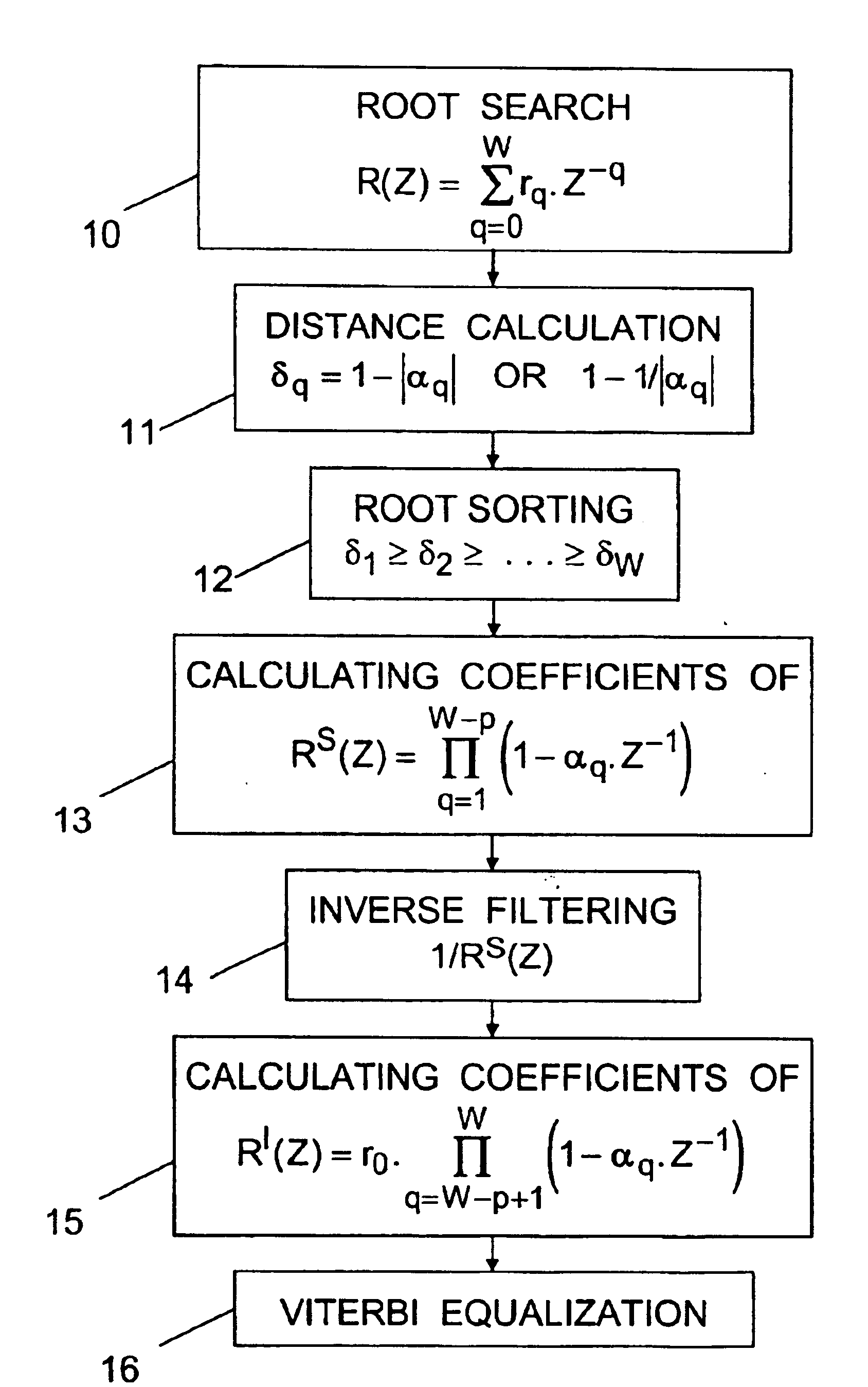
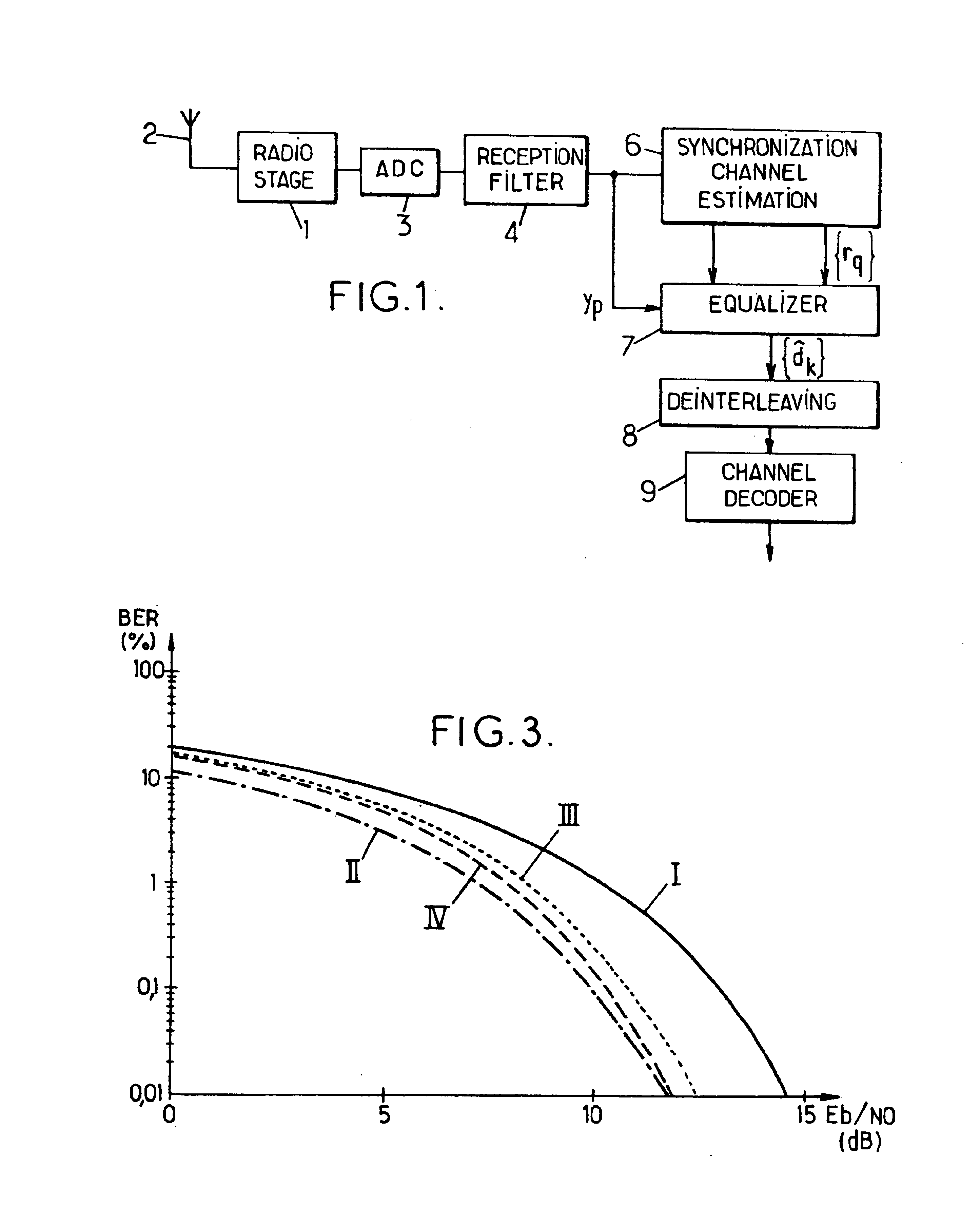
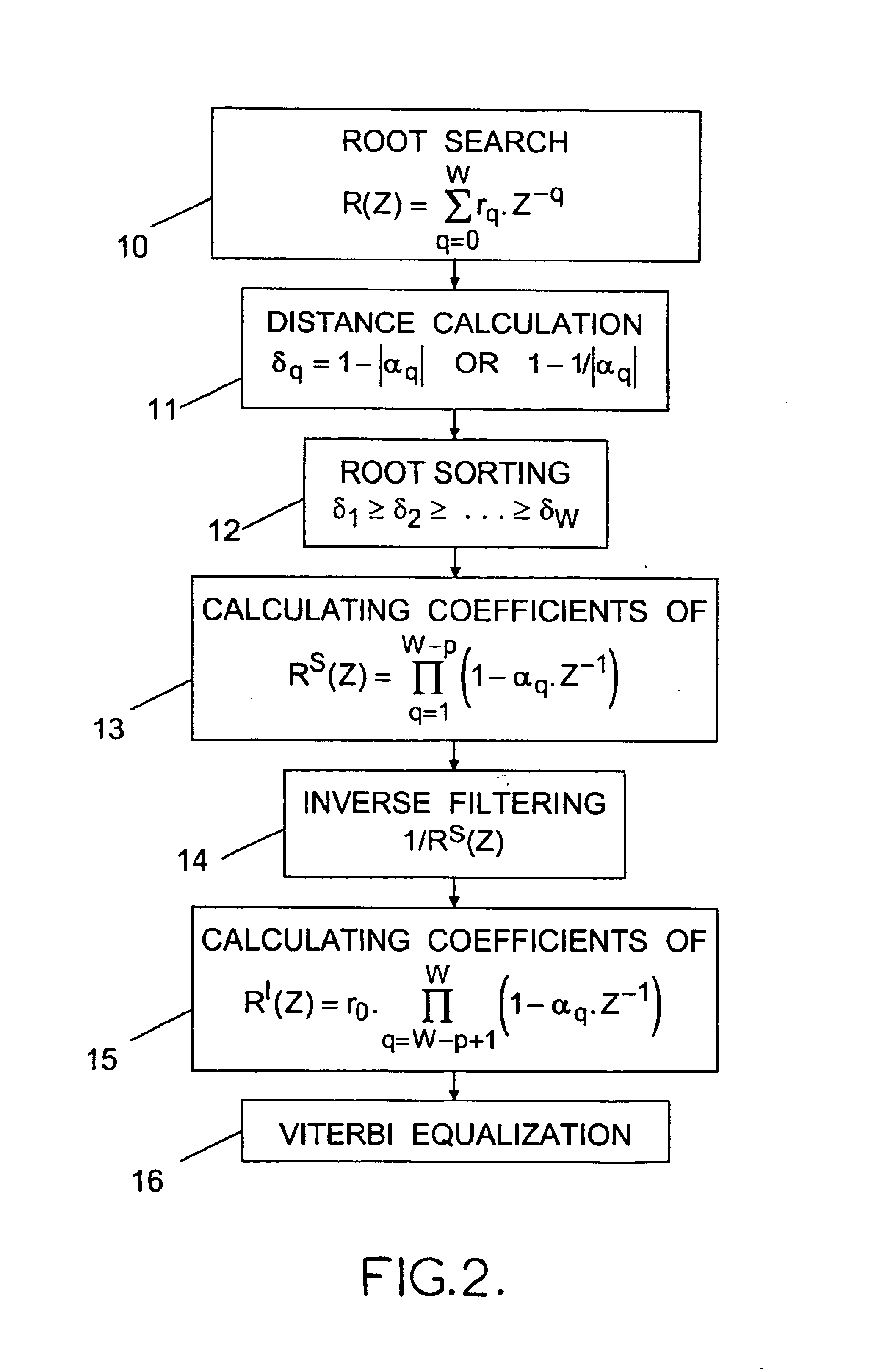
InactiveUS6850562B1Increase valueSolution value is not highMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationChannel impulse responsePartition of unity
For processing samples of a signal received via a channel represented by an impulse response of W−1 coefficients, the method comprises: determining the W roots of the Z-transform of the channel impulse response; producing an intermediate signal by equalizing the received signal by a zero-forcing method or the like based on an impulse response whose Z-transform is a Z−1 polynomial of degree W-p having as roots those of the W roots which are furthest from the unit circle of the complex plane; and then obtaining estimations of the transmitted signal symbols by applying a Viterbi-type equalization method or the like based on an impulse response whose Z-transform is a Z−1 polynomial of degree p having as roots those of the W roots which are nearest to the unit circle.
Owner:APPLE INC
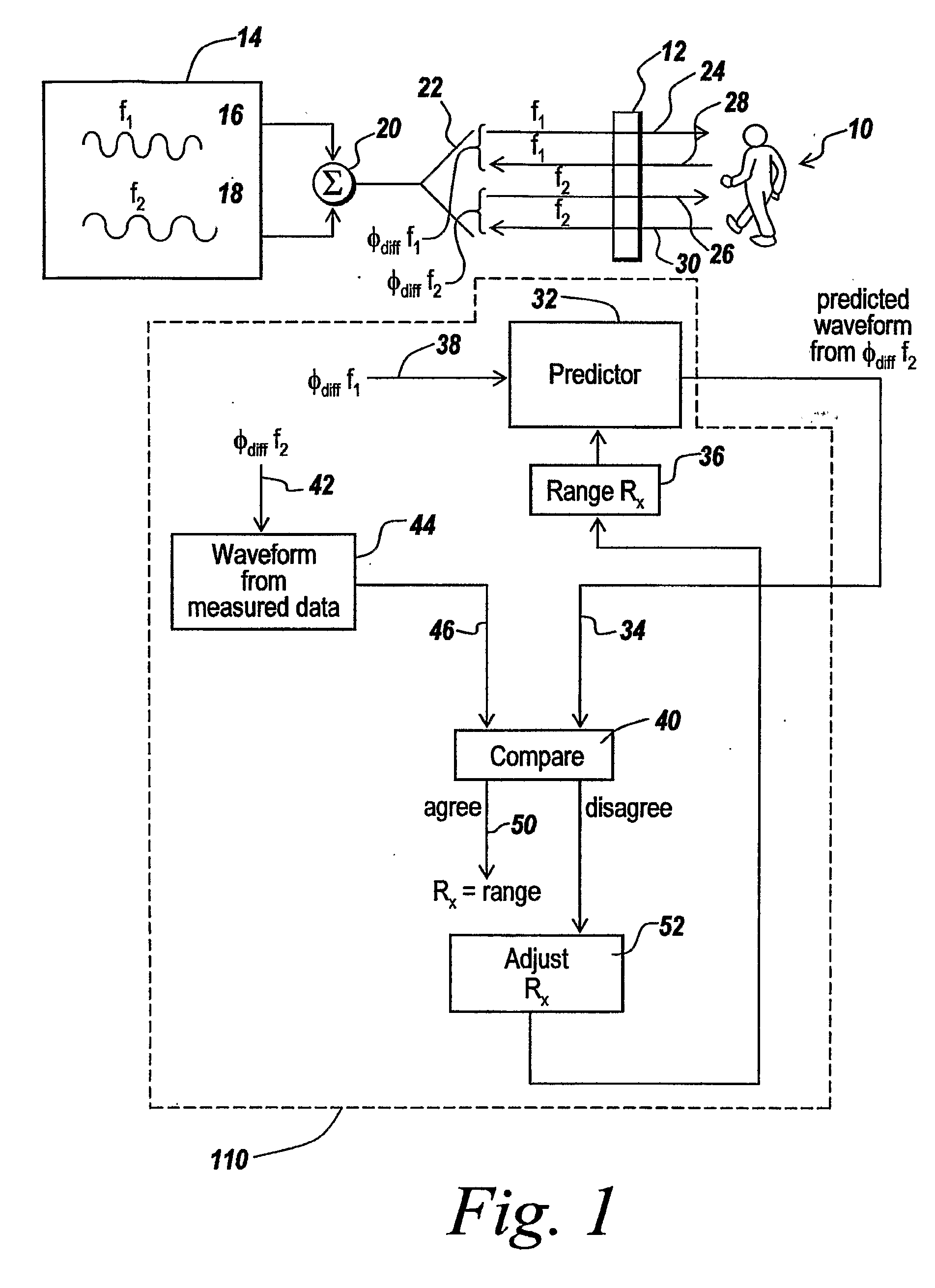
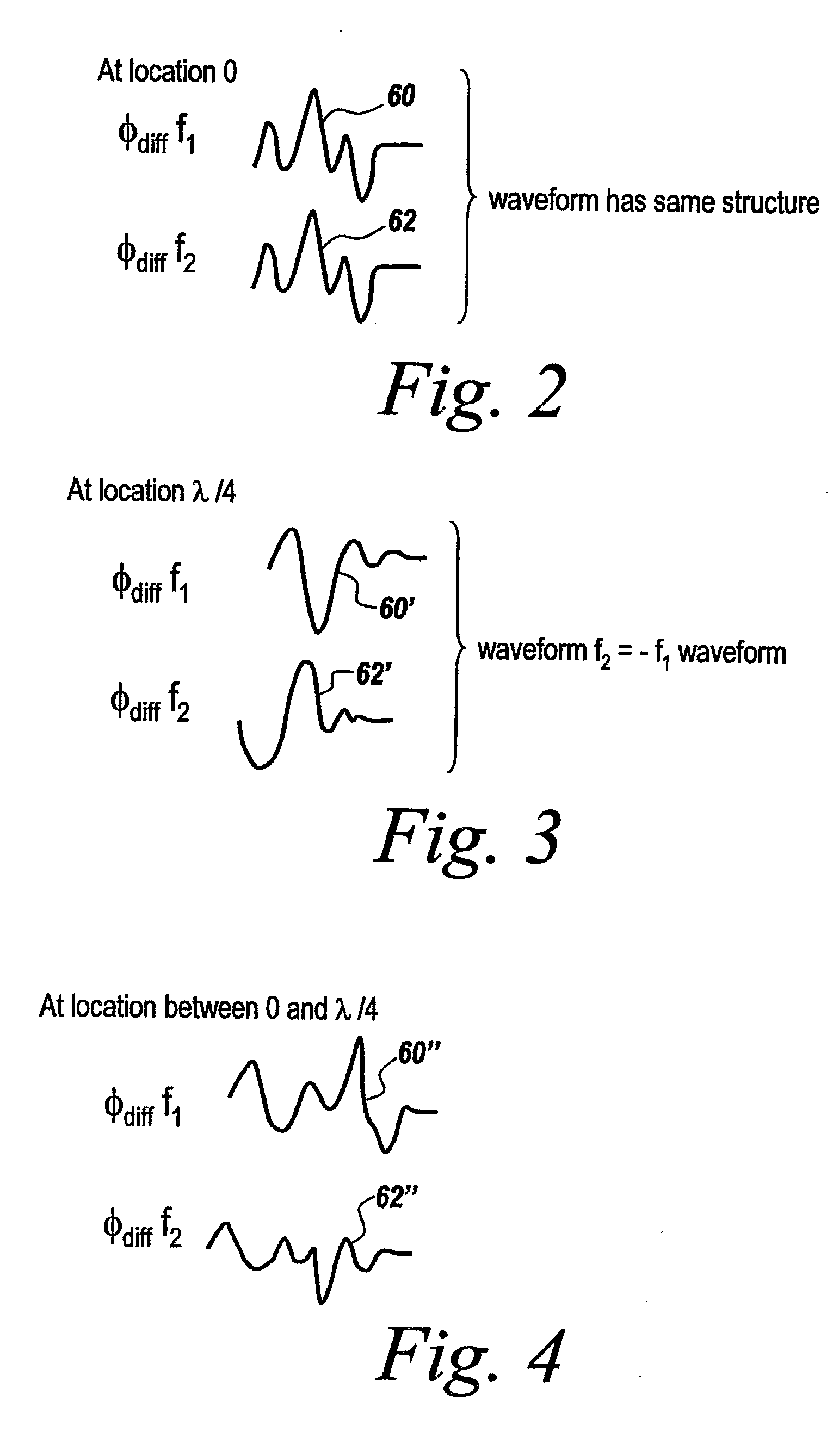
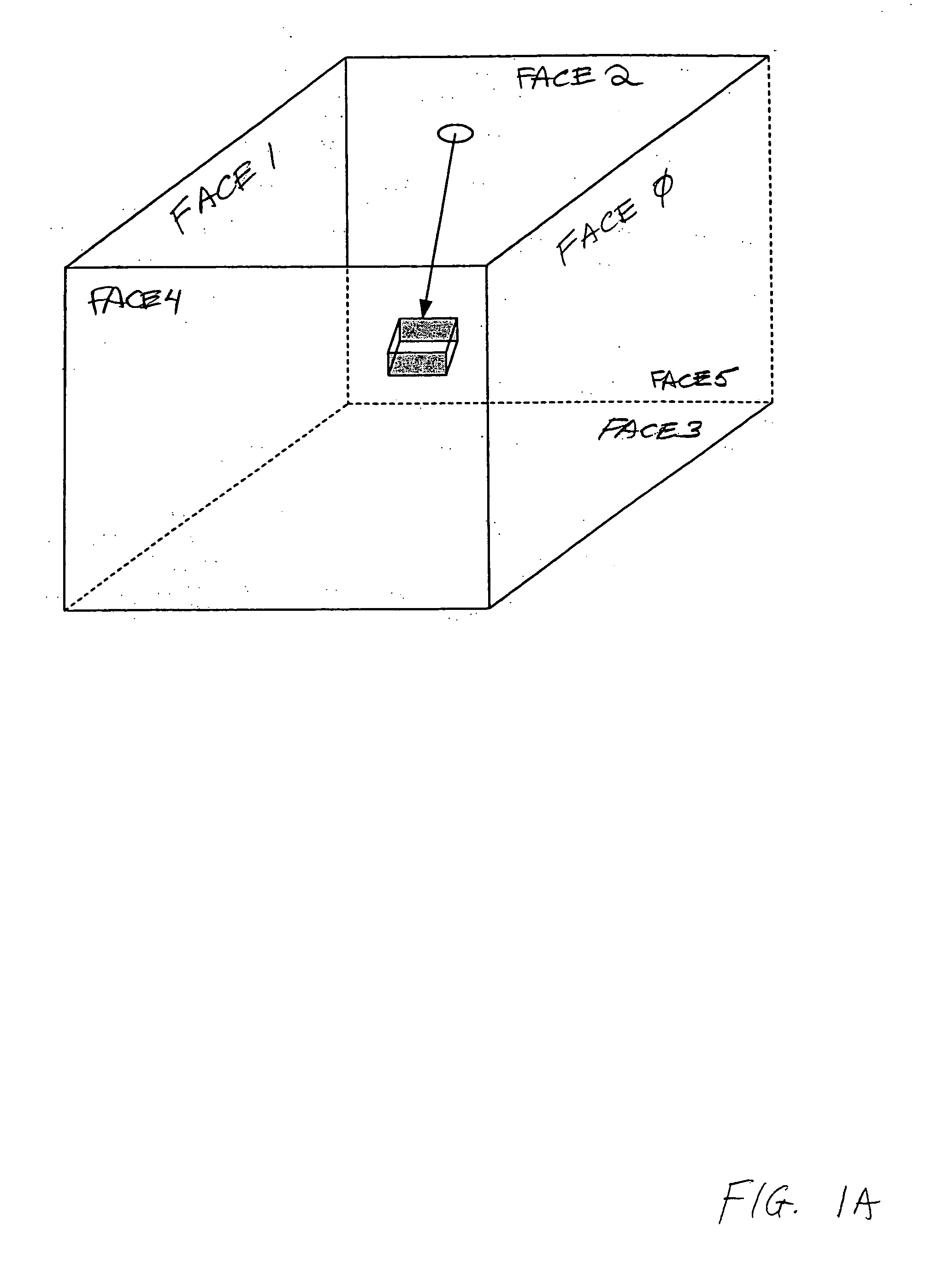
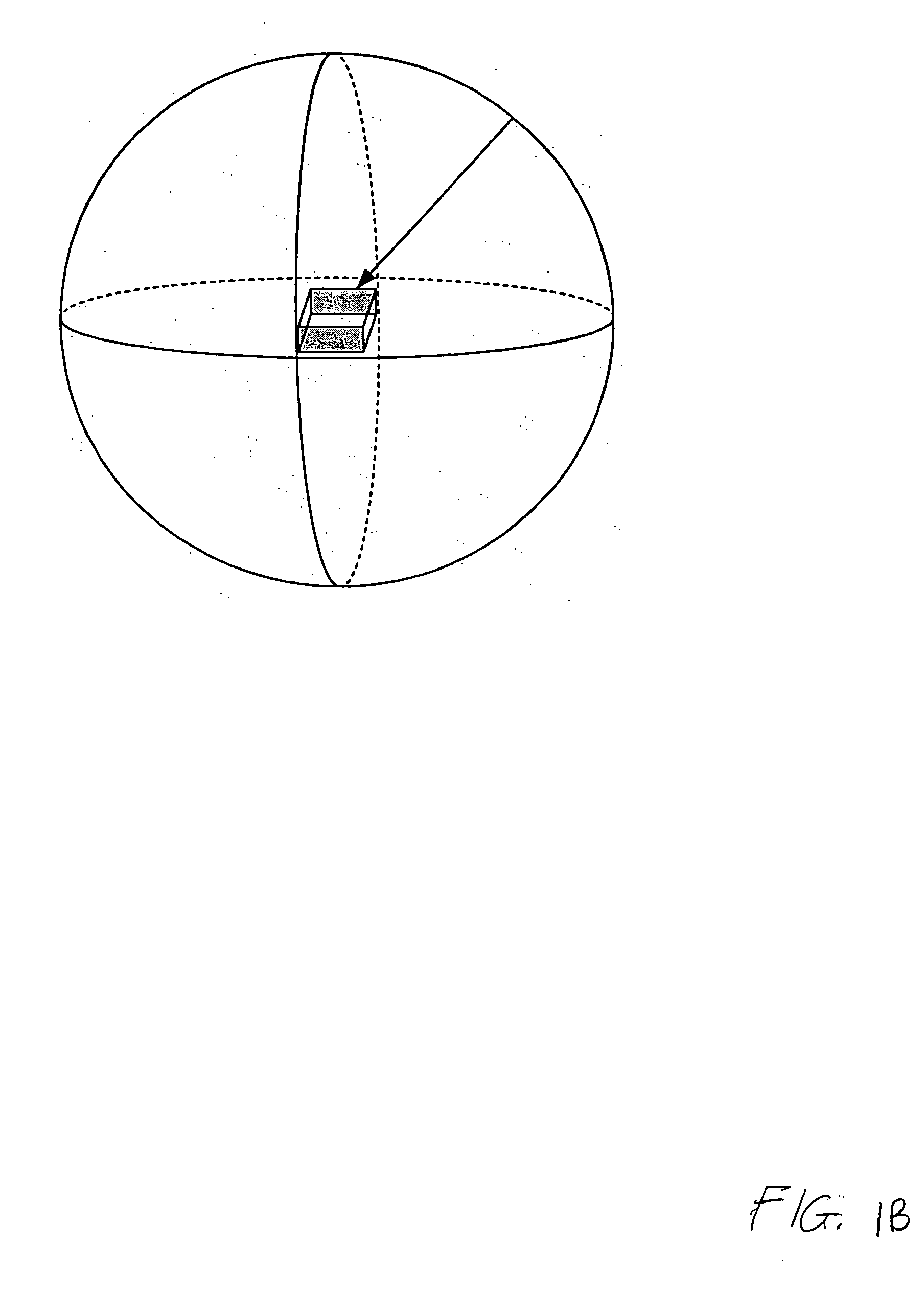
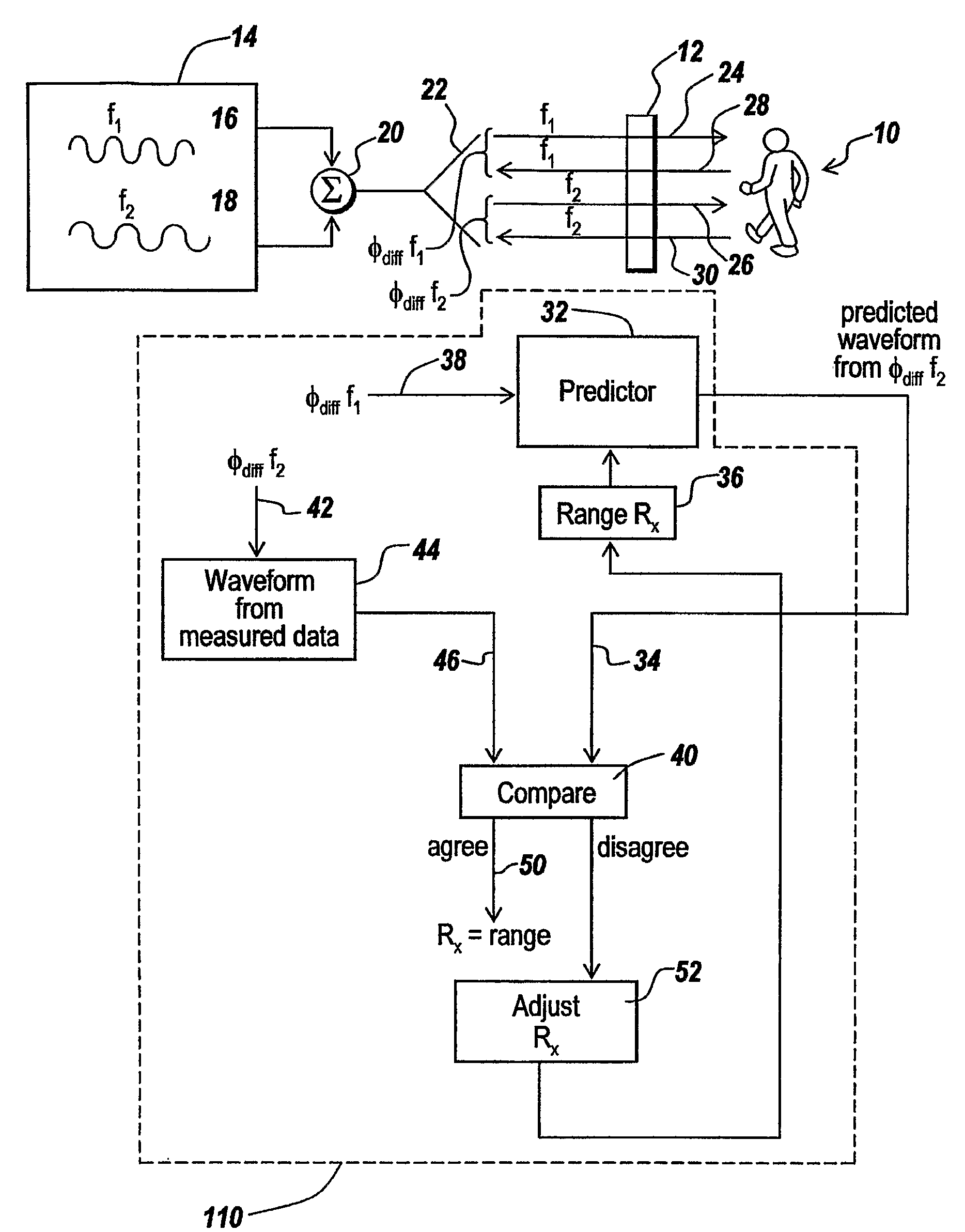
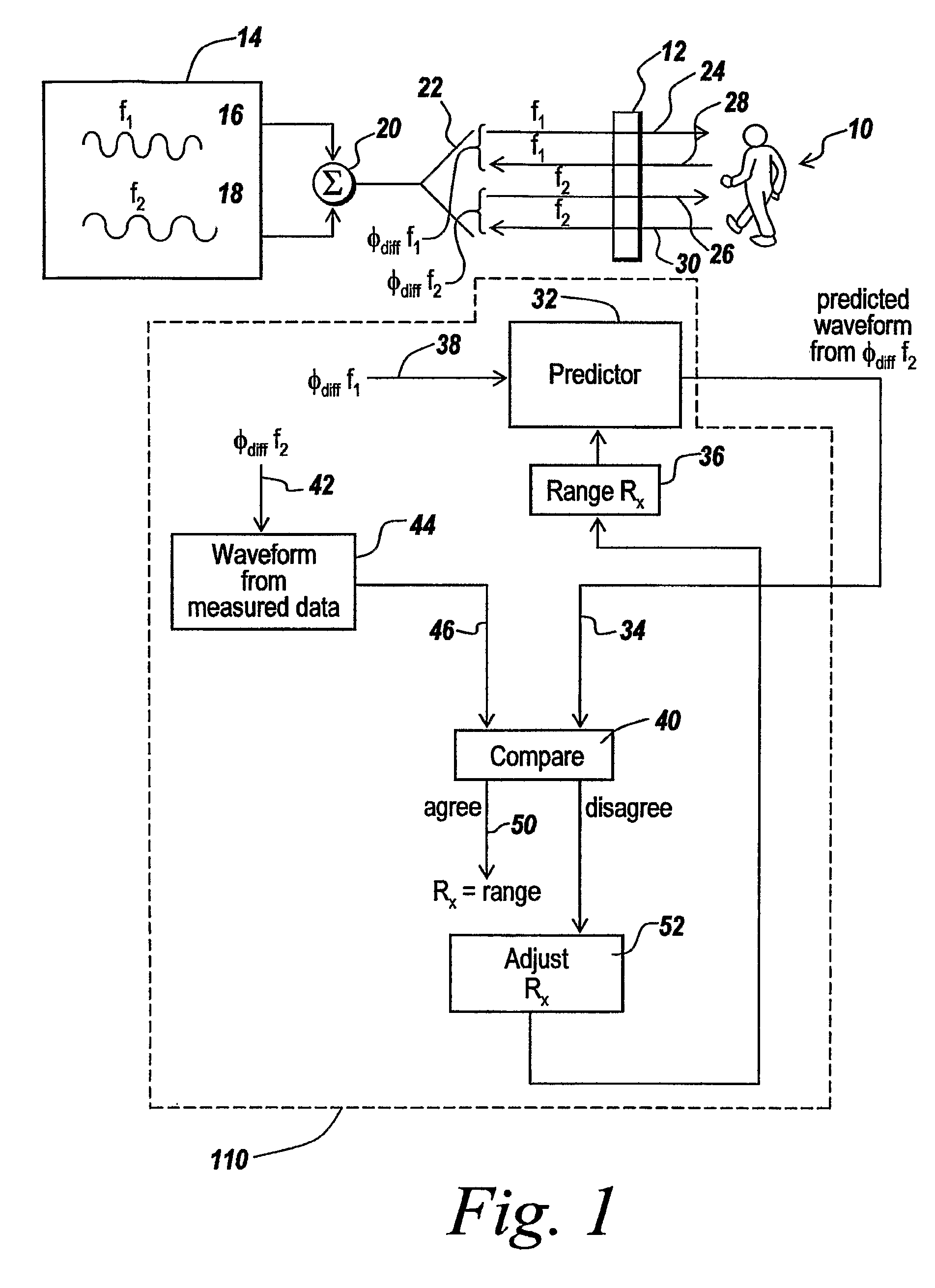
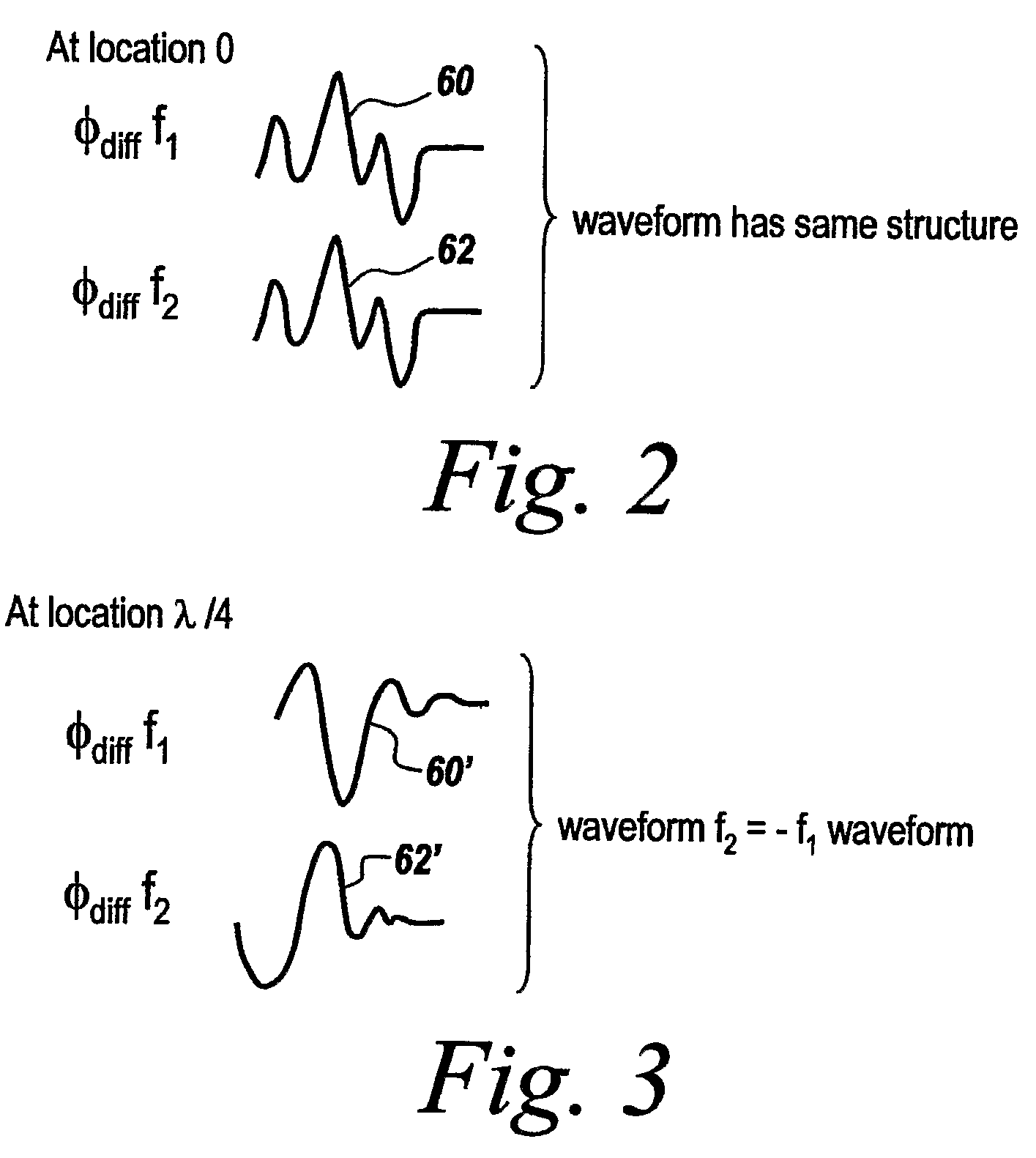
Multiple frequency through-the-wall motion detection and ranging using a difference-based estimation technique
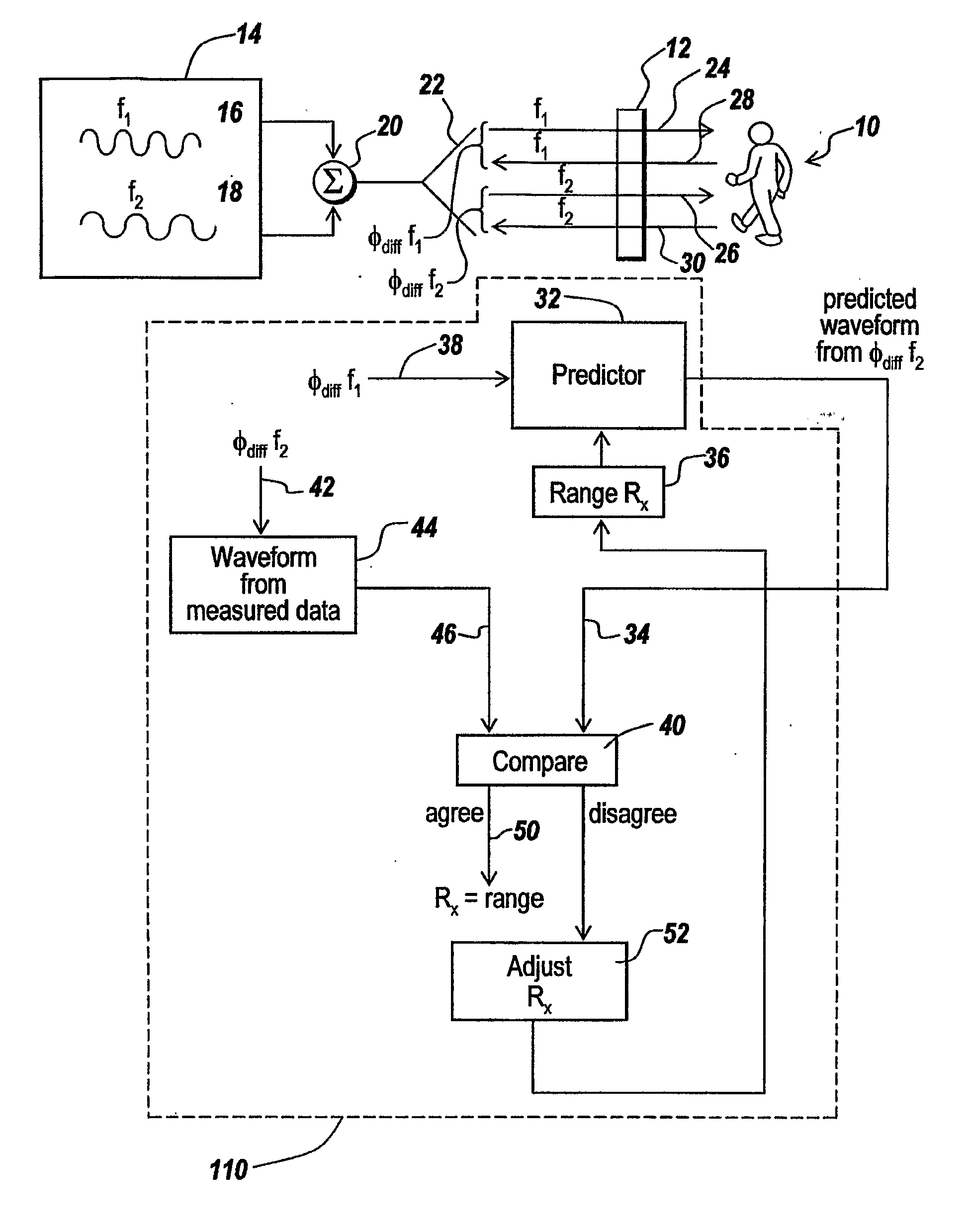
InactiveUS20070024487A1Easy to carryLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPartition of unityPhase difference
A multi-tone CW radar (14) is used to project signals from an antenna (22) and to receive returns with the same antenna. The phase differences between the outgoing signals and the returns are analyzed to determine the existence of motion and the range to a moving object (10). A model is made which has range as its major parameter. A waveform associated with the phase difference between outgoing signals and returns for one of the tones is compared to templates produced by the model to determine which has a range that most closely matches. By varying the range parameters, when a match is detected the range to the object can be obtained even if its motion is pseudorandom. If the range is measured with multiple units it is possible to measure the location of the object. This can be done assuming a grid and algorithmically combining the ranges from the units.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Lattice structures
A unit cell for a lattice structure includes eight unit trusses disposed at vertices of the unit cell. A single unit truss is disposed at a centroid of the unit cell. Each of the nine unit trusses includes fourteen struts. Lattice structures are commonly used to connect various loads within a volume of space. Most such structures, however, have a rigid definition for their topology, and are unable to conform to shape or load directions. Additionally, conventional lattice structures are homogeneous, having dimensions and properties that are consistent throughout. These constraints, generally imposed for ease of manufacturing and assembly, prevent the development of highly robust and efficient structures, and limit the potential for multi-functional applications.
Owner:MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING
Method and apparatus for designing and manufacturing electronic circuits subject to process variations
ActiveUS20050235232A1Additional circuitryImprove the environmentDetecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designDisplay deviceTrade offs
Methods and apparatus are described in which, at design-time a thorough analysis and exploration is performed to represent a multi-objective “optimal” trade-off point or points, e.g. on Pareto curves, for the relevant cost (C) and constraint criteria. More formally, the trade-off points may e.g. be positions on a hyper-surface in an N-dimensional Pareto search space. The axes represent the relevant cost (C), quality cost (Q) and restriction (R) criteria. Each of these working points is determined by positions for the system operation (determined during the design-time mapping) for a selected set of decision knobs (e.g. the way data are organized in a memory hierarchy). The C-Q-R values are determined based on design-time models that then have to be “average-case” values in order to avoid a too worst-case characterisation. At processing time, first a run-time BIST manager performs a functional correctness test, i.e. checks all the modules based on stored self-test sequences and “equivalence checker” hardware. All units that fail are deactivated (so that they cannot consume any power any more) and with a flag the run-time trade-off controllers, e.g. Pareto controllers, are informed that these units are not available any more for the calibration or the mapping. At processing time, also a set of representative working points are “triggered” by an on-chip trade-off calibration manager, e.g. a Pareto calibration manager, that controls a set of monitors which measure the actual C-Q-R values and that calibrates the working points to their actual values. Especially timing monitors require a careful design because correctly calibrated absolute time scales have to be monitored.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
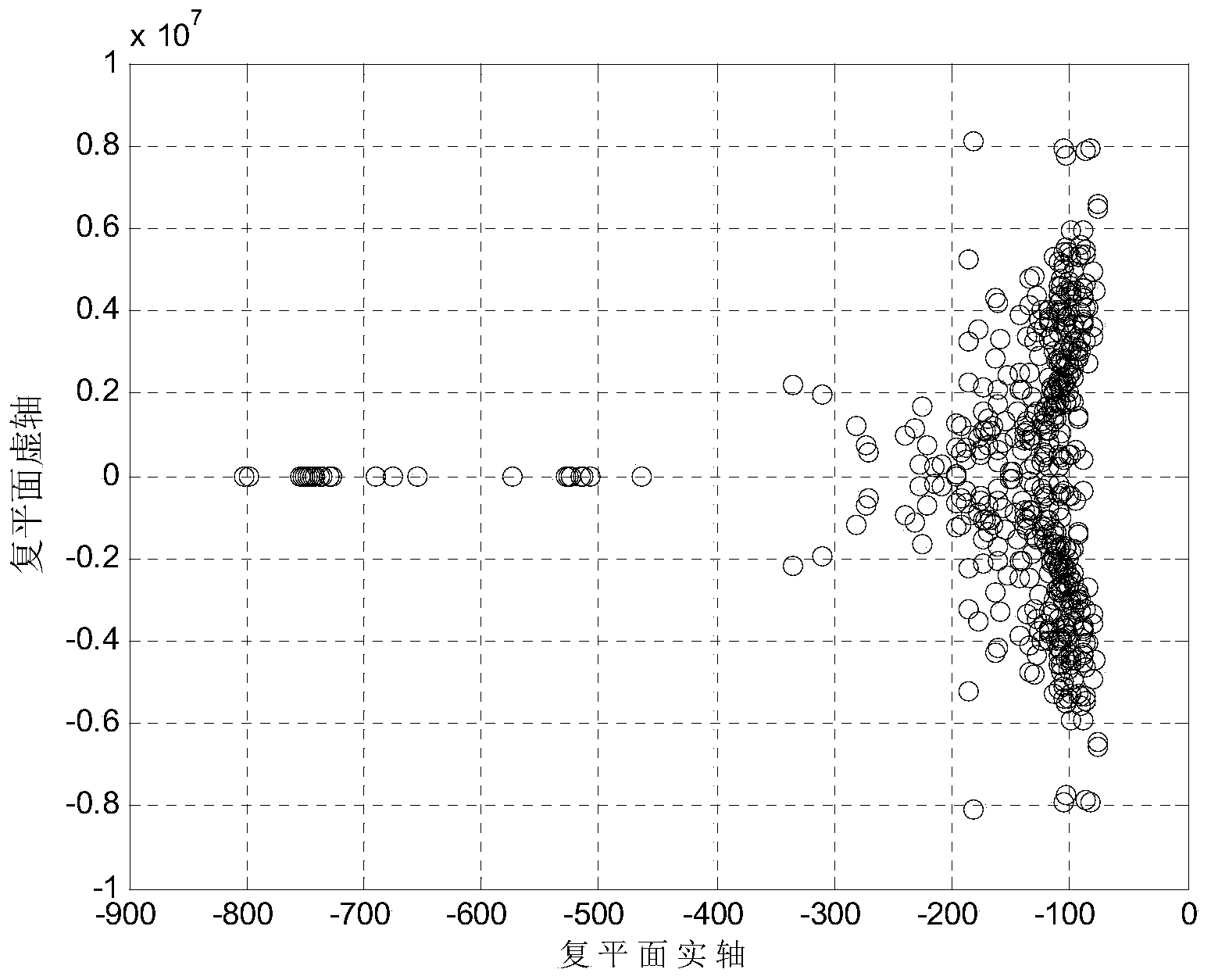
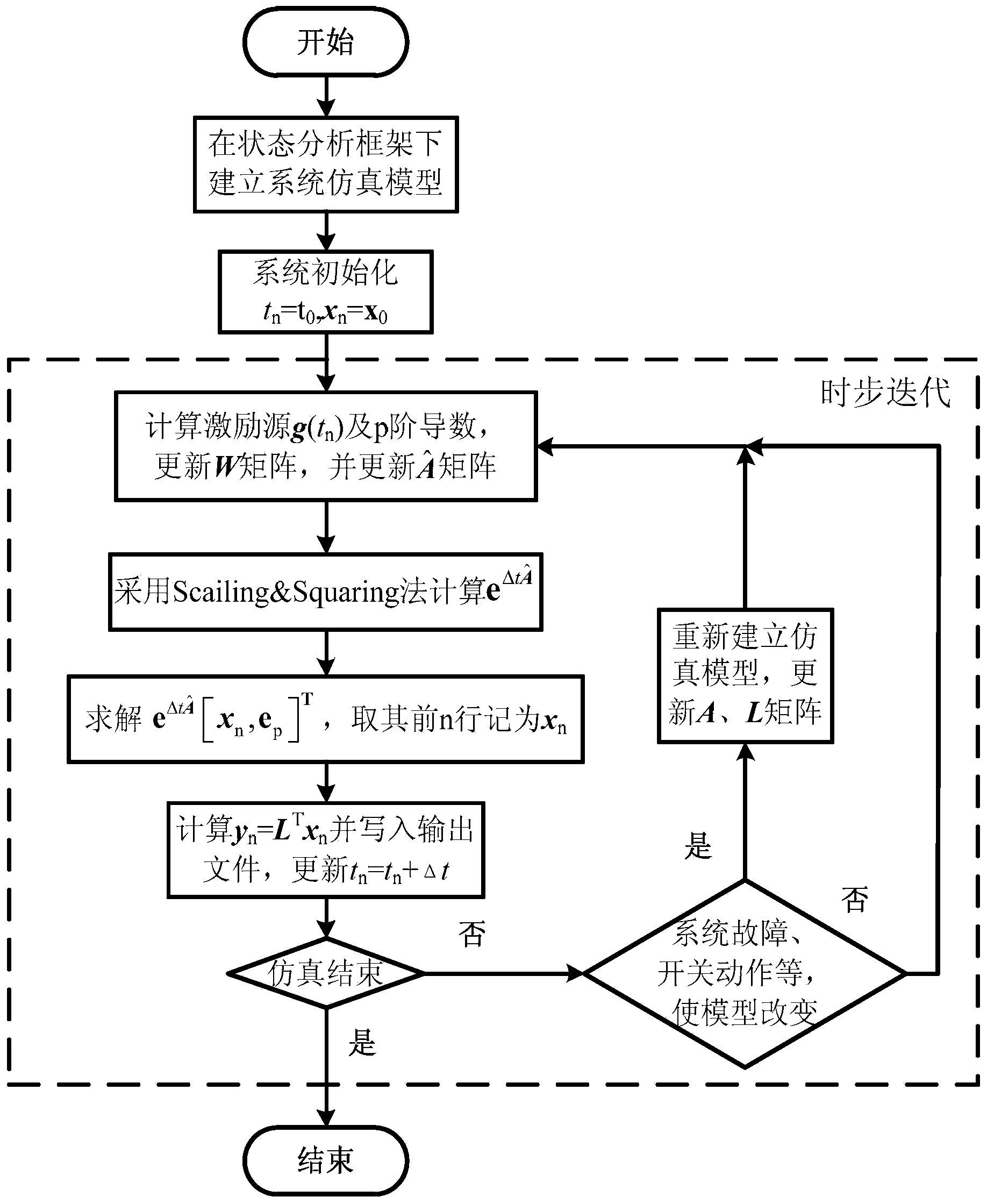
Electromagnetic transient simulation method of electric system based on matrix exponential
ActiveCN103646152AGuaranteed numerical stabilityGuaranteed accuracySpecial data processing applicationsTransient stateElectric power system
An electromagnetic transient simulation method of an electric system based on a matrix exponential comprises the steps of establishing an electromagnetic transient simulation model, as shown in the specification, of the system to be studied under a state analysis frame, starting a simulation program after setting simulation step sizes delta t and relevant simulation parameters, forming an augmented state matrix with an excitation source g(t) of the current moment, each derivative information and a state matrix A in each simulation step size, solving the matrix exponential e<delta t A> by a Scaling and Squaring algorithm, performing matrix vector multiplication on an augmented state vector formed with a state variable vector x(t) and a p-dimensional unit vector, taking a result as a state variable of the current moment, obtaining an output vector y(t) through an output equation, writing into an output file, simulating and boosting one step size, and judging a short circuit, an open circuit and switch motion firstly in the next simulation step size. The method can achieve electromagnetic transient modeling simulation of the electric system with a complicated structure, asymmetric height, and the model having the characteristic of rigidity.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
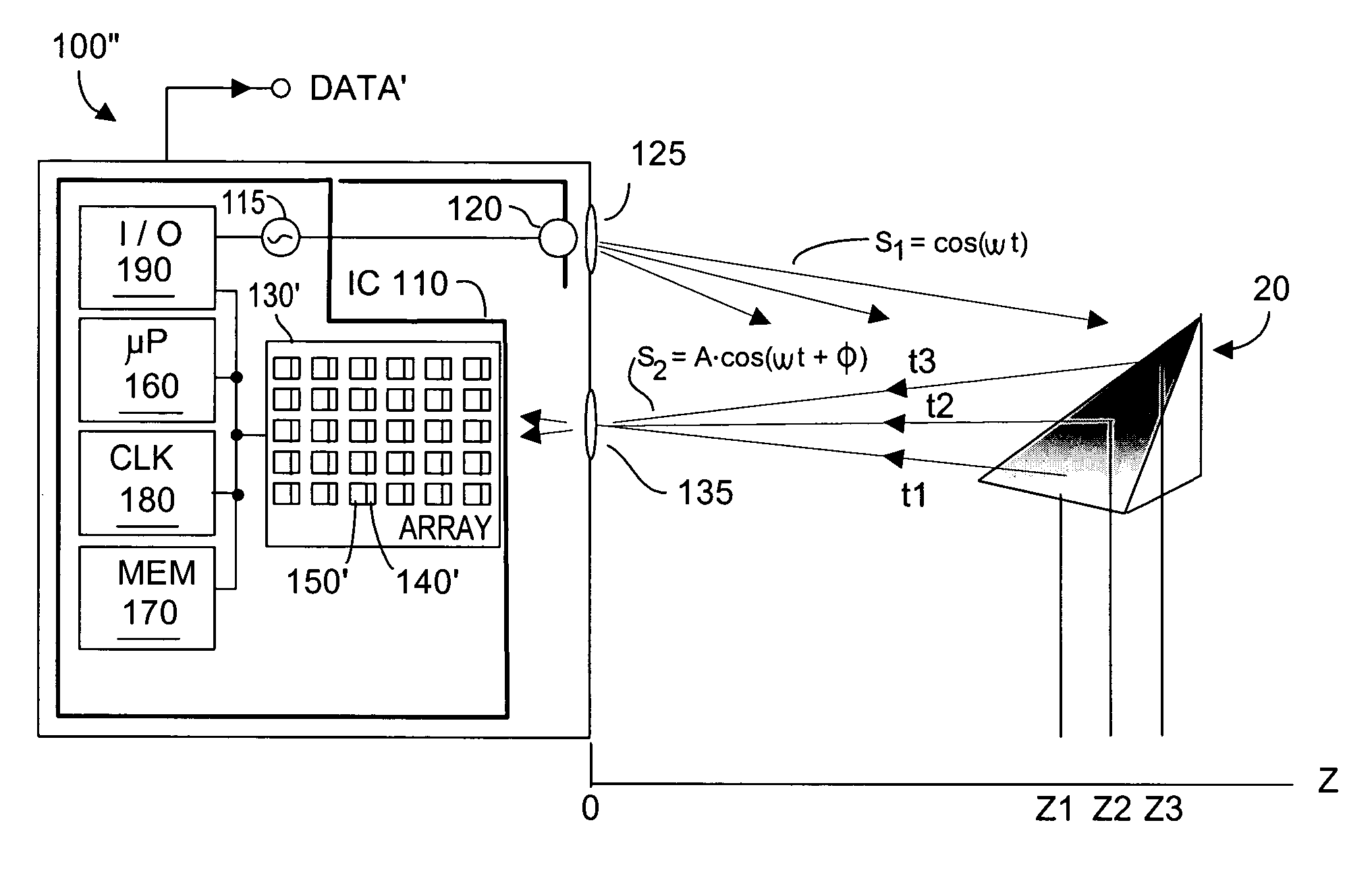
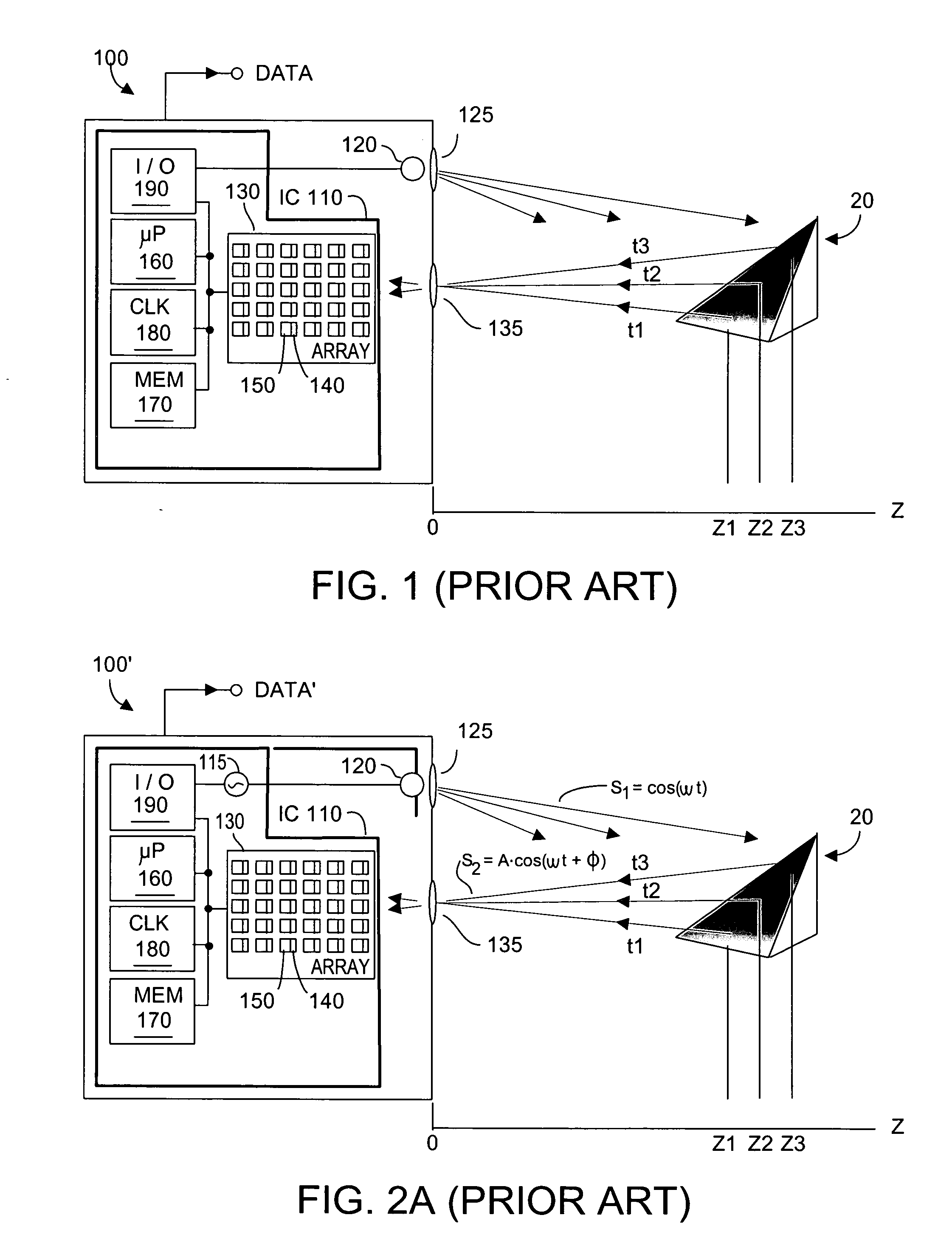
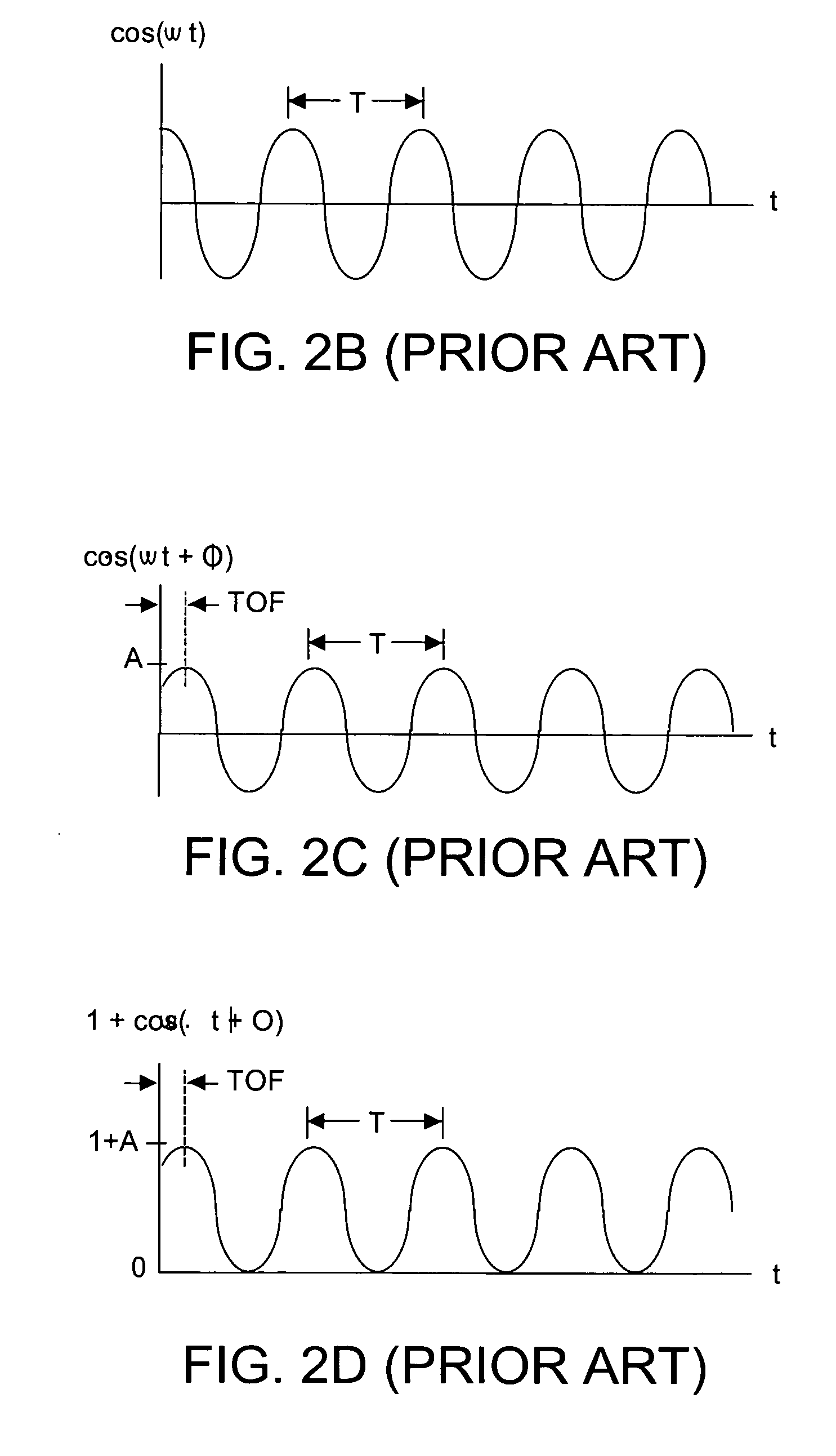
Method and system to correct motion blur and reduce signal transients in time-of-flight sensor systems
ActiveUS20060176469A1Reduces signal integrity problemReduce transferOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationTime of flight sensorPartition of unity
TOF system shutter time needed to acquire image data in a time-of-flight (TOF) system that acquires consecutive images is reduced, thus decreasing the time in which relative motion can occur. In one embodiment, pixel detectors are clocked with multi-phase signals and integration of the four signals occurs simultaneously to yield four phase measurements from four pixel detectors within a single shutter time unit. In another embodiment, phase measurement time is reduced by a factor (1 / k) by providing super pixels whose collection region is increased by a factor “k” relative to a normal pixel detector. Each super pixel is coupled to k storage units and four-phase sequential signals. Alternatively, each pixel detector can have k collector regions, k storage units, and share common clock circuitry that generates four-phase signals. Various embodiments can reduce the mal-effects of clock signal transients upon signals, and can be dynamically reconfigured as required.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
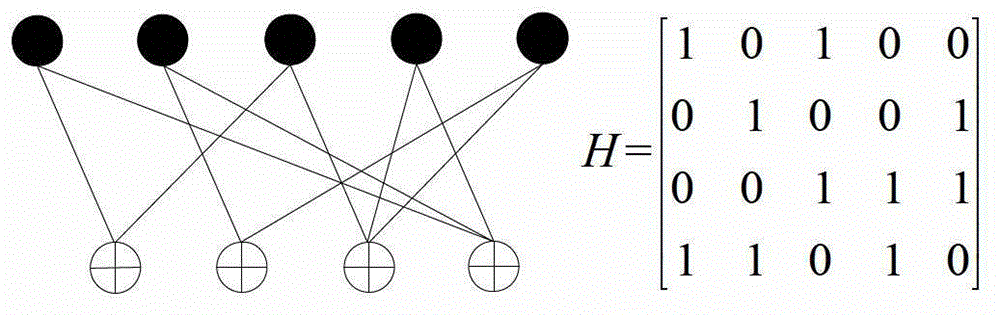
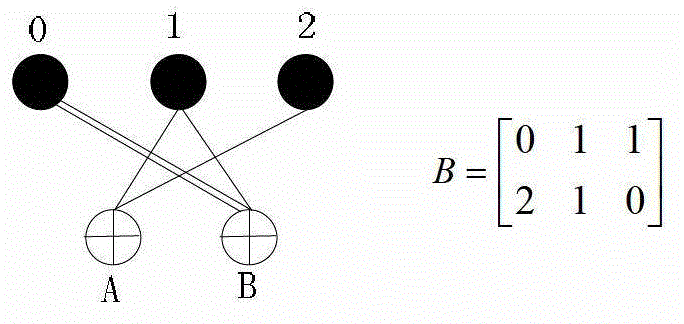
Quasi-cyclic low density parity check code (LDPC) construction method and device based on protographs
InactiveCN103152056AConsider complexityError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsMultiple edgesExpansion factor
The invention discloses a quasi-cyclic low density parity check code (LDPC) construction method and a device based on protographs. The protographs are expanded for two times in the construction method. A first expansion time L1 is smaller. A correcting progressive edge growth (PEG) algorithm is adopted to remove multiple edges of protographs. The girths of codes which are expanded are increased. A second expansion time is L2 and a cyclic shift offset is selected for connection which is established in the first expansion. Each connection corresponds to a unit cyclic matrix, wherein the size of the unit cyclic matrix is L2 * L2. The method references a local optimization idea of the PEG algorithm to construct a basis matrix of the quasi-cyclic LDPC code. The connection is established between each row of variable nodes and checking nodes and is confirmed in corresponding cyclic shift offset process. According to the correcting PEG algorithm, new rings formed in the basis matrix caused by the newly established connection are gone through. The fact that expansion factors A of the rings are larger than one is guaranteed. Thus, the rings with length of four are avoided. The number of short rings is reduced. The short rings which are small in connectivity emerge in a checking matrix are avoided by utilizing an ACE multiplication principle.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
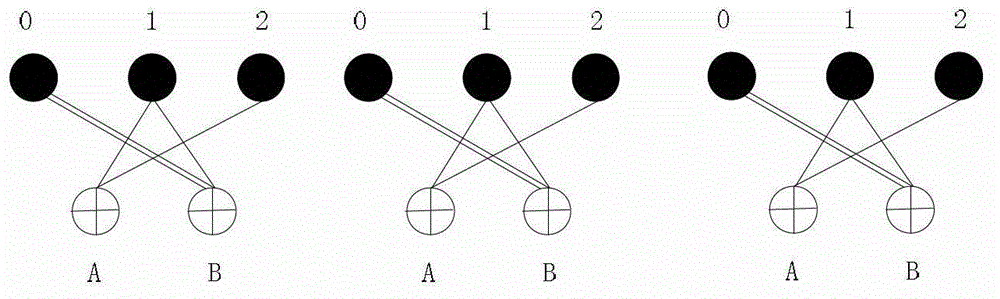
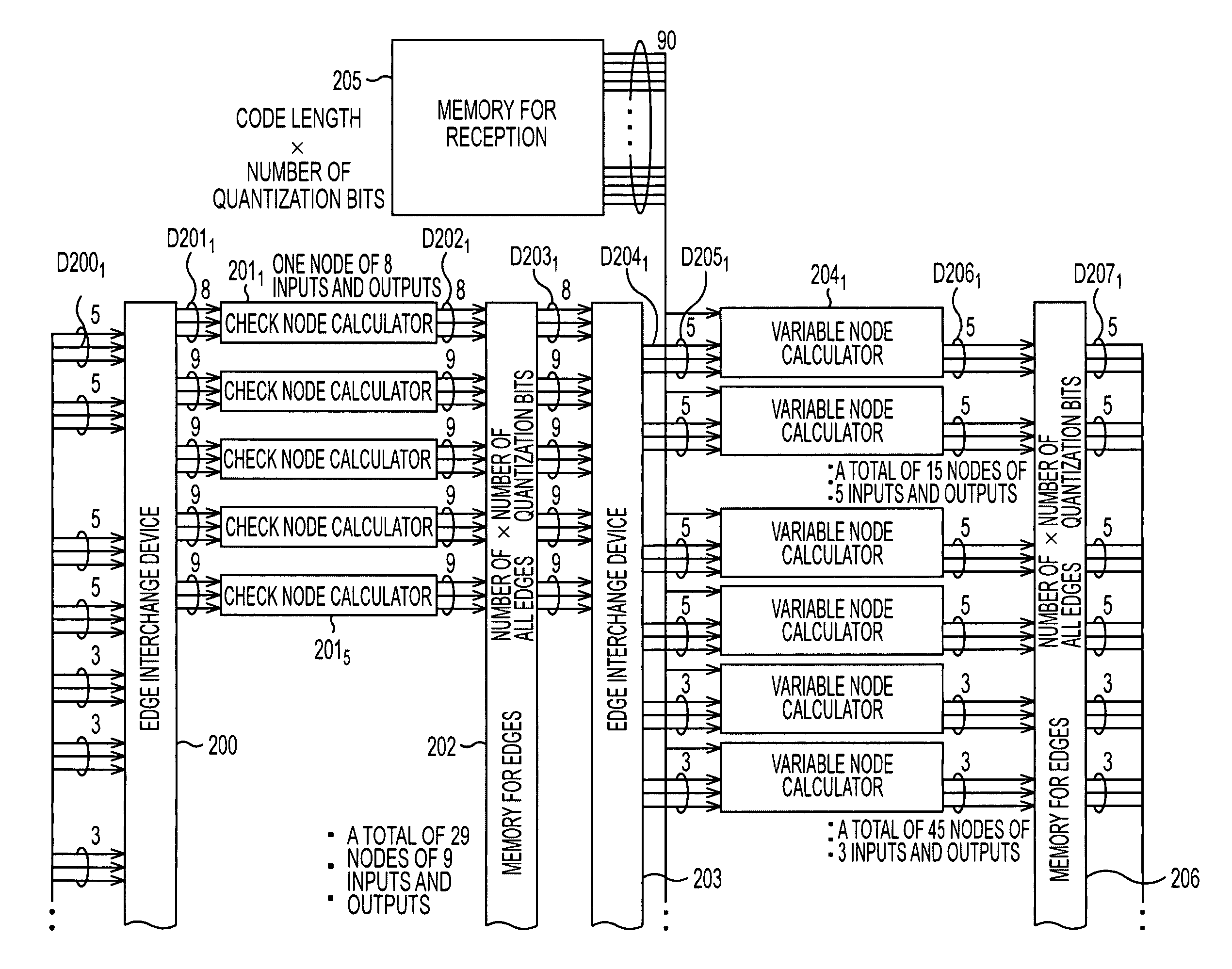
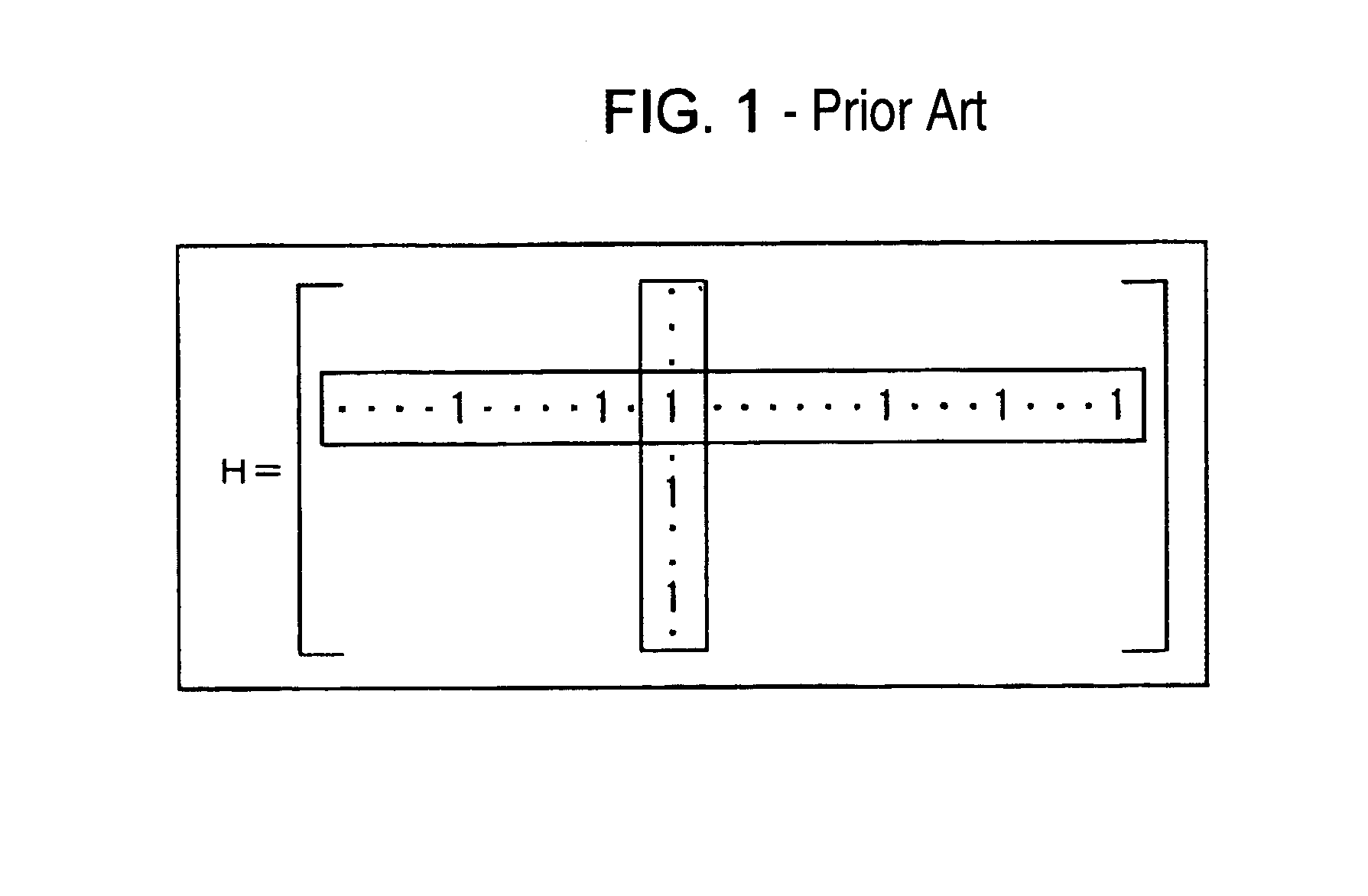
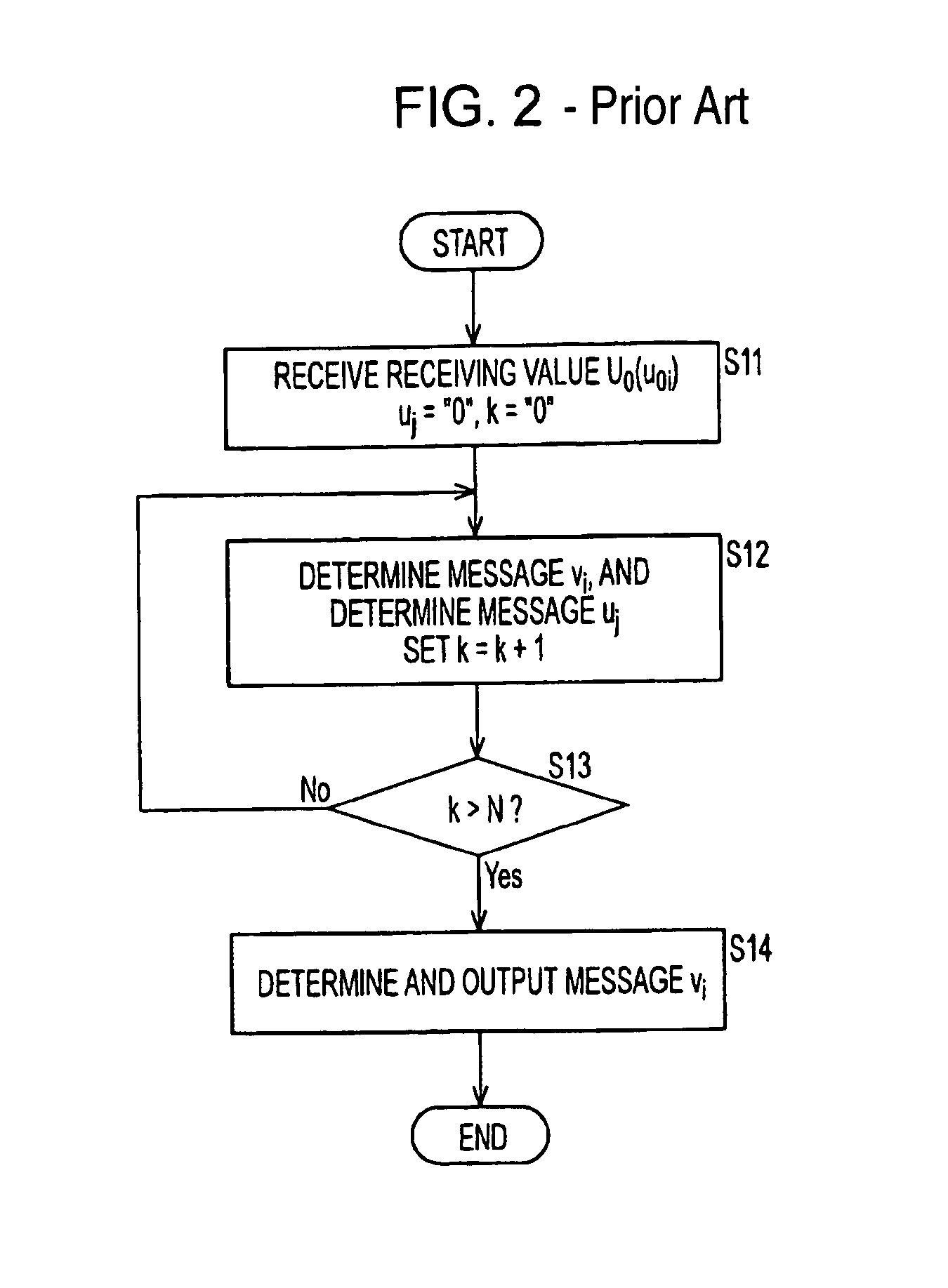
Decoding method, decoding apparatus, and program to decode low density parity check codes
ActiveUS7318186B2Easy to controlSuppression frequencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionFormation matrixPartition of unity
Owner:SONY CORP
Abstract convex lower-bound estimation based protein structure prediction method
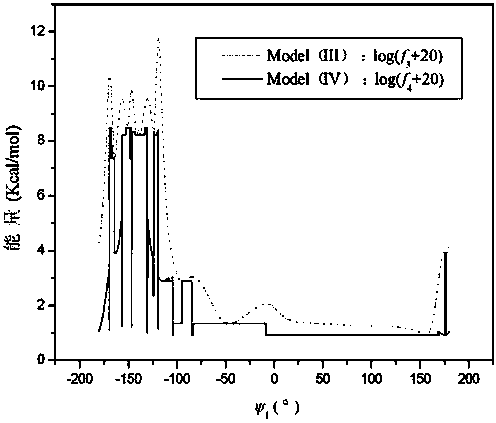
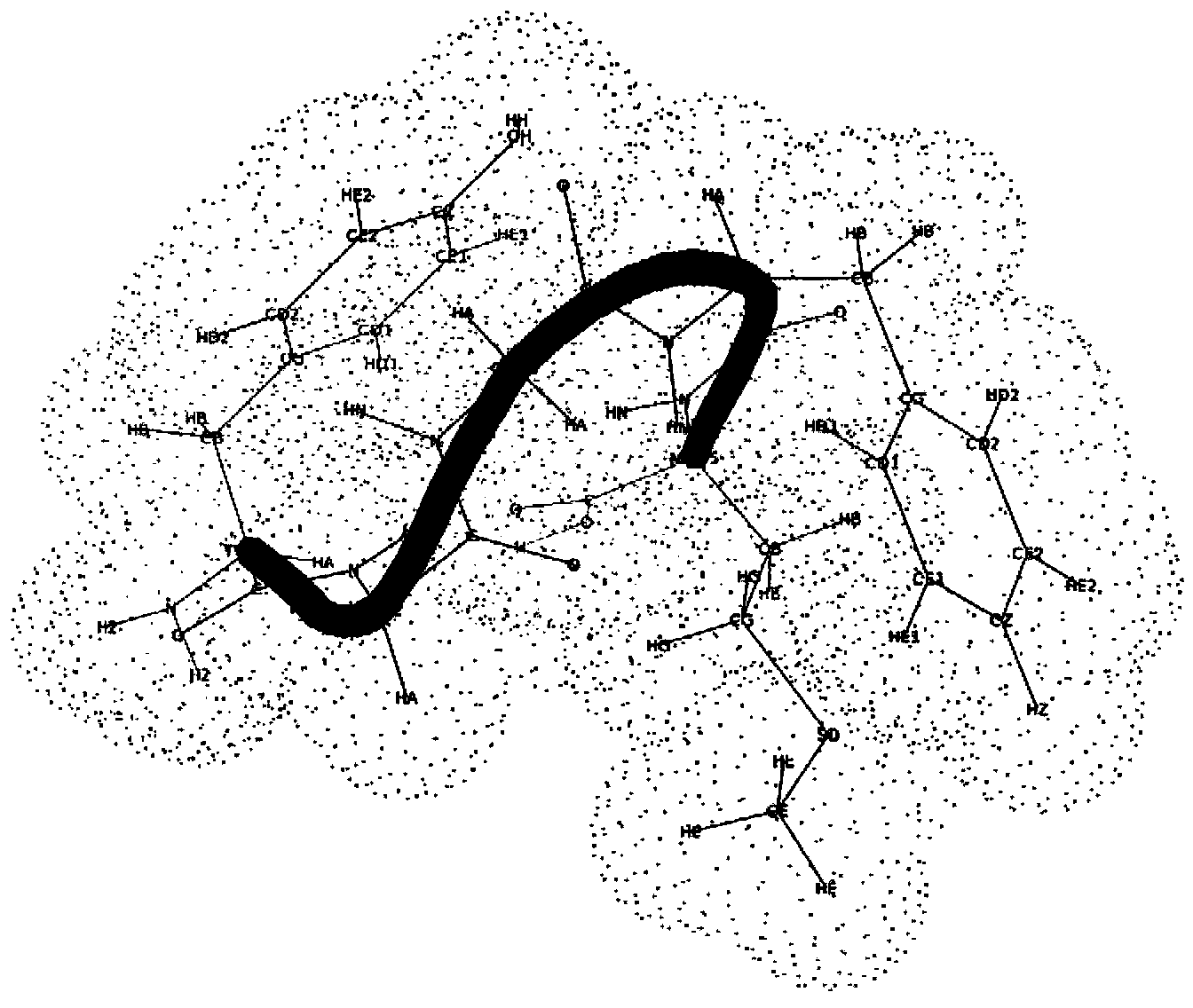
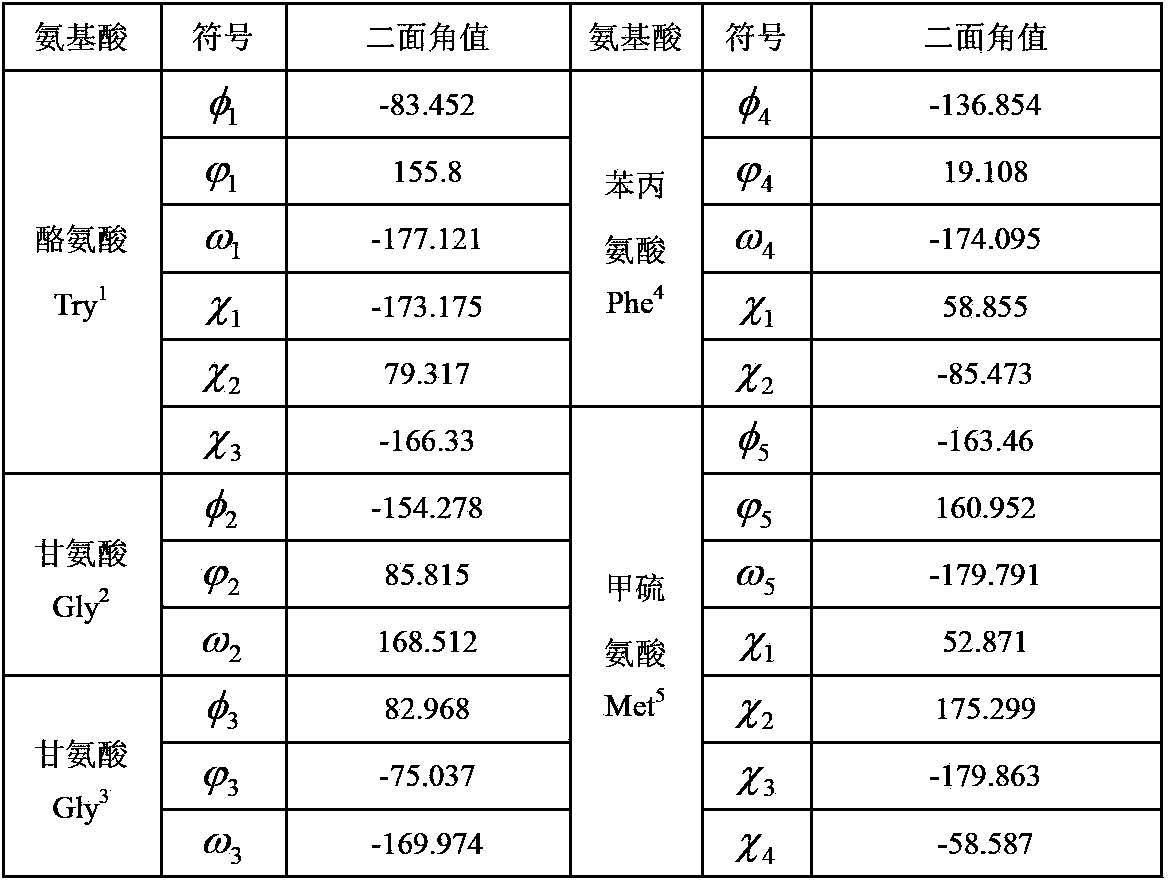
Disclosed is an abstract convex lower-bound estimation based protein structure prediction method. The method includes: firstly, aiming for high-dimensional conformational spatial sampling problems for proteins, adopting a series of transform methods to transform an ECEPP / 3 force field model into an increasing radial convex function in unit simple constraint conditions; secondly, based on an abstract convex theory, proving and analyzing to give out a supporting hyperplane set of the increasing radial convex function; thirdly, constructing a lower-bound underestimate supporting plane on the basis of population minimization conformation subdifferential knowledge under a differential evolution population algorithm framework; fourthly, by the aid of a quick underestimate supporting plane extreme point enumeration method, gradually decreasing a conformational sampling space to improve sampling efficiency; fifthly, utilizing the lower-bound underestimate supporting plane for quickly and cheaply estimating an energy value of an original potential model to effectively decrease evaluation times of a potential model objective function; finally, verifying effectiveness of the method by methionine-enkephalin (TYR1-GLY2-GLY3-PHE4-MET5) conformational spatial optimization examples. The abstract convex lower-bound estimation based protein structure prediction method is high in reliability, low in complexity and high in computation efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for supervised teaching of a recurrent artificial neural network
A method for the supervised teaching of a recurrent neutral network (RNN) is disclosed. A typical embodiment of the method utilizes a large (50 units or more), randomly initialized RNN with a globally stable dynamics. During the training period, the output units of this RNN are teacher-forced to follow the desired output signal. During this period, activations from all hidden units are recorded. At the end of the teaching period, these recorded data are used as input for a method which computes new weights of those connections that feed into the output units. The method is distinguished from existing training methods for RNNs through the following characteristics: (1) Only the weights of connections to output units are changed by learning—existing methods for teaching recurrent networks adjust all network weights. (2) The internal dynamics of large networks are used as a “reservoir” of dynamical components which are not changed, but only newly combined by the learning procedure—existing methods use small networks, whose internal dynamics are themselves completely re-shaped through learning.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method for generating a 3D reconstruction of a body
InactiveUS7742557B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPartition of unityBack projection
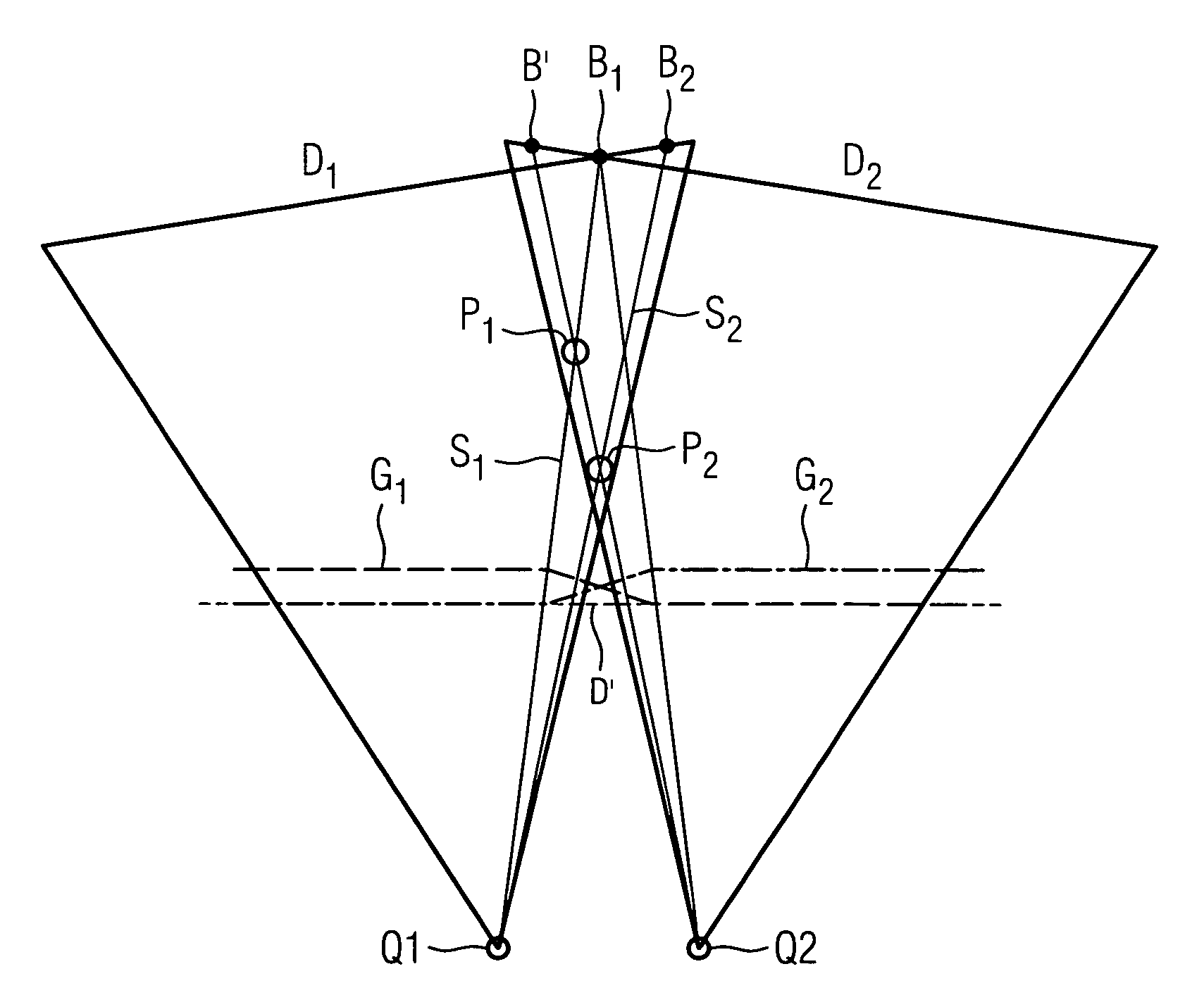
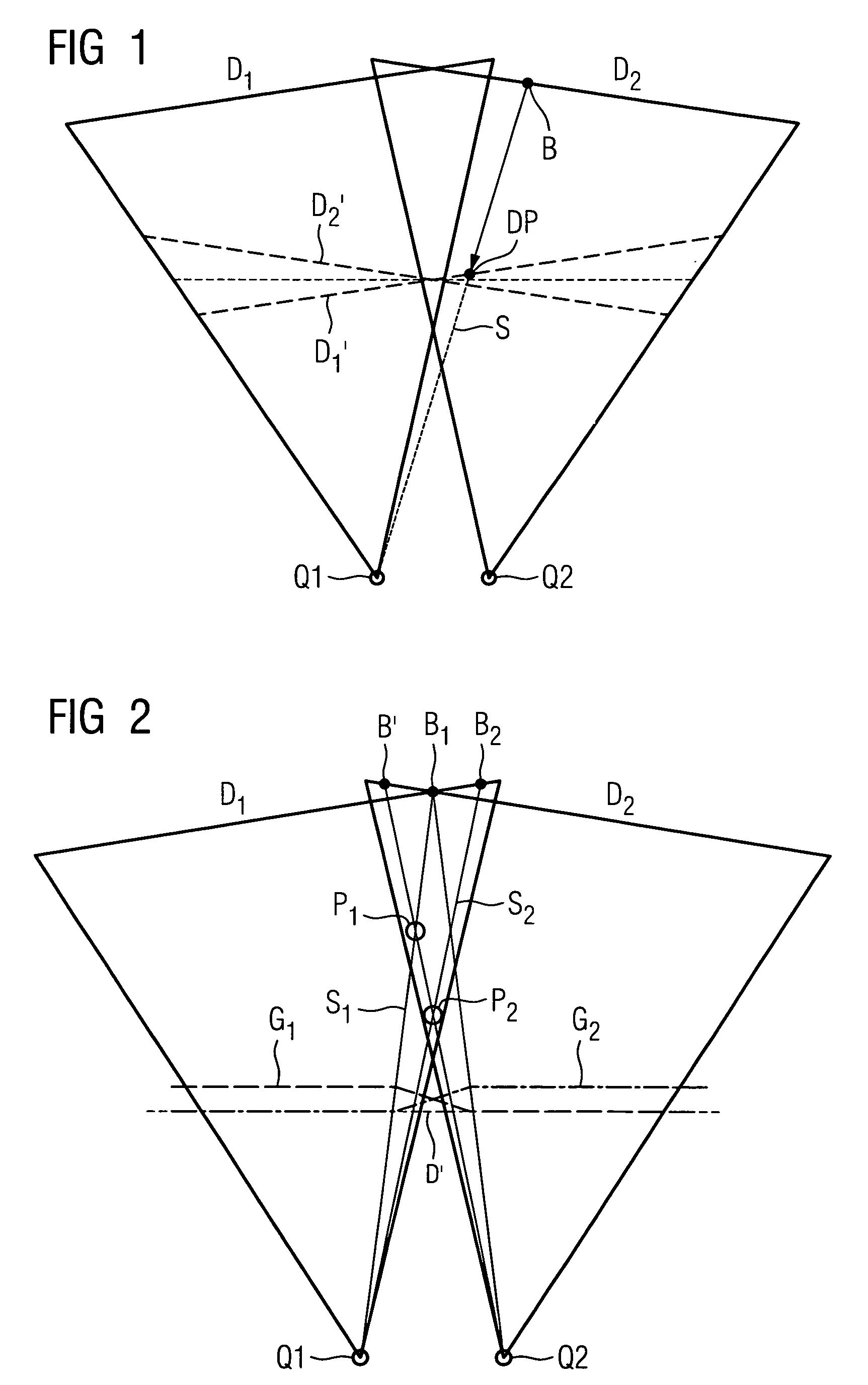
The invention relates to a method for generating a 3D reconstruction of an especially large body that cannot be captured by a single projection by capturing at least two projections, which together capture the body, at each of the positions taken up by a C-arm X-ray unit. Data from the two projections is projected onto a virtual detector and the data from the virtual detector is then used for the filtered back projection procedure. It is assumed here that the real source remains motionless and that only the detector moves. A virtual detector D1′ / D2′ is only used in order to carry out large scale filtering in the event that real sources Q1 and Q2 for the two projections do not coincide. A return is then made to two independent projections. These two independent projections are used separately in the filtered back projection procedure to generate the 3D reconstruction.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
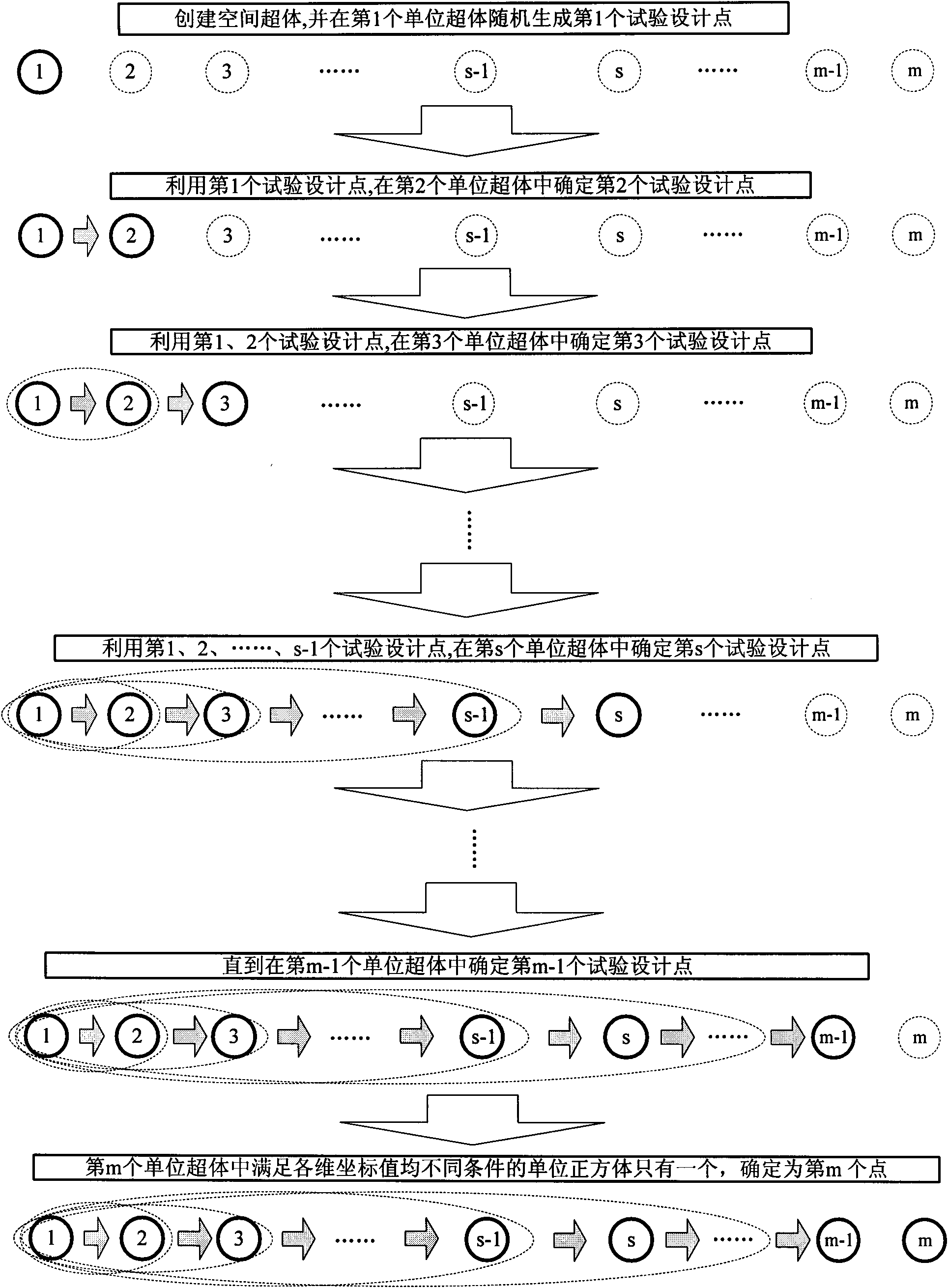
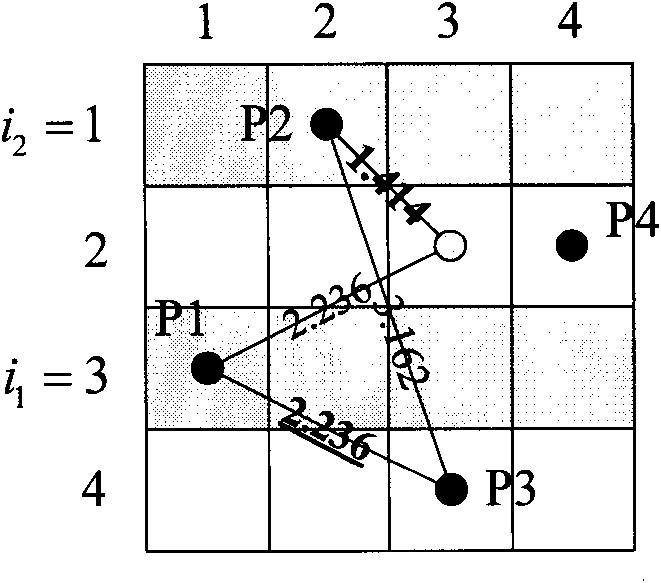
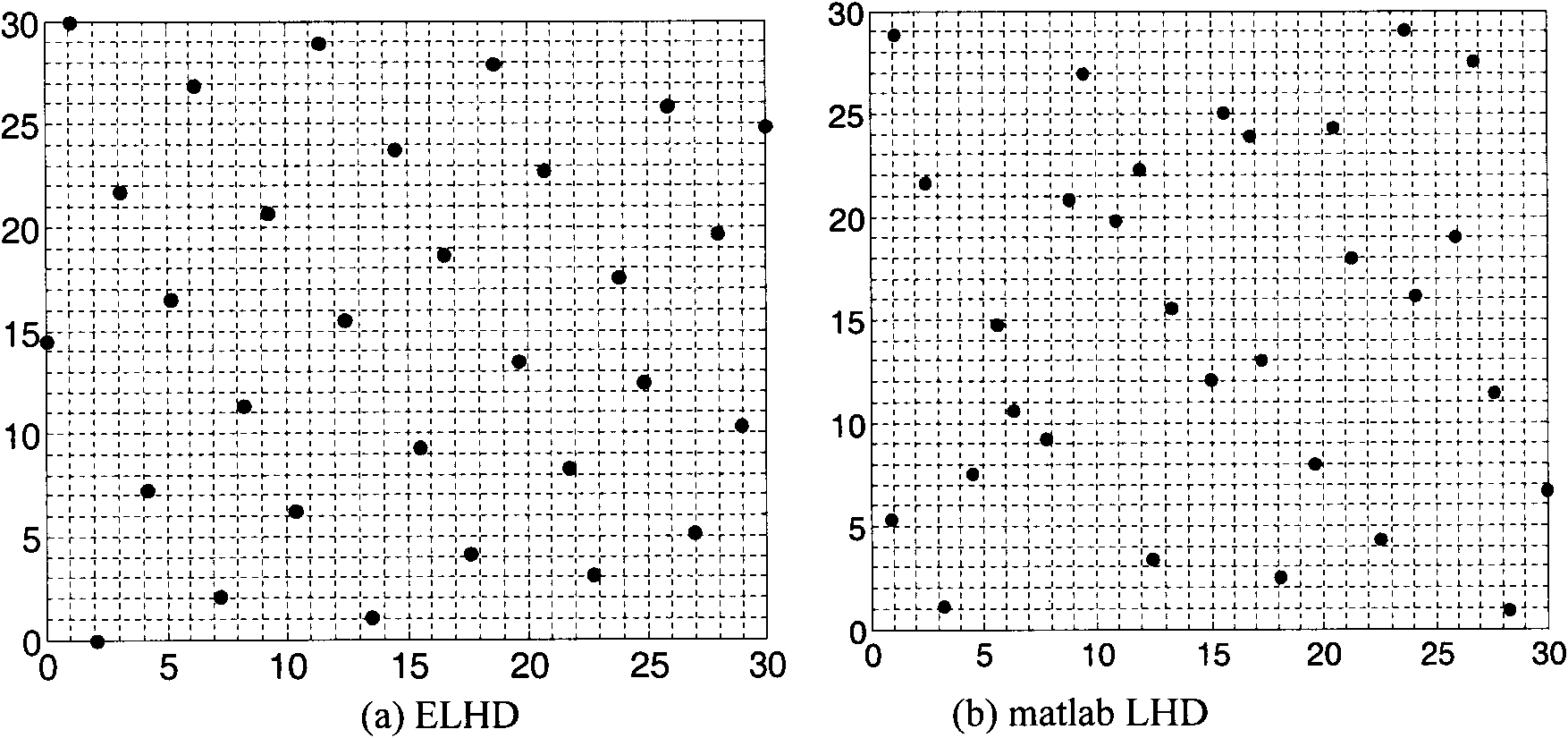
High-efficiency Latin hypercube experimental design method
InactiveCN101923590AImprove sampling efficiencySimple designSpecial data processing applicationsPartition of unityEngineering
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
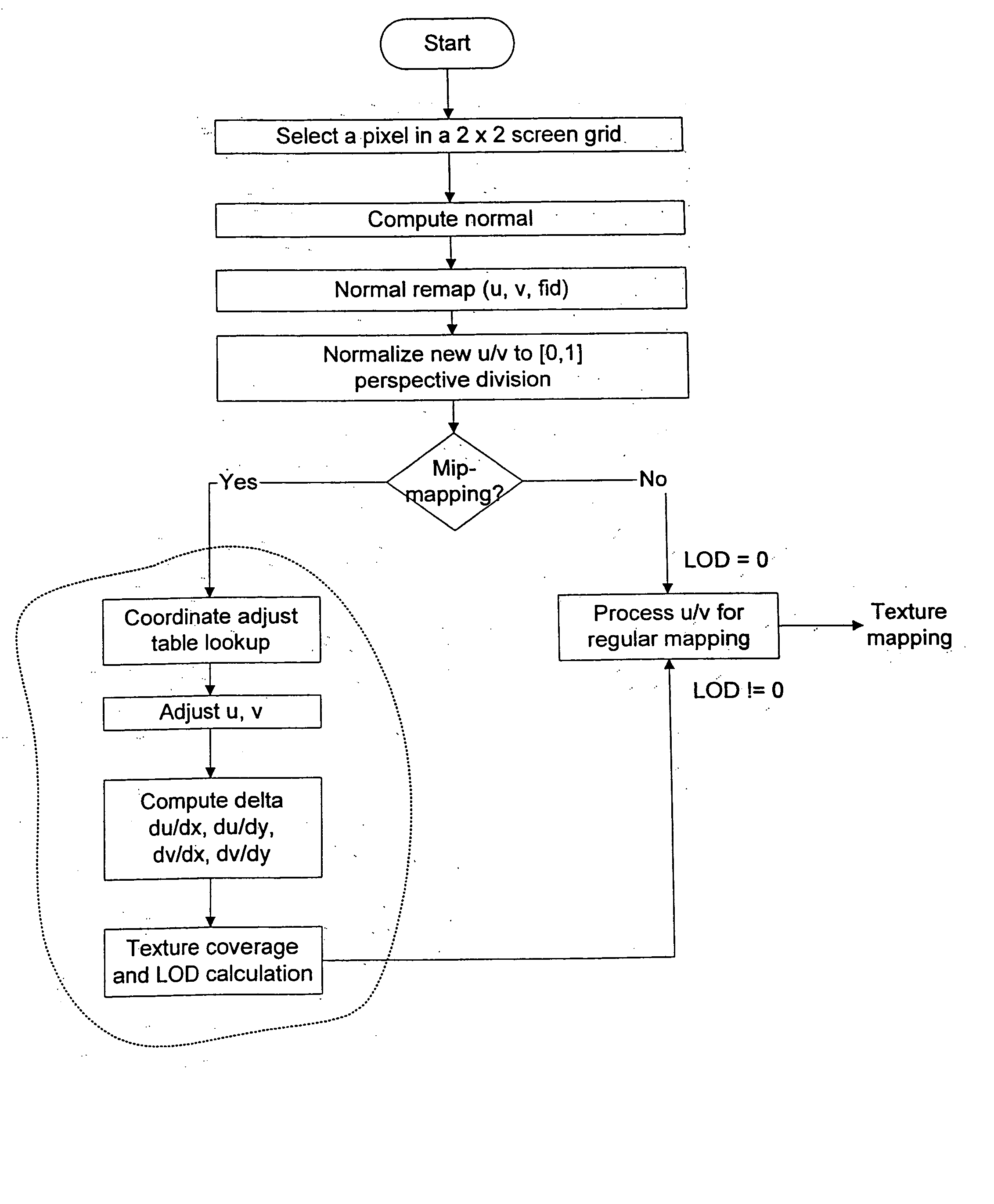
Approximation of level of detail calculation in cubic mapping without attribute delta function
ActiveUS20050017983A1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsLevel of detailPartition of unity
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Multiple frequency through-the-wall motion detection and ranging using a difference-based estimation technique
InactiveUS7460052B2High resolutionEasy to separateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPartition of unityPhase difference
A multi-tone CW radar (14) is used to project signals from an antenna (22) and to receive returns with the same antenna. The phase differences between the outgoing signals and the returns are analyzed to determine the existence of motion and the range to a moving object (10). A model is made which has range as its major parameter. A waveform associated with the phase difference between outgoing signals and returns for one of the tones is compared to templates produced by the model to determine which has a range that most closely matches. By varying the range parameters, when a match is detected the range to the object can be obtained even if its motion is pseudorandom. If the range is measured with multiple units it is possible to measure the location of the object. This can be done assuming a grid and algorithmically combining the ranges from the units.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
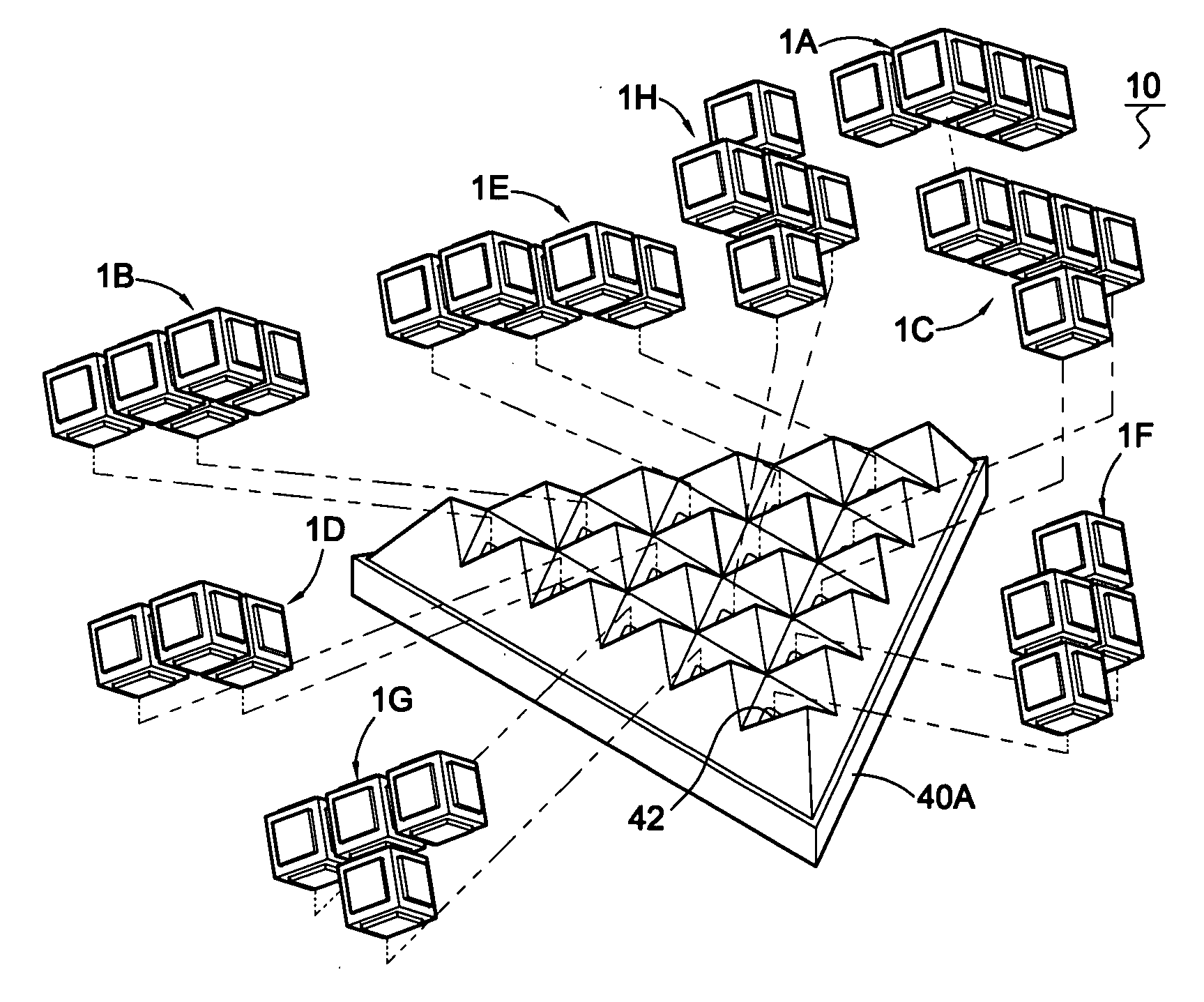
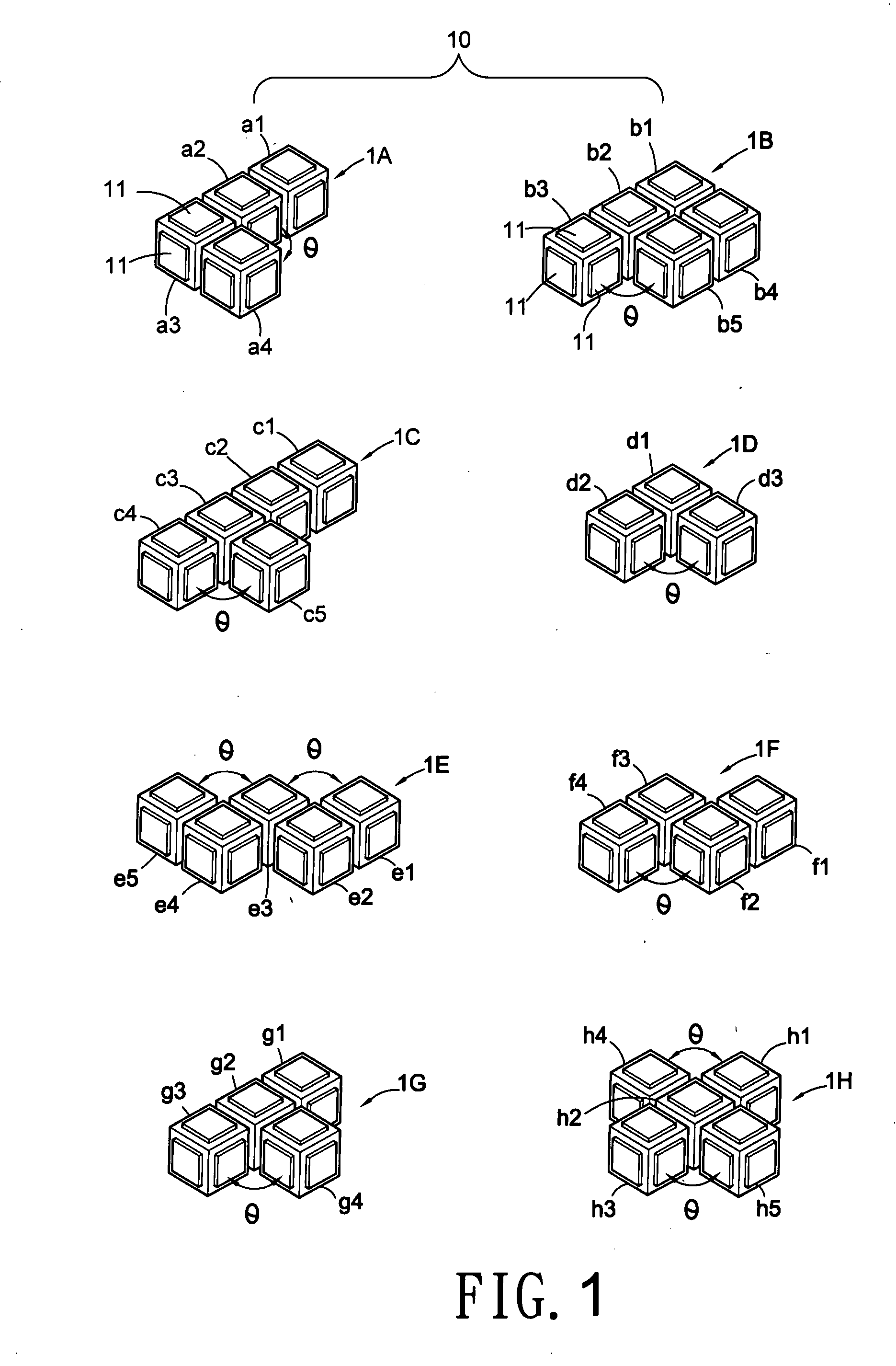
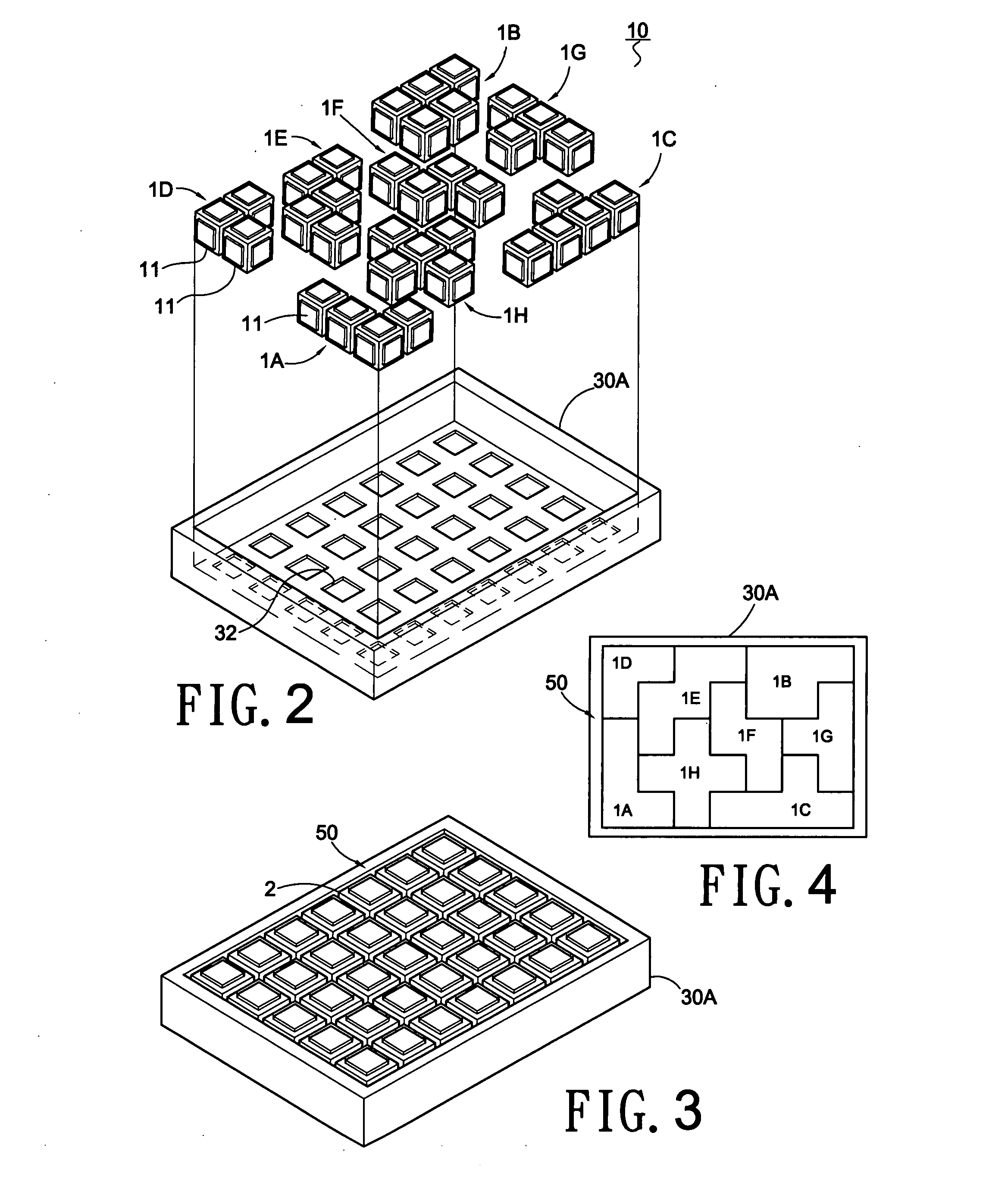
Building base plates assembled to build block sets in two or three dimensional configurations
The present invention relates to building base plates assembled to make two or three dimensional pyramids. Eight building base plates (1A˜1H) can be arranged as a rectangular plane (50) with seven cubic units in longitudinal direction, five cubic units in transversal direction; or assembled to build a five-layer (61˜65) pyramid (60) on a triangular frame each side arrayed five cubic units, a first layer arrayed fifteen cubic units. Furthermore, four building base plates (1I˜1L) with different shapes added to the eight building base plates (1A˜1H), totally fifty six cubic units of those twelve building base plates make a rectangular shape (70) with eight cubic units in longitudinal direction, seven cubic units in transversal direction, or assembled to build a six-layer (81˜86) pyramid (80) on a triangular frame, each side arrayed six cubic units, a first layer of the pyramid arrayed twenty one cubic units.
Owner:LONPOS BRAINTELLIGENT
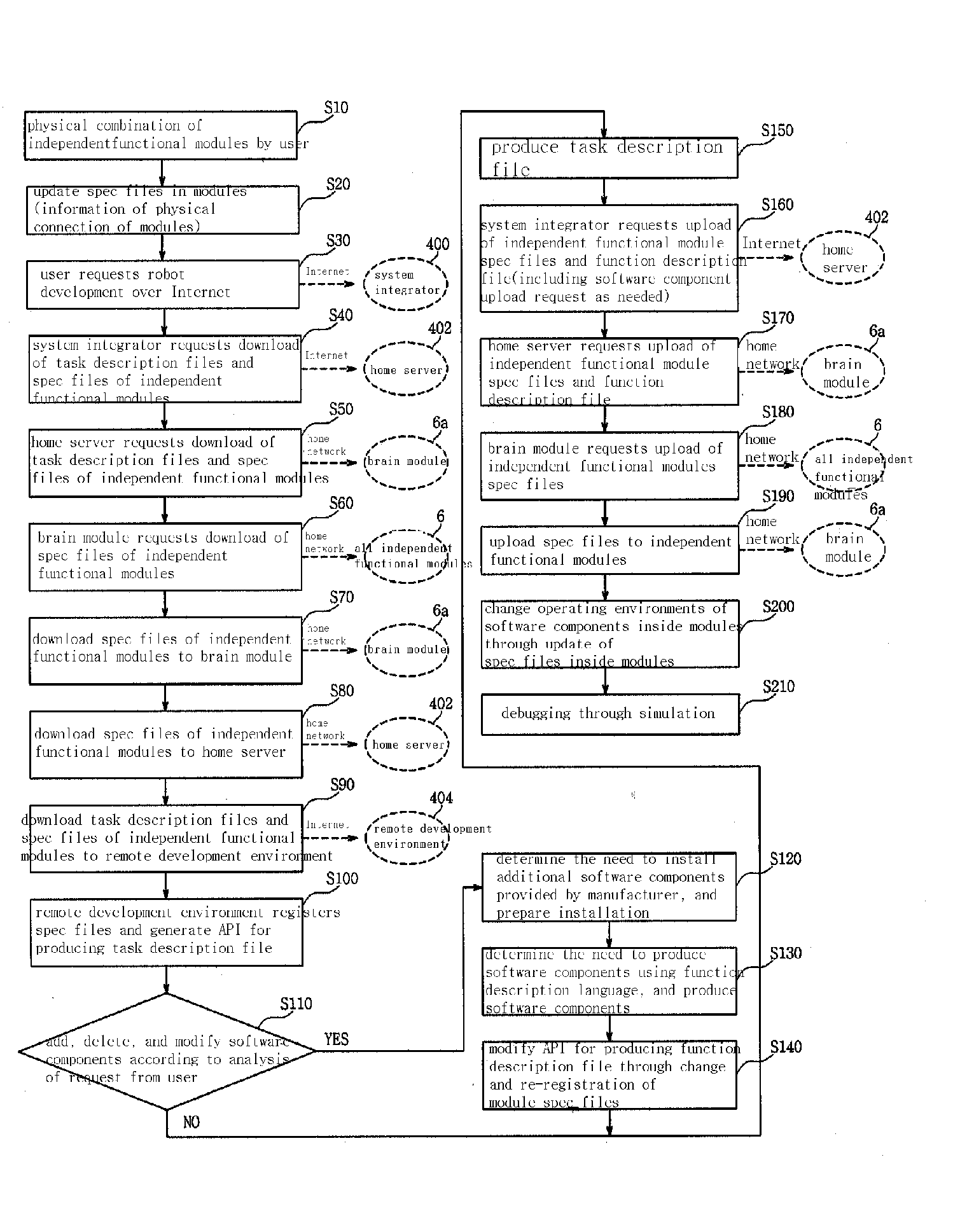
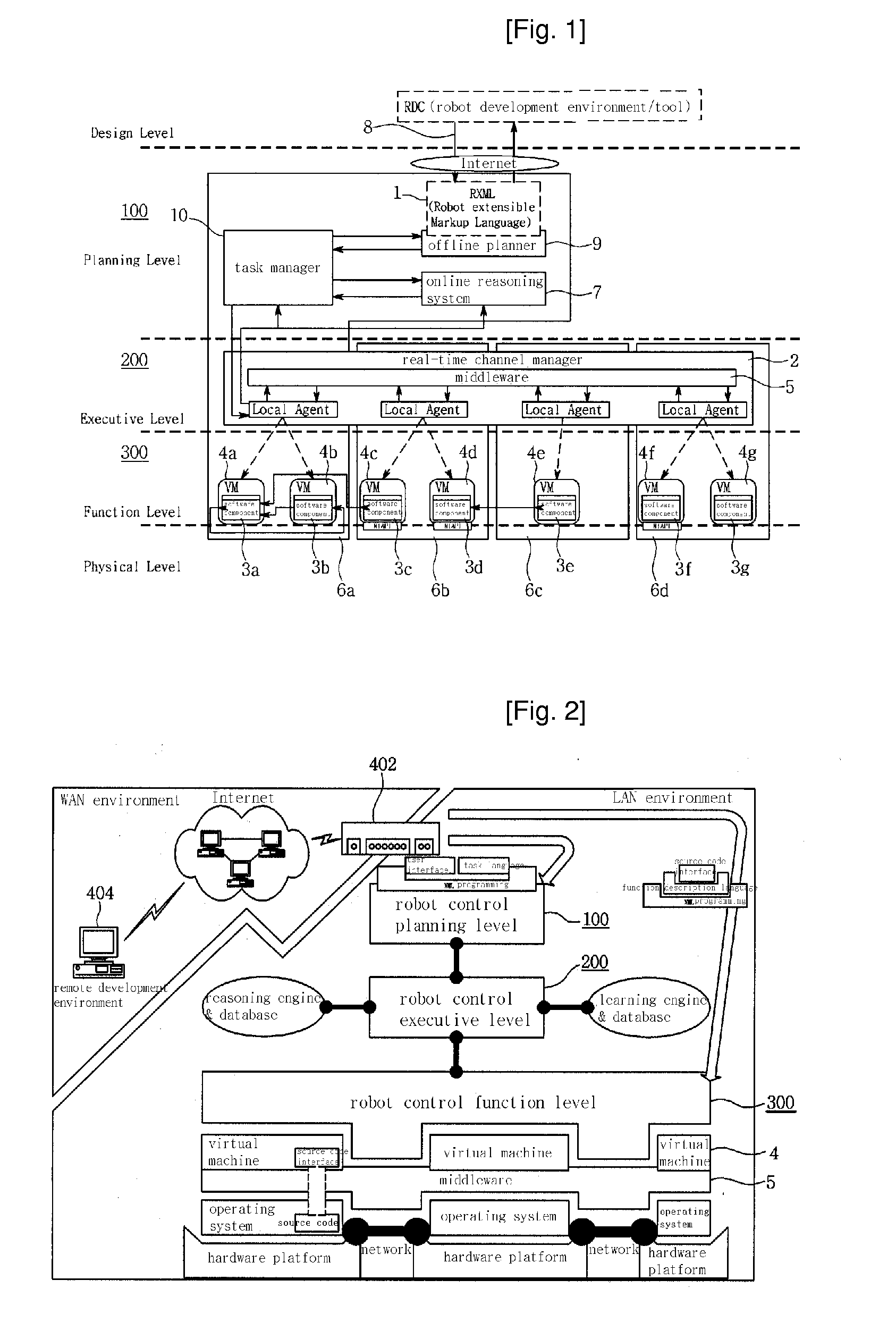
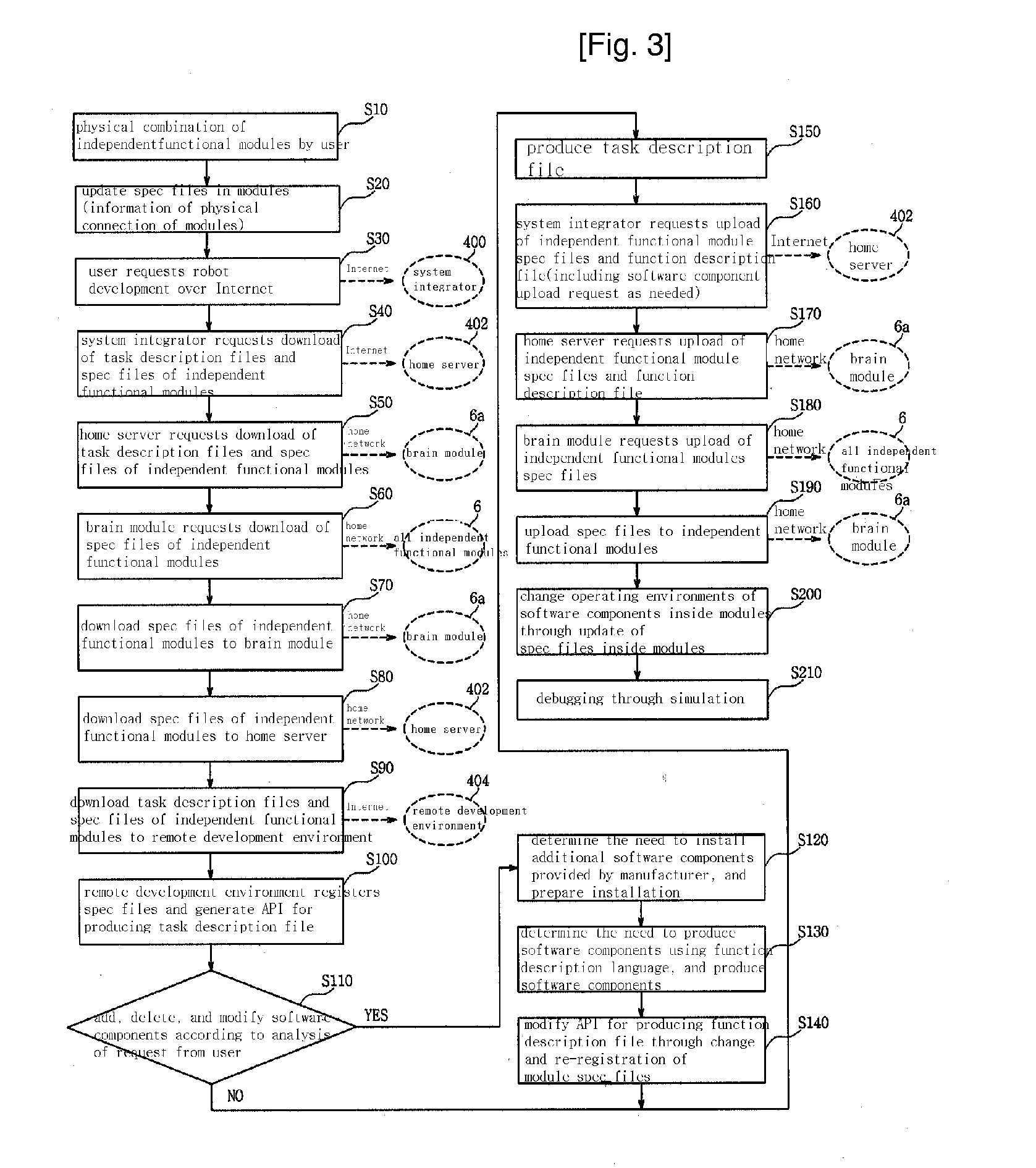
Integrated Service Method of Distribution Software for Robot Development Based on Open Internet Network
InactiveUS20070294662A1Advancing technology developmentIncrease heightProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorTechnology developmentService development
A distributed software integration service method for open robot development based on the Internet is disclosed, which makes it possible to manufacture a user-oriented robot through combination of independent heterogeneous modules. The invention involves a robot development procedure and a new robot development environment / tool for providing user-oriented services and for integrated operating of distributed software installed in the modules over the Internet. The robot development procedure includes three independent specialized development stages, i.e., a platform development stage, a module development stage, and a user-oriented robot development / user service development stage. The invention makes it possible to mass-produce autonomous robots in units of interoperable functional modules. It is also possible to meet various demands of consumers, achieve specialization, and accelerate technology development since the development procedures are specialized in an independent manner and are suitable for manufacturing a wide variety of robot products in small quantities.
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH
Method for the numerical simulation of a physical phenomenon with a preferential direction
ActiveUS7239990B2Improving numerical toolReduce Simulation CostsComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPartition of unityAdvection
The invention provides a method of simulating behavior of a flow interacting with an object. The invention improves the accuracy of the approximation of the spatial pth derivative Dp, p≧1, and therefore reduces the cost of the simulation. It includes in the approximation values of the parameter at points which do not lay on grid lines passing through the point of computation P, and by using these values to optimize the approximation. The use of these additional points depends on a preferential direction, such as determined by the advection direction of the flow. The points used in the approximation extend beyond a unit cube on the computational grid. The simulation is in three or more dimensions. The numerical simulation produces output which can be used in the design or optimization of the object which interacts with the flow. In certain cases, it is the output by itself which is important.
Owner:STRUIJS ROBERT
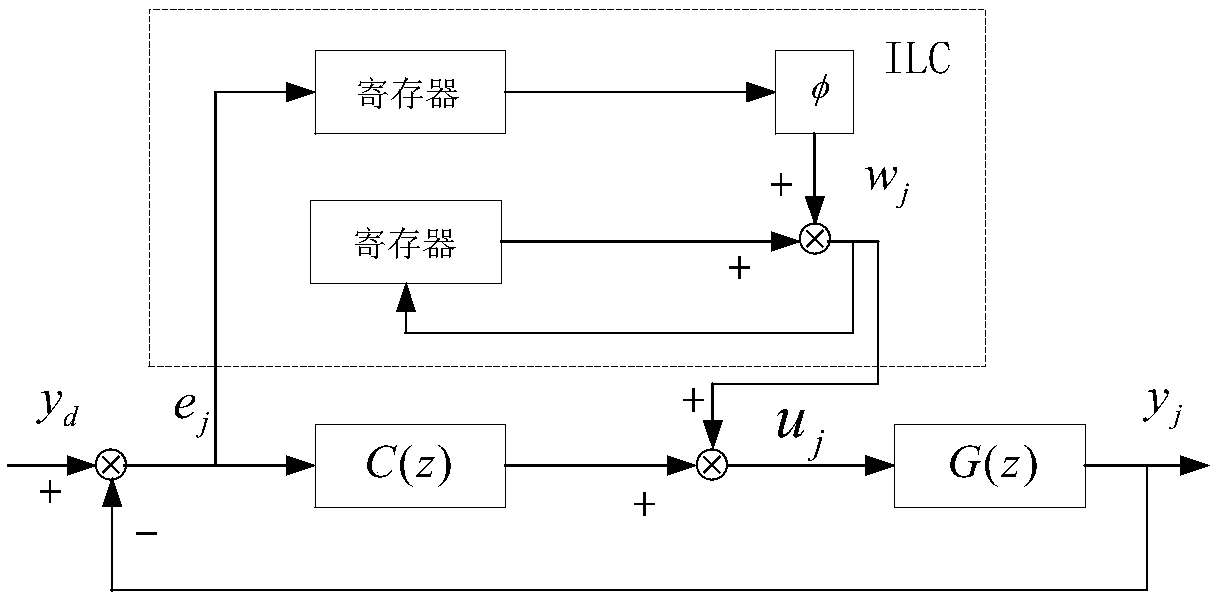
Method for correcting track errors generated during iterative learning of industrial robot
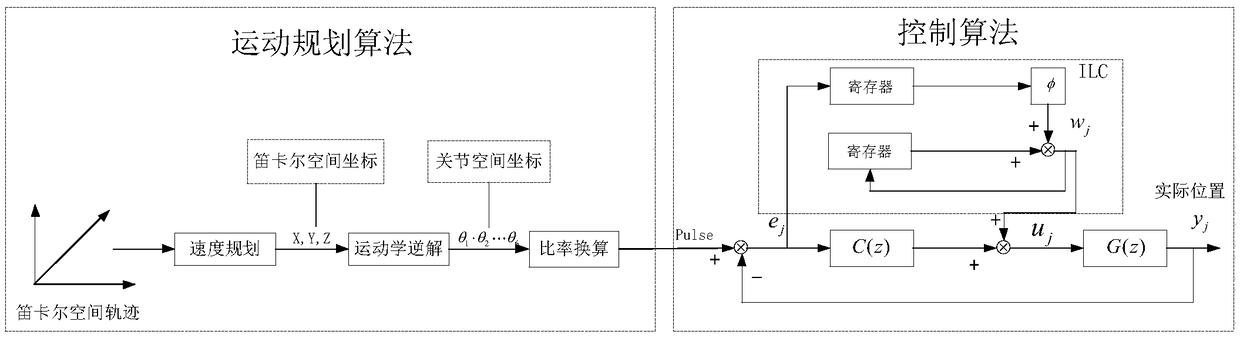
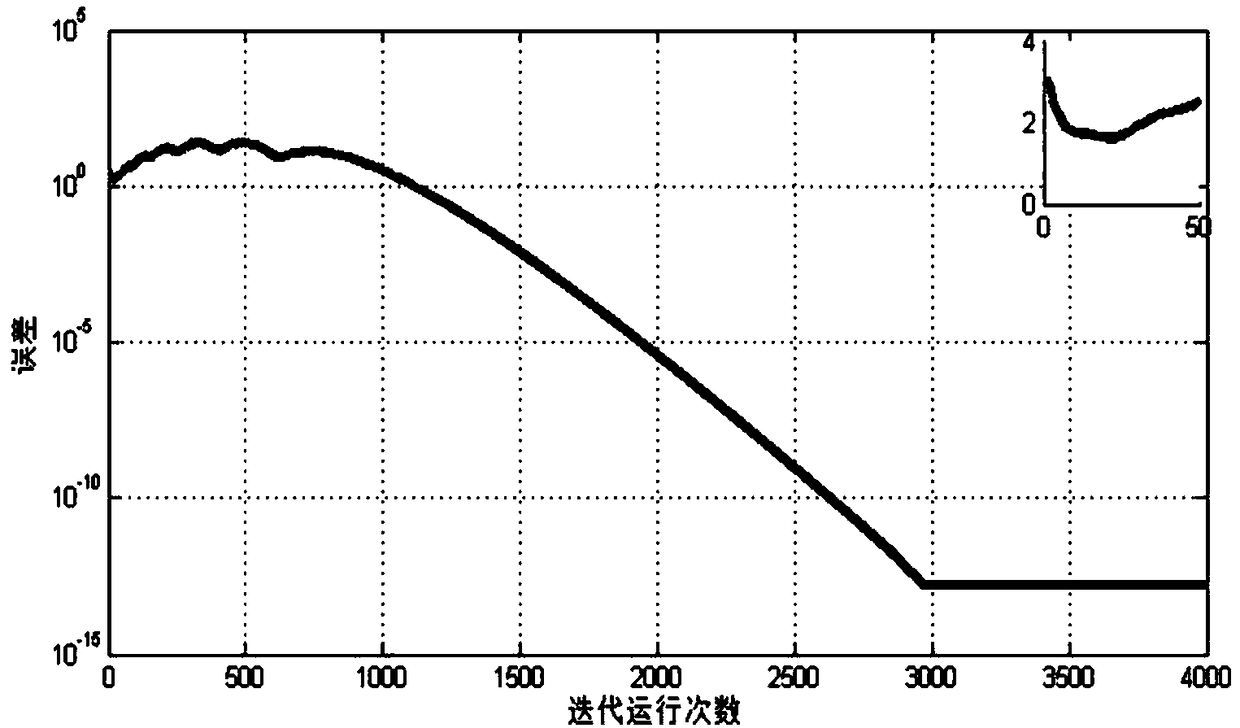
InactiveCN109015661ARun accuratelyImprove accuracyProgramme-controlled manipulatorSpecial data processing applicationsPartition of unityClosed loop
A method for correcting track errors generated during iterative learning of an industrial robot comprises the following steps that firstly, a specific controlled object is determined, an electric current loop or a speed closed loop is adopted as the controlled object, and optimizing and setting of control parameters are carried out on a whole control loop; and secondly, according to the formula (please see the specification), the learning gain phi is changed, the position of the starting point of a N(z) Nyquist curve and the amplitude of the curve are adjusted, introduced offline lead compensation factors enable the N(z) Nyquist curve to achieve translation, more curves fall into a unit circle, gamma=1,2,3...n, and in the formula, q is the feedback gain, and gamma is the number of samplingperiods. According to the method, the design of a robot iterative learning controller is provided according to the characteristic that the industrial robot operates on the same track multiple times,the robot has the self correction capacity, the experience in the previous operating track process is gained to guide operating of subsequent tracks, the more the robot operates, the higher the accuracy is, following errors are reduced greatly, and the accuracy of track operating is improved.
Owner:重庆固高科技长江研究院有限公司
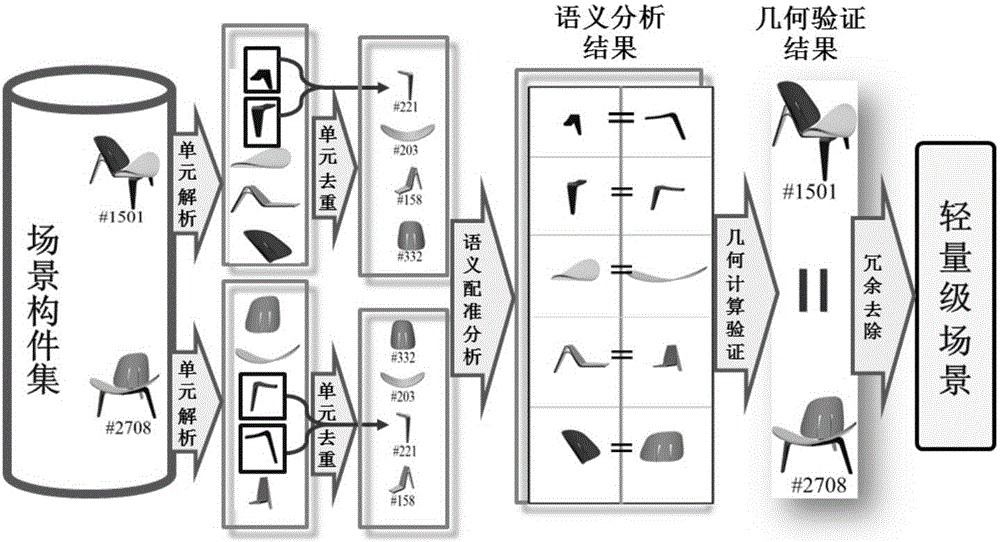
Lightweight BIM big data online visualization method and system
ActiveCN106776963AMeet Online VisualizationReduce data volumeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationRelational structureGranularity
The invention relates to a lightweight BIM big data online visualization method and system. The method includes the following steps that lightweight analysis based on semantic guidance is conducted on a BIM scenario component set to obtain a lightweight component base; the interior structure of a BIM building is automatically partitioned to generate multiple relatively independent spaces and a relation structure chart of the relatively independent spaces; a multilayer data index structure with multi-granularity decomposition is established according to the relation structure chart and the component set in each space; the lightweight component base is called according to the multilayer data index structure to achieve progressive visualization of the BIM building, and in the visualization process, with each space as the unit, data in the next space relative to the current space is cached and data in the last space is deleted. Compared with the prior art, the method and system have the advantages of automation, lightweight, fine granularity and the like.
Owner:JILIN ANIMATION INST +1
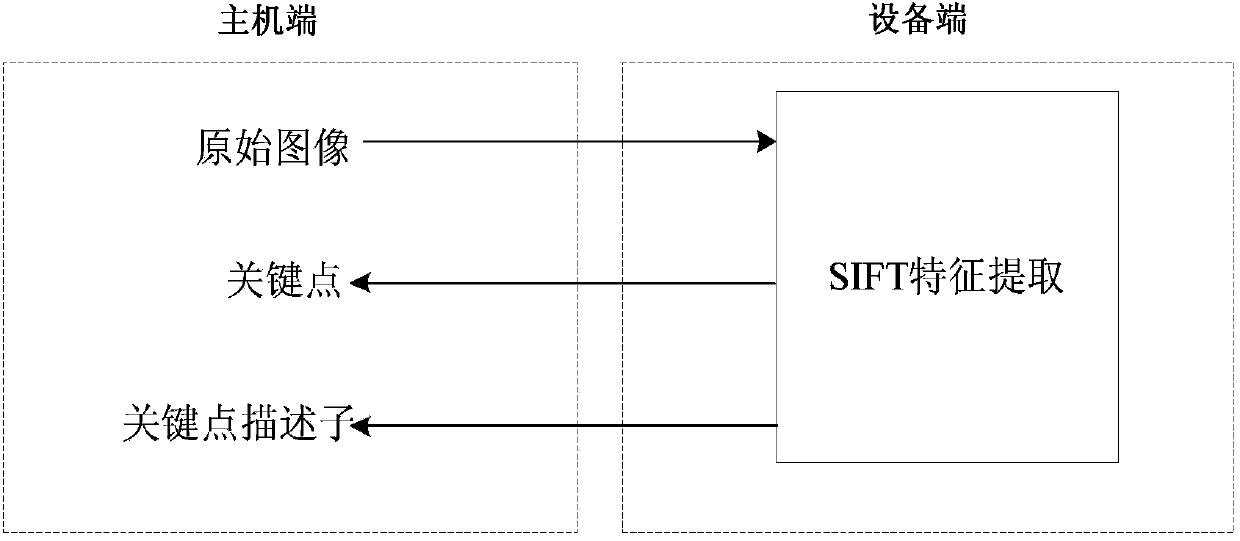
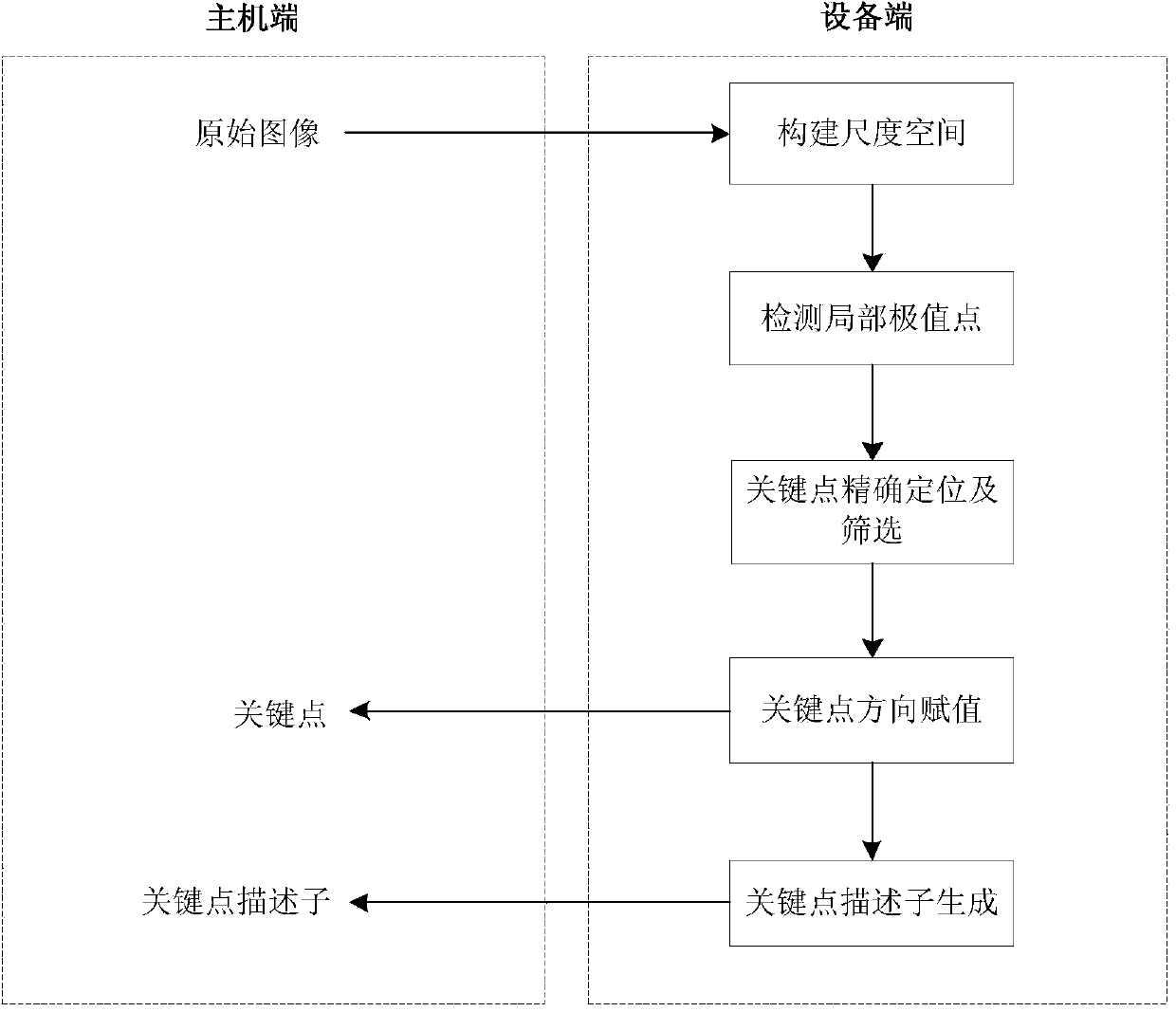
SIFT parallelization system and method based on recursion Gaussian filtering on CUDA platform
InactiveCN103593850ACalculation speedMeet real-time requirementsImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionImage transfer
Provided are an STFT parallelization system and method based on recursion Gaussian filtering on a CUDA platform. The method comprises the steps that first, original images are transmitted to a GPU end for conducting a series of Gaussian filtering and downsampling to establish a Gaussian pyramid, Gaussian filtering is conducted through a recursion Gaussian filter, and then substraction is conducted on the adjacent images to obtain a Gaussian difference pyramid; second, a thread block is used as a unit to load in an image, each thread is used for processing one pixel, and the pixel is compared with the adjacent 26 pixels to obtain local extreme points; third, each thread is used for processing one local extreme point, and positioning and selecting of key points are conducted; fourth, one thread block is used for calculating the direction of one key point, one thread is used for calculating the direction and the amplitude value of one pixel in the neighbourhood of the key point, the direction and the amplitude valve are accumulated to a gradient histogram through an atomic addition provided by a CUDA, and the information such as the coordinates and the directions of the key points are transmitted to a host end according to the directions of the key points obtained by the gradient histogram; fifth, one thread block is used for calculating one key point descriptor, then a calculating result is transmitted to the host end, and SIFT feature extraction is achieved. The STFT parallelization system and method based on the recursion Gaussian filtering on the CUDA platform improve the calculating speed of an SIFT algorithm.
Owner:北京航空航天大学深圳研究院
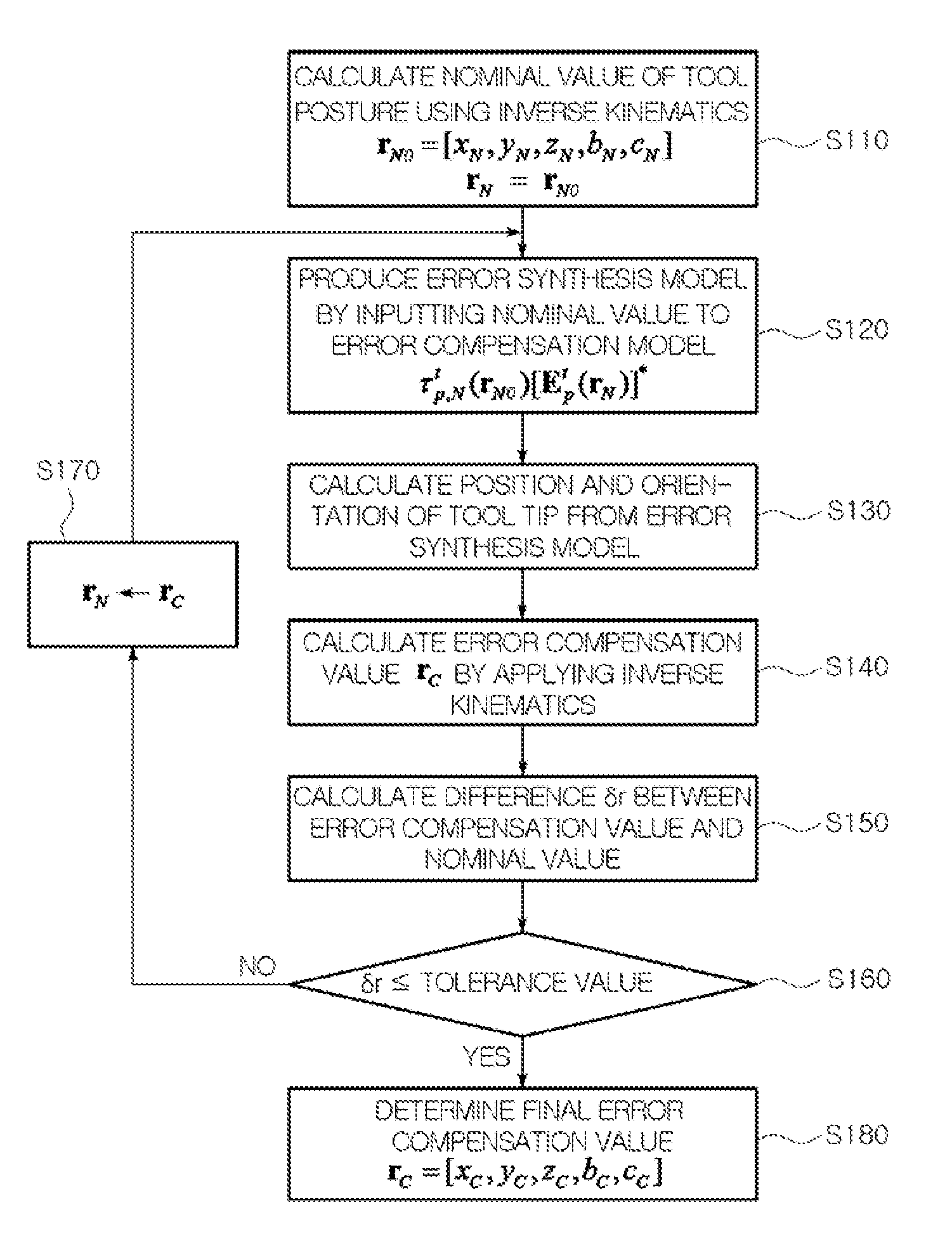
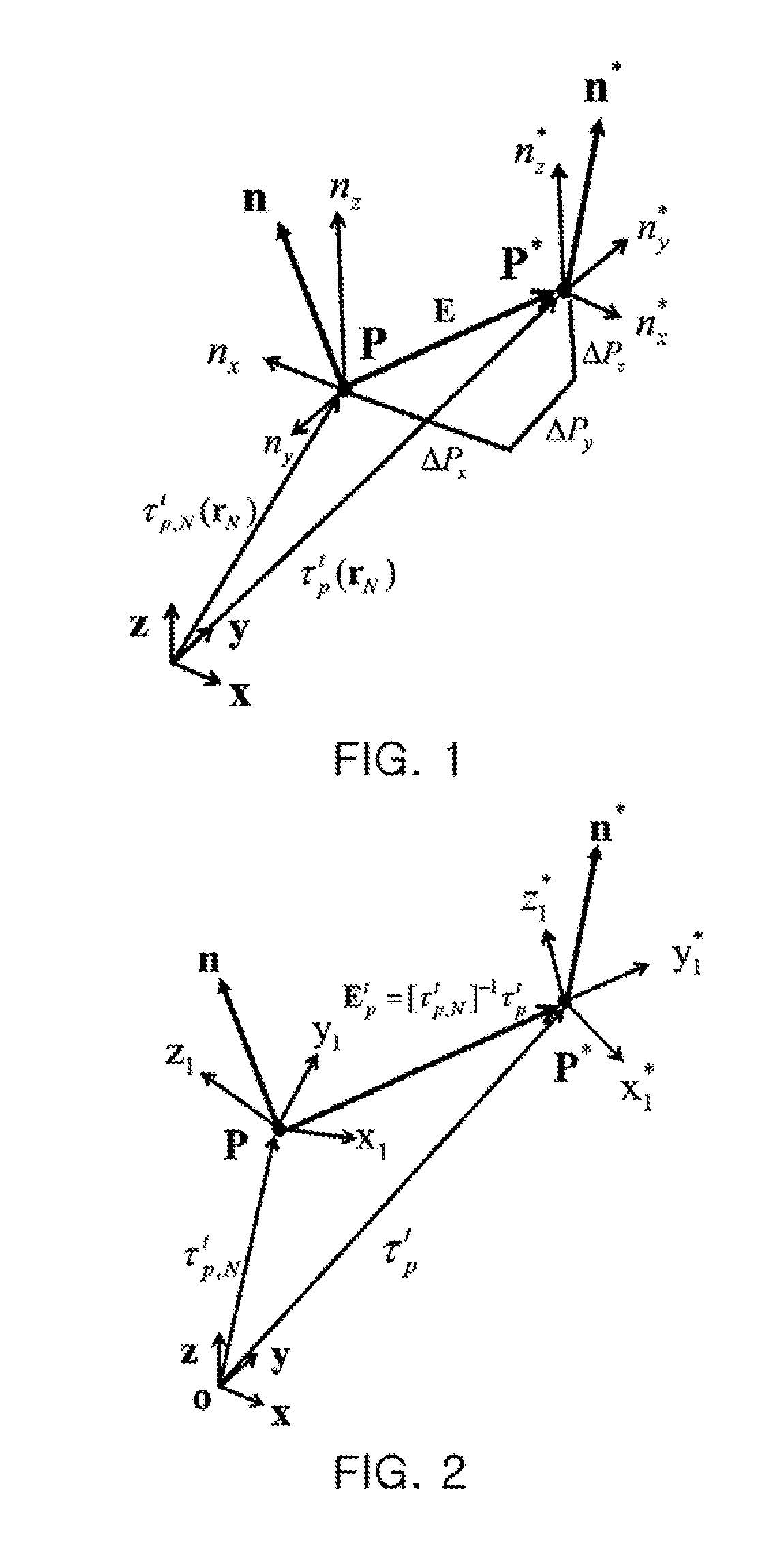
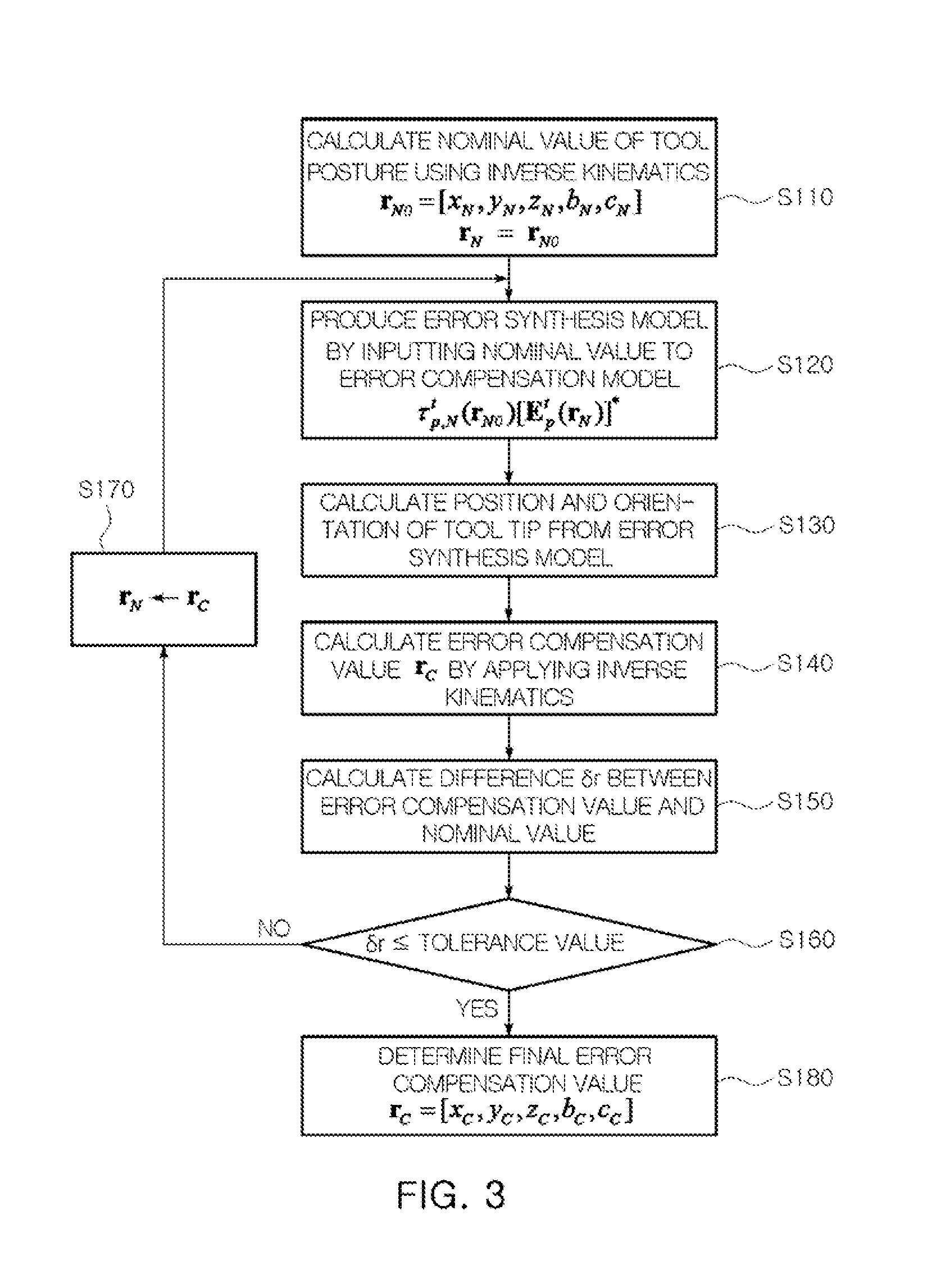
Error compensation method for multi-axis controlled machines
ActiveUS20110224958A1Efficient productionReduce errorsProgramme controlMeasurement devicesGeometric errorPartition of unity
An error compensation method for multi-axis controlled machines generates an error compensation model for compensating for geometric error of a multi-axis controlled machine by separating an error matrix of a tool tip from an error synthesis model of a multi-axis controlled machine and calculates an error compensation value using the error compensation model and an inverse kinematic model so that the error matrix becomes an identity matrix. The error compensation method can reduce calculation error and calculation time due to complicated numerical analysis and compensate for error in the multi-axis controlled machine, regardless of its configuration.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com