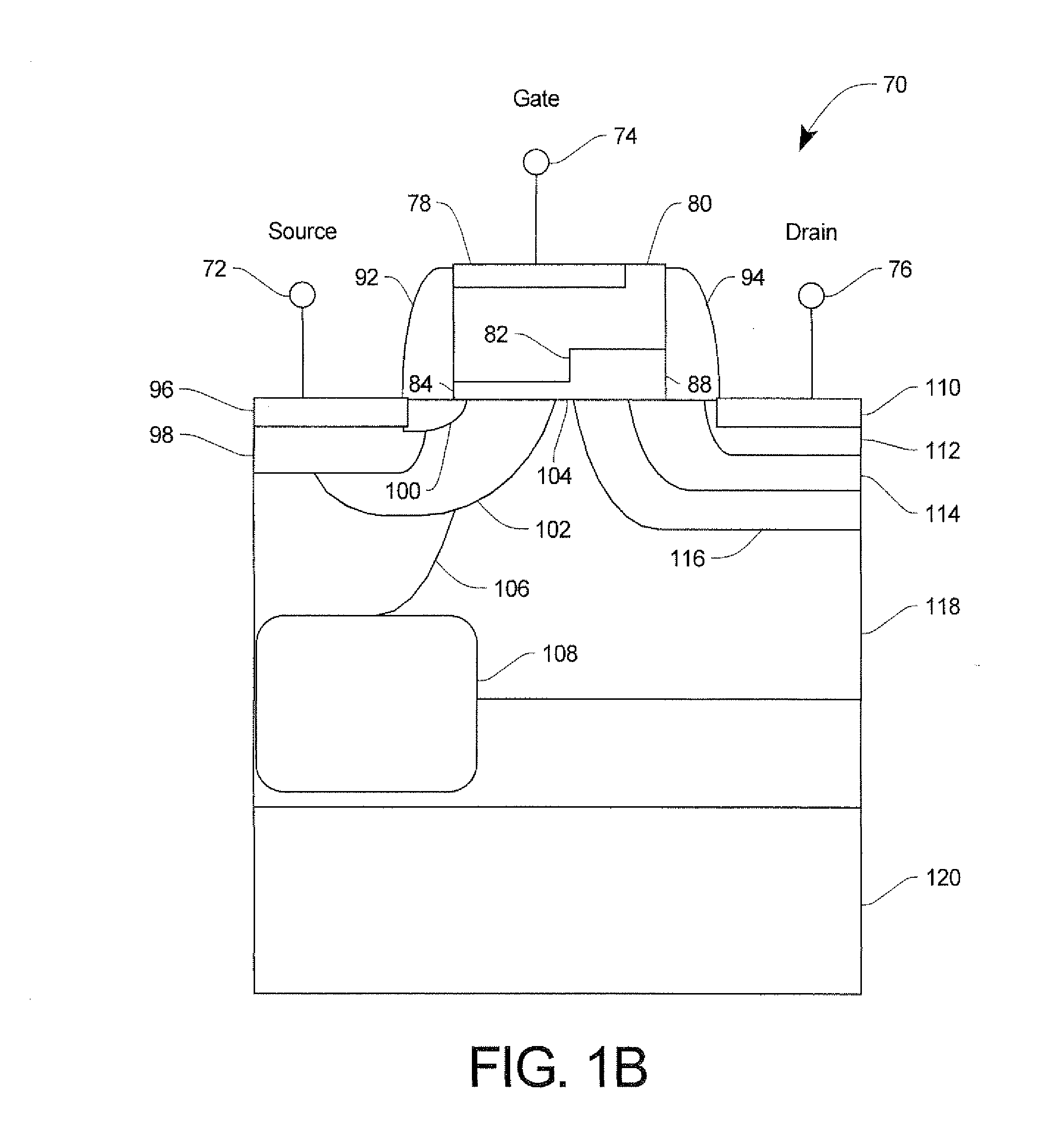
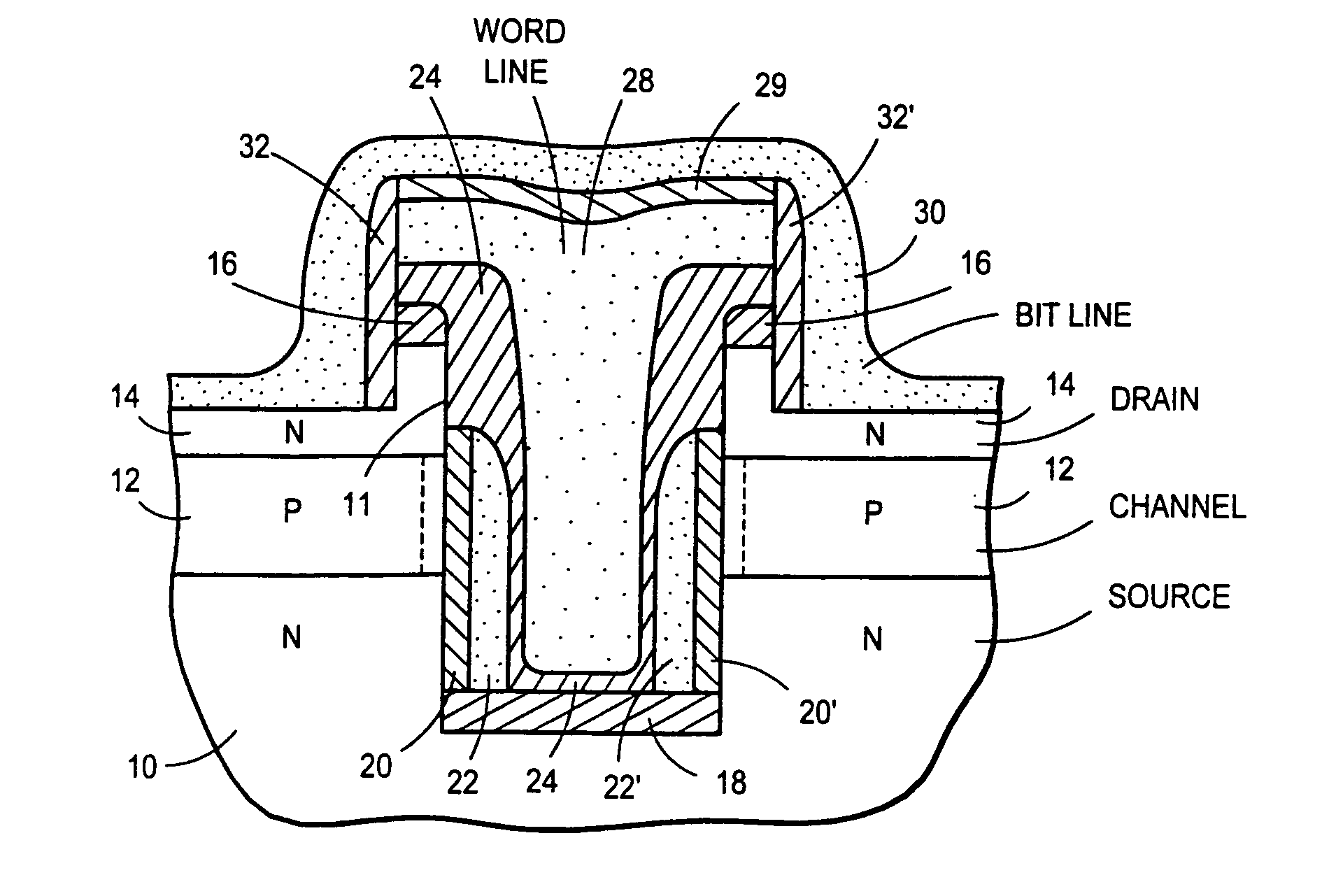
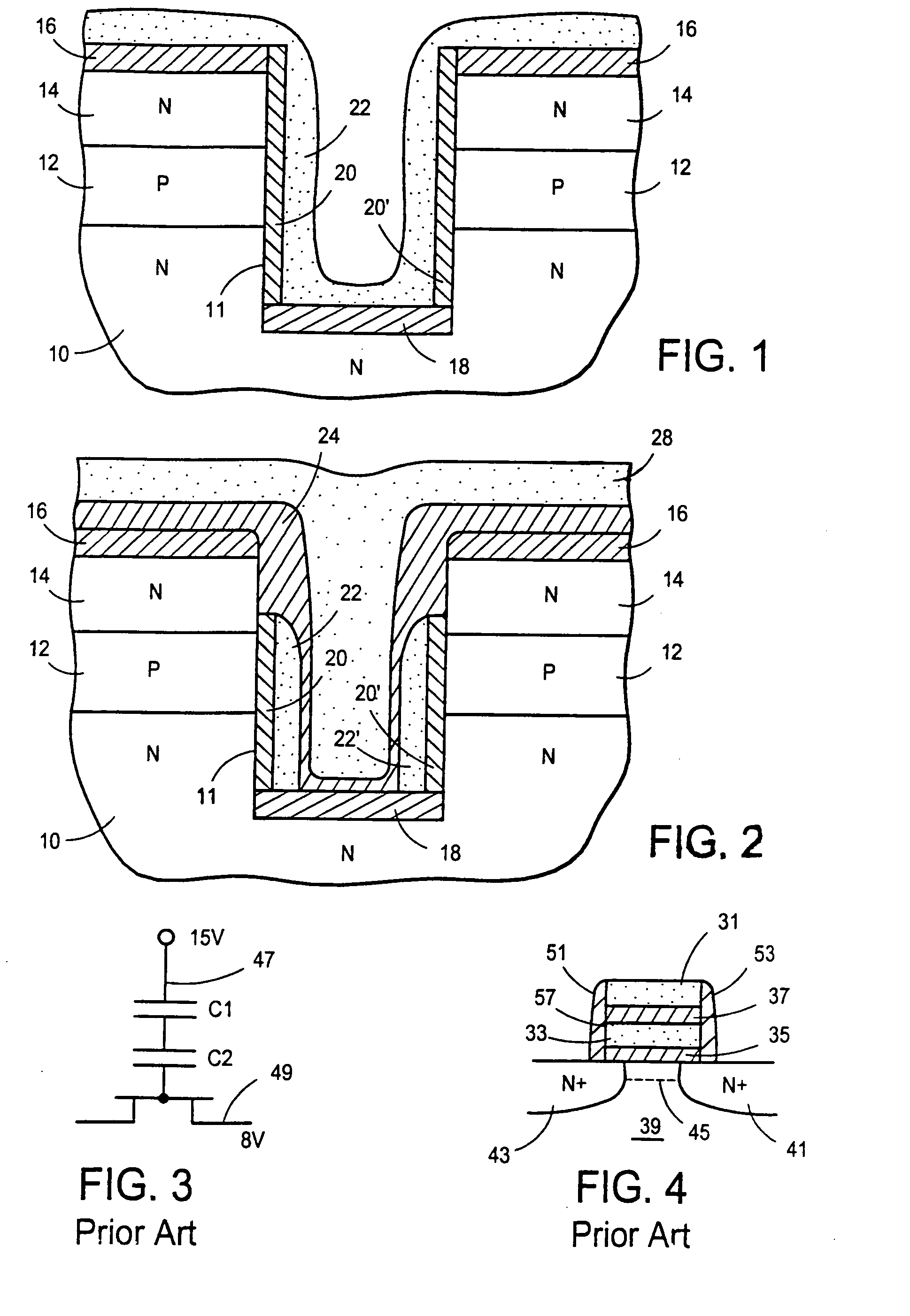
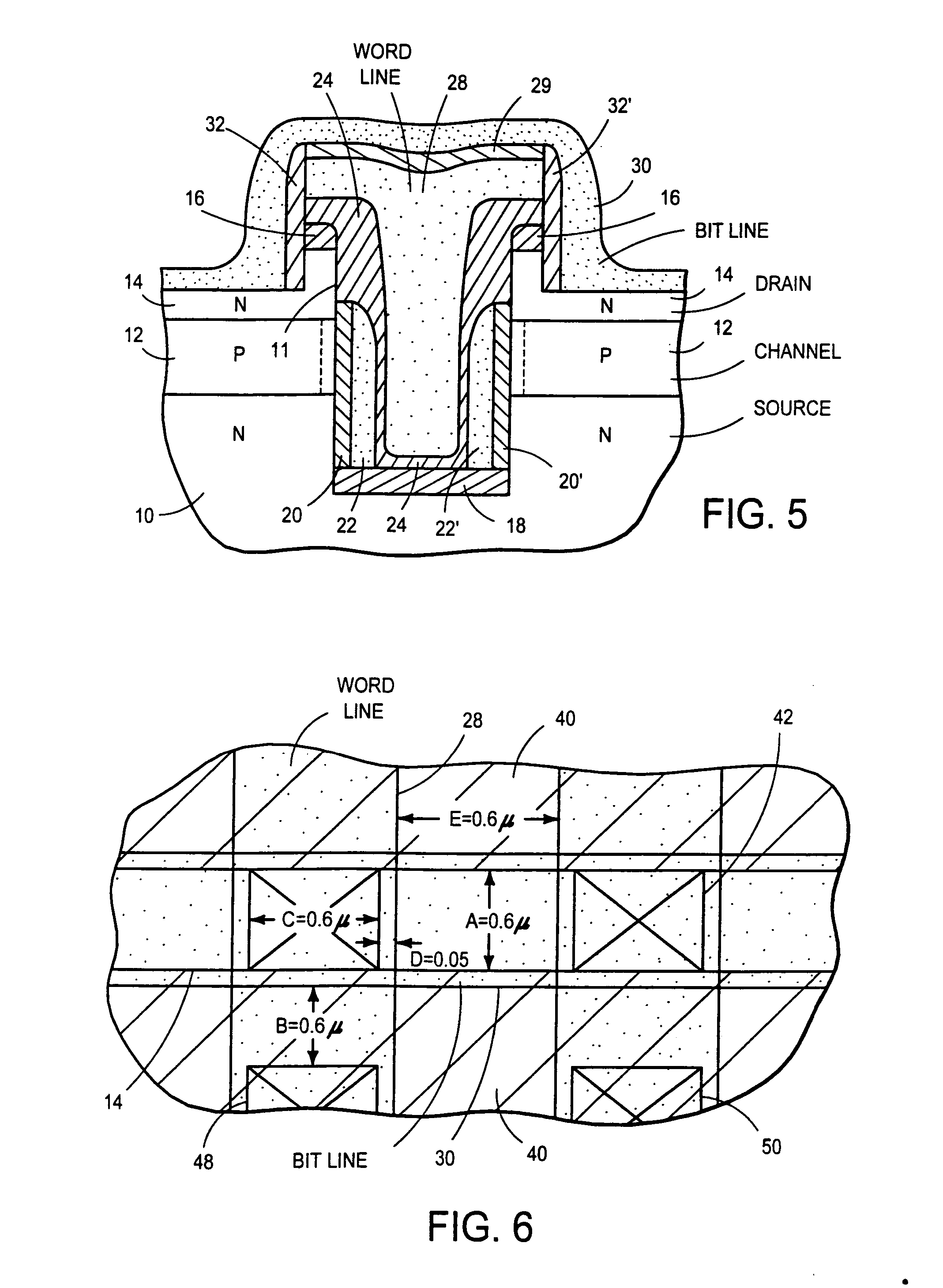
Patents
Literature
281 results about "Thin gate oxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
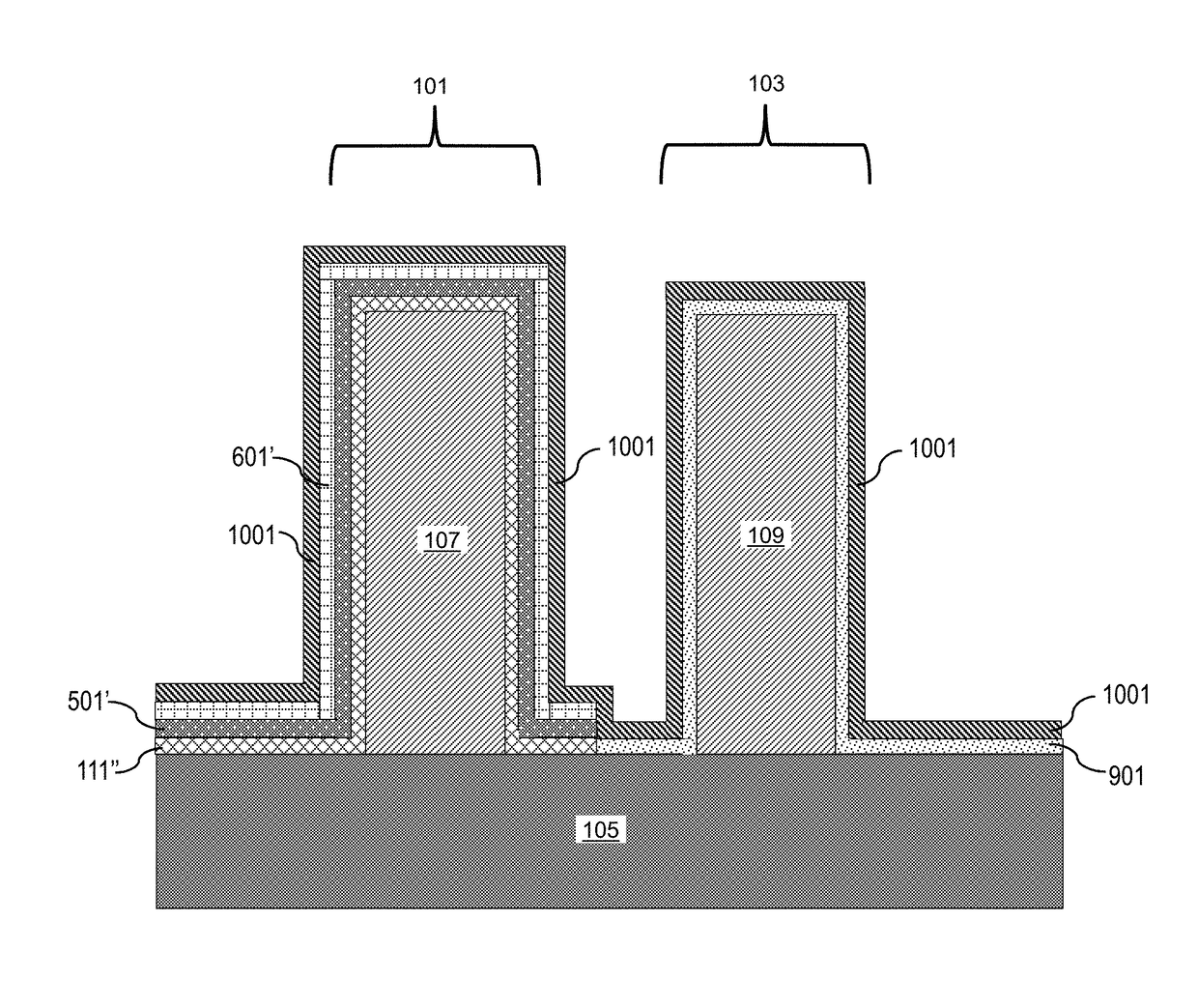
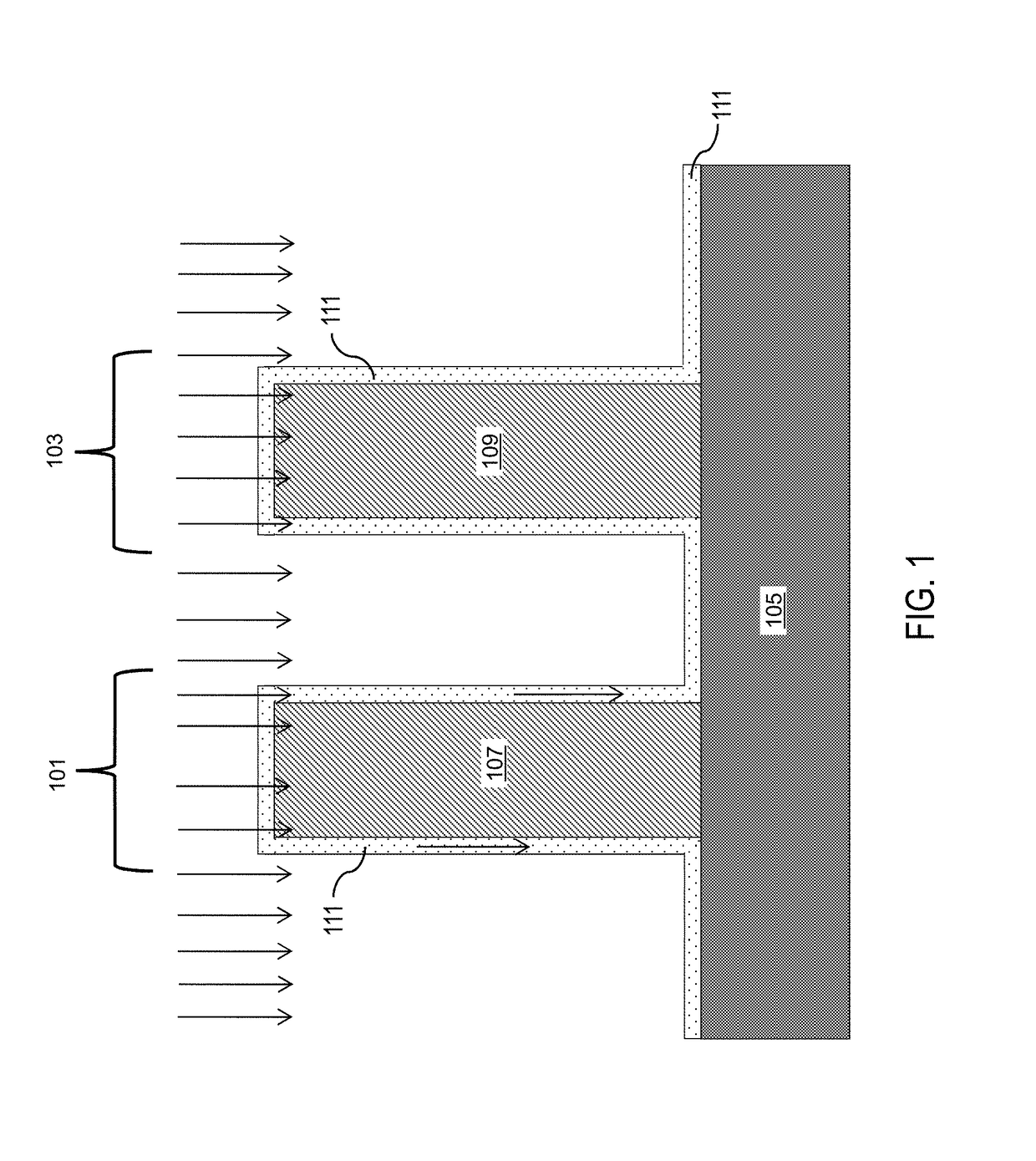
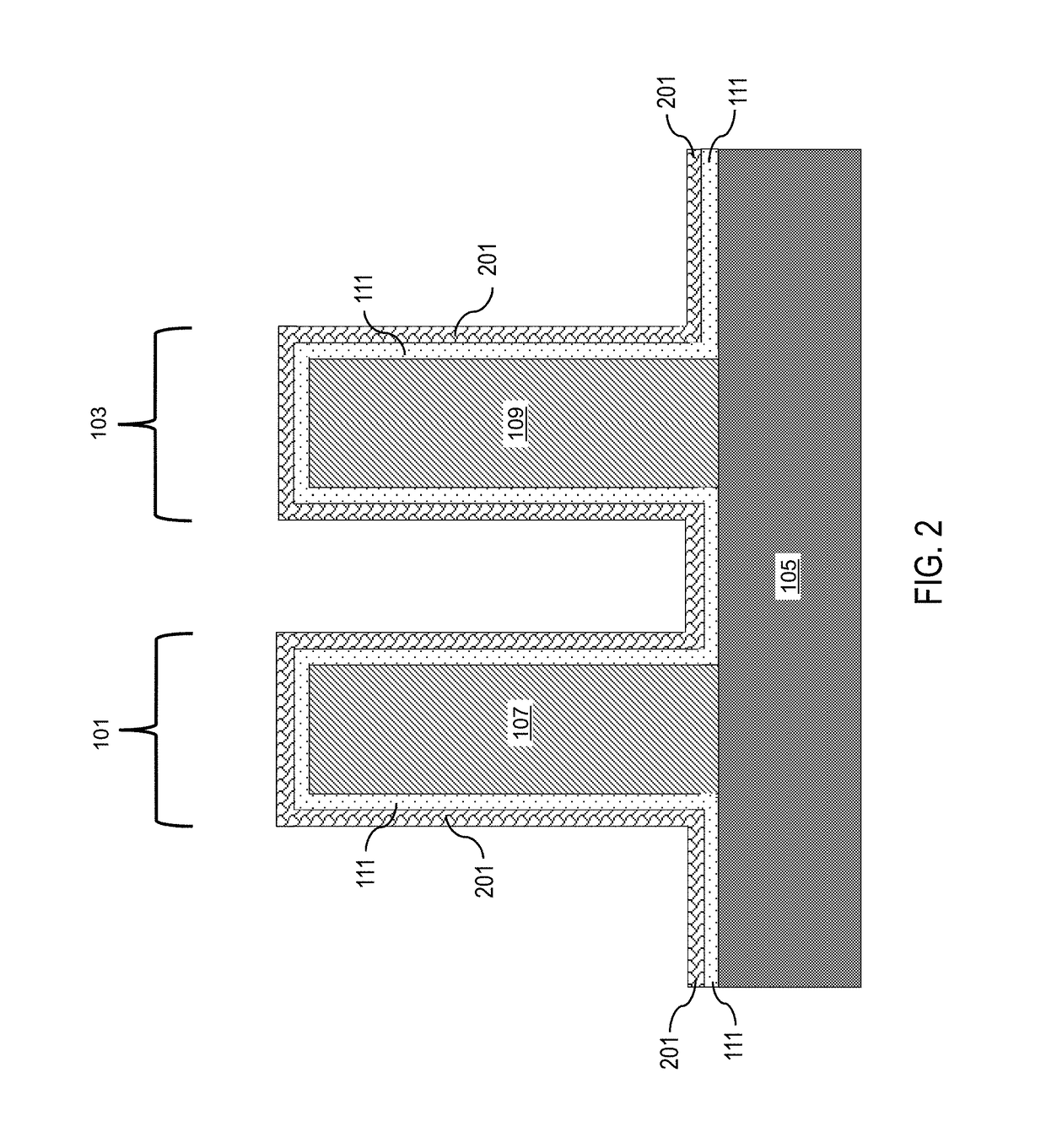
Thermal oxide equivalent low temperature ALD oxide for dual purpose gate oxide and method for producing the same
ActiveUS10106892B1Nitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsSolid-state devicesNitrideThermal oxide
Methods of forming conformal low temperature gate oxides on a HV I / O and a core logic and the resulting devices are provided. Embodiments include providing a HV I / O and core logic laterally separated on a Si substrate, each having a fin; forming a gate oxide layer over each fin and the Si substrate; forming a silicon oxy-nitride layer over the gate oxide layer; forming a sacrificial oxide layer over the silicon oxy-nitride layer; removing the sacrificial oxide and silicon oxy-nitride layers and thinning the gate oxide layer; forming a second gate oxide layer over the thinned gate oxide layer; forming a silicon oxy-nitride layer over the second gate oxide layer; removing the silicon oxy-nitride and second gate oxide layers over the core logic fin portion; forming an IL over the core logic fin portion; and forming a HfOx layer over the second silicon oxy-nitride layer and ILs.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
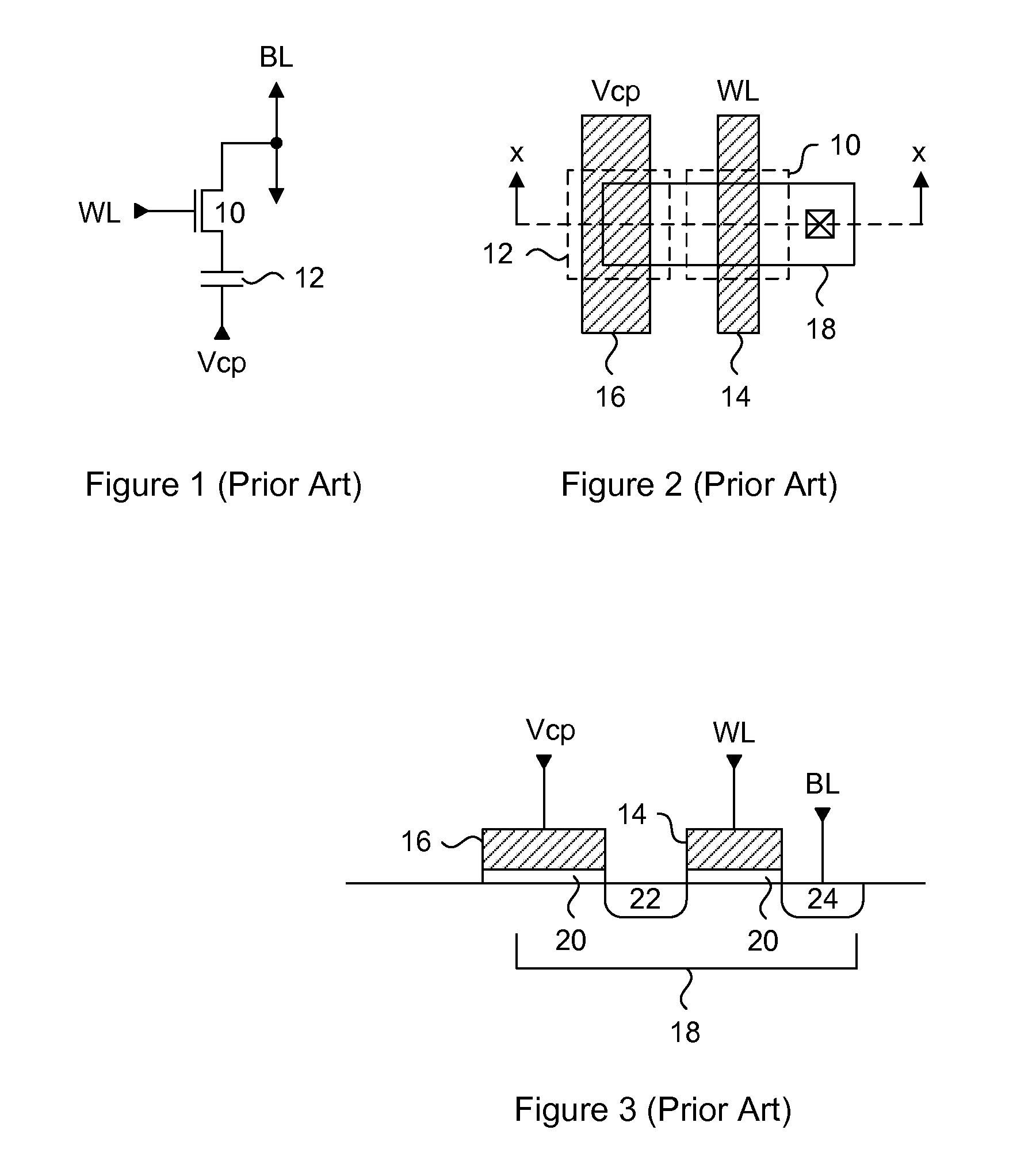
Split-channel antifuse array architecture
InactiveUS20060244099A1Limited over-voltage exposureSimplify and improve and accessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCMOSEngineering
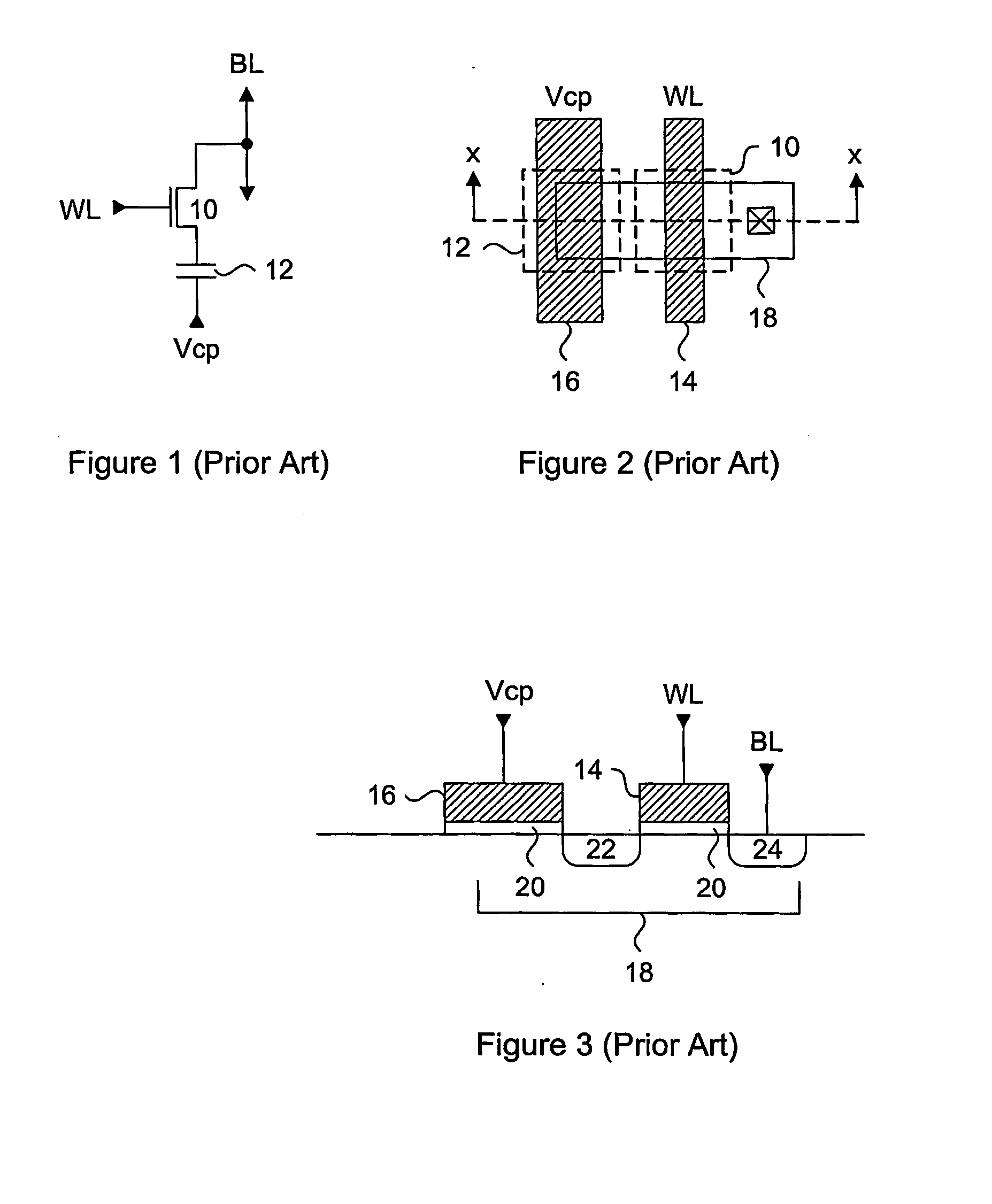
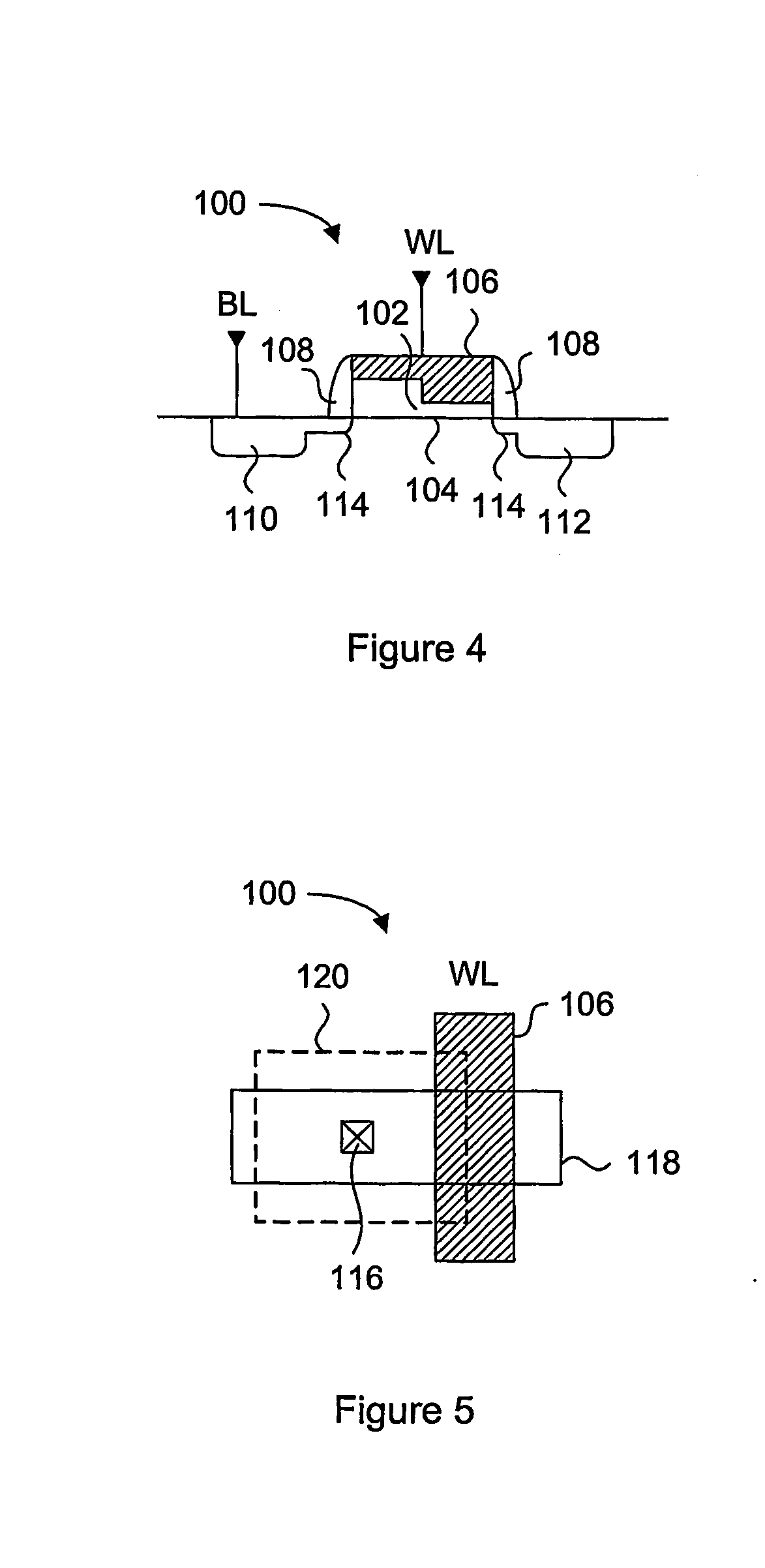
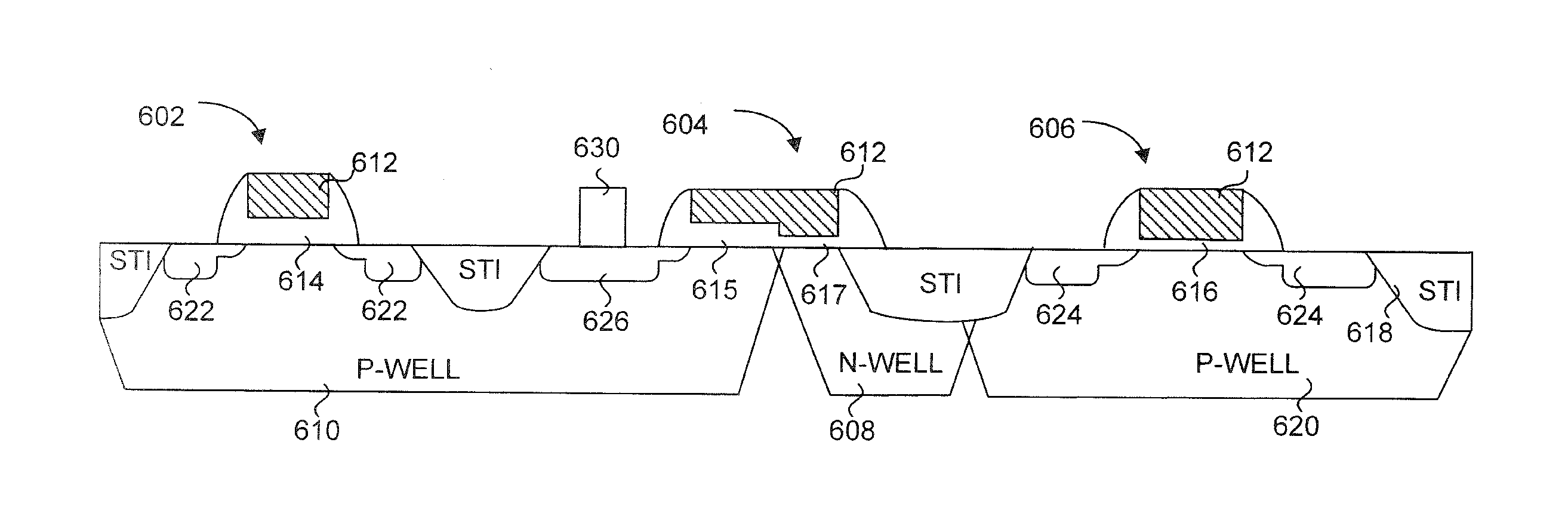
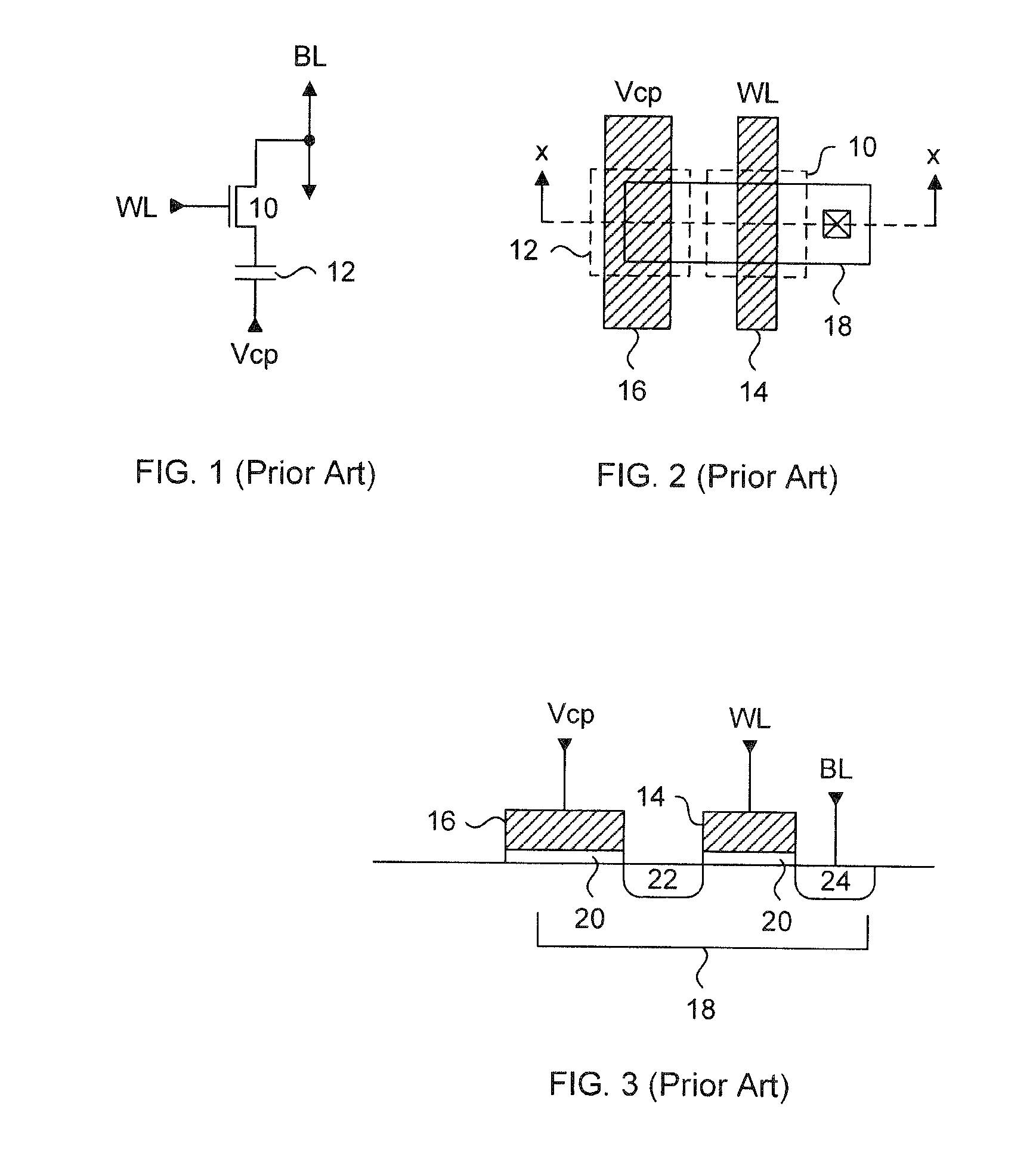
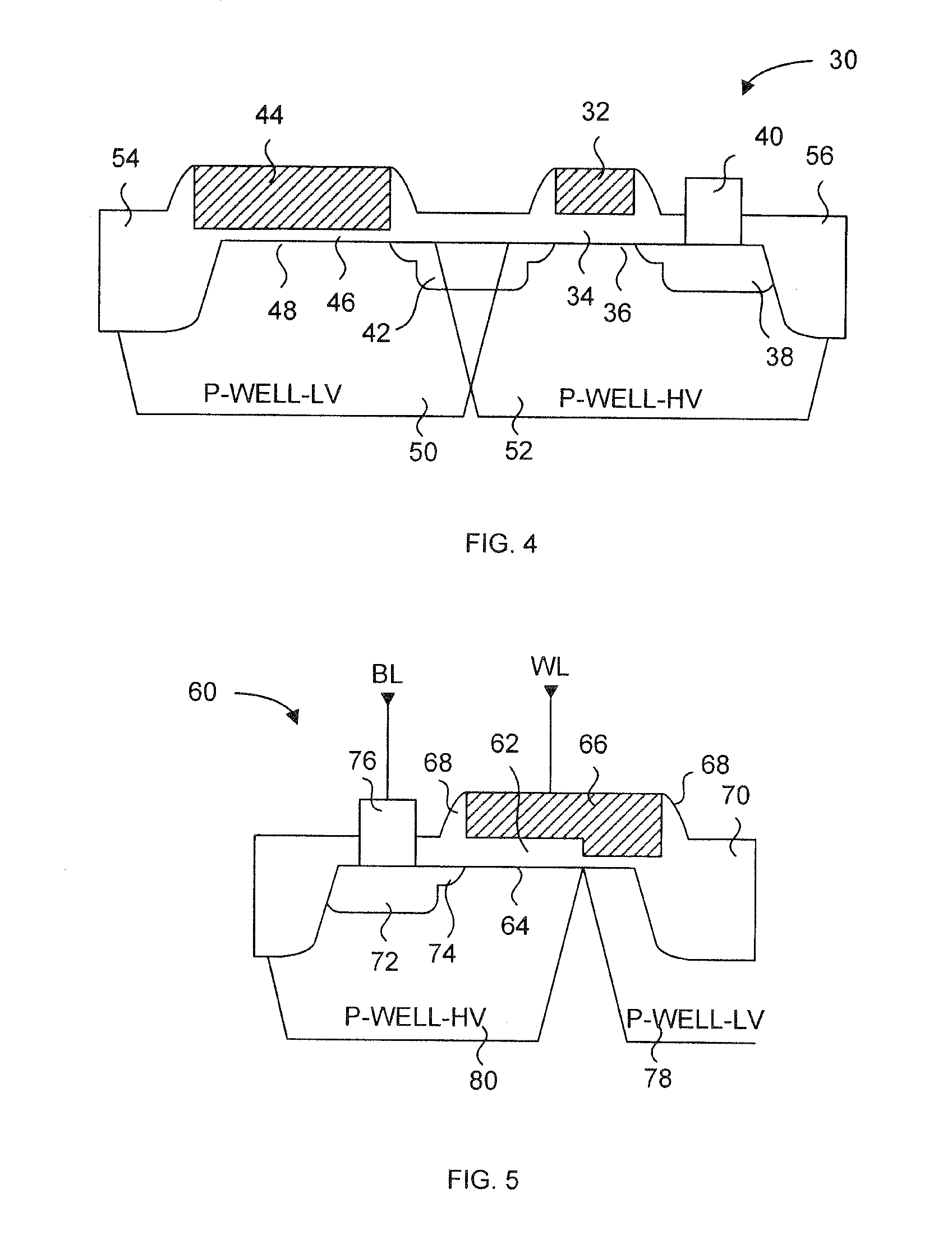
Generally, the present invention provides a variable thickness gate oxide anti-fuse transistor device that can be employed in a non-volatile, one-time-programmable (OTP) memory array application. The anti-fuse transistor can be fabricated with standard CMOS technology, and is configured as a standard transistor element having a source diffusion, gate oxide, polysilicon gate and optional drain diffusion. The variable gate oxide underneath the polysilicon gate consists of a thick gate oxide region and a thin gate oxide region, where the thin gate oxide region acts as a localized breakdown voltage zone. A conductive channel between the polysilicon gate and the channel region can be formed in the localized breakdown voltage zone during a programming operation. In a memory array application, a wordline read current applied to the polysilicon gate can be sensed through a bitline connected to the source diffusion, via the channel of the anti-fuse transistor. More specifically, the present invention provides an effective method for utilizing split channel MOS structures as an anti-fuse cell suitable for OTP memories.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
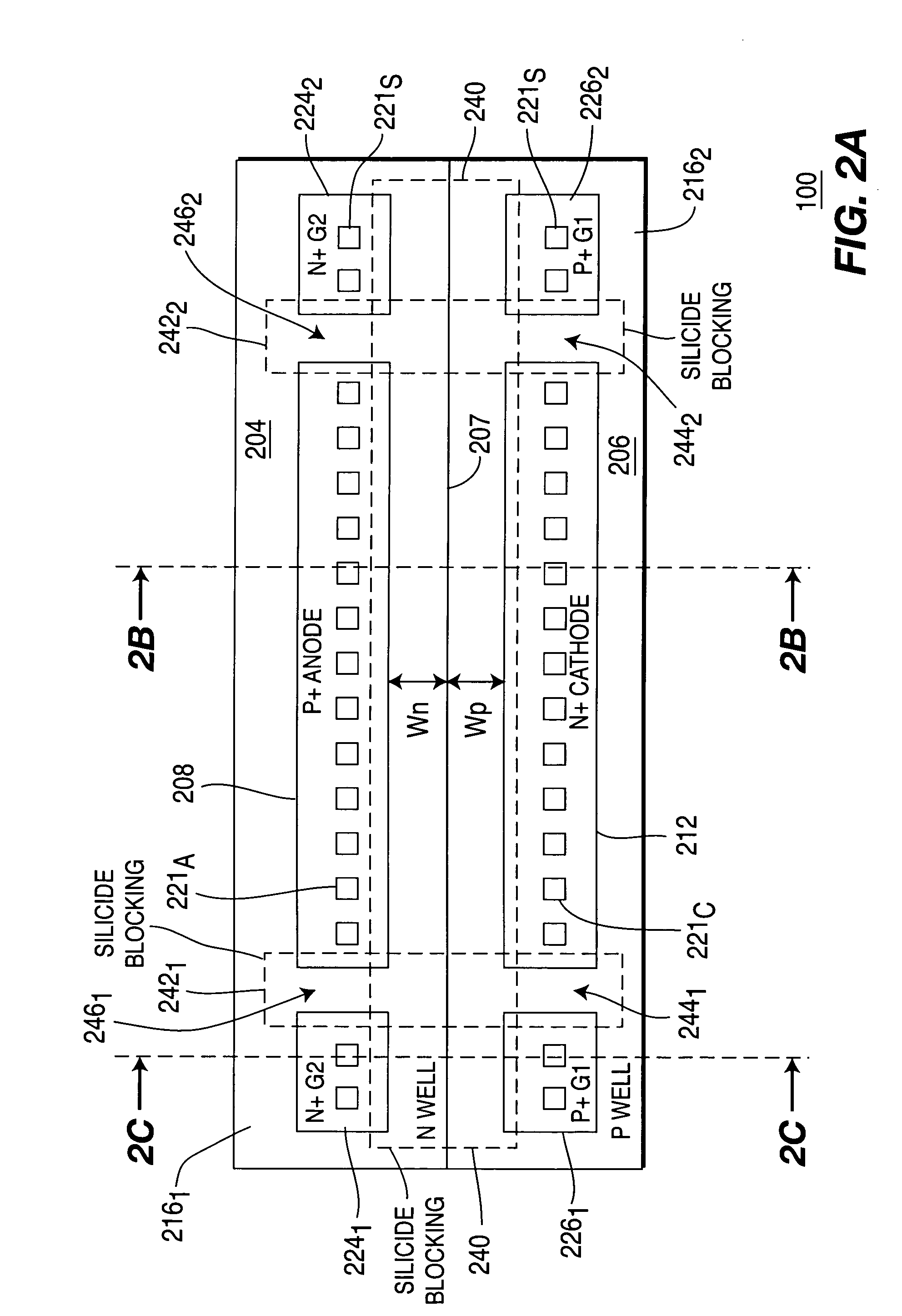
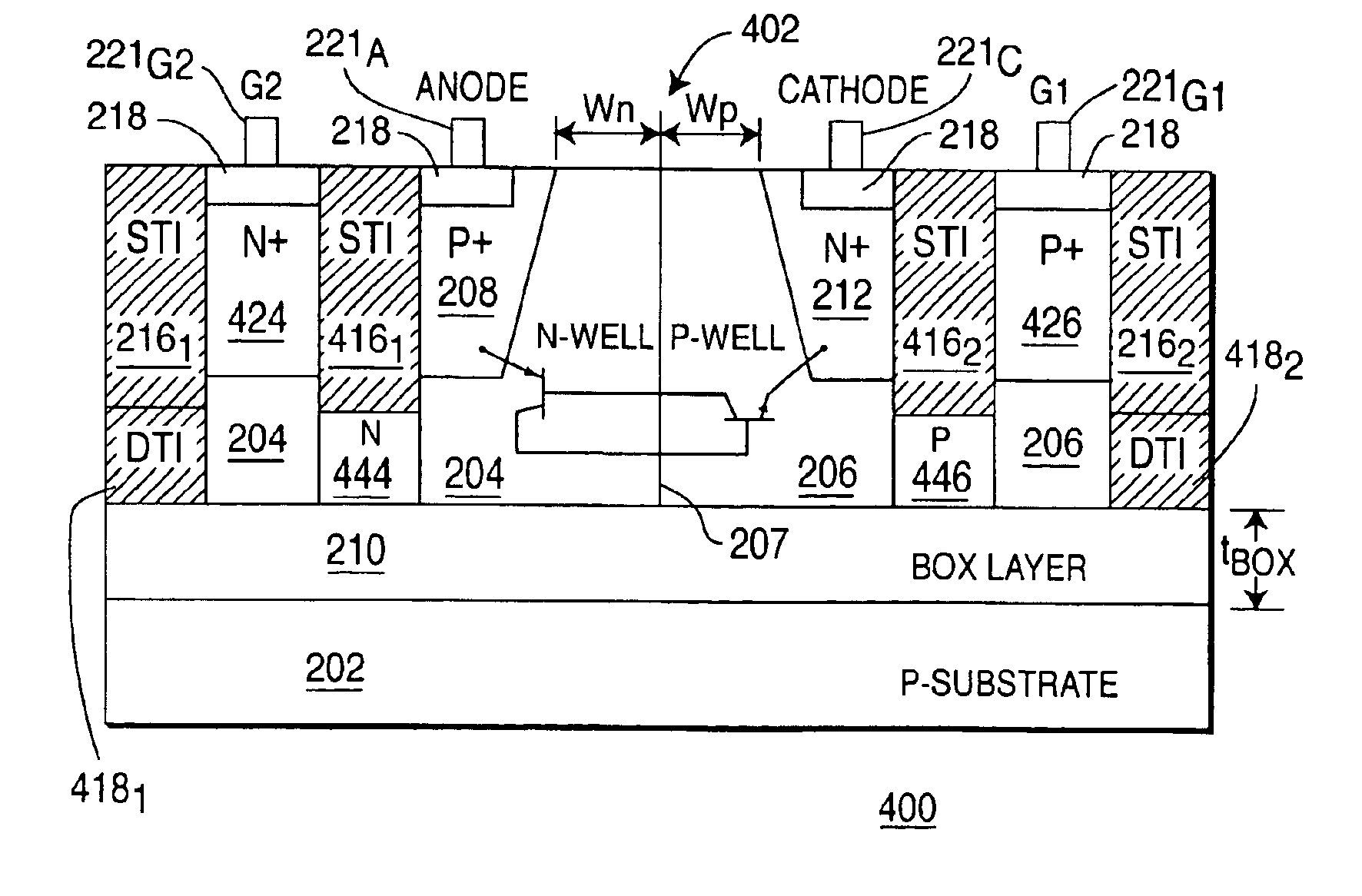
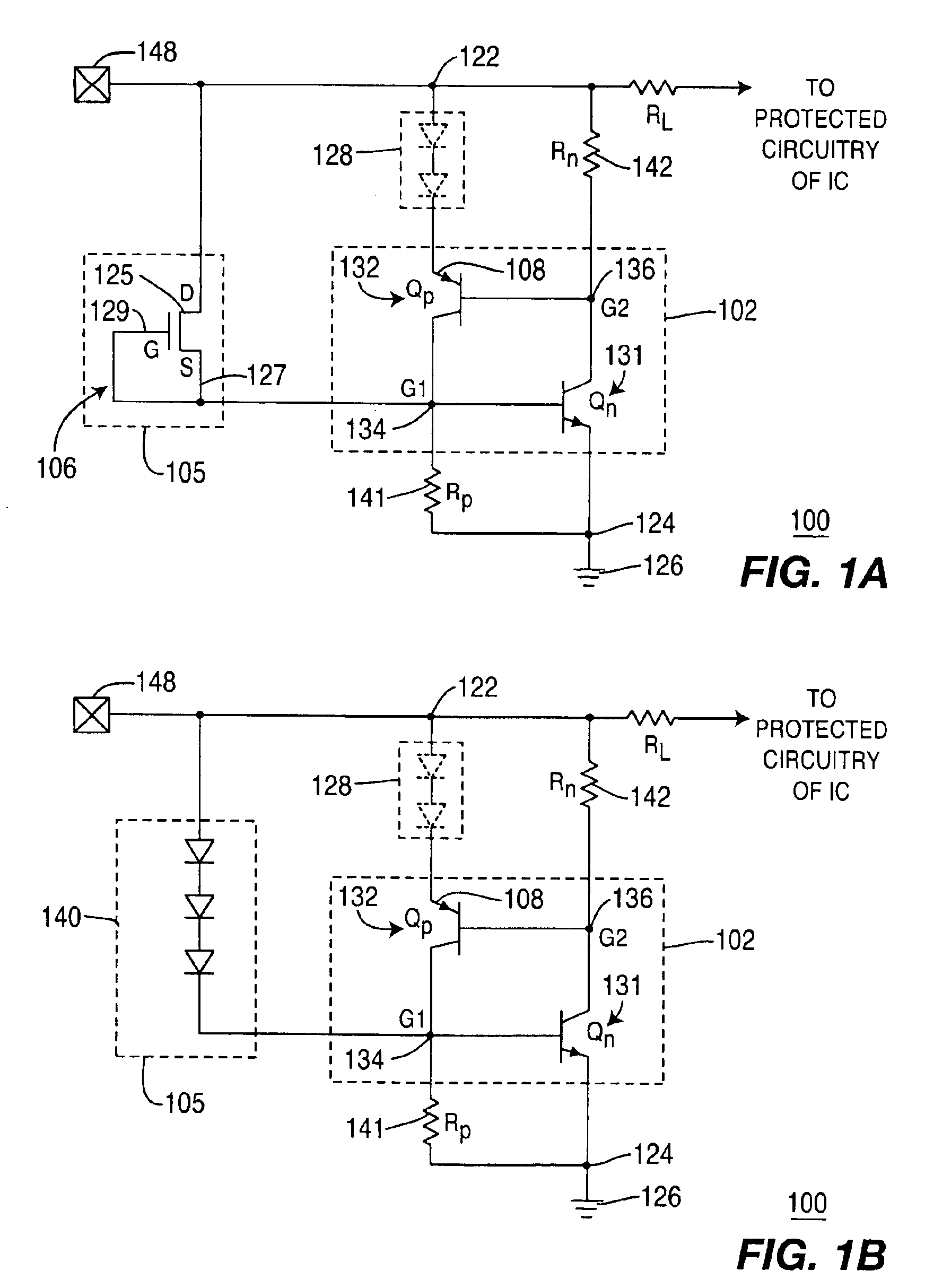
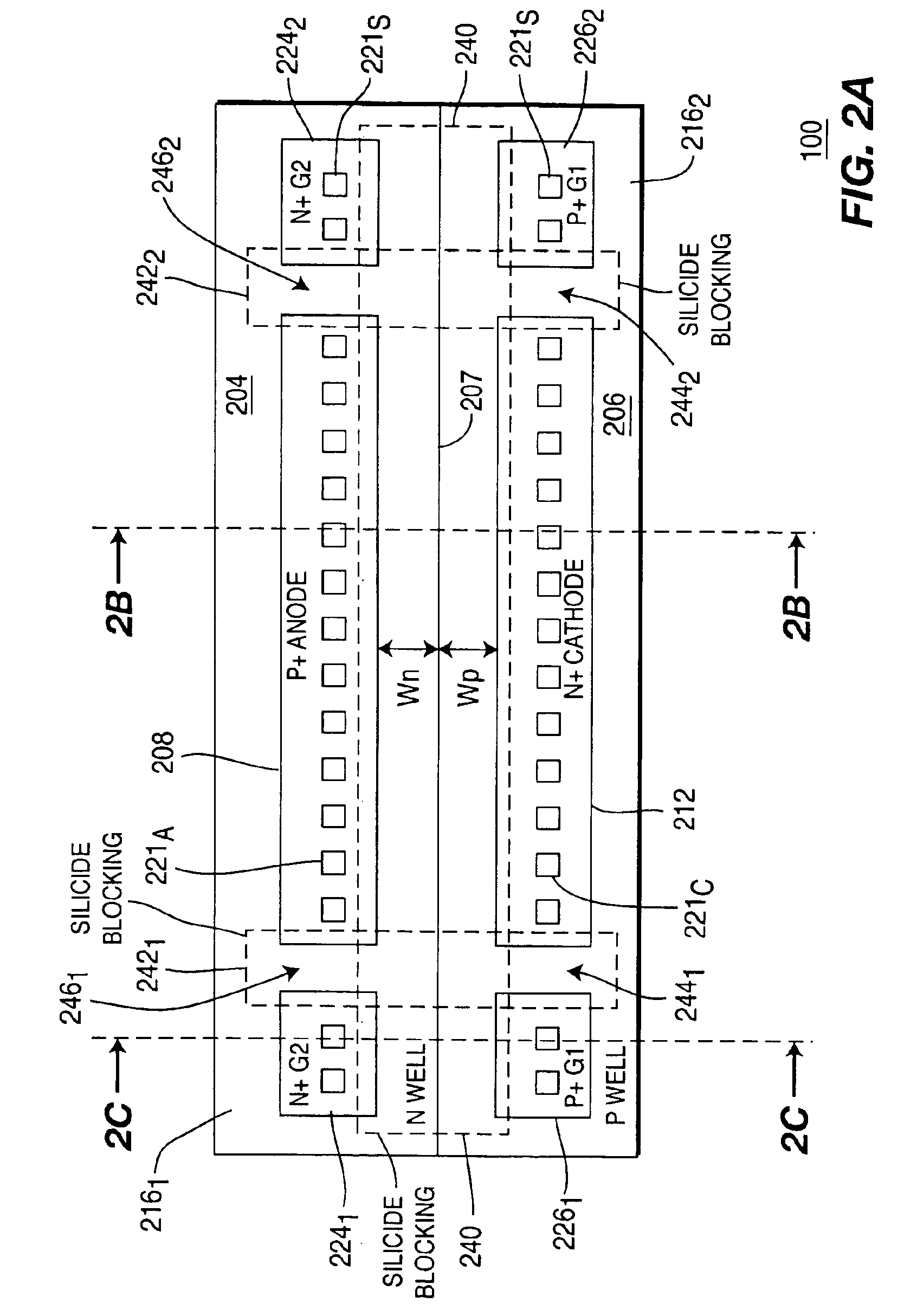
Low voltage silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) for electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection of silicon-on-insulator technologies
InactiveUS20050212051A1Low triggeringLow holding voltageTransistorThyristorSilicon-controlled rectifierLow voltage
Owner:SOFICS BVBA
Low voltage silicon controlled rectifier (SCR) for electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection of silicon-on-insulator technologies
ActiveUS6909149B2Low triggeringLow holding voltageTransistorThyristorSilicon-controlled rectifierLow voltage
A silicon-on-insulator (SOI) electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection device that can protect very sensitive thin gate oxides by limiting the power dissipation during the ESD event, which is best achieved by reducing the voltage drop across the active (protection) device during an ESD event. In one embodiment, the invention provides very low triggering and holding voltages. Furthermore, the SOI protection device of the present invention has low impedance and low power dissipation characteristics that reduce voltage build-up, and accordingly, enable designers to fabricate more area efficient protection device
Owner:SOFICS BVBA
Method for dual gate oxide dual workfunction CMOS
InactiveUS6087225AIncrease flexibilityIncrease junction formation flexibilityTransistorSolid-state devicesThin oxideCMOS
A method of forming integrated circuit chips including two dissimilar type NFETs and / or two dissimilar type PFETs on the same chip, such as both thick and thin gate oxide FETs. A DRAM array may be constructed of the thick oxide FETs and logic circuits may be constructed of the thin oxide FETs on the same chip. First, a gate stack including a first, thick gate SiO2 layer is formed on a wafer. The stack includes a doped polysilicon layer on the gate oxide layer, a silicide layer on the polysilicon layer and a nitride layer on the silicide layer. Part of the stack is selectively removed to re-expose the wafer where logic circuits are to be formed. A thinner gate oxide layer is formed on the re-exposed wafer. Next, gates are formed on the thinner gate oxide layer and thin oxide NFETs and PFETs are formed at the gates. After selectively siliciding thin oxide device regions, gates are etched from the stack in the thick oxide device regions. Finally, source and drain regions are implanted and diffused for the thick gate oxide devices.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Anti-fuse memory cell
ActiveUS20070257331A1Simple and reliable processHigh densityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVariable thicknessCondensed matter physics
An anti-fuse memory cell having a variable thickness gate oxide. The variable thickness gate oxide has a thick gate oxide portion and a thin gate oxide portion, where the thing gate oxide portion has at least one dimension less than a minimum feature size of a process technology. The thin gate oxide can be rectangular in shape or triangular in shape. The anti-fuse transistor can be used in a two-transistor memory cell having an access transistor with a gate oxide substantially identical in thickness to the thick gate oxide of the variable thickness gate oxide of the anti-fuse transistor.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
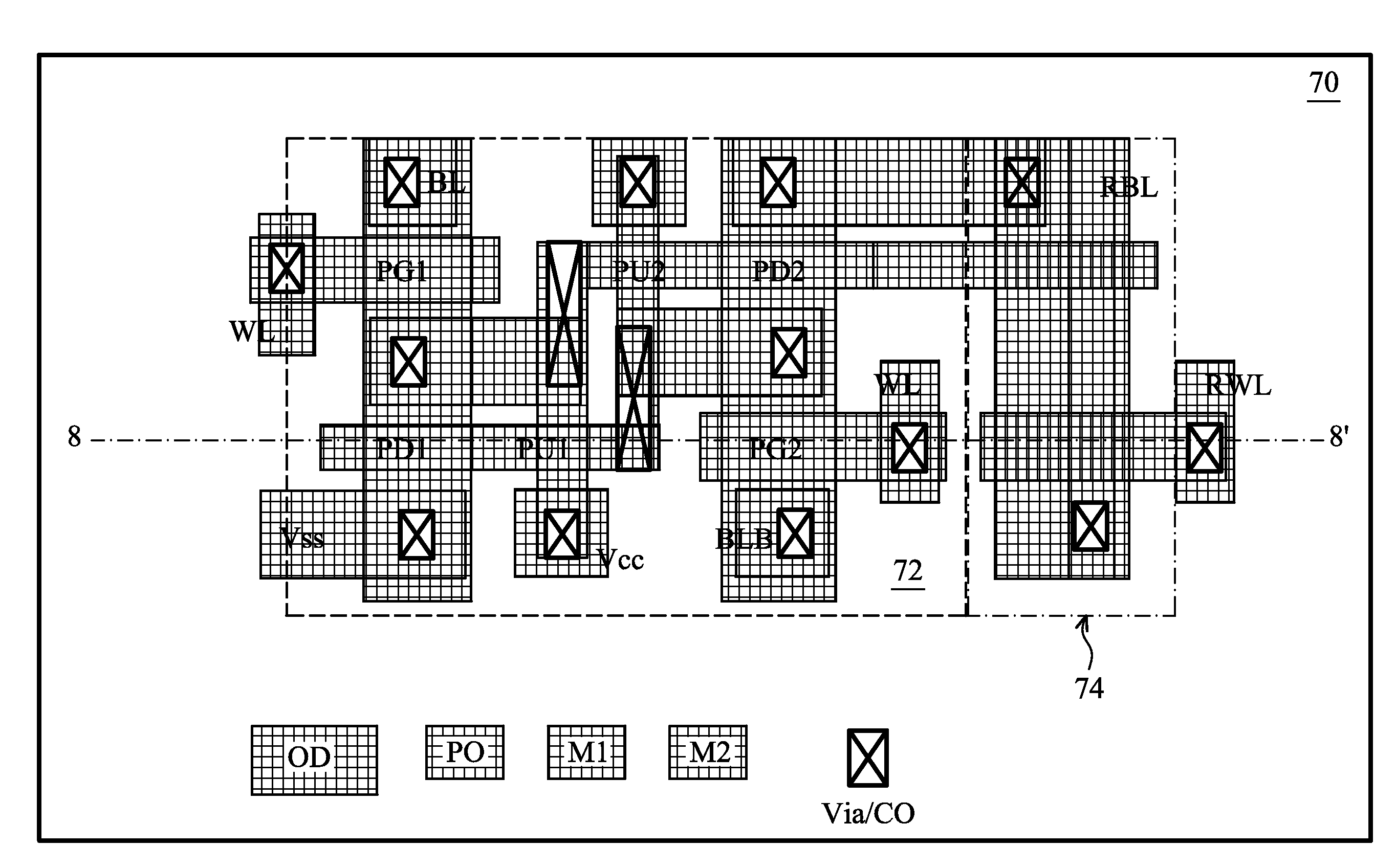
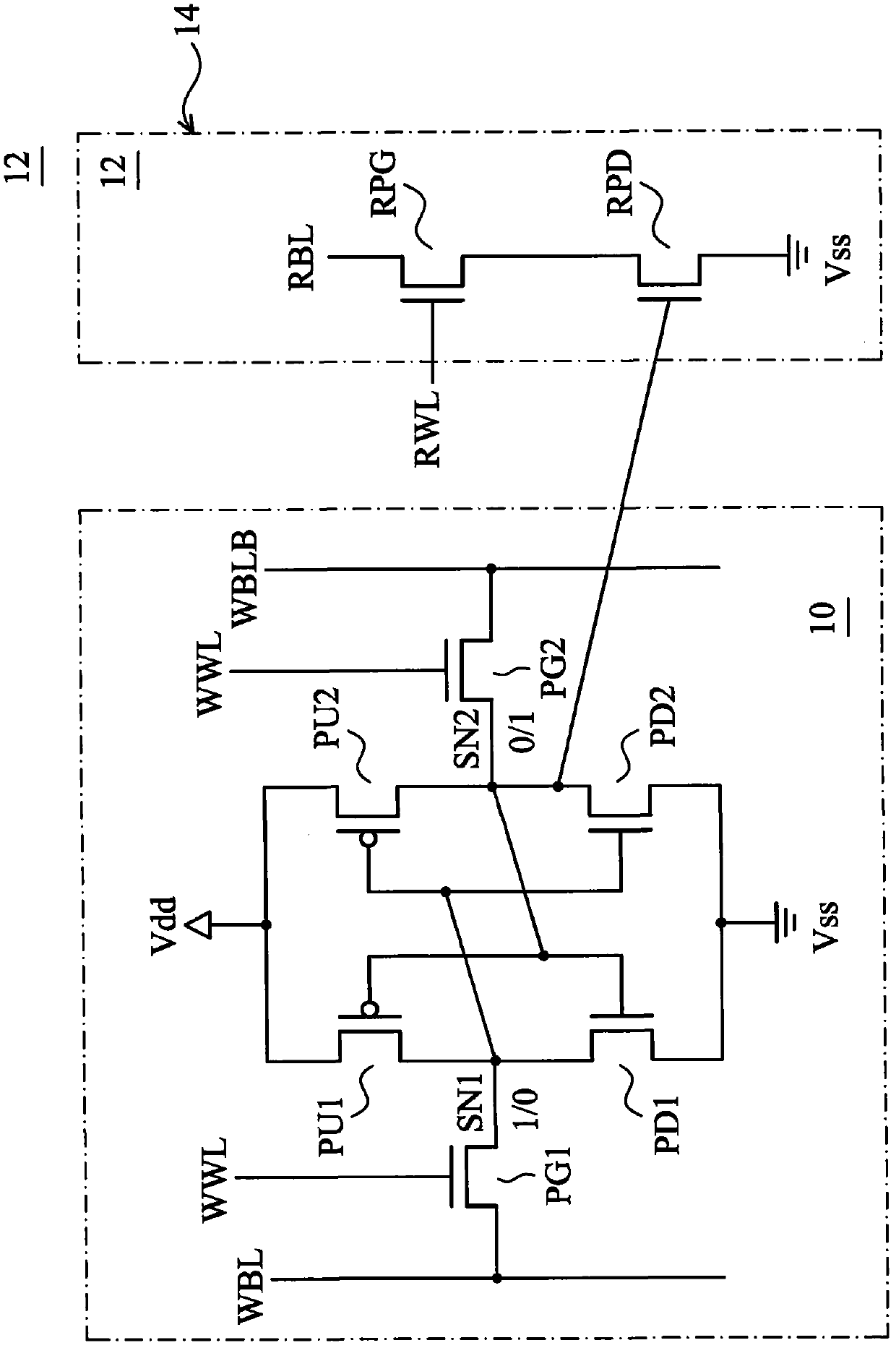
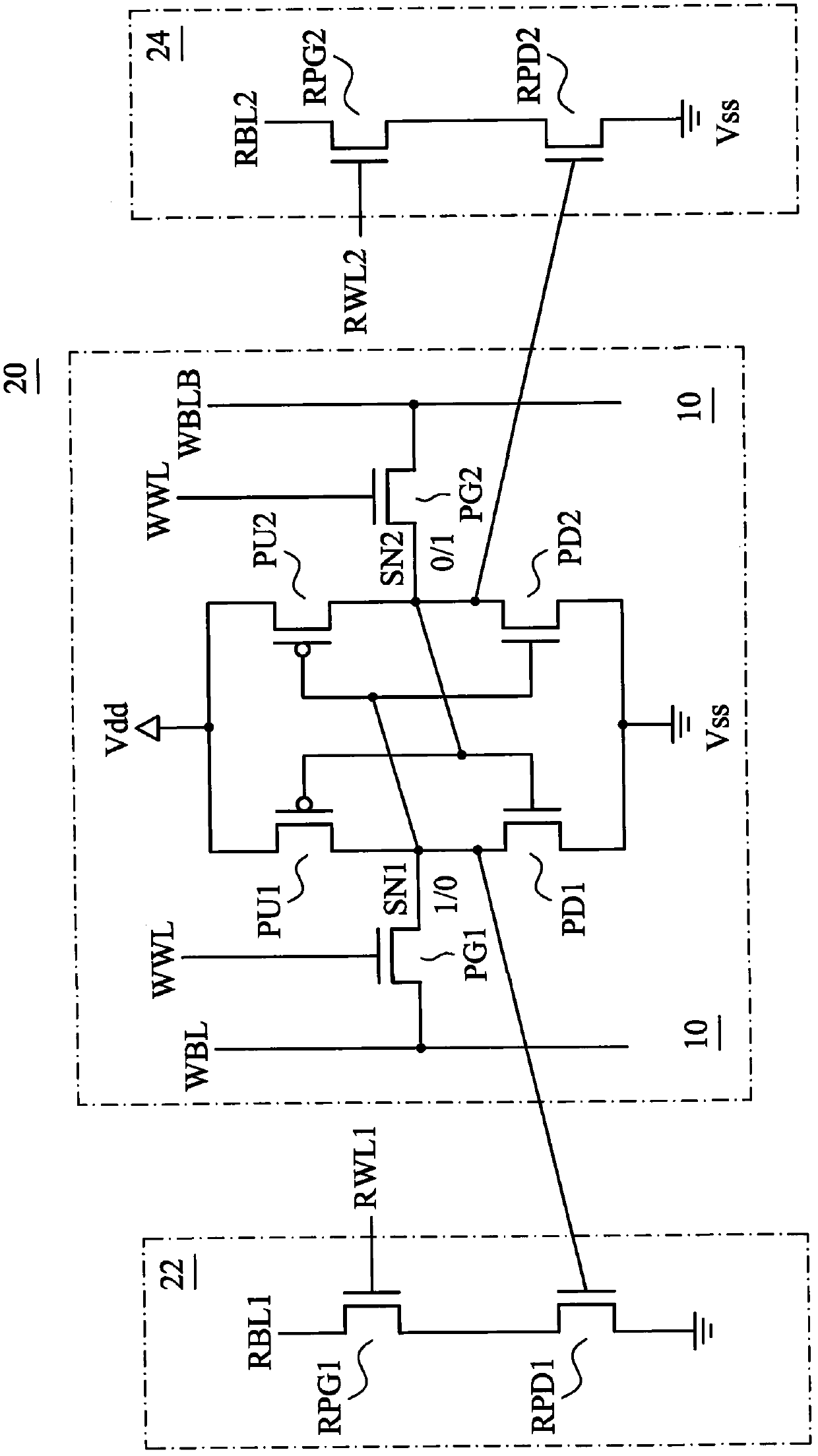
Methods and apparatus for SRAM bit cell with low standby current, low supply voltage and high speed
ActiveUS8294212B2Data stabilityLower average currentTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricGate dielectric
Circuits and methods for providing an SRAM or CAM bit cell. In one embodiment, a bit cell portion with thicker gate oxides in the storage cell transistors, and thinner gate oxides in a read port section having transistors are disclosed. The use of the thick gate oxides in the storage cell transistors provides a stable storage of data and lower standby leakage current. The use of the thinner gate oxides in the read port transistors provides fast read accesses and allows a lower Vcc,min in the read port. The methods used to form the dual gate oxide thickness SRAM cells have process steps compatible with the existing semiconductor manufacturing processes. Embodiments using high k gate dielectrics, dual gate dielectric materials in a single bit cell, and using finFET and planar devices in a bit cell are described. Methods for forming the structures are disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
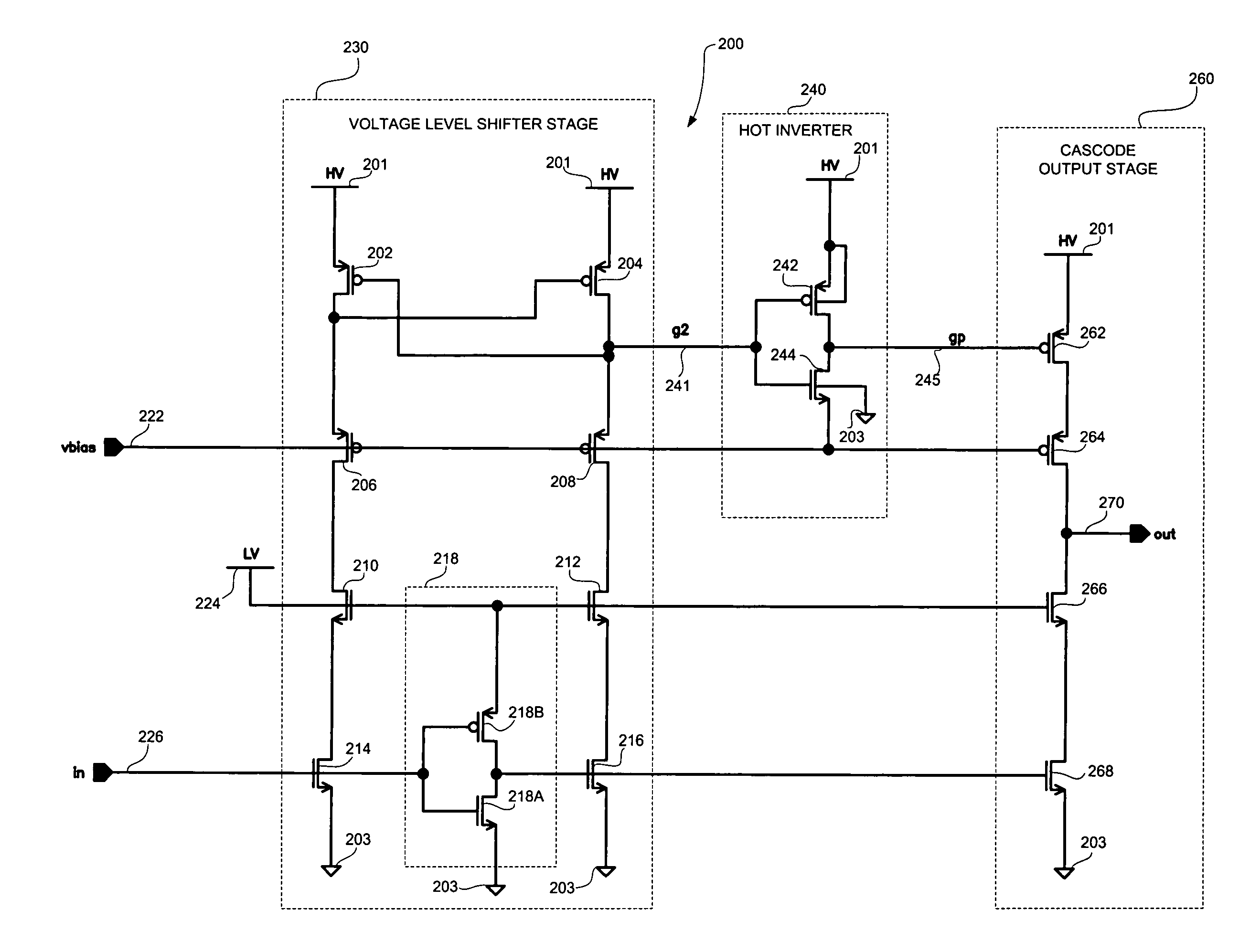
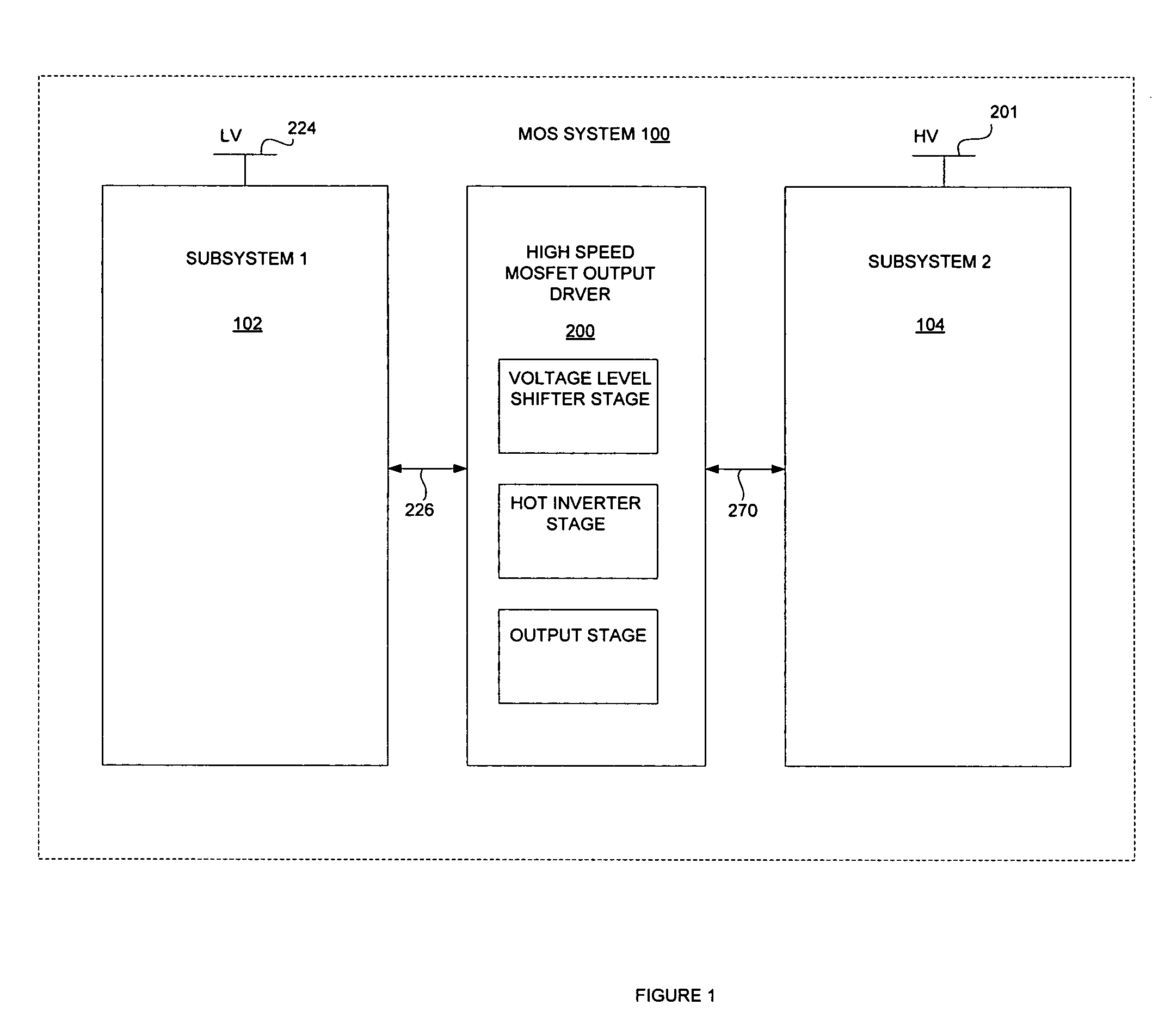
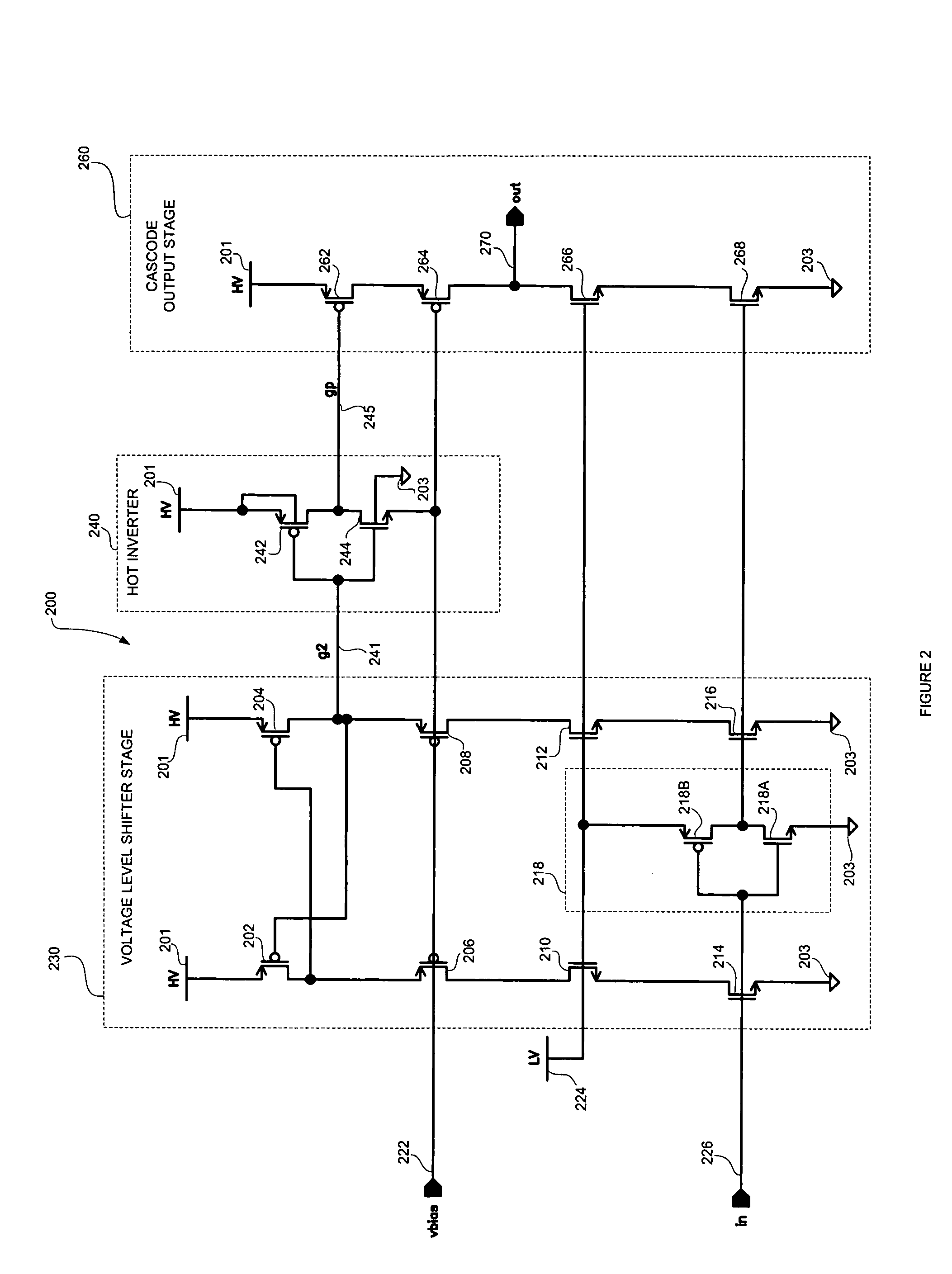
High speed MOSFET output driver
ActiveUS7227400B1High voltage gainReducing minimum voltage levelSwitching accelaration modificationsPulse automatic controlMOSFETEngineering
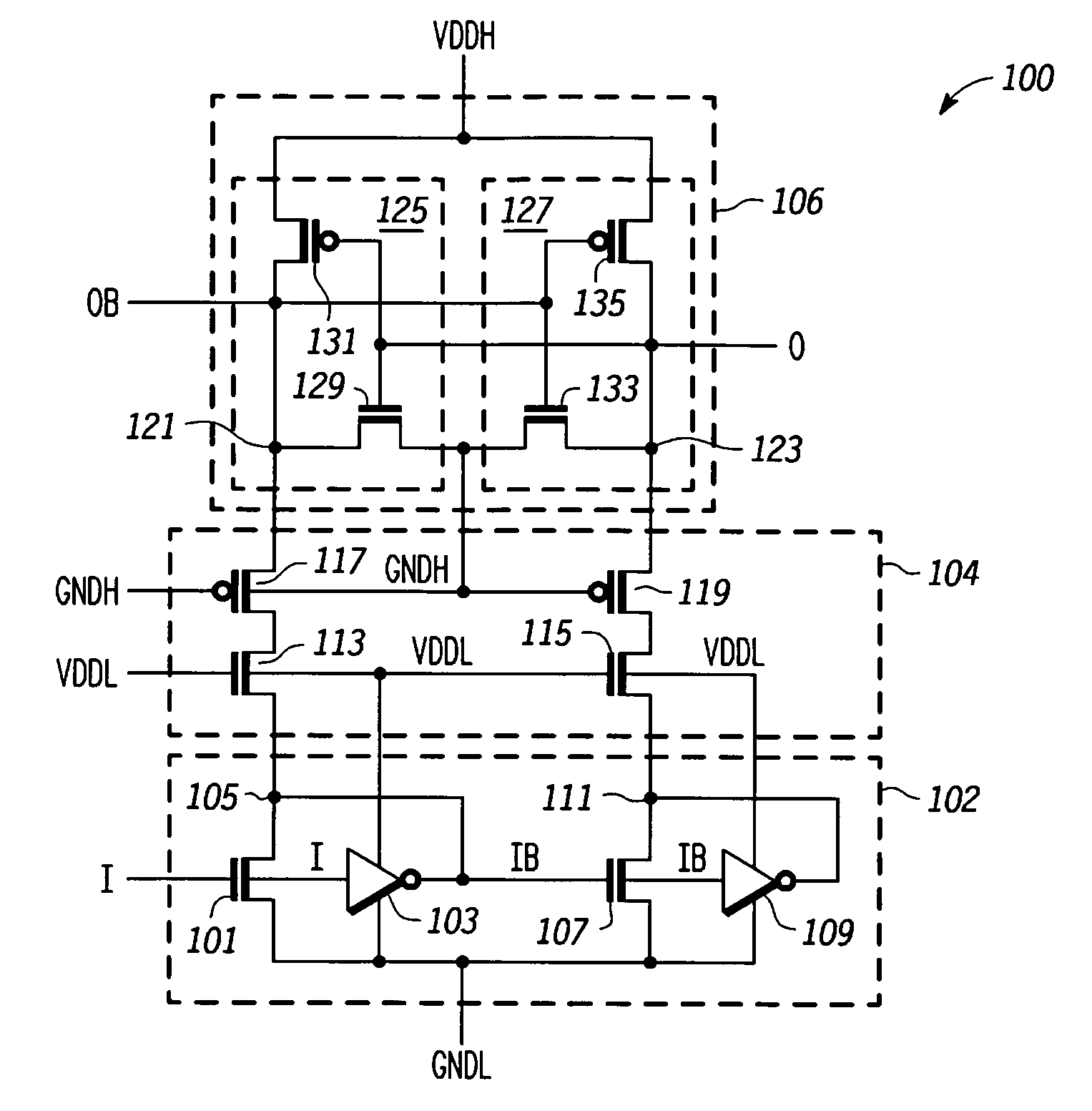
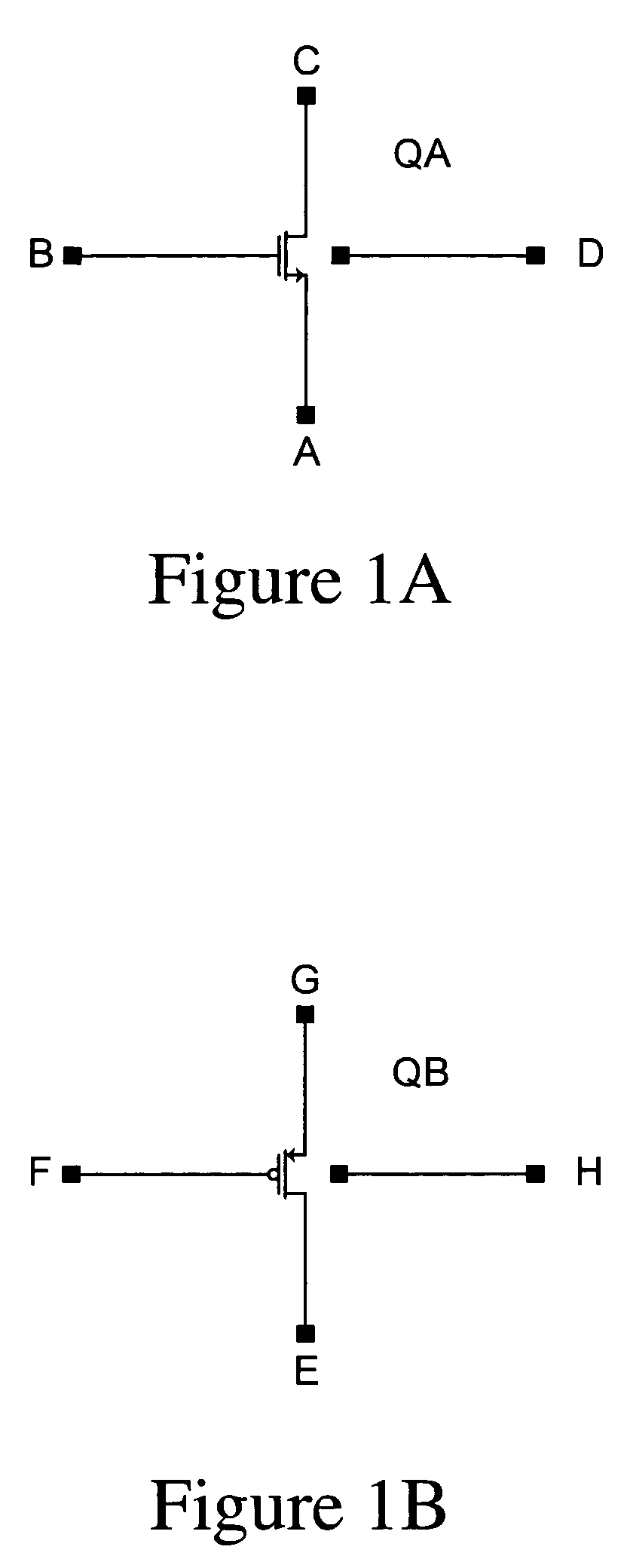
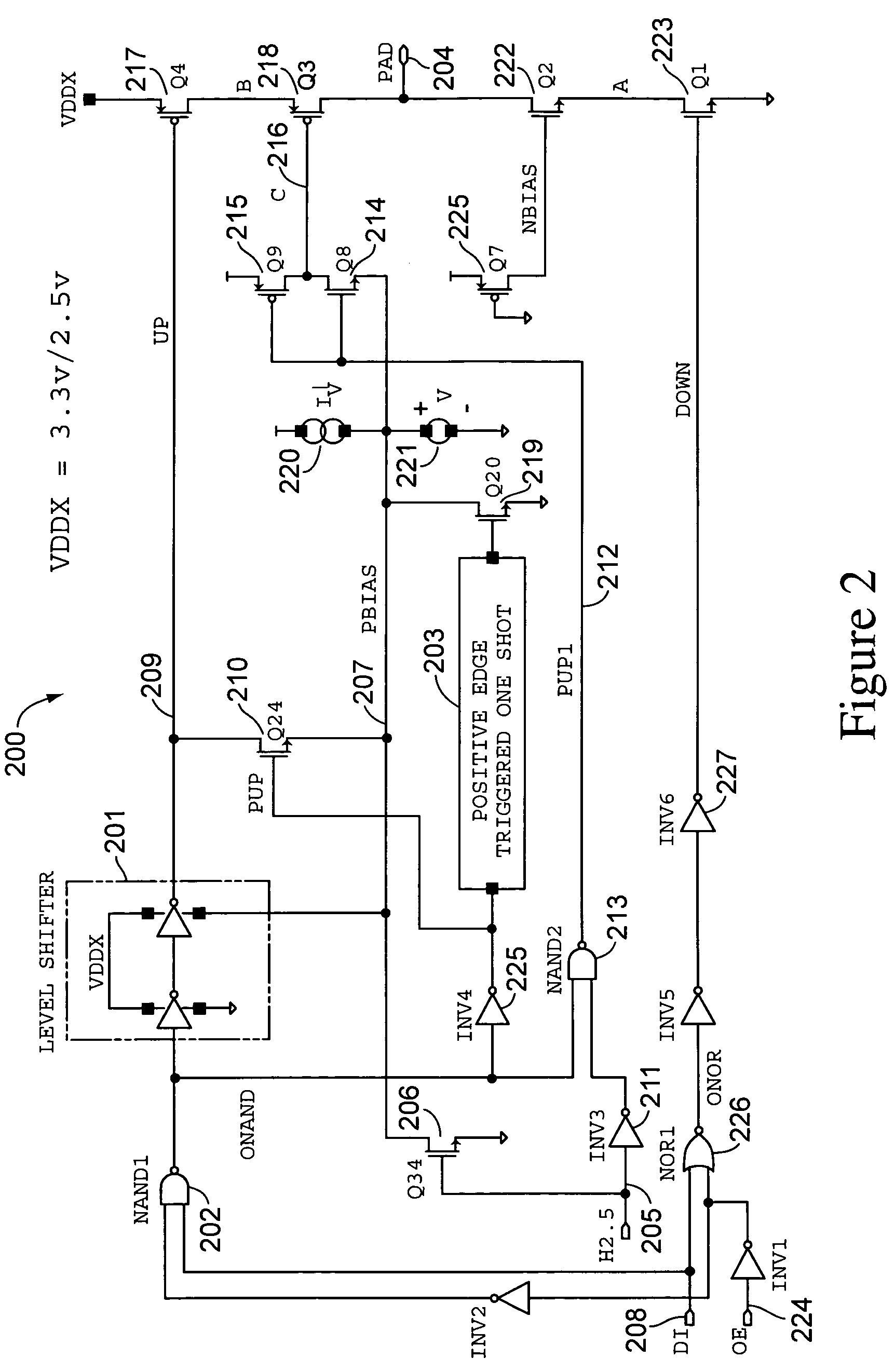
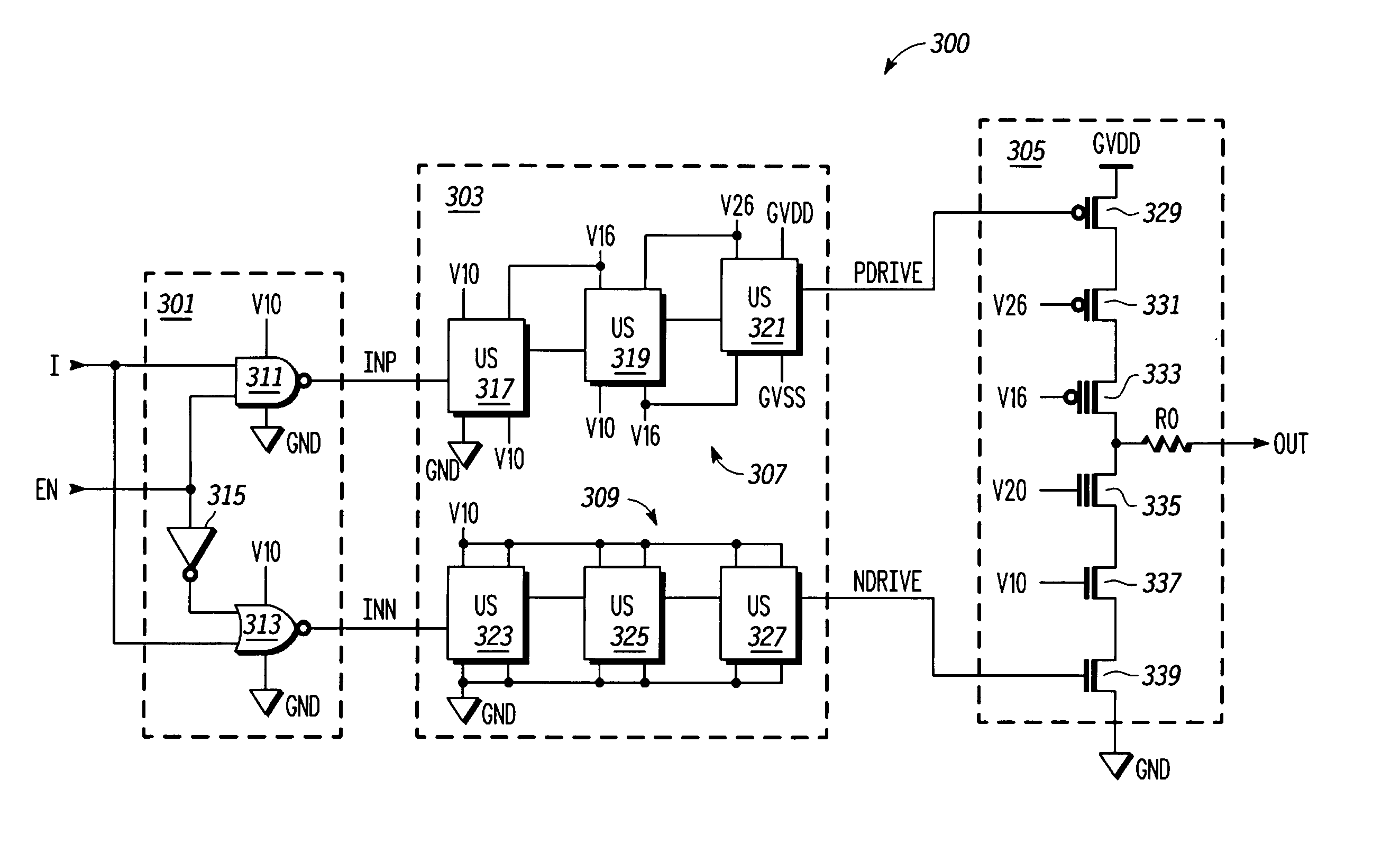
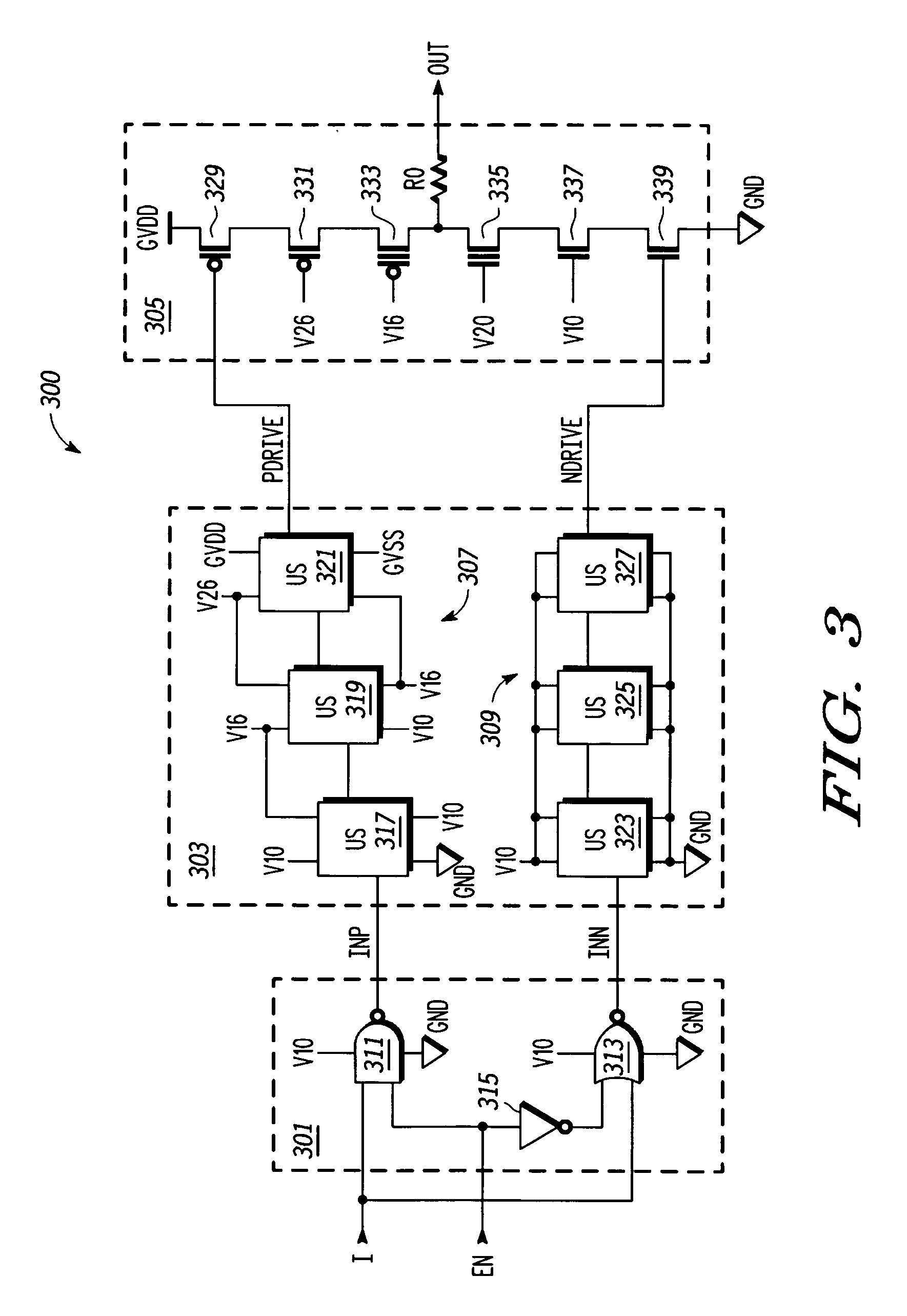
A high speed MOSFET output driver is disclosed that includes a voltage level shifter stage operable to transition an input signal at a first voltage level to an output signal at a second voltage level, an output stage operable to drive high voltage output load, and a hot inverter, biased between the second voltage level and the bias voltage such that the voltage gain of the output signal is increased and at the same time the minimum voltage level of the output signal introduced to the output stage is decreased, improving the control and the transition time of the output signal and allowing all components of the high speed MOSFET output driver of the present invention to be fabricated using a single thin gate oxide process.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Methods and Apparatus for SRAM Bit Cell with Low Standby Current, Low Supply Voltage and High Speed
ActiveUS20110068400A1Data stabilityLower average currentTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectricGate dielectric
Circuits and methods for providing an SRAM or CAM bit cell. In one embodiment, a bit cell portion with thicker gate oxides in the storage cell transistors, and thinner gate oxides in a read port section having transistors are disclosed. The use of the thick gate oxides in the storage cell transistors provides a stable storage of data and lower standby leakage current. The use of the thinner gate oxides in the read port transistors provides fast read accesses and allows a lower Vcc,min in the read port. The methods used to form the dual gate oxide thickness SRAM cells have process steps compatible with the existing semiconductor manufacturing processes. Embodiments using high k gate dielectrics, dual gate dielectric materials in a single bit cell, and using finFET and planar devices in a bit cell are described. Methods for forming the structures are disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
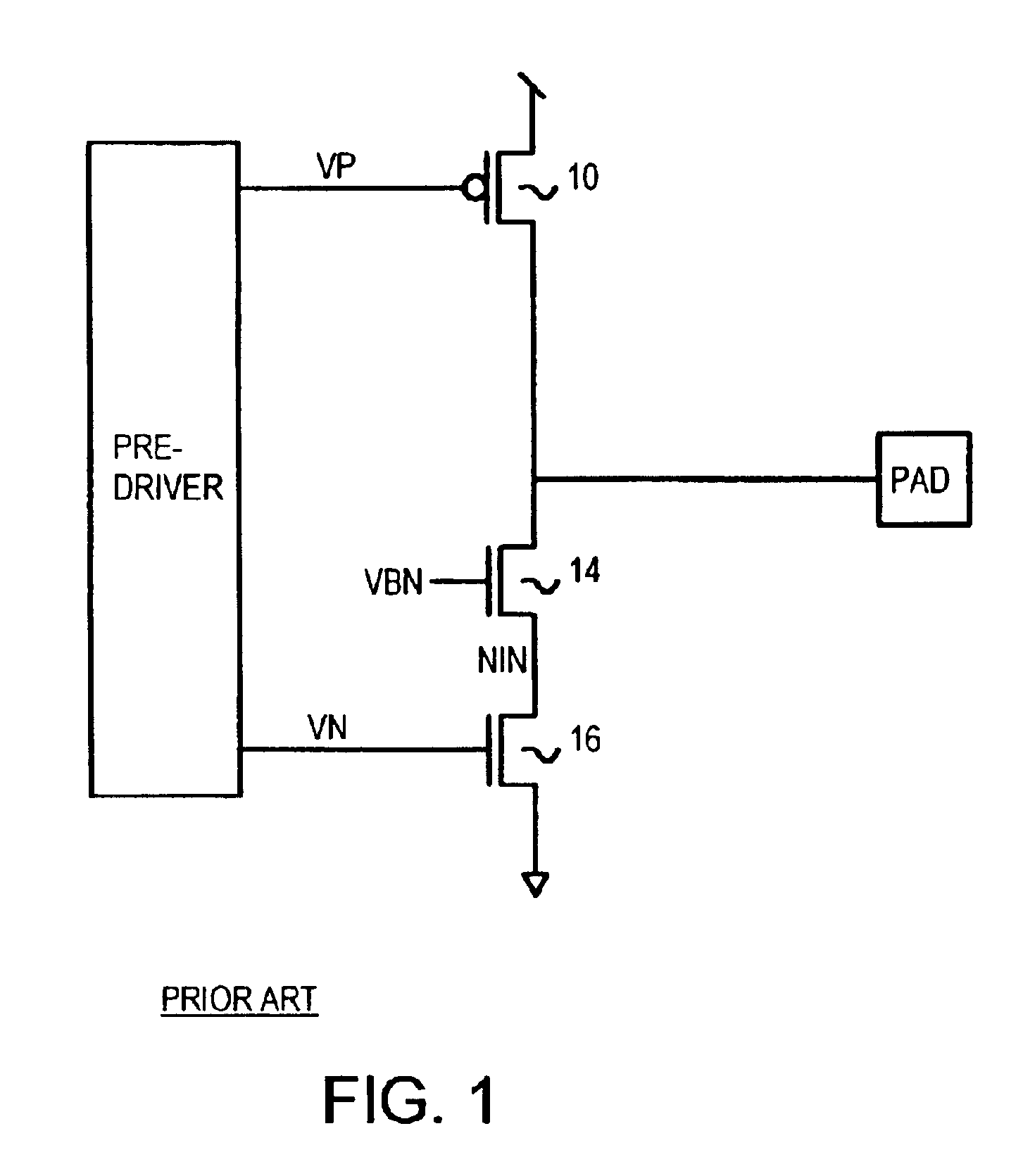
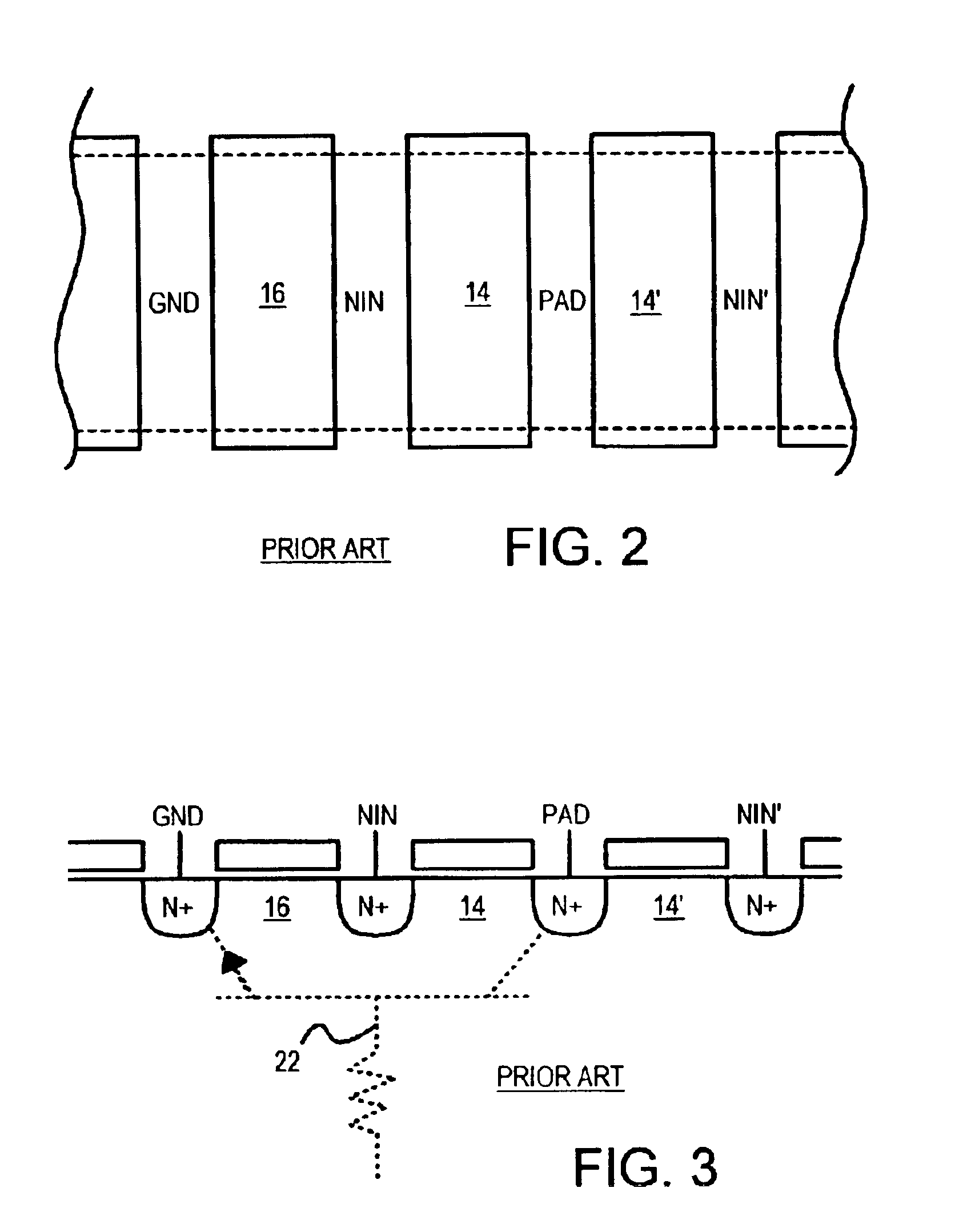
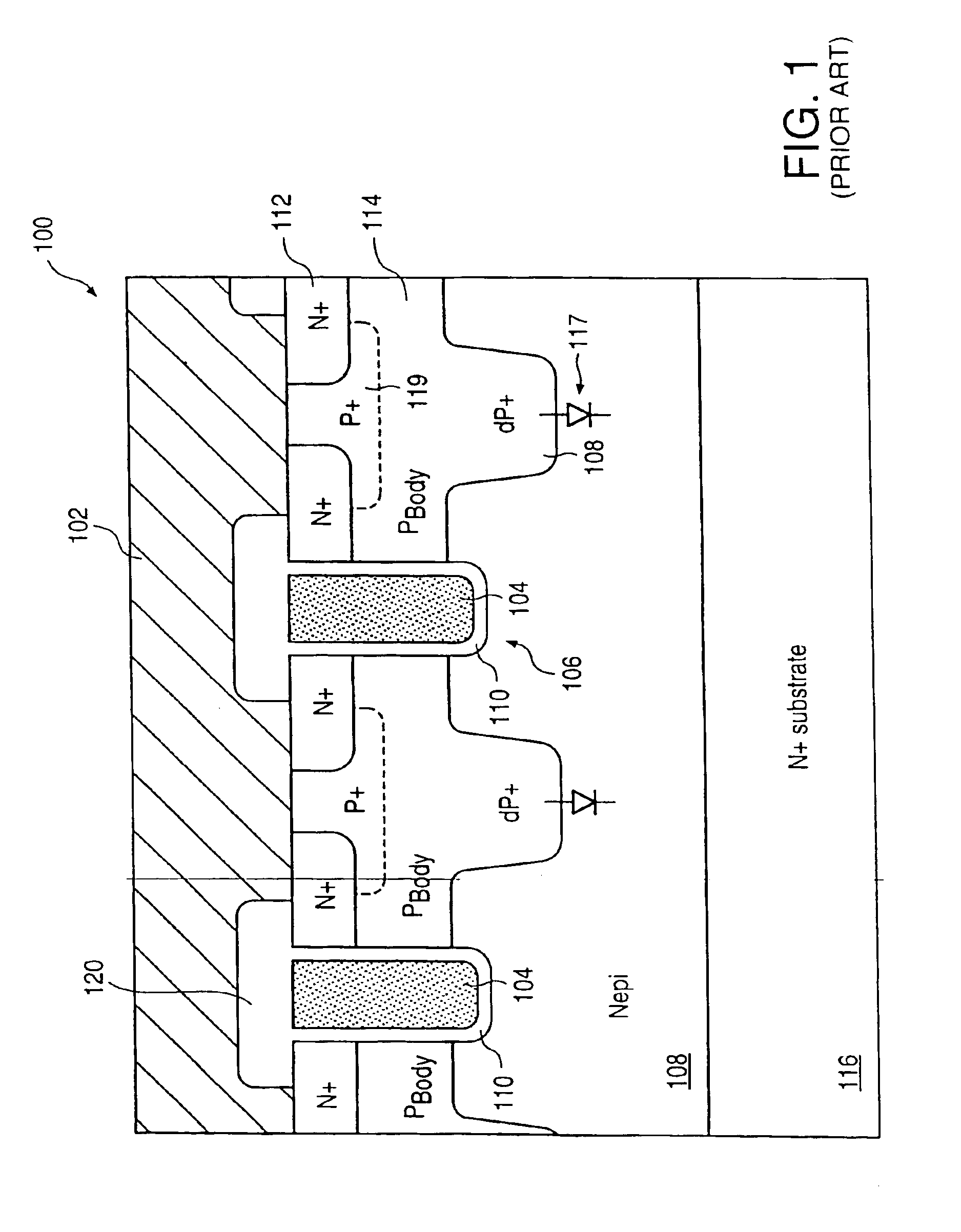
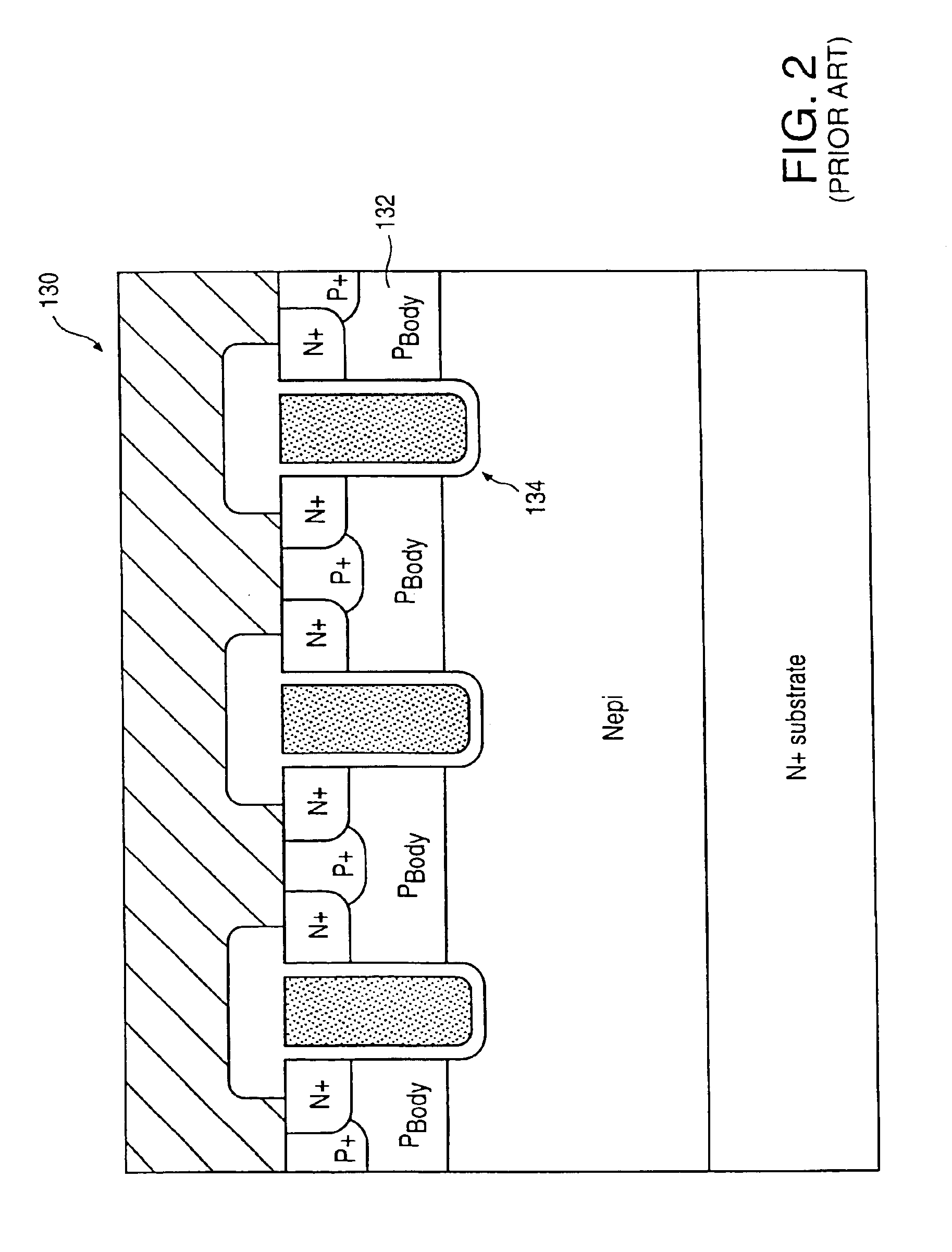
Stacked-NMOS-triggered SCR device for ESD-protection
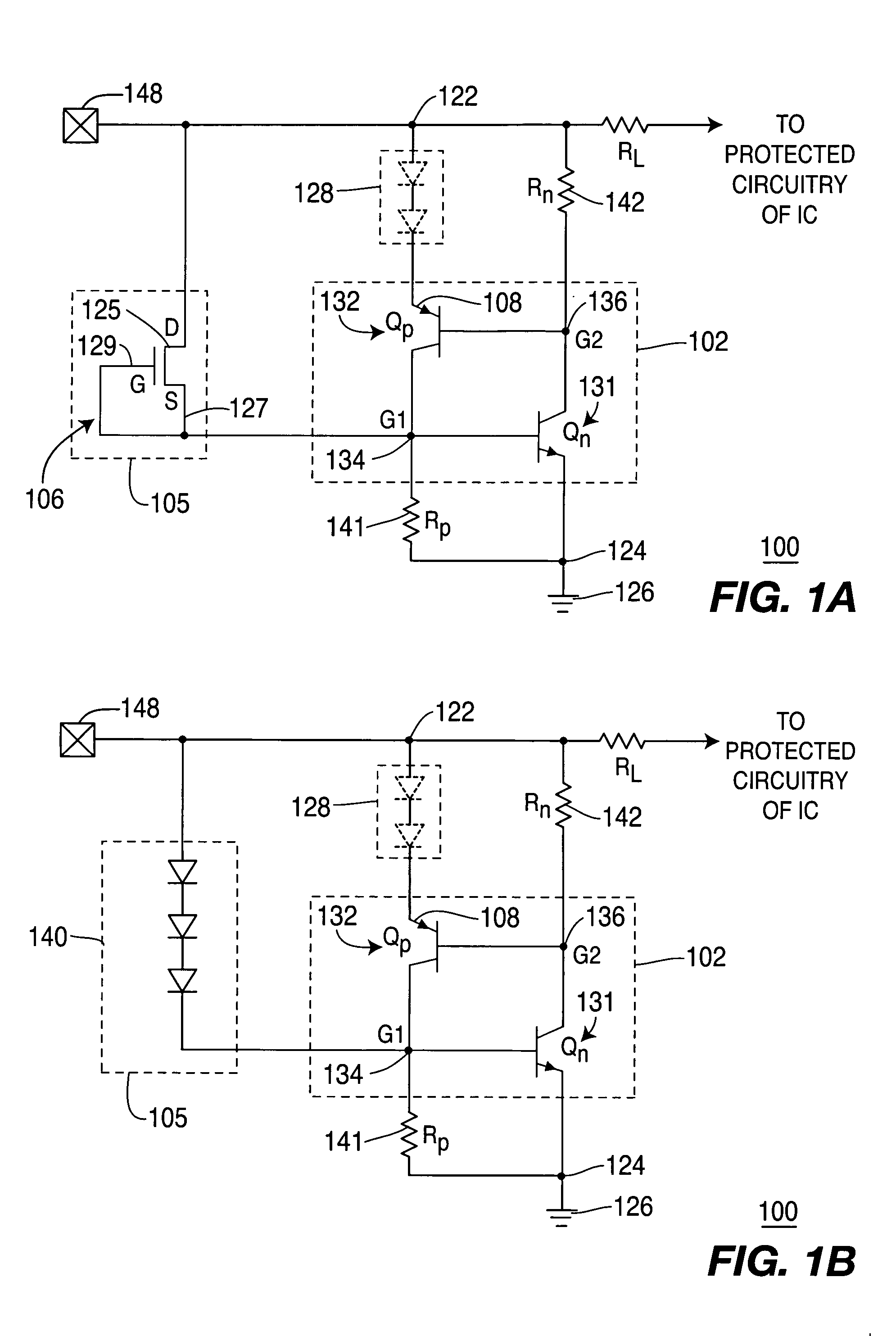
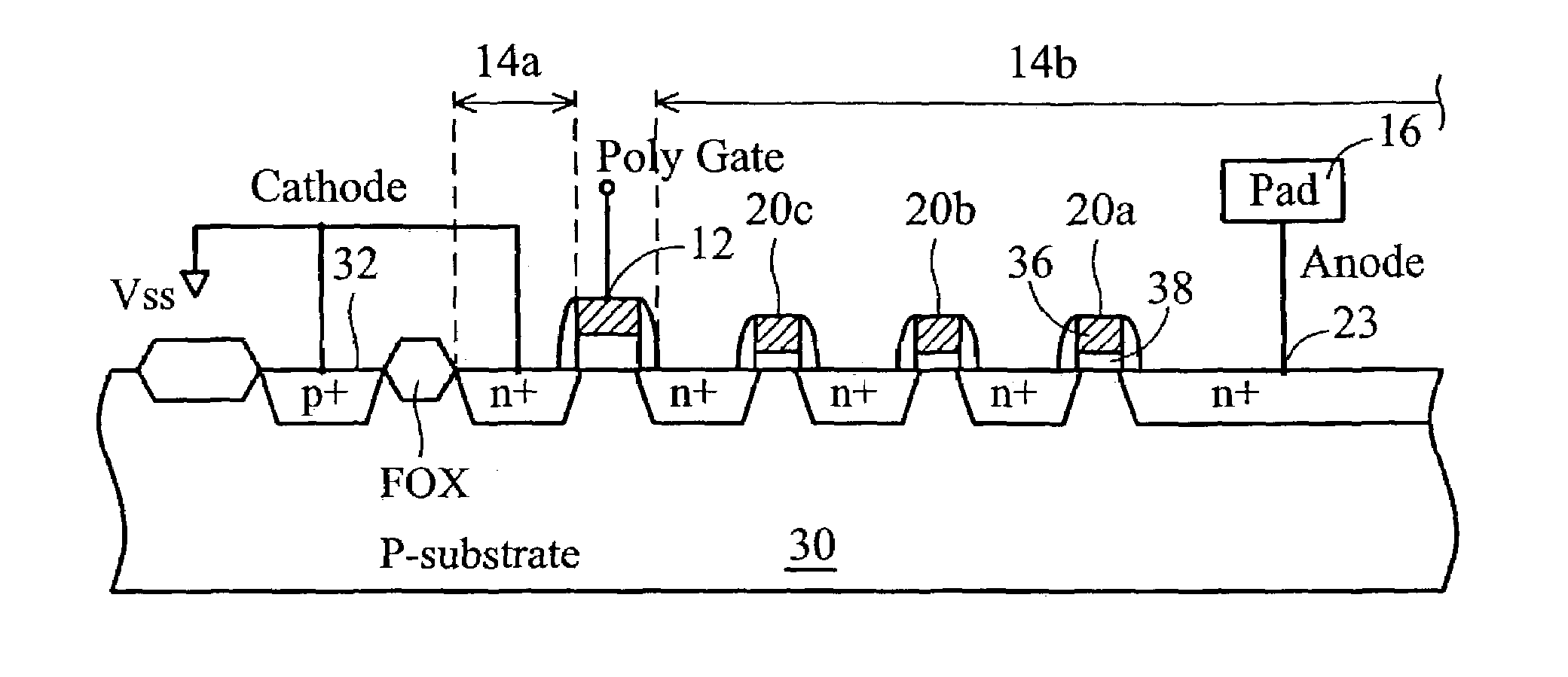
Transistors with very thin gate oxides are protected against oxide failure by cascading two or more transistors in series between an output pad and ground. The intermediate source / drain node between the two cascaded transistors is usually floating during an ESD test, delaying snapback turn-on of a parasitic lateral NPN transistor. This intermediate node is used to drive the gate of an upper trigger transistor. A lower trigger transistor has a gate node that is charged by the ESD pulse on the pad through a coupling capacitor. When the coupled ESD pulse turns on the trigger transistors, the trigger transistors turn on a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) that is integrated with the trigger transistors.
Owner:DIODES INC
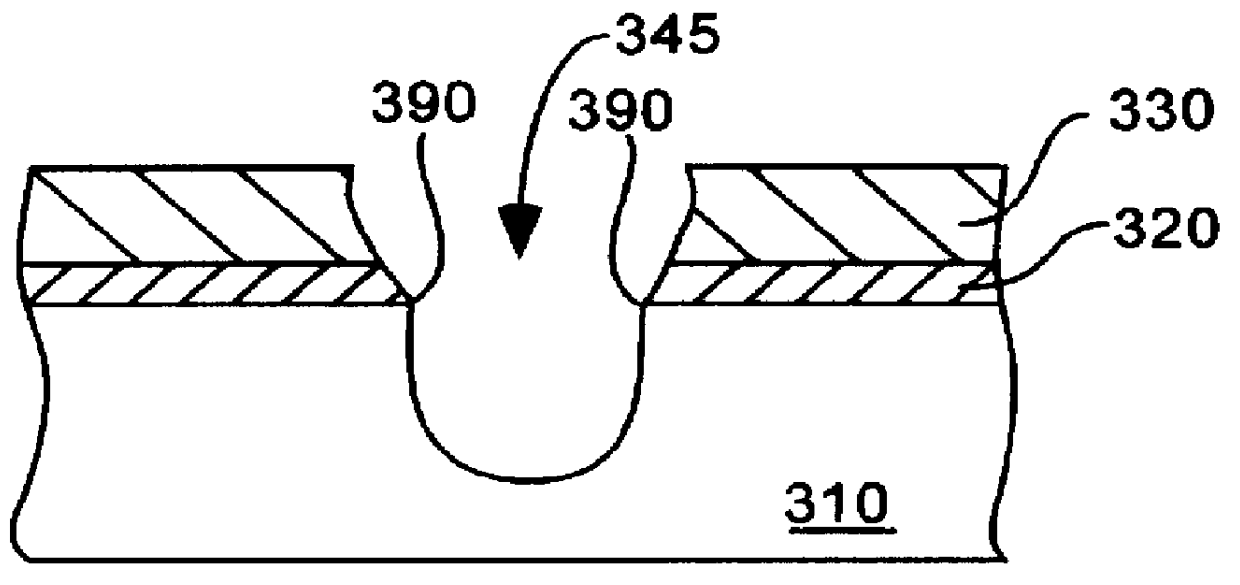
Advanced trench sidewall oxide for shallow trench technology
A method of forming an isolation structure in a semiconductor substrate is described. A trench is first etched into a semiconductor substrate. The trench is subjected to a nitrogen-oxide gas ambient and is annealed to form a silicon-oxynitride surface along the trench sidewalls. A first oxide layer is then formed within the trench. The first oxide layer is subjected to a nitridation step and is annealed to form an oxy-nitride surface on the first oxide layer and a silicon-oxynitride interface between the first oxide layer and the semiconductor substrate. A second oxide layer is then deposited over the oxy-nitride surface of the first oxide layer. The method and isolation structure of the present invention reduce dopant outdiffusion, reduce trench stresses, allow more uniform growth of thin gate oxides, and permit the use of thinner gate oxides.
Owner:INTEL CORP
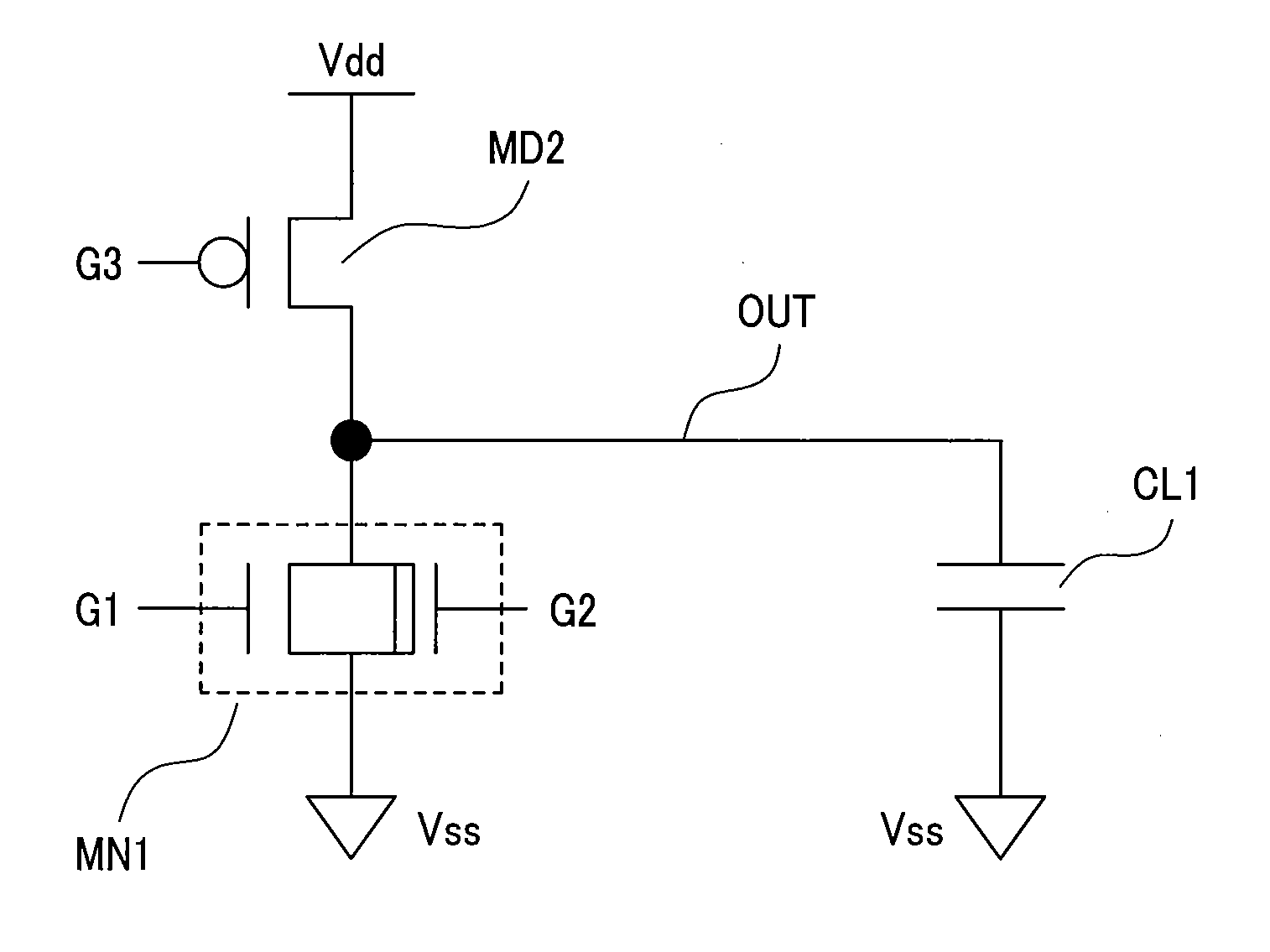
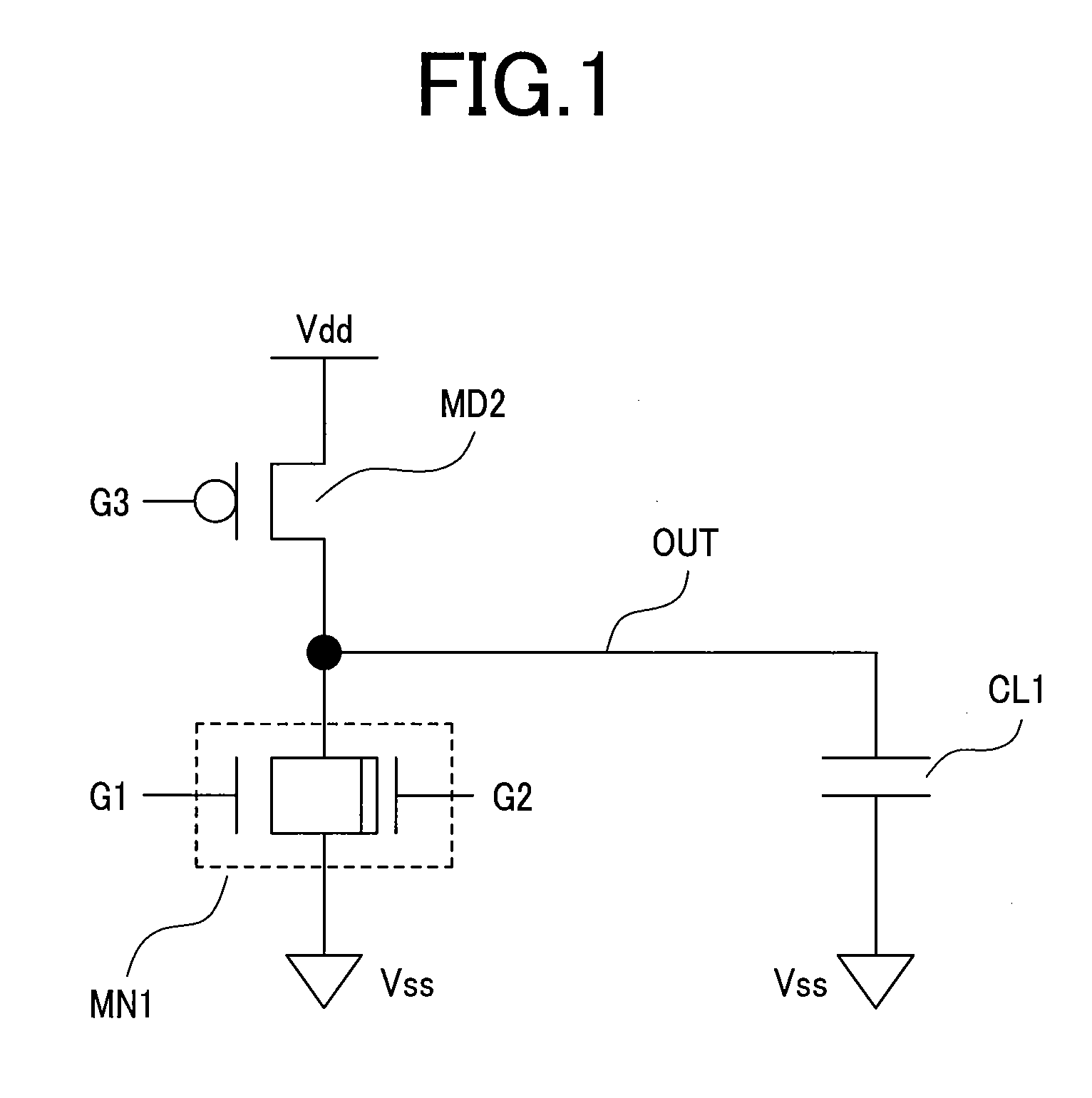
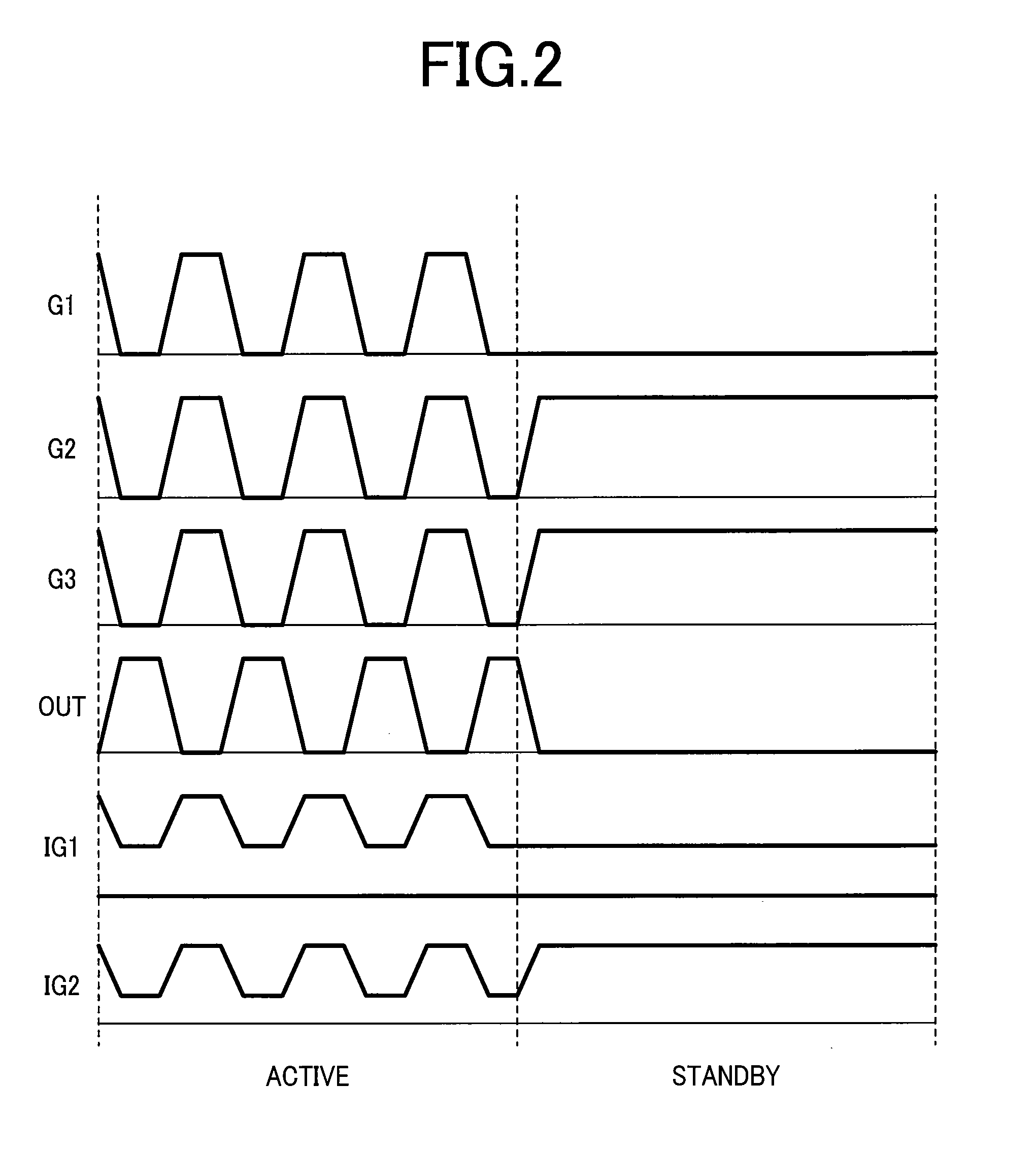
Semiconductor integrated circuit device
ActiveUS20070139072A1Reduce leakage currentReduce power consumptionReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalDrain currentDouble gate
An object of the present invention is to provide a technique of reducing the leakage current of a drive circuit for driving a circuit that must retain a potential (or information) when in its standby state. A semiconductor integrated circuit device of the present invention includes a drive circuit for driving a circuit block. This drive circuit is made up of a double gate transistor with gates having different gate oxide film thicknesses. When the circuit block is in its standby state, the gate of the double gate transistor having a thinner gate oxide film is turned off and that having a thicker gate oxide film is turned on. This arrangement allows a reduction in the leakage currents of both the circuit block and the drive circuit while allowing the drive circuit to deliver or cut off power to the circuit block.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
High voltage reset method for increasing the dynamic range of a CMOS image sensor
InactiveUS6864920B1Extended imaging rangeHigh voltage levelTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSEngineering
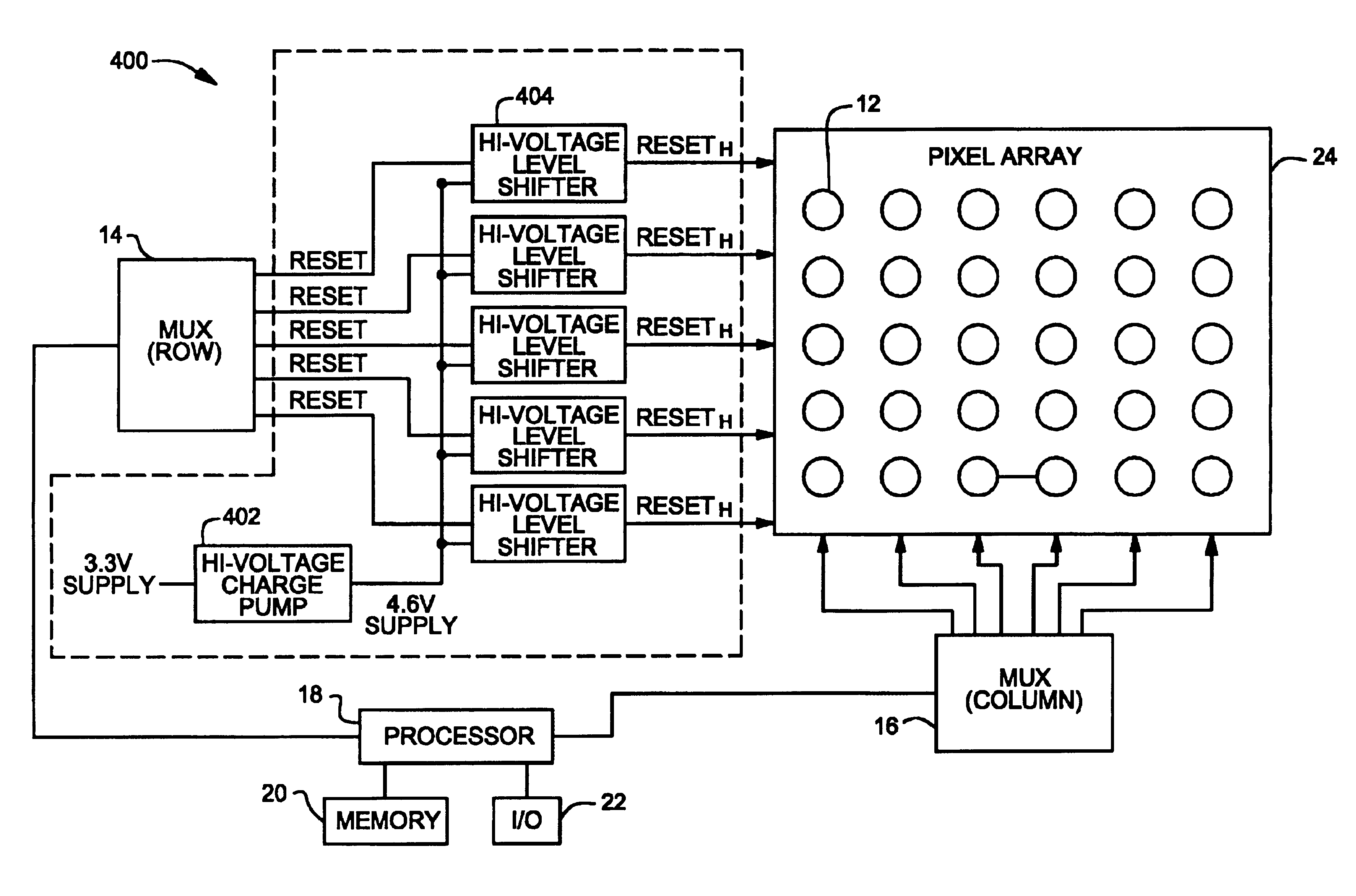
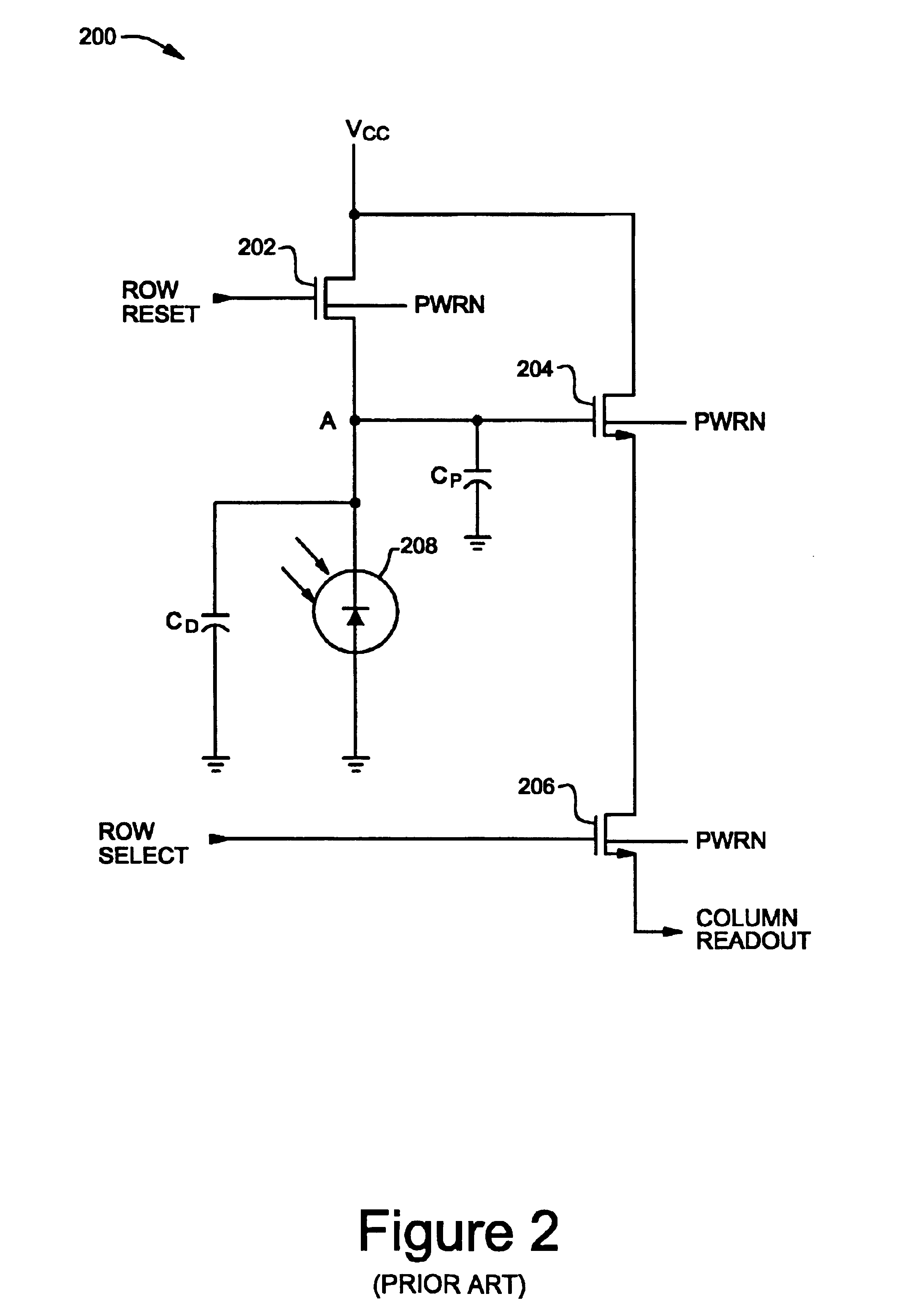
A circuit and method for increasing the dynamic range of CMOS image sensors designed with a thin gate oxide layer. The circuit includes a high voltage supply circuit and a high voltage level shifter circuit. The high voltage supply circuit is configured to supply a voltage to the shifter circuit. The voltage has a voltage level higher than the maximum supply voltage of the associated fabrication process. The shifter circuit is configured to output a high reset signal based on a reset signal generated to reset a pixel circuit of a pixel array. Instead of the reset signal, the high reset signal is coupled to a gate of the reset transistor in the pixel circuit. The high reset signal allows the reset transistor to maintain a gate to source potential less than the maximum supply voltage even when the high reset signal is greater than the maximum supply voltage.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
ESD protection devices and methods for reducing trigger voltage
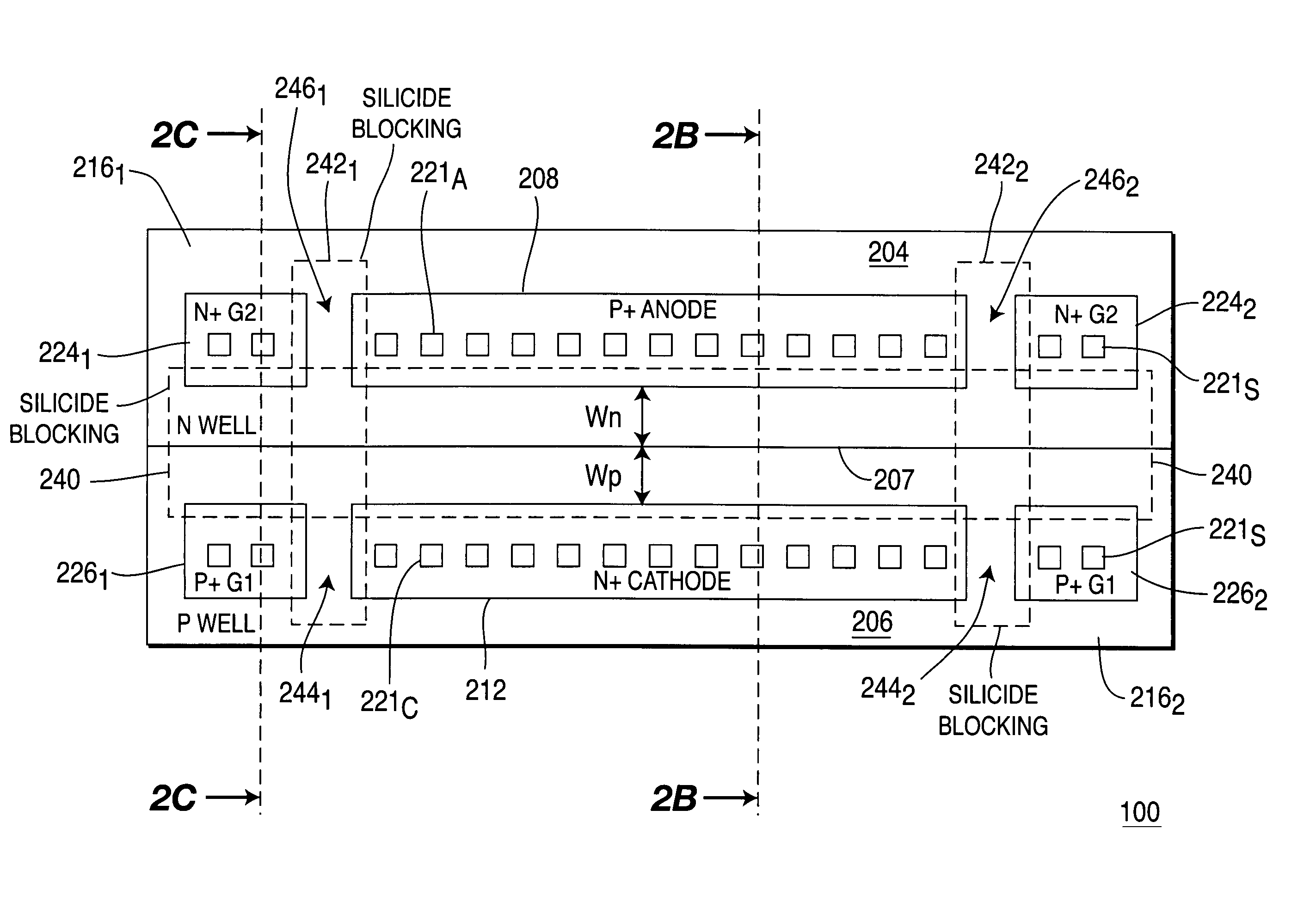
InactiveUS7009252B2Quicker trigger mechanismBetter ESD protection levelTransistorThyristorP–n junctionBreakdown voltage
ESD protection devices and methods to form them are provided in this invention. By employing the thin gate oxide fabricated by a dual gate oxide process, ESD protection devices with a lower trigger voltage are provided. The NMOS for ESD protection according to the present invention has islands with thin gate oxides and a control gate with a thick gate oxide. These islands overlap the drain region of the NMOS to reduce the breakdown voltage of the PN junction in the drain region, thereby reducing the ESD trigger voltage and improving the ESD protection level of the NMOS. Furthermore, the invention is applicable to general integrated-circuit processes as well as various ESD protection devices.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Integrated complementary low voltage rf-ldmos
InactiveUS20080164537A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLDMOSLow voltage
Complementary RF LDMOS transistors have gate electrodes over split gate oxides. A source spacer of a second conductivity type extends laterally from the source tap of a first conductivity type to approximately the edge of the gate electrode above the thinnest gate oxide. A body of a first conductivity type extends from approximately the bottom center of the source tap to the substrate surface and lies under most of the thin section of the split gate oxide. The source spacer is approximately the length of the gate sidewall oxide and is self aligned with gate electrode. The body is also self aligned with gate electrode. The drain is surrounded by at least one buffer region which is self aligned to the other edge of the gate electrode above the thickest gate oxide and extends to the below the drain and extends laterally under the thickest gate oxide. Both the source tap and drain are self aligned with the gate side wall oxides and are thereby spaced apart laterally from the gate electrode.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Vertically integrated flash EPROM for greater density and lower cost
InactiveUS20070004134A1Increase cell areaImprove the coupling ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon implantationPhotolithography
Owner:VORA MADHUKAR B
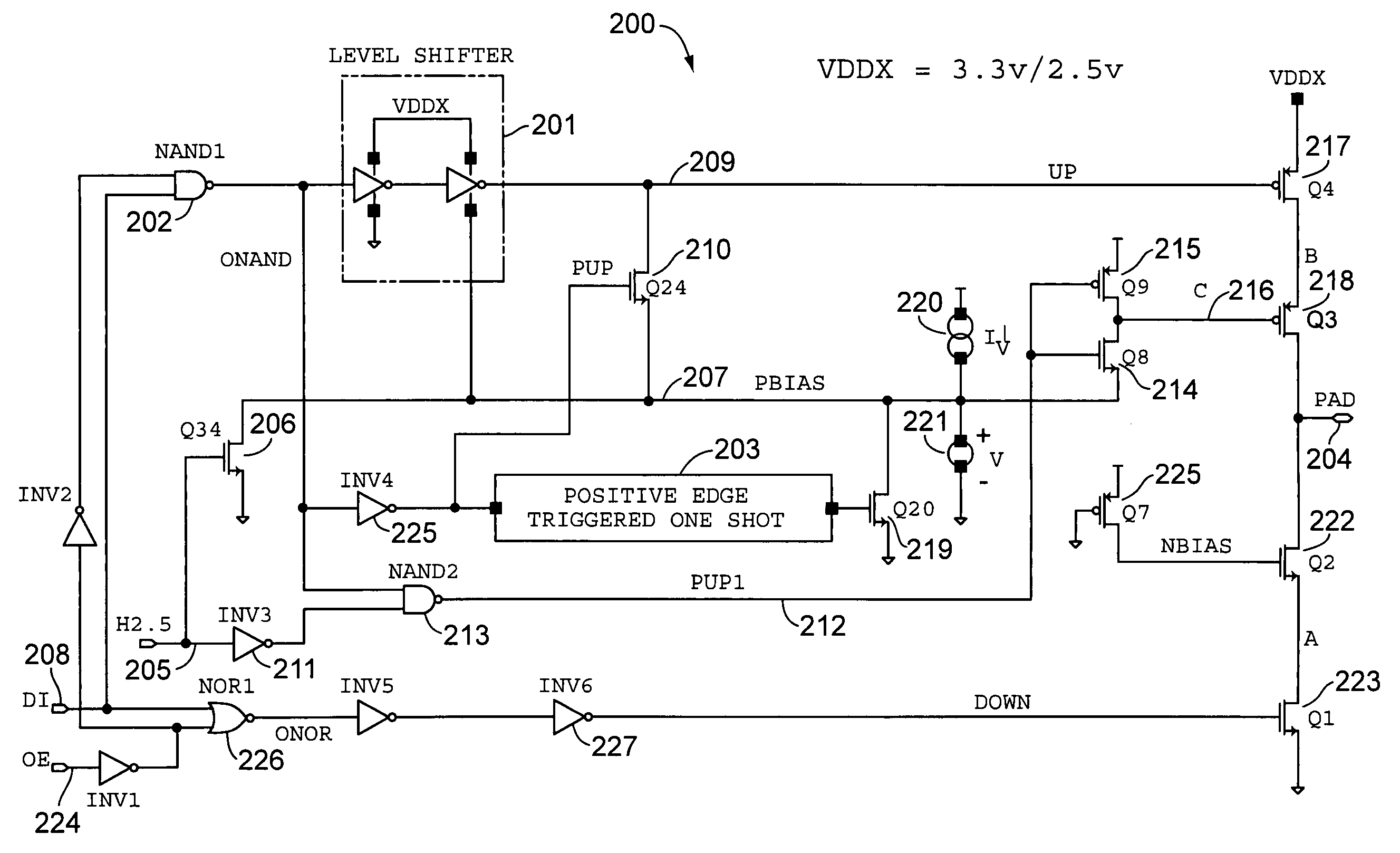
Cascadable level shifter cell
ActiveUS7268588B2Electric pulse generatorLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsVoltage rangeProtection layer
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
Anti-fuse memory cell
ActiveUS7755162B2Improve reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsVariable thicknessCondensed matter physics
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
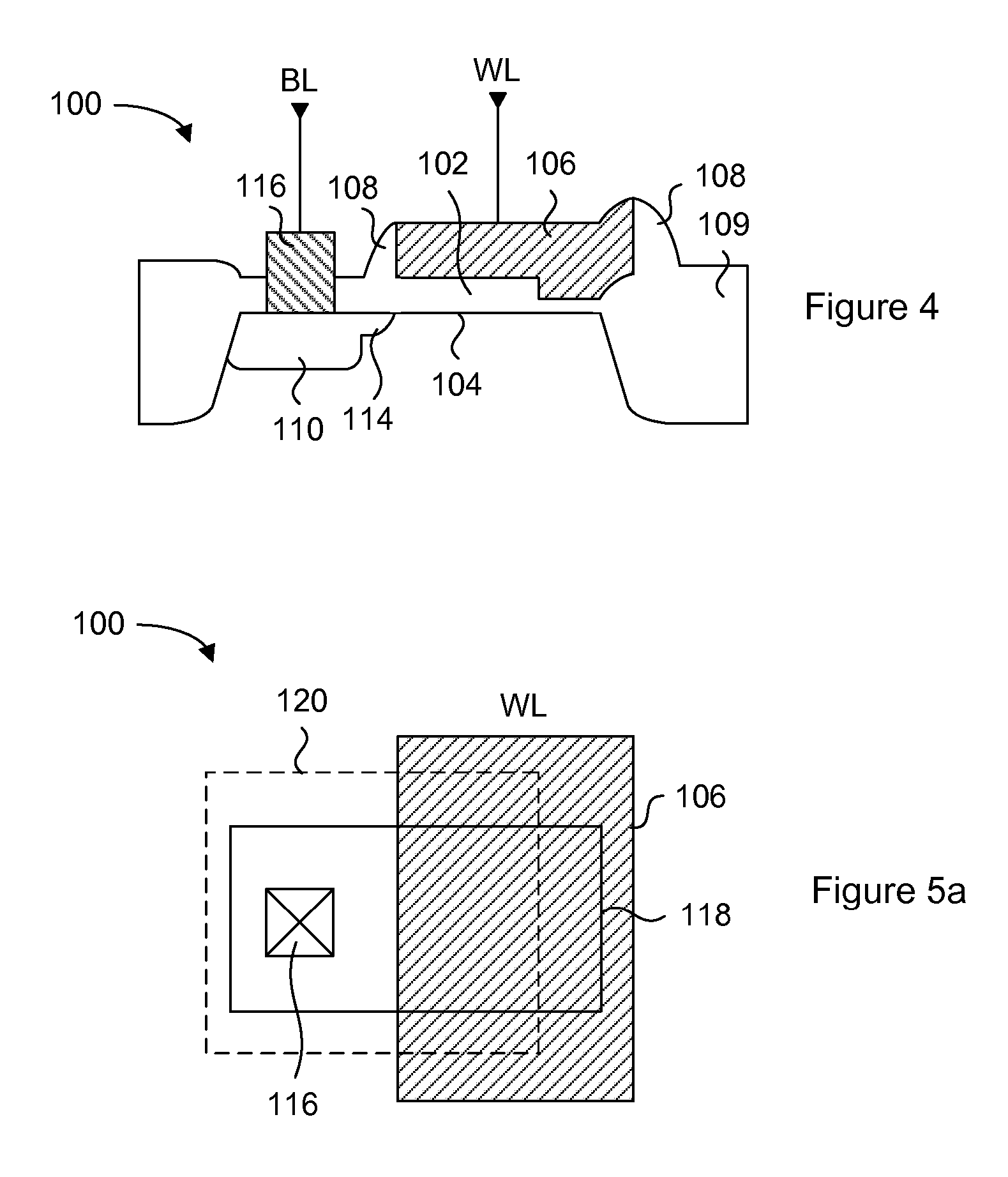
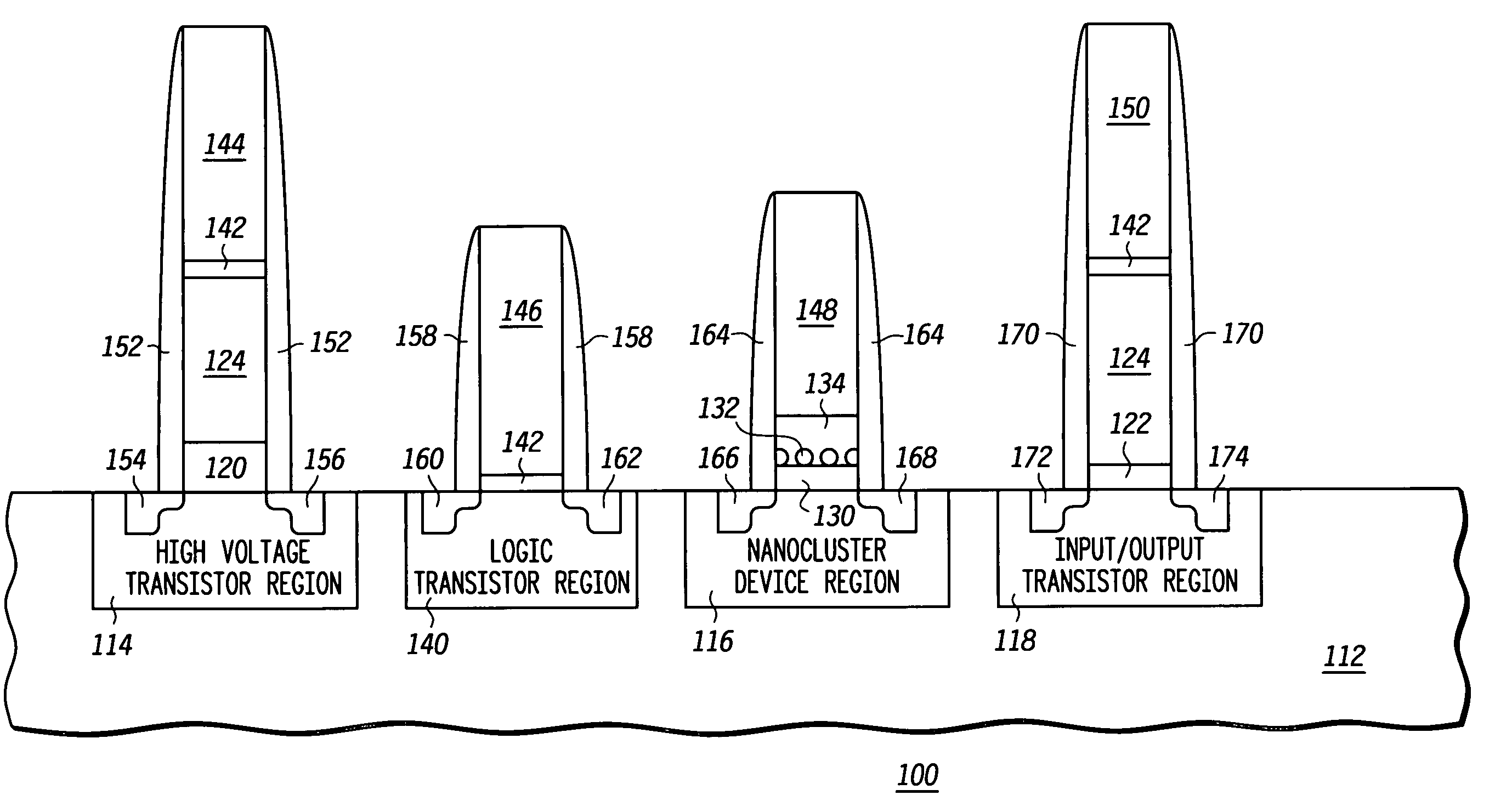
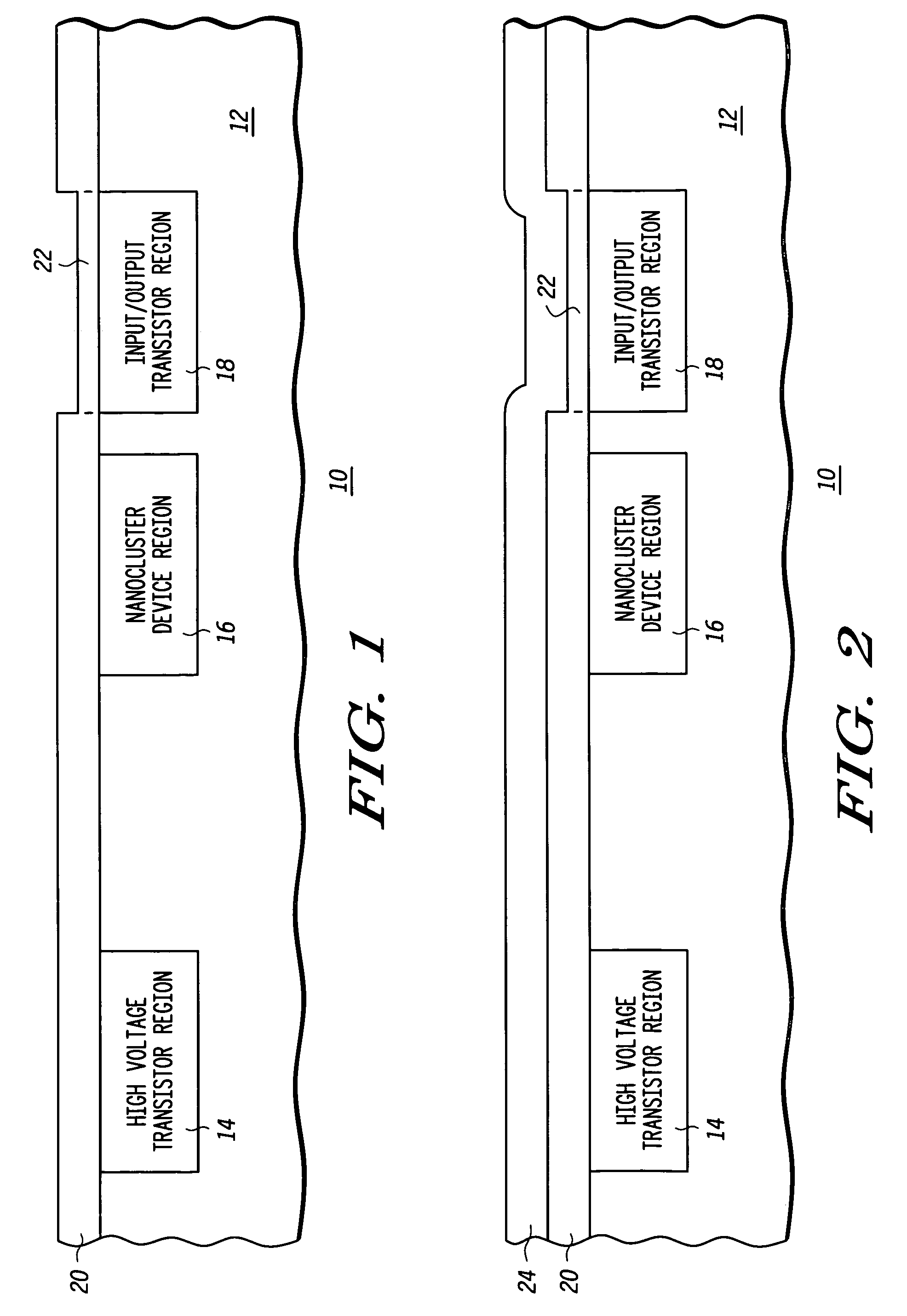
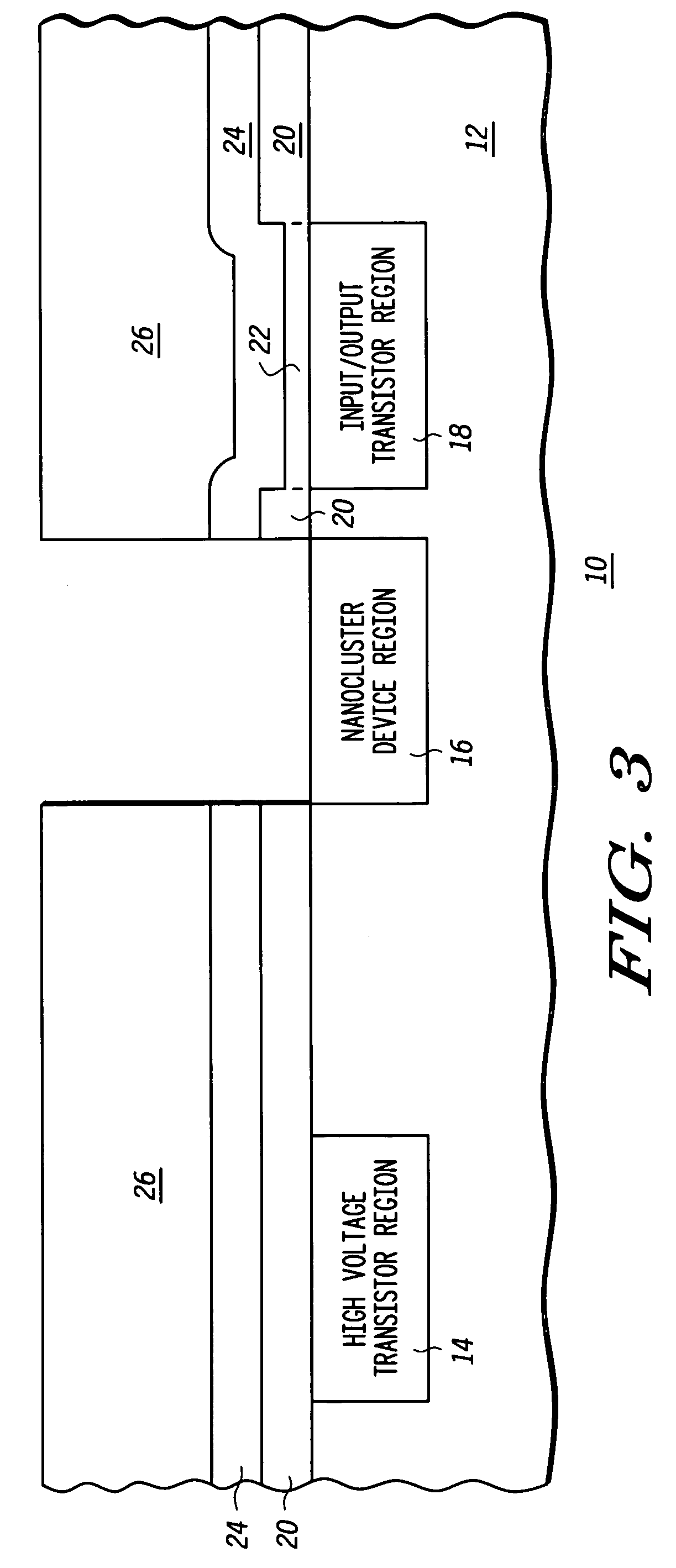
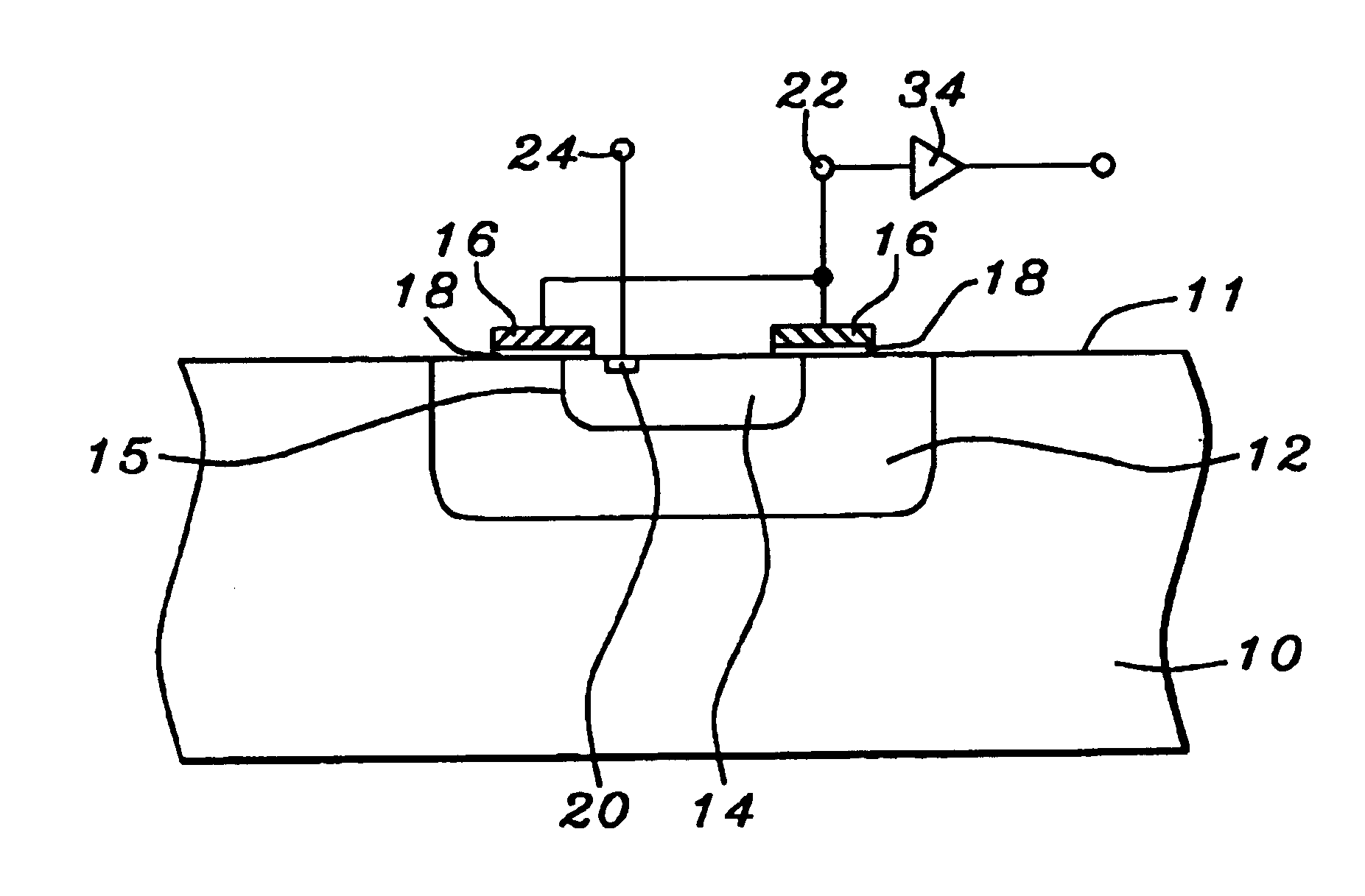
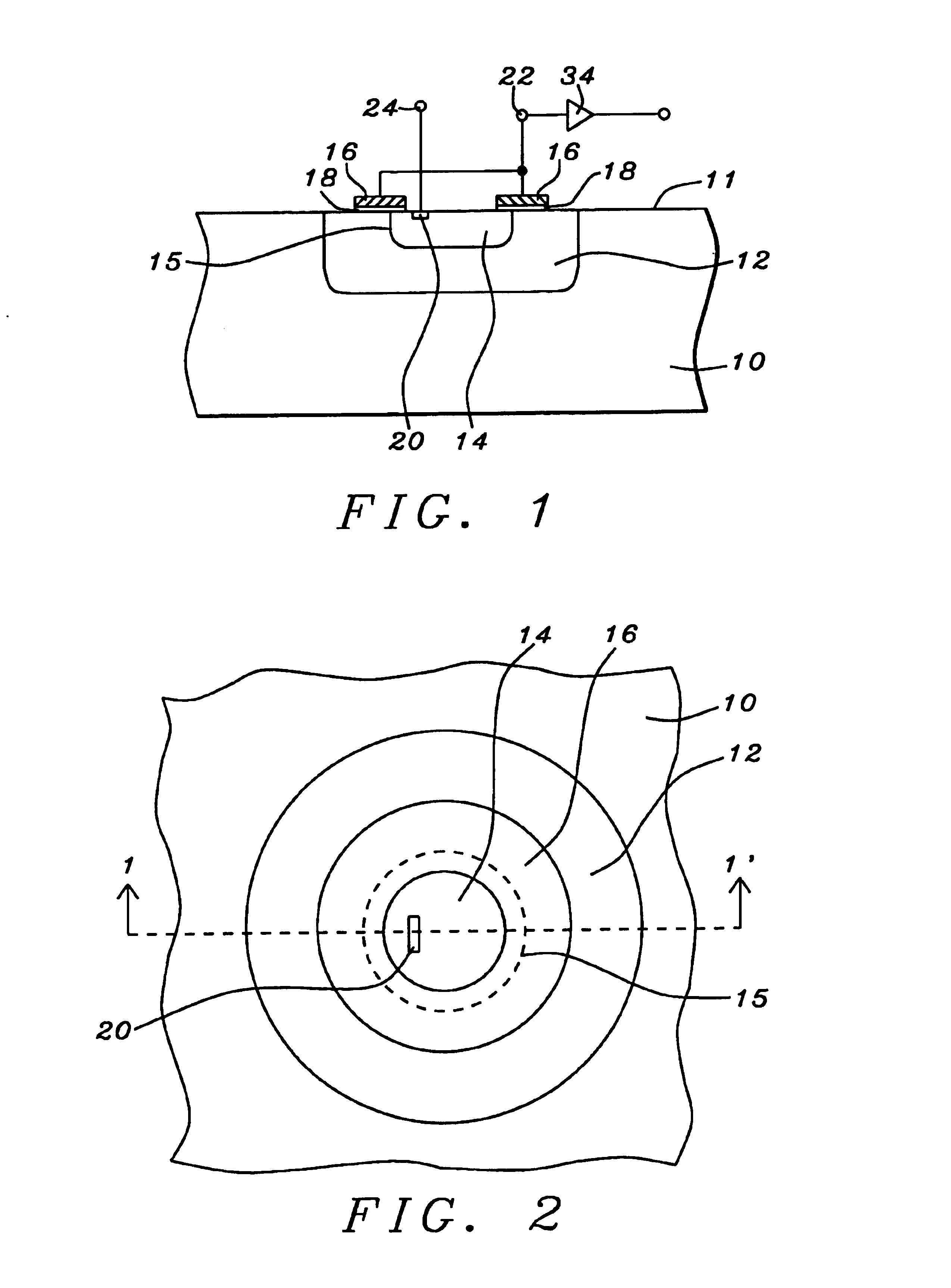
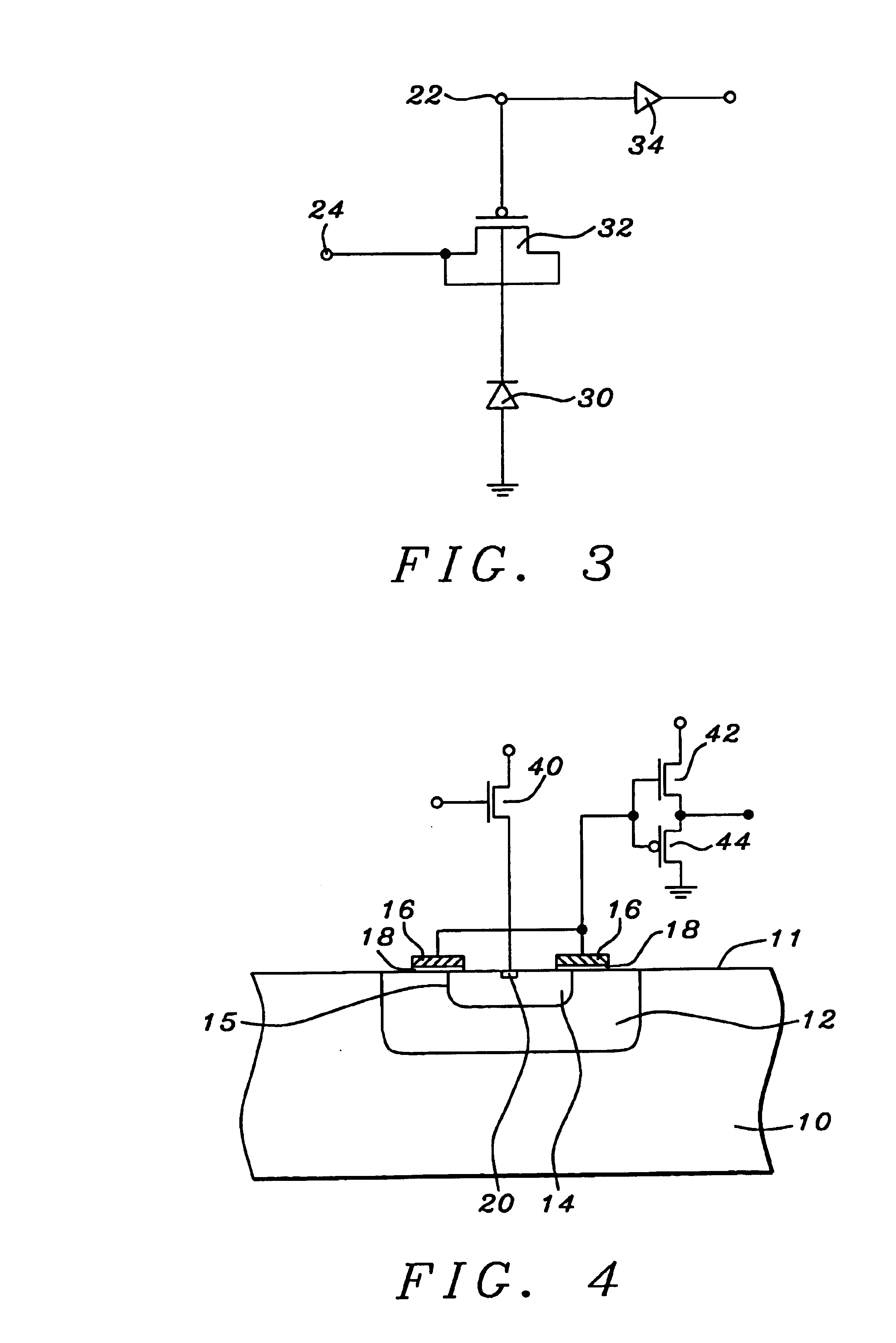
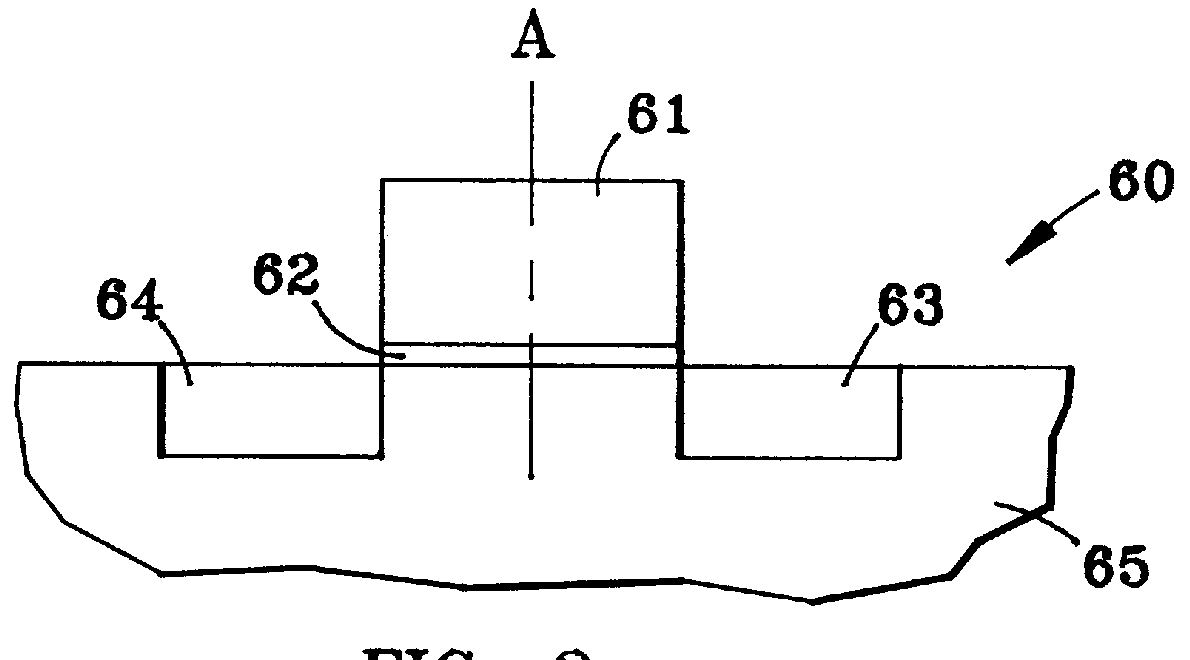
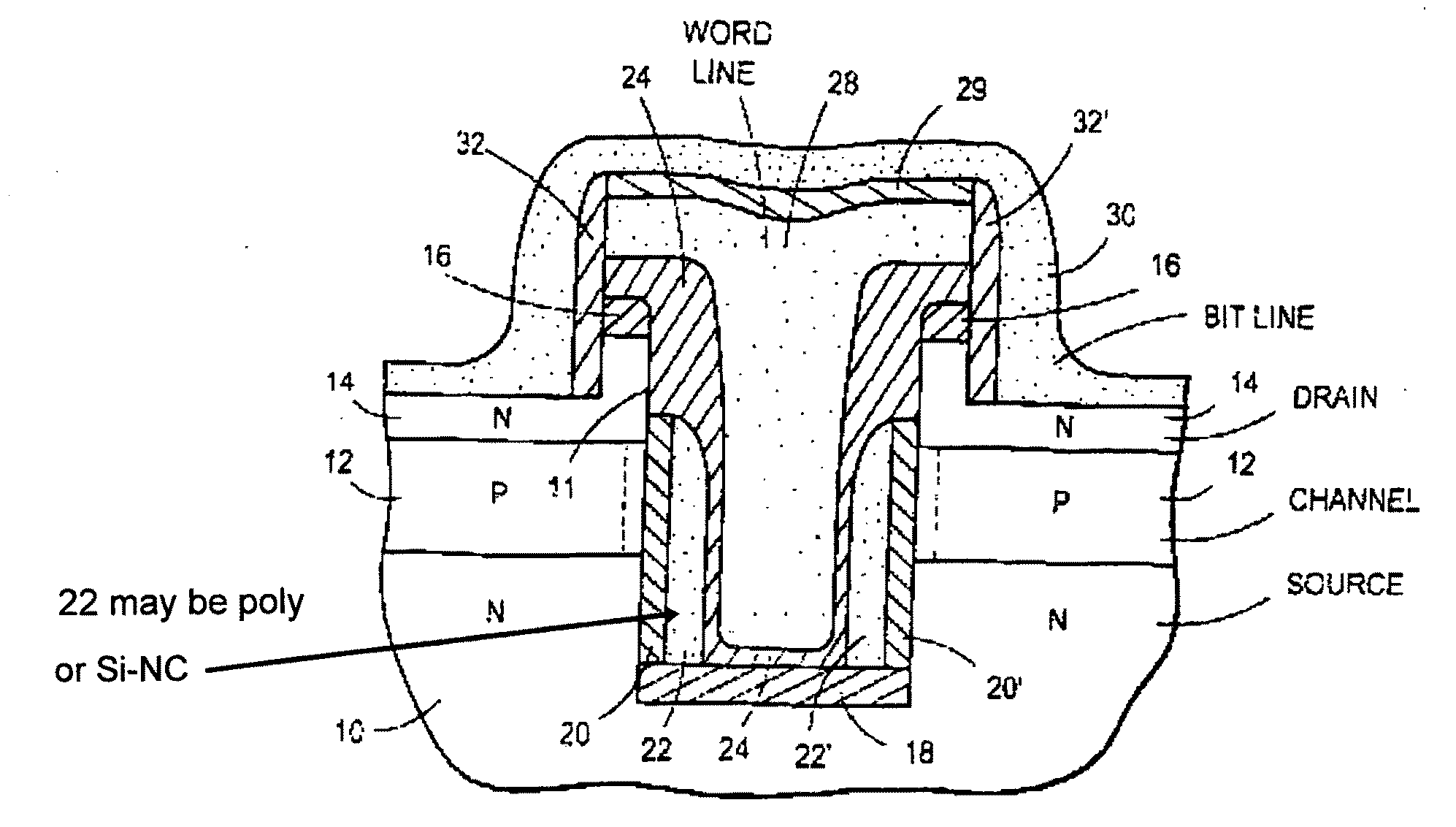
Method of forming an integrated circuit having nanocluster devices and non-nanocluster devices
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Tunneling floating gate APS pixel
A floating gate pixel is described which is formed by forming an N well in a P type silicon substrate. A P well is formed in the N well A gate is formed over a thin gate oxide, about 25 Angstroms thickness, such that the gate is directly over part of the P well and part of the N well. A P+ contact in the P well allows connection to a reset voltage source, usually through a reset transistor, to reset the pixel. The pixel is reset by setting the potential between the P well and the substrate, which is usually held at ground potential. When the pixel is reset tunneling current through the thin gate oxide sets the voltage of the floating gate. During the charge integration cycle an input signal to the pixel, such as a light signal, changes the potential of the pixel. After the charge integration cycle the tunneling current through the gate oxide changes the potential of the floating gate by an amount related to the input signal to the pixel. The potential of the floating gate can then be read out to determine the input signal to the pixel. The pixel can also be embodied using a P well formed in an N type substrate, an N well formed in the P well, and an N+ contact formed in the N well.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
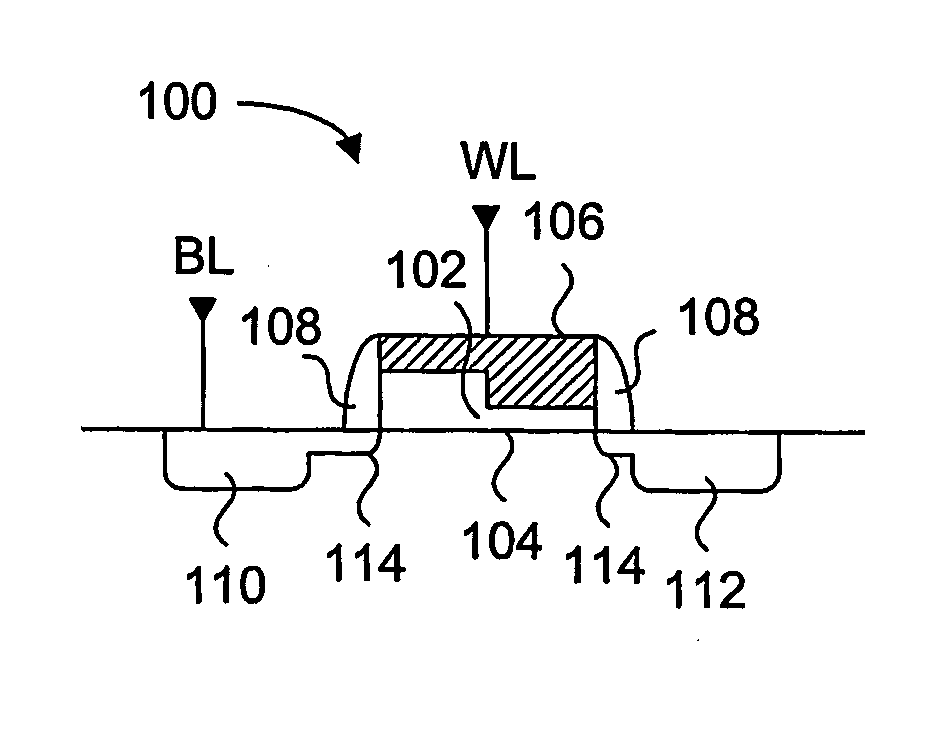
Otp memory cell having low current leakage
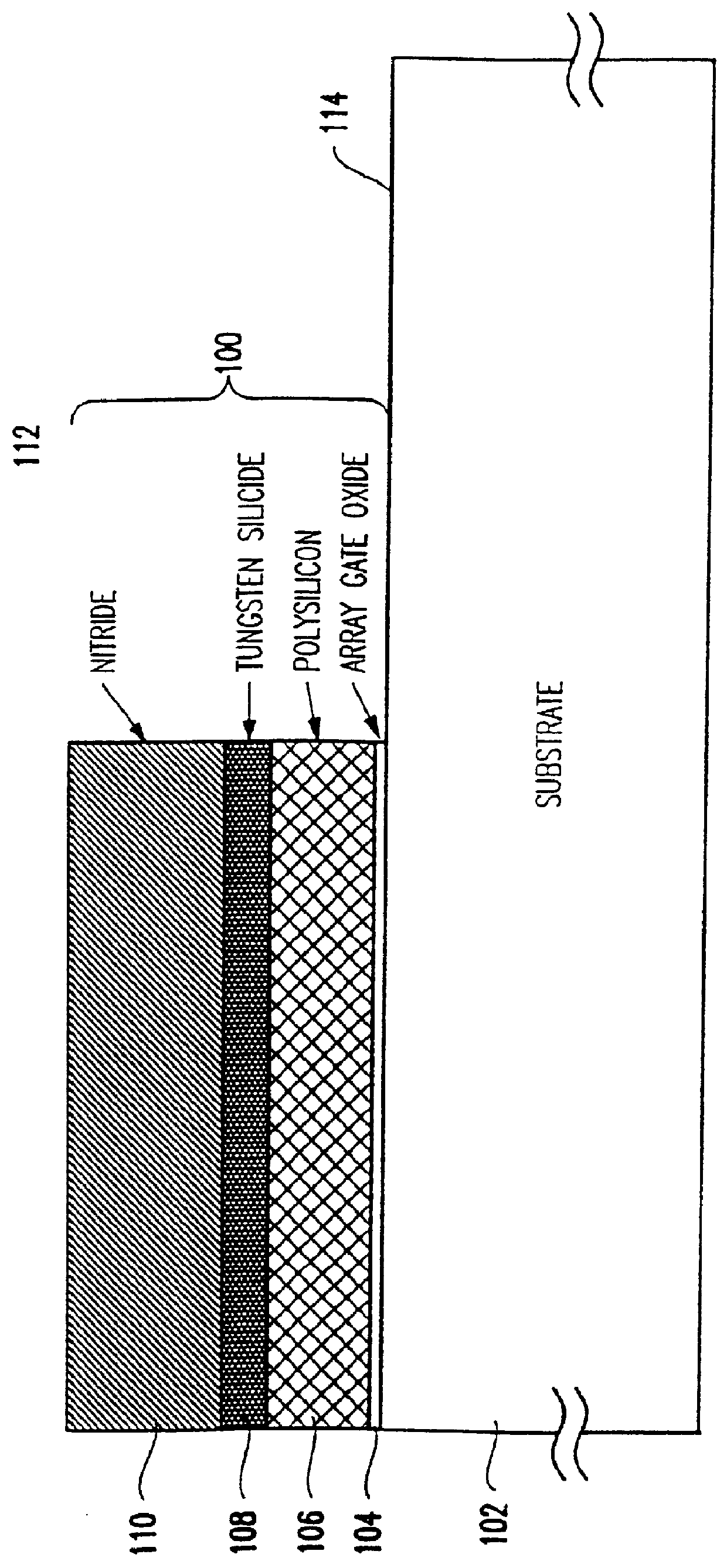
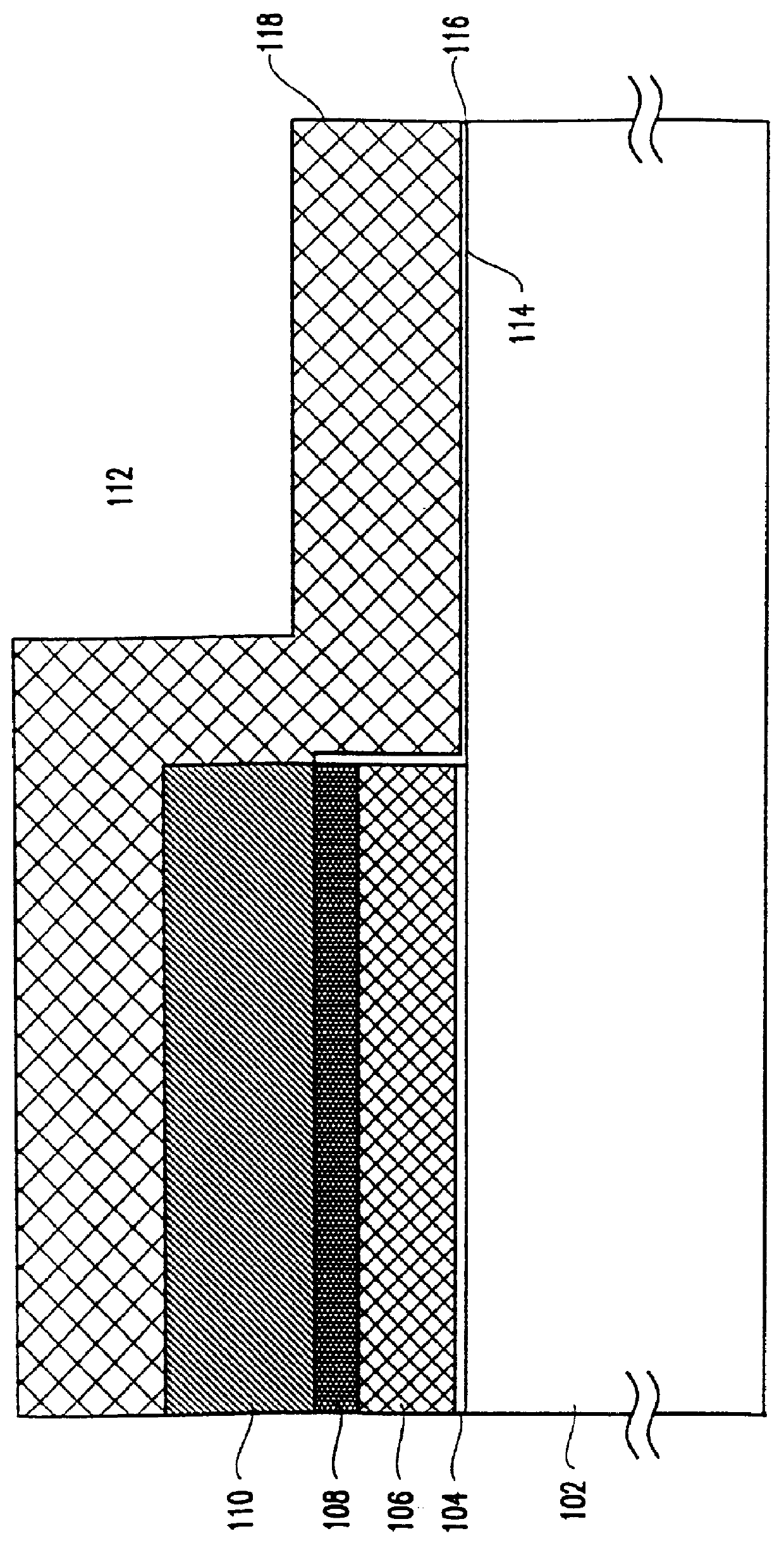
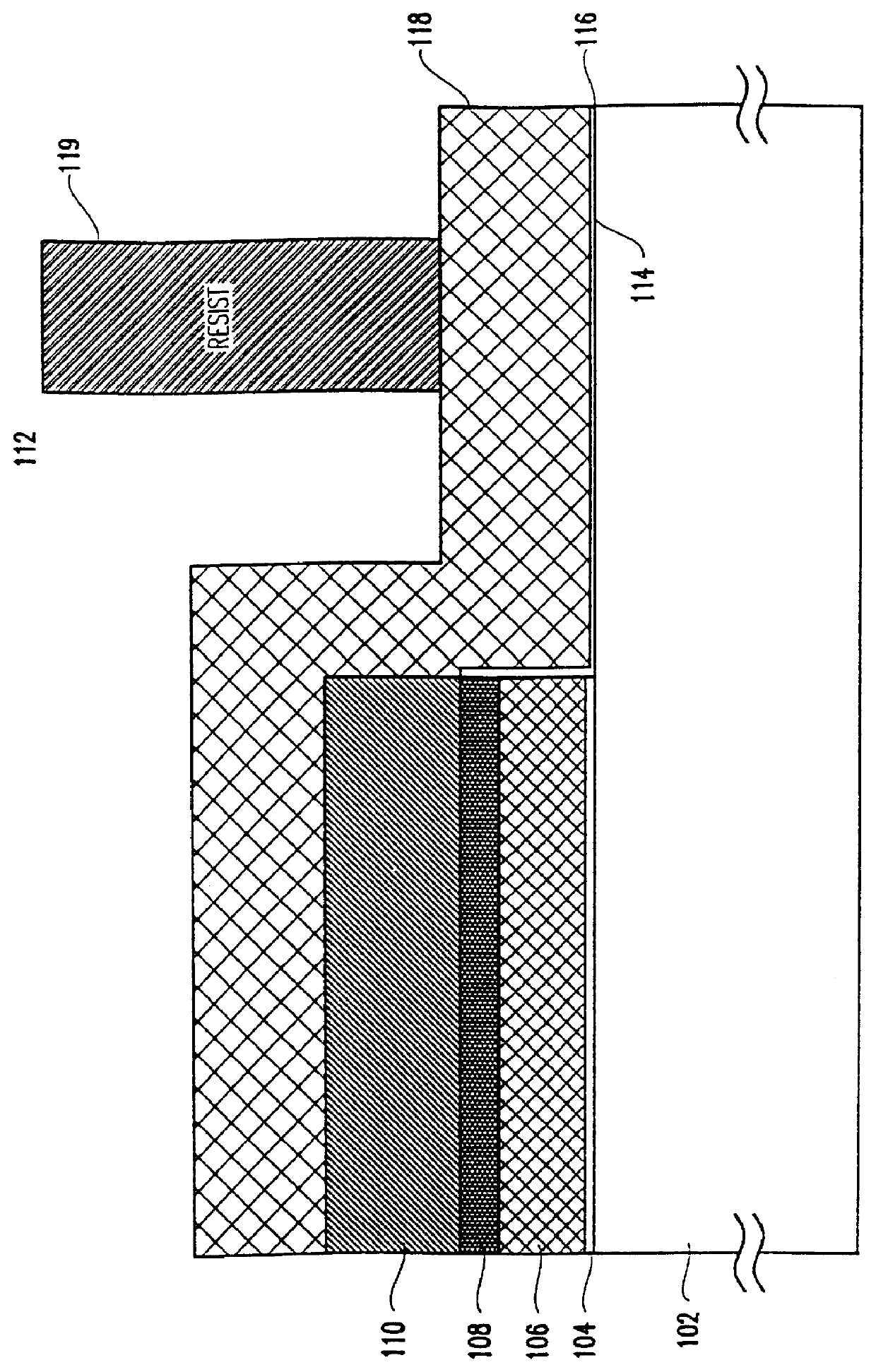
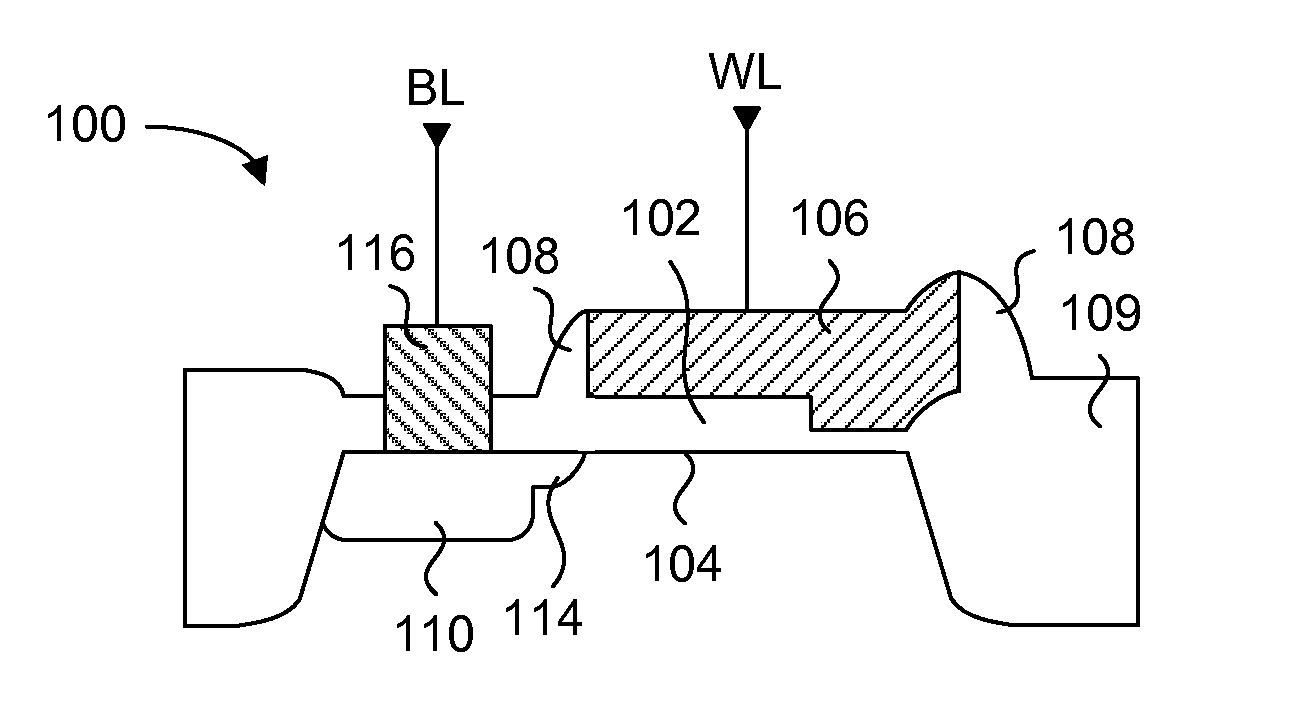
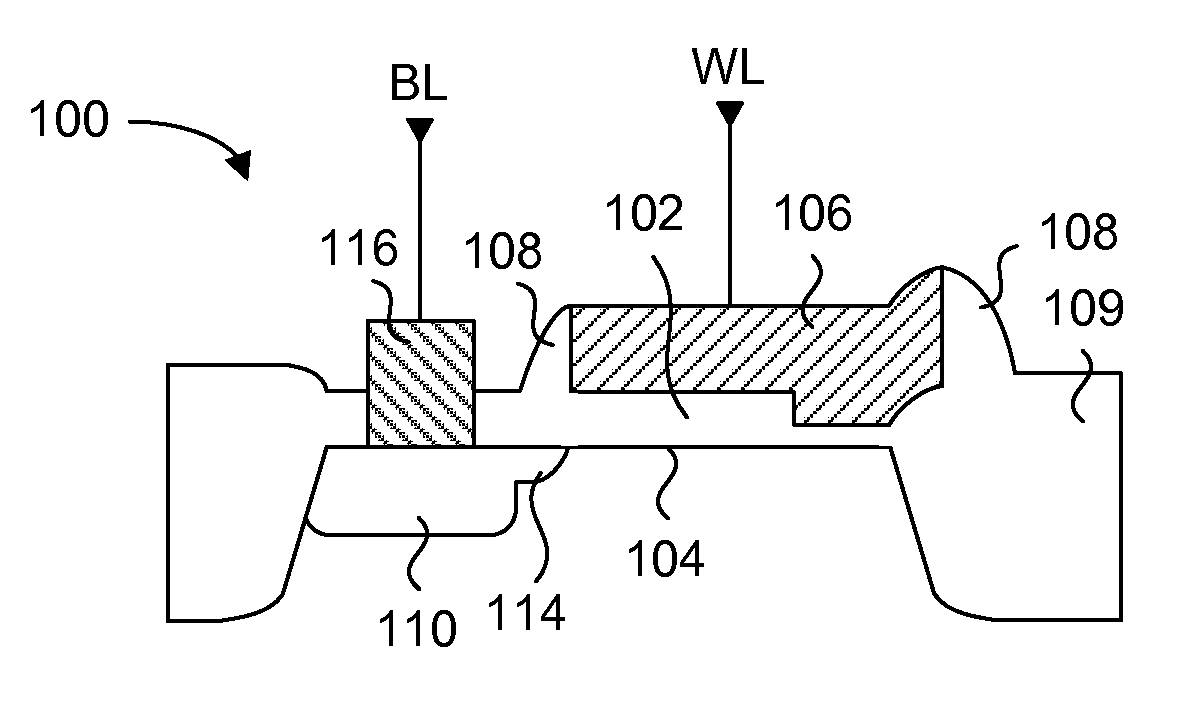
A one time programmable memory cell having twin wells to improve dielectric breakdown while minimizing current leakage. The memory cell is manufactured using a standard CMOS process used for core and I / O (input / output) circuitry. A two transistor memory cell having an access transistor and an anti-fuse device, or a single transistor memory cell 100 having a dual thickness gate oxide 114&116, are formed in twin wells 102&104. The twin wells are opposite in type to each other, where one can be an N-type well 102 while the other can be a P-type well 104. The anti-fuse device is formed with a thin gate oxide and in a well similar to that used for the core circuitry. The access transistor is formed with a thick gate oxide and in a well similar to that used for I / O circuitry.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Trench semiconductor device having gate oxide layer with multiple thicknesses and processes of fabricating the same
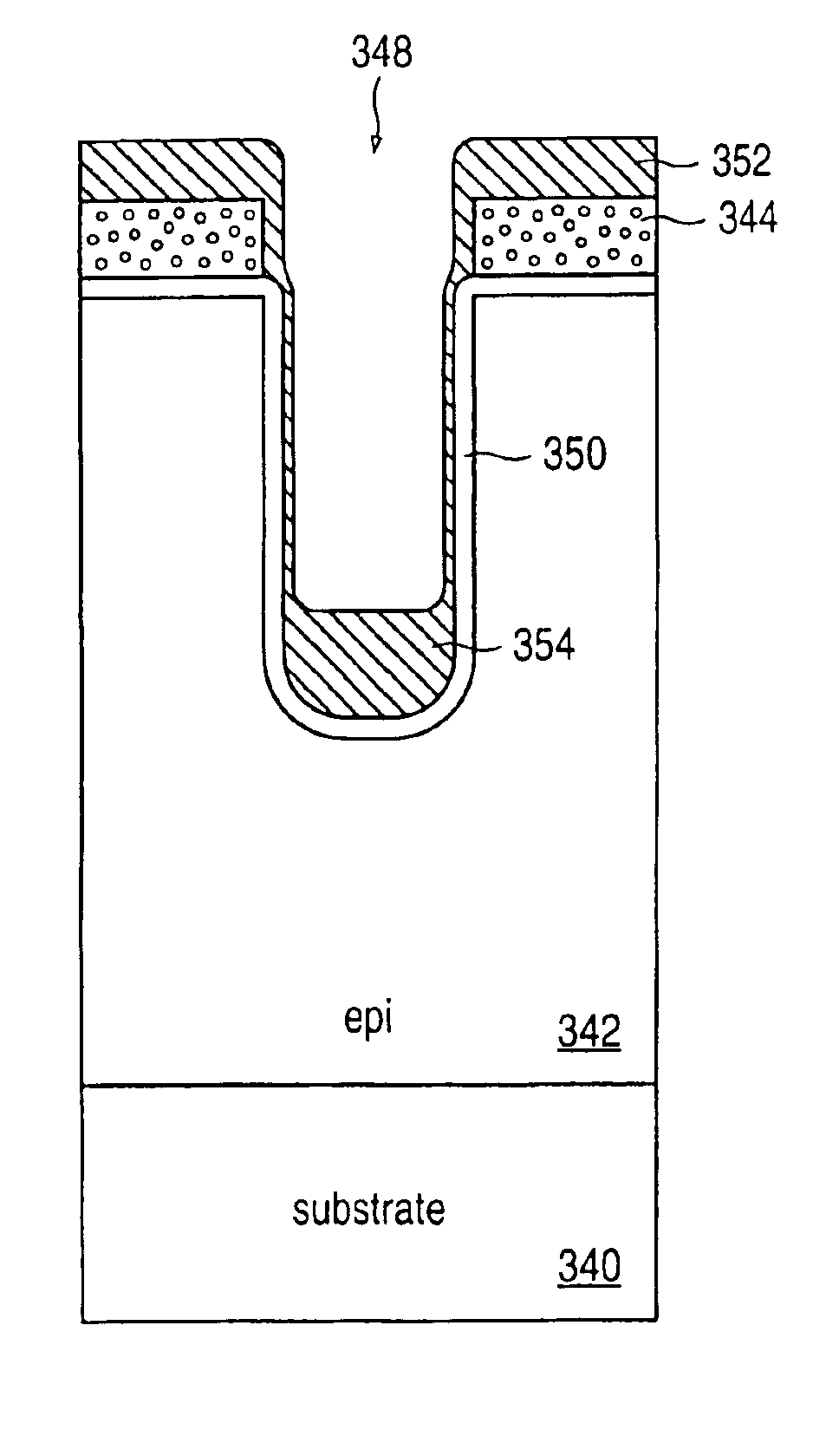
InactiveUS6900100B2Reduce electric field strengthReduce capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeSilicon oxidePower MOSFET
The a trench semiconductor device such as a power MOSFET the high electric field at the corner of the trench is diminished by increasing the thickness of the gate oxide layer at the bottom of the trench. Several processes for manufacturing such devices are described. In one group of processes a directional deposition of silicon oxide is performed after the trench has been etched, yielding a thick oxide layer at the bottom of the trench. Any oxide which deposits on the walls of the trench is removed before a thin gate oxide layer is grown on the walls. The trench is then filled with polysilicon in or more stages. In a variation of the process a small amount of photoresist is deposited on the oxide at the bottom of the trench before the walls of the trench are etched. Alternatively, polysilicon can be deposited in the trench and etched back until only a portion remains at the bottom of the trench. The polysilicon is then oxidized and the trench is refilled with polysilicon. The processes can be combined, with a directional deposition of oxide being followed by a filling and oxidation of polysilicon. A process of forming a “keyhole” shaped gate electrode includes depositing polysilicon at the bottom of the trench, oxidizing the top surface of the polysilicon, etching the oxidized polysilicon, and filling the trench with polysilicon.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
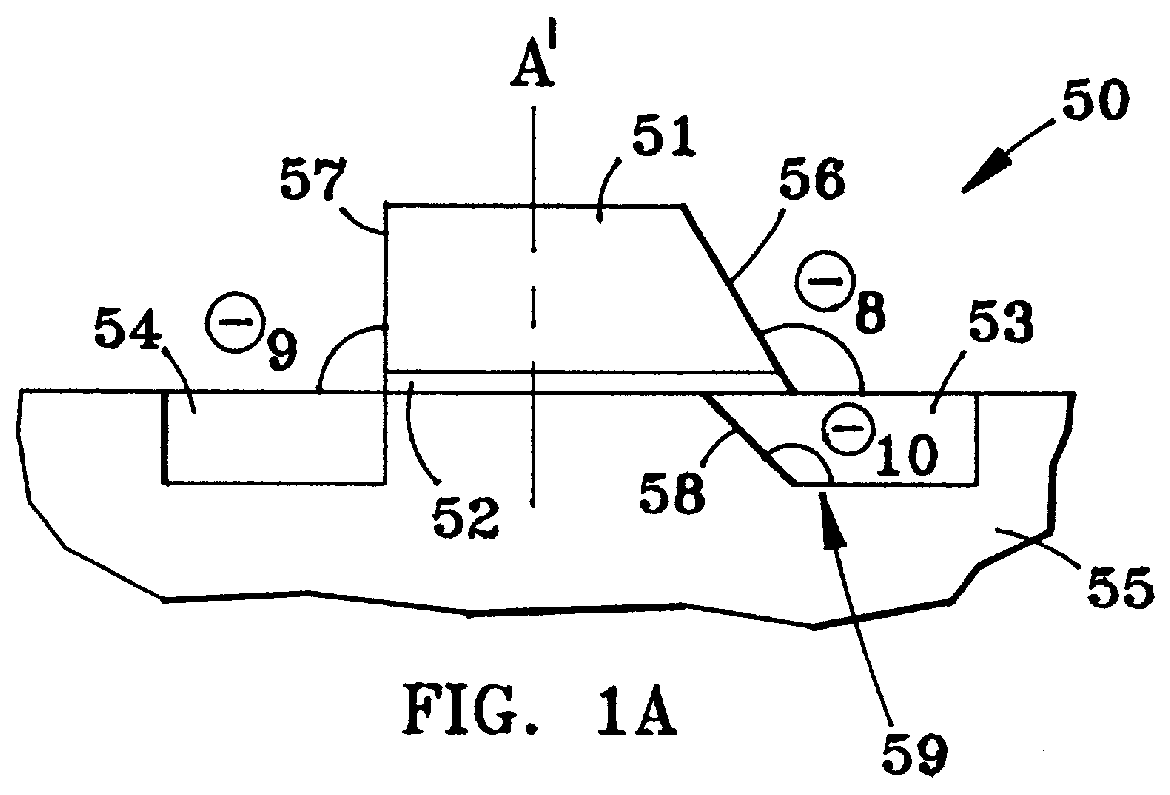
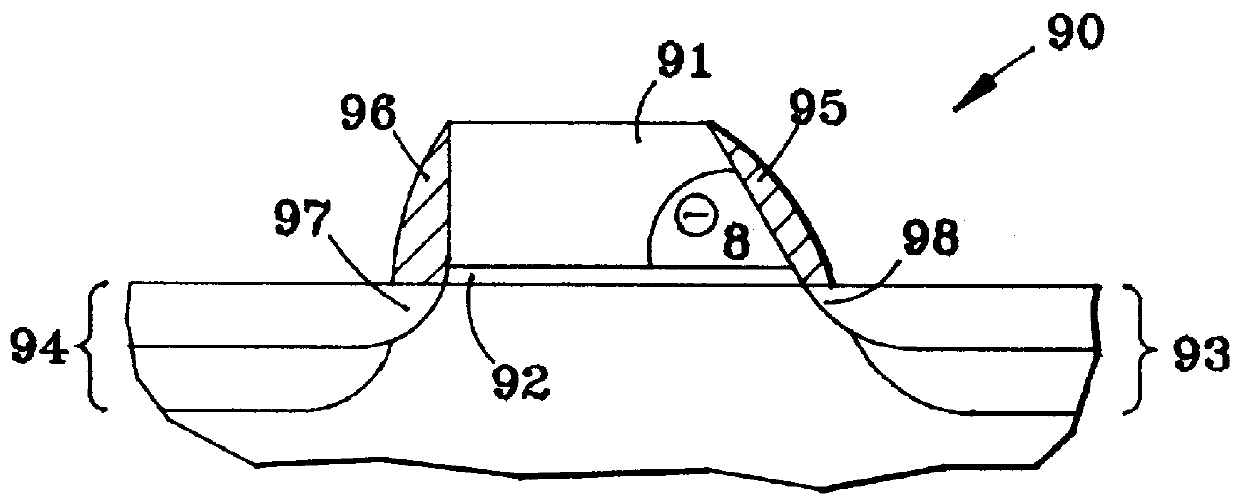
Asymmetrical field effect transistor
InactiveUS6015991AReduce decreaseImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesField-effect transistorCondensed matter physics
Disclosed is an asymmetric field effect transistor which comprises a first region serving as source, a second region serving as drain, a thin gate oxide and a gate electrode. The gate electrode is asymmetric and one of its sidewalls is sloped. The second region extends underneath said sloped sidewall. The part of said second region which extends underneath said gate electrode is less doped than the remaining part of said second region. Furthermore, said second region has a sloped junction edge underneath said gate electrode.
Owner:IBM CORP
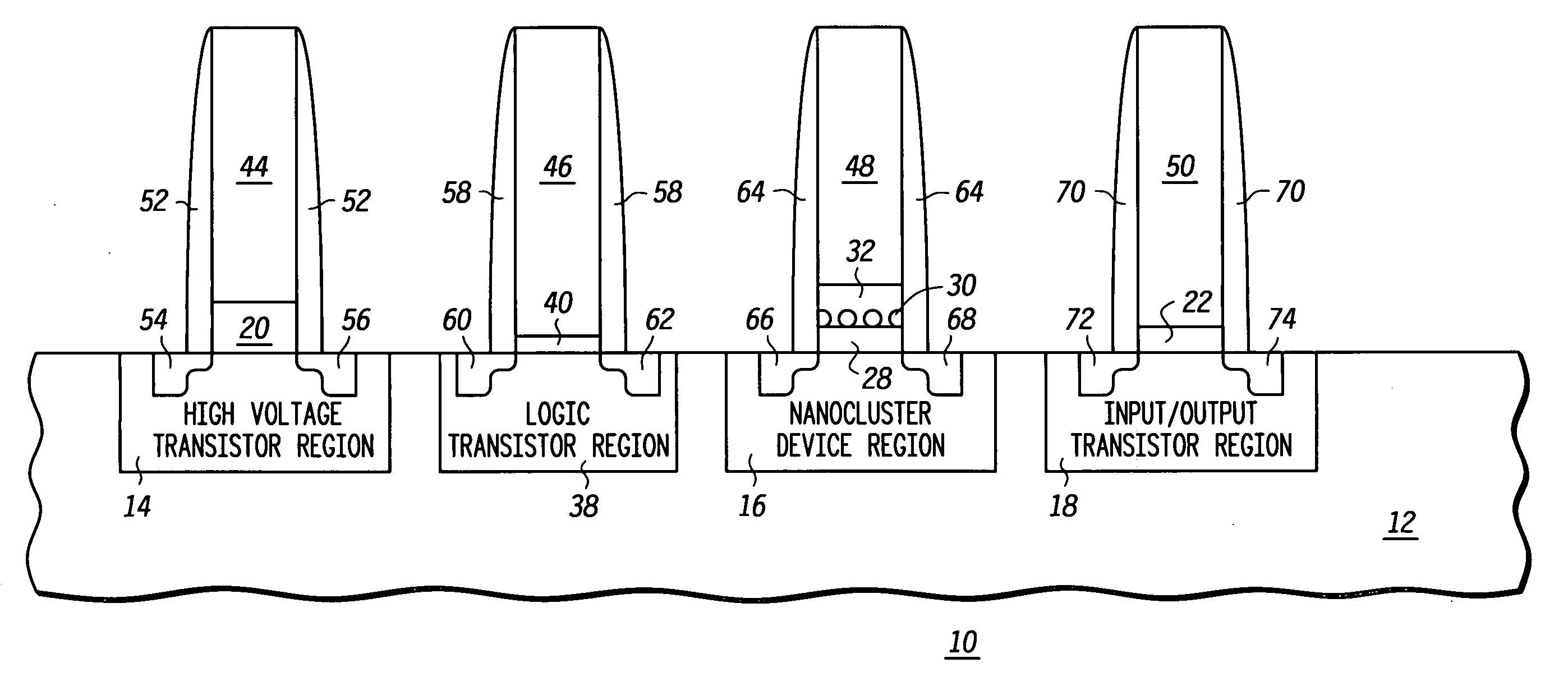
Method of forming an integrated circuit having nanocluster devices and non-nanocluster devices
An integrated circuit is formed by identifying multiple regions, each having transistors that have a gate oxide thickness that differs between the multiple regions. One of the regions includes transistors having a nanocluster layer and another of the regions includes transistors with a thin gate oxide used for logic functions. Formation of the gate oxides of the transistors is sequenced based upon the gate oxide thickness and function of the transistors. Thin gate oxides for at least one region of transistors are formed after the formation of gate oxides for the region including the transistors having the nanocluster layer.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Vertically integrated flash EPROM for greater density and lower cost
InactiveUS20090039407A1Increase cell areaImprove the coupling ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesIon implantationPolycrystalline silicon
A nonvolative memory in the form of a vertical flash EPROM with high density and low cost. A vertical MOS transistor is formed in well etched into a semiconductor substrate, the substrate having source, body and drain regions formed by ion implantation. A thin gate oxide or oxide-nitride-oxide (ONO) layer is formed in the well and a self-aligned floating gate of polysilicon is formed over the gate oxide in the well to overlie the body region. An anisotropic etch is used to form the self aligned floating gate so as to remove all horizontal components and leave no portion of said floating gate extending beyond the perimeter of said well such that its lateral extents are determined by the anisotropic etch and not photolithography. Leff is determined by the energy of the implants used for form the source and drain regions and not by lithography. A deep field oxide bounding parts of said well keeps the coupling ratio good at all feature sizes. A vertically oriented NMOS and PMOS transistor are also disclosed.
Owner:VORA MADHUKAR B
Output drive circuit that accommodates variable supply voltages
ActiveUS7224195B2Increase charging rateSwitching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsDriver circuitEngineering
In accordance with the invention, a driver circuit is described that permits a single thin gate oxide process to be utilized where a dual oxide process may normally be necessary. Circuits employing only thin gate oxide devices are used as the design basis for a single product with a single set of tooling and manufacturing process to operate within the same timing specifications for a core voltage output drive as well as for a higher system drive.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Method of making ultra thin gate oxide using aluminum oxide
InactiveUS6100204ATransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEquivalent oxide thicknessGate dielectric
A transistor and a method of making the same are provided. The method includes the step of forming a gate dielectric layer on the substrate where the gate dielectric layer is composed of an aluminum oxide containing material. A gate electrode is formed on the gate dielectric layer and first and second source / drain regions are formed in the substrate laterally separated to define a channel region beneath the gate electrode. The aluminum oxide containing material may be, for example, Al2O3. Aluminum oxide provides for a gate dielectric with a thin equivalent thickness of oxide in a potentially single crystal form.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Cascadable level shifter cell
ActiveUS20070008001A1Electric pulse generatorLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsVoltage rangeProtection layer
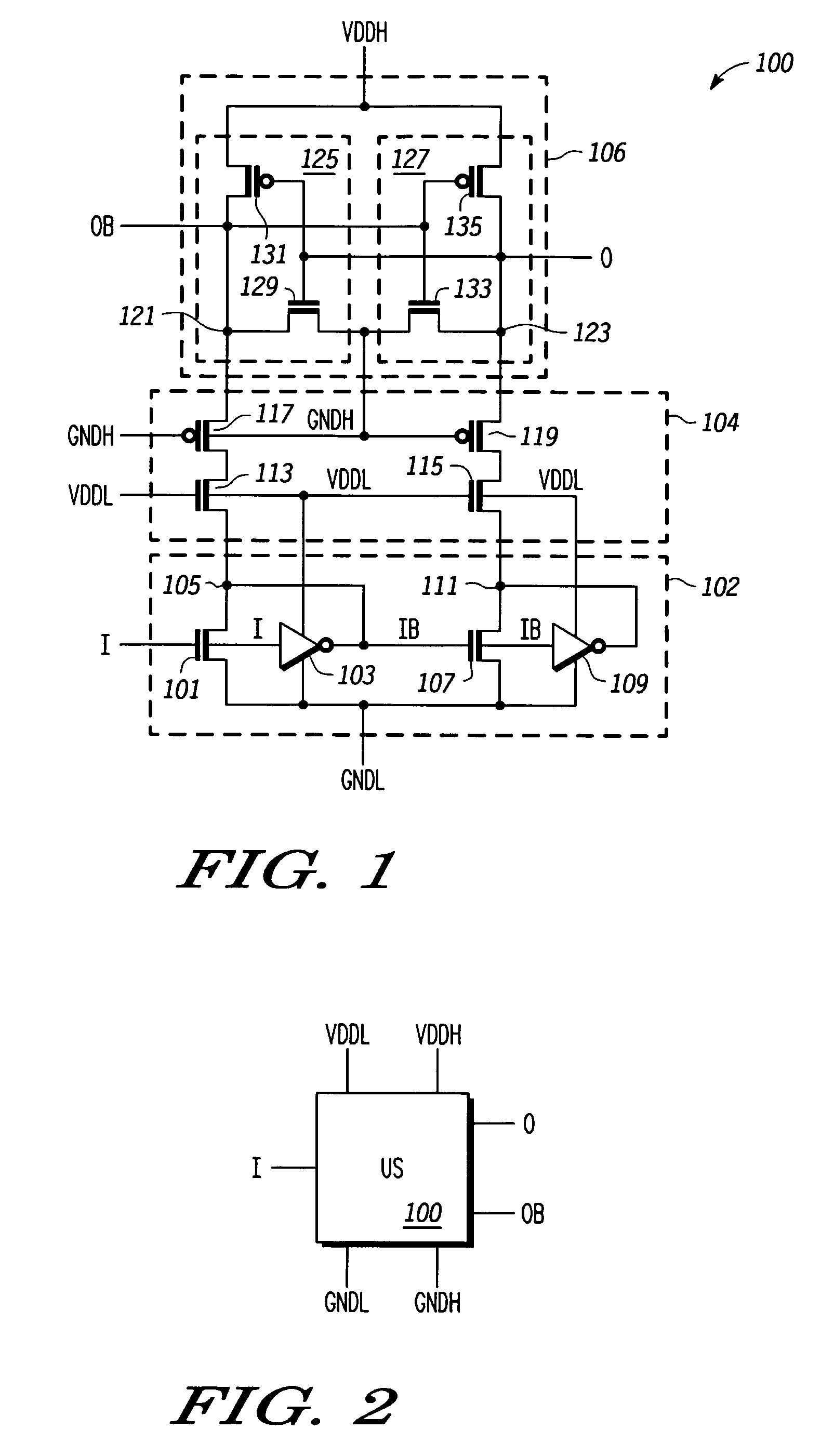
A level shifter circuit including first and second circuits and a protection layer. The first circuit receives an input signal and switches first and second nodes to opposite states within a first voltage range between first and second supply voltages. The second circuit switches the third and fourth nodes to opposite states within a second voltage range between third and fourth supply voltages in response to switching of the first and second nodes. The protection layer couples the first and second nodes to third and fourth nodes via respective first and second isolation paths. The isolation paths operate to keep the first and second nodes within the first voltage range and to keep the third and fourth nodes within the second voltage range. Isolation enables the use of thin gate-oxide devices for speed while extending the voltage range beyond the maximum voltage allowable for a single thin gate-oxide device.
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
To prevent a thick gate oxide film from being damaged by a cleaning and hydrofluoric-acid treatment preprocess performed prior to formation of a thin gate oxide film. A thick first gate oxide film is formed, and an insulating film, having etching resistance against the cleaning and hydrofluoric-acid treatment process for formation of thin second gate oxide film, is formed in an upper region of the first gate oxide film. A resist is then formed in a region where a thick gate insulating film is to be formed, and etching is performed on the first gate oxide film with the resist as a mask. The resist is stripped, then cleaning and hydrofluoric-acid treatment are performed on the silicon surface in a region where a thin gate insulating film is to be formed, and the thin second gate oxide film is formed.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Apparatus for providing SRAM and CAM bit cell
ActiveCN102024819AImprove VccImprove access speedSolid-state devicesDigital storageDielectricStatic random-access memory
The invention provides circuits and methods for providing an SRAM and CAM bit cell. In one embodiment, a bit cell portion with thicker gate oxides in the storage cell transistors, and thinner gate oxides in a read port section having transistors are disclosed. The use of the thick gate oxides in the storage cell transistors provides a stable storage of data and lower standby leakage current. The use of the thinner gate oxides in the read port transistors provides fast read accesses and allows a lower Vcc,min in the read port. The methods used to form the dual gate oxide thickness SRAM cells have process steps compatible with the existing semiconductor manufacturing processes. Embodiments using high k gate dielectrics, dual gate dielectric materials in a single bit cell, and using finFET and planar devices in a bit cell are described. Methods for forming the structures are disclosed.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com