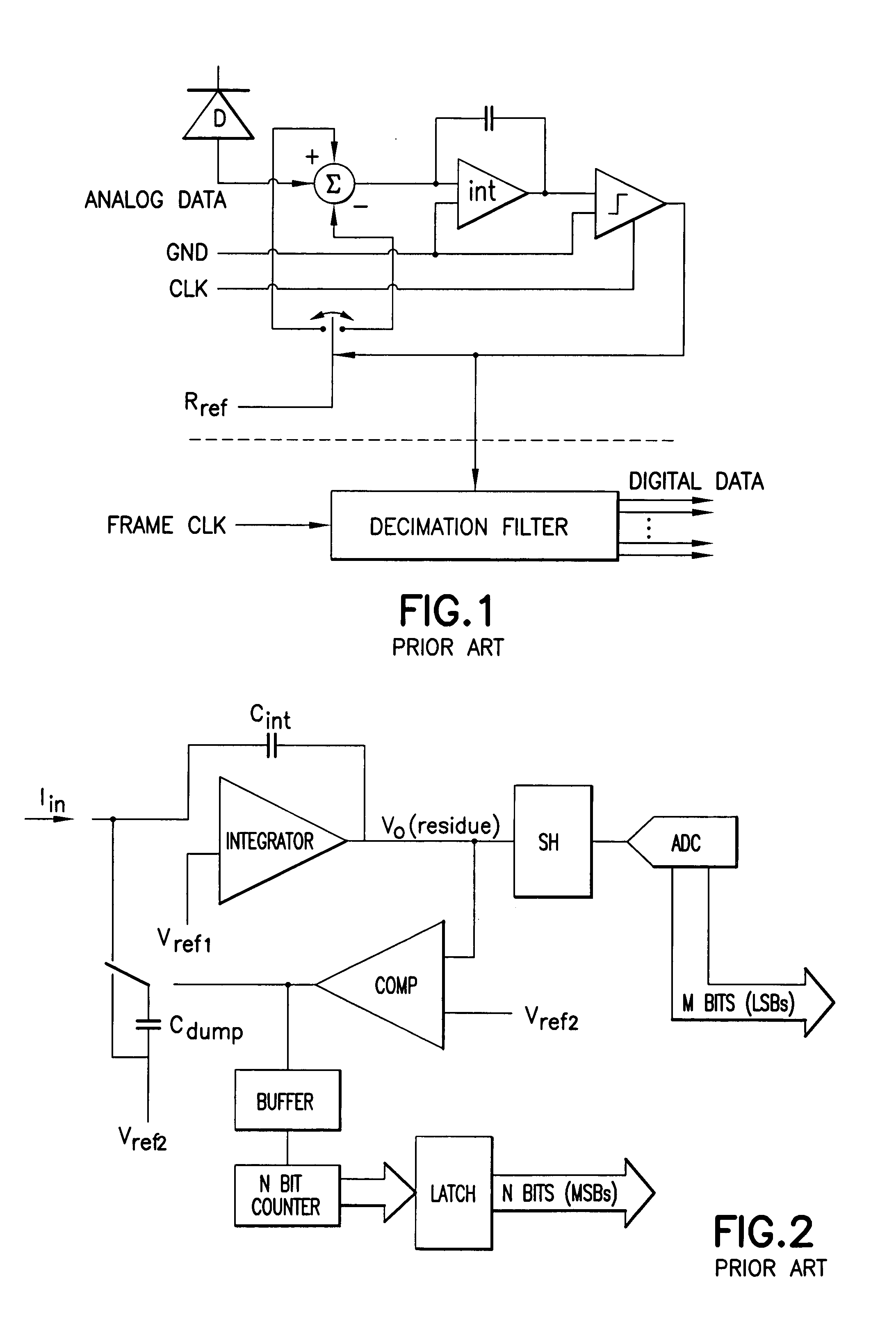
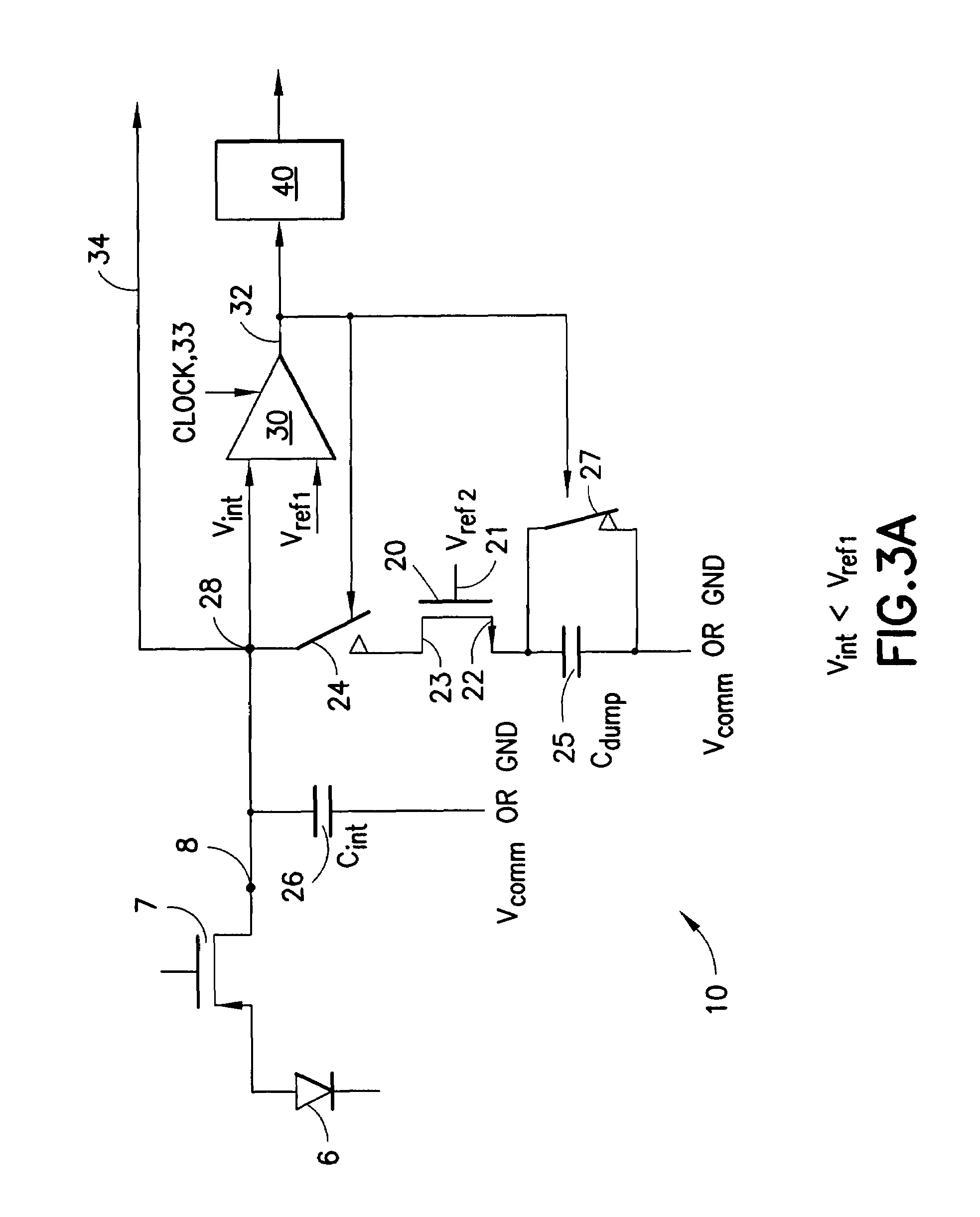
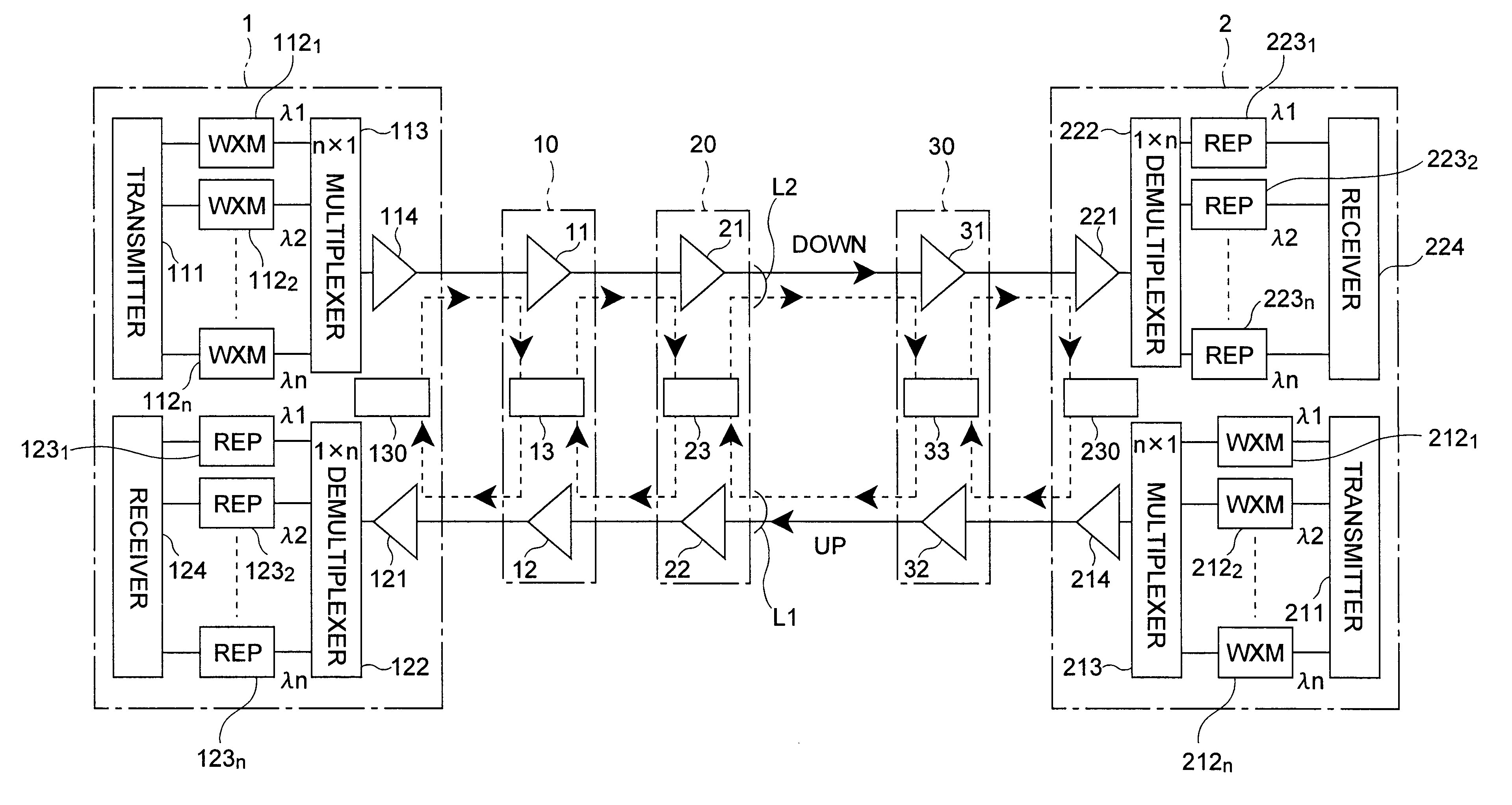
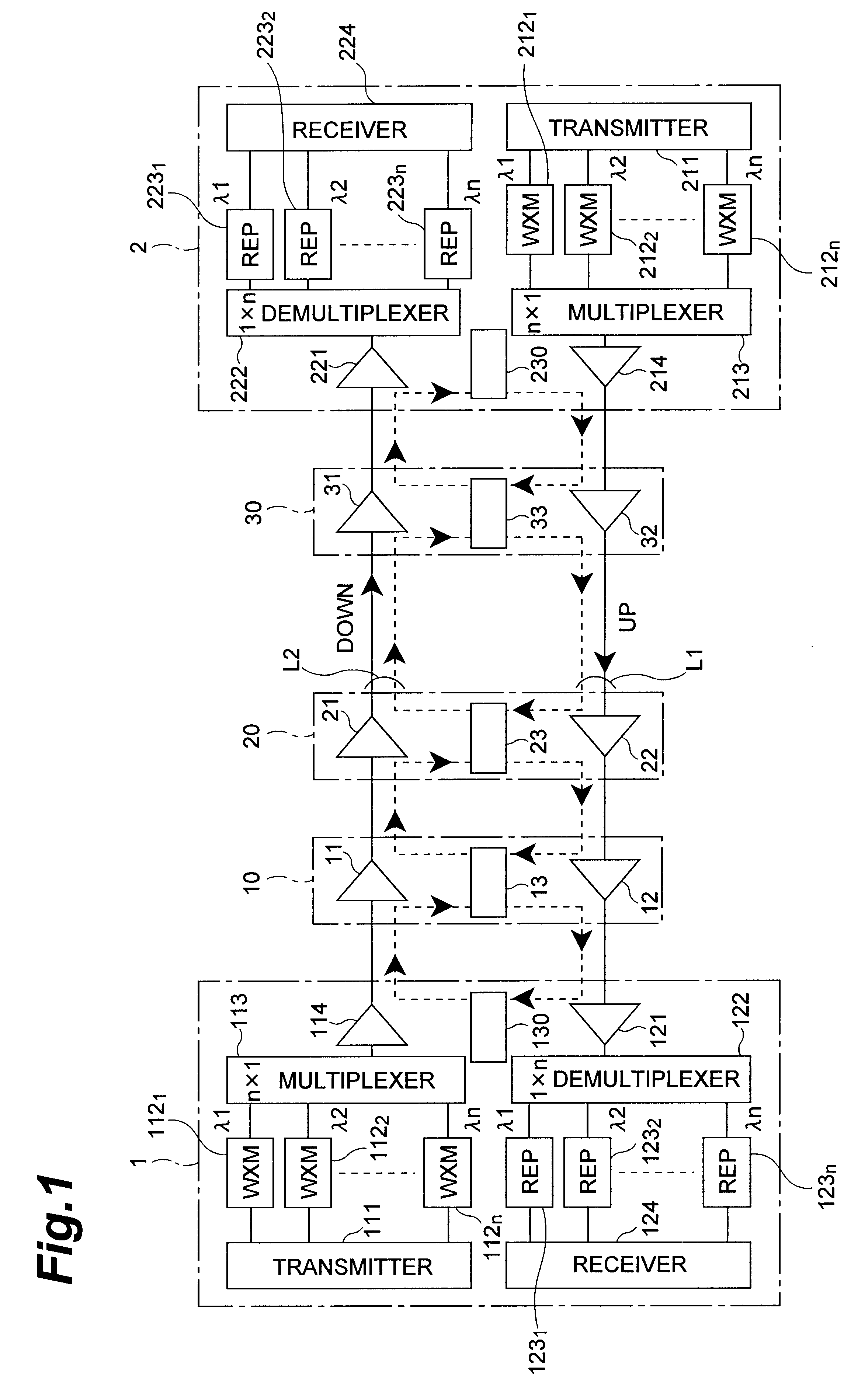
Patents
Literature
13638 results about "Operational amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An operational amplifier (often op-amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals. Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to perform mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear, and frequency-dependent circuits.
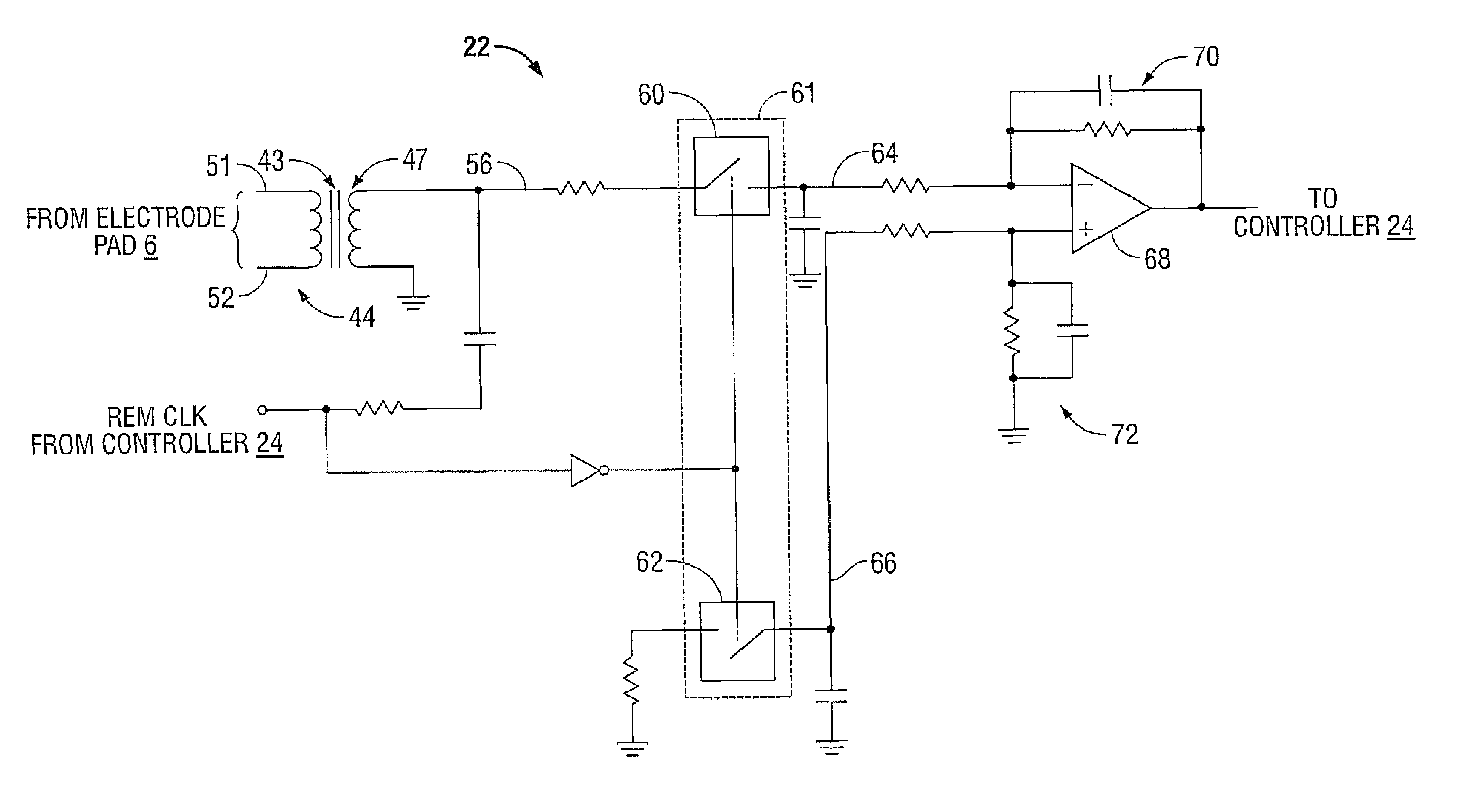
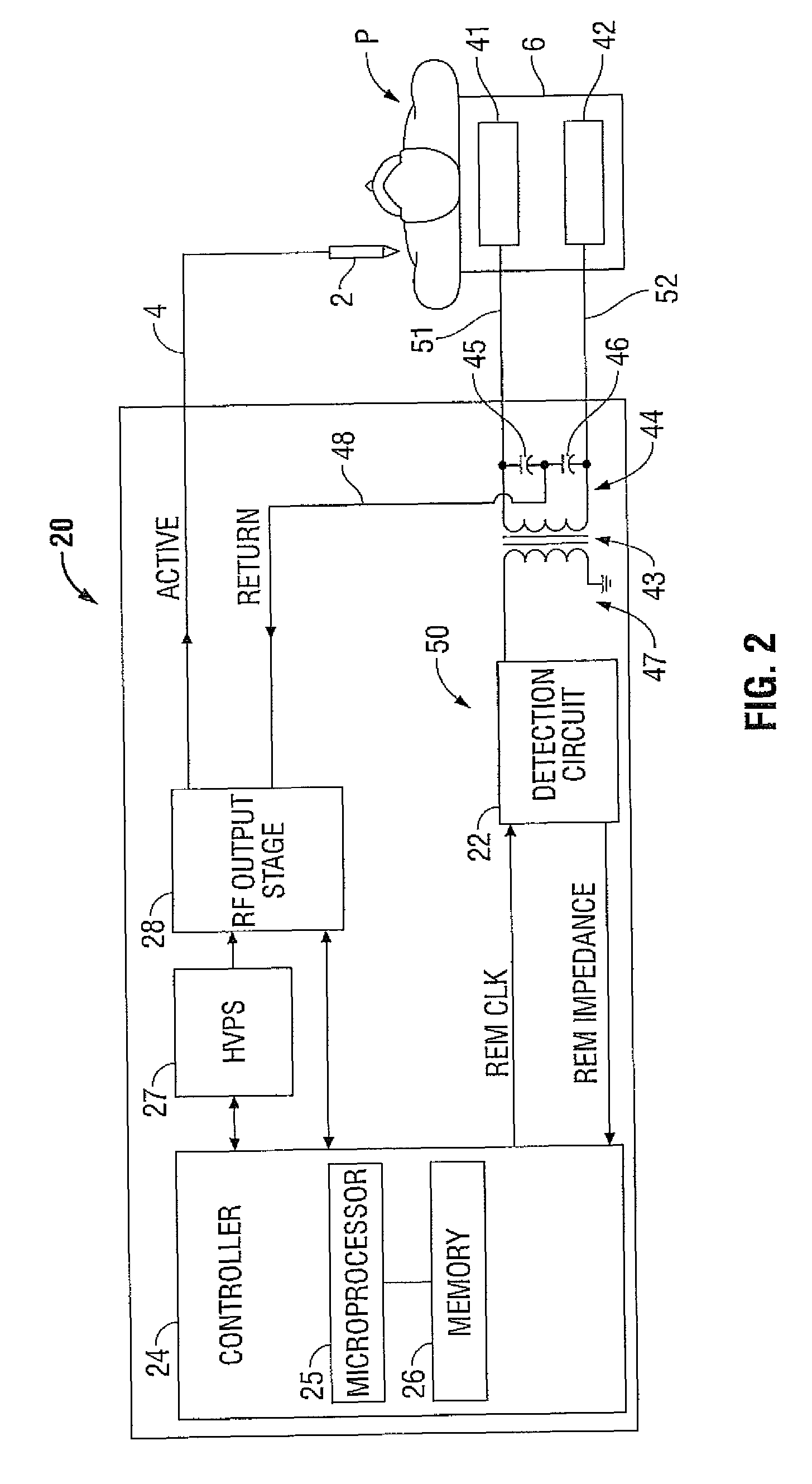
System and method for return electrode monitoring
A detection circuit for return electrode monitoring is disclosed. The detection circuit includes a transformer operatively coupled to a pair of split electrode pads, wherein the transformer is configured to transceive a return electrode sense signal. The detection circuit also includes a first switch coupled to the transformer and a neutrally-referenced second switch, wherein the first switch and the second switch are disposed on a single die. The detection circuit further includes an operational amplifier coupled to the first switch and the neutrally-referenced second switch. The operational amplifier is configured to subtract a noise signal from the return electrode sense signal.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Power supply driver circuit
InactiveUS7138786B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
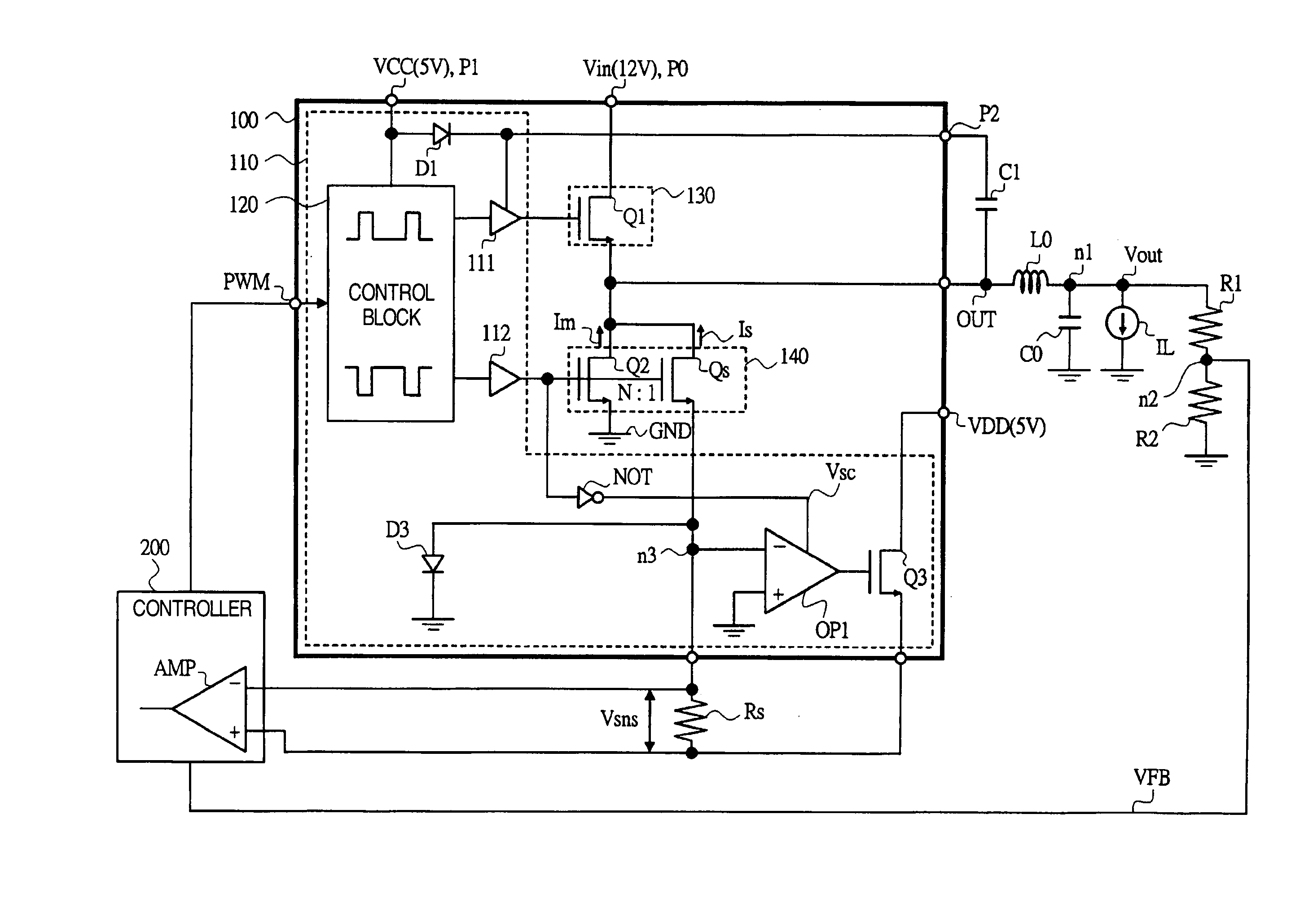
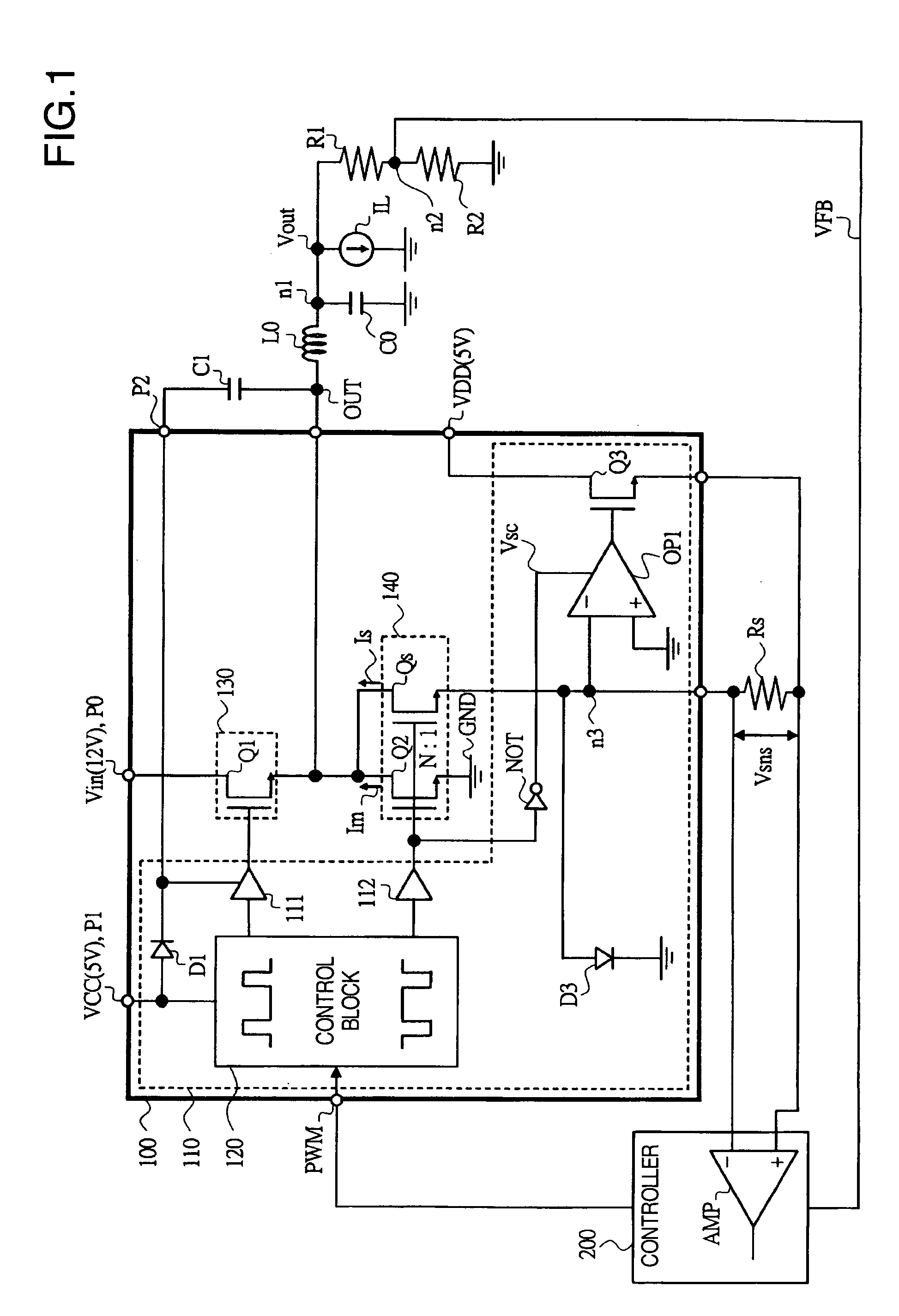
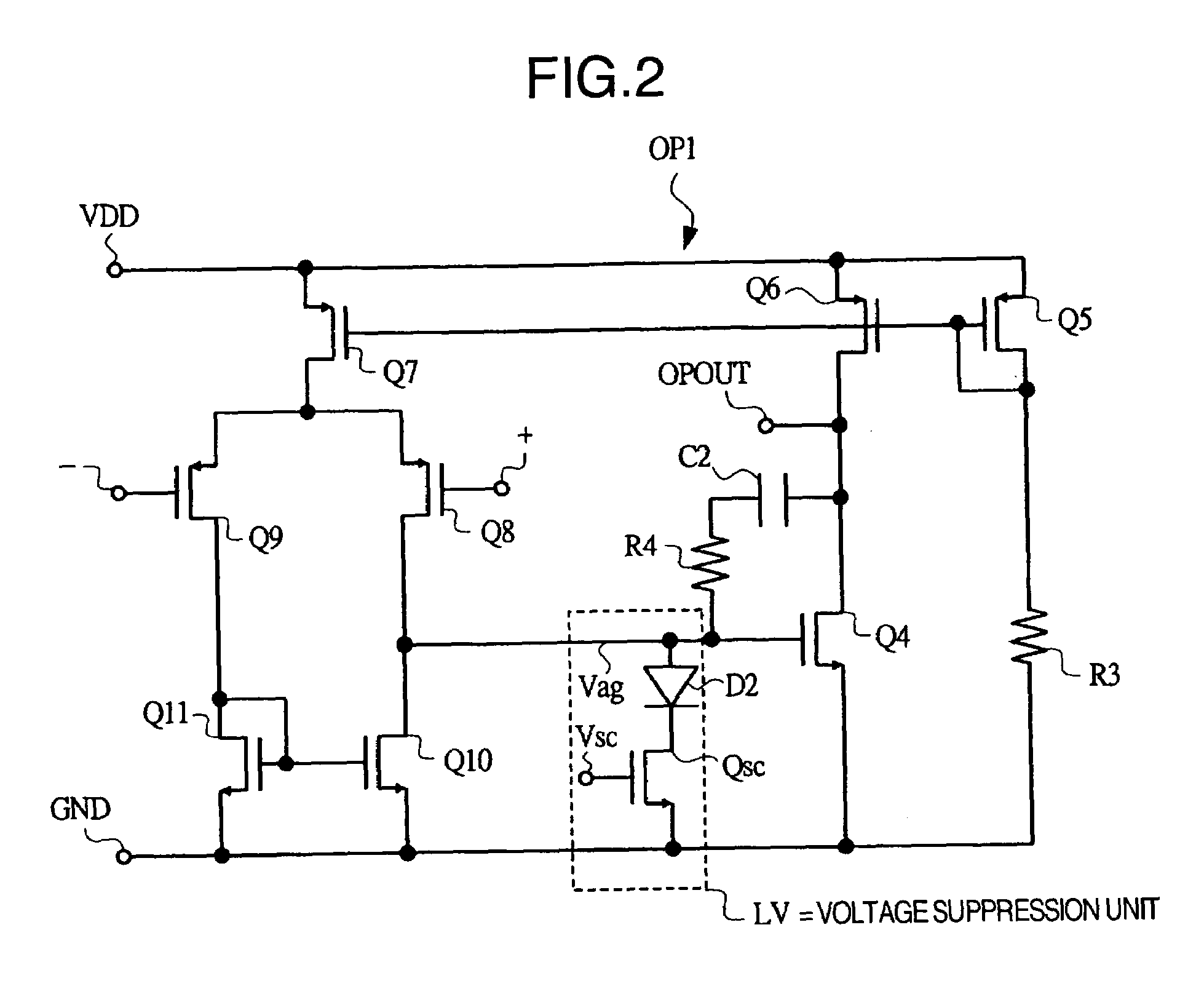
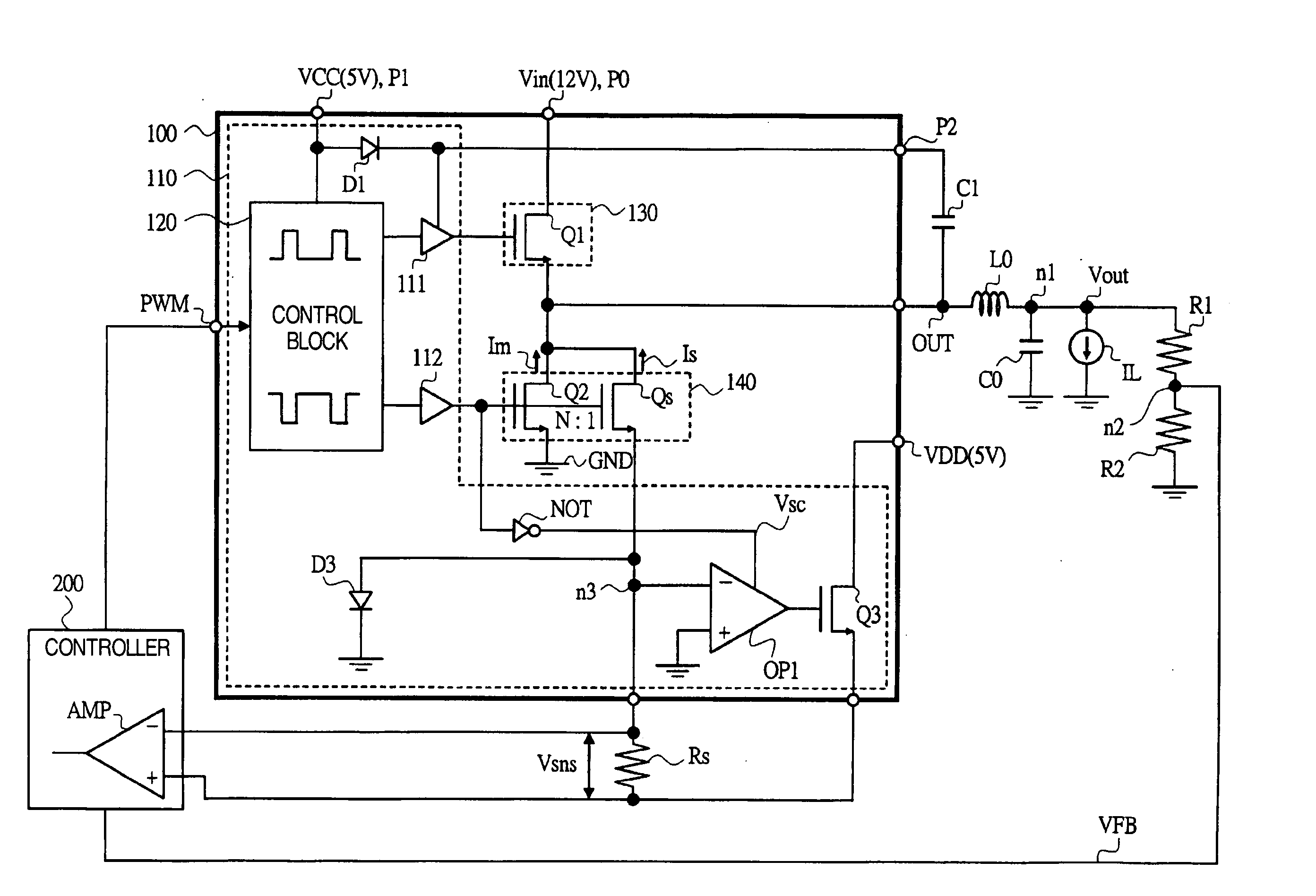
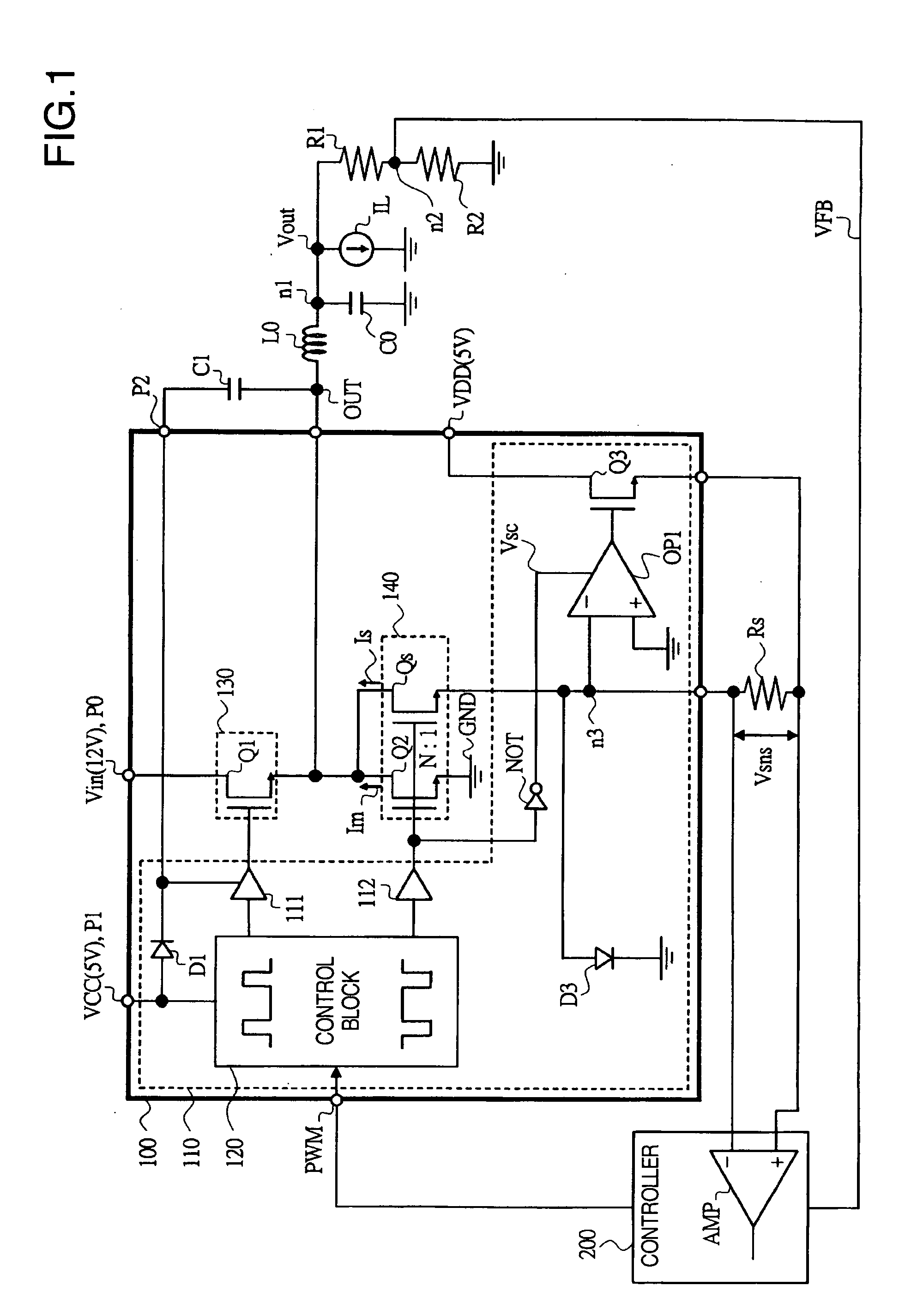
A power supply driver circuit with low power losses and desired response characteristics with respect to changes in output and its miniaturization is provided. In a driver IC constituting a switched-mode power supply equipment controlling the switching, by pulse width modulation, of first and second power transistors passing a current in a coil, and outputting a voltage bucked or boosted from an input voltage, current sensing with desired responsiveness is enabled by providing a switching transistor between an inverted input terminal and a non-inverted input terminal of an operational amplifier, preventing, while the second power transistor is ON, the generation of a potential which is undefined when first power transistor is ON, i.e. when the second power transistor is OFF, and maintaining a node potential in a state in which the potential is well defined.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
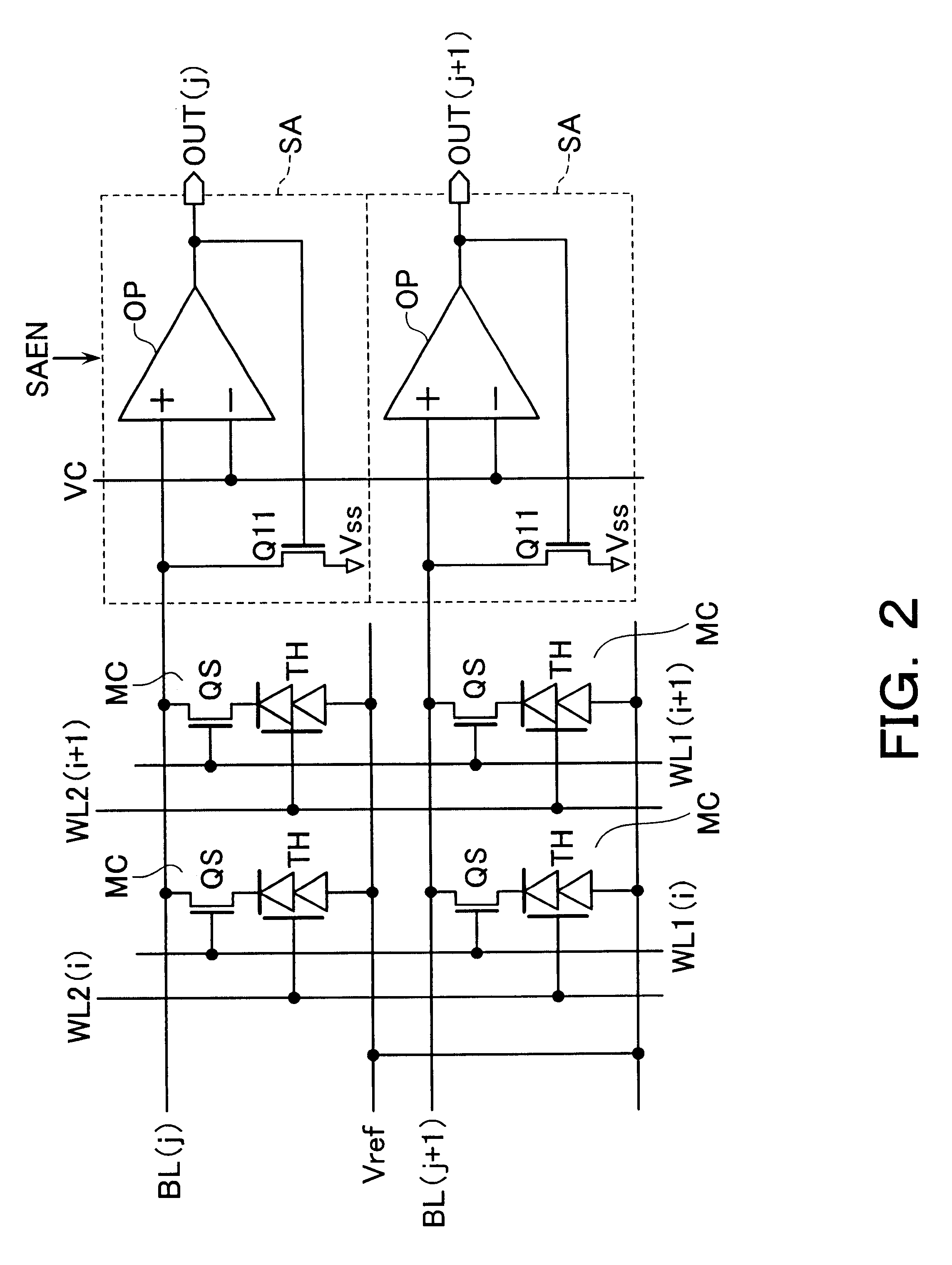
Magnetoresistive memory device
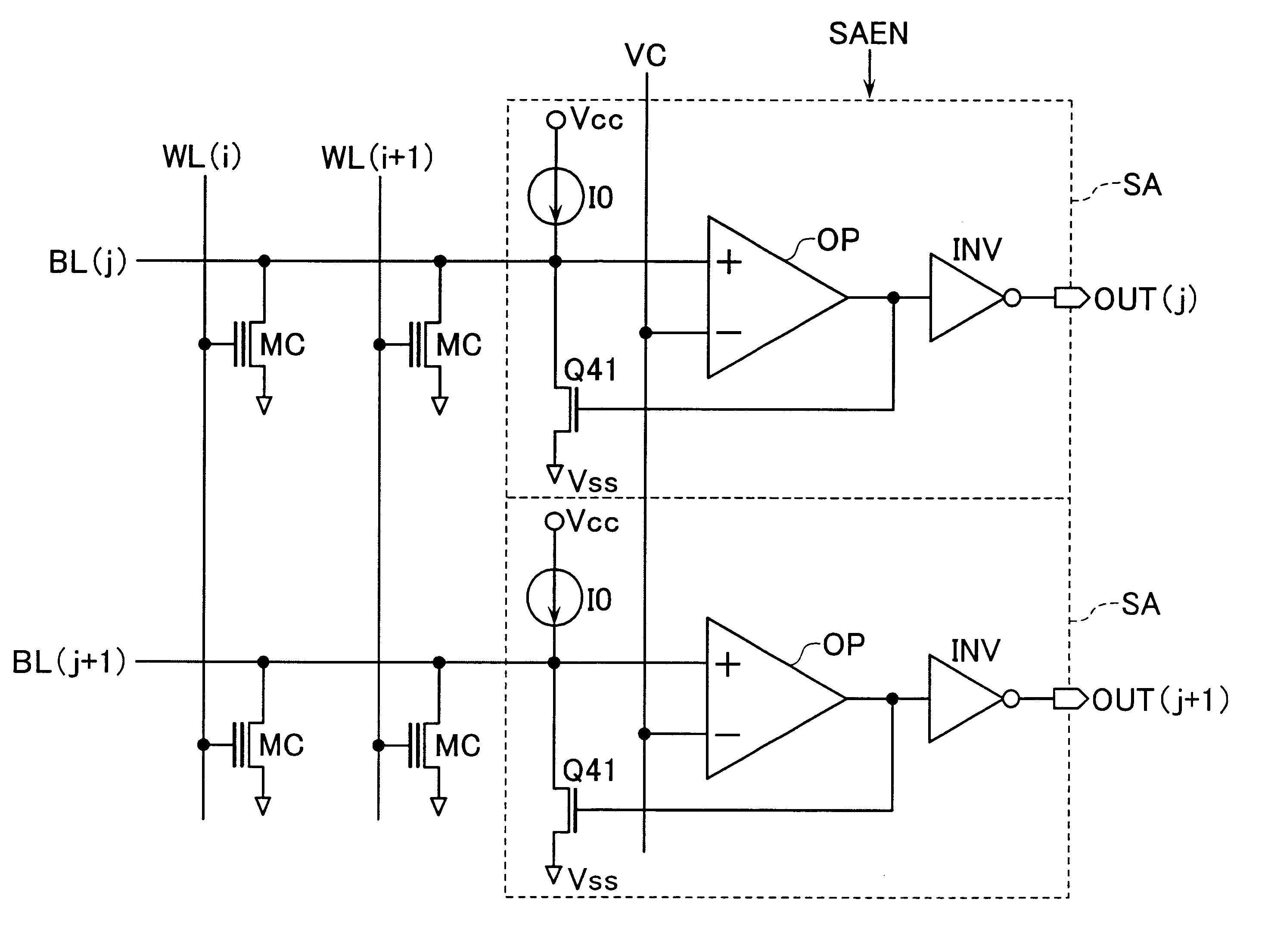
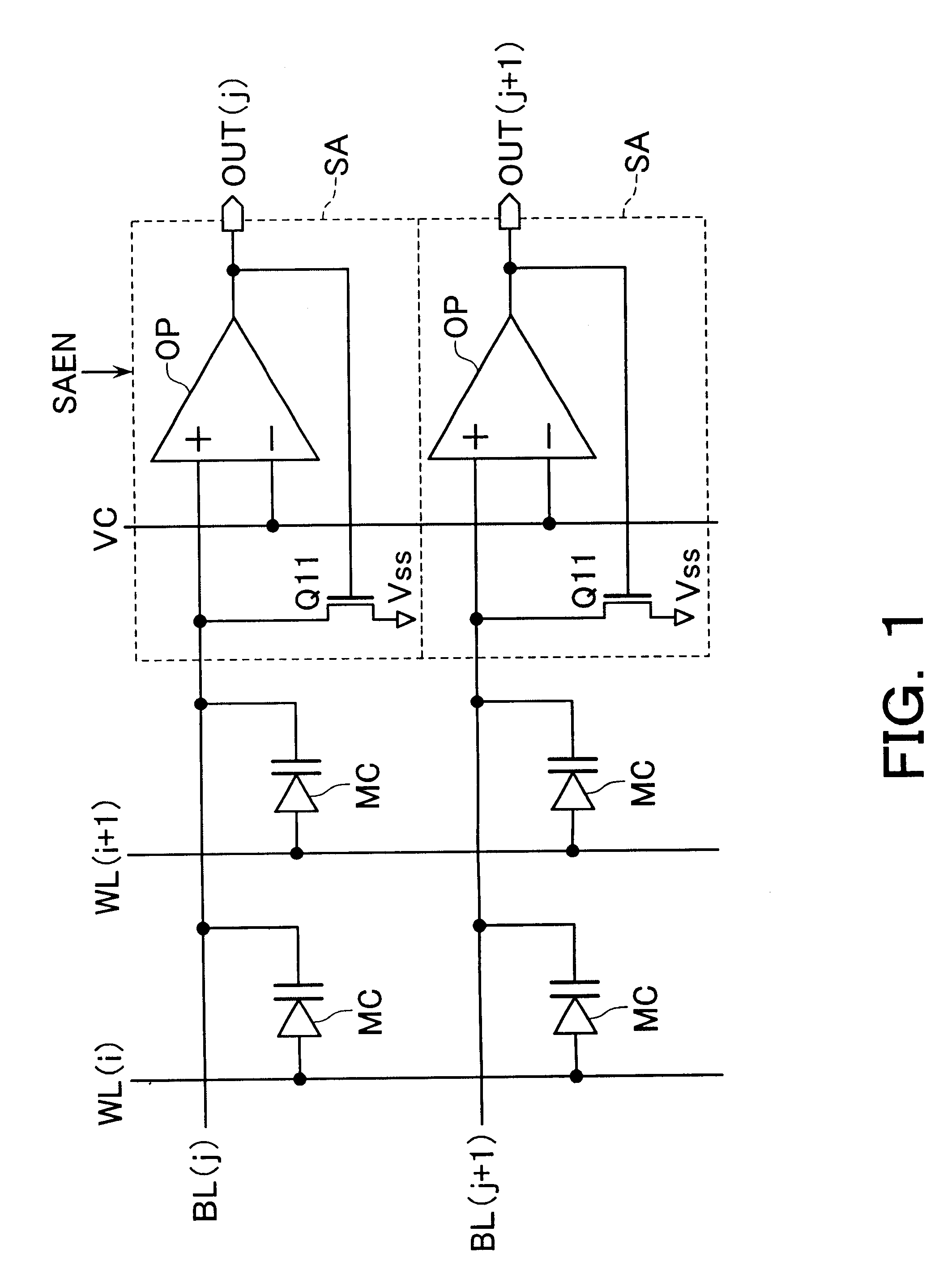
An integrated semiconductor memory device with an array of memory cells MC using magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) cells is disclosed. A sense amplifier SA that is connected to a bit line BL for data readout of a selected memory cell MC is arranged using an operational amplifier OP. The operational amplifier OP has an inverting input terminal which is connected to the bit line BL and a non-inverting input terminal, to which a potentially fixed constant voltage VC is given. A PMOS transistor Q31 is provided, which can also do double-duty as a current source load. This PMOS transistor has its drain and gate that are connected to the inverting input terminal, and a source as connected to an output terminal of the operational amplifier OP whereby the transistor is under feedback control in response to an output of the operational amplifier OP so that a clamped voltage potential of the bit lime BL is fixed to the voltage VC.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
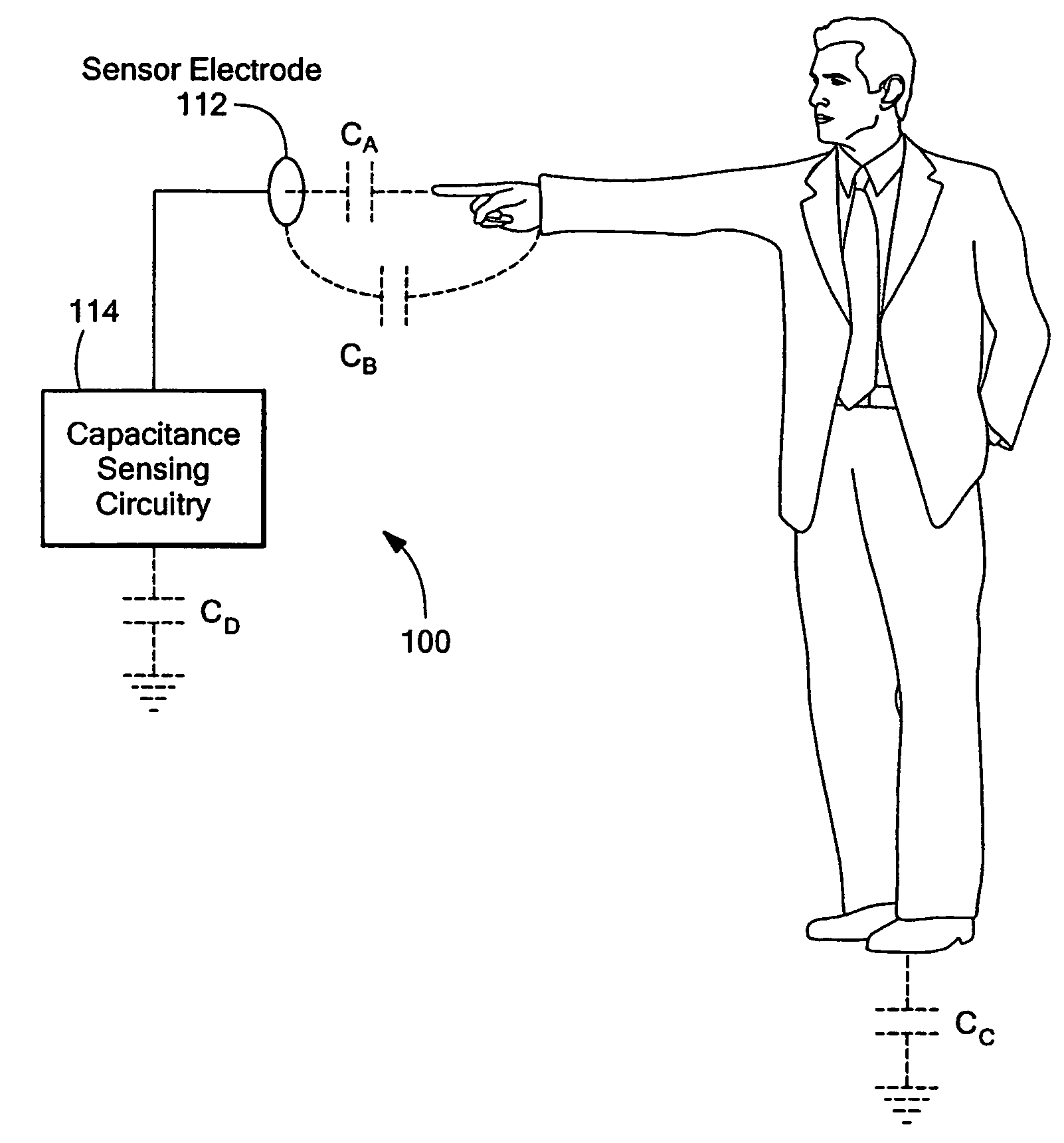
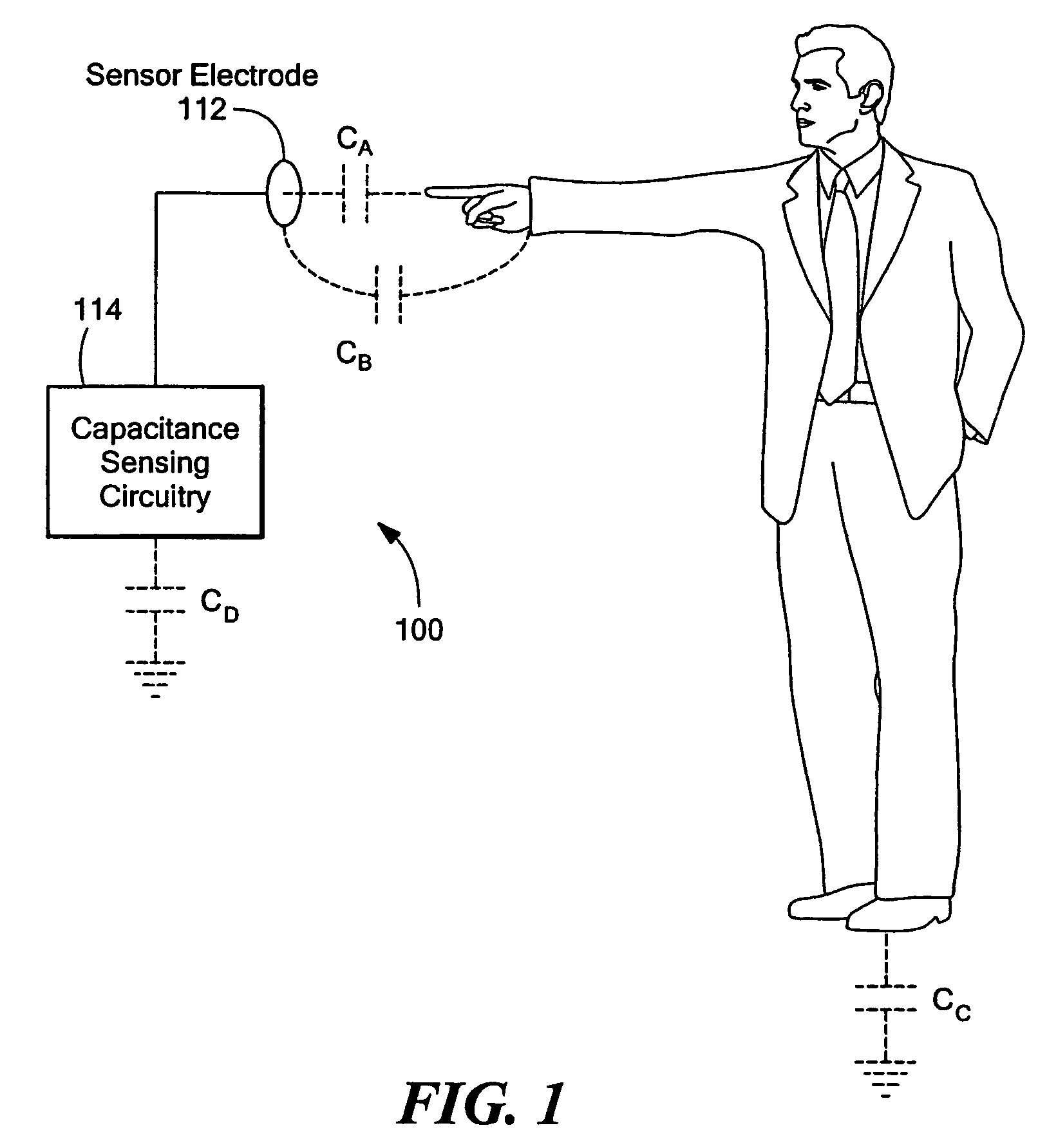
Linear capacitance measurement and touchless switch
InactiveUS7498822B2Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityResistance/reactance/impedenceElectronic switchingNegative feedbackProximity sensor
Owner:LEE YING LAU
Power supply driver circuit
InactiveUS20060113979A1Improve responseImproving Current Sensing AccuracyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
A power supply driver circuit with low power losses and desired response characteristics with respect to changes in output and its miniaturization is provided. In a driver IC constituting a switched-mode power supply equipment controlling the switching, by pulse width modulation, of first and second power transistors passing a current in a coil, and outputting a voltage bucked or boosted from an input voltage, current sensing with desired responsiveness is enabled by providing a switching transistor between an inverted input terminal and a non-inverted input terminal of an operational amplifier, preventing, while the second power transistor is ON, the generation of a potential which is undefined when first power transistor is ON, i.e. when the second power transistor is OFF, and maintaining a node potential in a state in which the potential is well defined.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
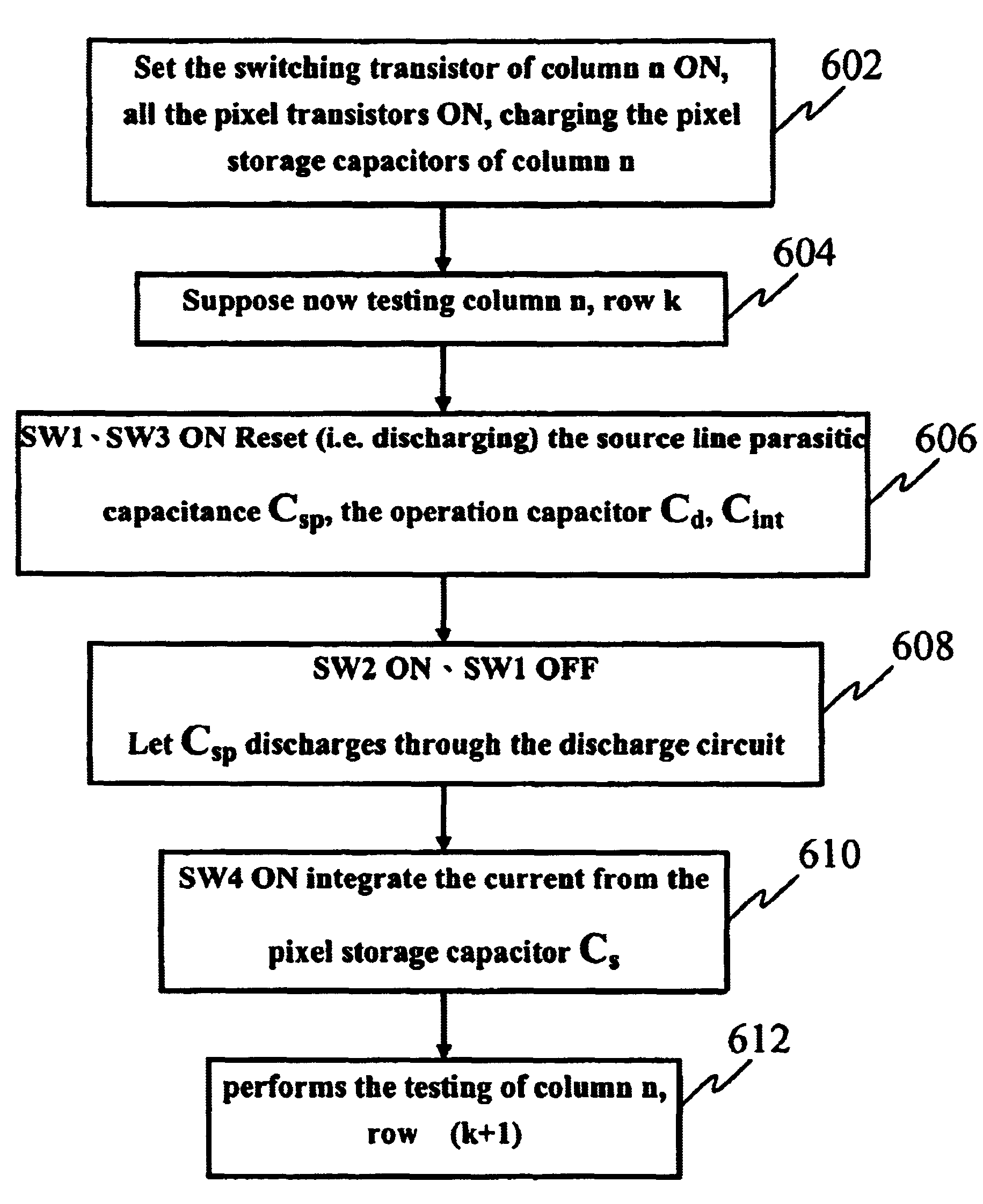
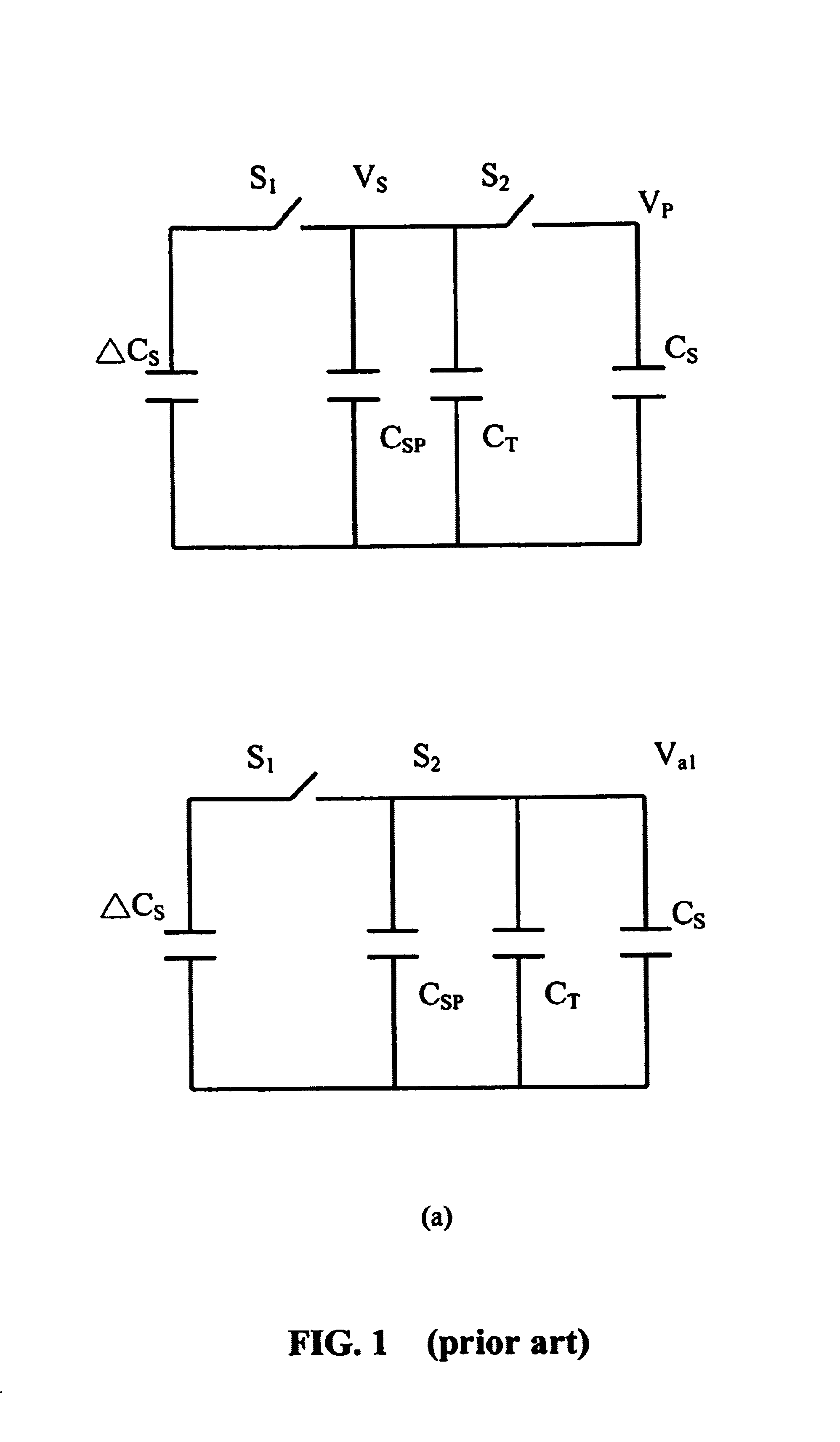
Testing apparatus and method for thin film transistor display array
InactiveUS20050024081A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityDigital circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceTransistor arrayHemt circuits
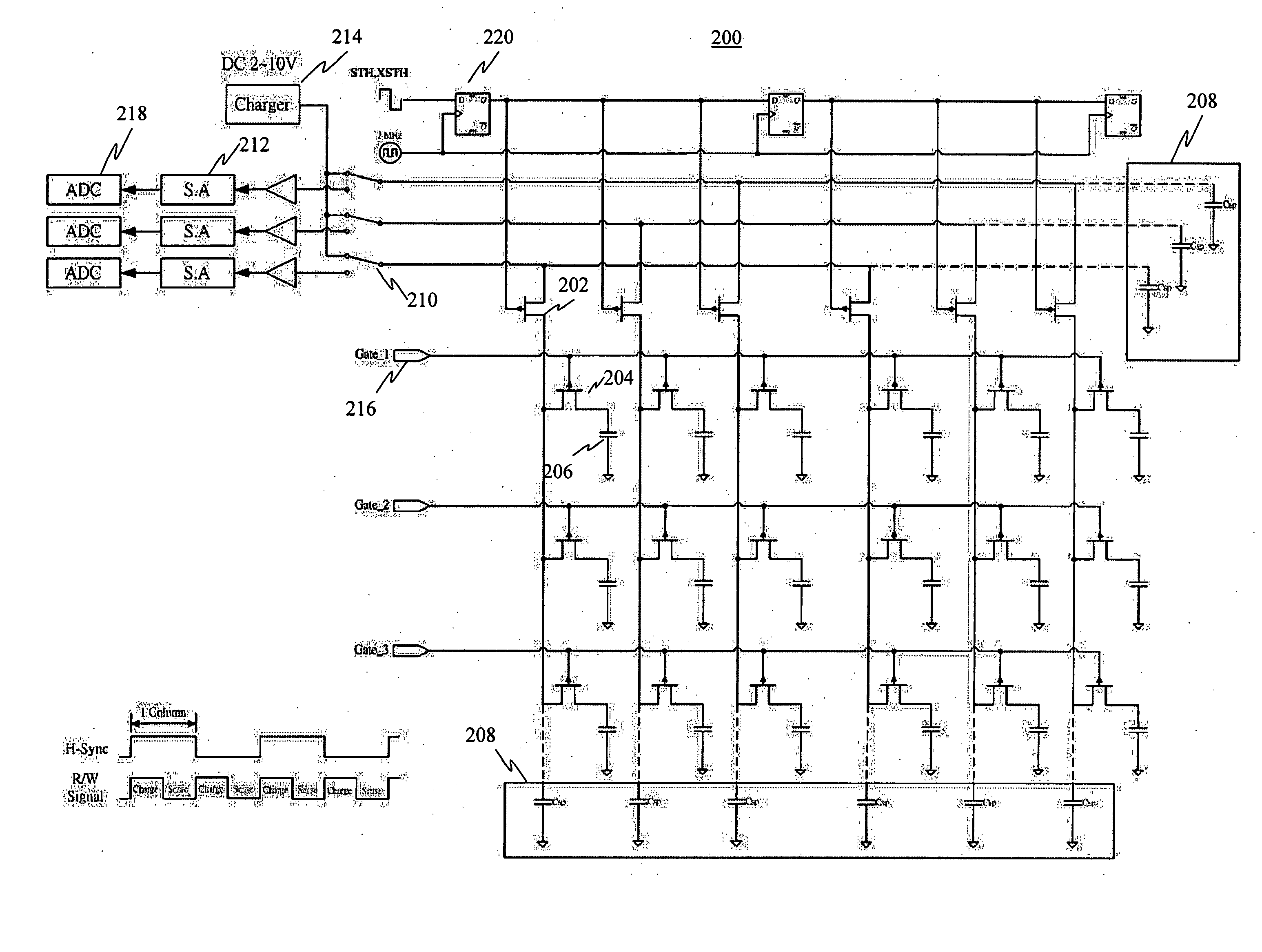
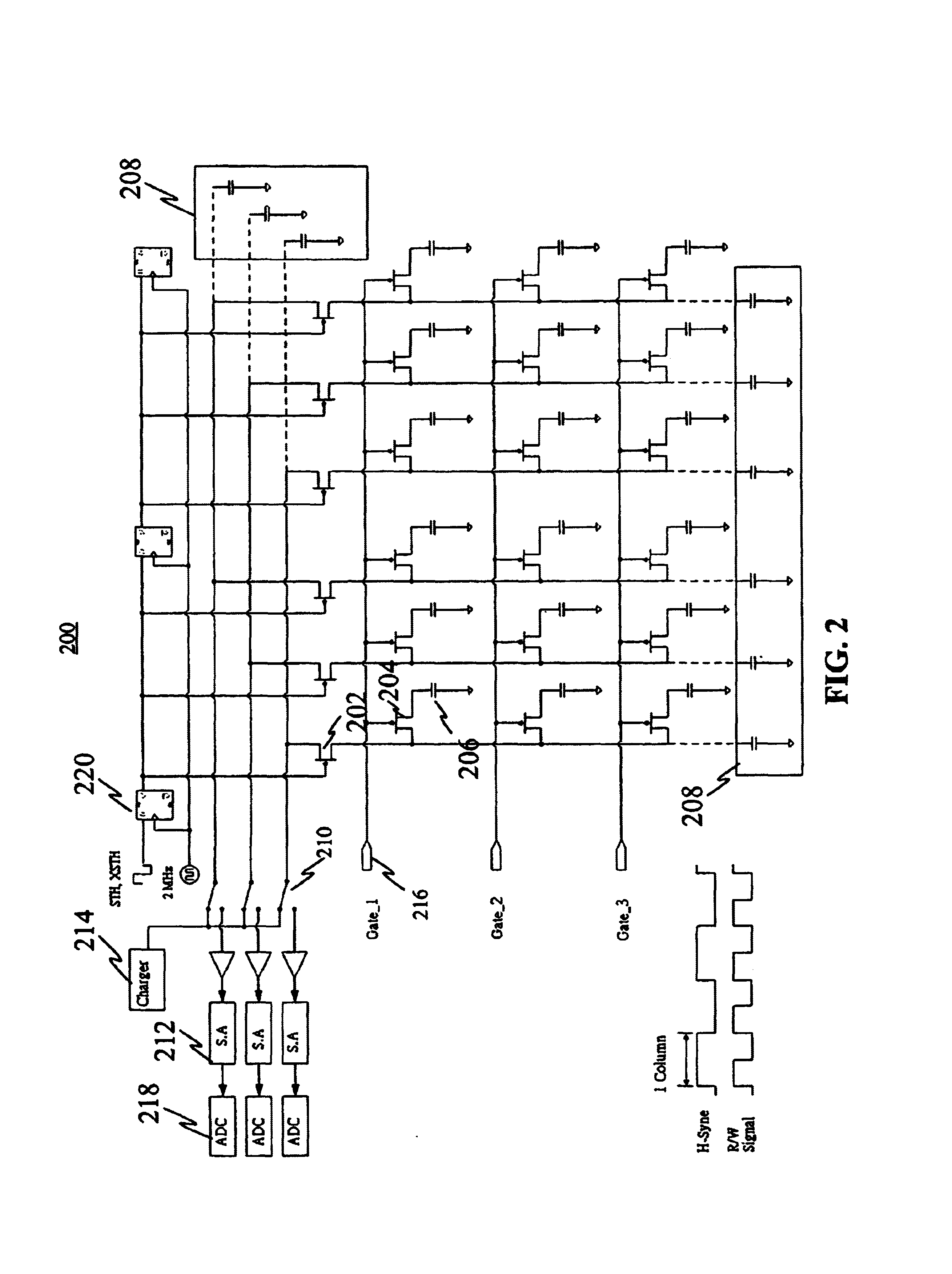
The present invention discloses a testing circuit and method for thin film transistor display array, for testing the yield of thin film transistor array. The testing circuit comprising: An array tester, a test panel (DUT), a sense amplifier array. The sense amplifier is composed by a plurality of trans- impedance amplifier unit and a plurality of parasitic capacitance discharge circuit unit. Every sense amplifier includes: a trans-impedance amplifier, which is implemented by an operational amplifier, two switches and an operation capacitance, the trans-impedance amplifier is used to form an integrated circuit, the output is transmitted to a sampling / hold circuit via a switch; a parasitic capacitance discharge circuit is used to form a discharge rout for the charge of the parasitic capacitance.
Owner:PRIMETECH INT CORP
Current-to-voltage-converter for a biosensor
InactiveUS6908535B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsVoltage converterAudio power amplifier
An integrated current-to-voltage conversion circuit converts a first current to an output voltage representative of the first current. The circuit includes a first contact pad and second and third contact pads capable of being coupled across a first resistor. A first operational amplifier has a first input coupled to the first contact pad for producing a first voltage thereat, a second input for receiving a reference voltage, and a first output coupled to the third contact pad. A second voltage appears at the third contact pad. A second operational amplifier has a second output at which a third voltage appears, a first input coupled to the second output, and a second input coupled to the second contact pad. The output voltage is substantially equal to the difference between the second and third voltages.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
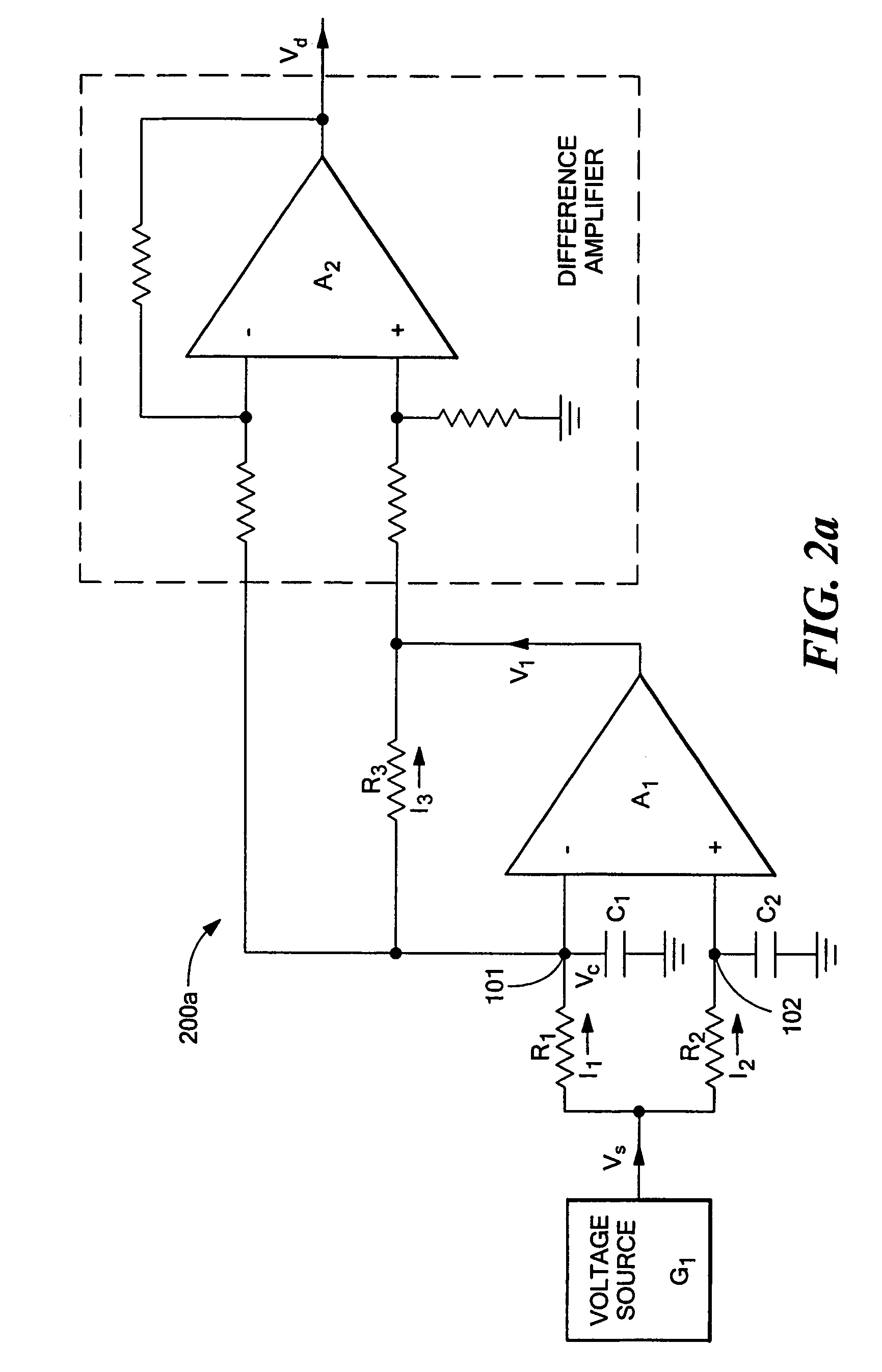
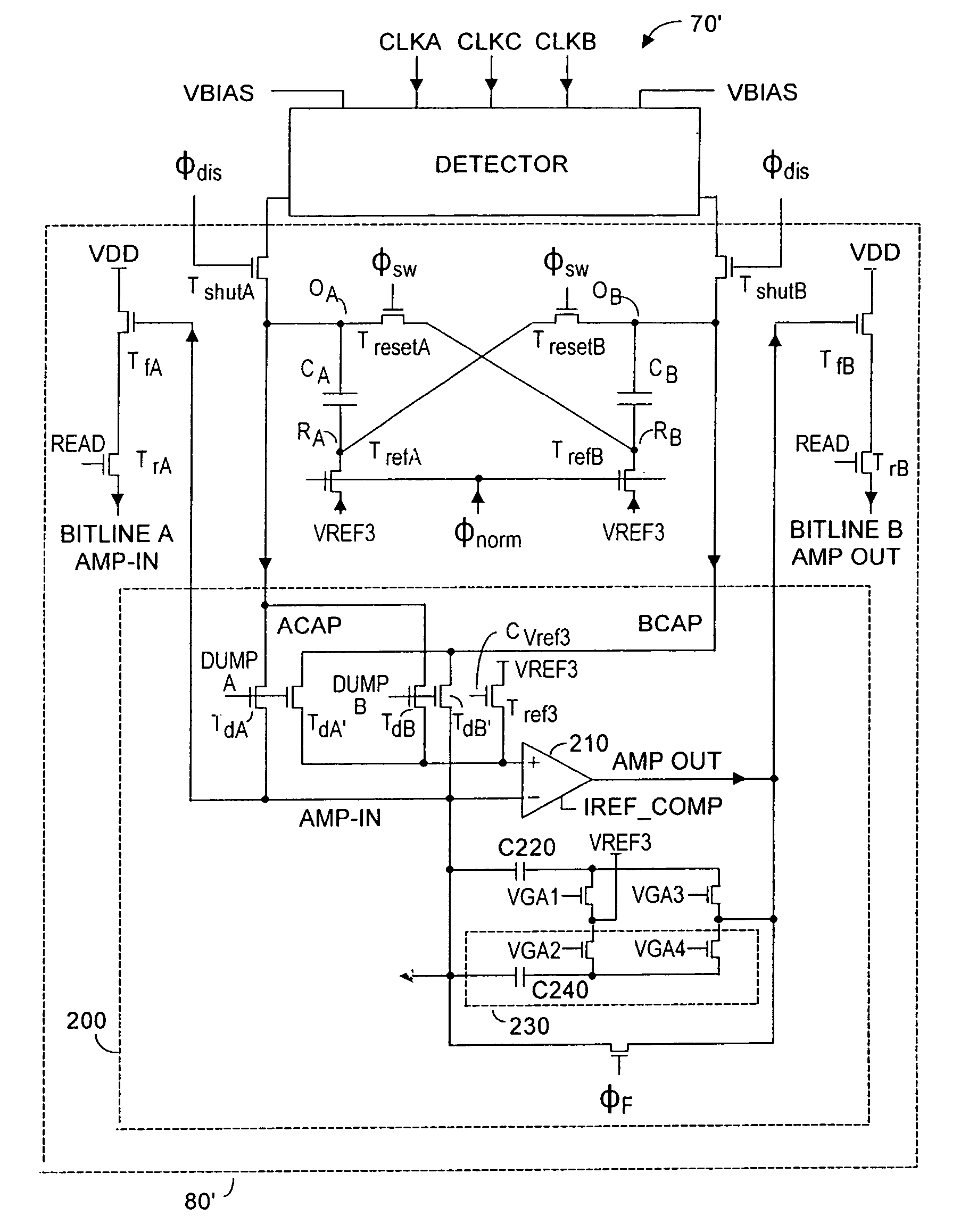
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
ActiveUS7157685B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersCMOSCapacitor voltage
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system to differentially enhance sensor dynamic range using enhanced common mode reset
ActiveUS7176438B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierPhotodetector
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
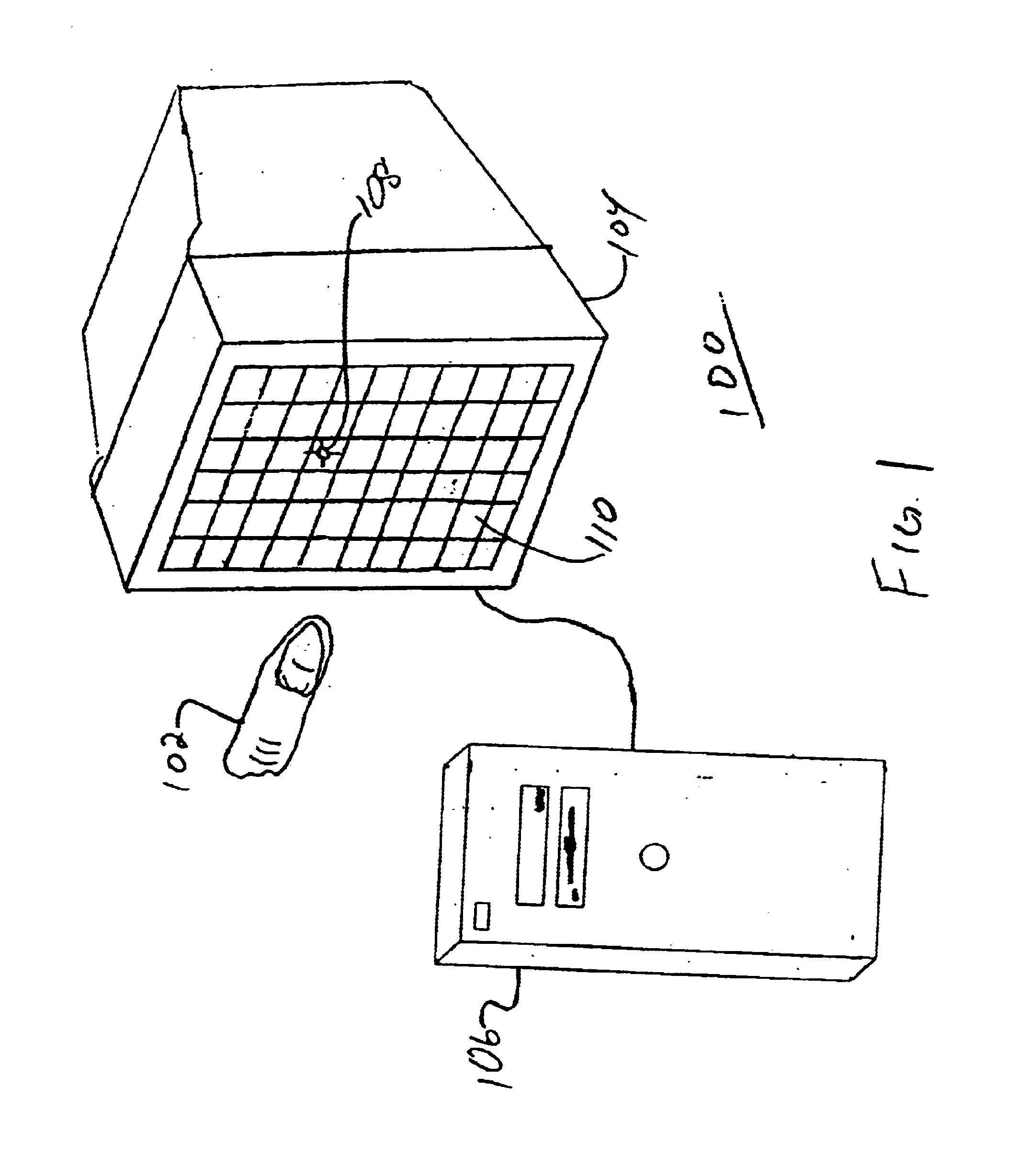
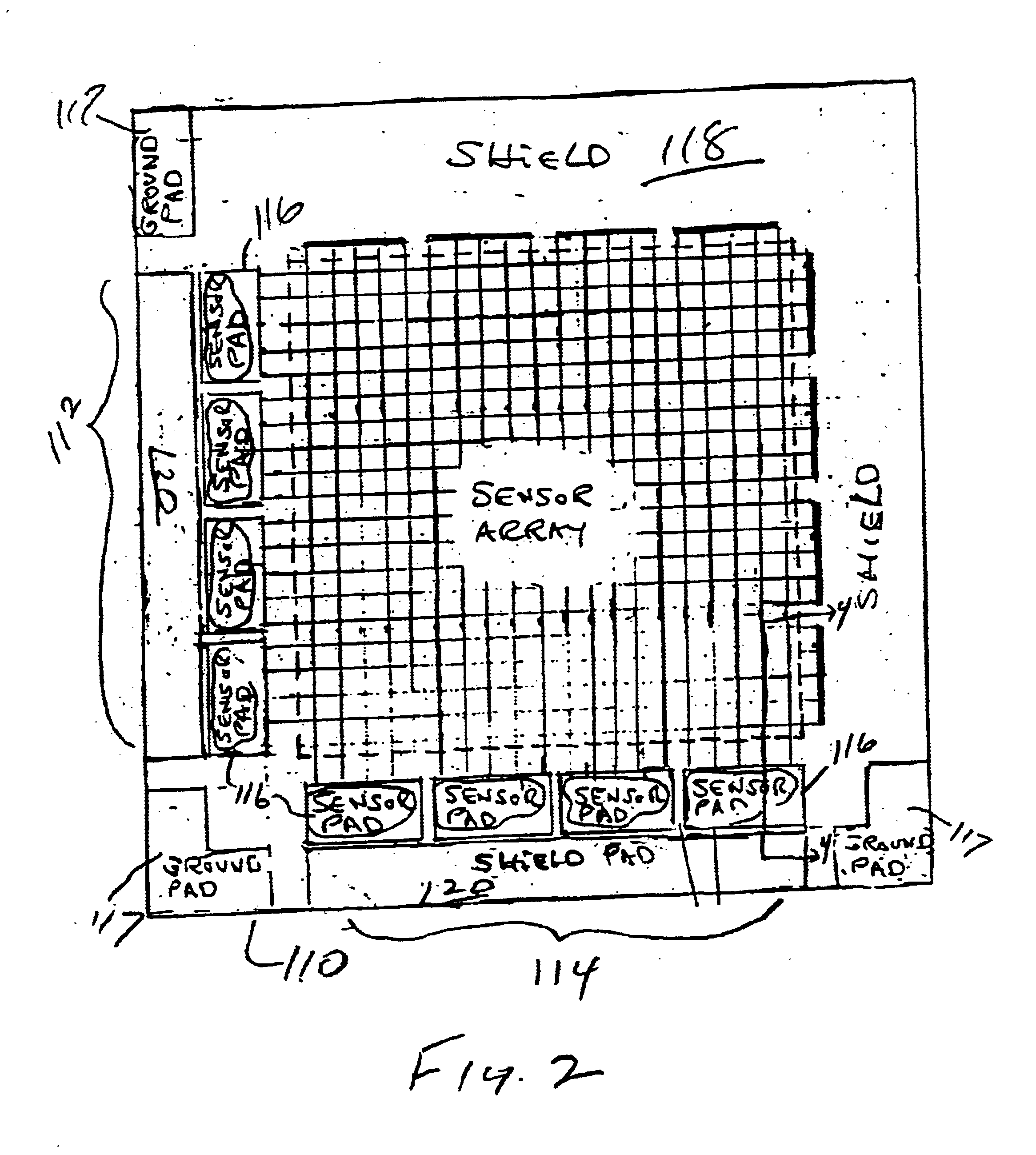
Three dimensional interactive display
InactiveUS6847354B2Improve manual input to displayed response coordinationIncrease inputInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsAudio power amplifierDisplay device
A three-dimensional (3-D) interactive display and method of forming the same, includes a transparent capaciflector (TC) camera formed on a transparent shield layer on the screen surface. A first dielectric layer is formed on the shield layer. A first wire layer is formed on the first dielectric layer. A second dielectric layer is formed on the first wire layer. A second wire layer is formed on the second dielectric layer. Wires on the first wire layer and second wire layer are grouped into groups of parallel wires with a turnaround at one end of each group and a sensor pad at the opposite end. An operational amplifier is connected to each of the sensor pads and the shield pad biases the pads and receives a signal from connected sensor pads in response to intrusion of a probe. The signal is proportional to probe location with respect to the monitor screen.
Owner:NASA
Testing apparatus and method for thin film transistor display array
InactiveUS7102378B2Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityDigital circuit testingResistance/reactance/impedenceTransistor arrayAudio power amplifier
A testing circuit and method for thin film transistor display array, for testing the yield of a thin film transistor array is provided. The testing circuit includes an array tester, a test panel (DUT) and a sense amplifier array. The sense amplifier is composed of a plurality of trans-impedance amplifier units and a plurality of parasitic capacitance discharge circuit units. Every sense amplifier includes a trans-impedance amplifier, which is implemented by an operational amplifier, two switches and an operation capacitance. The trans-impedance amplifier is used to form an integrated circuit and the output is transmitted to a sampling / hold circuit via a switch. Also included is a parasitic capacitance discharge circuit that is used to form a discharge route for the charge of the parasitic capacitance.
Owner:PRIMETECH INT CORP
Dual loop voltage regulation circuit of power supply chip
InactiveUS7193453B2Increase jitterShorten the timeTransistorElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierVoltage regulation
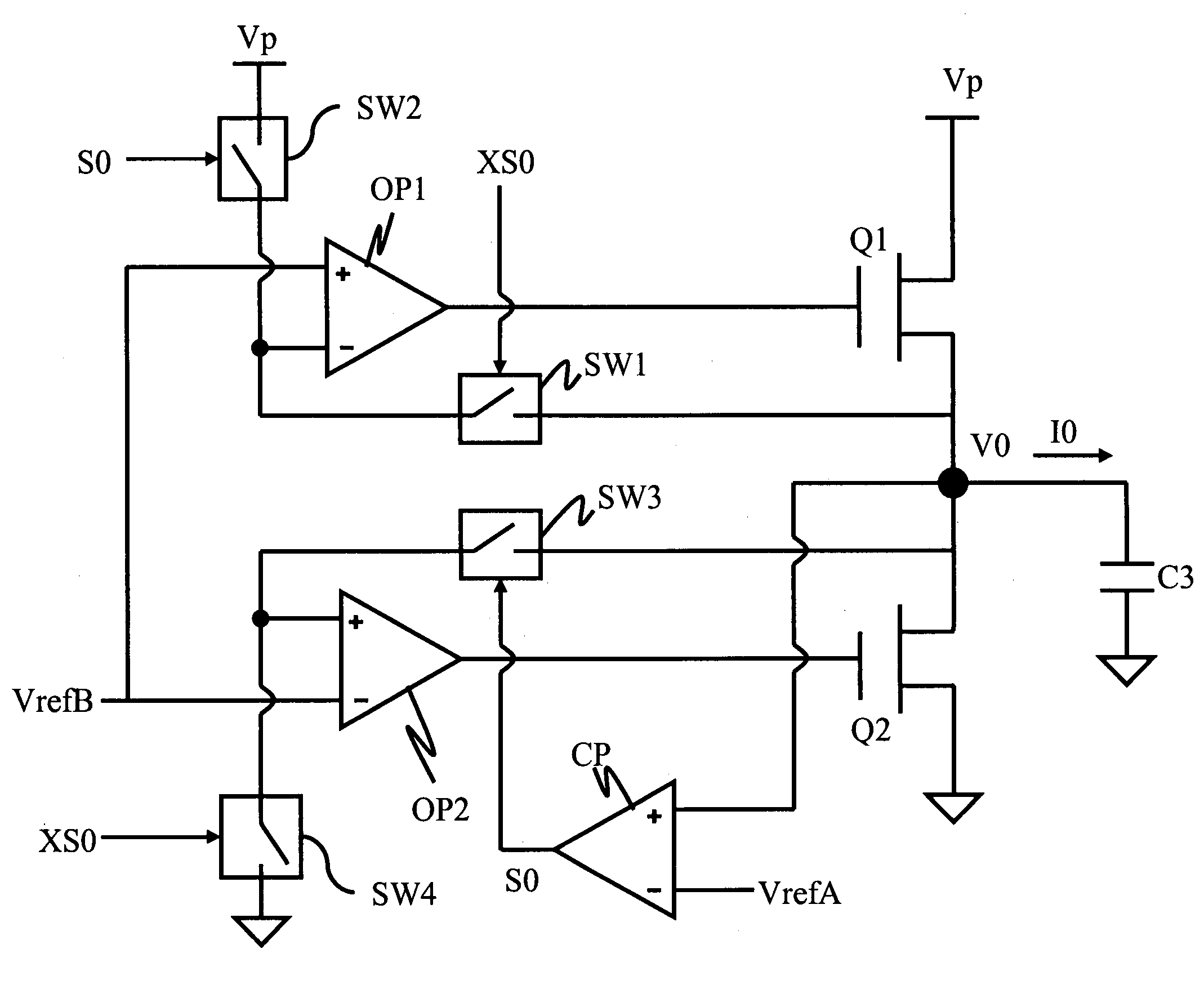
A dual loop voltage regulation circuit of power supply chip is provided, comprising a capacitor for providing a voltage signal, a comparator for comparing a first reference voltage signal and the voltage signal to output forward or backward trigger signal, a first switch triggered by a forward trigger signal, a second switch triggered by a backward trigger signal, a first operational amplifier generating a first drive signal while the first and second switches are on, a first transistor switch triggered to be on by a first drive signal to provide a current source loop, a third switch triggered by a forward trigger signal, a fourth switch triggered by a backward trigger signal, a second operational amplifier generating a second drive signal while the third and fourth switches are on, and a second transistor switch triggered to be on by a second drive signal to provide a current sink loop.
Owner:LEADTREND TECH
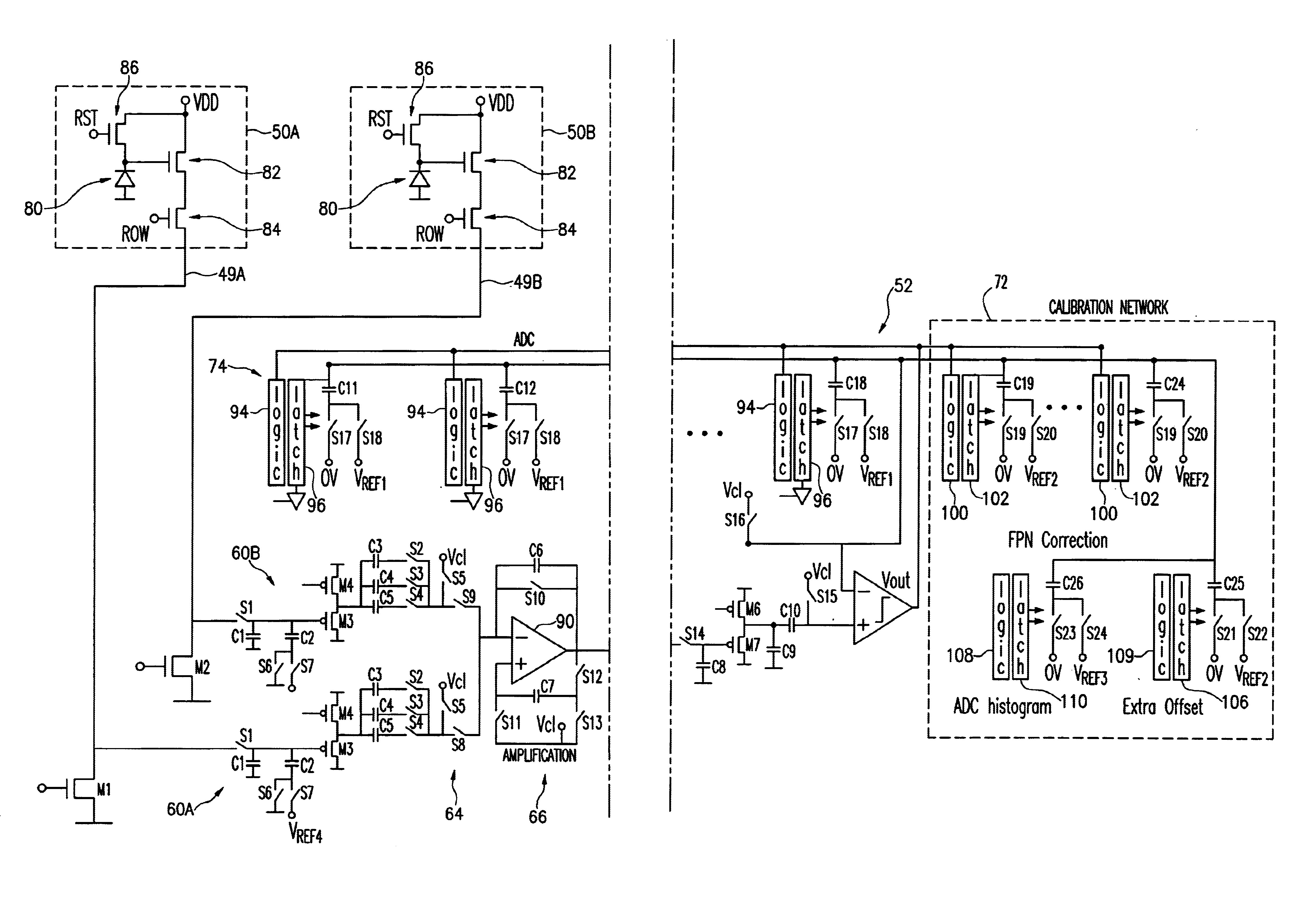
Readout circuit with gain and analog-to-digital a conversion for image sensor
InactiveUS6885396B1Increase parallel structureAttenuation bandwidthTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsSensor arrayCMOS sensor
A CMOS imager includes an array of active pixel sensors, wherein each pixel is associated with a respective column in the array. The imager also includes multiple circuits for reading out values of pixels from the active sensor array. Each readout circuit can be associated with a respective pair of columns in the array and can include first and second sample-and-hold circuits. The first and second sample-and-hold circuits are associated, respectively, with first and second columns of pixels in the array. Each readout circuit also includes an operational amplifier-based charge sensing circuit that selectively provides an amplified differential output signal based on signals sampled either by the first sample-and-hold circuit or the second sample-and-hold circuit. The readout circuit also has an analog-to-digital converter for converting the differential output to a corresponding digital signal using a successive approximation technique. Use of the readout circuit can increase the parallel structure of the overall chip, thereby reducing the bandwidth which each readout circuit must be capable of handling.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Method and system to enhance differential dynamic range and signal/noise in CMOS range finding systems using differential sensors
InactiveUS7321111B2Extend effective differential dynamic range of differentialInhibitionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSAudio power amplifier
Dynamic range of a differential pixel is enhanced by injecting, synchronously or asynchronously, a compensating offset (ΔCOMP) into a differential signal capacitor whenever magnitude of the differential signal across the capacitor exceeds a predetermined value. Positive and negative magnitudes of ΔCOMP need not be equal. The number (N) of ΔCOMP offsets made is counted. Effective differential signal capacitor voltage V(t)=Vo±N·ΔCOMP, where Vo is capacitor voltage. In other embodiments magnitude of ΔCOMP in a sequence of compensations can differ, and the sum total of compensations in recorded. Differential pixel signal / noise ratio is increased by dynamically maximizing operational amplifier gain AG for each differential pixel.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
High PSRR, high accuracy, low power supply bandgap circuit
ActiveUS7199646B1Improve accuracyIncrease output impedanceElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierCascode
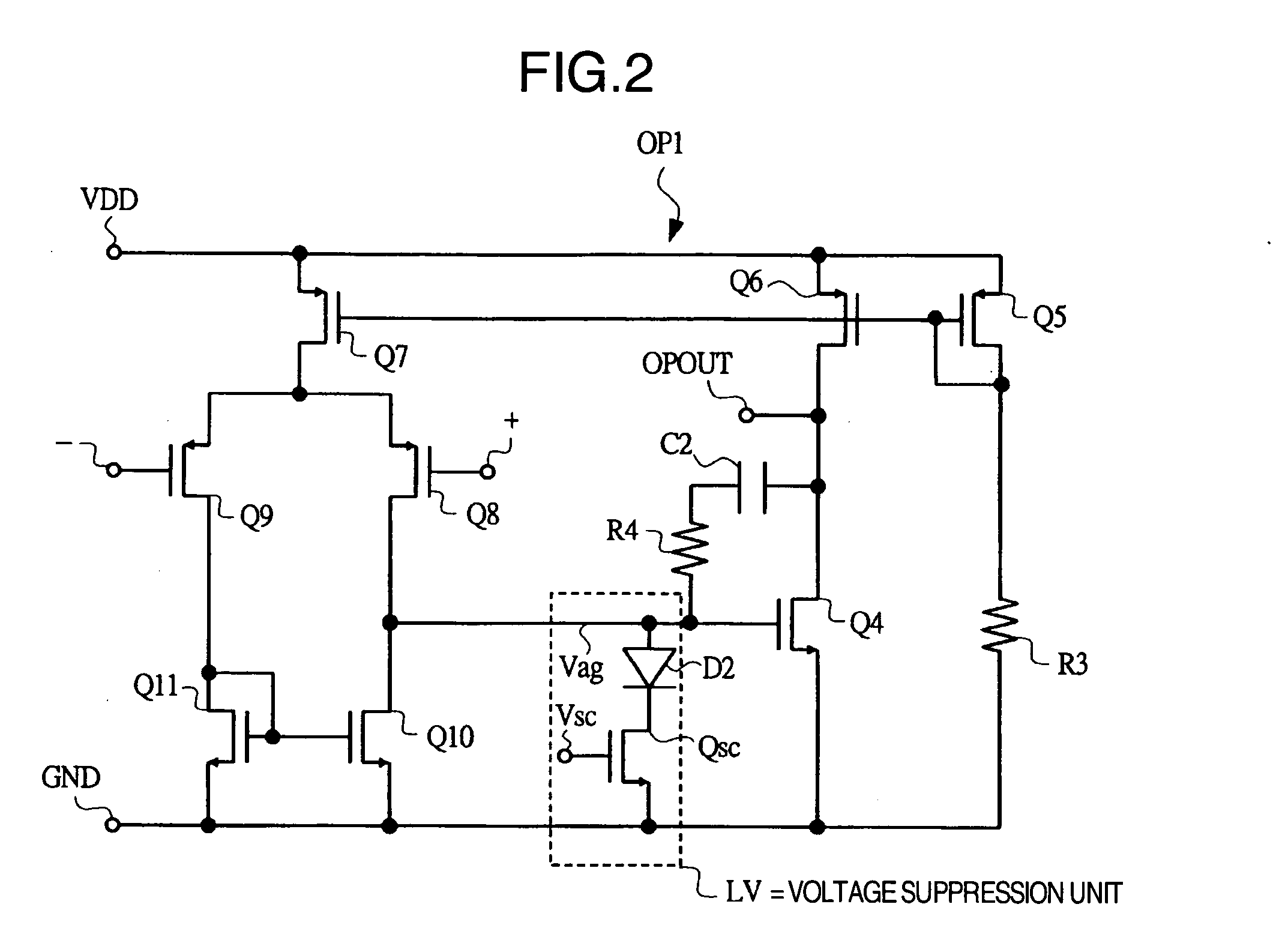
A bandgap circuit comprising a current generation circuit and a current replication circuit is provided herein. The output current of the current generation circuit is generated as a weighted sum of two currents. The circuit configuration of the current generation circuit allows it to function at low power supply voltages, e.g., on the order of 1 V. The current replication circuit includes an operational amplifier, which when configured in conjunction with MOS cascode current sources and the current generation circuit, significantly increases the accuracy and insensitivity to power supply noise of the bandgap circuit output current. A resistor may be included between the bandgap circuit output node and ground for generating a reference voltage with increased accuracy and insensitivity to power supply noise.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
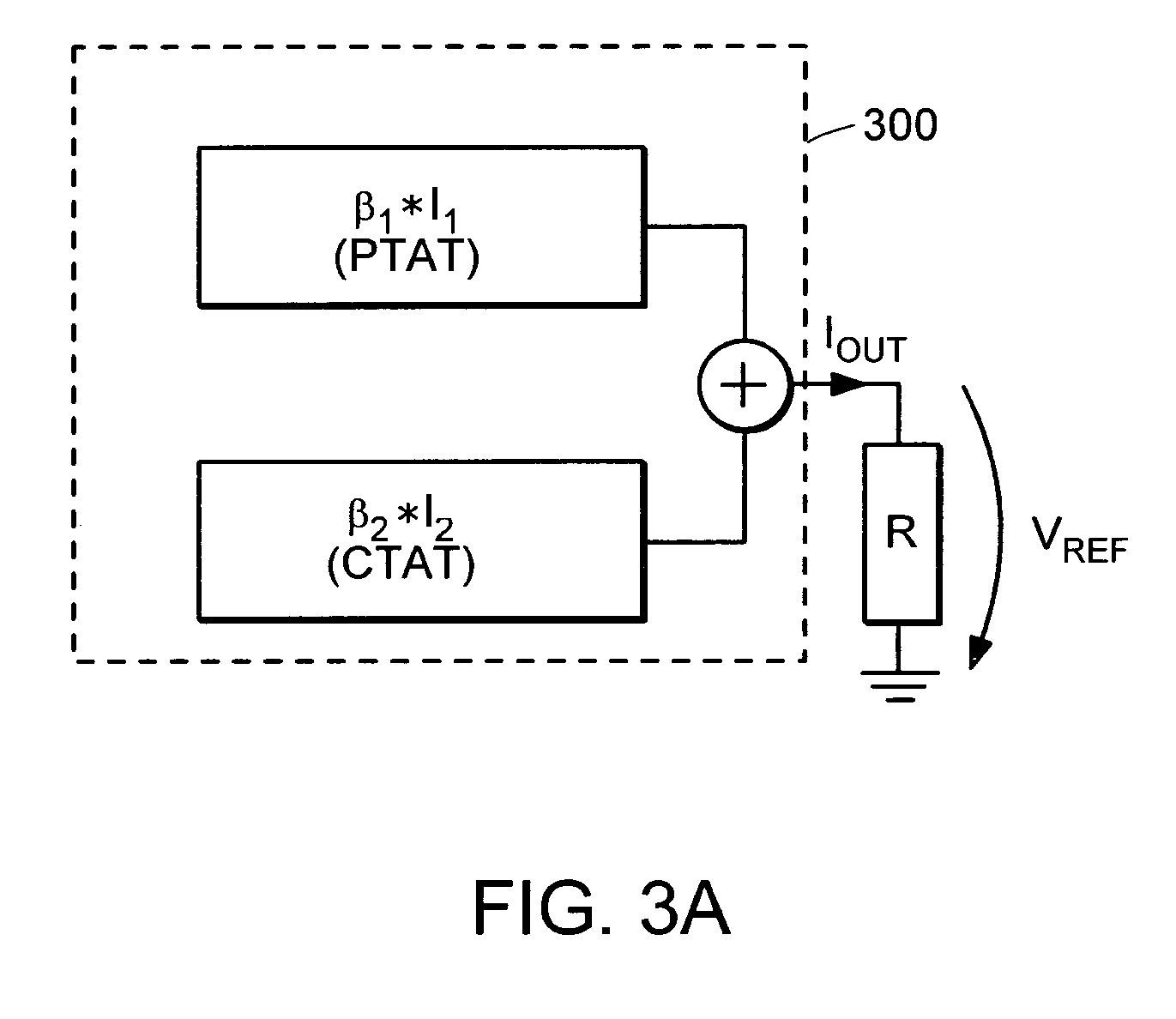
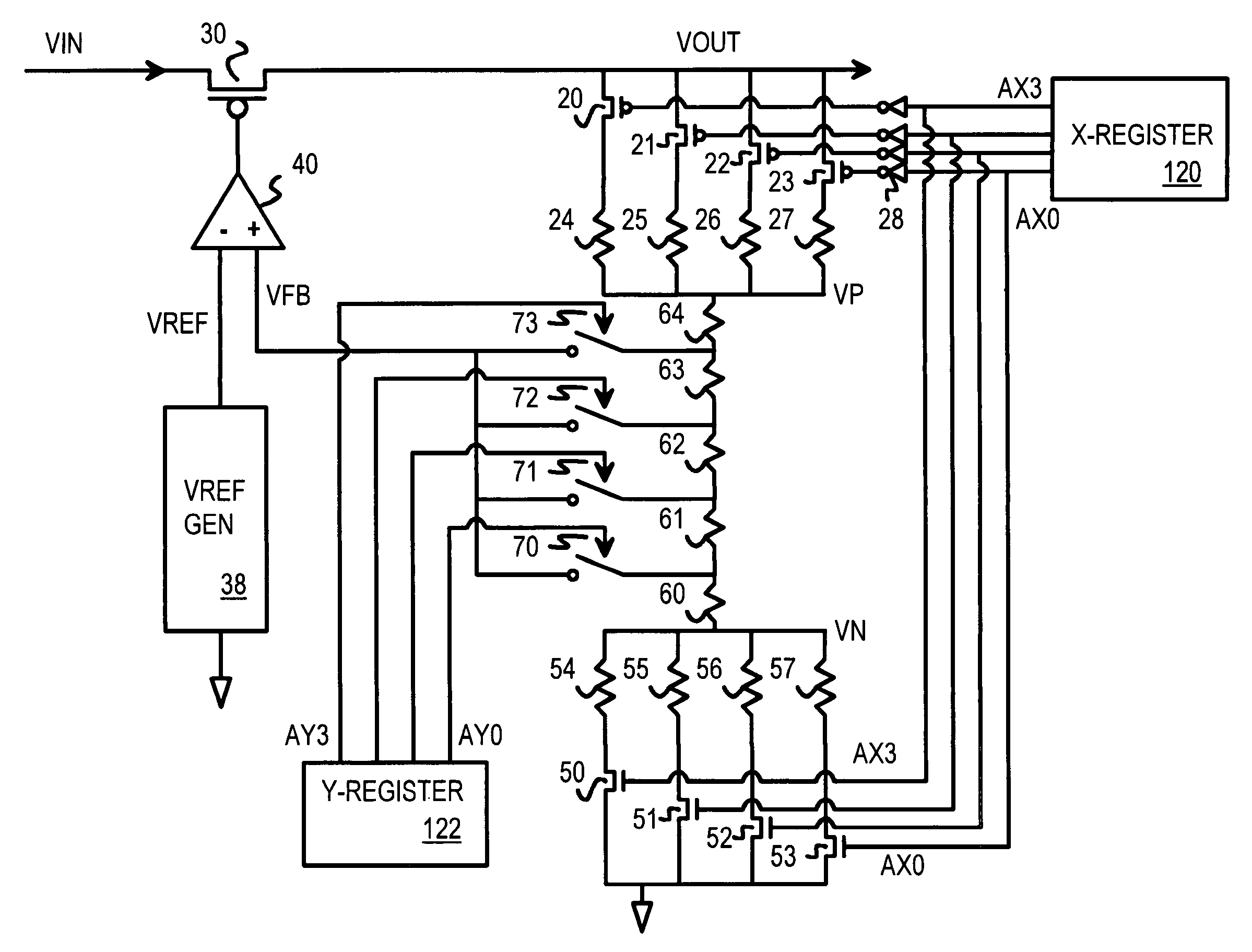
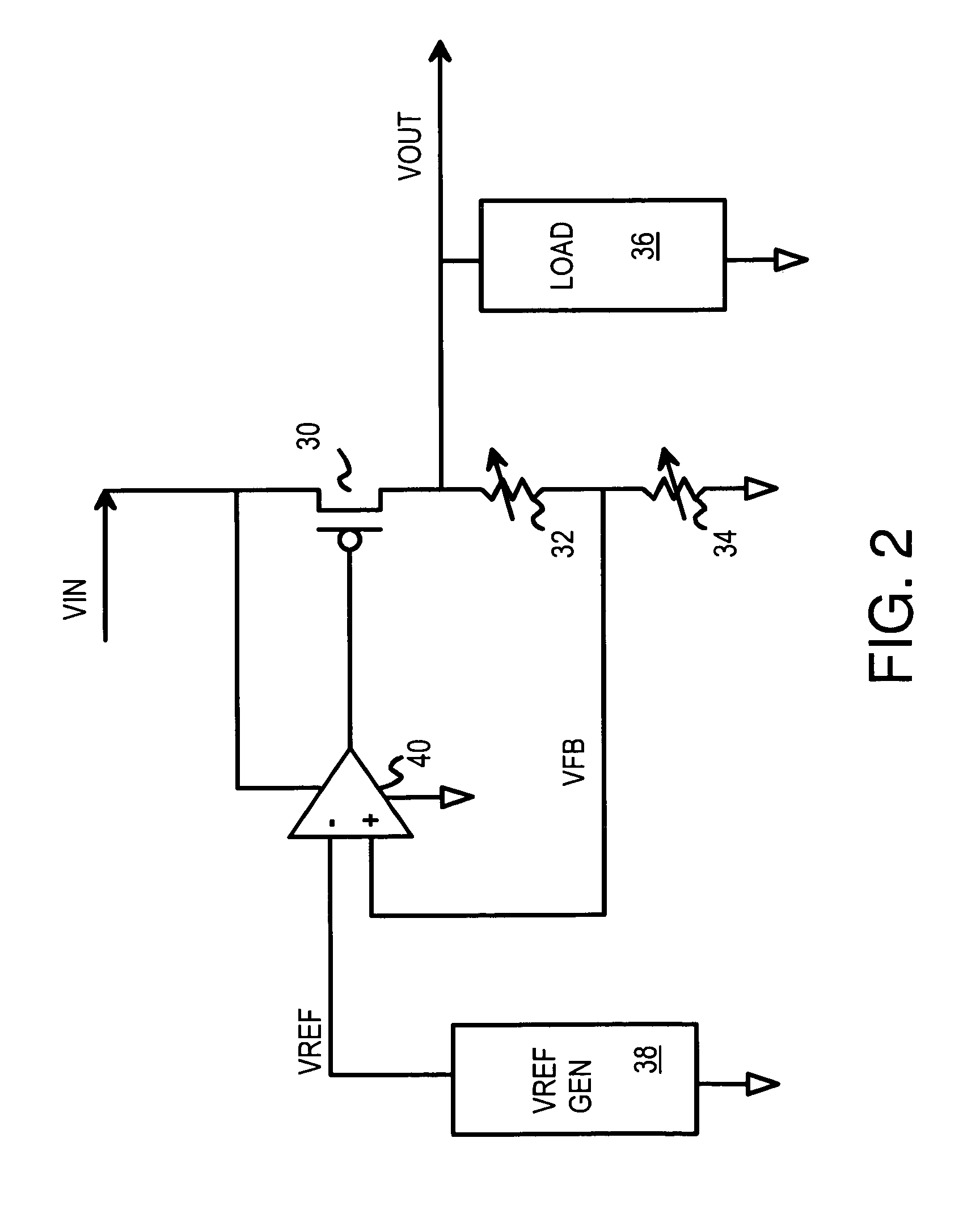
Low dropout voltage regulator with programmable on-chip output voltage for mixed signal embedded applications
ActiveUS7619402B1Multiple-port networksOne-port networksElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage generator
A programmable voltage generator has software-programmable registers that may be decoded to generate control bits that turn on select transistors that control a variable resistor network. An external power voltage is input to a regulator transistor, which has a channel resistance controlled by a gate voltage. The channel resistance of the regulator transistor produces a regulated voltage as an output. An op amp compares a reference voltage to a feedback voltage to generate the gate voltage. The feedback voltage is taken from a tap within the variable resistor network. The variable resistor network has select transistors that select one resistor between the regulated voltage and an upper node, and that select one resistor between a lower node and ground. Switches select a tap within a series of resistors between the upper and lower nodes. Y (fine) control bits select the tap while X (coarse) control bits enable select transistors.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
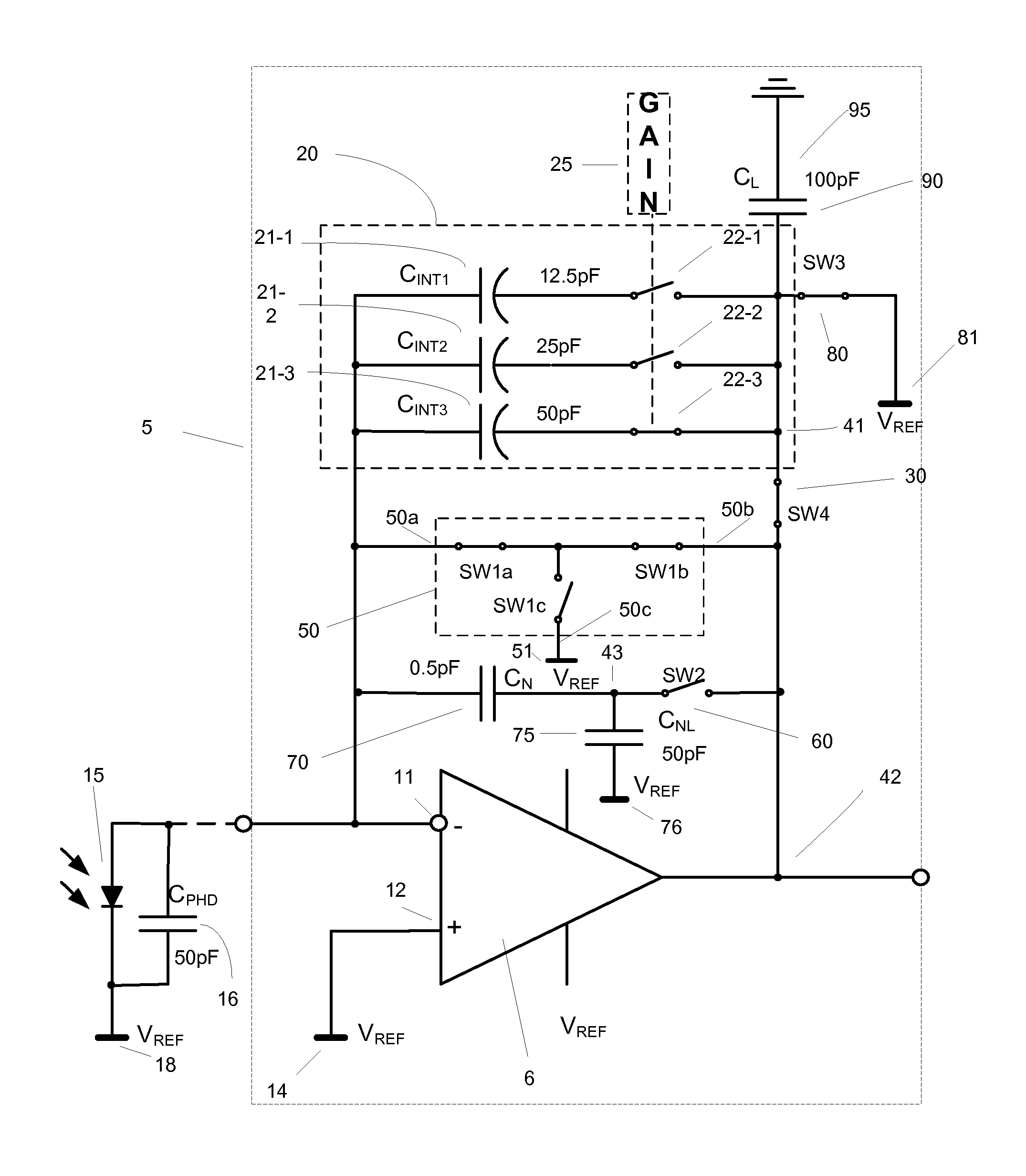
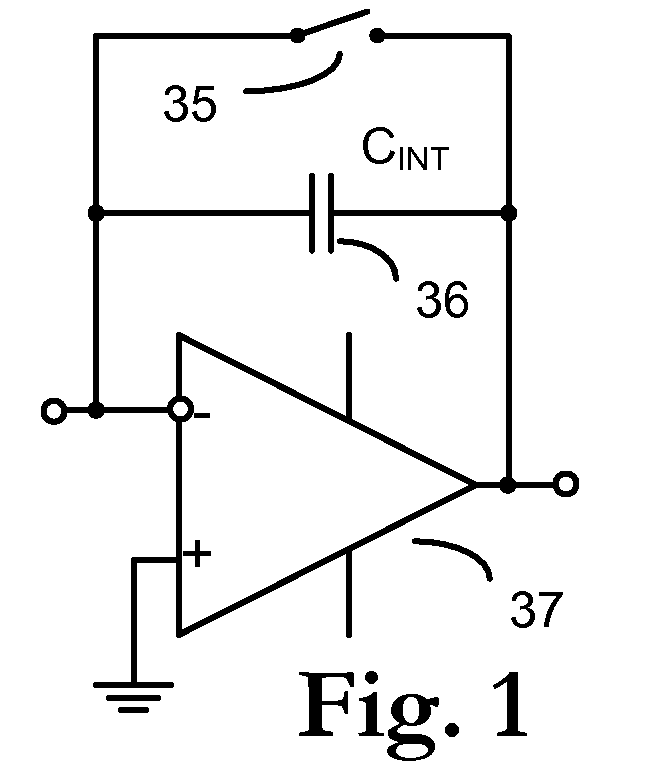
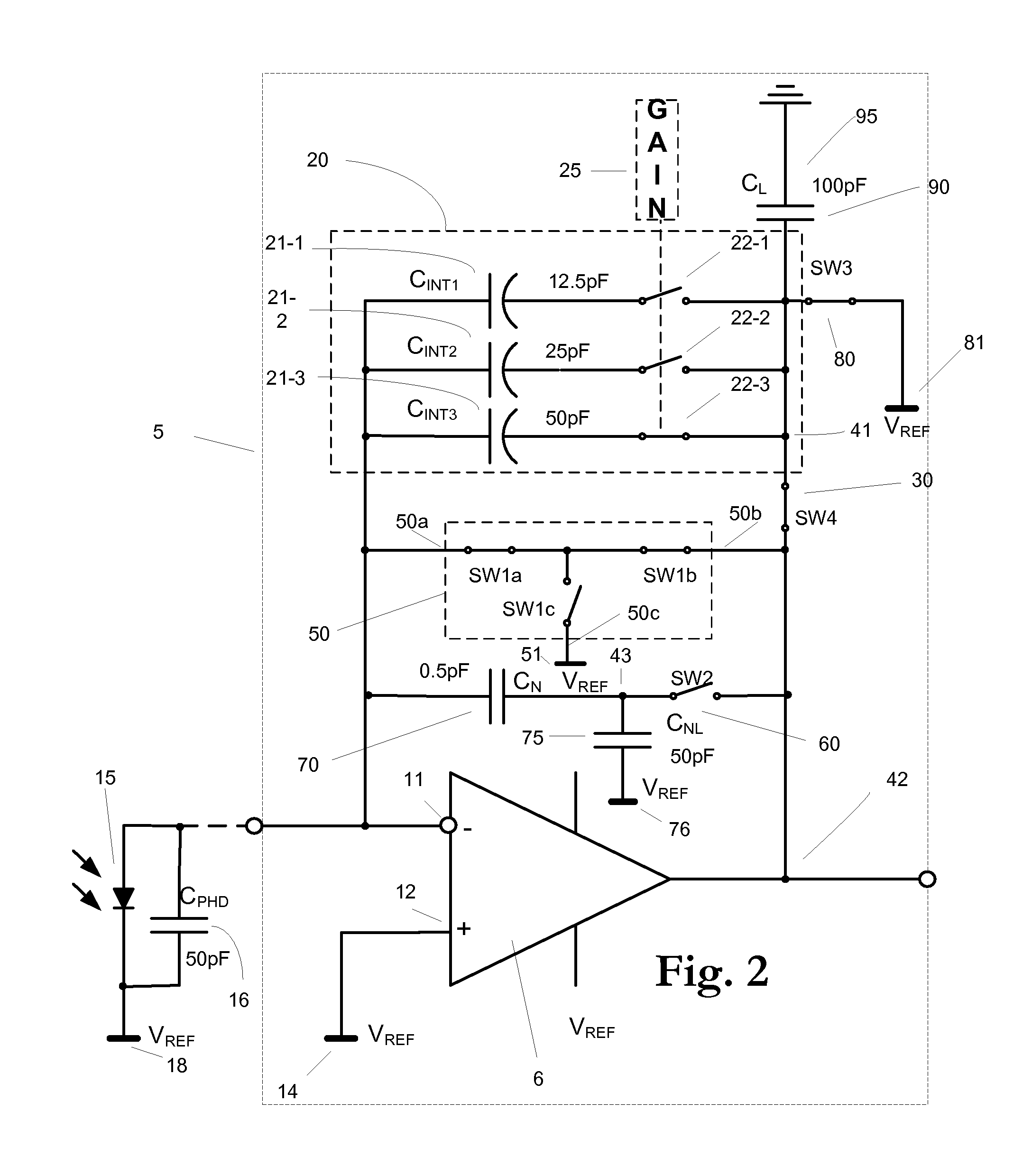
Apparatus for current-to-voltage integration for current-to-digital converter
InactiveUS20090273386A1Reduce charge injectionReduce demandComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationDigital down converterIntegrator
Owner:CUSTOM ONE DESIGN
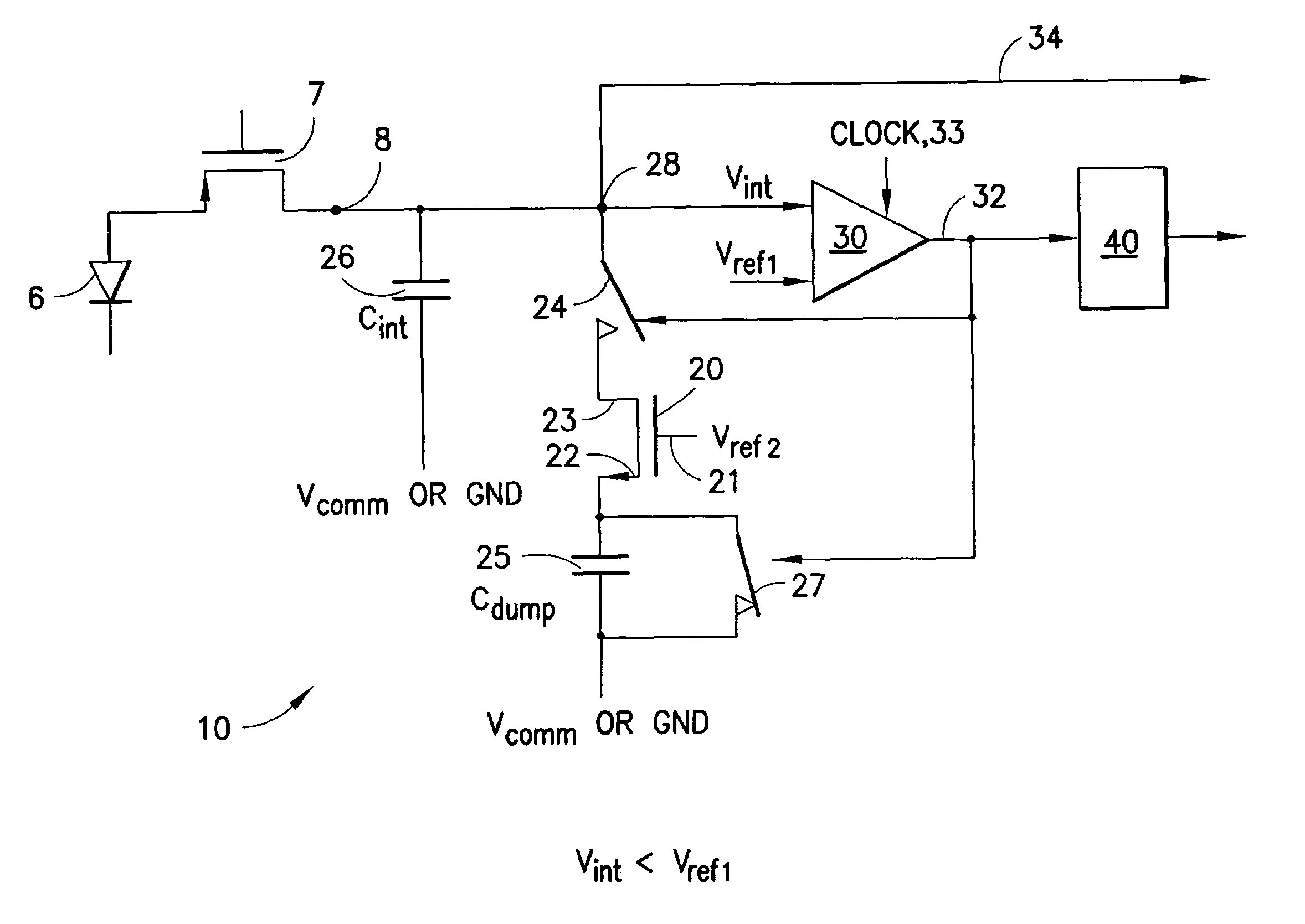
Low power current input delta-sigma ADC using injection FET reference
A low power delta-sigma analog to digital converter 10 for converting current mode signals without an amplifier includes an integration capacitor 26, a comparator 30, and a first switch 24 in parallel with one another and coupled to an integration node 28. A FET 20 and the first switch are disposed in series between a dump capacitor 25 and the integration node. A second switch 27 operates to discharge the dump capacitor, and an output of the comparator controls both switches in opposition. Preferably, no op-amps are included in the circuit, and current is supplied by an imaging component 5. In a first comparator state, the first capacitor charges, the first switch is open and the second switch is closed, and the dump capacitor discharges. In a comparator second state, the first switch is closed and the second switch is open, and the integration capacitor transfers a fixed amount of charge into the dump capacitor through an injection FET operating in saturation.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Optical amplifier repeater system
InactiveUS6259554B1Reliable transmissionOperational securityLaser detailsFibre transmissionAudio power amplifierSignal light
A repeater station 10 detects whether or not an abnormality exists in each of signal light and monitor light having arrived from a terminal station 1 or a repeater station 20, and controls, according to the result of detection, operations of optical amplifiers 11 and 12 and the monitor light. In the case where both of the signal light and monitor light arriving from the terminal station 1 via the optical transmission line for the downstream direction are abnormal, the optical amplifier 11 for the downstream direction stops its amplifying operation by itself, whereas a monitor control apparatus 13 stops the amplifying operation of the other optical amplifier for the upstream direction and also stops transmitting the monitor light to the terminal station 1 in the upstream direction.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Low voltage differential signal driver circuit and method
InactiveUS6900663B1Small RC-delaysSpeed maximizationTransmission line coupling arrangementsLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsDriver circuitElectronic load
Embodiments of the present invention relate to a low voltage differential signal driver (LVDS) circuit which comprises a current source, logic controlled switches for controlling the driver's output, an electronic load circuit coupled across the circuit, and a common-mode resistor feedback circuit coupled across the circuit, in parallel with the RC load, for tuning the driver's impedance. The driver is enabled to operate without op-amps and achieves optimum performance at 1.8 v supply voltages.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
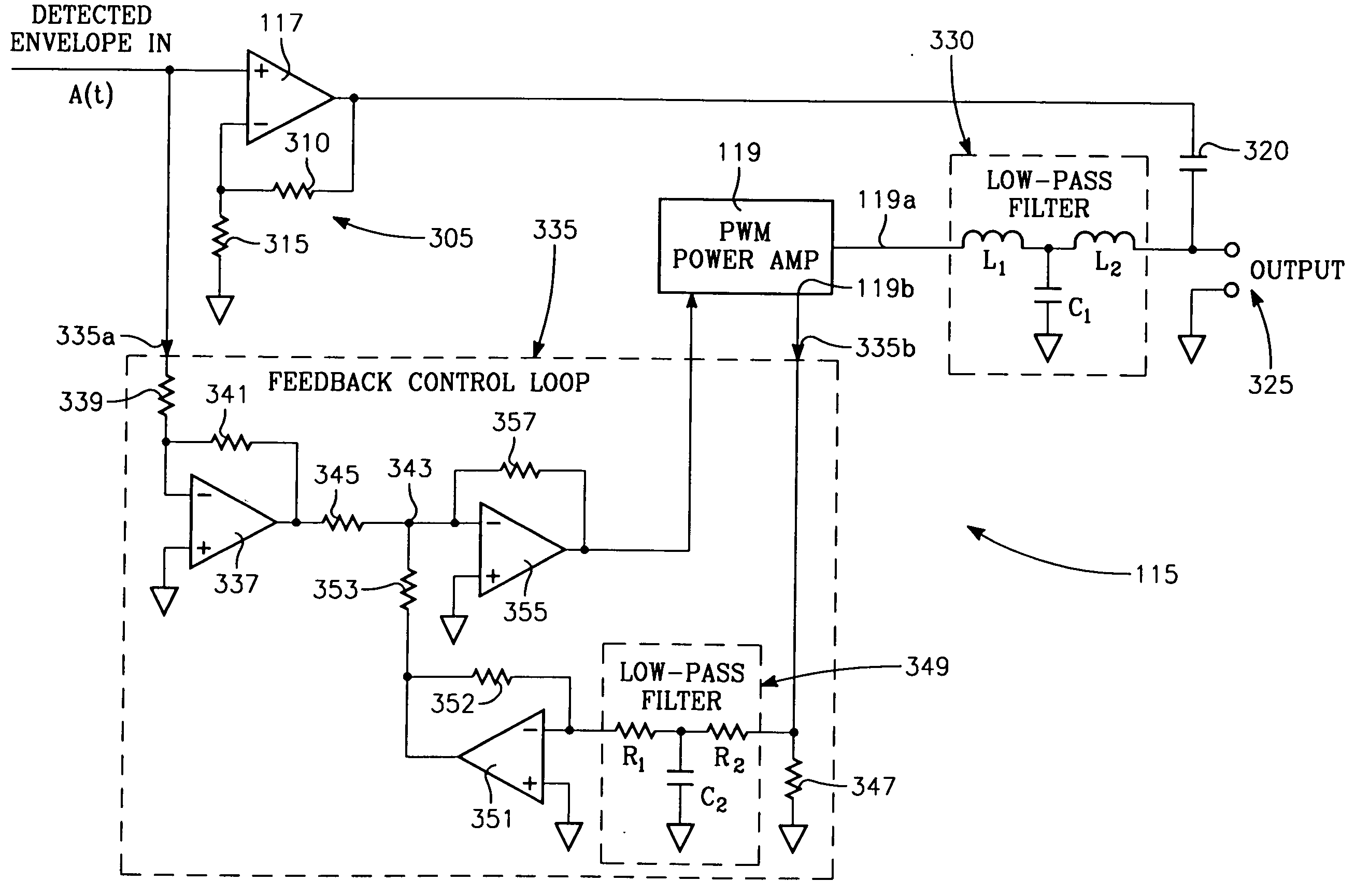
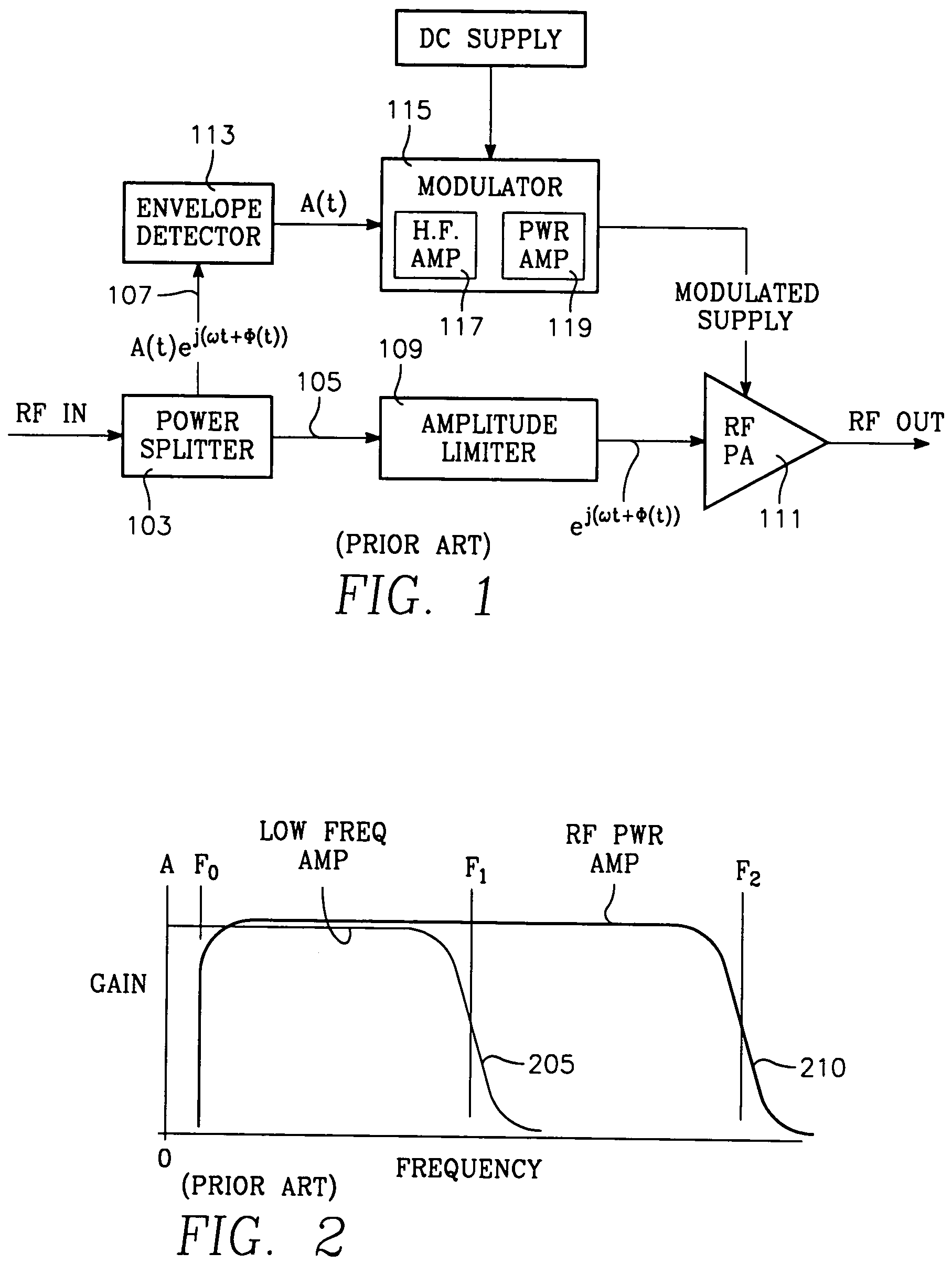
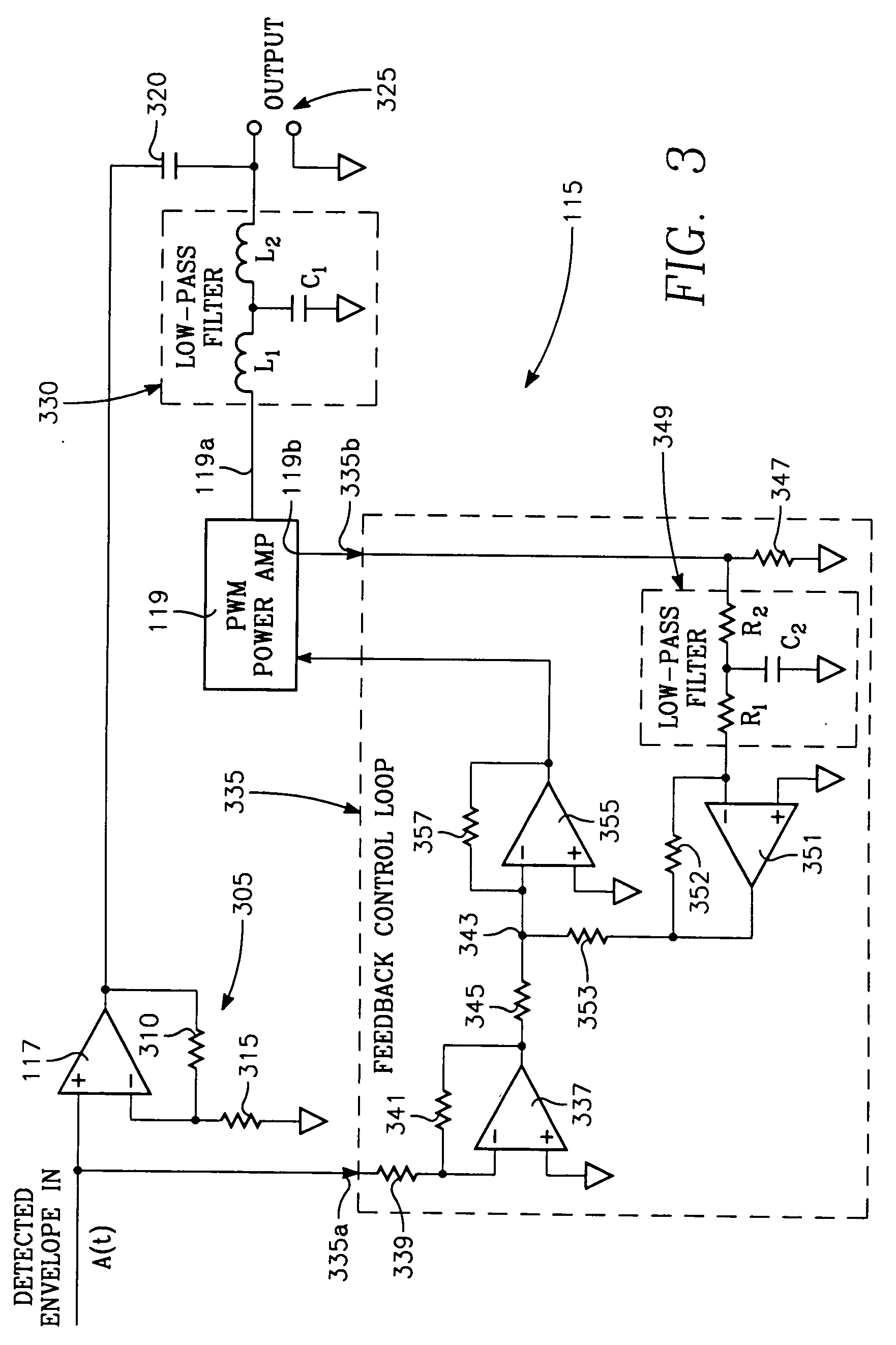
EER modulator with power amplifier having feedback loop providing soft output impedance
ActiveUS20050122163A1Efficient powerImprove efficiencyGain controlAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
An EER amplifier for amplifying an RF signal includes: (II) a first RF amplifier for amplifying the phase portion of the signal; (III) an EER modulator for amplifying the envelope or baseband portion of the signal, including: A) a high frequency operational amplifier; B) a power amplifier; C) a feedback control loop including: (1) a current-to-voltage conversion amplifier having an input coupled to a current monitoring output of the power amplifier and an output, (2) an input buffer amplifier having an input coupled to receive the envelope signal and an output; (3) a summing amplifier having: (a) an input coupled to the outputs of: (a) the current-to-voltage conversion amplifier and (b) the input buffer amplifier, and (b) an output coupled to the current control input of the power amplifier.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
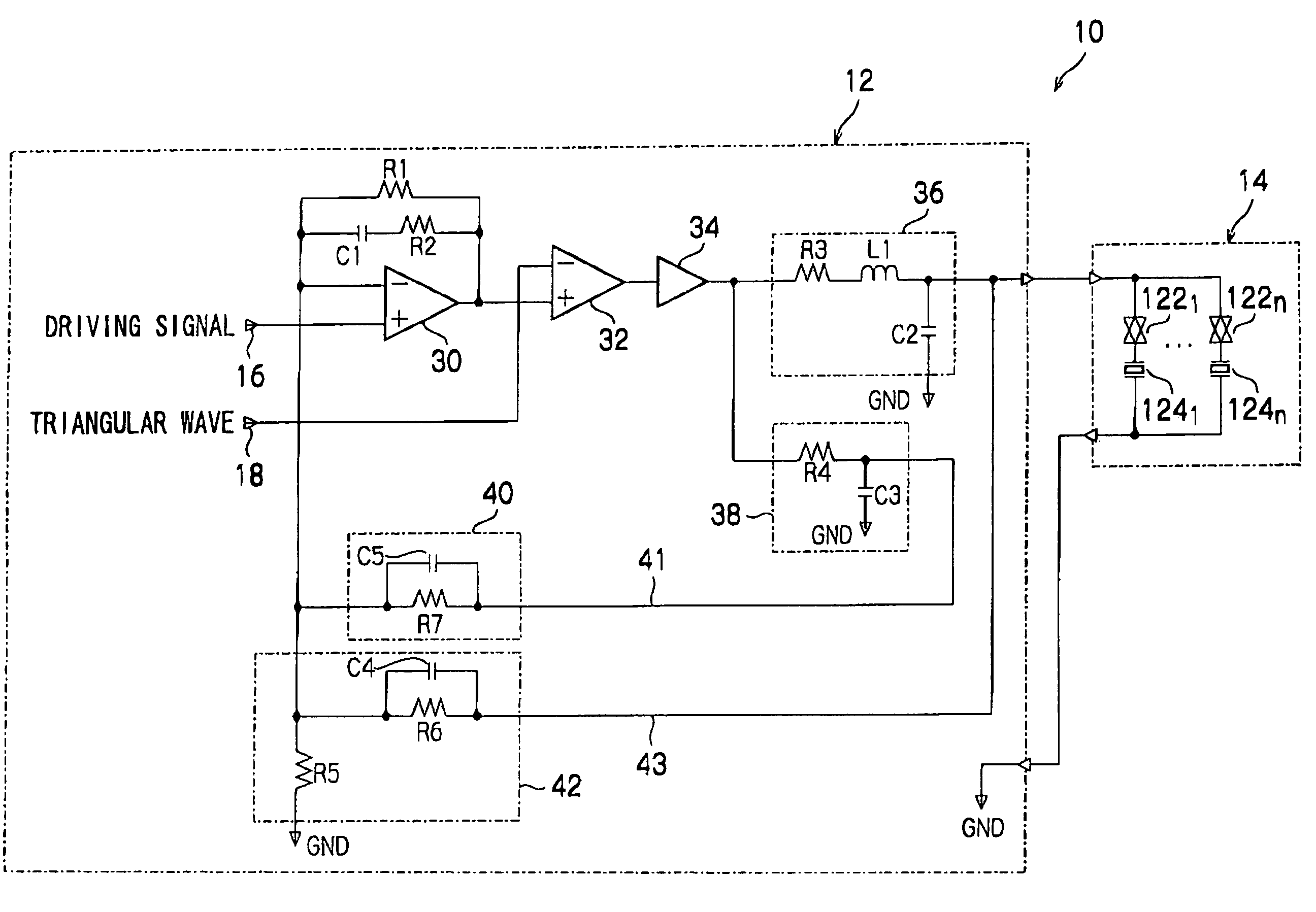
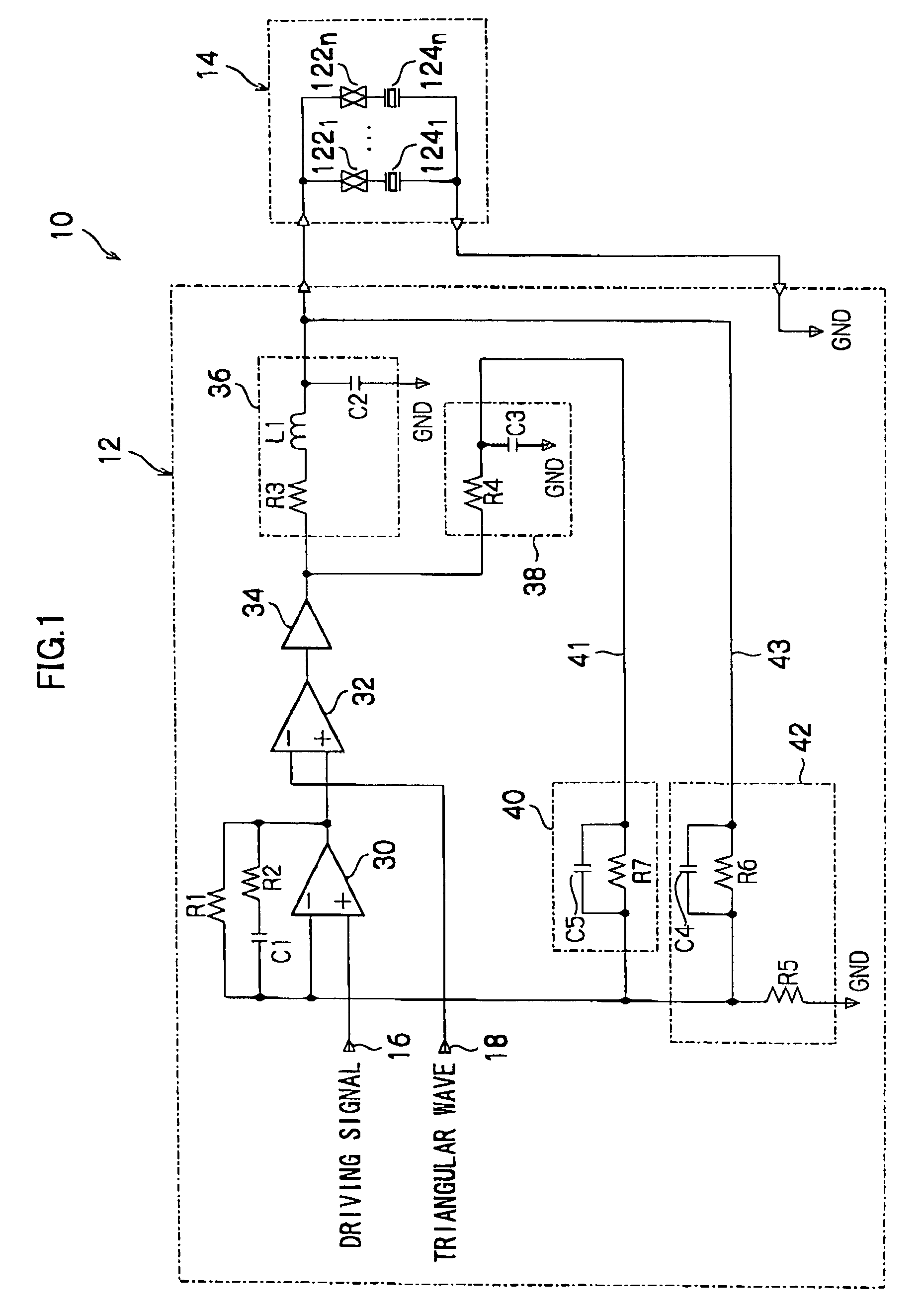
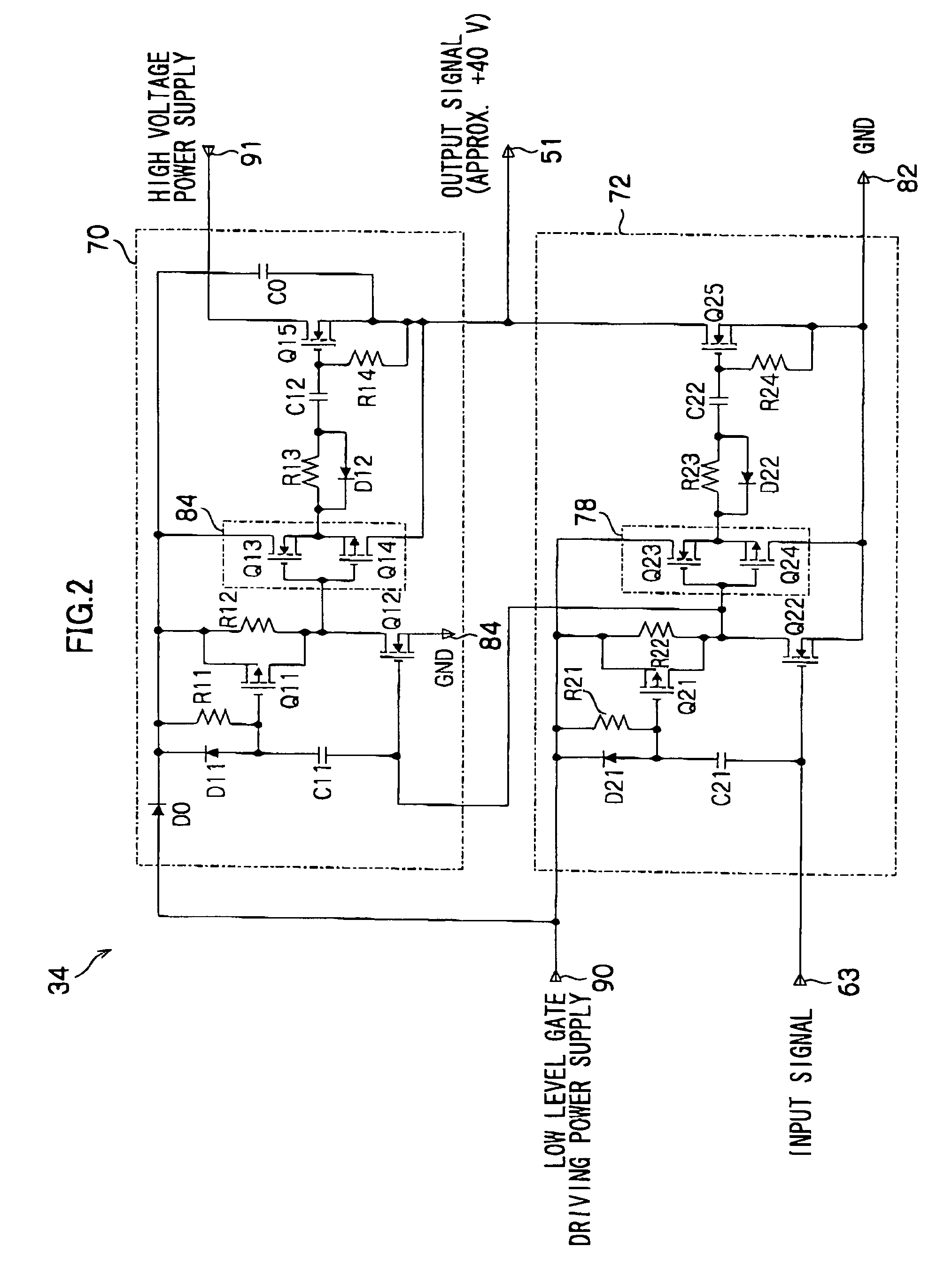
Capacitive load driving circuit, droplet ejection device, droplet ejection unit and inkjet head driving circuit
InactiveUS20050231179A1Reduced stabilityOther printing apparatusAc network voltage adjustmentCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A capacitive load driving circuit which includes an operational amplifier, a pulse width modulator, a digital power amplifier, a first filter, a first feedback circuit and a second feedback circuit. The operational amplifier outputs a differential signal between a signal fed back to the inverting input terminal and an input signal inputted to the non-inverting input terminal. The pulse width modulator pulse width-modulates output from the operational amplifier and outputs a digital signal. The digital power amplifier amplifies power of the digital signal. The first filter smooths output of the digital power amplifier and inputs the smoothed signal to the capacitive load as the driving signal. The first feedback circuit feeds back the driving signal outputted from the first filter to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier. The second feedback circuit feeds back a signal outputted from the digital power amplifier, which signal includes a phase which is advanced relative to the driving signal, to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
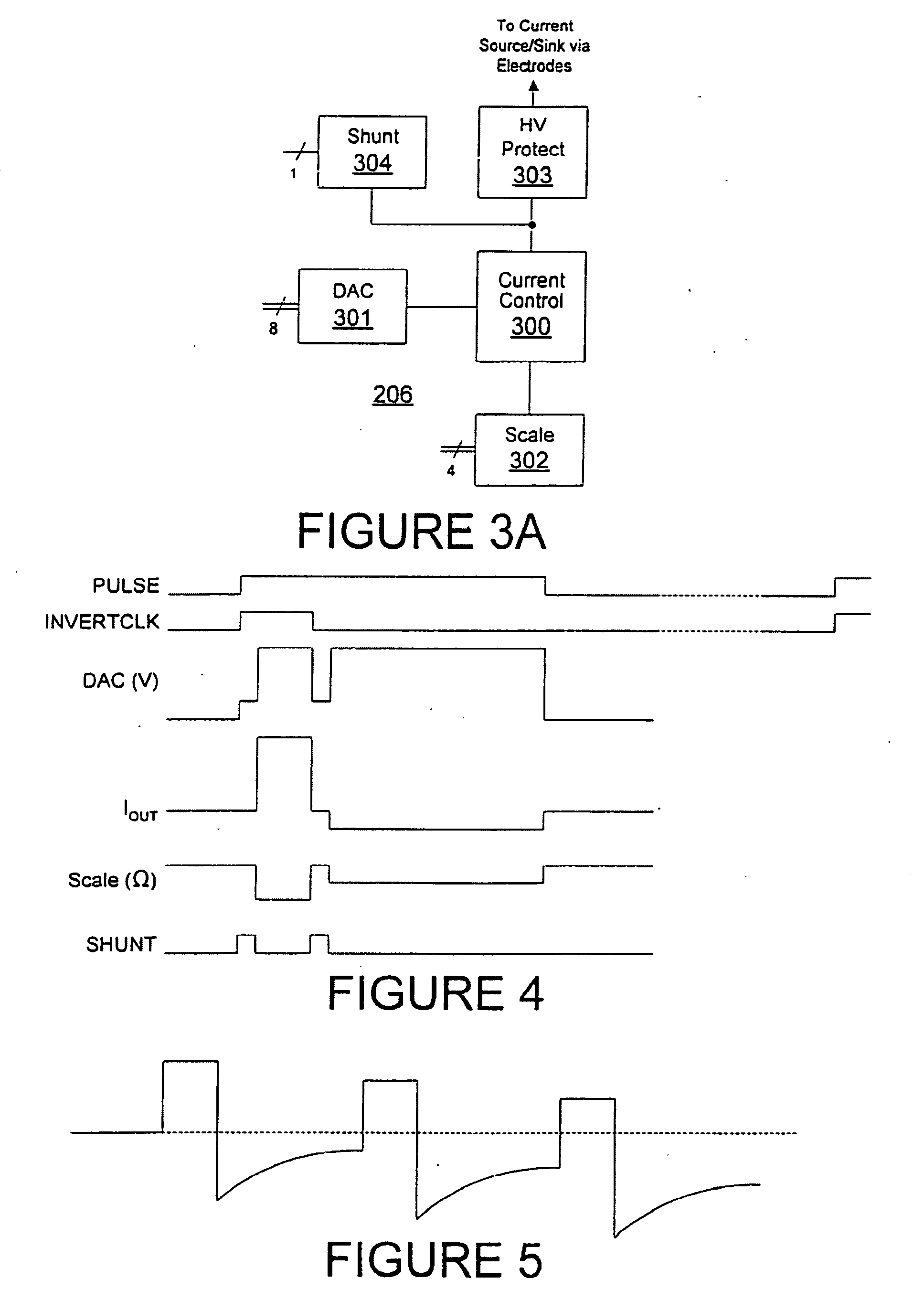
Systems and methods for precharging circuitry for pulse generation
ActiveUS20050245978A1Low powerLow costElectrotherapyApparatus without intermediate ac conversionLeading edgeAudio power amplifier
A low power (and lower cost) implementation for amplifier used in delivering a stimulation pulse is provided according to embodiments through use of a pre-charge period for each pulse. For example, a voltage at a variable output terminal of a digital-to-analog converter is increased on the leading edge of PULSE and INVERTCLK signals to result in an output of an operational amplifier increasing to a predetermined voltage prior to output of a stimulation pulse, according to an embodiment. A shunt path may be implemented to shunt current away from a load during the pre-charge period.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
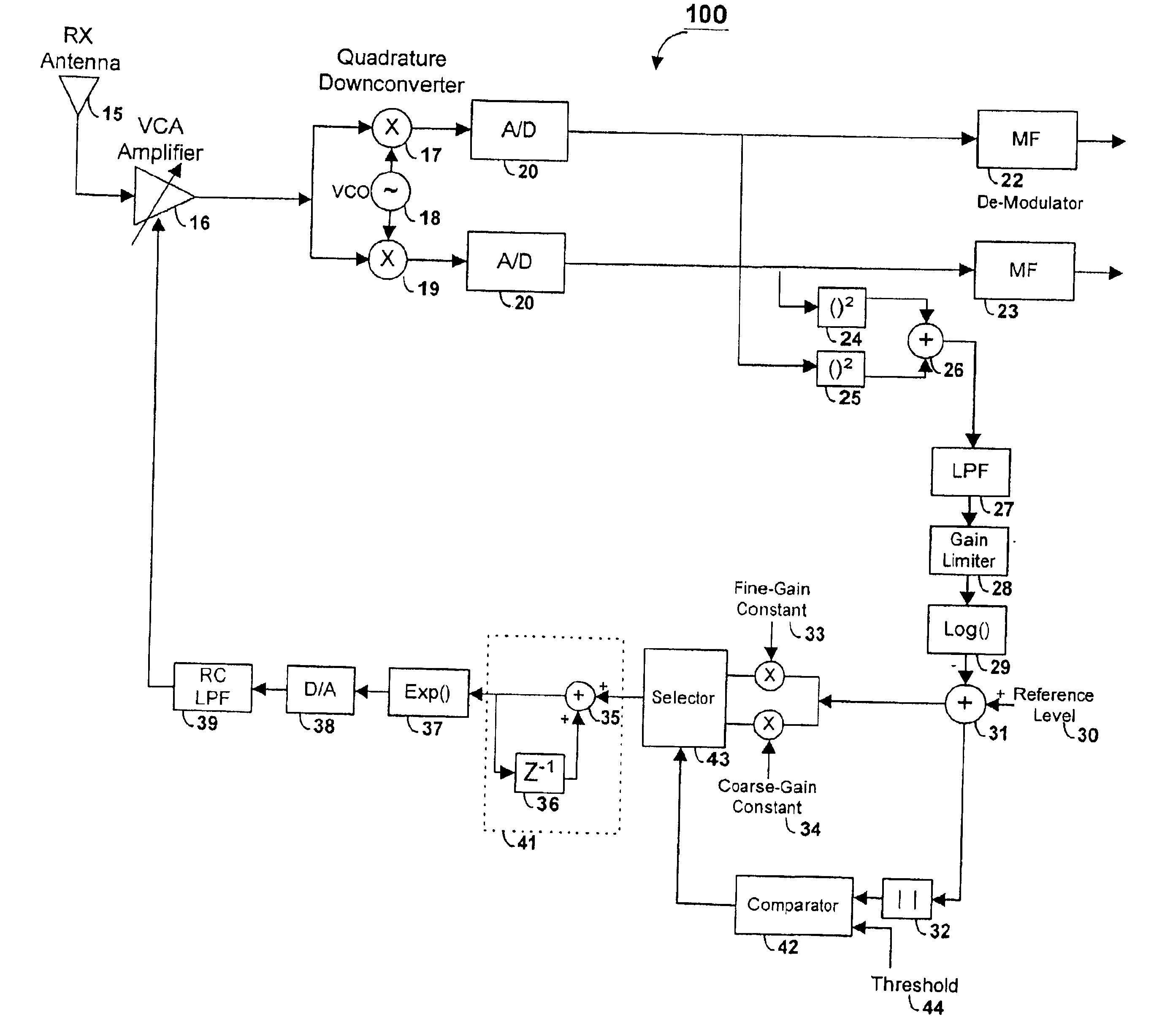
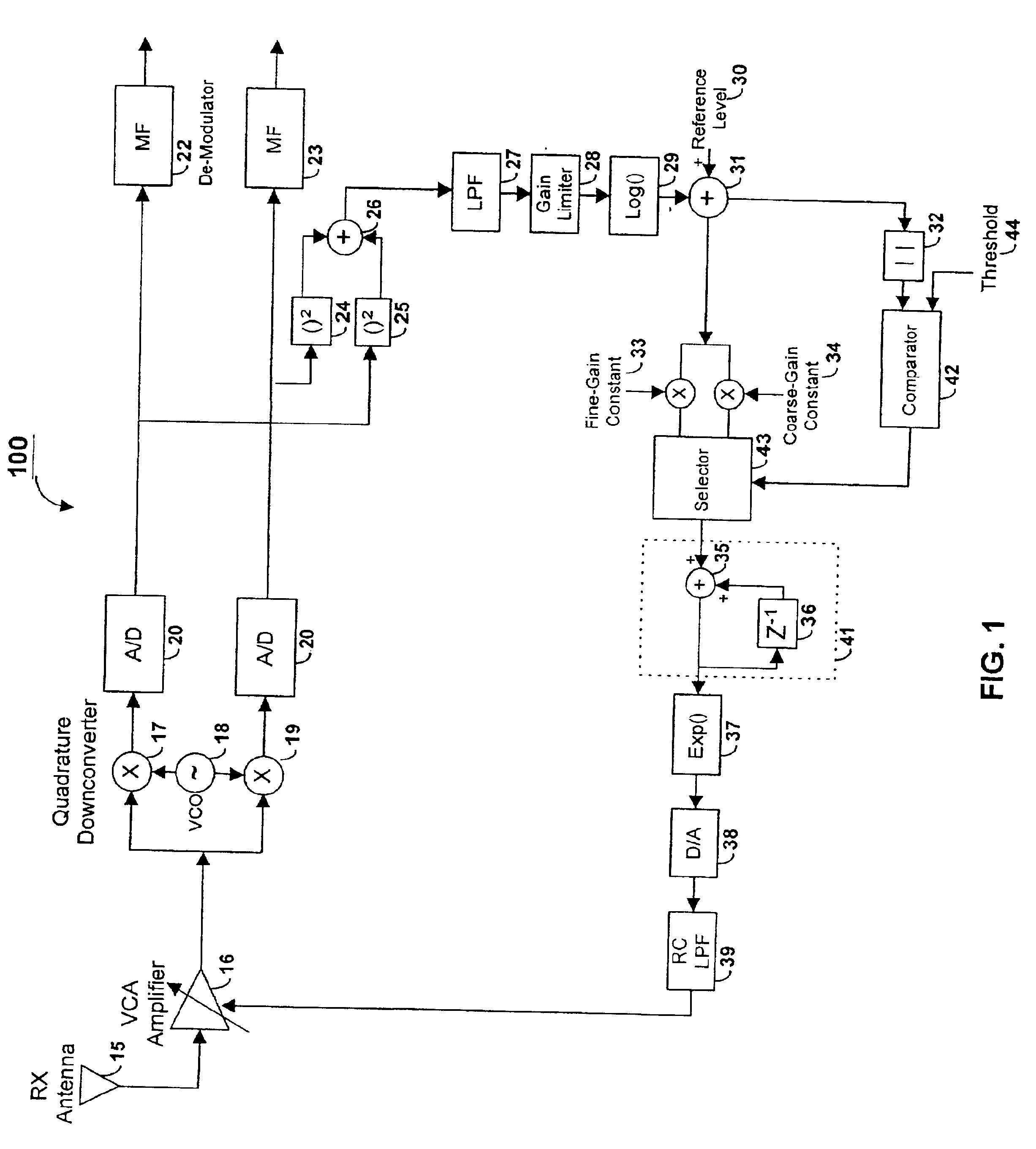
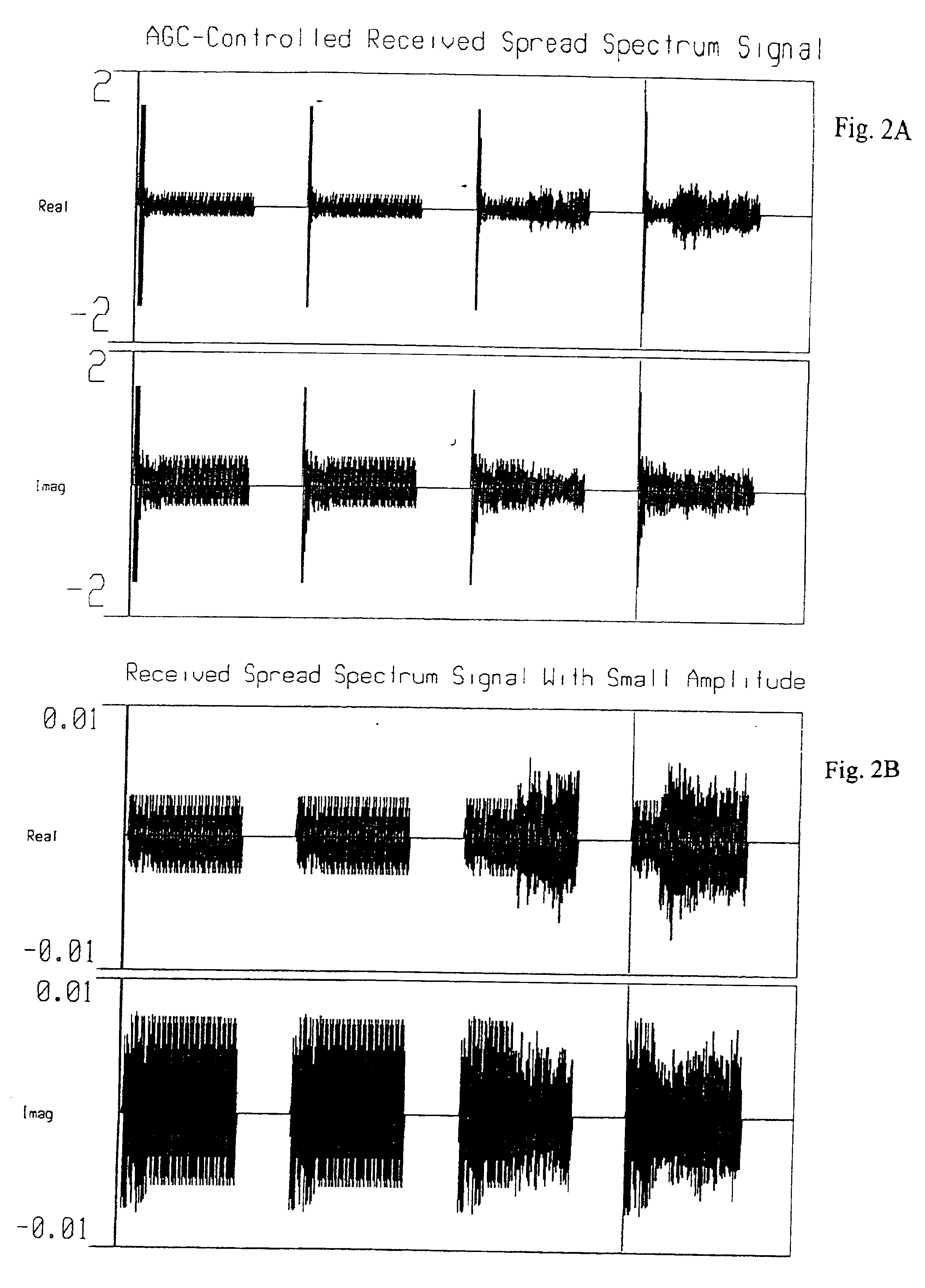
Method and apparatus of a fast two-loop automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS6843597B1Small sizeLow costGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
In a burst-mode, high-speed spread-spectrum communications system, faster convergence of a receiver's automatic gain control (AGC) circuit reduces the time required to bring a received signal within the operating range of an operation amplifier and other radio-frequency and digital sections of the receiving system. A gain control circuit includes a coarse-gain feedback loop and a fine-gain feedback loop to improve convergence speed and at the same time maintain the stability of the AGC circuit. The coarse-gain feedback loop quickly brings the received signal, using a large gain signal, to the desired operating range. The fine-gain feedback loop uses a smaller gain signal to gradually smooth the received signal to avoid saturation on the A / D converters.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
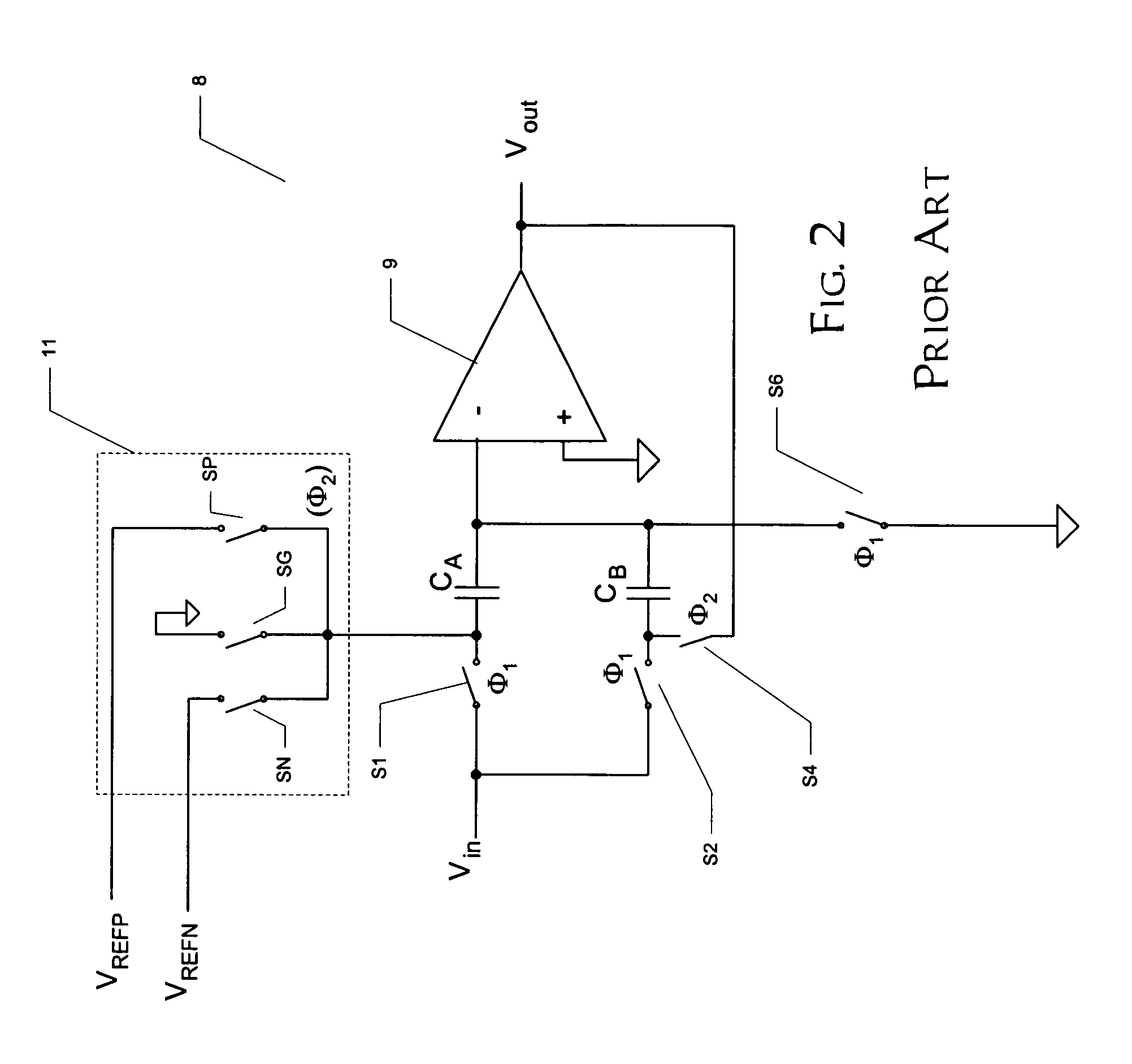
Switched-capacitor circuit with scaled reference voltage
ActiveUS7009549B1Improve precisionImprove stabilityElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
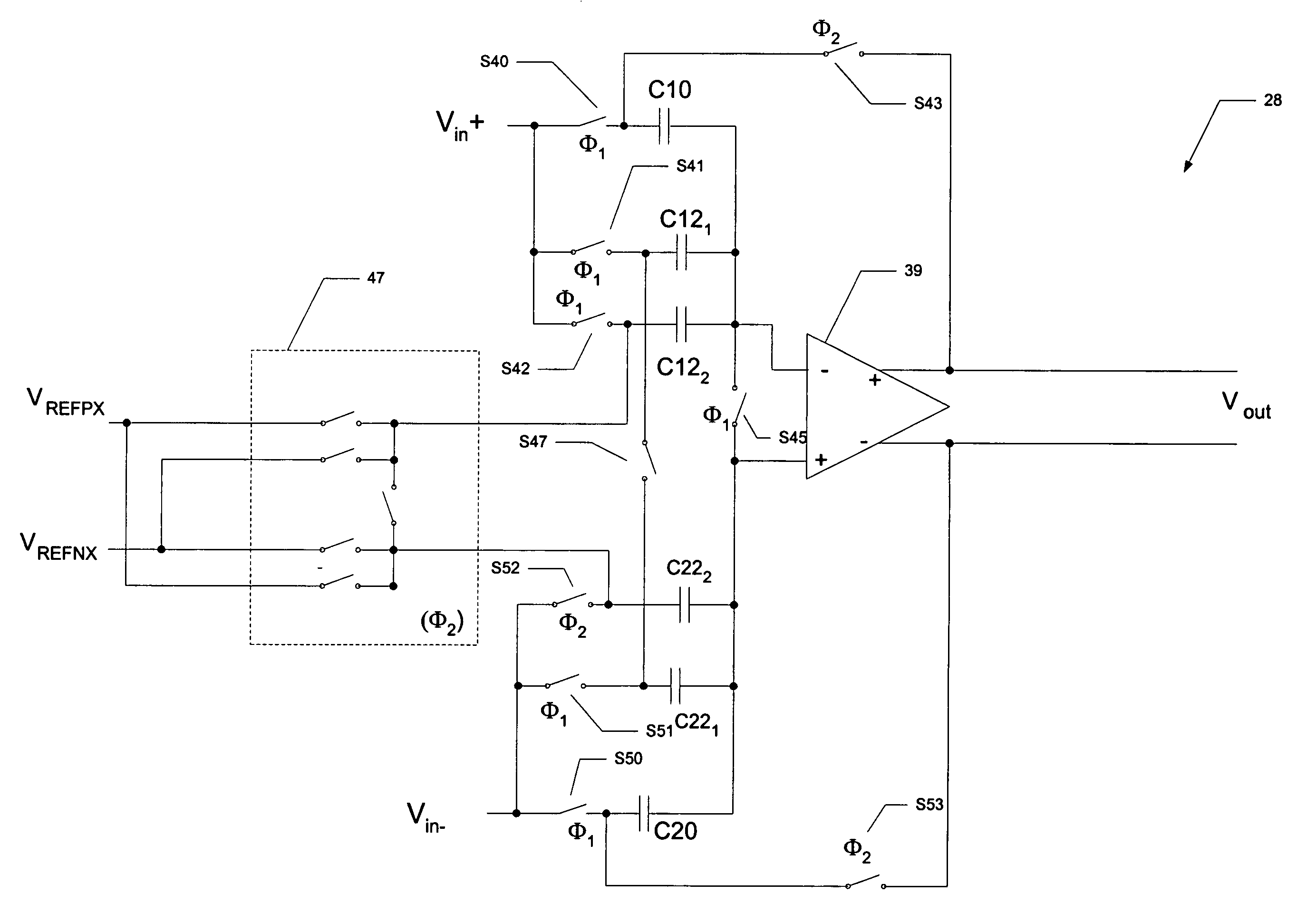
A pipelined analog-to-digital converter (ADC) (30) with improved precision is disclosed. The pipelined ADC (30) includes a sequence of stages (20), each of which includes a sample-and-hold circuit (22), an analog-to-digital converter (23), and the functions of a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) (25), an adder (24), and a gain stage (27) at which a residue signal (RES) is generated for application to the next stage (20) in the sequence. A multiplying DAC (28) performs the functions of the DAC (25), adder (24), and gain stage (27) in the stage (20), and is based on an operational amplifier (29). Sample capacitors (C10, C20) and reference capacitors (C122, C222) receive the analog input from the sample-and-hold circuit (22) in a sample phase; parallel capacitors (C121, C221) are provided to maintain constant circuit gain. Extended reference voltages (VREFPX, VREFNX) at levels that exceed the output range (V0+, V0−) of the operational amplifier (29) are applied to the reference capacitors, in response to the digital output of the analog-to-digital converter (23) in its stage (20). The reference capacitors (C12, C22) are scaled according to the extent to which the extended reference voltages (VREFPX, VREFNX) exceed the op amp output levels (V0+, V0−). The effects of noise on the reference voltages (VREFPX, VREFNX) on the residue signal (RES) are thus greatly reduced.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
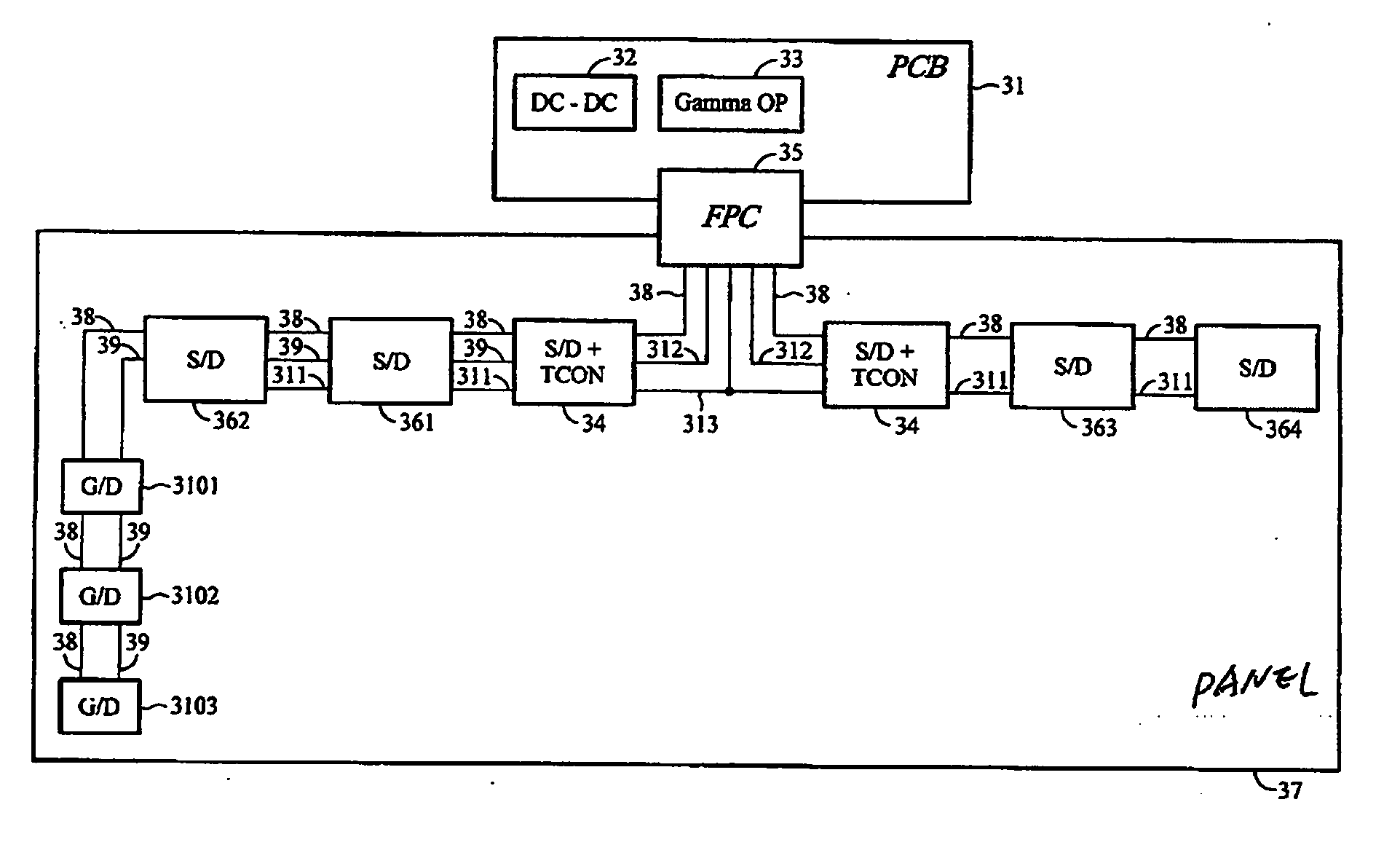
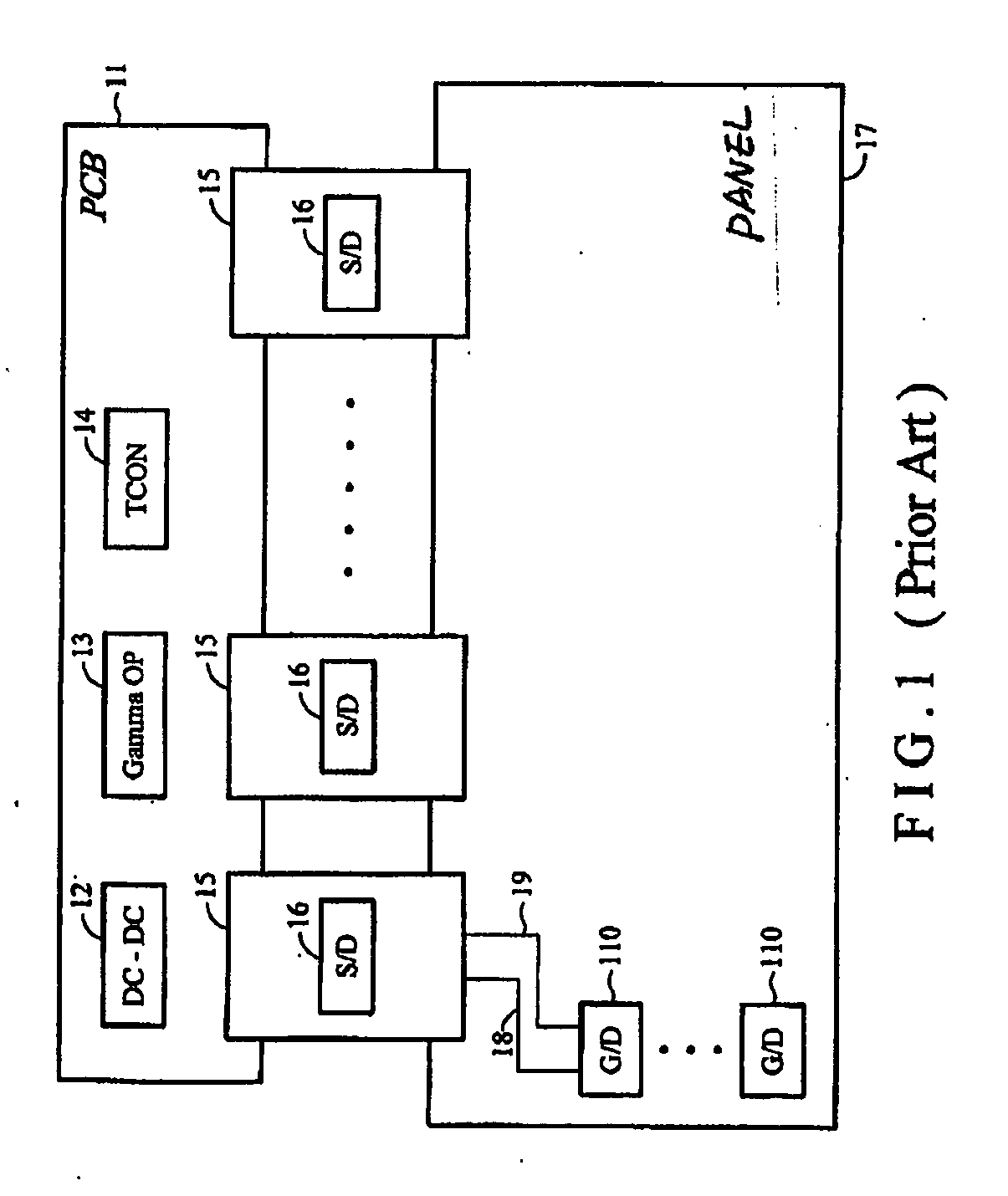
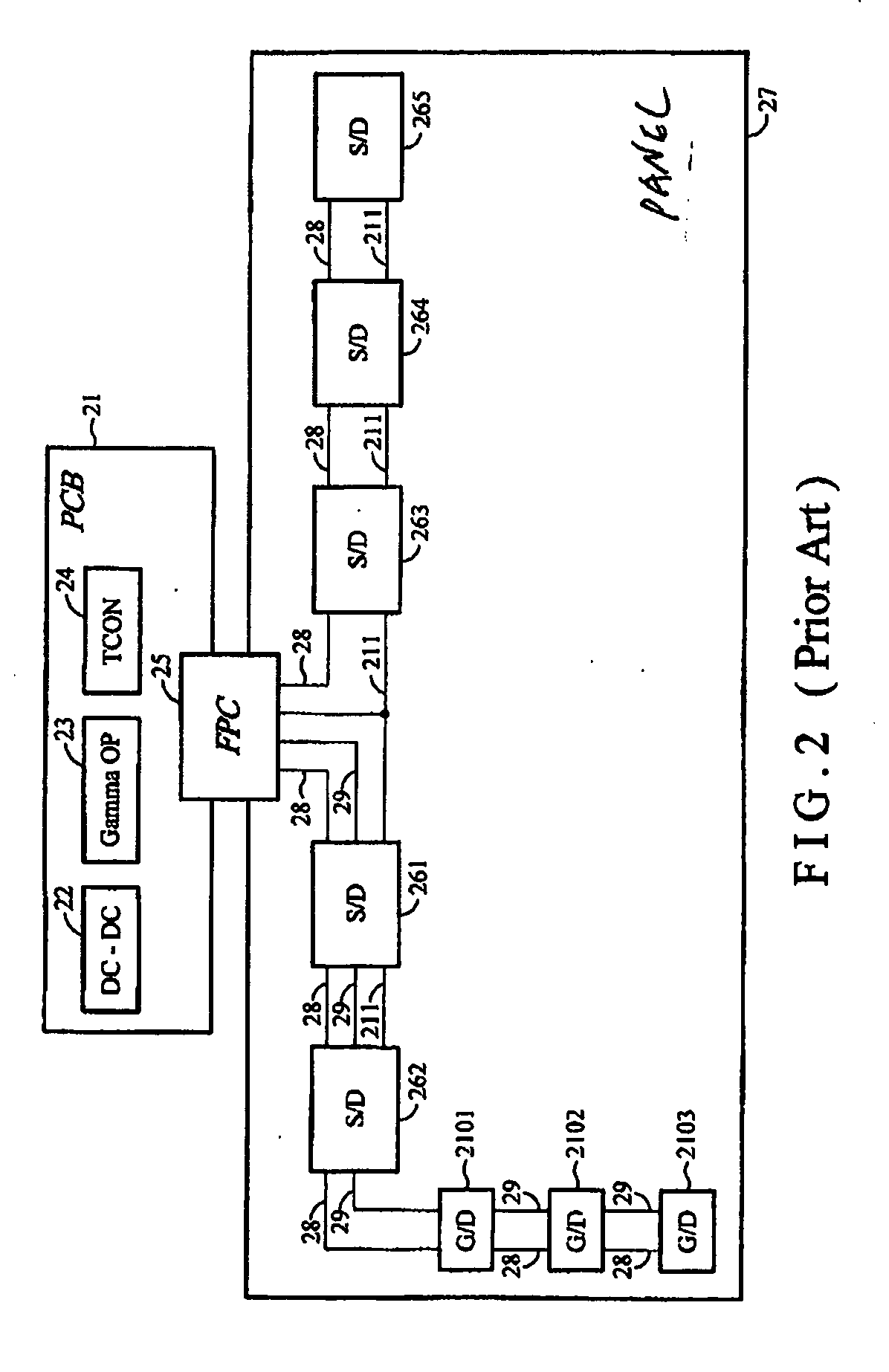
WOA panel architecture
InactiveUS20060232579A1Low costSmall sizeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingSpatial correlationLiquid-crystal display
The present invention provides solutions to simplify and reduce the resources needed for manufacturing liquid crystal display modules. Failure of mid-process steps during mass production can result in significant costs. According to certain embodiments of the present invention, a WOA display panel architecture requires fewer LCM resources or has no PCB. Although the COG process and WOA method provide higher reliability in temporary LCD production, the costs associated with the space required for wires on the PCB or display panel for larger panel sizes remains expensive. Larger panel sizes also requires an increased number of driver ICs to construct a flat display panel. Similarly, the number of wires connecting each driver IC to a timing controller IC, gamma operational amplifier IC and DC-to-DC converter IC creates spacing problems that translate into higher production costs. These problems can be solved by certain embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
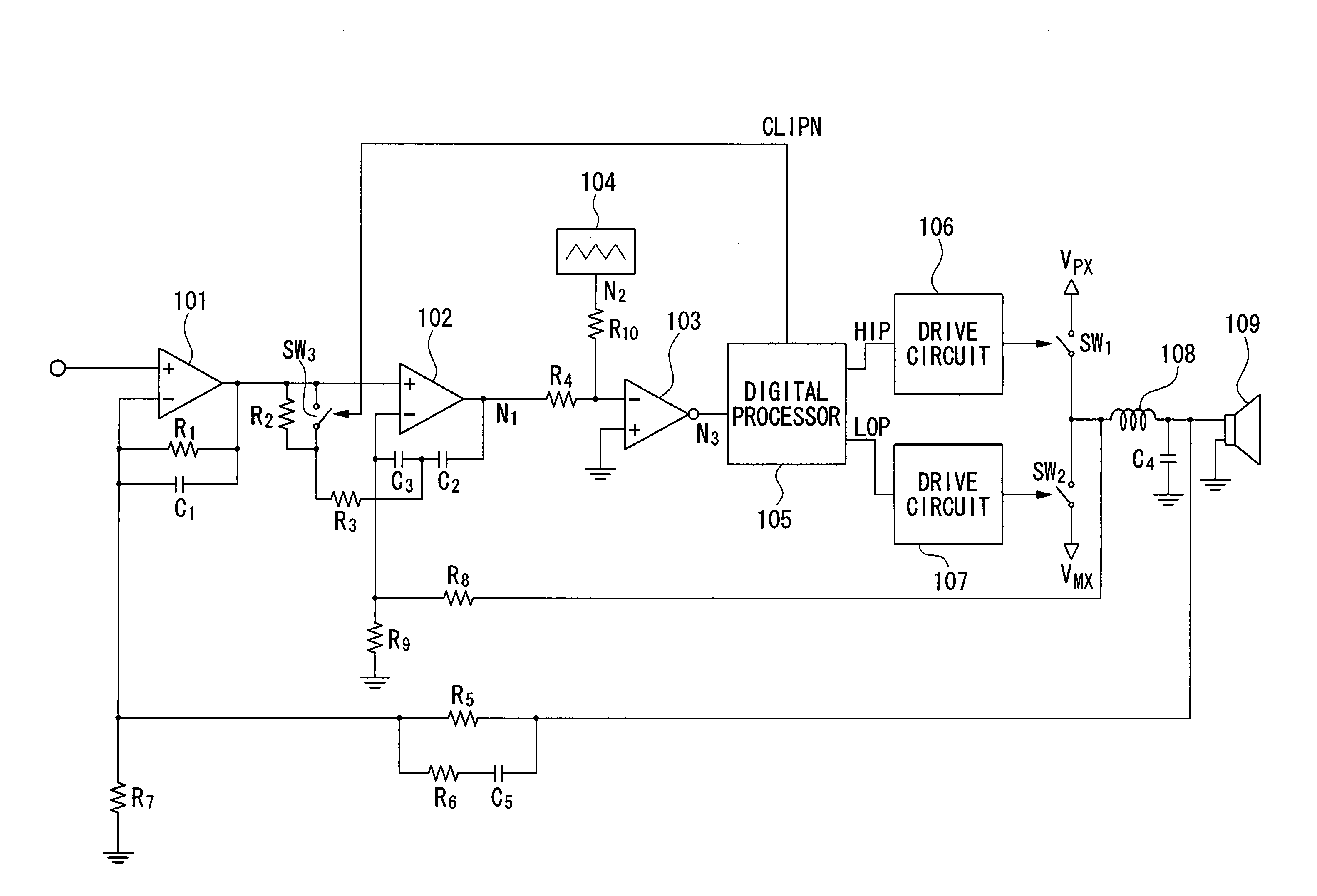
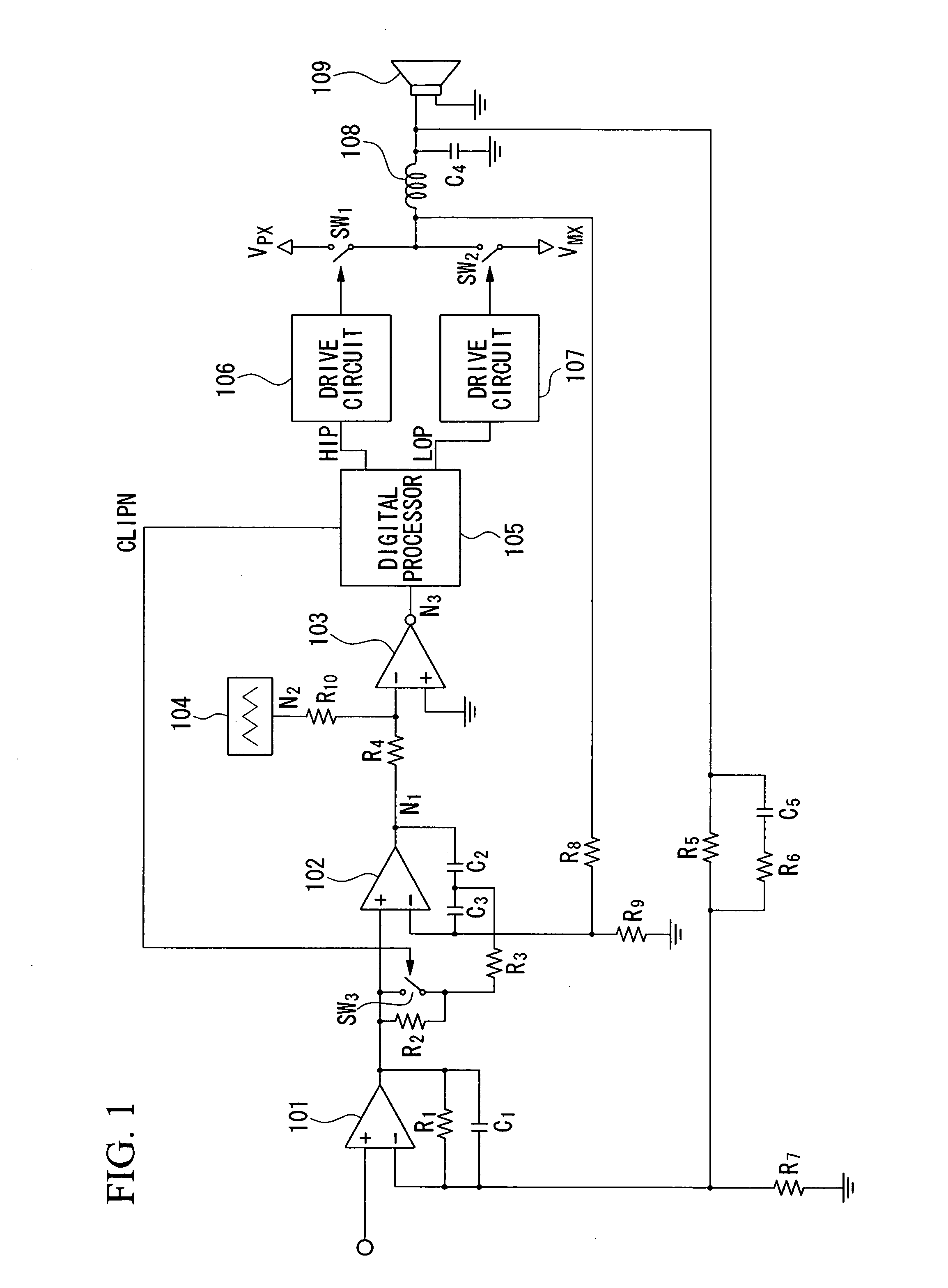
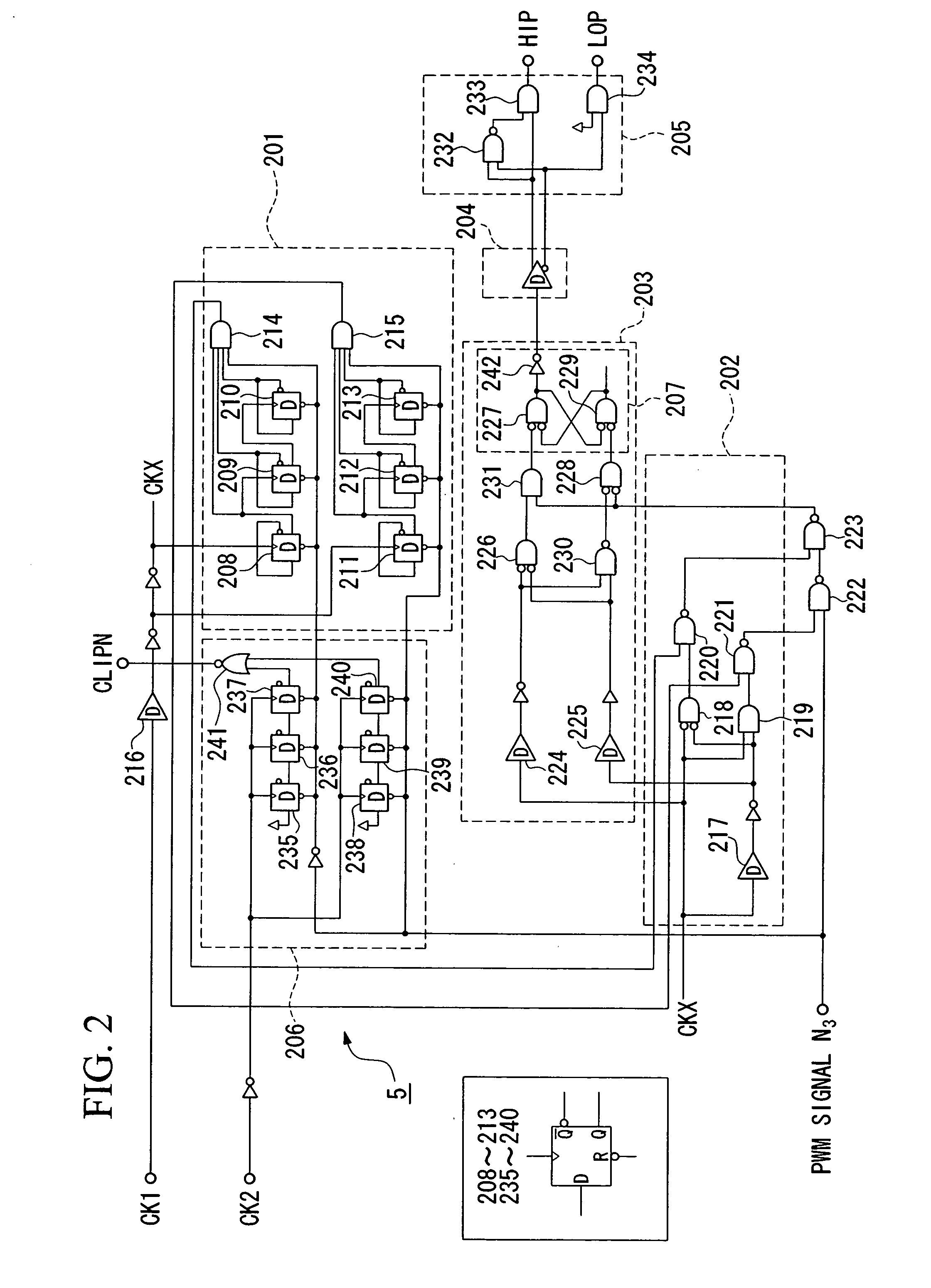
Pulse-width modulation amplifier and suppression of clipping therefor
ActiveUS20060008095A1Avoid excessive currentPower use efficiency decreaseAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlLeading edgeAudio power amplifier
A pulse-width modulation (PWM) amplifier is adapted to a class-D amplifier in which an analog input signal is subjected to integration, pulse-width modulation, and switched amplification, wherein a glitch elimination circuit eliminates noise from a pulse-width modulated signal, from which a high pulse signal and a low pulse signal are isolated such that each pulse is delayed by a dead time at the leading-edge timing thereof. When both of them are simultaneously set to a high level, one of them is reduced in level. In response to the occurrence of clipping, an integration constant applied to an operational amplifier is automatically changed from a primary integration constant to a secondary integration constant. When the clipped state is sustained for a prescribed time, an inversion pulse is compulsorily introduced into the pulse-width modulated signal.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Capacitive load driving circuit, droplet ejection device, droplet ejection unit and inkjet head driving circuit
InactiveUS7244007B2Reduced stabilityDc network circuit arrangementsOther printing apparatusAudio power amplifierDifferential signaling
A capacitive load driving circuit which includes an operational amplifier, a pulse width modulator, a digital power amplifier, a first filter, a first feedback circuit and a second feedback circuit. The operational amplifier outputs a differential signal between a signal fed back to the inverting input terminal and an input signal inputted to the non-inverting input terminal. The pulse width modulator pulse width-modulates output from the operational amplifier and outputs a digital signal. The digital power amplifier amplifies power of the digital signal. The first filter smooths output of the digital power amplifier and inputs the smoothed signal to the capacitive load as the driving signal. The first feedback circuit feeds back the driving signal outputted from the first filter to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier. The second feedback circuit feeds back a signal outputted from the digital power amplifier, which signal includes a phase which is advanced relative to the driving signal, to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
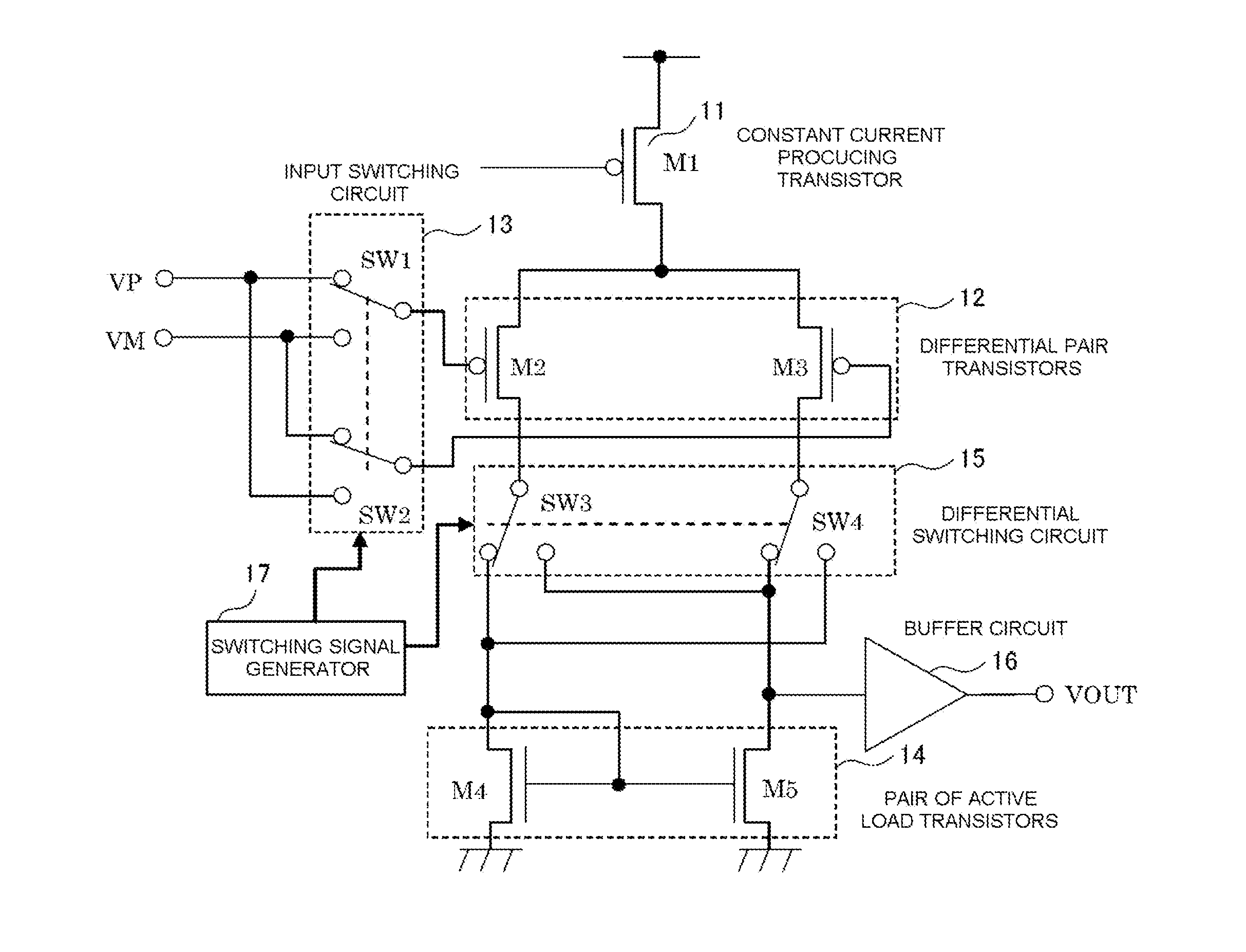
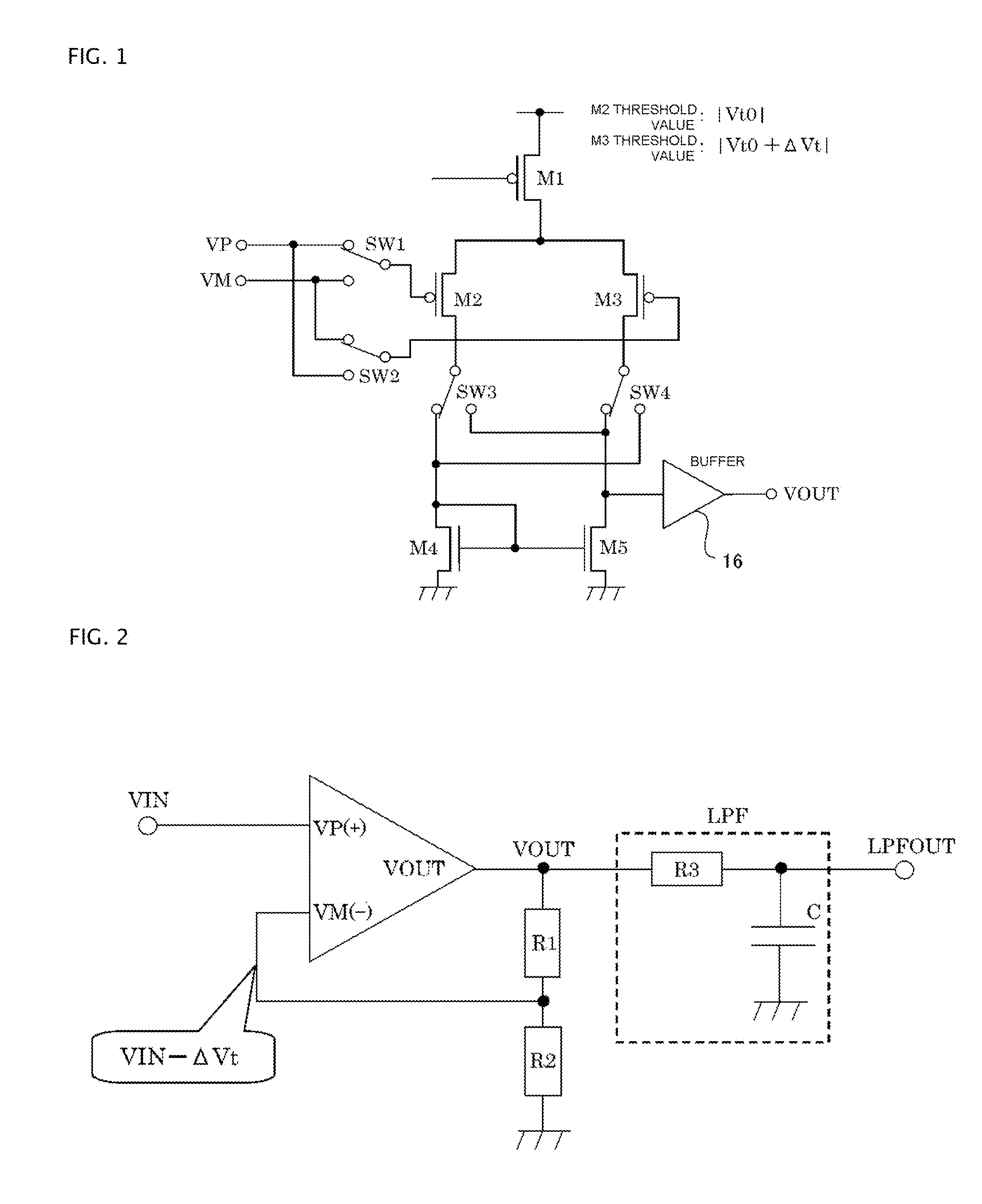
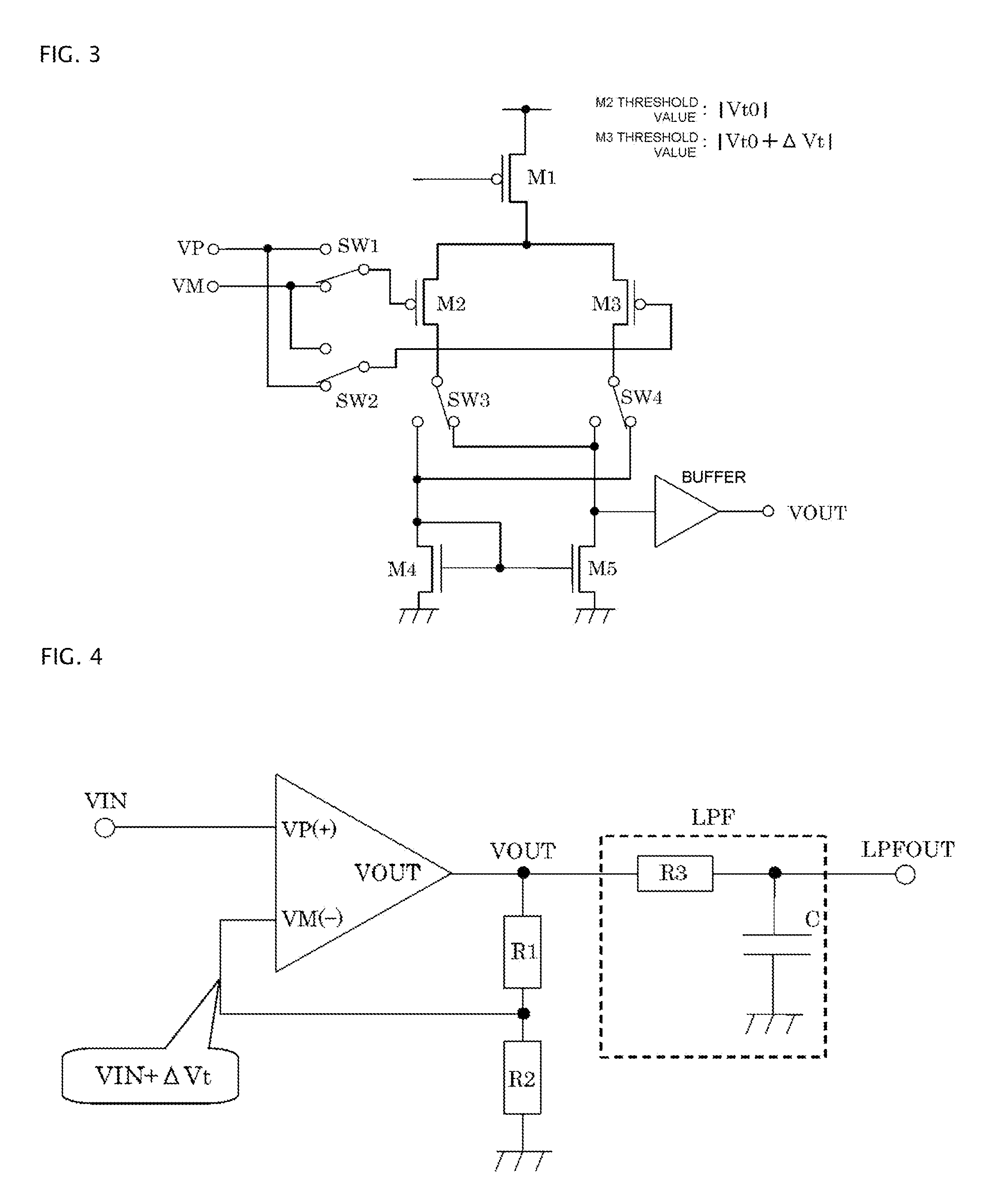
Auto-zero amplifier and feedback amplifier circuit using the auto-zero amplifier
ActiveUS20130147553A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
In aspects of the invention, at normal operation, an operational amplifier circuit has feedback applied from the output thereof to the input thereof so that currents equal to each other flow in differential pair transistors, respectively. While, in order that currents equal to each other may flow in the differential pair transistors, respectively, for compensating the difference in threshold voltages in the differential pair transistors, a voltage lower by a certain voltage difference than the voltage applied to the gate terminal of the transistor must be applied to the gate terminal of the transistor. From this, the switching of switches, when a virtual short circuit occurs, can make the output voltage of the operational amplifier circuit become a signal in which positive and negative rectangular ripples, with the values thereof being proportional to the value of the certain voltage difference, are superimposed on a true value.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
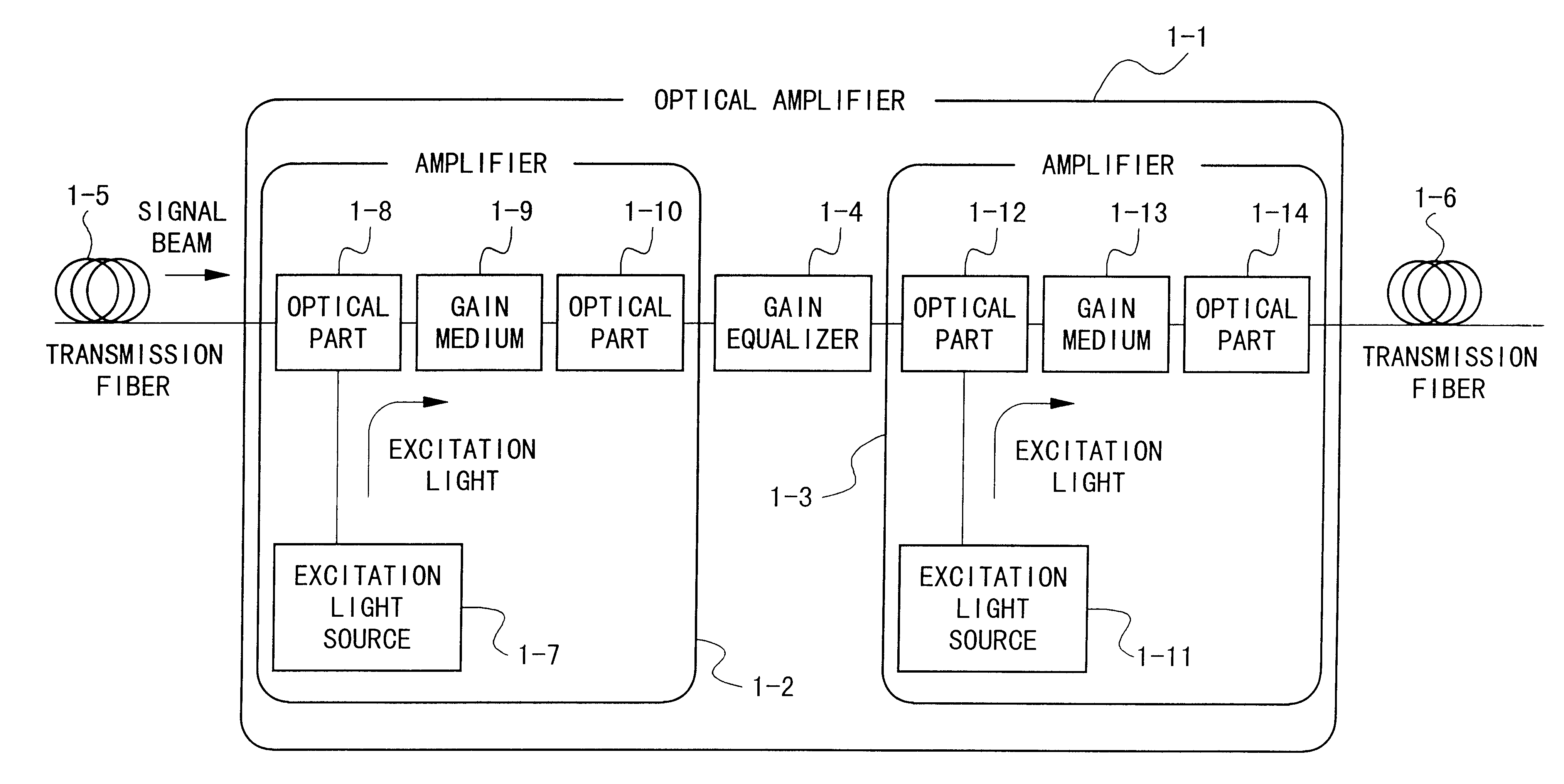
Optical amplifier and transmission system using the same
InactiveUS6172803B1Laser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesFiberErbium doping
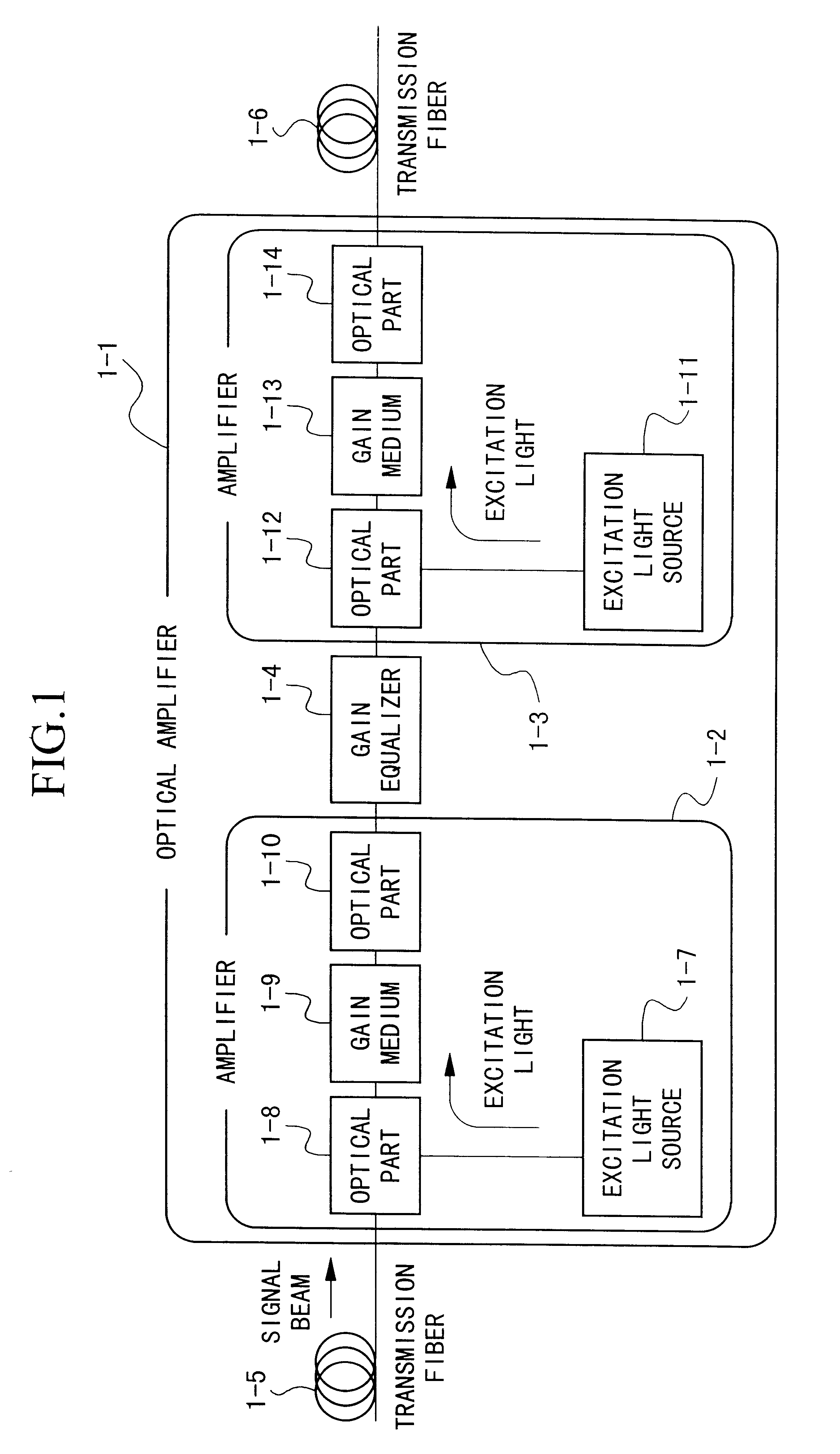
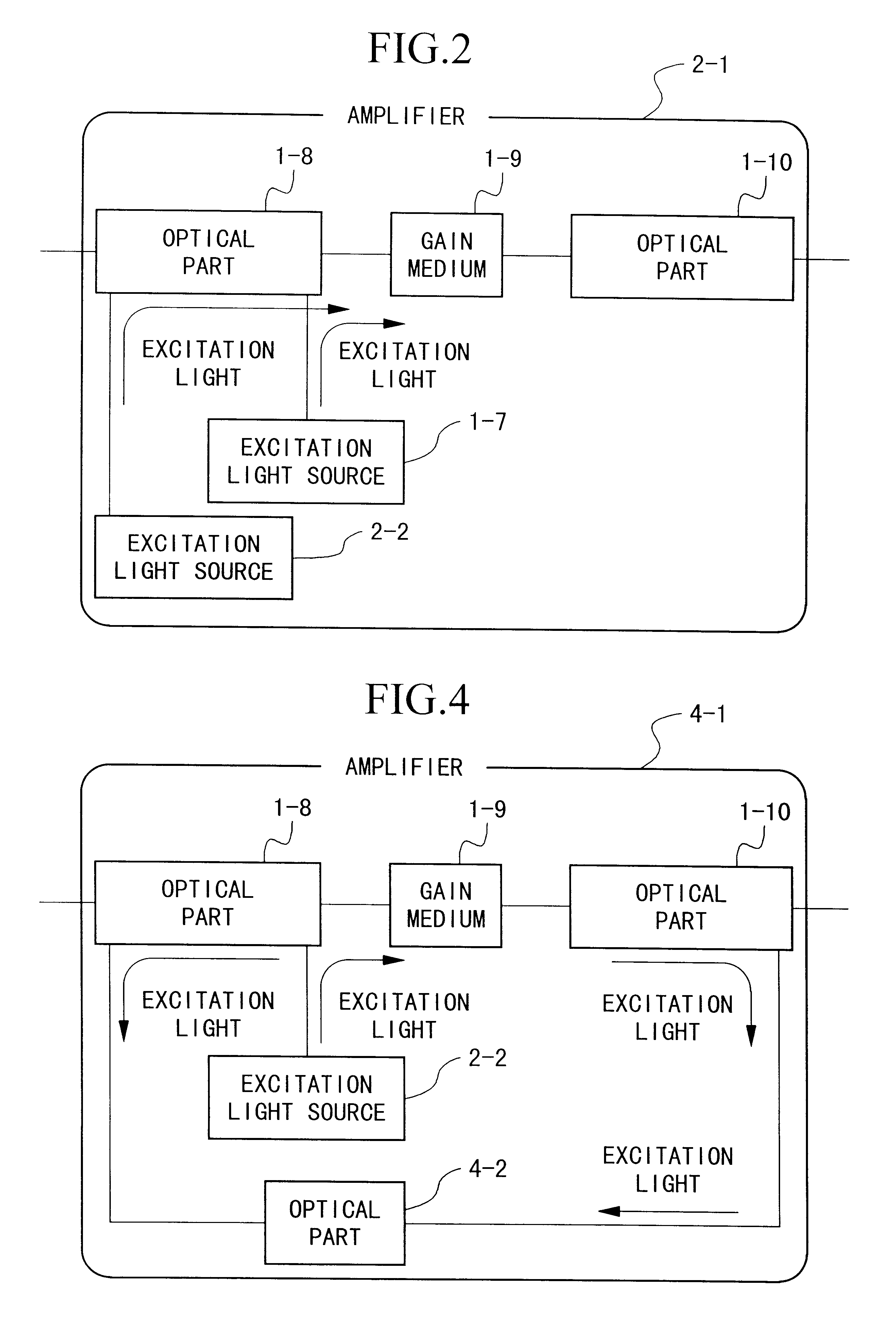
An optical amplifier having a two-stage construction using an erbium doped fiber (EDF) as a gain medium. The erbium dopant concentration is 1000 ppm, and the unsaturated absorption coefficient of the signal beam at 1550 nm is 1 dB / m. The length of the EDF 14-8 is 10 m, and the length of the EDF 14-12 is 70 m. The excitation light sources 14-6 and 14-10 are semiconductor lasers of 1.53 mum, and the excitation light power is 100 mW. Multiplexers 14-7 and 14-11 are inductive multi-layer film filters, and the gain equalizer 14-4 is a Fourier filter. The peak loss of the Fourier filter is 17 dB. The gain of the EDF 14-8 is 25 dB, and the gain of the EDF 14-12 is 15 dB. Two optical isolators are installed on a pre-stage amplifier, and one on a post-stage amplifier in order to prevent laser oscillation.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com