Patents
Literature
262 results about "Overdrive voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
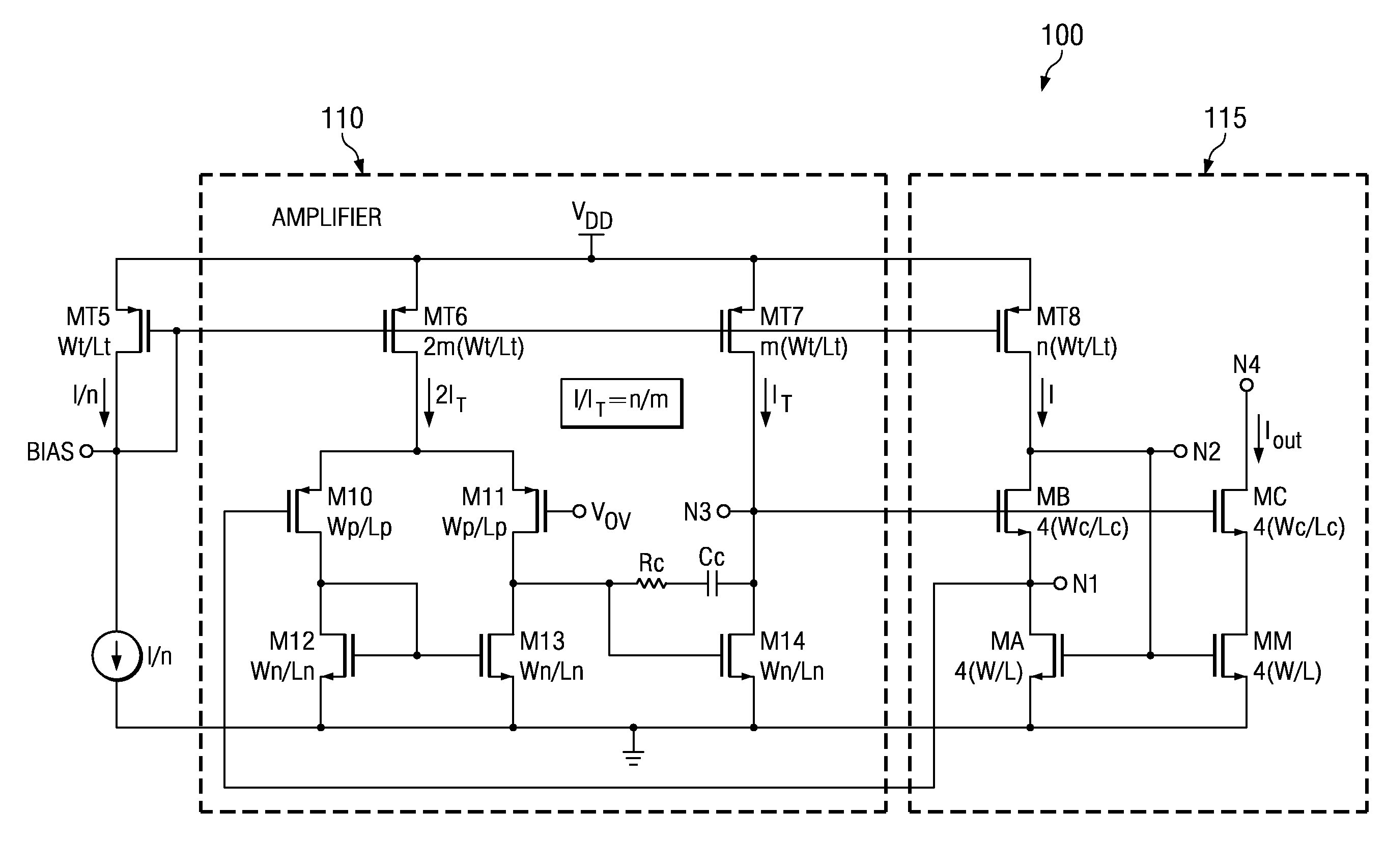
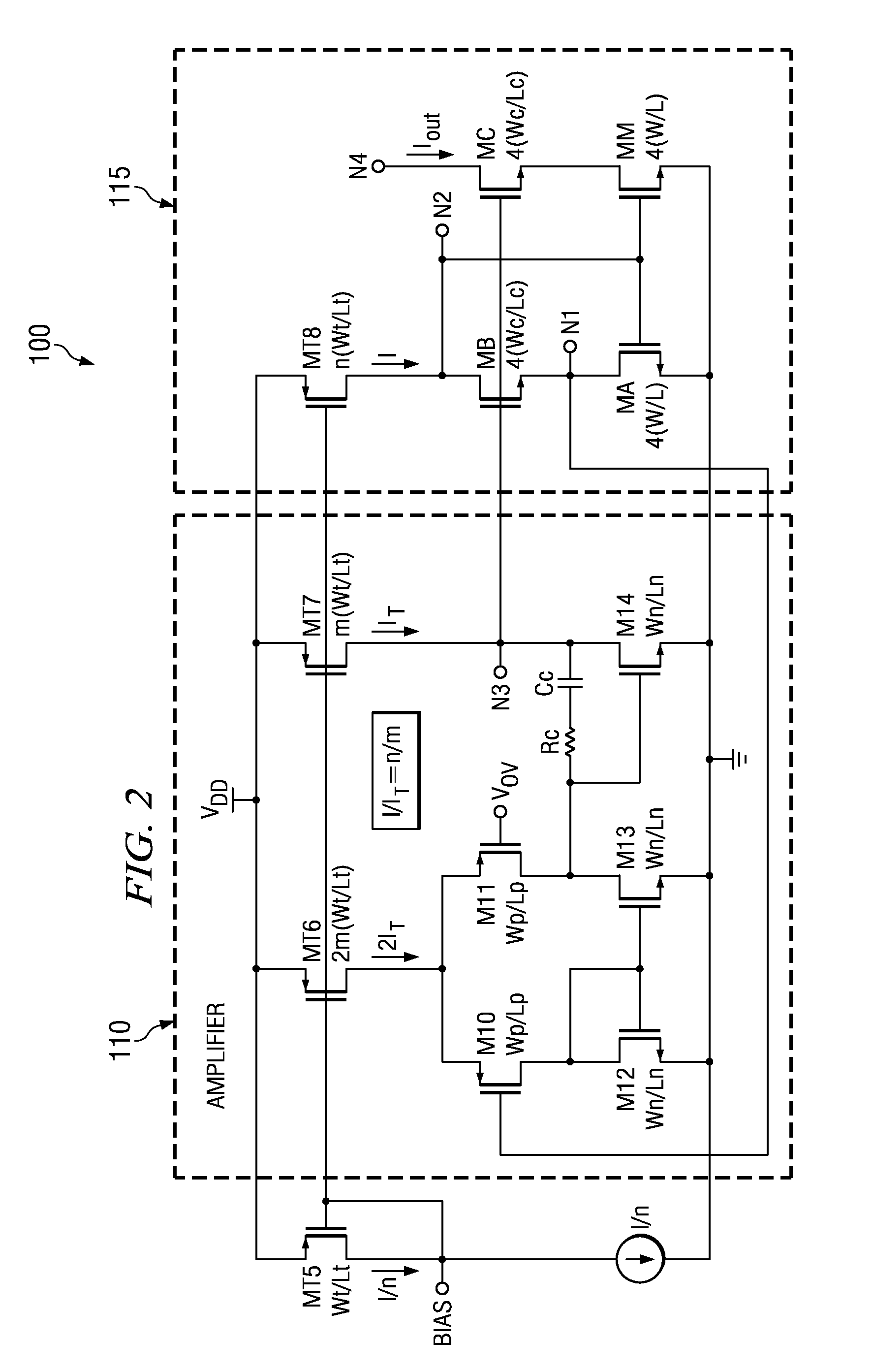
Overdrive voltage, usually abbreviated as VOV, is typically referred to in the context of MOSFET transistors. The overdrive voltage is defined as the voltage between transistor gate and source (VGS) in excess of the threshold voltage (VTH) where VTH is defined as the minimum voltage required between gate and source to turn the transistor on (allow it to conduct electricity). Due to this definition, overdrive voltage is also known as "excess gate voltage" or "effective voltage." Overdrive voltage can be found using the simple equation: VOV = VGS − VTH.
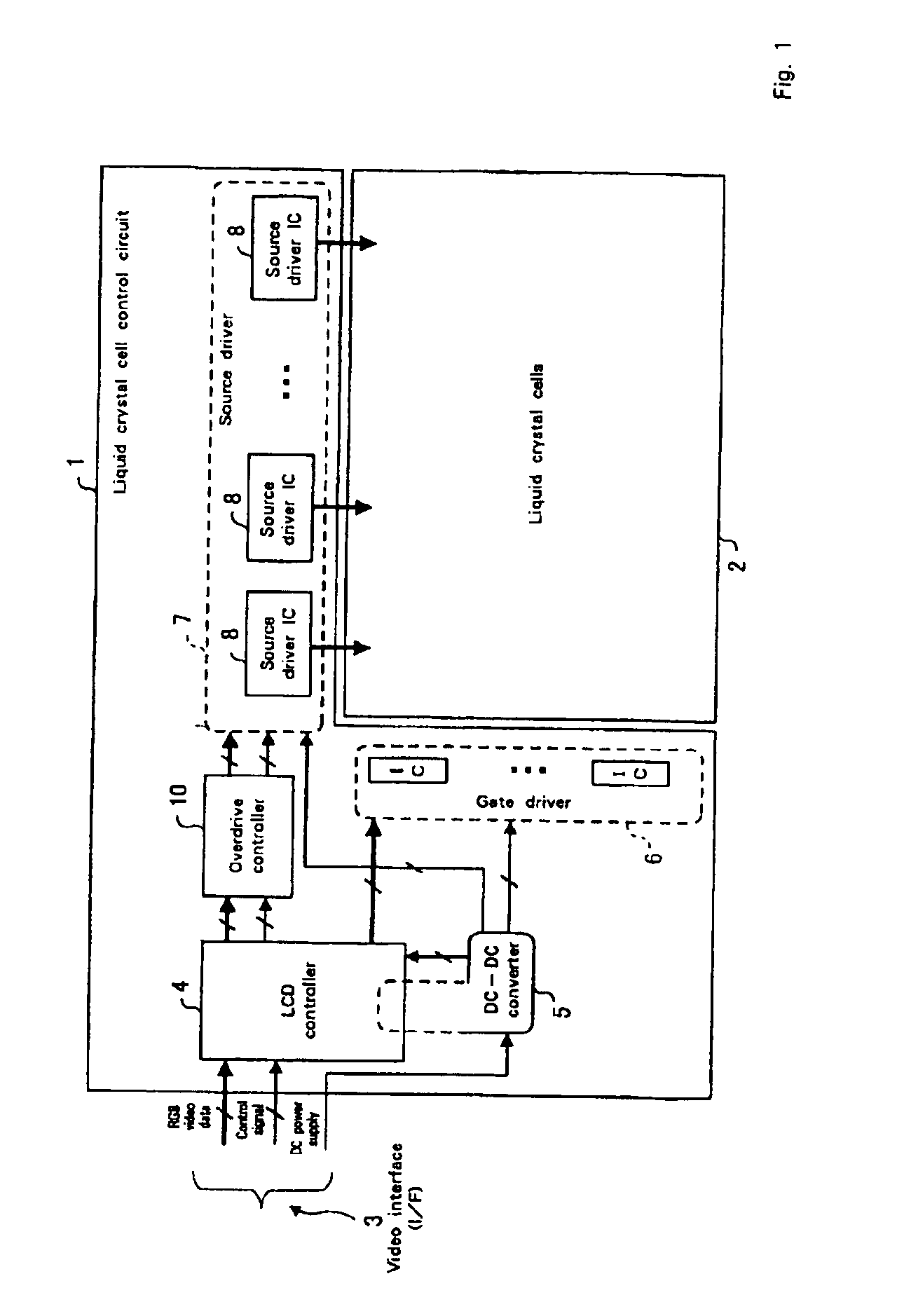
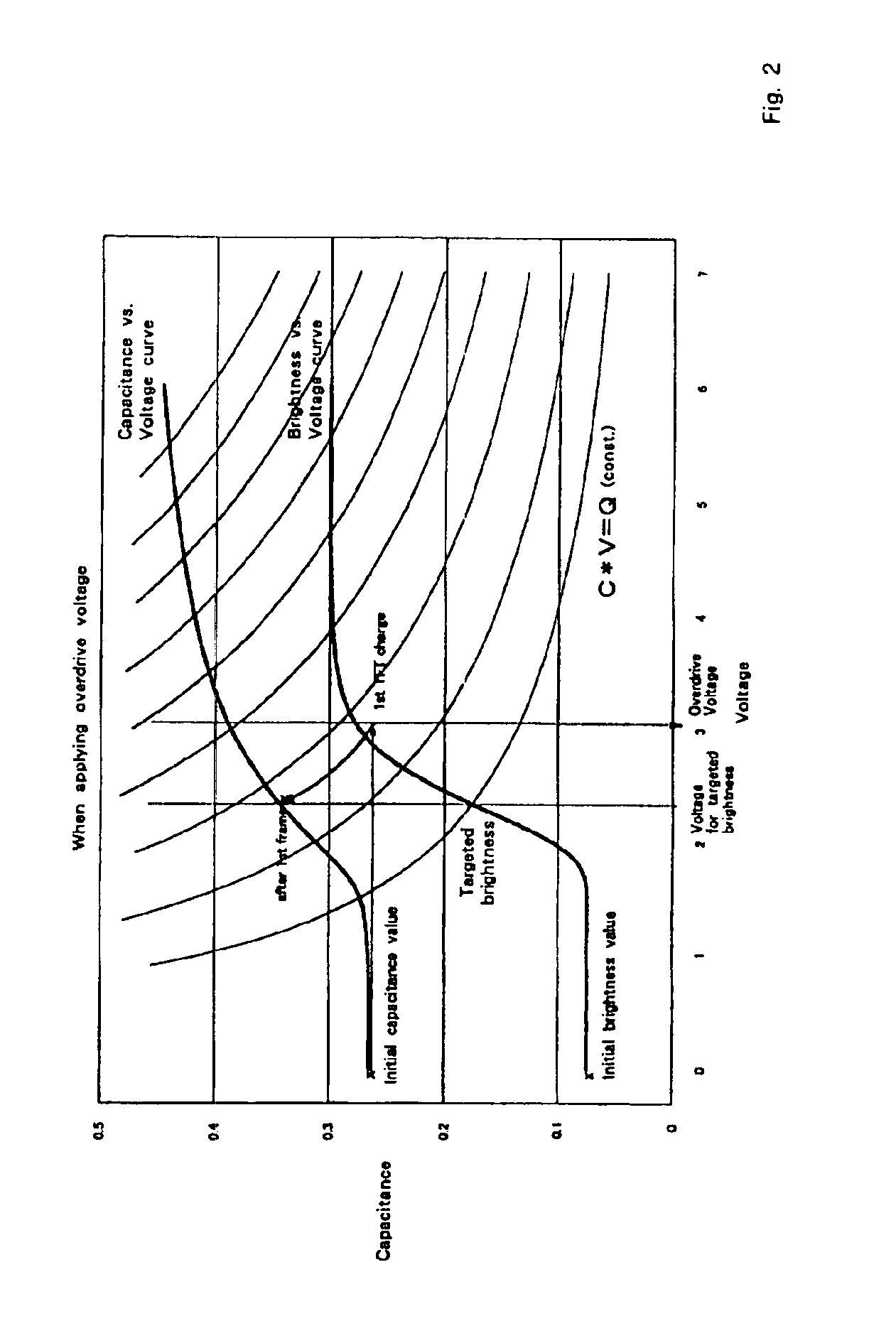
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7034793B2Fully appreciatedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
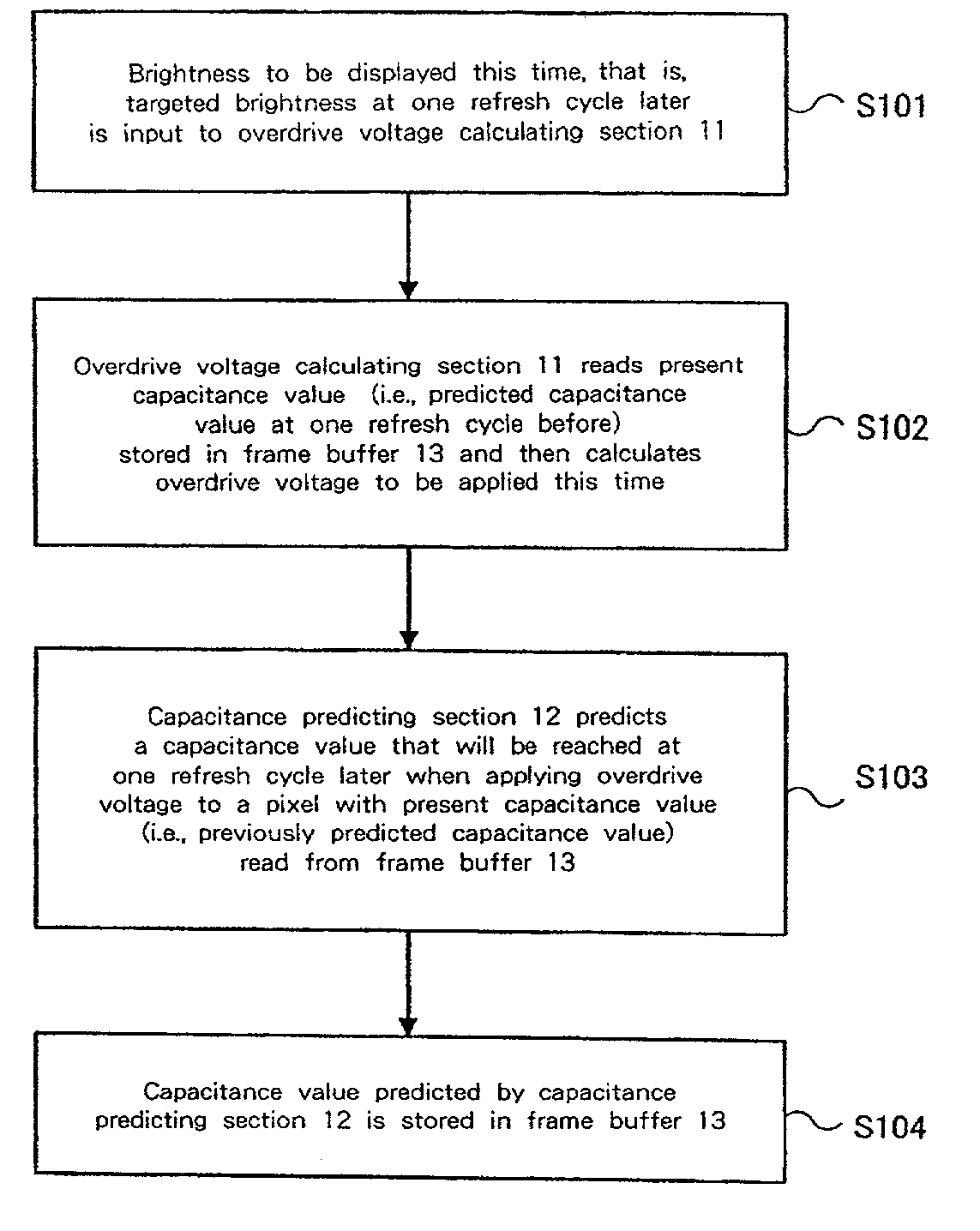
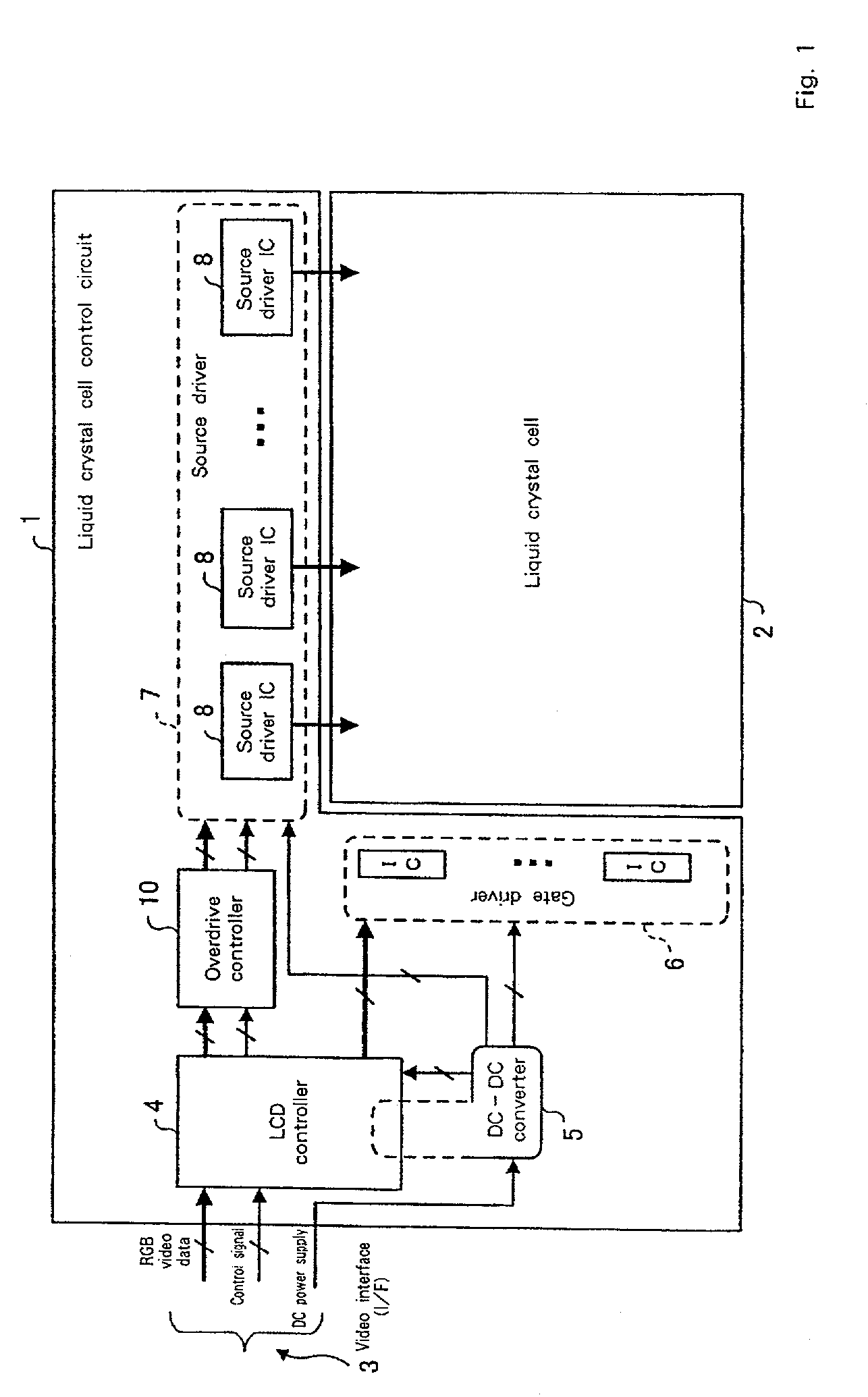
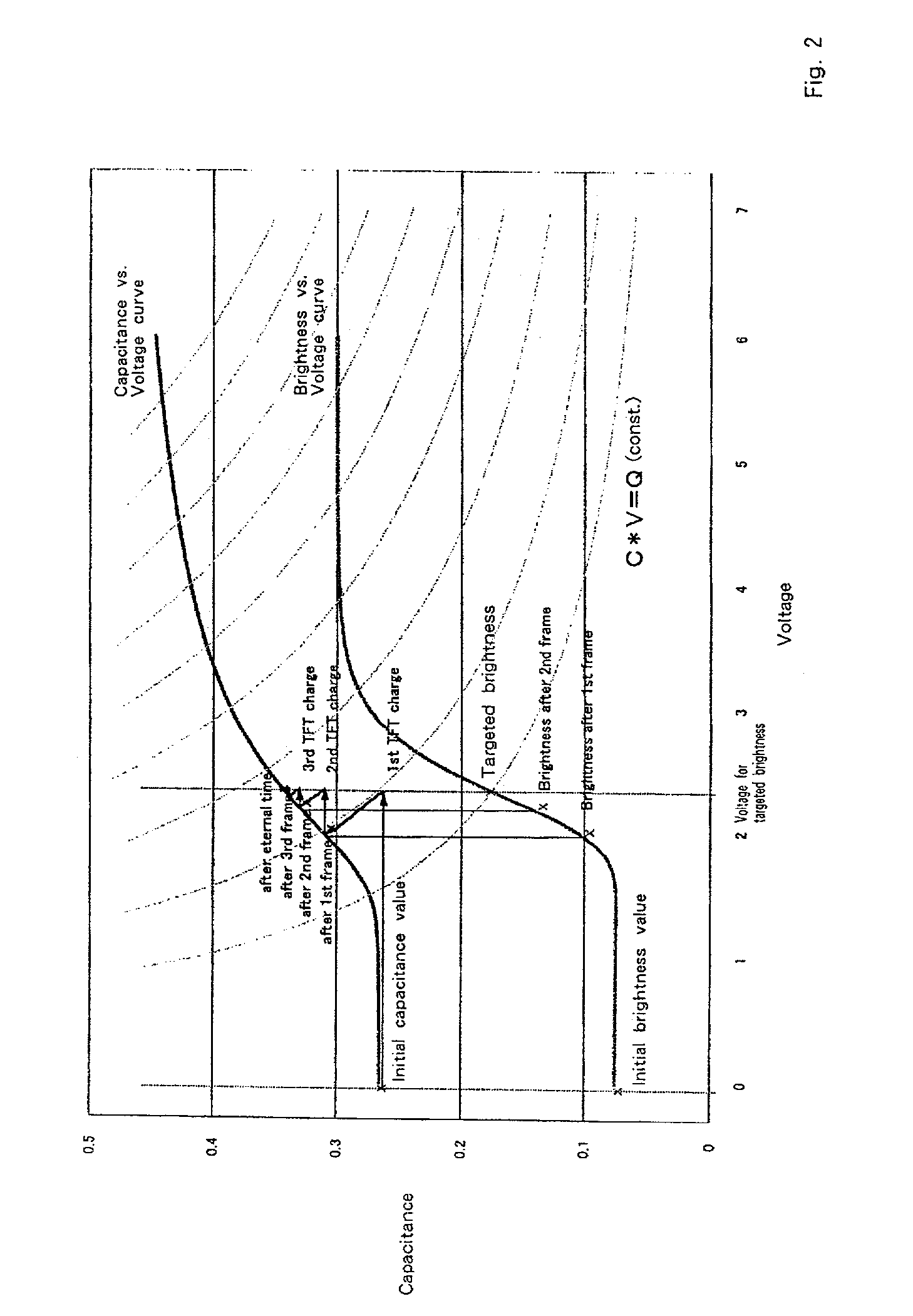
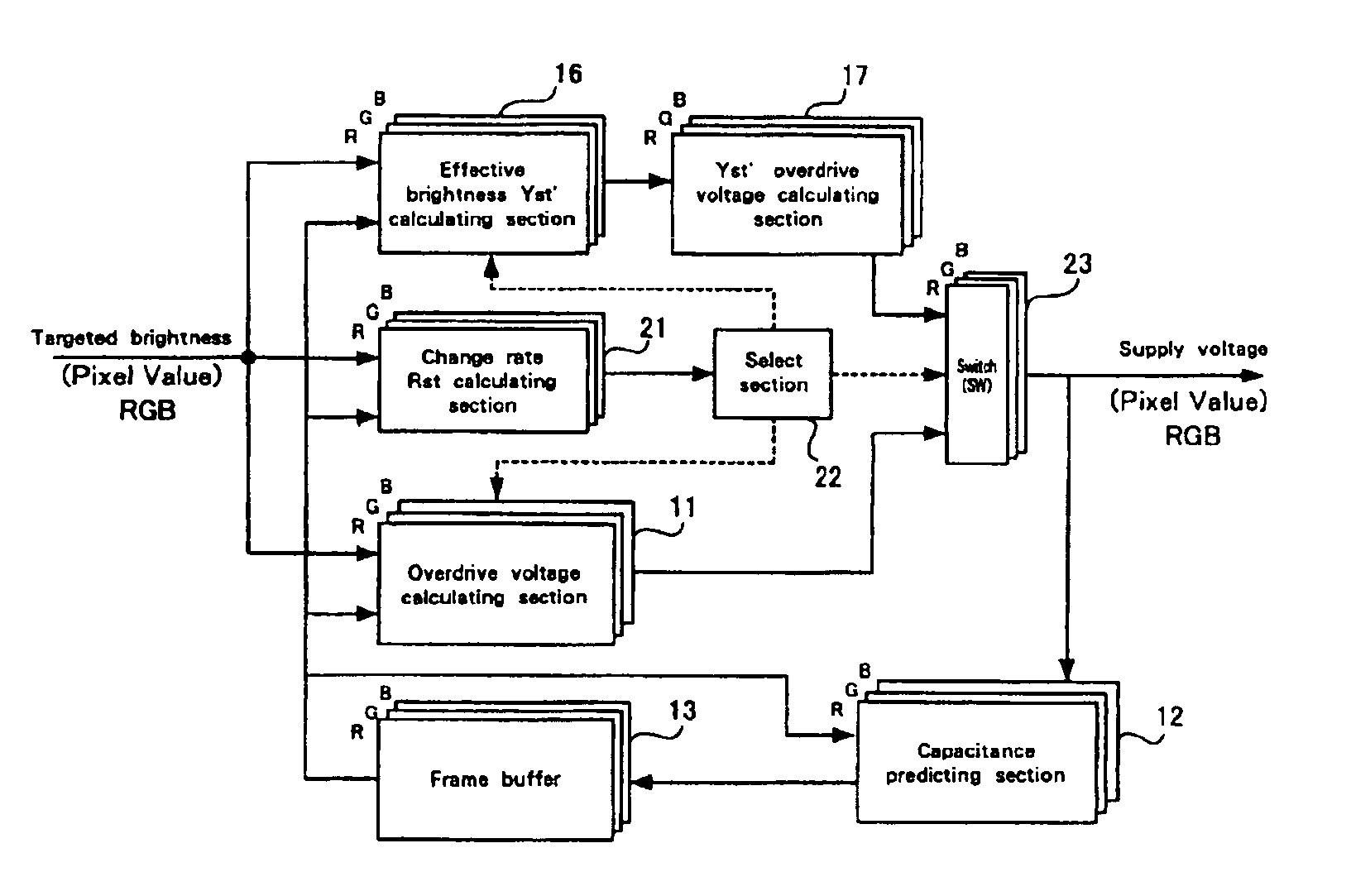
A liquid crystal display drive circuit includes capacitance predicting section for predicting a capacitance value each pixel will reach at one refresh cycle later when applying a predetermined voltage for targeted brightness, a frame buffer for storing the predicted capacitance value, and overdrive voltage calculating section for calculating a voltage to be applied to each pixel based on targeted brightness at one refresh cycle later and the stored capacitance value in frame buffer.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Liquid crystal display driving system and method for driving the same
InactiveUS20080284775A1Short response timeQuality improvementCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
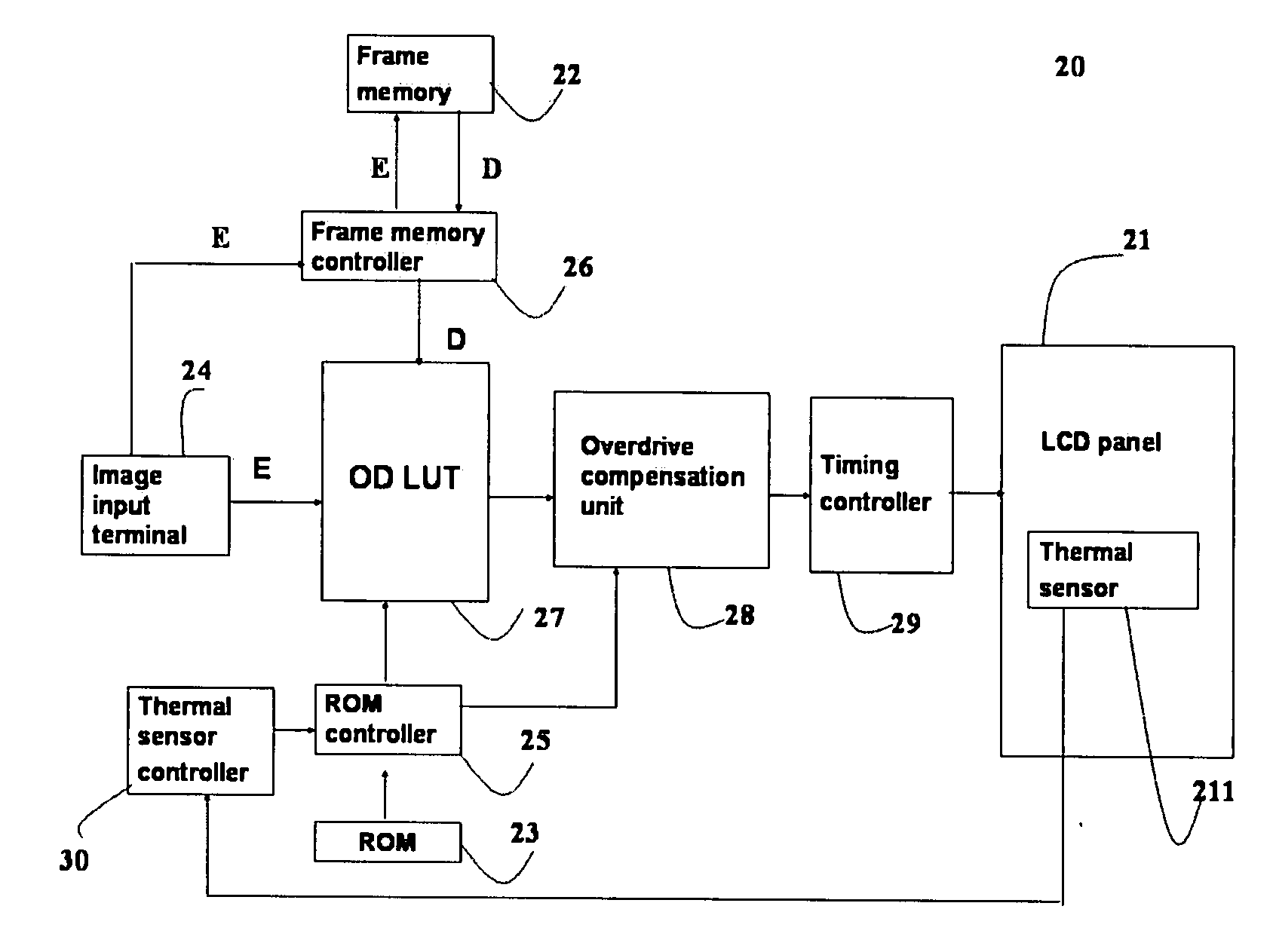
The present invention discloses a liquid crystal display driving system that uses at least one temperature sensor to detect a temperature of a LCD panel, and outputs a gamma compensation voltage value according to the detected temperature, and further uses an overdrive compensation unit to receive the gamma compensation voltage value, and obtains the overdrive compensation voltage value of two gamma overdrive compensation curves of a temperature gradient corresponding to a region of the LCD panel by a gamma mapping method, or uses an overdrive compensation unit to derive a corresponding partial compensation data table according to the temperature and the compensation data table, and at least one overdrive compensation table (OD compensation table) corresponding to the change of temperature gradient in a region of the LCD panel is derived, an outputted display image after being processed by an overdrive lookup table (OD LUT) is compensated, so as to adjust the overdrive voltage of the LCD panel and enhance the response time of the liquid crystal display.
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
Method and apparatus for providing a modulation current
ActiveUS7154923B2Easy to adjustLaser detailsPulse modulationChannel length modulationFeedback circuits
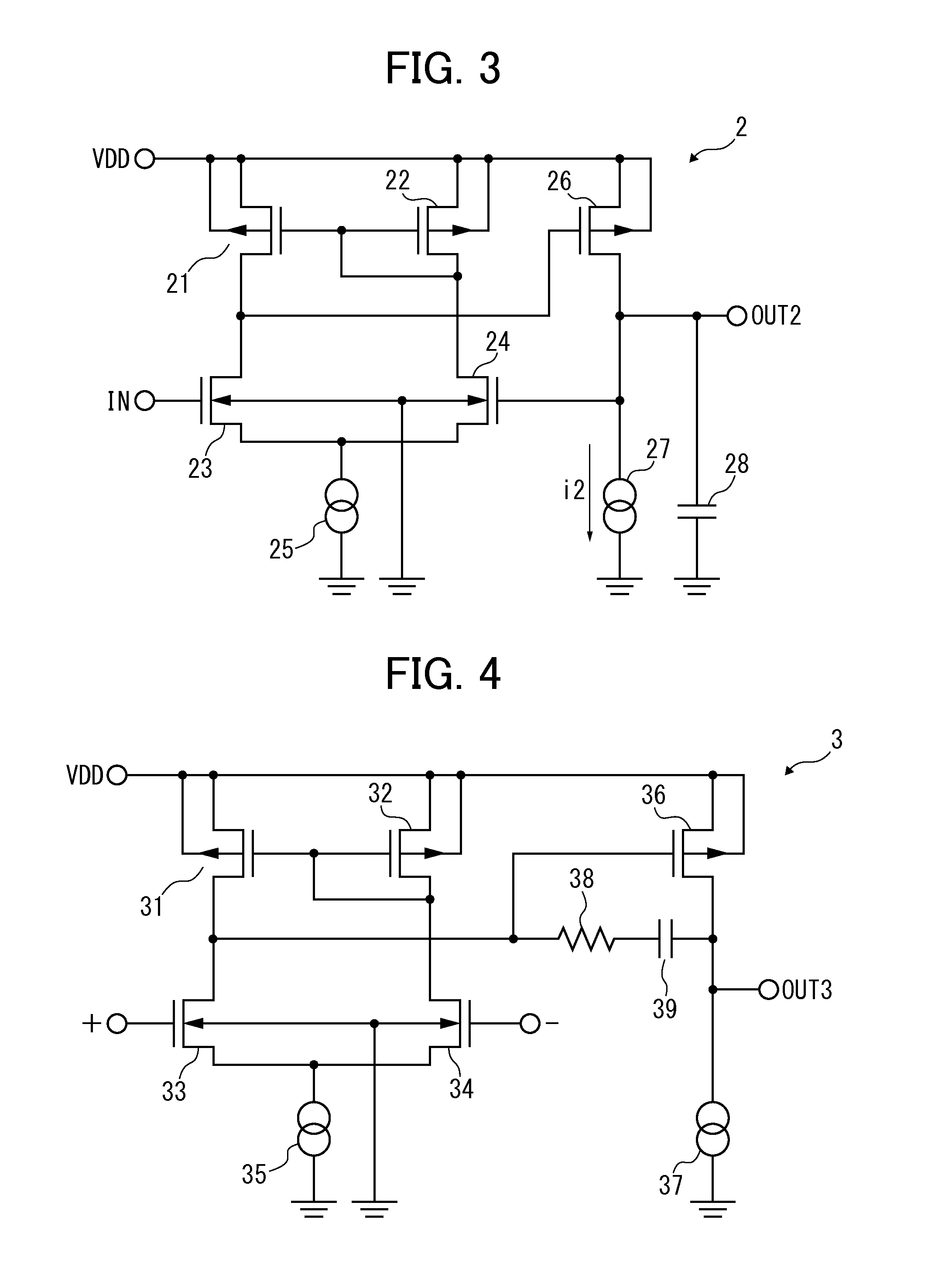
Techniques are disclosed for providing modulation current that includes output impedance compensation with a feed-forward bandwidth enhancement and pre-distortion modulation to control waveform transition symmetry. A feedback circuit senses output node voltage and increases the overdrive voltage of a current source. This offsets the loss of current due to channel length modulation and increases the effective output impedance of the source. A feed-forward circuit enhances the bandwidth of the impedance compensation feedback loop. Waveform transition symmetry is improved by pre-distorting a laser modulation current by introducing an undershoot current on the falling edge of the modulating current.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20080224980A1Improve display qualityReduce manufacturing costStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A liquid crystal display includes a plurality of gate lines having odd-numbered gate lines and even-numbered gate lines, a plurality of source lines, a first gate driver which drives the odd-numbered gate lines, a second gate driver which drives the even-numbered gate lines and a driving controller which outputs an overdriven image signal in at least one driving period of a plurality of driving periods and outputs a normal image signal in remaining driving periods of the plurality of driving periods. The overdriven image signal is obtained by adding an overdrive voltage to the normal image signal, and the overdrive voltage is set according to a level of the normal image signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
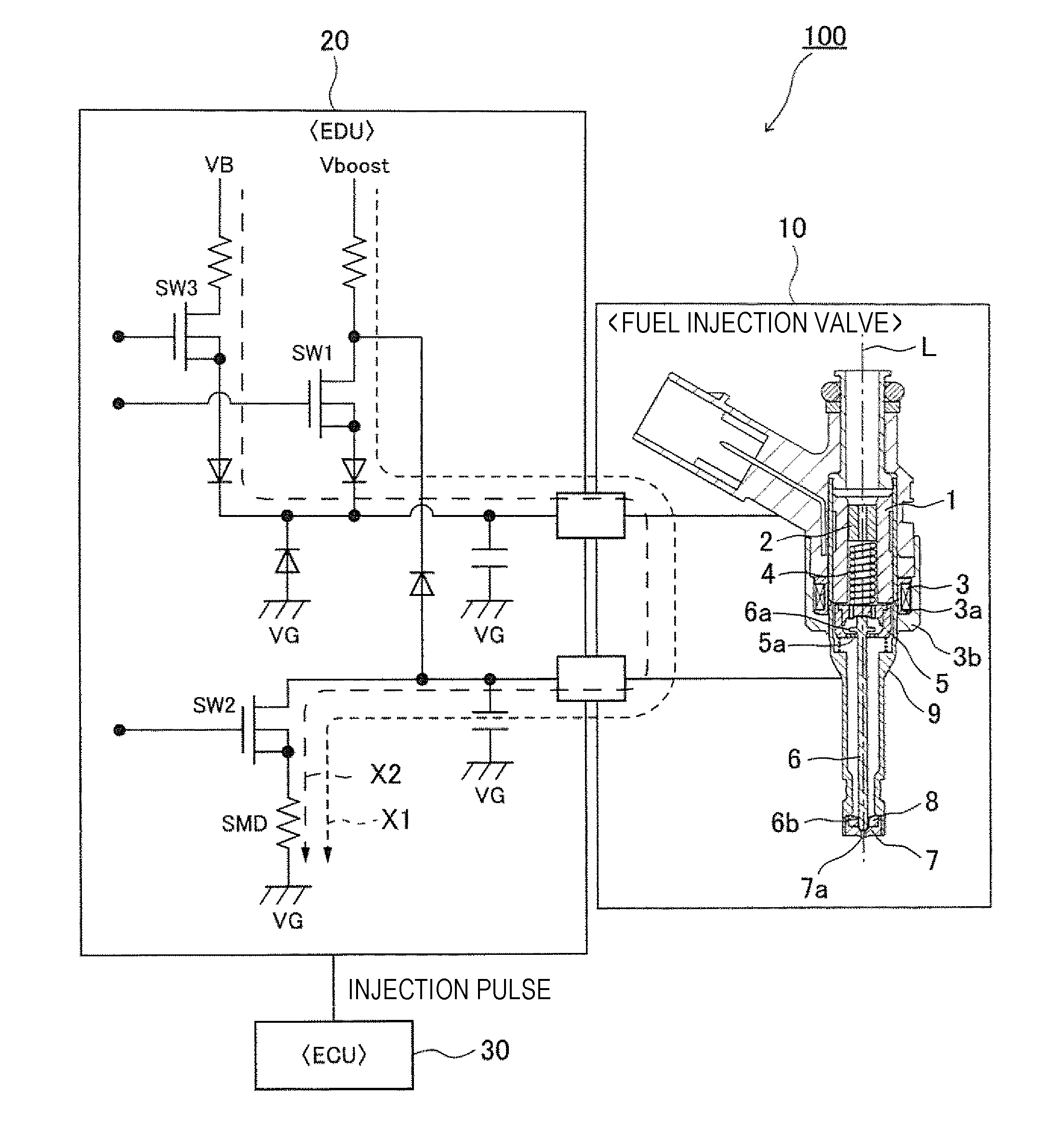
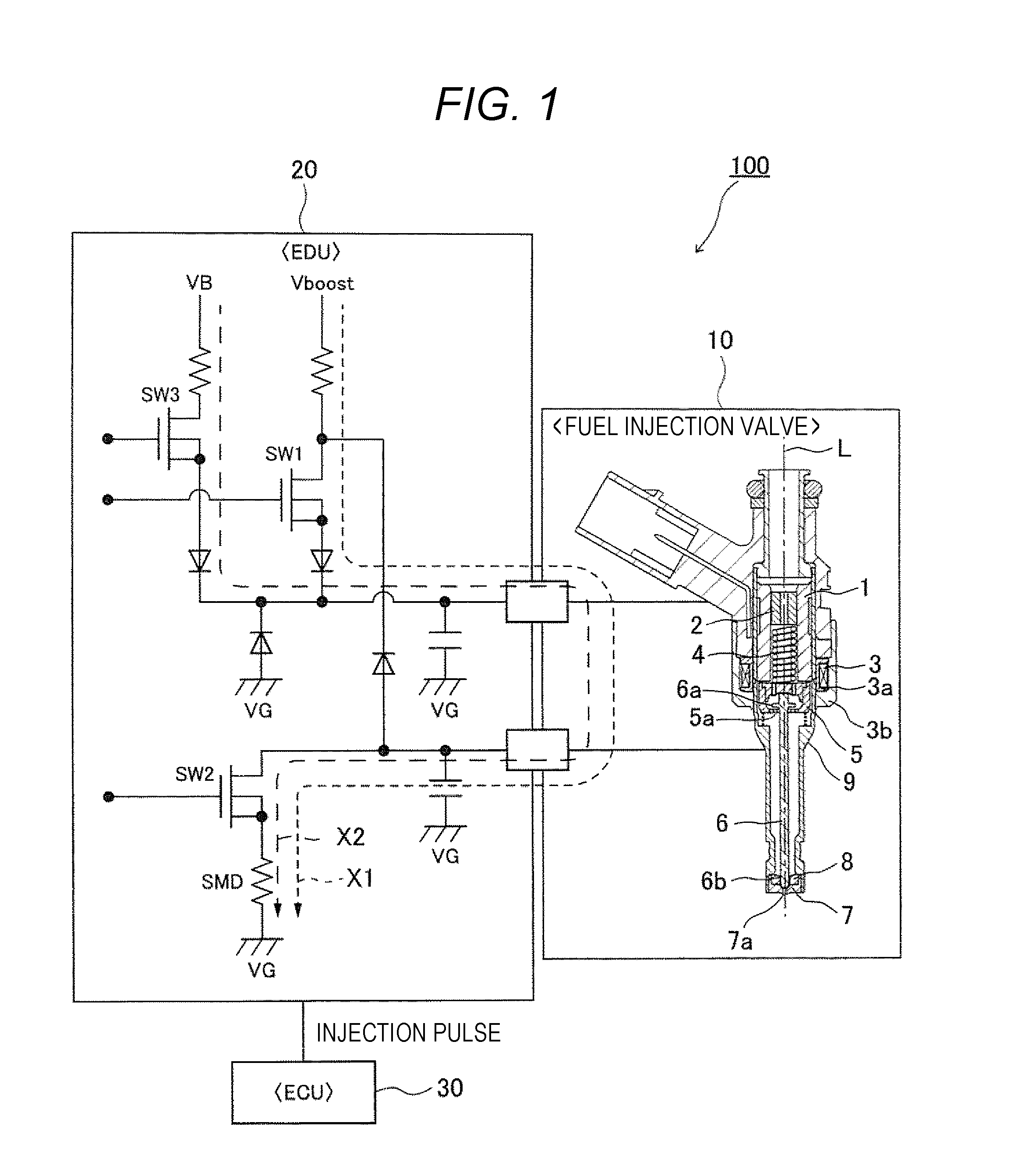
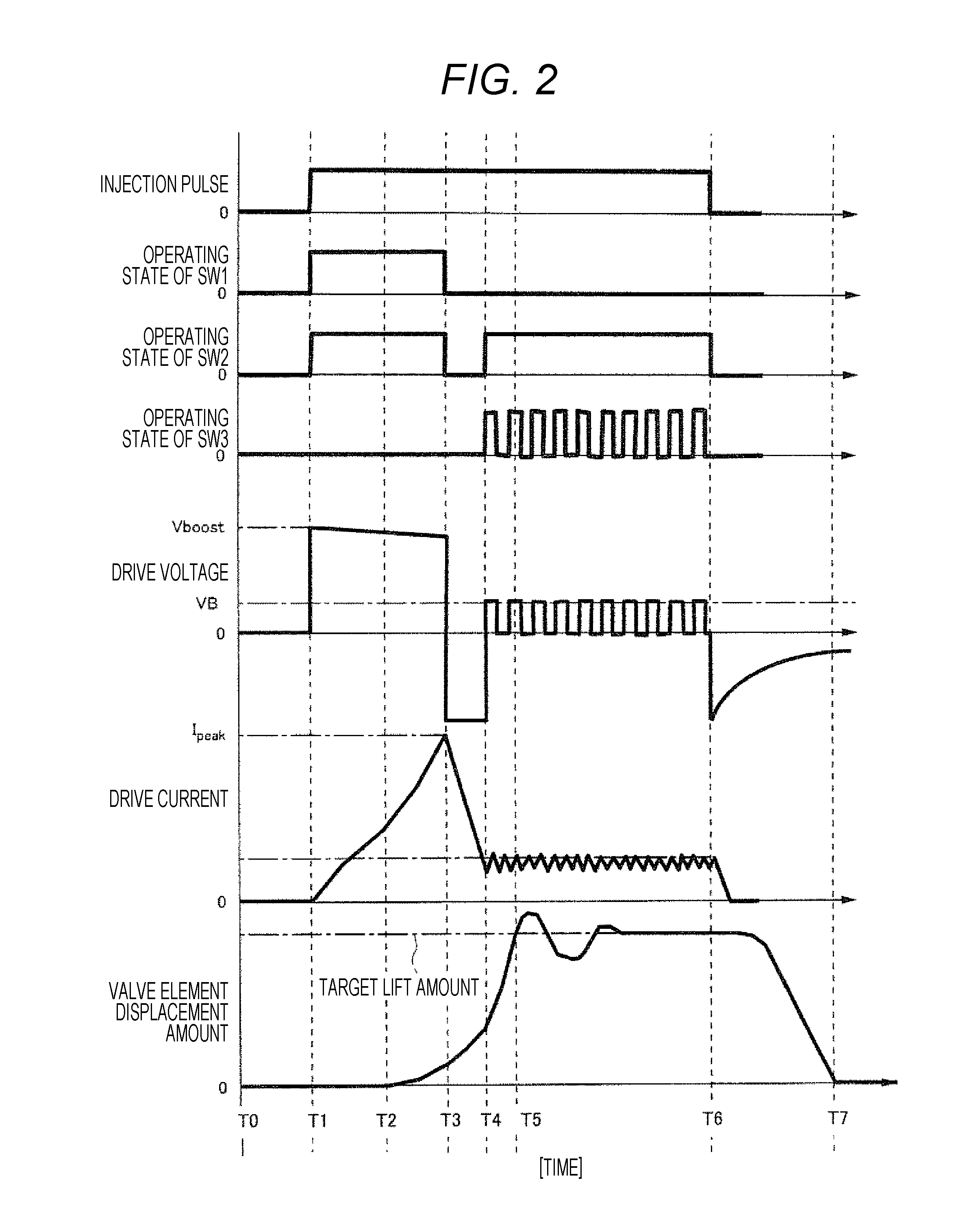
Electromagnetic Valve Control Unit and Internal Combustion Engine Control Device Using Same
Provided are an electromagnetic valve control unit and a fuel injection control device using the same that can precisely detect a change of an operating state of an electromagnetic valve, that is, a valve opening time or a valve closing time of the electromagnetic valve, precisely correct a drive voltage or a drive current applied to the electromagnetic valve, and appropriately control opening / closing of the electromagnetic valve, with a simple configuration. In an electromagnetic valve control unit for controlling opening / closing of an electromagnetic valve by a drive voltage and a drive current to be applied, the drive voltage and the drive current applied to the electromagnetic valve are corrected on the basis of a detection time of an inflection point from time series data of the drive voltage and the drive current when the electromagnetic valve is opened / closed.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
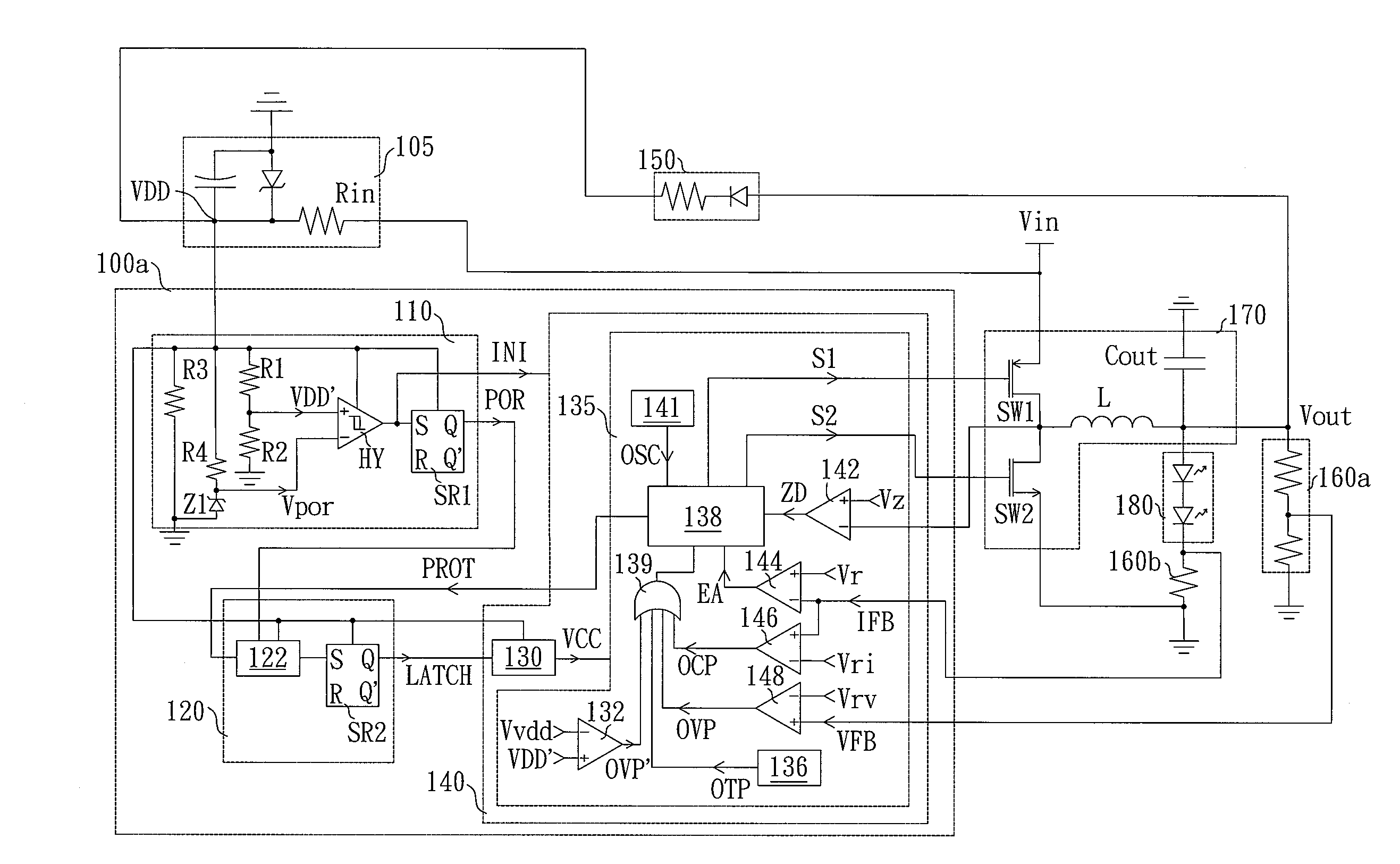
Power converting circuit and controller thereof
ActiveUS20100315017A1Shortened life-spanProcess safetyElectroluminescent light sourcesAc-dc conversionEngineeringElectric power
A controller which receives electric power required for operating through a driving voltage terminal and controls a converting circuit to convert an input voltage into an output voltage is provided. The controller is latched to stop providing a part or all of functions until the input voltage is removed. Therefore, the issues of the converting circuit in related arts in shortened life-span and safety of users due to can be avoided in the present invention.
Owner:GREEN SOLUTION TECH CO LTD
Oscillator, and clock generator, semiconductor device, and electronic device including the same
InactiveUS20120154066A1Reduce extraneous power consumptionInhibit deteriorationPulse automatic controlApparatus using electrochemical resonatorsVoltage generatorDriving current
An oscillator includes a reference voltage generator, an oscillation element configured to oscillate by either a drive voltage or a drive current and output an oscillation signal, a peak hold element configured to detect a peak level of the oscillation signal for output; and a controller configured to increase or decrease the drive voltage or drive current in accordance with the reference voltage generated by the reference voltage generator and the peak level output from the peak hold element.
Owner:RICOH ELECTRONIC DEVICES CO LTD
Over-drive D/A converter and source pole driver and its method
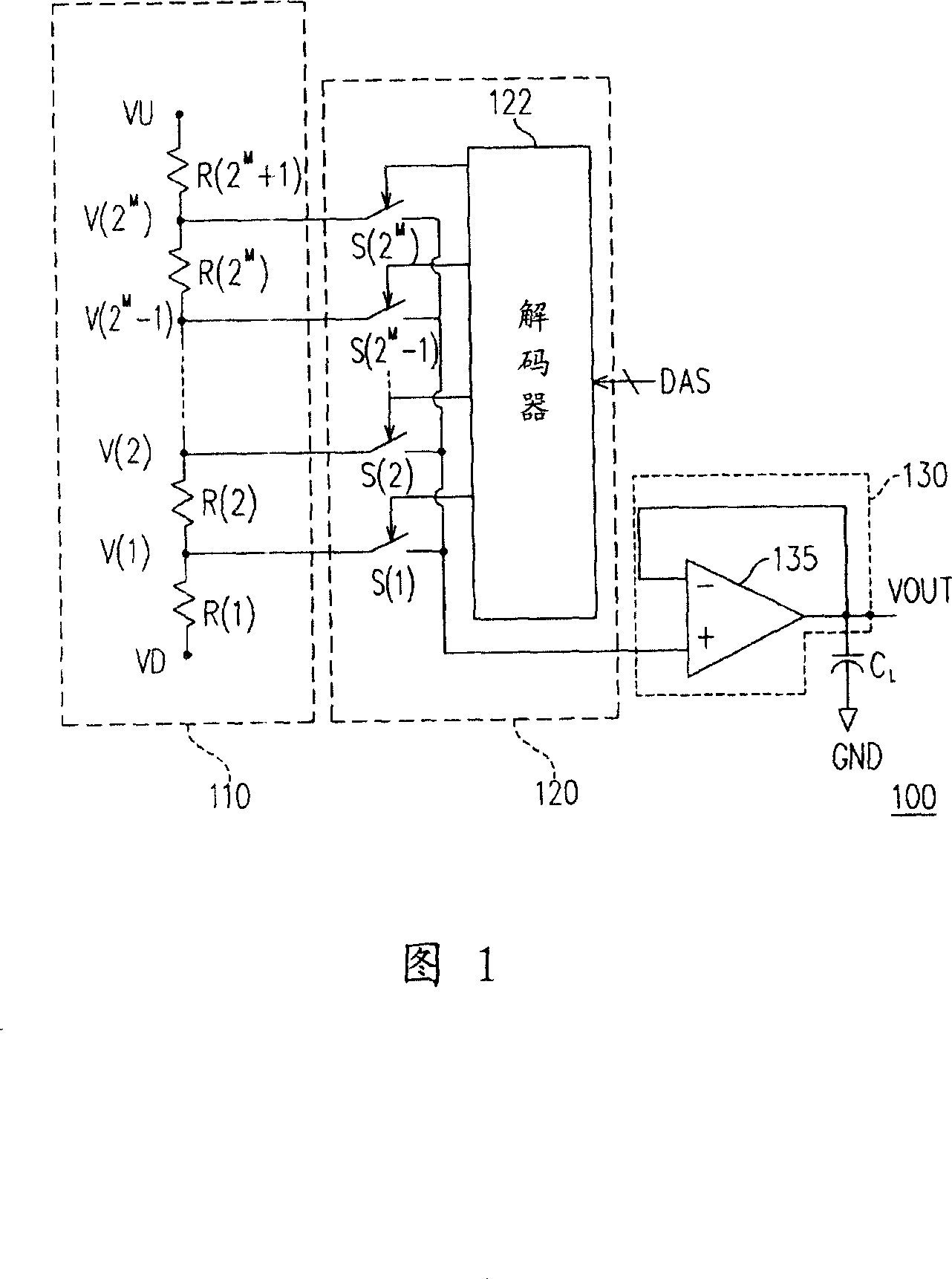
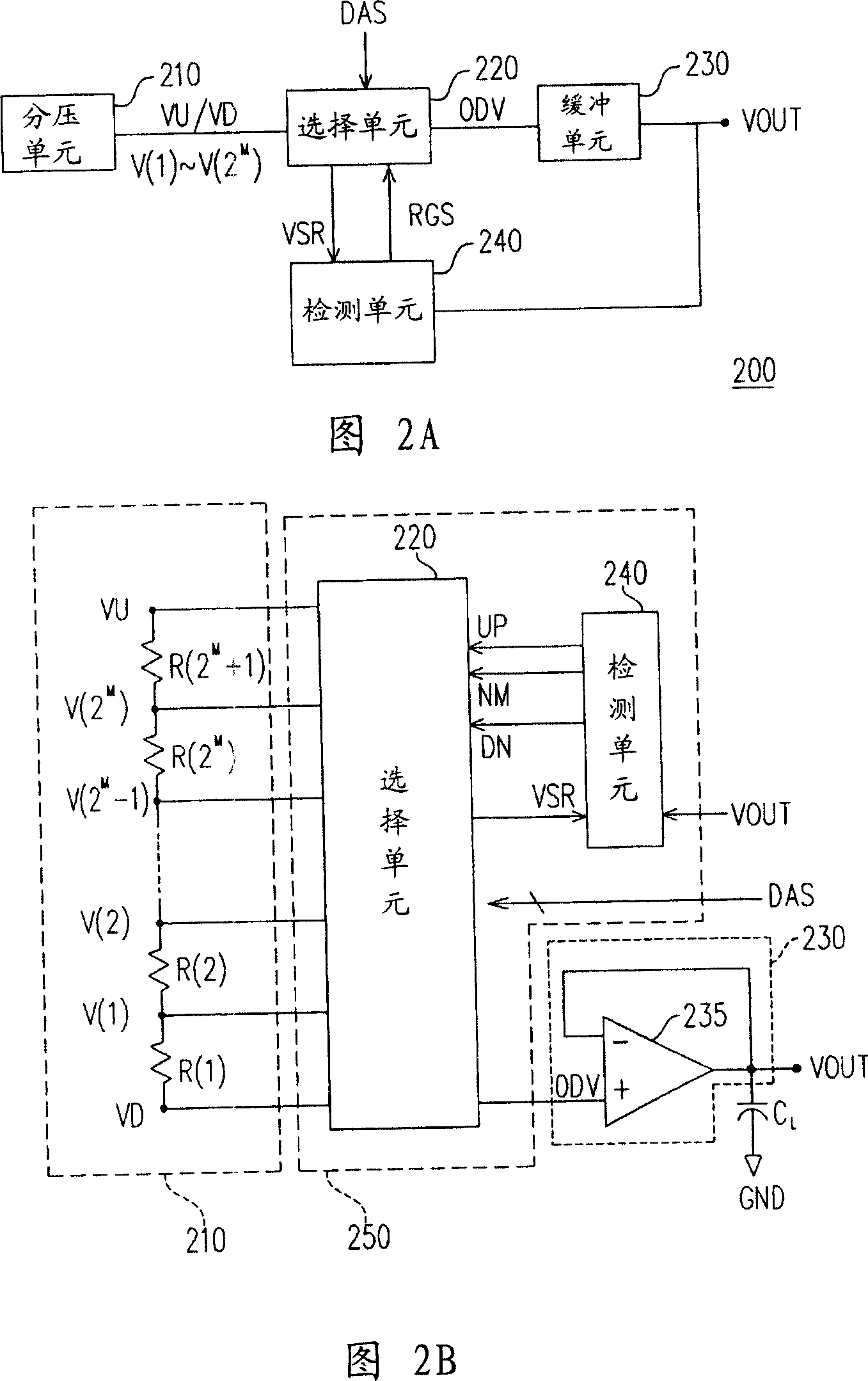
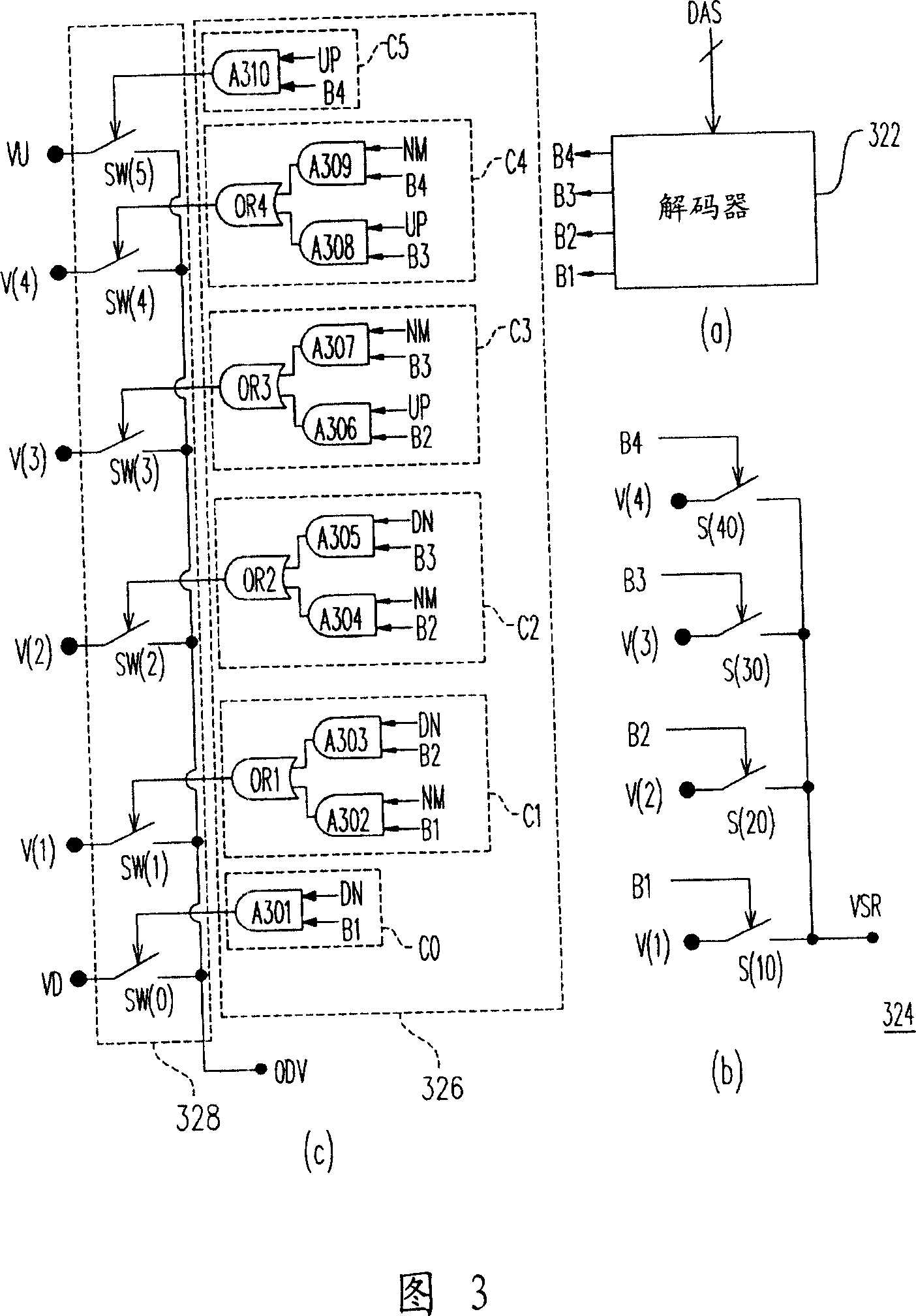
InactiveCN101145781AIncrease turn rateHigh speedStatic indicating devicesDigital-analogue convertorsDigital analog converterVoltage reference
The invention provides an overdriven digital-analog converter, a source electrode driver and a method thereof. The digital-analog converter comprises a voltage division unit, a selecting unit, a buffering unit and a detection unit. The voltage division unit provides multiple reference voltages, and the detection unit outputs a regulation signal based on the comparison result between the output voltage of the buffering unit and a specific reference voltage corresponding to an input digital signal. the selecting unit regulates the overdriven voltage outputted to the buffering unit based on the regulation signal and input digital signal, so as to accelerate the output voltage variation of the buffering unit, thereby improving the conversion speed of the digital-analog converter.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Low-dynamic maladjusted high-speed low-power consumption comparator circuit
InactiveCN108832916AImprove stabilityReduce complexityMultiple input and output pulse circuitsDifferential signalingComparators circuits
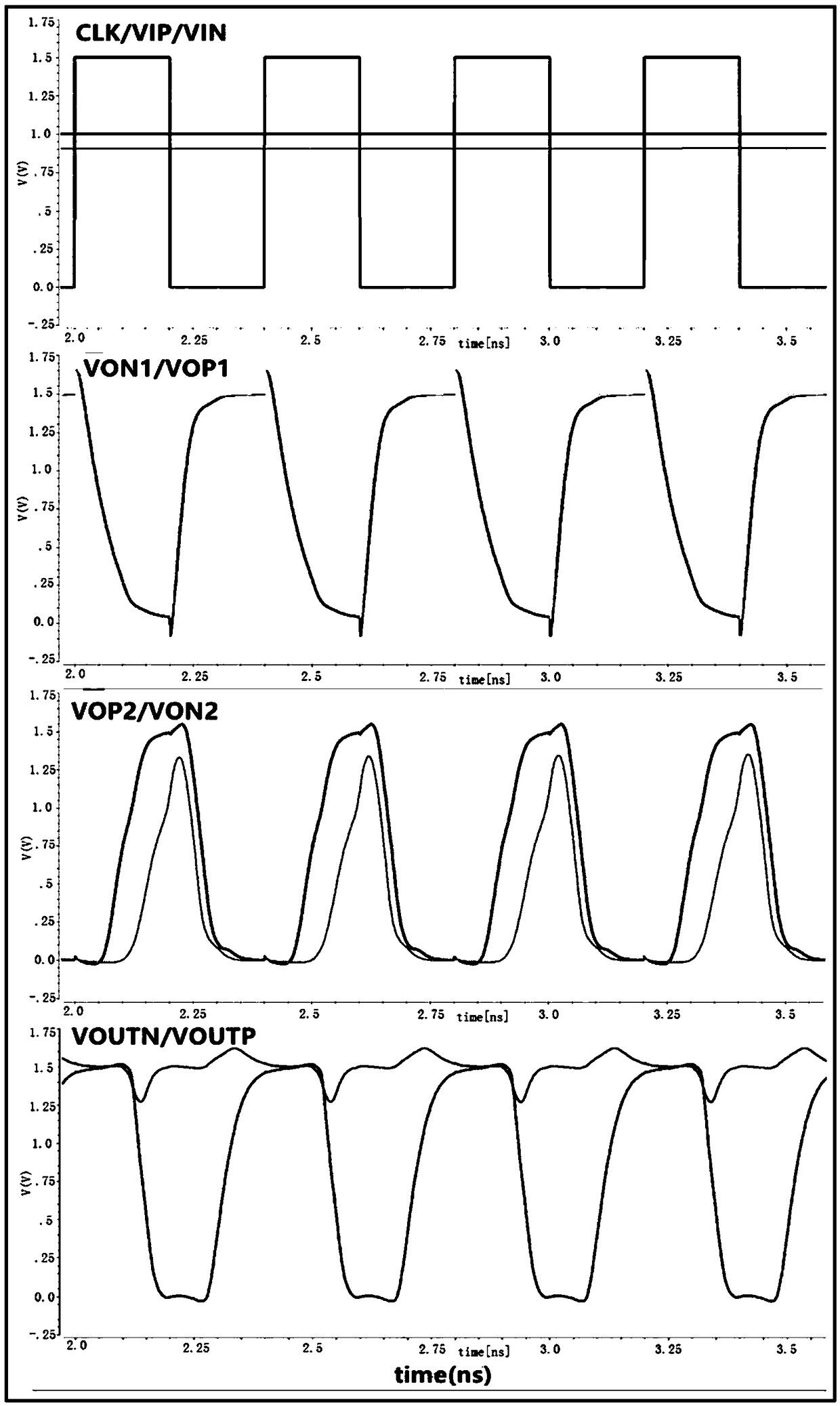
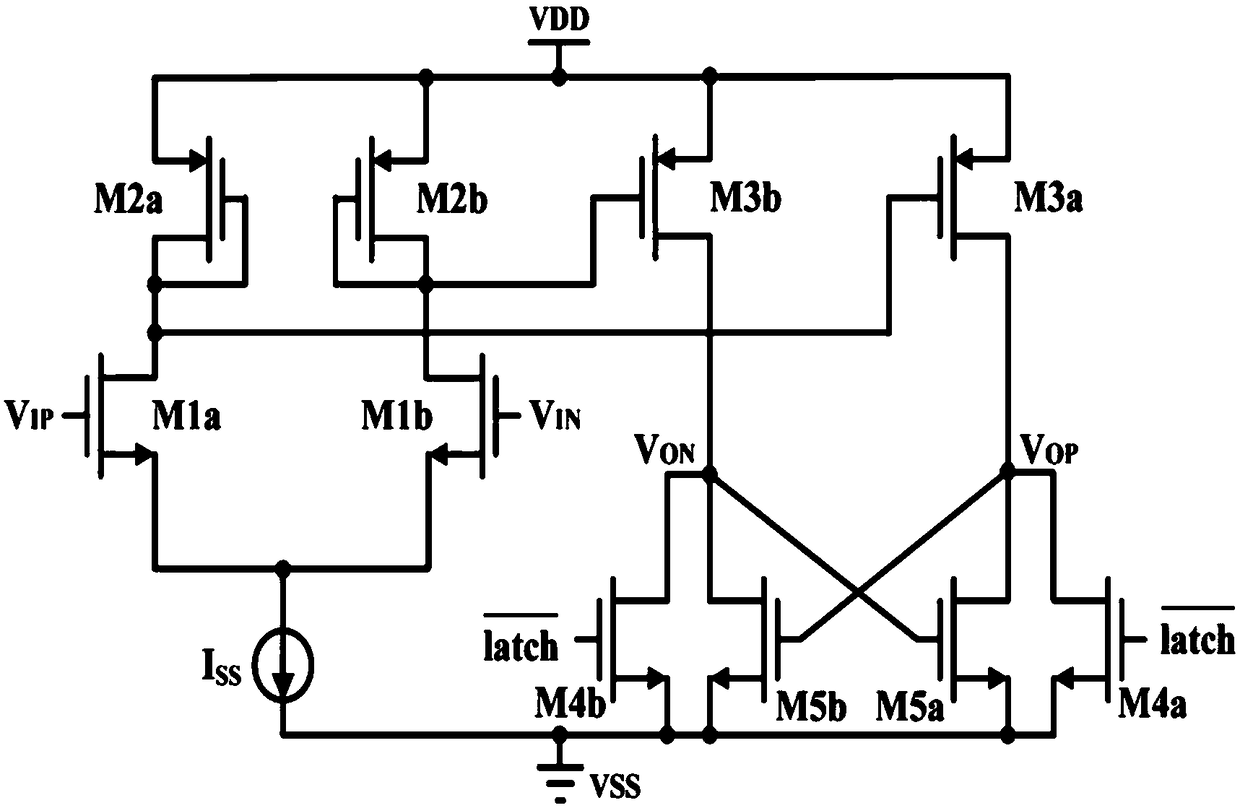
The invention discloses a low-dynamic maladjusted high-speed low-power consumption comparator circuit. The circuit comprises a first-stage pre-amplifying circuit and a second-stage positive-feedback latch circuit; the comparator circuit controls a comparison stage and a reset stage of the comparator circuit by adopting a clock signal; the comparator circuit is located at the comparison stage whenthe clock signal is located at high level, a pair of differential input signals are respectively amplified through the first-stage pre-amplifying circuit so as to form a pair of primary differential signals; the second-stage feedback latch circuit inversely amplifies a pair of primary differential signals and forms a pair of secondary differential signals, and performs the positive feedback latching on the secondary differential signals so as to obtain a pair of differential output signals. By adopting a tail current source biased by a bias voltage and a cascade switch tube controlled by the clock signal, the static power consumption is eliminated, the stability on the tube over-driving voltage by the differential input is guaranteed, and the dynamic maladjustment is effectively reduced.
Owner:ANHUI CHUANSI MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS6930663B2Improve abnormal appearance of colorSuppress colorStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
An overdrive controller for driving a liquid crystal display includes a change rate Rst calculating section for comprehending a transition state from a present brightness to a targeted brightness for each of R, G and B sub-pixels, a select section for selecting the sub-pixel with the slowest transition and the other sub-pixels from the comprehended transition states, and an overdrive voltage calculating section for calculating a voltage to accelerate a transition of brightness for the sub-pixel with the slowest transition. The overdrive controller further includes, an effective brightness Yst′ calculating section and Yst′ overdrive voltage calculating section for calculating a voltage to accelerate or to decelerate a transition of brightness for the other sub-pixels in order to coordination with each other, wherein the voltage is switched by a switch 23 to be supplied.
Owner:VIDEOCON GLOBAL
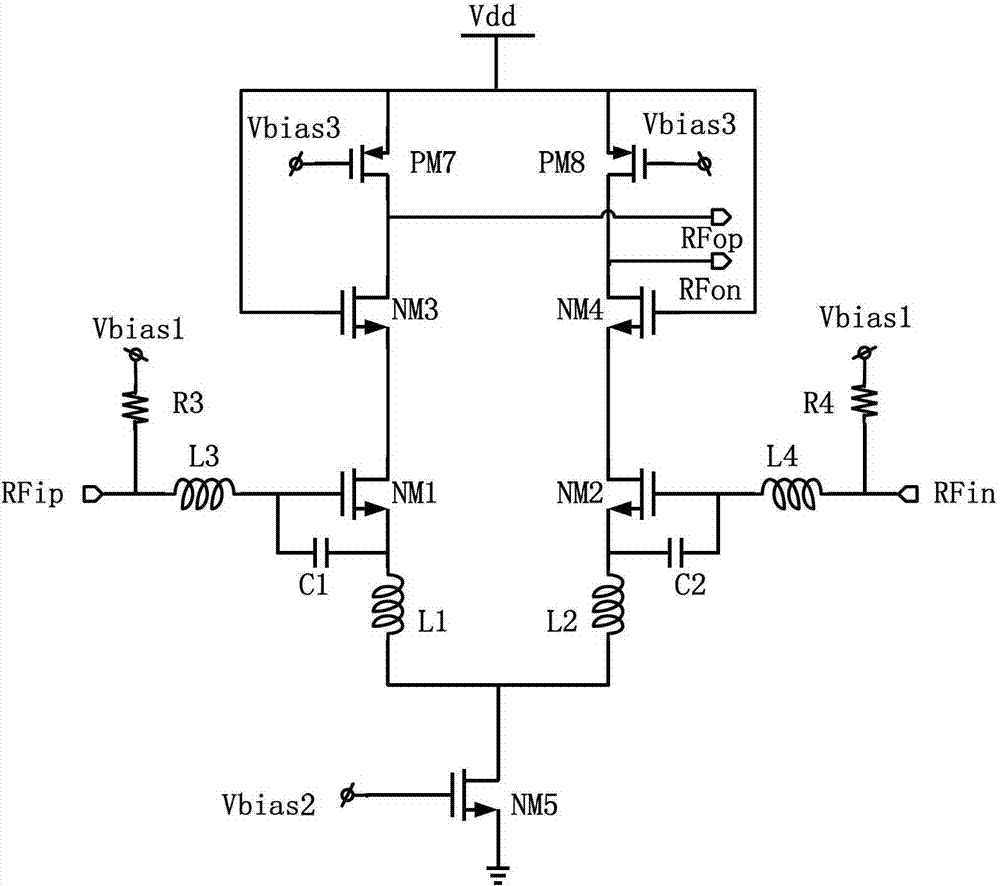
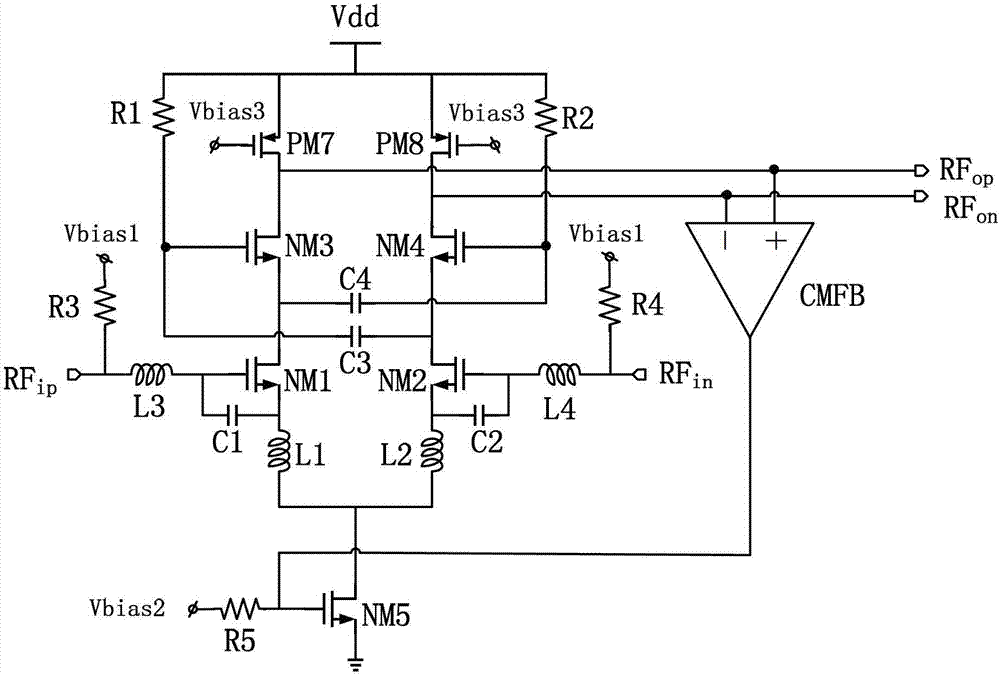
High-linearity low-noise amplifier
ActiveCN103248324AImprove linearityIncrease the overdrive voltageAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionLow noise
The invention provides a high-linearity low-noise amplifier of the front end of an ultrahigh-frequency RFID (radio frequency identification) receiver. The amplifier detects two common levels from two differential output ends of a full-differential amplifier through a common-feedback circuit, bias current of the amplifier is adjusted validly and feedback voltage is outputted to a grid of a tail current source, and accordingly, overdrive voltage of the tail current source is increased, input current is increased and linearity is improved. Meanwhile, the problem of non-linear distortion caused by instability of the output common levels is solved. In addition, a coupling capacitor is crossed interstagely to increase power grain, and noise figure is reduced to improve noise performance. The high-linearity low-noise amplifier has the advantages of low noise figure, low power consumption, and high linearity, and solves the problem of carrier leak in ultrahigh-frequency RFID receivers and zero intermediate frequency receivers, and linearity of the low-noise amplifier is improved, so that weak available signals can be amplified linearly and distortionlessly in the process of receiving block signals.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM INST AT NANJING CO LTD
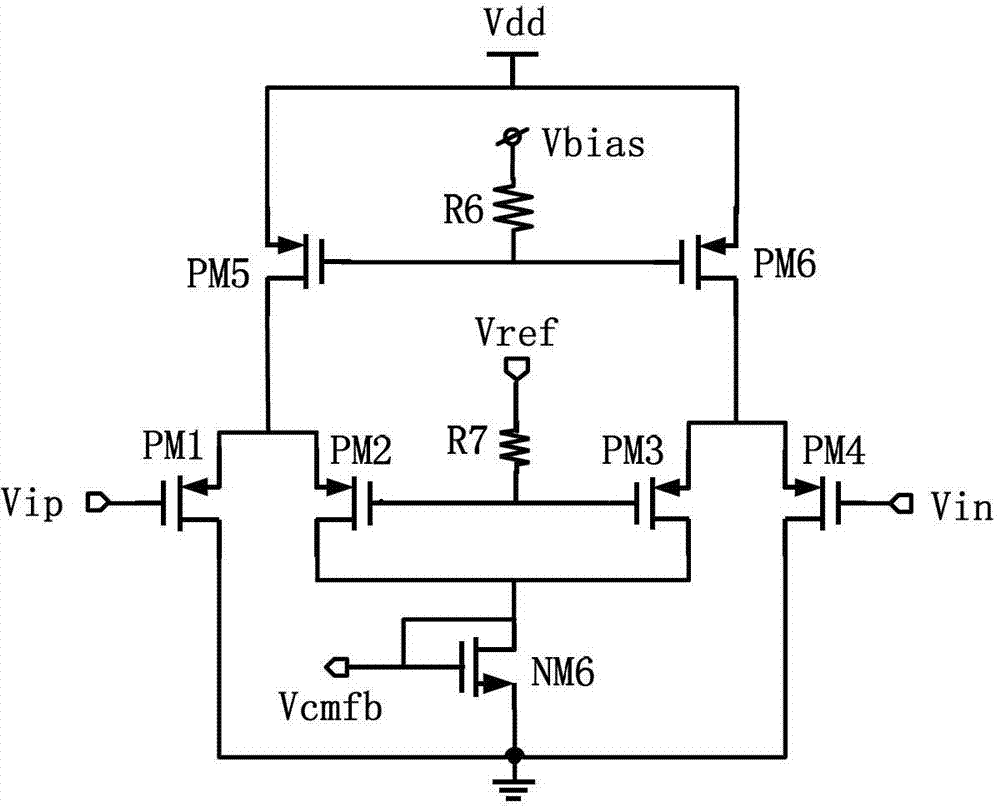
Voltage buffer and its source electrode driver
ActiveCN101131807ALarge load capacitanceChange the voltage levelStatic indicating devicesAudio power amplifierOperational amplifier
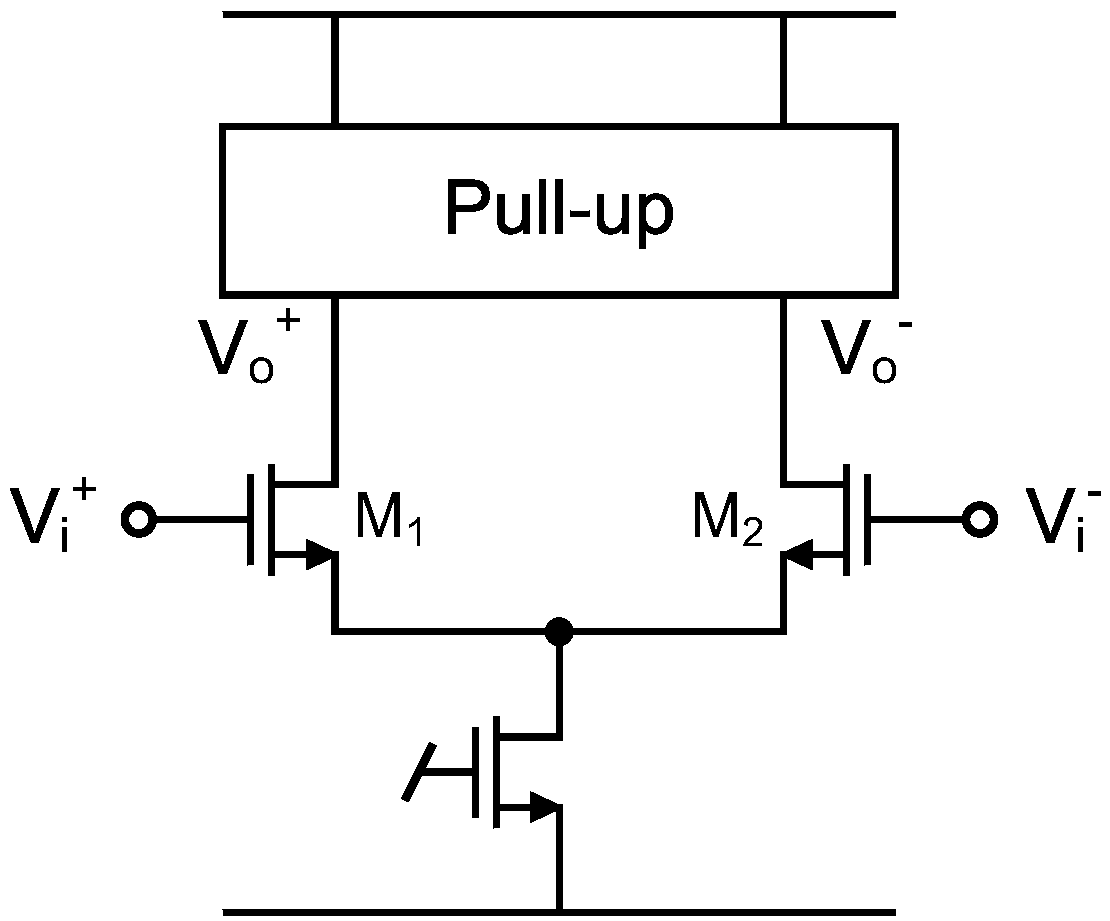
A pressure buffer and its source drivers, the said pressure buffer includes operation amplifier and overdrive cell, its operation amplifier output a output pressure. The overdrive cell couples between a output pressure and the operation amplifier, to compare the input pressure and the output one, and output a overdrive pressure to the positive output end of the operation amplifier. If the input pressure is bigger than the output pressure, the overdrive pressure is bigger than the input pressure, if the input pressure is smaller than the output pressure, the overdrive pressure is smaller than the input pressure, if the input pressure is equal to the output pressure, the overdrive pressure is equal to than the input pressure.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method for driving liquid crystal display and apparatus employing the same
InactiveUS20070063947A1Picture quality is deterioratedQuality improvementCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayComputer vision
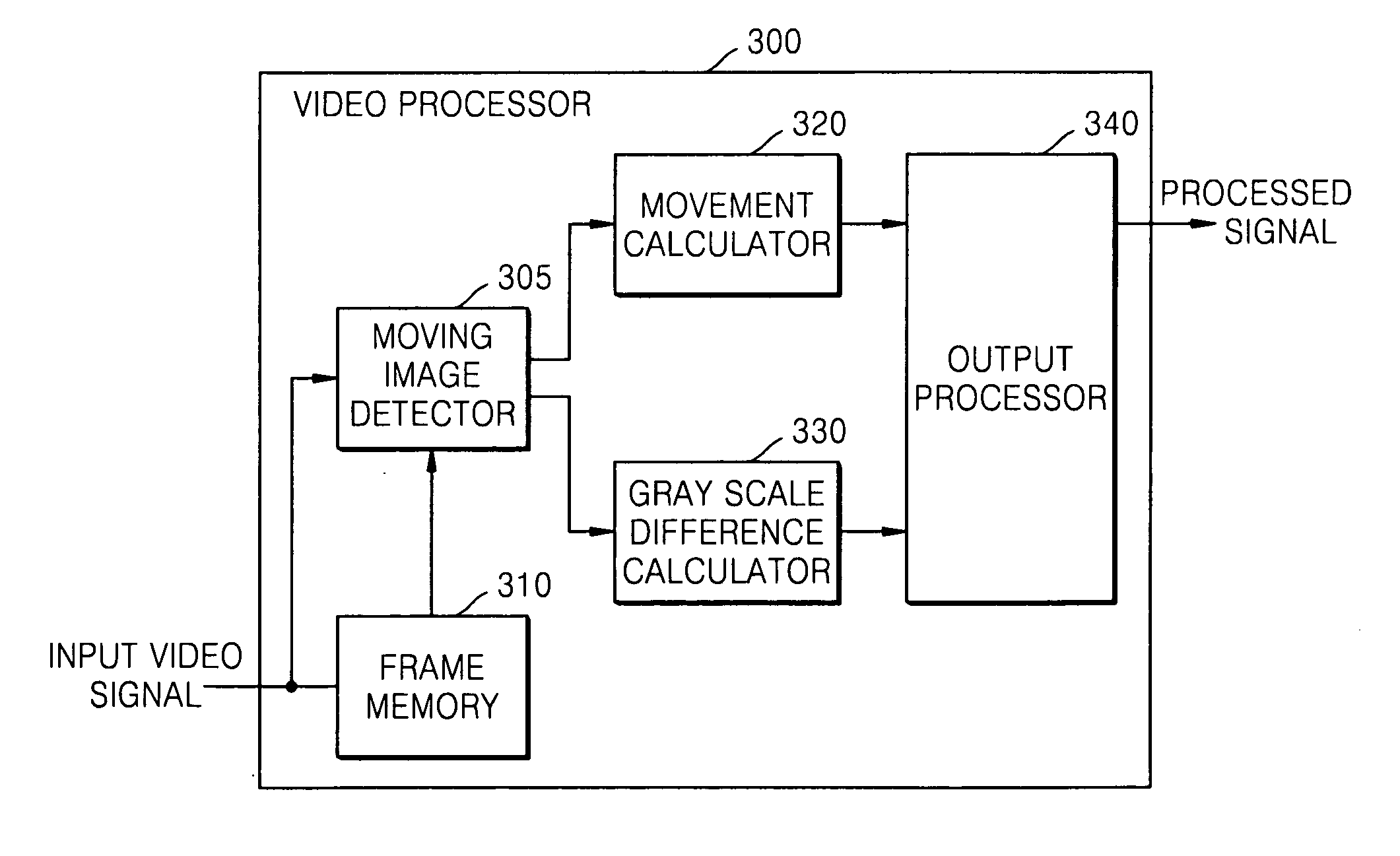
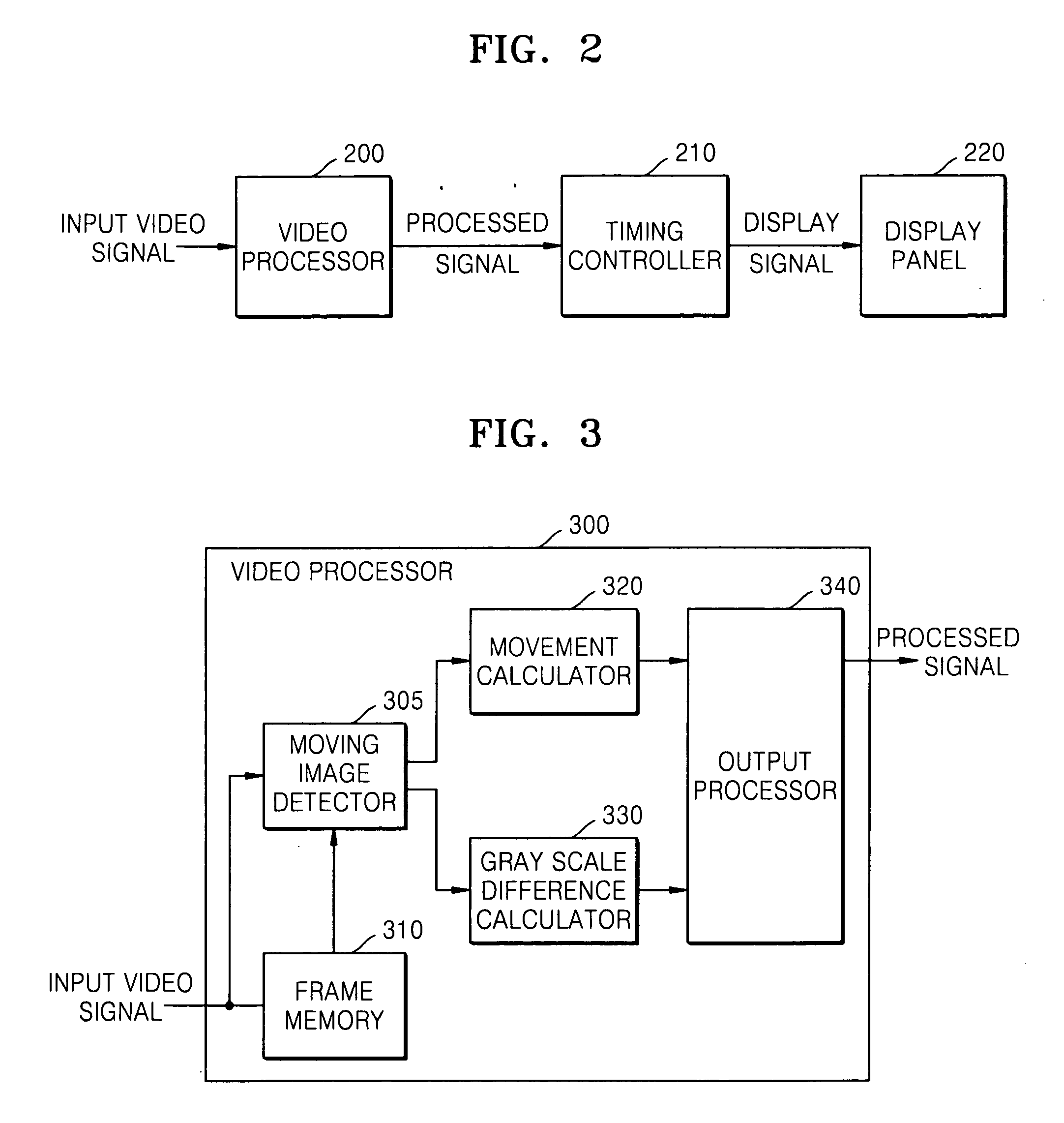
Provided are a method and apparatus for driving a liquid crystal display. The apparatus includes: a moving image detector which reads an input signal frame by frame and compares gray-scale data of a previous frame to gray-scale data of the current frame to detect a moving pattern; a gray-scale difference calculator which calculates a gray-scale difference in the detected pattern to discriminate the boundary of the pattern from the inside of the pattern; and an output processor that generates an over-driving voltage for over-driving pixels corresponding to the inside of the pattern and applies the over-driving voltage to pixels of liquid crystal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
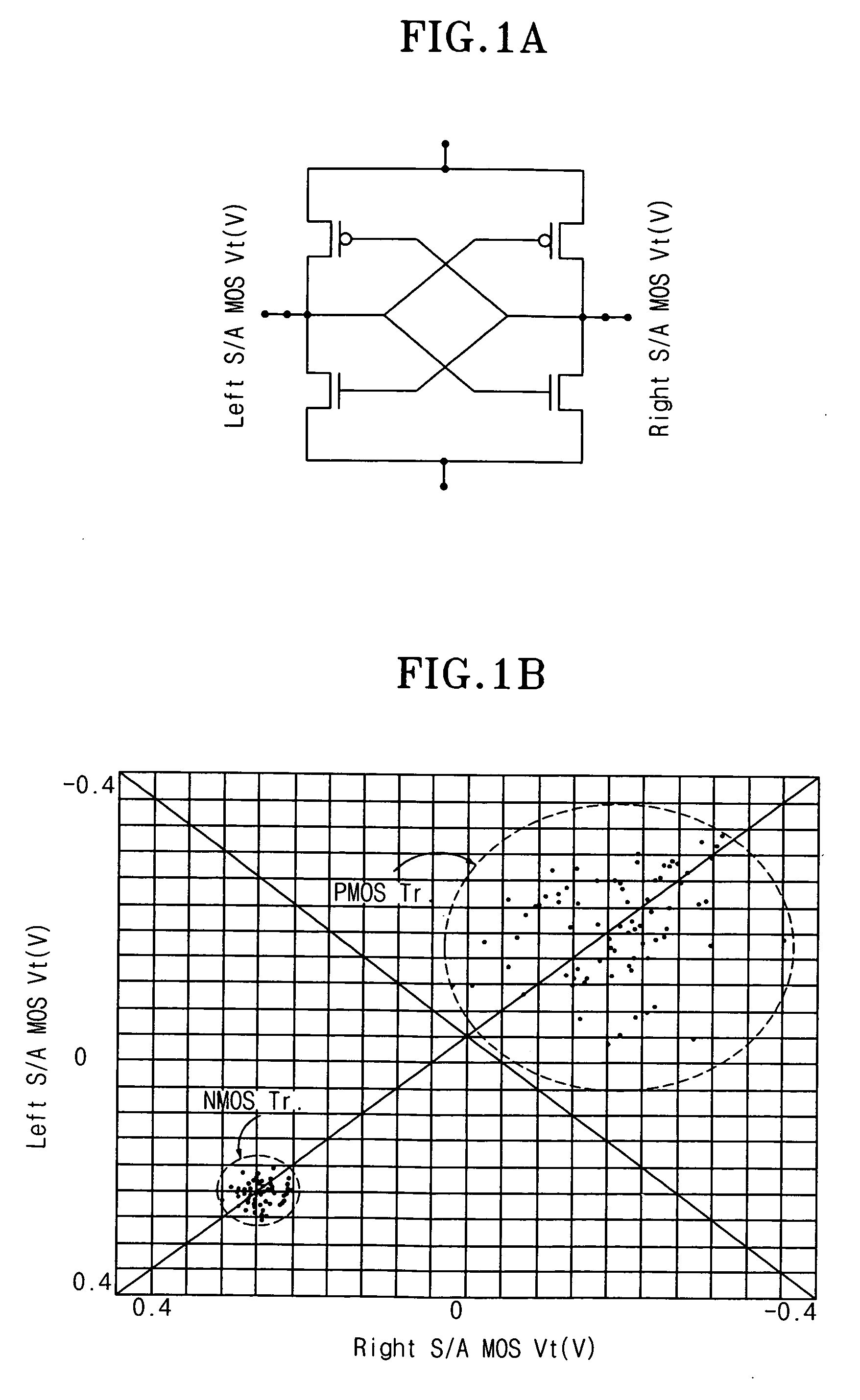
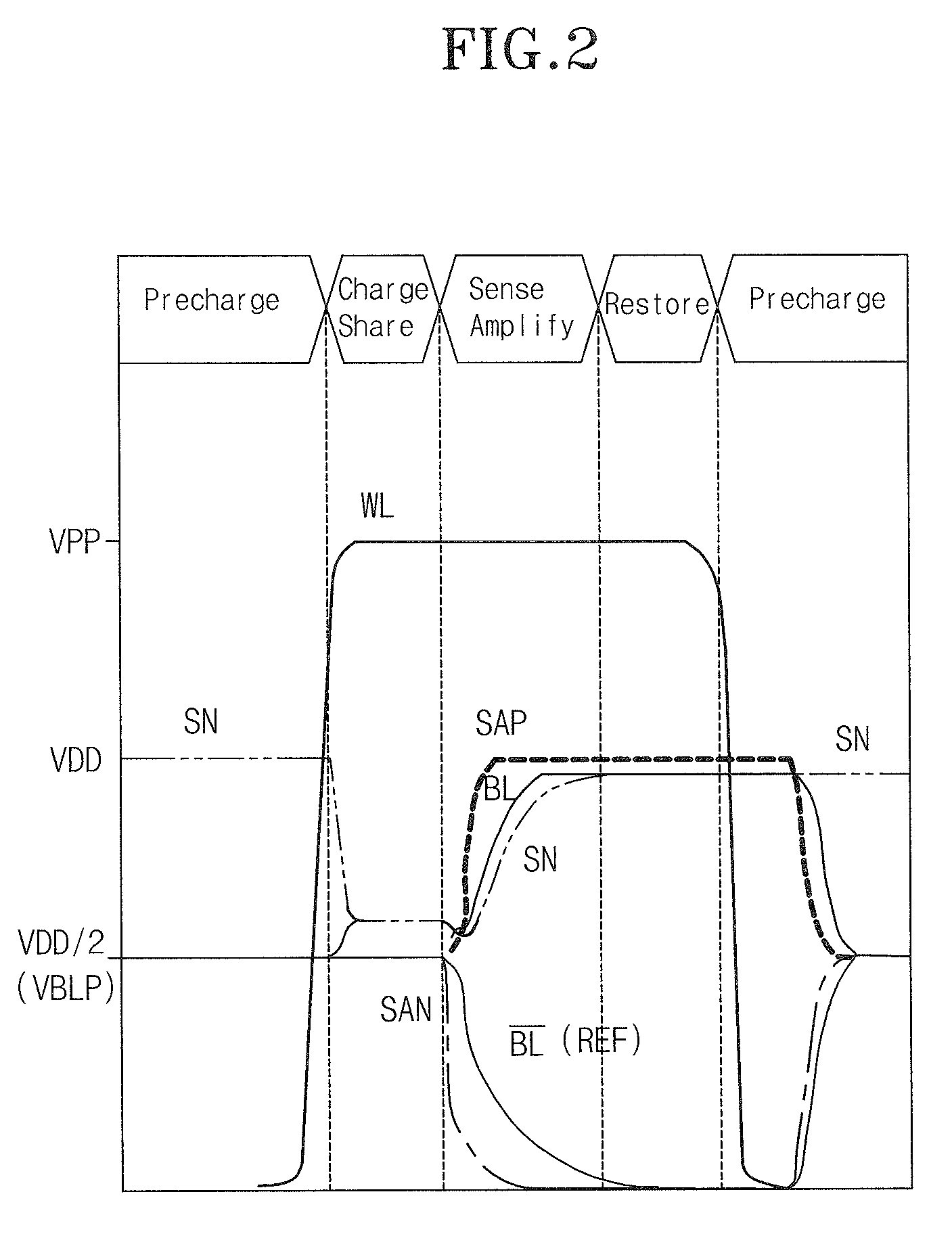
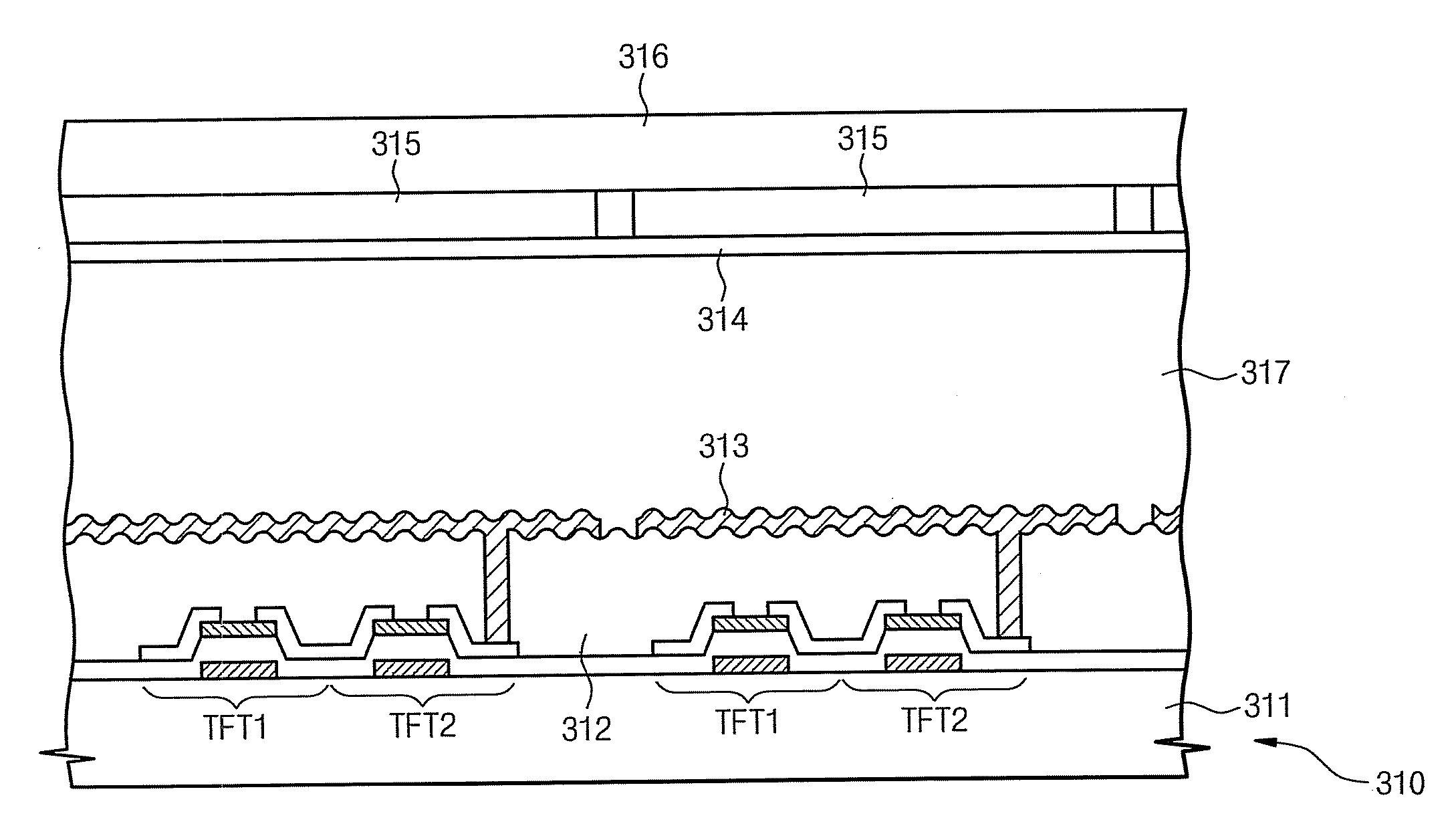
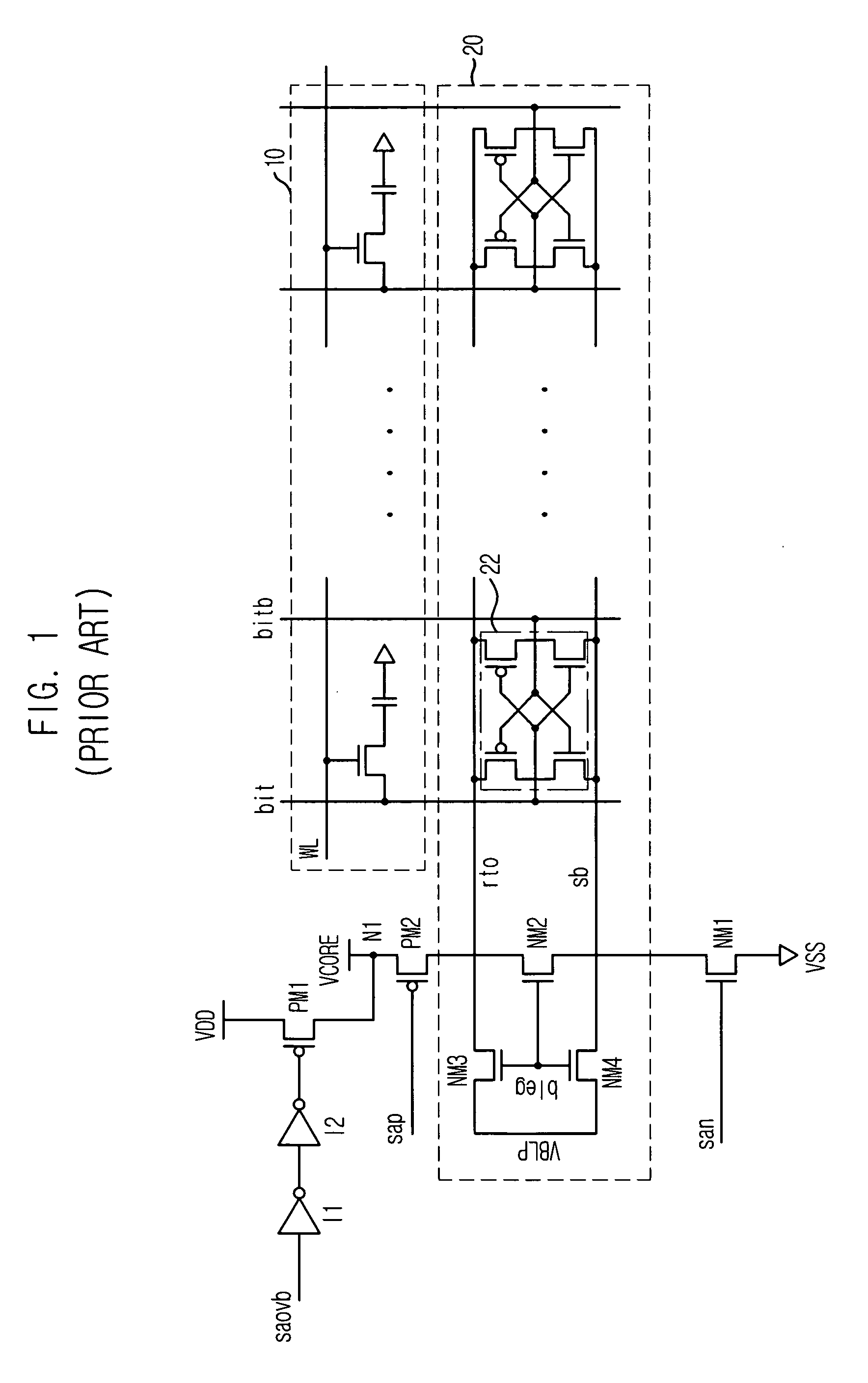
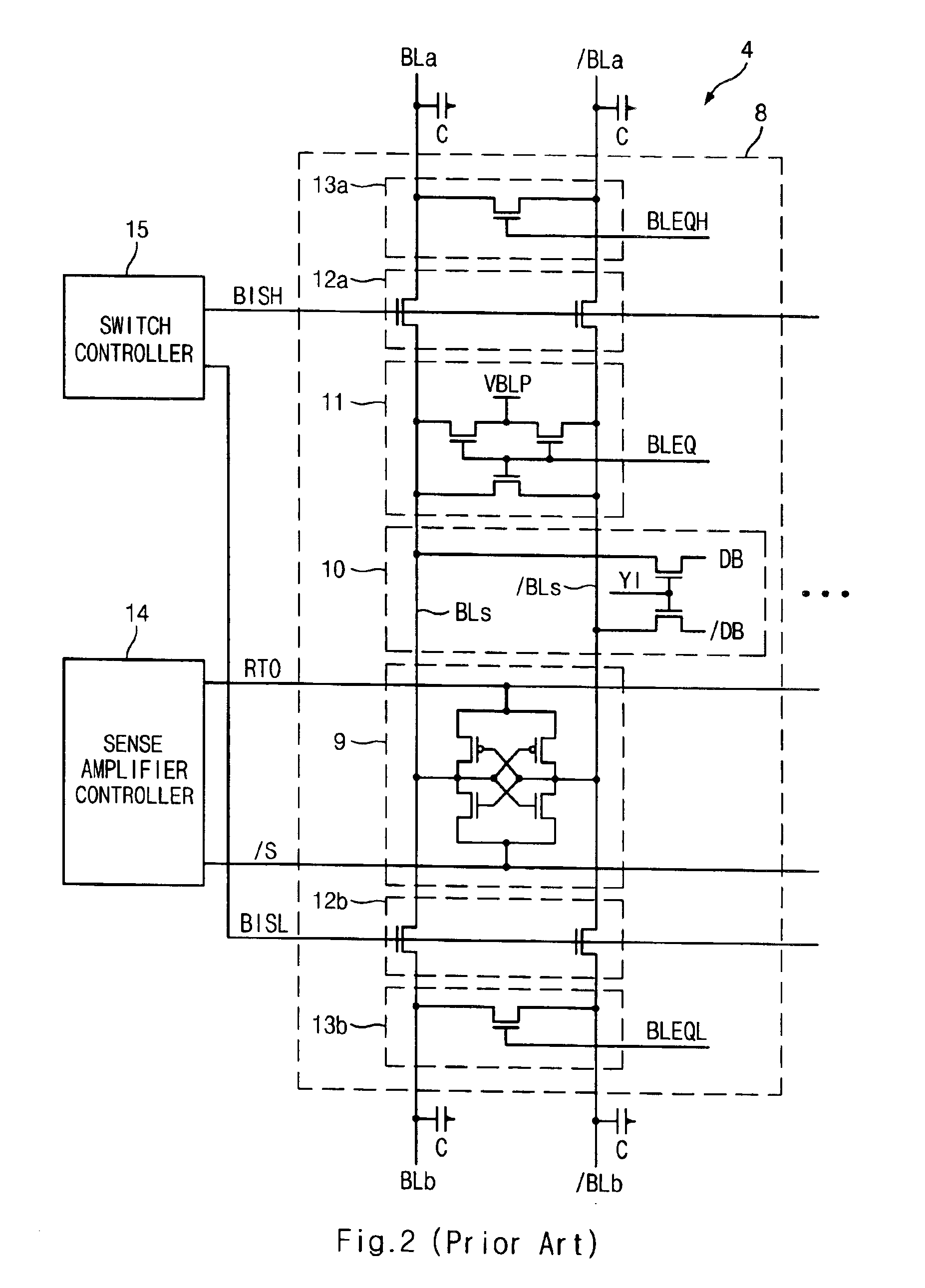
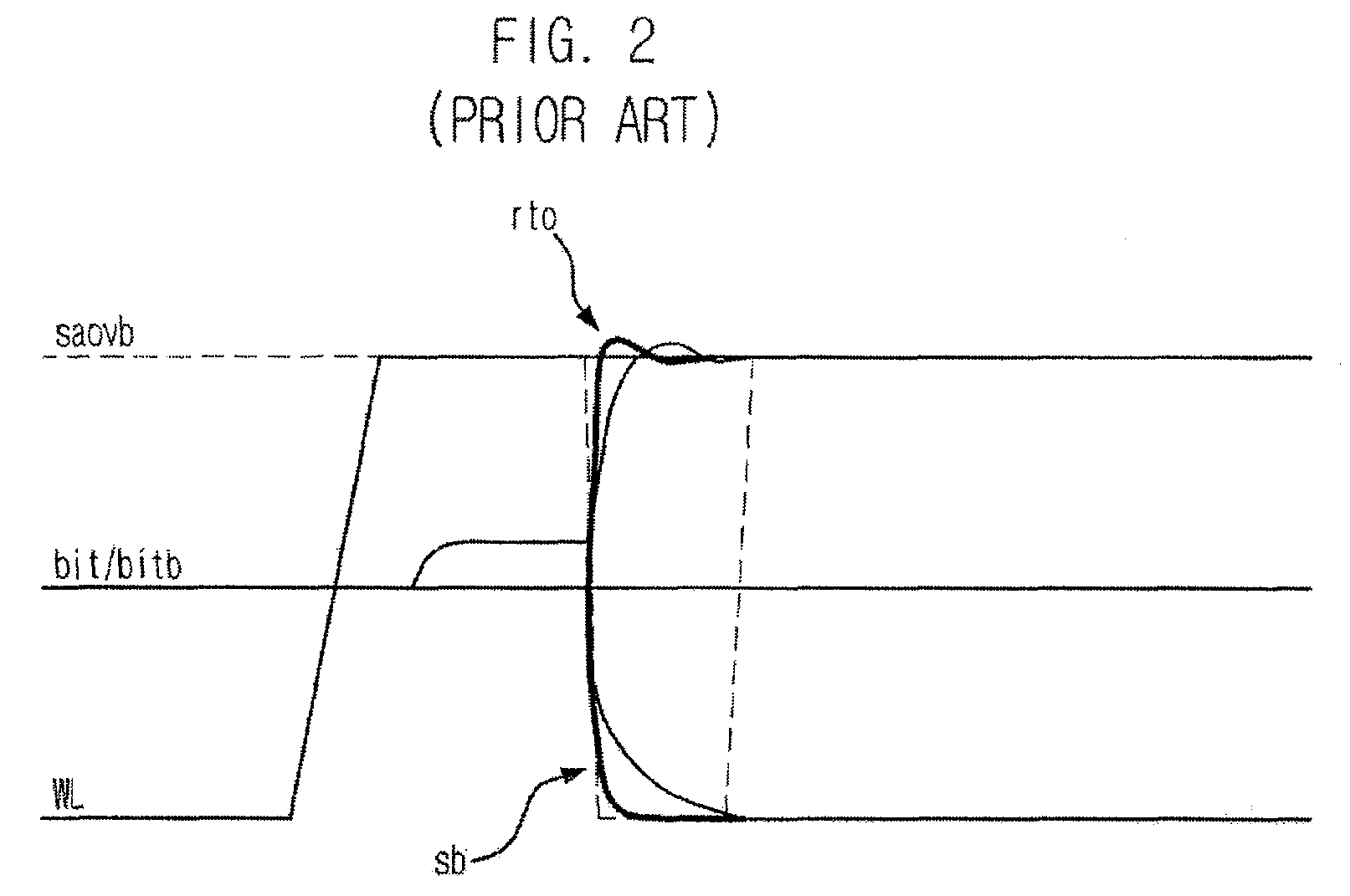
Sense amplifier and driving method thereof, and semiconductor memory device having the sense amplifier
InactiveUS20090147604A1Drive capability can be improvedLayout improvementDigital storageAudio power amplifierBack bias
The semiconductor memory device includes a bank having a cell array and a sense amplifier. A back bias voltage generating unit supplies a back bias voltage to the cell array of the bank. A negative drive voltage generating unit generates negative driving voltages including a normal pull-up voltage, an overdrive voltage, a normal pull-down voltage, and a negative voltage and supplies the negative driving voltages to the sense amplifier of the bank. A switching unit opens a connection between the back bias voltage generating unit and the negative drive voltage generating unit when in active mode and shares the back bias voltage between the back bias voltage generating unit and the negative drive voltage generating unit when in a refresh mode, in response to an external command.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Display device and gate drive circuit and gate drive unit circuit thereof
ActiveCN104732904ADrift Speed SuppressionExtend working lifeStatic indicating devicesWorking lifeDisplay device
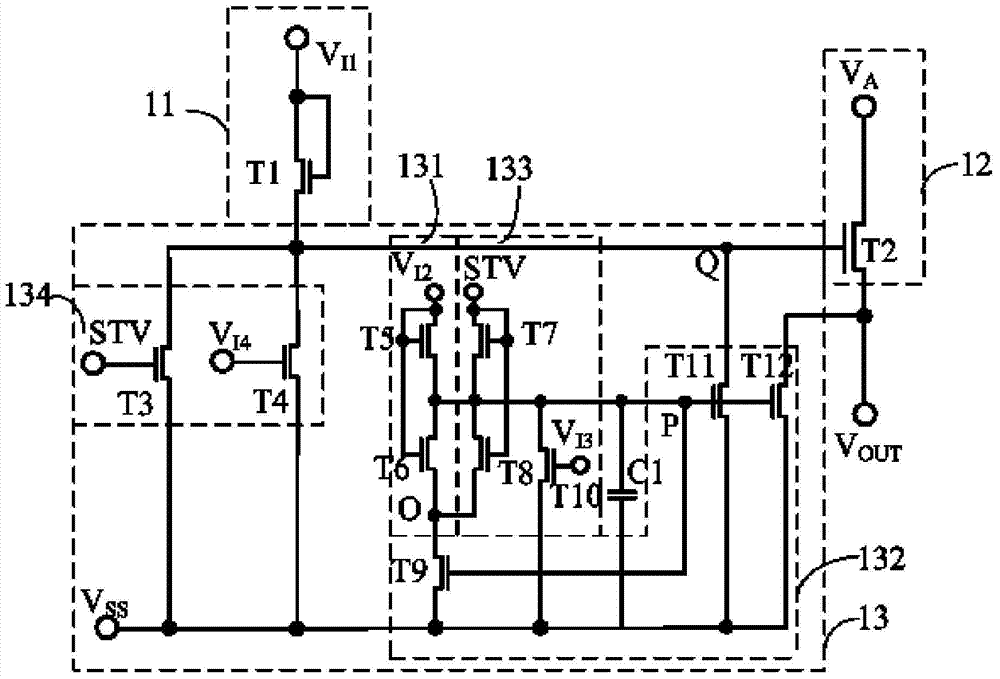
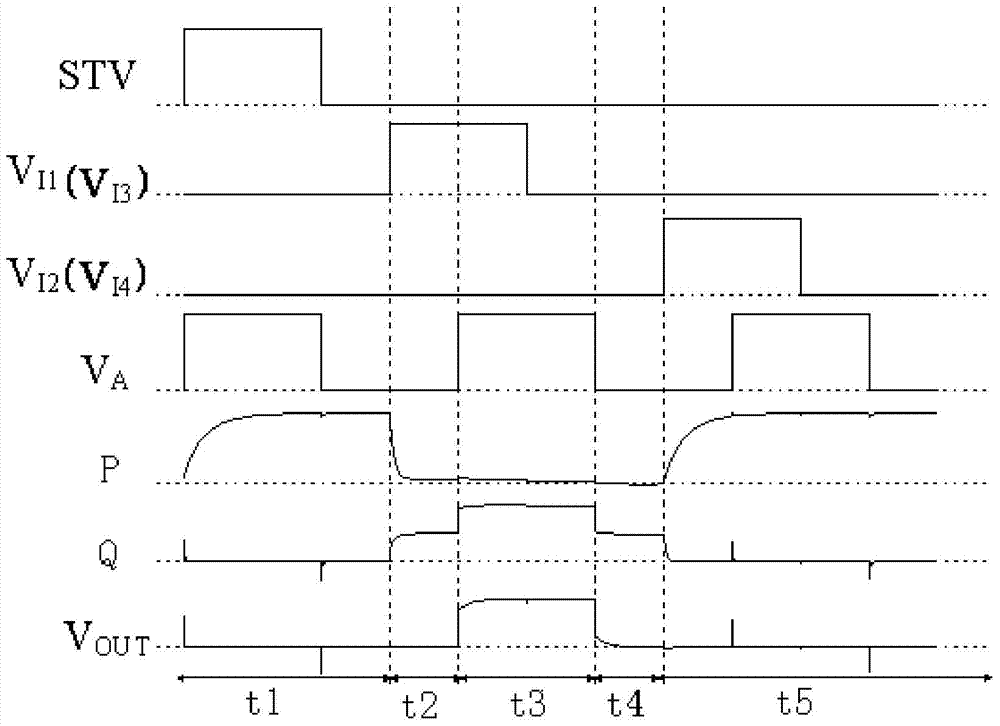
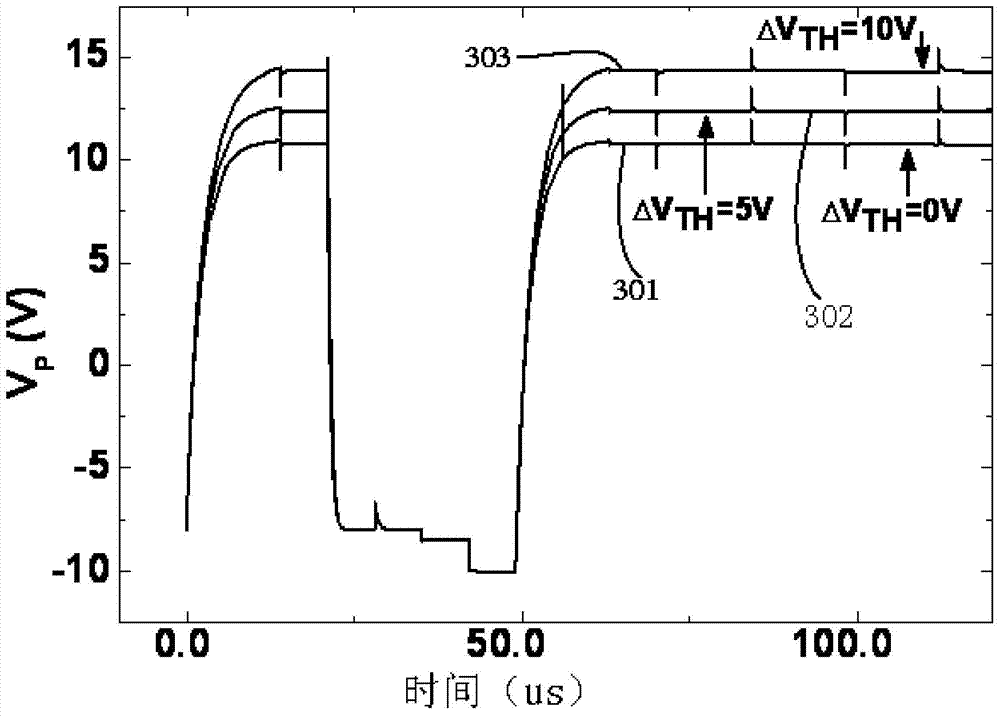
The invention provides a display device and a gate drive circuit and a gate drive unit circuit thereof, the gate drive unit circuit comprises an input module, a driving module and a low level maintaining module, and the low level maintaining module comprises a first charging unit and a threshold voltage self compensating unit. The voltage of a second node P in the threshold voltage self compensating unit changes along with the threshold voltage of a drop-down transistor in the low level maintaining module in a self-adaptive mode, therefore, the gate overdrive voltage of the drop-down transistor maintains a constant value, the drift amplitude of the threshold voltage of the drop-down transistor is increased, due to the fact that the overdrive voltage value is small, and the drift speed of the threshold voltage of the drop-down transistor is restrained, the gate drive unit circuit has the advantage of being long in working life.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Liquid crystal display driving method, liquid crystal display and display device
InactiveCN105913825AGuaranteed picture qualityIncrease charging rateStatic indicating devicesVoltage amplitudeDisplay device
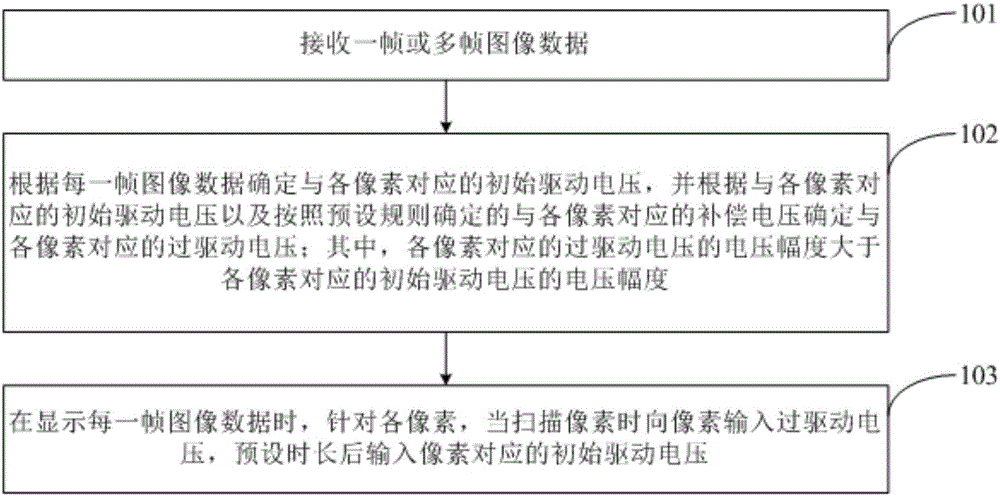
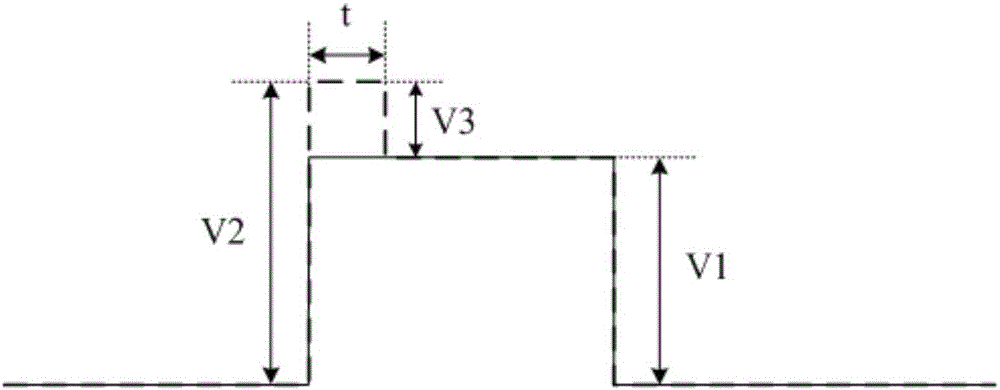
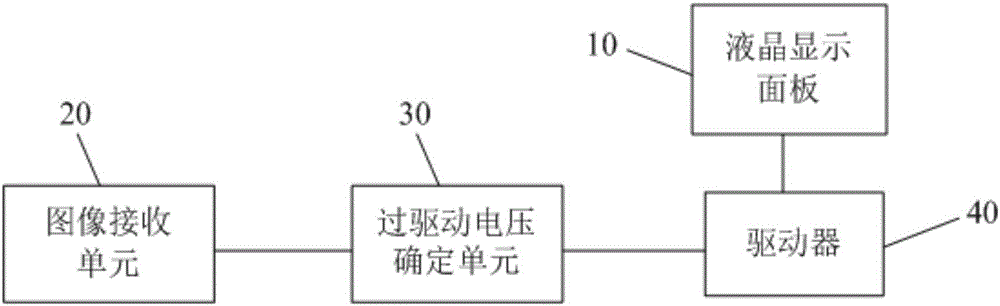
The invention discloses a liquid crystal display driving method, a liquid crystal display and a display device. In display of image data of each frame, overdrive voltage with voltage amplitude greater than preset duration of the voltage amplitude of an initial driving voltage is firstly applied to each pixel so that liquid crystal molecules approach to a target deflecting angle, and then corresponding initial driving voltage is applied to each pixel so that the liquid crystal molecules quickly reach the target deflecting angle to improve the charging rate of the pixel, thus ensuring the picture quality of the liquid crystal display.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Liquid crystal display device, method of driving the same, and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080013007A1Static indicating devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
In a liquid crystal display device includes; a plurality of pixels arranged substantially in a matrix pattern; wherein each of the plurality of pixel includes; first and second thin film transistors including current paths connected to a source line in series, a storage capacitor line, a first capacitor connected between the first and second thin film transistors and connected to the storage capacitor line, a second capacitor connected between one of the source and the drain of the second thin film transistor and a pixel electrode and connected to the storage capacitor line, and a third capacitor including the pixel electrode, a common electrode, and a liquid crystal between the pixel electrode and the common electrode, wherein an overdrive voltage Vover satisfying equation Vover=C 1C 2+C lc·Vsigis added to a display signal voltage Vsig and a resultant voltage is applied to the source line.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
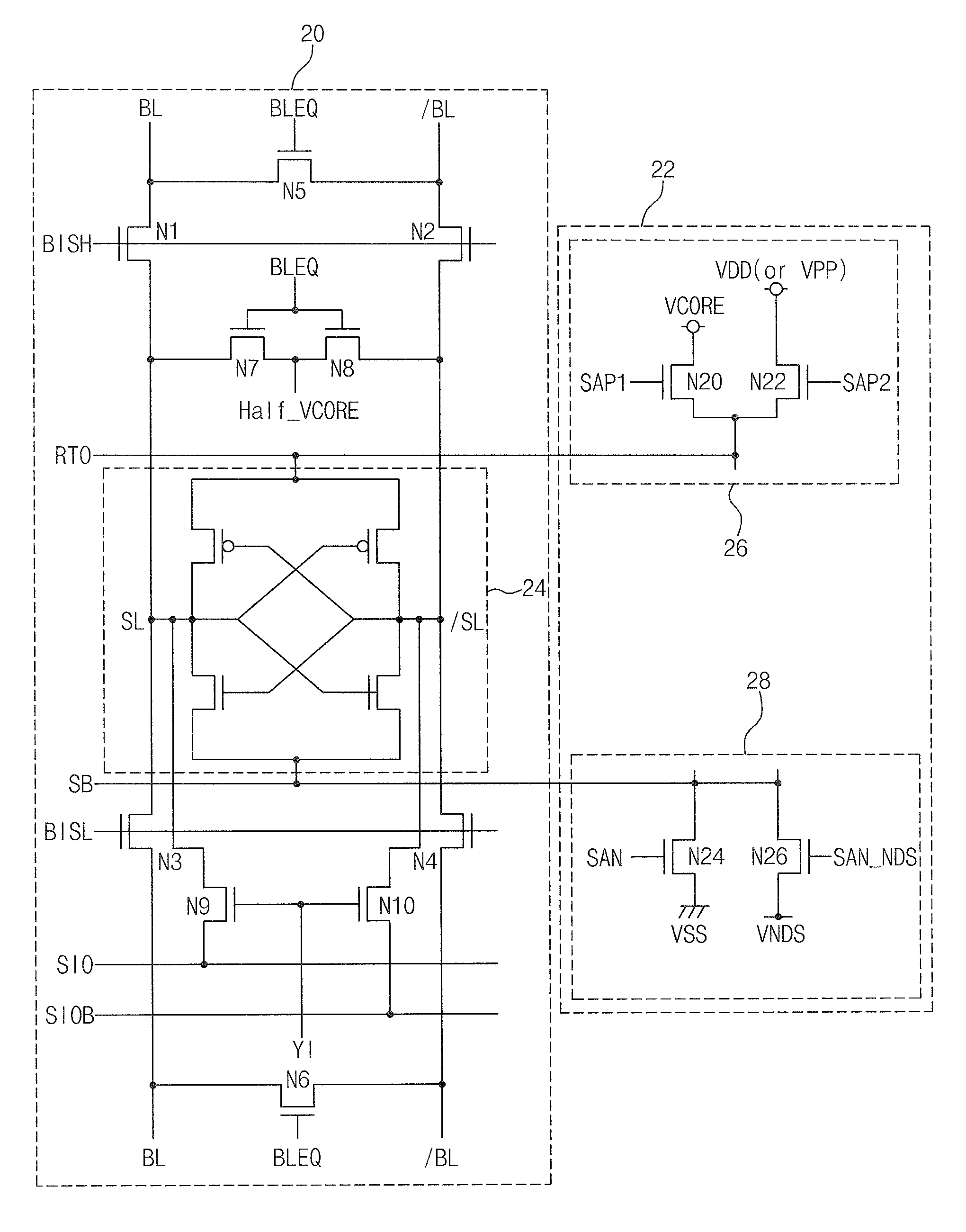
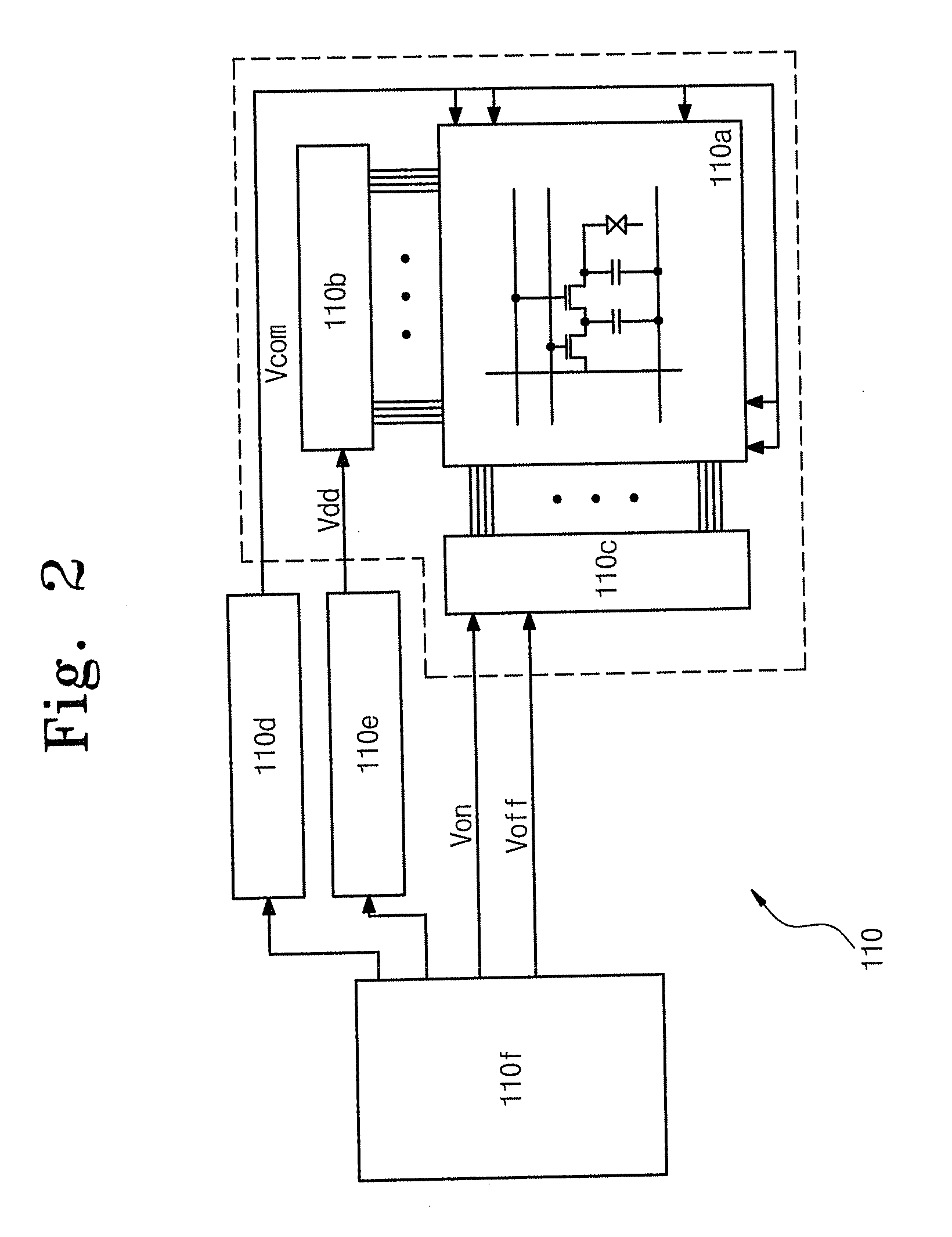
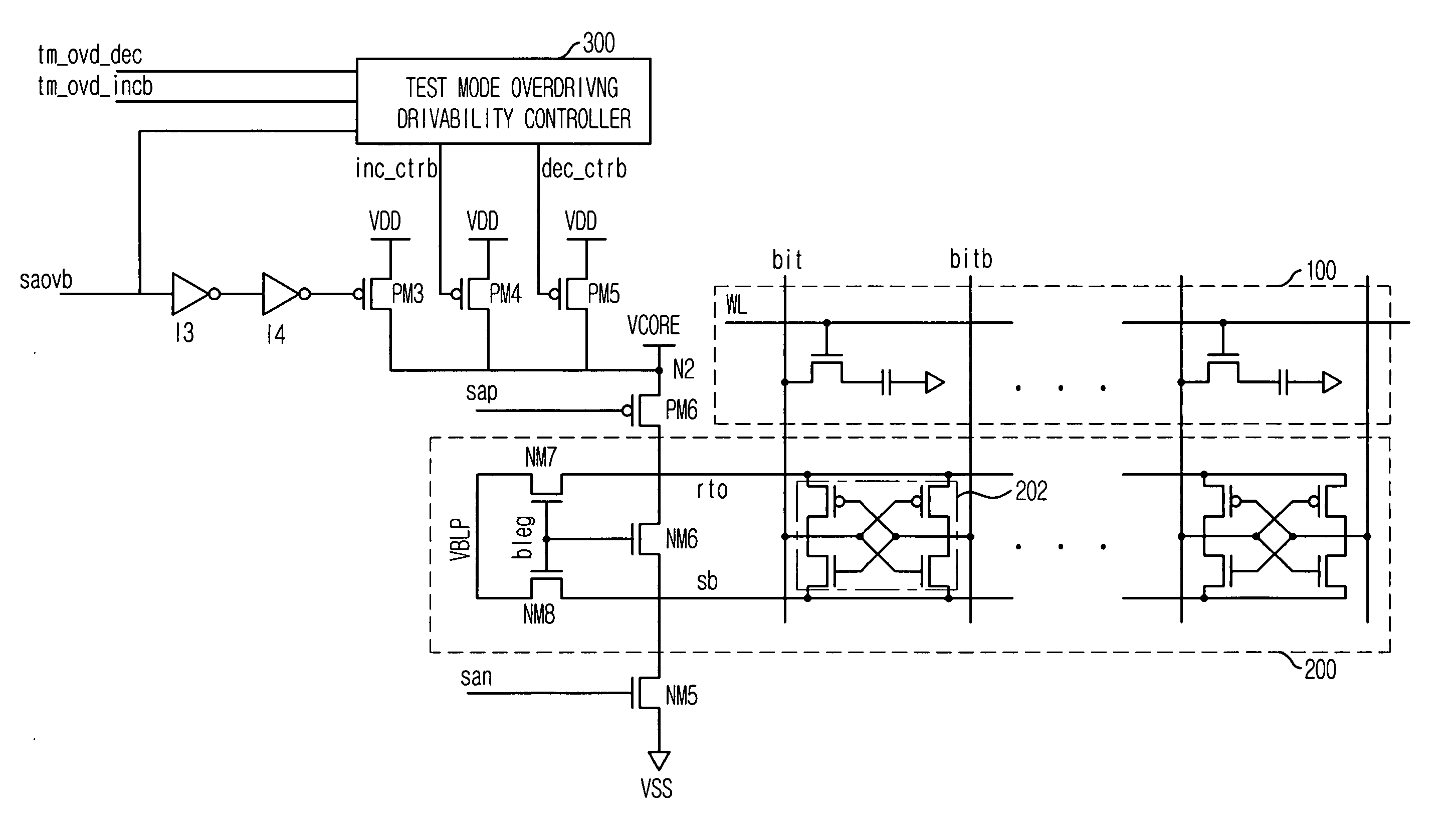
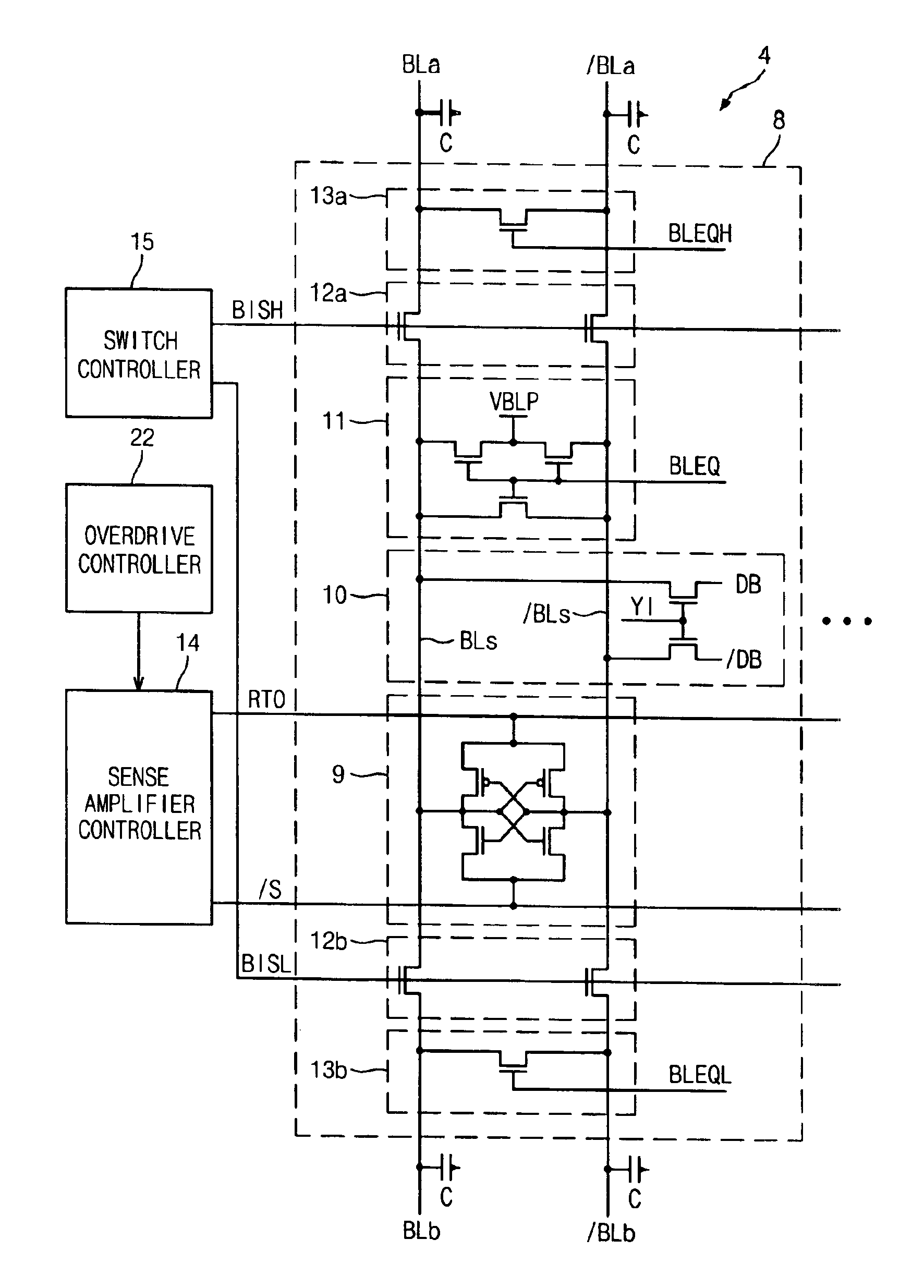
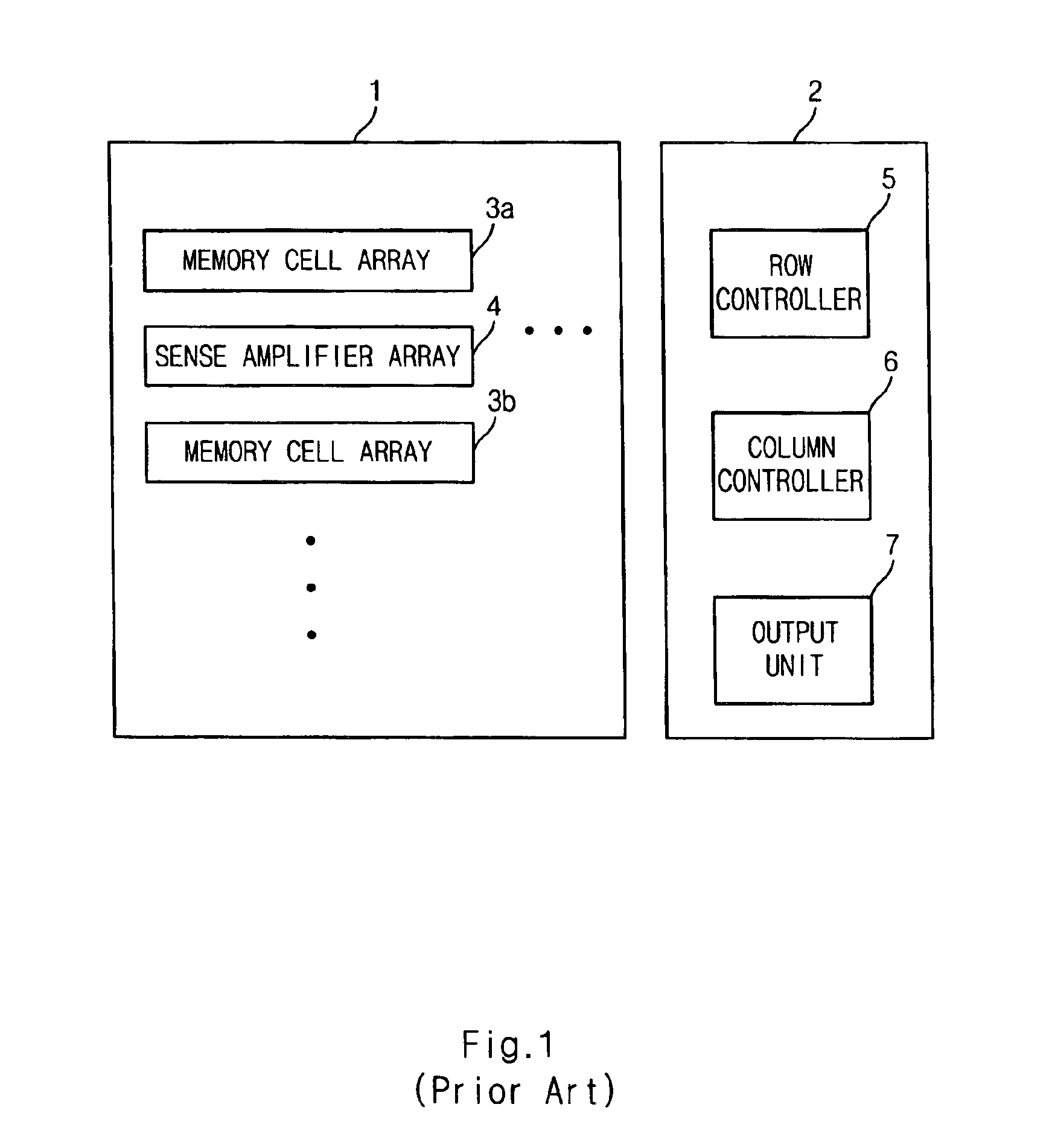
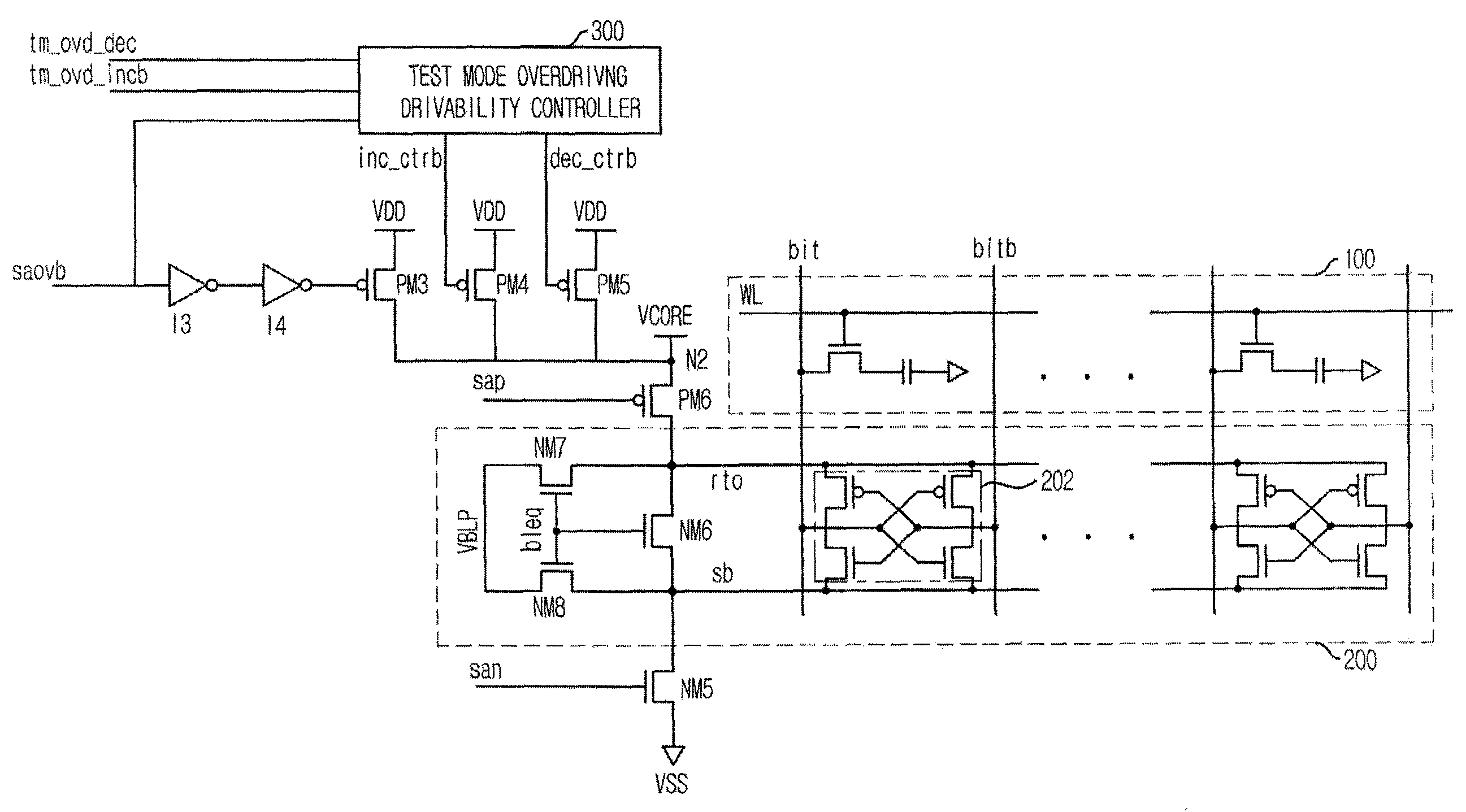
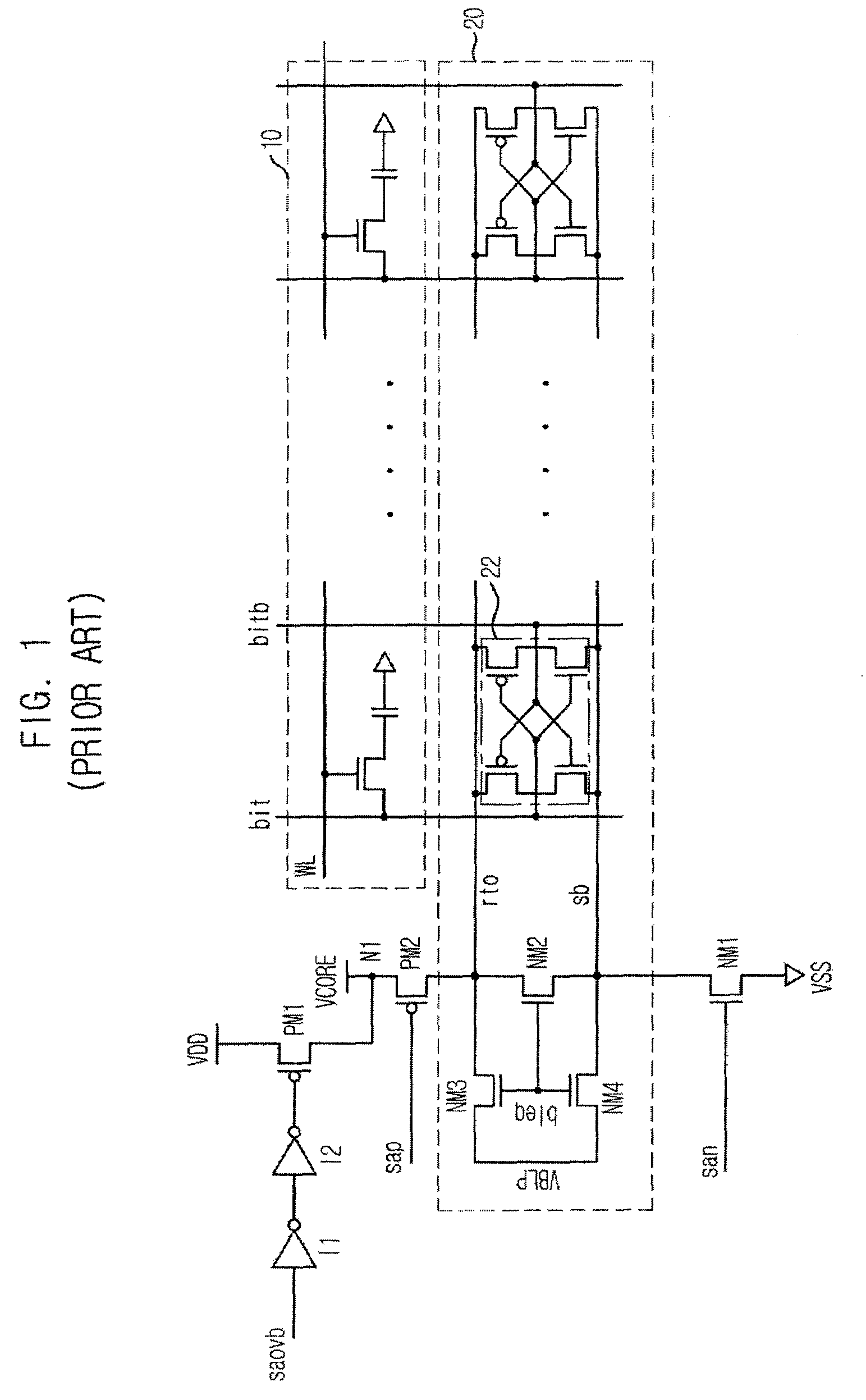
Semiconductor memory device capable of controlling drivability of overdriver
A semiconductor memory device capable of controlling a drivability of an overdriver is provided. The semiconductor memory device includes: a first power supply for supplying a normal driving voltage; a memory cell array block; a bit line sense amplifier block for sensing and amplifying voltage difference between bit line pair of the memory cell array block; a first driver for driving a power supply line of the bit line sense amplifier block to a voltage of a node connected with the first power supply in response to a driving control signal; a plurality of second drivers for driving the node to an overdriving voltage higher than the normal driving voltage; and an overdriving drivability controller for selectively activating the second drivers in response to a test-mode drivability control signal inputted during an activation period of an overdriving signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Semiconductor memory device having sense amplifier and method for overdriving the sense amplifier
A semiconductor memory device comprises a plurality of memory cell arrays, a plurality of sense amplifiers, a connection unit, a driver and an over-driver. The plurality of memory cell arrays comprise a plurality of memory cells. The plurality of sense amplifiers sense and amplify data stored in the plurality of memory cells. The connection unit selectively connects the plurality of sense amplifiers to the plurality of memory cell arrays. The driver drives the sense amplifier to a predetermined voltage. The over-driver applies an overdrive voltage to the driver for a predetermined time after the sense amplifier is temporarily separated from the selected memory cell array. In the semiconductor device since data in a bitline can be rapidly amplified, the restoration time of data stored in a memory cell is reduced, and the parameter tRCD. Accordingly, the operation speed of the semiconductor memory device can be improved.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
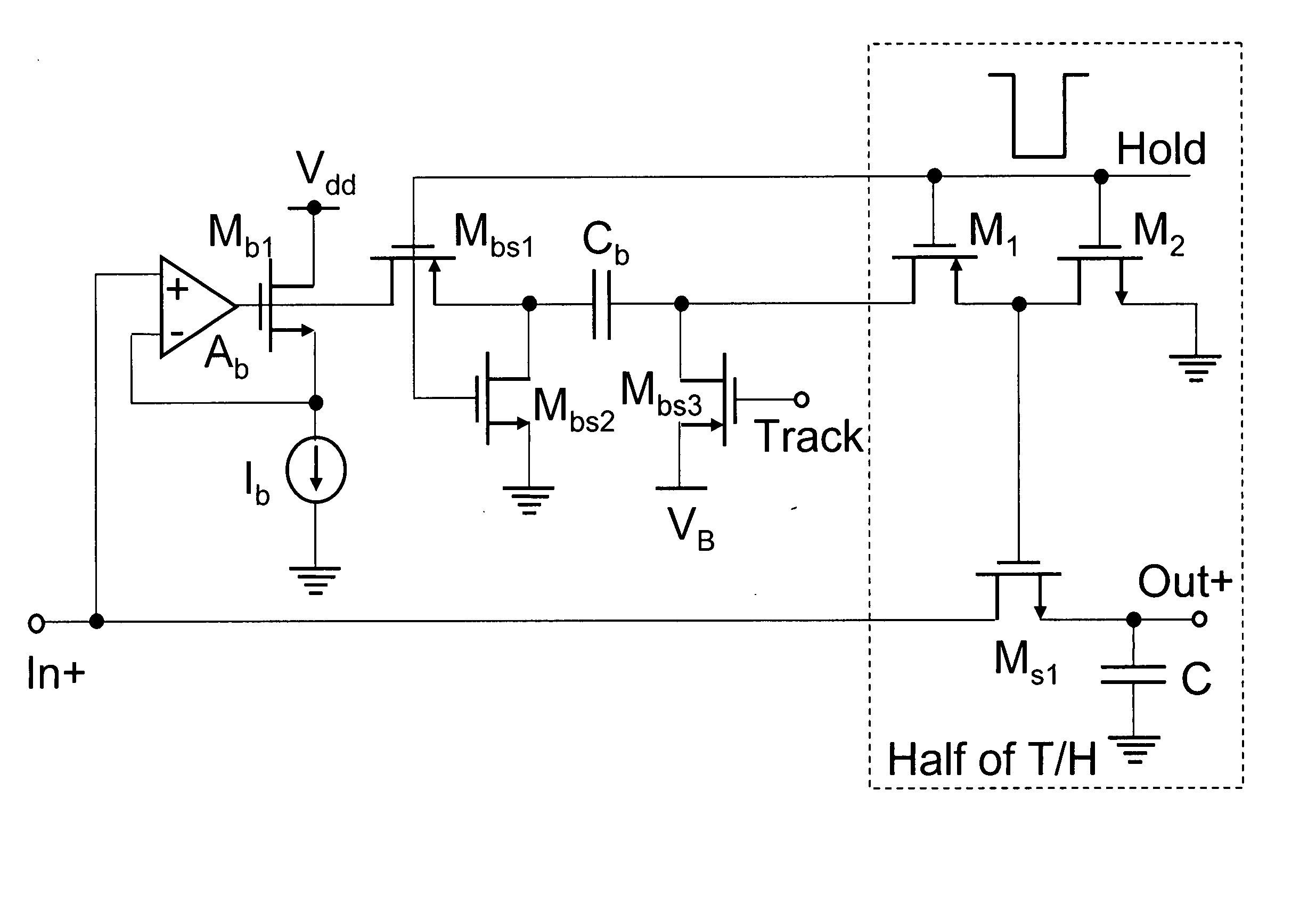
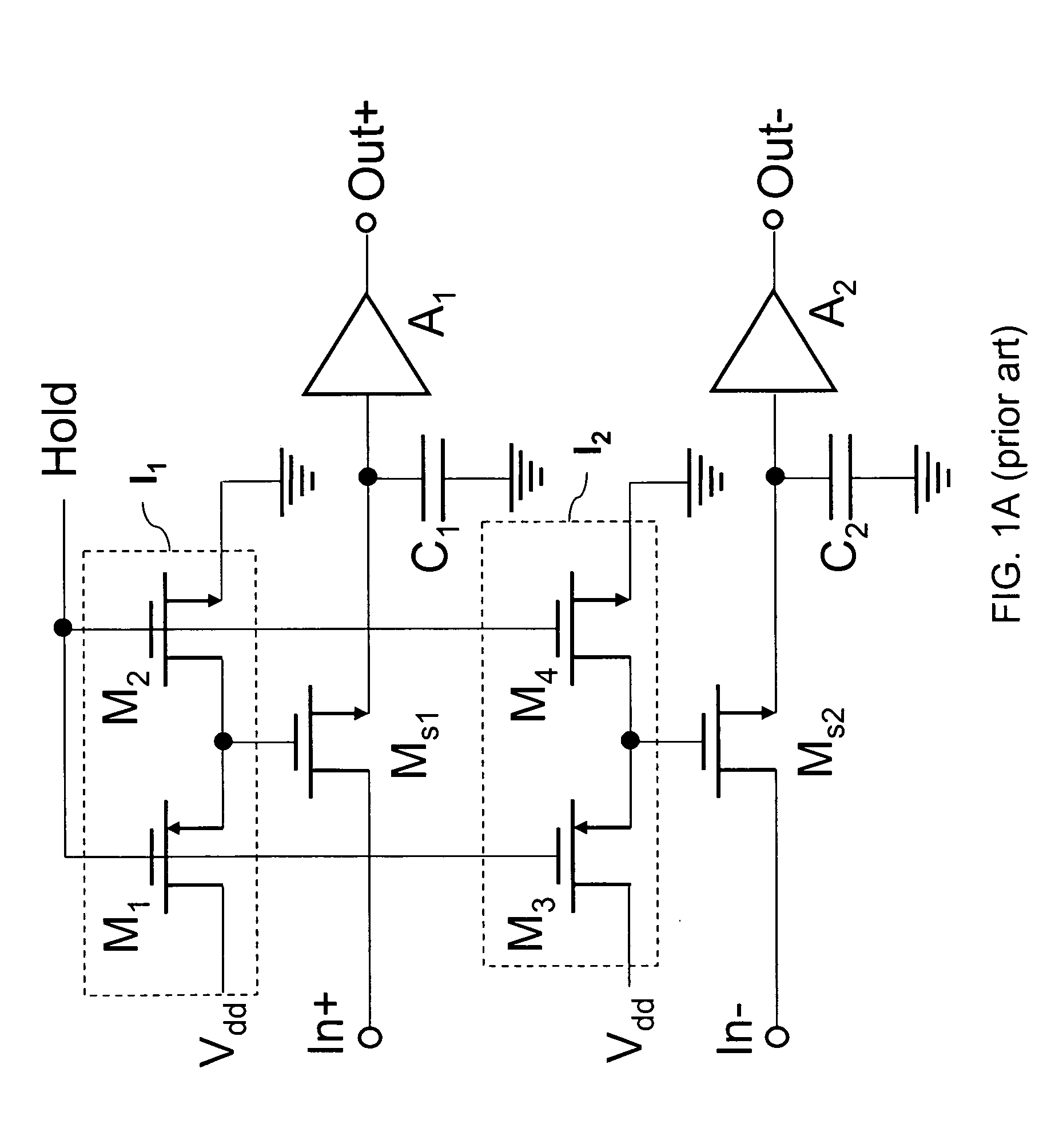
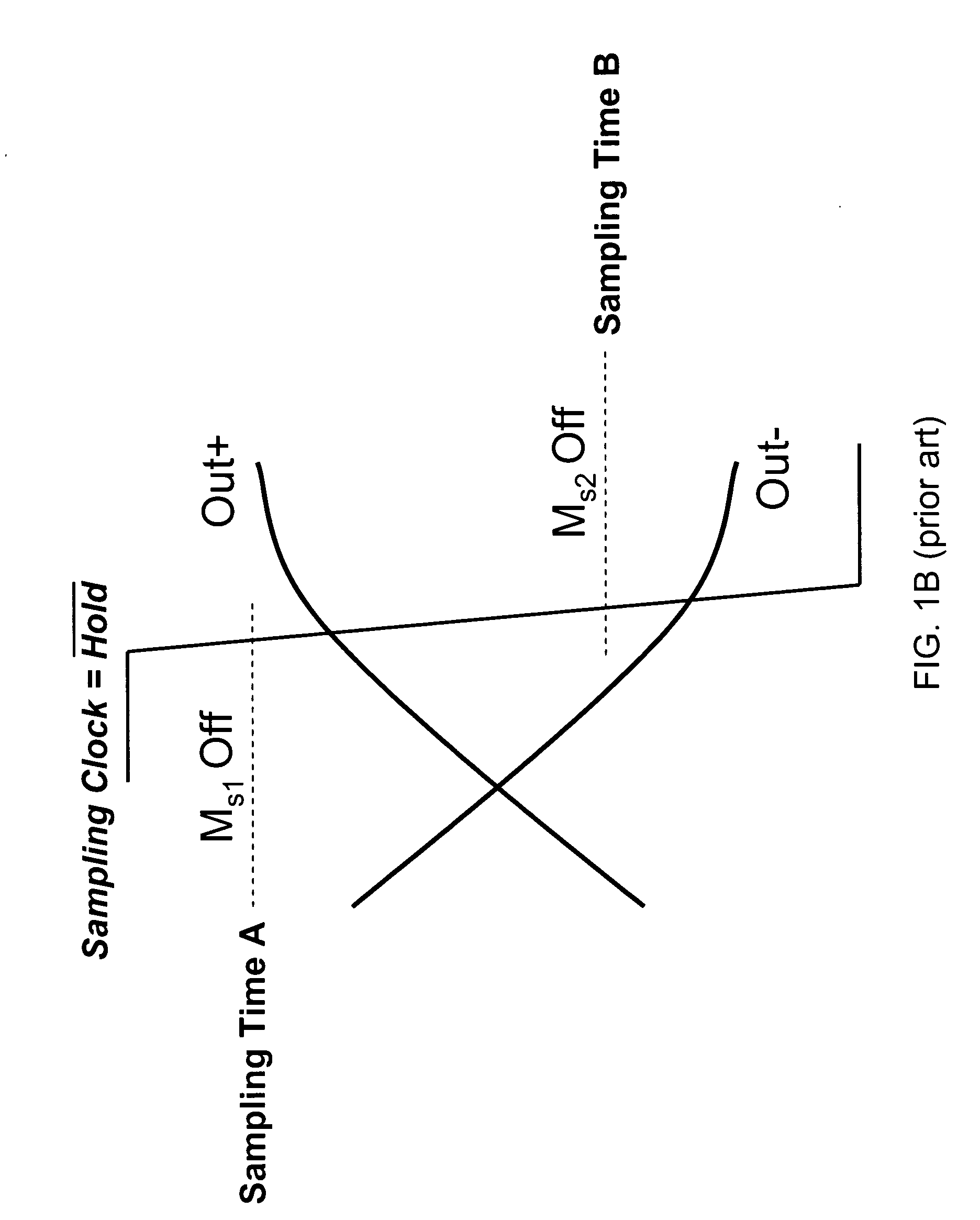
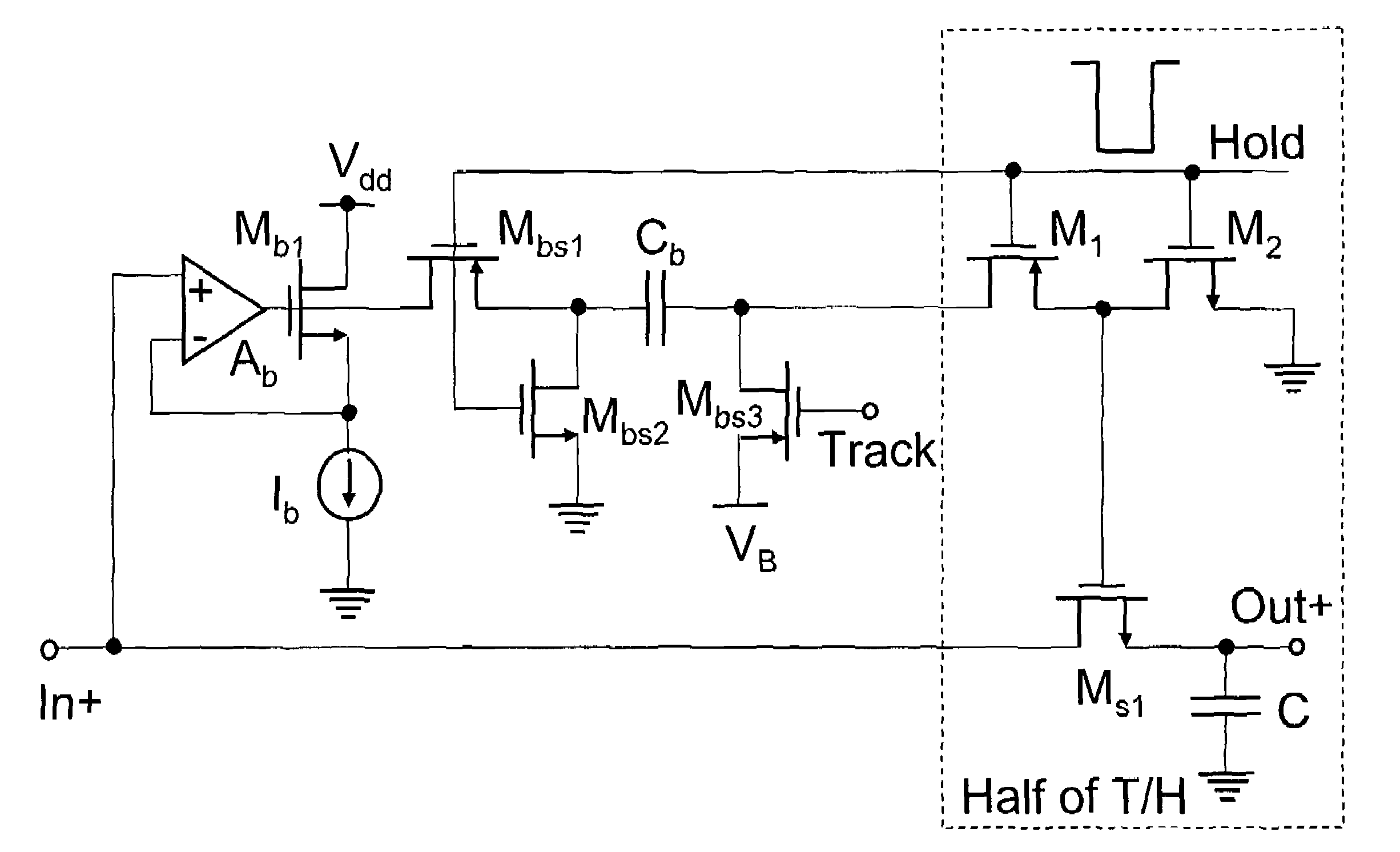
Switch linearized track and hold circuit for switch linearization
Circuits that provide a gate boost to address non-linear threshold voltage variation in a CMOS T / H circuit. In embodiments of the invention, a boost capacitor and a feedback amplifier add a signal-dependent threshold voltage to the switch gate over-drive voltage of a switch that controls track and hold circuit sampling. In a modified embodiment, capacitive boost is omitted and the feedback amplifier provides the signal-dependent threshold voltage boost. In another embodiment, a boost capacitor and a diode connected transistor provide the signal-dependent threshold voltage boost. In a modified embodiment, capacitive boost is omitted and the diode connected transistor provides the signal-dependent threshold voltage.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
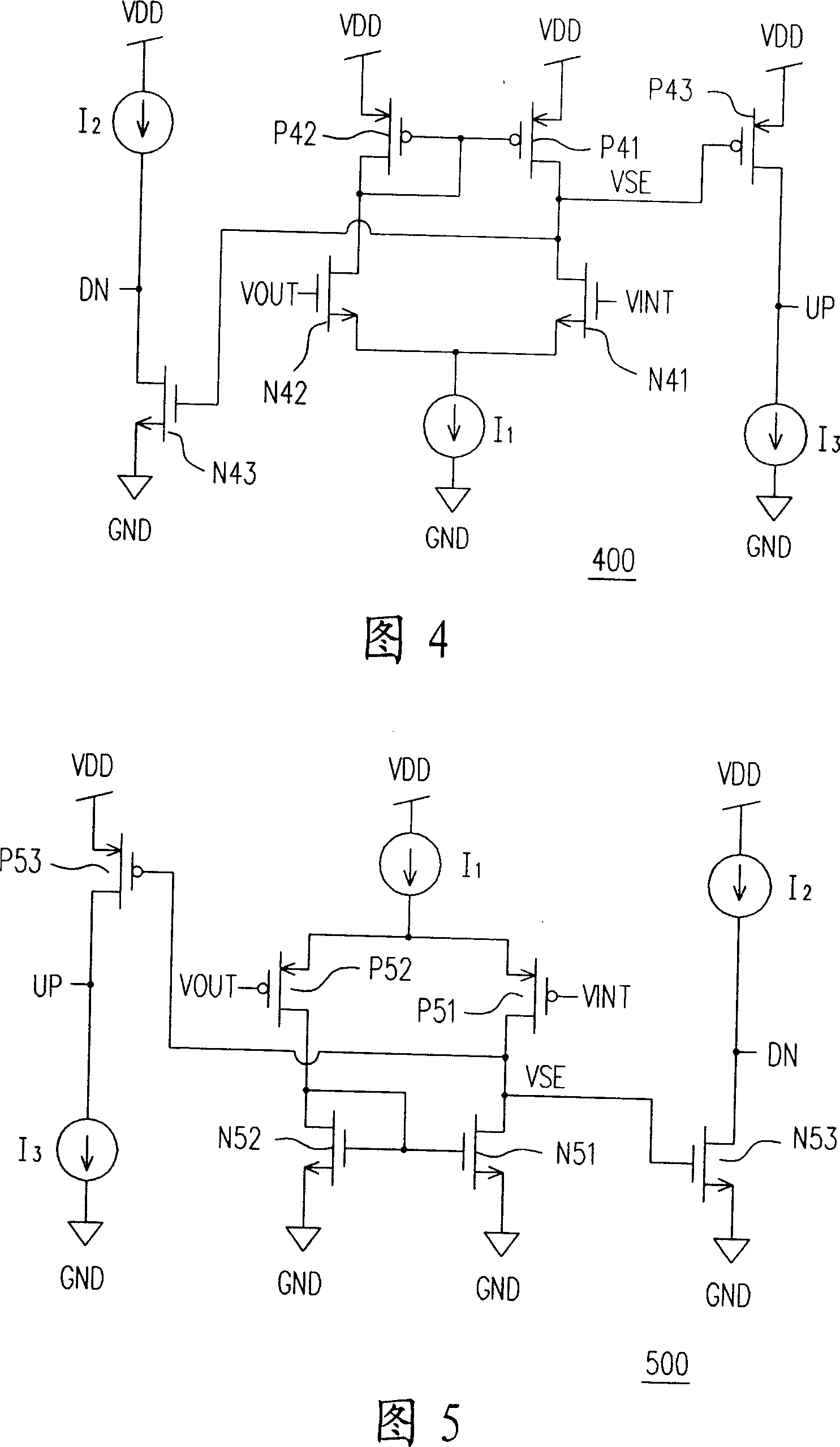
Biasing Scheme for Low-Voltage MOS Cascode Current Mirrors
ActiveUS20080186101A1Easy to trackAmplifier detailsElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierLow voltage
A circuit and a method for biasing a compound cascode current mirror (CCCM) that enables high-voltage swing at the output and accurate current mirroring is presented. The CCCM has mirror transistors and cascode transistors which may be of a different technology kind. The drain-source voltage Vds of the mirror transistor on the input leg of the CCCM is held at a voltage Vov that is generated by the biasing circuit; Vov is the overdrive voltage of the input mirror transistor of the CCCM and the value of Vov is maintained by the bias circuit and a feed-back amplifier such that the mirror transistor remains on the edge of its active region, over manufacture deviations and tracks even over operational conditions such as temperature and supply variations. The feed-back amplifier drives the gates of the cascode transistors and uses its feedback node to hold the Vds at Vov.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Liquid crystal display device and driving method thereof
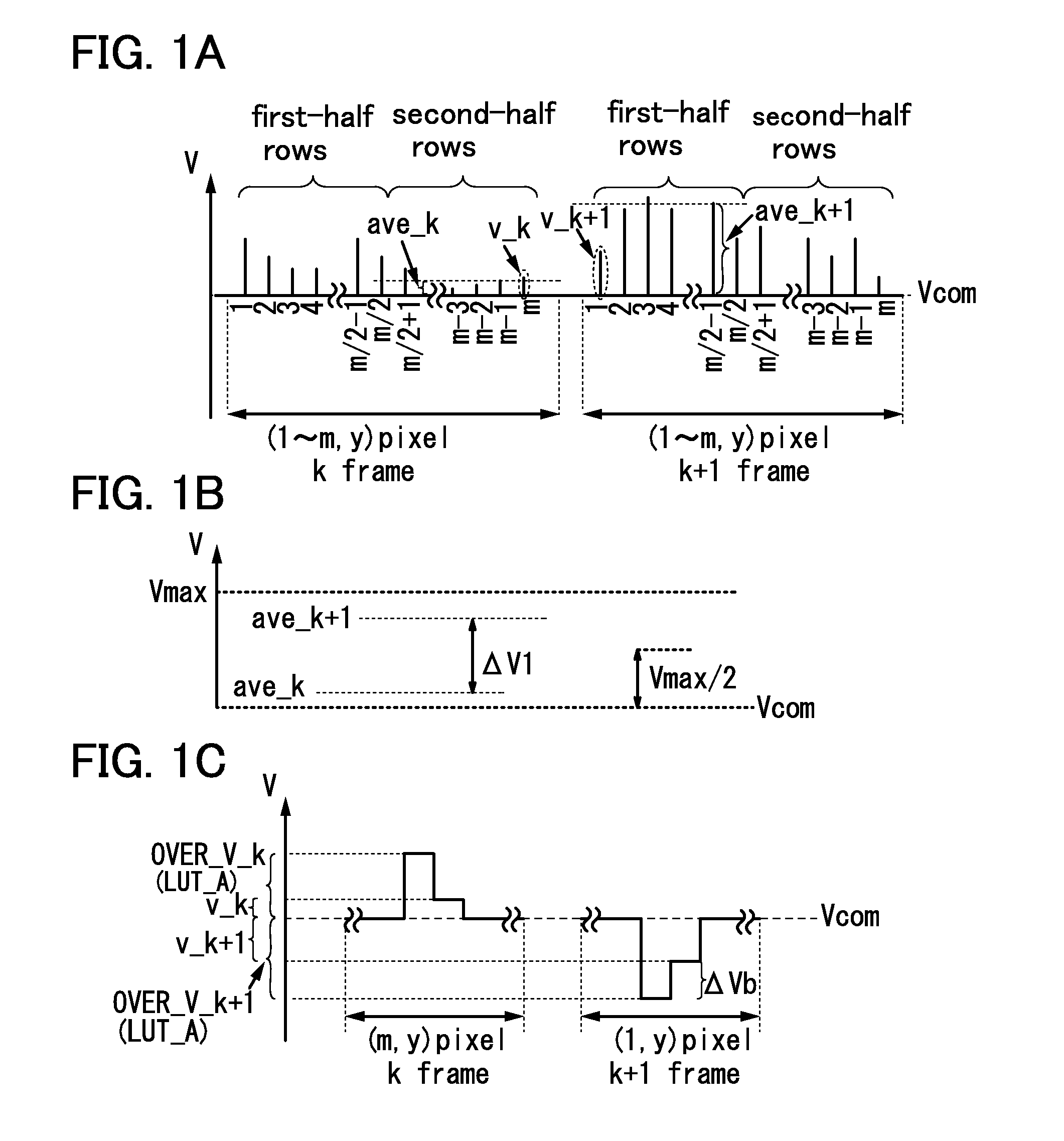
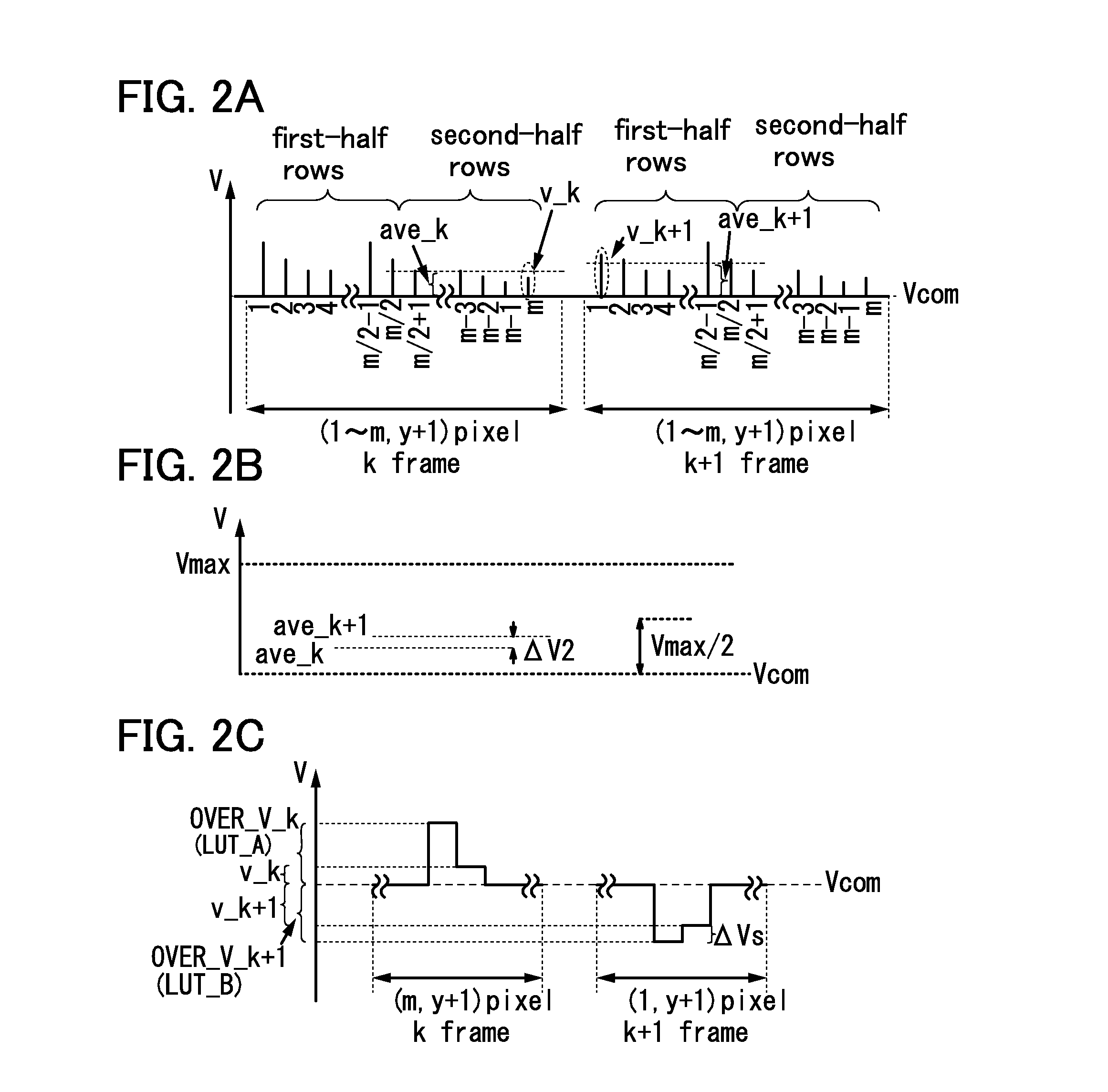
ActiveUS20140104262A1Prevent display quality degradationIncrease opening ratioCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayComparators circuits
In a video voltage comparator circuit, an average of first video voltages applied to pixel electrodes of pixels in the second-half rows in a k-th frame period (k is a natural number) is compared with an average of second video voltages applied to pixel electrodes of pixels in the first-half rows in a (k+1)th frame period for each row. In an overdrive voltage switching circuit, when a difference obtained from the comparison in the video voltage comparator circuit is greater than or equal to a threshold value, the overdrive voltage in the (k+1)th frame period is switched to a first overdrive voltage, and when the difference obtained from the comparison in the video voltage comparator circuit is less than the threshold value, the overdrive voltage in the (k+1)th frame period is switched to a second overdrive voltage lower than the first overdrive voltage.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device capable of controlling drivability of overdriver
A semiconductor memory device capable of controlling a drivability of an overdriver is provided. The semiconductor memory device includes: a first power supply for supplying a normal driving voltage; a memory cell array block; a bit line sense amplifier block for sensing and amplifying voltage difference between bit line pair of the memory cell array block; a first driver for driving a power supply line of the bit line sense amplifier block to a voltage of a node connected with the first power supply in response to a driving control signal; a plurality of second drivers for driving the node to an overdriving voltage higher than the normal driving voltage; and an overdriving drivability controller for selectively activating the second drivers in response to a test-mode drivability control signal inputted during an activation period of an overdriving signal.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
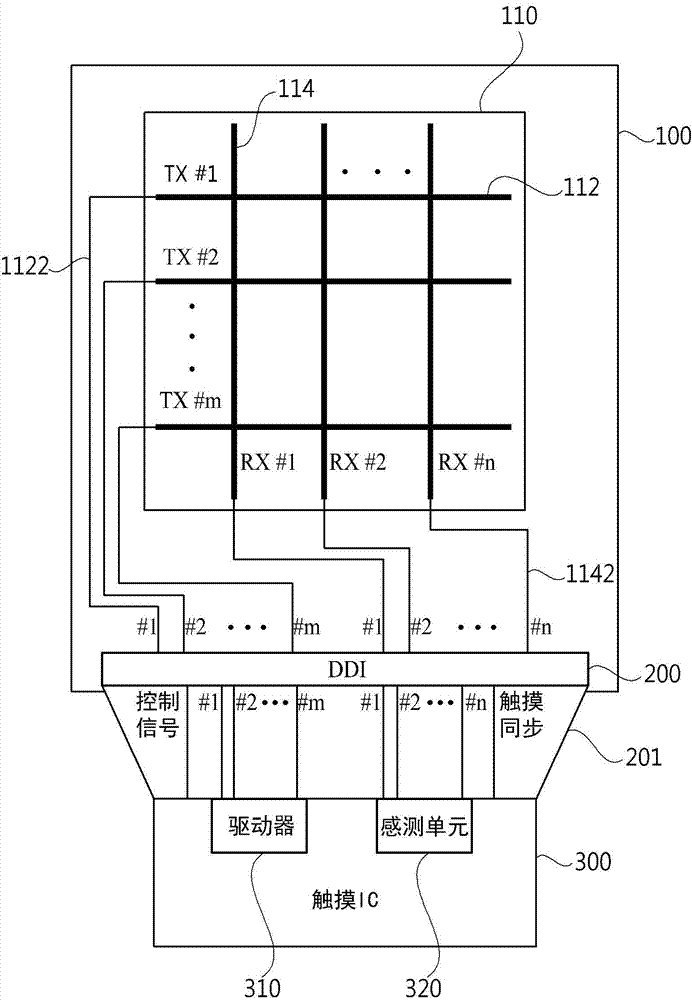
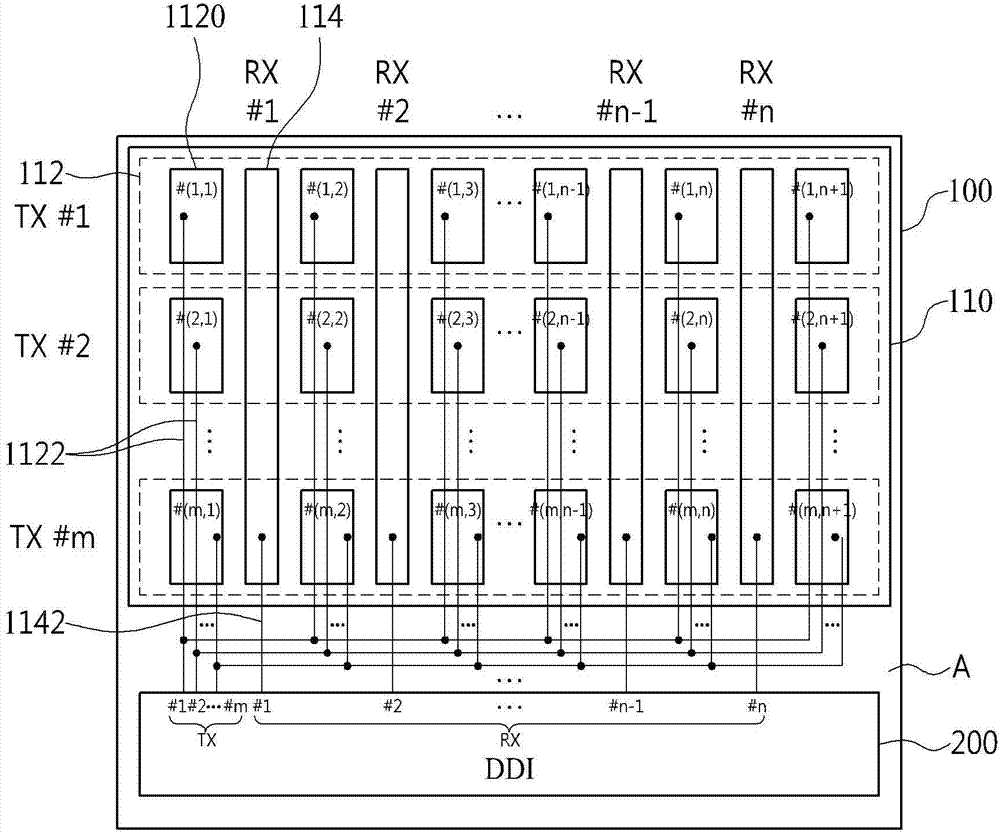
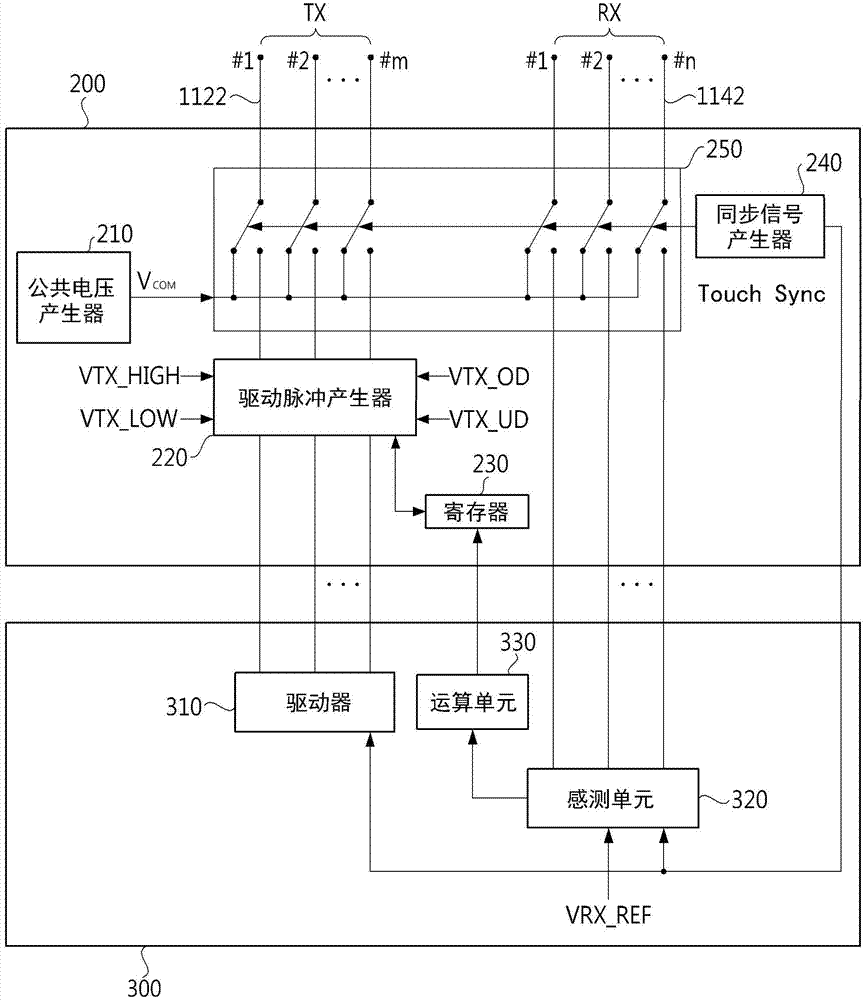
Display device with integrated touch screen and driving method thereof
ActiveCN104731402ACathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingTouchscreenDriving mode
Disclosed is a display device with integrated touch screen (110). The display device includes a panel (100) configured to include a plurality of driving electrodes (112) and a plurality of sensing electrodes (114) and a display driver IC (200) configured to apply a common voltage to the plurality of driving electrodes (112) and the plurality of sensing electrodes (114) when the panel (100) operates in a display driving mode, and when the panel (100) operates in a touch driving mode, generate a driving pulse, which includes a maximum voltage with an overdriving voltage applied thereto and a minimum voltage with an under-driving voltage applied thereto, according to a timing pulse to apply the driving pulse to the plurality of driving electrodes (112), and respectively receive a plurality of sensing signals from the plurality of sensing electrodes (114).
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Overdrive apparatus for advancing the response time of a liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20090122052A1Short response timeReduce image sizeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayChipset
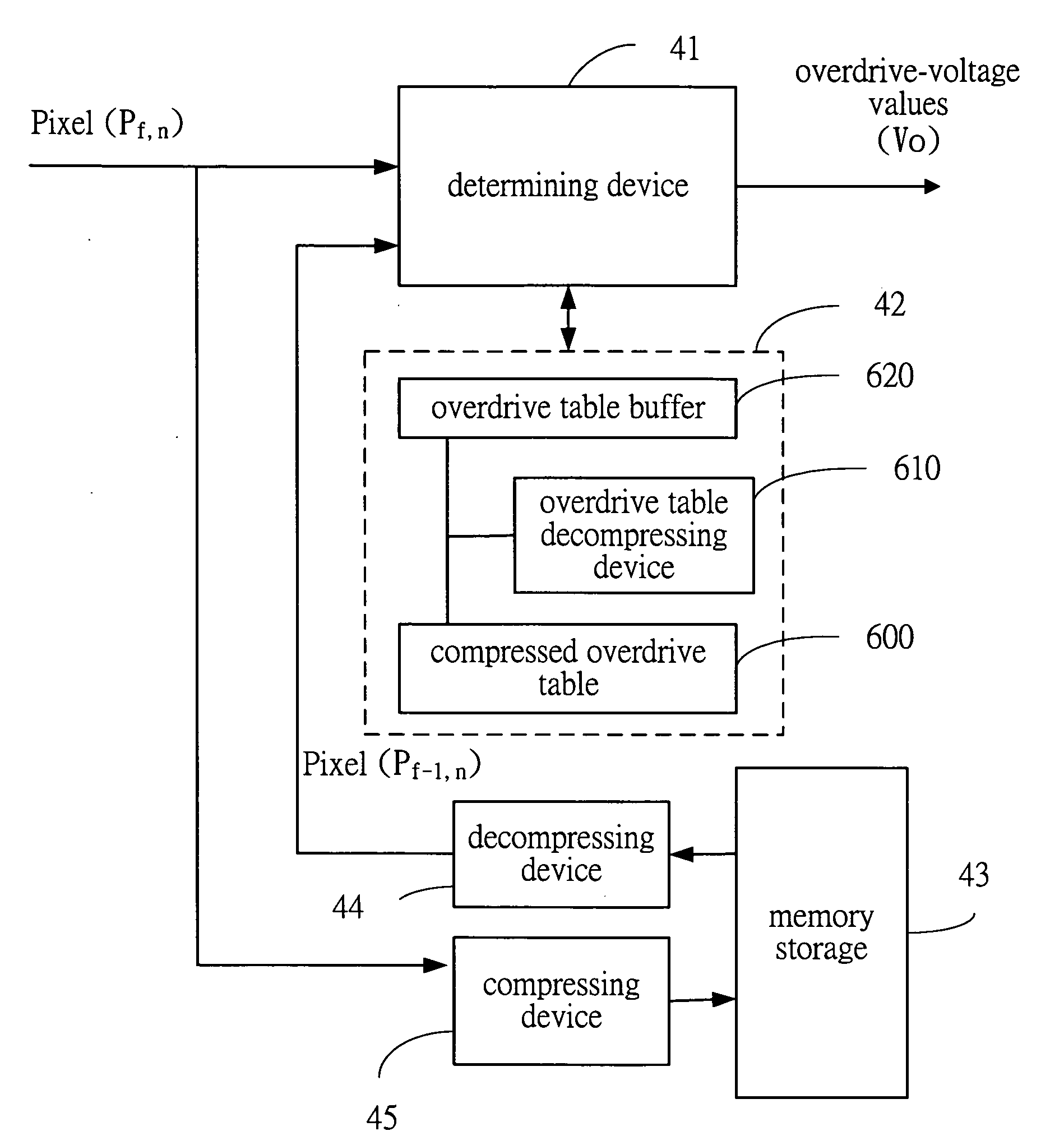
An overdrive apparatus for advancing the response time of a liquid crystal display (LCD) is disclosed, comprising a overdrive table, a memory storage, and a determining device, wherein the overdrive table is used for saving a plurality of overdrive-voltage values, the memory storage is used for saving a first frame, the determining device receives a first pixel, which is corresponding with a second pixel of the first frame, wherein the determining device can select an overdrive-voltage value from the overdrive table according to the first pixel and the second pixel, wherein the memory storage is provided within a first chipset, which comprises a first active face and a plurality of first bond pads provided on the first active face; the determining device is provided within a second chipset, which comprises a second active face and a plurality of second bond pads provided on the second active face, wherein the first chipset and the second chipset are stacked with each other, and the second bond pads are electrically connected to the first bond pads.
Owner:ETRON TECH INC
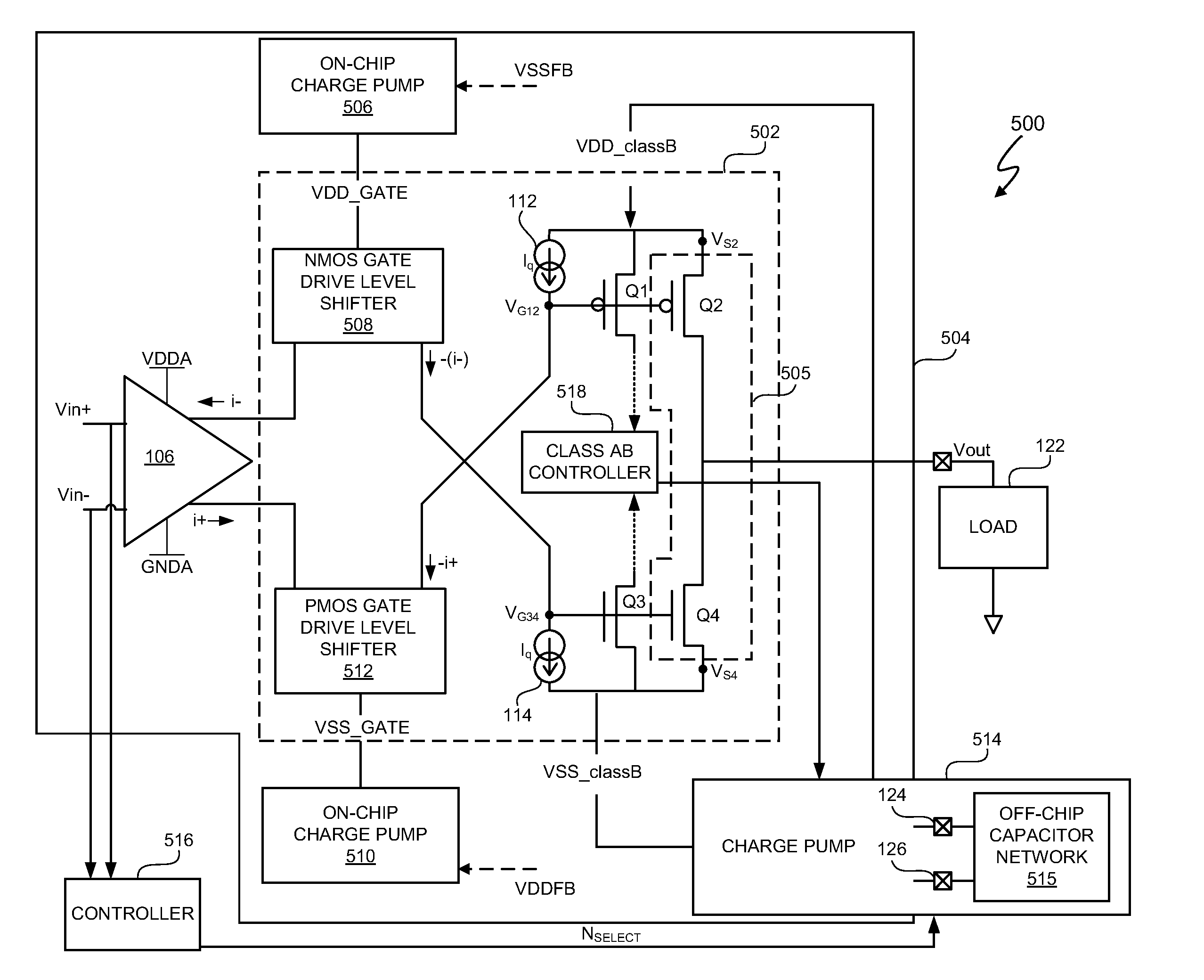
Gate-boosted, variable voltage supply rail amplifier
ActiveUS8008975B1Amplifier detailsAmplifiers with semiconductor devices onlyElectronic systemsAudio power amplifier
In at least one embodiment, an electronic system includes an amplifier having an on-chip charge pump to provide a gate boost voltage to boost a gate voltage of at least one on-chip field effect transistor (FET) of an output stage of an amplifier. In at least one embodiment, the gate boost voltage boosts the gate voltage higher than the supply voltage rail to increase an overdrive voltage of the on-chip FET. In at least one embodiment, the gate boost voltage boosts the DC bias of an input signal and, thus, generation of gate boost voltage by the on-chip charge pump is signal-independent, i.e. independent of the input signal. Increasing the overdrive voltage increases the efficiency of the amplifier by decreasing the difference between the maximum swing of the output voltage and the voltage supply rails of the at least one on-chip FET relative to conventional designs.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Switch linearized track and hold circuit for switch linearization
Circuits that provide a gate boost to address non-linear threshold voltage variation in a CMOS T / H circuit. In embodiments of the invention, a boost capacitor and a feedback amplifier add a signal-dependent threshold voltage to the switch gate over-drive voltage of a switch that controls track and hold circuit sampling. In a modified embodiment, capacitive boost is omitted and the feedback amplifier provides the signal-dependent threshold voltage boost. In another embodiment, a boost capacitor and a diode connected transistor provide the signal-dependent threshold voltage boost. In a modified embodiment, capacitive boost is omitted and the diode connected transistor provides the signal-dependent threshold voltage.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Adjusting control gate overdrive of select gate transistors during programming of non-volatile memory
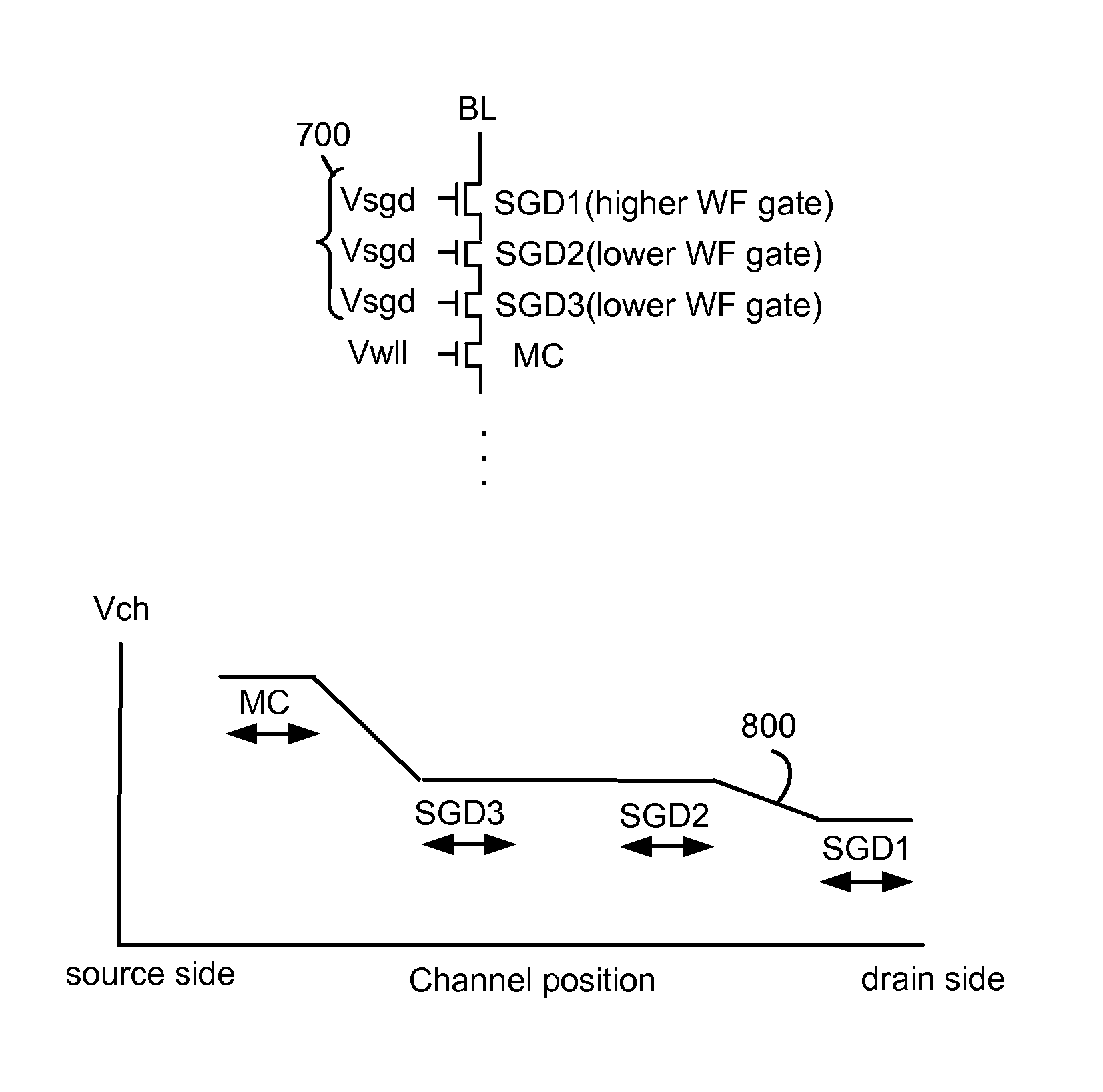
In a 3D stacked non-volatile memory device, multiple smaller drain-end selected gate (SGD) transistors replace one larger SGD transistor. The SGD transistors have different control gate overdrive voltages so that, during a programming operation, a discontinuous channel potential is created in an inhibited NAND string. The SGD transistor closest to the bit line has a lower control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is lower, and the next SGD transistor has a higher control gate overdrive voltage so that the channel potential under it is higher. The different control gate overdrive voltages can be provided by programming different threshold voltages, or by providing different control gates voltages, for the SGD transistors. Undesirable reductions in a Vsgd window due to drain-induced barrier lowering can be avoided.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
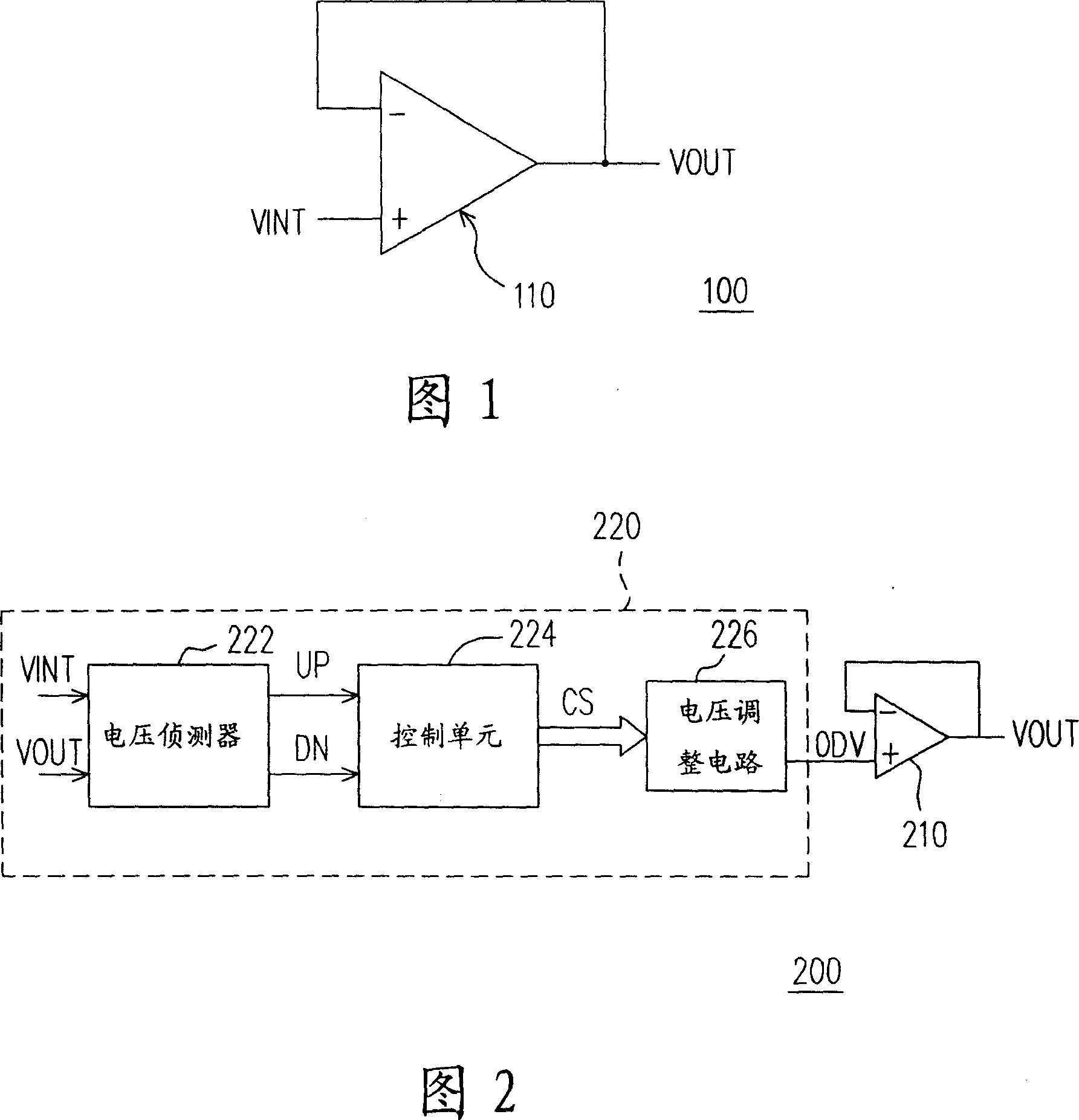
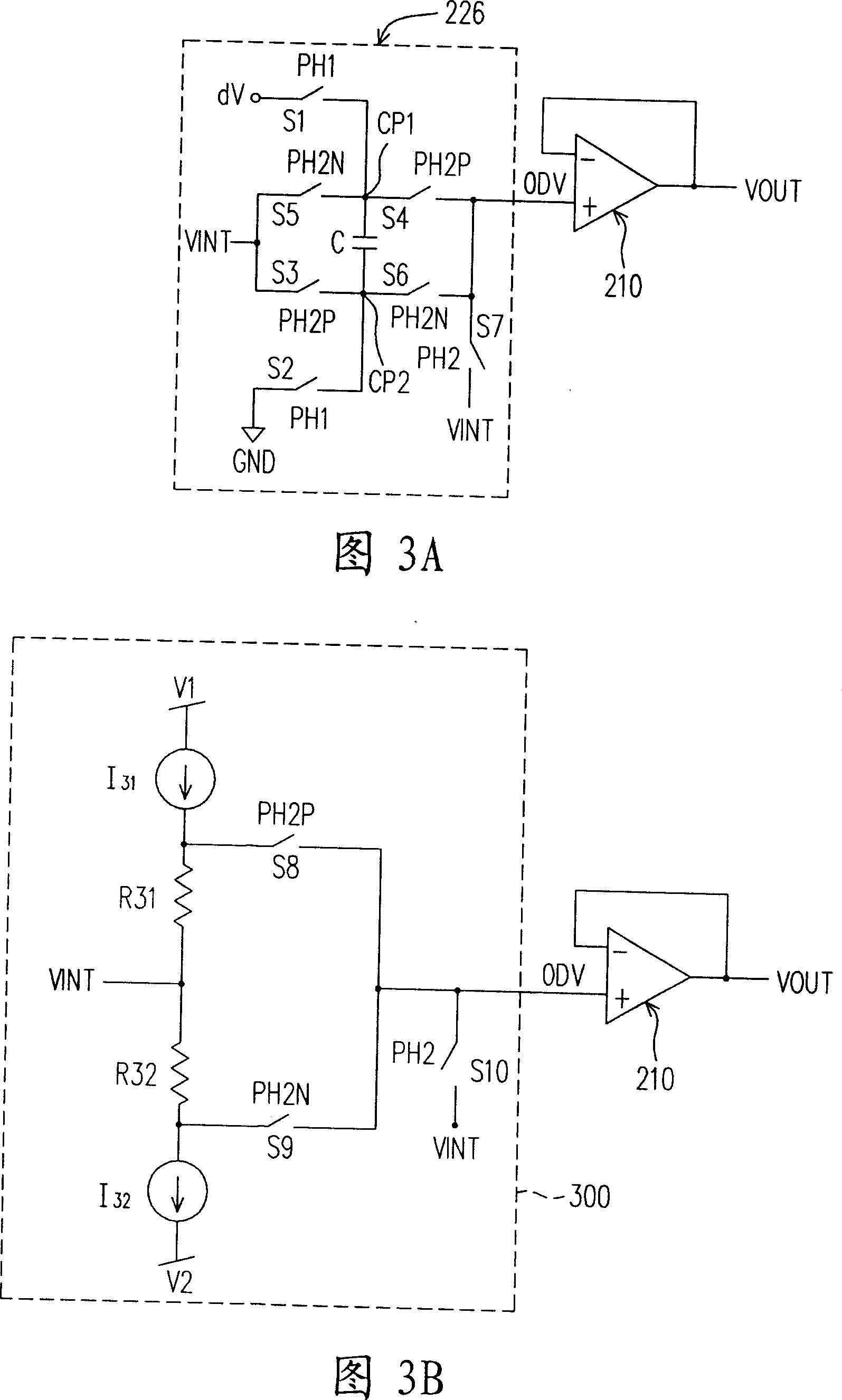
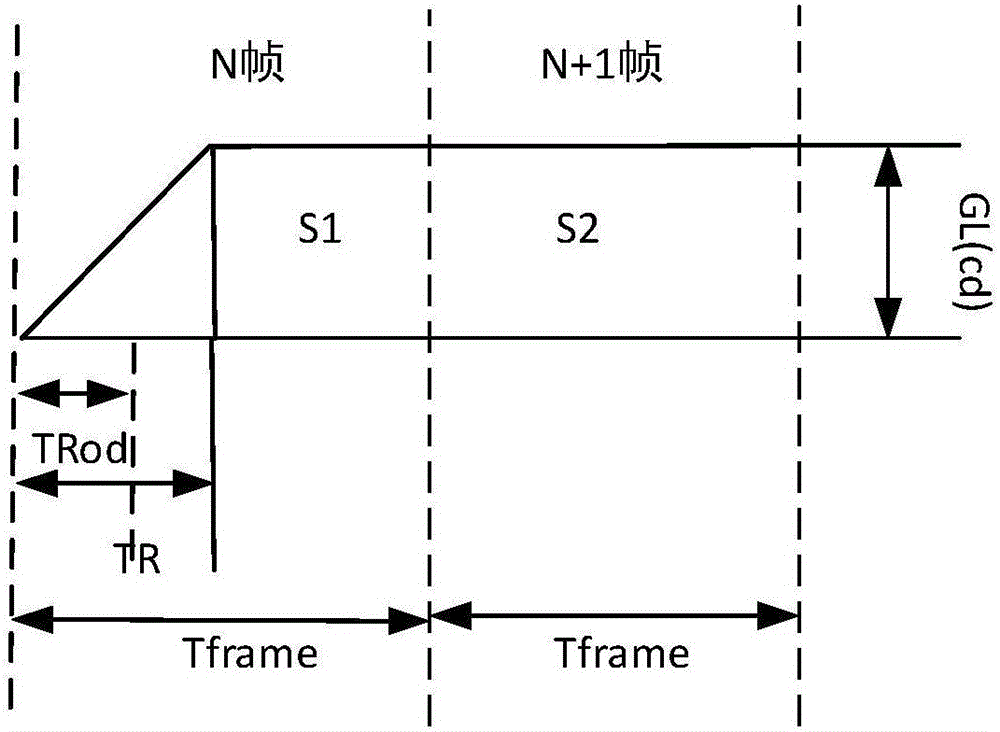
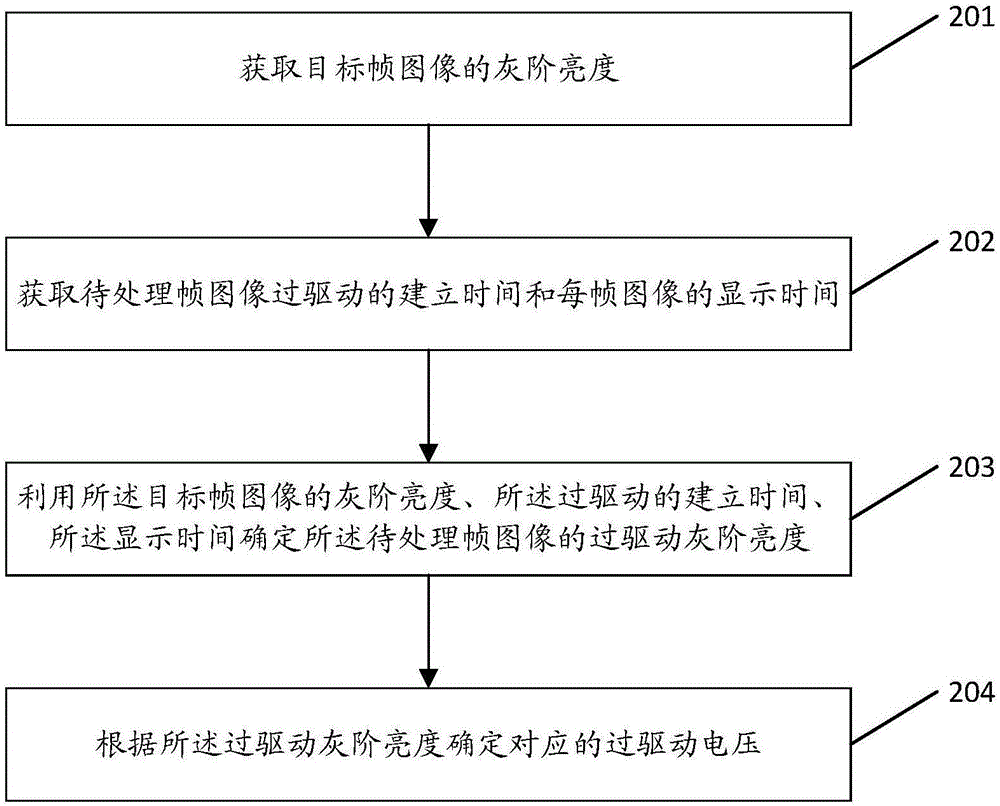
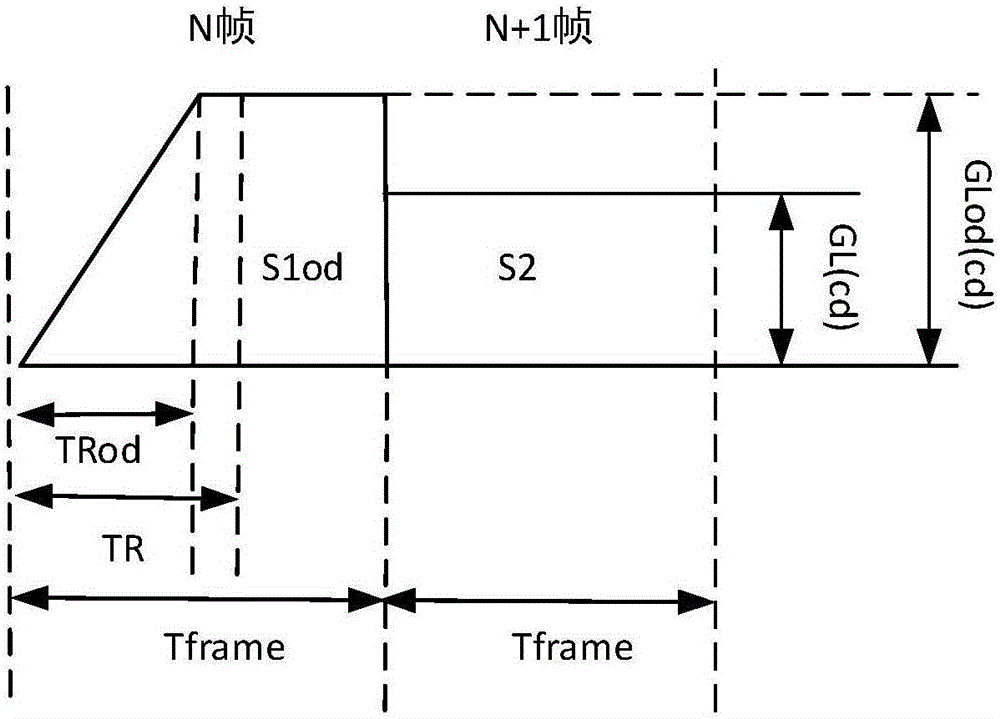
Method and device for determining overdrive voltage as well as display device
ActiveCN106324875AReduce workloadStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
The invention provides a method and a device for determining overdrive voltage as well as a display device, relates to the technical field of liquid crystal display and is used for reducing the workload during determination of overdrive gray scale brightness. The method for determining the overdrive voltage comprises steps as follows: acquiring gray scale brightness of a target frame image; acquiring the setting time of overdrive of to-be-processed frame images and display time of each frame of one image; determining the overdrive gray scale brightness of the to-be-processed frame images according to the gray scale brightness of the target frame image, the setting time of overdrive and the display time; determining the corresponding overdrive voltage according to the overdrive gray scale brightness. The method and the device for determining the overdrive voltage as well as the display device are mainly applied to the technical field of liquid crystal display.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
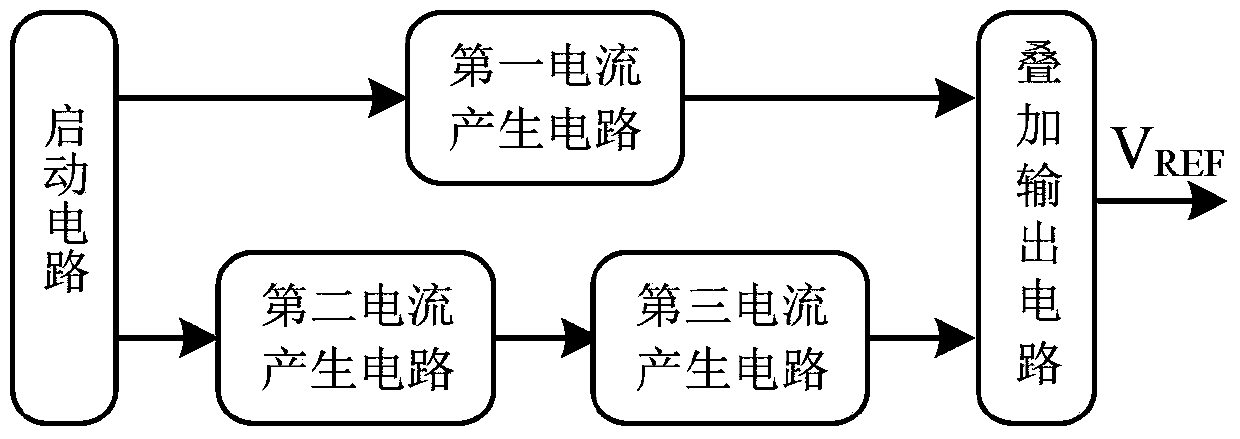
Low-voltage bandgap-free reference voltage source
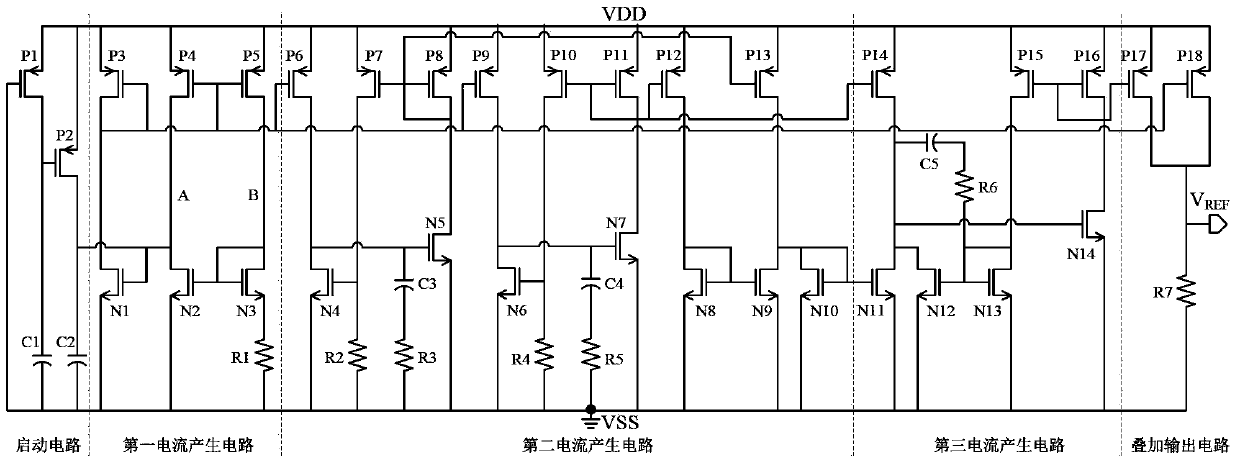
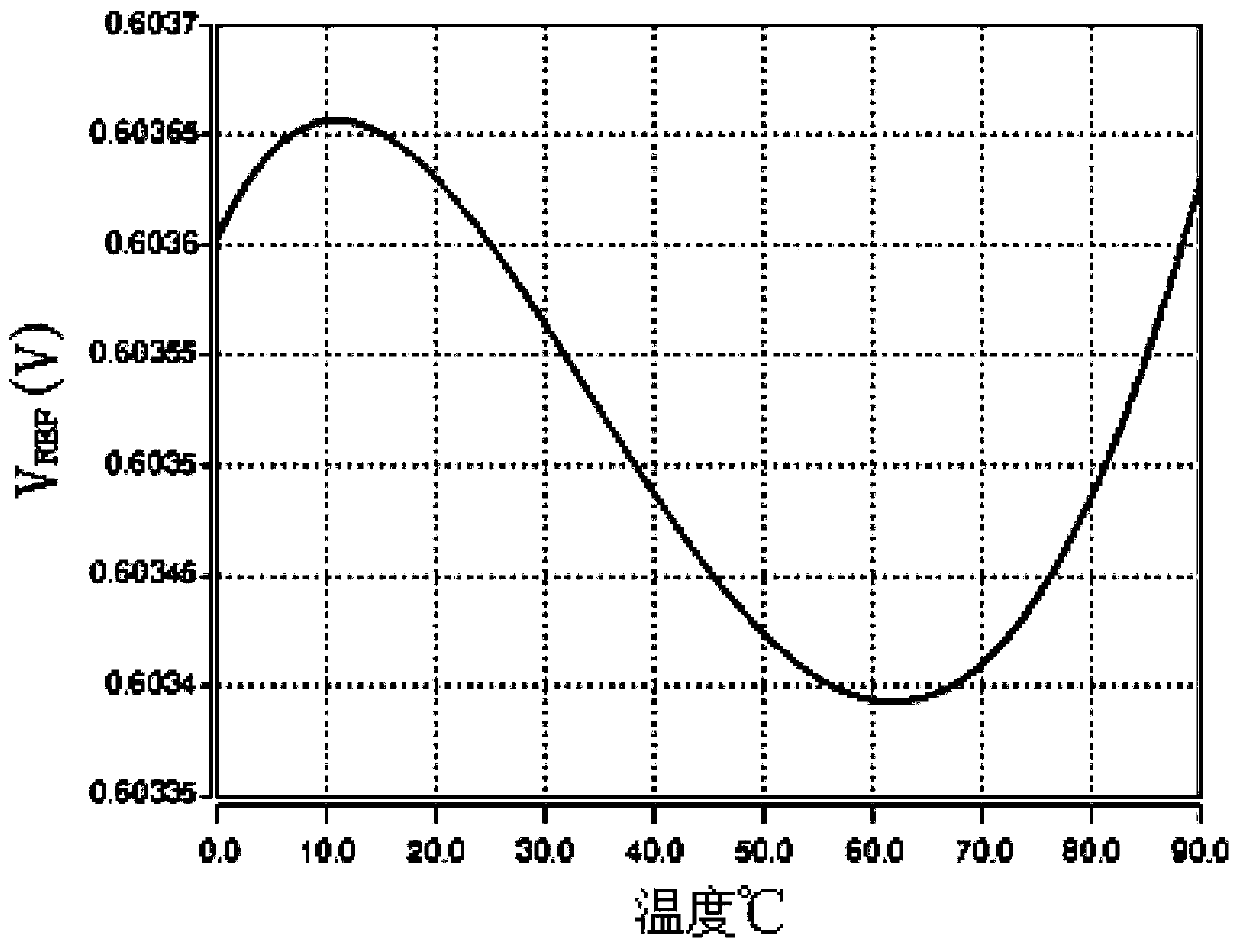
The invention relates to the integrated circuit technique and discloses a low-voltage bandgap-free reference voltage source. According to the technical scheme, the low-voltage bandgap-free reference voltage source comprises a starting circuit composed of a CMOS transistor circuit, a first current generating circuit, a second current generating circuit, a third current generating circuit and an overlaying output circuit, wherein the starting circuit is used for providing a starting bias voltage for the whole circuit, the first current generating circuit is used for generating a current IPTAT in direct proportion to the temperature, the second current generating circuit is used for generating a current IPTOD in direct proportion to an overdriving voltage, the third current generating circuit is used for generating a current IPTTV in direct proportion to a threshold voltage, the current IPTTV is inversely proportional to the temperature, and the overlaying output circuit is used for overlaying of the current IPTAT and the current IPTTV and outputting a reference voltage VREF. The low-voltage bandgap-free reference voltage source has the advantages that the working voltage is low, the output voltage can be adjusted, influence of a technique on the low-voltage bandgap-free reference voltage source is little, and the area of a chip is small.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com