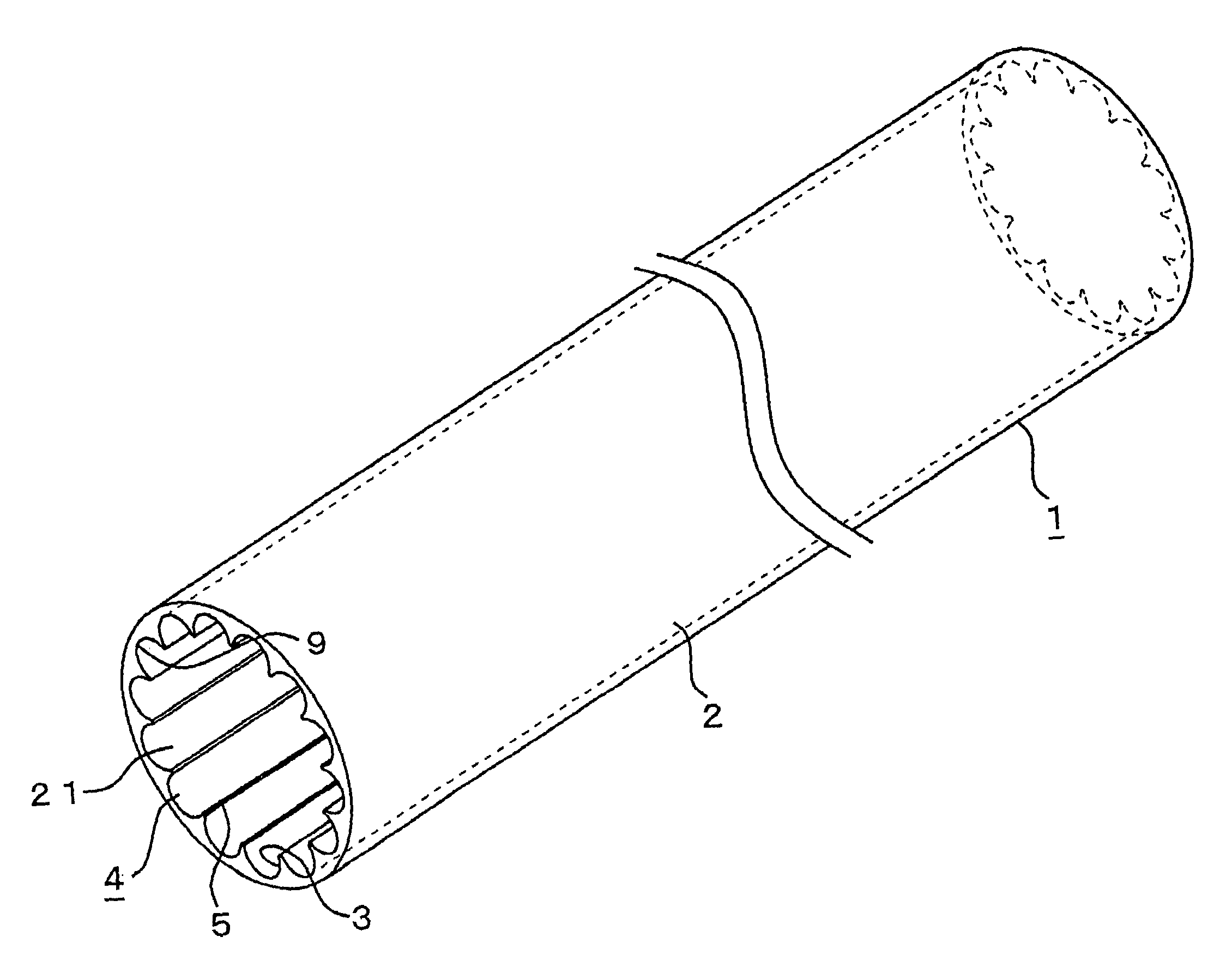
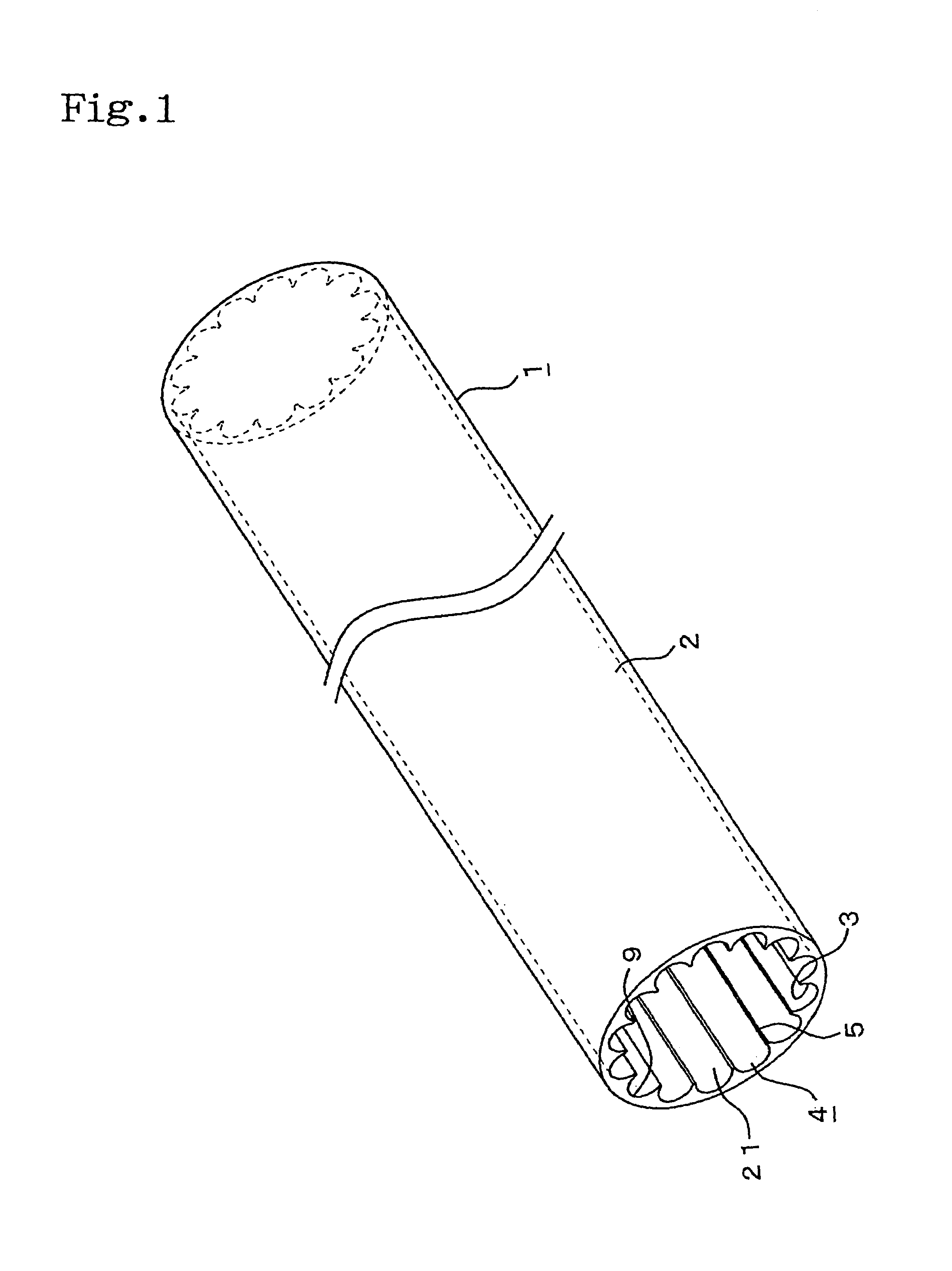
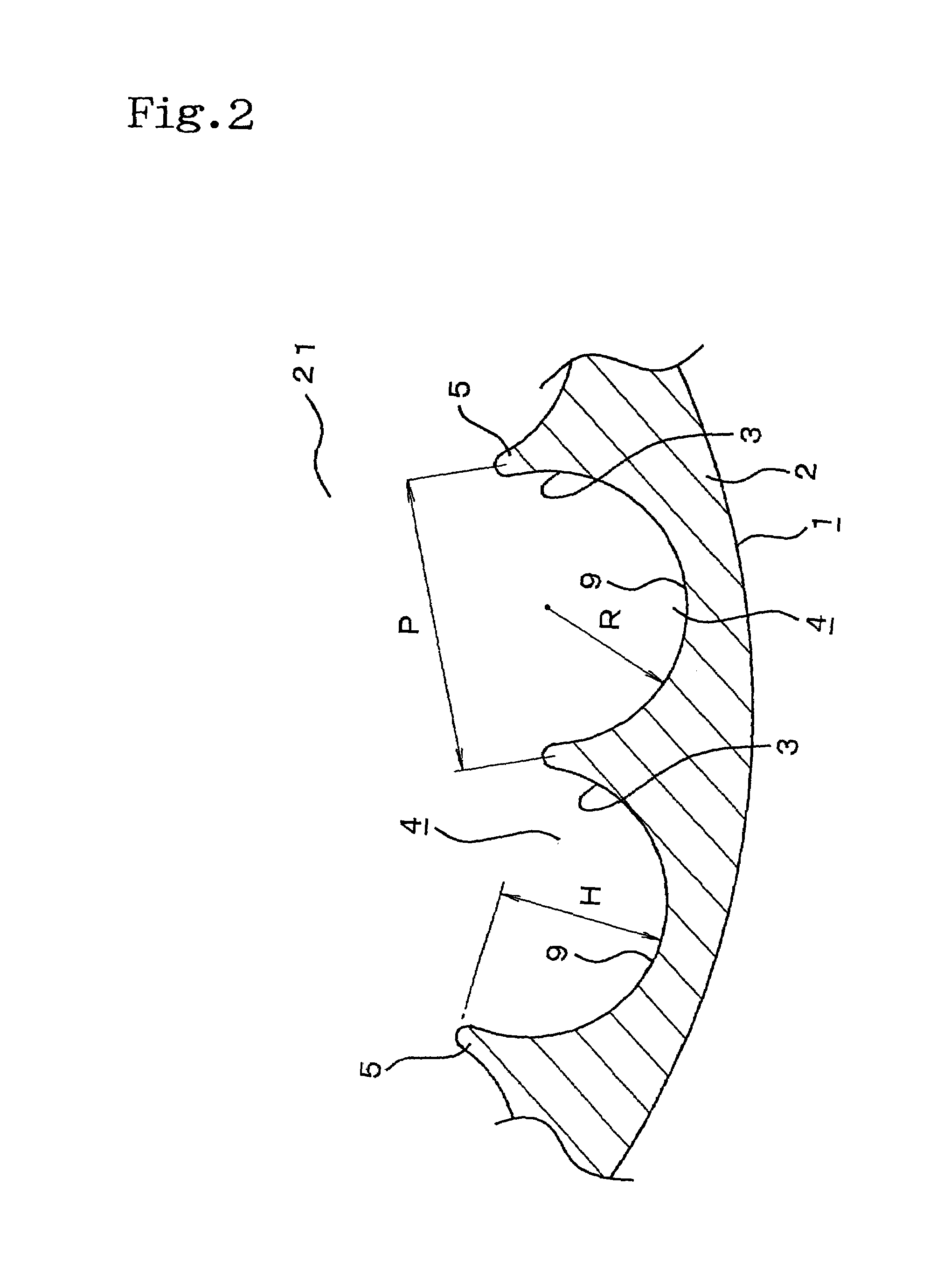
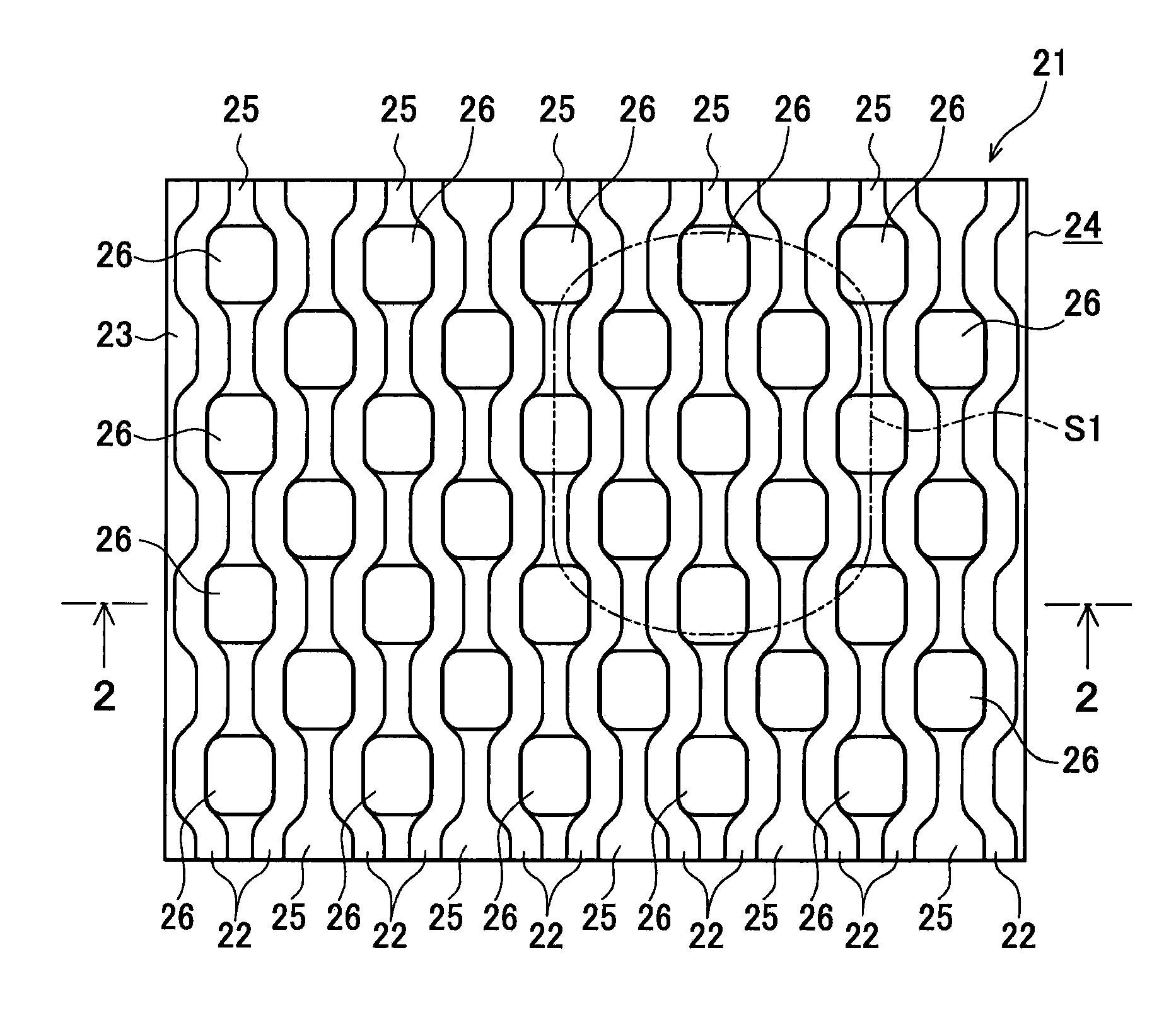
Patents
Literature
1282results about "Heat exhanger fins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
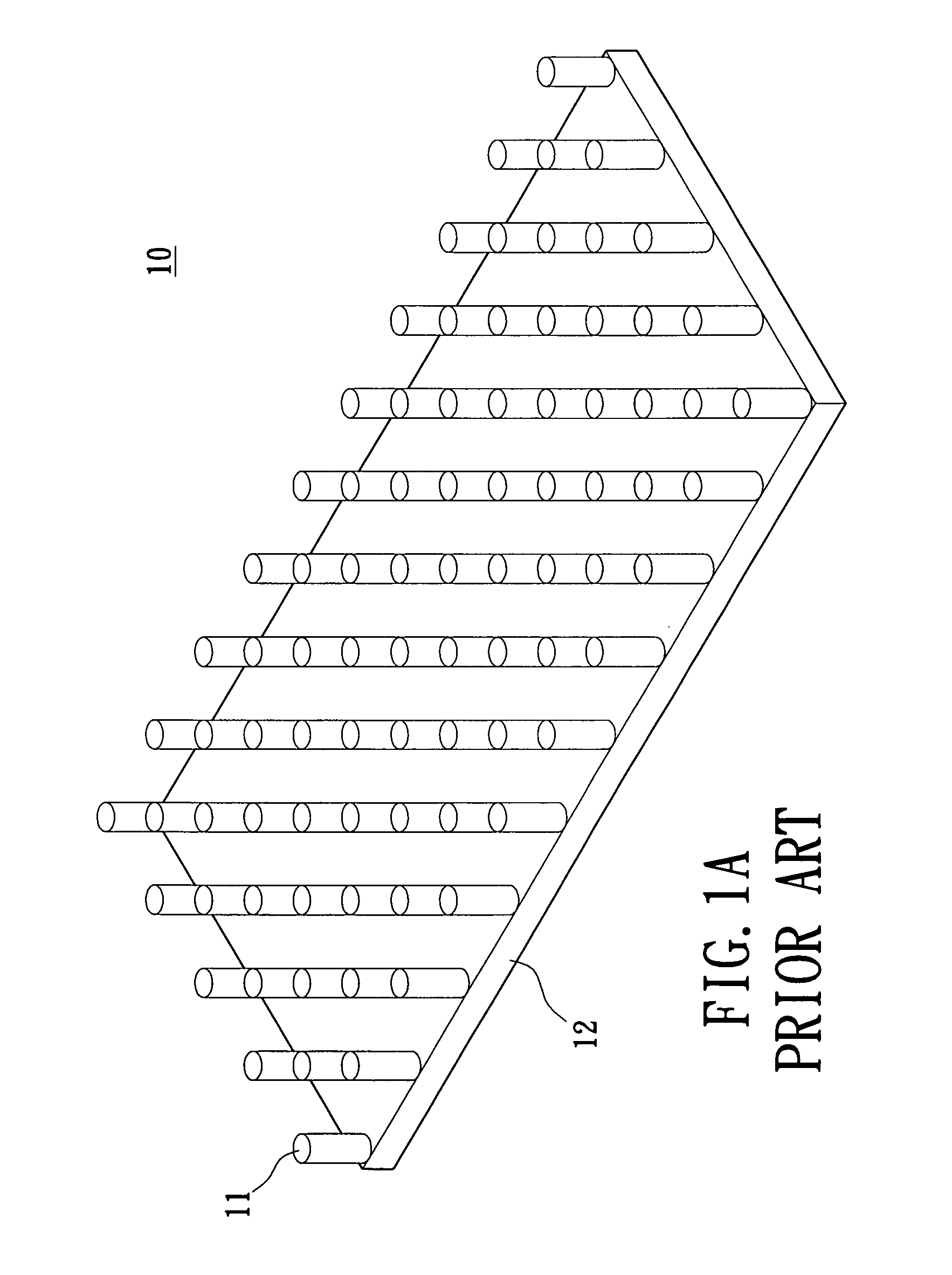
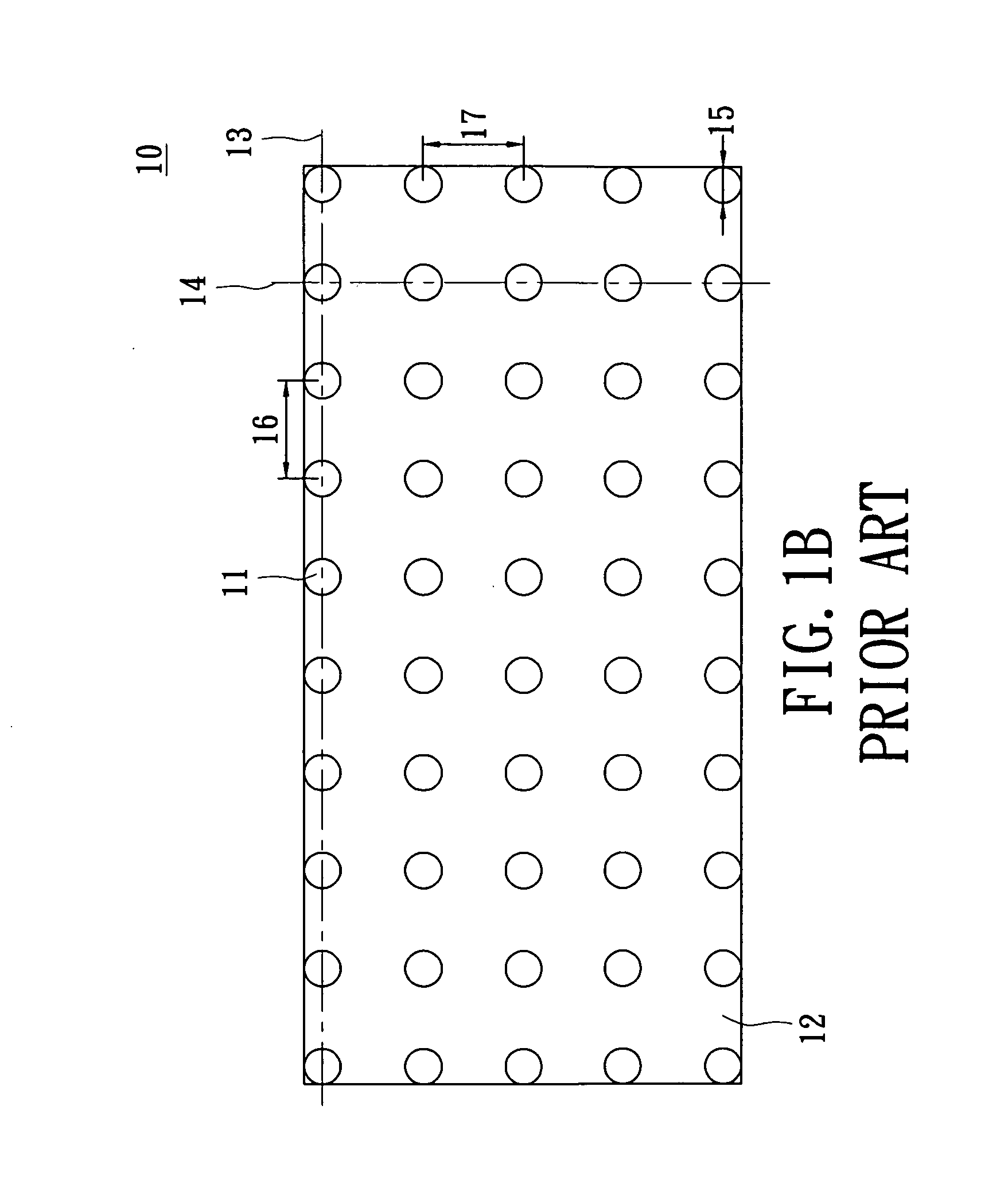
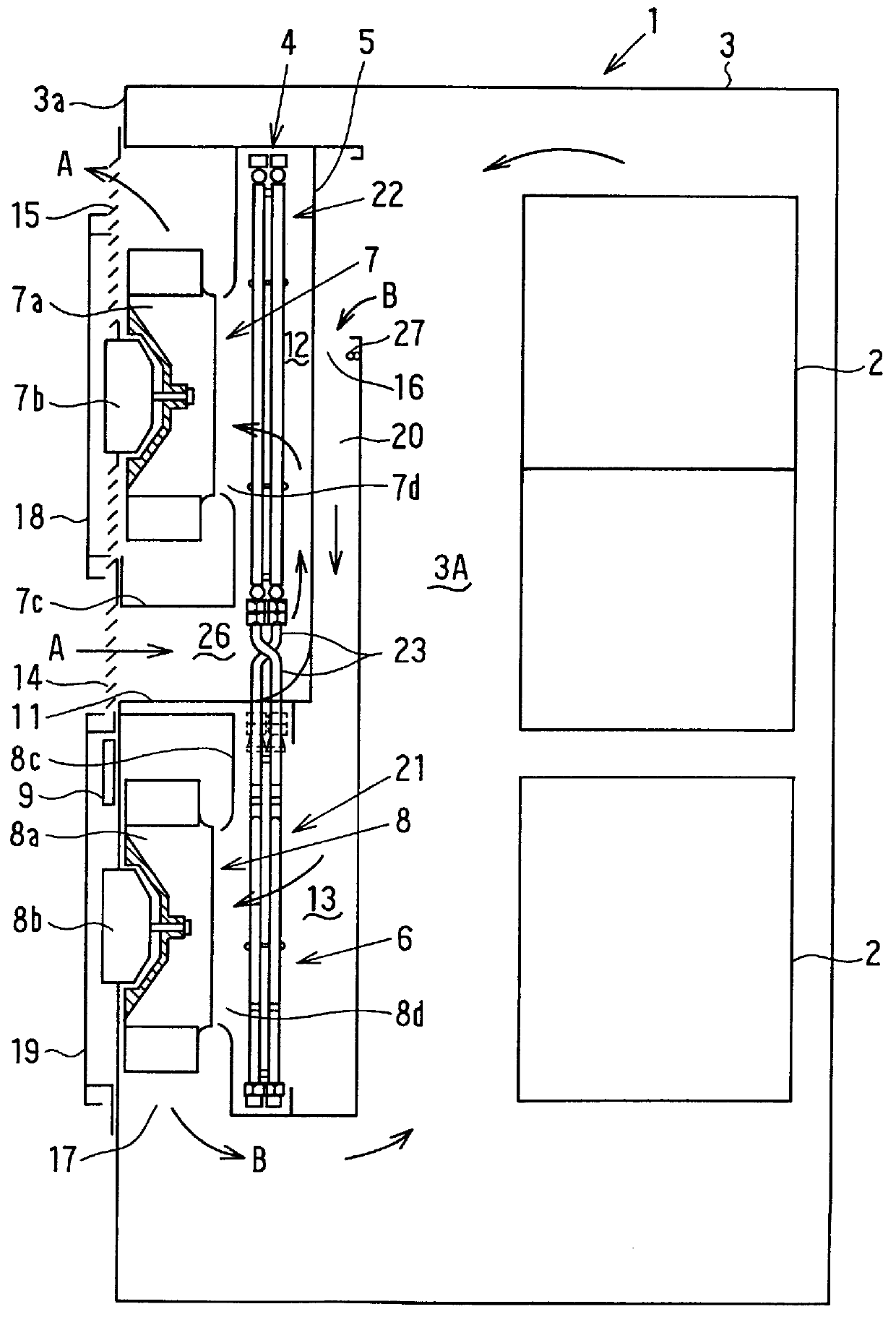
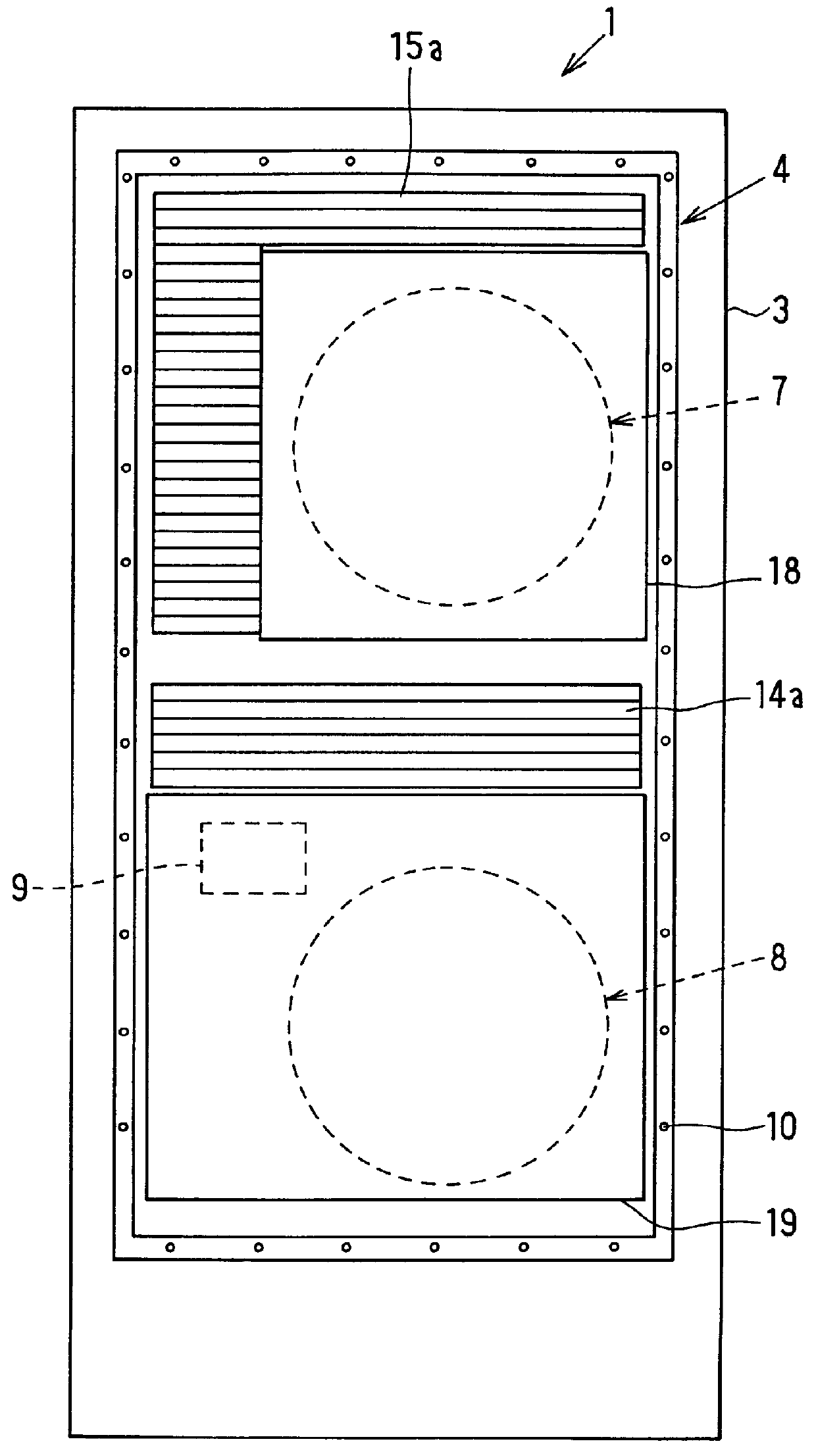
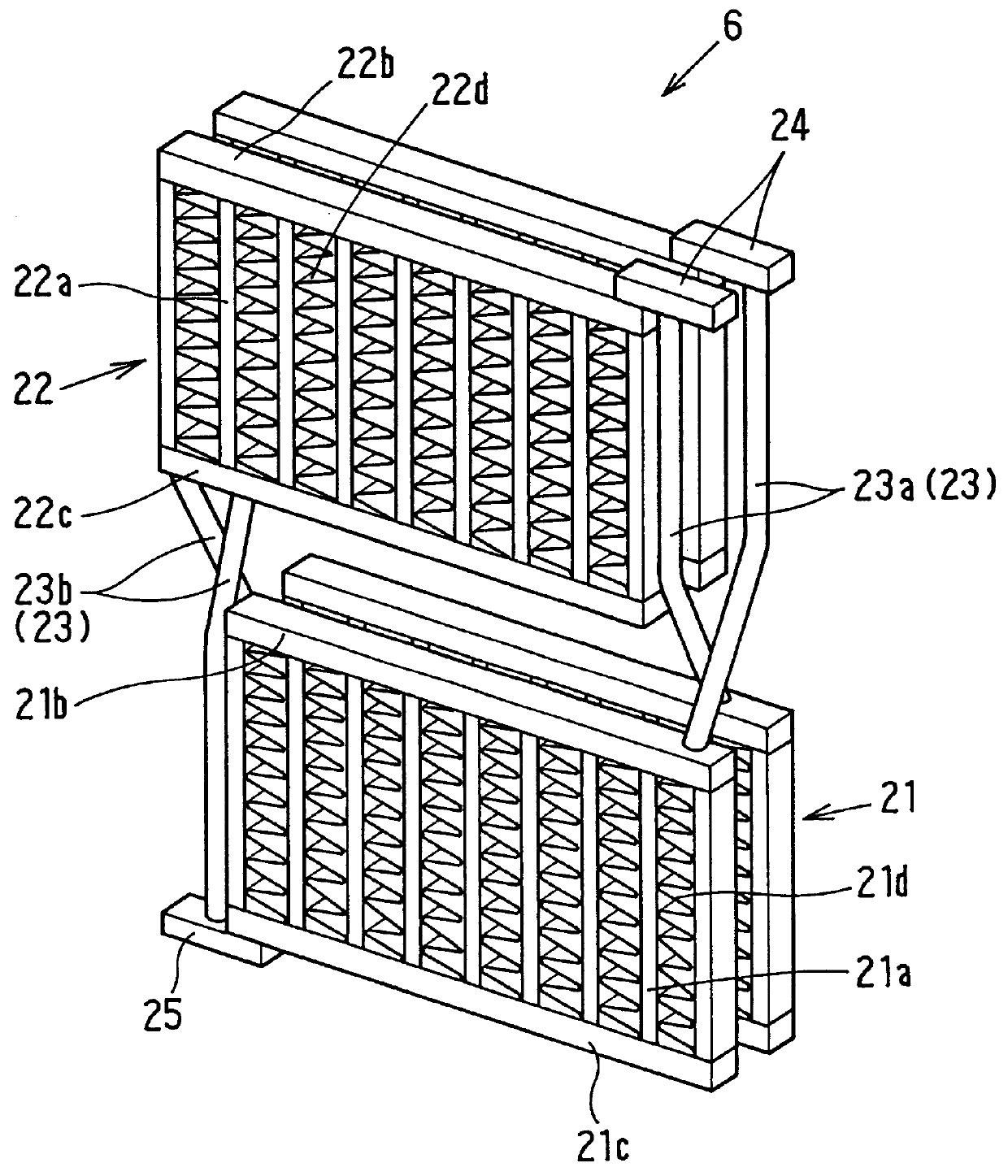
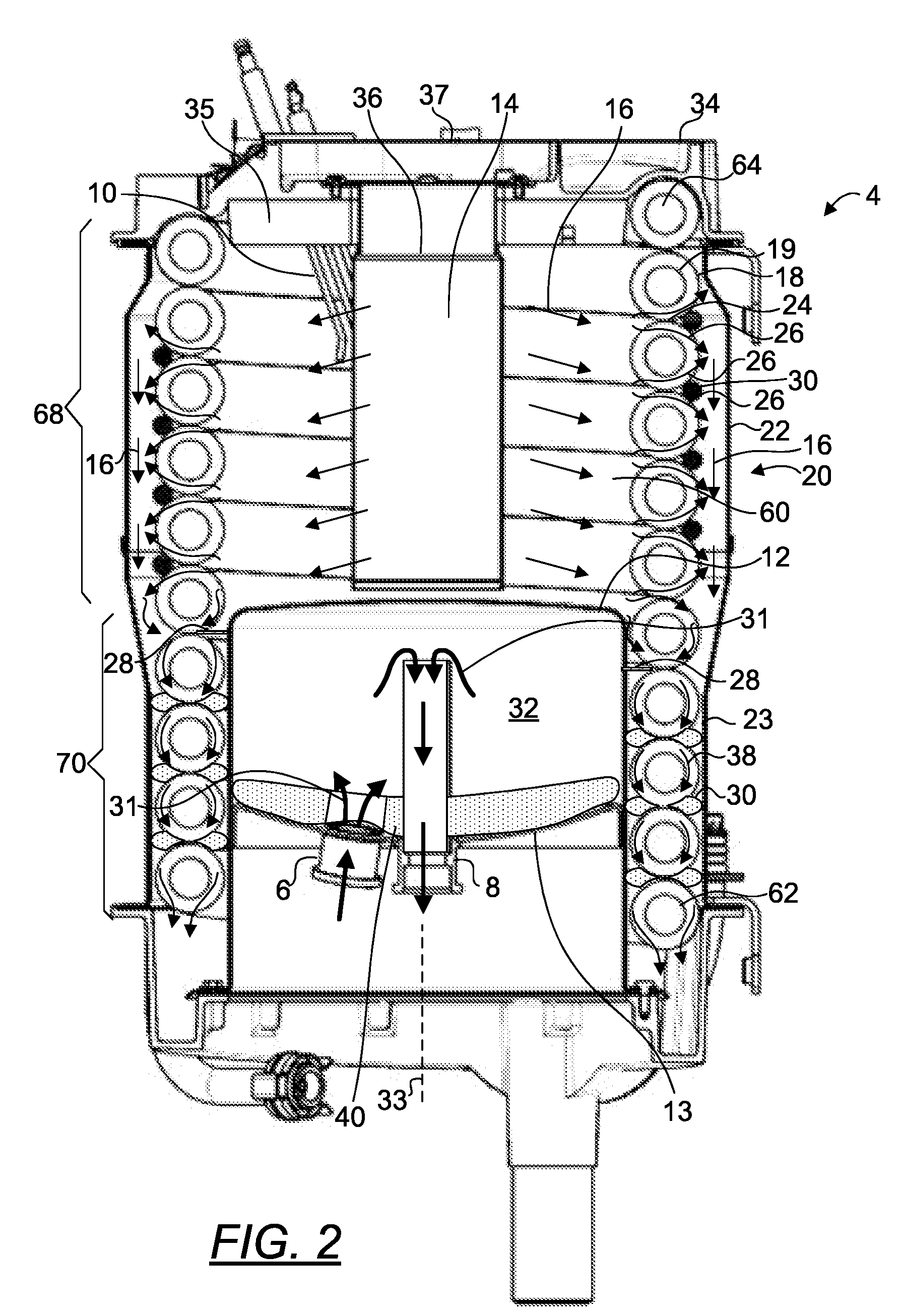
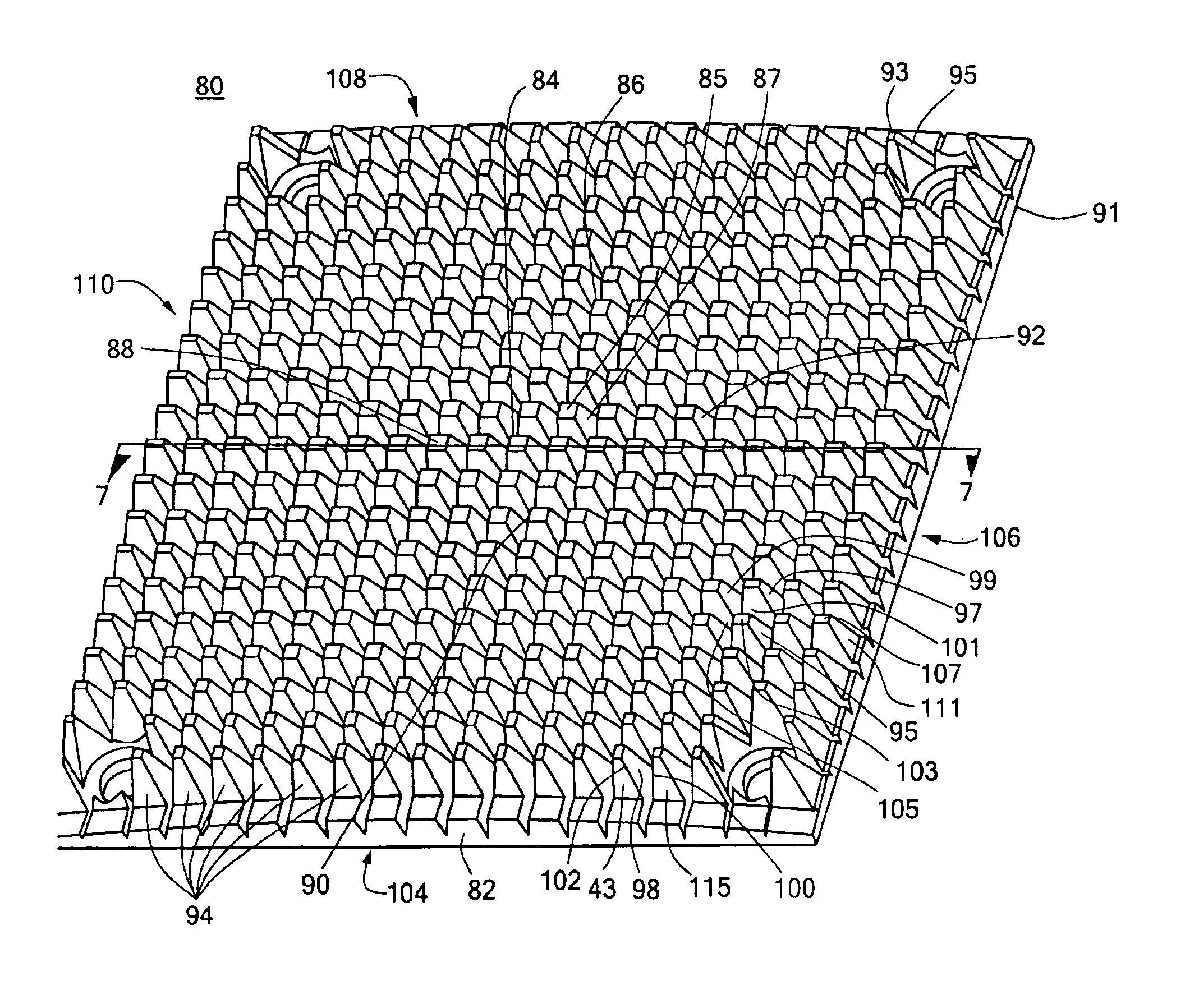
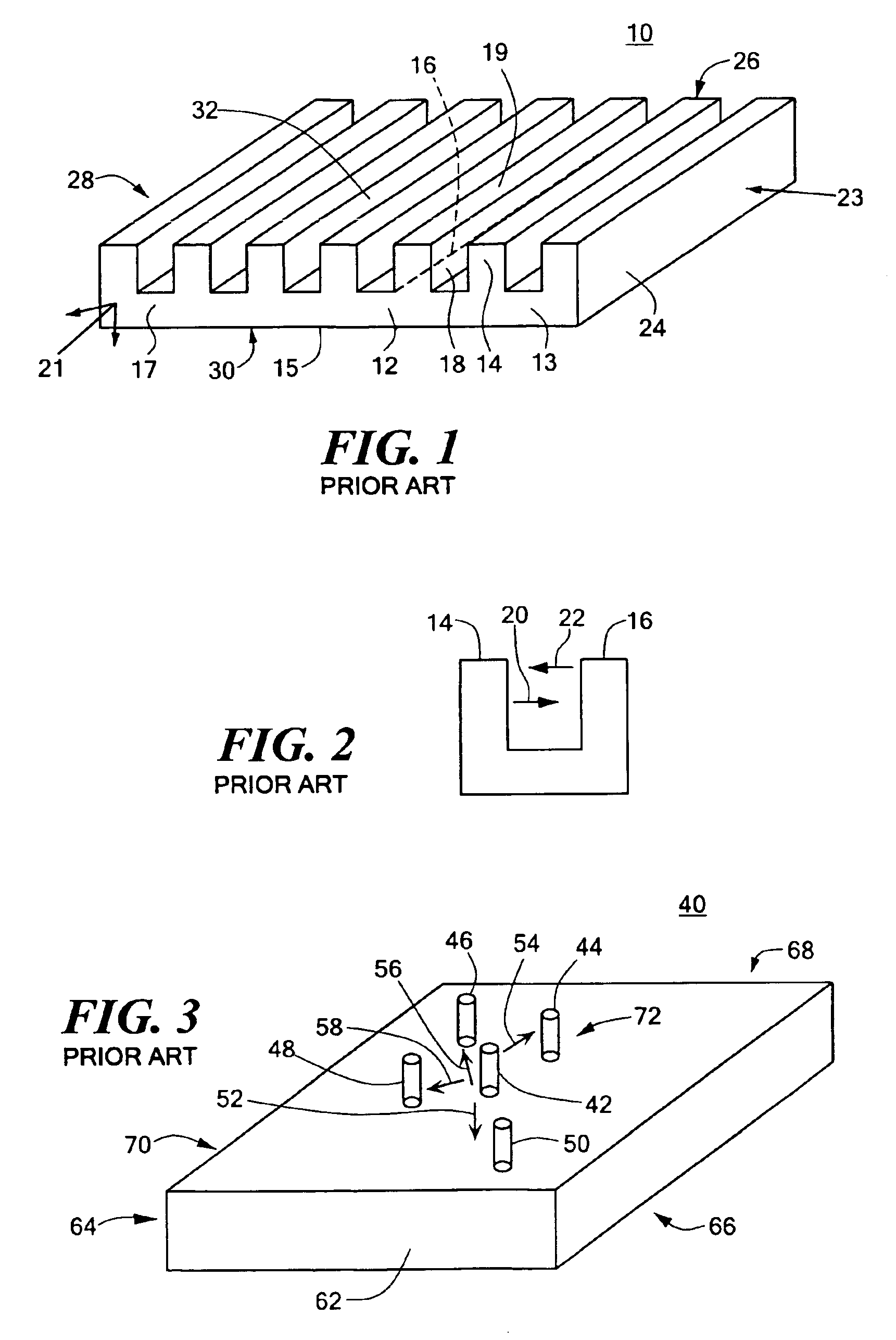
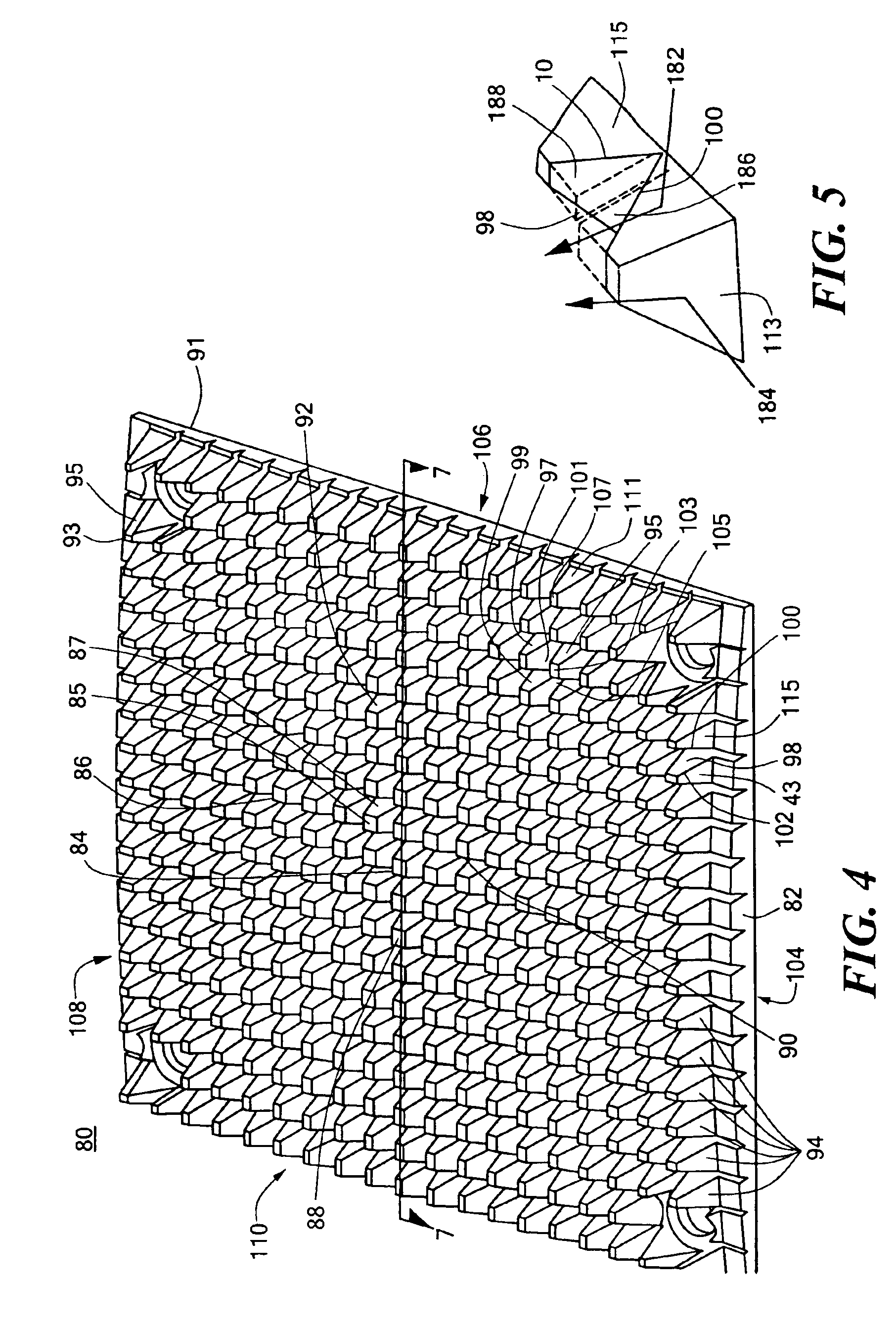
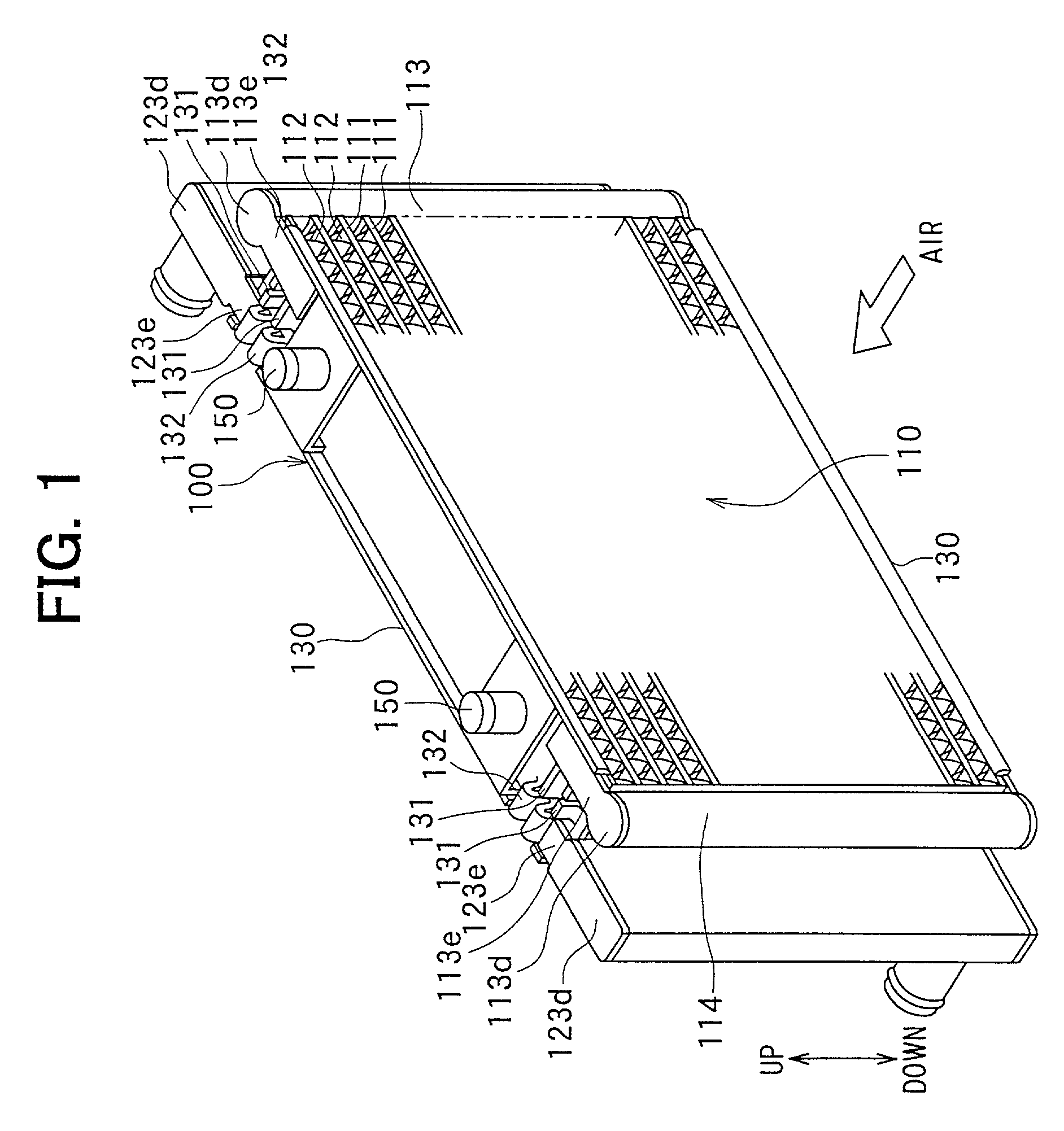
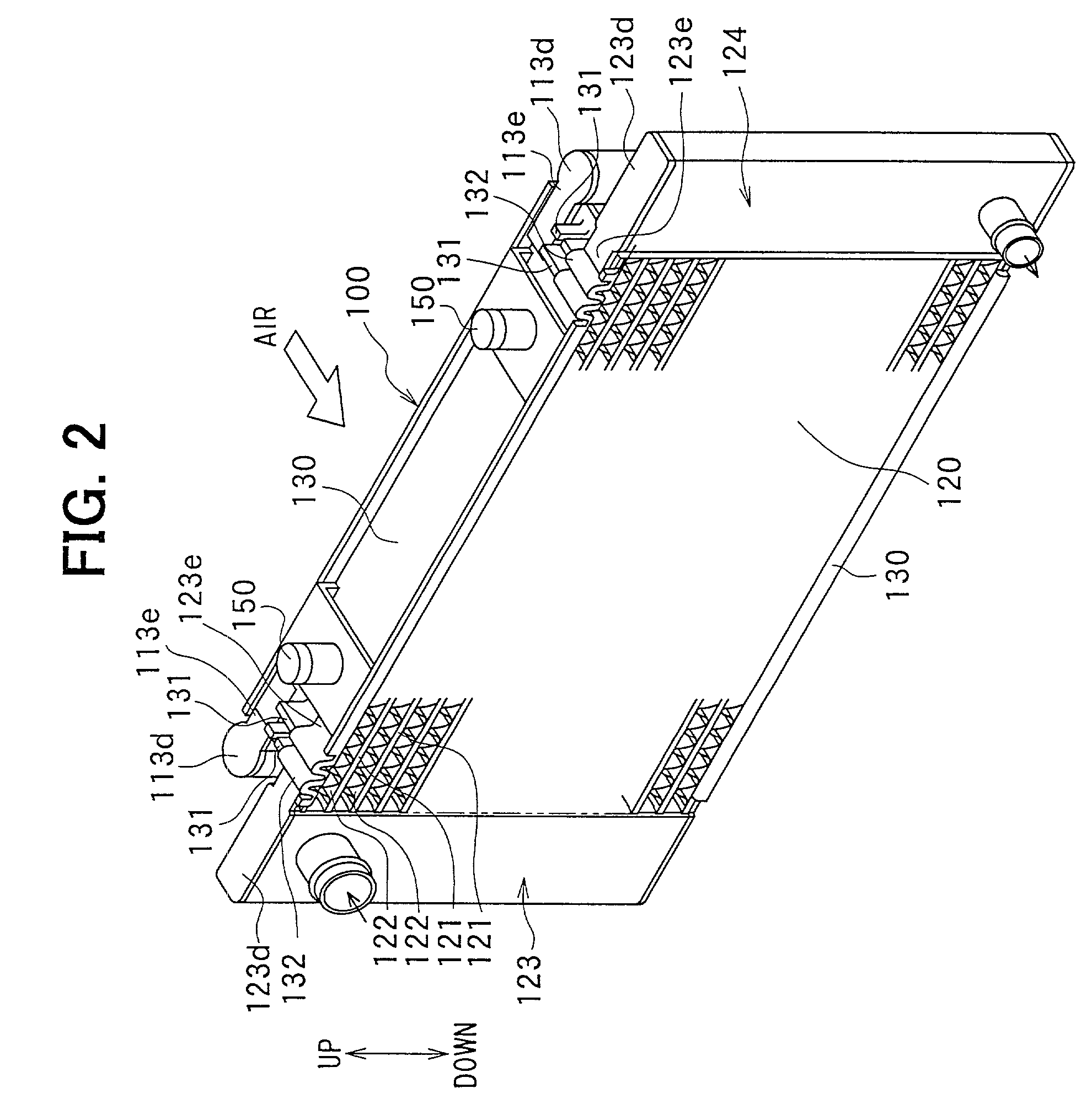
Heat exchanger
InactiveUS6964296B2Eliminate requirementsImprove relationshipSoldering apparatusHeat exhanger finsEngineeringMechanical engineering
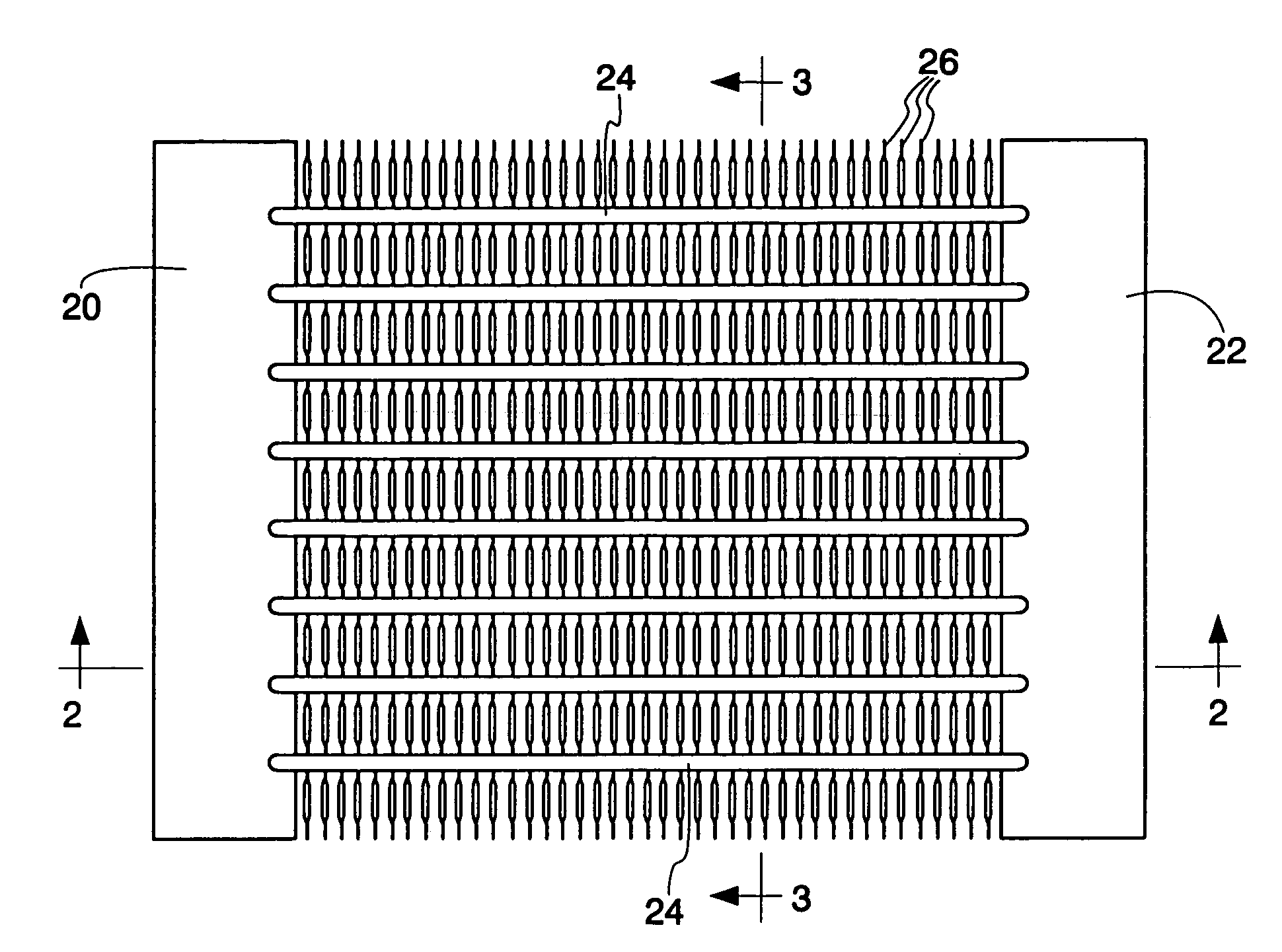
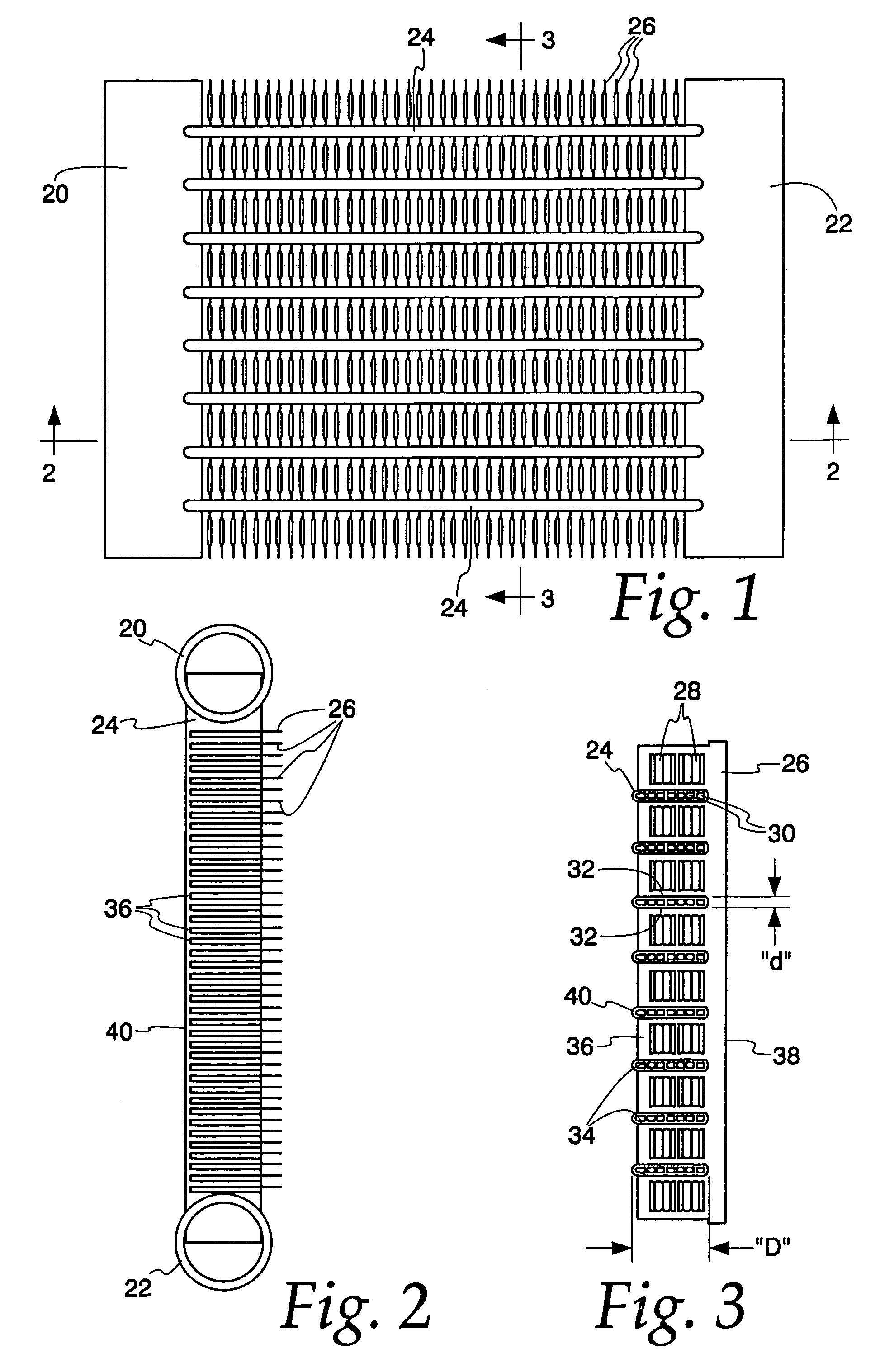
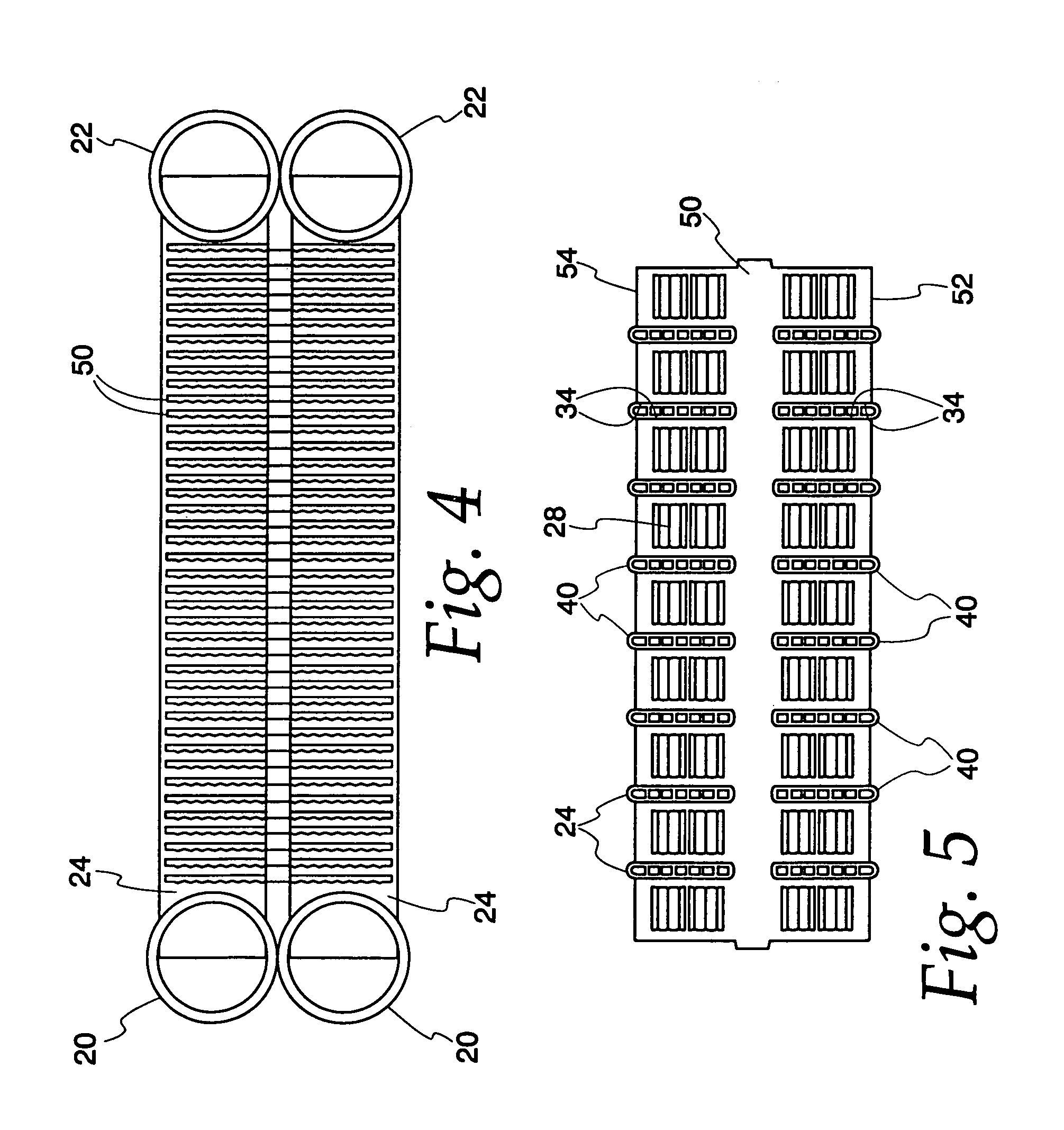
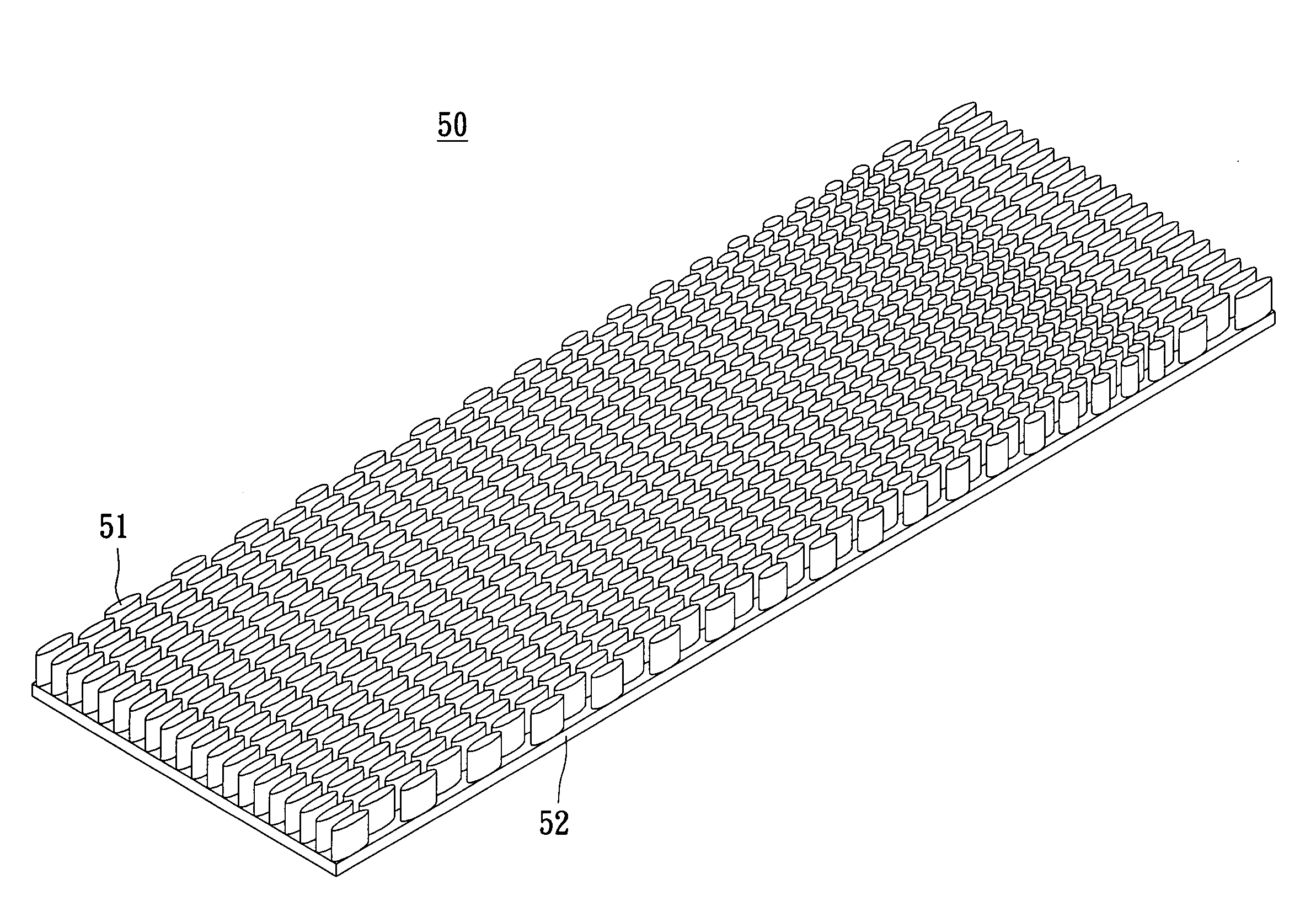
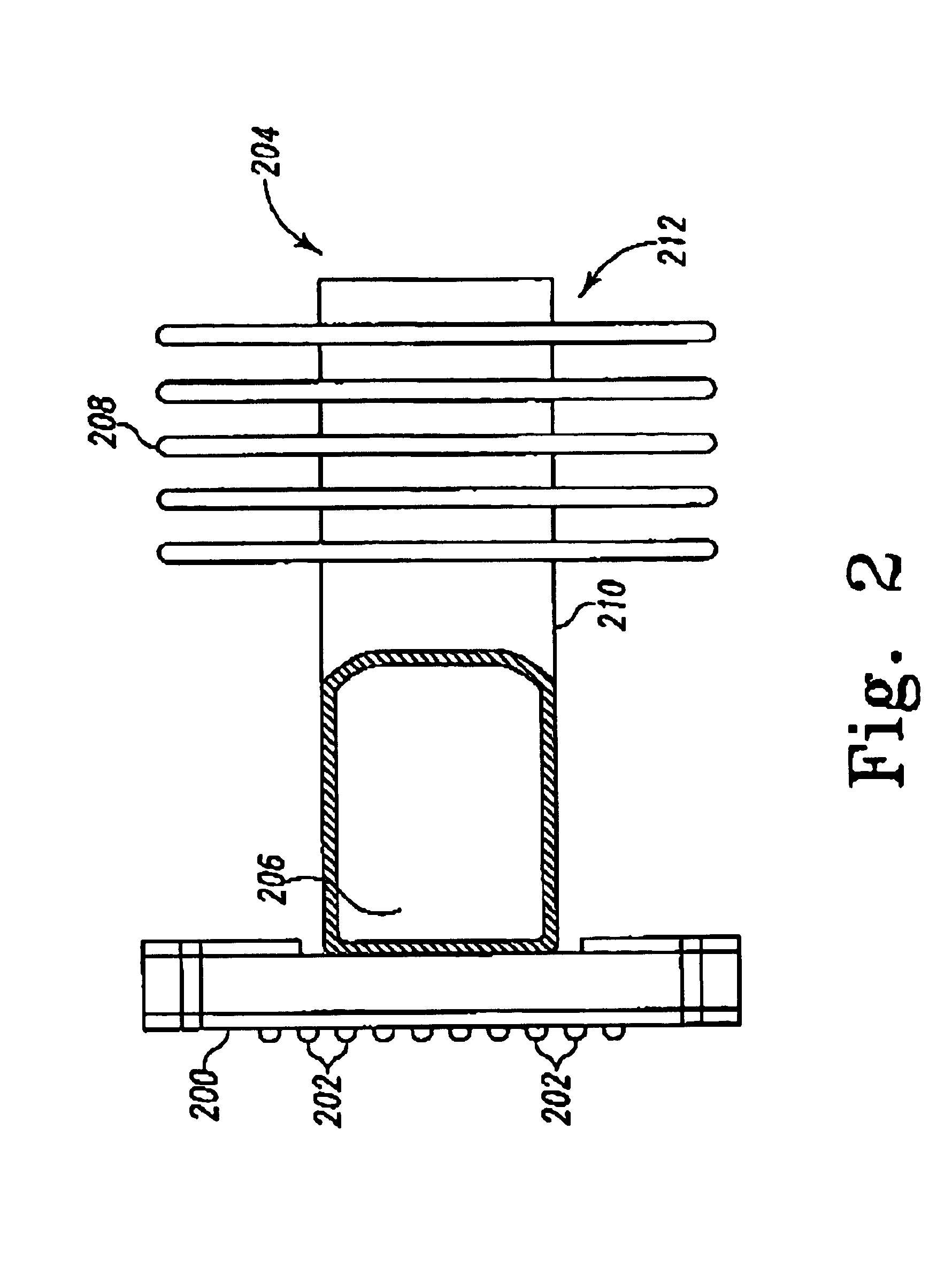
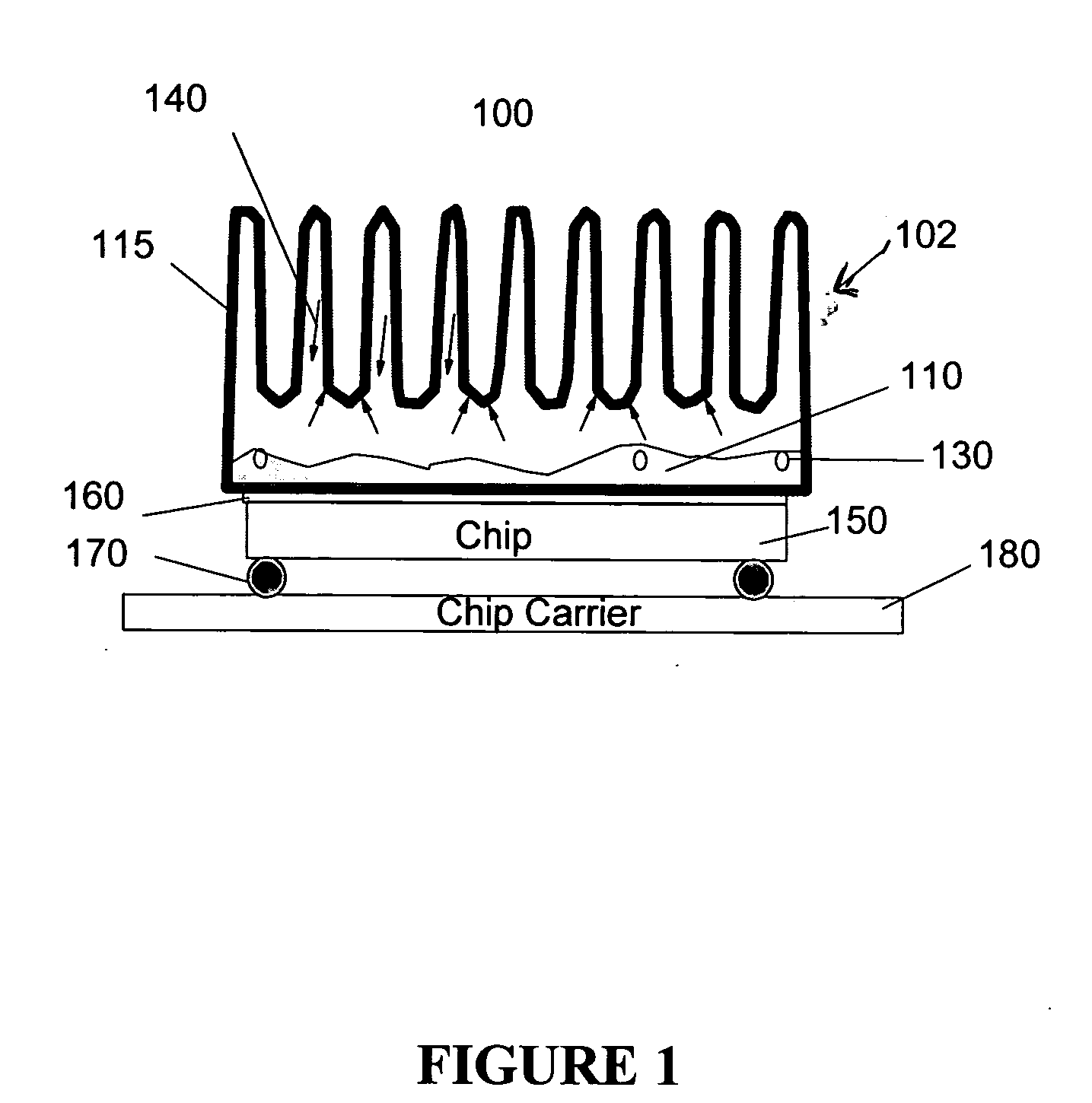
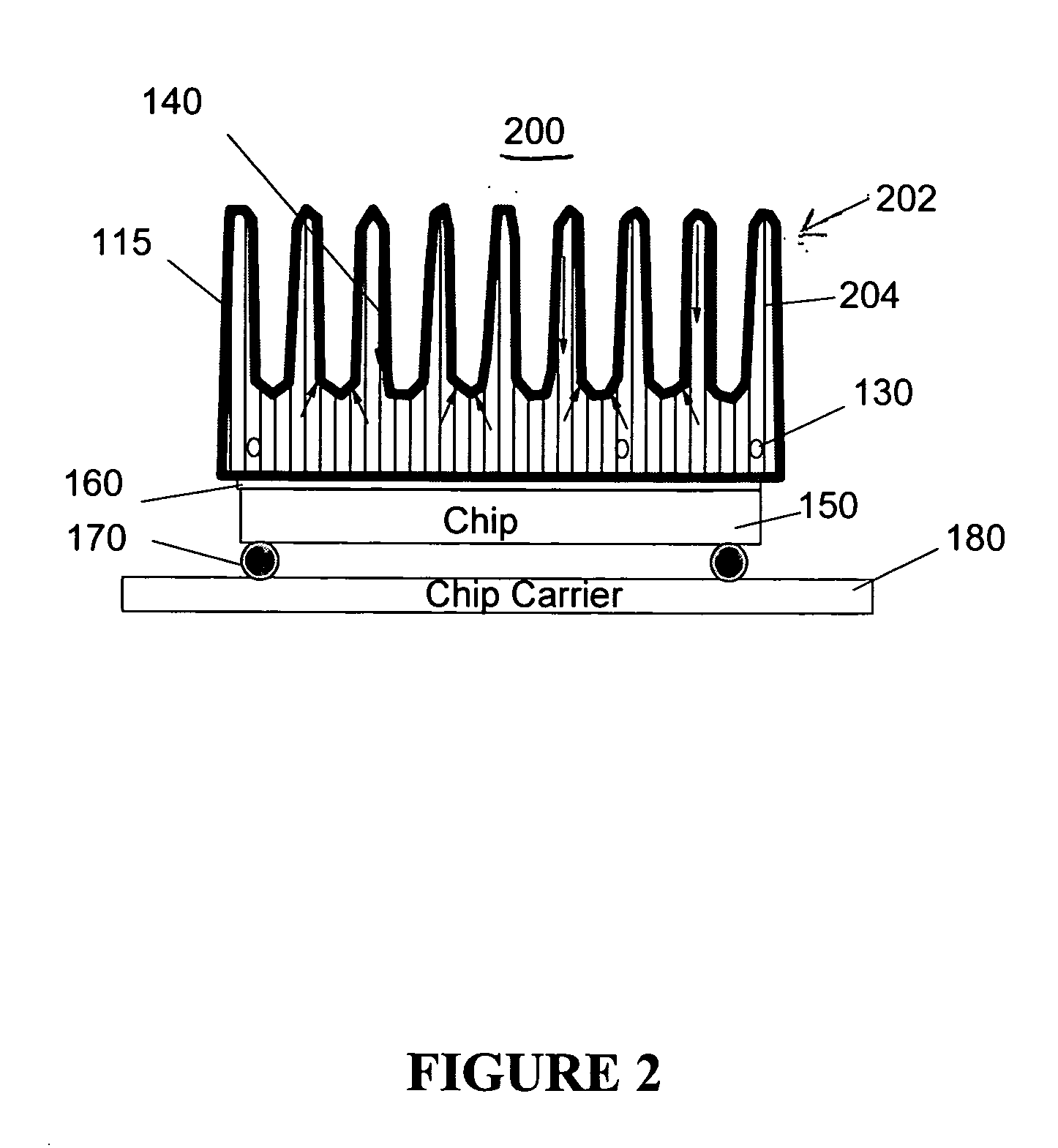
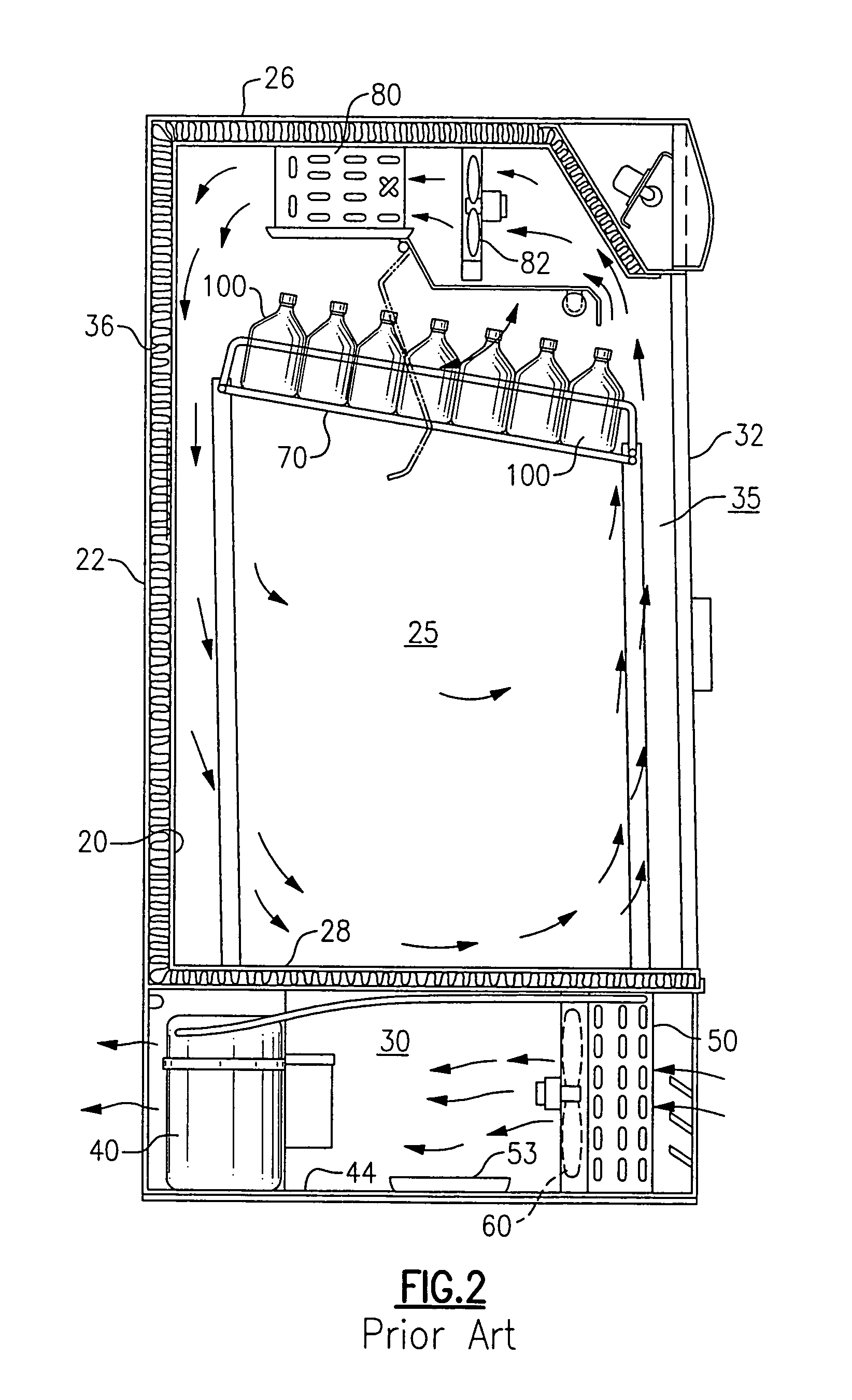
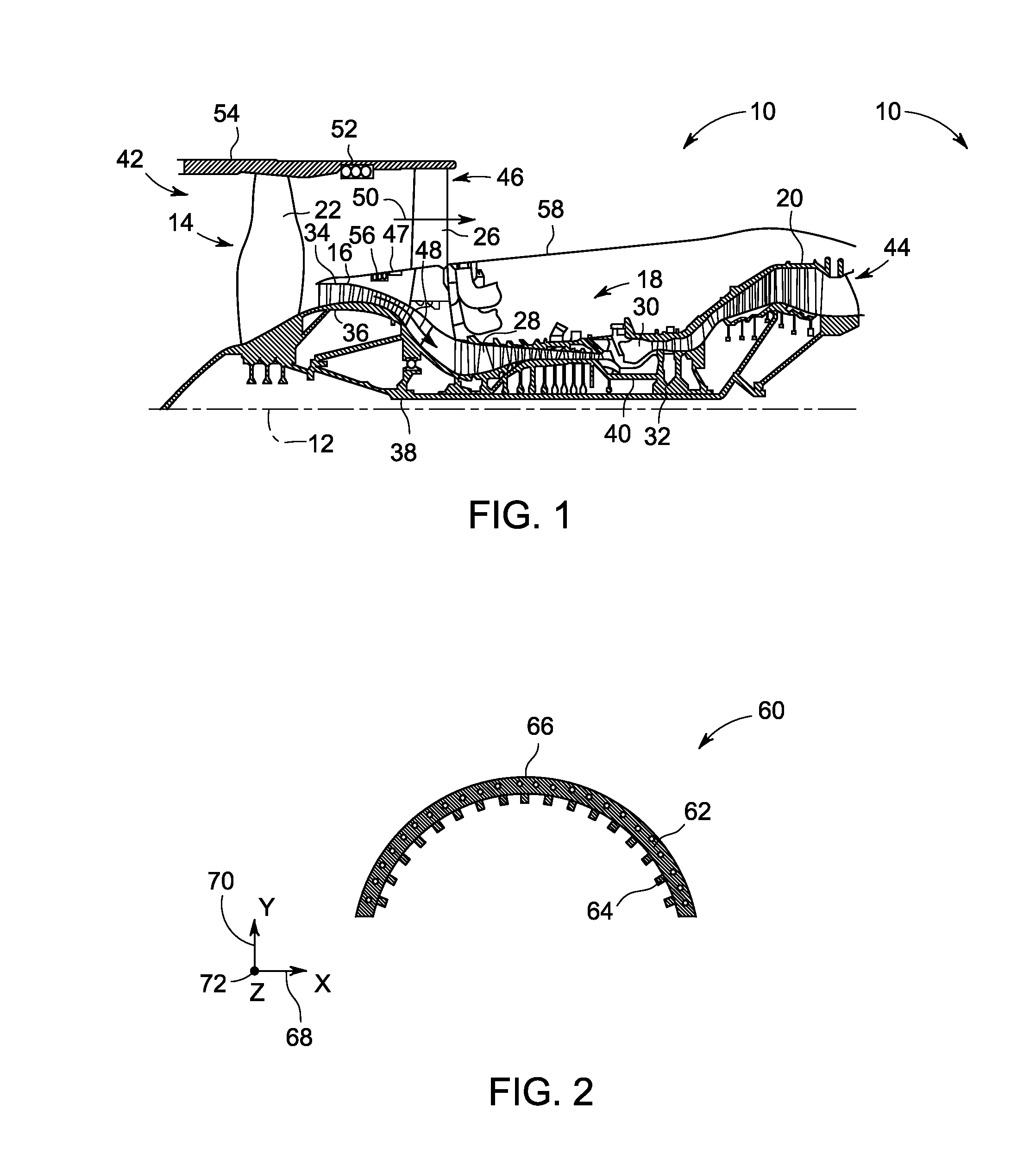
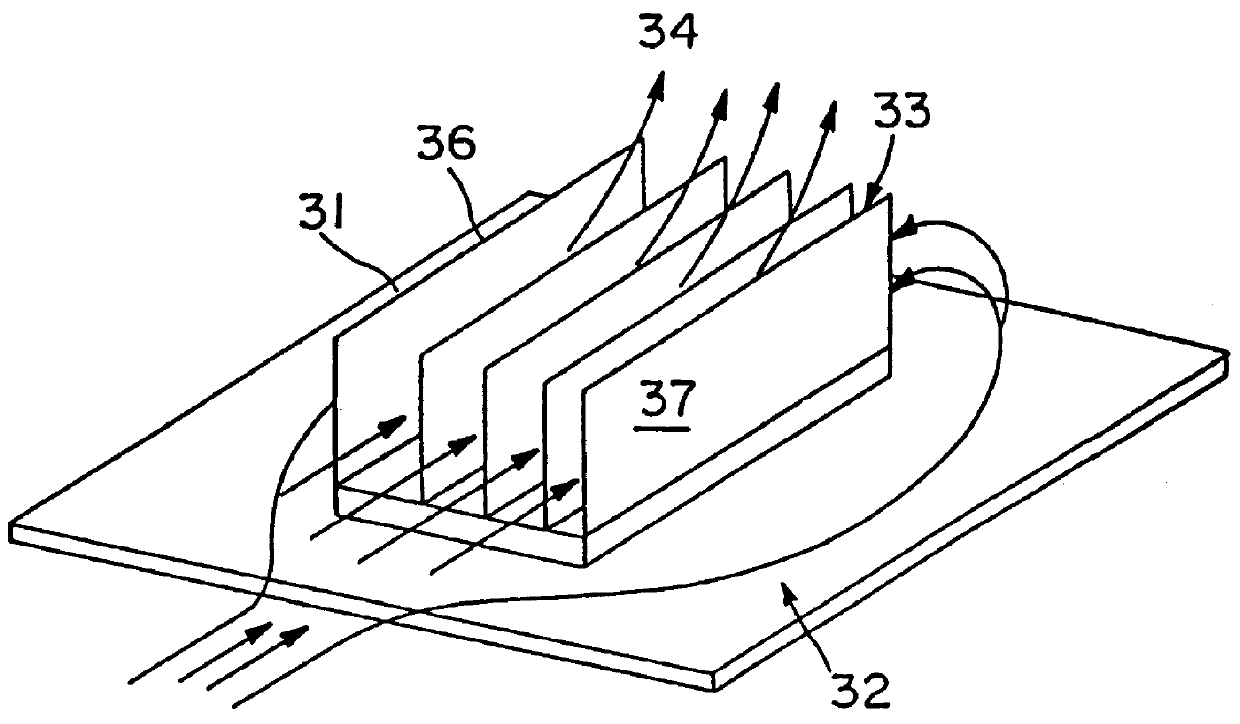
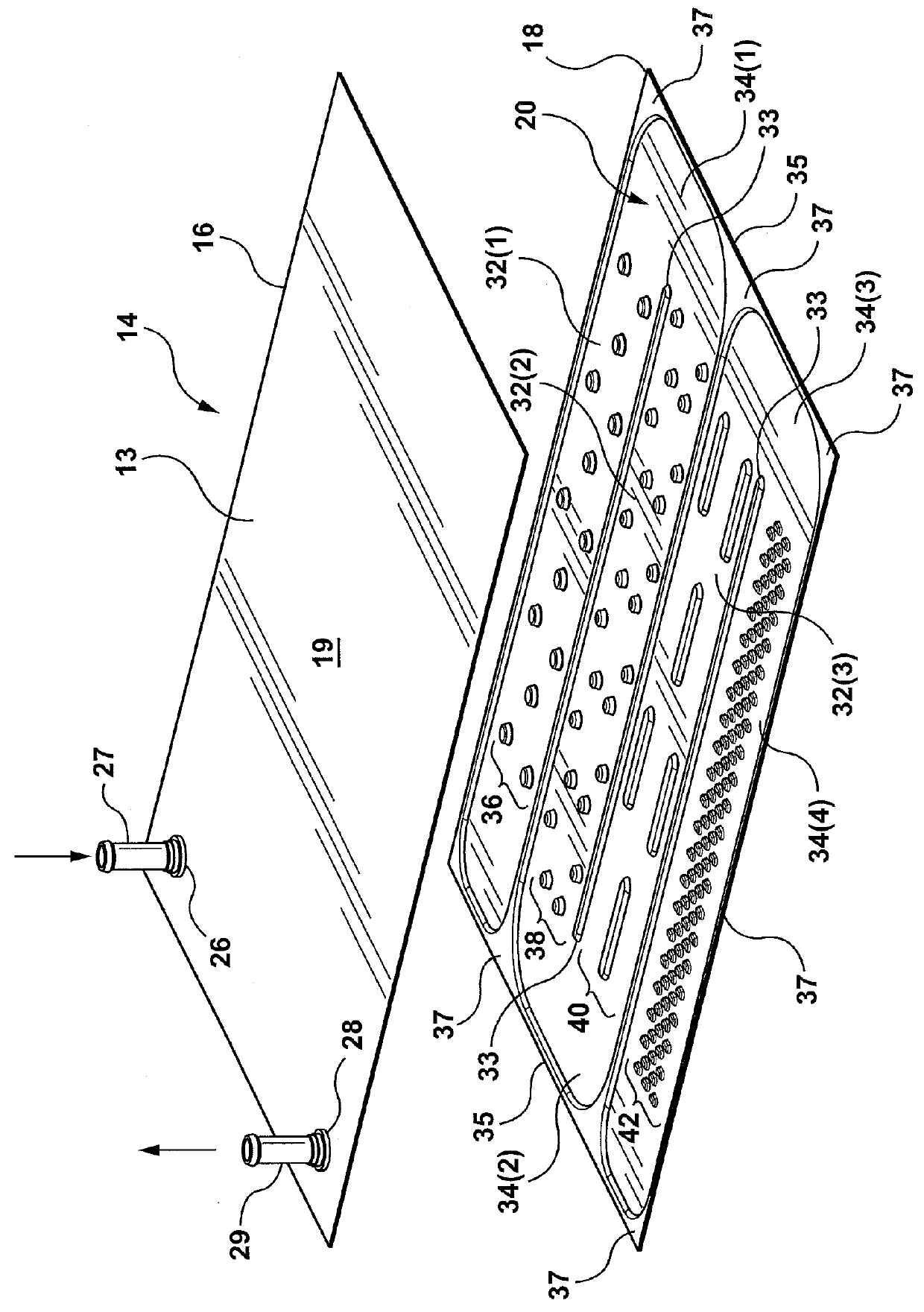
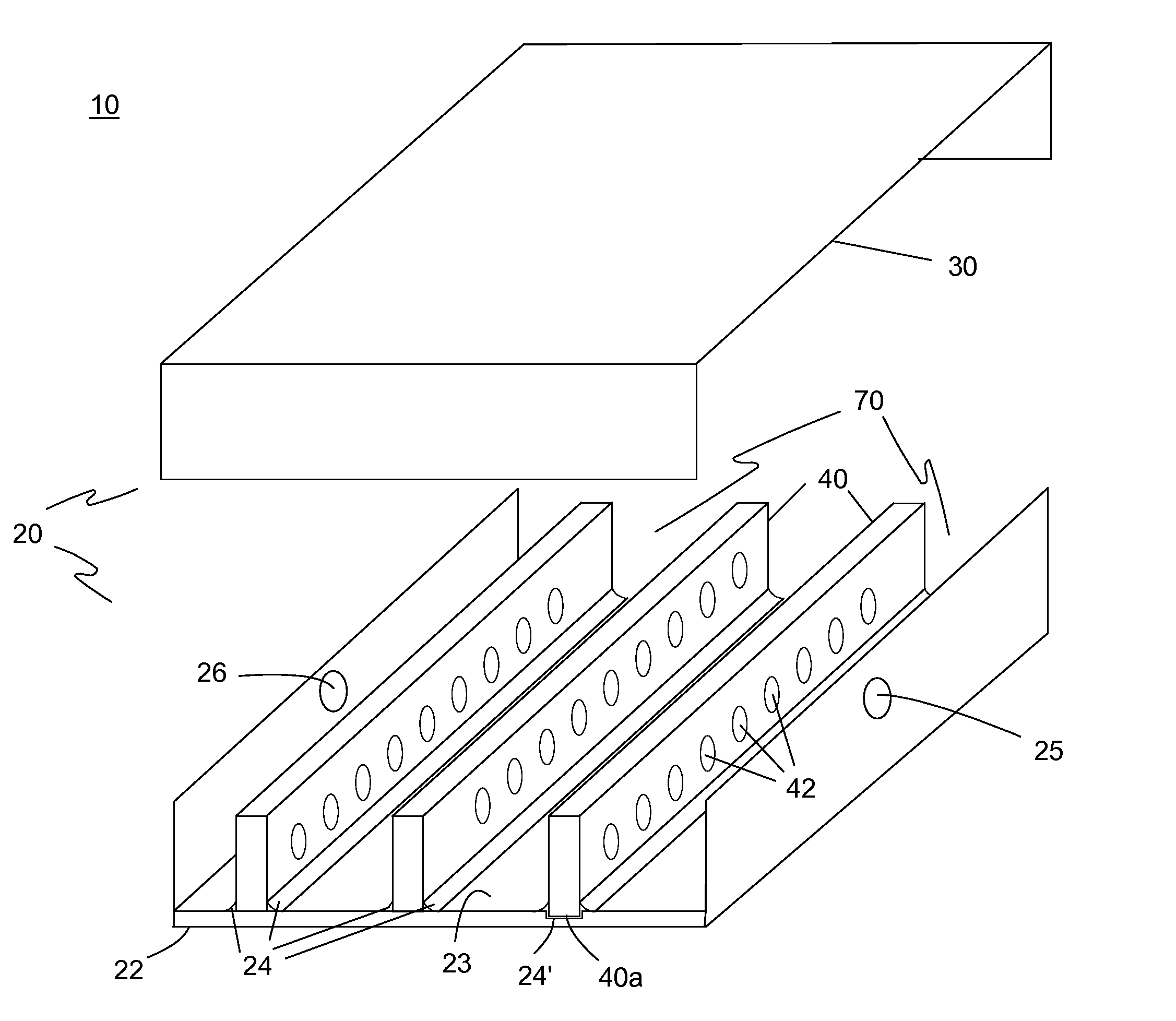
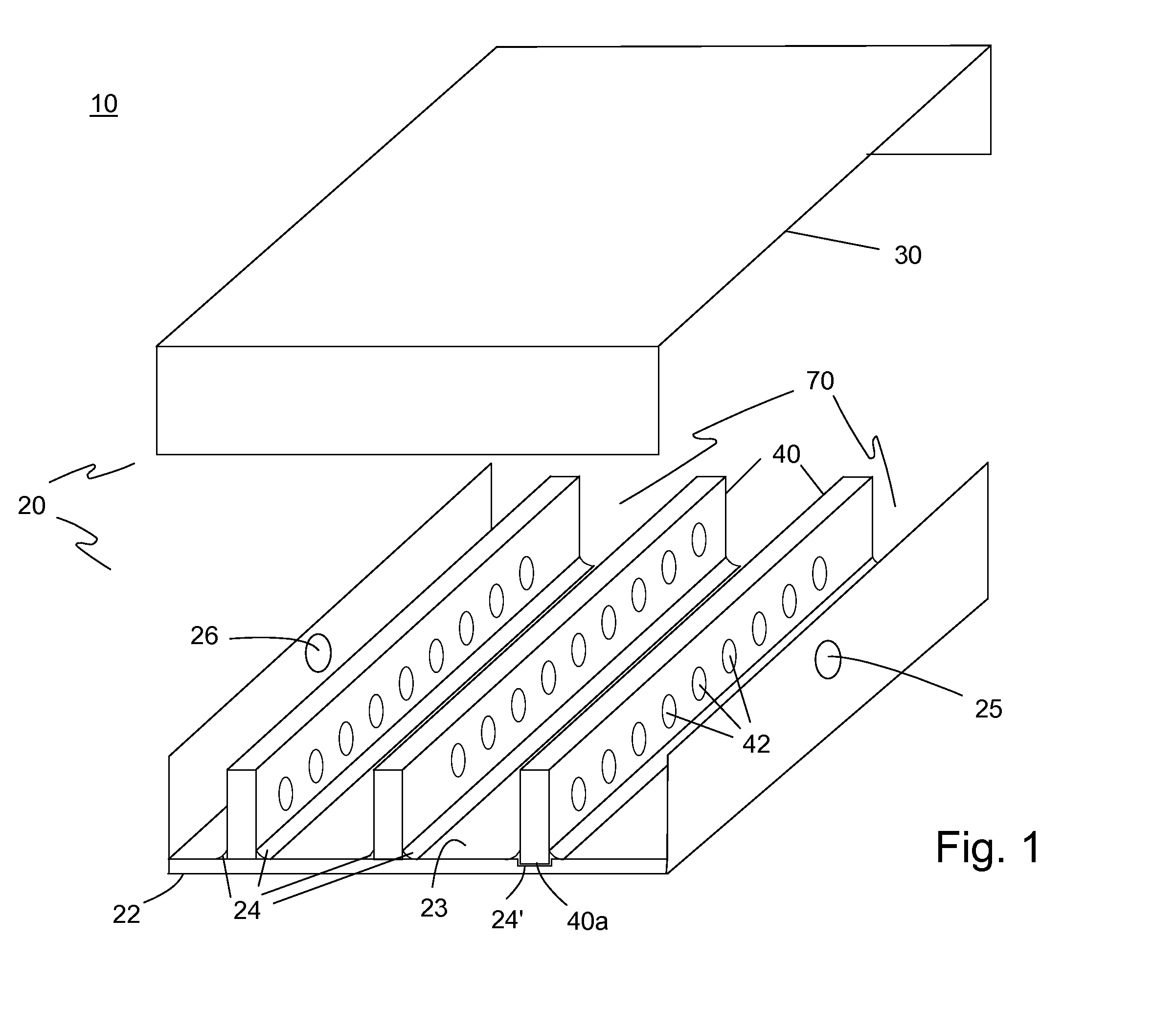
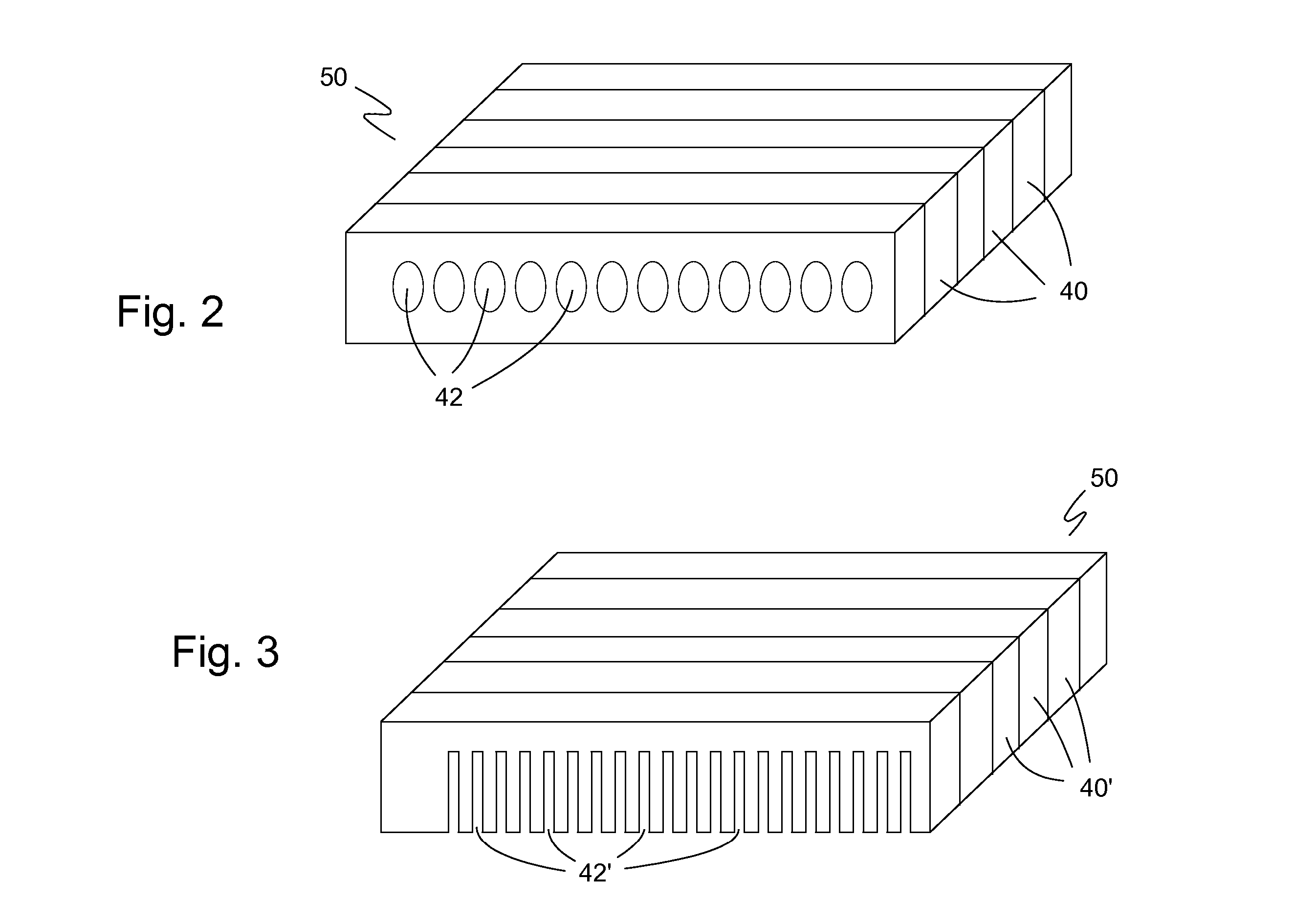
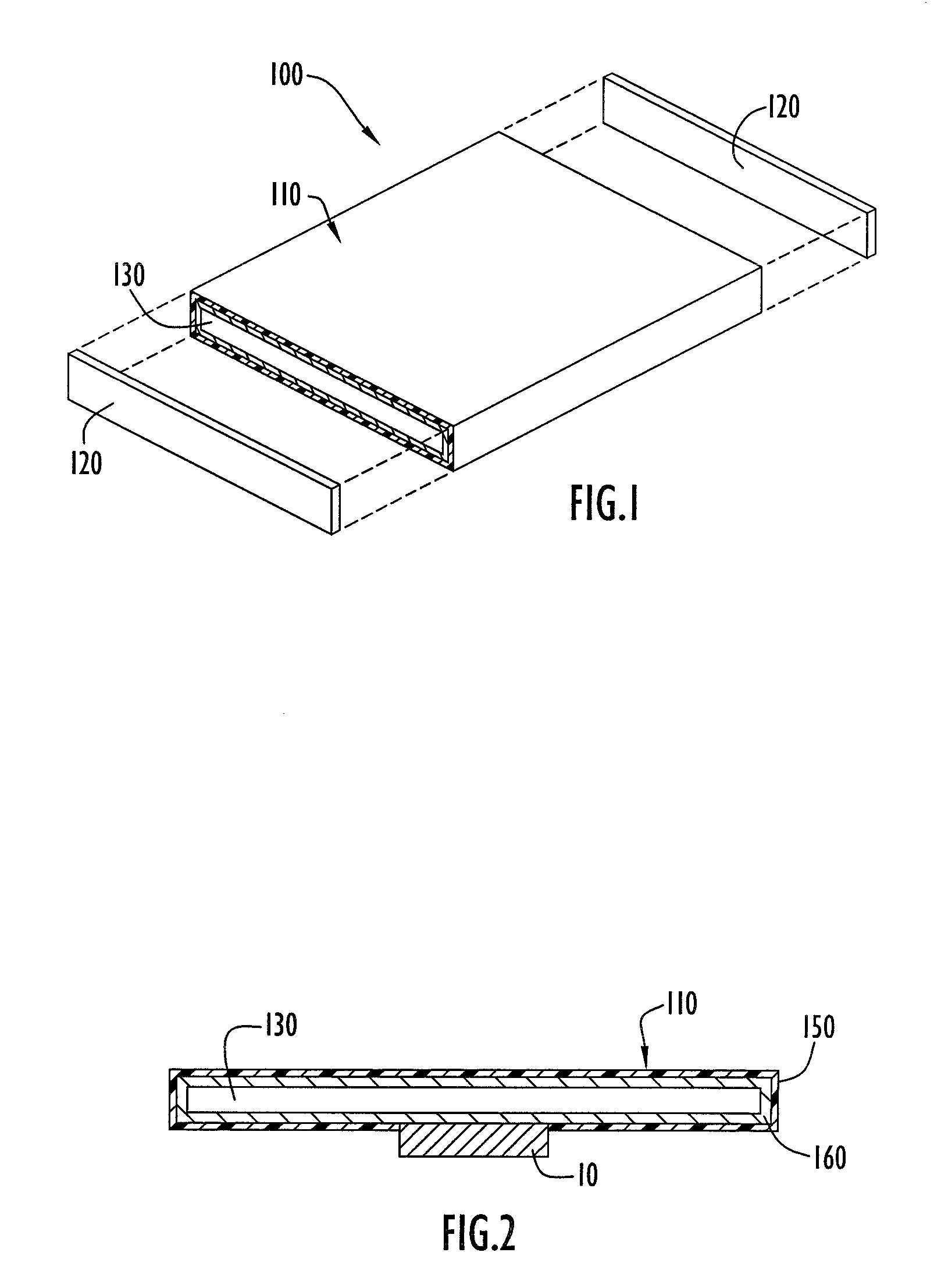
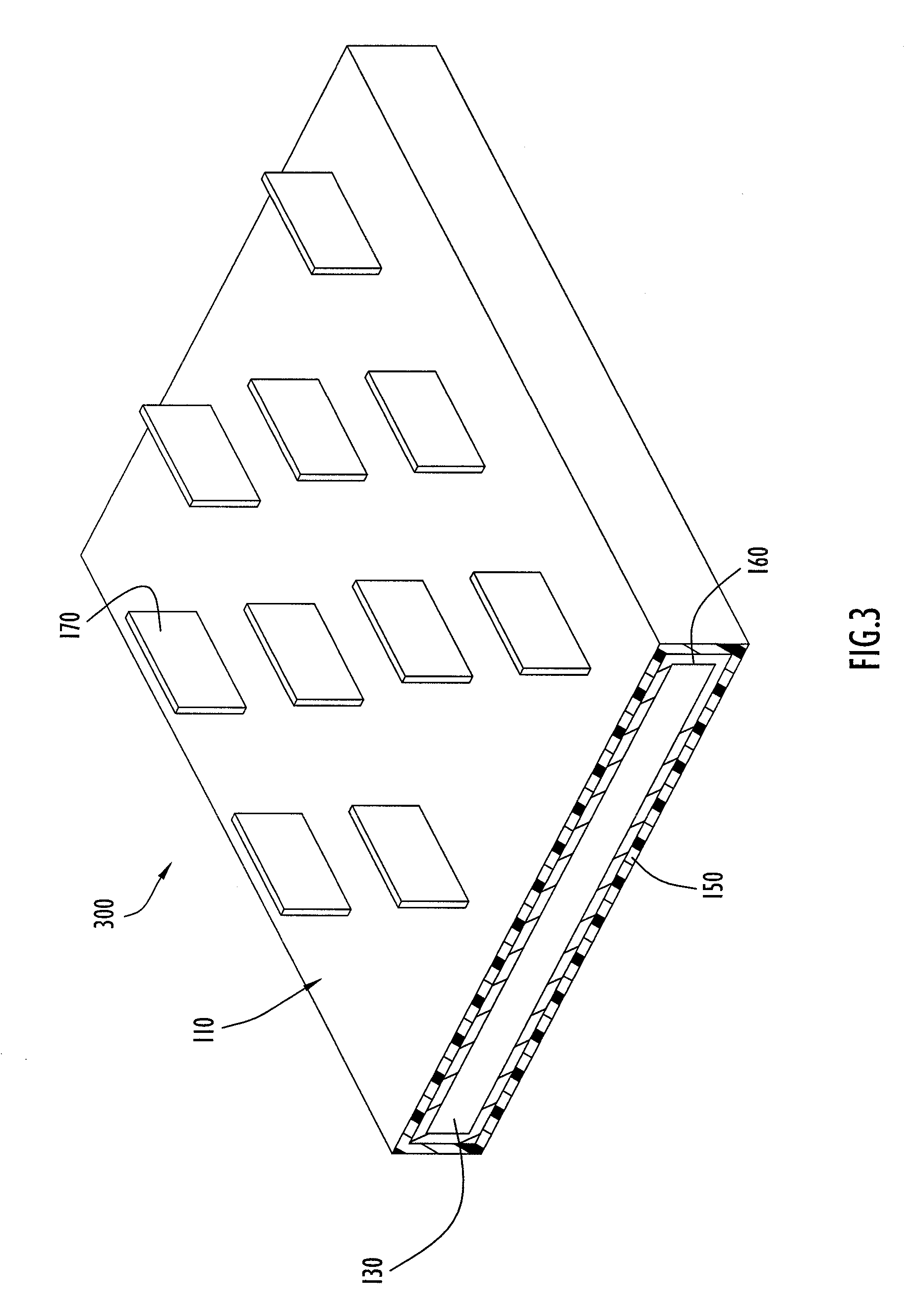
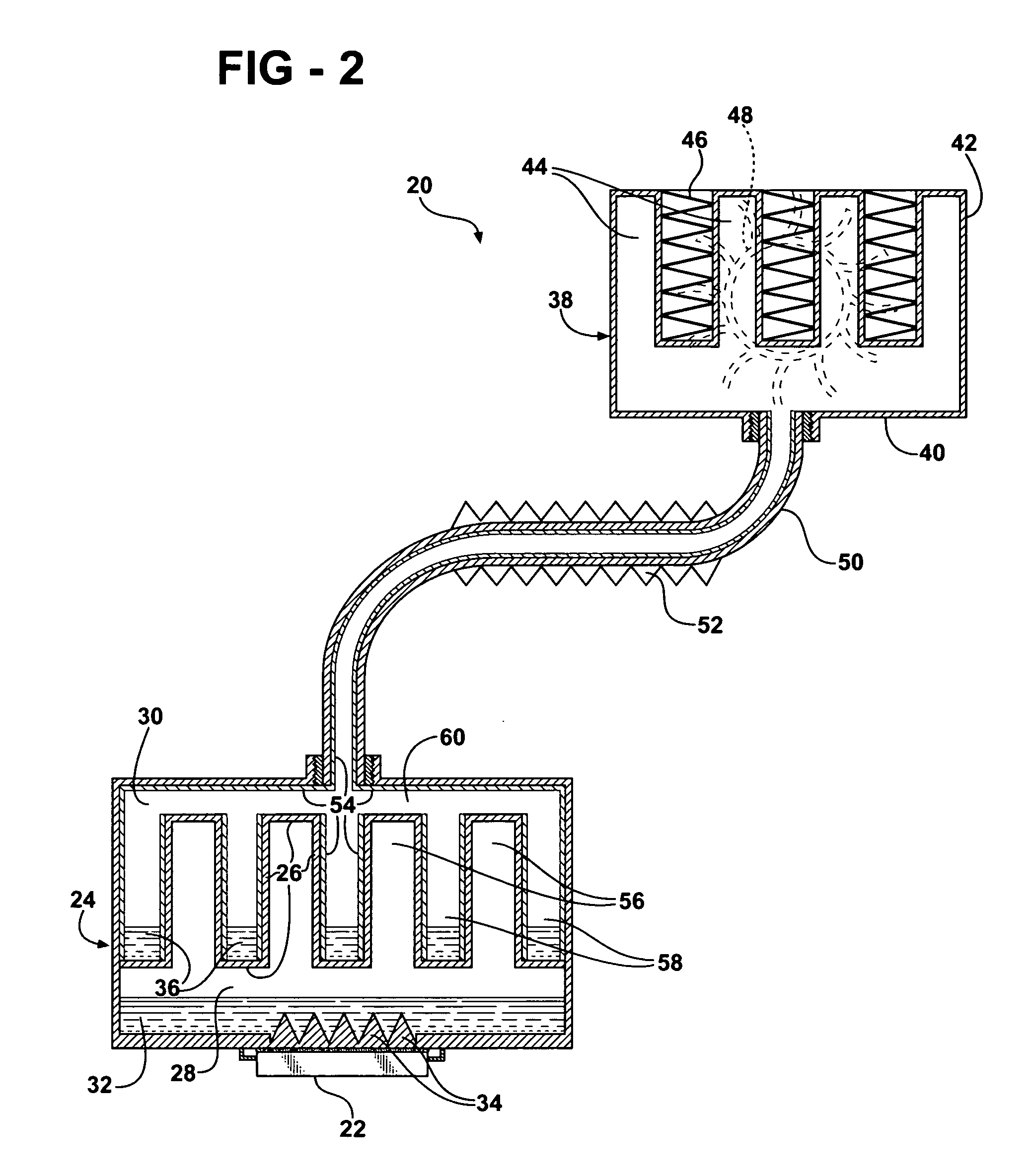
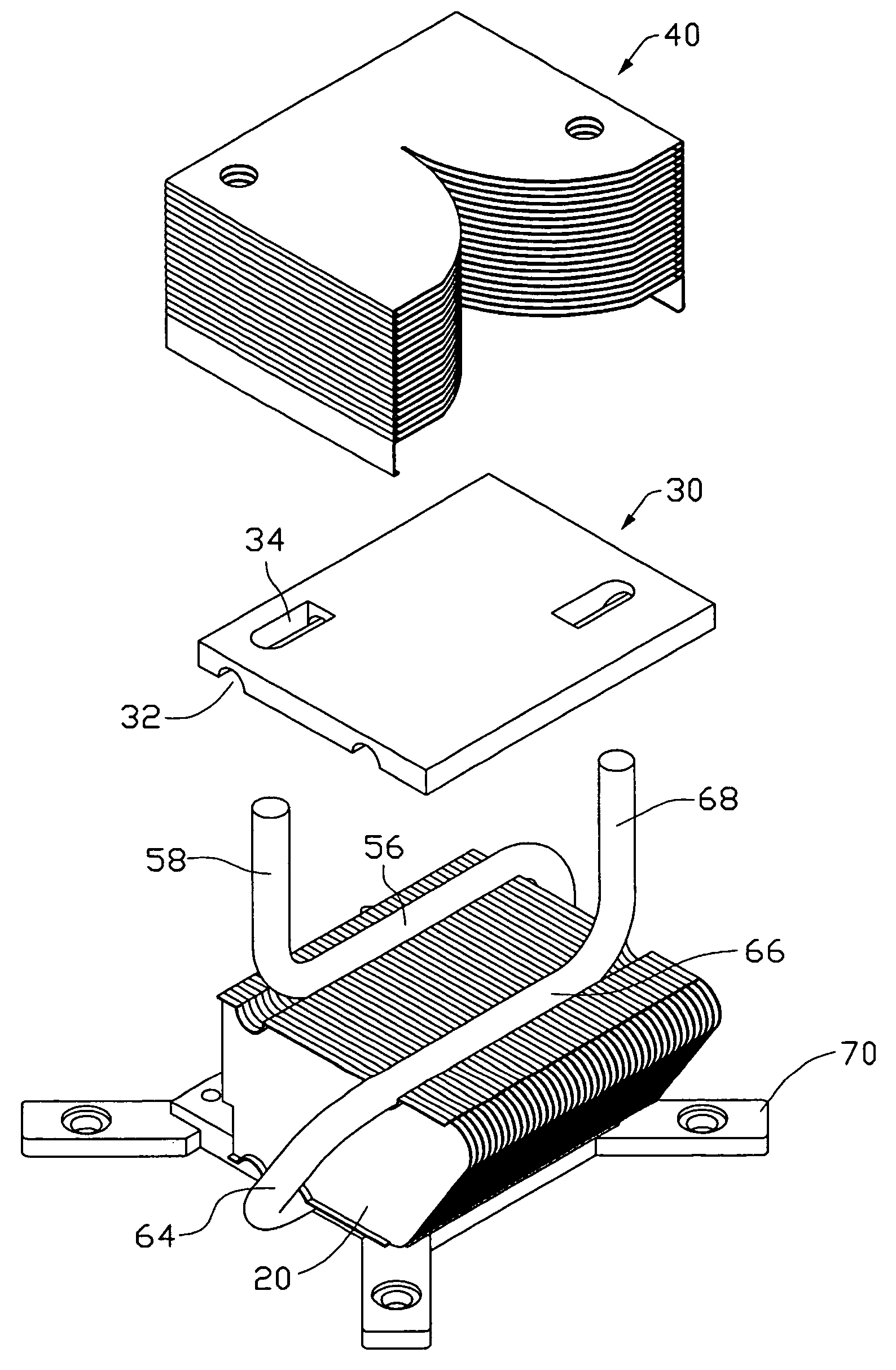
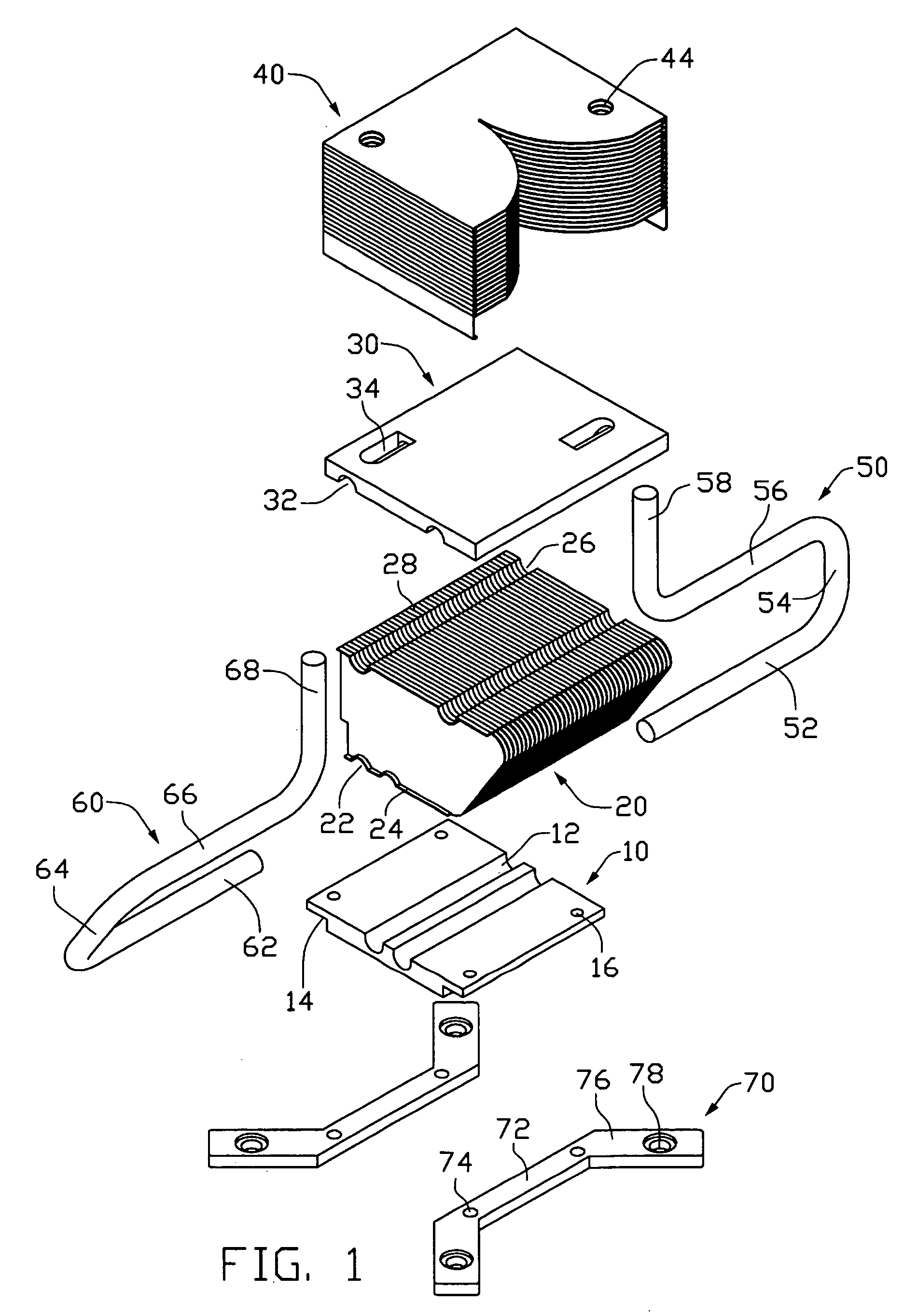
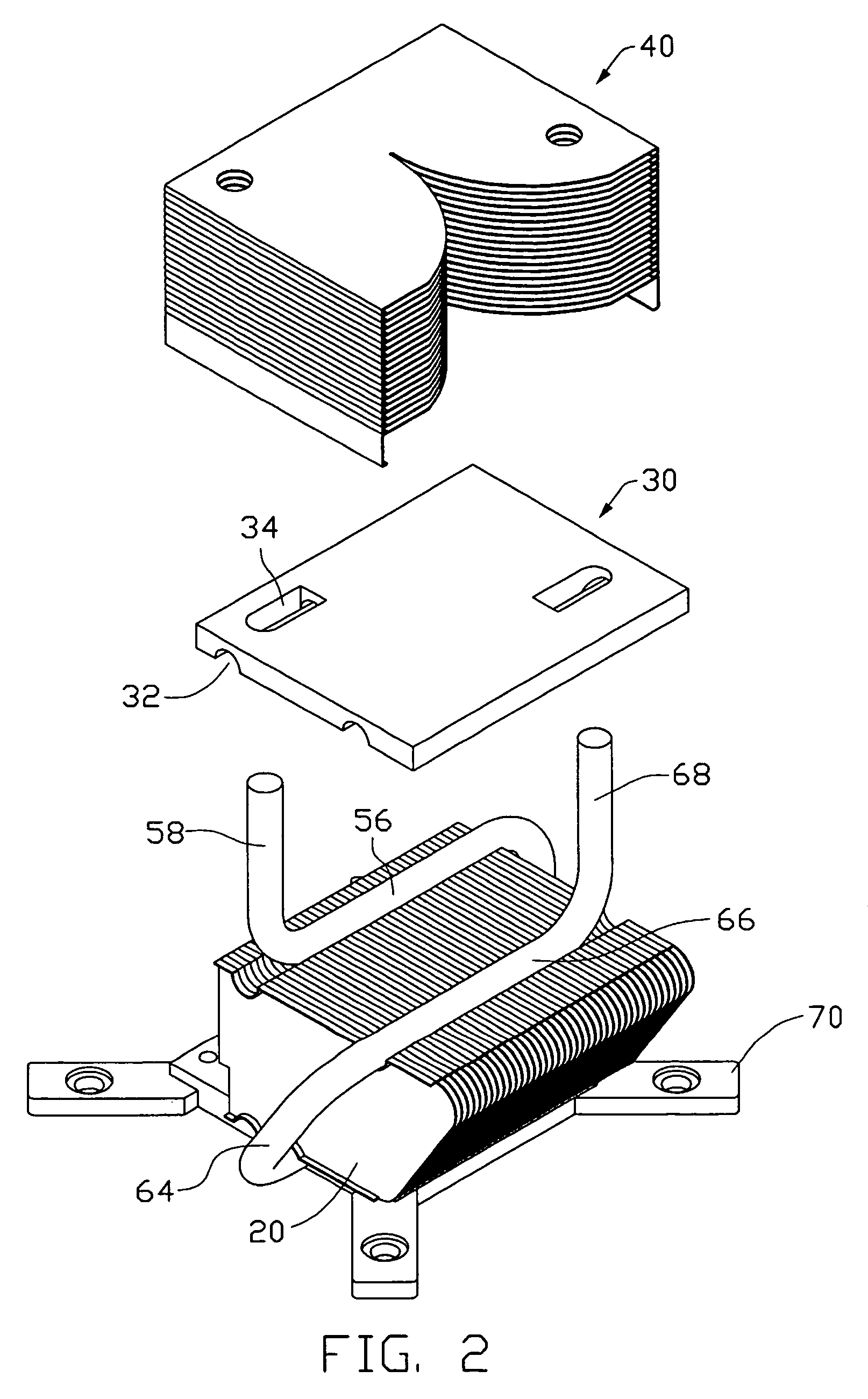
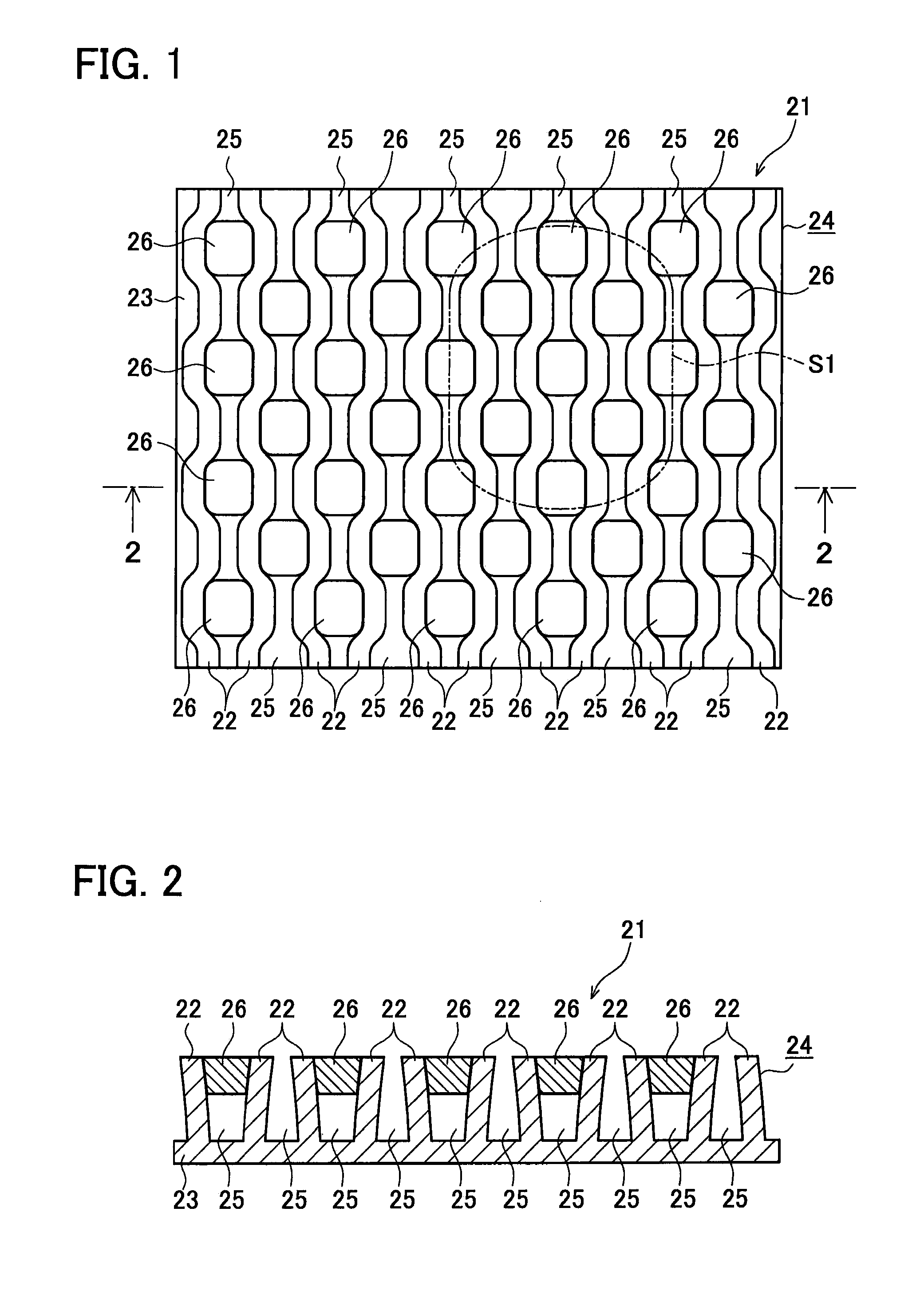
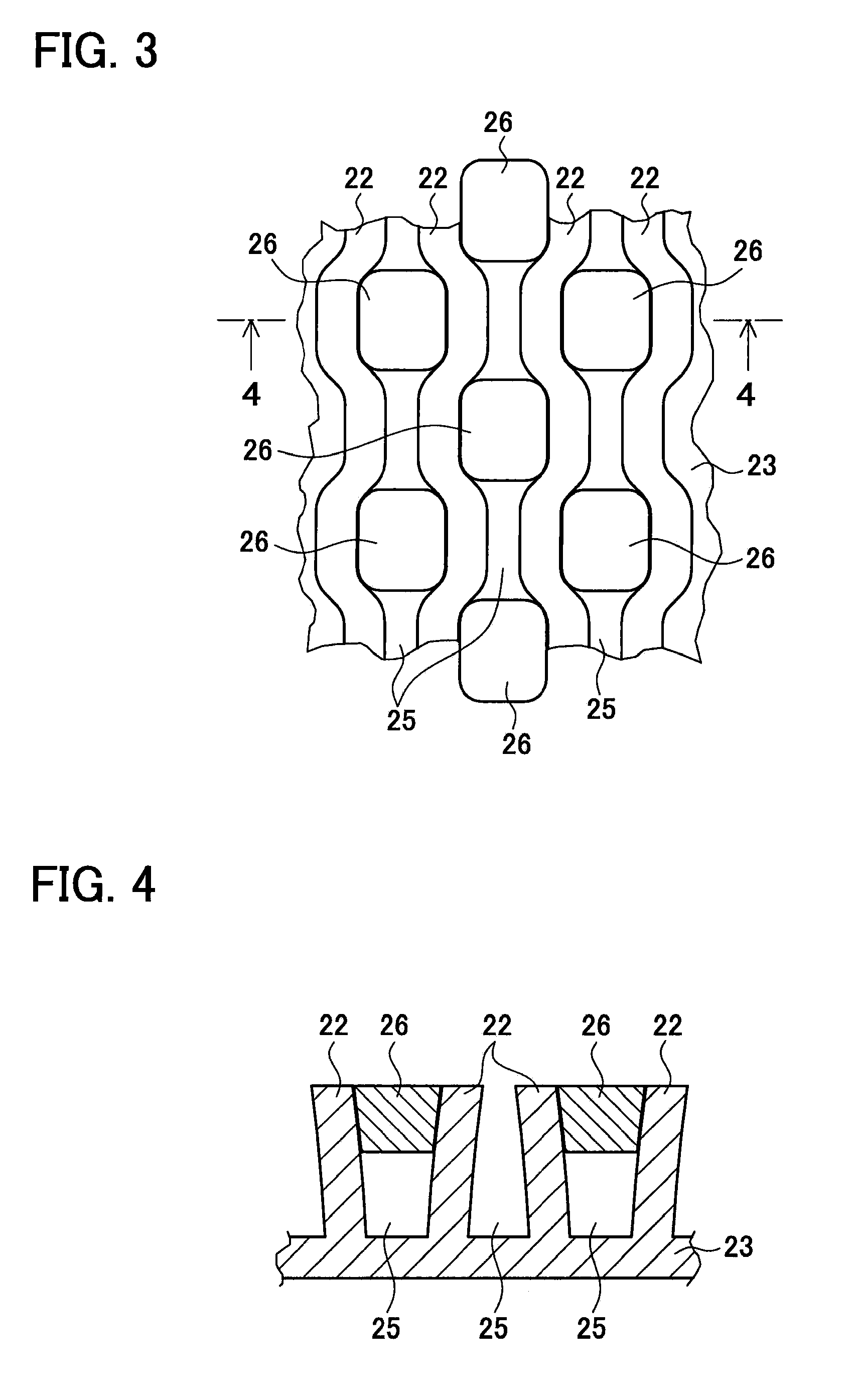
Heat exchange inefficiencies found in round tube plate fin heat exchangers are eliminated in an aluminum heat exchanger that includes first and second headers (20), (22) and at least one flattened tube (24), (70) extending between the headers (20), (22). A plurality of generally parallel tube runs are defined and each has opposite edges. A plurality of plate fins (26), (50) are arranged in a stack and each has a plurality of open ended slots (34), one for each run of the tubes (24), (70). Each of the tube runs (24), (70) is nested within corresponding slots (26) and the fins (26), (50) with one of the edges (40) of the tube runs extending outwardly of the corresponding fin (34). The assembly is brazed together.
Owner:MODINE MFG CO
Non-linear fin heat sink
InactiveUS20090145581A1Improve power densityDissipating/removing heatSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCoolant flowEngineering
A non-linear fin heat sink is provided for dissipating / removing heat uniformly from a device, where the heat generation is non-uniform over that device, while also providing a small and relatively lightweight heat sink. The heat sink has extended surface protrusions that are optimally shaped in recognition of convective heat transfer, conductive heat transfer, and flow resistance allowing the heat sink to offset the temperature rise of a coolant media and provide enhanced cooling for the coolant temperature, deliver optimized cooling efficiency per the local physical properties of the coolant media, be used with a fluid for effectuating heat transfer; either liquid coolant, gas coolant or a combination thereof. Furthermore the heat sink features turbulence enhancement of the coolant stream by a pin array through which coolant stream passes, such fin array featuring a non-linear shape, spacing, and height pattern to provide optimal cooling while simultaneously reducing volume and flow resistance.
Owner:THERMAL TECH
Automotive lighting assembly cooling system
InactiveUS6910794B2Point-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsMobile vehicleEffect light
An automotive lighting assembly cooling system includes a heat pipe with an evaporation area proximate to a heat generating component, such as a Light Emitting Diode (LED), and a condensing area located remote from the evaporation area. Evaporation of fluid within the heat pipe transfers heat away from the heat generating component. The efficiency of the cooling system in one embodiment is increased by including fins associated with the condensing area and placing the fins in an area where air flow external to a moving vehicle assists in cooling the fins.
Owner:GUIDE
Heat sink
InactiveUS20080066888A1Minimized pressure dropImprove cooling effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRADIUSHeat spreader
A heat sink comprises a base panel having a top surface and a bottom surface. A plurality of pin fins extend outwardly from the top surface and each fin has a cross-sectional configuration with two radiuses, a first radius and a second radius, wherein the first radius is larger than the second radius. The first and second radiuses are tangentially interconnected by intermediate portions, giving the pin fin cross-sectional configuration a raindrop shape, thereby generating low pressure drop across the heat sink by minimizing the drag force effects and maintaining large exposed surface area available for heat transfer.
Owner:DANAHER MOTION STOCKHOLM AB
Cooling member for heat containing device
InactiveUS20110299244A1Fixed capacitor electrodesDigital data processing detailsBiomedical engineeringIrregular shape
Owner:TOYOTA MOTOR CO LTD
Vapor chamber structure and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090040726A1Improve structural strengthImprove sealingSpacing meansReinforcing meansWorking fluidEngineering
A vapor chamber structure includes a casing, a working fluid, a wick layer, a plurality of structure strengthening bodies, and a plurality of backflow accelerating bodies. The casing has an airtight vacuum chamber. The working fluid is filled into the airtight vacuum chamber. The wick layer is formed on a surface of the airtight vacuum chamber. The structure strengthening bodies are respectively arranged in the airtight vacuum chamber for supporting the casing. The backflow accelerating bodies are respectively arranged in the airtight vacuum chamber for increasing the backflow velocity of the working fluid. Therefore, the present invention can maintain the completeness of the vapor chamber structure and increase the backflow velocity of the working fluid due to the match of the structure strengthening bodies and backflow accelerating bodies. Because the backflow velocity of the working fluid is increased, the heat-transmitting efficiency is increased.
Owner:THERMAL TECH
Method and apparatus for cooling an electronic device
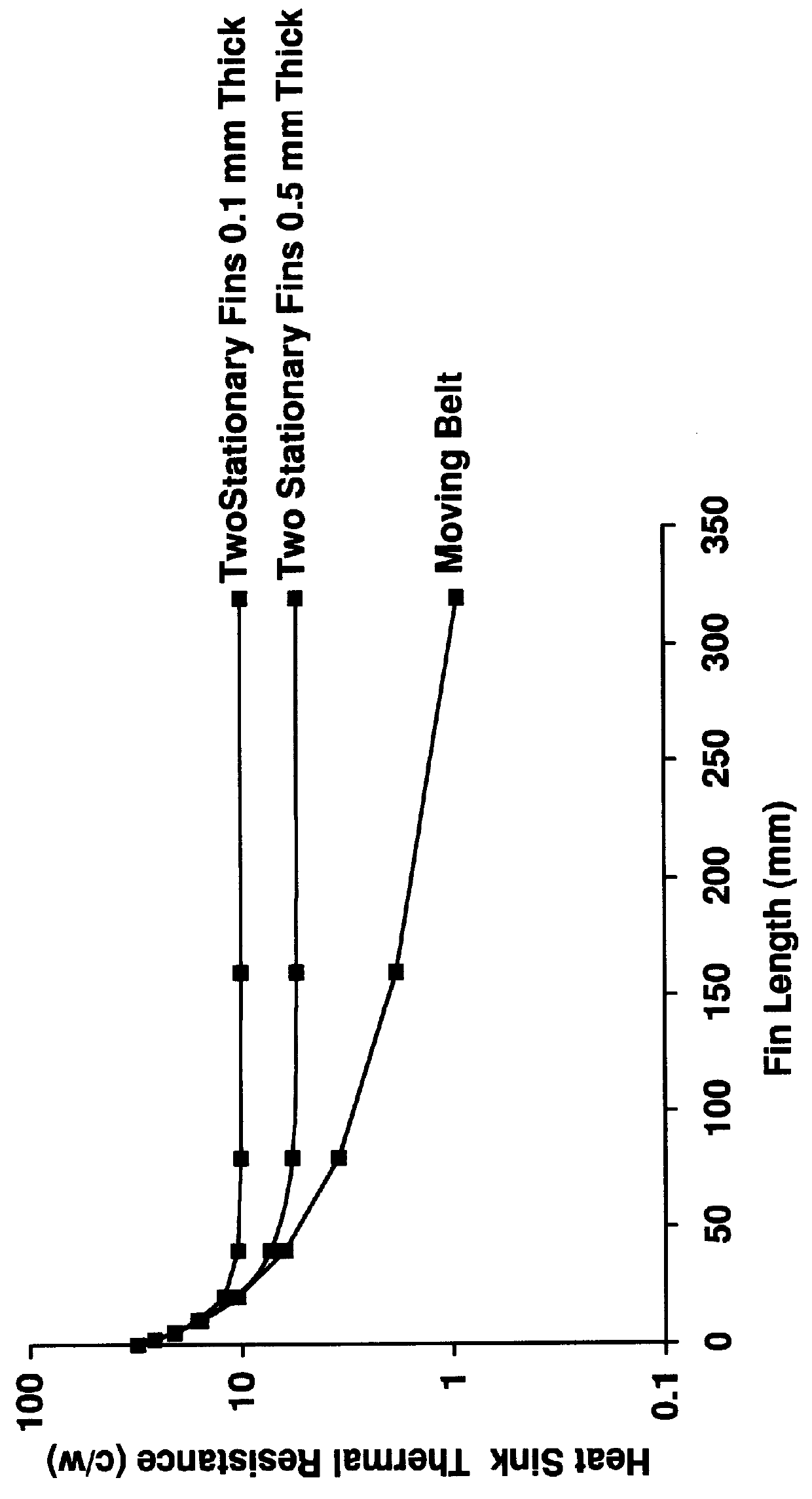
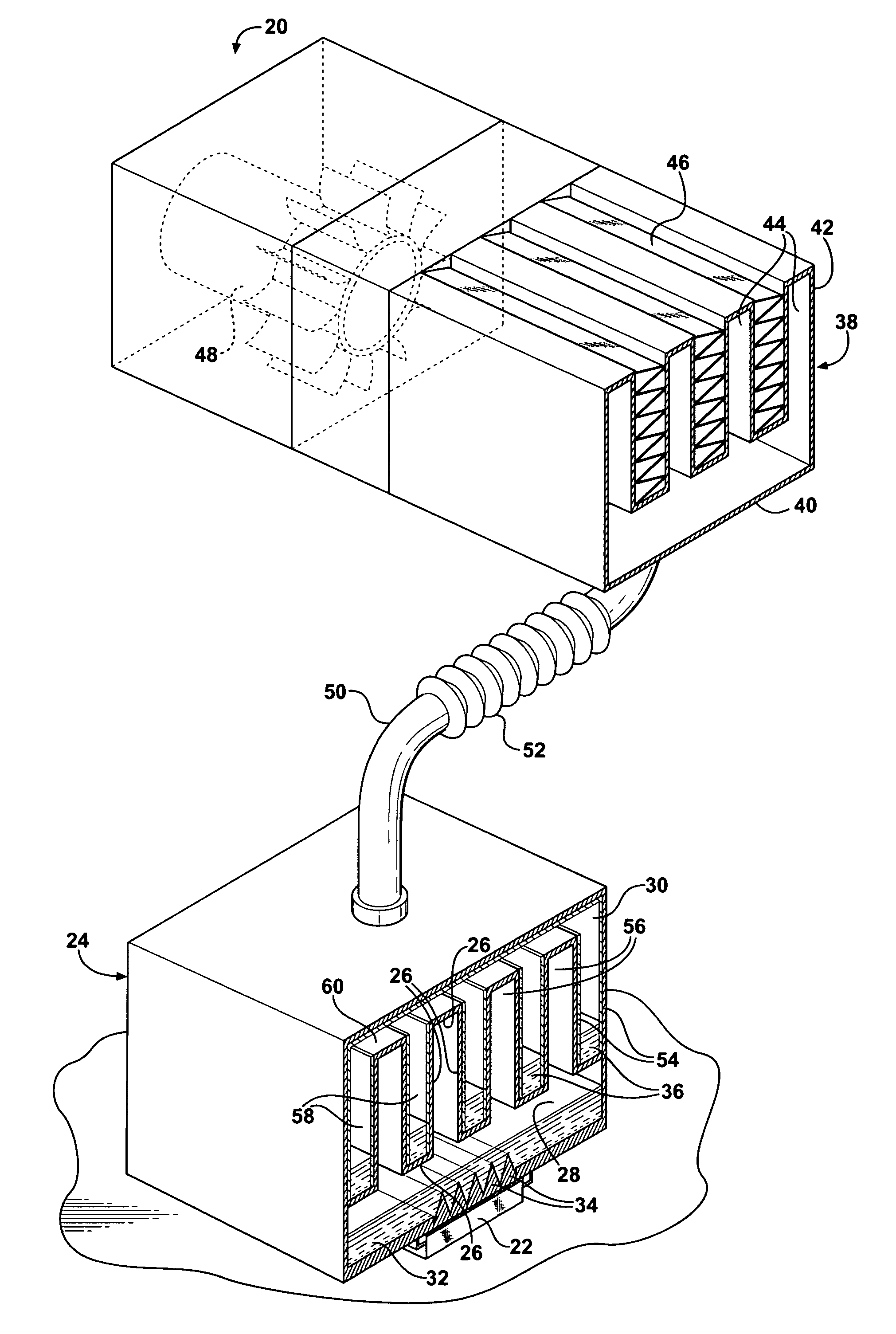
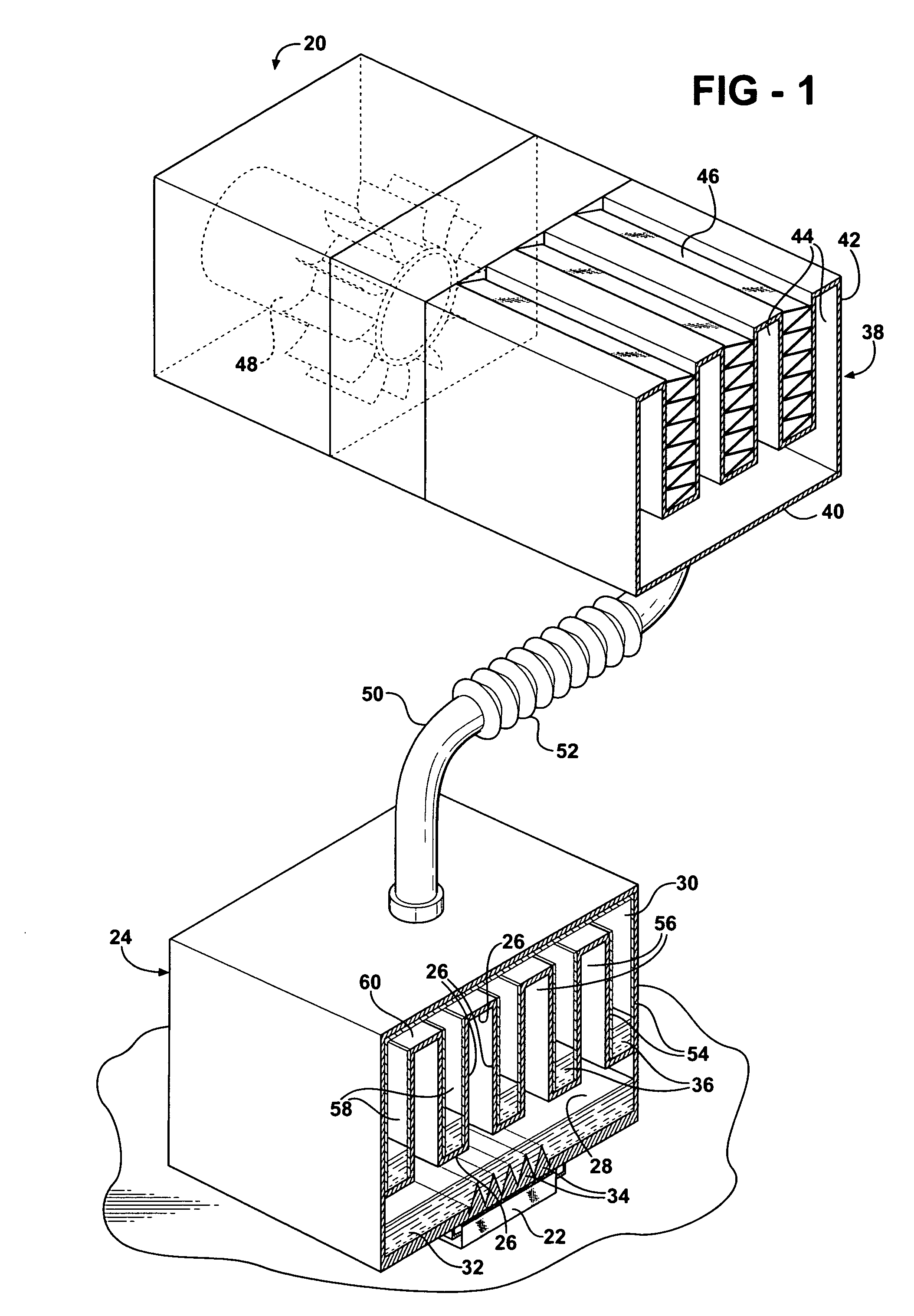
A heat dissipation apparatus for cooling one or more electronic devices. The apparatus utilizes a moving heat sink a portion of which is in contact with the device to be cooled. The moving heat sink may be in the form of a rotating disk, moving belt or strip. The heat sink may be made from various materials such as metals or plastics.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatuses for dissipating heat from semiconductor devices
ActiveUS7369410B2Increase surface areaImprove cooling efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devices3d shapesEngineering
An apparatus for providing two-phase heat transfer for semiconductor devices includes a vapor chamber configured to carry a cooling liquid, the vapor chamber having base section, and a plurality of three-dimensional (3D) shaped members. The plurality of 3D-shaped members have interior and exterior sidewalls, the 3D-shaped members being connected to the base section so that vapor carrying latent heat can reach the respective interior sidewalls and get transferred to the respective exterior sidewalls configured to be in contact with an external coolant. The vapor chamber is configured to be in contact with a semiconductor device in order to remove heat therefrom.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Cooling device boiling and condensing refrigerant
A cooling device includes: a partition plate for partitioning an interior of a case into a first fluid passage through which first fluid having a high temperature flows and a second fluid passage through which second fluid having a low temperature flows; a heat receiving portion disposed in the first fluid passage; a heat radiating portion disposed in the second fluid passage; and a connection pipe for communicating the heat receiving portion and the heat radiating portion. The heat radiating portion is disposed at an upper side of the heat receiving portion in such a manner that the second fluid from a front side of the heat radiating portion flows into a rear side of the heat radiating portion through a pipe space between the heat radiating portion and the heat receiving portion, and further passes through the heat radiating portion from the rear side toward the front side of the heat radiating portion. Thus, the cooling device has a small size while improving the cooling capacity of the cooling device.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Apparatuses for dissipating heat from semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20070258213A1Increase surface areaImprove two-phase cooling efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devices3d shapesDevice material
An apparatus for providing two-phase heat transfer for semiconductor devices includes a vapor chamber configured to carry a cooling liquid, the vapor chamber having base section, and a plurality of three-dimensional (3D) shaped members. The plurality of 3D-shaped members have interior and exterior sidewalls, the 3D-shaped members being connected to the base section so that vapor carrying latent heat can reach the respective interior sidewalls and get transferred to the respective exterior sidewalls configured to be in contact with an external coolant. The vapor chamber is configured to be in contact with a semiconductor device in order to remove heat therefrom.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Foul-resistant condenser using microchannel tubing
ActiveUS7000415B2Reducing and eliminating occurrenceShow cabinetsEvaporators/condensersFiberEngineering
A condenser coil for a refrigerated beverage and food service merchandiser includes a plurality of parallel fins between adjacent tubes. In order to reduce the likelihood of fouling by the bridging of fibers therebetween, the spacing of the fins is maintained at a distance of 0.4 to 0.8 inches apart. In one embodiment, the tubes comprise microchannel tubes, with no fins therebetween, and the spacing between the microchannel tubes is maintained in the range of 0.75 inches to optimize the heat transfer performance while minimizing the occurrence of fouling. A supporting structure is provided between microchannel tubes when no fins are included. Also, plural rows of microchannel tubes are provided with separate inlet headings and with the rows being staggered in transverse relationship to enhance the heat transfer characteristic while minimizing the likelihood of fouling.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
High performance fan tail heat exchanger
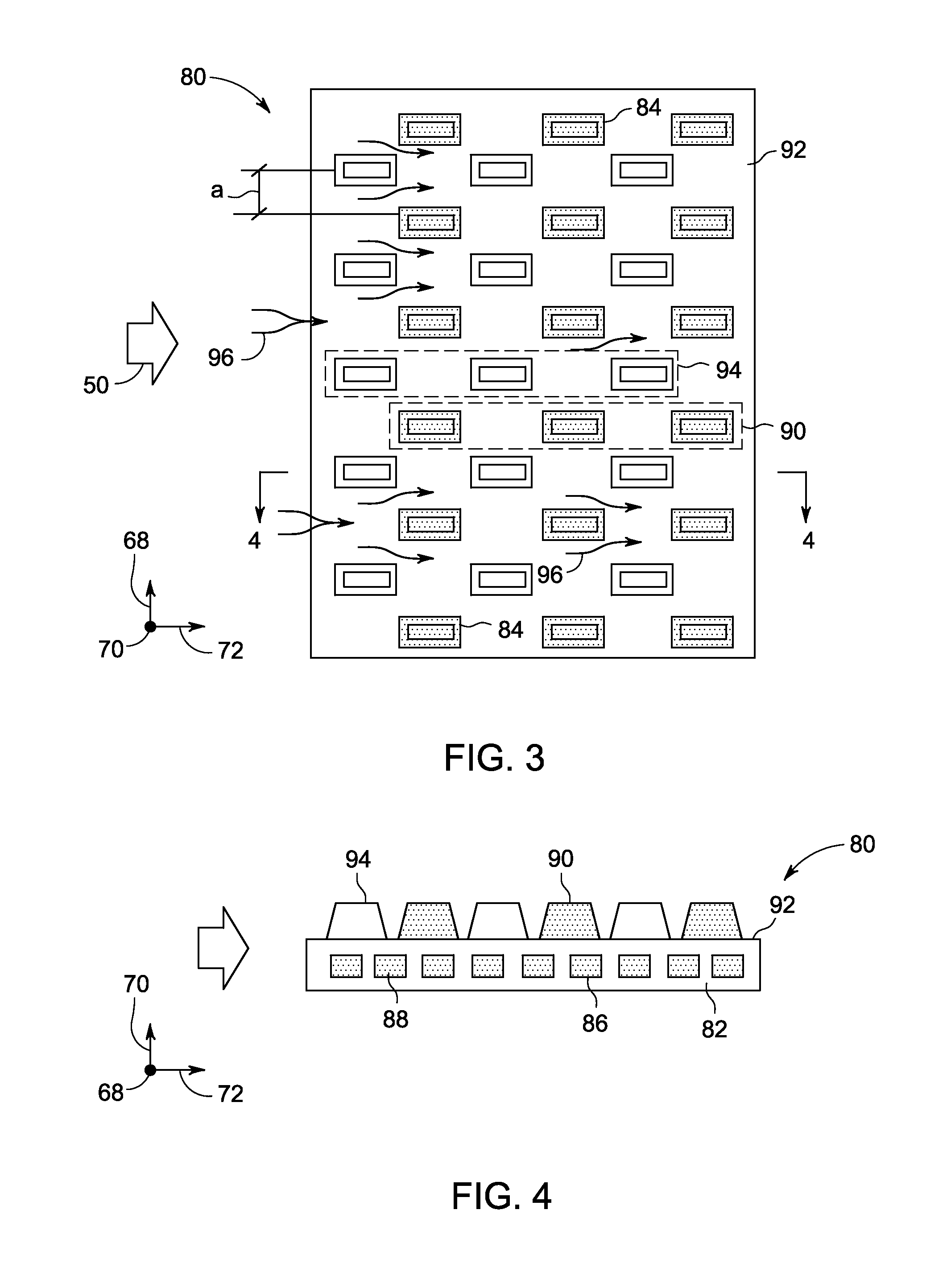
InactiveUS6308771B1Increased control volumeOptimize volumeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAcute angleEngineering
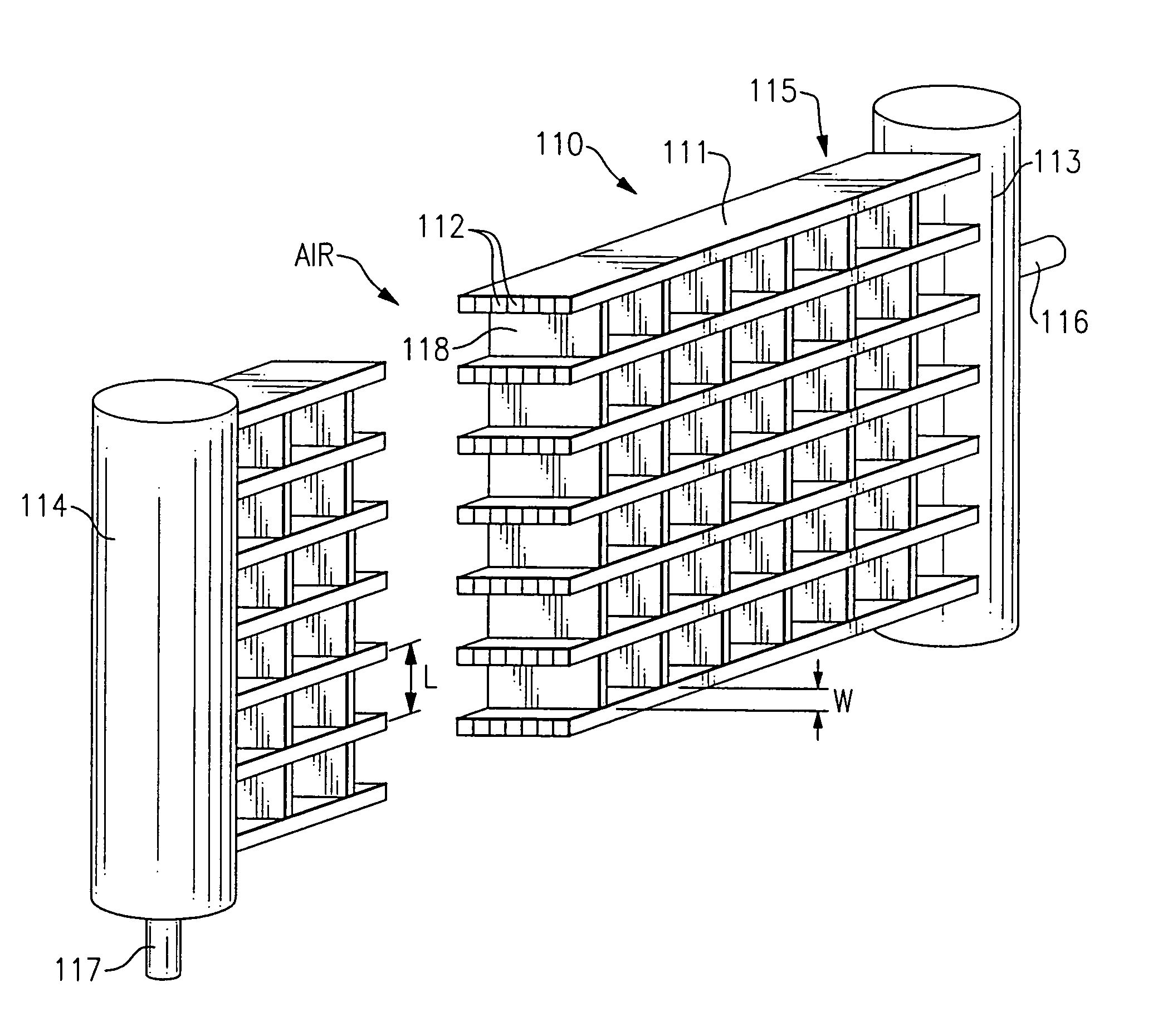
A novel plate fin heat exchanger adapted for high and low velocity fluid flows for dissipating heat from a heat generating component. The heat exchanger comprises an array of fins being affixed to and in thermal communication with a thermally conductive base, wherein the fins are arranged in a fan tail configuration for minimizing flow bypass, and further providing reduced thermal resistance for fluid passing through the fin field. The fins are affixed to and in thermal communication with the base at an acute angle, such that the effective width of the array of fins exceeds the width of the base. The enlarged effective width of the fin array in comparison to conventional heat exchanger provides an increased volume for fluid flow, thereby allowing a greater volume of fluid to enter the fin field and a greater surface area of plate fins for cooling the fluid passing through the heat exchanger. In addition, the heat exchanger comprises a fin density of at least ten fins per inch or greater of base length thereby providing a narrow channel heat exchanger with a fan tail. The aspect ratio of the individual channels between the fins, as compared to parallel fins affixed perpendicular to the base through an extrusion method, generates a reduced pressure drop across the heat exchanger. Accordingly, the heat exchanger of the present invention expands the envelope of cooling performance provided by fluid flow over an array of thermally conductive plates.
Owner:ADVANCED THERMAL SOLUTION
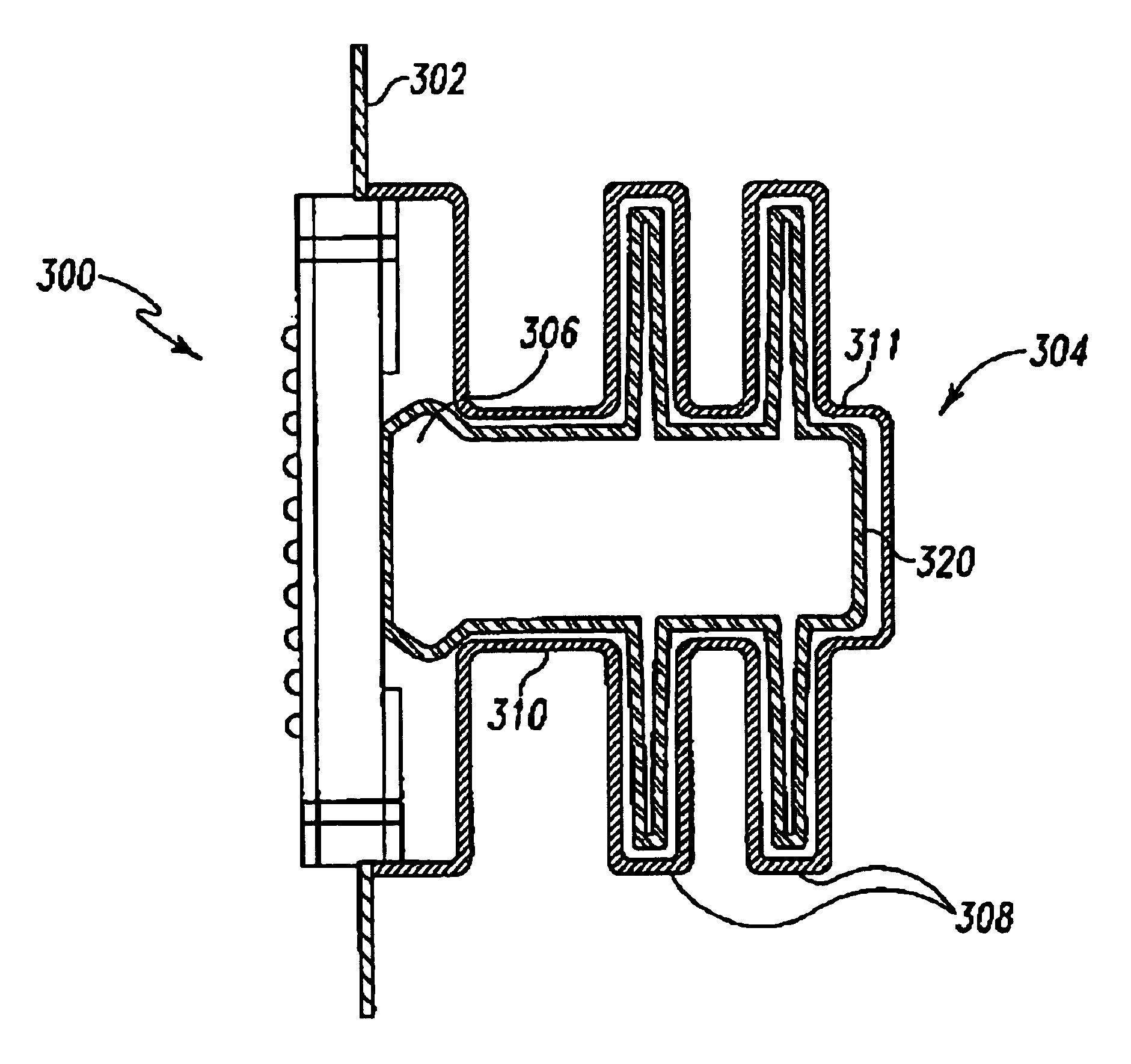
Cooling system and electronic apparatus applying the same therein
ActiveUS20110048676A1Small total thermal resistanceThermal resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSiphonEngineering
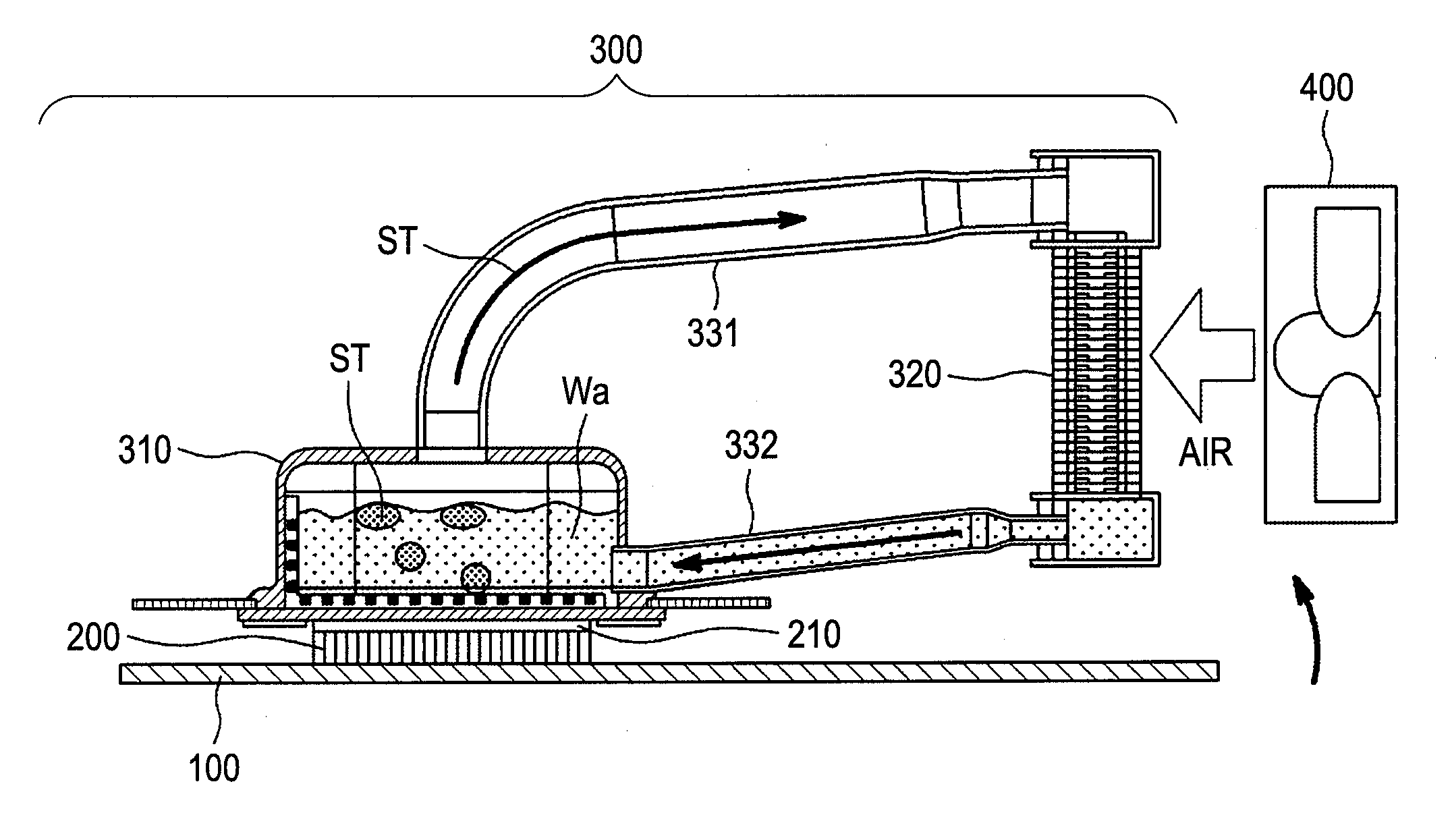
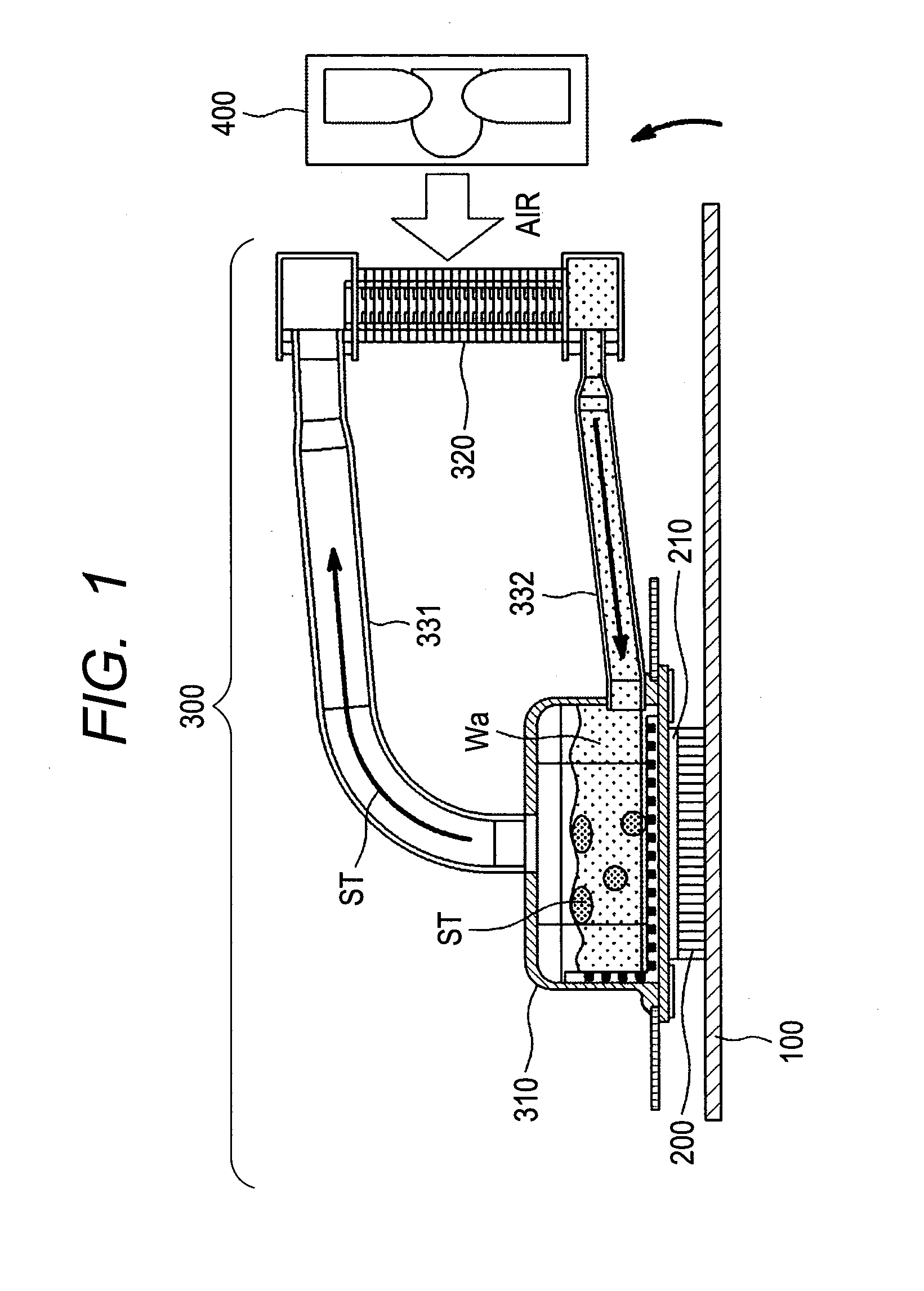
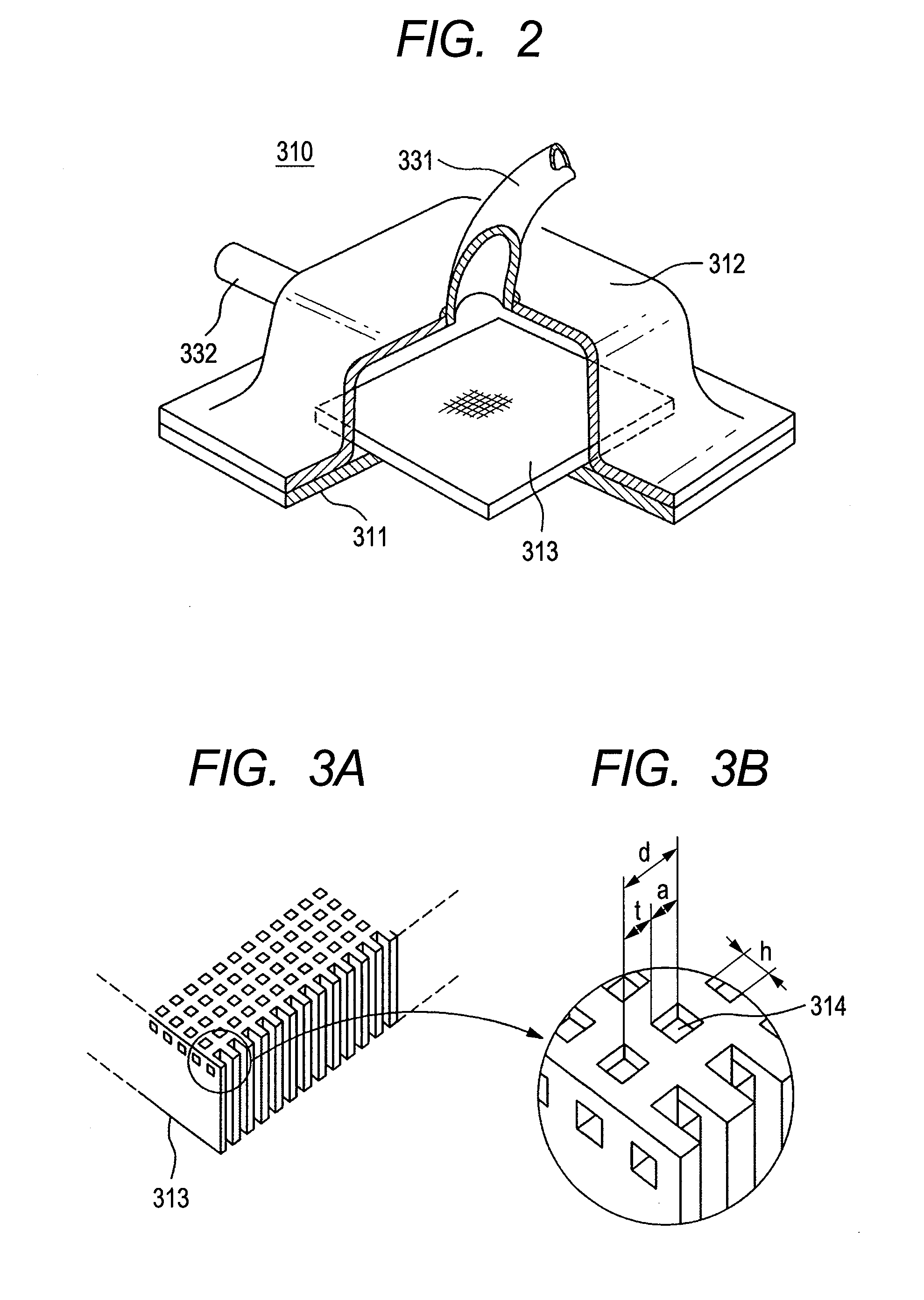
A cooling system applying a thermo siphon therein, being superior in energy saving and / or ecology, with an effective cooling, and also an electronic apparatus applying that therein, in particular, for cooling a CPU 200 mounted on a printed circuit board 100 within a housing thereof, comprises a heat-receiving jacket 310, being thermally connected with a surface of the CPU generating heats therein, and for evaporating liquid refrigerant stored in a pressure-reduced inner space with heat generation thereof, a condenser 320 for receiving refrigerant vapor from the heat-receiving jacket within a pressure-reduced inner space thereof and for condensing the refrigerant vapor into a liquid by transferring the heats into an outside of the apparatus, a vapor tube 331, and a liquid return tube 332, with applying the thermo siphon for circulating the refrigerant due to phase change thereof, wherein the condenser forms fine grooves on an inner wall surface thereof along a direction of flow of the refrigerant, and is also formed flat in a cross-section thereof, for cooling the refrigerant vapor from the heat-receiving jacket on the inner wall surface thereof, efficiently.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Air-cooled engine surface cooler
ActiveUS20140027102A1Improve heat transfer performanceIncreasing turbulence levelEngine fuctionsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingSurface coolingEngineering
A surface cooler comprises a plate-like layer and a plurality of spaced-apart fins extending substantially perpendicular from an uppermost layer of the plate-like layer. The plurality of fins defining a plurality of air flow paths. The plurality of spaced-apart fins are configured to augment heat transfer of the surface cooler by increasing the turbulence levels of a fluid flowing through the airflow paths by promoting increased mixing with a resulting increase in the heat transfer coefficient of the surface cooler. A method of forming the surface cooler and an engine including the surface cooler.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Heat sink with arc shaped fins
InactiveUS6161610AMinimize formationHeat dissipationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFluid controlEngineering
A heat exchanger and a method of manufacturing the heat exchanger is disclosed for dissipating heat from a heat generating component. The heat exchanger comprises a thermally conductive base in thermal communication with the component, a plurality of thermally conductive plate fins affixed to the base wherein the plate fins define a fin field and channels, and fluid control for controlling the fluid flow within the fin field. The individual fins of the heat exchanger comprise an arc shape with diametrically opposed legs extending vertically downward from each end of the fins. The individual fins are comprised of thermally conductive material affixed to and in thermal communication with the base. The individual fins are arcuately shaped sections separated by arcuately shaped channels. The fins, together with the channels and base form a fin field having an inlet region, a middle region and an outlet region. Additionally, the fins may comprise a plurality of orifices, slots and / or apertures to enhance cross channel fluid communication, and / or textured surface regions in the form of surface anomalies for disrupting formation of a boundary layer along said fins.
Owner:AZAR KAVEH
Extruded and Ribbed Thermal Interface for use with a Battery Cooling System
ActiveUS20110212356A1Cell temperature controlHeat exhanger conduitsInterface layerThermal management system
A cooling manifold assembly for use in a battery pack thermal management system is provided. The cooling manifold assembly includes a coolant tube that is interposed between at least a first row of cells and a second row of cells, where the first and second rows of cells are adjacent and preferably offset from one another. A thermal interface layer is attached to the cooling tube, the thermal interface layer including a plurality of pliable fingers that extend away from the cooling tube and are interposed between the cooling tube and the first row of cells, and interposed between the cooling tube and the second row of cells, where the pliable fingers are deflected by, and in thermal contact with, the cells of the first and second rows of cells.
Owner:TESLA INC
Photovoltaic module with adjustable heat sink and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20060137733A1Facilitating laminationPV power plantsSolid-state devicesEngineeringHeat spreader
The present invention provides a photovoltaic module (20) comprising a photovoltaic material and a heat sink in thermal communication with the photovoltaic material proximate a mounting surface of the heat sink. The heat sink comprises a plurality of fins (12) that are movable between a first position parallel to the mounting surface and a second position non-parallel to the mounting surface. Orientation of the fins in the first position may be particularly desirable during fabrication of the module when the heat sink is attached to the photovoltaic material. As such, the present invention provides a method for fabricating a photovoltaic module comprising providing a photovoltaic material and providing the heat sink having movable fins. The fins are oriented in the first position and the heat sink is then attached to the photovoltaic material. After the heat sink is attached, the fins may be unfolded into the second position.
Owner:SCHRIPSEMA JASON E +1
Foul-resistant condenser using microchannel tubing
A condenser coil for a refrigerated beverage and food service merchandiser includes a plurality of parallel fins or V-shaped fins between adjacent tubes. In order to reduce the likelihood of fouling by the bridging of fibers therebetween, the spacing of the fins is maintained at a distance of 0.4 to 0.8 inches apart. In one embodiment, the coil includes a plurality of flat multichannel tubes, with no fins therebetween, and the spacing between the multichannel tubes is maintained in the range of 0.4 to 0.8 inches. In one embodiment, the coil includes at least one serpentine shaped, multichannel tubes, with no fins therebetween, and the spacing between flat, parallel segments of the multichannel tubes is maintained in the range of 0.4 to 0.8 inches.
Owner:CARRIER COMML REFRIGERATI
Battery cell heat exchanger with graded heat transfer surface
A battery cell heat exchanger formed by a pair of mating plates that together form an internal tubular flow passage. The tubular flow passage is generally in the form of a serpentine flow passage extending between an inlet end and an outlet end and having generally parallel flow passage portions interconnected by generally U-shaped flow passage portions. The flow passage provides a graded heat transfer surface within each generally parallel flow passage portion and / or a variable channel width associated with each flow passage portion to provide improved temperature uniformity across the surface of the heat exchanger. The graded heat transfer surface may be in the form of progressively increasing the surface area associated with the individual flow passage portions with heat transfer enhancement features or surfaces arranged within the flow passage portions. The channel width and / or height may also be varied so as to progressively decrease for each flow passage portion.
Owner:DANA CANADA CORP
High Efficiency Fluid Heat Exchanger and Method of Manufacture
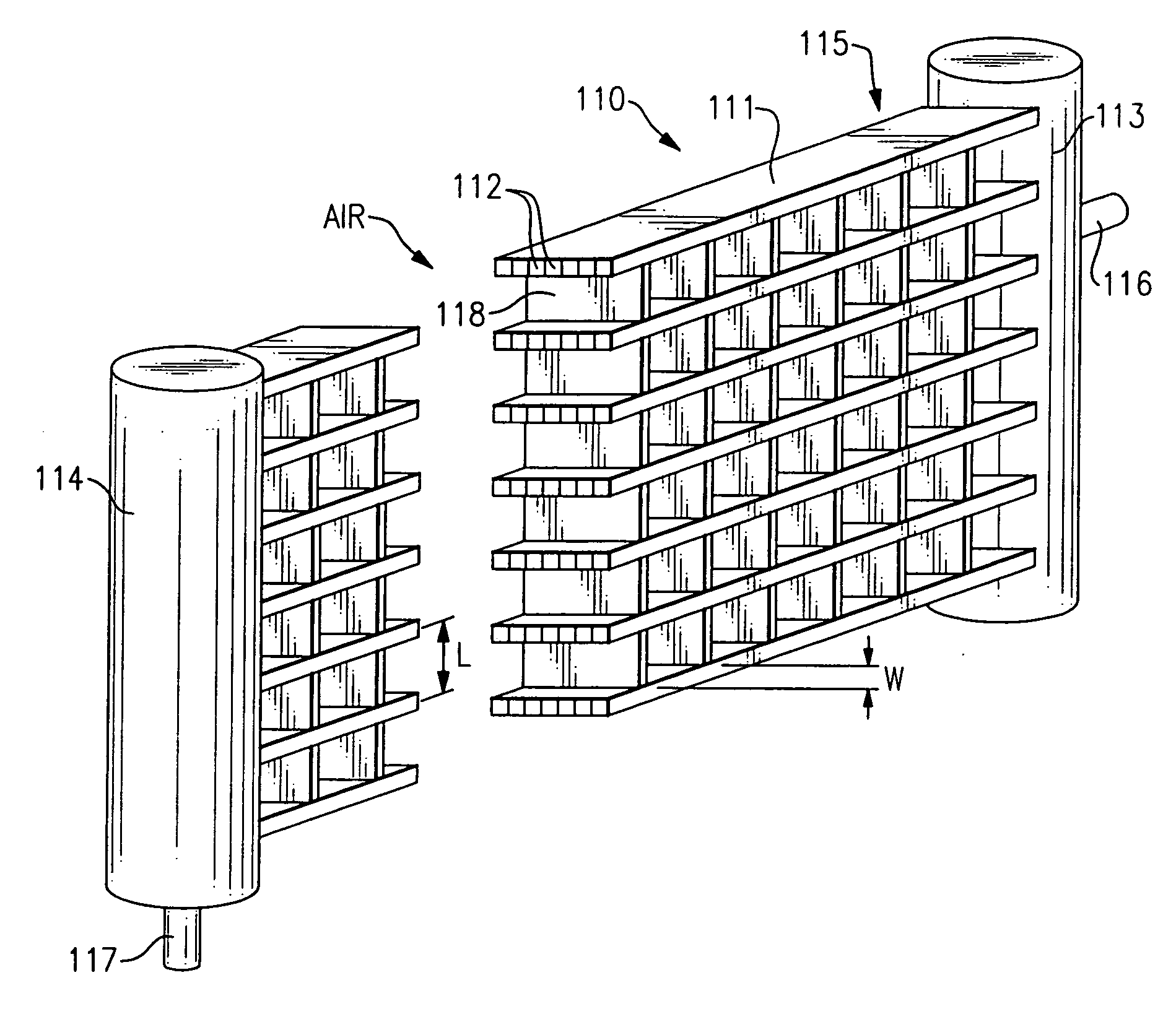
InactiveUS20060237166A1Good thermally conductive bondIncrease surface areaMetal-working apparatusHeat exhanger finsEngineeringHeat exchanger
A fluid heat exchanger has a housing having a thermally conductive base, a plurality of fin members connected to the base in a parallel, spaced relationship, a heat exchanger fluid inlet on one side of the plurality of fin members, and a heat exchanger fluid outlet on the opposite side of the plurality of fin members. The plurality of fin members each have a plurality of passageways and are arranged in the housing so that the passageways of one fin member are offset from the passageways of adjacent fin members.
Owner:FERROTEC USA CORP
Heat Sink Having a Cooling Structure with Decreasing Structure Density
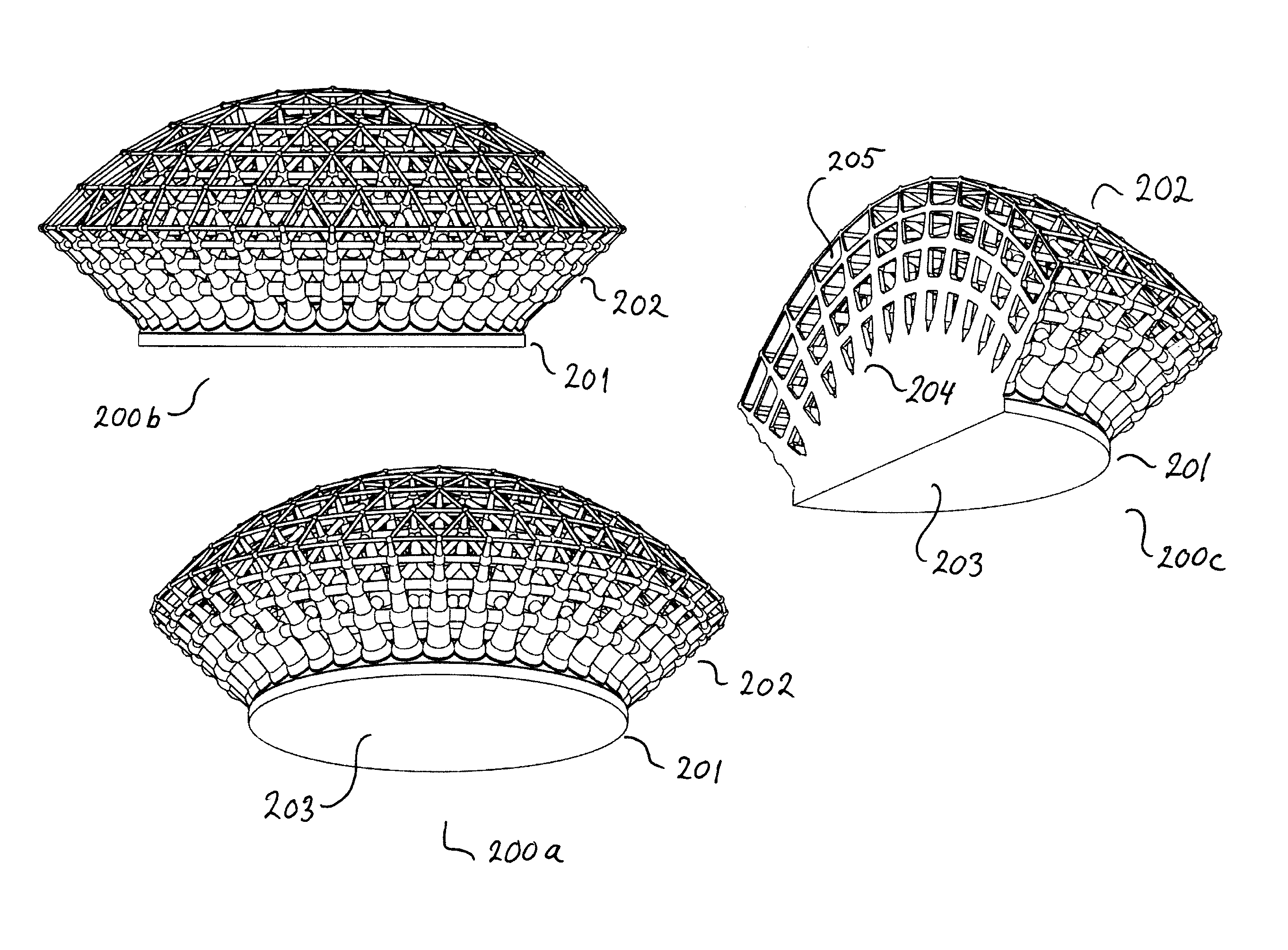
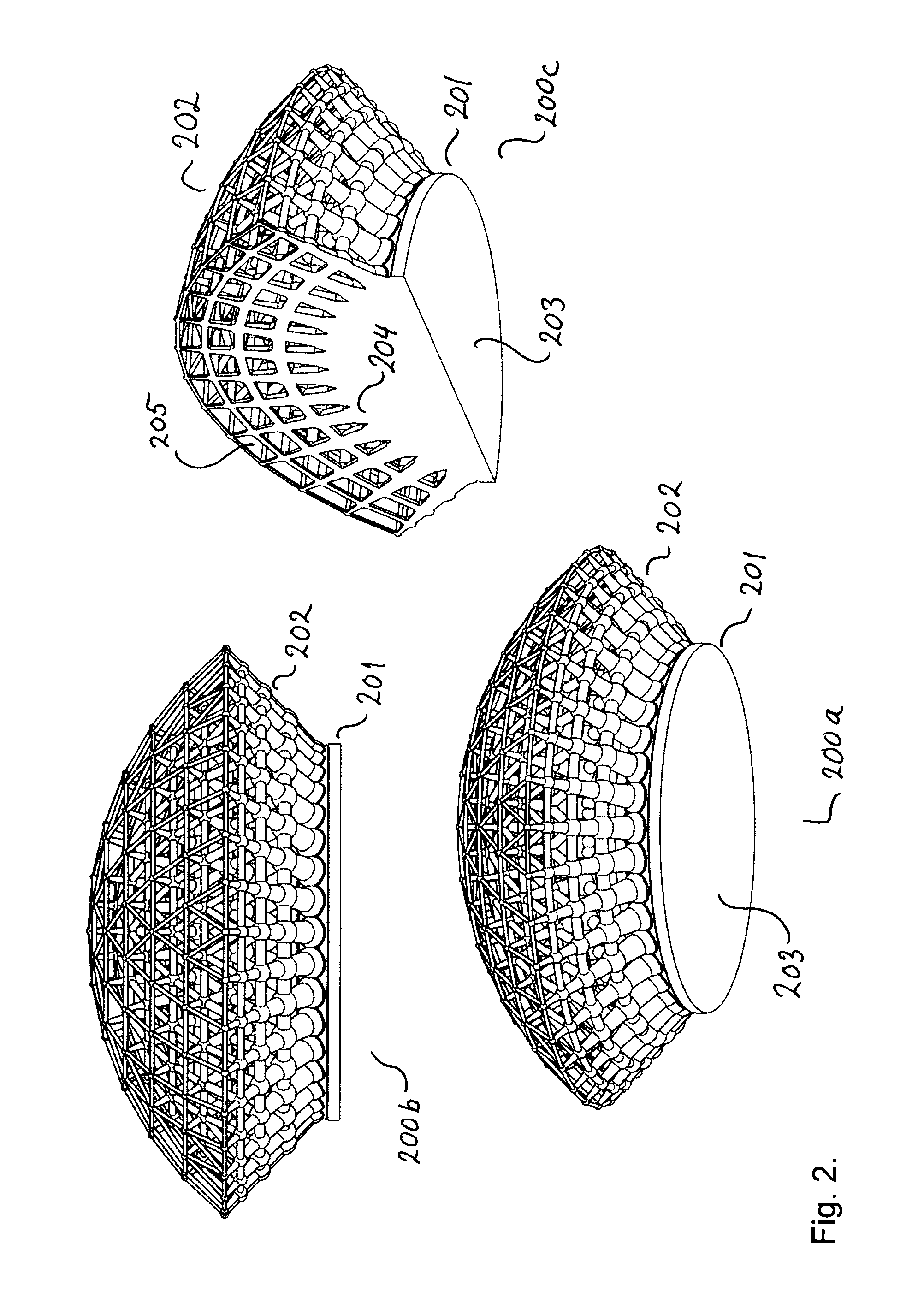
InactiveUS20160069622A1Increase distanceReduce material densityLighting support devicesDigital data processing detailsSelective laser meltingCarbon nanotube
A heat sink for cooling a heat generating device comprises a body part with a first surface for contacting the heat generating device, and a second surface contacting a cooling part, and the cooling part including a cooling structure. The structure density of the cooling structure decreases with increasing distance to body part. The cooling structure may be a three dimensional structure e.g. a grid or a lattice, but the cooling structure may also be fins projecting or extending from the second surface of the body part. The heat sink can be manufactured using additive manufacturing e.g. selective laser melting process (SLM). The heat sink can be made of metals e.g. aluminum, copper, ceramics e.g. aluminium nitride (AlN), silicon carbide or a composite containing graphite, graphene or carbon nanotubes.
Owner:ALEXIOU & TRYDE HLDG APS
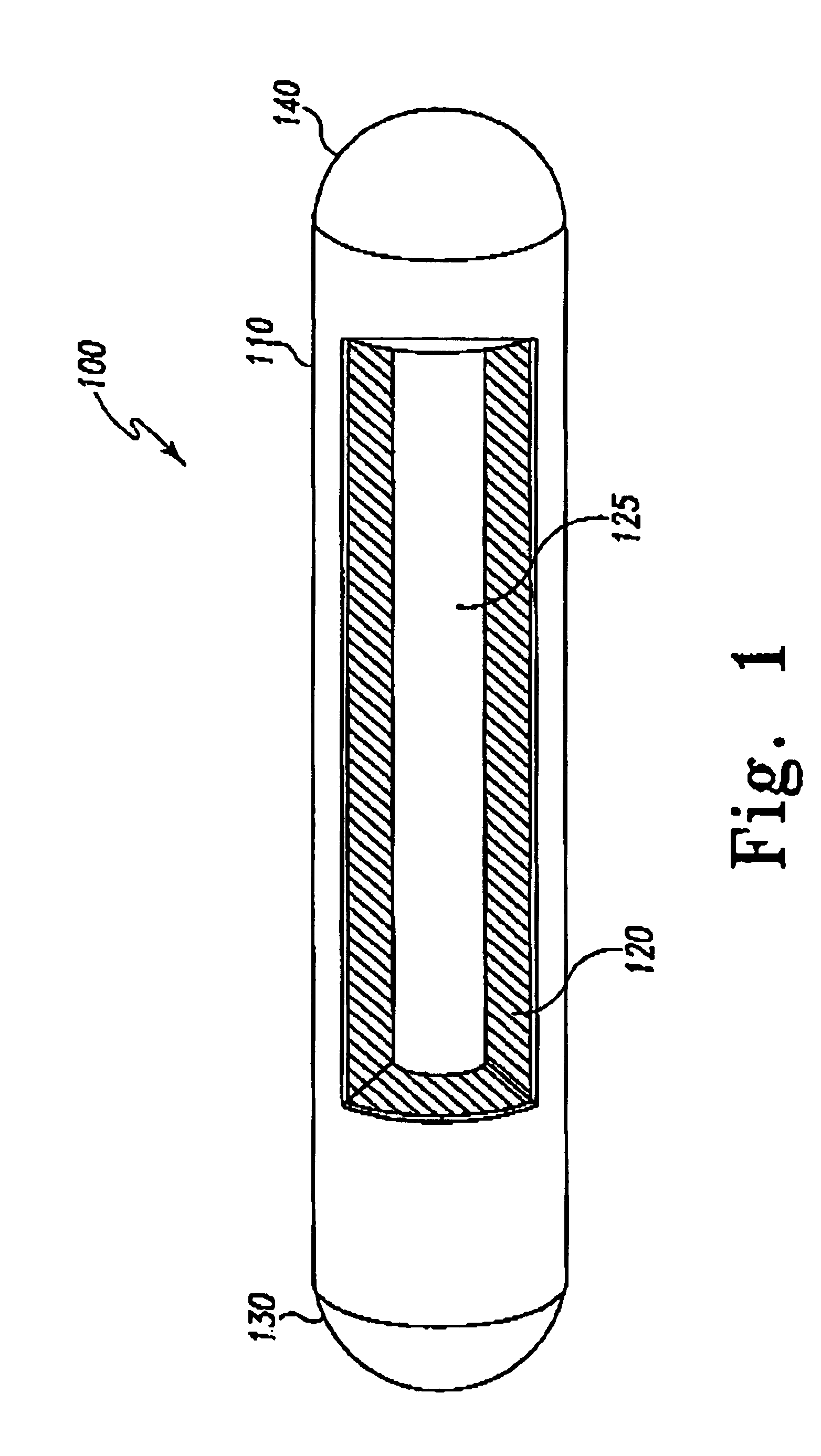
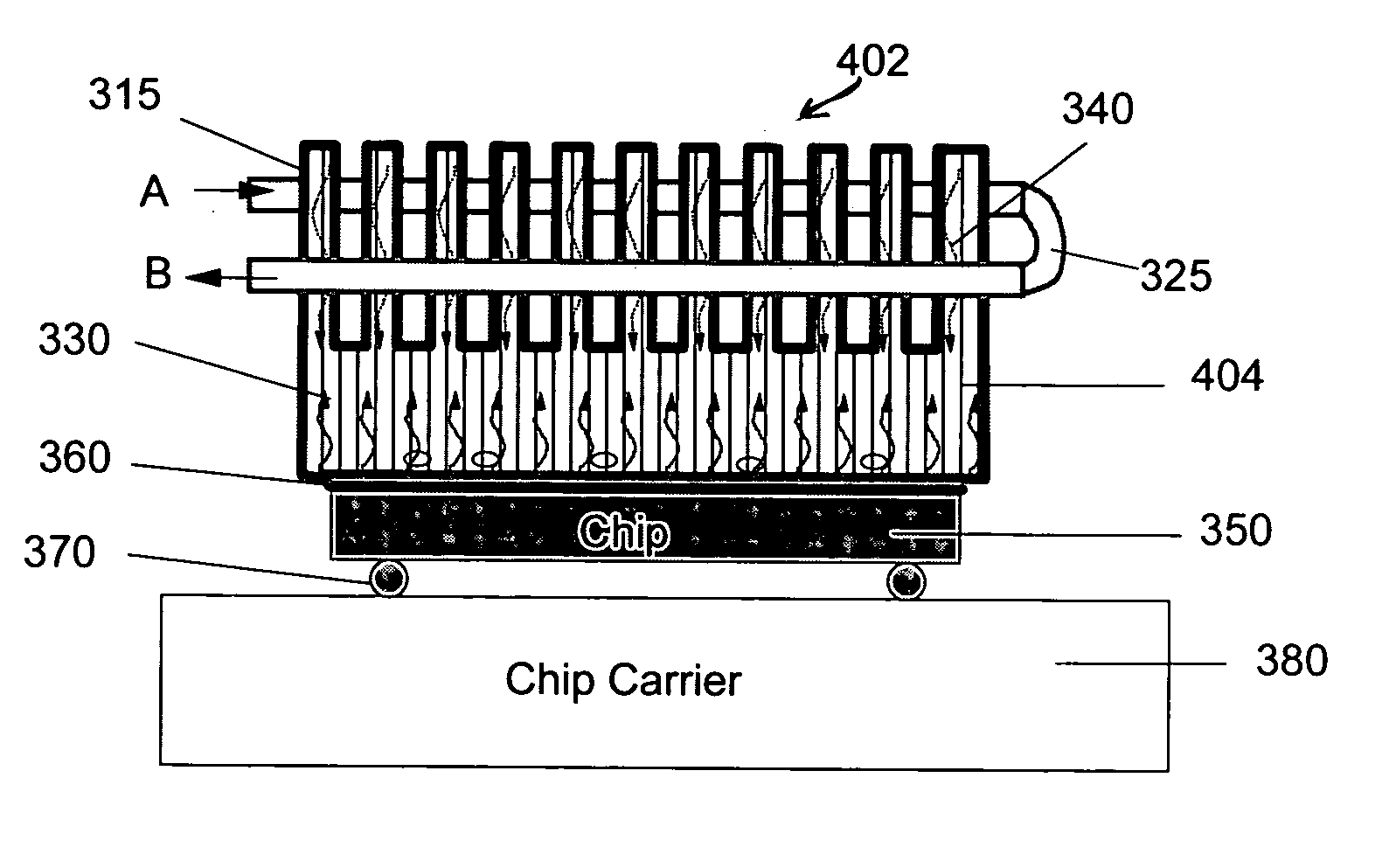
Heat Transfer Device
InactiveUS20070012429A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolid structureEngineering
A heat transfer device includes a vapor chamber that houses a phase change material such as water. The heat transfer device may be selectively formed from a combination of polymeric and non-polymeric materials. In one embodiment, the vapor chamber is formed from a polymer layer surrounding a sealing layer formed from non-polymeric material. The heat transfer device may further include one or more fin members operable to diffuse heat from the vapor chamber to the ambient / outside environment. The fins may be solid structures, or may each define a fin chamber in communication with the vapor chamber. In one embodiment, the fin members are formed from non-polymeric material.
Owner:CONVERGENCE TECH LTD
Evaporatively cooled thermosiphon
InactiveUS20070227703A1Increase surface areaImprove heat transfer performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringRefrigerant
A thermosiphon cooling assembly cools an electronic device with a first refrigerant disposed in the lower boiling chamber of a housing for liquid-to-vapor transformation and a second refrigerant disposed in an upper evaporating chamber of a housing for liquid-to-vapor transformation. The partition separating the lower boiling chamber of the housing from the upper evaporating chamber of the housing creates a series of vapor chambers within the lower boiling portion for condensing vapor boiled off the first refrigerant. The upper evaporating chamber contains a series of refrigerant pockets interleaved vertically with the vapor chambers to increase the surface area for heat transfer between the refrigerant vapor and the second refrigerant for absorbing heat by the second refrigerant for liquid-to-vapor transformation.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Heat dissipation device having heat pipe
InactiveUS7100681B1Efficient removalEven heat distributionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A heat dissipation device includes a base, a plurality of first fins, a plate, a plurality of second fins and two heat pipes. Each heat pipe includes a heat-receiving portion sandwiched between the base and the first fins, a heat-exchange portion sandwiched between the plate and the first fins, a connecting portion connecting the heat-receiving portion and the heat-exchange portion, a heat-discharging portion extending through the plate and inserted into the second fins. At least one of the heat pipes defines two different planes which intercross at the heat-exchange portion of the at least one of the heat pipes.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Heat transfer pipe and heat exchange incorporating such heat transfer pipe
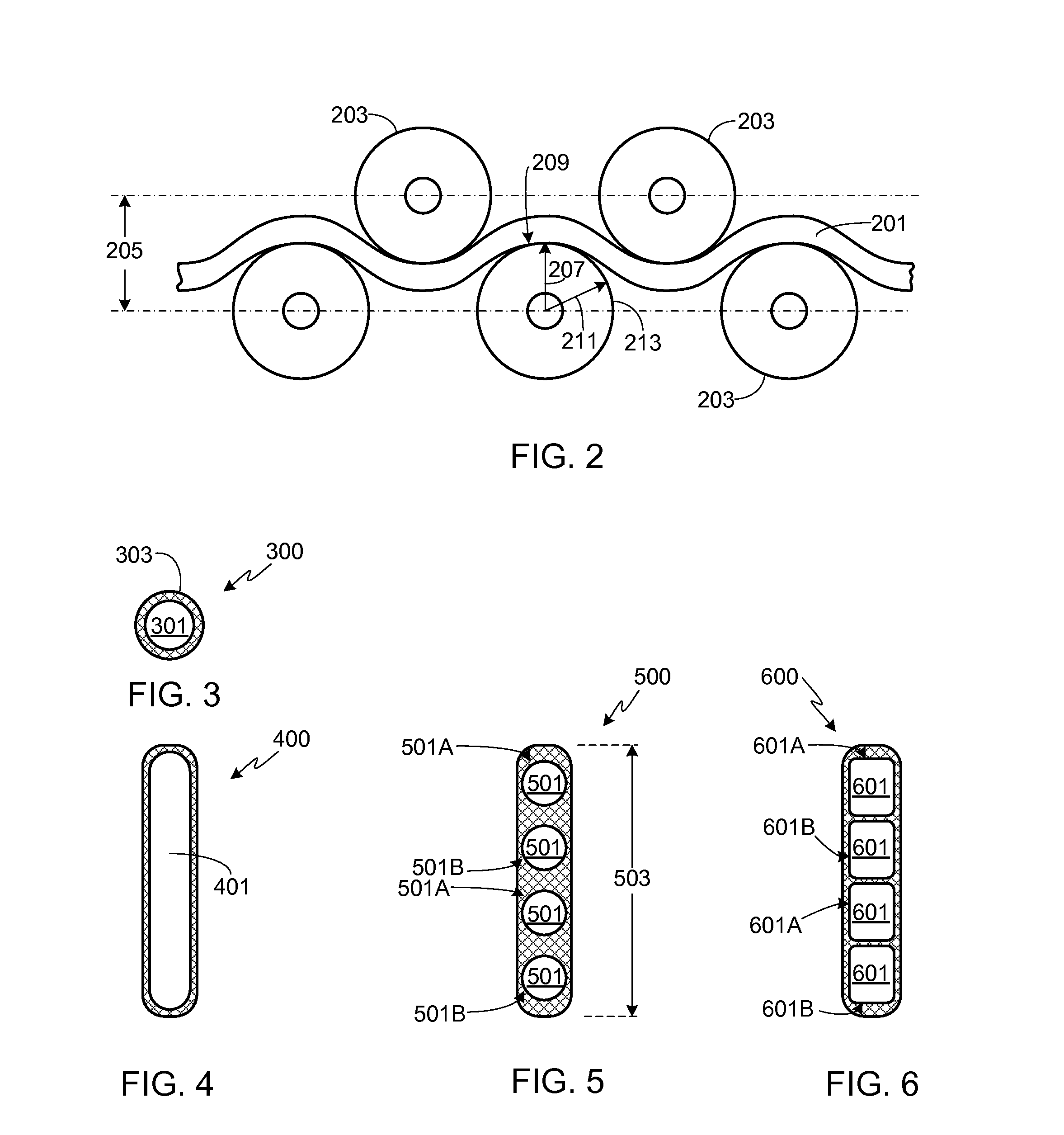
InactiveUS7044210B2Facilitate conductionLarge heat exchange surfaceCorrosion preventionHeat exhanger finsPlate heat exchangerHeat transfer efficiency
Soot adhering to the inner surface of a heat transfer pipe can be removed without lowering the heat transfer efficiency that is the inherent object of the heat transfer pipe or without stopping the cooling operation of the heat transfer pipe. Further, this soot removal can be effected when the amount of soot adhering to the inner surface of the heat transfer pipe is small, thus minimizing the soot-caused lowering in the heat transfer efficiency of the heat transfer pipe. A heat transfer pipe (1) wherein the inner peripheral surface of an element pipe (2) through which fluid can flow is formed with longitudinal grooves (4) as recessed grooves (3) of cross-section with a given depth such that the longitudinal grooves are parallel with the pipe axis and circumferentially continuous, and a partition wall (5) of given thickness is formed between the longitudinal grooves (4): and a heat exchanger incorporating this heat transfer pipe (1).
Owner:USUI KOKUSAI SANGYO KAISHA LTD
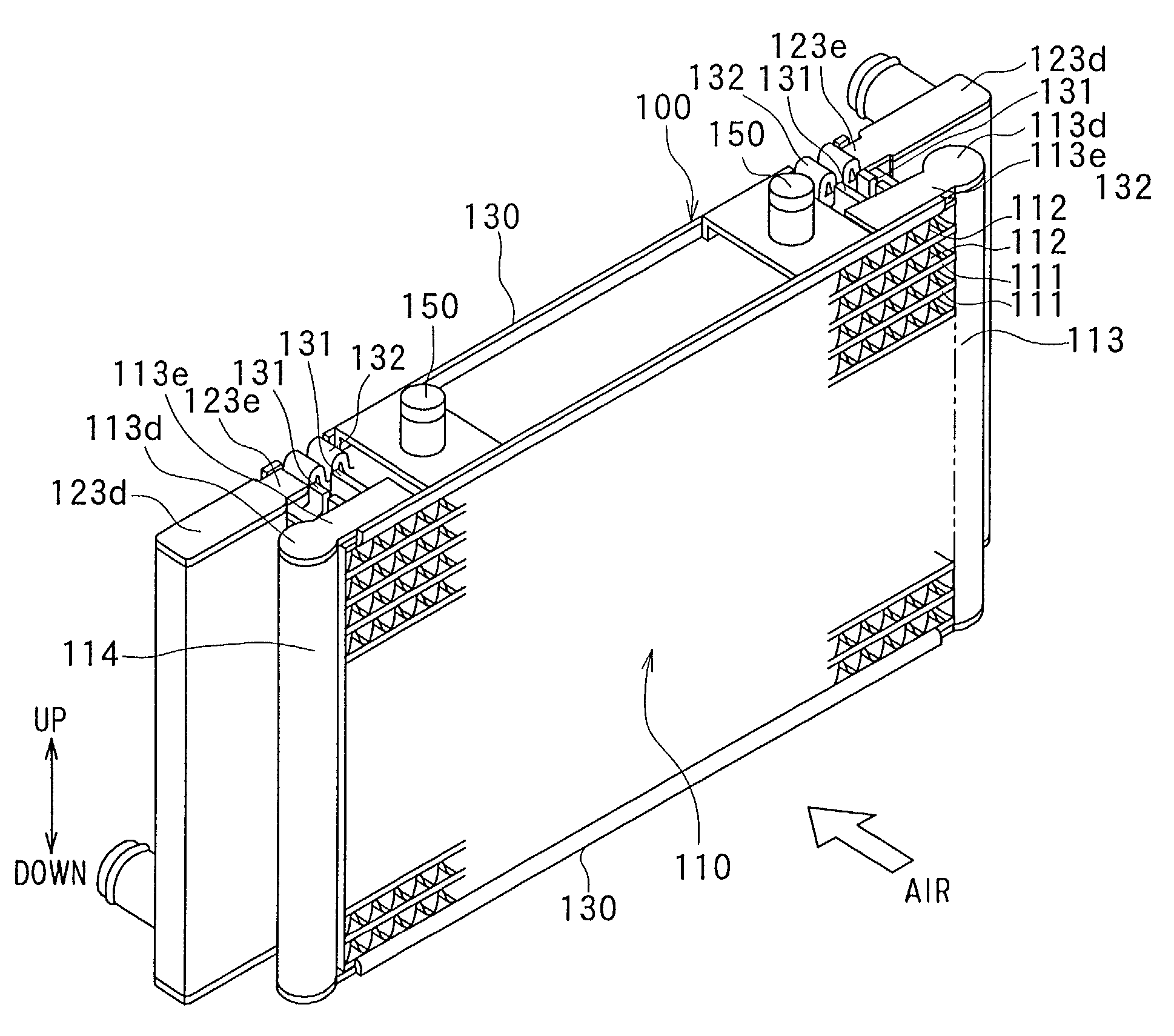
Heat exchanger and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20120012295A1Increase heatImprove rigiditySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetal-working apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
A heat exchanger is provided with a cooling fin including a plurality of fin portions and a base portion supporting the fin portions, and a plurality of pins press-fitted into the fin portions. In the heat exchanger, the pins each having a wider width than each space between the fin portions formed in advance in parallel straight shapes are press-fitted into the spaces in a direction from a top end of each fin portion toward the base portion. Accordingly, the fin portions are formed into corrugated shapes by plastic deformation, thereby fixing the pins between the fin portions in positions apart from the base portion. In each space, the pins are arranged at intervals in a longitudinal direction of each space. The pins arranged in adjacent spaces are placed with a displacement in alternating pattern.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Coil tube heat exchanger for a tankless hot water system
A novel water heat exchanger with a helix coil incorporated into a stainless steel elongated variable diameter cylindrical housing. A buffer tank is incorporated within the lumen of the helix coil. In one embodiment, the heat exchanger utilizes a radial direct-firing burner and a blower-driven hot flue gas to heat water for domestic and commercial use. In one embodiment, at least a rope seal is disposed between adjacent coil loops of a portion of the helix coil for enhancing heat transfer to the helix coil. In one embodiment, solar and electric heating systems are combined with the helix coil heat exchanger and disposed within the buffer tank to provide supplemental heating. In another embodiment, the heat exchanger further comprises a Stirling engine comprised of a free piston having hot and cold ends that is disposed within the cavity taken up the buffer tank, wherein the hot end receives heat from the burner and the cold end is cooled by the incoming cold water line to form an electric power generator.
Owner:INTELLIHOT
Flow diverters to enhance heat sink performance
InactiveUS20090321046A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringFlow diverter
A heat sink includes a base and fins attached to the base. A flow diverter is in contact with the base or at least one of the fins and is configured to disturb a laminar flow region of a fluid flowing adjacent to at least one of the fins or the base.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Uniform heat dissipating and cooling heat sink
InactiveUS6942025B2Reduce airflow resistanceIncrease air velocitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVariable thicknessEngineering
Owner:DEGREE CONTROLS
Double heat exchanger with condenser and radiator
InactiveUS20020023735A1Reduce decreaseReduce heat stressSafety devices for heat exchange apparatusHeat exhanger finsWave shapeEngineering
In a double heat exchanger with a condenser and a radiator, a flexible portion formed into a wave shape to be flexible is provided in a side plate at least at one side of connection portions of the side plate, connected to condenser header tanks and radiator header tanks. Further, a slit is provided to be recessed from one longitudinal end of the side plate to the flexible portion. Accordingly, a heat stress generated in condenser tubes and radiator tubes can be absorbed by the flexible portion even when a length of the slit is made shorter.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com