Patents
Literature
1653results about "Low frequency amplifiers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
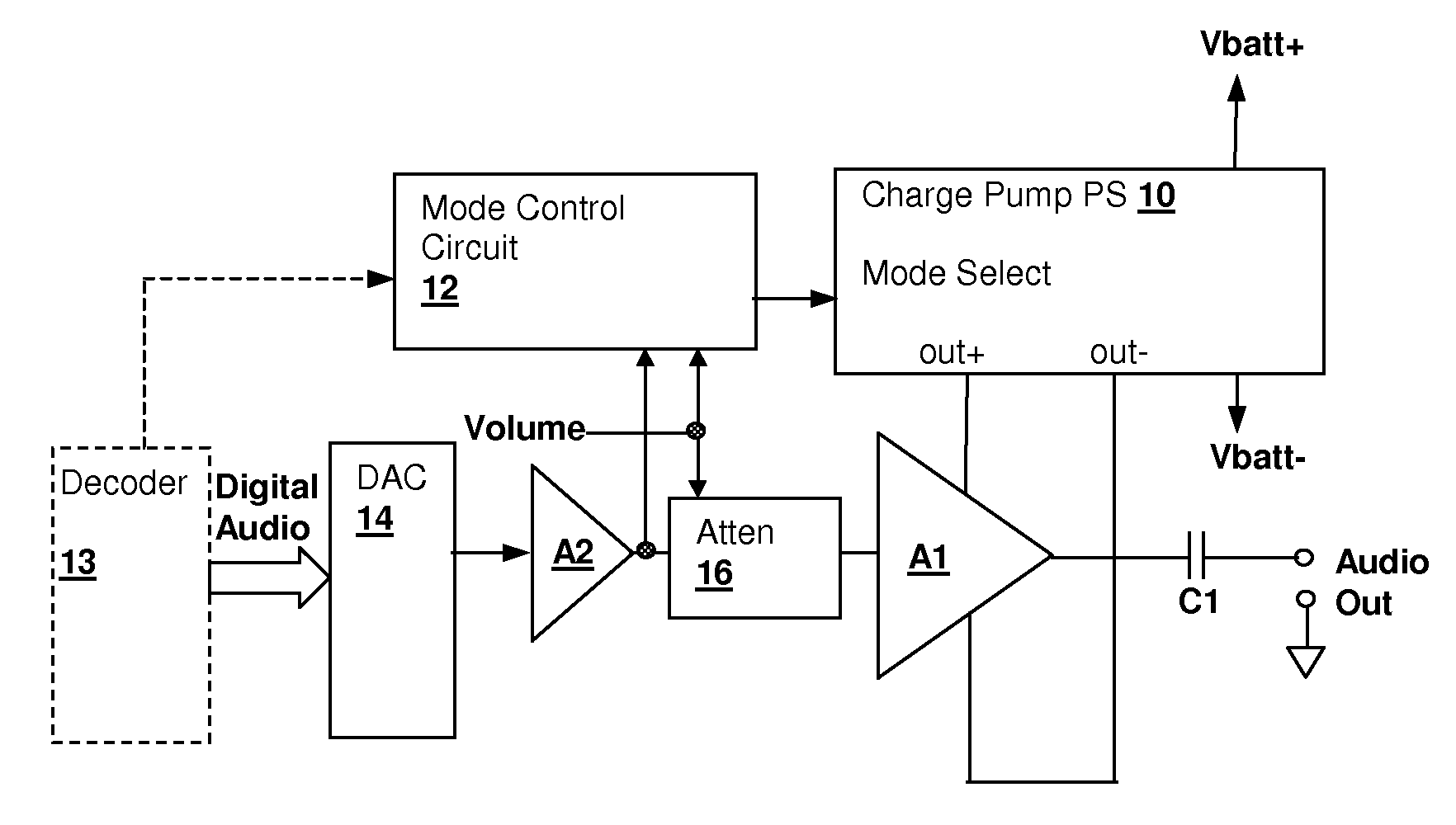
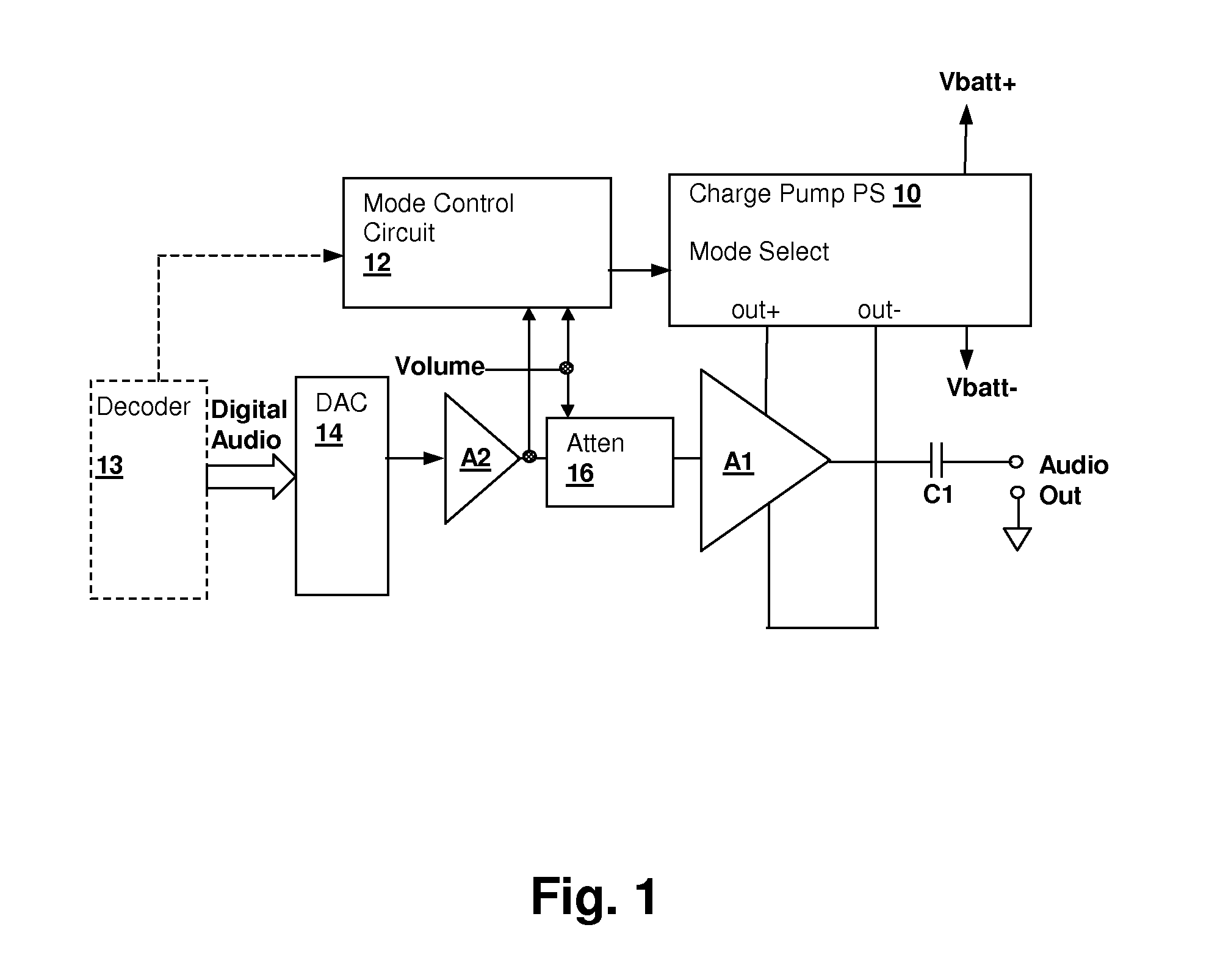
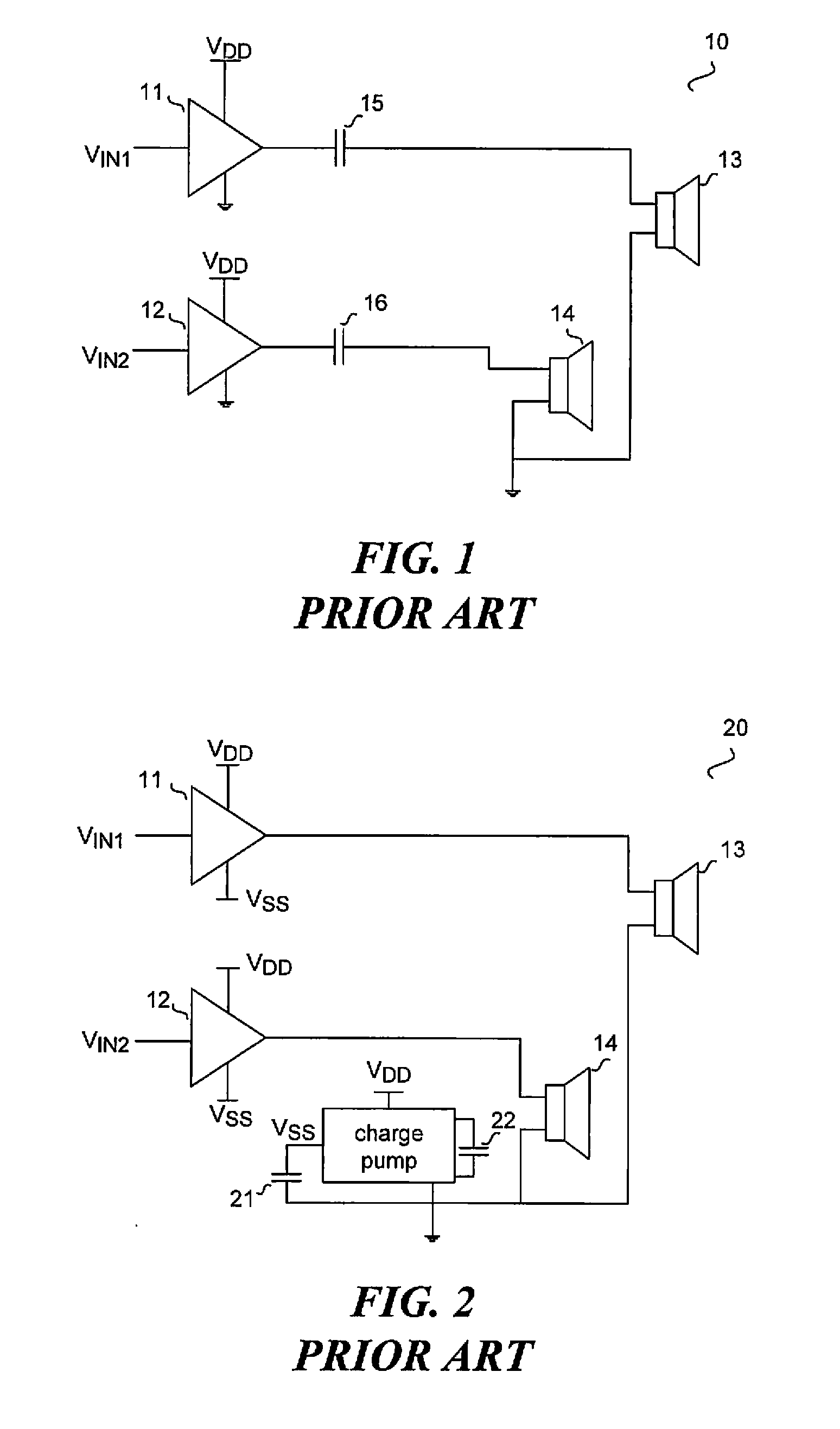
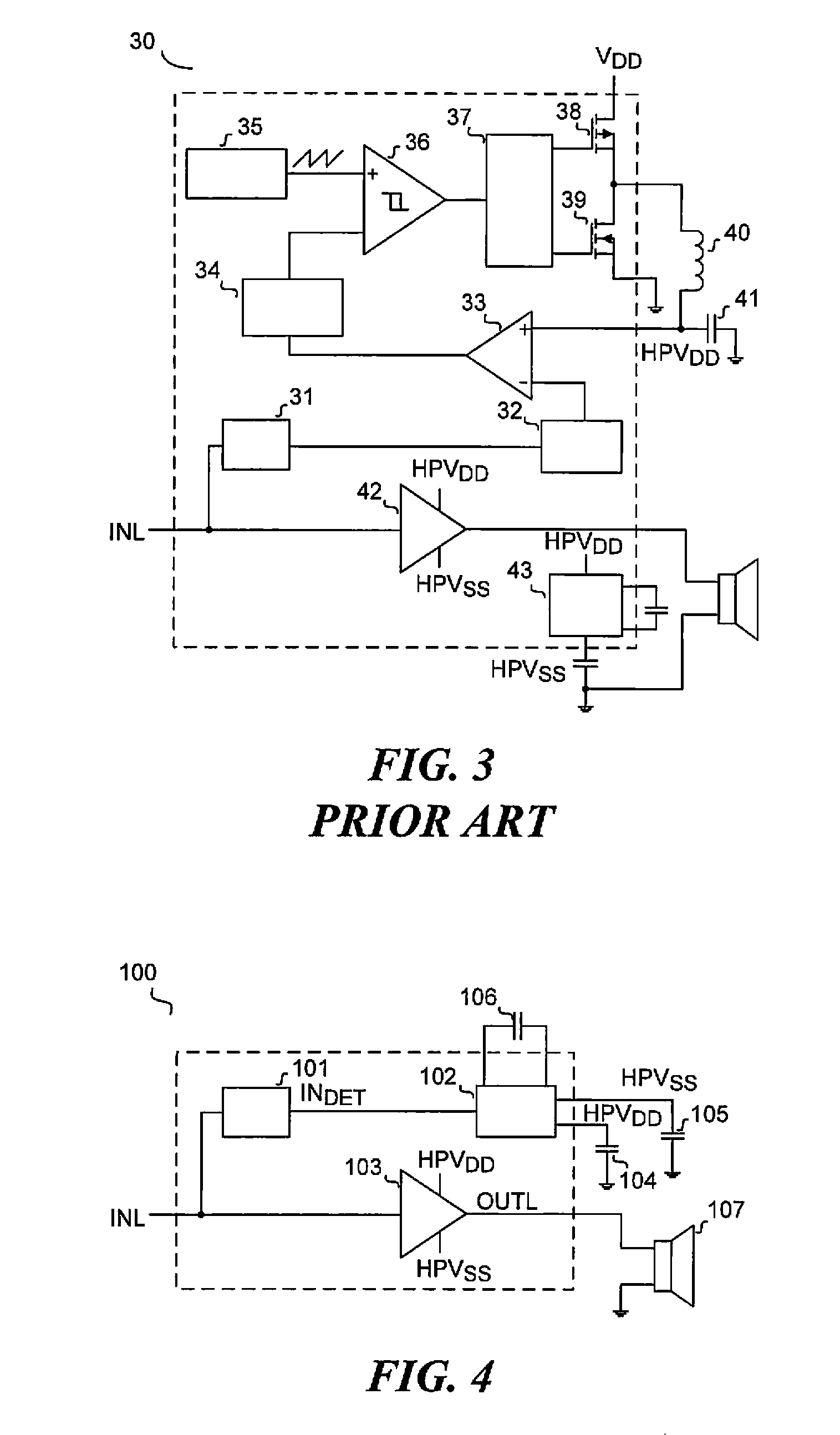
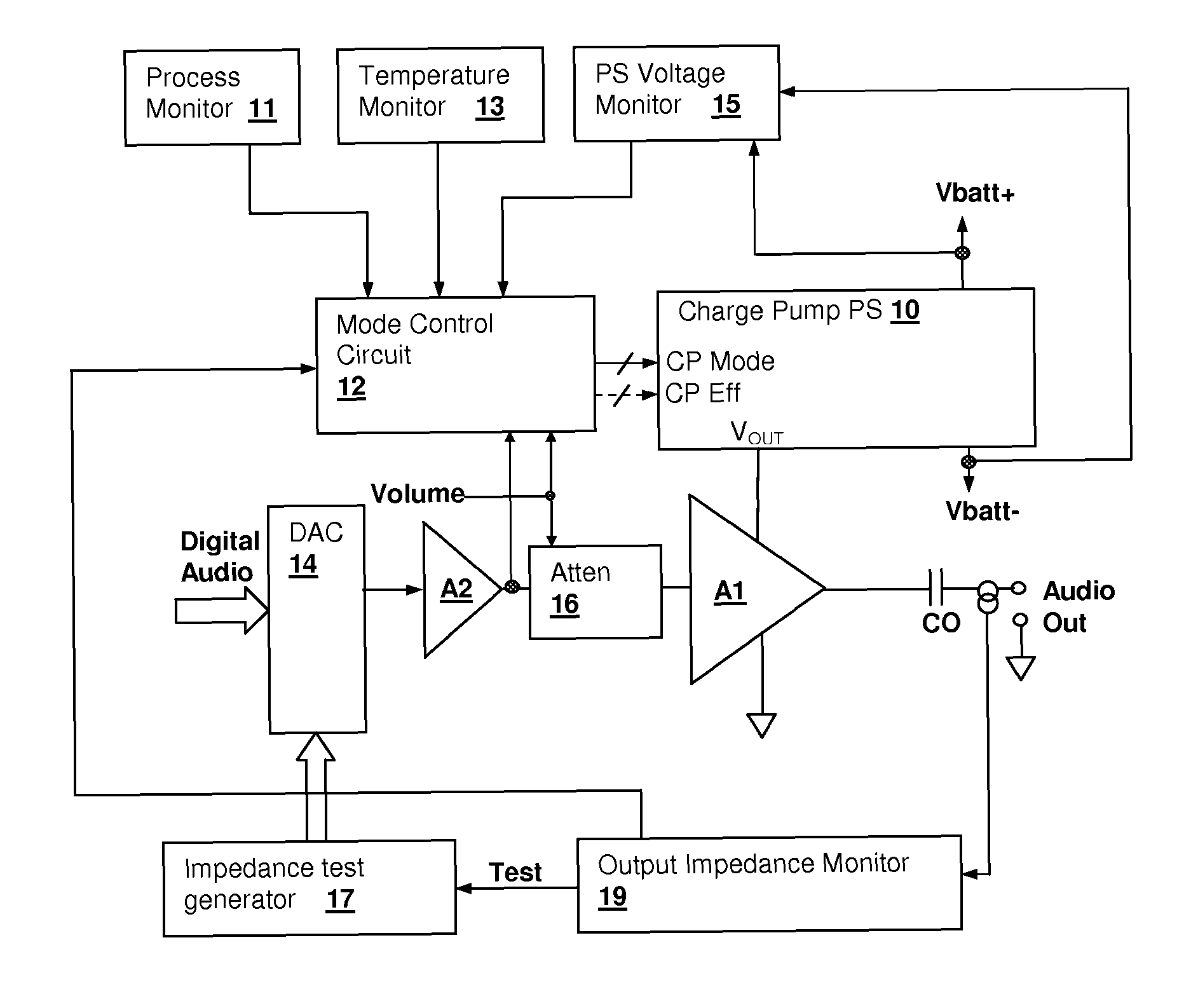
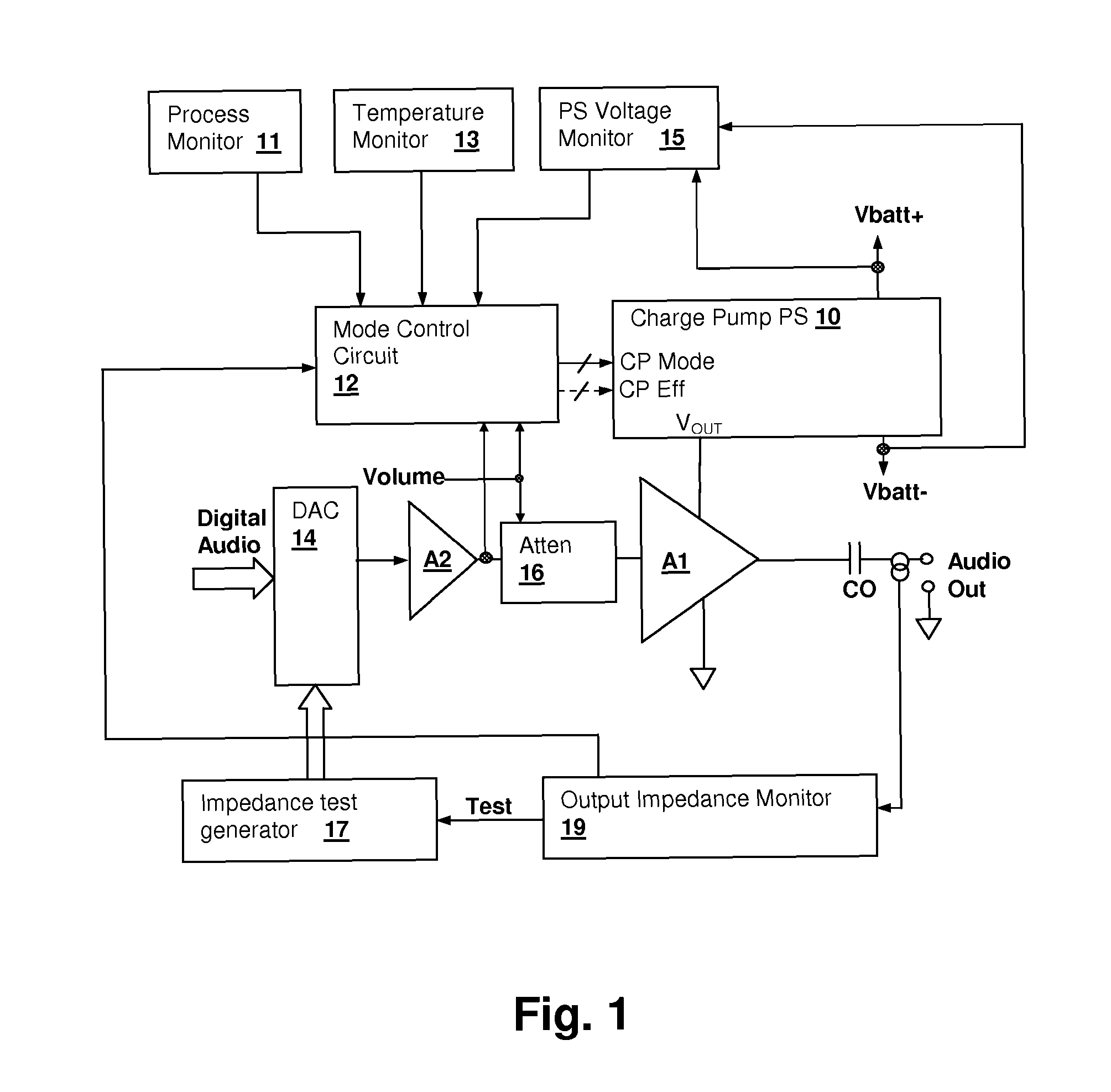
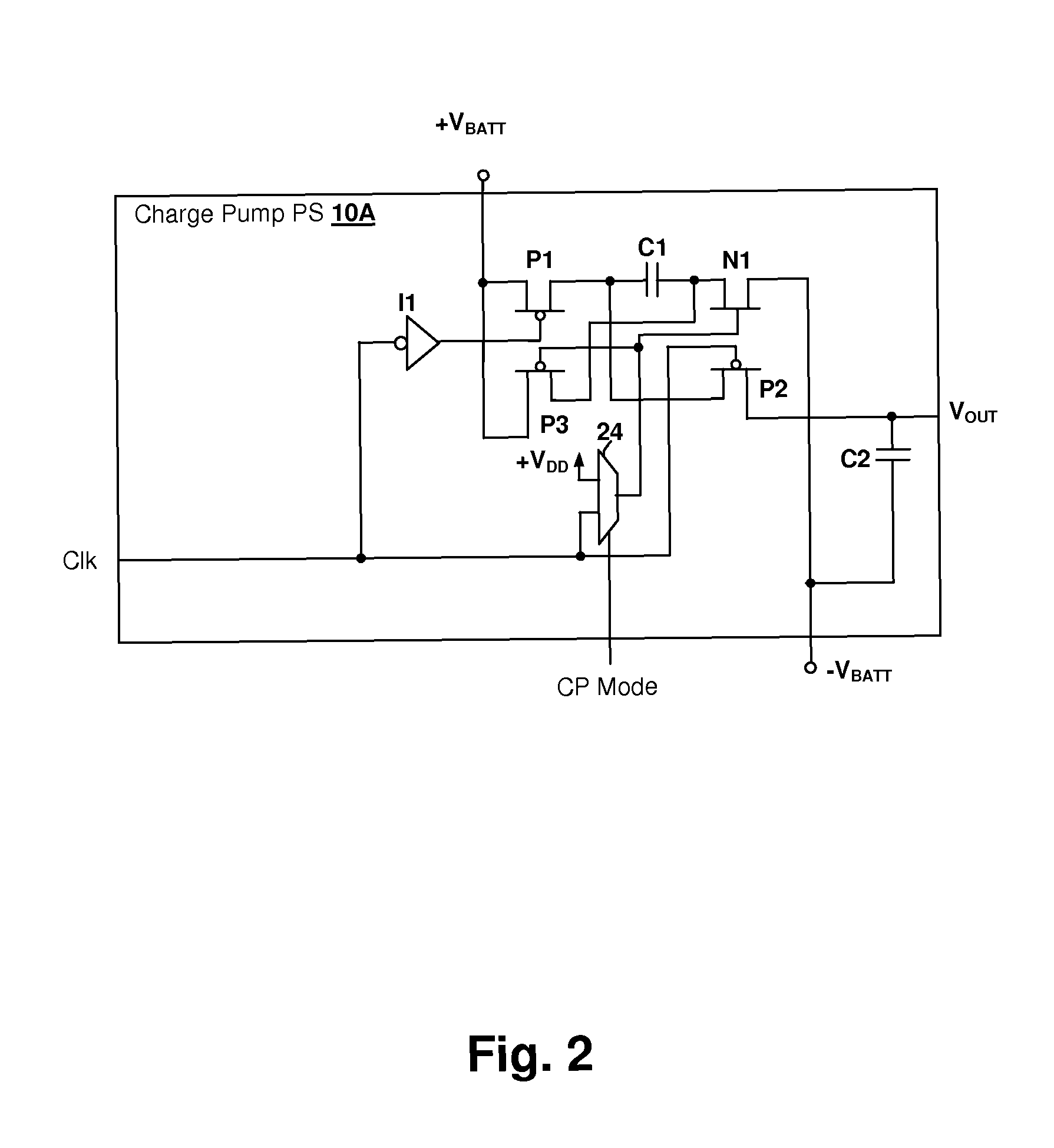
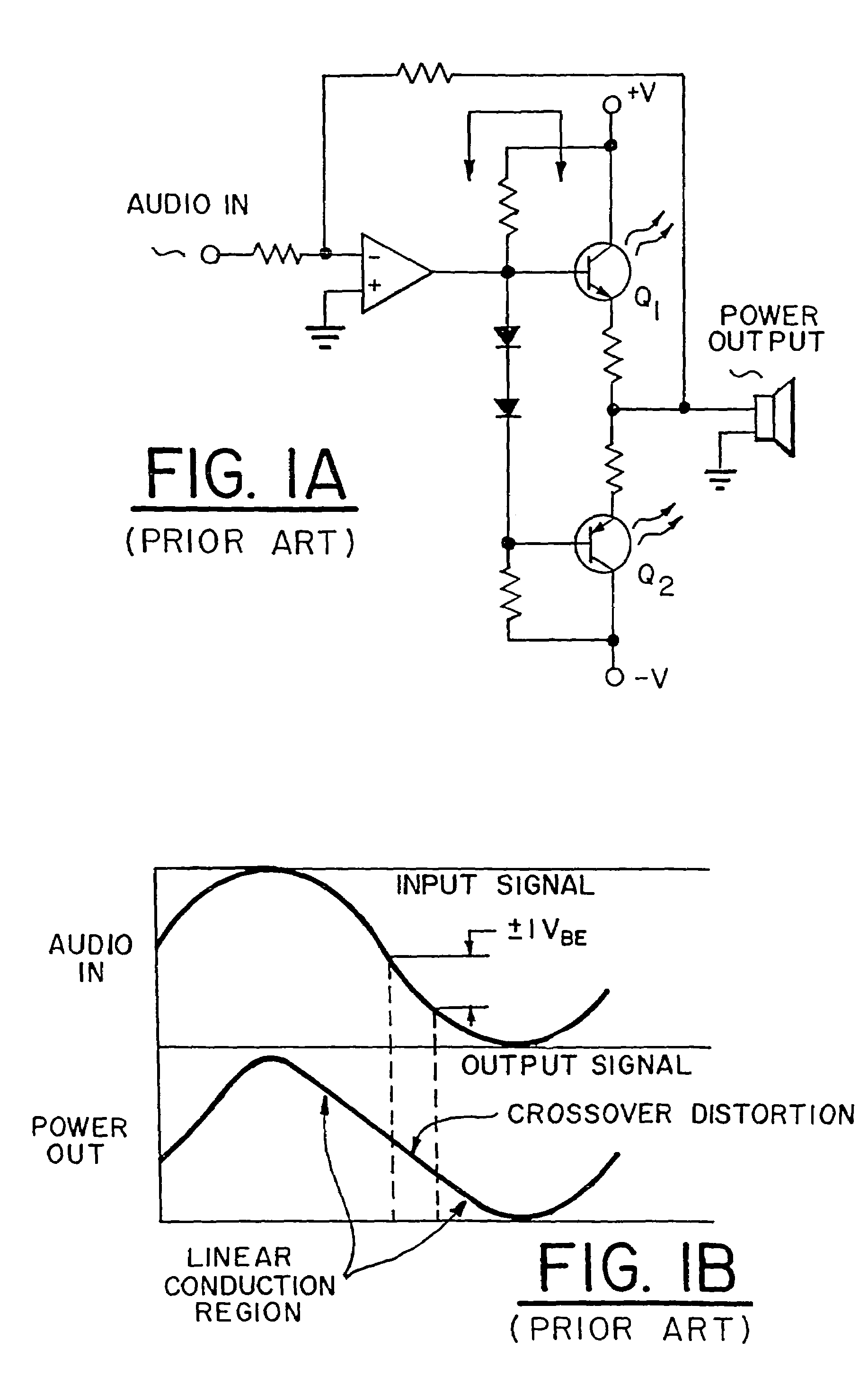
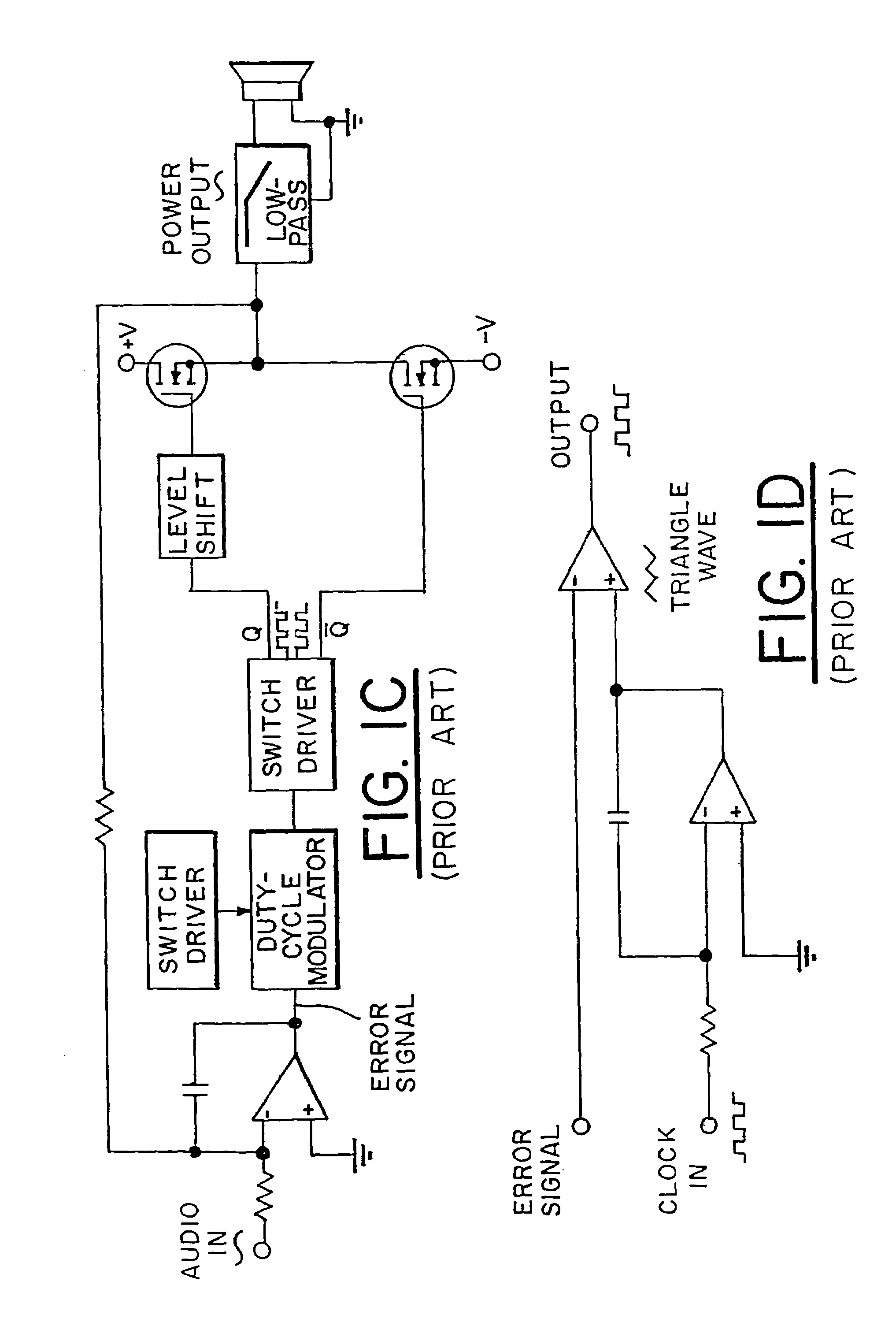
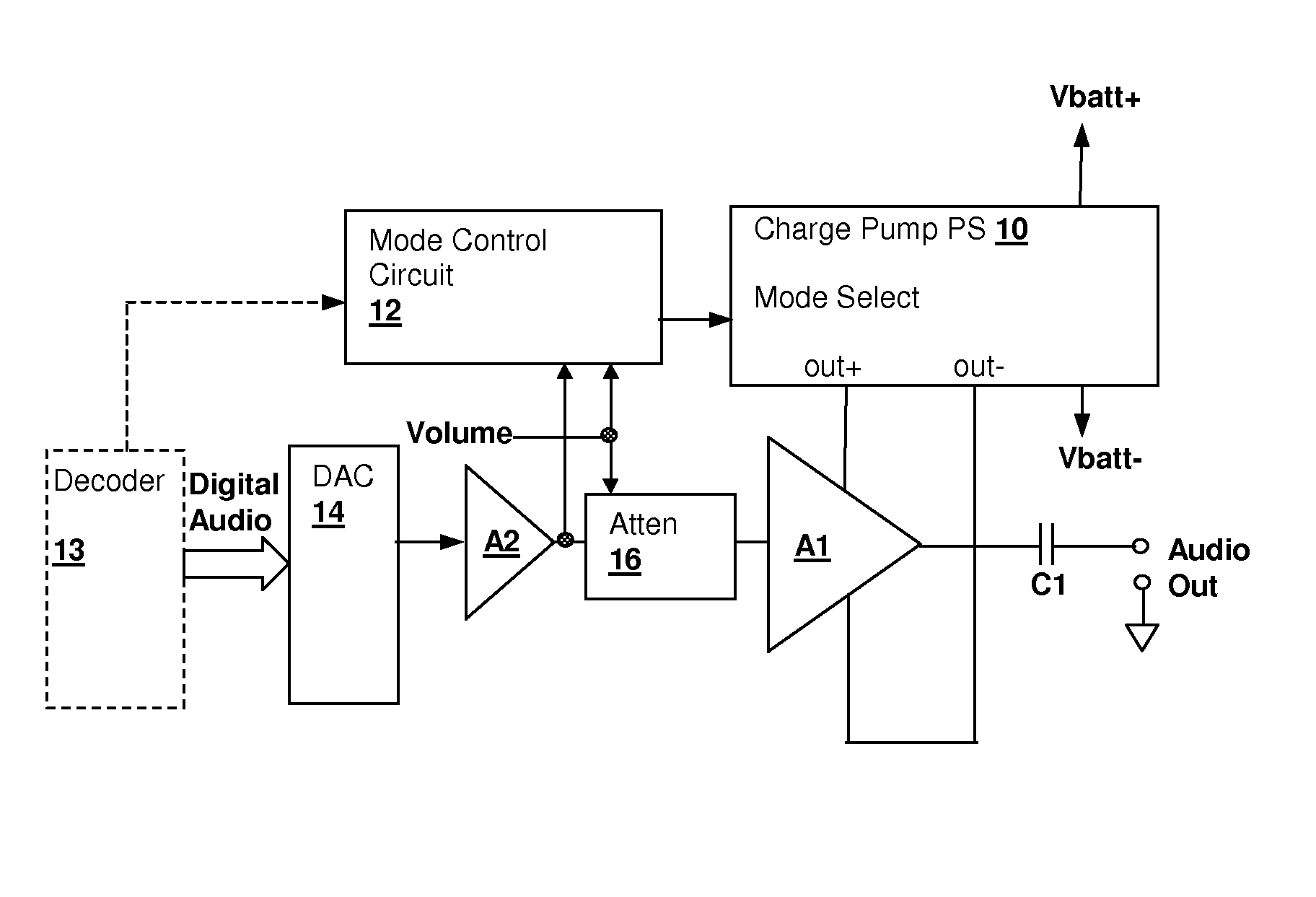
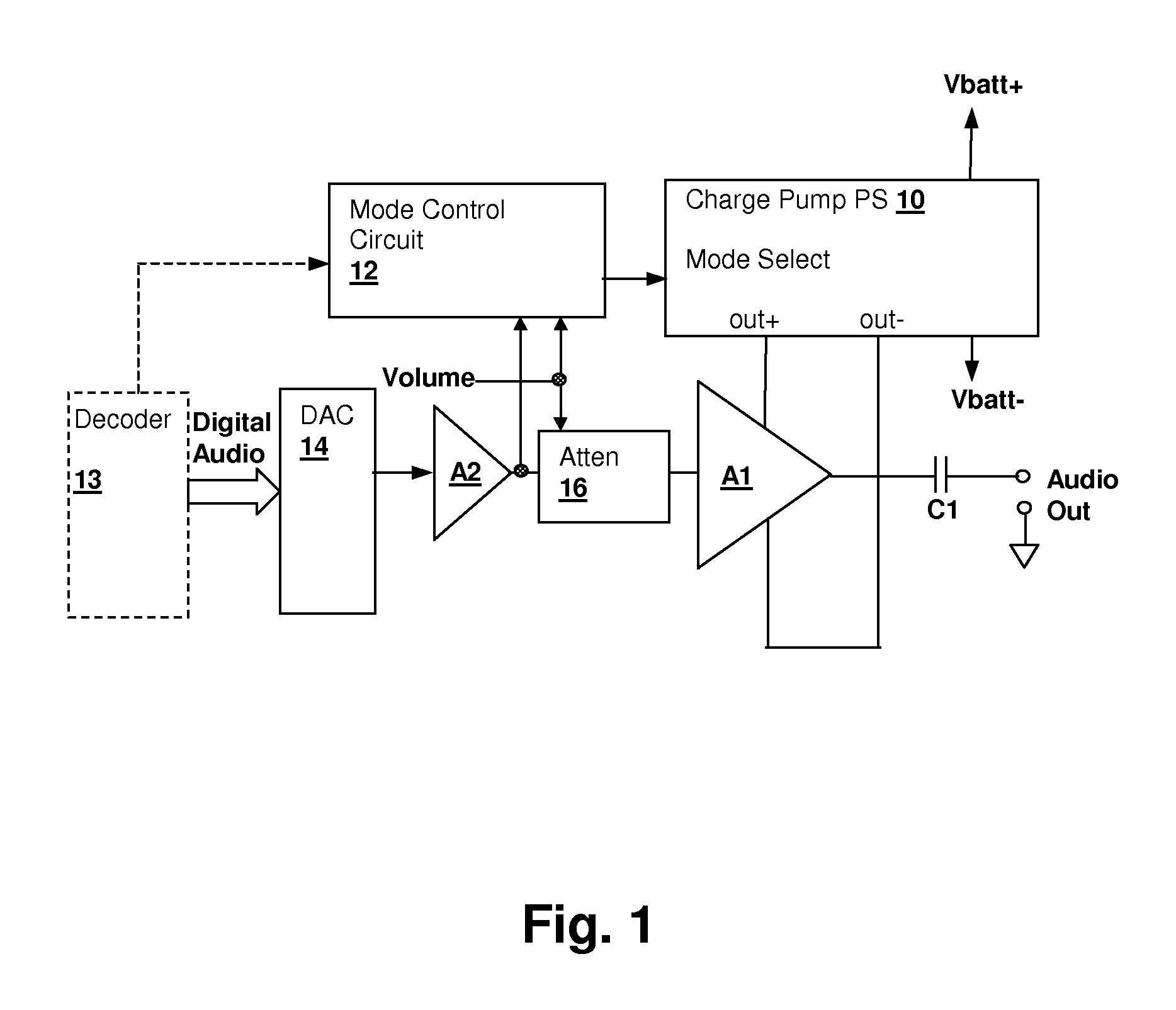
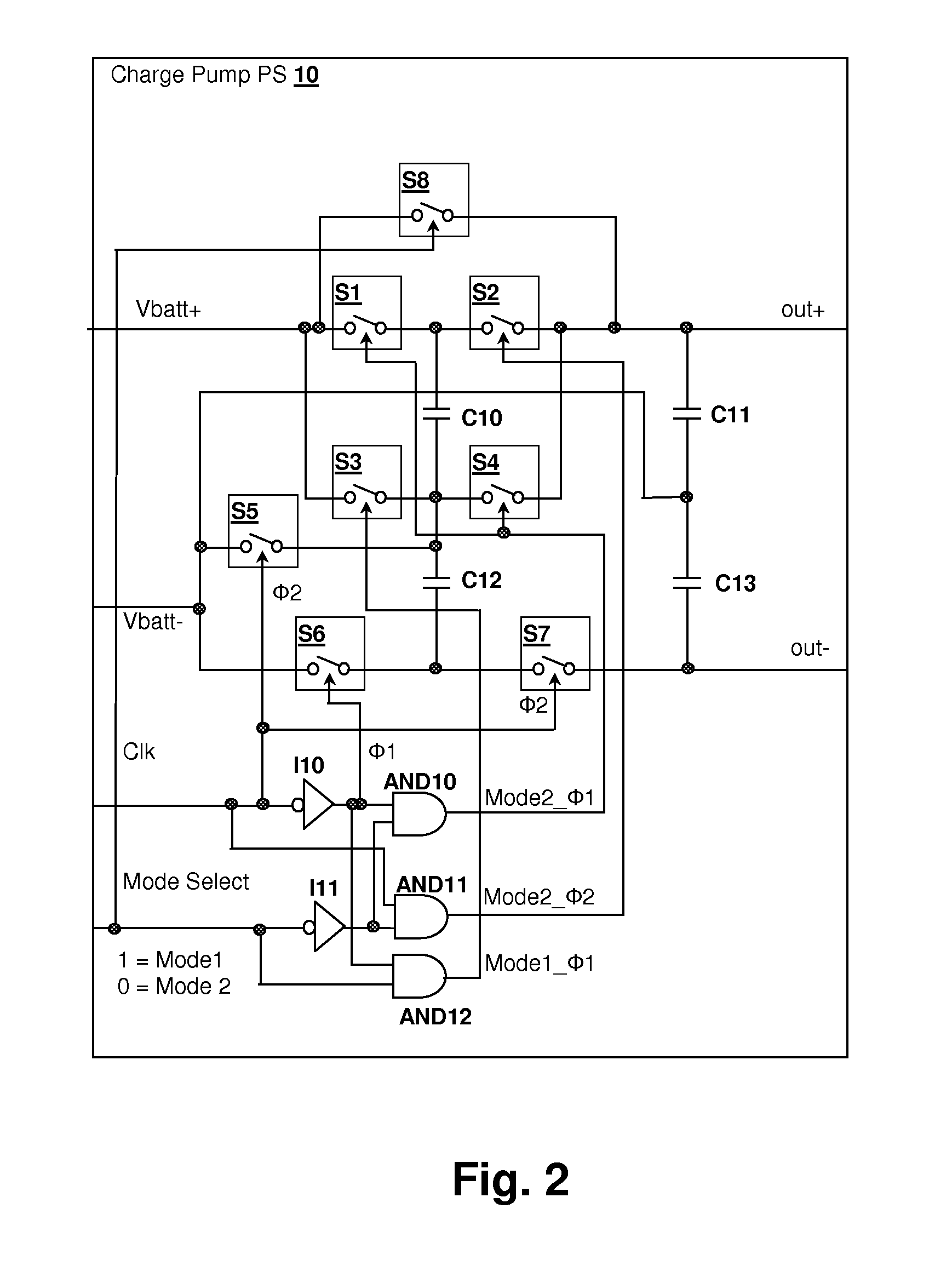
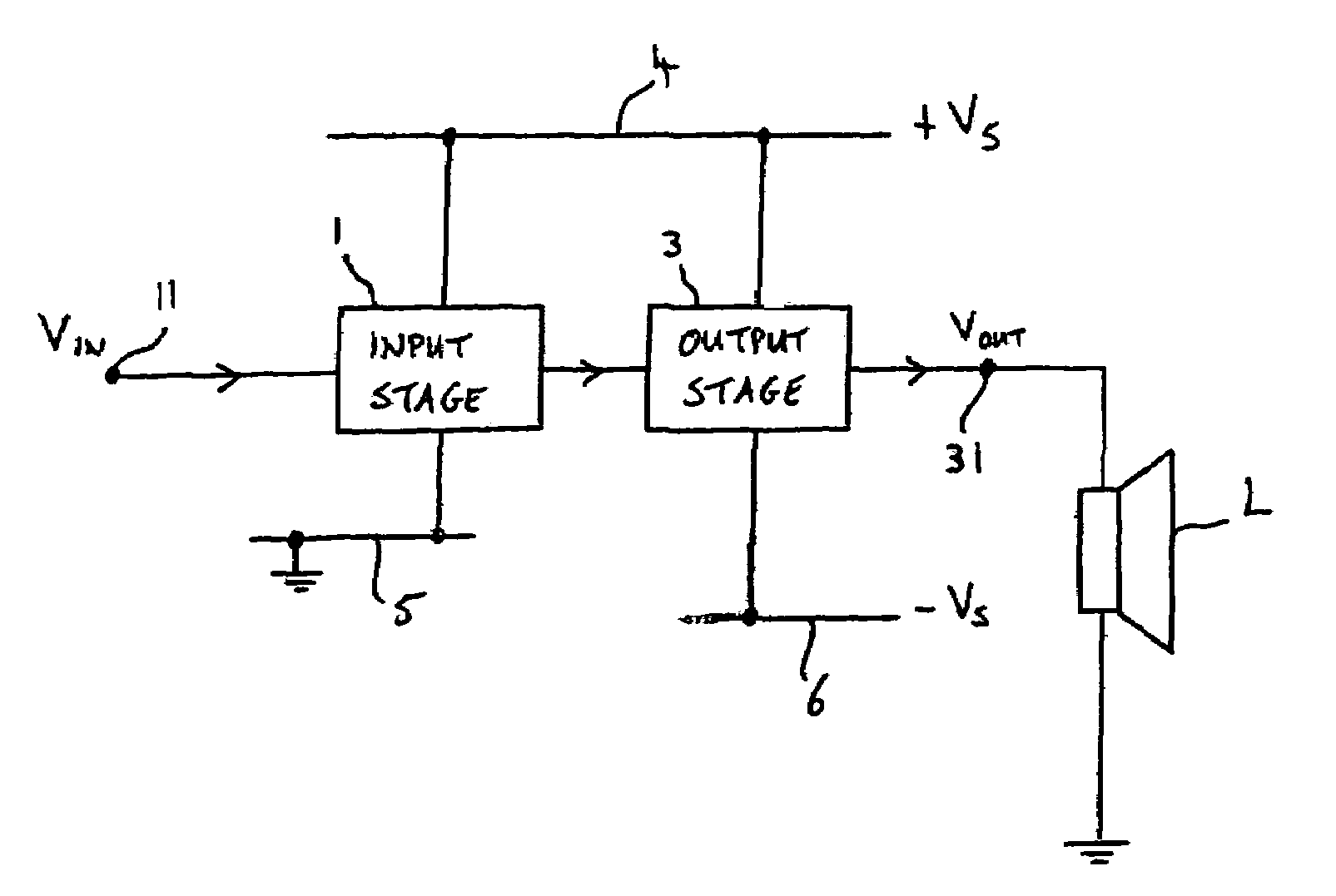
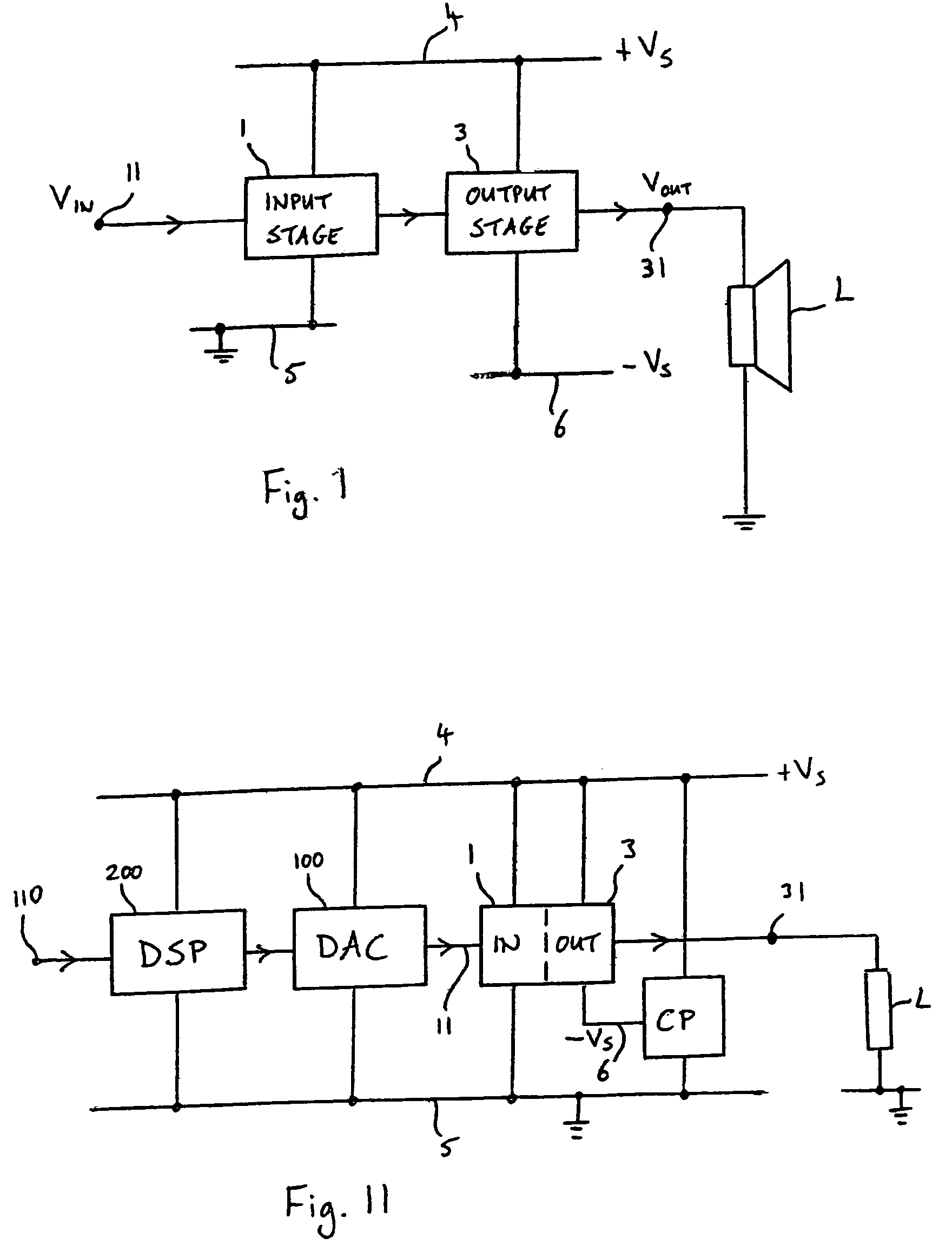
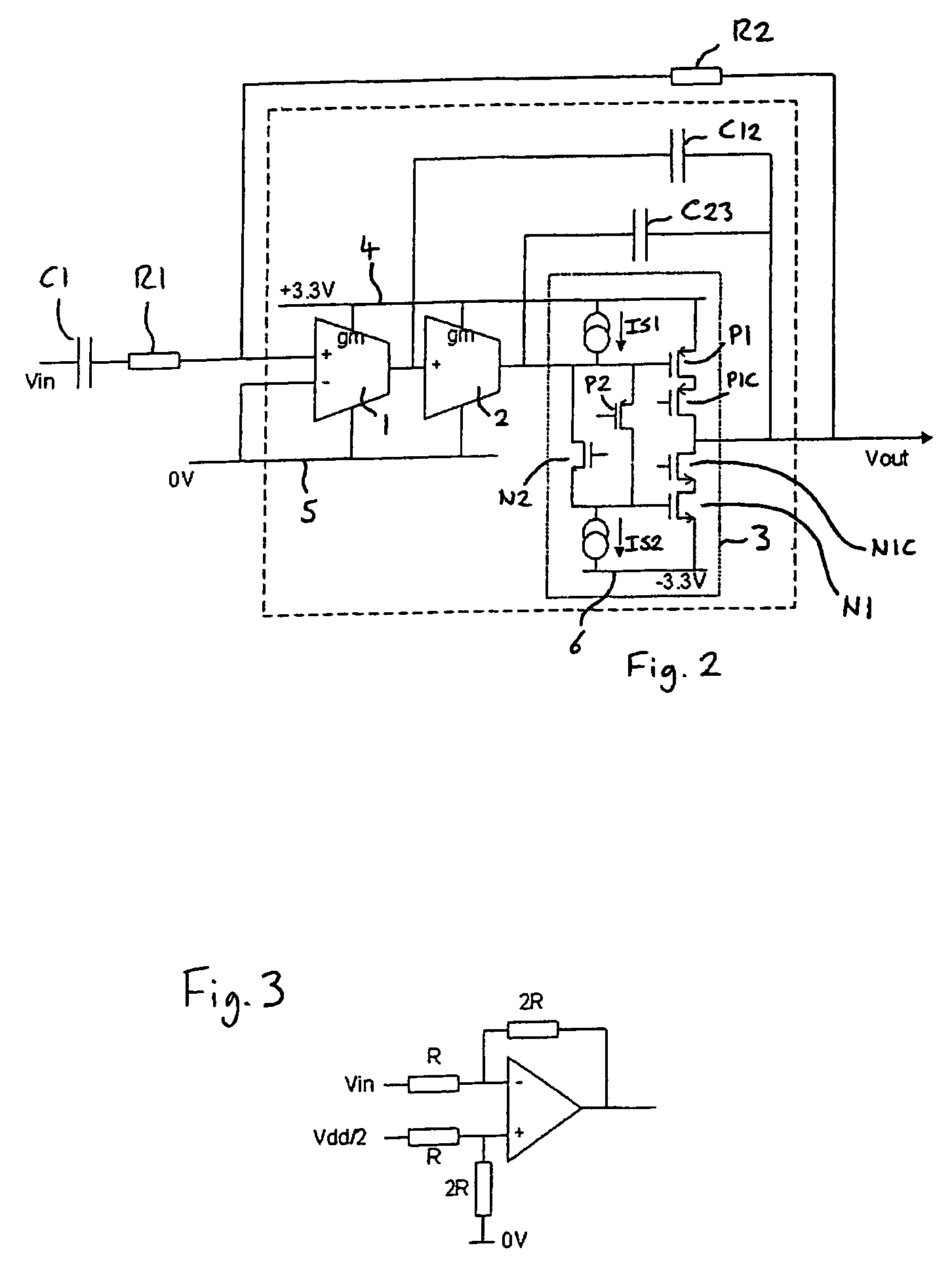
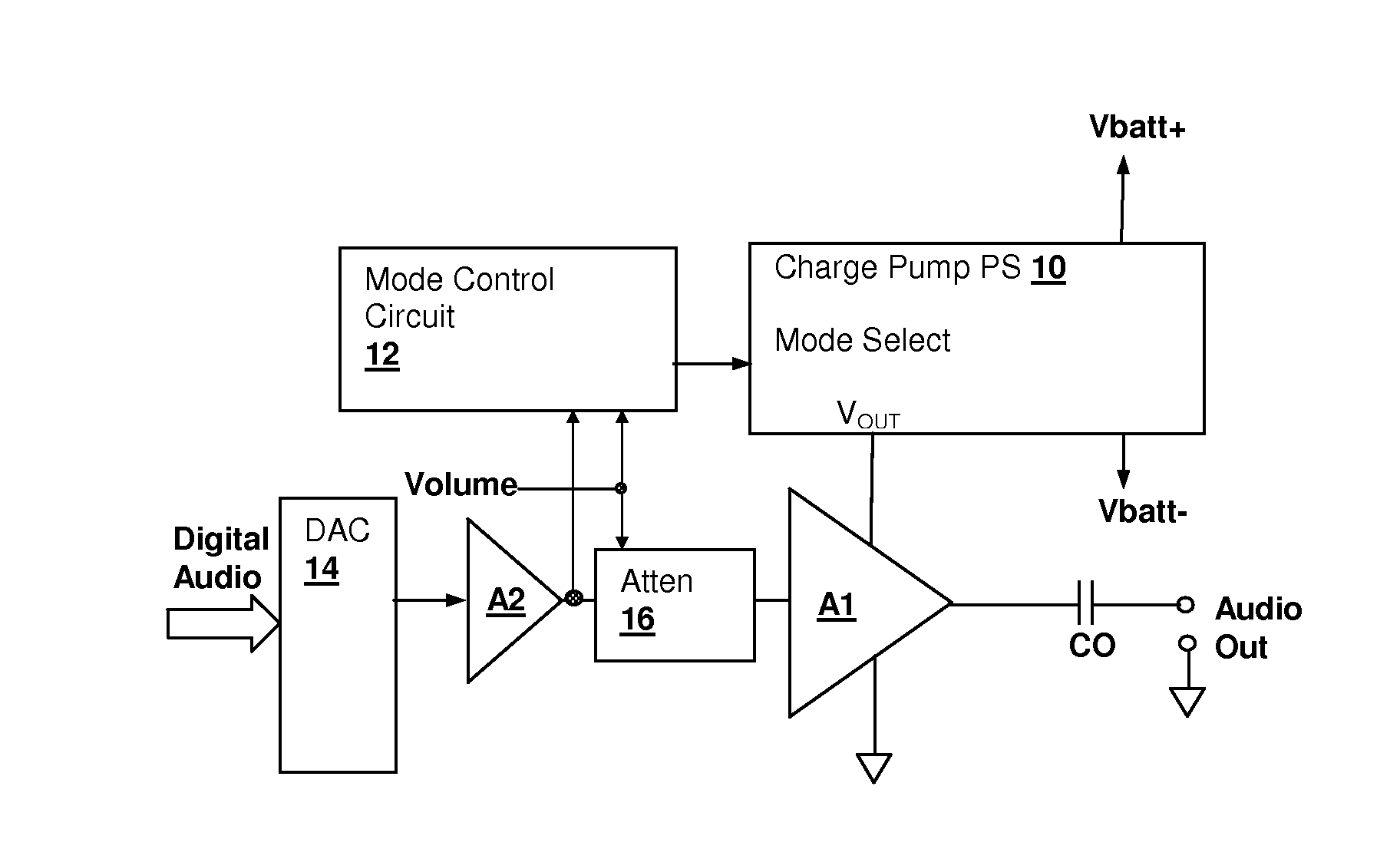
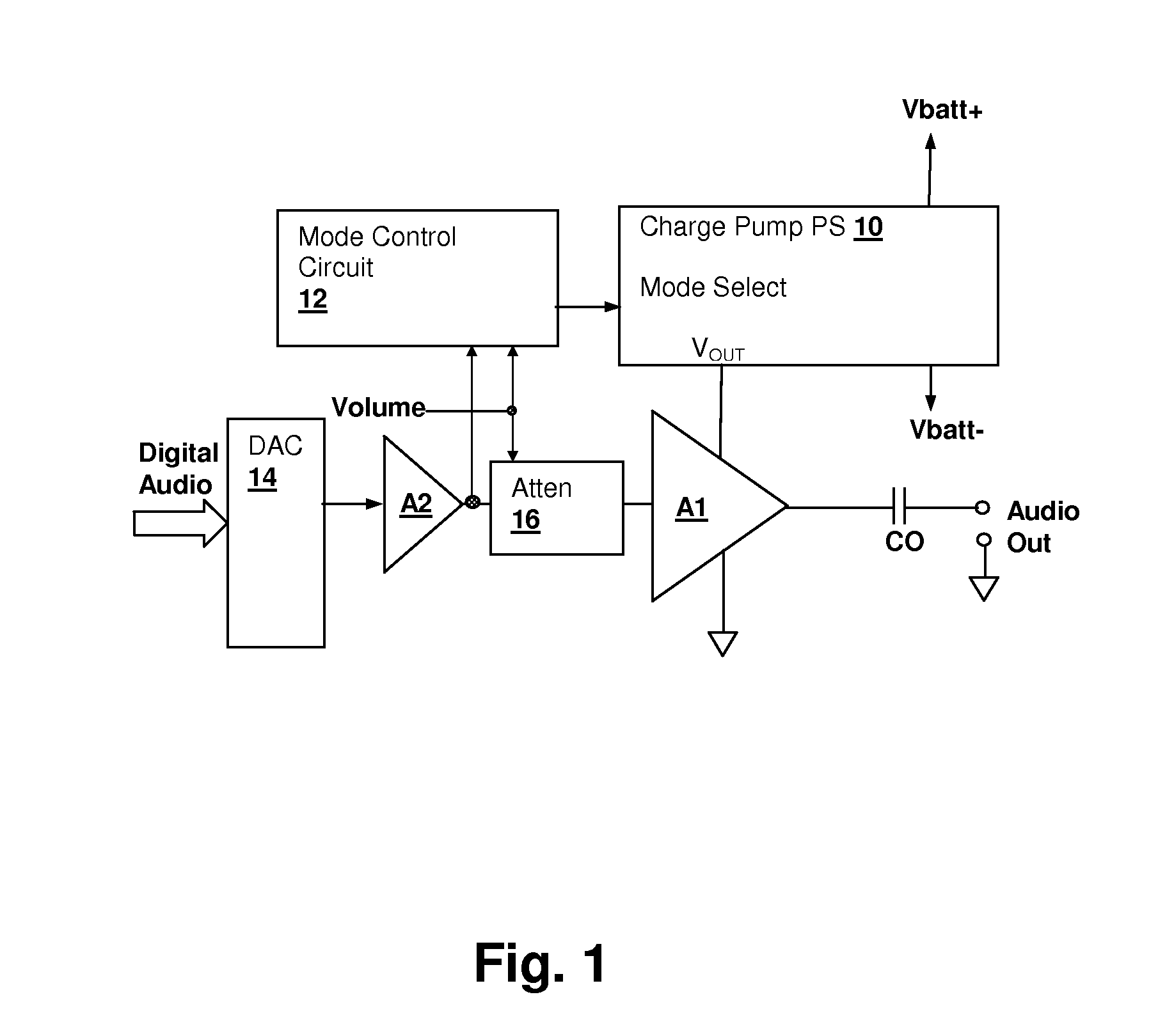
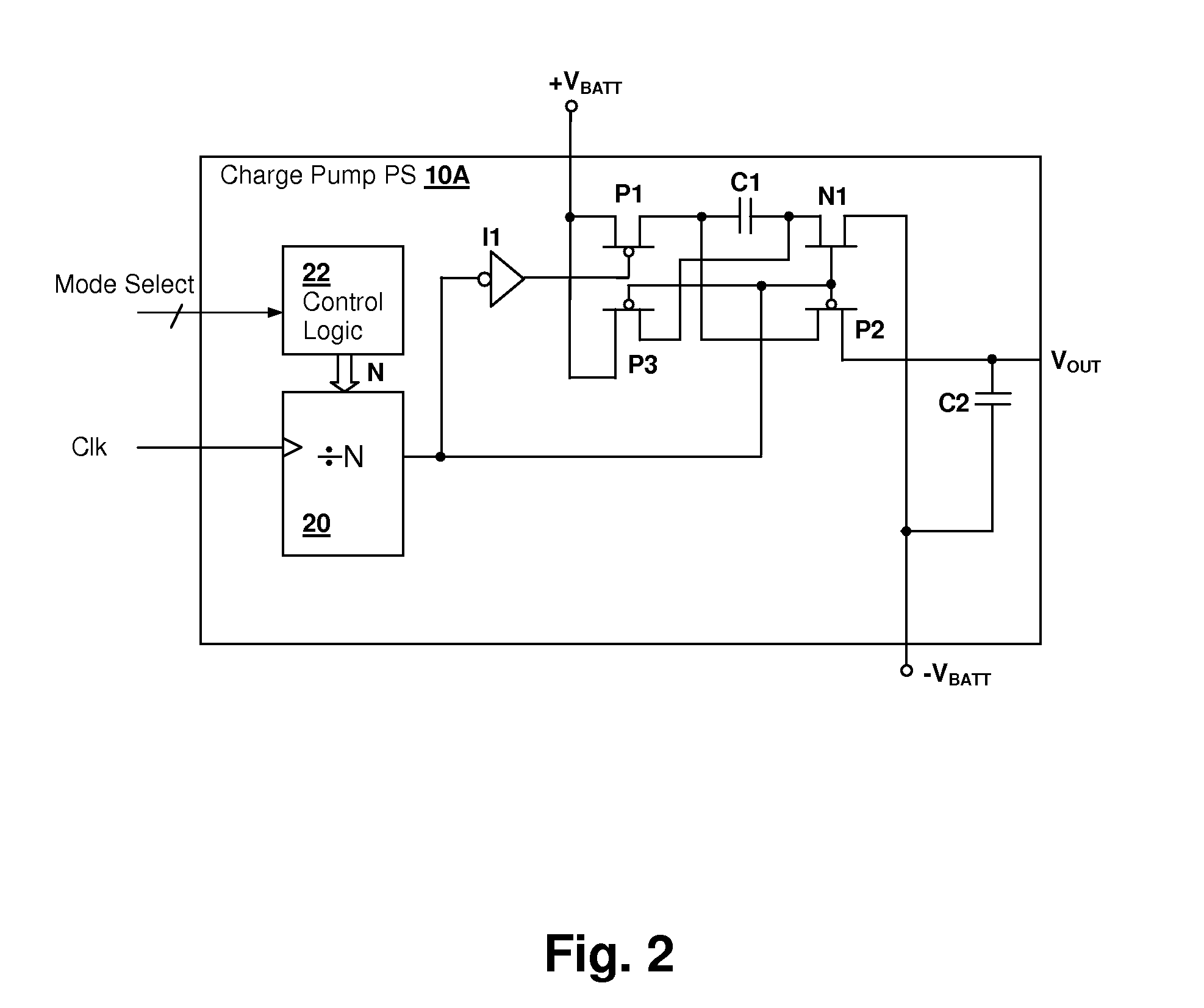
Energy-efficient consumer device audio power output stage
ActiveUS20080044041A1Improve efficiencyReduce power consumptionPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersCapacitive dividerOperation mode
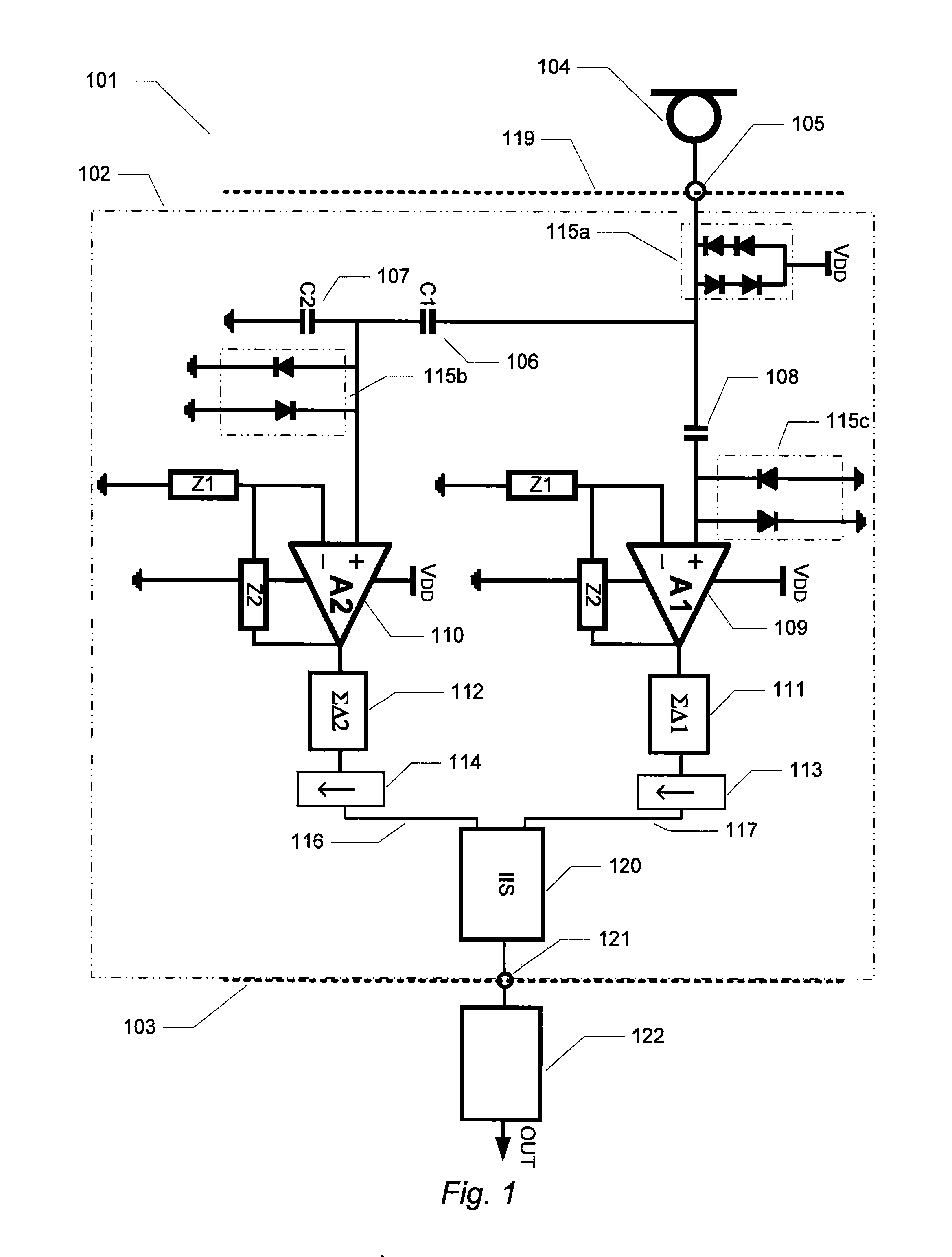
An energy-efficient consumer device audio power output stage provides improved battery life and reduced power dissipation. A power supply having a selectable operating mode supplies the power supply rails to the power amplified output stage. The operating mode is controlled in conformity with the audio signal level, which may be determined from a volume control setting of the device and / or from a signal level detector that determines the amplitude of the signal being amplified. The power supply may be a charge pump in which the operating mode uses a capacitive divider to provide for selection of a power supply output voltage that is a rational fraction of the power supply output voltage in a full-voltage operating mode.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Signal repeater system
InactiveUS8059576B2Secures repeatabilityReduce mutual interferenceInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsAnalog signalEngineering
The present invention concerns analog signal repeater system solutions of the general kind. It concerns in particular stability with analog signal repeater systems.
Owner:VAVIK GEIR MONSEN
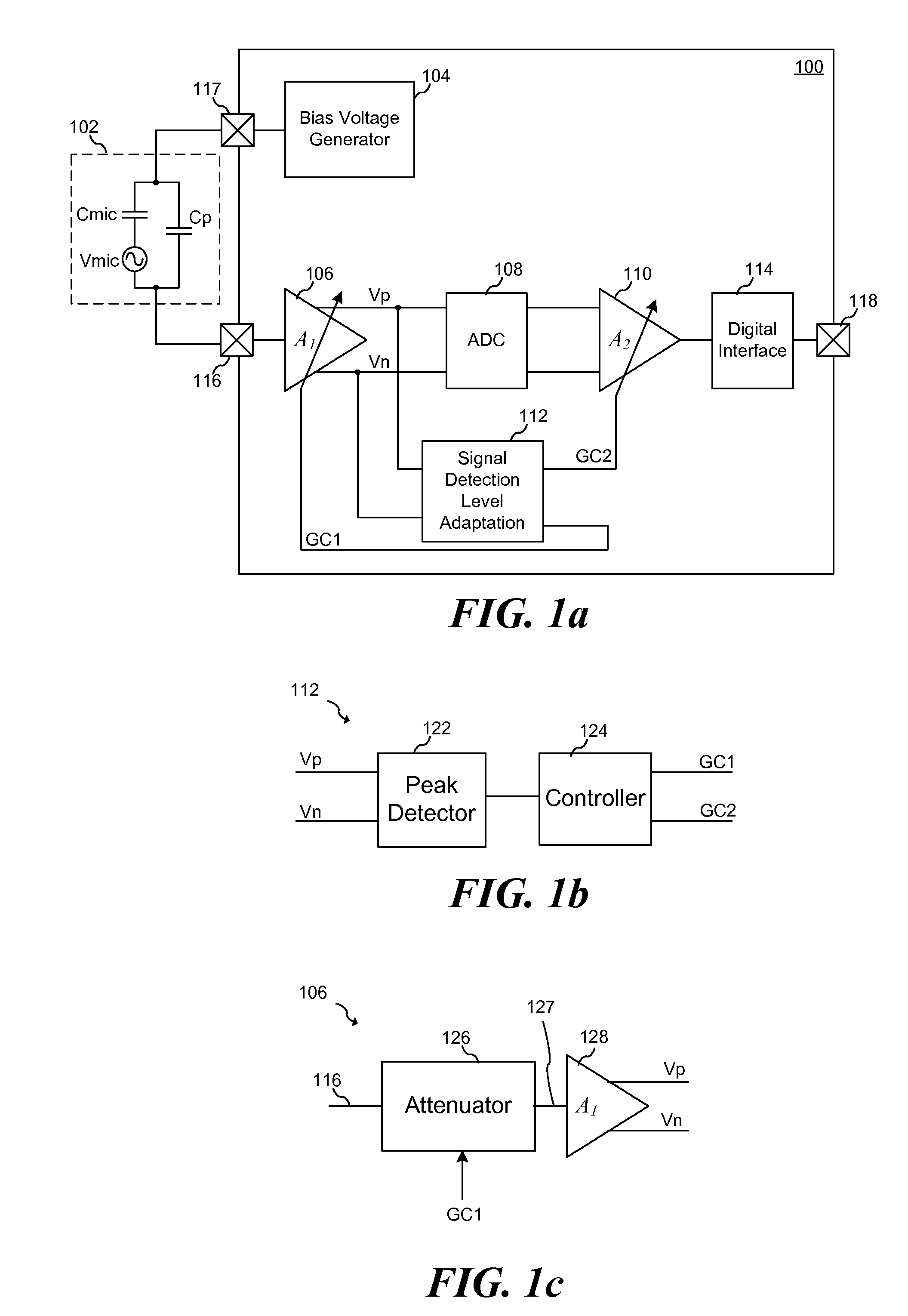
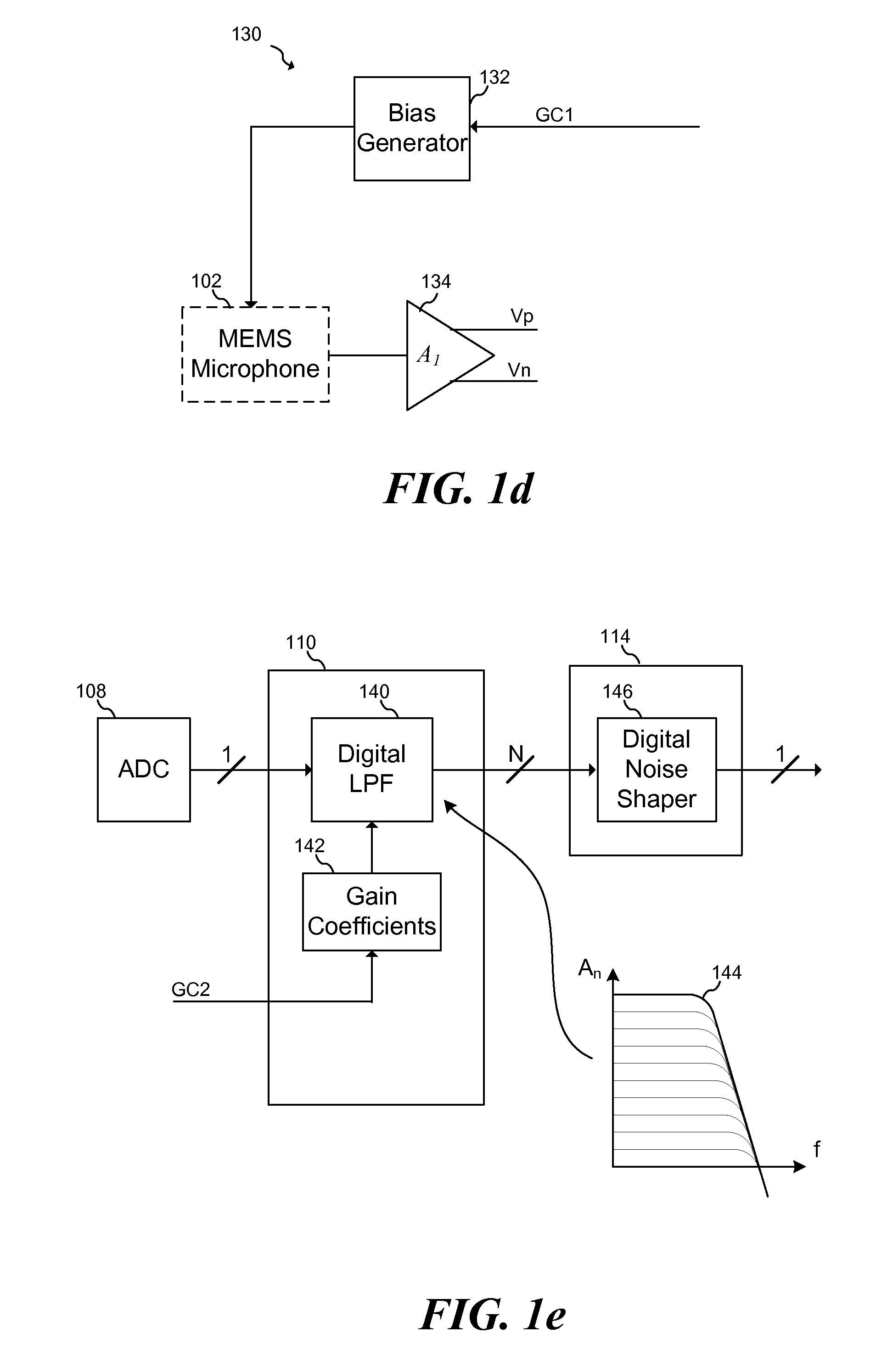
System and Method for Low Distortion Capacitive Signal Source Amplifier
ActiveUS20130051582A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationCapacitanceLow distortion
According to an embodiment, a method includes amplifying a signal provided by a capacitive signal source to form an amplified signal, detecting a peak voltage of the amplified signal, and adjusting a controllable impedance coupled to an output of the capacitive signal source in response to detecting the peak voltage. The controllable impedance is adjusted to a value inversely proportional to the detected peak voltage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Power-MOSFETs with Improved Efficiency for Multi-channel Class-D Audio Amplifiers and Packaging Thereof
InactiveUS20080252372A1Lower on-resistanceSimple preparation techniqueTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGround contactAudio power amplifier
A stereo class-D audio system includes a first die including four monolithically integrated NMOS high-side devices and a second a second die including four monolithically integrated PMOS low-side devices. The audio system also includes a set of electrical contacts for connecting the high and low-side devices to components within the a stereo class-D audio system, the set of electrical contacts including at least one supply contact for connecting the drains of the high-side devices to a supply voltage (Vcc) and at least one ground contact for connecting the drains of the low-side devices to ground, the electrical contacts also including respective contacts for each source of the high and low-side devices allowing the source of each high-side device to be connected to the source of a respective low-side device to form two H-bridge circuits.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
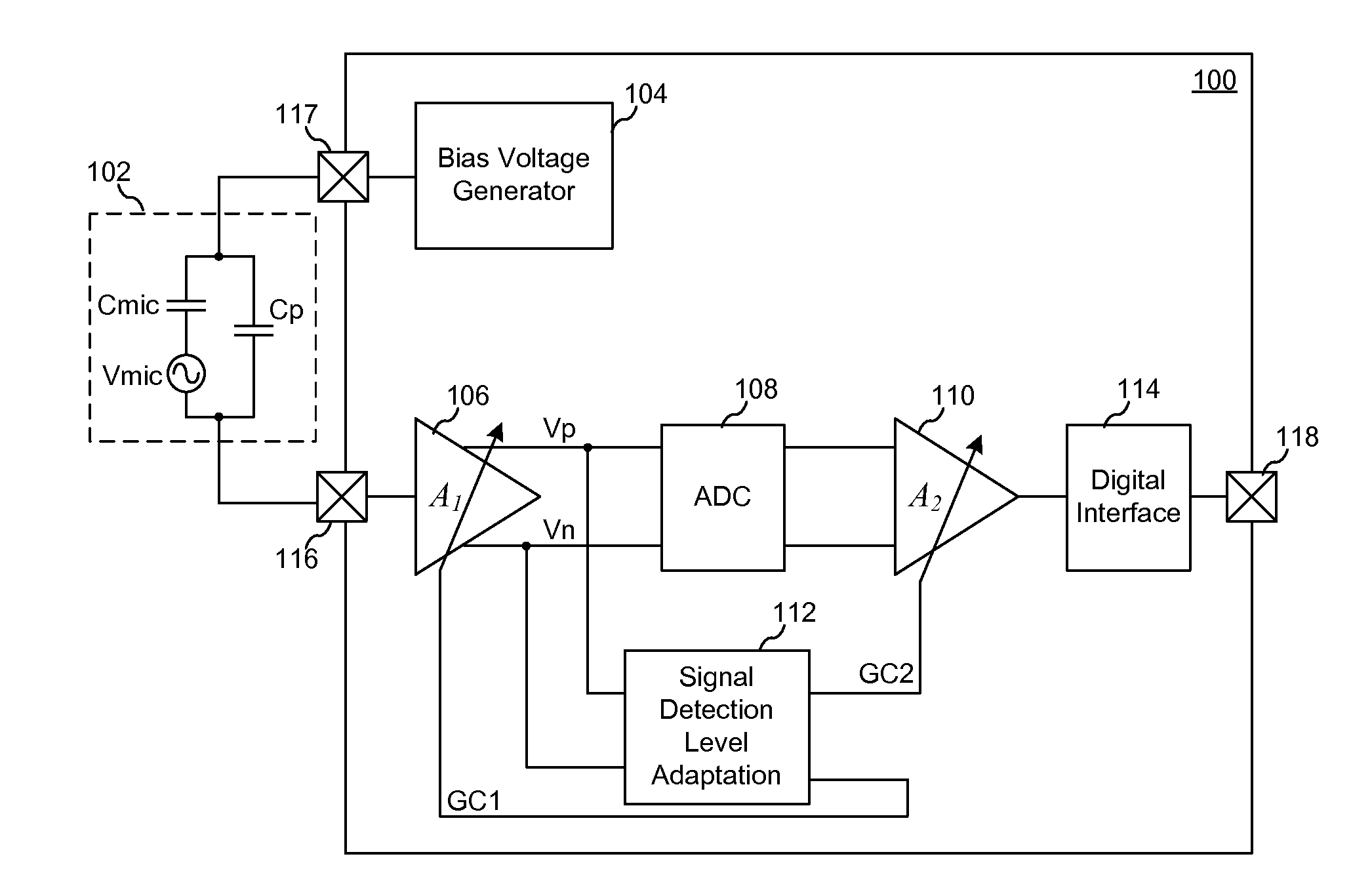
Preamplifier for two terminal electret condenser microphones
ActiveUS6888408B2Low costLimited space availableLow frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The present invention relates to a preamplifier suitable for use with Electret Condenser Microphones such as used within telecommunication equipment. More particularly the invention relates to a preamplifier specially suited for the demands to such a preamplifier within telecommunication equipment: low input capacitance, gain and a combined terminal for output and supply voltage, thus making the preamplifier suitable for two terminal microphone assemblies. These features are obtained with a two stage amplifier with a first stage optimised for low input capacitance and the second stage being able to provide gain. The preamplifier may be implemented using an ASIC, thus making the preamplifier suitable for applications with very limited space available, such as for integration within microphone assemblies.
Owner:SONION
System and Method for High Input Capacitive Signal Amplifier
ActiveUS20130271307A1Electric signal transmission systemsVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
In accordance with an embodiment, a method includes determining an amplitude of an input signal provided by a capacitive signal source, compressing the input signal in an analog domain to form a compressed analog signal based on the determined amplitude, converting the compressed analog signal to a compressed digital signal, and decompressing the digital signal in a digital domain to form a decompressed digital signal. In an embodiment, compressing the analog signal includes adjusting a first gain of an amplifier coupled to the capacitive signal source, and decompressing the digital signal comprises adjusting a second gain of a digital processing block.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
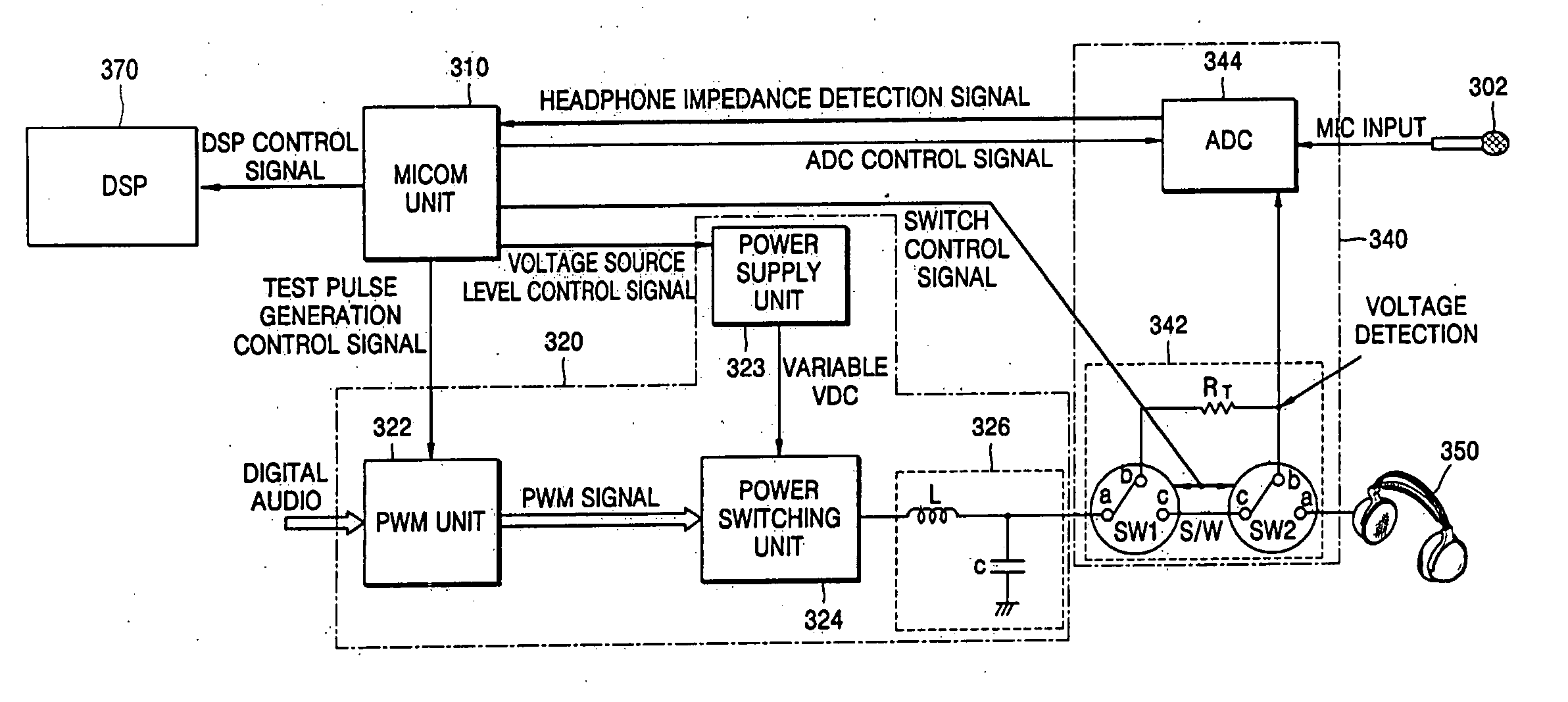
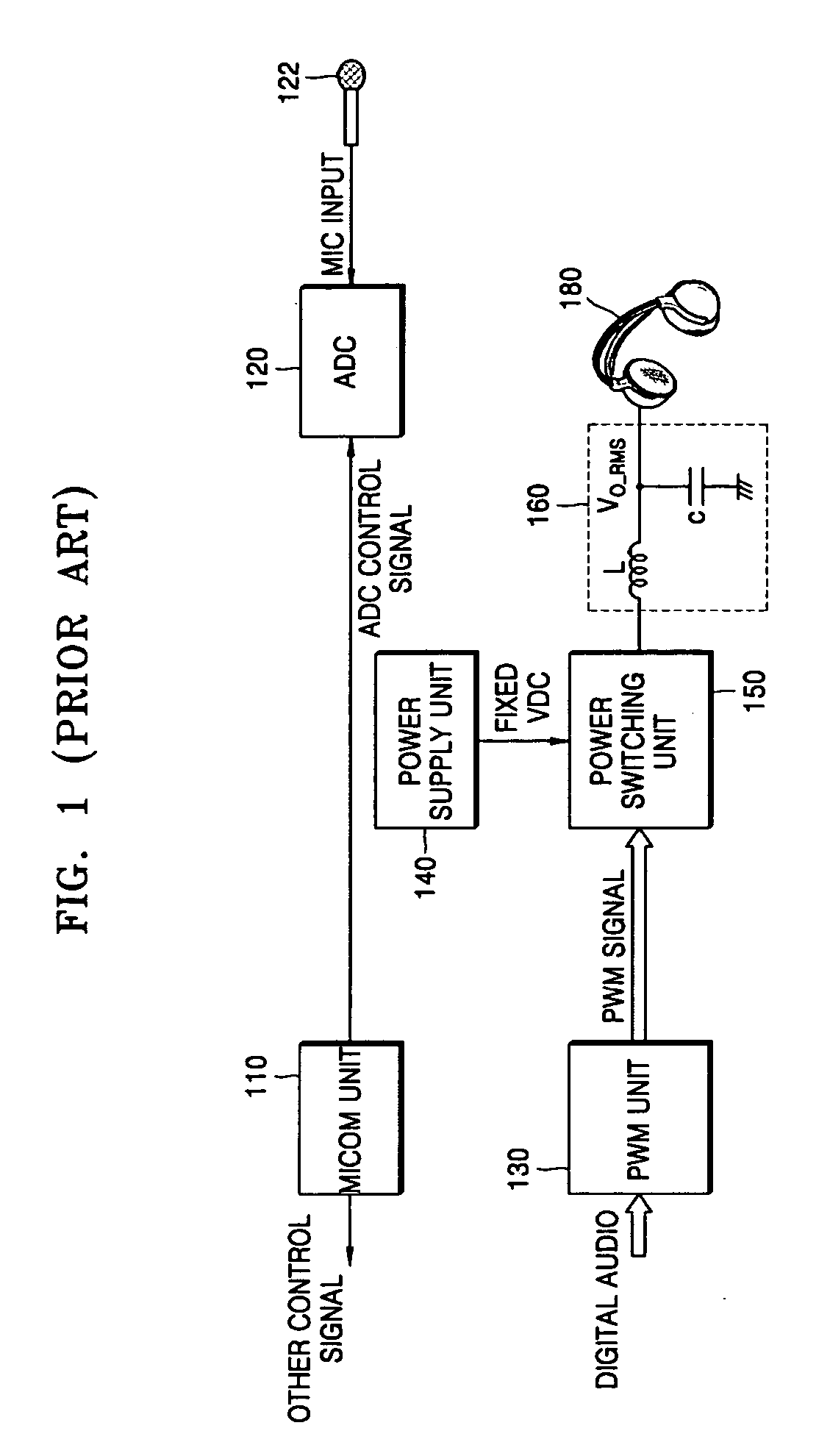
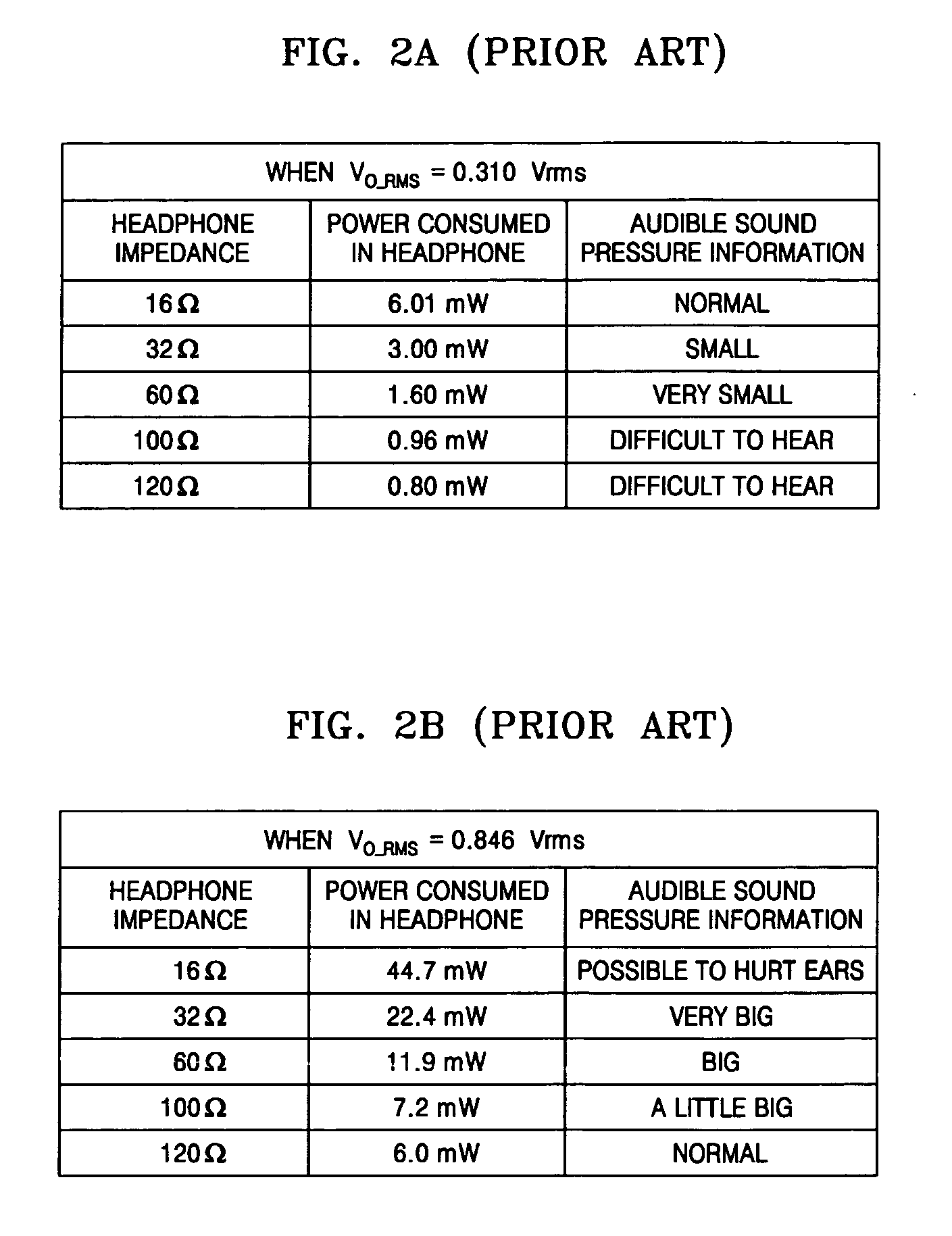
Method and apparatus to control output power of a digital power amplifier optimized to a headphone and a portable audio player having the same
ActiveUS20070098190A1Adjustable levelHeadphones for stereophonic communicationStereophonic circuit arrangementsControl signalEngineering
A method and apparatus to control output power of a digital amplifier capable of automatically determining an impedance of an earphone or headphone connected to a portable audio device and outputting a power that is optimized according to the impedance. The apparatus is usable with a digital amplification device and includes a signal processing unit to convert a pulse signal into a direct current (DC) voltage by power-amplifying the pulse signal, an impedance measuring unit to connect a resistance device between the signal processing unit and a speaker unit and to detect a voltage value applied to the resistance device and the speaker unit, and a micom unit to generate a pulse signal having a predetermined duty cycle in the signal processing unit if the speaker unit is connected to the device, to determine an impedance of the speaker unit based on the voltage value detected by the impedance measuring unit, to control a power amplification by providing a voltage level control signal to the signal processing unit according to the determined impedance, and to control an audio level in an audio reproduction mode accordingly.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
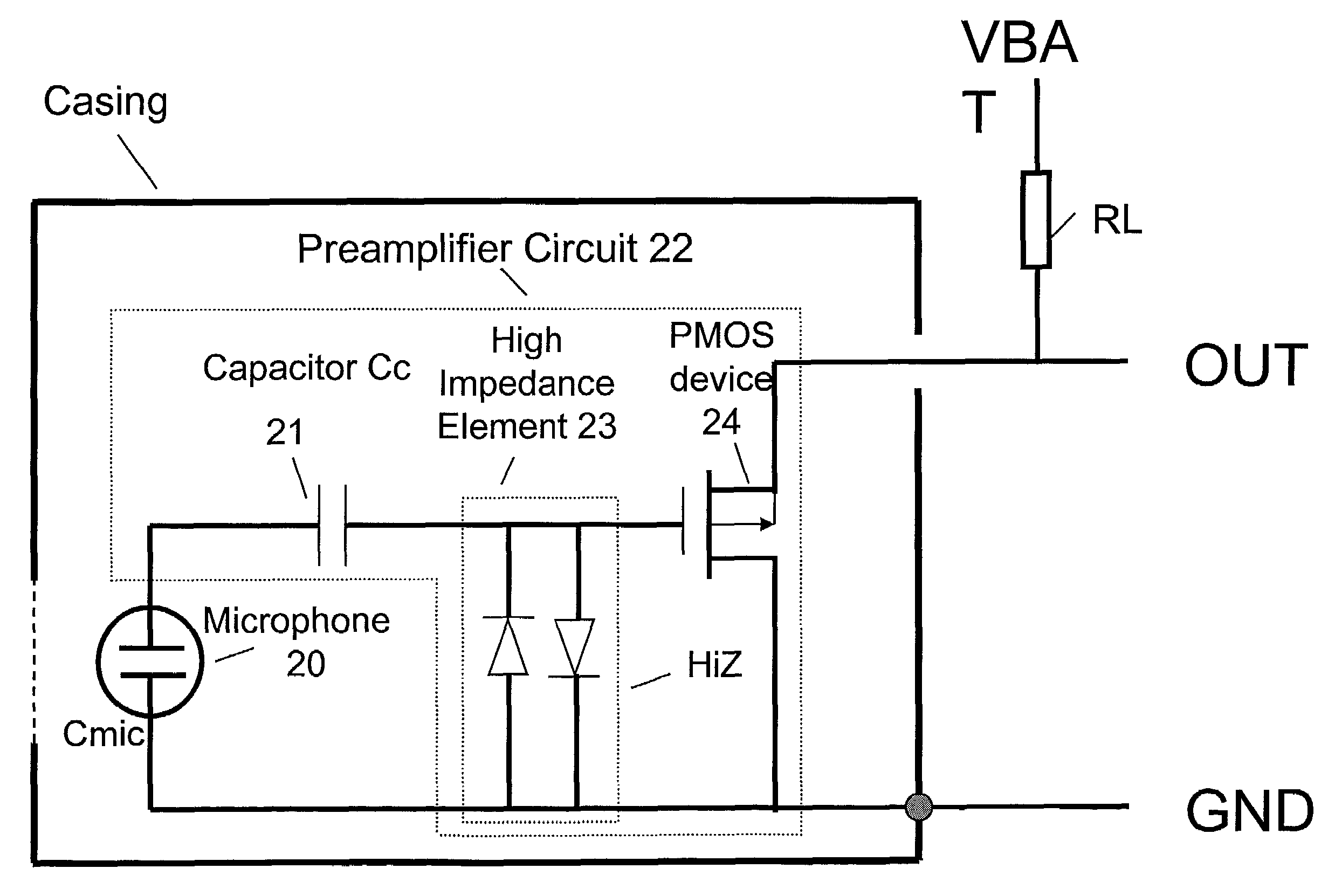
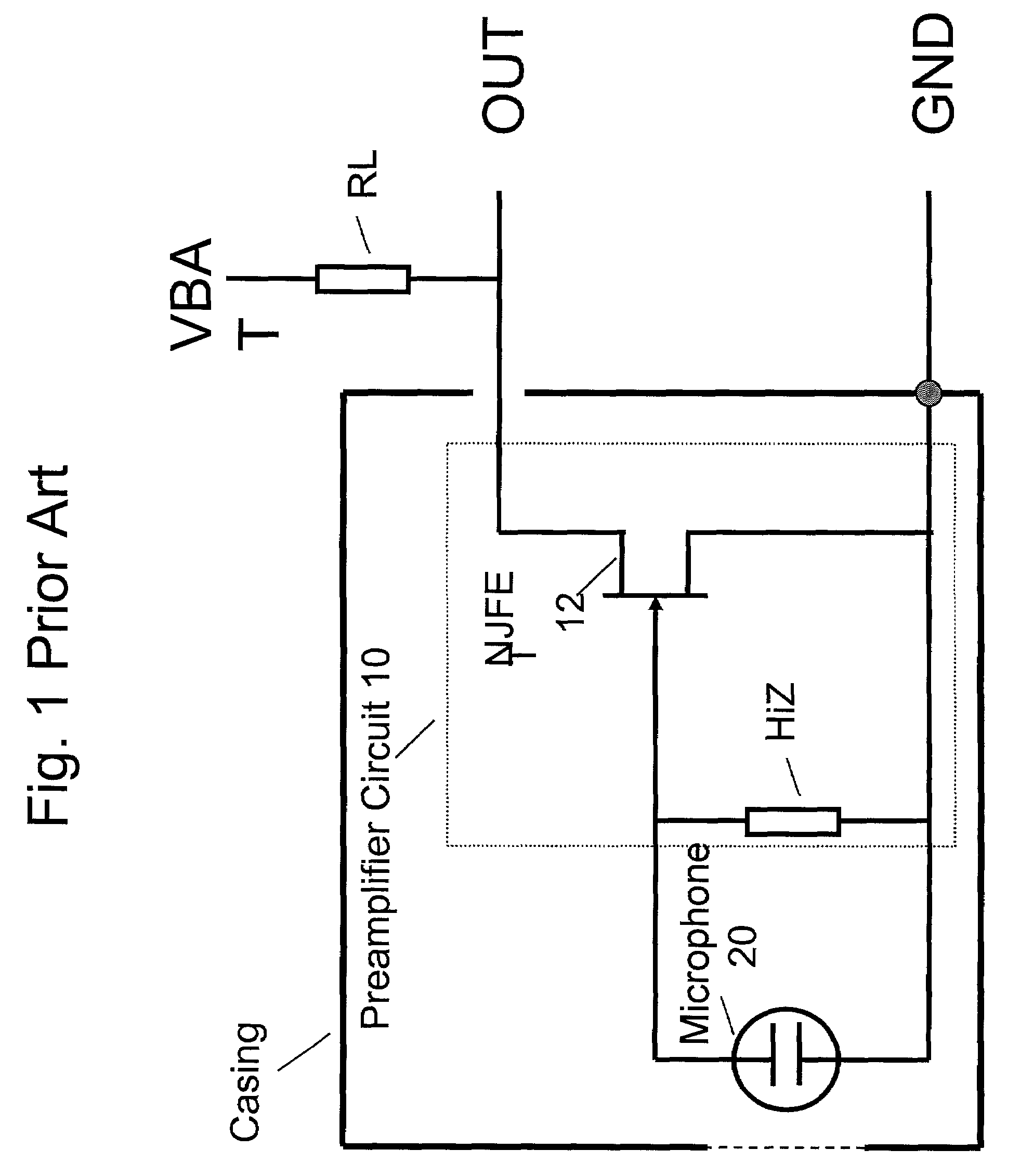
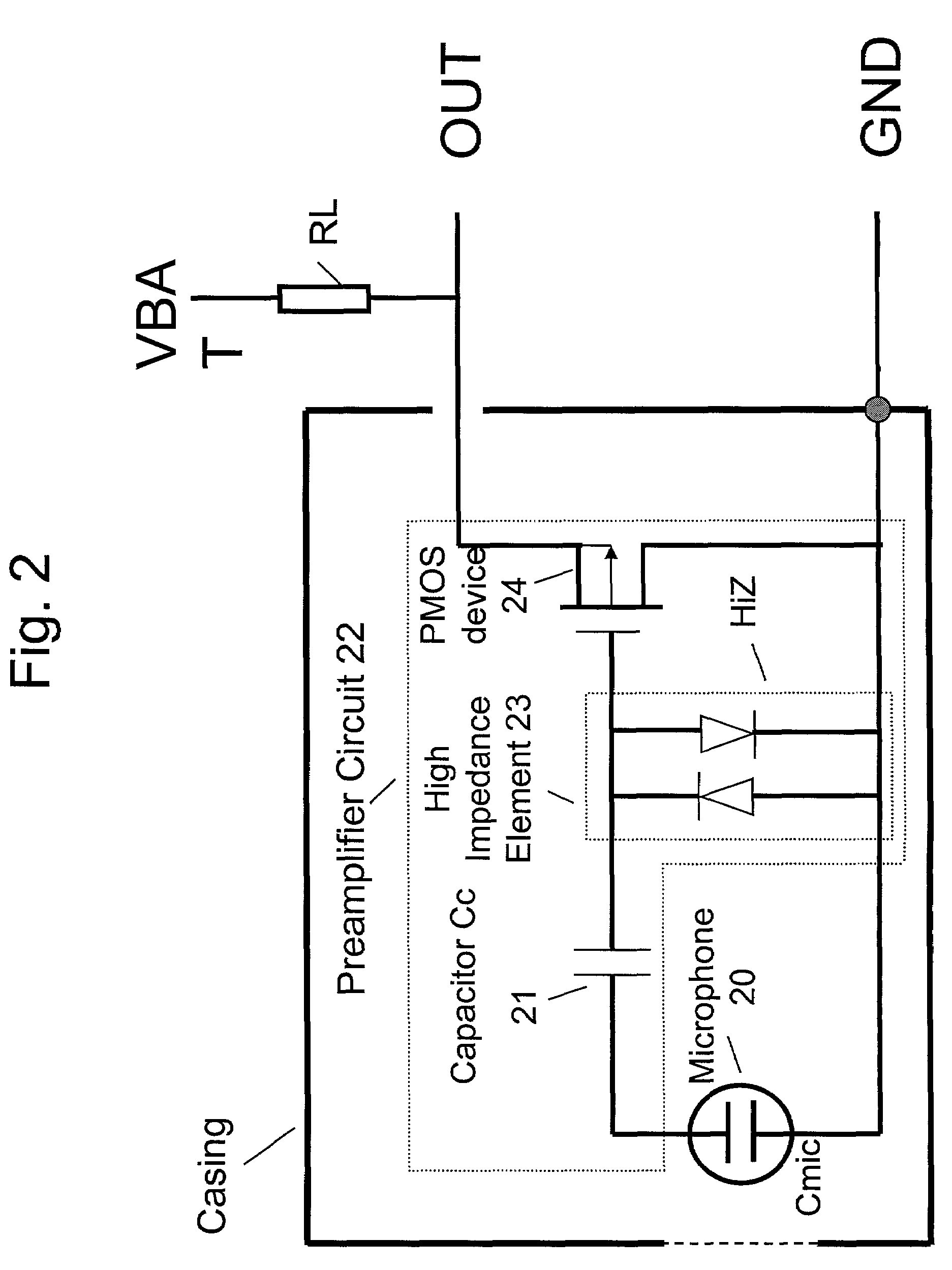
Electret condensor microphone preamplifier that is insensitive to leakage currents at the input
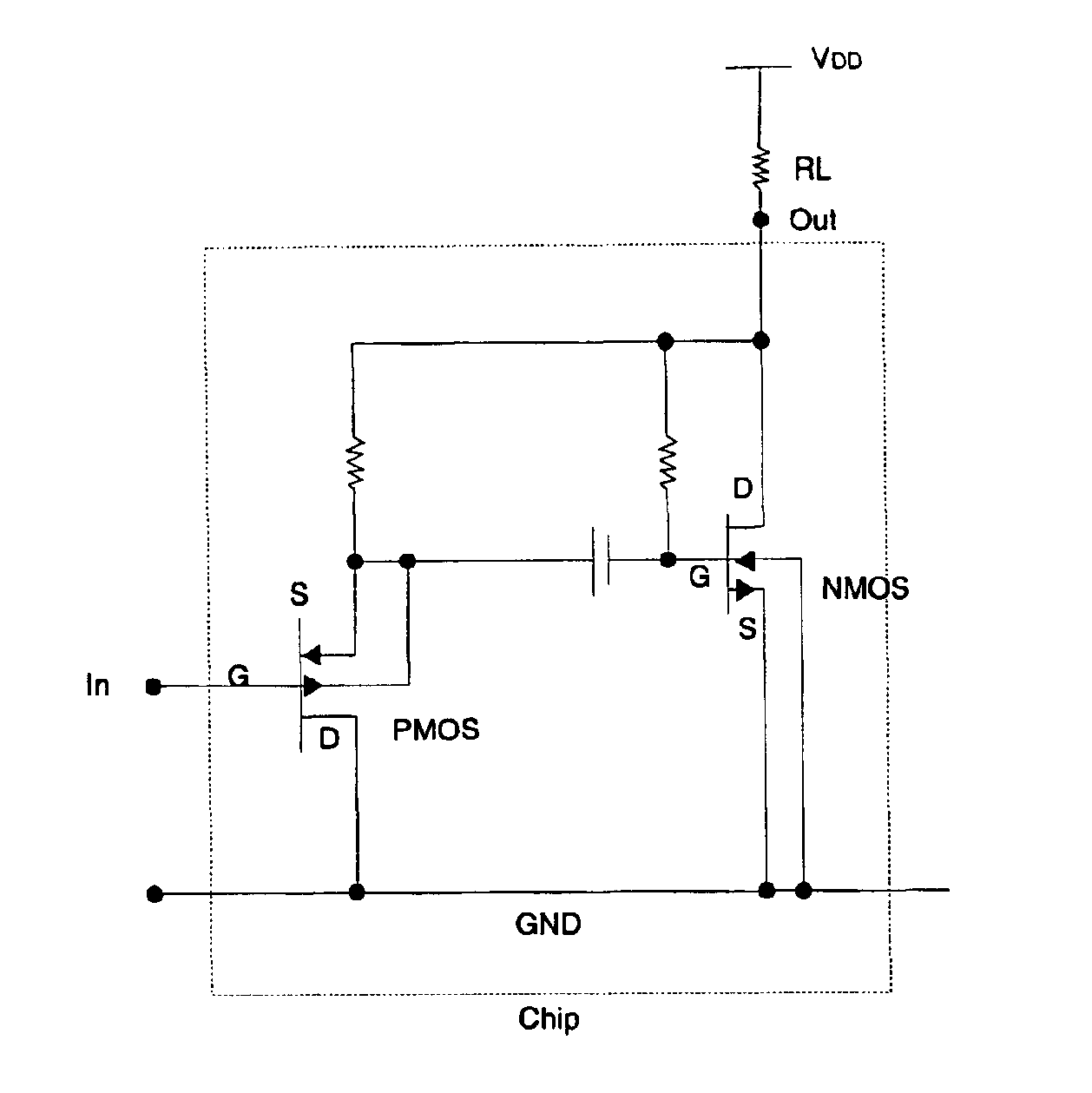
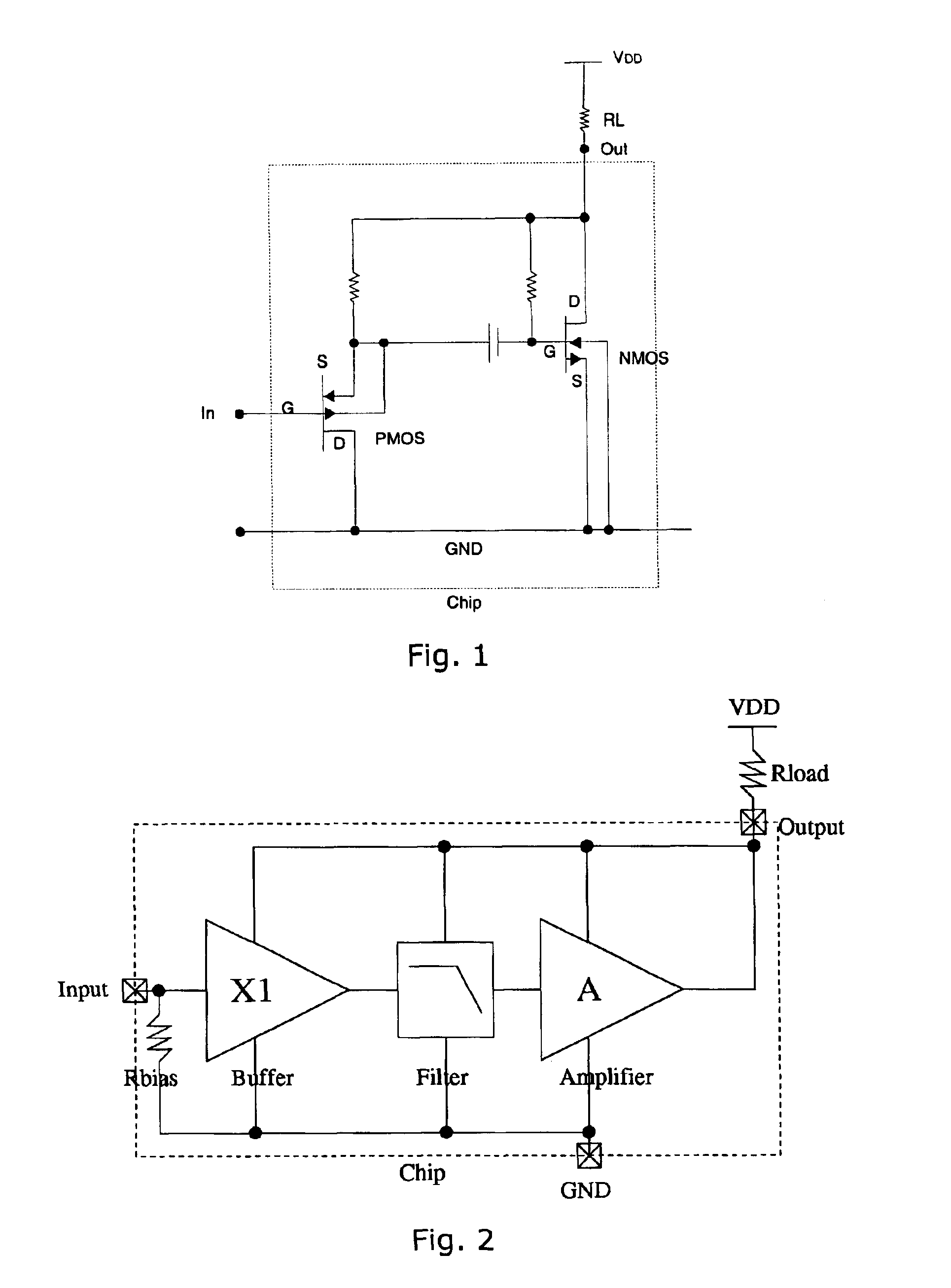
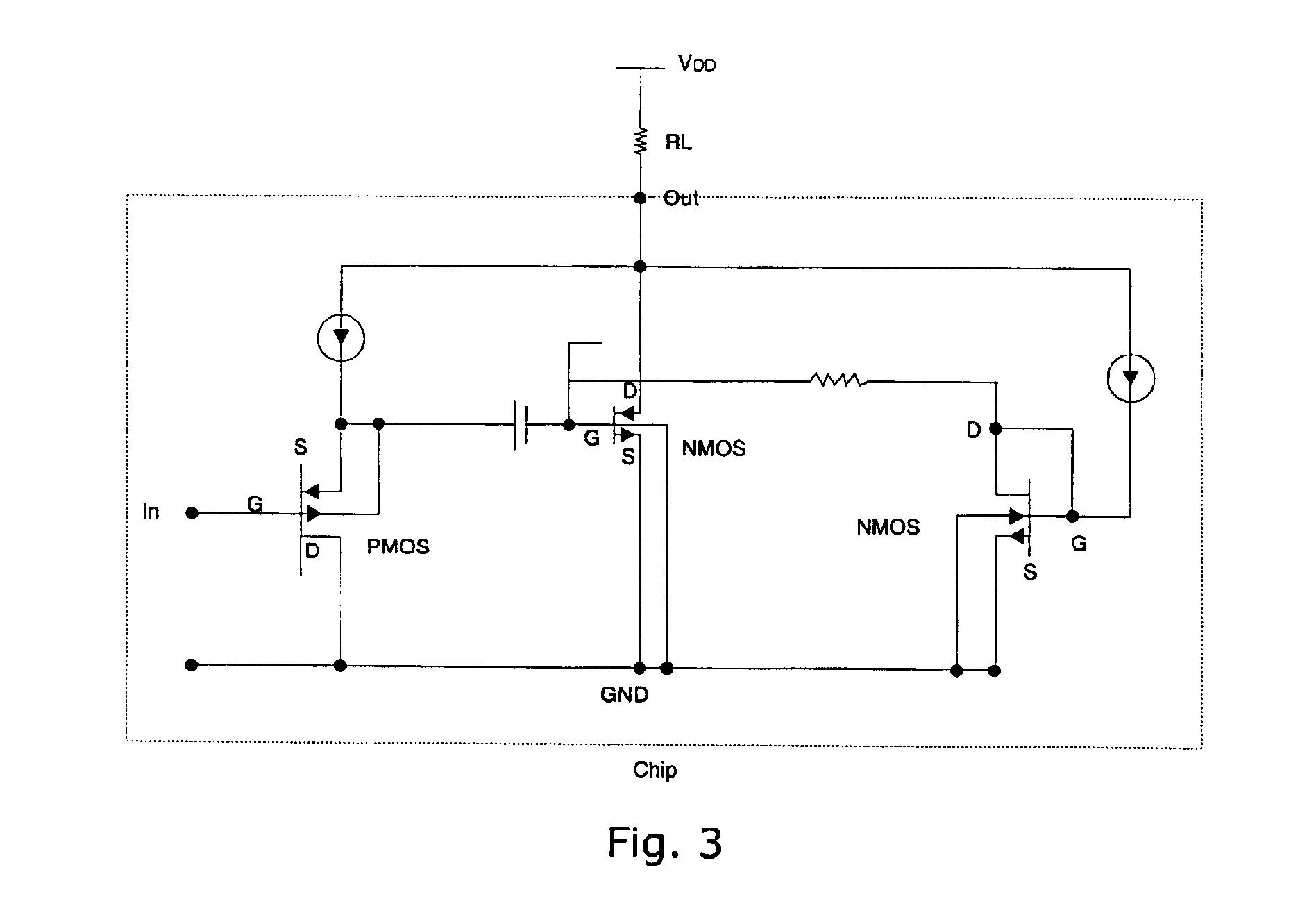
InactiveUS7110560B2Reduce input leakage currentAvoid leakage currentLow frequency amplifiersTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsCapacitanceOperating point
A preamplifier having extremely high input impedance amplifies the electrical signal output from an electret condenser microphone (ECM) without suffering from the effects of a DC leakage current at the input. The preamplifier circuit includes a pair of cross-coupled PN junction diodes setting the input impedance, a PMOS device, and a load resistor configured similarly to a conventional preamplifier. A capacitor is placed between the input and the cross-coupled diodes such that a DC path no longer exists to bias the cross-coupled diodes. Therefore, leakage currents are prevented from upsetting the DC operating point of the preamplifier and biasing the cross-coupled diodes. Consequently, small signal gain distortion, excessive demodulation products and increased noise can be avoided.
Owner:SONION
Audio signal controller
ActiveUS20110029109A1Lower Level RequirementsLow costSignal processingLow frequency amplifiersDigital audio signalsAudio frequency
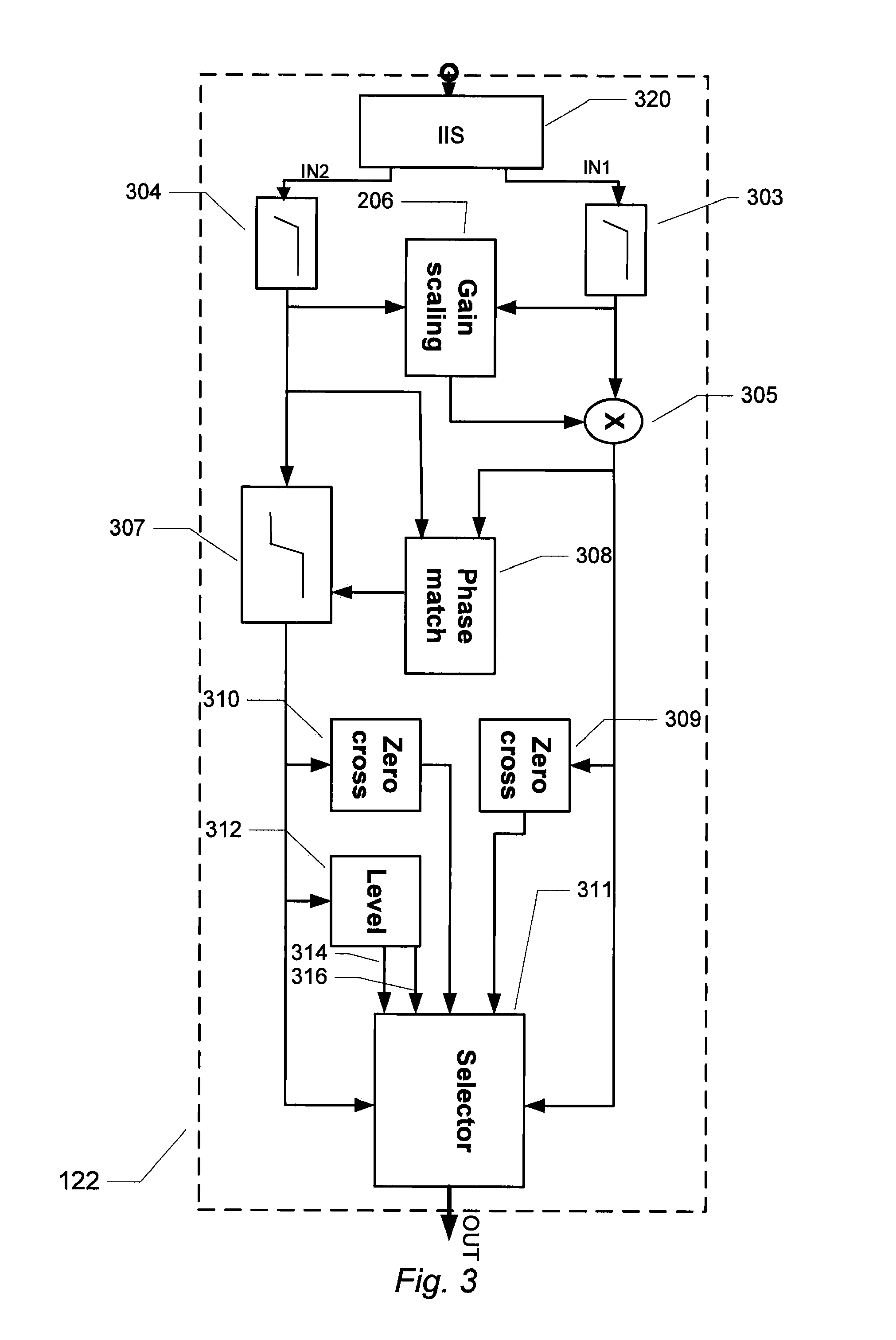
The present invention relates to an audio signal controller adapted to receiving first and second digital audio signals and estimating a signal feature of the first or second digital audio signal. The estimated signal feature is compared with a predetermined feature criterion and the audio signal controller switches from conveying the first digital audio signal to conveying the second digital audio signal to a controller output, or vice versa, at a zero-crossing of the first digital audio signal or the second digital audio signal based on the comparison between the estimated signal feature and the predetermined feature criterion.
Owner:INVENSENSE
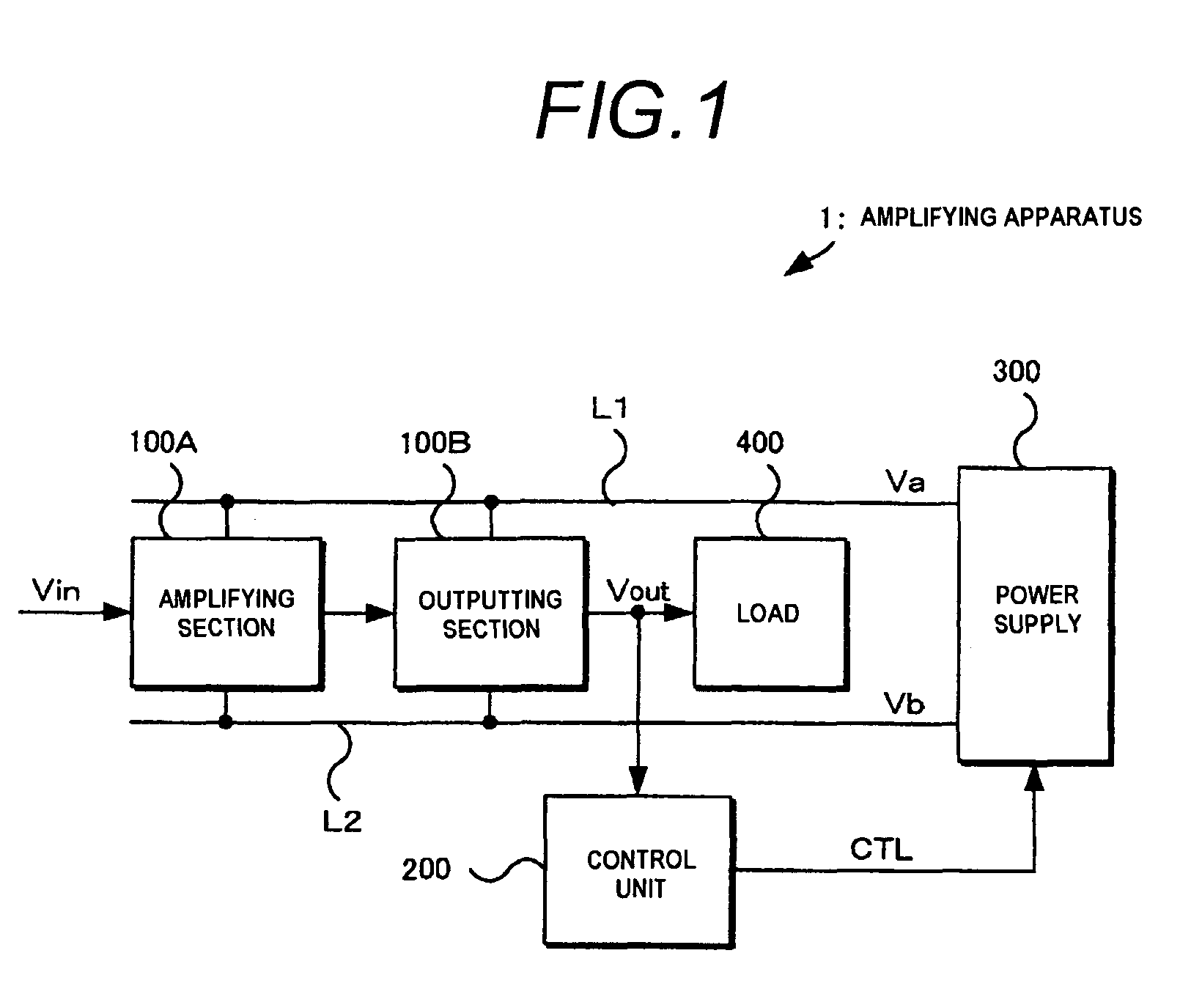
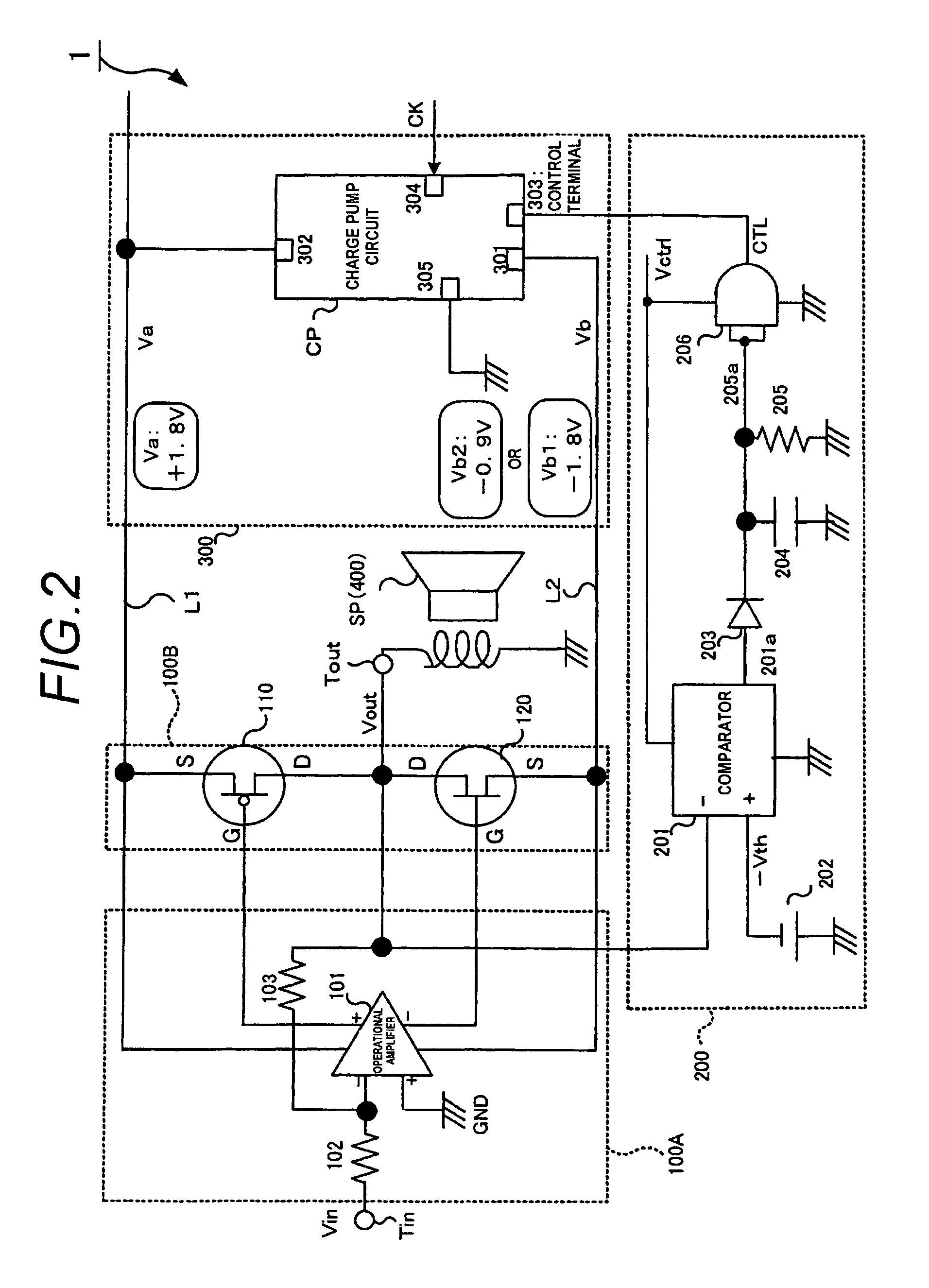
Amplifying apparatus
ActiveUS8164388B2Improve power efficiencyHigh voltageLow frequency amplifiersAmplififers with field-effect devicesLow voltageEngineering
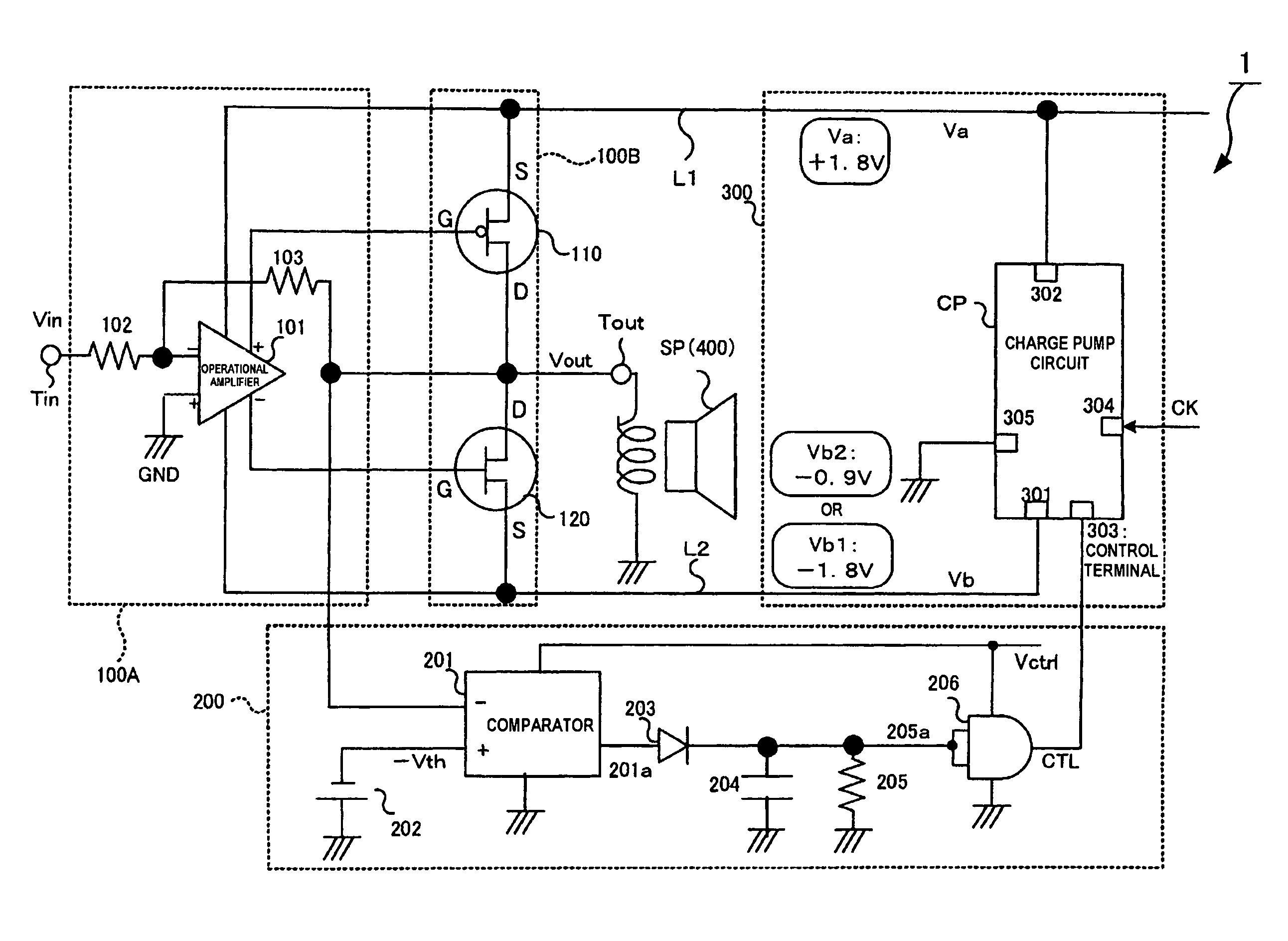
An amplifying apparatus amplifies an input signal supplied to an input terminal and outputs an output signal from an output terminal. The apparatus includes a high-potential power supply line through which a high voltage is supplied; a low-potential power supply line through which a low voltage is supplied; a control unit; and a power supply in which one of the high and low voltages is a fixed voltage, and which generates, as the other of the high and low voltages, one of a first voltage in which a polarity of the fixed voltage is inverted, and a second voltage which is closer to the ground potential than the first voltage is. The control unit controls the power supply to cause the other of the high and low voltages to be switched between the first voltage and the second voltage in accordance with a signal level of the output signal.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
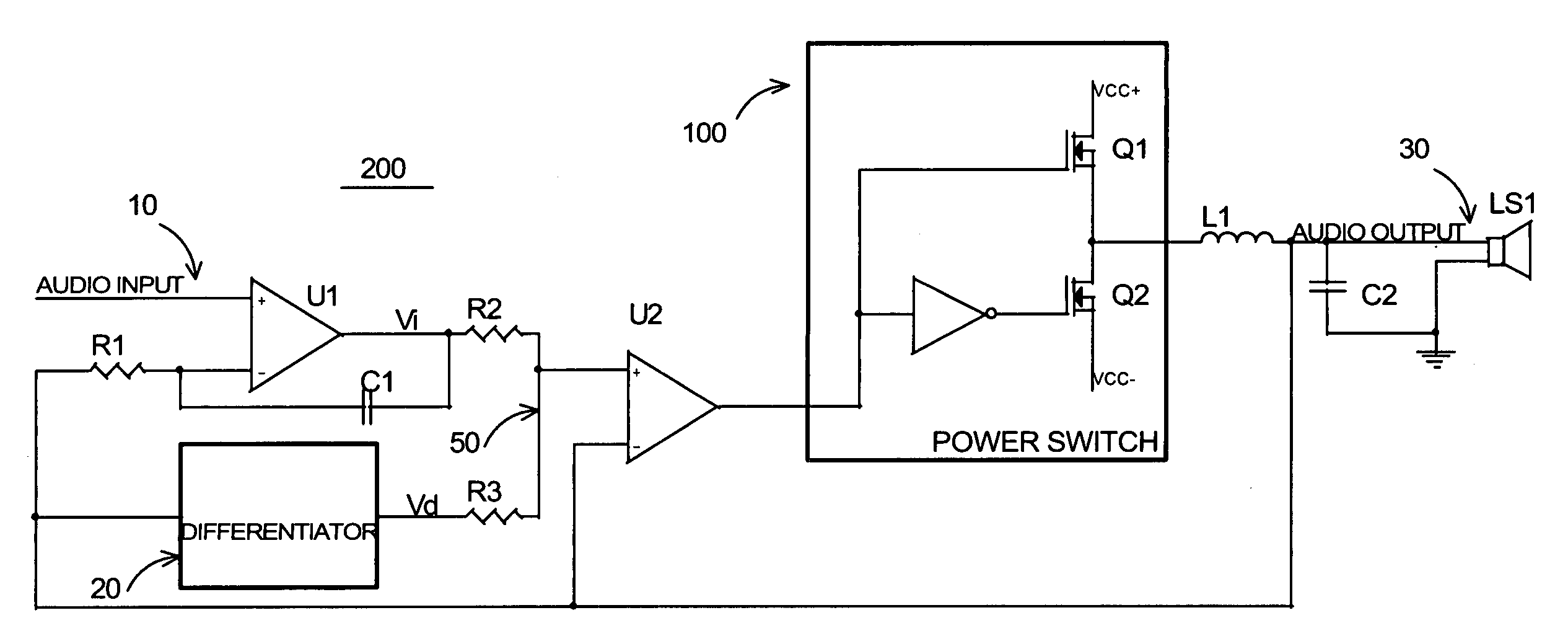
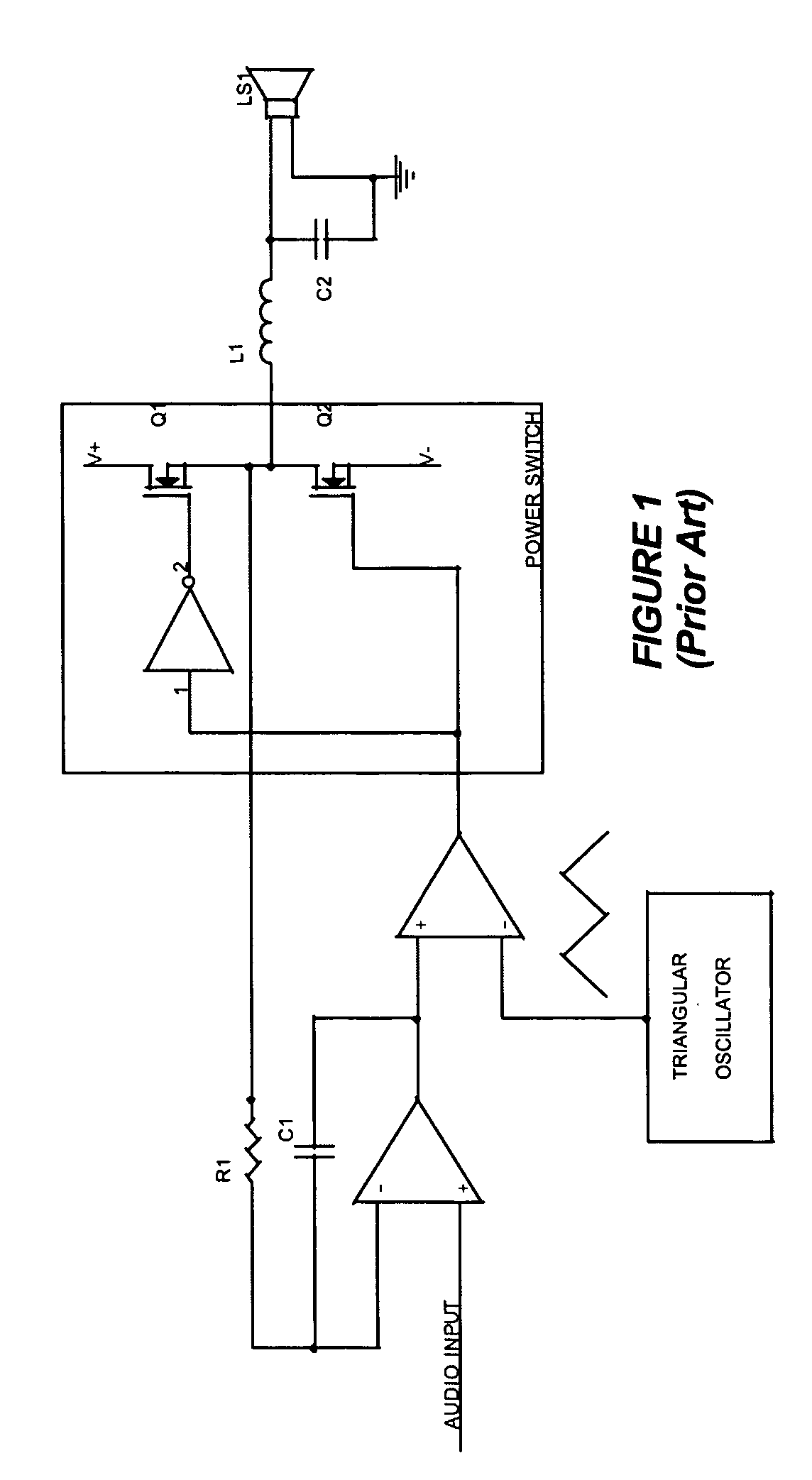
Self-oscillating switching amplifier
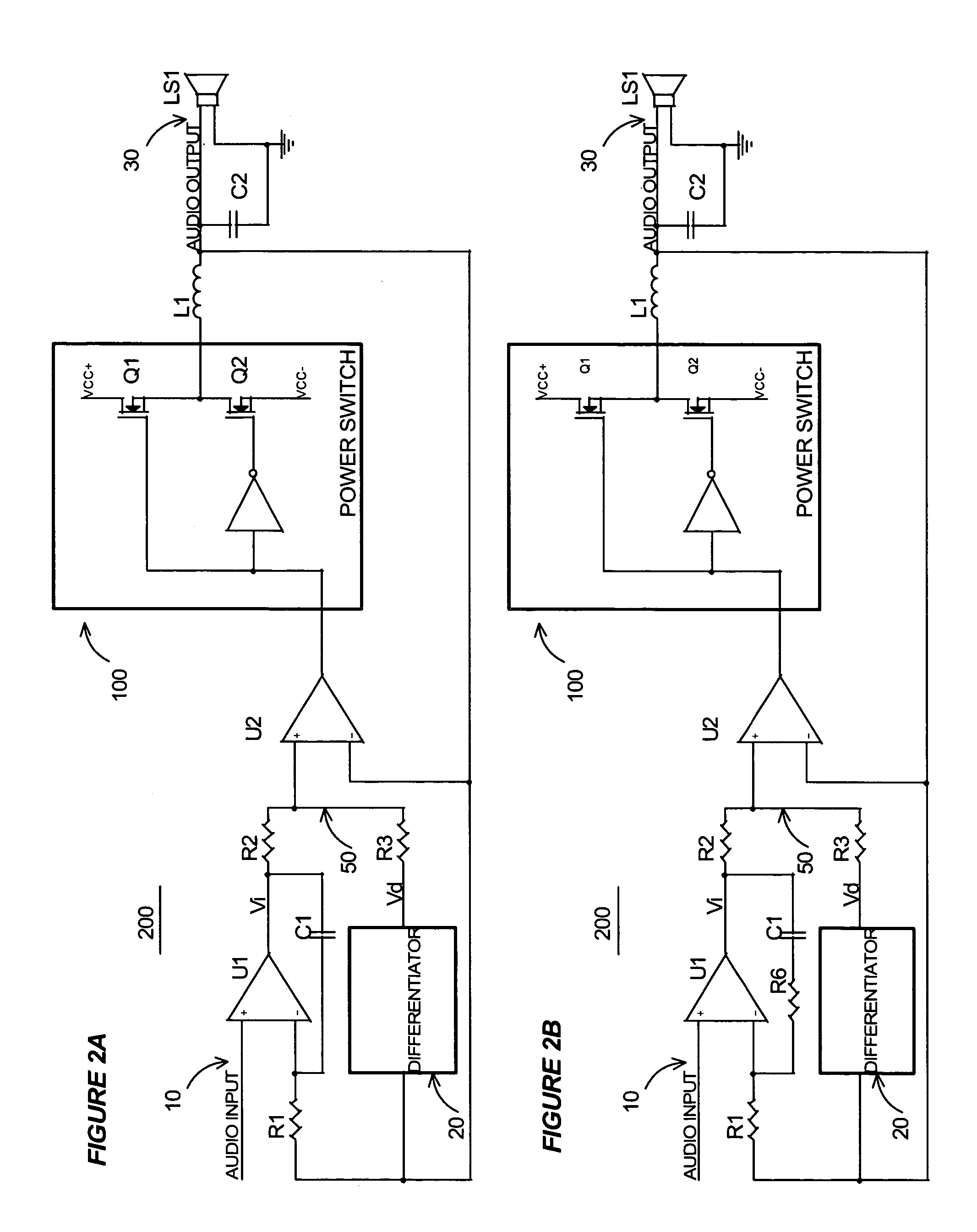
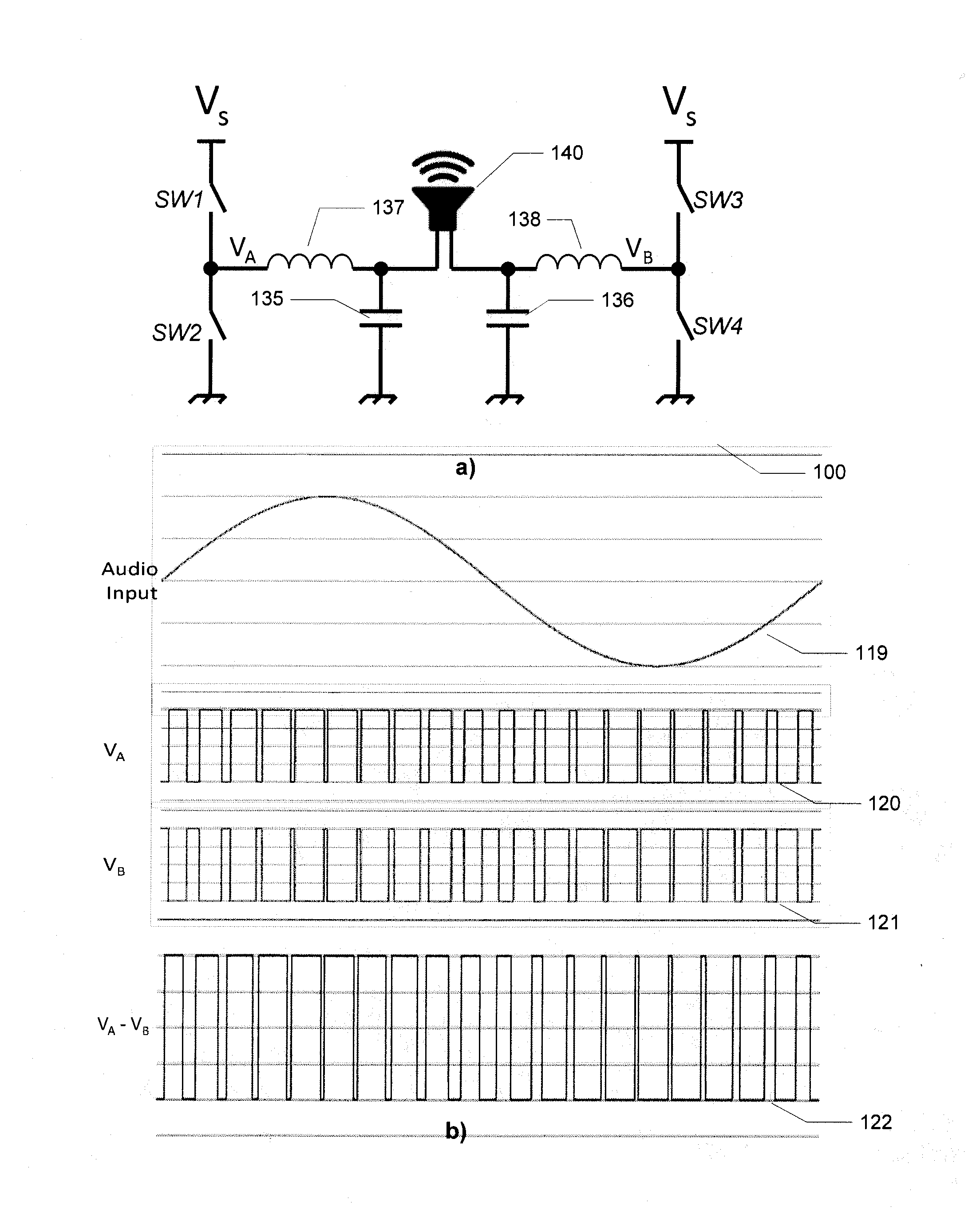
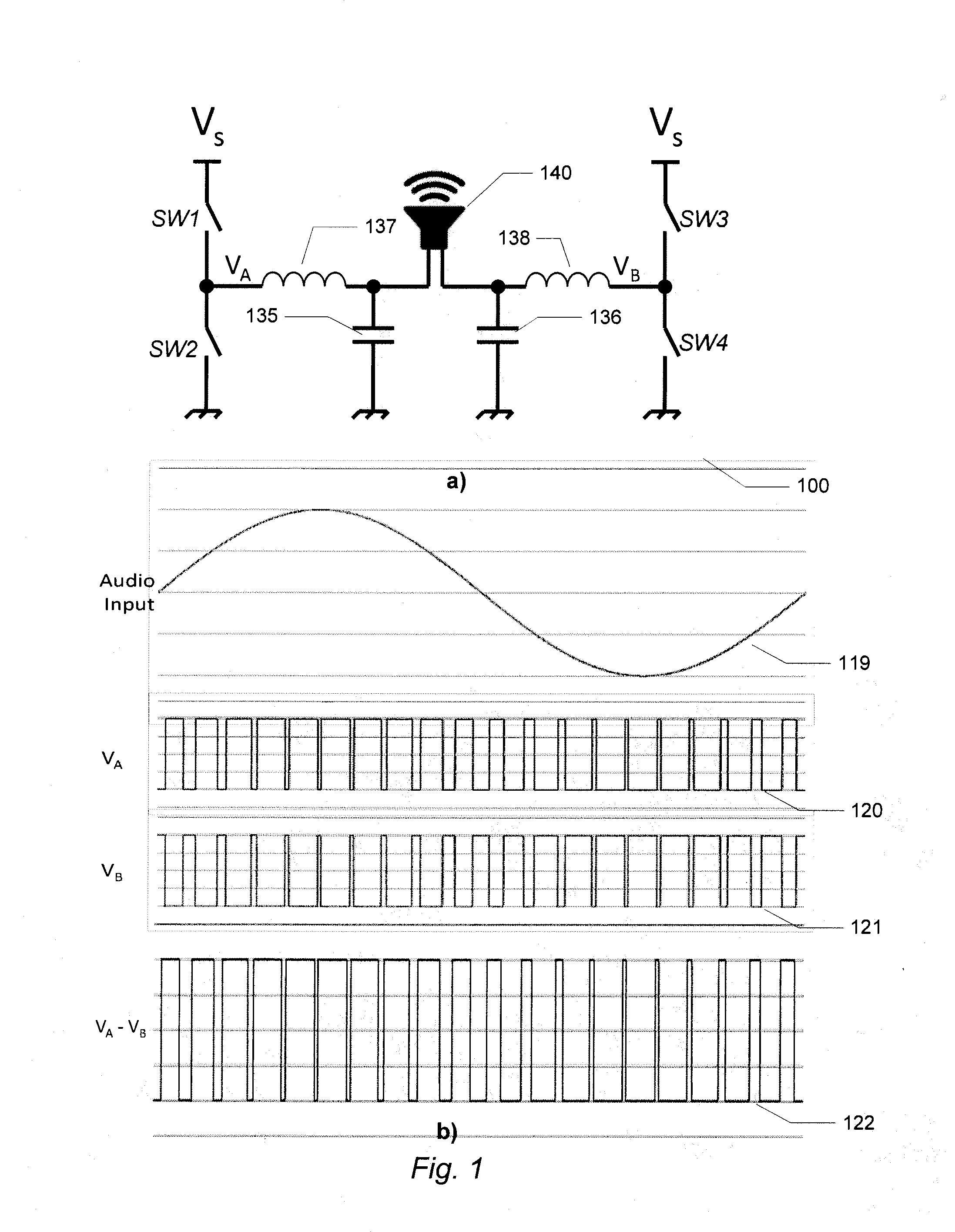
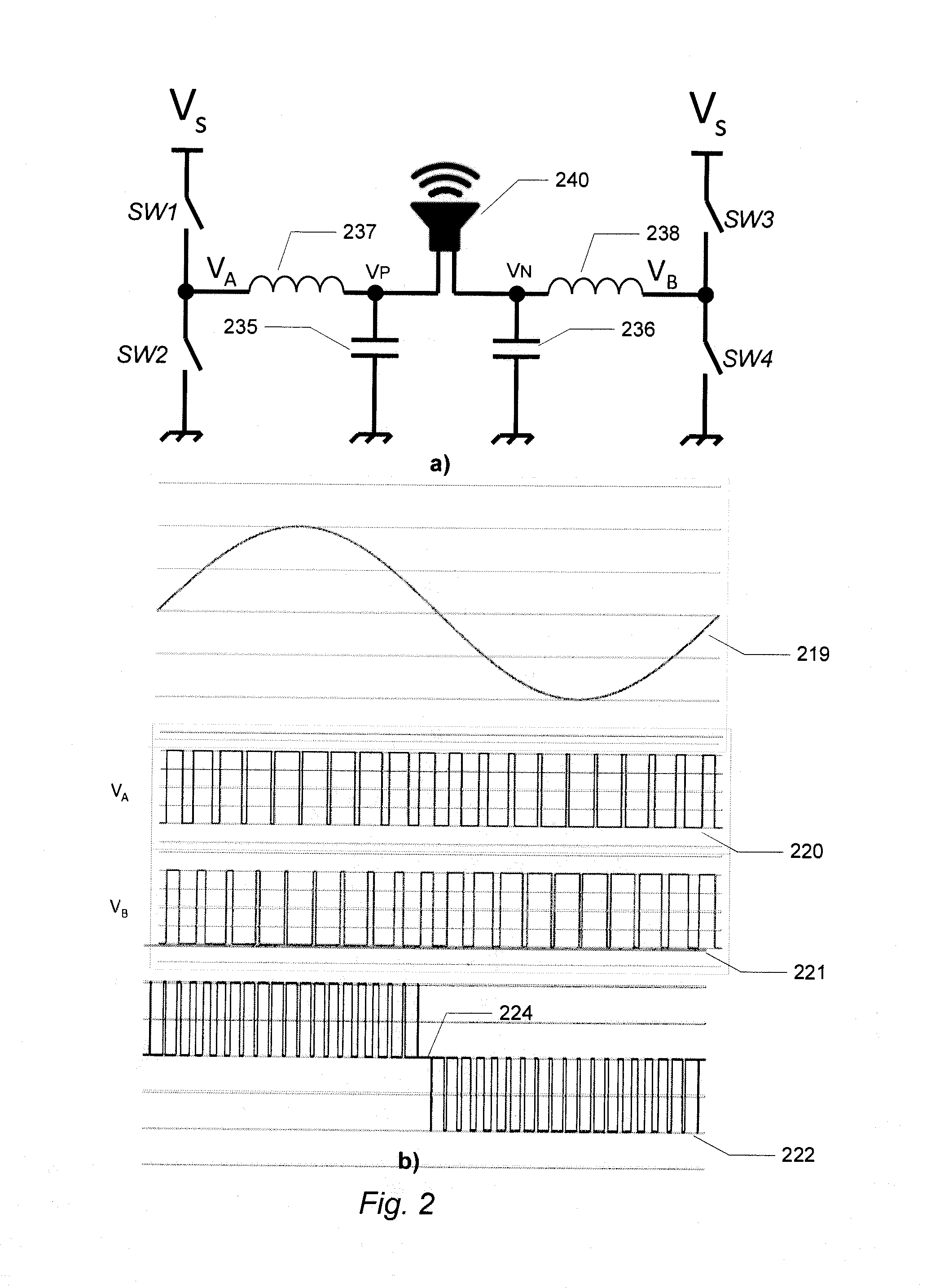
InactiveUS7221216B2Improve audio performanceMinimize distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionLow frequency amplifiersDifferentiatorLc resonant circuit
A self-oscillating switching amplifier having an error amplifier output combined with the output of an output signal differentiator according predetermined weighing factors to force a small oscillation around the averaged output signal at a high frequency. The feedback voltage is sensed at the output of the switching amplifier. Additional feedback can be derived from a switching node of the power switch. The switching of the power switch can be dynamically changed from binary switching when the amplitude of the audio signal is low, to ternary switching when the amplitude of the input signal is high to minimize distortion of the output signal. The amplifier can be supplied with a pulsing voltage. In certain embodiments the output signal differentiator is simply a capacitor or a LC resonance circuit coupled directly to an appropriate speaker terminal for the highest possible self-oscillating frequency of the switching amplifier.
Owner:CORETRONIC
Audio amplifier using multi-level pulse width modulation
ActiveUS20130223651A1Reduce switching frequencyReduce power lossAc-dc conversionLow frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present invention relates in one aspect to a class D audio amplifier with improved output driver topology supporting multi-level output signals such as 3-level, 4-level or 5-level pulse width or pulse density modulated output signals for application to a loudspeaker load. The present class D audio amplifiers are particularly well-suited for high-volume consumer audio applications and solutions.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
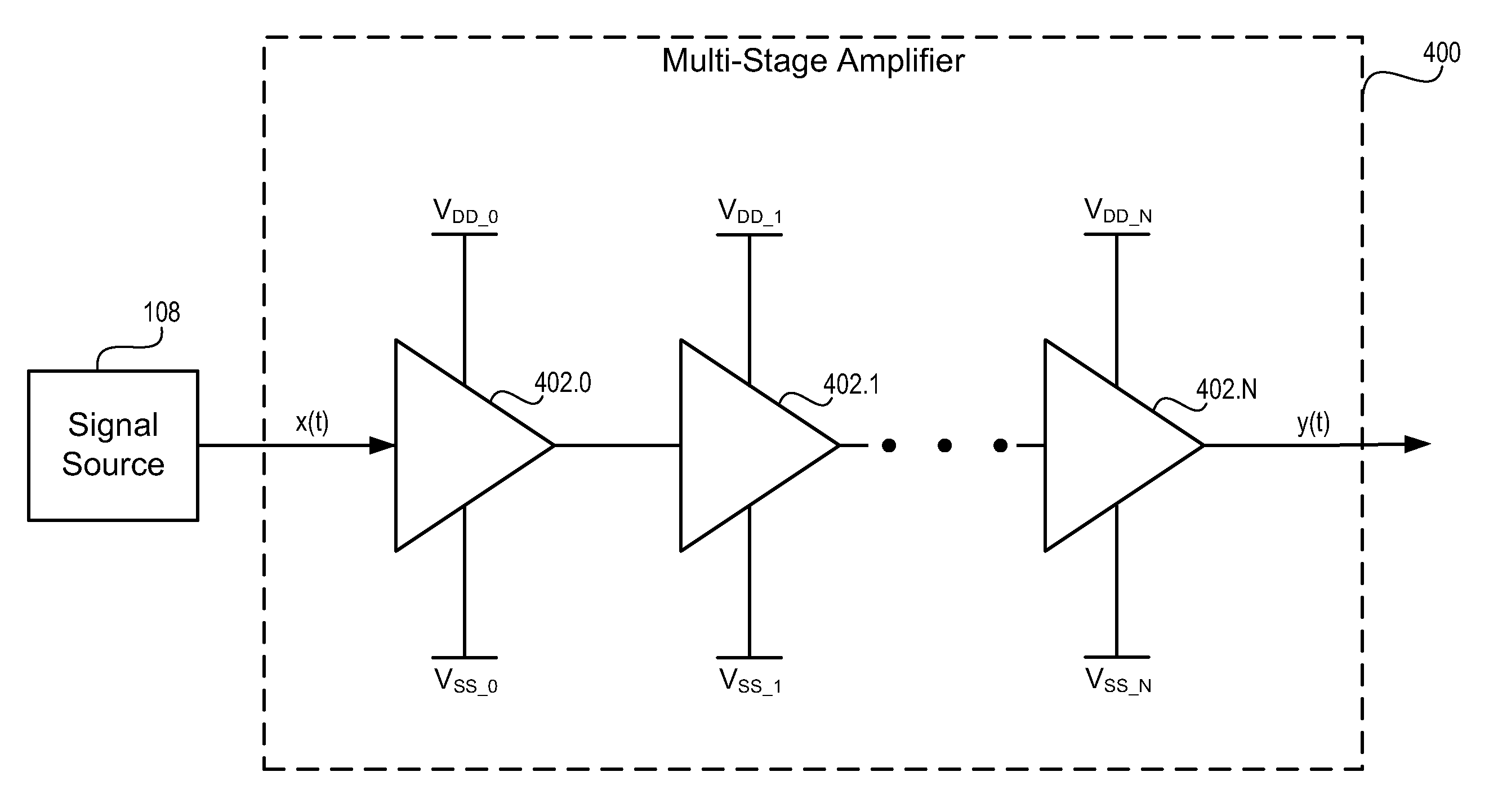
Multi-stage amplifier with multiple sets of fixed and variable voltage rails
A signal processing system and method utilizes a multi-stage amplifier to amplify an input signal. The multi-stage amplifier uses a mixed set of voltage rails to improve the operating efficiency of at least one of the amplification stages while allowing other amplification stages to operate in a predetermined operating mode. Efficiency of at least one of the stages is improved by supplying at least one variable voltage rail to an amplification stage of the multi-stage amplifier. The variable voltage rail varies in response to changes in an input signal voltage to the amplification stage. Accordingly, at least one amplification stage utilizes a variable voltage rail, and all amplification stages are supplied with a set of voltage rails that provides sufficient input signal headroom, thus, providing amplification stage efficiency and adequate voltage to allow operation of all amplification stages.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Class g audio amplifiers and associated methods of operation
ActiveUS20110123048A1High outputLow efficiencyPower amplifiersLow frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The present technology is directed to class G audio amplifiers and the associated methods of operation. In one embodiment, a class G audio amplifier includes an input port, an audio output stage, a level detector, and a charge pump. The class G audio amplifier regulates the power supplies of the audio output stage according to the input signal, so as to realize high efficiency and high quality audio output.
Owner:MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Distortion suppression in high-level capable audio amplification circuit
ActiveUS20120121106A1Enhances small signal transfer function matchingEasy to controlGain controlSemiconductor electrostatic transducersAudio power amplifierLinear element
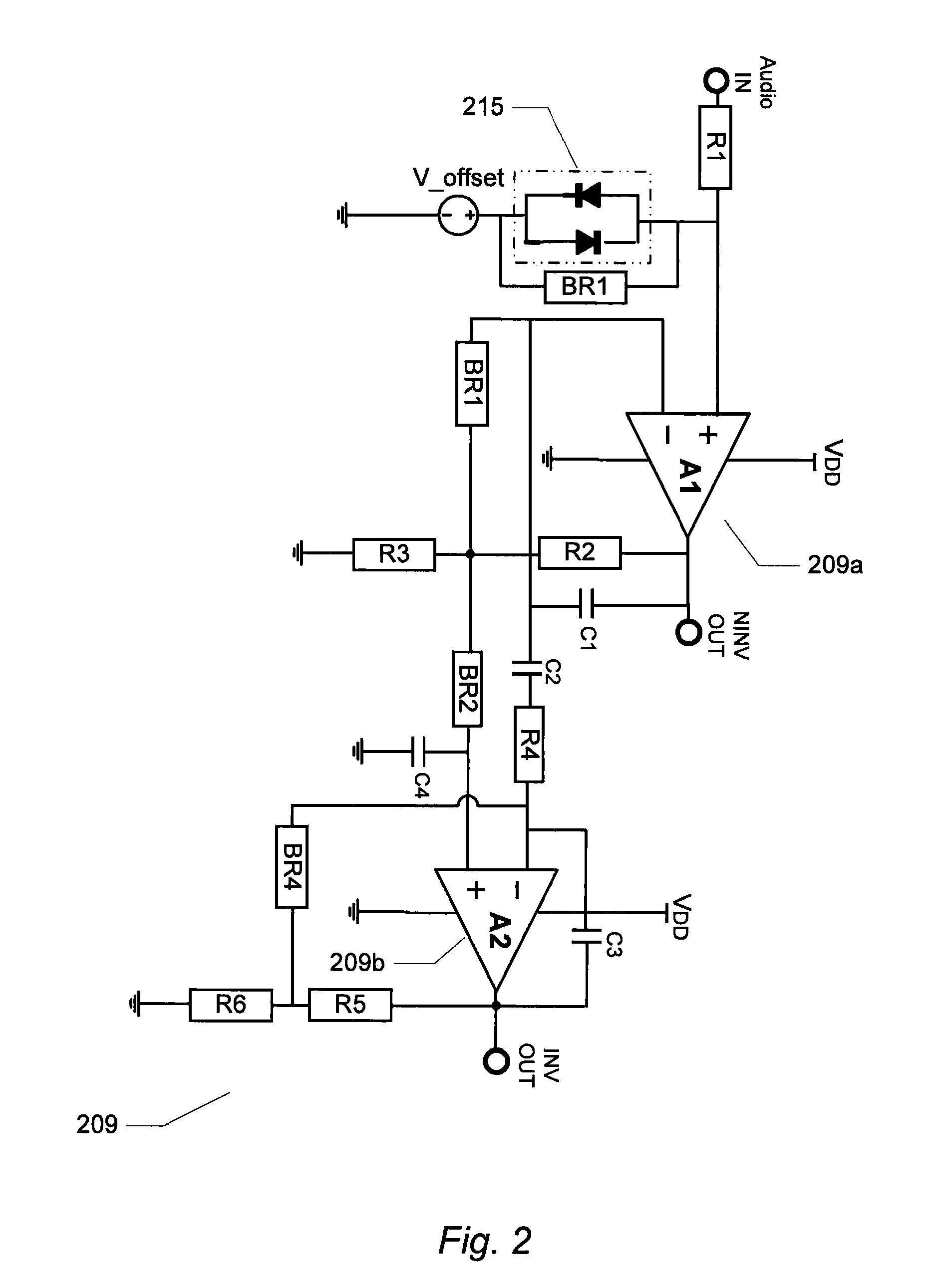
The present invention relates to an audio amplification circuit comprising a first preamplifier for receipt of an audio input signal and a second preamplifier comprising a first differential input for receipt of an attenuated audio input signal. The attenuated audio input signal is generated by an attenuator coupled to the audio input signal. A non-linear element is coupled to a first input of the first preamplifier thereby distorting the audio input signal at the first input at large signal levels. A distortion compensation network is adapted to supply a distortion compensation signal from the first input of the first preamplifier to a second differential input of the second preamplifier such that distortion in the output signal of the second preamplifier is cancelled or attenuated. The invention further relates to a corresponding method of compensating an audio amplification circuit for distortion induced by a non-linear element.
Owner:INVENSENSE
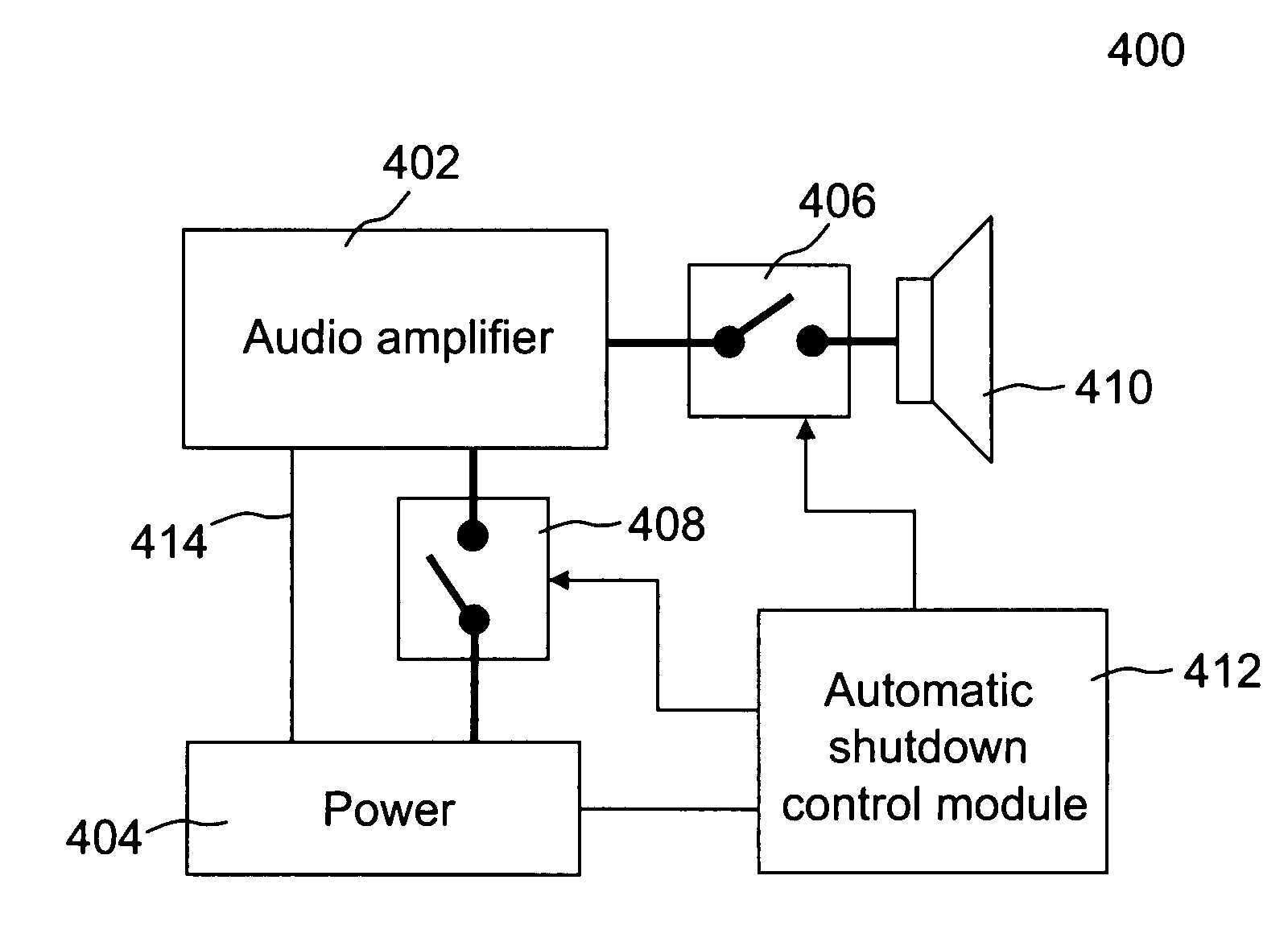
Method and system for controlling amplifiers
ActiveUS20110299696A1Digital data processing detailsPublic address systemsTelecommunicationsAudio power amplifier
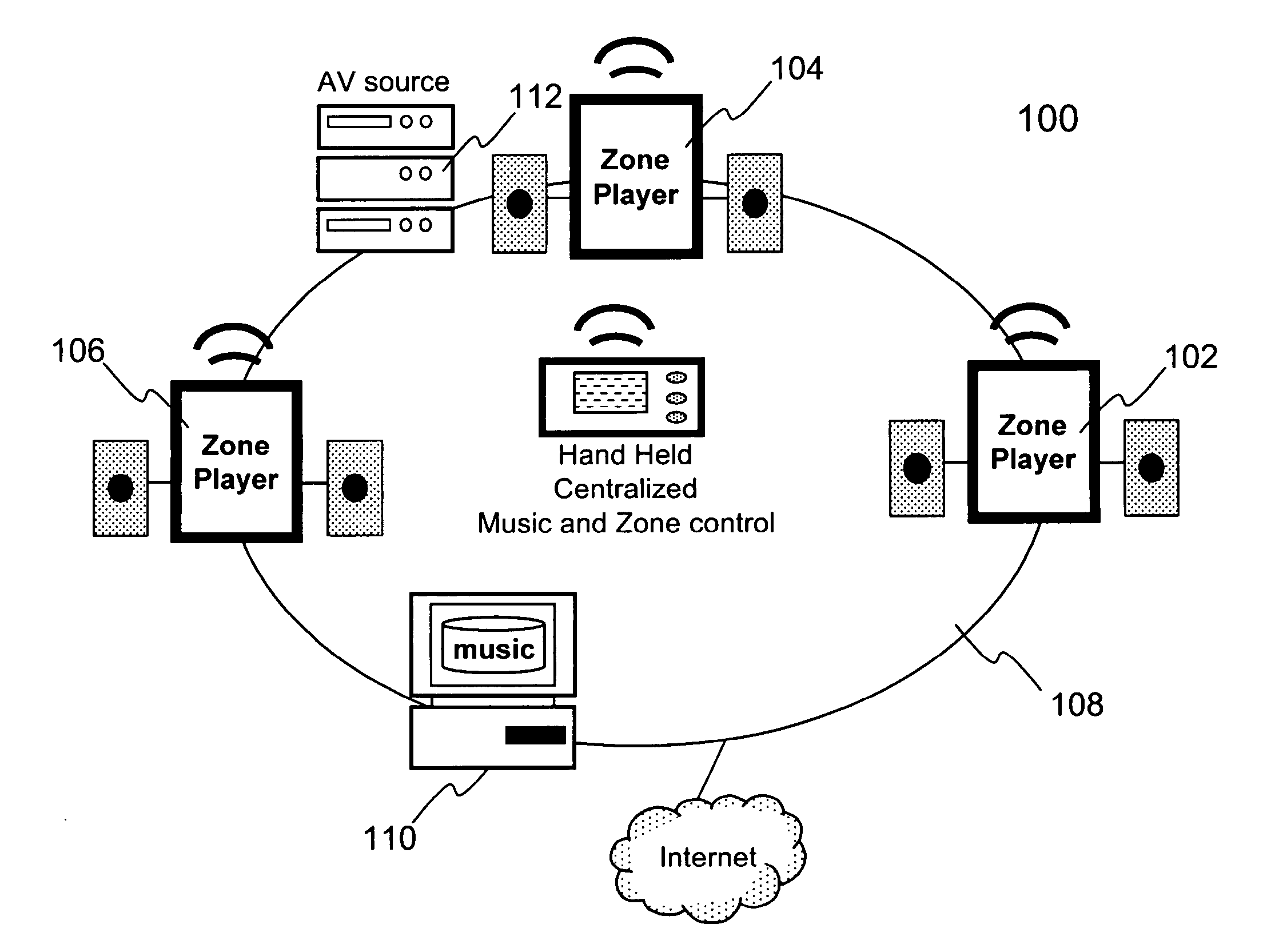
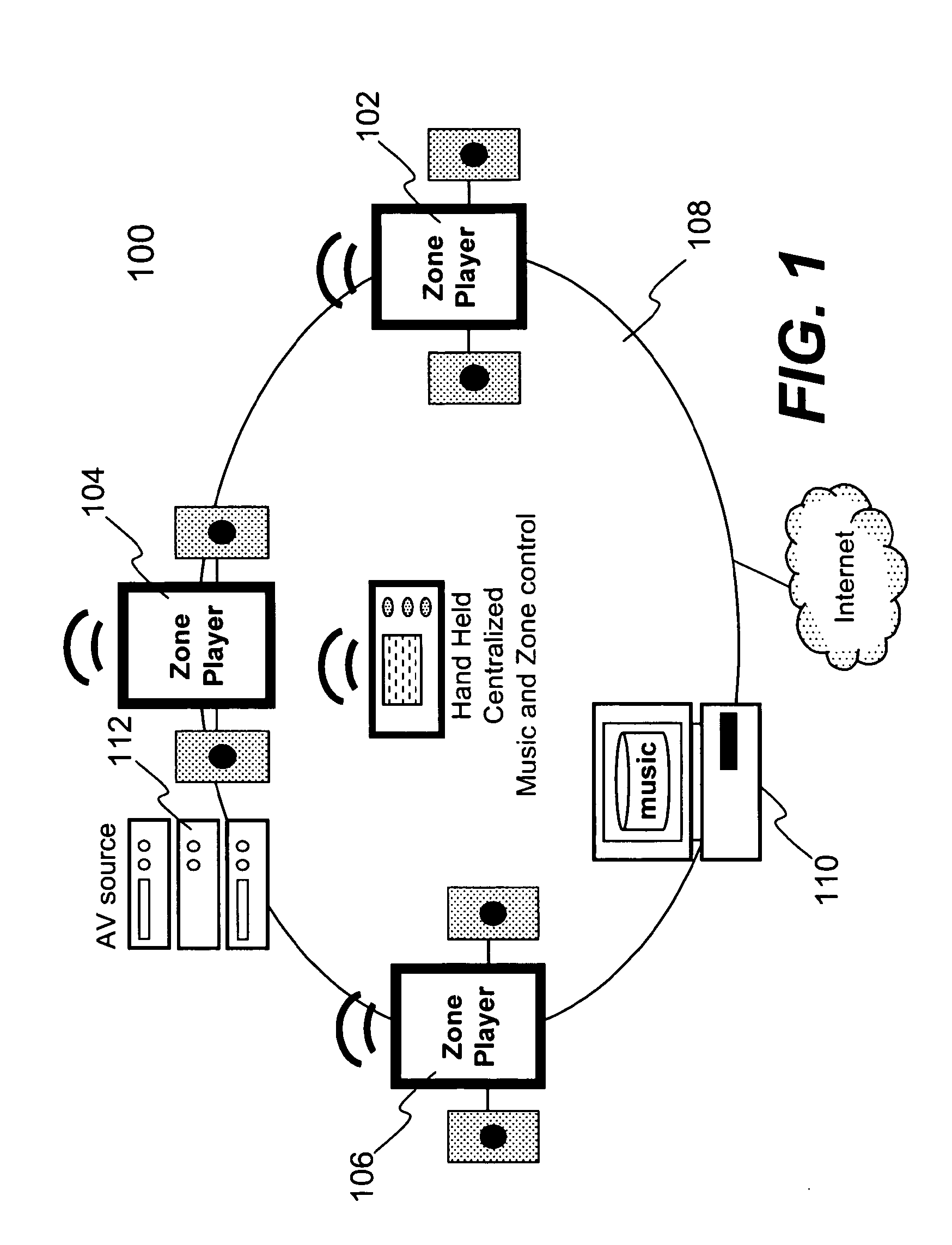
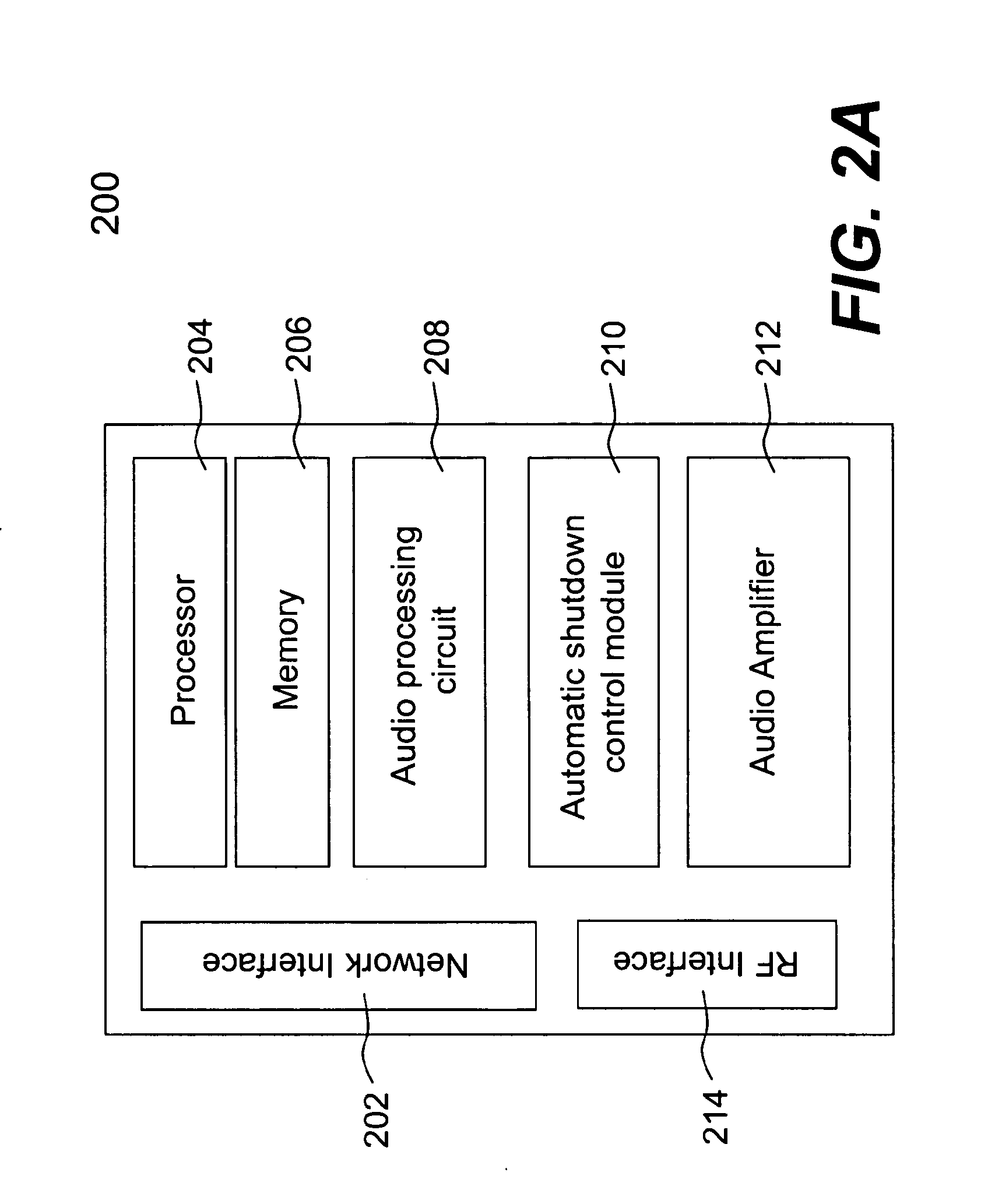
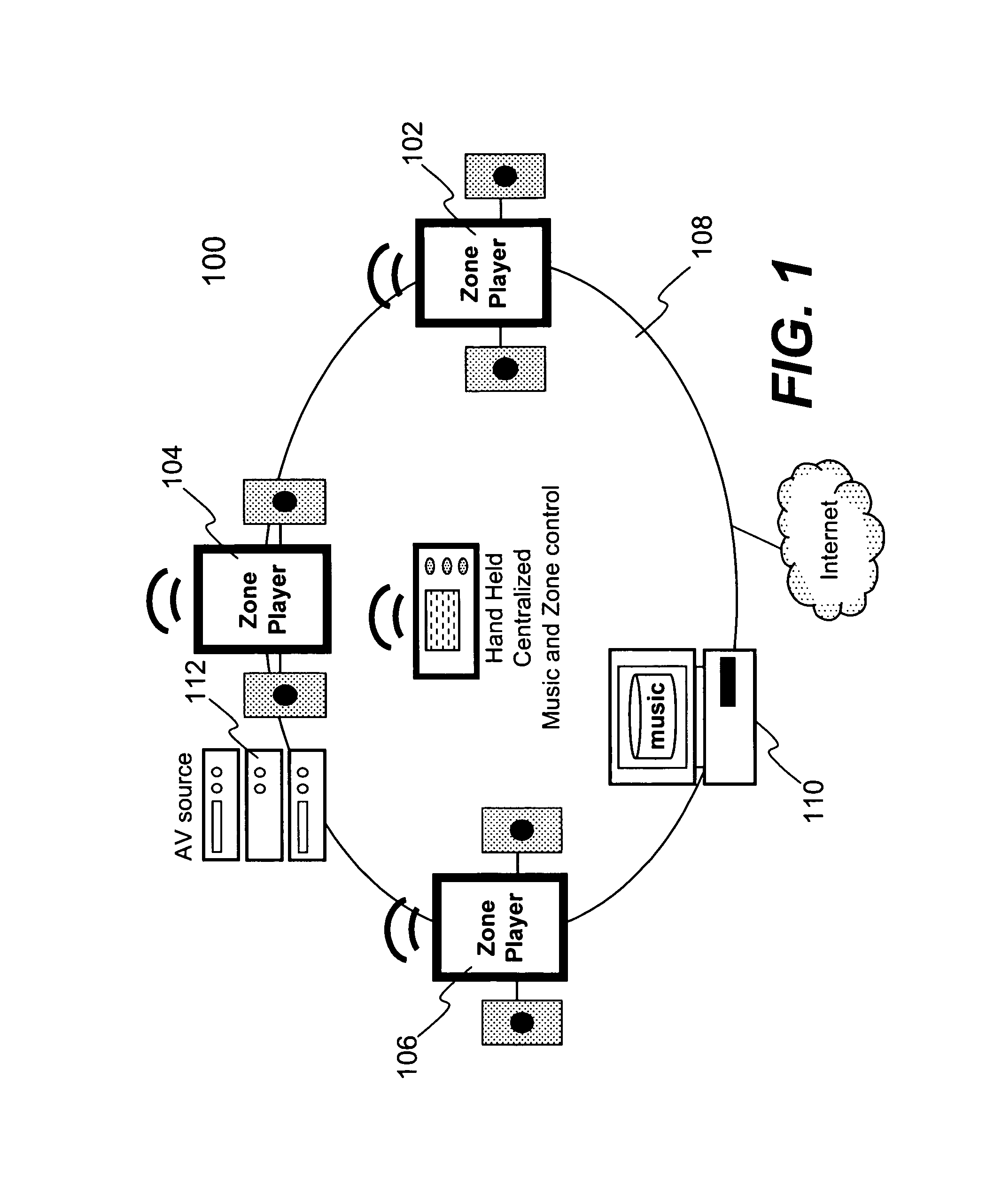
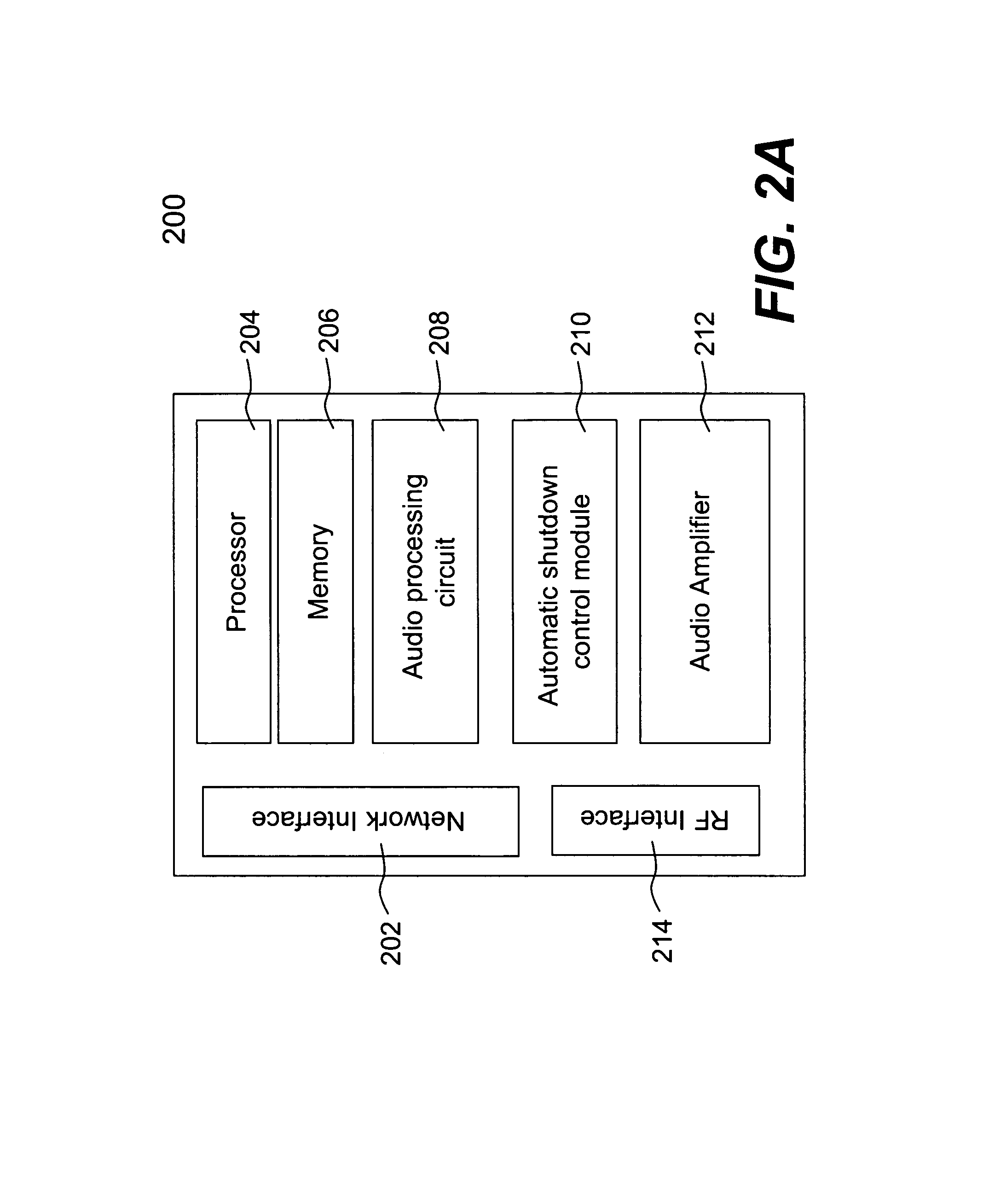
Techniques for controlling one or more audio amplifiers in or associated with a device coupled on a local area network are disclosed. The device receives at least one selected source from other devices also coupled on the network According to one aspect of the techniques, an automatic shutdown control module is provided in the device to power down the audio amplifiers when there is no audio data flow coming to the device or power up the audio amplifiers when there is audio data flow coming to the device. In one embodiment, the procedure to power down or power up the amplifiers is in accordance with a hysteresis, wherein the hysteresis, being lagging of an effect behind its cause, protects the amplifiers and makes the powering-down or powering-up procedure unnoticeable to a user.
Owner:SONOS
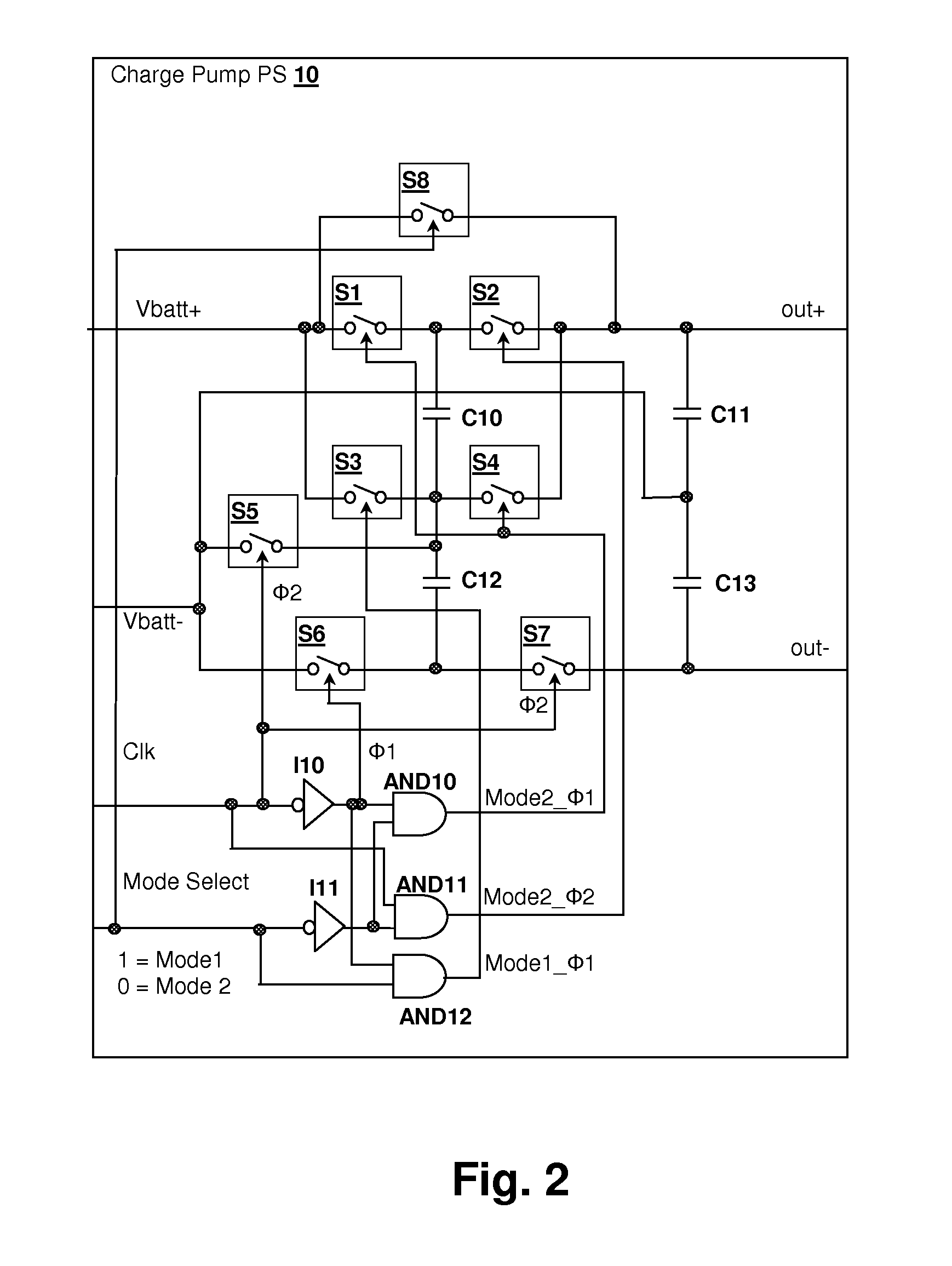
Operating environment and process position selected charge-pump operating mode in an audio power amplifier integrated circuit
ActiveUS7808324B1Improve efficiencyPower amplifiersLow frequency amplifiersOperation modeEngineering
A charge pump power supply for an audio power amplifier integrated circuit has an operating mode selected according to an indication of operating environment and / or a process position of the integrated circuit. The operating mode selects the output voltage provided by the charge pump and may also select efficiency by selecting a frequency of operation of the charge pump and / or the effective size of a switching transistor bank. The selection is made in conformity with an indication of a process position of the integrated circuit and / or an indication of an environment of the integrated circuit, such as temperature, power supply voltage and / or load impedance values, and generally also in conformity with a volume (gain) setting, or a detected signal level, so that internal power consumption of the amplifier and charge pump is reduced when a high signal level is not being reproduced at the audio power stage.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
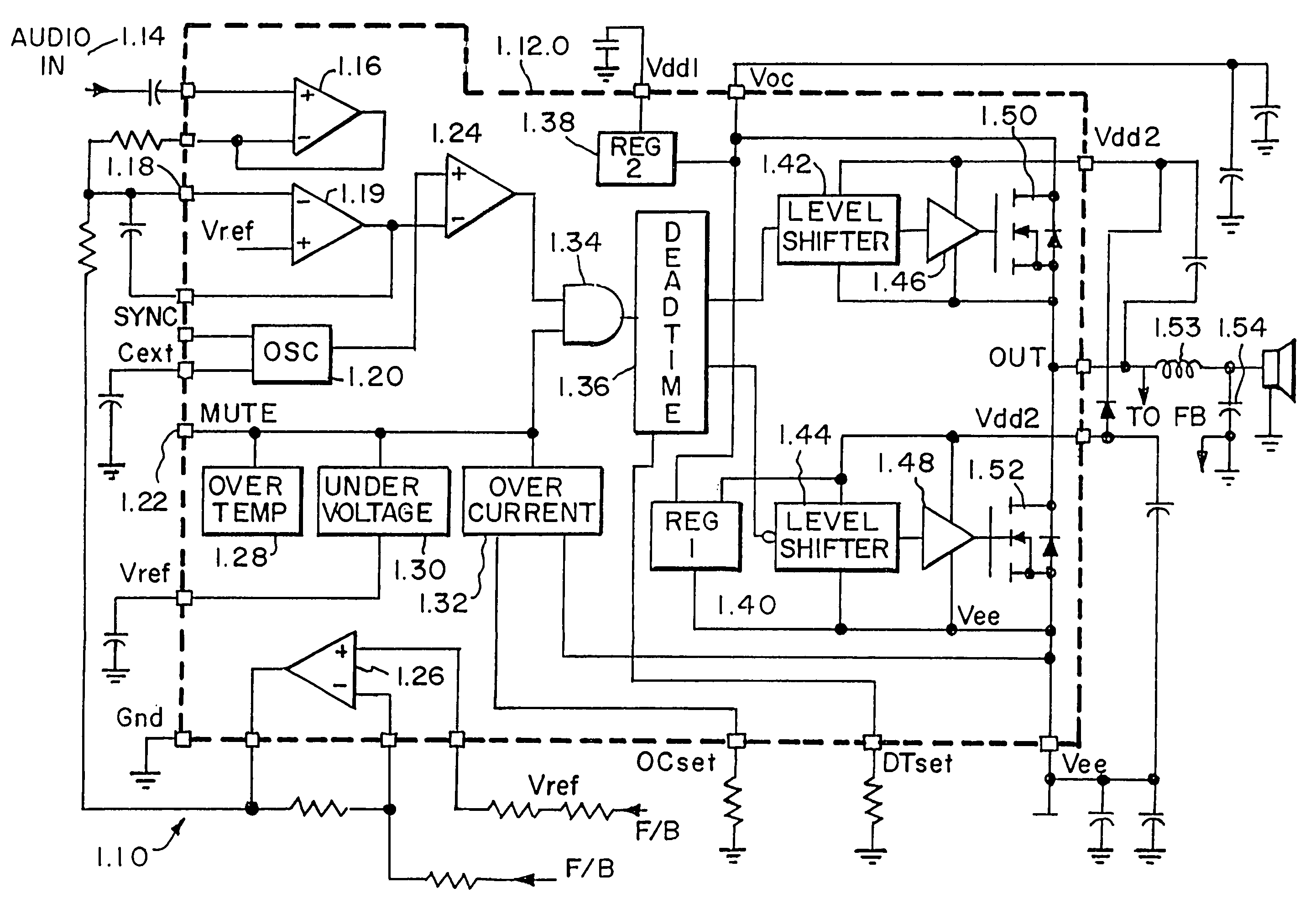
Monolithic class D amplifier
InactiveUS7076070B2Minimized cell areaMaximizing specific channel widthTransistorGated amplifiersDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
A monolithic 1.75 is mounted in a speaker cabinet 1.71 to drive the voice coil 1.74 of the speaker 1.70. The monolithic integrated circuit may be a class D amplifier 1.10, and is at least a half-bridge or full bridge power MOSFET device. Structures and process for forming the mos switching devices 2.20 of the bridge driver circuits are disclosed. Also disclosed is the N+ buried layer 4.14 of the QVDMOS transistors 4.43 of the bridge circuits.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Mixed-mode (current-voltage) audio amplifier
ActiveUS20050134374A1Total current dropReduce voltageNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsLow frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierCurrent voltage
A method and system for providing a mixed-mode (current- and voltage-source) audio amplifier is disclosed. The mixed-mode amplifier includes a voltage sensing feedback path including a first network comprising at least one circuit; and a current sensing feedback path including a second network comprising at least one circuit. According to the method and system disclosed herein, the first and second networks vary an output impedance or transconductance of the amplifier as a function of frequency of the input voltage signal, such that at a first frequency range, the amplifier operates substantially as a current amplifier, and at a second frequency range, the amplifier operates substantially as a voltage amplifier, thereby inheriting distortion reduction of the current amplifier and stability of the voltage amplifier.
Owner:TYMPHANY HK
Modular charger for hearing aid
A battery charger for a hearing aid includes a housing that defines at least one socket for receiving any one of a plurality of adapters. Each adapter closely fits and at least partially contains one hearing aid to hold the hearing aid in place during charging. The hearing aid includes a plurality of electrical contacts in a pattern and the adapter defines a plurality of apertures in the same pattern. Resilient contacts in the charger extend through the apertures in the adapter to contact the hearing aid.
Owner:ZOUNDS LLC FORMERLY ZOUNDS ACQUISITION
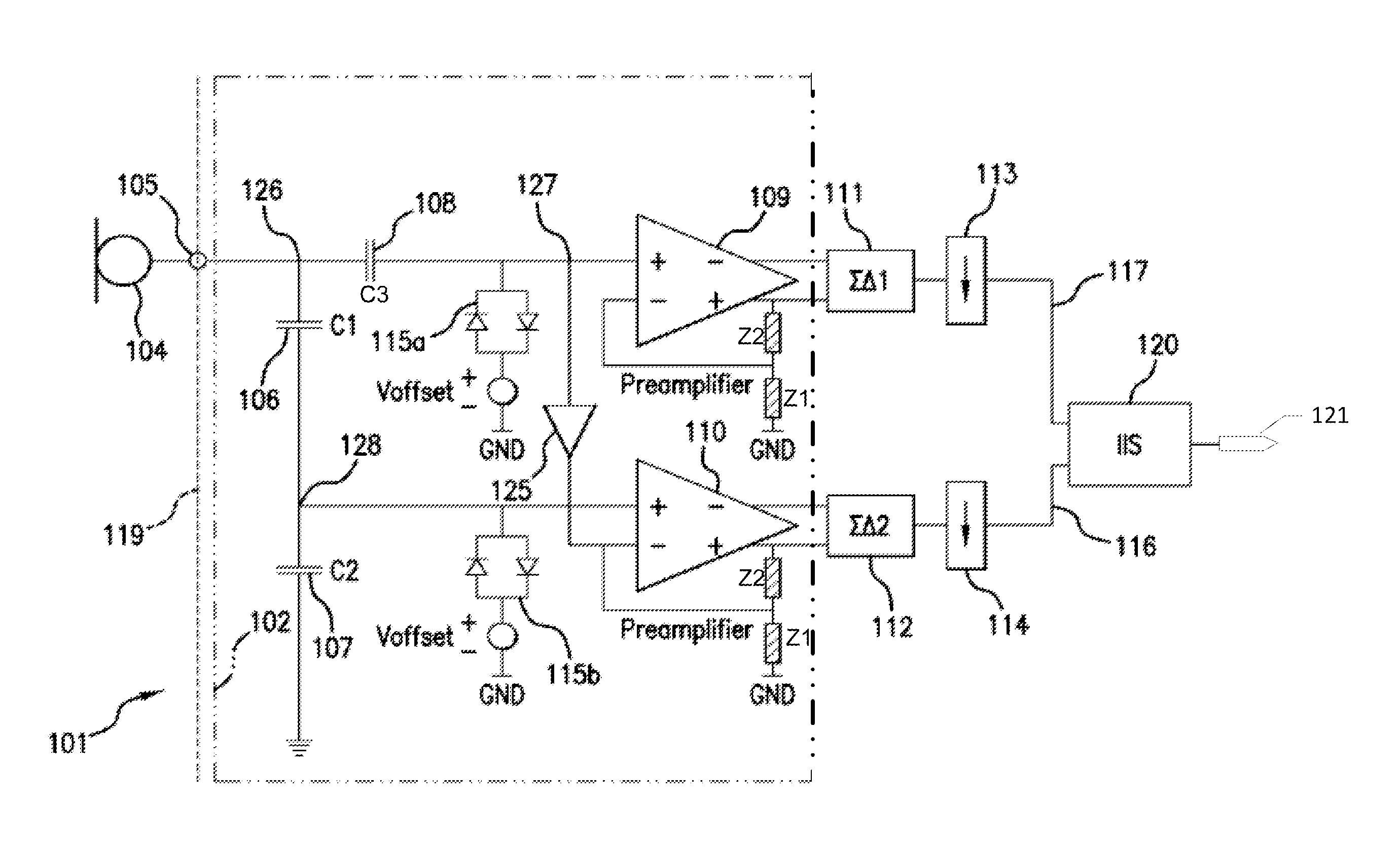
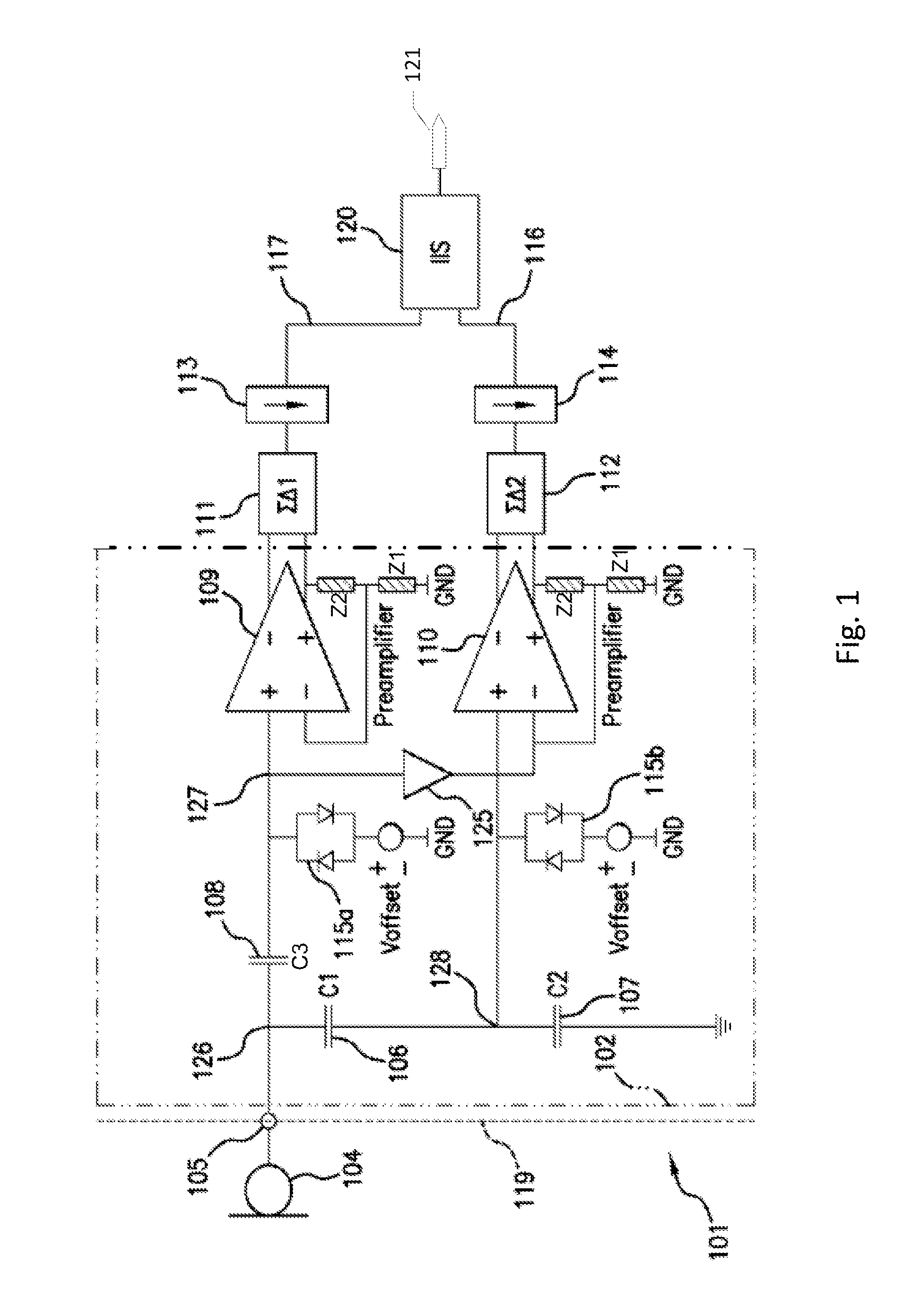
Transducer amplification circuit
ActiveUS20150281836A1Accurate representationImprove responseAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionSemiconductor electrostatic transducersSonificationTransducer
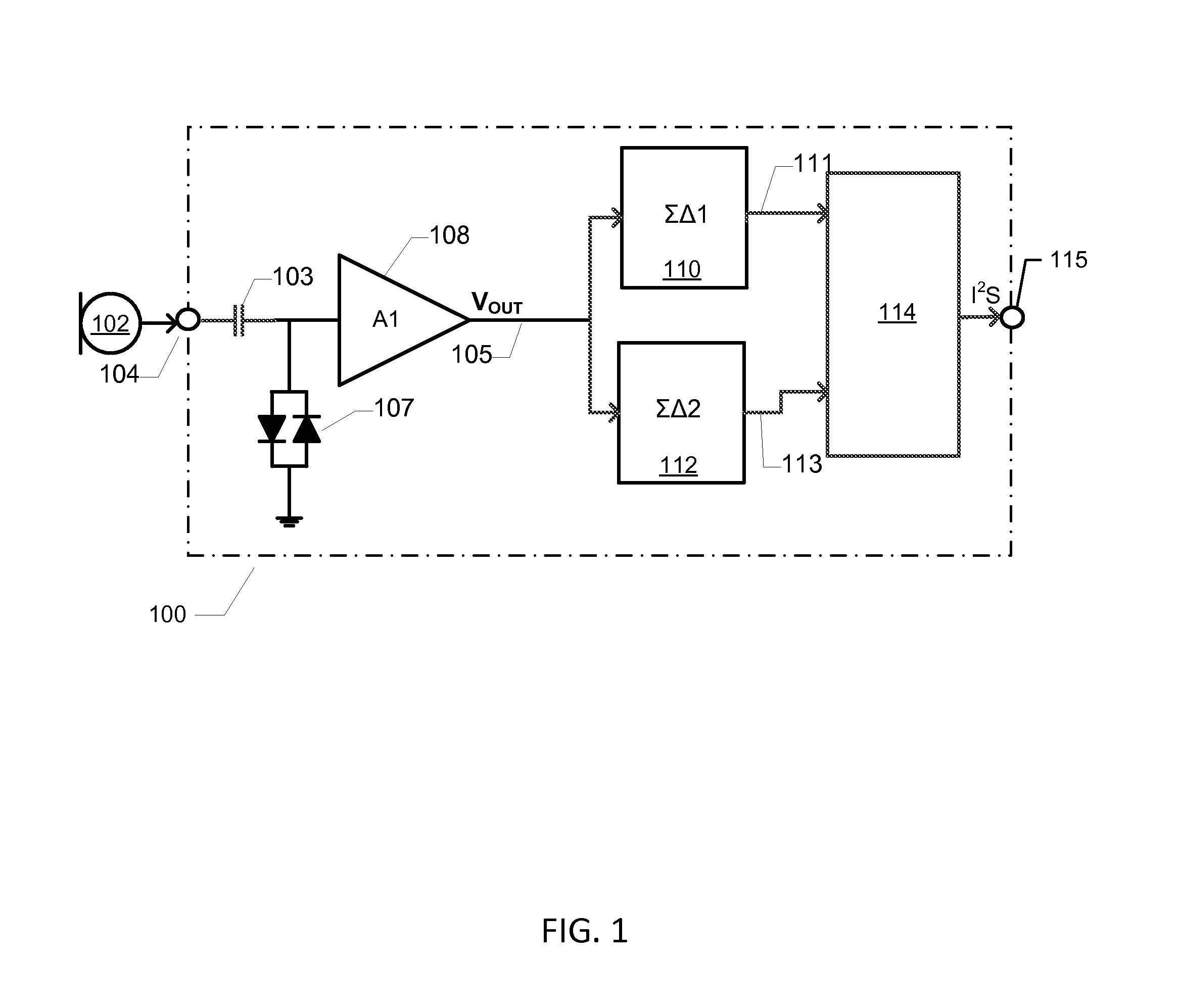
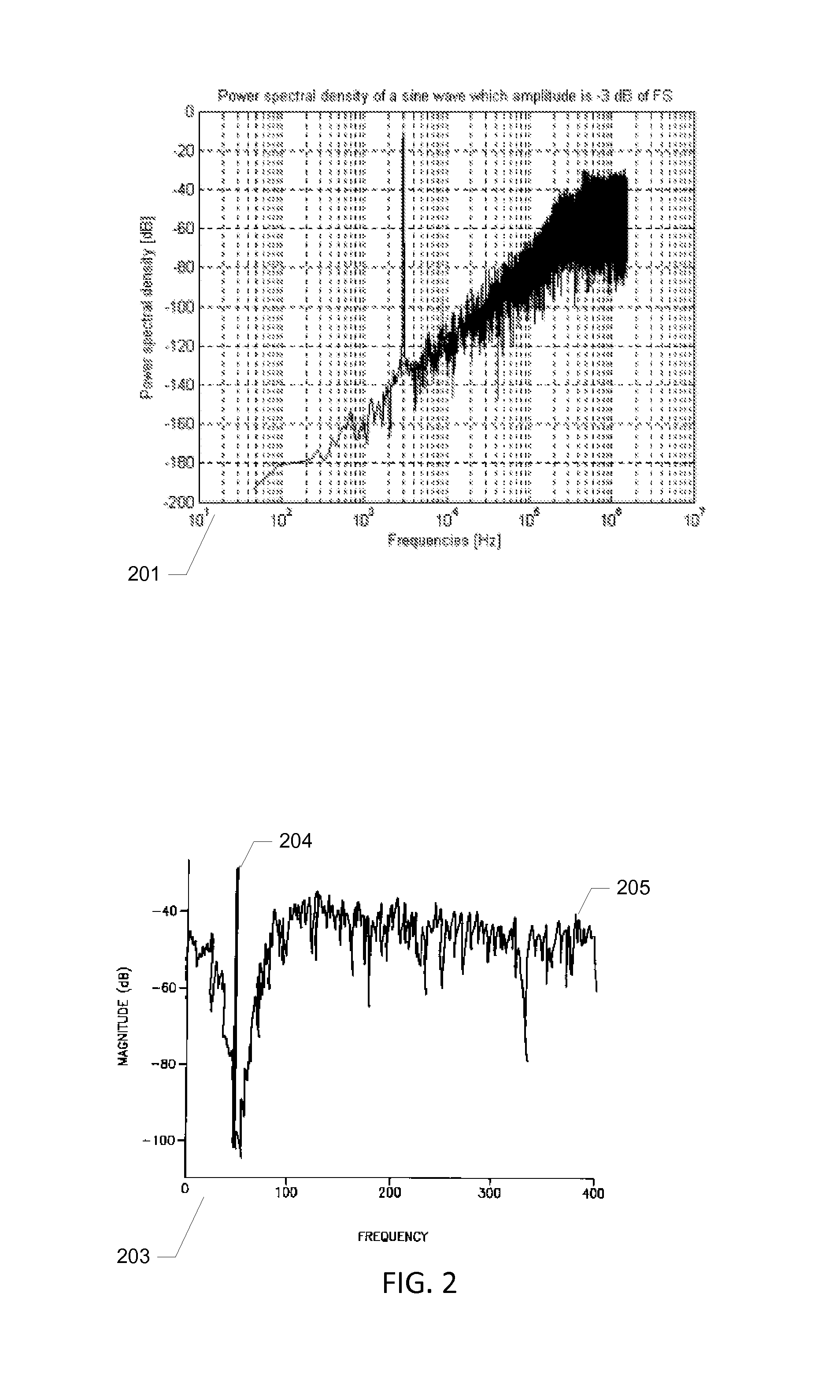
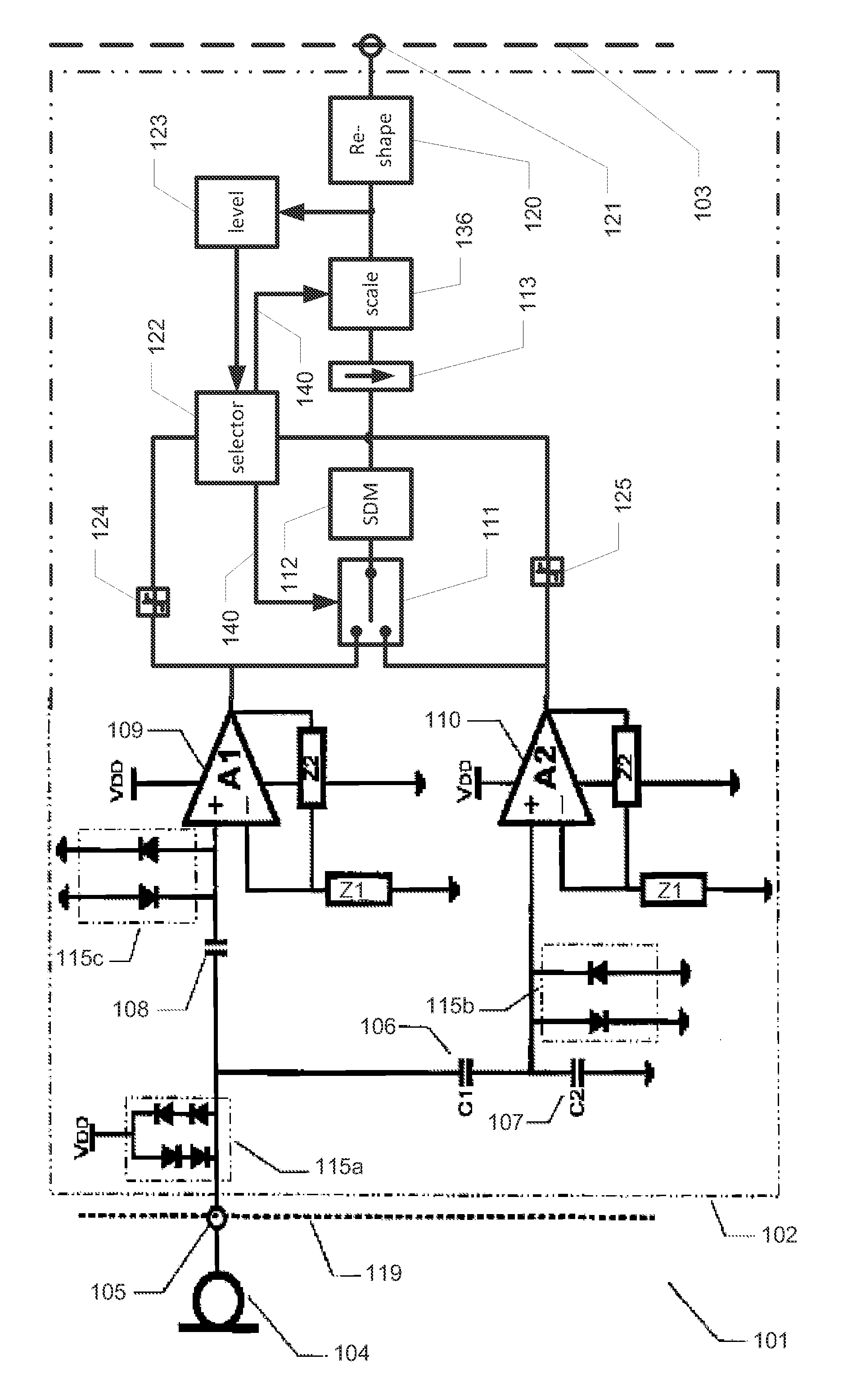
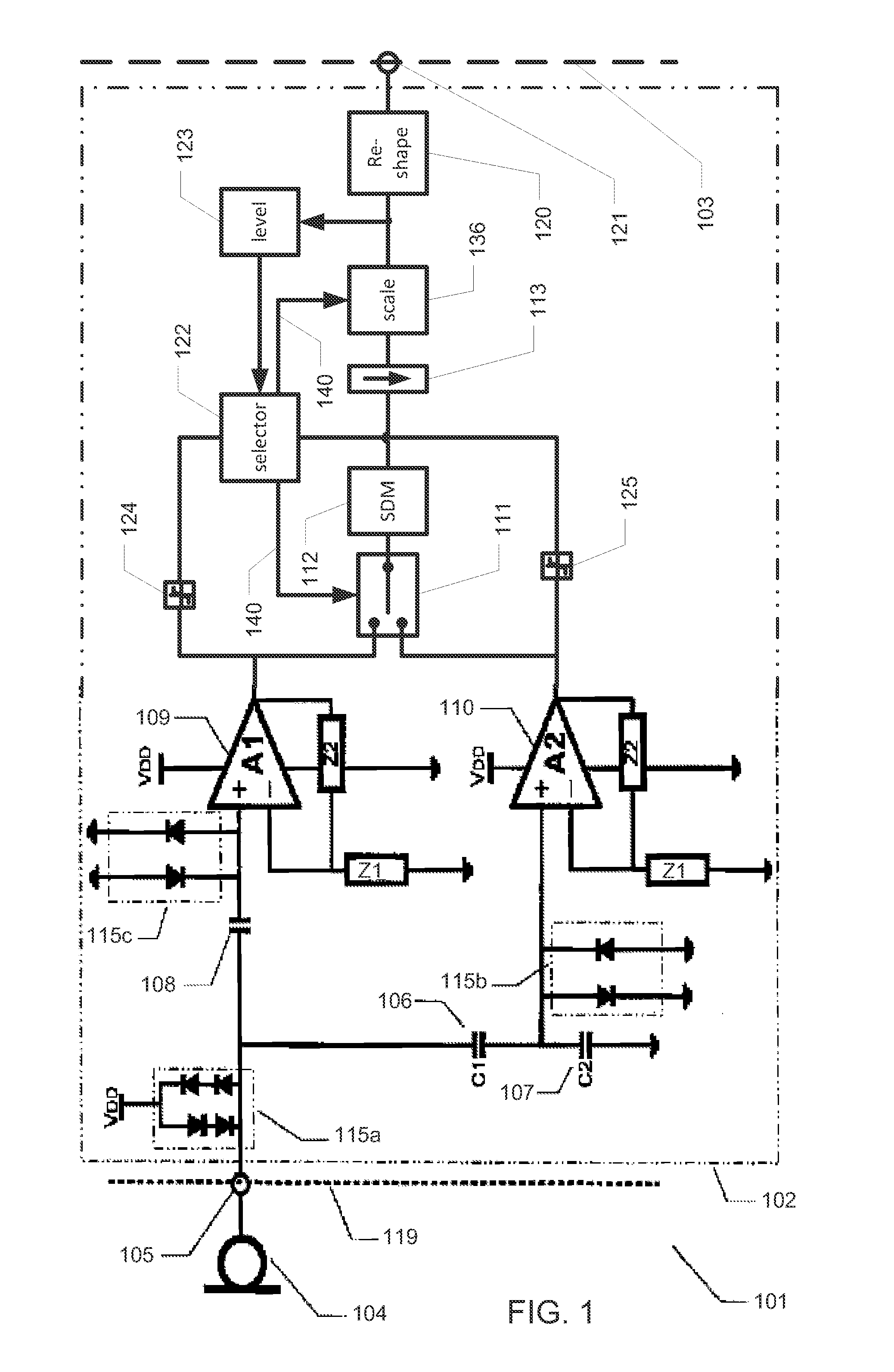
A transducer amplification circuit may include a preamplifier circuit with a signal input receiving a transducer signal to provide an amplified transducer signal comprising audible frequency components and ultrasonic frequency components. The transducer amplification circuit may include a first sigma-delta modulator configured to sample and quantize the amplified transducer signal to generate a first digital transducer signal comprising a first quantization noise signal. The first sigma-delta modulator may include a first noise transfer function having a high pass response in at least a portion of an audible frequency range to push the quantization noise signal to ultrasonic frequencies. A second sigma-delta modulator is configured to sample and quantize the amplified transducer signal to generate a second digital transducer signal comprising a second quantization noise signal. The second sigma-delta modulator may include a second noise transfer function with a magnitude minimum placed at the ultrasonic frequencies.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
Audio amplification circuit
InactiveUS20130129117A1Increase investmentEfficiently maskedHearing device energy consumption reductionSemiconductor electrostatic transducersAudio power amplifierA d converter
Disclosed is an audio amplification circuit comprising: an input terminal for receipt of an audio input signal; a first preamplifier having an input operatively coupled to the input terminal and operable to provide a first amplified audio signal with a first signal amplification; a second preamplifier having an input operatively coupled to the input terminal and operable to provide a second amplified audio signal with a second signal amplification, smaller than the first signal amplification; a switch having a first input operatively coupled to the first preamplifier, a second input operatively coupled to the second preamplifier, and an output; an analogue-to-digital converter operatively coupled to the output of the switch and operable to provide a digital audio signal; a signal selection circuit operable to control the switch to selectively provide one of the first and second amplified audio signals on the output of the switch.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES GLOBAL
Systems and methods for automatically adjusting channel timing
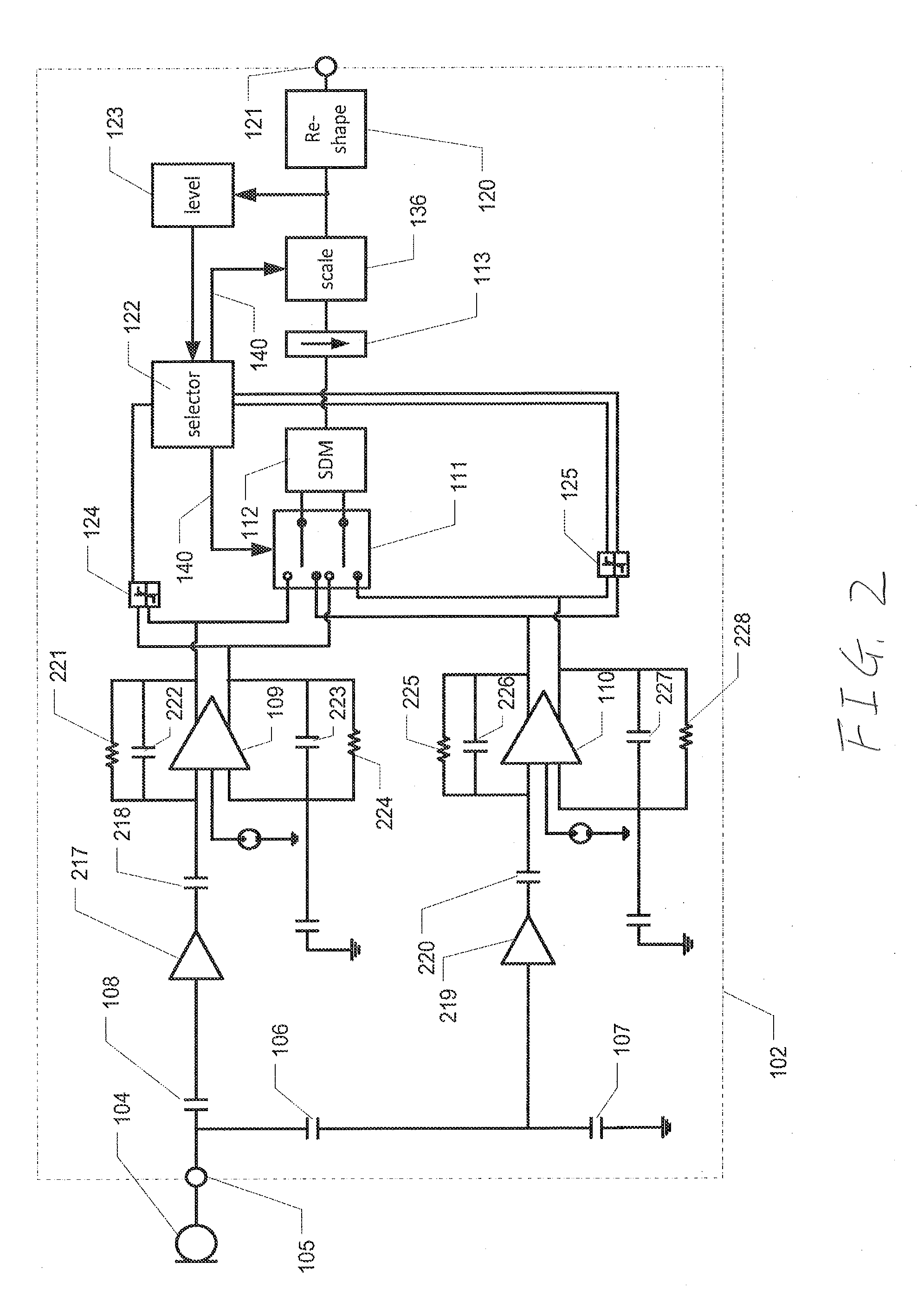
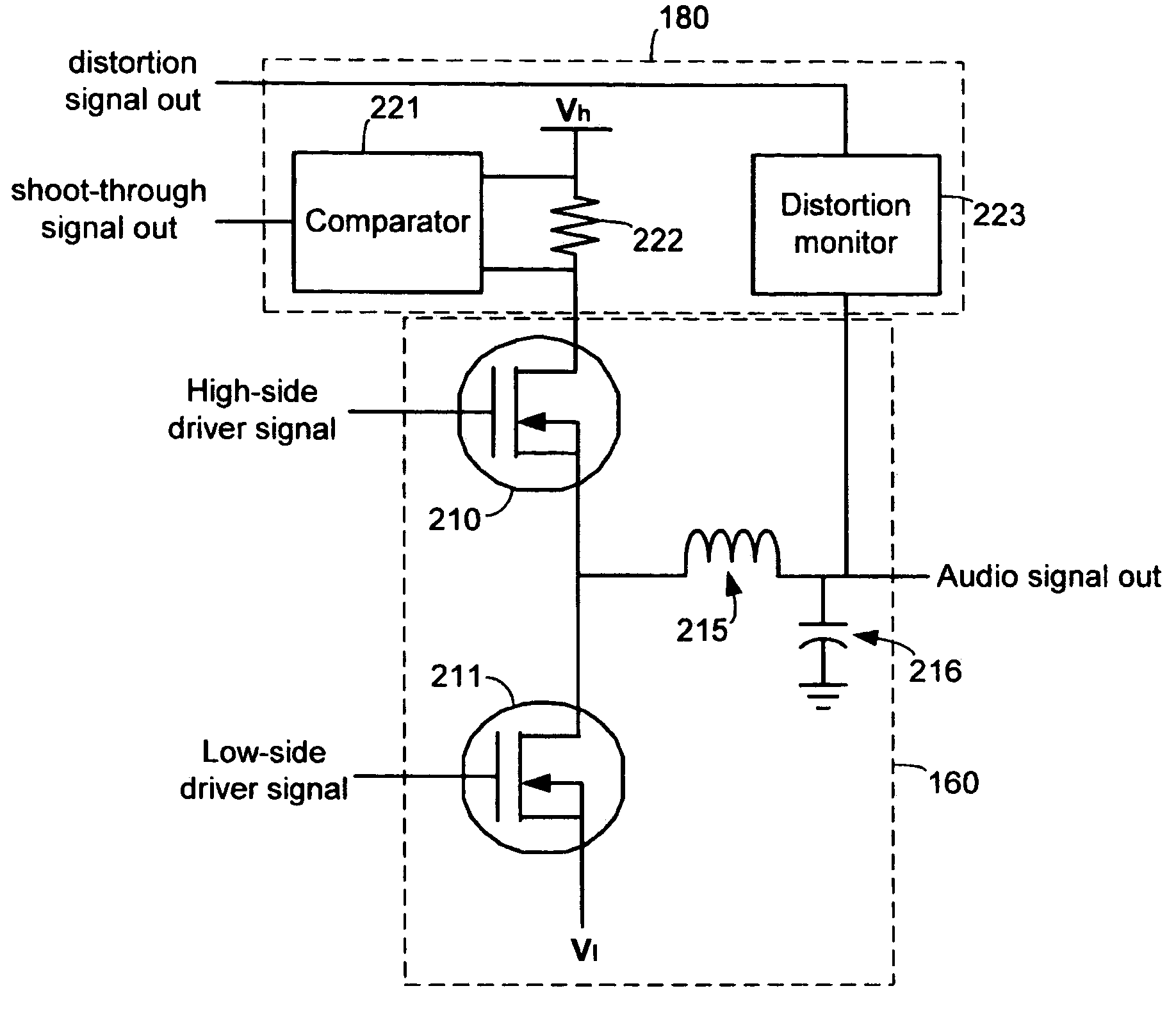
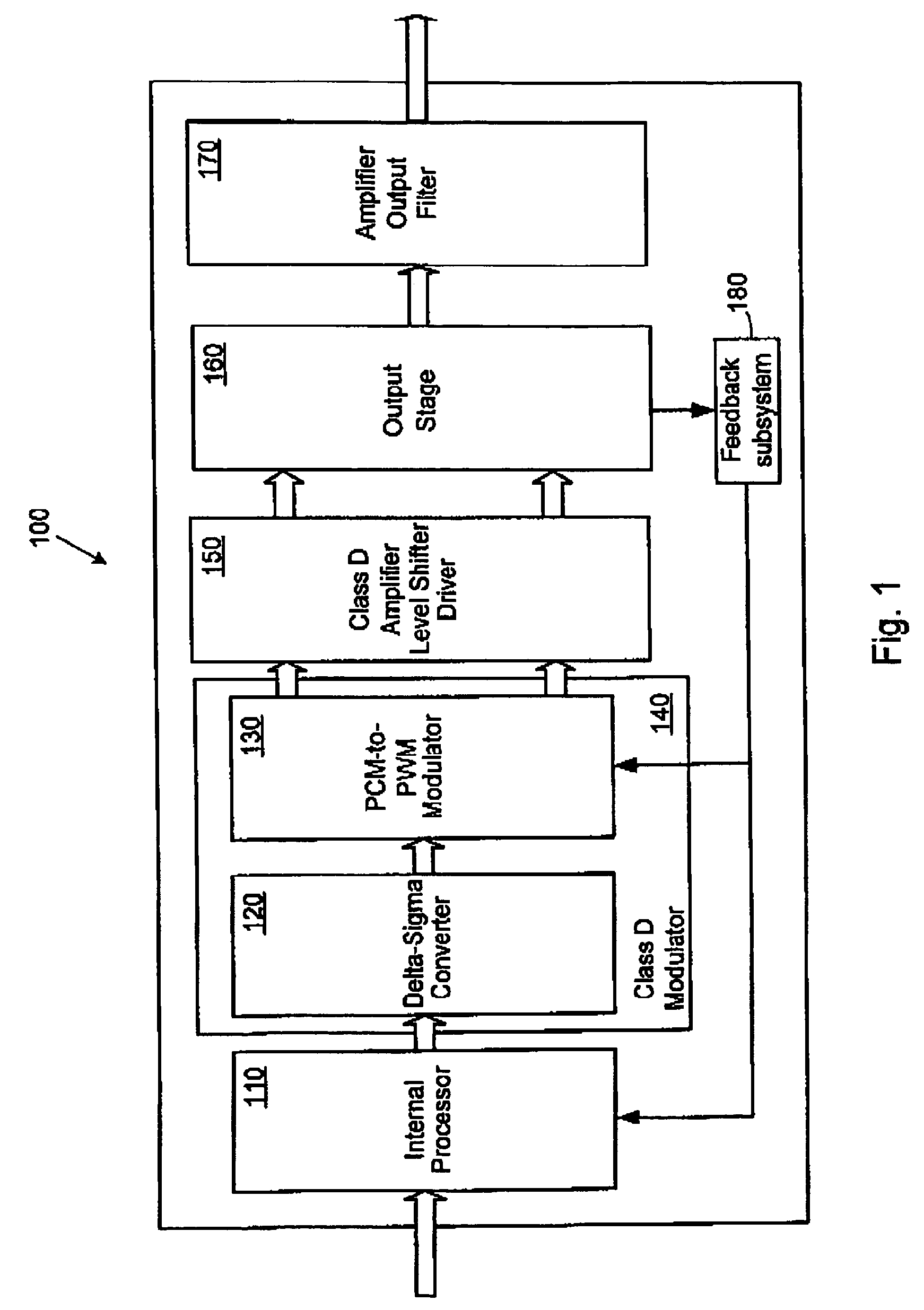
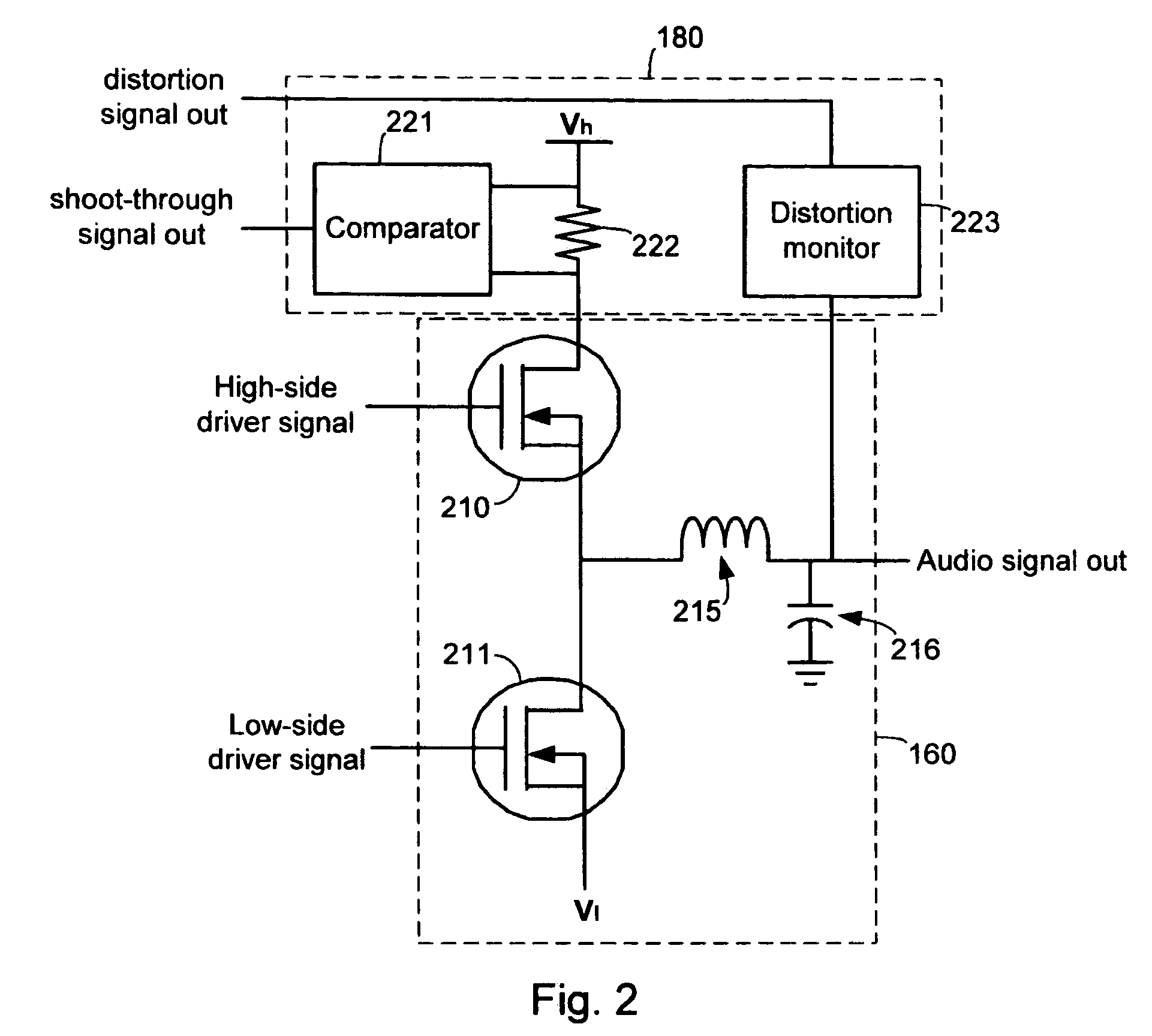
ActiveUS7023268B1Extended dead timeImprove shoot-through conditionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionLow frequency amplifiersAuto regulationAudio power amplifier
Systems and methods for automatically adjusting the alignment of high-side and low-side pulse width modulated signals to improve dead time and shoot-through conditions. In one embodiment, a system includes a digital amplifier controller, an amplifier output stage coupled to the controller and configured to receive audio signals from the controller, and one or more sensors coupled to the output stage. The sensors are configured to detect and / or measure various parameters, such as shoot-through current and distortion, which are associated with the operation of the output stage. The sensors provide feedback to an internal processor or modulator of the controller, which then adjusts the timing of the high-side and low-side signals to improve the operating conditions of the output stage by minimizing shoot-through current and / or distortion.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Energy-efficient consumer device audio power output stage
ActiveUS8311243B2Improve efficiencyReduce power consumptionPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersCapacitive dividerOperation mode
An energy-efficient consumer device audio power output stage provides improved battery life and reduced power dissipation. A power supply having a selectable operating mode supplies the power supply rails to the power amplified output stage. The operating mode is controlled in conformity with the audio signal level, which may be determined from a volume control setting of the device and / or from a signal level detector that determines the amplitude of the signal being amplified. The power supply may be a charge pump in which the operating mode uses a capacitive divider to provide for selection of a power supply output voltage that is a rational fraction of the power supply output voltage in a full-voltage operating mode.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Method and system for controlling amplifiers
Techniques for controlling one or more audio amplifiers in or associated with a device coupled on a local area network are disclosed. The device receives at least one selected source from other devices also coupled on the network According to one aspect of the techniques, an automatic shutdown control module is provided in the device to power down the audio amplifiers when there is no audio data flow coming to the device or power up the audio amplifiers when there is audio data flow coming to the device. In one embodiment, the procedure to power down or power up the amplifiers is in accordance with a hysteresis, wherein the hysteresis, being lagging of an effect behind its cause, protects the amplifiers and makes the powering-down or powering-up procedure unnoticeable to a user.
Owner:SONOS
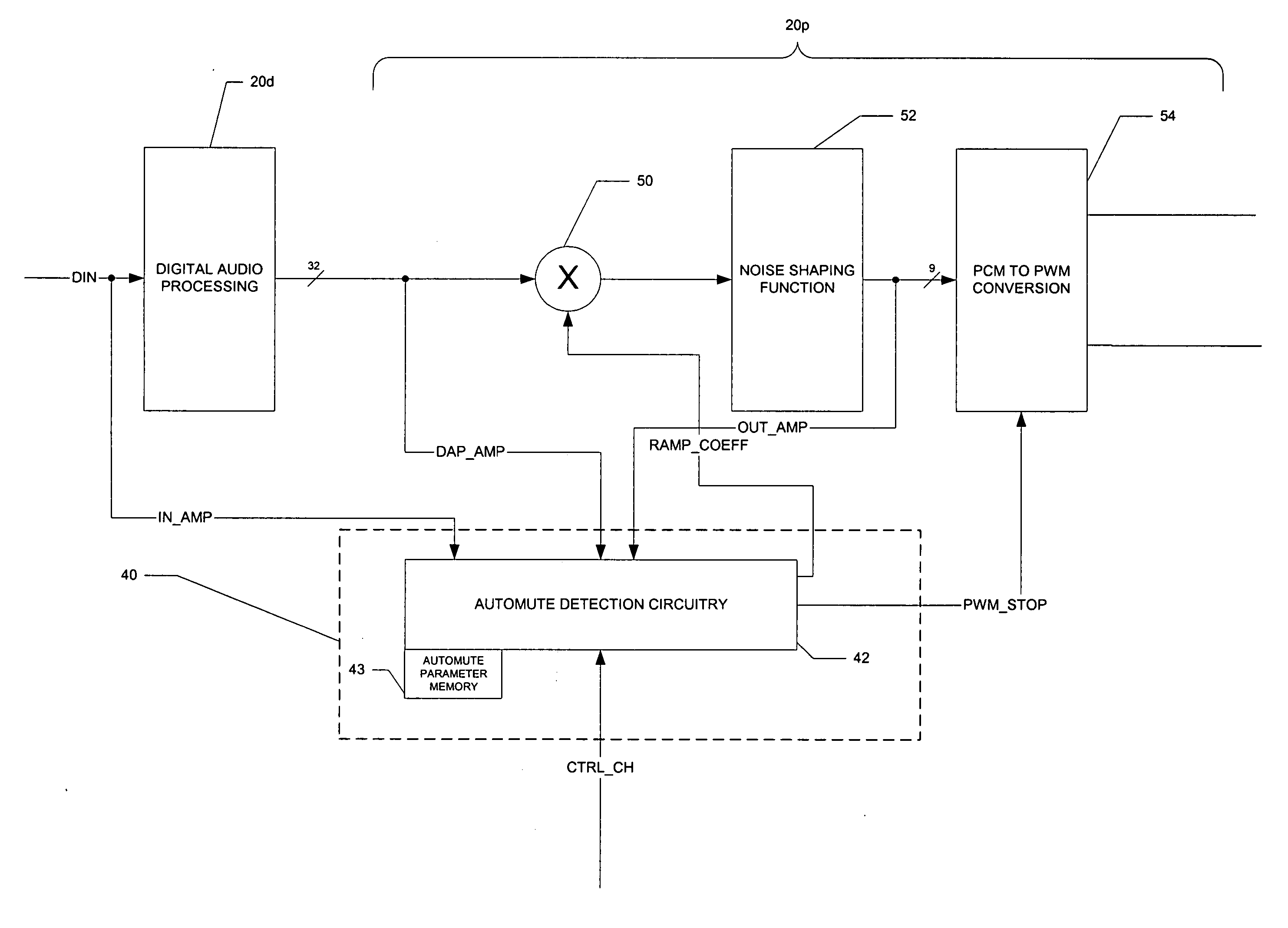
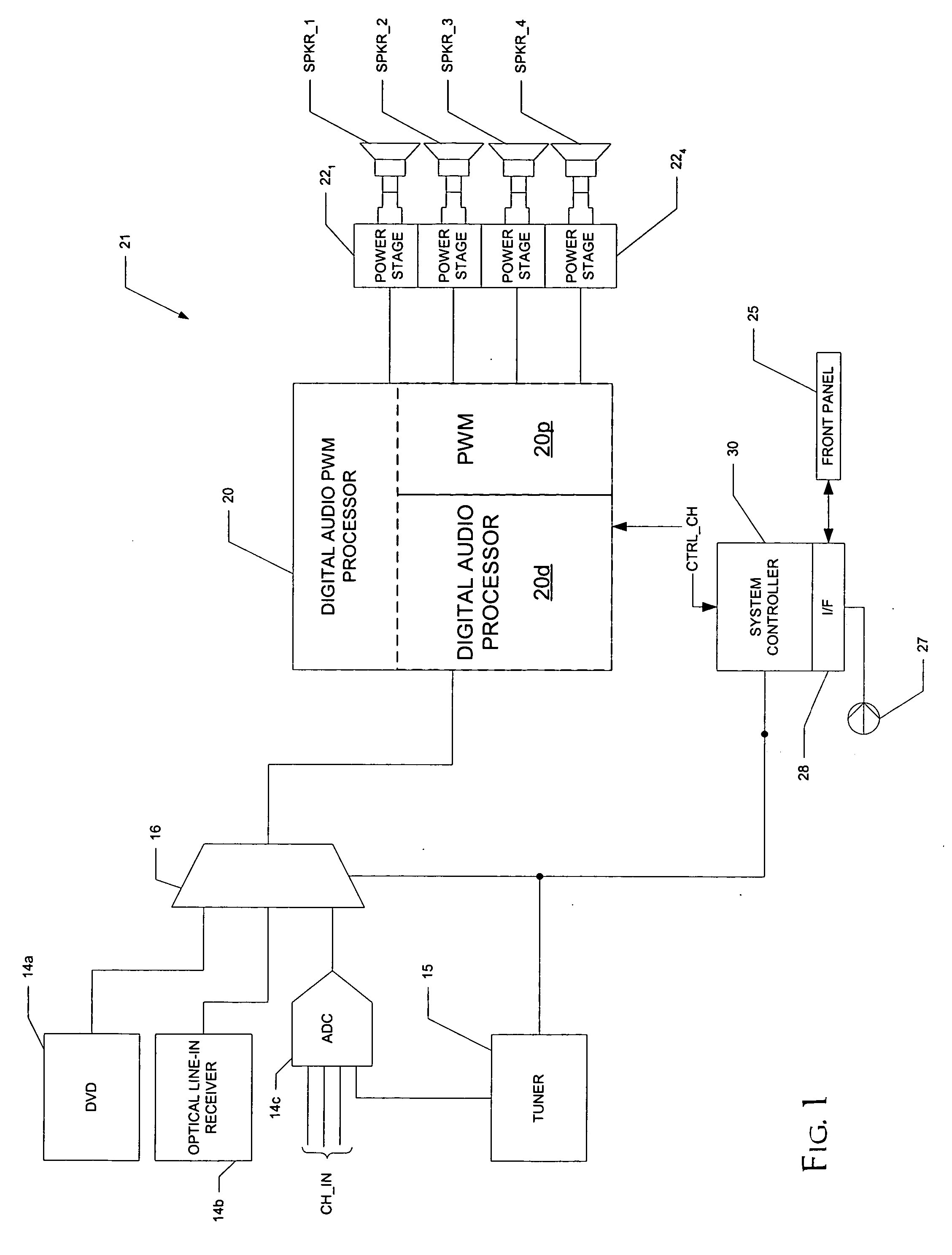
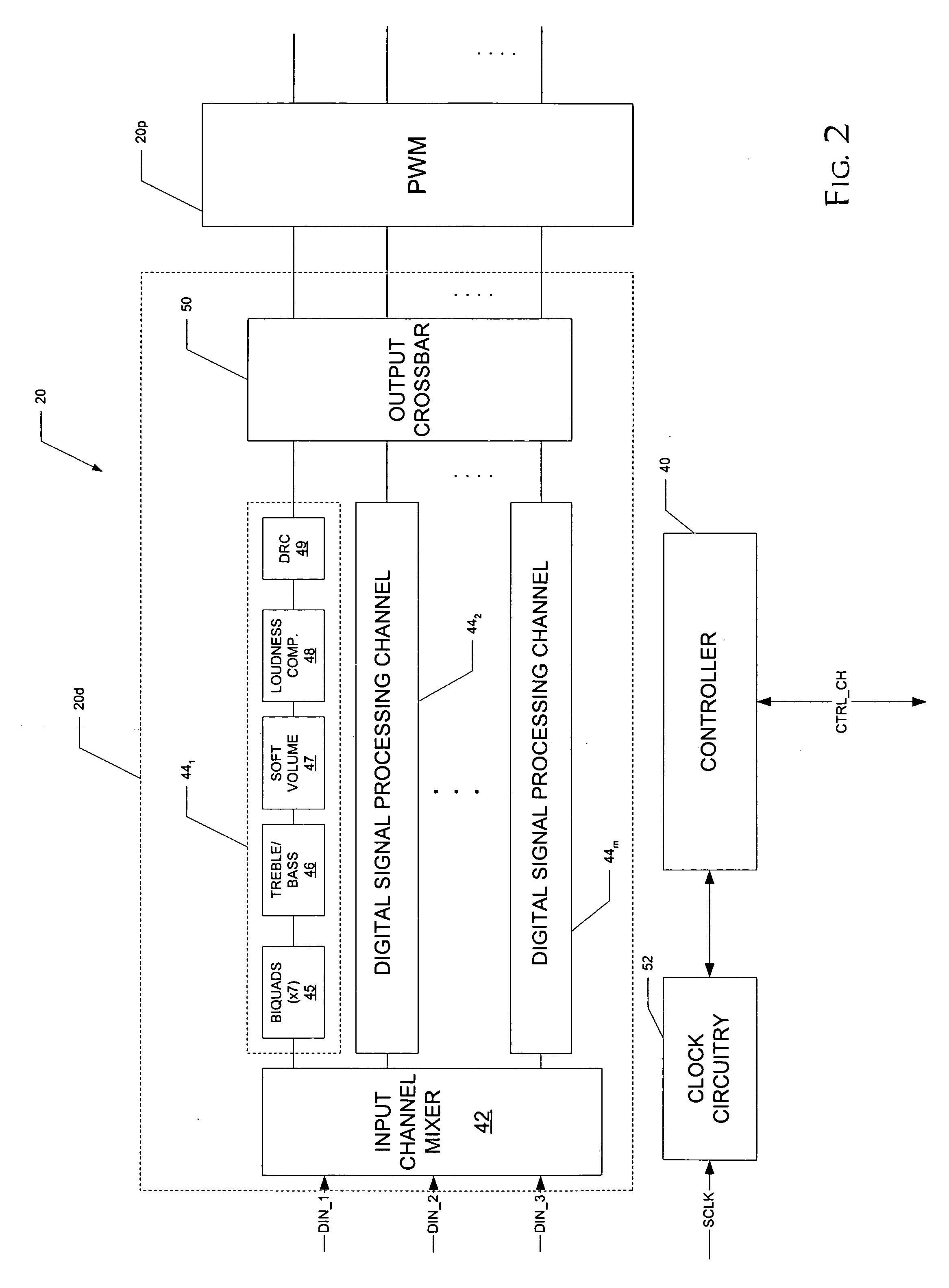
Automute detection in digital audio amplifiers
ActiveUS20070005160A1Rapidly automuteRapidly unmuteAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGain controlHysteresisDigital filter
A digital audio processor (20) for a digital audio receiver (21) having an improved automute sequence is disclosed. The digital audio processor (20) includes automute detection circuitry (42) that monitors the amplitude of digital audio signals before and after the application of digital filters by digital audio processing circuitry (20d). The amplitude of the input signals are compared against a first threshold level, while the amplitude of the output signals are compared against a second threshold level. In response to the amplitude of the input signals for all of the audio channels (44) falling below the first threshold for a selected time period, a gain stage (50) in each channel ramps down the volume to a mute level, and pulse-width-modulation circuitry (54) is disabled. If the output signal amplitude falls below a second threshold for a channel, the pulse-width-modulation circuitry (54) for that channel is disabled. Hysteresis for the input signal amplitude is preferably added into the automute exit determination.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Charging circuit and amplifier
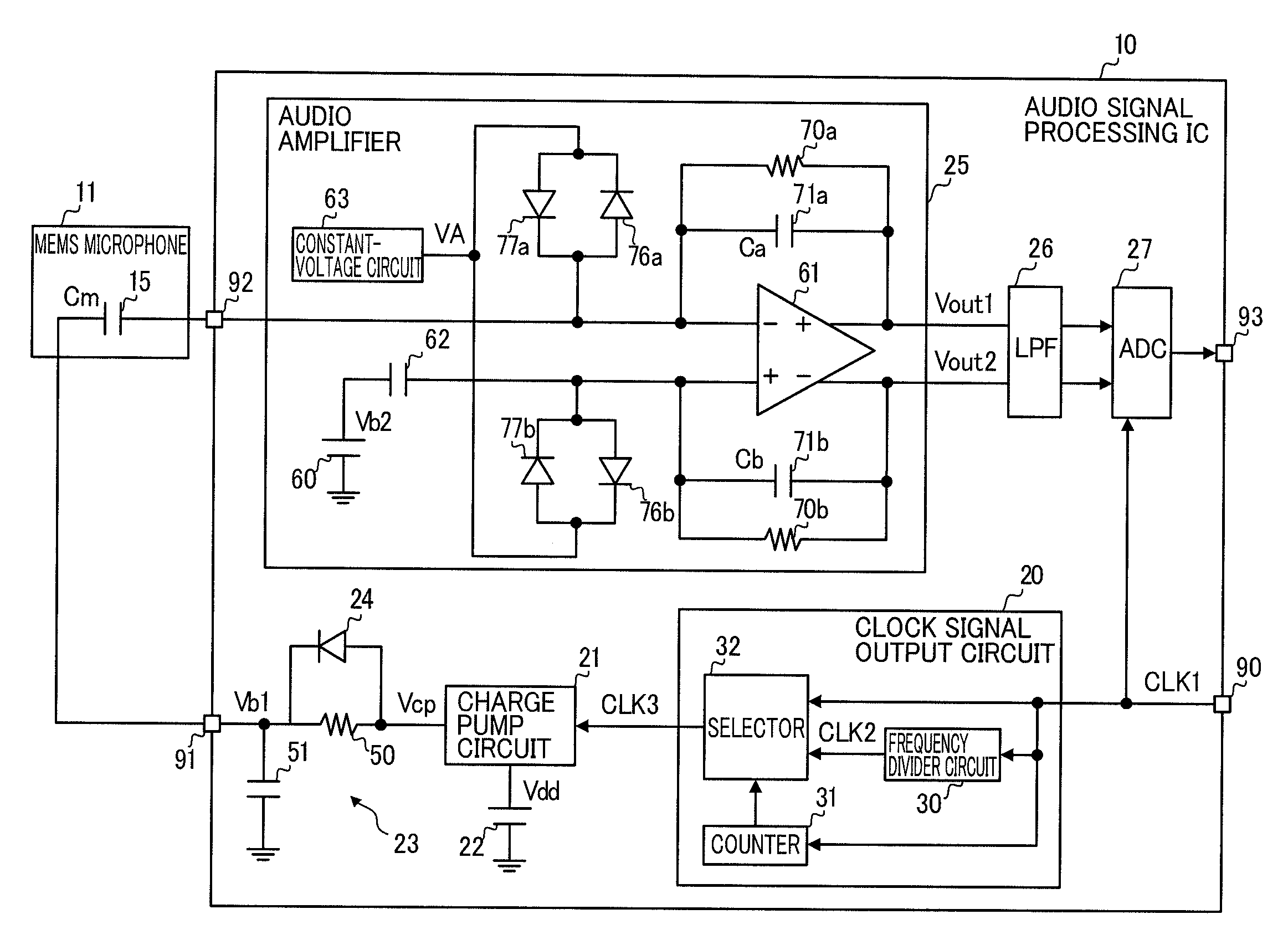
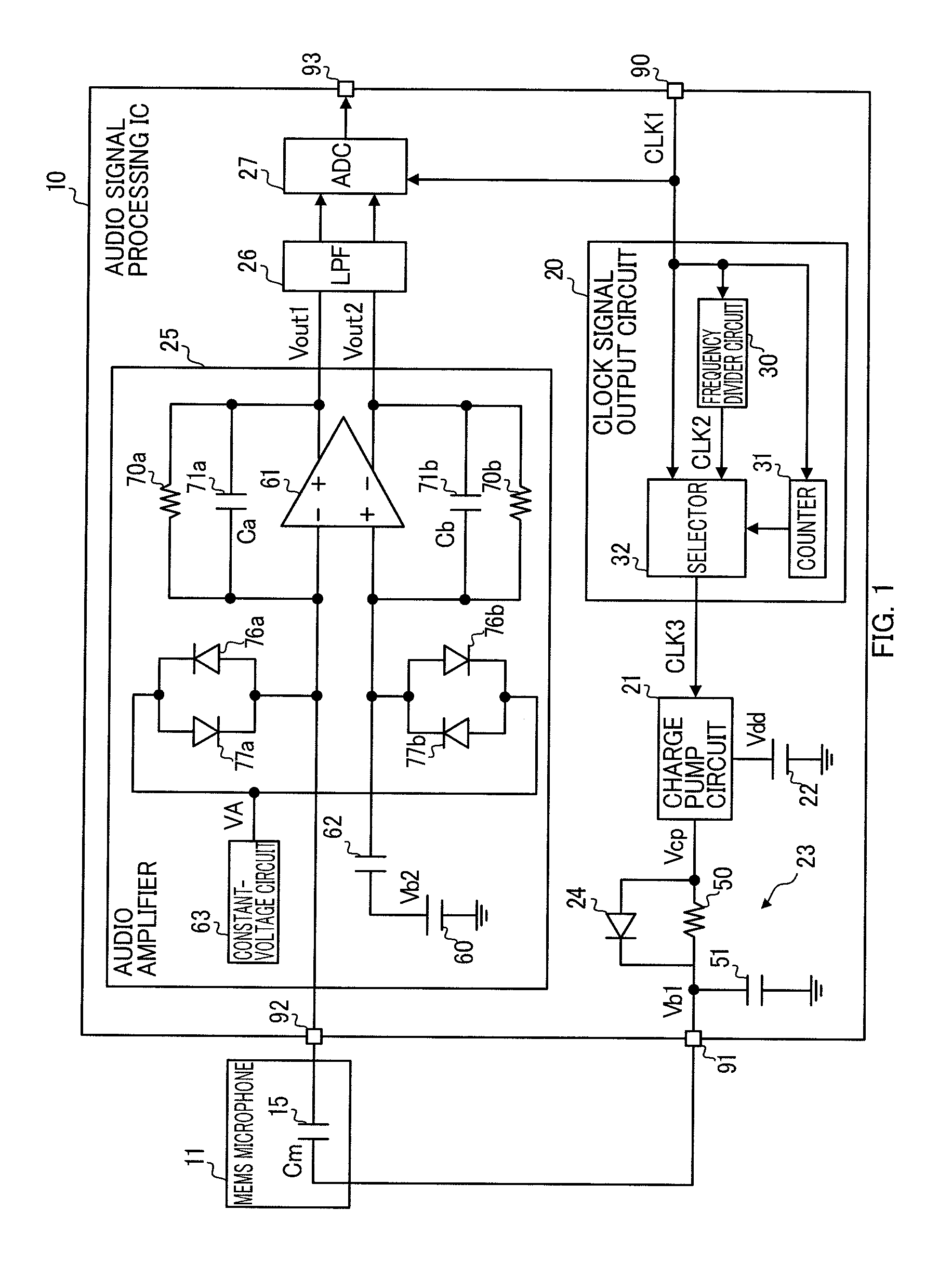
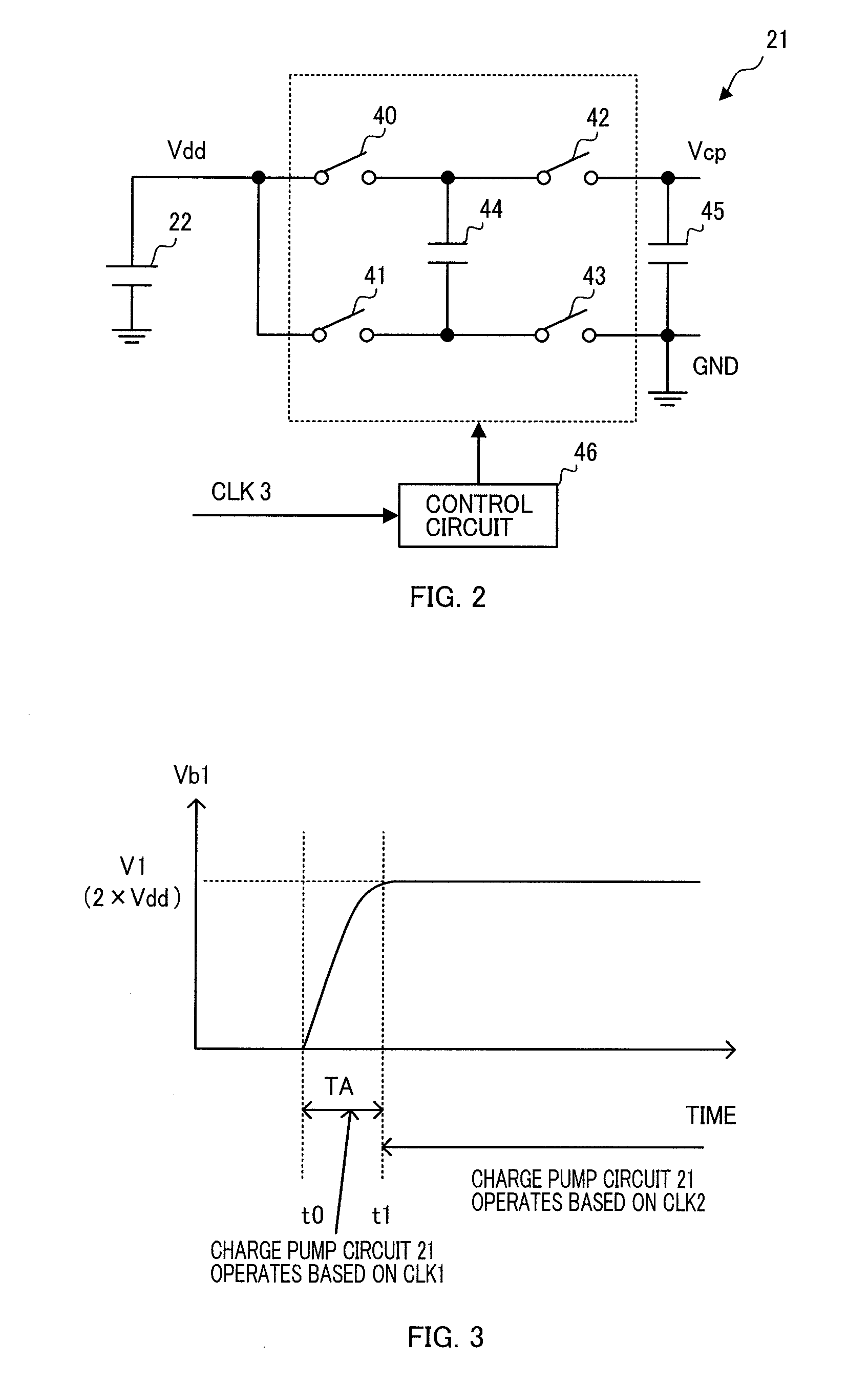
ActiveUS20110150243A1Boost voltageLow frequency amplifiersApparatus without intermediate ac conversionAudio power amplifierEngineering
A charging circuit comprising:a charge-pump circuit configured to generates a boosted voltage obtained by boosting an input voltage at each time interval shorter in accordance with an increase of a frequency of an input clock signal;an integrating circuit configured to integrate the boosted voltage to apply the integrated boosted voltage to a capacitor; anda clock signal output circuit configured to output a second clock signal higher in frequency than a first clock signal to the charge-pump circuit as the clock signal, and thereafter output the first clock signal to the charge-pump circuit as the clock signal, in order that a charge voltage of the capacitor reaches a predetermined voltage level in a time shorter than a time in which the charge voltage of the capacitor reaches the predetermined voltage level when the first clock signal is input to the charge-pump circuit as the clock signal.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Amplifier
ActiveUS7030699B2Reduce noiseMore stressStereophonic circuit arrangementsLow frequency amplifiersCMOSAudio power amplifier
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
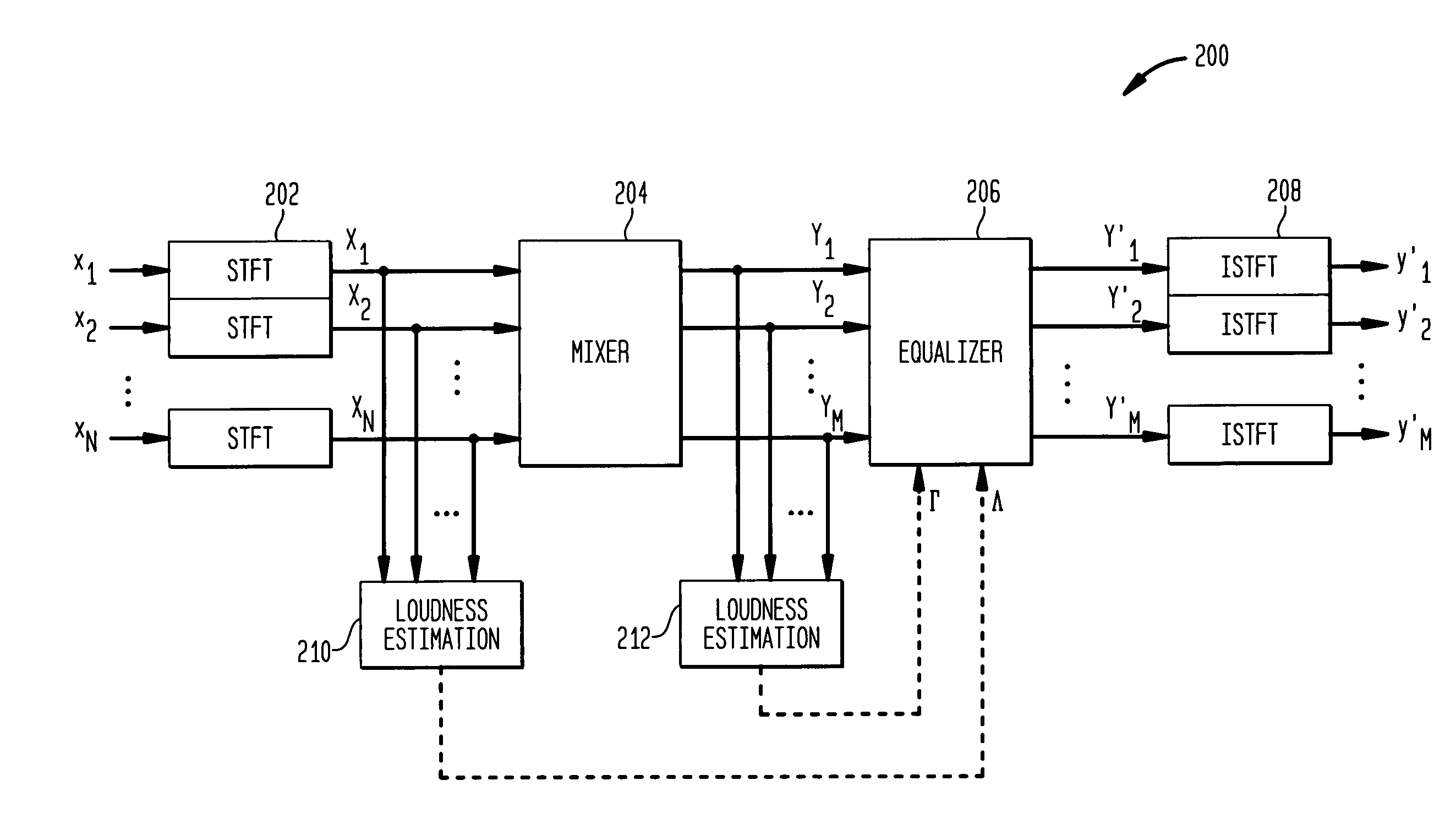
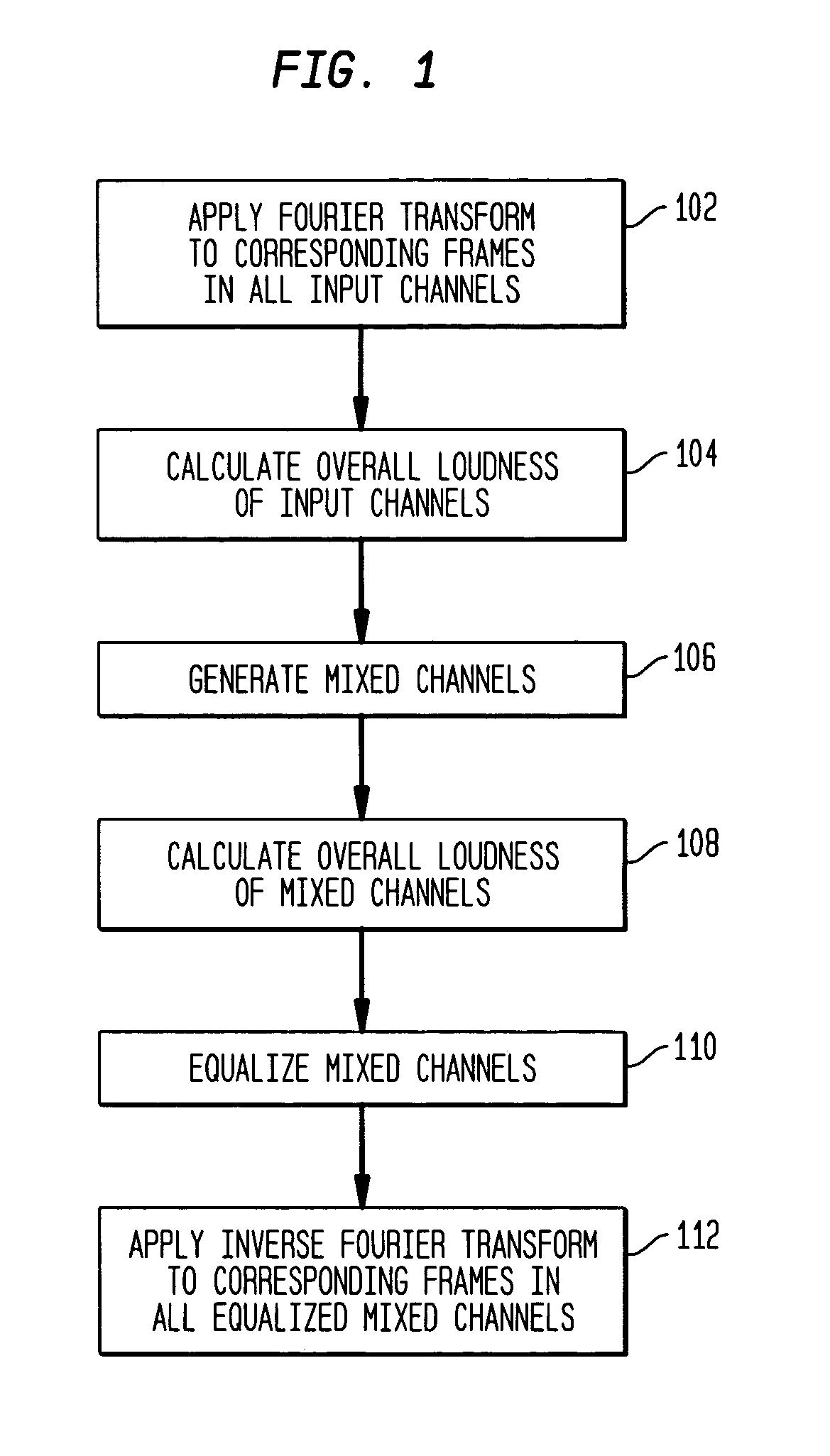
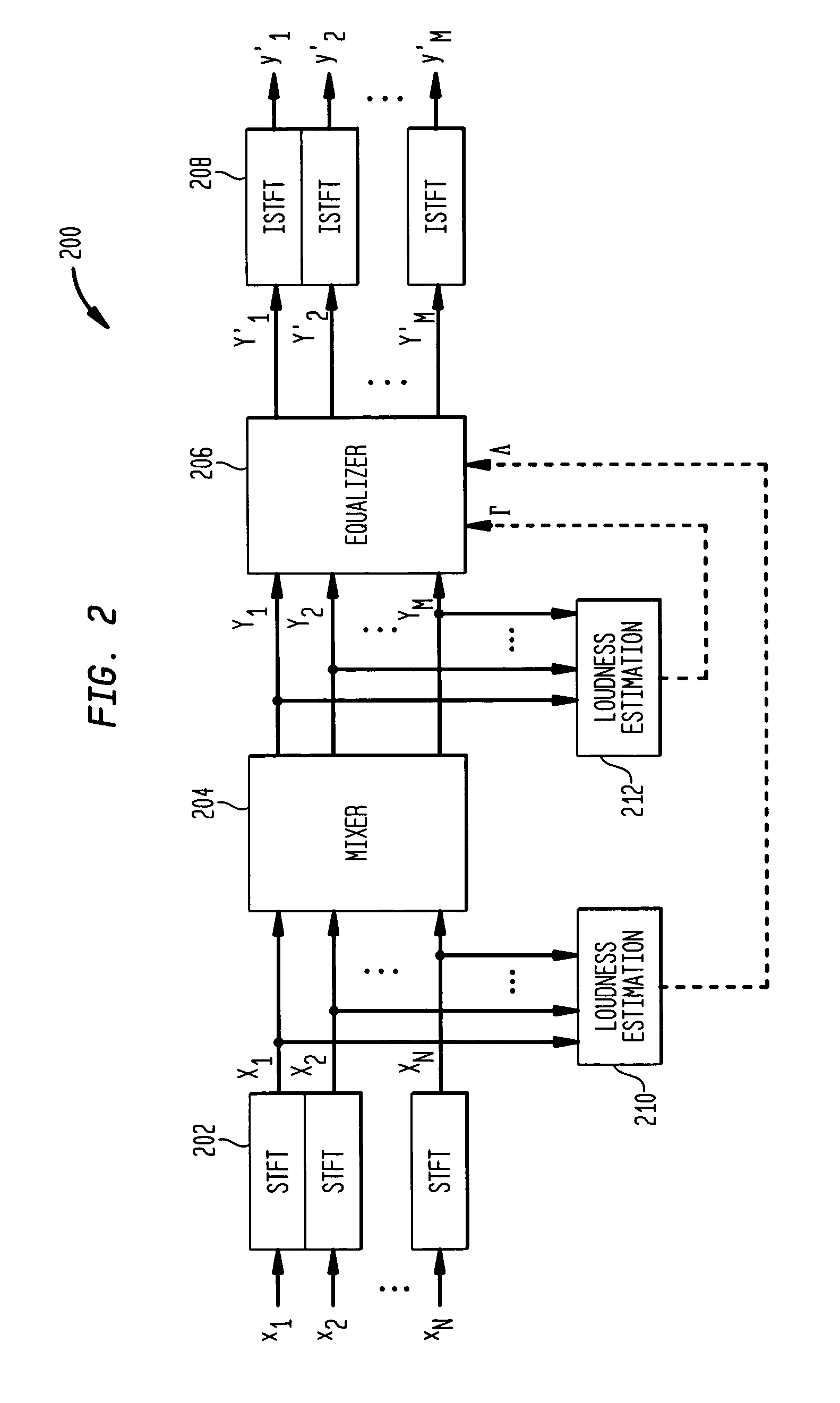
Equalization for audio mixing
During mixing of an N-channel input signal to generate an M-channel output signal, the mixed channel signals are equalized (e.g., amplified) to maintain the overall energy / loudness level of the output signal substantially equal to the overall energy / loudness level of the input signal. In one embodiment, the N input channel signals are converted to the frequency domain on a frame-by-frame basis, and the overall spectral loudness of the N-channel input signal is estimated. After mixing the spectral components for the N input channel signals (e.g., using weighted summation), the overall spectral loudness of the resulting M mixed channel signals is also estimated. A frequency-dependent gain factor, which is based on the two loudness estimates, is applied to the spectral components of the M mixed channel signals to generate M equalized mixed channel signals. The M-channel output signal is generated by converting the M equalized mixed channel signals to the time domain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Signal level selected efficiency in a charge pump power supply for a consumer device audio power output stage
ActiveUS7830209B1Improve efficiencyIncreased power output capabilityManually-operated gain controlLow frequency amplifiersCapacitanceDriver circuit
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com