Patents
Literature
454 results about "Refresh cycle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
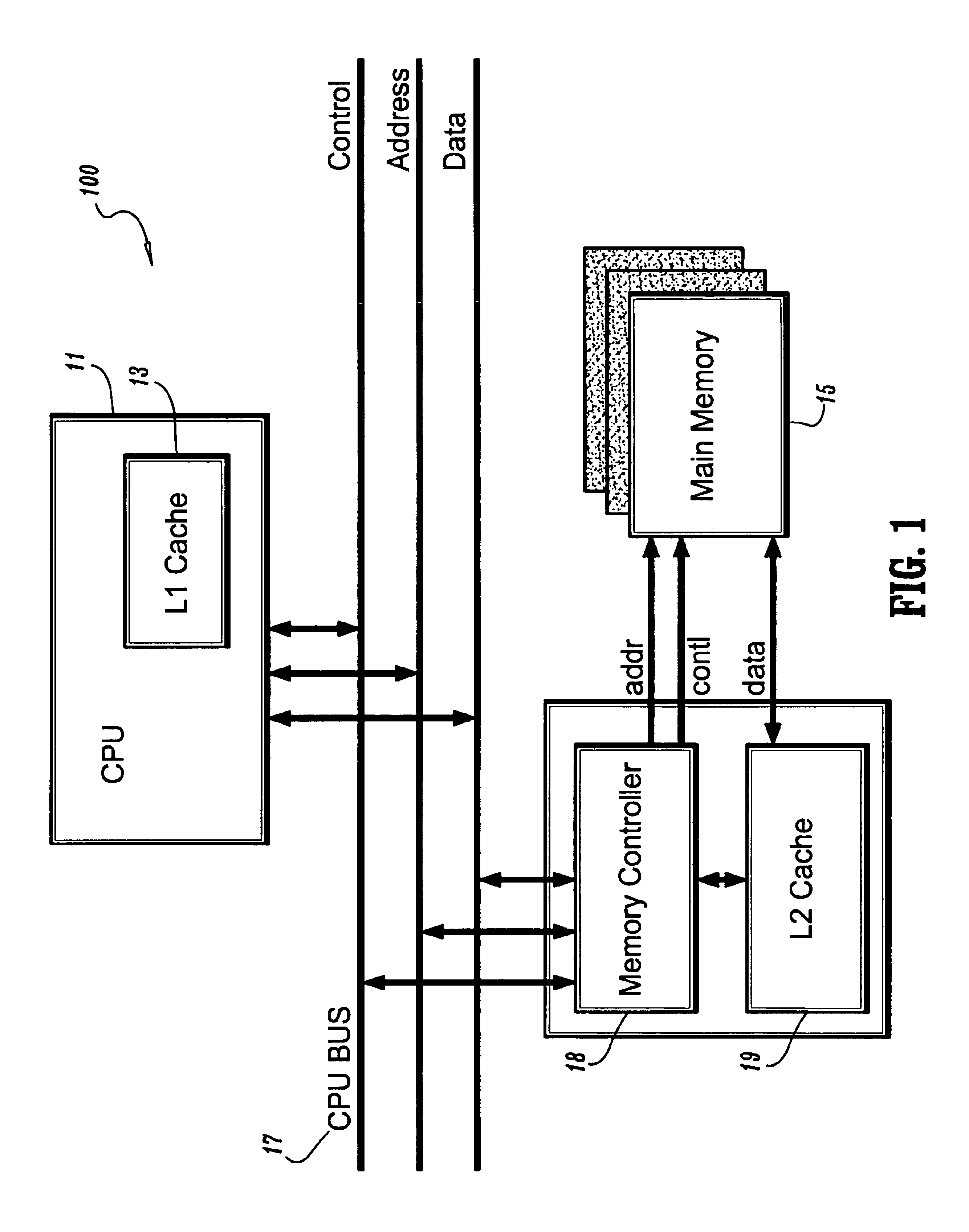
The server refresh cycle is the length of time that normally passes between installations of new servers and related hardware in a data center. Traditionally, refresh cycles have averaged around five years, but they have accelerated during the last decade.
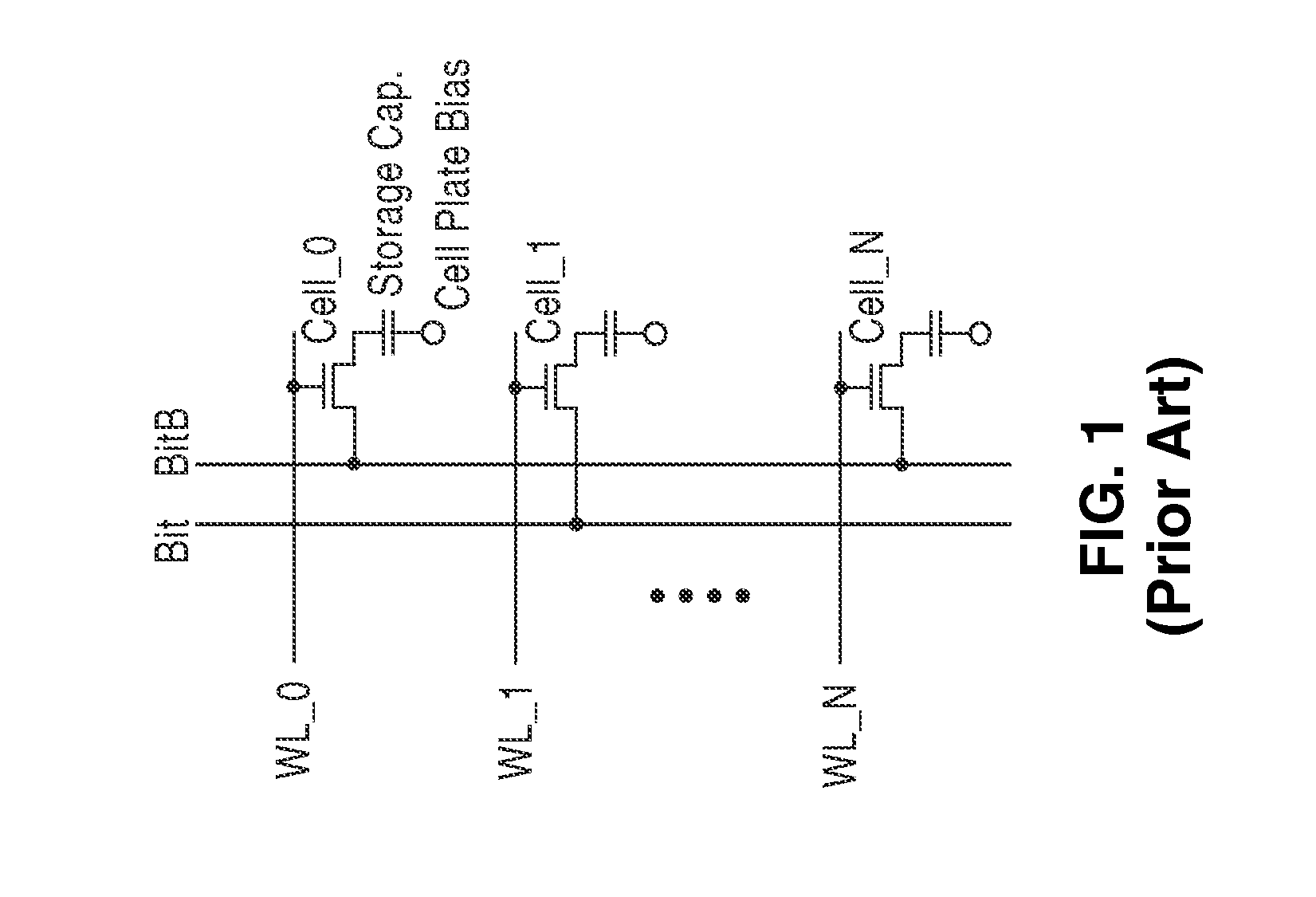
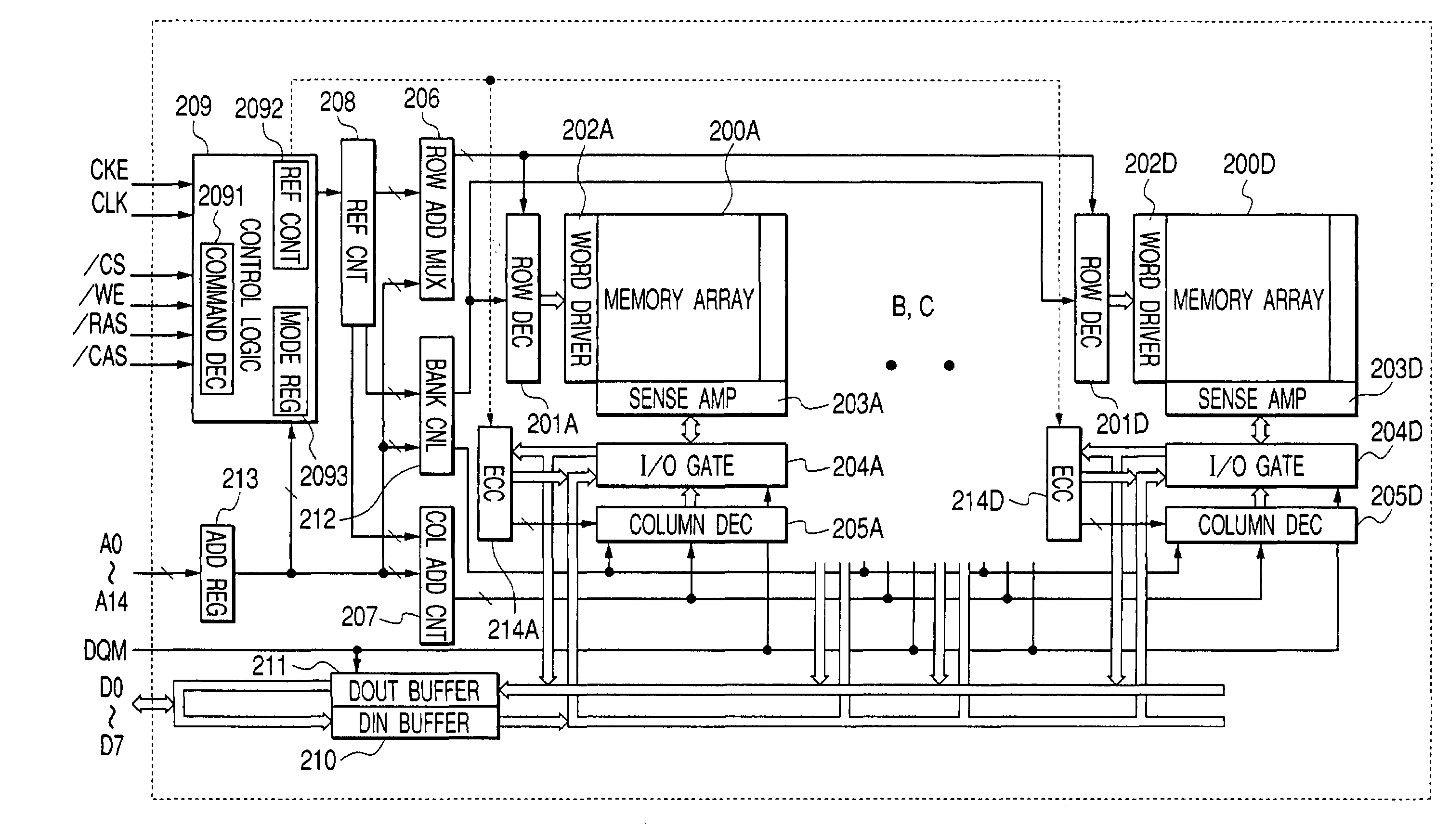
Planar capacitor memory cell and its applications
InactiveUS7209384B1Less complicated to fabricateImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
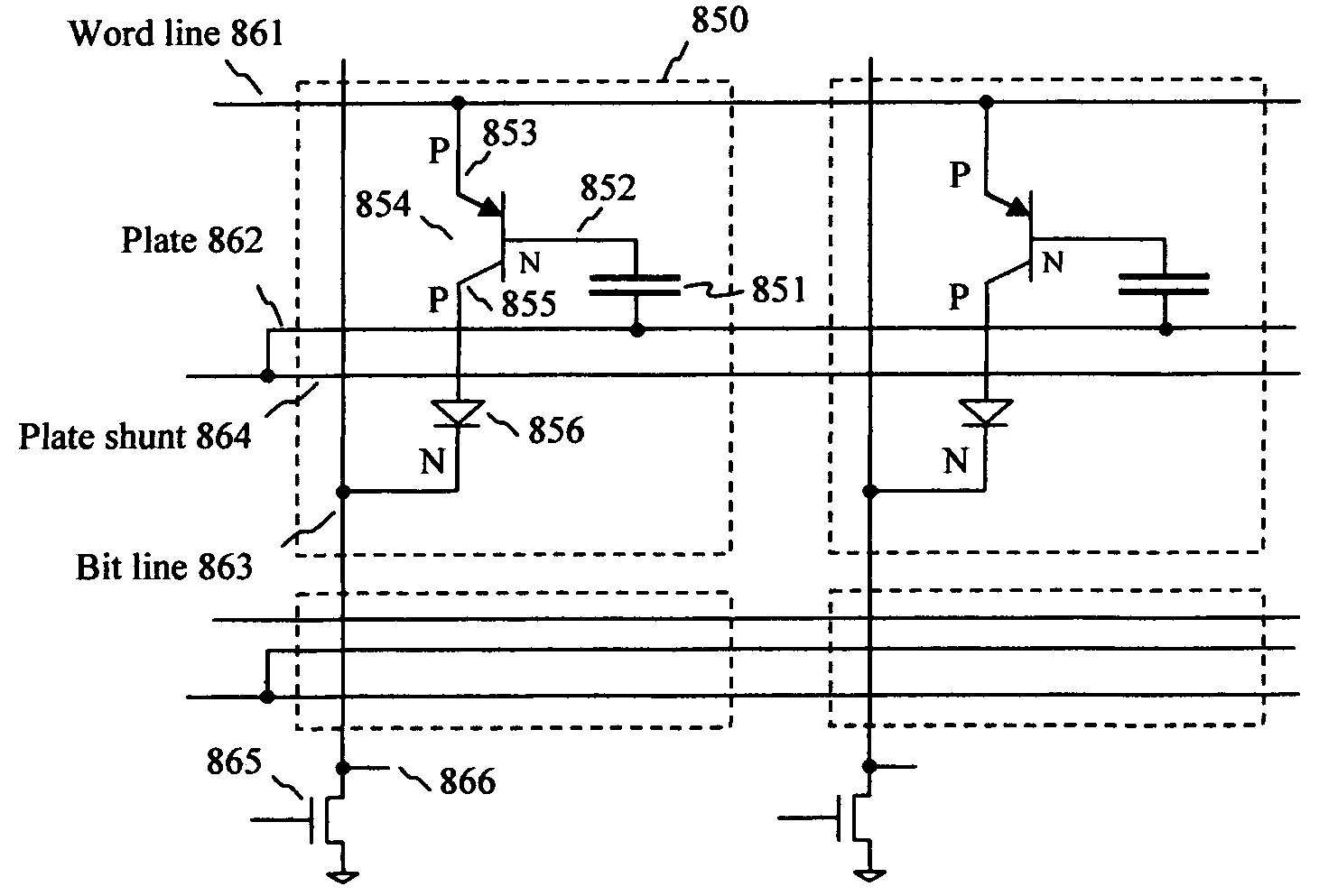
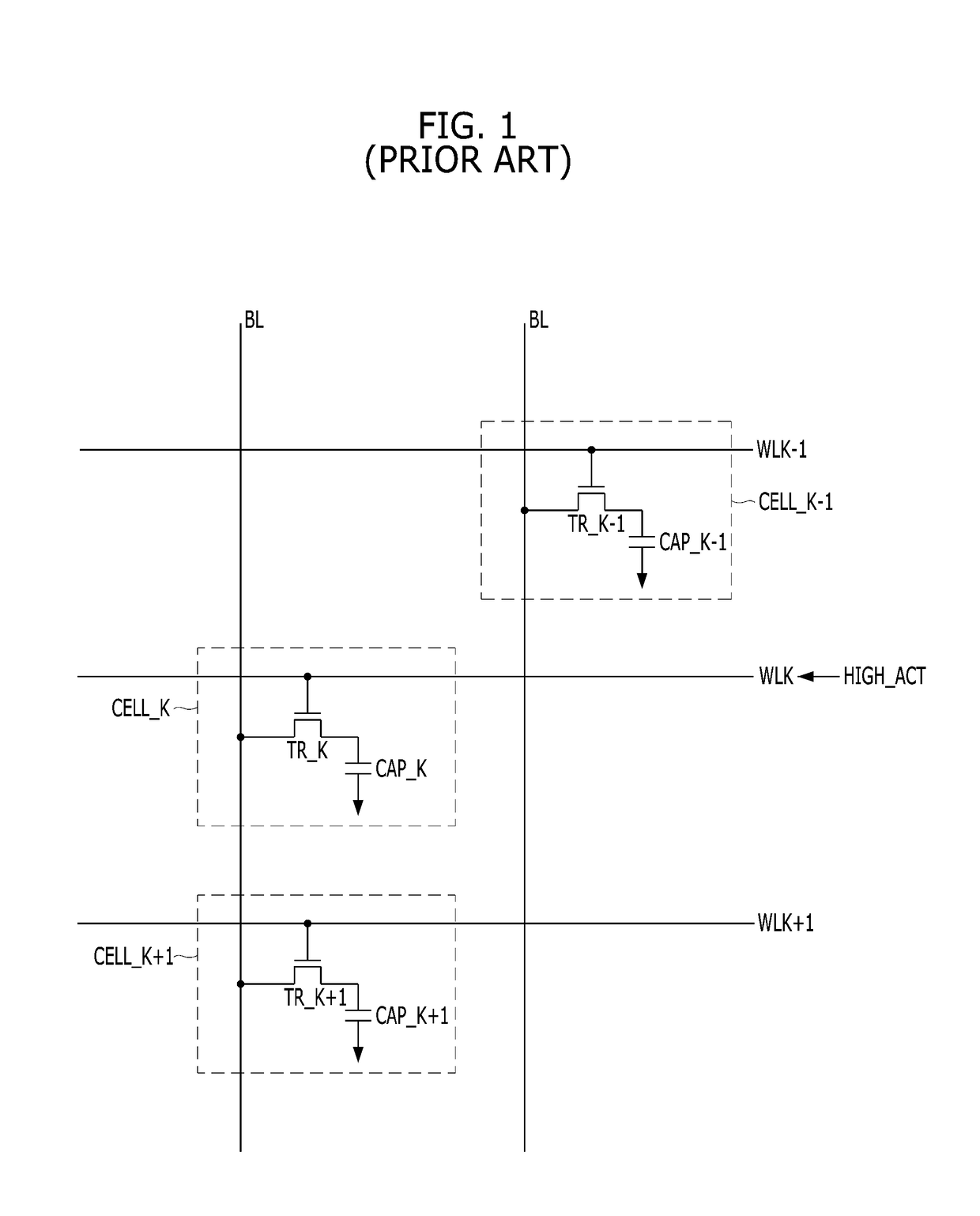
A capacitor memory is realized, wherein a capacitor stores data and a diode controls to store data “1” or “0”. Diode has four terminals wherein first terminal serves as word line, second terminal serves as storage node, third terminal is floating, and fourth terminal serves as bit line, wherein back channel effect is suppressed adding additional ions in the bottom side of third terminal or applying negative voltage in the well or substrate. A capacitor plate couples to second terminal, which plate has no coupling region to first, third and fourth terminal. With no coupling, the inversion layer of plate in the storage node is isolated from the adjacent nodes. In doing so, the plate can swing ground level to positive supply level to write. As a result, no negative generator is required for controlling plate. Word line and bit line keep ground level during standby, and rise to supply level for read or write operation. In this manner, no holding current is required during standby, and operating current is dramatically reduced with no negative generator. Write has a sequence to clear the state of cell before writing to store data regardless of previous state. Refresh cycle is periodically asserted to sustain data. The present invention can be applied for destructive read, or for nondestructive read adding pull-down device to bit line. The height of cell is almost same as control circuit on the bulk or SOI wafer.
Owner:KIM JUHAN
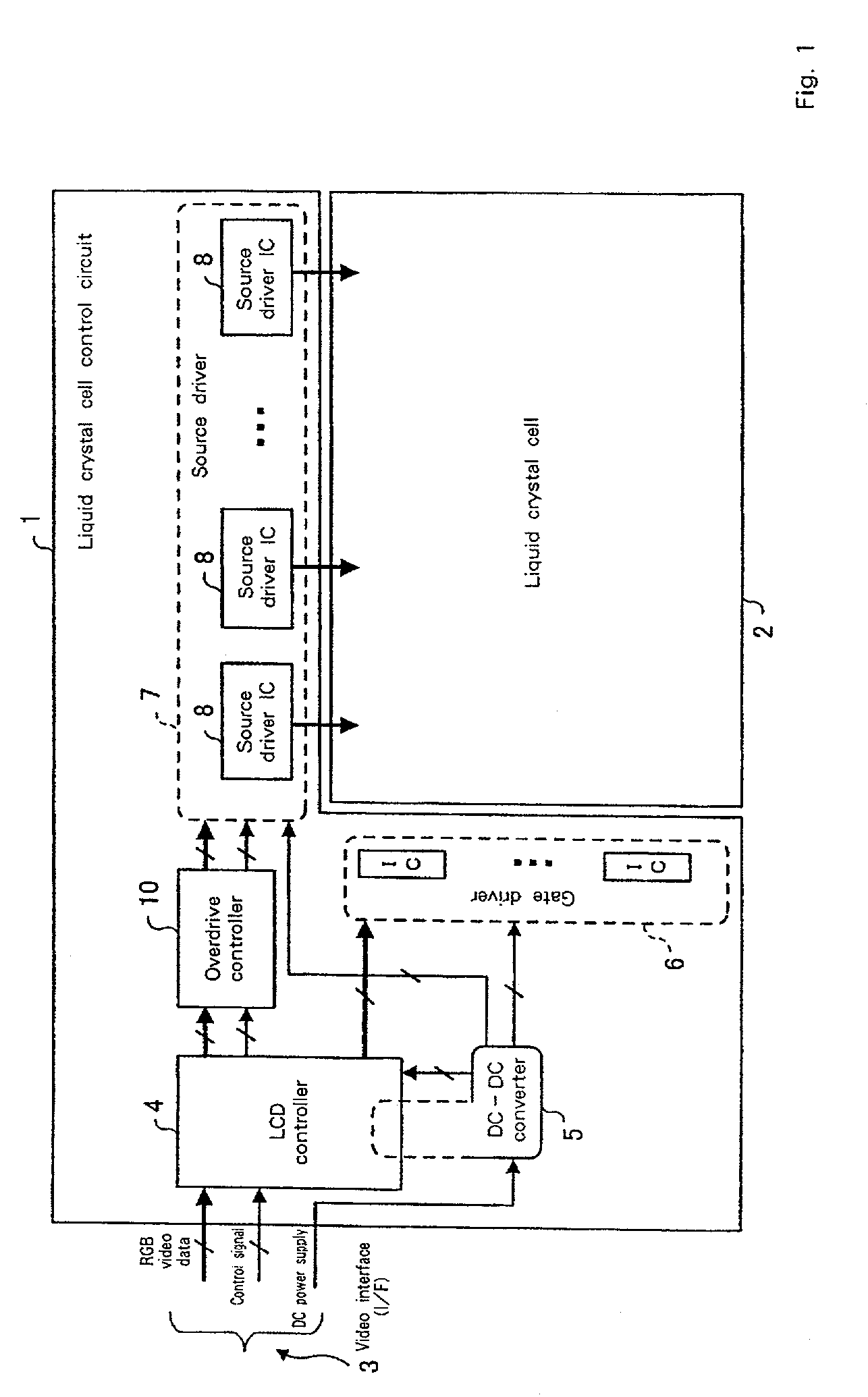
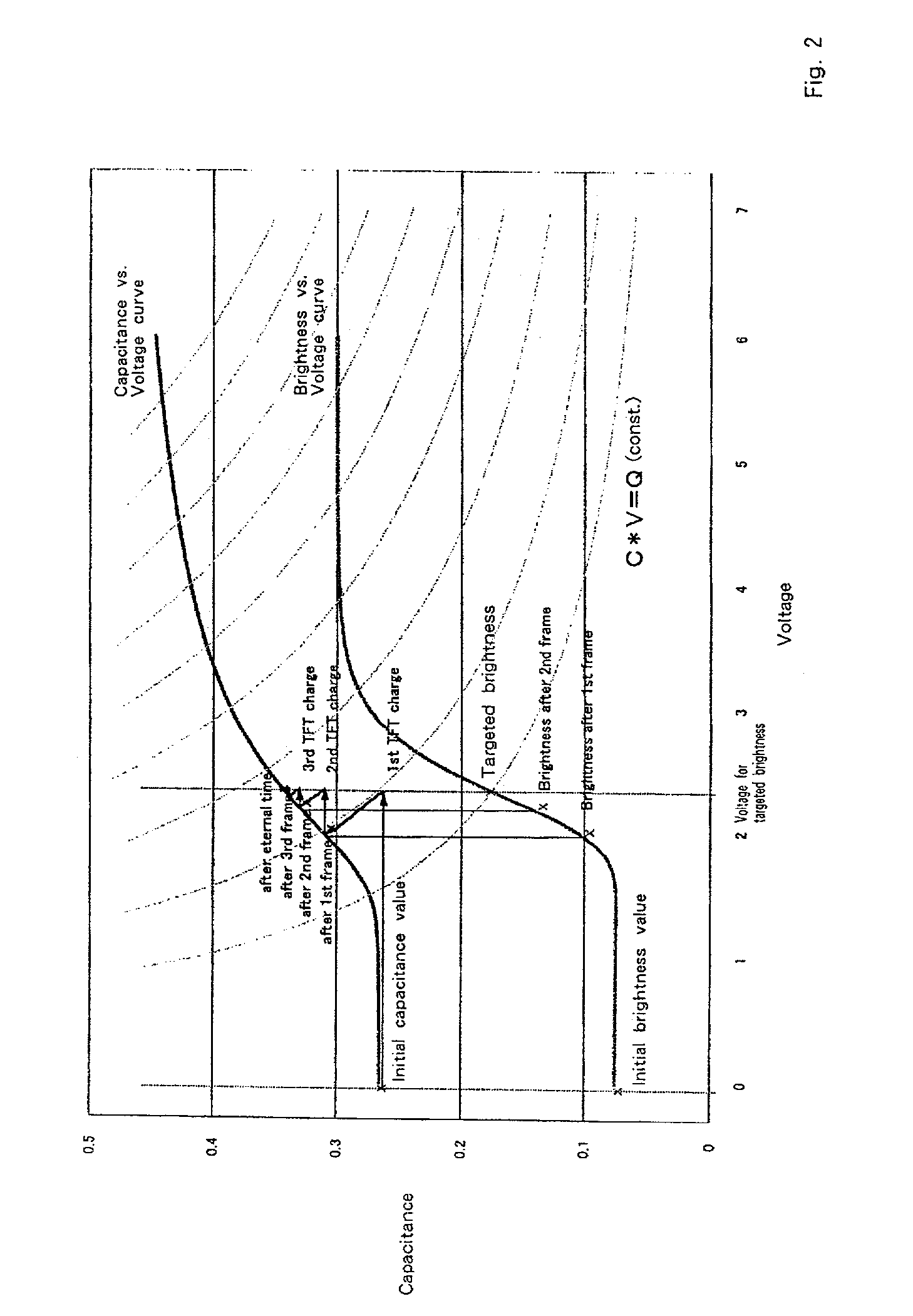
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7034793B2Fully appreciatedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
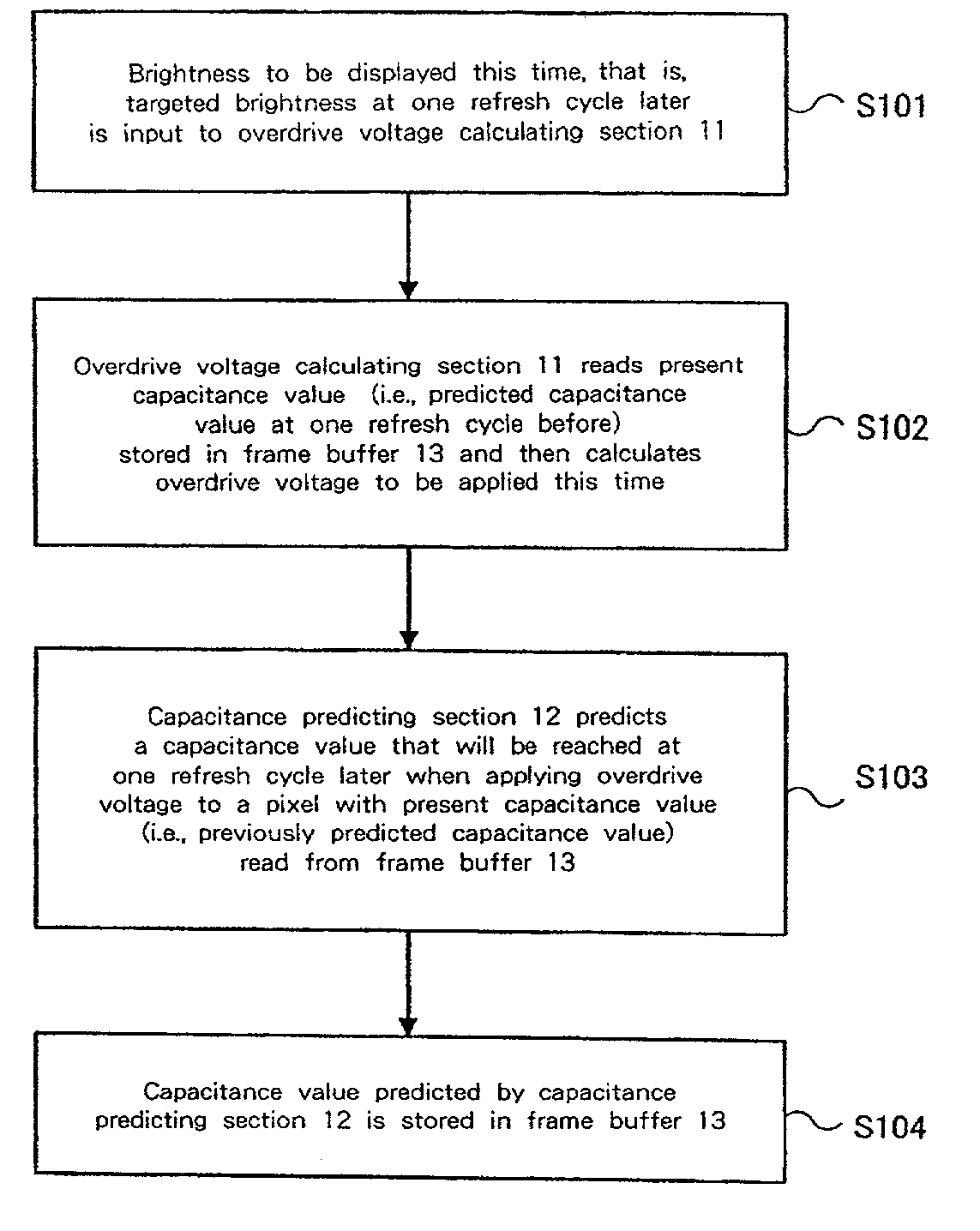
A liquid crystal display drive circuit includes capacitance predicting section for predicting a capacitance value each pixel will reach at one refresh cycle later when applying a predetermined voltage for targeted brightness, a frame buffer for storing the predicted capacitance value, and overdrive voltage calculating section for calculating a voltage to be applied to each pixel based on targeted brightness at one refresh cycle later and the stored capacitance value in frame buffer.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
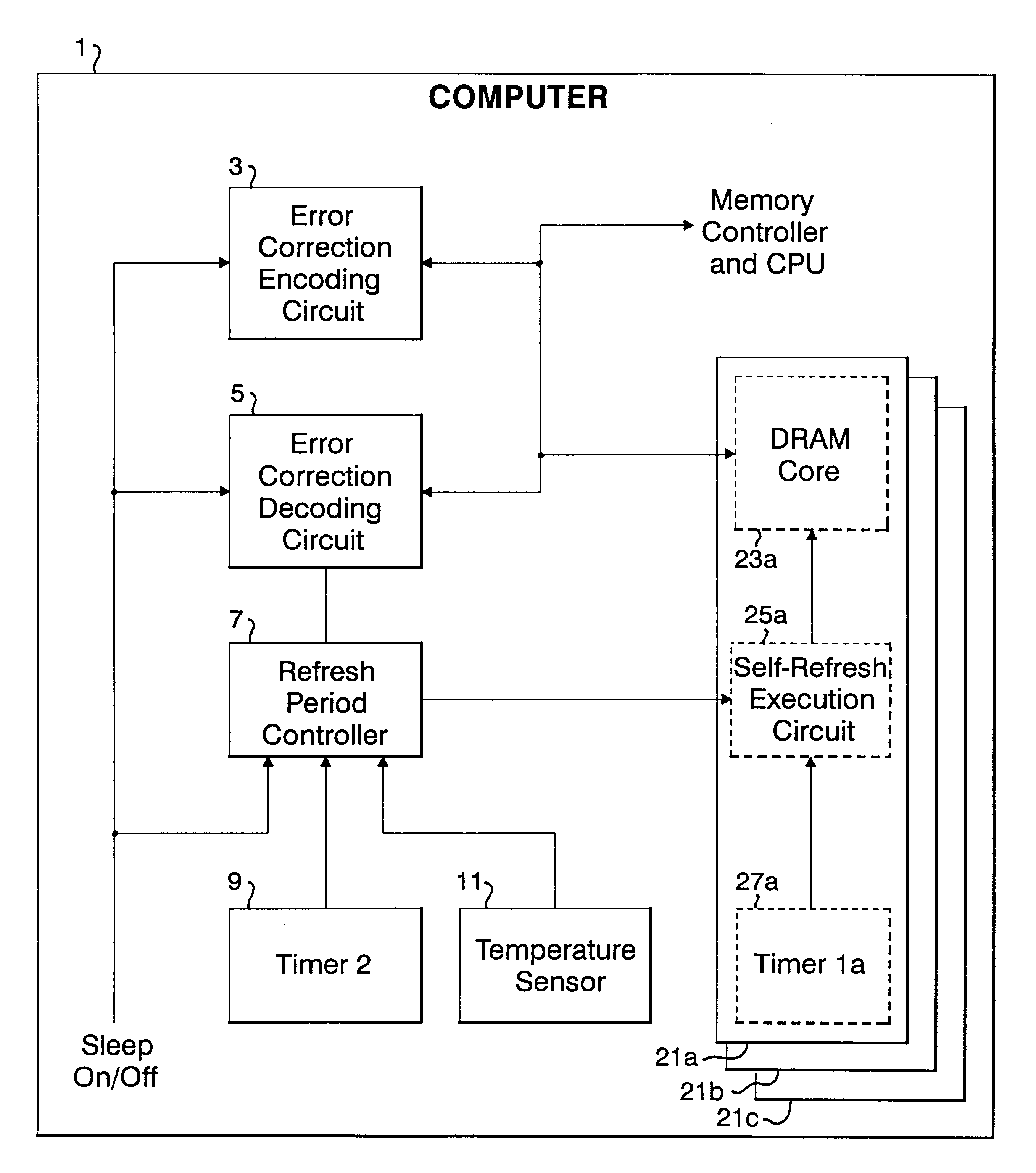
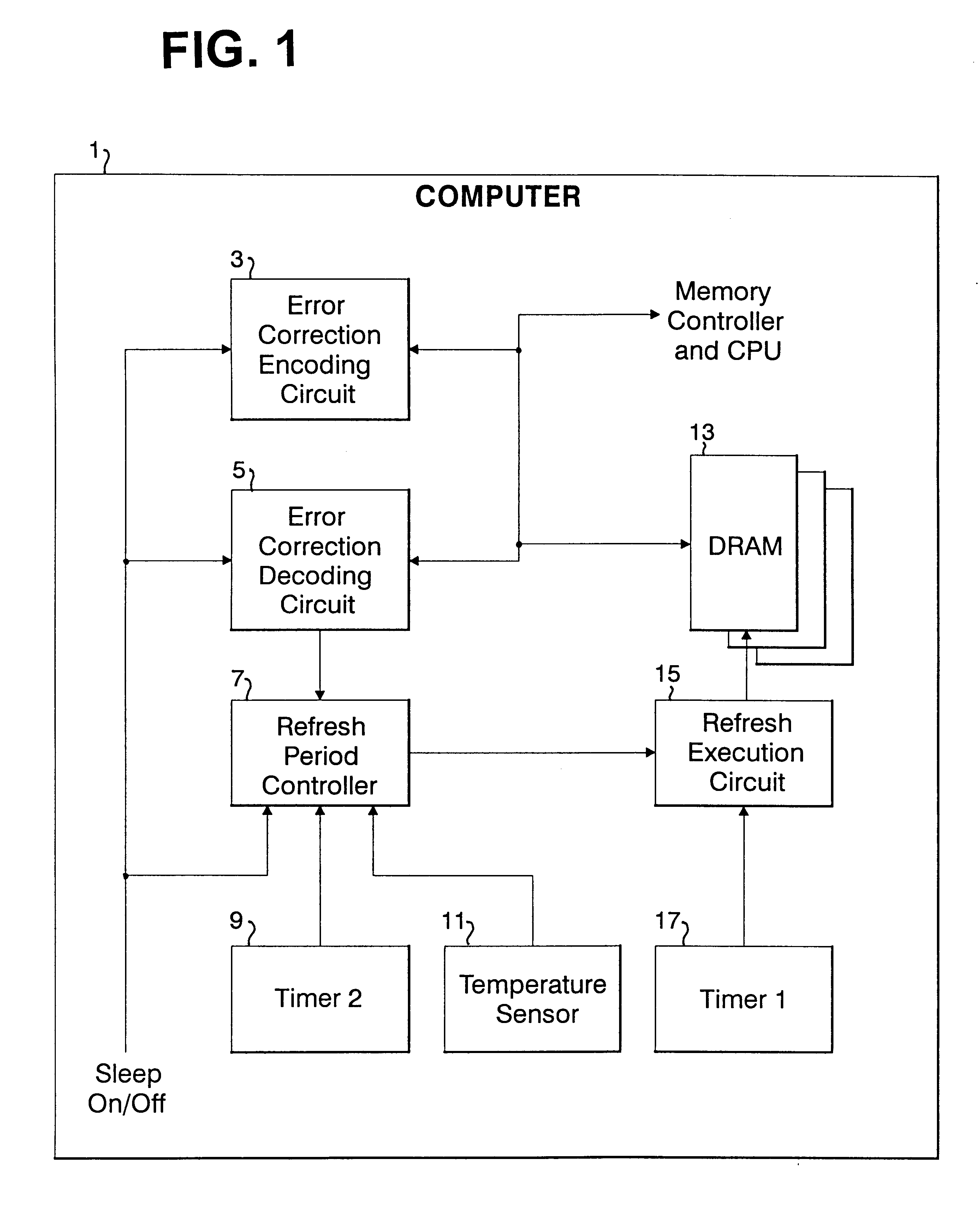
Refresh period control apparatus and method, and computer
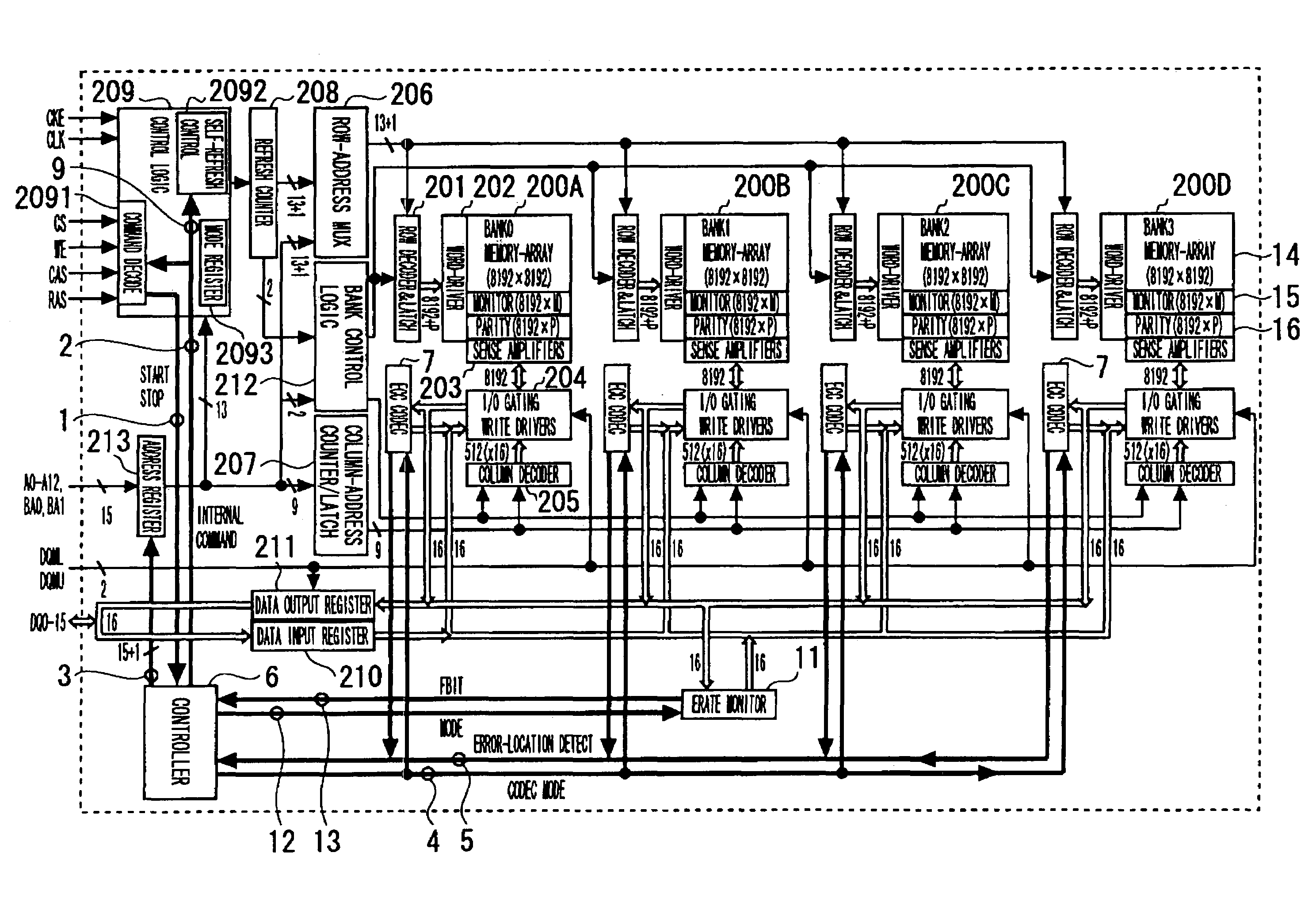
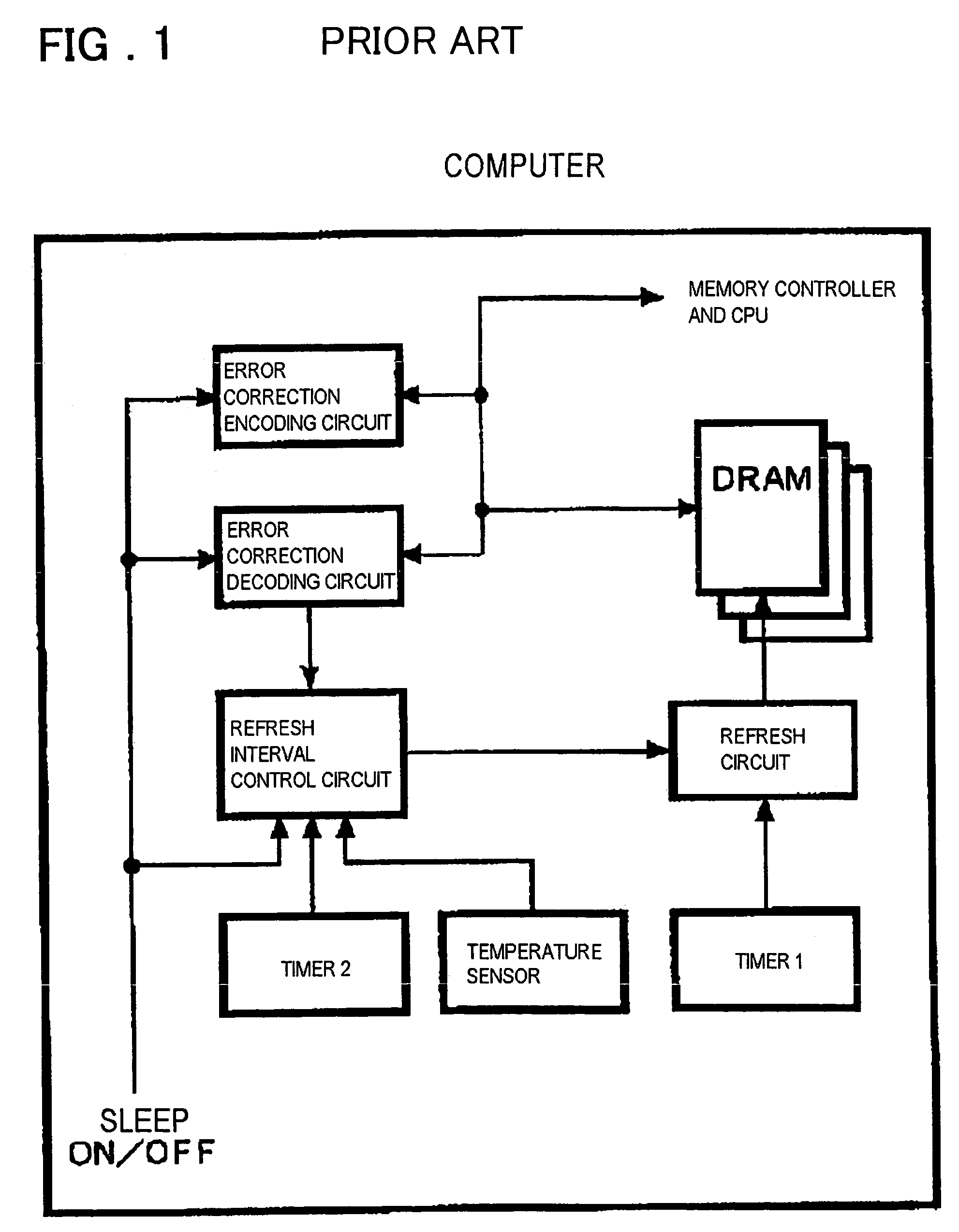
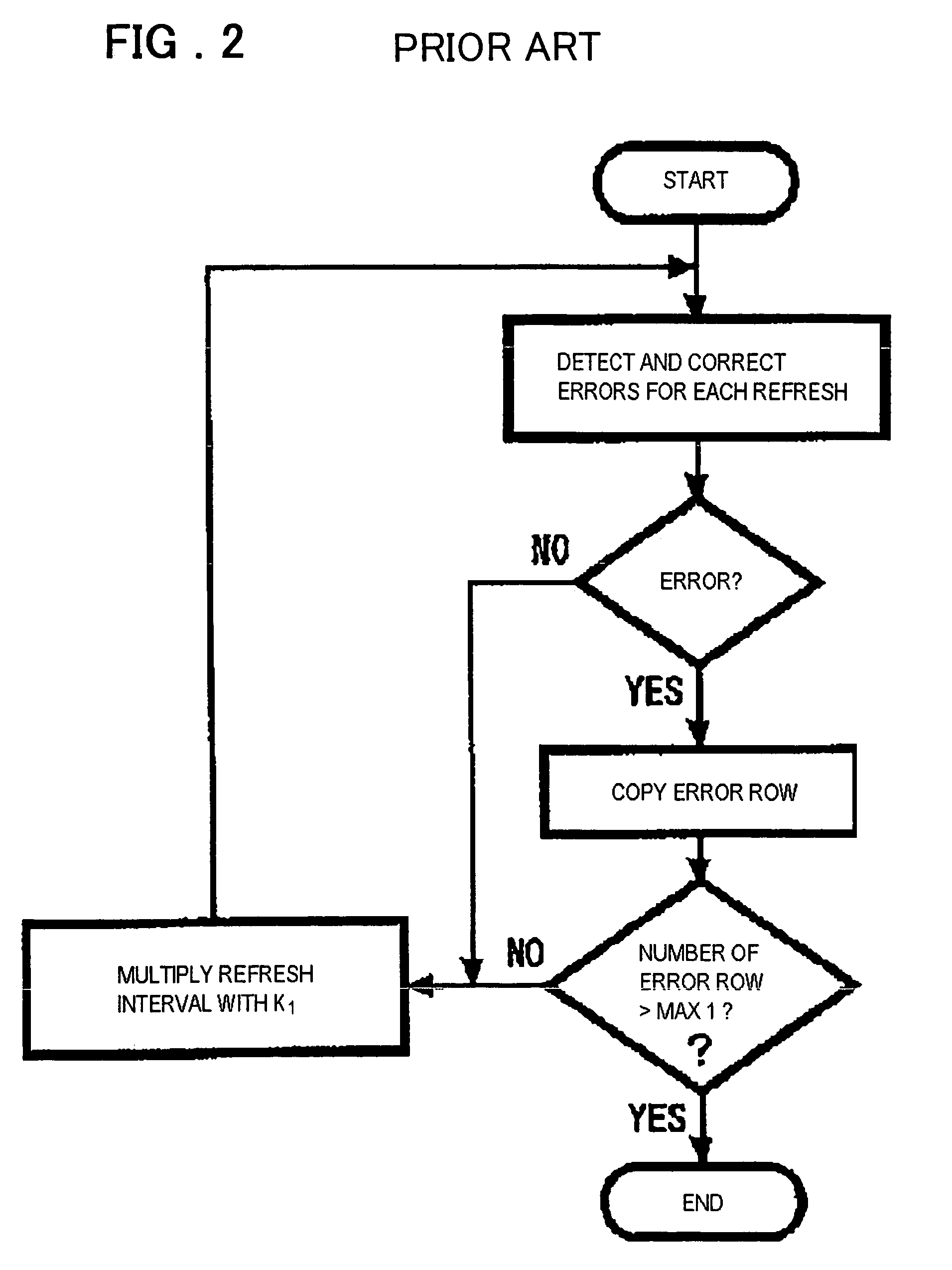
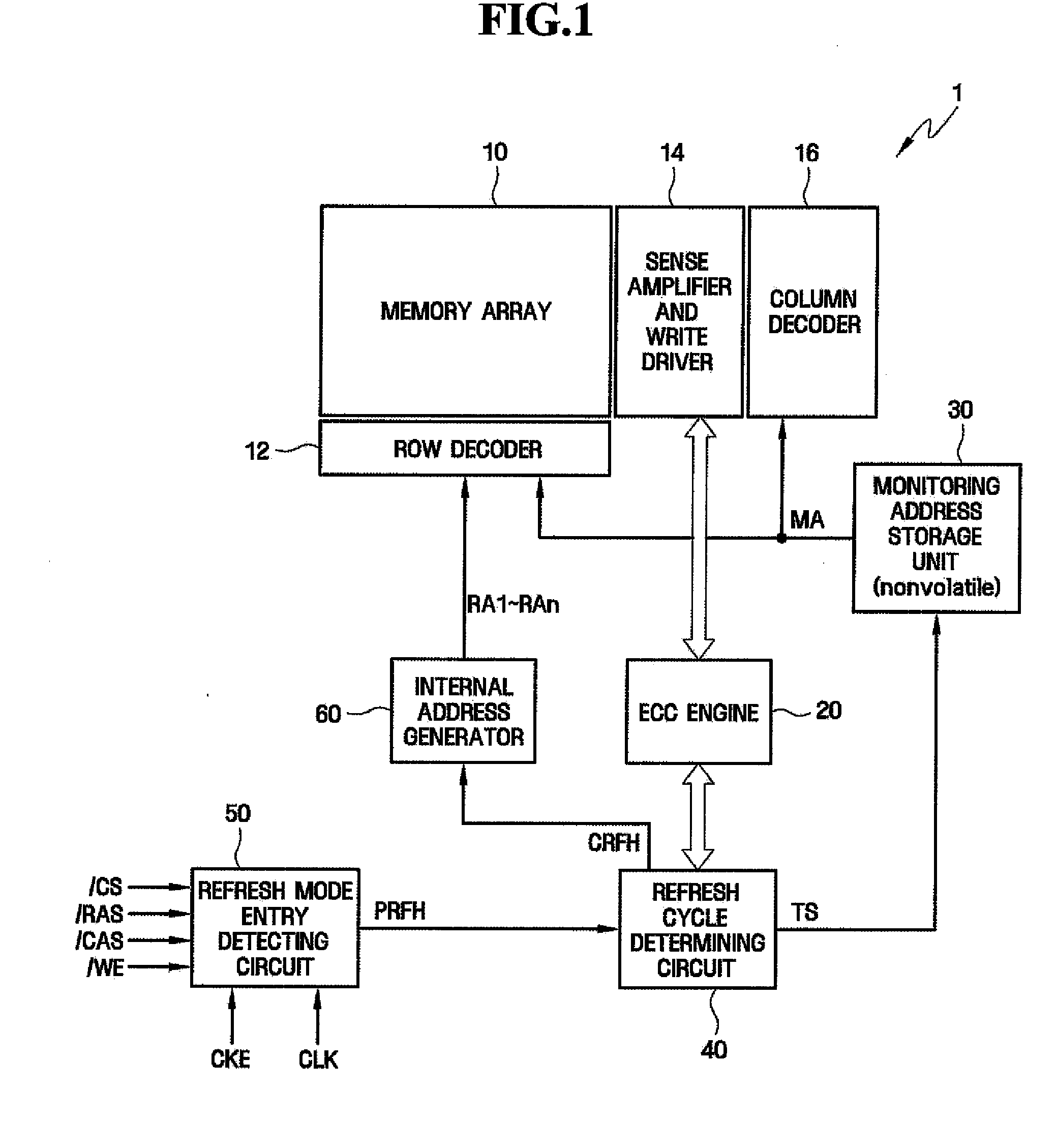
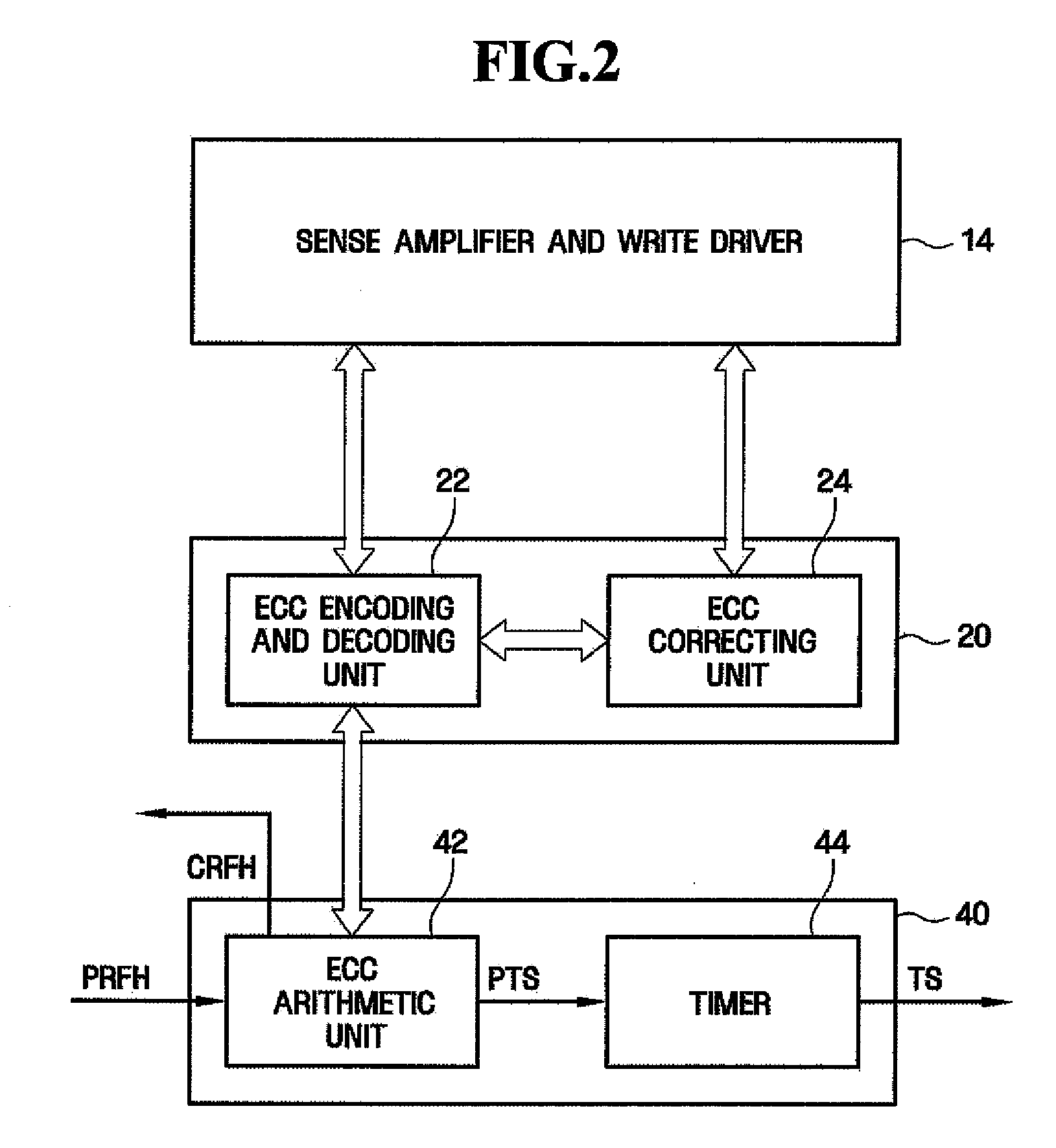
InactiveUS6199139B1Highly effective error correction functionLow costEnergy efficient ICTCode conversionComputer hardwareRefresh cycle
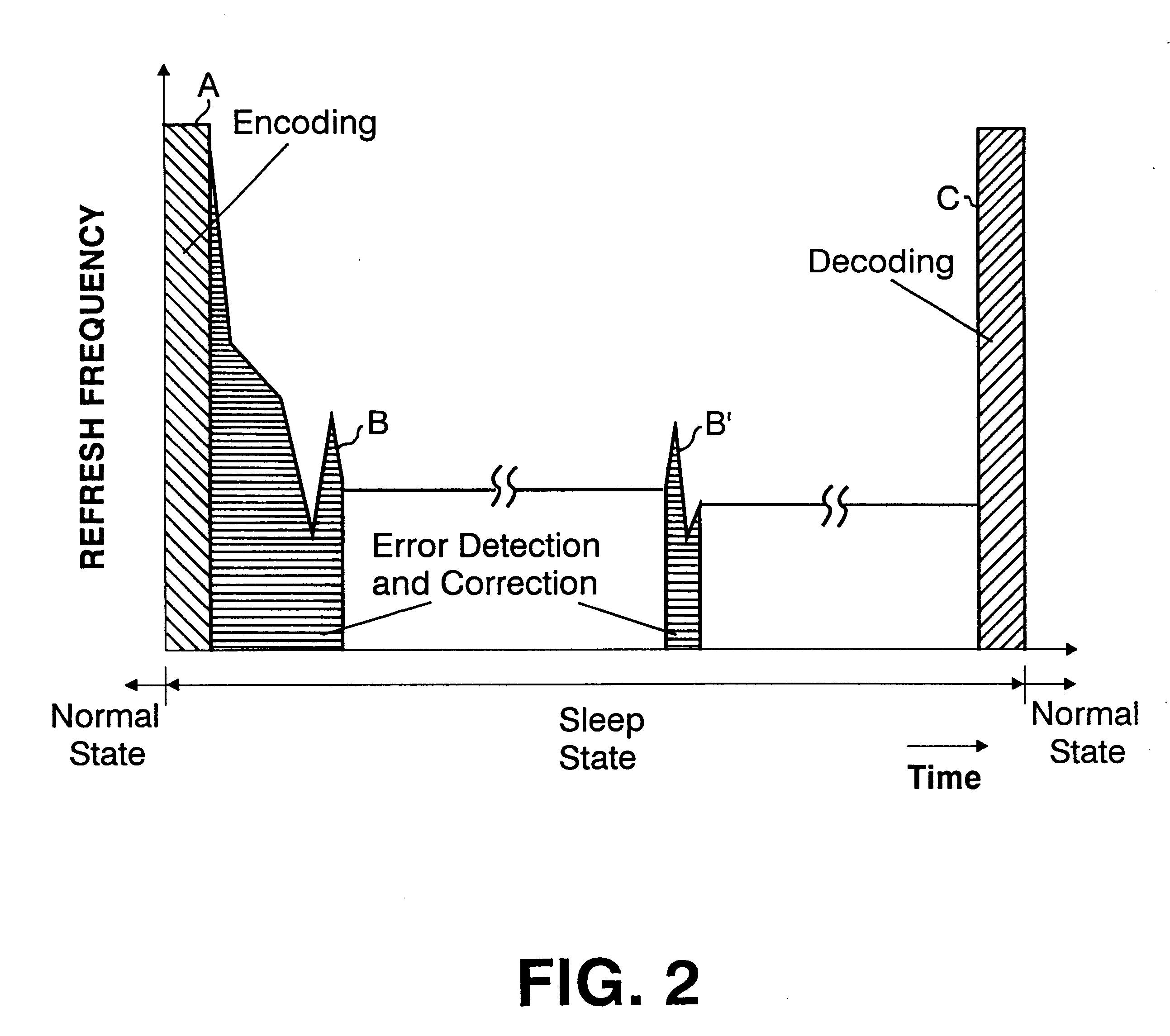
The present invention provides a memory system that optimizes, during a sleep mode, a refresh period for a memory device, such as DRAM, which stores meaningful data and for which a refresh operation is required to prevent the loss of data. More particularly, the present invention is directed to an apparatus for controlling, in a sleep mode, a refresh period for a memory device 13 that requires a refresh operation, comprises: an encoding circuit 3 for encoding data to obtain code that can be used to correct errors equal to or more than dual errors; a decoding circuit 5 for correcting errors and for decoding the corrected code; and a refresh period controller 7 for, following a transition to the sleep mode, changing a refresh period by using data, which is stored in the memory device 13 and encoded by the encoding circuit 3, until the refresh period becomes longest in a condition where there is no error that can not be corrected by the decoding circuit 5 and the number of correctable errors does not exceed a predetermined count, and where a refresh execution circuit 15 for performing the refresh operation for the memory device can deal with the changed refresh period, and for, following the first end of the change of the refresh period, setting the refresh execution circuit 15 so that the refresh of the memory device 13 is performed at the refresh period at the first end of the change of the refresh period.
Owner:IBM CORP
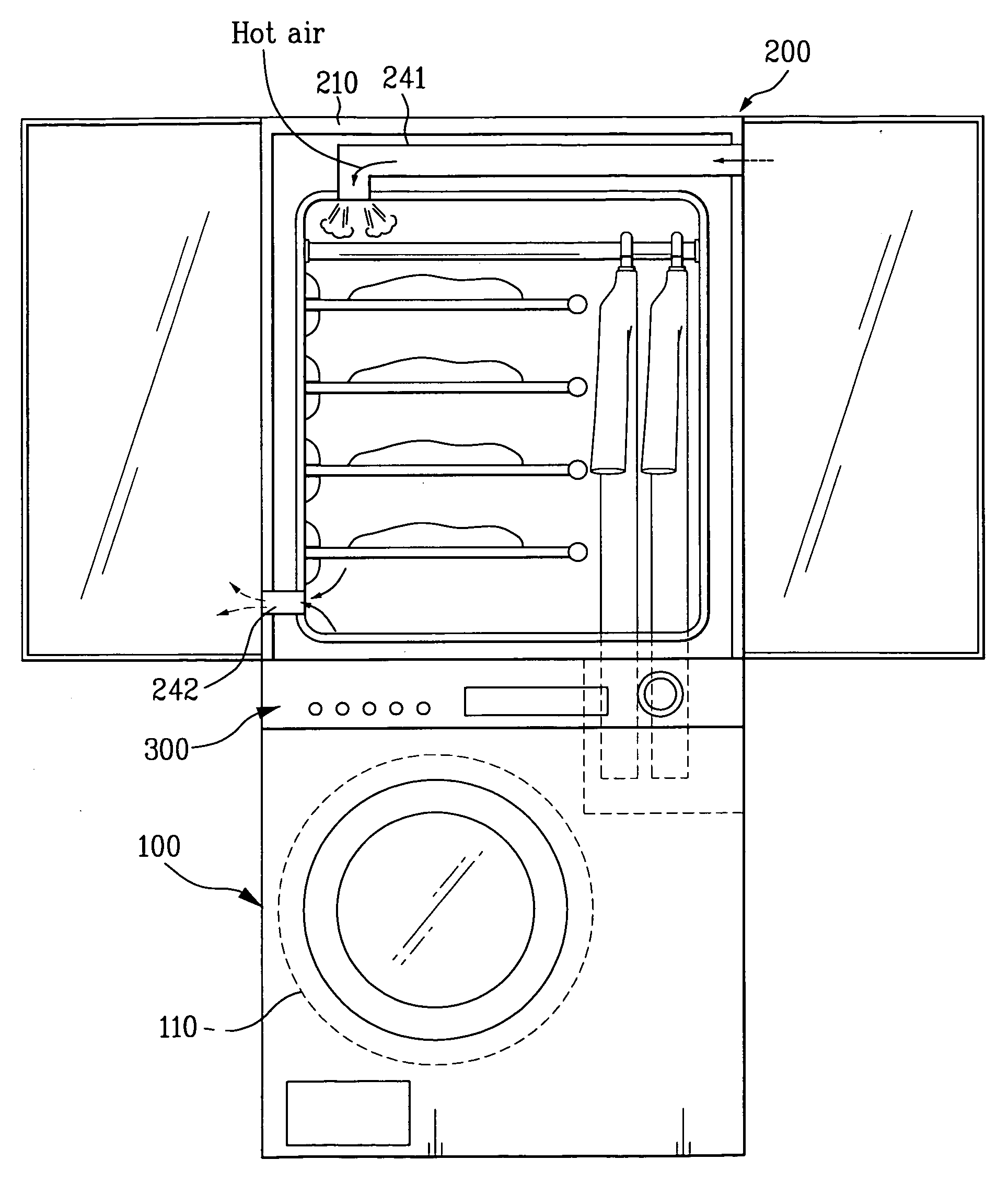
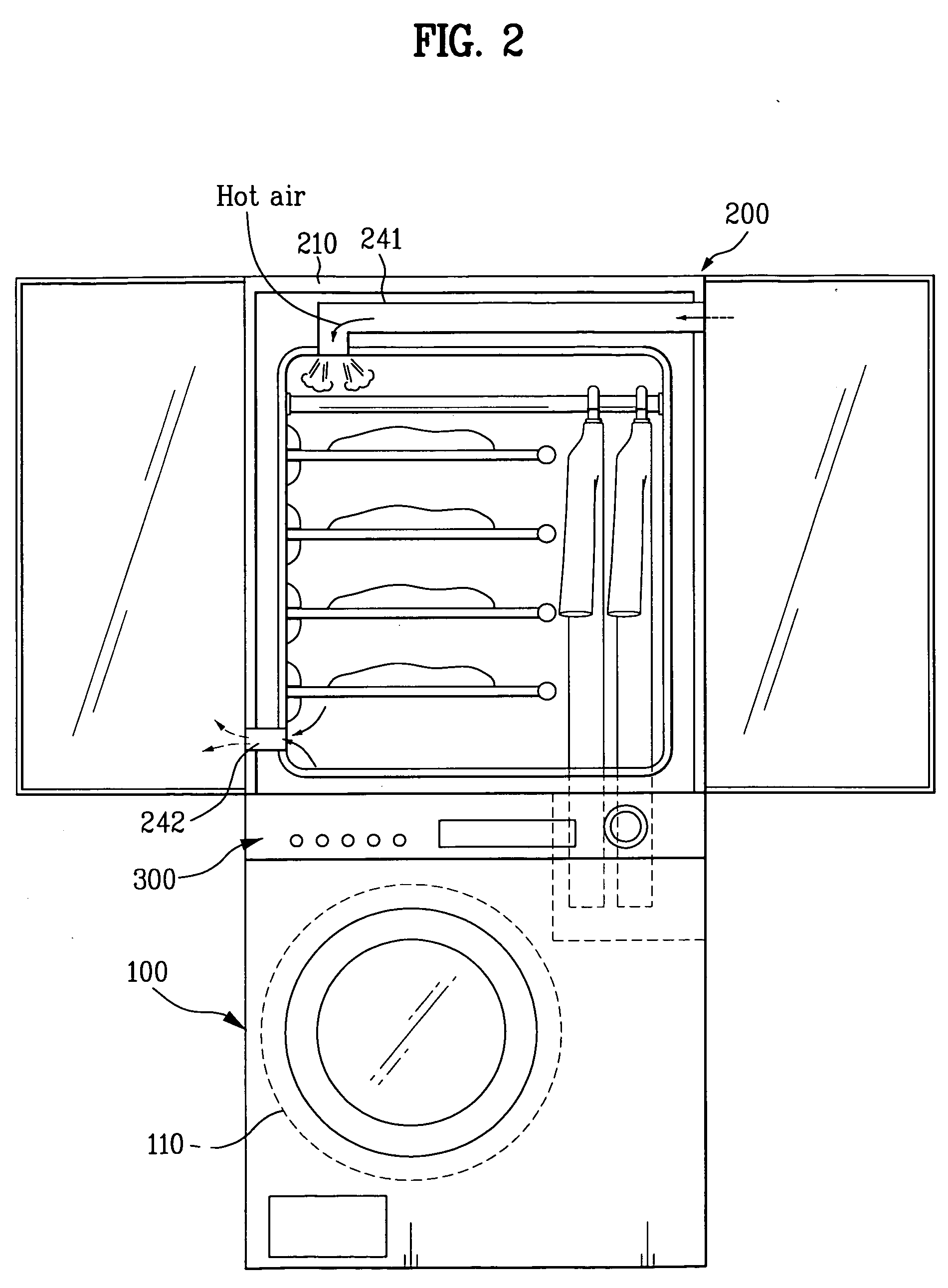
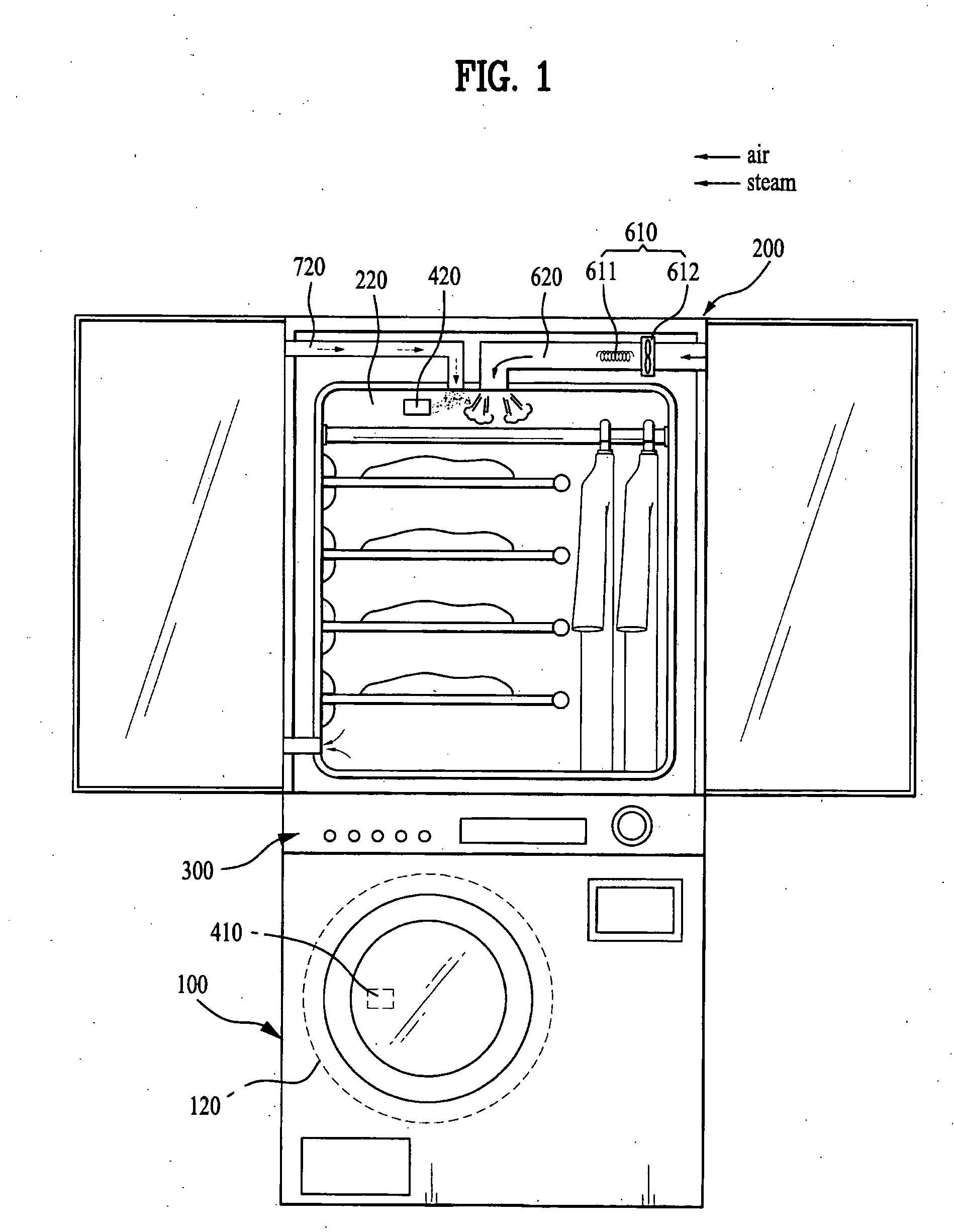
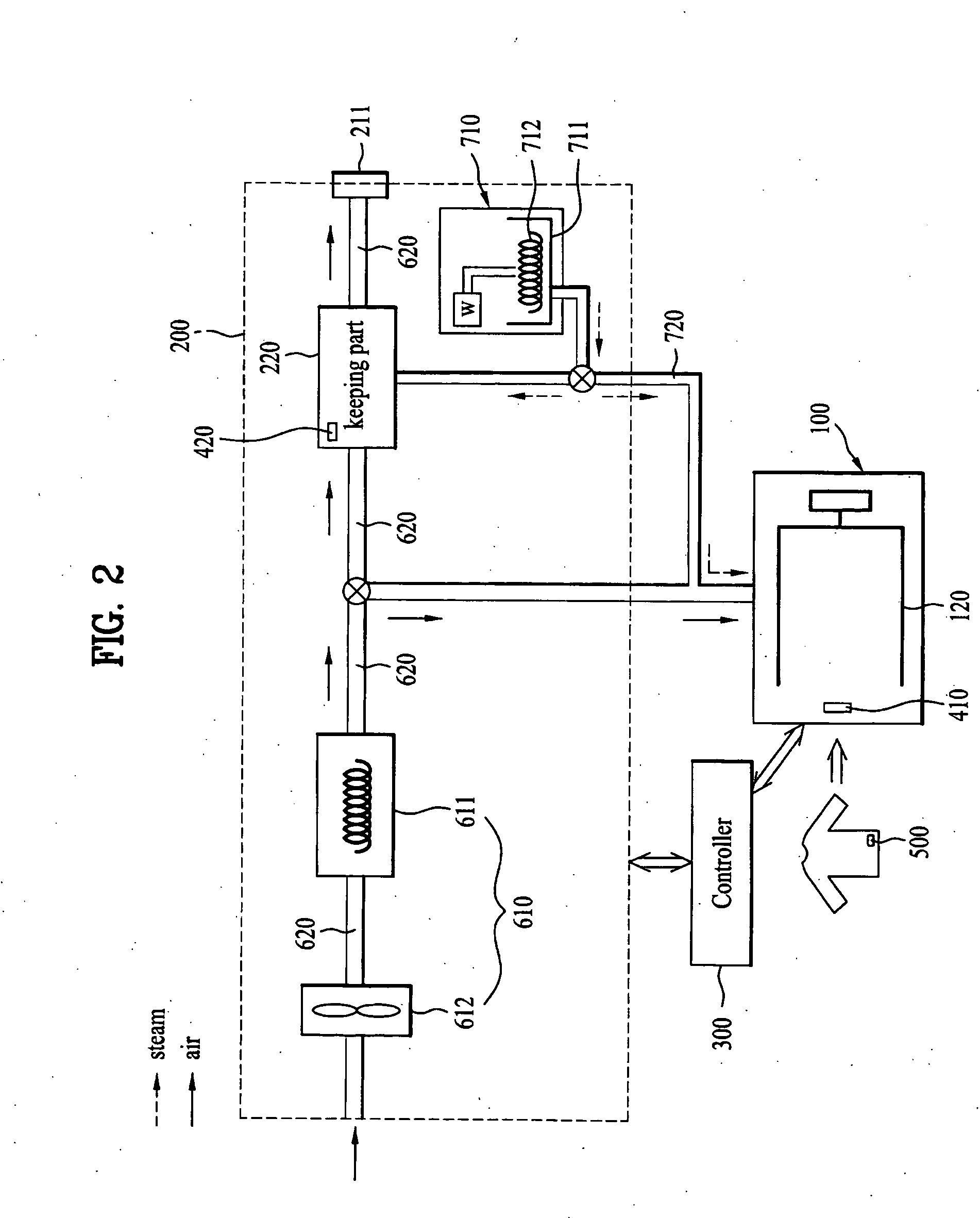
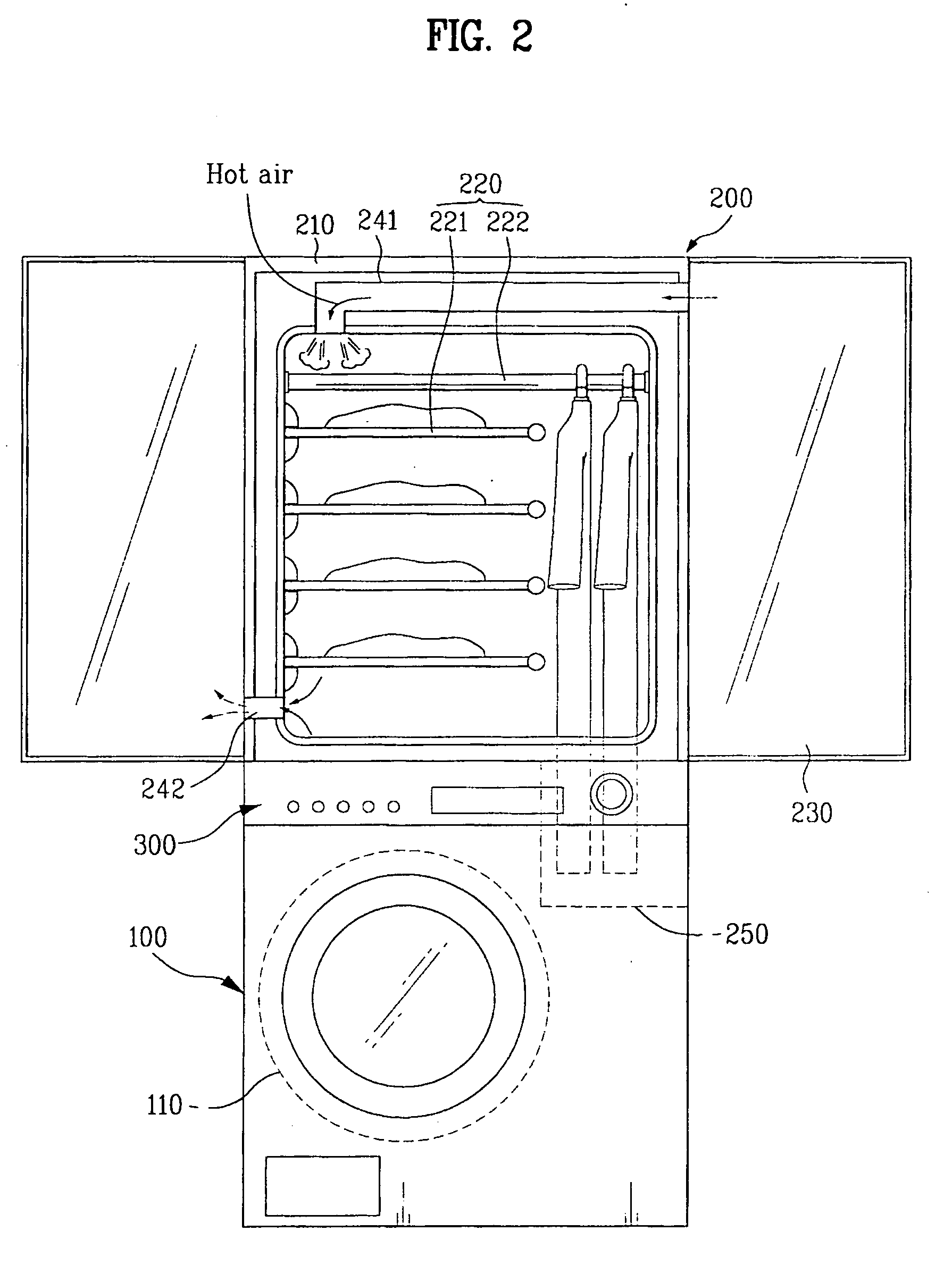
Operation method for combination dryer
InactiveUS20060112585A1Eliminate the problemDrying gas arrangementsOther washing machinesCyclic processRefresh cycle
An operation method for a combination dryer is disclosed. The present invention relates to a combination dryer, and more particularly, to an operation method for a combination dryer which enables air in a drying drum and a cabinet for drying the laundry to circulate continuously and enables condensed water generated in the circulation process to perform a refreshing cycle by using the water.
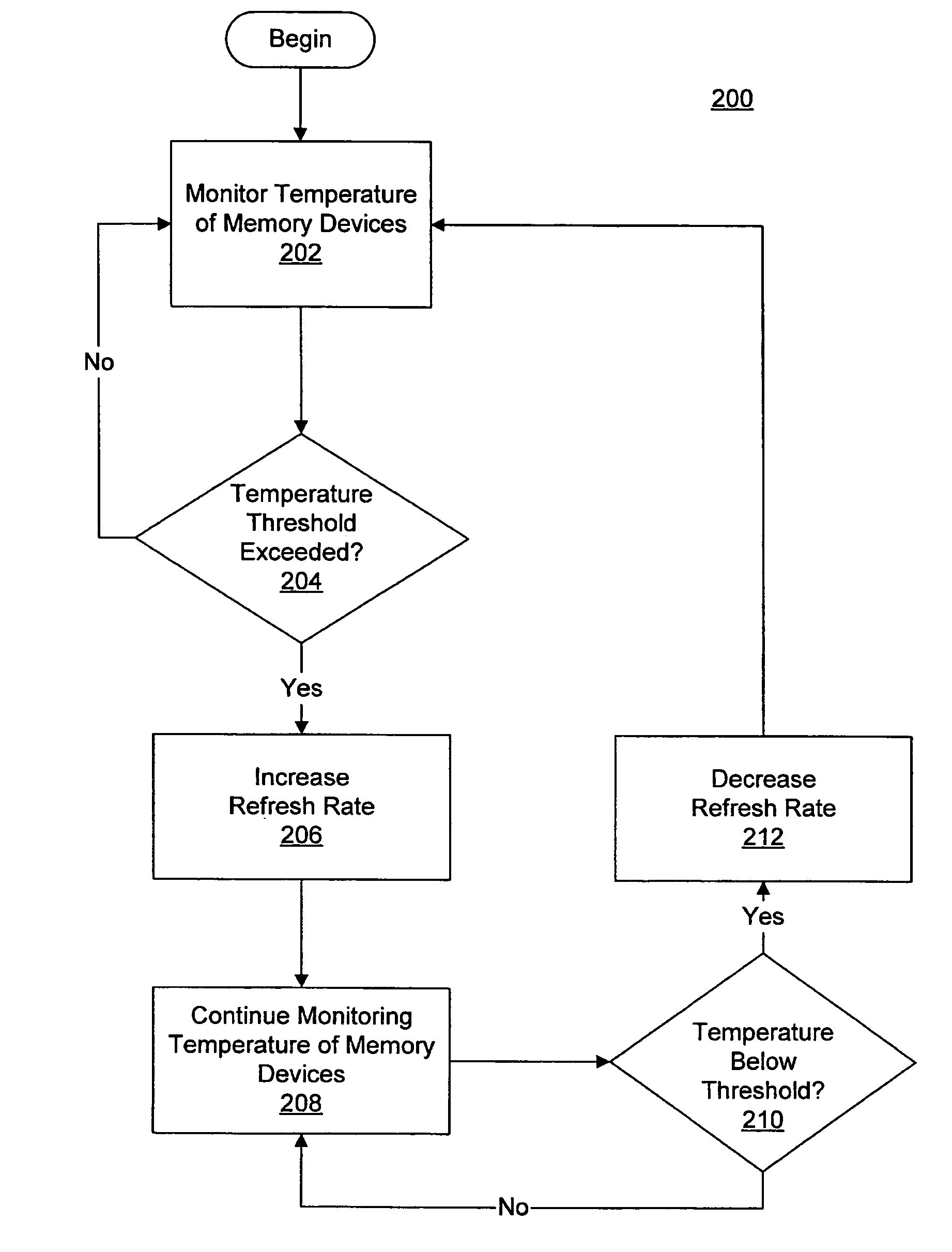
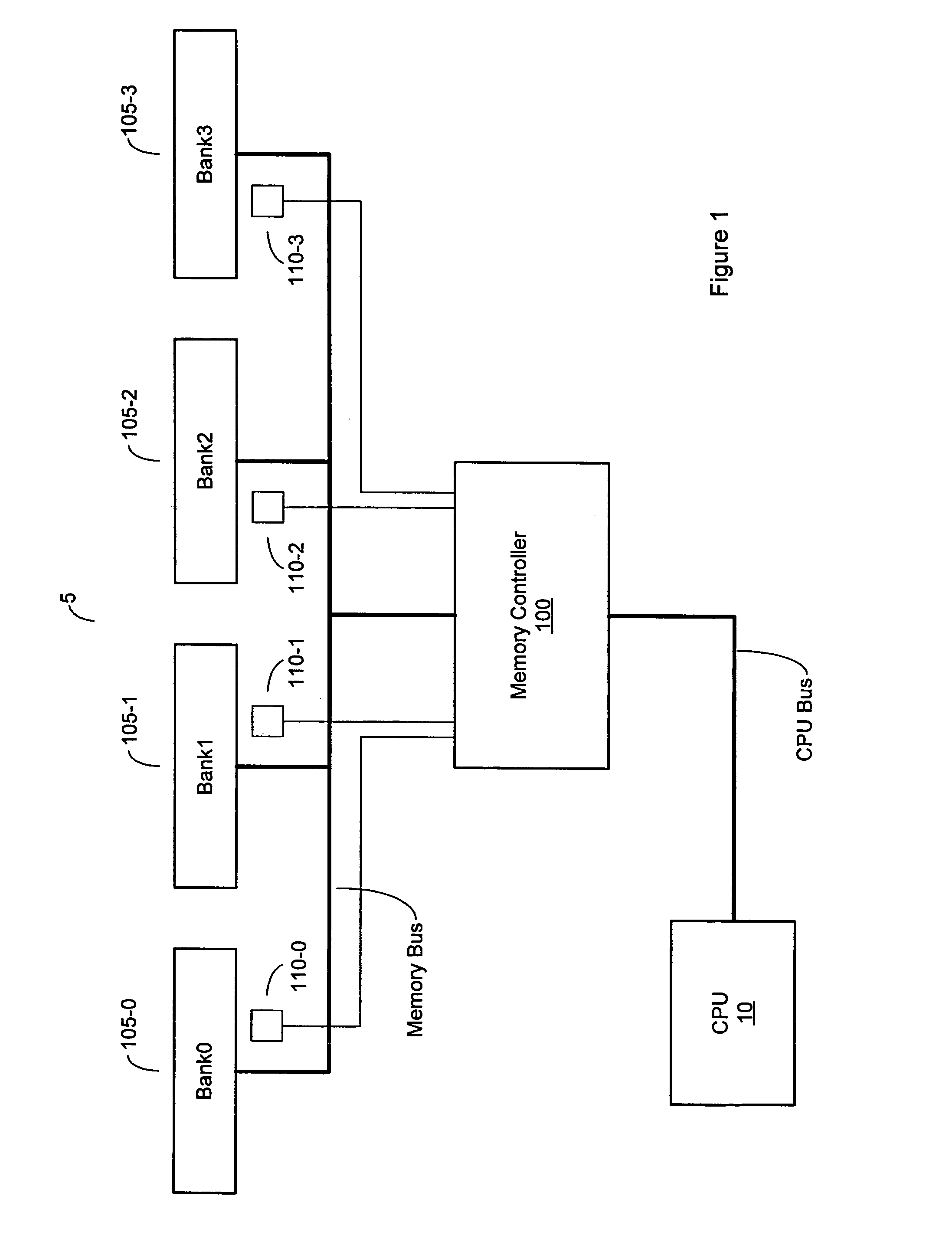
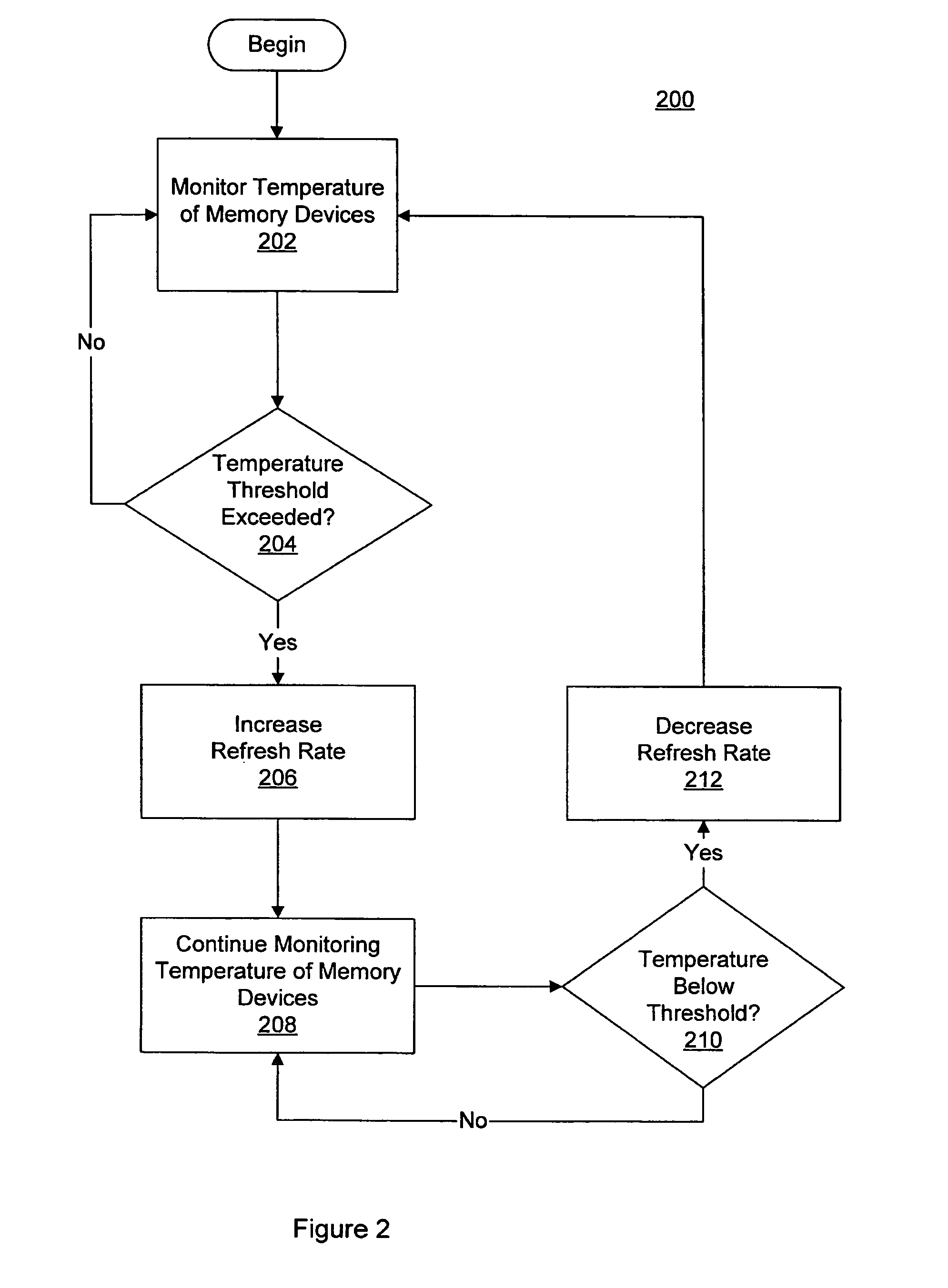
Variable memory refresh rate for DRAM
A method and apparatus for controlling a DRAM refresh rate. In one embodiment, a computer system includes a memory subsystem having a memory controller and one or more DRAM (dynamic random access memory) devices. The memory controller is configured to periodically initiate a refresh cycle to the one or more DRAM devices. The memory controller is also configured to monitor the temperature of the one or more DRAM devices. If the temperature exceeds a preset threshold, the memory controller is configured to increase the rate at which the periodic refresh cycle is performed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Dram CAM cell with hidden refresh
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method, apparatus, and system for active refresh management
A method, apparatus, and system to enable a partial refresh scheme for DRAM which includes specifying at least a refresh start value, or a refresh start value and a refresh end value, to reduce the number of rows that must be refreshed during a refresh cycle, thus reducing the amount of power consumed during refresh.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Low-power band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit
InactiveUS6876250B2Short refresh cycle timeIncrease temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLow voltageMicroprocessor
A combined low-voltage, low-power band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit is provided for providing a band-gap reference parameter and for sensing the temperature of a chip, such as an eDRAM memory unit or CPU chip, using the band-gap reference parameter. The combined sensor circuit is insensitive to supply voltage and a variation in the chip temperature. The power consumption of both circuits, i.e., the band-gap reference and the temperature sensor circuits, encompassing the combined sensor circuit is less than one μW. The combined sensor circuit can be used to monitor local or global chip temperature. The result can be used to (1) regulate DRAM array refresh cycle time, e.g., the higher the temperature, the shorter the refresh cycle time, (2) to activate an on-chip or off-chip cooling or heating device to regulate the chip temperature, (3) to adjust internally generated voltage level, and (4) to adjust the CPU (or microprocessor) clock rate, i.e., frequency, so that the chip will not overheat. The combined band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit of the present invention can be implemented within battery-operated devices having at least one memory unit. The low-power circuits of the sensor circuit extend battery lifetime and data retention time of the cells of the at least one memory unit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Graphics power savings system and method
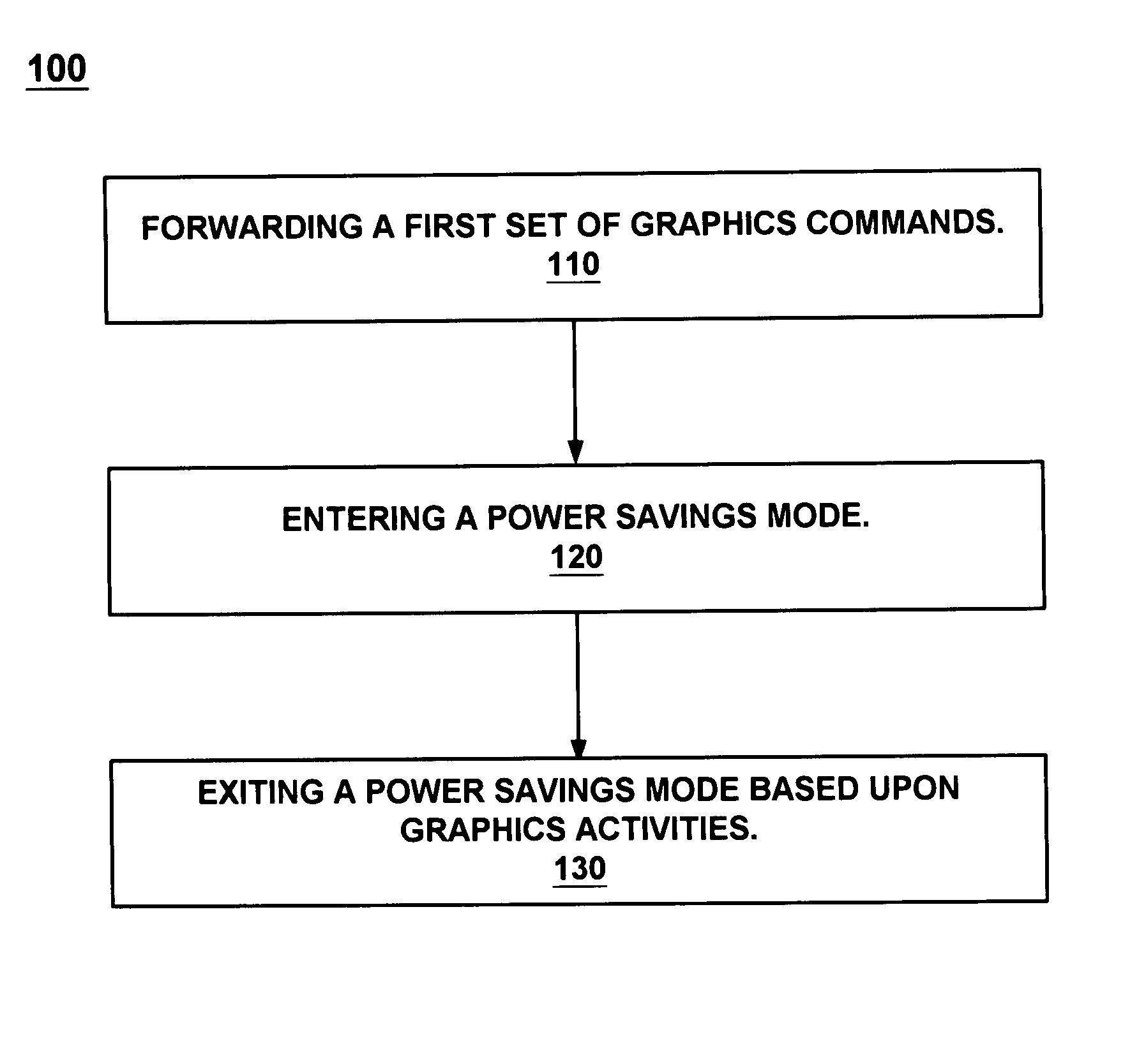
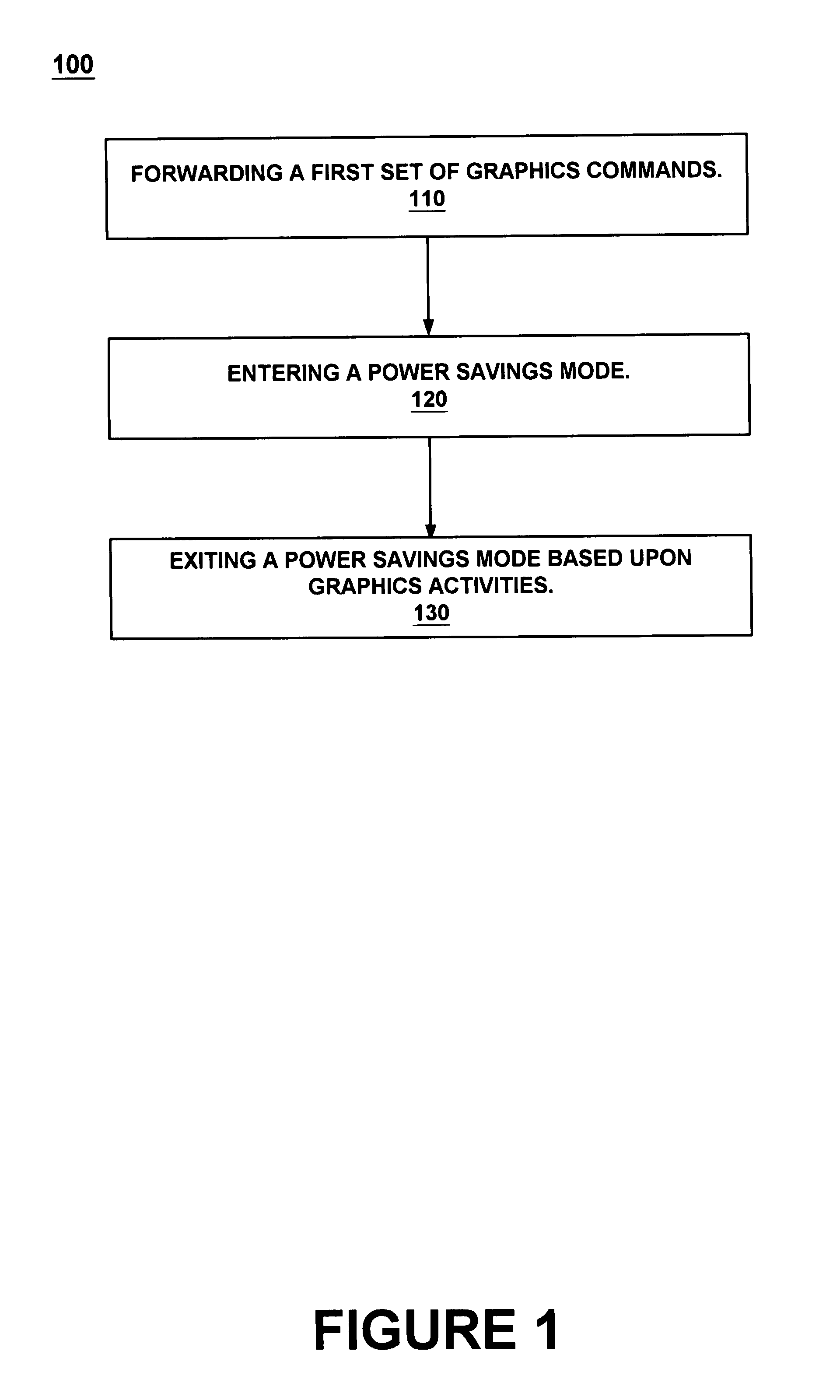
InactiveUS7256788B1Efficient power savingConvenient and flexible useEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementComputer hardwareGraphics
The present invention facilitates utilization of flexible and efficient power savings in graphics systems. A graphics power management method loads a first set of graphics commands from a CPU into a GPU at the beginning of a frame cycle. The CPU is put into a power saving mode after the loading is complete. The GPU processes the commands and forwards the results to a graphics buffer. The display begins the presentation of the data at the beginning of the following refresh cycle. The CPU leaves the power savings mode at end of the frame cycle to begin loading a second set of commands. The CPU recognizes the end of the frame cycle by counting a predetermined number of frame flip interrupt requests. After the CPU counts the predetermined number of frame flip interrupt requests the CPU begins to communicate additional graphics commands and then returns to the power savings mode.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Combination laundry device and method thereof
A combination laundry device and a method thereof are disclosed. The present invention relates to a combination laundry device that can interchange information between two laundry mechanisms, and that can automatically set operation conditions for a washing and a drying and / or a refreshing cycle based on information from each information tag attached on the laundry without a user's inputting additional conditions.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Refresh for dynamic cells with weak retention
Methods and circuit configurations for utilizing memory cells having weak retention times are provided. For some embodiments, rows identified as having weak retention cells may be refreshed more often than “normal retention” cells. As an example, if a normal refresh period is TREF, weak retention cells may be refreshed every TREF / 2 or TREF / 4 (possibly depending on the actual measured retention time).
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Semiconductor memory device having a DRAM cell structure and handled as a SRAM
InactiveUS20040130959A1Access time of the read/write operation for the input address can be reducedShorten access timeSolid-state devicesDigital storageRefresh cycleComputer architecture
A semiconductor memory device includes a memory cell array including a plurality of memory cells having a DRAM cell structure and is treated as a SRAM memory device without controlling the data refreshing cycle for the memory cells. The refreshing cycle is separated into a read operation and a write operation, which sandwich therebetween a read / write operation for the input address of the memory cell. The data read in the refreshing cycle is saved in a refreshing sense amplifier during the read / write operation and stored in the memory cell after the read / write operation.
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
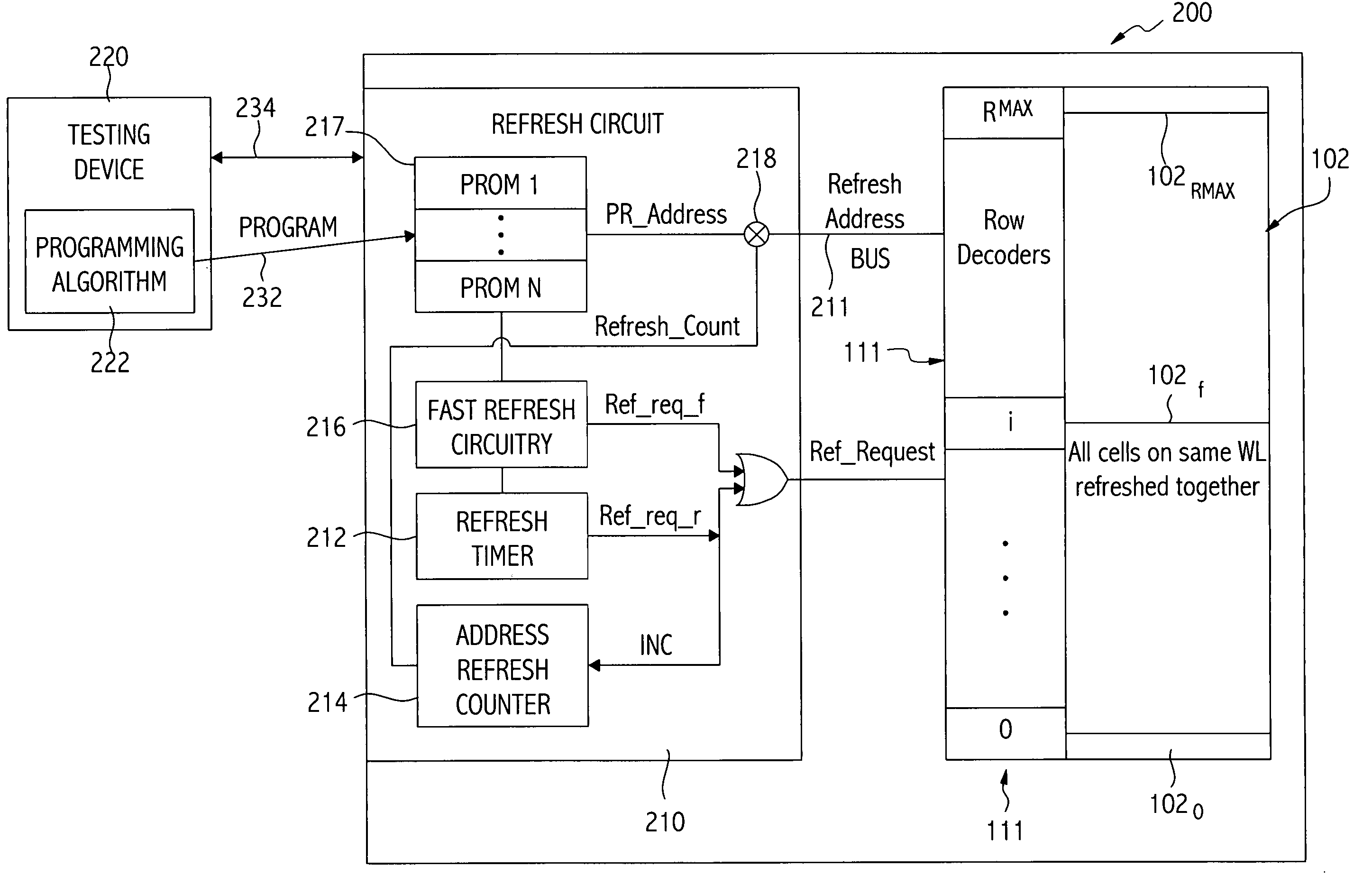
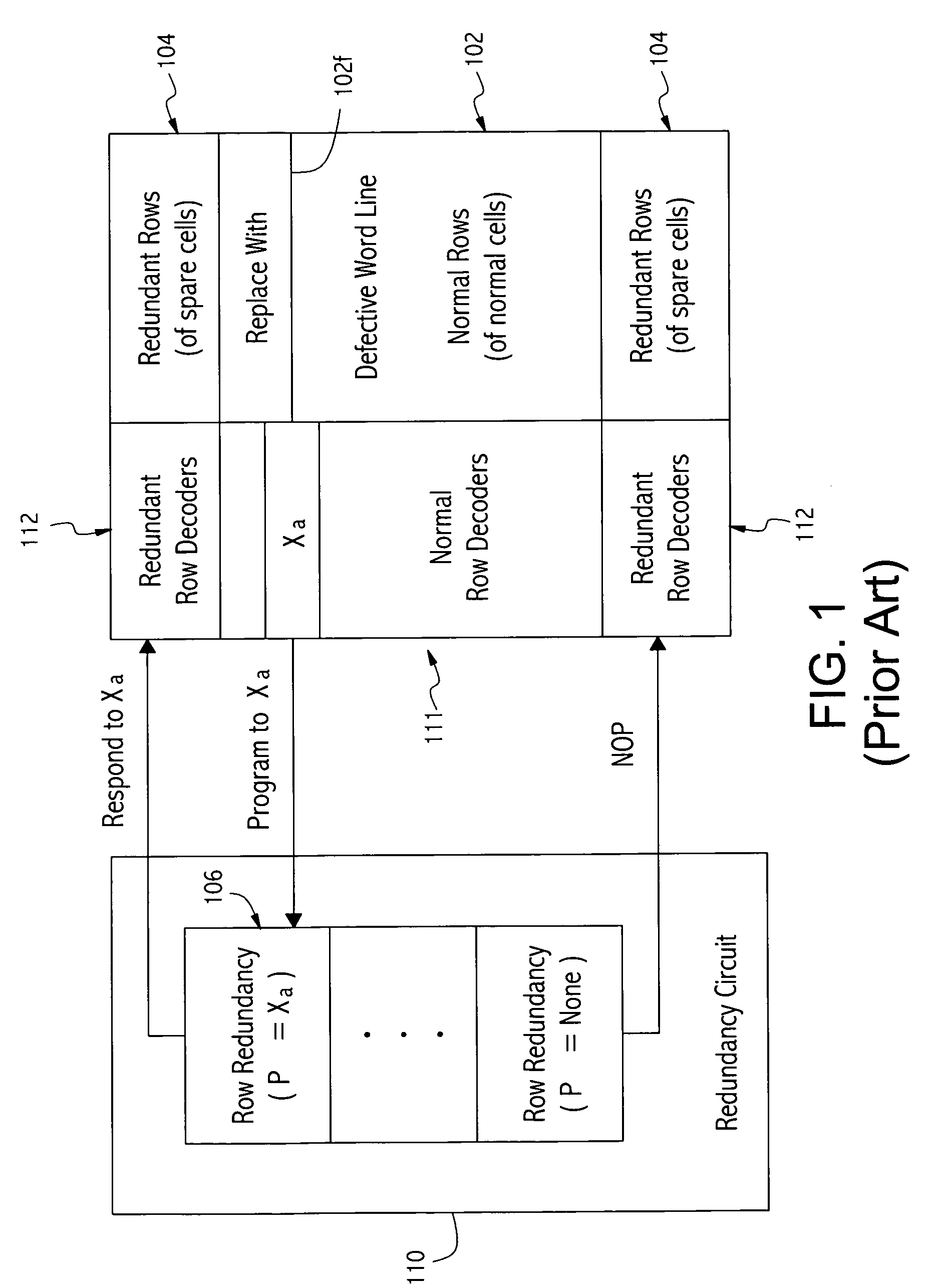
Dynamic memory refresh configurations and leakage control methods
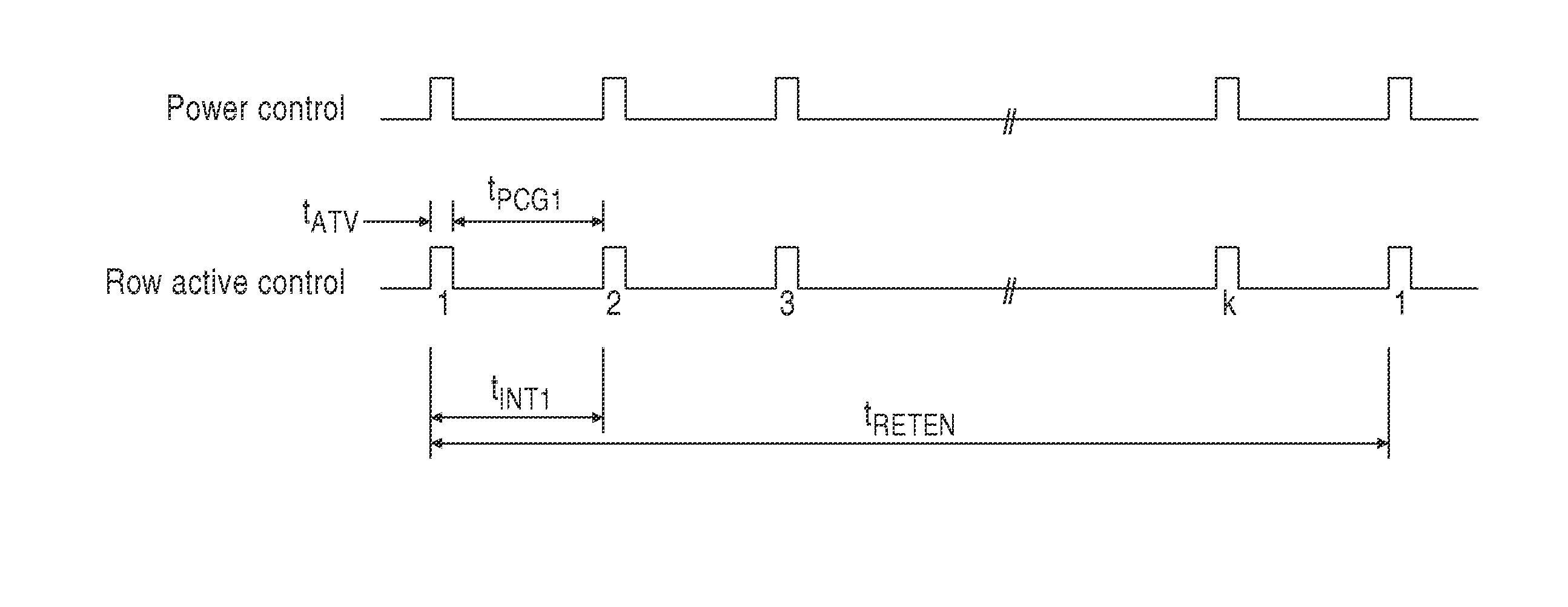
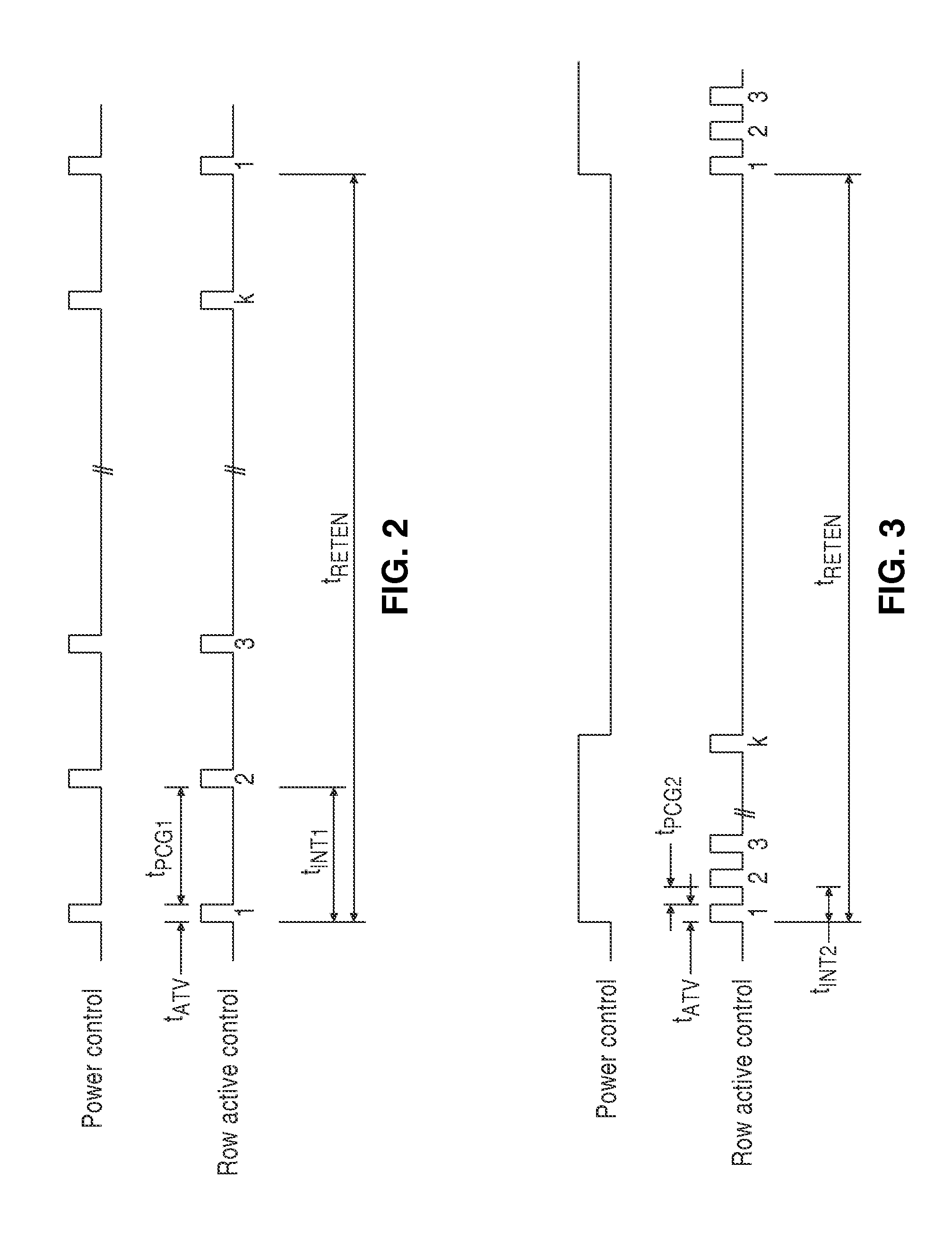
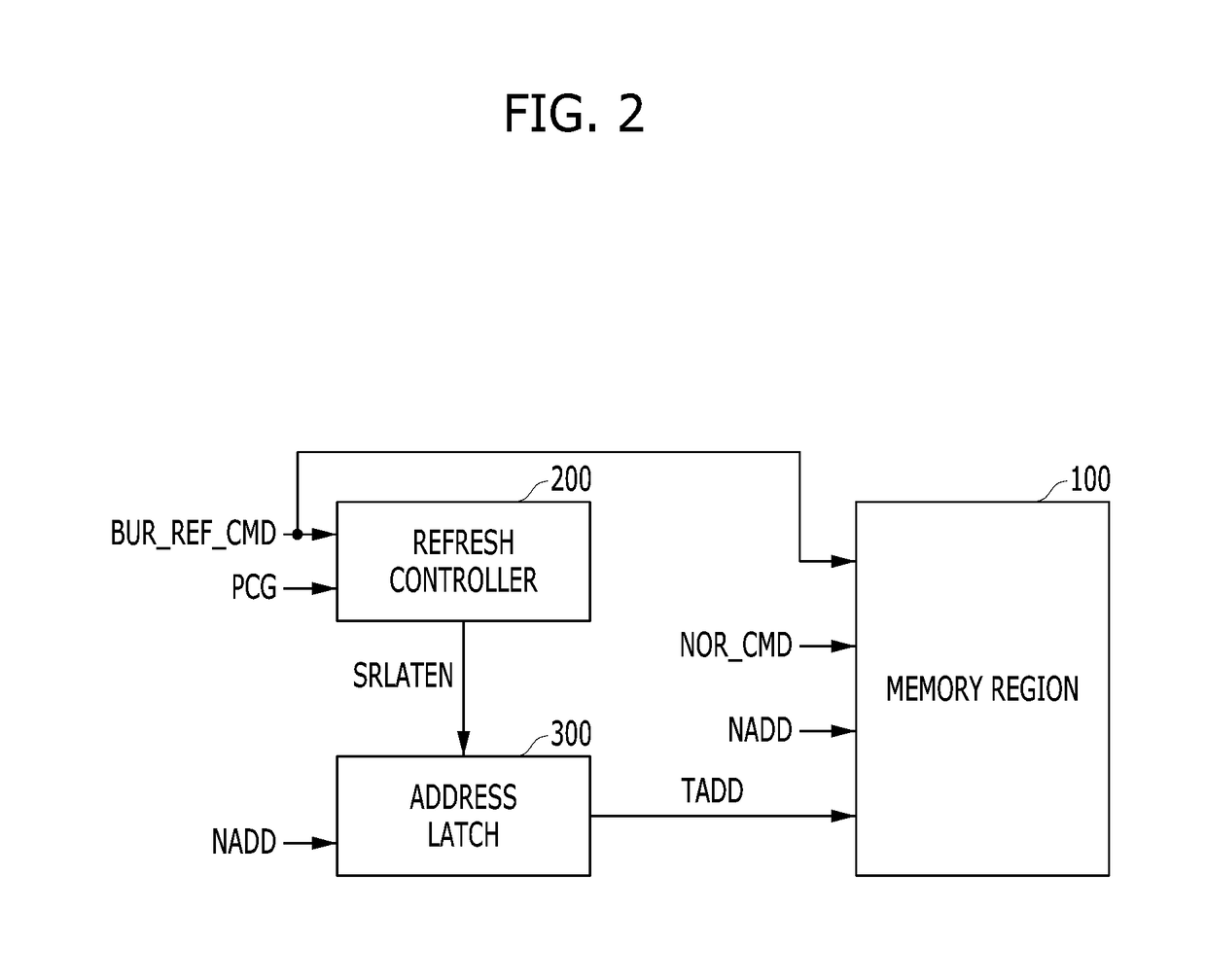
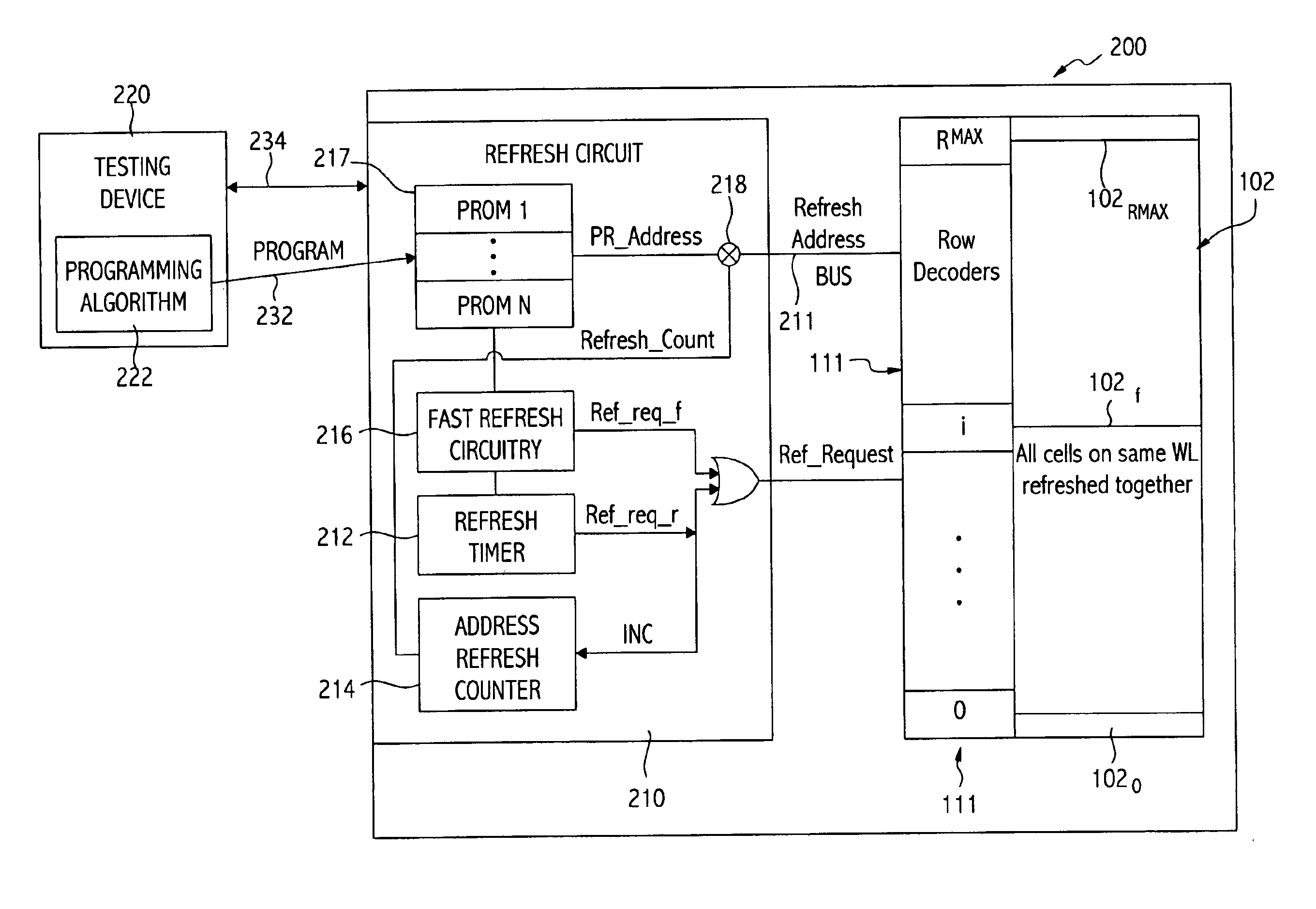
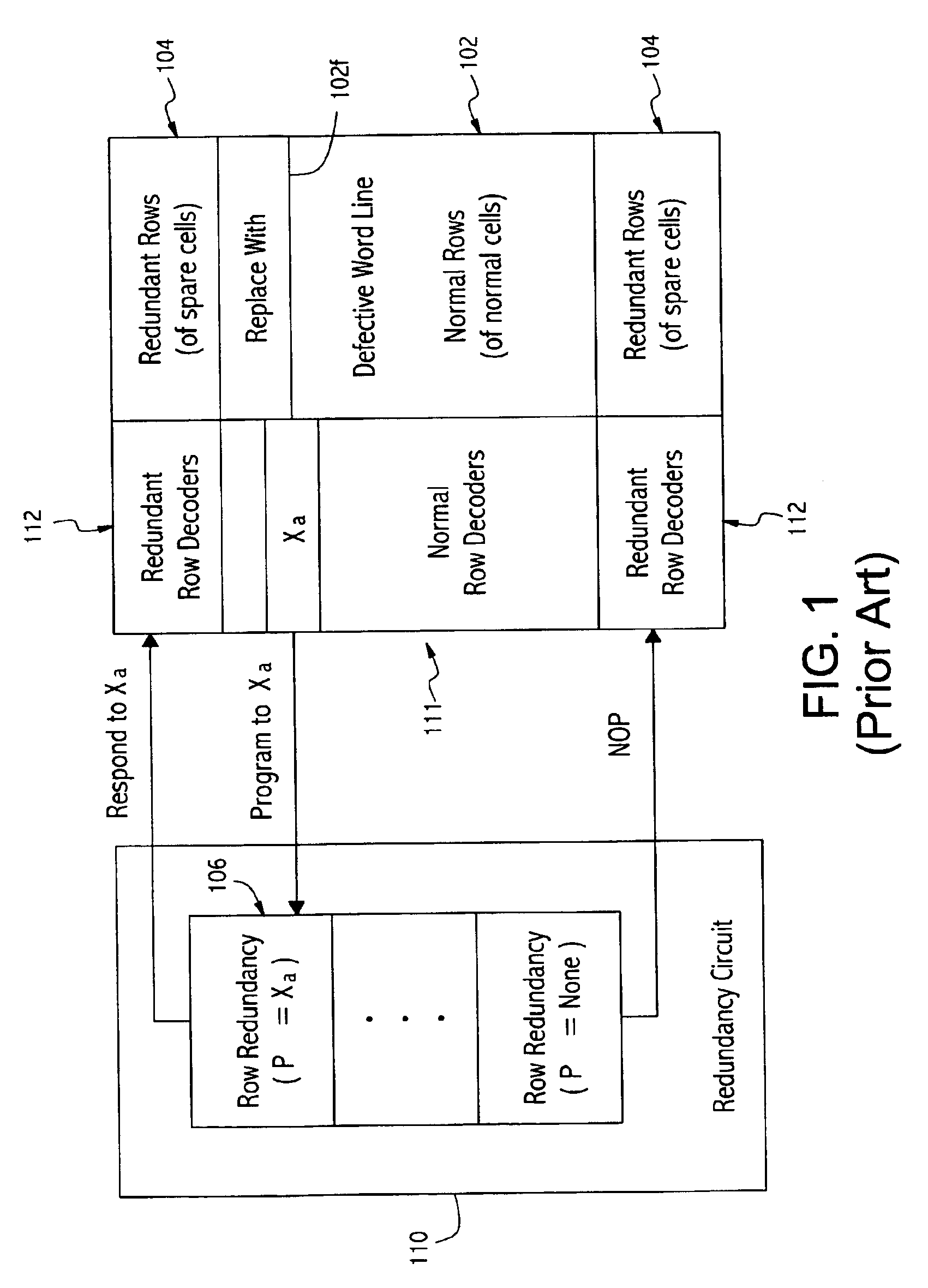
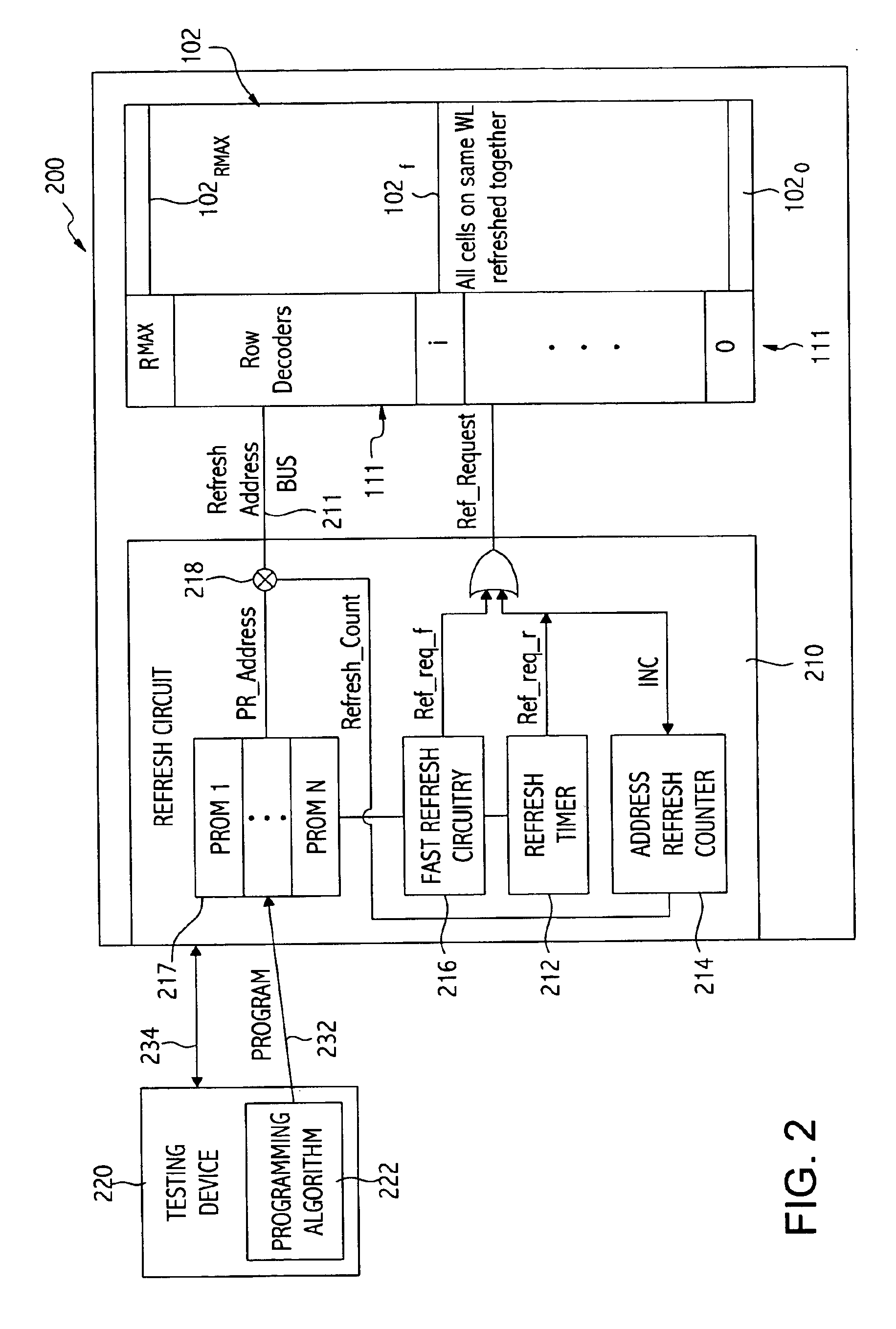
Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) circuits and methods are described for reducing leakage and increasing repaired yield. These objects are accomplished according to the invention by grouping refresh cycles within a single activation of power control, the use of limiting circuits or fuses to mitigate power losses associated with micro-bridging of bit-lines and word-lines, modulating the bit-line voltage at the end of precharge cycles, configuring refresh control circuits to use redundant word-lines in generating additional refresh cycles for redundant rows of memory cells, and combinations thereof. In one aspect, word-line fuses indicate modes of use as: unused, replacement, additional refresh, and replacement with additional refresh. The refresh control circuit utilizes these modes in combination with the X-address stored in the word-line fuses for controlling the generation of additional refresh cycles toward overcoming insufficient data retention intervals in select memory cell rows.
Owner:ZMOS TECH
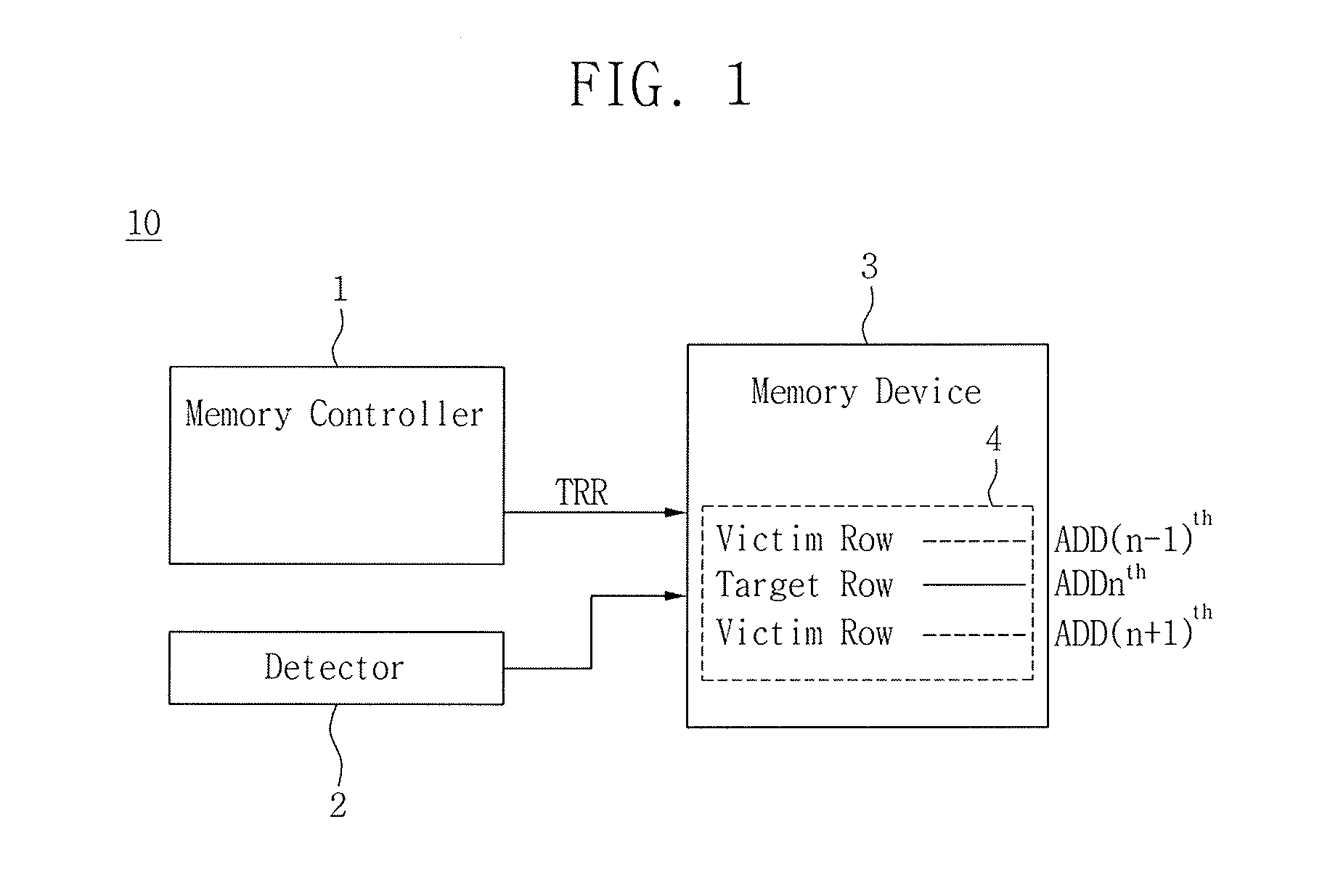
Semiconductor memory device that performs a refresh operation
A semiconductor memory device includes a memory circuit including a plurality of memory cells and a refresh control circuit. The refresh control circuit is configured to determine a number of times to perform a target row refresh (TRR) in response to a mode register set (MRS) code signal, wherein the MRS code signal is generated in response to a temperature change, and the refresh control circuit is configured to maintain a refresh cycle of at least two of the memory cells for a period of time when the refresh cycle is changed due to the temperature change.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
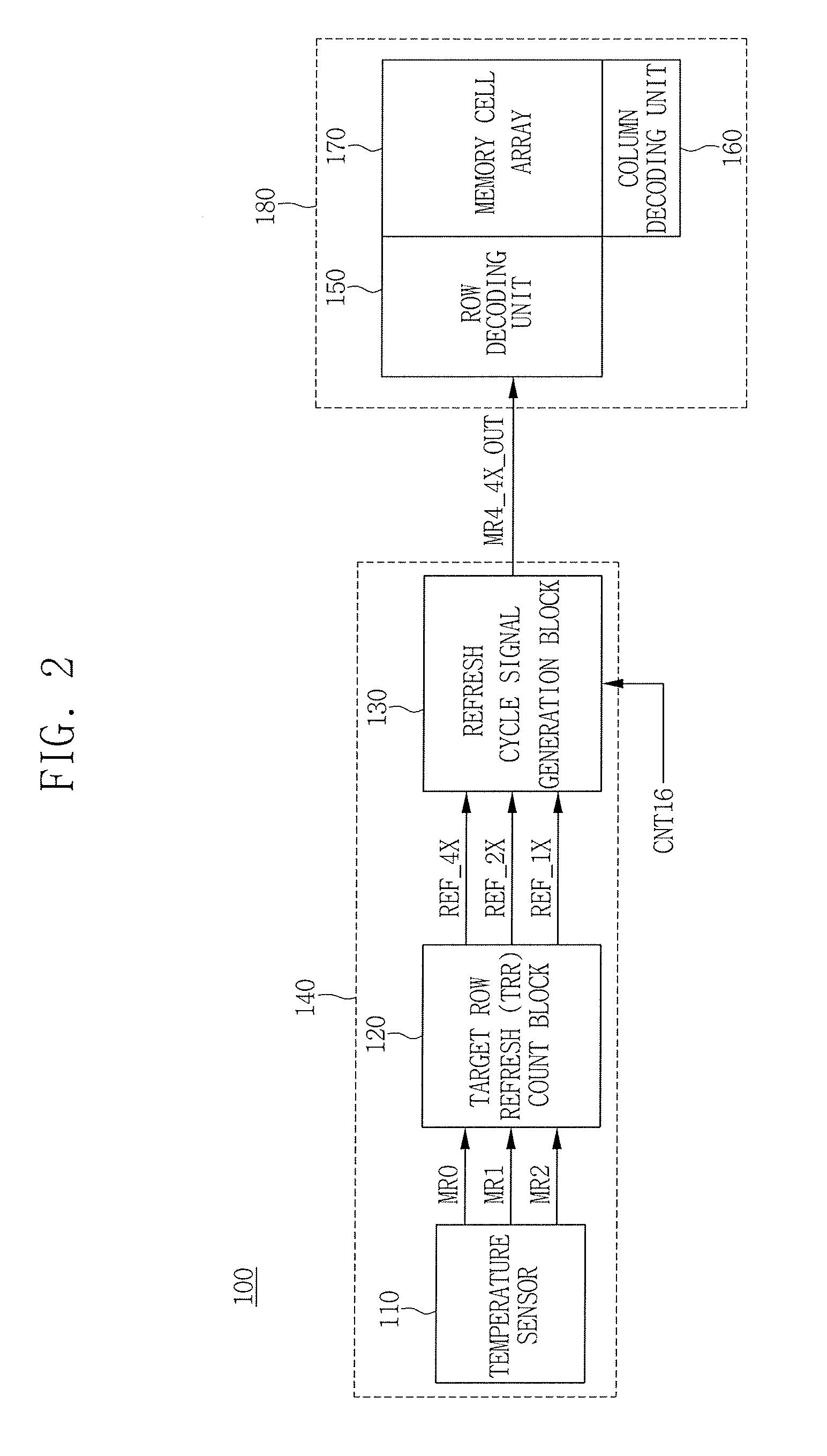
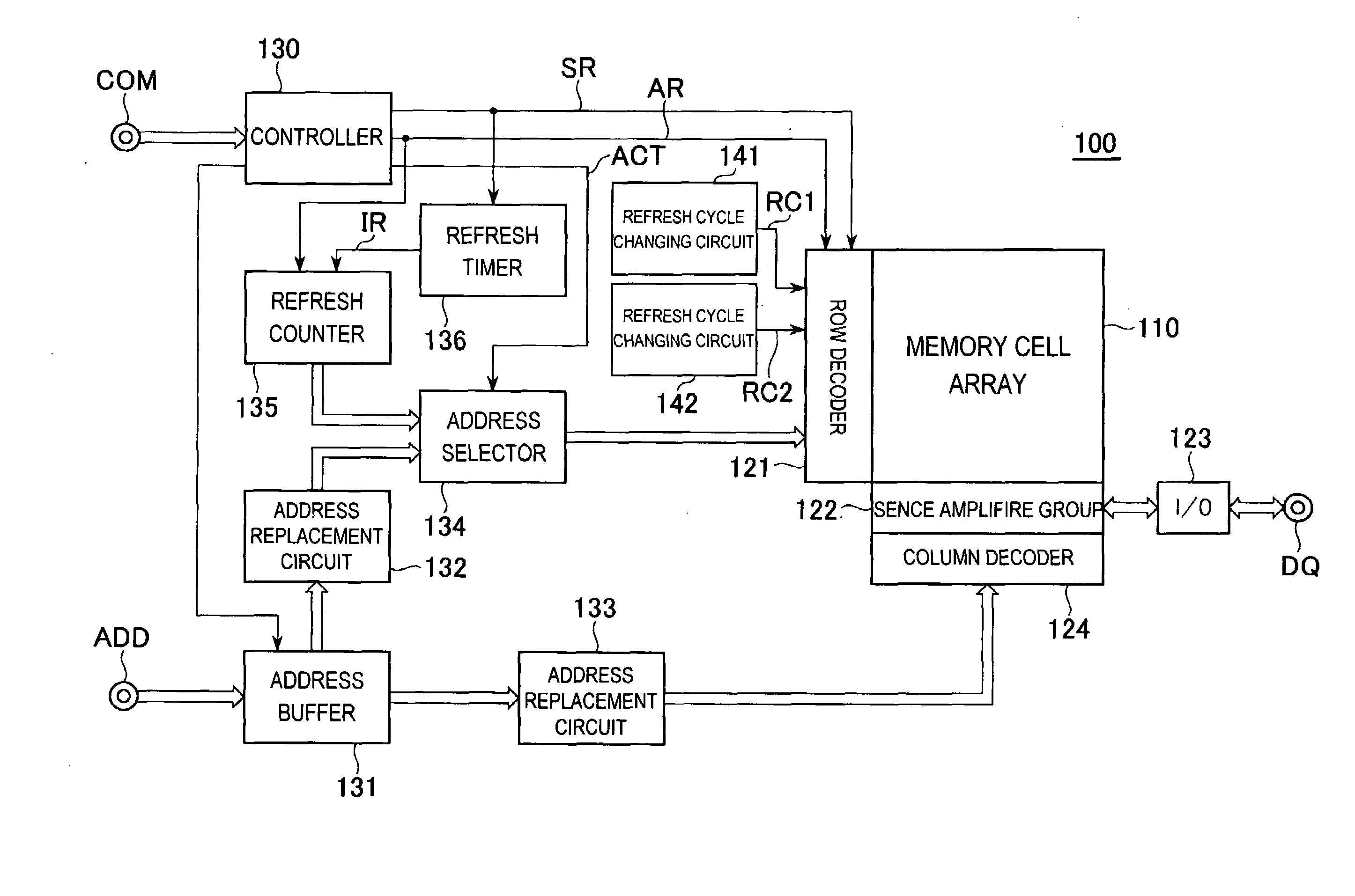
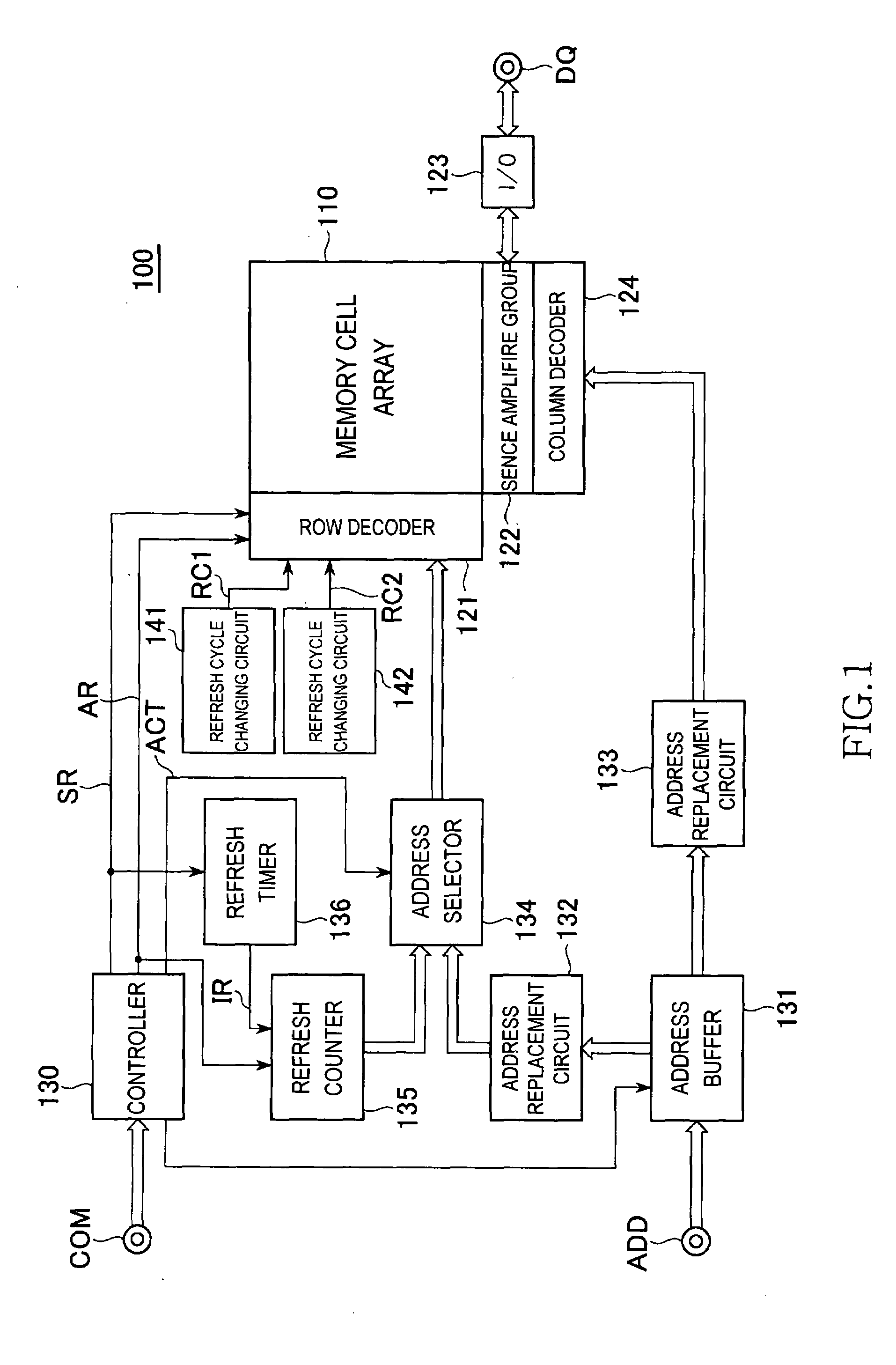
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20080130394A1Time consumingReduce power consumptionRead-only memoriesCode conversionRefresh cycleHemt circuits
A semiconductor memory device includes a first refresh cycle changing circuit that changes a refresh cycle according to an auto-refresh mode, without giving influence to a refresh cycle according to a self-refresh mode, and a second refresh cycle changing circuit that changes a refresh cycle according to the self-refresh mode, without giving influence to a refresh cycle according to the auto-refresh mode. In this way, according to the present invention, the refresh cycle according to the auto-refresh mode and the refresh cycle according to the self-refresh mode can be controlled independently. Therefore, refresh operation considering the characteristic of each mode can be executed.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
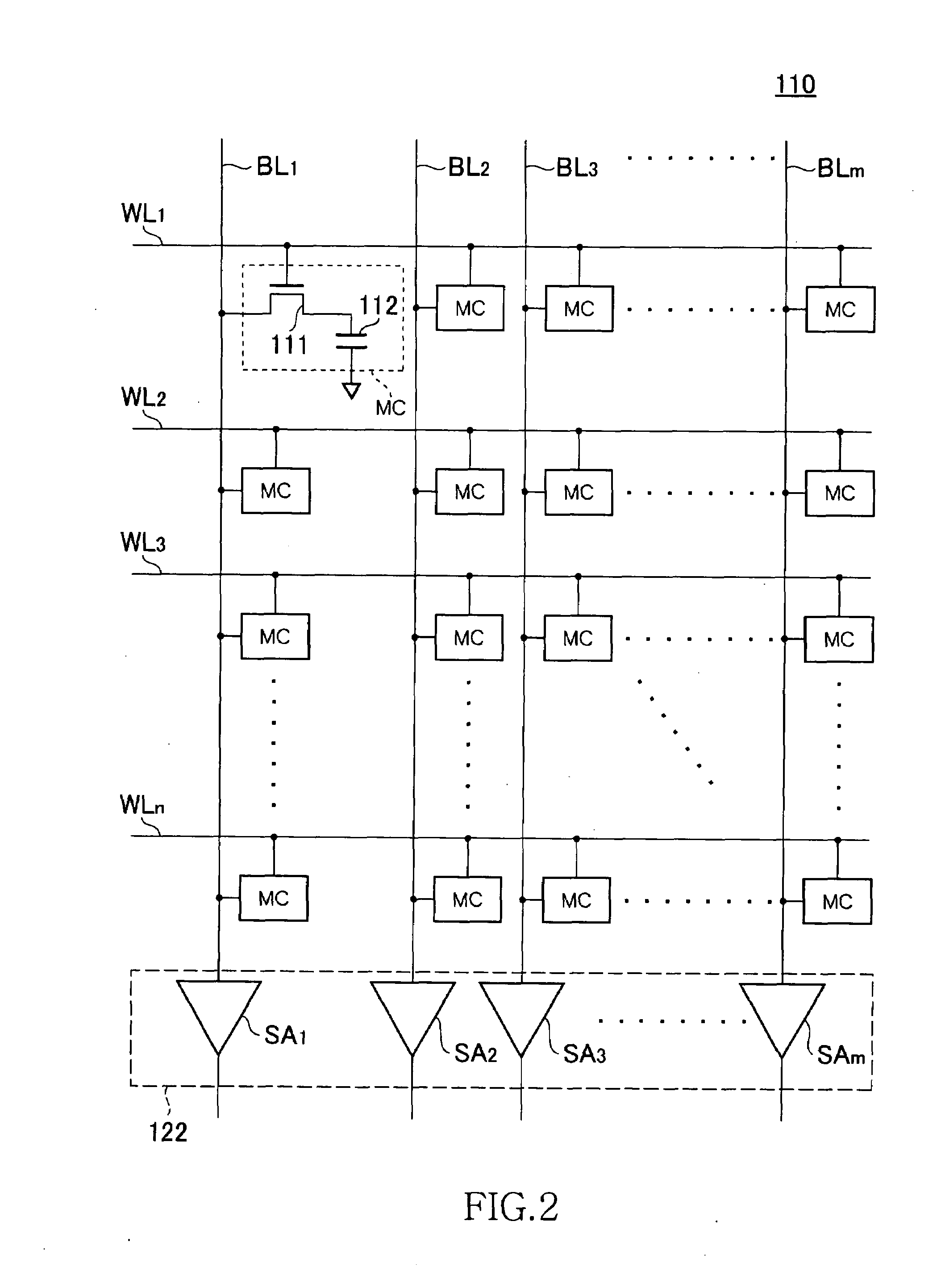
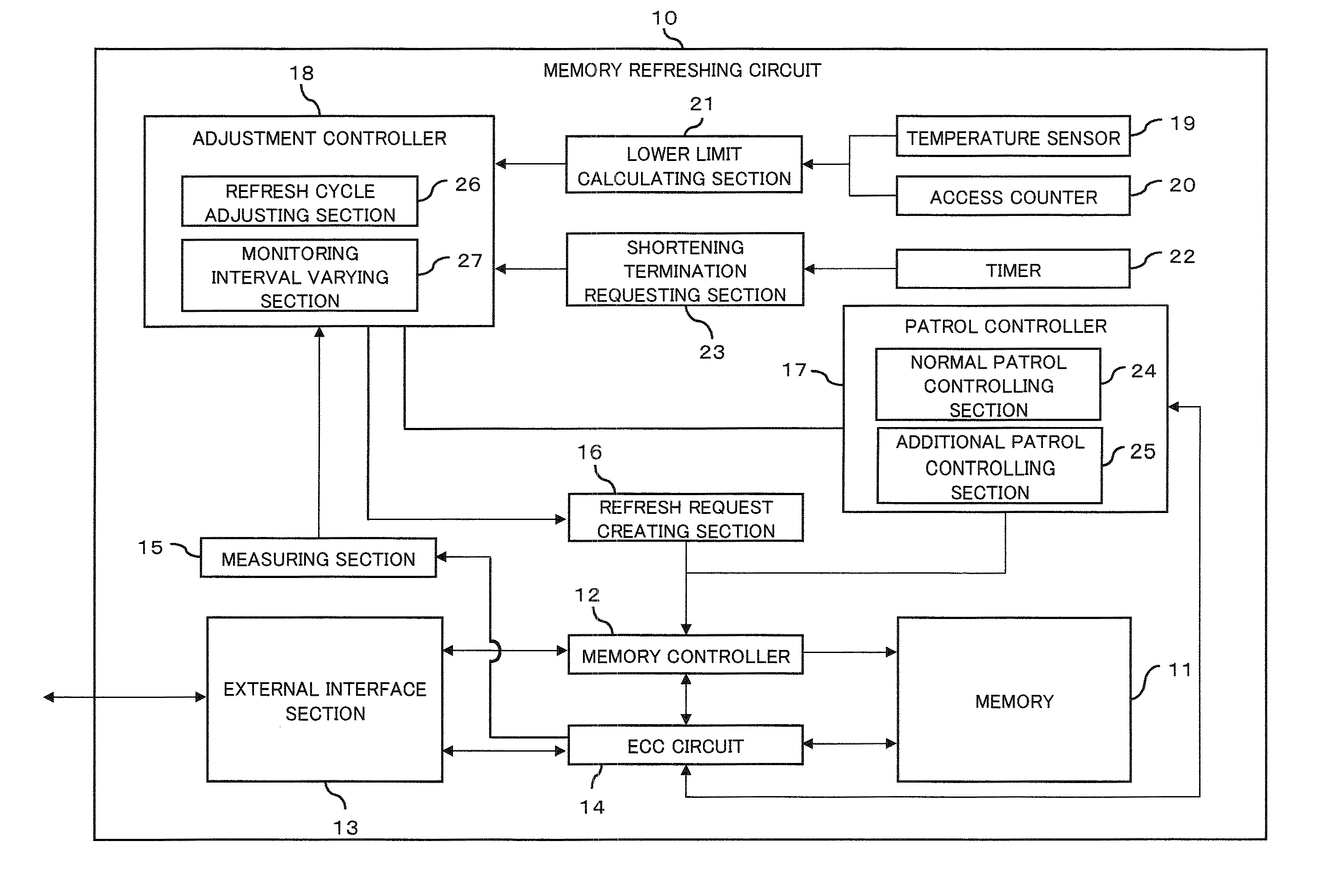
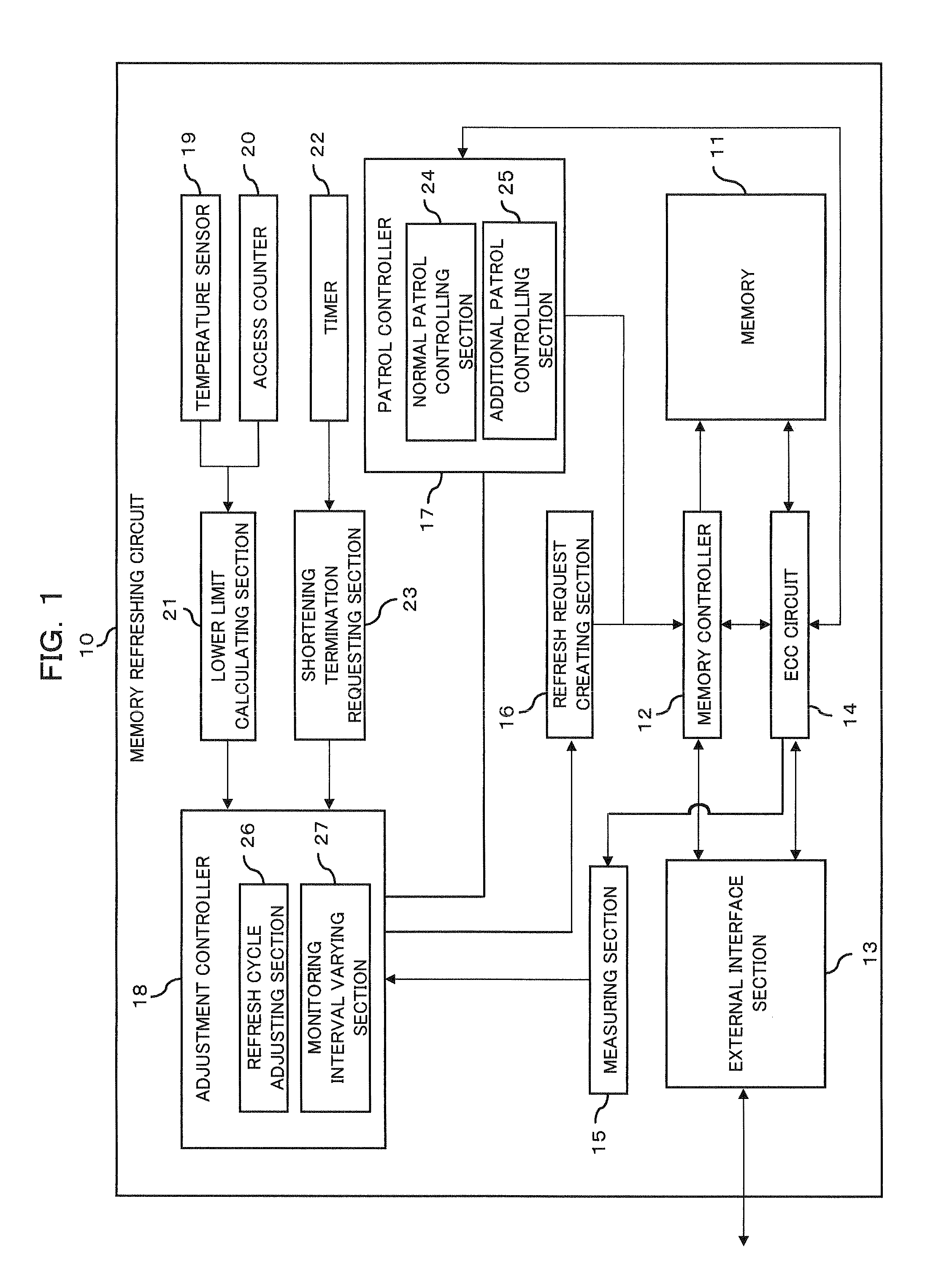
Memory refreshing apparatus and method for memory refresh
InactiveUS20100106901A1Error detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRefresh cycleComputer science
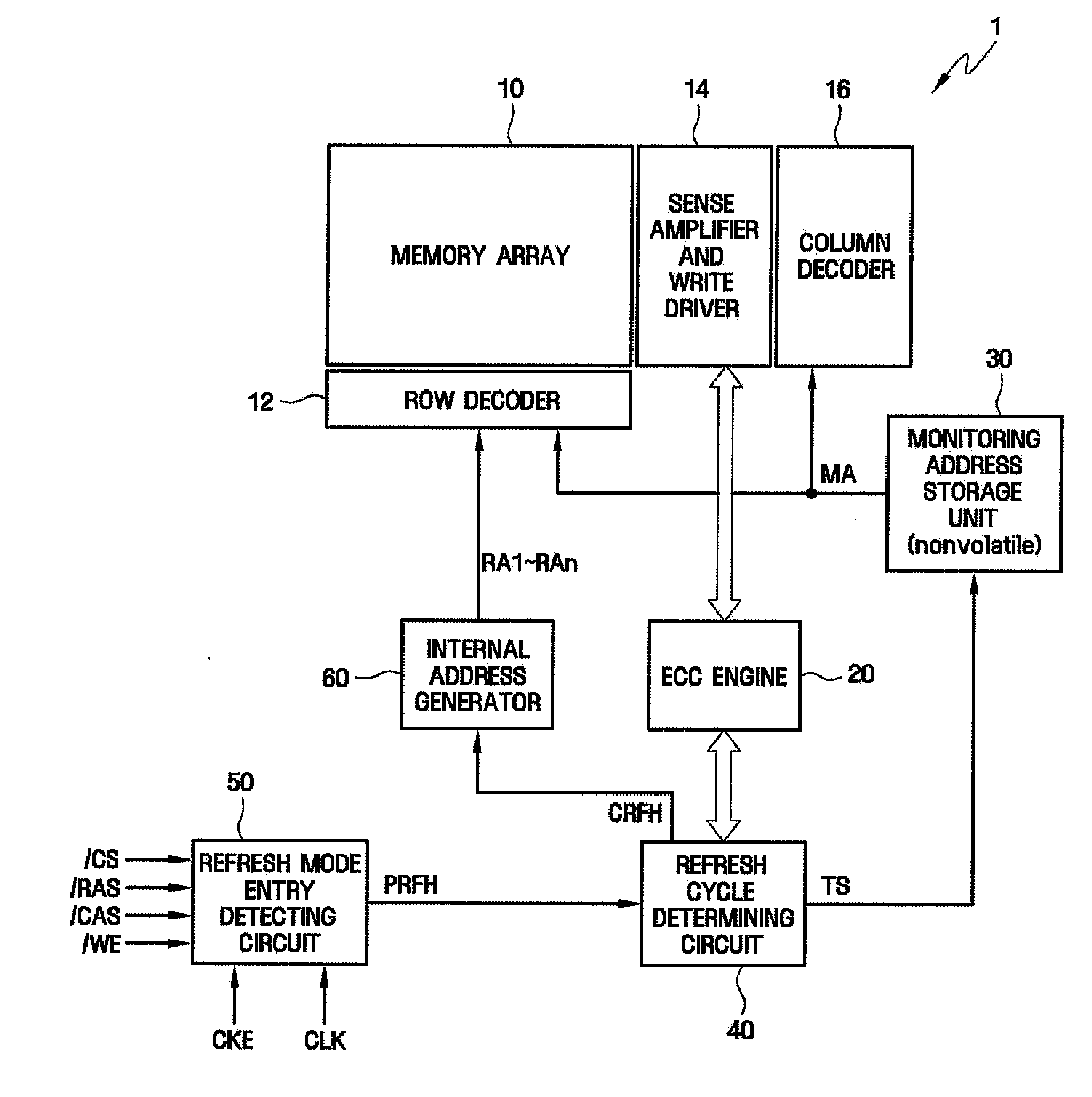
The optimization of a refresh cycle is carried out in harmony with the error occurrence state in the memory with the presence of a normal patrol controlling section controlling a normal patrol operation that patrols the memory; an additional patrol controlling section controlling an additional patrol operation that patrols, if a first error in the memory is detected during the normal patrol operation, an error occurring area in which the first error occurs and which is included in the memory; a measuring section (15) measuring, if a second error is detected in the error occurring area during the additional patrol operation, an error frequency representing information of error in the error occurring area; and a refresh cycle adjusting section adjusting the refresh cycle in accordance with the error frequency measured by the measuring section.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Semiconductor device
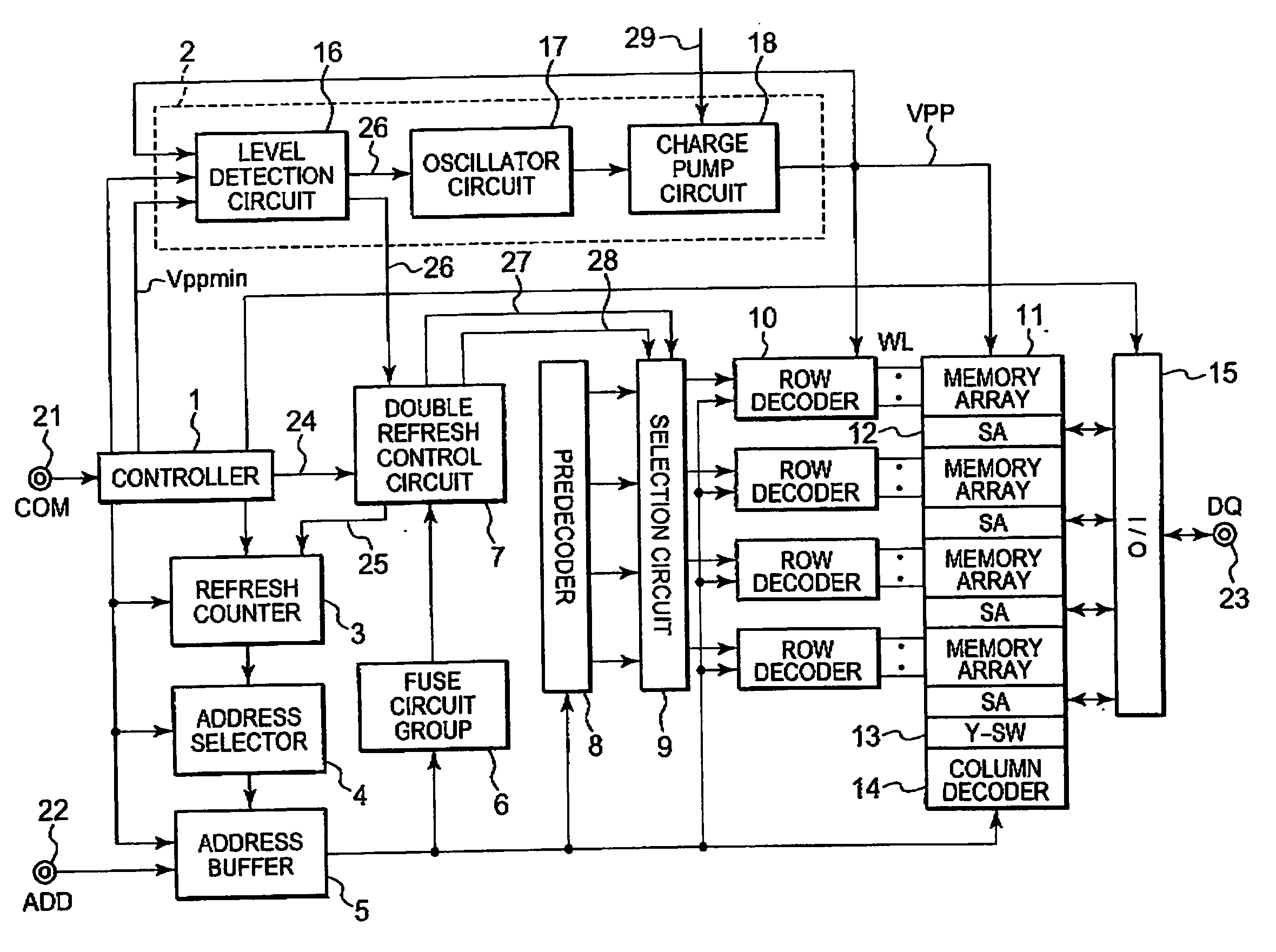
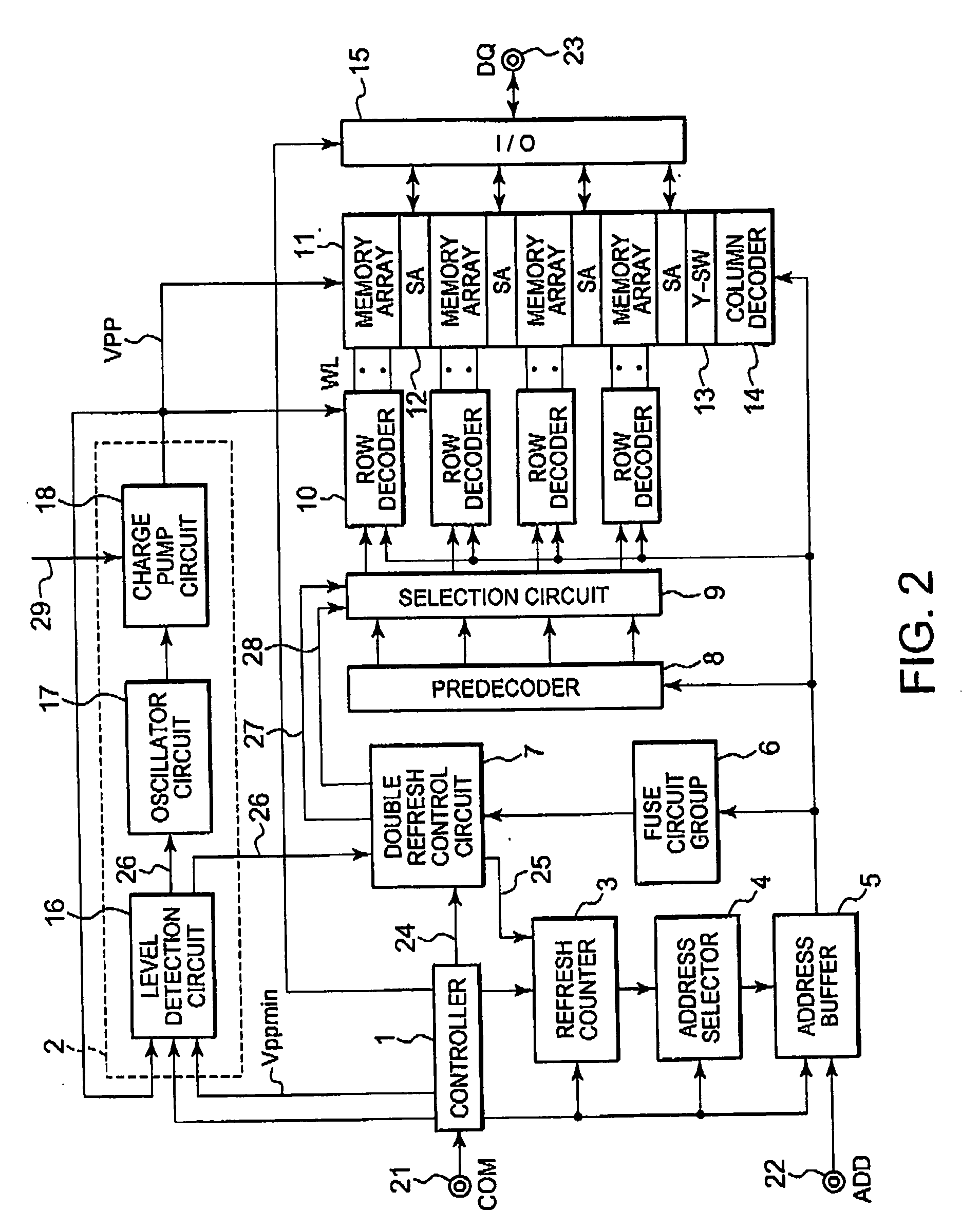
InactiveUS20070008799A1Raise the voltage levelImprove refresh featureDigital storageLower limitRefresh cycle
In a semiconductor device, an internally-generated power supply voltage VPP is monitored. If the internally-generated power supply voltage VPP is lower than a lower limit voltage, serial refresh is selected as a double refresh operation mode. In the serial refresh, double refresh for a pair address is inserted in a next refresh cycle. By the serial refresh, decrease of the internally-generated power supply voltage VPP is suppressed.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Self-initiated self-refresh mode for memory modules
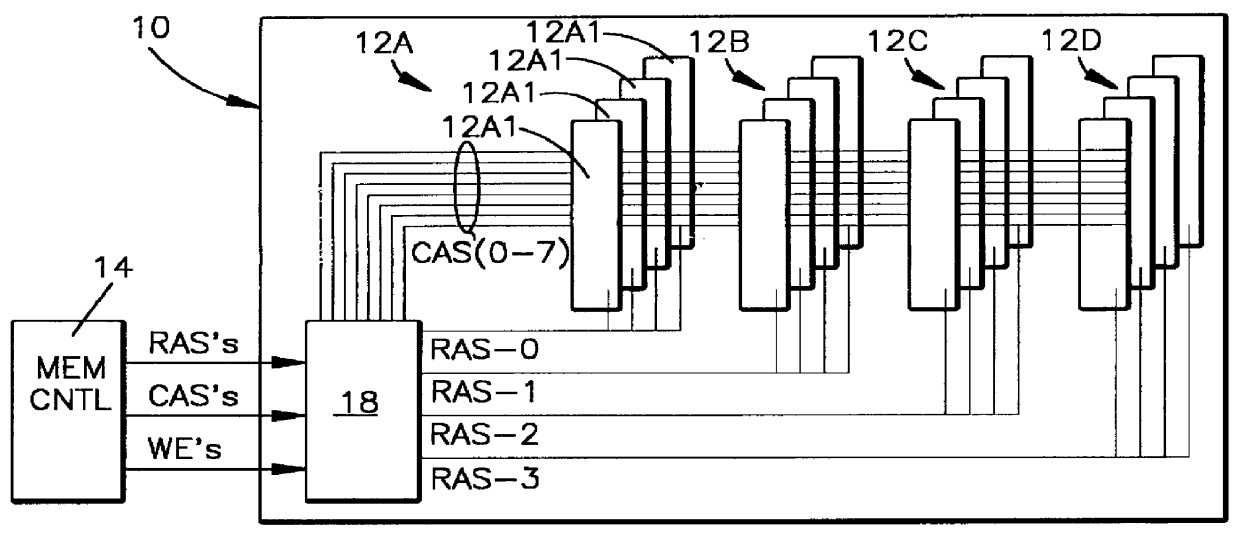
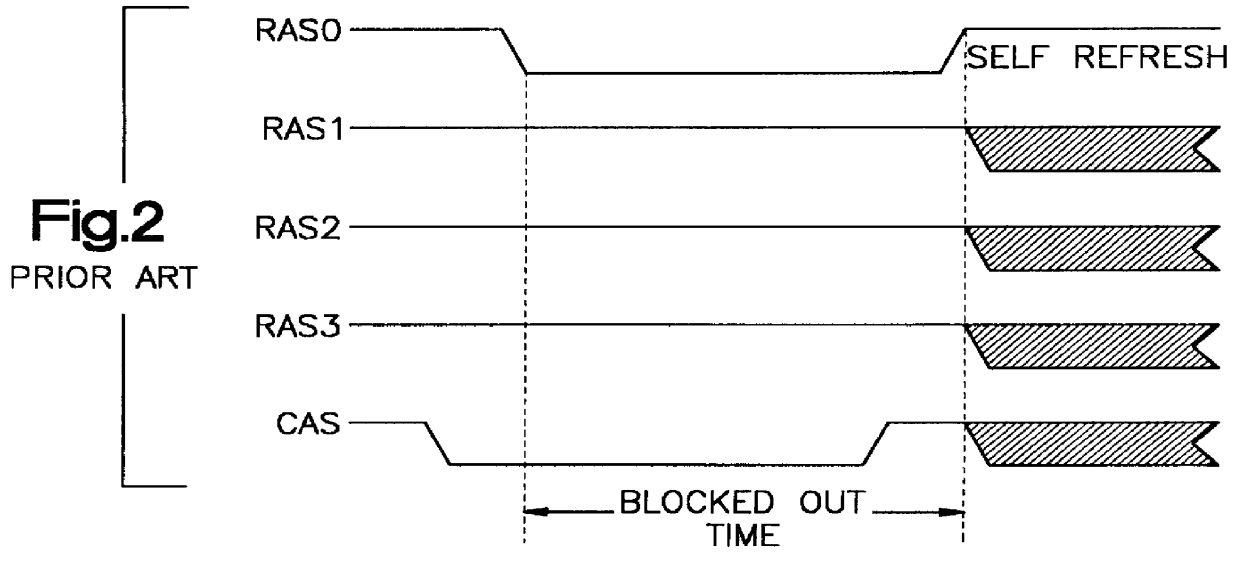
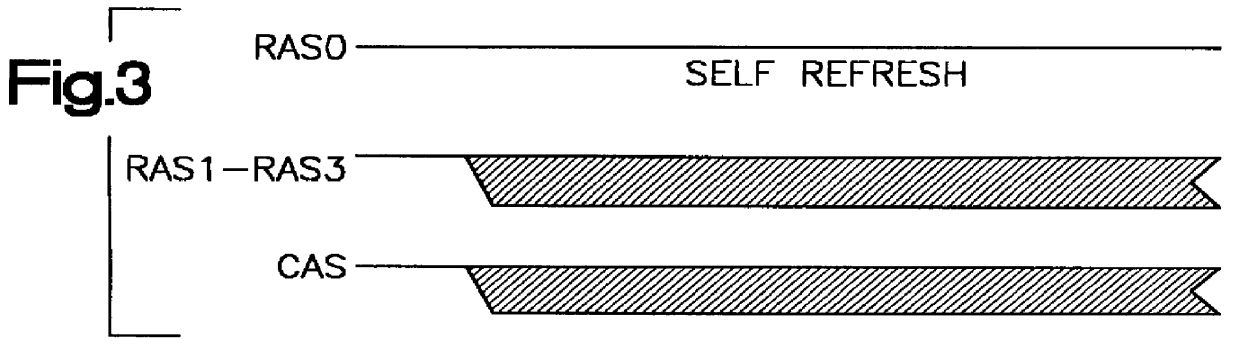
A method and apparatus for selectively causing each bank of a number of banks of DRAMs of a DRAM memory card to enter into the self-refresh mode without affecting the operation of any other bank. In the computer system incorporating the SIMM or DIMM type DRAM cards, each bank of memory on each card has a RAS signal specific to that specific bank. One or more CAS signals are supplied across all of the memory banks, on all cards. Thus, each memory bank is accessed separately for a read / write operation by the RAS becoming active before the CAS becomes active; and refresh takes place by the CAS signal becoming active before the RAS signal becomes active. The number of clock cycles or refresh cycles between active RAS signals to each memory bank are counted. If RAS does not become active for N clock or refresh cycles, a signal is provided within each respective memory bank and that memory bank will immediately, or preferably after M additional clock or refresh cycles enter self-refresh mode without affecting the operation of any other bank. At the same time, the memory controller counts cycles of RAS inactivity for each DRAM bank it controls. A signal is also provided to a register to require a double read / write on the next active read / write cycle to that bank, for reactivating that bank from the self-refresh mode when RAS signal specific to that bank becomes active while CAS is inactive.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
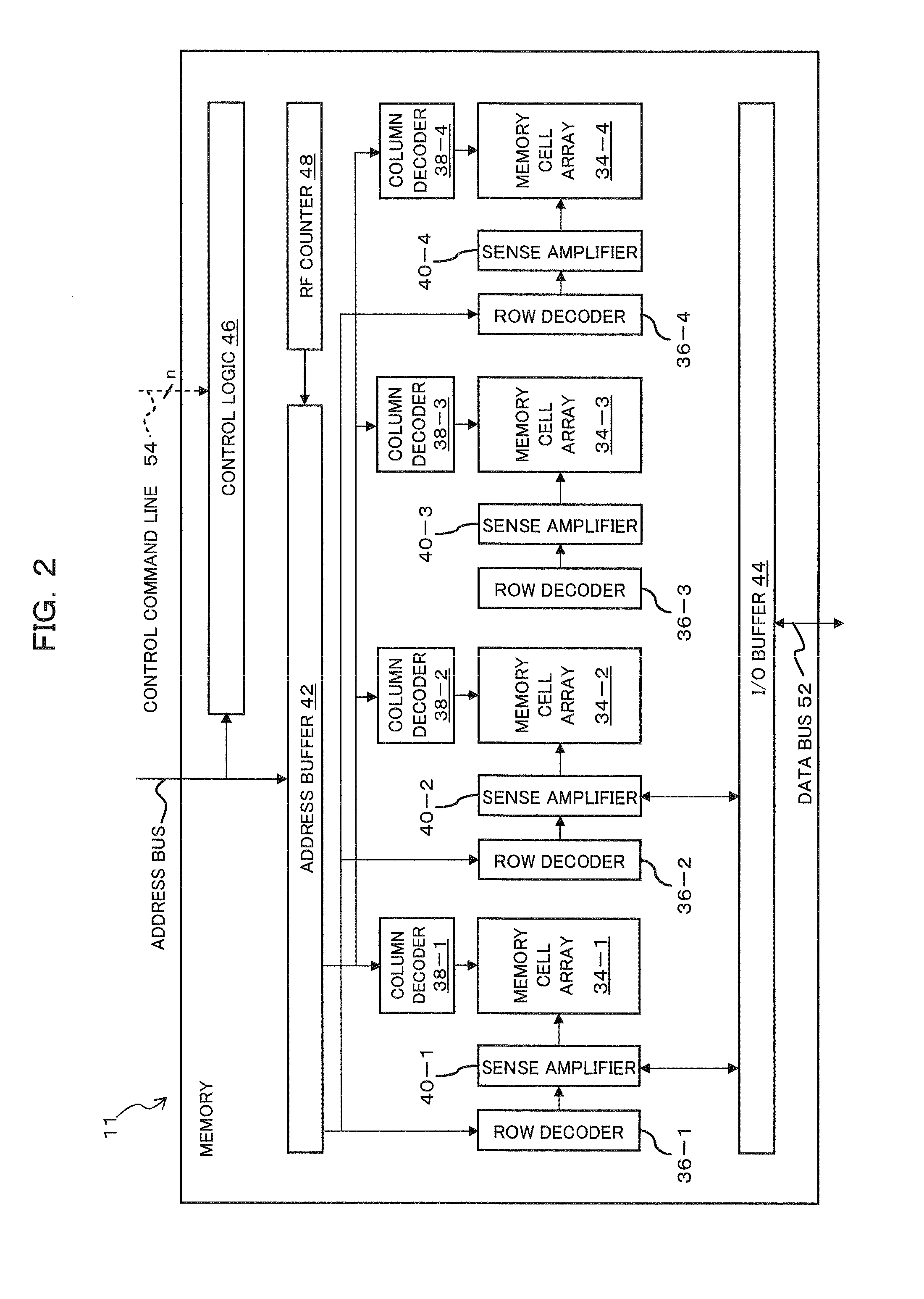
Semiconductor memory device
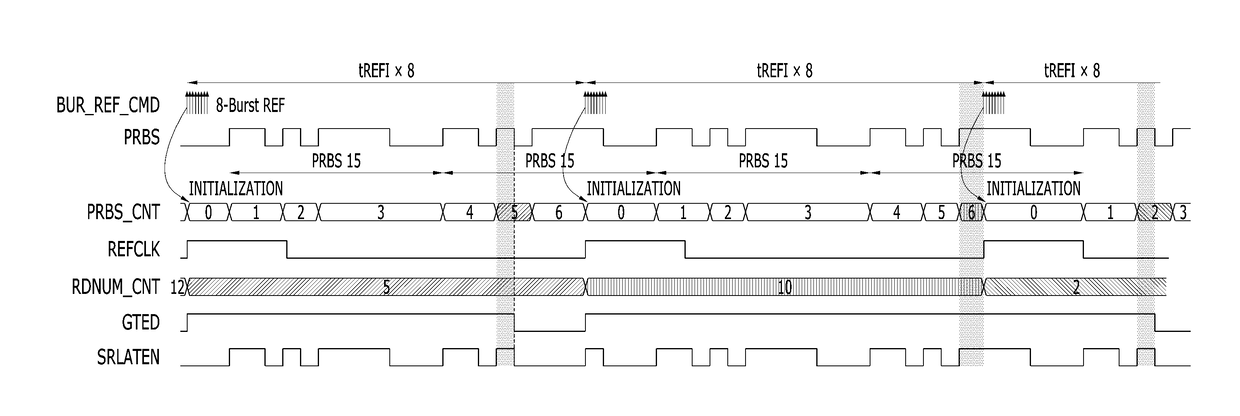
A semiconductor memory device includes a first count circuit suitable for counting a first clock signal which continuously toggles in each burst refresh cycle, and generating a first count code signal, based on a burst refresh command signal; a cycle guide circuit suitable for generating a second clock signal which toggles once in each burst refresh cycle, based on the burst refresh command signal and a precharge signal; a second count circuit suitable for counting the second clock signal and generating a second count code signal; and a control circuit suitable for generating a latch control signal for latching a target address in each burst refresh cycle, based on the first count code signal and the second count code signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Refresh for dynamic cells with weak retention
Methods and circuit configurations for utilizing memory cells having weak retention times are provided. For some embodiments, rows identified as having weak retention cells may be refreshed more often than “normal retention” cells. As an example, if a normal refresh period is TREF, weak retention cells may be refreshed every TREF / 2 or TREF / 4 (possibly depending on the actual measured retention time).
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Semiconductor memory device and refresh period controlling method
InactiveUS7493531B2Reduce dataFacilitates temperature compensationError detection/correctionCode conversionControl circuitSemiconductor
Disclosed is a memory device including an error rate measurement circuit and a control circuit. The error rate measurement circuit, carrying a BIST circuit, reads out and writes data for an area for monitor bits every refresh period to detect an error rate (error count) with the refresh period. The control circuit performs control for elongating and shortening the refresh period so that a desired error rate will be achieved. The BIST circuit issues an internal command and an internal address and drives the DRAM from inside. The BIST circuit writes and reads out desired data, compares the monitor bits to expected values (error decision) and counts the errors.
Owner:PS4 LUXCO SARL
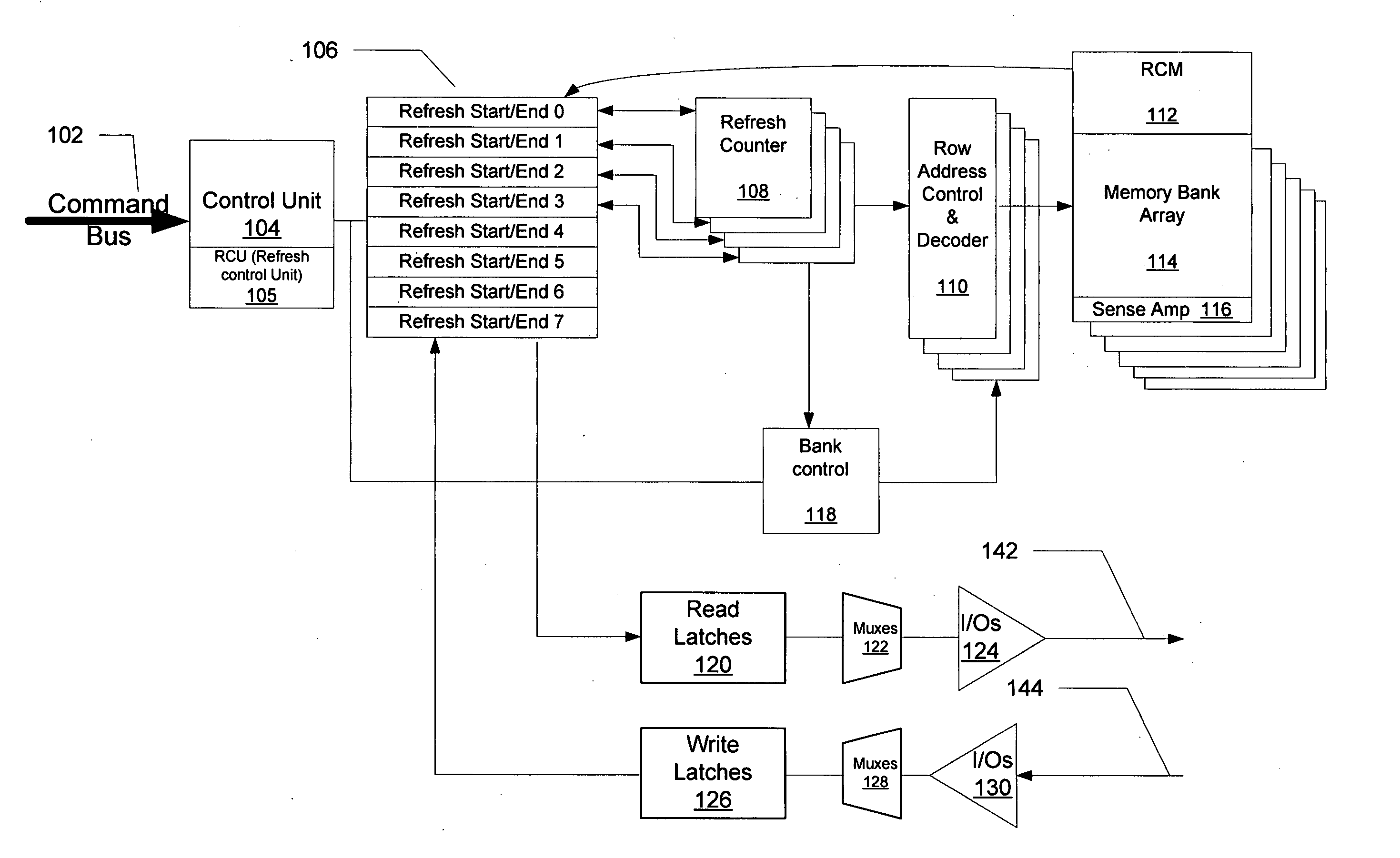
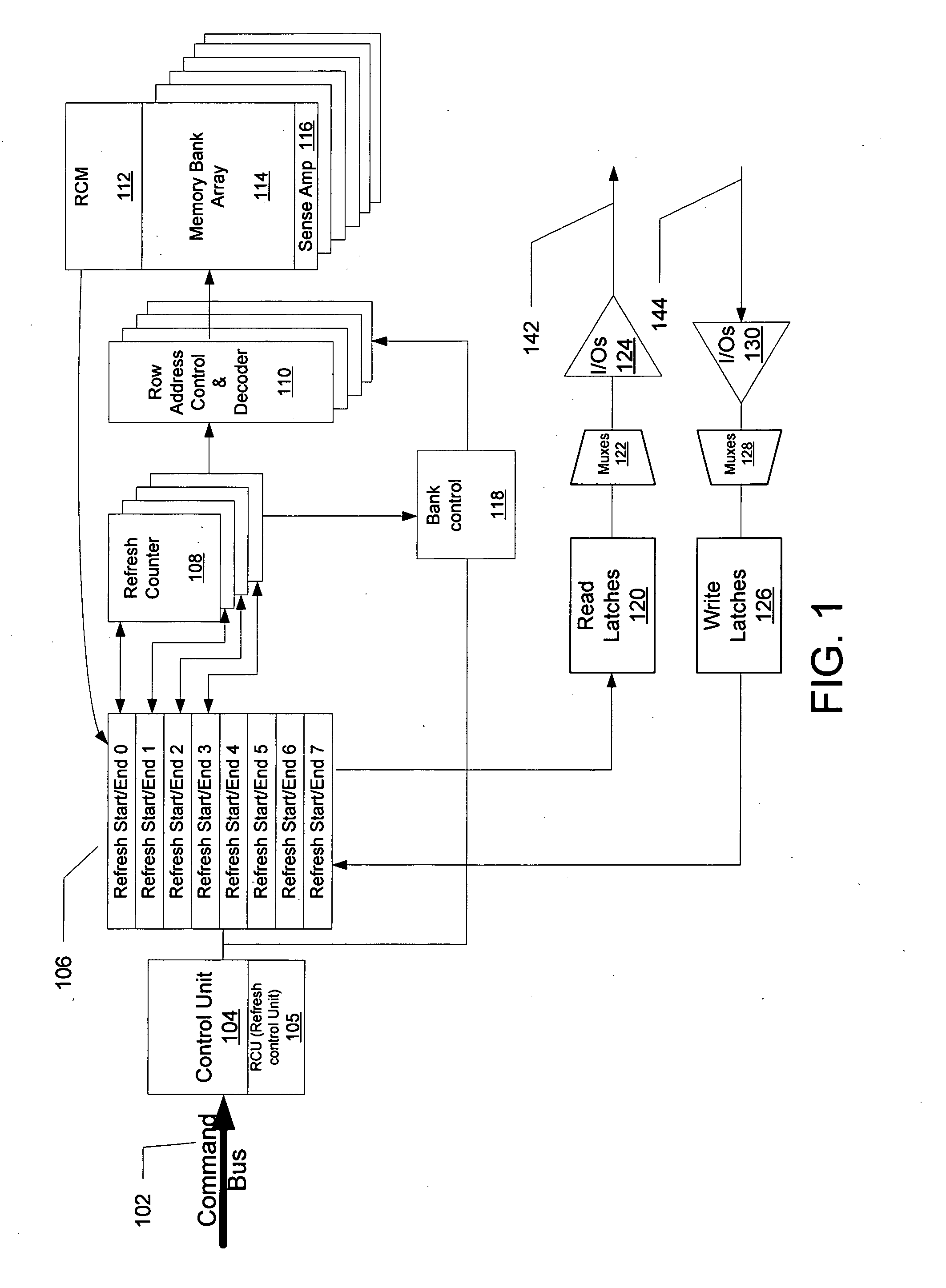
Dynamic random access memory device and method of determining refresh cycle thereof
Provided are a dynamic random access memory device having reduced power consumption and a method of determining a refresh cycle of the dynamic random access memory device. The method includes: selecting one or more monitoring bits during first through n-th self refresh cycles, where “n” is a natural number equal to or greater than one; detecting whether the monitoring bits have errors during (n+1)-th through m-th self refresh cycles, where “m” is a natural number equal to or greater than n+1; and adjusting an (m+1)-th self refresh cycle according to whether the monitoring bits have errors.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Gain cell type non-volatile memory having charge accumulating region charged or discharged by channel current from a thin film channel path
InactiveUS6876023B2Reduce leakage currentWrite performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringLow power dissipation
A semiconductor memory element subject to a threshold voltage controlling method other than those based on low leak currents or on the implantation of impurities. Such semiconductor elements are used to form semiconductor memory elements that are employed in scaled-down structures and are conducive to high-speed write operations thanks to a sufficiently prolonged refresh cycle. These semiconductor memory elements are in turn used to constitute a semiconductor memory device. A very thin semiconductor film is used as channels so that leak currents are reduced by the quantum-mechanical containment effect in the direction of film thickness. An amount of electrical charges in each charge accumulating region is used to change conductance between a source and a drain region of each read transistor structure, the conductance change being utilized for data storage. A channel of a transistor for electrically charging or discharging each charge accumulating region is made of a semiconductor film 5 nm thick at most. The arrangement affords both high-speed data write performance and an extended data retention time. The invention provides a high-speed, power-saving semiconductor device of high integration particularly advantageous for producing a small-scale system of low-power dissipation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
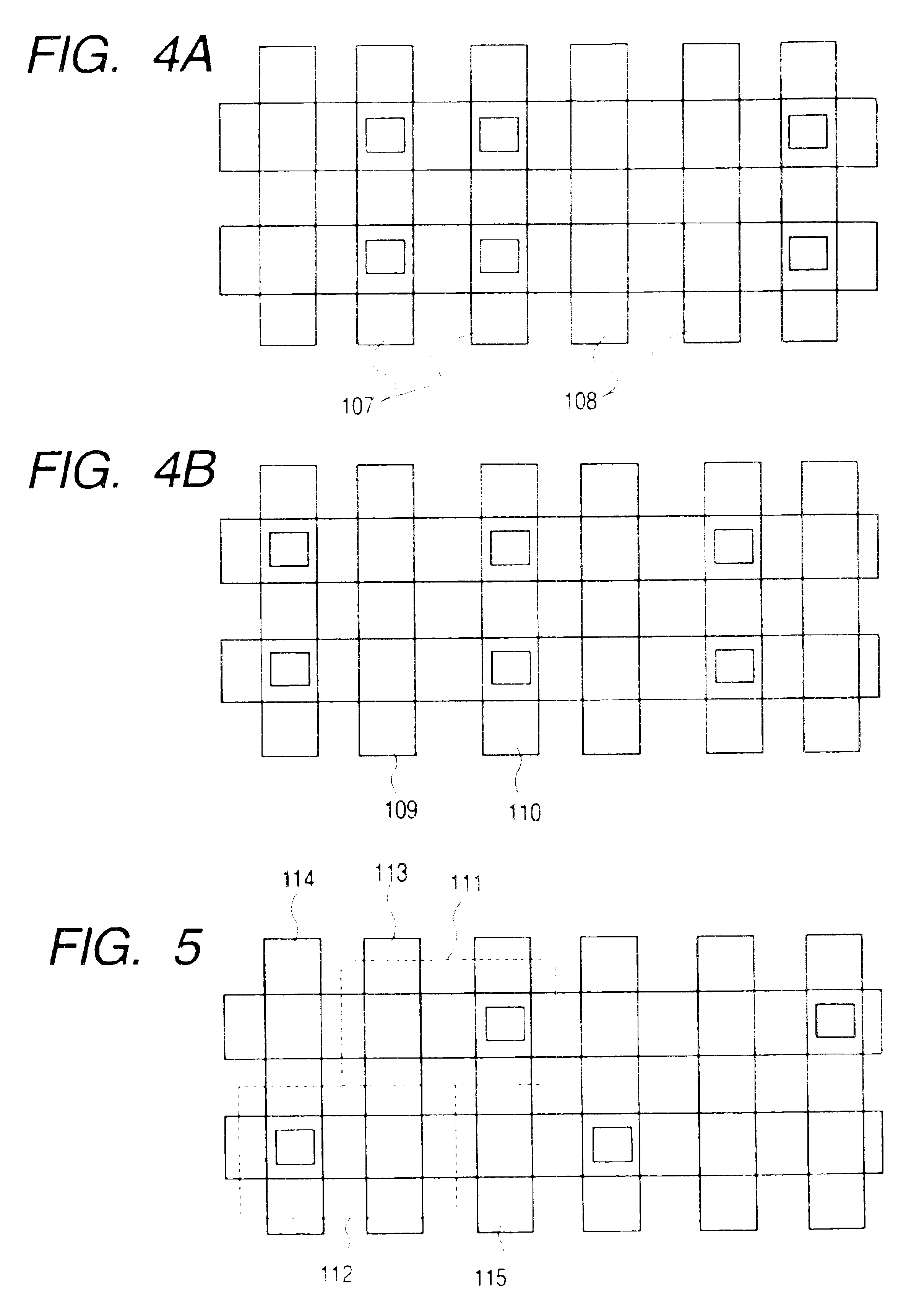
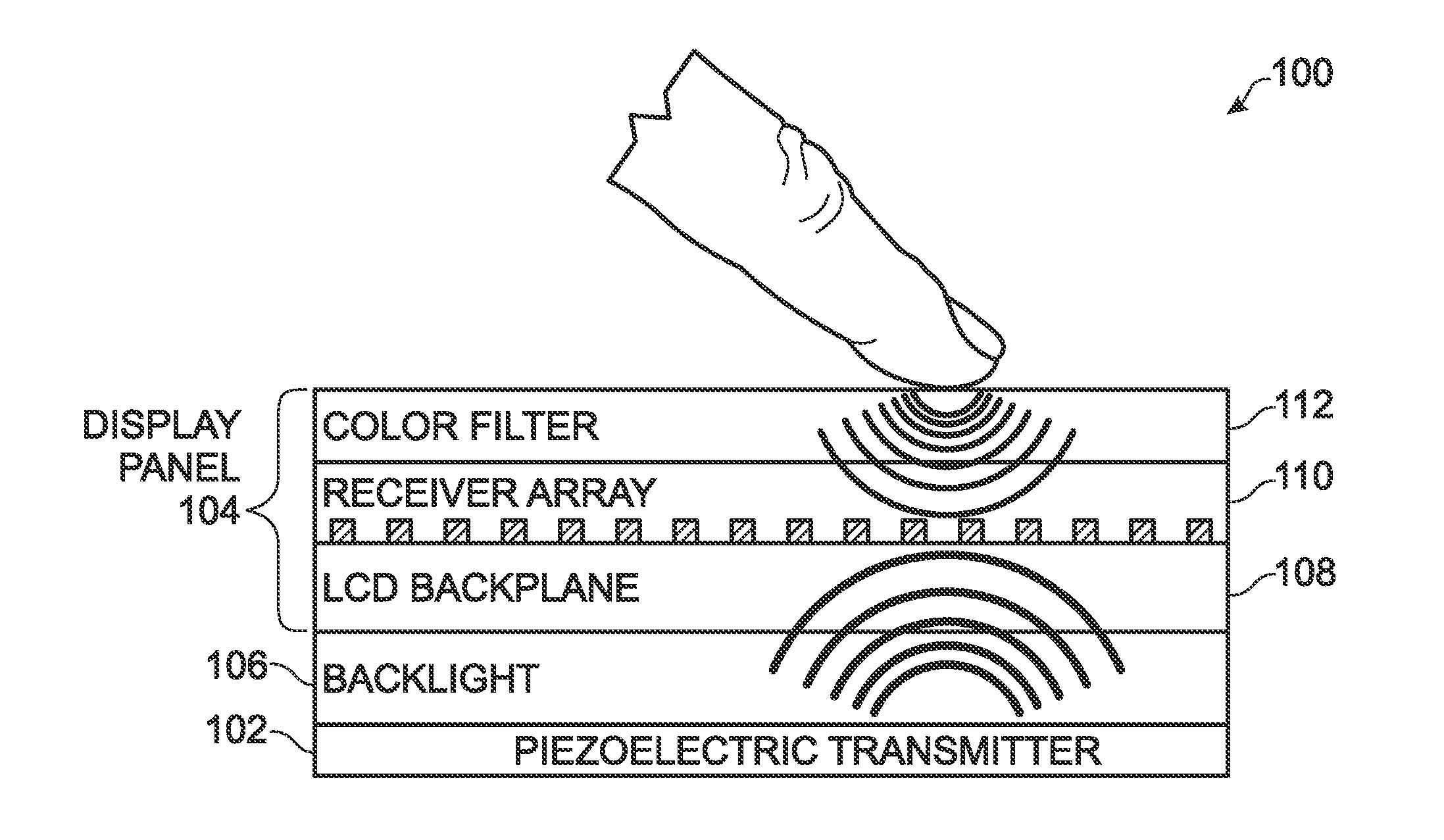
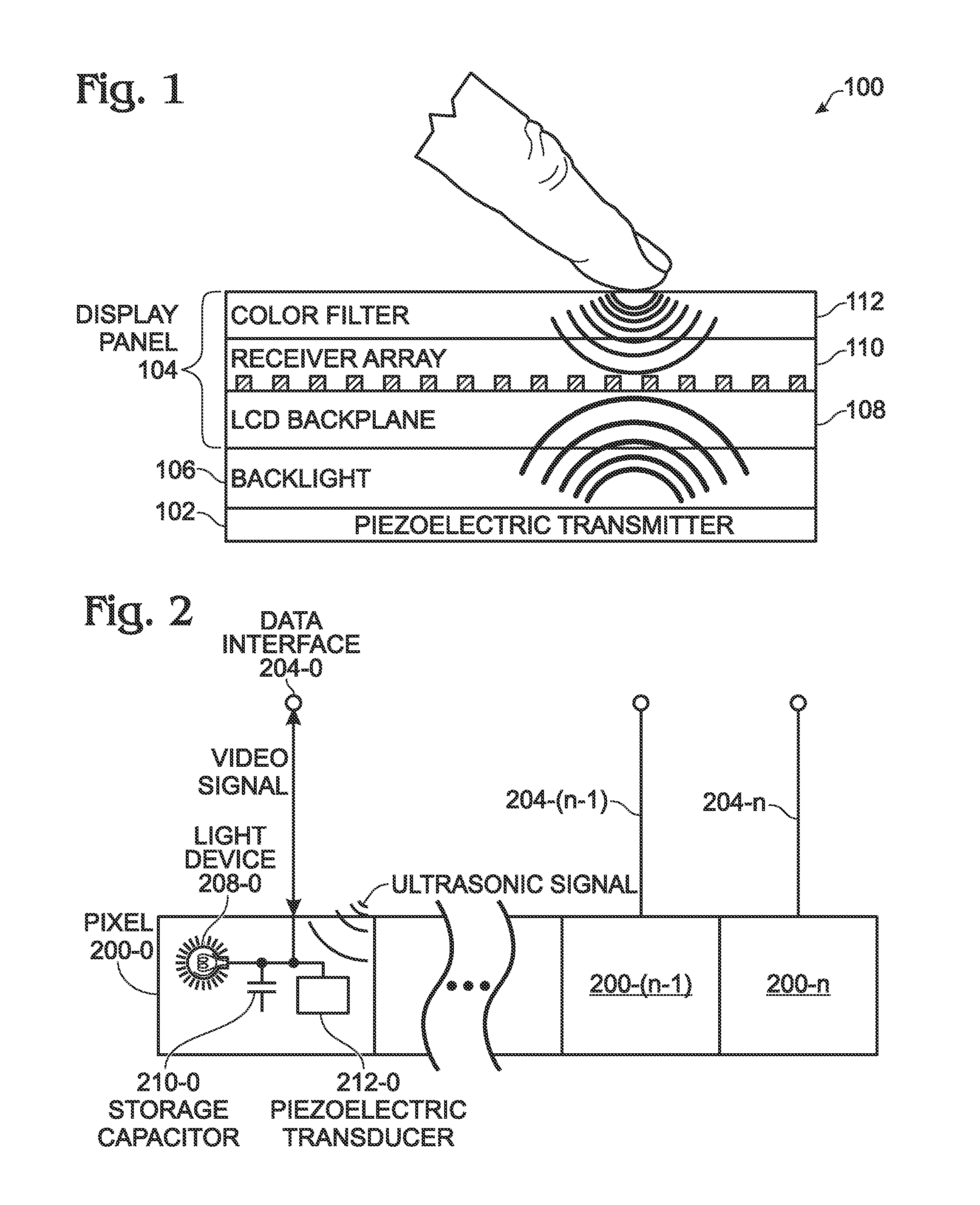
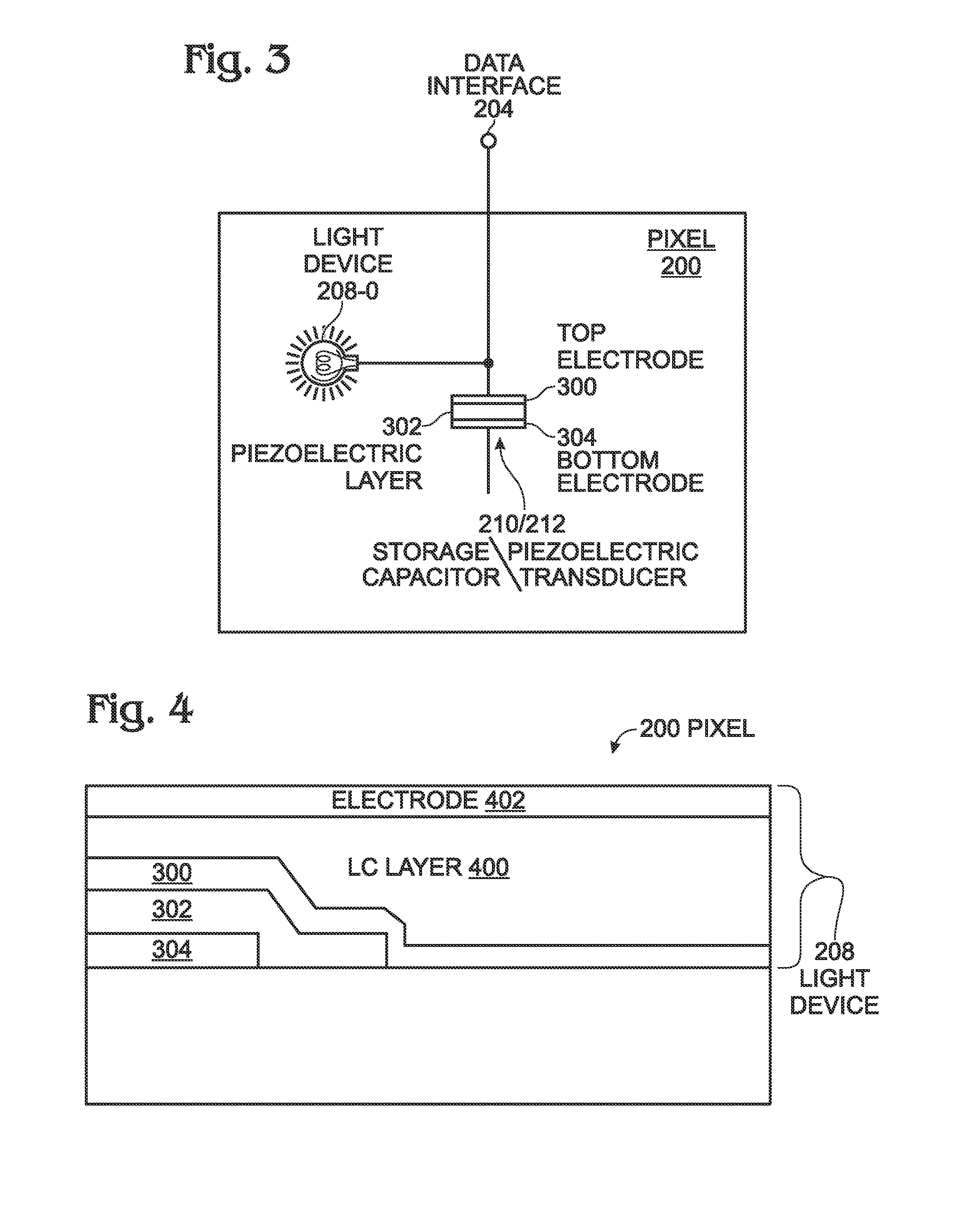
In-Pixel Ultrasonic Touch Sensor for Display Applications
InactiveUS20140198072A1Increase costEliminate attachmentInput/output processes for data processingSonificationDisplay device
A video display is provided with a planar piezoelectric transmitter to transmit ultrasound signals, and a display panel including a plurality of pixels. Each pixel has a data interface to accept a video signal with a variable voltage associated with a range of light intensity values, and to supply a touch signal with a variable voltage derived from a range of reflected ultrasound signal energies. Each pixel is made up of a light device to supply light with an intensity responsive to the video signal voltage, and a storage capacitor to maintain a video signal voltage between refresh cycles. A piezoelectric transducer accepts a reflected ultrasound signal energy and maintains a touch signal voltage between refresh cycles. In one aspect, the storage capacitor and the piezoelectric transducer are the same device. The light device may be a liquid crystal (LC) layer or a light emitting diode.
Owner:SHARP KK
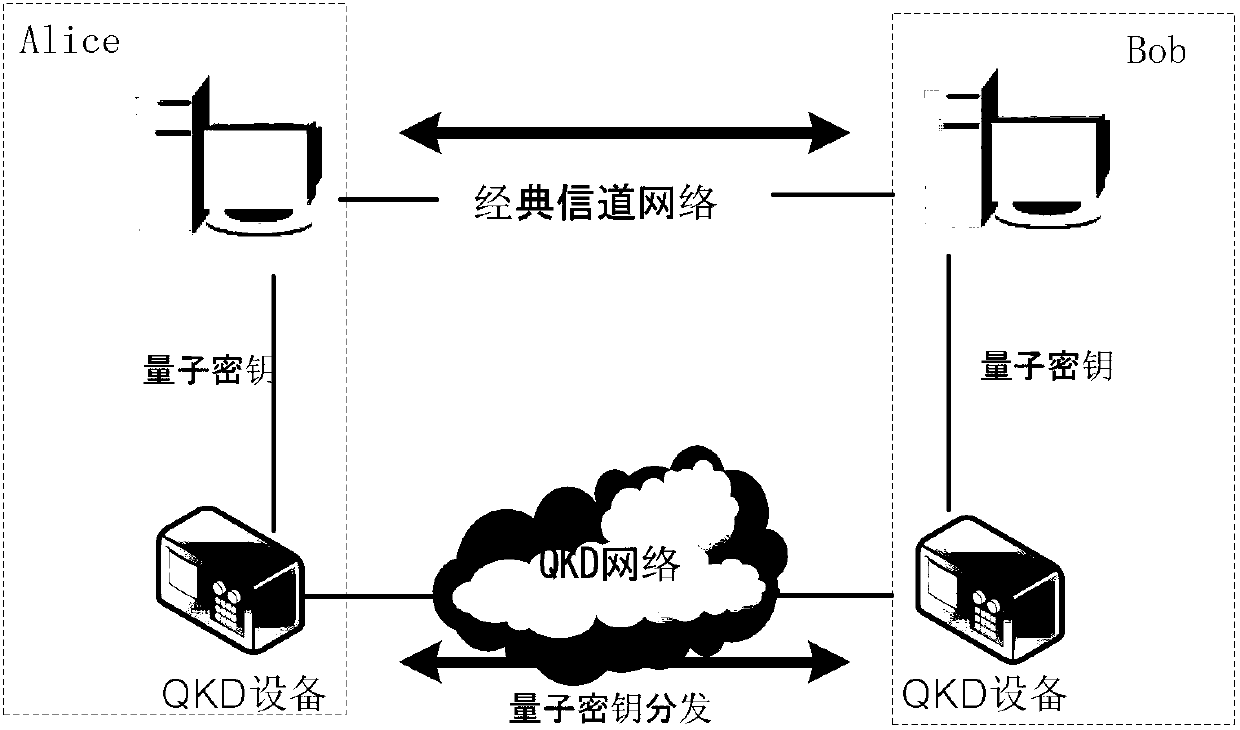
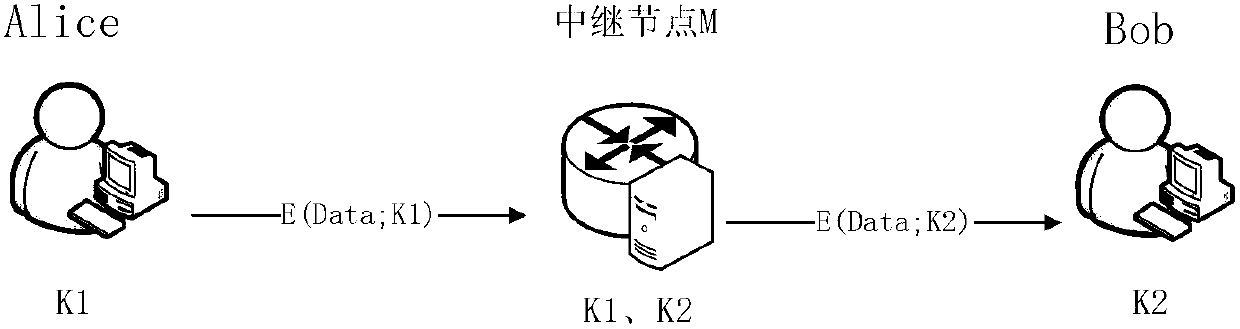
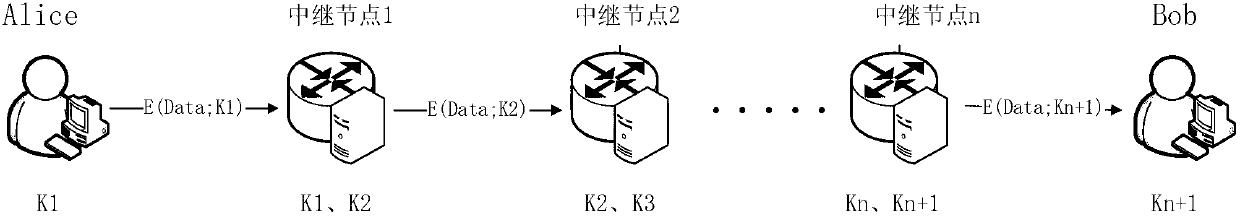
Quantum cryptography network dynamic routing method
ActiveCN103001875AConvenient for dynamic expansionFast convergenceKey distribution for secure communicationData switching networksRefresh cycleRoute server
The invention discloses a quantum cryptography network dynamic routing method. According to the method, dynamic routing selection of encryption communication is performed by utilizing quantum cryptography according to changes of the quantum key quantity between relay nodes of a quantum cryptography network. According to the method, a route server is arranged for the relay nodes of the whole quantum cryptography network, and topology refresh cycles of the quantum cryptography network are set; in each topology refresh cycle, each relay node collects and processes state information of the relay node and reports results to the route server. After the route server collects the topology state information of each relay node, quantum cryptography network topology state information of a next topology refresh cycle is generated and sent to all the relay nodes of the quantum cryptography network. According to the quantum cryptography network topology state information obtained from the route server, a target relay node is calculated and determined to be a next skip route of communication data of a random other relay node according to a shortest path law through each relay node.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF QUANTUM SCI & TECH +2
Data storing method of dynamic RAM and semiconductor memory device
When a DRAM enters an operation mode in which only a data storing operation is performed, a check bit for error detection and correction for plural data is generated and stored. Refresh operation is performed in a refresh cycle which is made long within an allowable range of an error occurrence by an error correcting operation using the check bit. Before the DRAM returns to the normal operation mode from the data holding operation mode, an error bit is corrected by using the data and the check bit.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
Combination dryer and method thereof
InactiveUS20060130354A1Avoid changeDrying using combination processesDrying gas arrangementsCyclic processRefresh cycle
An operation method for a combination driver is disclosed. The present invention relates to a combination dryer, and more particularly, to an operation method for a combination dryer which enables air in a drying drum and a cabinet for drying the laundry to circulate continuously and enables water generated in the circulation process to perform a refreshing cycle by using the water.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
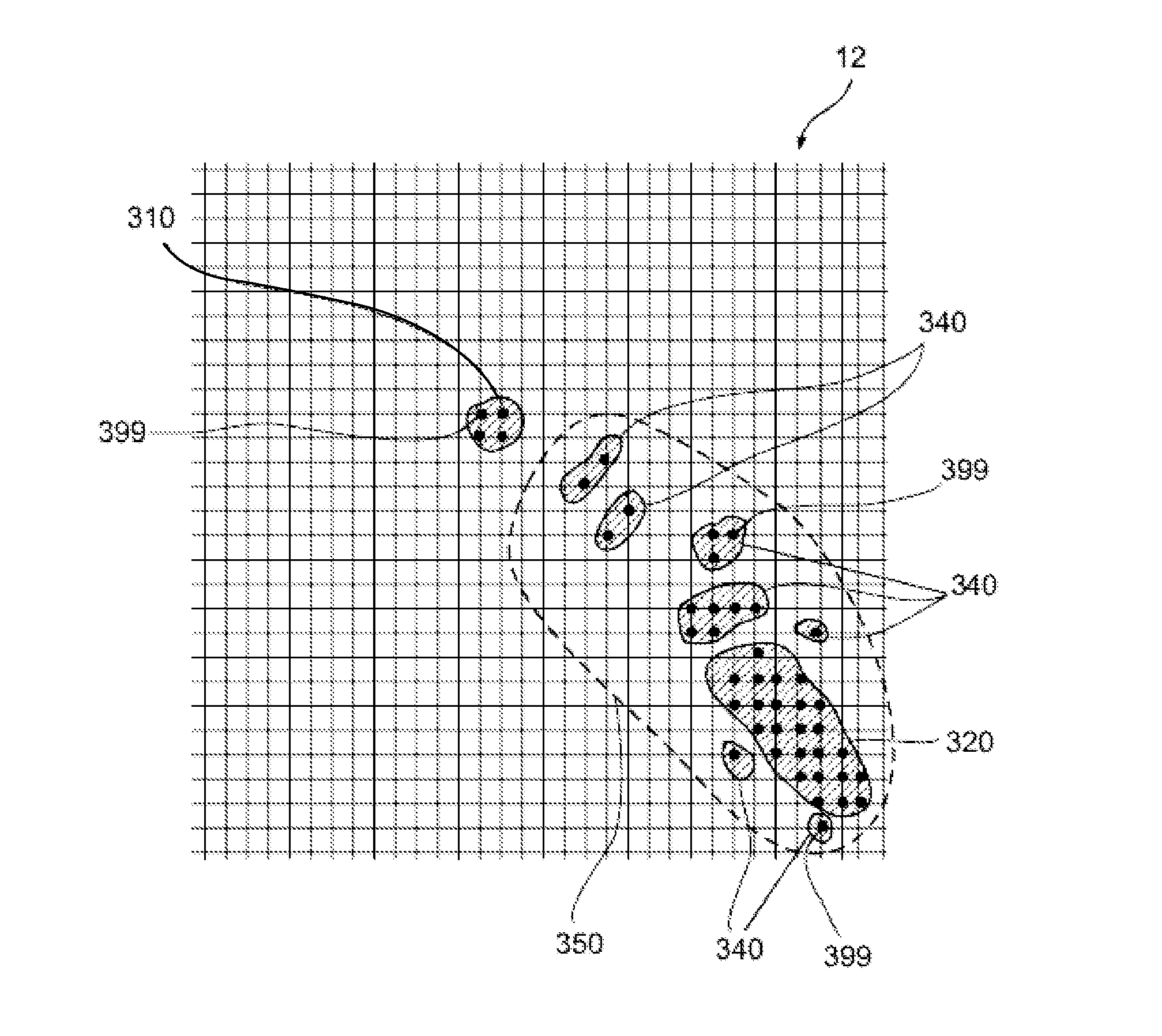
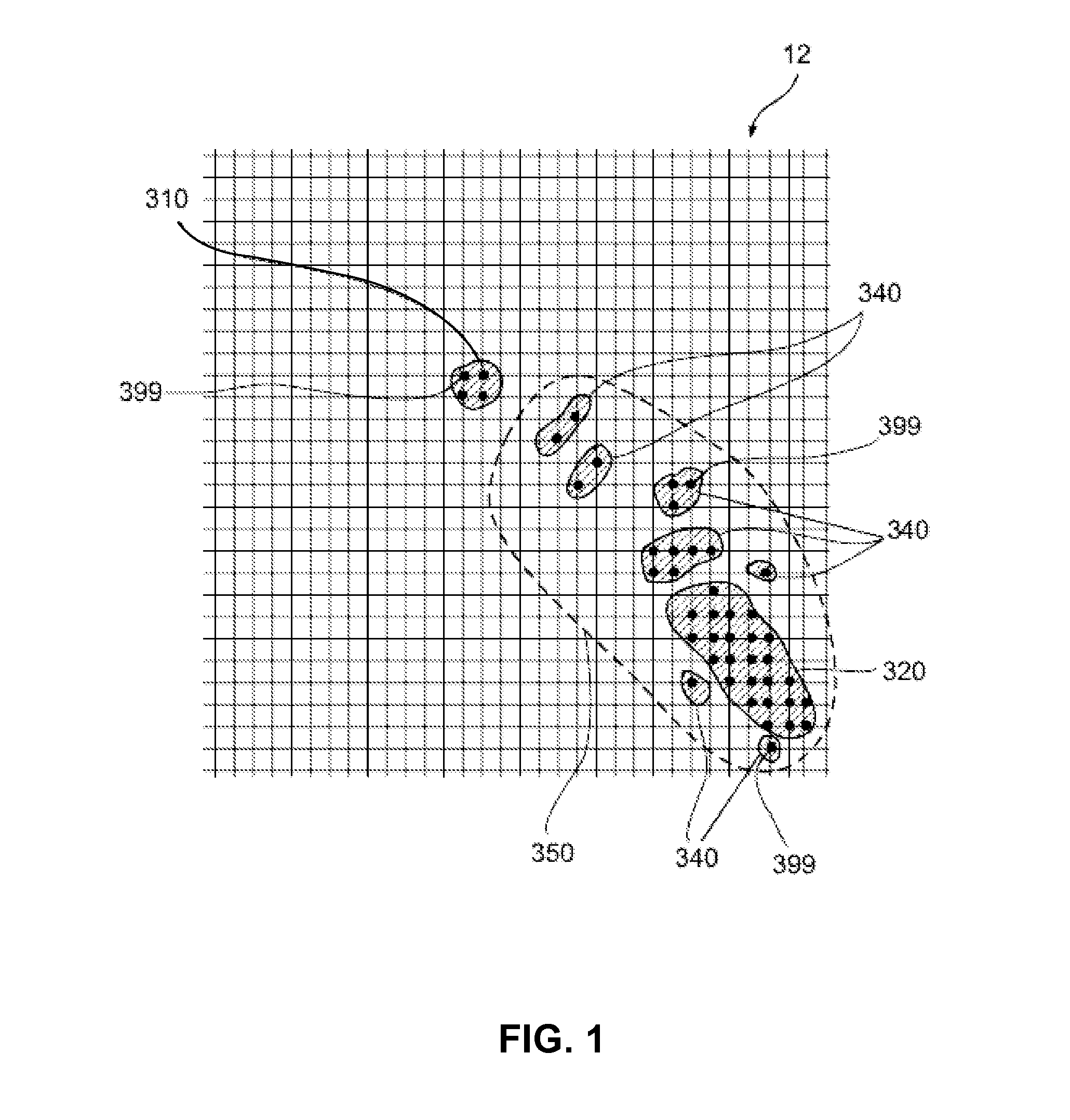
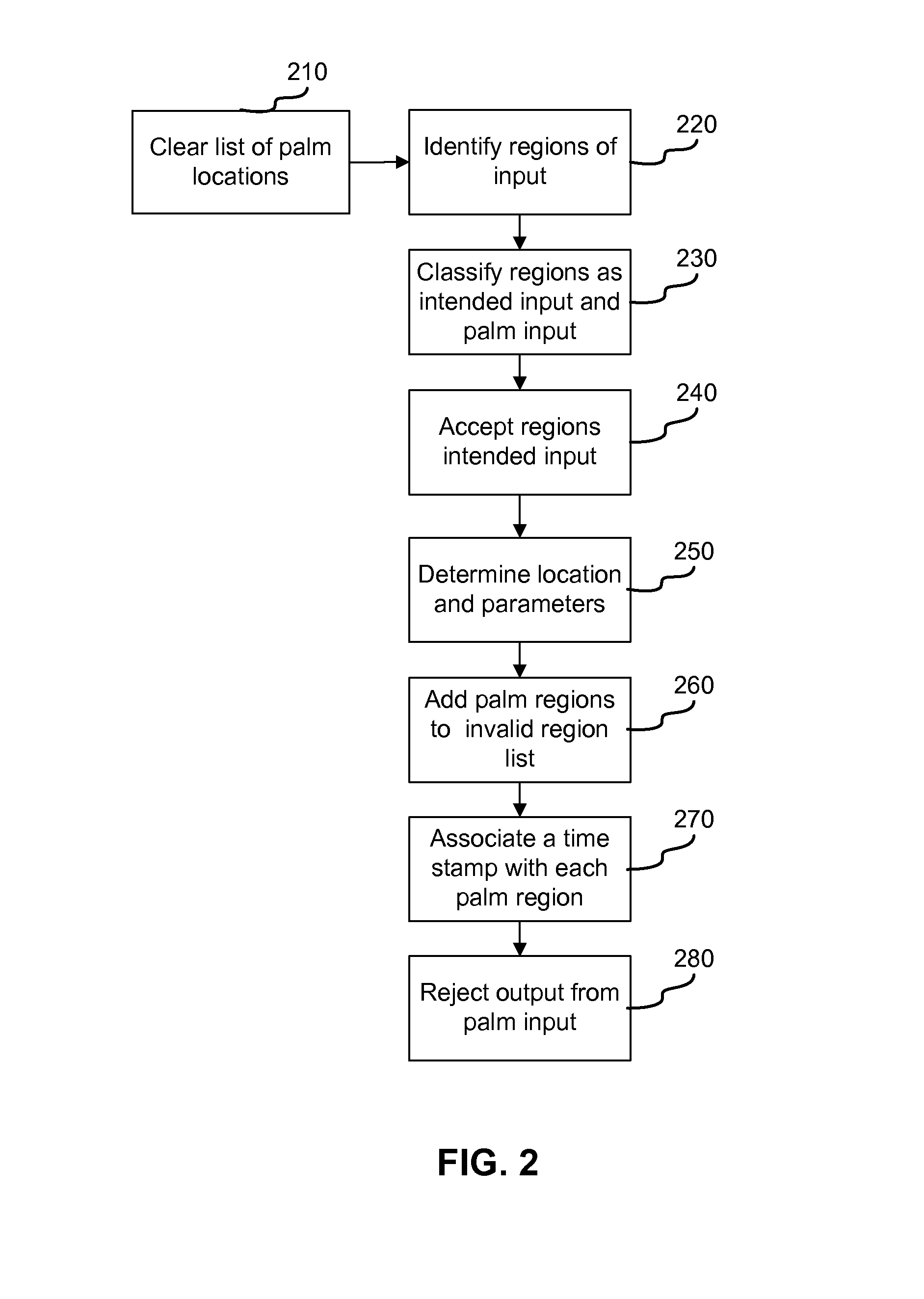
Tracking input to a multi-touch digitizer system
ActiveUS20130328832A1Improve robustnessImprove stabilityInput/output processes for data processingRefresh cycleDigital converter
A method for identifying intended input to a digitizer sensor includes identifying a plurality of regions of input to a digitizer sensor over a plurality of refresh cycles, classifying each of the plurality regions as one of intended input and unintended input, the classifying performed for each of the plurality of refresh cycles, storing a list of locations of regions classified as unintended input regions, where each entry of the list stored for a pre-defined time period and then subsequently removed from storage and invalidating output obtained from a region classified as a region of intended input, responsive to the region overlapping a location listed in the list of locations classified as unintended input regions.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
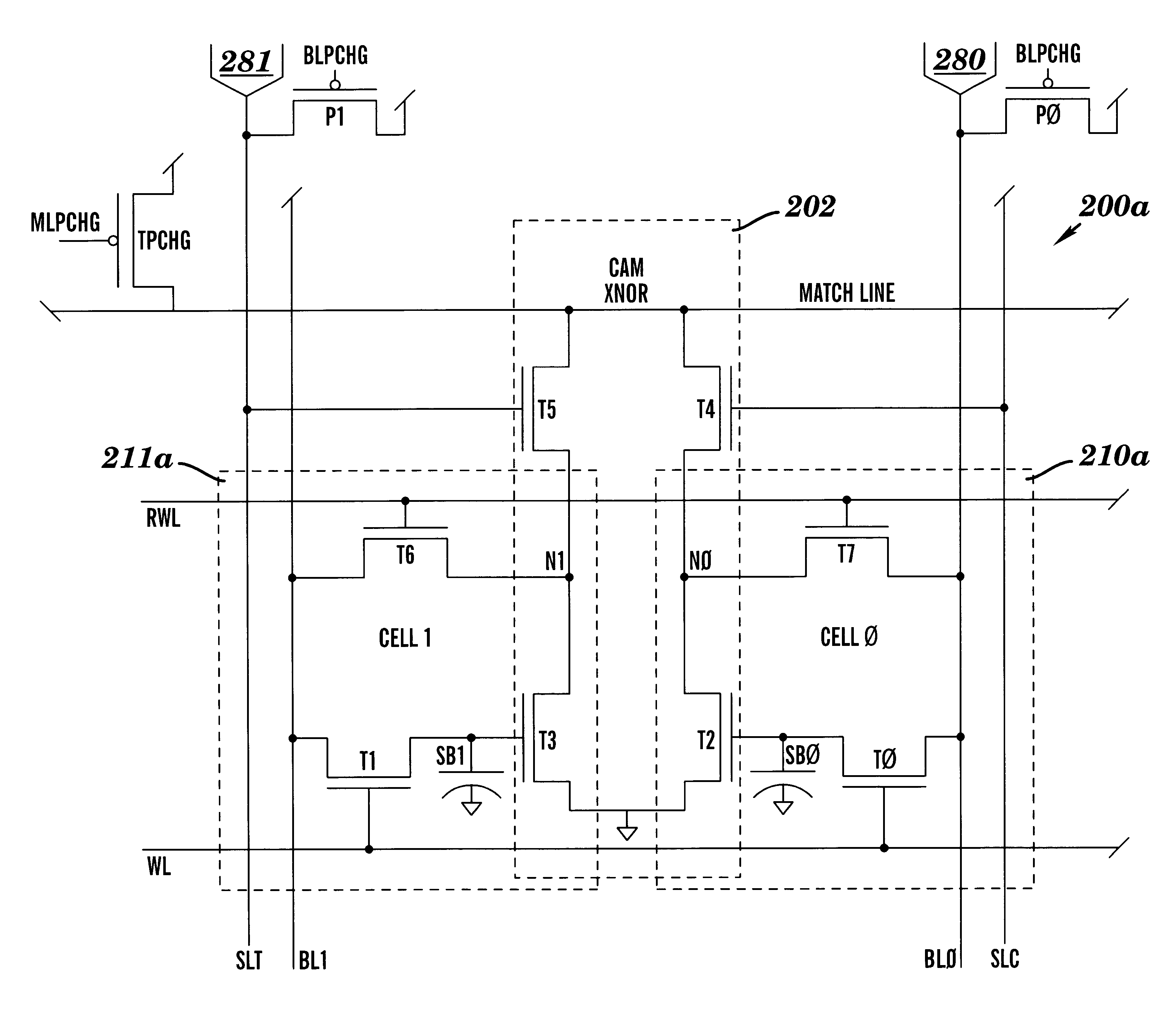
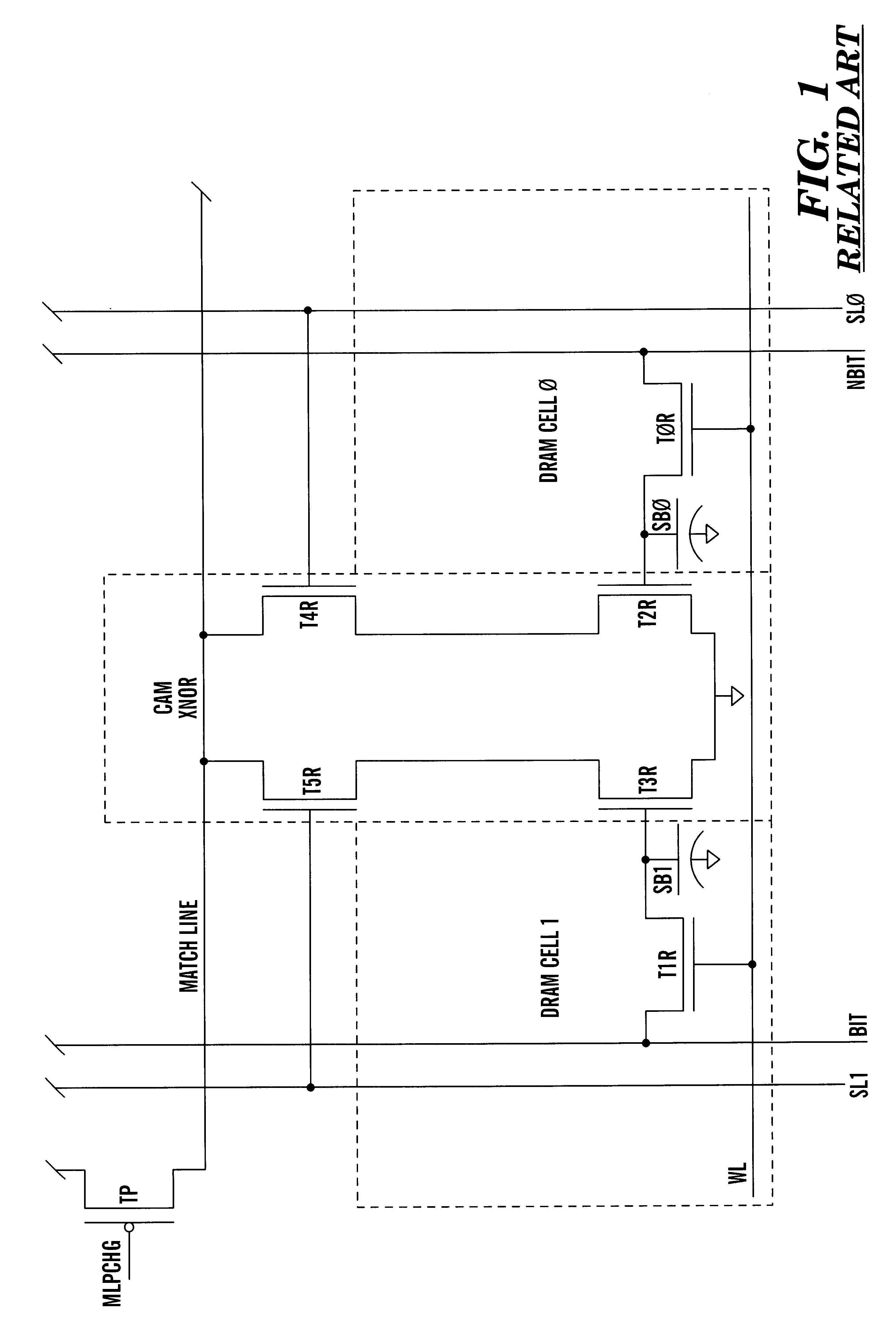
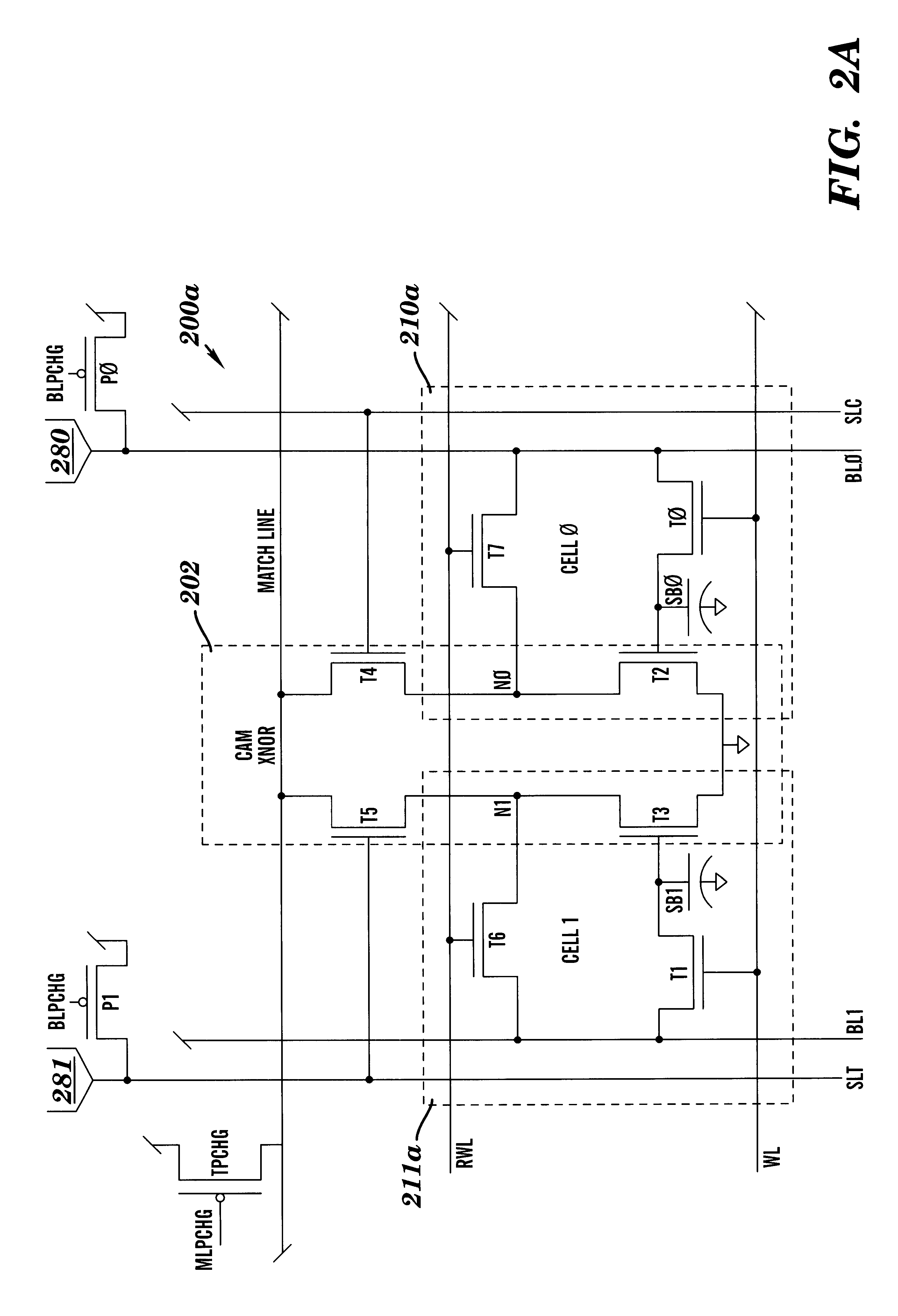
Dram cam cell with hidden refresh
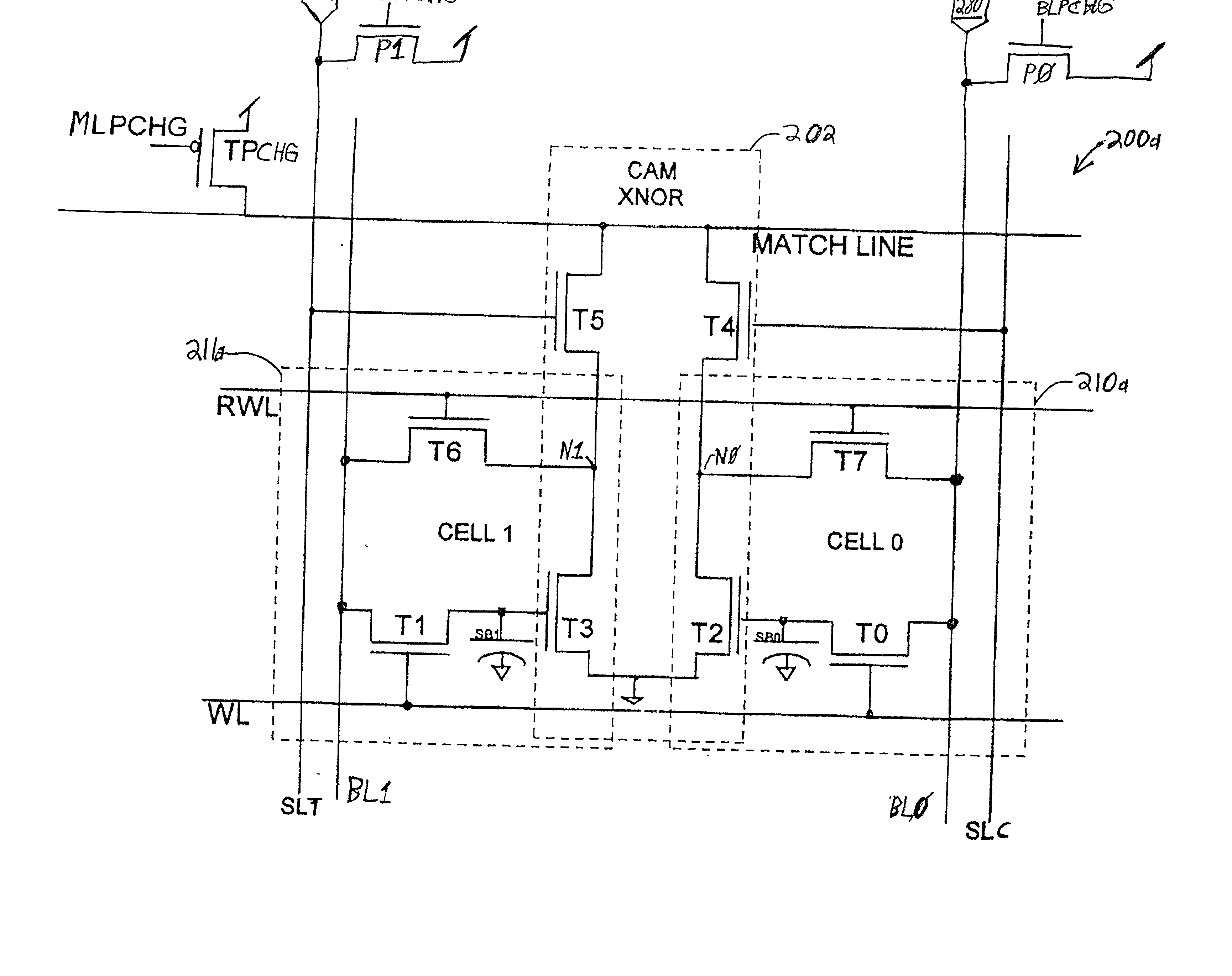
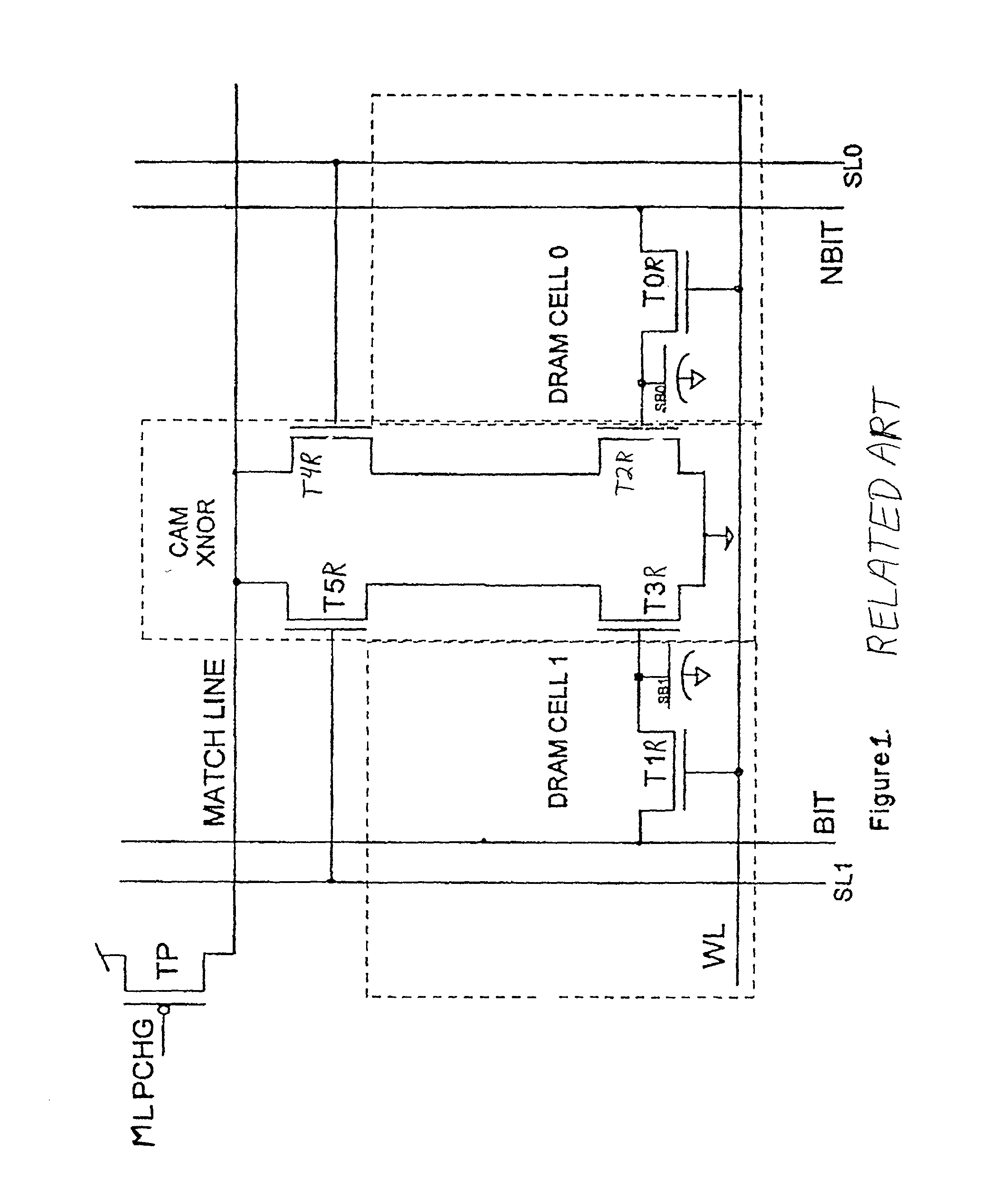
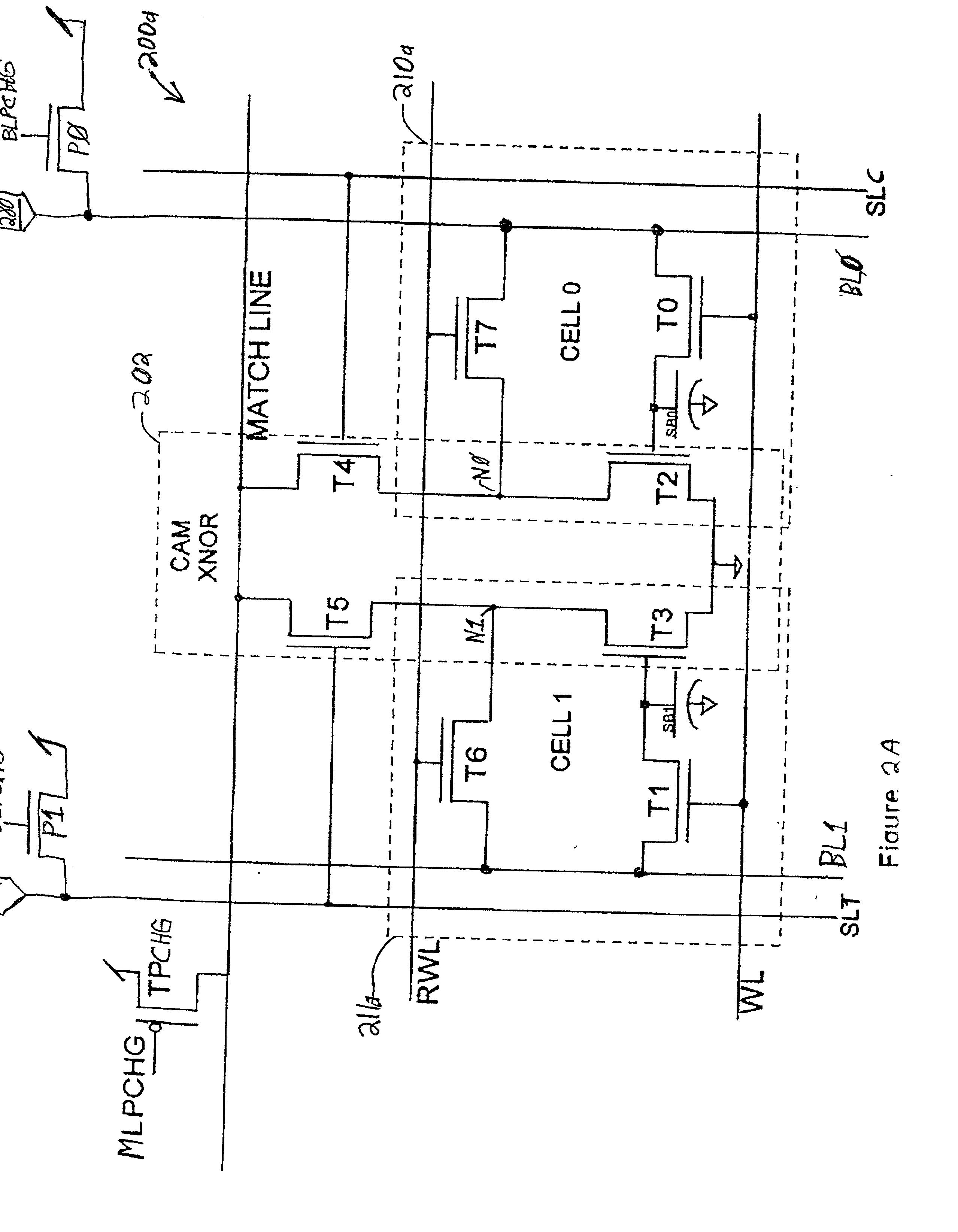
A Dynamic Content Addressable Memory (DCAM) cell topology that contains fewer that can perform a "hidden" refresh of stored data that does not delay nor interrupt the CAM search cycle, thereby providing SCAM-like performance. A non-destructive read operation, is performed such that the stored-data does not have to be written back because of a refresh-read operation. A reliable CAM search can be performed after a read operation and before or even while the refresh-data is being written back. Soft-error detection processes can be performed on each CAM entry during the pendency of the refresh cycle. The DCAM cell can be used in a digital system such as a digital computer and a Network Router.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Bank address mapping according to bank retention time in dynamic random access memories
InactiveUS6920523B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTStatic random-access memoryRetention time
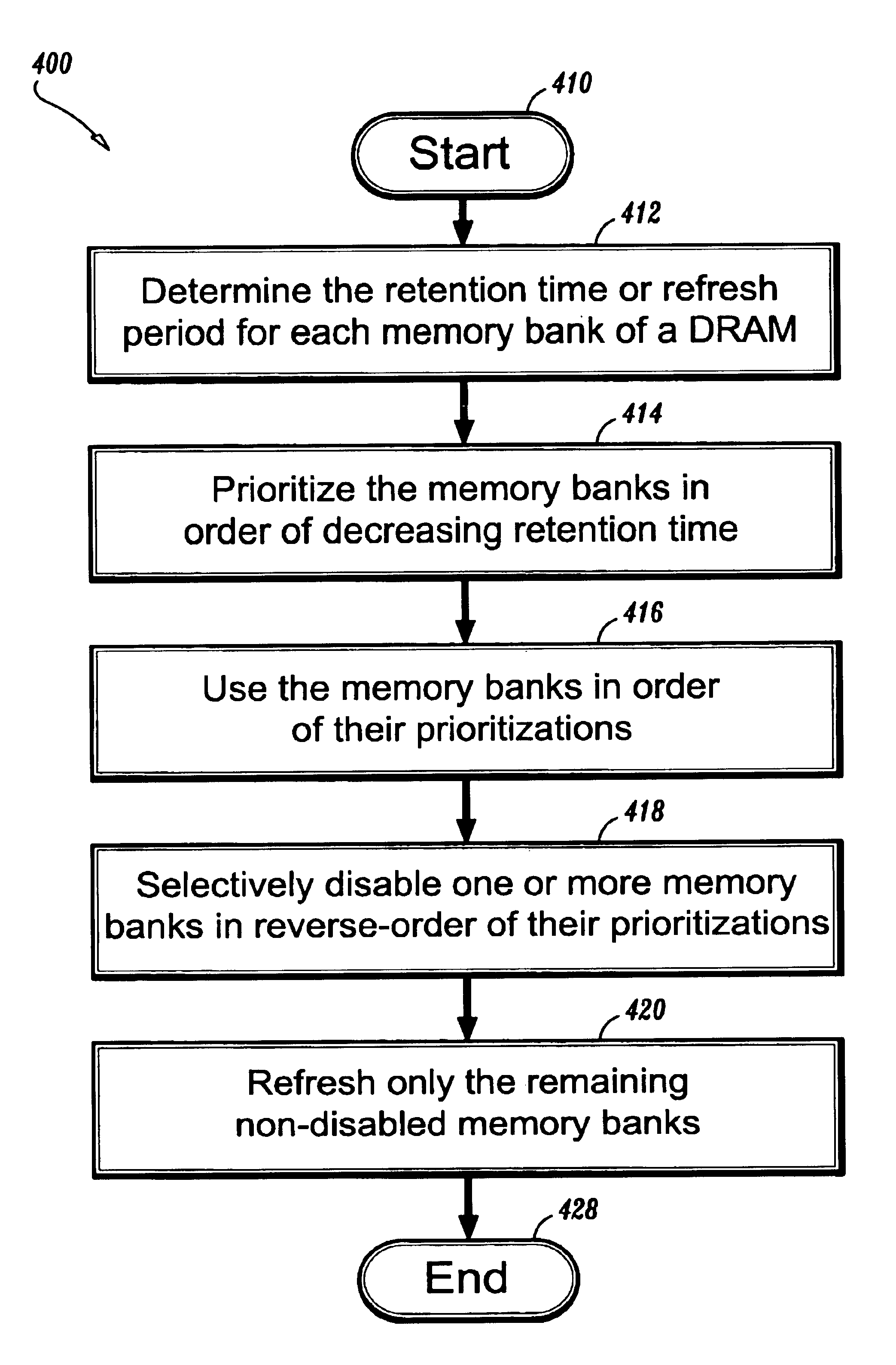
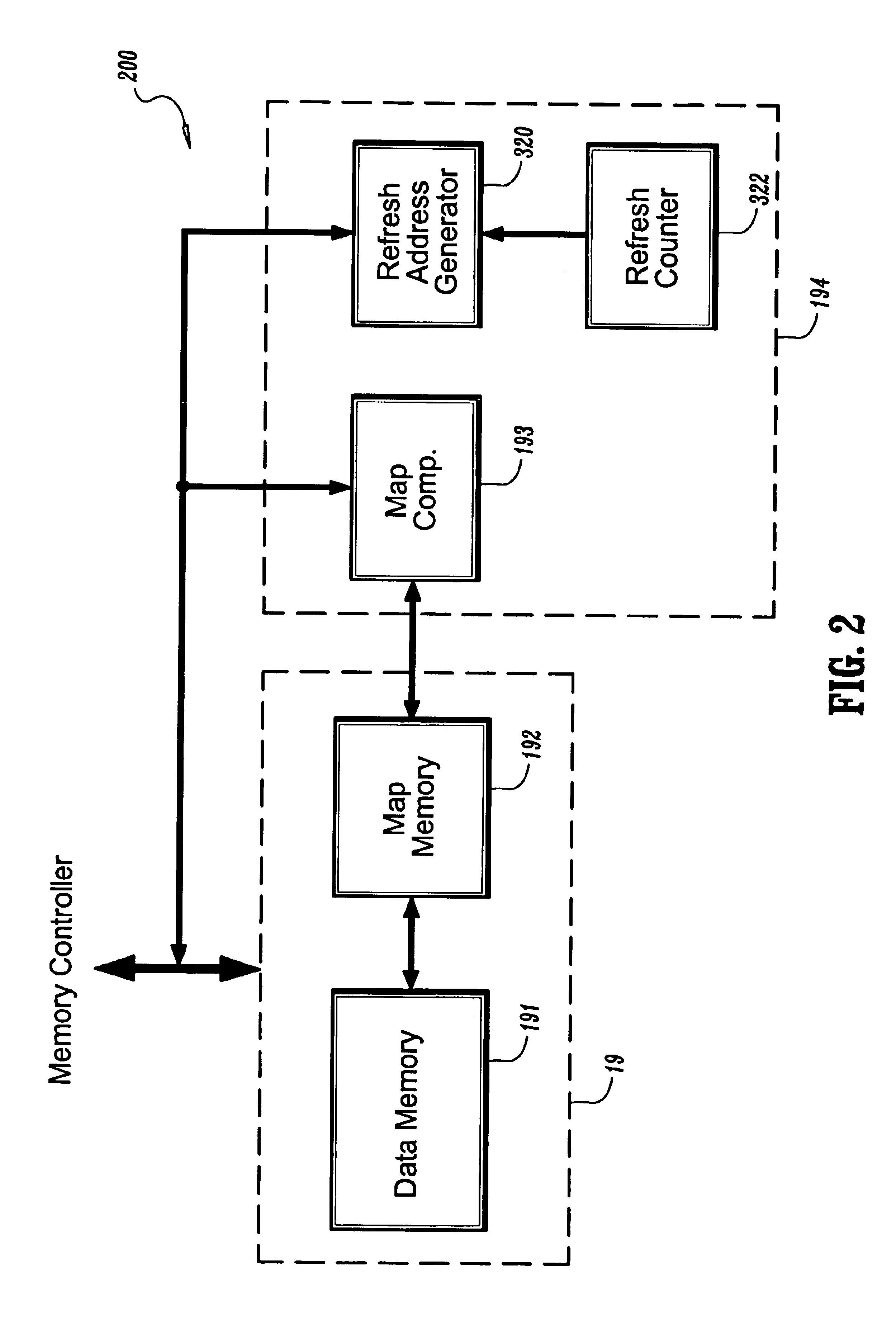
A system and method for refreshing data in a dynamic random access memory (“DRAM”) is provided, where the system includes a data memory having a plurality of memory banks, a map memory in signal communication with the data memory for translating an internal address of each of the plurality of memory banks into a corresponding external address, a map comparator in signal communication with the map memory for selectively enabling a memory bank in accordance with its external address, a refresh address generator in signal communication with the map comparator for selectively refreshing the enabled memory bank in accordance with its external address, and a refresh counter in signal communication with the refresh address generator for signaling a refresh in accordance with the maximum required refresh time of the enabled memory bank; and where the corresponding method includes determining the maximum required refresh period for each of the memory banks, respectively, prioritizing the memory banks in accordance with their respective refresh periods, utilizing the memory banks in order of their respective prioritizations, selectively disabling at least one of the memory banks in reverse-order of their respective prioritizations, and refreshing only the remaining non-disabled memory banks.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com