Patents
Literature
155results about How to "Improve the coupling ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
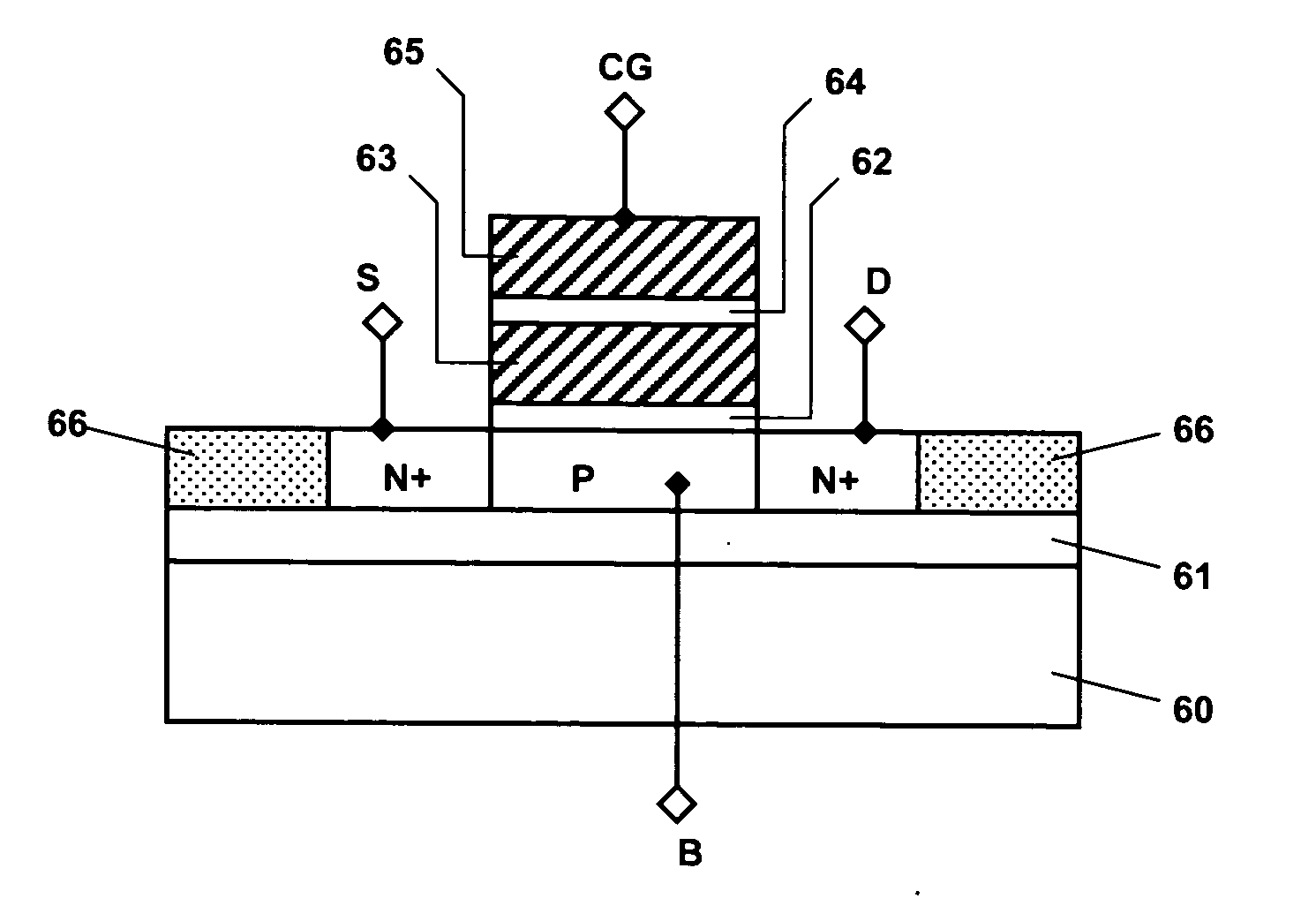
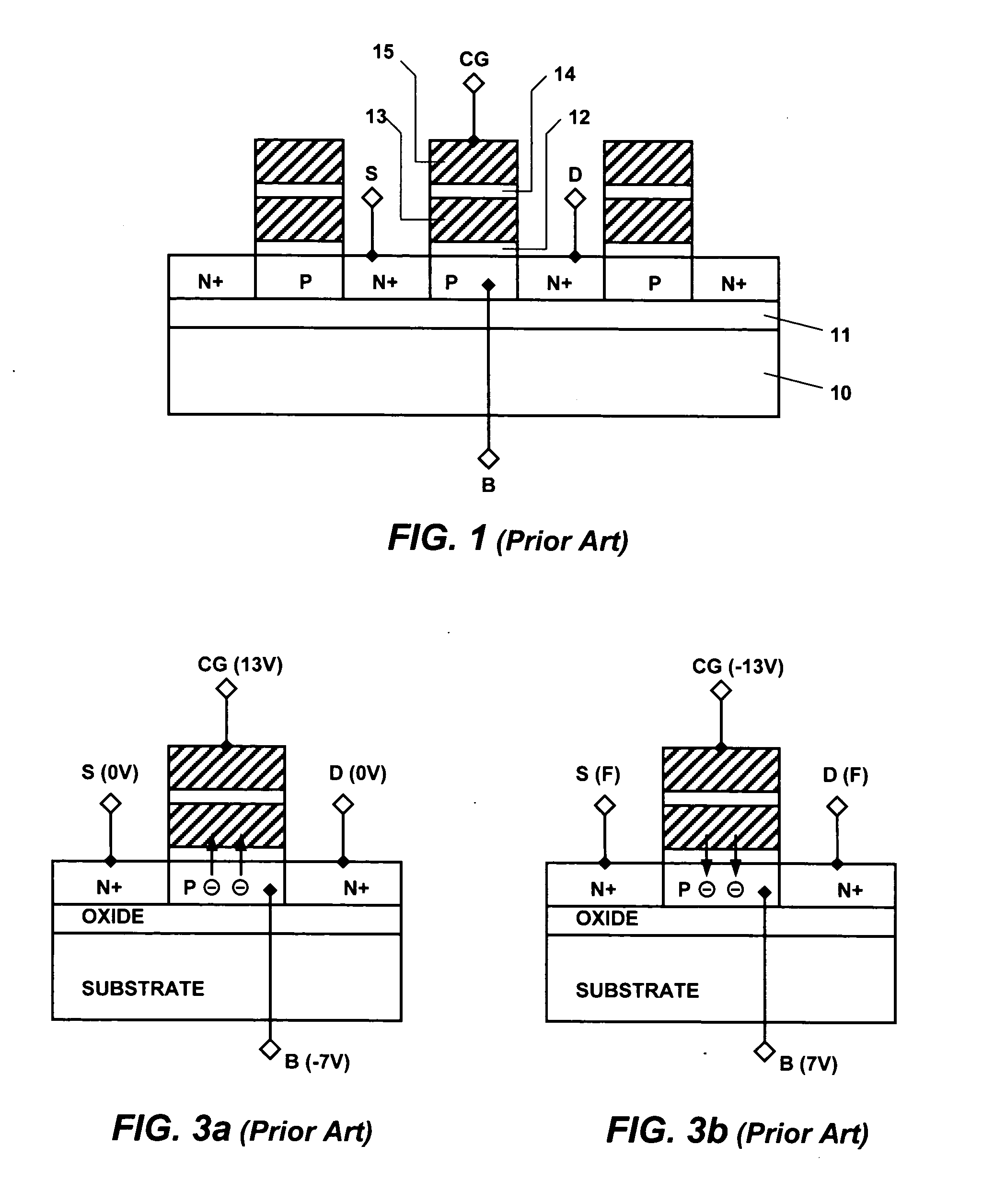
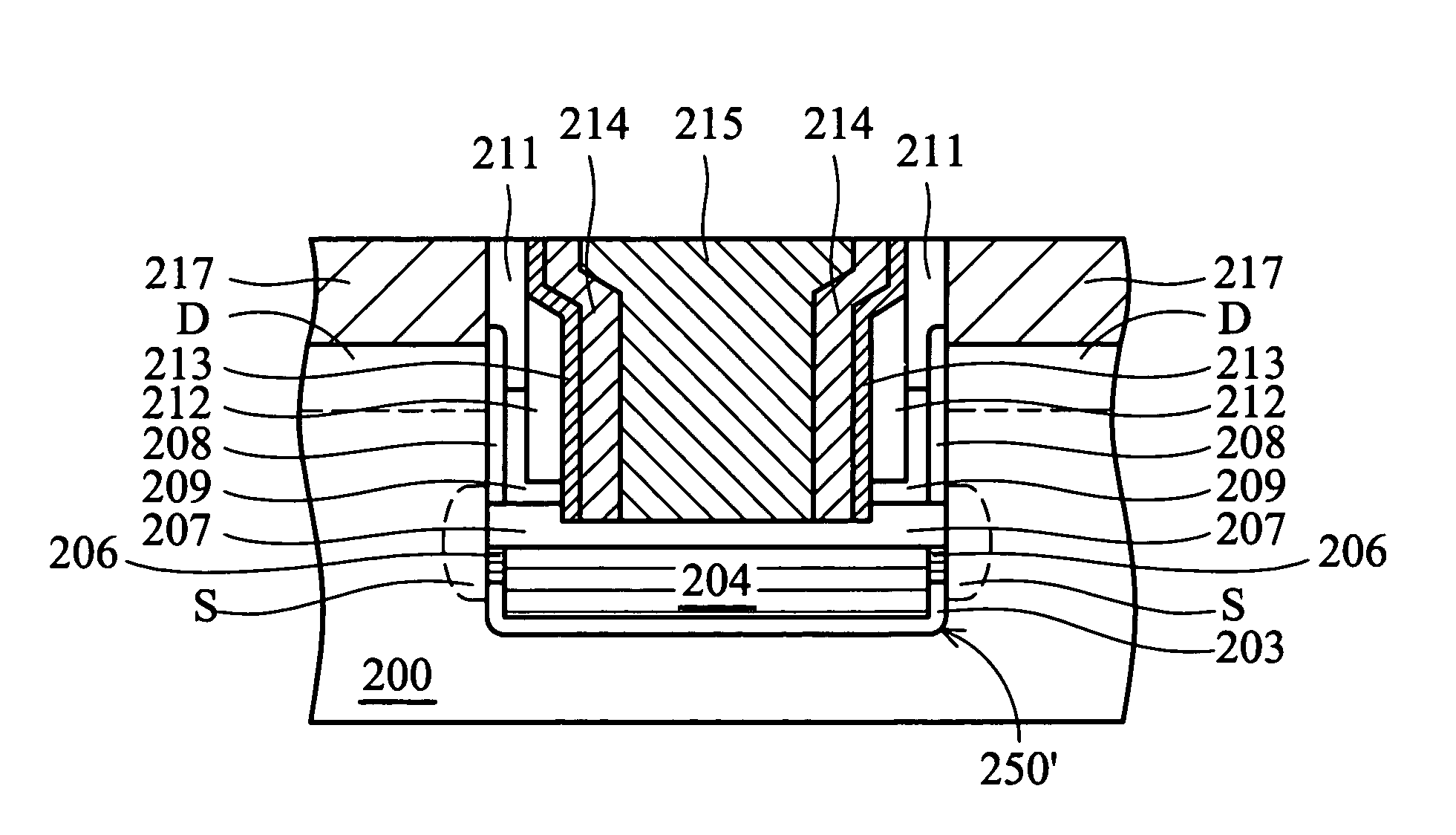
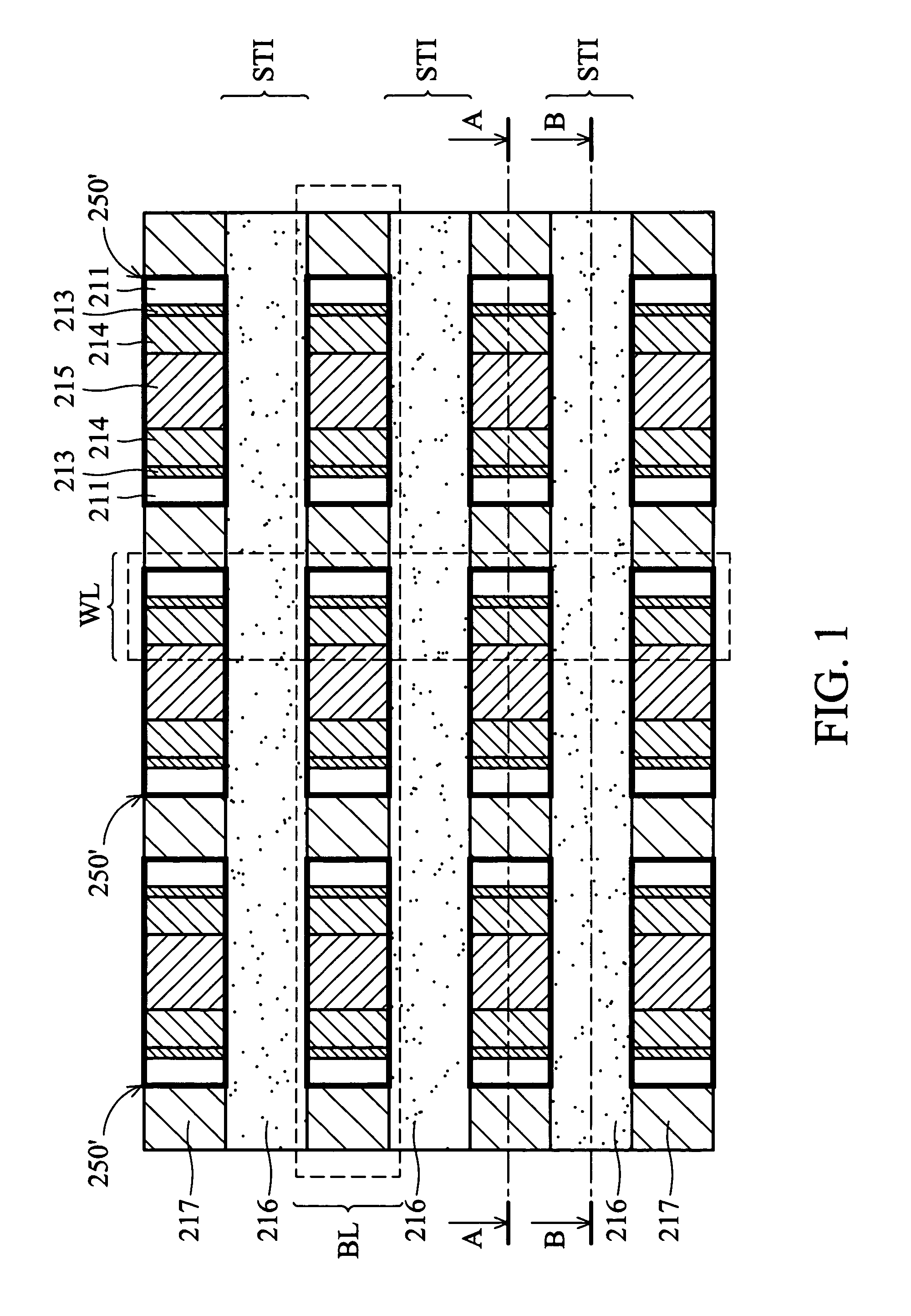
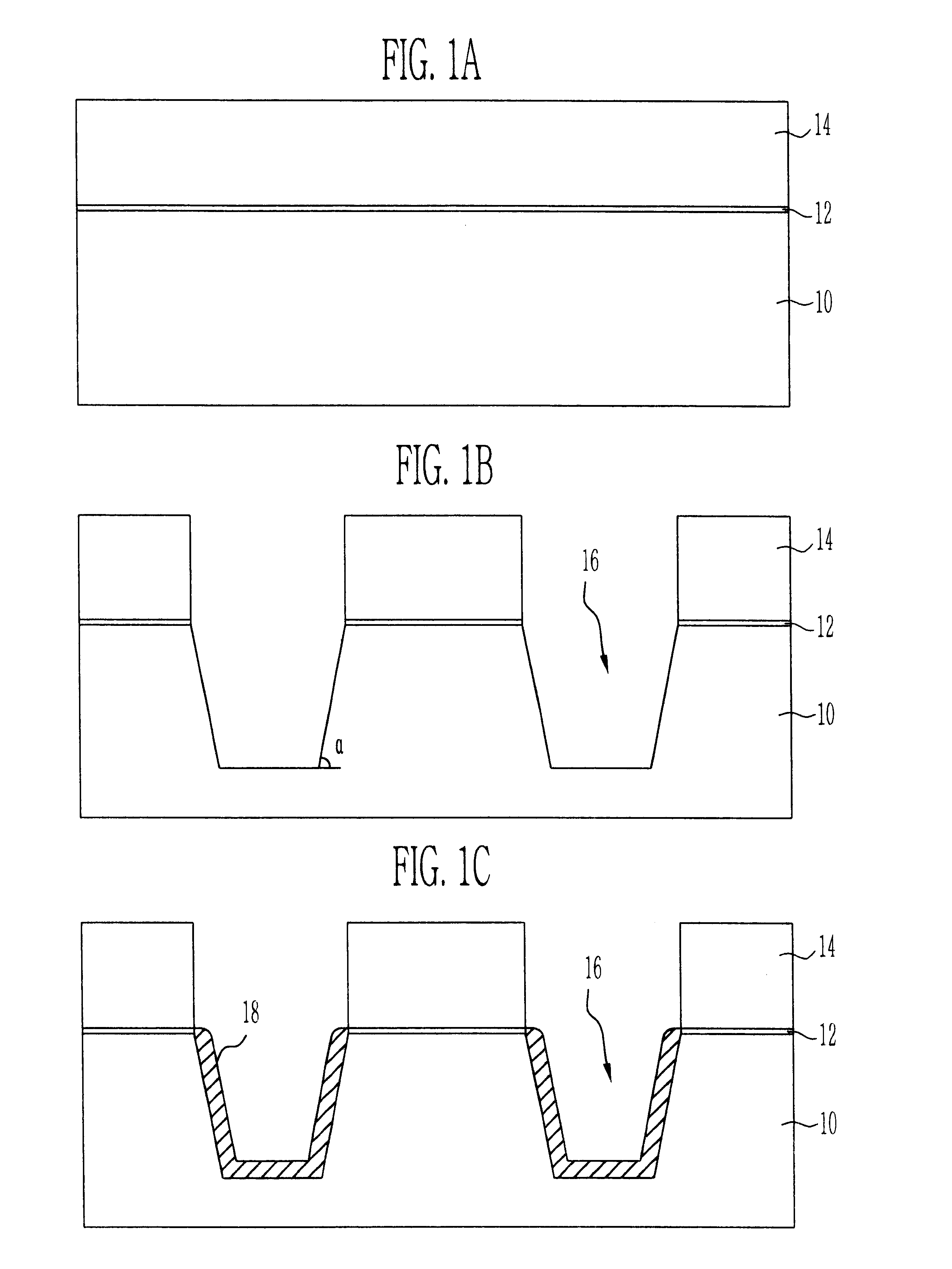
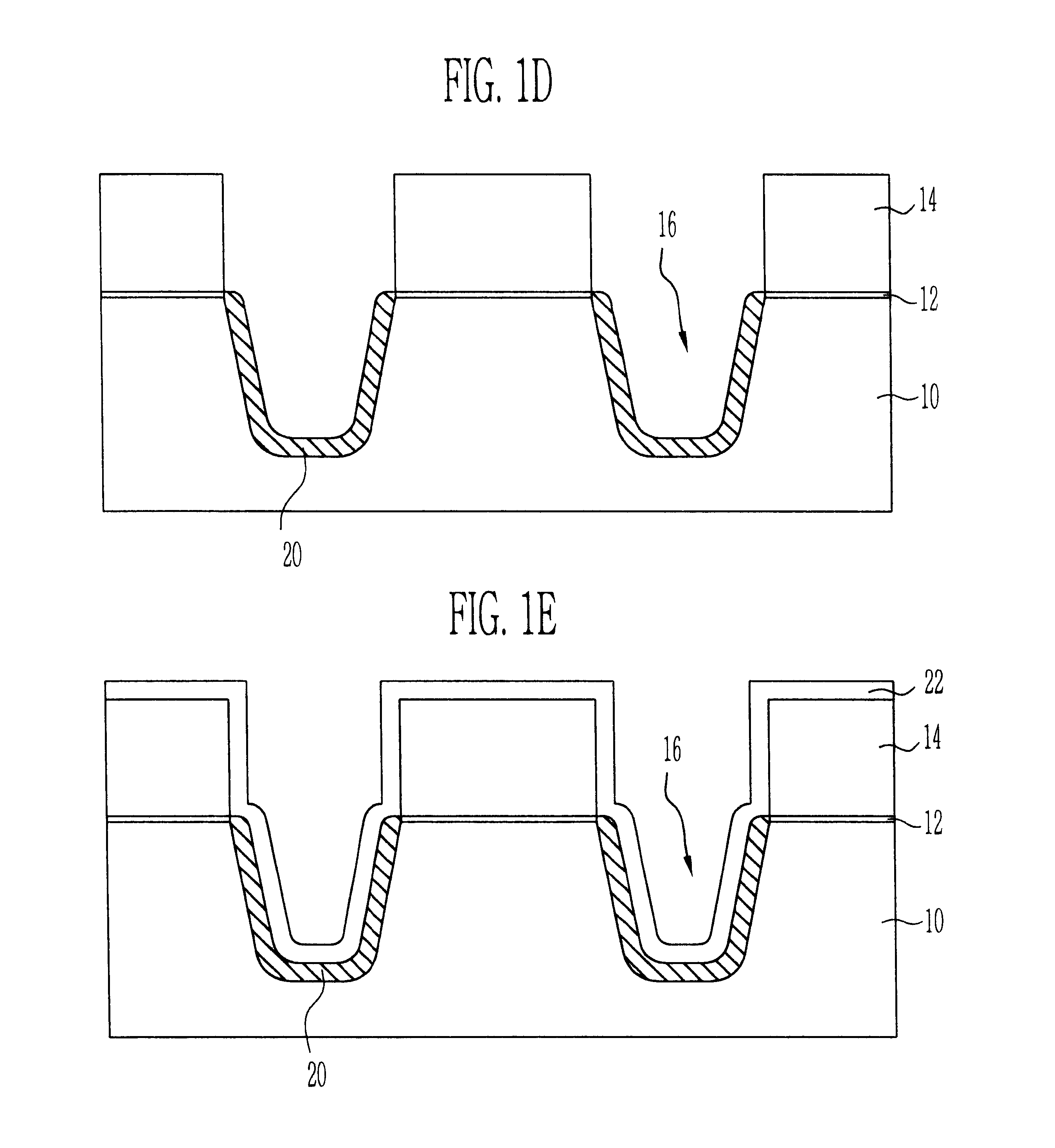
Flash memory device using semiconductor fin and method thereof
ActiveUS20060044915A1Improve scalabilityProgramming and erasing efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling ratioEngineering
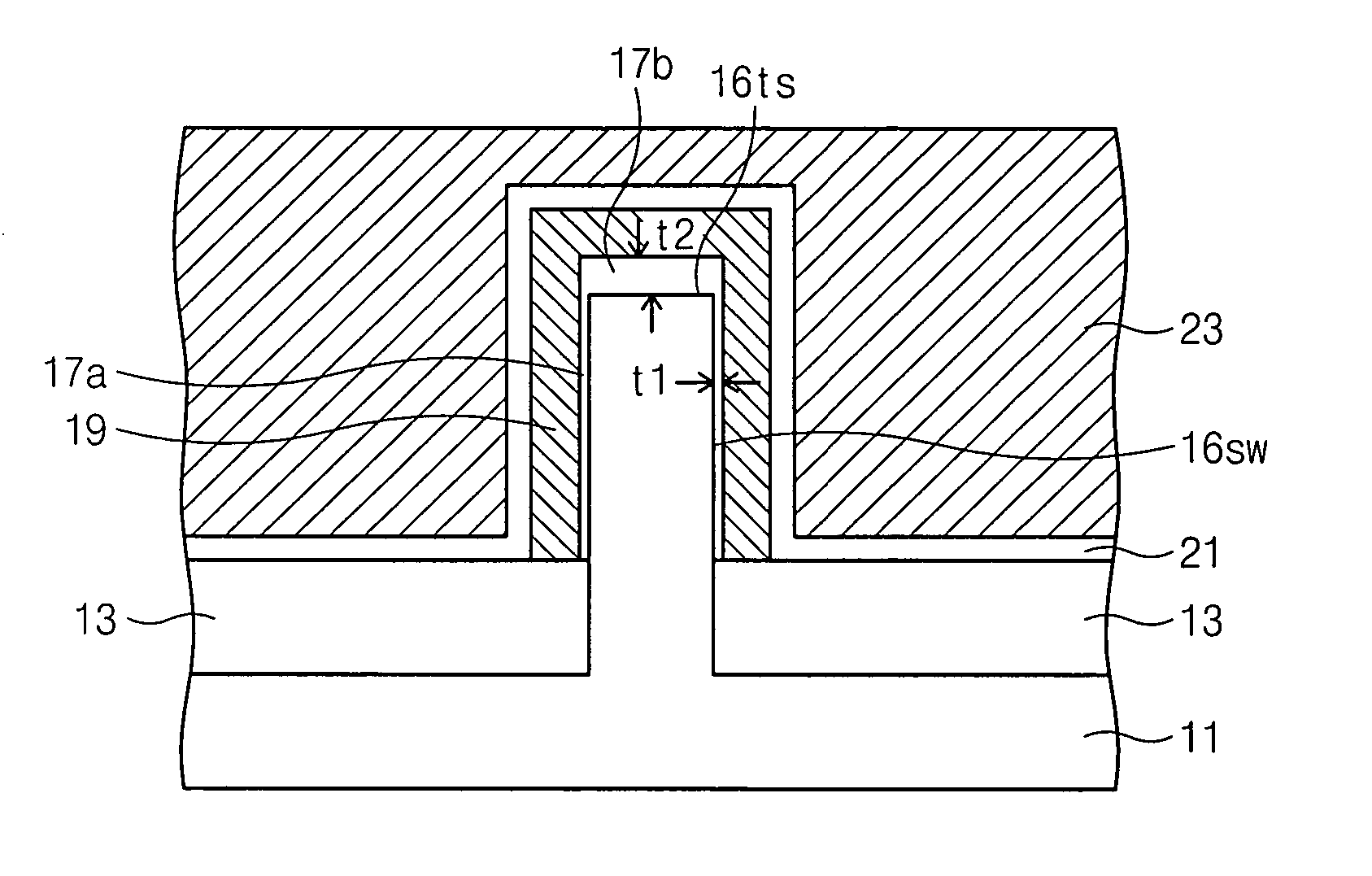
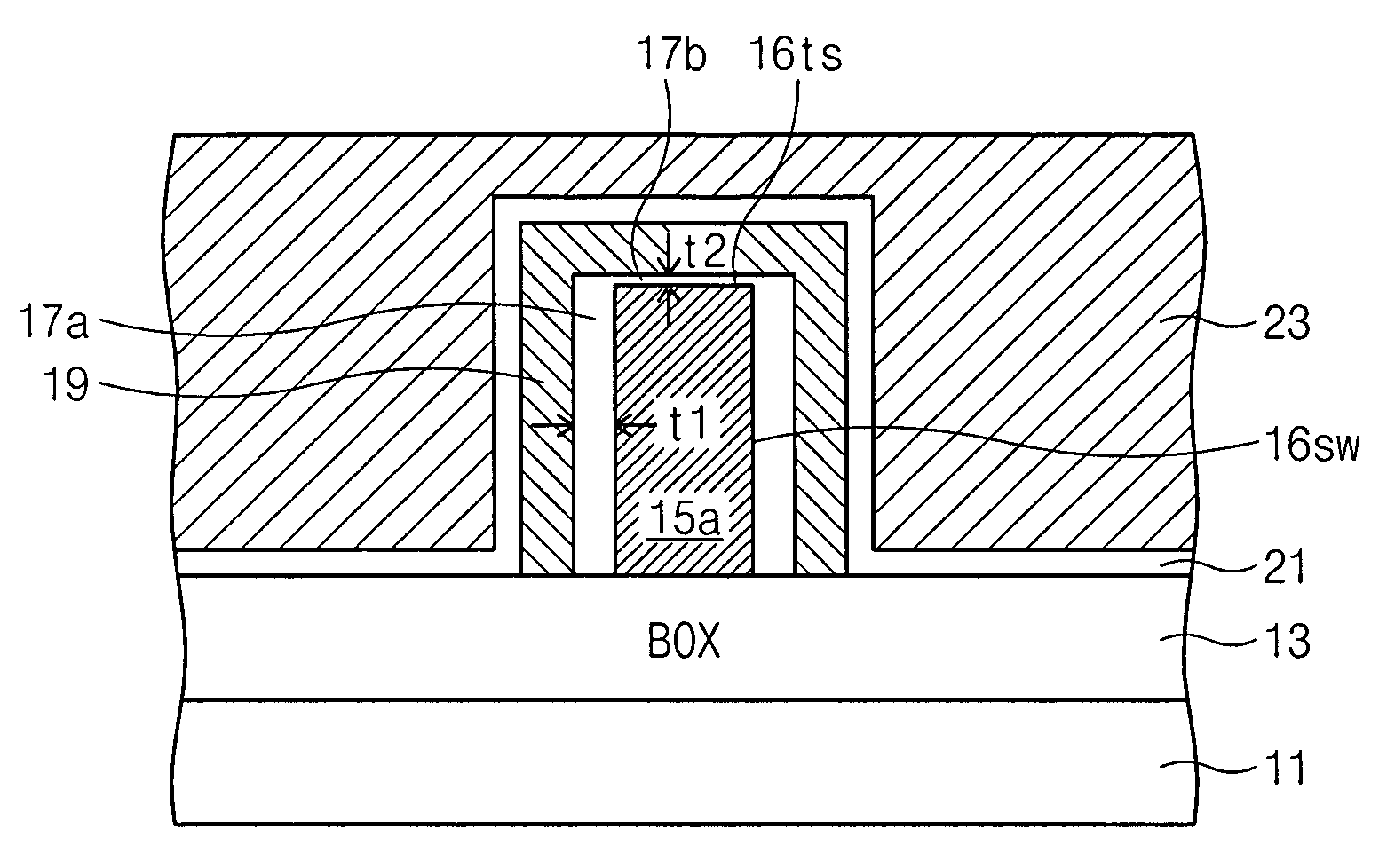
A flash memory device according to the present invention includes a semiconductor fin including a top surface and a side surface originated from different crystal planes. The flash memory device comprises: insulating layers having different thicknesses formed on a side surface and a top surface of the semiconductor fin, a storage electrode, a gate insulating layer and a control gate electrode sequentially formed on the insulating layers. A thin insulating layer enables charges to be injected or emitted through it, and a thick insulating layer increases a coupling ratio. Accordingly, it is possible to increase an efficiency of a programming or an erase operation of a flash memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Flash memory device using semiconductor fin and method thereof
ActiveUS7285820B2Improve scalabilityProgramming and erasing efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesCoupling ratioCrystal plane
A flash memory device according to the present invention includes a semiconductor fin including a top surface and a side surface originated from different crystal planes. The flash memory device comprises: insulating layers having different thicknesses formed on a side surface and a top surface of the semiconductor fin, a storage electrode, a gate insulating layer and a control gate electrode sequentially formed on the insulating layers. A thin insulating layer enables charges to be injected or emitted through it, and a thick insulating layer increases a coupling ratio. Accordingly, it is possible to increase an efficiency of a programming or an erase operation of a flash memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
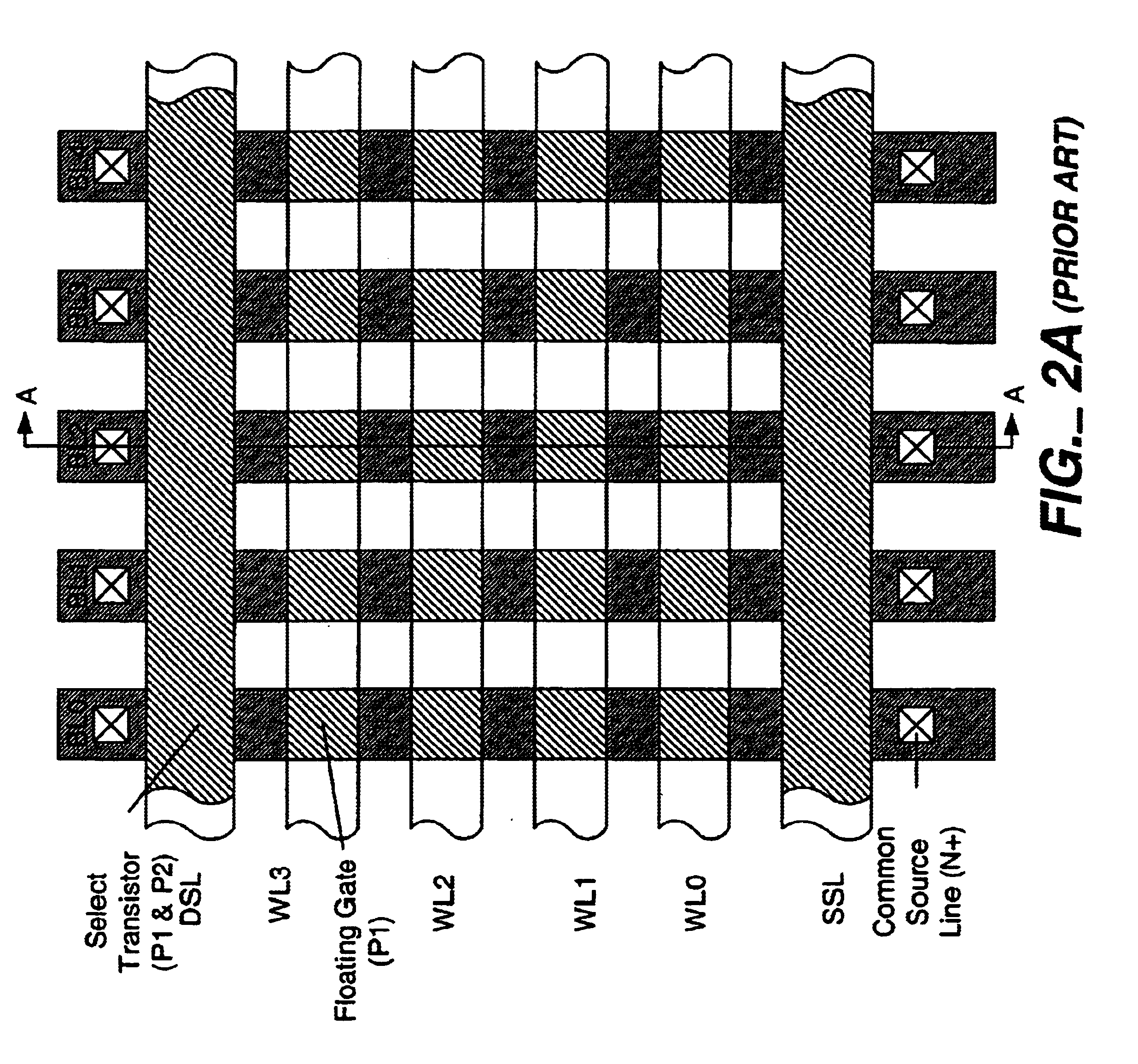
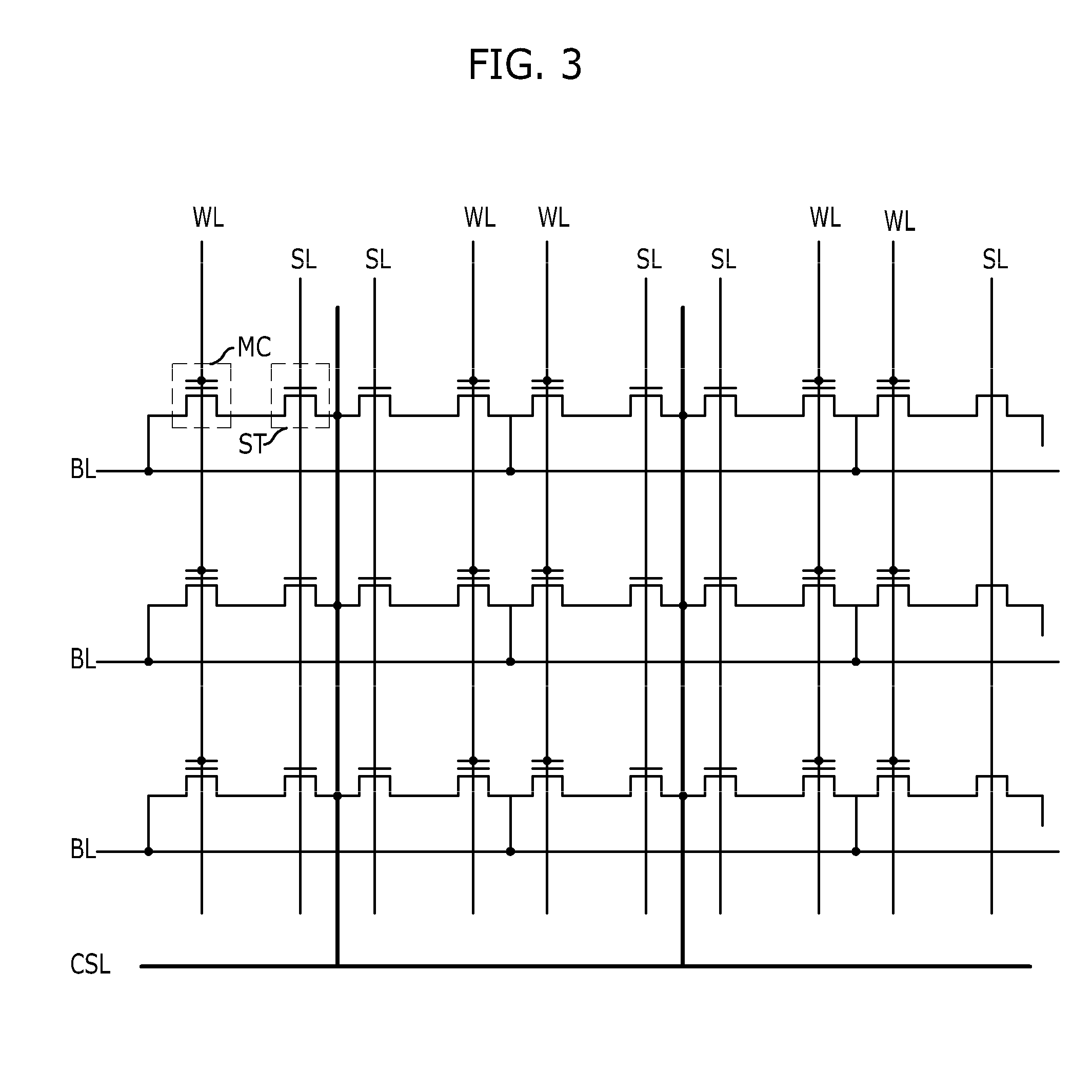
Flash memory cell arrays having dual control gates per memory cell charge storage element
InactiveUS6888755B2Increase coupling areaImprove the coupling ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceImage resolution
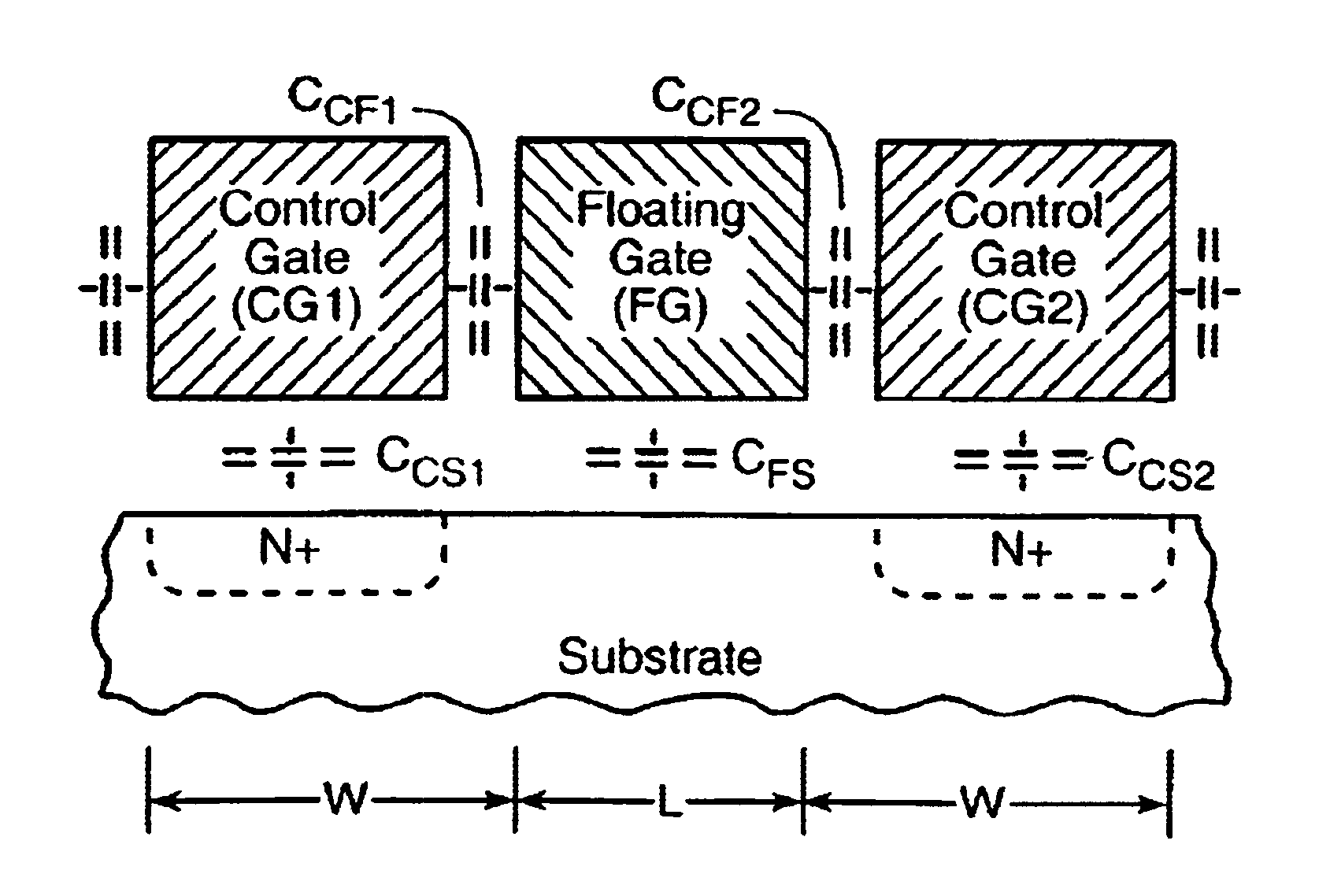
A flash NAND type EEPROM system with individual ones of an array of charge storage elements, such as floating gates, being capacitively coupled with at least two control gate lines. The control gate lines are preferably positioned between floating gates to be coupled with sidewalls of floating gates. The memory cell coupling ratio is desirably increased, as a result. Both control gate lines on opposite sides of a selected row of floating gates are usually raised to the same voltage while the second control gate lines coupled to unselected rows of floating gates immediately adjacent and on opposite sides of the selected row are kept low. The control gate lines can also be capacitively coupled with the substrate in order to selectively raise its voltage in the region of selected floating gates. The length of the floating gates and the thicknesses of the control gate lines can be made less than the minimum resolution element of the process by forming an etch mask of spacers.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Nor-type channel-program channel-erase contactless flash memory on SOI
InactiveUS20060018164A1Improve good performanceImprove circuit performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesProgrammable read-only memoryDevice material
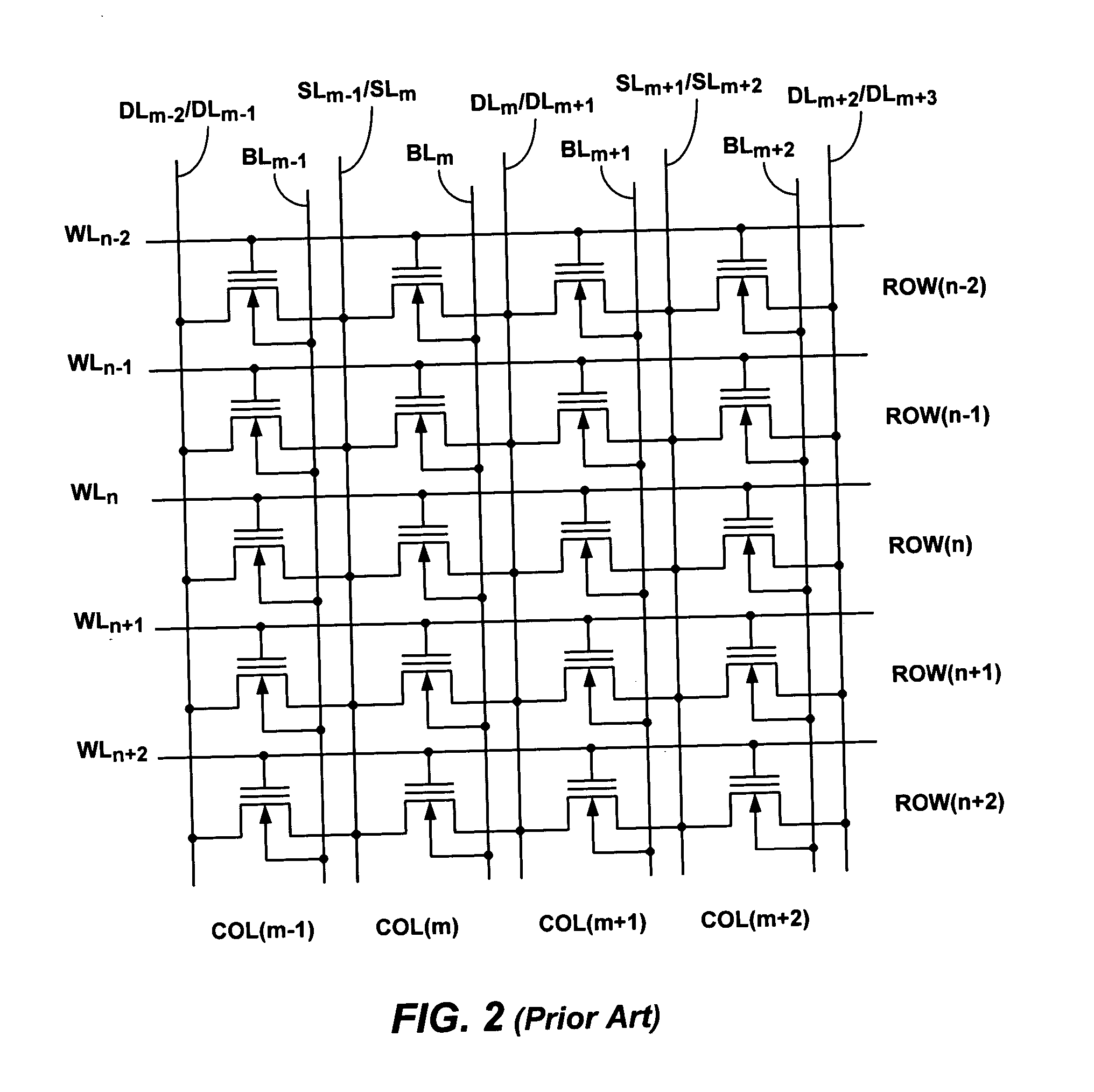
A semiconductor device having an electrically erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM) comprises a contactless array of EEPROM memory cells disposed in rows and columns and constructed over a silicon-on-insulator wafer. Each EEPROM memory cell comprises a drain region, a source region, a gate region, and a body region. The semiconductor device further comprises a plurality of gate lines each connecting the gate regions of a row of EEPROM memory cells, a plurality of body lines each connecting the body regions of a column of EEPROM memory cells, a plurality of source lines each connecting the source regions of a column of EEPROM memory cells, and a plurality of drain lines each connecting the drain regions of a column of EEPROM memory cells. The source lines and the drain lines are buried lines, and the source regions and the drain regions of a column of EEPROM memory cells are insulated from the source regions and the drain regions of the adjacent columns of EEPROM memory cells.
Owner:WU KOUCHENG
Nor-type channel-program channel-erase contactless flash memory on SOI
InactiveUS20050179079A1Improve good performanceImprove circuit performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesProgrammable read-only memoryDevice material
A semiconductor device having an electrically erasable programmable read only memory (EEPROM) comprises a contactless array of EEPROM memory cells disposed in rows and columns and constructed over a silicon-on-insulator wafer. Each EEPROM memory cell comprises a drain region, a source region, a gate region, and a body region. The semiconductor device further comprises a plurality of gate lines each connecting the gate regions of a row of EEPROM memory cells, a plurality of body lines each connecting the body regions of a column of EEPROM memory cells, a plurality of source lines each connecting the source regions of a column of EEPROM memory cells, and a plurality of drain lines each connecting the drain regions of a column of EEPROM memory cells. The source lines and the drain lines are buried lines, and the source regions and the drain regions of a column of EEPROM memory cells are insulated from the source regions and the drain regions of the adjacent columns of EEPROM memory cells.
Owner:WU KOUCHENG
Method to increase coupling ratio of source to floating gate in split-gate flash
InactiveUS20050207264A1Improve the coupling ratioIncrease lateral couplingTransistorSolid-state devicesFirst FillCoupling ratio
A split-gate flash memory cell having a three-dimensional source capable of three-dimensional coupling with the floating gate of the cell, as well as a method of forming the same are provided. This is accomplished by first forming an isolation trench, lining it with a conformal oxide, then filling with an isolation oxide and then etching the latter to form a three-dimensional coupling region in the upper portion of the trench. A floating gate is next formed by first filling the three-dimensional region of the trench with polysilicon and etching it. The control gate is formed over the floating gate with an intervening inter-poly oxide. The floating gate forms legs extending into the three-dimensional coupling region of the trench thereby providing a three-dimensional coupling with the source which also assumes a three-dimensional region. The leg or the side-wall of the floating gate forming the third dimension provides the extra area through which coupling between the source and the floating gate is increased. In this manner, a higher coupling ratio is achieved without an increase in the cell size while at the same time alleviating the punchthrough and junction break-down of source region by sharing gate voltage along the side-wall.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS7476582B2Easy to integrateImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesCell regionEngineering
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device which simultaneously possesses a non-volatile memory cell region which possesses an isolating insulation film which has been formed selectively within a semiconductor substrate, which also possesses a first electroconductive film (floating gate electrode) via a first gate insulating film which has been formed on the semiconductor substrate surface, and which also possesses a metal film (control gate electrode) via a second gate insulating film which has been formed above said electroconductive film and a peripheral transistor region which possesses a metal film (gate electrode) via a third gate insulating film which has been formed above the semiconductor substrate surface.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Flash memory cell arrays having dual control gates per memory cell charge storage element
InactiveUS7075823B2Increase coupling areaImprove the coupling ratioSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCapacitanceMemory cell
A flash NAND type EEPROM system with individual ones of an array of charge storage elements, such as floating gates, being capacitively coupled with at least two control gate lines. The control gate lines are preferably positioned between floating gates to be coupled with sidewalls of floating gates. The memory cell coupling ratio is desirably increased, as a result. Both control gate lines on opposite sides of a selected row of floating gates are usually raised to the same voltage while the second control gate lines coupled to unselected rows of floating gates immediately adjacent and on opposite sides of the selected row are kept low. The control gate lines can also be capacitively coupled with the substrate in order to selectively raise its voltage in the region of selected floating gates. The length of the floating gates and the thicknesses of the control gate lines can be made less than the minimum resolution element of the process by forming an etch mask of spacers.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method of forming an insulation layer structure and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the same
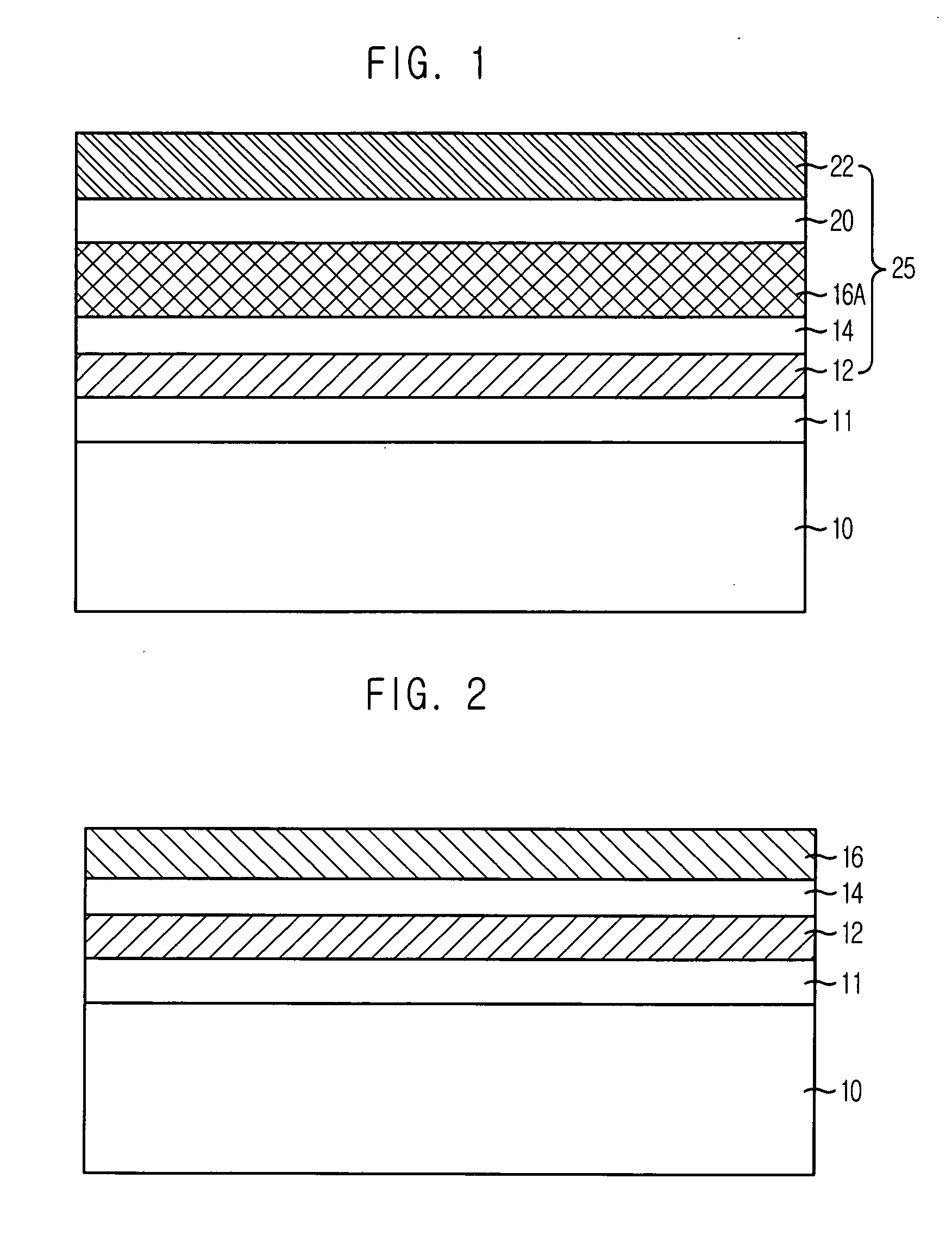
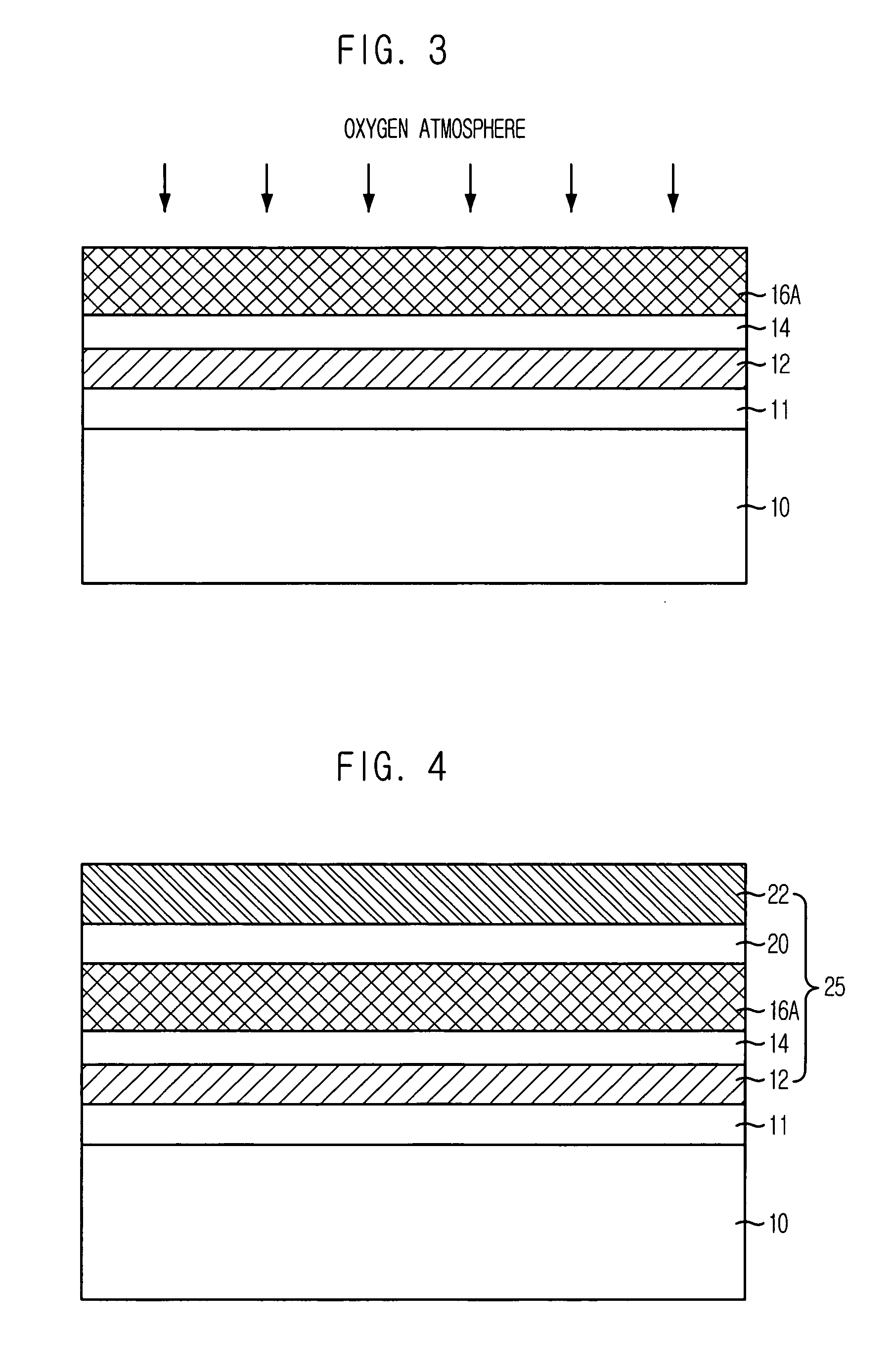
InactiveUS20060246657A1Improve the coupling ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerDevice material
A method of forming an isolation layer structure for a semiconductor device includes forming a first structure on a substrate, the first structure including an insulation layer pattern having a sacrificial pattern therein, the sacrificial pattern having an etching rate that is different from the insulation layer pattern, partially removing the insulation layer pattern until the sacrificial pattern is exposed to form a second structure, partially removing the sacrificial pattern from the insulation layer pattern to form a third structure having a recessed portion at a central portion thereof, and removing an upper portion of the third structure such that a top surface of the third structure is concave with respect to a top surface of the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ferroelectric non-volatile memory device having integral capacitor and gate electrode, and driving method of a ferroelectric non-volatile memory device
InactiveUS6898105B2Increase the areaImprove the coupling ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorCoupling ratio
A ferroelectric non-volatile memory device that allows the coupling ratio to be increased and the effect of voltage distribution to the ferroelectric capacitor to be improved without increasing the area of the gate electrode of a detection MIS field effect transistor is provided. In a memory cell structure, a semiconductor including regions for a source, a channel, and a drain, a gate insulator on the channel region, a floating gate conductor, a ferroelectrics, and an upper electrode conductor are layered in this order. The structure includes a paraelectric capacitor having one end connected to the floating gate conductor and the other end connected to the source region.
Owner:SEIKO NPC +1
Method and apparatus for controlling pitch and flap angles of a wind turbine
InactiveUS7530785B1Large coupling ratioReduce eliminatePropellersWind motor controlControl systemCoupling ratio
A wind turbine with improved response to wind conditions is provided. Blade flap angle motion is accompanied by a change in pitch angle by an amount defining a pitch / flap coupling ratio. The coupling ratio is non-constant as a function of a flap angle and is preferably a substantially continuous, non-linear function of flap angle. The non-constant coupling ratio can be provided by mechanical systems such as a series of linkages or by configuring electronic or other control systems and / or angle sensors. A link with a movable proximal end advantageously is part of the mechanical system. The system can provide relatively large coupling ratios and relatively large rates of coupling ratio changes especially for near-feather pitches and low flap angles.
Owner:THE WIND TURBINE
Split gate non-volatile memory devices and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20080093647A1Increased floating gate coupling ratioAccelerated programTransistorCoupling ratioEngineering
Non-volatile memory devices and methods for fabricating non-volatile memory devices are disclosed. More specifically, split gate memory devices are provided having frameworks that provide increased floating gate coupling ratios, thereby enabling enhanced programming and erasing efficiency and performance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Scaled EEPROM cell by metal-insulator-metal (MIM) coupling
InactiveUS6818936B2Reduce cell areaReduce areaTransistorSolid-state devicesMetal-insulator-metalCoupling
A single-poly EEPROM cell is disclosed with a vertically formed metal-insulator-metal (MIM) coupling capacitor, which serves as a control gate in place of a laterally buried control gate thereby eliminating the problem of junction breakdown, and at the same time reducing the size of the cell substantially. A method of forming the single-poly cell is also disclosed. This is accomplished by forming a floating gate over a substrate with an intervening tunnel oxide and then the MIM capacitor over the floating gate with another intervening dielectric layer between the top metal and the lower metal of the capacitor where the latter metal is connected to the polysilicon floating gate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Low-voltage fast-write PMOS nvsram cell
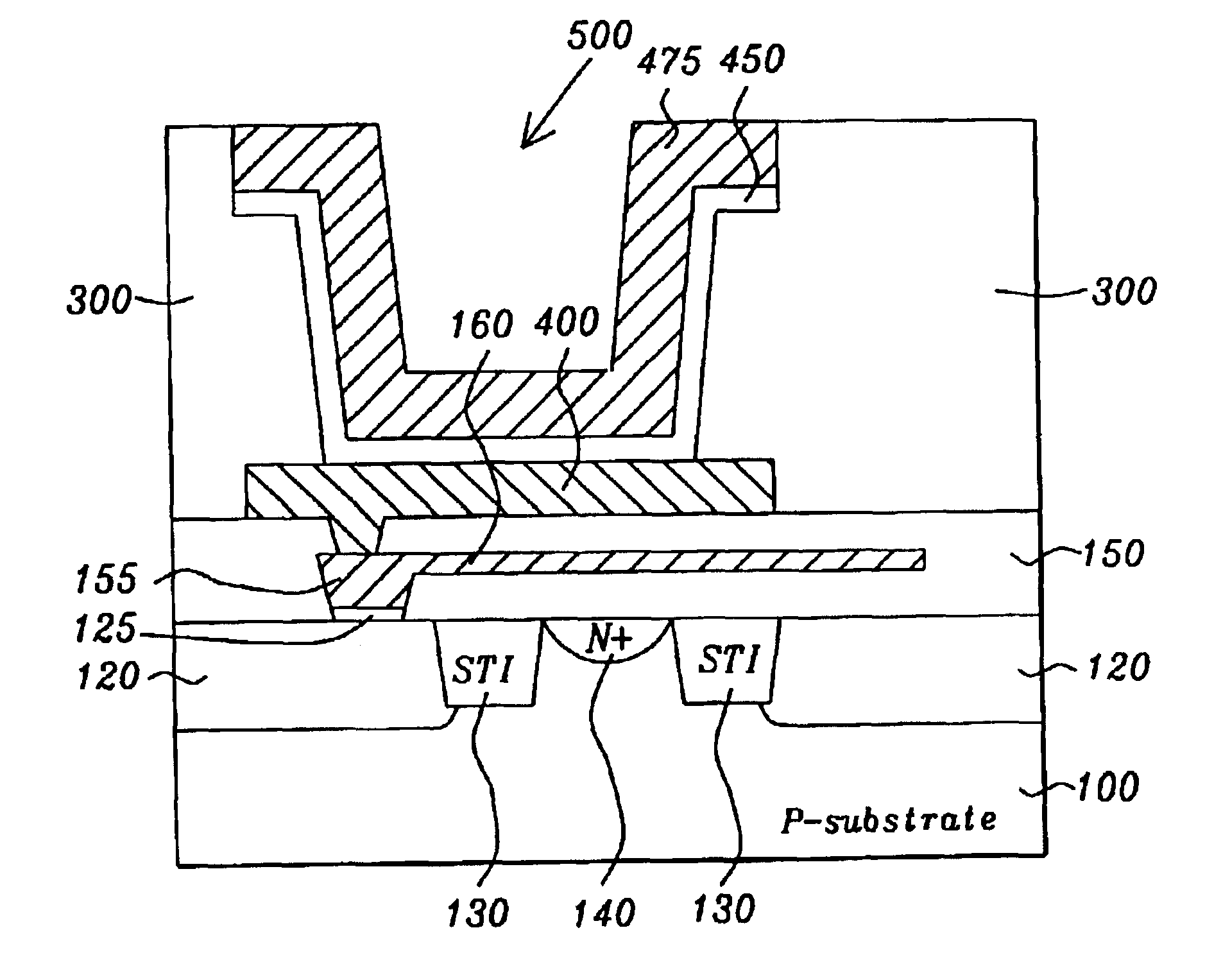
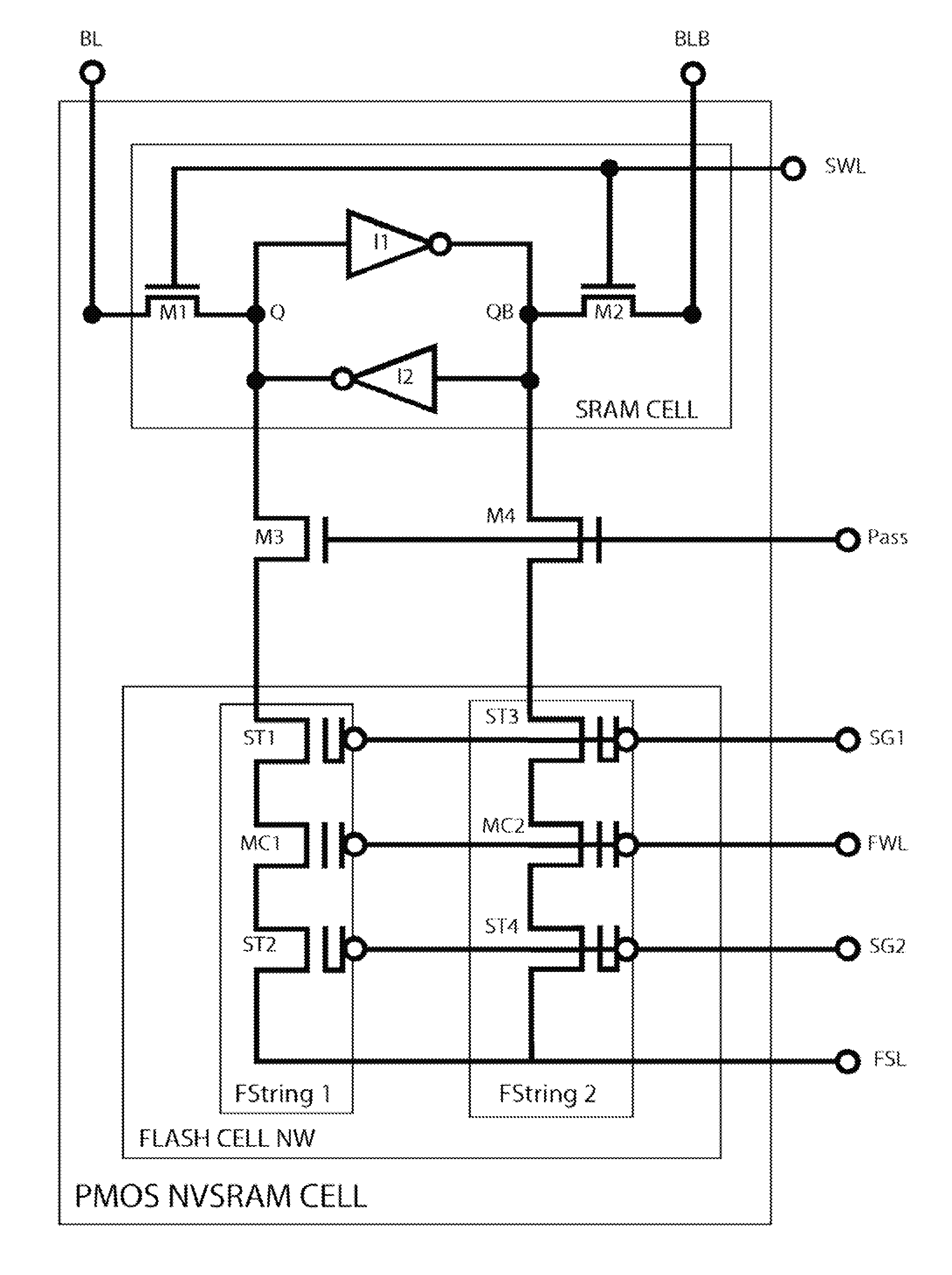
InactiveUS20140050025A1Junction breakdown can be preventedImprove the coupling ratioRead-only memoriesDigital storageLow voltageComputer science
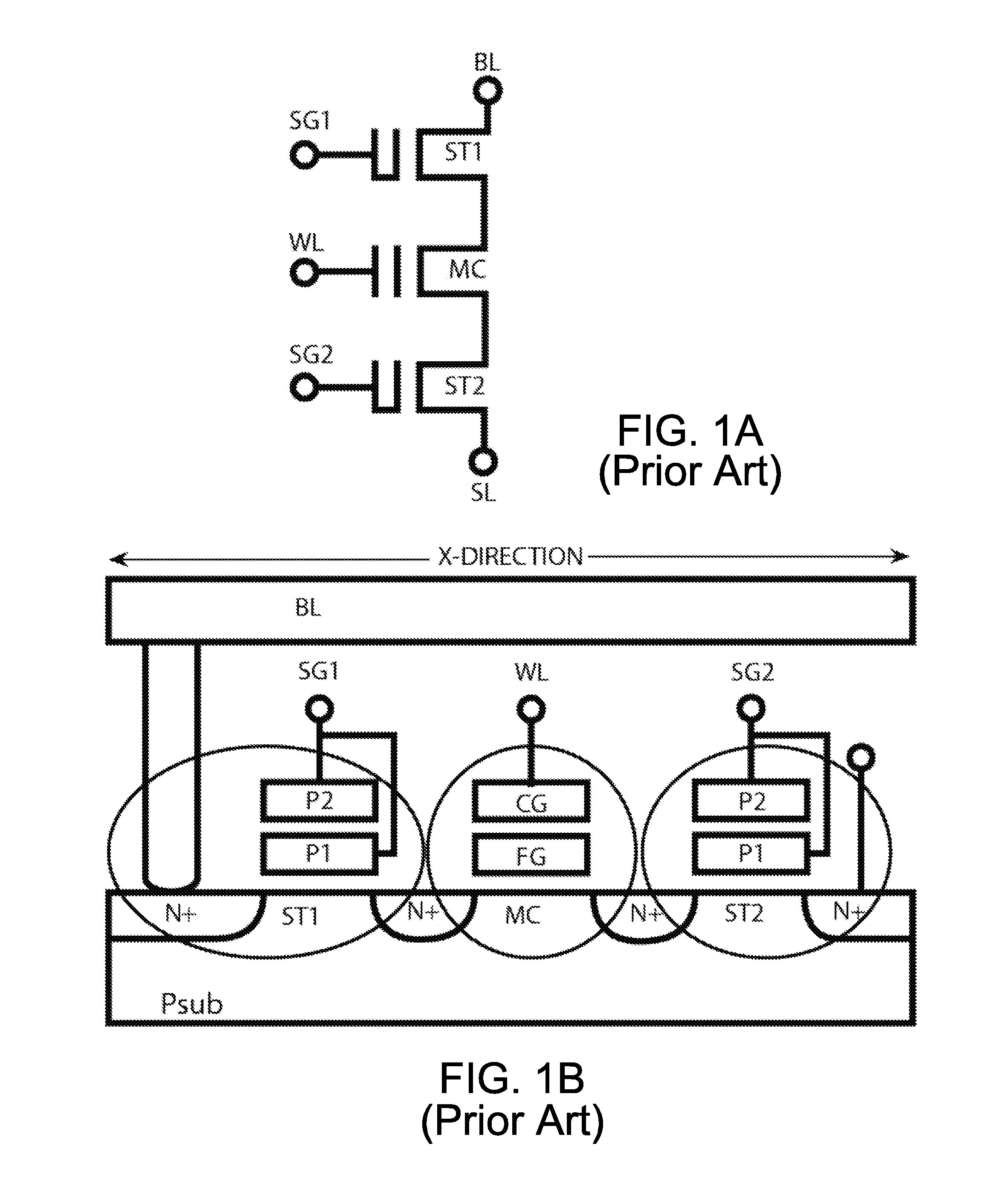
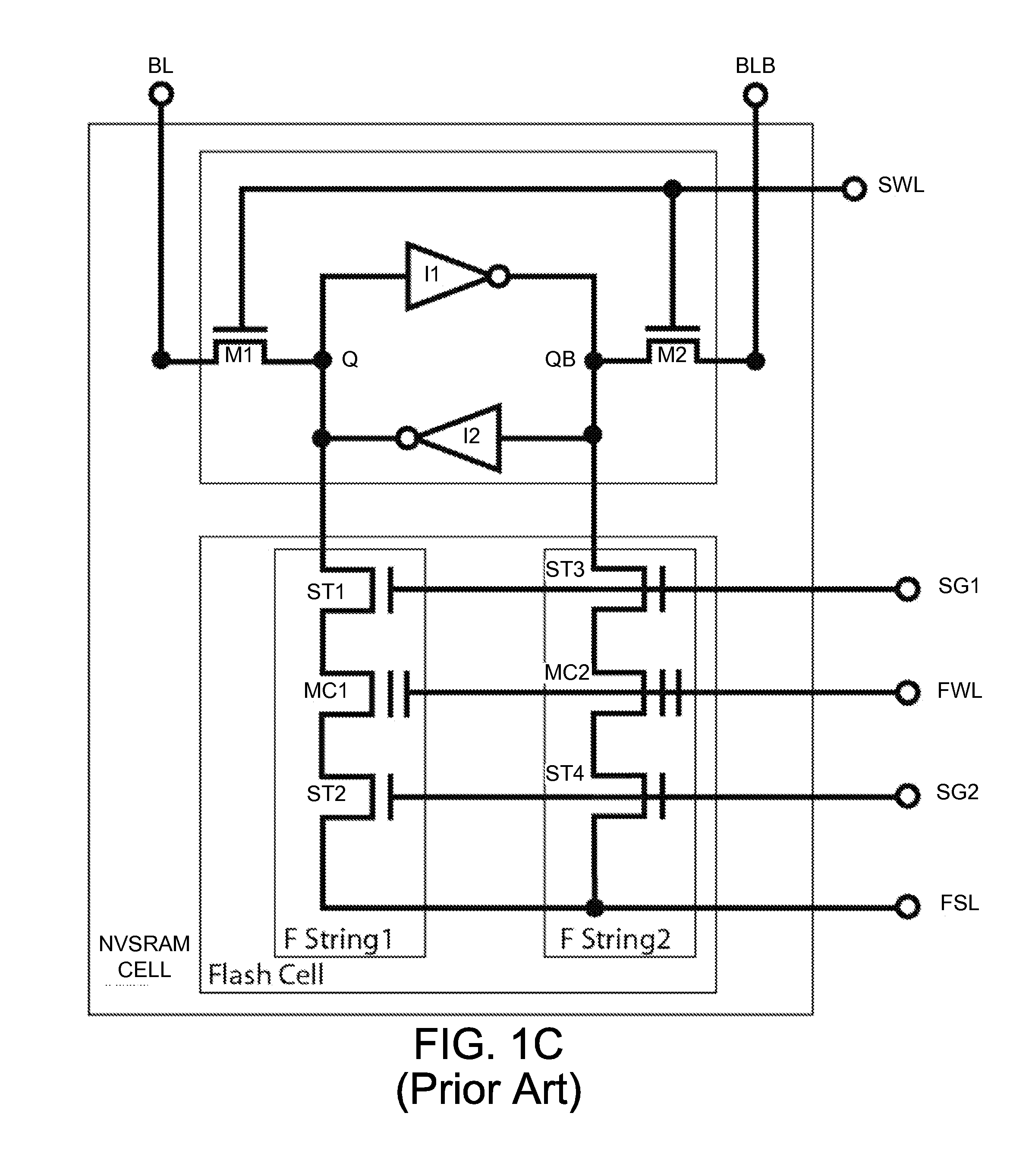
This invention discloses a low-voltage fast-write 12T or 14T PMOS NVSRAM cell structure which comprises a 6T LV SRAM cell and one pairs of two 3T or 4T HV PMOS Flash strings. Due to reverse threshold voltage definition of PMOS and NMOS flash cell, this PMOS NVSRAM cell has the advantage over the NMOS NVSRAM cell to have the same data polarity between SRAM and Flash pairs during the data writing operation. In addition, this PMOS NVSRAM's PMOS Flash cell uses similar low-current FN-tunneling scheme as NMOS NVSRAM, thus the fast data program and erase can be achieved in a big density up to 100 Mb simultaneously. As a result, low power voltage operation of NVSRAM with 1.2V VDD can be much easier to be designed without coupling the FSL line to any VDD level during the flash data loading into SRAM cell during a power-on period.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Nonvolatile memory cell and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20100270605A1Guaranteed uptimeSmall sizeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDielectric layer
A nonvolatile memory cell and a method for fabricating the same can secure stable operational reliability as well as reducing a cell size. The nonvolatile memory cell includes a drain region formed in a substrate, a source region formed in the substrate to be separated from the drain region, a floating gate formed over the substrate between the drain region and the source region, a halo region formed in the substrate in a direction that the drain region is formed, a dielectric layer formed on sidewalls of the floating gate, and a control gate formed over the dielectric layer to overlap with at least one sidewall of the floating gate.
Owner:KEY FOUNDRY CO LTD
Stacked gate flash memory device and method of fabricating the same
A stacked gate flash memory device and method of fabricating the same. A cell of the stacked gate flash memory device is disposed in a cell trench within a substrate to achieve higher integration of memory cells.
Owner:NAN YA TECH
Non-Volatile Memory Devices Having L-Shaped Floating Gate Electrodes and Methods of Forming Same
InactiveUS20070053223A1Reduced cell-to-cell coupling capacitanceImprove the coupling ratioSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesNon-volatile memoryVertical segment
A flash EEPROM array includes a first row of EEPROM cells having a first floating gate electrode therein and a second row of EEPROM cells having a second floating gate electrode therein. The first floating gate electrode includes at least one horizontal segment and at least one vertical segment, which collectively define a first L-shaped portion of the first floating gate electrode that faces a first direction. The second floating gate electrode includes at least one horizontal segment and at least one vertical segment that collectively define a second L-shaped portion of the second floating gate electrode that faces a second direction opposite the first direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of forming a self-aligned floating gate in flash memory cell
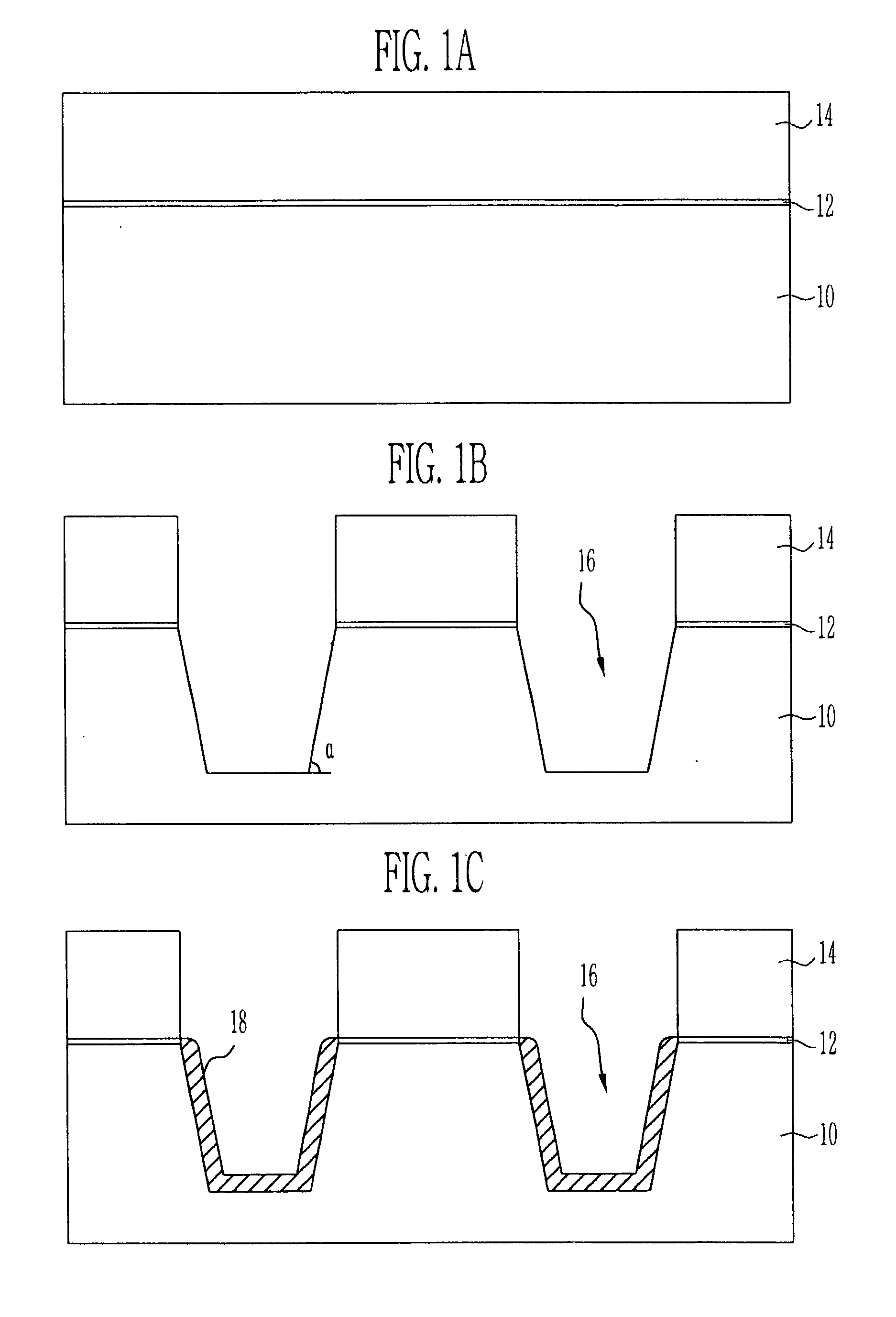
InactiveUS6656793B2Space minimizationAvoid it happening againTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of forming a self-aligned floating gate in a flash memory cell. A capping layer is formed on a trench insulating film. An etching process is then performed to etch the trench insulating film to a desired dimension. Therefore, generation of a moat in the trench insulating film is avoided. Further, spacing of a floating gate formed in a subsequent process can be minimized.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Flash Memory Cell Arrays Having Dual Control Gates Per Memory Cell Charge Storage Element
InactiveUS20060176736A1Increase coupling areaImprove the coupling ratioSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCapacitanceImage resolution
A flash NAND type EEPROM system with individual ones of an array of charge storage elements, such as floating gates, being capacitively coupled with at least two control gate lines. The control gate lines are preferably positioned between floating gates to be coupled with sidewalls of floating gates. The memory cell coupling ratio is desirably increased, as a result. Both control gate lines on opposite sides of a selected row of floating gates are usually raised to the same voltage while the second control gate lines coupled to unselected rows of floating gates immediately adjacent and on opposite sides of the selected row are kept low. The control gate lines can also be capacitively coupled with the substrate in order to selectively raise its voltage in the region of selected floating gates. The length of the floating gates and the thicknesses of the control gate lines can be made less than the minimum resolution element of the process by forming an etch mask of spacers.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method of fabricating memory cell structure of flash memory having annular floating gate
InactiveUS6518110B2Improve equipment reliabilityImprove reliabilityTransistorRead-only memoriesCapacitanceDielectric
The present invention relates to a memory cell structure of a flash memory and a method for fabricating the same and, more particularly, to a flash memory having annular floating gates. The present invention uses the capacitance coupling between the source and the floating gate to form a channel in the substrate under the floating gate. Hot electrons are injected into the floating gate or released from the floating gate to the control gate through inerpoly dieletric by injection point on the top of floating gate In the proposed memory cell, a floating gate is etched to form an annular shape situated between a drain, a source, and two field oxides. An interpoly dielectric and a control gate are stacked in turn on the floating gate and on the surface of the substrate not covered by the floating gate through means of self-alignment. An injection point not covered by the SiN film of the interpoly dielectric is formed on the top of the floating gate. Thereby the present invention can not only achieve self-alignment to form the control gate and apply to high-integration memory cells with small areas, but also can release electrons from the floating gate to the control gate by the FN tunneling effect to effectively increase efficiency of erasing data and reliability of devices.
Owner:WEN WEN YING
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080014760A1Easy to implementImprove the coupling ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
When microfabrication is done, a reliable semiconductor device is offered.A semiconductor device has a semiconductor substrate which has a main front surface, a plurality of convex patterns formed on the main front surface of a semiconductor substrate so that each might have a floating gate and a control gate, a first insulating film formed so that the upper surface and the side surface of each of a plurality of convex patterns might be covered, and so that width might become large rather than the portion which covers the lower part side surface of a convex pattern in the portion which covers an upper part side surface, and a second insulating film that covers the upper surface and the side surface of the first insulating film so that the cavity between the adjacent convex patterns may be occluded. The position occluded by the second insulating film of a cavity is a position higher than the upper surface of a floating gate, and is a position lower than the upper surface of a control gate.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device with dielectric structure and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070048929A1Increase currentImprove the coupling ratioSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPhysicsTitanium dioxide
A semiconductor device with a dielectric structure and a method for fabricating the same are provided. A capacitor in the semiconductor device includes: a bottom electrode formed on a substrate; a first dielectric layer made of titanium dioxide (TiO2) in rutile phase and formed on the bottom electrode; and an upper electrode formed on the first dielectric layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method of forming a self-aligned floating gate in flash memory cell
InactiveUS20030119259A1Space minimizationAvoid it happening againTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical and Electronics engineeringFlash memory
A method of forming a self-aligned floating gate in a flash memory cell. A capping layer is formed on a trench insulating film. An etching process is then performed to etch the trench insulating film to a desired dimension. Therefore, generation of a moat in the trench insulating film is avoided. Further, spacing of a floating gate formed in a subsequent process can be minimized.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method for manufacturing a non-volatile memory device
InactiveUS20050090059A1Reduce in sizeObtain capacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesBuried oxideOxide
A method for manufacturing a non-volatile memory device which can increase the coupling ratio and can avoid affecting the height of a control gate by forming a trench in a cell region and forming a floating gate in a concave shape in the trench is disclosed. The method comprises: forming a first trench having a first depth on a silicon substrate of a peripheral circuit region, burying the same with a buried oxide film and planarizing the same; forming a second trench having a second depth on the silicon substrate of the cell region; carrying out channel ion implantation to the cell region, forming a tunnel oxide film in the second trench and depositing a floating gate material; forming a floating gate by etching the floating gate material; forming a source / drain junction in the cell region; forming wells in the peripheral circuit and cell regions and depositing a dielectric film; depositing a gate material while leaving the dielectric film only in the channel portion of the cell region; and forming a gate in the peripheral circuit region and a control gate in the cell region by etching the gate material.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Non-volatile memory cell and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7038267B2Highly integratedImprove the coupling ratioTransistorSolid-state devicesTrappingDielectric layer
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
NAND flash memory cell row and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060040440A1Improve memory performanceIncrease erasing speedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
A NAND flash memory cell row includes first and second stacked gate structures, control and floating gates, inter-gate dielectric layer, a tunnel oxide layer, doping regions and source / drain regions. The first stacked gate structures has an erase gate dielectric layer, an erase gate and a first cap layer. Each of the second stacked gate structure has a select gate dielectric layer, a select gate and a second cap layer. The control gate is between each of the first stacked gate structures, and between each of the second stacked gate structures and the adjacent first stacked gate structure. The floating gate is between the control gate and substrate. The inter-gate dielectric layer is disposed between the control and floating gates. The tunnel oxide is between the floating gate and substrate. The doping regions are disposed under the first stacked gate structure, and the source / drain regions are in the exposed substrate.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20090283812A1Improve the coupling ratioSuppress errorTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
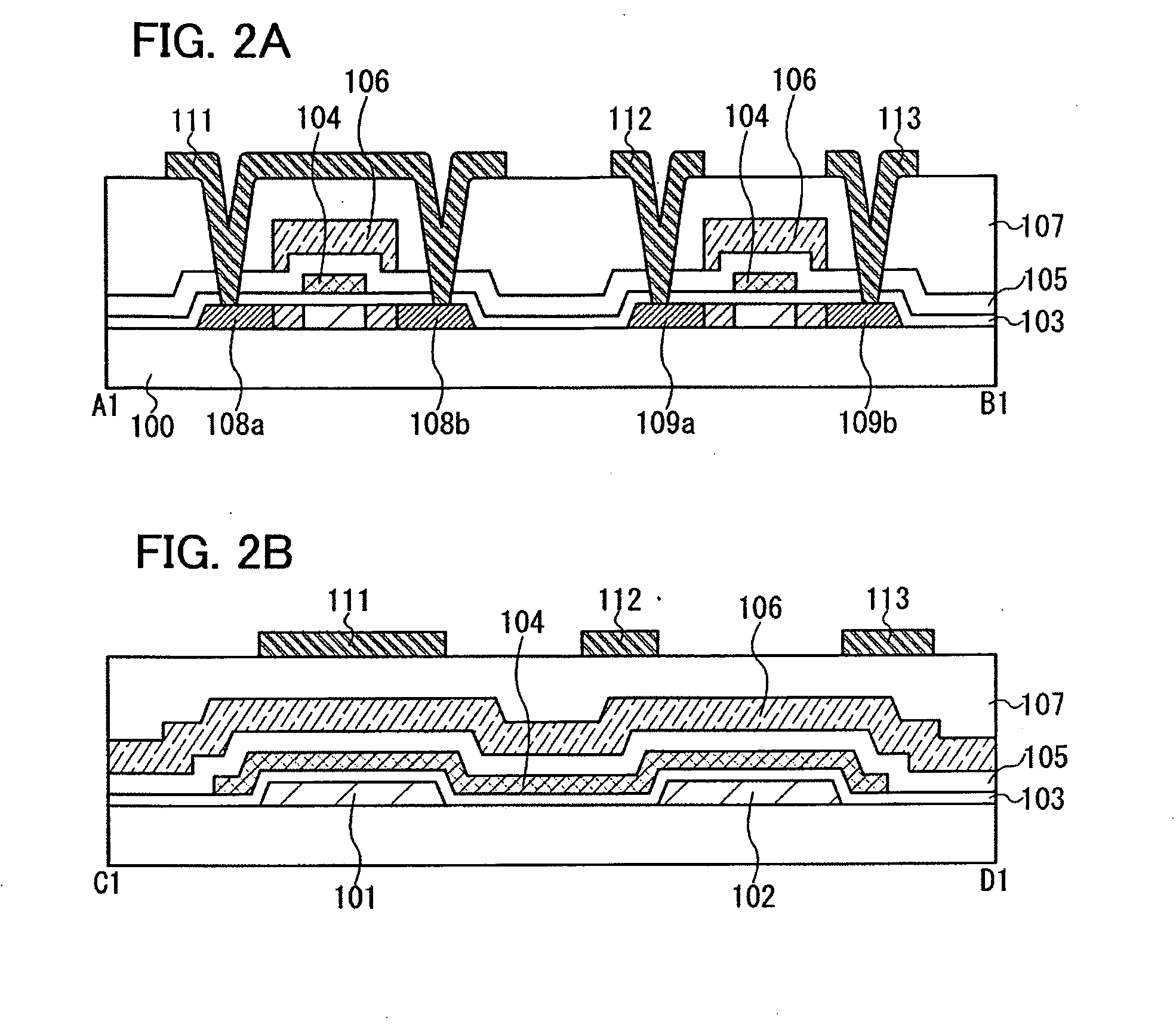
An object is to suppress reading error even in the case where writing and erasing are repeatedly performed. Further, another object is to reduce writing voltage and erasing voltage while increase in the area of a memory transistor is suppressed. A floating gate and a control gate are provided with an insulating film interposed therebetween over a first semiconductor layer for writing operation and erasing operation and a second semiconductor layer for reading operation which are provided over a substrate; injection and release of electrons to and from the floating gate are performed using the first semiconductor layer; and reading is performed using the second semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Non-volatile memory device and method of manufacturing the same
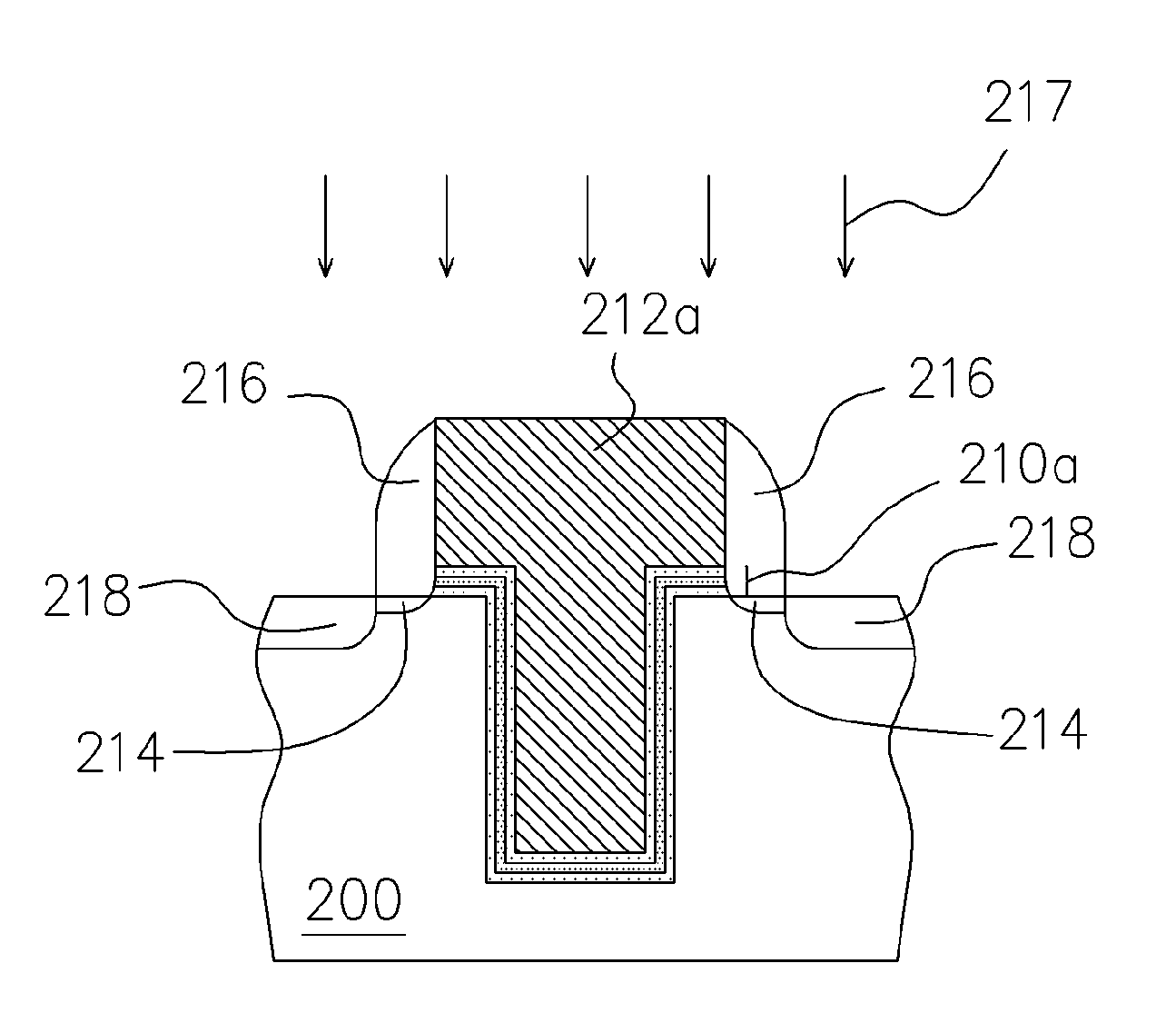
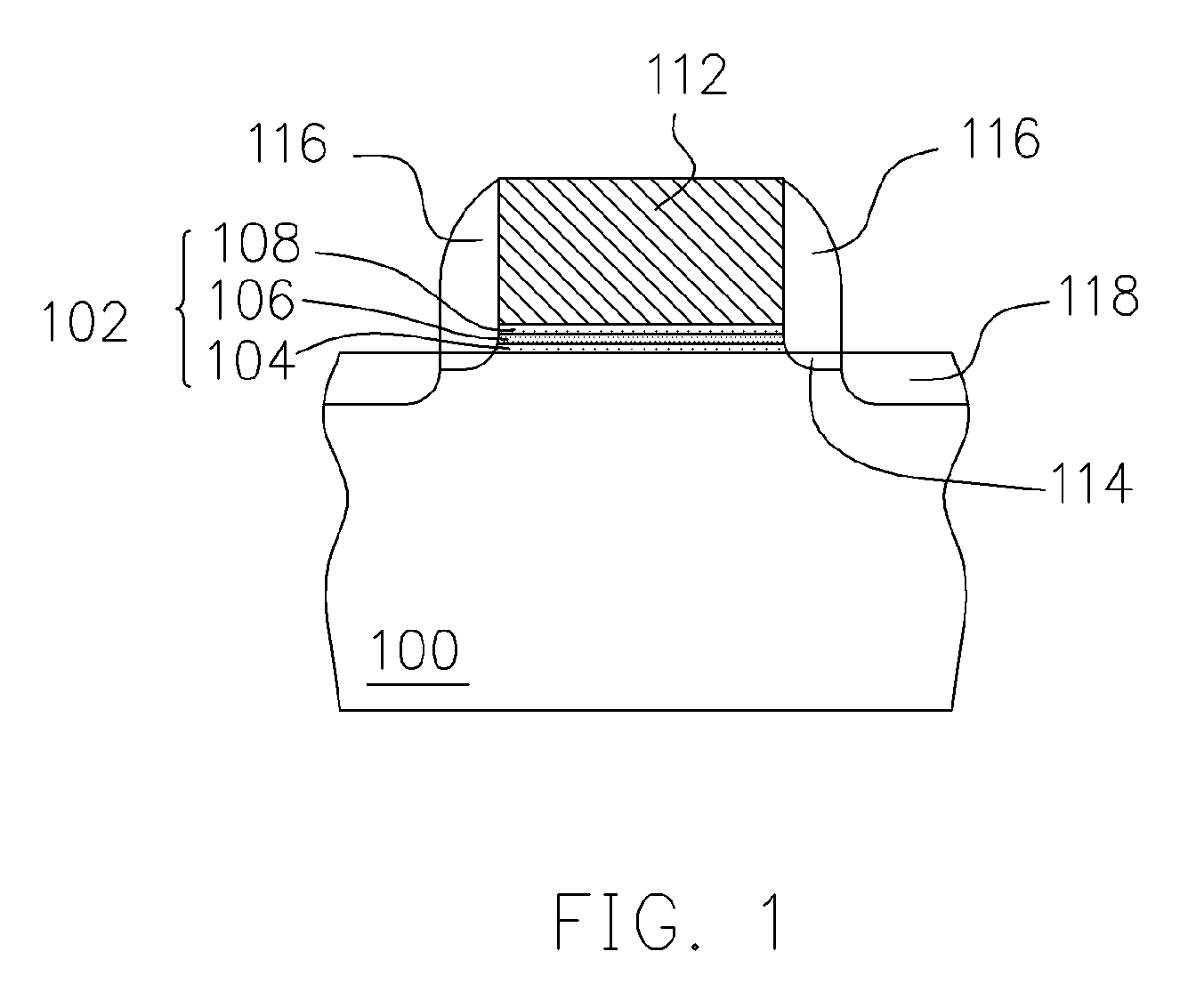
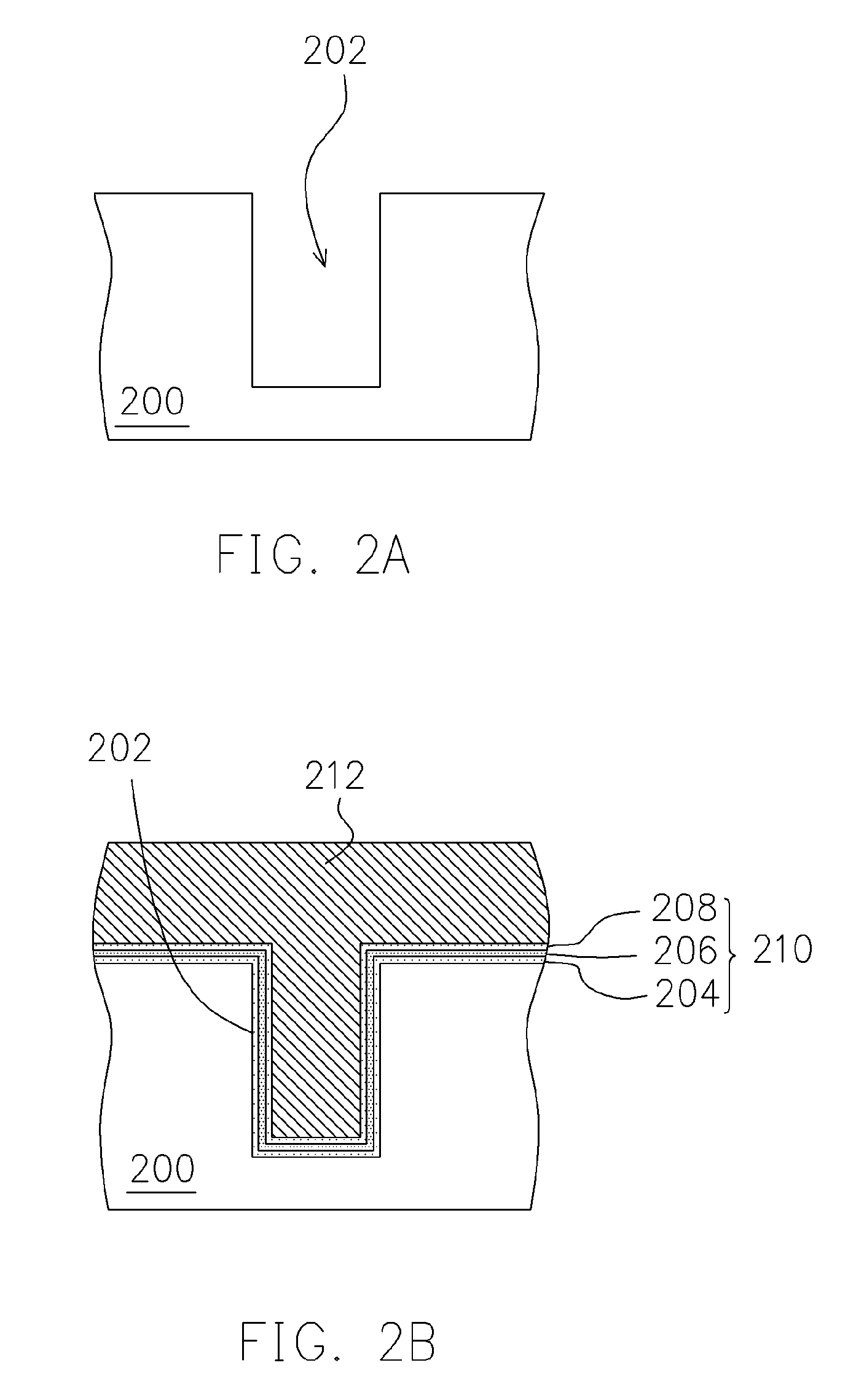
ActiveUS7091550B2Small dimensionImprove the coupling ratioTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrappingCoupling ratio
A non-volatile memory device and method of manufacturing the same is provided. A substrate is provided and then a trench is formed in the substrate. Thereafter, a bottom oxide layer, a charge-trapping layer and a top oxide layer are sequentially formed over the substrate and the surface of the trench. A conductive layer is formed over the top oxide layer filling the trench. The conductive layer is patterned to form a gate over the trench. The top oxide layer, the charge-trapping layer and the bottom oxide layer outside the gate are removed. A source / drain doping process is carried out. Because the non-volatile memory device is manufactured within the trench, storage efficiency of the device is improved through an increase in the coupling ratio. Furthermore, more charges can be stored by increasing the depth of the trench.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Method of manufacturing semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20090233434A1Stable structureThreshold voltage uniformSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorsDevice materialNitrogen
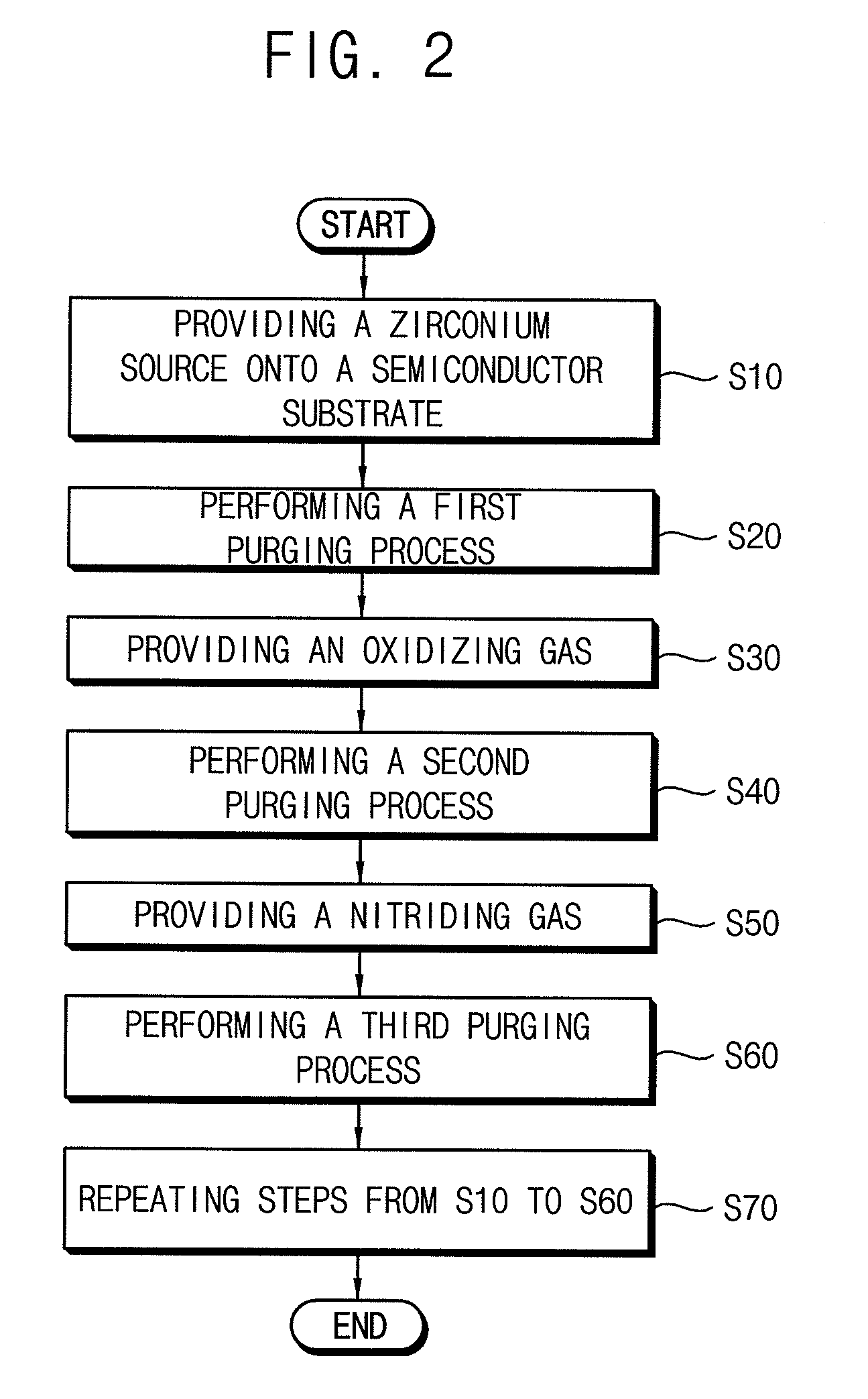
In semiconductor devices and methods of manufacturing semiconductor devices, a zirconium source having zirconium, carbon and nitrogen is provided onto a substrate to form an adsorption layer of the zirconium source on the substrate. A first purging process is performed to remove a non-adsorbed portion of the zirconium source. An oxidizing gas is provided onto the adsorption layer to form an oxidized adsorption layer of the zirconium source on the substrate. A second purging process is performed to remove a non-reacted portion of the oxidizing gas. A nitriding gas is provided on the oxidized adsorption layer to form a zirconium carbo-oxynitride layer on the substrate, and a third purging process is provided to remove a non-reacted portion of the nitriding gas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Coupling Device with Compensated Birefringence
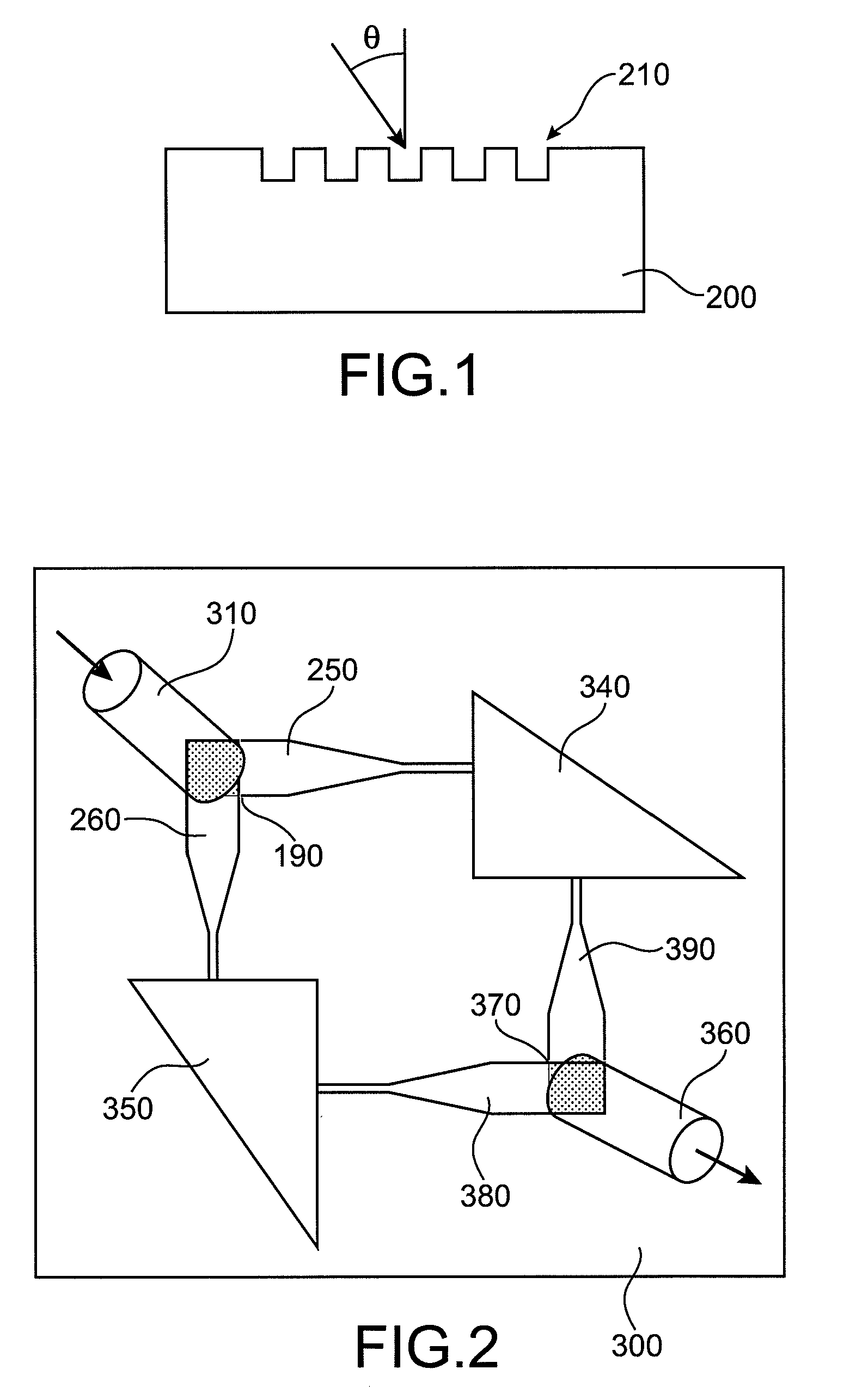
InactiveUS20100172615A1Polarization insensitiveImprove the coupling ratioOptical articlesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLength waveSecondary layer
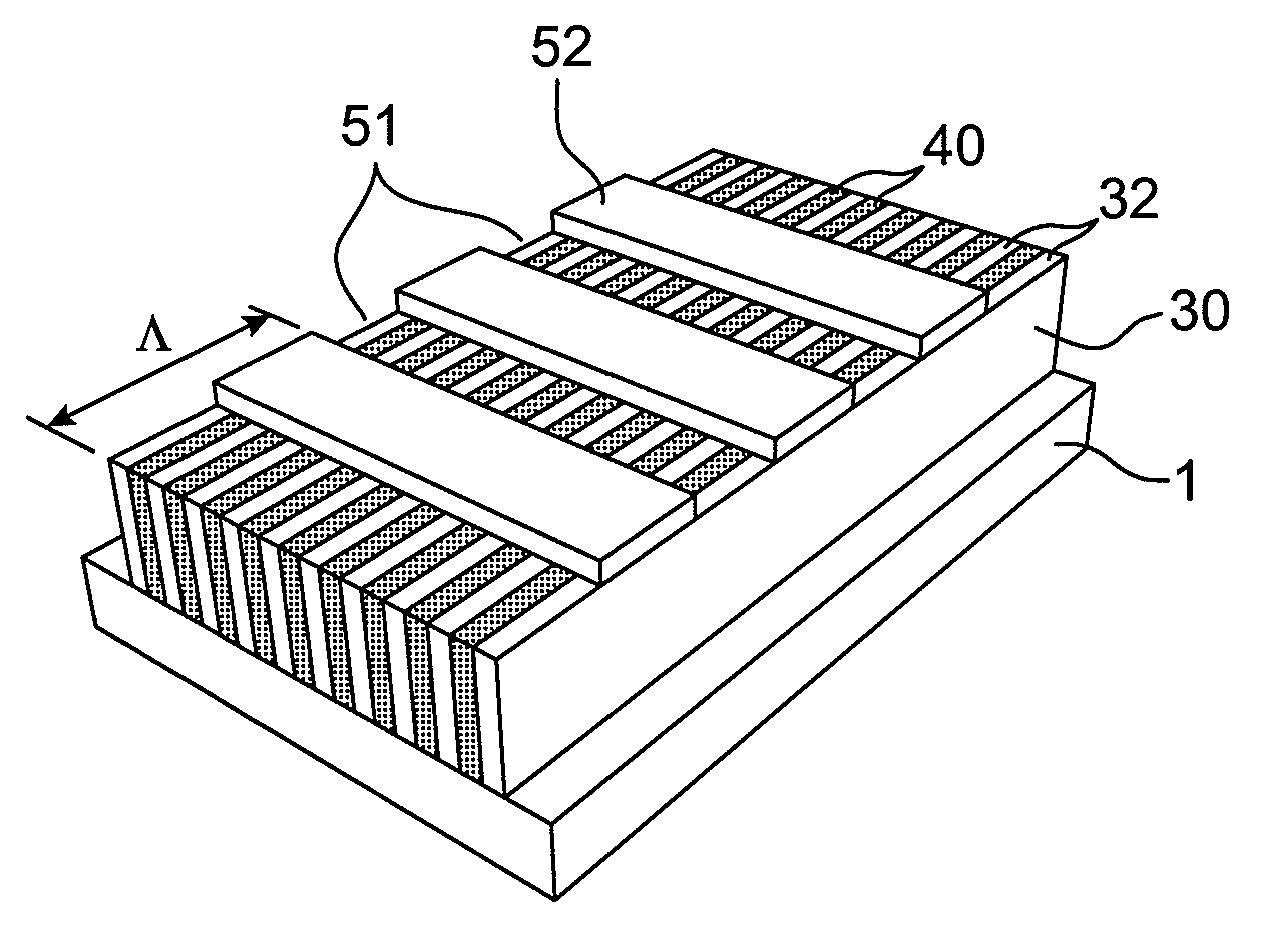
The invention relates to a coupling device comprising a support substrate; a first layer arranged on the support substrate and comprising first patterns produced within the thickness of said first layer, said first patterns being arranged in parallel and periodic rows; a second layer arranged on the first layer and comprising second patterns passing through the thickness of said second layer, said second patterns being arranged in parallel and periodic rows. The direction of periodicity of the rows of the first patterns is perpendicular to the direction of periodicity of the rows of the second patterns. The rows of the first patterns extend over a distance greater than or equal to the wavelength in the void of the optical wave intended to be coupled. The first patterns have a width less than or equal to a tenth of the wavelength of the optical wave intended to be coupled, and the period of these patterns is between 50 nm and 1 μm. The second patterns are arranged so as to form a periodic diffraction grating.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com