Patents
Literature
194results about How to "Improve memory performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
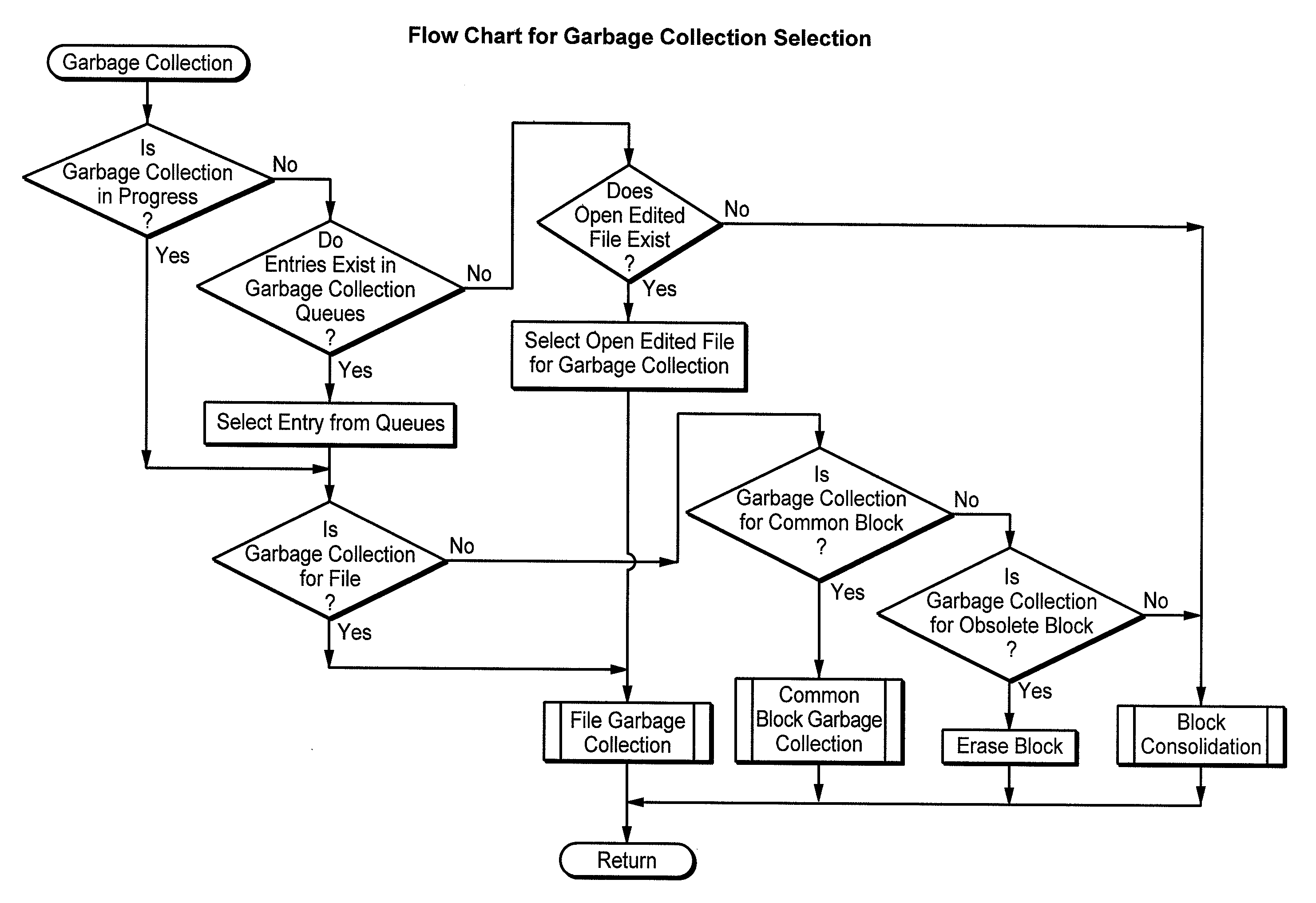
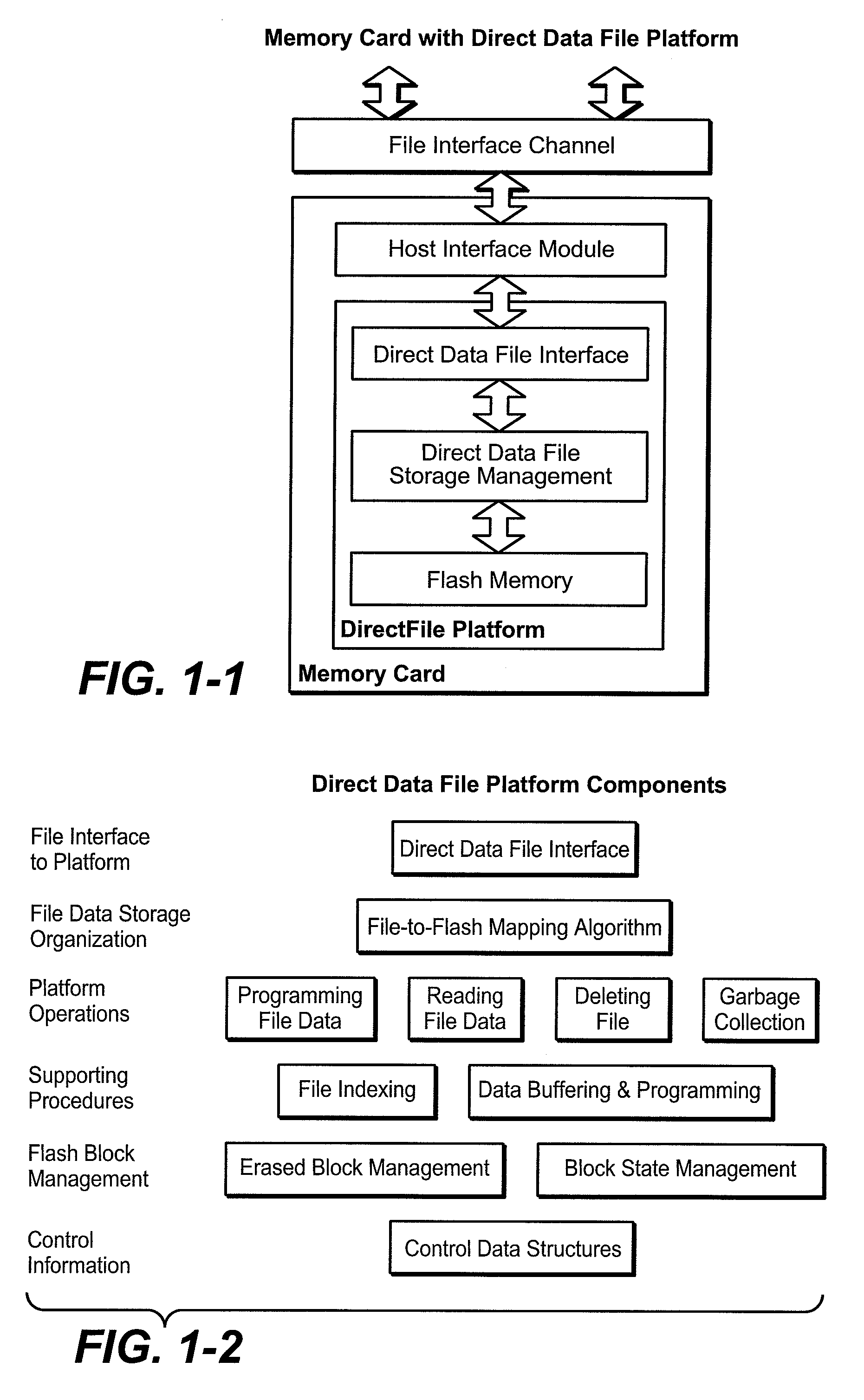
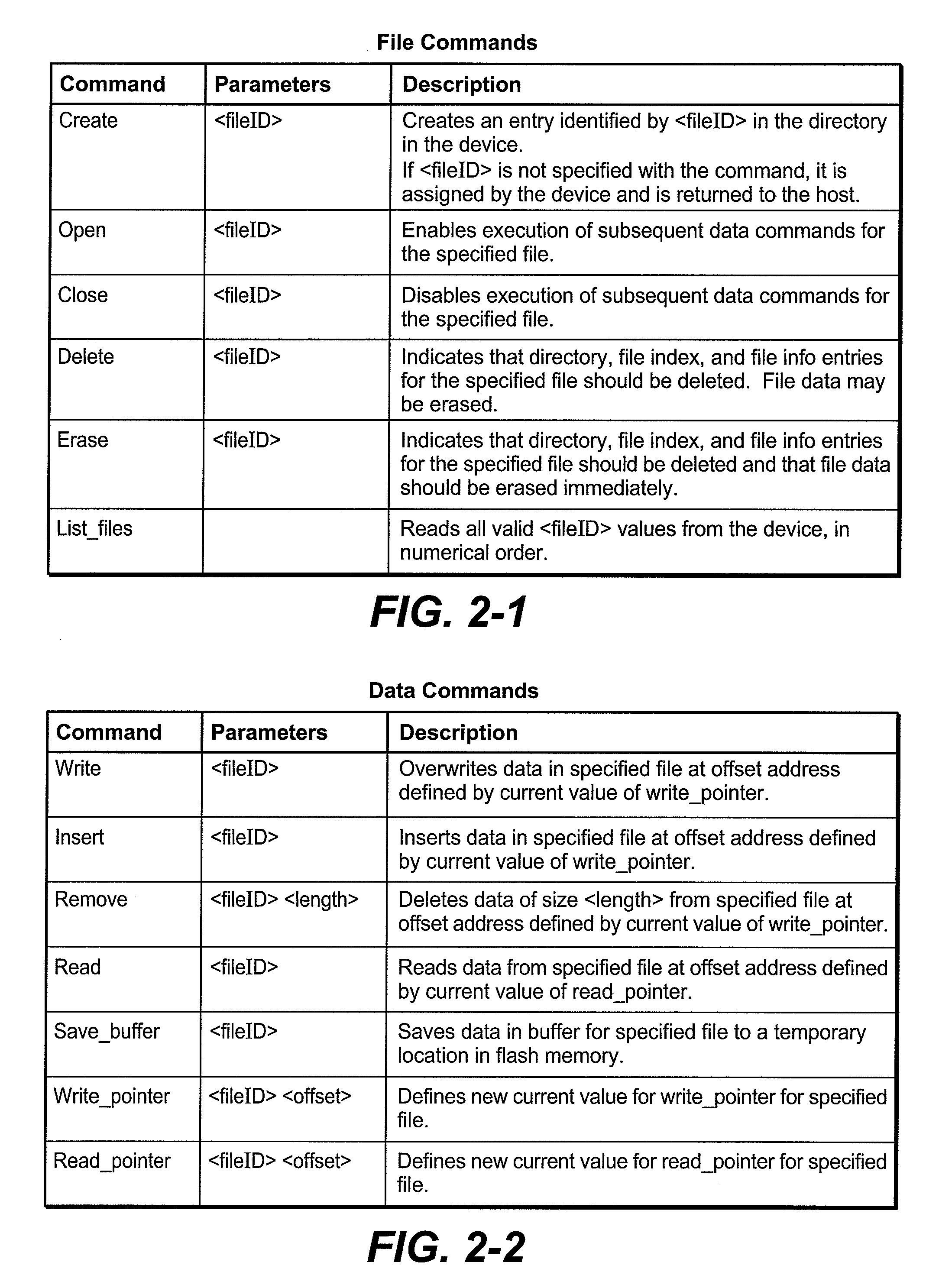
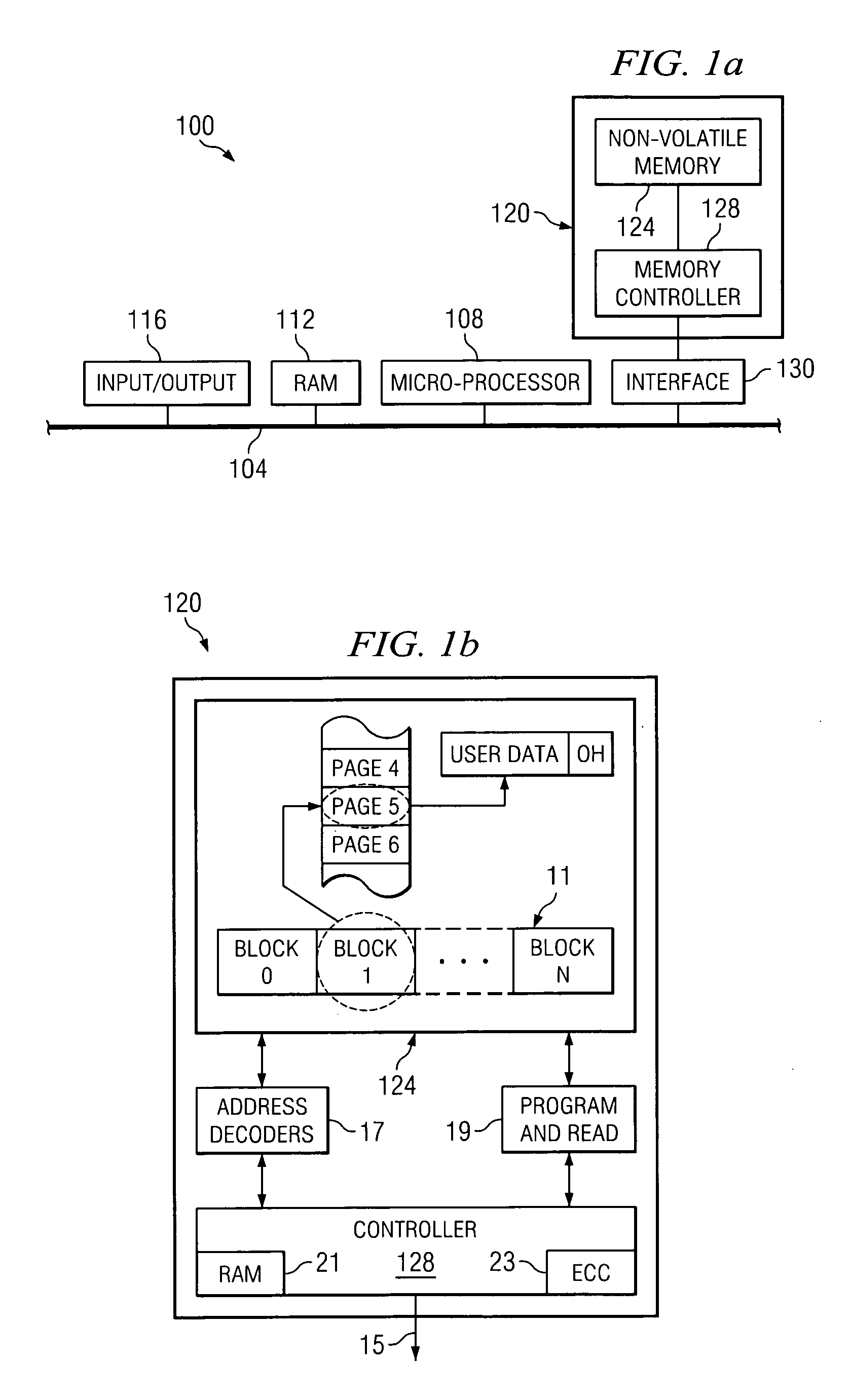
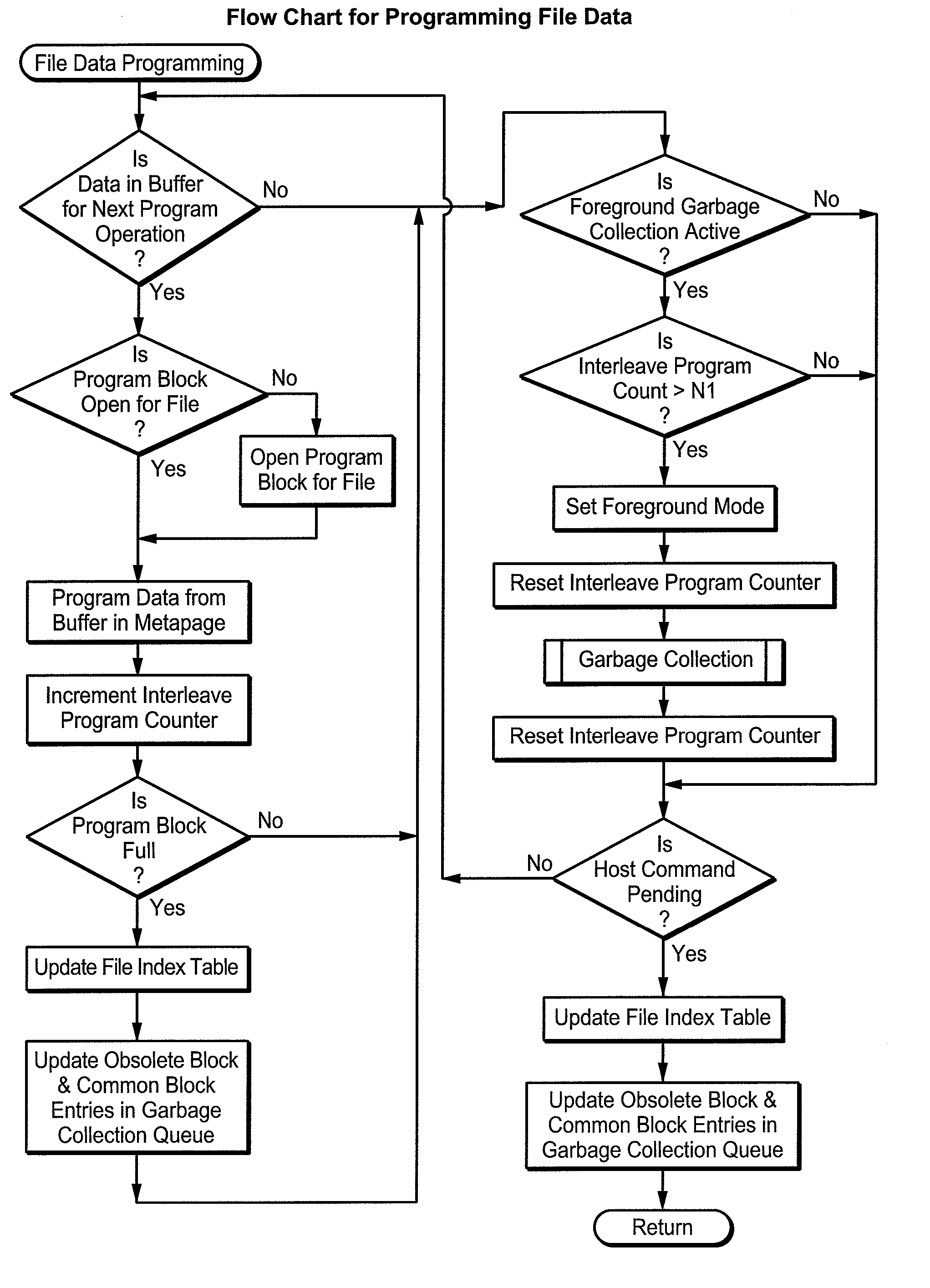
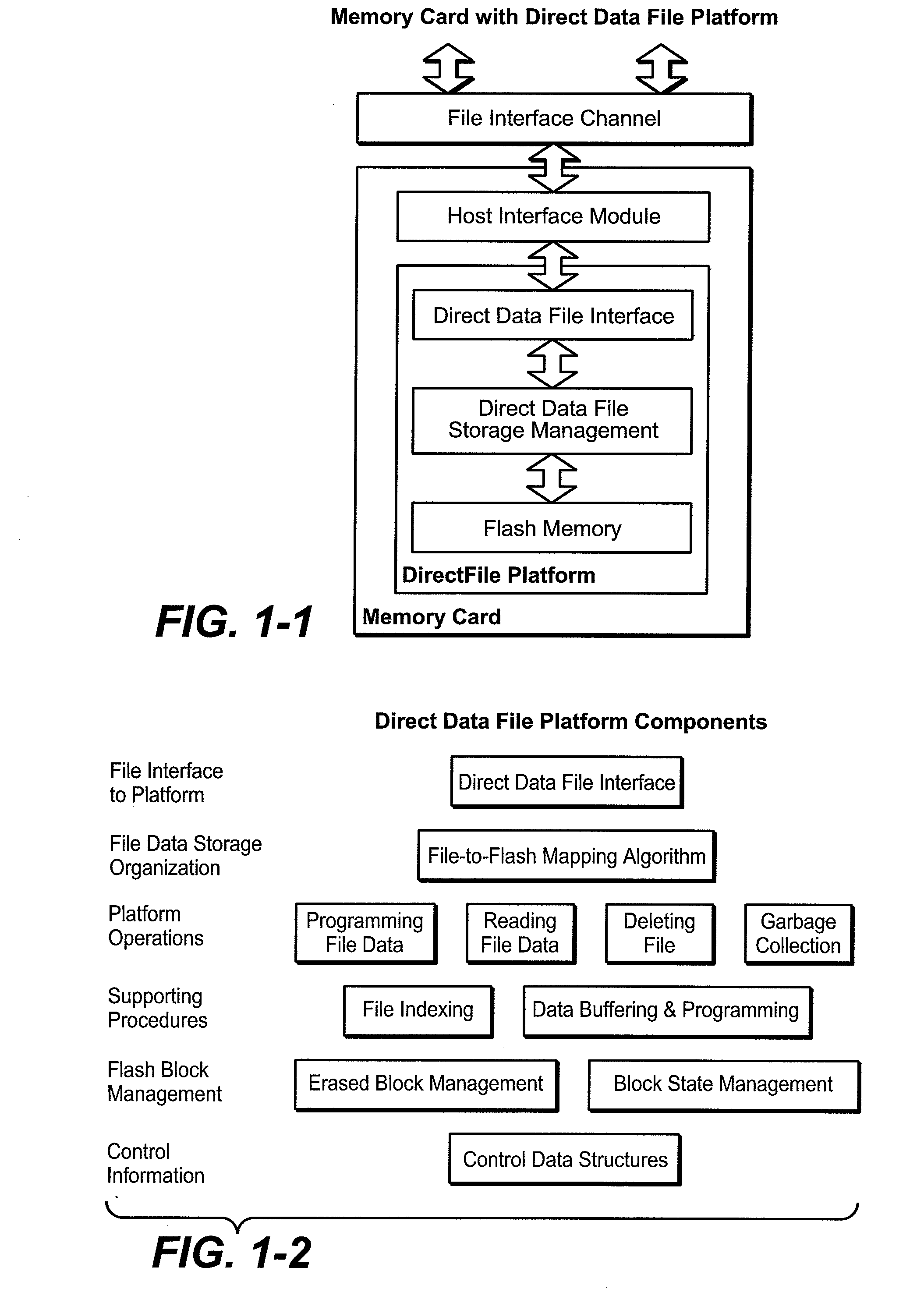
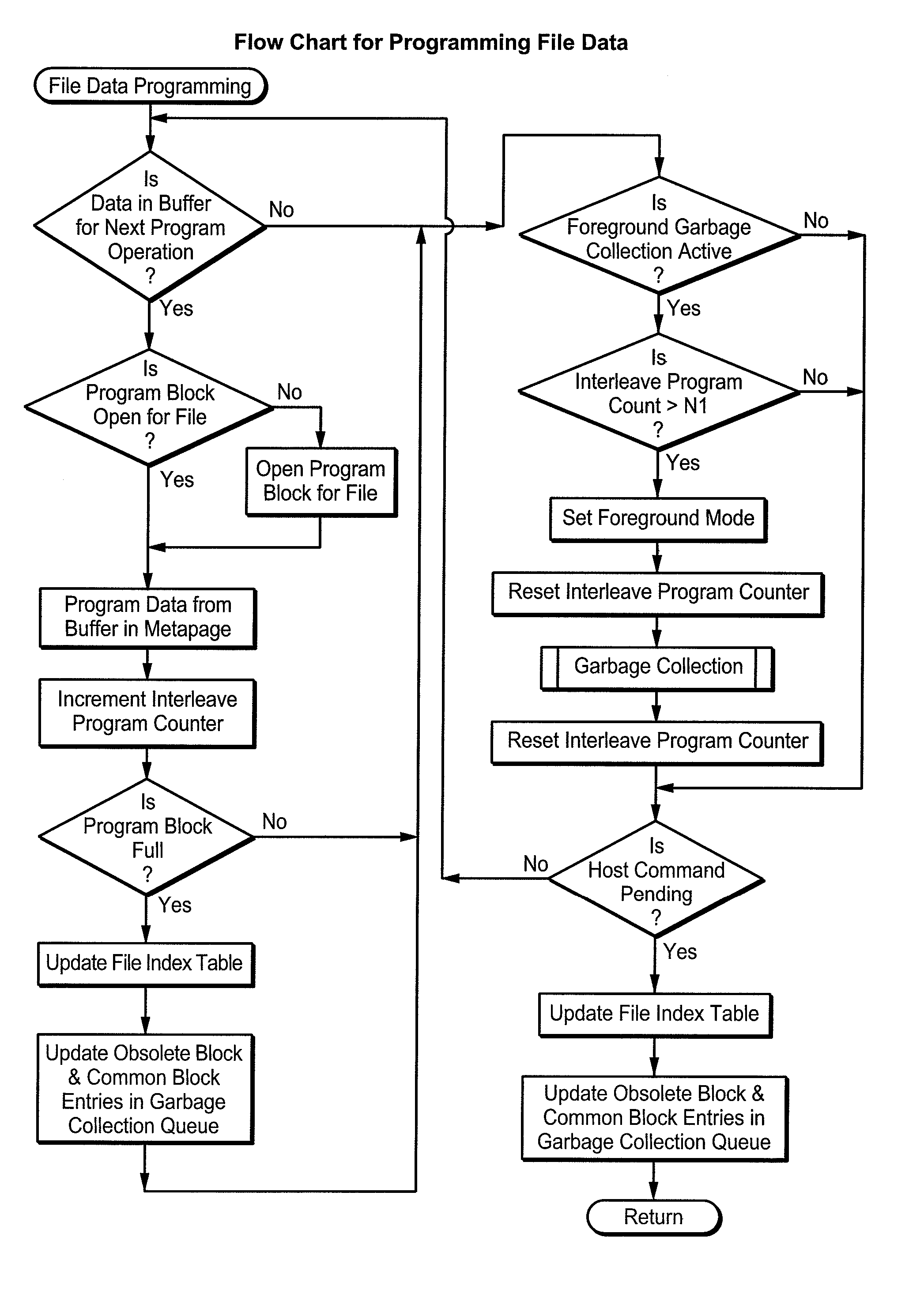
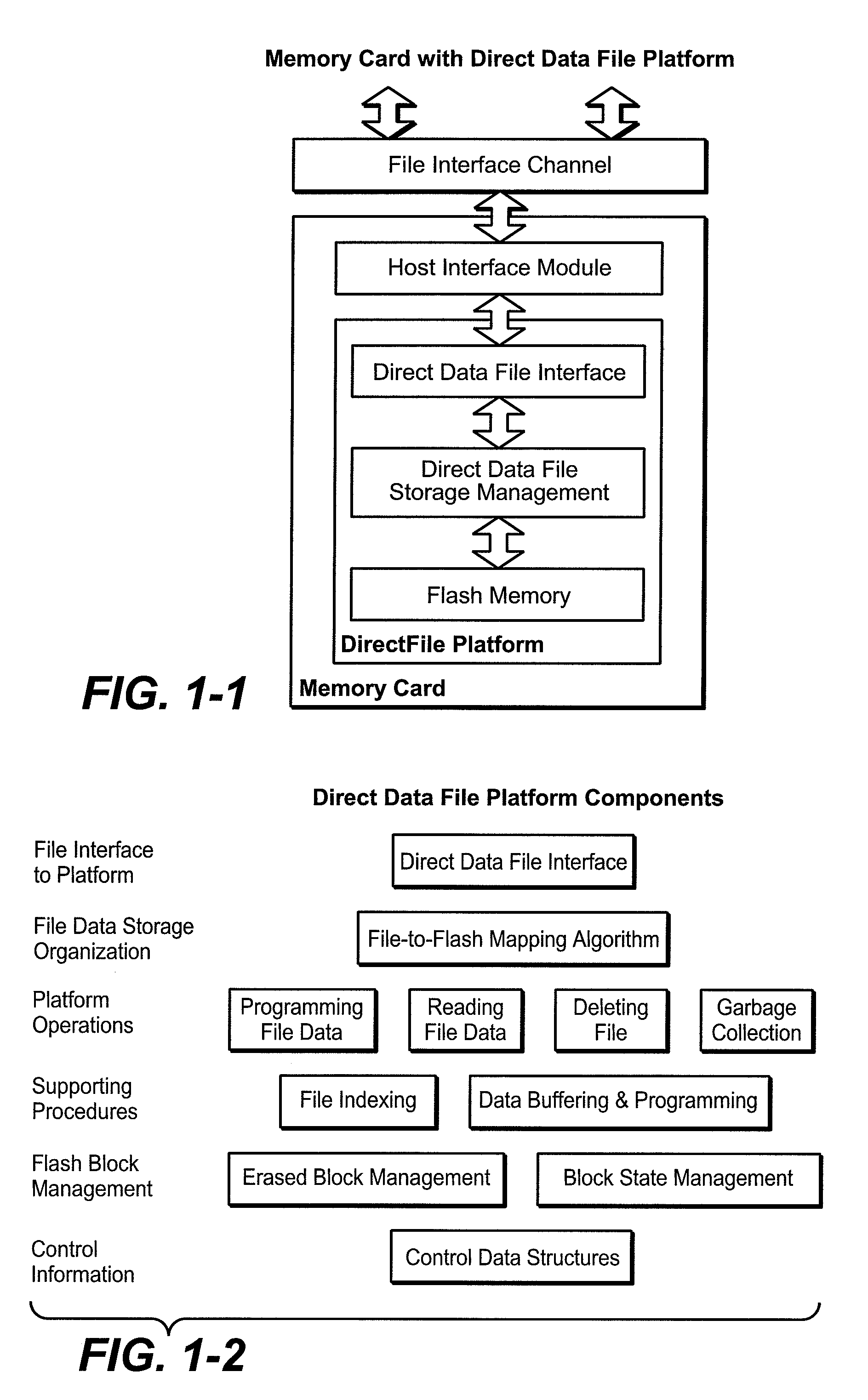
Flash Memory Systems With Direct Data File Storage Utilizing Data Consolidation and Garbage Collection
ActiveUS20070186032A1Prevent ConsolidationImprove memory performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data information retrievalData fileTerm memory
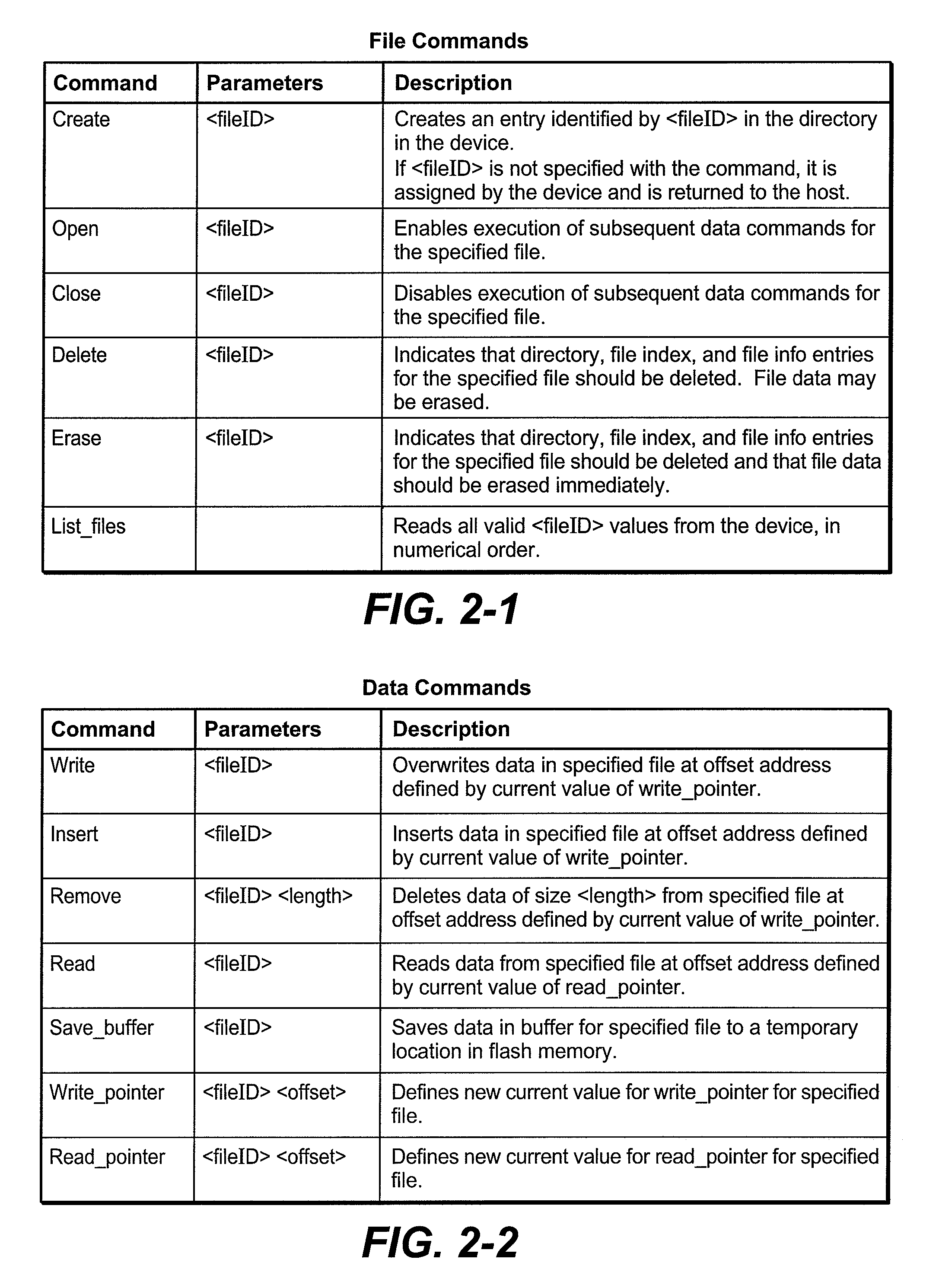
Host system data files are written directly to a large erase block flash memory system with a unique identification of each file and offsets of data within the file but without the use of any intermediate logical addresses or a virtual address space for the memory. Directory information of where the files are stored in the memory is maintained within the memory system by its controller, rather than by the host.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
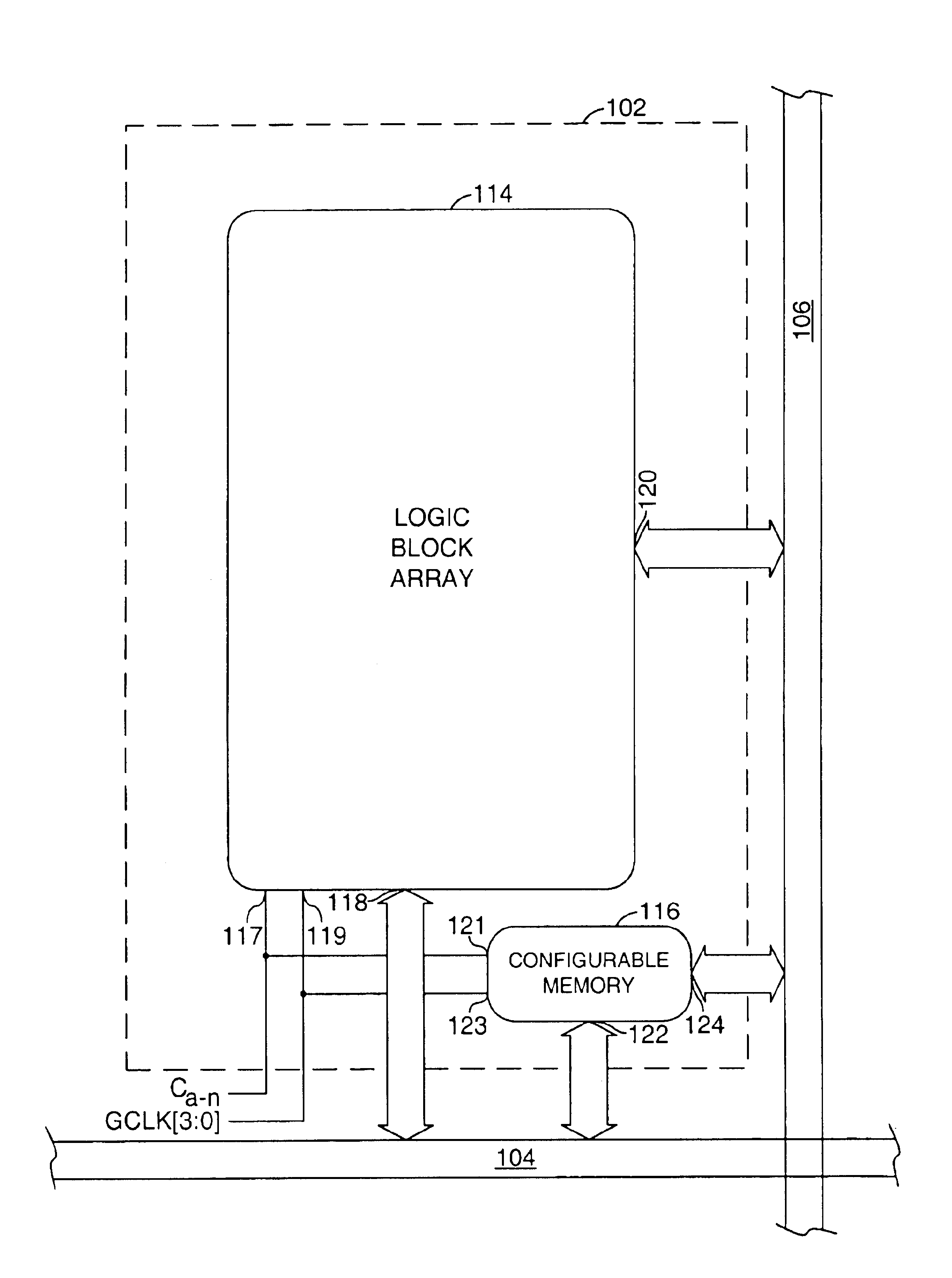
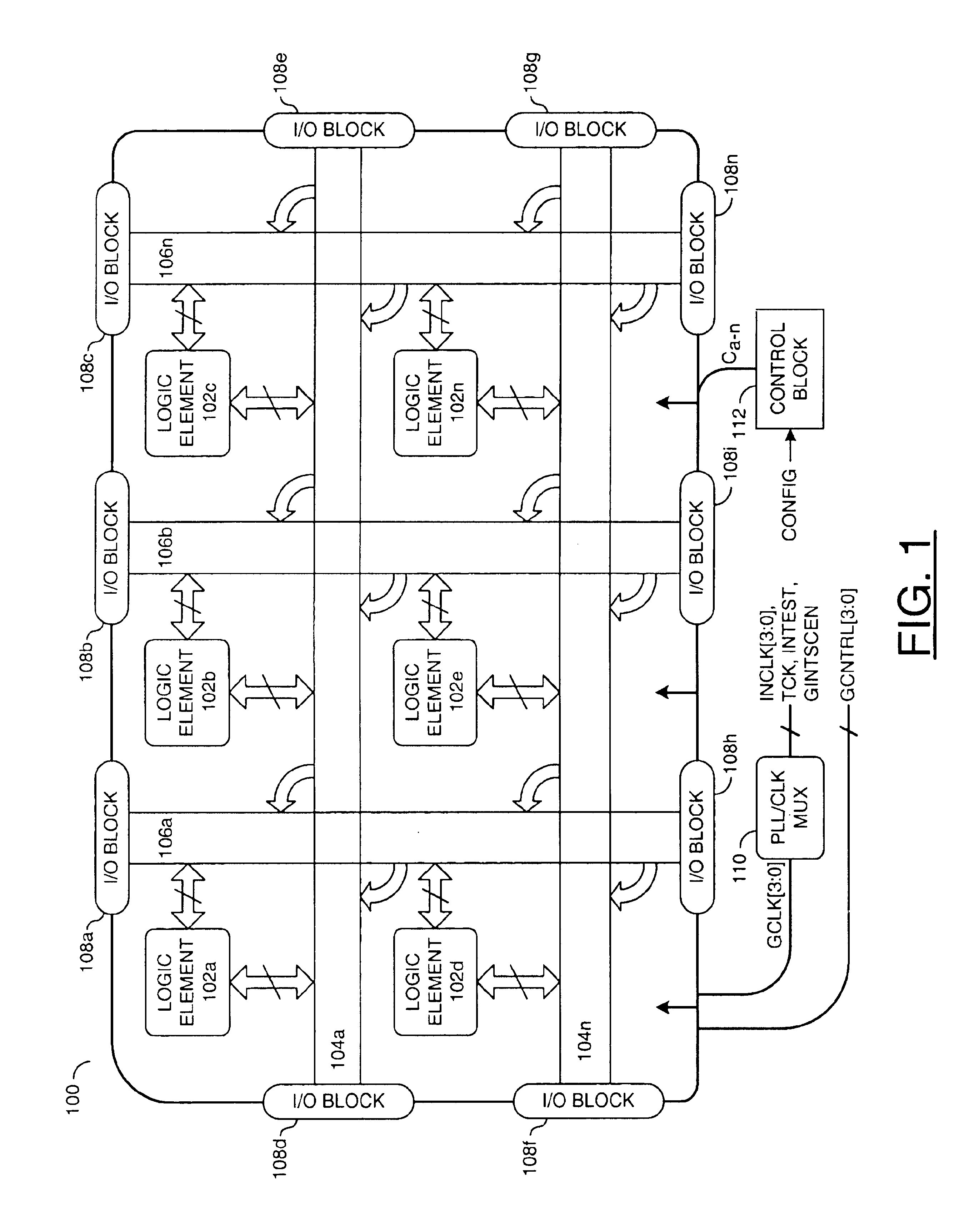
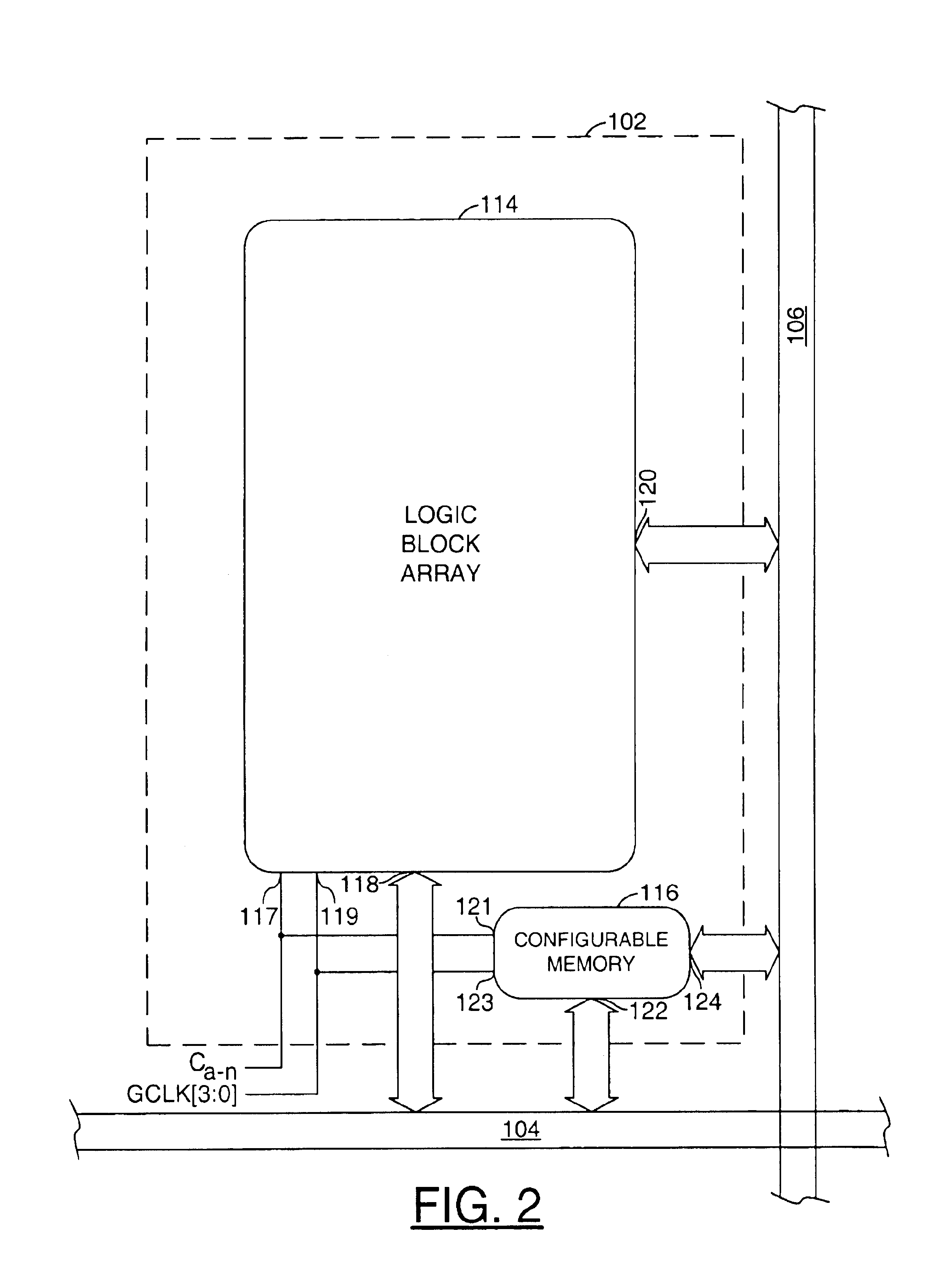
Programmable logic device
InactiveUS6864710B1Increase capacityHigh voltageSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsProgrammable logic deviceParallel computing
A programmable logic device comprising one or more horizontal routing channels, one or more vertical routing channels, and a logic element. Each logic element may be configured to connect between one of the horizontal routing channels and one of the vertical routing channels. The logic element may comprise a logic block cluster and a memory block.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
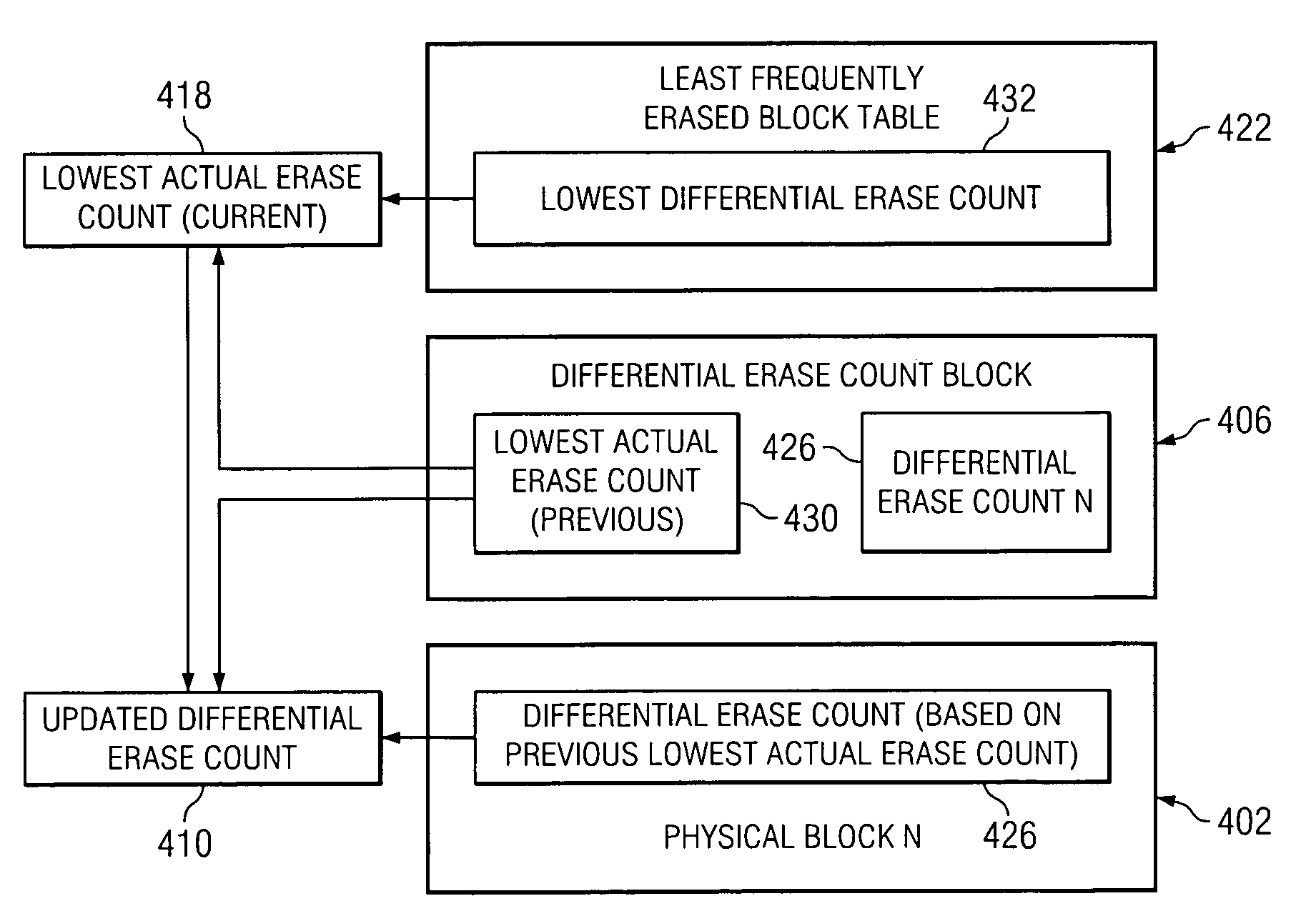
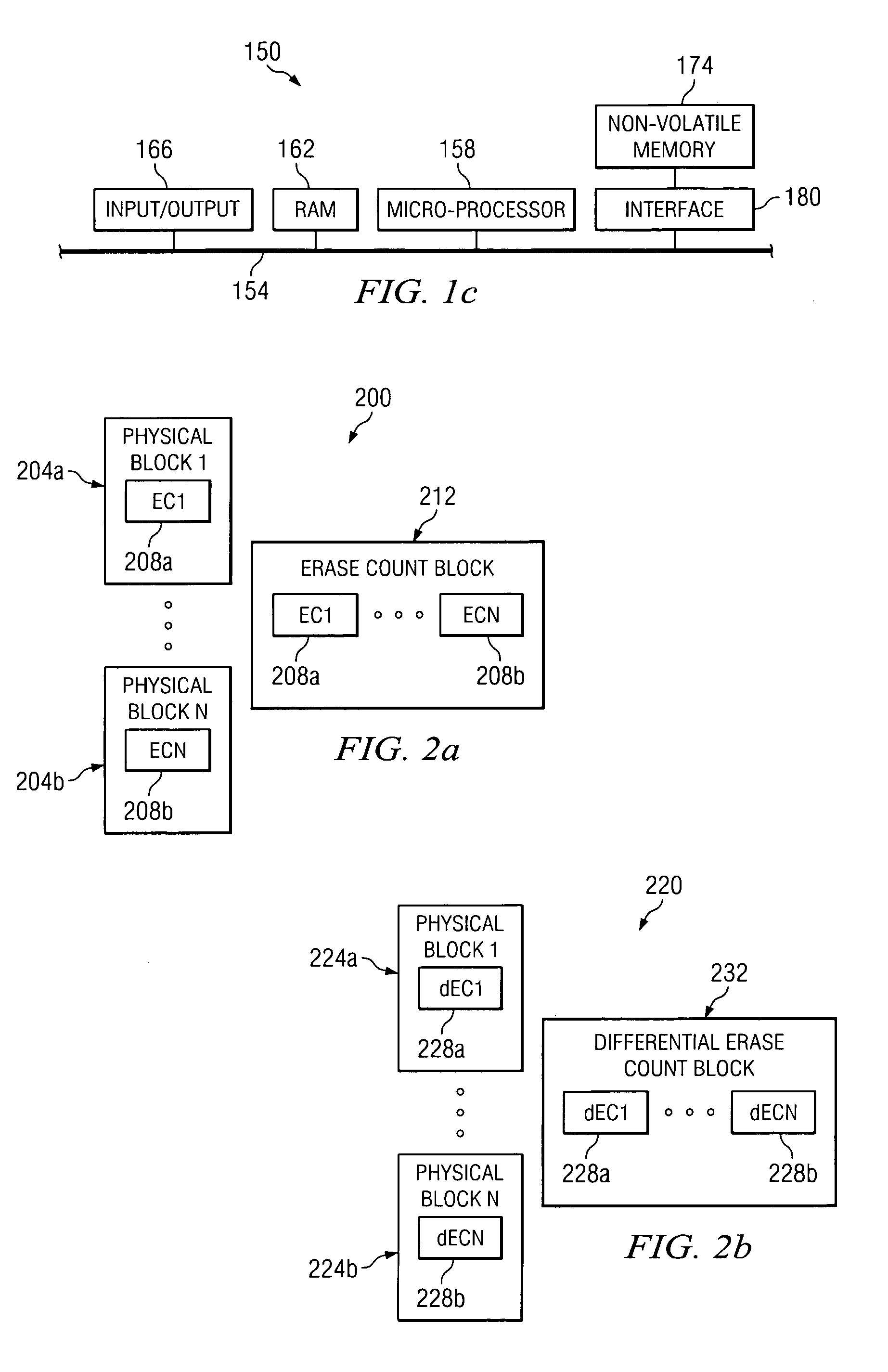
Erase count differential table within a non-volatile memory system
ActiveUS7032087B1Improve performanceMemory spaceMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesVolatile memoryDatabase
Methods and apparatus for efficiently tracking the usage of physical blocks of non-volatile memory are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method for maintaining a data structure that stores contents relating to the usage of physical blocks includes determining when to update the contents stored in the data structure, and obtaining a first differential erase count from the data structure when the contents are to be updated. The first differential erase count provides information on a number of times a first physical block has been erased. The method also includes determining a first actual erase count when the contents are to be updated. The first actual erase count is associated with a second physical block, and provides a number of times the second physical block has been erased. Finally, the method includes updating the first differential erase count when the contents are to be updated.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Flash Memory Systems Utilizing Direct Data File Storage
ActiveUS20070033378A1Prevent movementPrevent ConsolidationMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data information retrievalData fileTerm memory
Host system data files are written directly to a large erase block flash memory system with a unique identification of each file and offsets of data within the file but without the use of any intermediate logical addresses or a virtual address space for the memory. Directory information of where the files are stored in the memory is maintained within the memory system by its controller, rather than by the host.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Data Operations in Flash Memories Utilizing Direct Data File Storage
ActiveUS20070033377A1Prevent ConsolidationImprove memory performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data information retrievalData operationsData file
Host system data files are written directly to a large erase block flash memory system with a unique identification of each file and offsets of data within the file but without the use of any intermediate logical addresses or a virtual address space for the memory. Directory information of where the files are stored in the memory is maintained within the memory system by its controller, rather than by the host.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
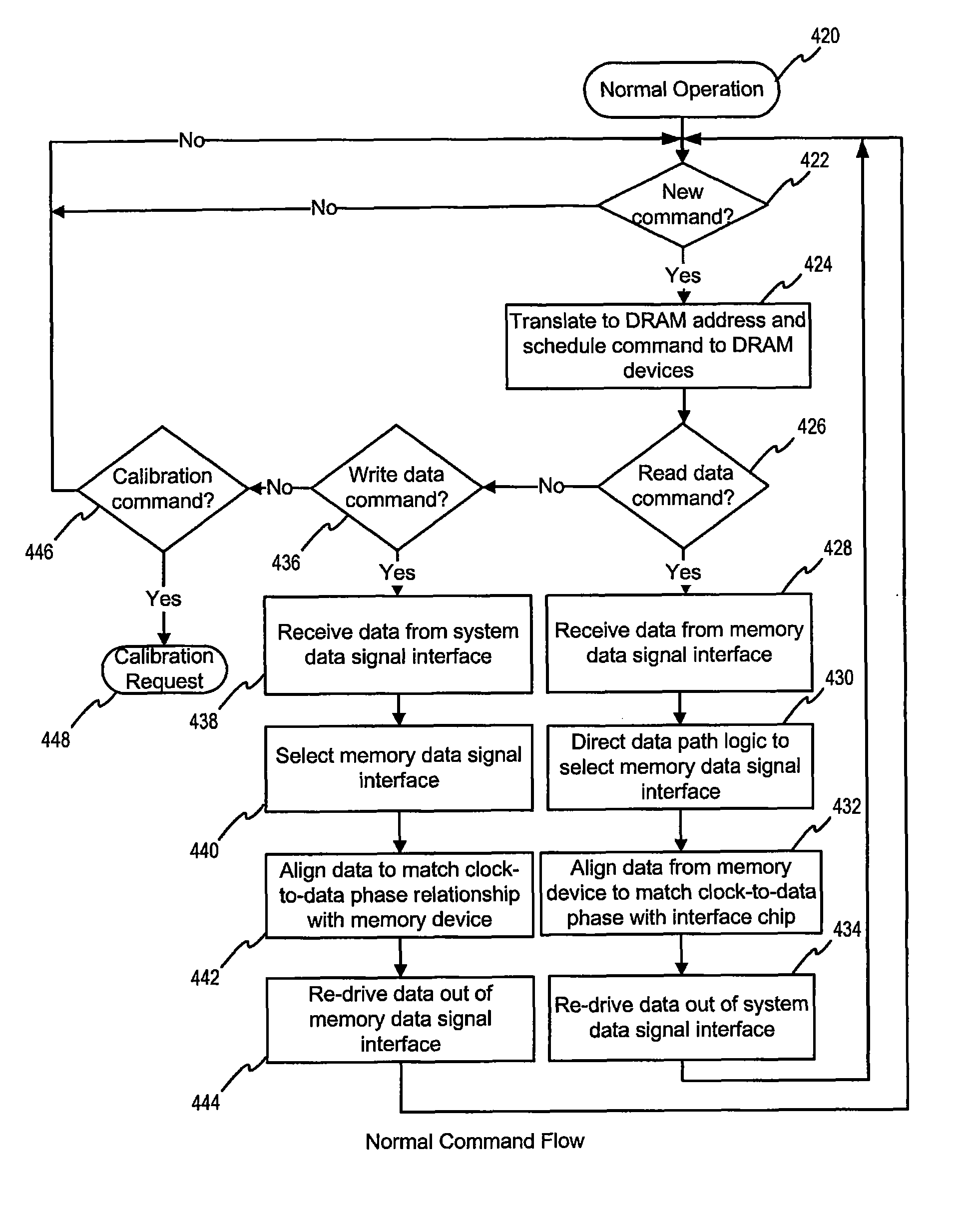
Multi-bank scheduling to improve performance on tree accesses in a DRAM based random access memory subsystem
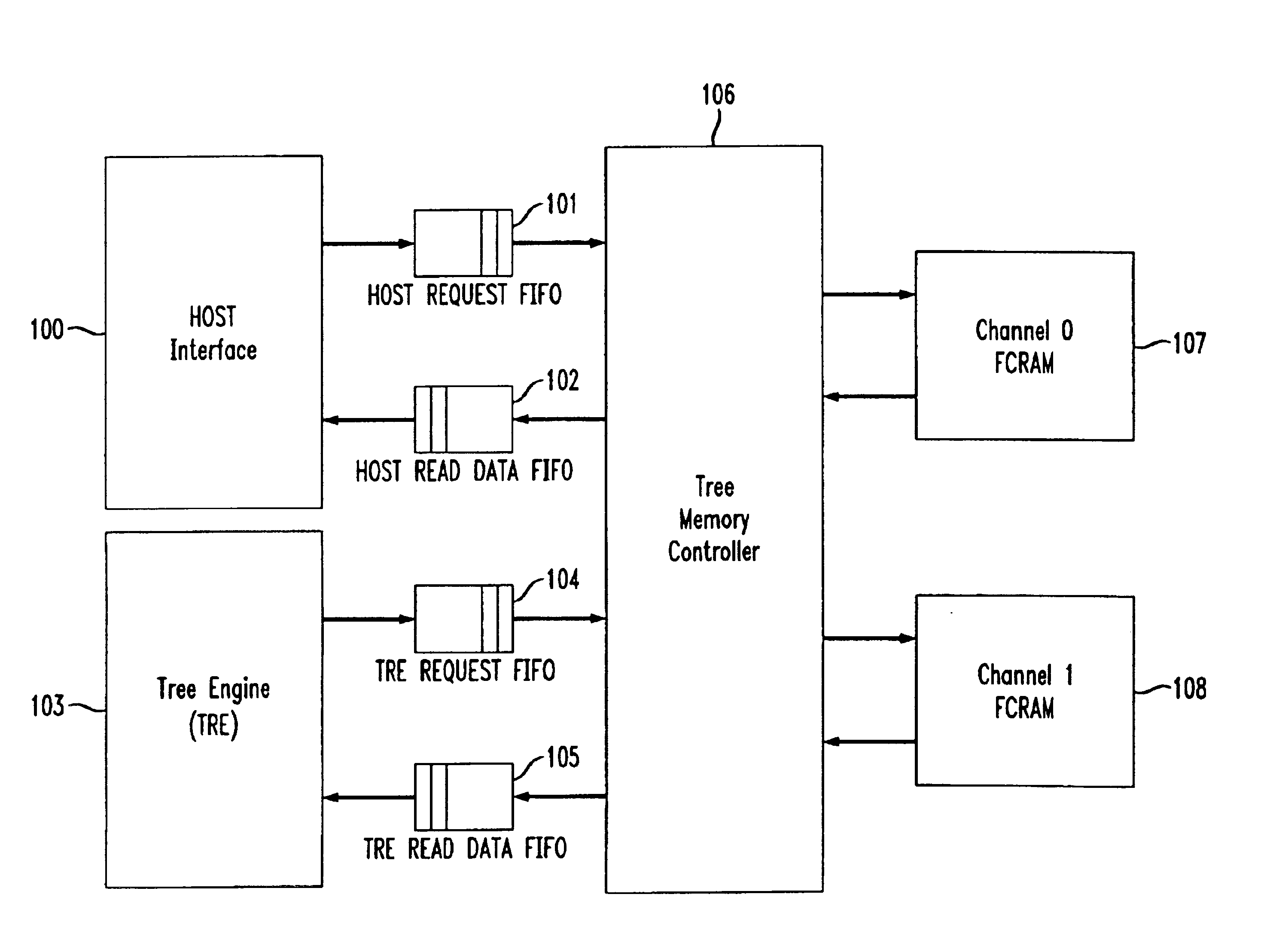
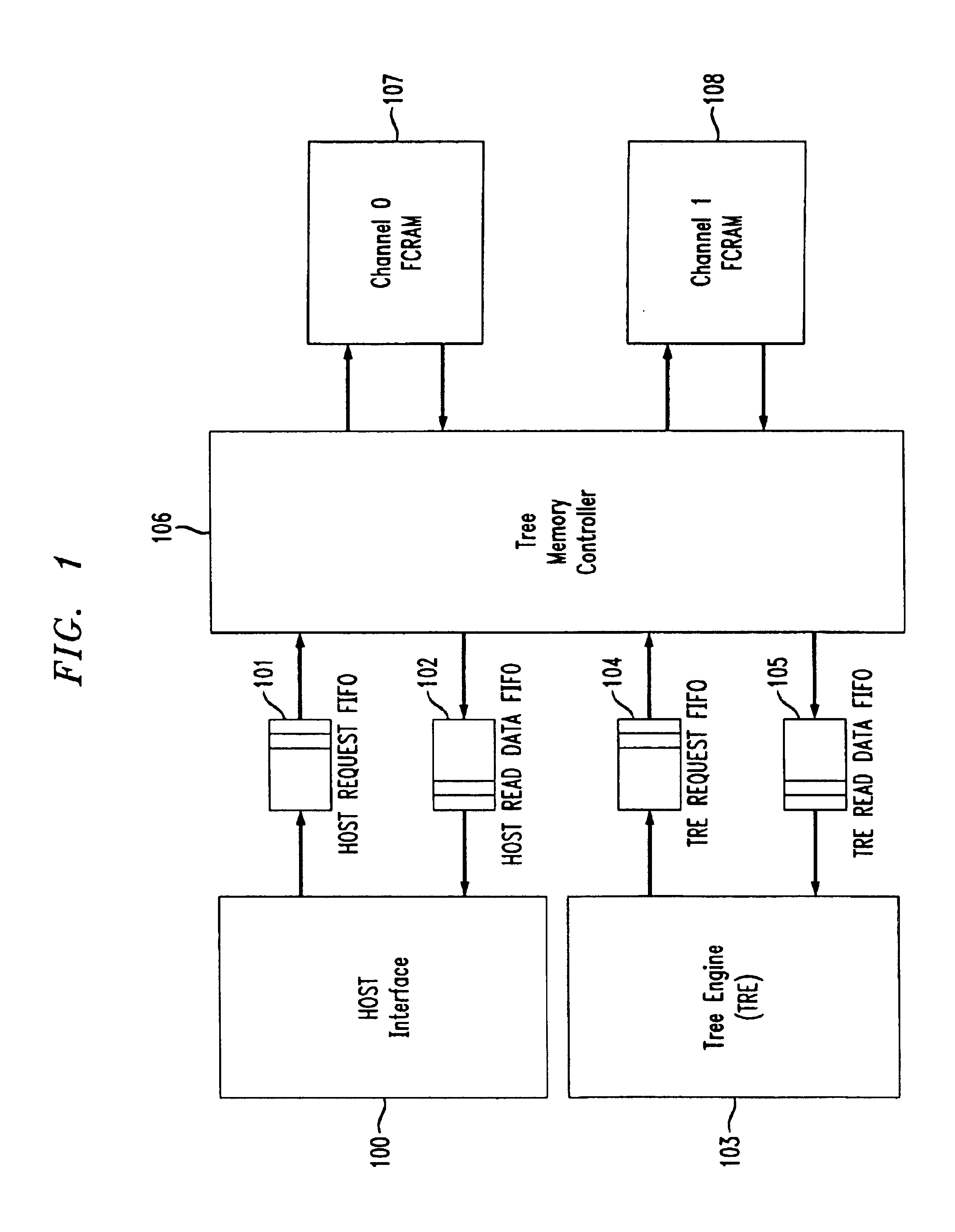
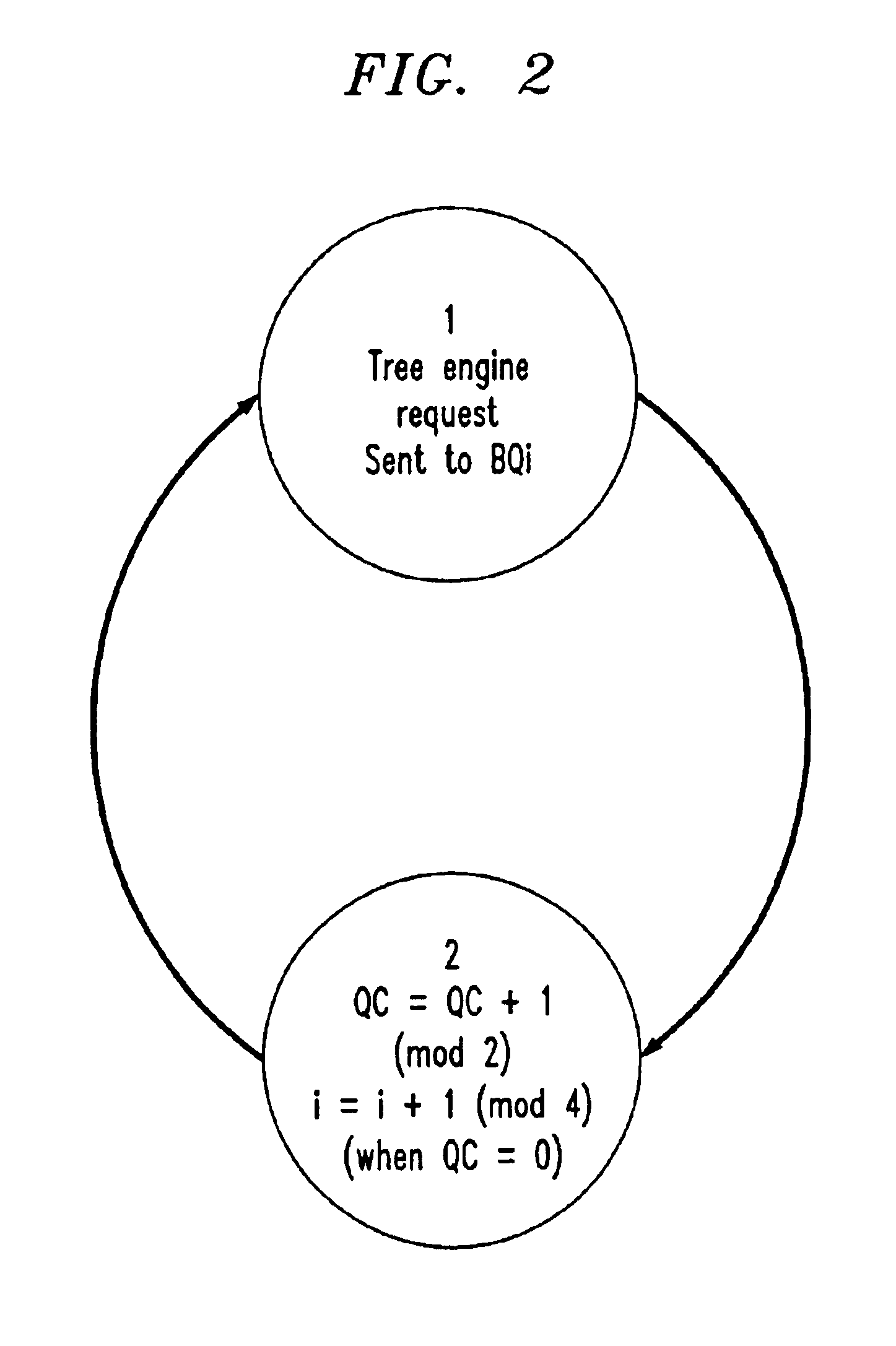
InactiveUS6839797B2Reduced time requirementHigh memory performanceEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory controllerComplete data
A method and system of memory management incorporates multiple banks of memory devices organized into independent channels wherein each bank of memory devices contains duplicate data. A tree memory controller controls data read and write accesses to each of the banks in each of the channels. A bank queue for each bank in each channel keeps track of bank availability. When read or write requests are received at the tree memory controller, the controller checks the availability of each bank in a channel, identifies a first available bank, and executes the read request from the first available bank. In response to a write request, the controller blocks all read requests once it has confirmed that data to be written is complete for the selected memory word length. As soon as each bank queue for read requests is empty, the controller initiates burst mode transfer of the completed data word to all banks concurrently.
Owner:AGERE SYST GUARDIAN
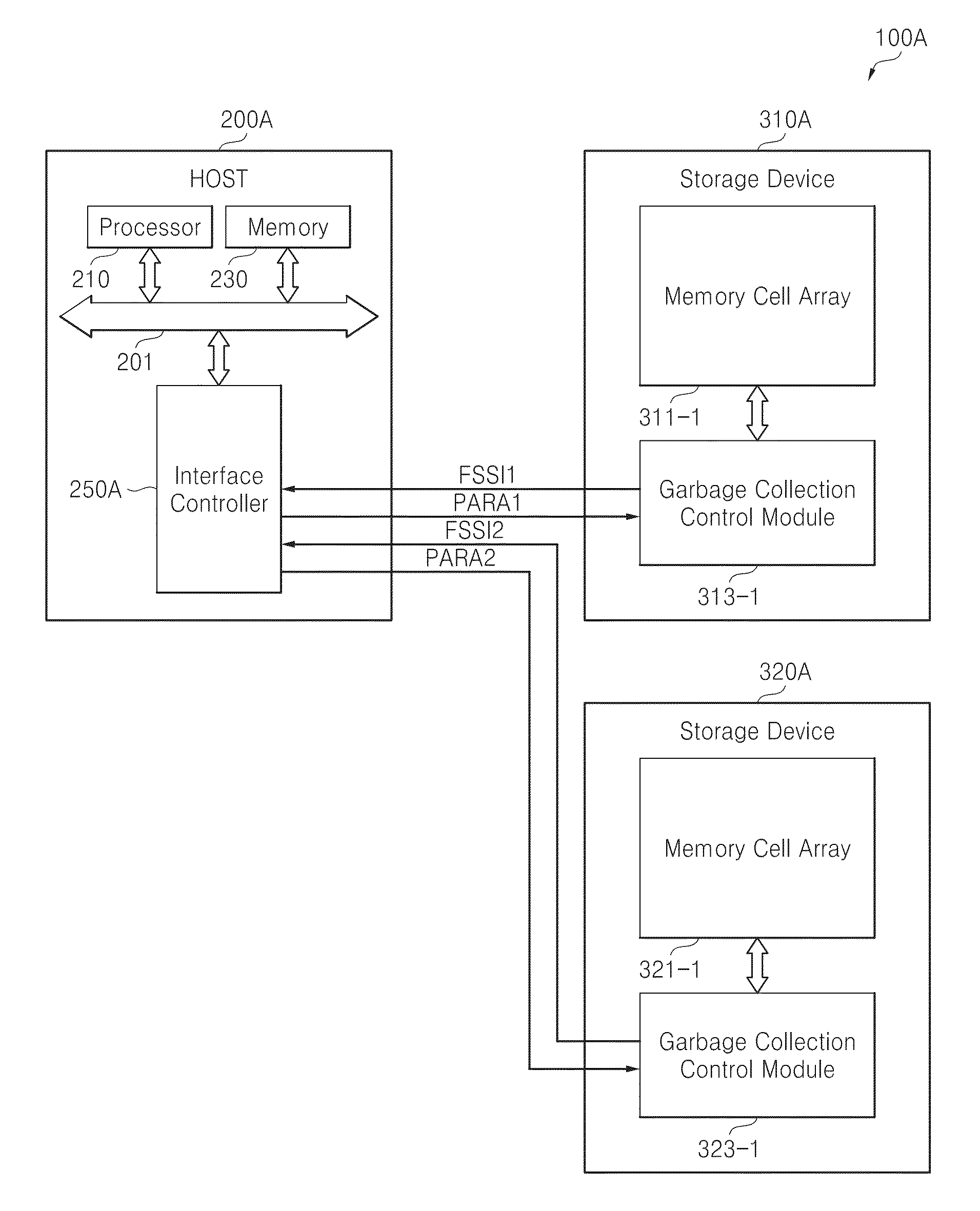
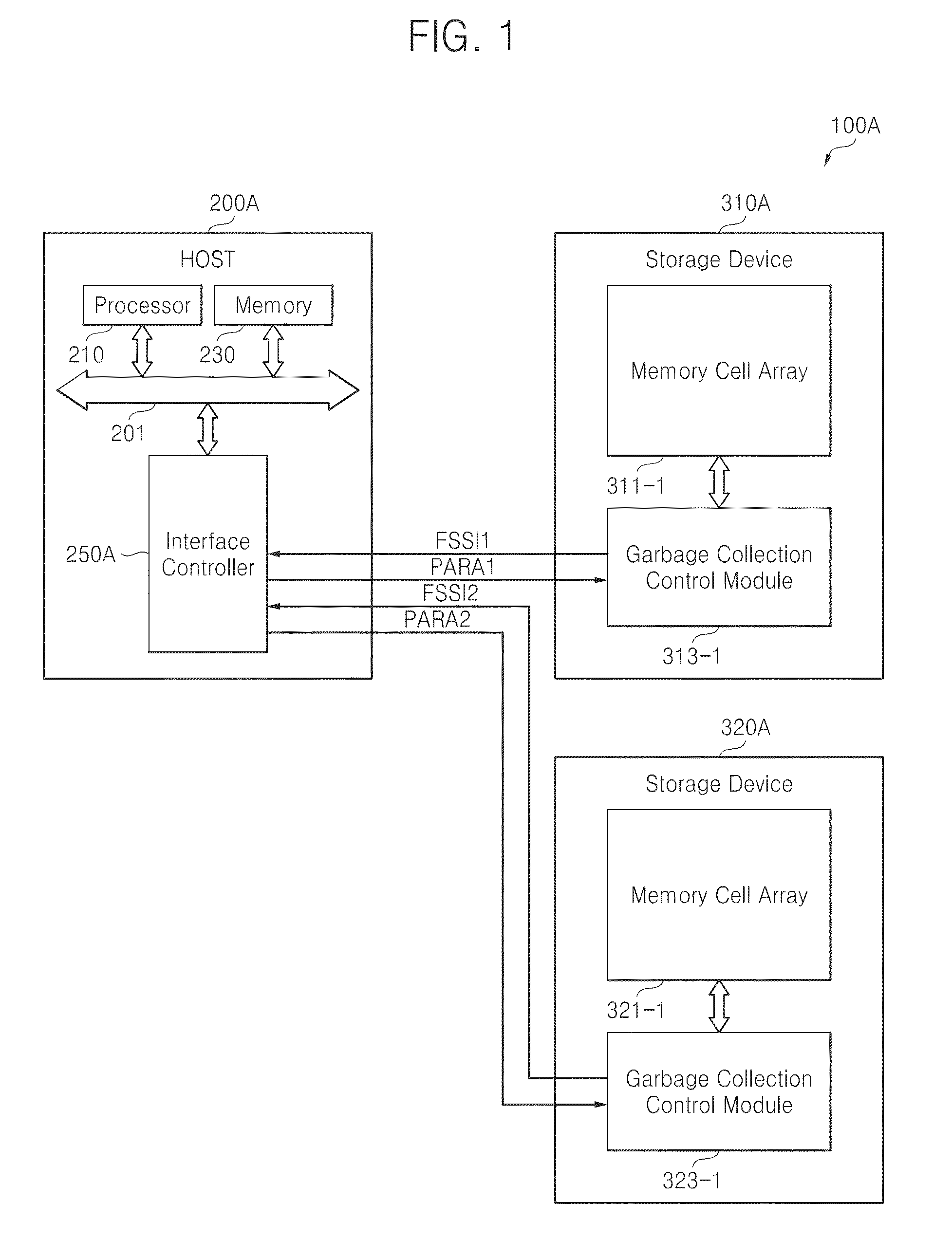
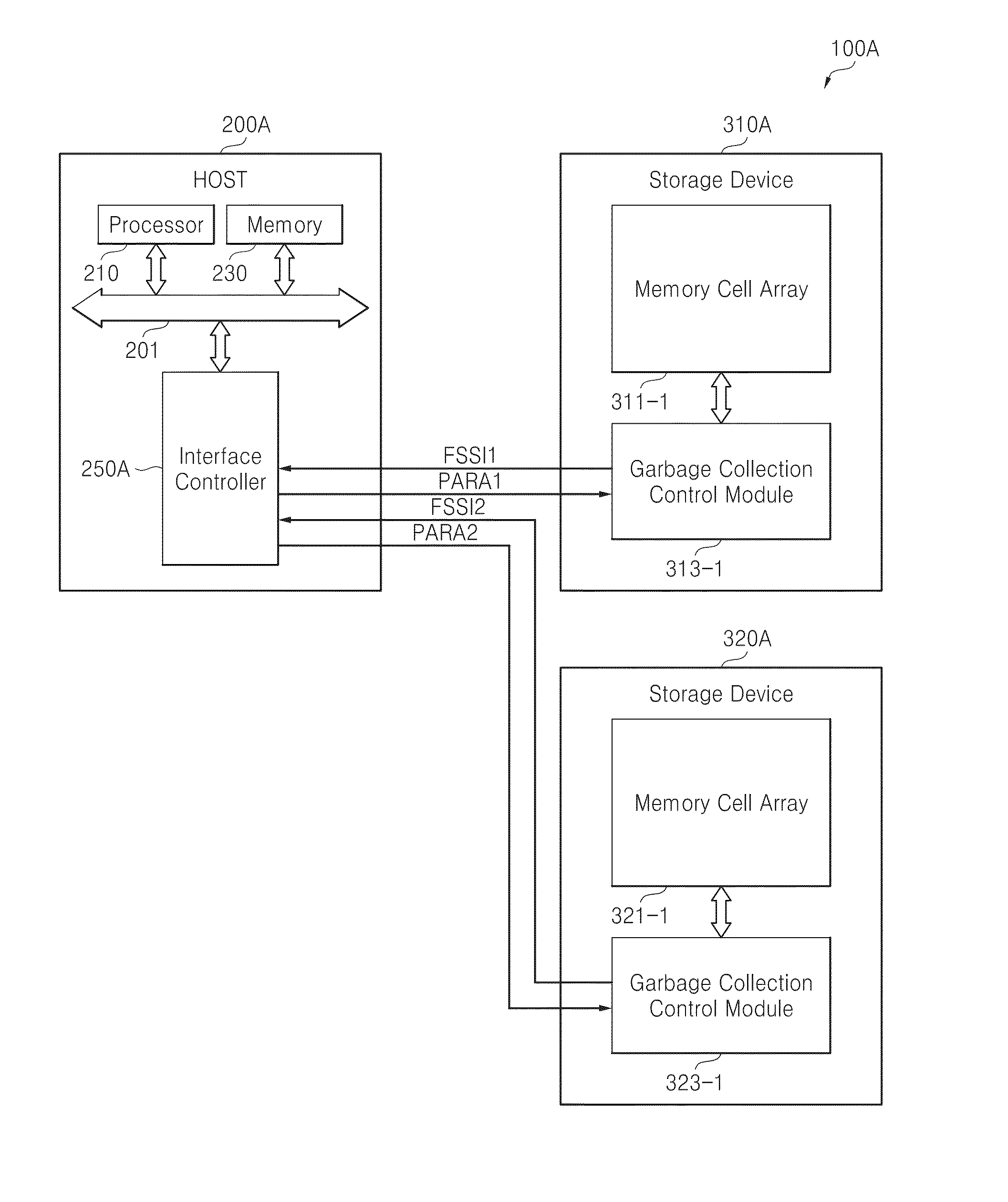
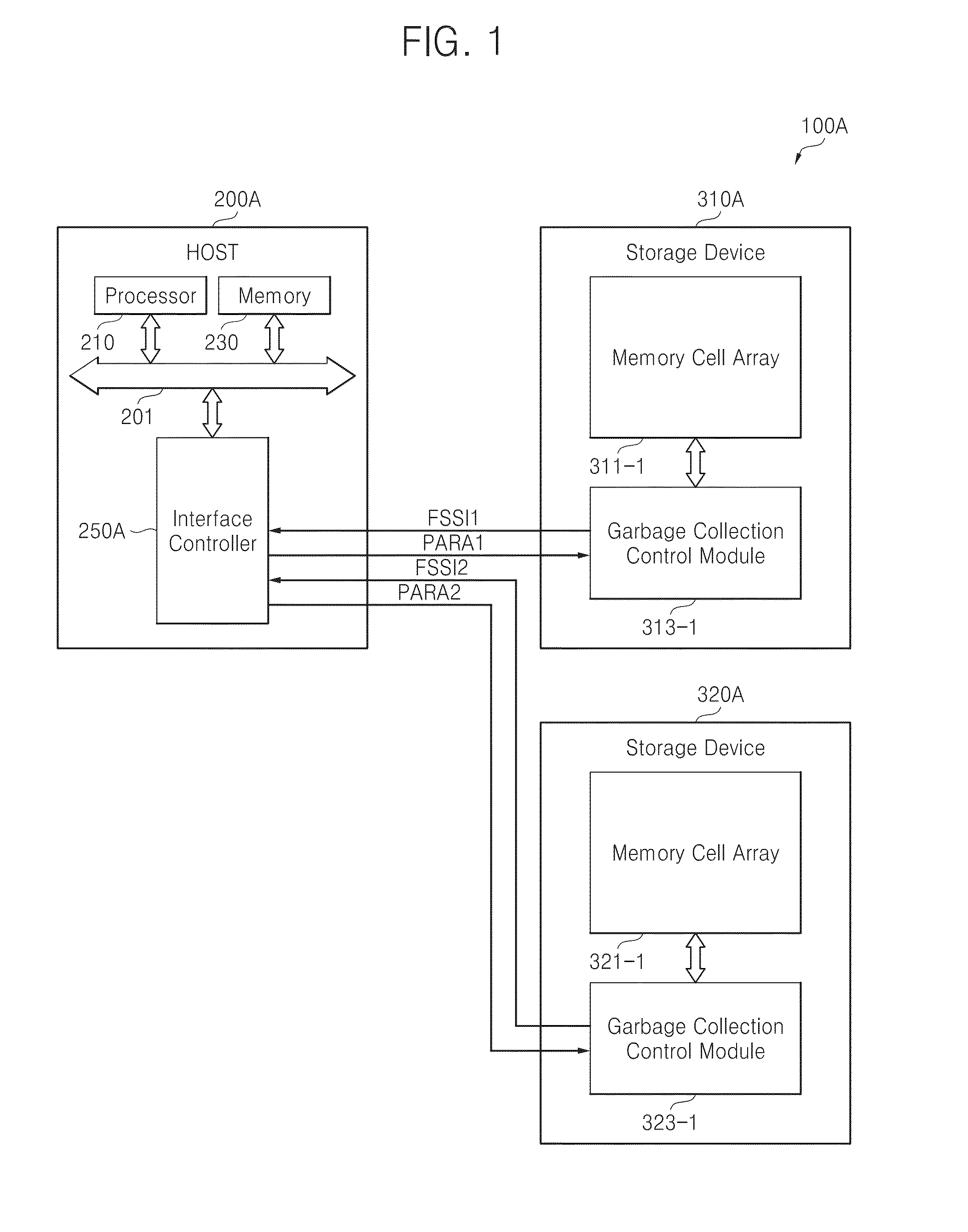
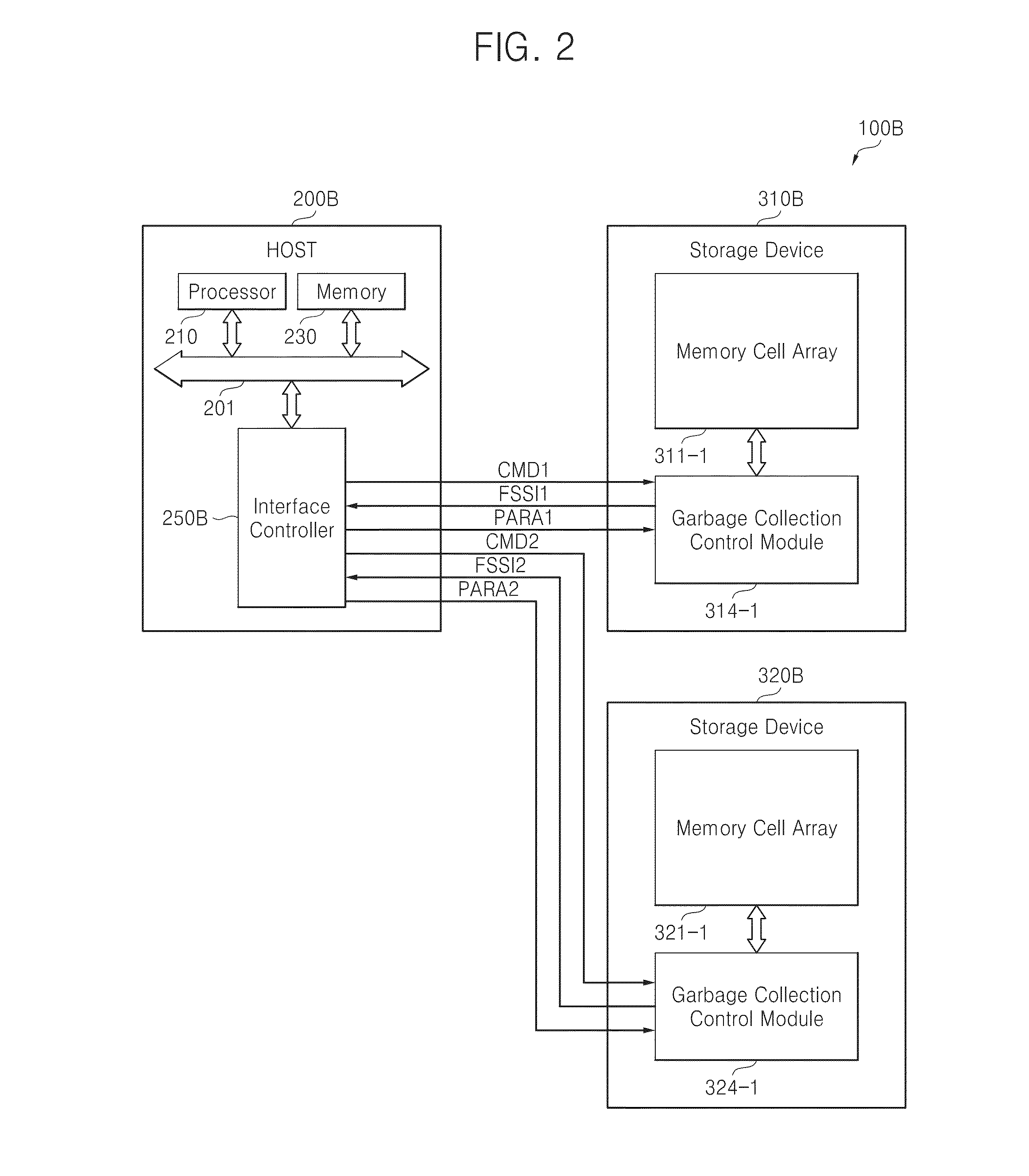
Host-driven garbage collection
ActiveUS20140281338A1Improve performanceAdjust I/O latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersOperating systemInformation control
A host receives information related to garbage collection of a storage device, and it controls selective execution of garbage collection by the storage device according to the received information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
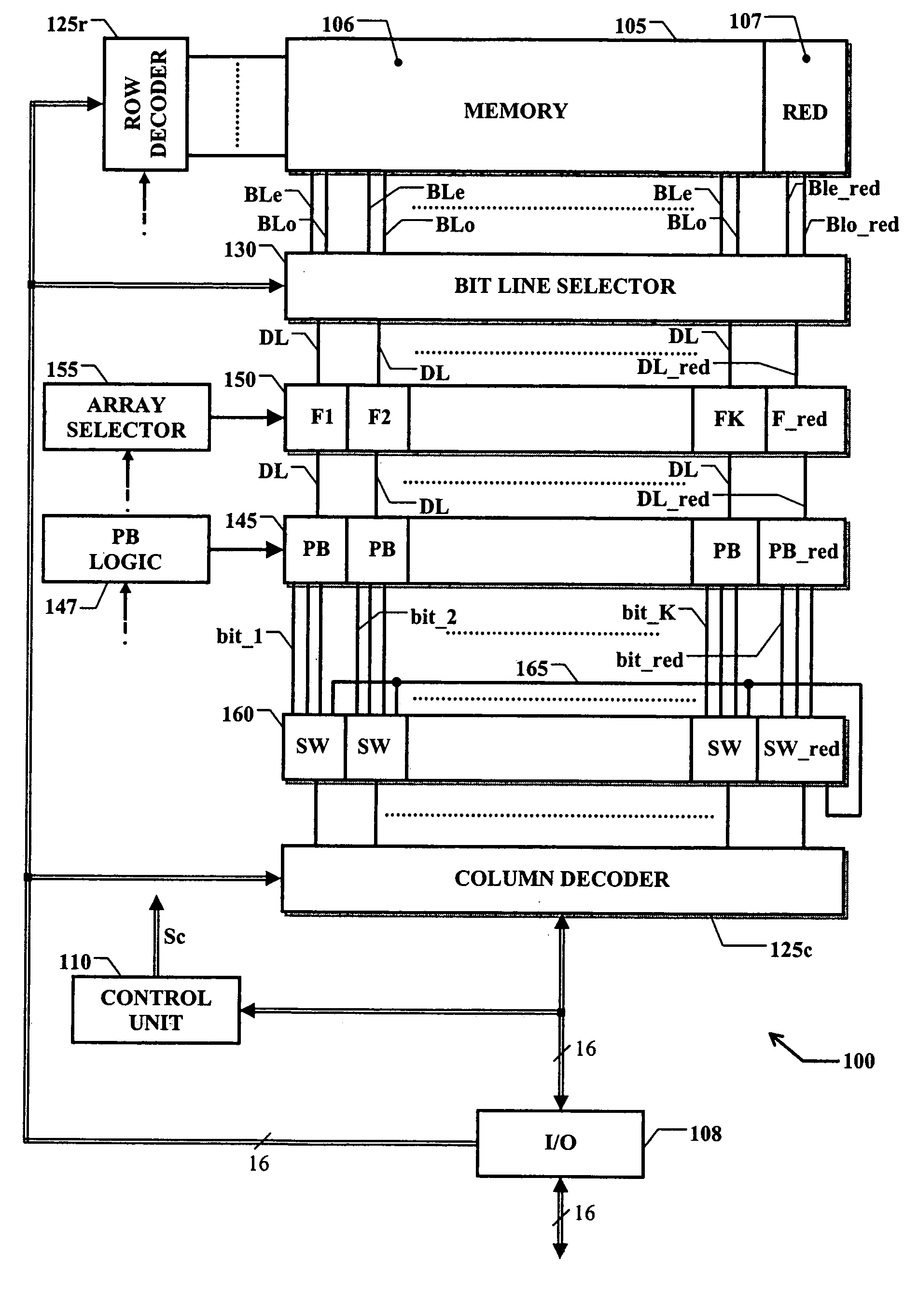
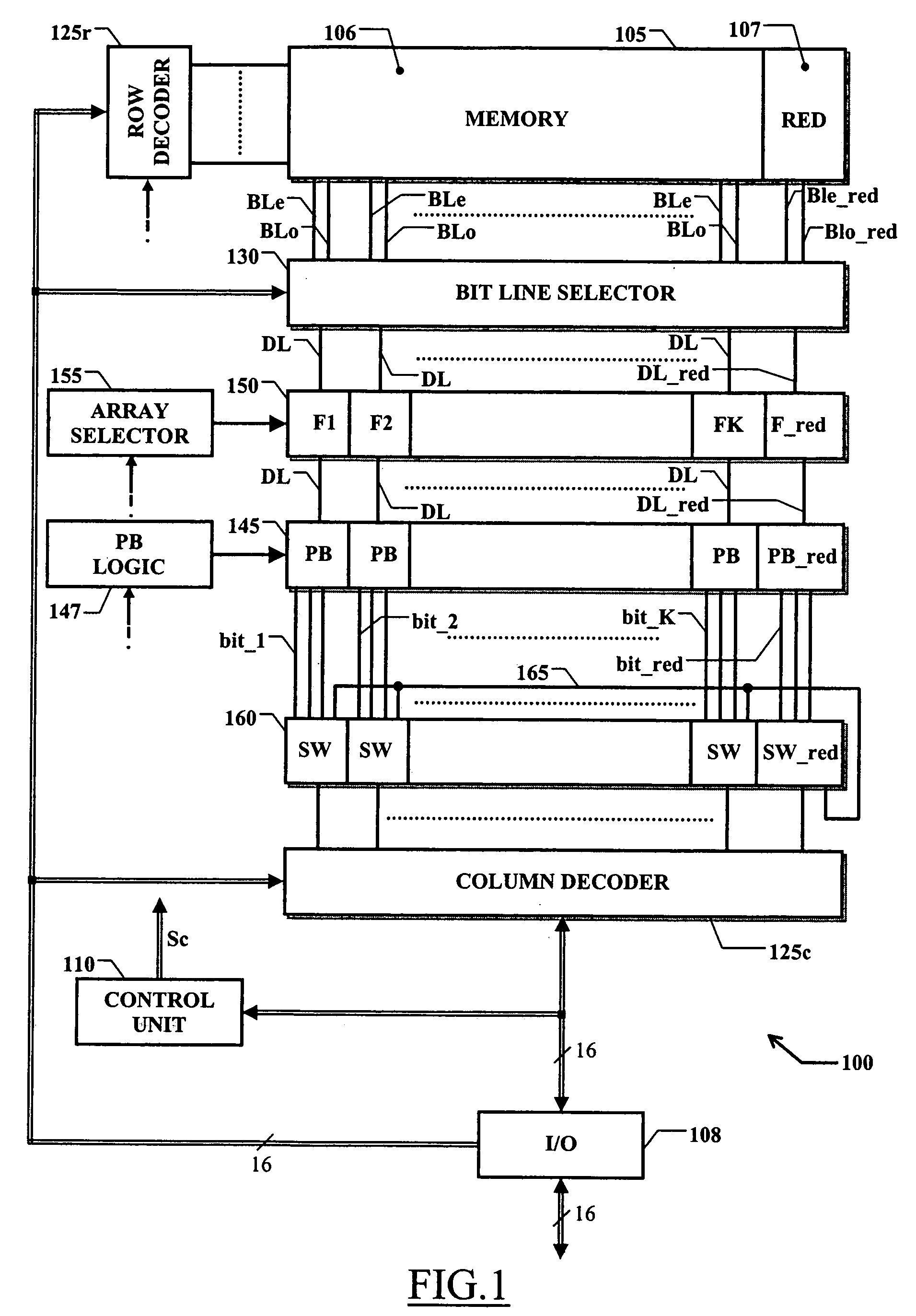
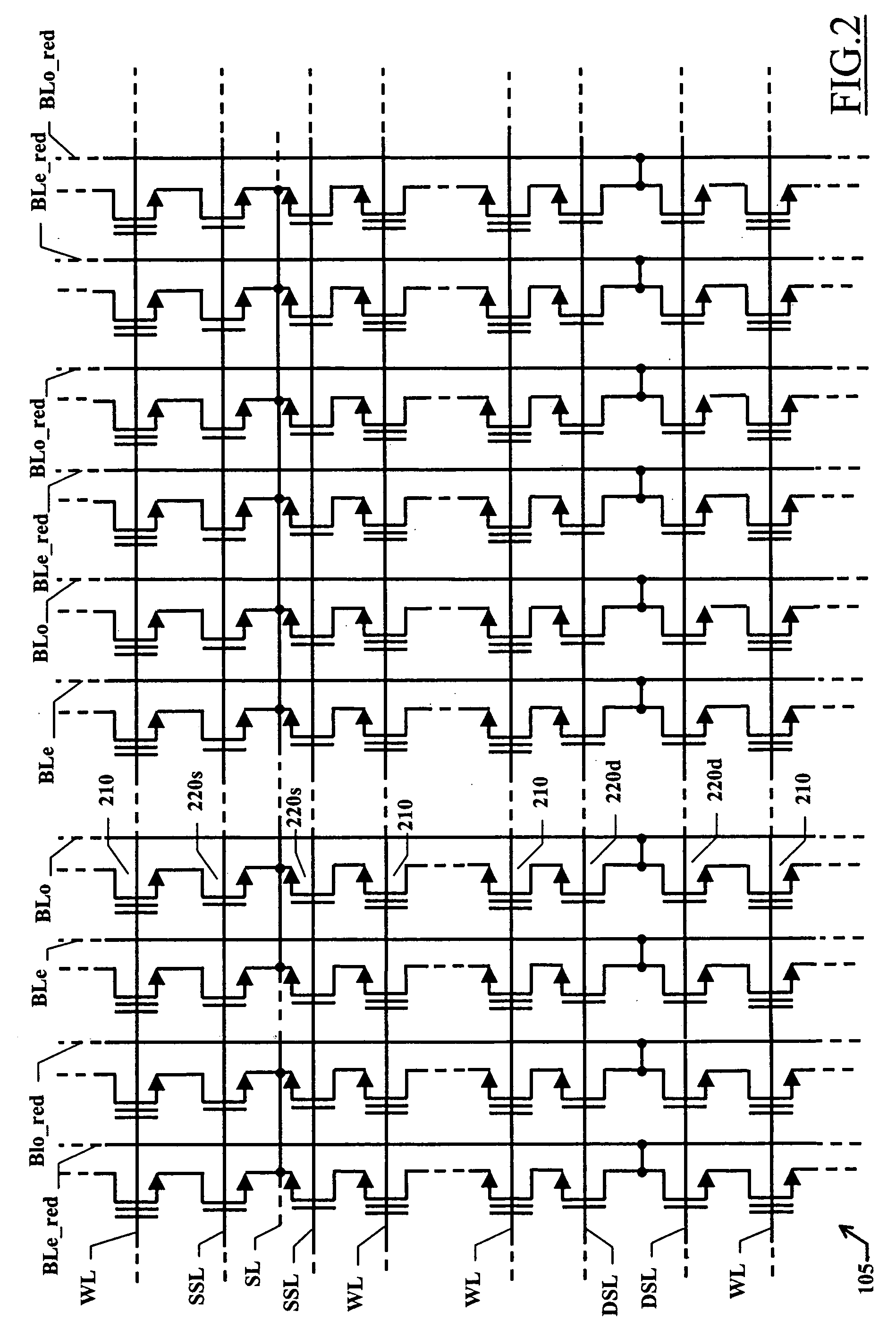
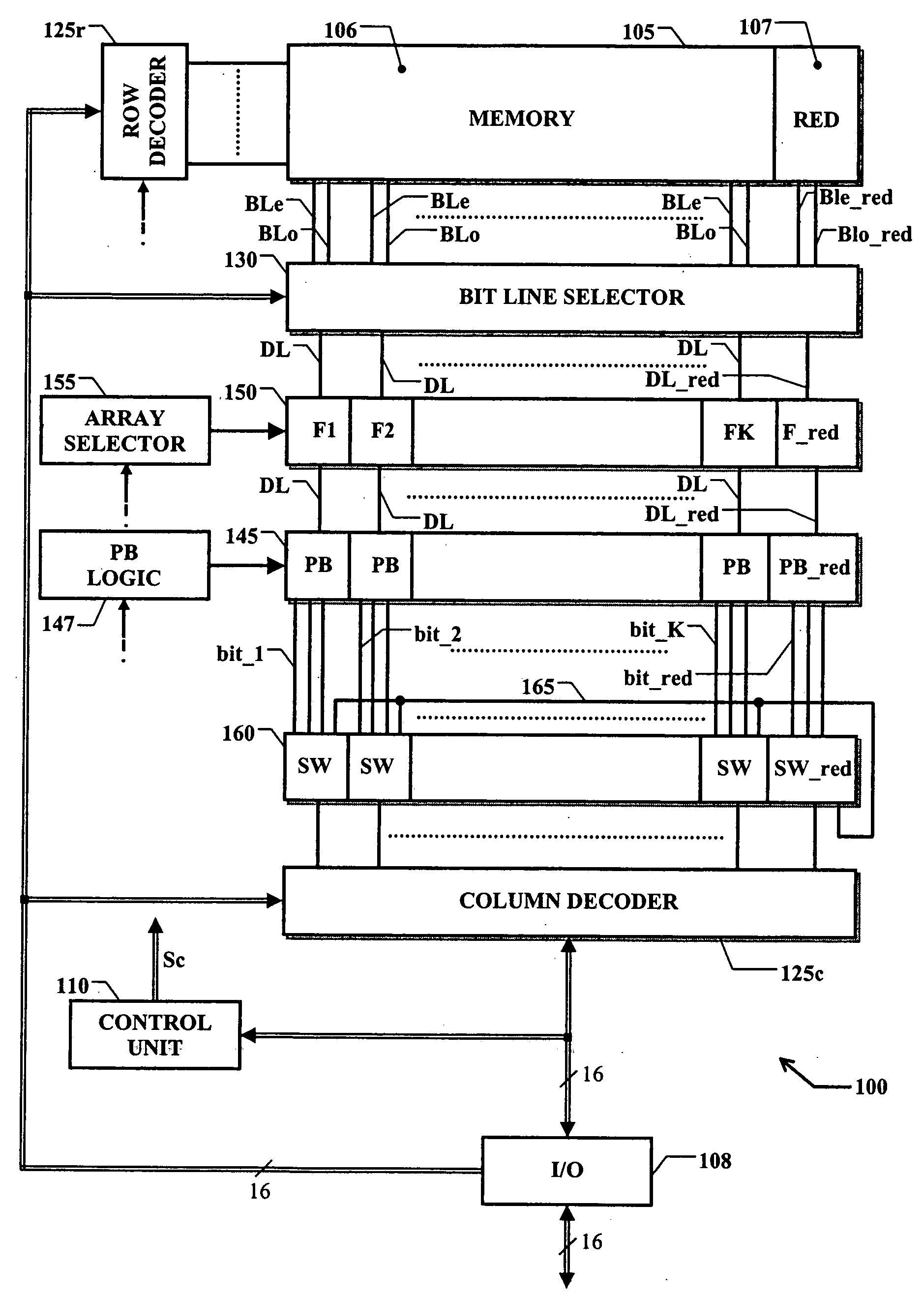
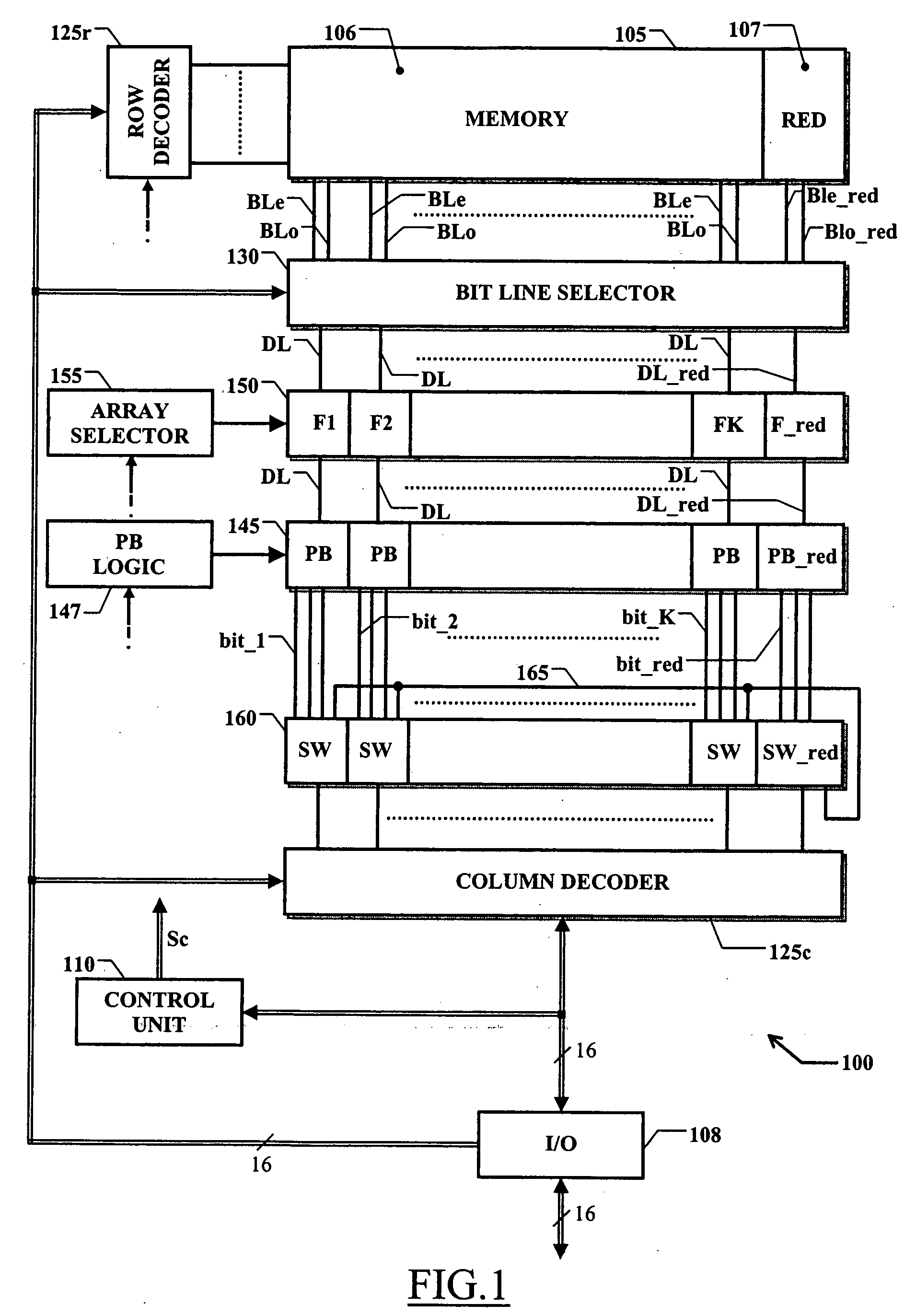
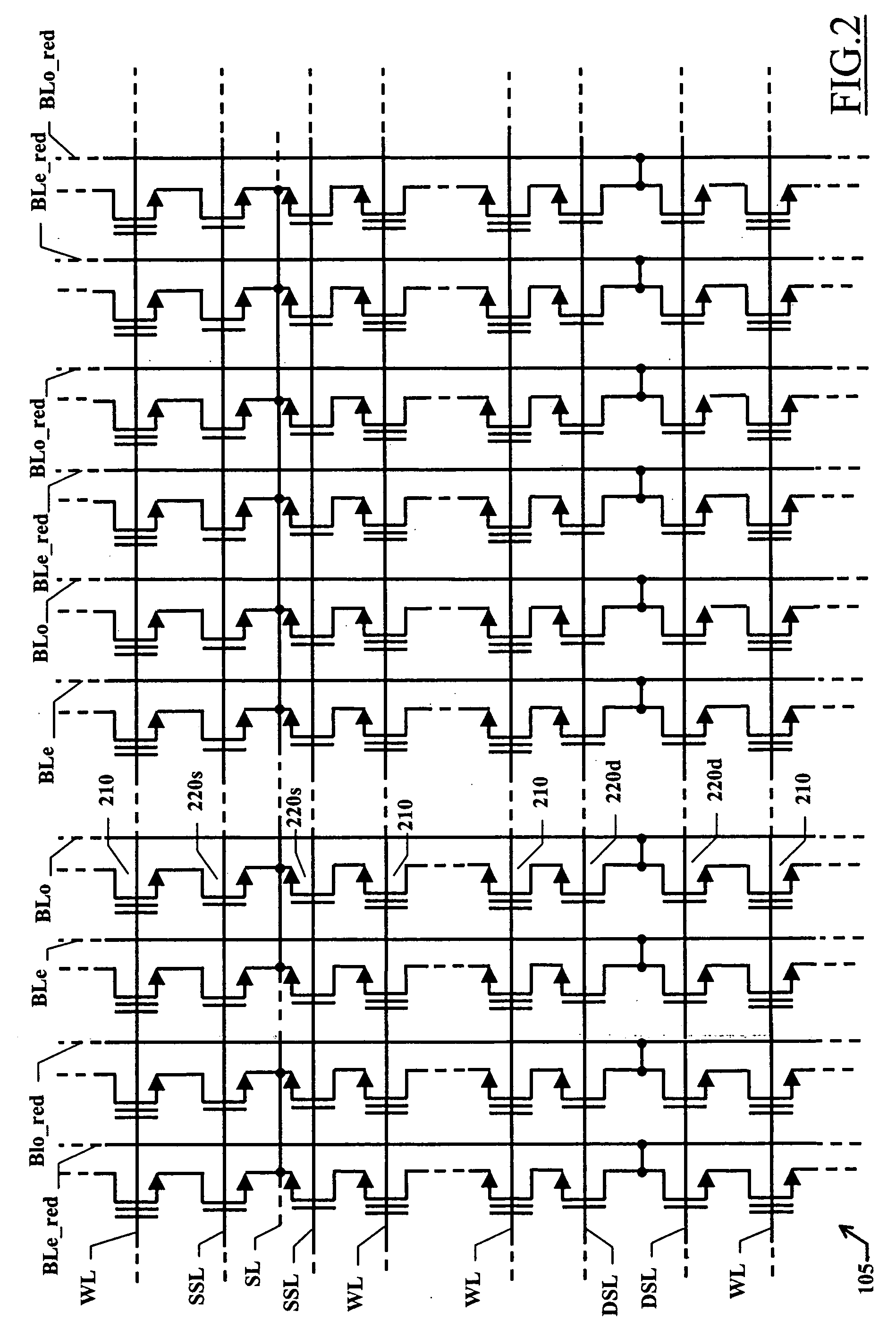
Programmable memory device with an improved redundancy structure
ActiveUS20060034137A1Improve memory performanceSimplify the management processDigital storageComputer scienceStorage cell
An electrically programmable memory device is proposed including: a matrix of memory cells arranged in a plurality of memory arrays and at least one redundancy array; and a substituting structure that substitutes the use of each memory array with the use of one of the at least one redundancy array in response to a failure of the memory array, wherein the memory arrays are grouped into at least one set. The substituting structure includes: a structure for associating each set with a predetermined one of the at least one redundancy array; a flag for each memory array indicative of the failure of the memory array; and a selecting for enabling each memory array or the associated redundancy array according to the corresponding flag.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
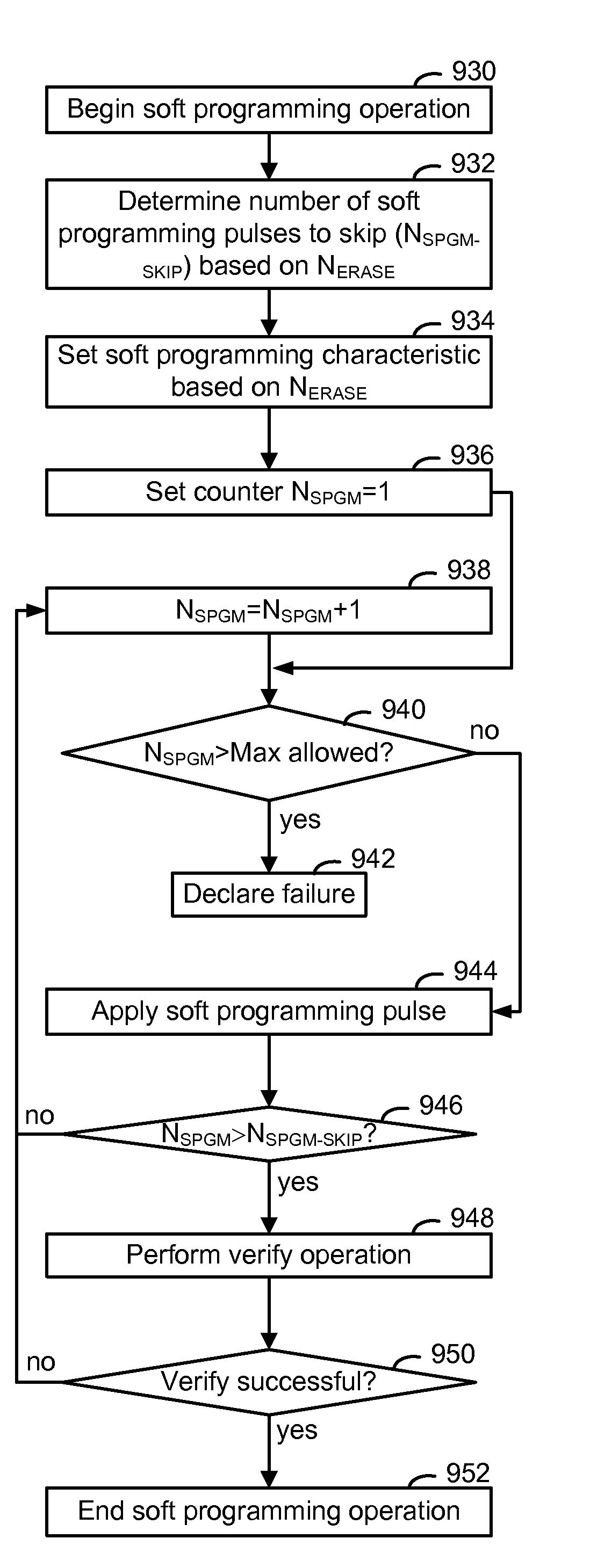
Adaptive erase and soft programming for memory
ActiveUS7839690B2Improve memory performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageSelf adaptivePulse duration
An erase sequence of a non-volatile storage device includes an erase operation followed by a soft programming operation. The erase operation applies one or more erase pulses to the storage elements, e.g., via a substrate, until an erase verify level is satisfied. The number of erase pulses is tracked and recorded as an indicia of the number of programming-erase cycles which the storage device has experienced. The soft programming operation applies soft programming pulses to the storage elements until a soft programming verify level is satisfied. Based on the number of erase pulses, the soft programming operation time is shortened by skipping verify operations for a specific number of initial soft programming pulses which is a function of the number of erase pulses. Also, a characteristic of the soft programming operation can be optimized, such as starting amplitude, step size or pulse duration.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
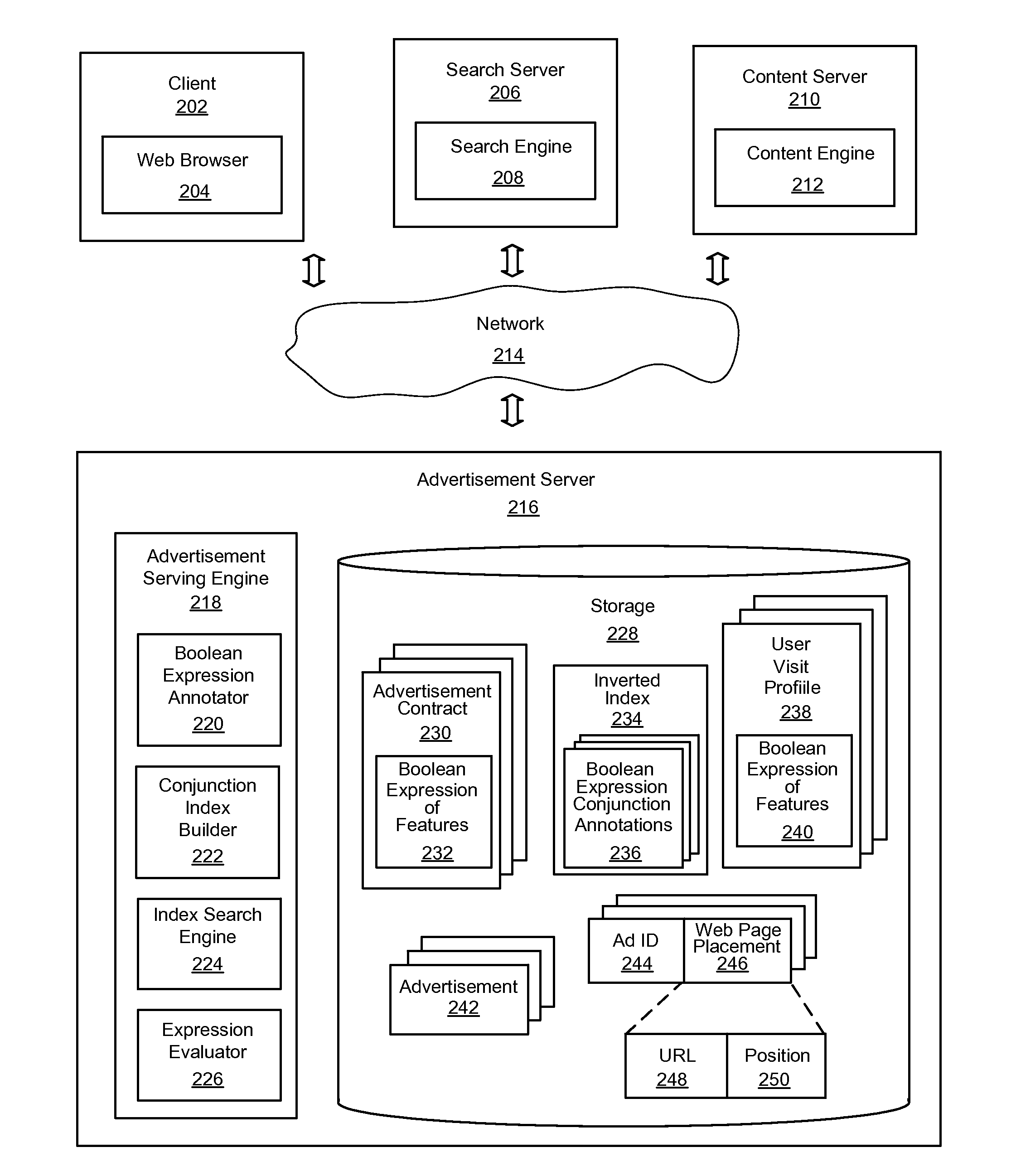
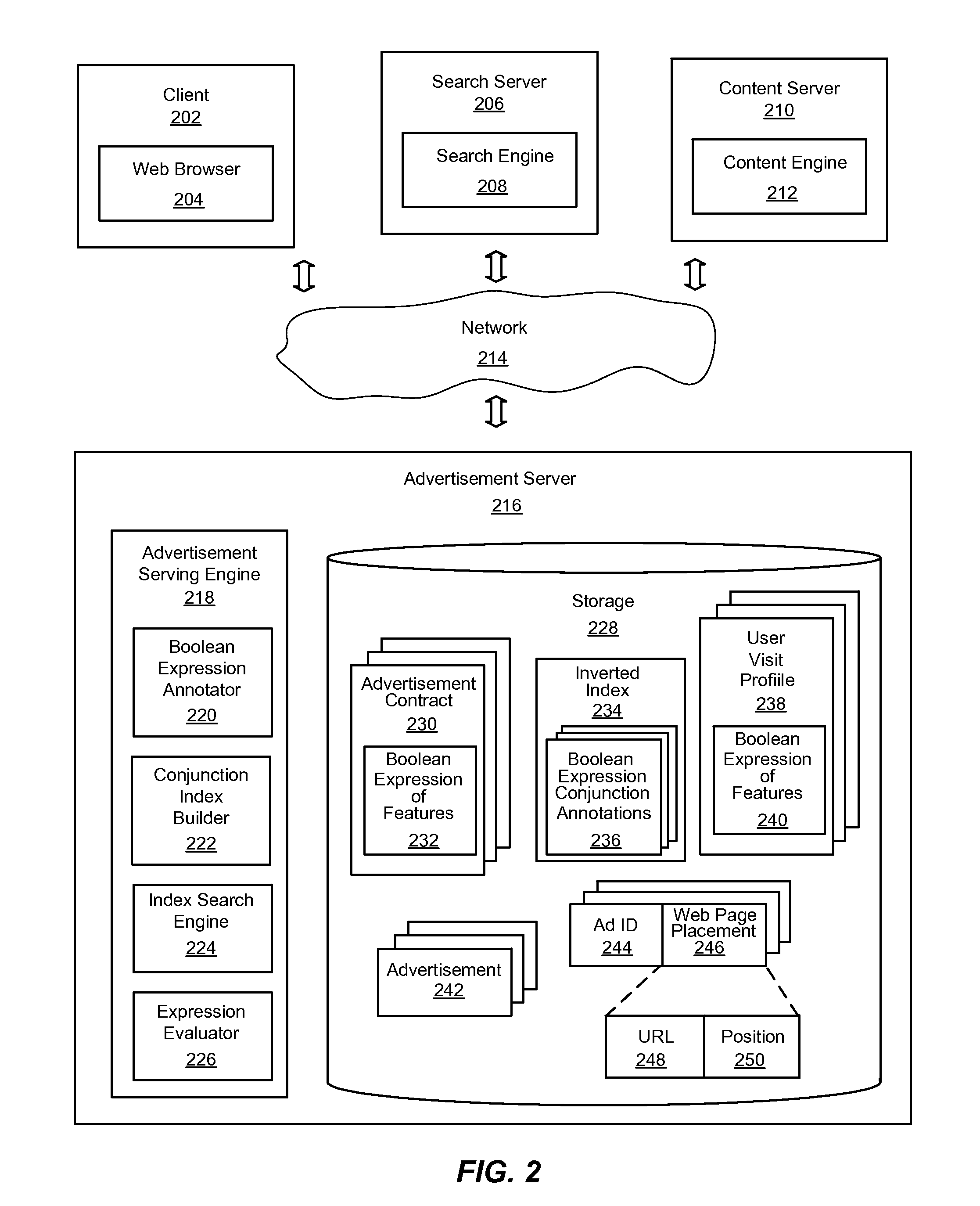
System and Method for Efficiently Evaluating Complex Boolean Expressions
InactiveUS20110225038A1Effective evaluationImprove indexing speedDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceInverted index
An improved system and method for efficiently evaluating complex Boolean expressions is provided. Leaf nodes of Boolean expression trees for objects represented by Boolean expressions of attribute-value pairs may be assigned a positional identifier that indicates the position of a node in the Boolean expression tree. The positional identifiers of each object may be indexed by attribute-value pairs of the leaf nodes of the Boolean expression trees in an inverted index. Given an input set of attribute-value pairs, a list of positional identifiers for leaf nodes of virtual Boolean expression trees may be found in the index matching the attribute-value pairs of the input set. The list of positional identifiers of leaf nodes may be sorted in order by positional identifier for each contract. An expression evaluator may then verify whether a virtual Boolean expression tree for each contract is satisfied by the list of positional identifiers.
Owner:YAHOO INC
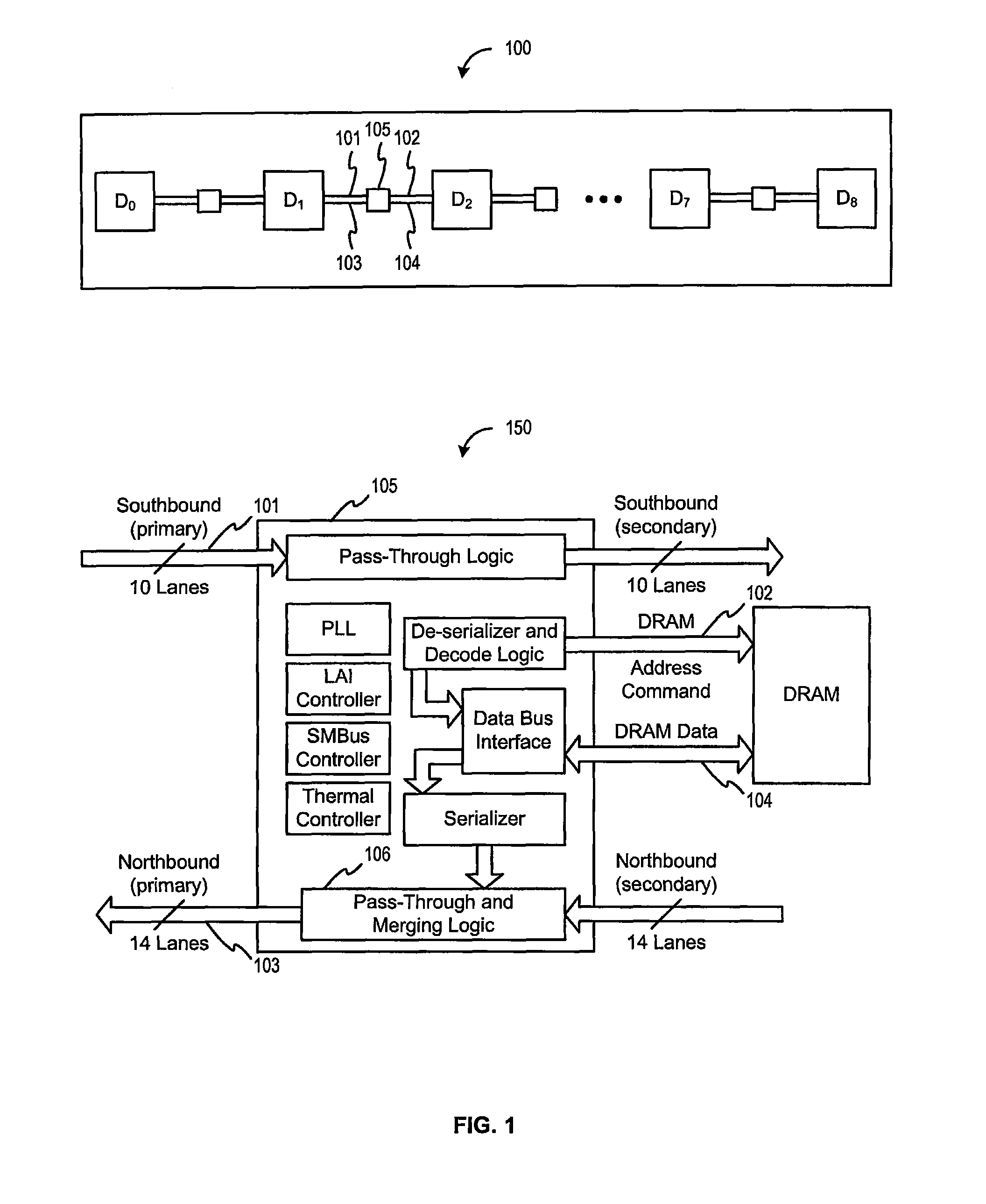
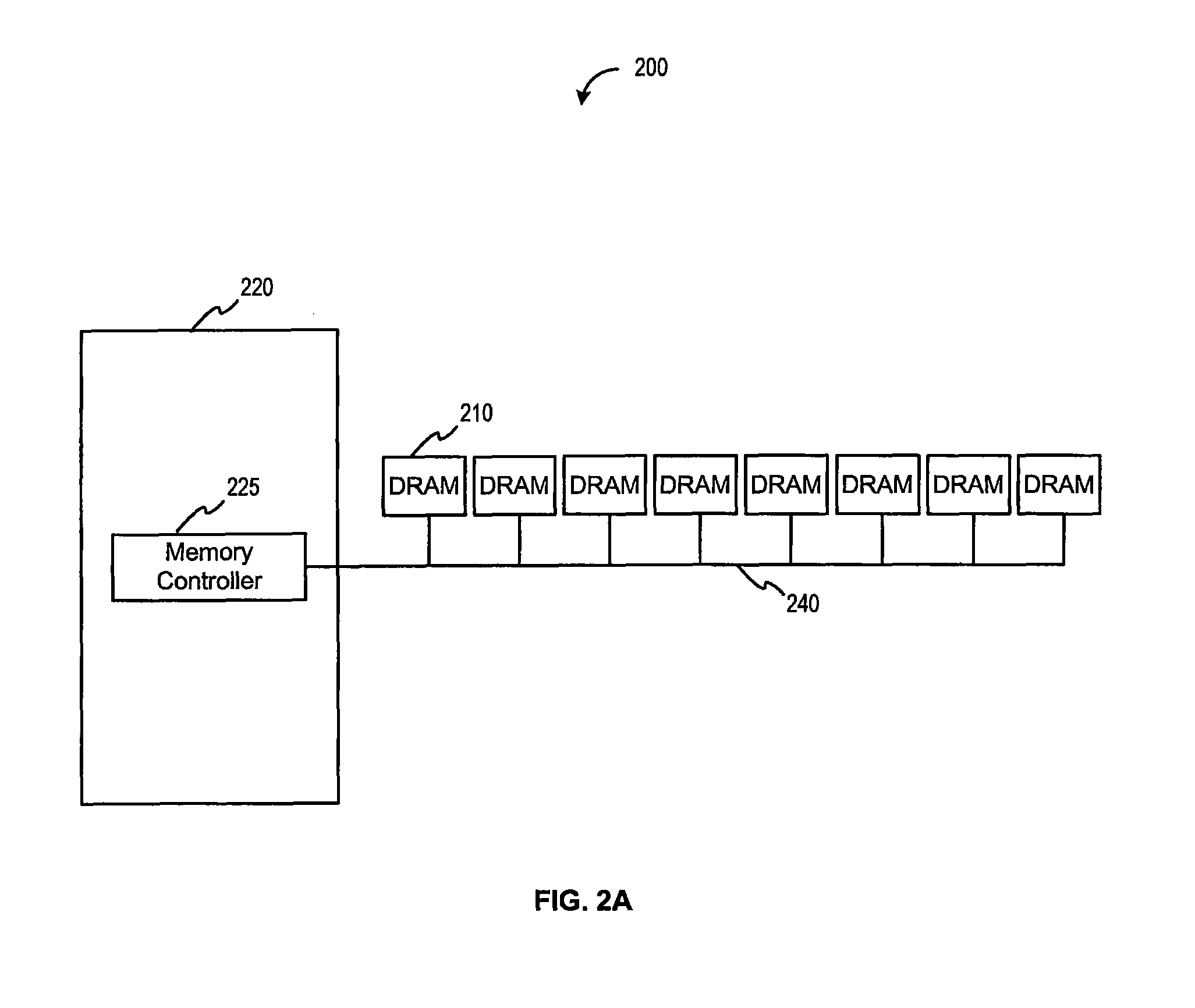
Stacked DIMM memory interface
ActiveUS8386722B1Improve memory performanceDigital storageGenerating/distributing signalsDIMMMemory interface
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth an interface circuit configured to combine time staggered data bursts returned by multiple memory devices into a larger contiguous data burst. As a result, an accurate timing reference for data transmission that retains the use of data (DQ) and data strobe (DQS) signals in an infrastructure-compatible system while eliminating the cost of the idle cycles required for data bus turnarounds to switch from reading from one memory device to reading from another memory device, or from writing to one memory device to writing to another memory device may be obtained, thereby increasing memory system bandwidth relative to the prior art approaches.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method of manufacturing high coupling ratio flash memory having sidewall spacer floating gate electrode
InactiveUS6875660B2Reduce operating speedImprove memory performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricCoupling ratio
A method of manufacturing a flash memory is provided. First, a substrate with a first gate structure and a second gate structure thereon is provided. The first gate structure and the second gate structure each comprises of a dielectric layer, a first conductive layer and a cap layer. A tunneling oxide layer is formed over the substrate and then a first spacer is formed on the sidewall of the first conductive layer. Thereafter, a second conductive layer is formed on one side designated for forming a source region of the sidewalls of the first gate structure and the second gate structure. Then, the source region is formed in the substrate in the designated area. Next, an inter-gate dielectric layer is formed over the second conductive layer and then an insulating layer is formed over the source region. After forming a third conductive layer over the area between the first gate structure and the second gate structure, a drain region is formed in the substrate.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Non-volatile memory and manufacturing method and operating method thereof
InactiveUS20060197145A1Highly integratedImprove device performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricComputer science
A non-volatile memory having a plurality of memory units is provided. Each memory unit includes a first memory cell and a second memory cell. The first memory cell is disposed on the substrate. The second memory cell is disposed on one sidewall of the first memory cell and the substrate. The first memory cell includes a first control gate disposed on the substrate and a composite layer disposed between the first control gate and the substrate. The second memory cell includes a pair of floating gates disposed on the substrate, a second control gate disposed on the upper surface of the two floating gates, an inter-gate dielectric layer disposed between the floating gate and the second control gate, a tunneling dielectric layer disposed between the floating gate and the substrate and a gate dielectric layer disposed between the bottom of the second control gate and the substrate.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
Partial FinFET memory cell
ActiveUS20080105932A1Improve performanceImprove memory performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureField-effect transistor
A semiconductor structure includes a semiconductor substrate, a planar PMOS device at a surface of the semiconductor substrate, and an NMOS device at the surface of the semiconductor substrate, wherein the NMOS device is a Fin field effect transistor (FinFET).
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for rasterizing in a hierarchical tile order
InactiveUS20050088448A1Enhance performanceIncrease temporal localityDrawing from basic elementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsBase addressGraphics
A method and apparatus for efficiently rasterizing graphics is provided. The method is intended to be used in combination with a frame buffer that provides fast tile-based addressing. Within this environment, frame buffer memory locations are organized into a tile hierarchy. For this hierarchy, smaller low-level tiles combine to form larger mid-level tiles. Mid-level tiles combine to form high-level tiles. The tile hierarchy may be expanded to include more levels, or collapsed to included fewer levels. A graphics primitive is rasterized by selecting an starting vertex. The low-level tile that includes the starting vertex is then rasterized. The remaining low-level tiles that are included in the same mid-level tile as the starting vertex are then rasterized. Rasterization continues with the mid-level tiles that are included in the same high-level tile as the starting vertex. These mid-level tiles are rasterized by rasterizing their component low-level tiles. The rasterization process proceeds bottom-up completing at each lower level before completing at higher levels. In this way, the present invention provides a method for rasterizing graphics primitives that accesses memory tiles in an orderly fashion. This reduces page misses within the frame buffer and enhances graphics performance.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Partial FinFET memory cell
ActiveUS7592675B2Improve performanceImprove memory performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureField-effect transistor
A semiconductor structure includes a semiconductor substrate, a planar PMOS device at a surface of the semiconductor substrate, and an NMOS device at the surface of the semiconductor substrate, wherein the NMOS device is a Fin field effect transistor (FinFET).
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
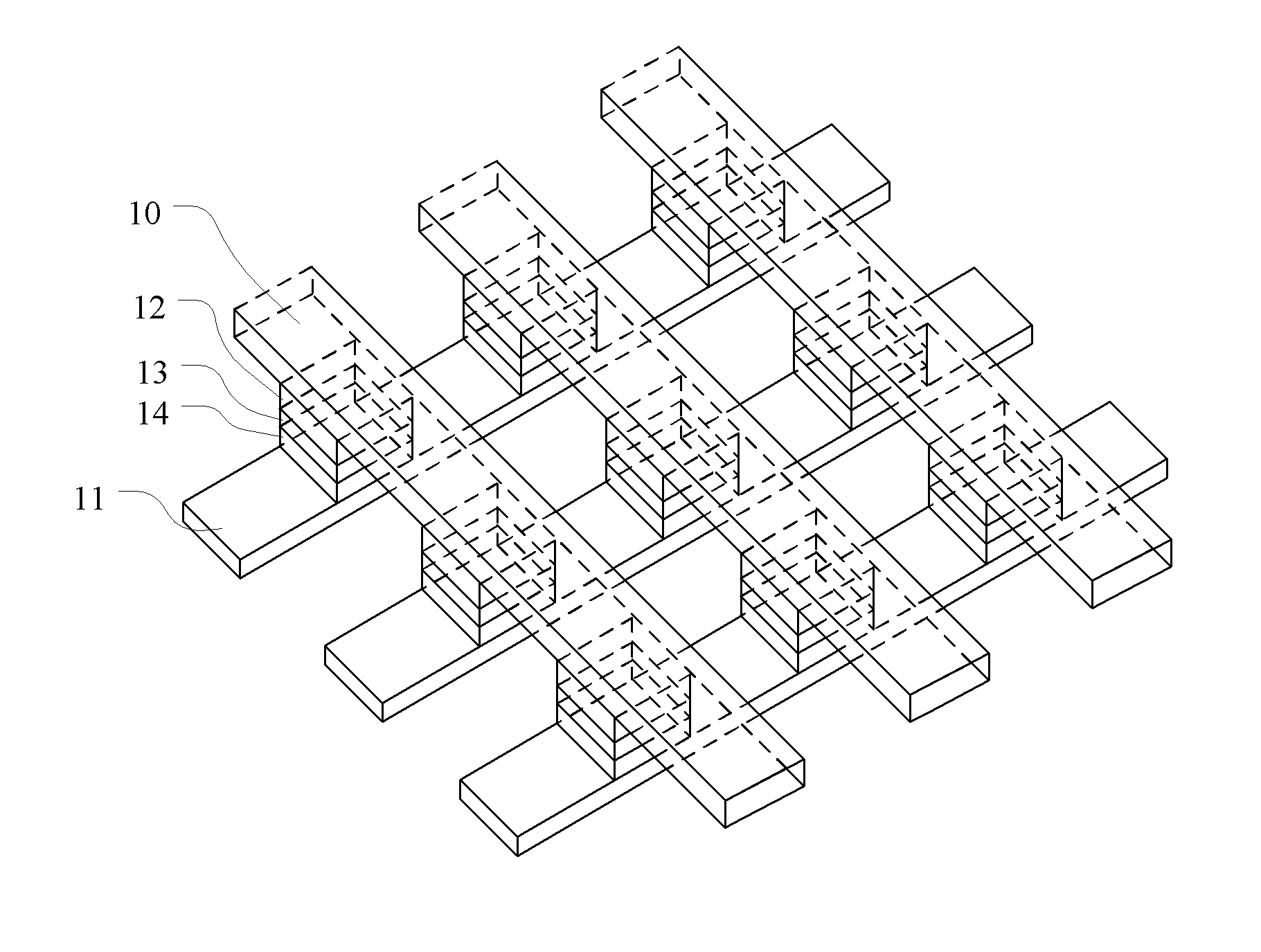
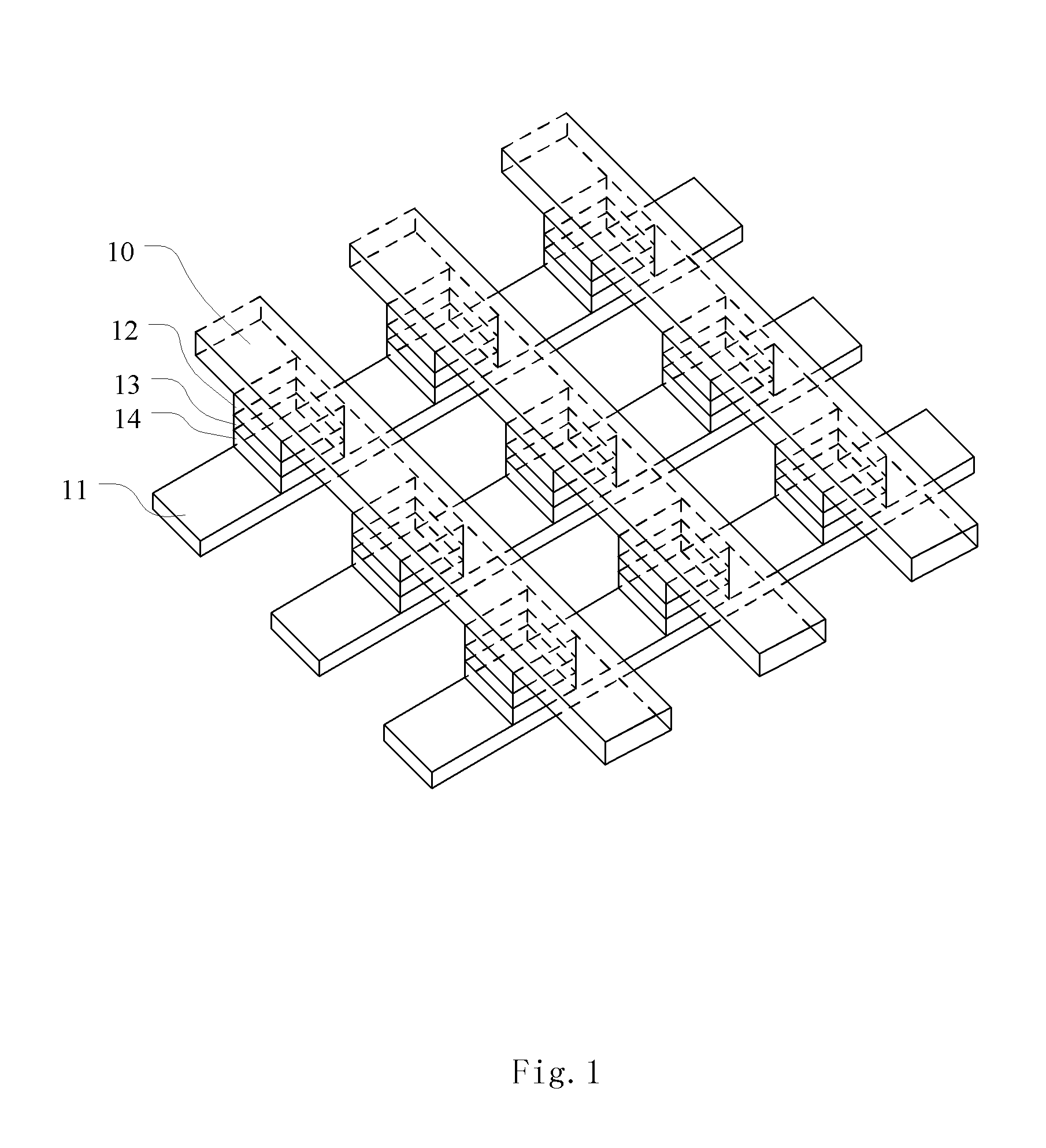
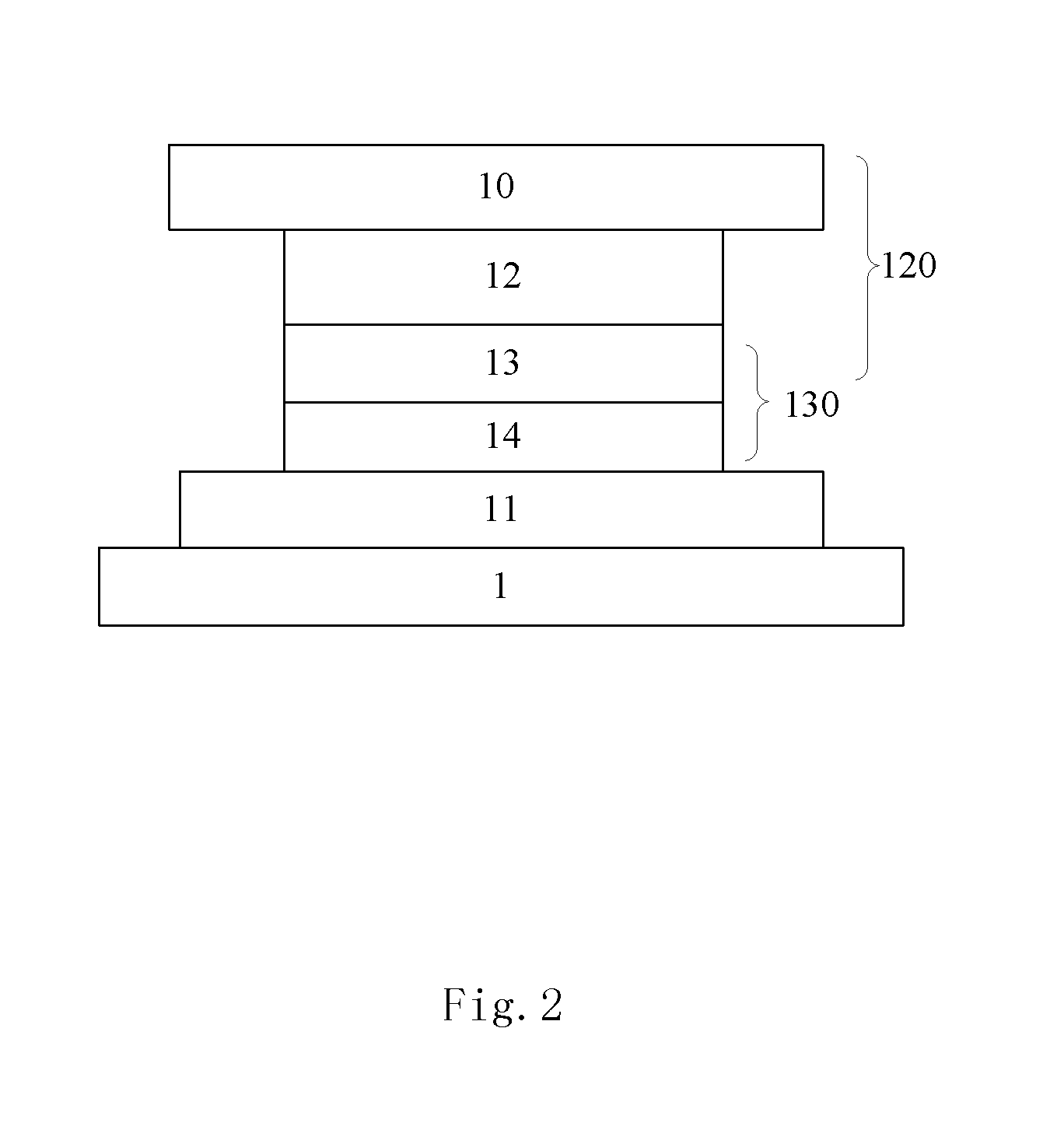
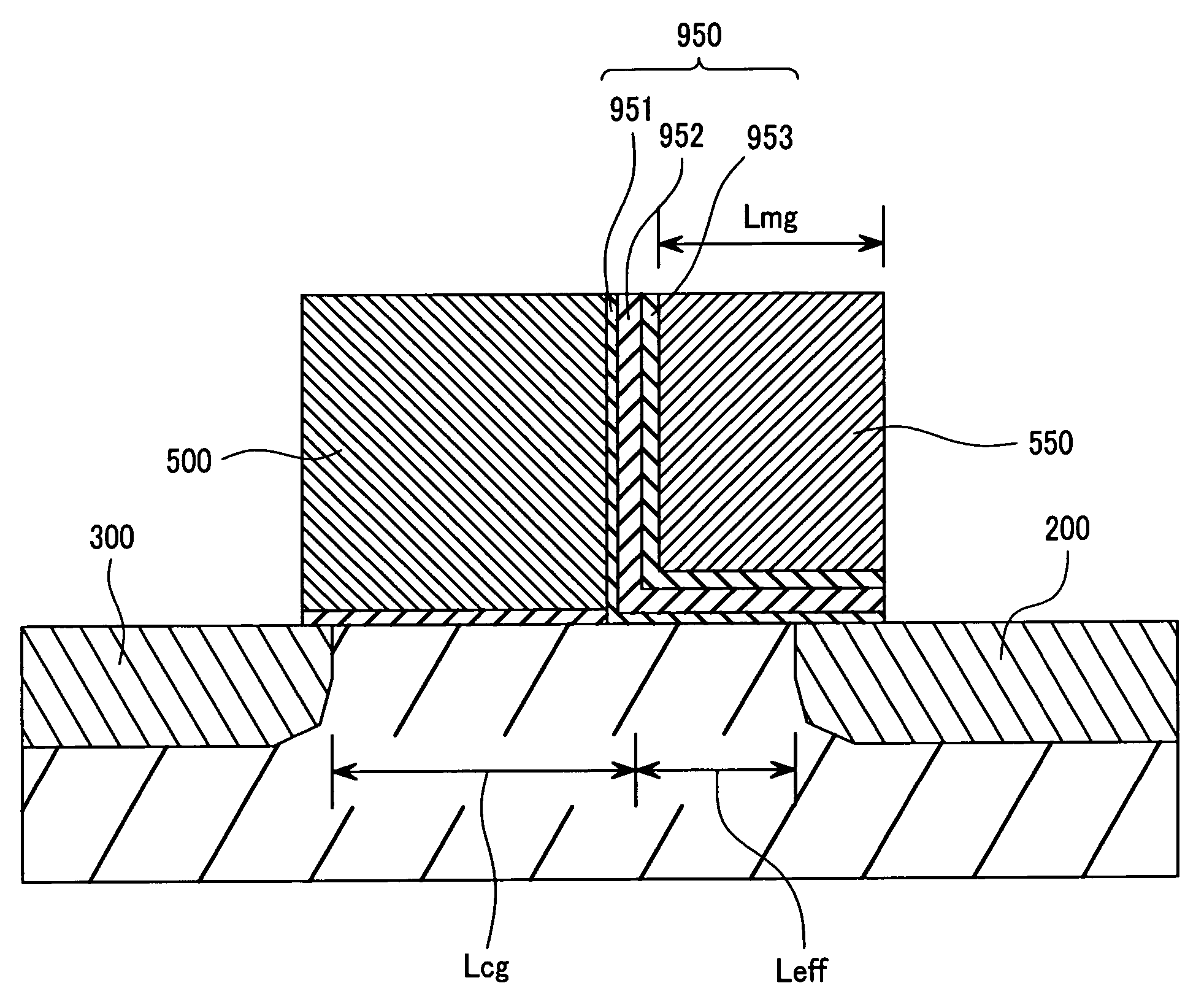
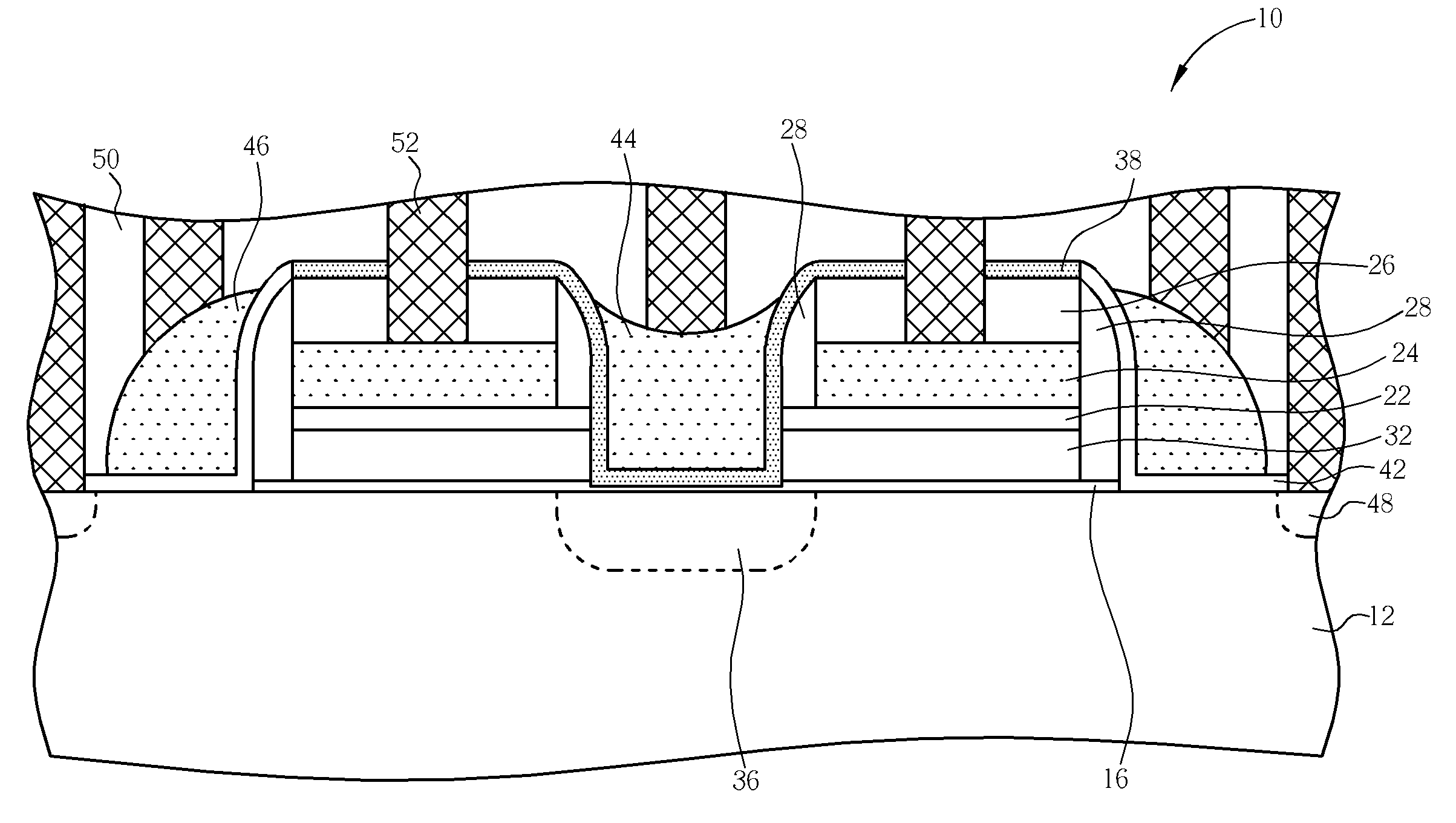
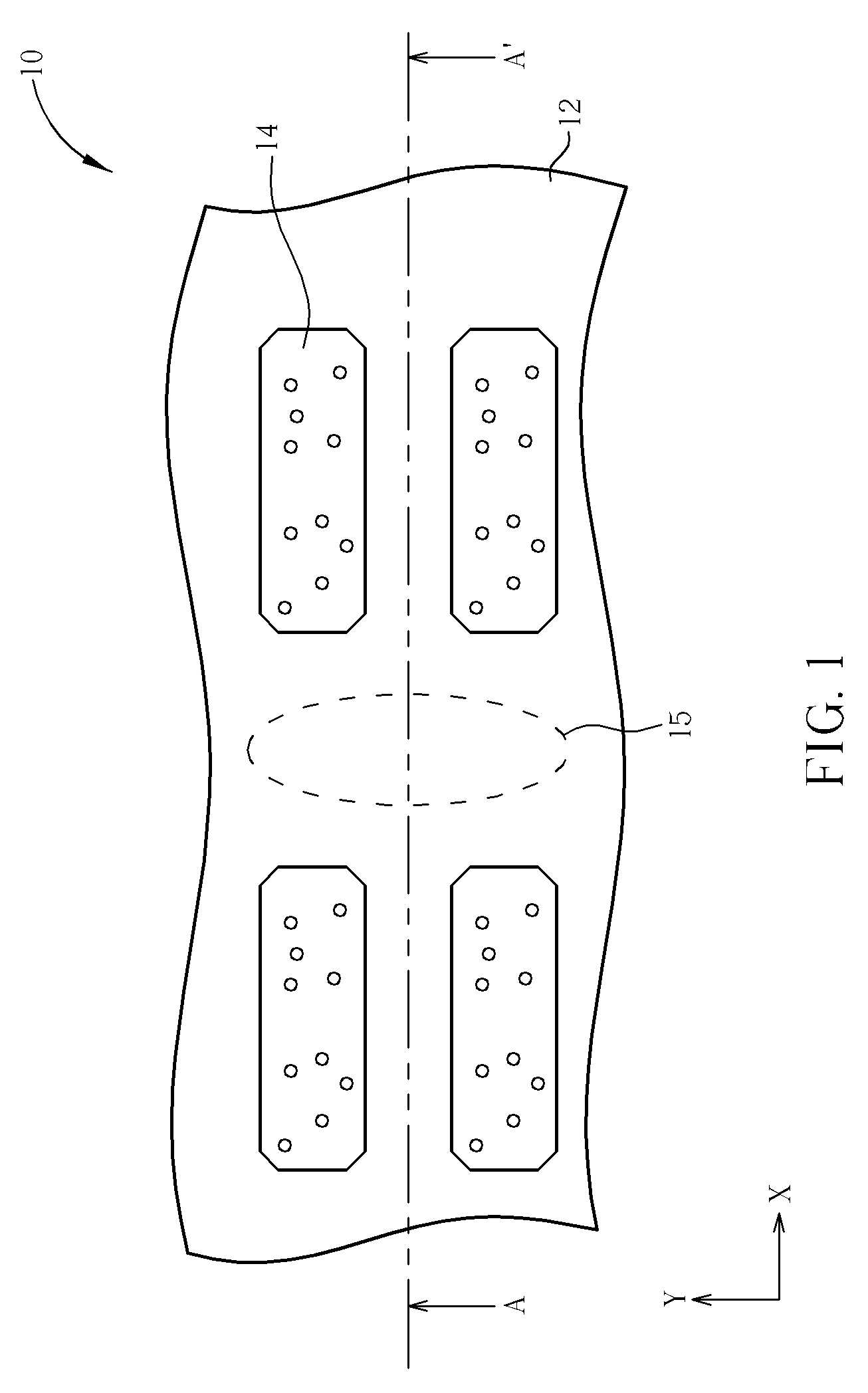
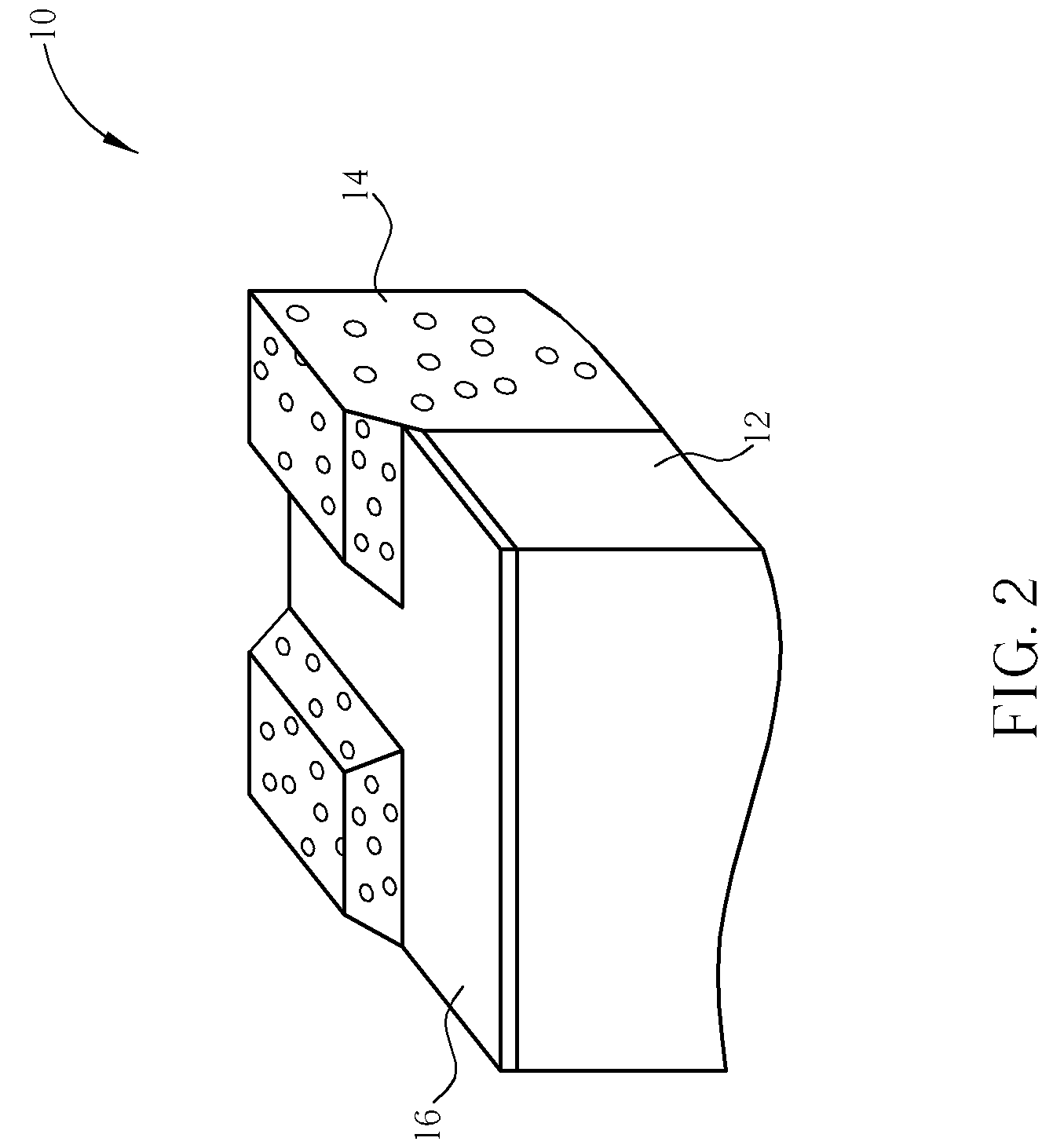
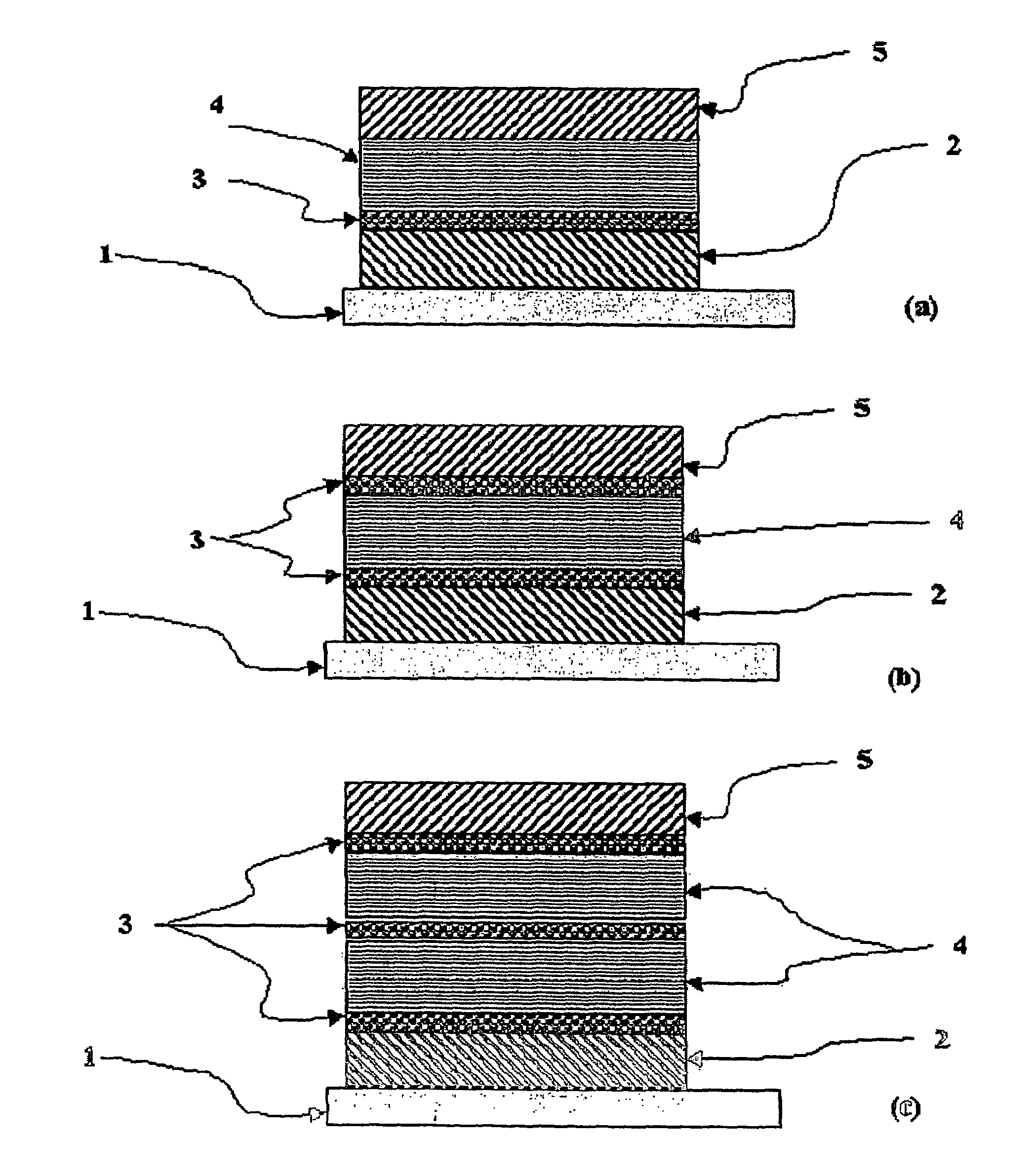
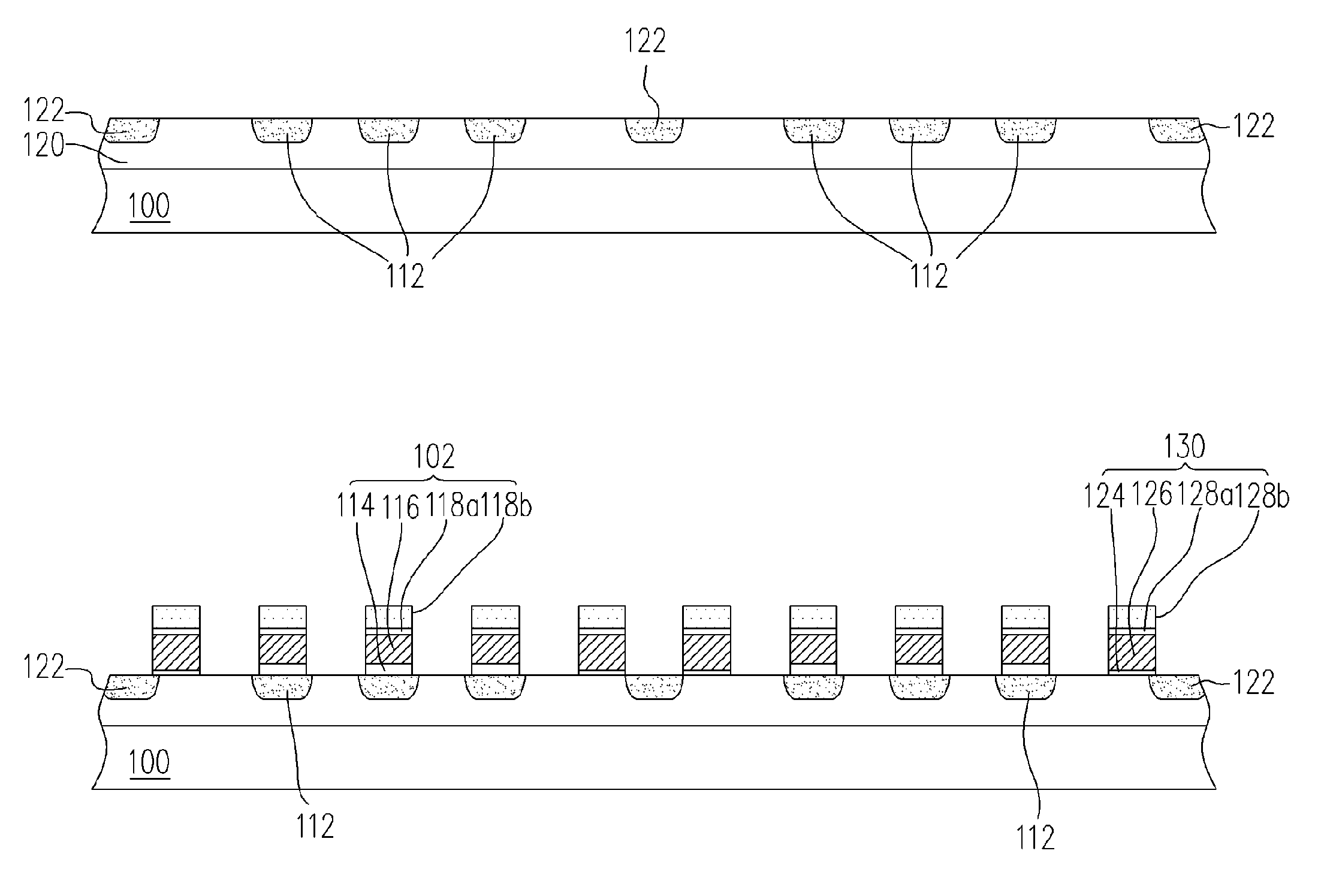
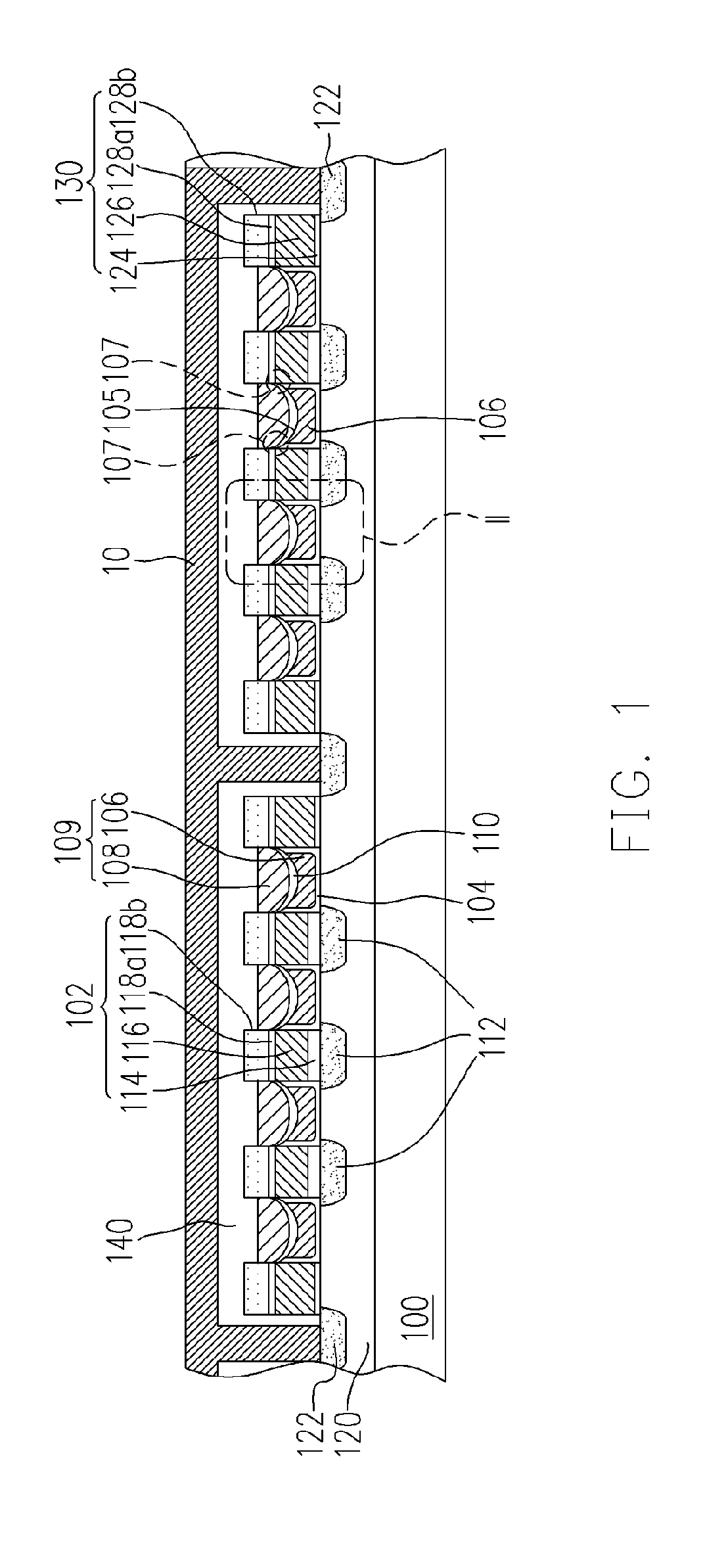
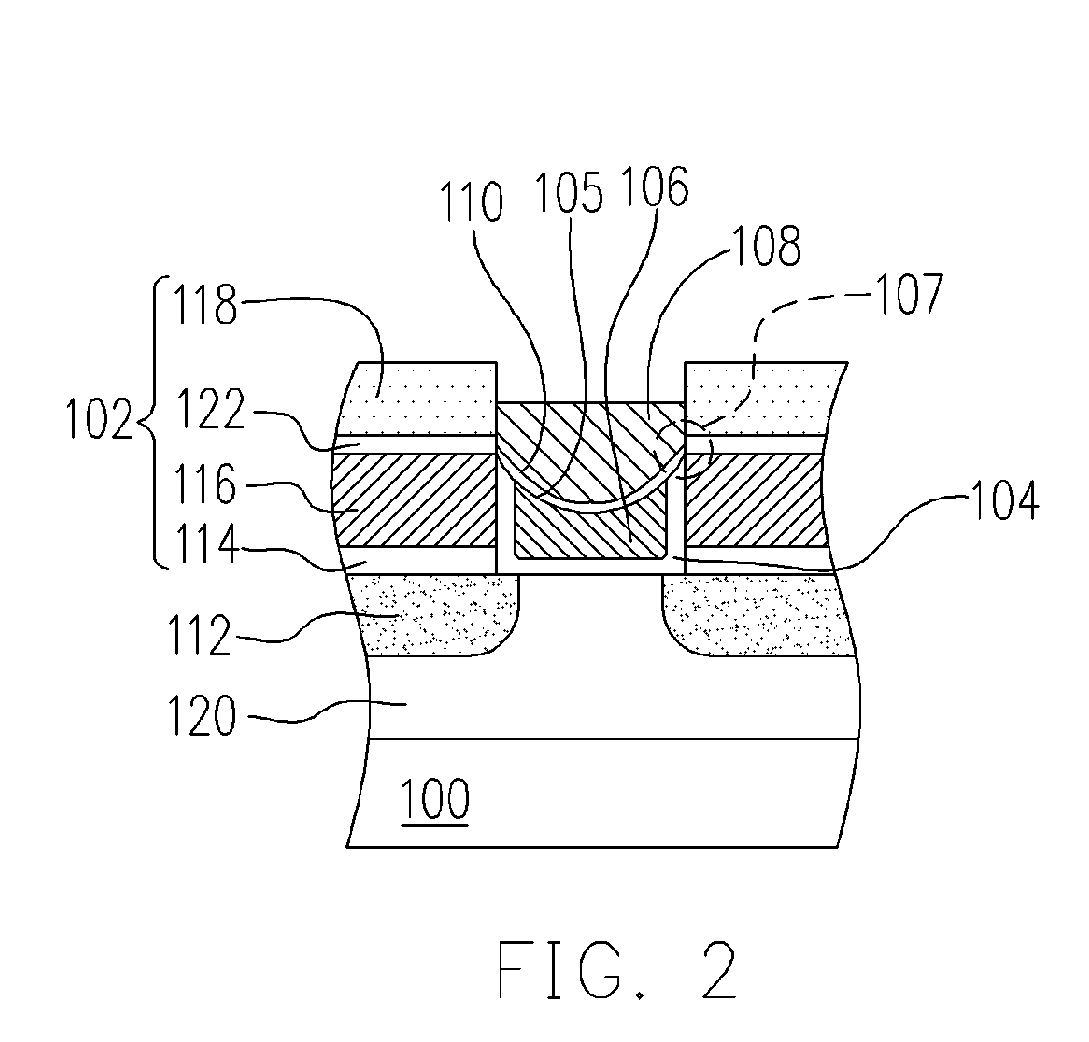
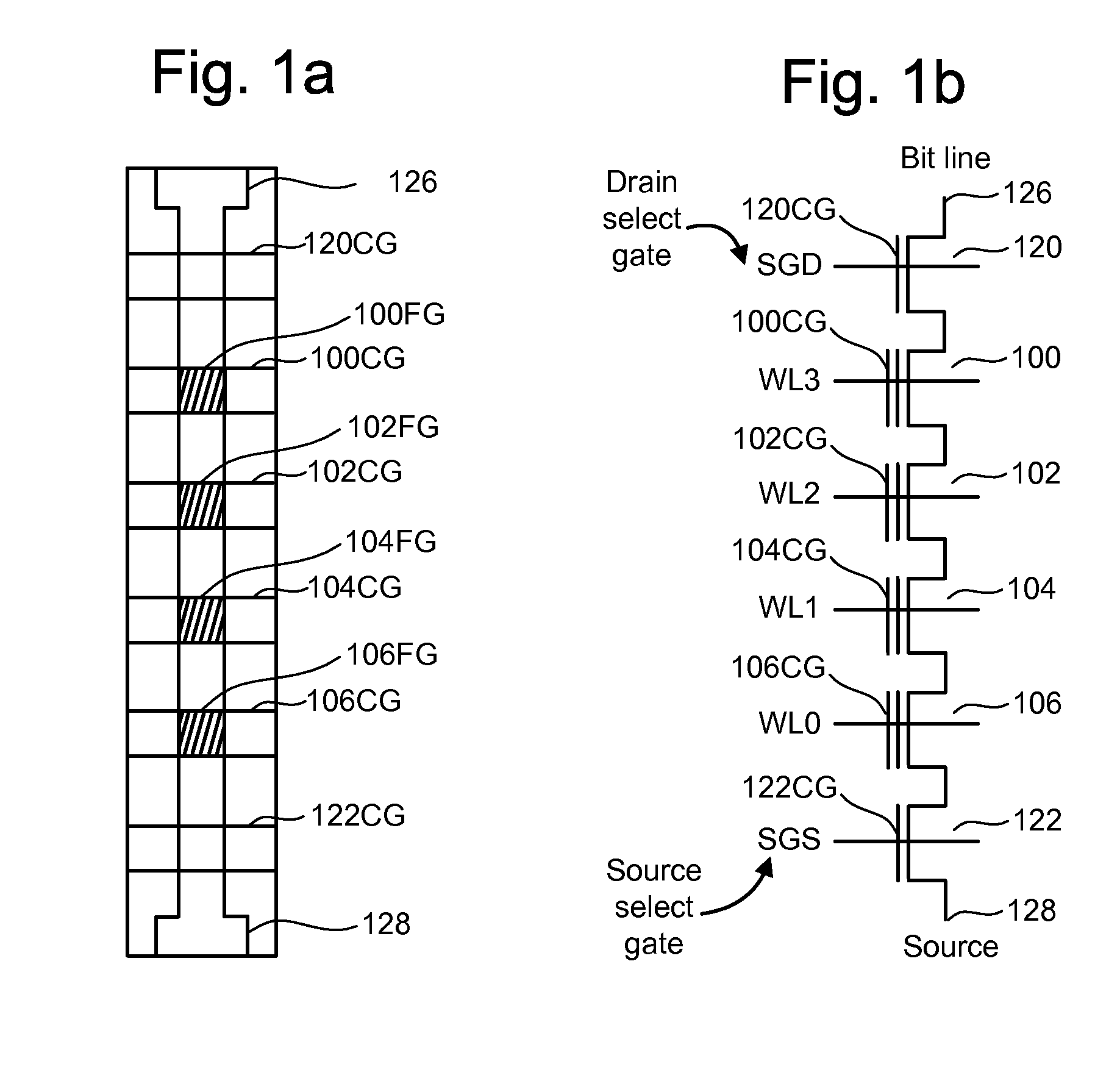
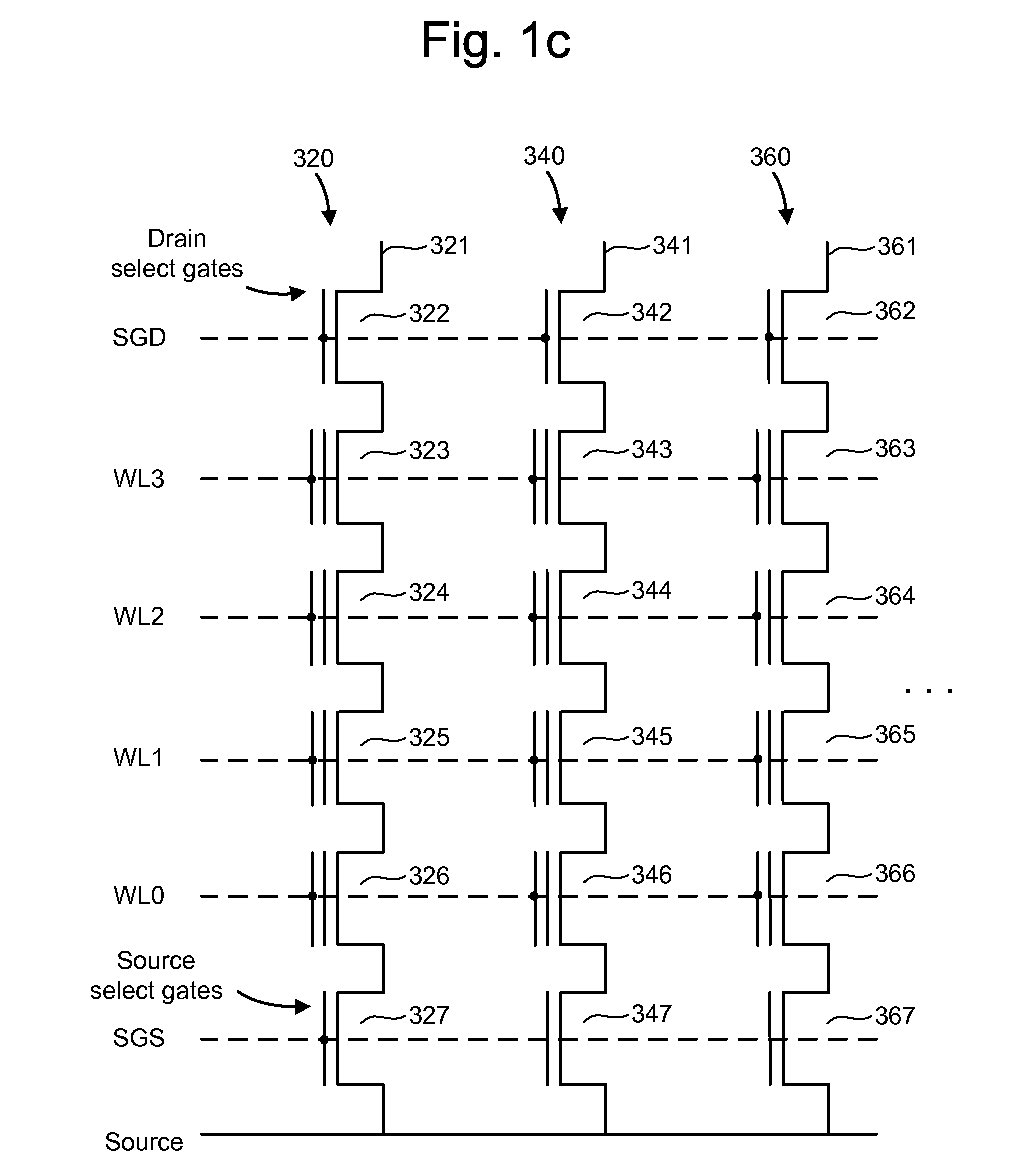
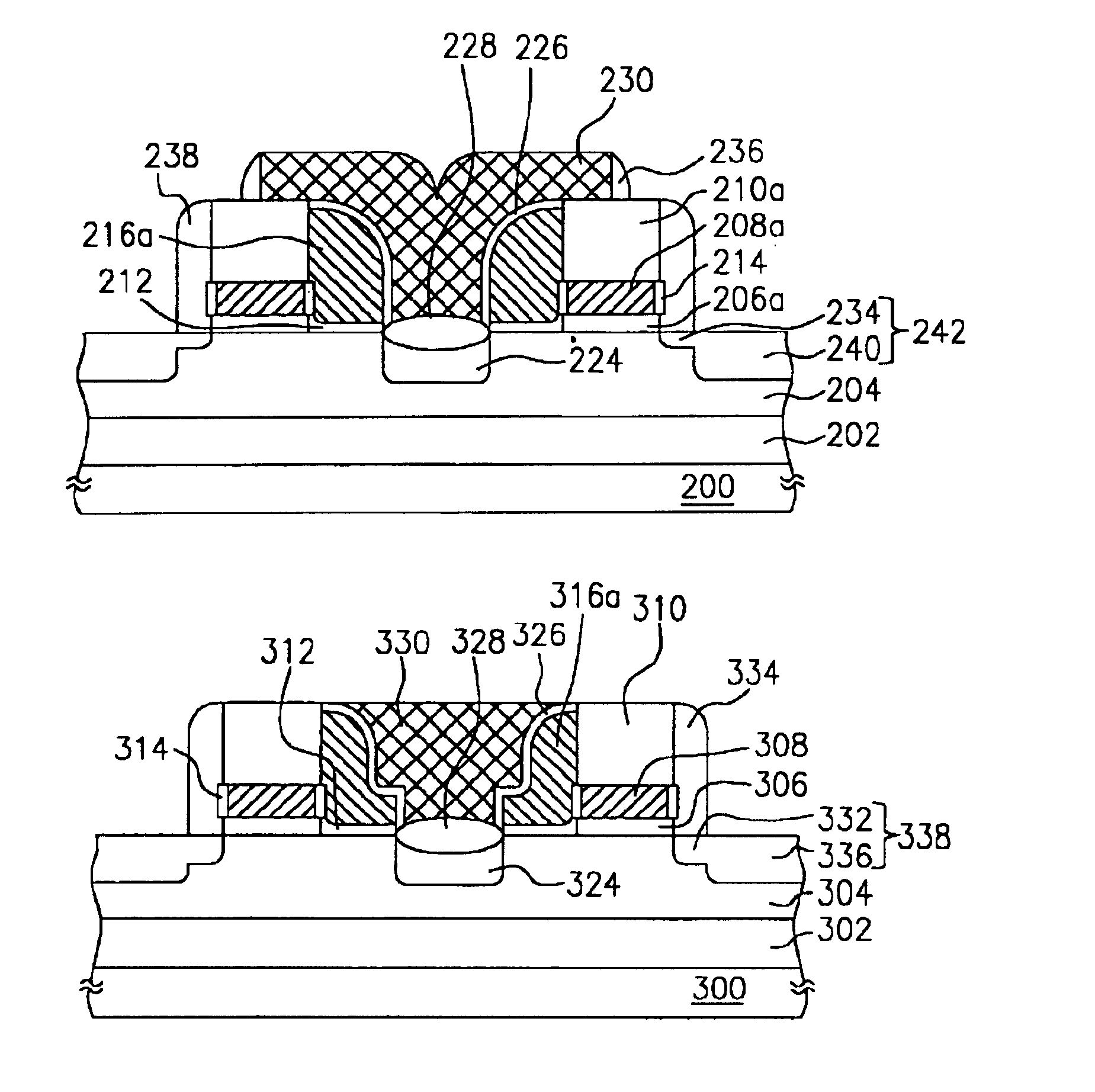
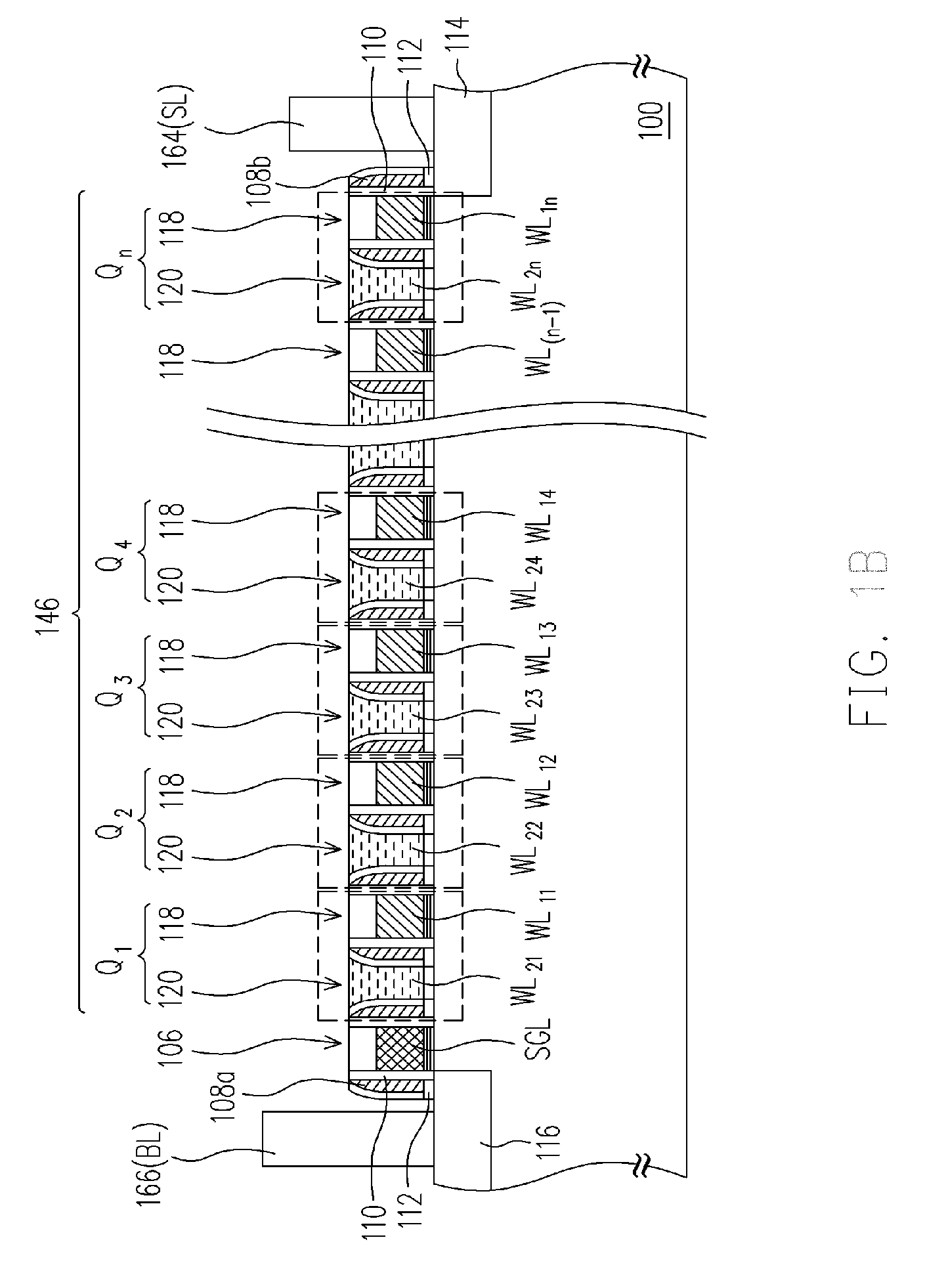
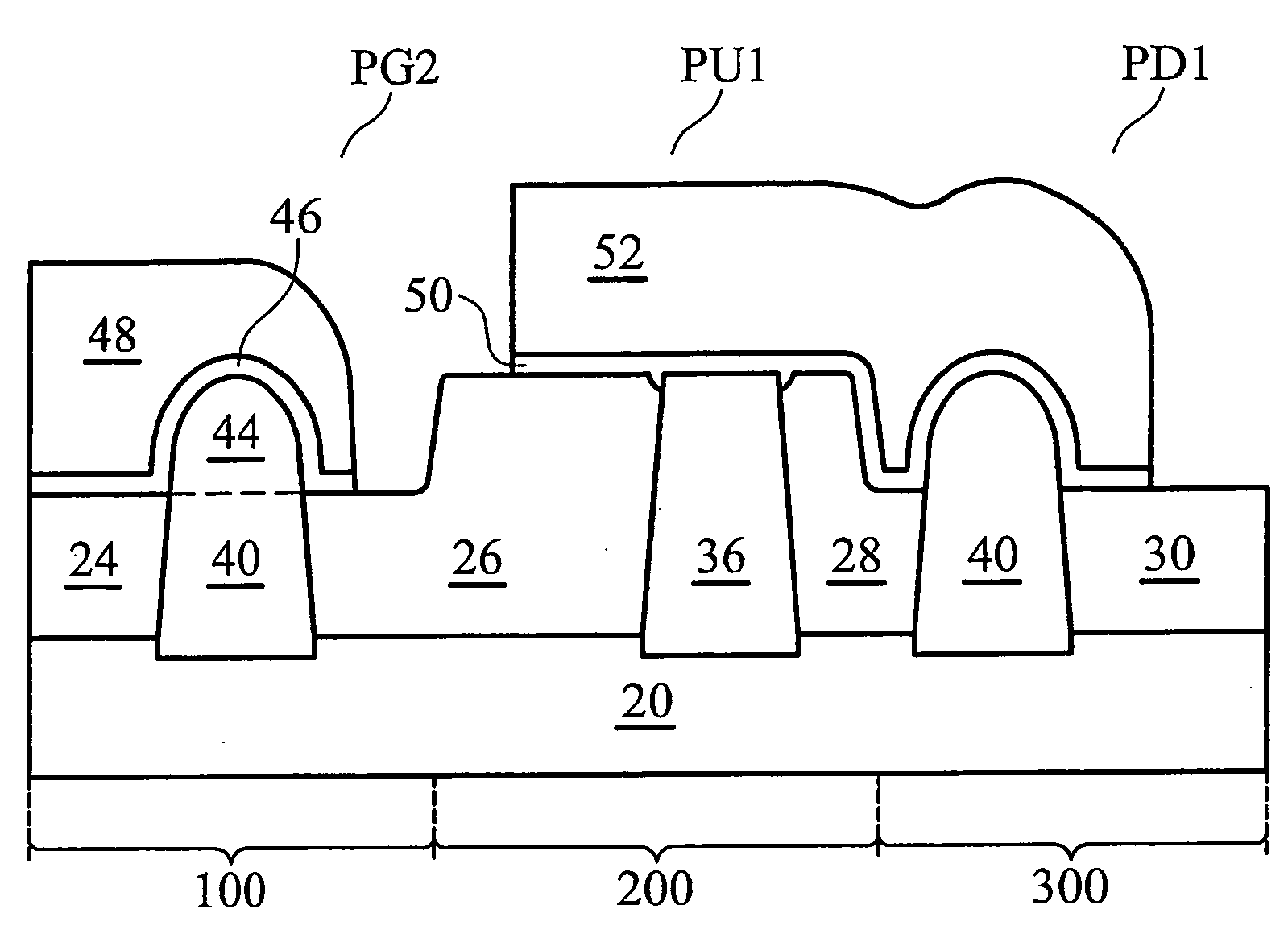
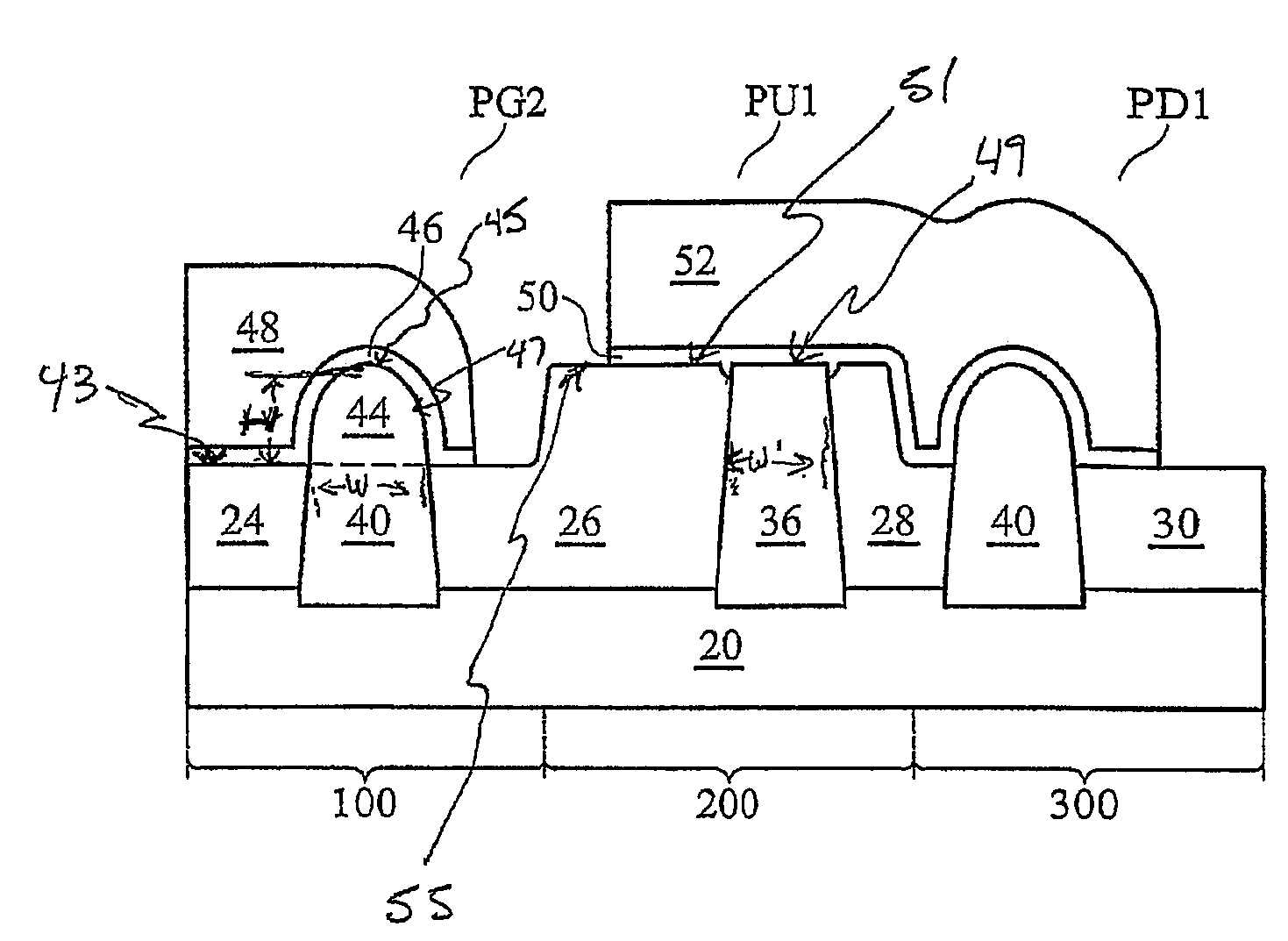
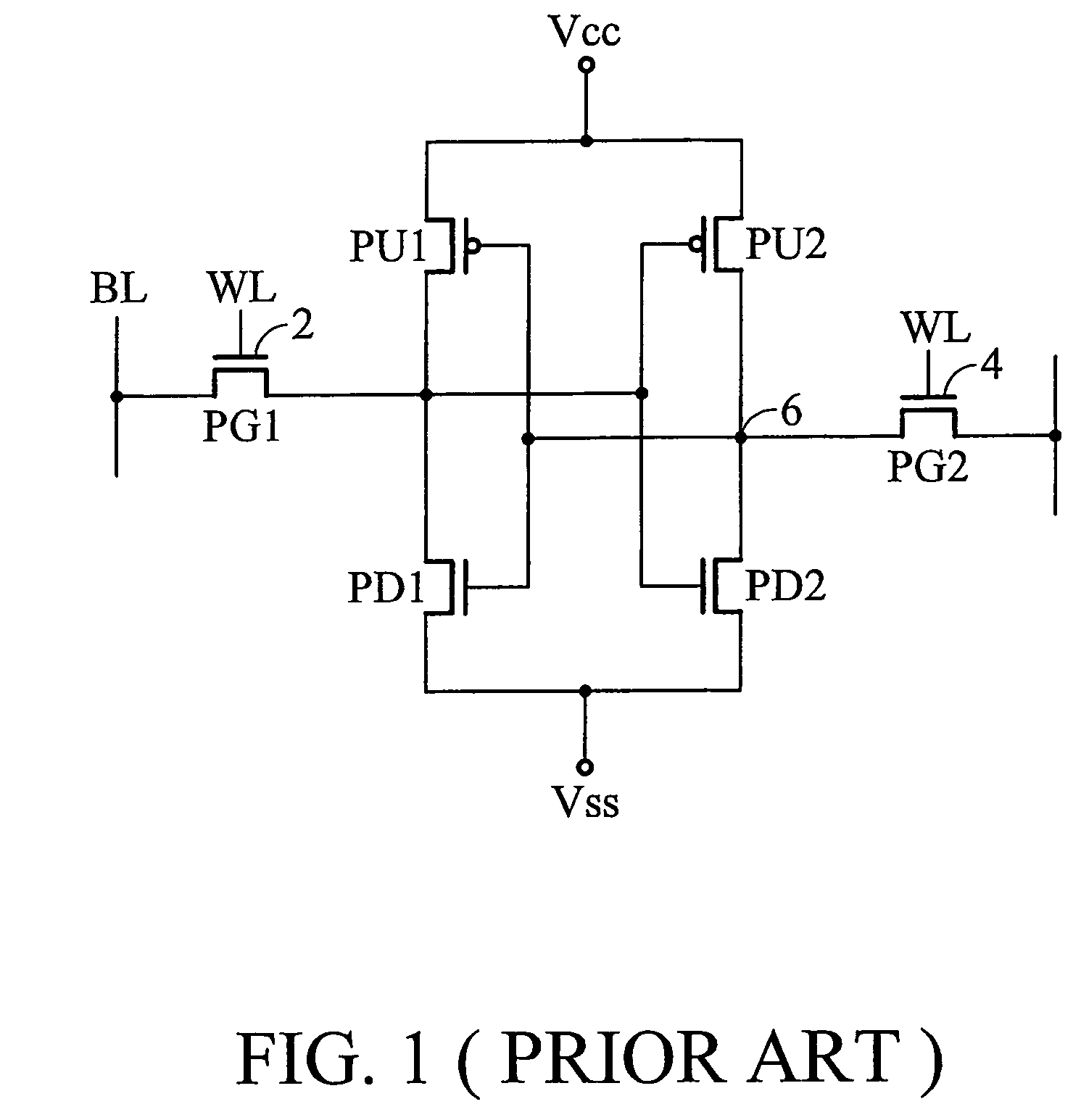
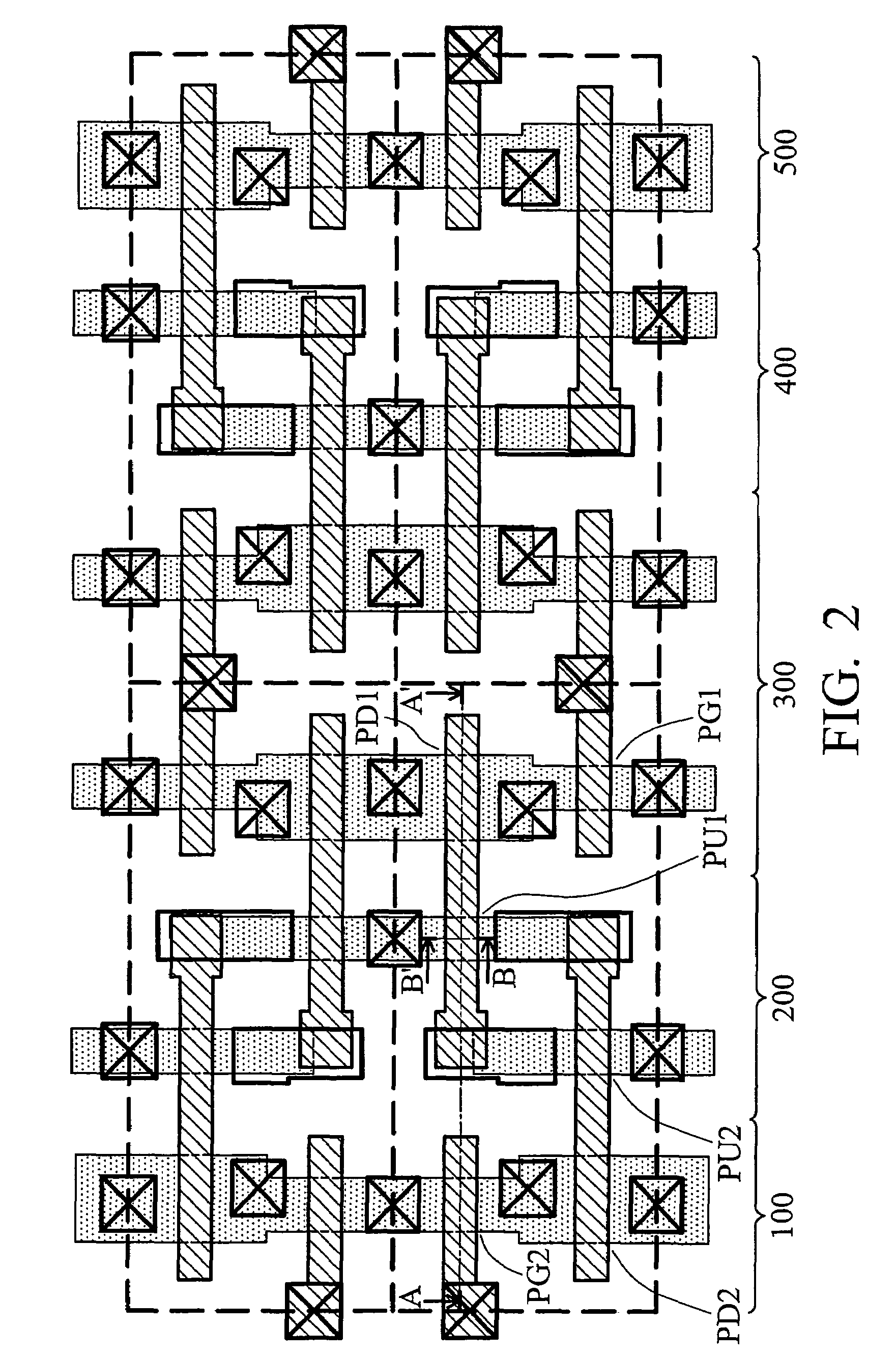
[non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof]
InactiveUS20050224858A1Easy to manufactureImprove programming speedSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesGate dielectricDielectric layer
A non-volatile memory including a substrate, a plurality of gate structures, a plurality of select gate structures, spacers and source region / drain region is provided. Each gate structure on the substrate further includes a bottom dielectric layer, an electron trapping layer, an upper dielectric layer, a control gate and a cap layer. The select gate structures are disposed on one side of the respective each gate structure. Each select gate structure includes a select gate dielectric layer and a select gate. The select gate structures and the gate structures are connected in series to form a memory cell row. The spacers are disposed between the select gate structures and the gate structures. The source region and the drain region are disposed in the substrate on each side of the memory cell row.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
Insulin-associated peptides with effects on cerebral health
InactiveUS7655619B2Efficiently enter brainImprove performanceNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMemory retentionInsulin A Chain
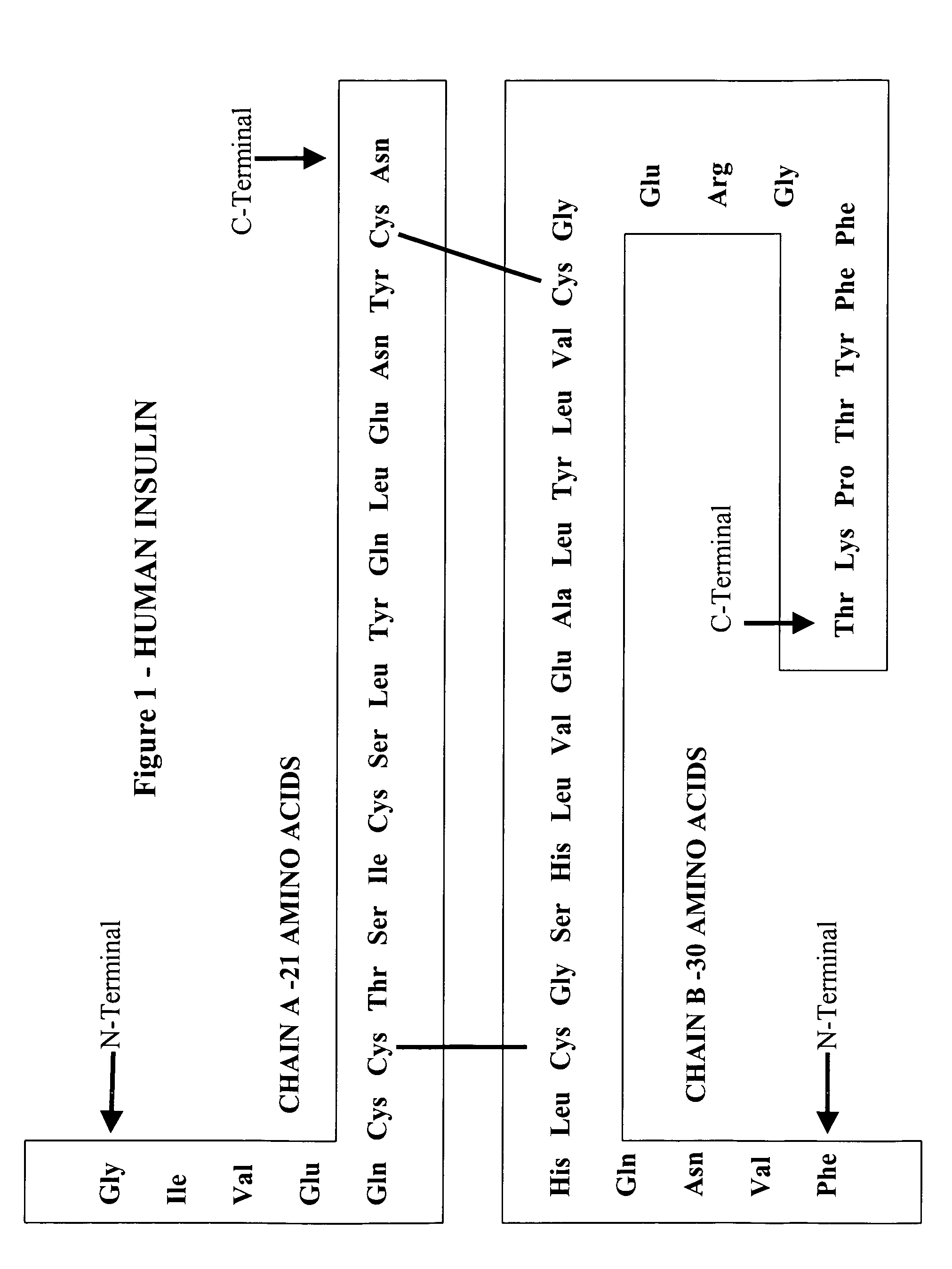
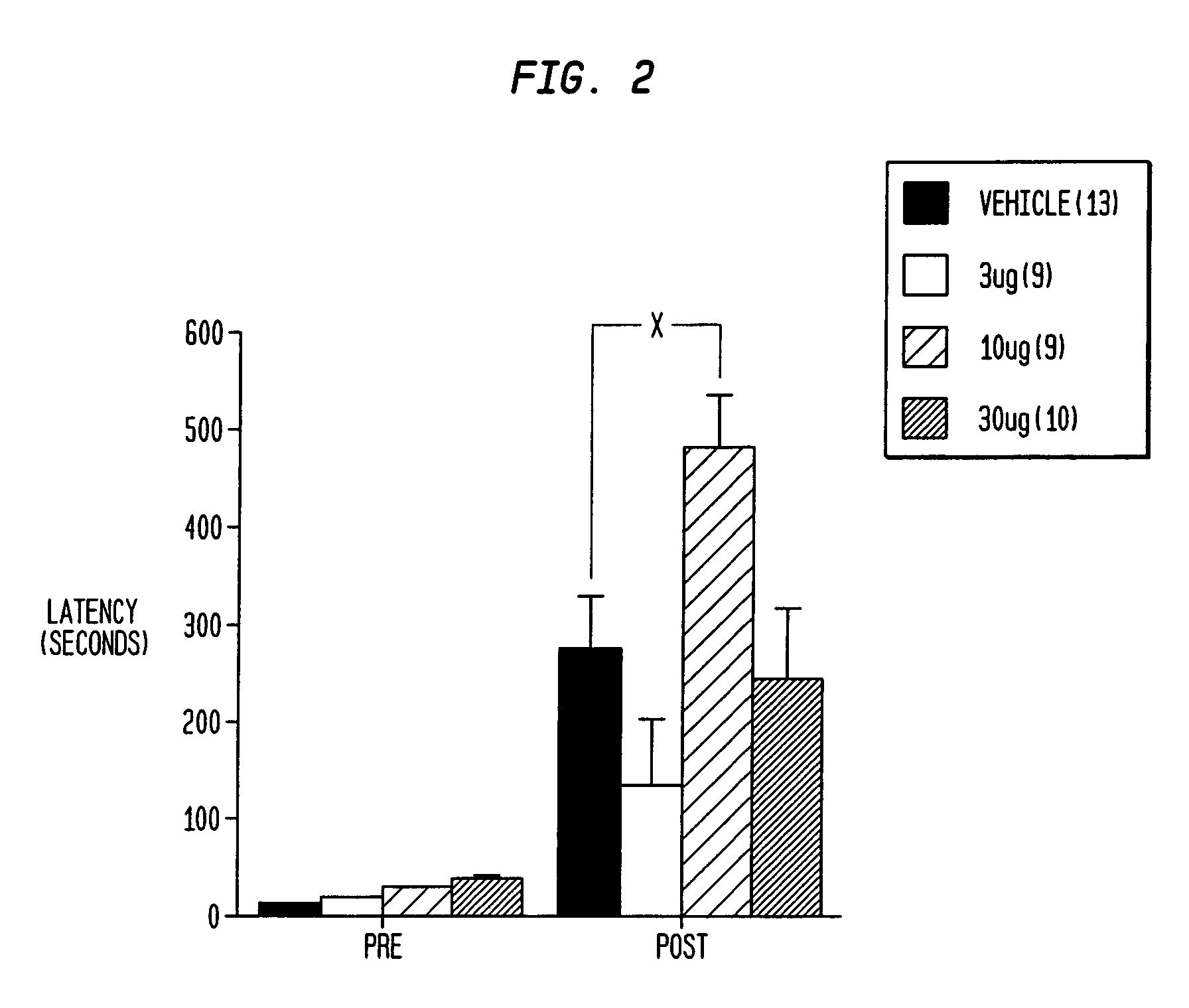
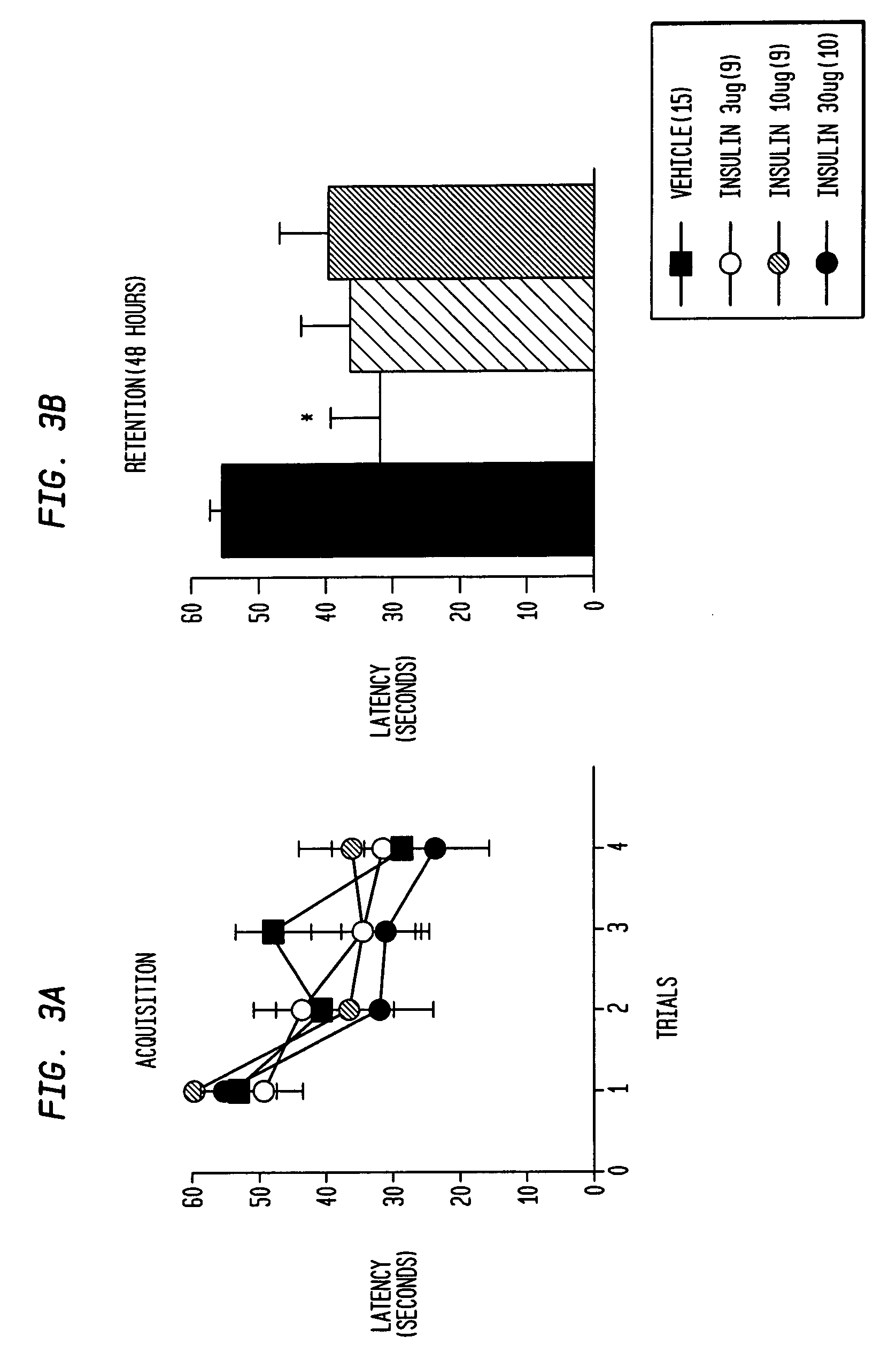
The present invention provides compositions and methods for ameliorating neurological, attention, or memory disorders and improving learning and cognition through the delivery of insulin A-chain and analogs thereof to a subject. Insulin A-chain, peptides comprising the 21 amino acid sequence GIVEQ CCASV CSLYQ LENYC N (SEQ ID NO:1), and functional analogs thereof are disclosed to modulate neurological activity when administered to a subject. The methods of the invention can be used to prevent or treat neurological disorders as well as improve memory retention and acquisition. The invention includes pharmaceutical compositions comprising a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of insulin A-chain peptide or a functional analogs thereof.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Resistive radom access memory device, method for manufacturing the same, and method for operating the same
ActiveUS20130128653A1Improve memory performanceFast switching speedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRandom access memoryEngineering
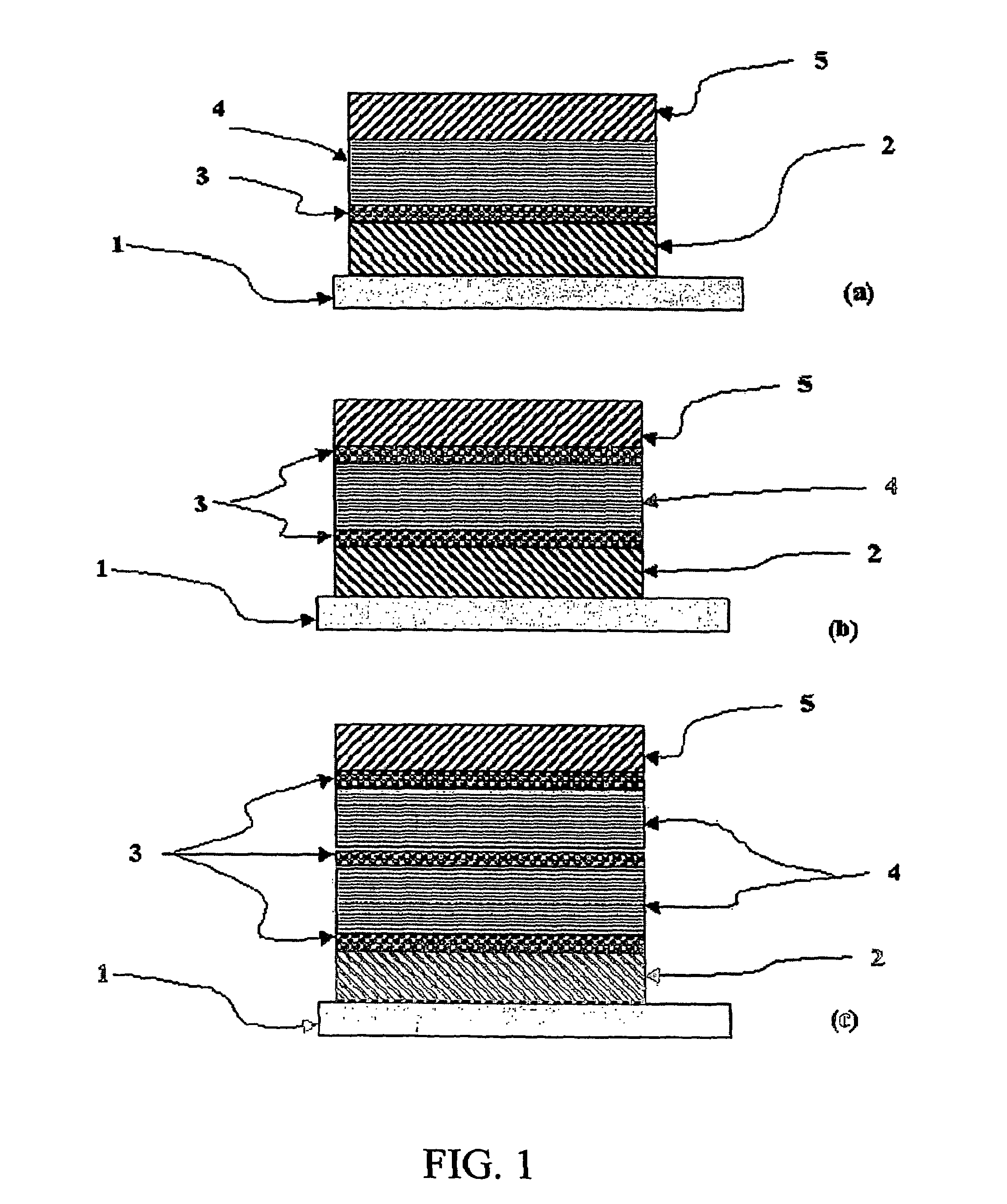
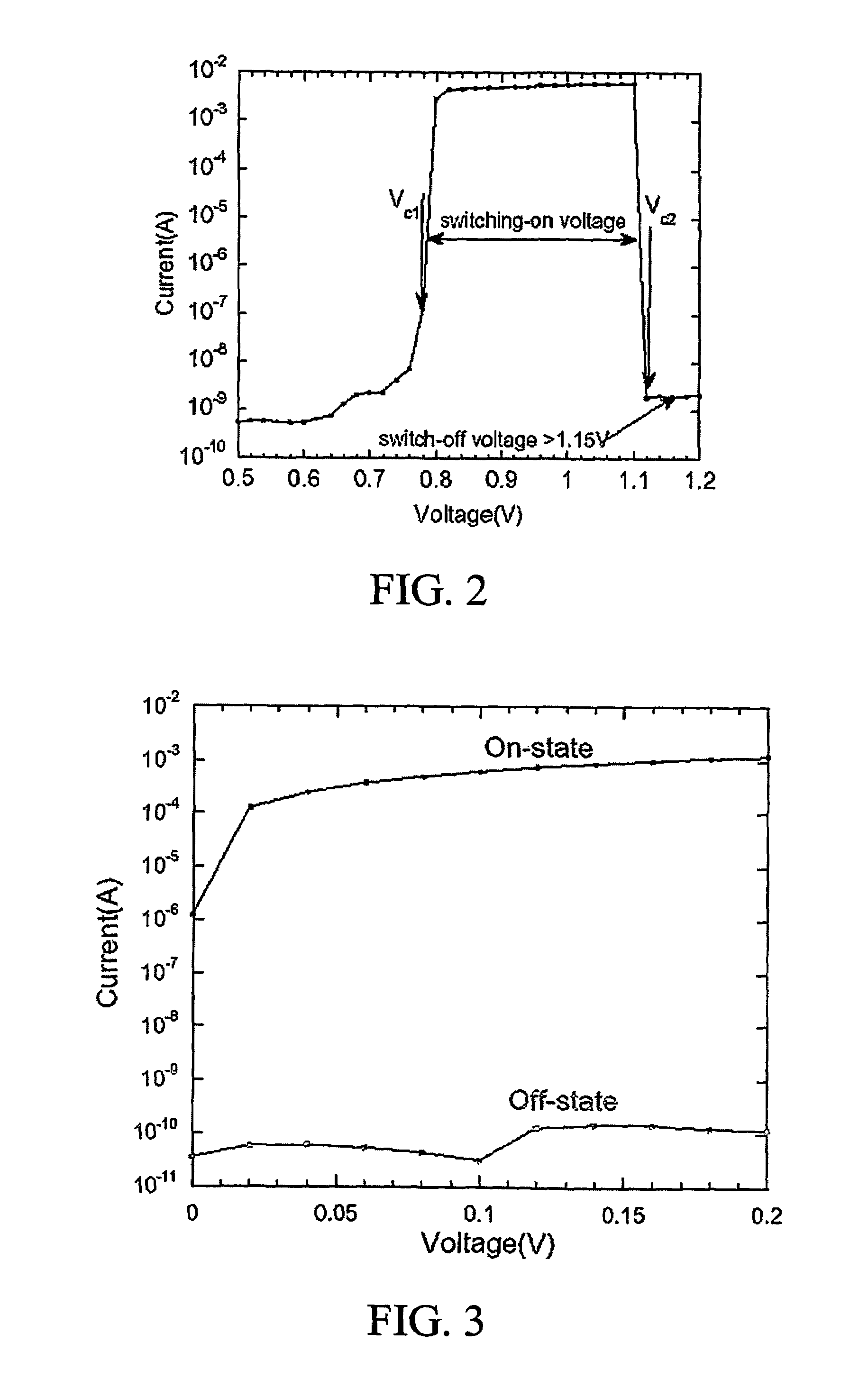
A resistive random access memory device, a method for manufacturing the resistive random access memory device, and a method for operating the resistive random access memory device are disclosed. The resistive random access memory device includes a resistive switching memory element including two electrodes and a layer of variable-resistance material between the two electrodes, wherein the layer of variable-resistance material exhibits bipolar resistive switching behavior; and a Schottky diode including a metal layer and a p-doped semiconductor layer which contact each other, wherein the metal layer of the Schottky diode is coupled to one of the two electrodes of the resistive switching memory element. The present disclosure provides the resistive random access memory device operating in bipolar resistive switching scheme.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Integrated semiconductor nonvolatile storage device
ActiveUS7723779B2Improve performanceIncrease currentSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesComputer architectureSemiconductor storage devices
An object of the present invention is to provide an integrated semiconductor nonvolatile storage device that can be read at high speed and reprogrammed an increased number of times.In the case of conventional nonvolatile semiconductor storage devices having a split-gate structure, there is a tradeoff between the read current and the maximum allowable number of reprogramming operations. To overcome this problem, an integrated semiconductor nonvolatile storage device of the present invention is configured such that memory cells having different memory gate lengths are integrated on the same chip. This allows the device to be read at high speed and reprogrammed an increased number of times.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Dual port memory core cell architecture with matched bit line capacitances
InactiveUS7002258B2Reduce the overall heightShorten the lengthTransistorSolid-state devicesBit lineCapacitance
A Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) dual port memory with an improved core cell design having internally matched capacitances and decreased bit line capacitance is disclosed. The core cell is fabricated on a substrate divided into three approximately equal columns of different substrate materials. In a preferred embodiment, the memory cell is fabricated on a central p-type column that in turn is sandwiched between two n-type columns. The three-column substrate architecture permits reduced bit line height, with an accompanying reduction in bit line capacitance, which increases the speed at which the core cell can operate. The architecture also permits separating the core cell's bitline and complement bitline, reducing capacitive coupling between these lines and increasing the core cell's operating speed. The architecture further permits better matching of internal node capacitances.
Owner:ARM INC
Programmable memory device with an improved redundancy structure
ActiveUS7289364B2Improve memory performanceSimplify the management processRead-only memoriesDigital storageProgrammable logic deviceComputer science
An electrically programmable memory device is proposed including: a matrix of memory cells arranged in a plurality of memory arrays and at least one redundancy array; and a substituting structure that substitutes the use of each memory array with the use of one of the at least one redundancy array in response to a failure of the memory array, wherein the memory arrays are grouped into at least one set. The substituting structure includes: a structure for associating each set with a predetermined one of the at least one redundancy array; a flag for each memory array indicative of the failure of the memory array; and a selecting for enabling each memory array or the associated redundancy array according to the corresponding flag.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +1
Method of fabricating a flash memory
InactiveUS20090098721A1Improve memory performanceShort lifeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDielectric layer
A method of fabricating a flash memory includes providing a semiconductor substrate with STIs and an active area between two adjacent STIs along a first direction; successively forming a floating-gate insulating layer, a conductive layer, a dielectric layer, a control gate, and a cap layer on the semiconductor substrate; forming spacers on the sidewalls of the cap layer and the control gate; removing the dielectric layer, the conductive layer, and the floating-gate insulating layer not covered by the spacers and the cap layer; performing a selective epitaxial growth process to form an epitaxial layer on the exposed semiconductor substrate in the active area; and forming a source in the epitaxial layer and the semiconductor substrate in the active area.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON CORP
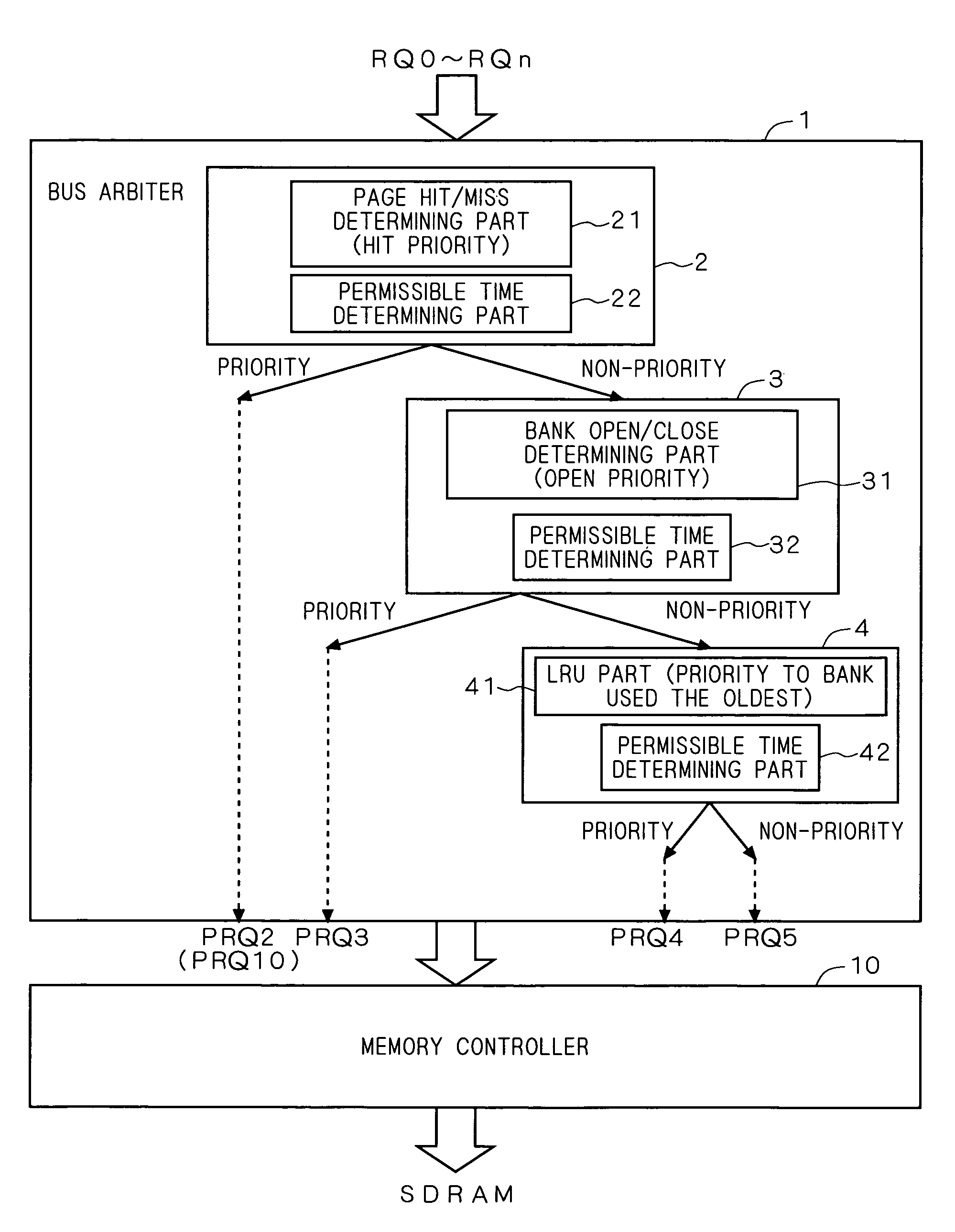
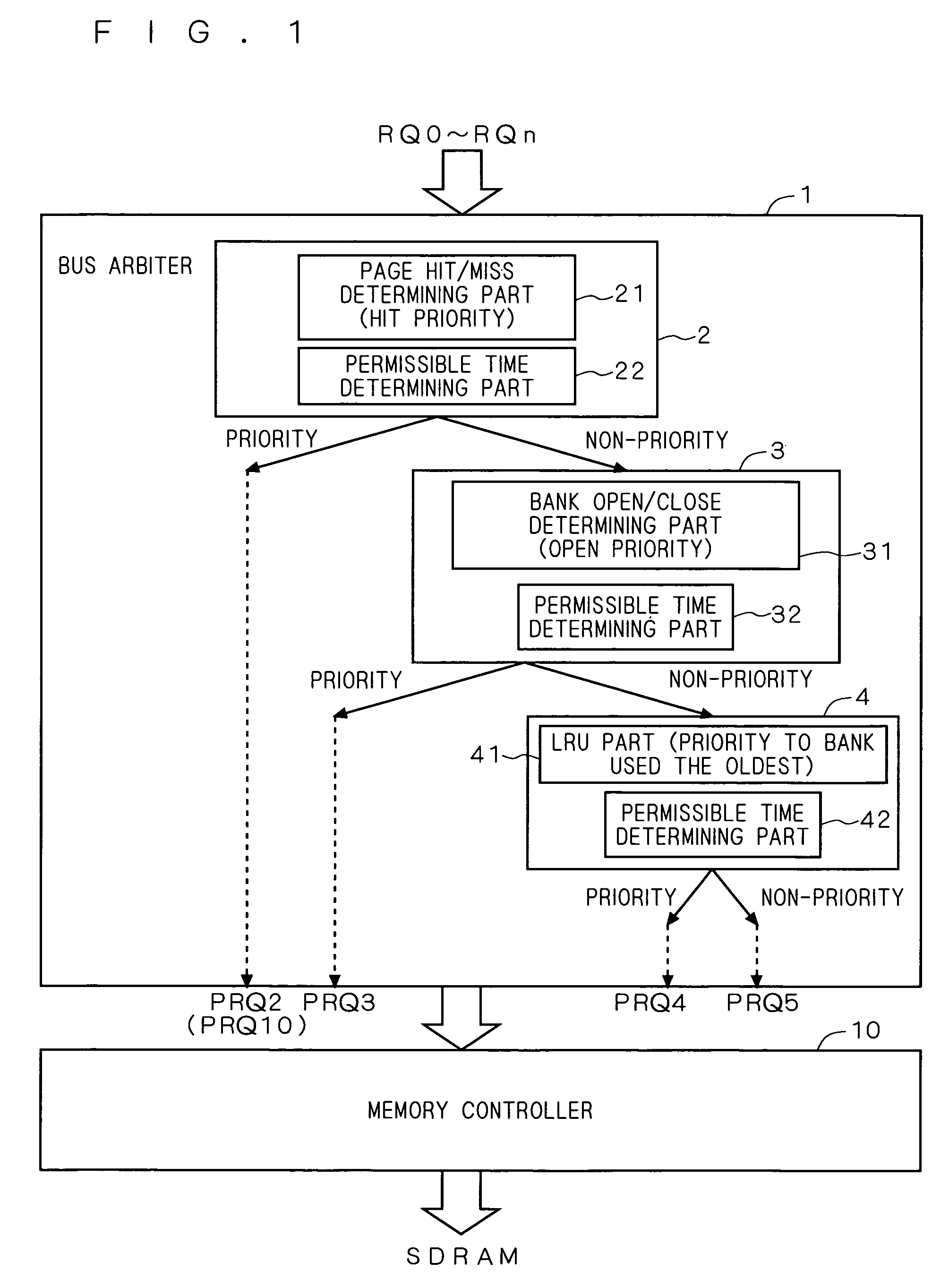
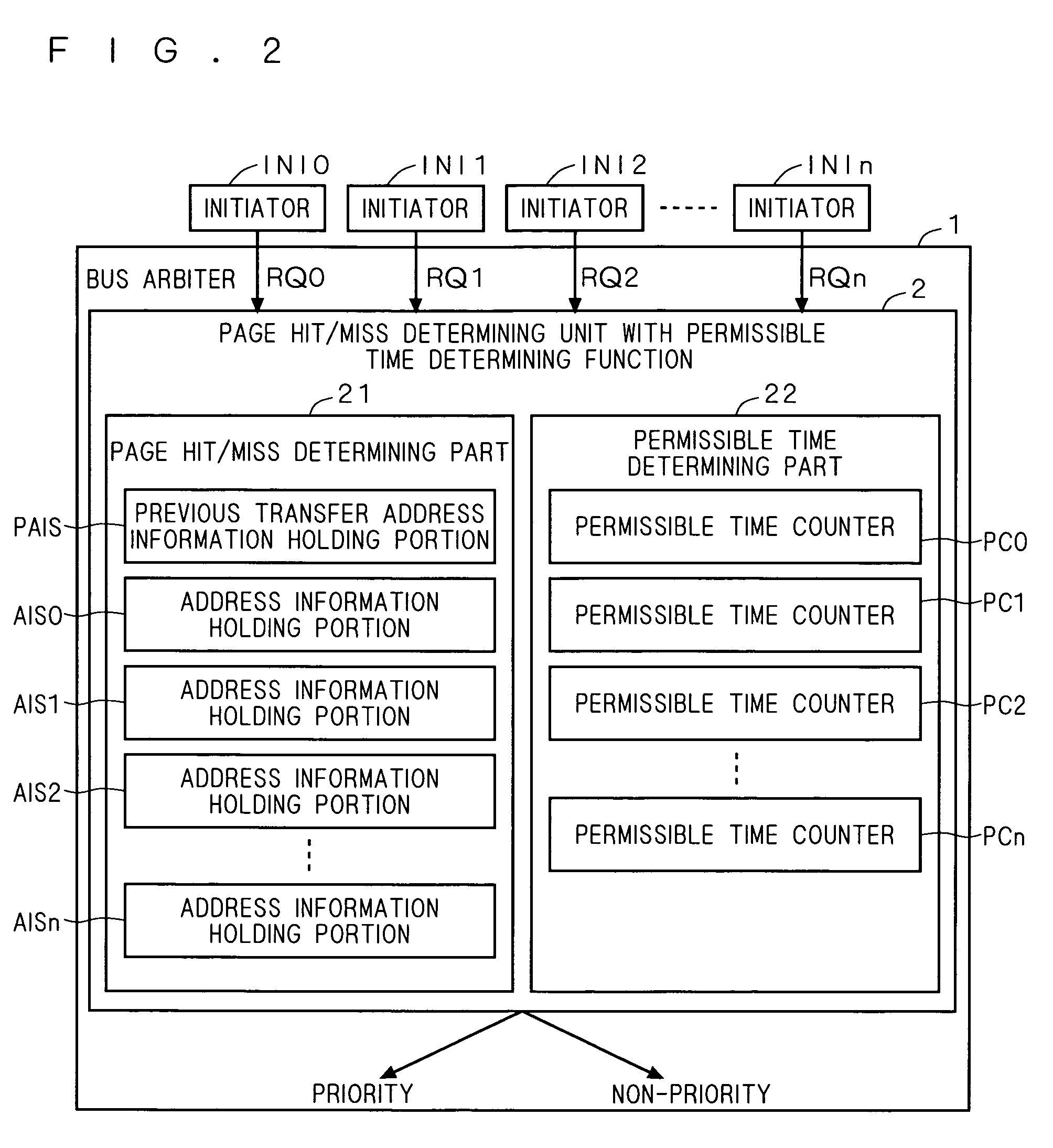
Request arbitration device and memory controller
InactiveUS7925849B2Improve memory performanceImprove performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory controllerBus priority
A bus arbiter receives requests of initiators, and internally includes a page hit / miss determining unit with permissible determining function, a bank open / close determining unit with permissible determining function, and an LRU unit with permissible determining function. Regarding the priority of the request arbitration on the requests, the bank priority on the SDRAM is determined in the order of page hit, bank open, and LRU. Furthermore, each determining unit internally includes a permissible time determining unit, and processes, at top priority, the request of the initiator which the corresponding permissible time is below the count threshold value in the priority processing of the determining unit.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
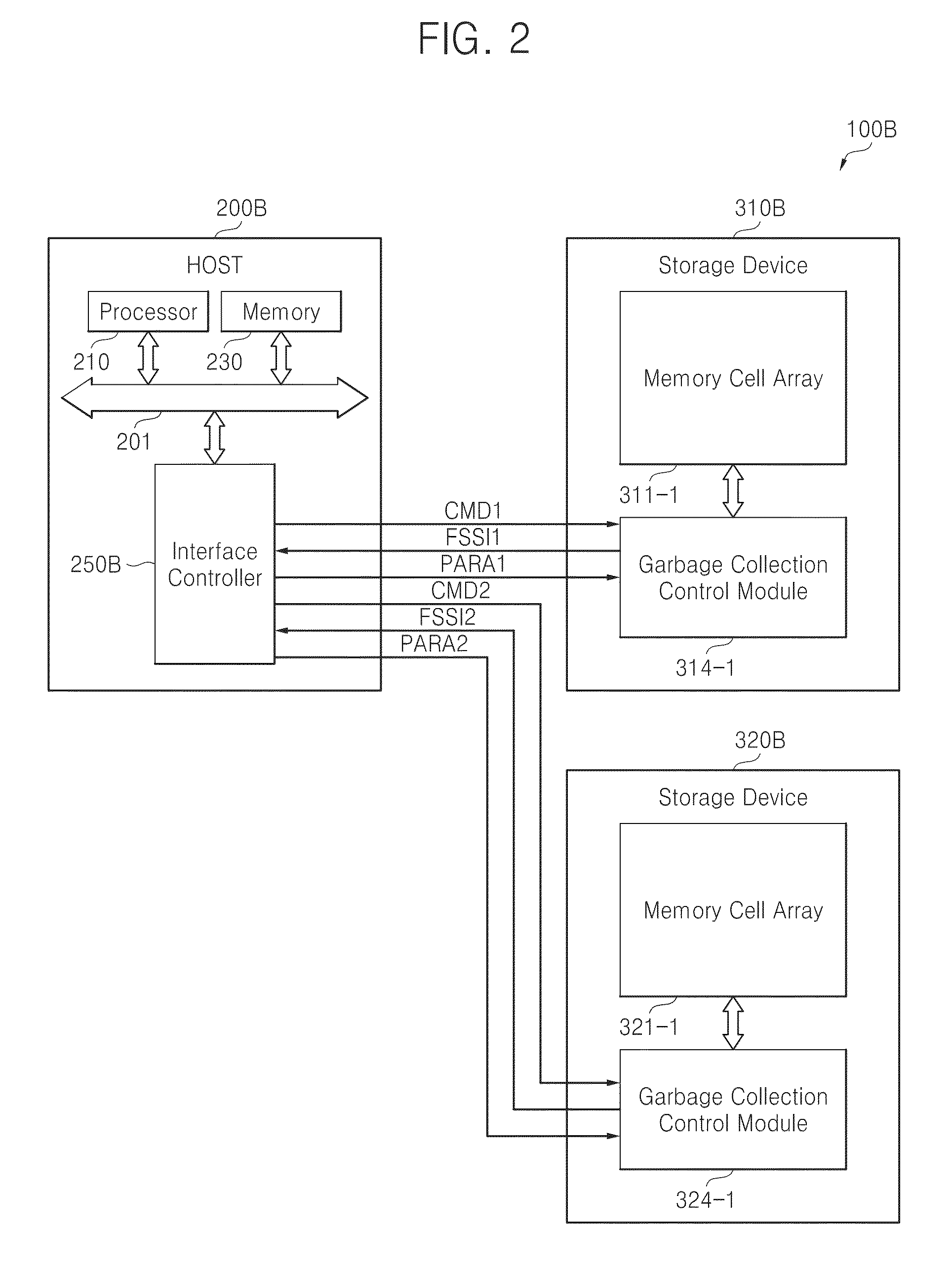
Host-driven garbage collection
ActiveUS9348749B2Improve memory performanceAdjust I/O latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersRefuse collectionOperating system
A host receives information related to garbage collection of a storage device, and it controls selective execution of garbage collection by the storage device according to the received information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nonvolatile memory erase method and device
ActiveCN103426474AShorten the timeReduce the risk of Over ProgramRead-only memoriesGate voltageOperating system
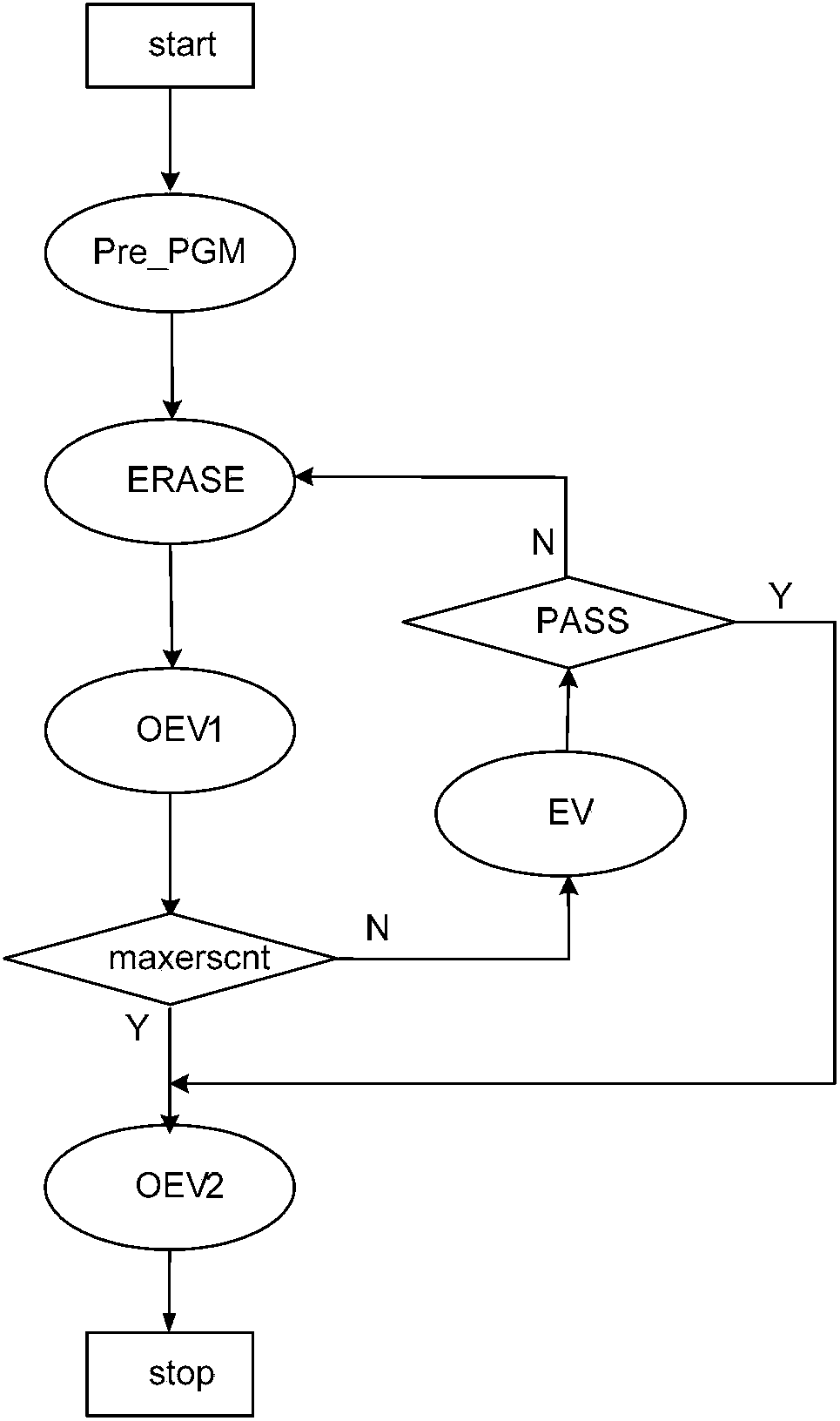
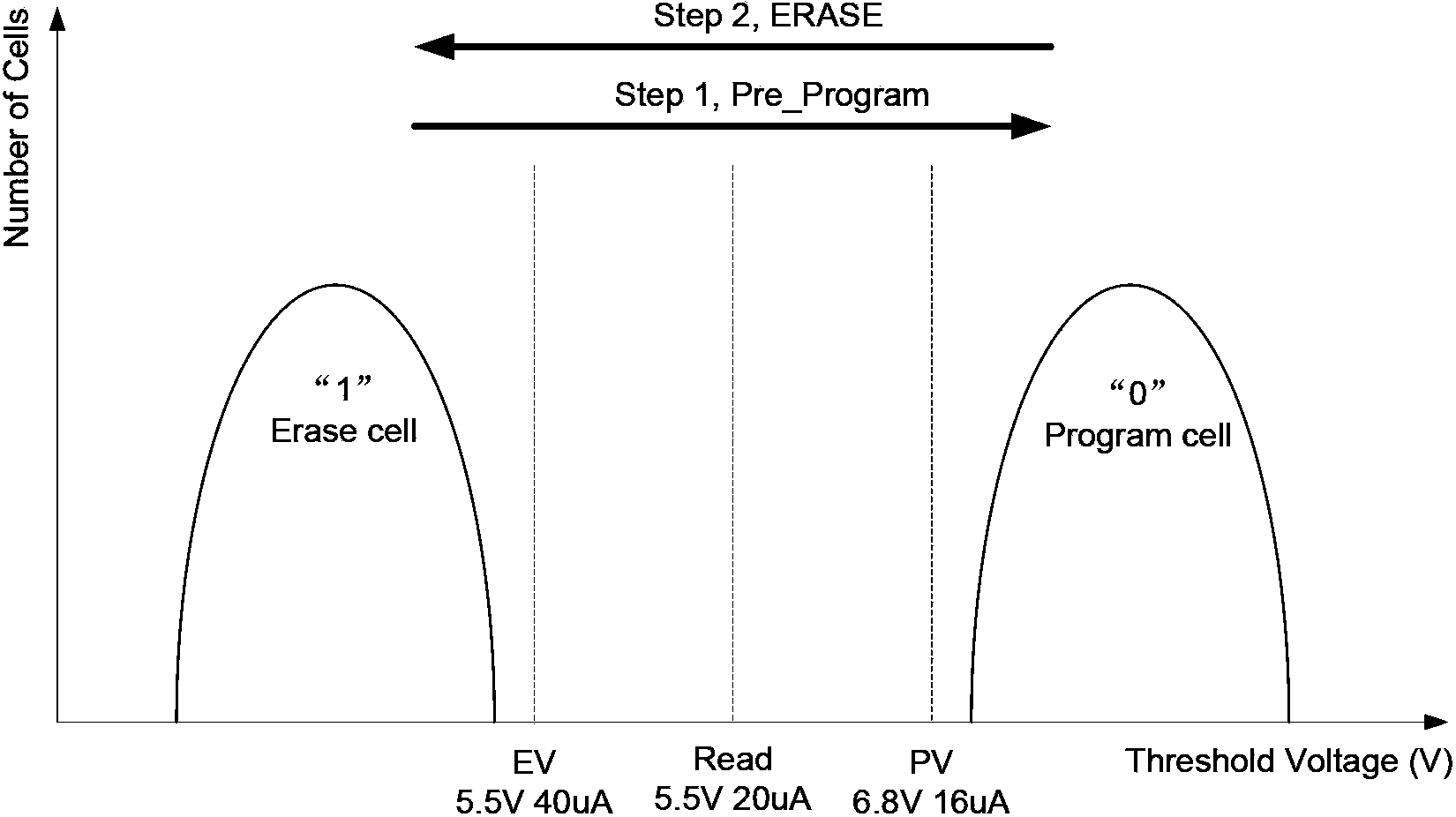
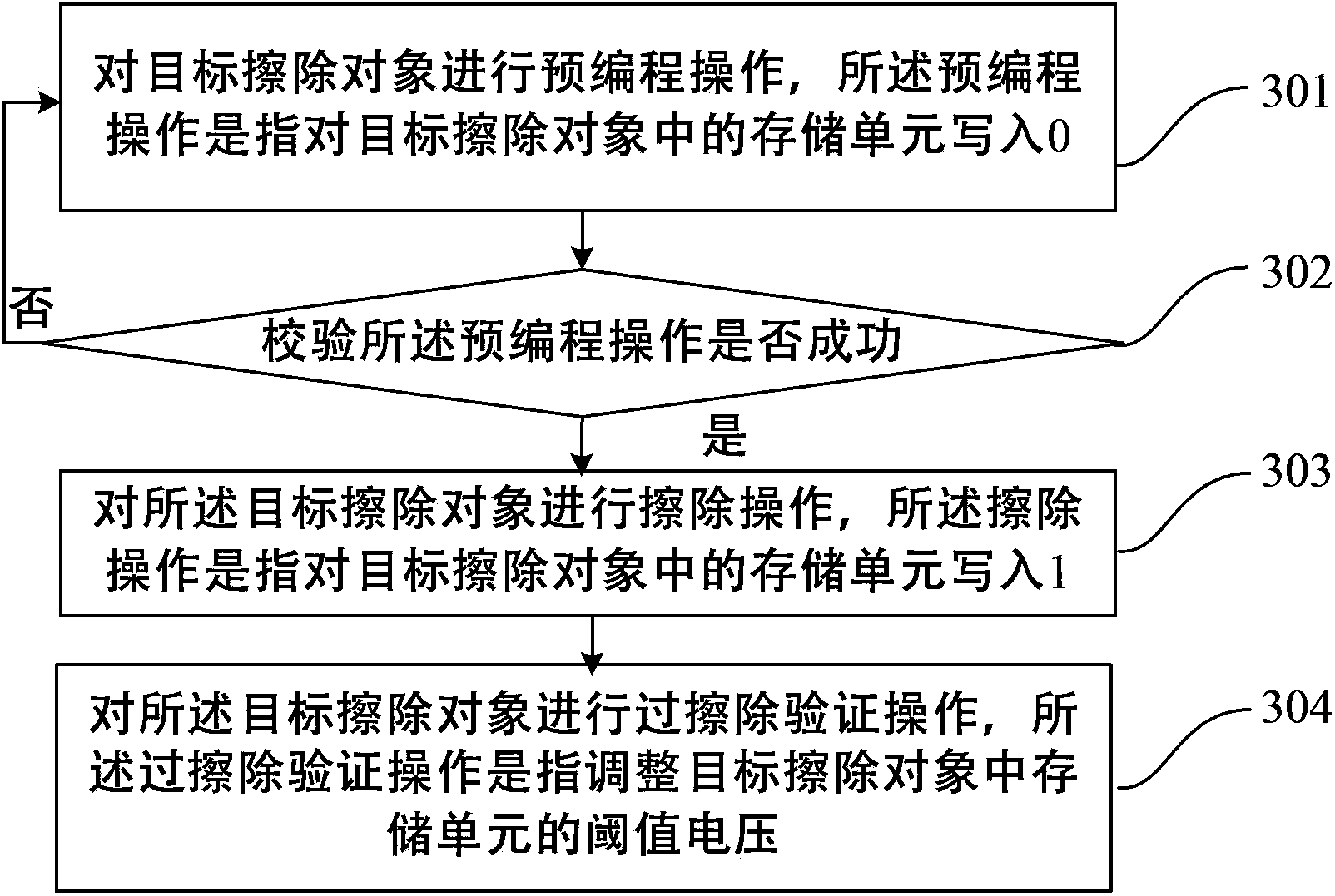
The invention discloses a nonvolatile memory erase method and a nonvolatile memory erase device. The method comprises the steps that: a target erasing target is subjected to a preprogramming operation, wherein the preprogramming operation is that 0 is written into memory units of the target erase object; whether the preprogramming operation is successful is examined, wherein the examining is that whether currents of the memories in the target erase object processed through the preprogramming operation under a certain gate voltage are all smaller than a target current value which is a current value with current margin; if the preprogramming operation is successful, a next step is executed, and if not, the progress is turned back to the execution of the preprogramming operation; the target erase object is subjected to an erase operation, wherein the erase operation is that 1 is written into memory units of the target erase object; and the target erase object is subjected to an over-erase examine operation, wherein the over-erase examine operation is that threshold voltage of memory units in the target erase object is adjusted. With the method and device provided by the invention, nonvolatile memory erase speed can be improved, and memory performance can be improved.
Owner:GIGADEVICE SEMICON (BEIJING) INC
Rewritable nano-surface organic electrical bistable devices
InactiveUS7482621B2Improve memory performanceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A bistable electrical device that is convertible between a low resistance state and a high resistance state. The device includes at least one layer of organic low conductivity material that is sandwiched between two electrodes. A buffer layer is located between the organic layer and at least one of the electrodes. The buffer layer includes particles in the form of flakes or dots of a low conducting material or insulating material that are present in a sufficient amount to only partially cover the electrode surface. The presence of the buffer layer controls metal migration into the organic layer when voltage pulses are applied between the electrodes to convert the device back and forth between the low and high resistance states.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for making high performance semiconductor memory devices
InactiveUS20050169090A1Improve performanceReduce Noise SensitivityDigital storageBit lineComputer architecture
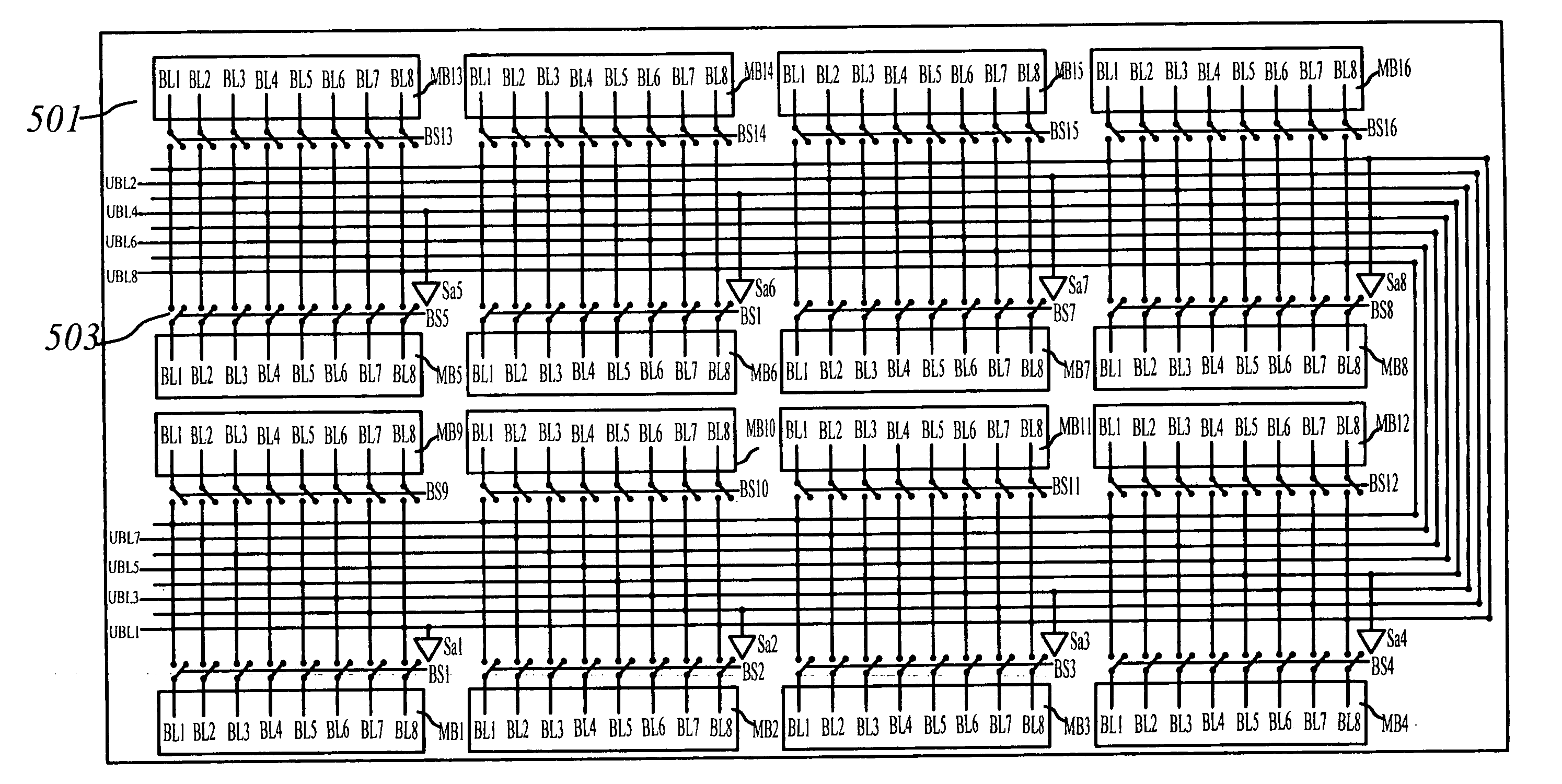
High performance memory devices have been realized by applying an Evenly Scaled Multiple Level Architecture (ESMLA) using block select arrangement. A single-bit-line-write mechanism allows us to reduce the number of bit lines by 50% for static memory devices. The resulting memory device can be as fast as registers files while its area is smaller than prior art high-density memory devices. The scaling method of the memory architecture also assures that the speed of the memory devices will scale in the same rate as logic circuits in future IC manufacture technologies.
Owner:SHAU JENG JYE
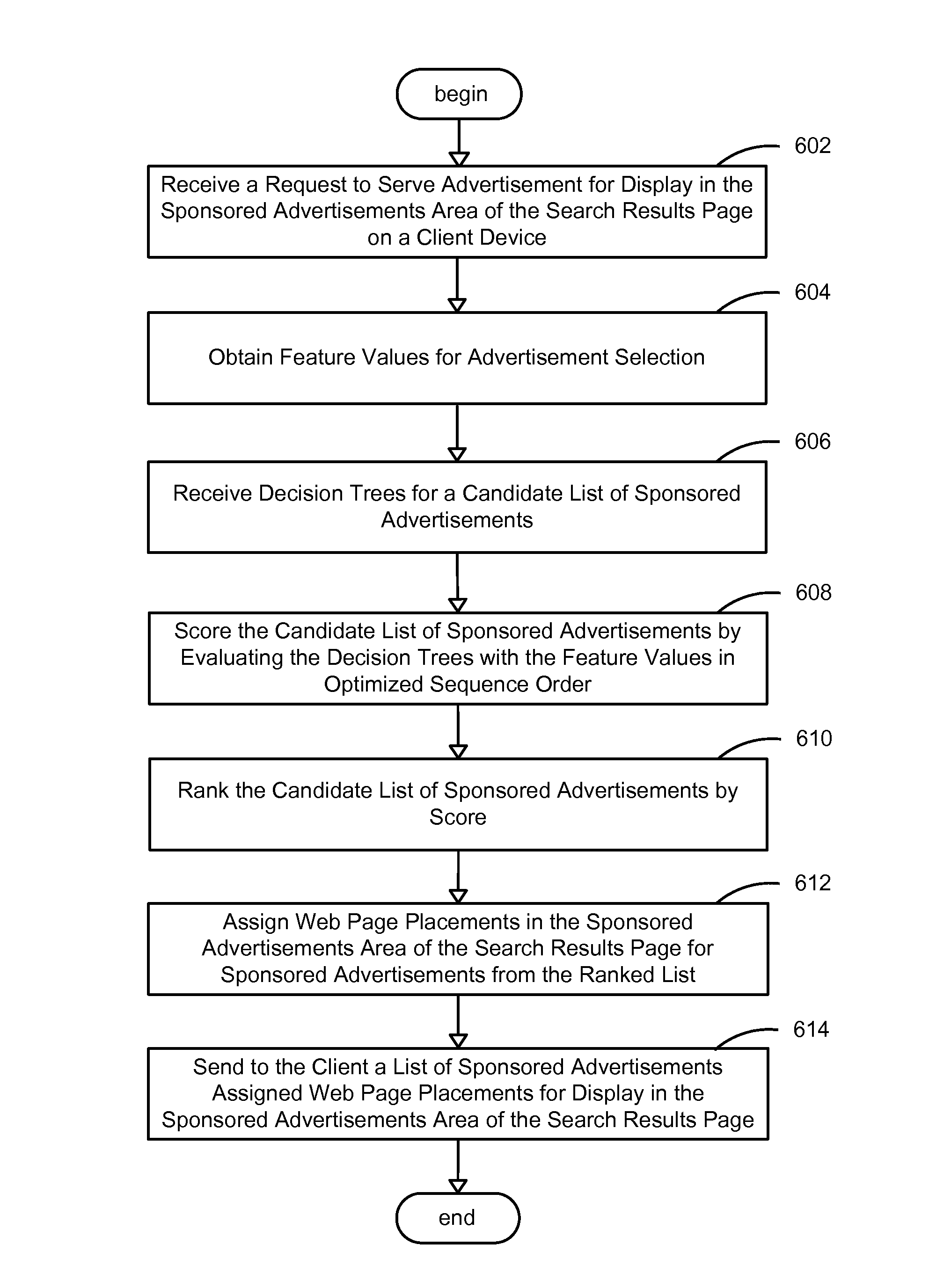
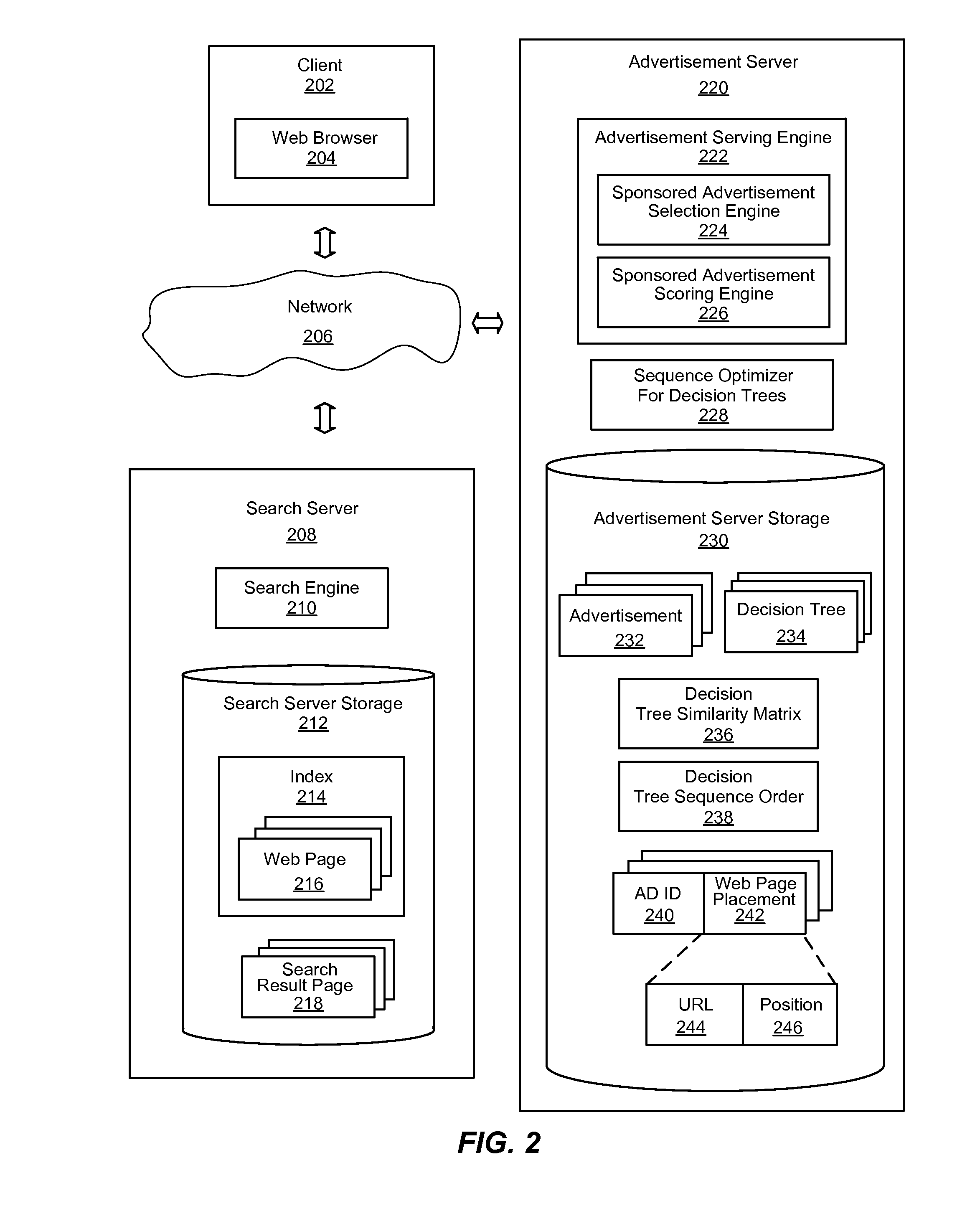
System and method for optimizing selection of online advertisements
InactiveUS20110131093A1Optimize ranking advertisementImprove run time memory performanceInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsDecision takingSimilarity matrix
An advanced system and method for optimizing selection of online advertisements is provided. Decision trees with expressions to evaluate feature values for advertisements may be received, and a decision tree similarity matrix of decision tree similarity values between pairs of decision trees may be generated that represent the number of common features between two decision trees. The edges of the decision tree similarity matrix may be sorted in non-increasing order by edge value, and the decision trees of each edge retrieved from the sorted order may be placed in an optimized sequence order for evaluation. In response to a request to serve advertisements, advertisements may be scored by evaluating the decision trees of advertisements in the optimized sequence order. The advertisements may then be ranked in descending order by score, and advertisement with the highest scores may be sent for display.
Owner:OATH INC
NAND flash memory cell row and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060040440A1Improve memory performanceIncrease erasing speedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
A NAND flash memory cell row includes first and second stacked gate structures, control and floating gates, inter-gate dielectric layer, a tunnel oxide layer, doping regions and source / drain regions. The first stacked gate structures has an erase gate dielectric layer, an erase gate and a first cap layer. Each of the second stacked gate structure has a select gate dielectric layer, a select gate and a second cap layer. The control gate is between each of the first stacked gate structures, and between each of the second stacked gate structures and the adjacent first stacked gate structure. The floating gate is between the control gate and substrate. The inter-gate dielectric layer is disposed between the control and floating gates. The tunnel oxide is between the floating gate and substrate. The doping regions are disposed under the first stacked gate structure, and the source / drain regions are in the exposed substrate.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![[non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof] [non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/754b3ed3-8dc8-4ae1-afef-ef843bfb71df/US20050224858A1-20051013-D00000.png)
![[non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof] [non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/754b3ed3-8dc8-4ae1-afef-ef843bfb71df/US20050224858A1-20051013-D00001.png)
![[non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof] [non-volatile memory structure and manufacturing method thereof]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/754b3ed3-8dc8-4ae1-afef-ef843bfb71df/US20050224858A1-20051013-D00002.png)