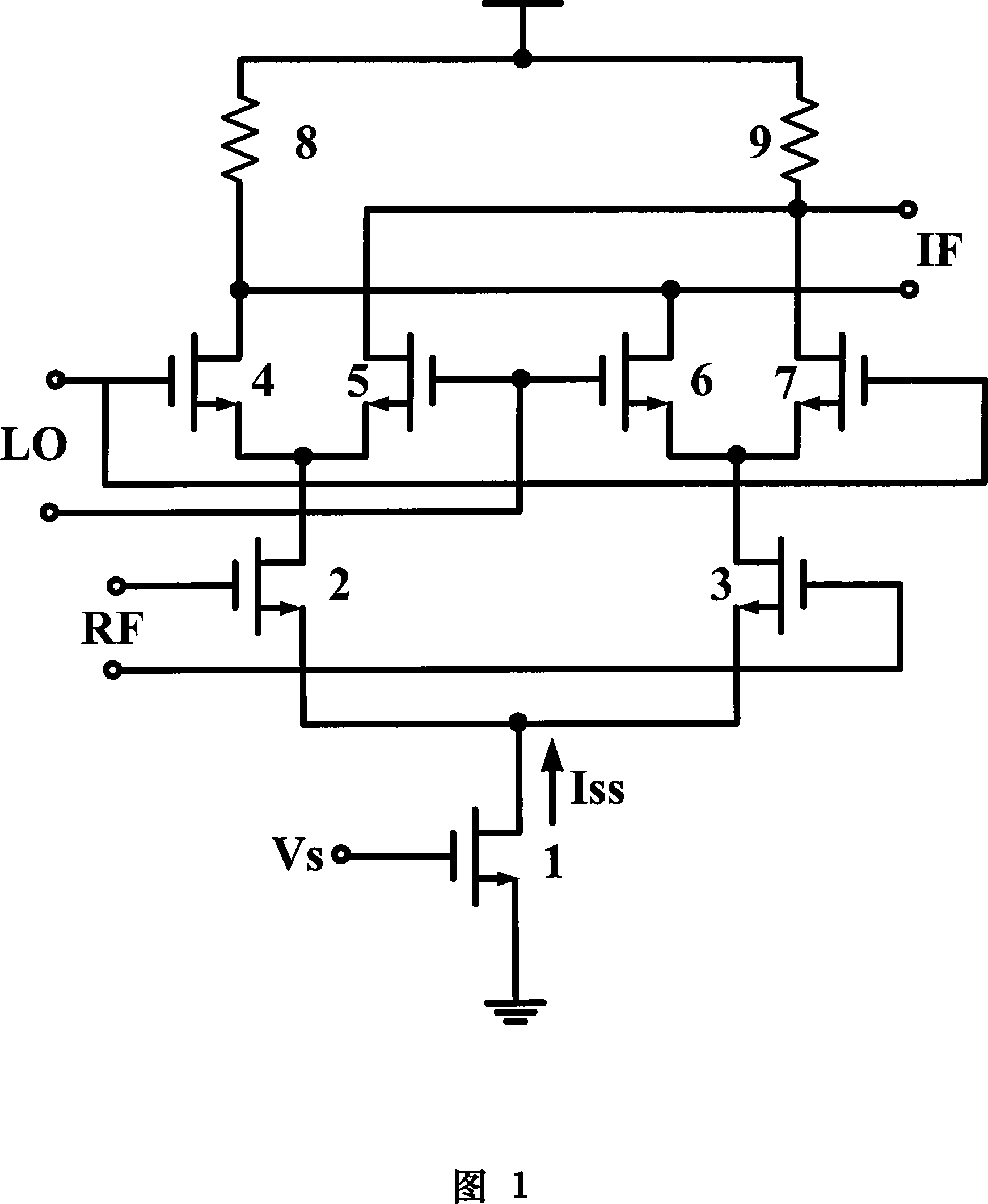
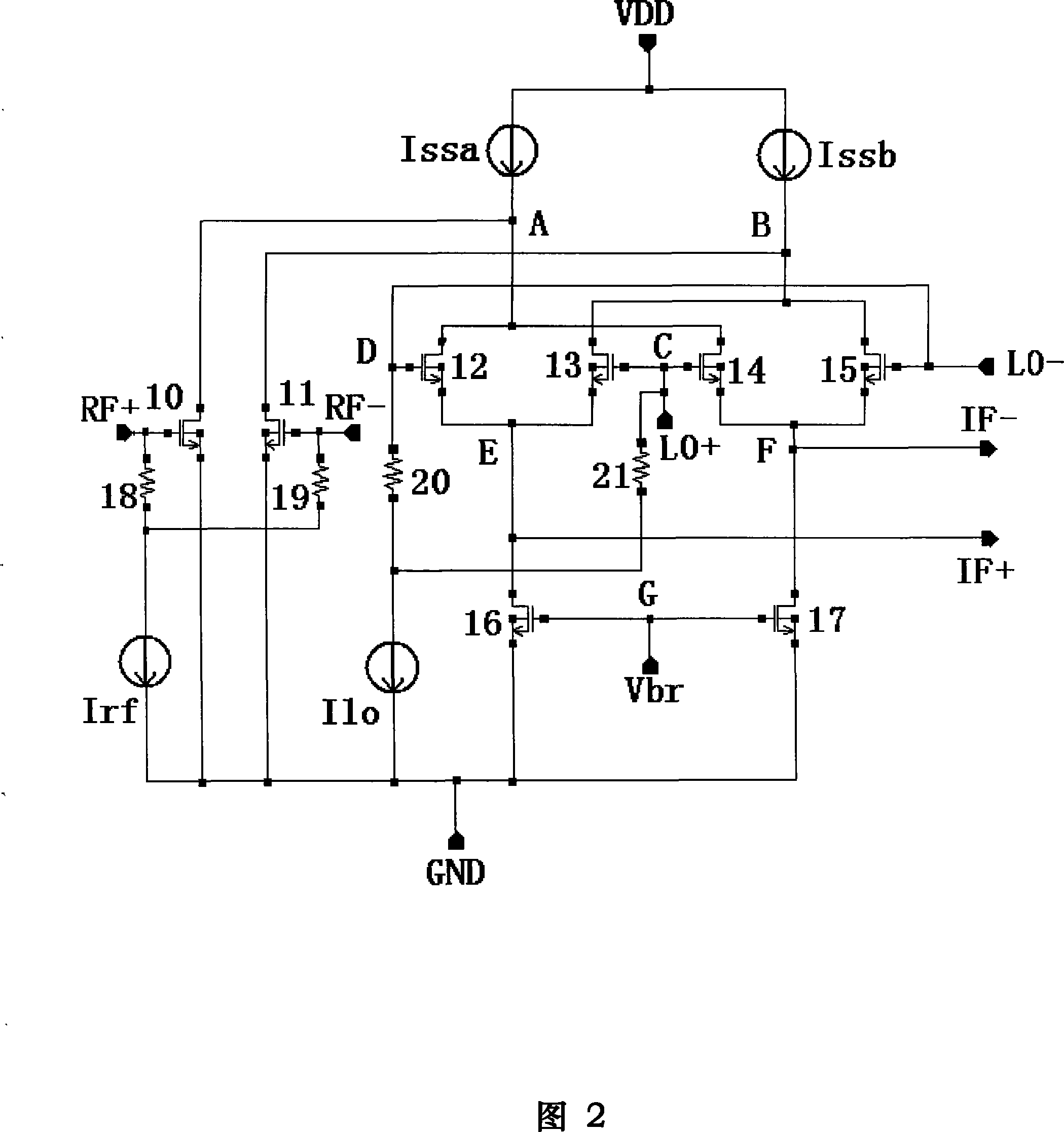
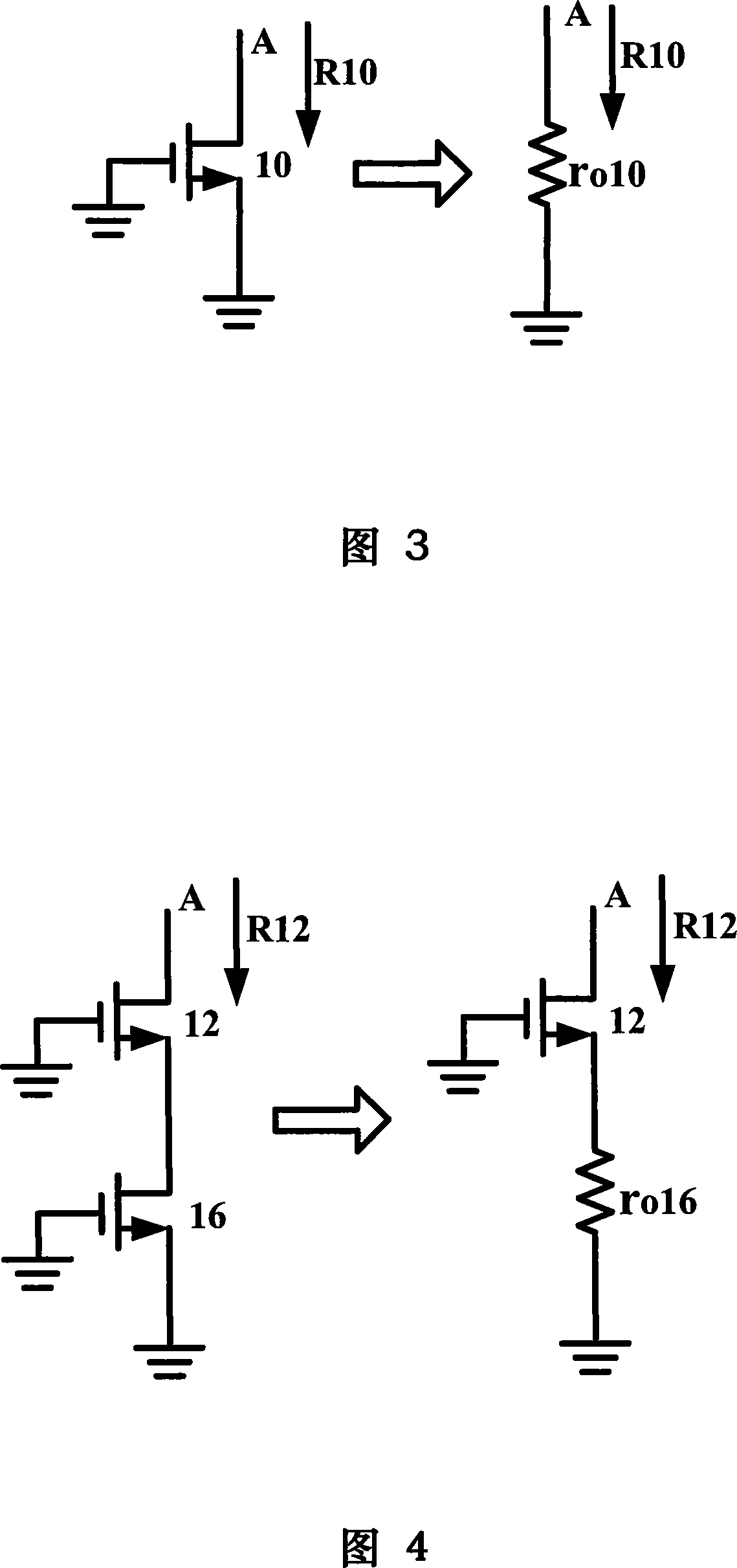
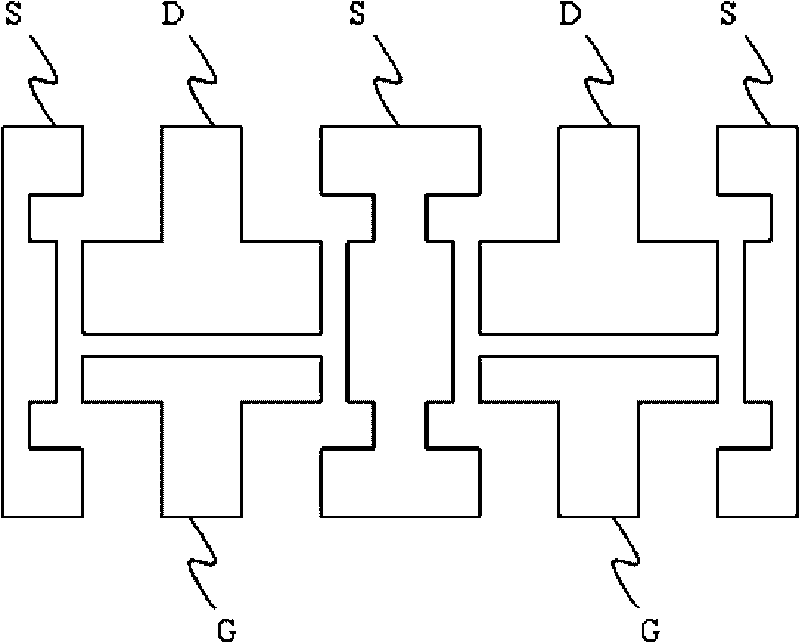
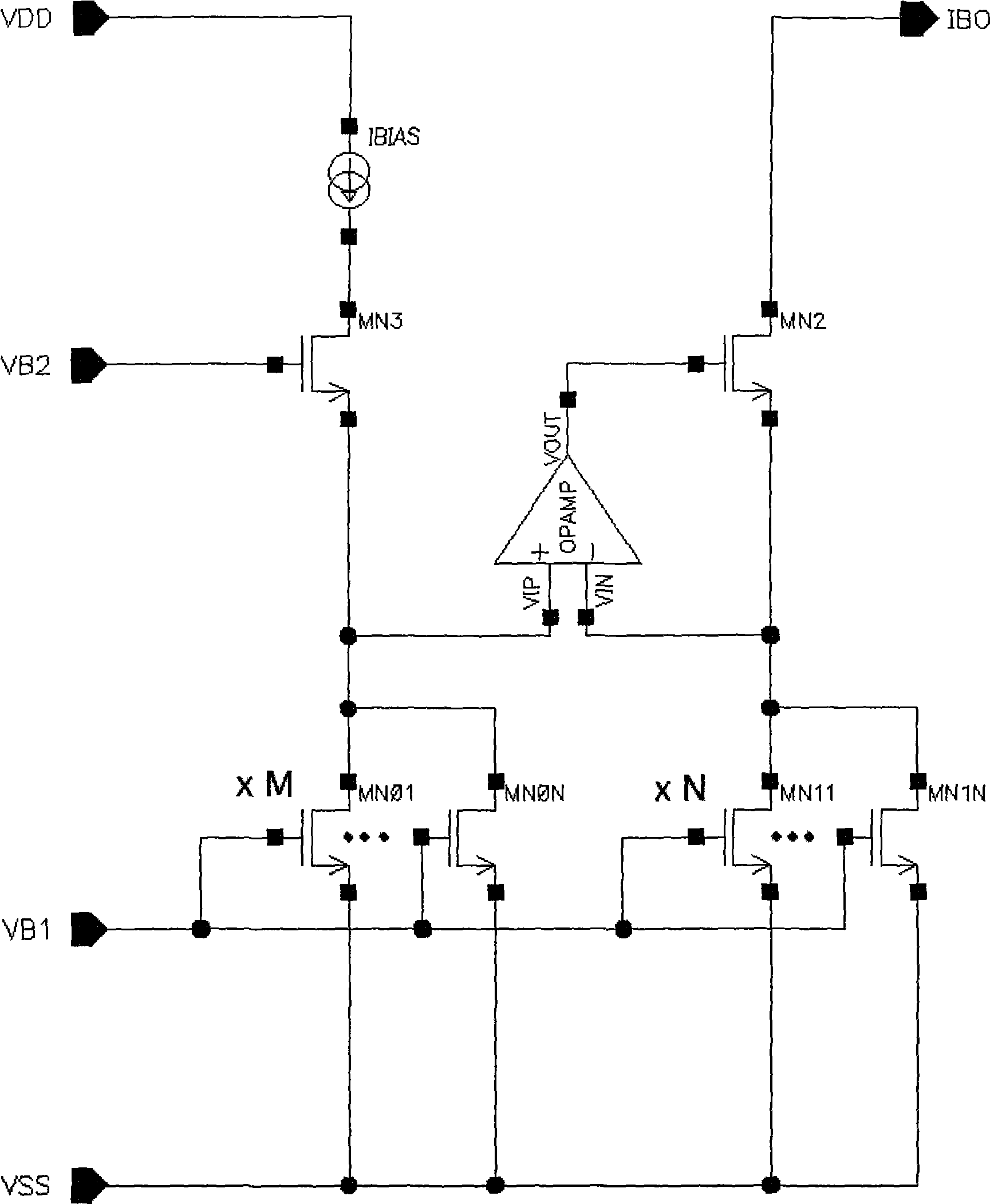
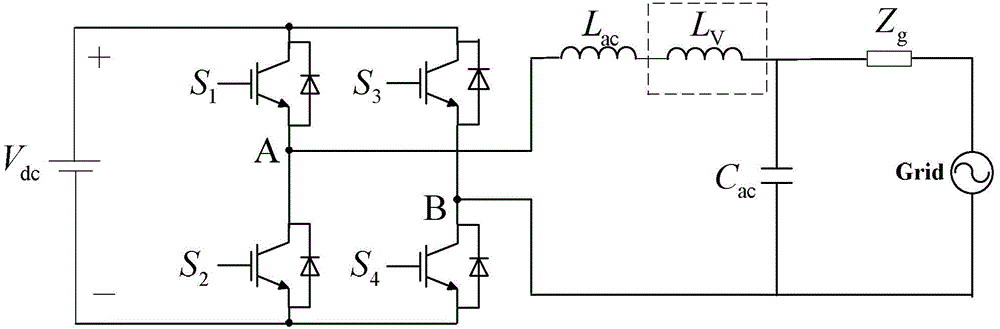
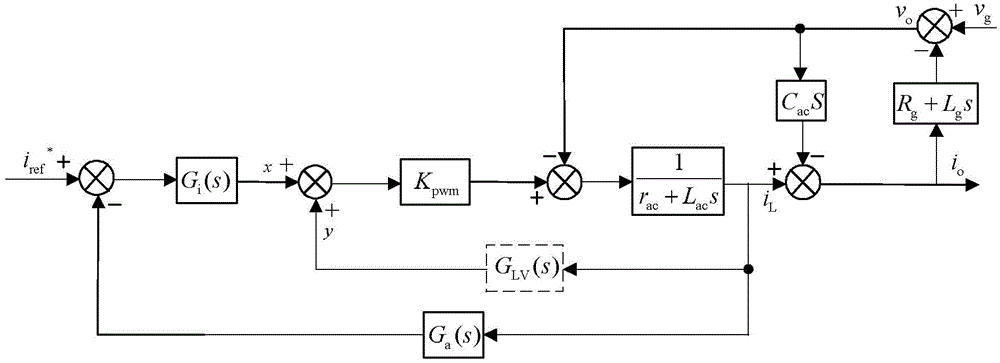
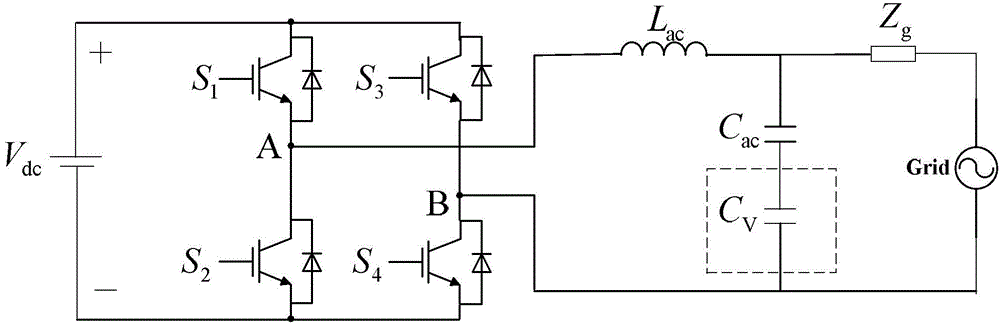
Patents
Literature
220results about How to "Increase output impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
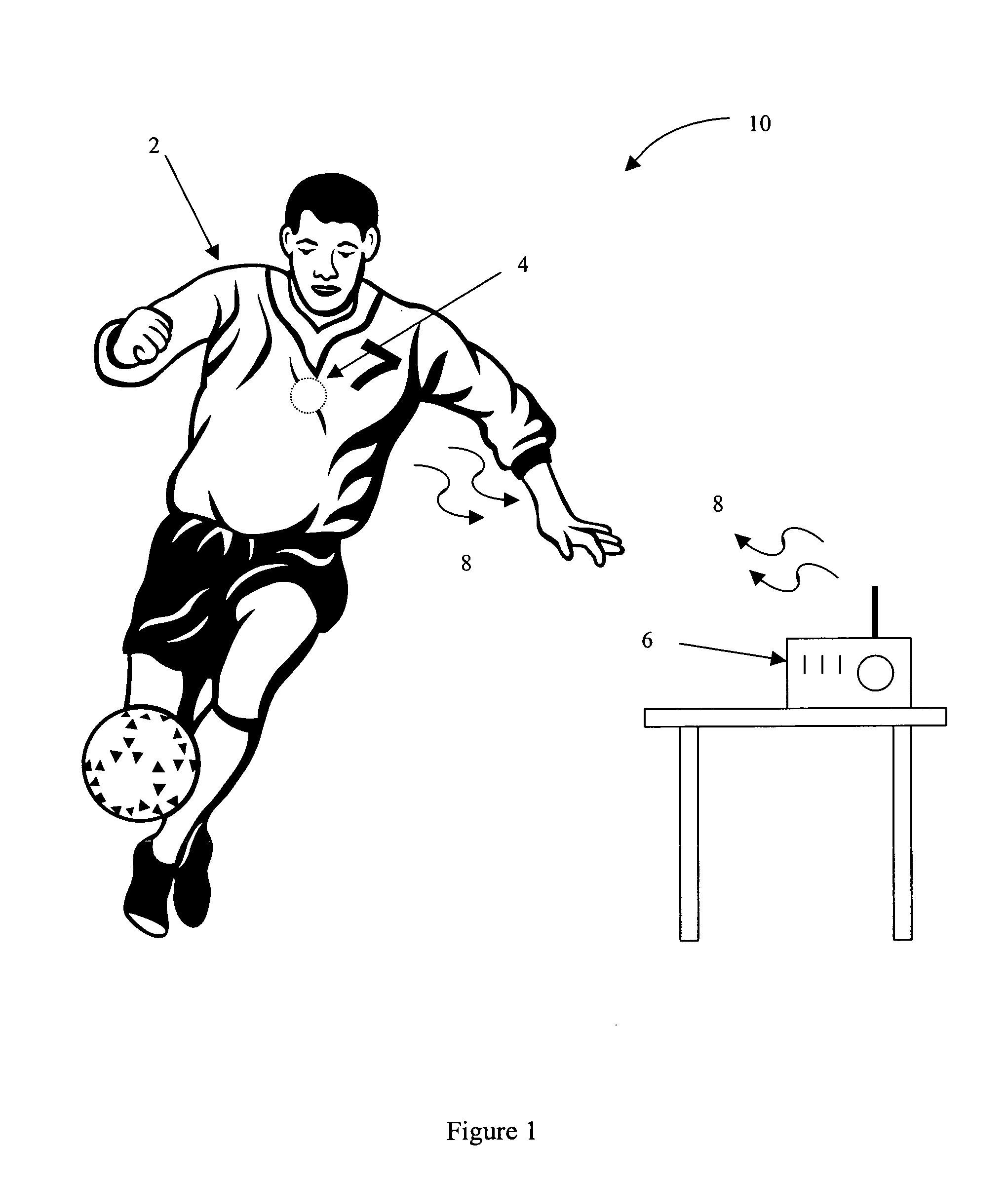
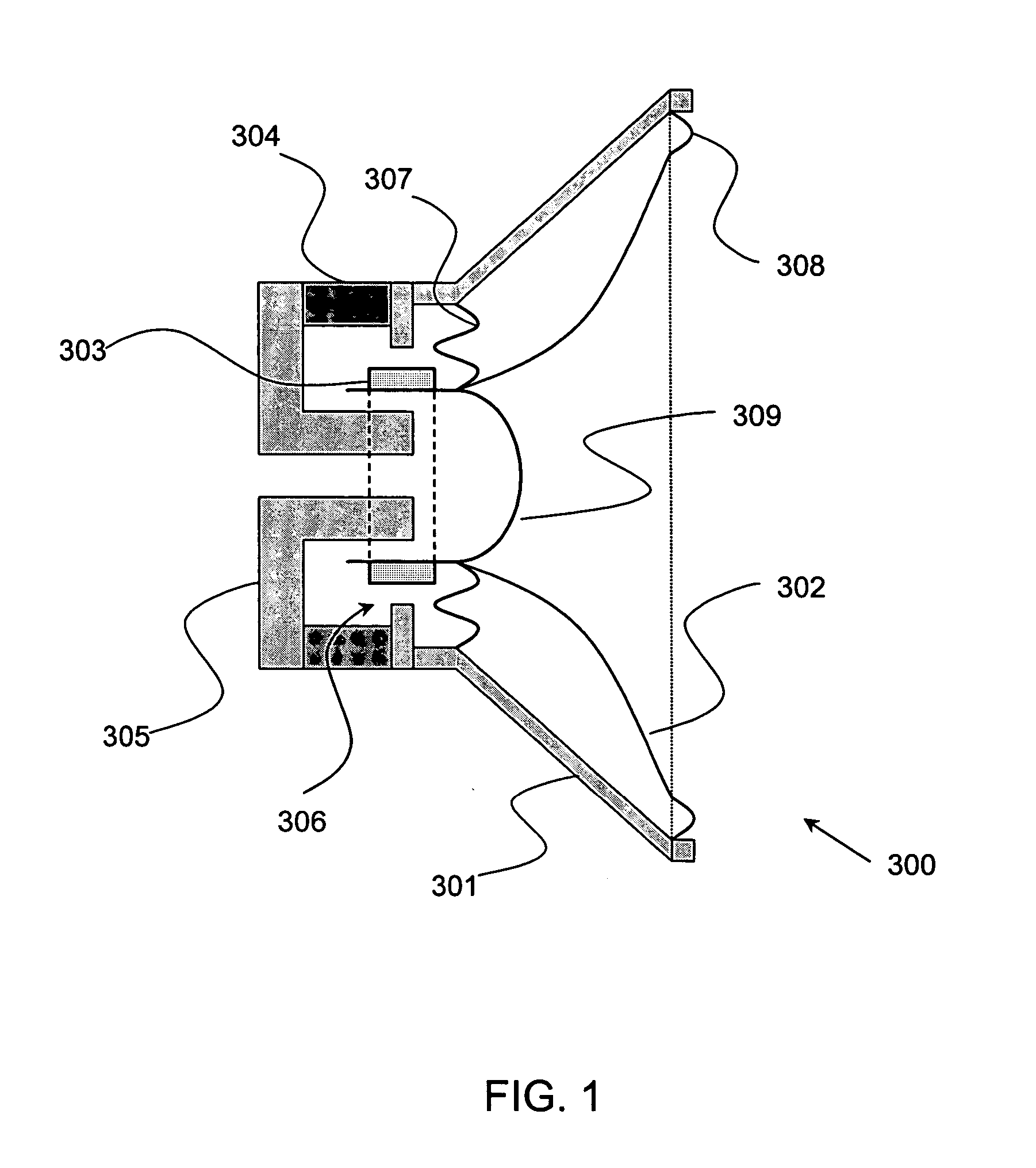
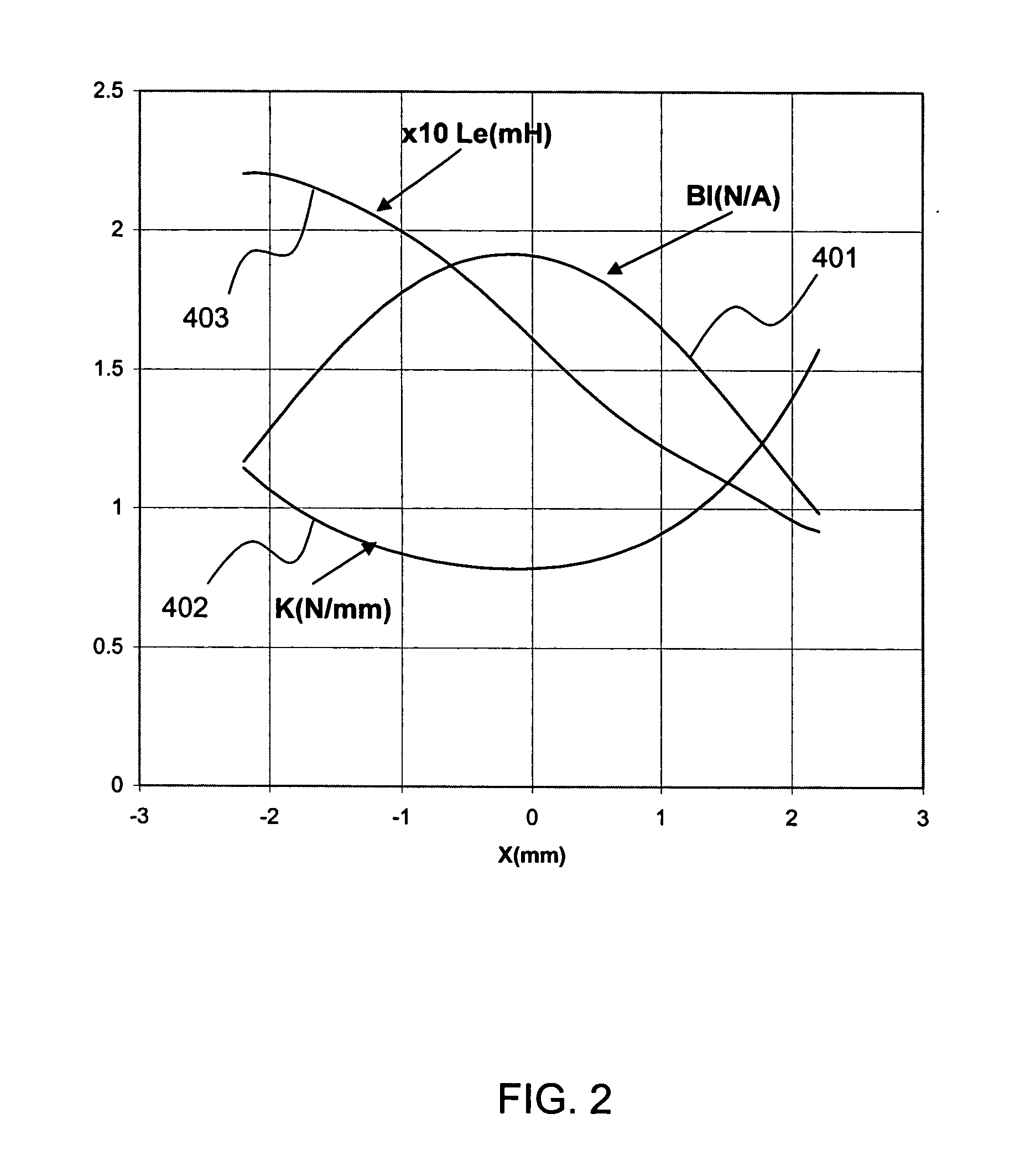
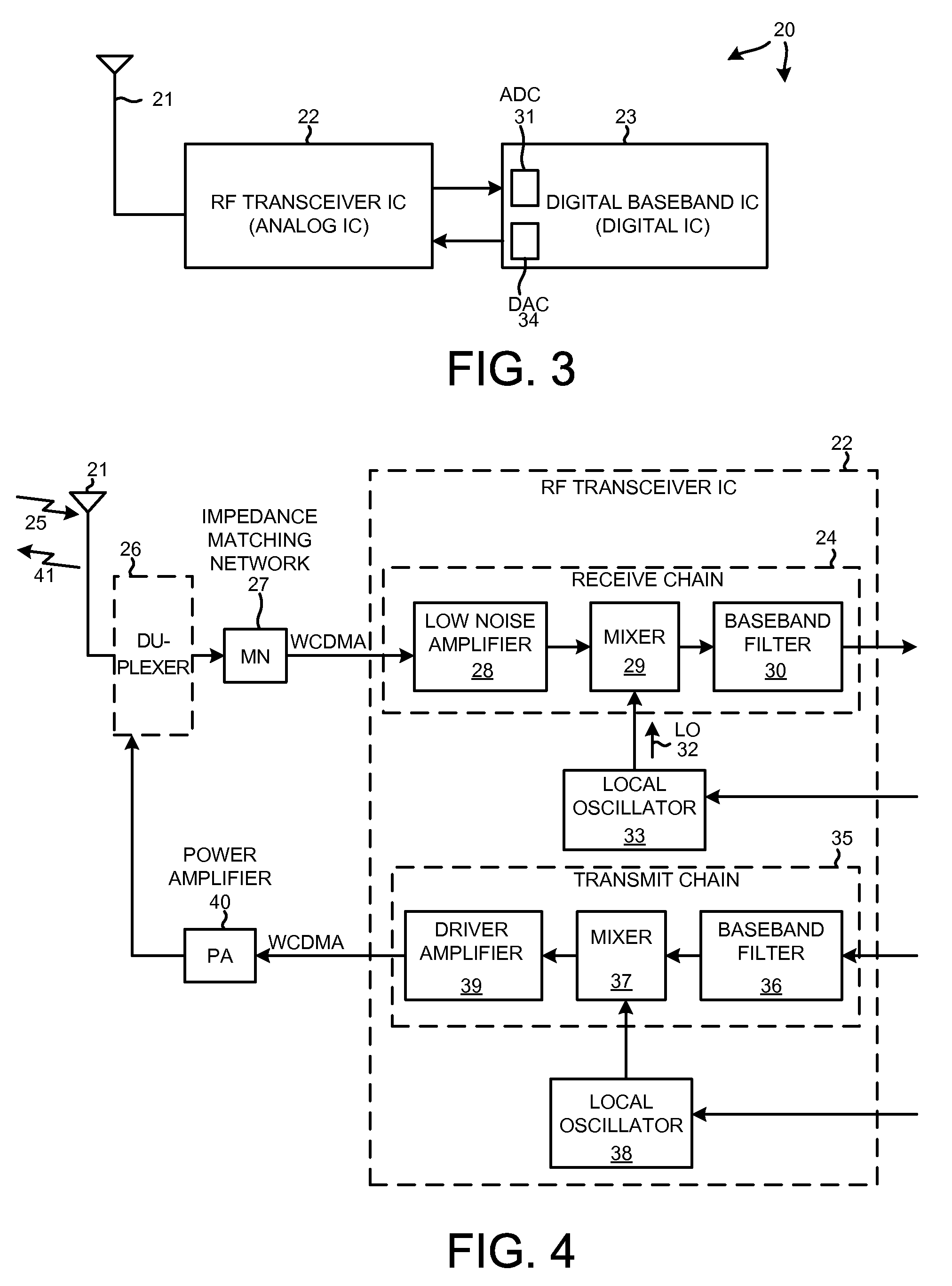
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20050197677A1Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic field
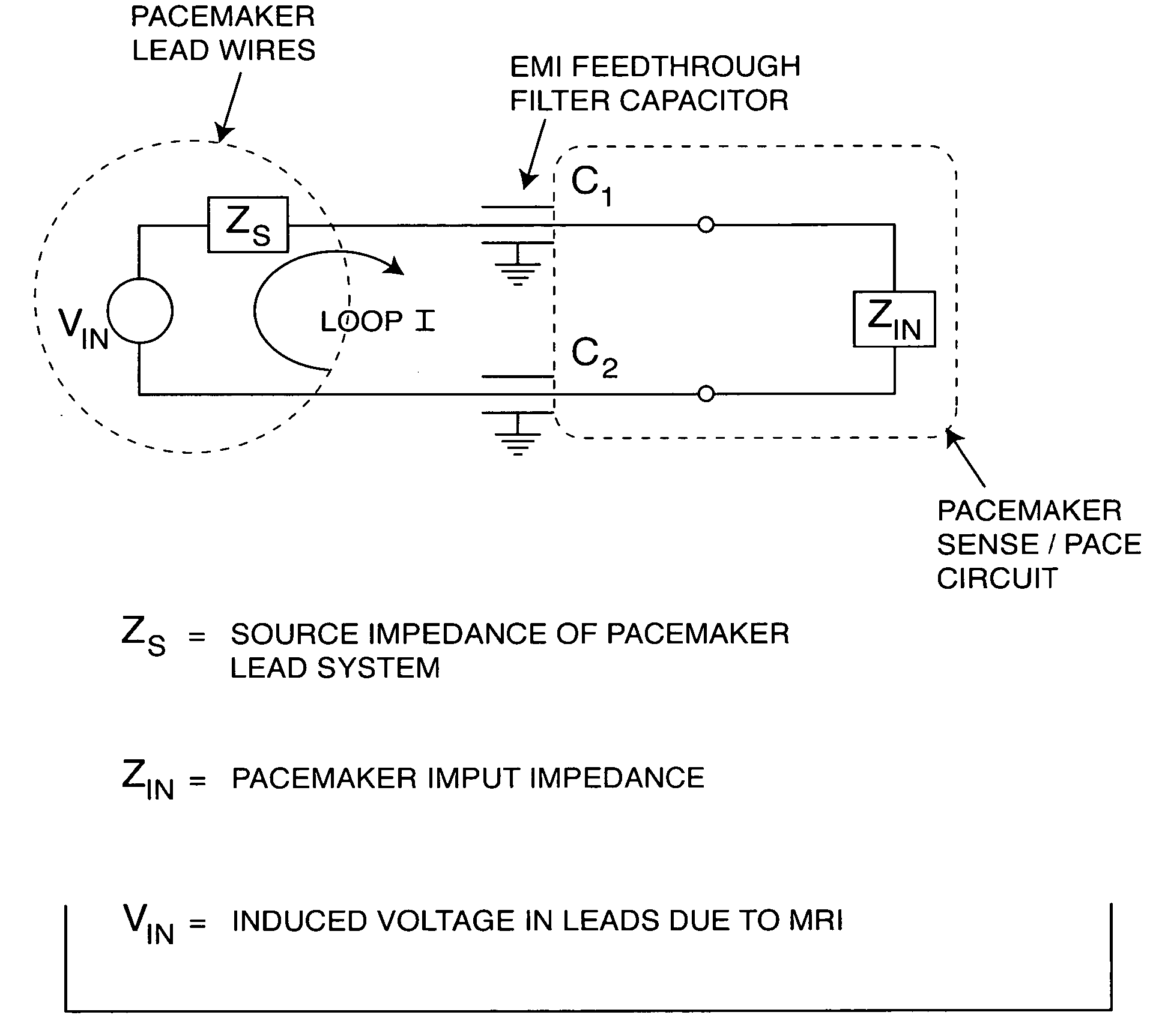
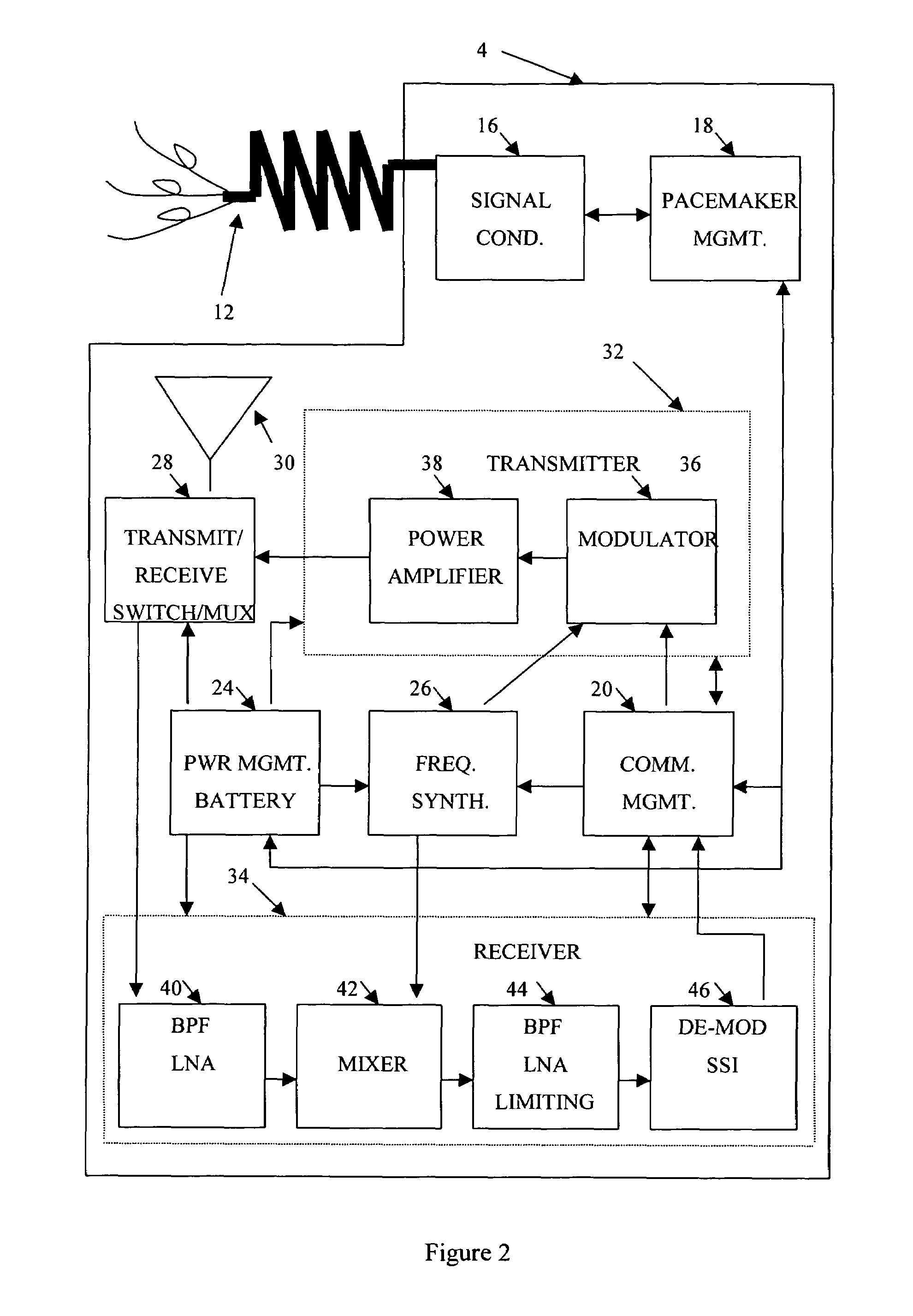
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
High frequency wireless pacemaker
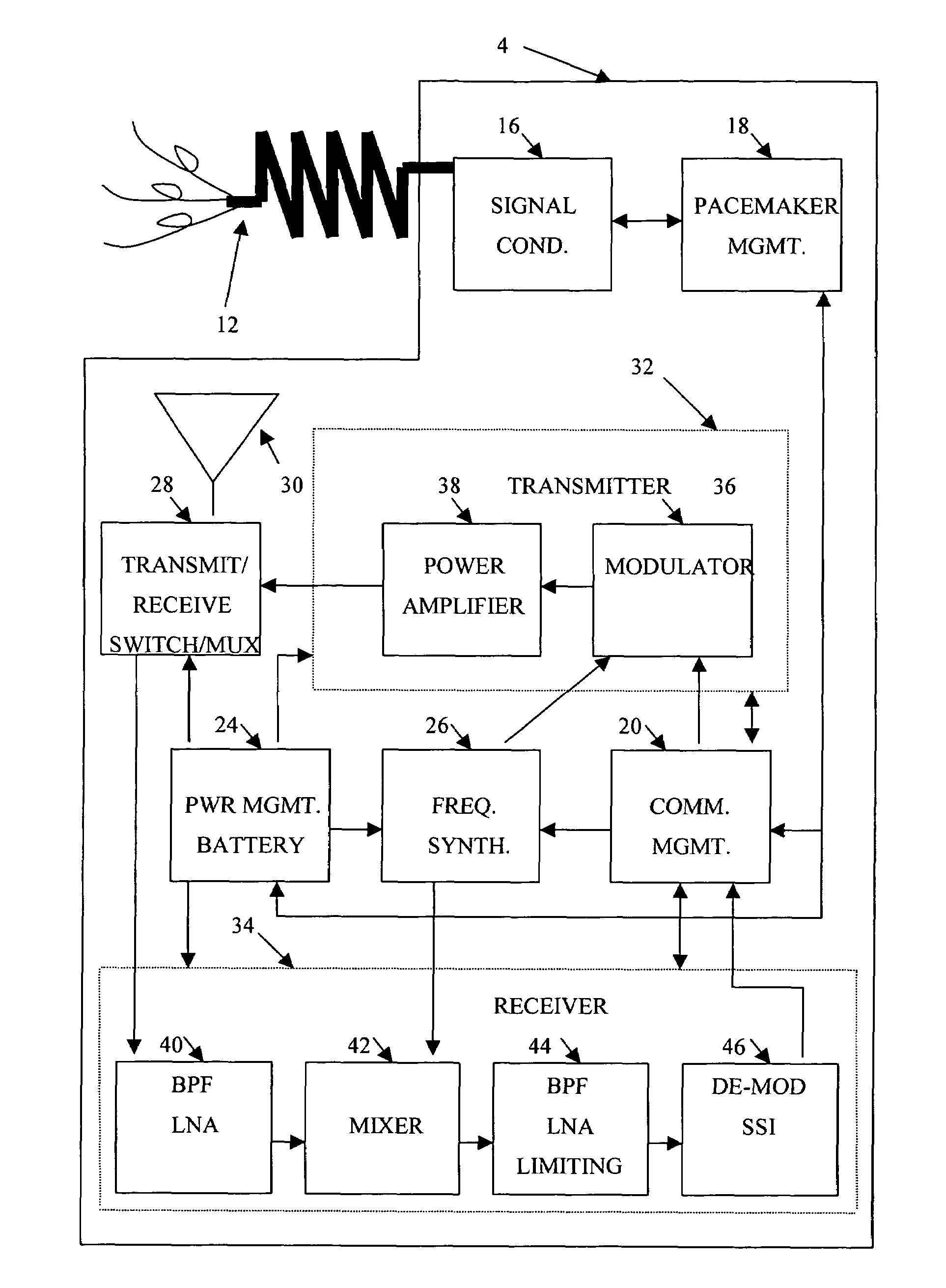
InactiveUS7289853B1High-frequency operationLow pacemaker power consumptionHeart stimulatorsCommunications systemCardiac pacemaker electrode
A wireless communications system optimizes performance by dividing communications functionality between a wireless pacemaker and a wireless monitoring base station according to the design constraints imposed by the system elements. Typical design constraints include high frequency operation, low pacemaker power consumption, reasonable range, high data rate, minimal RF radiation of internal circuitry, small pacemaker antenna system, simple pacemaker RF circuit design, high reliability, low pacemaker cost, and use of existing pacemaker construction methodologies.
Owner:CAMPBELL DAVID +1
Apparatus and process for reducing the susceptability of active implantable medical devices to medical procedures such as magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7765005B2Improving impedanceReducing magnetic flux core saturationAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyPhase cancellationElectromagnetic interference
A feedthrough terminal assembly for an active implantable medical device (AIMD) includes a plurality of leadwires extending from electronic circuitry of the AIMD, and a lossy ferrite inductor through which the leadwires extend in non-conductive relation for increasing the impedance of the leadwires at selected RF frequencies and reducing magnetic flux core saturation of the lossy ferrite inductor through phase cancellation of signals carried by the leadwires. A process is also provided for filtering electromagnetic interference (EMI) in an implanted leadwire extending from an AIMD into body fluids or tissue, wherein the leadwire is subjected to occasional high-power electromagnetic fields such as those produced by medical diagnostic equipment including magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:GREATBATCH SIERRA INC
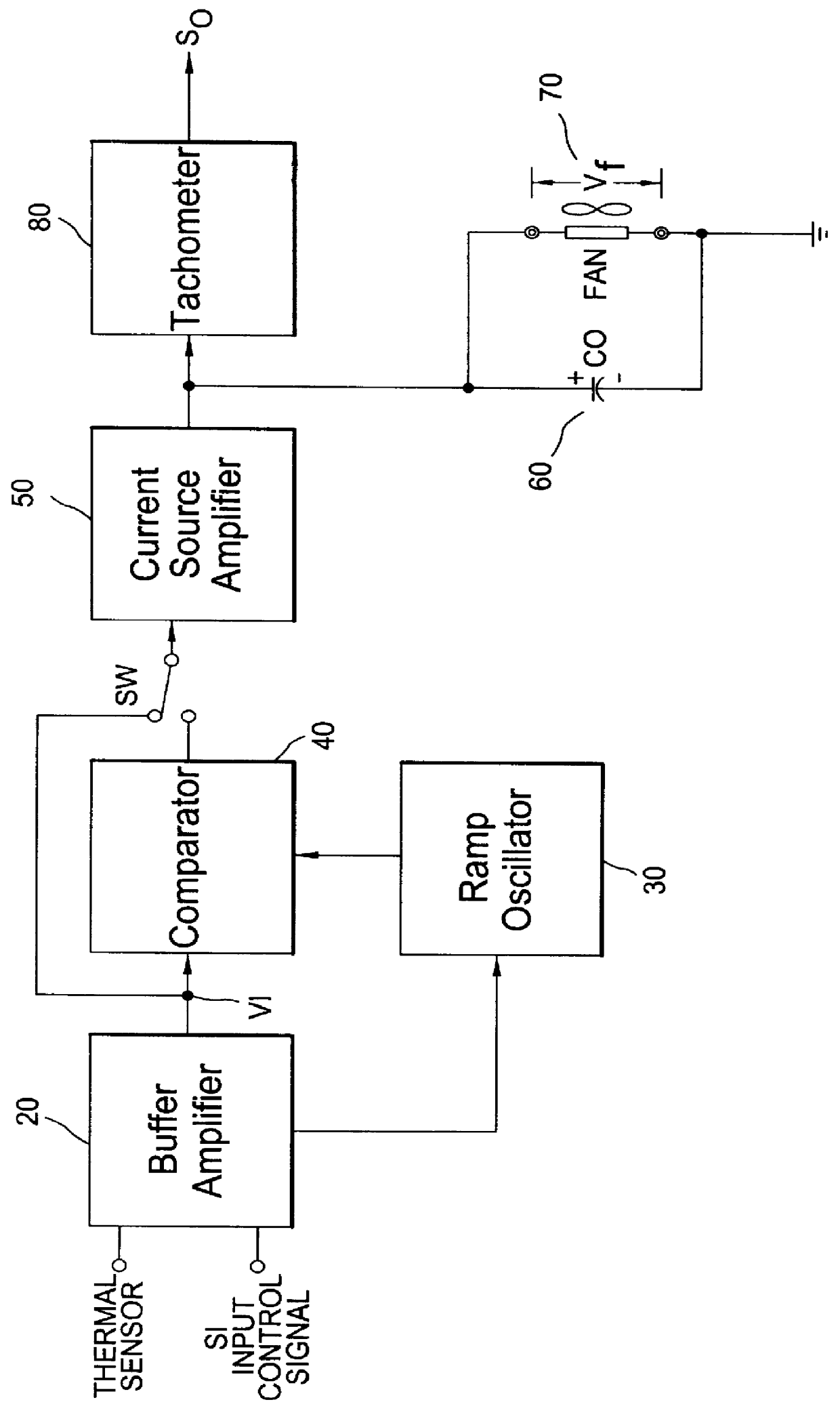
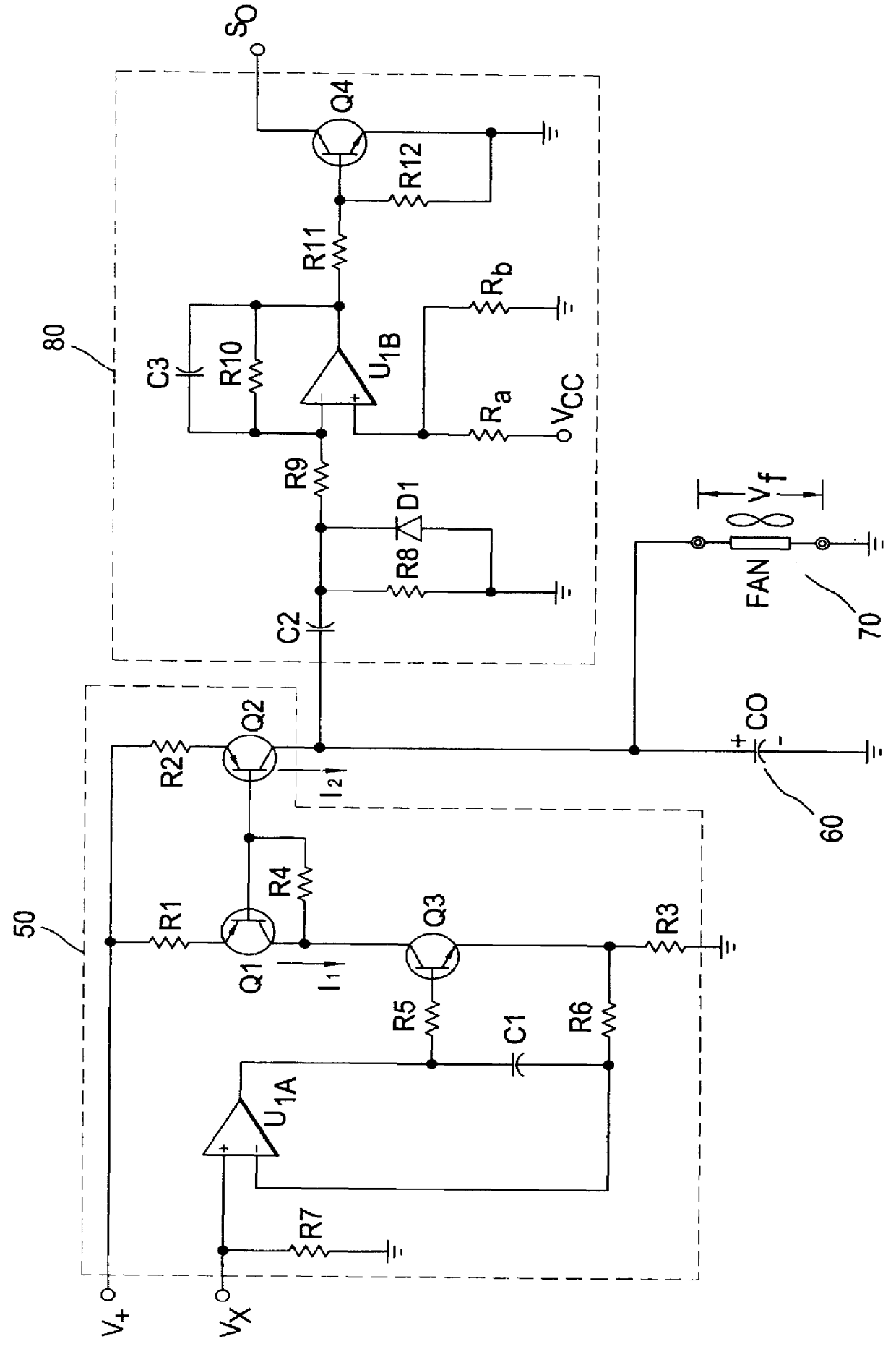
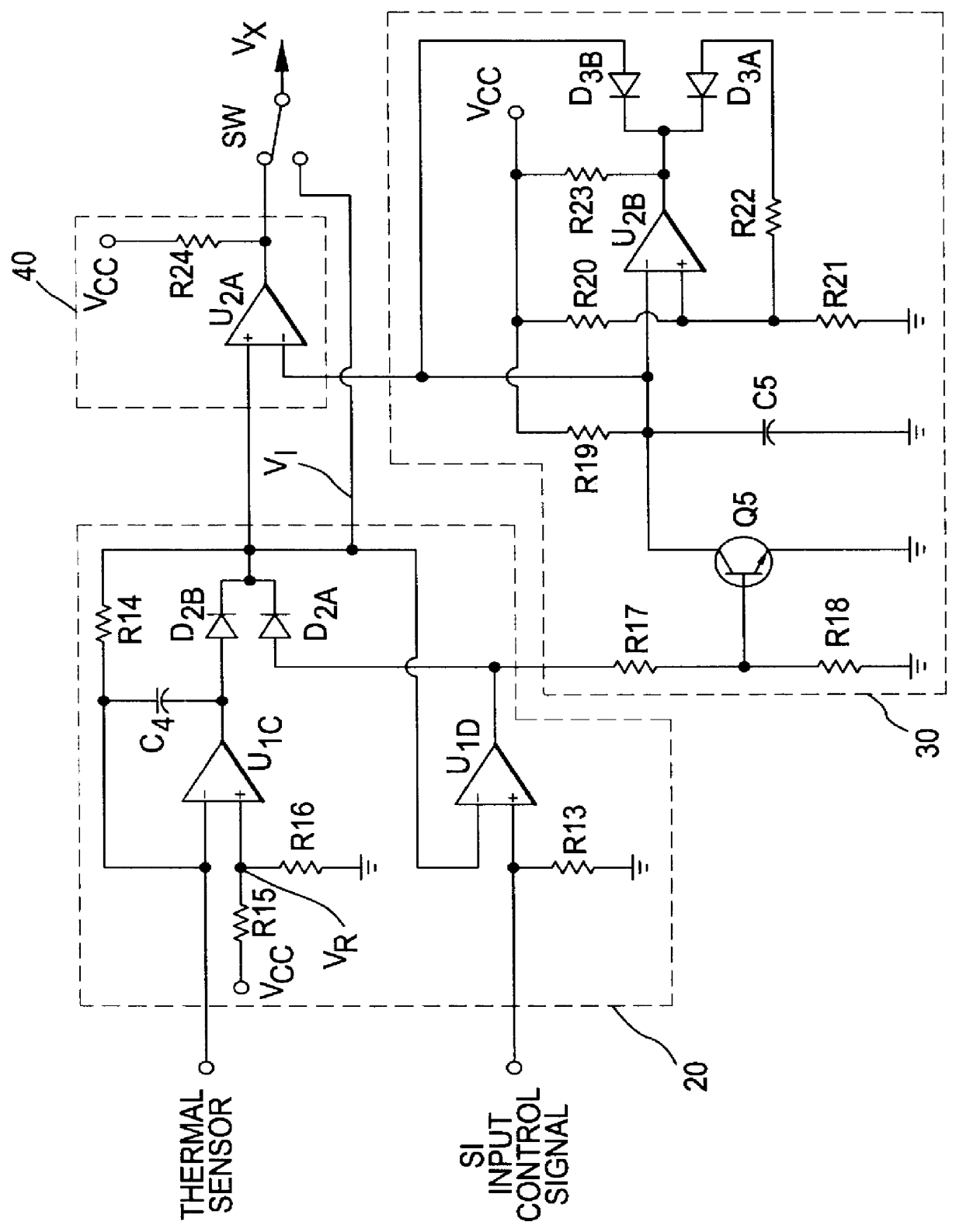
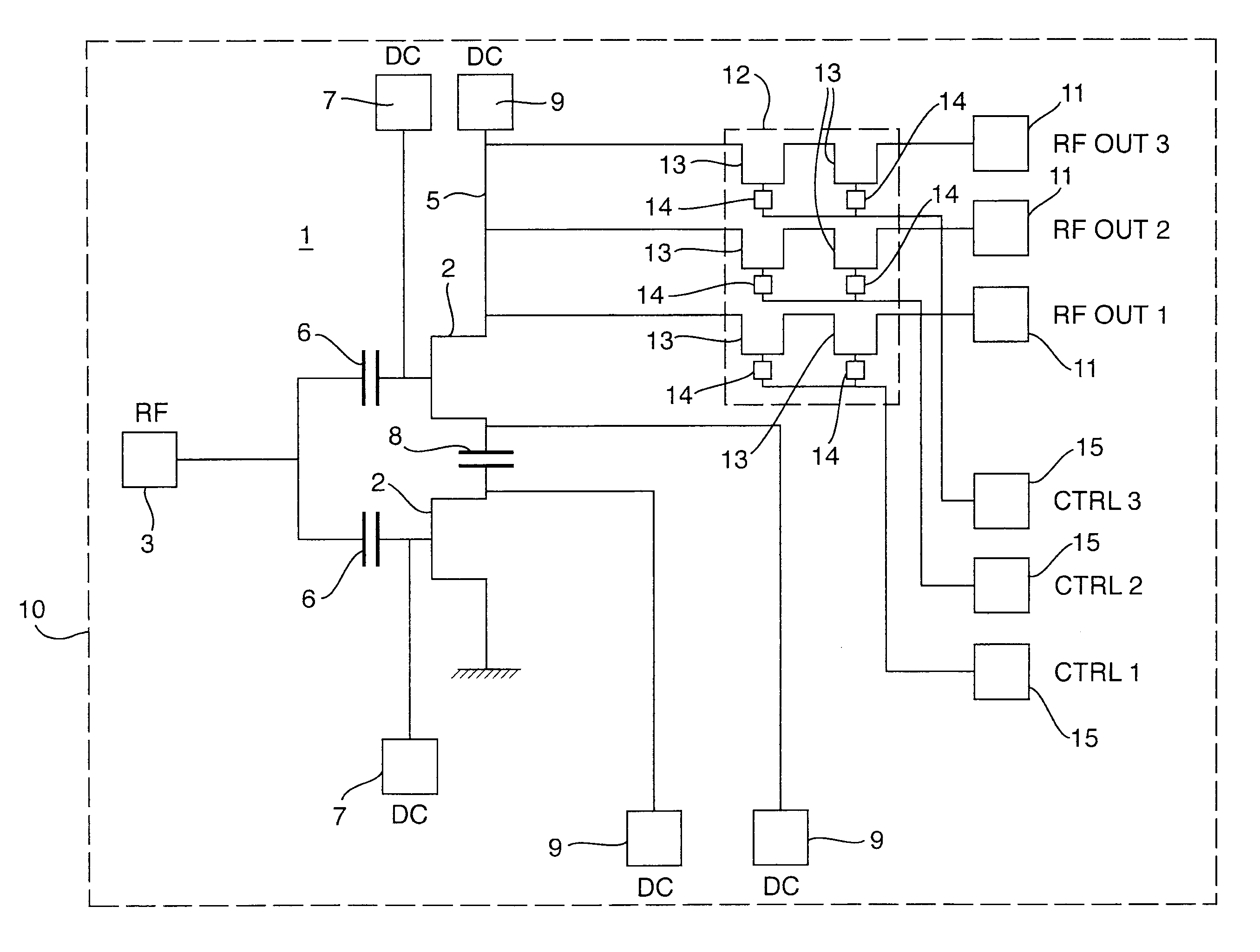
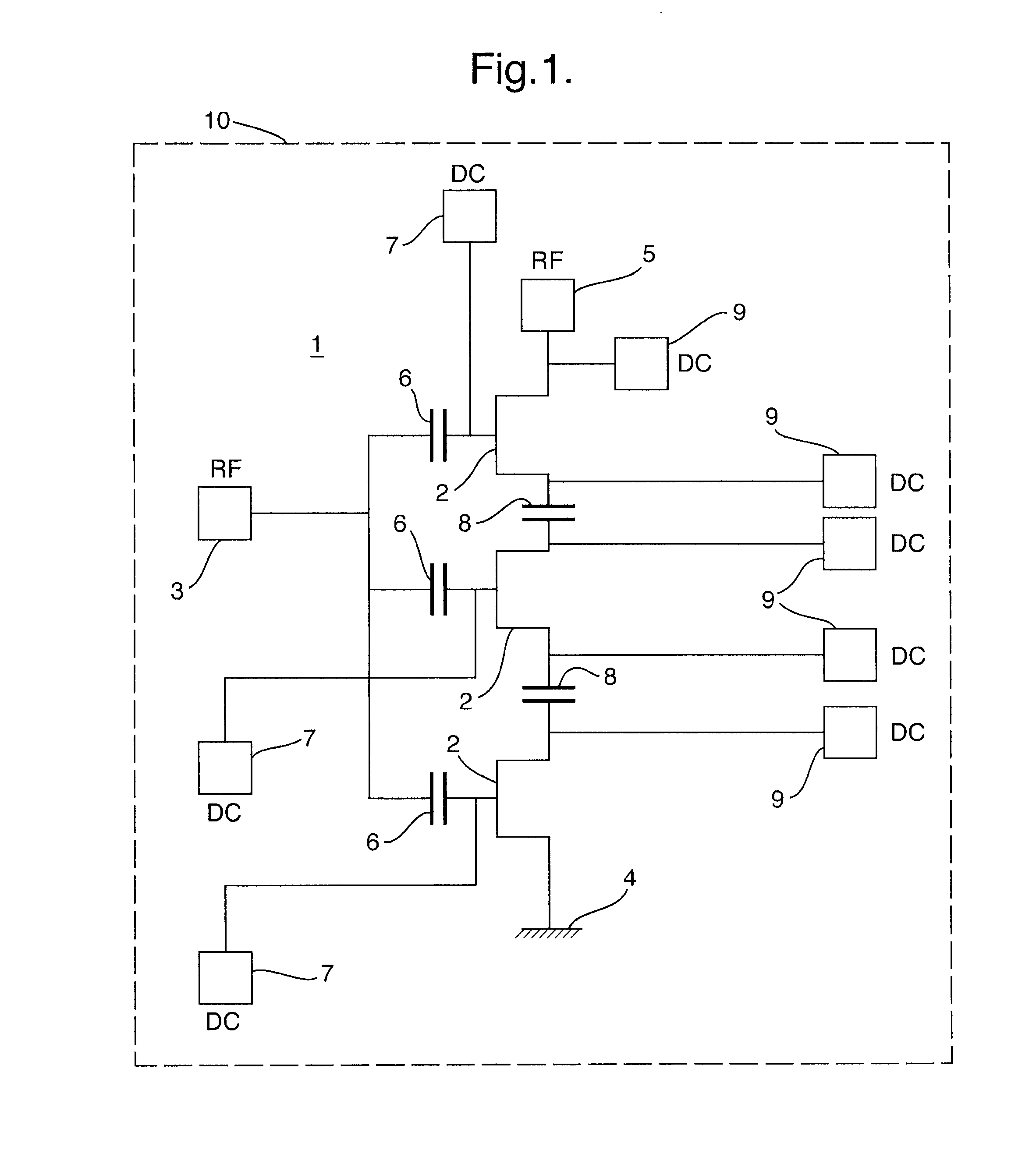
Interface apparatus for fan monitoring and control
InactiveUS6135718ADifficult to filterIncrease output impedancePump componentsTemperatue controlCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
An interface apparatus for fan monitoring and control includes a current source amplifier that generates a programmable current in response to its input voltages. Associated with an output capacitor, which is able to reduce noise, the programmable current drives the fan at a desired speed. The rotating fan induces a ripple signal in the output capacitor, which is fed to a band-pass amplifier to produce a tachometer pulse. Through a buffer amplifier, an input control signal combined with a thermal sensor signal has direct control over the current source amplifier. Alternatively, a PWM circuit having a comparator, a ramp oscillator and the output of the buffer amplifier drives the current source amplifier in switching mode. Since the ramp oscillator can be synchronized by the input, both analog and pulse signals can function as the input control signals.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Mixed-mode (current-voltage) audio amplifier
ActiveUS20050134374A1Total current dropReduce voltageNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsLow frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierCurrent voltage
A method and system for providing a mixed-mode (current- and voltage-source) audio amplifier is disclosed. The mixed-mode amplifier includes a voltage sensing feedback path including a first network comprising at least one circuit; and a current sensing feedback path including a second network comprising at least one circuit. According to the method and system disclosed herein, the first and second networks vary an output impedance or transconductance of the amplifier as a function of frequency of the input voltage signal, such that at a first frequency range, the amplifier operates substantially as a current amplifier, and at a second frequency range, the amplifier operates substantially as a voltage amplifier, thereby inheriting distortion reduction of the current amplifier and stability of the voltage amplifier.
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
Power amplifier
ActiveUS8253485B2Reduce voltageReduces cost and complexityGated amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierCoupling
Owner:SONY EUROPE BV
Programmable low-voltage differential signaling output driver
ActiveUS7236018B1Increase output impedanceInhibit currentGated amplifiersElectric pulse generatorLow voltageEngineering
The present invention relates to a programmable low-voltage differential signaling (LVDS) output driver. The programmable LVDS output driver may include circuitry for tri-stating the output to allow several programmable LVDS output drivers to be coupled to a single receiver. The programmable LVDS output driver may also include programmable current sources for varying the output current, as well as providing additional current to circuitry within the driver (e.g., impedance circuitry). The programmable LVDS output driver may also include an impedance circuit for adjusting the output impedance of the output driver, while only diverting a small amount of source current. The current diverted by the impedance circuit may be compensated for by increasing the source current from the programmable current sources. The programmable LVDS output driver may also include pre-emphasis circuitry for boosting the edge rates of output signals.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Condenser microphone
InactiveUS20080219482A1Improve environmental adaptabilityImprove abilitiesSolid-state devicesElectrostatic transducer microphonesCapacitanceResonance
An electroacoustic transducer includes a condenser microphone, which includes a package having a cavity and a through-hole, a plate whose thickness is thinner than the length of the through-hole and which has a sound hole overlapping with the through-hole in plan view, and an electroacoustic transducer die, which is stored in the cavity of the package. The electroacoustic transducer die includes a fixed electrode and a diaphragm electrode, which are positioned opposite to each other and which are supported by and enclosed inside of a support. The sound hole of the plate is reduced in dimensions realizing a small sectional area and a small depth, thus realizing a high resonance frequency higher than the audio frequency range.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Signal conditioner with suppression of interfering signals
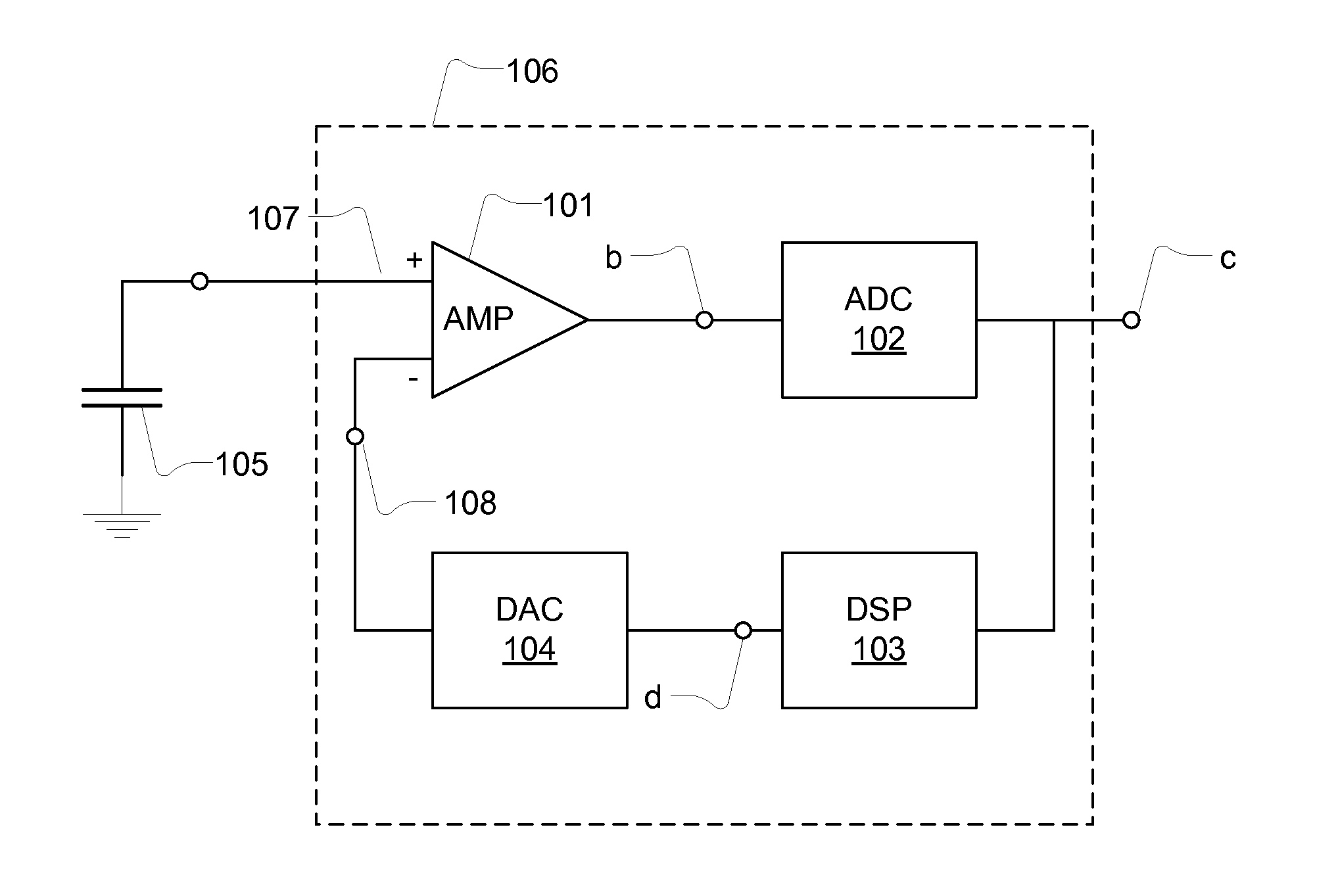
InactiveUS20110051954A1Reduce the amplitudeLow frequency signalAnalogue/digital conversionMicrophone structural associationSemiconductor chipA d converter
A semiconductor die with an integrated circuit providing a signal conditioner (106) for a capacitive transducer (105), comprising: a gain stage (101) configured to receive an analogue transducer signal; an analogue-to-digital converter (102) coupled to receive a signal outputted from the gain stage (101) and to provide a digital signal. A feedback signal is provided via a digital-to-analogue converter (104) and a digital signal processor (103) that receives the digital signal; and the gain stage (101) is configured with a first input (107) and second input (108) coupled to receive the analogue transducer signal and the feedback signal, respectively.
Owner:INVENSENSE
Degenerated passive mixer in saw-less receiver
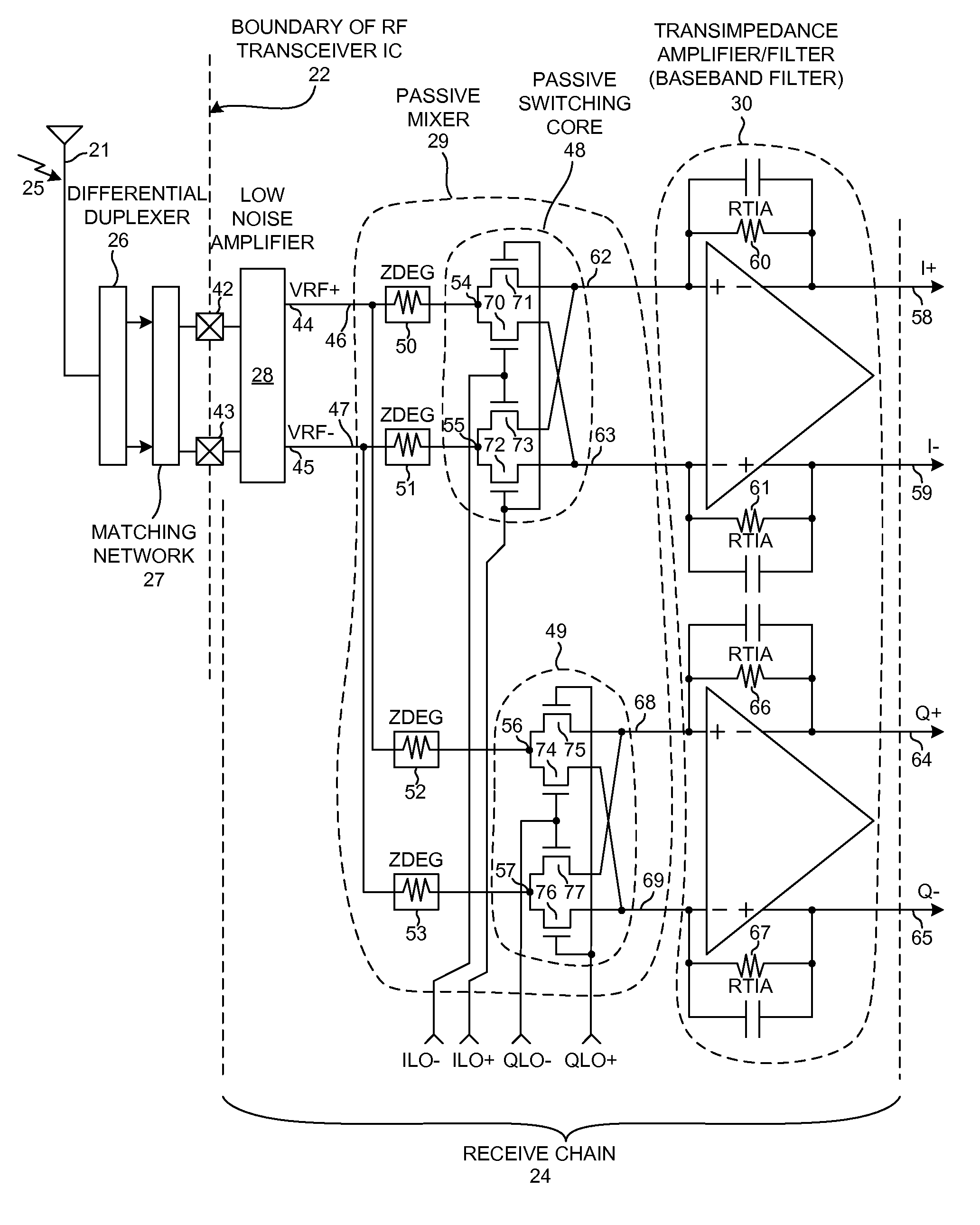
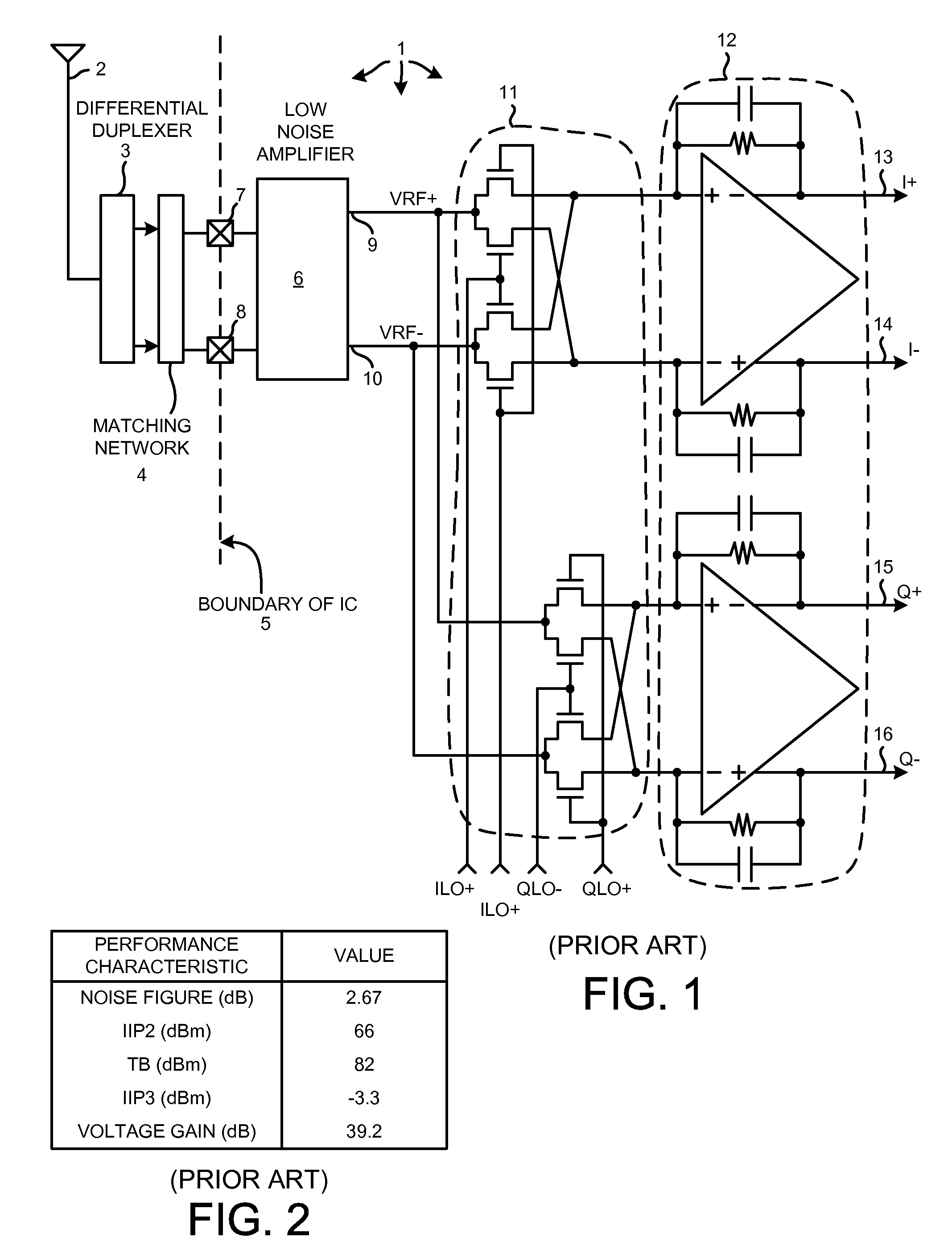
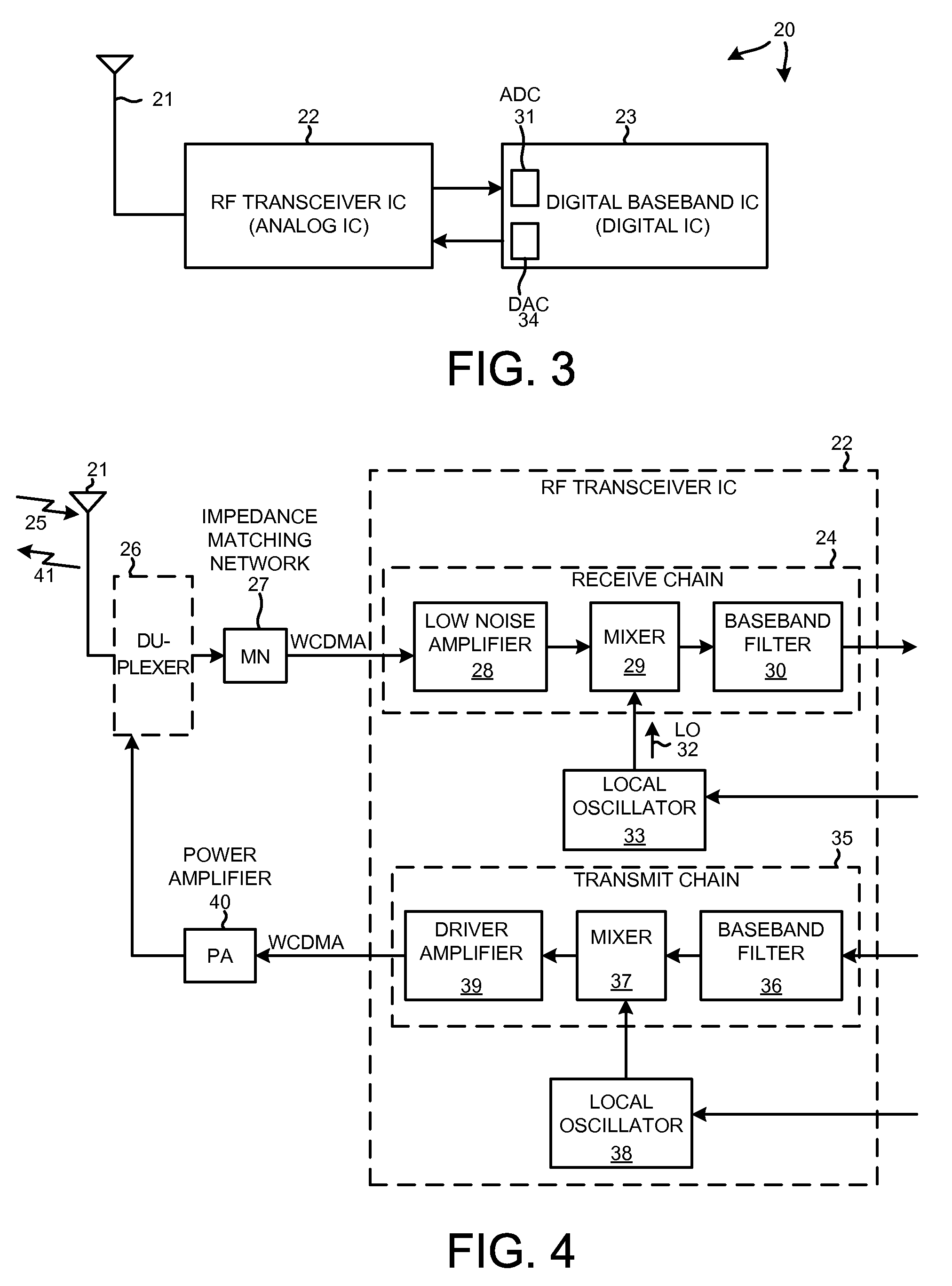
ActiveUS20090111420A1Increase output impedanceReduce noiseSubstation equipmentTransmissionElectrical impedanceAudio power amplifier
In a SAW-less receiver involving a passive mixer, novel degenerative impedance elements having substantial impedances are disposed in incoming signal paths between the differential signal output leads of a low-noise amplifier (LNA) and the differential signal input leads of the passive mixer. The passive mixer outputs signals to a transimpedance amplifier and baseband filter (TIA). Providing the novel degenerative impedance elements decreases noise in the overall receiver as output from the TIA, with only minimal degradation of other receiver performance characteristics. In some examples, the passive mixer receives local oscillator signals having duty cycles of substantially less than fifty percent. In some examples, the degenerative impedance elements can have one of several impedances.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Low pressure difference voltage stabilizer
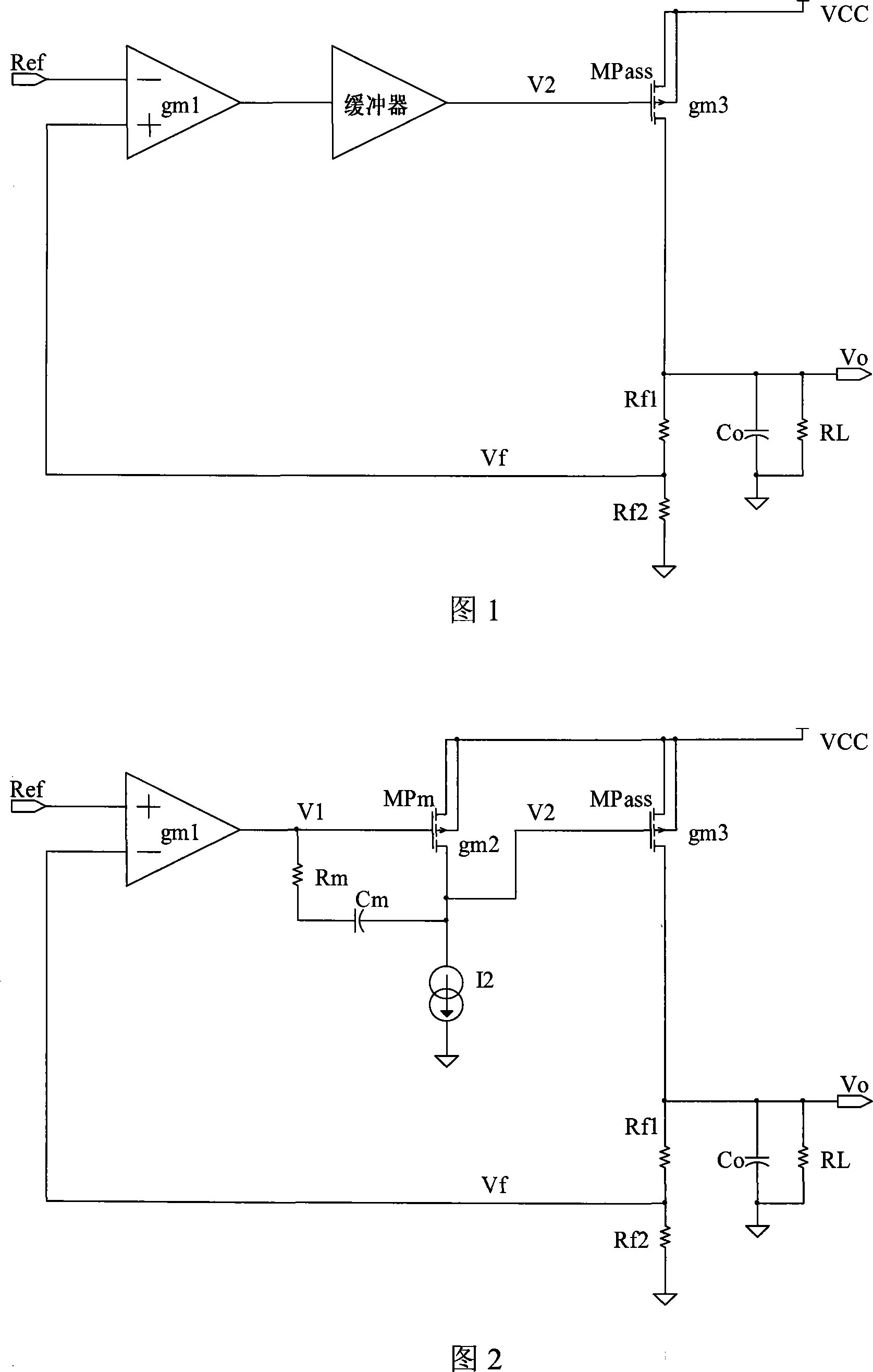
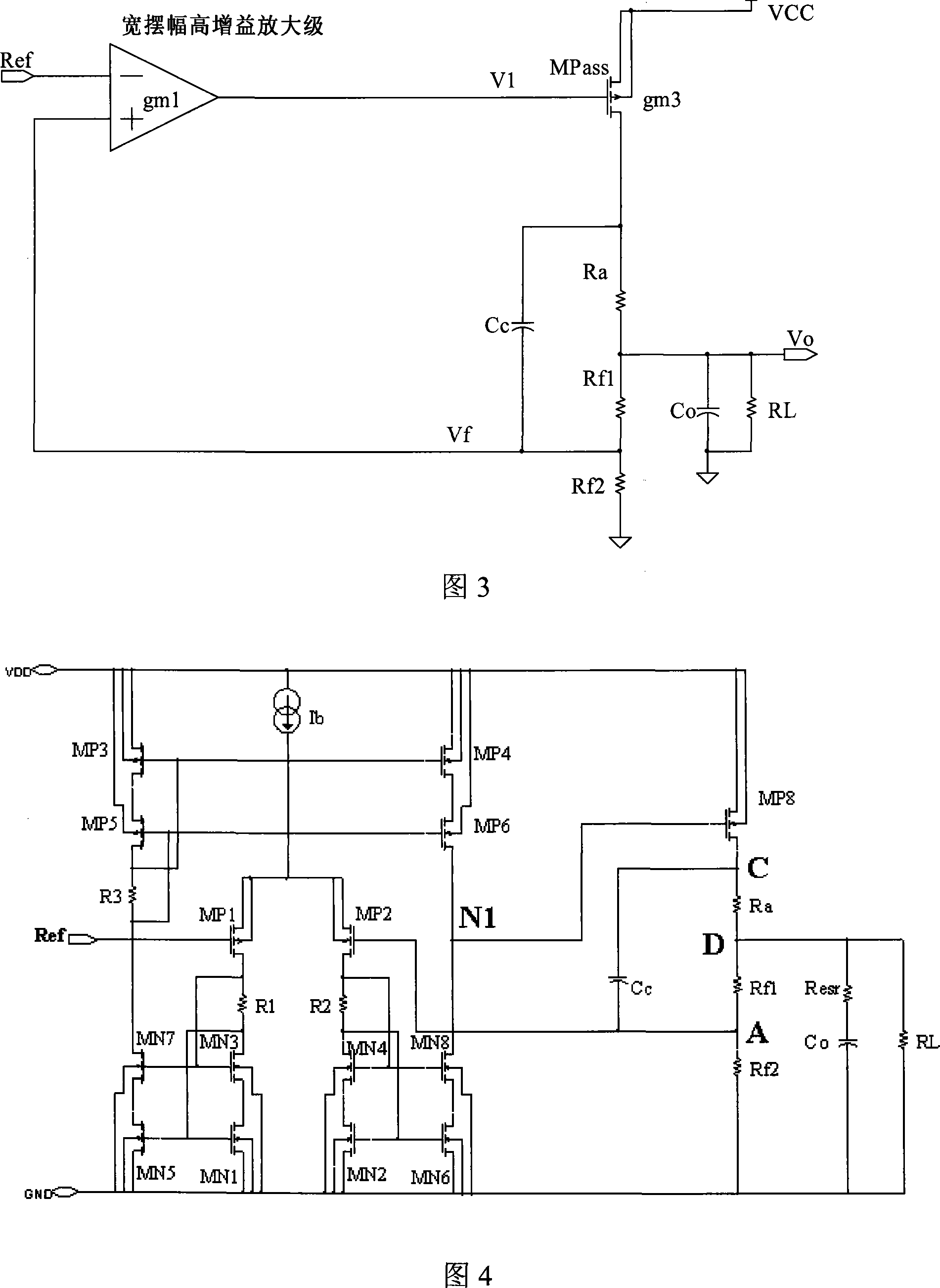
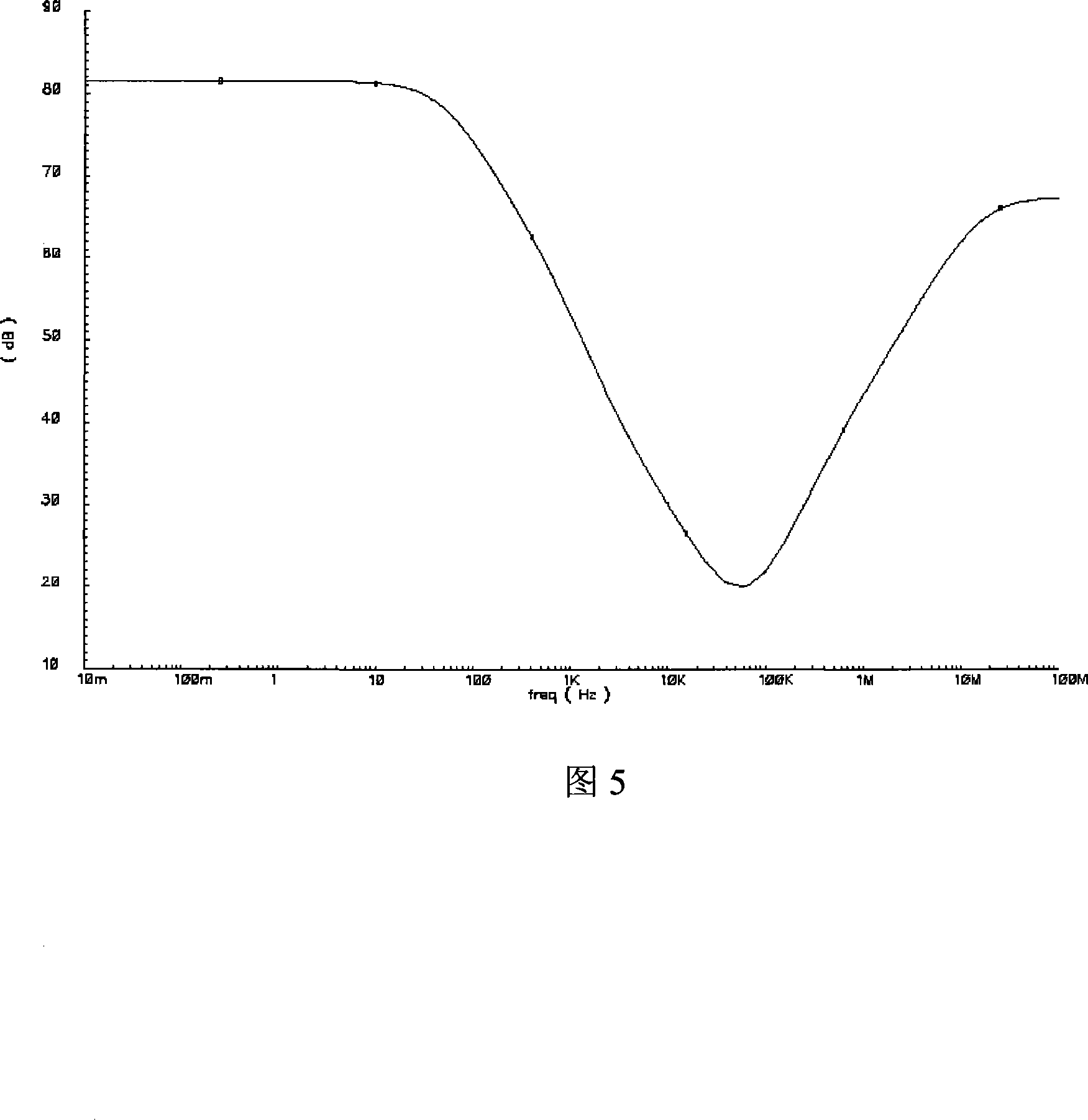
InactiveCN101183270AReduce consumptionIncrease output impedanceElectric variable regulationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A kind of low-dropout regulator, comprising a differential amplifier circuit, an output amplifier circuit and a voltage divider circuit, said output amplifier circuit comprises a PMOS transistor MPass1 whose source is connected to the input supply voltage Vdd, and connected between the voltage output point and The output capacitor Co between the ground, the two input terminals of the differential amplifier circuit are respectively connected to the reference voltage Ref and the voltage division point of the voltage divider circuit, the output terminal of the differential amplifier circuit is connected to the gate of the PMOS transistor, and the The voltage divider circuit is connected between the voltage output point and the ground, and is characterized in that it also includes a resistor Ra connected between the drain of the PMOS transistor MPass1 and the voltage output point, and a resistor Ra connected between the drain of the PMOS transistor MPass1 and the capacitor Cc between the voltage divider points. The low dropout voltage regulator provided by the invention has the advantages of low quiescent current, high power supply suppression, strong stability, low dropout voltage and low cost, and meets the needs of practical applications.
Owner:WUXI ZGMICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Degenerated passive mixer in saw-less receiver
ActiveUS7899426B2Increase output impedanceReduce noiseSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionLocal oscillator signalAudio power amplifier
In a SAW-less receiver involving a passive mixer, novel degenerative impedance elements having substantial impedances are disposed in incoming signal paths between the differential signal output leads of a low-noise amplifier (LNA) and the differential signal input leads of the passive mixer. The passive mixer outputs signals to a transimpedance amplifier and baseband filter (TIA). Providing the novel degenerative impedance elements decreases noise in the overall receiver as output from the TIA, with only minimal degradation of other receiver performance characteristics. In some examples, the passive mixer receives local oscillator signals having duty cycles of substantially less than fifty percent. In some examples, the degenerative impedance elements can have one of several impedances.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
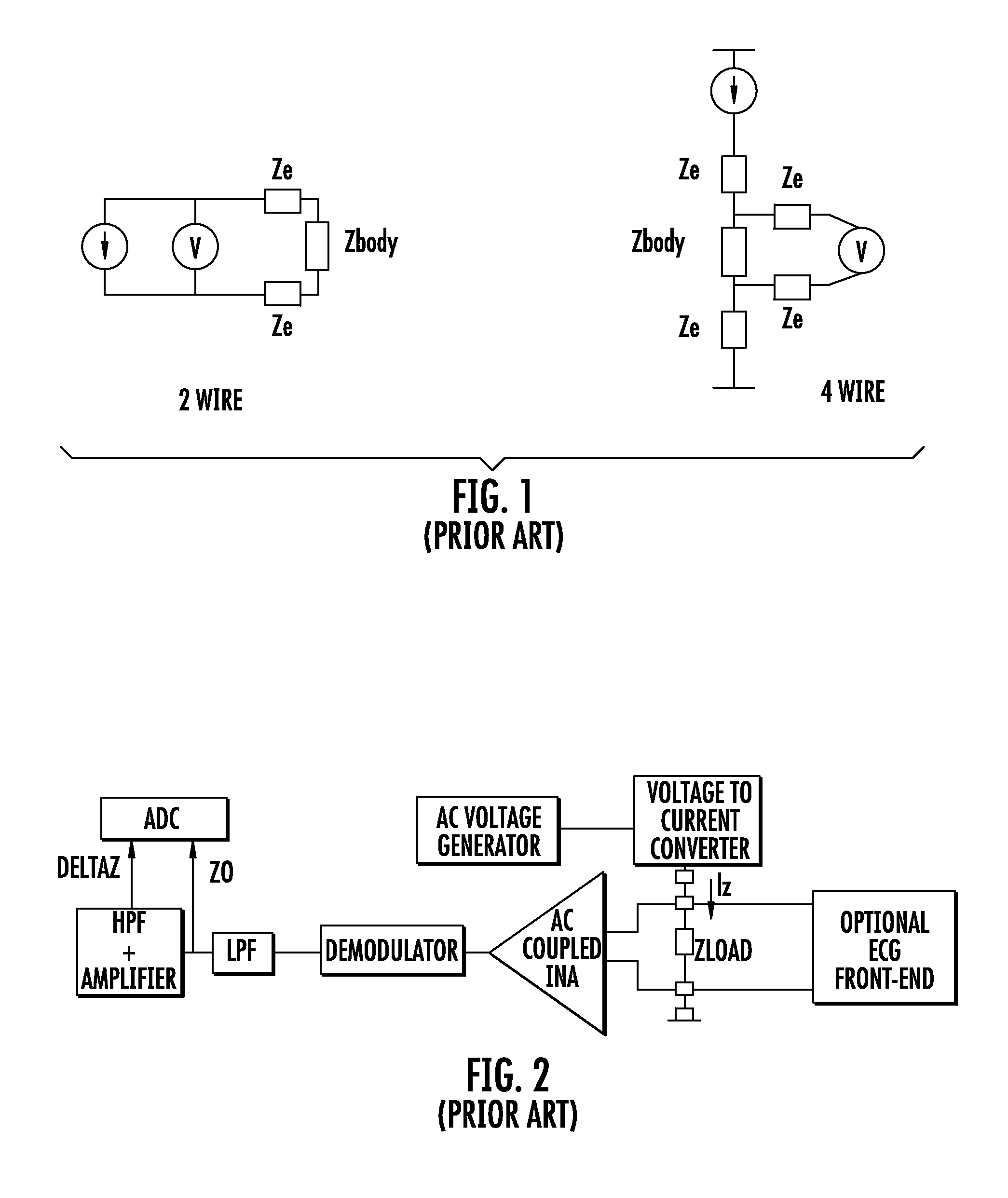
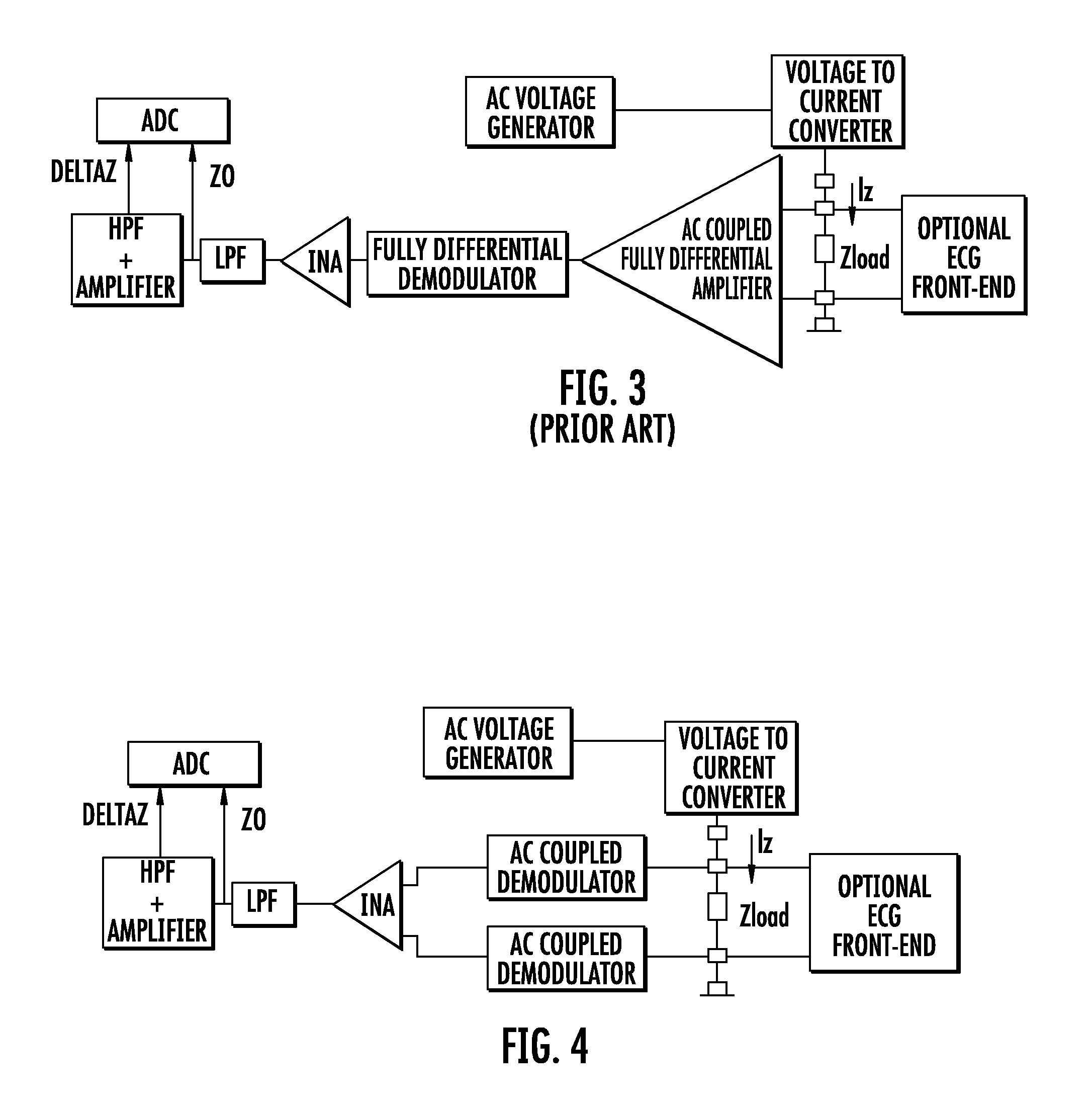
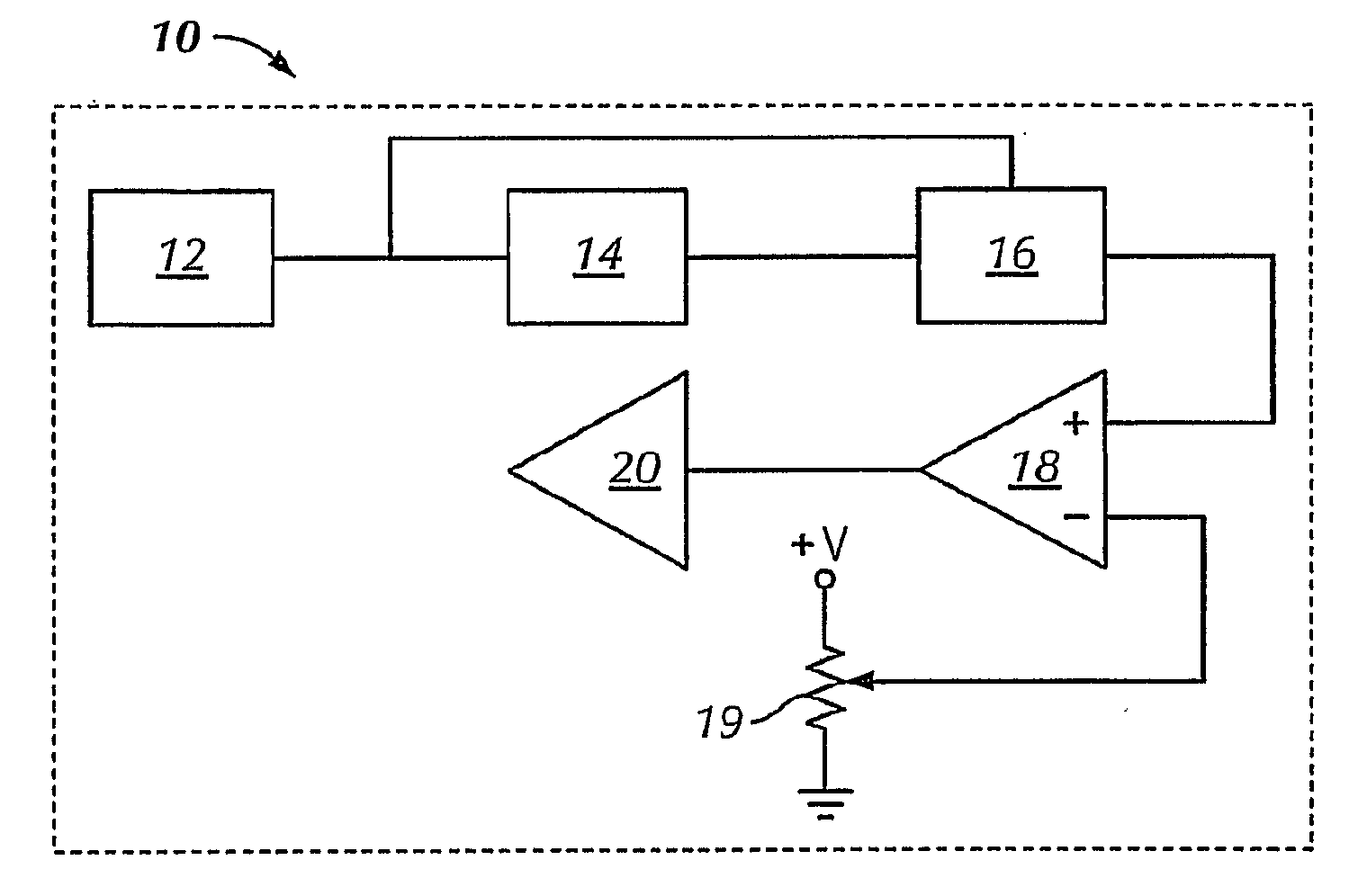
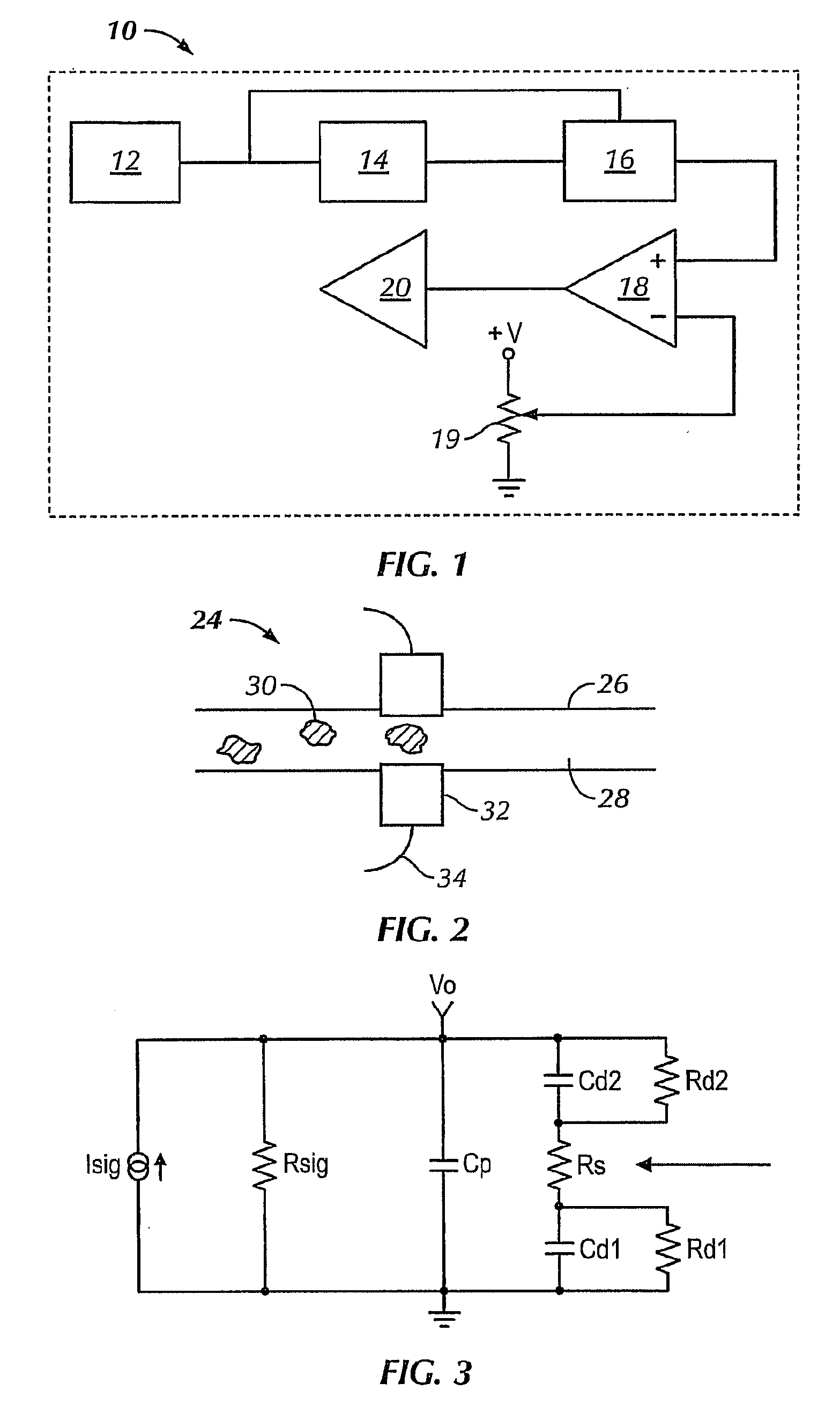
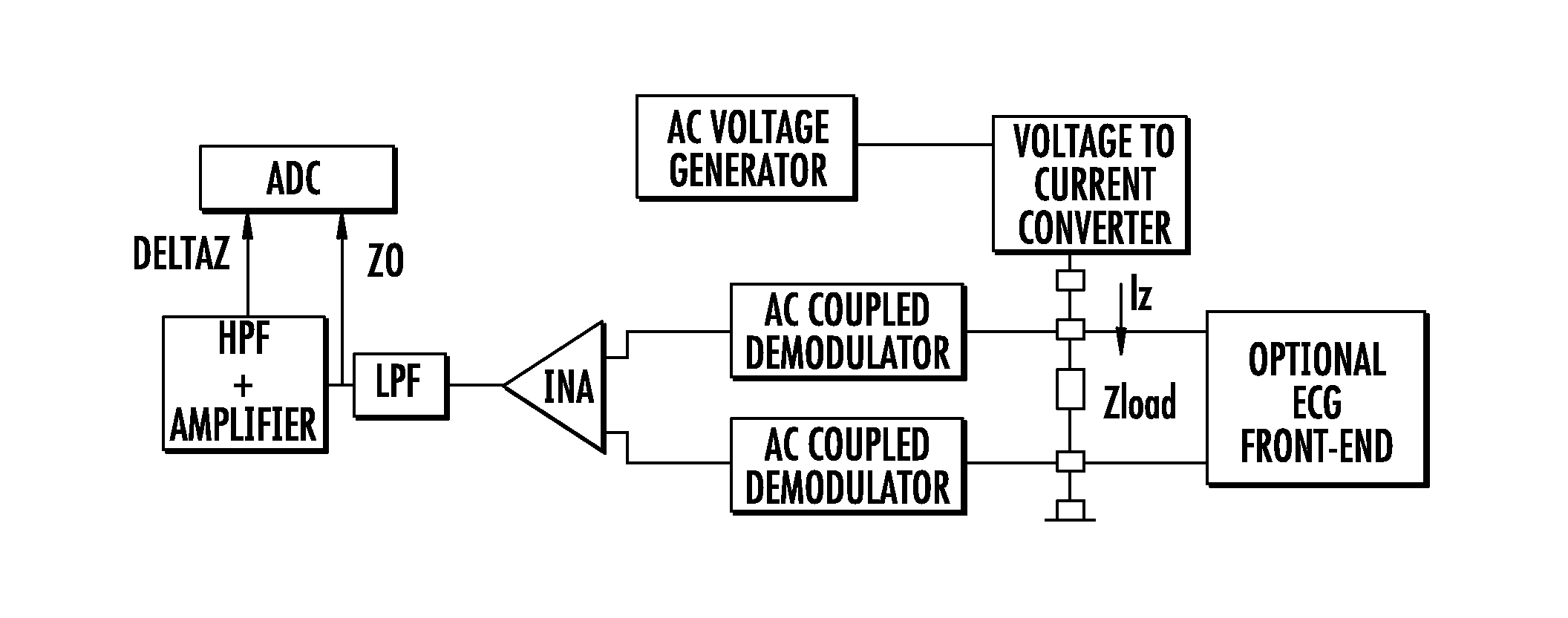
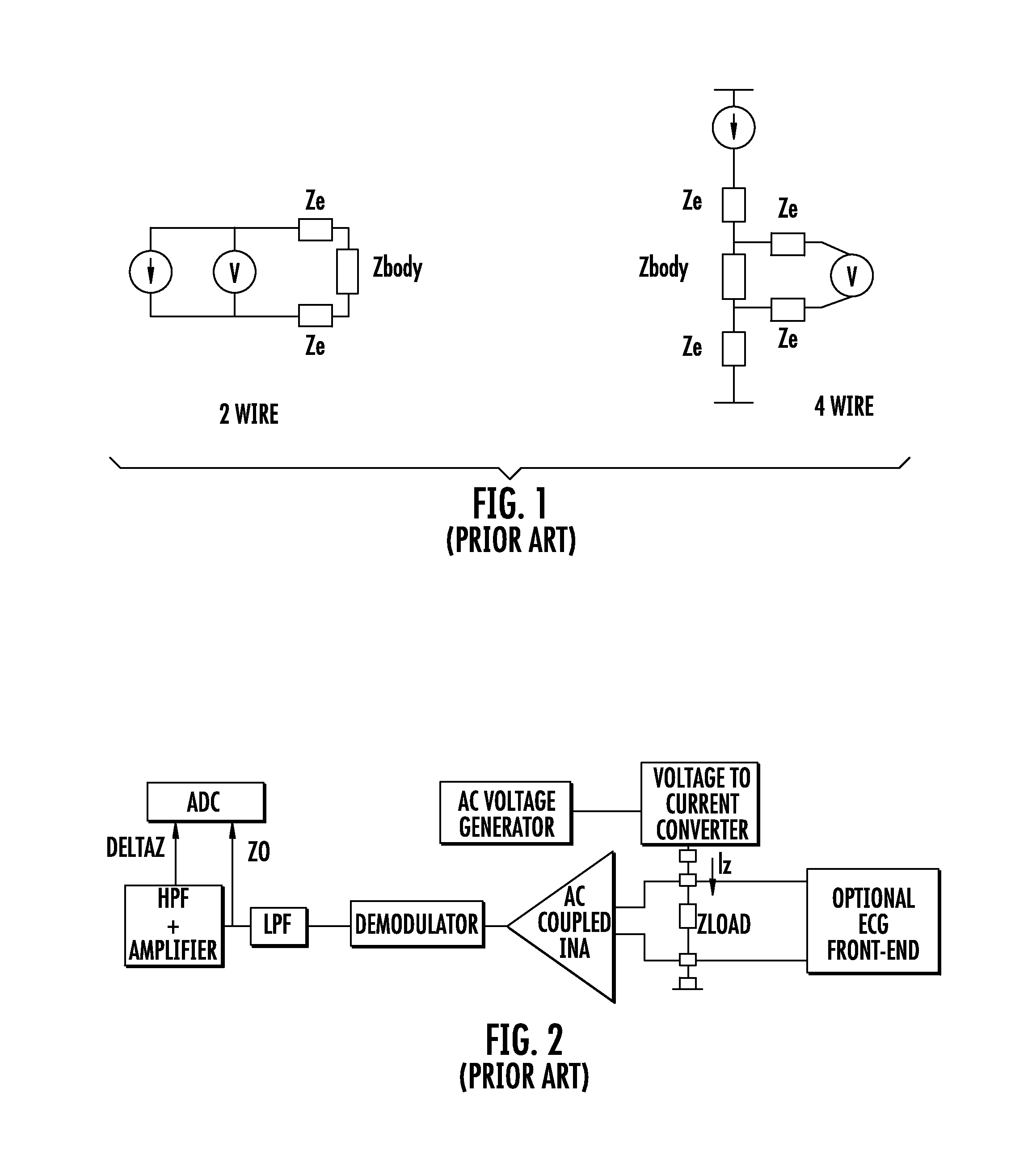
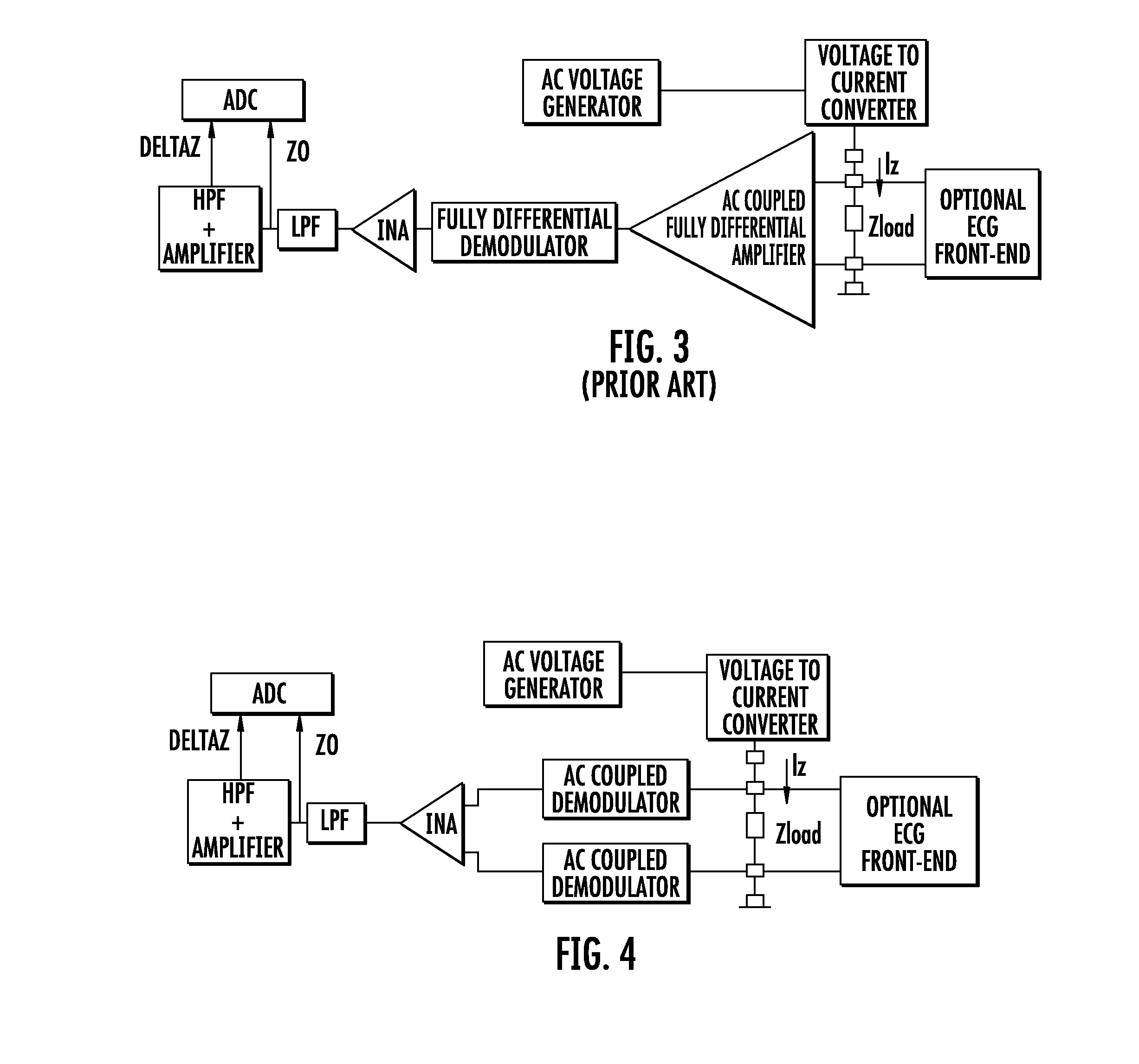
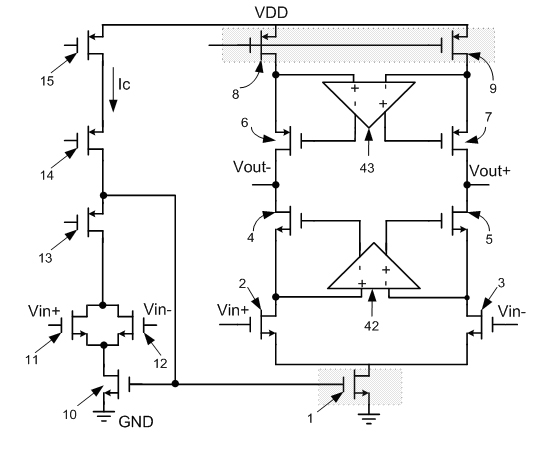
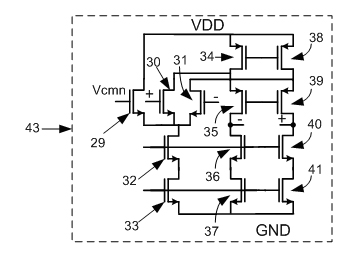
Device for measuring impedance of biologic tissues including an alternating current (AC) coupled voltage-to-current converter
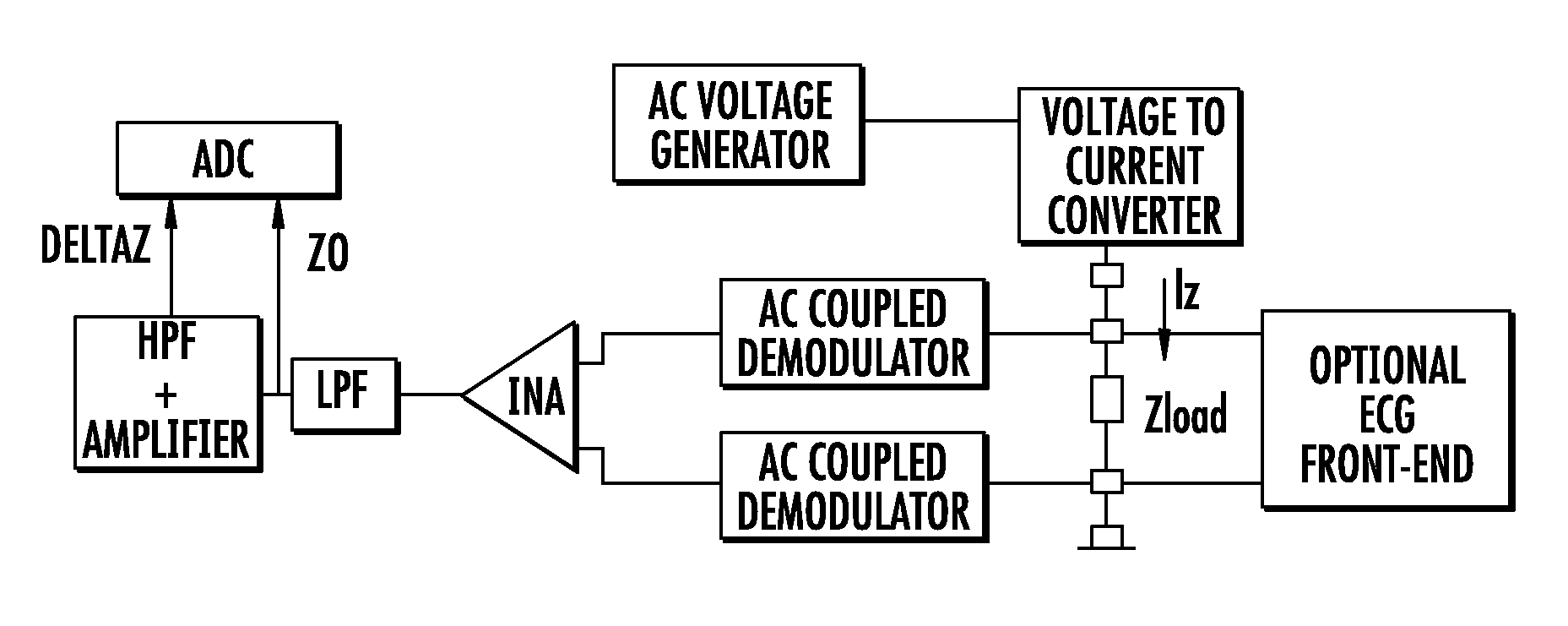
ActiveUS9510768B2Increase output impedanceTotal current dropResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsAc componentsAudio power amplifier
A device for measuring impedance of biological tissue may include electrodes and a voltage-to-current converter coupled to the electrodes to drive an alternating current (AC) through the tissue and sense an AC voltage. The converter may include an amplifier having first and second inputs and an output, a first voltage divider coupled to the first input, a second voltage divider coupled to the second input, a filter capacitor coupled between the output and the second voltage divider, a current limiting resistor coupled between the second input the second voltage divider, and a bypass capacitor coupled to the second input of the amplifier and in parallel with the resistor. A single-ended amplitude modulation (AM) demodulator may demodulate the AC voltage and generate a corresponding baseband voltage representing the impedance. The device may also include an output circuit to generate output signals representative of DC and AC components of the baseband voltage.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Conductivity Counter
ActiveUS20090212788A1Eliminate capacitanceImprove signal-to-noise ratioFluid resistance measurementsMaterial impedanceCapacitancePhase sensitive
A conductivity counter and method of determining conductivity of a fluid sample are disclosed. The counter is suitable for high-speed, accurate counting of discrete events or items, such as cancer cells, passing through a fluid sample cell. A variable frequency current source is used to supply an excitation current to a sample cell connected in parallel with an inductance or the electrical equivalence of an inductance. This configuration can be accurately modeled as a parallel RLC circuit when the system is operated at a stable frequency. The current source frequency is tuned to the resonance frequency of the equivalent RLC circuit, which effectively eliminates the capacitive and inductive components of the impedance, leaving only purely resistive components. The output of the equivalent RLC circuit is connected to a high input impedance buffer amplifier and then to a phase sensitive detector, which detects the phase shift resulting from the equivalent RLC circuit. The output is filtered and a differencing amplifier is used to zero out the output signal due to the system components and the sample cell buffer solution prior to taking active readings. The remaining output signal is due to perturbations in the fluid sample, such as passing cancer cells. This output is sent to a high-gain output amplifier and then supplied to a suitable signal processing device or system, such as a computer.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Power amplifier
ActiveUS20110241782A1Reduce voltageReduces cost and complexityGated amplifiersAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierCoupling
A power amplifier comprises a series stack of power amplifier devices, connected in parallel to the amplifier input for receiving an RF input signal, and having output terminals being connected in series to the amplifier output. An intermediate coupling capacitor is connected between each adjacent pair of power amplifier devices in the series stack of power amplifier devices for DC isolation of said power amplifier devices. This reduces the required DC supply voltage, as well as allowing shorting of individual power amplifier devices in response to variation in the DC supply voltage.
Owner:SONY EUROPE BV
Wideband Highly-Linear Low Output Impedance D2S Buffer Circuit
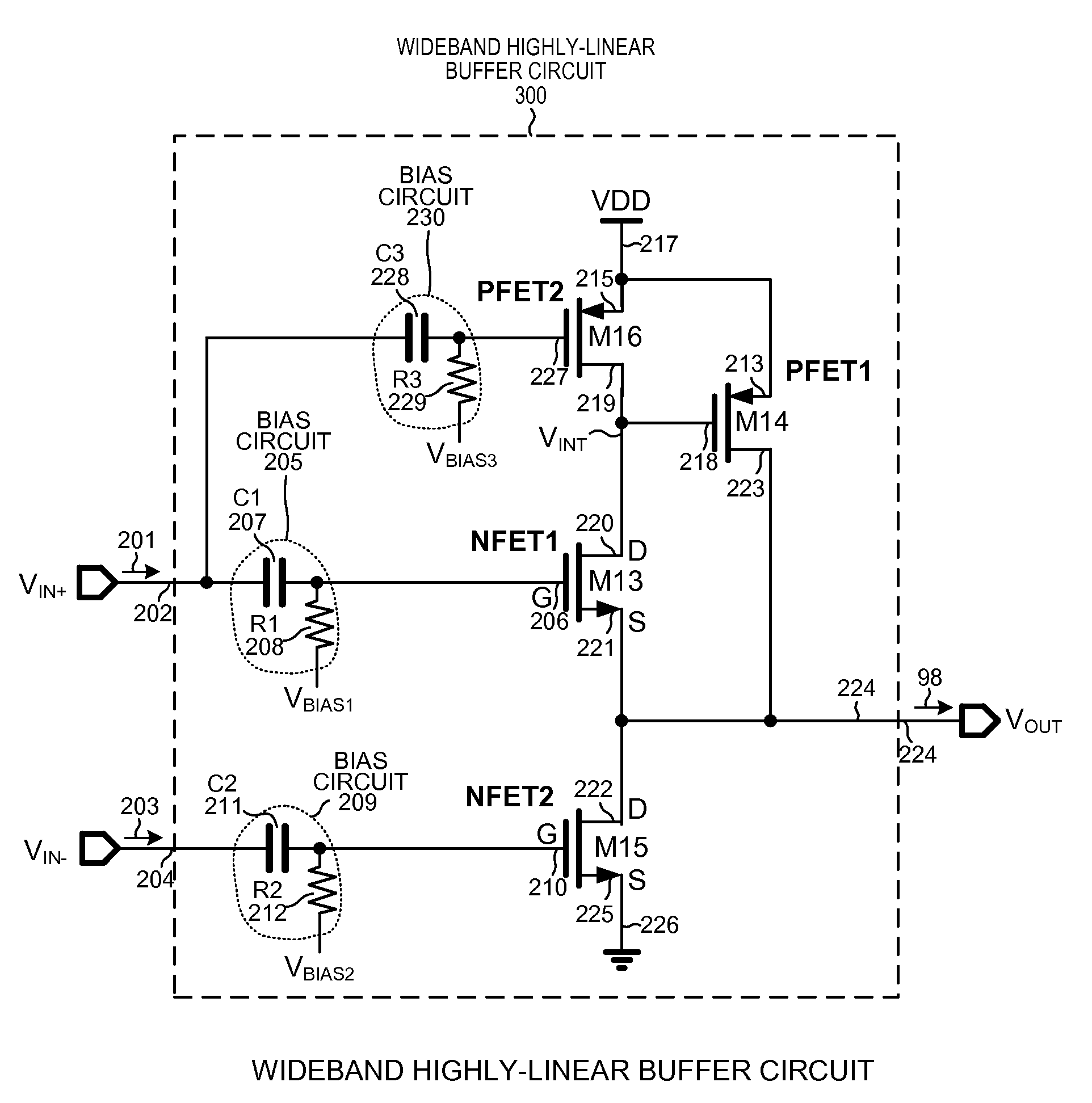
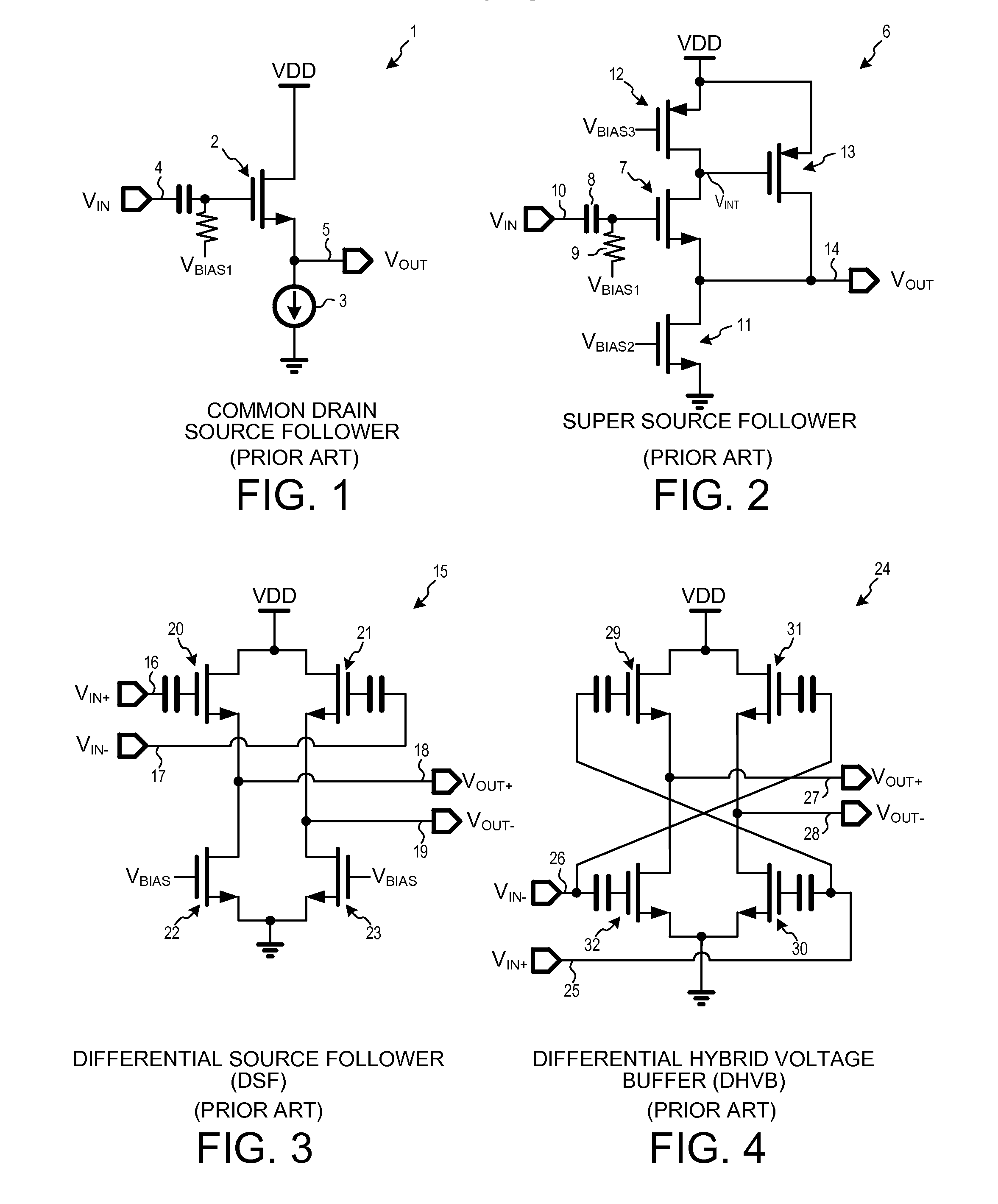
ActiveUS20160365859A1Low output impedanceImprove linearityLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesOutput impedanceWideband
A wideband highly-linear buffer circuit exhibiting a low output impedance comprises a first PFET (PFET1), a second PFET (PFET2), a first NFET (NFET1), and a second NFET (NFET2). Sources of PFET1 and PFET2 are coupled to VDD. PFET1's drain is coupled to an output lead. PFET2 acts as a current source. NFET1's drain is coupled to PFET2's drain and to PFET1's gate. NFET1's source is coupled to the output lead. NFET2's source is coupled to ground. NFET2's drain is coupled to NFET1's source and to the output lead. NFET1's gate is AC coupled to a first input lead. In a single-ended input example, NFET2's gate is AC coupled NFET1's drain. In a differential input example, NFET2's gate is AC coupled to a second input lead. In another differential input example, PFET2 is not just a current source, but rather PFET2's gate is AC coupled to the first input lead.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Axial magnetic path multi-pole pair reluctance type rotary transformer
InactiveCN102034596AImprove performanceReduce volumeTransformersTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsEngineeringElectrical impedance
The invention relates to an axial magnetic path multi-pole pair reluctance type rotary transformer, belonging to the technical field of transformers. The invention solves the problems that an air gap is increased and input output impedance is reduced in the variable reluctance design of the existing reluctance type rotary transformer. An air gap is formed between a stator and a rotor, the upper section of the stator and the lower section of the stator are in the same shape, the inner circle surface is distributed with 4PN convex teeth along the peripheral direction, a tooth groove is arranged between adjacent convex teeth, and the inner diameter of the tooth groove is the same as the middle section of the stator; the middle section of the permeability material of the rotor is corrugate along the peripheral direction, and the number of peaks is P; an exciting winding is arranged in a groove which is formed on the stator inner surface at the middle section of the stator and is coaxial with the stator; and N adjacent convex teeth at the same positions of the upper section of the stator and the lower section of the stator form a group, A phase signal windings and B phase signal windings are alternately arranged on 4P groups of convex teeth, homopolar in-phase signal windings are wound on the same group of convex teeth, and homopolar in-phase homopolar signal windings are connected in forward series. The invention is used for measuring speed and position of a servo system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
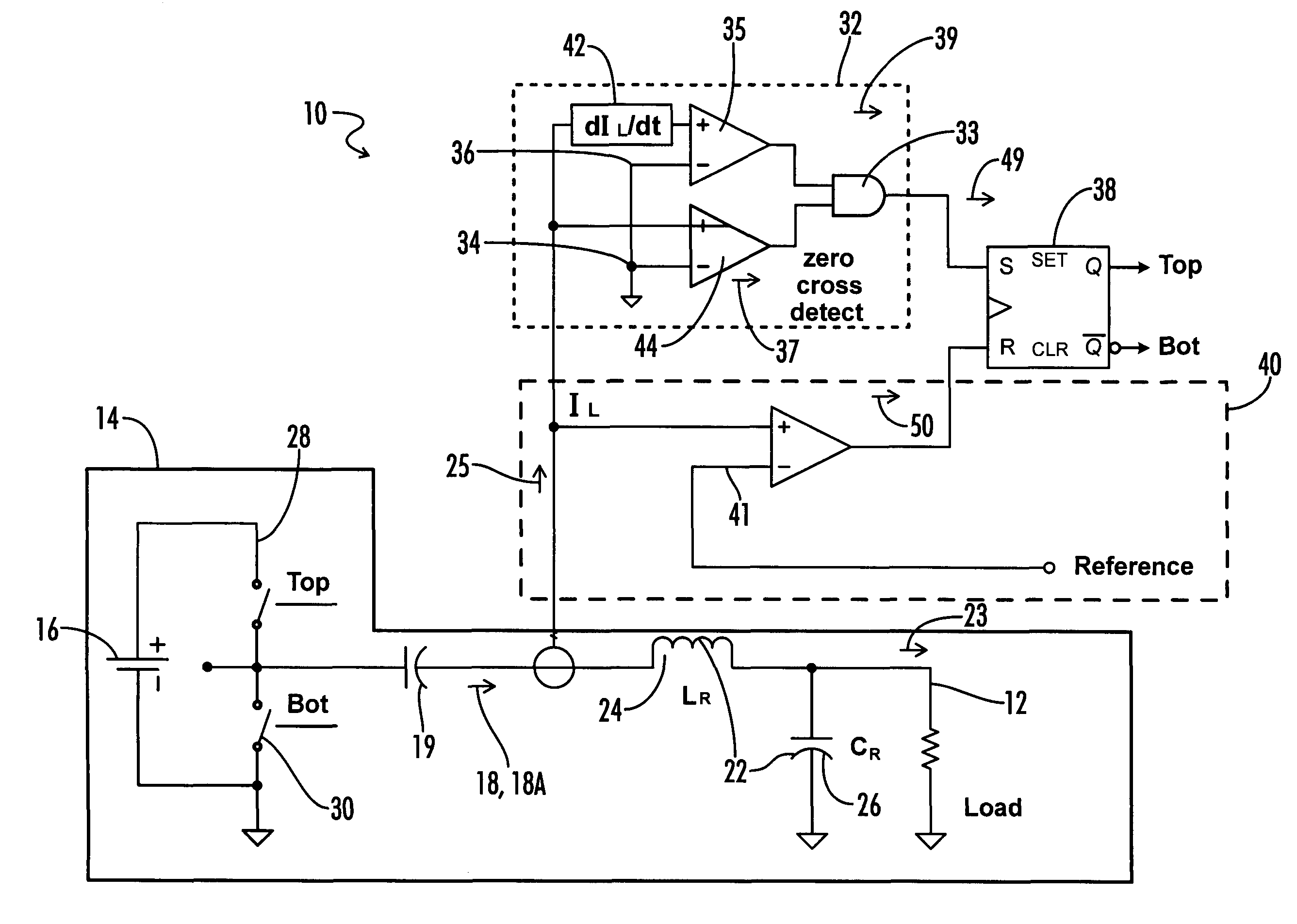
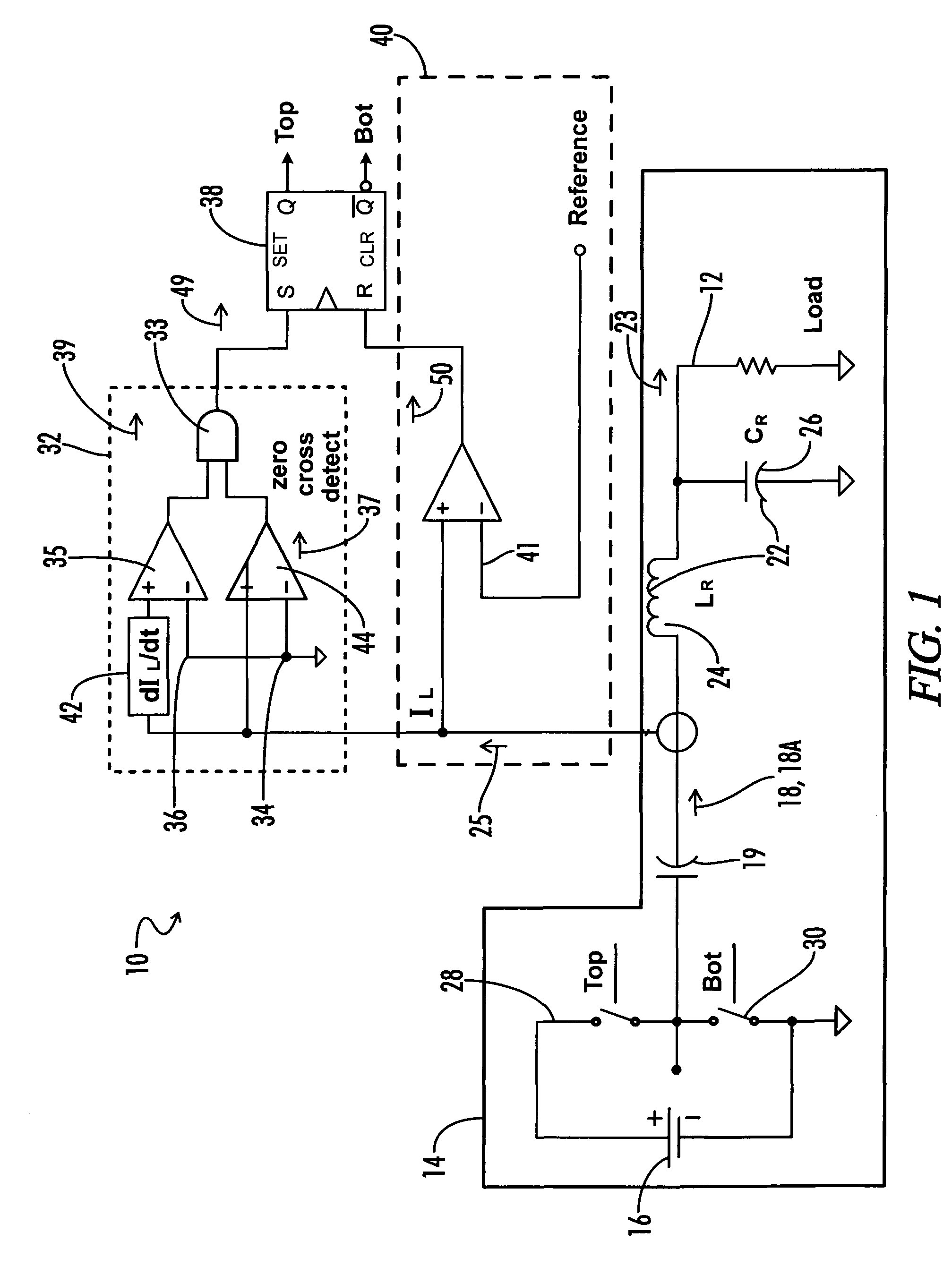
Method of operating a resonant inverter using zero current switching and arbitrary frequency pulse width modulation
InactiveUS7800928B1Increase output impedanceExtended maintenance periodConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionResonant inverterGas-discharge lamp
A method of controlling a series-resonant, half-bridge inverter includes turning off the bottom switch and turning on the top switch the inverter when the current through the resonant inductor crosses the zero axis while the current is increasing, thereby insuring zero voltage switching of the inverter switches and increases the overall switching period so that the actual inverter frequency is closer to the resonant frequency of the series-resonant circuit. Using an on-time control circuit, the method further includes controlling the current delivered to the load (such as a gas discharge lamp) by varying the on-time of the top inverter switch.
Owner:UNIVERSAL LIGHTING TECHNOLOGIES
Amplification device with a bias circuit
InactiveUS20050134384A1Stable bias voltageImprove reliabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationLow frequency amplifiersMOSFETAudio power amplifier
An operational amplifier amplifies a signal received through its input terminal connected directly to a piezoelectric device. A bias voltage generating section includes a voltage divider between the power supply terminal and the ground terminal. The drain and source of a p-channel MOSFET are connected to the input terminal of the operational amplifier and the ground terminal. Since the voltage divider applies a bias voltage to the gate and the backgate, the p-channel MOSFET maintains the OFF state. Since a drain-backgate parasitic diode clamps the drain potential to the bias voltage, the bias voltage is applied to the input terminal of the operational amplifier. Then, the drain-backgate resistance is extremely high. The p-channel MOSFET is embedded on a substrate together with other circuits of the amplification device. Thus, the amplification device with an extremely high input impedance is configured as a single integrated circuit.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
A low-voltage frequency mixer
InactiveCN101188402ALower requirementReduce power consumptionModulation transference balanced arrangementsBeacon systems using radio wavesLow noiseEngineering
The invention provides a low-voltage CMOS folding co-source co-grid mixer. The mixer includes the following parts: a pair of transconductance poles composed of NMOS tubes, tow pairs of switch poles composed of NMOS tubes, a pair of load poles composed of NMOS, and a current source. In the structure of the mixer circuit, the transconductance poles are connected with the switch poles in a co-source co-grid method. The invention solves the problems of the high power supply high voltage caused by the overlapping of the transconductance poles and the switch poles of the traditional Gilbert mixer, and the compromise design between the high transconductance and the high linearity of the transconductance poles and the low noise of the switch poles. The invention can be used in the application of the deep submicron RF CMOS circuit, in particular in the design developing of the satellite navigation double-system compatible receiver radio frequency integrated circuit. The invention has bright application prospect in both the military and the civilian fields.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Hybrid microwave integrated circuit
InactiveCN101740556AImprove thermal conductivityFlexible and adjustableSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesState of artMicrowave
The invention relates to a hybrid microwave integrated circuit. Aiming at the defects that the hybrid microwave integrated circuit of a large-size high-frequency power device has infirm welding and poor heat conducting performance and is easy to produce oscillation in the prior art, the invention discloses the hybrid microwave integrated circuit suitable for manufacturing the large-size high-frequency power device. In order to solve the technical problems, the invention adopts the technical scheme that the hybrid microwave integrated circuit comprises a substrate encapsulated in a tube shell, and at least two power devices manufactured on the substrate; the power device consists of field effect transistors; a matching circuit and an extraction electrode are manufactured on the substrate; the power device is connected with the extraction electrode through the matching circuit; the extraction electrode is connected with a pin; and gate electrodes of chips of the field effect transistors are welded in parallel through metal wires, drain electrodes of the chips of the field effect transistors are welded in parallel through metal wires, and the gate electrodes and the drain electrodes connected in parallel are welded on the matching circuit through the metal wires respectively.
Owner:SICHUAN LONGRUI MICROELECTRONICS
Current mirror circuit with feedback regulation and method thereof
InactiveCN101498950AHigh precisionIncrease output impedanceElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierMirror image
The invention discloses a current mirror image circuit with feedback adjustment and method, comprising monitored MOS tube and mirror image MOS tube; the gate ends are both connected with bias voltage; the source ends are connected with power or ground; the drain ends are in cascade connection with the MOS tube; the drain ends are simultaneously connected with input ends of the operational amplifier; output end of the operational amplifier is connected with the cascade MOS tube; the drain end voltage difference between the monitored MOS tube and mirror image MOS tube is detected and is amplified by the operational amplifier and fed-back to the gate voltage of the mirror image MOS tube cascade MOS tube; the equivalent impedance of the mirror image MOS tube cascade MOS tube is adjusted, thereby indirectly adjusting the drain end voltage of the mirror image MOS tube following the monitored MOS tube; the instant bias is substituted by dynamically adjusting the gate voltage by feedback mode such that the output impedance observably increases and reduces the shunt current to obtain a mirror current with higher precision; because the operational amplifier clamps the drain ends of the monitored MOS tube and mirror image MOS tube, the mirror image current difference is little.
Owner:IPGOAL MICROELECTRONICS (SICHUAN) CO LTD
Method for controlling virtual reactance of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
InactiveCN104158220AIncrease output impedanceThe method of increasing the actual capacity of the filter inductor to increase the output impedanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationCapacitanceFull bridge
The invention discloses a method for controlling the virtual reactance of a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter, and relates to the technical field of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter control. The problem that an existing photovoltaic grid-connected inverter is poor in stability is solved. The method includes the following steps: obtaining the virtual inductance value, the equivalent internal resistance of the virtual inductance value and the virtual capacitance according to the actual power grid resistance, the inverter output impedance and the inverter output impedance stability criterion; obtaining the equivalent feedforward passage transfer function of a virtual inductor in cooperation with full-bridge gains according to the virtual inductance value and the equivalent internal resistance of the virtual inductance value; obtaining the equivalent feedforward passage transfer function of a virtual capacitor in cooperation with the full-bridge gains, the actual filter capacitance, the filter inductor, the parasitic resistance of the filter inductor, the electric current loop transfer function and the feedback filter loop transfer function according to the virtual capacitance of the virtual capacitor; conducting discretization on the equivalent feedforward passage transfer functions of the virtual inductor and the virtual capacitor to obtain a difference equation; overlaying the difference equation and the electric current loop output value. The method is suitable for controlling the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
General closed-loop control system for providing positive and negative constant flow sources for aircraft engines
InactiveCN103605393AImprove compatibilityIncrease output impedanceElectric variable regulationLinear variable differential transformerLoop control
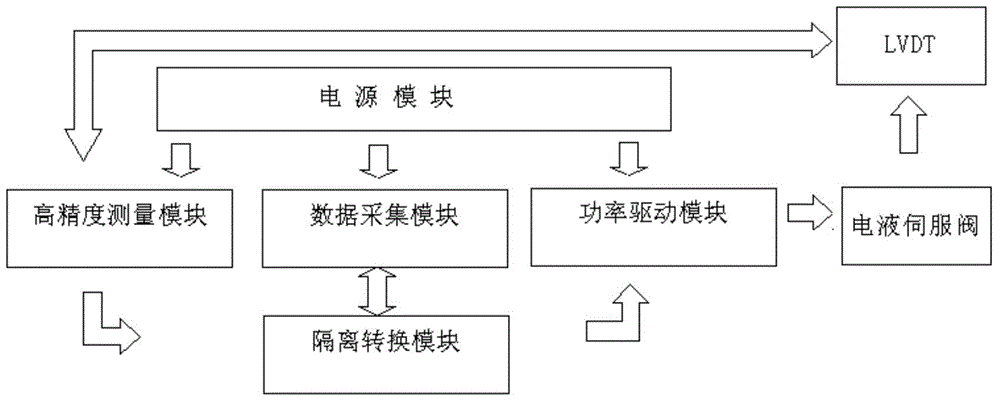
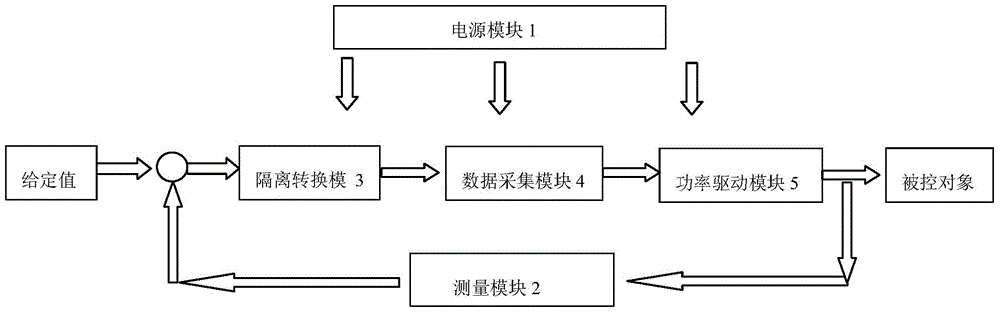
The invention belongs to the technical field of engine control and particularly relates to a practical aircraft engine fuel electronic control system. A general closed-loop control system for providing positive and negative constant flow sources for aircraft engines is mainly applied to performance adjustment and static testing for an engine with an electro-hydraulic servo valve being served as an electro-hydraulic conversion device and can be used for primarily calibrating steady state characters of the engine. According to the general closed-loop control system for providing the positive and negative constant flow sources for the aircraft engines, a high-precision measuring module which provides excitation signals for an LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer) collects a current position of the LVDT, a preset instruct state of the closed-loop system is changed, PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) calculation is performed on the current position and a preset position of the LVDT under a closed-loop control state, and the flow of the engine is controlled. The closed-loop control system needs to maintain current values to be at steady state values during a testing process.
Owner:BEIJING HANGKE ENGINE CONTROL SYST SCI & TECH
Input buffer circuit for high-speed pipeline analog-to-digital converter
InactiveCN101800550AMeet the input requirementsReduce load capacitanceAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceNegative feedback
The invention provides a input buffer circuit for high-speed pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The input buffer circuit comprises an input pair transistor, a current mirror load, a gain-boosted amplifier and a compensation capacitor, wherein the input pair transistor consists of a first MOS (metal oxide semi-conductor) transistor and a second MOS transistor of a source negative-feedback resistor; the current mirror load consists of a third MOS transistor and a fourth transistor which are connected to each other by a gate; the positive input terminal of the gain-boosted amplifier is connected with the drain of the first MOS transistor, the negative input terminal thereof is connected with the drain of the second MOS transistor, and the output terminal thereof is connected with the gate of the third MOS resistor; and one terminal of the compensation capacitor is connected with the gate of the third MOS transistor, and the other terminal thereof is connected with the drain of the third MOS transistor. The input buffer circuit of the invention is capable of meeting the requirements for the input of high-speed signals, effectively reducing the inputted load capacitance and increasing the outputted impedance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Elastic wave filter device and duplexer
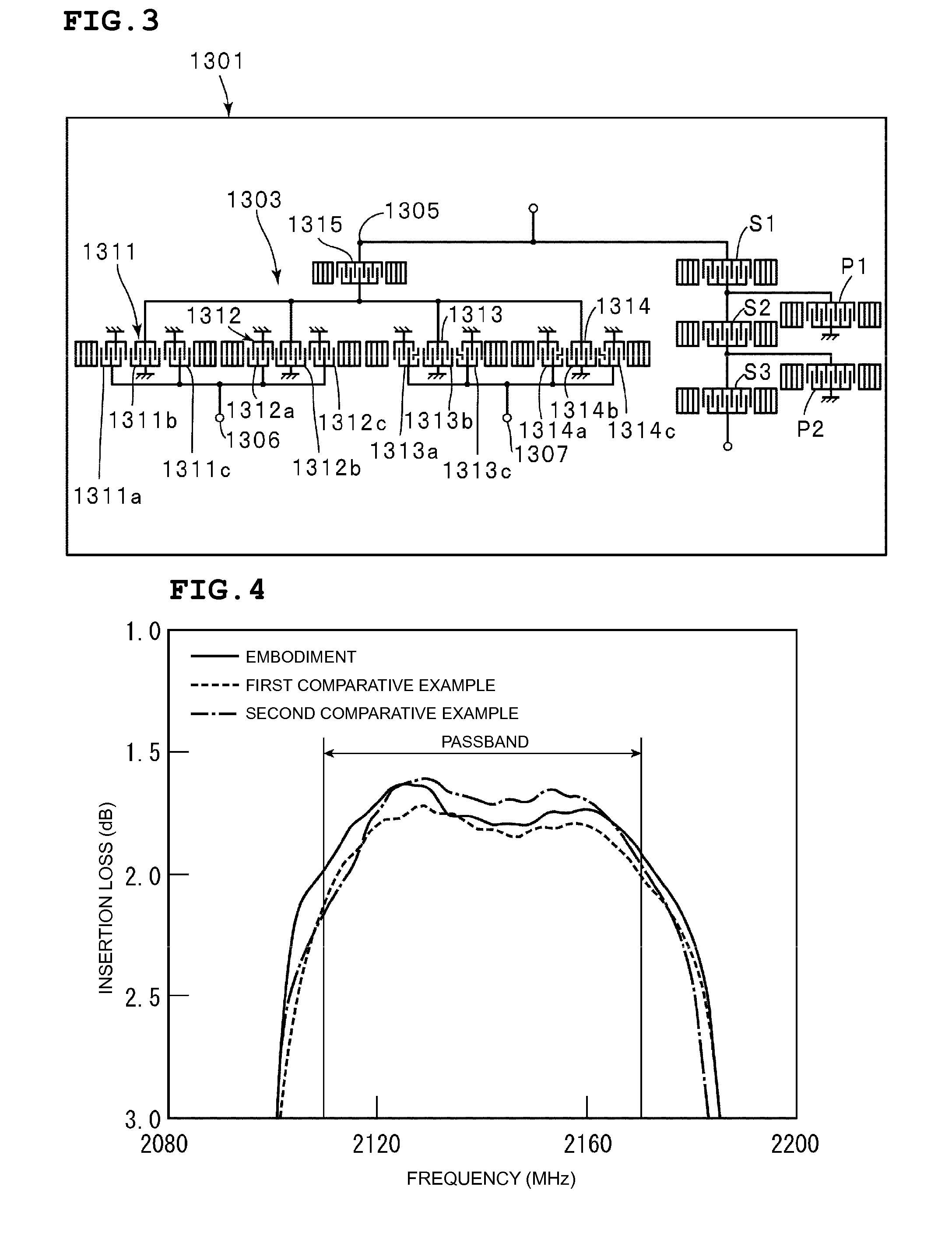
InactiveUS20070296522A1Reduce the impactIncreasing ohmic lossImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesPhase differenceSurface acoustic wave
In an elastic wave acoustic device, input ends of first to third longitudinally coupled resonator surface acoustic wave filters are connected to an unbalanced signal terminal, the output end of the first longitudinally coupled resonator surface acoustic wave filter, and a first IDT defining a first output terminal of the second longitudinally coupled resonator surface acoustic wave filter are connected to a first balanced signal terminal, the output end of the third longitudinally coupled resonator surface acoustic wave filter, and a third IDT defining a second output terminal of the second longitudinally coupled resonator surface acoustic wave filter are connected to a second balanced signal terminal, and the phase of an output signal to an input signal of the first longitudinally coupled resonator surface acoustic wave filter differs by about 180 degrees from the phase of an output signal to an input signal of the third longitudinally coupled resonator surface acoustic wave filter. Thus, the elastic wave filter device has a balanced-to-unbalanced conversion function and an impedance conversion function, and reduces an insertion loss within a passband.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Low noise amplifier with adjustable gain
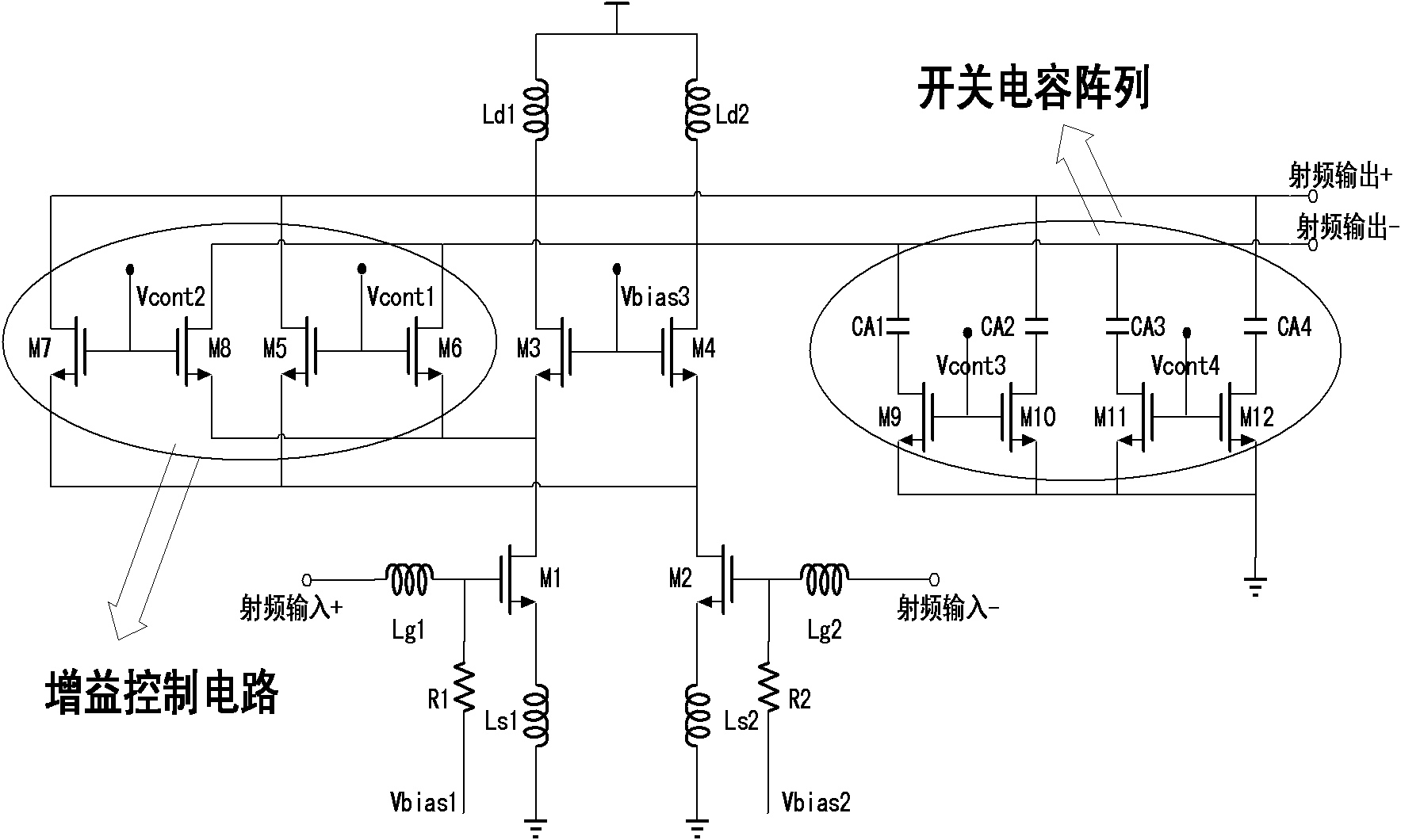
InactiveCN102045028AIncrease output impedanceEnhanced inhibitory effectAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceRadio frequencyPositive current
The invention discloses a low noise amplifier with adjustable gain. The low noise amplifier provided by the invention is characterized in that two groups of cascode tubes are crossed and connected in parallel on a main body cascode tube; the amplified current of a transitron is crossed and shunted; partial radio frequency (RF) input positive current flows to a negative output end; and partial RF input negative current flows to a positive output end, thus a gain control circuit which can adjust the gain of the low noise amplifier is formed through crossed cancellation. Compared with the traditional method for controlling the gain of the low noise amplifier, the low noise amplifier with adjustable gain has the characteristics that the system noises is not increased when the gain is adjusted, the gain control is accurate, the bias and input impedance are not influenced, and the power consumption is not increased.
Owner:东南大学无锡分校
Multifrequency synchronous excitation current source used in bio-electrical impedance frequency spectrum measurement
InactiveCN102048537AImprove stabilityIncrease output impedanceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFrequency spectrumFinite-state machine
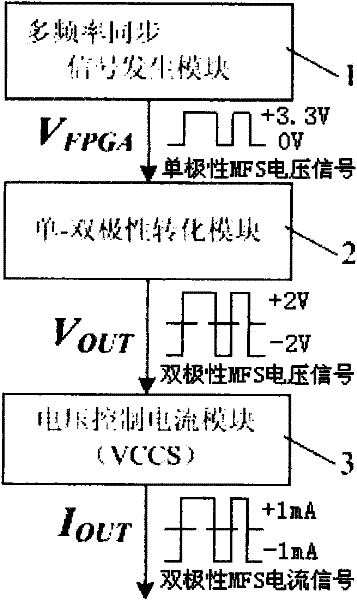
The invention discloses a multifrequency synchronous excitation current source used in bio-electrical impedance frequency spectrum measurement, which comprises a multifrequency synchronous signal generating module, a unipolar-bipolar conversion module, and a voltage control current source module in sequential connection, wherein the multifrequency synchronous signal generating module adopts an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) as a carrier, performs hardware programming through utilizing a Verilog HDL (Hardware Description Language), generates unipolar MFS voltage signal V FPGA based on finite state machine principles, and inputs the signal V FPGA to the unipolar-bipolar conversion module; the unipolar-bipolar conversion module is used for converting unipolar MFS voltage signal V FPGA into symmetric bipolar MFS voltage signal V OUT, and inputting the signal V FPGA into the voltage control current source module; and the voltage control current source module is used for converting the bipolar MFS voltage signal V OUT output by the unipolar-bipolar conversion module into bipolar MFS current signal IOUT and directly exerting the bipolar MFS current signal IOUT onto a tested biomass target receiving BIS (Bispectral) measurement. The multifrequency synchronous excitation current source provided by the invention lays a foundation for the realization of BIS multifrequency synchronous measurement.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Device for measuring impedance of biologic tissues including an alternating current (AC) coupled voltage-to-current converter
ActiveUS20150051505A1Increase output impedanceCancellation effectResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsAc componentsCurrent limiting
A device for measuring impedance of biological tissue may include electrodes and a voltage-to-current converter coupled to the electrodes to drive an alternating current (AC) through the tissue and sense an AC voltage. The converter may include an amplifier having first and second inputs and an output, a first voltage divider coupled to the first input, a second voltage divider coupled to the second input, a filter capacitor coupled between the output and the second voltage divider, a current limiting resistor coupled between the second input the second voltage divider, and a bypass capacitor coupled to the second input of the amplifier and in parallel with the resistor. A single-ended amplitude modulation (AM) demodulator may demodulate the AC voltage and generate a corresponding baseband voltage representing the impedance. The device may also include an output circuit to generate output signals representative of DC and AC components of the baseband voltage.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
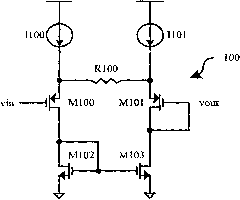
High-speed low-power consumption large-swing operational amplifier for analog-digital converter of production line
ActiveCN101895264AReduce power consumptionHigh gainAnalogue-digital convertersDifferential amplifiersAnalog-to-digital converterPower supply rejection ratio
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuits, in particular to a high-speed low-power consumption large-swing operational amplifier for an analog-digital converter of a production line. The operational amplifier consists of an input tail current source tube, differential input geminate transistors, an N-type co-gate tube, a P-type co-gate tube, a P-type load tube, a duplicate circuit and a bootstrap circuit. A gain-boosting sleeve type cascade structure is adopted, so the tail current source tube and the PMOS load tube work in a linear area to increase the output swing; and the duplicate circuit dynamically regulates the grid voltage of the tail current source to maintain constant current and increase output impedence so as to improve the common-mode rejection ratio and the power rejection ratio. The operational amplifier realizes high speed, low power consumption, large output swing, high common-mode rejection ratio and high power rejection ratio.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com