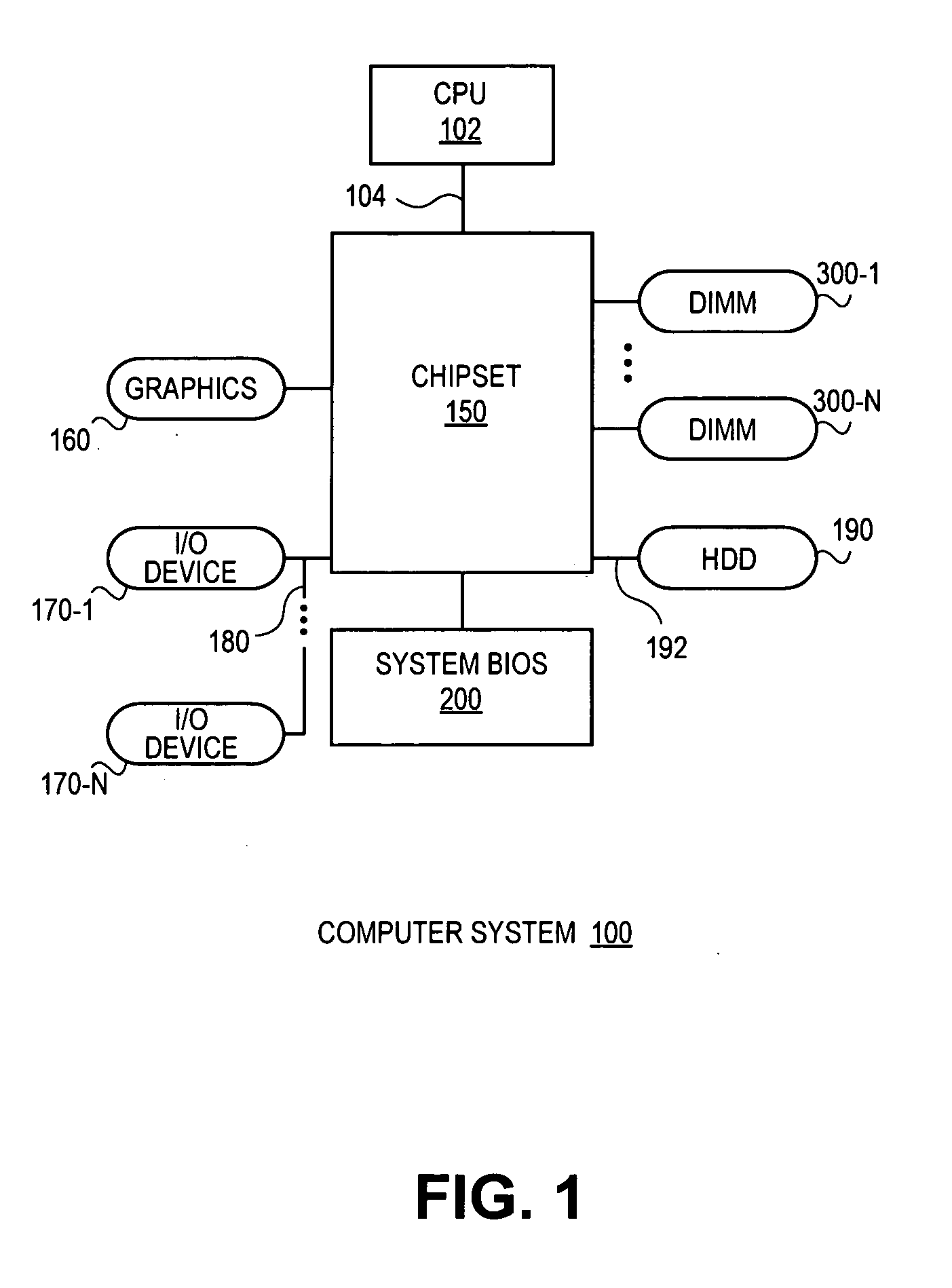
Patents
Literature
277 results about "DIMM" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
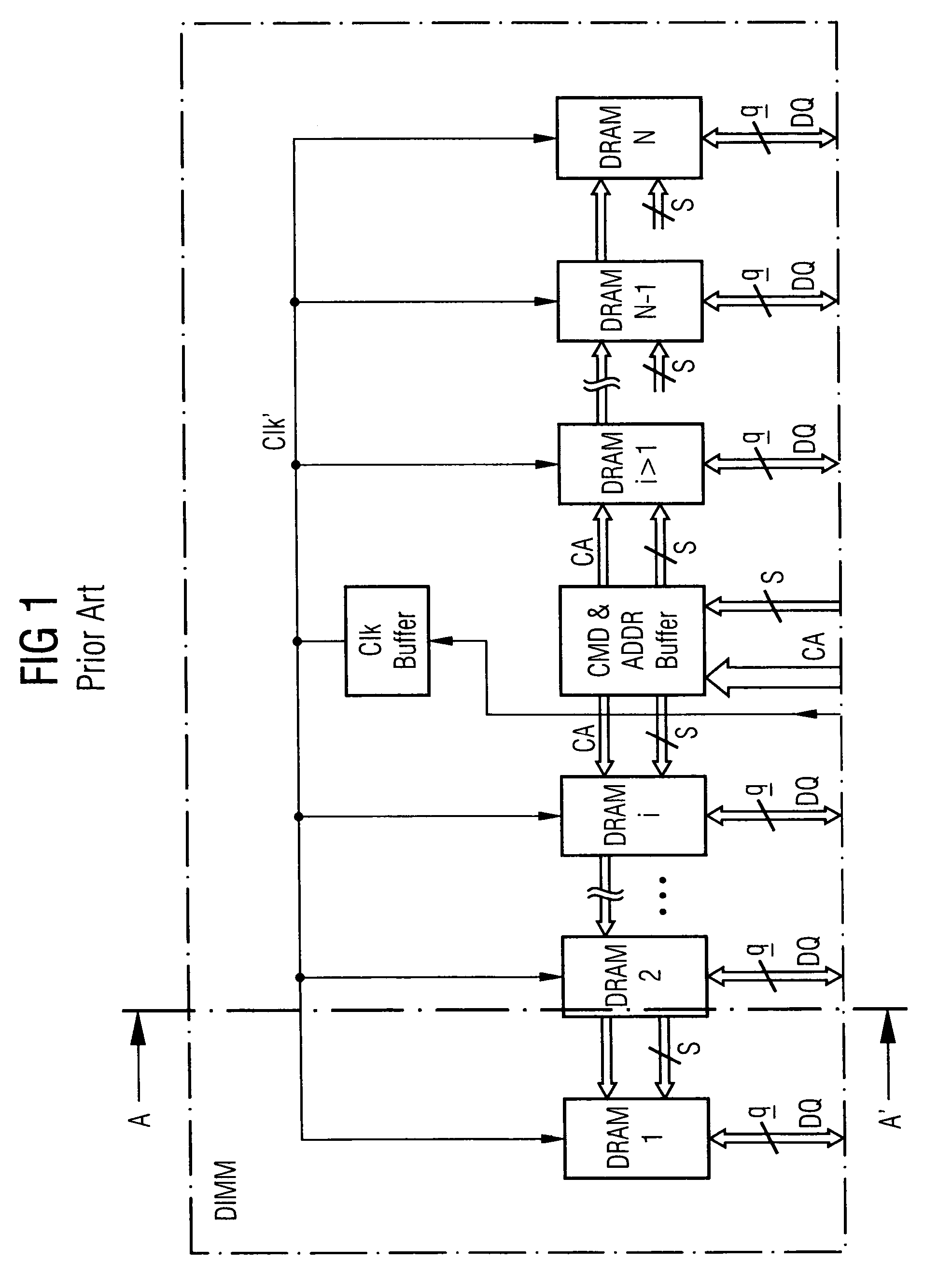
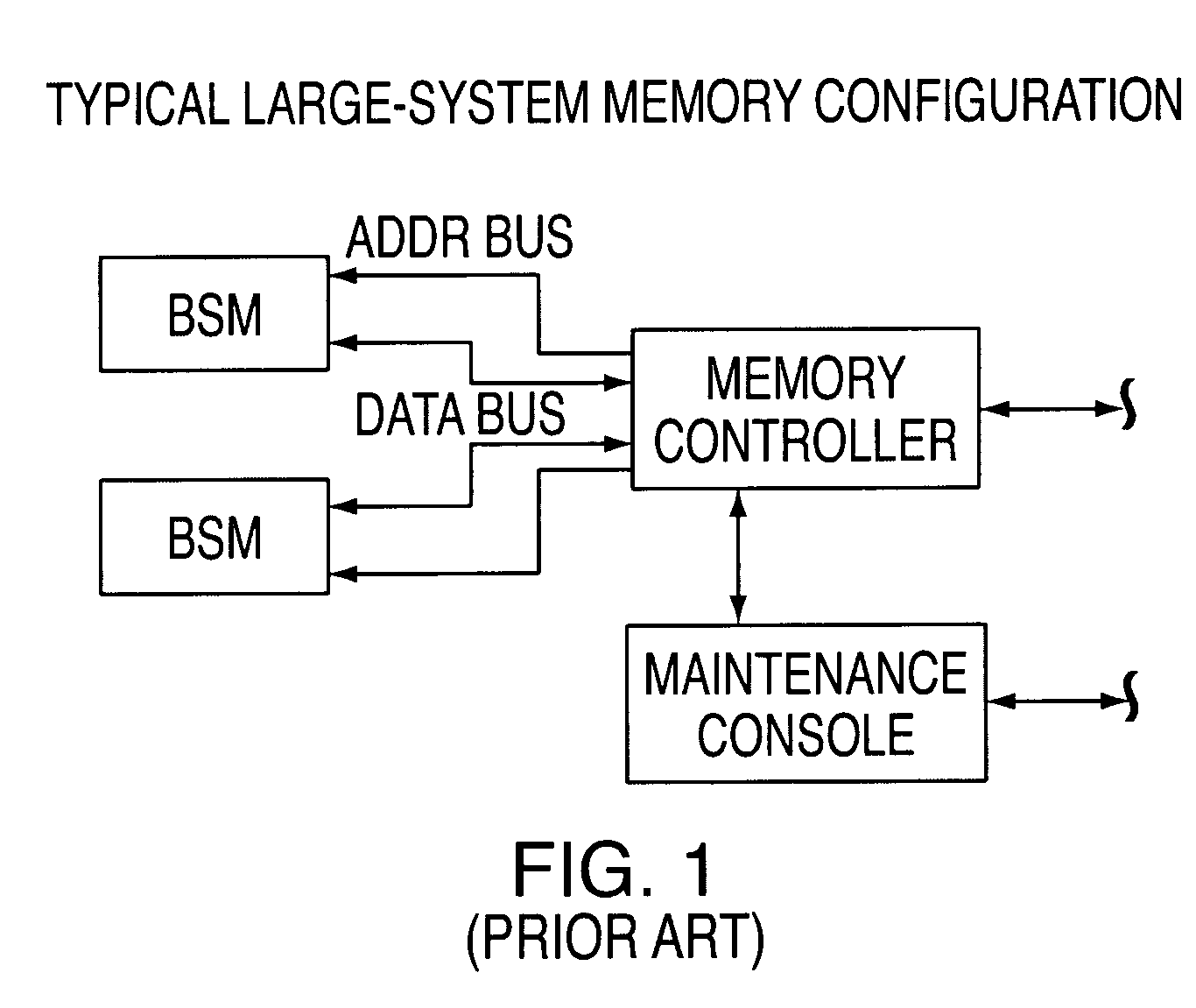
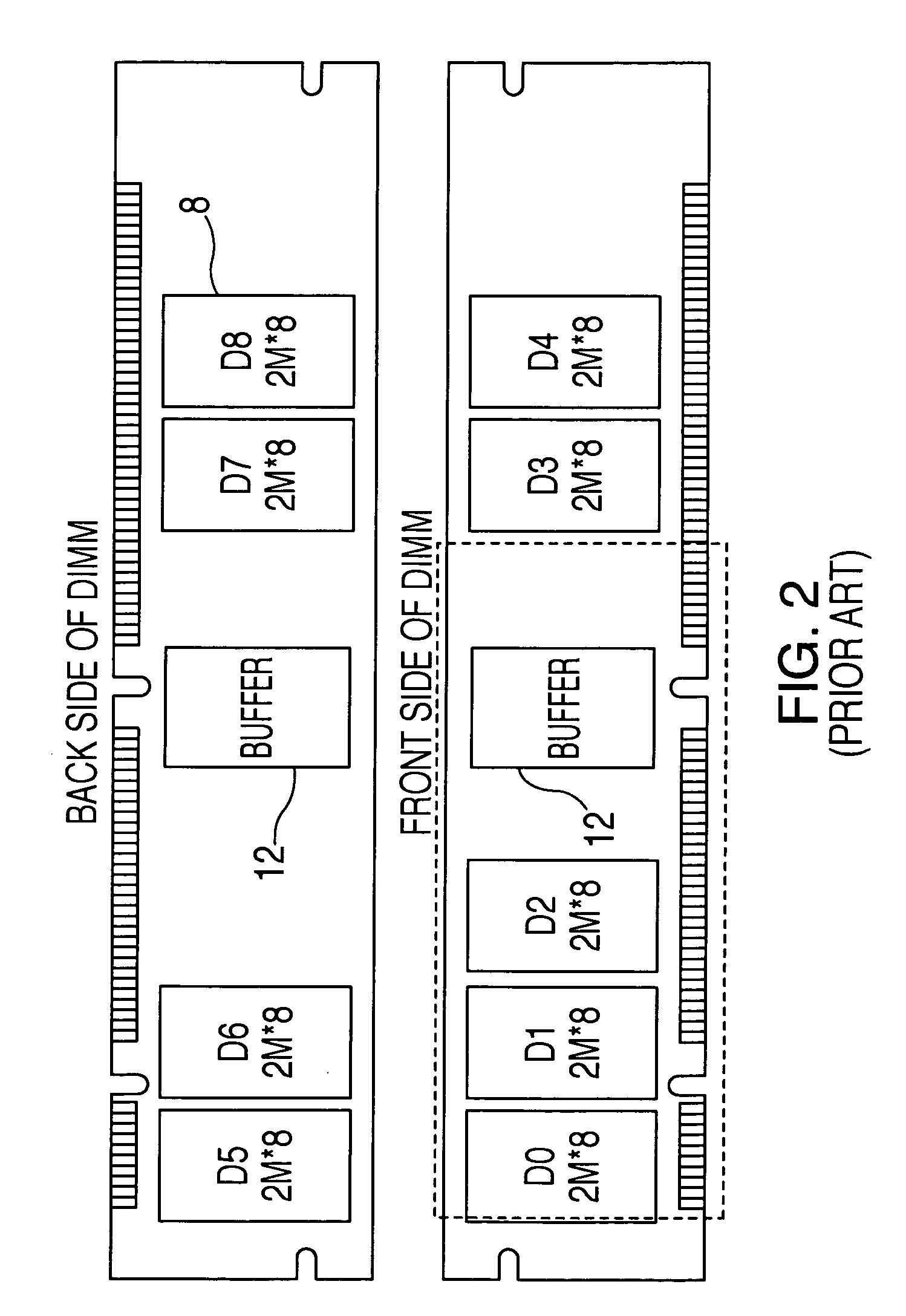
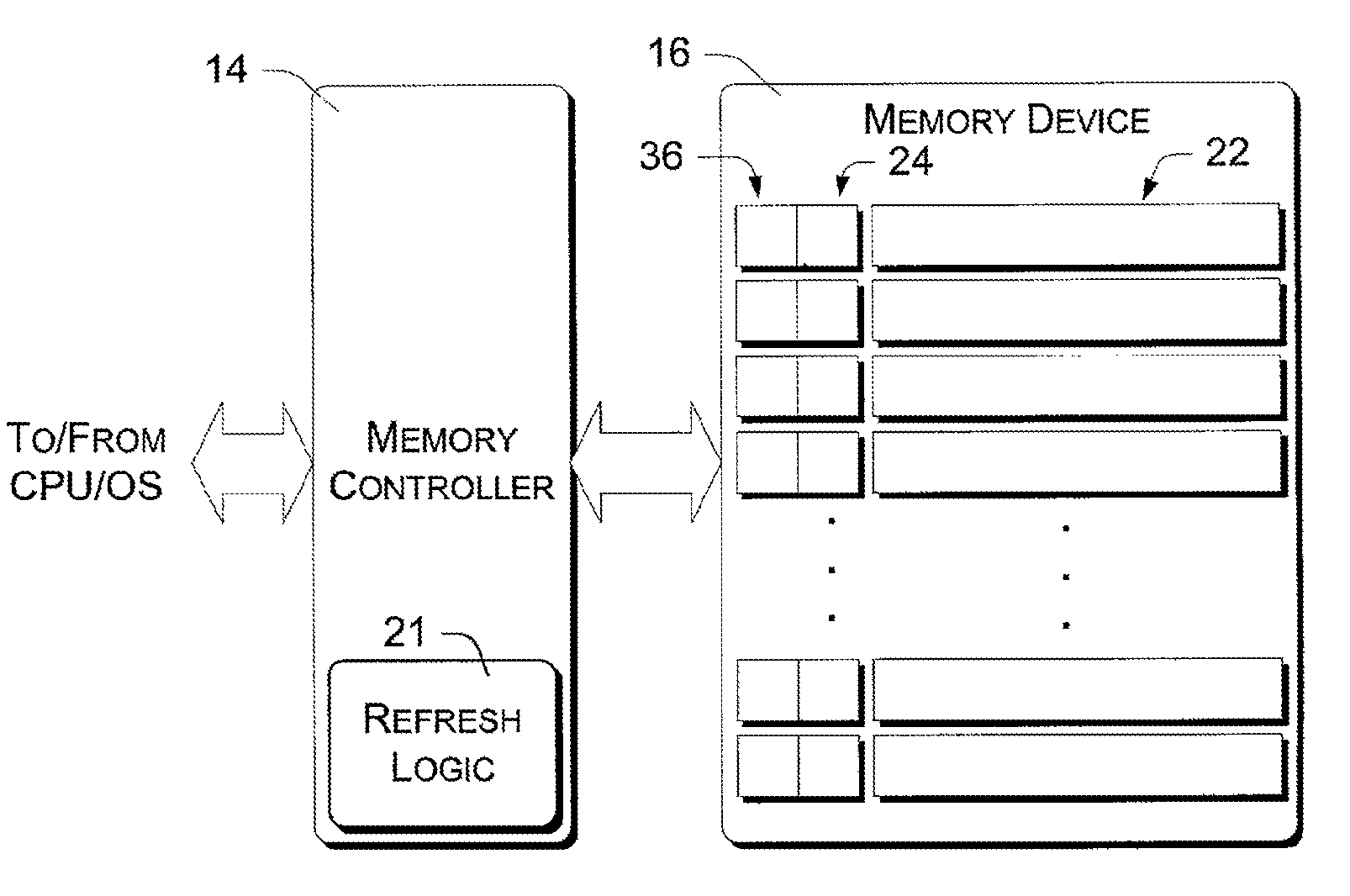
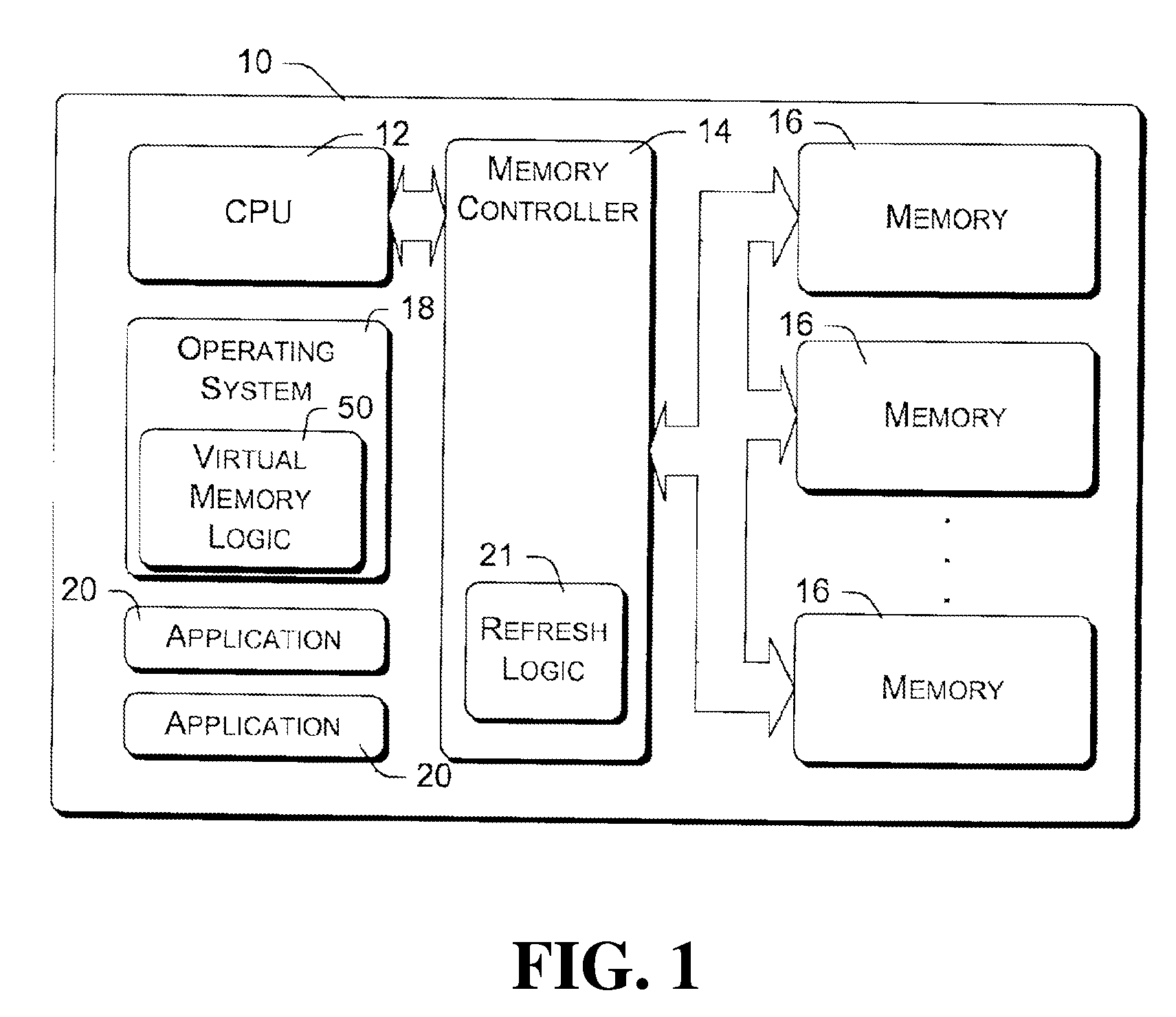
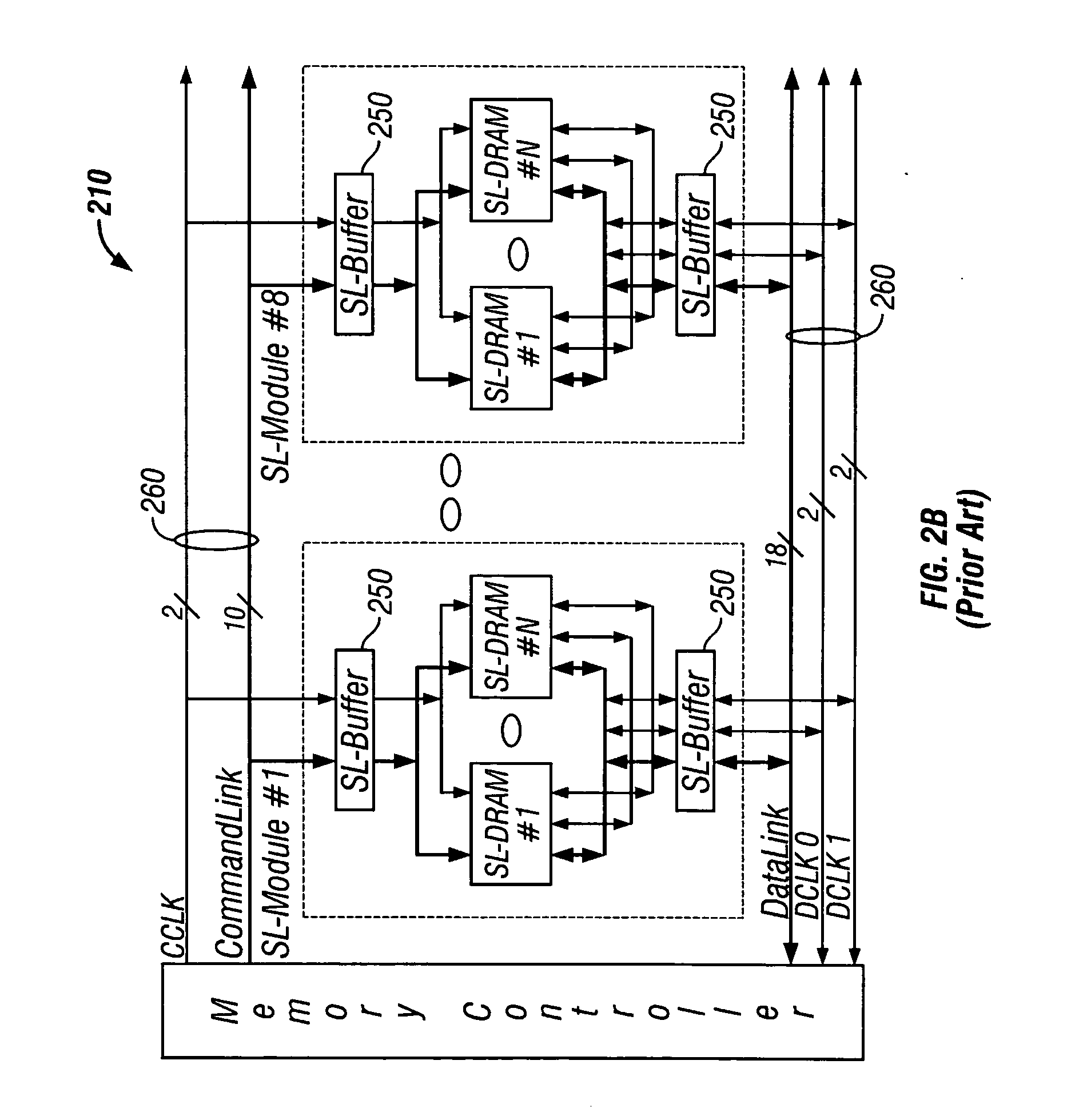
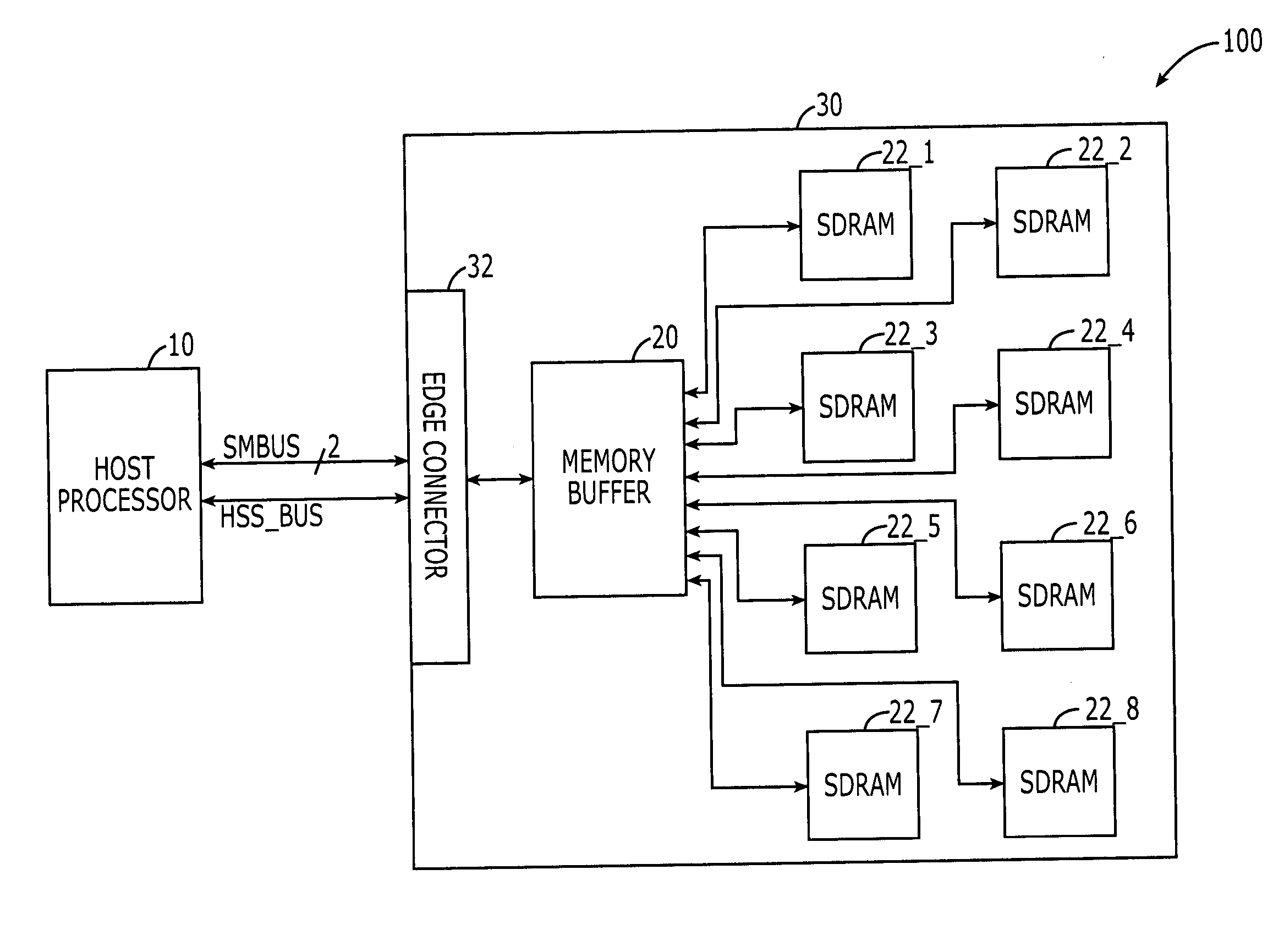
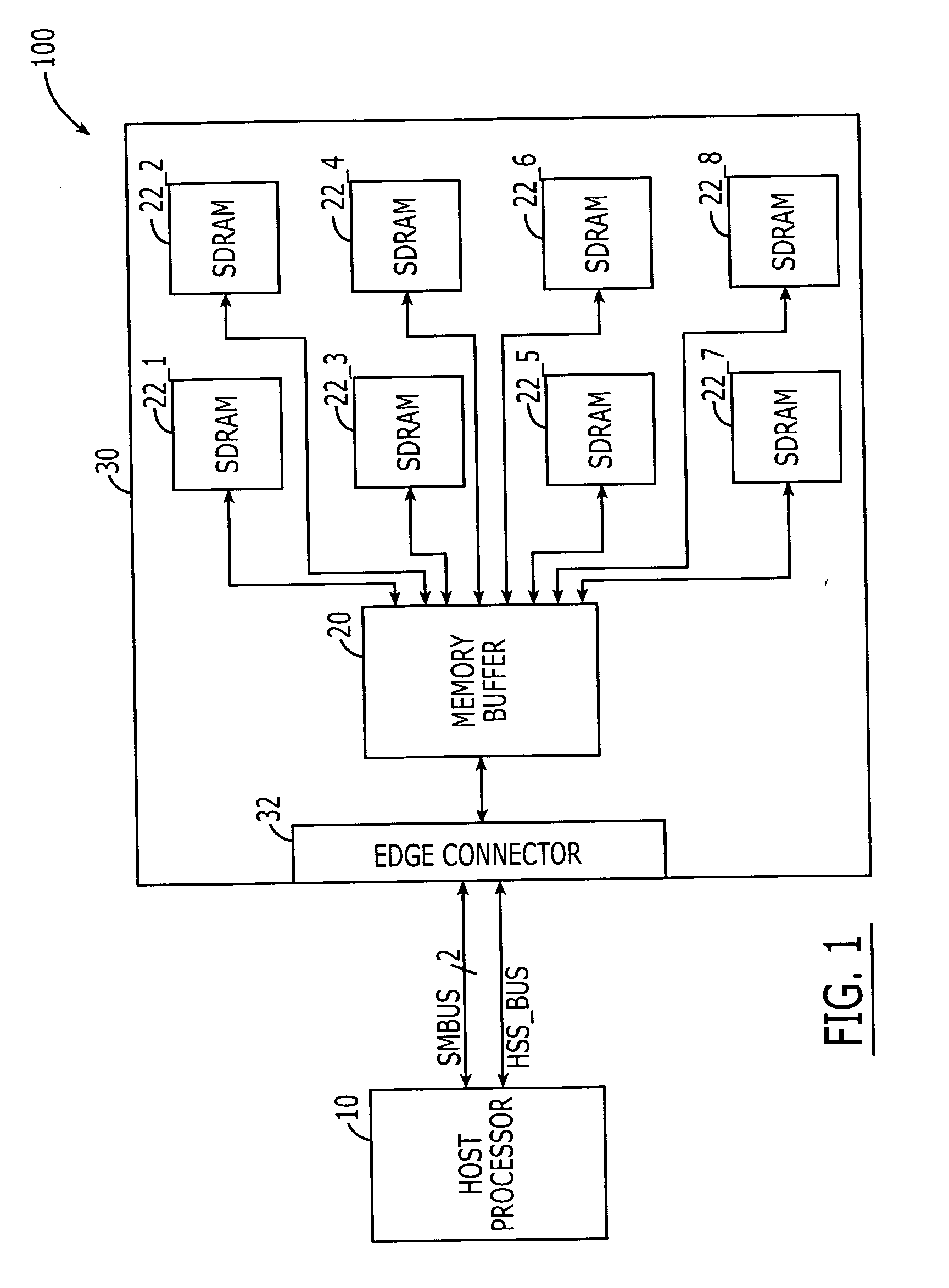
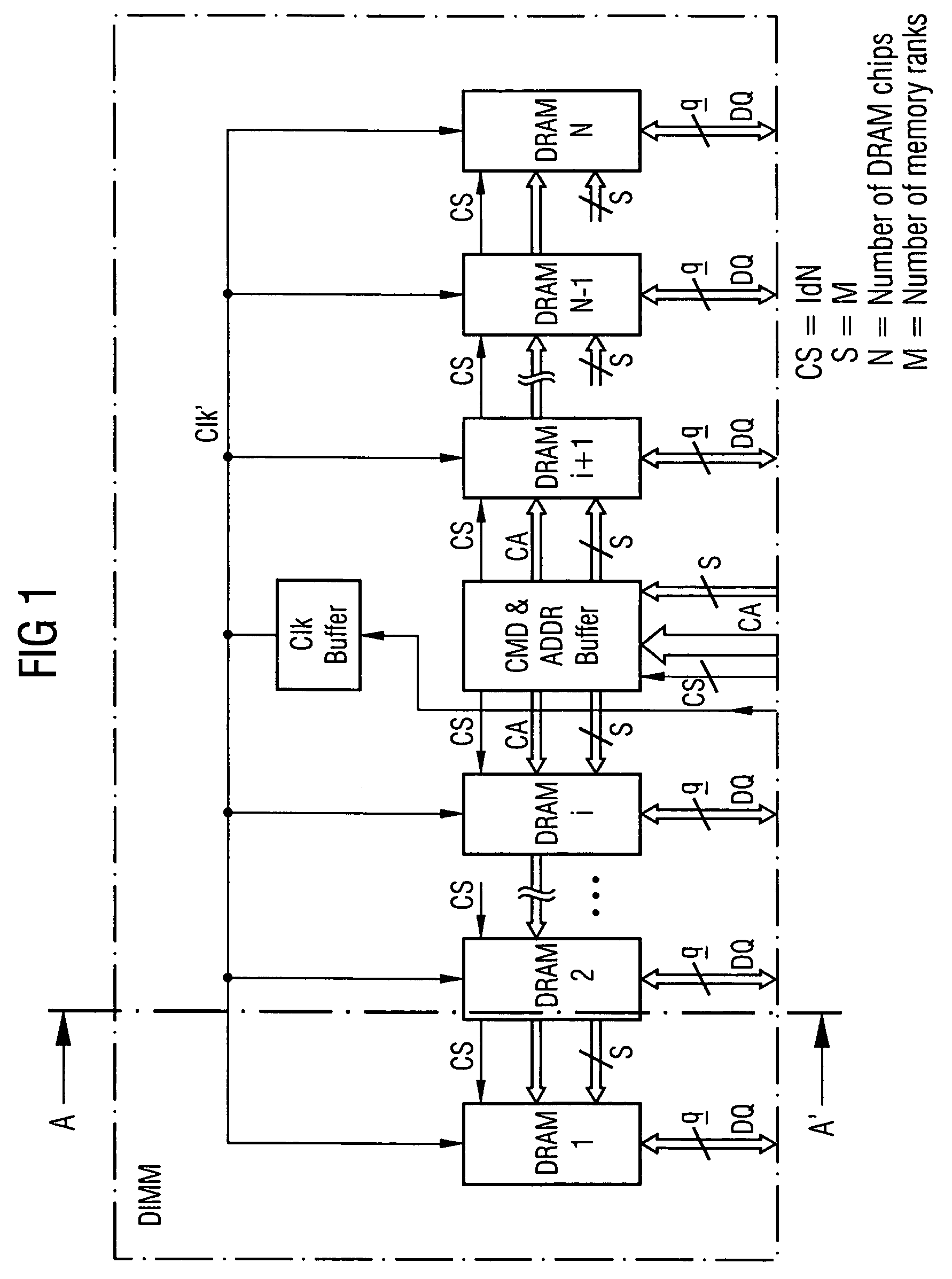
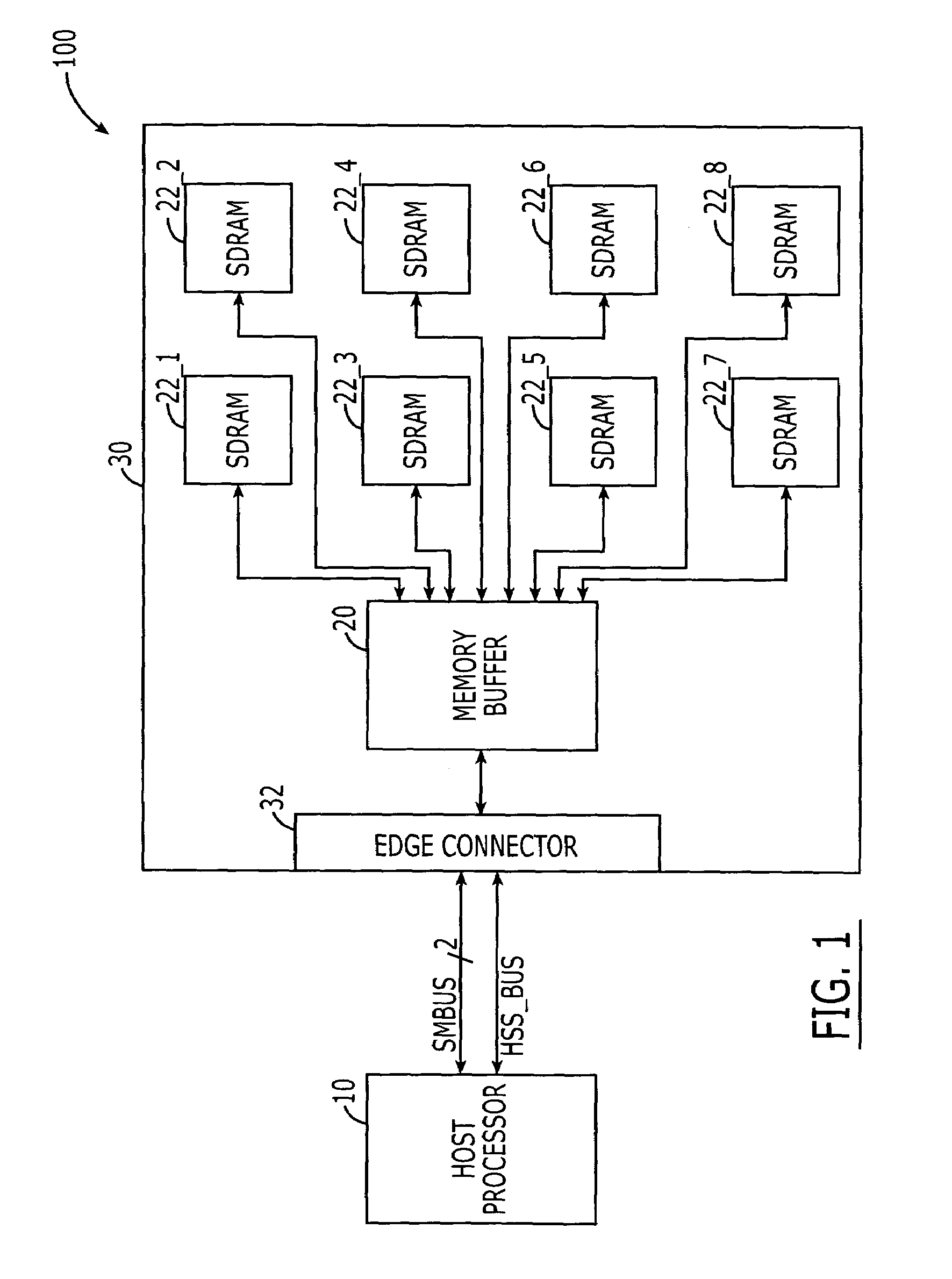
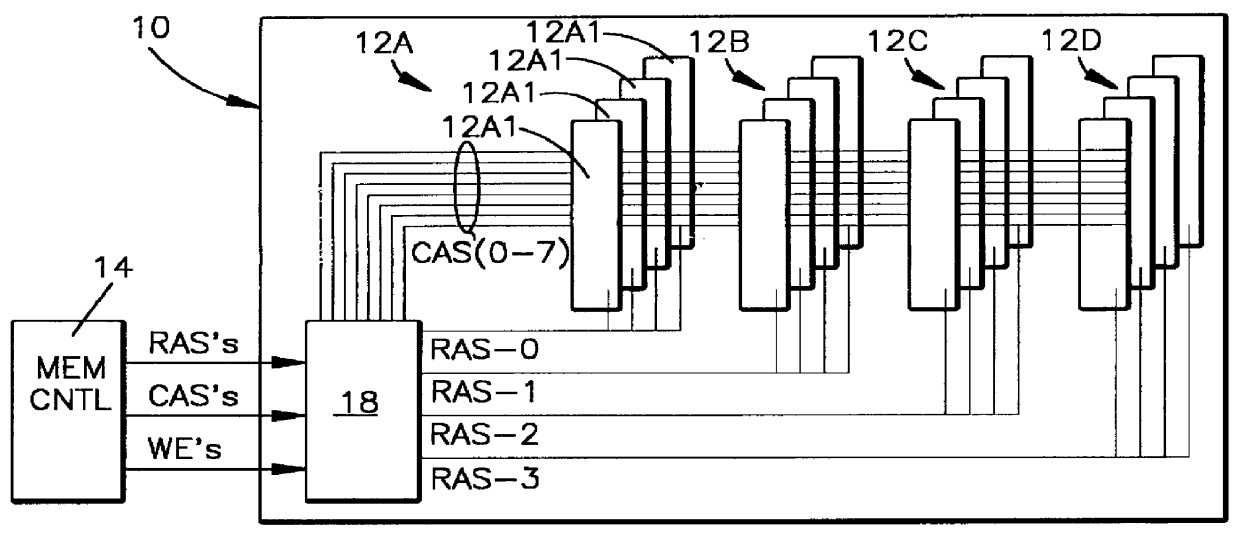
A DIMM or dual in-line memory module comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits. These modules are mounted on a printed circuit board and designed for use in personal computers, workstations and servers. DIMMs began to replace SIMMs (single in-line memory modules) as the predominant type of memory module as Intel P5-based Pentium processors began to gain market share.
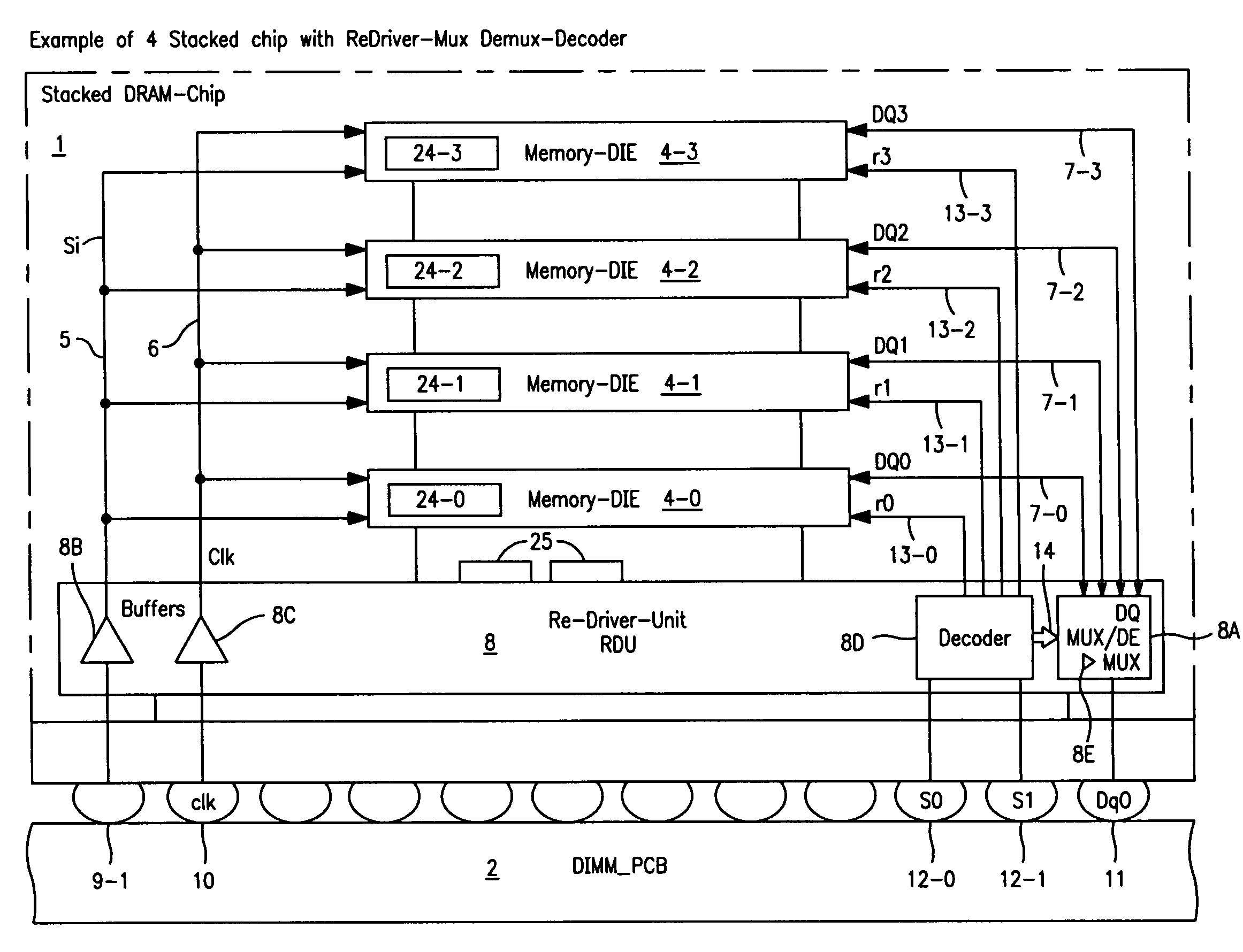
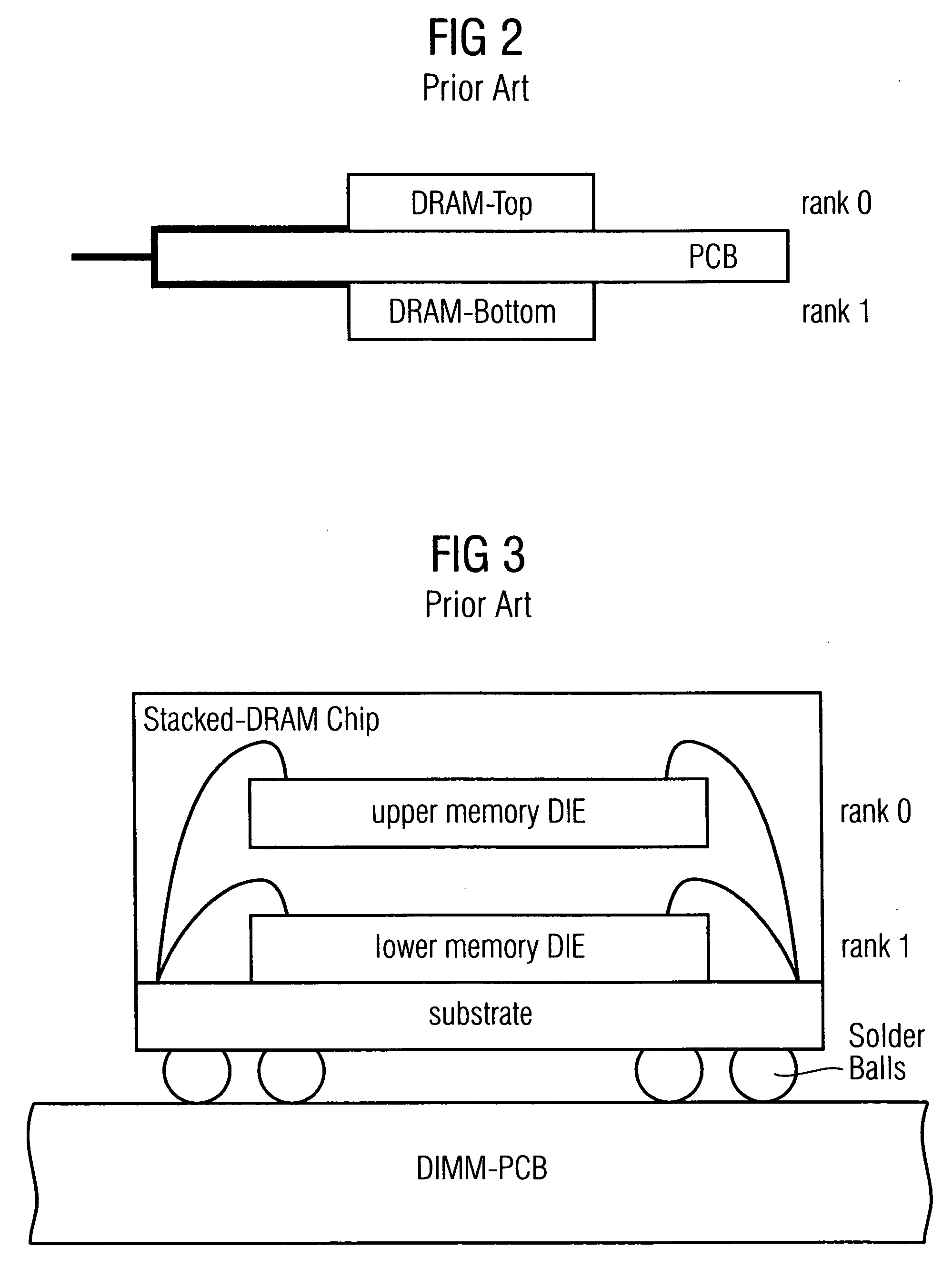
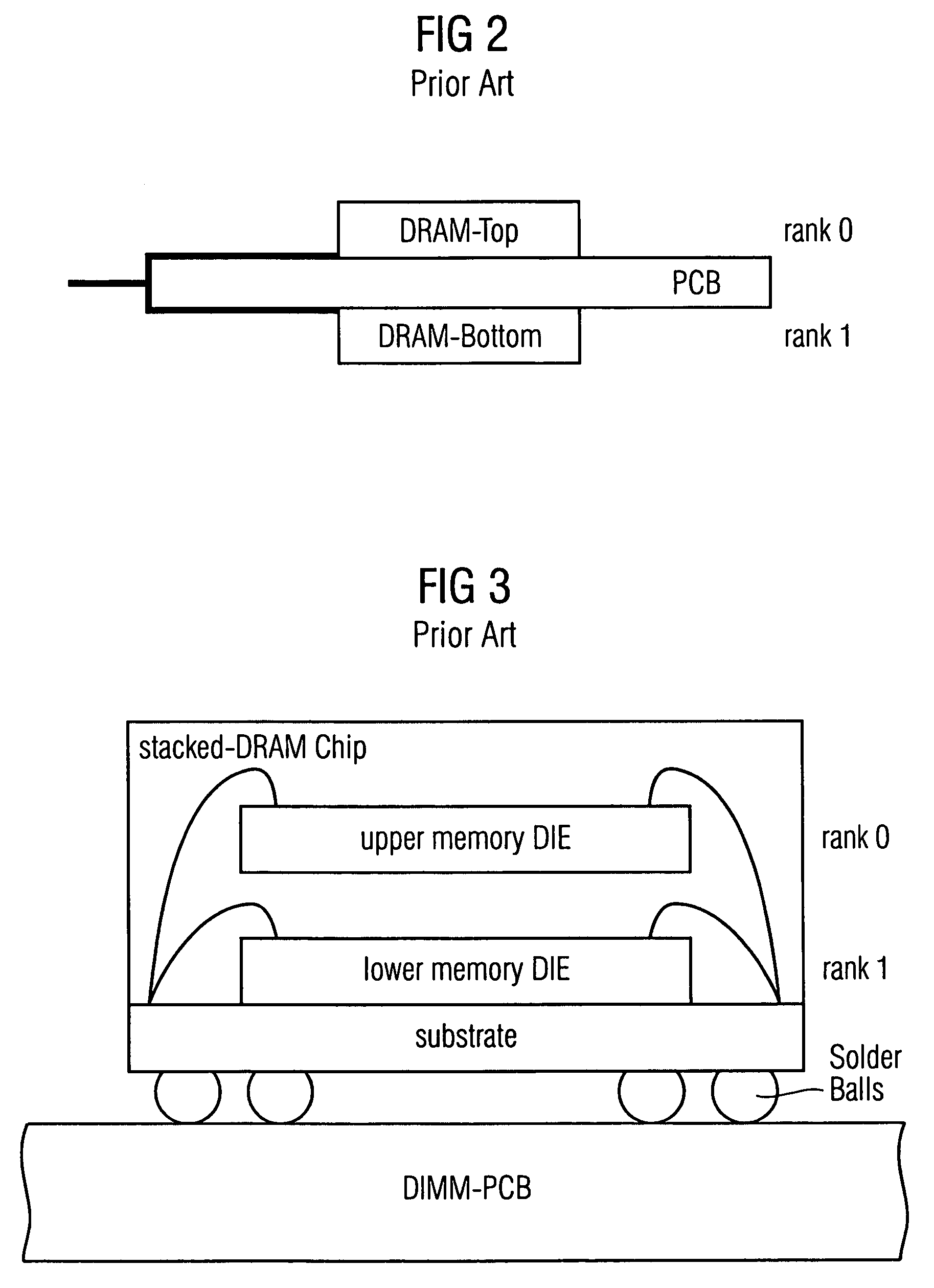
Stacked DRAM memory chip for a dual inline memory module (DIMM)
ActiveUS7200021B2Increase the number ofSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsInternal memoryMemory chip
A stacked DRAM memory chip for a Dual In Line Memory Module (DIMM) is disclosed. According to one aspect, the DRAM memory chip comprises at least four stacked DRAM memory dies. Further, the memory dies are each selectable by a corresponding internal memory rank signal. Each memory die comprises an array of memory cells. A common internal address bus is provided for addressing the memory cells and is connected to all stacked DRAM memory dies. Internal data buses are provided for writing data into the memory cells and reading data out of the memory cells of the DRAM memory dies. An integrated redriving unit comprises buffers for all internal address lines provided for driving external address signals applied to address pads of the DRAM memory chip. A multiplexer / demultiplexer switches the internal data lines of the selected DRAM memory die. A memory rank decoder selects a corresponding memory die.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
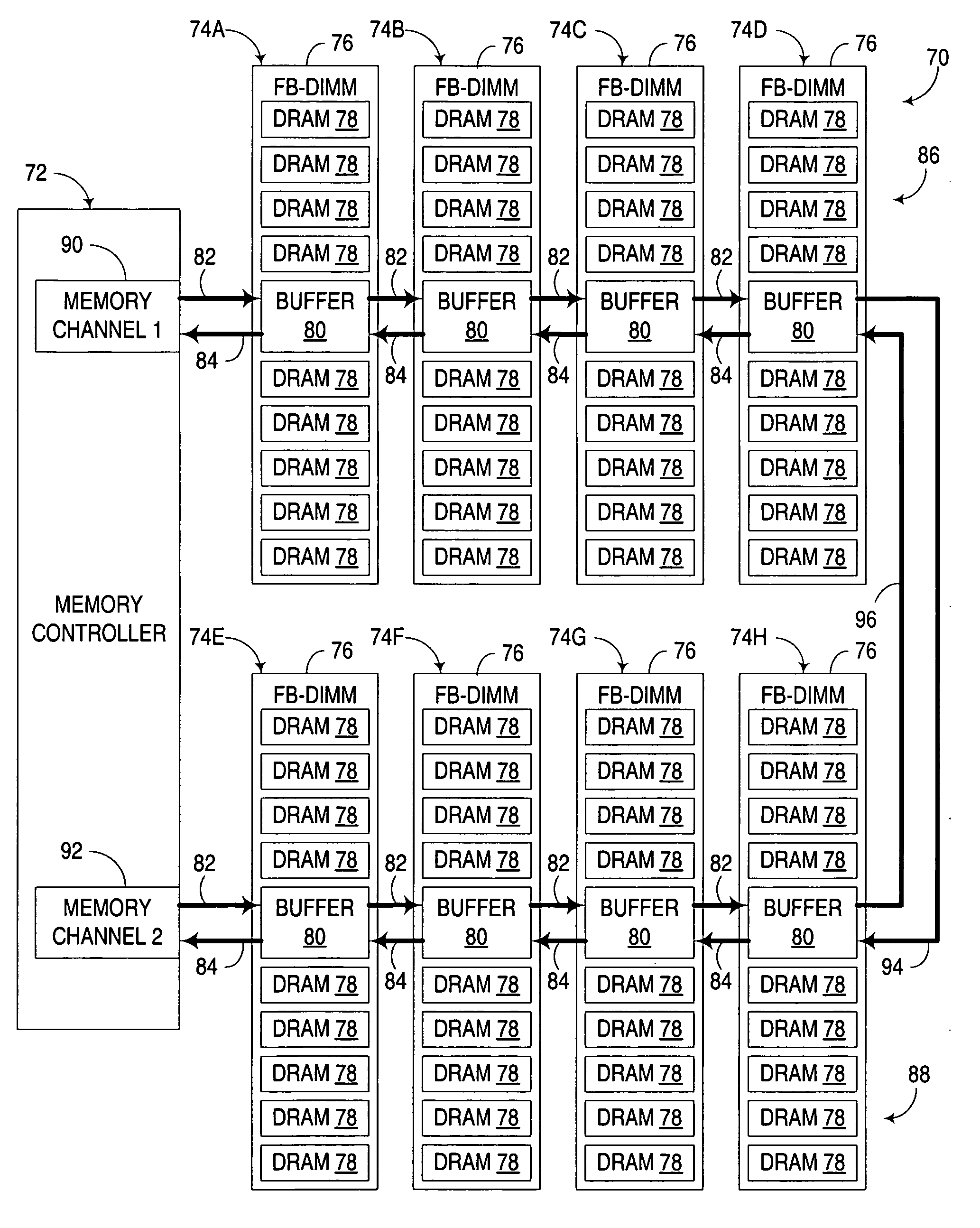
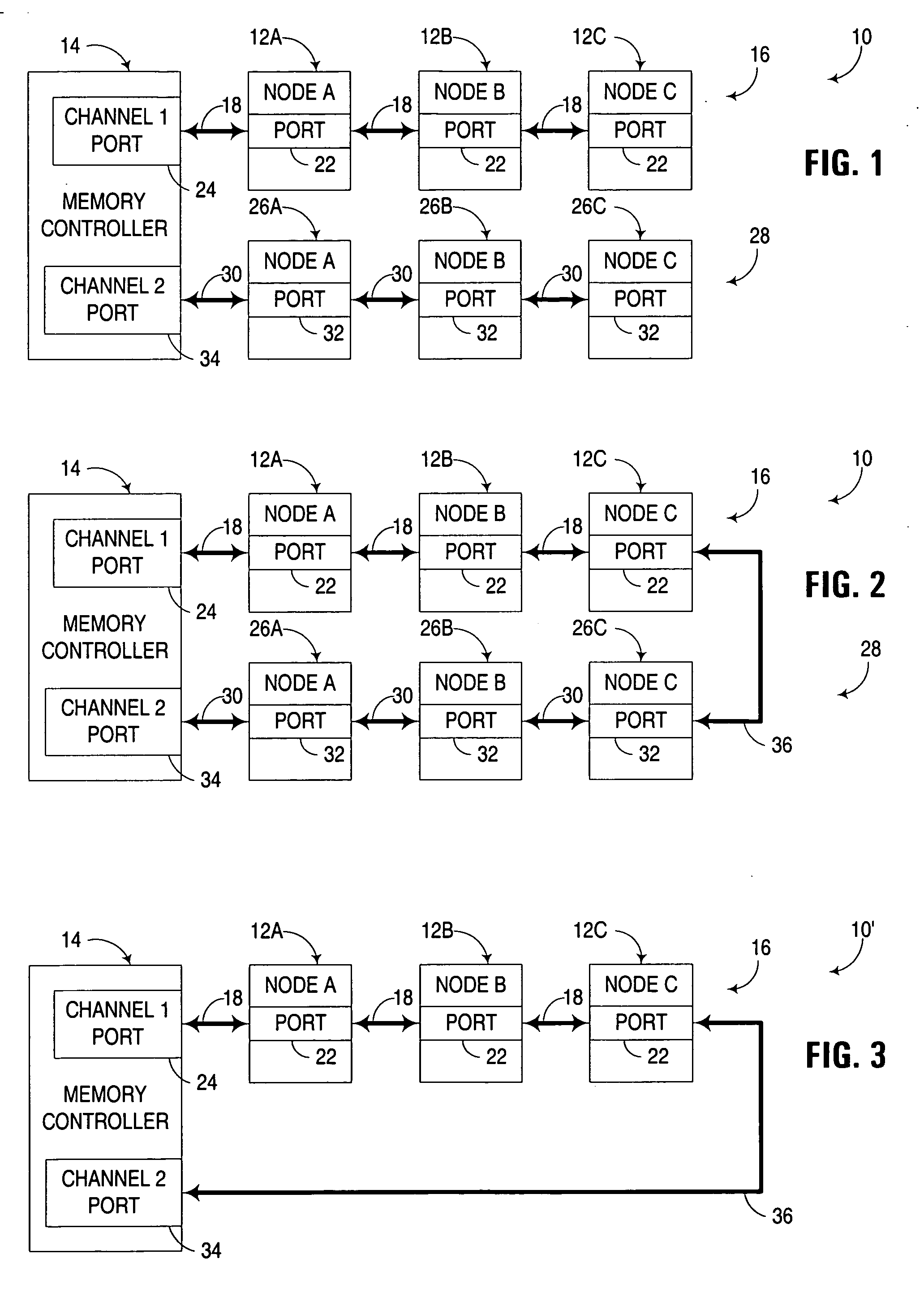
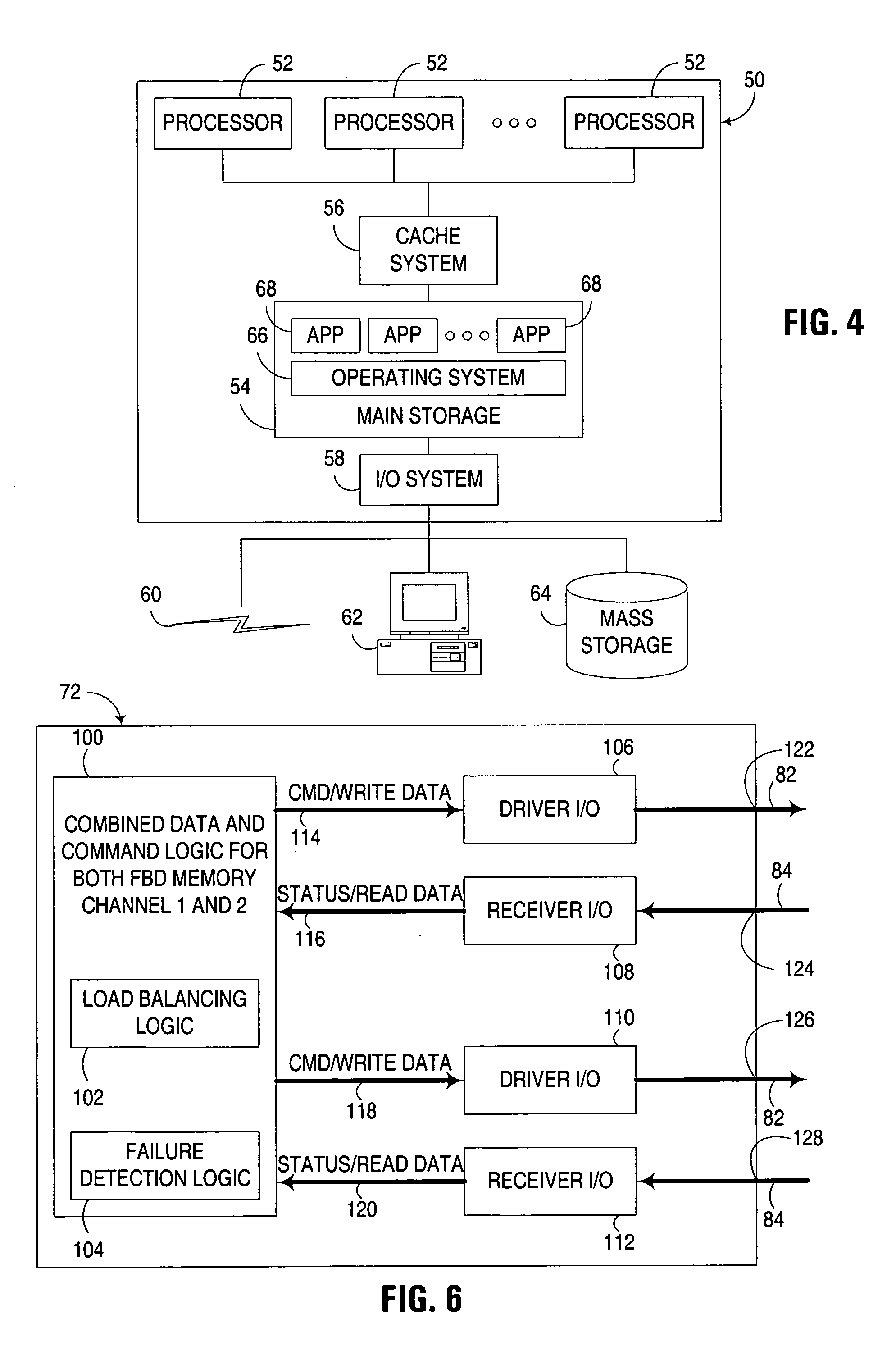
Multi-channel memory architecture for daisy chained arrangements of nodes with bridging between memory channels
InactiveUS20060095592A1Optimize latencyImprove utilizationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDIMMParallel computing
Multiple memory channels of a multi-channel memory architecture are effectively bridged together to enable data traffic associated with various nodes in daisy chain arrangement to be communicated over both memory channels. For example, a daisy chain arrangement of nodes, such as FB-DIMM memory modules disposed in a first memory channel may be coupled to a second memory channel, with support for communicating data associated with one of the nodes over either or both of the first and second memory channels.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
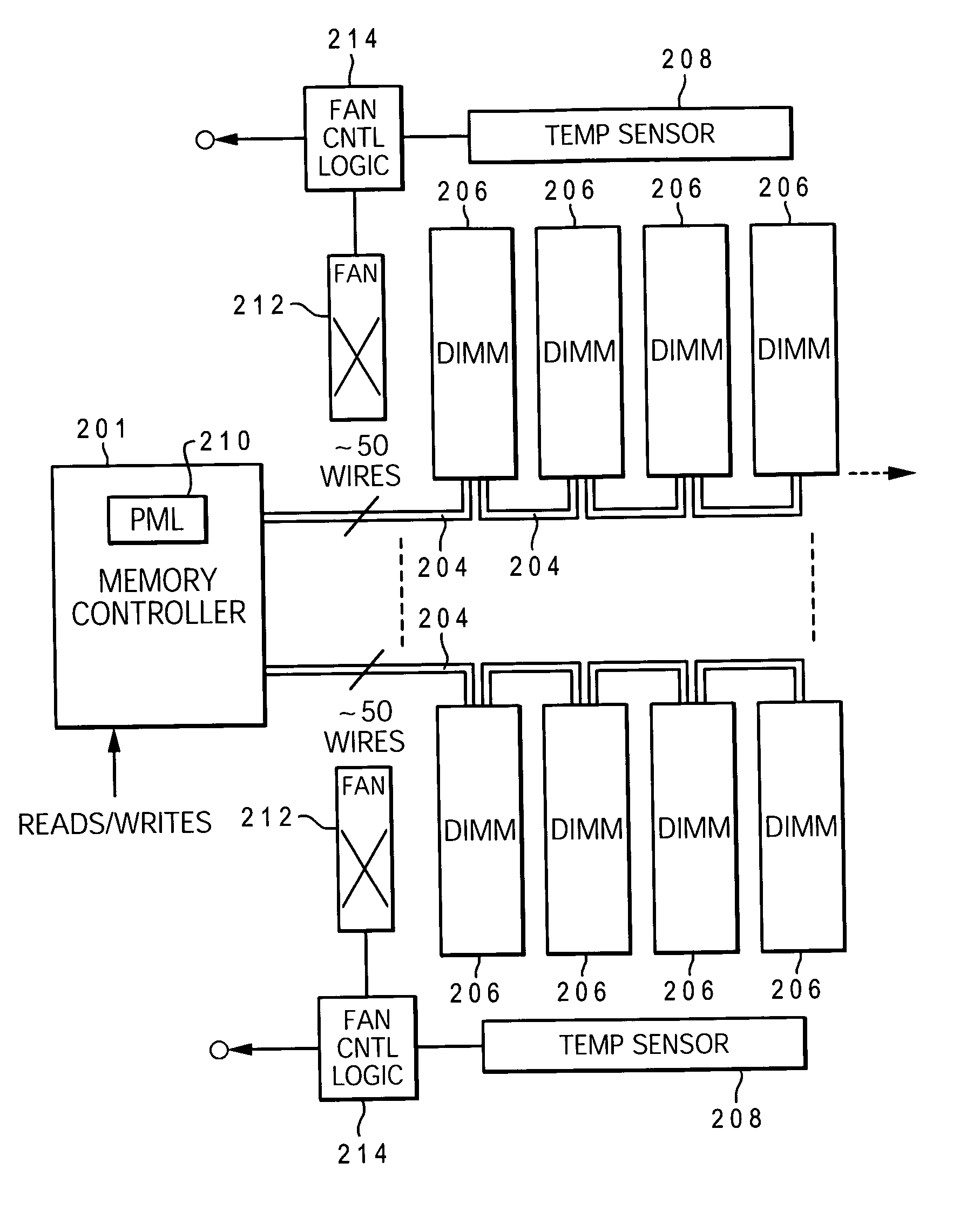
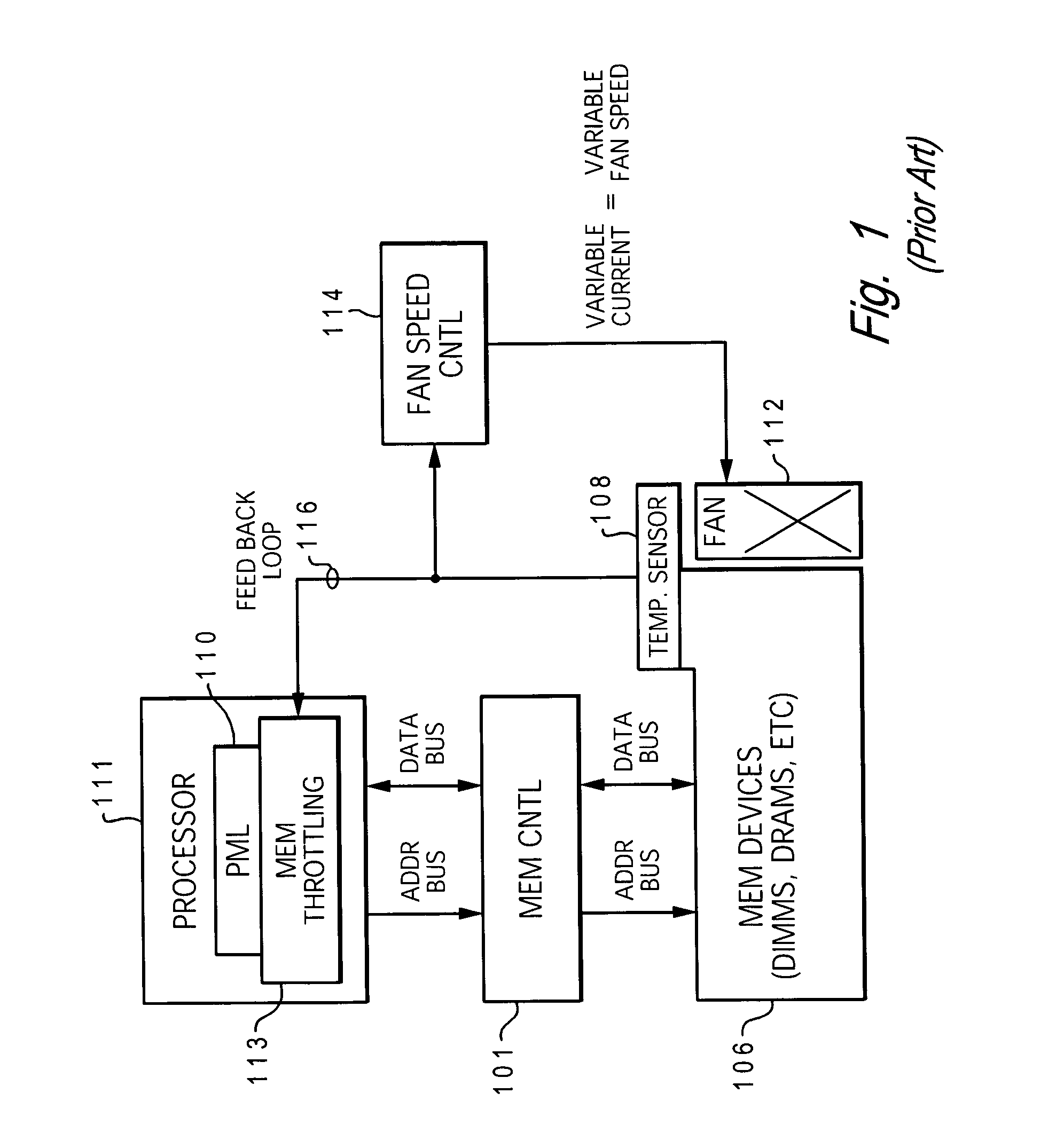
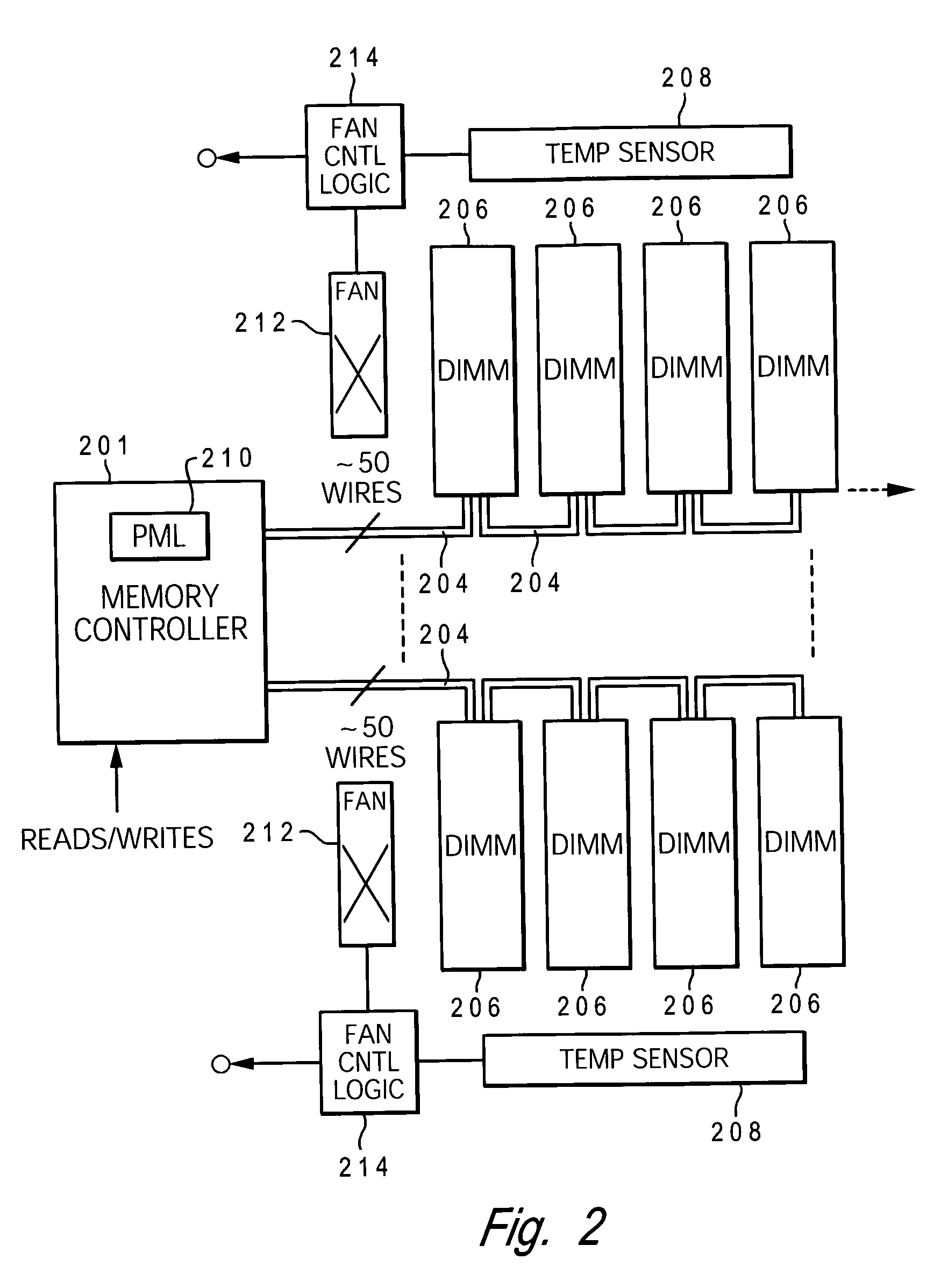
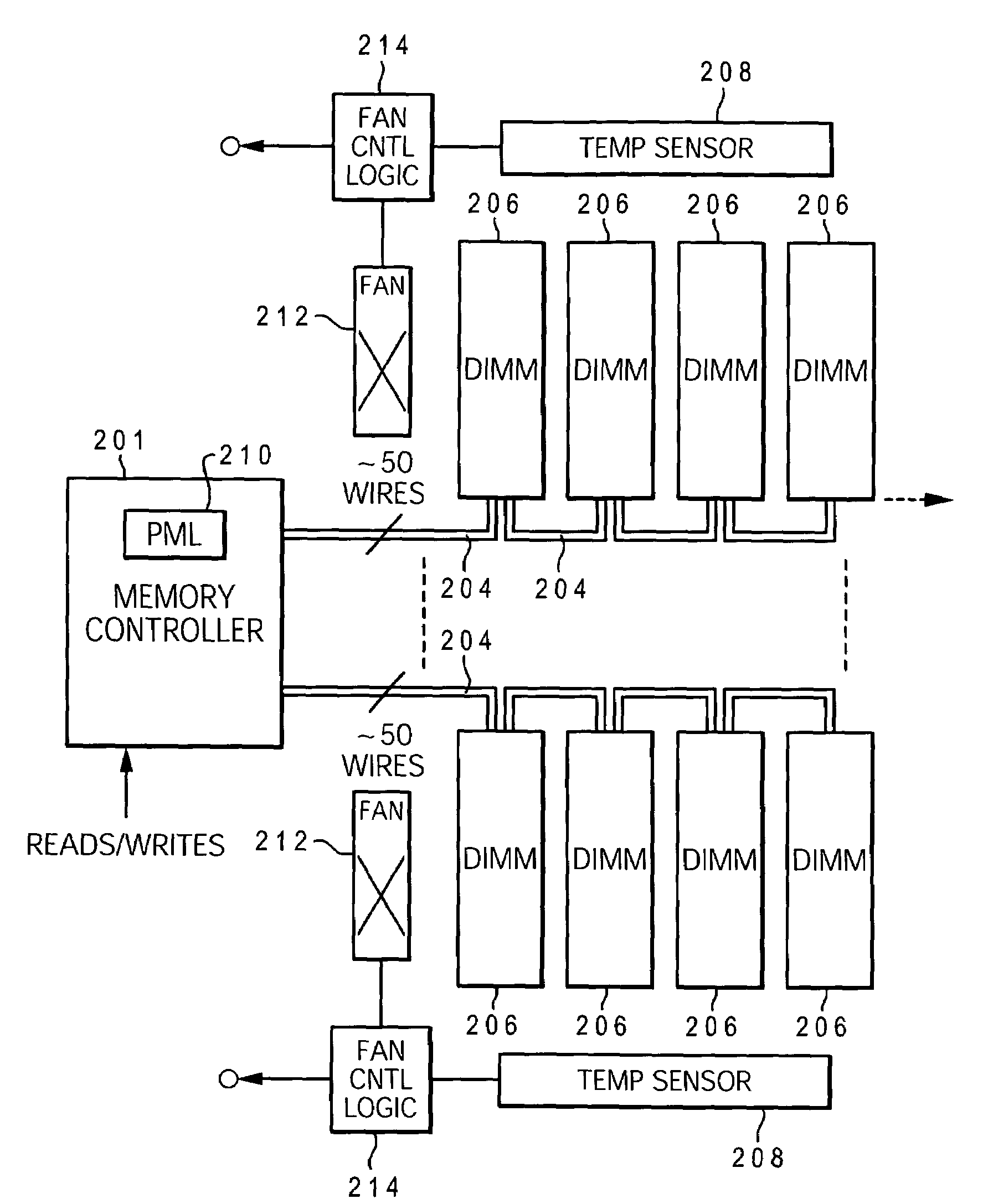
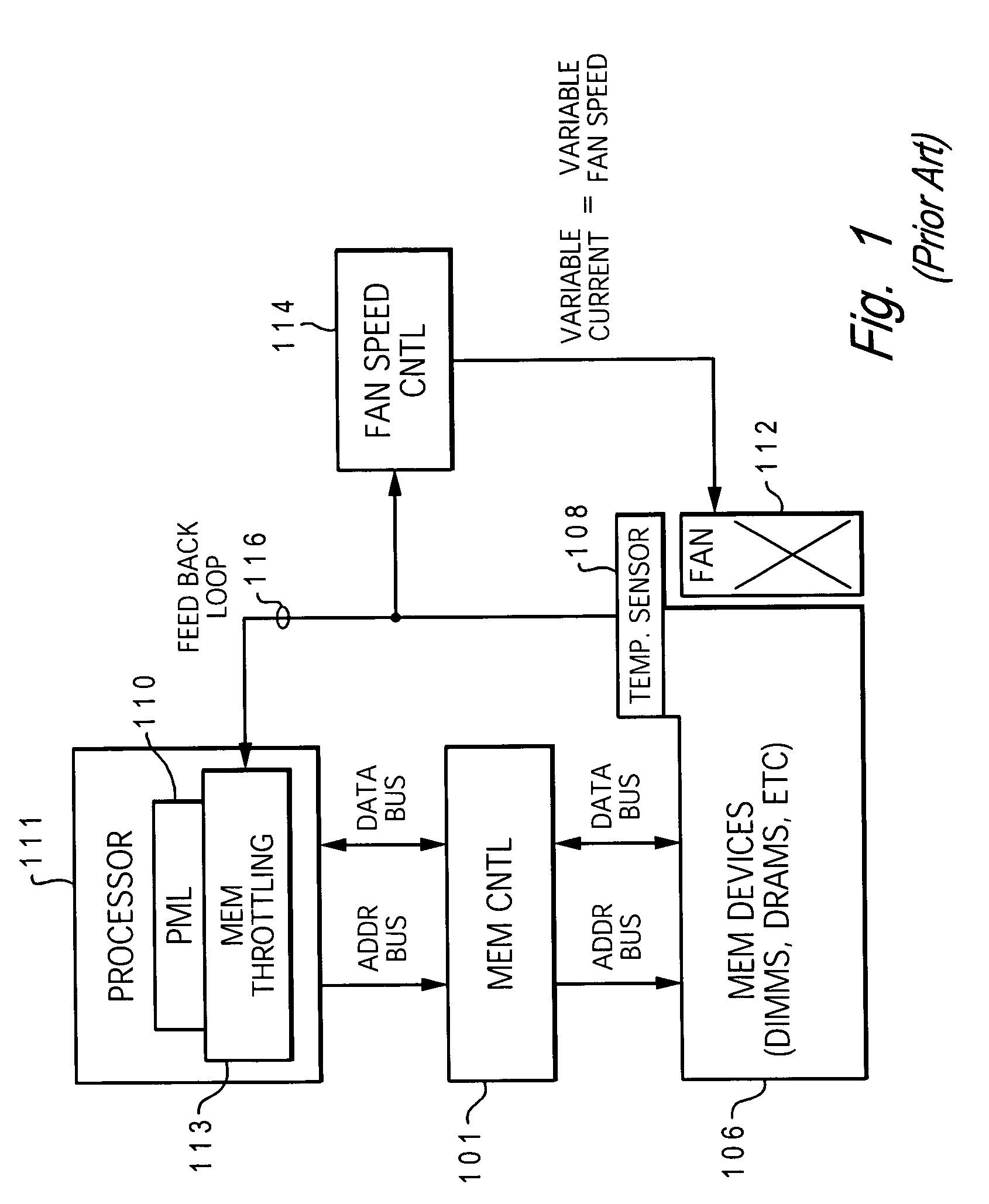
Dynamic power management via DIMM read operation limiter
InactiveUS20060179334A1Little or no usePower usageEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDIMMDynamic power management
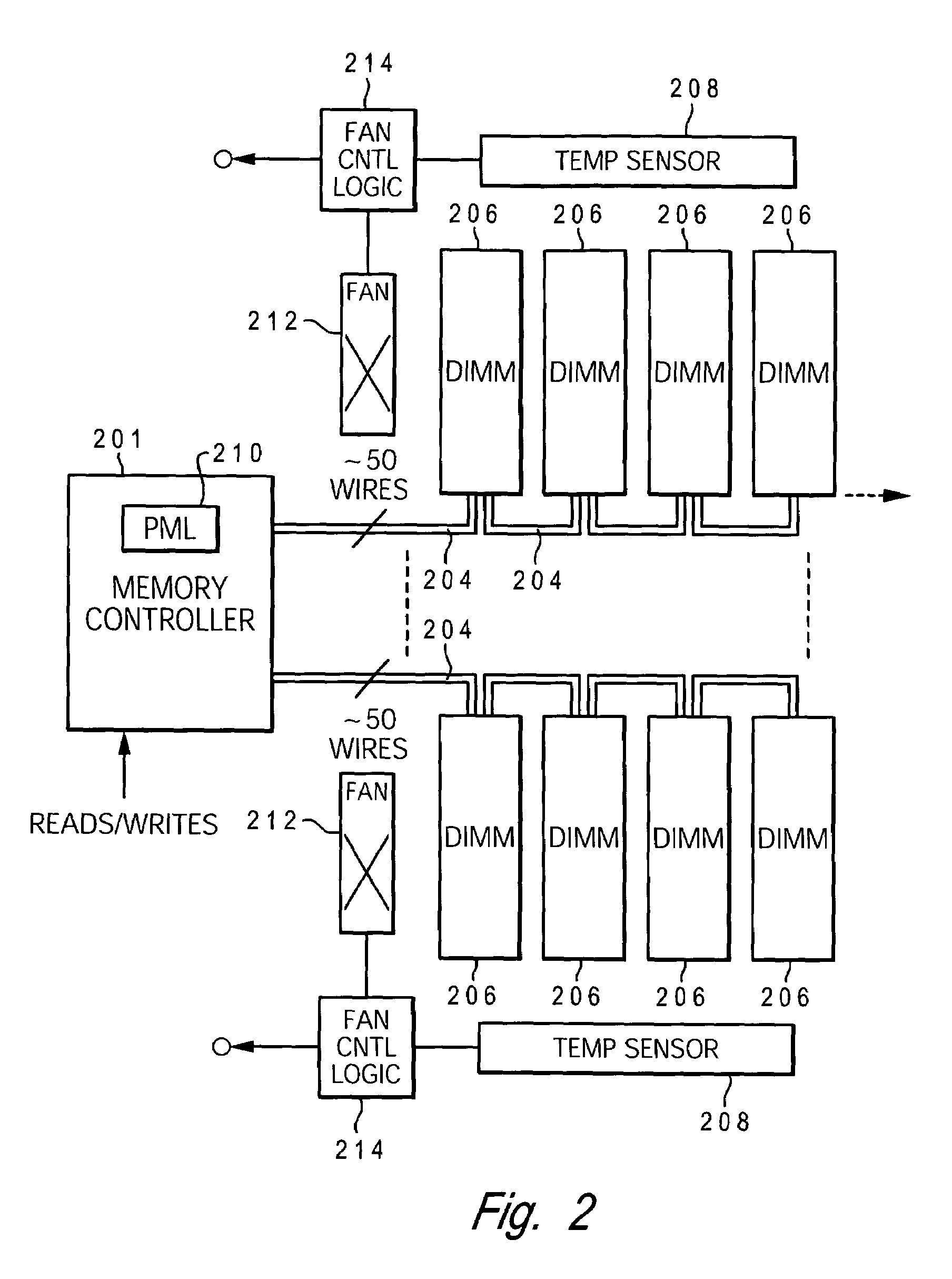
A method and system for enabling directed temperature / power management at the DIMM-level and / or DRAM-level utilizing intelligent scheduling of memory access operations received at the memory controller. Hot spots within the memory subsystem, caused by operating the DIMMs / DRAMs above predetermined / preset threshold power / temperature values for operating a DIMM and / or a DRAM, are avoided / controlled by logic within the memory controller. The memory controller logic throttles the number / frequency at which commands (read / write operations) are issued to the specific DIMM / DRAM based on feedback data received from the specific DIMM / DRAM reaching the preset threshold power usage value.
Owner:IBM CORP
Redistribution of memory to reduce computer system power consumption
InactiveUS20070106860A1Limited amount of powerLowering thermal profileEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDIMMPower mode
A method, apparatus and system are disclosed for redistributing memory allocation to portions of dynamic random access memory (DRAM) and dual in-line memory module (DIMM) devices that are underutilized, in order to balance memory usage more evenly amongst active devices so as to limit the amount of power and the thermal load consumed by an individual memory component. The disclosed method, apparatus and system are capable of identifying and tracking memory usage to minimize power consumption in a way that lessens the detrimental effects of “throttling” or reduced power modes for memory devices.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
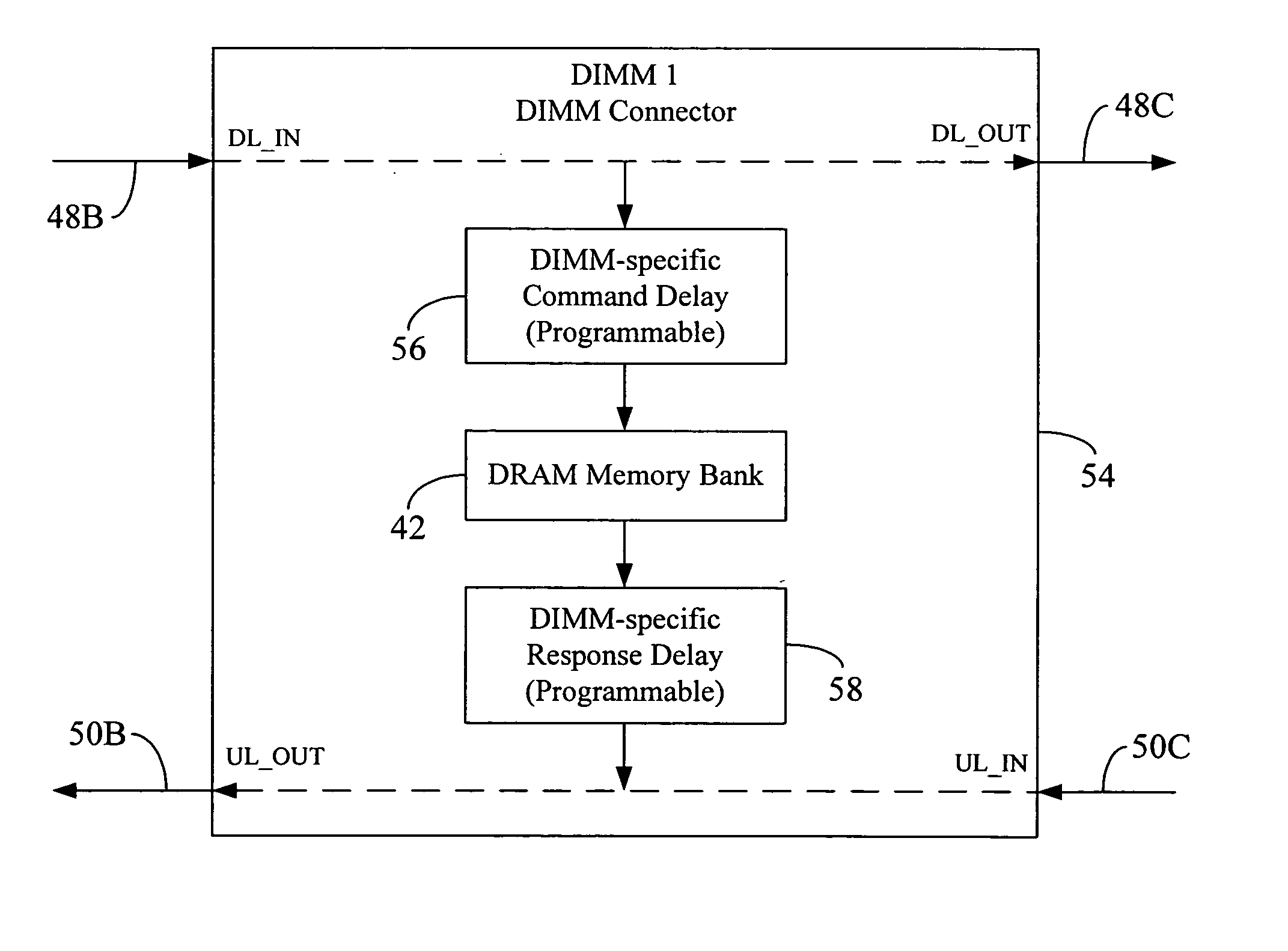
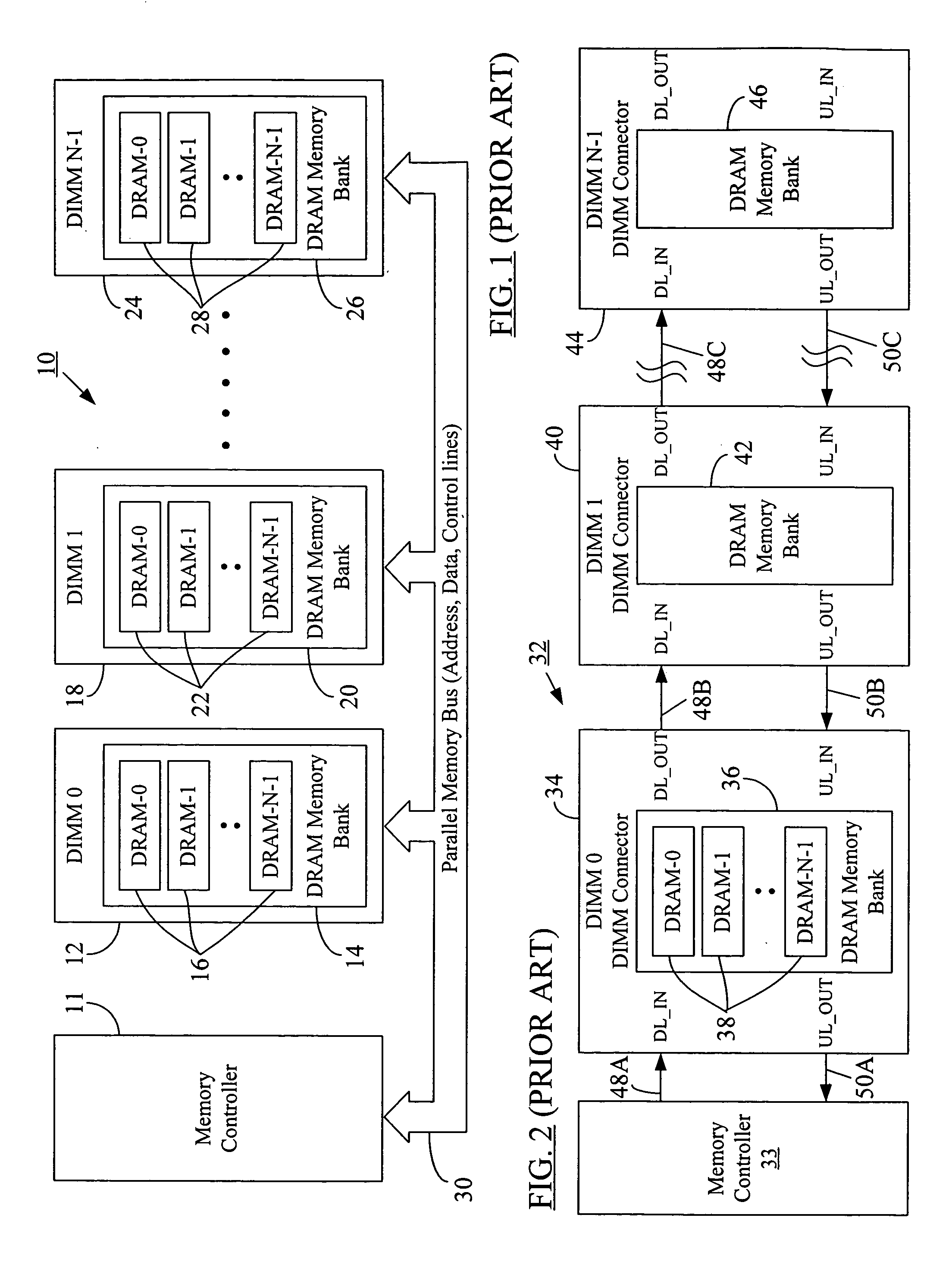
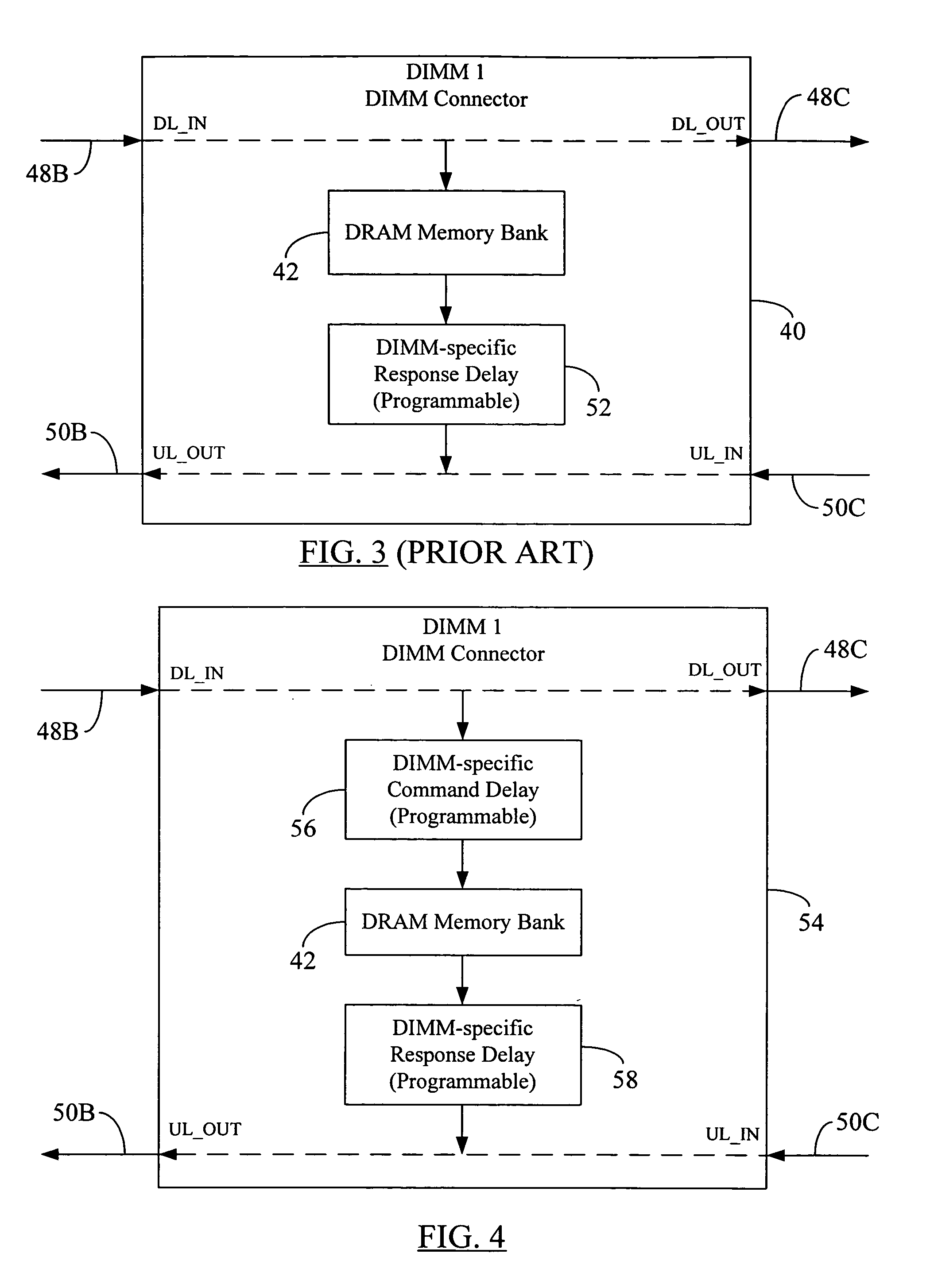
Memory command delay balancing in a daisy-chained memory topology
InactiveUS20060041730A1Effective predictionAccurately ascertainedEnergy efficient ICTDigital storageDIMMControl power
A methodology for a daisy-chained memory topology wherein, in addition to the prediction of the timing of receipt of a response from a memory module (DIMM), the memory controller can effectively predict when a command sent by it will be executed by the addressee DIMM. By programming DIMM-specific command delay in the DIMM's command delay unit, the command delay balancing methodology according to the present disclosure “normalizes” or “synchronizes” the execution of the command signal across all DIMMs in the memory channel. With such ability to predict command execution timing, the memory controller can efficiently control power profile of all the DRAM devices (or memory modules) on a daisy-chained memory channel. A separate DIMM-specific response delay unit in the DIMM may also be programmed to provide DIMM-specific delay compensation in the response path, further allowing the memory controller to accurately ascertain the timing of receipt of a response thereat, and, hence, to better manage further processing of the response.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
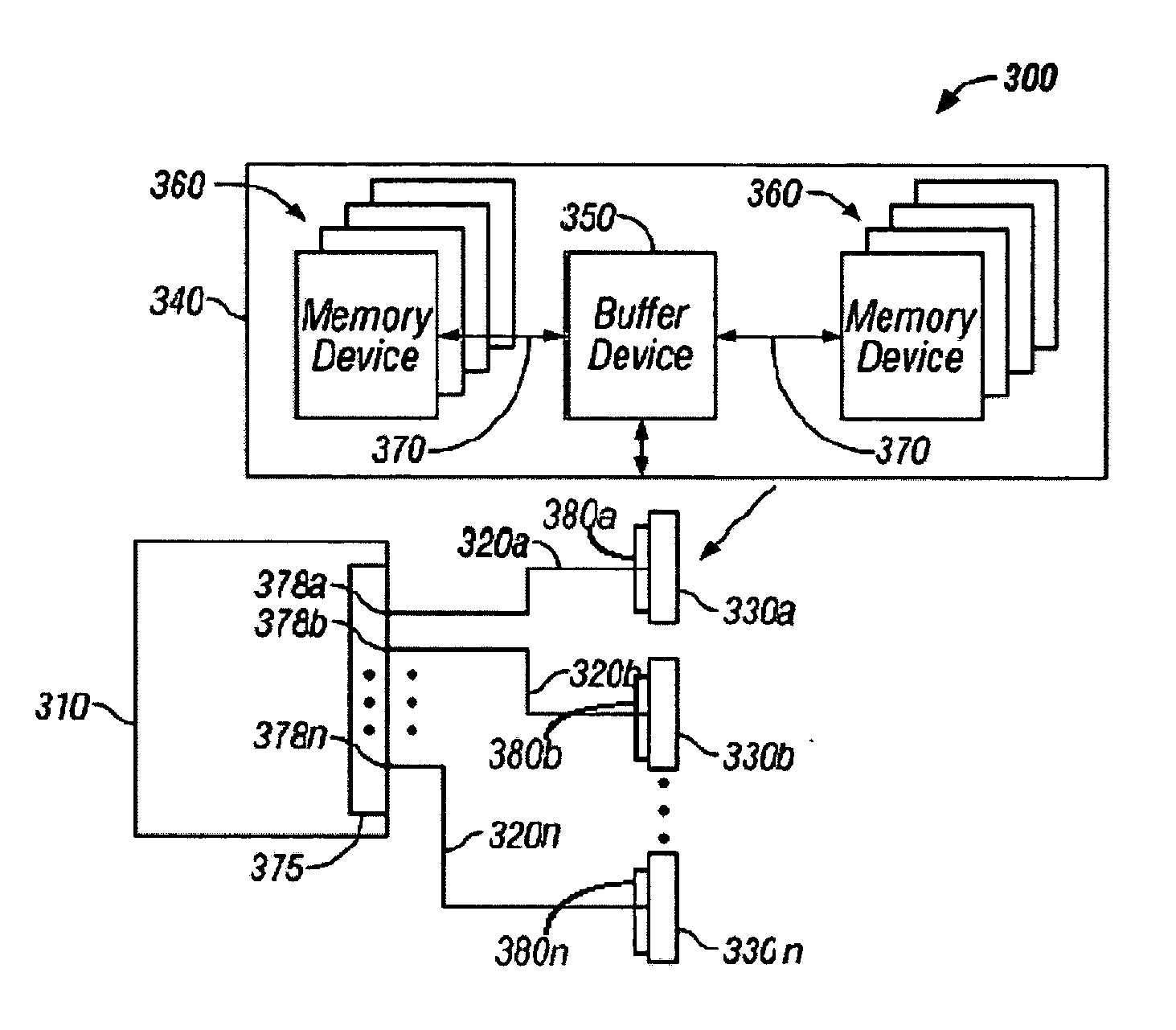
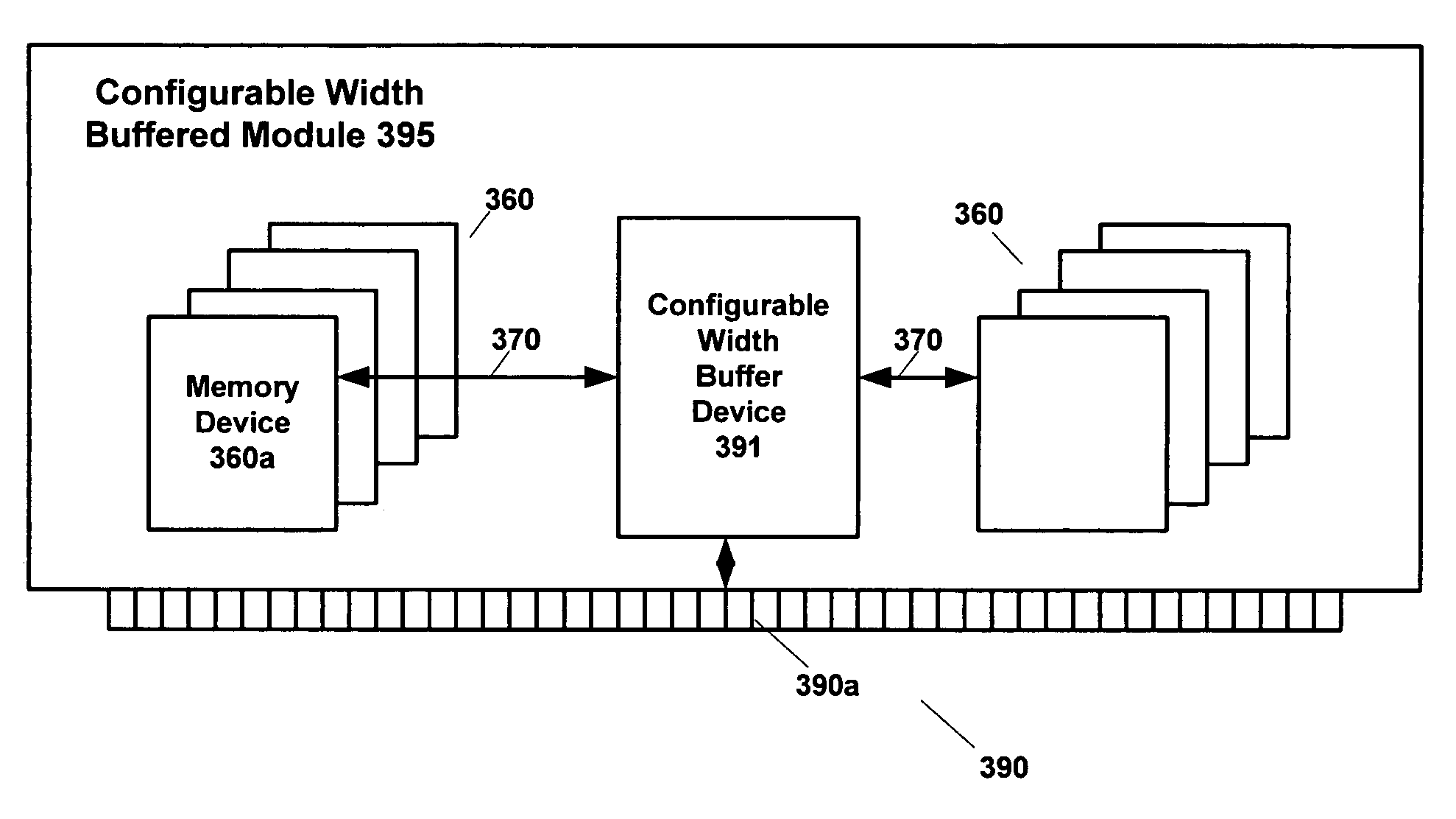
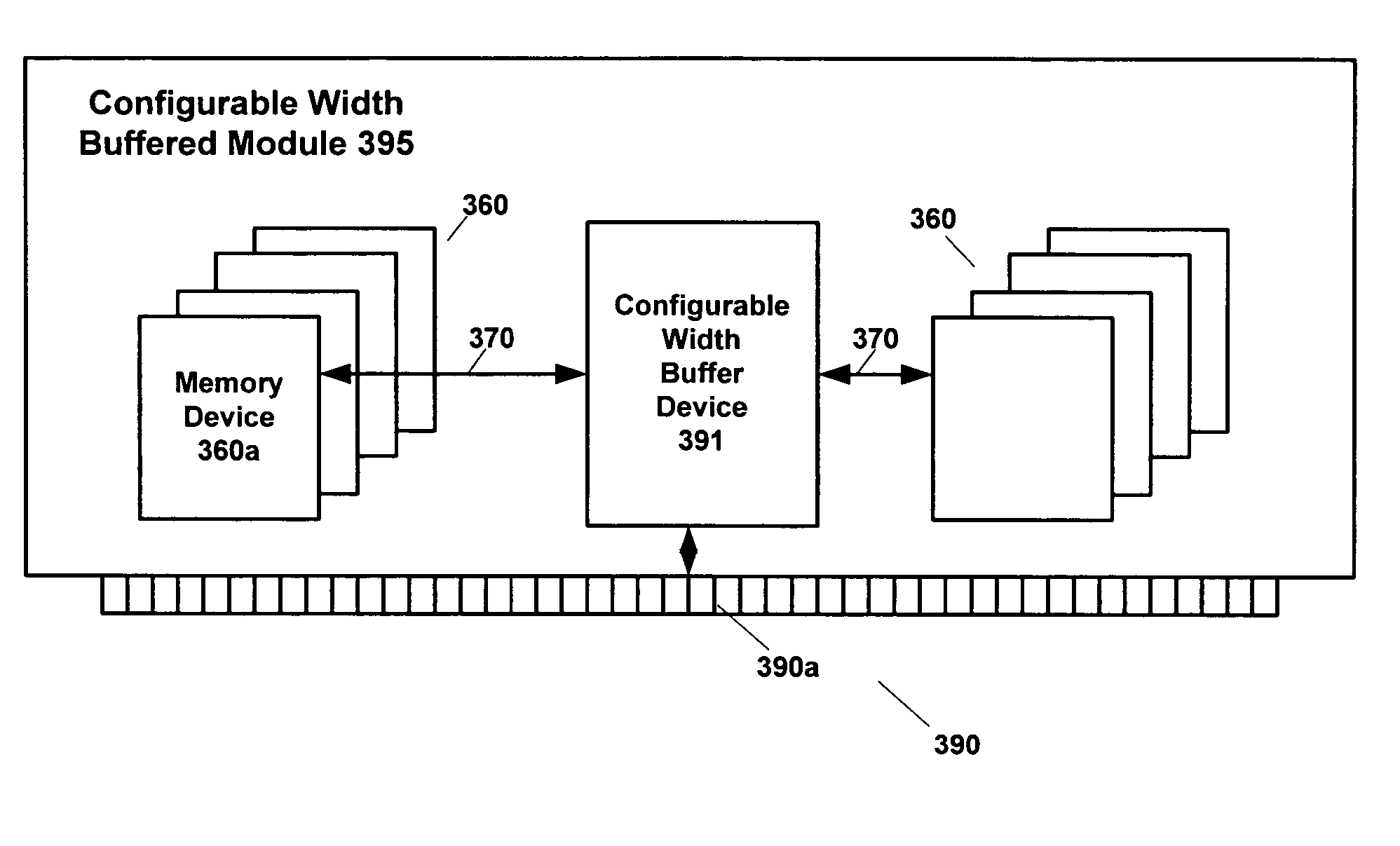
Configurable width buffered module having switch elements
A memory system architecture / interconnect topology includes a configurable width buffered memory module having a configurable width buffer device with at least one switch element. A buffer device, such as a configurable width buffer device, is positioned between or with at least one integrated circuit memory device positioned on a substrate surface of a memory module, such as a DIMM. A switch element is positioned on or off a memory module and includes two transistors in embodiments of the invention. One or more switch elements are coupled to one or more channels to allow for upgrades of memory modules in a memory system. An asymmetrical switch topology allows for increasing the number of memory modules to more than two memory modules without adding switch elements serially on each channel. Switch elements allow for increasing the number of ranks of memory modules in a system, while also achieving many of the benefits associated with point-to-point topology.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
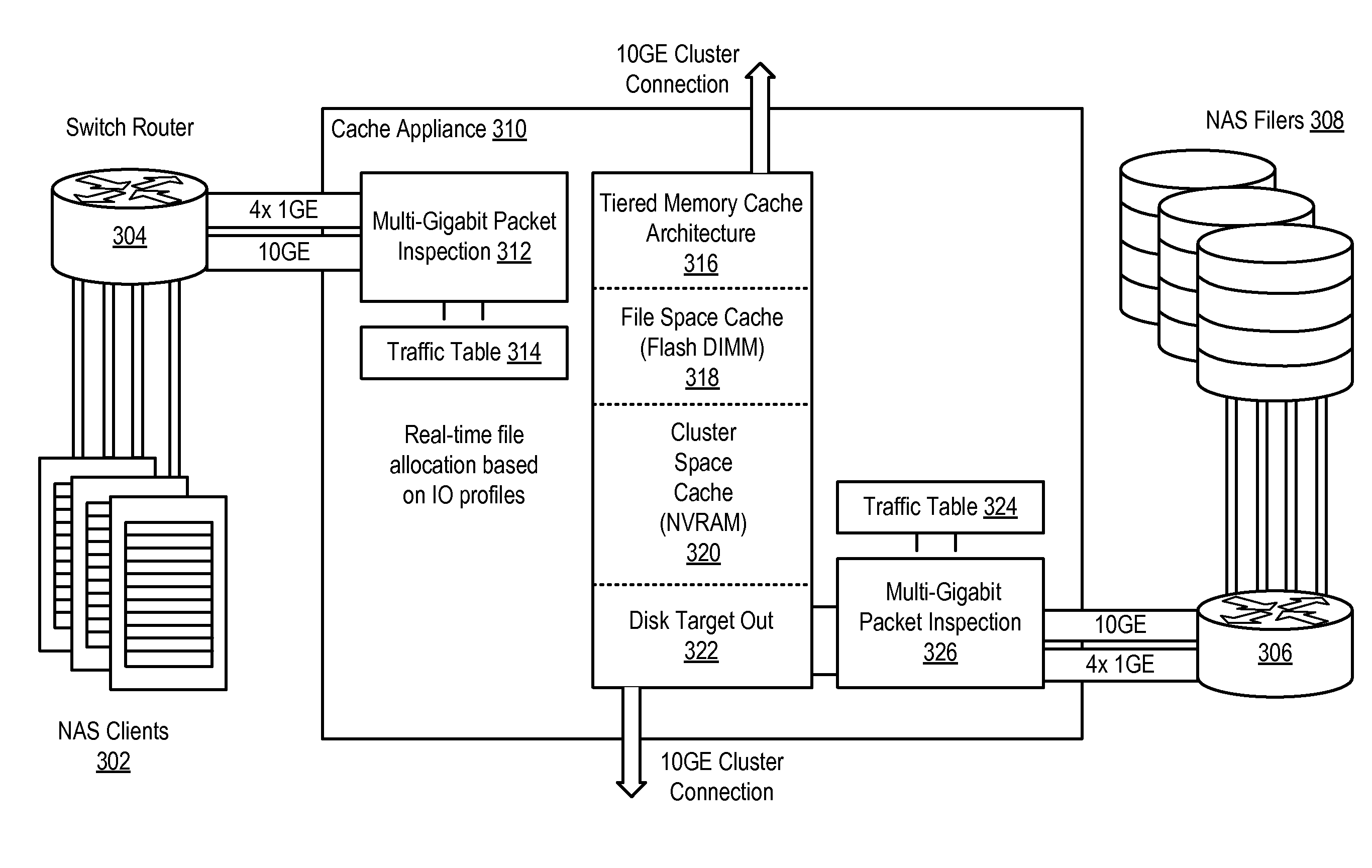
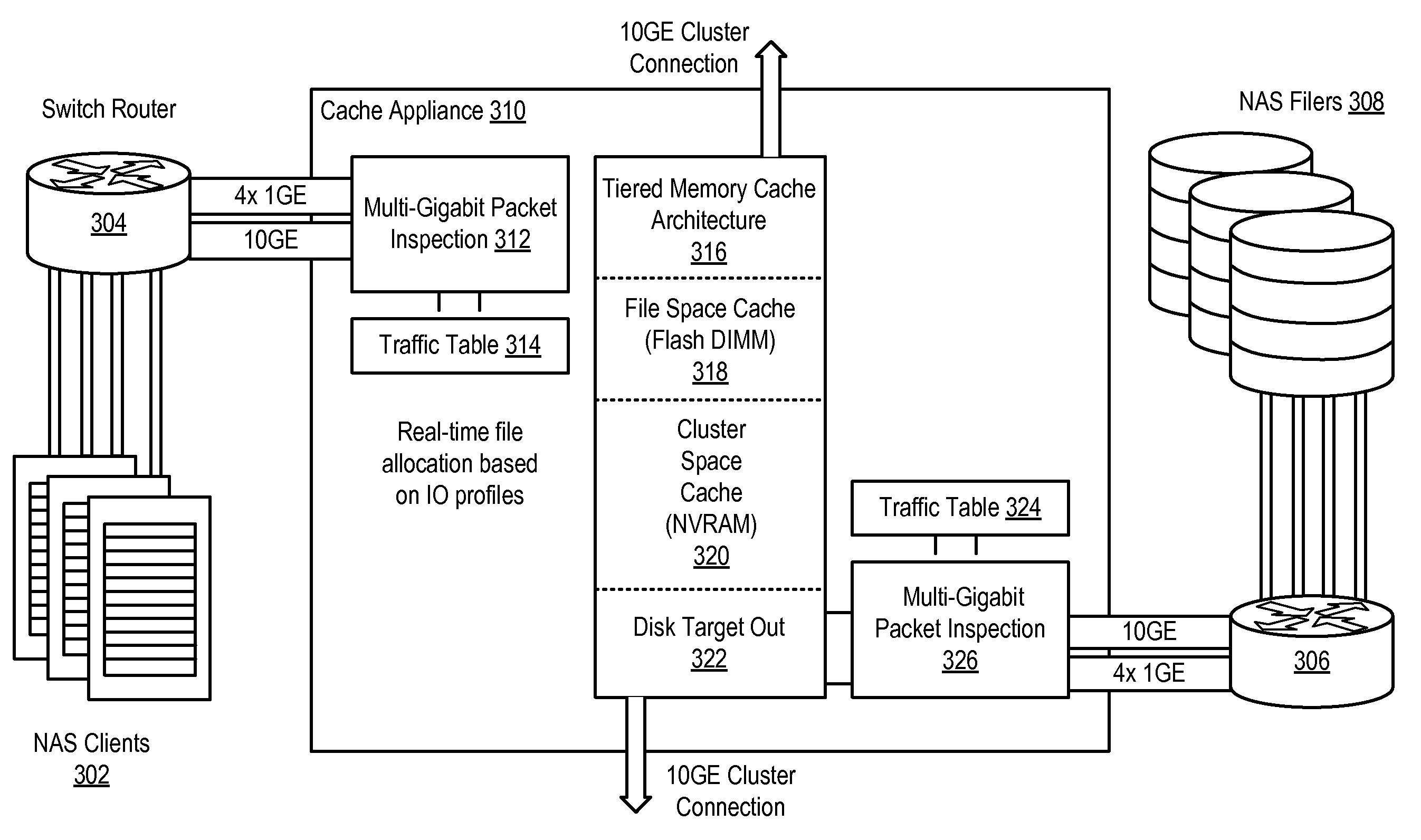
Flash DIMM in a Standalone Cache Appliance System and Methodology
InactiveUS20100023674A1Low costLess power consumptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDIMMClient-side
A method, system and program are disclosed for accelerating data storage in a cache appliance cluster that transparently monitors NFS and CIFS traffic between clients and NAS subsystems and caches files in a multi-rank flash DIMM cache memory by pipelining multiple page write and page program operations to different flash memory ranks, thereby improving write speeds to the flash DIMM cache memory.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Flash DIMM in a standalone cache appliance system and methodology
InactiveUS7941591B2Low costLess power consumptionMemory architecture accessing/allocationTransmissionDIMMClient-side
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
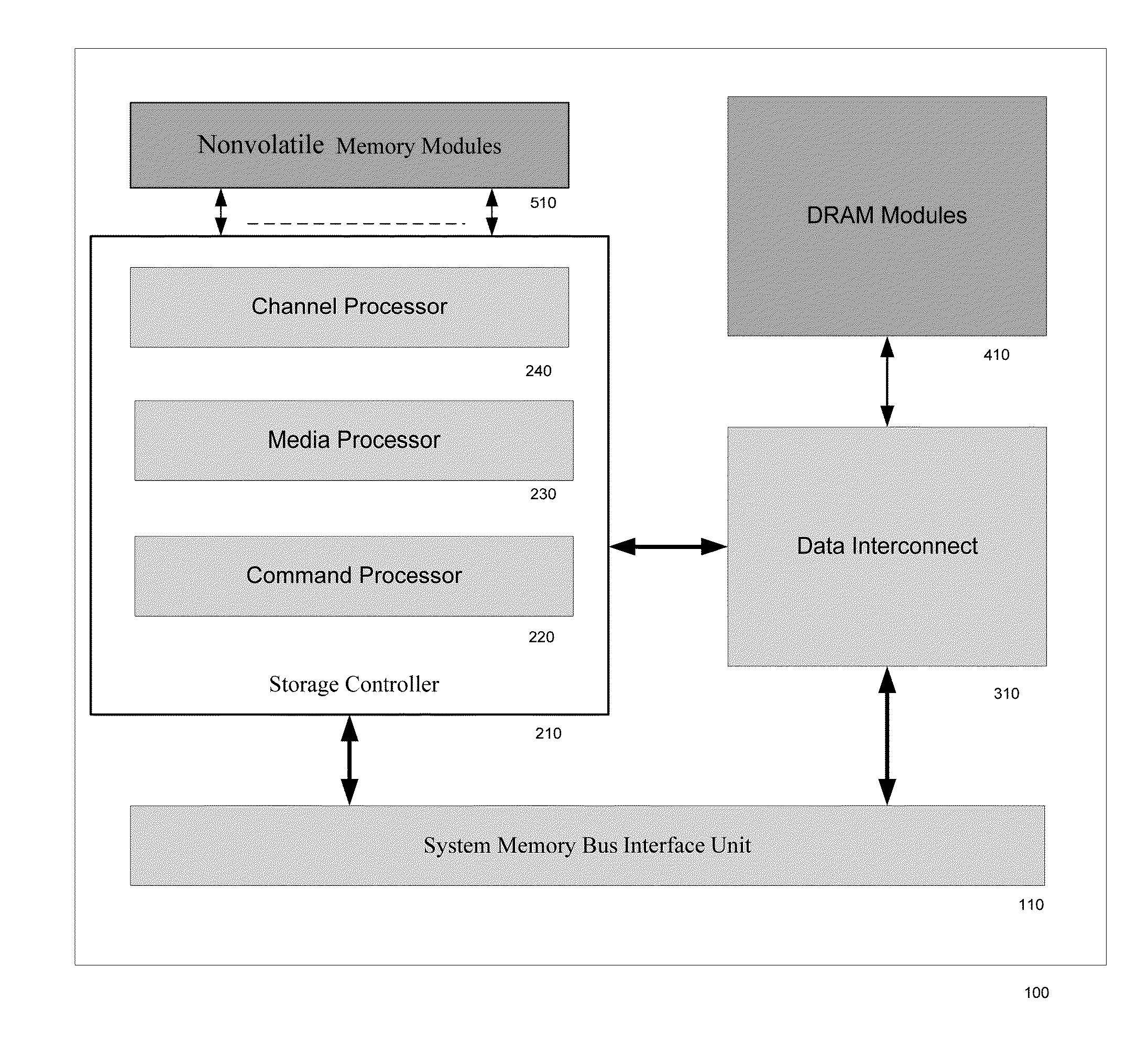
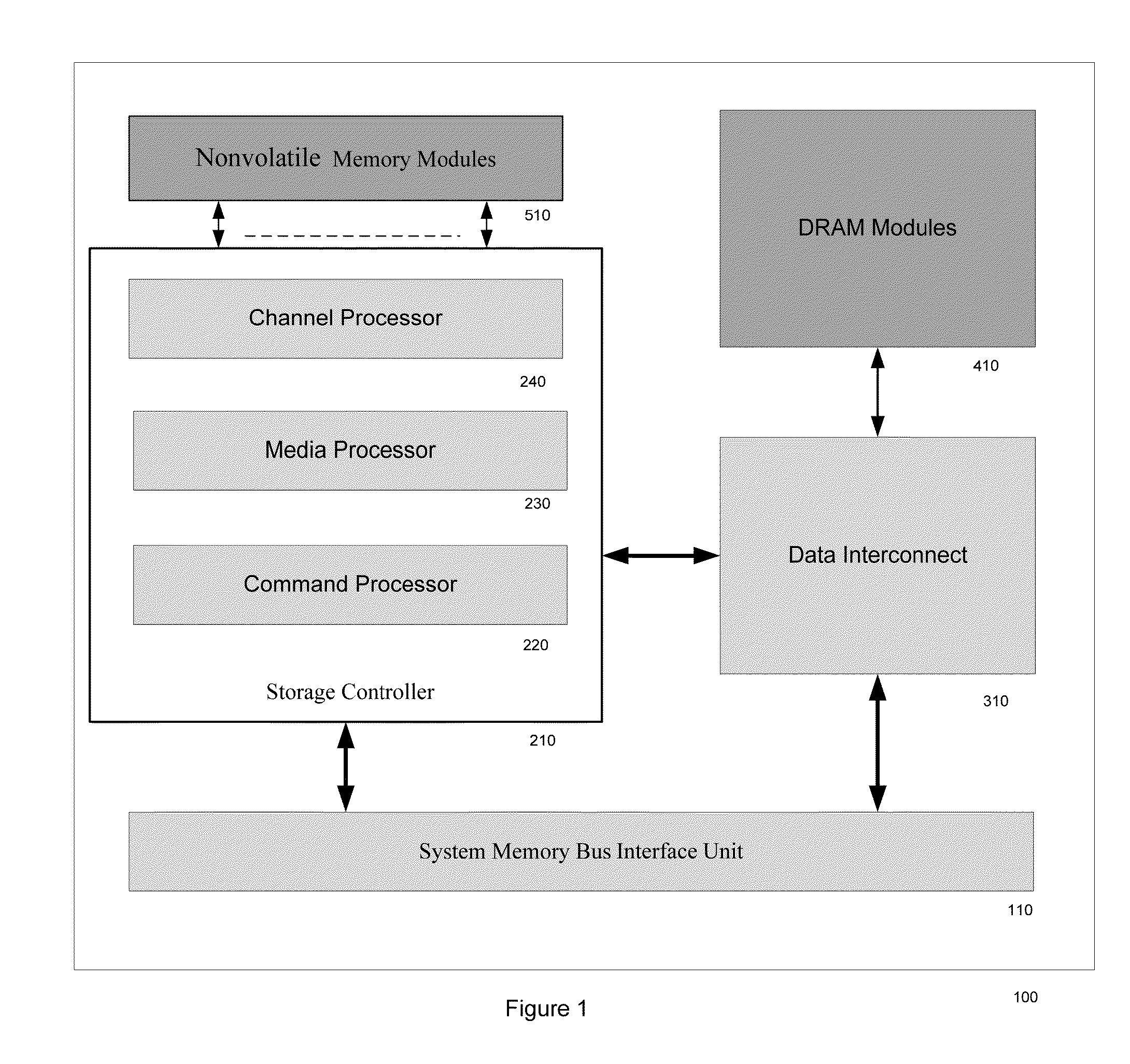
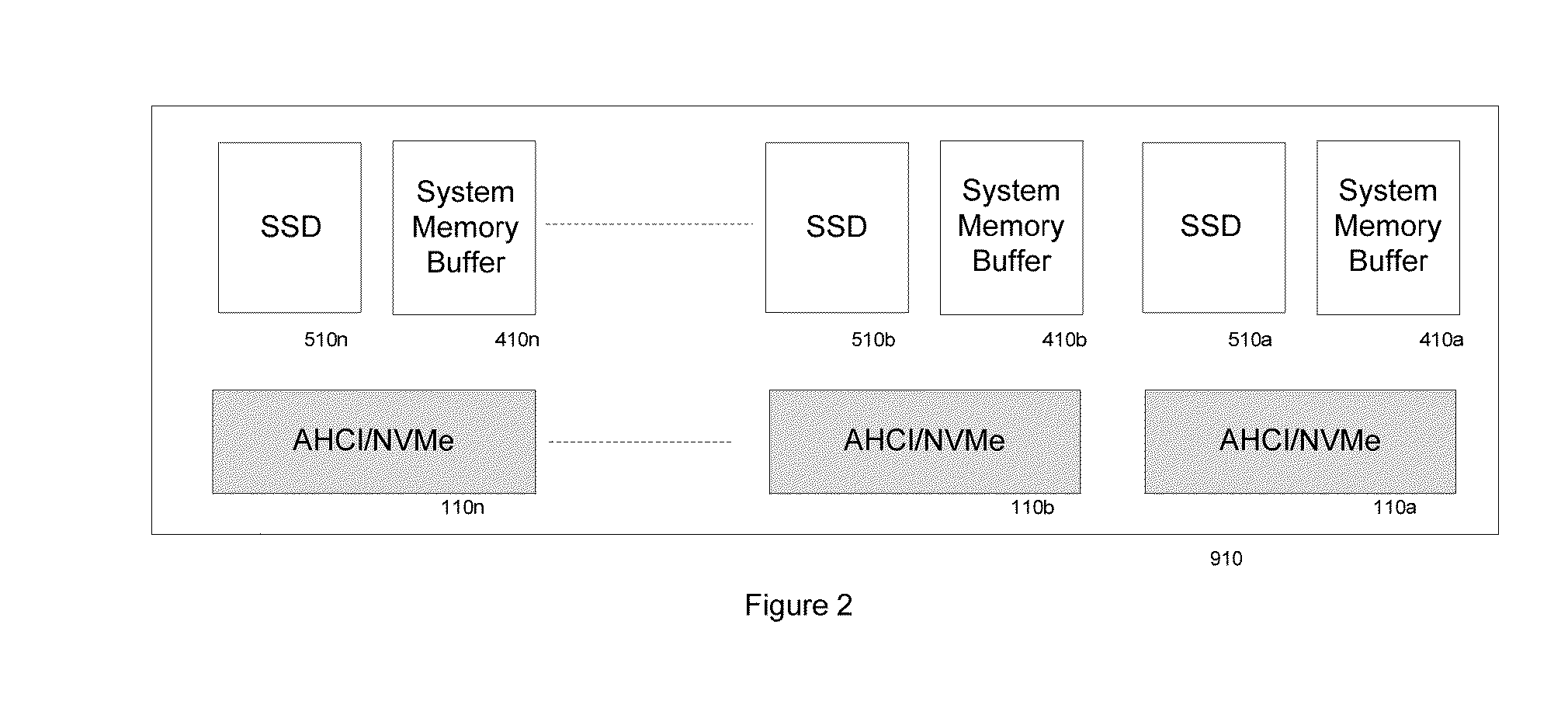
METHOD OF DIRECT CONNECTING AHCI OR NVMe BASED SSD SYSTEM TO COMPUTER SYSTEM MEMORY BUS
A SSD system directly connected to the system memory bus includes at least one system memory bus interface unit, one storage controller with associated data buffer / cache, one data interconnect unit, one nonvolatile memory (NVM) module, and flexible association between storage commands and the NVM module. A logical device interface, the Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) or NVM Express (NVMe), is used for the SSD system programming. The SSD system appears to the computer system physically as a dual-inline-memory module (DIMM) attached to the system memory controller, and logically as an AHCI device or an NVMe device. The SSD system may sit in a DIMM socket and scaling with the number of DIMM sockets available to the SSD applications. The invention moves the SSD system from I / O domain to the system memory domain.
Owner:HUANG MING +1
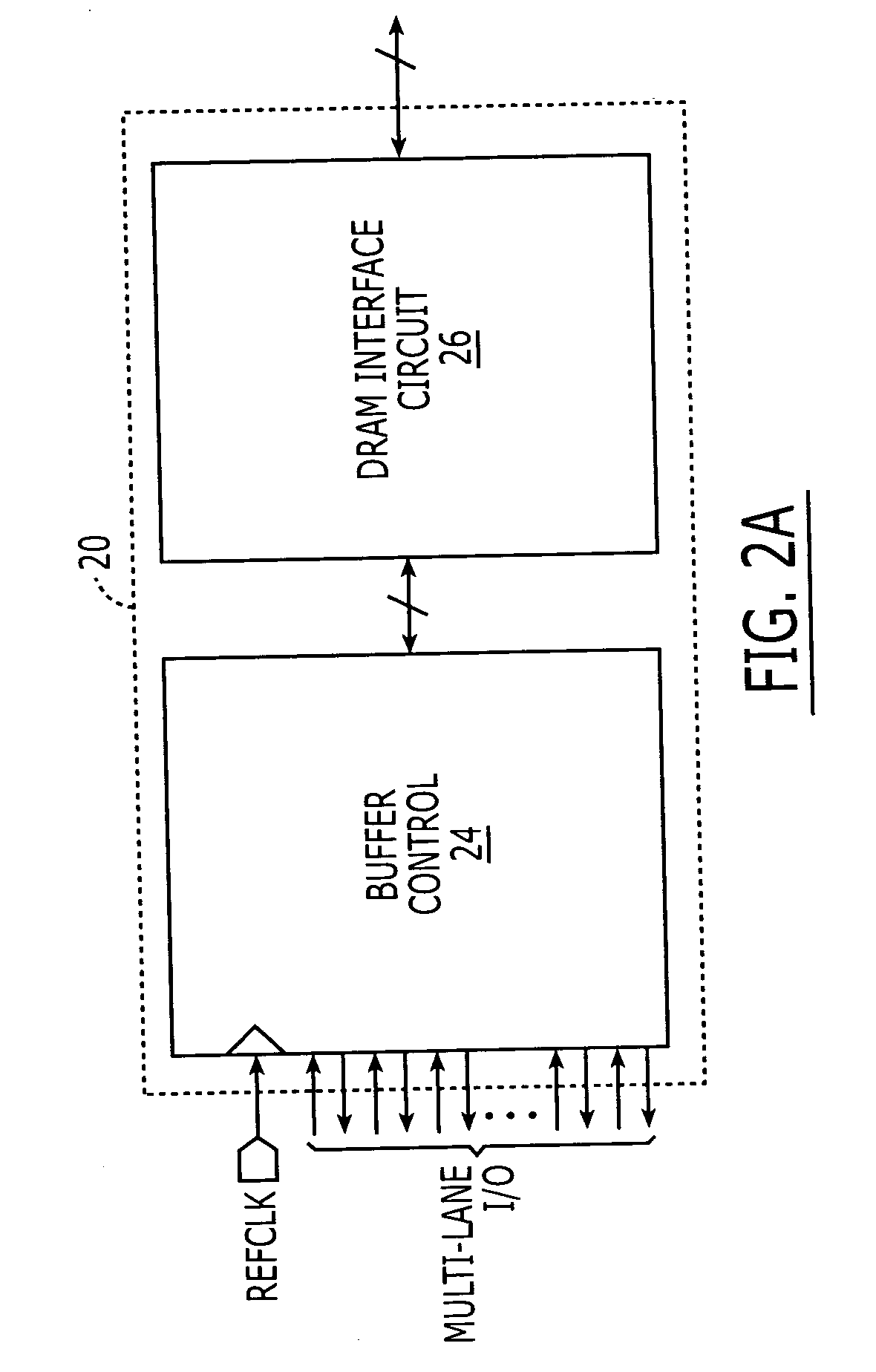
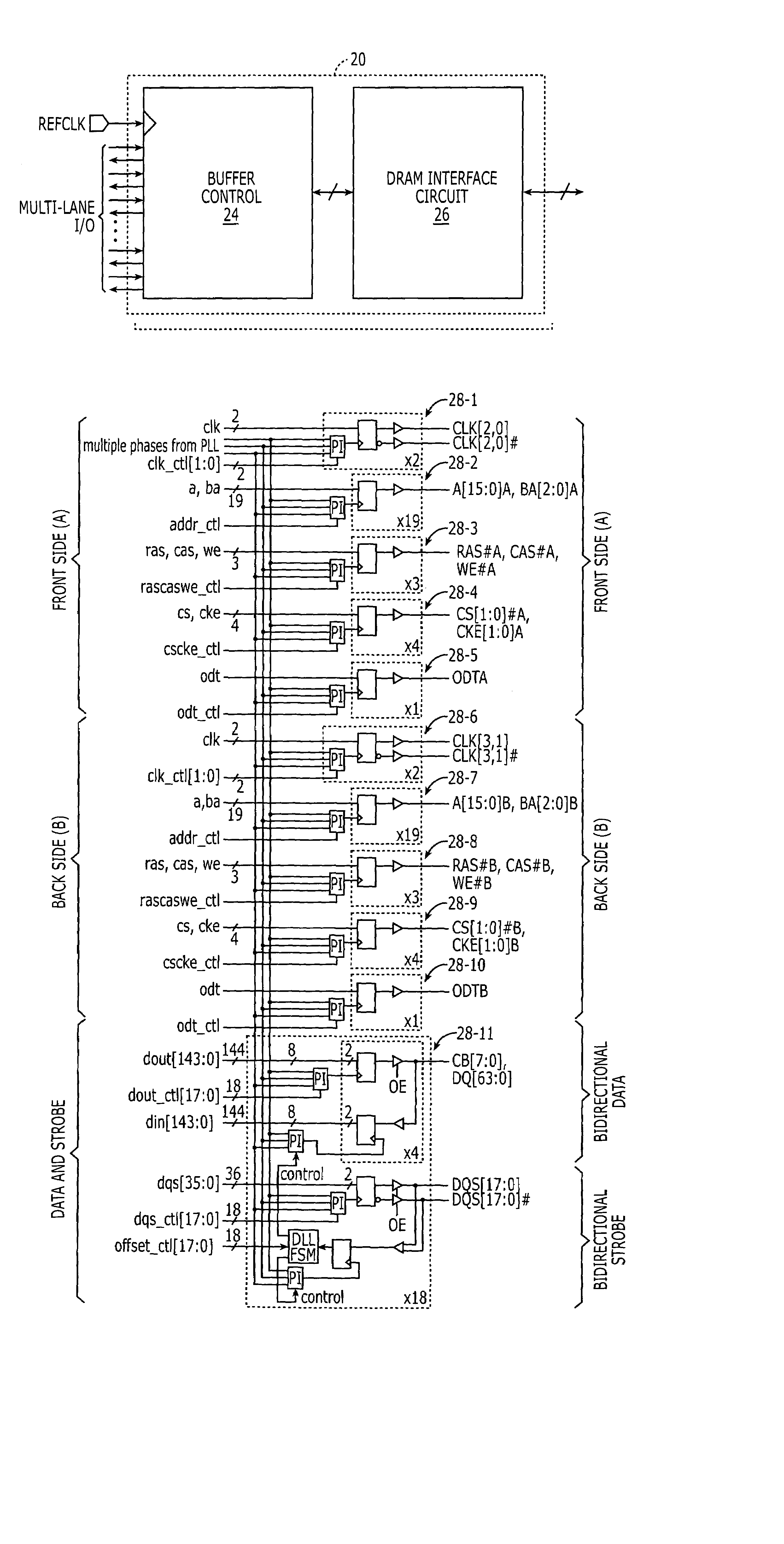
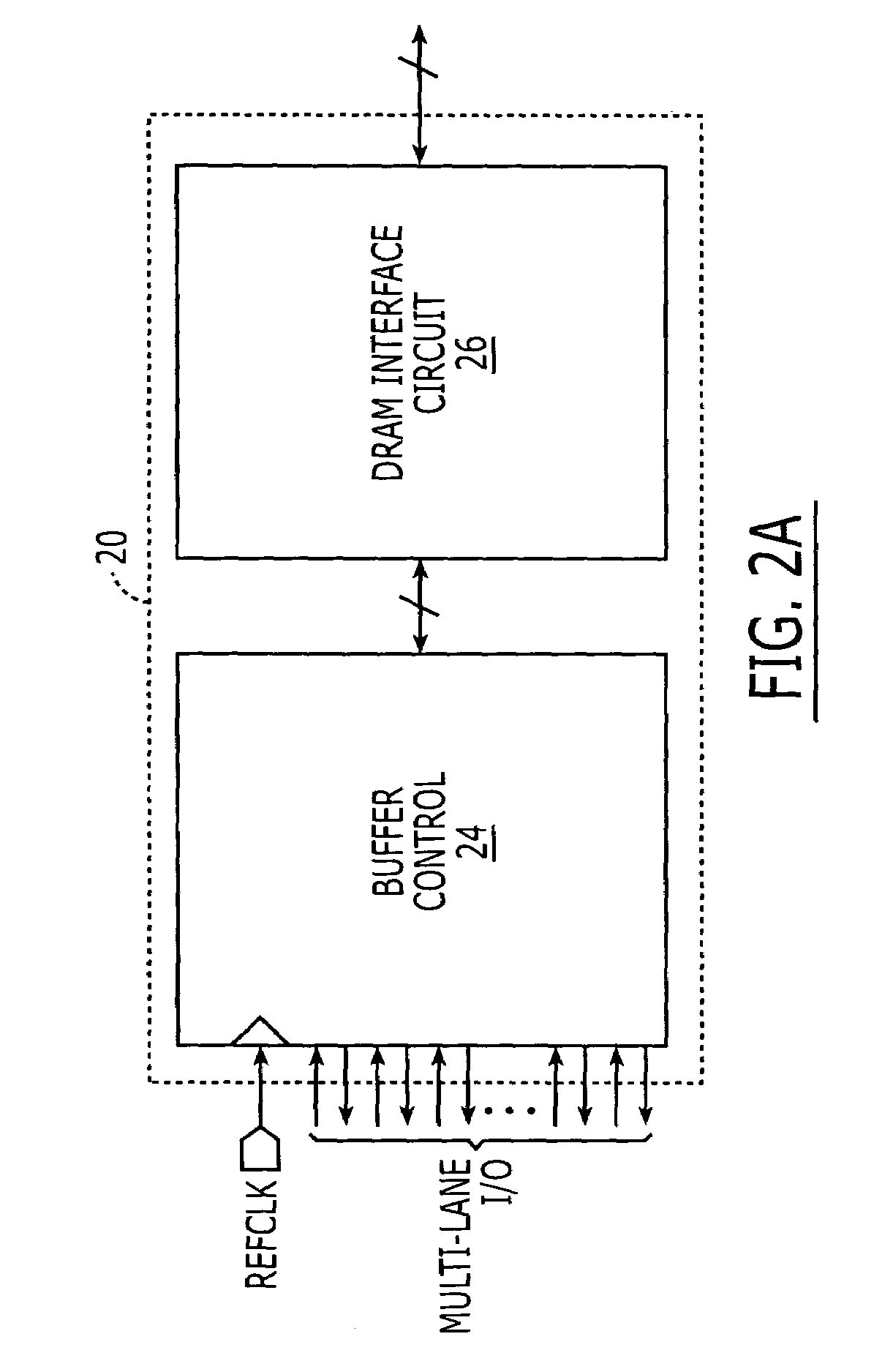
DRAM interface circuits having enhanced skew, slew rate and impedance control
Fully-buffered dual in-line memory modules (FB-DIMM) include advanced memory buffers (AMBs) having enhanced skew, slew rate and output impedance control. The AMB includes user accessible registers that can be programmed to carefully control the edge placement (or phase) of signals generated from the AMB to multiple DRAMs on the module. This control of edge placement, which may be performed independently for each group of signals: clock (CLK, CLK#), command (RAS, CAS, WE), address (including bank address), data (DQ) and data strobe (DQS), provides 360 degrees of control (or one period). This means that any group of signals can be moved independently by one complete period relatively to any other group.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
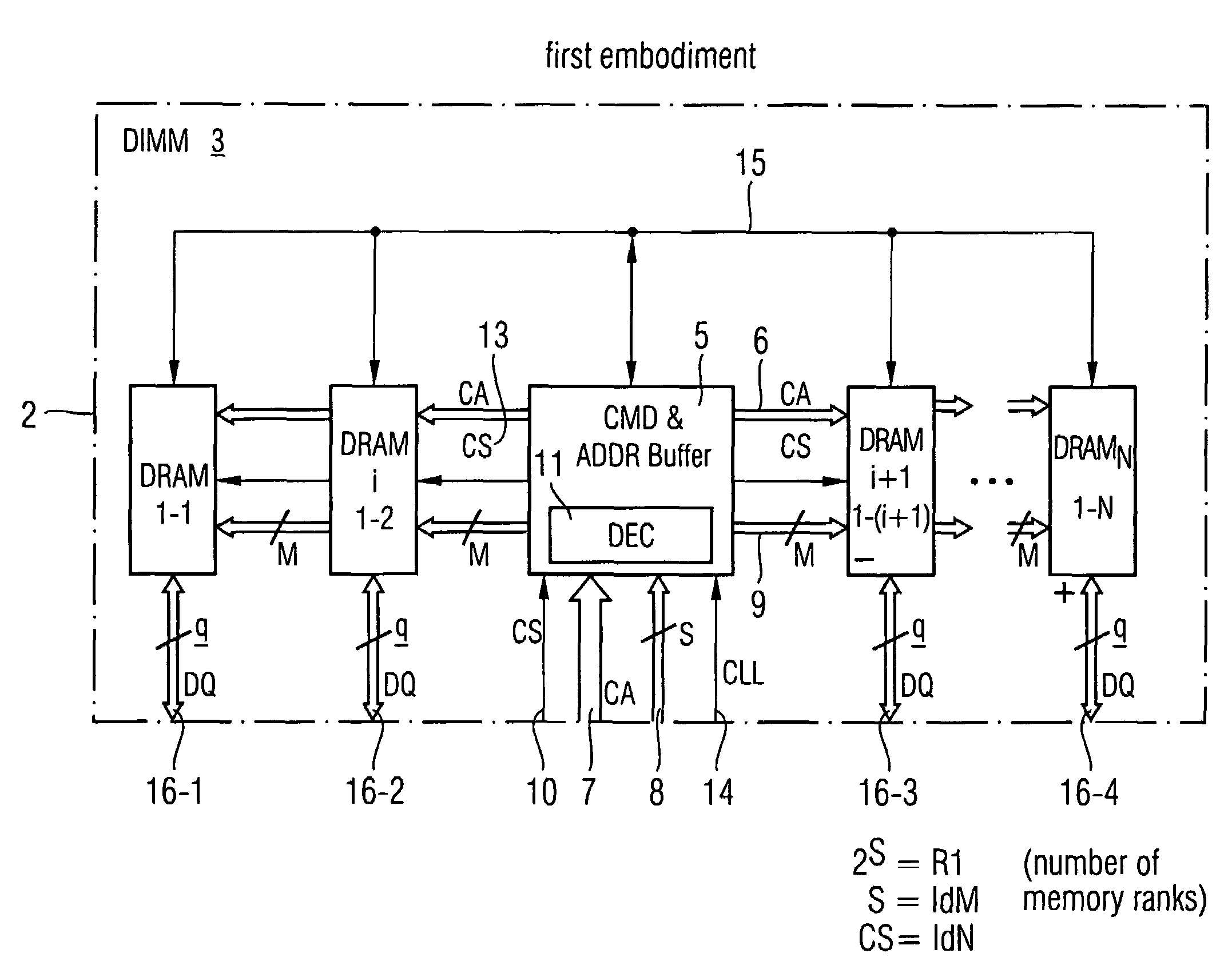
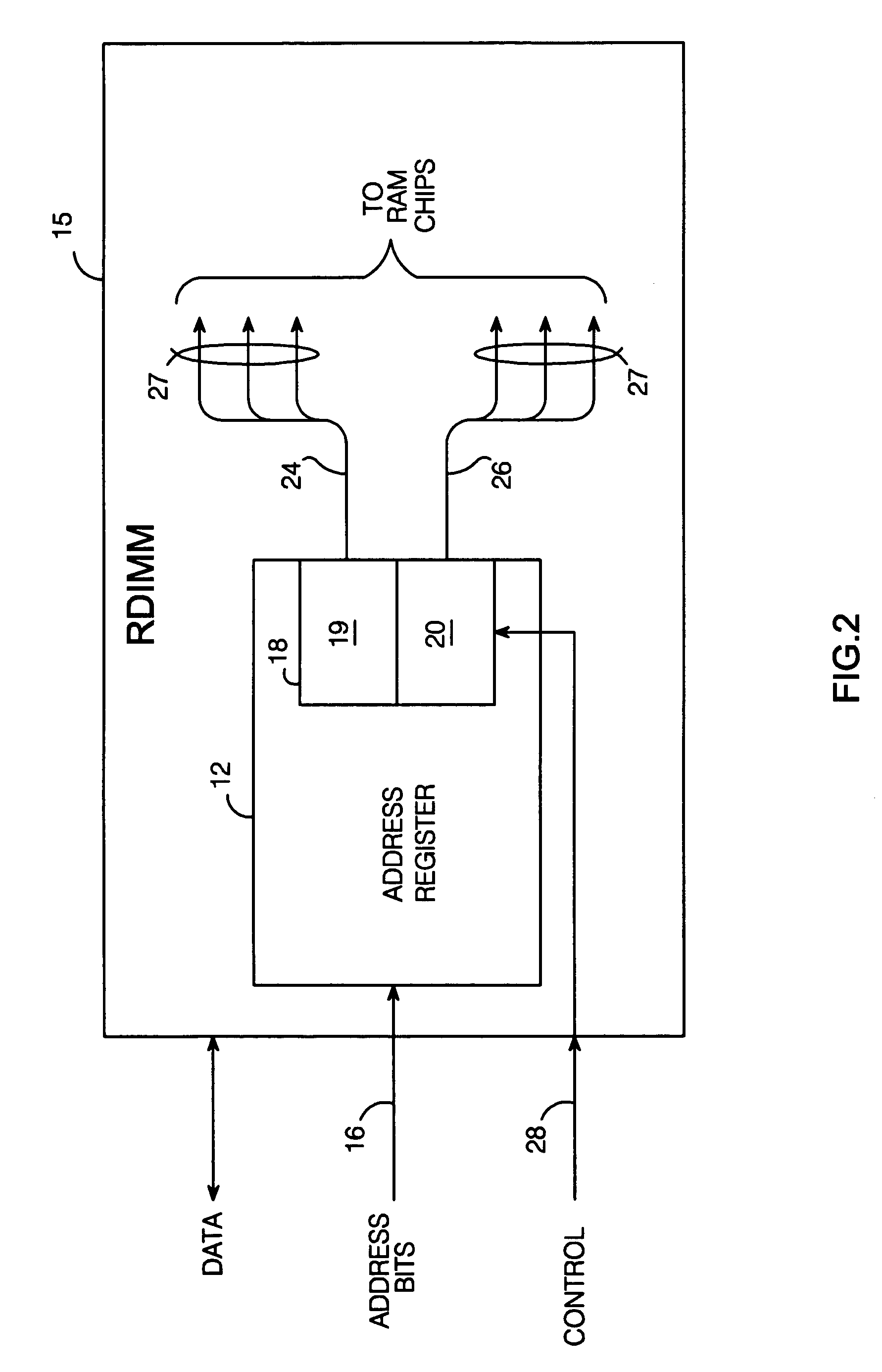
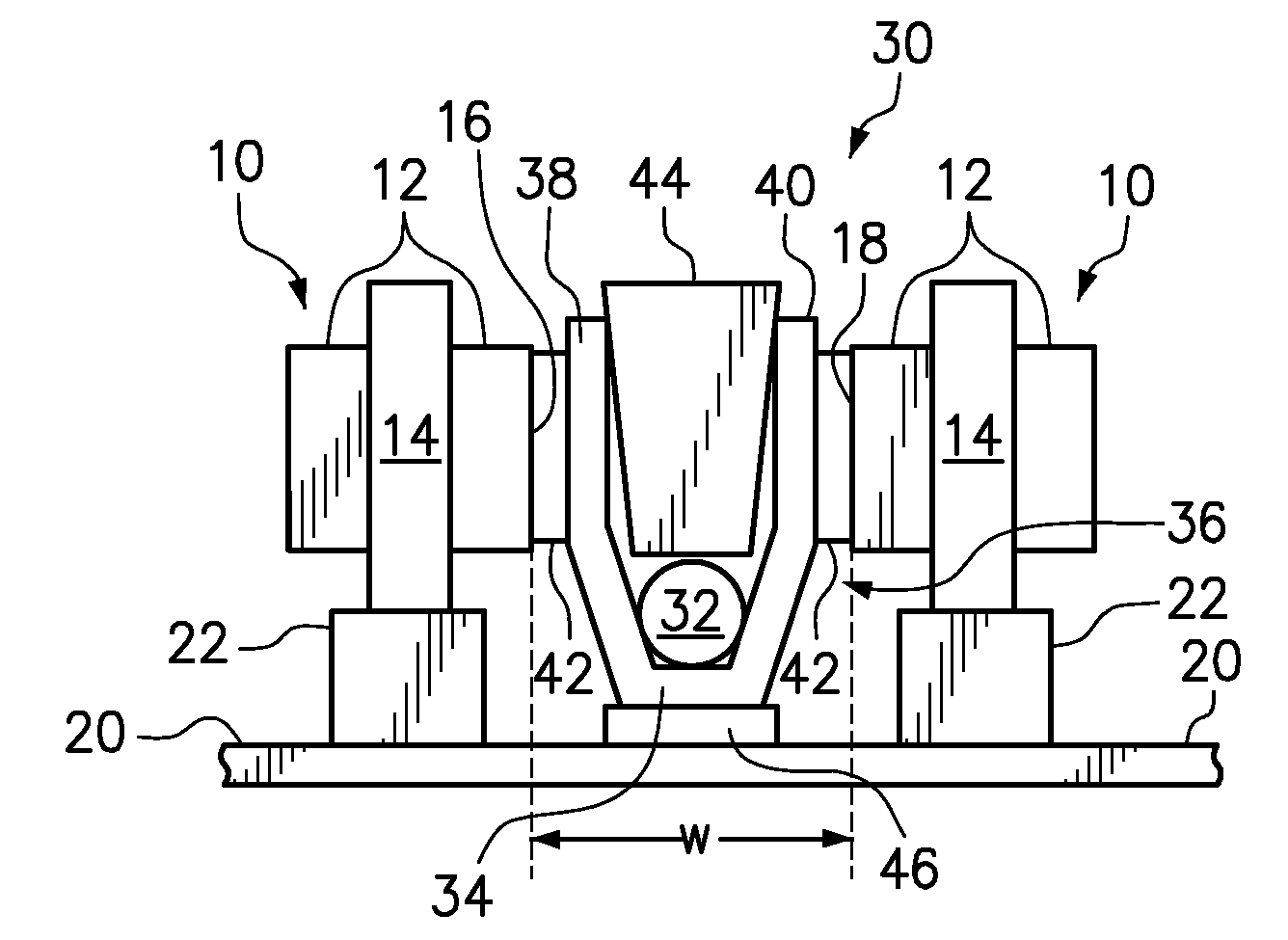
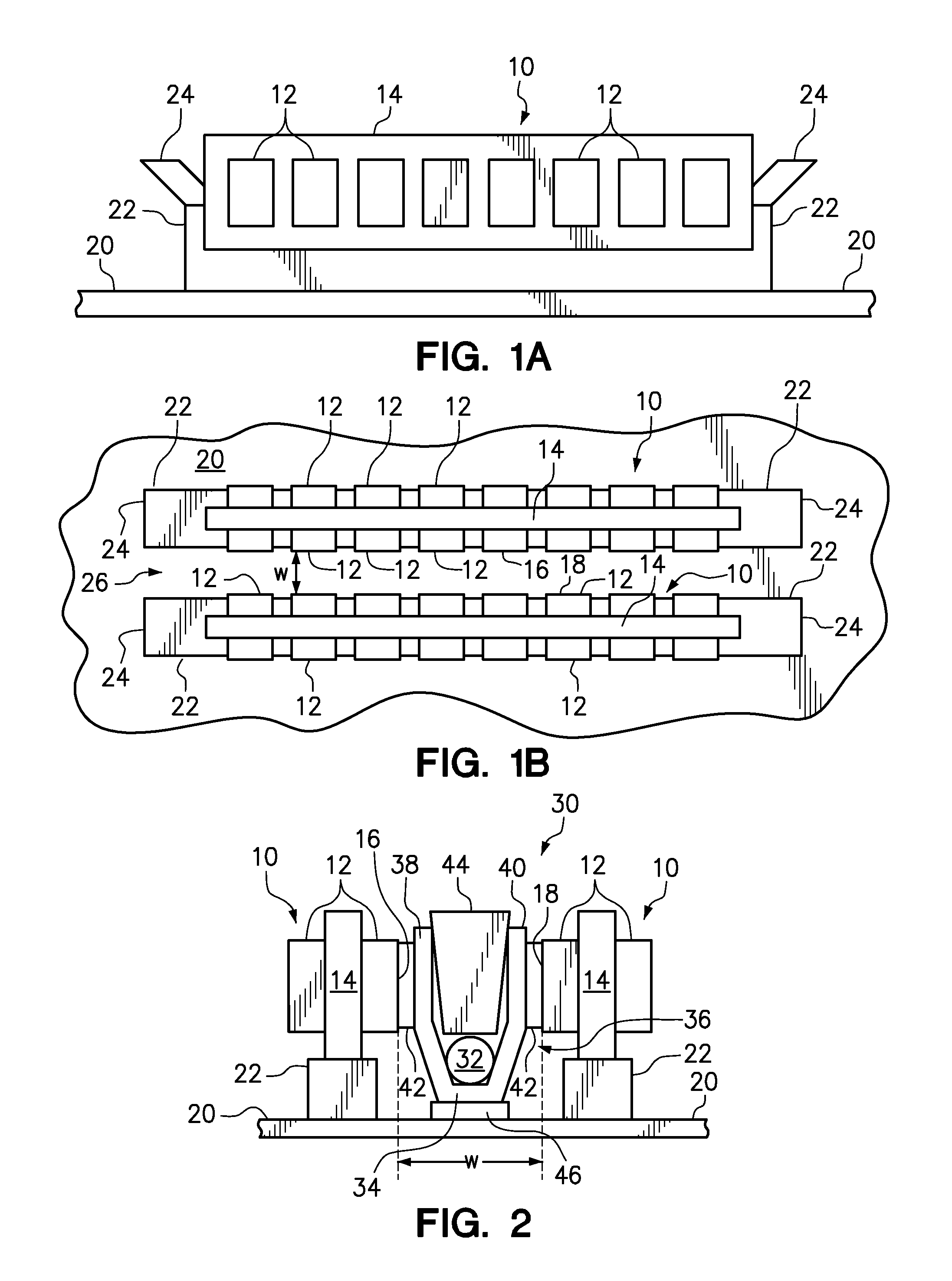
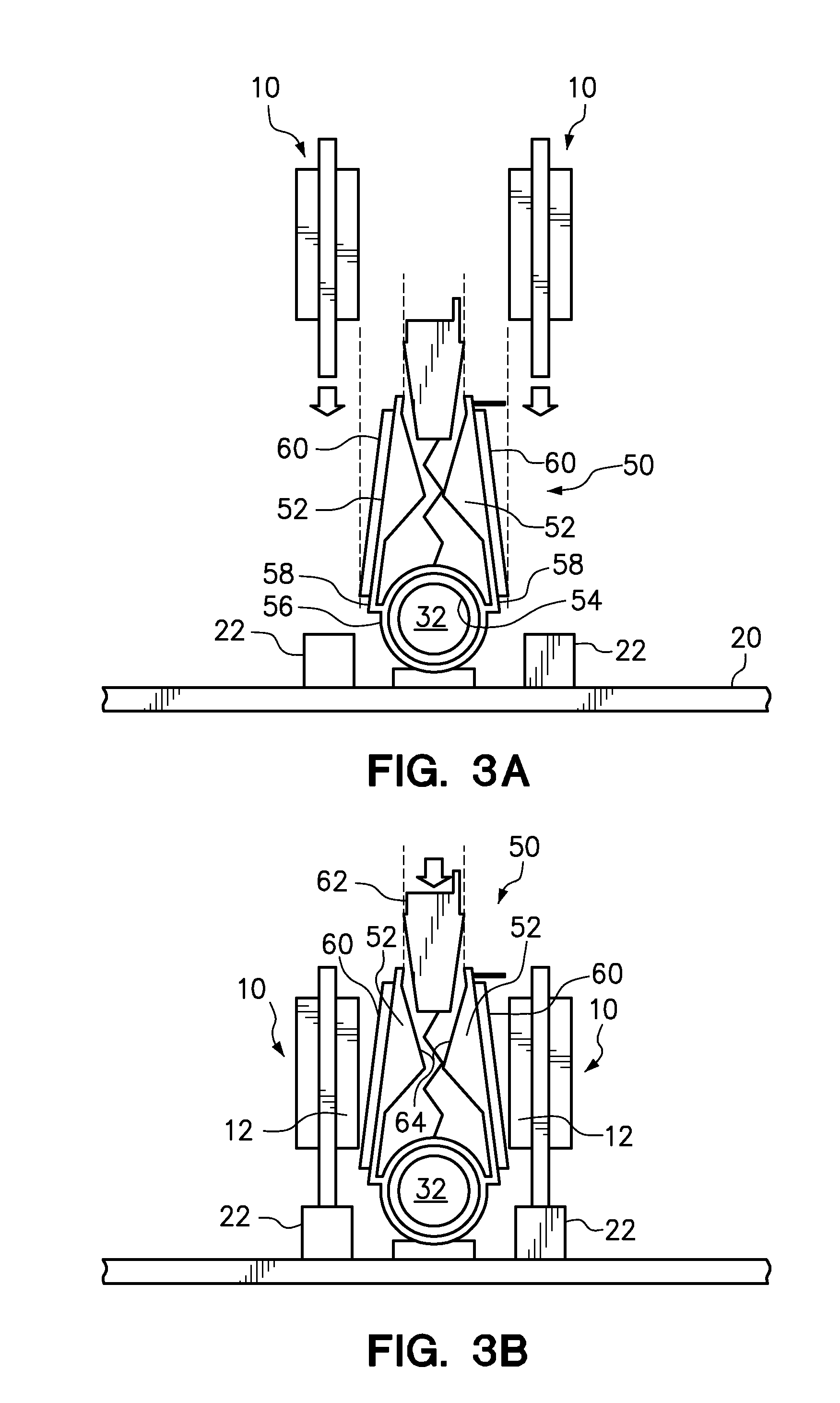
Memory rank decoder for a multi-rank Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM)
The invention refers to a Memory Rank Decoder for a Multi-Rank Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) having a predetermined number of DRAM memory chips mounted on a printer circuit board (PCB), wherein each DRAM memory chip comprises a predetermined number of stacked DRAM memory dies which are selectable by a memory rank selection signal (r), wherein the memory rank decoder generates the memory rank selection signal (r) in response to external selection signals applied to the dual inline module (DIMM).
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
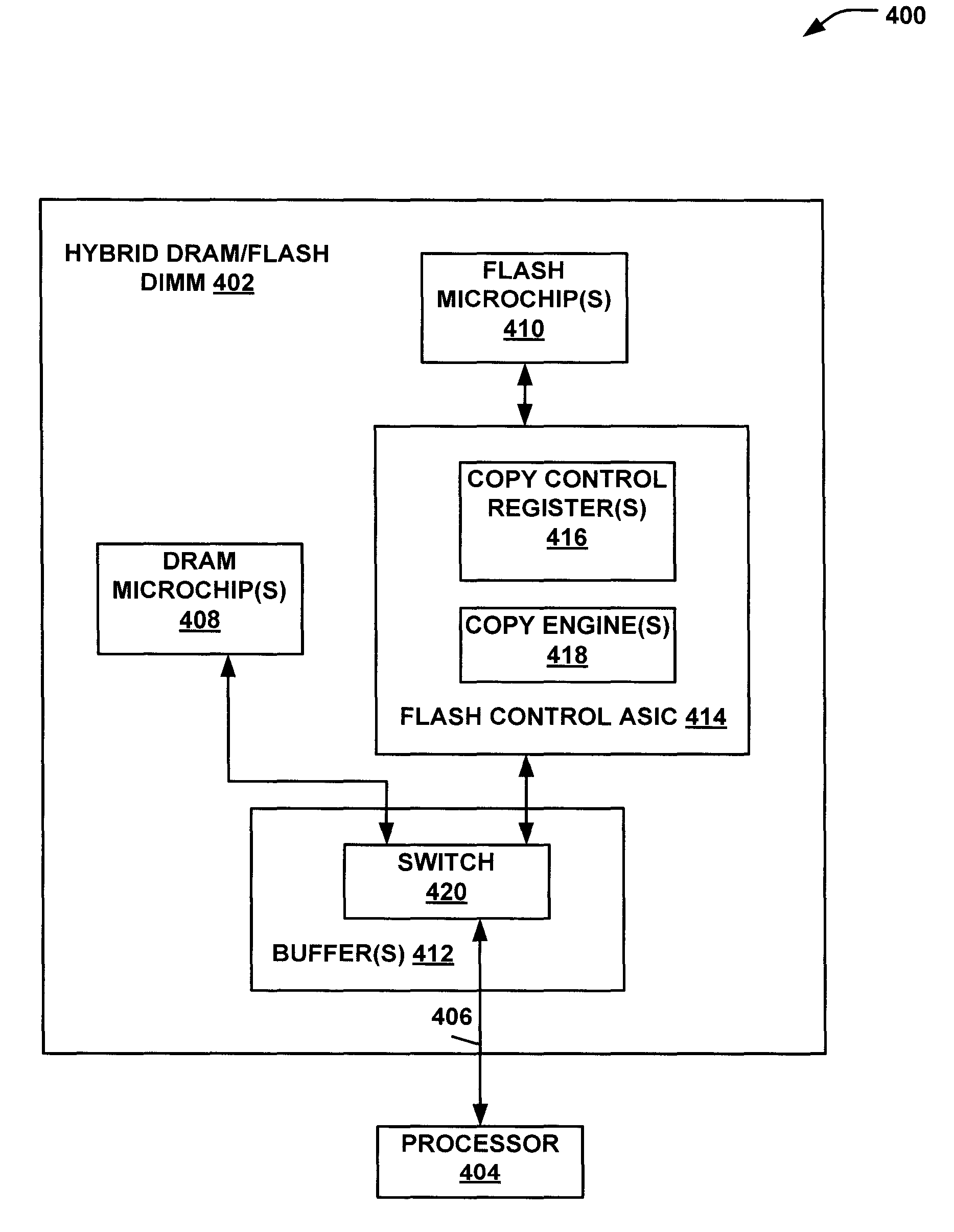
Flash memory dual in-line memory module management
InactiveUS20140095769A1Improve work performanceImprove system performanceRead-only memoriesDigital storageDIMMComputer module
Systems and methods to manage memory on a dual in-line memory module (DIMM) are provided. A particular method may include receiving at a flash application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) a request from a processor to access data stored in a flash memory of a DIMM. The data may be transferred from the flash memory to a switch of the DIMM. The data may be routed to a dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) of the DIMM. The data may be stored in the DRAM and may be provided from the DRAM to the processor.
Owner:LENOVO ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS SINGAPORE
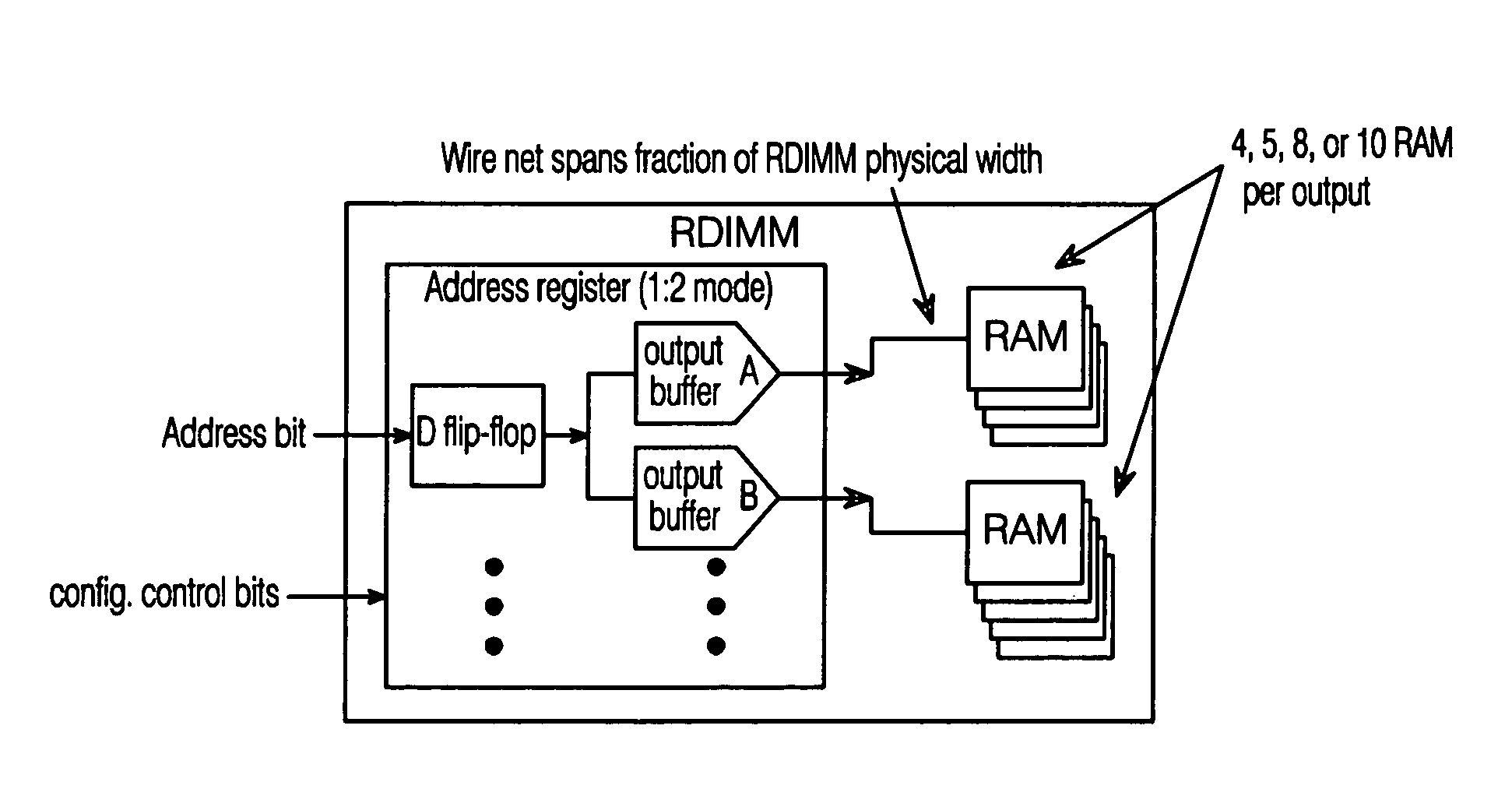
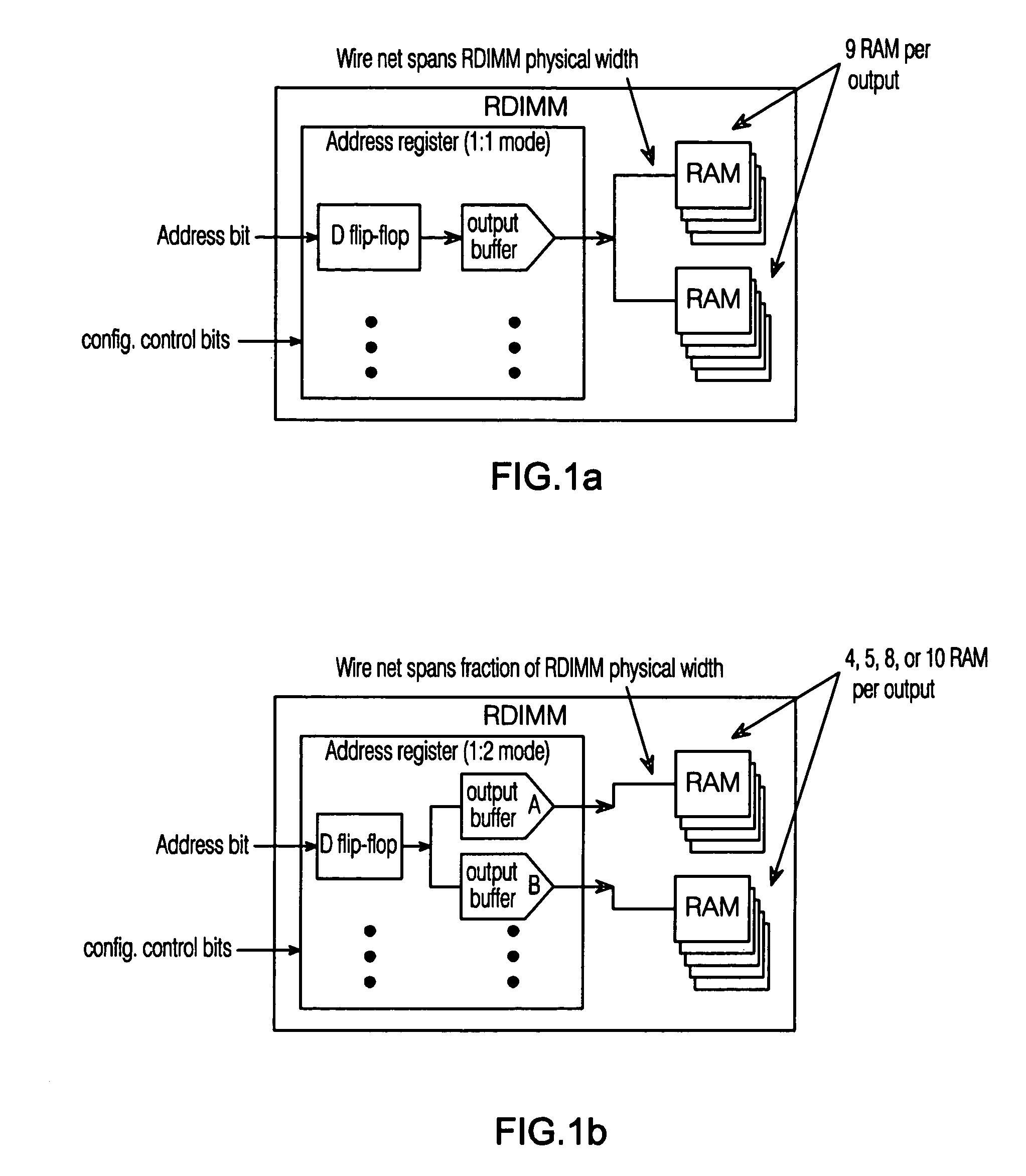
Programmable strength output buffer for RDIMM address register
Owner:RAMBUS INC
DRAM interface circuits having enhanced skew, slew rate and impedance control
Fully-buffered dual in-line memory modules (FB-DIMM) include advanced memory buffers (AMBs) having enhanced skew, slew rate and output impedance control. The AMB includes user accessible registers that can be programmed to carefully control the edge placement (or phase) of signals generated from the AMB to multiple DRAMs on the module. This control of edge placement, which may be performed independently for each group of signals: clock (CLK, CLK#), command (RAS, CAS, WE), address (including bank address), data (DQ) and data strobe (DQS), provides 360 degrees of control (or one period). This means that any group of signals can be moved independently by one complete period relatively to any other group.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Memory read/write reordering
InactiveUS7047374B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingDIMMMemory bandwidth
Owner:INTEL CORP
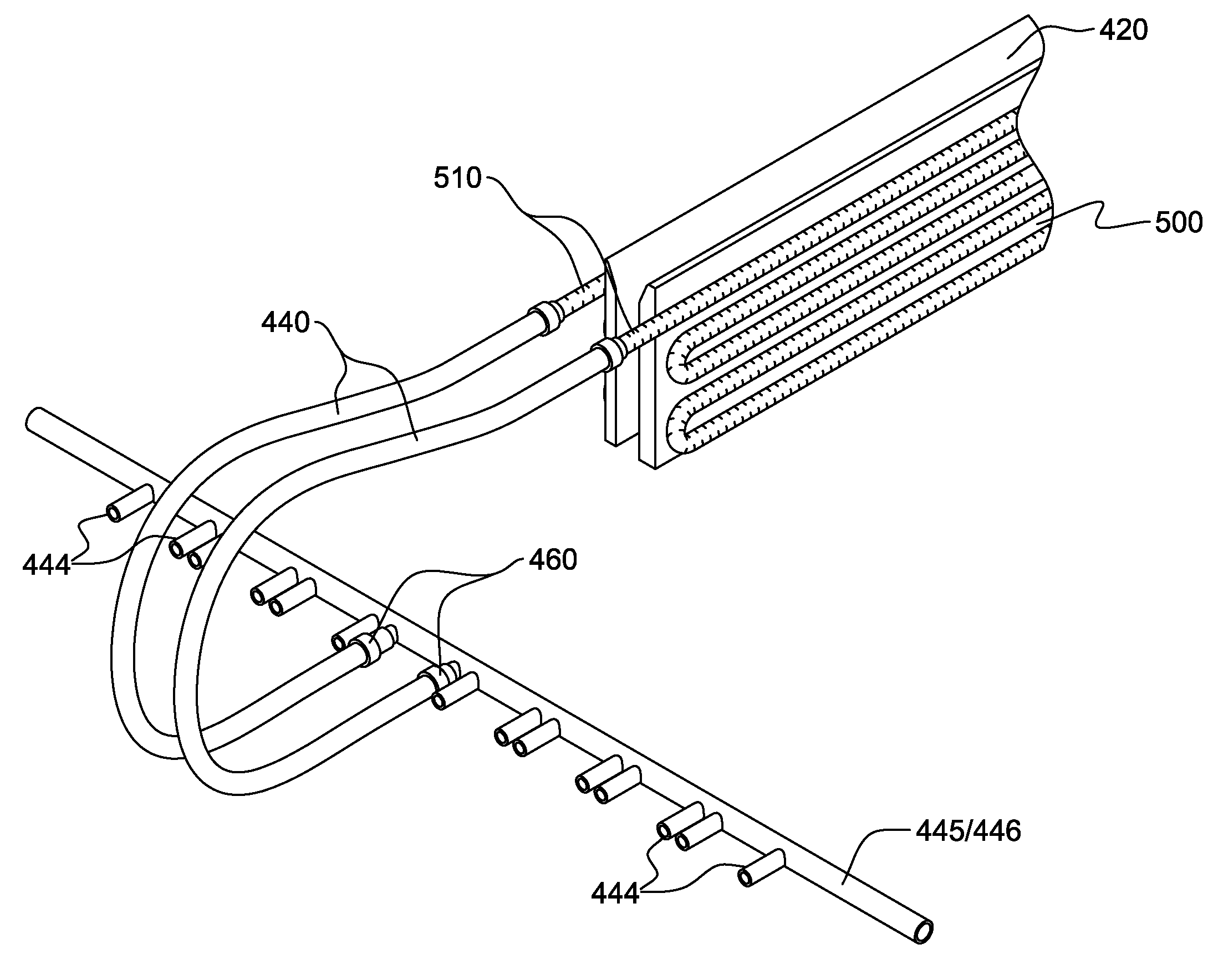
High performance dual-in-line memory (DIMM) array liquid cooling assembly and method
A method and associated assembly for cooling electronic heat generating components of a computer including dual-in-line memory (DIMM) array(s) is provided. The assembly comprises a cooling component having a plate with a first and a second (reverse) side, thermally coupling to the heat generating components including the DIMM array(s). The first plate side has a coolant conduit connected at one end to a supply manifold via flexible tubing and at another end to a return manifold via another flexible tubing such that when coolant is supplied, the coolant circulates from the supply manifold to the return manifold by passing through said first plate's conduit.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
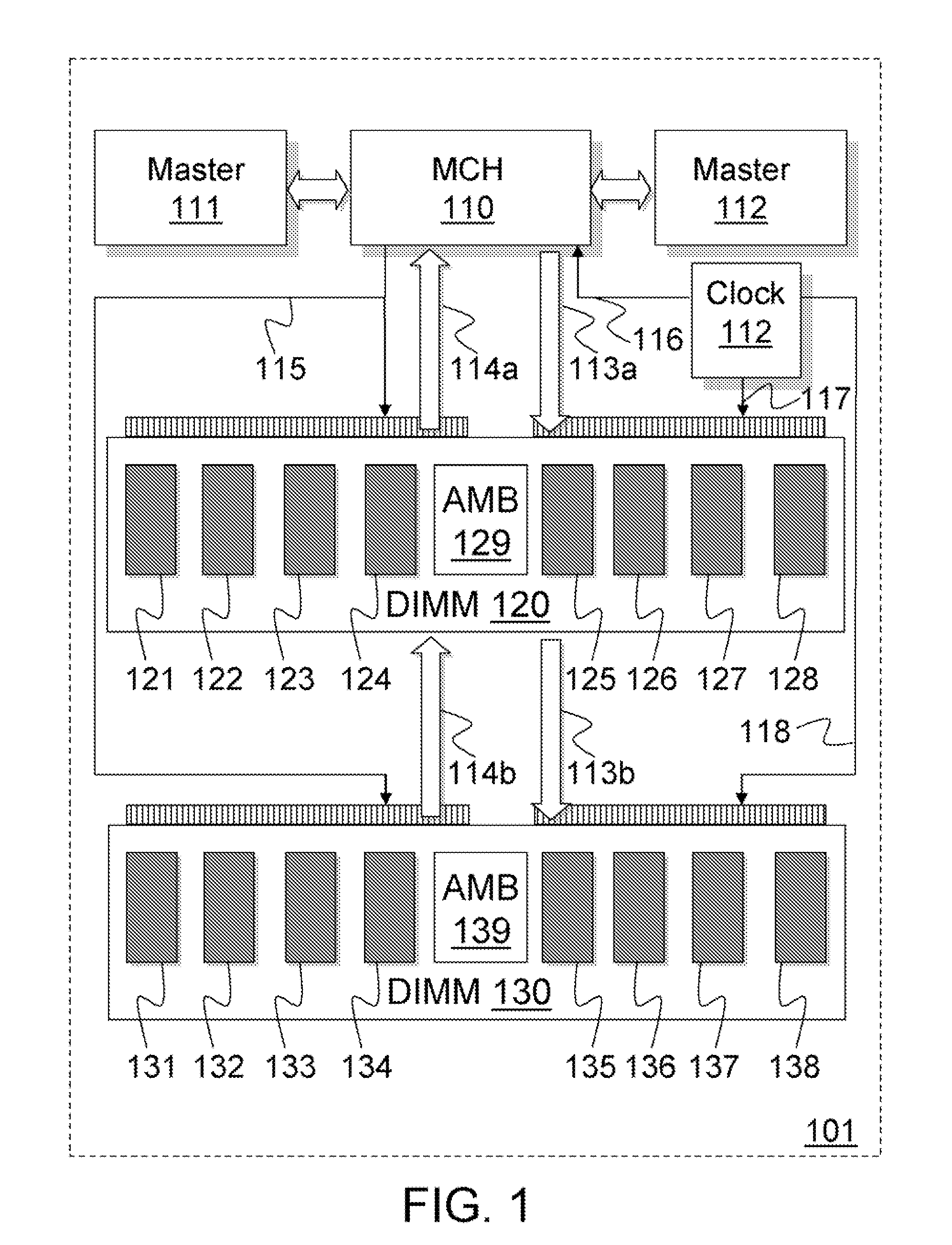
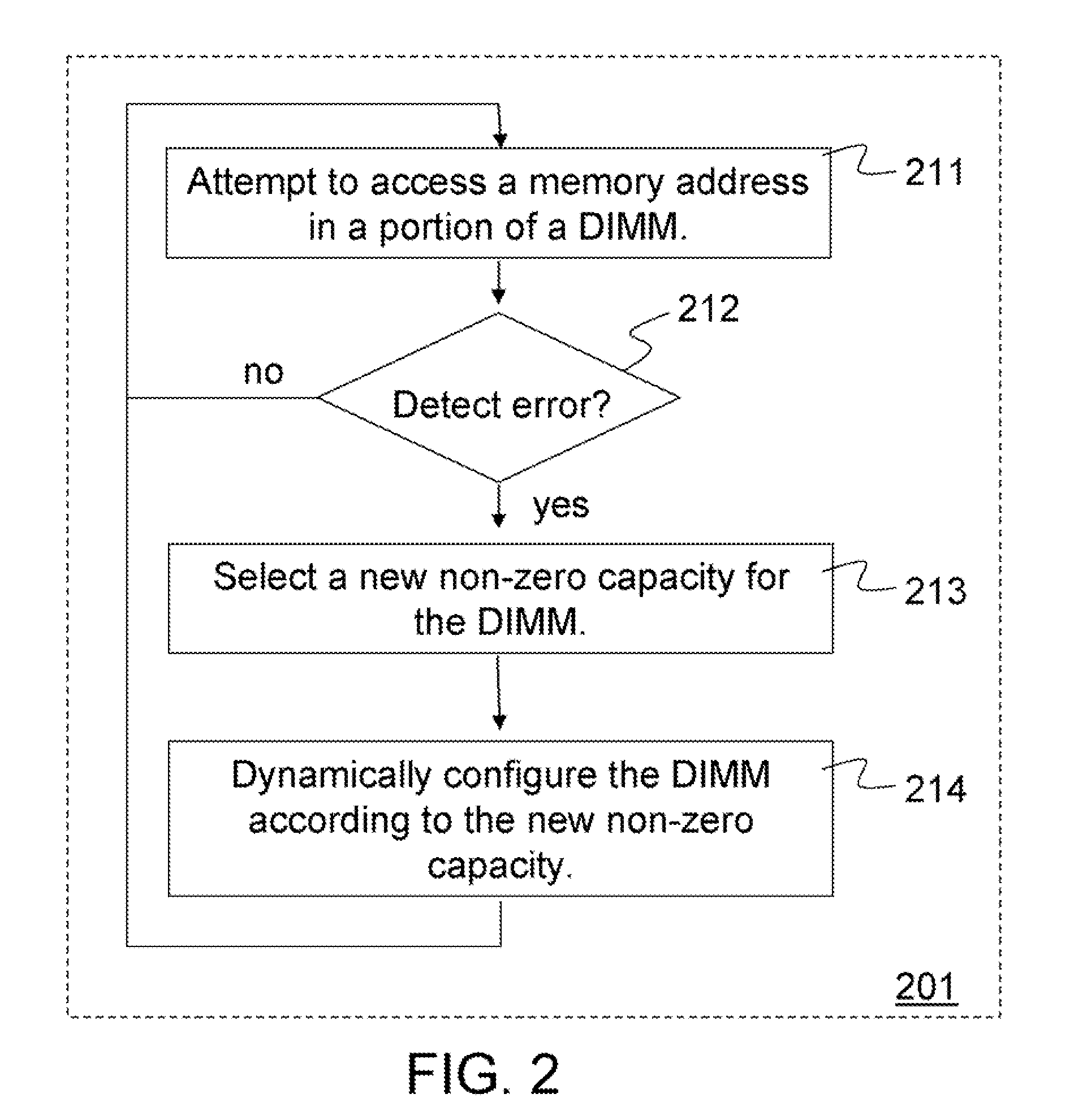
Method and apparatus for improved memory reliability, availability and serviceability
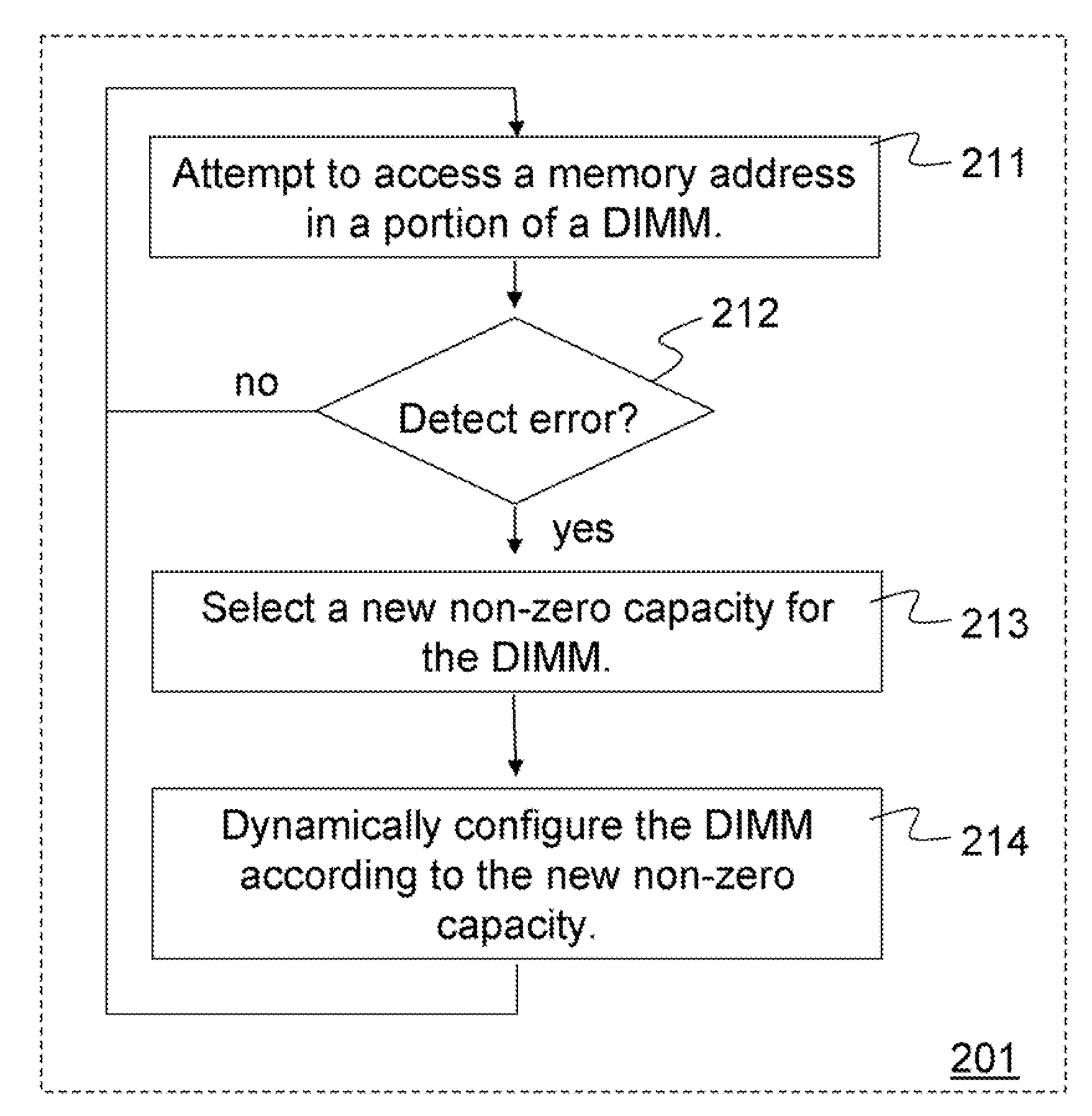
Methods and apparatus dynamically reconfigure storage or channel capacities in a memory system. A fully-buffered dual in-line memory module (DIMM) is configured for a particular storage capacity and a particular channel capacity. An error may be detected at a memory address in some portion of the DIMM. To resolve the problem, the storage capacity or the channel capacity may be reduced and the DIMM may be dynamically reconfigured according to the reduced capacity. For one embodiment the DIMM may be reconfigured by mapping the portion of the DIMM containing the error as unavailable and taking that portion off-line without taking the entire DIMM off-line. For another embodiment the DIMM may be reconfigured by throttling the DIMM at a reduced frequency. The portion of the DIMM containing the error may be retested at the reduced frequency. If no errors are detected, the DIMM may be made available at the reduced frequency.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dynamic power management via DIMM read operation limiter
InactiveUS7421598B2Little or no usePower usageEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementDIMMDynamic power management
A method and system for enabling directed temperature / power management at the DIMM-level and / or DRAM-level utilizing intelligent scheduling of memory access operations received at the memory controller. Hot spots within the memory subsystem, caused by operating the DIMMs / DRAMs above predetermined / preset threshold power / temperature values for operating a DIMM and / or a DRAM, are avoided / controlled by logic within the memory controller. The memory controller logic throttles the number / frequency at which commands (read / write operations) are issued to the specific DIMM / DRAM based on feedback data received from the specific DIMM / DRAM reaching the preset threshold power usage value.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Power Management of a Spare DRAM on a Buffered DIMM by Issuing a Power On/Off Command to the DRAM Device
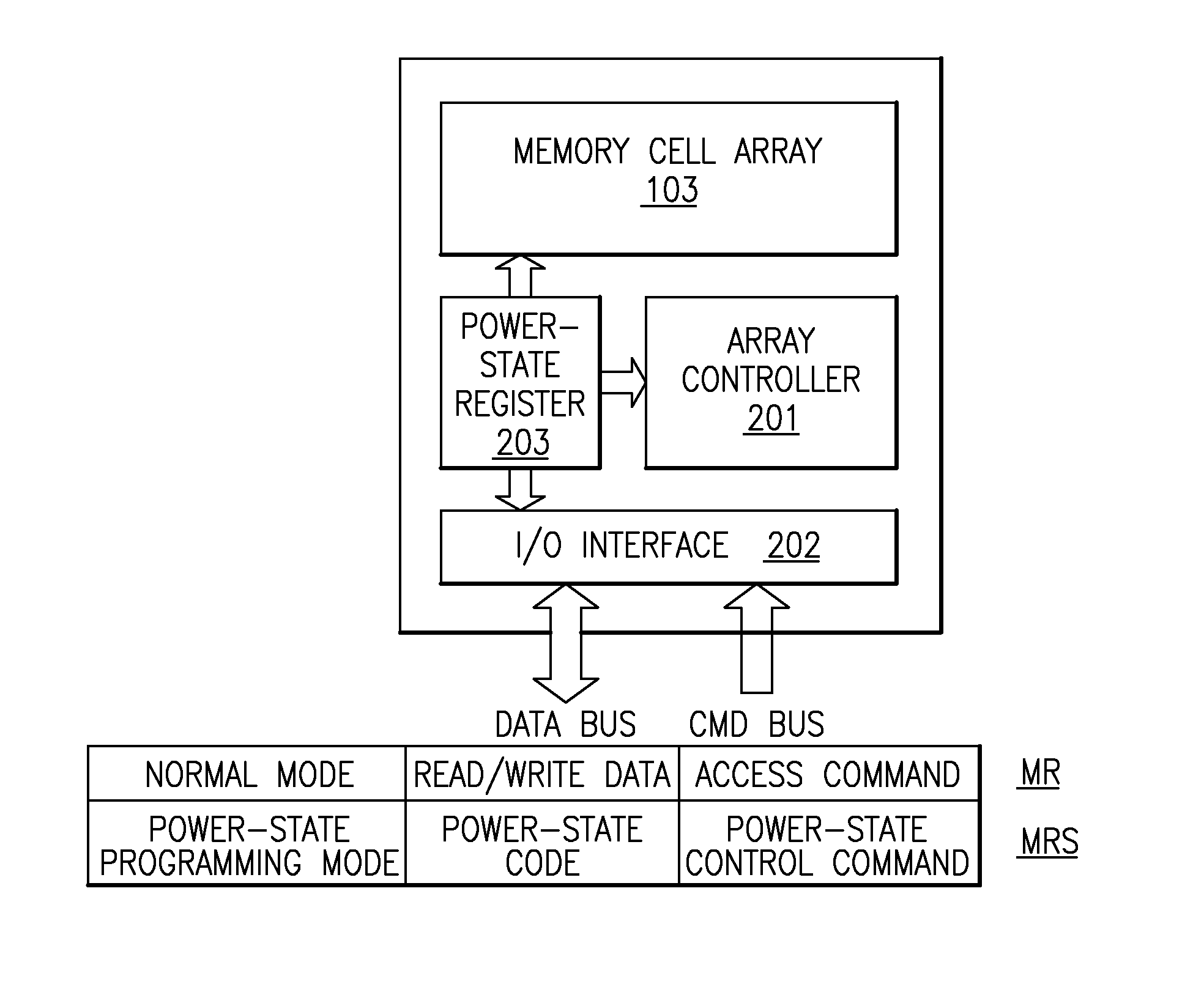
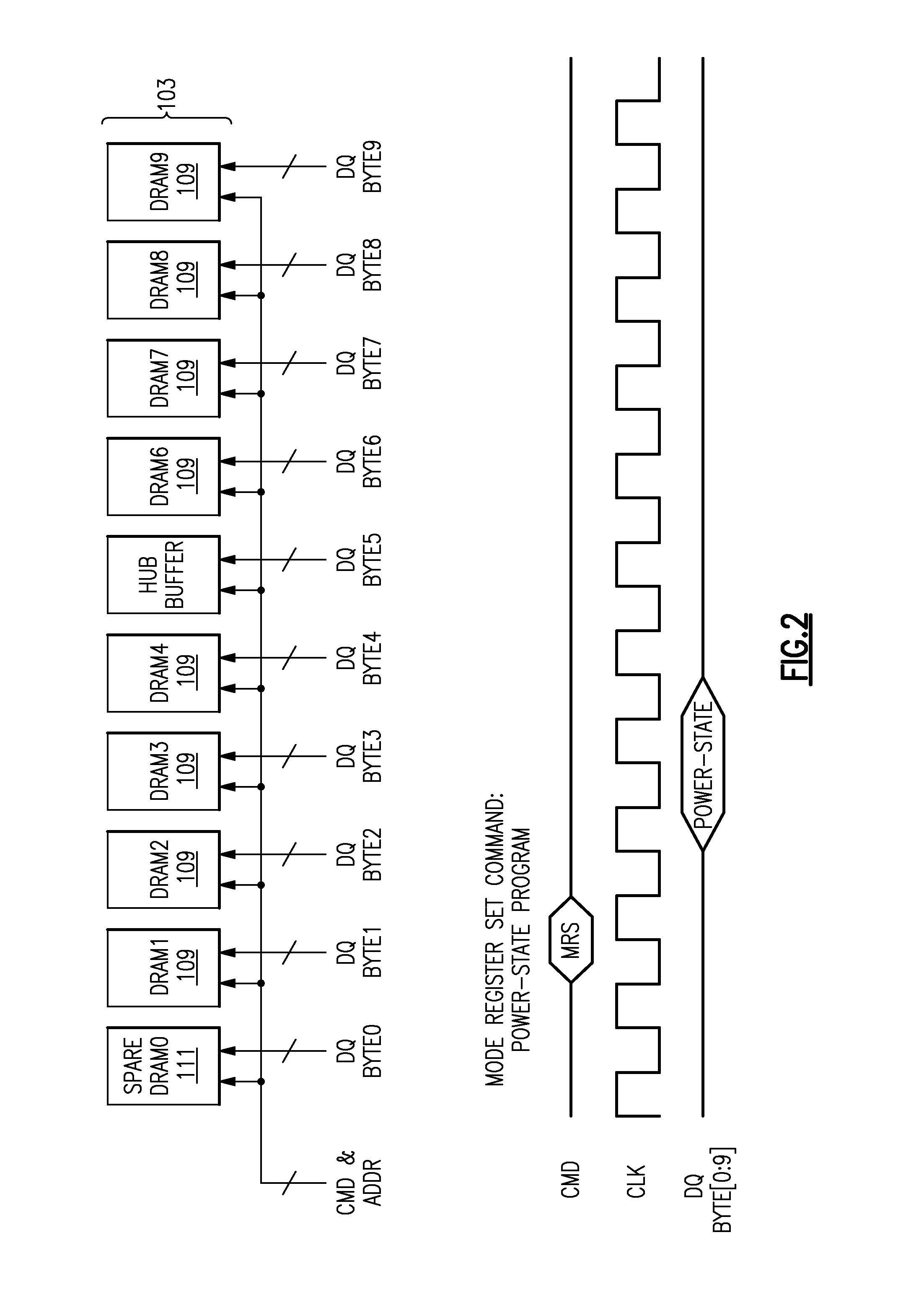
A computer memory, having one or more of a semiconductor memory device having an internal memory array comprising a plurality of semiconductor dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cells arranged in a matrix of rows and columns, and provided as a memory module rank of such memory devices arranged in an array on a DIMM of one or more of said semiconductor memory device on a substrate which can be coupled via a memory device data interface to a memory system as a memory subsystem, each of said memory device having a low power shut-down state that can be activated using a common memory data interface. Control of power to a DRAM issues over the data interface two commands to a DRAM power control command decode, a power-state program signal and a power-state reset signal as a power-state control commands to control the power state of said DRAM, and to activate for READ / WRITE a memory cell as a normal active or spare device.
Owner:IBM CORP
System for cooling memory modules
DIMMs are cooled by positioning a thermally conductive base between adjacent DIMMs. The thermally conductive base, such as a heat pipe or metal rod, receives heat from the DIMMs through thermally conductive elements that are selectively biased outward against the installed DIMMs. The base transfers the heat to a liquid conduit extending along the end of the DIMMs, where a circulating liquid carries away the heat. The thermally conductive elements provide an adjustable span to accommodate variations in distance between the DIMM surfaces. Embodiments of the invention may be installed without extending above the height of the DIMM.
Owner:IBM CORP
Self-initiated self-refresh mode for memory modules
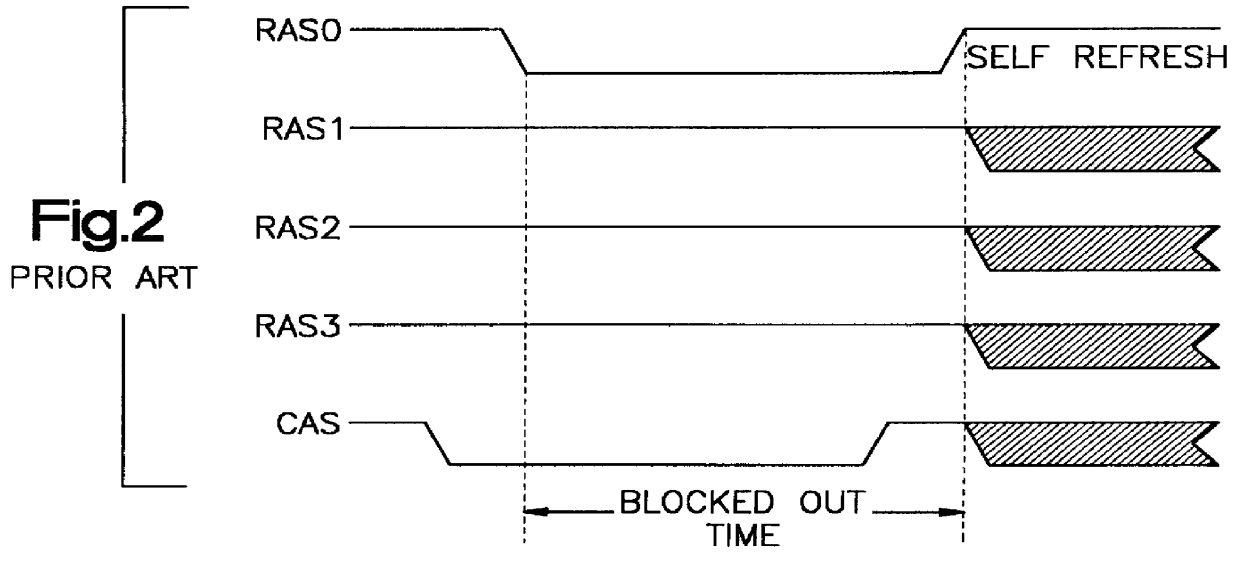
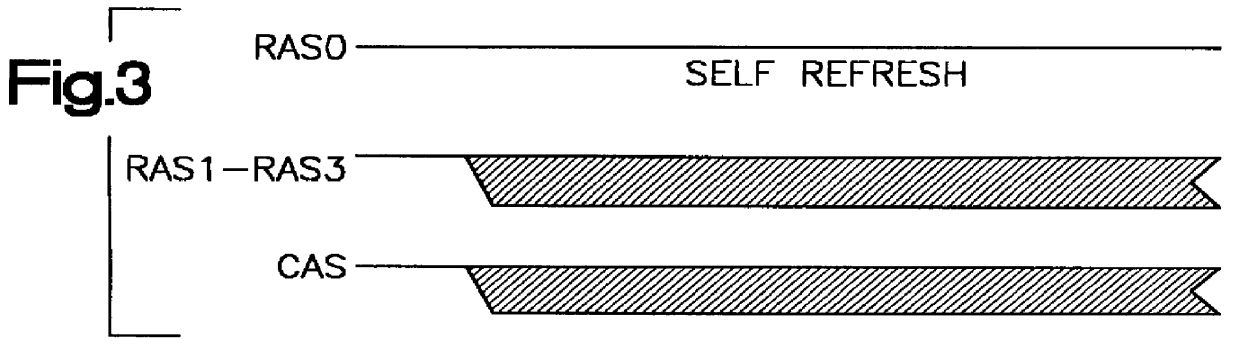
A method and apparatus for selectively causing each bank of a number of banks of DRAMs of a DRAM memory card to enter into the self-refresh mode without affecting the operation of any other bank. In the computer system incorporating the SIMM or DIMM type DRAM cards, each bank of memory on each card has a RAS signal specific to that specific bank. One or more CAS signals are supplied across all of the memory banks, on all cards. Thus, each memory bank is accessed separately for a read / write operation by the RAS becoming active before the CAS becomes active; and refresh takes place by the CAS signal becoming active before the RAS signal becomes active. The number of clock cycles or refresh cycles between active RAS signals to each memory bank are counted. If RAS does not become active for N clock or refresh cycles, a signal is provided within each respective memory bank and that memory bank will immediately, or preferably after M additional clock or refresh cycles enter self-refresh mode without affecting the operation of any other bank. At the same time, the memory controller counts cycles of RAS inactivity for each DRAM bank it controls. A signal is also provided to a register to require a double read / write on the next active read / write cycle to that bank, for reactivating that bank from the self-refresh mode when RAS signal specific to that bank becomes active while CAS is inactive.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
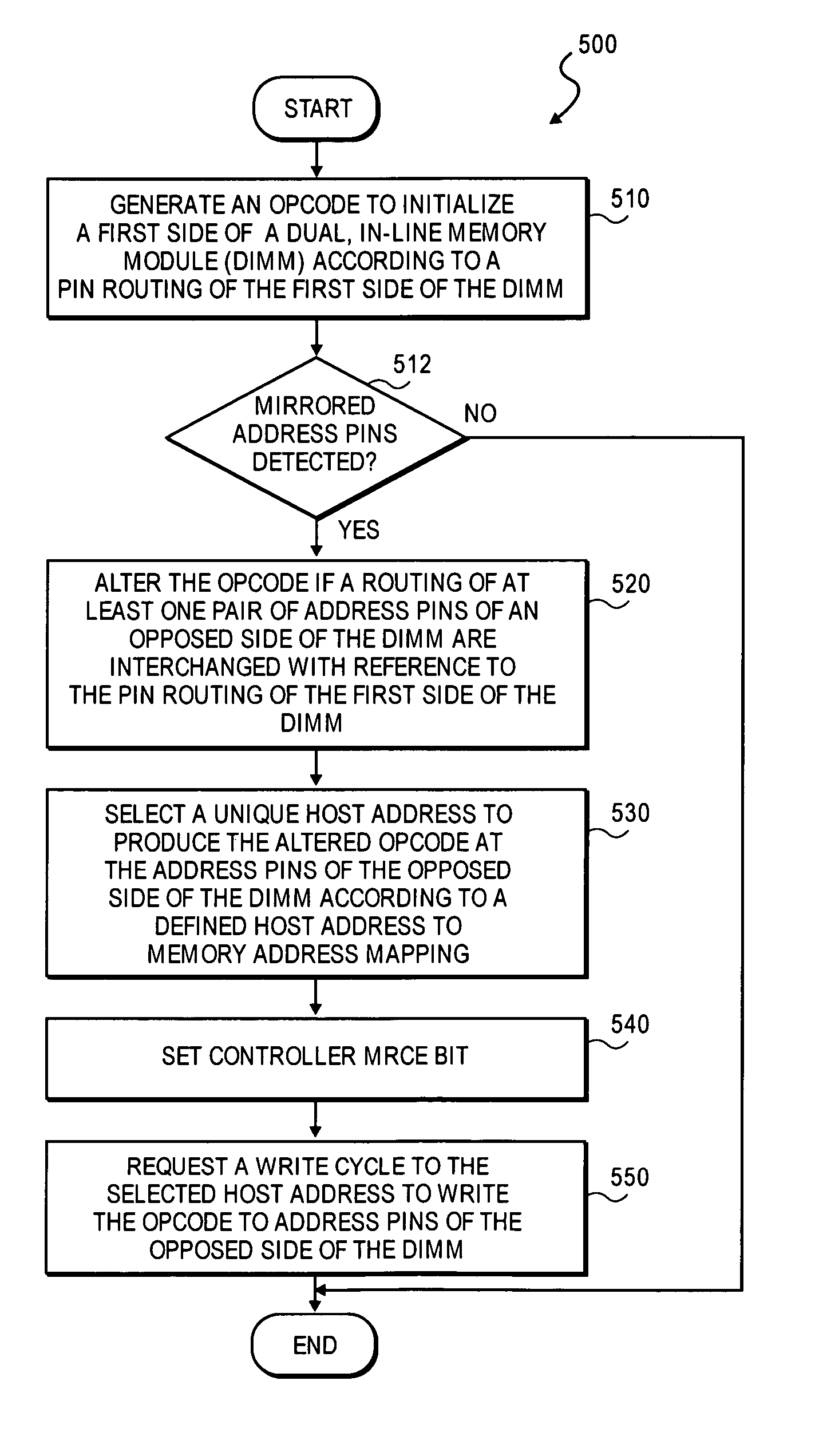
Apparatus and method for initialization of a double-sided dimm having at least one pair of mirrored pins
A method and apparatus for initialization of a double-sided memory module having a least one pair of mirrored pins. In one embodiment, the method includes the generation of an opcode to initialize a first side of the memory module according to a first side pin routing. In one embodiment, the opcode is written to a host address selected for the first side of the memory module according to a system host address to memory address mapping. In one embodiment, the opcode is altered if a routing of address pins of the opposed side of the memory module are interchanged with reference to the first side pin routing. Subsequently, a unique host address is selected to produce the altered opcode at the address pins of the opposed side of the memory module according to a defined host address to memory address mapping. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
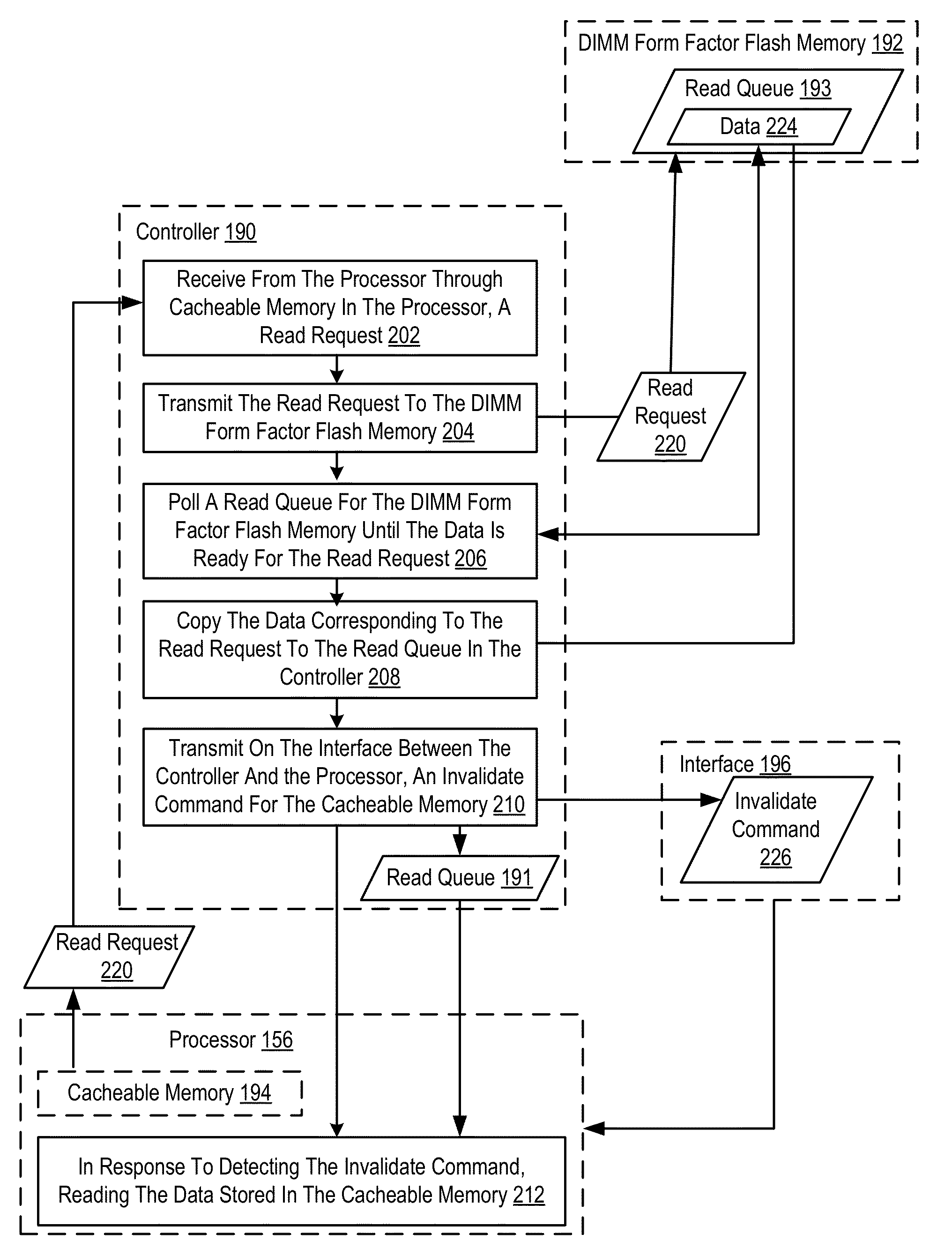
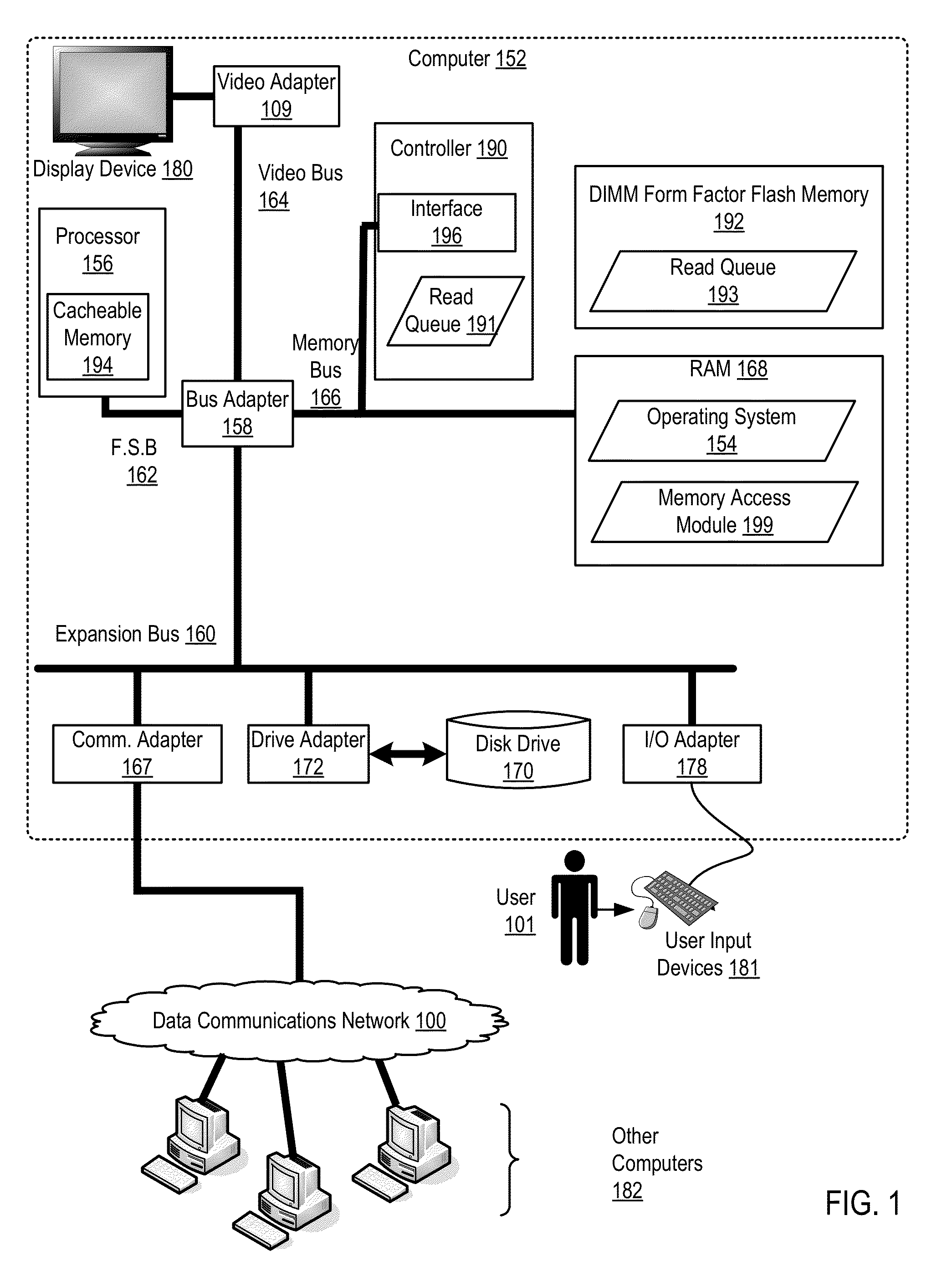
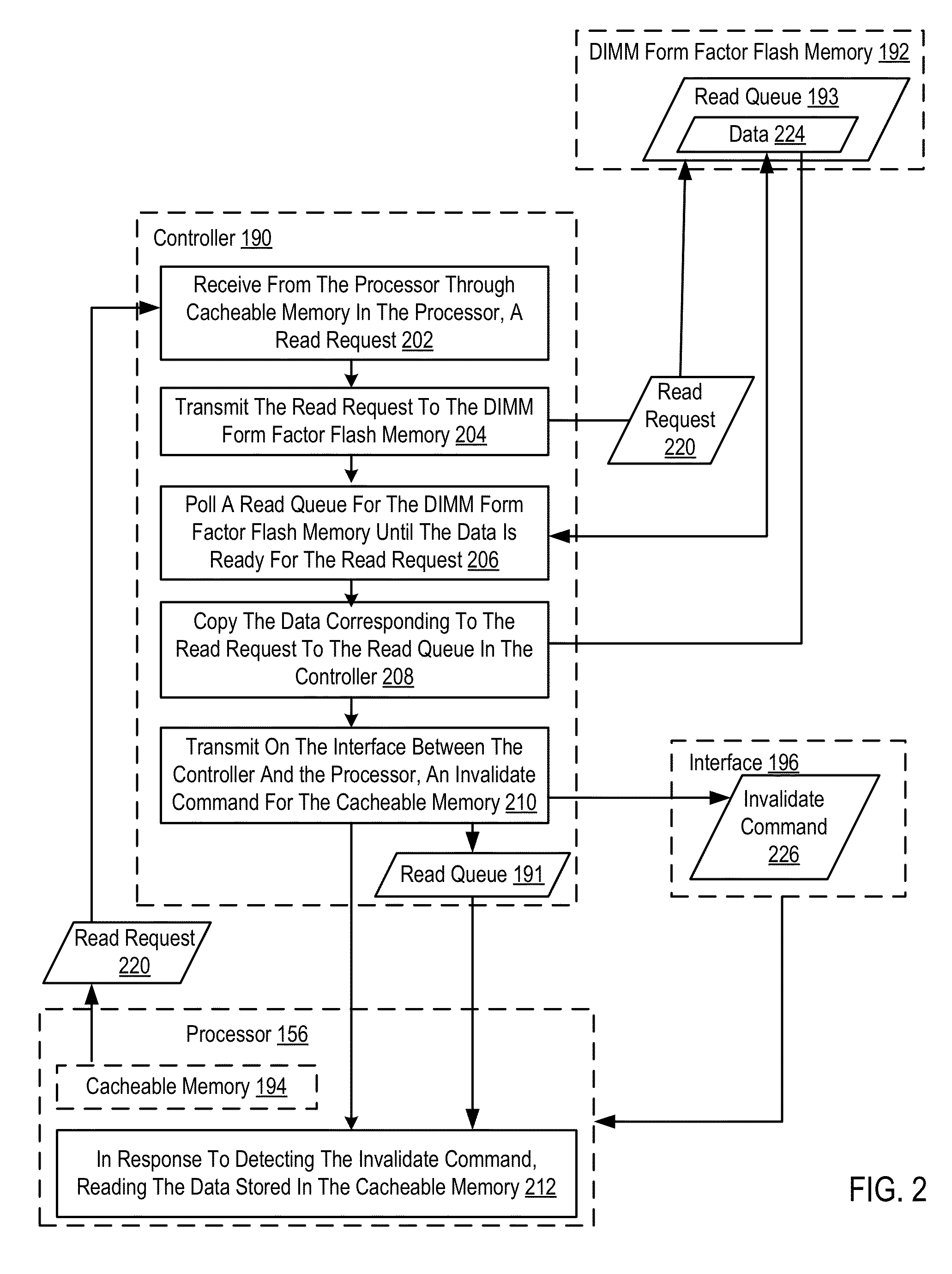
Memory access to a dual in-line memory module form factor flash memory
ActiveUS8607003B2Improve system performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDIMMData preparation
Methods, apparatuses, and computer program products for memory access to a dual in-line memory module (DIMM) form factor flash memory are provided. Embodiments include receiving, by a controller from a processor through cacheable memory in the processor, a read request; transmitting, by the controller, the read request to the DIMM form factor flash memory; polling, by the controller, a read queue in the DIMM form factor flash memory until data is ready for the read request; copying from the DIMM form factor flash memory, by the controller, the data corresponding to the read request to a read queue in the controller; transmitting, by the controller on an interface between the controller and the processor, an invalidate command for the cacheable memory; and in response to receiving the invalidate command, reading by the processor the data stored in the read queue in the controller.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Configurable width buffered module having a bypass circuit
InactiveUS7356639B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStatic storageInterconnect topologyDIMM
A memory system architecture / interconnect topology includes a configurable width buffered memory module having a configurable width buffer device with at least one bypass circuit. A buffer device, such as a configurable width buffer device, is positioned between or with at least one integrated circuit memory device positioned on a substrate surface of a memory module, such as a DIMM. The configurable width buffer device is coupled to at least one memory device (by way of an internal channel), entry pin and exit pin on the memory module. The configurable width buffer device includes a multiplexer / demultiplexer circuit coupled to the entry pin and the internal channel for accessing the memory device. A bypass circuit is coupled to the entry pin and the exit pin in order to allow information to be transferred through the memory module to another coupled memory module in the memory system by way of an external channel. In an alternate embodiment of the present invention, two bypass circuits are coupled to a pair of entry and exit pins. In an embodiment of the present invention, a memory system may include at least four interfaces, or sockets, for respective memory modules having configurable width buffer devices with bypass circuits that enable additional upgrade options while reducing memory system access delays.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Data bus
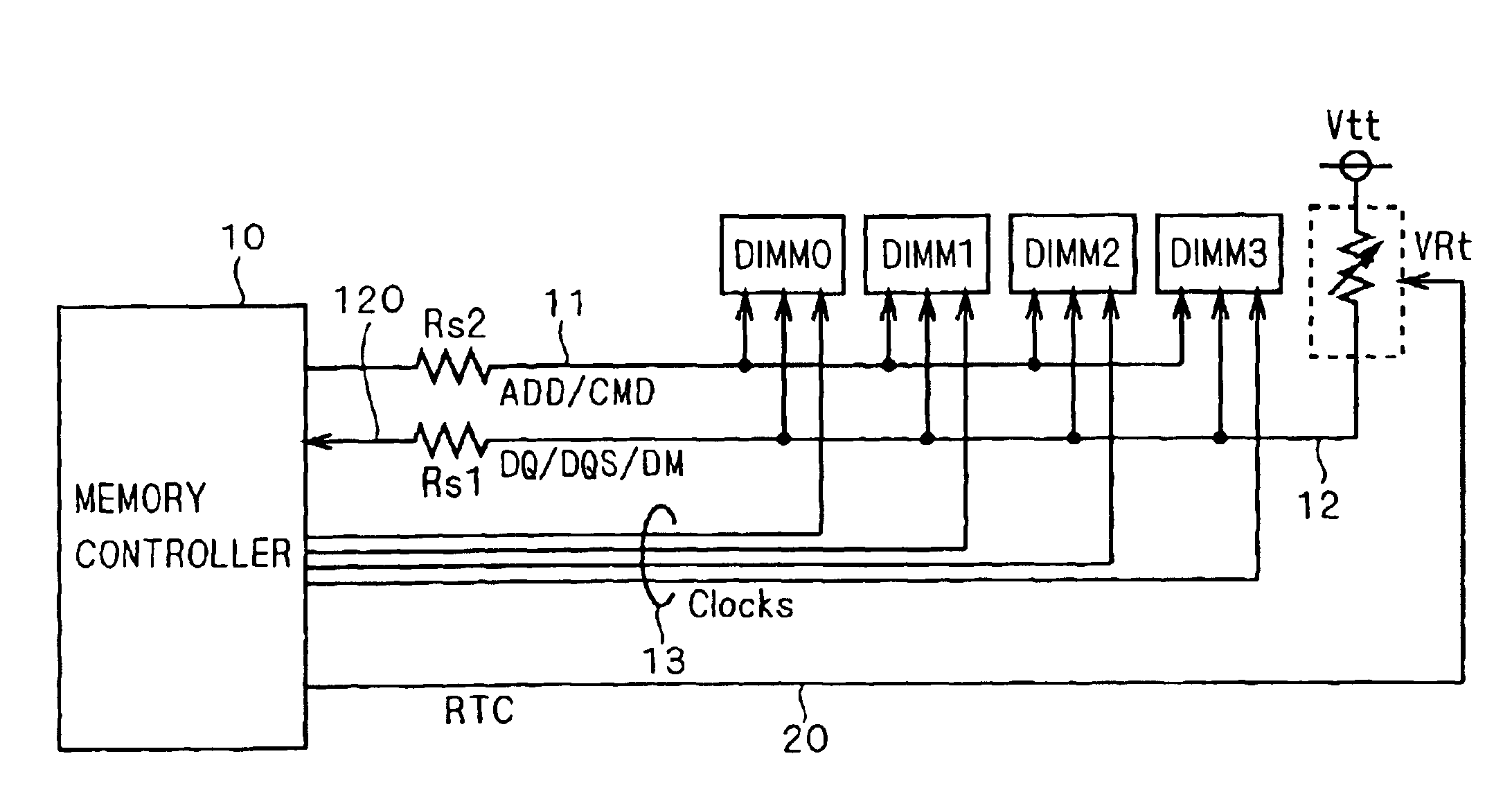
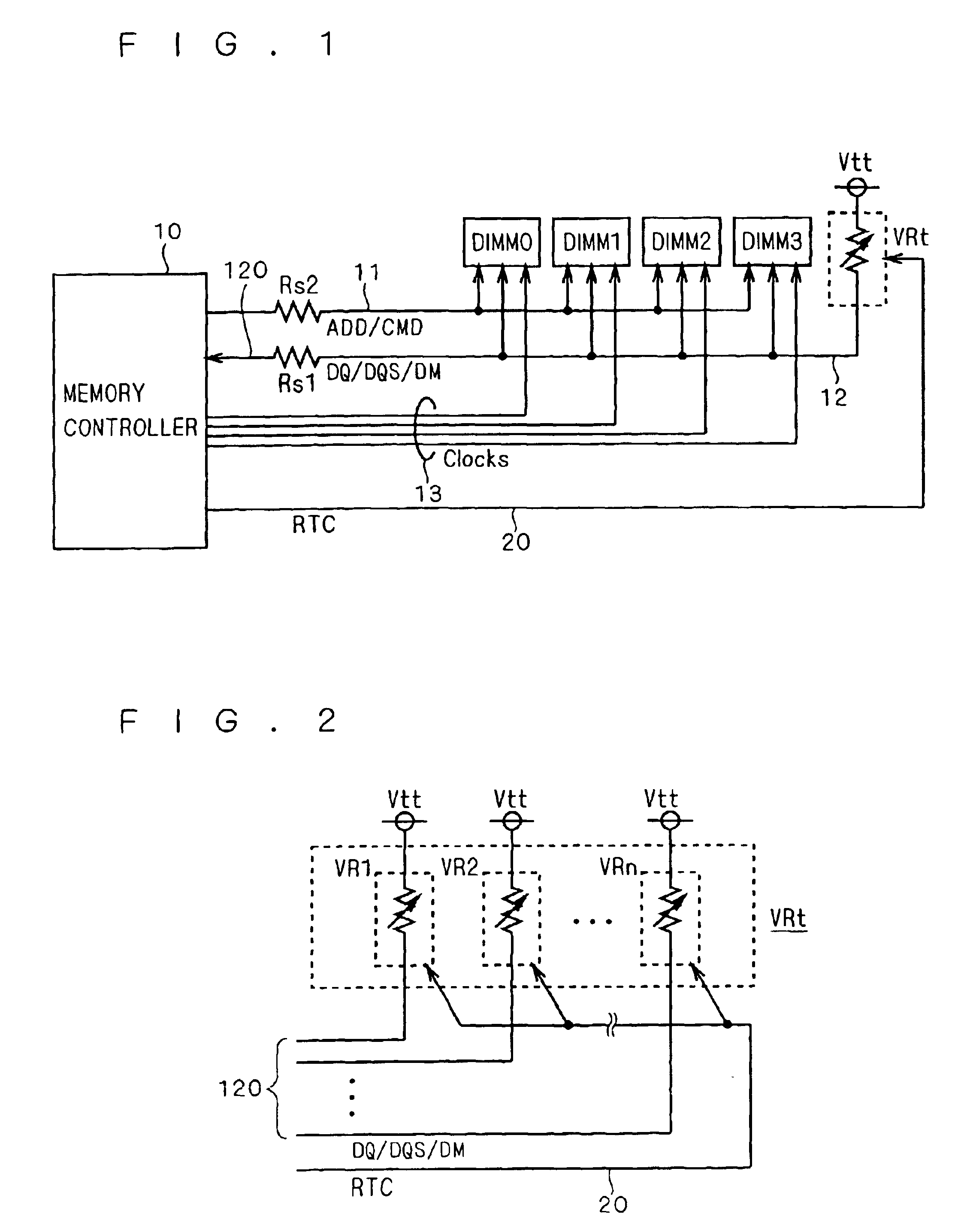
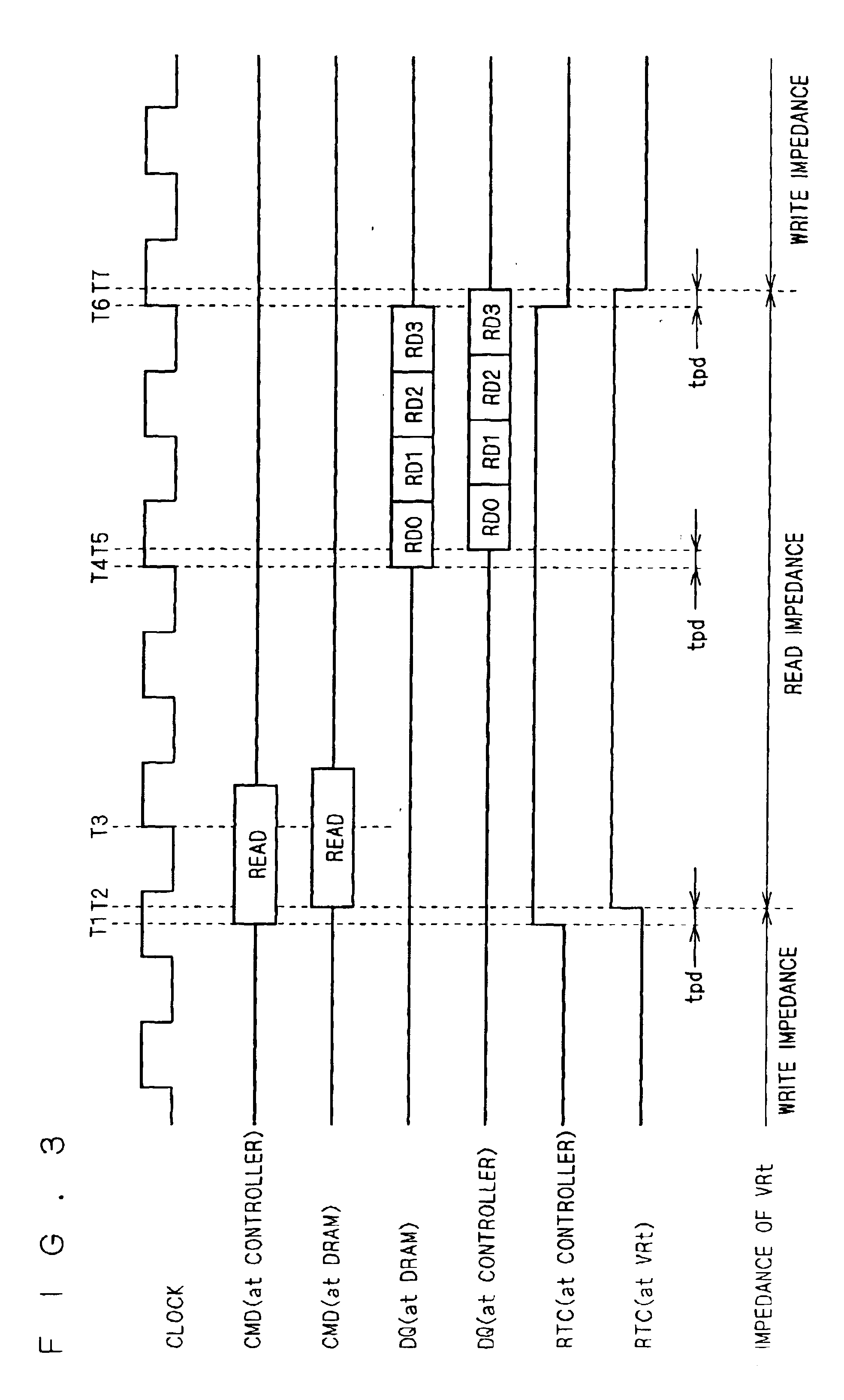
InactiveUS6844754B2Highly reliably transferring dataReliable dataReliability increasing modificationsElectronic switchingDIMMComputer hardware
In a memory system having a data bus transferring data in either direction, highly reliable data transfer is provided regardless of the direction in which data is transferred. The signal lines of a data bus (12) bidirectionally transfer data. That is to say, during data write operations to a DIMM, the signal lines transfer data from a memory controller (10) to the DIMM, and during data read operations, they transfer data from the DIMM to the memory controller (10). The signal lines have, as terminating resistors, terminating variable resistors (VRt) whose impedance is controlled by the memory controller (10). During data write operations to the DIMM, the memory controller (10) sets the impedance of each terminating variable resistor (VRt) at a value suitable for writing, and during data read operations, it sets the impedance of each terminating variable resistor (VRt) at a value suitable for reading.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Configurable width buffered module having flyby elements
A memory system architecture / interconnect topology includes a configurable width buffered memory module having a configurable width buffer device and at least one flyby element. A buffer device, such as a configurable width buffer device, is positioned between or with at least one integrated circuit memory device positioned on a substrate surface of a memory module, such as a DIMM. A flyby element is positioned on a memory module and / or in the buffer device and includes conductive element or signal line in embodiments of the invention. One or more flyby elements are coupled to one or more memory modules to allow for upgrades of memory modules in a memory system. An asymmetrical flyby topology allows for increasing the number of memory modules to more than two memory modules without increasing any more delay than is present in with two memory modules.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Dual-edged DIMM to support memory expansion
A method and system for expanding the number of memory modules that can be coupled to a motherboard such as a server blade is presented. A stack of multiple Dual In-line Memory Modules (DIMMs) is formed using novel double-connector-edge DIMMs, which each have connector pins on their opposite edges. Alternatively, the double-connector-edge DIMM is used to couple the motherboard to a memory expansion card that has multiple single-edge pinned DIMMs coupled in a “daisy-chain.”
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
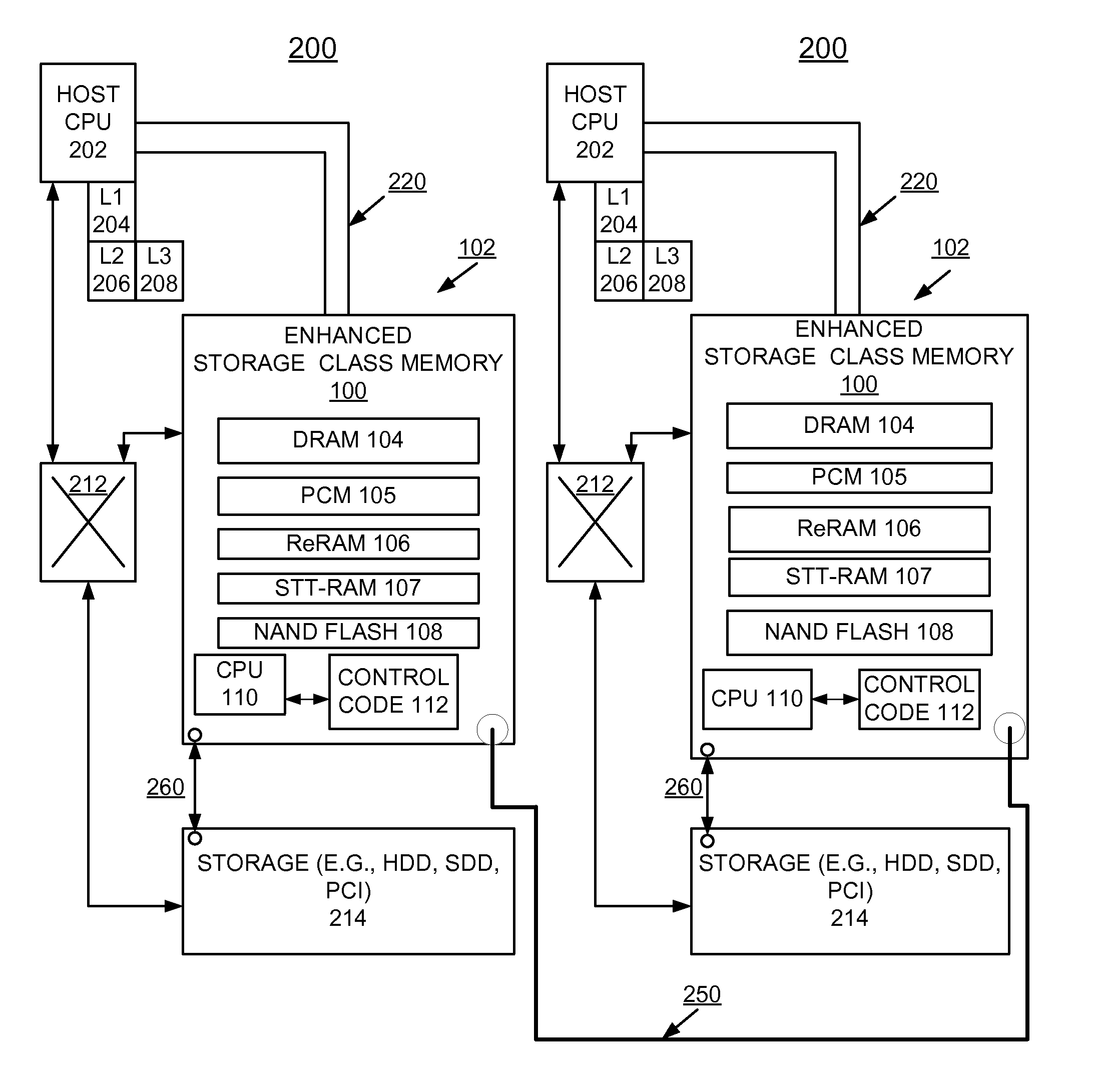
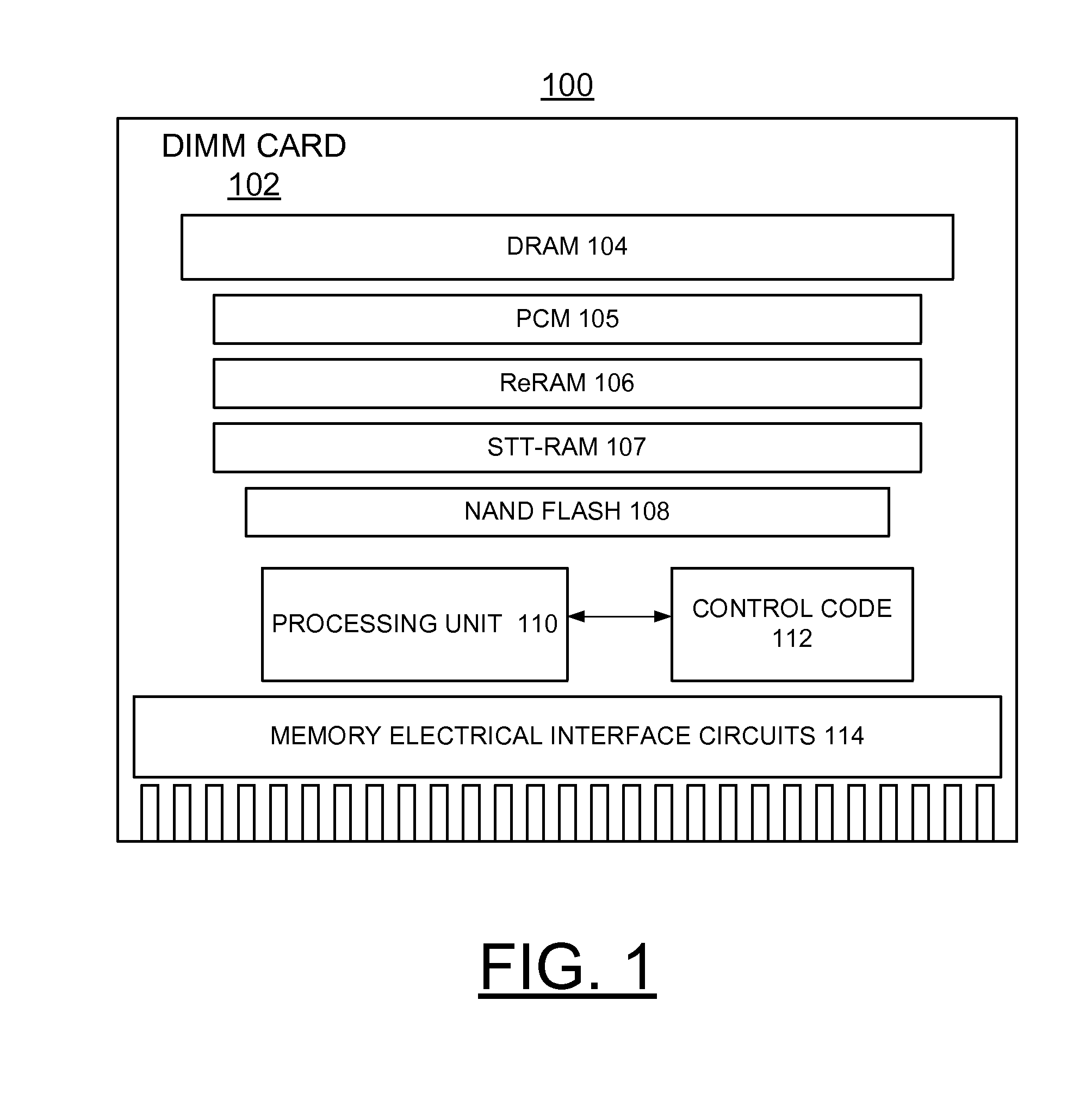
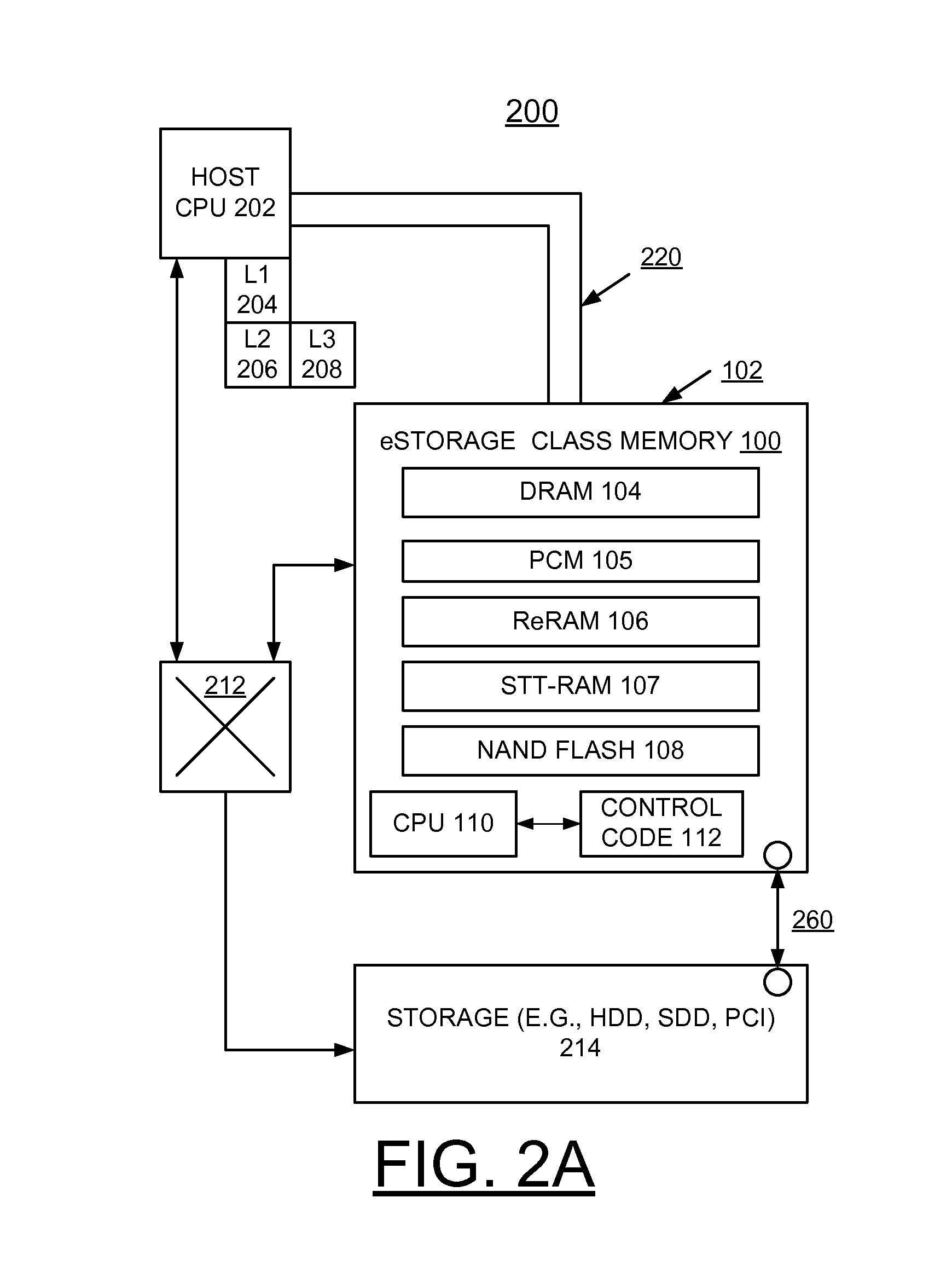
Apparatus and method for low power low latency high capacity storage class memory
InactiveUS20140101370A1Enhanced solid-state storage usageOvercome disadvantagesMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSolid-state storageDIMM
A method and a storage system are provided for implementing enhanced solid-state storage class memory (eSCM) including a direct attached dual in line memory (DIMM) card containing dynamic random access memory (DRAM), and at least one non-volatile memory, for example, Phase Change memory (PCM), Resistive RAM (ReRAM), Spin-Transfer-Torque RAM (STT-RAM), and NAND flash chips. An eSCM processor controls selectively allocating data among the DRAM, and the at least one non-volatile memory primarily based upon a data set size.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
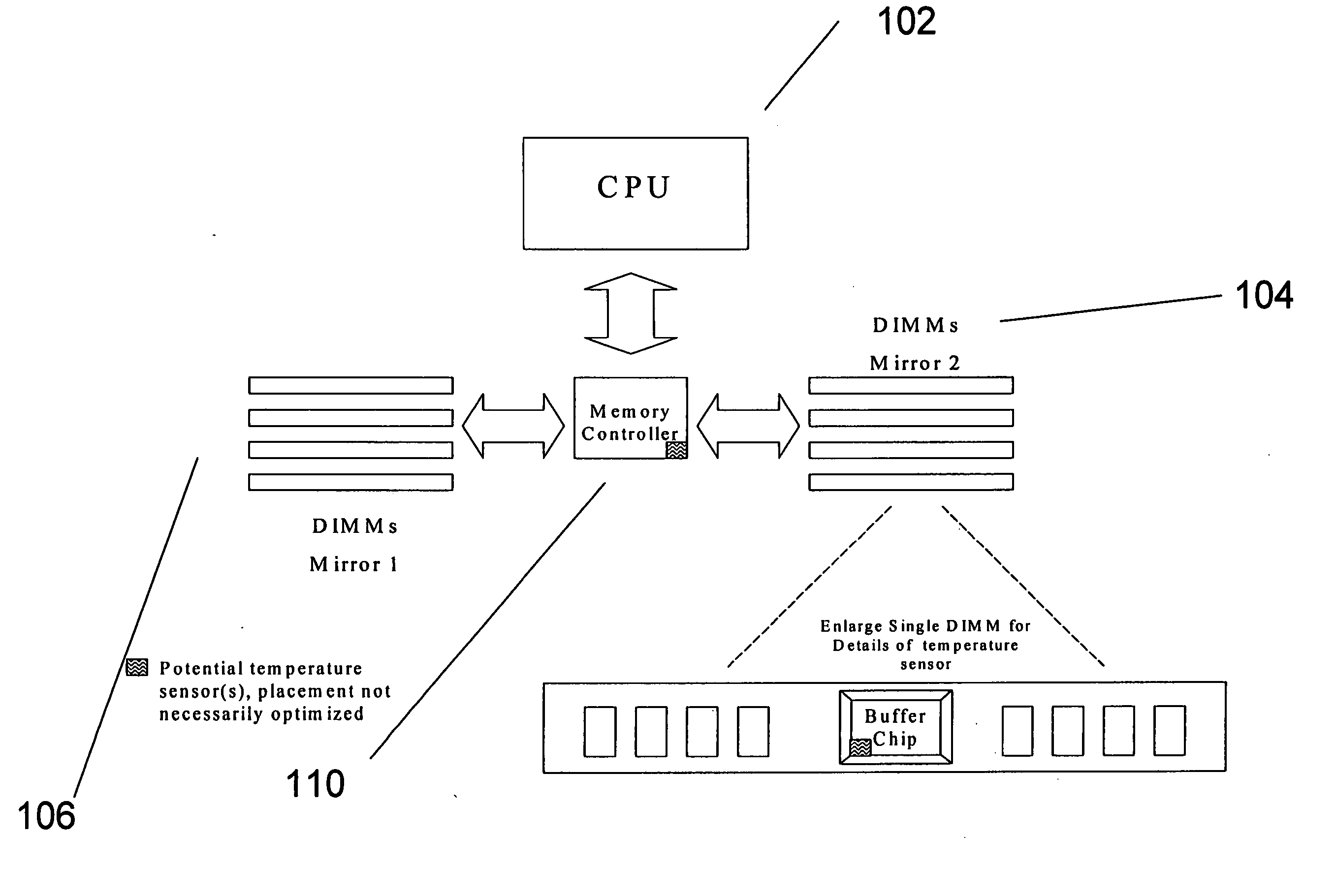
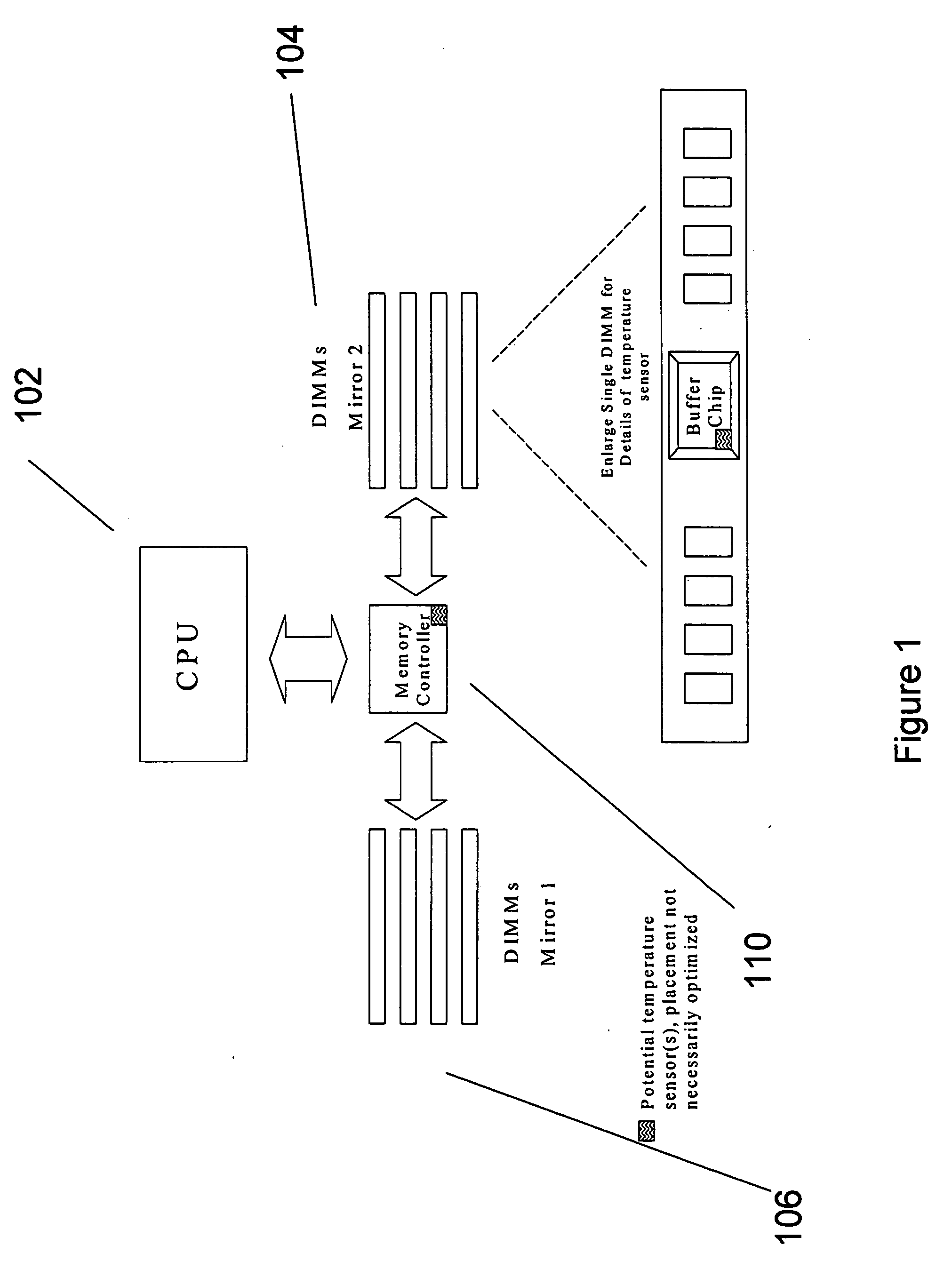
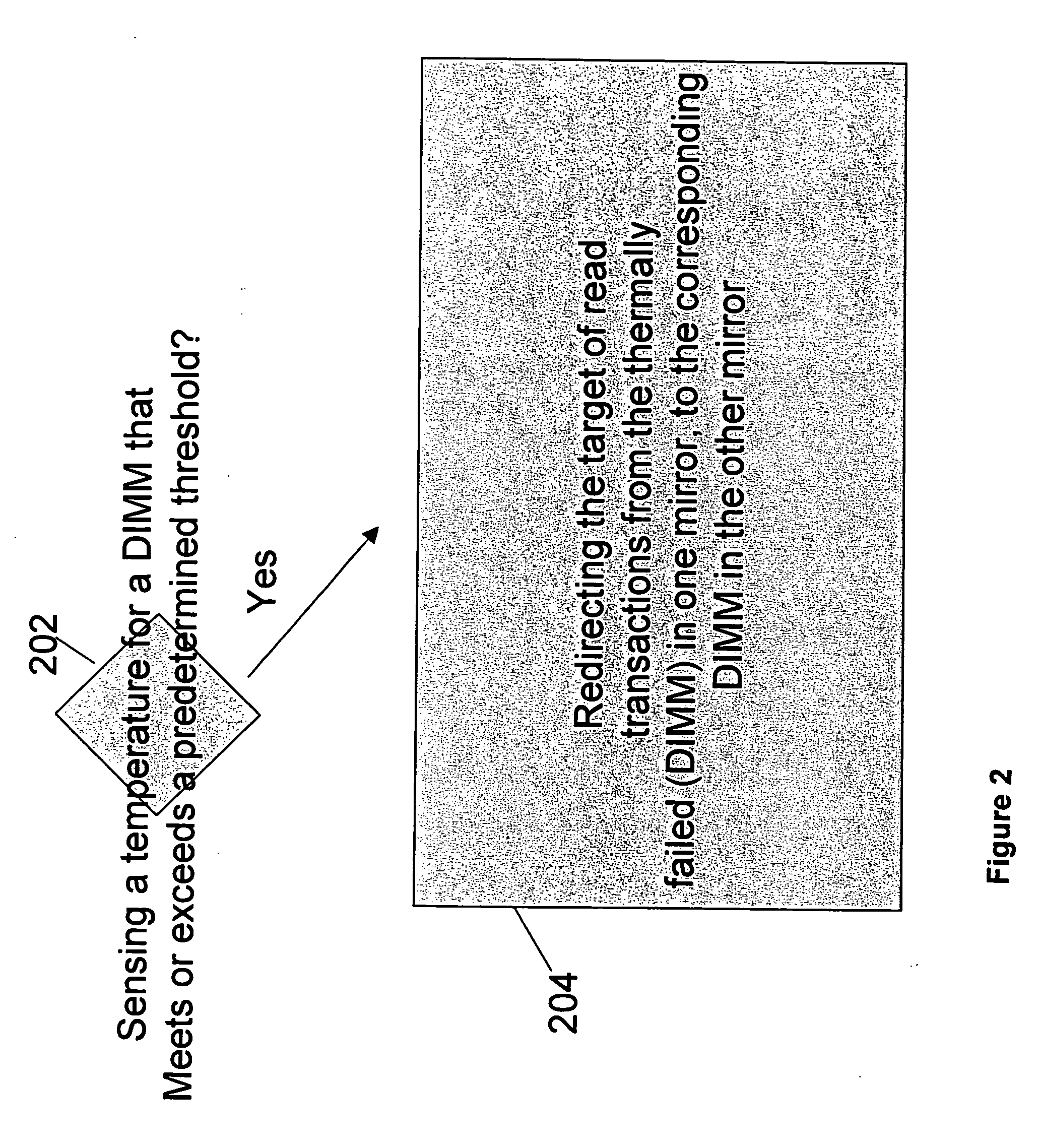
Method, apparatus, and system for memory read transaction biasing in mirrored mode to provide thermal management
ActiveUS20060111866A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionDIMMMemory controller
A thermal management that redirects the target of read transactions from a thermally failed Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) in one mirror, to the corresponding DIMM in the other mirror. The memory controller or MCH would effectively bias the read transactions toward the mirror that is best able to respond based on thermal feedback. Likewise, this may be used as a temporary redirection that continues for only as long as was required to reduce the operating temperature in the failing DIMM.
Owner:SONY CORP OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com