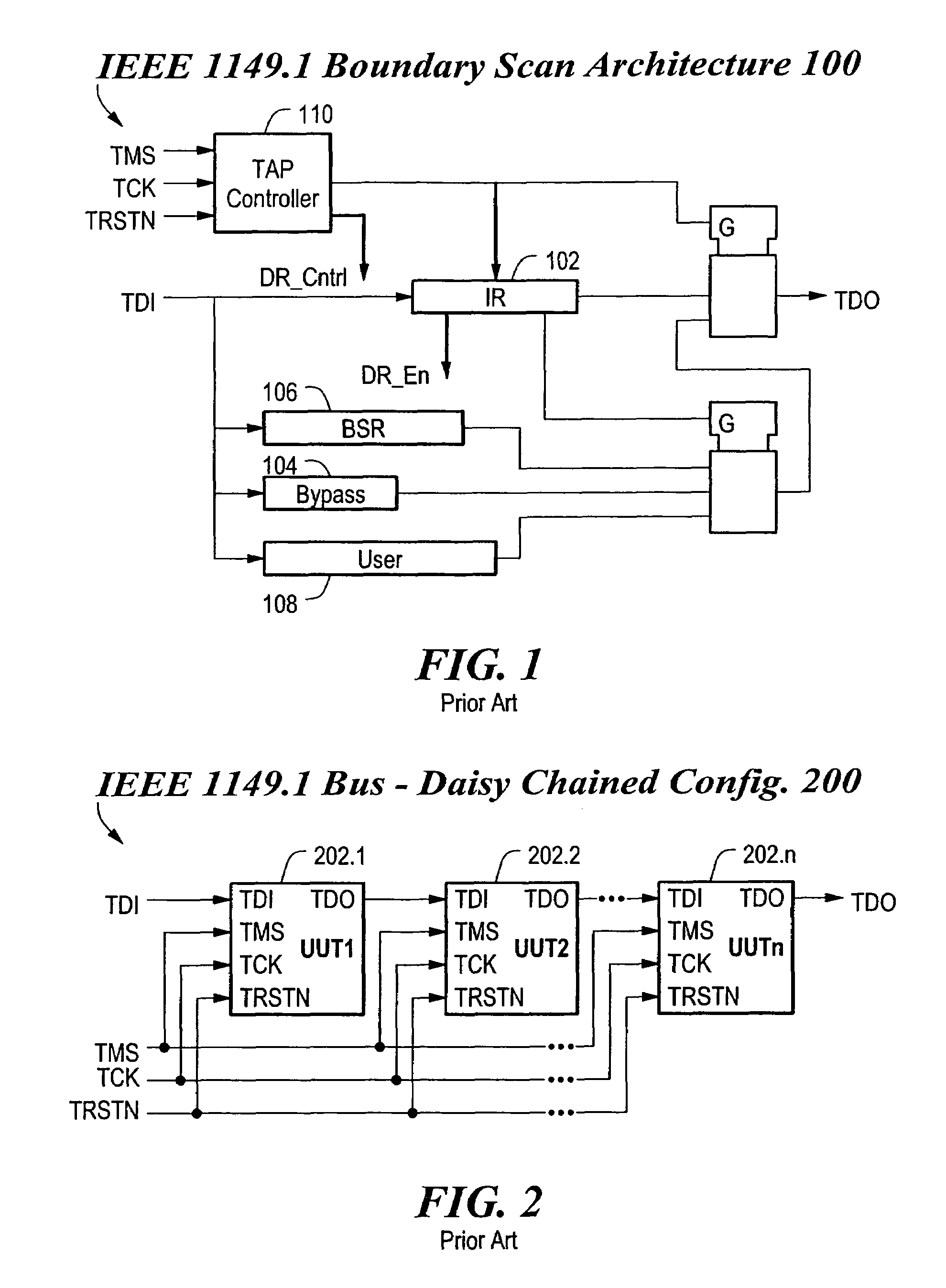
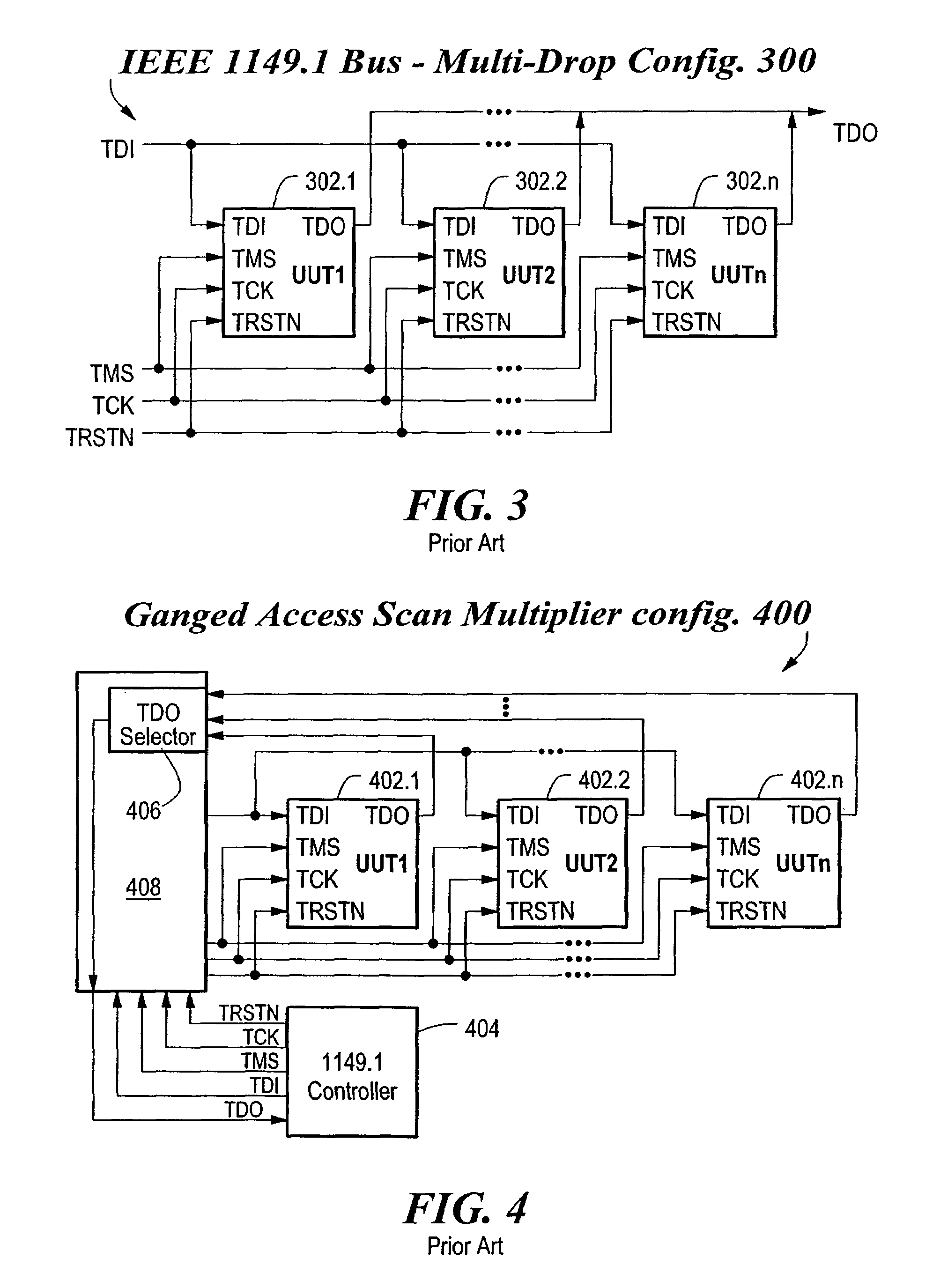
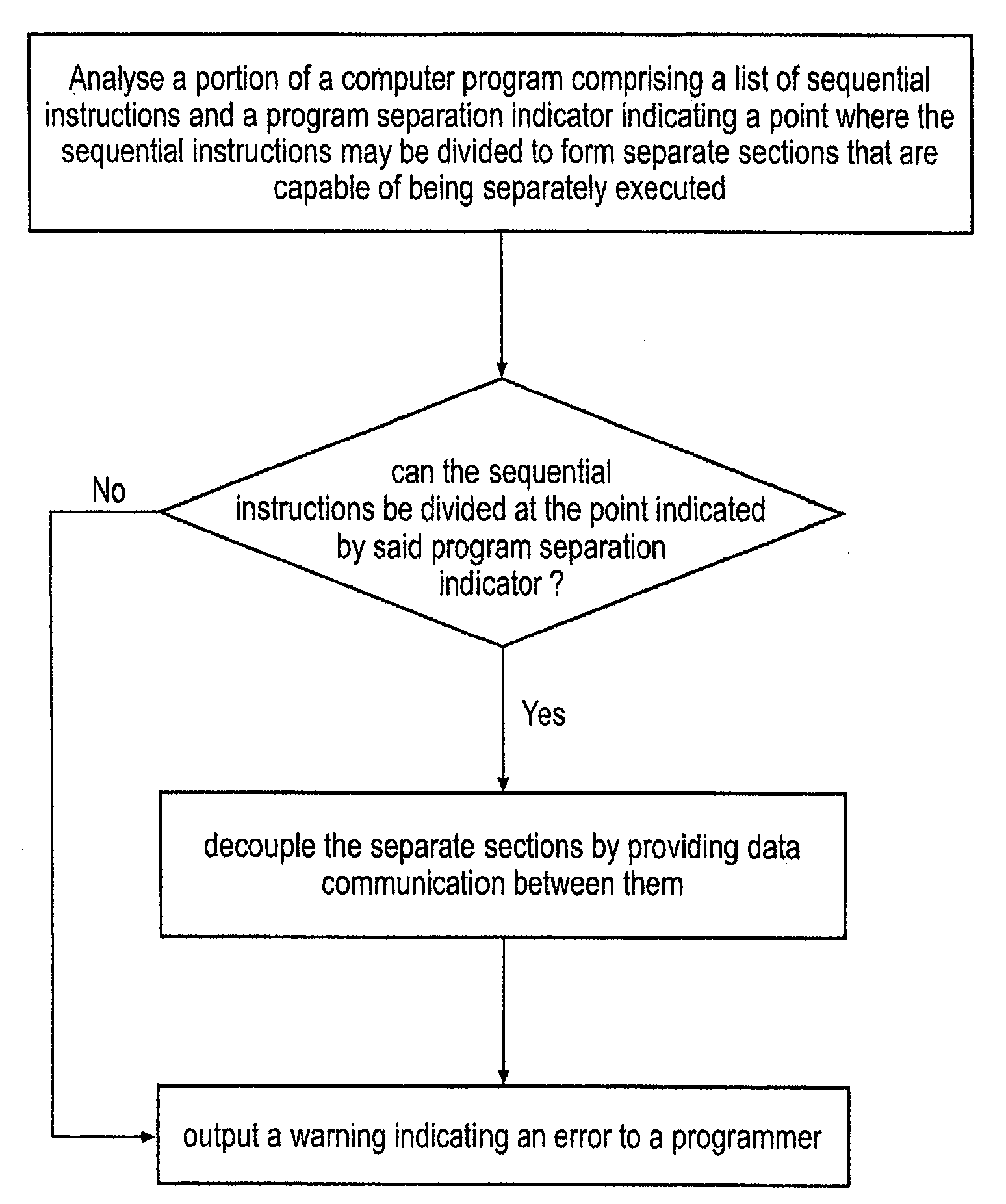
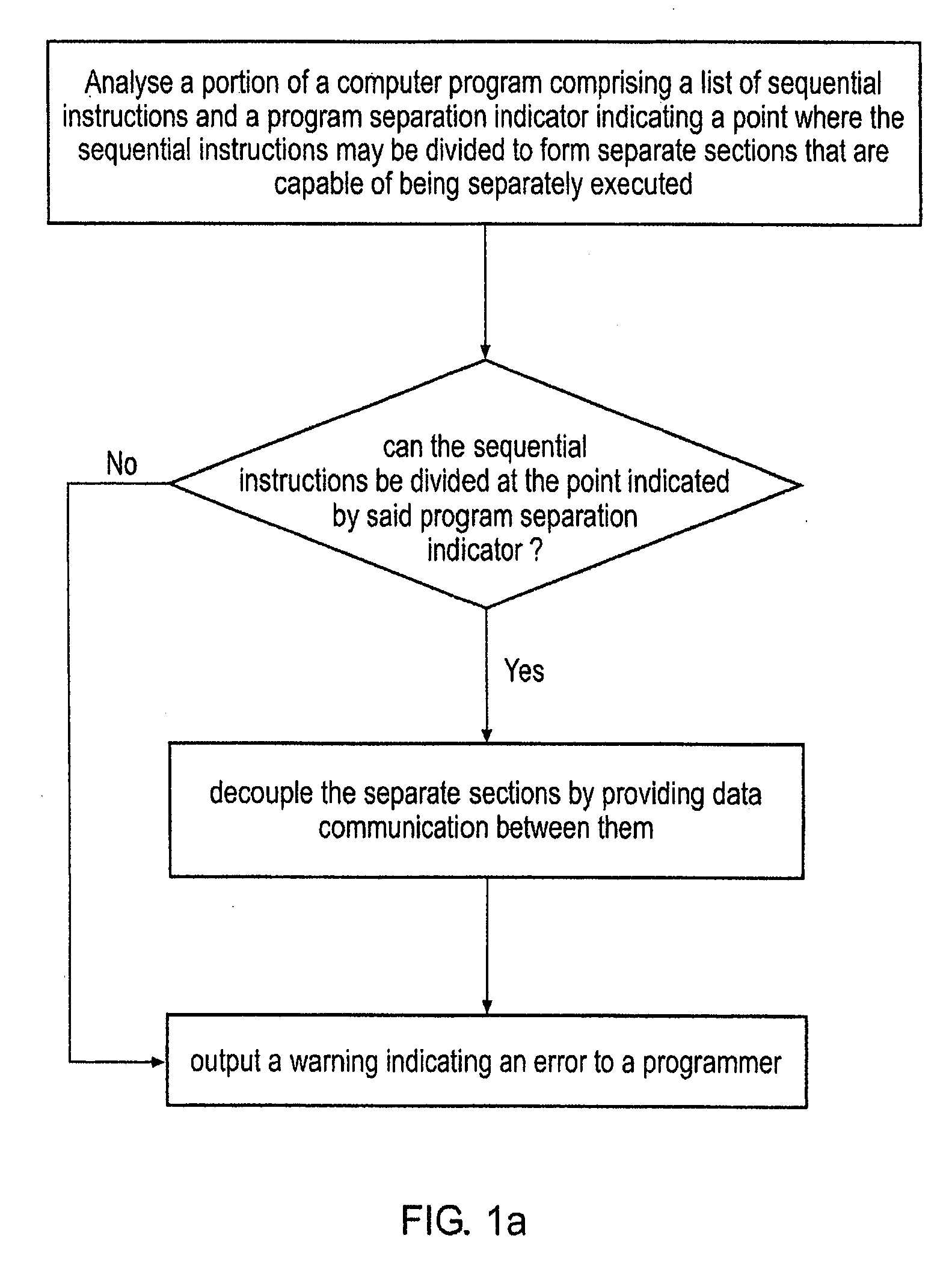
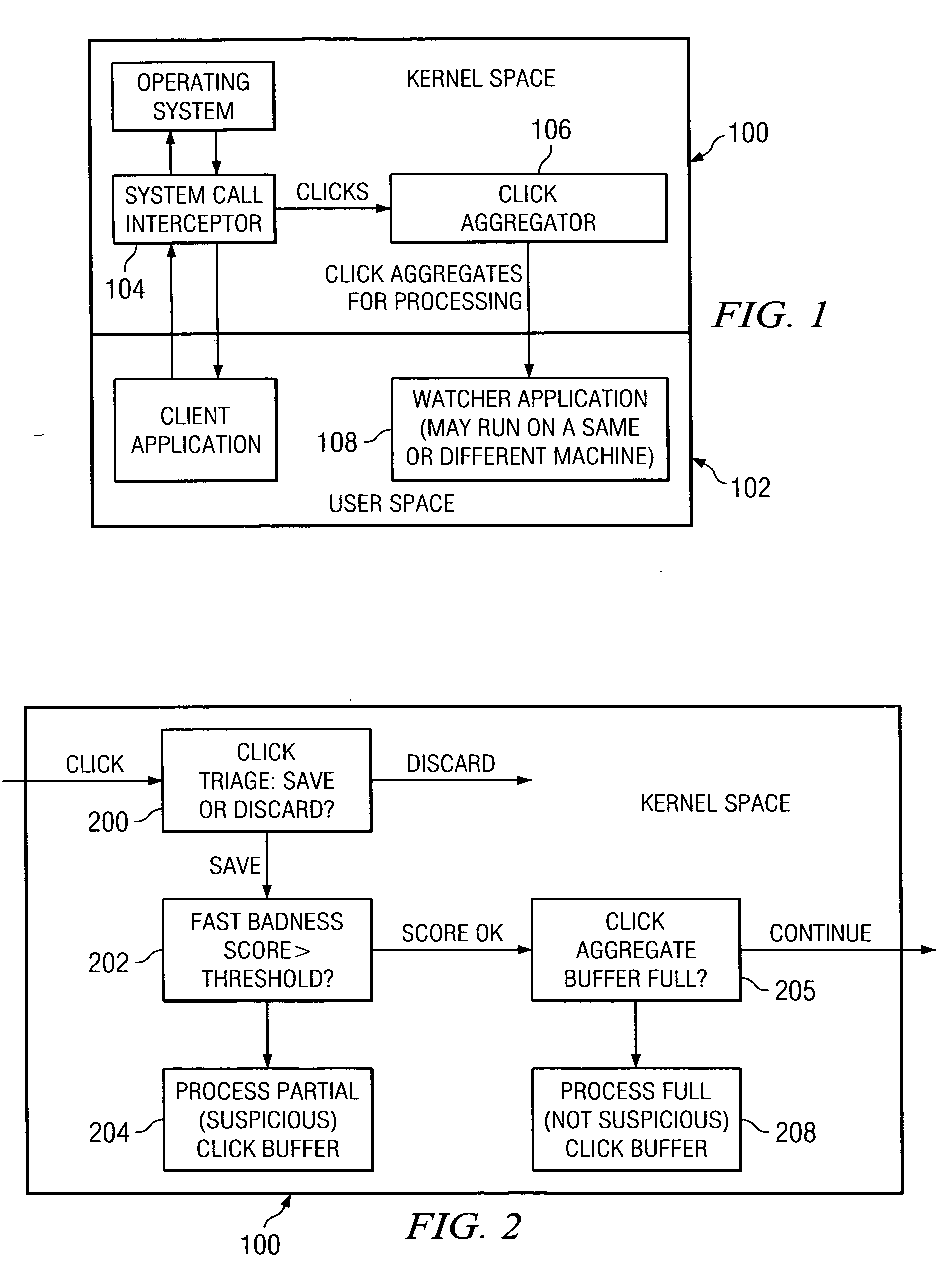
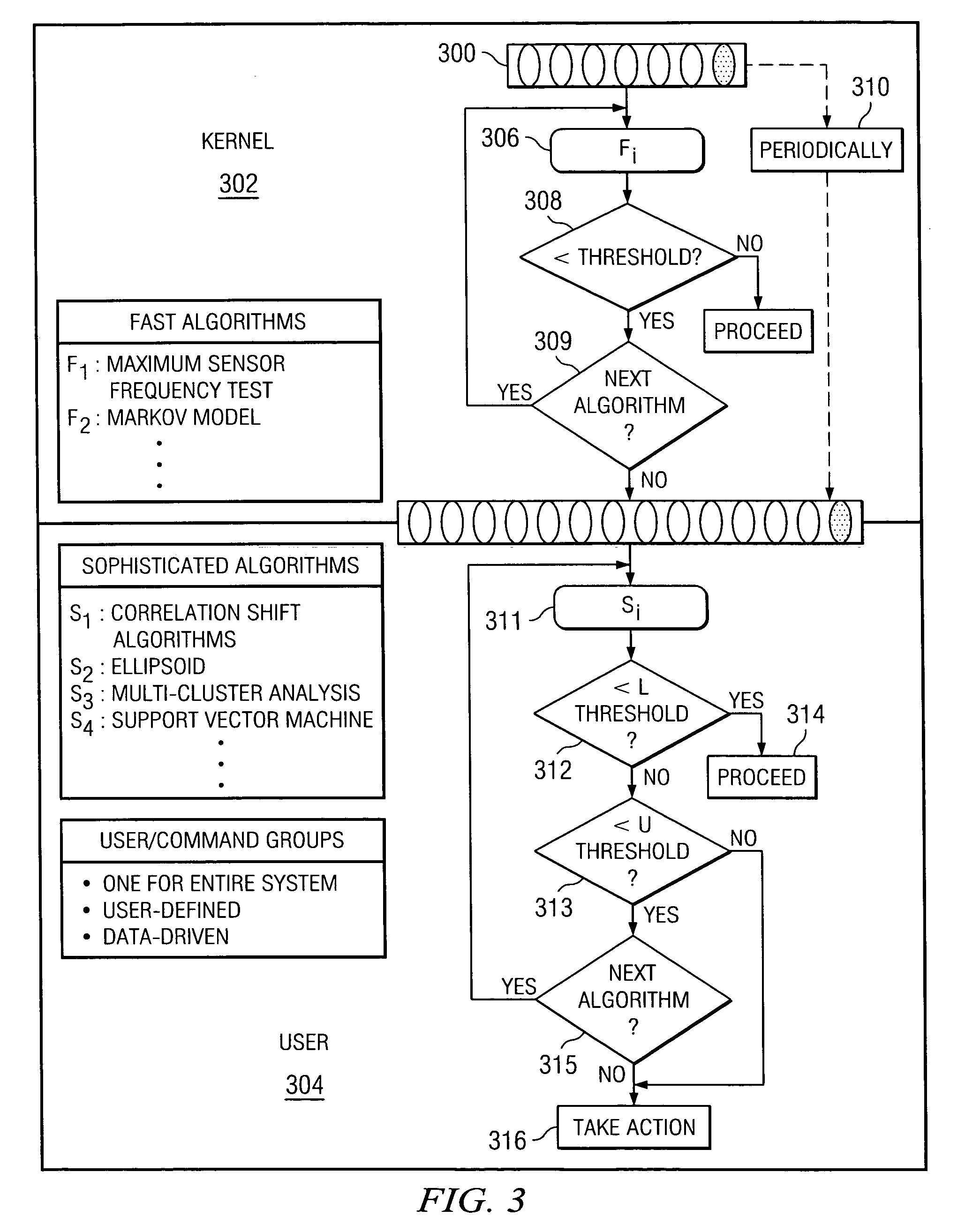
Patents
Literature
7040results about "Detecting faulty computer hardware" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
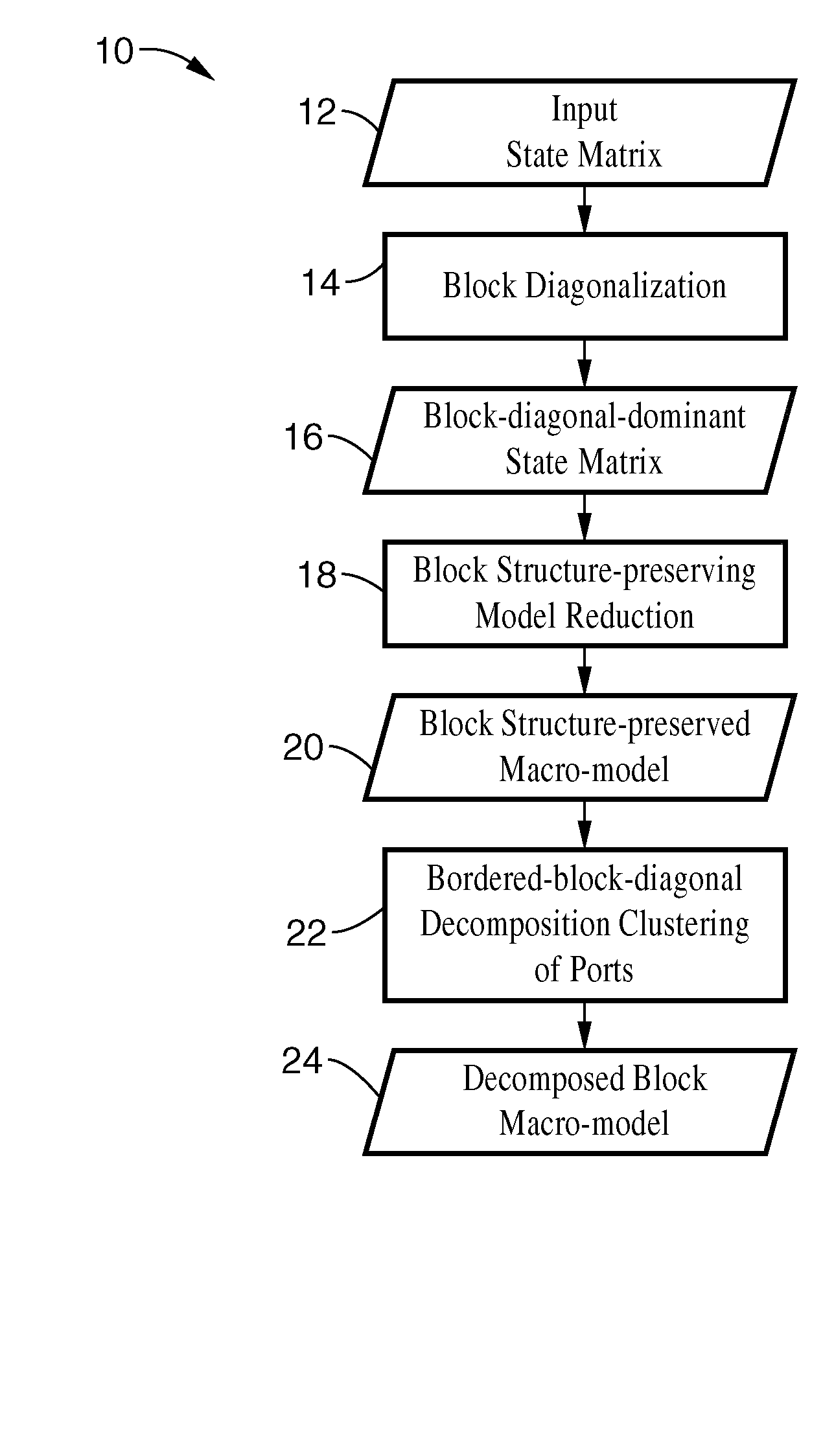
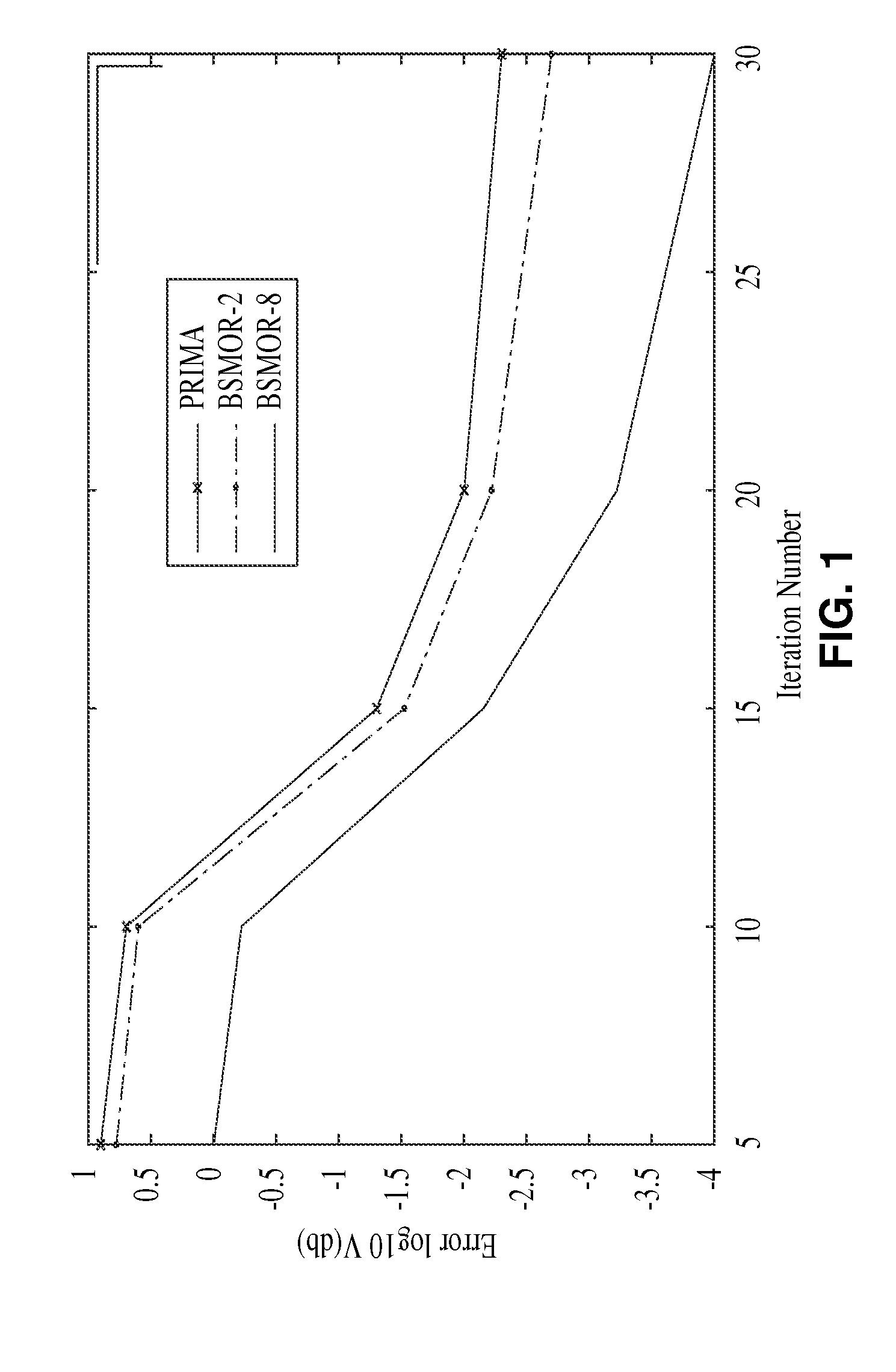
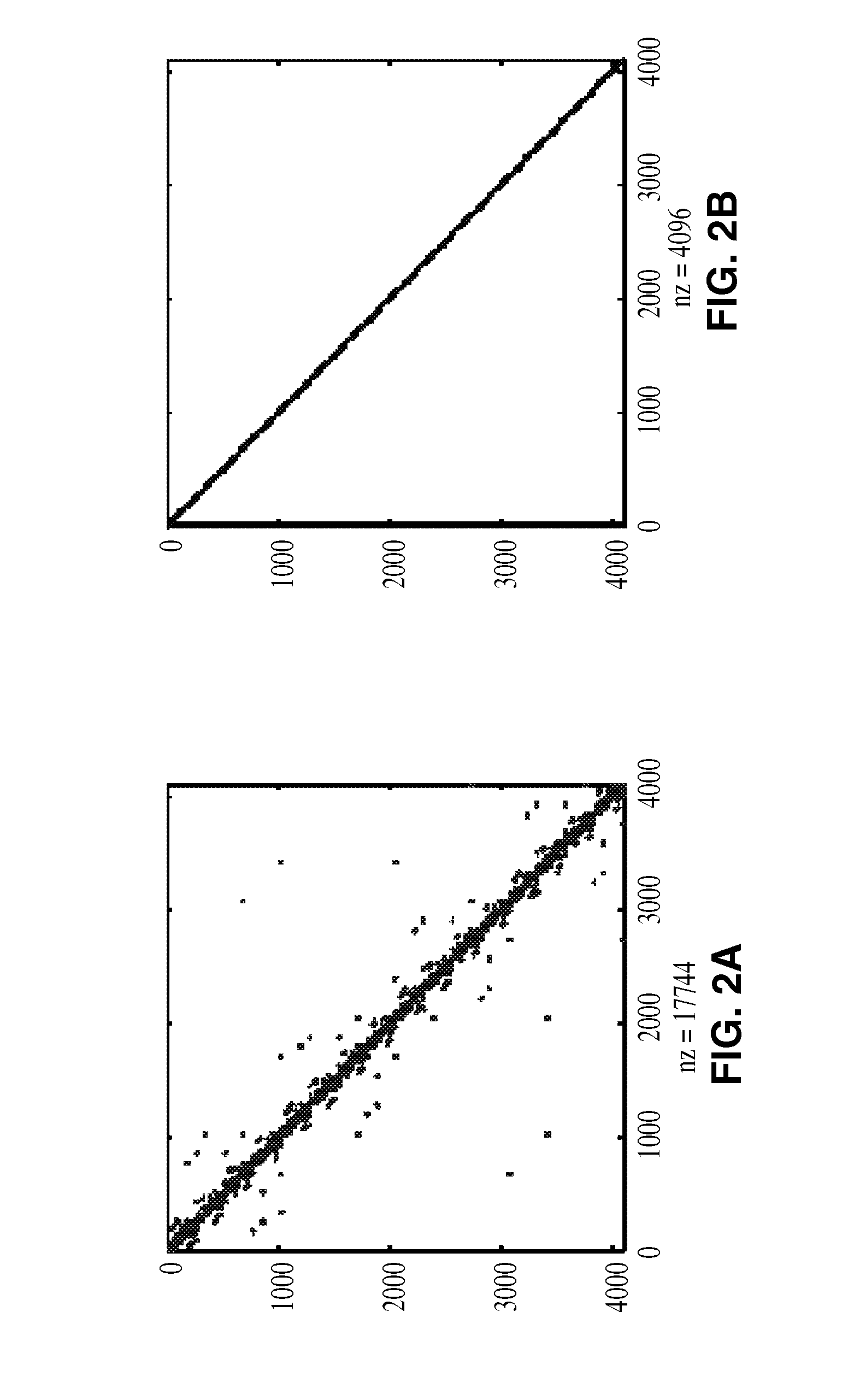
Structured and parameterized model order reduction
InactiveUS20080072182A1Reduce redundancyNon-uniformity is constantDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationStructured modelOrder reduction
Model-order reduction techniques are described for RLC circuits modeling the VLSI layouts. A structured model order reduction is developed to preserve the block-level sparsity, hierarchy and latency. In addition, a structured and parameterized model order reduction is developed to generate macromodels for design optimizations of VLSI layouts. The applications are thermal via allocation under the dynamic thermal integrity and via stapling to simultaneously optimize thermal and power integrity.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
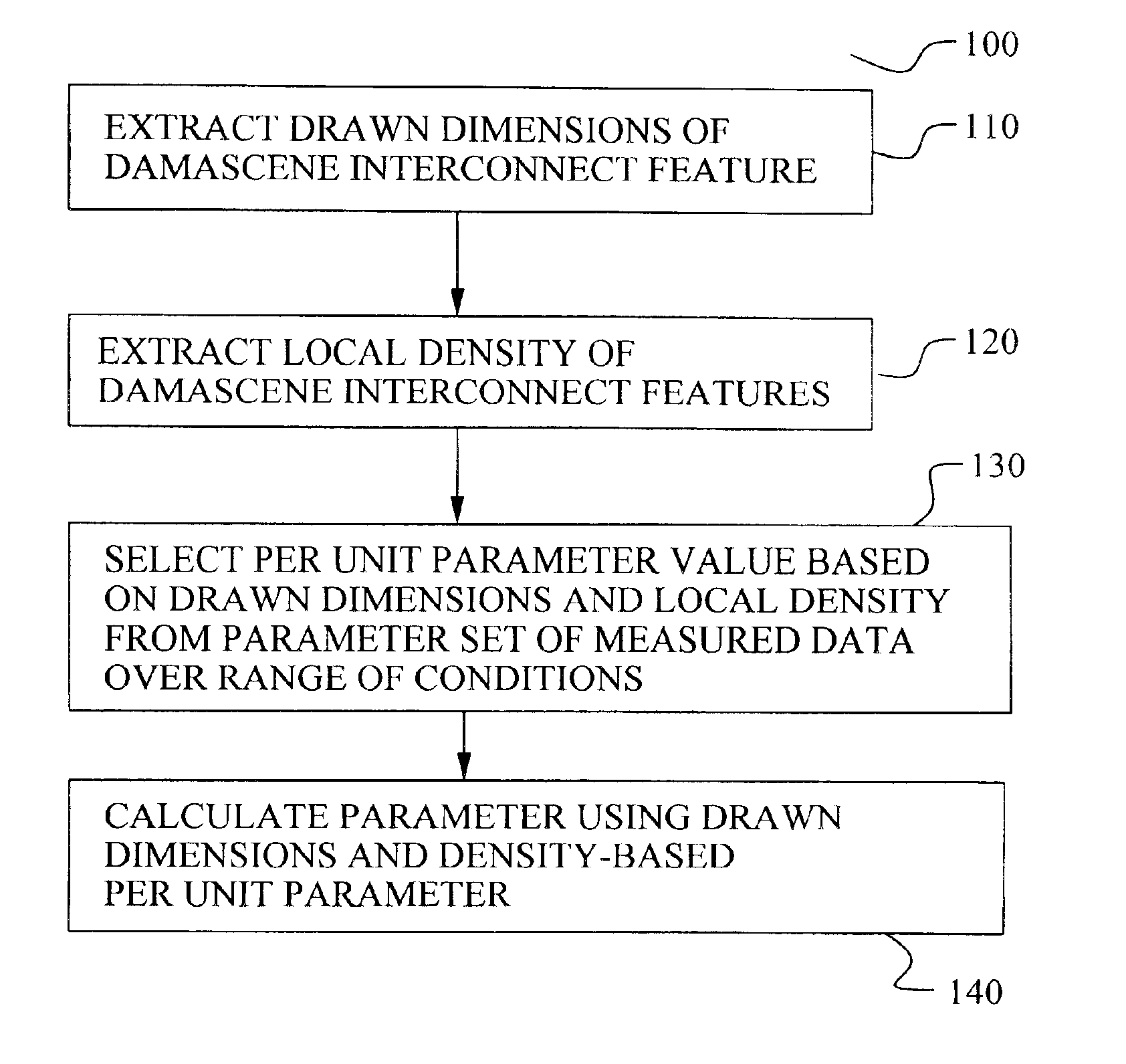
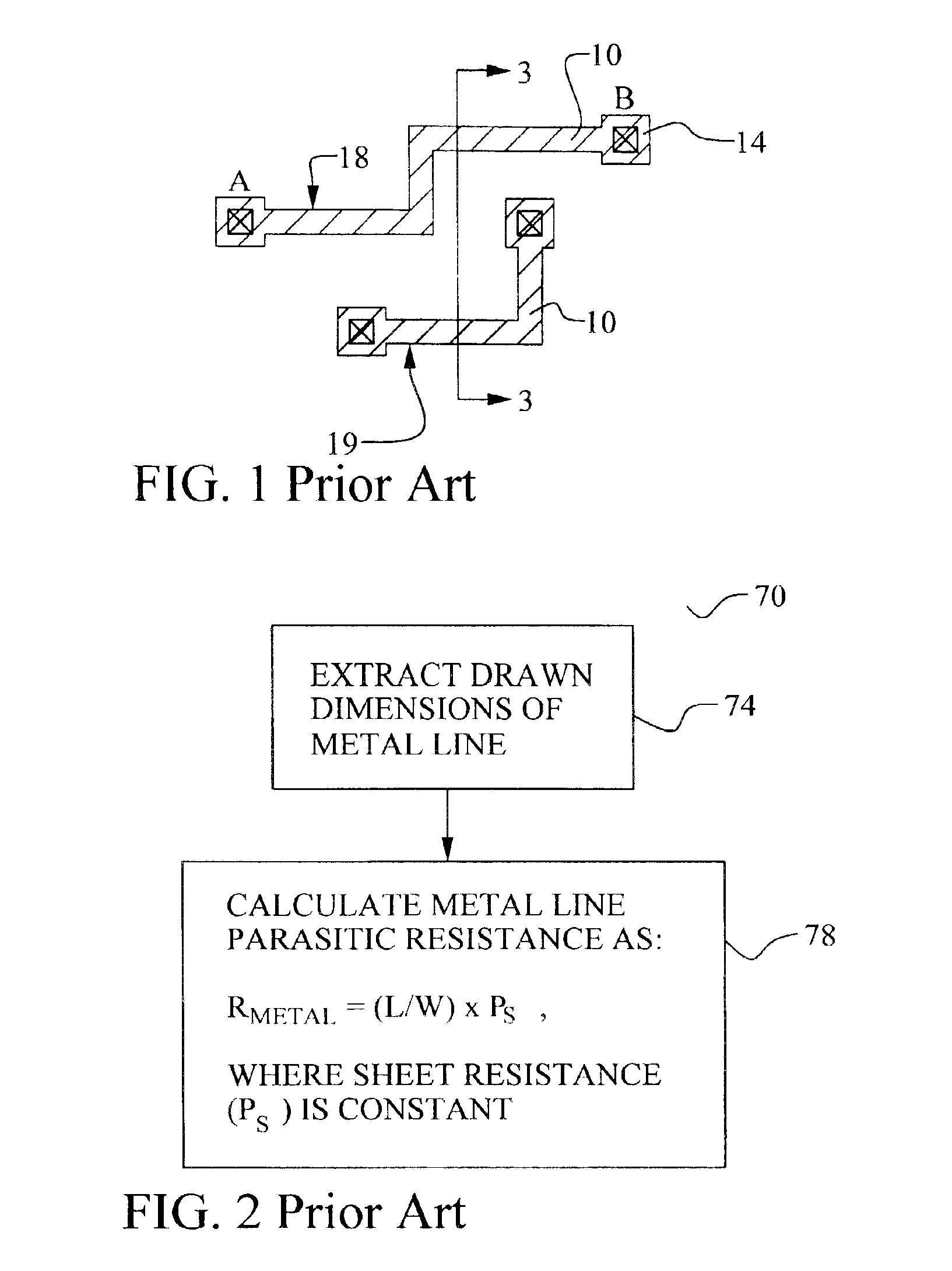
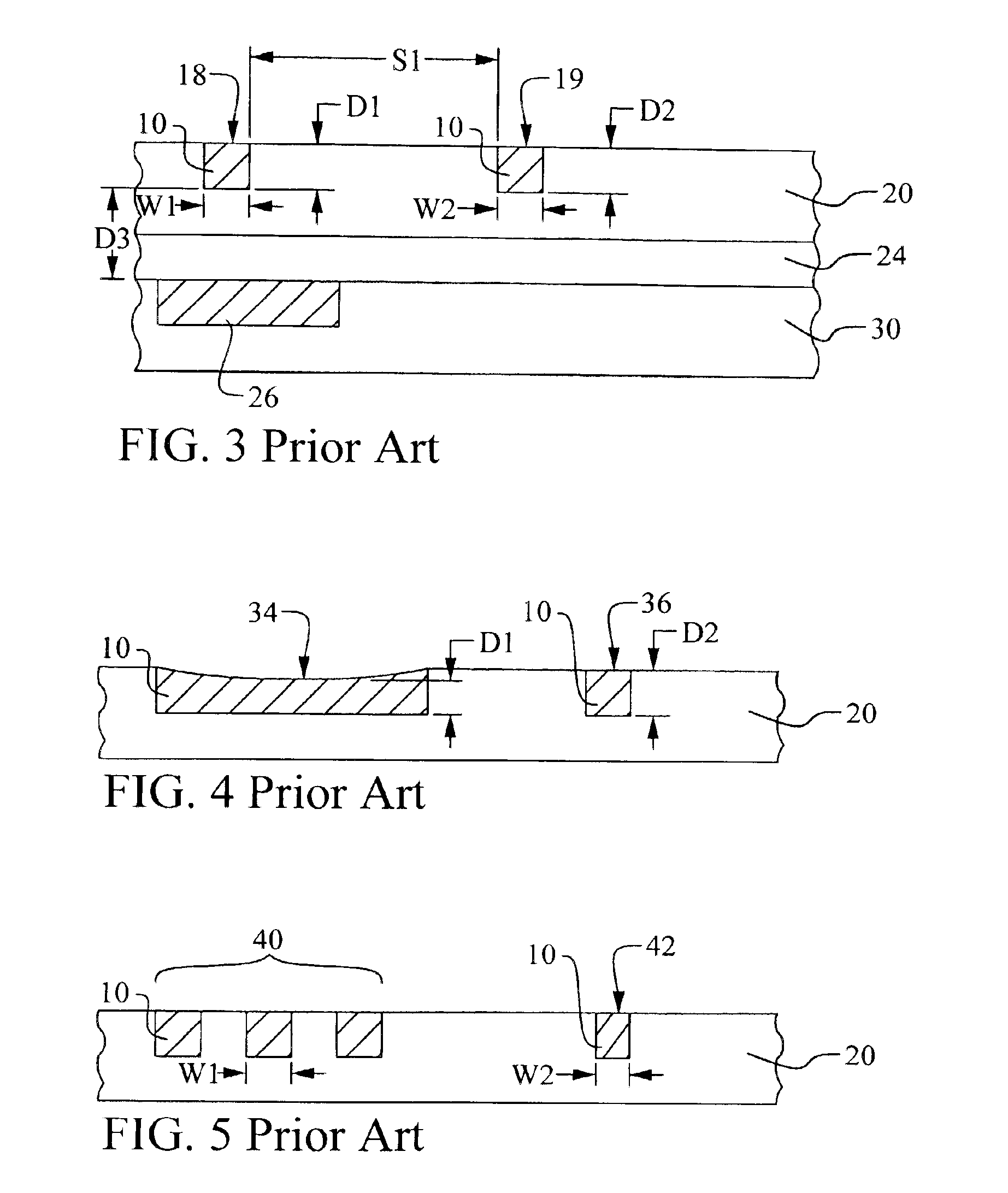
Methodology to characterize metal sheet resistance of copper damascene process
InactiveUS6854100B1Efficiently determinedSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty computer hardwareCopper damasceneIntegrated circuit
A new method to determine a parameter of a damascene interconnect in an integrated circuit device is achieved. Drawn dimensions and local pattern density of a damascene interconnect are extracted in an integrated circuit device. A parameter of the damascene interconnect is calculating using the drawn dimensions and the local pattern density to select a per unit value from a set of per unit values measured over a range of drawn dimension and pattern density combinations. The method may be used to improve the accuracy of extracted damascene metal line resistance and parasitic capacitance.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
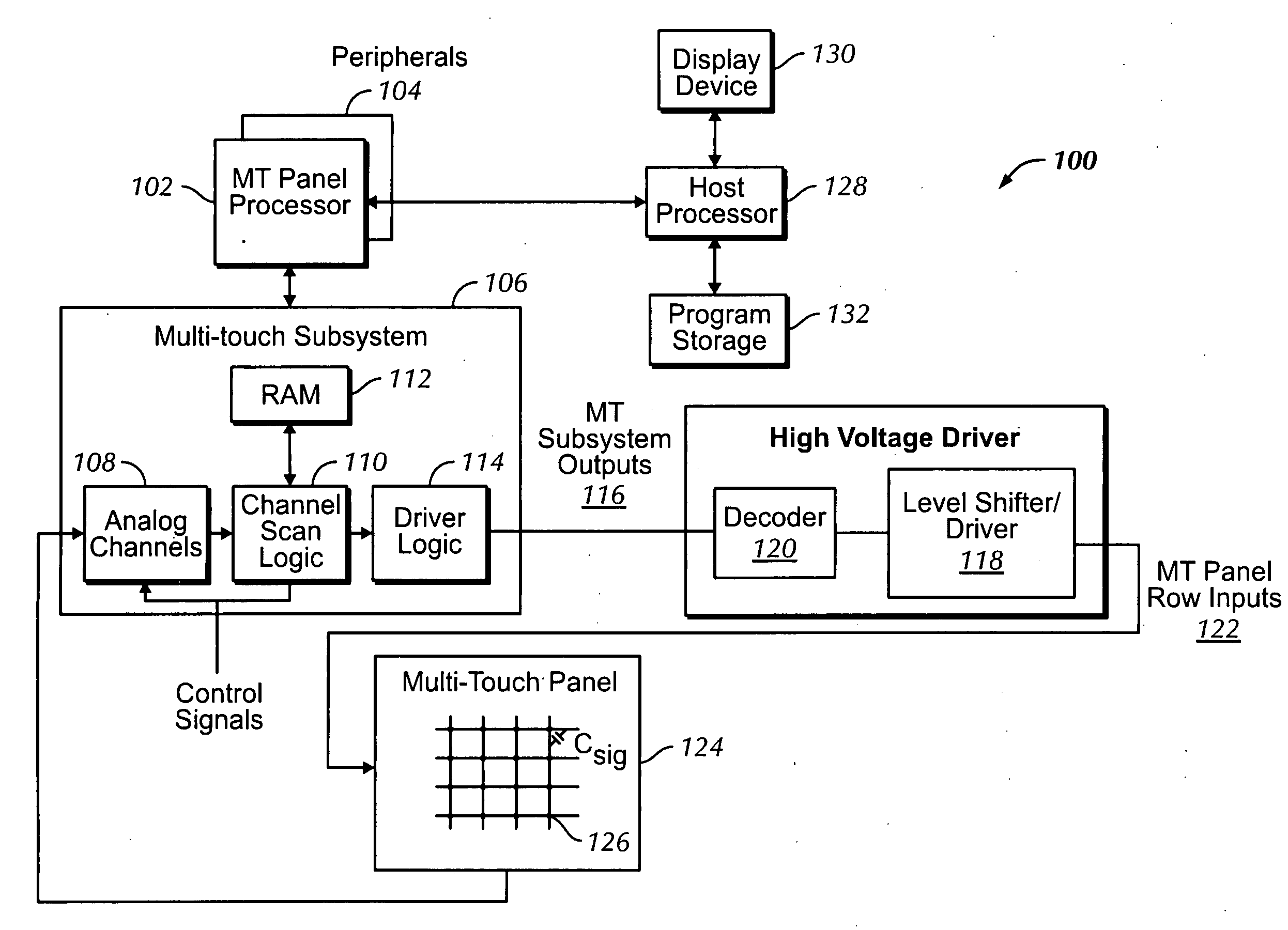
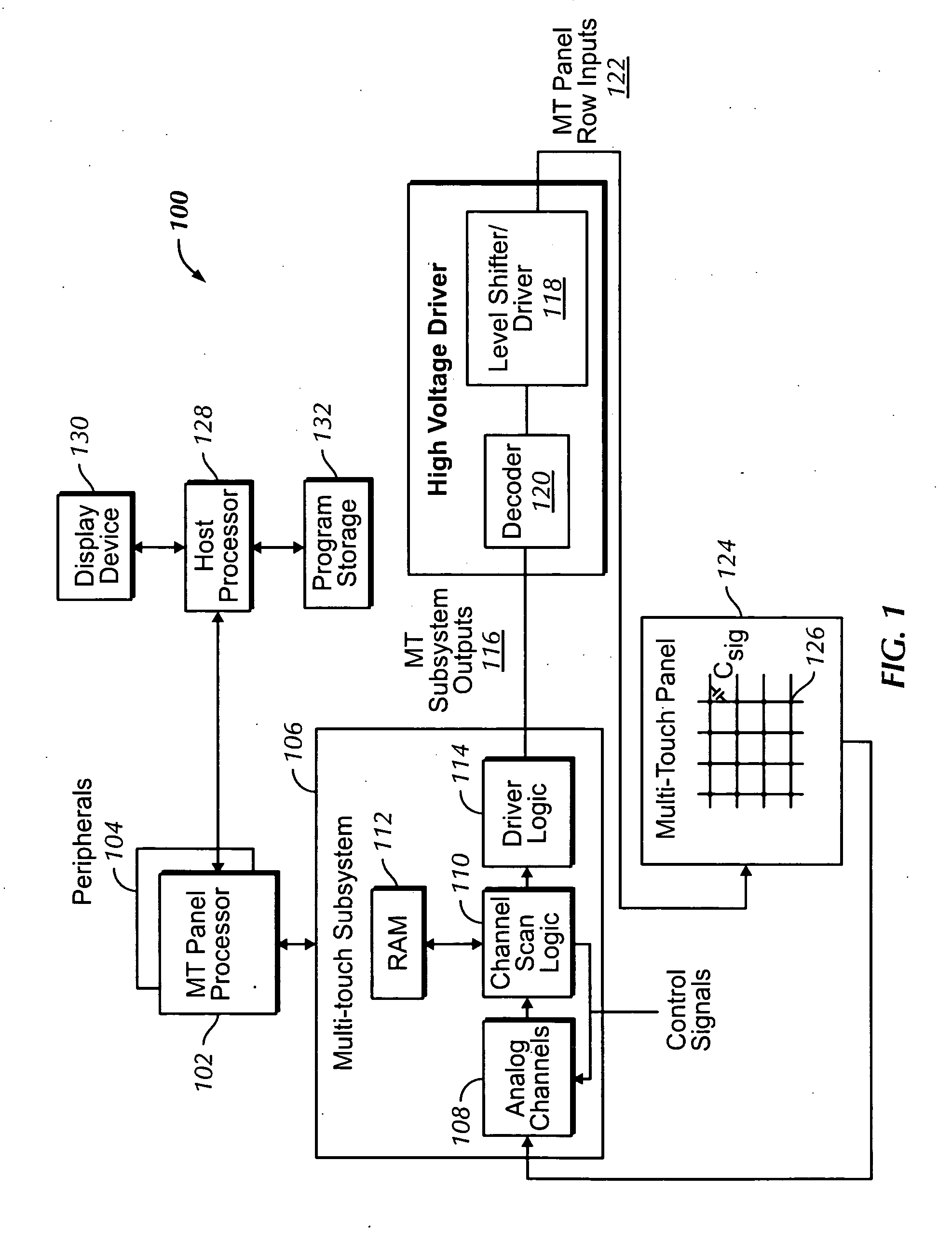
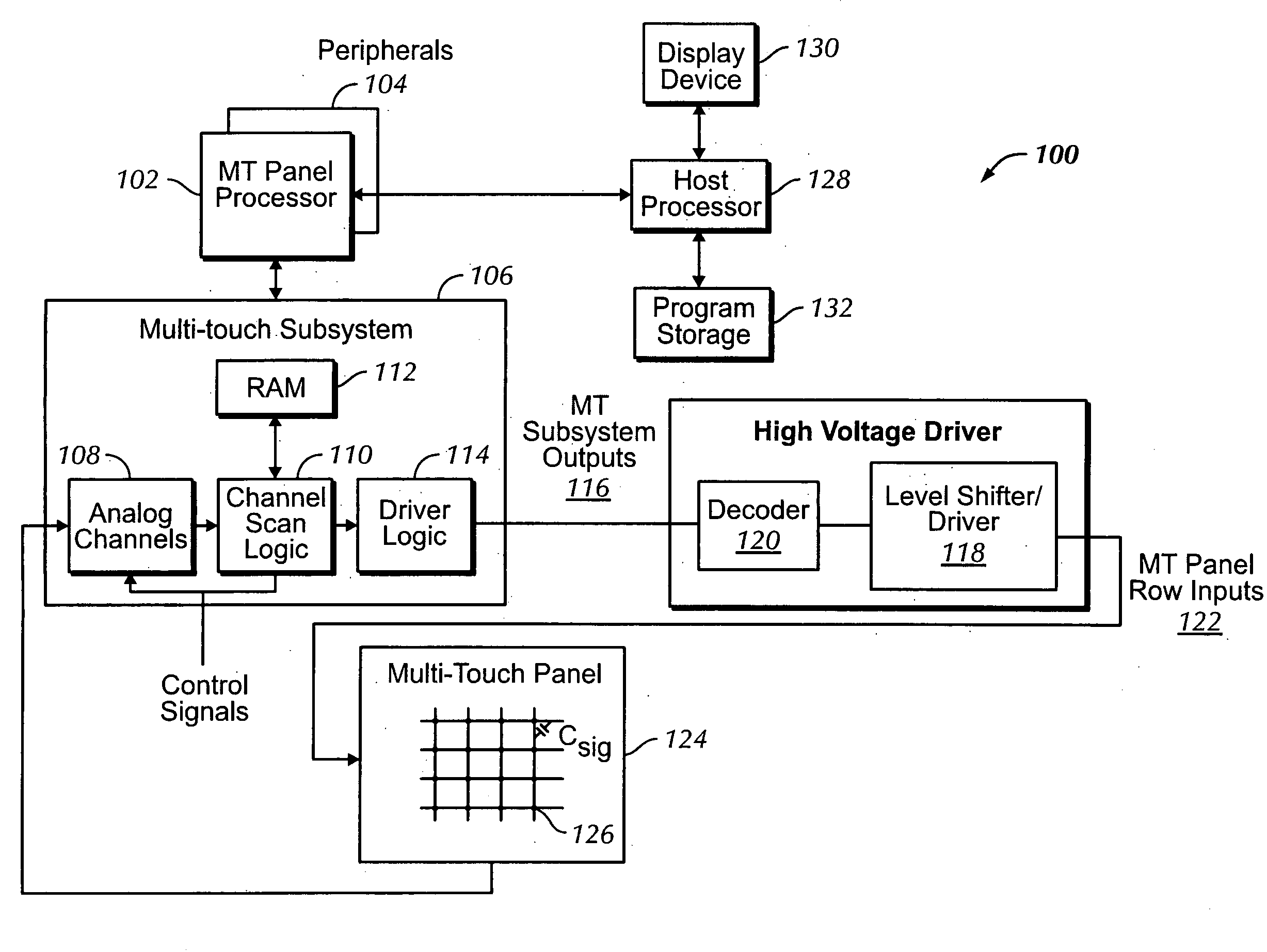
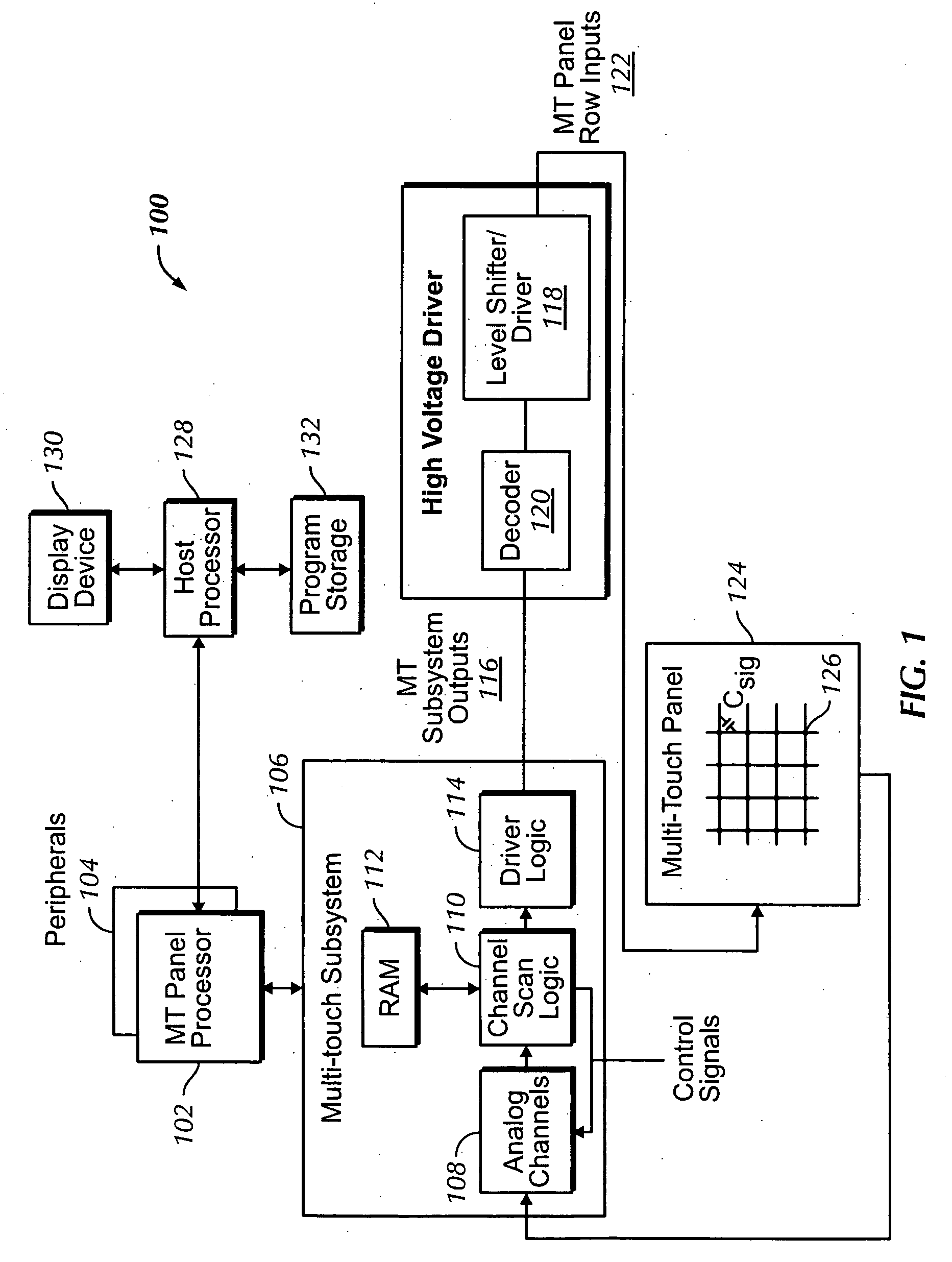
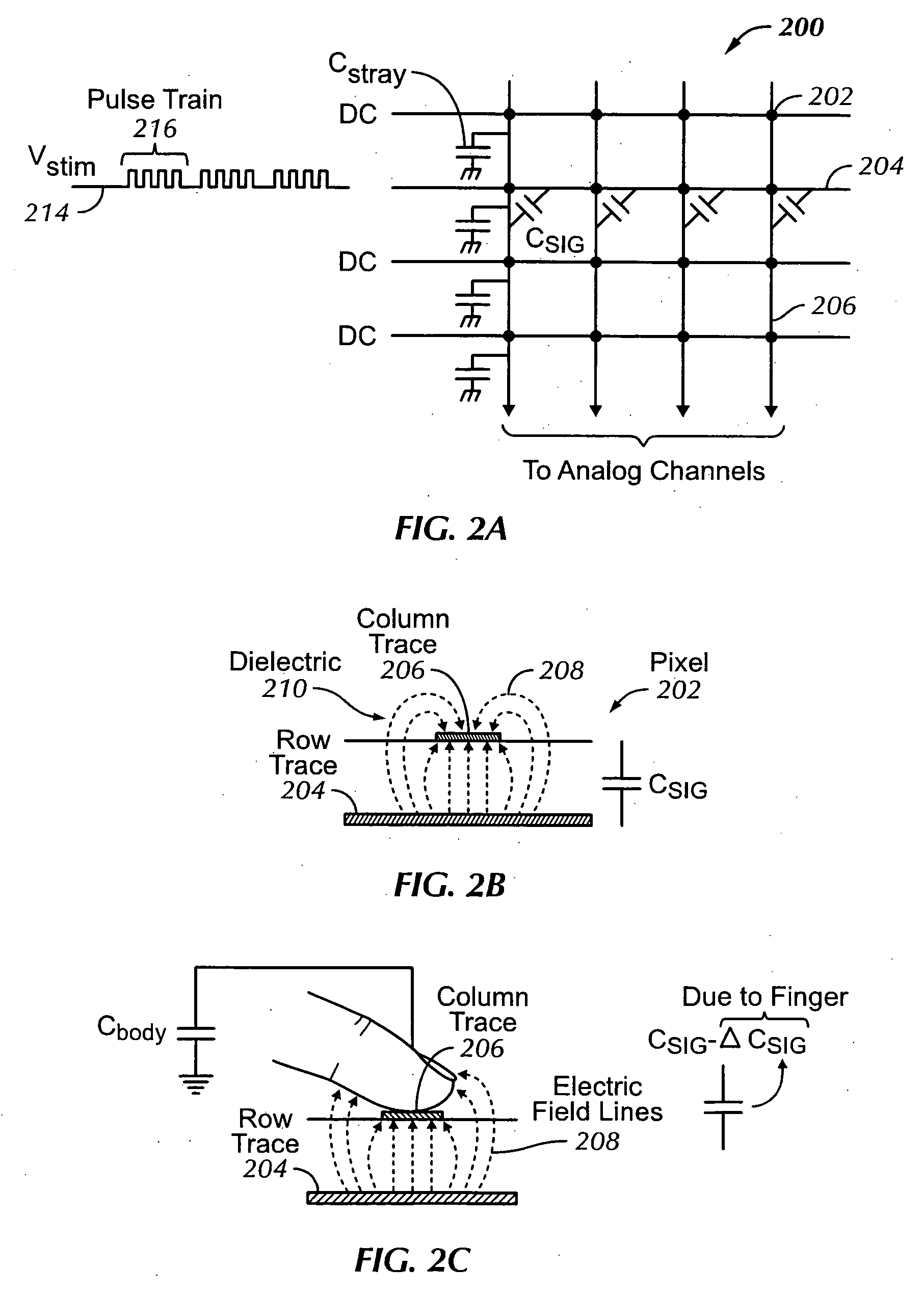
Multi-touch auto scanning
ActiveUS20080162996A1Digital data processing detailsDetecting faulty computer hardwareEngineeringCalibration function
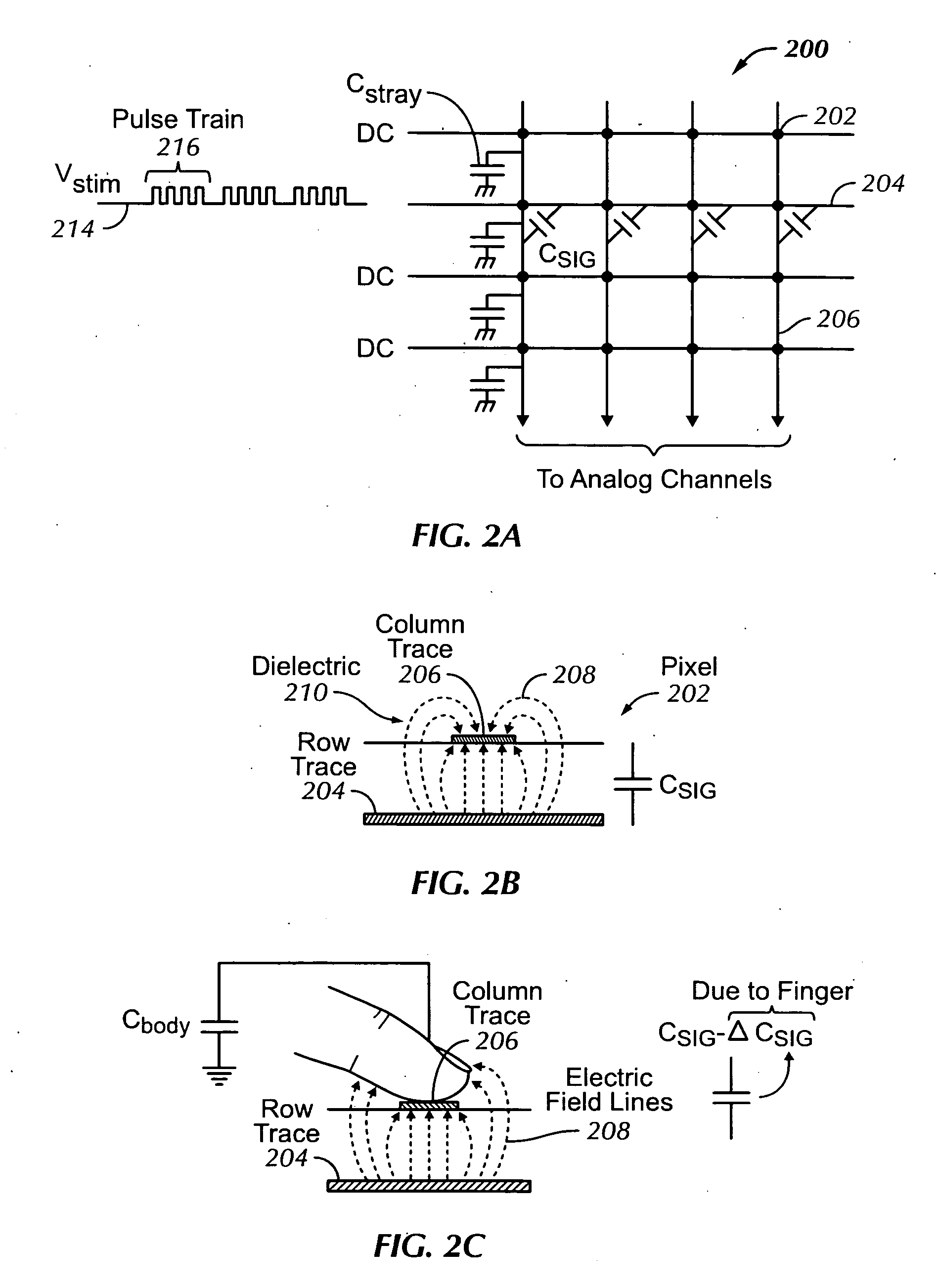
A system and method for autonomously scanning a sensor panel device, such as a multi-touch panel, is disclosed. In one embodiment, the system and method disables a sensor panel processor after a first predetermined amount of time has elapsed without the sensor panel device sensing any events. One or more system clocks can also be disabled to conserve power. While the processor and one or more system clocks are disabled, the sensor panel device can periodically autonomously scan the sensor panel for touch activity. Accordingly, if one or more results from the autonomous scans exceed a threshold, the sensor panel device re-enables the processor and one or more clocks to actively scan the sensor panel. If the threshold is not exceeded, then the sensor panel device continues to periodically autonomously scan the sensor panel without intervention from the processor. Furthermore, the sensor panel device can periodically perform calibration functions to account for any drift that may be present in the system.
Owner:APPLE INC
Diagnosis of programmable modules
InactiveUS20050258963A1Memory record carrier reading problemsDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer hardwareDiagnostic data
An electronic diagnostic device for testing electronic monitoring tags for devices such as replaceable modules for a printing apparatus includes a tag reader with a reader wireless communication element. The tag reader is adapted to read tag diagnostic information from an electronic monitoring tag. The electronic diagnostic device further includes a data processor in communication with the tag reader. The data processor is adapted to determine from the tag diagnostic data whether the electronic monitoring tag is operating within predetermined parameters, to identify one of a predetermined set of error categories if the electronic monitoring tag is operating outside the predetermined parameters, and to generate error category information. The electronic diagnostic device further includes a results communication element adapted to communicate the error category information generated by the data processor. The diagnostic device may also communicate correction information to the electronic monitoring tag.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and system for providing tamper-resistant software
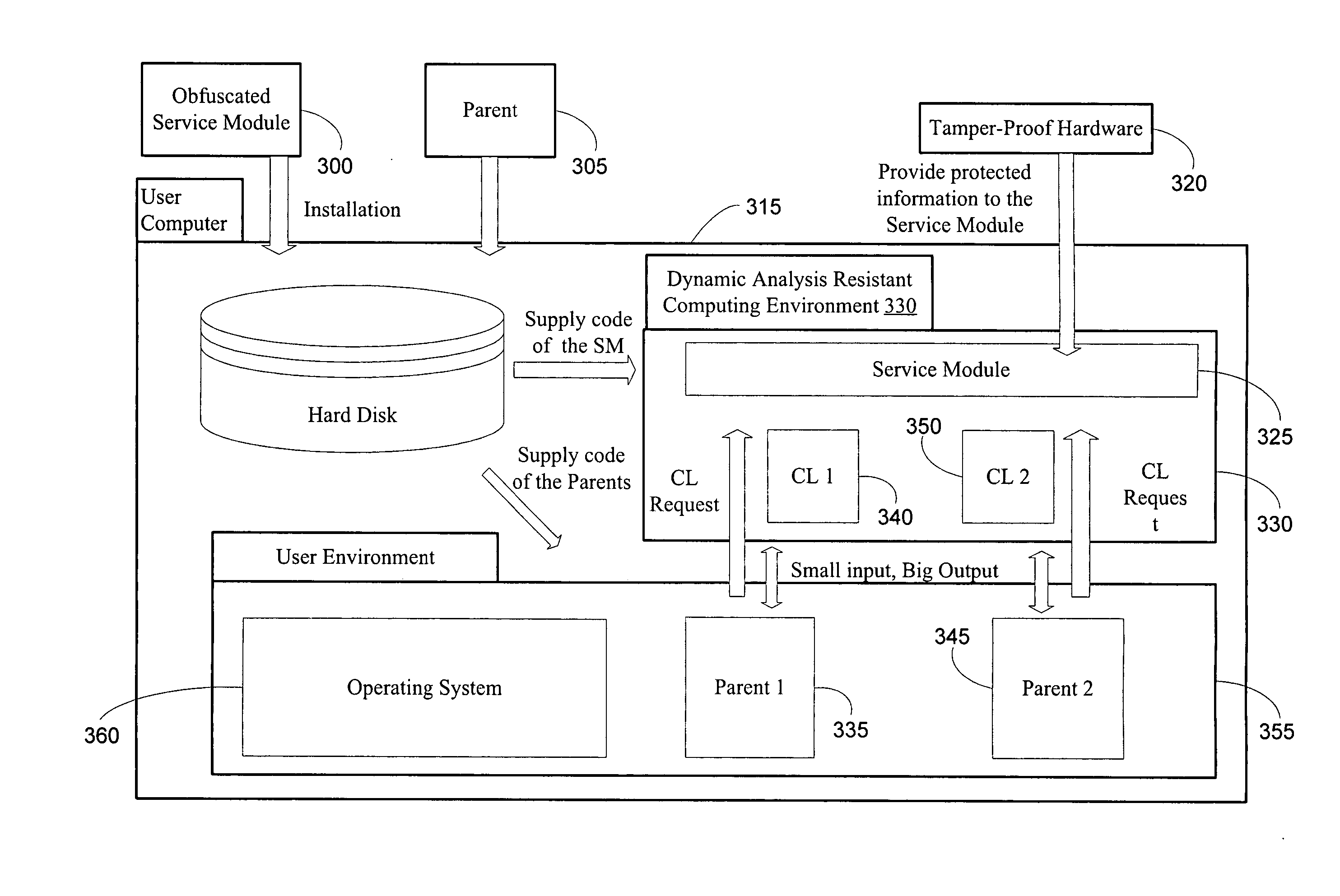
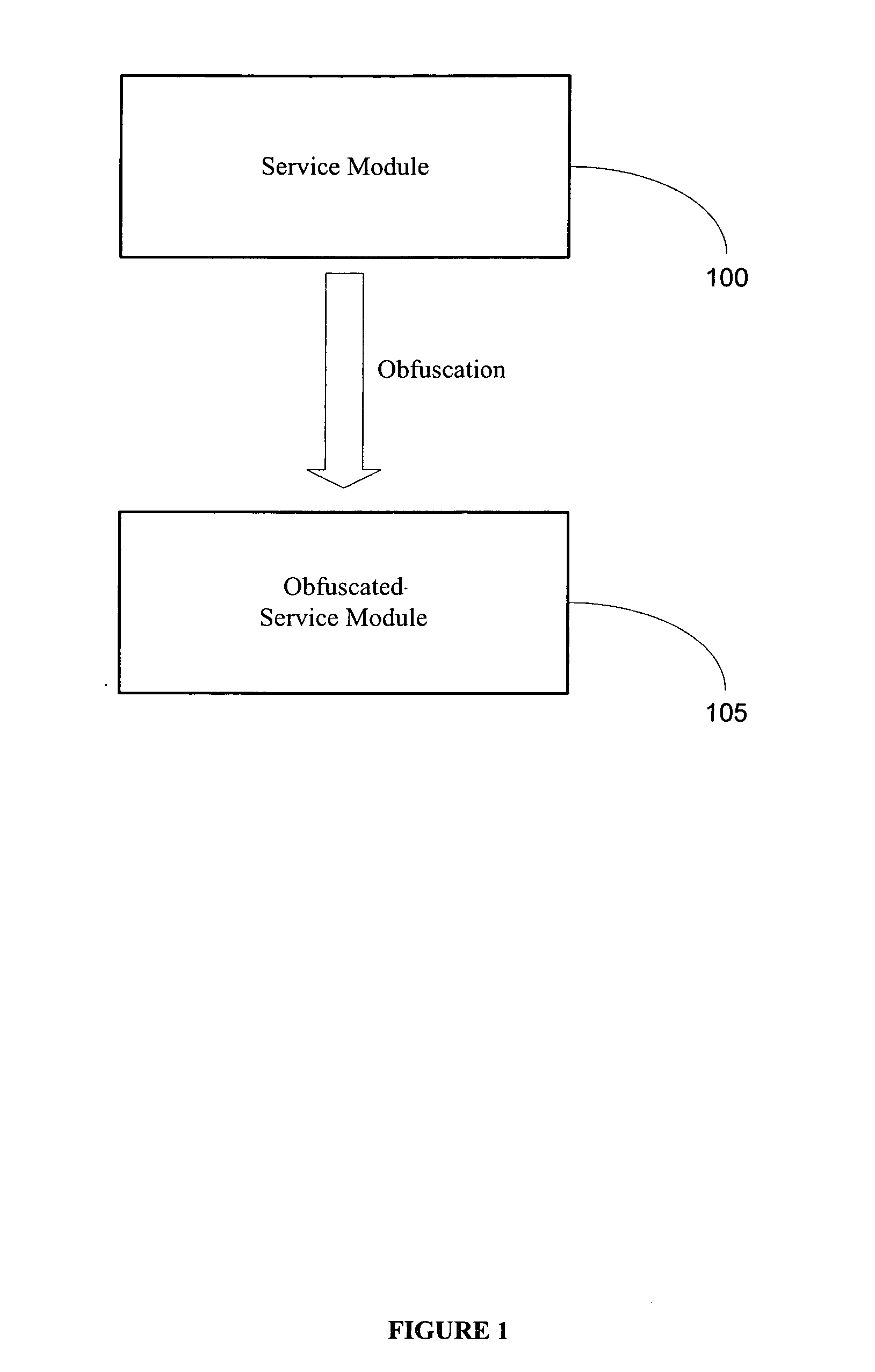
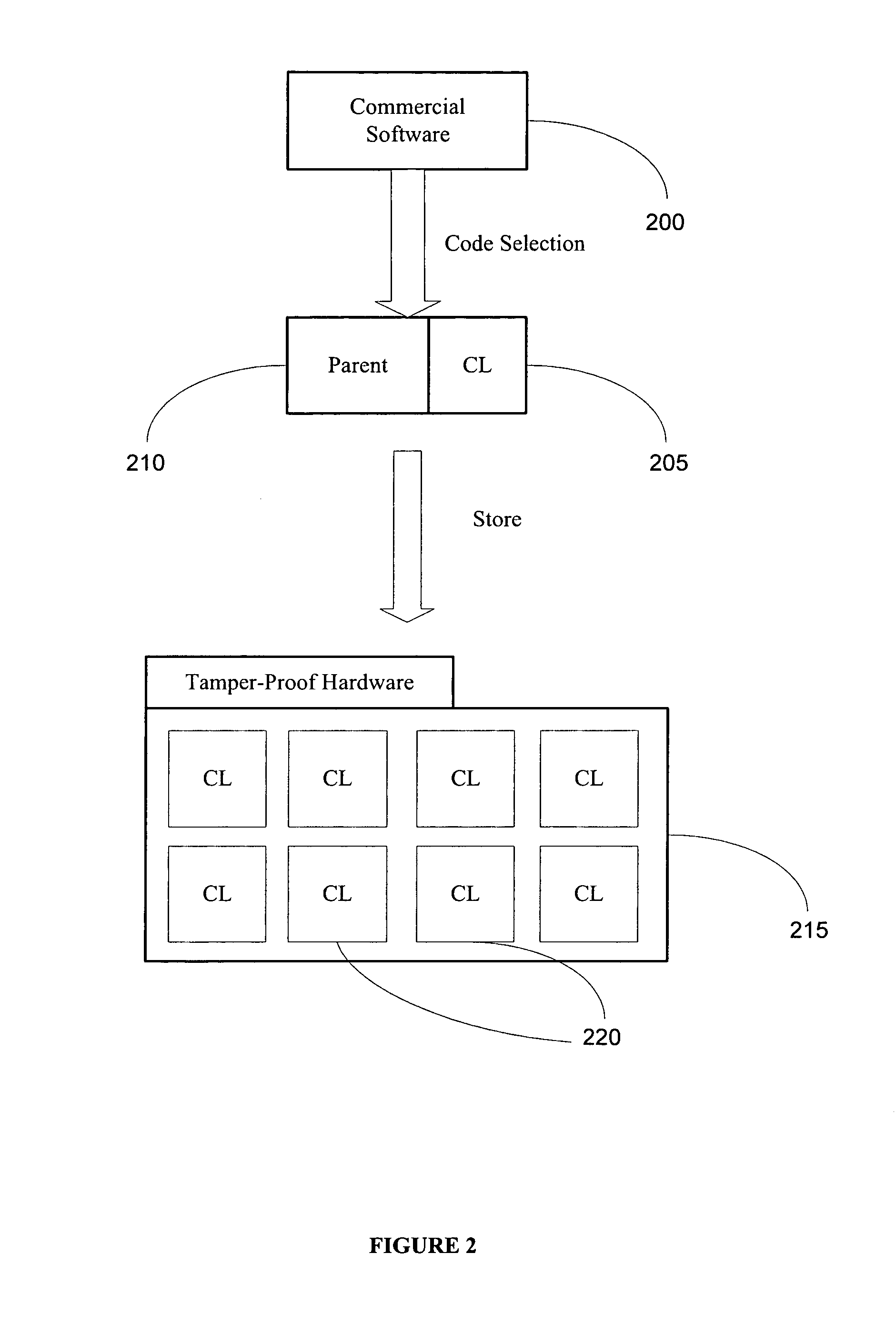
InactiveUS20060048223A1Performance penaltyImprove tamper resistanceMemory loss protectionDetecting faulty computer hardwareTamper resistanceObfuscation
A method and system for protecting only a portion of the software to be protected against tampering is described. Such a portion may be stored in a tamper-resistant physical device, with optional encryption, for downloading when needed for execution. Several layers of tamper resistance are provided without excessively impacting performance of the protected software. For instance, obfuscation is applied to the code for the service module to minimize the large expense associated with obfuscation. The invention includes embodiments that deliver critical logic, policy information and other similar information with the help of mobile agents, which may be hosted by a server in a smart card.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
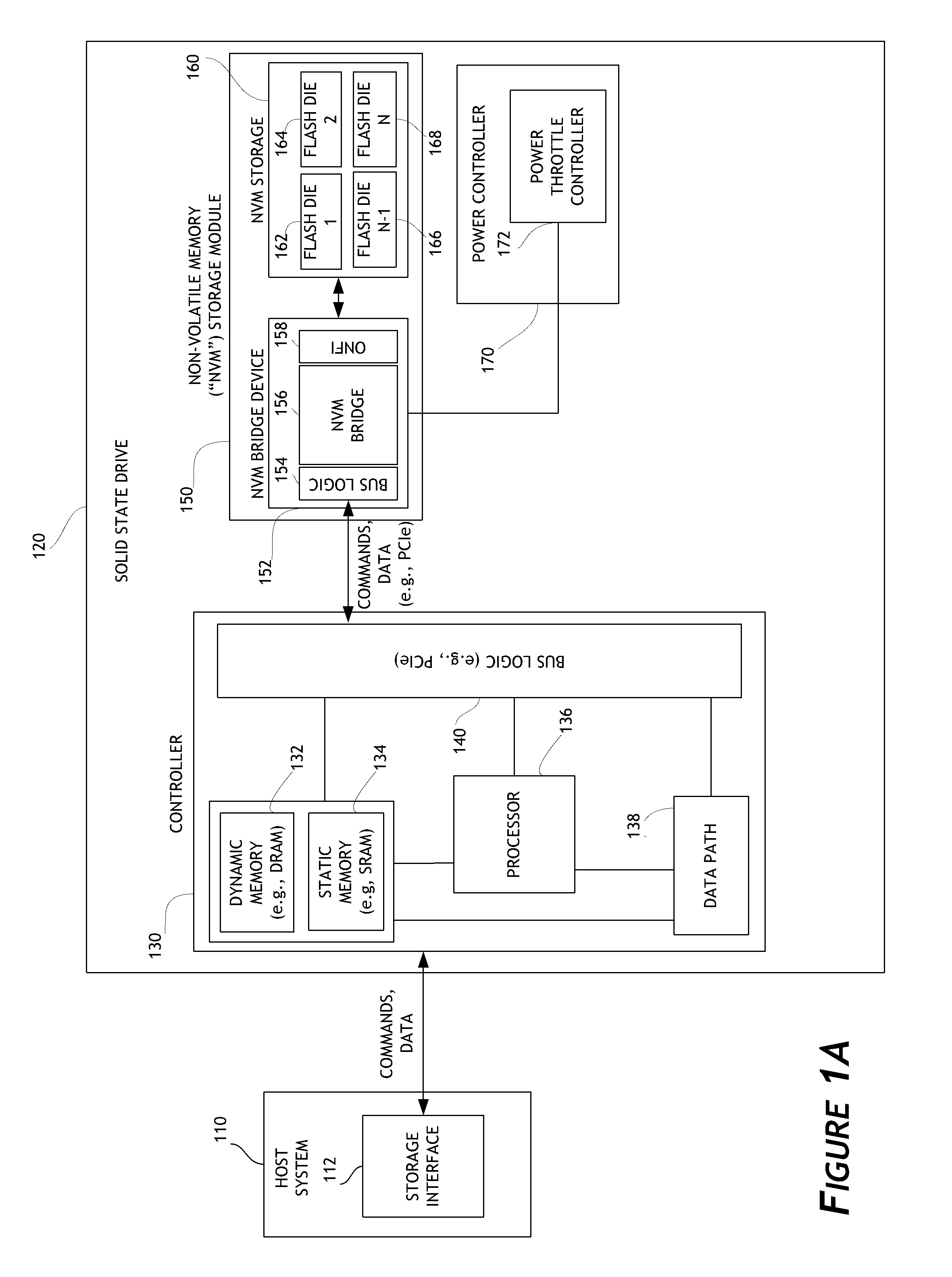
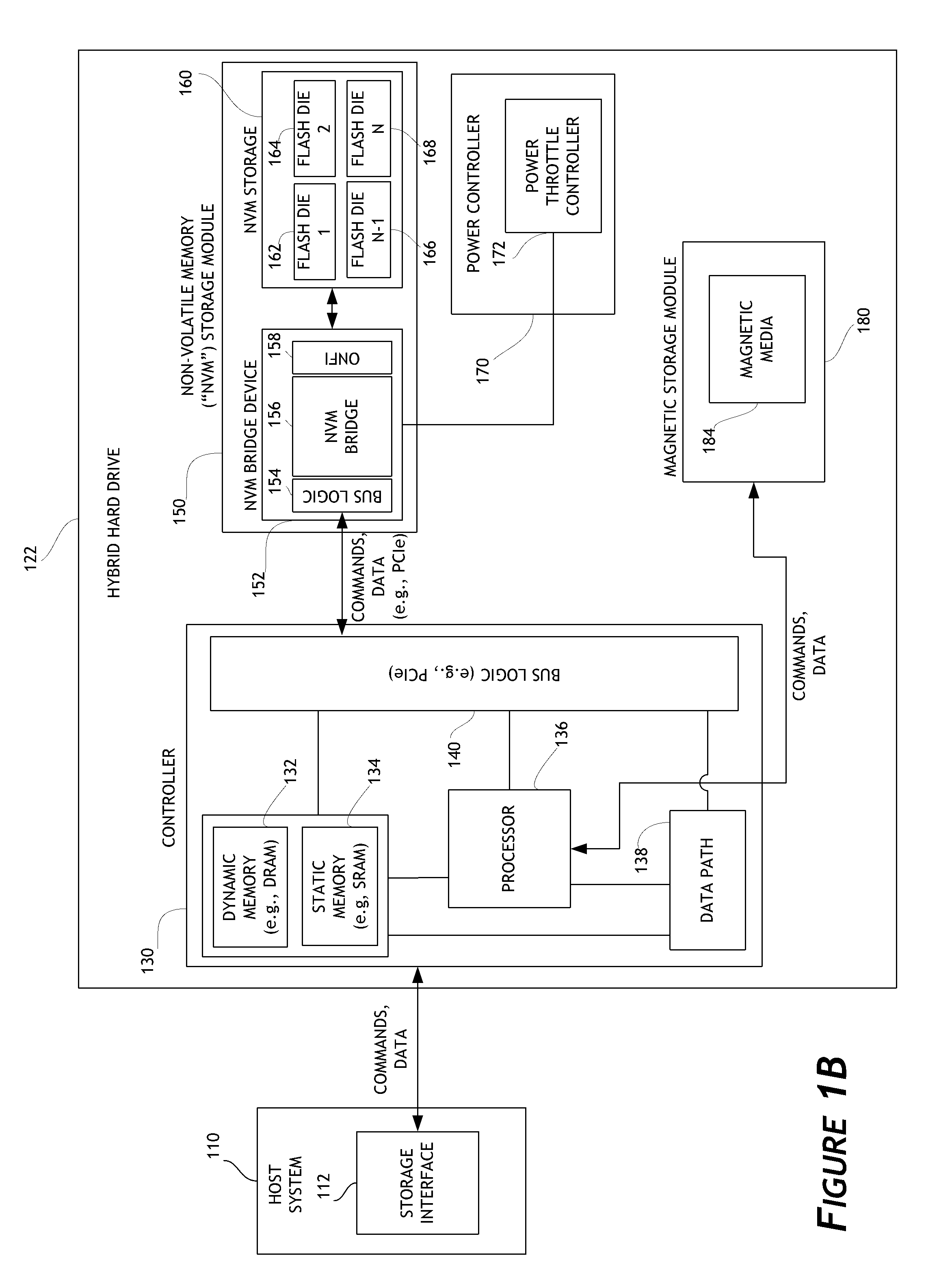
Systems and methods for error injection in data storage systems
ActiveUS8707104B1Solving precise measurementsTested and reliableDetecting faulty computer hardwareRead-only memoriesSolid-state storageHybrid storage system
Embodiments of the solid-state storage system provided herein are configured to perform improved mechanisms for testing of error recovery of solid state storage devices. In some embodiments, the system is configured to introduce or inject errors into data storage commands or operations performed in the non-volatile memory. Injected errors include corruption of data stored in the non-volatile memory, deliberate failure to execute storage operations, and errors injected into communication protocols used between various elements of the device. In some embodiments, injected errors can include direct errors that trigger an immediate execution of error recovery mechanisms and delayed errors that trigger execution of error recovery mechanisms at a later time. Error recovery mechanisms can be tested in an efficient, reliable, and deterministic manner to help ensure effective operation of storage devices. The integrity of non-volatile memory can also be tested.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
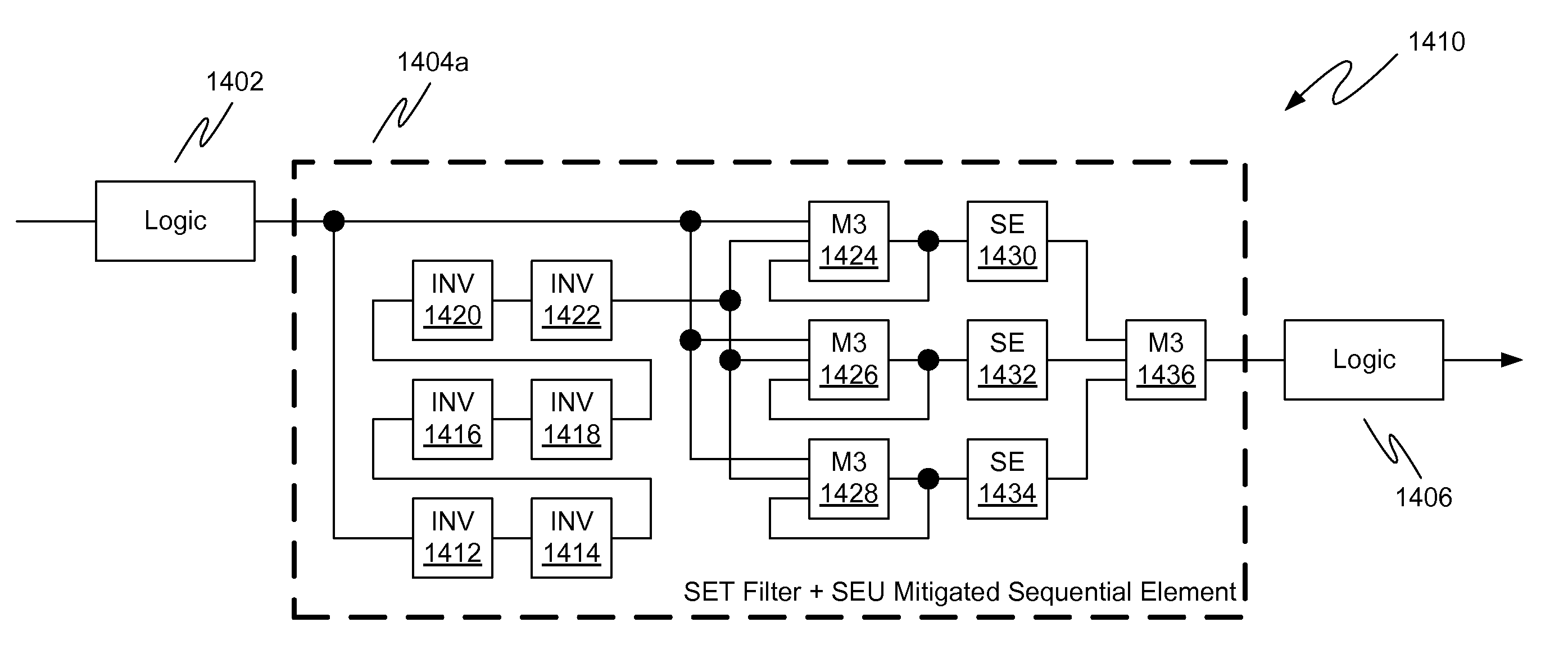
Single event transient mitigation and measurement in integrated circuits
ActiveUS20090204933A1Fail-safe circuitsDetecting faulty computer hardwareIntegrated circuit layoutComputer science
A method for single event transient filtering in an integrated circuit device is described. The device comprises three sequential elements, each having a data input and a data output with each of the three data outputs coupled to one of three inputs of a voting gate. The method comprises generating first and second nominally equivalent logic signals in first and second SET domains, converting the first and second nominally equivalent logic signals into first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels, and transmitting the first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels to the data inputs of the first, second and third sequential elements. Provision is made for applying the method to logic designs implemented in programmable logic integrated circuit devices.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
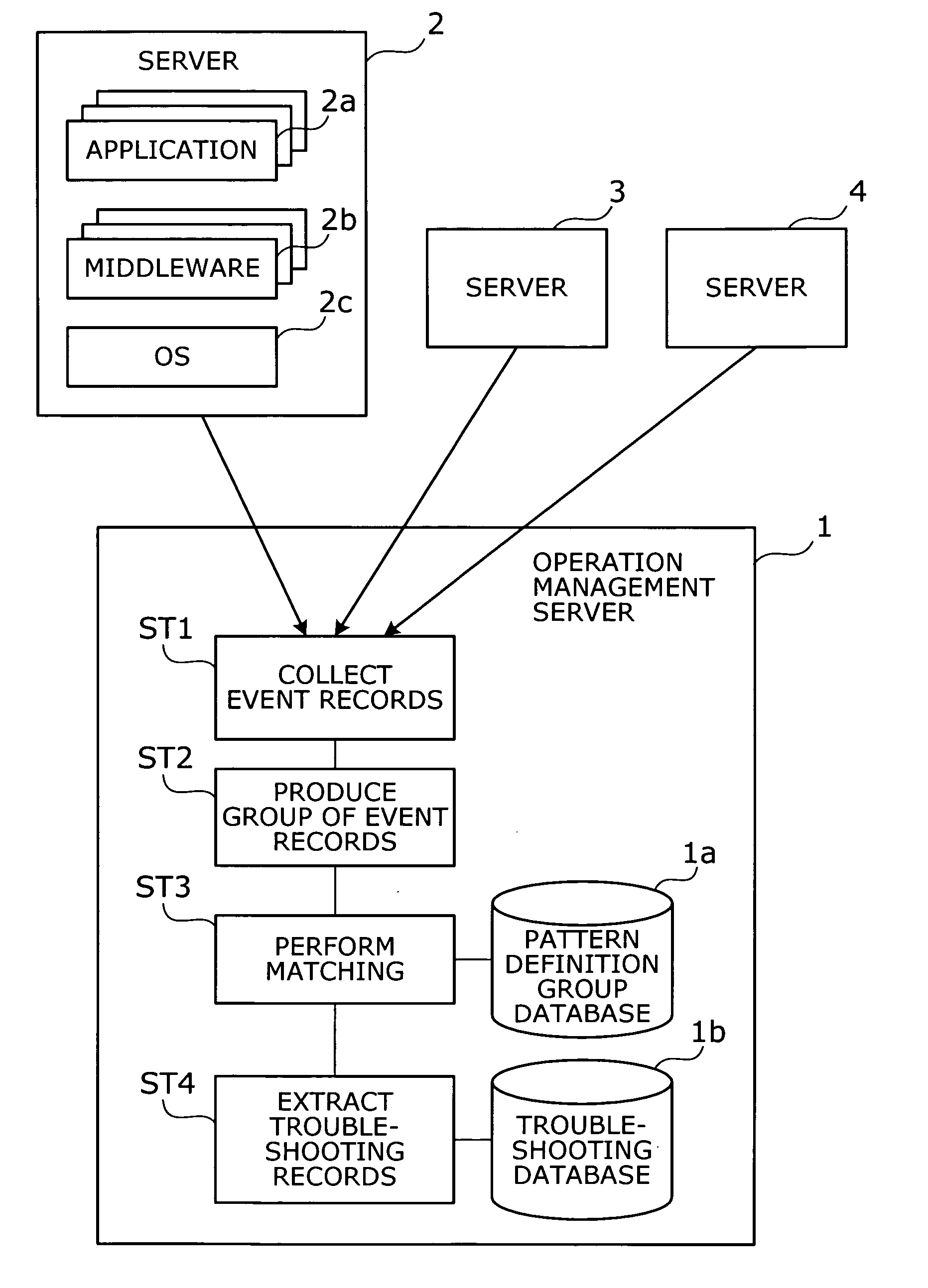
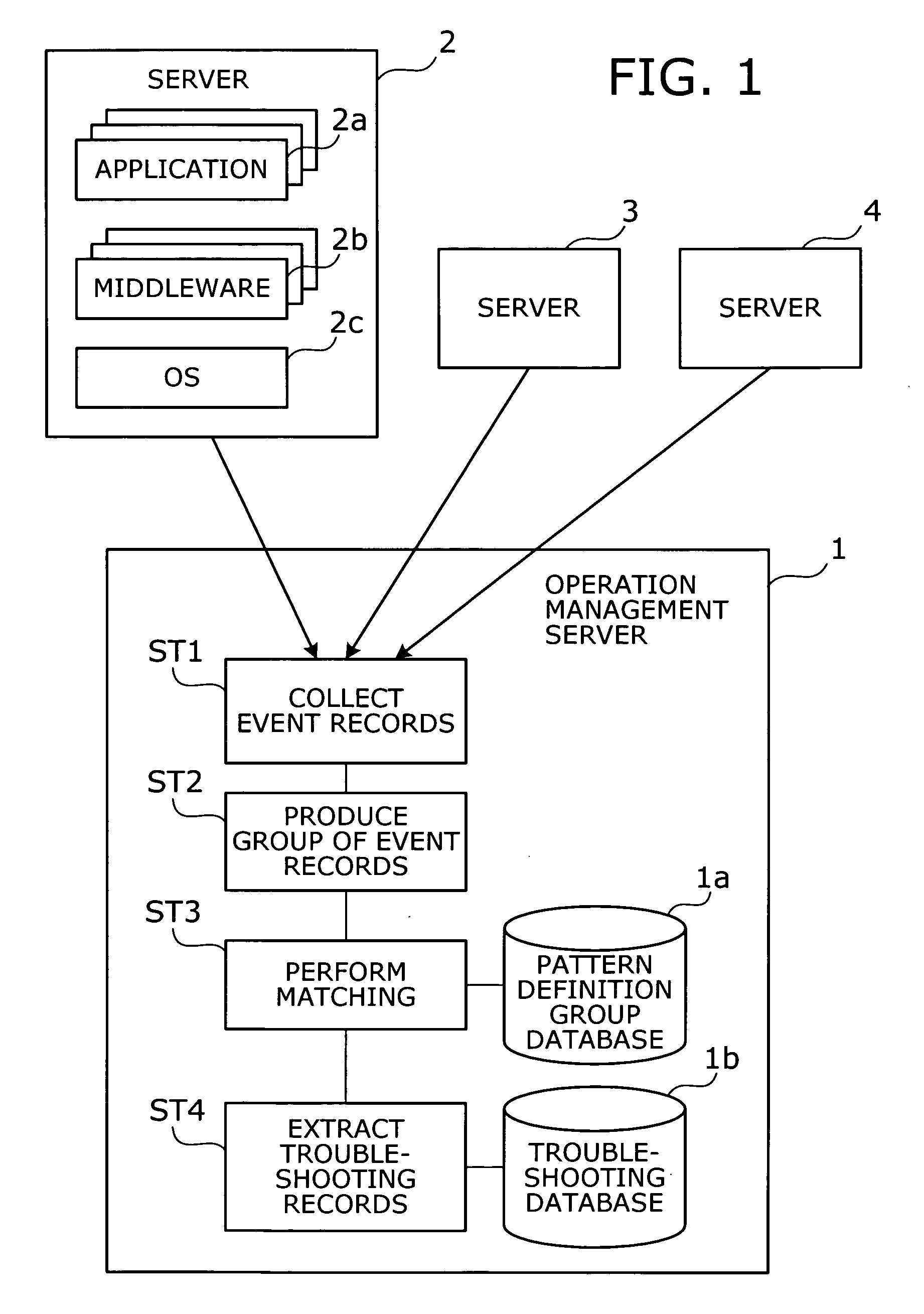
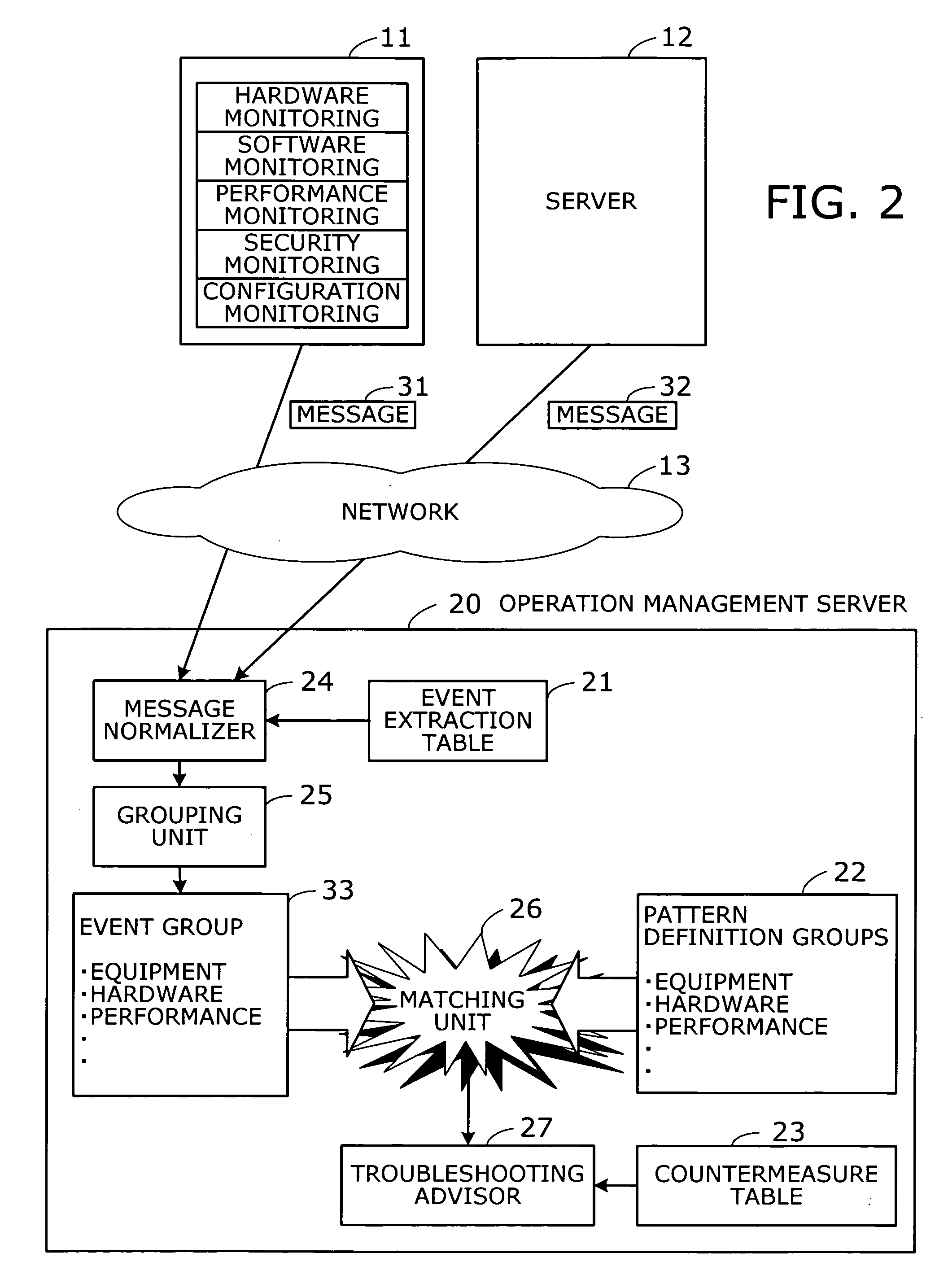
Operation management method and operation management server
InactiveUS20050172162A1Data processing applicationsDetecting faulty computer hardwareSoftwareReal-time computing
A method is provided to point out which software program is causing a problem. Event records are collected from target objects being monitored. An event group is then produced by grouping the collected event records. The event group is compared with a plurality of pattern definition groups in terms of occurrence patterns of event records, where each pattern definition group defines a pattern of event records that would be produced upon occurrence of a particular problem. Subsequently a troubleshooting record is extracted. This troubleshooting record has previously been associated with a pattern definition group resembling the event group in terms of occurrence patterns of event records.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Channel scan logic
ActiveUS20080162997A1Digital data processing detailsDetecting faulty computer hardwareFrequency bandPower management
A device that can autonomously scan a sensor panel is disclosed. Autonomous scanning can be performed by implementing channel scan logic. In one embodiment, channel scan logic carries out many of the functions that a processor would normally undertake, including generating timing sequences and obtaining result data; comparing scan result data against a threshold value (e.g., in an auto-scan mode); generating row count; selecting one or more scanning frequency bands; power management control; and performing an auto-scan routine in a low power mode.
Owner:ALLLE INC
Fault diagnosis, repair and upgrades using the acoustic channel
InactiveUS20050028034A1Need be addressBroadcast information characterisationNon-redundant fault processingVocal tractEngineering
An acoustic channel is used for fault diagnosis, repair, and upgrades. Remote diagnosis uses self-test data encoded into sound waves. Repair data and upgrades are also encoded and transmitted as sound waves.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for parallel data preparation and processing of integrated circuit graphical design data
InactiveUS7434185B2Improve scalabilityIncrease loadDetecting faulty computer hardwareOriginals for photomechanical treatmentGraphicsComputer architecture
A method for implementing an ORC process to facilitate physical verification of an integrated circuit (IC) graphical design. The method includes partitioning the IC graphical design data into files by a host machine such that the files correspond to regions of interest or partitions with defined margins, dispersing the partitioned data files to available cpus within the network, processing of each job by the cpu receiving the file, wherein artifacts arising from bisection of partitioning margins during the partitioning, including cut-induced false errors, are detected and removed, and the shape-altering effects of such artifact errors are minimized and transmitting the results of processing at each cpu to the host machine for aggregate processing.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method, apparatus and computer program product for determination of noise in mixed signal systems
InactiveUS6941258B2Fast and accurate determinationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDetecting faulty computer hardwareEngineeringSignaling system
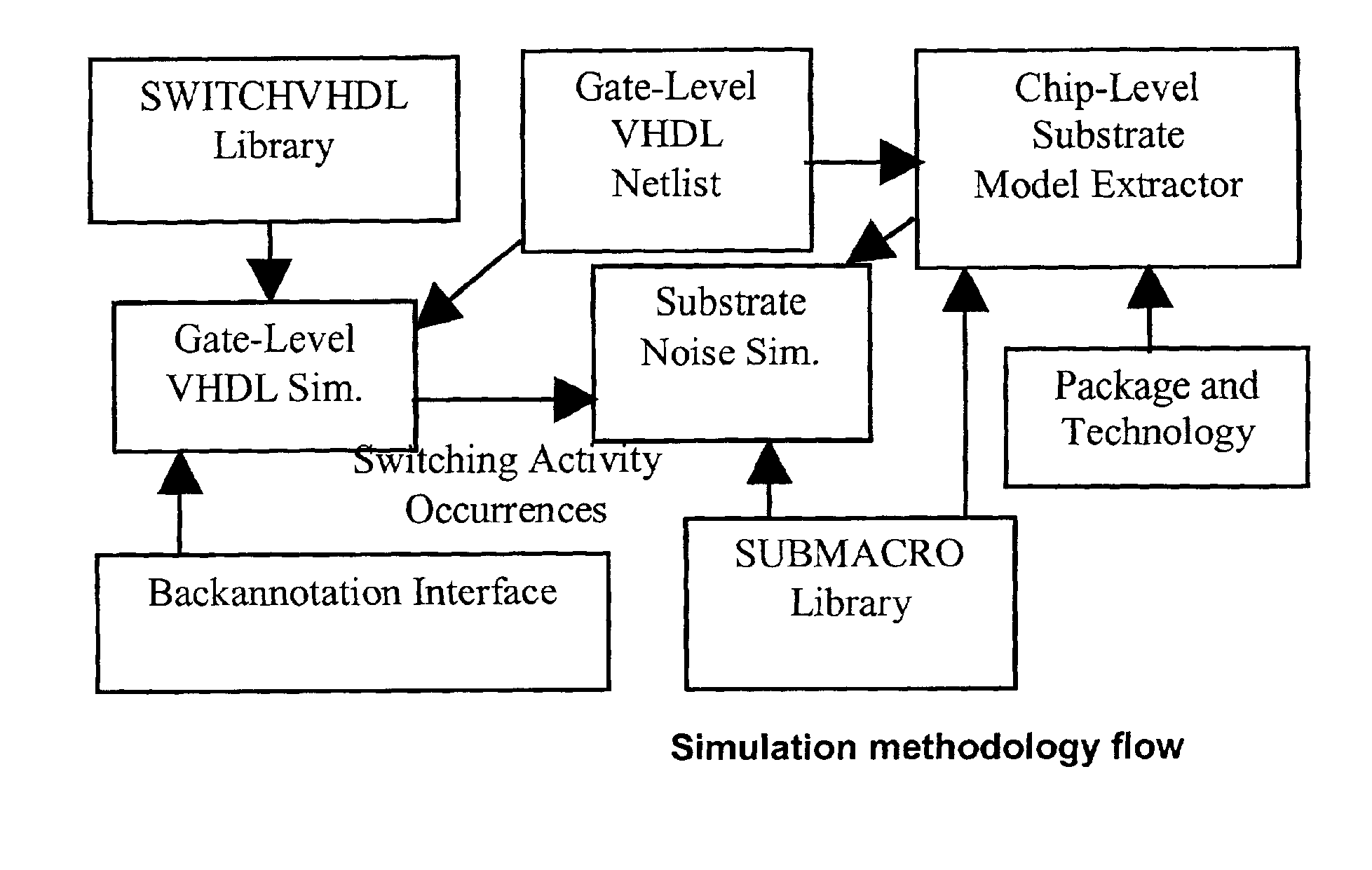
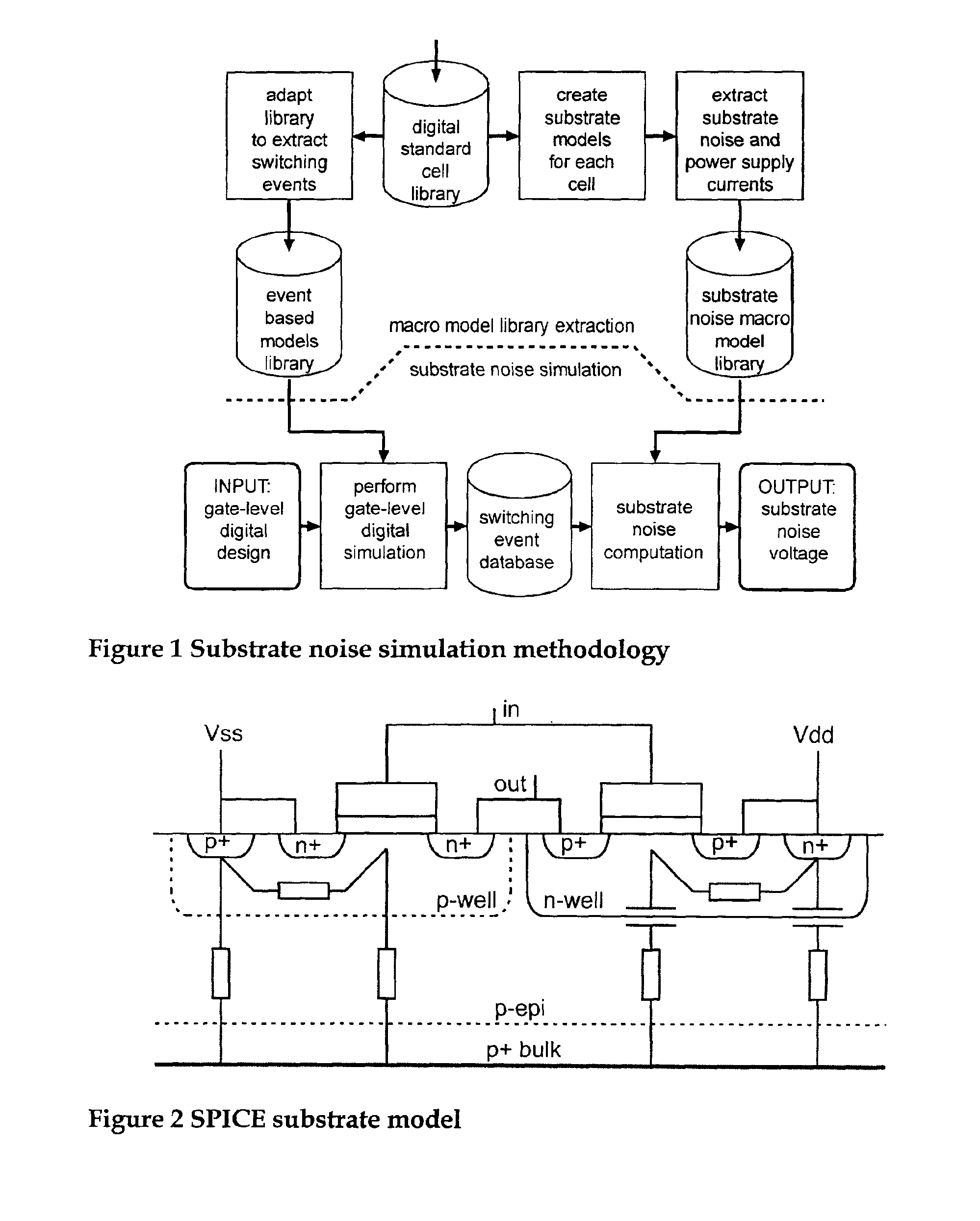
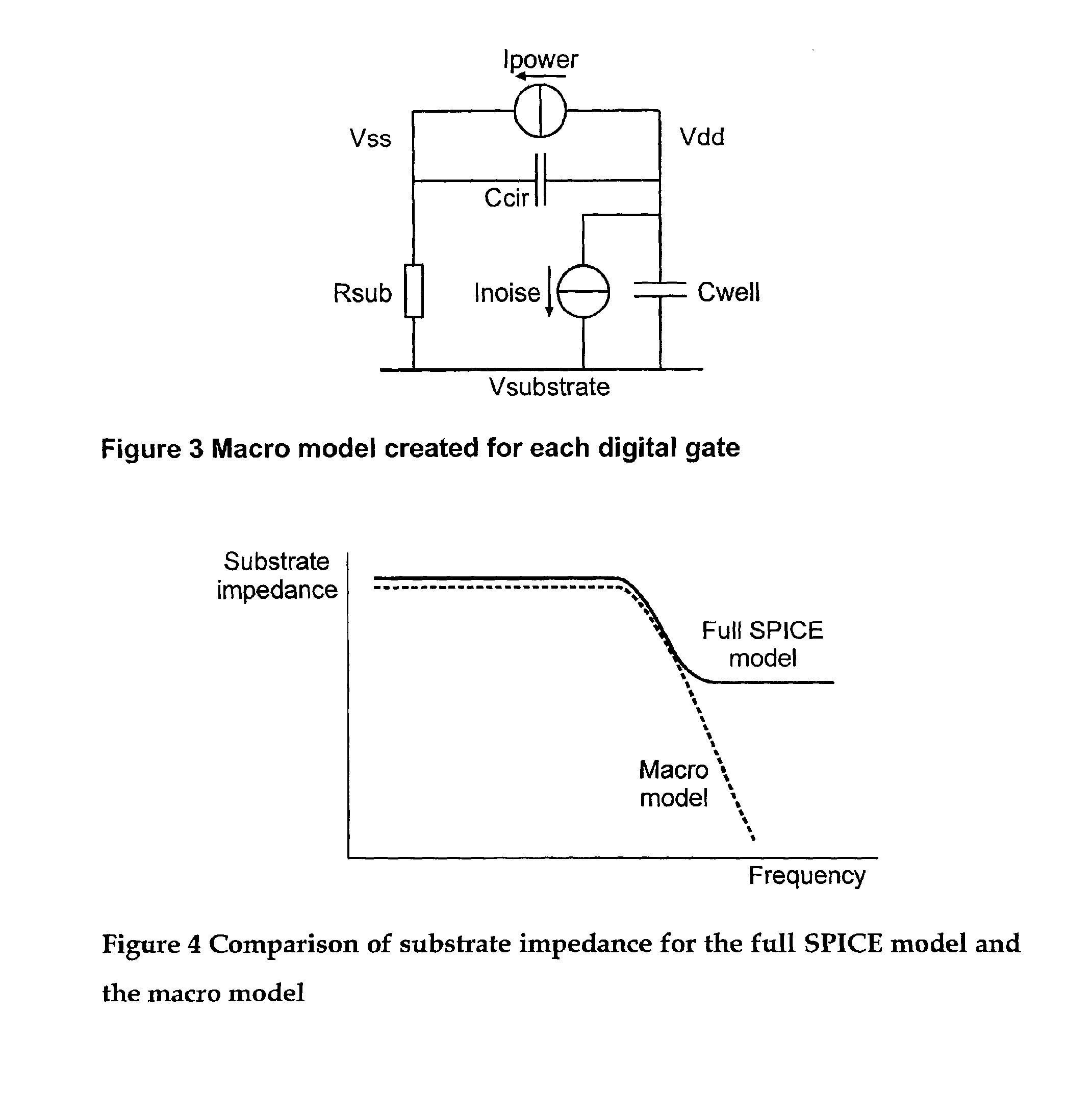
A simulation system is described for computing the overall signal generated in a substrate by a digital system comprising a plurality of gates associated with the substrate, wherein each gate is configured to perform a switching event. Output of a transistor-level model is compared with output of a lumped circuit model for each gate and the substrate, and signal contributions from each gate and switching event are determined based on the comparison. The system determines switching event signals for each of the plurality of gates. The signal contributions and the switching event signals are combined, and a combined lumped circuit model is derived based on a combination of lumped circuit models of the plurality of gates. The overall signal is computed based on the combined gate signal contributions and switching event signals, which are configured as an input to the combined lumped circuit model.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
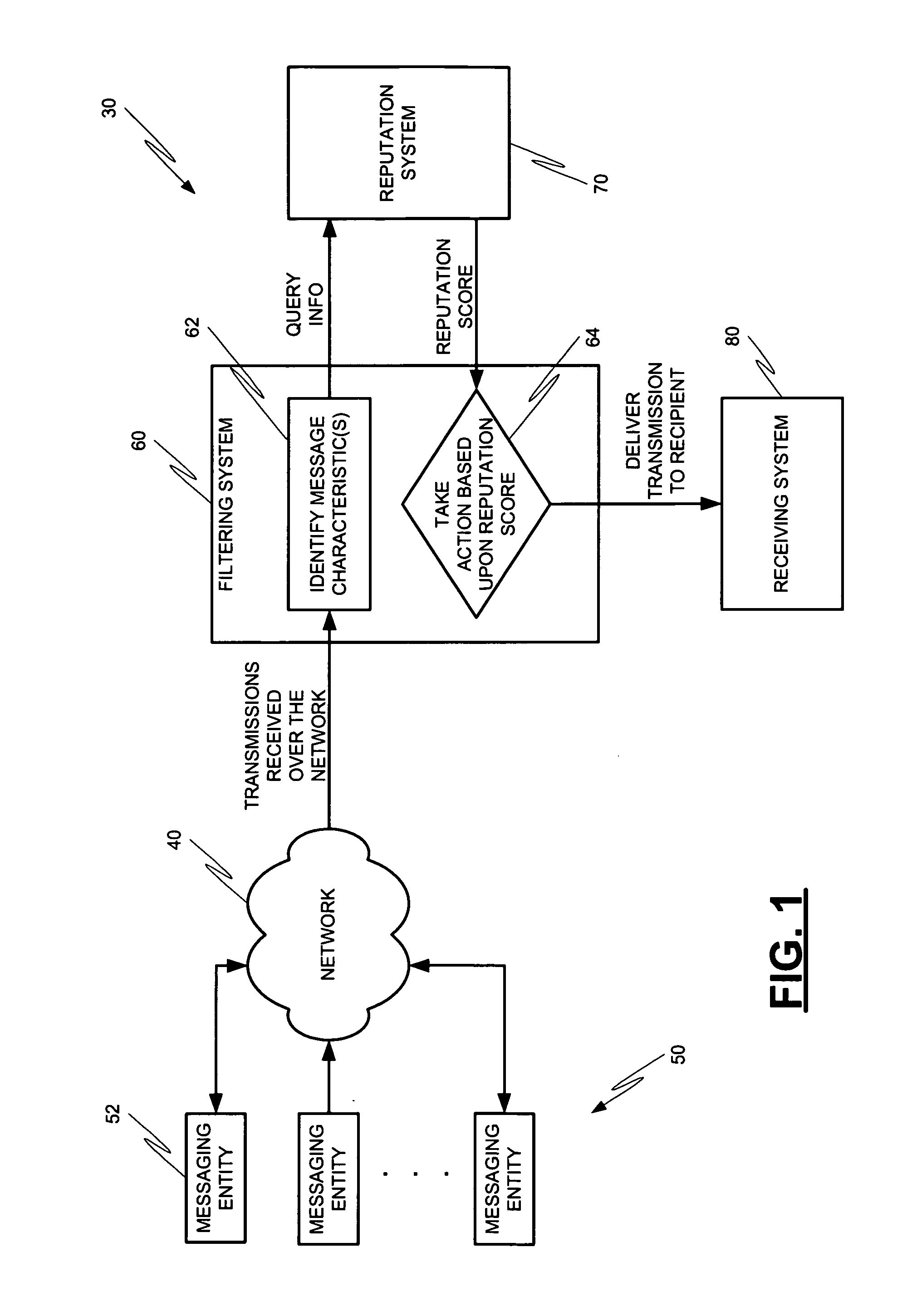
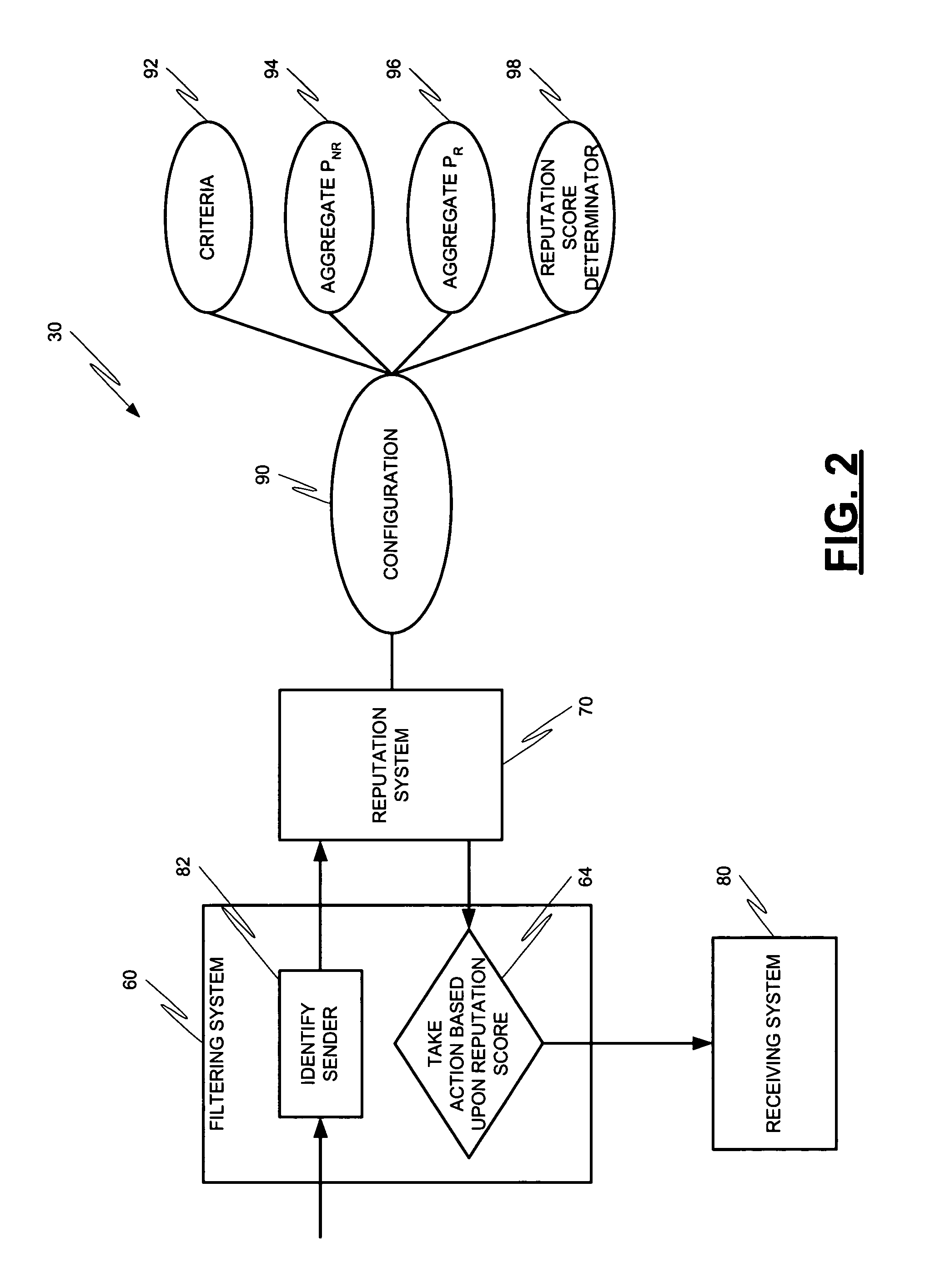
Systems and methods for classification of messaging entities
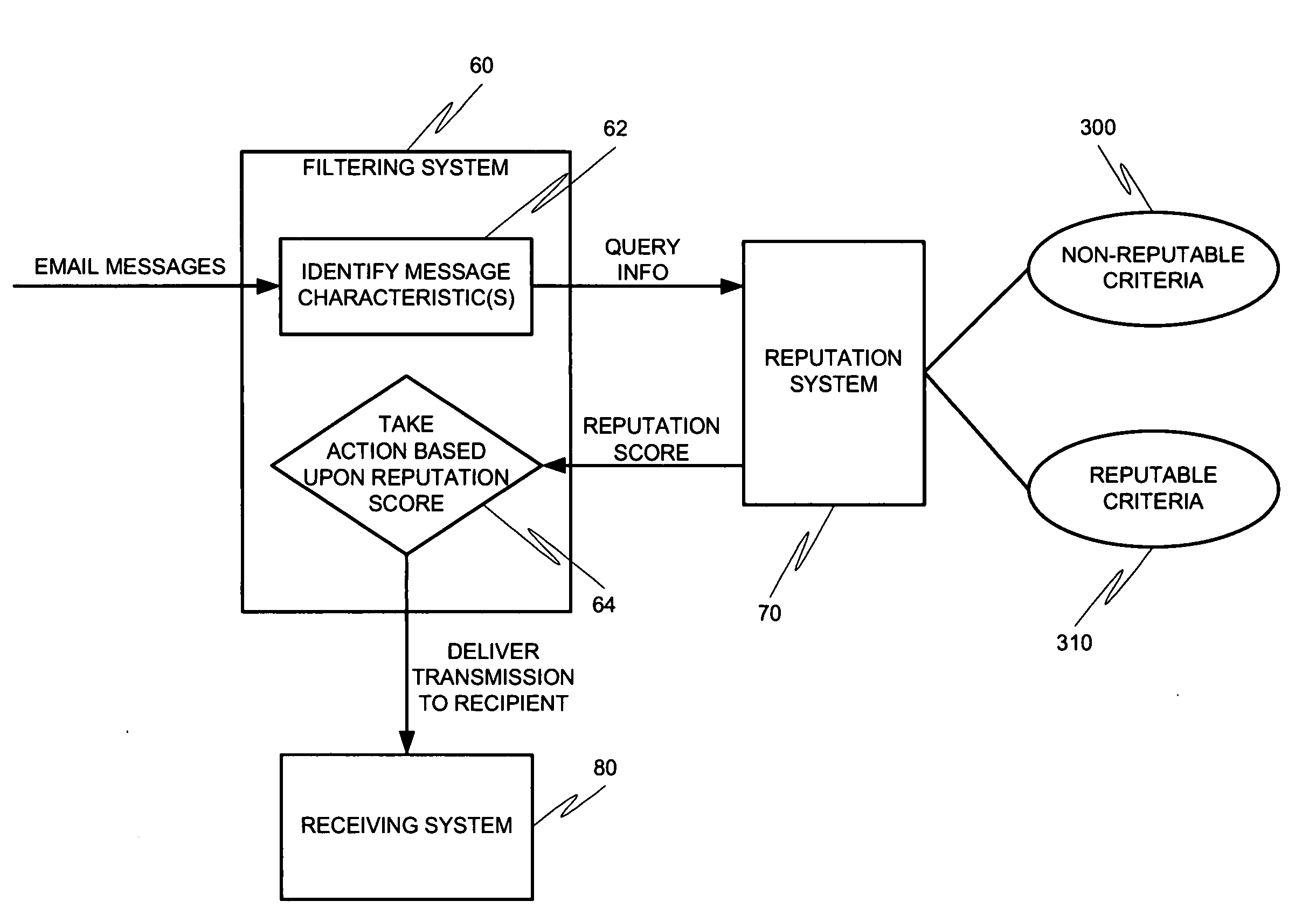
InactiveUS20060015942A1Memory loss protectionUser identity/authority verificationData treatmentMessage passing
Methods and systems for operation upon one or more data processors for assigning a reputation to a messaging entity. A method can include receiving data that identifies one or more characteristics related to a messaging entity's communication. A reputation score is determined based upon the received identification data. The determined reputation score is indicative of reputation of the messaging entity. The determined reputation score is used in deciding what action is to be taken with respect to a communication associated with the messaging entity.
Owner:MCAFEE INC
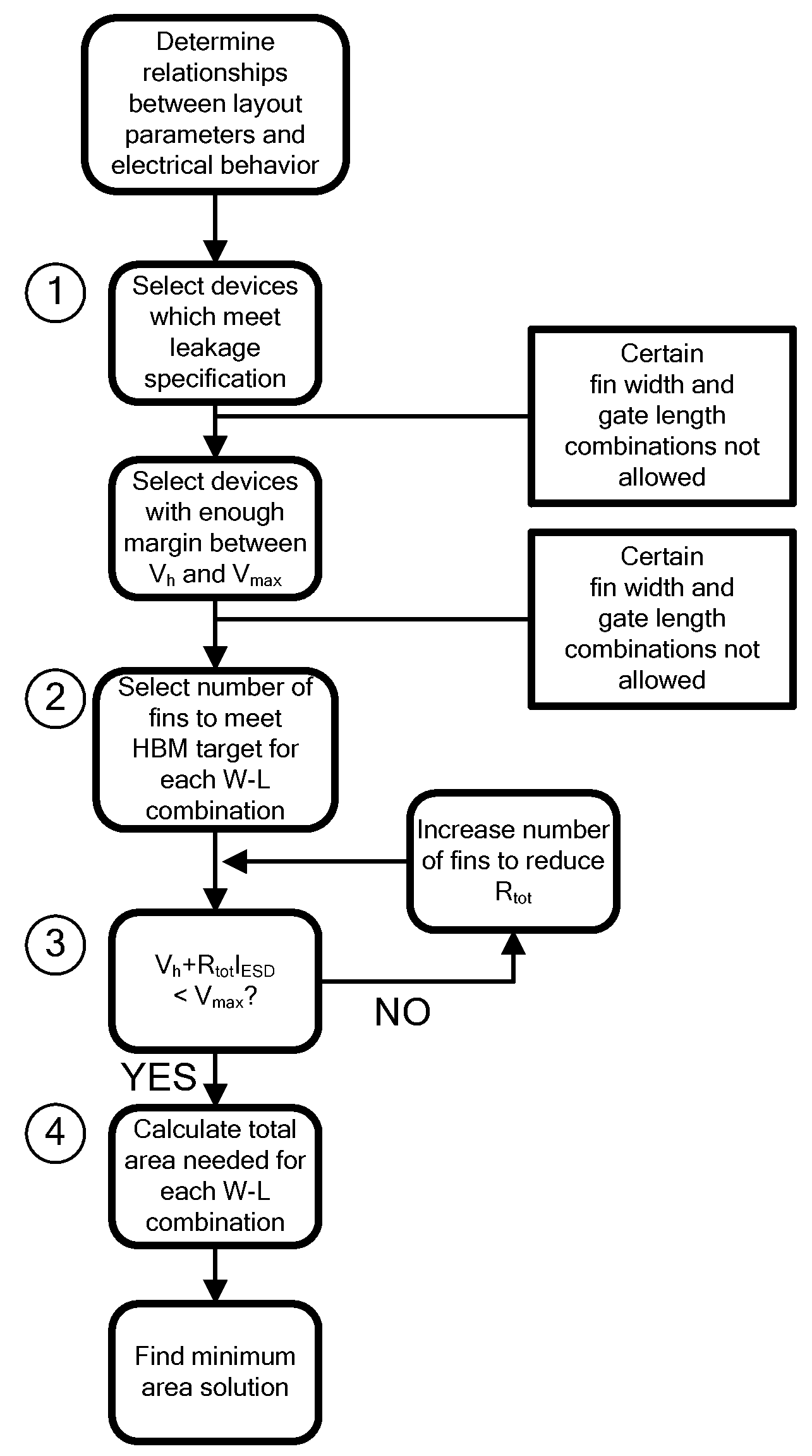
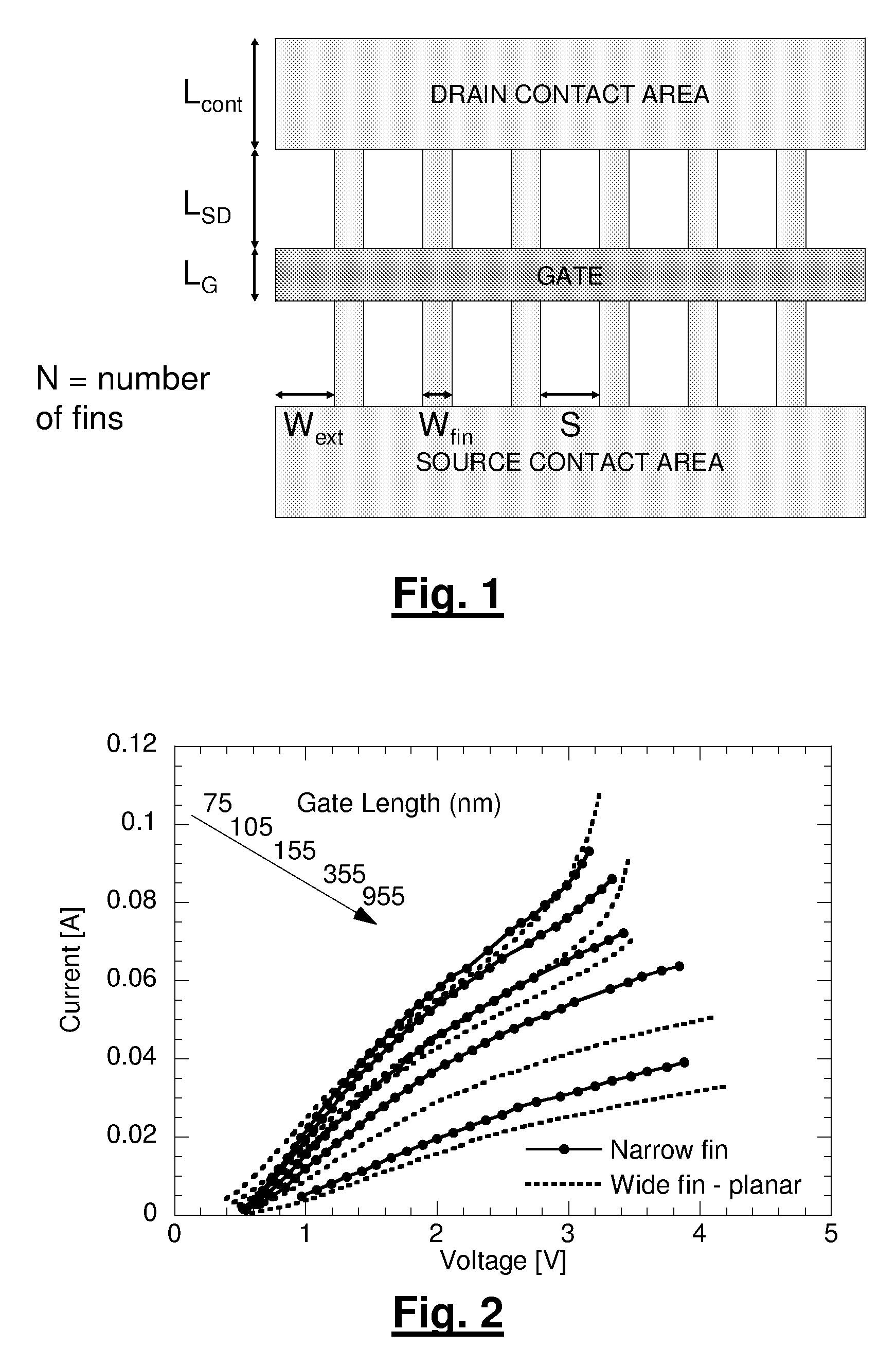
Design Methodology for MuGFET ESD Protection Devices
InactiveUS20090280582A1Easy to optimizePromote resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyEngineering
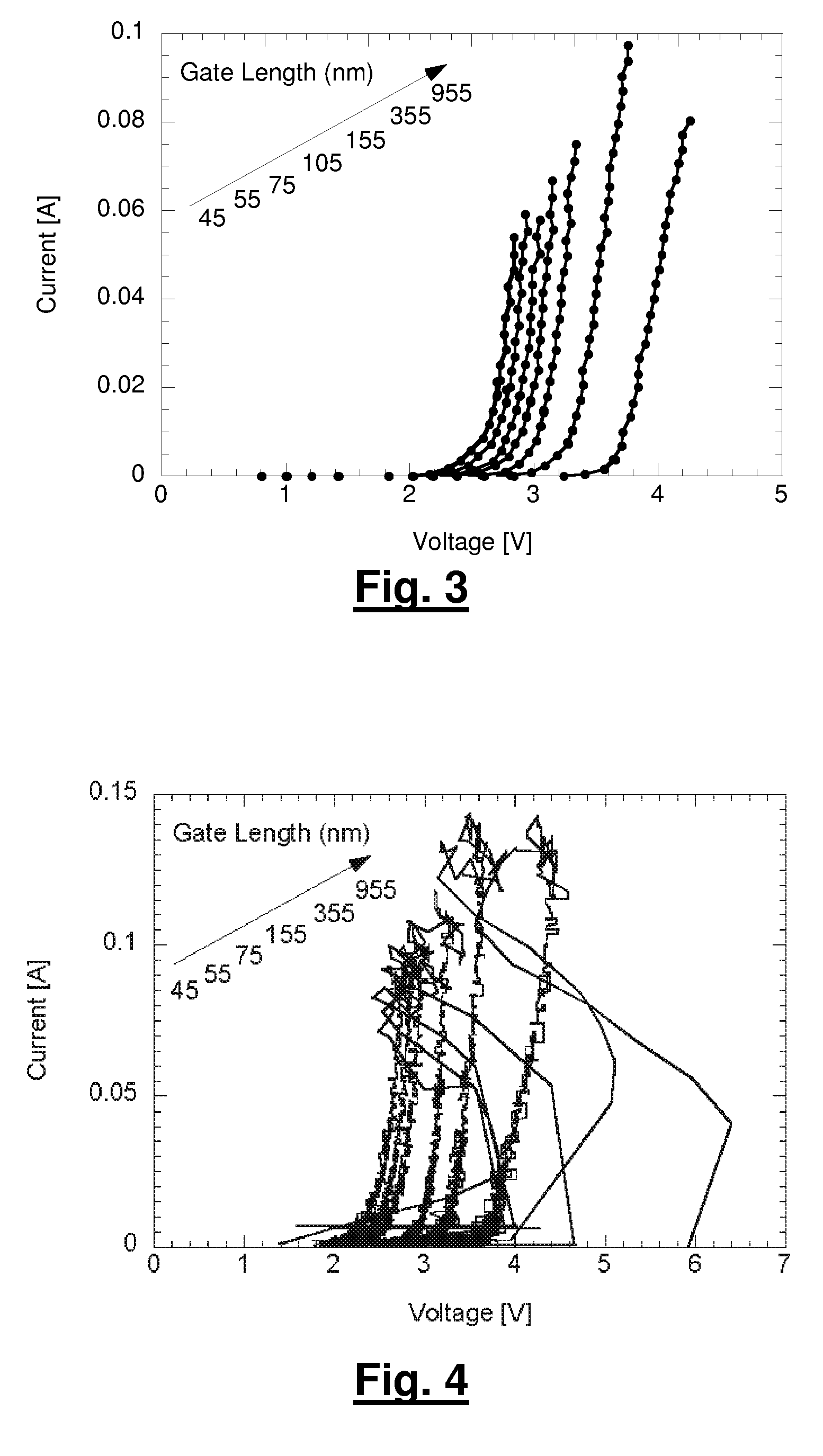
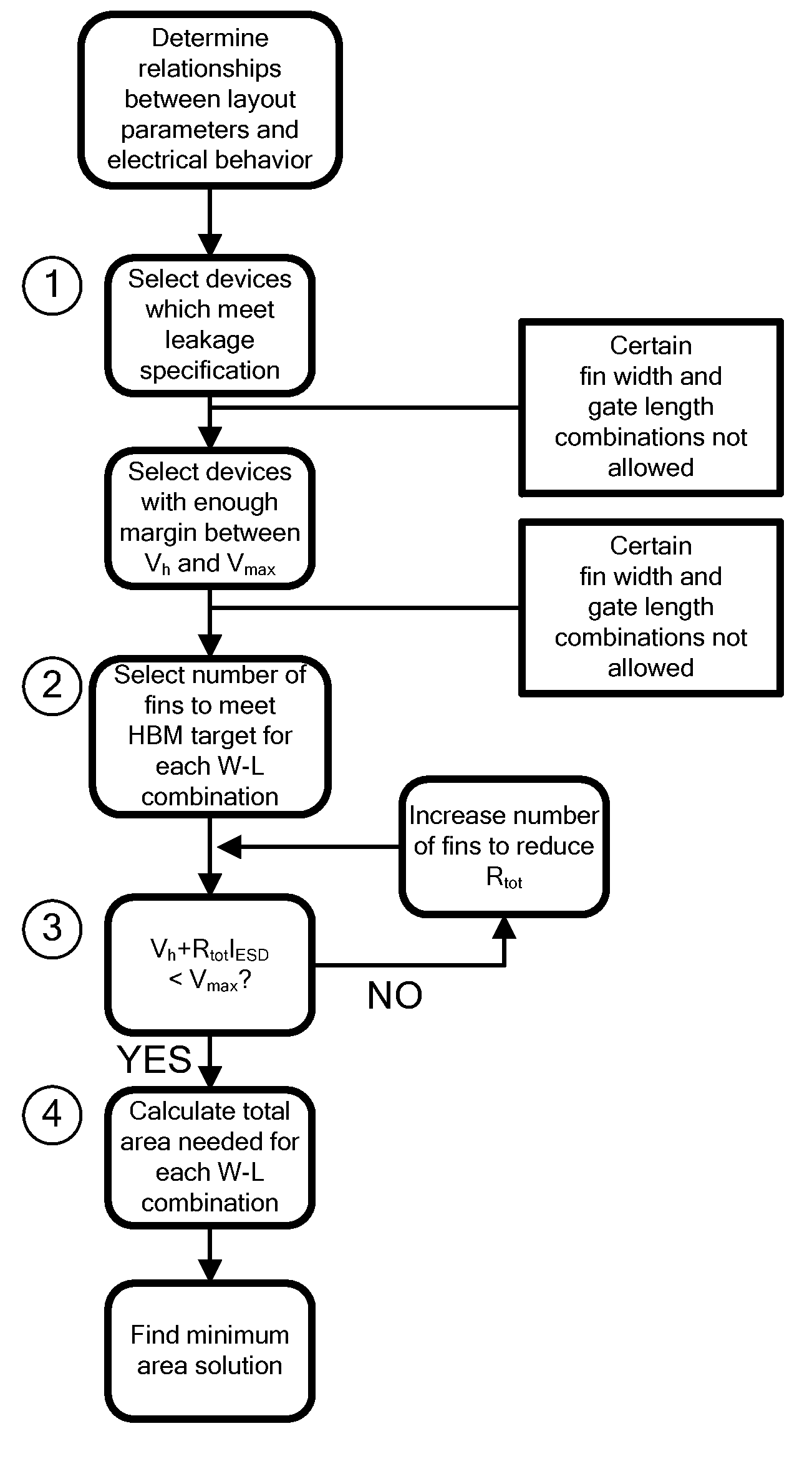
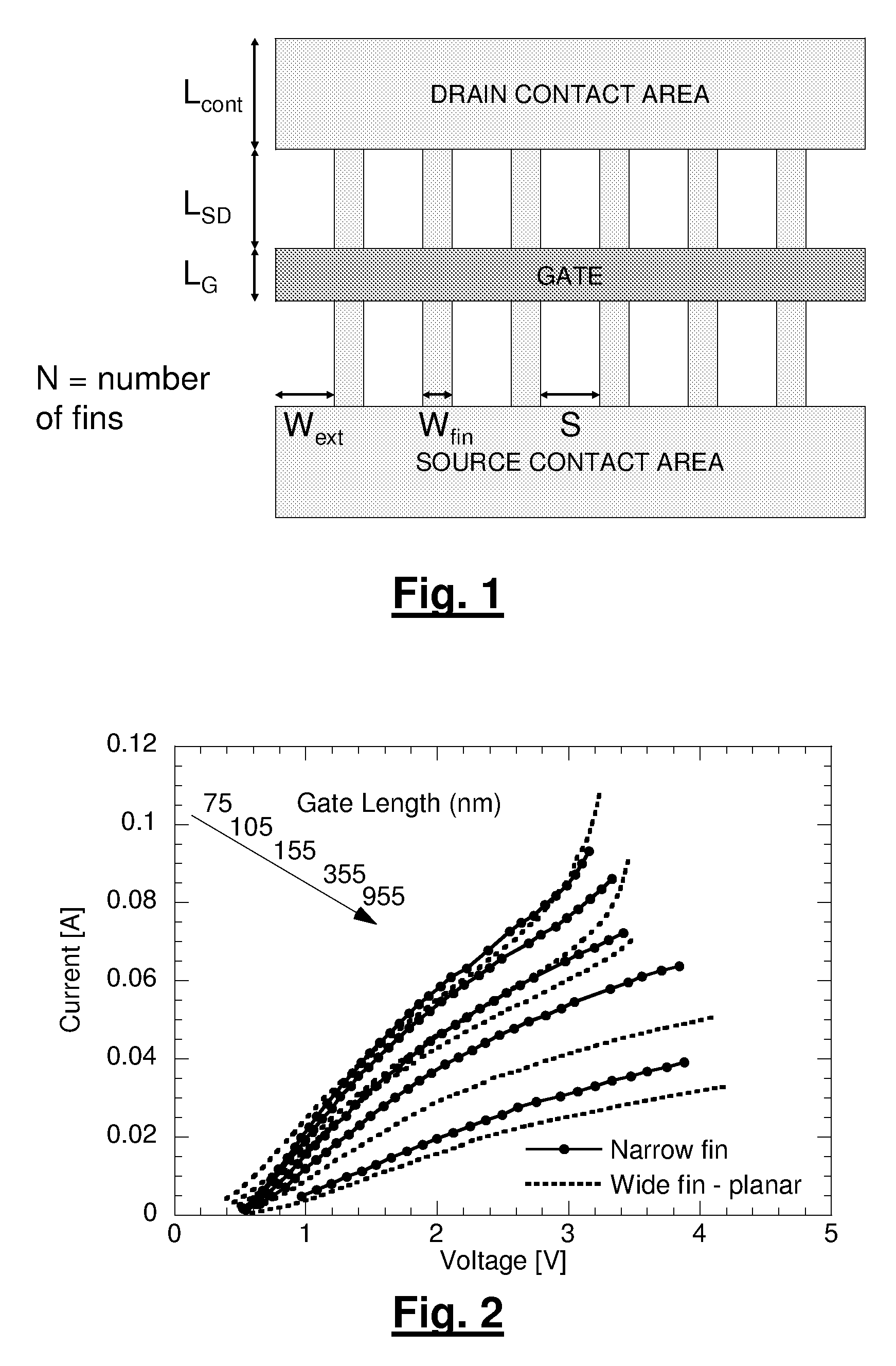
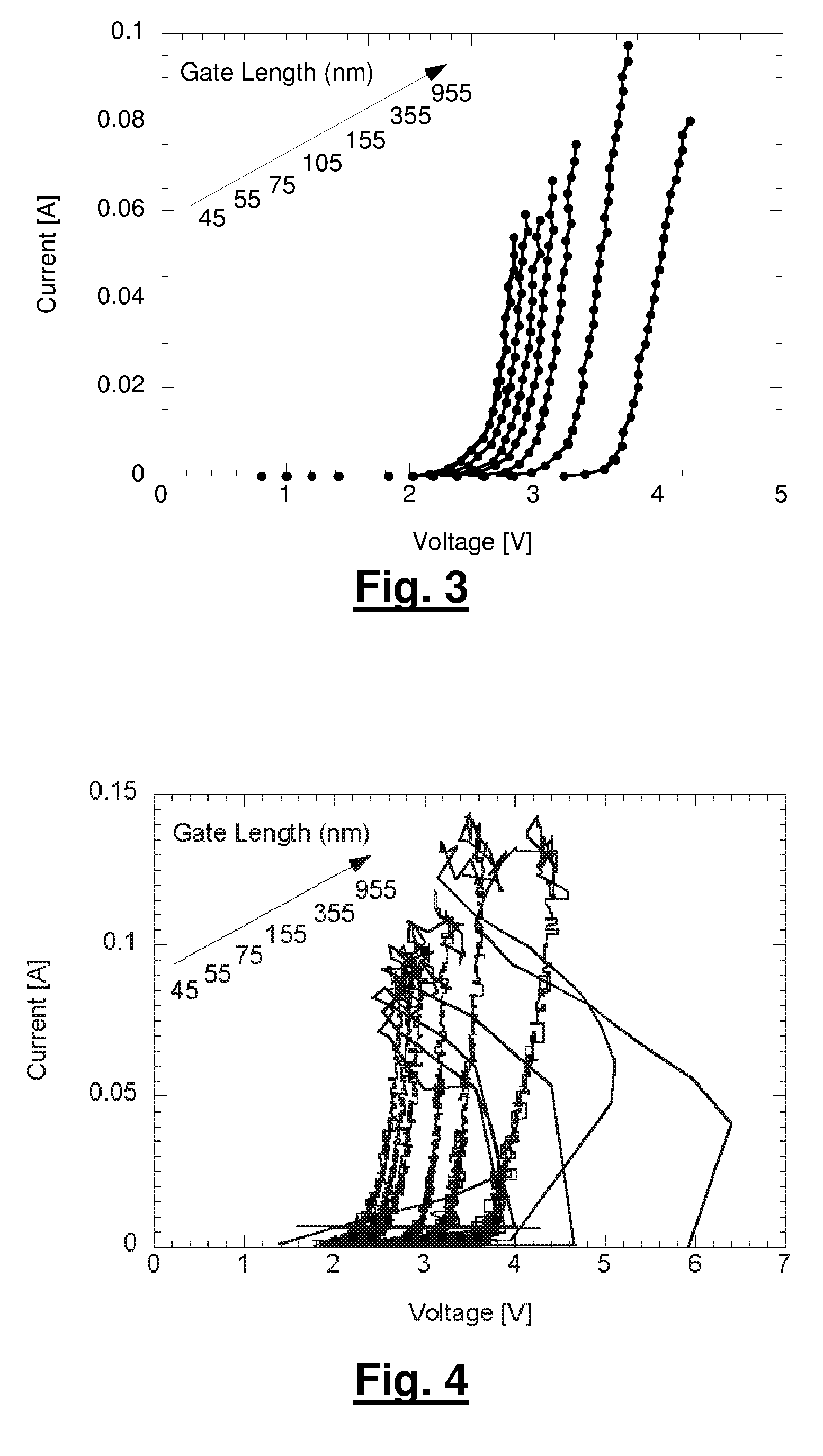
A method for manufacturing a MuGFET ESD protection device having a given layout by means of a given manufacturing process, the method comprising selecting multiple interdependent layout and process parameters of which a first set are fixed by said manufacturing process and a second set are variable, selecting multiple combinations of possible layout and process parameter values which meet predetermined ESD constraints; determining an optimum value for at least one other parameter in view of a predetermined design target apart from the predetermined ESD constraints; determining values for fin width (Wfin), gate length (LG) and number of fins (N) on the basis of the optimum value; and manufacturing said MuGFET ESD protection device using the given manufacturing and process values.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Design methodology for MuGFET ESD protection devices
InactiveUS7923266B2Promote resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyEngineering
A method for manufacturing a MuGFET ESD protection device having a given layout by means of a given manufacturing process, the method comprising selecting multiple interdependent layout and process parameters of which a first set are fixed by said manufacturing process and a second set are variable, selecting multiple combinations of possible layout and process parameter values which meet predetermined ESD constraints; determining an optimum value for at least one other parameter in view of a predetermined design target apart from the predetermined ESD constraints; determining values for fin width (Wfin), gate length (LG) and number of fins (N) on the basis of the optimum value; and manufacturing said MuGFET ESD protection device using the given manufacturing and process values.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Method for checking printability of a lithography target
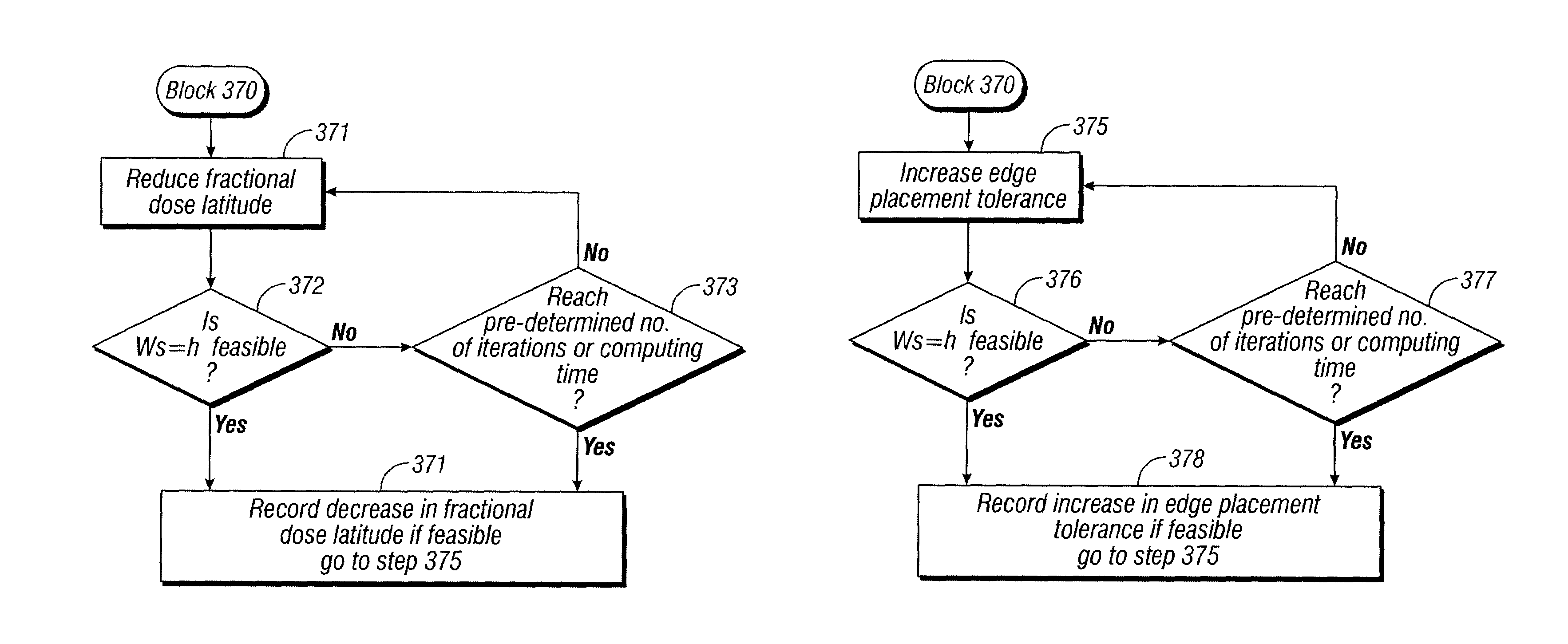
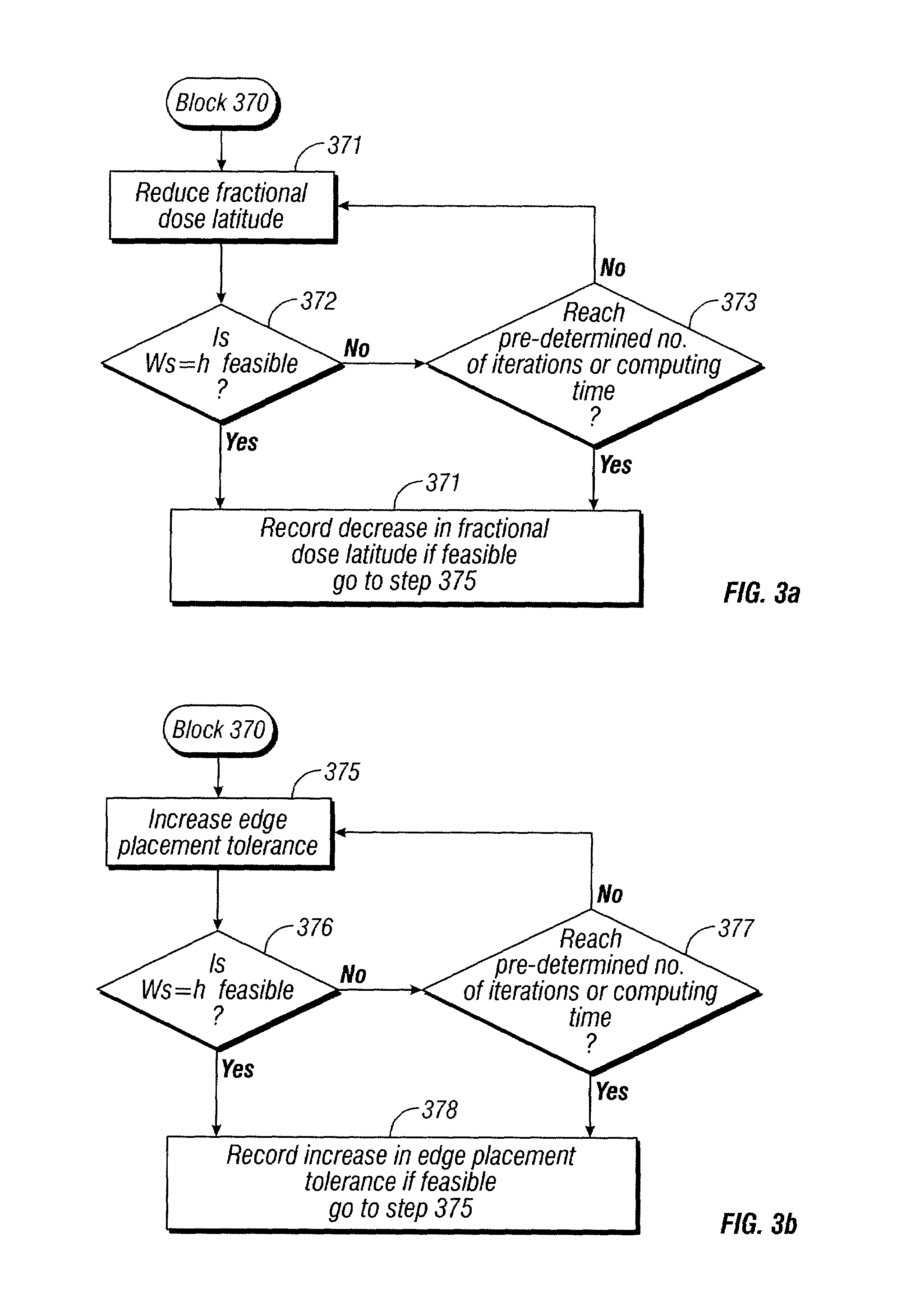
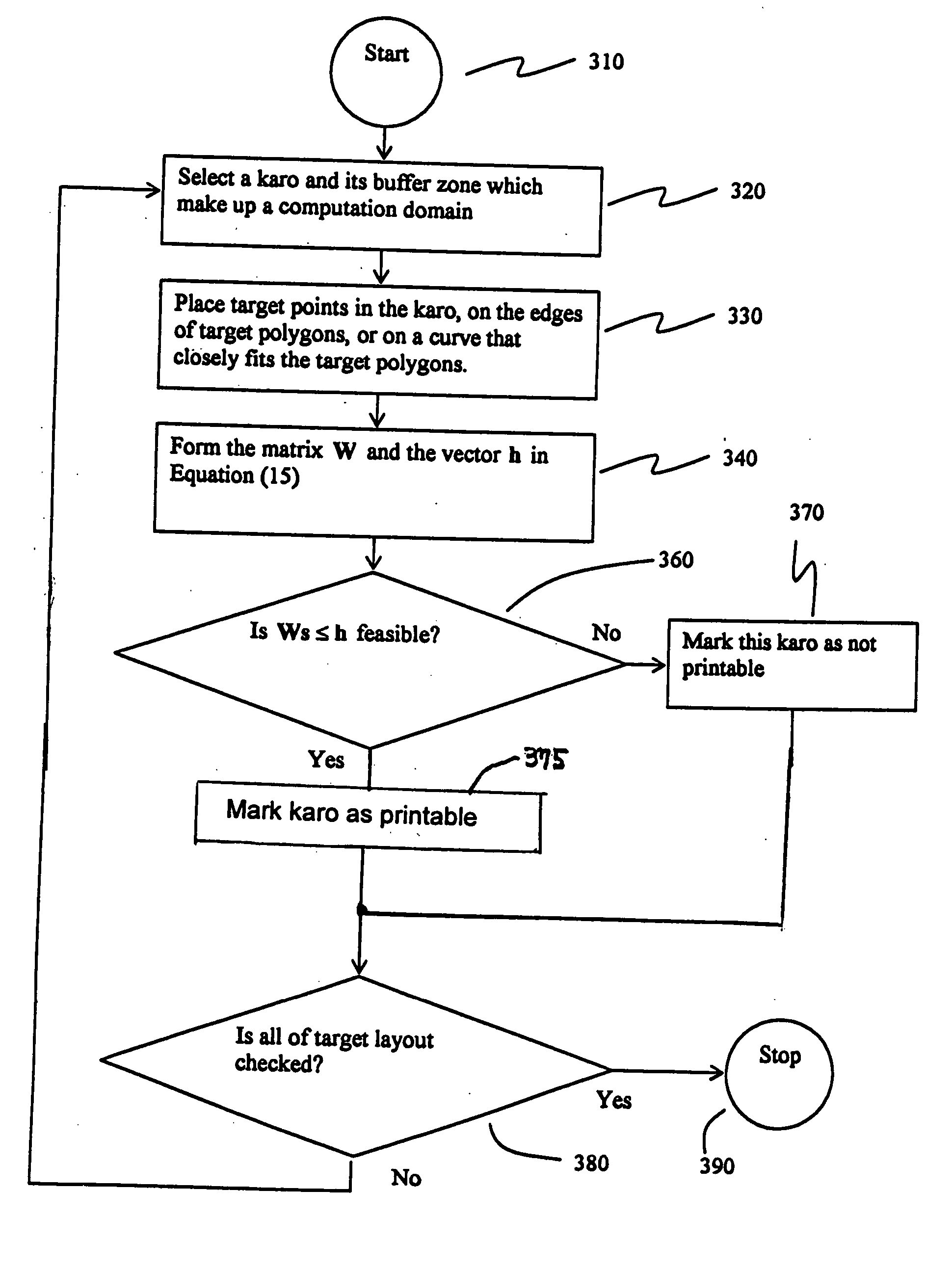
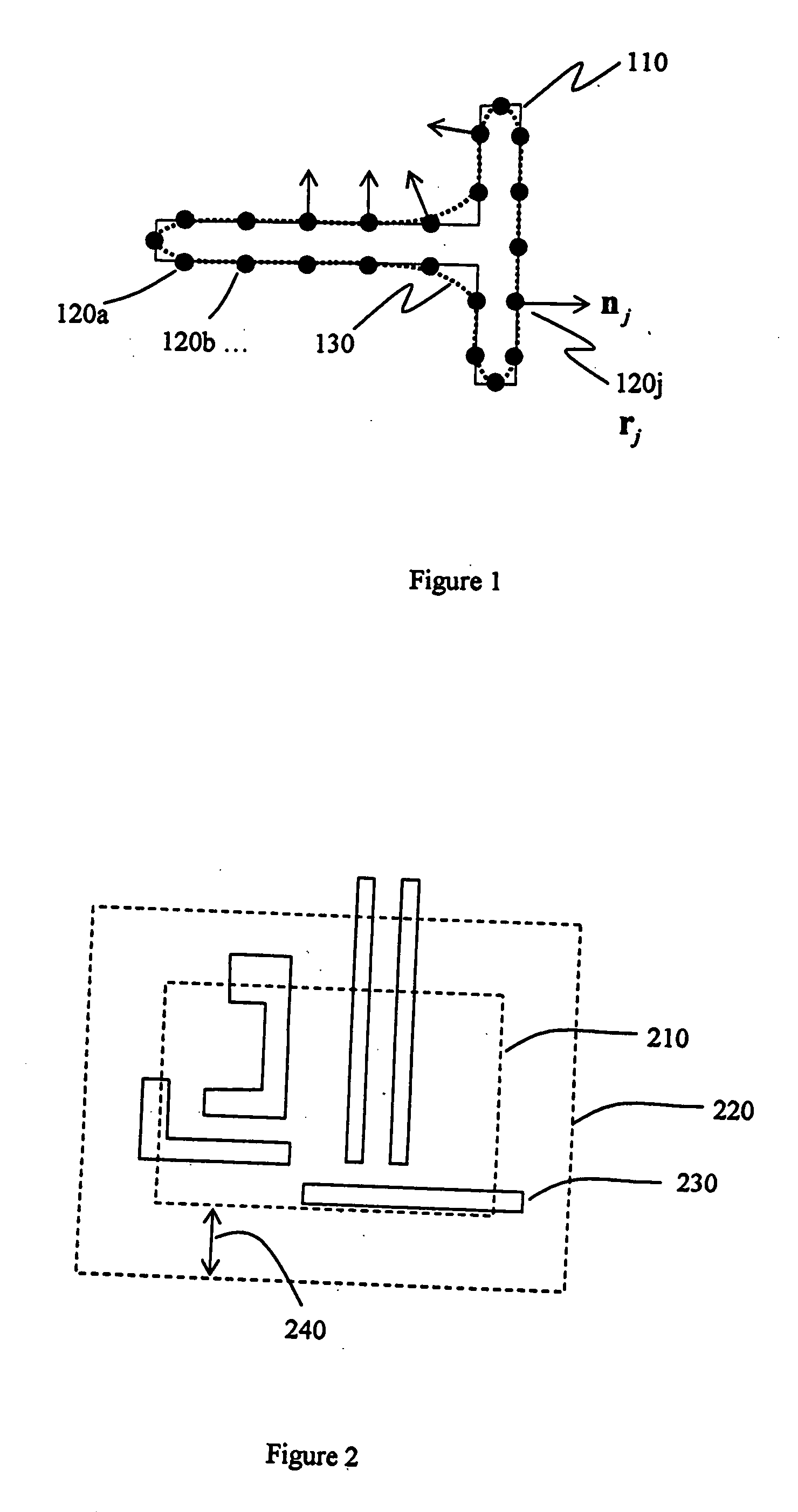
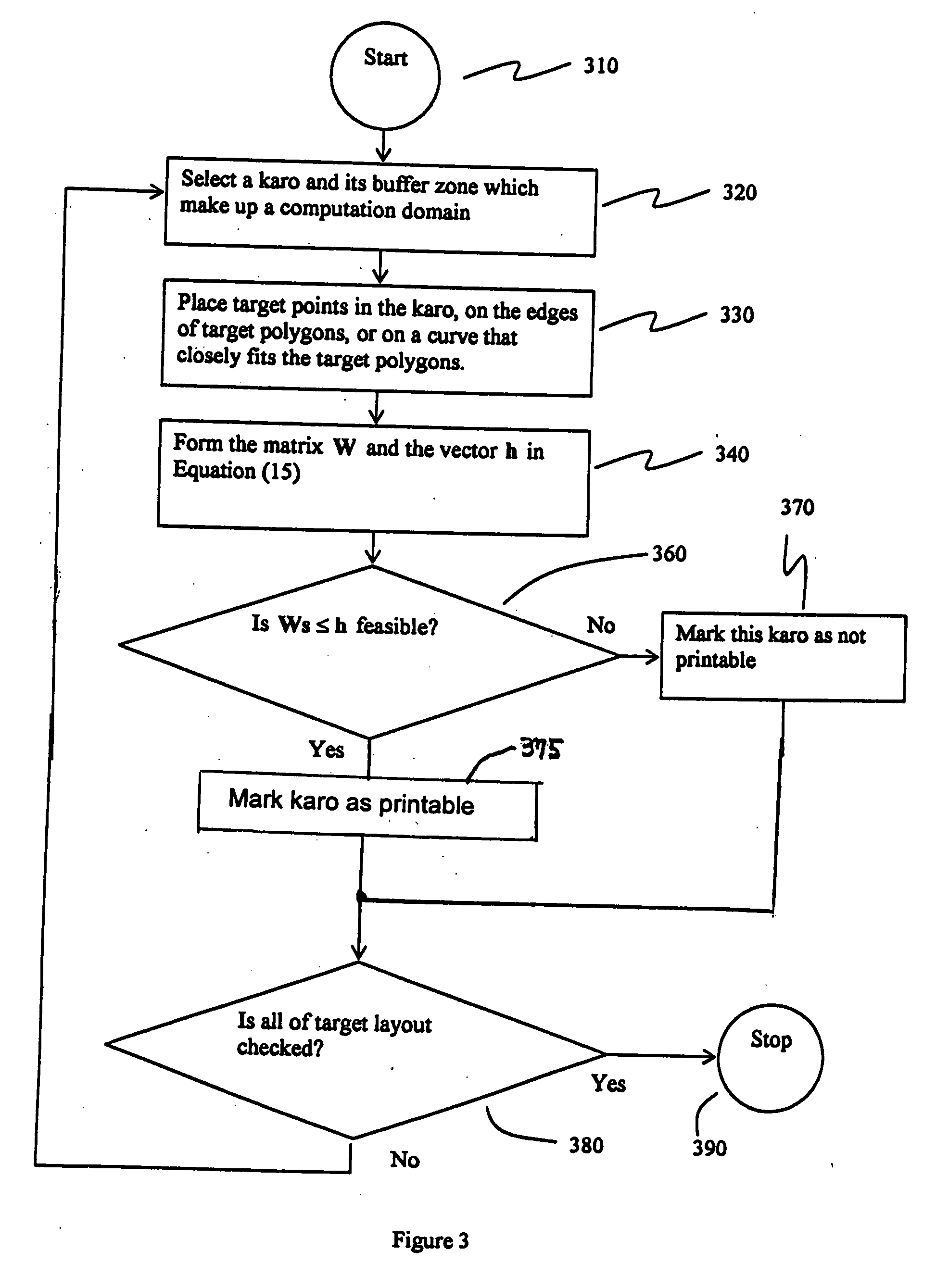
InactiveUS7568174B2Detecting faulty computer hardwarePhotomechanical apparatusOptical radiationLithographic artist
A technique for determining, without having to perform optical proximity correction, when the result of optical proximity correction will fail to meet the design requirements for printability. A disclosed embodiment has application to a process for producing a photomask for use in the printing of a pattern on a wafer by exposure with optical radiation to optically image the photomask on the wafer. A method is set forth for checking the printability of a target layout proposed for defining the photomask, including the following steps: deriving a system of inequalities that expresses a set of design requirements with respect to the target layout; and checking the printability of the target layout by determining whether the system of inequalities is feasible.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method for checking printability of a lithography target
InactiveUS20070094634A1Detecting faulty computer hardwarePhotomechanical apparatusOptical radiationLithographic artist
A technique for determining, without having to perform optical proximity correction, when the result of optical proximity correction will fail to meet the design requirements for printability. A disclosed embodiment has application to a process for producing a photomask for use in the printing of a pattern on a wafer by exposure with optical radiation to optically image the photomask on the wafer. A method is set forth for checking the printability of a target layout proposed for defining the photomask, including the following steps: deriving a system of inequalities that expresses a set of design requirements with respect to the target layout; and checking the printability of the target layout by determining whether the system of inequalities is feasible.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Methods and systems for content detection in a reconfigurable hardware
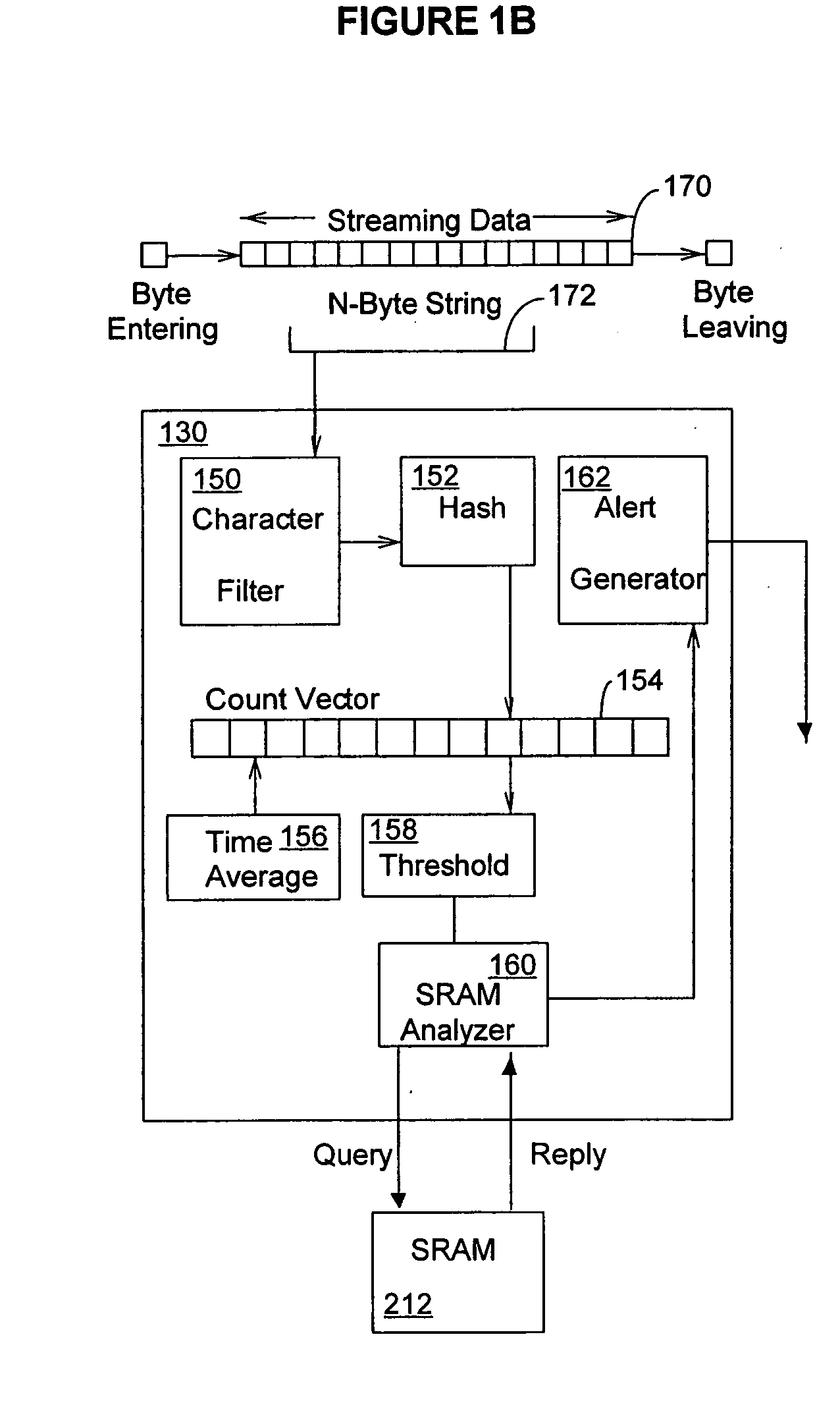
InactiveUS20060053295A1Improve throughputMaintain throughputMemory loss protectionPublic key for secure communicationDuplicate contentHash function
Methods and systems consistent with the present invention identify a repeating content in a data stream. A hash function is computed for at least one portion of a plurality of portions of the data stream. The at least one portion of the data stream has benign characters removed therefrom to prevent the identification of a benign string as the repeating content. At least one counter of a plurality of counters is incremented responsive to the computed hash function result. Each counter corresponds to a respective computed hash function result. The repeating content is identified when the at least one of the plurality of counters exceeds a count value. It is verified that the identified repeating content is not a benign string.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
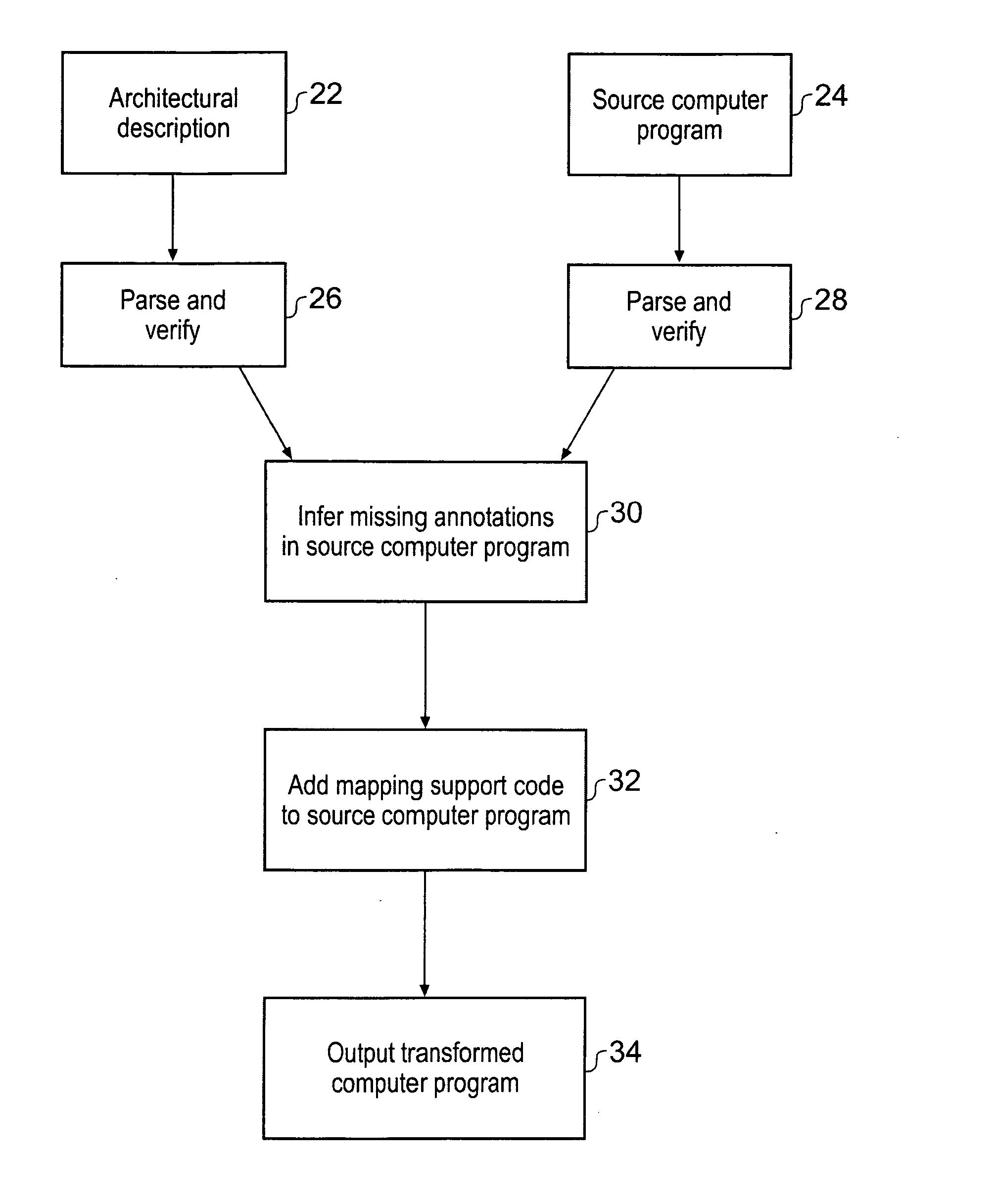
Mapping a computer program to an asymmetric multiprocessing apparatus
ActiveUS20080114937A1Quicker and less-expensiveNot easy to make mistakesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDetecting faulty computer hardwareMemory hierarchyTheoretical computer science
A computer implemented tool is provided for assisting in the mapping of a computer program to an asymmetric multiprocessing apparatus 2 incorporating an asymmetric memory hierarchy formed of a plurality of memories 12, 14. An at least partial architectural description 22, 40 is provided as an input variable to the tool and used to infer missing annotations within a source computer program 24, such as which functions are to be executed by which execution mechanisms 4, 6, 8 and which variables are to be stored within which memories 12, 14. The tool also adds mapping support commands, such as cache flush commands, cache invalidate commands, DMA move commands and the like as necessary to support the mapping of the computer program to the asymmetric multiprocessing apparatus 2.
Owner:ARM LTD
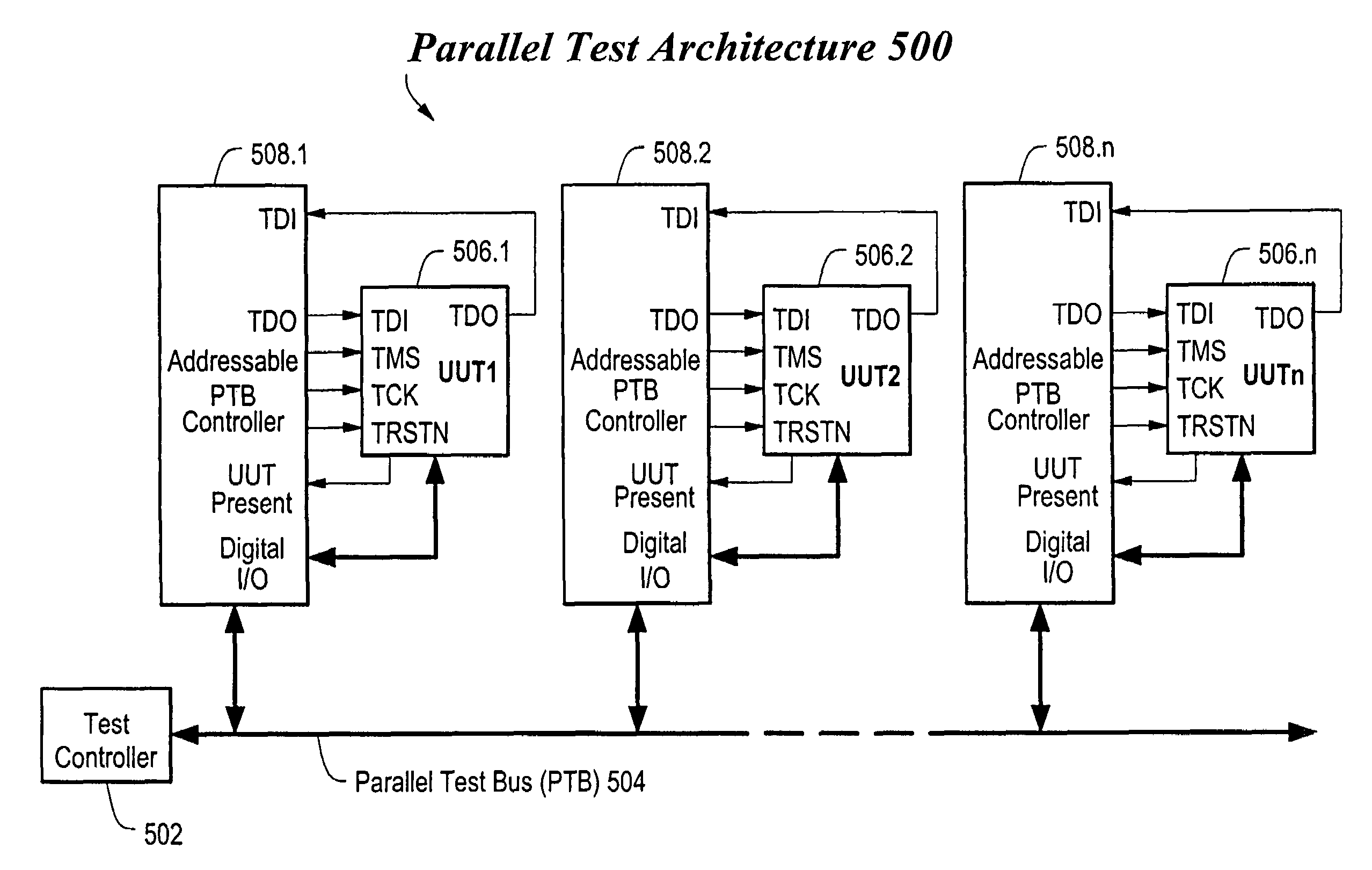
Method and apparatus for optimized parallel testing and access of electronic circuits
InactiveUS6988232B2Easy accessIncreased “ parallel ” testingElectronic circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareEngineeringElectronic circuit
An architecture that provides stimulus data and verifies the response of multiple electronic circuits substantially in parallel for optimized testing, debugging, or programmable configuration of the circuits. The architecture includes a test bus, a primary test controller connected to the bus, and a plurality of local test controllers connected to the bus, in which each local test controller is coupleable to a respective circuit. The primary test controller sends stimulus data and expected response data over the bus to the respective local test controllers to perform parallel testing, debugging or programmable configuration of the circuits. Each local test controller applies the stimulus data and verifies the circuit response against the expected response data. Further, each local test controller stores the result of the verification for later retrieval by the primary test controller.
Owner:INTELLITECH INC
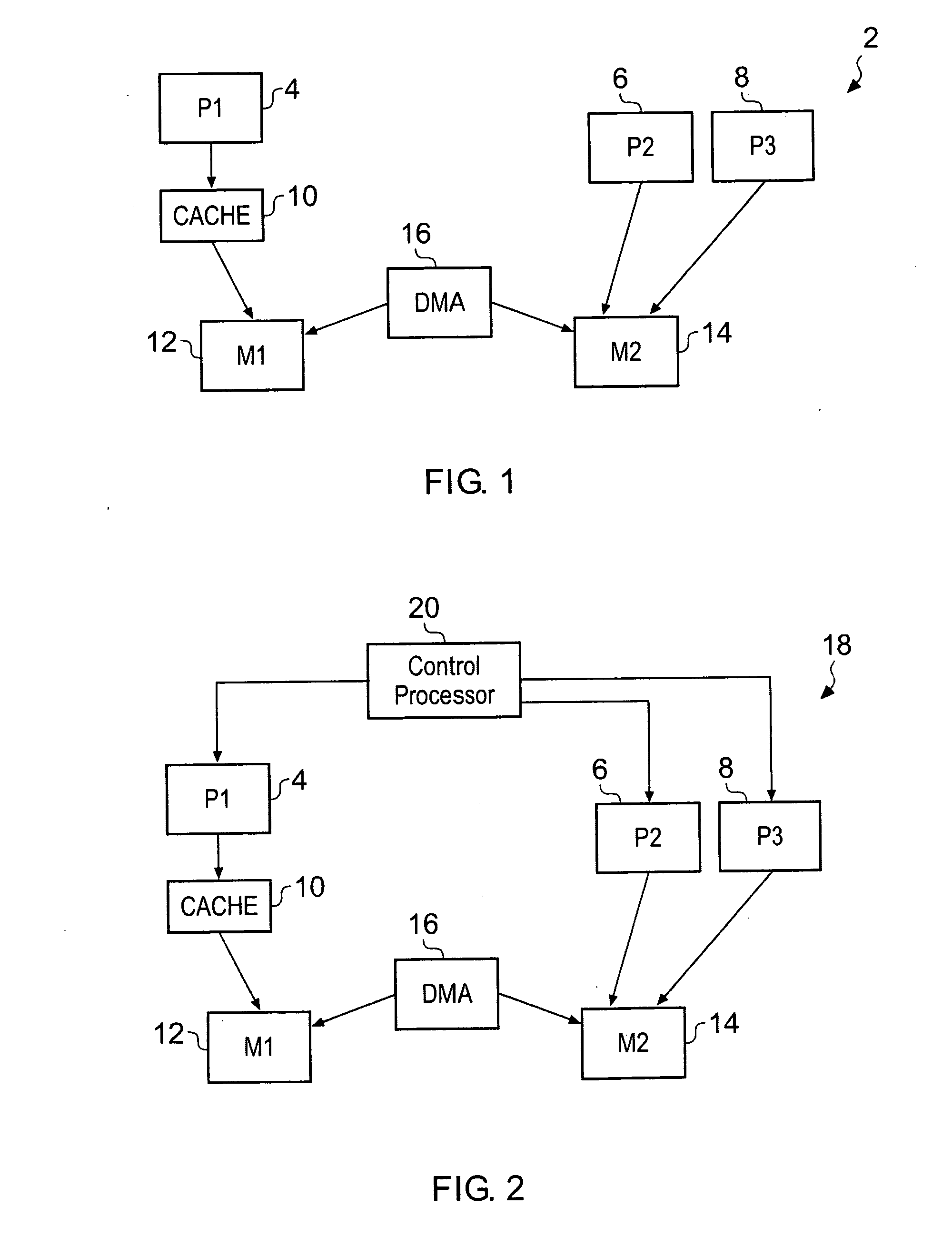
Analyzing and transforming a computer program for executing on asymmetric multiprocessing systems
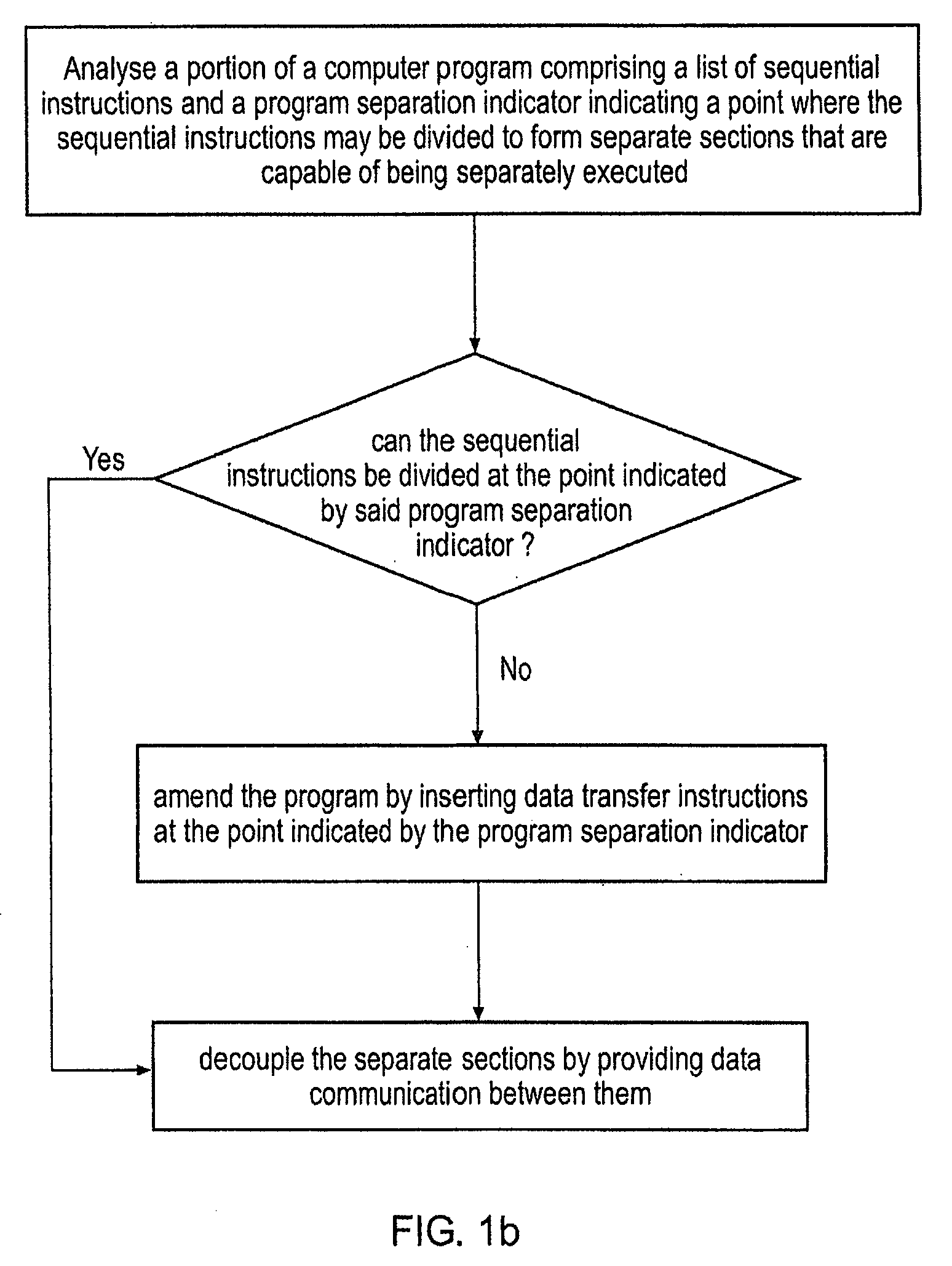
InactiveUS20080098208A1Easy to implementImprove system performanceDetecting faulty computer hardwareDigital computer detailsParallel computingData shipping
A method is disclosed for transforming a portion of a computer program comprising a list of sequential instructions comprising control code and data processing code and a program separation indicator indicating a point where said sequential instructions may be divided to form separate sections that are capable of being separately executed and that each comprise different data processing code. The m method comprises the steps of: (i) analysing said portion of said program to determine if said sequential instructions can be divided at said point indicated by said program separation indicator and in response to determining that it can: (iia) providing data communication between said separate sections indicated by said program separation indicator, such that said separate sections can be decoupled from each other, such that at least one of said sections is capable of being separately executed by an execution mechanism that is separate from an execution mechanism executing another of said separate sections, said at least one of said sections being capable of generating data and communicating said data to at least one other of said separate sections; and in response to determining it can not: (iib) not performing step (iia). If step (iia) is not performed then a warning may be output, or the program may be amended so it can be separated at that point, or the program separation indicator may be removed and the sections that were to be separated merged.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
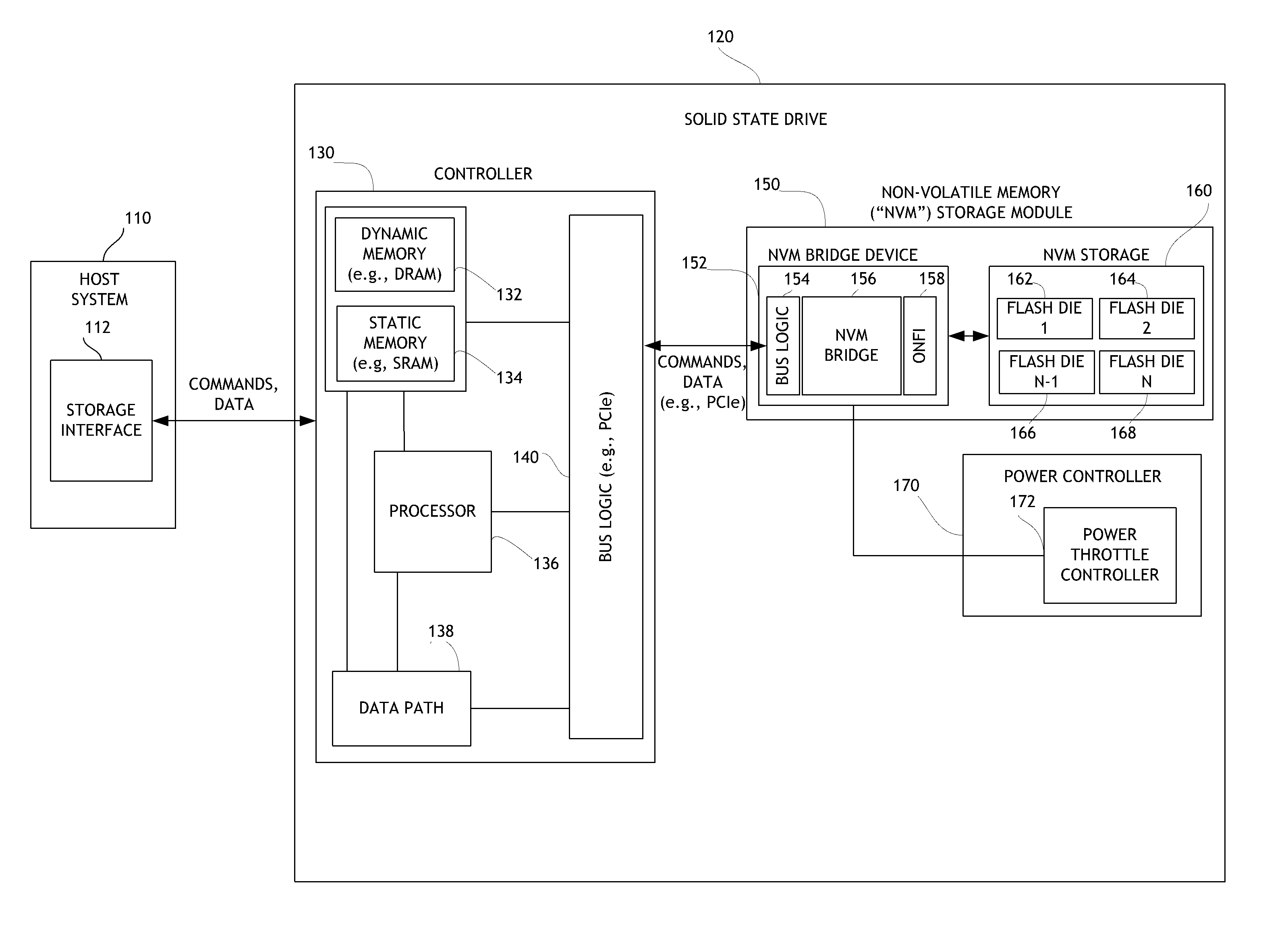
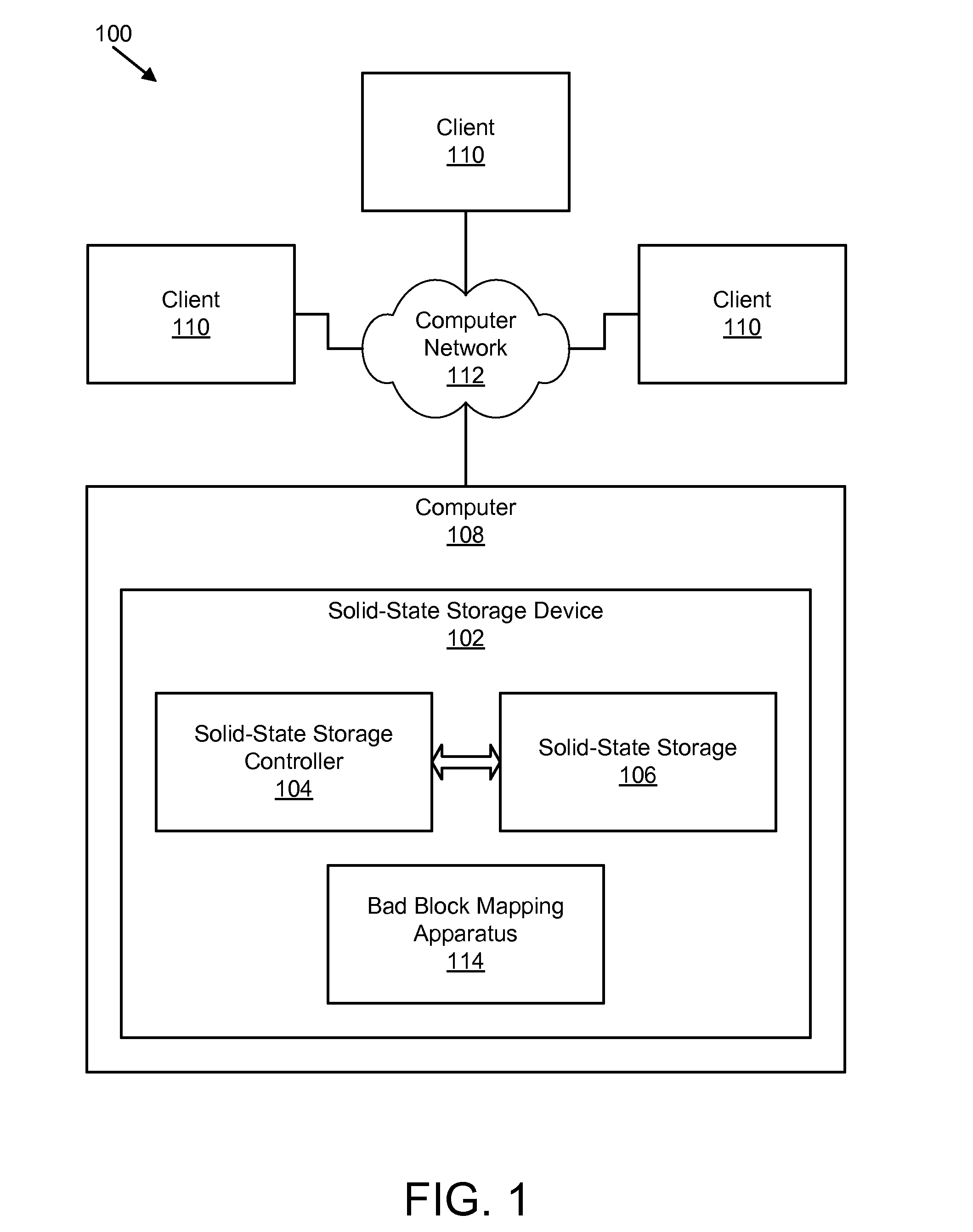
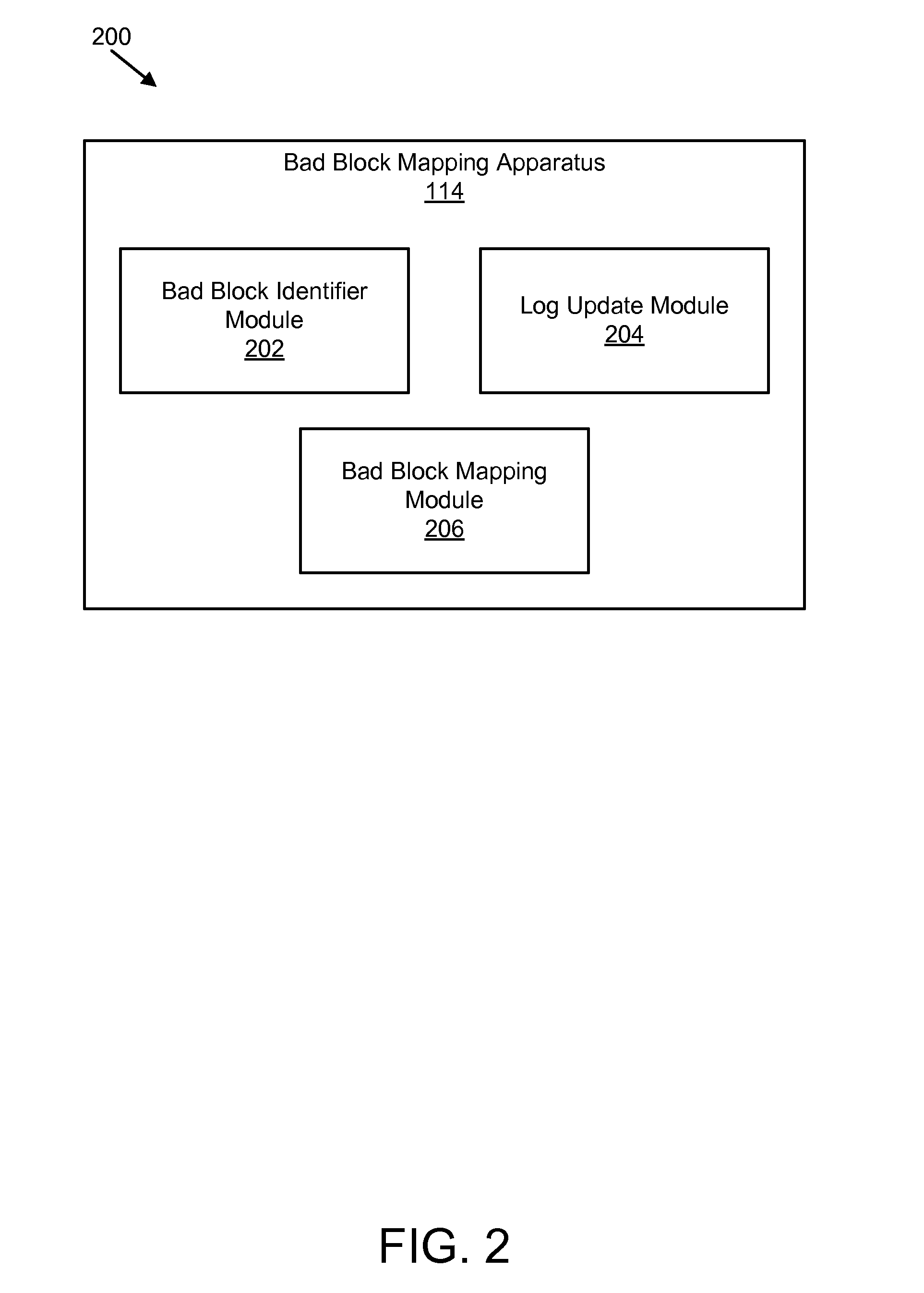
Apparatus, system, and method for bad block remapping
ActiveUS20090282301A1Improve reliabilityAvoid managementMemory architecture accessing/allocationError preventionSolid-state storageParallel computing
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for bad block remapping. A bad block identifier module identifies one or more data blocks on a solid-state storage element as bad blocks. A log update module writes at least a location of each bad block identified by the bad block identifier module into each of two or more redundant bad block logs. A bad block mapping module accesses at least one bad block log during a start-up operation to create in memory a bad block map. The bad block map includes a mapping between the bad block locations in the bad block log and a corresponding location of a replacement block for each bad block location. Data is stored in each replacement block instead of the corresponding bad block. The bad block mapping module creates the bad block map using one of a replacement block location and a bad block mapping algorithm.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
System and method for debugging a software program
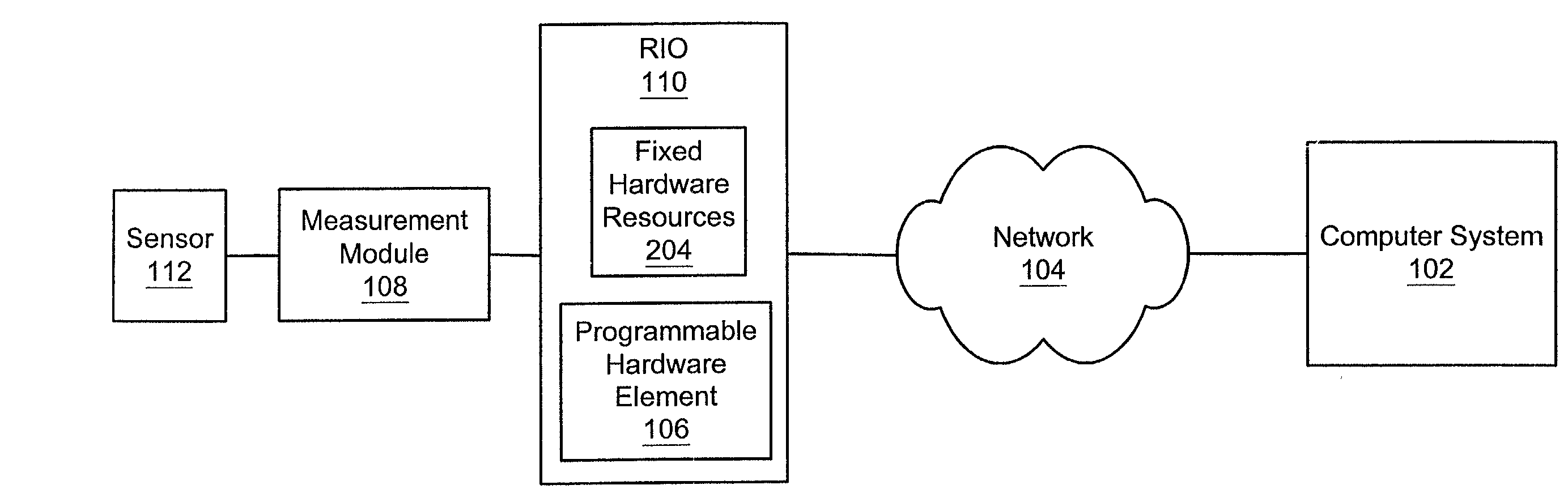
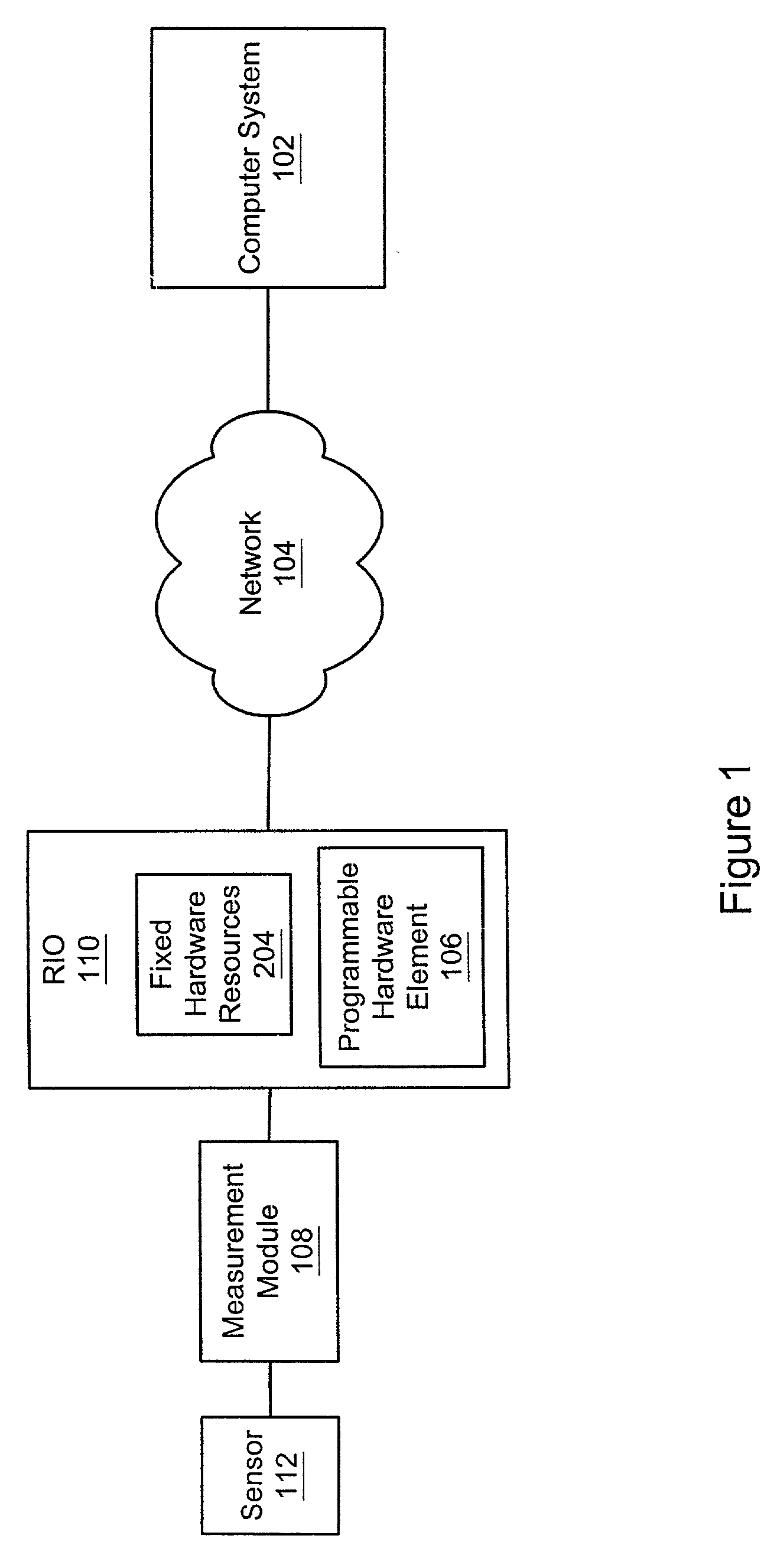
InactiveUS20030192032A1Fast and Accurate TestingAccurate and efficient matchingDetecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designComputerized systemProgrammable hardware
A system and method for debugging a program which is intended to execute on a reconfigurable device. A computer system stores a program that specifies a function, and which is convertible into a hardware configuration program (HCP) and deployable onto a programmable hardware element comprised on the device. The HCP is generated based on the program, specifies a configuration for the programmable hardware element that implements the function, and further specifies usage of one or more fixed hardware resources by the programmable hardware element in performing the function. A test configuration is deployable on the programmable hardware element by a deployment program, where, after deployment, the programmable hardware element provides for communication between the fixed hardware resources and the program. The program is executable by a processor in the computer system, where during execution the program communicates with the one or more fixed hardware resources through the programmable hardware element.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
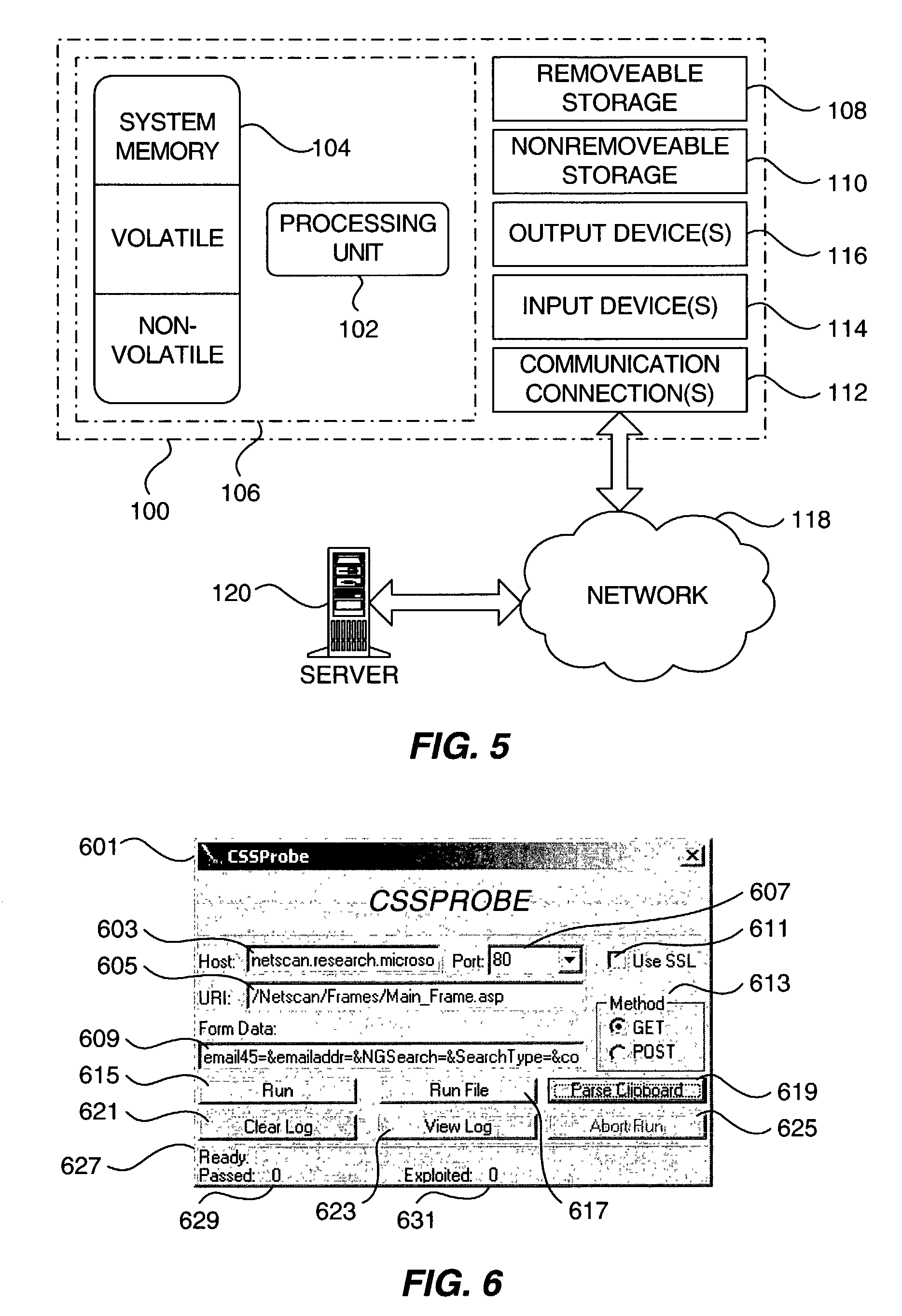
Automated detection of cross site scripting vulnerabilities
An automated method and system for testing a web site for vulnerability to a cross site scripting (XSS) attack are disclosed. The automated tool injects a tracer value into both GET and POST form data, and monitors the resultant HTML to determine whether the tracer value is returned to the local machine by the server to which it was sent. If the tracer value is returned, the automated tool attempts to exploit the web site by injecting a non-malicious script as part of an input value for some form data, based on the location in the returned HTML in which the returned tracer value was found. If the exploit is successful, as indicated by the non-malicious script, the automated tool logs the exploit to a log file that a user can review at a later time, e.g., to assist in debugging the web site.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
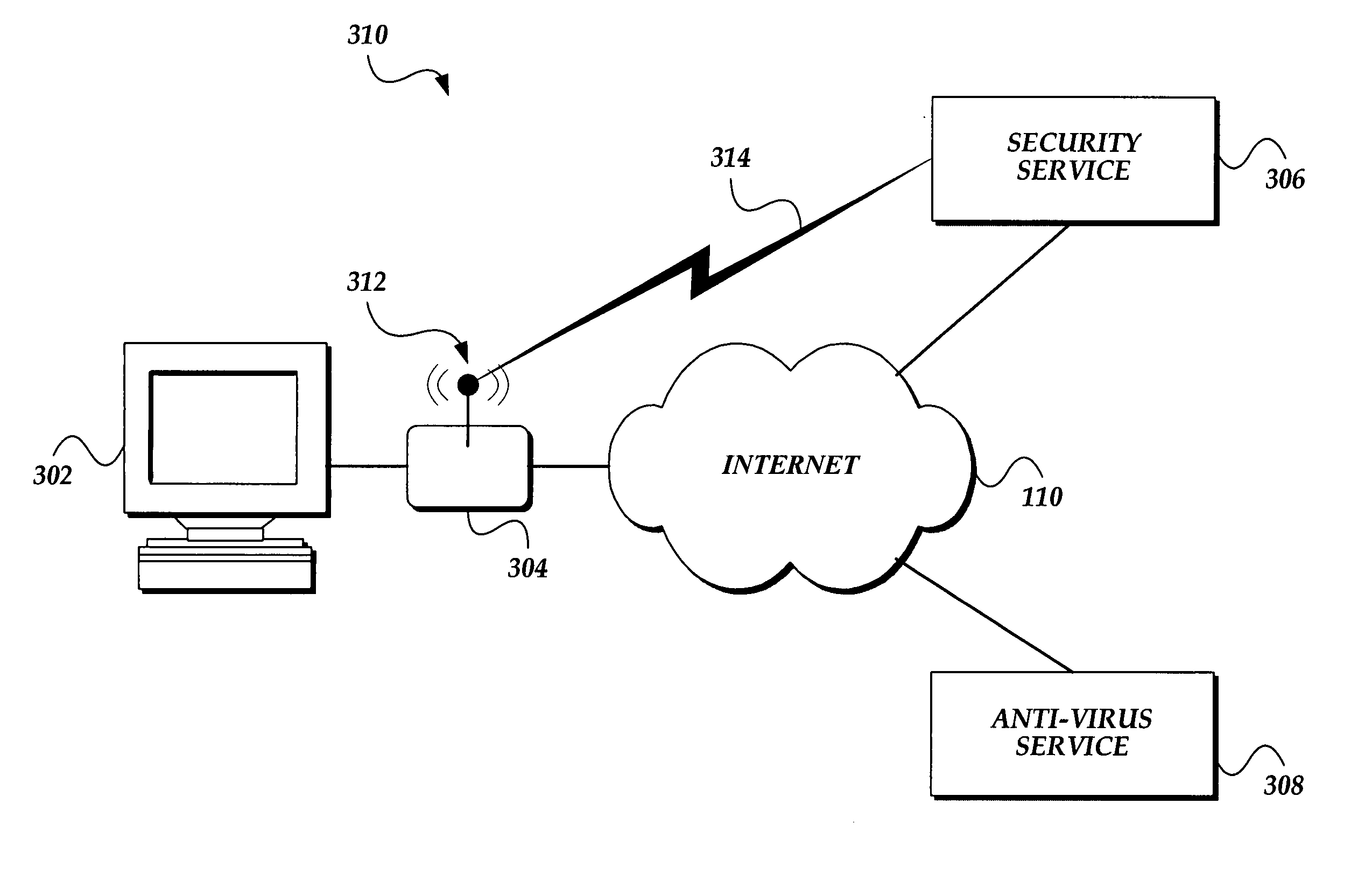
Network security device and method for protecting a computing device in a networked environment
ActiveUS20060095965A1Memory loss protectionDetecting faulty computer hardwareNetwork activitySecurity Measure
A network security module for protecting computing devices connected to a communication network from security threats is presented. The network security module is interposed, either logically or physically, between the protected computer and the communication network. The network security module receives security information from a security service. The security information comprises security measures which, when enforced by the network security module, protect the computer from a security threat to the computer. The network security module implements the security measures by controlling the network activities between the protected computer and the network. The network security module also temporarily implements security patches until corresponding patches are installed onto the protected computer.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
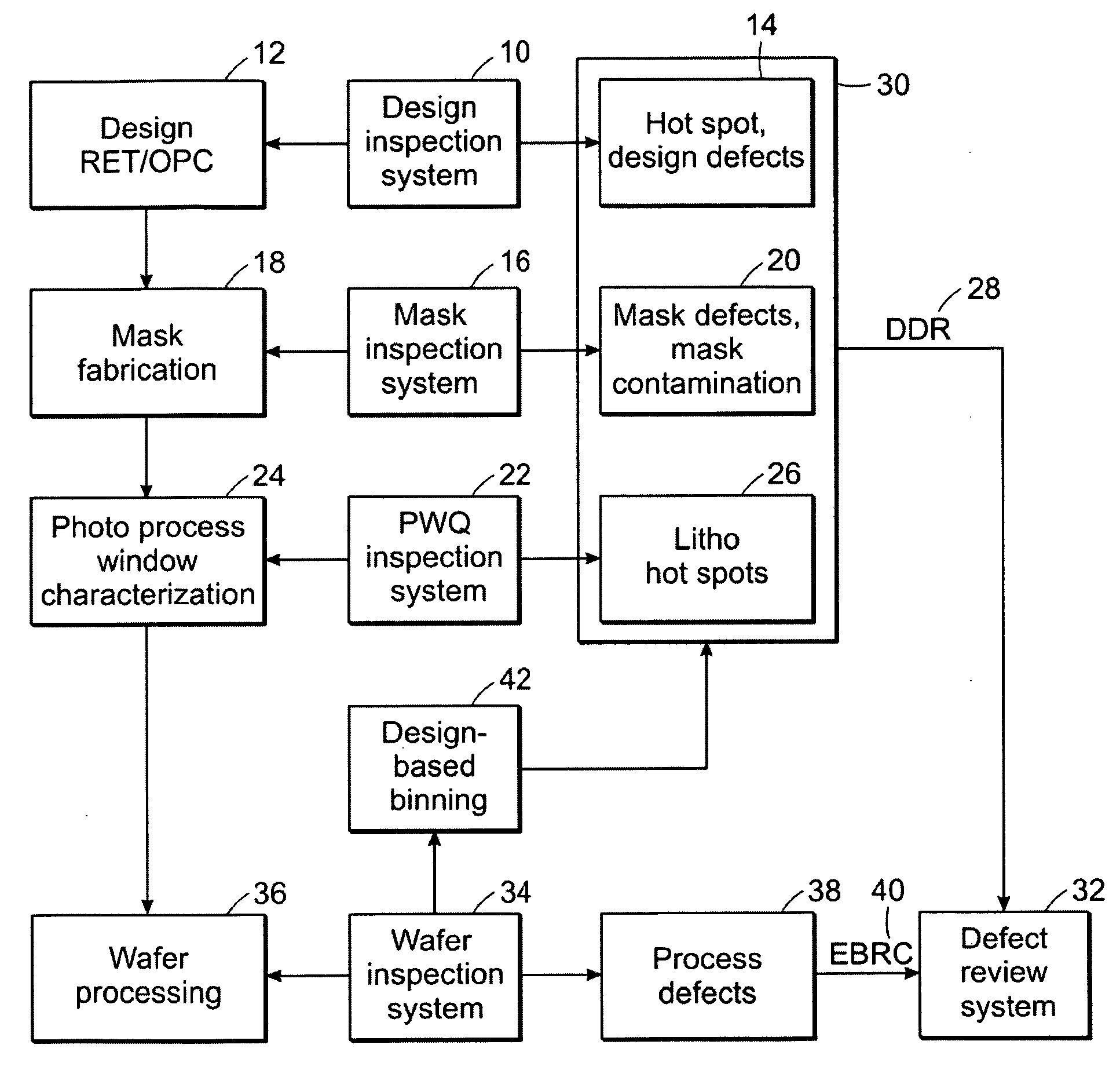
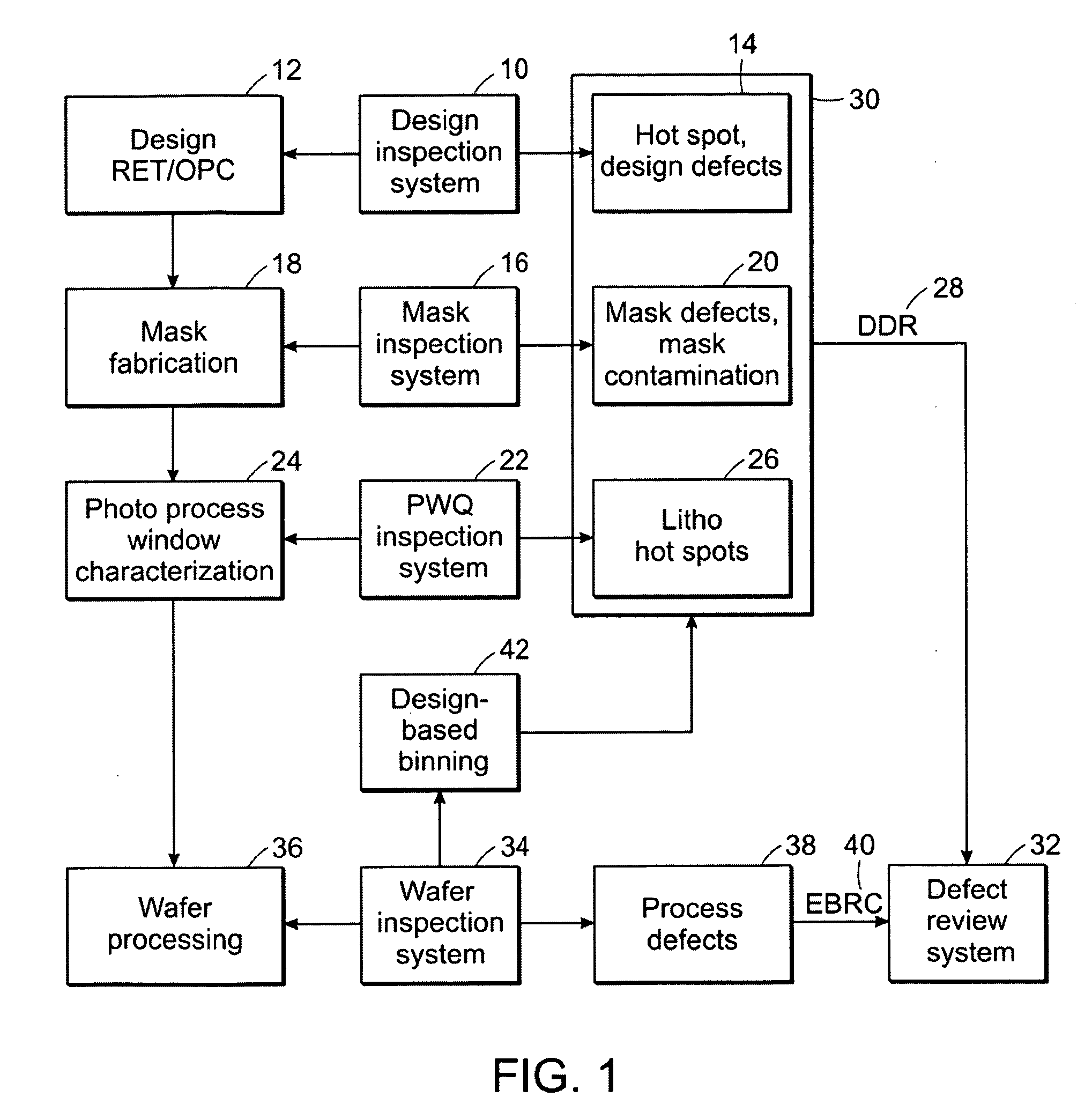
Methods, designs, defect review tools, and systems for determining locations on a wafer to be reviewed during defect review
ActiveUS20080163140A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceDetecting faulty computer hardwareWaferingSoftware engineering
Various methods, designs, defect review tools, and systems for determining locations on a wafer to be reviewed during defect review are provided. One computer-implemented method includes acquiring coordinates of defects detected by two or more inspection systems. The defects do not include defects detected on the wafer. The method also includes determining coordinates of the locations on the wafer to be reviewed during the defect review by translating the coordinates of the defects into the coordinates on the wafer such that results of the defect review performed at the locations can be used to determine if the defects cause systematic defects on the wafer.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
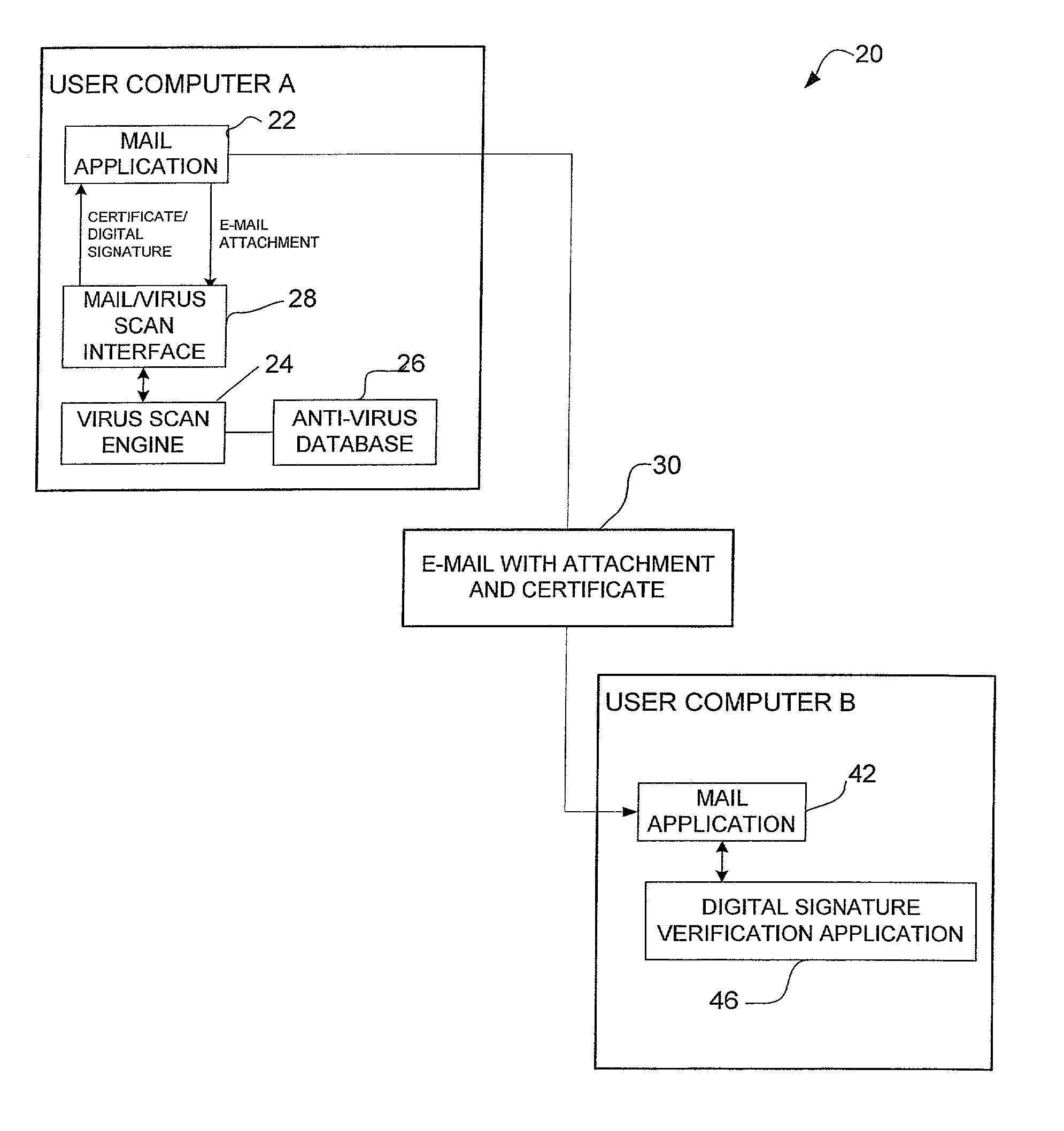
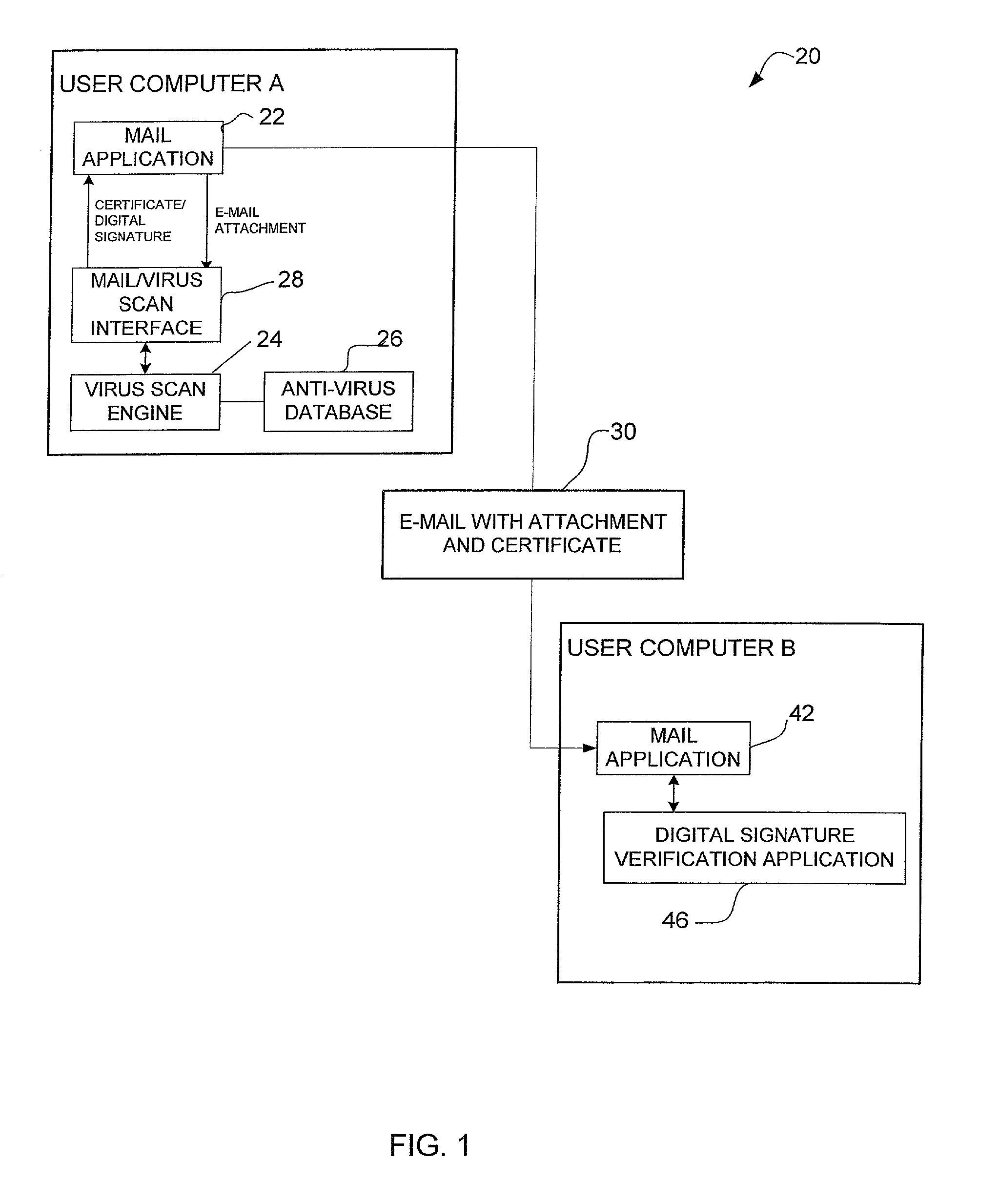
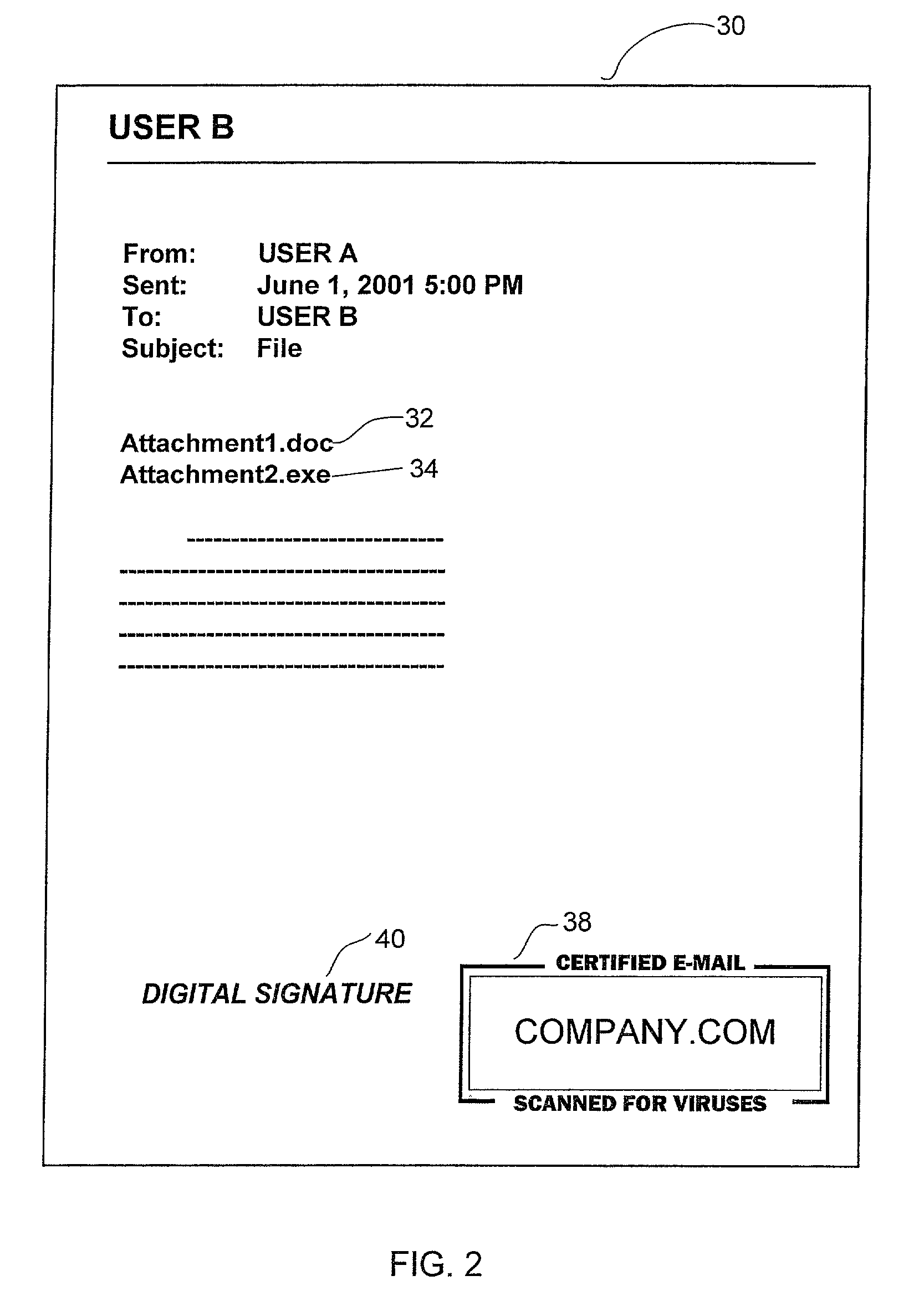
System and method for certifying that data received over a computer network has been checked for viruses
A method for certifying that data sent from a computer is free from viruses identified by an anti-virus database. The method includes scanning data for viruses before it is sent from the computer and attaching a certificate identifying the data as being scanned for viruses if no viruses are found during scanning. The data is sent with the certificate from the computer to a recipient computer. A method for certifying that content available on a host site is free from viruses is also disclosed.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
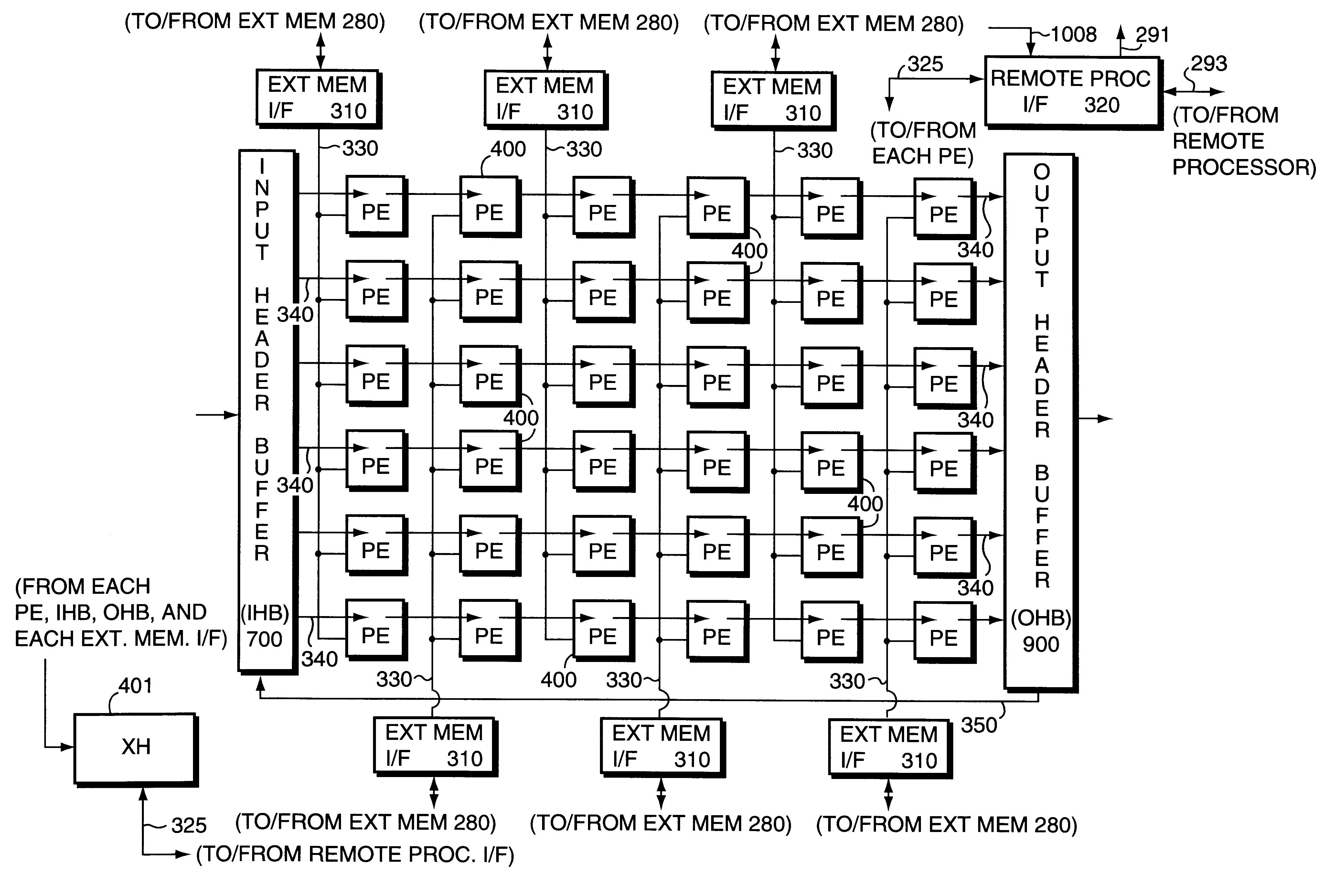
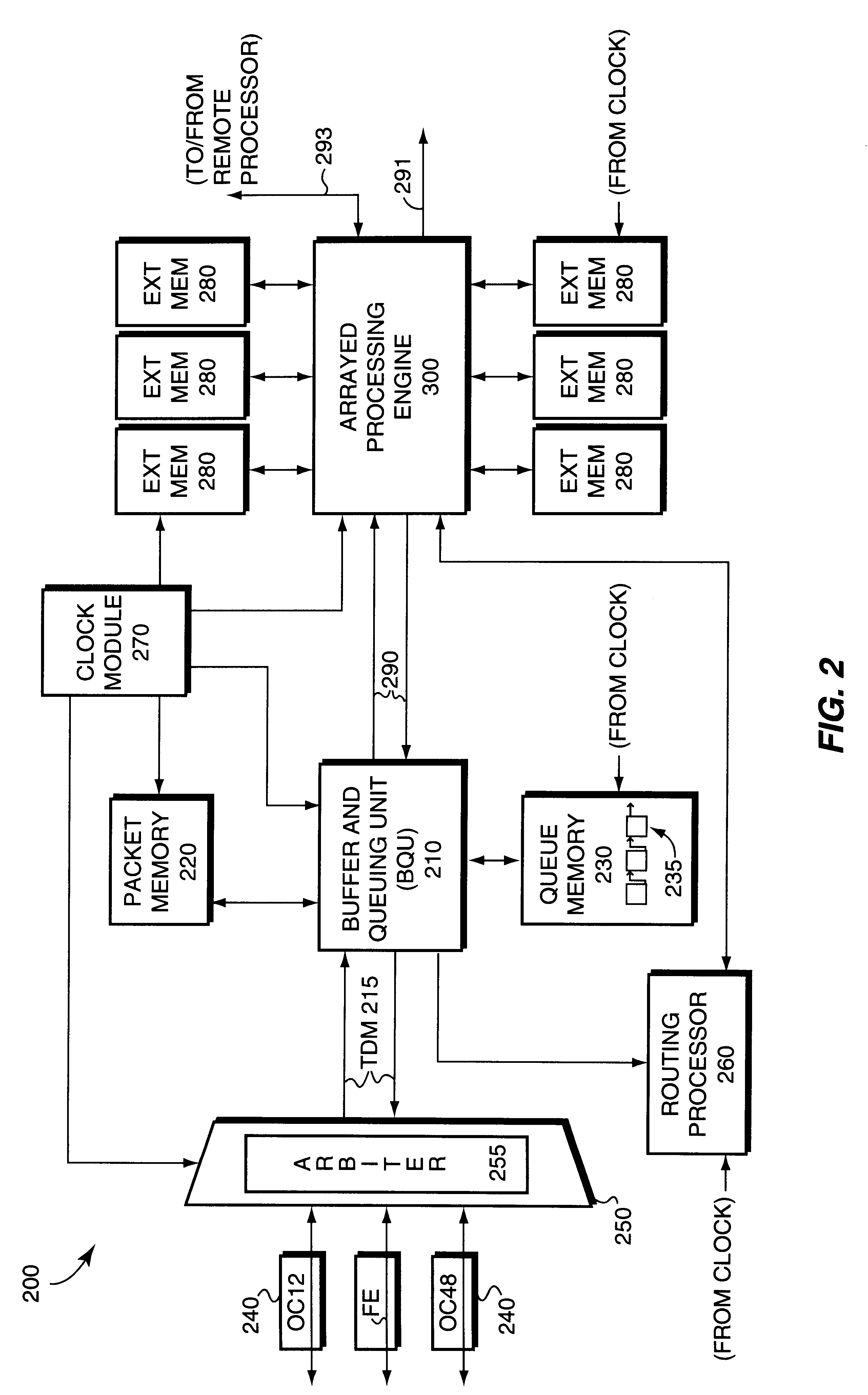
Parallel processor with debug capability
InactiveUS6173386B1Easy to checkReduce complexityDetecting faulty computer hardwareGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessing elementParallel processing
A parallel processor is provided that includes integrated debugging capabilities. The processor includes a pipelined processing engine, having an array of processing element complex stages, and input and output header buffers. A debug system is provided that, when triggered, may put some or all of the processing element complexes into a debug mode of operation. When a complex is in debug mode, examination of internal stages of the component circuits of the complex may occur, in order to facilitate debugging of software and hardware errors that may occur during operation of the processor.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Threshold voltage roll-off compensation using back-gated MOSFET devices for system high-performance and low standby power
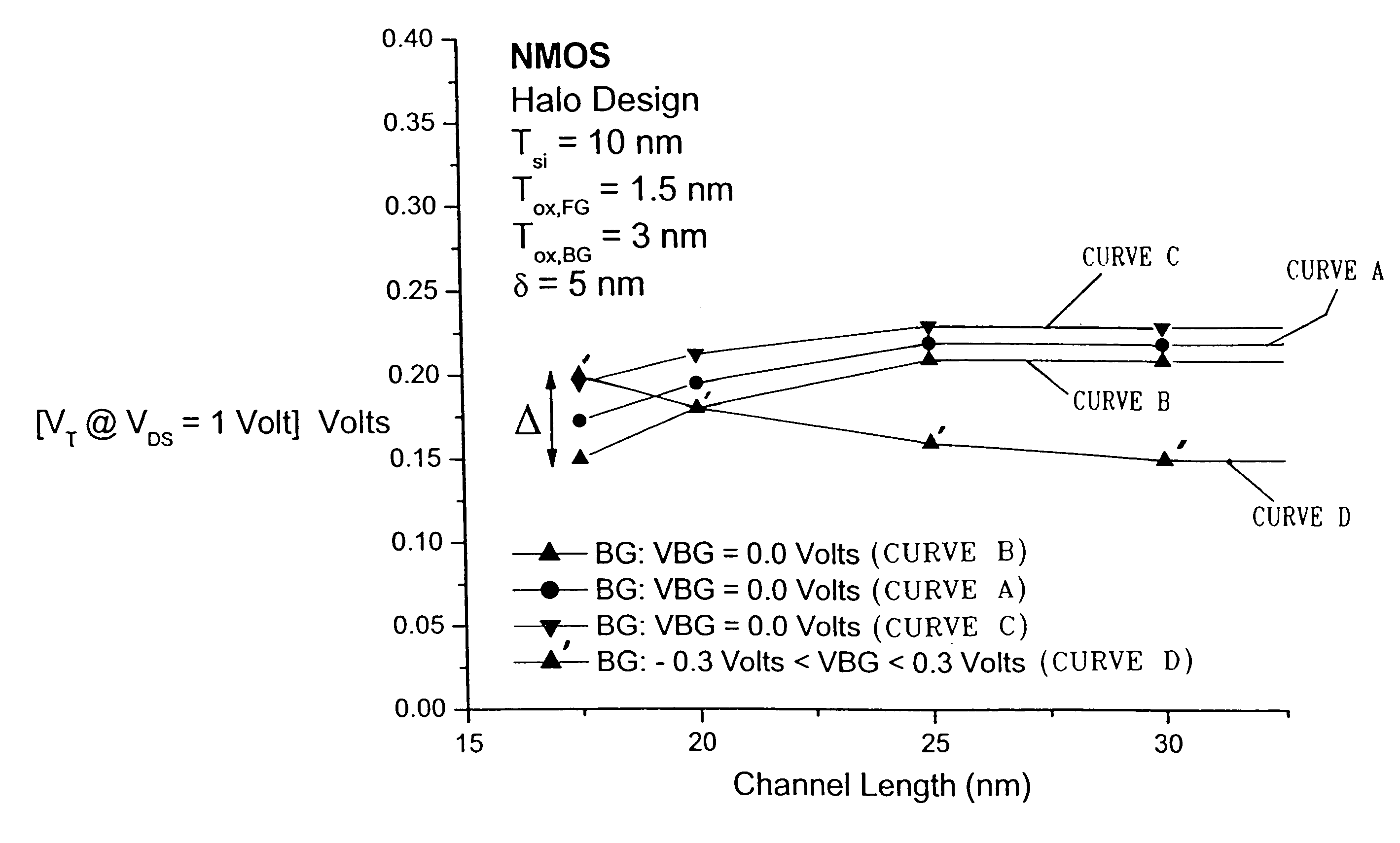
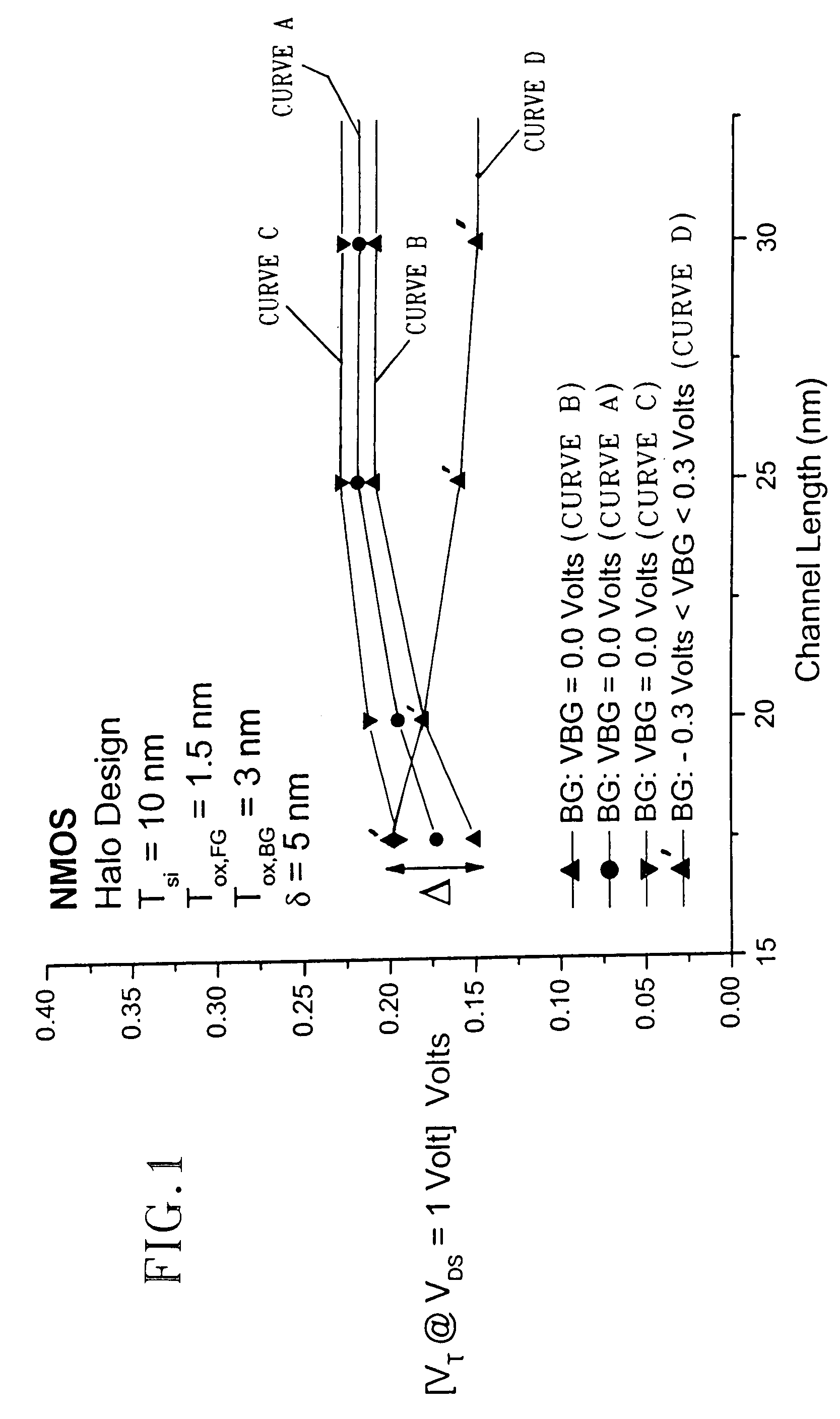
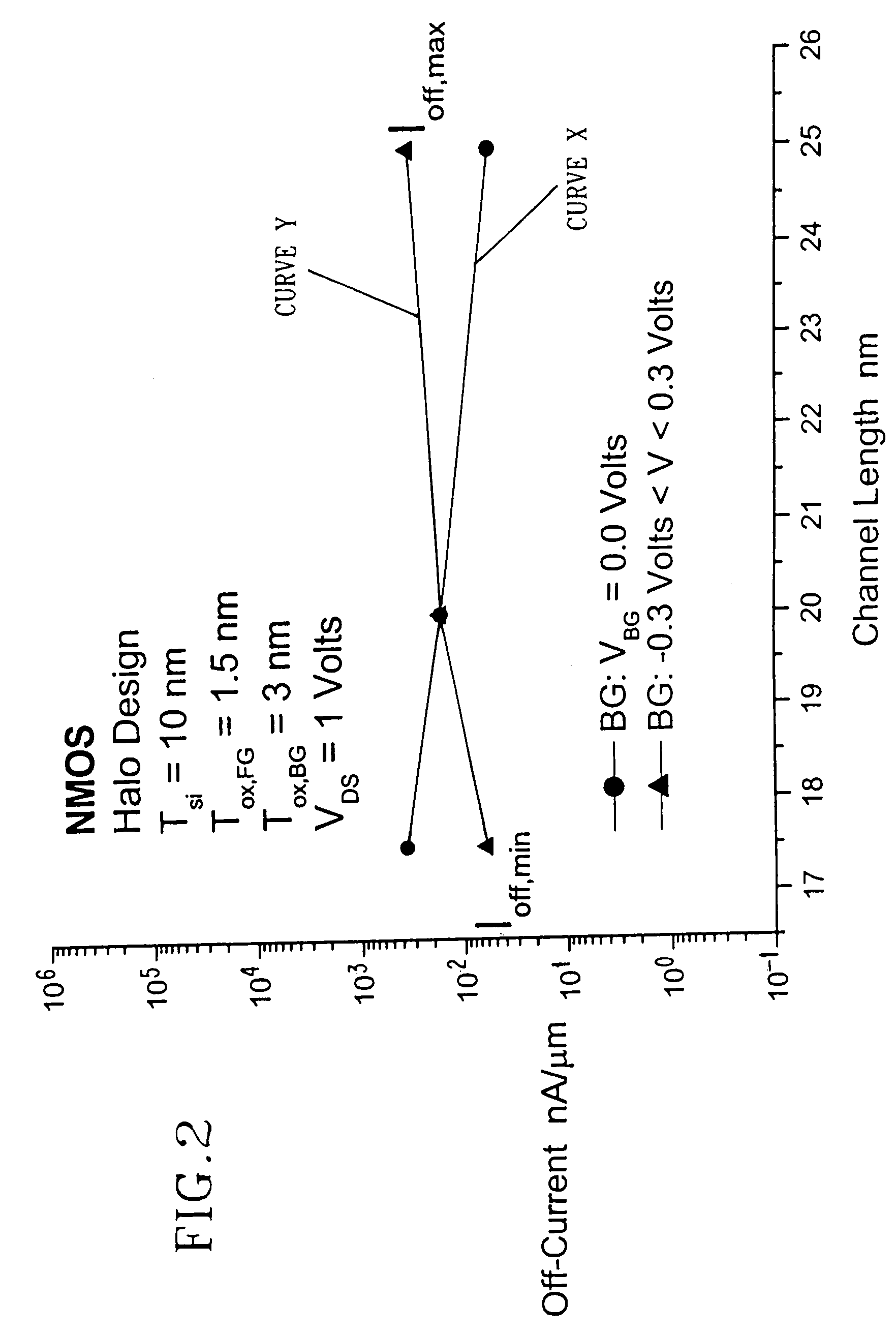
InactiveUS7089515B2Power reduction in field effect transistorsDetecting faulty computer hardwareMOSFETStandby power
A method for compensating the threshold voltage roll-off using transistors containing back-gates or body nodes is provided. The method includes designing a semiconductor system or chip having a plurality of transistors with a channel length of Lnom. For the present invention, it is assumed that the channel length of these transistors at the completion of chip manufacturing is Lmax. This enables one to set the off-current to the maximum value of I-offmax which is done by setting the threshold voltage value to Vtmin. The Vtmin for these transistors is obtained during processing by using the proper implant dose. After manufacturing, the transistors are then tested to determine the off-current thereof. Some transistors within the system or chip will have an off-current value that meets a current specification. For those transistor devices, no further compensation is required. For other transistors within the system or chip, the off-current is not within the predetermined specification. For those transistors, threshold voltage roll-off has occurred since they are transistors that have a channel length that is less than nominal. For such short channel transistors, the threshold voltage is low, even lower than Vtmin, and the off-current is high, even higher than I-offmax. Compensation of the short channel transistors is achieved in the present invention by biasing the back-gate or body node to give increased threshold voltage about equal to Vtmin and hence an off-current that meets the predetermined specification, which is about equal to I-offmax.
Owner:ETHICON INC +1
Method and system for detecting intrusive anomalous use of a software system using multiple detection algorithms
InactiveUS20060085854A1Improve detection accuracyAccurate detectionMemory loss protectionDetecting faulty computer hardwareCountermeasureSoftware system
A method of detecting an intrusion into (or an anomaly in a behavior of) a target software system begins by instrumenting the target software system to generate behavior data representing a current observation or observation aggregate. The method then determines whether the current observation or observation aggregate warrants a second level examination; preferably, this determination is made by processing the current observation or observation aggregate through a first level detection algorithm that provides a first, provisional indication of a possible intrusion. If a result of executing the first level detection algorithm indicates that the current observation or observation aggregate warrants a second level examination, the method continues by processing the current observation or observation aggregate through at least one or more second level detection algorithms to provide a second, more definite, fine grain indication of a possible intrusion. The observation aggregates used by the first and second level detection algorithms may be the same or different. The first and second level detection algorithms may be executed in the same or different systems, machines or processors. The target software system operation may be suspended as the current observation or observation aggregate is processed through the one or more second level detection algorithms. A given action (e.g., sending an alert, logging the event, activating a countermeasure, or the like) may be taken if the result of the second level examination indicates a possible intrusion. Multiple algorithms may be executed together within a single examination level, with the individual results then analyzed to obtain a composite result or output indicative of intrusive or anomalous behavior.
Owner:STRATACLOUD
Popular searches
Software simulation/interpretation/emulation Memory systems Complex mathematical operations Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Computer aided design Special data processing applications Input/output processes for data processing Co-operative working arrangements Visual presentation Electrographic process apparatus
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com