Patents
Literature
765 results about "Variable thickness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
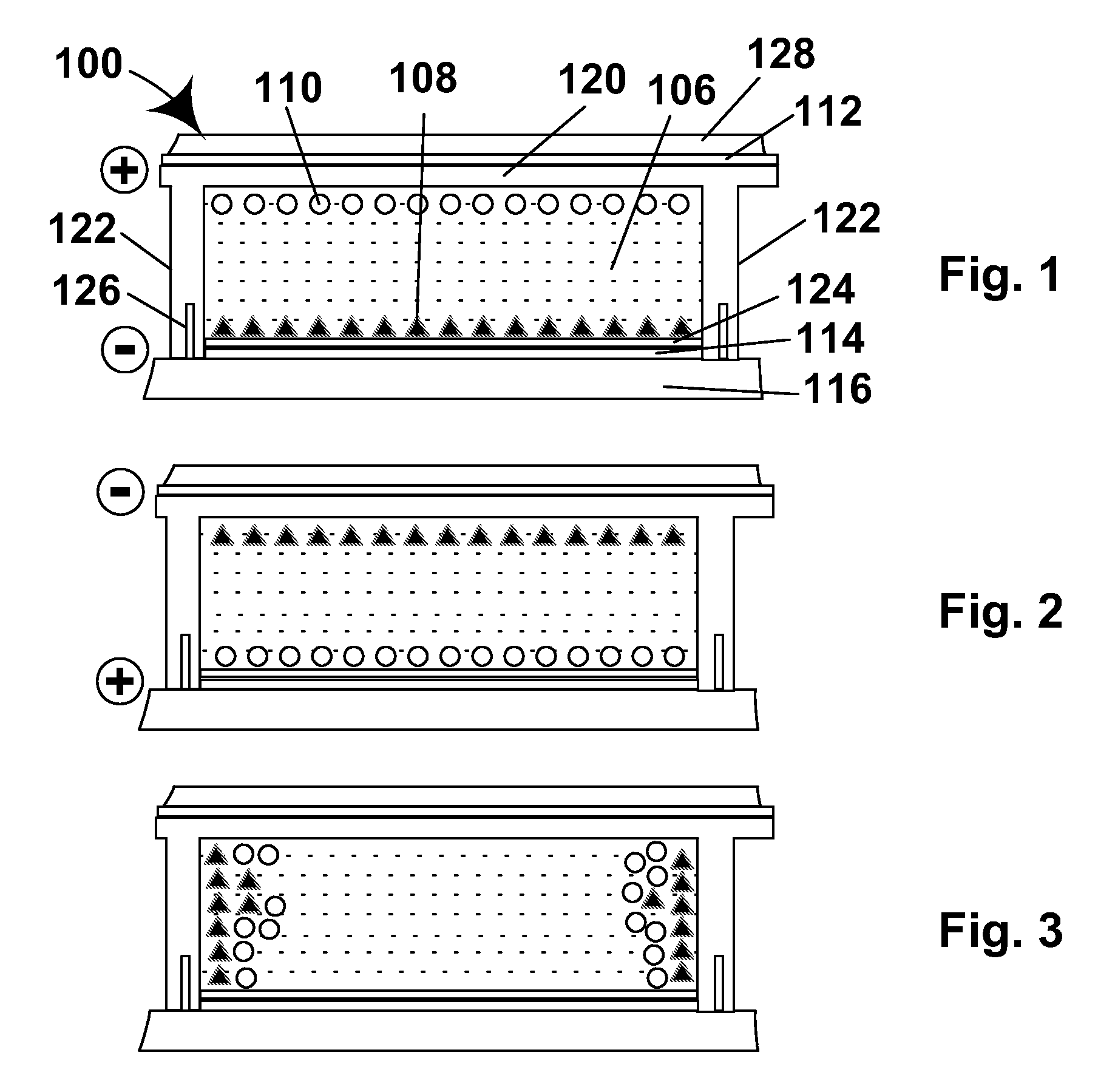
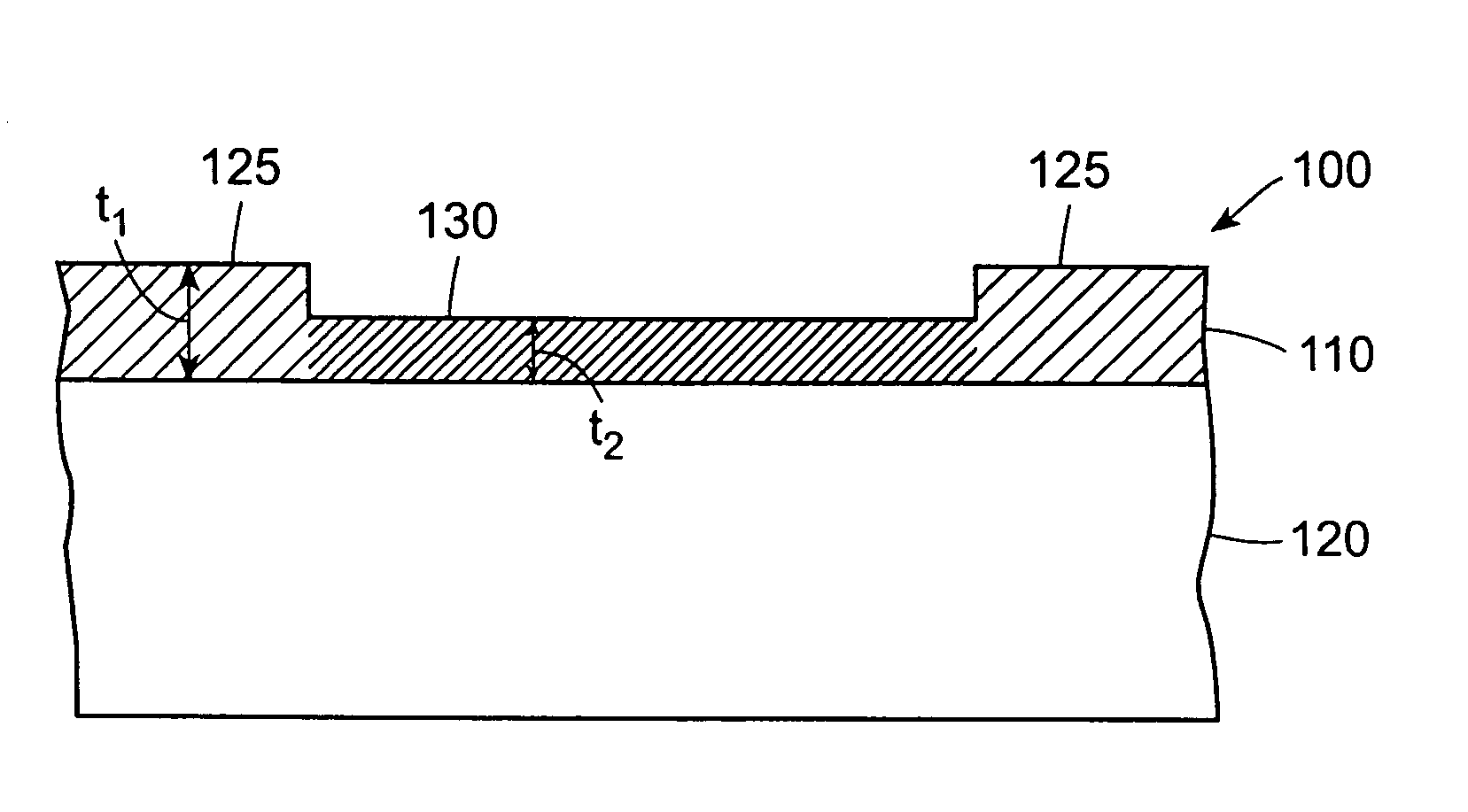
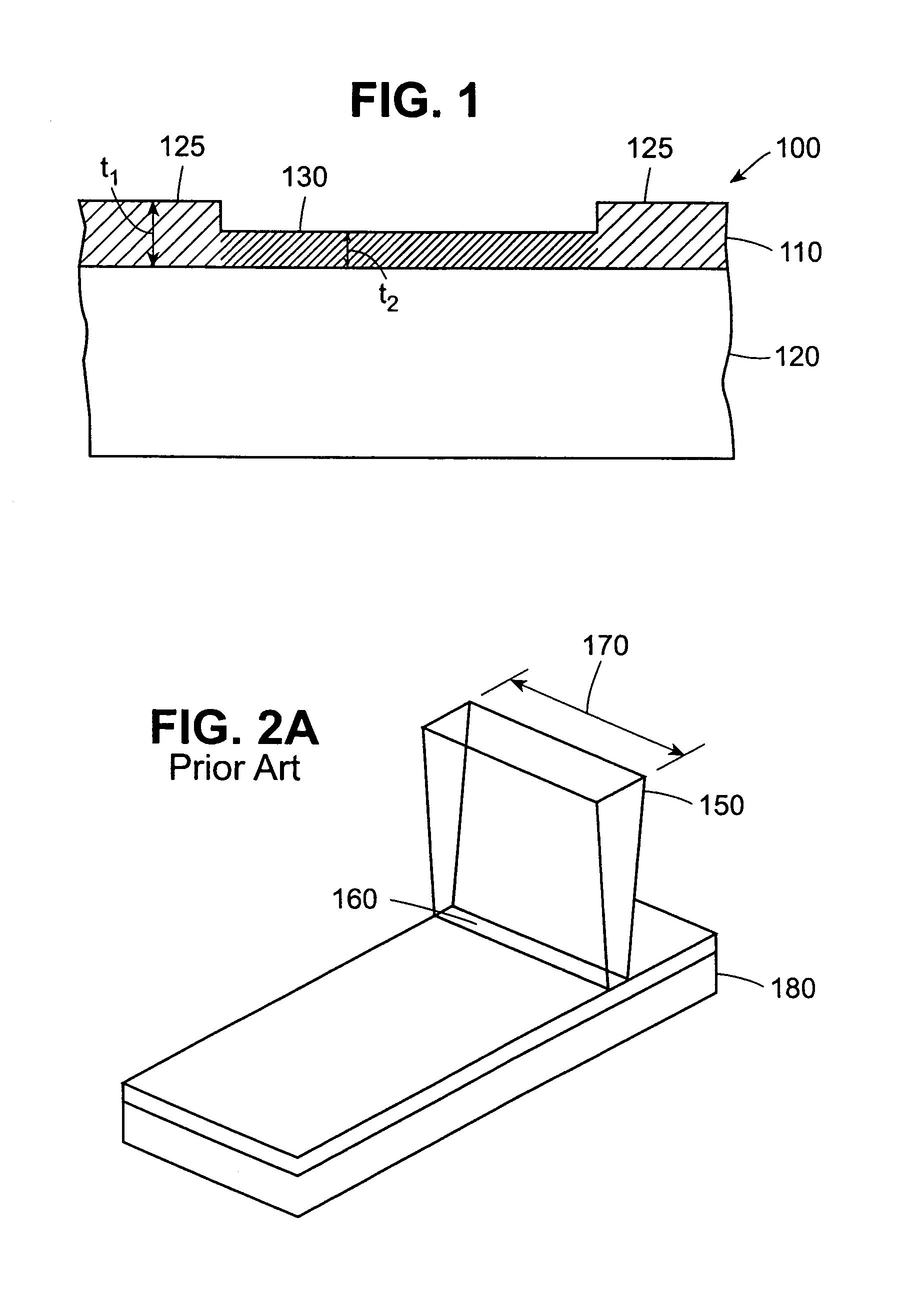
The purpose of a variable thickness face is to achieve more face flexing when the ball is hit off center while still having the proper amount of face flexing in the center of the face to keep the face within the USGA’s maximum limit for COR (coefficient of restitution) in the Rules of Golf.
Methods for the reduction and elimination of particulate contamination with CVD of amorphous carbon
InactiveUS20060014397A1Minimal defect formationReduce particle pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesVariable thicknessMicroparticle
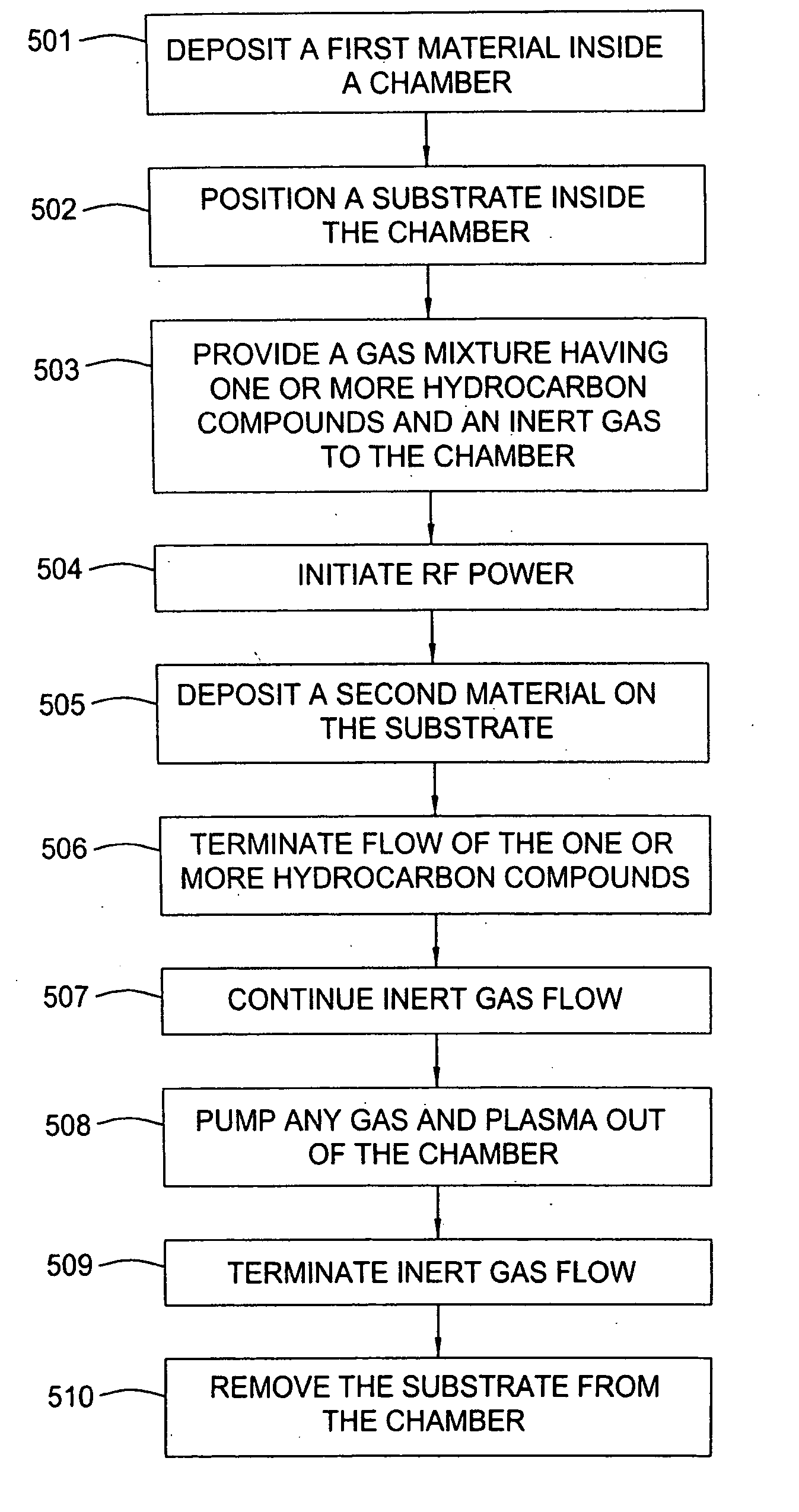
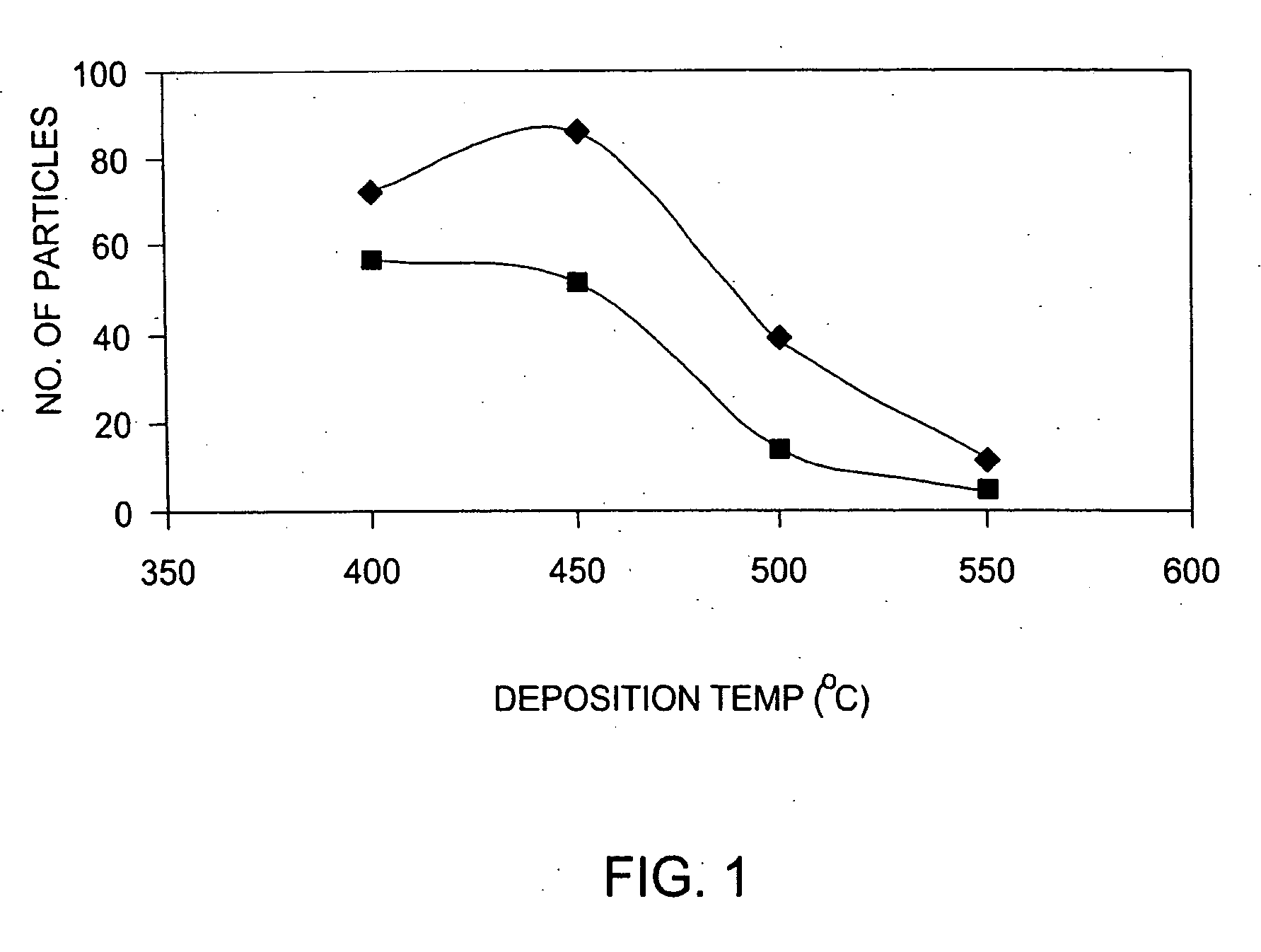
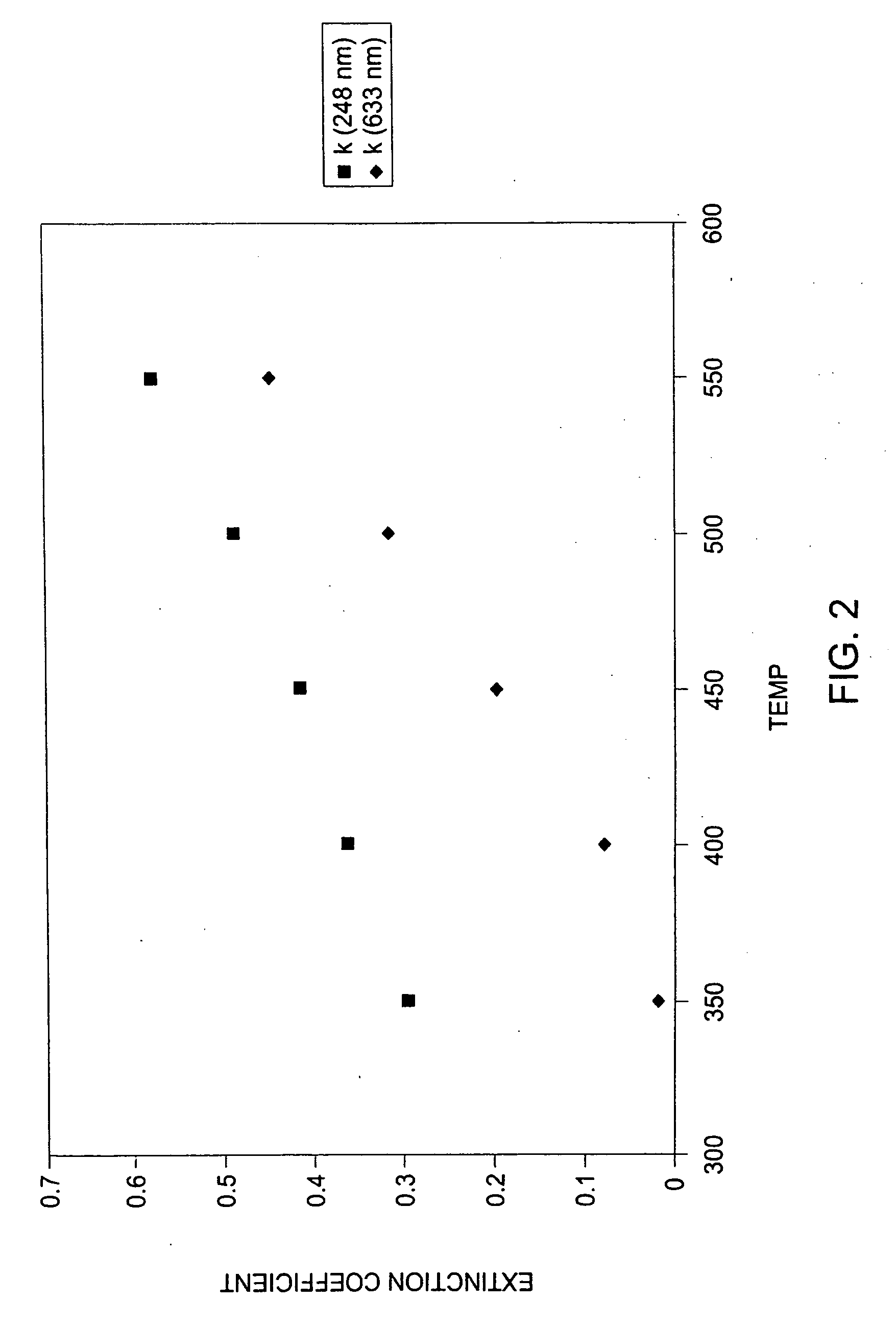
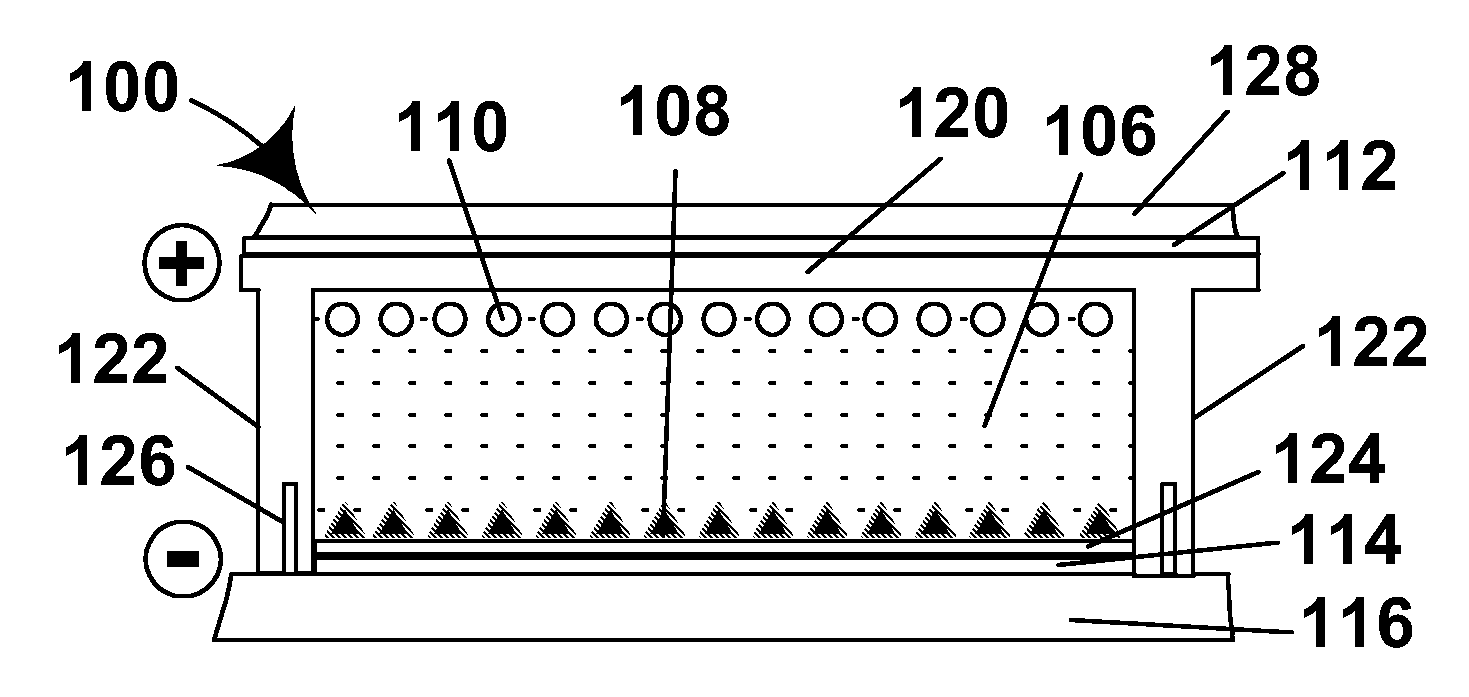
A method is provided for forming an amorphous carbon layer, deposited on a dielectric material such as oxide, nitride, silicon carbide, carbon doped oxide, etc., or a metal layer such as tungsten, aluminum or poly-silicon. The method includes the use of chamber seasoning, variable thickness of seasoning film, wider spacing, variable process gas flows, post-deposition purge with inert gas, and post-deposition plasma purge, among others, to make the deposition of an amorphous carbon film at low deposition temperatures possible without any defects or particle contamination.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
Electrophoretic displays using gaseous fluids
ActiveUS7230751B2Reduce transmissionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsVariable thicknessVitrification
Various improvements are provided in gas-based electrophoretic displays, including (a) the use of water getters to remove water from the gas; (b) the use of electron accepting or donating gases; (c) the use of electrophoretic polymer particles having high glass transition temperatures; (d) lateral movement of electrophoretic particles within the display; and (e) the use of variable thickness coatings on electrodes to provide for gray scale.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
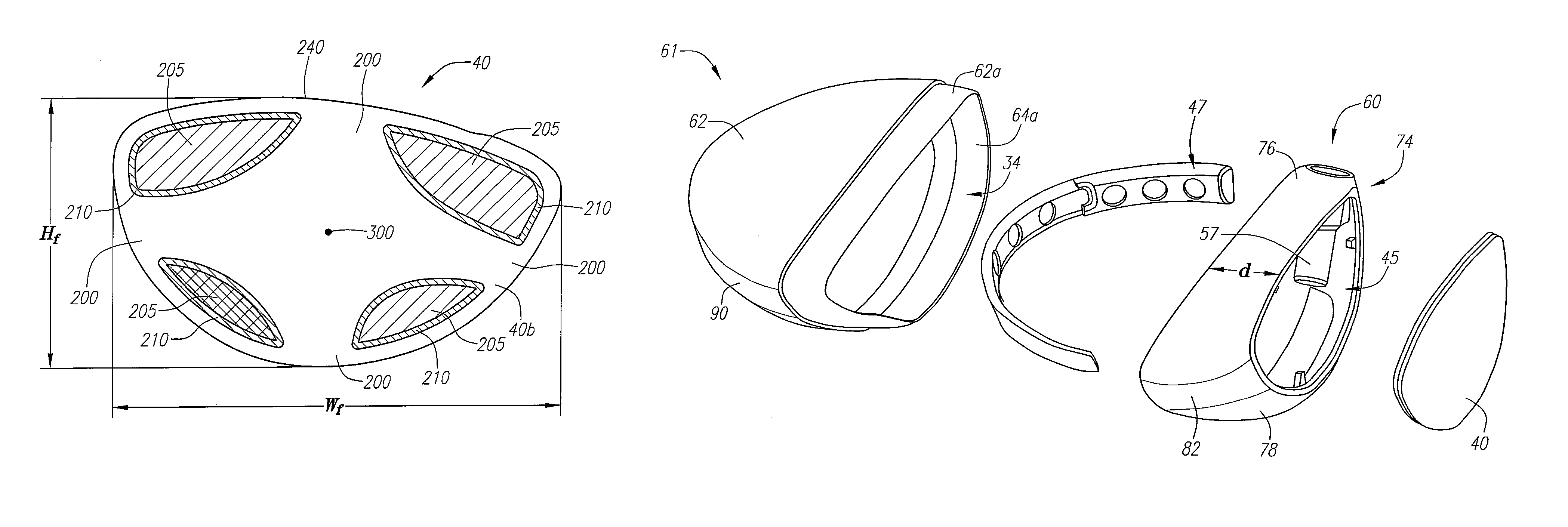
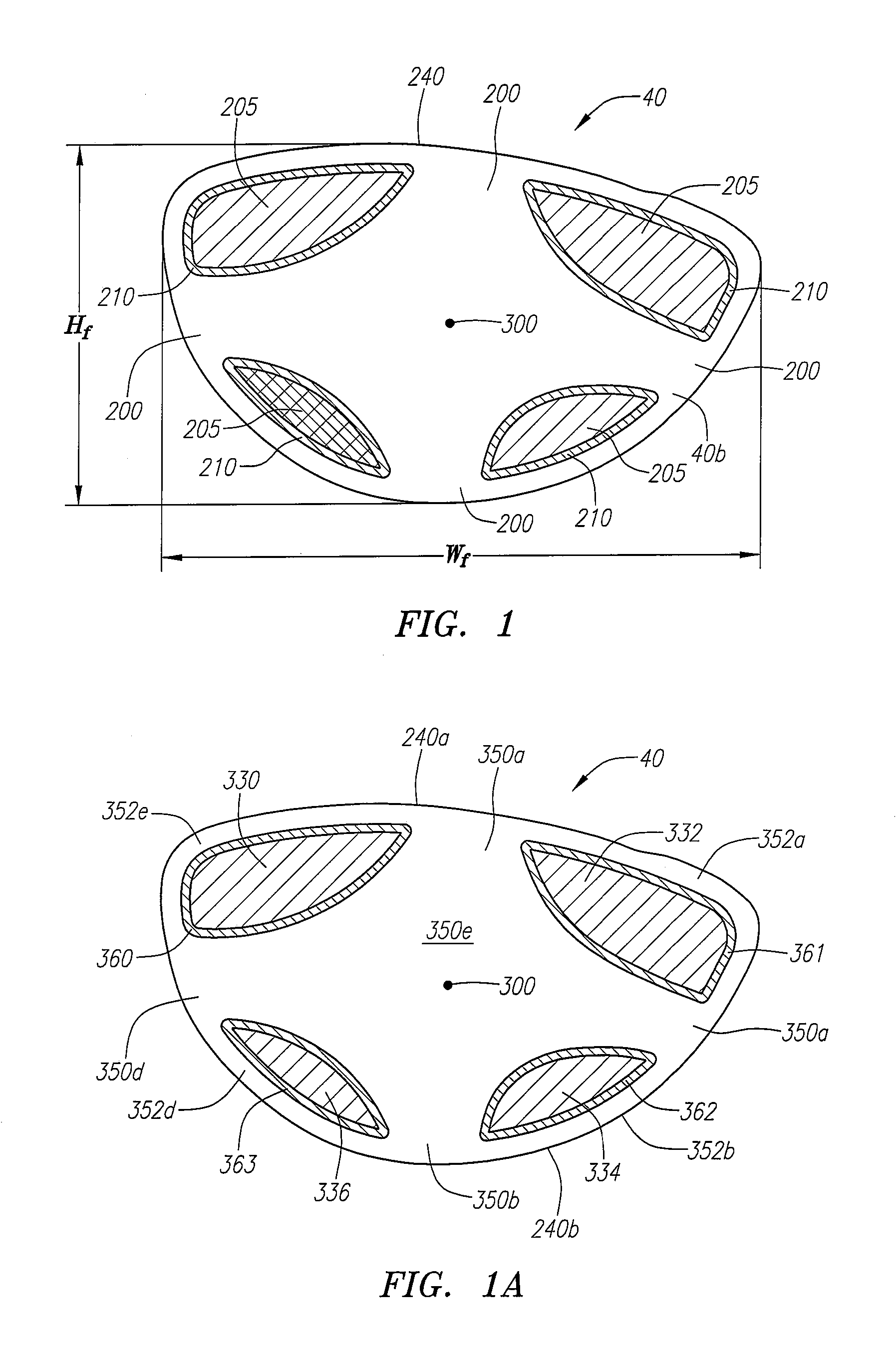
Golf club head with weight ports
ActiveUS8858362B1Excellent characteristicsIncrease gravityGolf clubsRacket sportsVariable thicknessEngineering
A golf club head having a face component, a crown, and a sole or a body patch with one or more weight ports for receiving one or more weight inserts is disclosed herein. At least part of each of the weight ports is integrally formed in the sole or body patch, and each of the weight ports includes an upper edge, a lower edge, and a wall having a variable thickness and varying radius.
Owner:CALLAWAY GOLF CO
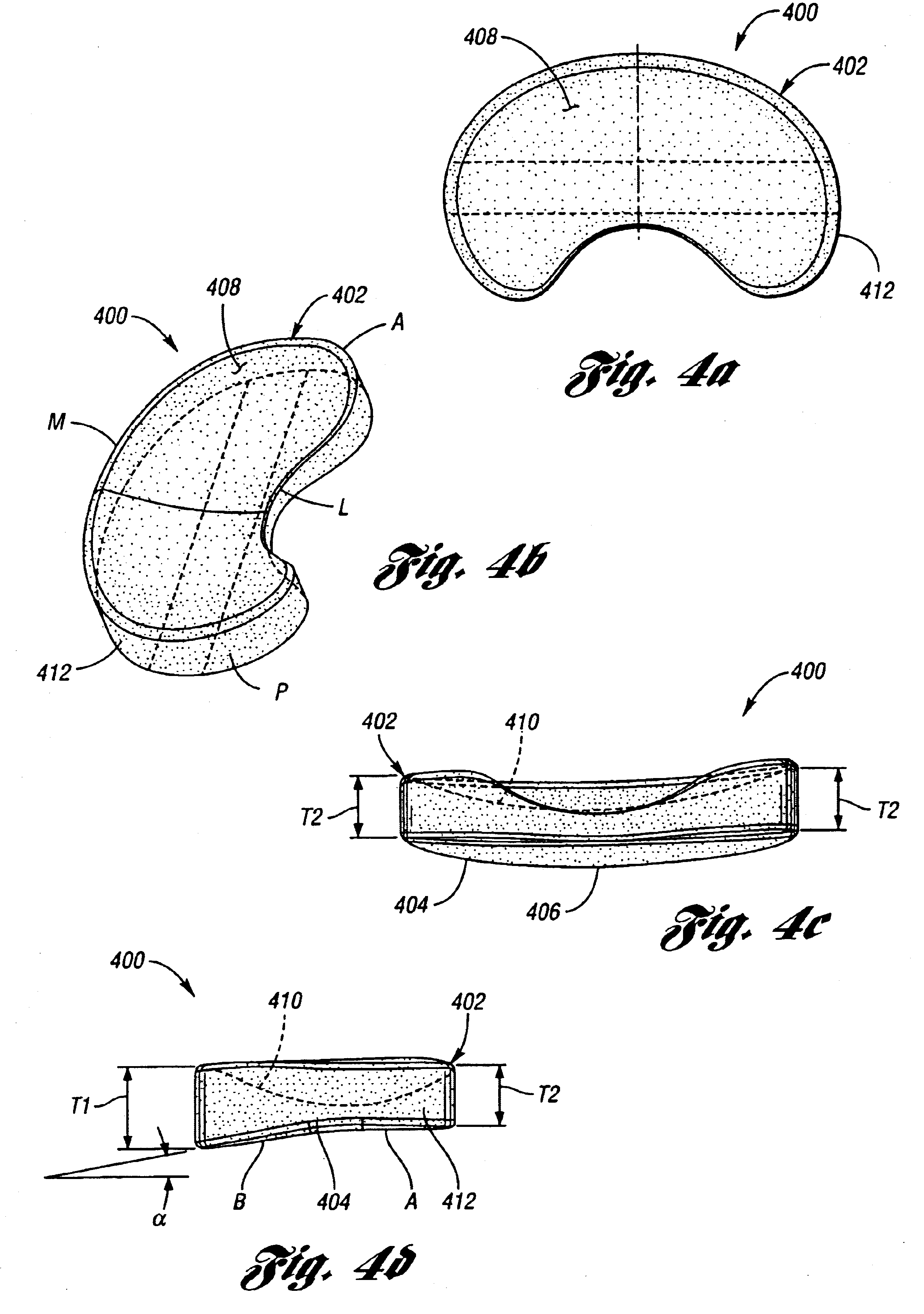
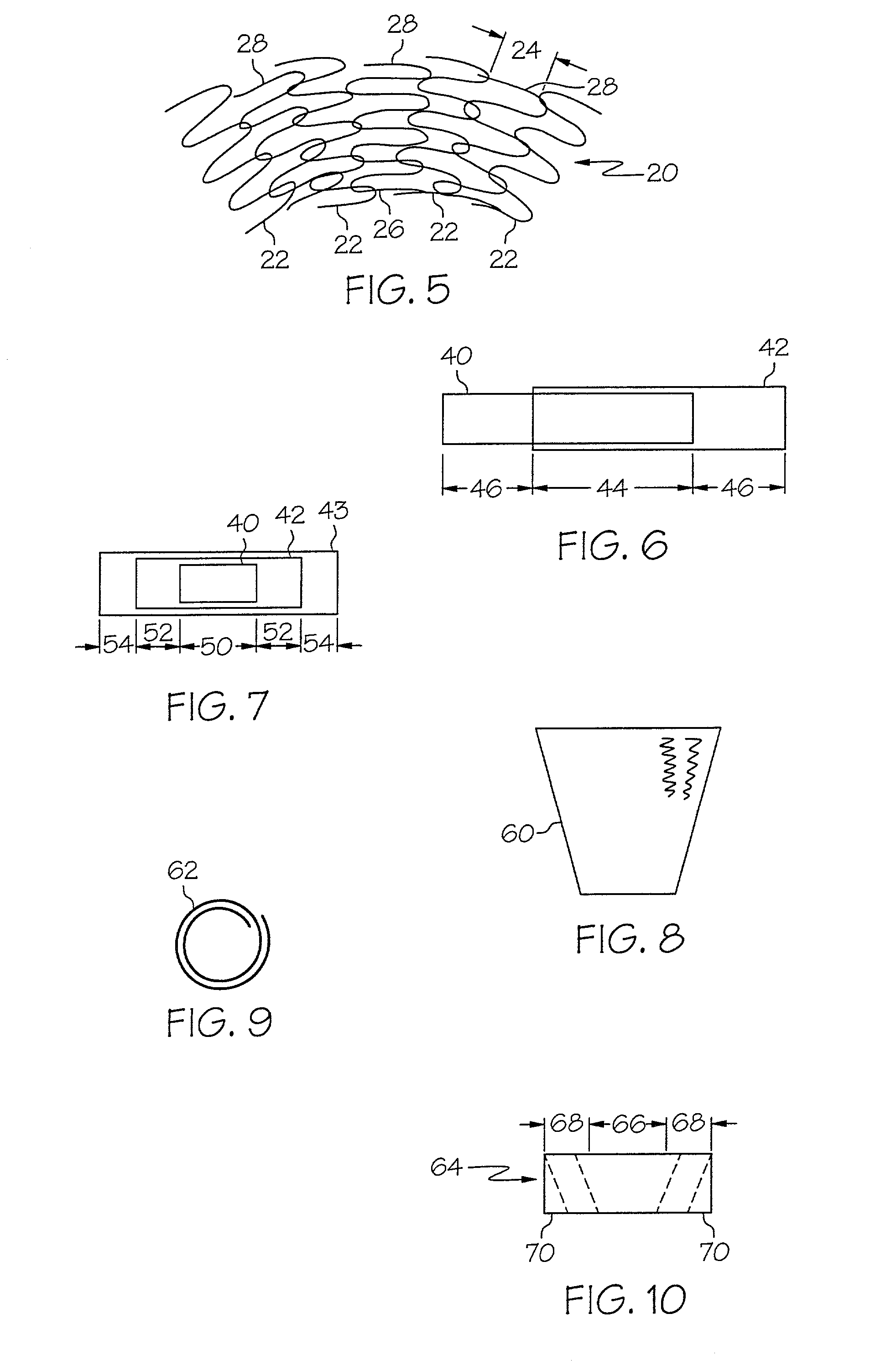
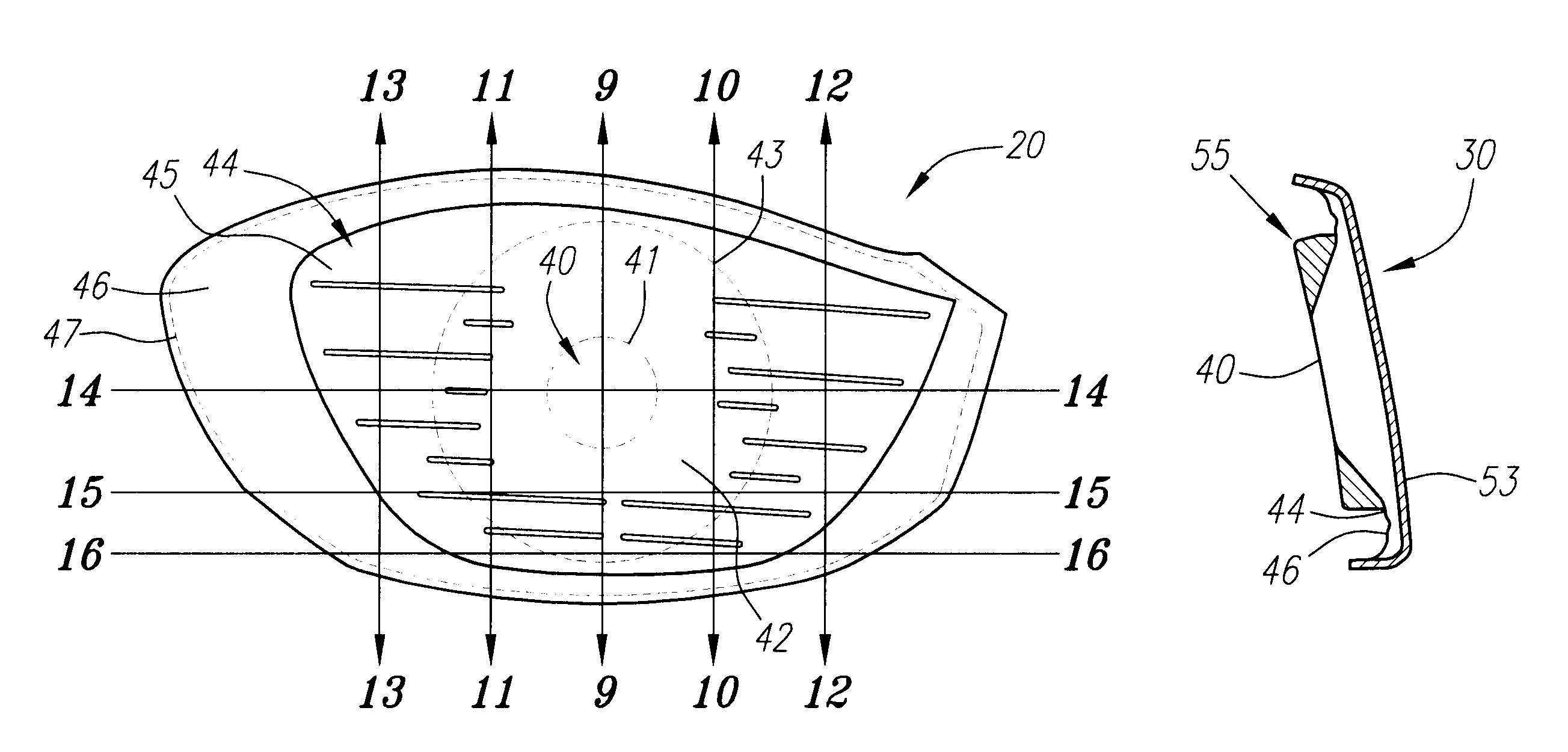
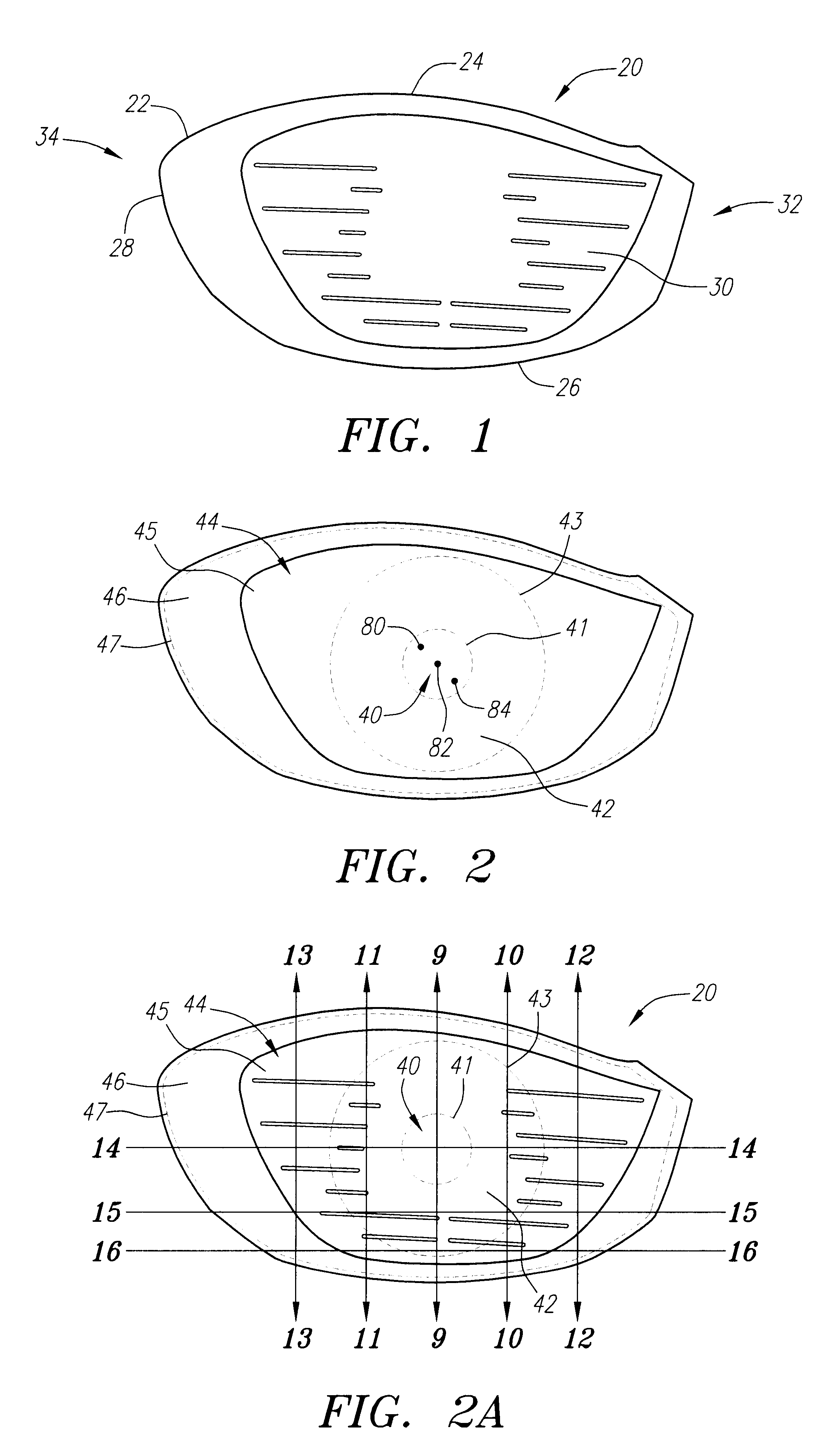
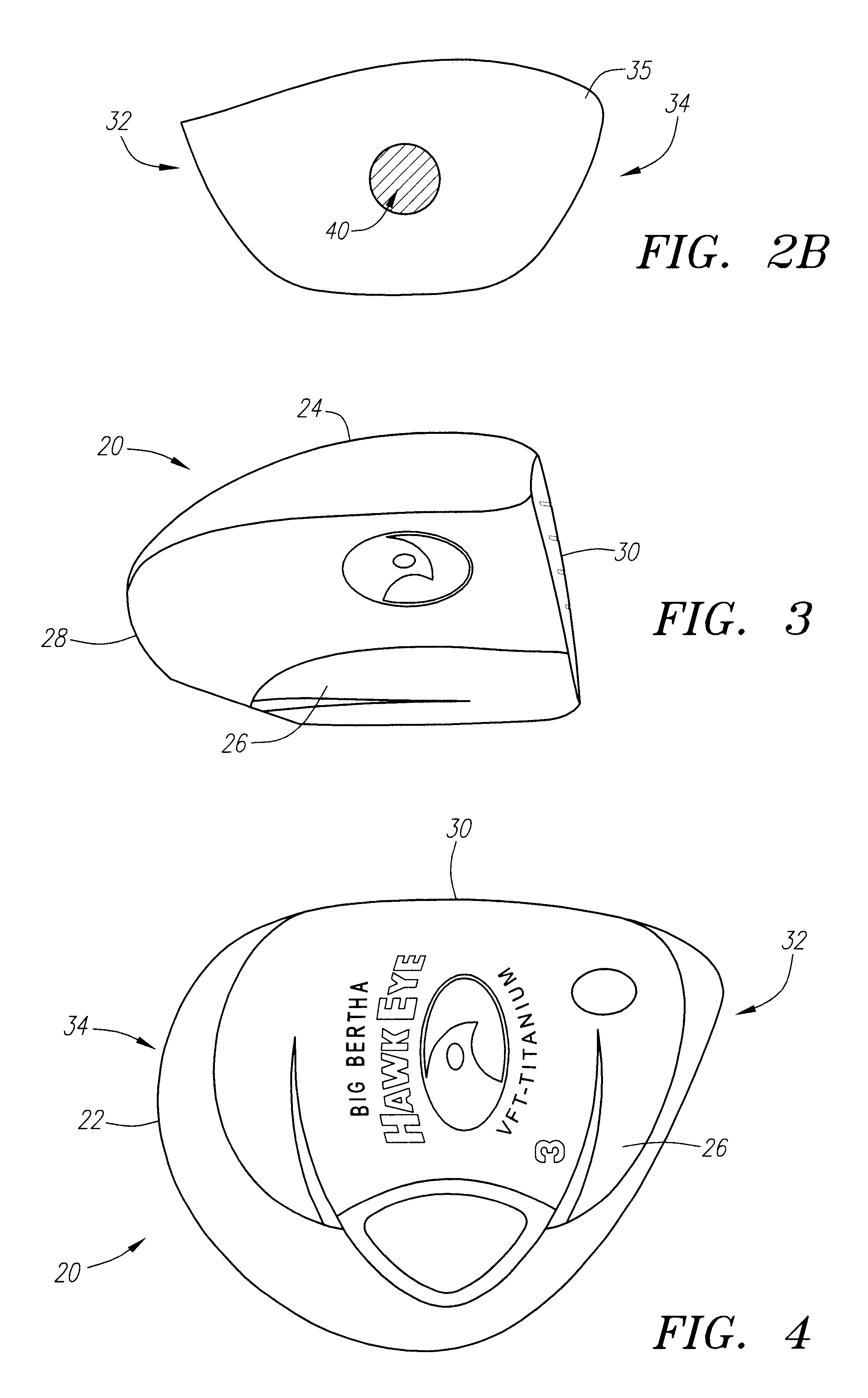
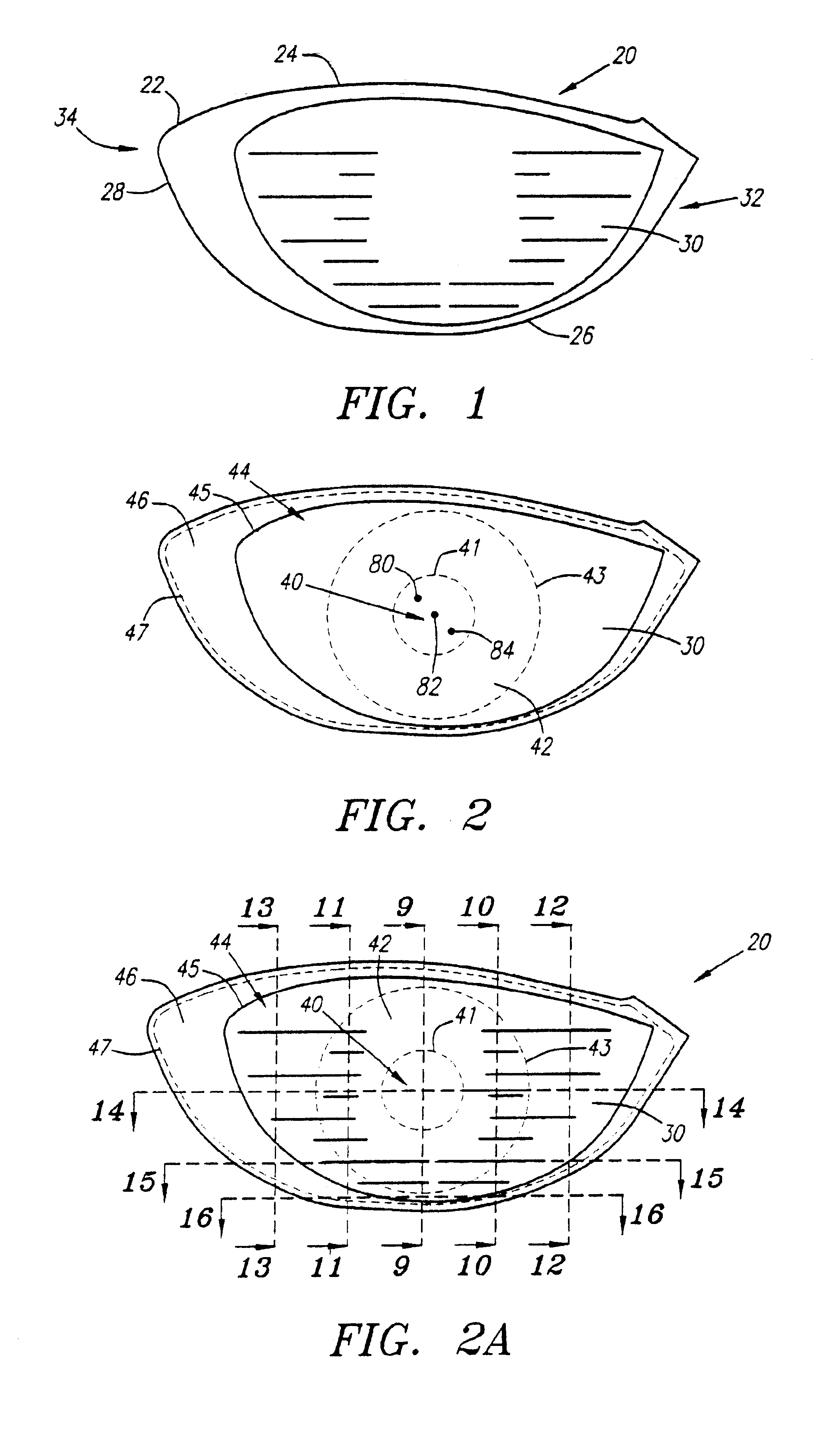
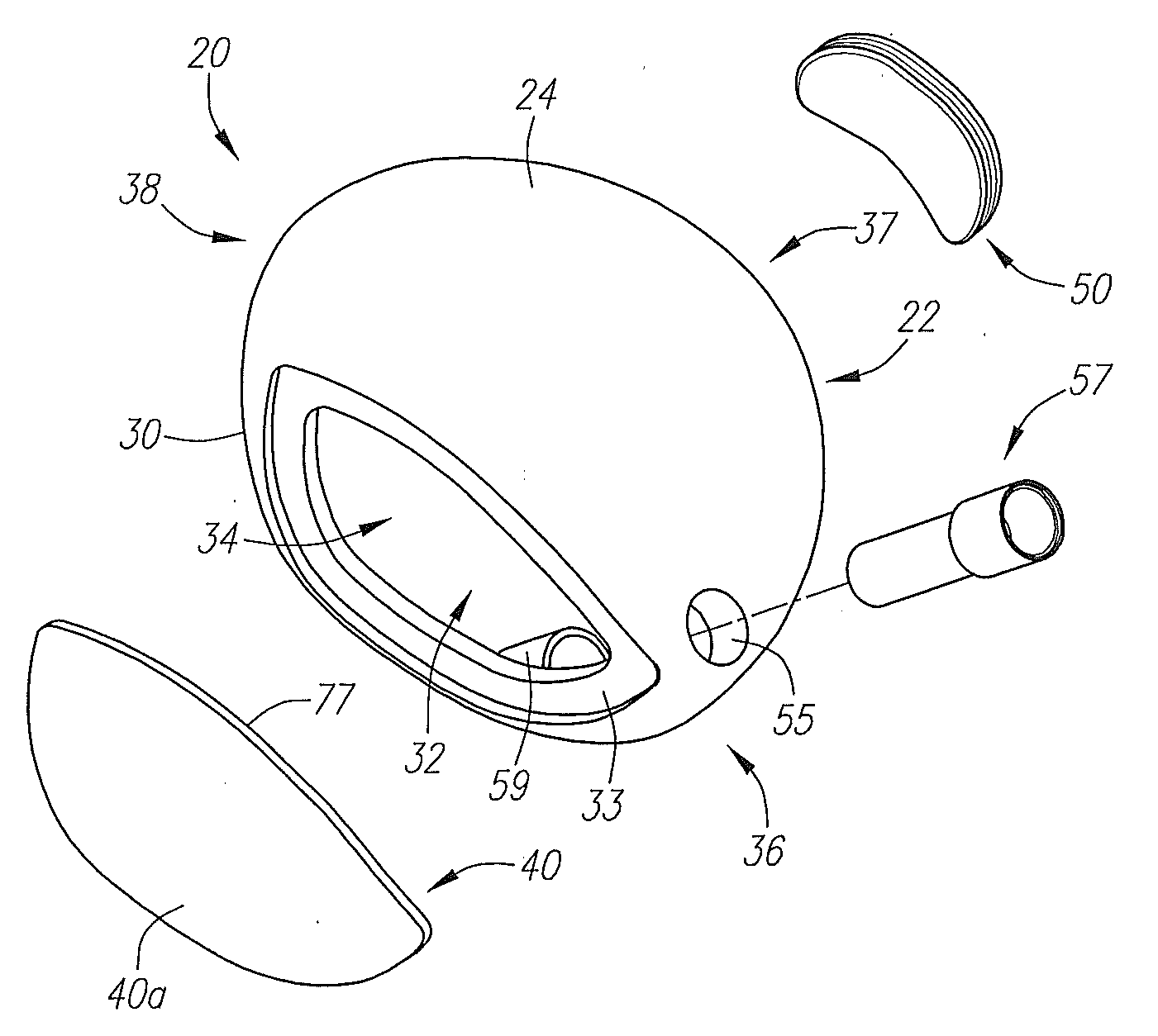
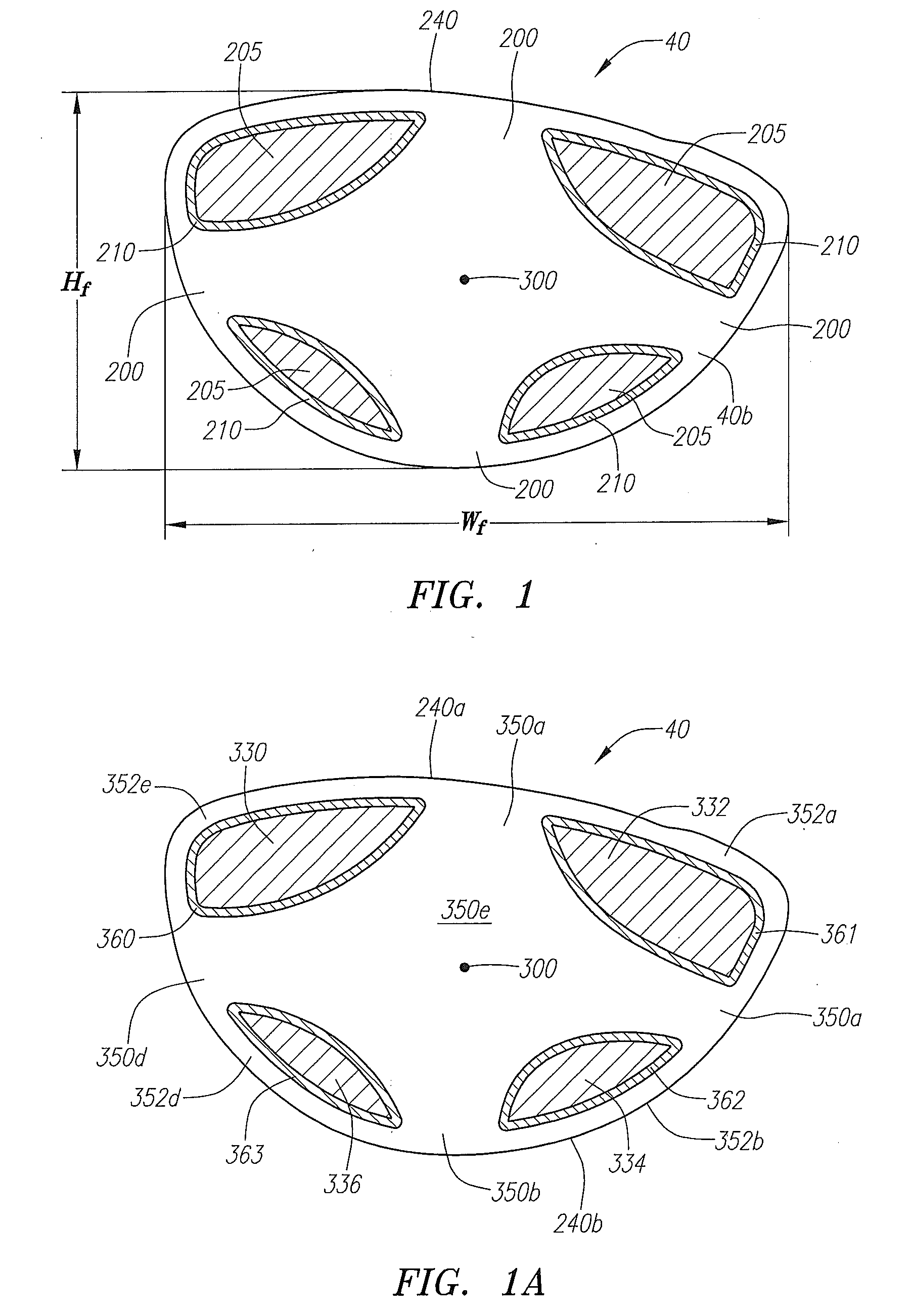
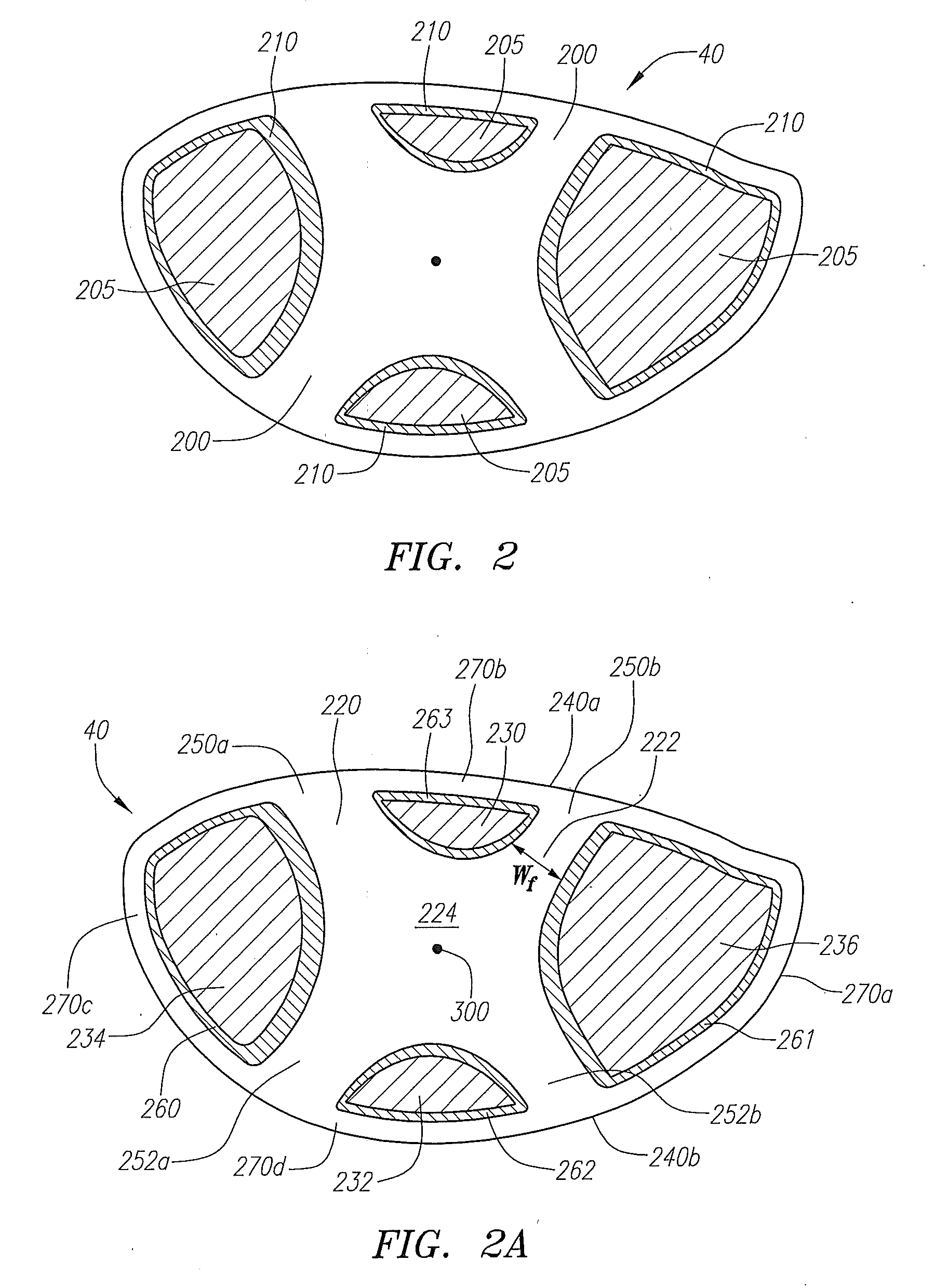
Golf club head with variable face thickness
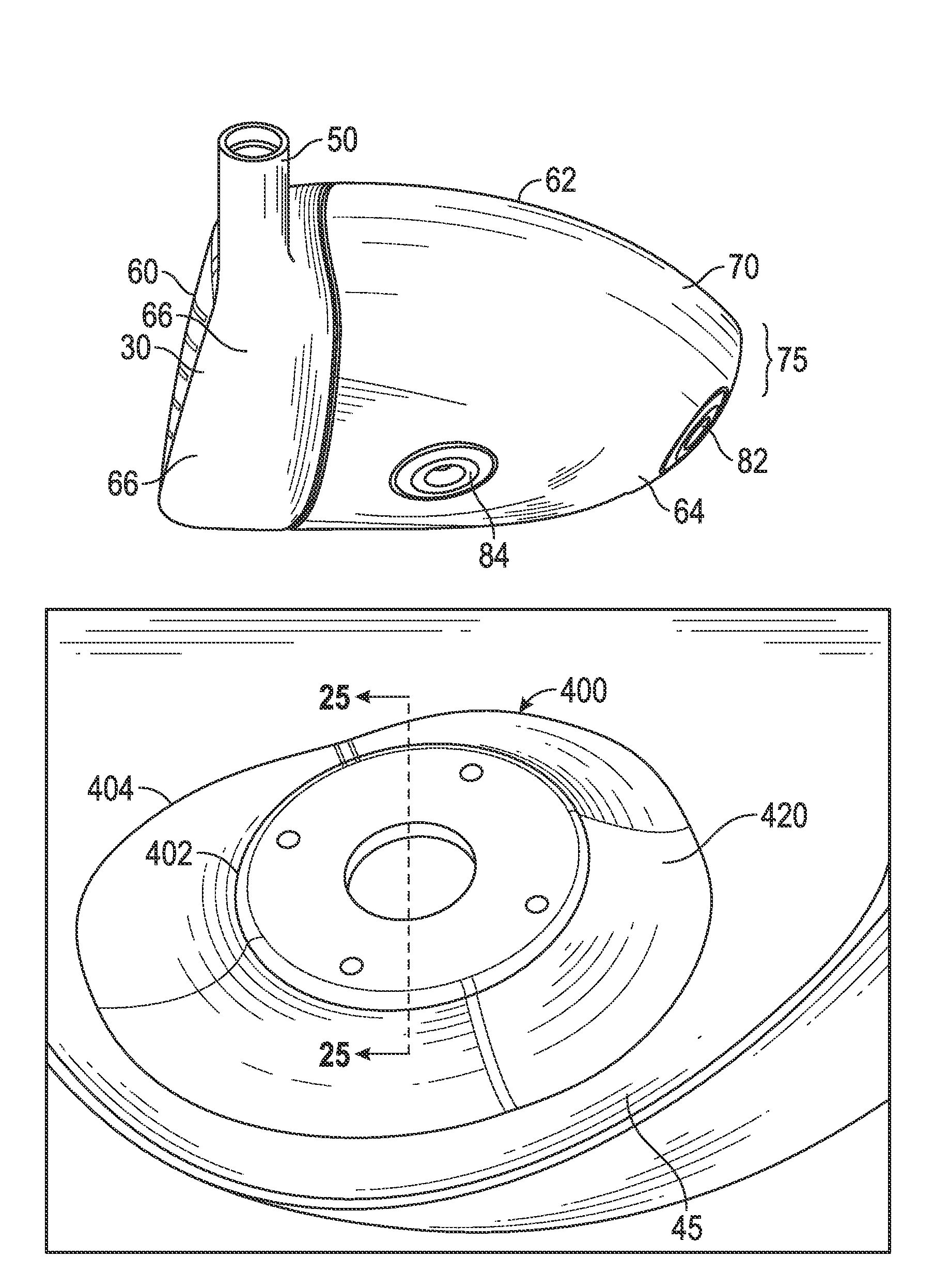
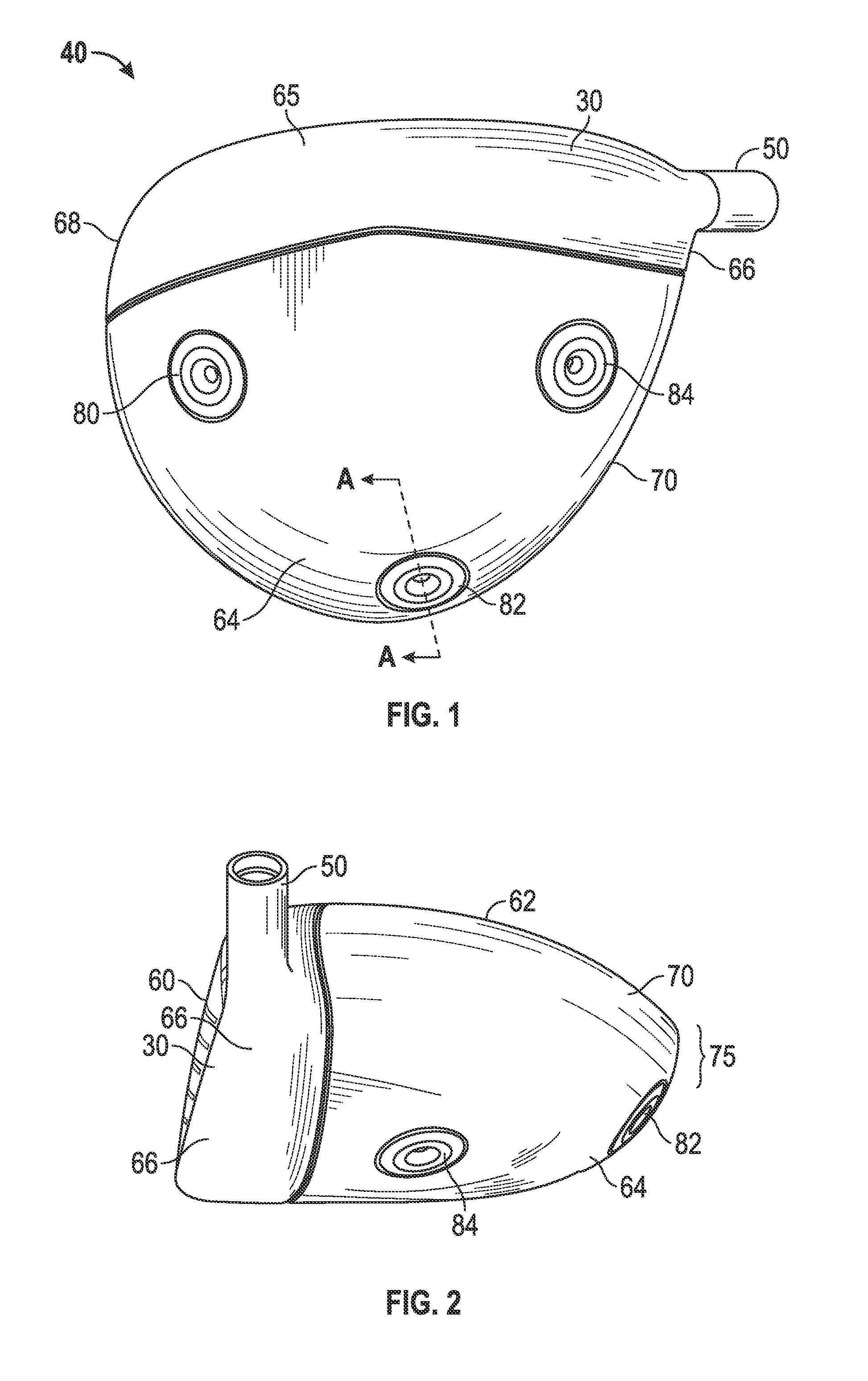
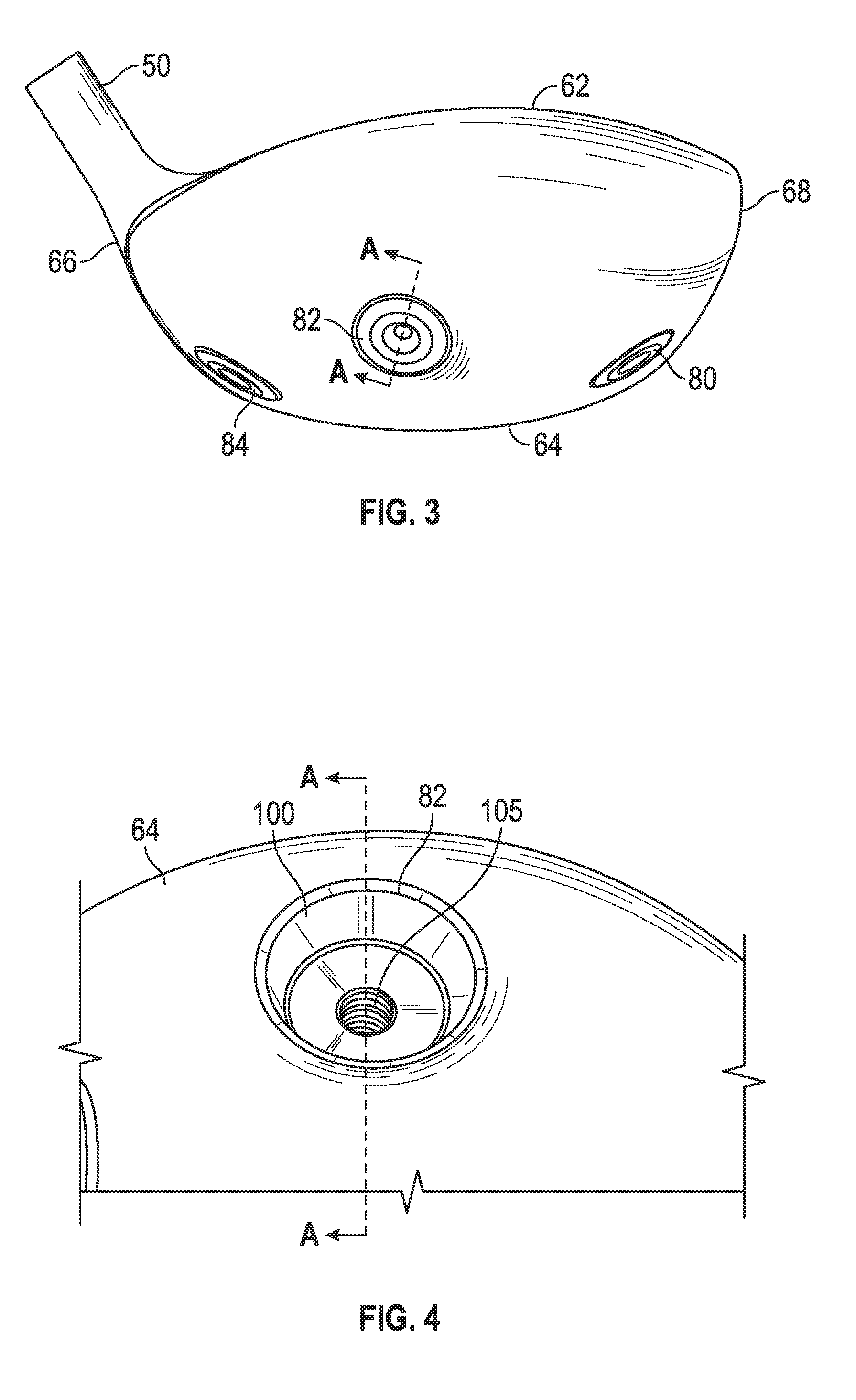
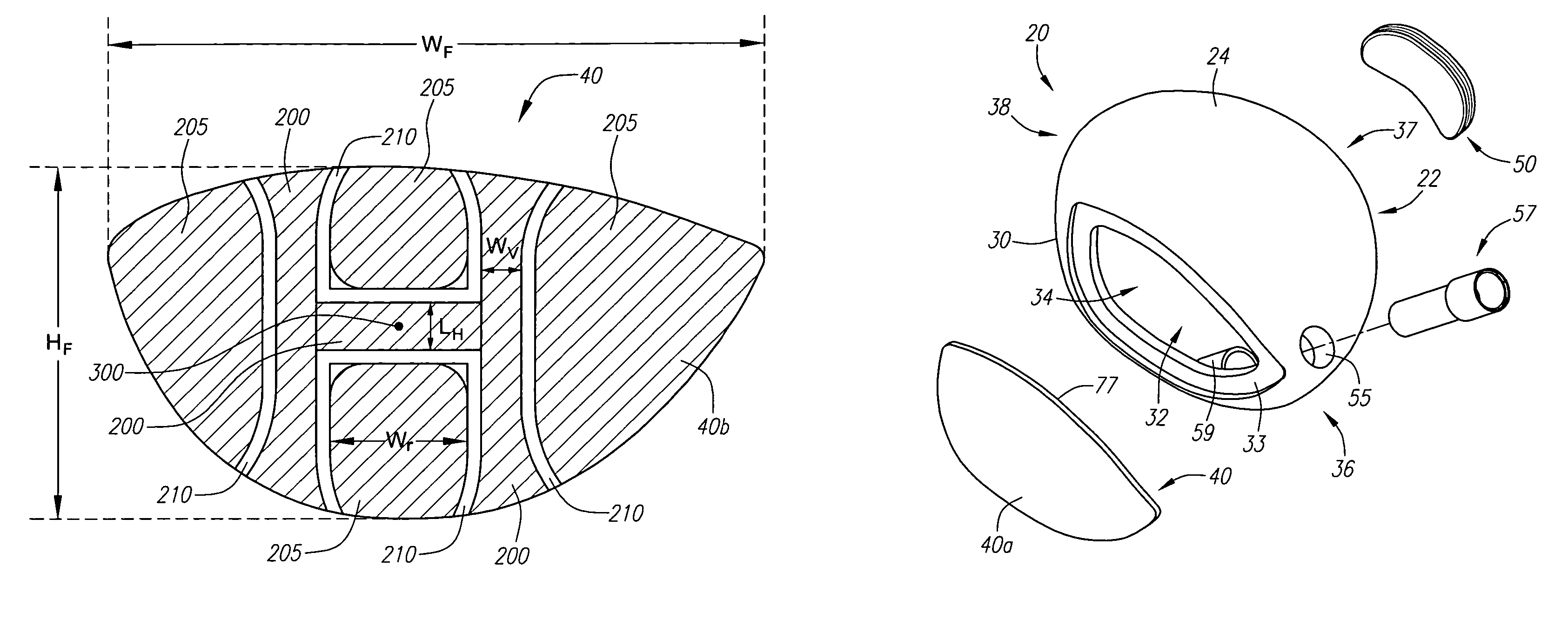
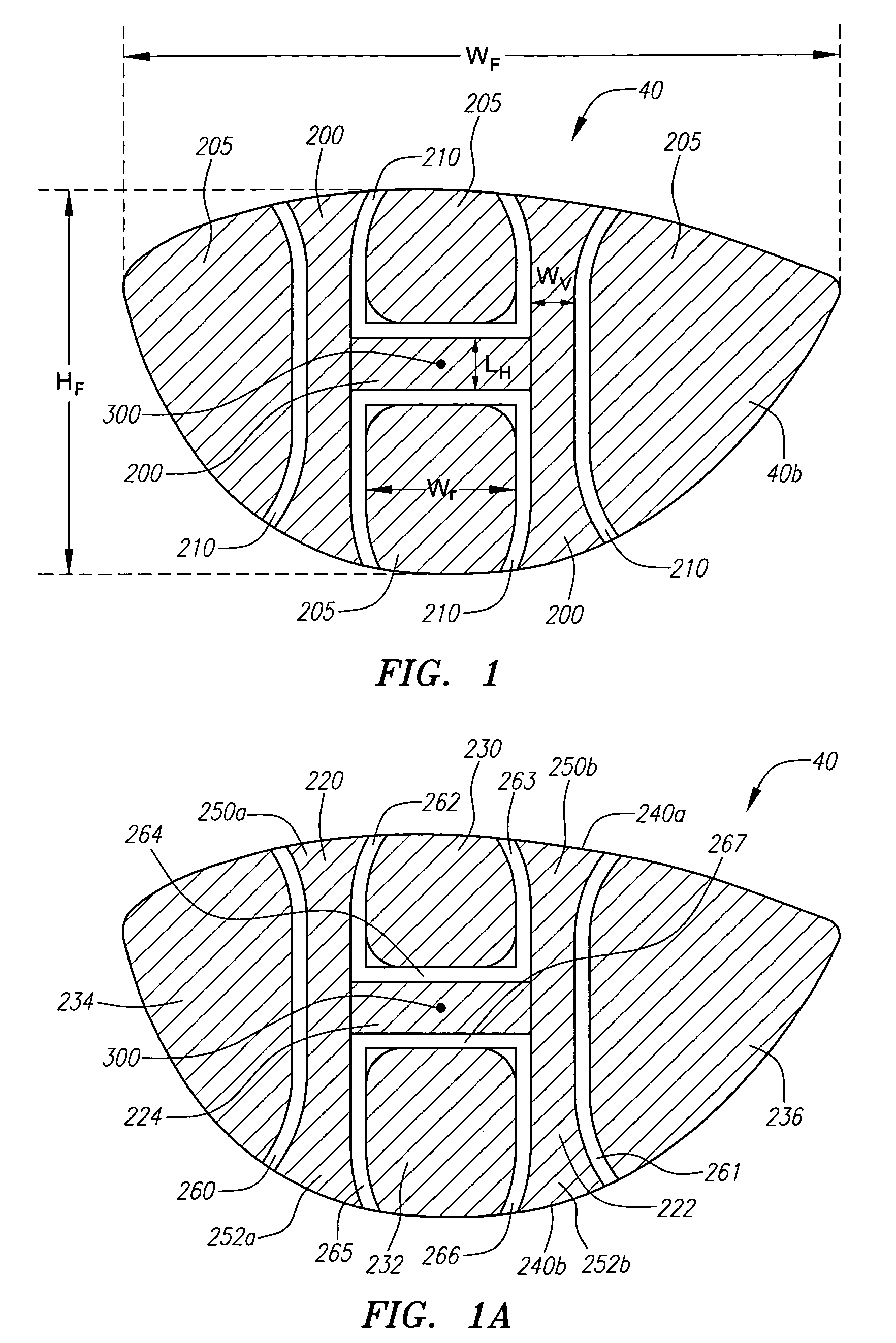
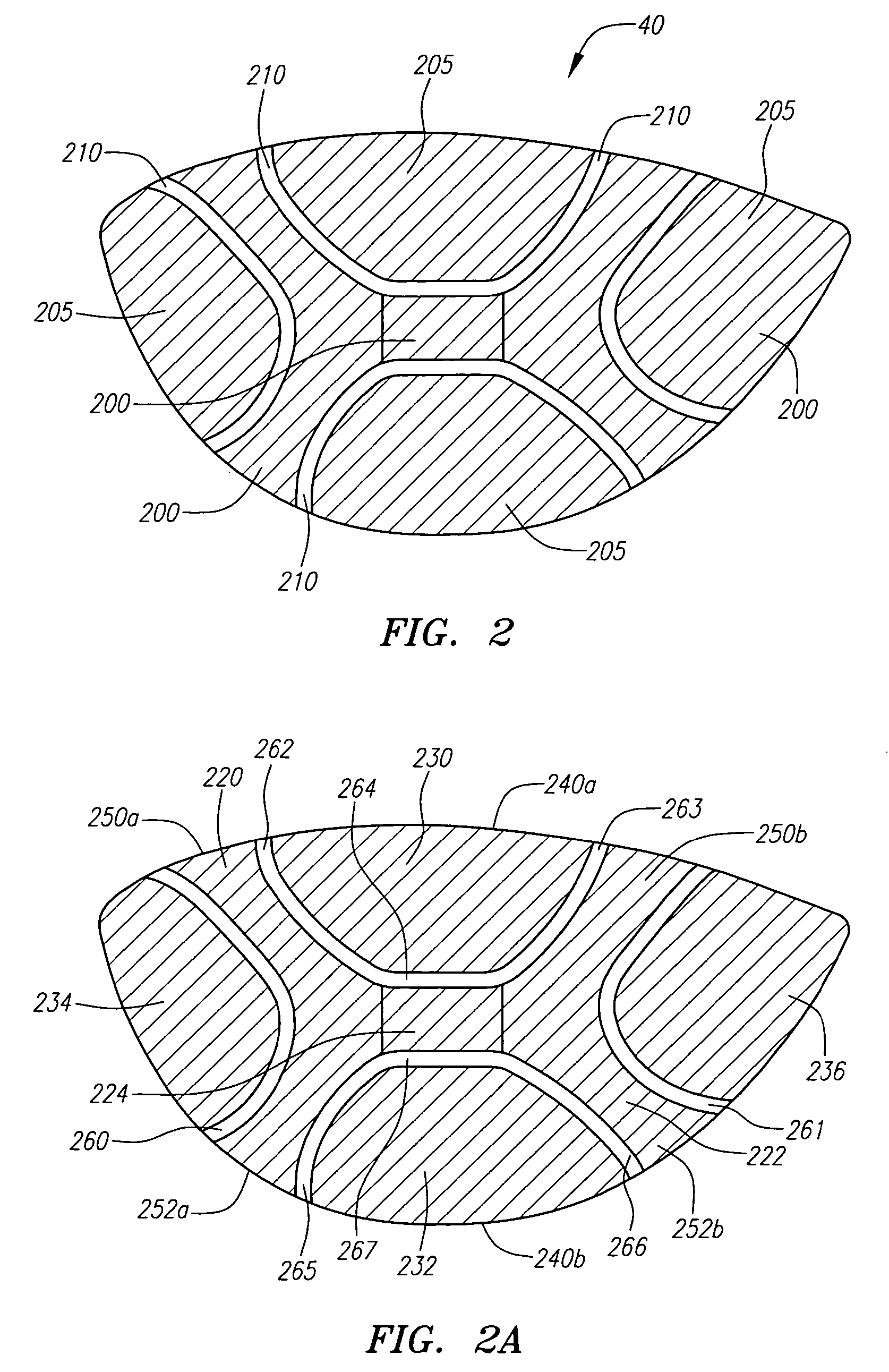
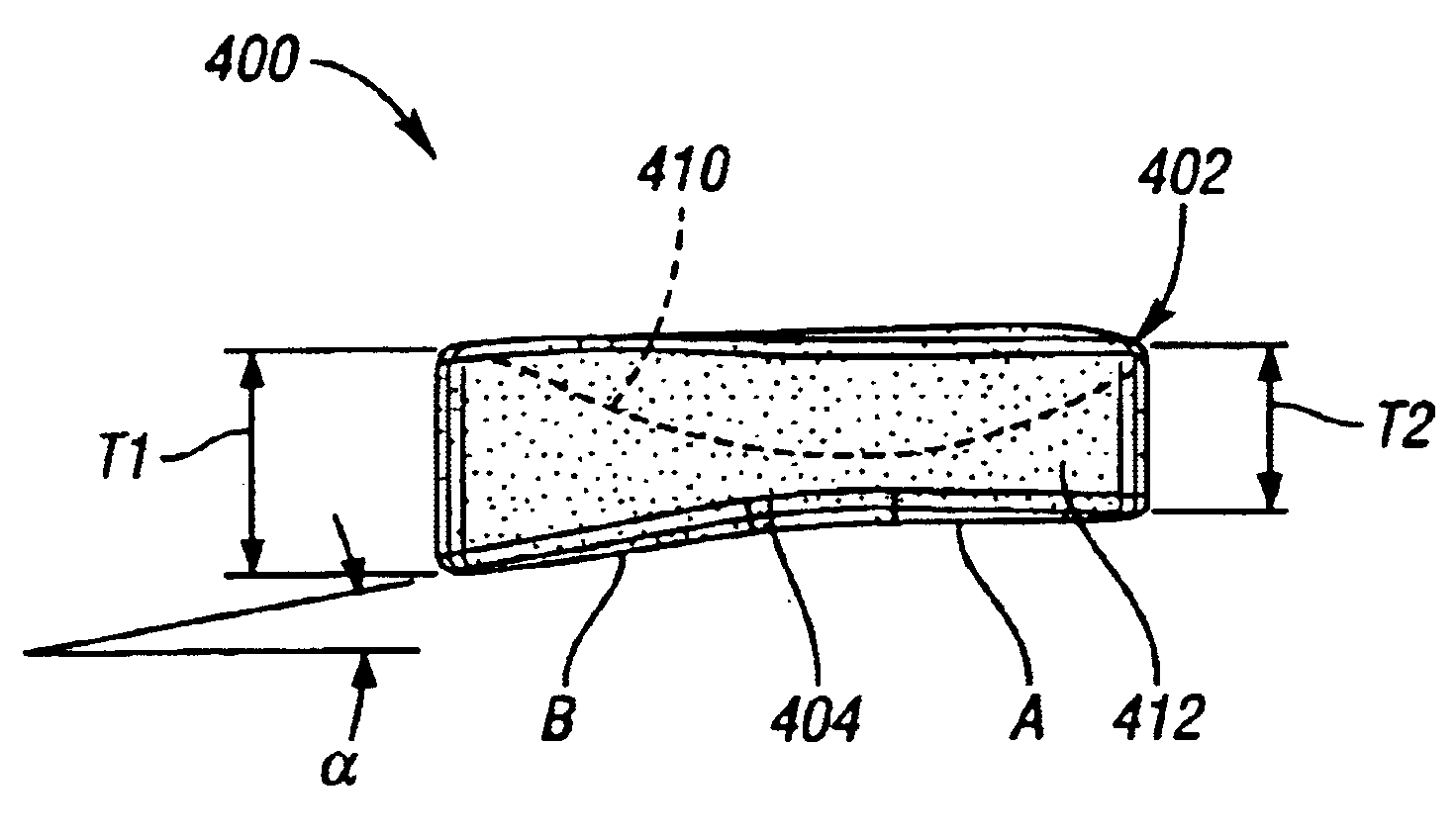
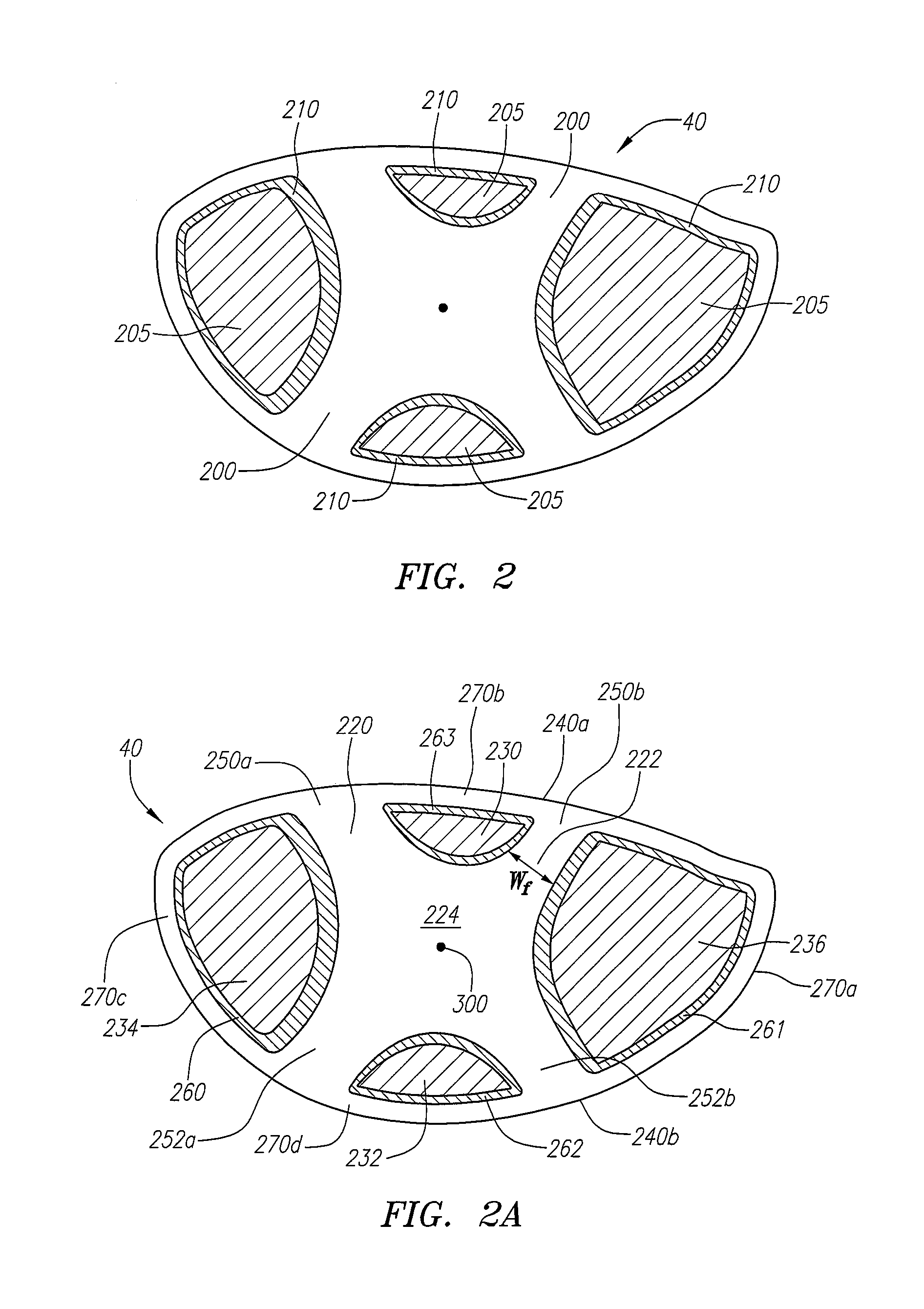
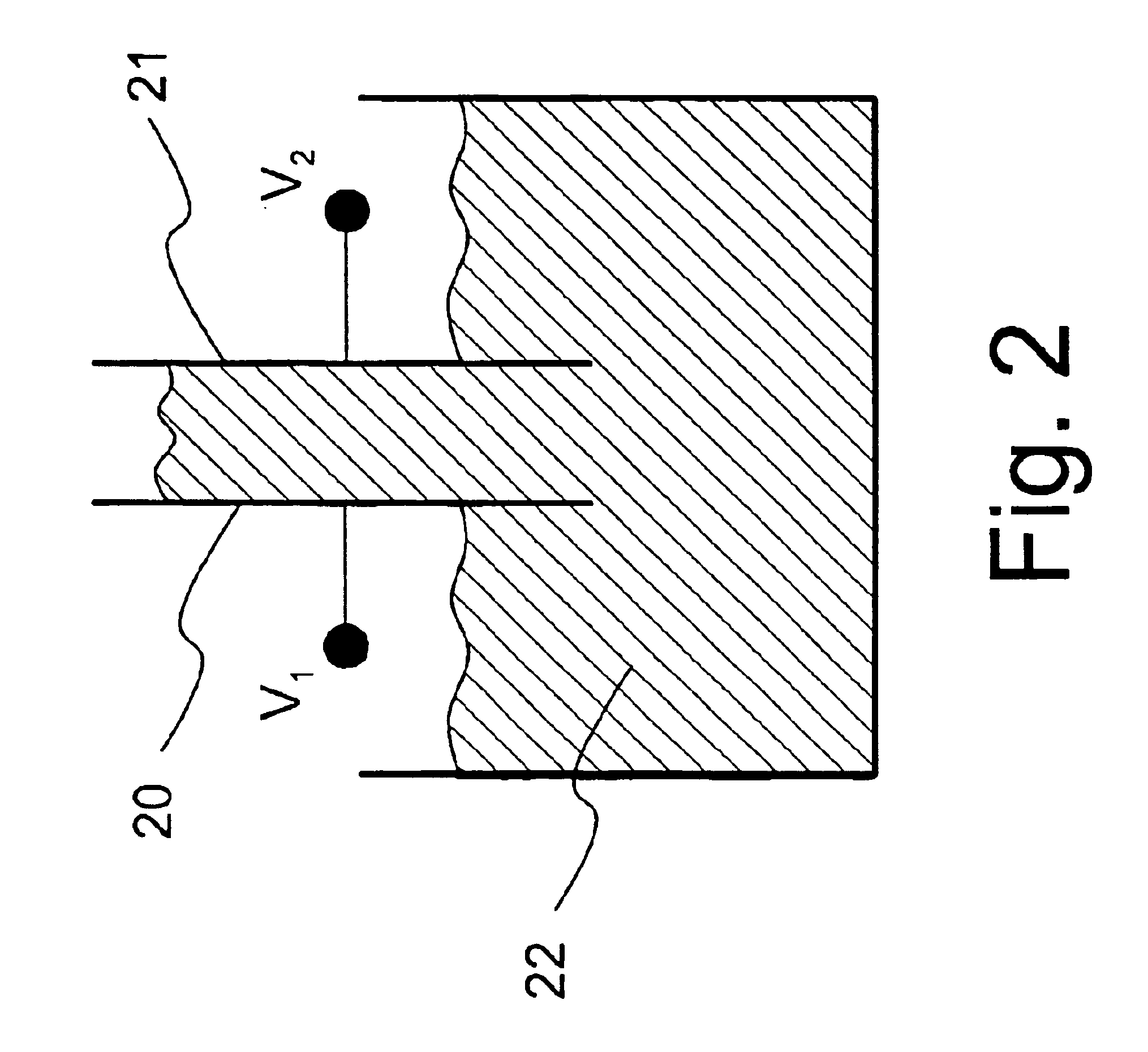
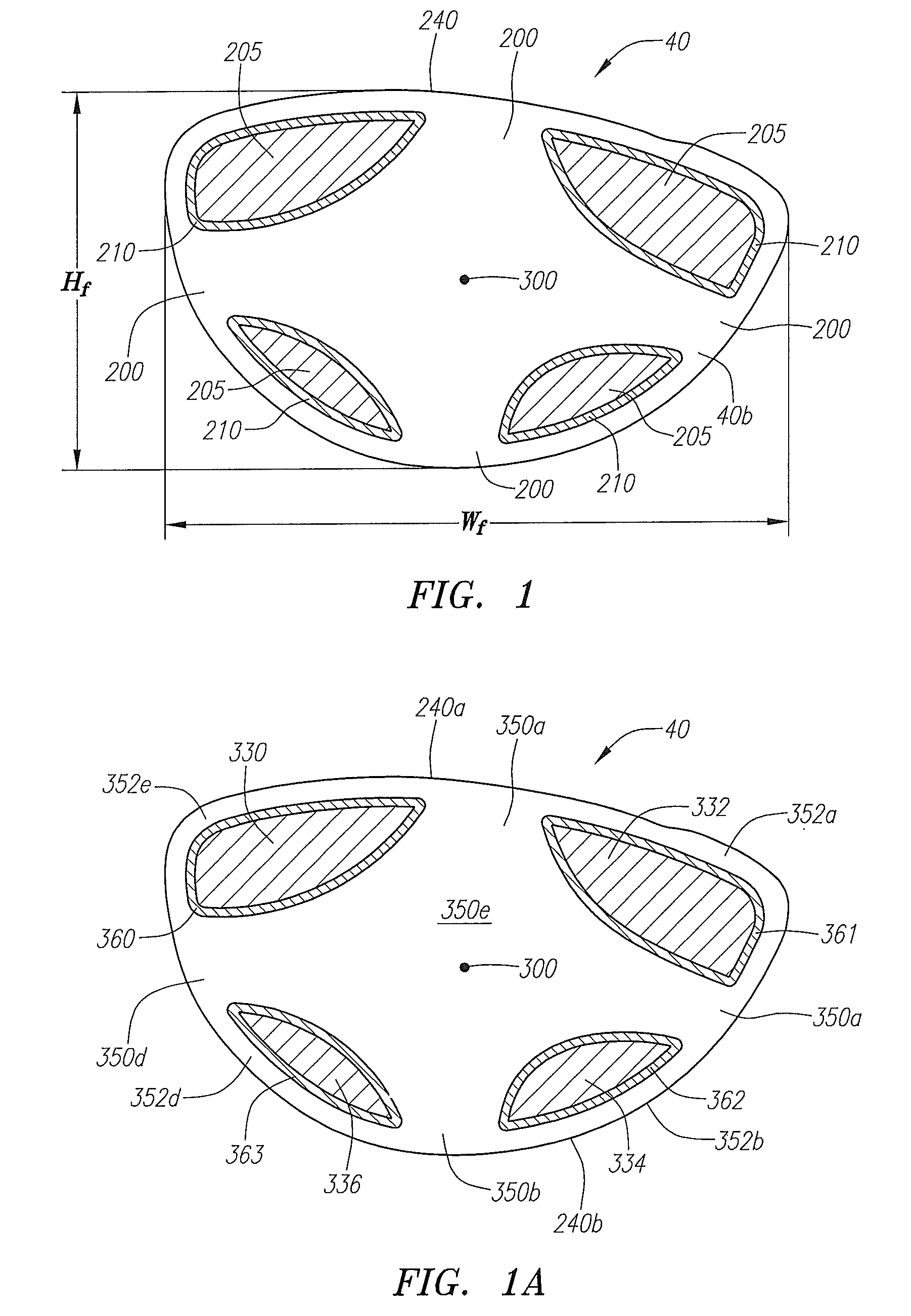
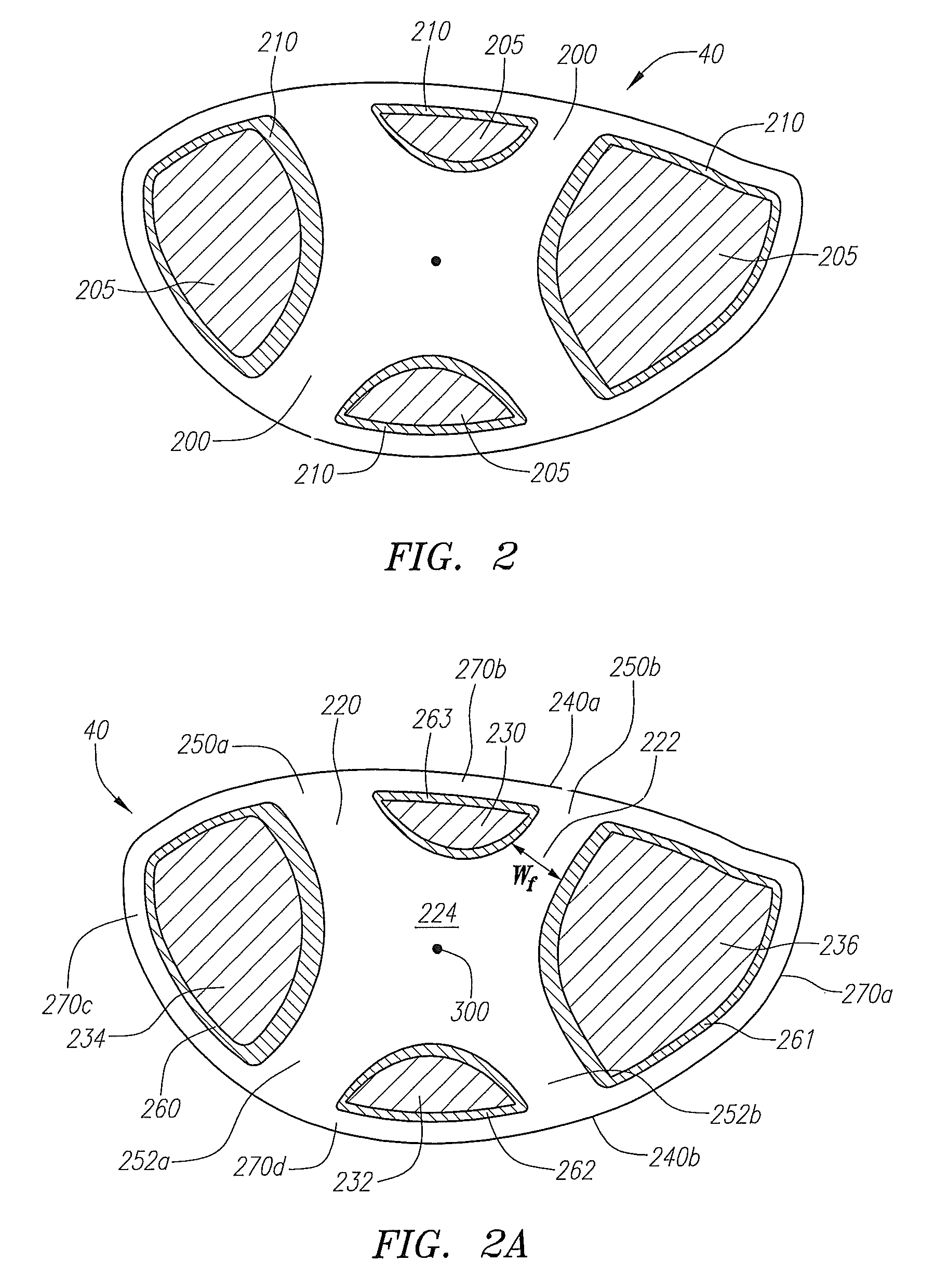
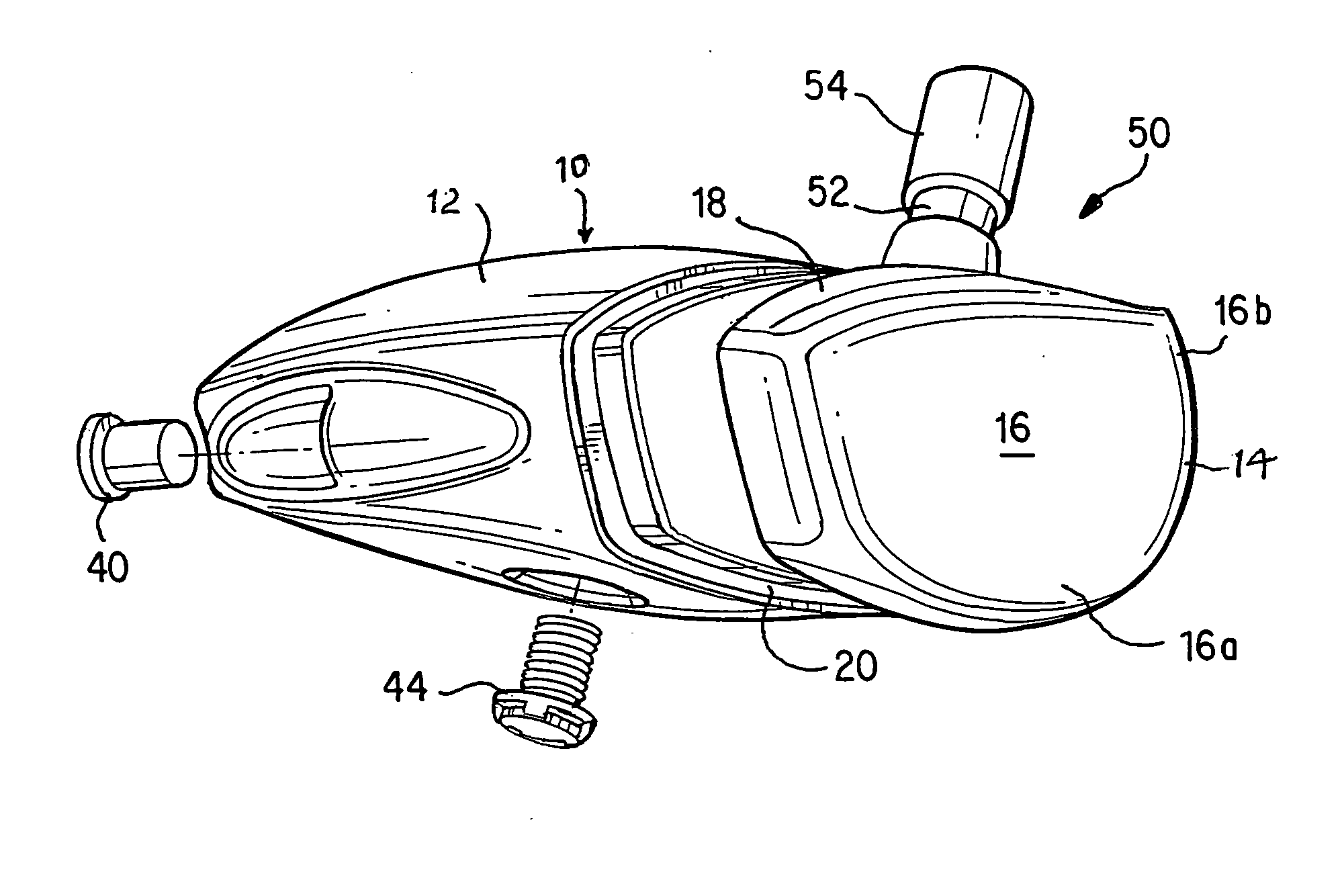
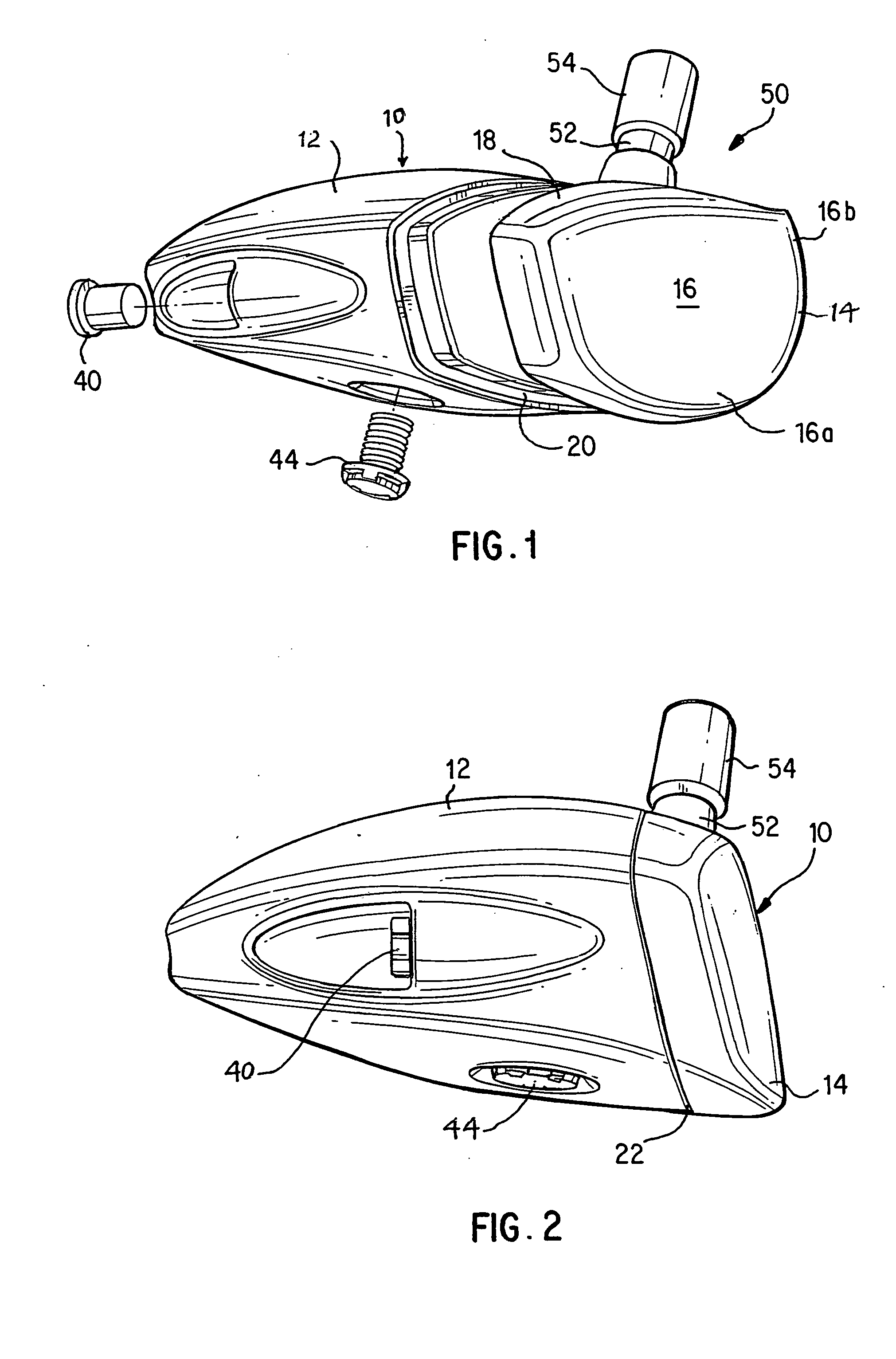
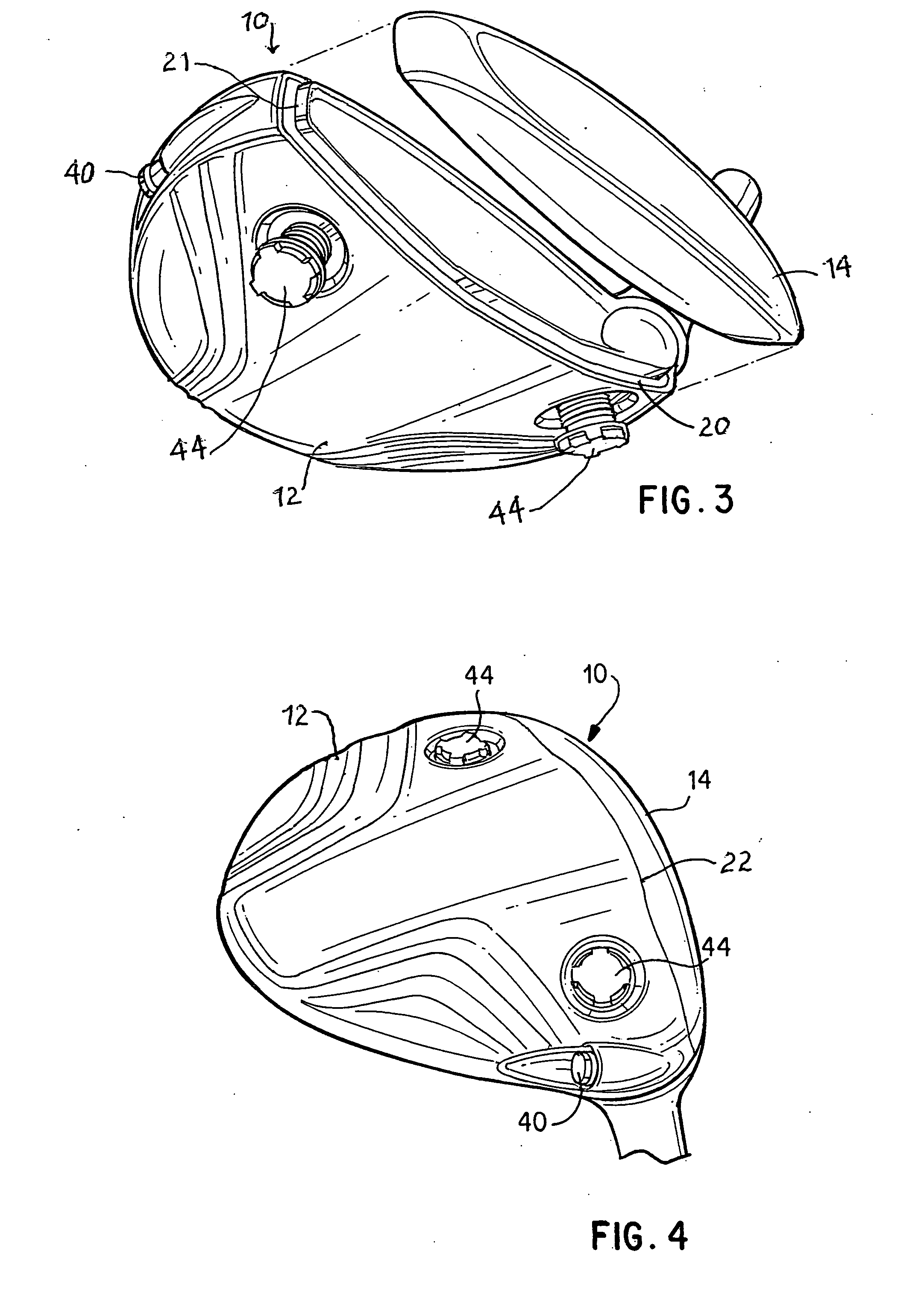
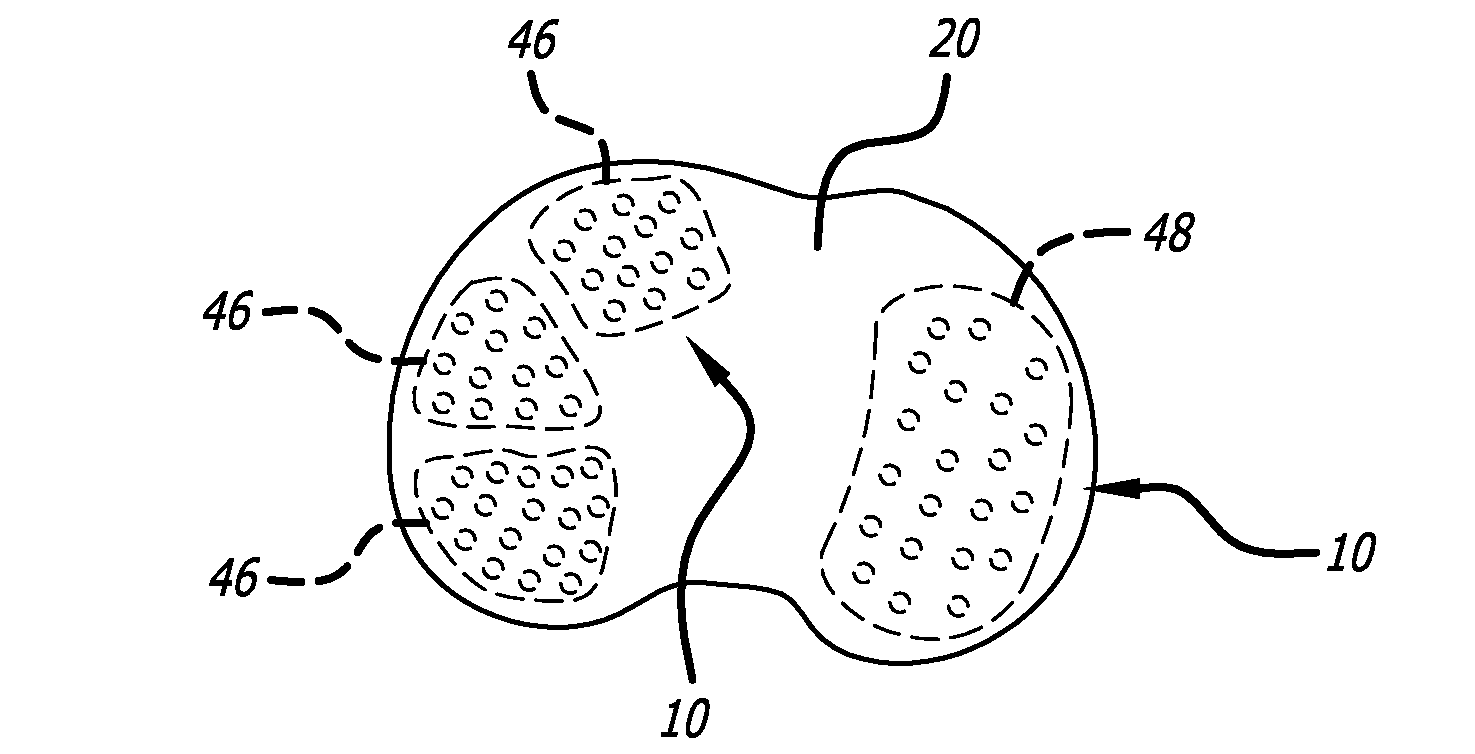
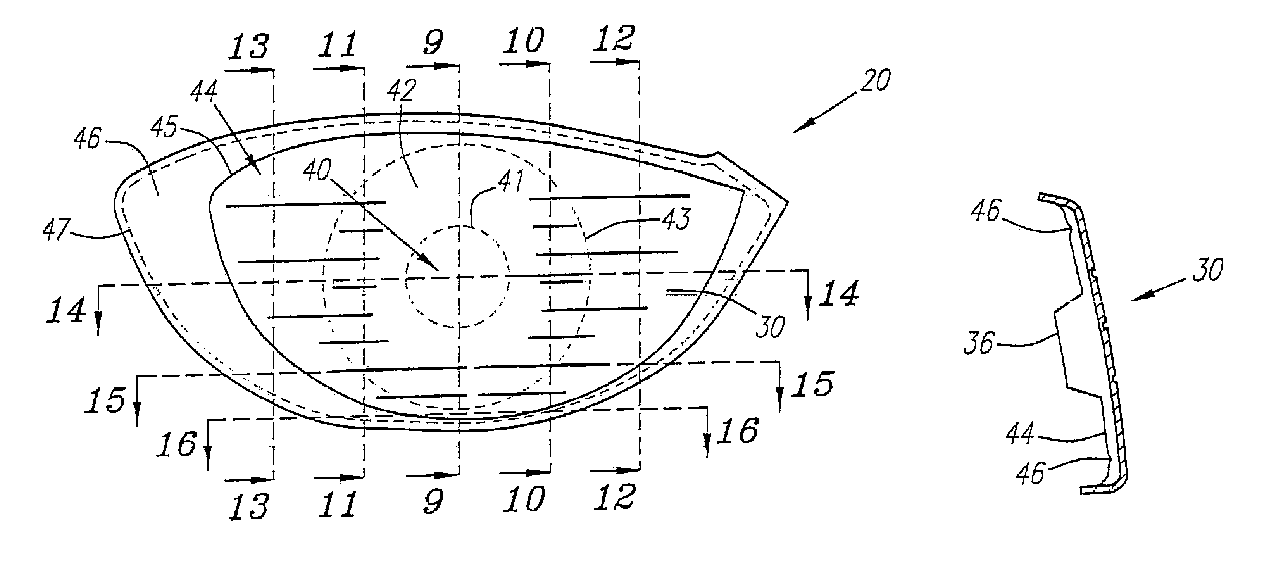
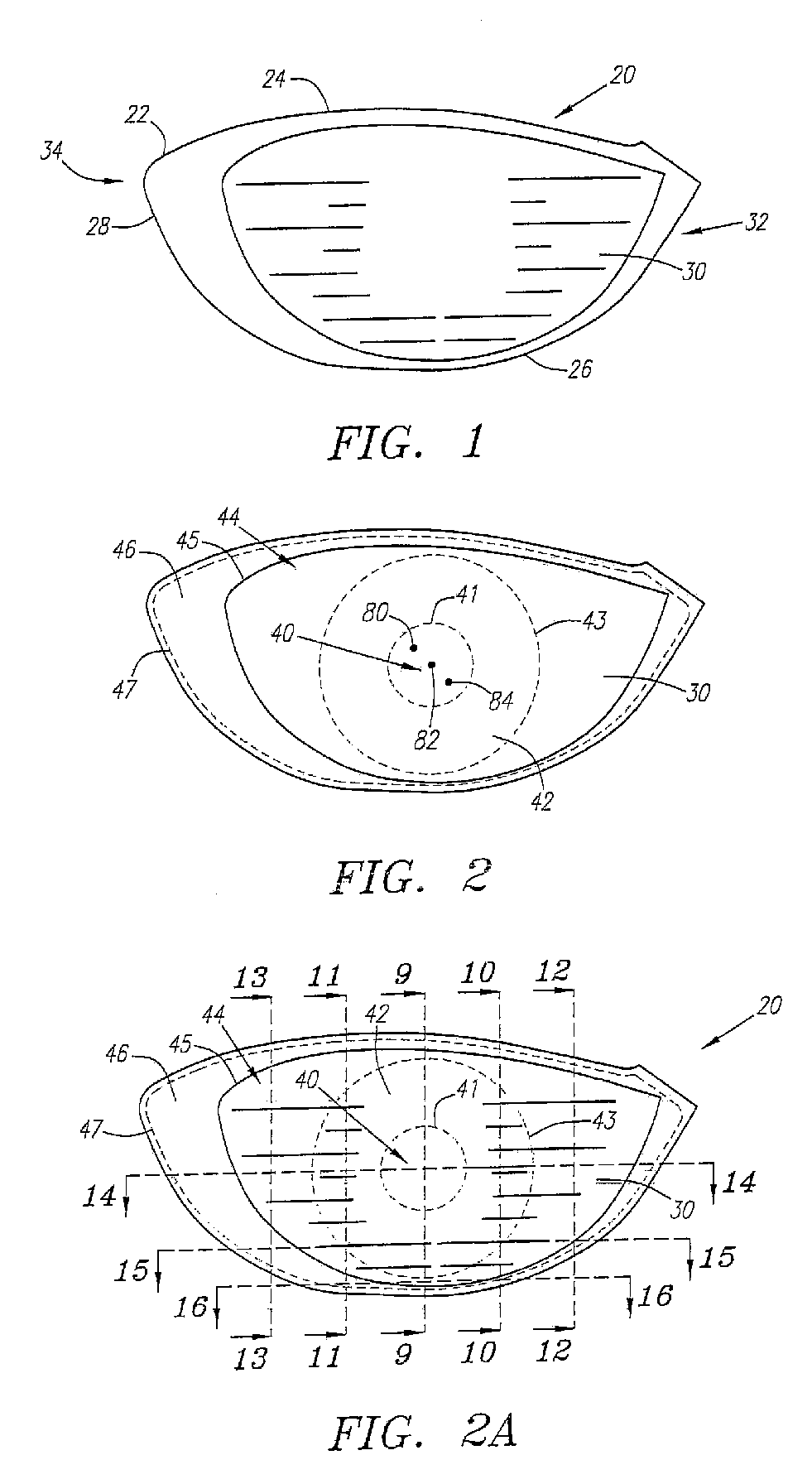
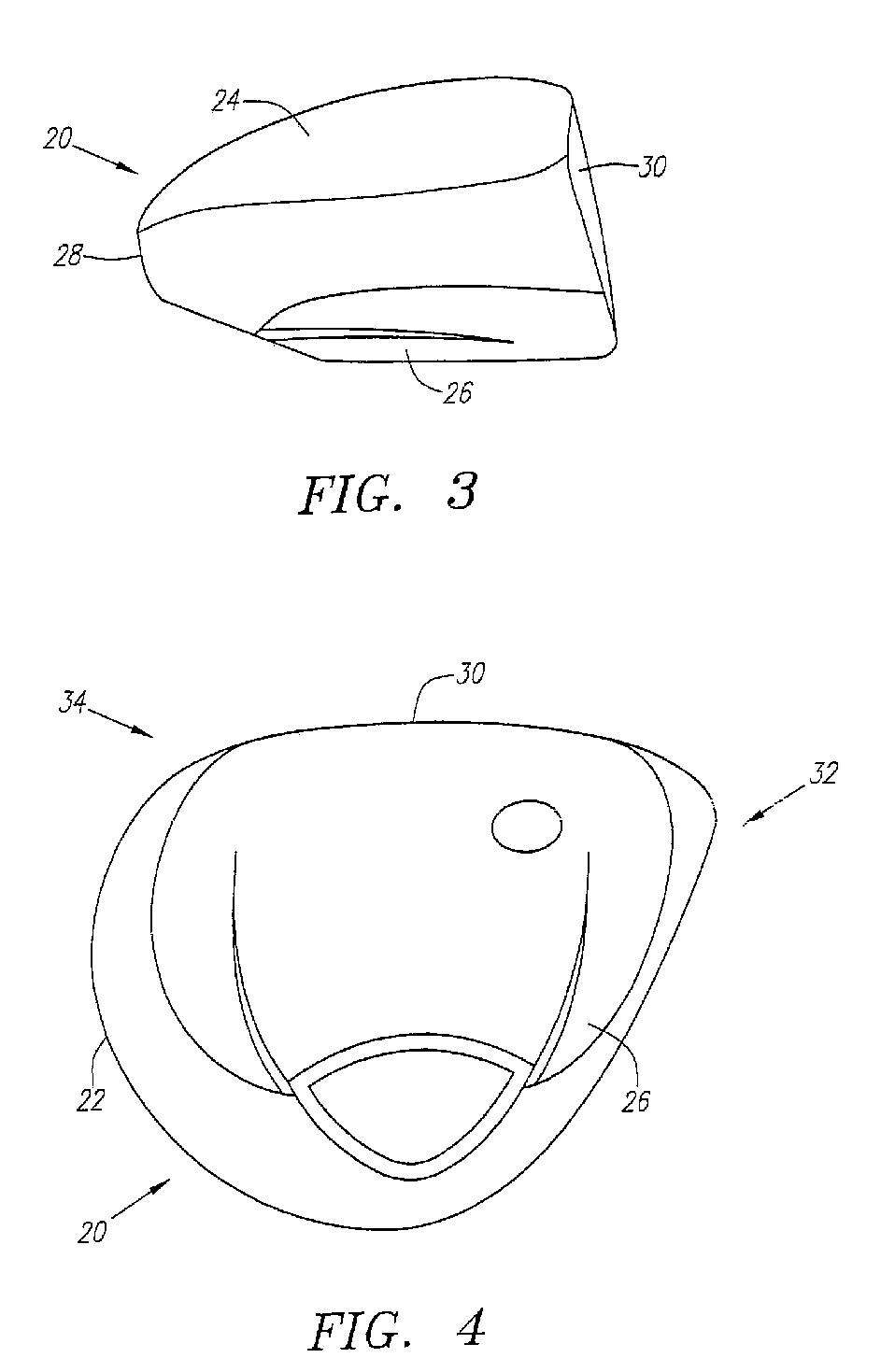
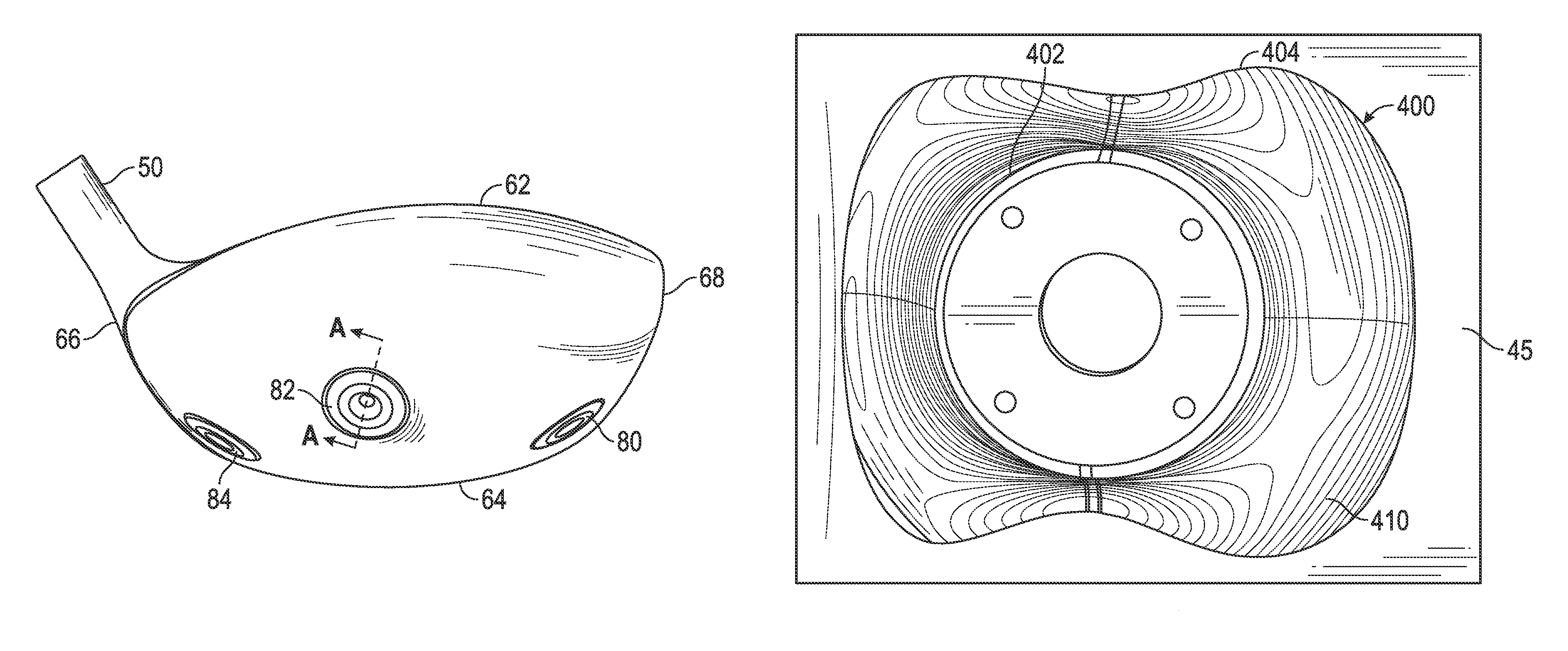
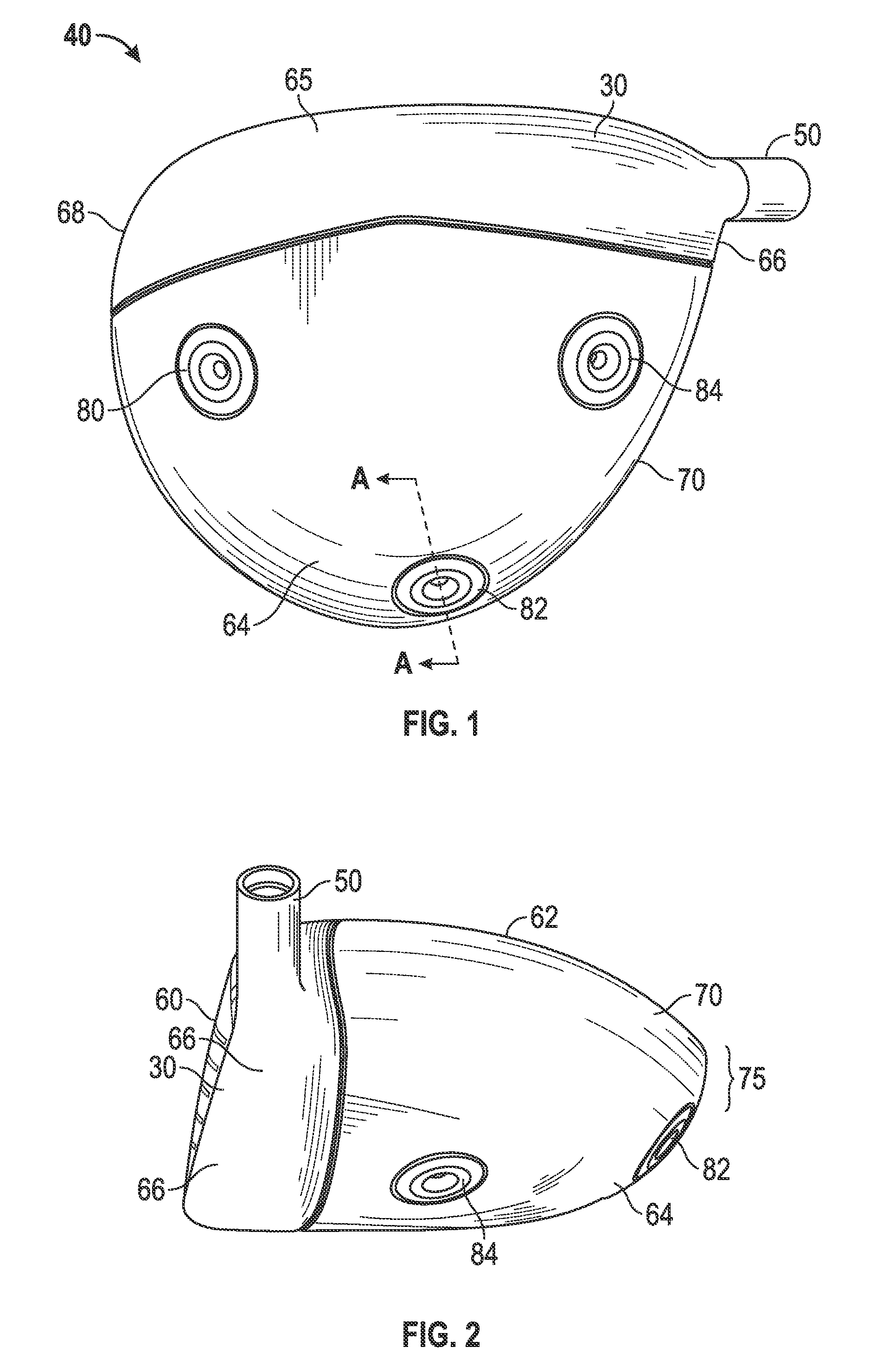
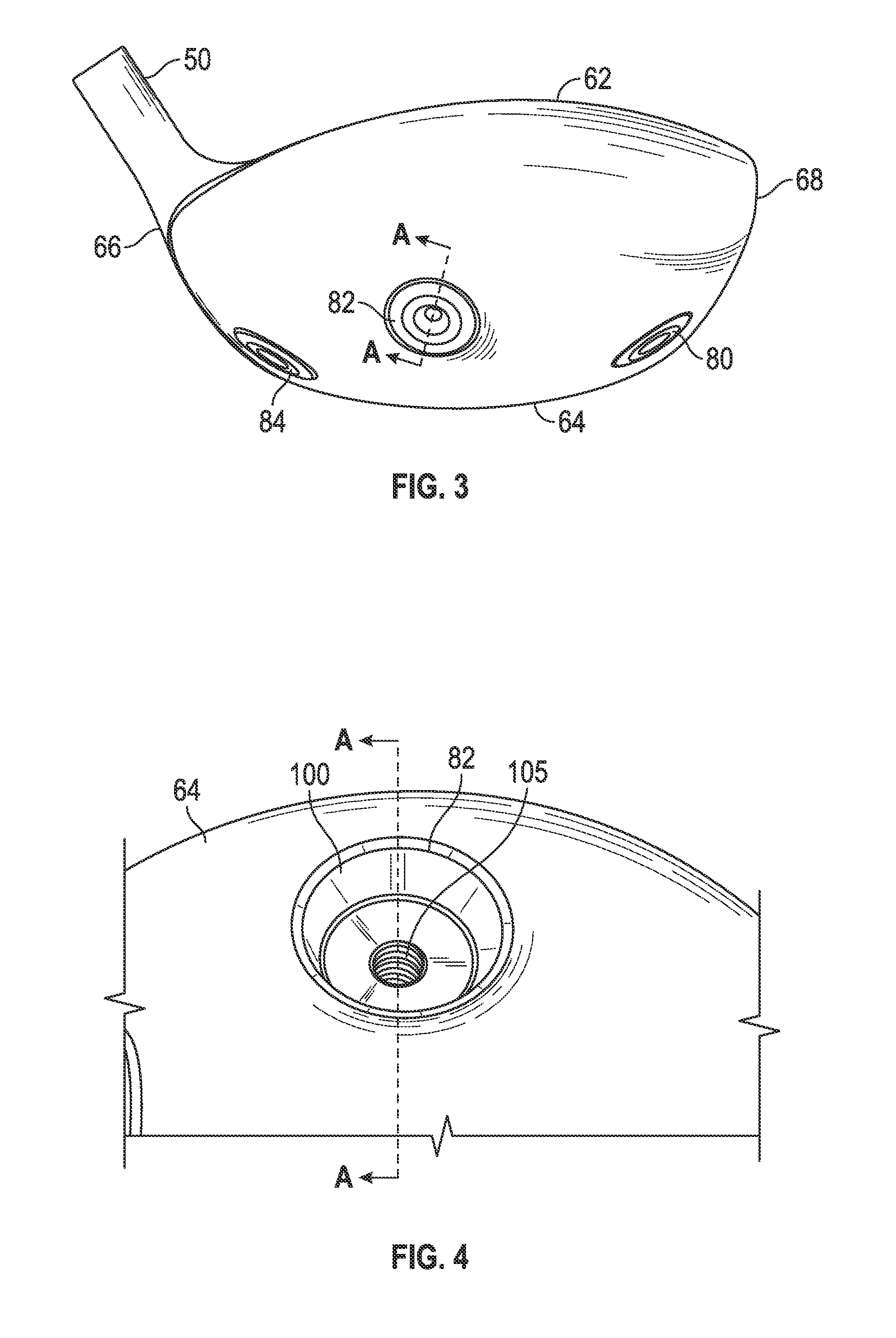
A face or face insert (40) for a golf club head (20) is disclosed herein. The face (40) has an interior surface (40a) with a first thickness section (200) and a second thickness region (205). The first thickness section (200) preferably has a thickness that is at least 0.025 inch greater than the thickness of the second thickness region (205). In a most preferred embodiment, the first thickness section (205) has an H shape. The face or face insert (40) with variable thickness allows for a face or face insert (40) with less mass in a golf club head (20) that conforms to the United States Golf Association regulations.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
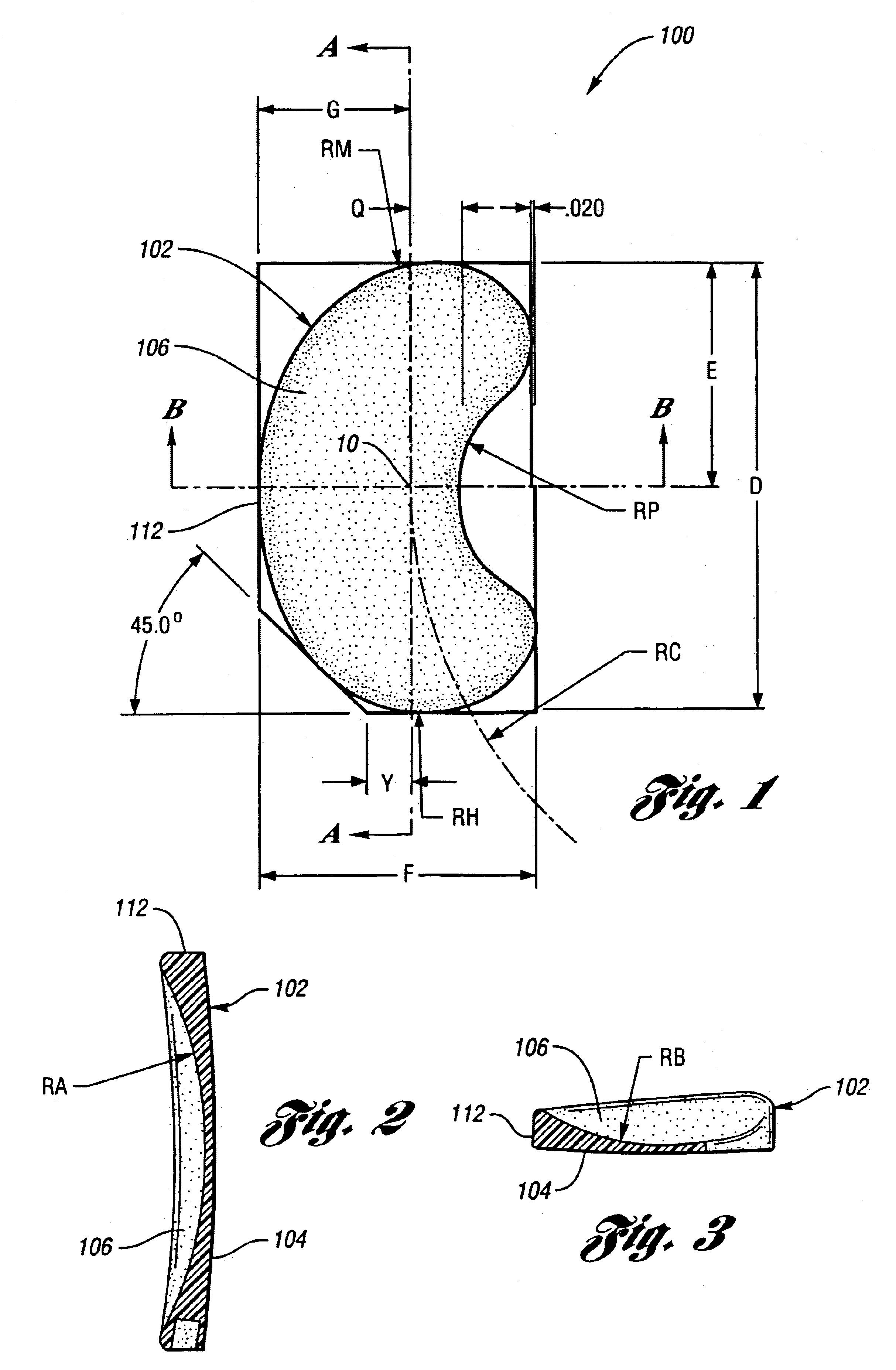
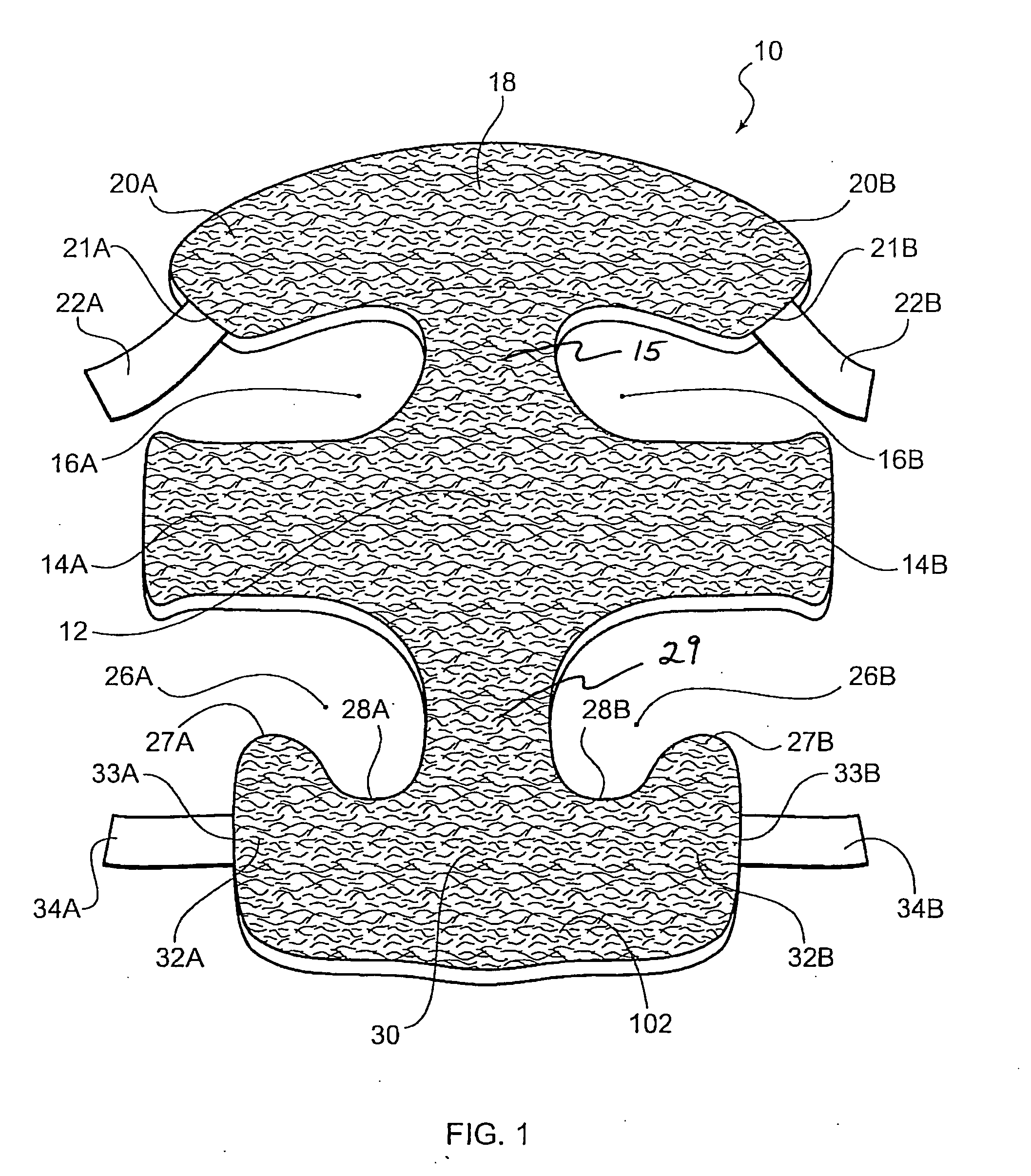
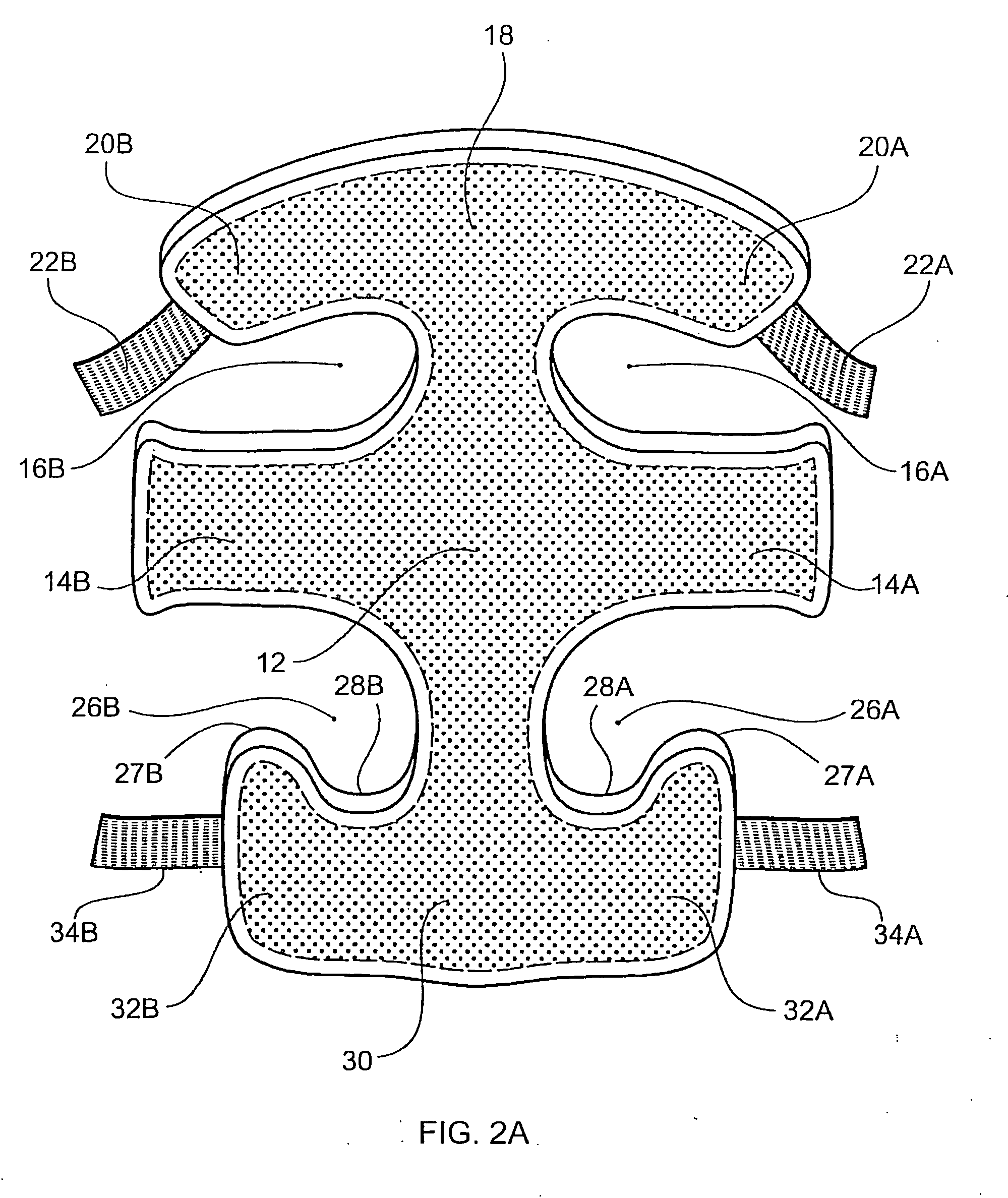
Surgically implantable knee prosthesis having medially shifted tibial surface
An implantable knee prosthesis includes a body having a substantially elliptical shape in plan and a pair of opposed faces. A peripheral edge of variable thickness extends between the faces and includes a first side, a second side opposite the first side, a first end and a second end opposite the first end. The thickness of the peripheral edge at the first side is greater than the thickness of the peripheral edge at the second side, the first end and the second end.
Owner:CENTPULSE ORTHOPEDICS
Golf club head with variable face thickness
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Method for manufacturing a golf club face
InactiveUS6904663B2Large thickness variationImprove performanceGolf clubsRacket sportsVariable thicknessAsymmetric face
A method of manufacturing a face plate for a golf club head is presented to provide face having substantial thickness variation for enhanced performance. The method includes the steps of providing a rolled sheet of metal material having an initial thickness and forming a blank having a prescribed outer shape from the material. The method also includes machining a second side of the blank such that the resulting face plate has a variable thickness. The machining is such that the plate has a first thickness less than or equal to the initial thickness, a second thickness less than the first thickness and a third thickness less than the second thickness. The machining is performed over a substantial portion of the surface area of the second side. Either a CNC lathe or milling machine may be used; however, for an axisymmetric face thickness a CNC lathe is preferred and for an asymmetric face thickness a CNC end mill is preferred. The club head may be a wood-type or iron, and titanium or steel alloys may be used.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
External cavity laser with rotary tuning element
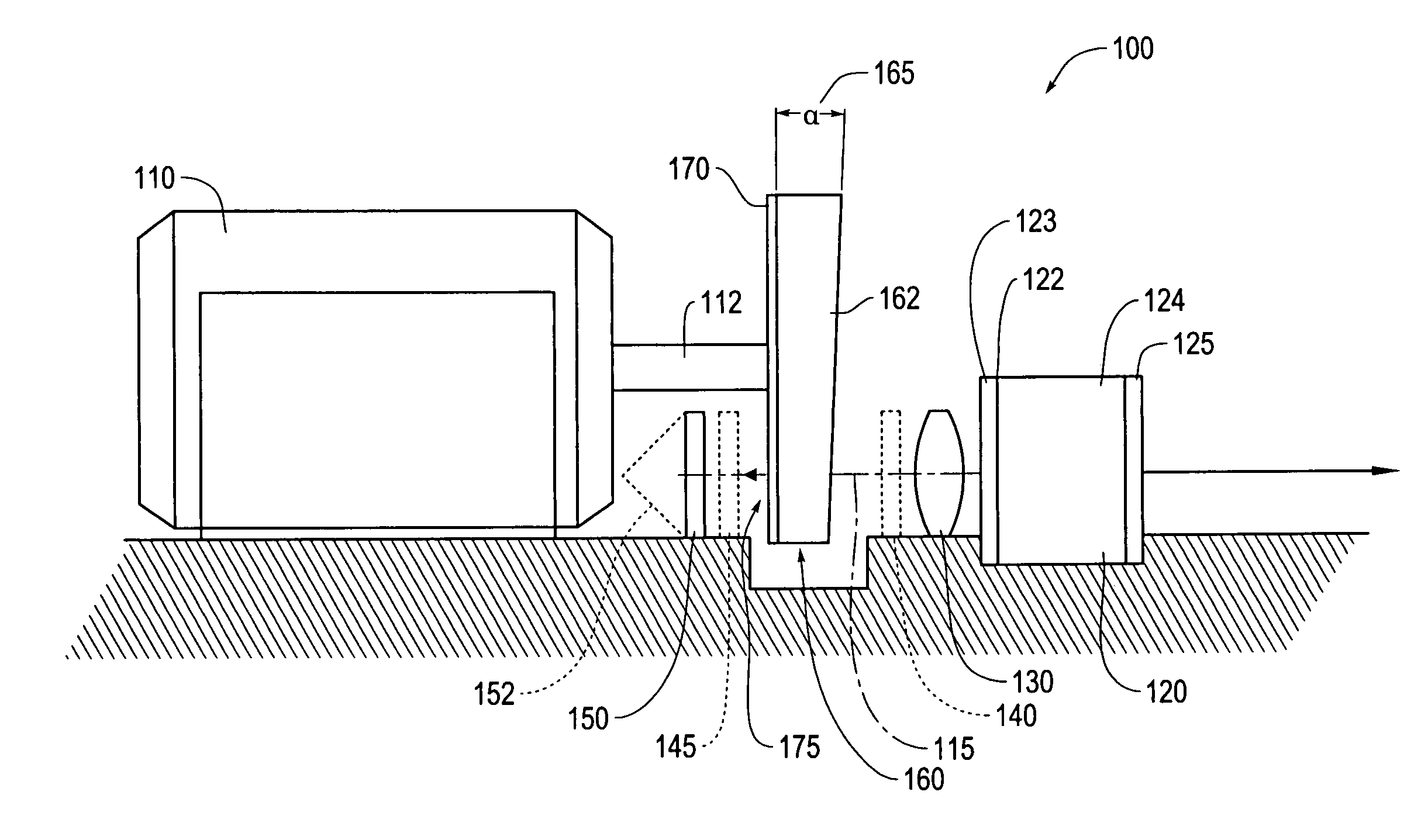
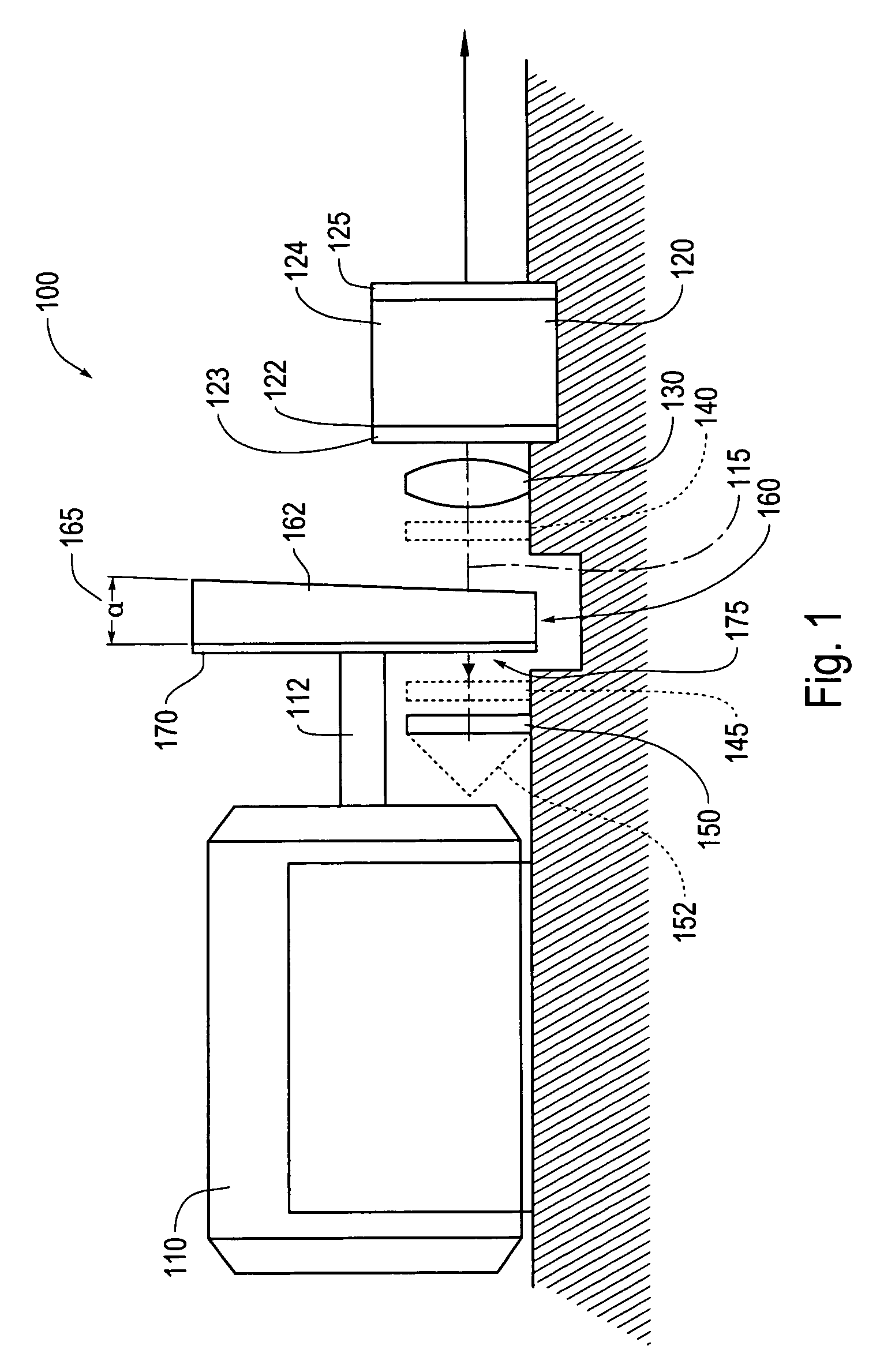
InactiveUS7130320B2Improve economyImprove reliabilityLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionVariable thicknessExternal cavity laser
An external cavity laser has a wavelength of the laser output that is tuned by a rotary tuning element mounted on the axle of a motor. The rotary tuning element includes a variable thickness interference film for wavelength selection, and a variable thickness compensation prism to adjust the cavity length appropriately for the selected wavelength, to stable wavelengths and mode-hop-free tuning ranges as the tuning element is rotated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
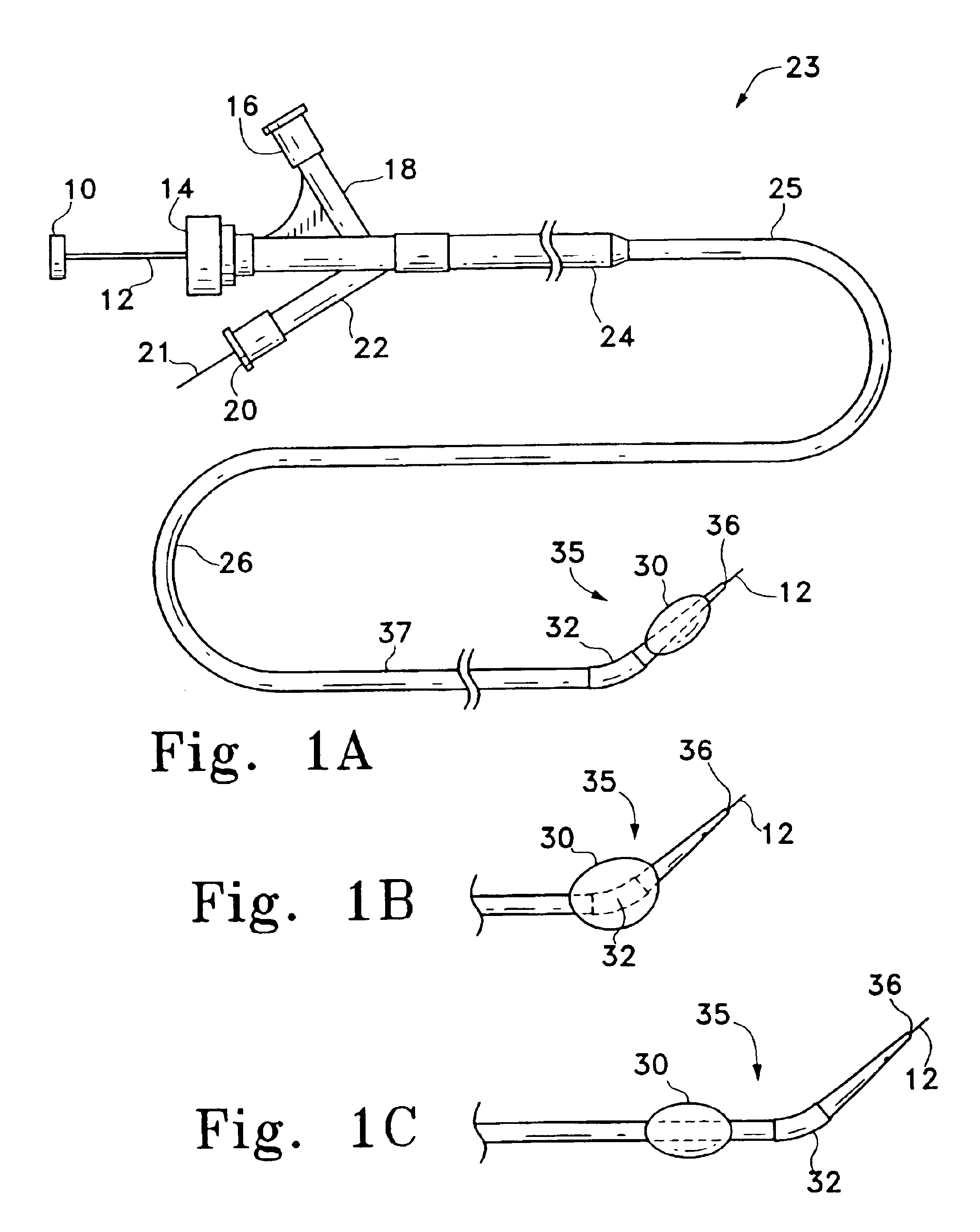
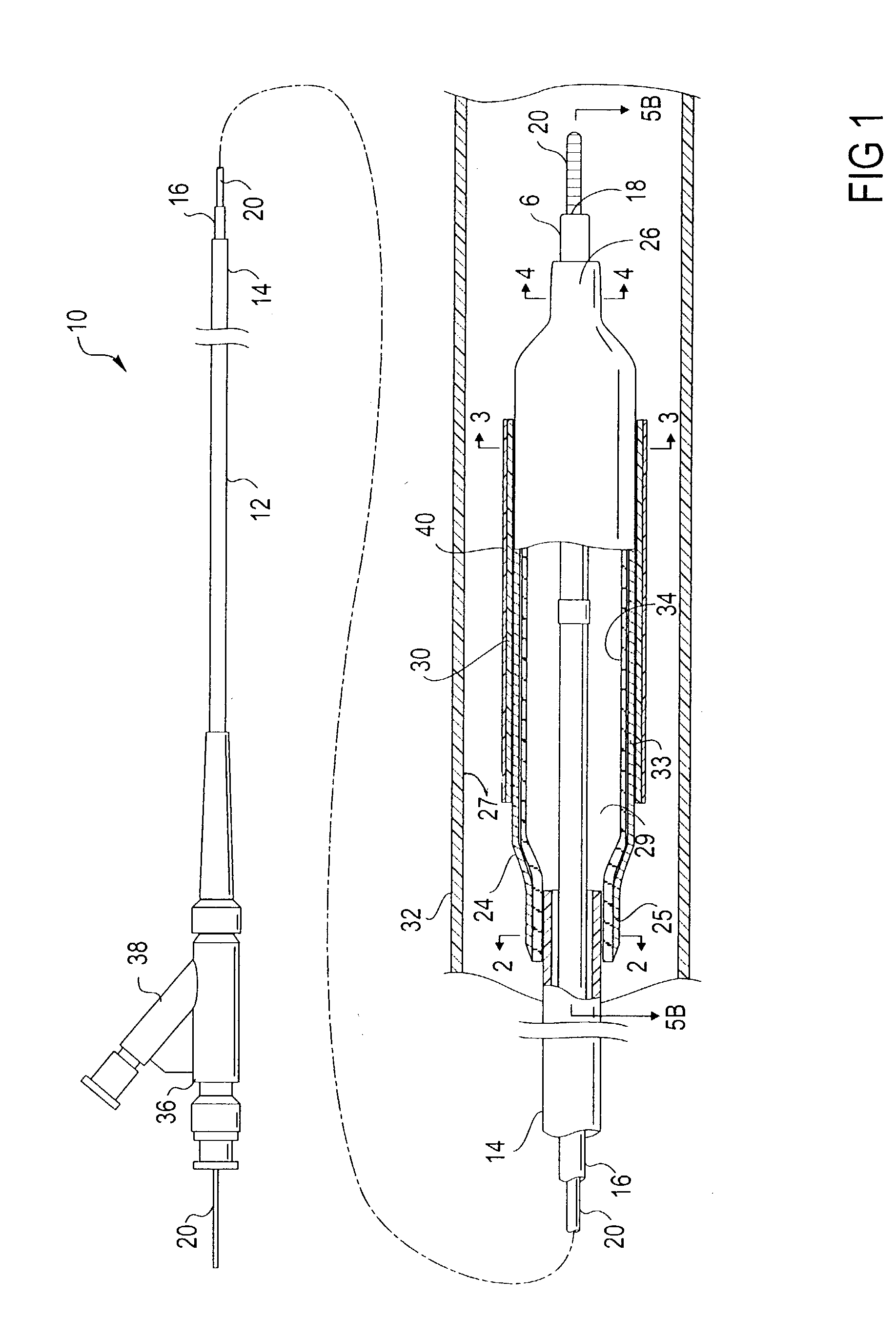
Manipulatable delivery catheter for occlusive devices (LL)
InactiveUS6976991B2Adjusting the flexibility of the joint regionReduce wall thicknessBalloon catheterMulti-lumen catheterVariable thicknessSurgical department
This is in the general field of surgical instruments and is specifically a delivery catheter with a flexible, proximally-manipulated hinge or joint region. The inventive catheter may have a balloon region. The catheter may have a shaft of varying flexibility which contains several lumen. The inner, or delivery, lumen generally may be used with a guidewire to access target sites within the body via the flexible, small diameter vessels of the body. The delivery lumen may be also used for placement of occlusive materials, e.g., in an aneurysm. Inflation of the micro-balloon, located near the distal tip of the catheter, is effected using the inflation lumen. The push / pull wire lumen contains a wire, which when manipulated, flexes the catheter's distal tip. The push / pull wire tubing may have a variable thickness to aid in adjusting the degree of flexibility. Moreover, the delivery catheter may be capable of twisting in a helical or corkscrew-like manner for traversing certain vasculature. This may be accomplished by winding the push / pull wire within the catheter and fixedly attaching it. The catheter may further include an entry in the catheter wall to allow for the insertion of a guidewire; this may facilitate the rapid exchange of catheter devices as desired by the user.
Owner:VASCULAR FX
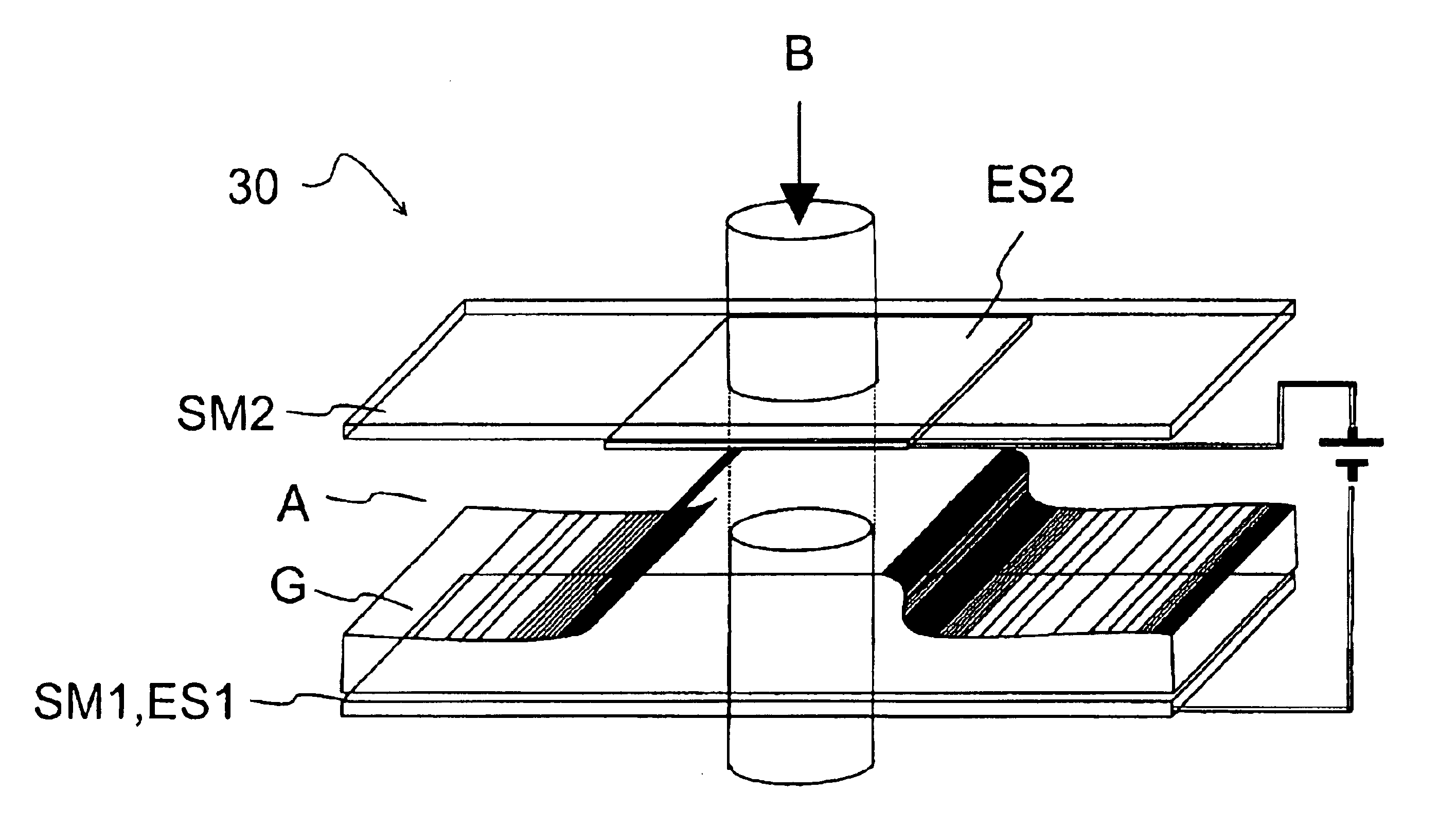
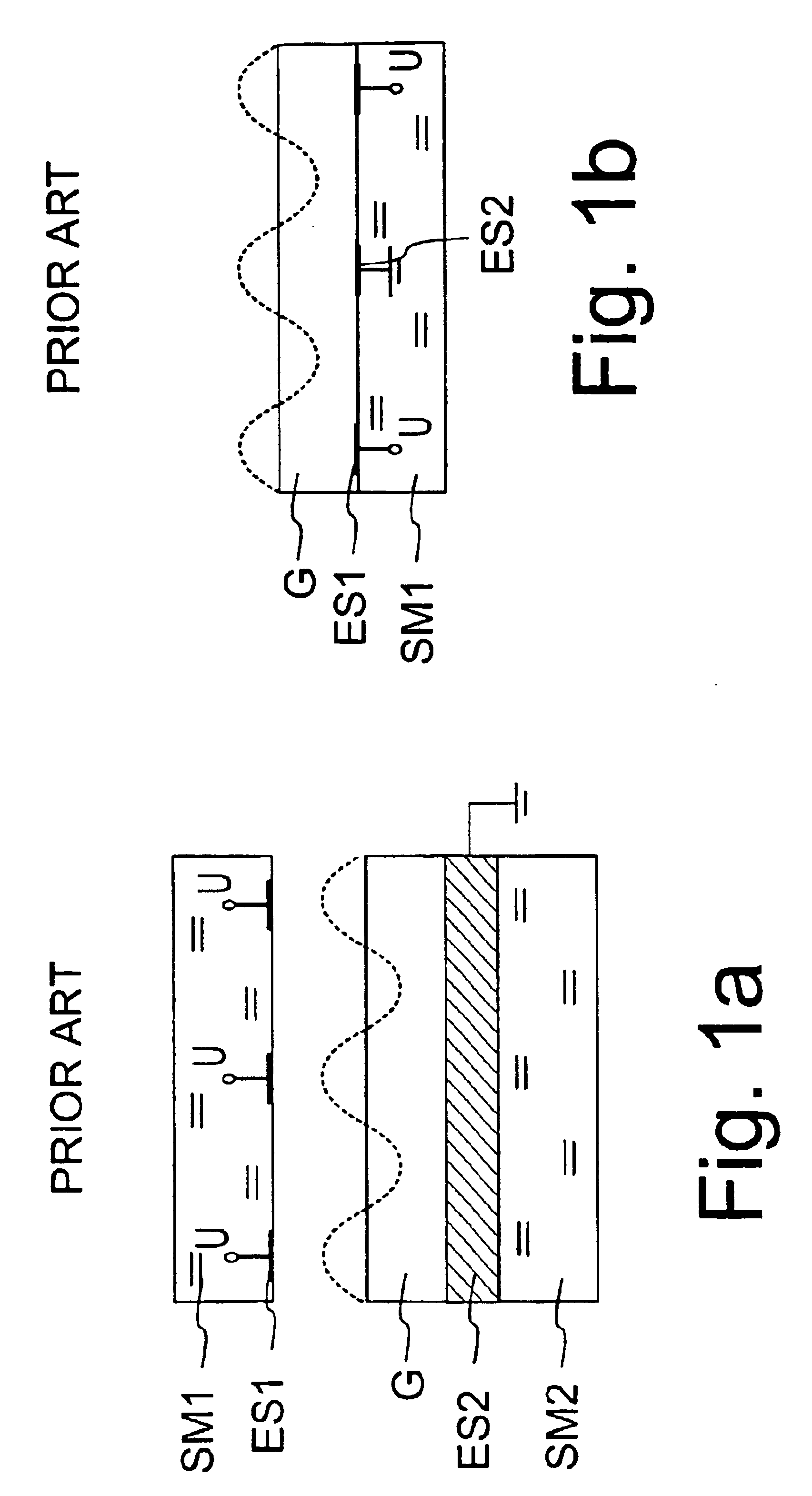
Electrically controlled variable thickness plate
InactiveUS6950227B2Easy and economical to manufactureNon-linear opticsOptical elementsElectricityVariable thickness
The invention refers to electrically controlled optical switching devices which are based on the use of a layer of dielectric and transparent viscoelastic material (G) located between transparent first (ES1) and transparent second (ES2) electrode structures. According to the invention, the first (ES1) and second (ES2) electrode structures are arranged in a manner that the thickness of the layer of the viscoelastic material (G) can be electrically altered maintaining the thickness of said layer substantially equal. This makes it possible to realize a generic, electrically controlled variable thickness plate (30). The generic variable thickness plate (30) can be further used to create optical switching devices based on a Fabry Perot Interferometer or a Mach-Zehnder Interferometer.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Golf club head with variable face thickness
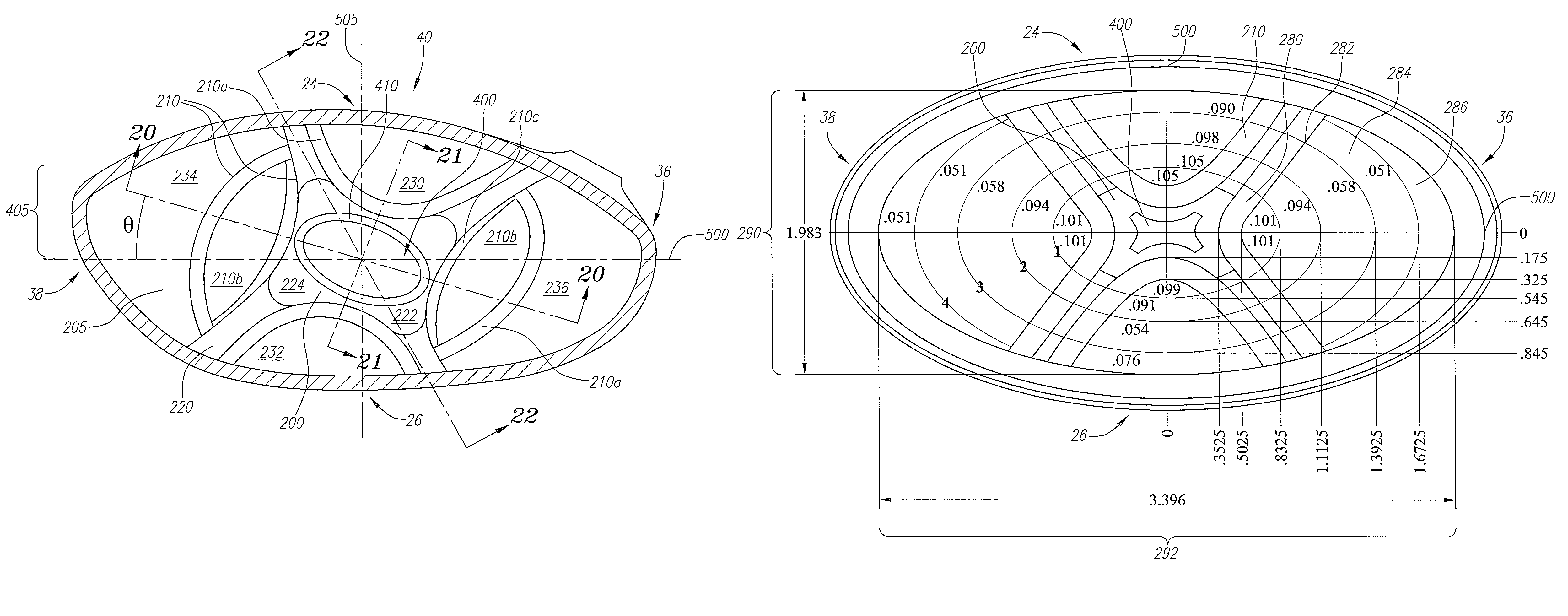
A face or face insert (40) for a golf club head (20) is disclosed herein. The face (40) has an interior surface (40b) with a first thickness section (200) and a second thickness region (205). The first thickness section (200) preferably has a thickness that is at least 0.025 inch greater than the thickness of the second thickness region (205). In a most preferred embodiment, the first thickness section (200) has an X shape that is rotated around the Y axis (500) by at least 10 degrees. In another preferred embodiment, the face has a first thickness section (200), a second thickness region (205), and a central region (400) having a third thickness. The face or face insert (40) with variable thickness allows for a face or face insert (40) with less mass in a golf club head (20) that conforms to the United States Golf Association regulations.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Laser-irradiated thin films having variable thickness
A crystalline film includes a first crystalline region having a first film thickness and a first crystalline grain structure; and a second crystalline region having a second film thickness and a second crystalline grain structure. The first film thickness is greater than the second film thickness and the first and second film thicknesses are selected to provide a crystalline region having the degree and orientation of crystallization that is desired for a device component.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
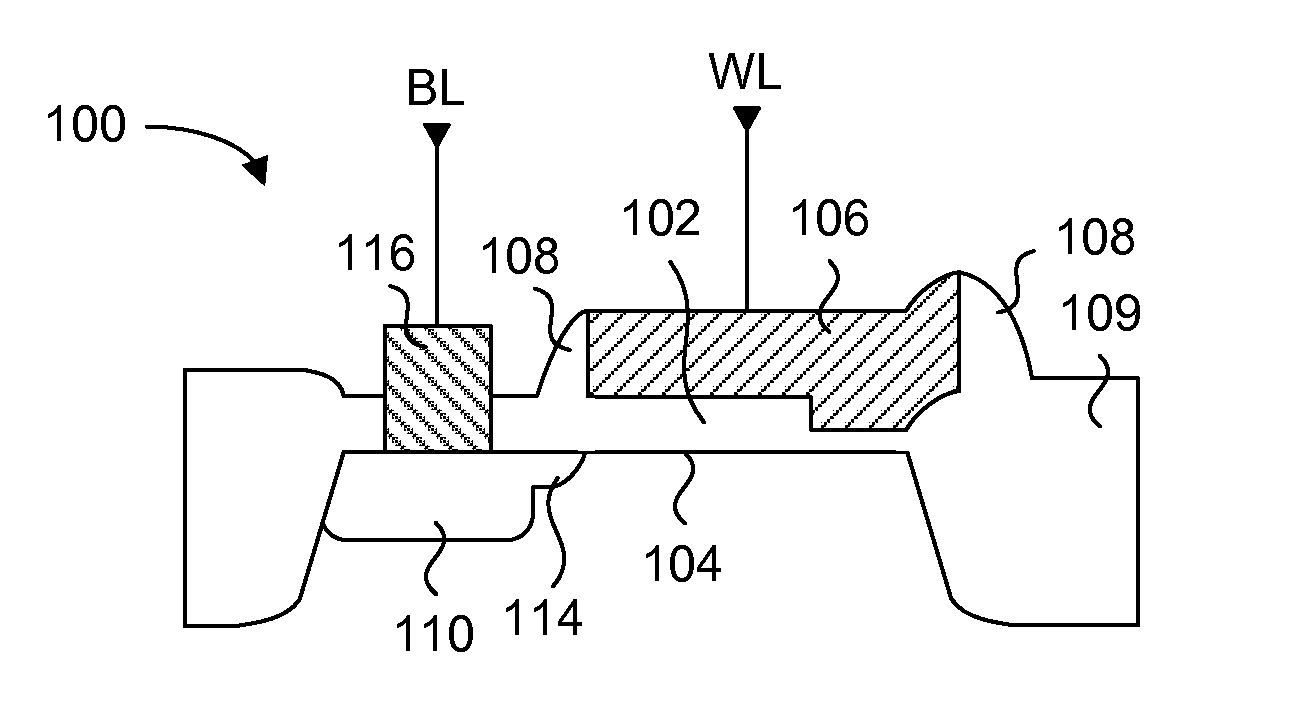
Anti-fuse memory cell
ActiveUS20070257331A1Simple and reliable processHigh densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVariable thicknessCondensed matter physics
An anti-fuse memory cell having a variable thickness gate oxide. The variable thickness gate oxide has a thick gate oxide portion and a thin gate oxide portion, where the thing gate oxide portion has at least one dimension less than a minimum feature size of a process technology. The thin gate oxide can be rectangular in shape or triangular in shape. The anti-fuse transistor can be used in a two-transistor memory cell having an access transistor with a gate oxide substantially identical in thickness to the thick gate oxide of the variable thickness gate oxide of the anti-fuse transistor.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Stent with variable properties
InactiveUS7226475B2Increase flexibilityExcellent fluoroscopic property propertyStentsMedical devicesVariable thicknessMedicine
A stent having variable thickness with improved radiopacity, MRI compatibility, radial stiffness, and flexibility and to the method of making such stents.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
High contrast surface marking using irradiation of electrostatically applied marking materials
InactiveUS6852948B1Quick tagSpeed up the processRecording apparatusRadiation applicationsVariable thicknessMaterials science
A method of radiantly marking substrates including metals, plastics, ceramic materials, glazes, glass ceramics, and glasses of any desired form, which comprises electrostatically applying to the material to be marked a variable thickness layer of marking material containing energy absorbing components and / or enhancers, then irradiating said layer with a radiant energy source such as a laser or diode based energy source such that the radiation is directed onto said layer, optionally in accordance with the form of the marking to be applied, preferably using a laser or diode based energy source of a wavelength which is sufficiently absorbed by the marking material so as to create a bonding of the marking material to the surface of the workpiece at the irradiated areas.
Owner:THERMAX LLC
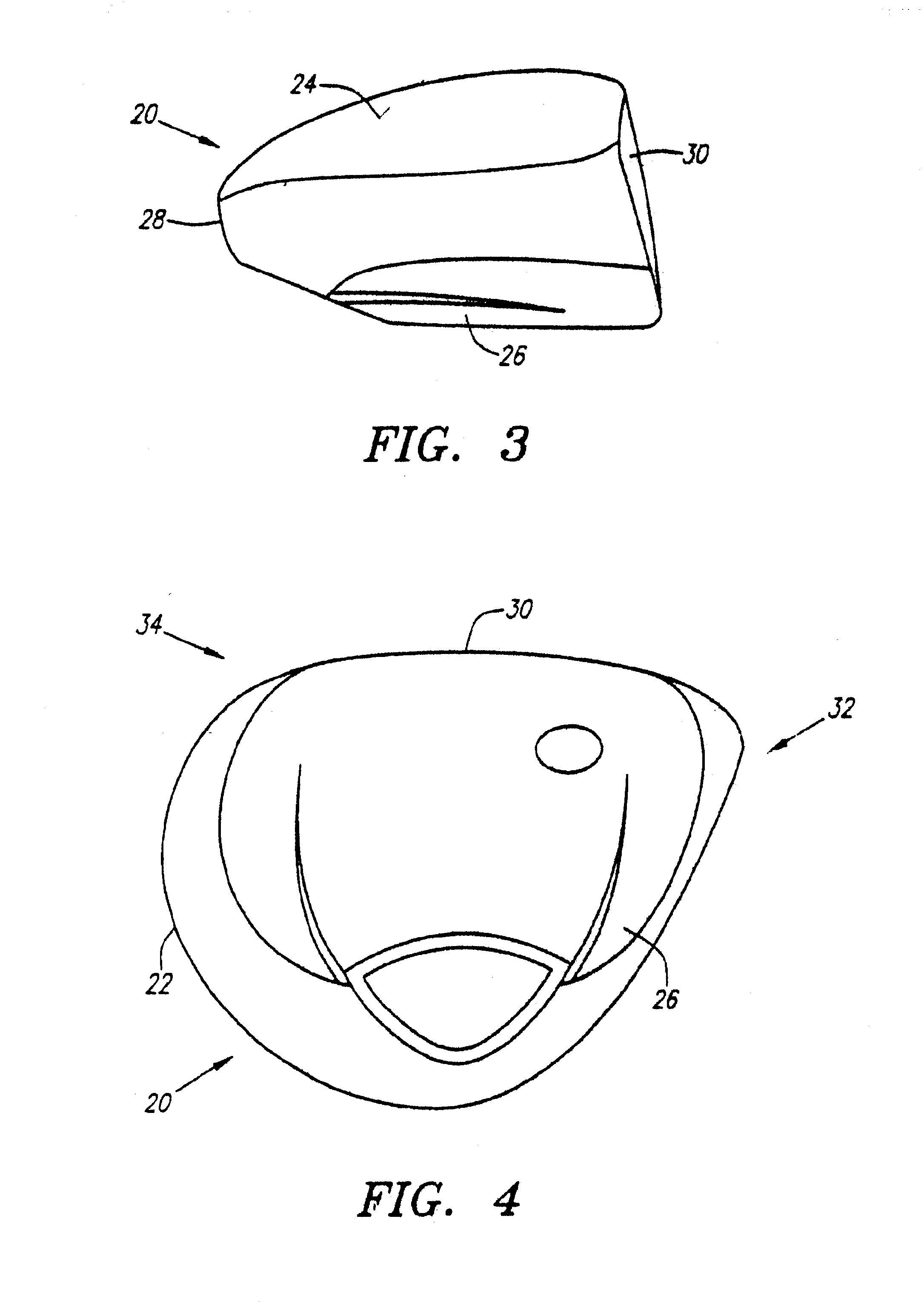
Fairway wood with titanium face member
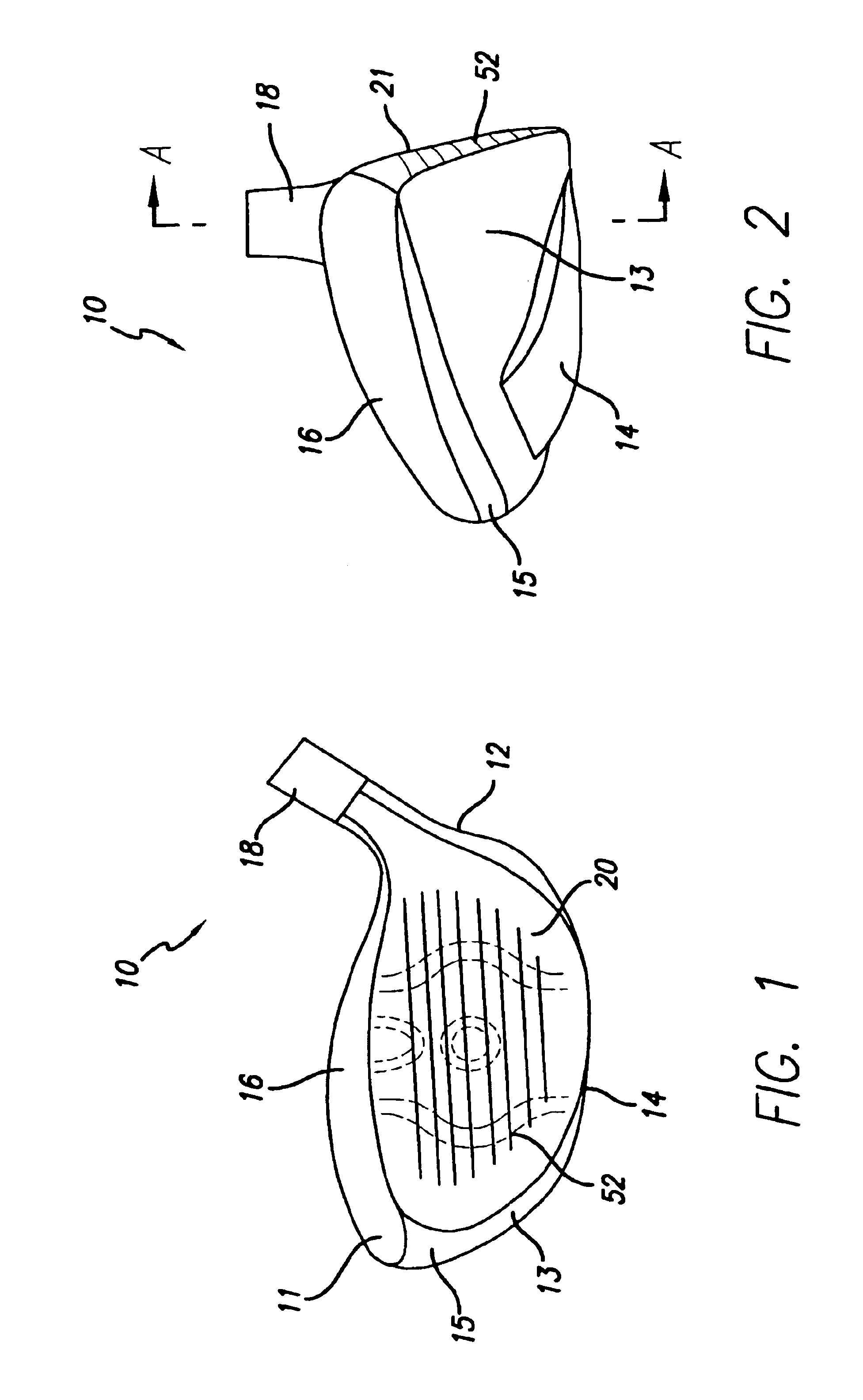
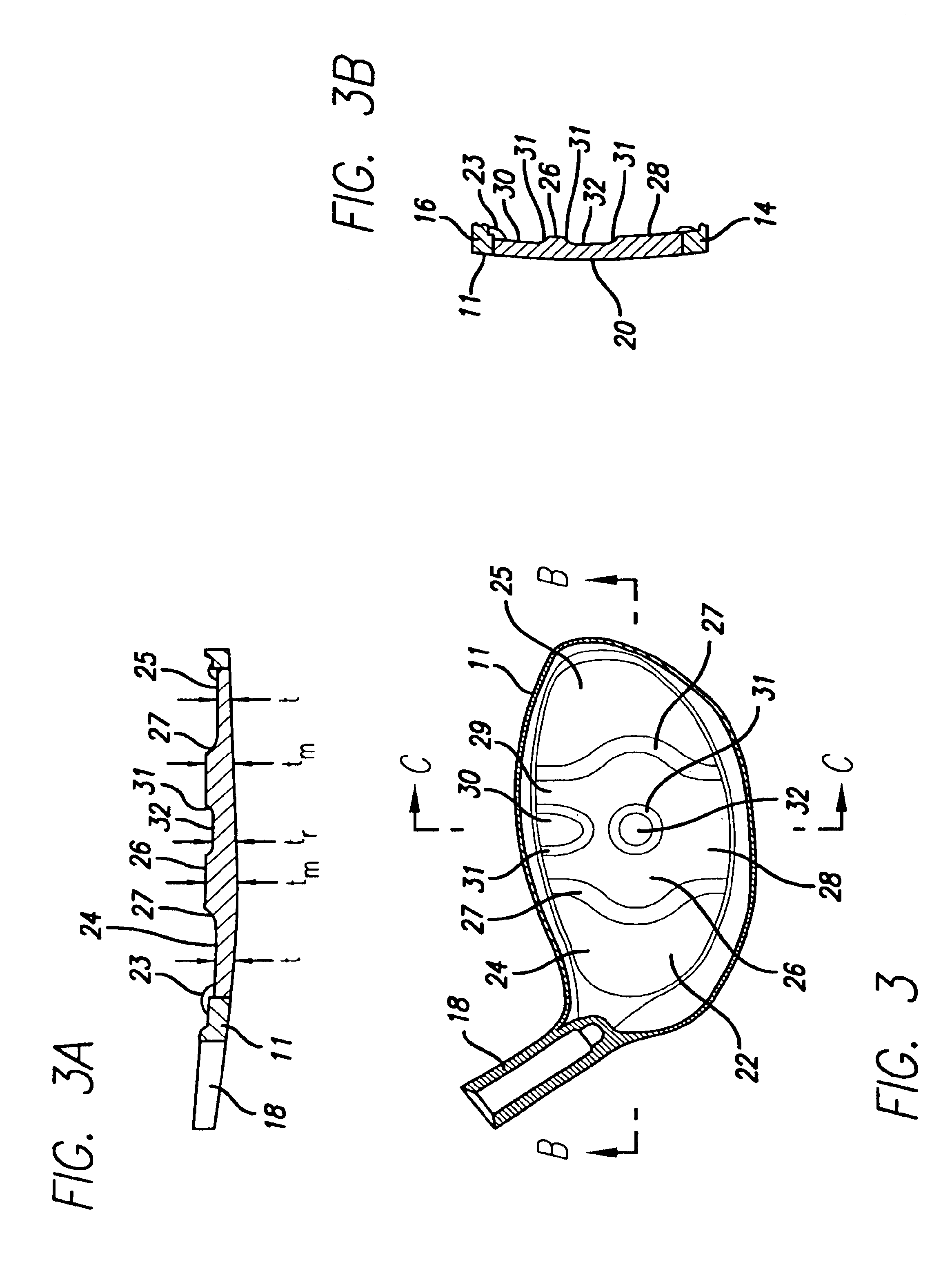
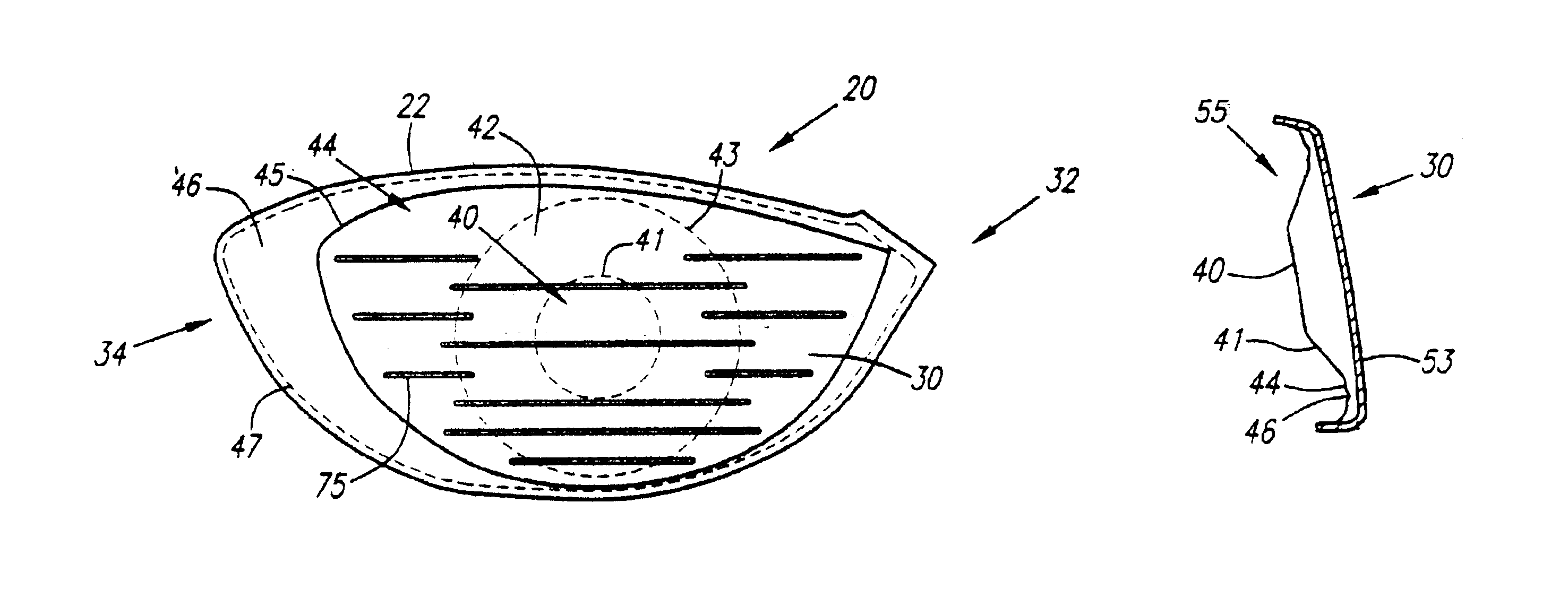
A fairway wood head comprises a stainless steel body and a cup-shaped titanium alloy face member attached by silver-nickel brazing to the body. The face member is preferably of variable thickness, being thicker at it's center than at it's outer periphery. Weights are attached at the toe and heel, respectively, of the body, to resist twisting of the head during an off-center hit. Weights are attached in the sole of the body on opposite sides of a front-to-rear center line of the head to lower the center of gravity of the head. The head has a hosel which includes a stainless steel inner portion and a titanium alloy outer sleeve portion disposed around and attached to the inner portion.
Owner:MACGREGOR GOLF
Joint support and subchondral support system
InactiveUS20100145451A1Increasing the thicknessImprove abilitiesSurgeryLigamentsVariable thicknessSupporting system
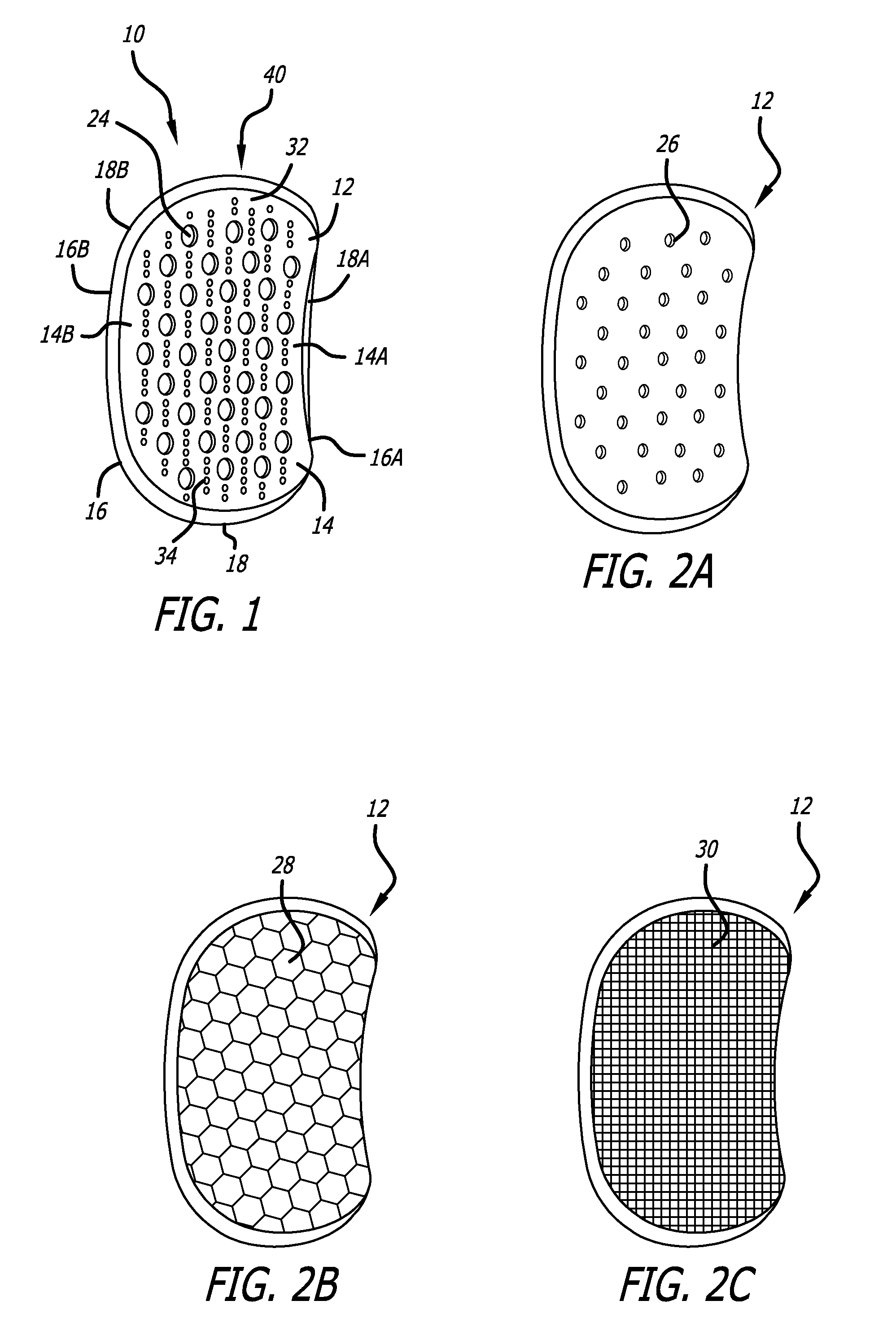
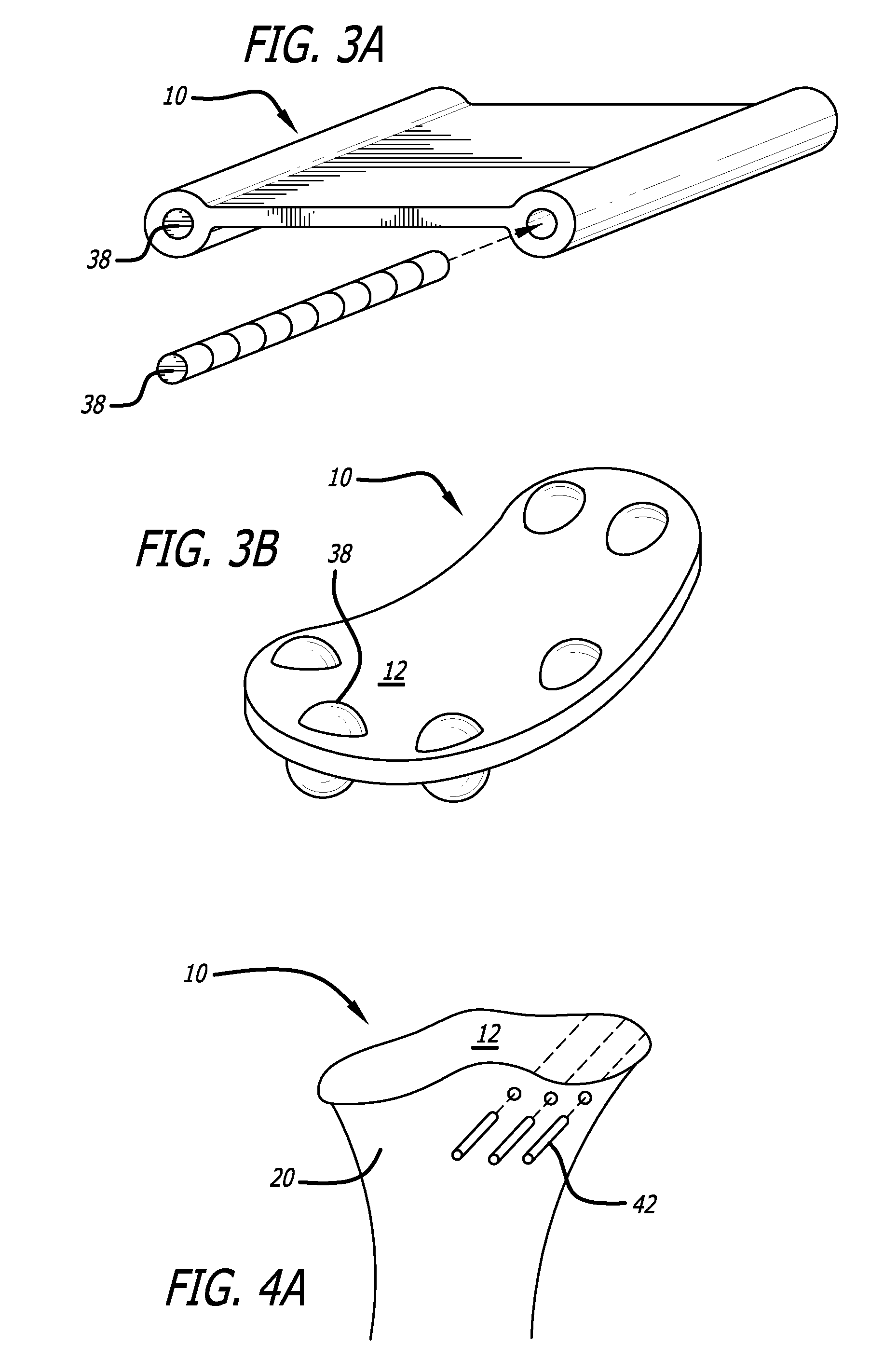
A joint support and subchondral support system for providing structural and dampening support to damaged subchondral bone in generalized or discrete arthritis includes a contoured, porous plate having a variable shaped inner surface, outer surface, and peripheral surface of variable thickness extending between the inner surface and the outer surface, suitable for insertion within the subchondral bone. The inner surface, outer surface and peripheral surface each have a concave portion and a convex portion. A guide pin hole or slot is located within the contoured, porous plate to aid in insertion and placement of the plate over at least one corresponding guide pin within the subchondral bone. The joint support and subchondral support system of the present invention is applicable to many parts of the joint as any area with cartilage disease has an adjoining subchondral component.
Owner:DEE DEREK
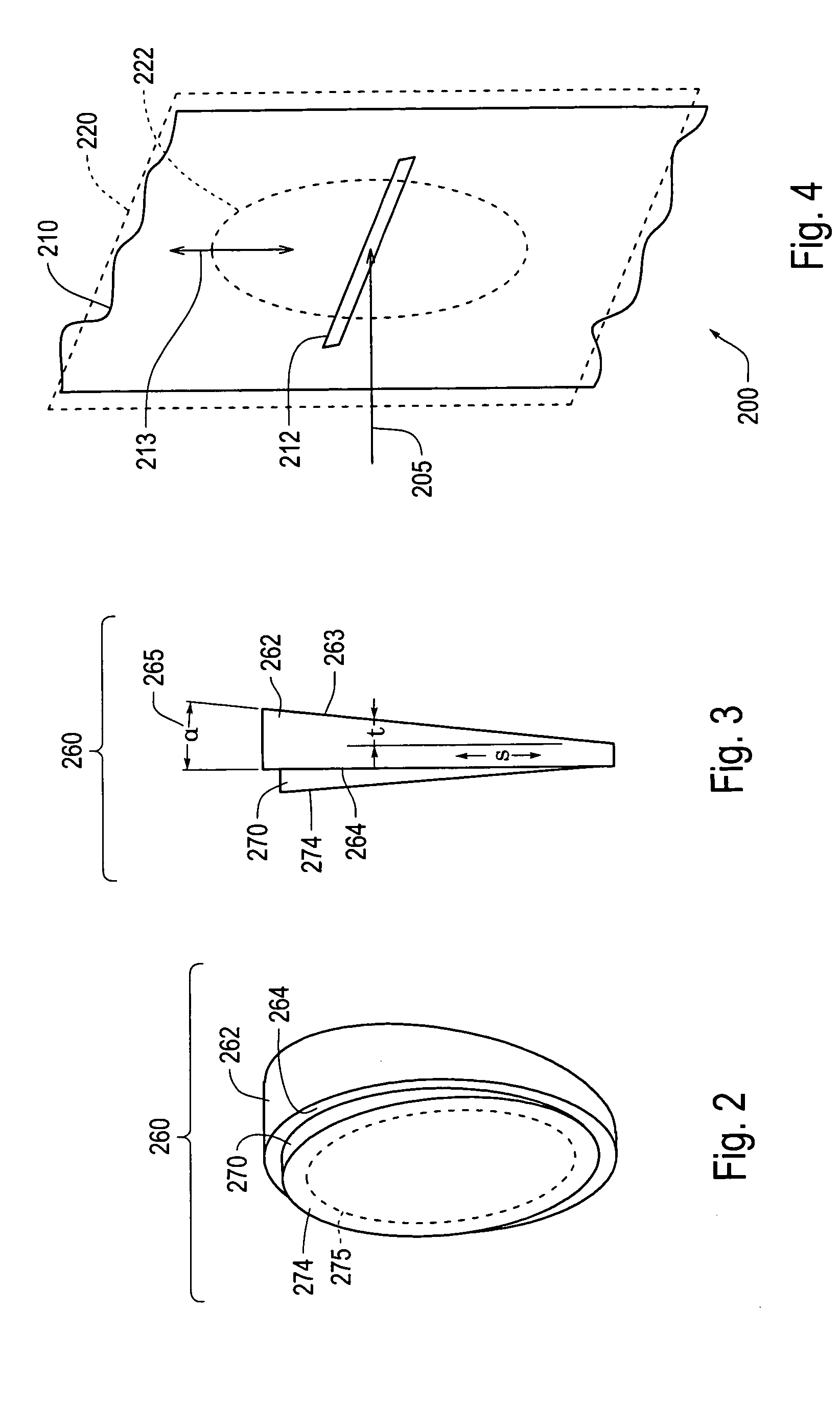
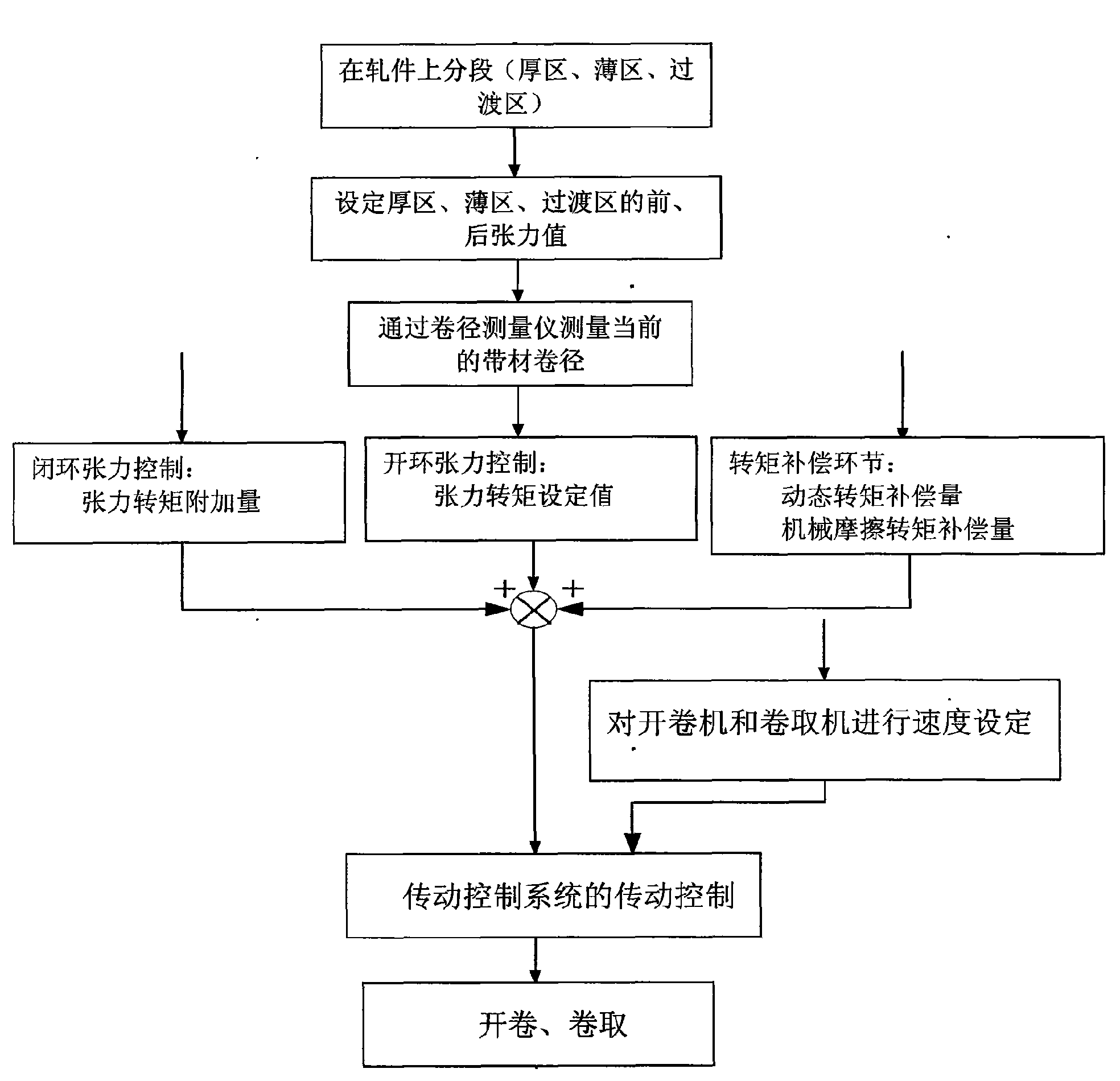
Periodic longitudinal variable-thickness strip and longitudinal variable-thickness plate and preparation method thereof
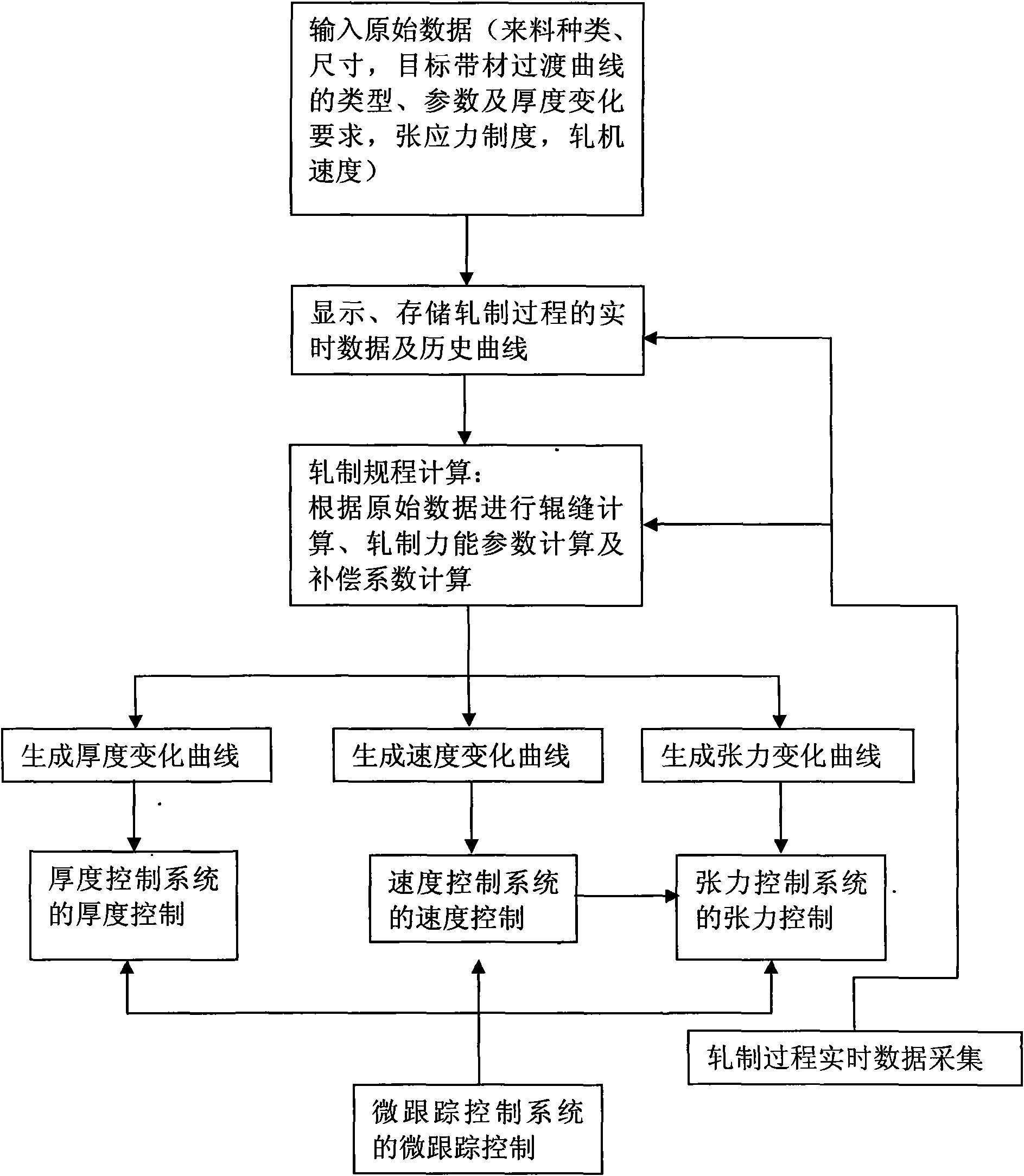
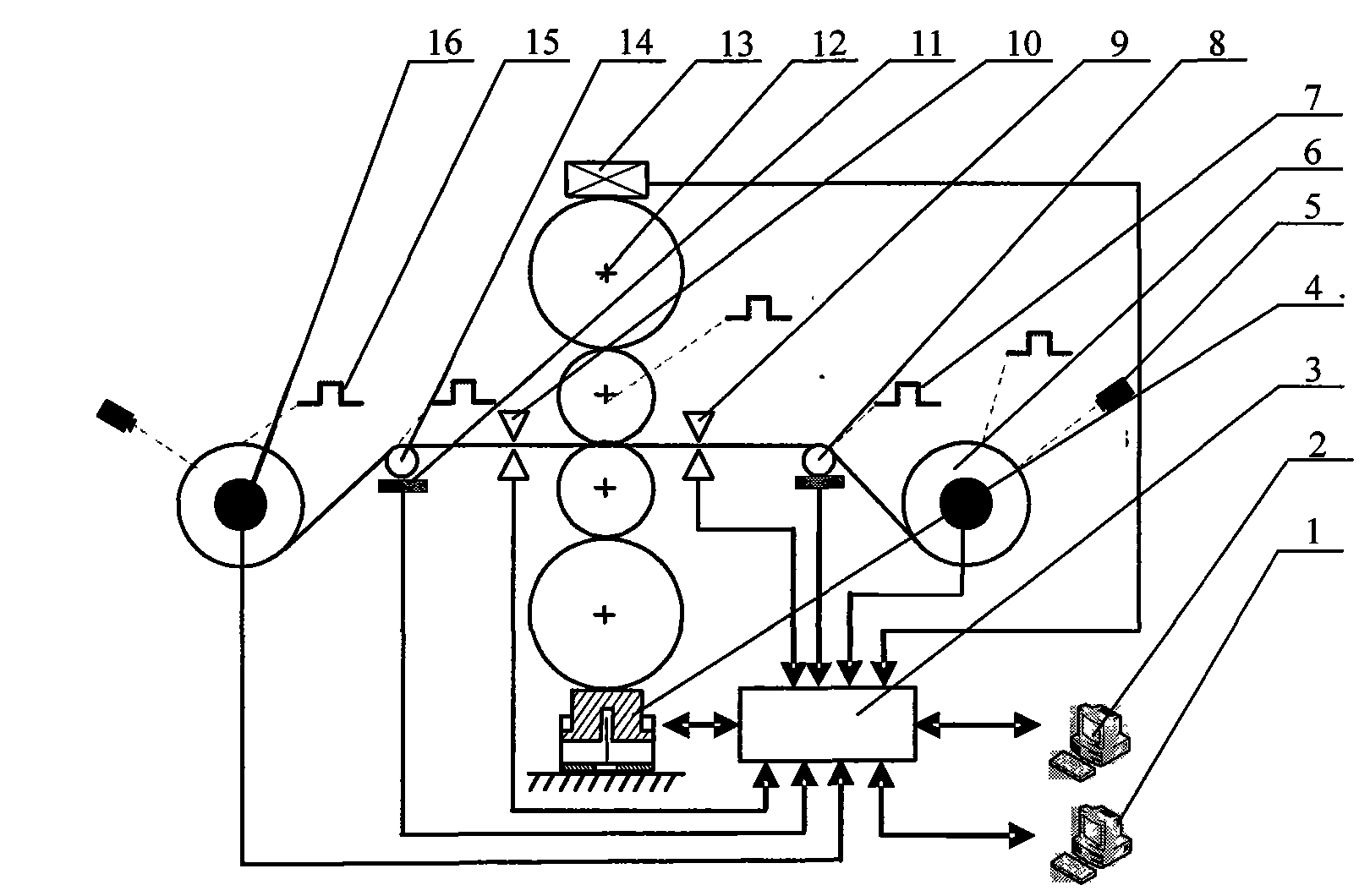
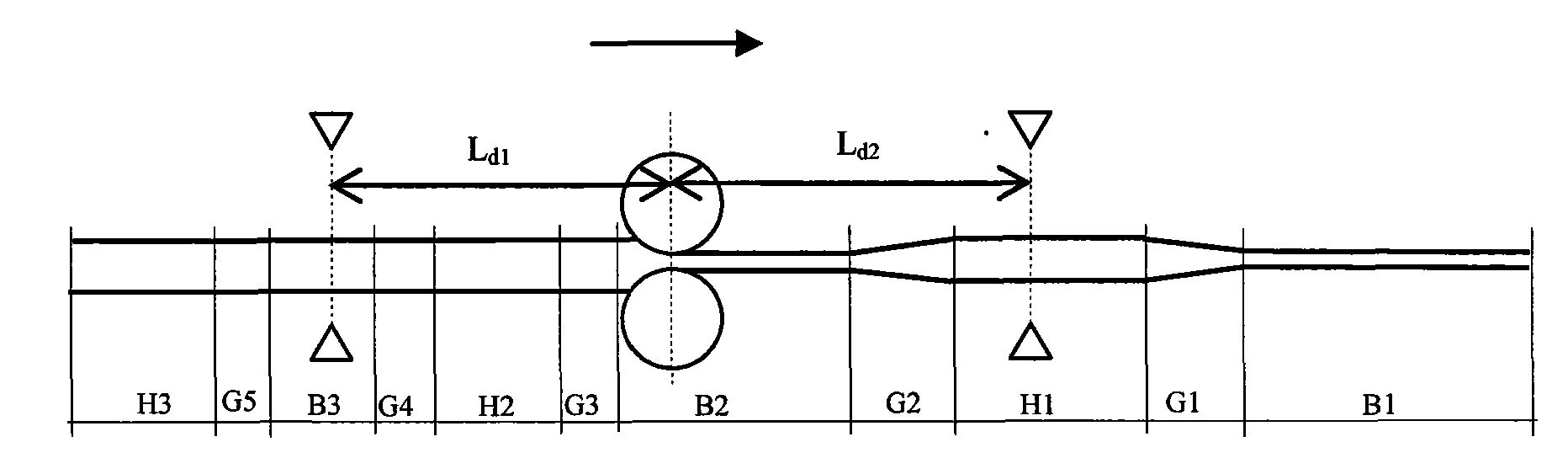
ActiveCN101607264AReduce welding processReduce manufacturing costProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersMetal rolling arrangementsComputer control systemVariable thickness
The invention belongs to the rolling technical field. The thickness of a periodic longitudinal variable-thickness strip changes periodically, the periodic longitudinal variable-thickness strip has more than two kinds of thicknesses regions and transition regions within a change period, and is formed by rolling. The control procedure of the periodic longitudinal variable-thickness strip comprises the following steps: inputting original data; displaying and storing real-time data and a history curve; computing the rolling procedure; generating a change curve; tracking the position of a rolling piece; and controlling the thickness, the speed and the tension. A device comprises a rolling mill, a reeling machine and a thickness measurer which are arranged at two sides of the rolling mill, and a length measuring roll arranged between the reeling machine and the rolling mill, wherein a reel diameter measurer is arranged on the reeling machine; a rolling force sensor and a hydraulic cylinder are arranged on the rolling machine; a pulse coder and a tension meter are respectively arranged on and below the length measuring roll; and the thickness measurer and the like are connected with a computer control system. A longitudinal variable-thickness plate has two or more kinds of different thickness regions, transition regions are arranged among the thickness regions, and the plate is formed by the strip through the steps of annealing, unreeling by an unreeler, leveling by a leveler, and cutting by a cutting machine.
Owner:SHENYANG DONGBAO HAIXING METAL MATERIAL TECH
Passive magnetic radome
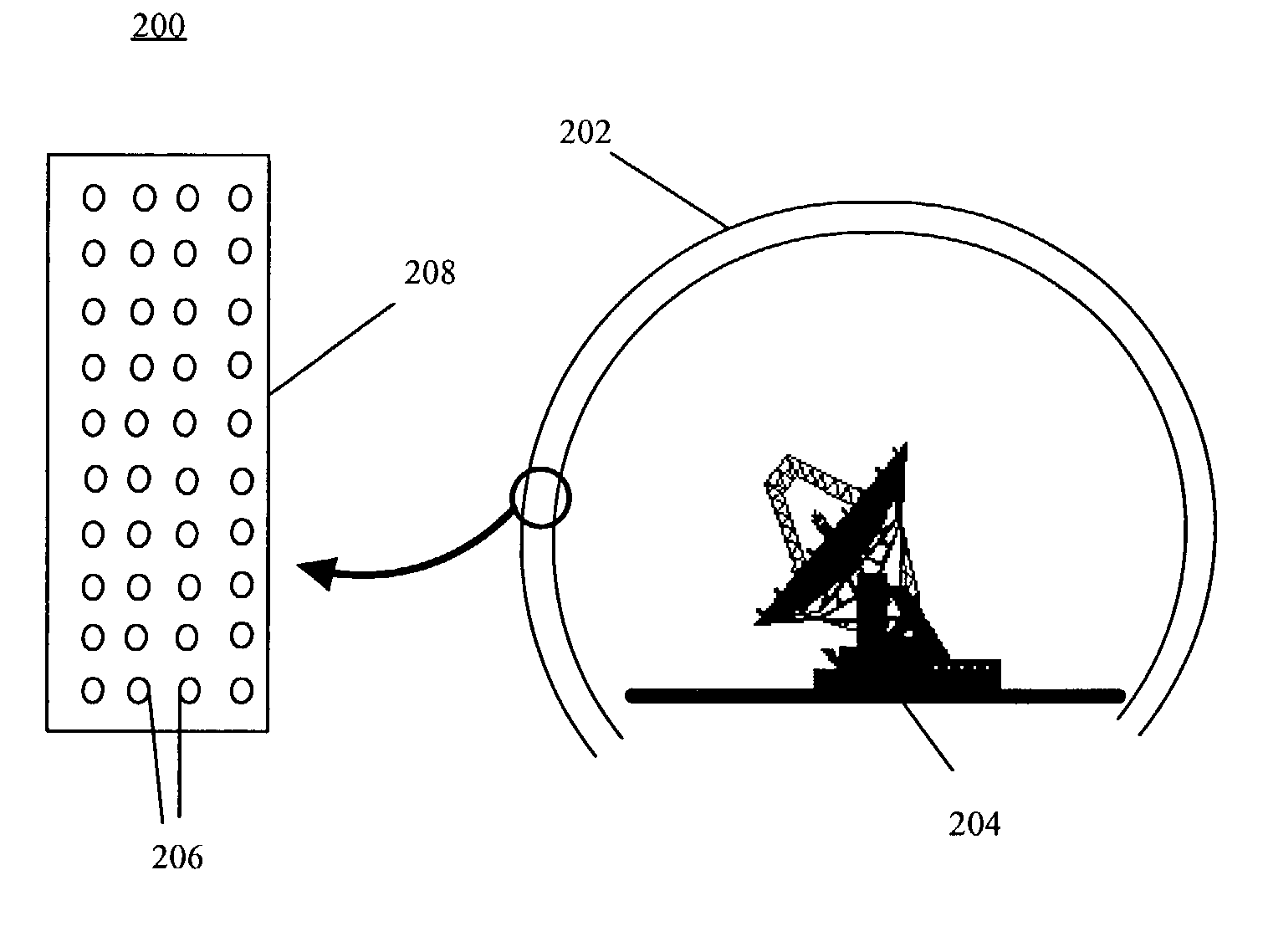
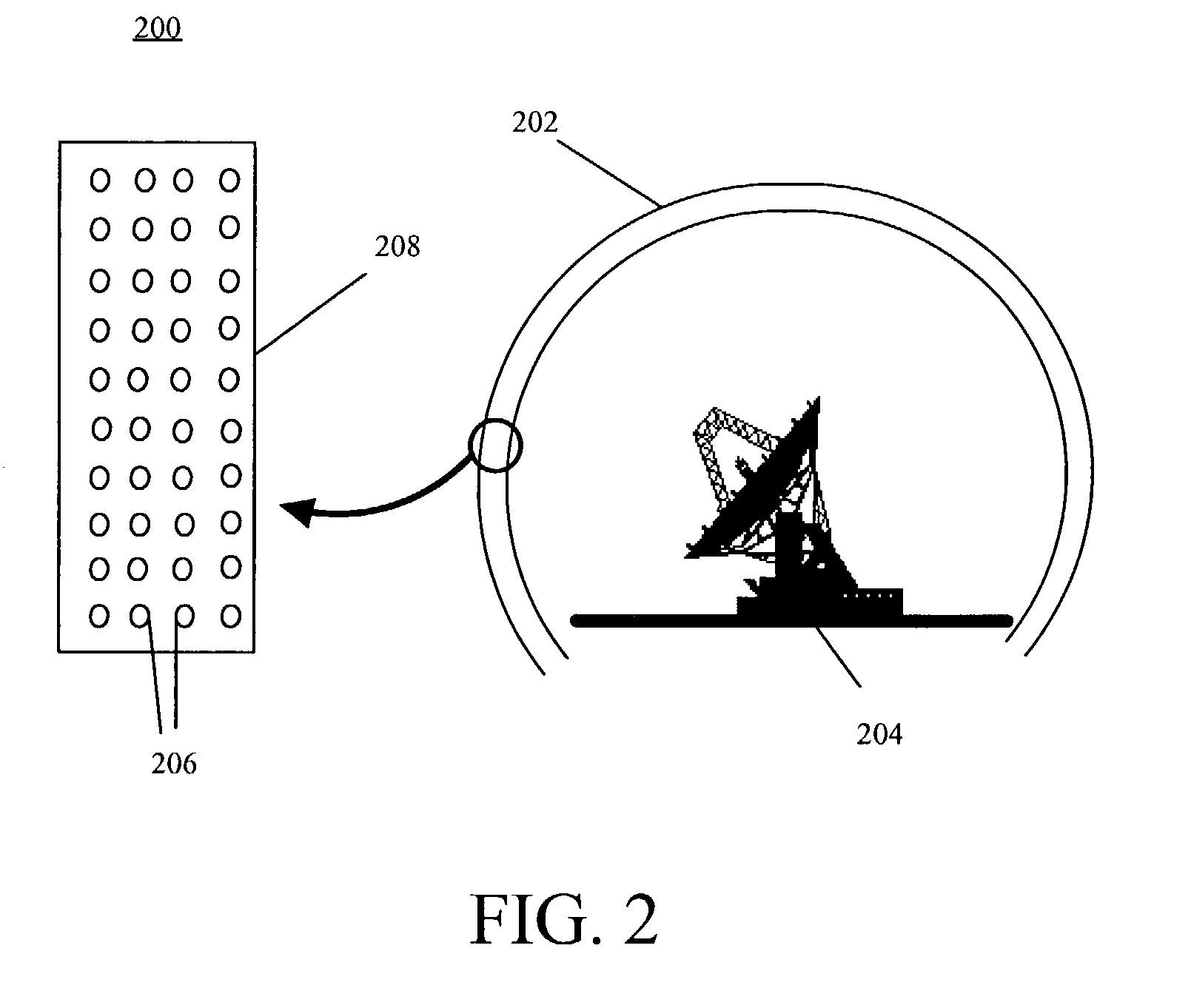
InactiveUS7006052B2Minimize reflectionProtective material radiating elementsRadiating element housingsVariable thicknessDielectric
A radome (202) includes a dome wall (208) formed from a dielectric material wherein at least a portion of the dielectric material includes a plurality of magnetic particles (206). Radomes according to the invention can form dome walls of variable thickness, yet still have high radiation efficiency across a wide frequency band. Magnetic radomes utilize dielectrics including magnetic particles (206) to match the impedances between medium boundaries, such as an air to dome boundary.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Golf club striking plate with variable thickness
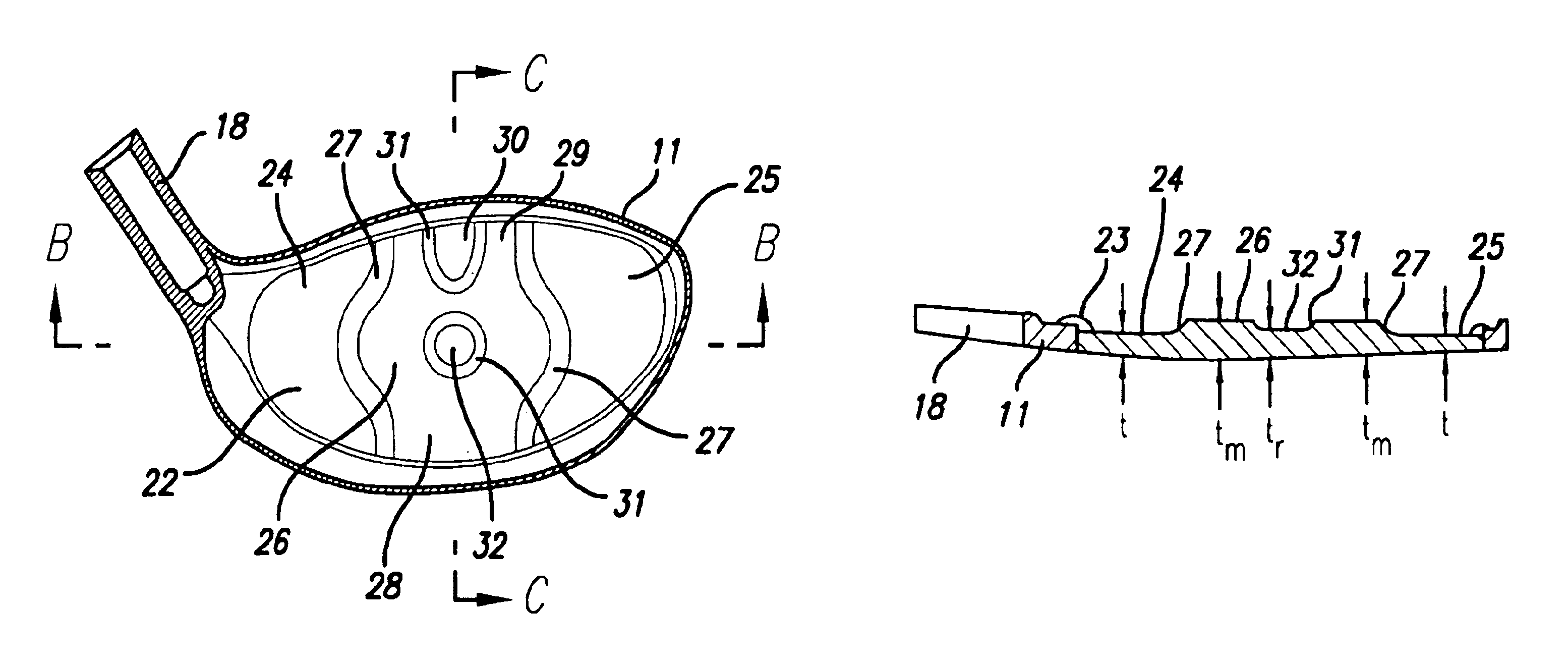
InactiveUS7014570B2Reduce thicknessReduce weightMetal-working apparatusGolf clubsVariable thicknessTitanium
A golf club head having a striking plate with regions of varying thickness is disclosed herein. A central region has a first thickness range that is thicker than the thickness range of any of the other regions. The thickness of the regions decreases outward from the center. The striking plate may be used on a fairway wood-type golf club head or a driver-type golf club head. The striking plate is preferably composed of steel or titanium.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
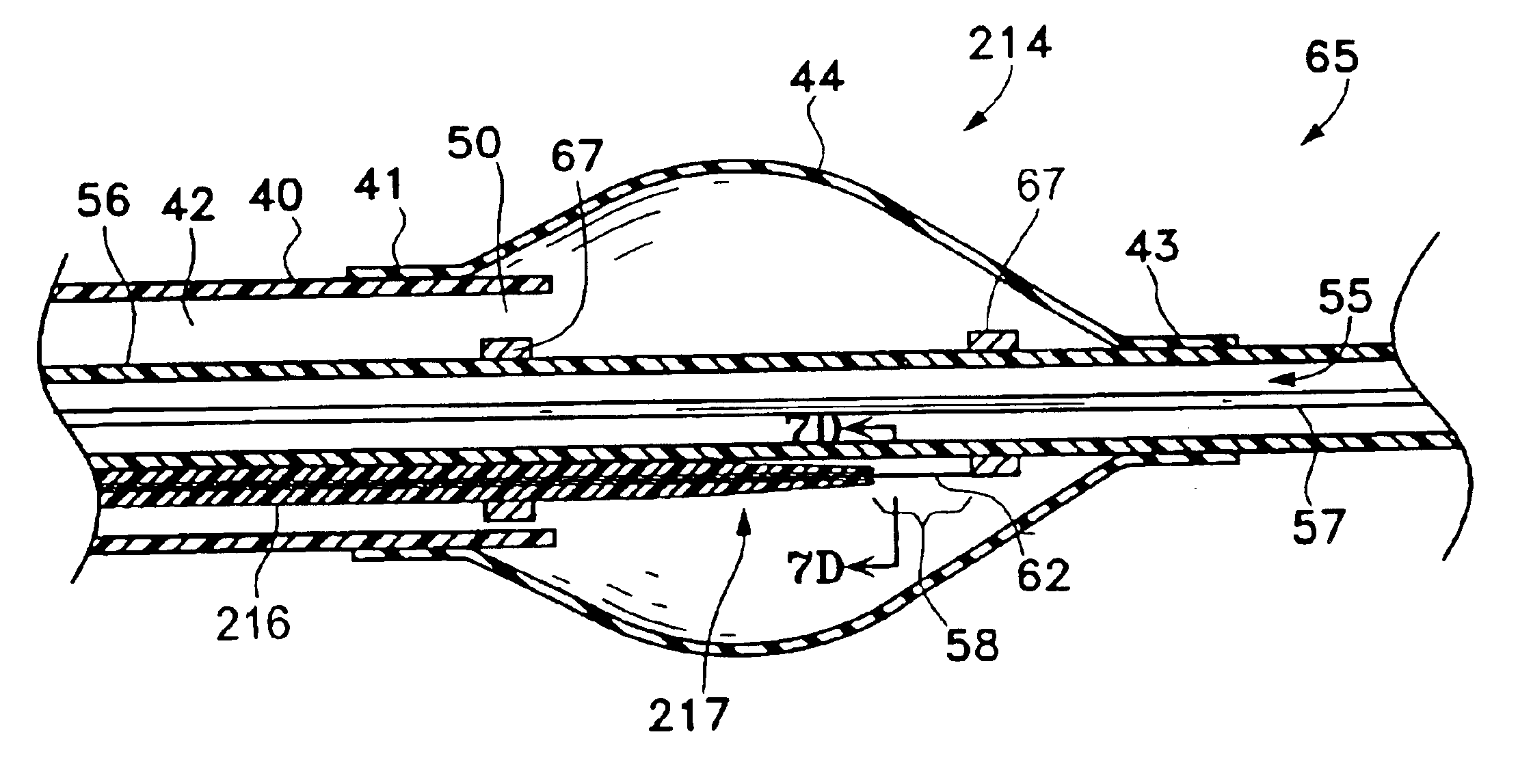
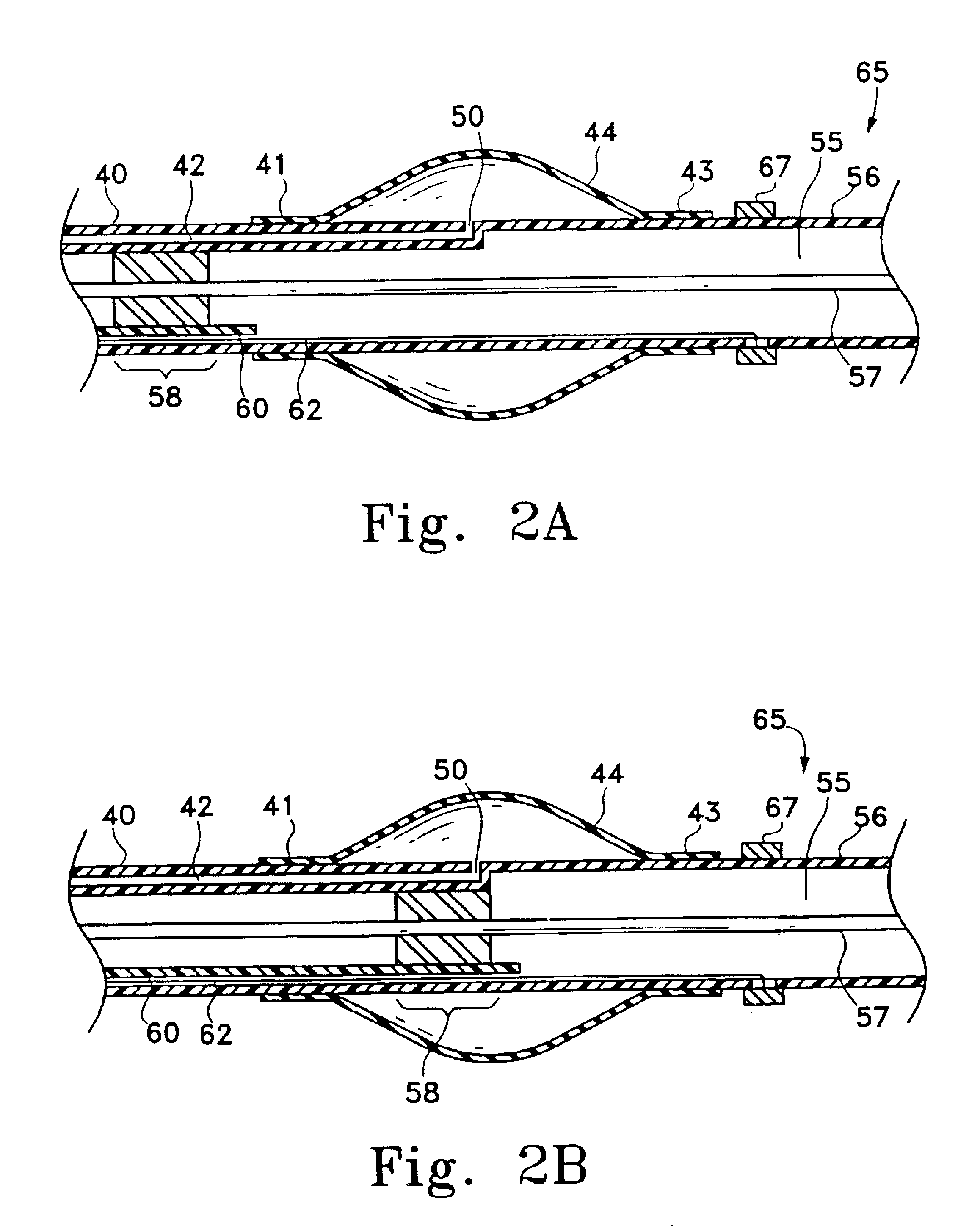
Catheter balloon liner with variable thickness and method for making same
InactiveUS7175607B2Improved high rupture pressureIncrease inner diameterBalloon catheterSurgeryVariable thicknessBalloon catheter
A method of making a catheter balloon, and a balloon catheter formed thereby, in which a layer of a catheter balloon is formed by providing a tubular member to serve as a non porous liner for cooperation with a polymeric tube, and enlarging radially a central or working section of the tubular member such that a first end of the tubular member is smaller in the radial direction with respect to the working section. The tubular member may also have a thickness at the working section that is less than a thickness of the first and second end portions. The first end section of the tubular member is bonded to a catheter shaft having a first outer diameter to form at least a portion of a skirt section of the balloon, and the second end section is bonded to the catheter shaft having a second outer diameter to form a portion of a skirt section, where the skirt sections have an improved high rupture pressure.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Golf club striking plate with vibration attenuation
A golf club head (20) having a striking plate (30) and means for vibration attenuation (35) disposed thereon. The vibration attenuation means (35) may be composed of a low-density. metallic, a polymer material, or a filled polymer material. The striking plate (30) may have a uniform thickness or a variable thickness. The overall thickness of the striking plate (30) and vibration attenuation means (35) is preferably in the range of 0.100 inch to 0.250 inch. The striking plate (30) is preferably composed of steel or titanium.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Control method and control system of tension in the process of rolling periodic variable-thickness strips
InactiveCN101602068AHigh precisionTension/compression control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsVariable thicknessMaximum torque
A control method and a control system of tension in the process of rolling periodic variable-thickness strips belong to the technical field of rolling. The method comprises the following steps: dividing segments on the rolled pieces, setting front and back tension values in each zone, realizing tension open-loop control and tension closed-loop control based on maximum torque limit and adding a dynamic torque compensation link and a mechanical friction torque compensation link; controlling torques of an uncoiler and a coiling machine motor and setting speed. The system comprises a rolling mill; coiling machines are arranged at both sides of the rolling mill respectively; length-measuring rollers are arranged between the coiling machines and the rolling mill; thickness gauges are arranged at both sides of the rolling mill respectively; coil diameter gauges are arranged on the coiling machines; a rolling force sensor and a hydraulic cylinder are arranged on the rolling mill; tensiometers are arranged below the length-measuring rollers and pulse coders are arranged on the length-measuring rollers; the thickness gauge, the coil diameter gauge, the rolling force sensor, a displacement sensor of the hydraulic cylinder, the tensiometer and the pulse coder are respectively connected with a computer control system.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Golf club head with composite weight port
ActiveUS8753226B2Excellent characteristicsIncrease gravityGolf clubsRacket sportsVariable thicknessEngineering
A golf club head having a face component, a crown, and a composite sole or a composite body patch with one or more weight ports for receiving one or more weight inserts is disclosed herein. At least part of each of the weight ports is integrally formed in the composite sole or composite body patch, and each of the weight ports includes an upper edge, a lower edge, and a wall having a variable thickness and varying radius.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Golf club striking plate with variable thickness
InactiveUS6863626B2Reduce thicknessReduce weightMetal-working apparatusGolf clubsVariable thicknessTitanium
A golf club having a striking plate with regions of varying thickness is disclosed herein. A central region has a first thickness range that is thicker than the thickness range of any of the other regions. The thickness of the regions decreases outward from the center. The striking plate may be used on a fairway wood-type golf club head or a driver-type golf club head. The striking plate is preferably composed of steel or titanium.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
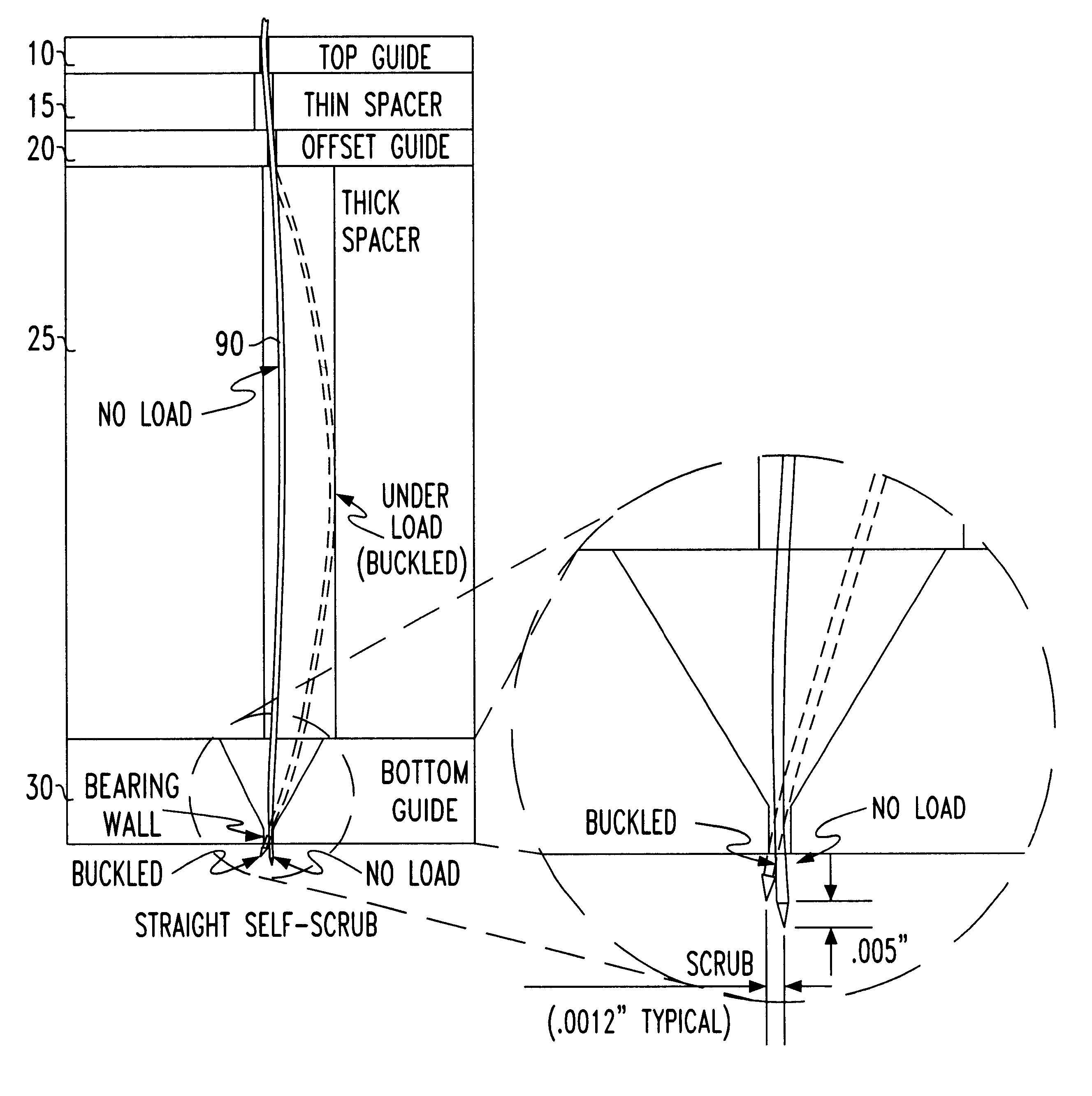
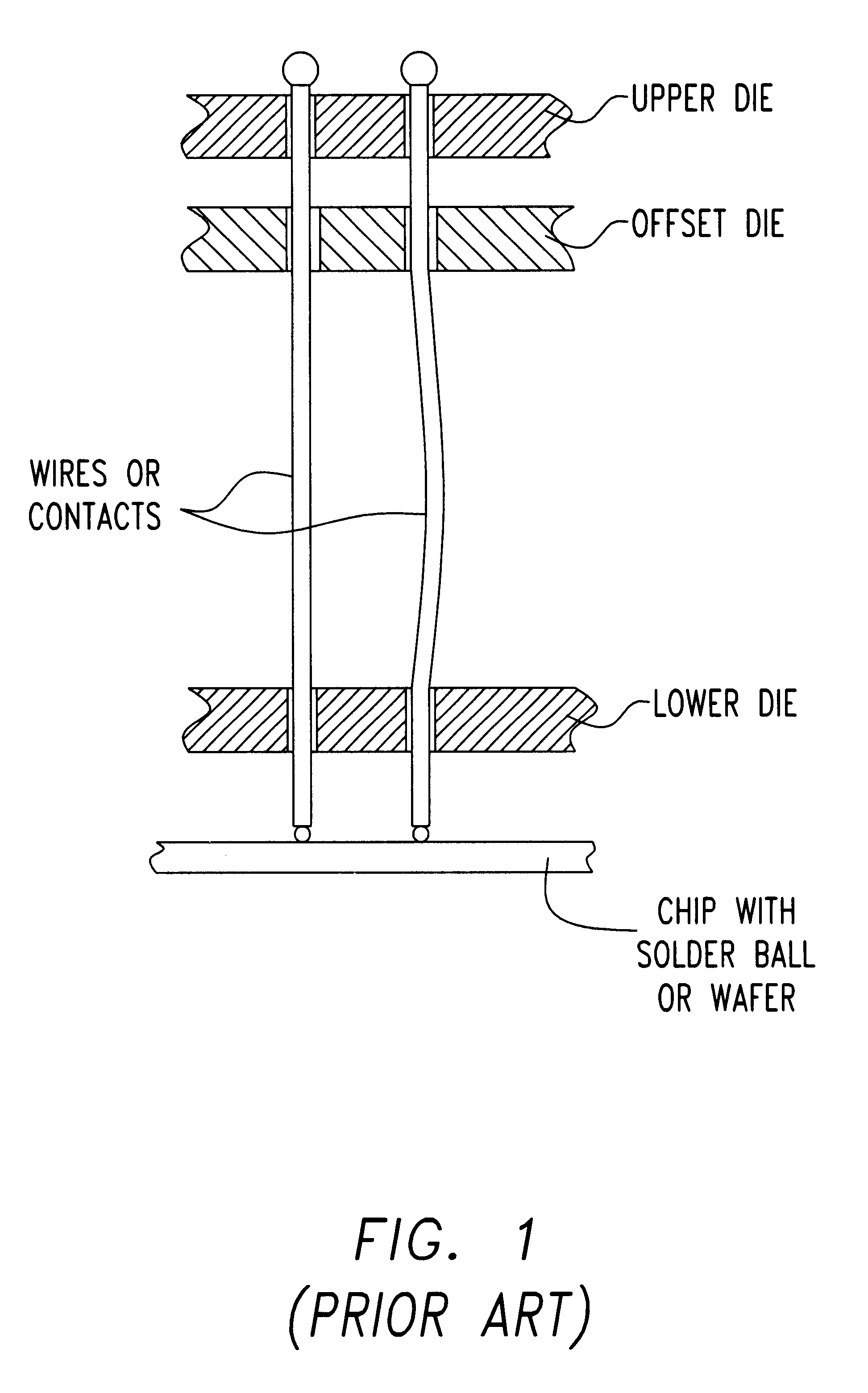
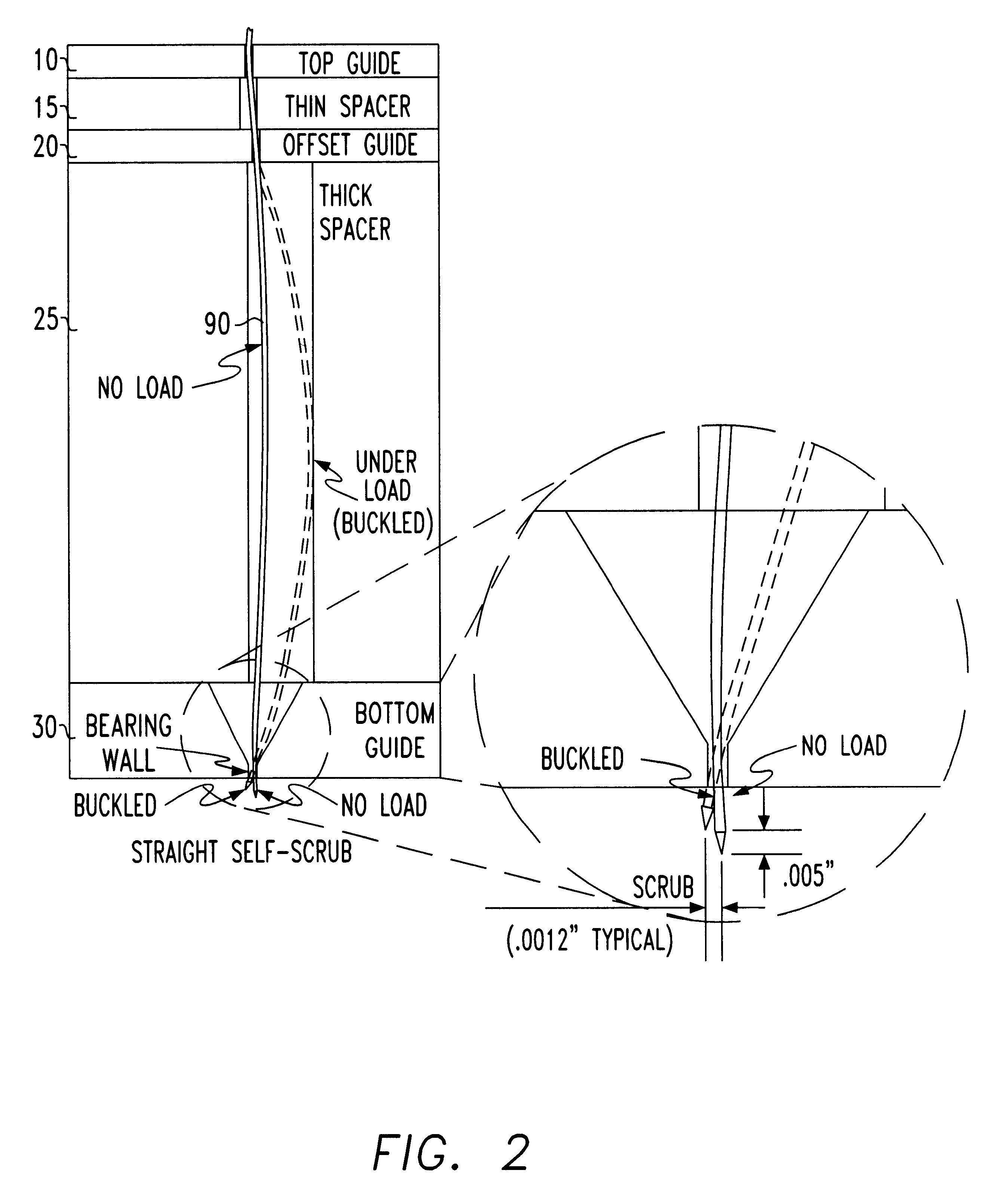
Self-scrub buckling beam probe
InactiveUS6529021B1Reduce resistanceAvoid stickingElectrical measurement instrument detailsCoupling device detailsRelative displacementVariable thickness
A self scrubbing buckling beam contactor for contacting an array of pads positioned on a device under test is described. The contactor consists of three insulating dies: a top, an offset and a lower die separated from each other by an insulated spacer of variable thickness. Each die is provided with holes. The buckling beam has an array of flexible wires positioned substantially perpendicular to the dies, each of the flexible wires crossing a corresponding hole in each of the top, offset and lower dies to allow each wire respectively contact a pad of the device under test. By shifting the center of the hole of the lower die relative to the center of the offset die, the tip of the wire exits from the lower die at an angle with respect to the plane formed by the pads of the device under test. The exit angle of the wire tip is controlled by the relative displacement of the offset die relative to the bottom die, such that the exit angle of the tip of the wire at the bottom die changes when the probe wire is under compression. By applying a reciprocating motion to the tip of the wire contacting the surface of the device under test, a scrubbing motion is achieved that lowers the resistance between the pad of the device under test. In this manner, the tip of the wire cleans the surface of the pads and prevents contaminants from adhering to the tip of the wire.
Owner:IBM CORP
Golf club head with variable face thickness
A face or face insert (40) for a golf club head (20) is disclosed herein. The face (40) has an interior surface (40b) with a first thickness section (200) and a second thickness region (205). The first thickness section (200) preferably has a thickness that is at least 0.025 inch greater than the thickness of the second thickness region (205). In a most preferred embodiment, the first thickness section (200) has an X shape that is rotated around the Y axis (500) by at least 10 degrees. In another preferred embodiment, the face has a first thickness section (200), a second thickness region (205), and a central region (400) having a third thickness. The face or face insert (40) with variable thickness allows for a face or face insert (40) with less mass in a golf club head (20) that conforms to the United States Golf Association regulations.
Owner:CALLAWAY GOLF CO
Uniform heat dissipating and cooling heat sink
InactiveUS6942025B2Reduce airflow resistanceIncrease air velocitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesVariable thicknessEngineering
Owner:DEGREE CONTROLS
Size adjustable safety and comfort liner for a helmet
ActiveUS20070163031A1User from adjustingInfinite adjustabilityHatsHeadwear capsVariable thicknessCushioning
A helmet liner that is infinitely adjustable by the user in the field is provided. The helmet liner includes front, center and rear cushioning portions with integrally formed spaces between the front and center portions, and the rear and center portions. The integrally formed spaces provide the liner with the ability to independently flex [in one degree of freedom] and bend [in a second degree of freedom] to collapse the spaces without any overlapping of cushioning portions and thereby conform the liner to the hemi-spherical shape of the wearer's head. The spaces provide ventilation for the wearer's head. The helmet liner may also provide for variable thickness of one or more of cushioning portions as well as antimicrobial treatment of the fabric. By increasing the thickness of the rear cushioning portion with respect to the front cushioning portion, the number of optimum fits achieved by the liner is maximized, while biasing the wearers head toward the front of the helmet, thereby increasing the wearer's field of view (FOV).
Owner:GENTEX CORP
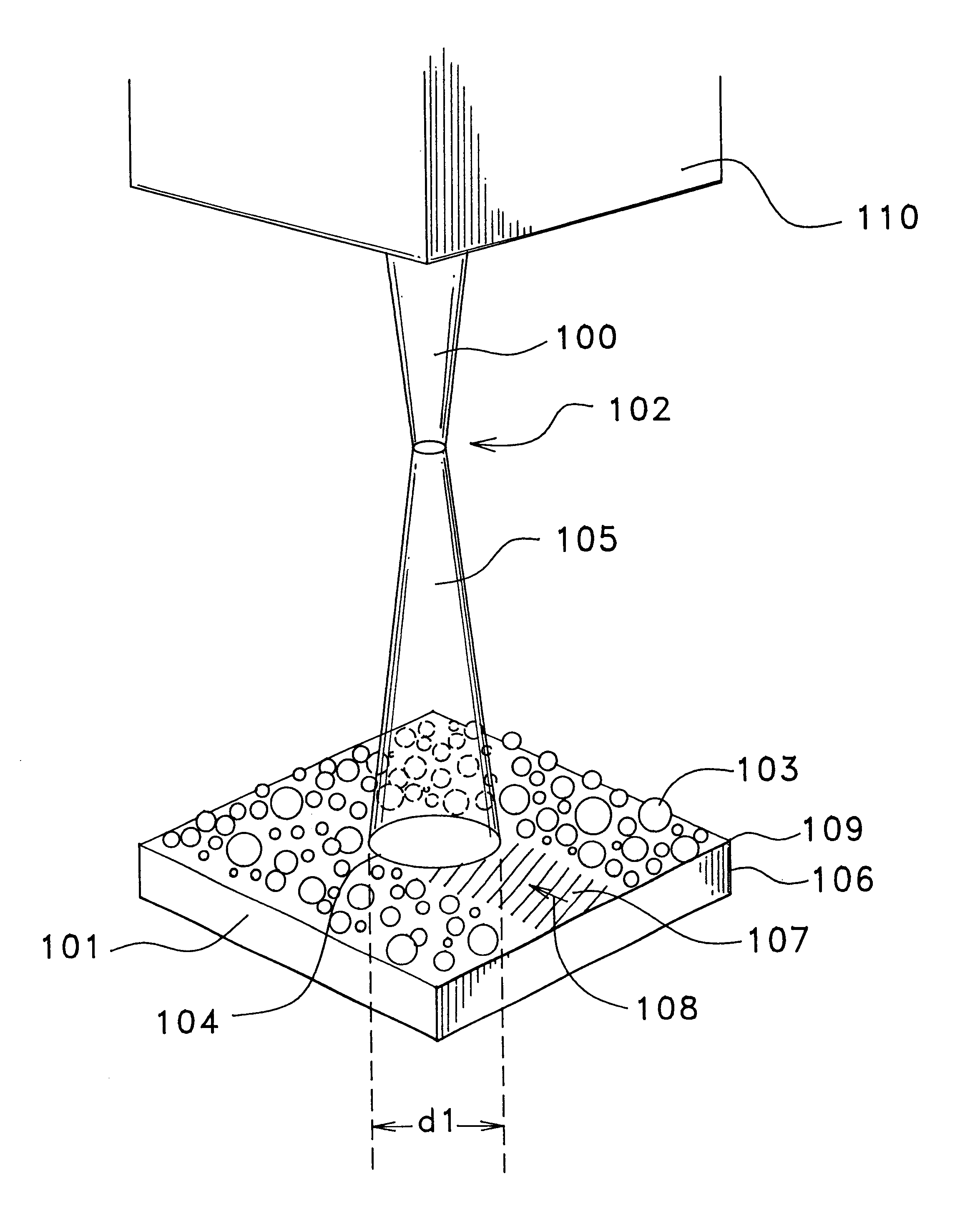
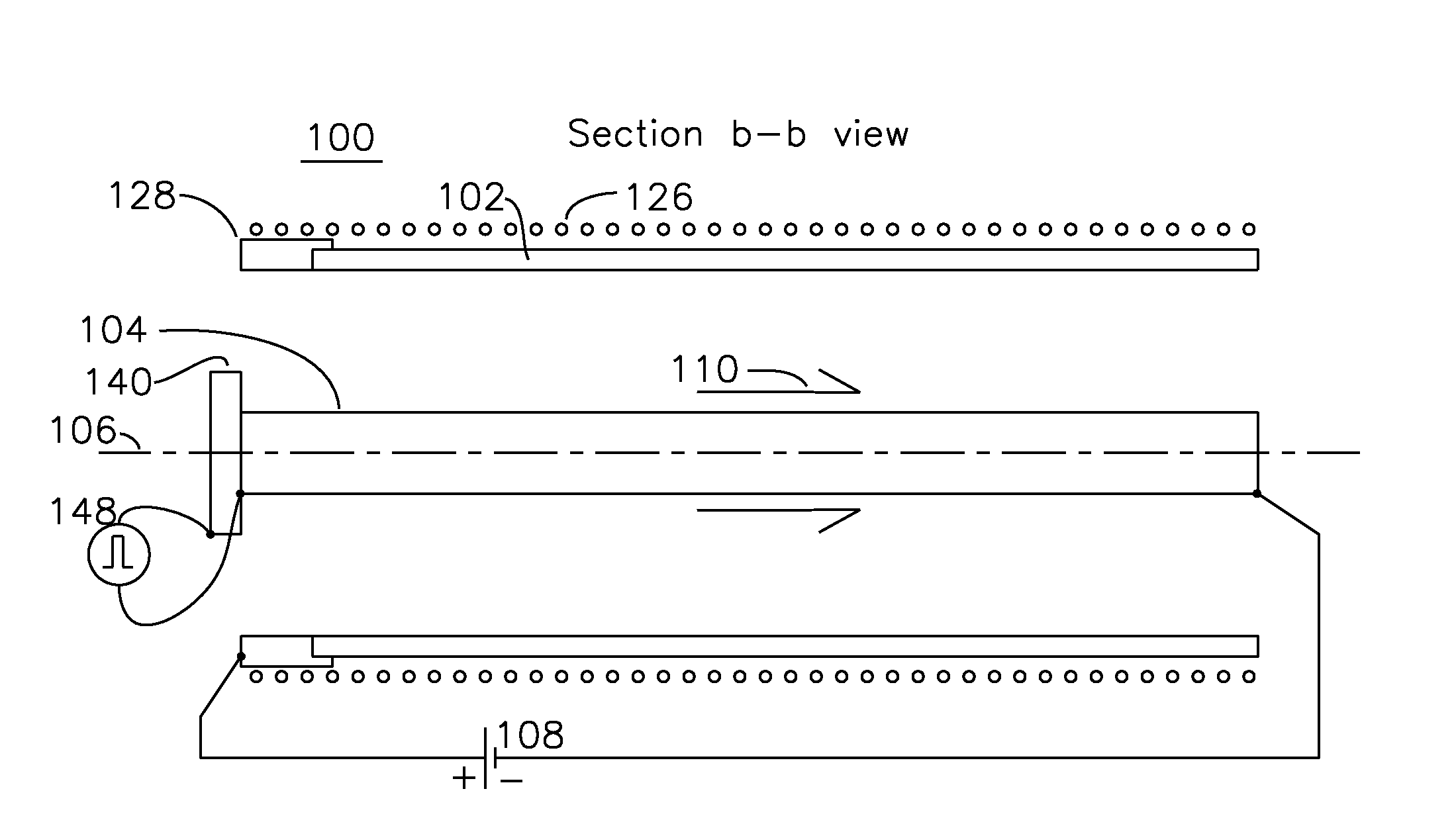
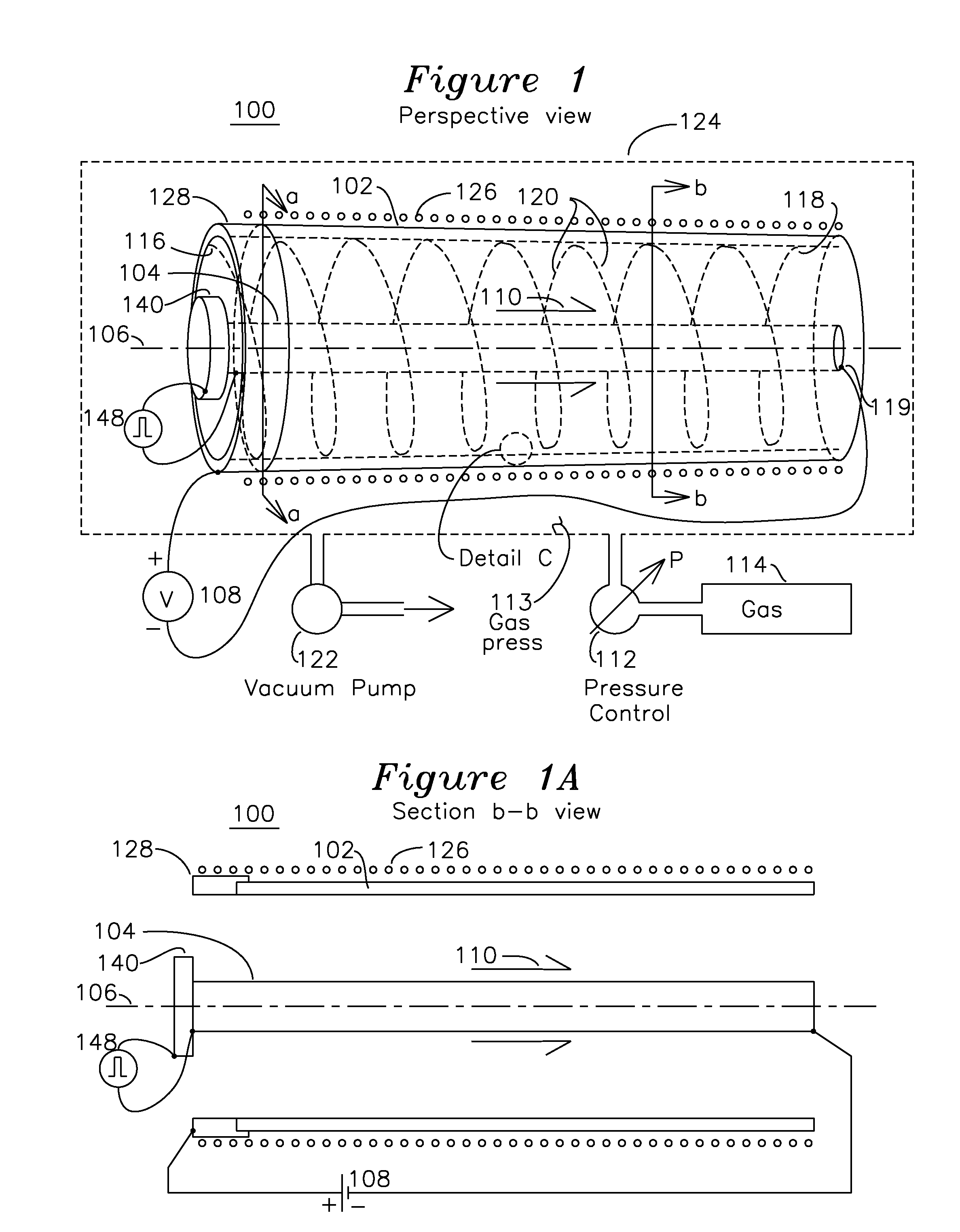
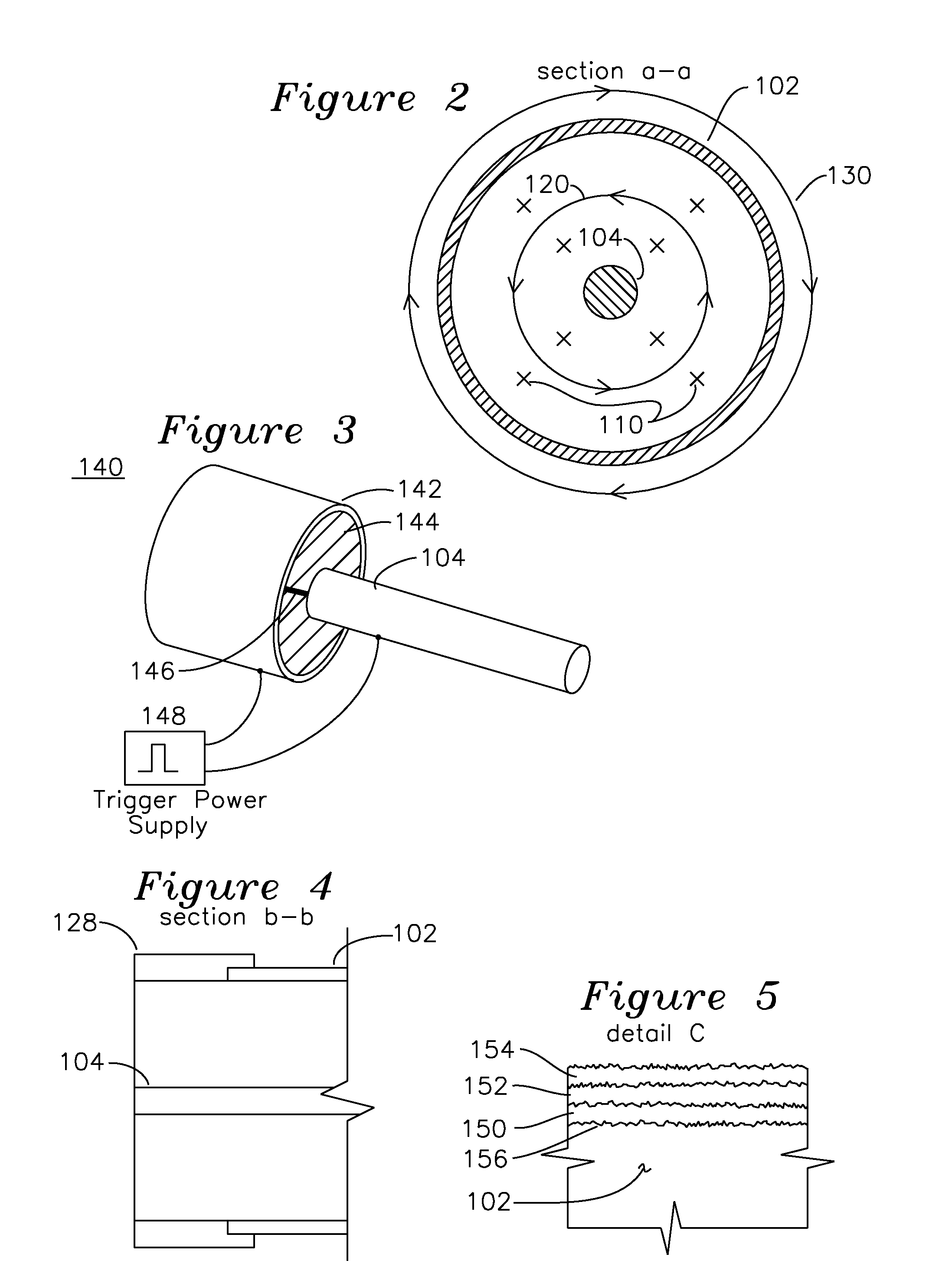
Coaxial plasma arc vapor deposition apparatus and method
An apparatus for the deposition of a variable thickness coating onto the inside of a cylindrical tube comprises a variable pressure gas, an cathode coaxially positioned within the cylinder, and a voltage source applied between the cathode and cylindrical tube, which functions as an anode. A radial plasma arc is generated between the anode and cathode at a starting point on the cylinder, and the plasma arc travels down the central axis of the cylinder, providing a helical deposition region on the inside of the cylinder. Selection of the combination of cathode material and gas enable the plasma to generate ionic material which is deposited on the anodic cylinder in the region of the plasma. By varying the pressure of variable pressure gas for each helical path, it is possible to vary the composition of this deposition film.
Owner:KRISHNAN MAHADEVAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com