Patents
Literature
68 results about "Fin width" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
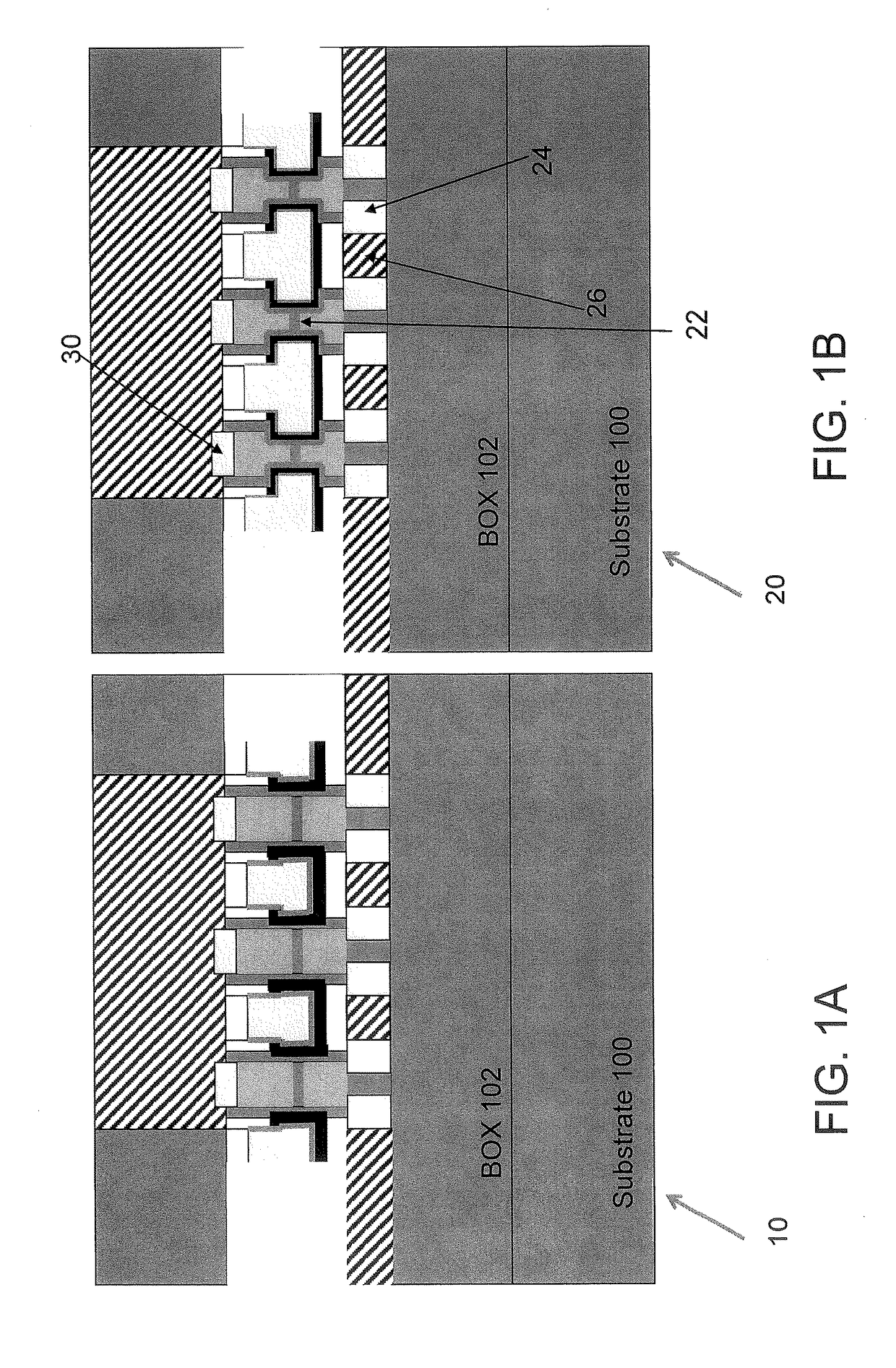
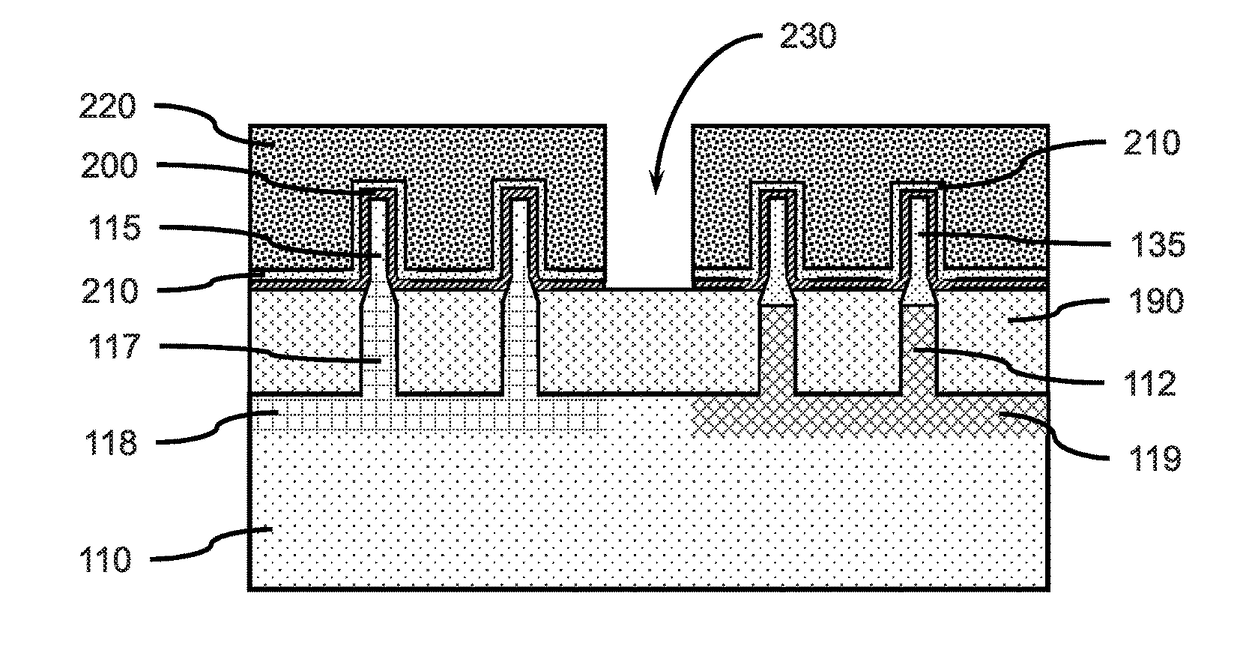
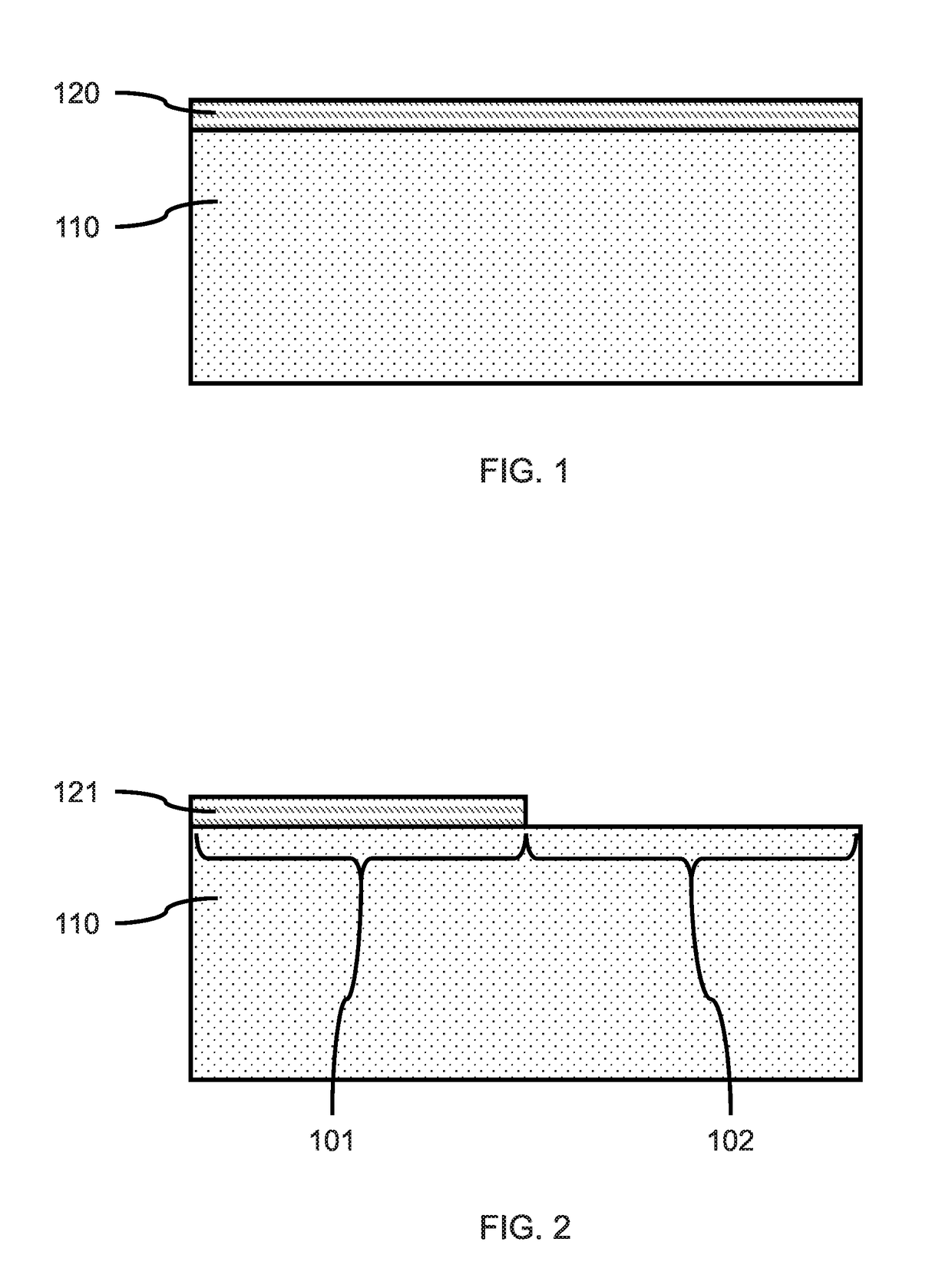
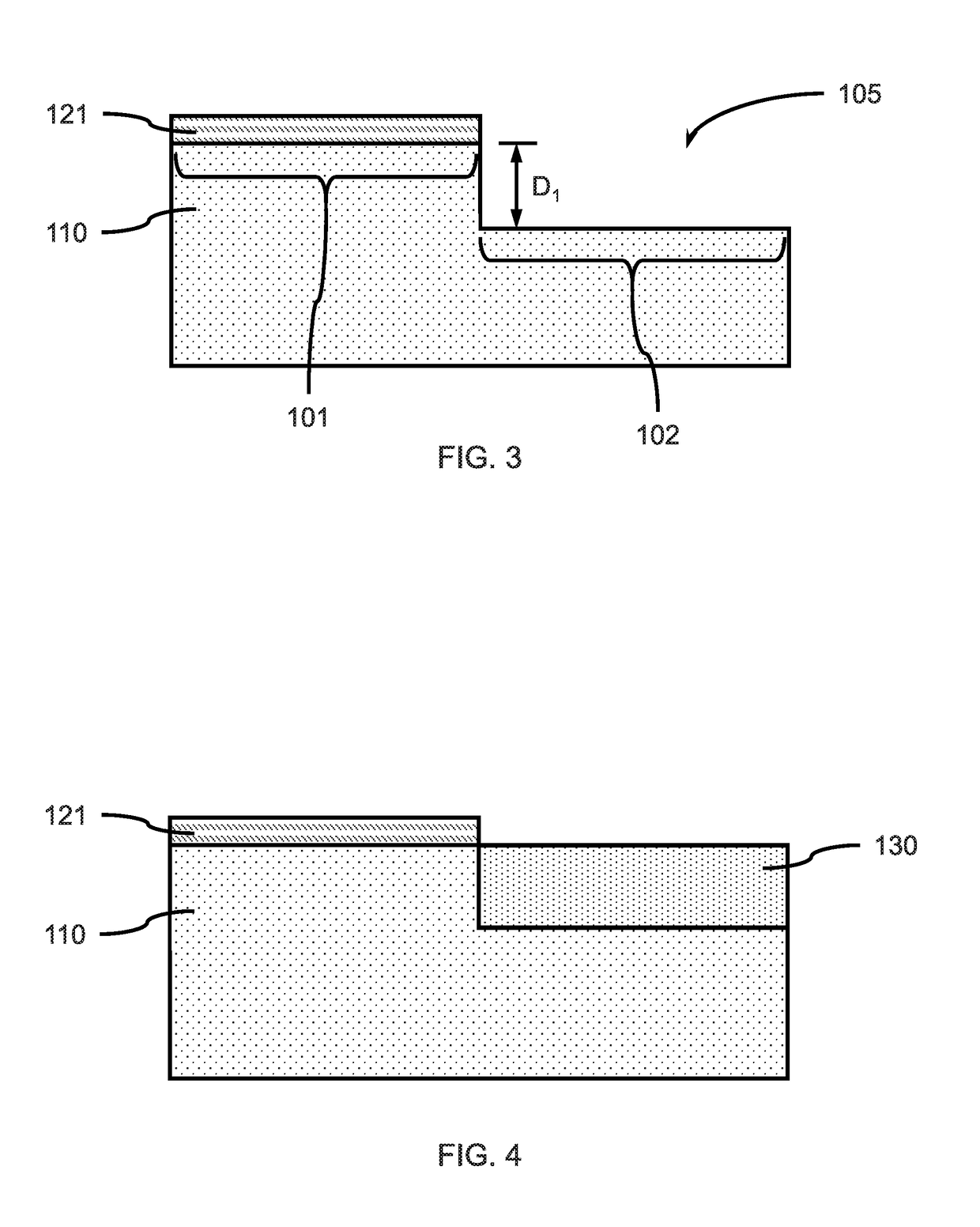
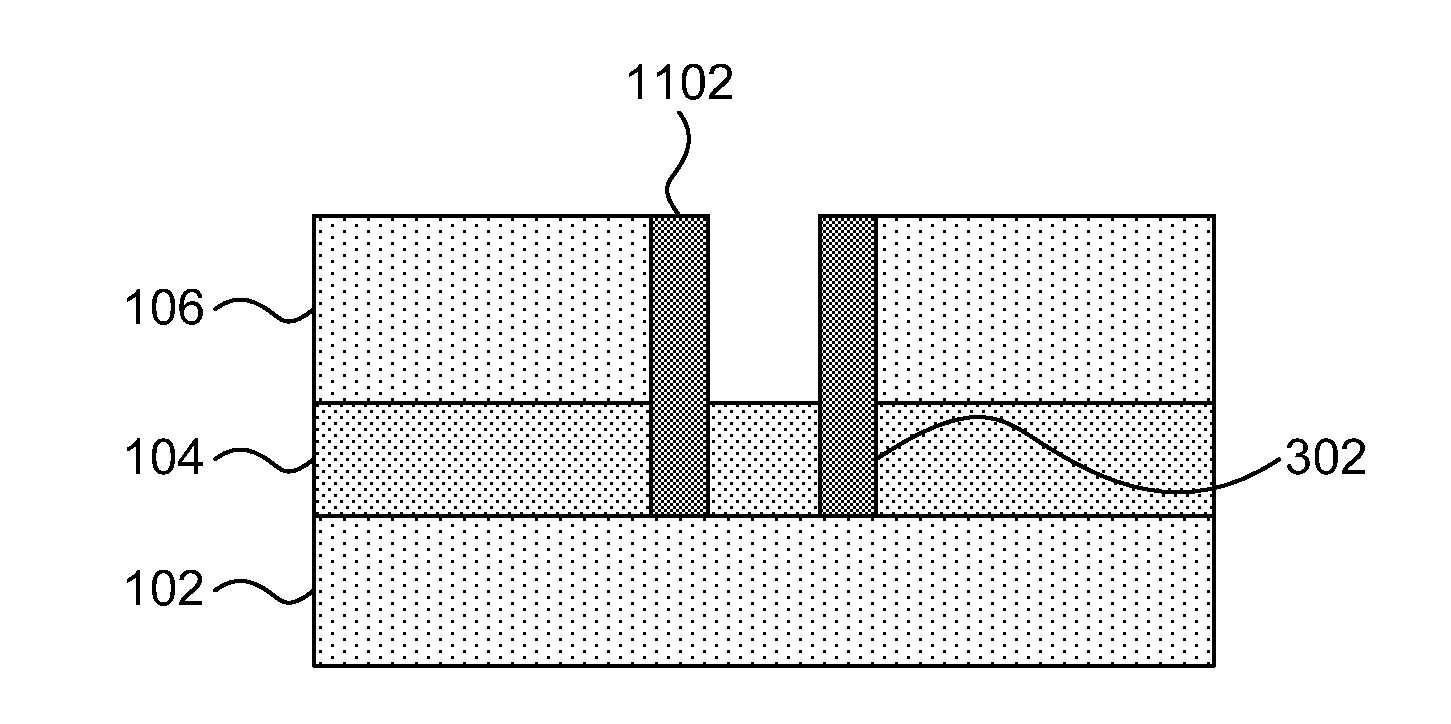
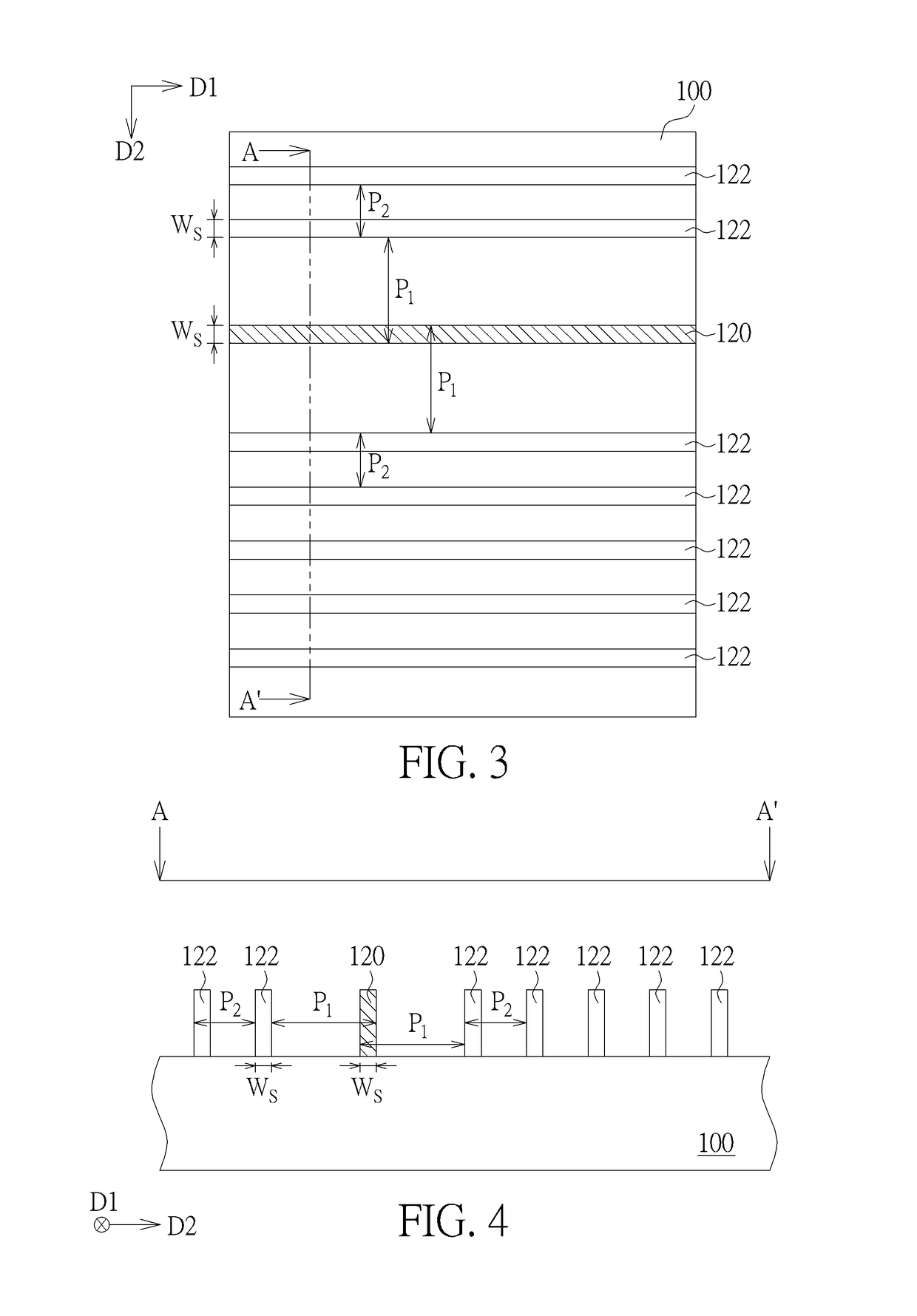
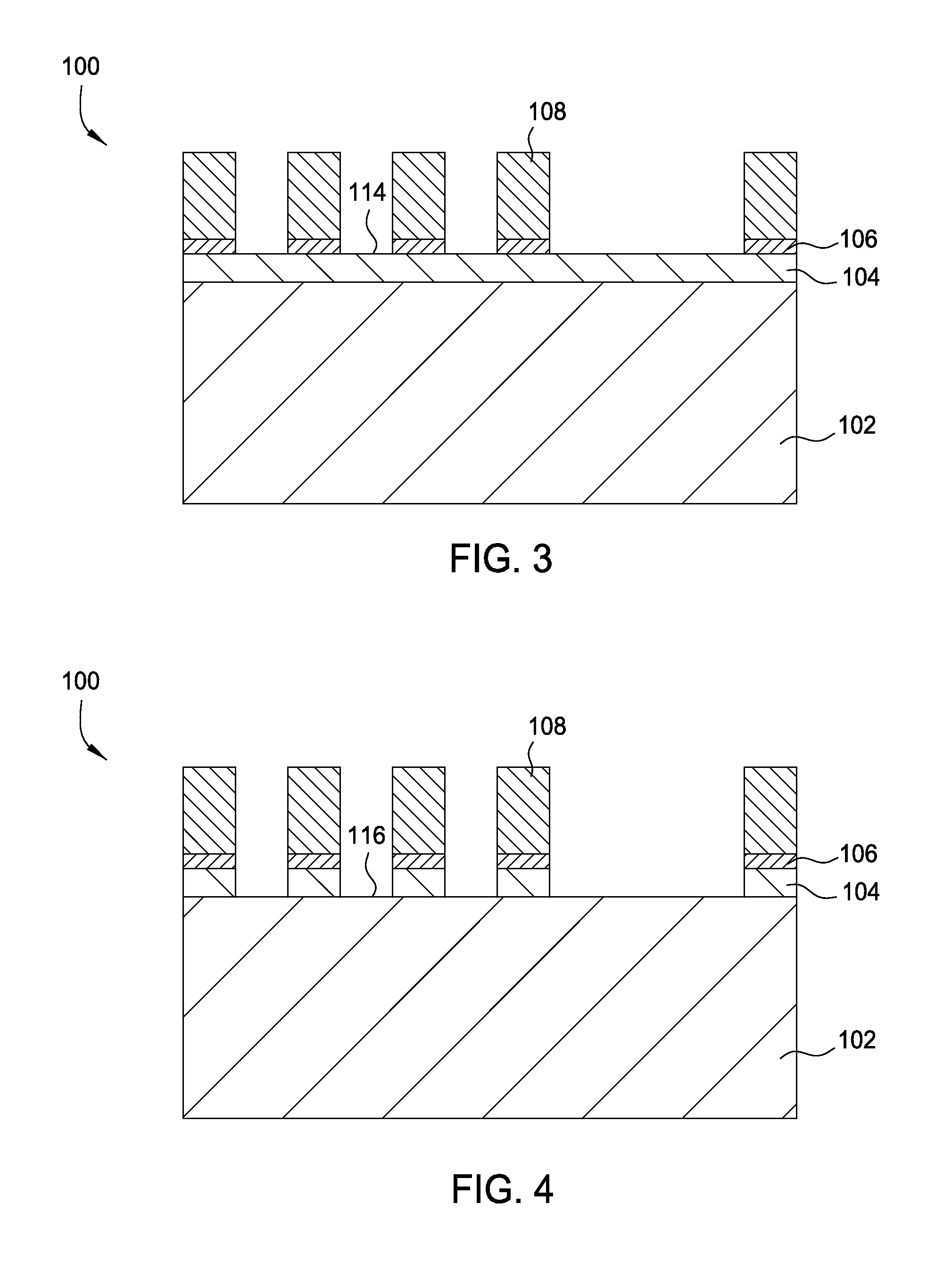
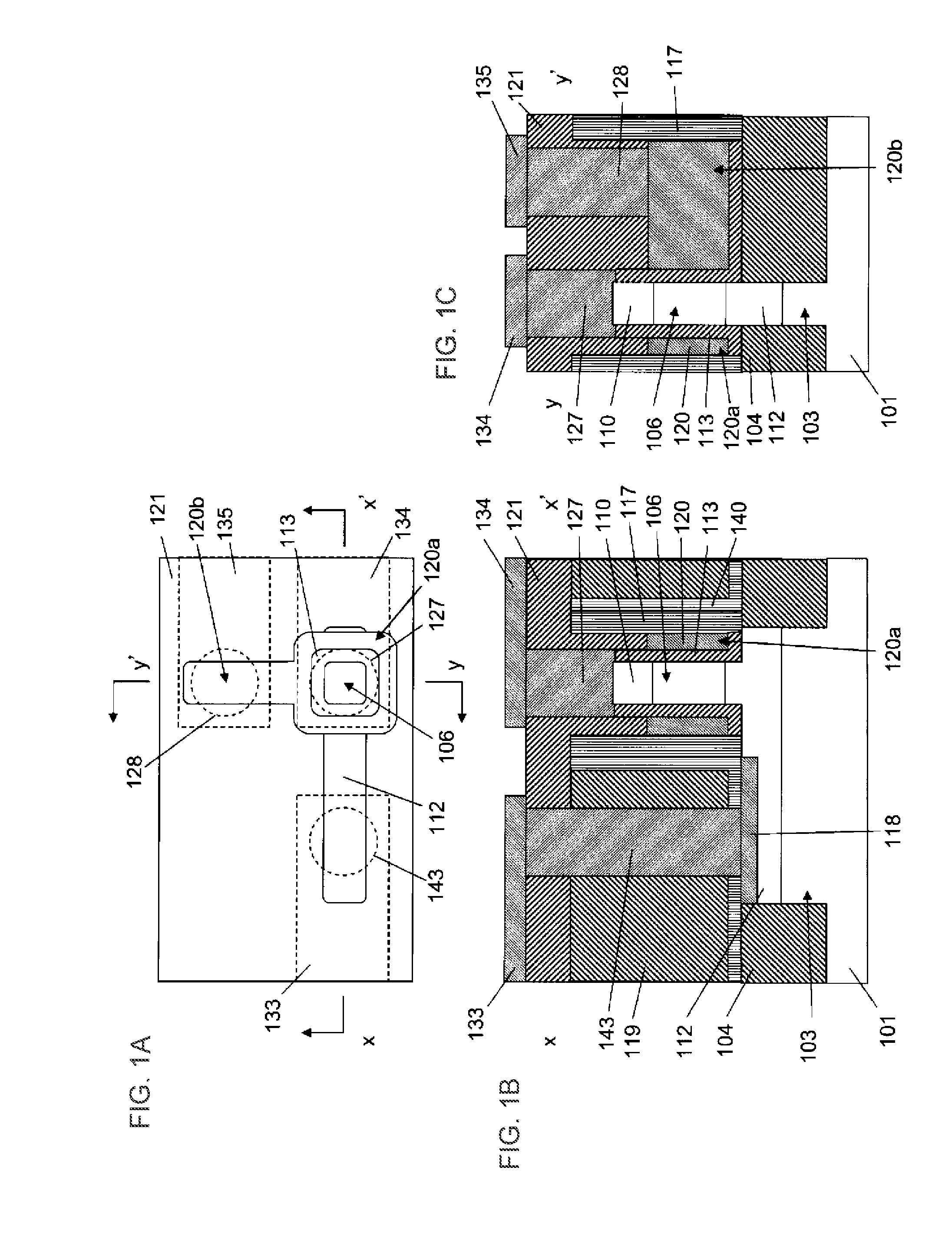
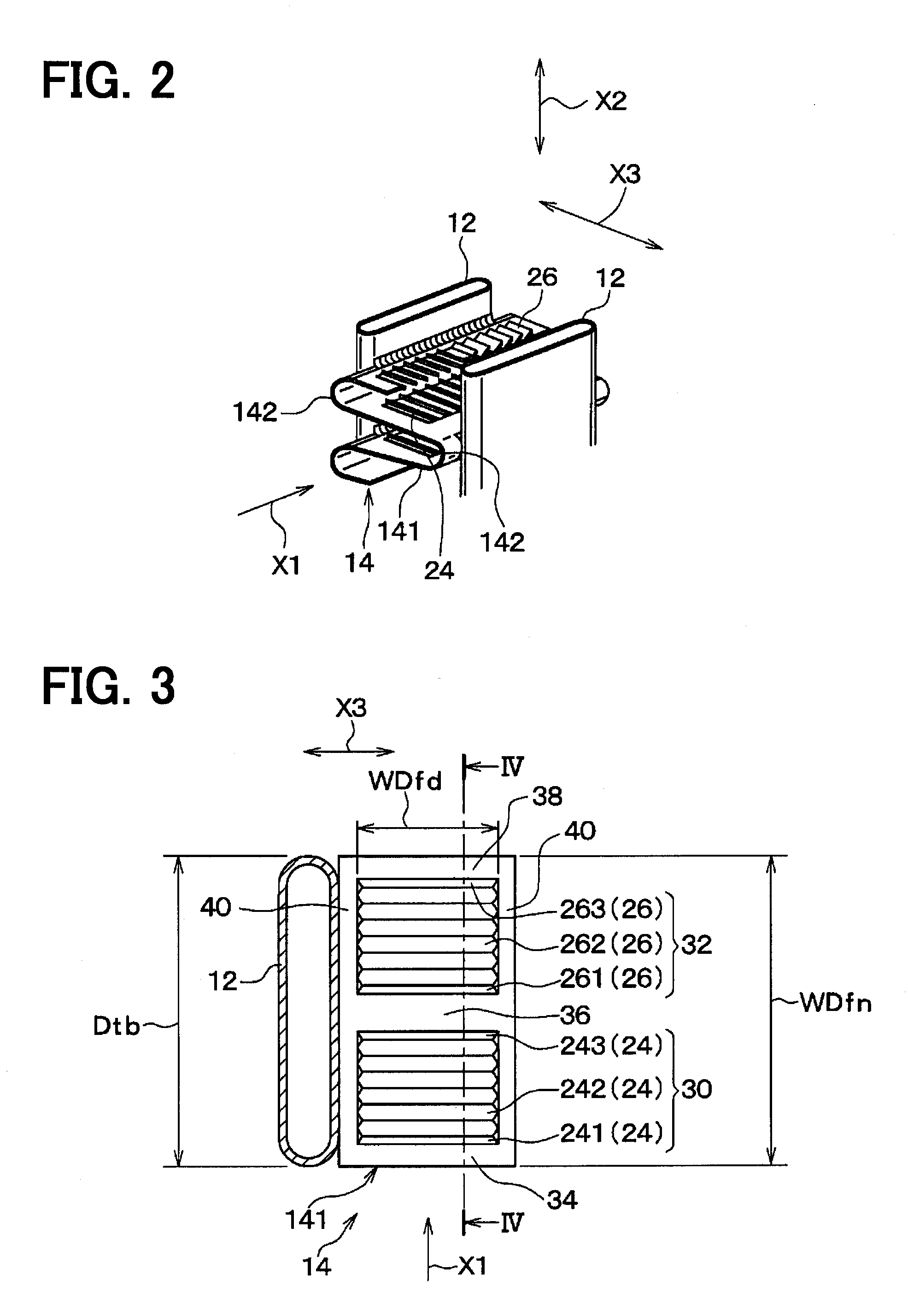
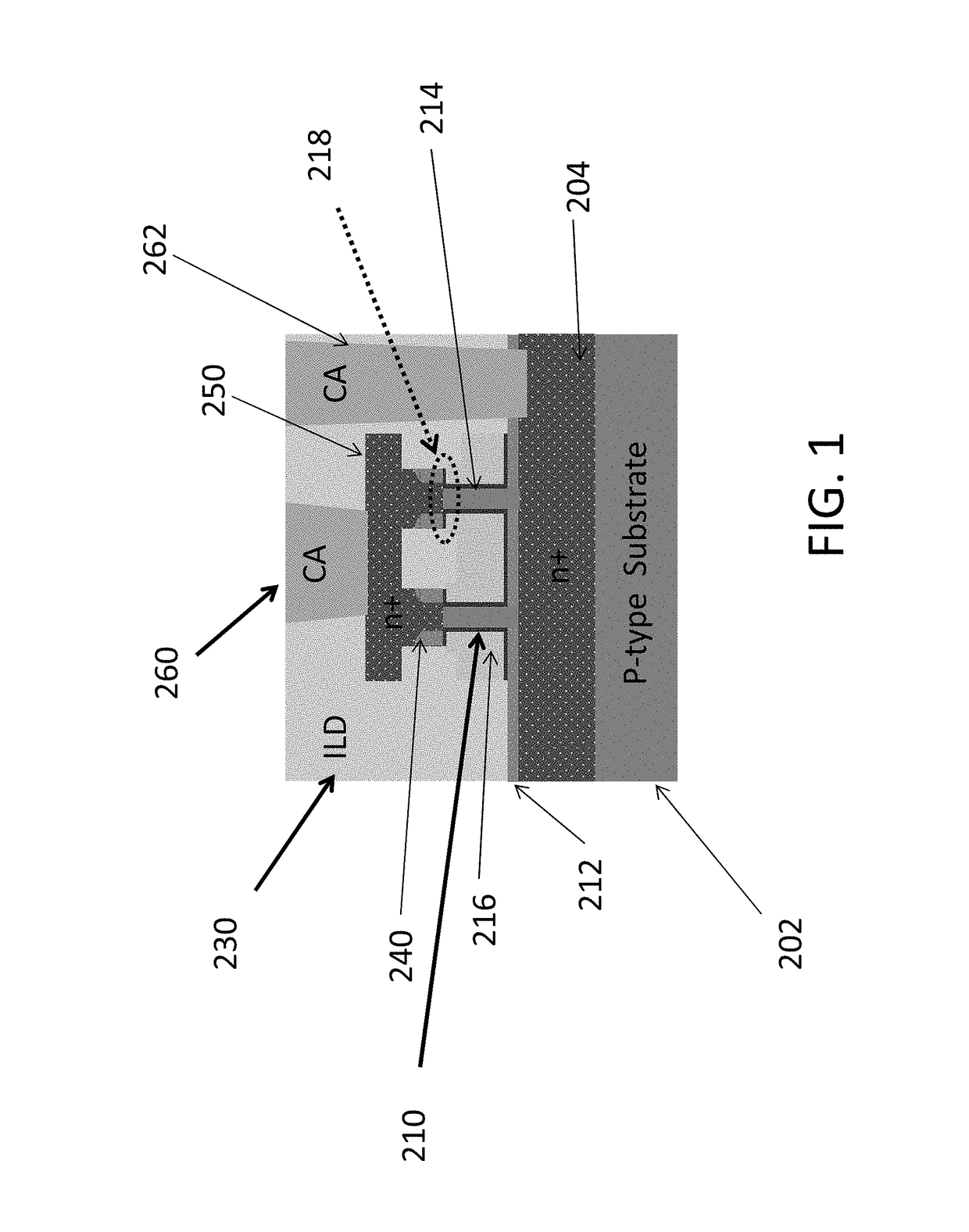
Semiconductor device
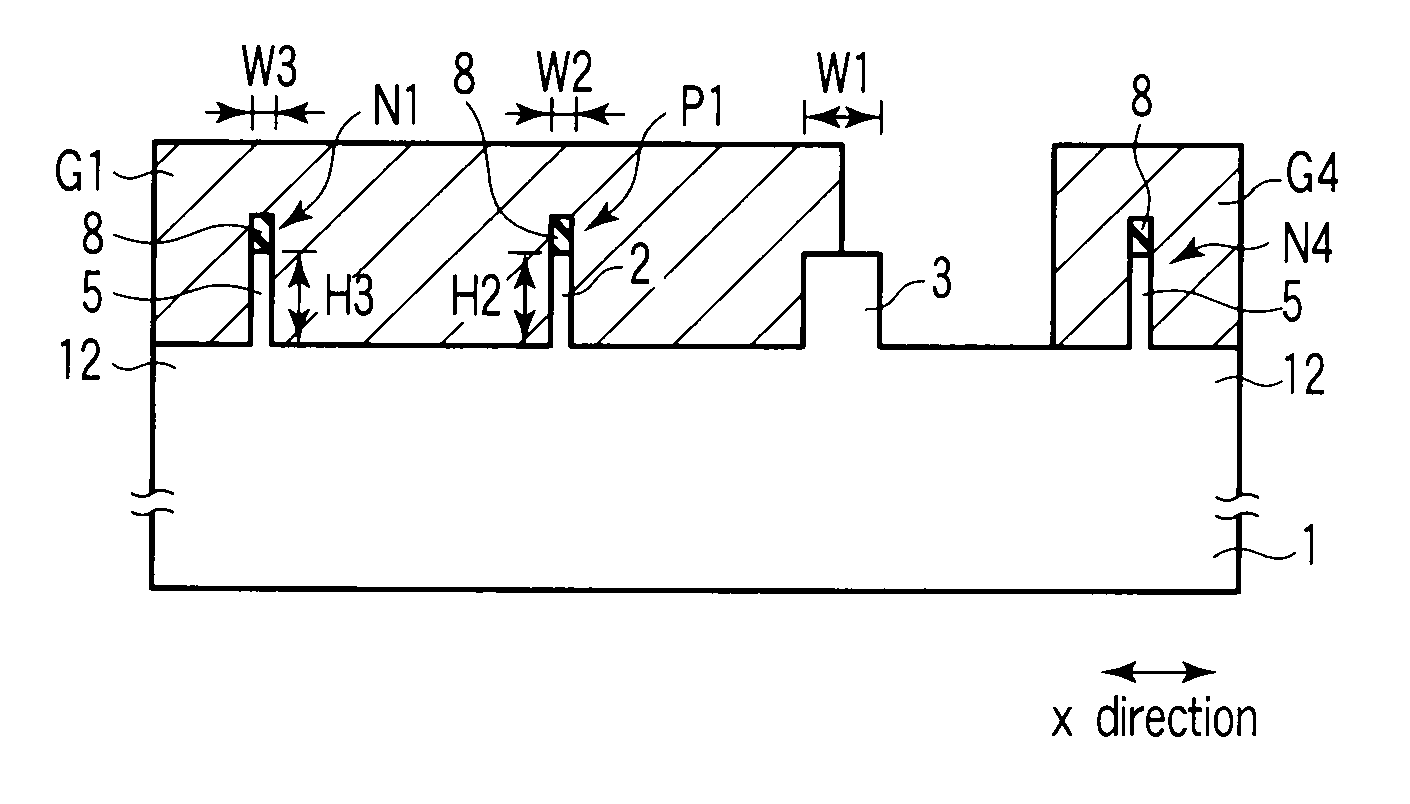
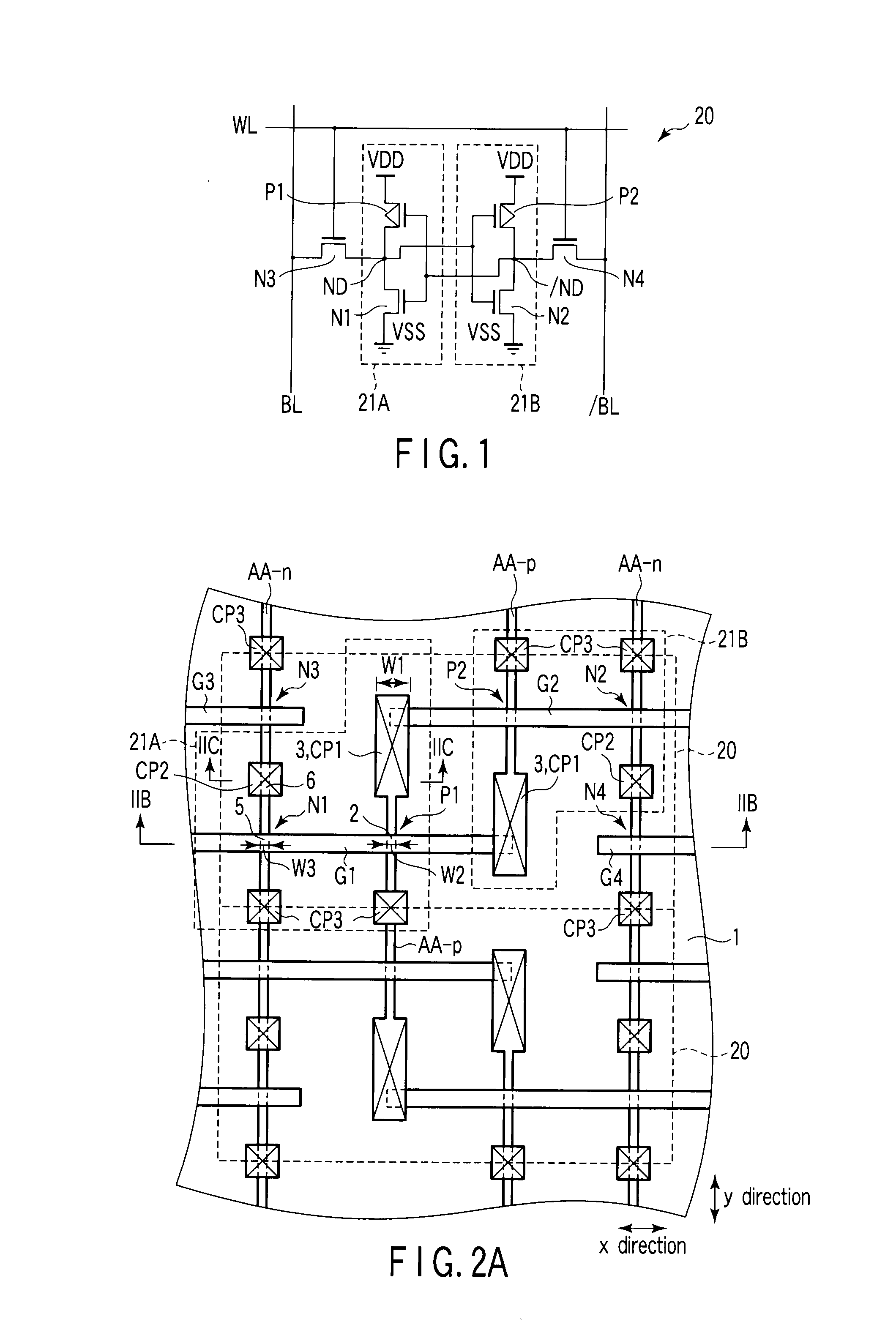
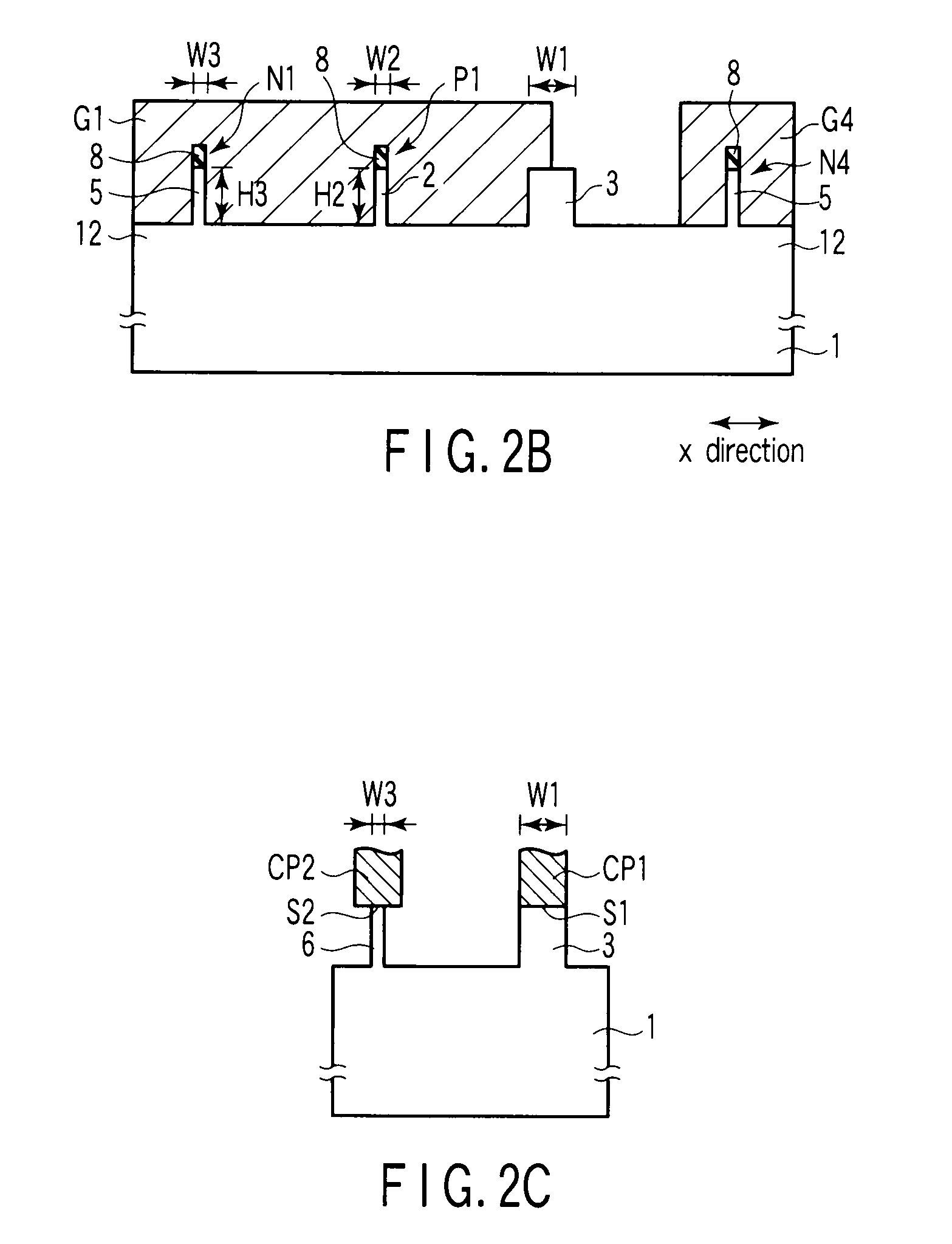
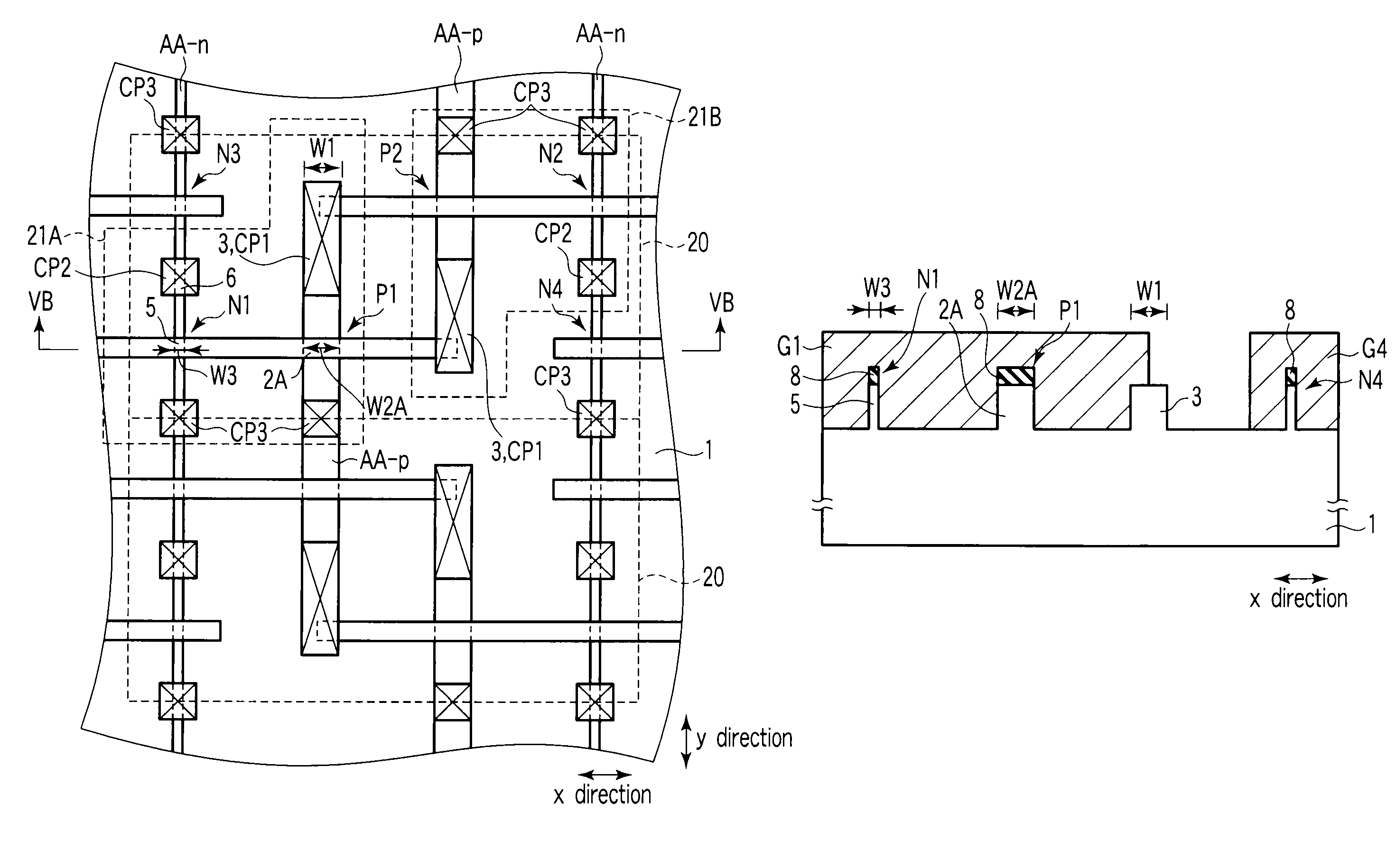
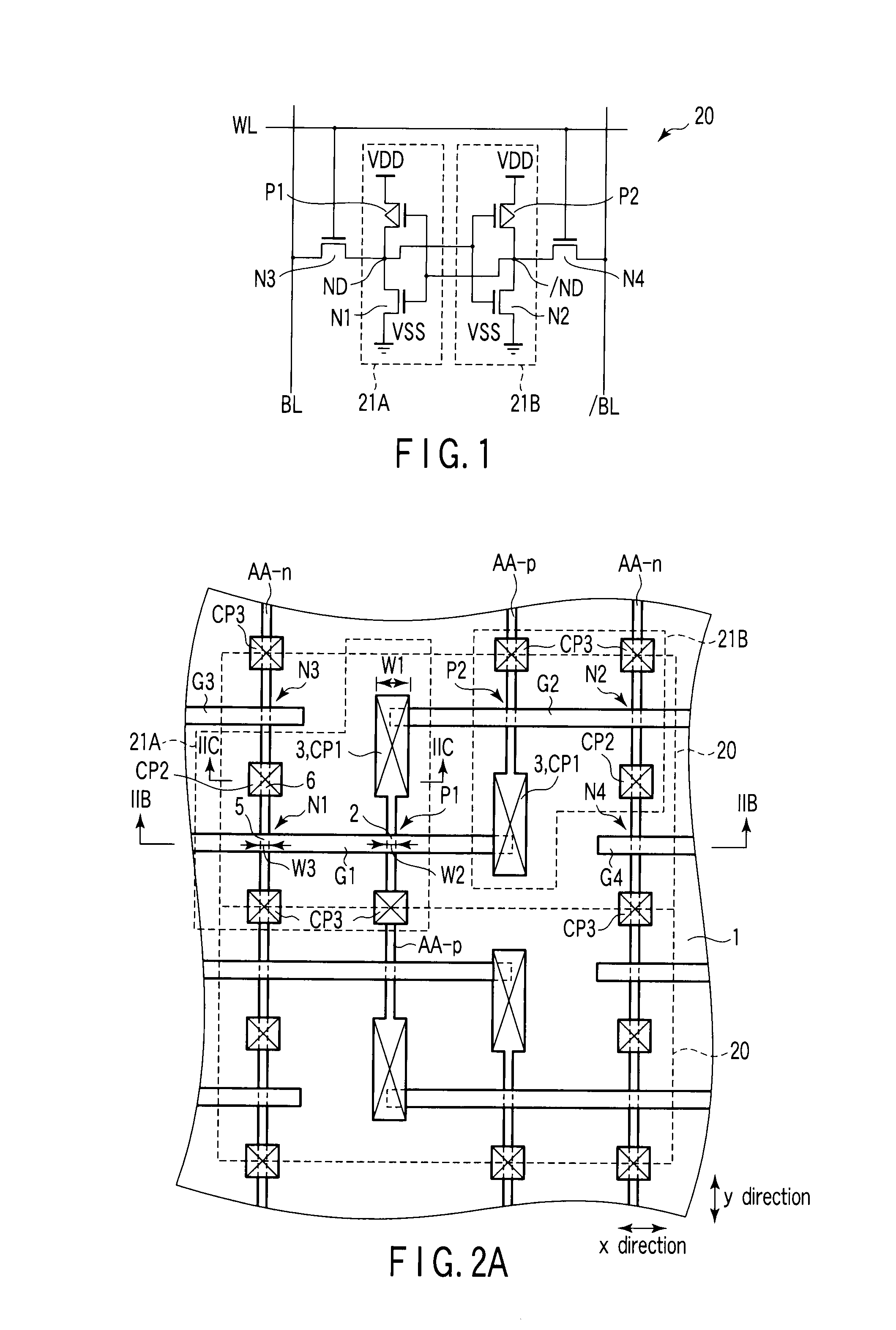
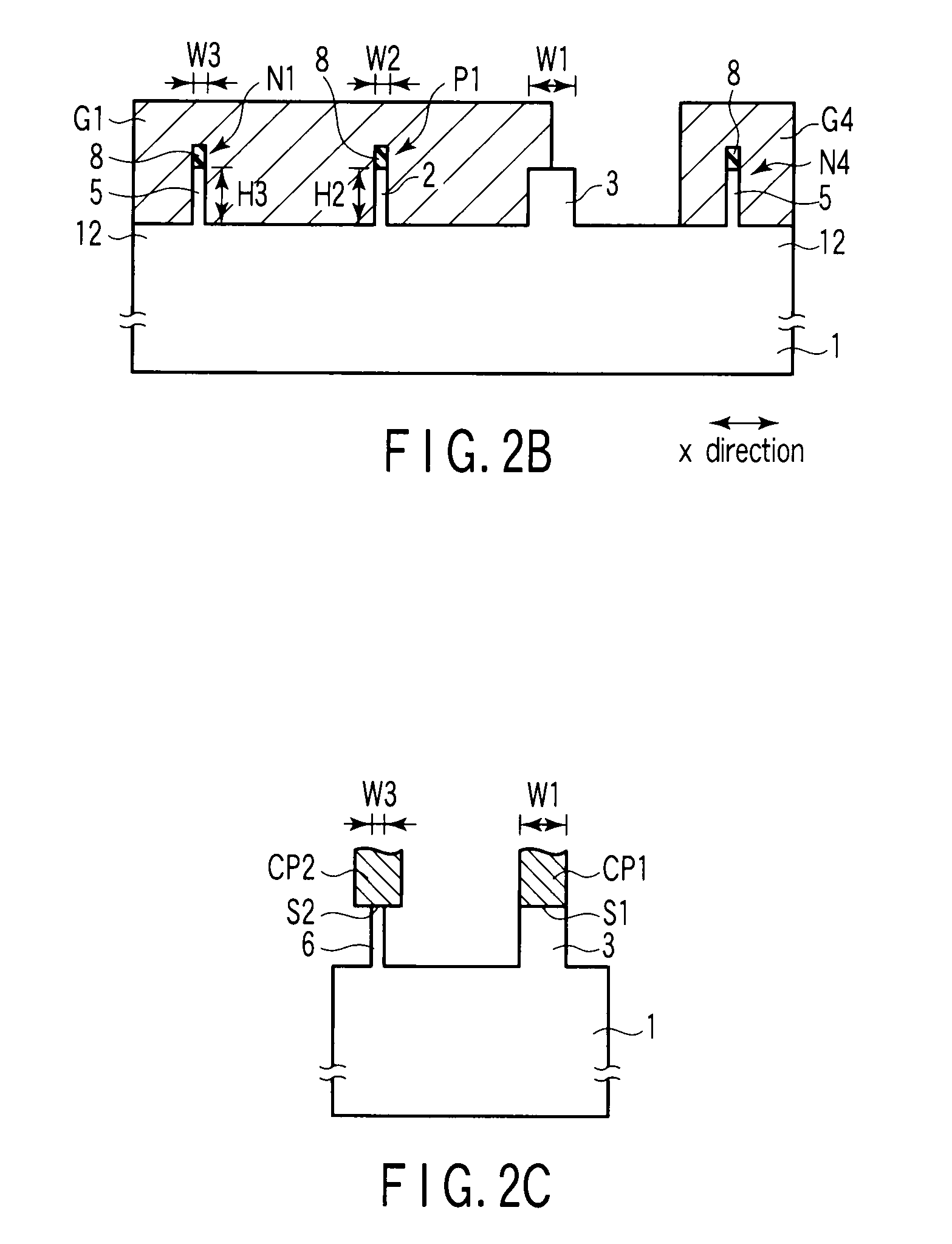
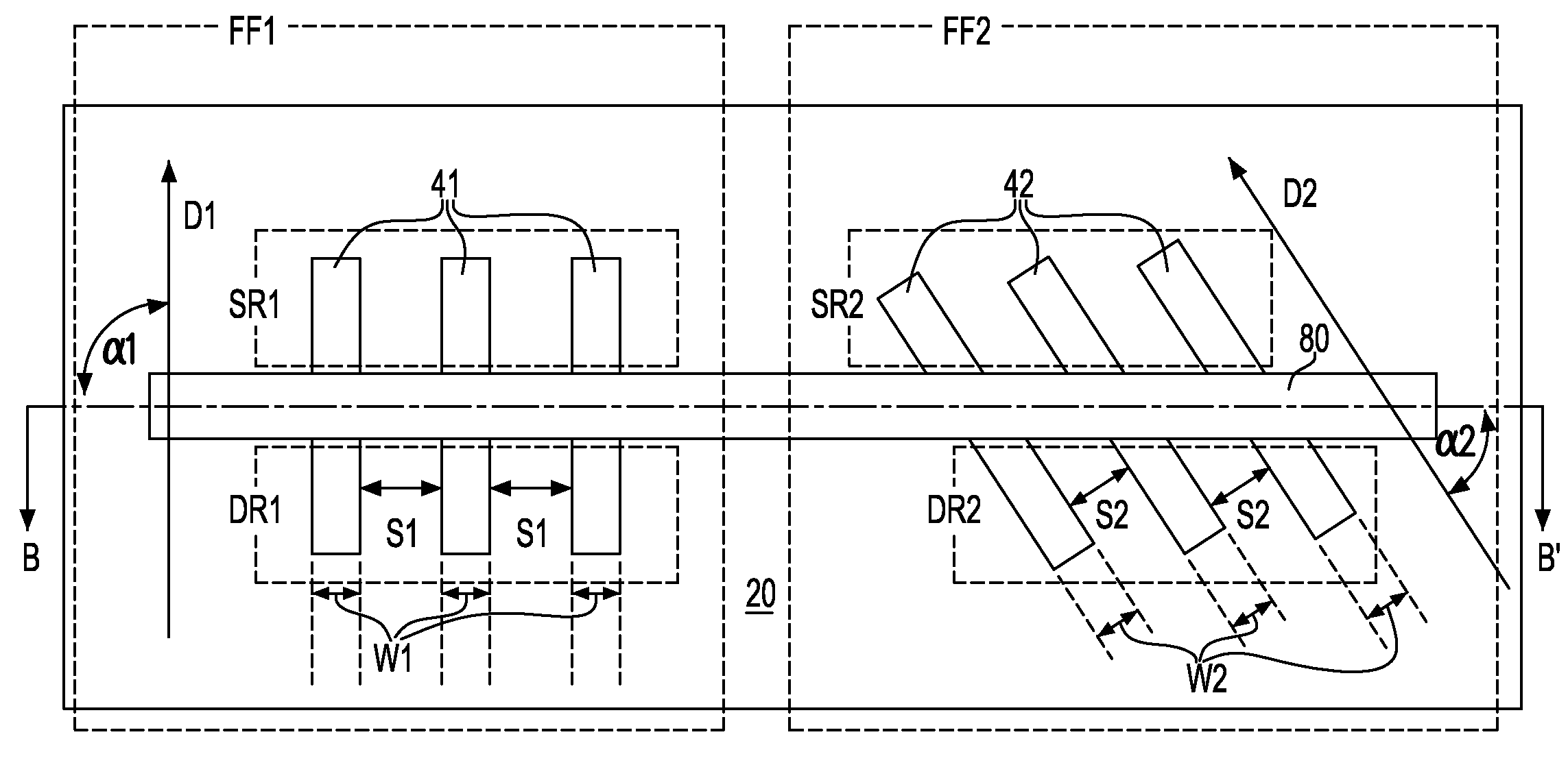
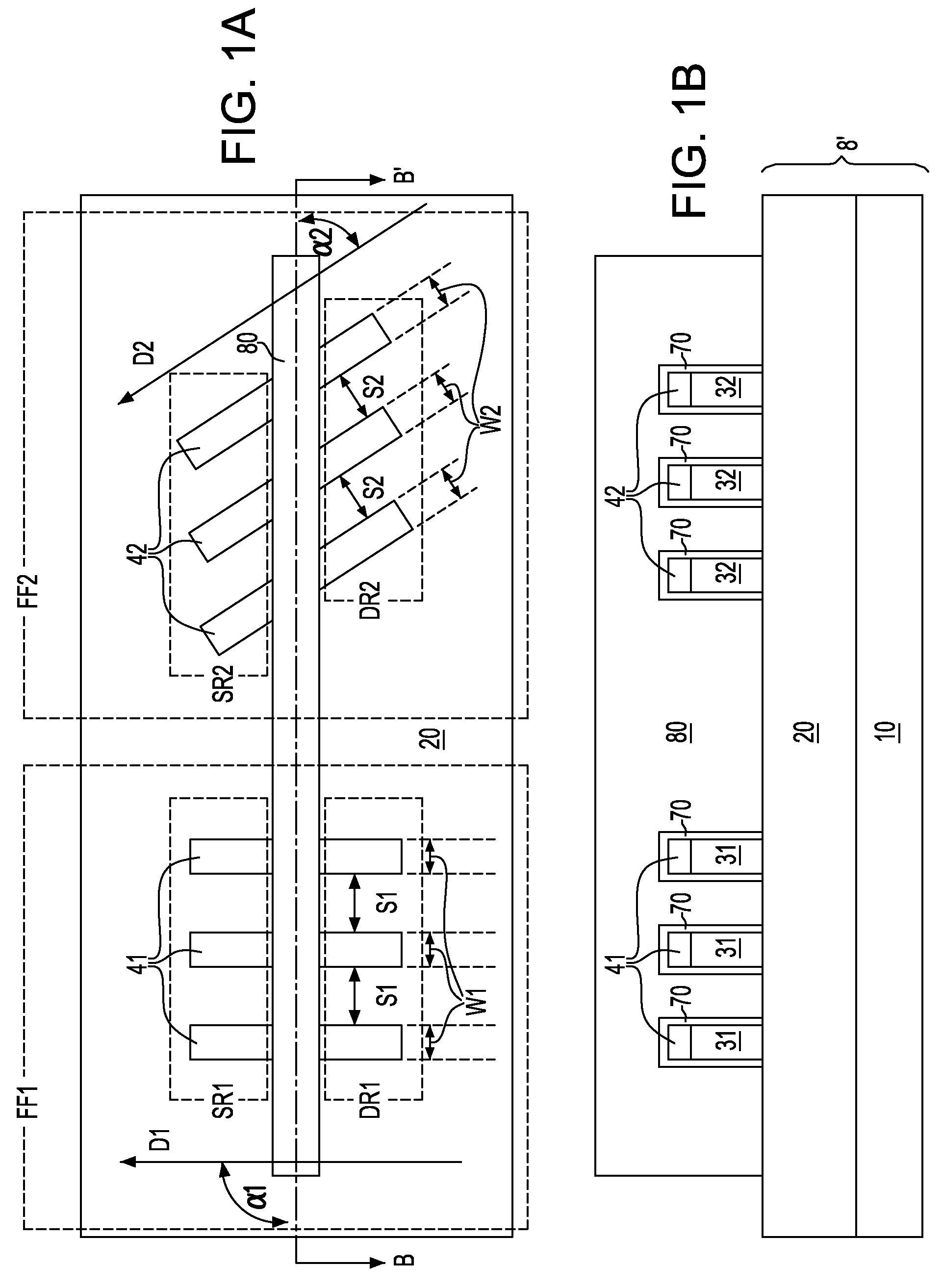
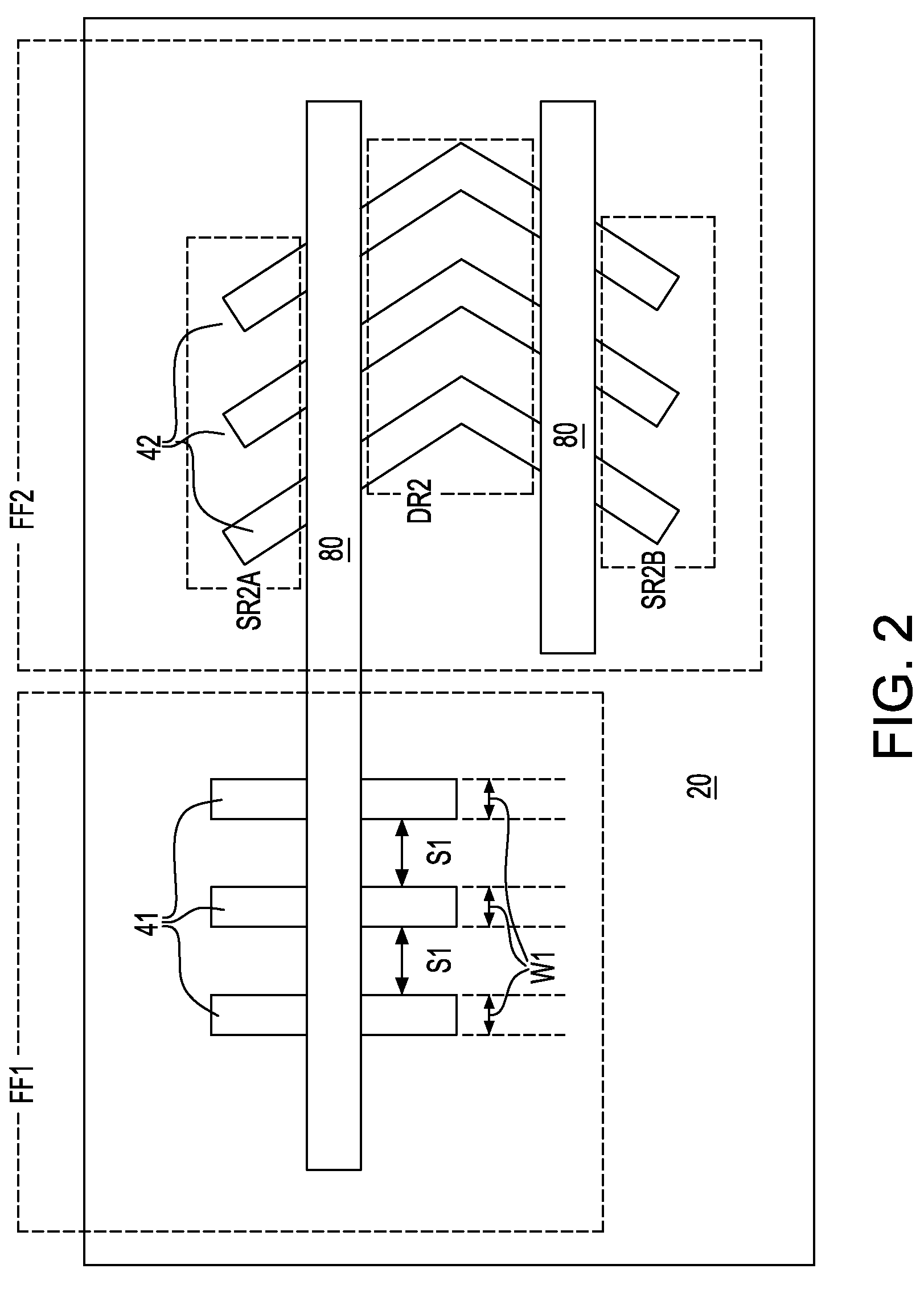
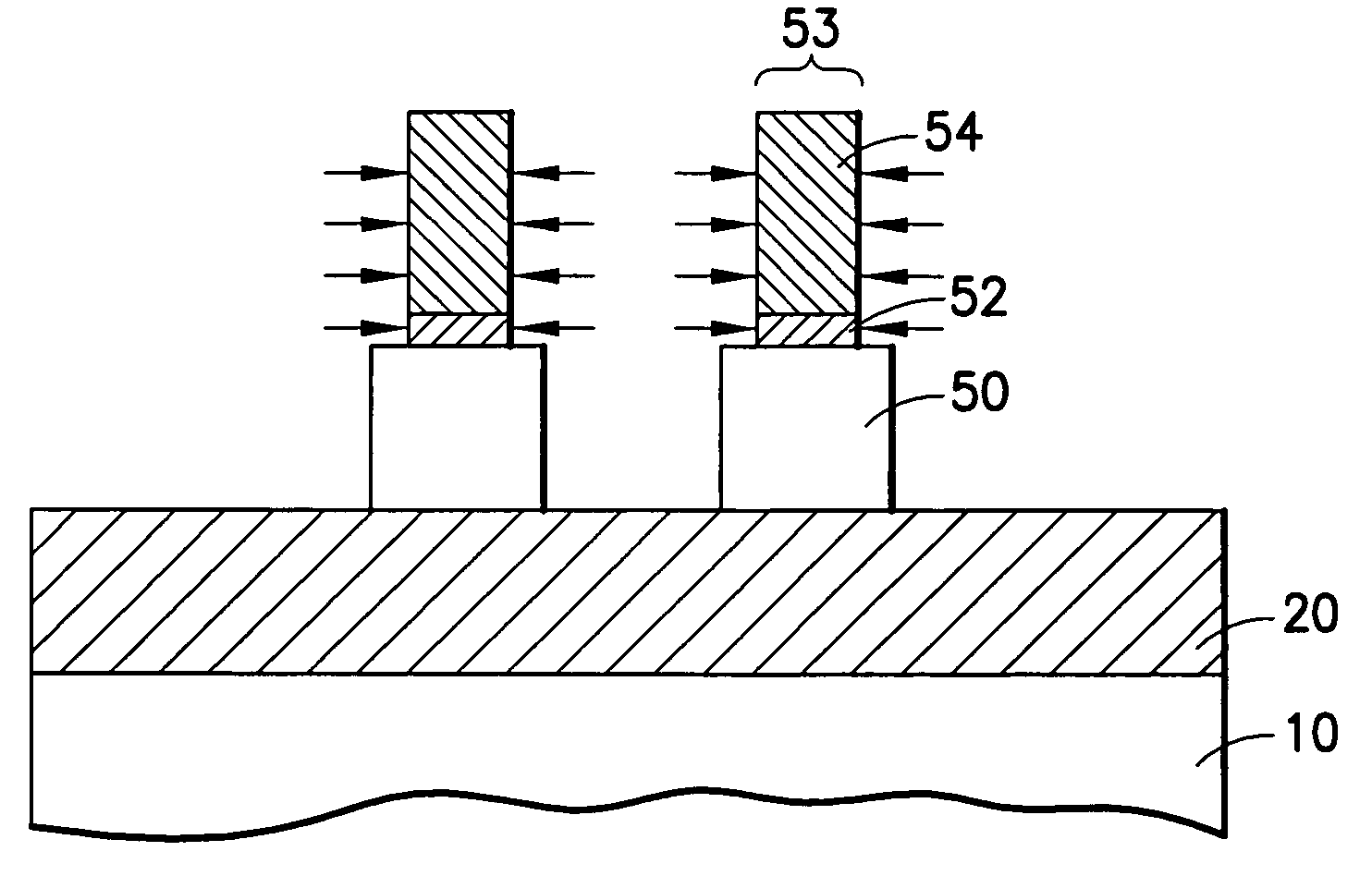
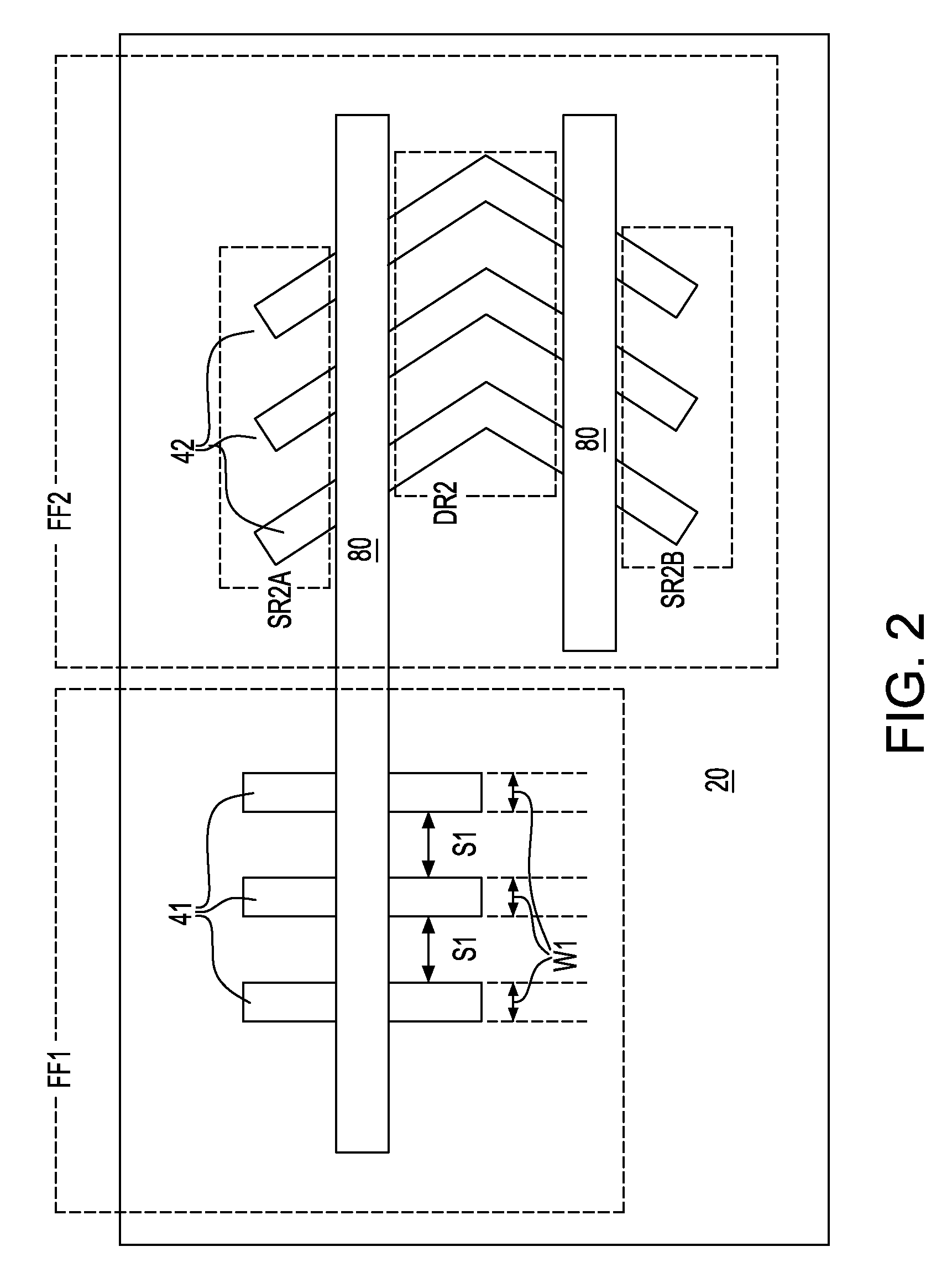
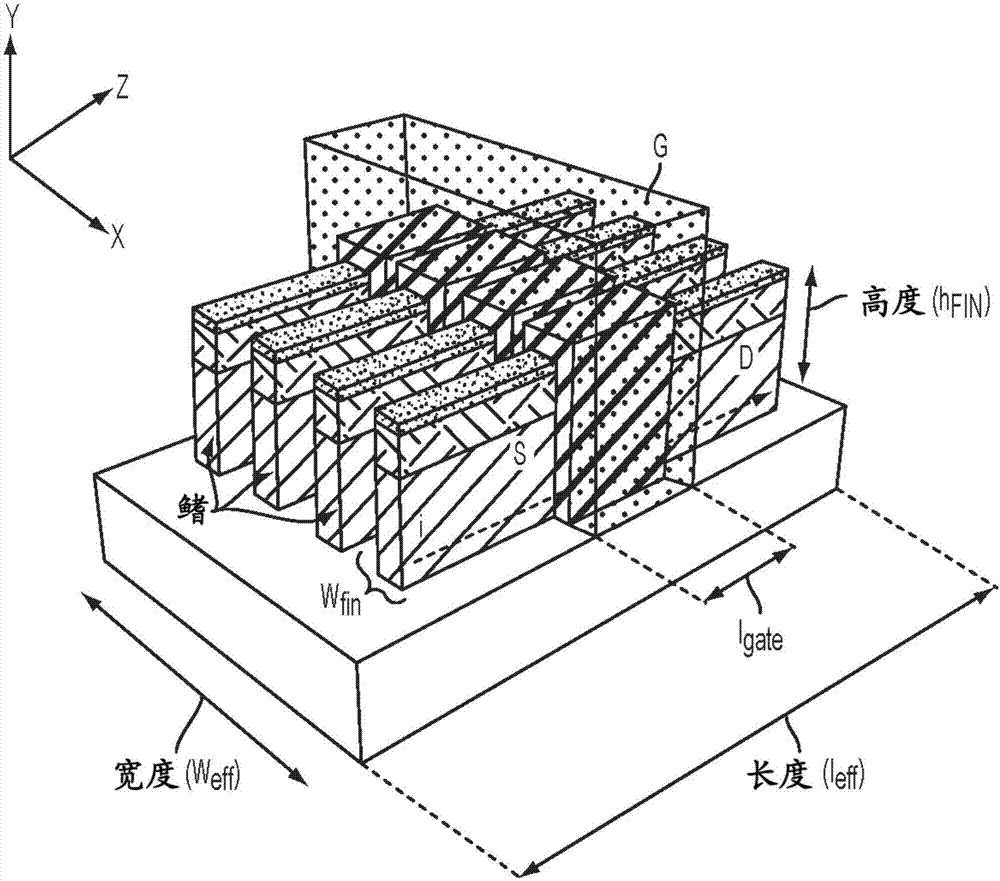
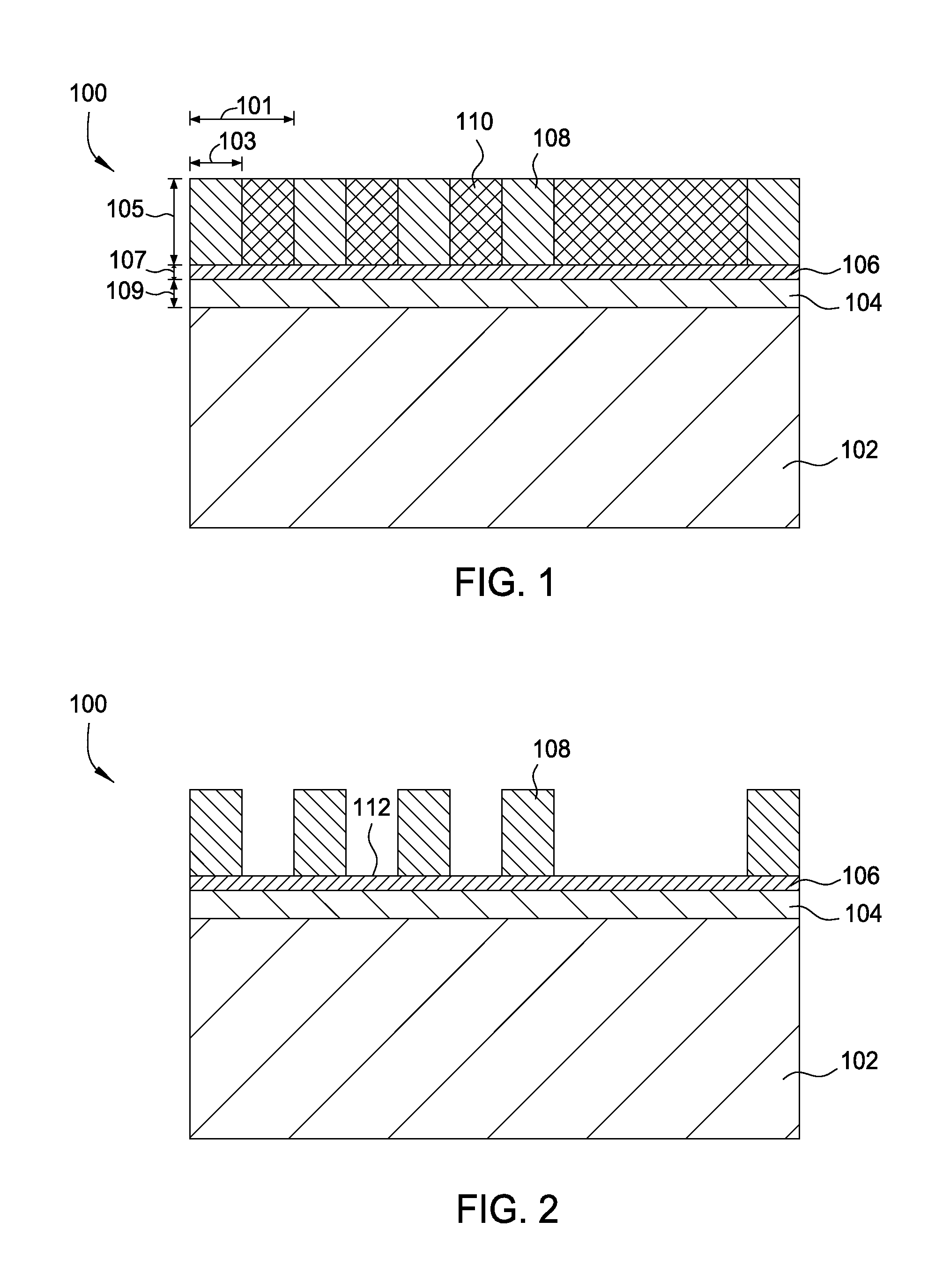
A semiconductor device according to an aspect of the invention comprises an n-type FinFET which is provided on a semiconductor substrate and which includes a first fin, a first gate electrode crossing a channel region of the first fin via a gate insulating film in three dimensions, and contact regions provided at both end of the first fin, a p-type FinFET which is provided on the semiconductor substrate and which includes a second fin, a second gate electrode crossing a channel region of the second fin via a gate insulating film in three dimensions, and contact regions provided at both end of the second fin, wherein the n- and the p-type FinFET constitute an inverter circuit, and the fin width of the contact region of the p-type FinFET is greater than the fin width of the channel region of the n-type FinFET.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device including n-type and p-type FinFET's constituting an inverter structure
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
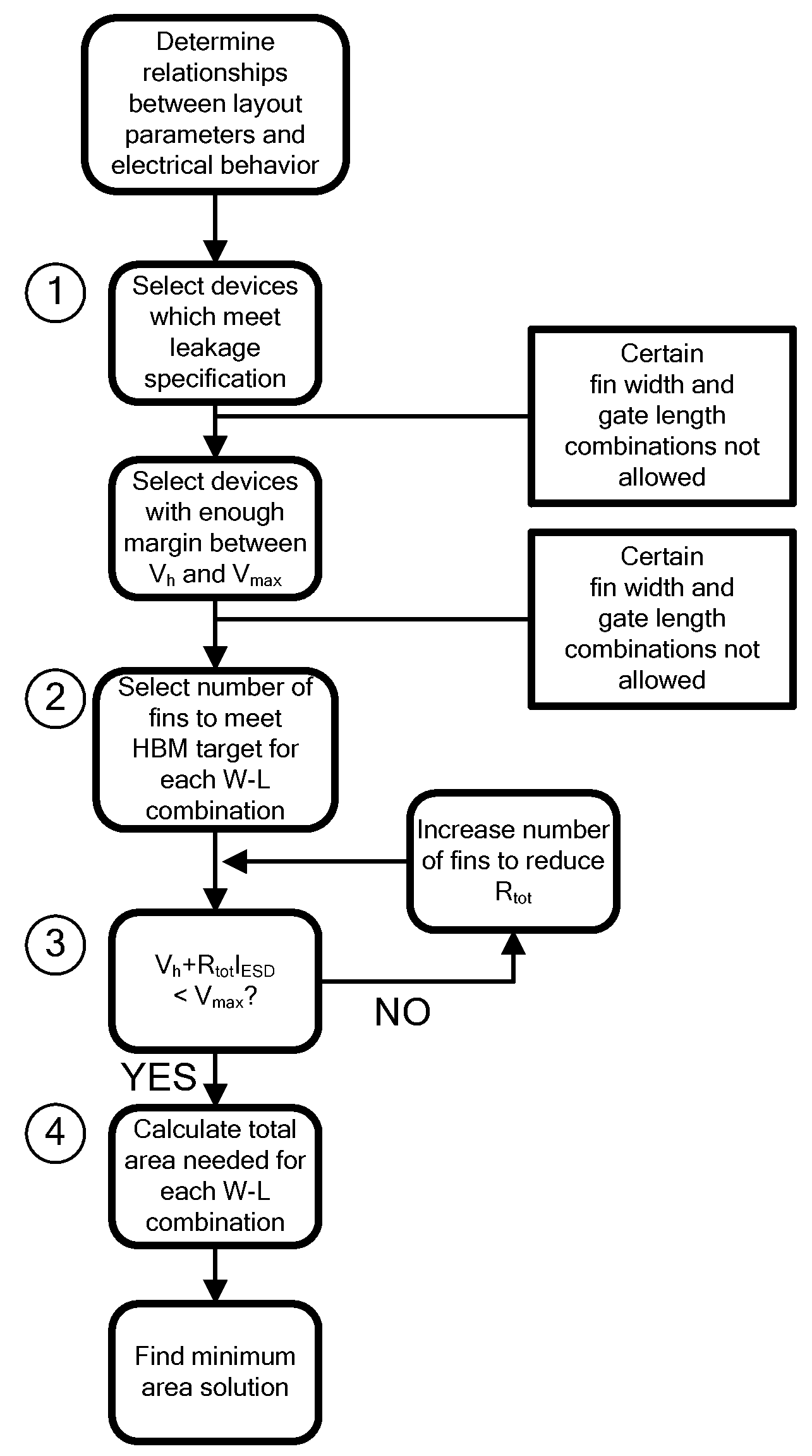
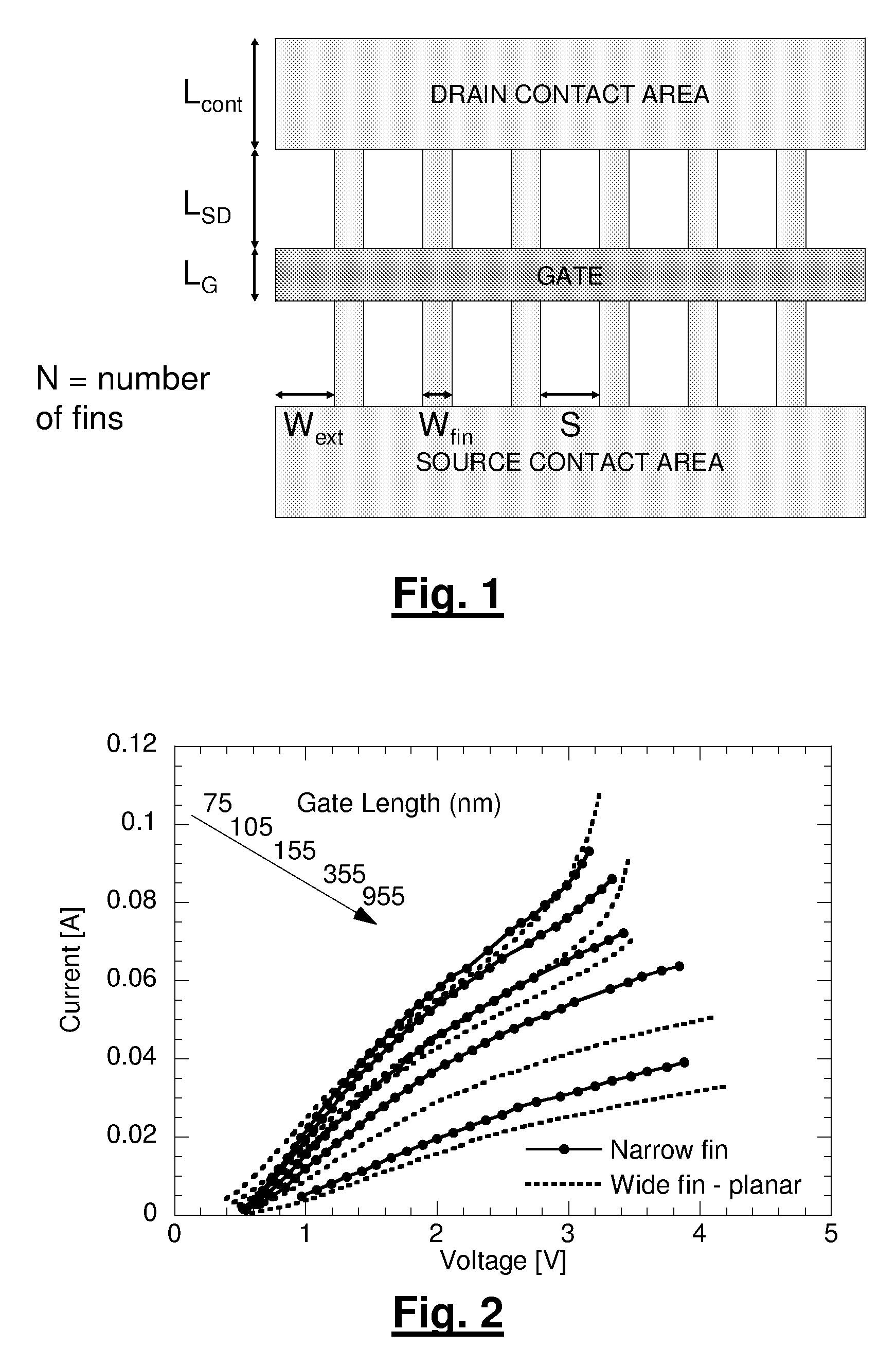
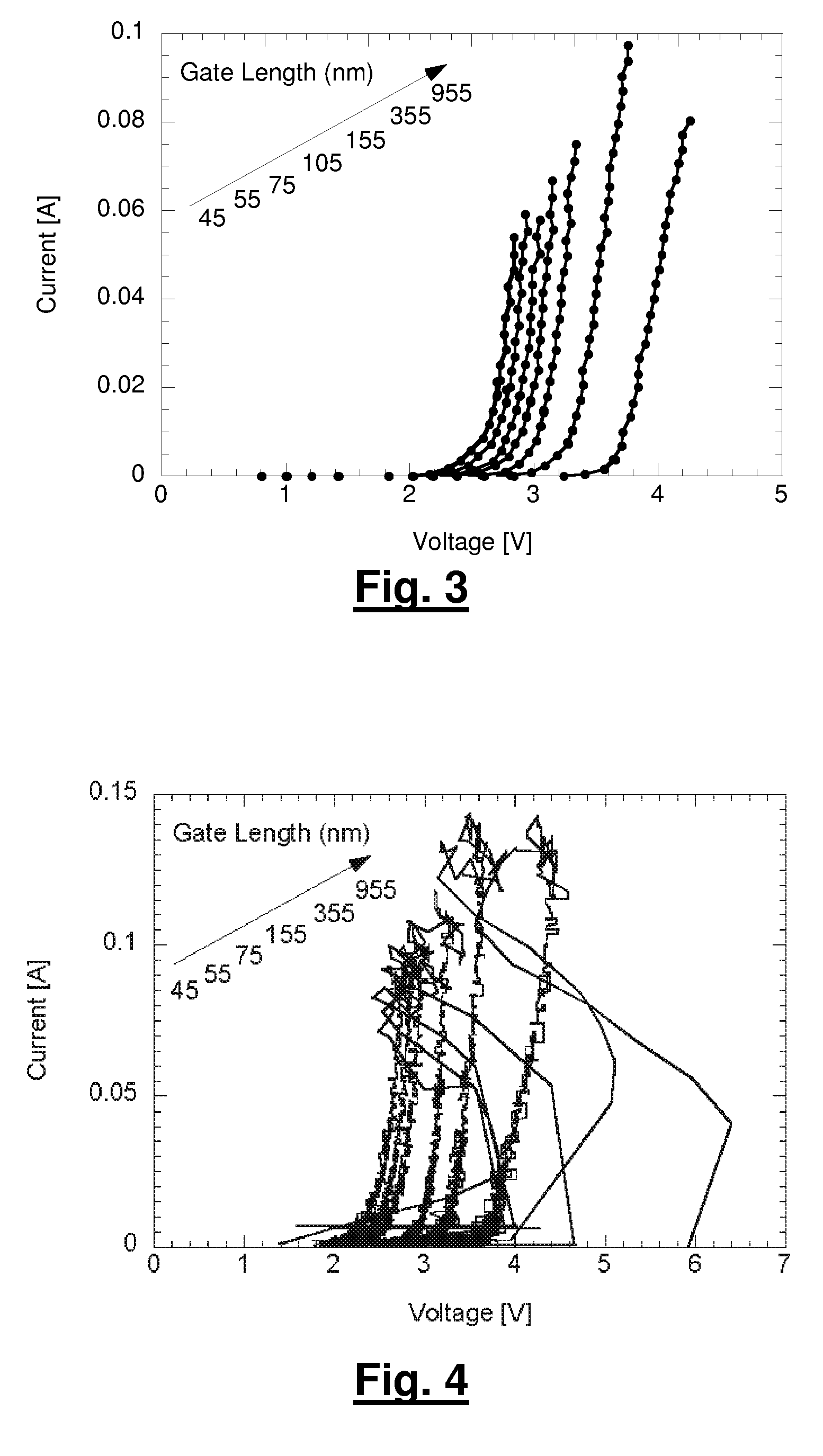
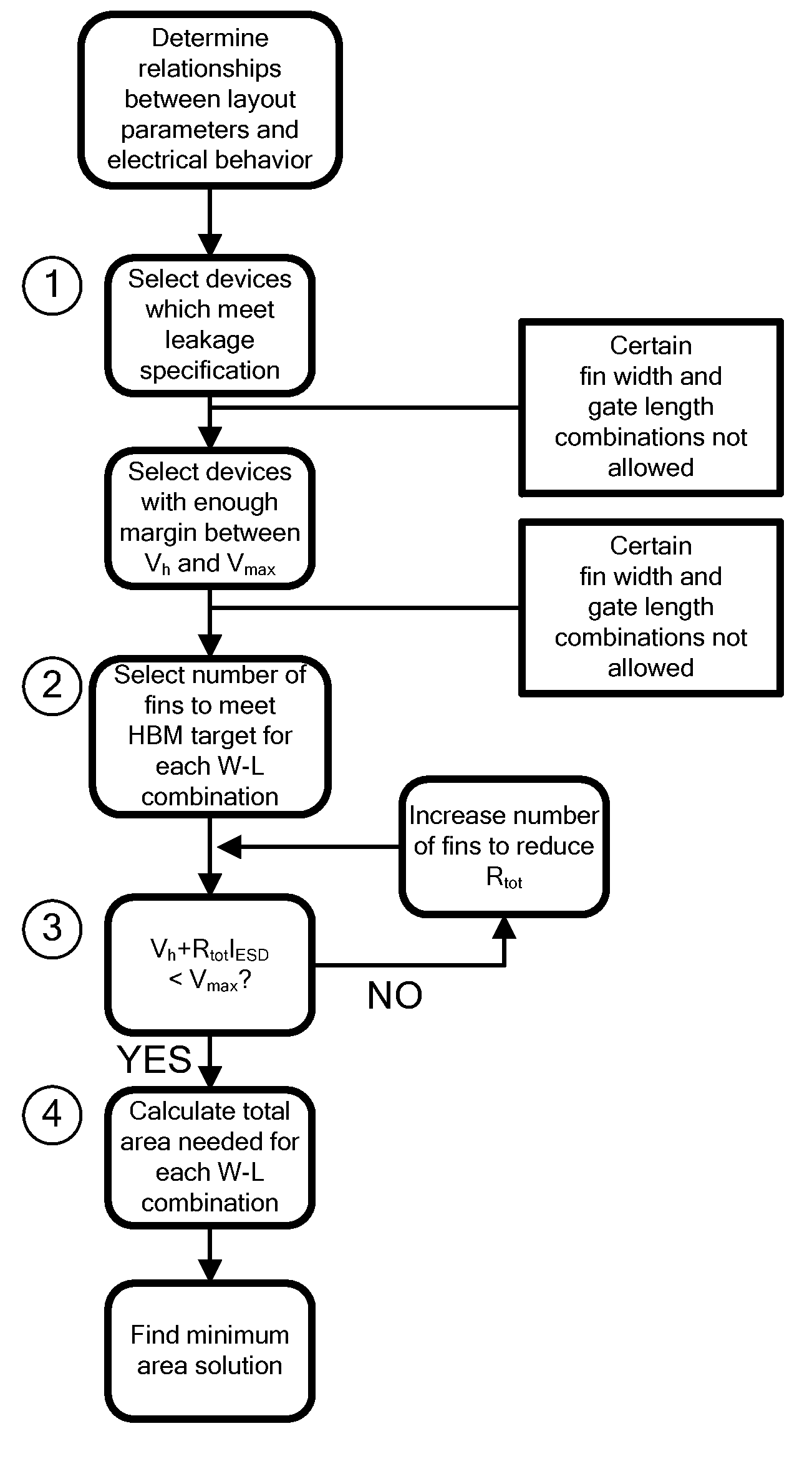
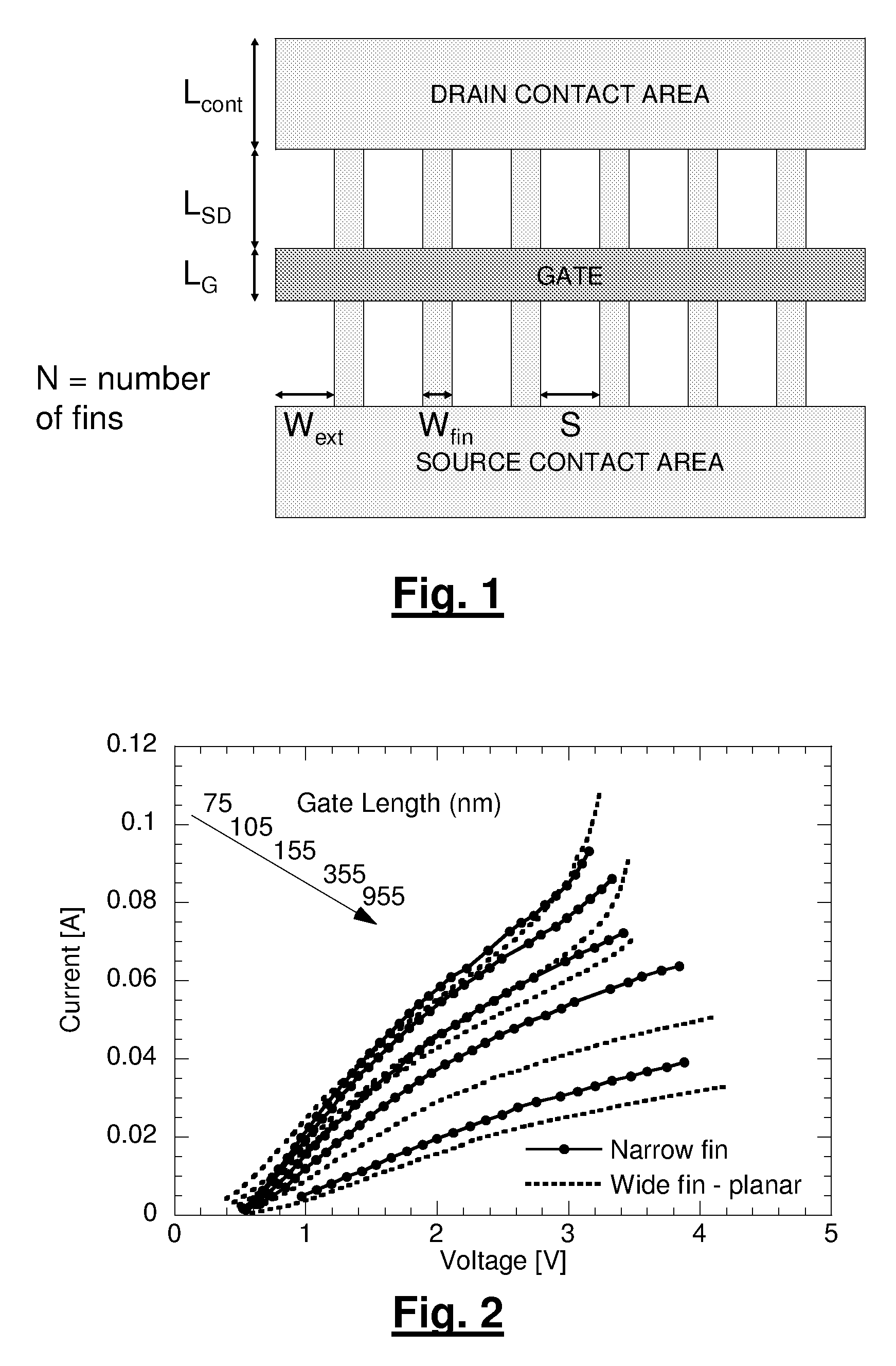
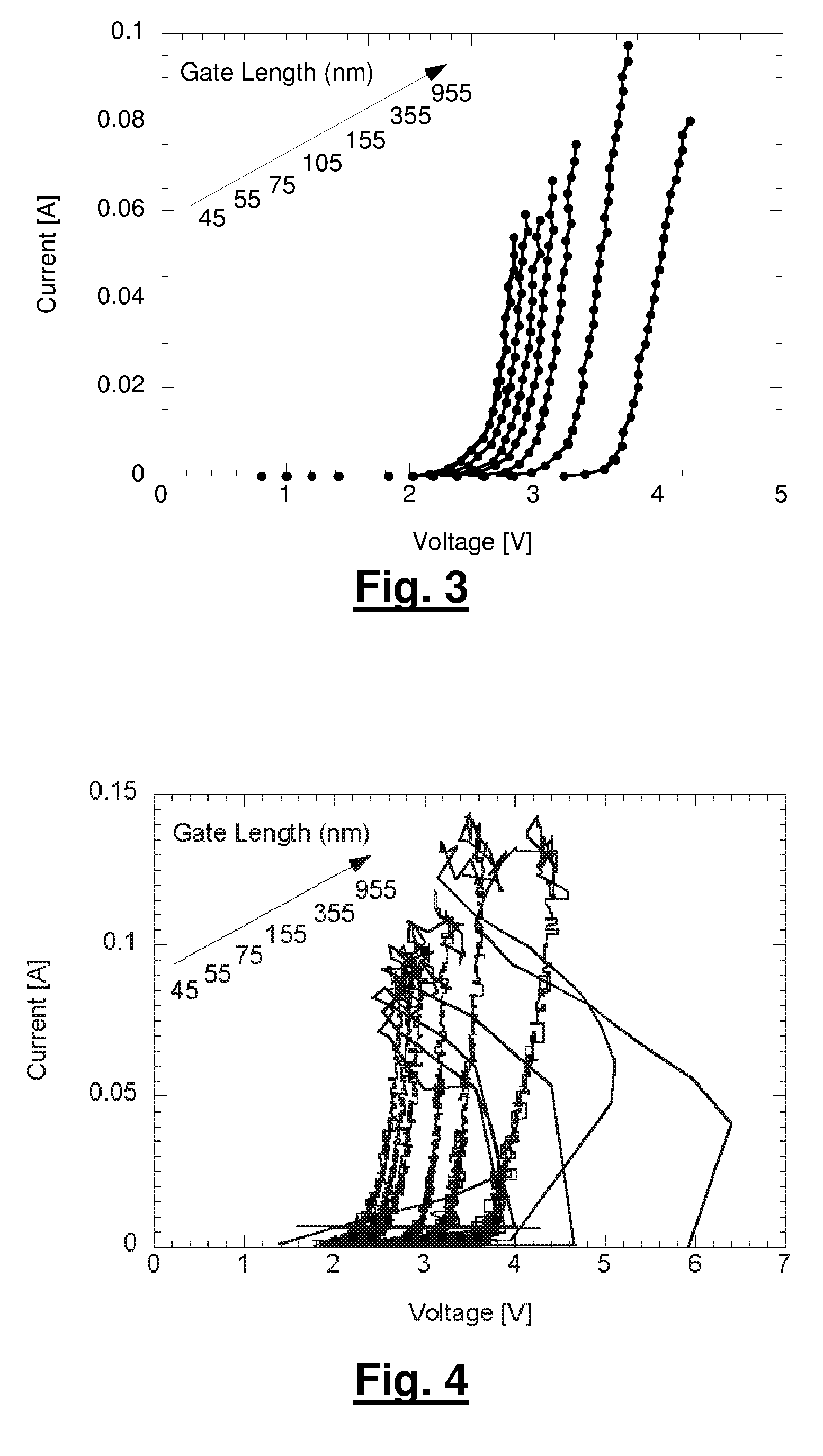
Design Methodology for MuGFET ESD Protection Devices
InactiveUS20090280582A1Easy to optimizePromote resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyEngineering
A method for manufacturing a MuGFET ESD protection device having a given layout by means of a given manufacturing process, the method comprising selecting multiple interdependent layout and process parameters of which a first set are fixed by said manufacturing process and a second set are variable, selecting multiple combinations of possible layout and process parameter values which meet predetermined ESD constraints; determining an optimum value for at least one other parameter in view of a predetermined design target apart from the predetermined ESD constraints; determining values for fin width (Wfin), gate length (LG) and number of fins (N) on the basis of the optimum value; and manufacturing said MuGFET ESD protection device using the given manufacturing and process values.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Design methodology for MuGFET ESD protection devices
InactiveUS7923266B2Promote resultsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyEngineering
A method for manufacturing a MuGFET ESD protection device having a given layout by means of a given manufacturing process, the method comprising selecting multiple interdependent layout and process parameters of which a first set are fixed by said manufacturing process and a second set are variable, selecting multiple combinations of possible layout and process parameter values which meet predetermined ESD constraints; determining an optimum value for at least one other parameter in view of a predetermined design target apart from the predetermined ESD constraints; determining values for fin width (Wfin), gate length (LG) and number of fins (N) on the basis of the optimum value; and manufacturing said MuGFET ESD protection device using the given manufacturing and process values.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
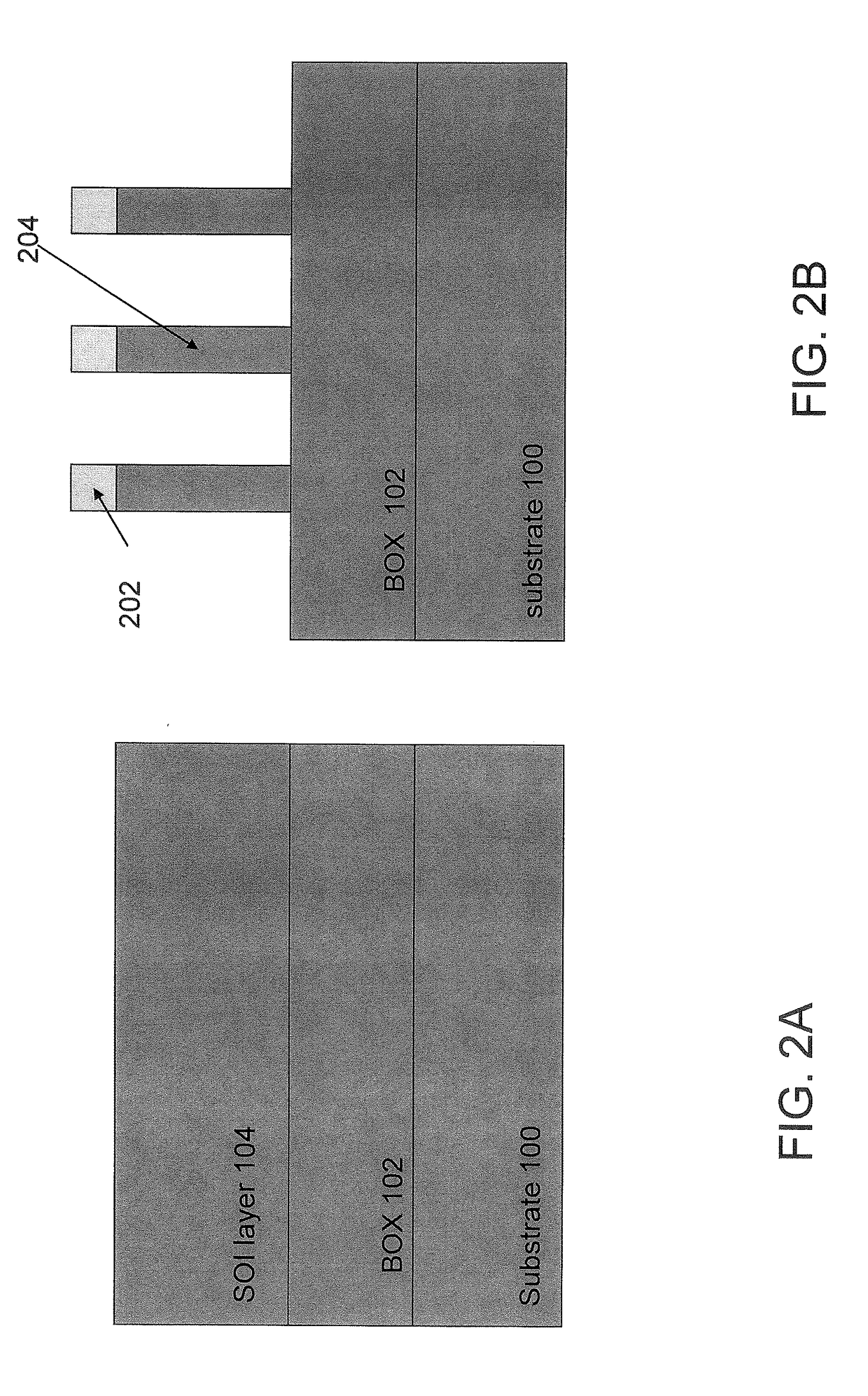
FinFET with sublithographic fin width
ActiveUS7625790B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCharge carrier mobility
At least one recessed region having two parallel edges is formed in an insulator layer over a semiconductor layer such that the lengthwise direction of the recessed region coincides with optimal carrier mobility surfaces of the semiconductor material in the semiconductor layer for finFETs to be formed. Self-assembling block copolymers are applied within the at least one recessed region and annealed to form a set of parallel polymer block lines having a sublithographic width and containing a first polymeric block component. The pattern of sublithographic width lines is transferred into the semiconductor layer employing the set of parallel polymer block lines as an etch mask. Sublithographic width semiconductor fins thus formed may have sidewalls for optimal carrier mobility for p-type finFETs and n-type finFETs.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Pull-back method of forming fins in FinFets
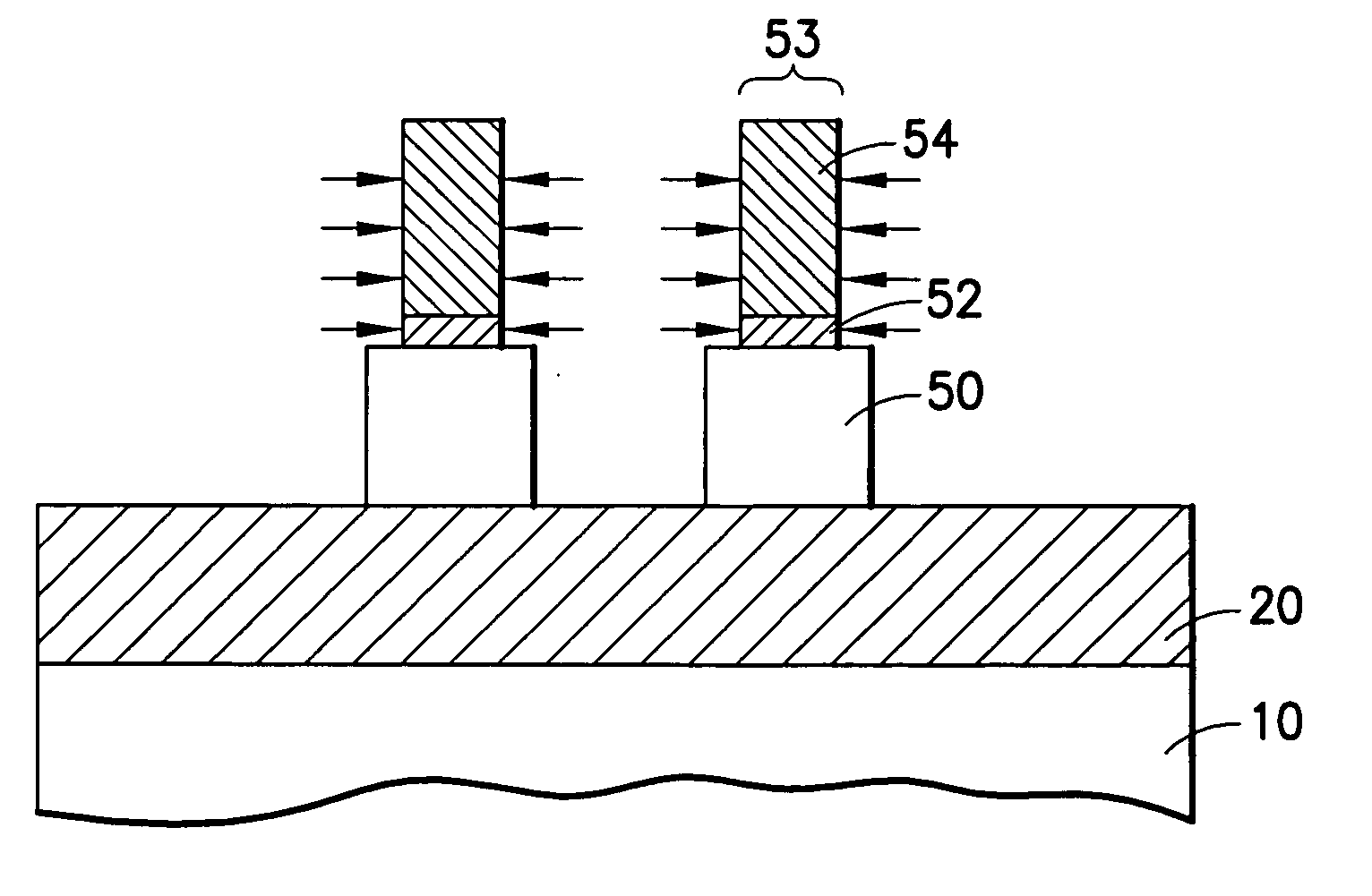
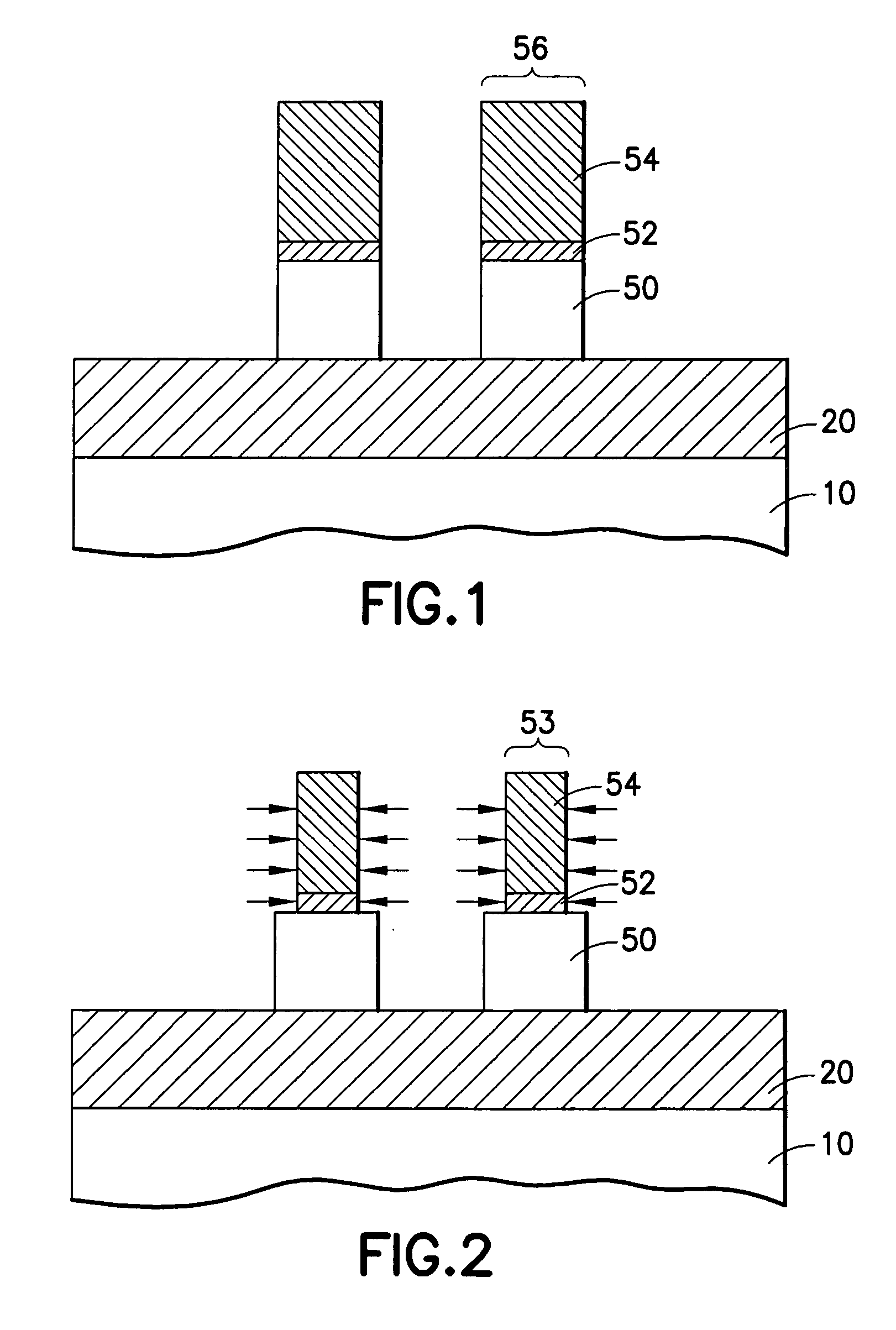
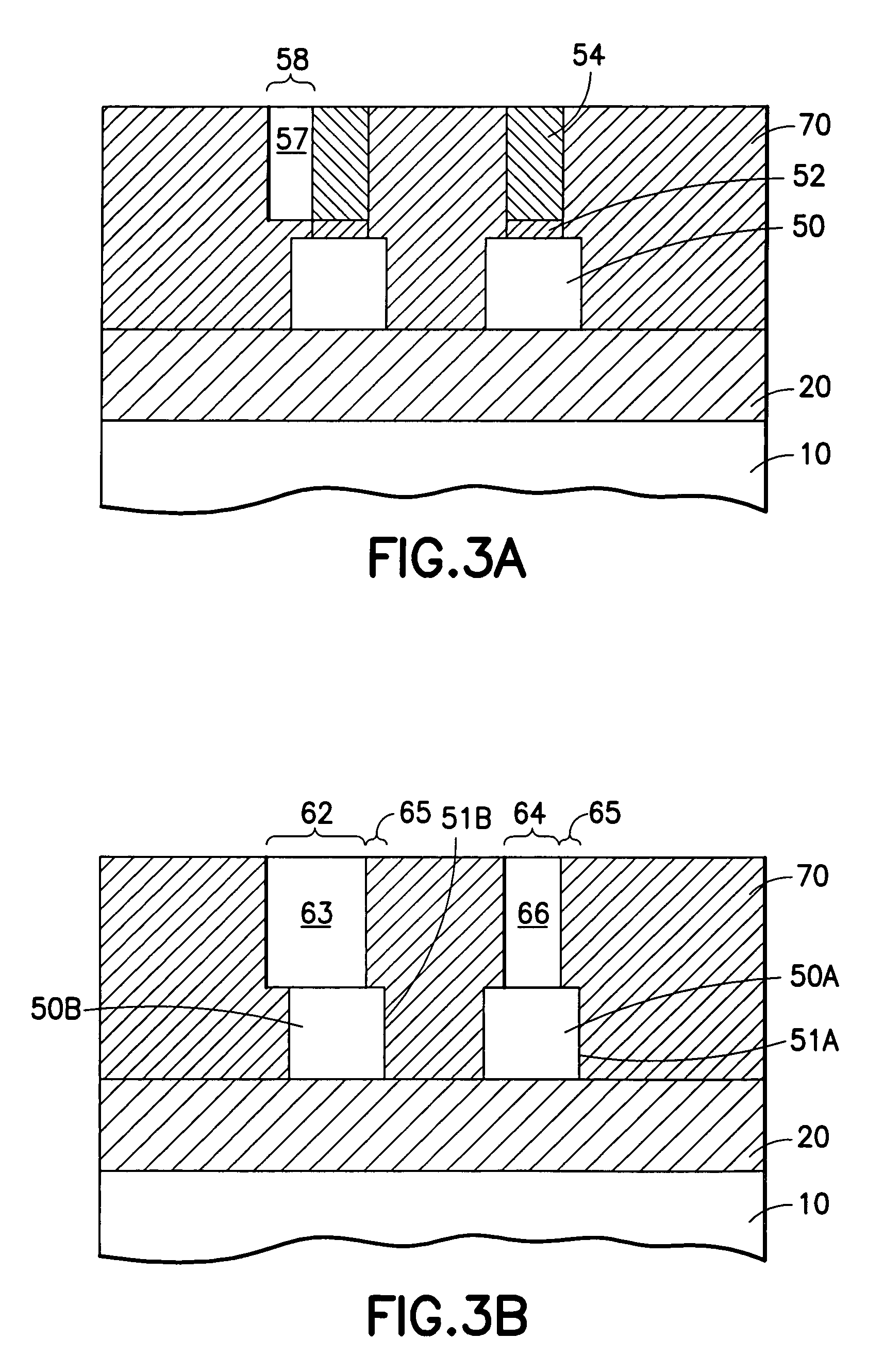
A method of forming integrated circuits having FinFET transistors includes a method of forming sub-lithographic fins, in which a mask defining a block of silicon including a pair of fins in reduced in width or pulled back by the thickness of one fin on each side, after which a second mask is formed around the first mask, so that after the first mask is removed, an aperture remains in the second mask having the width of the separation distance between the pair of fins. When the silicon is etched through the aperture, the fins are protected by the second mask, thereby defining fin thickness by the pullback step. An alternative method uses lithography of opposite polarity, first defining the central etch aperture between the two fins lithographically, then expanding the width of the aperture by a pullback step, so that filling the widened aperture with an etch-resistant plug defines the outer edges of the pair of fins, thereby setting the fin width without an alignment kstep.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Gate length controlled vertical fets
ActiveUS20180012993A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureEngineering
A semiconductor structure and a method a method of forming a vertical FET (Field-Effect Transistor), includes growing a bottom source-drain layer of a second type on a substrate of a first type, growing a channel layer on the bottom source-drain layer, forming a first fin from the channel layer with mask on top of the first fin. A width of the mask is wider than a final first fin width.
Owner:IBM CORP
Varying mugfet width to adjust device characteristics
InactiveUS20080303095A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotonic integrated circuitThreshold voltage
One embodiment of the present invention relates to an integrated circuit that includes a first multi-gate transistor that has a first fin width and a first threshold voltage. The integrated circuit also includes a second multi-gate transistor that has a second fin width that is greater than the first width and a second threshold voltage that is less than the first threshold voltage. Other circuits and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
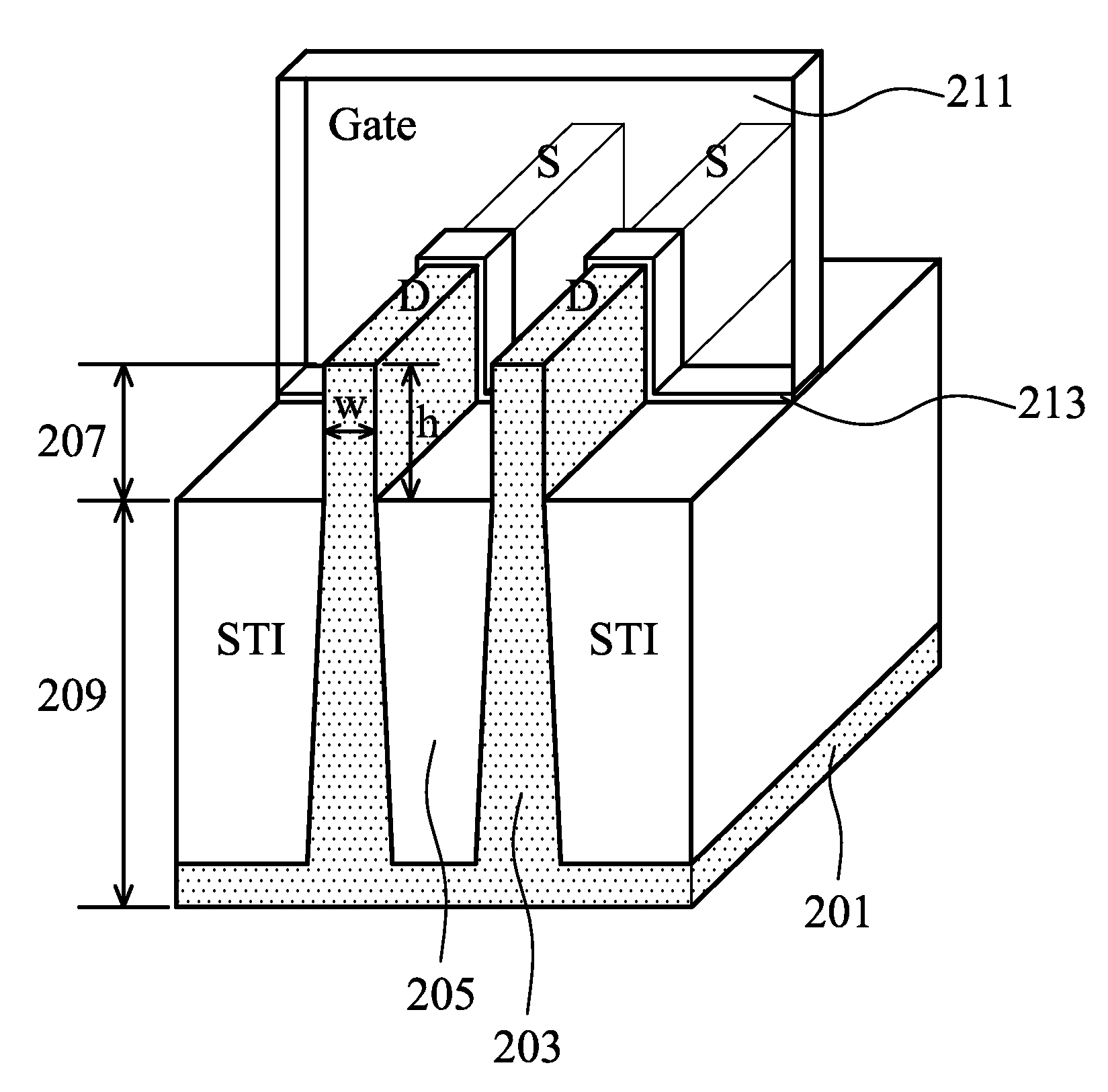
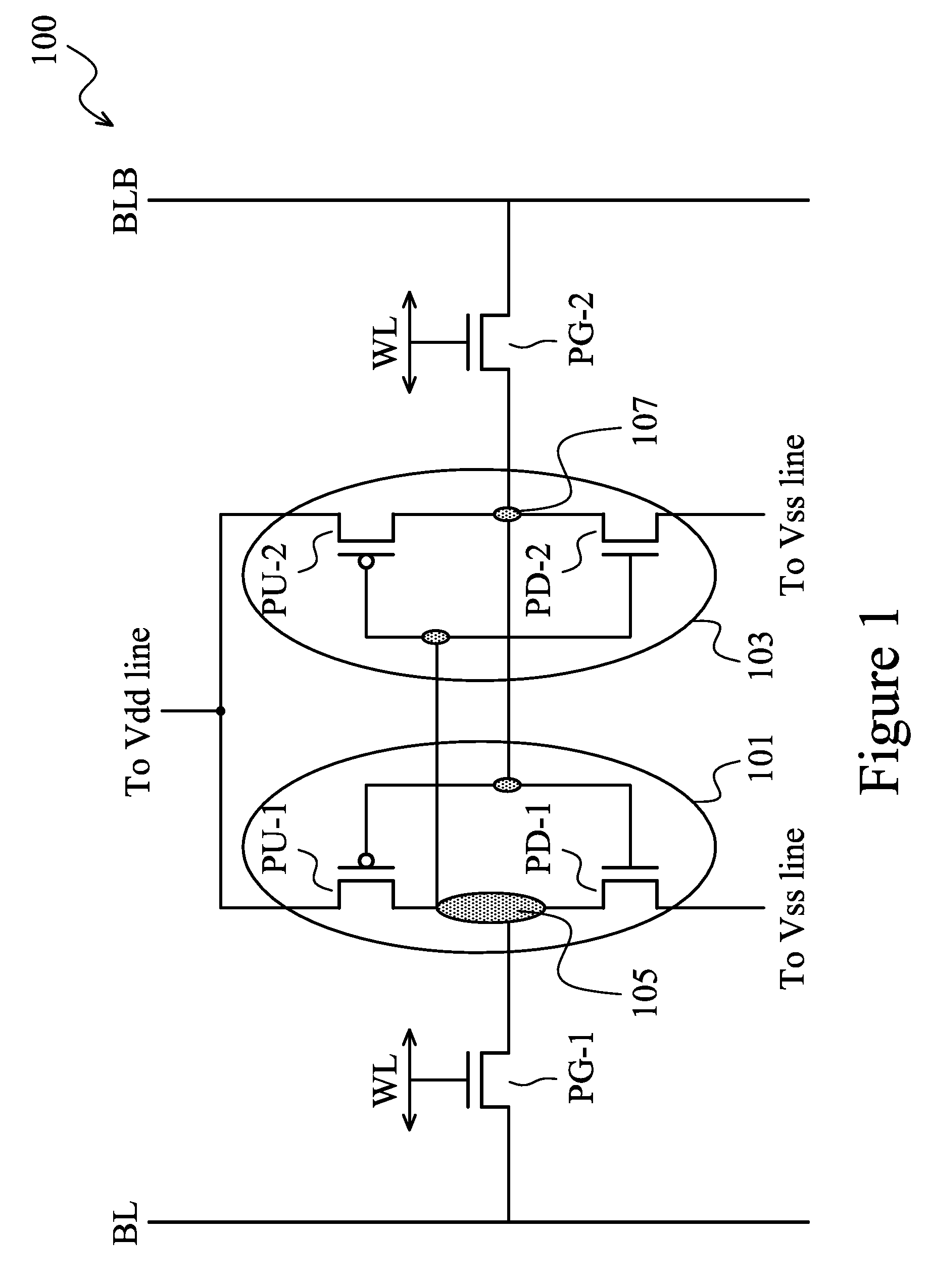
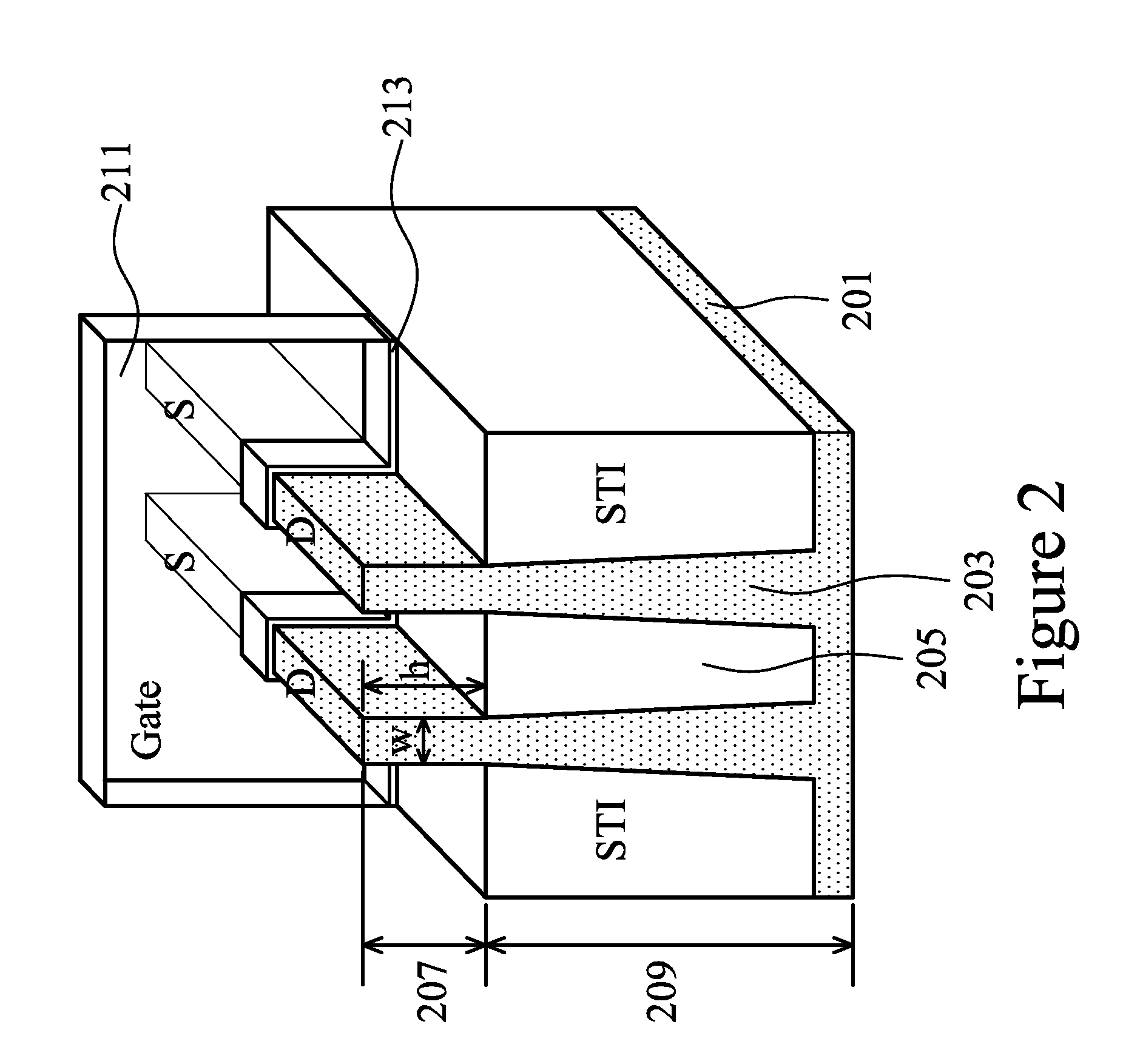
Cell Layout for SRAM FinFET Transistors
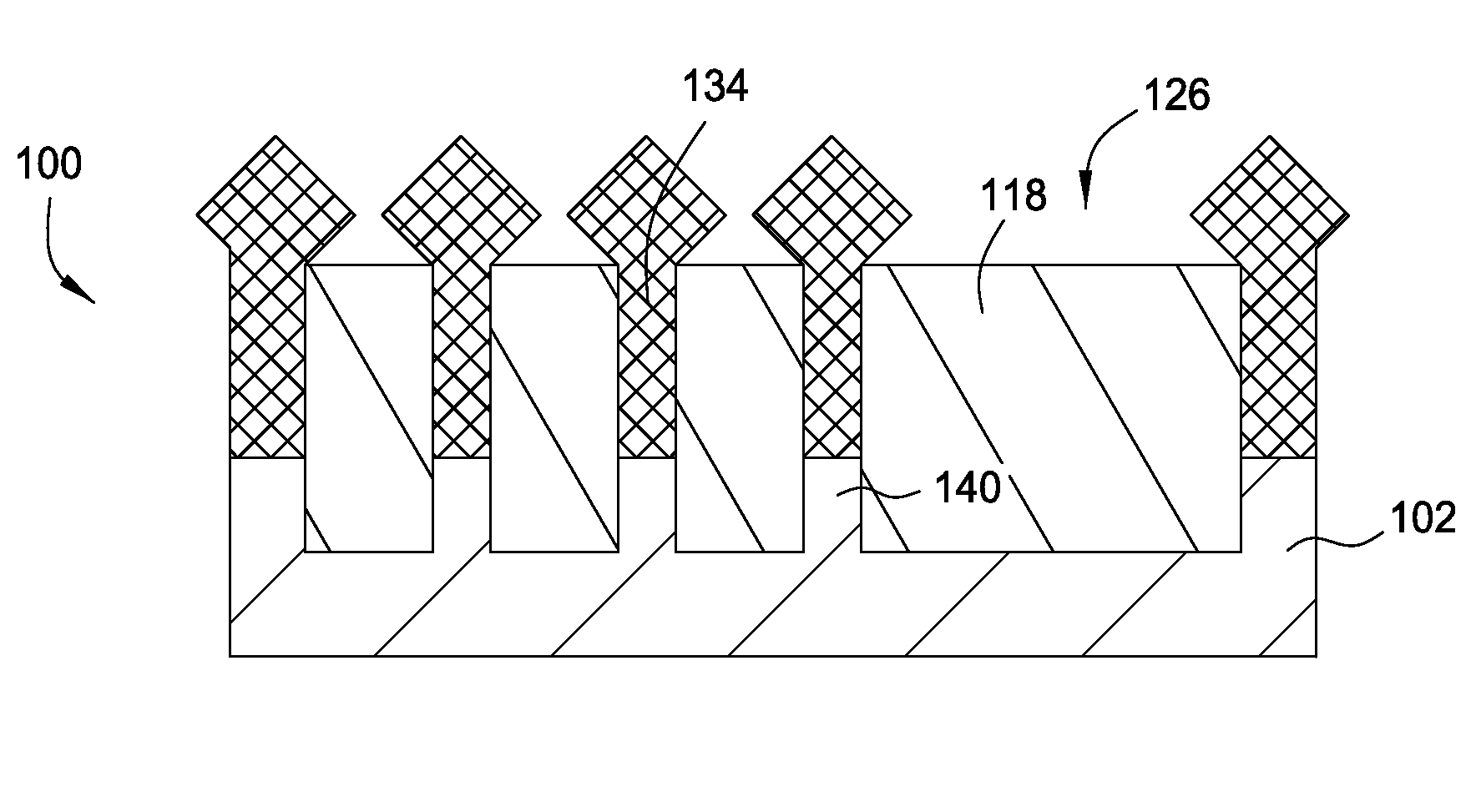
An SRAM array and method of making is disclosed. Each SRAM cell comprises two pull-up (PU), two pass-gate (PG), and two pull-down (PD) FinFETs. The PU transistors are adjacent to each other and include one active fin having a first fin width. Each PG transistor shares at least one active fin with a PD transistor. The active fin shared by a PG and a PD transistor has a second fin width smaller than the first fin width. The method includes patterning a plurality of fins including active fins and dummy fins and patterning and removing at least a portion of the dummy fins. No dummy fin is disposed between PU FinFETs in a memory cell. One dummy fin is disposed between a PU FinFET and the at least one active fin shared by a PG and a PD transistor. At least one dummy fin is disposed between adjacent memory cells.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Subtractive vfet process flow with replacement metal gate and metallic source/drain
A method and a semiconductor device includes a substrate, and a first device type formed on the substrate, the first device type including an active channel region including a first fin, the first fin including a first fin width which is narrower than a second fin width above and below the active channel region. A second device type can be formed on the same substrate, the second device type includes a second active channel region including a second fin, the second fin including a first fin width which is the same as the second fin width both above and below the second active channel region.
Owner:IBM CORP
Finfet with sublithographic fin width
ActiveUS20090026543A1Fine surfaceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsCharge carrier mobility
At least one recessed region having two parallel edges is formed in an insulator layer over a semiconductor layer such that the lengthwise direction of the recessed region coincides with optimal carrier mobility surfaces of the semiconductor material in the semiconductor layer for finFETs to be formed. Self-assembling block copolymers are applied within the at least one recessed region and annealed to form a set of parallel polymer block lines having a sublithographic width and containing a first polymeric block component. The pattern of sublithographic width lines is transferred into the semiconductor layer employing the set of parallel polymer block lines as an etch mask. Sublithographic width semiconductor fins thus formed may have sidewalls for optimal carrier mobility for p-type finFETs and n-type finFETs.
Owner:IBM CORP
Pull-back method of forming fins in FinFETs
A method of forming integrated circuits having FinFET transistors includes a method of forming sub-lithographic fins, in which a mask defining a block of silicon including a pair of fins in reduced in width or pulled back by the thickness of one fin on each side, after which a second mask is formed around the first mask, so that after the first mask is removed, an aperture remains in the second mask having the width of the separation distance between the pair of fins. When the silicon is etched through the aperture, the fins are protected by the second mask, thereby defining fin thickness by the pullback step. An alternative method uses lithography of opposite polarity, first defining the central etch aperture between the two fins lithographically, then expanding the width of the aperture by a pullback step, so that filling the widened aperture with an etch-resistant plug defines the outer edges of the pair of fins, thereby setting the fin width without an alignment kstep.
Owner:IBM CORP
Fabrication of fin field effect transistors utilizing different fin channel materials while maintaining consistent fin widths
A method of forming vertical fins on a substrate at the same time, the method including, forming a mask segment on a first region of the substrate while exposing the surface of a second region of the substrate, removing a portion of the substrate in the second region to form a recess, forming a fin layer in the recess, where the fin layer has a different material composition than the substrate, and forming at least one vertical fin on the first region of the substrate and at least one vertical fin on the second region of the substrate, where the vertical fin on the second region of the substrate includes a fin layer pillar formed from the fin layer and a substrate pillar.
Owner:IBM CORP
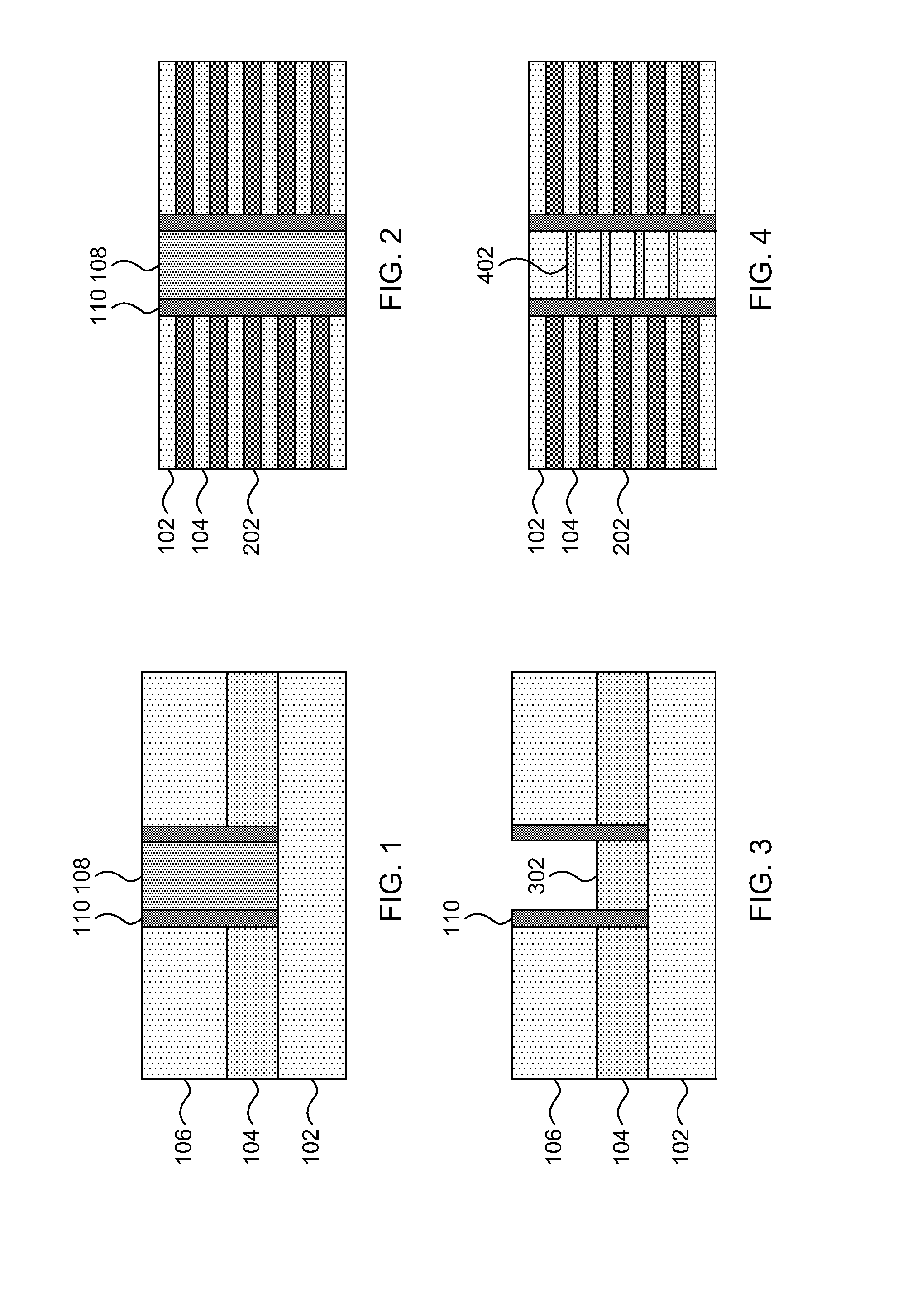
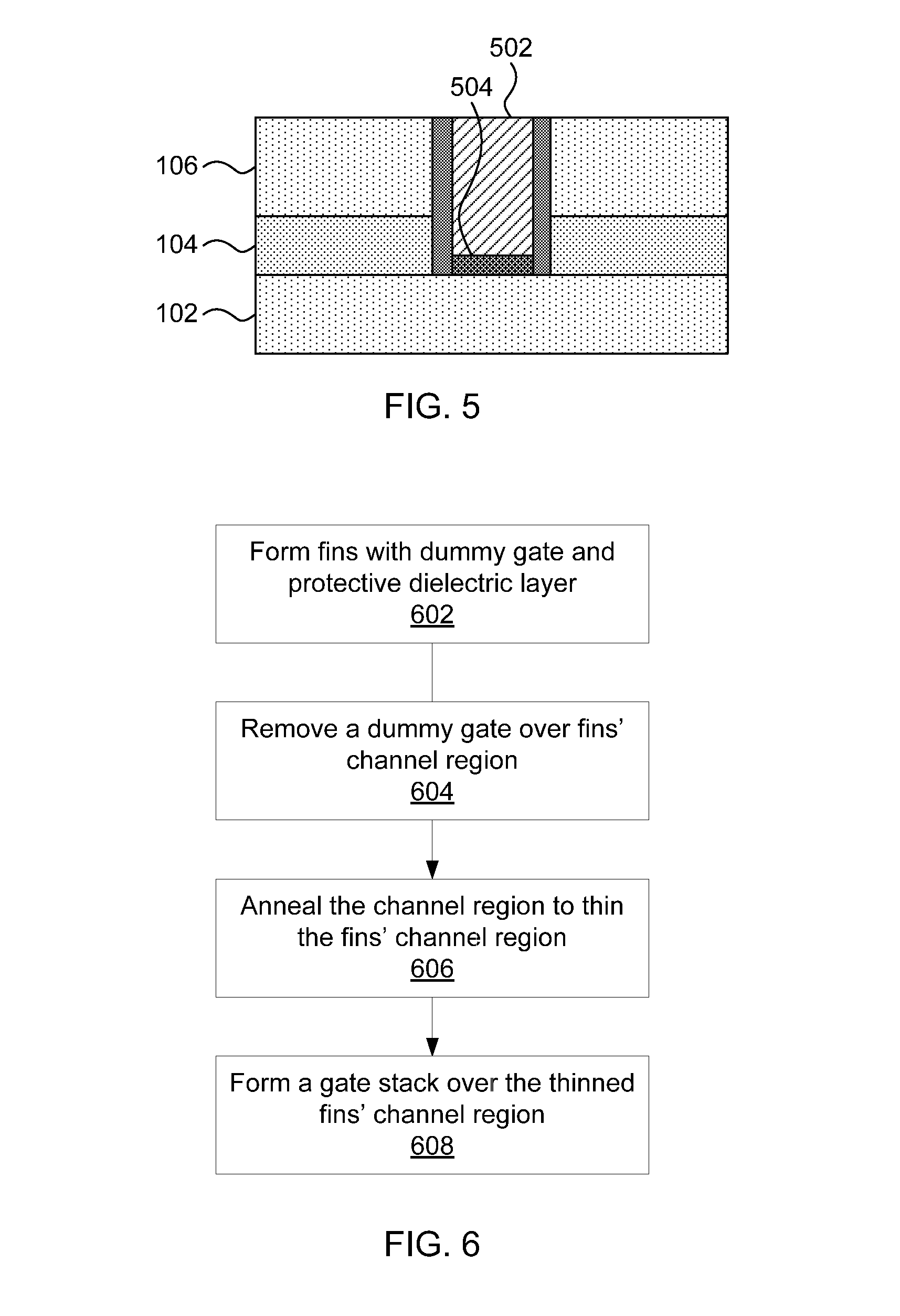
Localized fin width scaling using a hydrogen anneal
ActiveUS20140353735A1Reduce widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringProtection layer
Transistors and methods for fabricating the same include forming one or more semiconductor fins on a substrate; covering source and drain regions of the one or more semiconductor fins with a protective layer; annealing uncovered channel portions of the one or more semiconductor fins in a gaseous environment to reduce fin width and round corners of the one or more semiconductor fins; and forming a dielectric layer and gate over the thinned fins.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
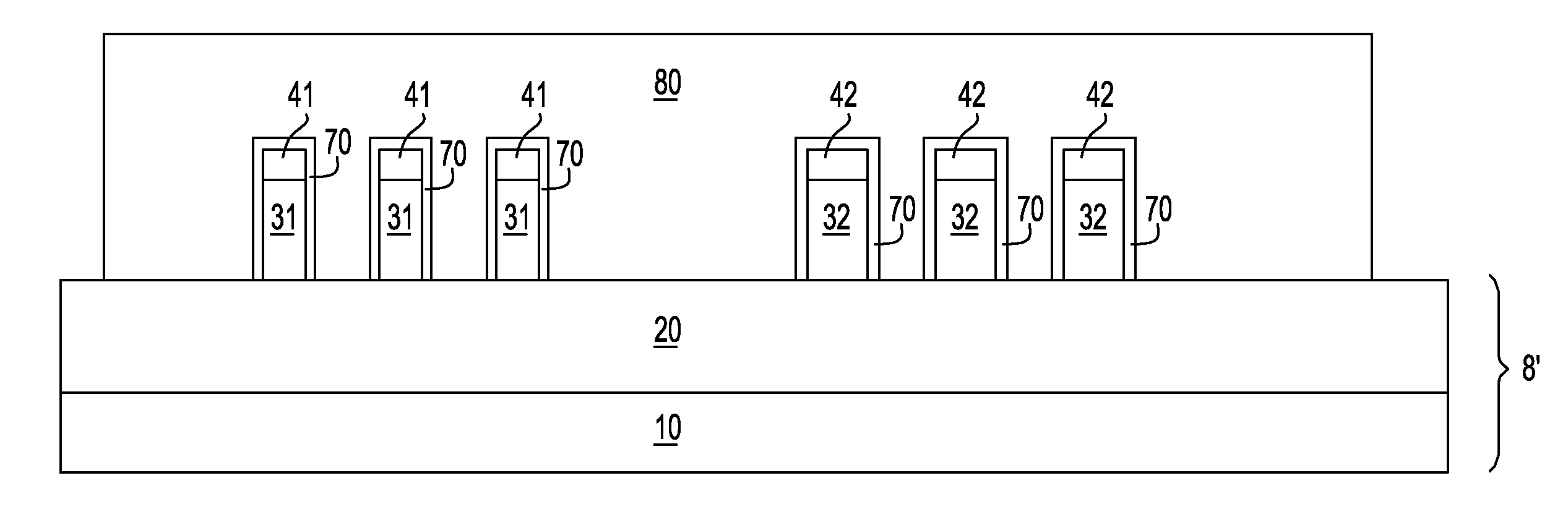
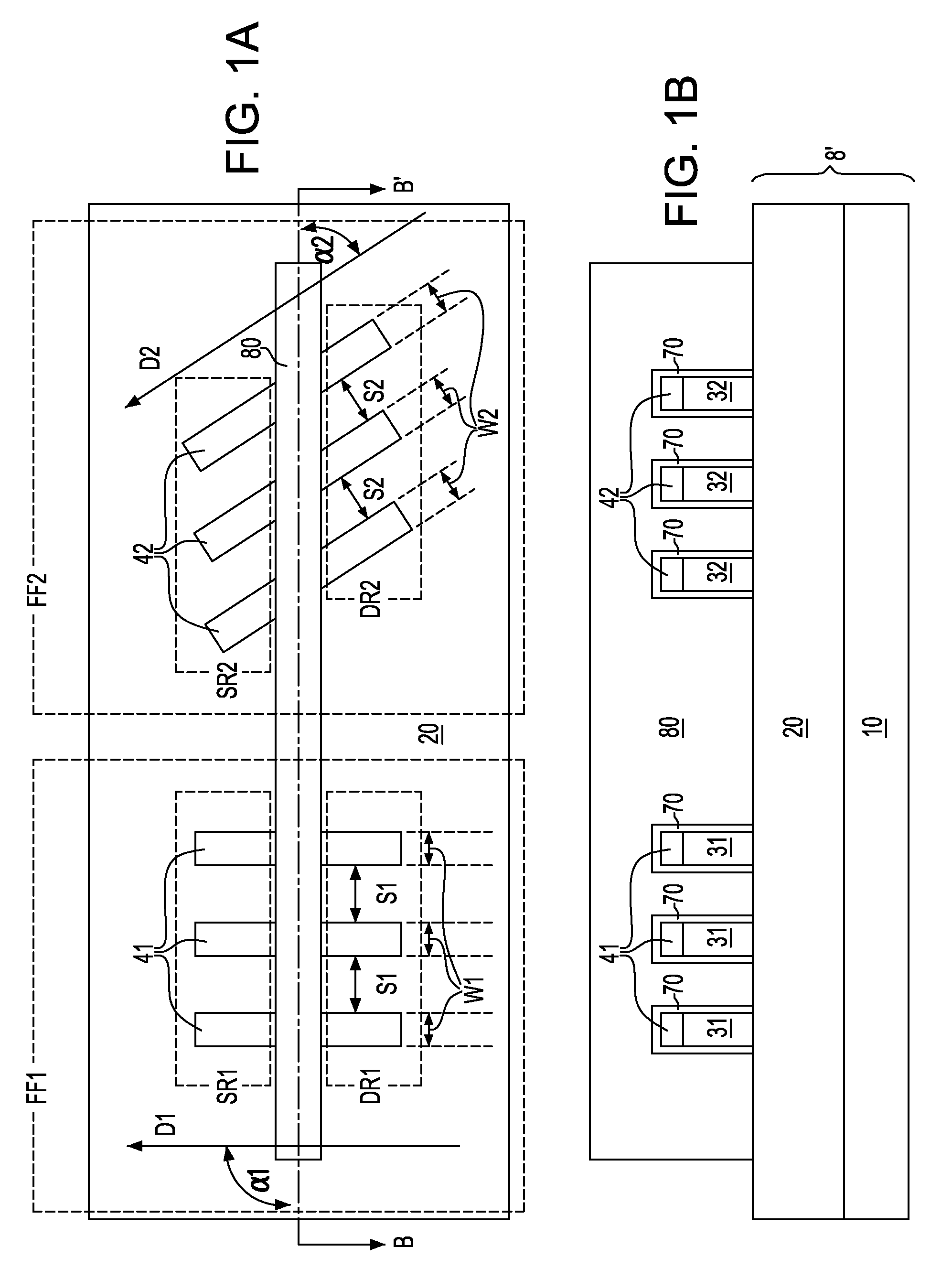
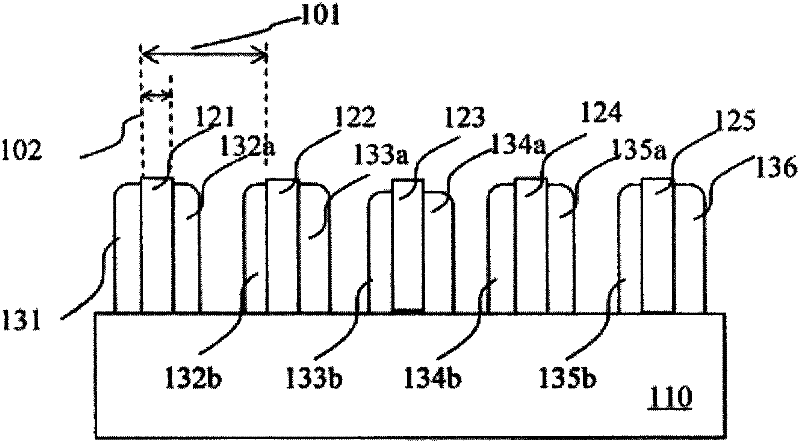
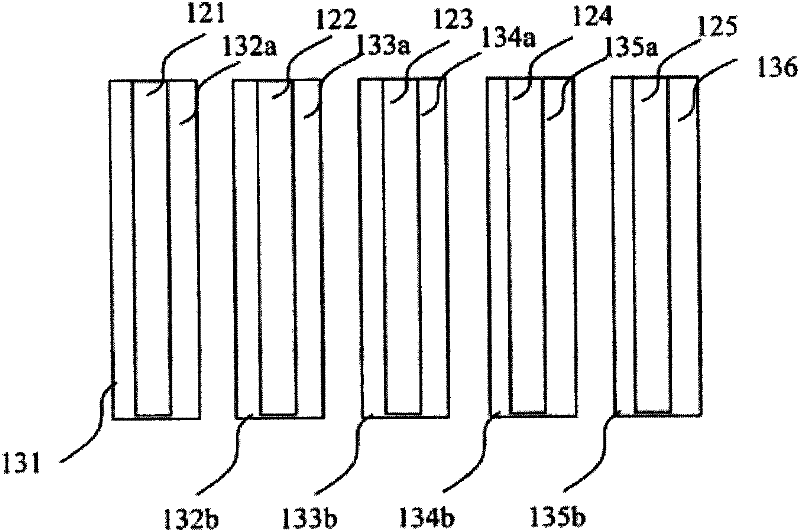
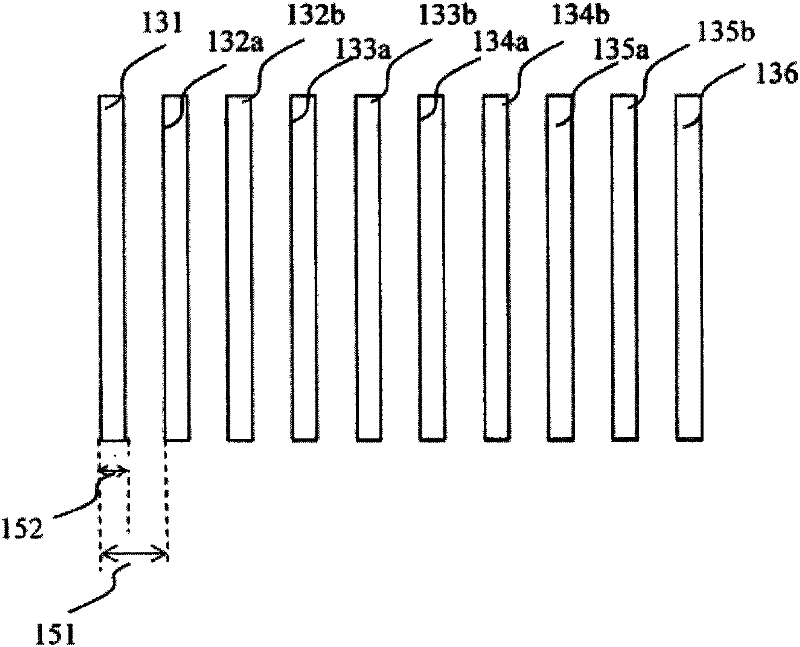
Semiconductor device having different fin widths
A semiconductor device includes at least one source region and at least one drain region. A plurality of fins extend between a source region and a drain region, wherein at least one fin has a different width than another fin. At least one gate is provided to control current flow through such fins. Fin spacing may be varied in addition to, or alternative to utilizing different fin widths.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Combined SADP fins for semiconductor devices and methods of making the same
A semiconductor cell includes a substrate and an array of at least five substantially parallel fins having substantially equal fin widths disposed on the substrate. The array includes a predetermined minimum spacing distance between at least one pair of adjacent fins within the array. The array has a first n-type fin for an n-type semiconductor device, and a first p-type fin for a p-type semiconductor device. The first p-type fin is disposed adjacent the first n-type fin and spaced a predetermined first n-to-p distance apart from the first n-type fin. The first n-to-p distance is greater than the minimum spacing distance and less than the sum of the fin width plus twice the minimum spacing distance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104752507ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate stackSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a substrate extending in a first direction to define a substrate length and a second direction perpendicular to the first direction to define a substrate width. A first semiconductor fin is formed on an upper surface of the substrate. The first semiconductor fin extends along the second direction at a first distance to define a first fin width. A first gate channel is formed between a first source / drain junction formed in the substrate and a second source / drain junction formed in the first semiconductor fin. A first gate stack is formed on sidewalls of the first gate channel. A first spacer is interposed between the first gate stack and the first source / drain junction.
Owner:IBM CORP
Trimming silicon fin width through oxidation and etch
InactiveUS20150140787A1Reduce widthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEtchingSemiconductor materials
Embodiments described herein generally relate to methods of forming sub-10 nm node FinFETs. Various processing steps are performed on a substrate to provide a trench defining a mandrel structure. Sidewalls of the mandrel structure and a bottom surface of the trench are oxidized and subsequently etched to reduce a width of the mandrel structure. The oxidation and etching of the mandrel structure may be repeated until a desired width of the mandrel structure is achieved. A semiconducting material is subsequently deposited on a regrowth region of the mandrel structure to form a fin structure. The oxidizing and etching the mandrel structure provides a method for forming the fin structure which can achieve sub-10 nm node dimensions and provide increasingly smaller FinFETs.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming fin structures for non-planar semiconductor device
ActiveUS20170263454A1Reduce adverse effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A method for forming fin structure includes following steps. A substrate is provided. A first mandrel and a plurality of second mandrels are formed on the substrate simultaneously. A plurality of spacers are respectively formed on sidewalls of the first mandrel and the second mandrels and followed by removing the first mandrel and the second mandrels to form a first spacer pattern and a plurality of second spacer patterns. Then the substrate is etched to simultaneously form at least a first fin and a plurality of second fins on the substrate with the first spacer pattern and the second spacer patterns serving as an etching mask. At least one of the second fins is immediately next to the first fin, and a fin width of the first fin is larger than a fin width of the second fins. Then, the second fins are removed from the substrate.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
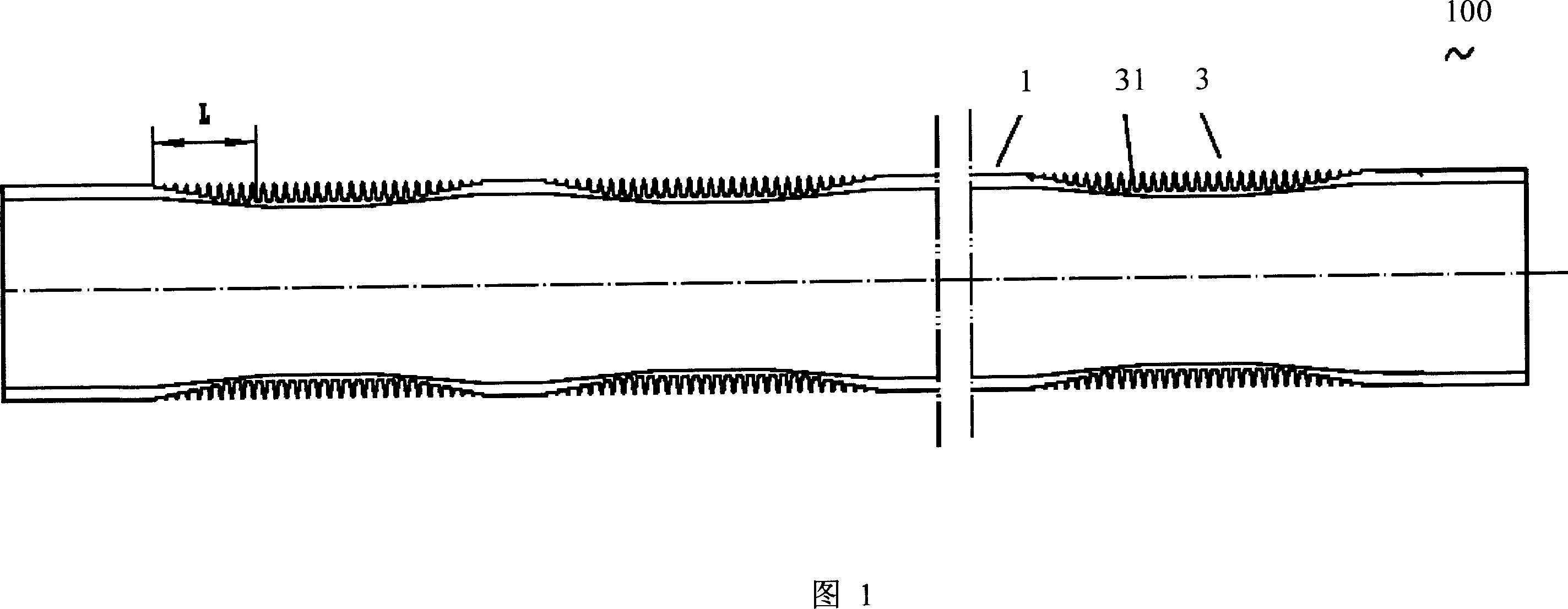
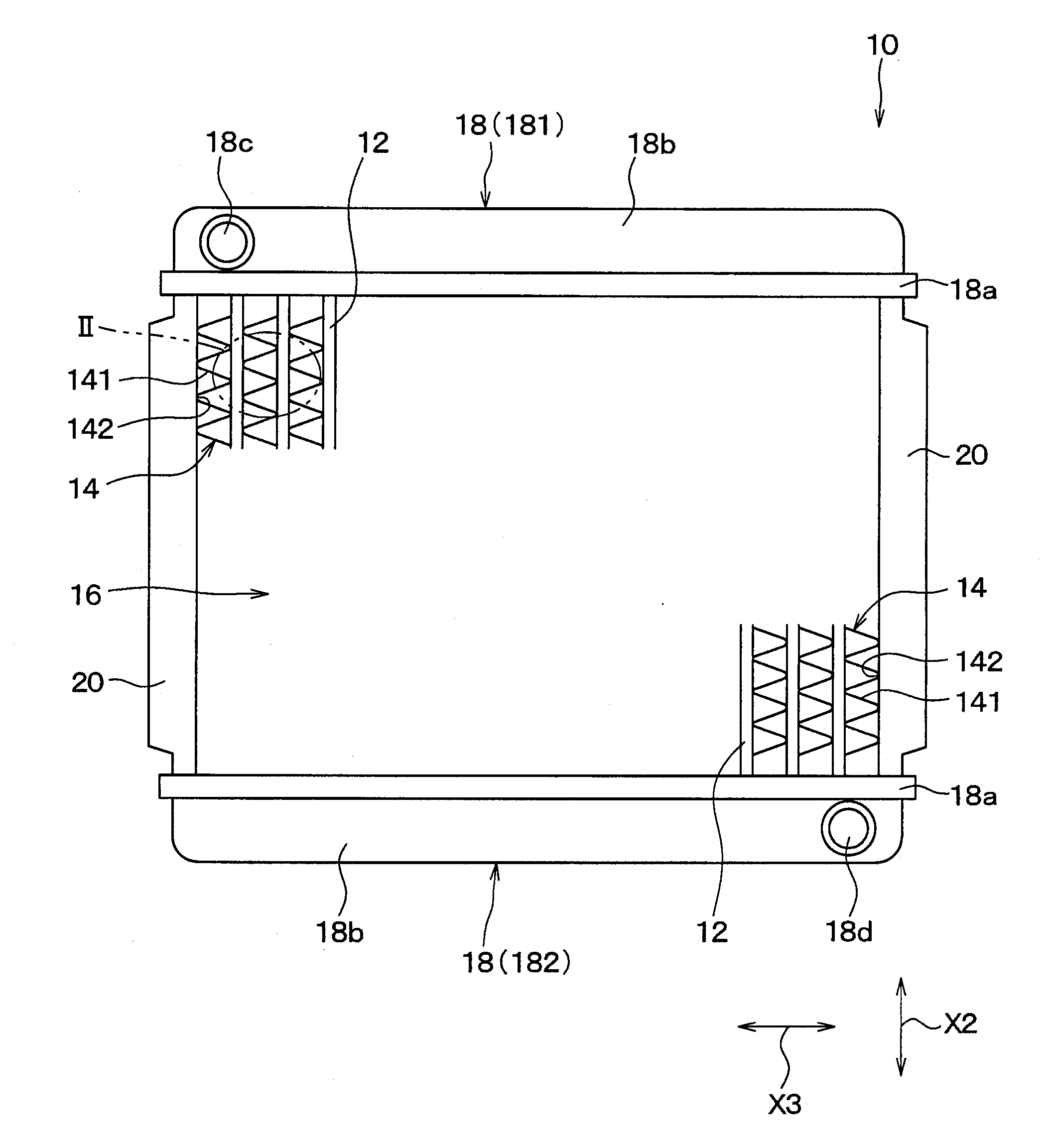
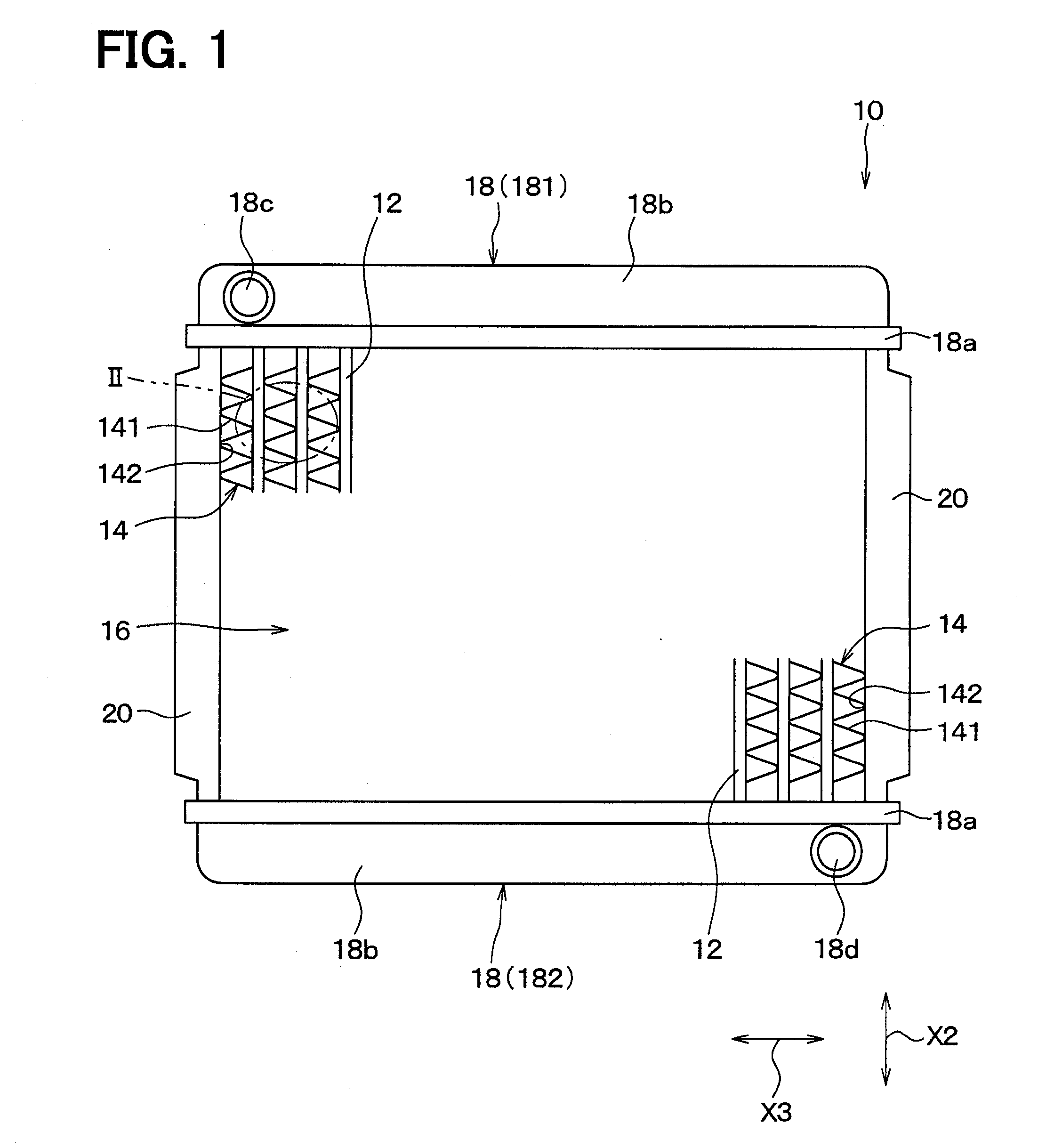
Corrugated fin
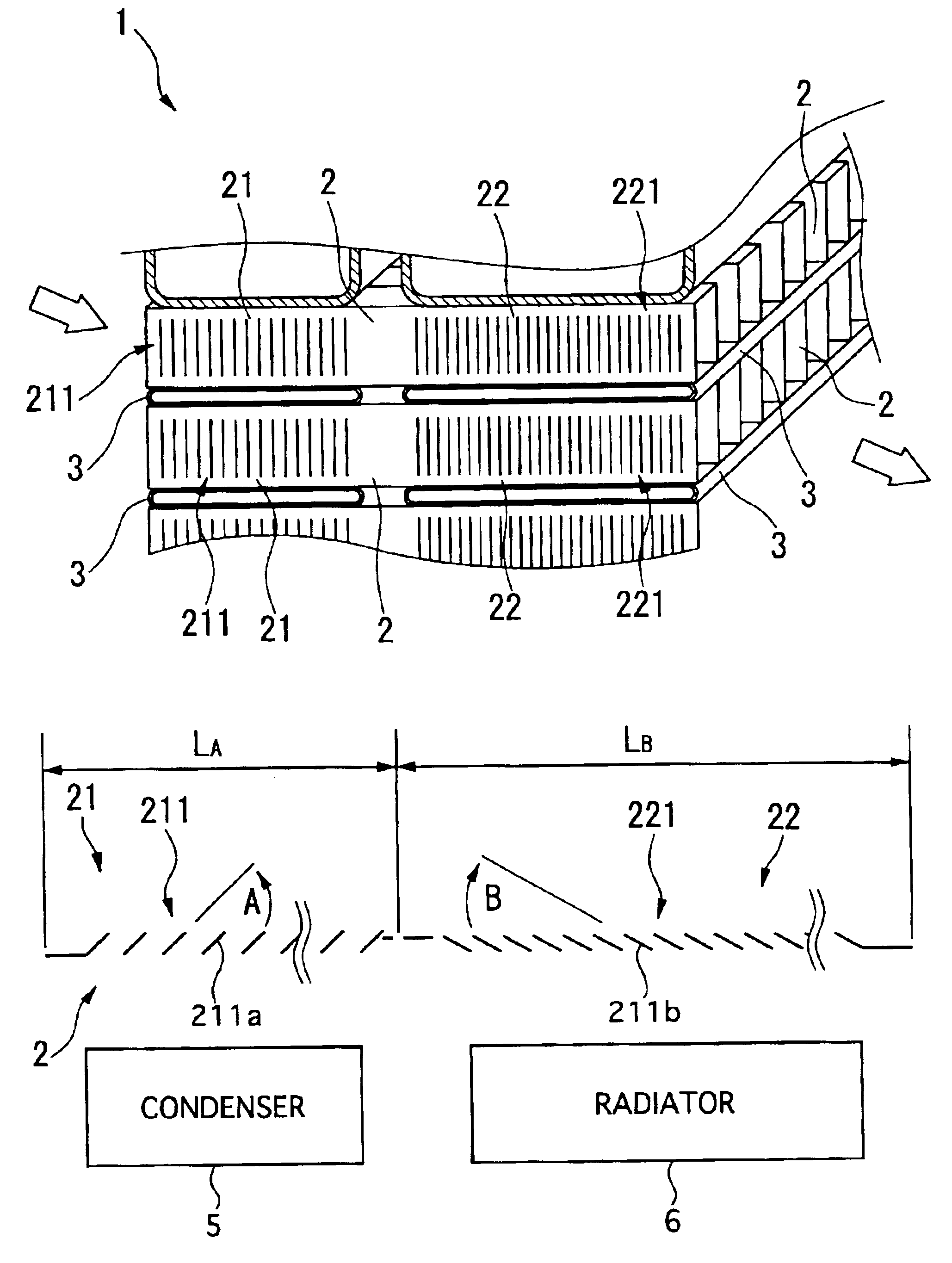
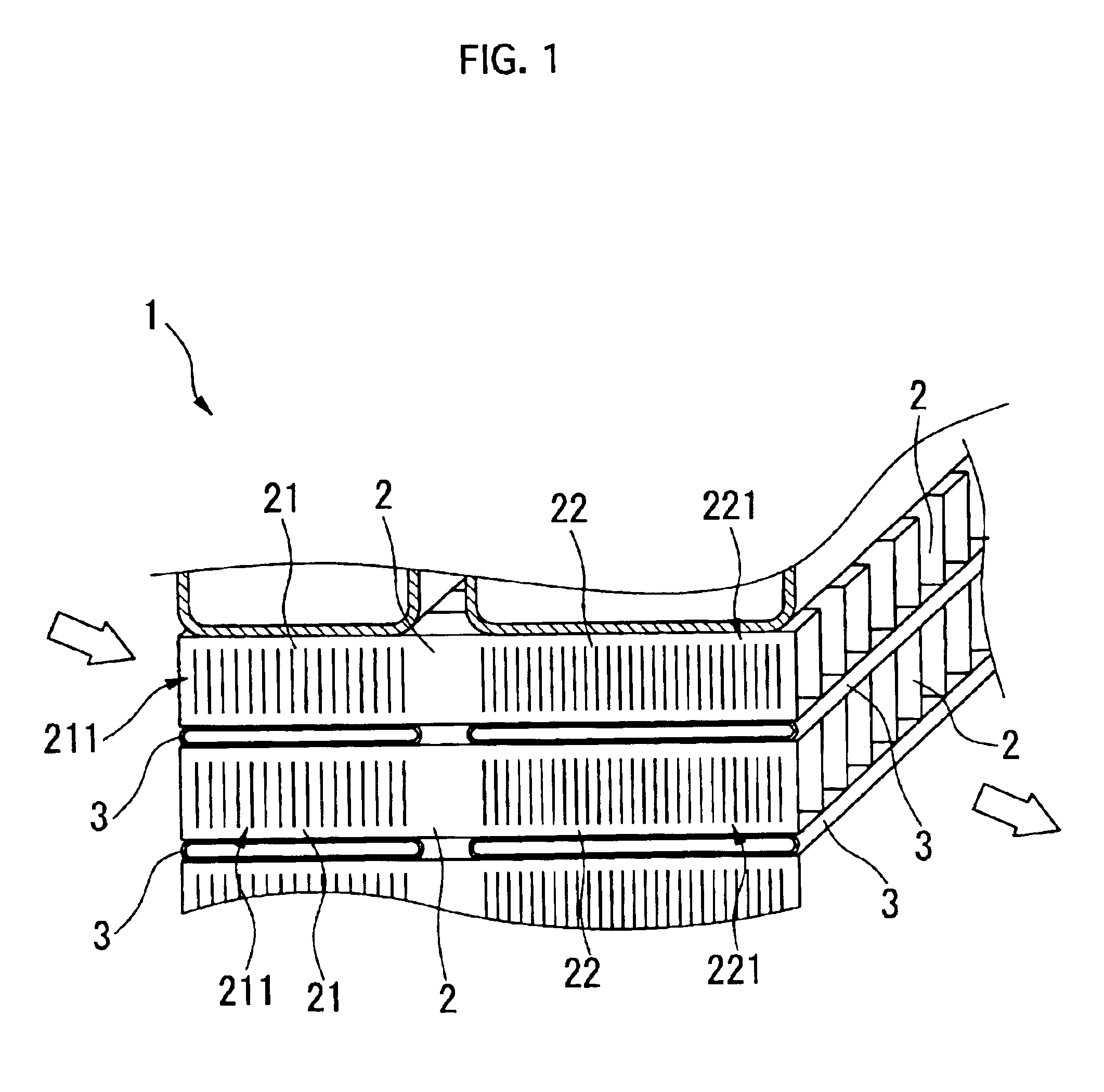
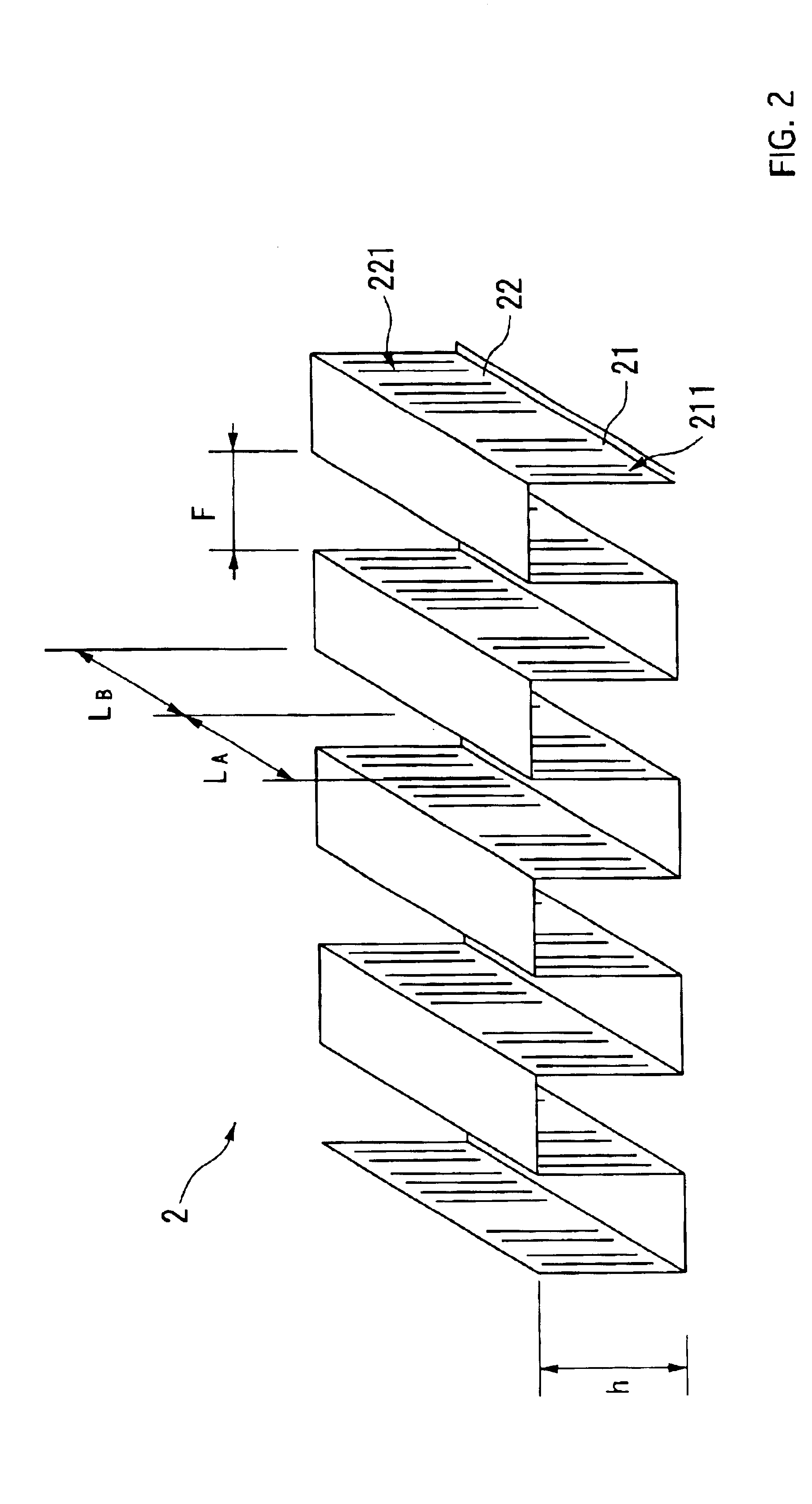
InactiveUS6938684B2Precise bendingDifferent widthLiquid coolingAir-treating devicesMobile vehiclePlate heat exchanger
A corrugated fin for a composite heat exchanger for motor vehicles includes a condenser portion and a radiator portion. The radiator portion is larger in fin width than the condenser portion. The condenser portion and the radiator portion respectively have first and second louvers formed corresponding to the fin widths. The first and second louvers respectively have first and second louver slats inclined in a direction which is different for each of the condenser portion and the radiator portion so as to oppose each other, and an inclination angle of the second louver slats is smaller than an inclination angle of the first louver slats.
Owner:CALSONIC KANSEI CORP
Method for adjusting fin width in integrated circuitry
ActiveCN102479754ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorIntegrated circuit
A method includes growing a plurality of parallel mandrels on a surface of a semiconductor substrate, each mandrel has at least two laterally opposite sidewalls and a predetermined width. The method further includes forming a first type of spacers on the sidewalls of the mandrels, wherein the first type of spacers between two adjacent mandrels are separated by a gap. The predetermined mandrel width is adjusted to close the gap between the adjacent first type of spacers to form a second type of spacers. The mandrels are removed to form a first type of fins from the first type of spacers, and to form a second type of fins from spacers between two adjacent mandrels. The second type of fins are wider than the first type of fins.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Copper heat-exchanging pipe of condenser for bromine refrigerator set
ActiveCN1982829AAvoid strandedReduce the numberEvaporators/condensersIndirect heat exchangersEngineeringCopper
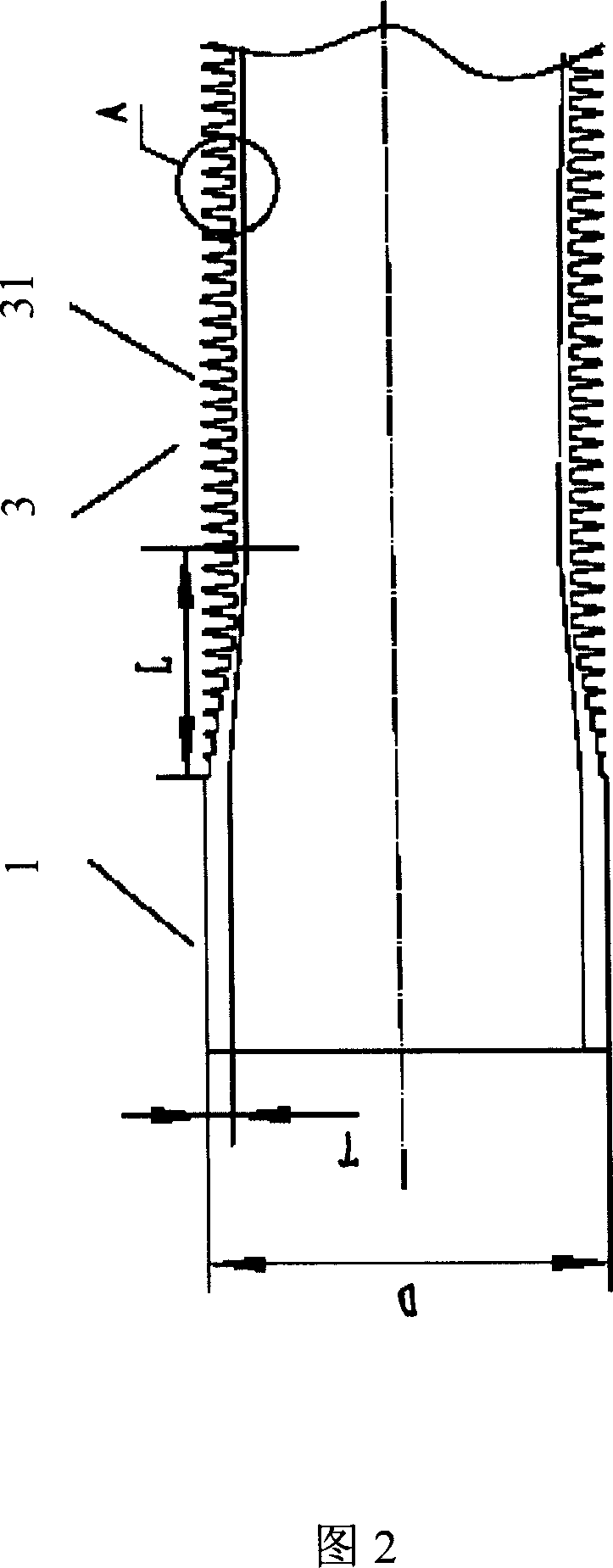
A copper heat-exchange tube for condensers of bromide refrigerating units is made up of at least one set of adjacent polish rod part and fins part. On the outside surface of the fins part are disposed continuous single-spiral fins and the section of the fin is triangle. The ratio of the fin width to the width of the fin slot bottom is 1 / 3-1 / 5, so as to extend the cooling area of the heat-exchange tube.
Owner:GOLDEN DRAGON PRECISE COPPER TUBE GROUP
Trimming silicon fin width through oxidation and etch
InactiveUS9412603B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEtchingSemiconductor materials
Embodiments described herein generally relate to methods of forming sub-10 nm node FinFETs. Various processing steps are performed on a substrate to provide a trench defining a mandrel structure. Sidewalls of the mandrel structure and a bottom surface of the trench are oxidized and subsequently etched to reduce a width of the mandrel structure. The oxidation and etching of the mandrel structure may be repeated until a desired width of the mandrel structure is achieved. A semiconducting material is subsequently deposited on a regrowth region of the mandrel structure to form a fin structure. The oxidizing and etching the mandrel structure provides a method for forming the fin structure which can achieve sub-10 nm node dimensions and provide increasingly smaller FinFETs.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Variable dual-tail-fin device for swimming
InactiveCN107224709AHas the characteristic of changing with speedImprove efficiencyGymnastic exercisingSwim finsEngineeringIntelligent control
The invention discloses a variable double tail fin equipment for swimming, which comprises a left tail fin, a right tail fin, and a double tail fin fixing rod. At least one caudal fin hinge structure is connected, and the fin span width or the fin span area of the left caudal fin plus the right caudal fin is variable; the variable double tail fin equipment for swimming also includes double tail fin intelligent control components, At least one of the left tail fin and the right tail fin is connected with the double tail fin control mechanism of the double tail fin intelligent control part through at least one linkage element between each other, which can realize the electric motor of fin width change or fin spread area change. Manipulation and automatic adjustment with speed; the variable double tail fin equipment for swimming is fixed or bound to at least one calf or at least one foot of the swimmer through the double tail fin fixing rod.
Owner:朱光
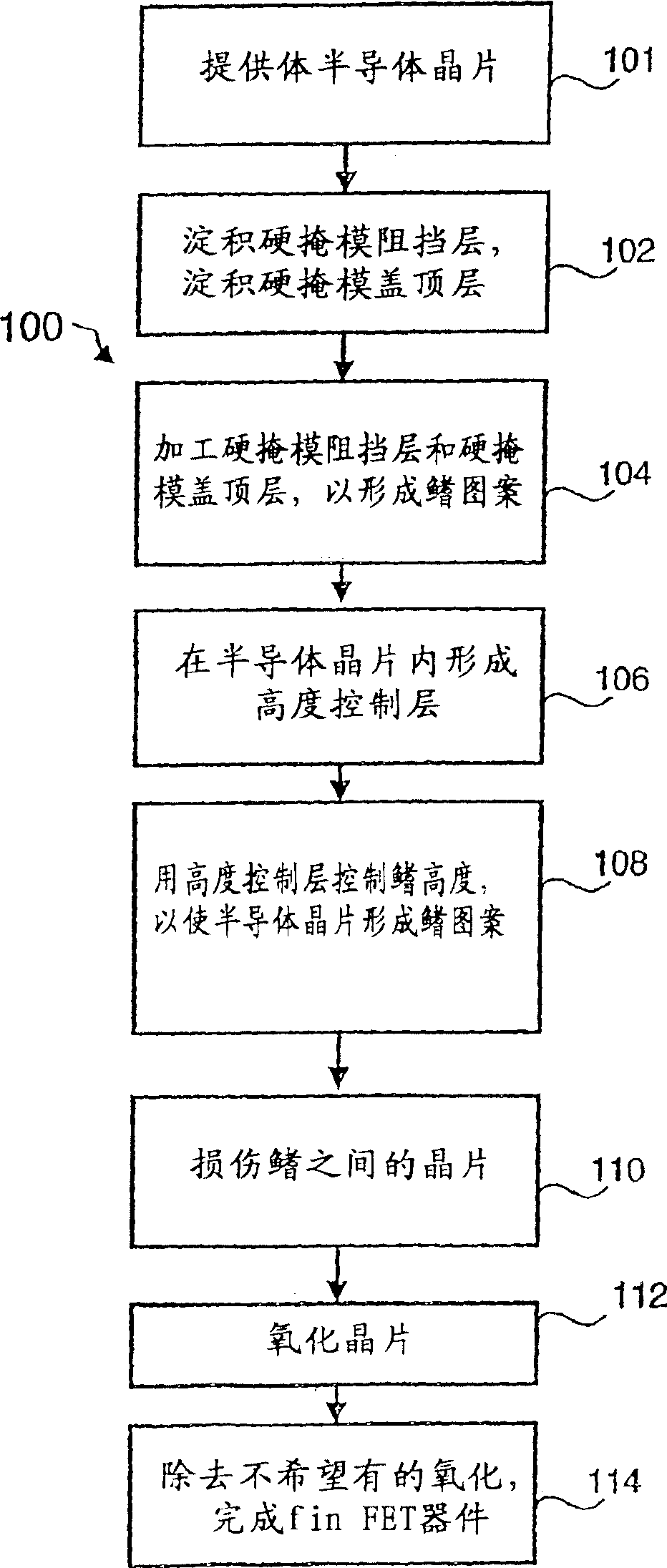
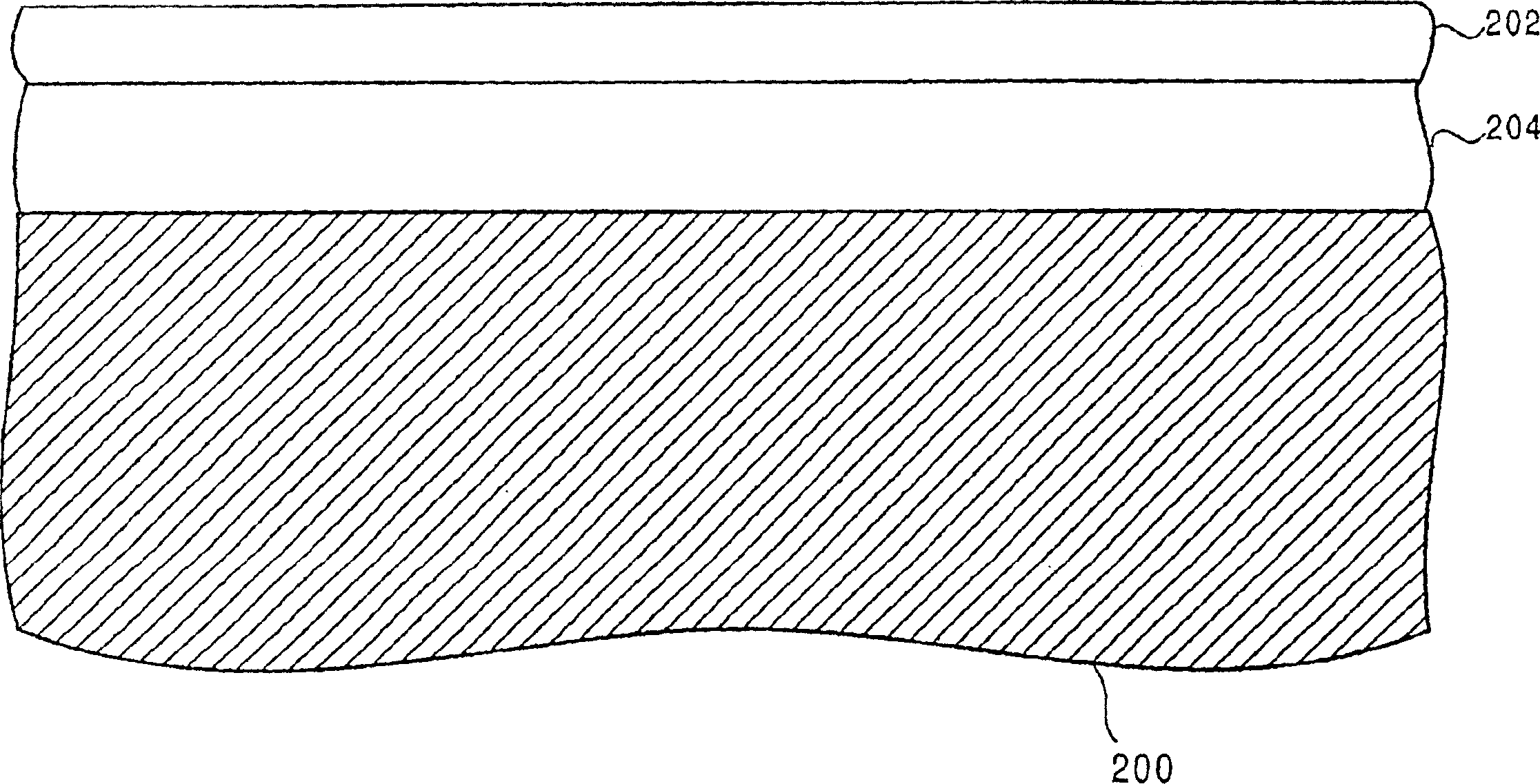
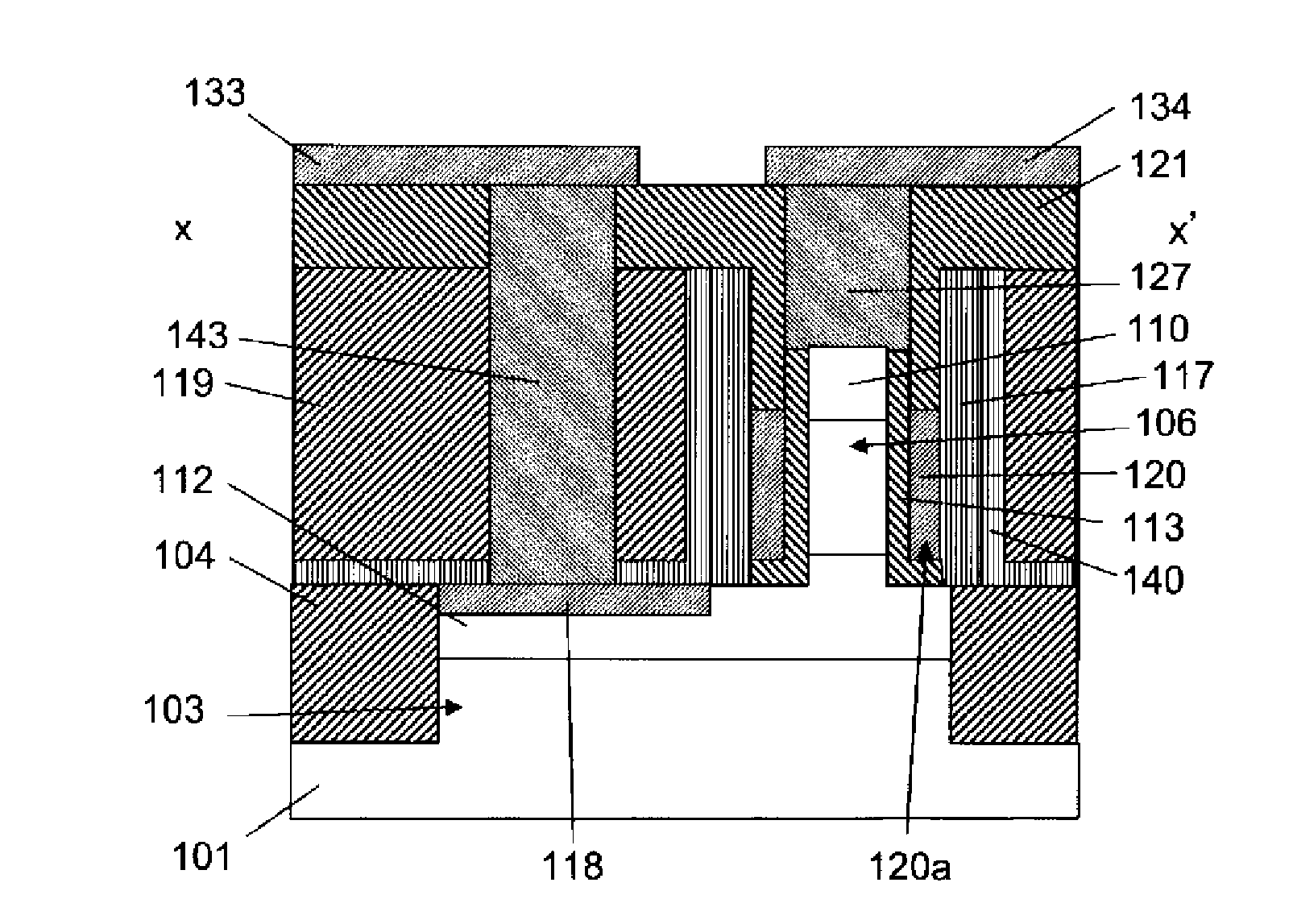
Fin FET devices from bulk semiconductor and method for forming
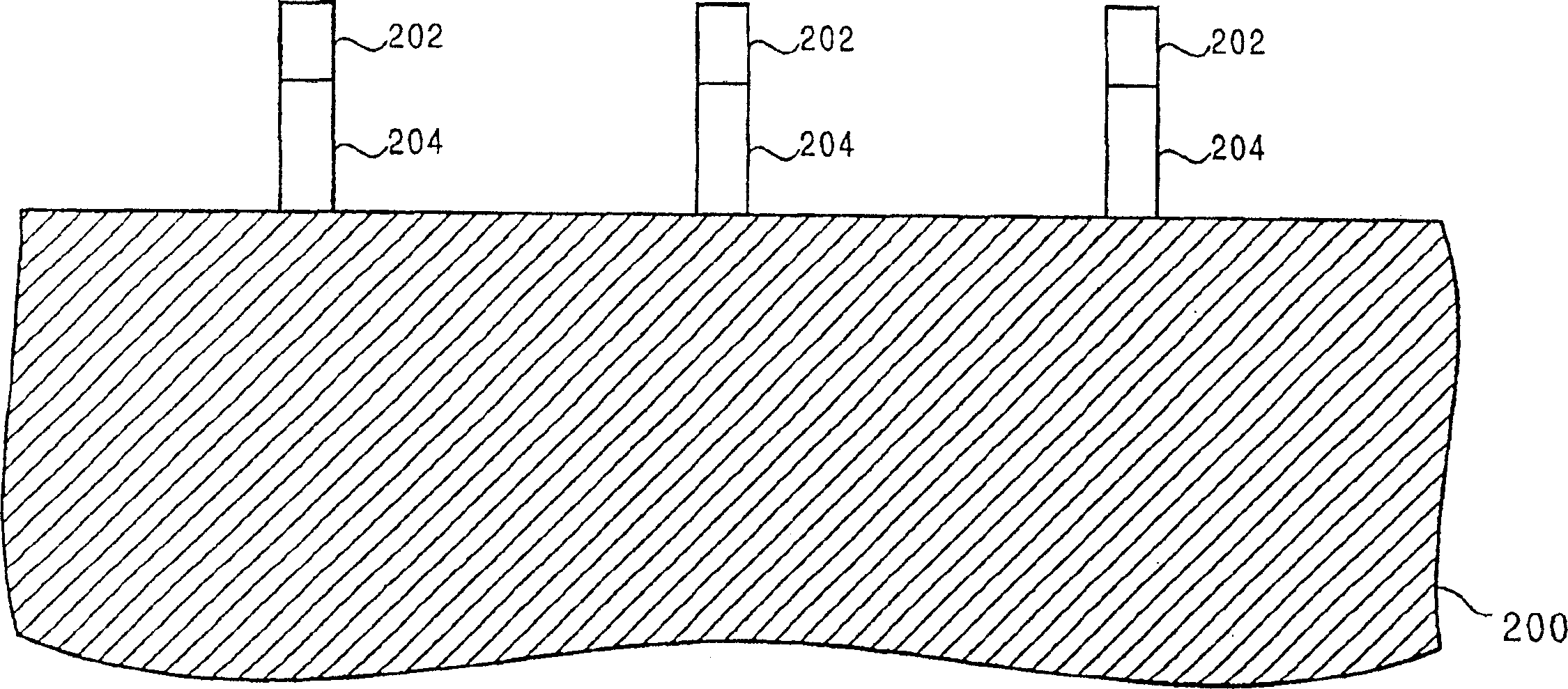
The present invention thus provides a device structure and method for forming fin Field Effect Transistors (FETs) that overcomes many of the disadvantages of the prior art. Specifically, the device structure and method provides the ability to form finFET devices from bulk semiconductor wafers while providing improved wafer to wafer device uniformity. Specifically, the method facilitates the formation of finFET devices from bulk semiconductor wafers with improved fin height control. Additionally, the method provides the ability to form finFETs from bulk semiconductor while providing isolation between fins and between the source and drain region of individual finFETs. Finally, the method can also provide for the optimization of fin width. The device structure and methods of the present invention thus provide the advantages of uniform finFET fabrication while using cost effect bulk wafers.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20160336400A1Increasing number of manufacturing stepPromote formationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering physics
A semiconductor device includes a fin-shaped semiconductor layer on a surface of a semiconductor substrate having a longitudinal axis extending in a first direction parallel to the surface. A first insulating film is around the fin-shaped semiconductor layer and a pillar-shaped semiconductor layer is on the fin-shaped semiconductor layer. A pillar diameter of the bottom of the pillar-shaped semiconductor layer is equal to a fin width of the top of the fin-shaped semiconductor layer, the pillar diameter and the fin width parallel to the surface. A gate insulating film is around the pillar-shaped semiconductor layer and a metal gate electrode is around the gate insulating film. A metal gate wiring is connected to the metal gate electrode and has a longitudinal axis extending in a second direction parallel to the surface and perpendicular to the first direction of the longitudinal axis of the fin-shaped semiconductor layer.
Owner:UNISANTIS ELECTRONICS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Heat exchanger and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20160025424A1Satisfactory performanceReduce widthHeat exhanger finsStationary conduit assembliesMarine engineeringFin width
In a heat exchanger, when louvers are viewed from an airflow direction, a louver tip end width becomes shorter with increase of a louver height. A fin width of the fin is 14 mm or shorter. Airflow-end louver lengths of an upstream-end first louver, a downstream-end first louver, an upstream-end second louver, and a downstream-end second louver are “⅝×LP” or longer, where LP is a louver pitch.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Soi finfet with reduced fin width dependence
ActiveUS20150214372A1Reduction of off-current spreadReduce transmissionTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringTransistor
The present invention relates to a method for polarizing at least a first finfet transistor and a second finfet transistor, wherein the first finfet transistor has a fin width bigger than the fin width of the second finfet transistor, and both the first finfet transistor and the second finfet transistor have a back gate, and the method comprising applying the same first voltage on the back gate of the first finfet transistor and on the back gate of the second finfet transistor so as to reduce the spread between the off-current value of the first finfet transistor and the off-current value of the second finfet transistor.
Owner:S O I TEC SILICON ON INSULATOR THECHNOLOGIES
Gate length controlled vertical FETs
ActiveUS10153367B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureEngineering
A semiconductor structure and a method a method of forming a vertical FET (Field-Effect Transistor), includes growing a bottom source-drain layer of a second type on a substrate of a first type, growing a channel layer on the bottom source-drain layer, forming a first fin from the channel layer with mask on top of the first fin. A width of the mask is wider than a final first fin width.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Heat exchanger and outdoor unit of air-conditioner having the same
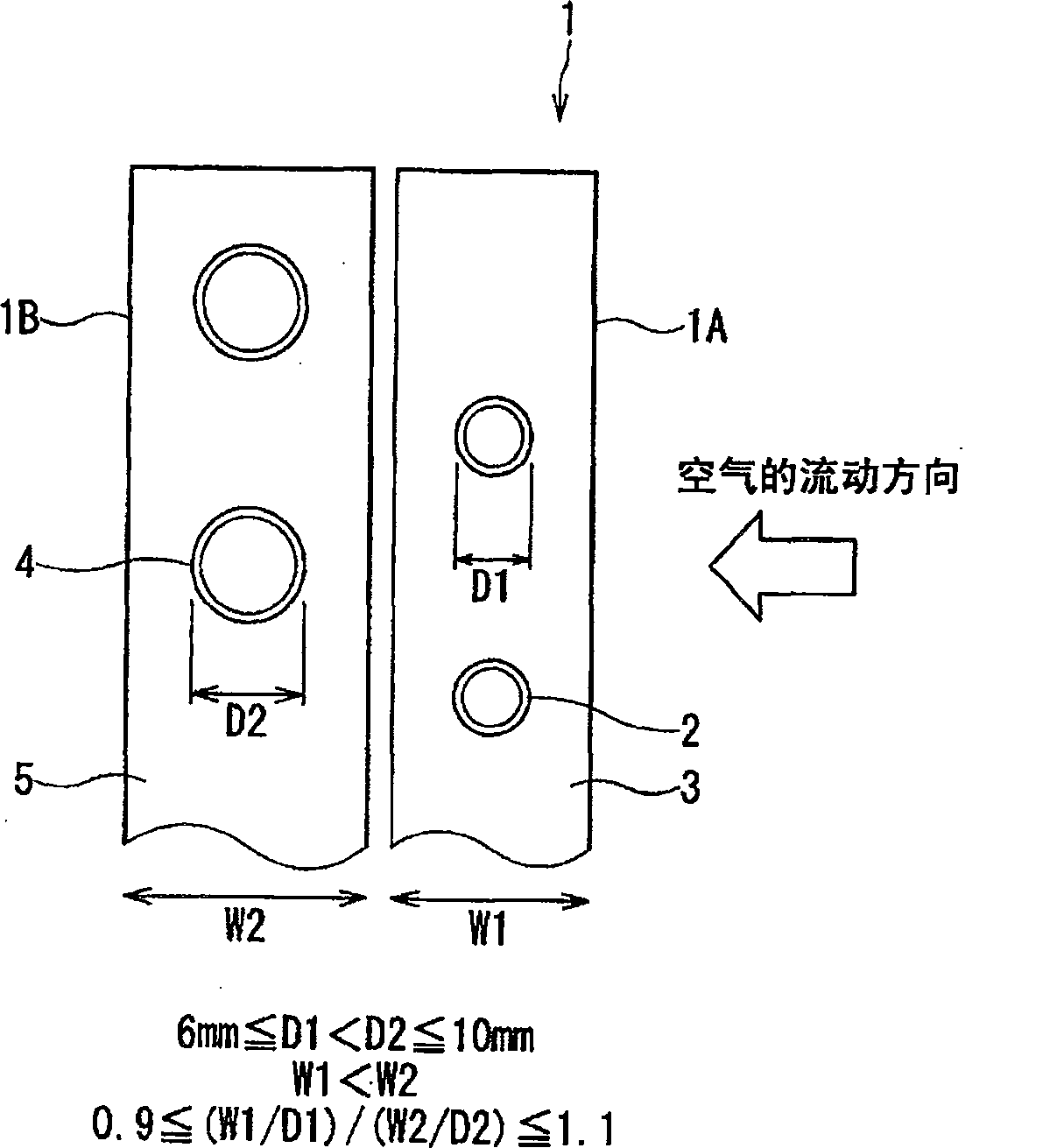
InactiveCN100533007CImprove heat transfer performanceLow efficiencyEvaporators/condensersTubular elementsEngineeringHeat sink
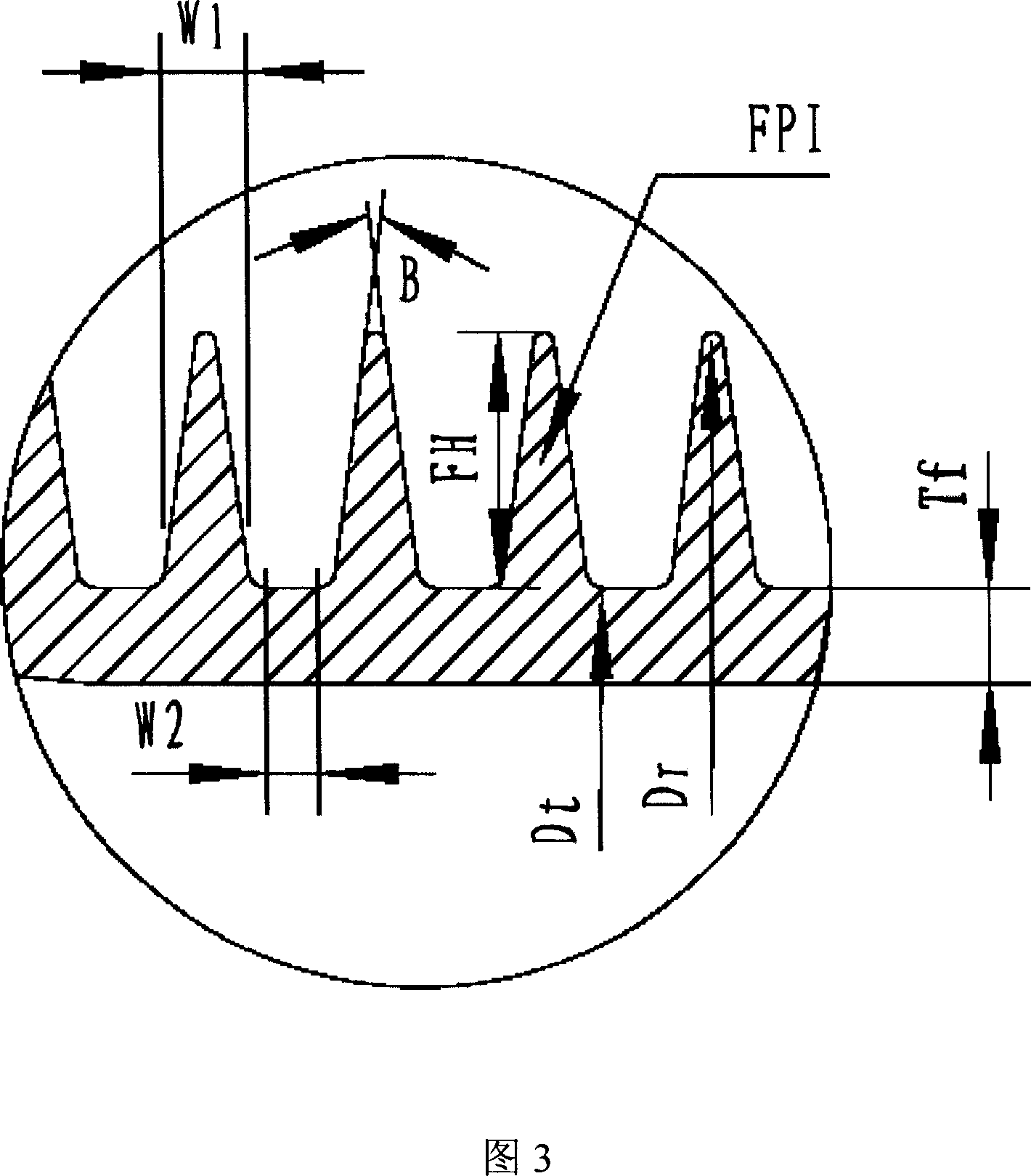
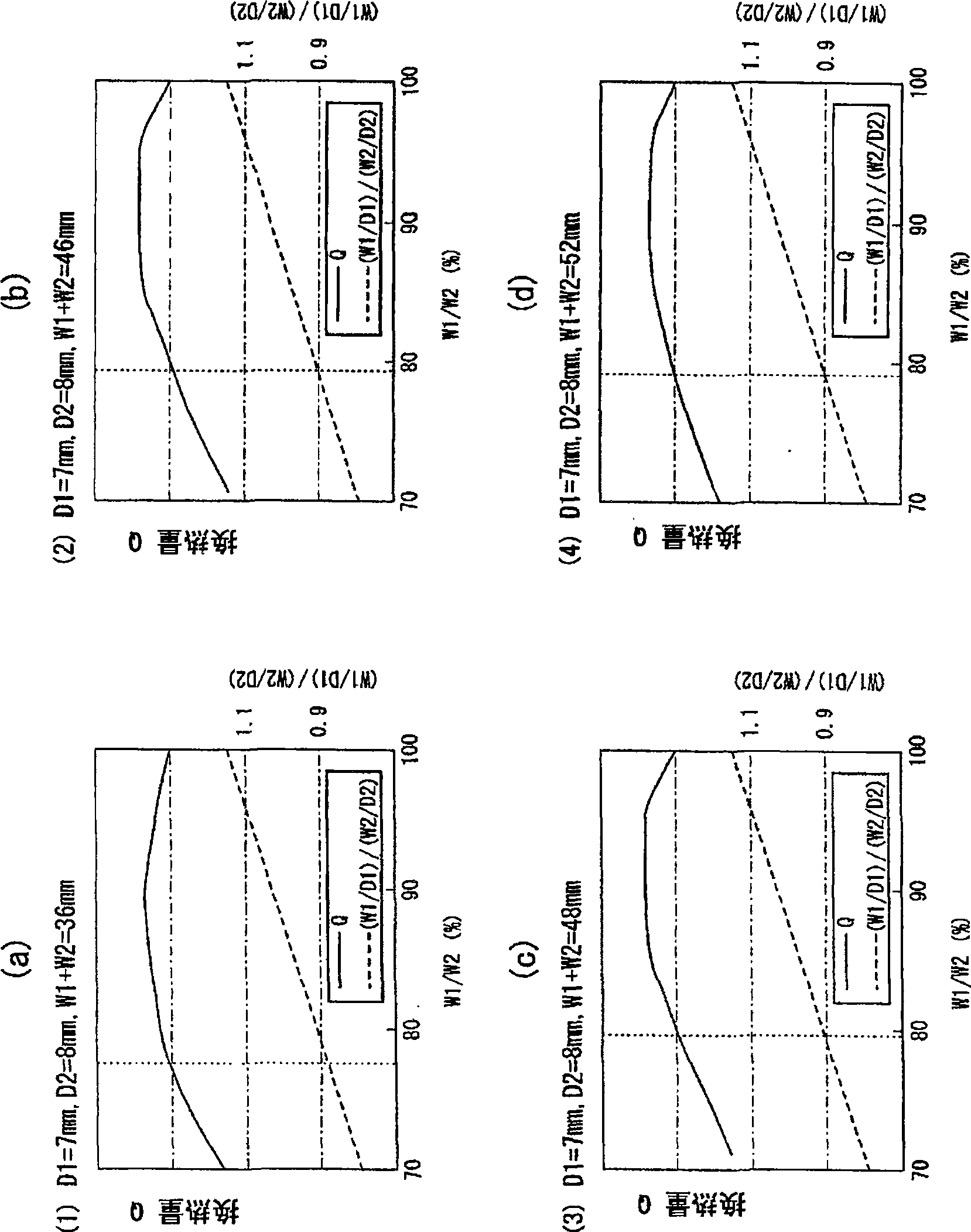
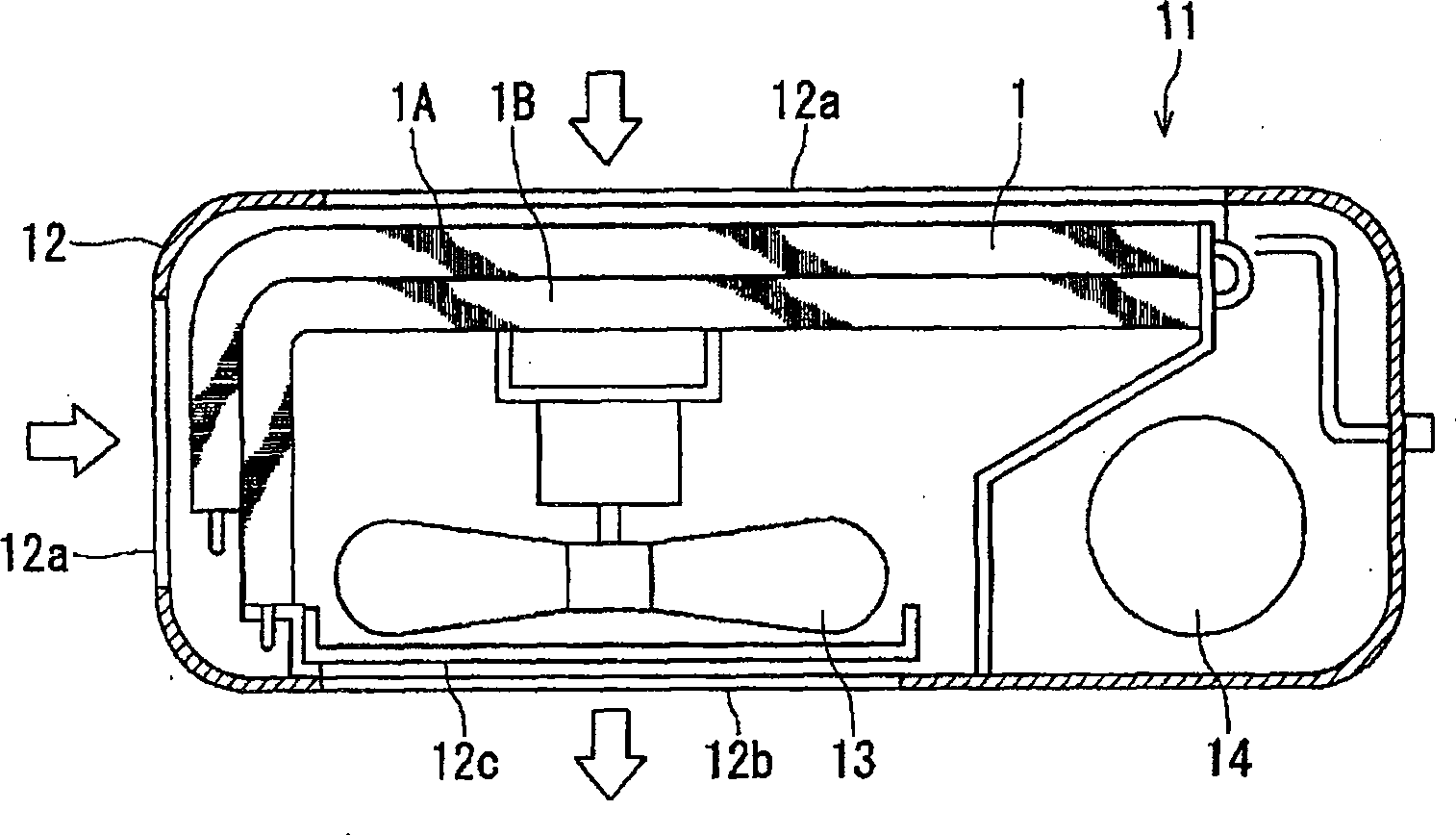
The present invention provides a method for improving the heat transfer performance of the refrigerant flowing in the tube by making the diameter of the heat transfer tube on the upwind side smaller than that of the heat transfer tube on the downwind side, and even if the heat transfer performance on the upwind side is reduced. The diameter of the heat pipe can also prevent the efficiency of the heat sink from decreasing in the heat exchanger with high heat transfer performance. The heat exchanger has: two rows of heat transfer tubes arranged along the airflow direction; and a plurality of cooling fins arranged separately for each row of the two rows of heat transfer tubes and arranged side by side with a predetermined gap, so that the heat exchange air flows along these gaps, The relationship between the outer diameter D1 of the heat transfer tube on the upper side of the wind and the outer diameter D2 of the heat transfer tube on the lower side of the wind is set as 6mm≤D1<D2≤10.5mm. When the width of the lower fin is W2, the fin widths W1 and W2 are set so that 0.9≦(W1 / D1) / (W2 / D2)≦1.11.
Owner:TOSHIBA CARRIER CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com