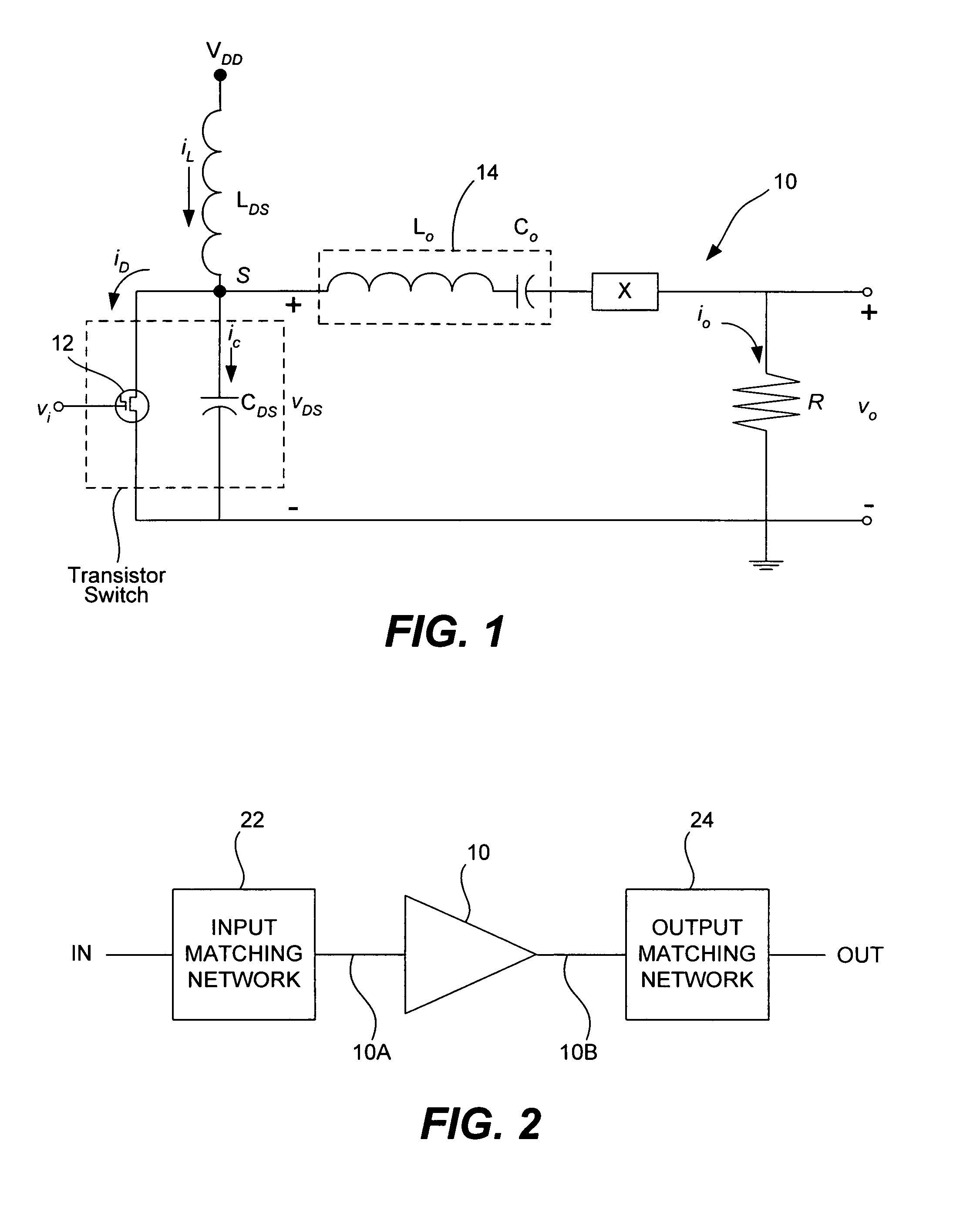
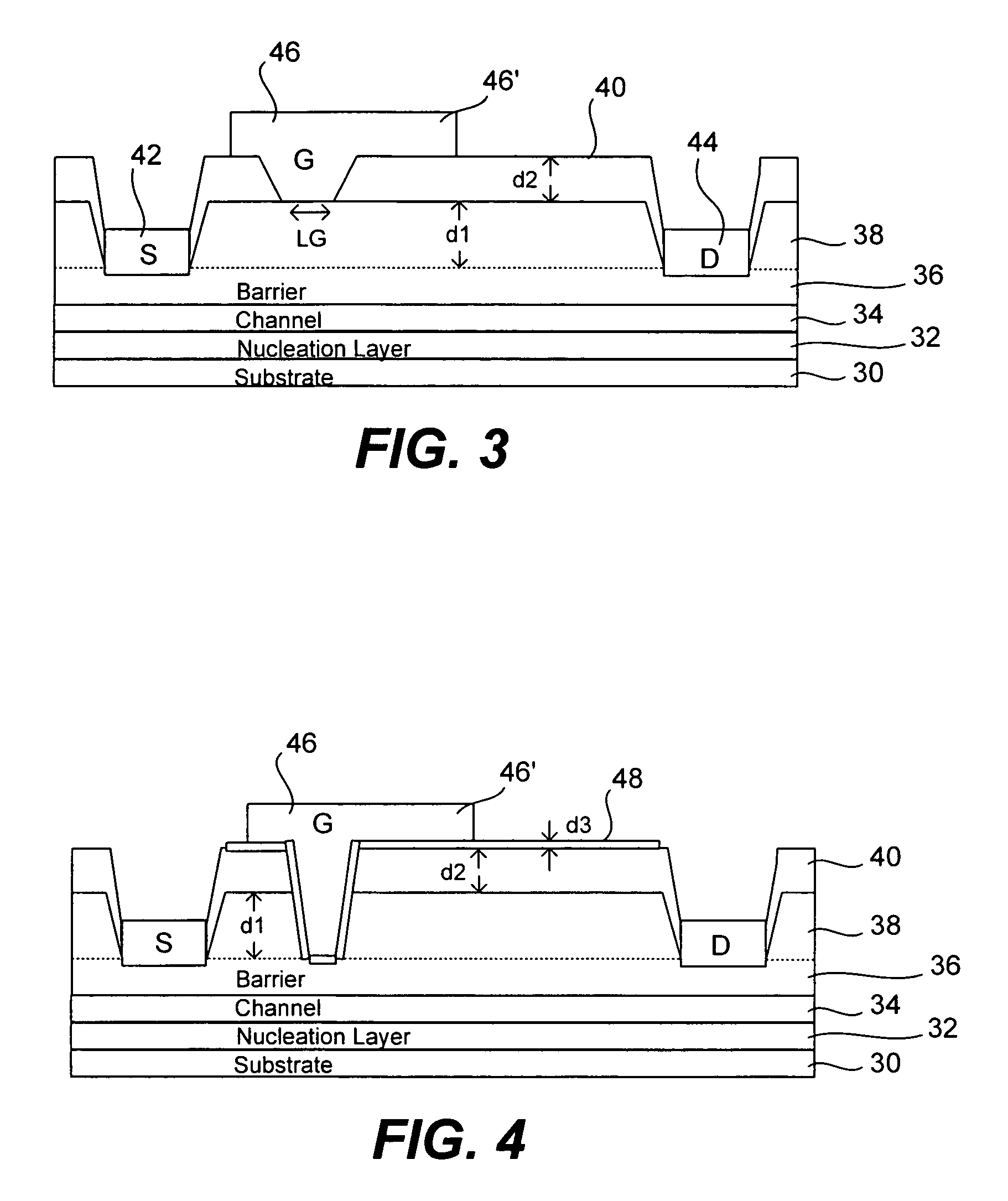
Patents
Literature
4285results about "High frequency amplifiers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
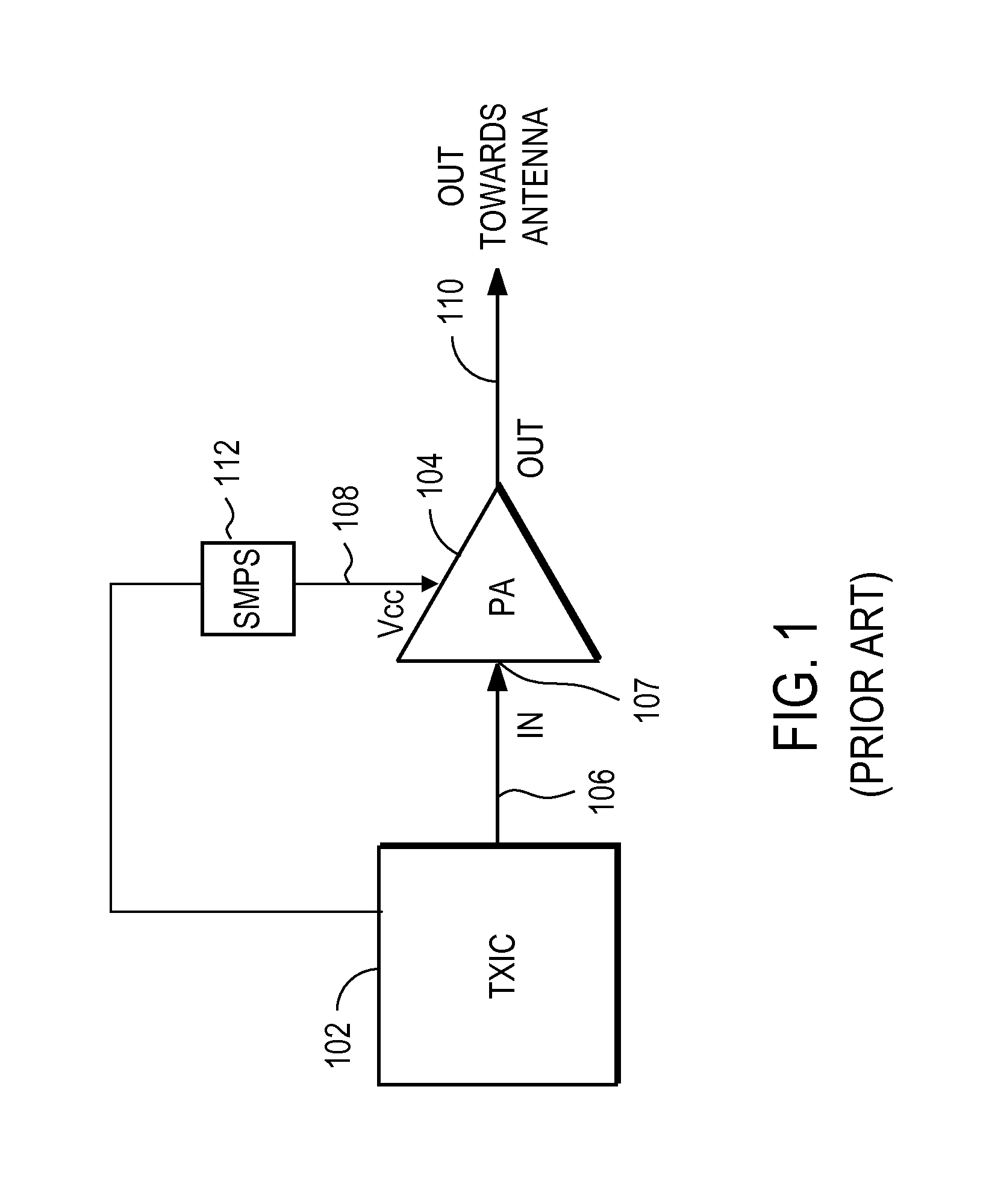
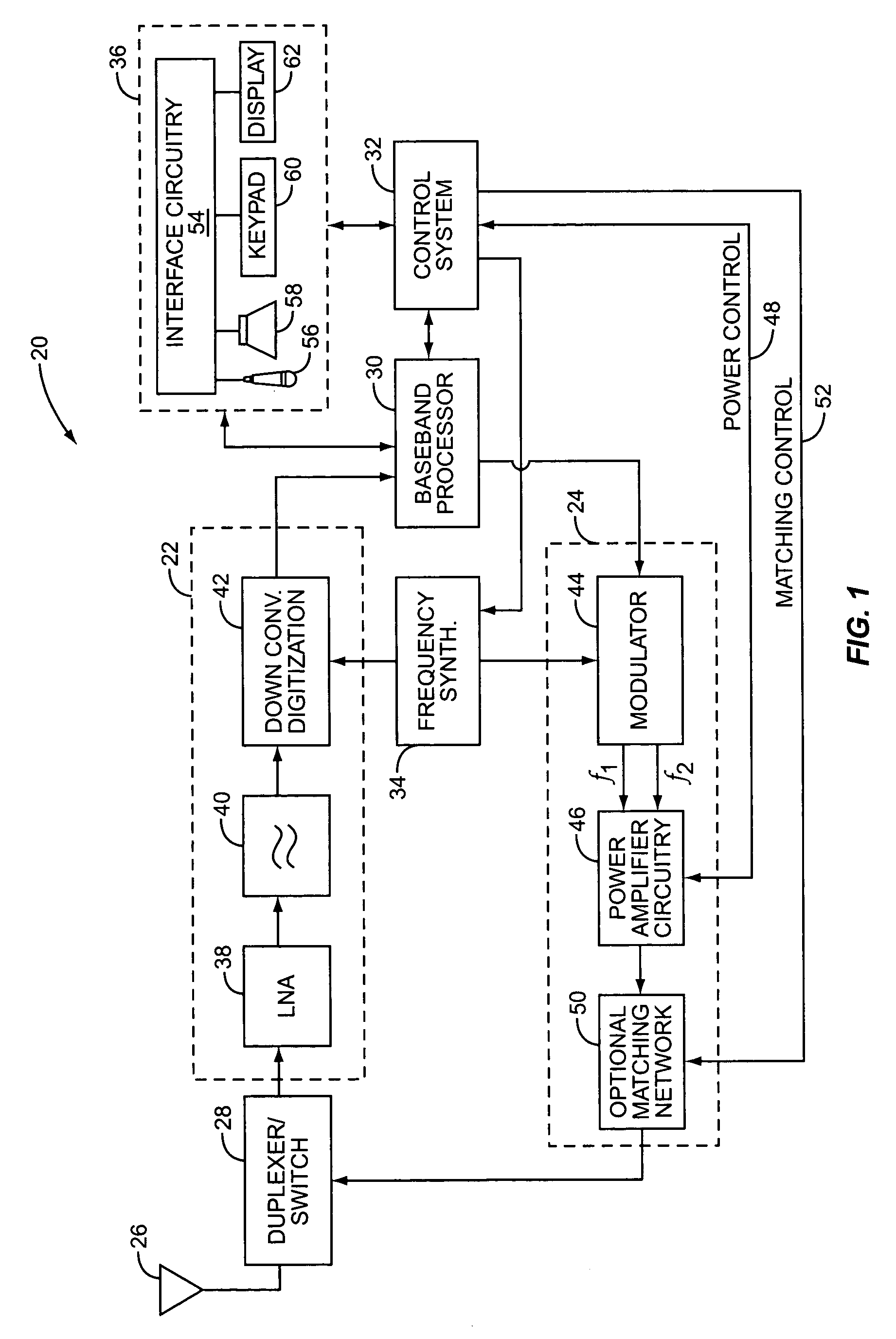
Transmission circuit and communication device
InactiveUS20120099675A1Smooth switchingPrevent stateHigh frequency amplifiersModulation with suppressed carrierAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
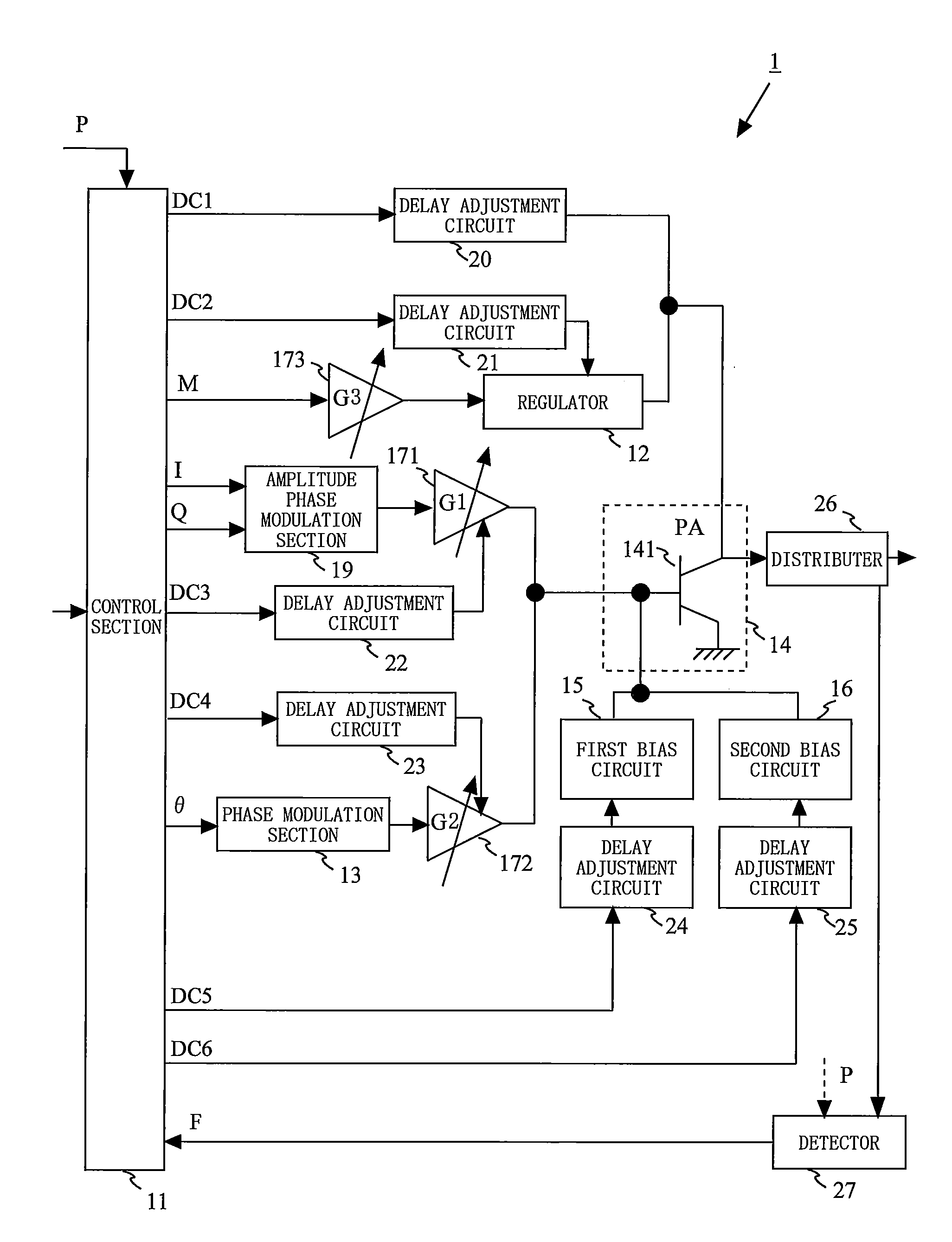
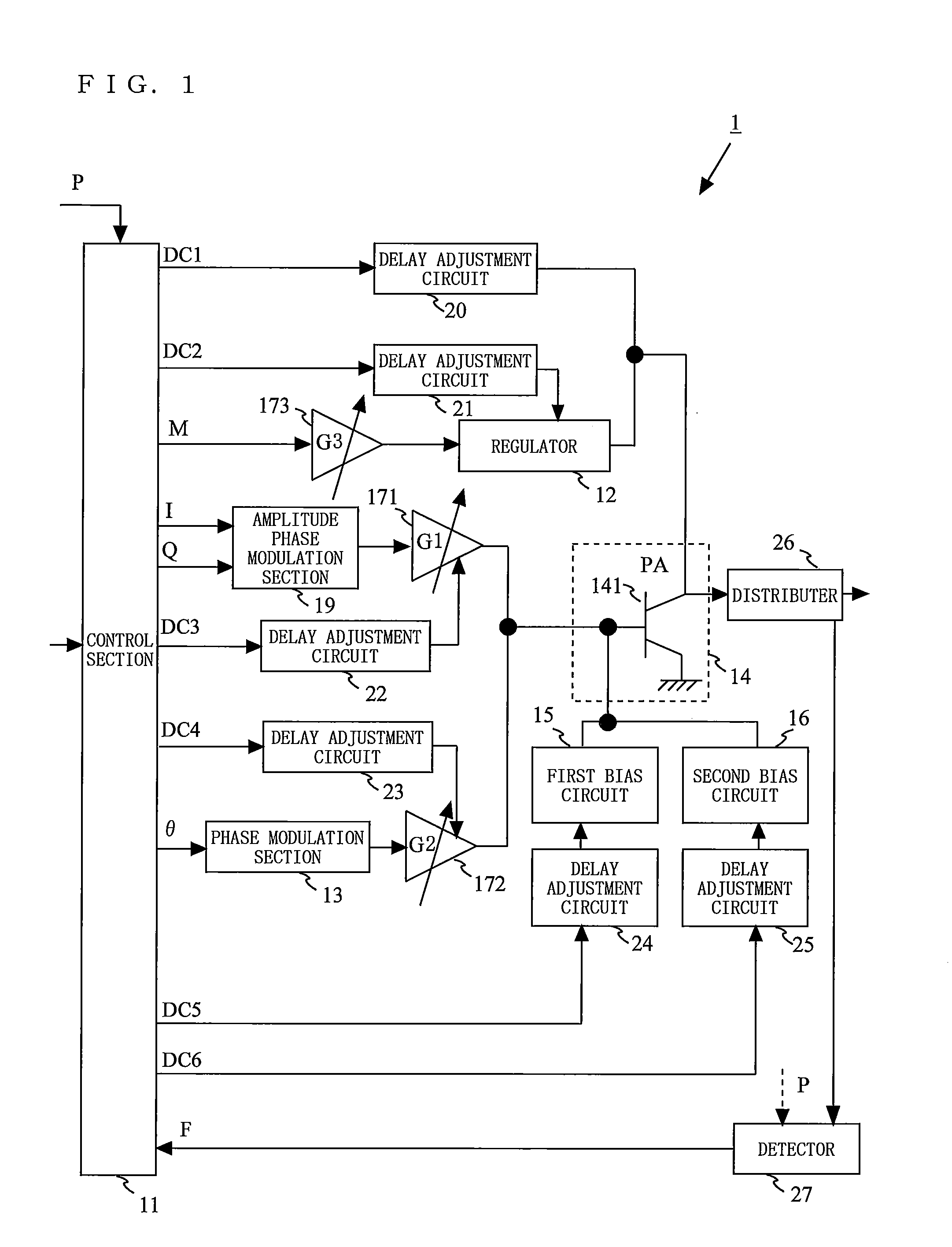
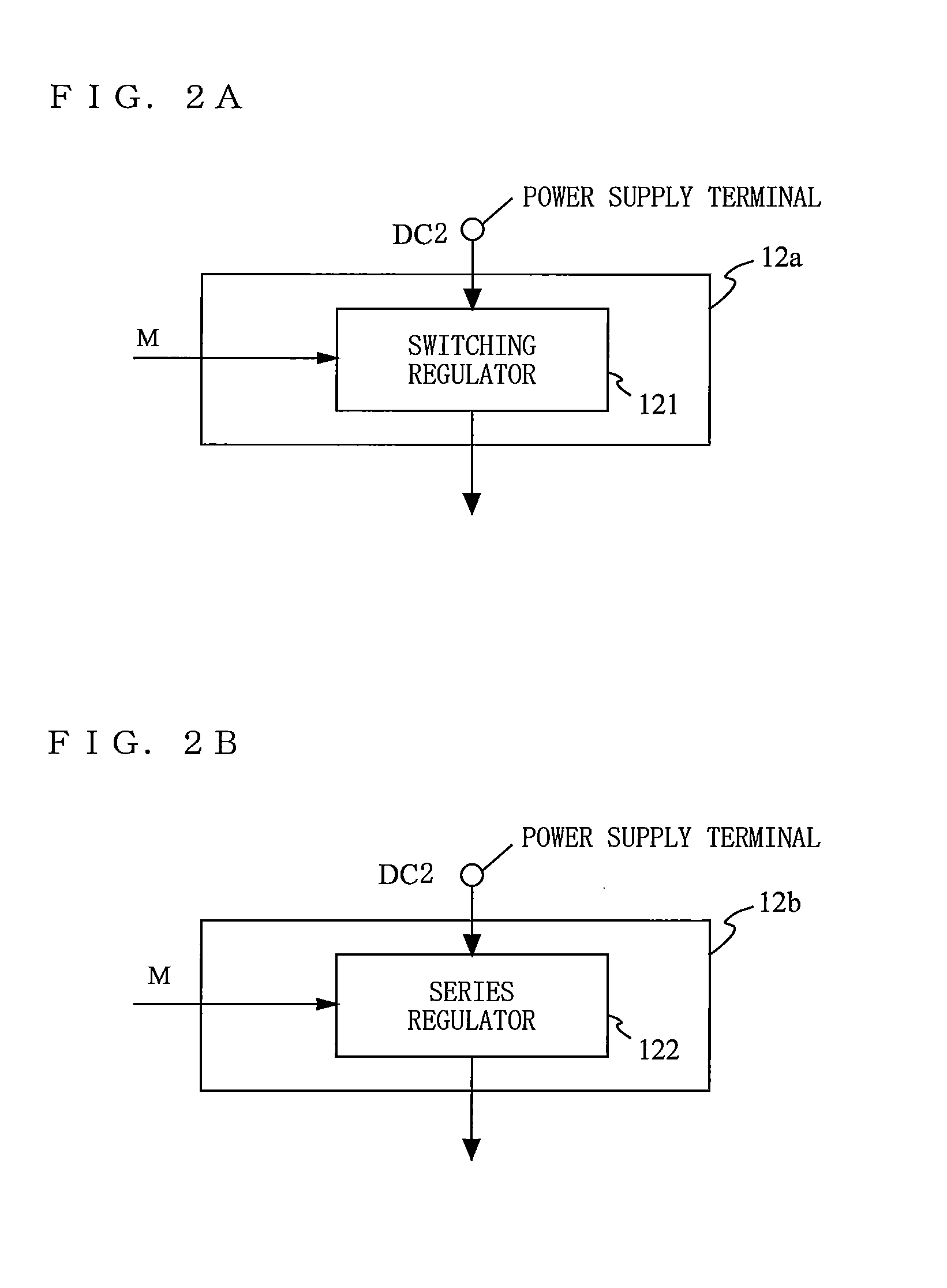
Provided is a transmission circuit which allows smooth switching of the operation mode when switching the operation mode of the transmission circuit. A power amplifier 14 includes: a first input terminal to which a direct-current voltage or a voltage in accordance with an amplitude signal M is supplied; a second input terminal to which an output signal from a first variable gain amplifier 171 or an output signal from a second variable gain amplifier 172 is inputted; and a third input terminal to which an output signal from a first bias circuit 15 or an output signal from a second bias circuit 16 is inputted. A control section 11 switches the operation mode of the transmission circuit so that at least one of the first input terminal, the second input terminal, and the third input terminal of the power amplifier is prevented from being in a no input state.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Switch mode power amplifier using MIS-HEMT with field plate extension
ActiveUS7548112B2Guaranteed uptimeIncrease heightTransistorHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierSilicon oxide
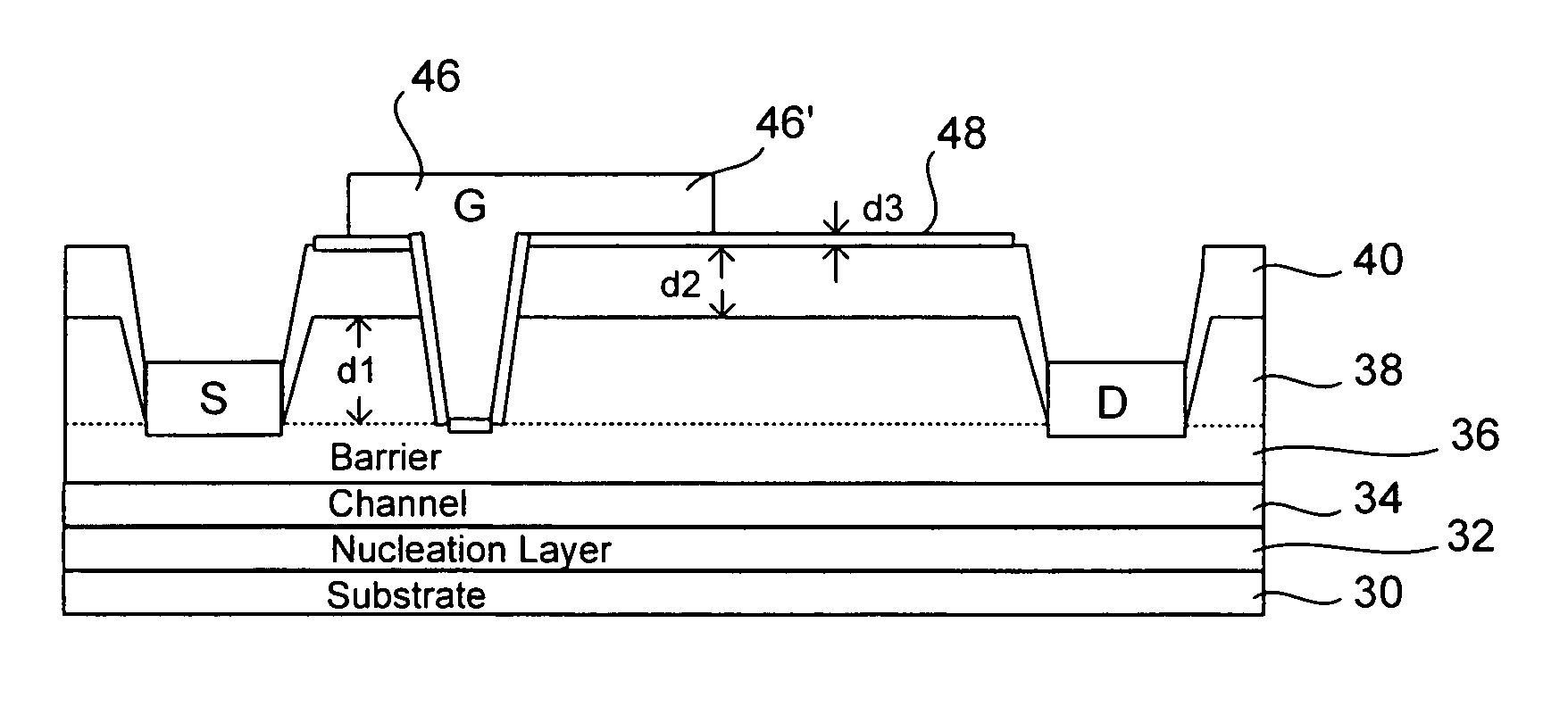
Disclosed are a switch mode power amplifier and a field effect transistor especially suitable for use in a switch mode power amplifier. The transistor is preferably a compound high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) having a source terminal and a drain terminal with a gate terminal therebetween and positioned on a dielectric material. A field plate extends from the gate terminal over at least two layers of dielectric material towards the drain. The dielectric layers preferably comprise silicon oxide and silicon nitride. A third layer of silicon oxide can be provided with the layer of silicon nitride being positioned between layers of silicon oxide. Etch selectivity is utilized in etching recesses for the gate terminal.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Signal repeater system
InactiveUS8059576B2Secures repeatabilityReduce mutual interferenceInterconnection arrangementsFrequency-division multiplex detailsAnalog signalEngineering
The present invention concerns analog signal repeater system solutions of the general kind. It concerns in particular stability with analog signal repeater systems.
Owner:VAVIK GEIR MONSEN
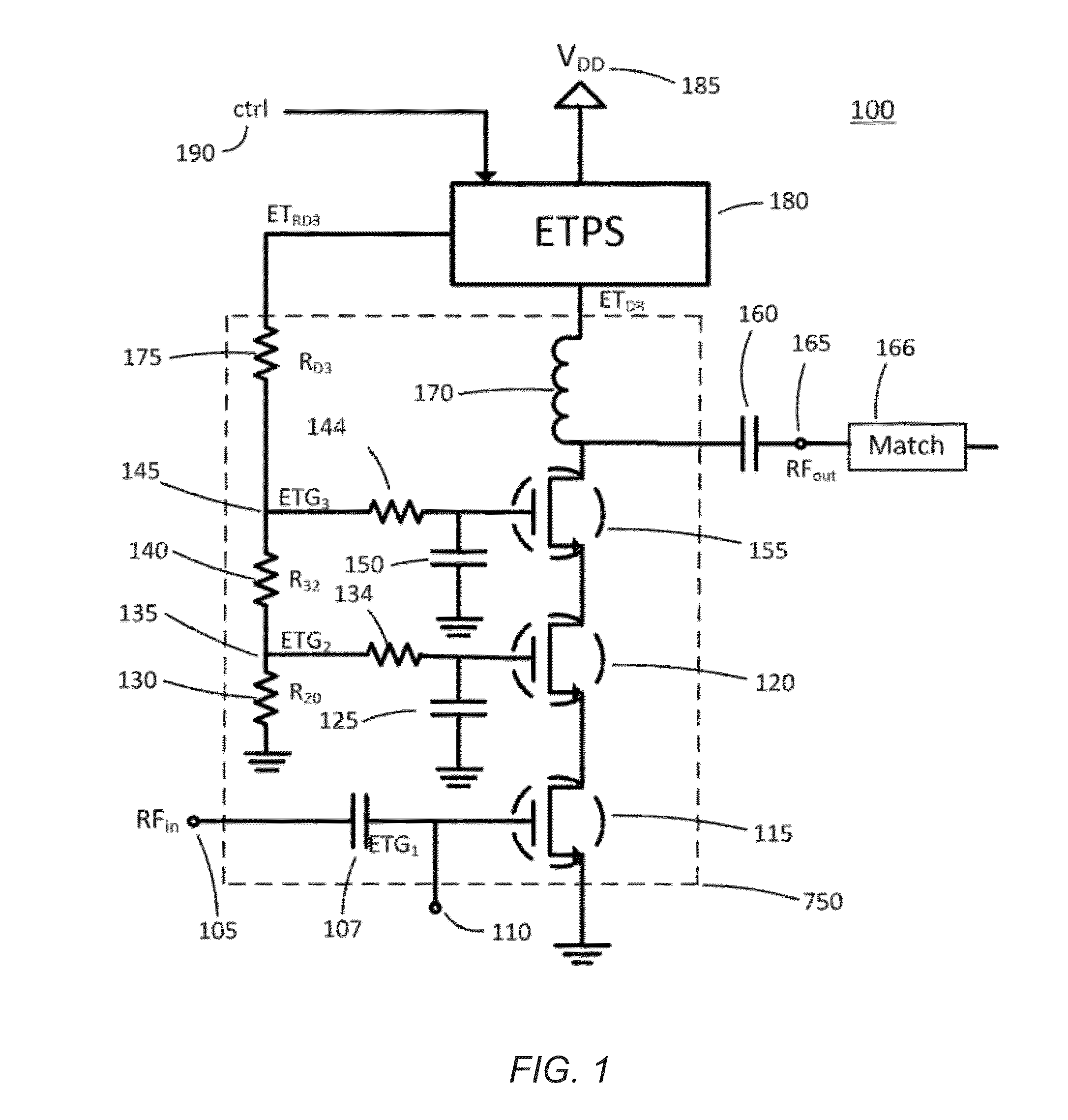
Bias Control for Stacked Transistor Configuration
Various methods and circuital arrangements for biasing one or more gates of stacked transistors of an amplifier are presented, where the amplifier can be an envelope tracking amplifier. Circuital arrangements to generate reference gate-to-source voltages for biasing of the gates of the transistors of the stack are also presented. Particular biasing for a case of an input transistor of the stack is also presented.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
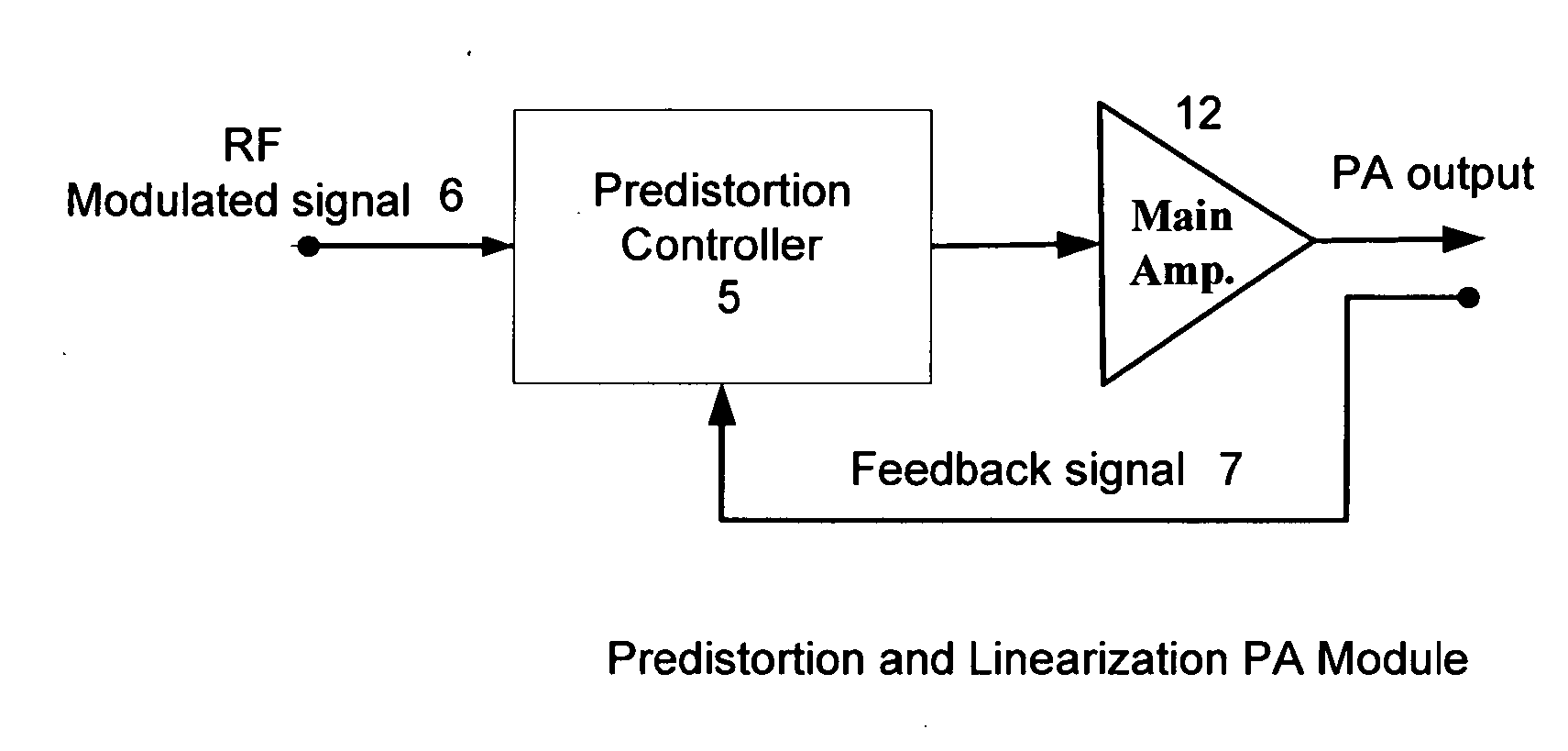
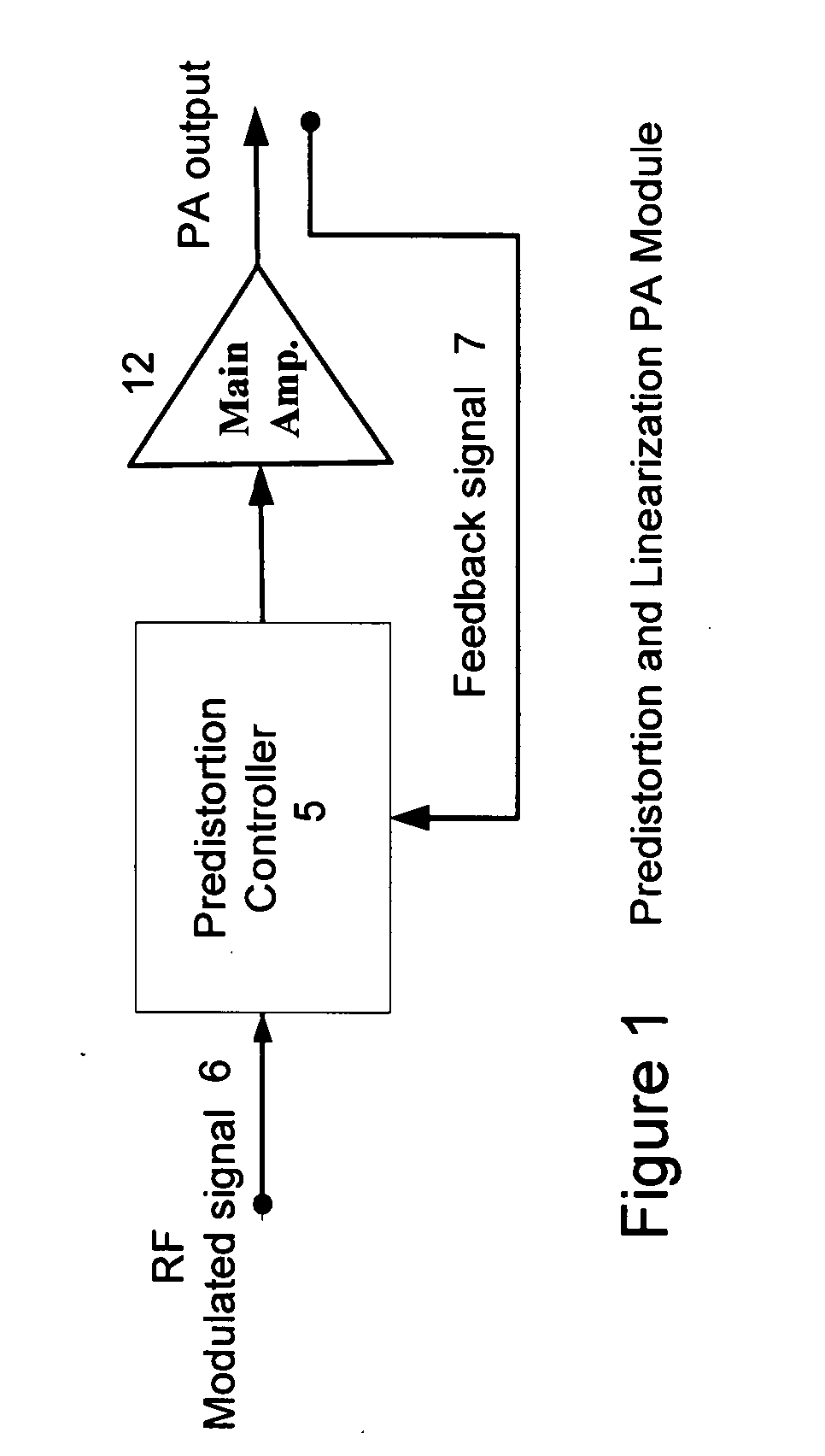
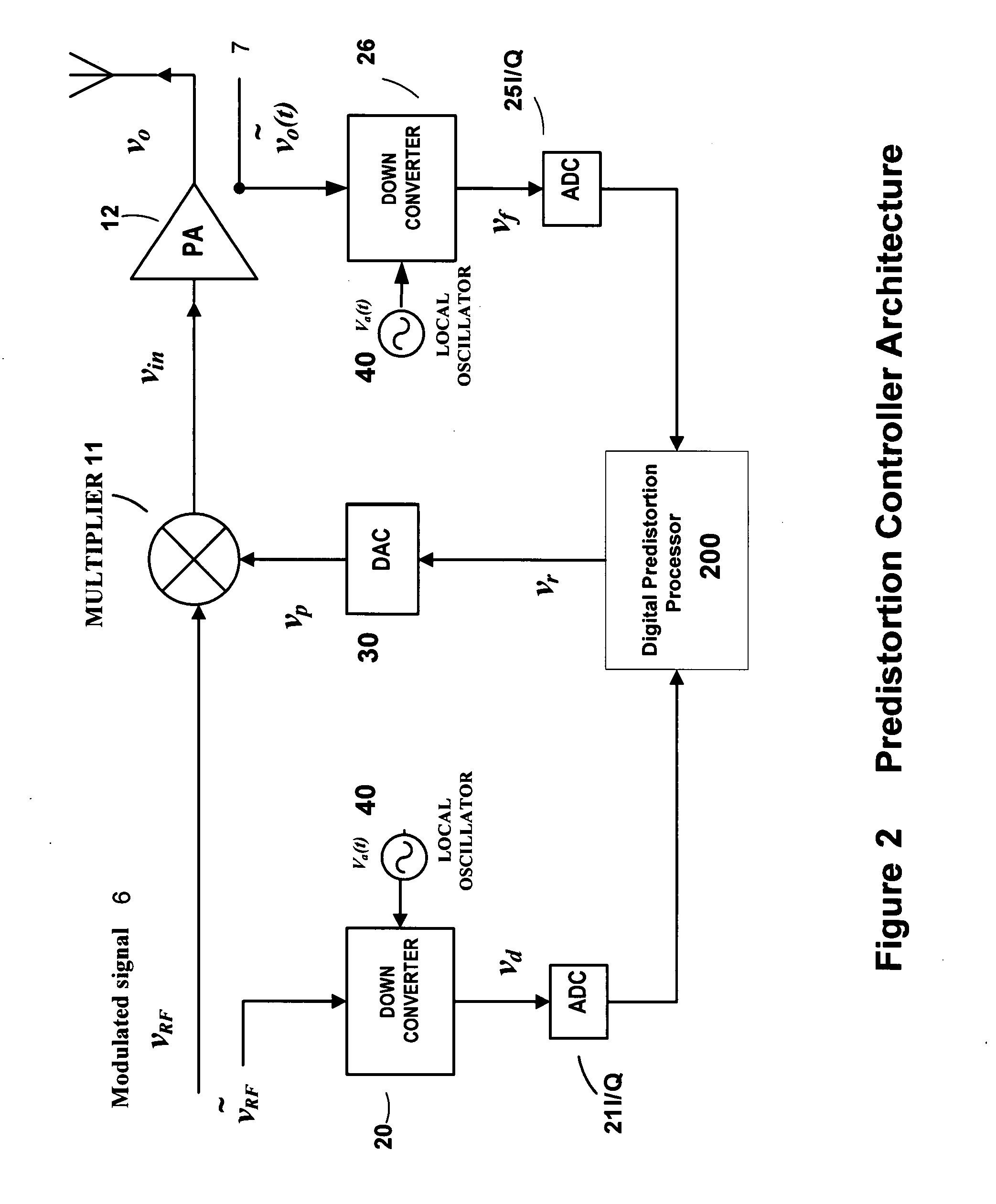
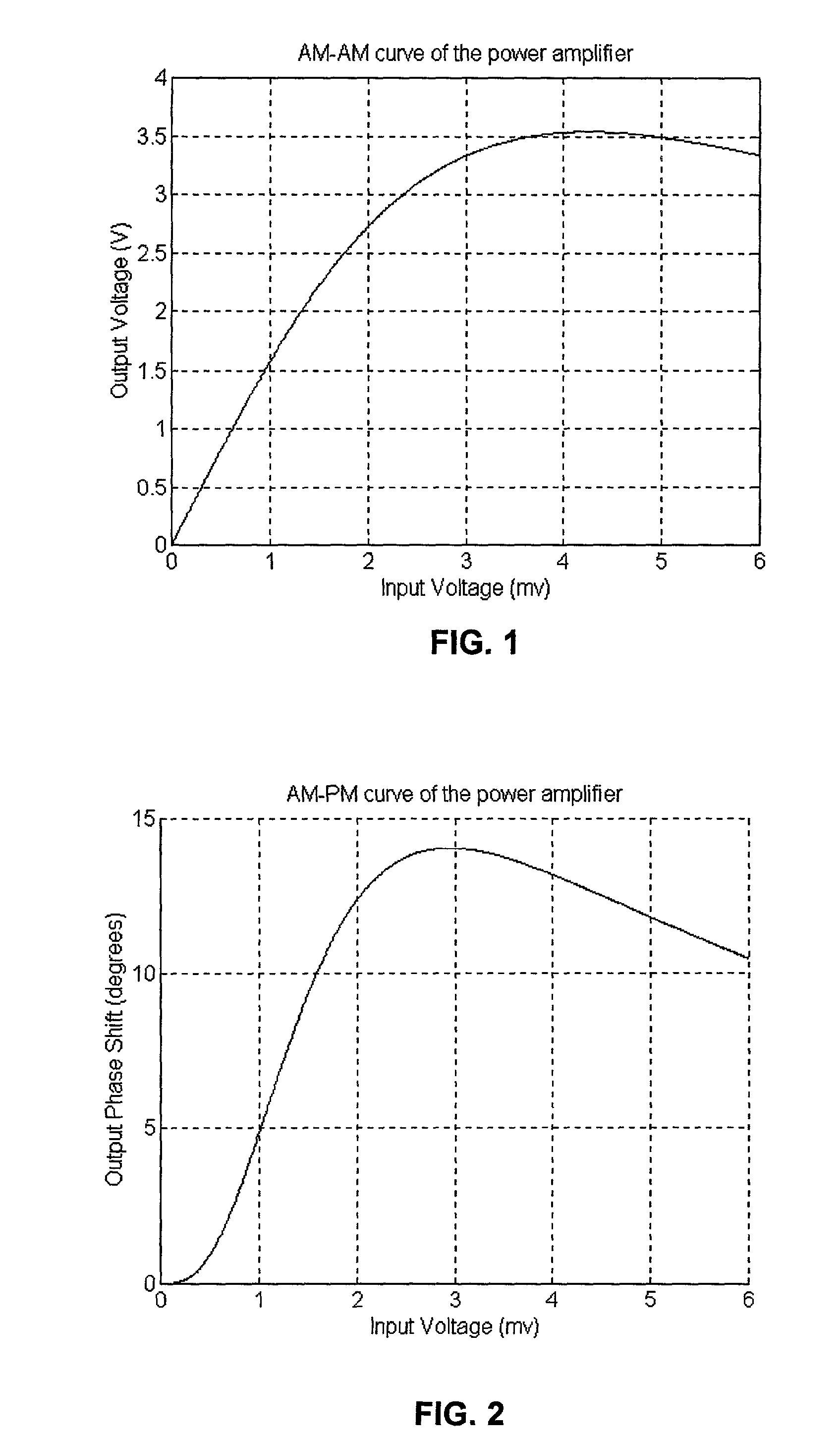
High efficiency linearization power amplifier for wireless communication
ActiveUS20070241812A1Improve efficiencyImprove linearityEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier details to increase power/efficiencyFrequency changerControl signal
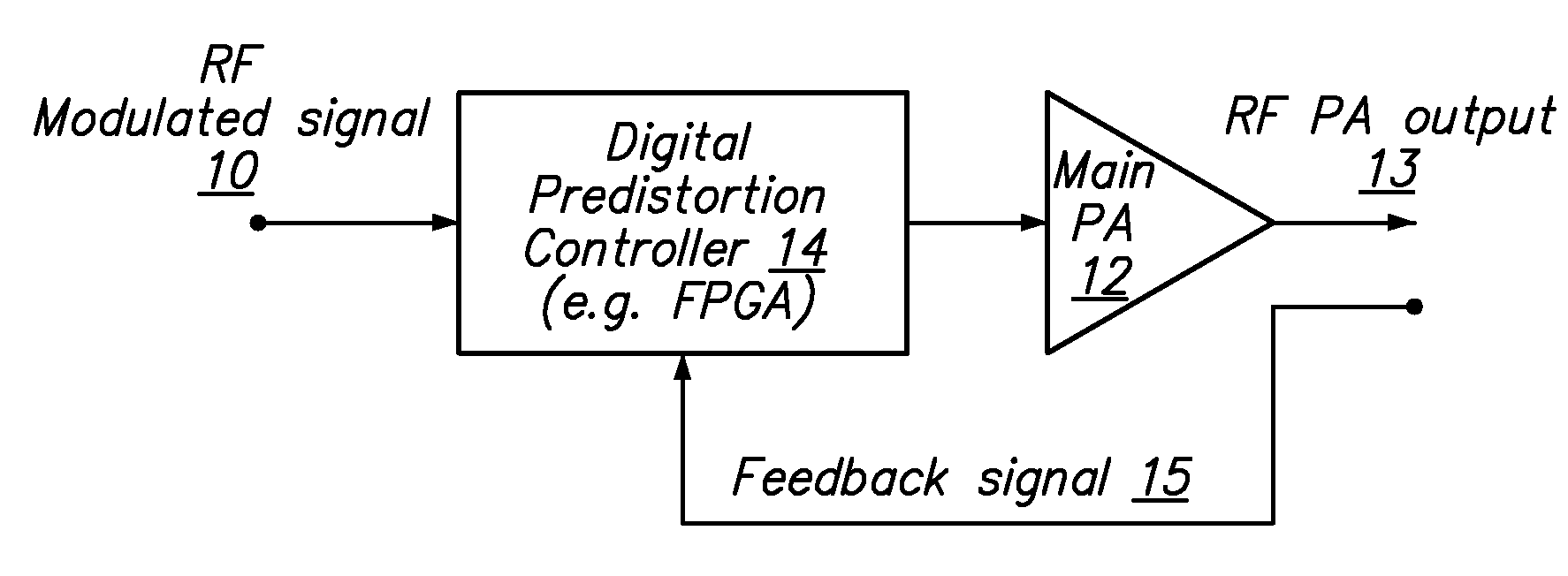
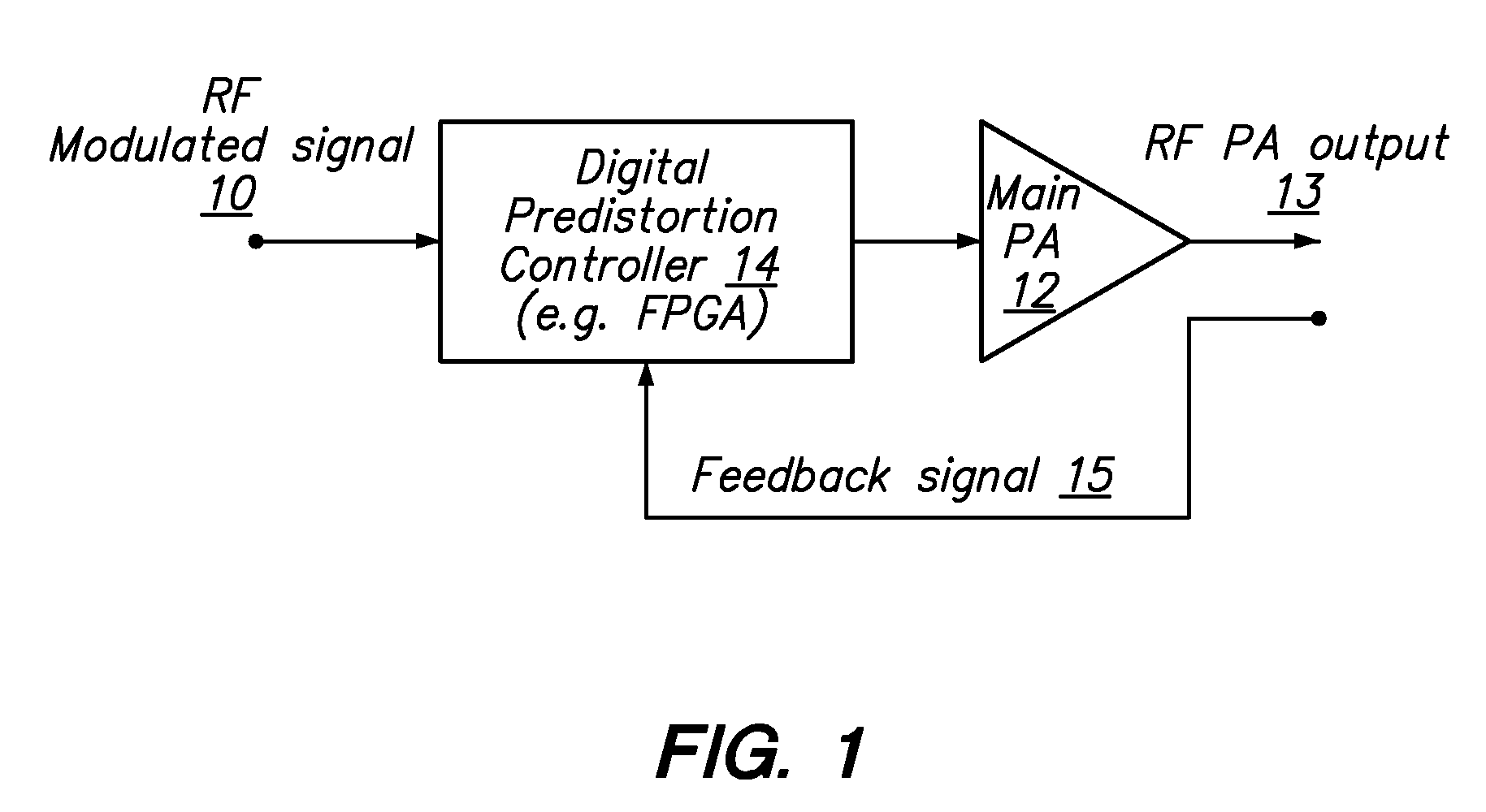
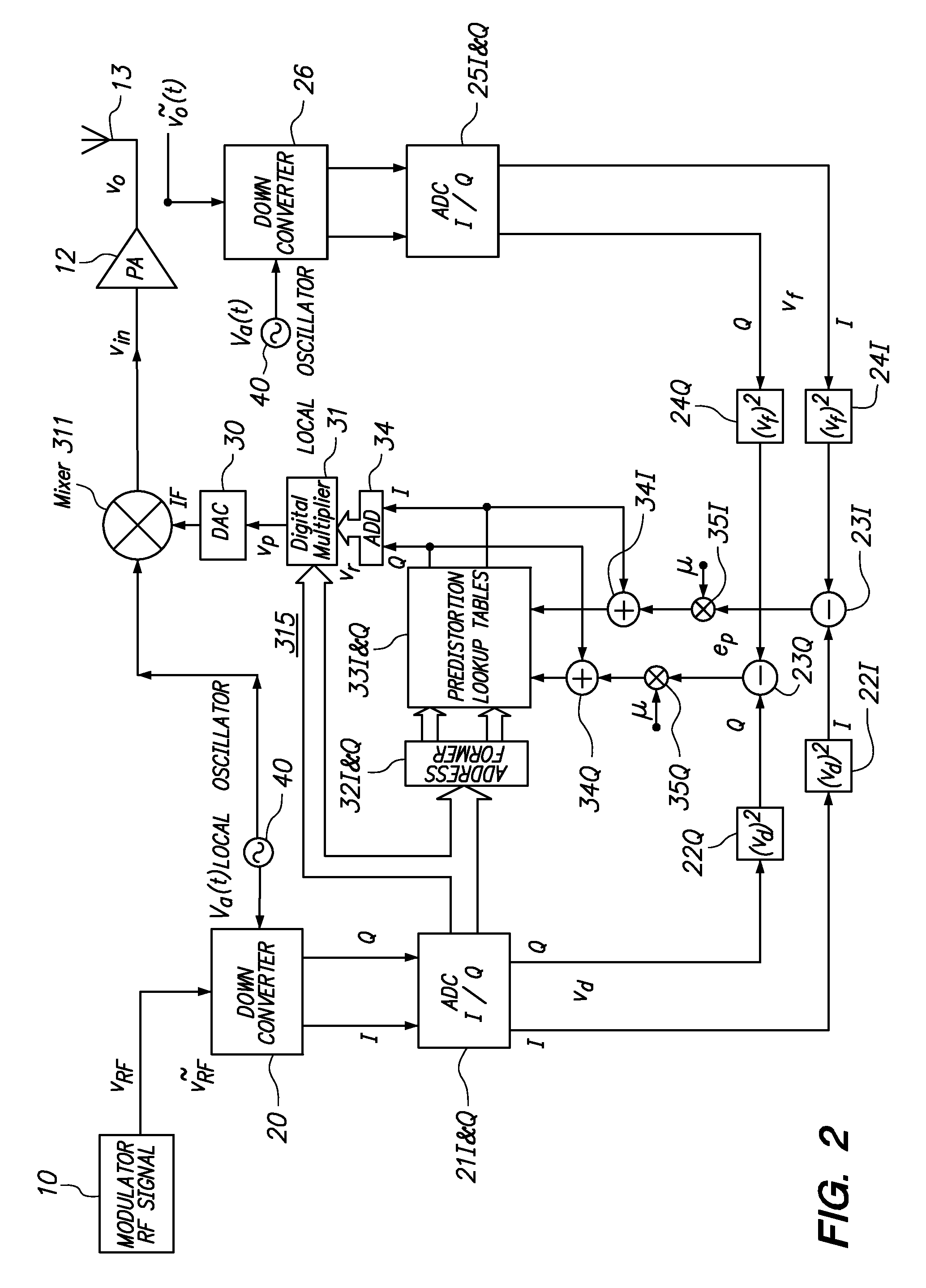
An embodiment of the invention uses a predistortion correction signal to combination the modulated RF signal by an analog multiplier for linearization of power amplifiers having nonlinear characteristics such as those used in wireless RF transmitters. A predistortion controller comprises a plurality of down converters for retrieving both the ideal non-distorted information and the feedback distorted information, together with pre-stored digitally-indexed predistortion information stored, for example, in a look-up table. The digitally-indexed information models nonlinear characteristics of the high power amplifier, and is stored prior to processing of pre-compensation in the power amplifier. When the predistortion information is combined with the modulated RF signal in the analog multiplier, the result is a substantially linear information transmission from the power amplifier. In an embodiment of the system, the modulated RF input signal and the feedback signal from PA output are down-converted, respectively, by analog devices, such as mixers, after which the analog intermediate frequency (IF) signals are digitized by analog-to-digital converters for digital predistortion correction processing, followed by predistortion processing performed by, for example, a DSP or FPGA chip to generate a digital correction control signal, which is then converted to an analog signal by a digital-to-analog converter, followed by combining the analog correction signal with the RF modulated input signal to yield the input to the power amplifier.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
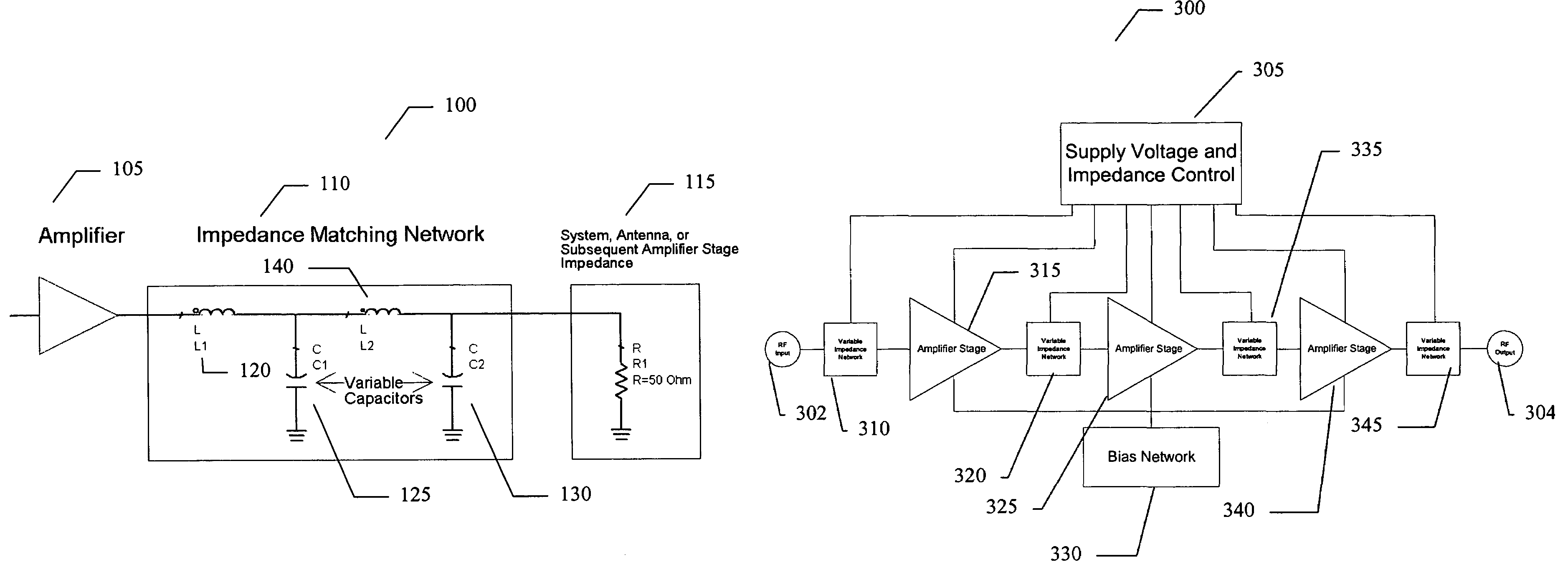
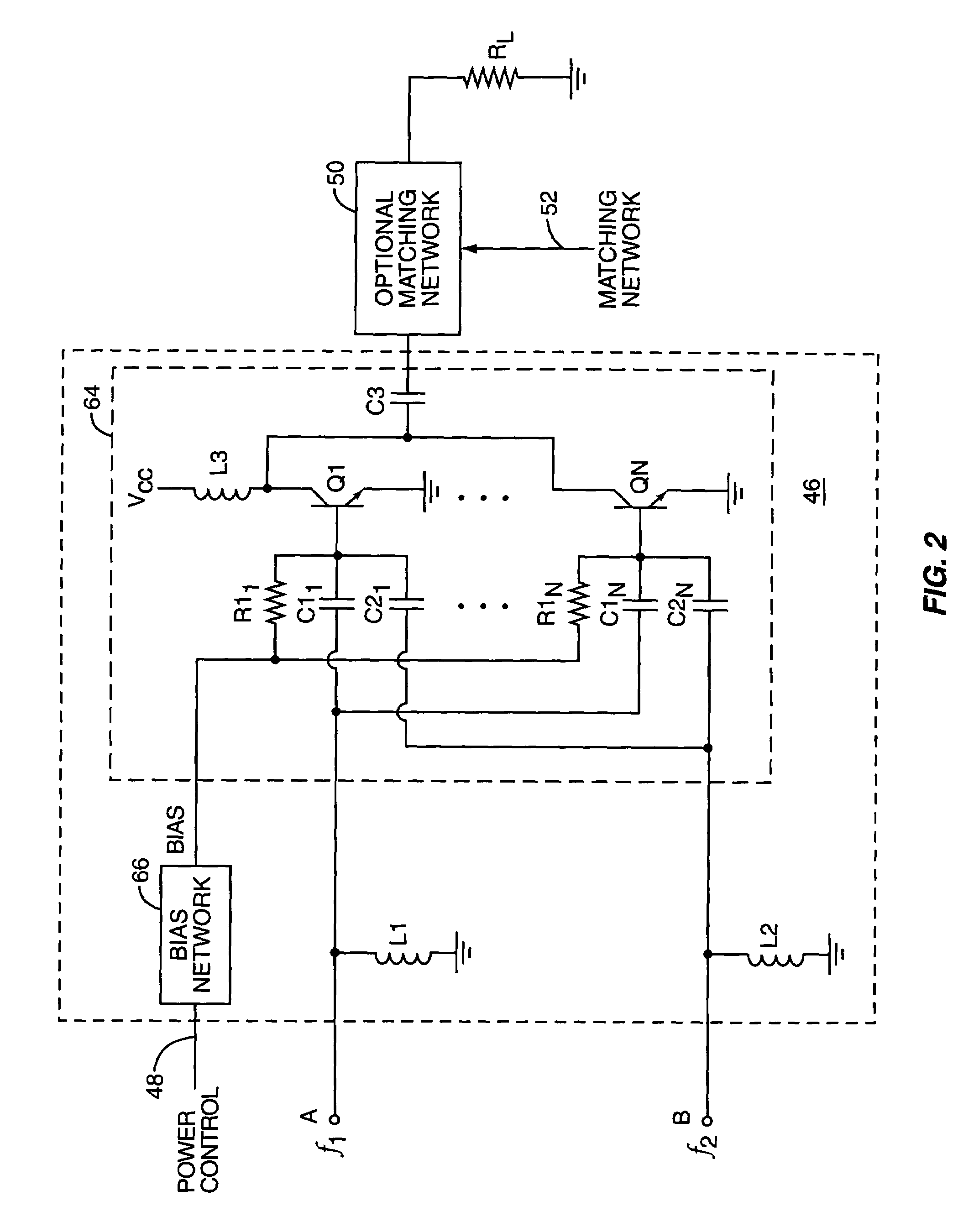
Amplifier system and method
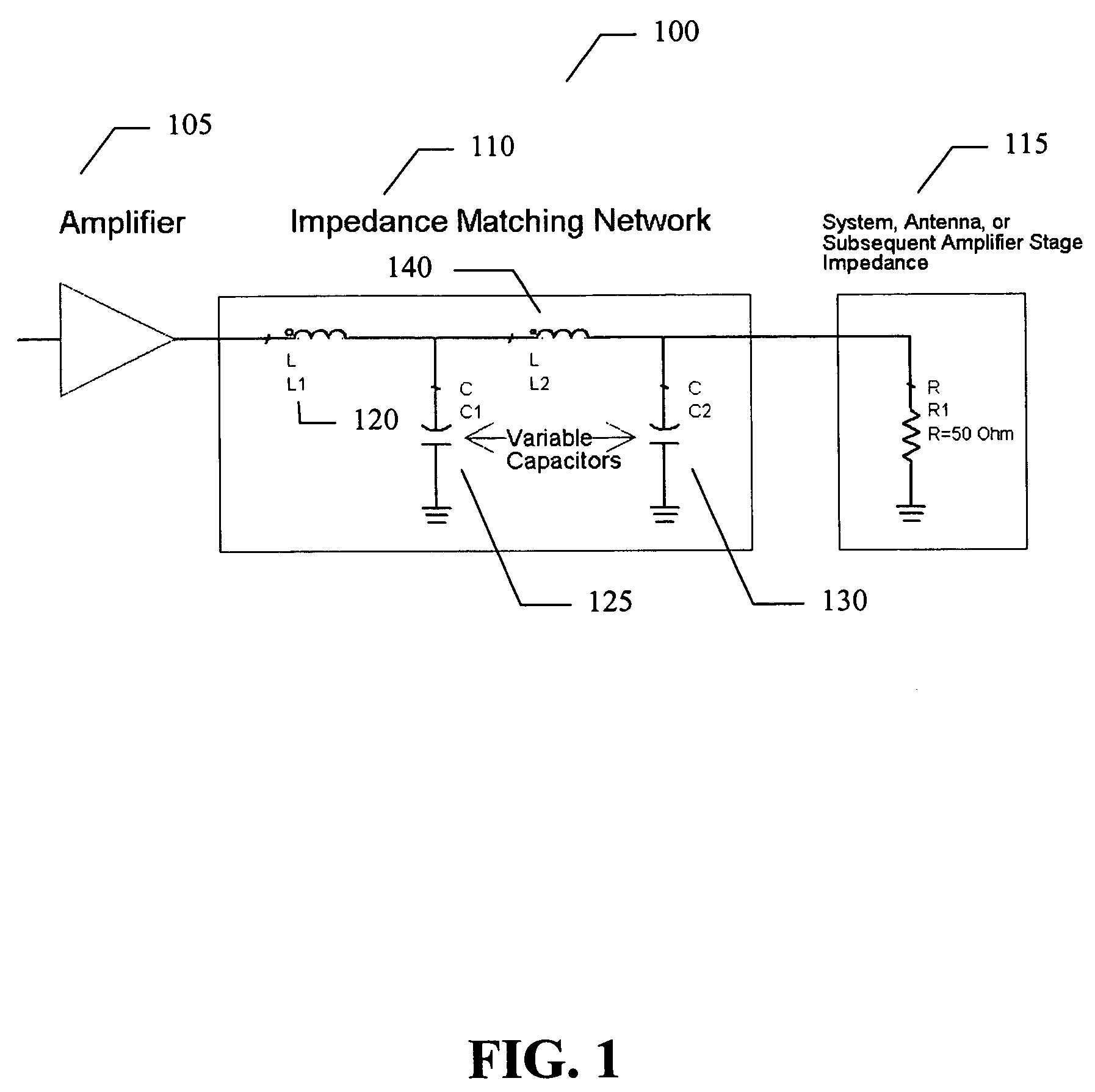
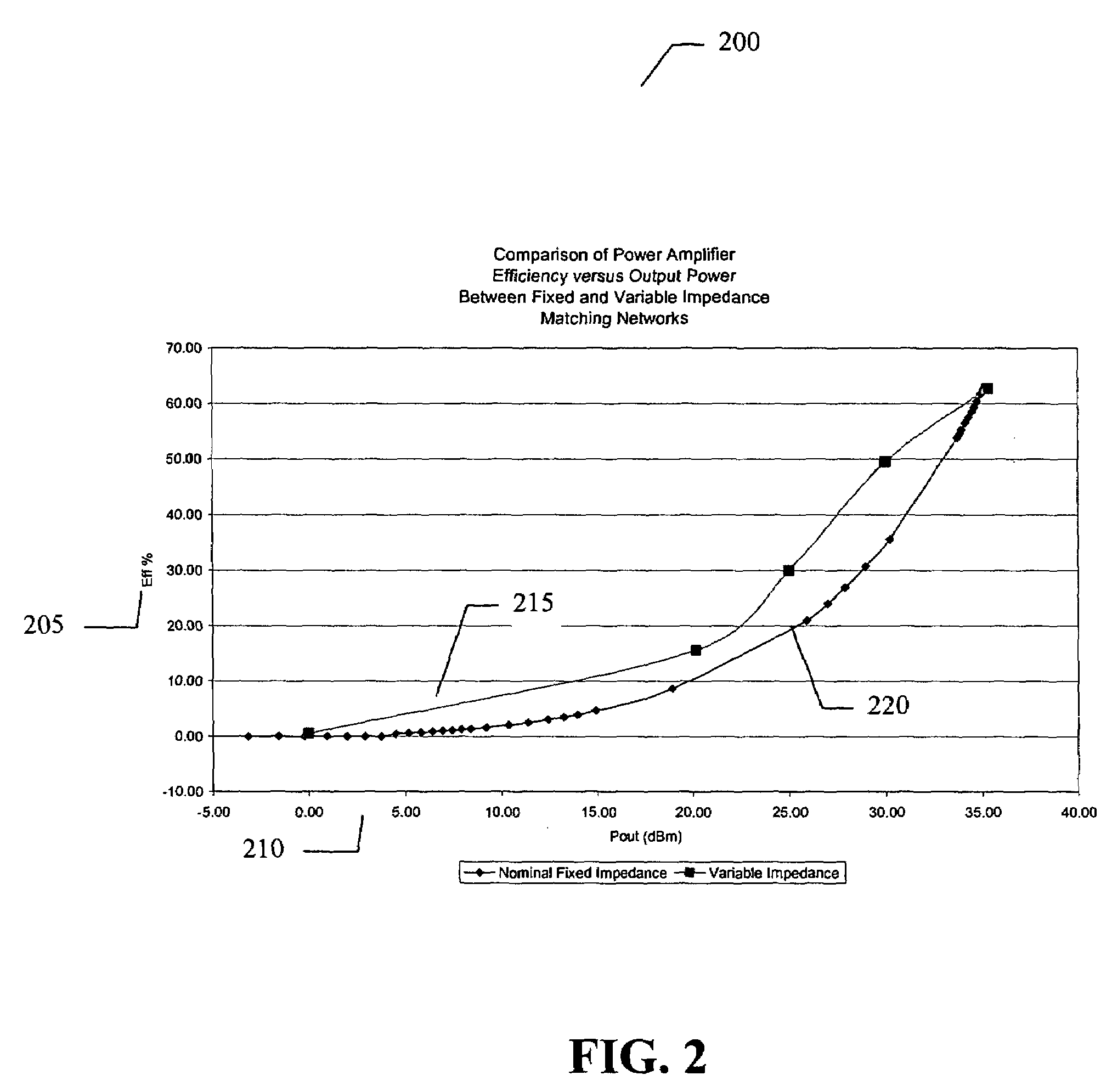
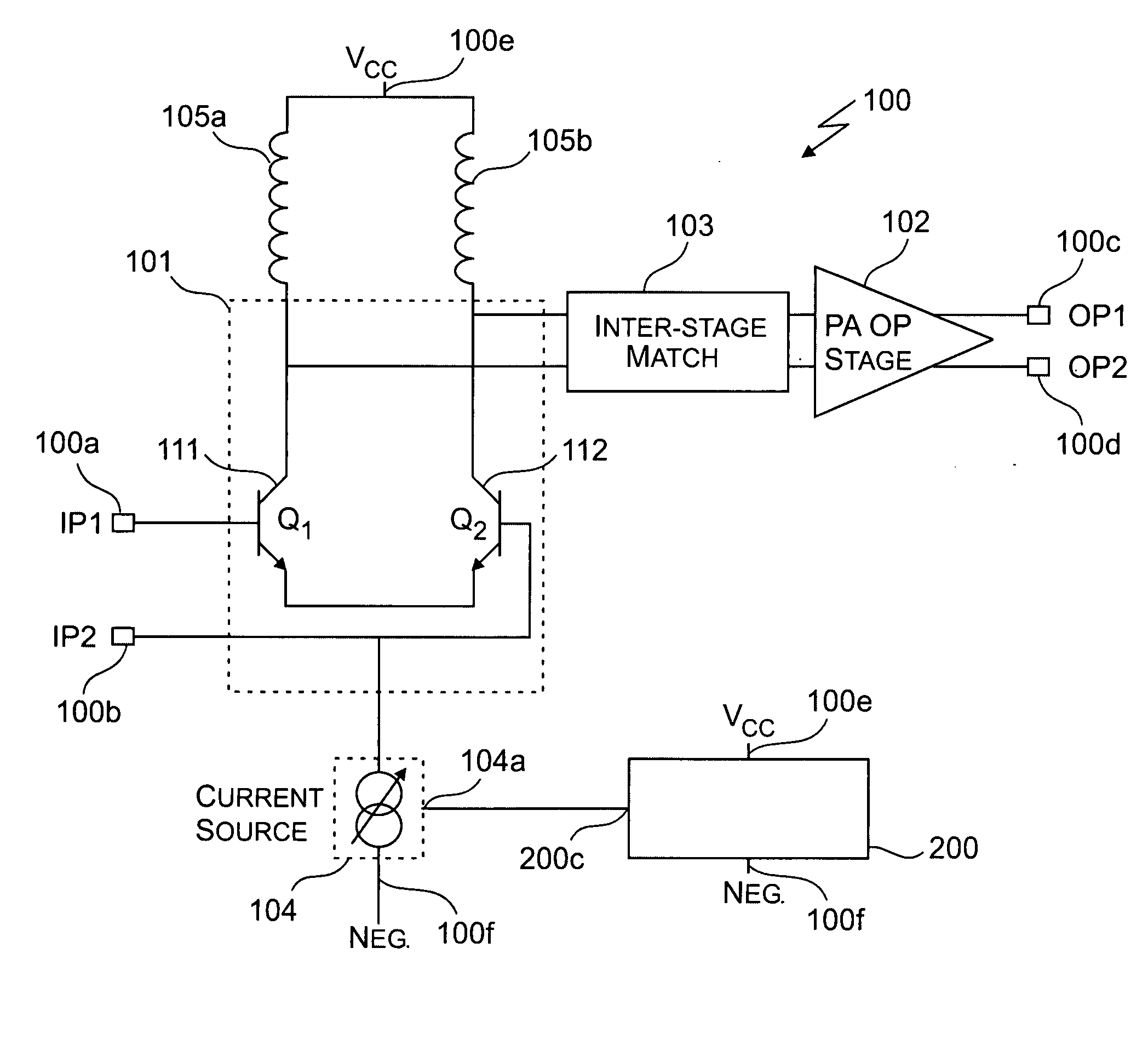
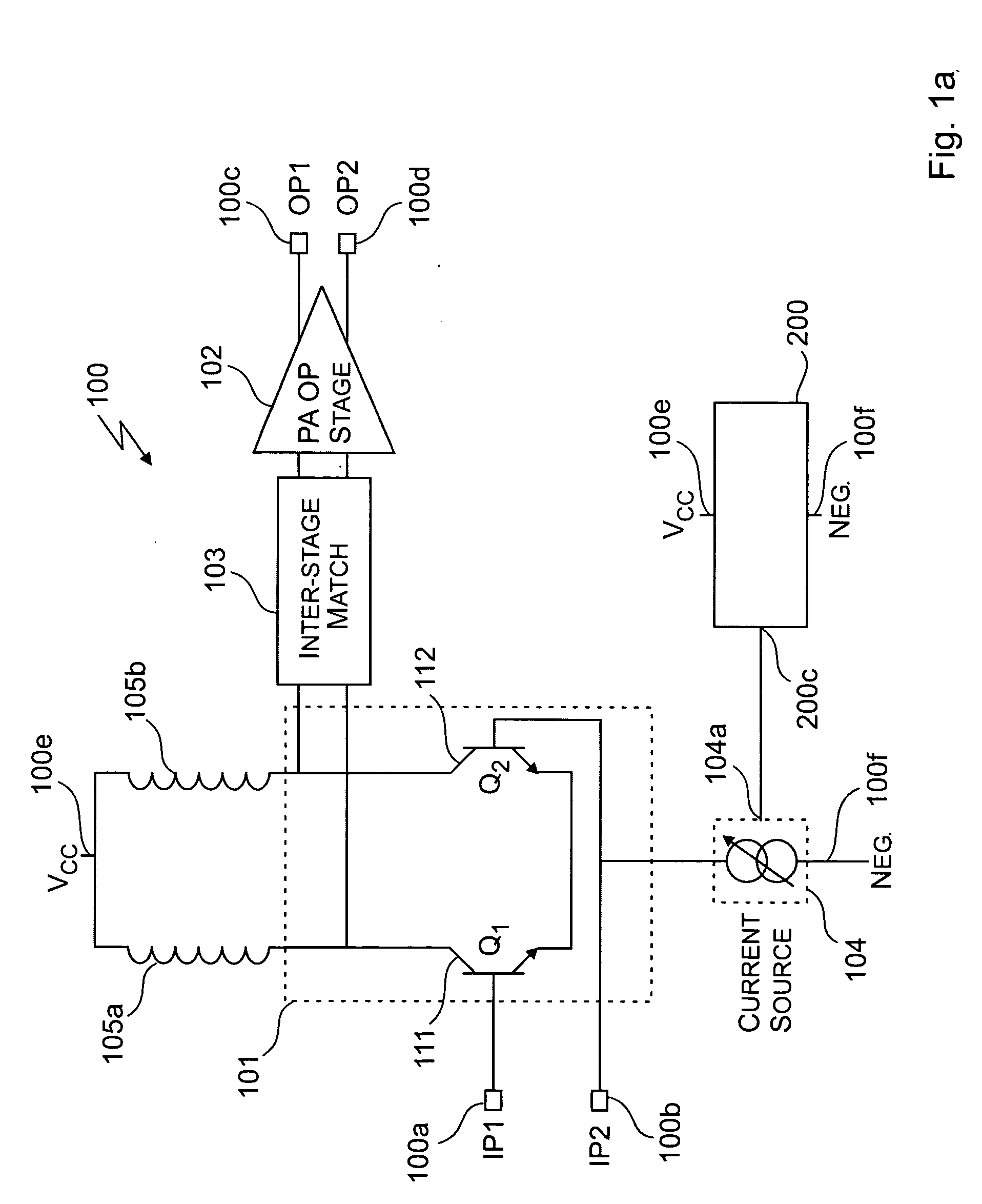
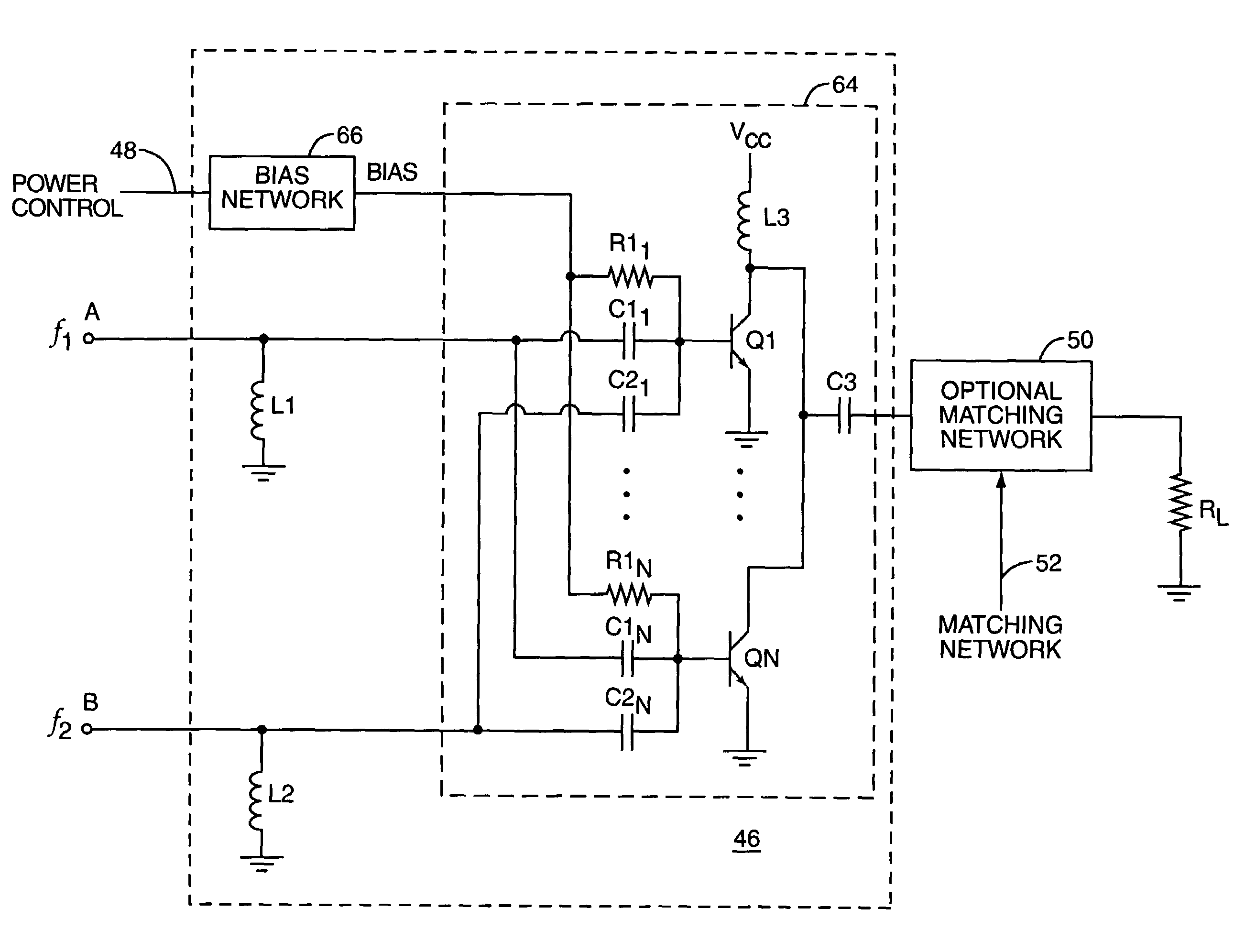
ActiveUS7151411B2High frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierImpedance matching
An embodiment of the present invention provides an amplifier system, comprising at least one variable impedance matching network, the output of which provides the input to at least one amplifier stage or provides an output of the power amplifier itself, and a bias network associated with the at least one amplifier stage. The amplifier system may further comprise a controller enabling impedance control to the at least one variable impedance matching network and a supply voltage provided to the at least one variable impedance network and / or the at least one amplifier stage and wherein the at least one variable impedance network and the at least one amplifier stage may be a plurality of impedance networks connected to a plurality of amplifier stages. The at least one variable impedance network may include at least one variable capacitor and the at least one variable capacitor may be a voltage tunable dielectric capacitor which may include Parascan® voltage tunable dielectric material.
Owner:NXP USA INC
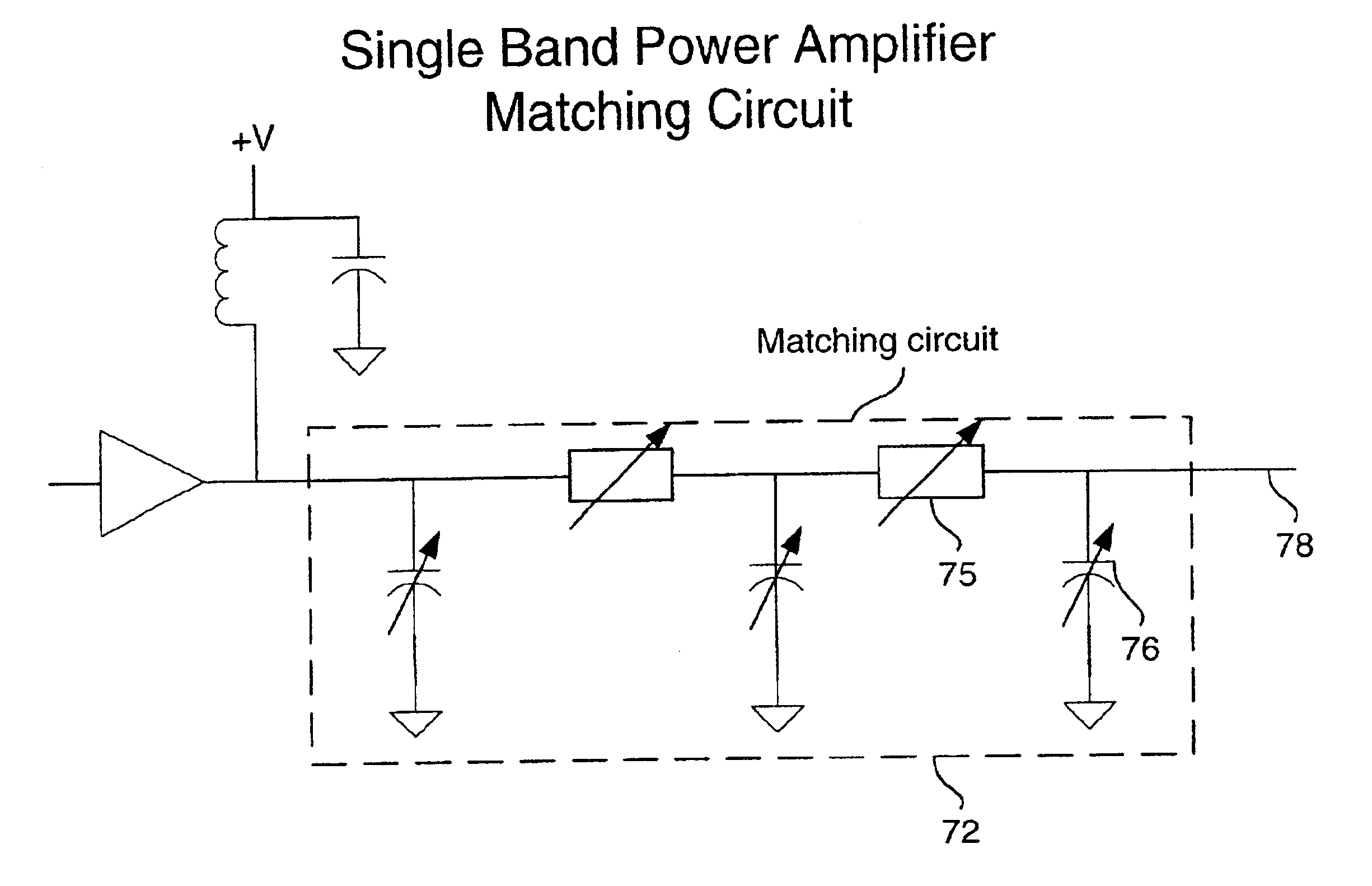
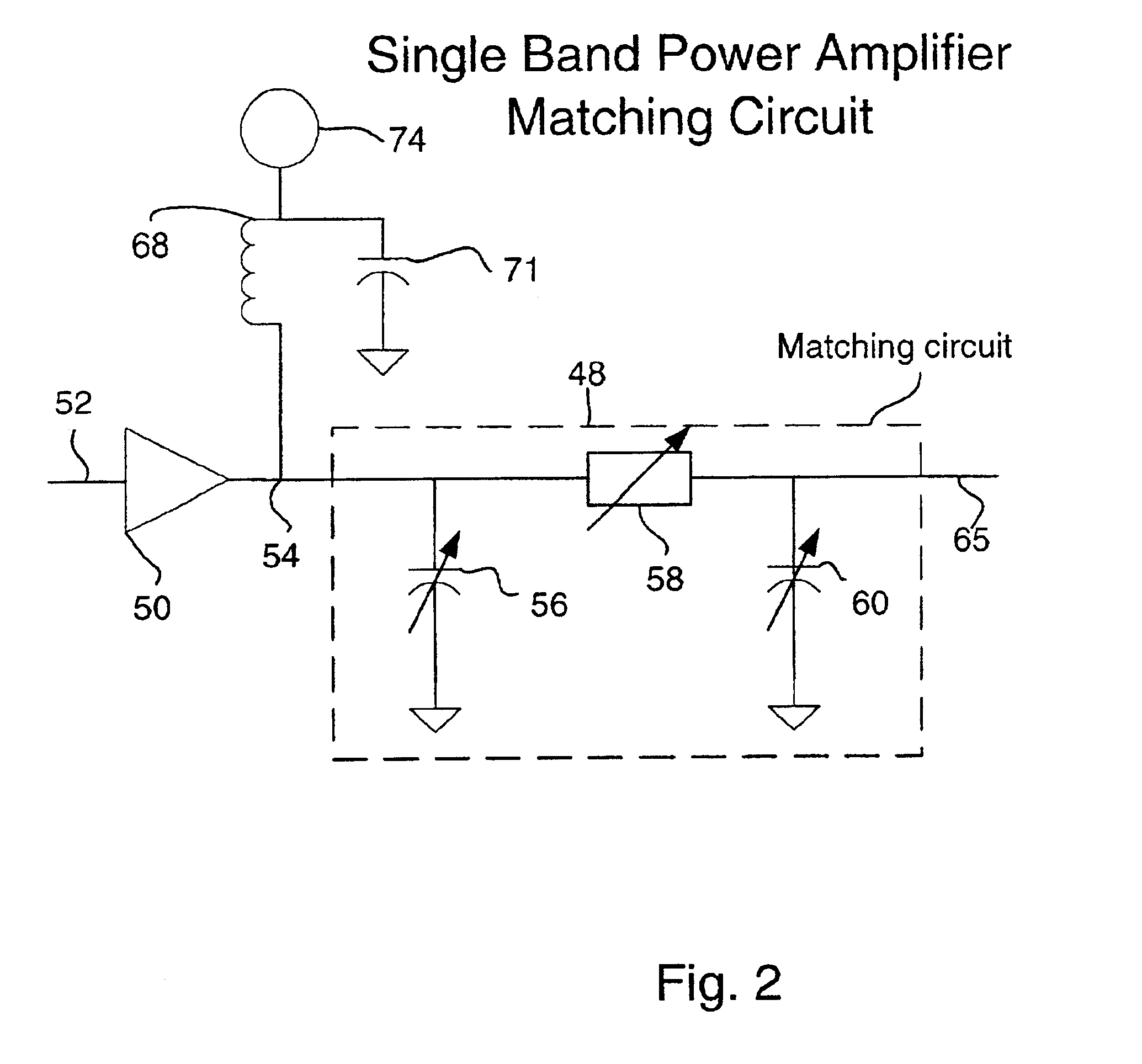
Tunable power amplifier matching circuit
InactiveUS6859104B2Reduce cost and size and power consumptionMultiple-port networksHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
A power amplifier matching circuit is provided. The matching circuit includes a ferro-electric tunable component. A control signal is applied to the tunable component, changing the component's impedance. This changes the impedance of the matching circuit.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
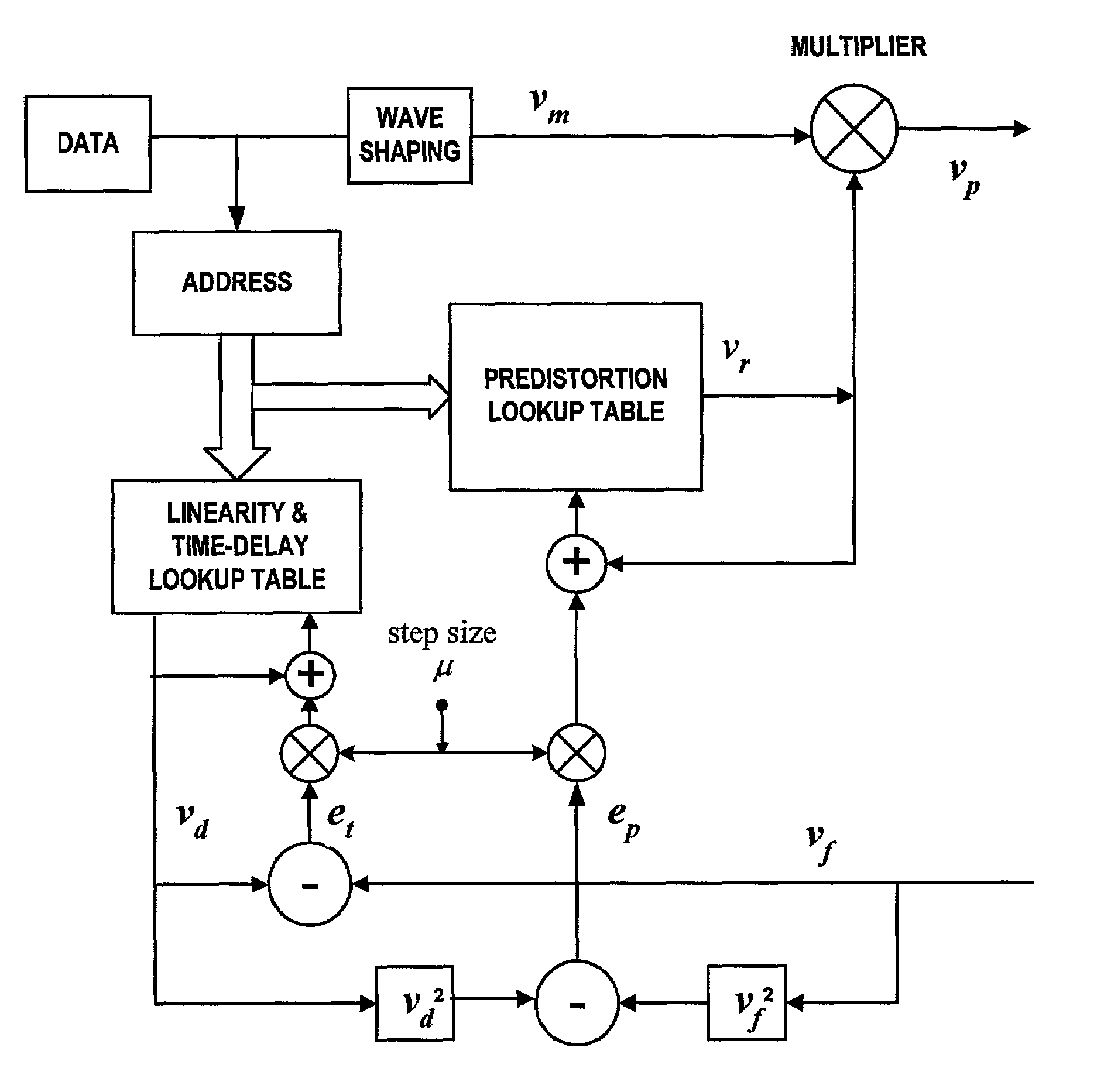
System and method for digital memorized predistortion for wireless communication
ActiveUS6985704B2Error preventionModulated-carrier systemsAudio power amplifierWireless transmission
An embodiment of the invention is a system for signal processing in preparation for wireless transmission, the wireless transmission being from a portable wireless communication device and including use of a power amplifier having nonlinear characteristics. The system includes memory for storing digitally-indexed information. The digitally-indexed information models nonlinear characteristics of the power amplifier, and the digitally-indexed information is stored prior to processing of a first signal that reflects information to be communicated. The system further includes first logic, configured to accept the first signal and to retrieve, based on the first signal, a portion of the digitally-indexed information stored in the memory, and second logic, configured to generate a second signal based on the portion of the digitally-accessed information and on the first signal. The second signal pre-compensates for the nonlinear characteristics of the power amplifier, and the second signal is for wireless transmission based on the second signal.
Owner:DALI WIRELESS
High efficiency amplification
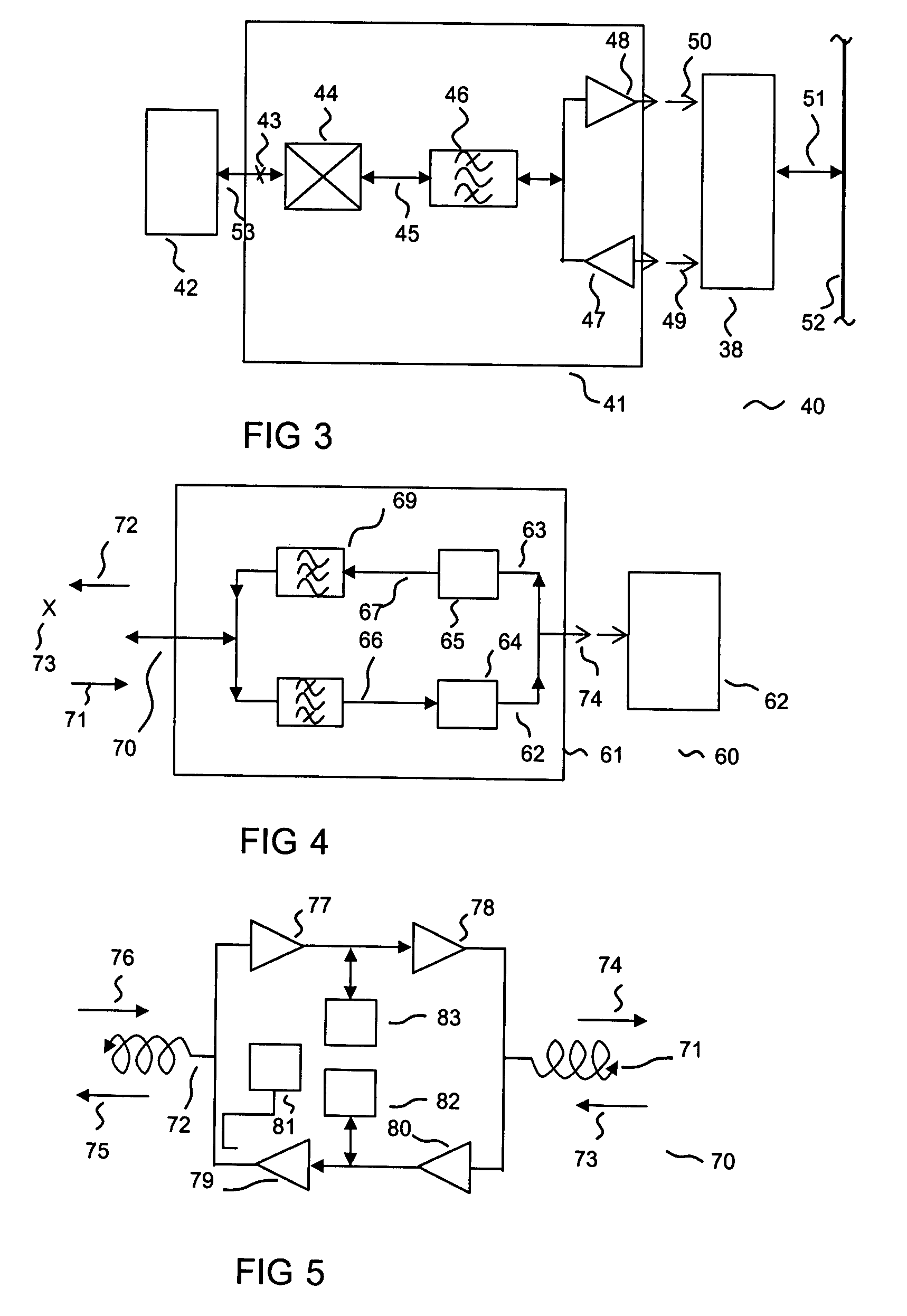
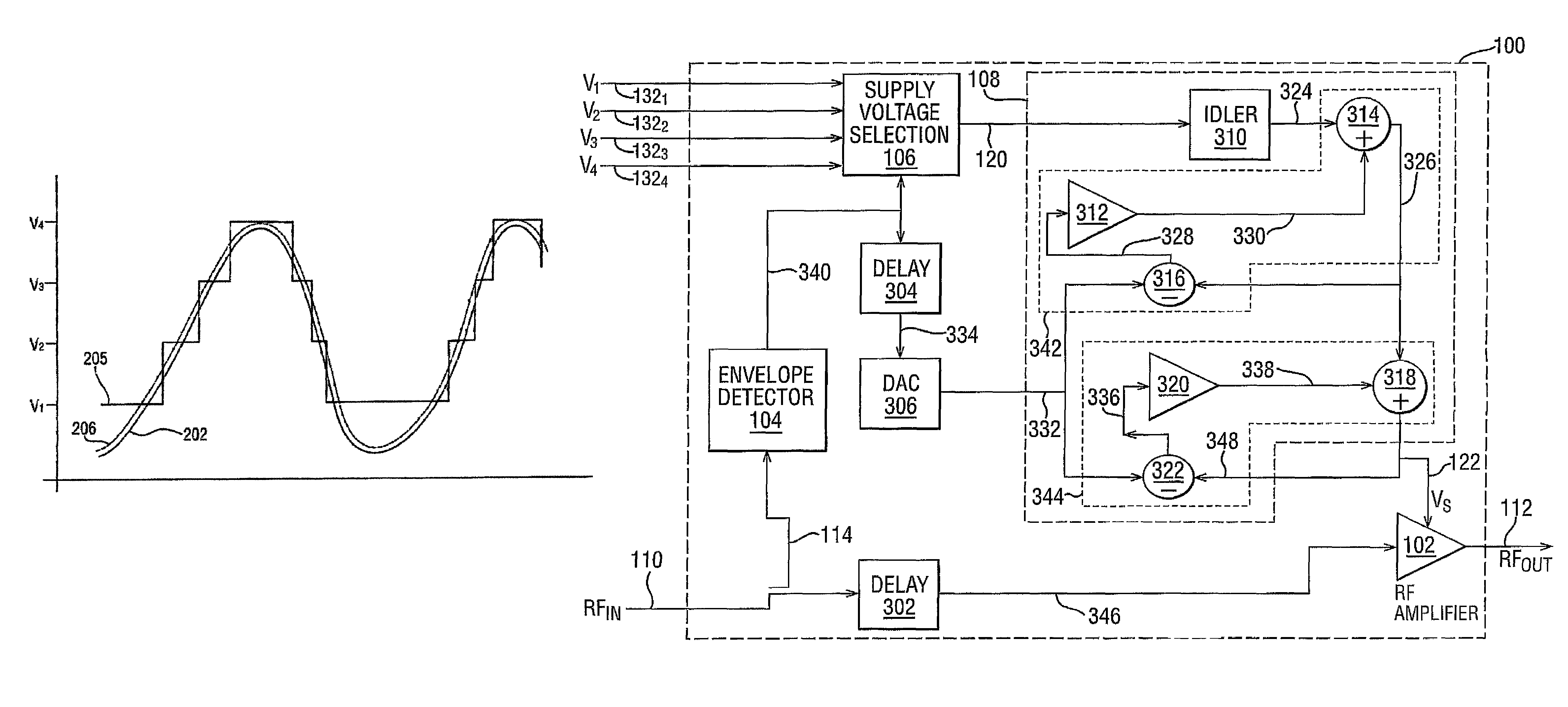
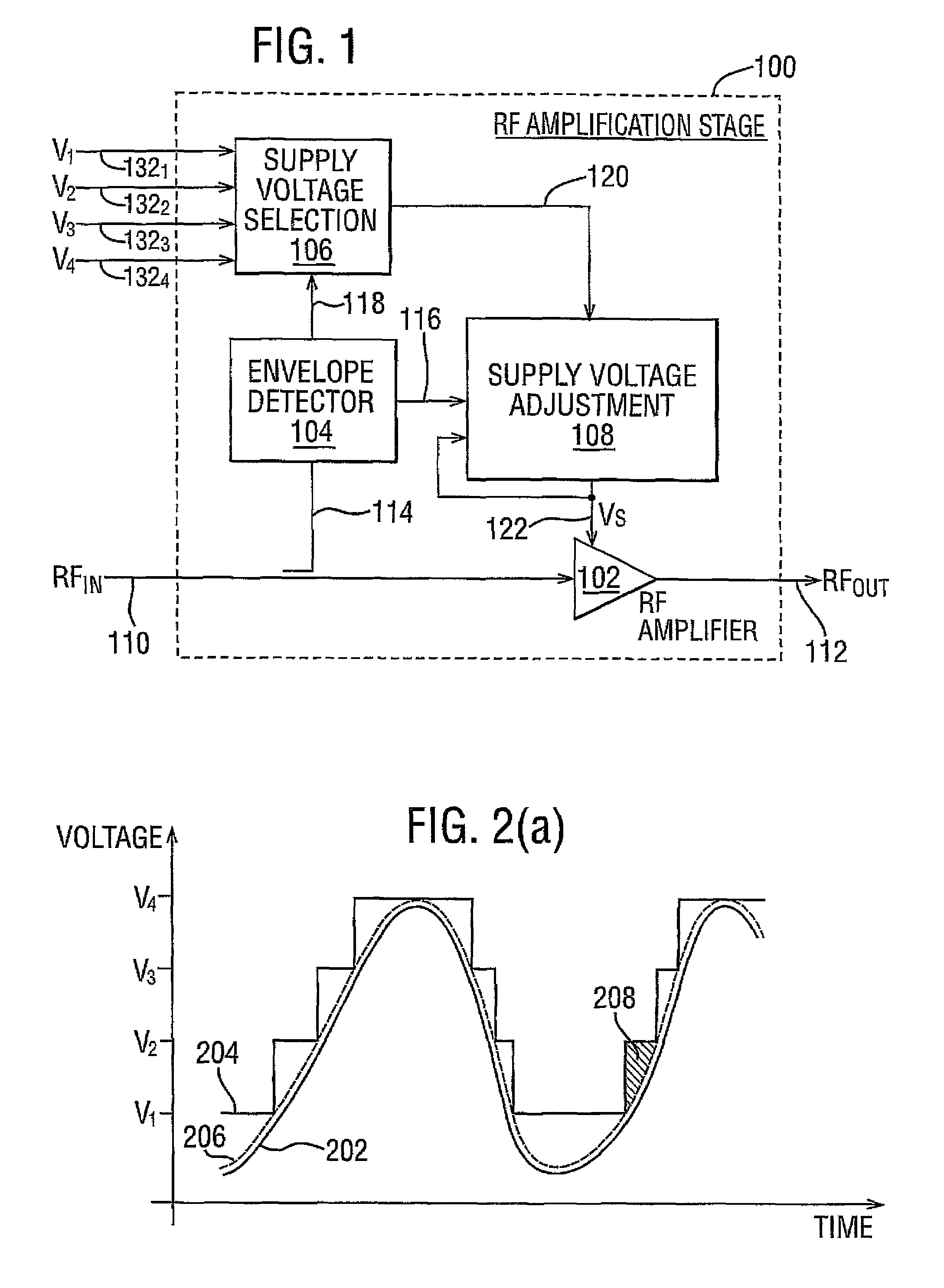
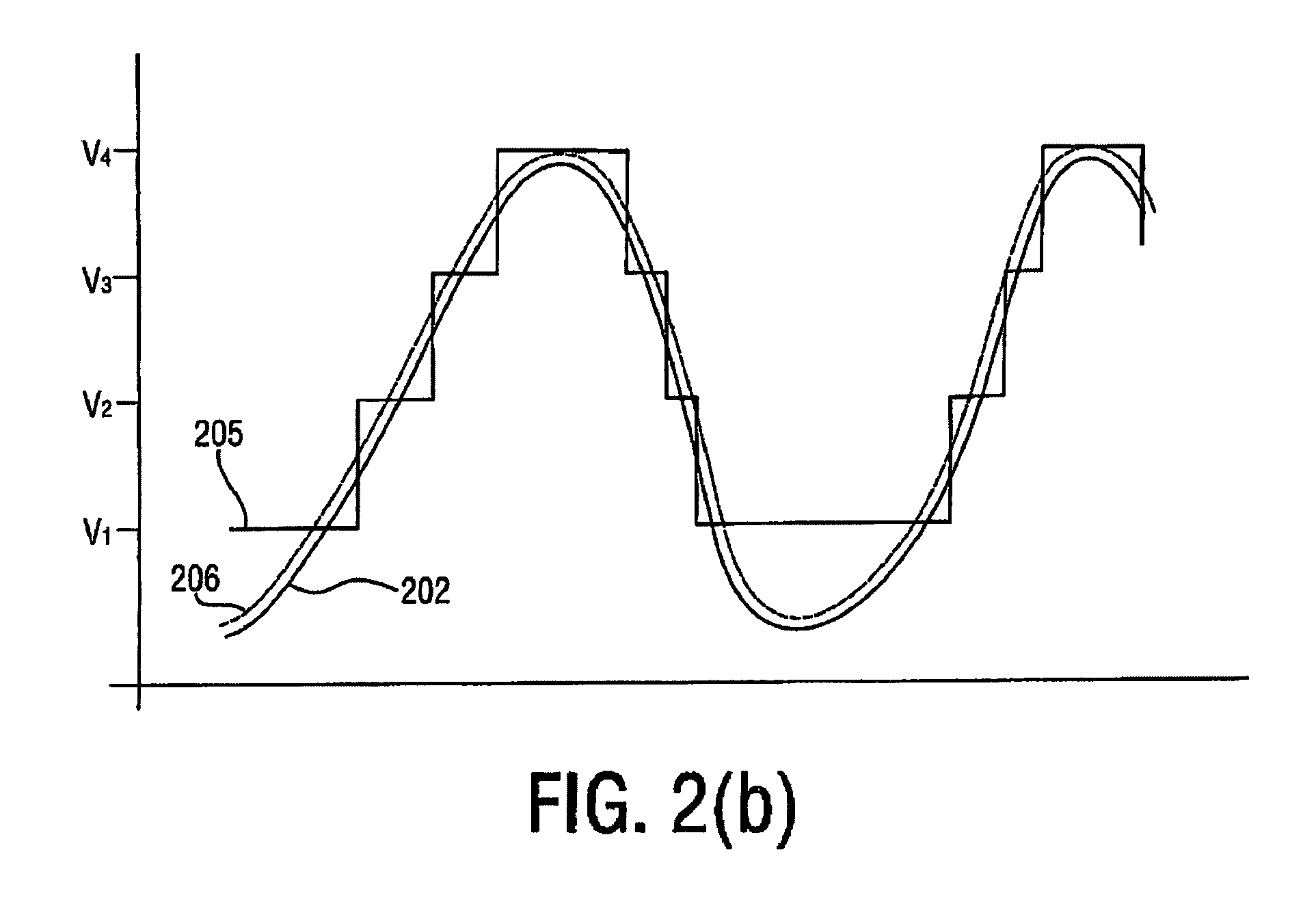
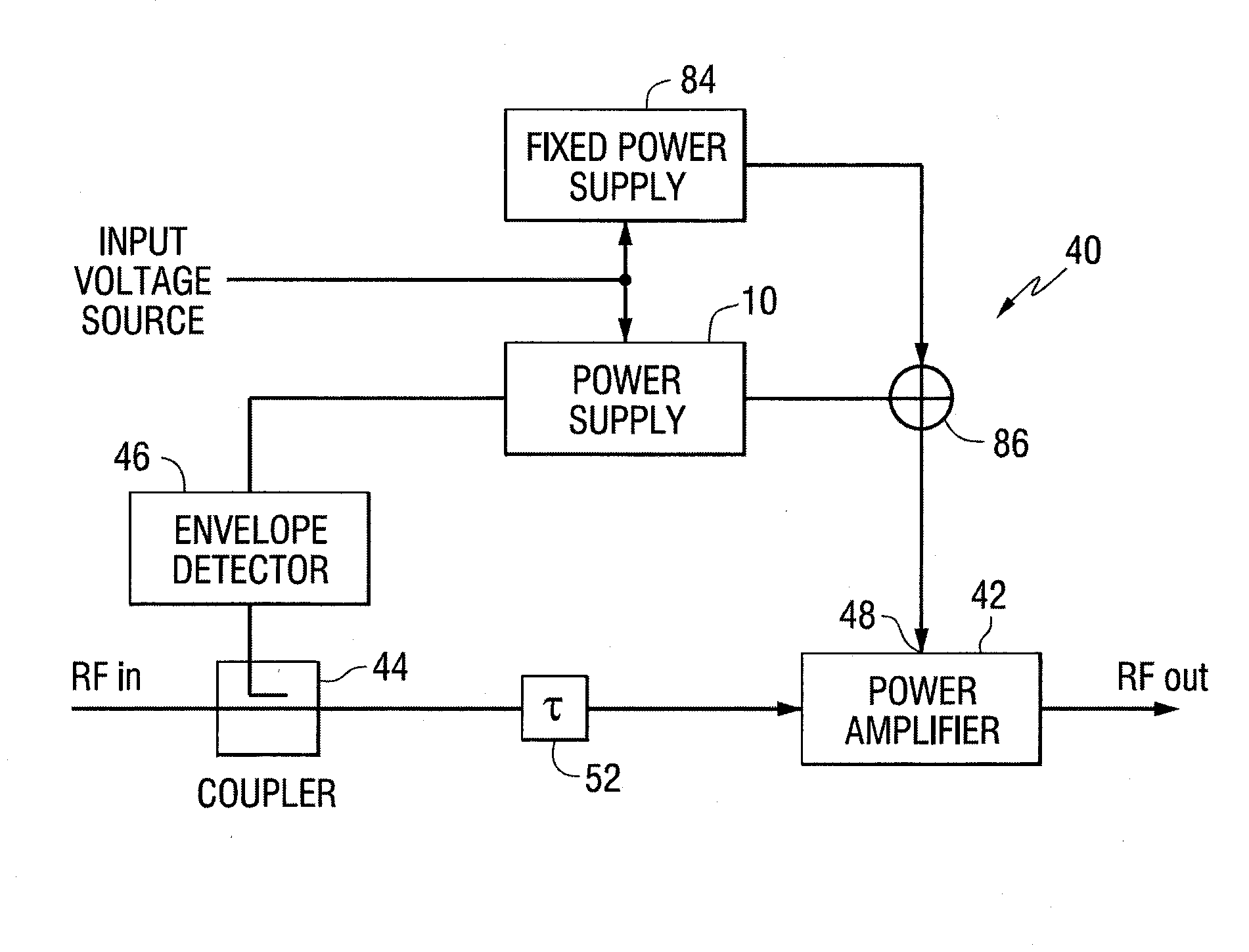
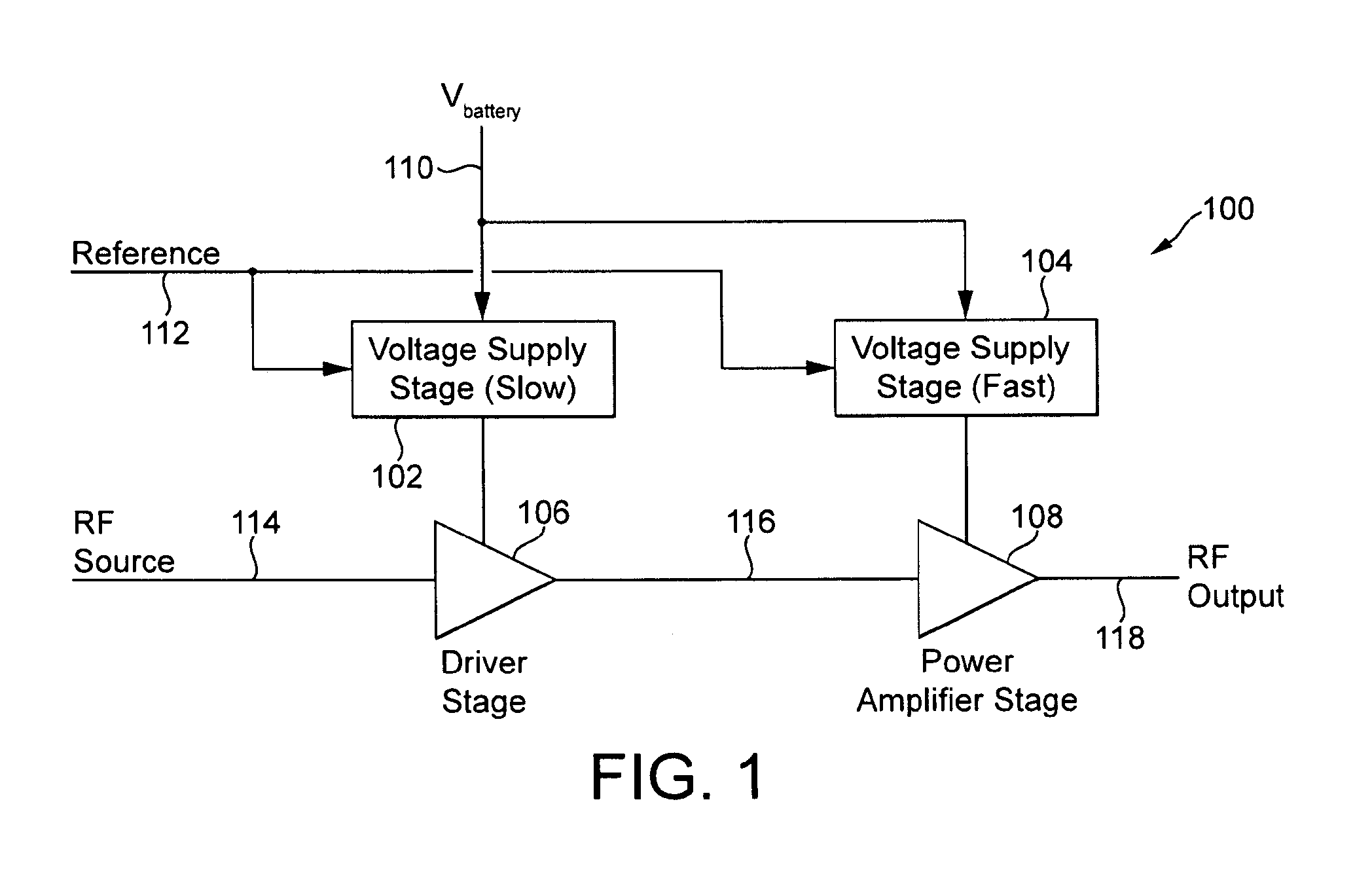
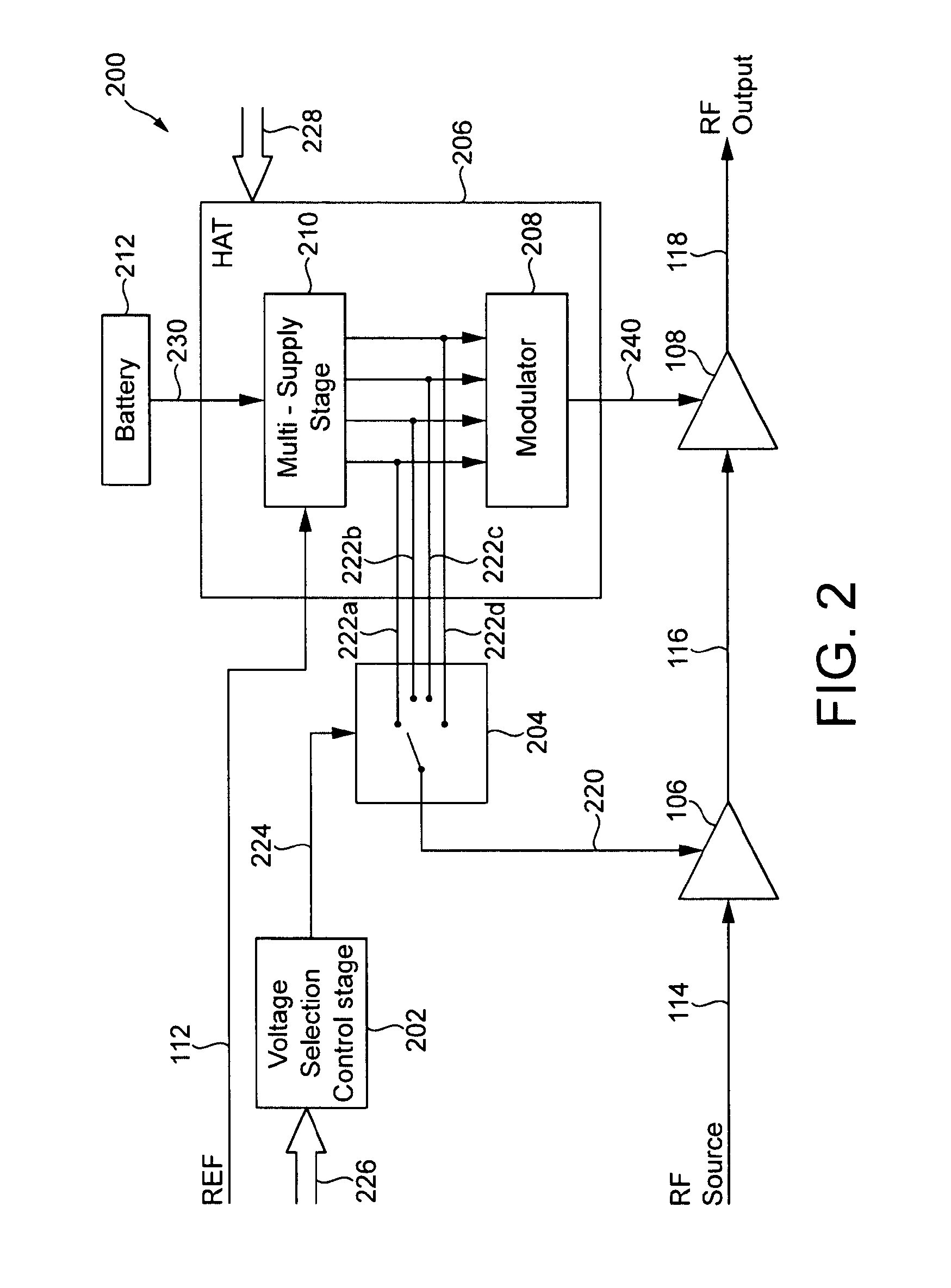
InactiveUS7482869B2Fast corrective loopWide bandwidthHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierSignal envelope
A radio frequency amplification stage including an amplifier for receiving an input signal to be amplified and a power supply voltage; and a power supply voltage stage for supplying said power supply voltage, including a circuit for providing a reference signal representing the envelope of the input signal; a circuit for selecting one of a plurality of supply voltage levels in dependence on the reference signal; and a circuit for generating an adjusted selected power supply voltage, including an ac amplifier for amplifying a difference between the reference signal and one of the selected supply voltage level or the adjusted selected supply voltage level, and a summer for summing the amplified difference with the selected supply voltage to thereby generate the adjusted supply voltage.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Gain boosting RF gain stage with cross-coupled capacitors
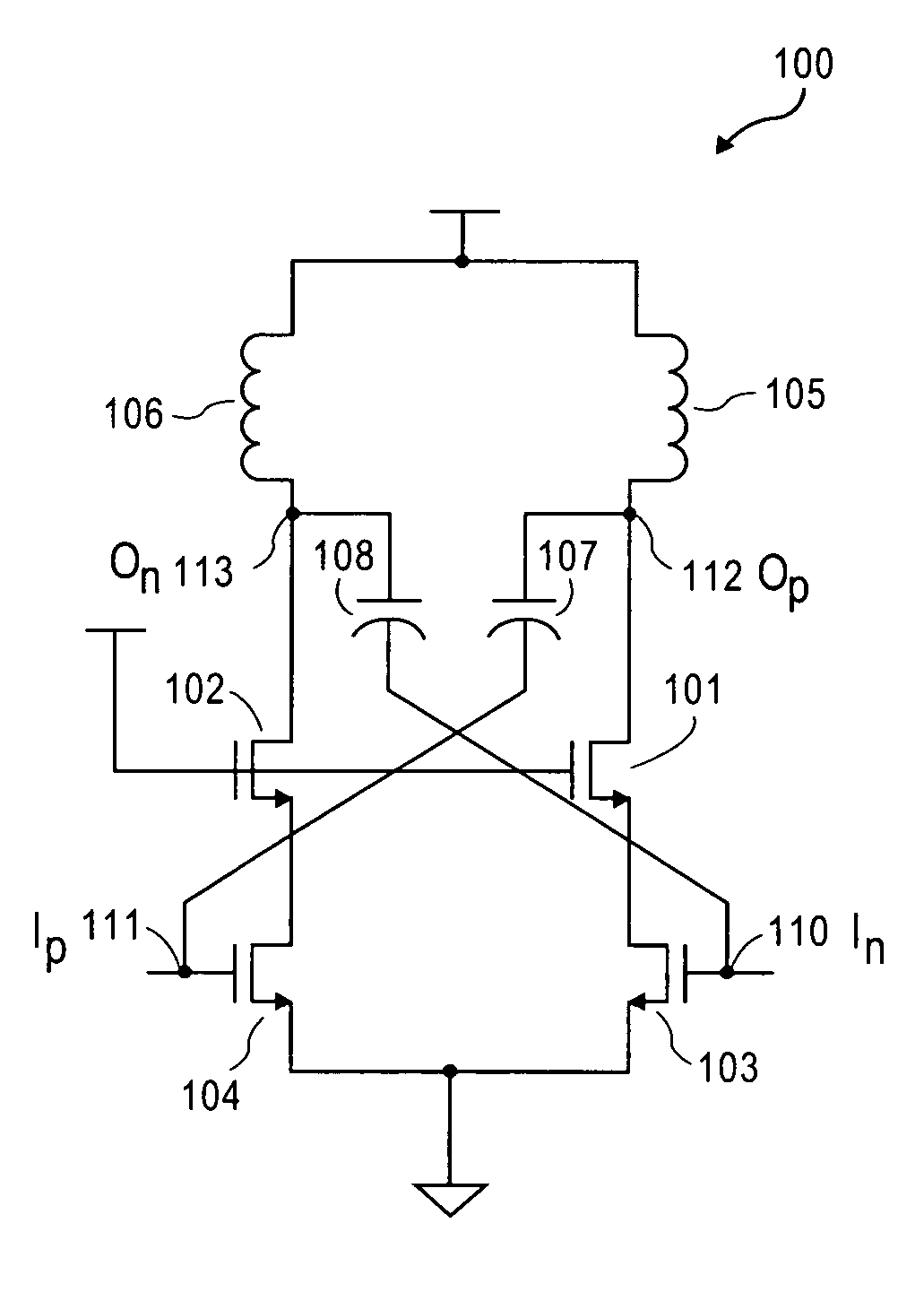
ActiveUS7697915B2Tighter current flow controlHigh gainHigh frequency amplifiersRadio transmissionCapacitanceGain stage
A RF differential gain stage has cross-coupled capacitors between input and output nodes of the amplifier stage to boost gain. The gain boost allows cancellation of the series resistance of an inductive load of the amplifier stage.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
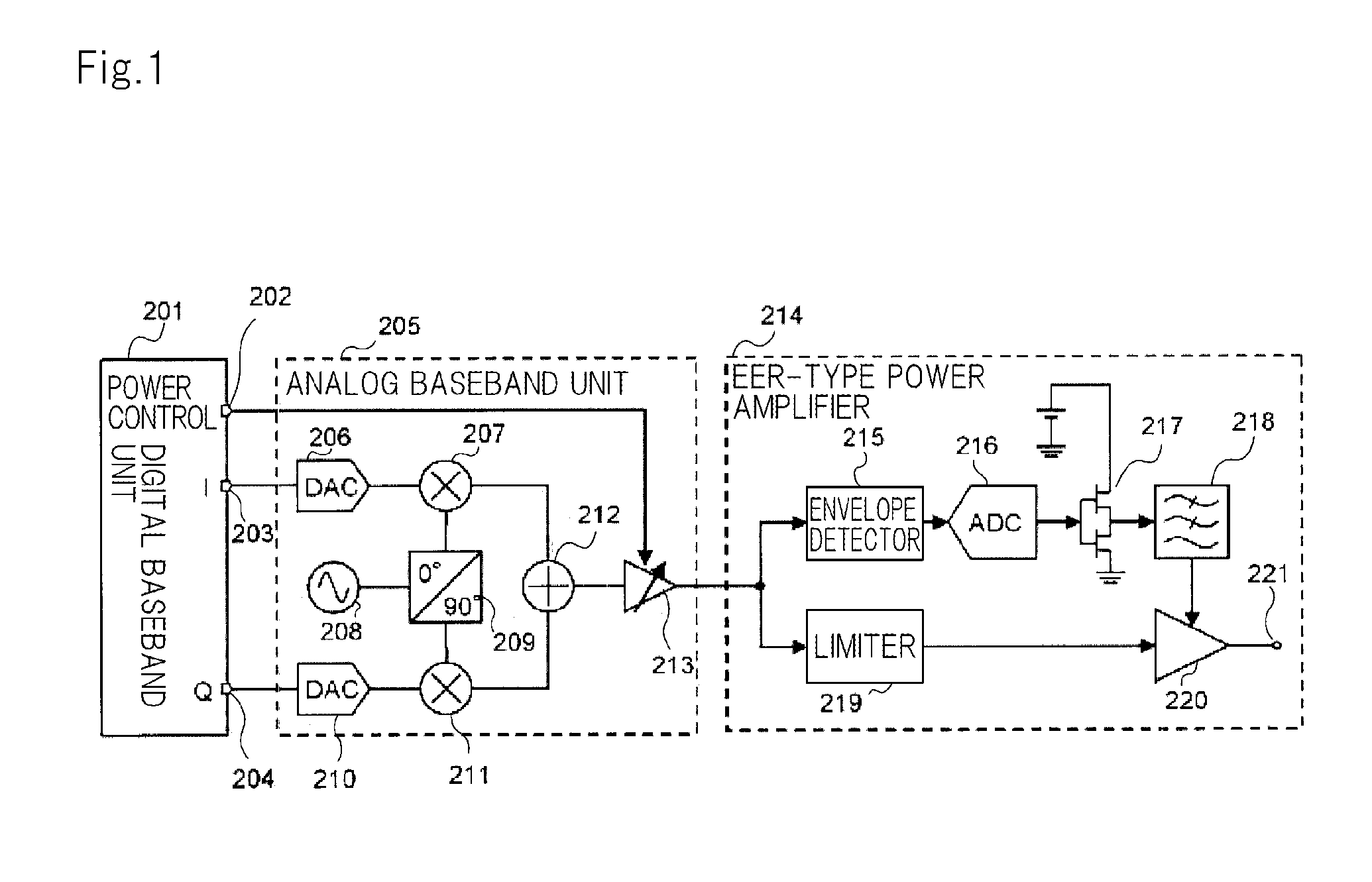
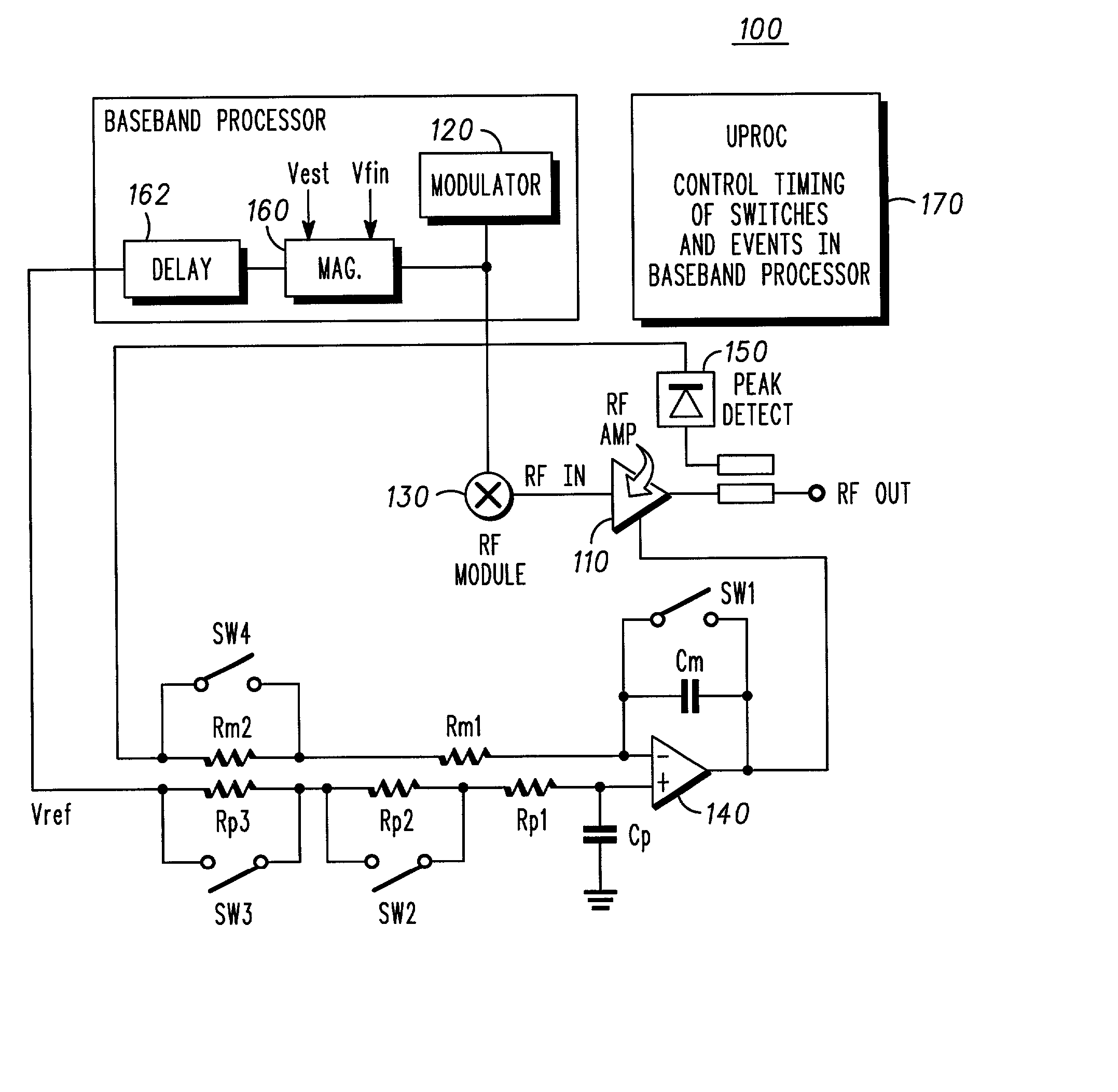
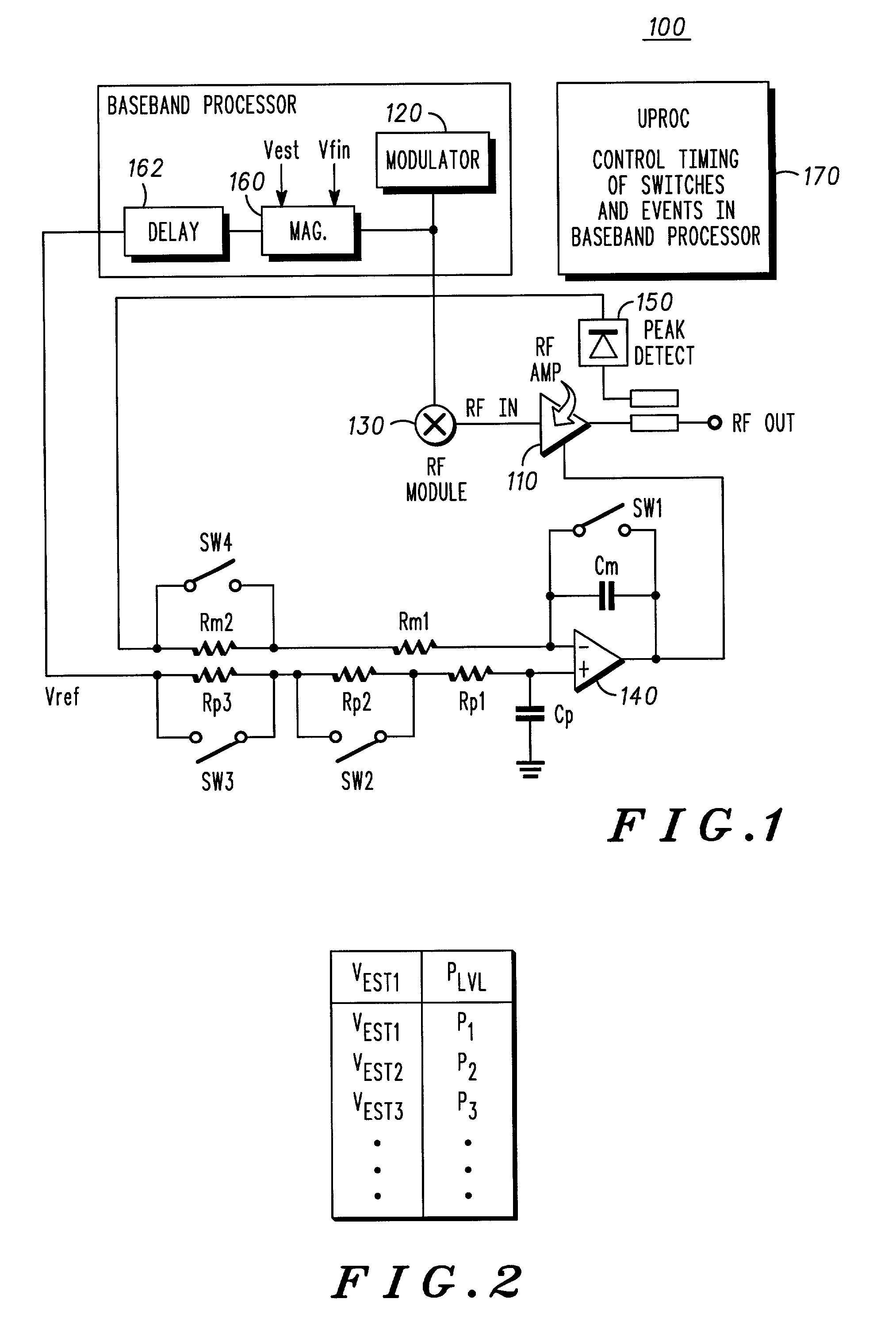
RF transmitter with variably biased RF power amplifier and method therefor
InactiveUS20070281635A1More powerSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasPeak valueWide band
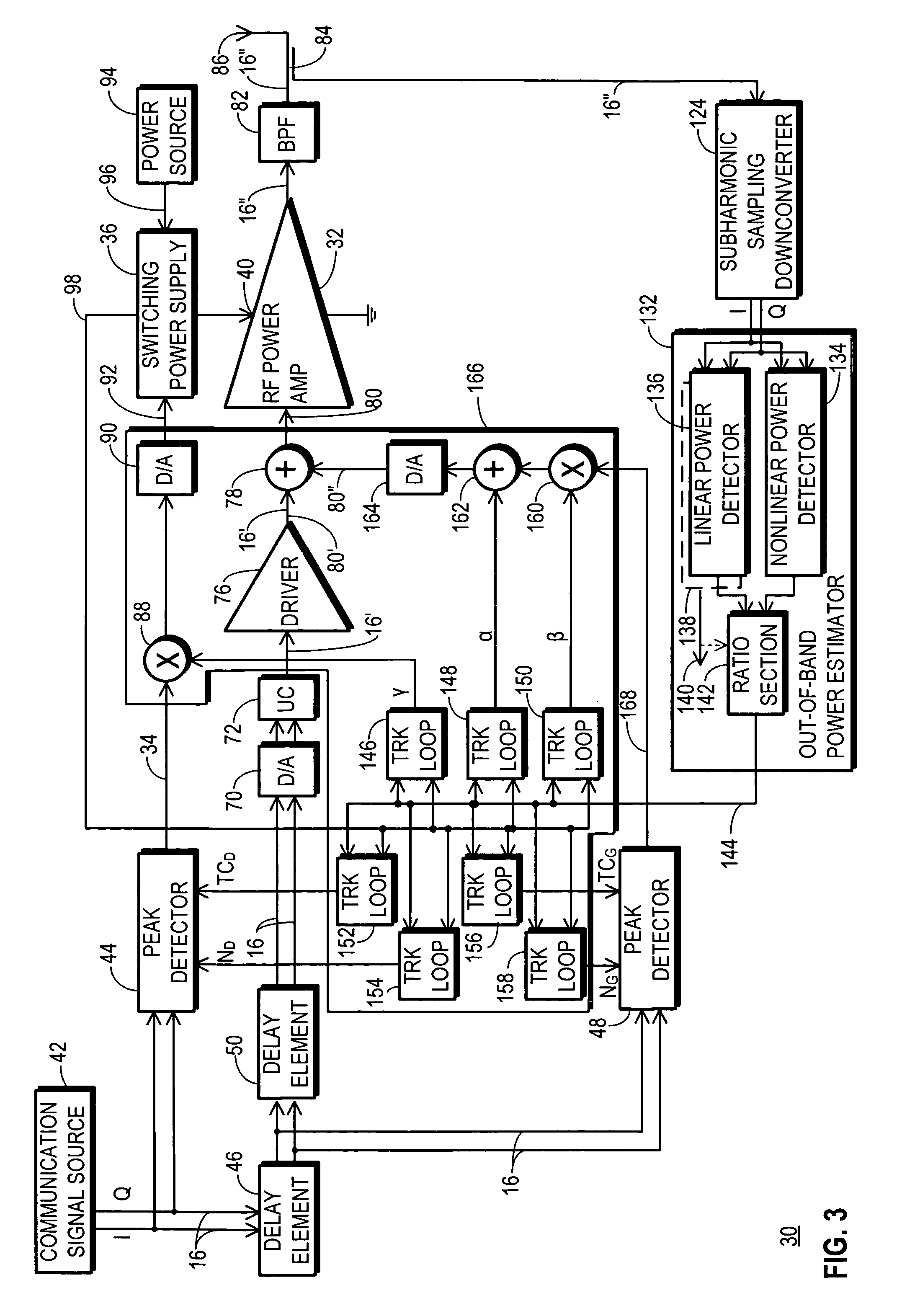
An RF transmitter (30) includes an RF power amplifier (32) for which the power input bias voltage (40) and signal input bias voltage (80) are controlled within feedback loops. A peak detector (44) generates a lowered-spectrum, peak-tracking signal (34) that follows the largest amplitude peaks of a wide bandwidth communication signal (16) but exhibits a lower bandwidth. This signal (34) is scaled in response to the operation of a drain bias tracking loop (146) then used to control a switching power supply (36) that generates the power input bias voltage. The tracking loop (146) is responsive to out-of-band power detected in a portion of the amplified RF communication signal (16″). A ratio of out-of-band power (128) to in-band power (126) is manipulated in the tracking loop (146) so that the power input bias voltage is modulated in a way that holds the out-of-band power at a desired predetermined level.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
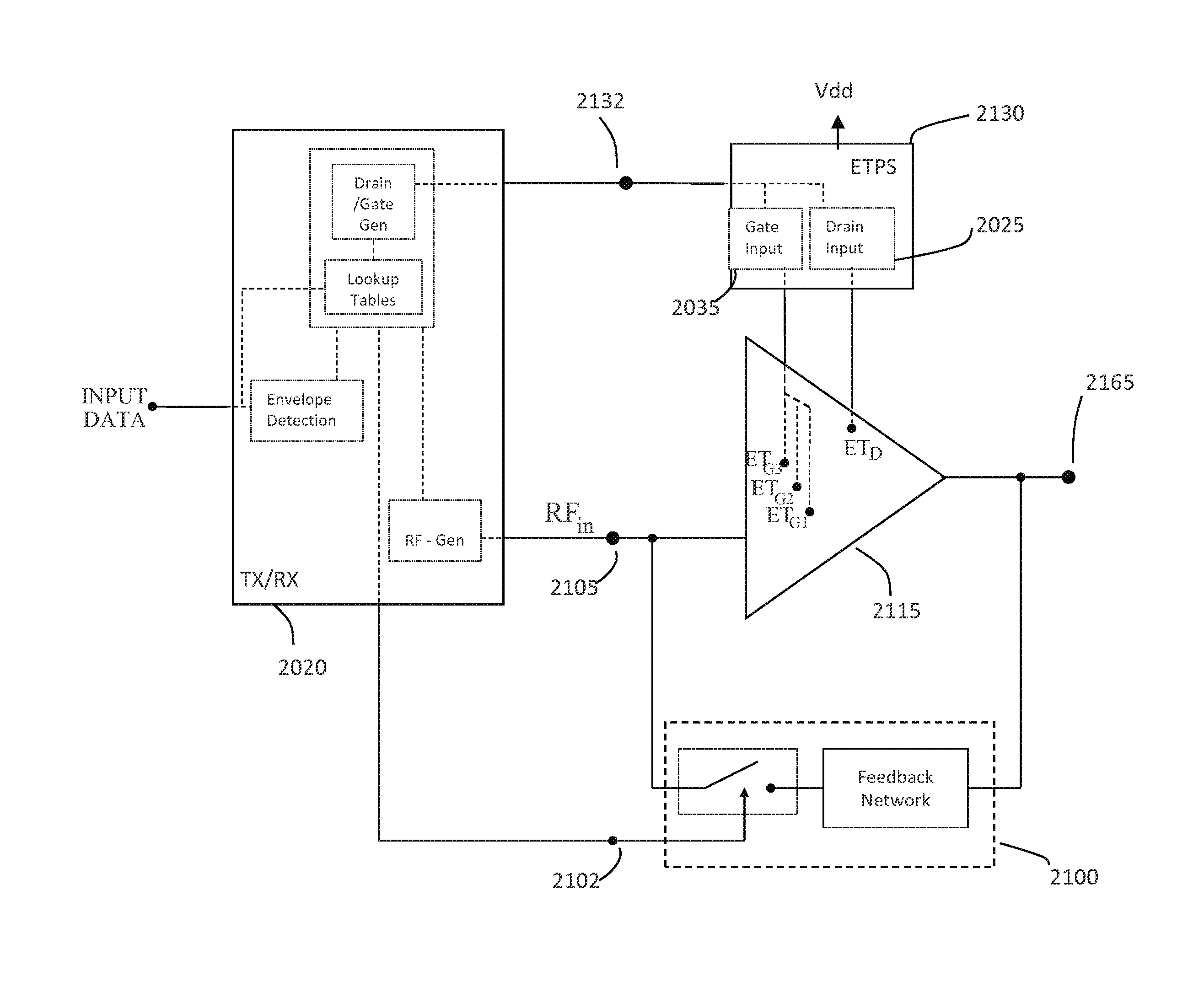
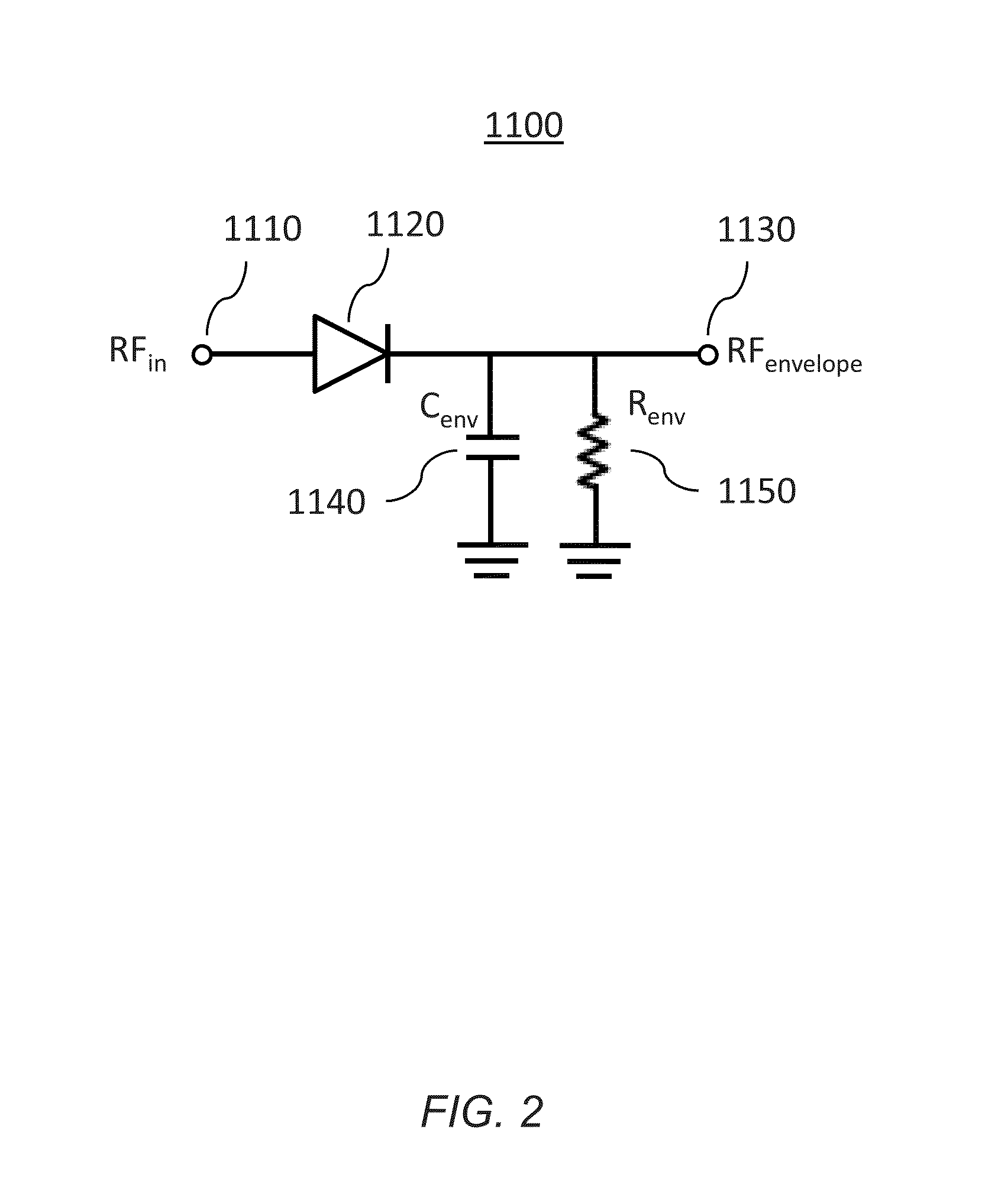
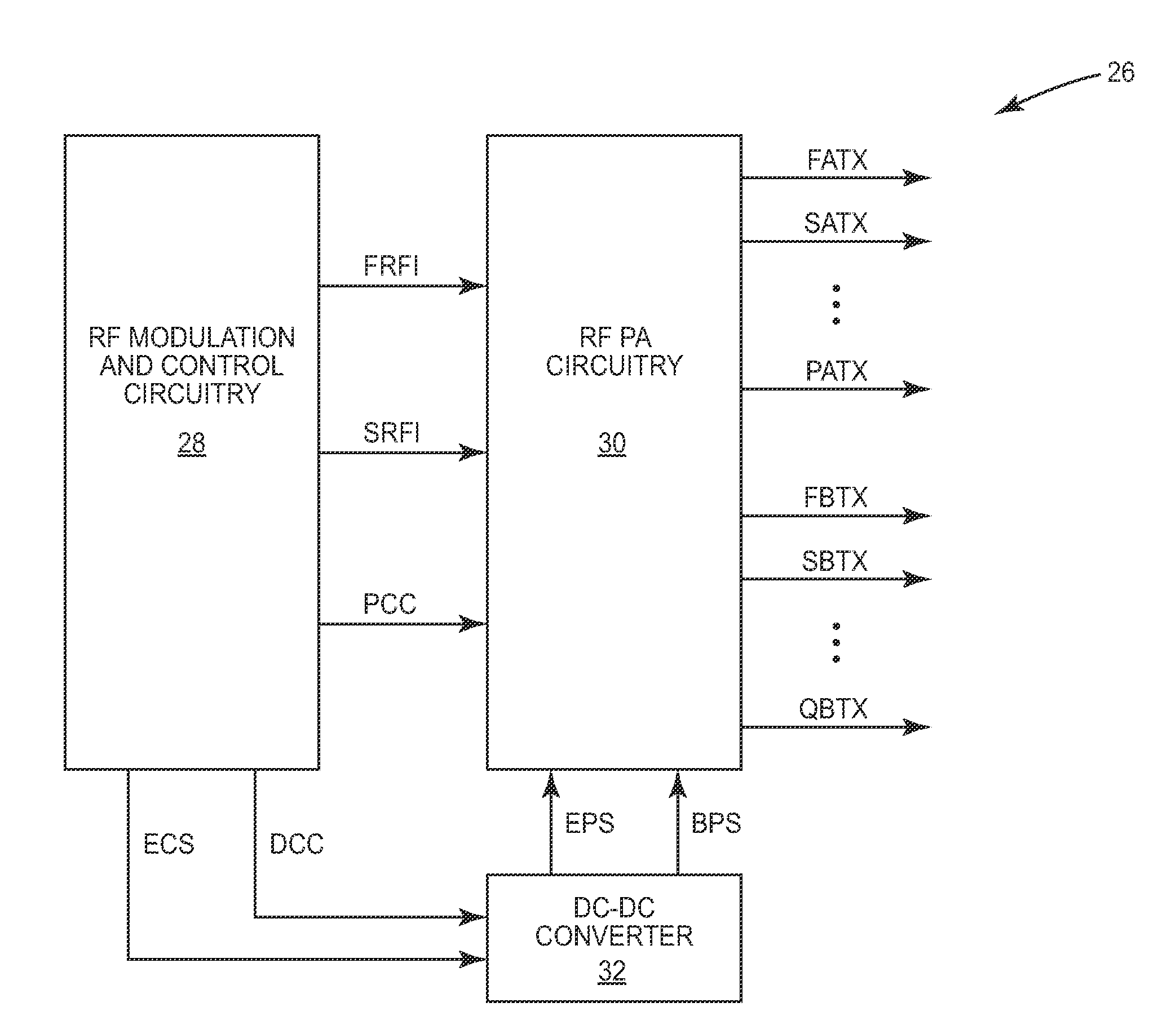
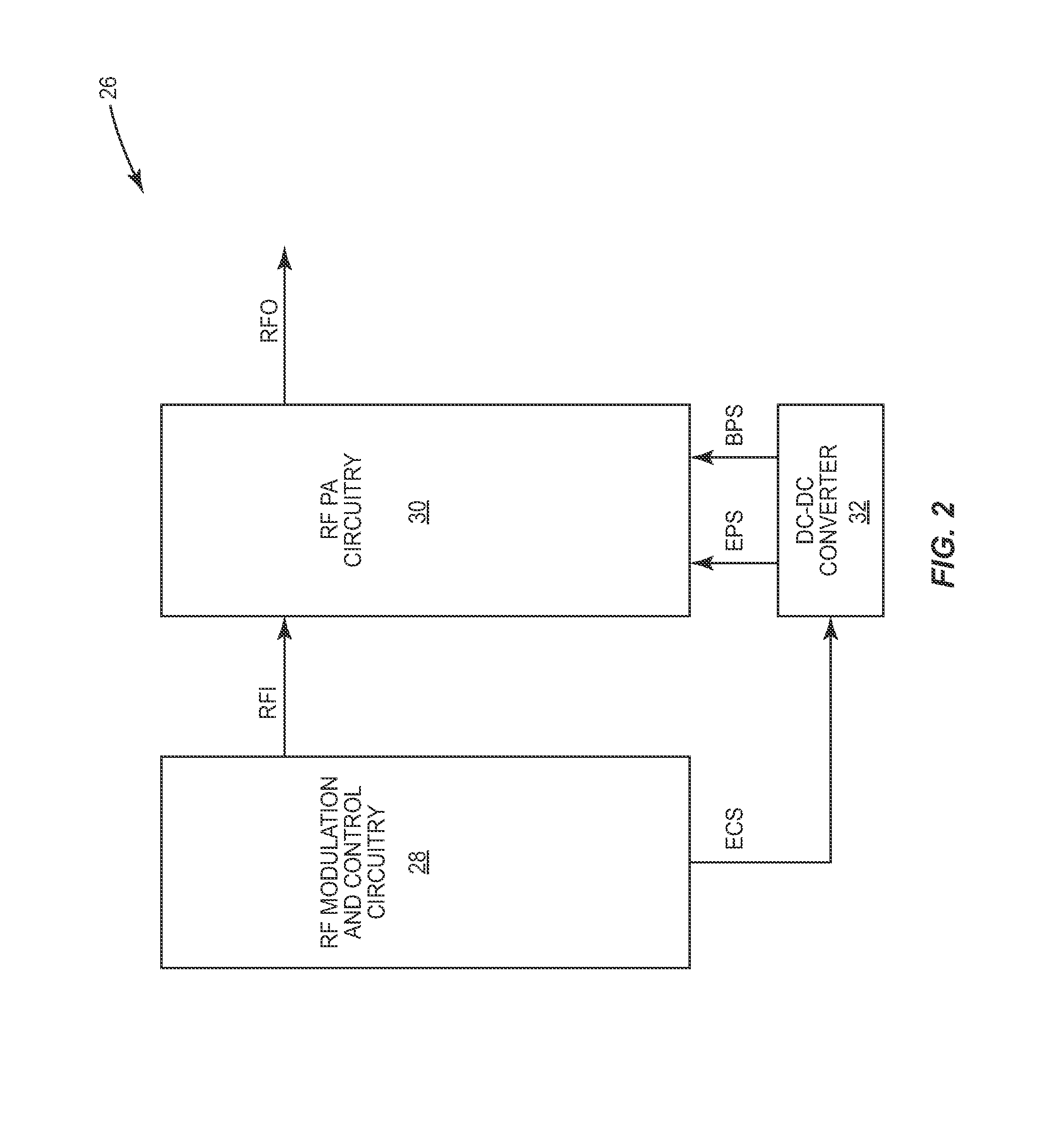
Pa envelope power supply undershoot compensation
ActiveUS20120299647A1Prevent undershootHigh frequency amplifiersGated amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
A power amplifier (PA) envelope power supply, which provides an envelope power supply signal to radio frequency (RF) PA circuitry, and a process to prevent undershoot of the PA envelope power supply is disclosed. The process includes determining if an envelope control signal to the PA envelope power supply has a step change from a high magnitude to a low magnitude that exceeds a step change limit. Such a step change may cause undershoot of the PA envelope power supply. As such, if the step change exceeds the step change limit, the envelope control signal is modified to use an intermediate magnitude for period of time. Otherwise, if the step change does not exceed the step change limit, the envelope control signal is not modified.
Owner:QORVO US INC
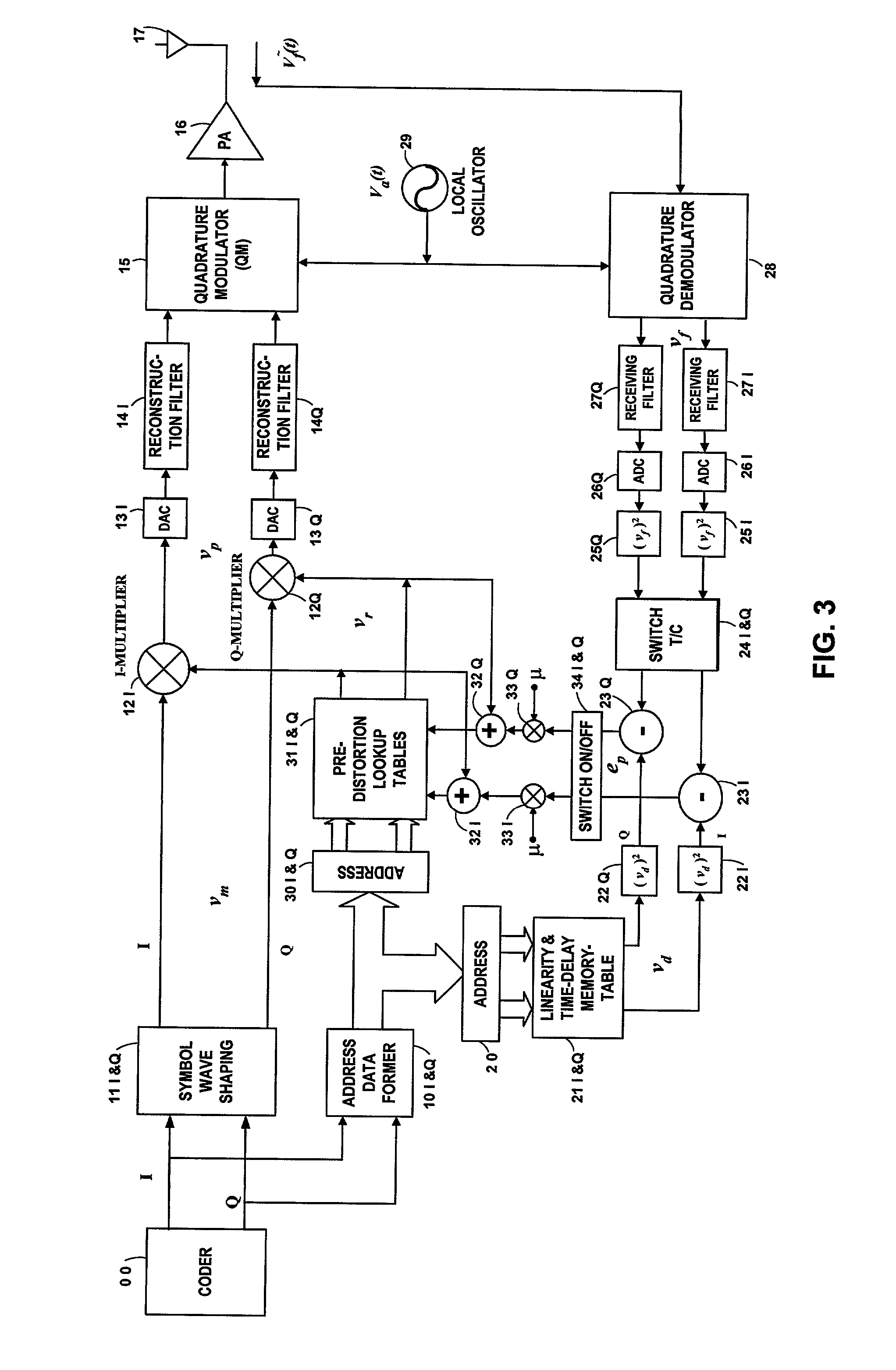
Digital Hybrid Mode Power Amplifier System
InactiveUS20080265996A1High performance and cost-effectiveImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersPeak valueMulti carrier
A RF-digital hybrid mode power amplifier system for achieving high efficiency and high linearity in wideband communication systems is disclosed. The present invention is based on the method of adaptive digital predistortion to linearize a power amplifier in the RF domain. The power amplifier characteristics such as variation of linearity and asymmetric distortion of the amplifier output signal are monitored by the narrowband feedback path and controlled by the adaptation algorithm in a digital module. Therefore, the present invention could compensate the nonlinearities as well as memory effects of the power amplifier systems and also improve performances, in terms of power added efficiency, adjacent channel leakage ratio and peak-to-average power ratio. The present disclosure enables a power amplifier system to be field reconfigurable and support multi-modulation schemes (modulation agnostic), multi-carriers and multi-channels. As a result, the digital hybrid mode power amplifier system is particularly suitable for wireless transmission systems, such as base-stations, repeaters, and indoor signal coverage systems, where baseband I-Q signal information is not readily available.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
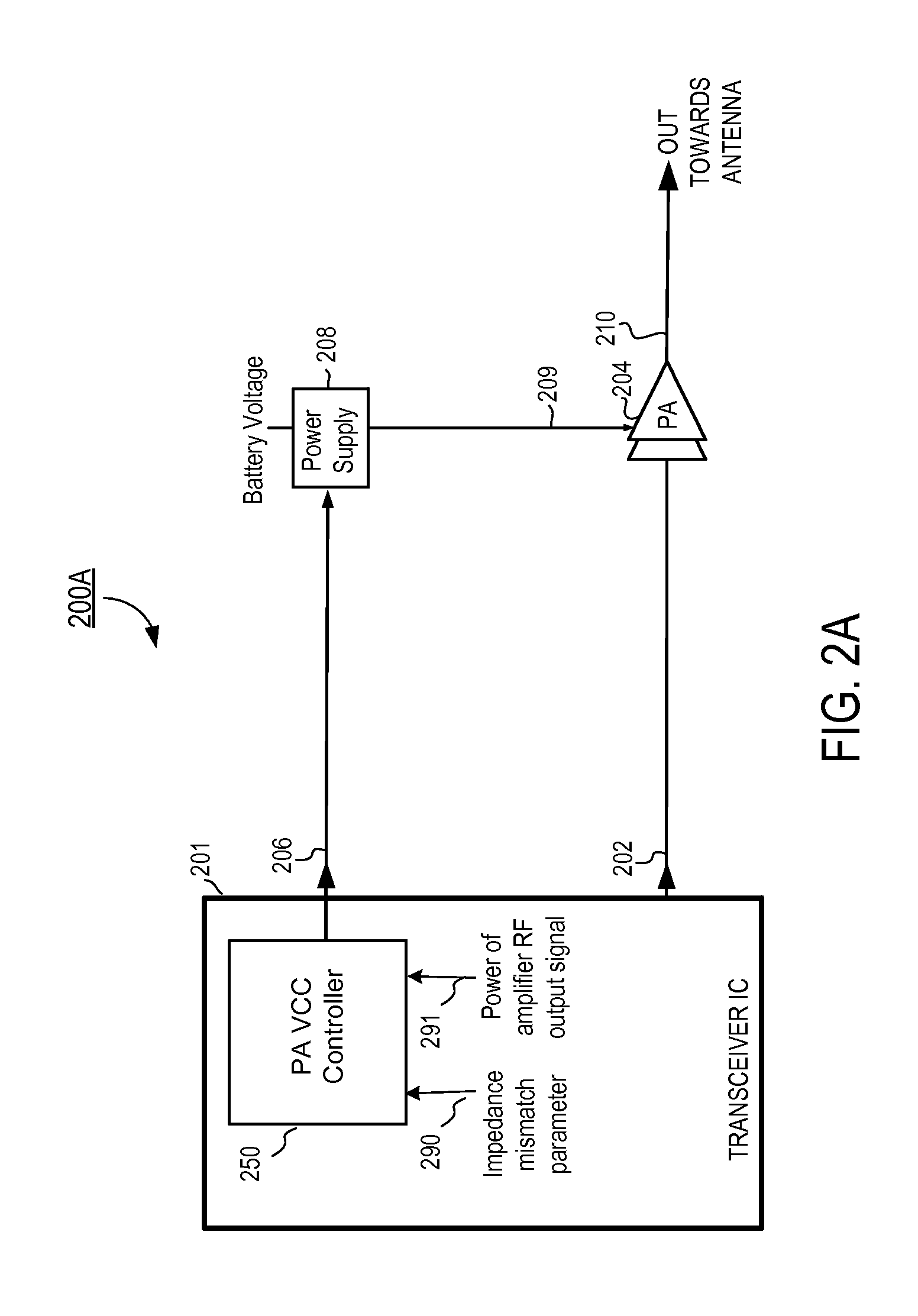
RF power amplifier circuit with mismatch tolerance
ActiveUS8183917B2Improve efficiencyReduce phase distortionHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
Owner:QUANTANCE
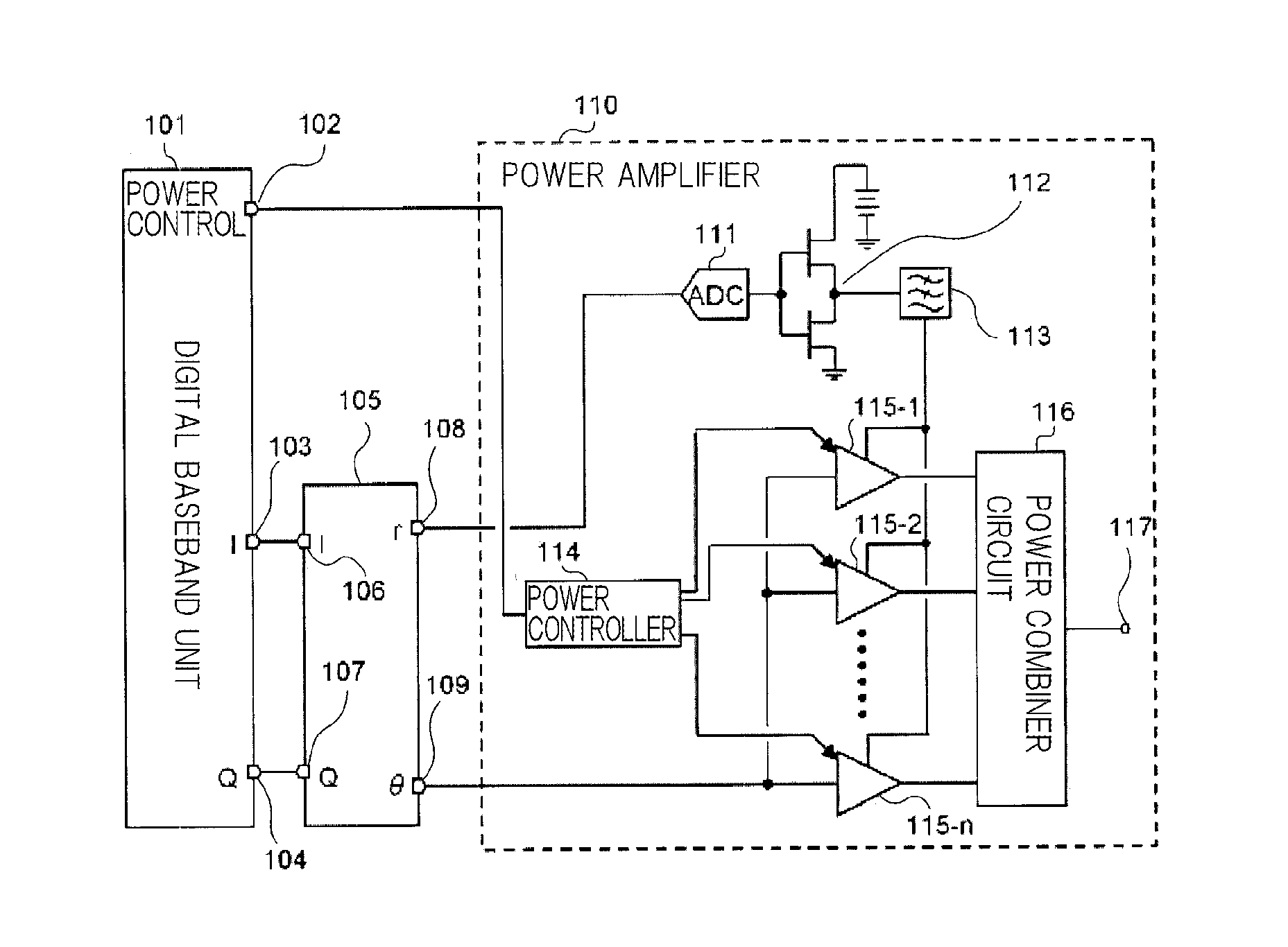
Power amplifier and radio wave transmitter having the same
ActiveUS20100266066A1Eliminate high frequency noiseNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsPower controllerHigh frequency power
A power amplifier (10) comprises: an A / D converter (11) for converting, to a time discrete signal, an envelope signal included in a high-frequency modulated signal and including only an amplitude modulated component of the high-frequency modulated signal; a switching amplifier (12) for amplifying the output signal of the A / D converter (11); a low-pass filter (13) for removing high frequency noise from the output signal of the switching amplifier (12); a plurality of high-frequency power amplifiers (15-1 to 15-n) for receiving the output signal of the low-pass filter (13) as a power supply and for amplifying a carrier signal included in the high-frequency modulated signal; and a power controller (14) for adjusting the average power of the output signal of the power amplifier (10) by controlling the total gains of the plurality of high-frequency power amplifiers (15-1 to 15-n).
Owner:NEC CORP
Remote radio head unit system with wideband power amplifier and method
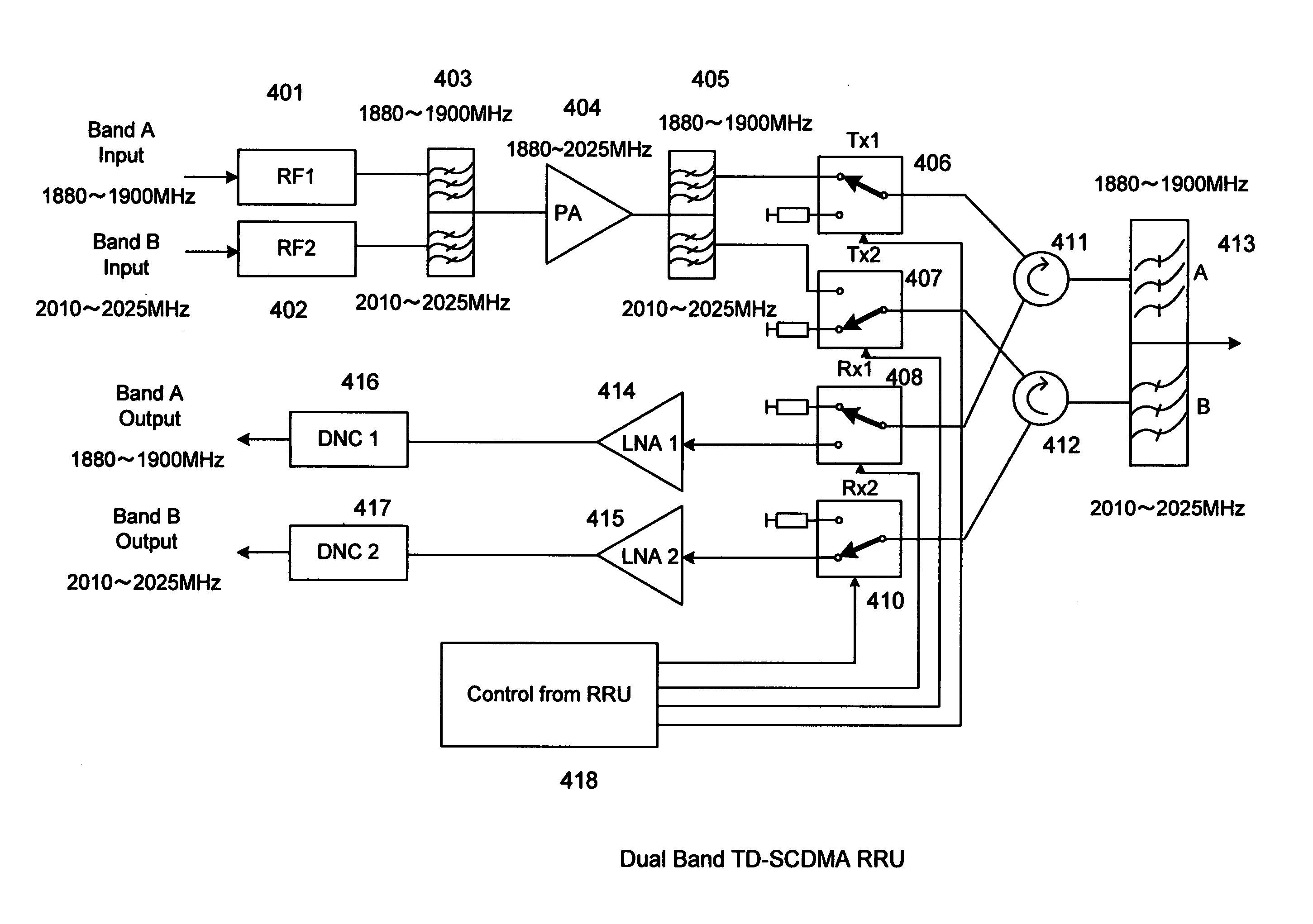
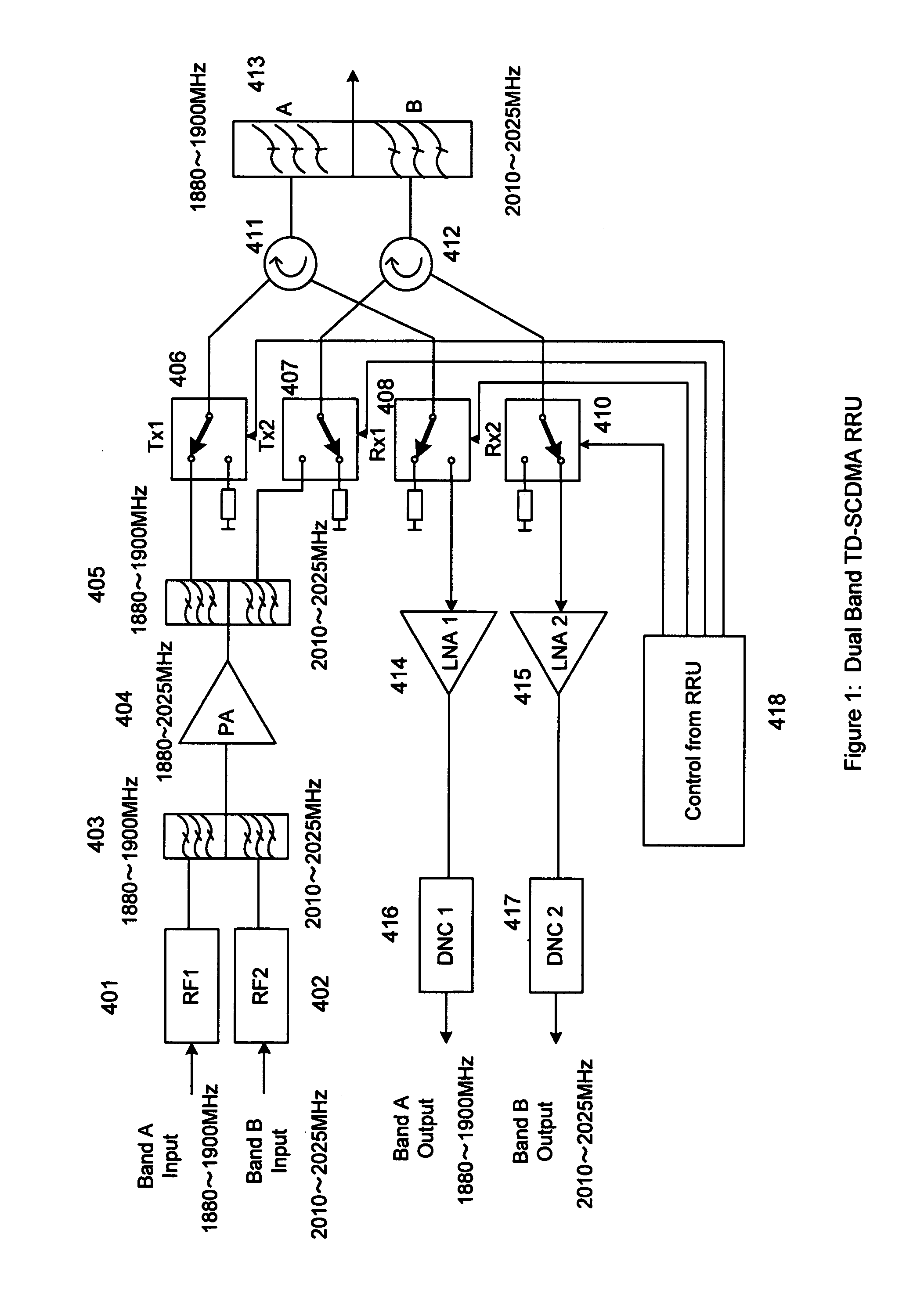
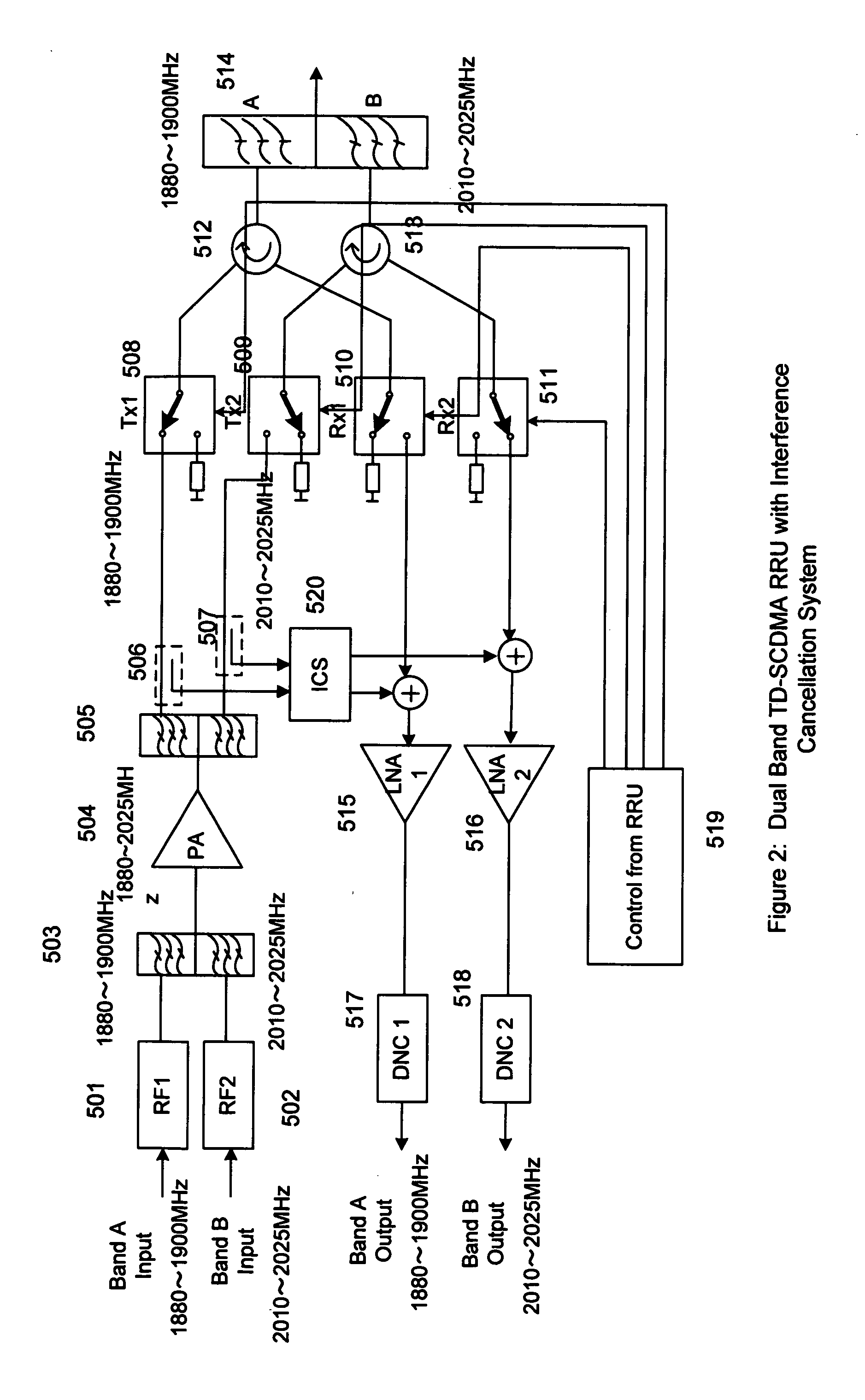
ActiveUS20110158081A1Improve performanceCost is economizedAmplifiers with memory effect compensationAmplifier with control circuitsMulti bandAudio power amplifier
A remote radio head unit (RRU) system for multiple operating frequency bands, multi-channels, driven by a single or more wide band power amplifiers. More specifically, the present invention enables multiple-bands RRU to use fewer power amplifers in order to reduce size and cost of the multi-band RRU. The present invention is based on the method of using duplexers and / or interference cancellation system technique to increase the isolation between the transmitter signal and receiver signal of the RRU.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
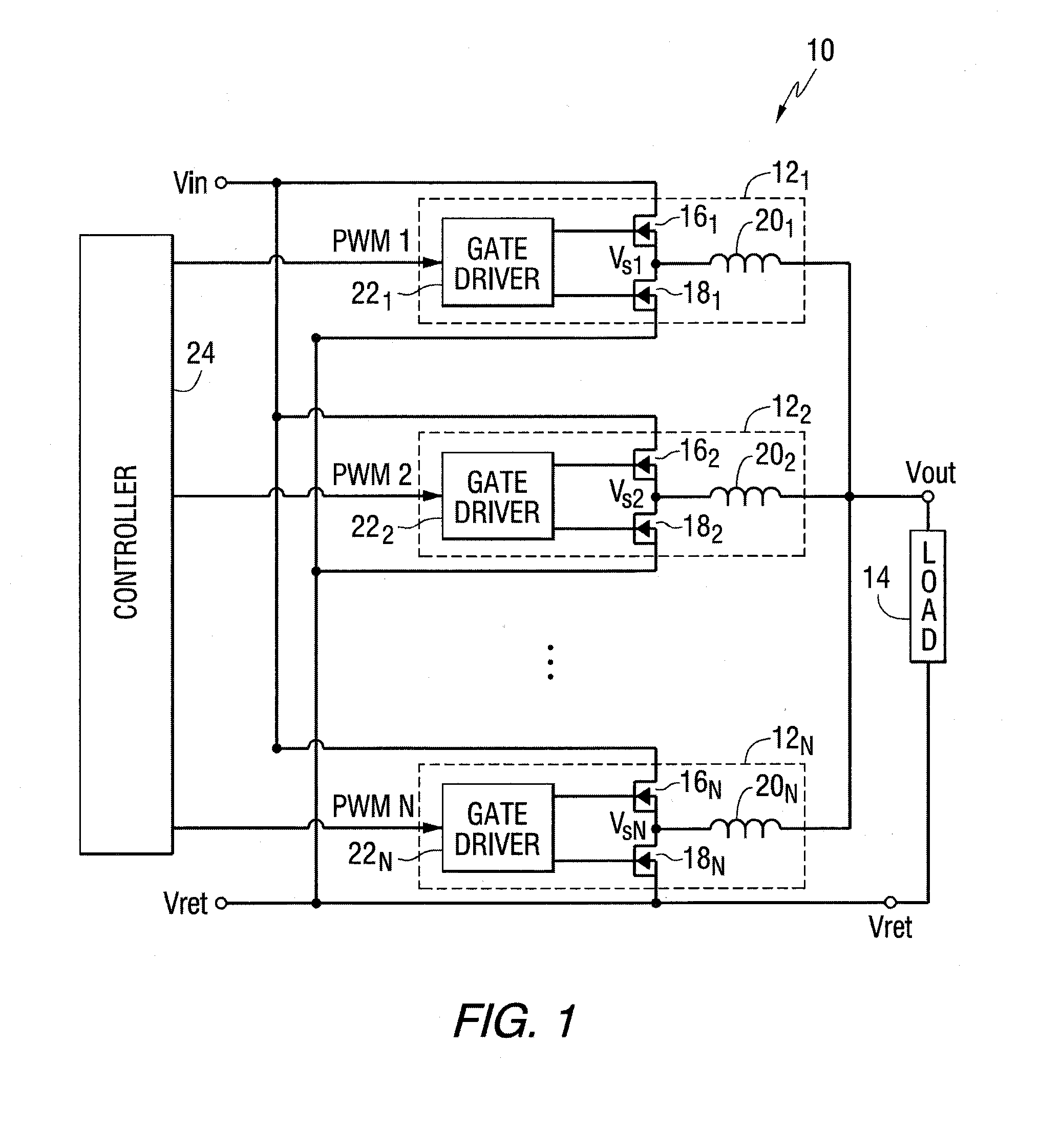
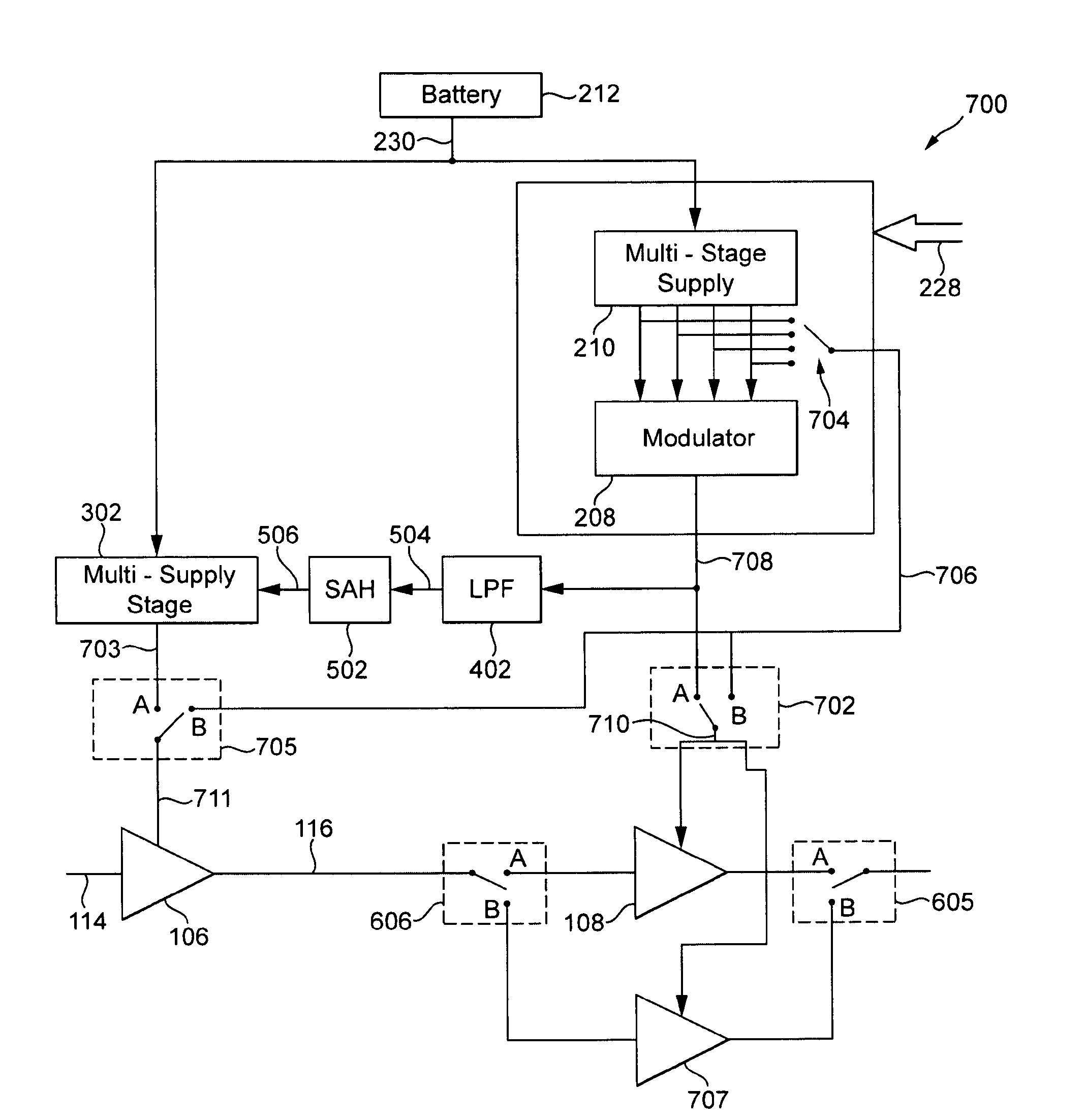
Direct current (DC)-dc converter having a multi-stage output filter
ActiveUS20130271221A1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersCapacitanceDc dc converter
A direct current (DC)-DC converter that includes a first switching converter and a multi-stage filter is disclosed. The multi-stage filter includes at least a first inductance (L) capacitance (C) filter and a second LC filter coupled in series between the first switching converter and a DC-DC converter output. The first LC filter has a first LC time constant and the second LC filter has a second LC time constant, which is less than the first LC time constant. The first switching converter and the multi-stage filter form a feedback loop, which is used to regulate the first switching power supply output signal based on the setpoint. The first LC filter includes a first capacitive element having a first self-resonant frequency, which is about equal to a first notch frequency of the multi-stage filter.
Owner:QORVO US INC
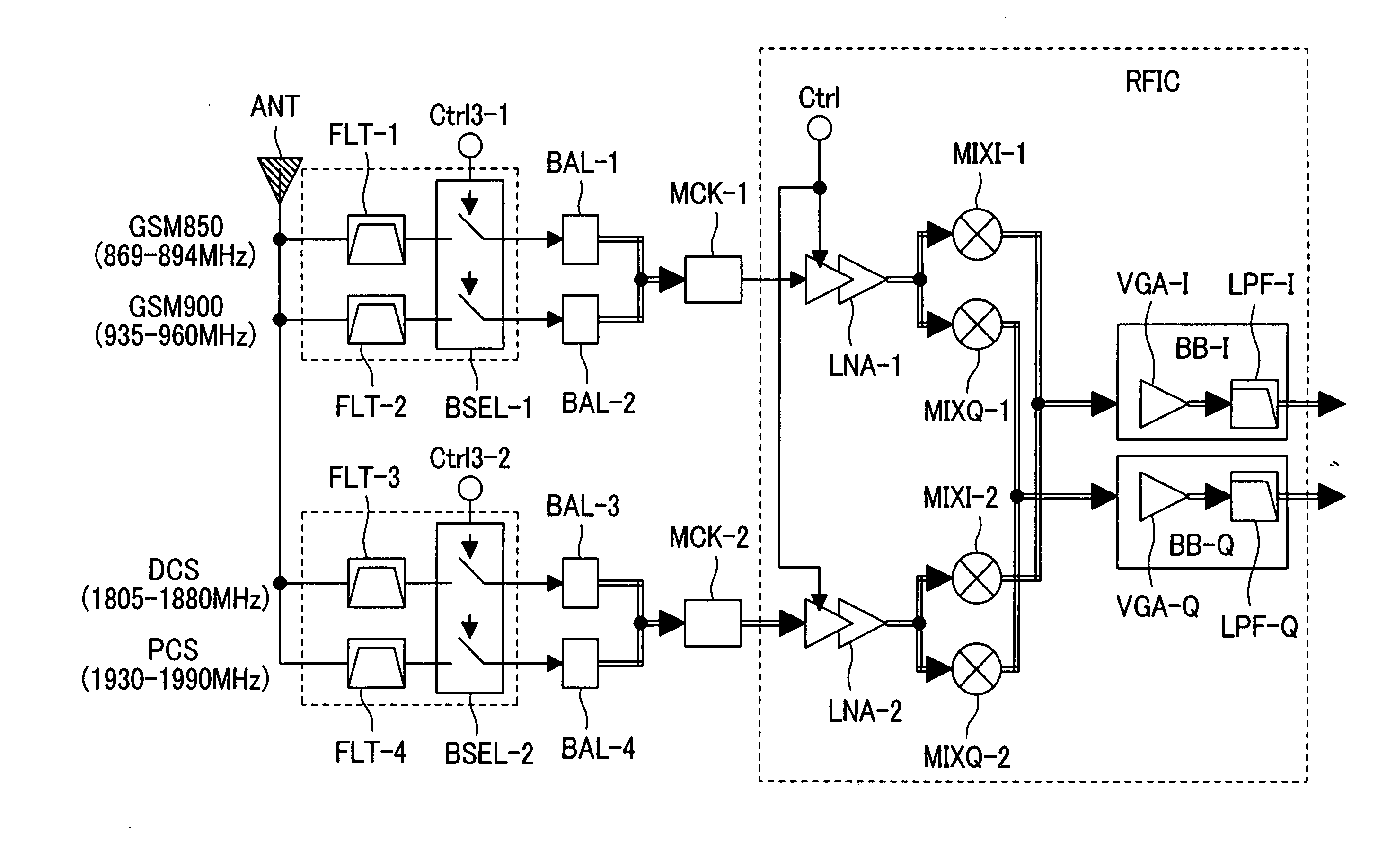
Radio frequency integrated circuit having an antenna diversity structure
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
RF power amplifier circuit with mismatch tolerance
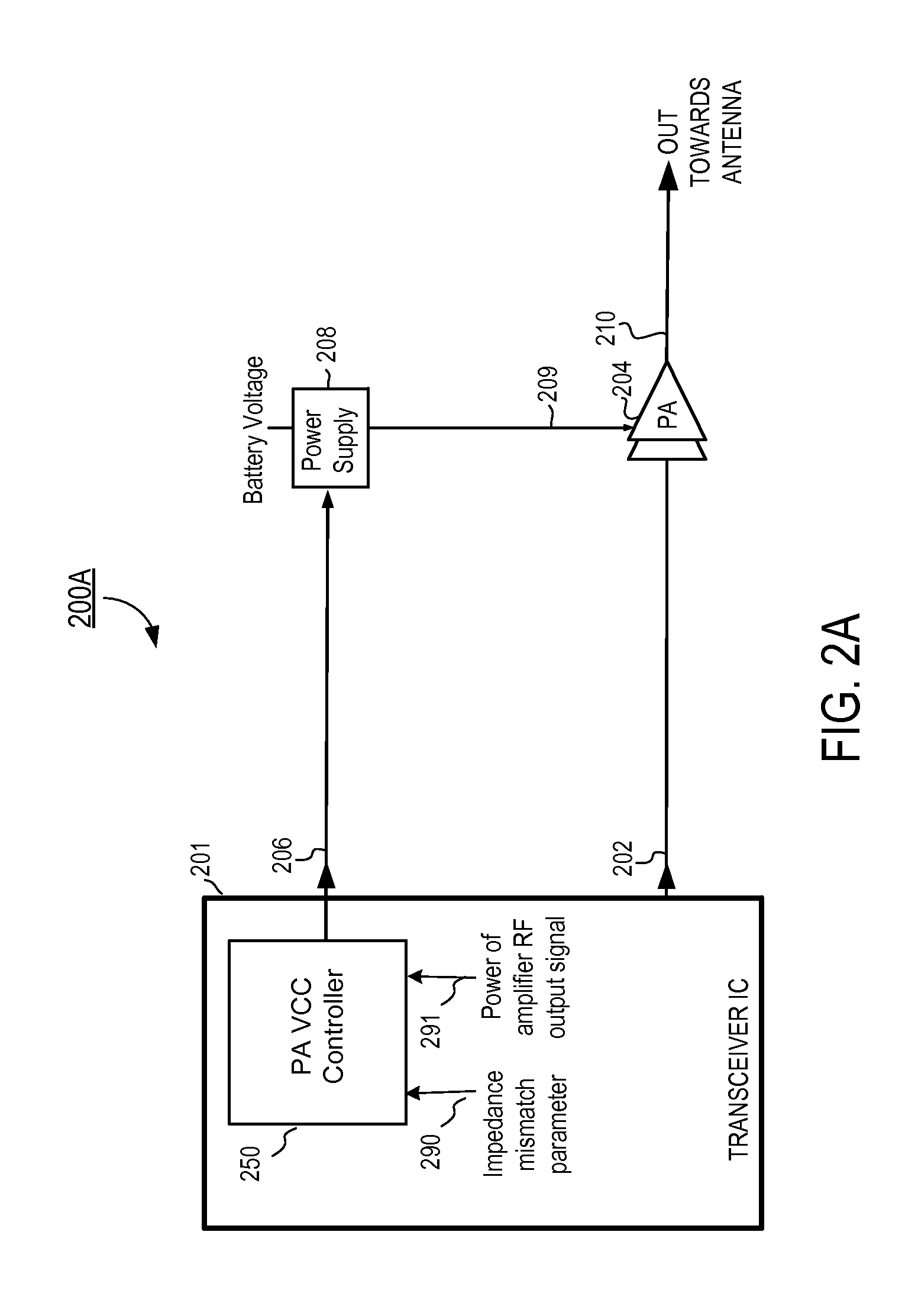
ActiveUS20110298539A1Efficiency of PA is improvedImprove efficiencyHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
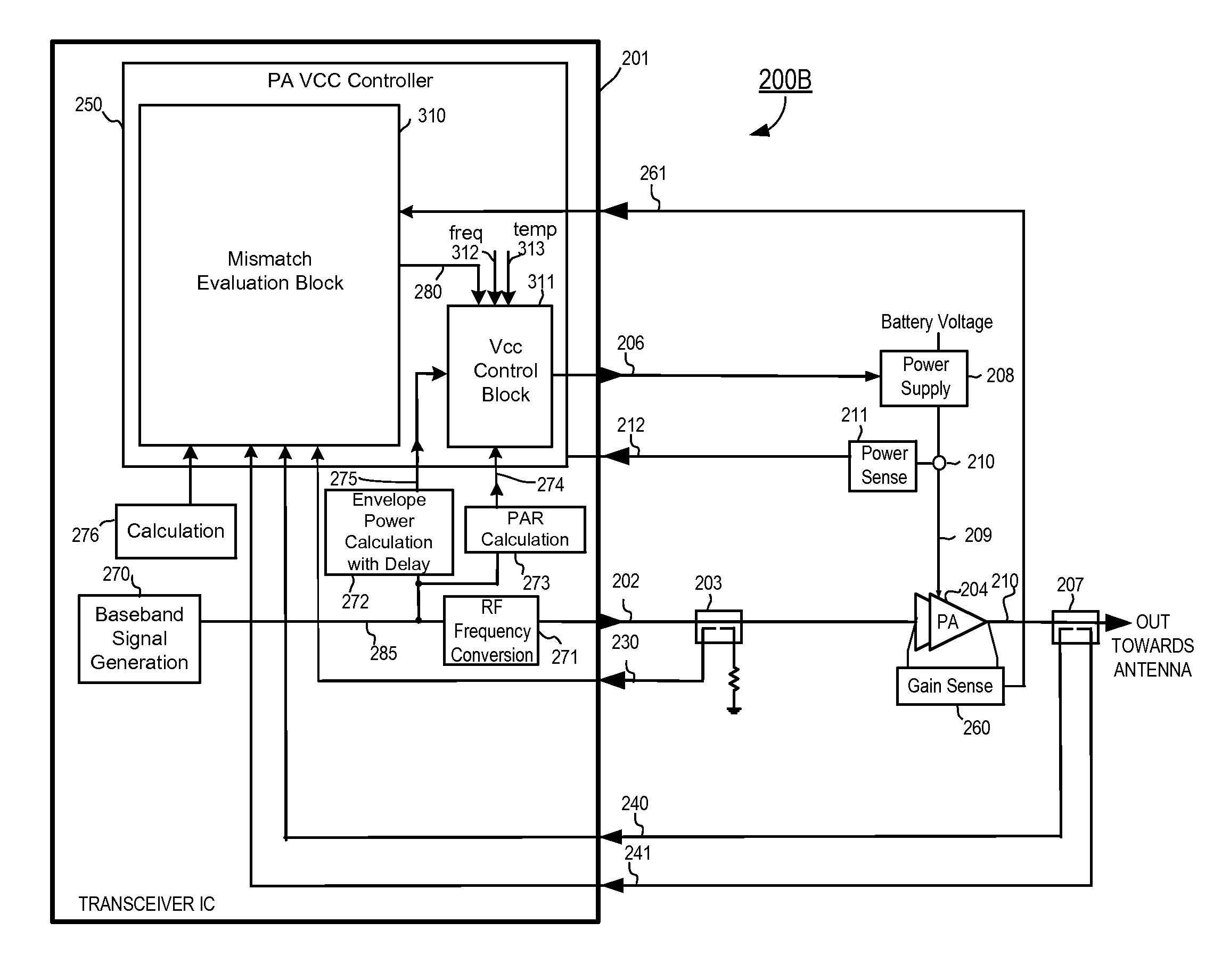
A radio frequency (RF) power amplifier system adjusts the supply voltage provided to a power amplifier (PA) adaptively, responsive to the measured or estimated power of the RF output signal of the PA. The RF PA system includes a power amplifier (PA) which receives and amplifies an RF input signal to generate an RF output signal at a level suitable for transmission to an antenna. A PA supply voltage controller generates a supply voltage control signal, which is used to control the supply voltage to the final stage of the PA. The supply voltage control signal is generated responsive to the measured or estimated power of the PA RF output signal, and also may be responsive to a parameter indicative of impedance mismatch experienced at the PA output. By controlling this supply voltage to the RF PA, the efficiency of the PA is improved.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Power supply providing ultrafast modulation of output voltage
A circuit for use with a power amplifier that amplifies an input signal. The circuit may comprise an amplitude correction circuit and an open-loop switching regulator. The amplitude correction circuit may be configured to generate a corrected envelope signal from an input envelope signal that represents an envelope of the input signal. The open-loop switching regulator may be connected to the amplitude correction circuit and may be for powering the power amplifier based on the corrected envelope signal. According to various embodiments, the corrected envelope signal generated by the amplitude correction circuit is a function of the input envelope signal and an error voltage of the open-loop switching regulator.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
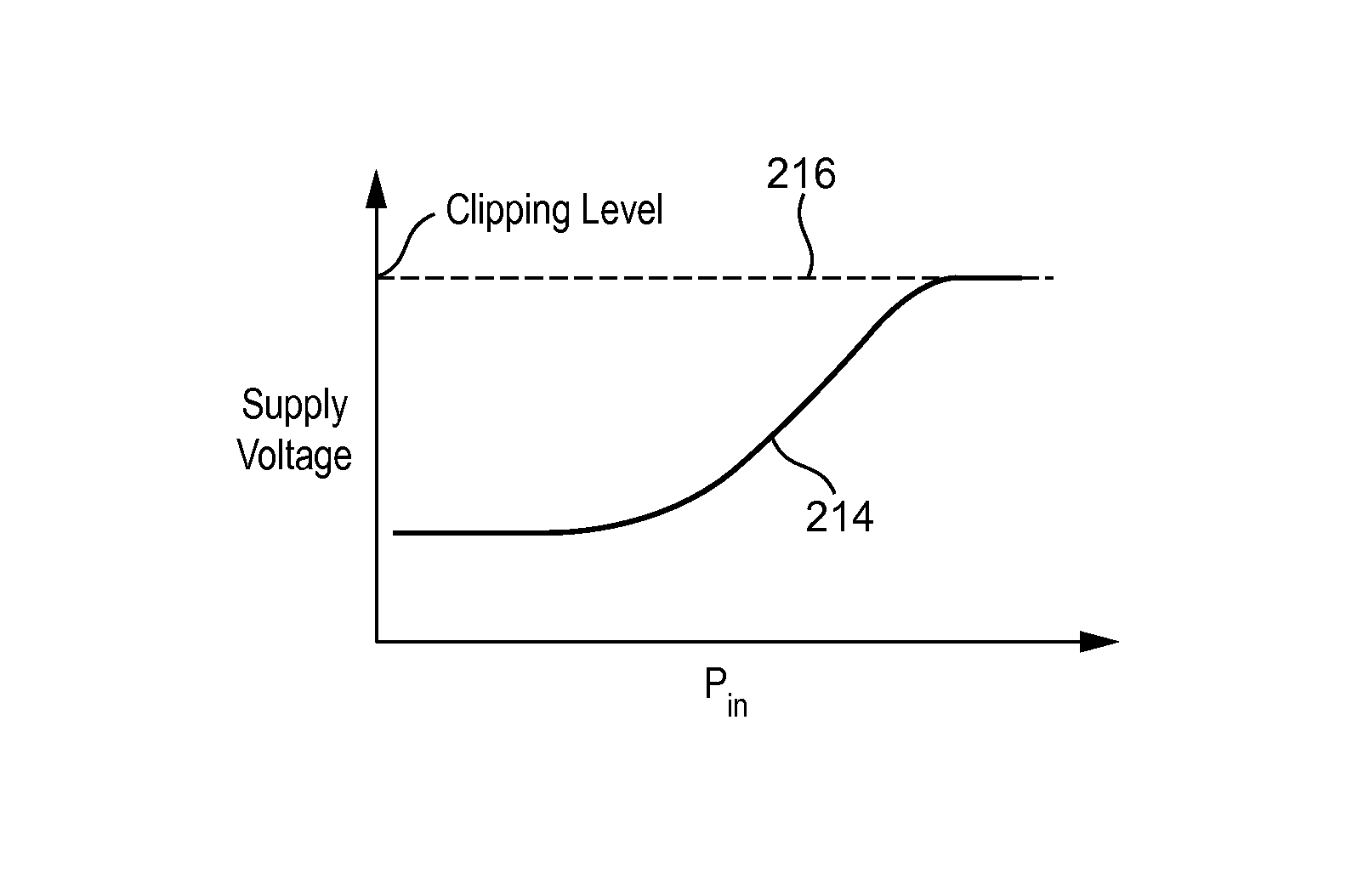
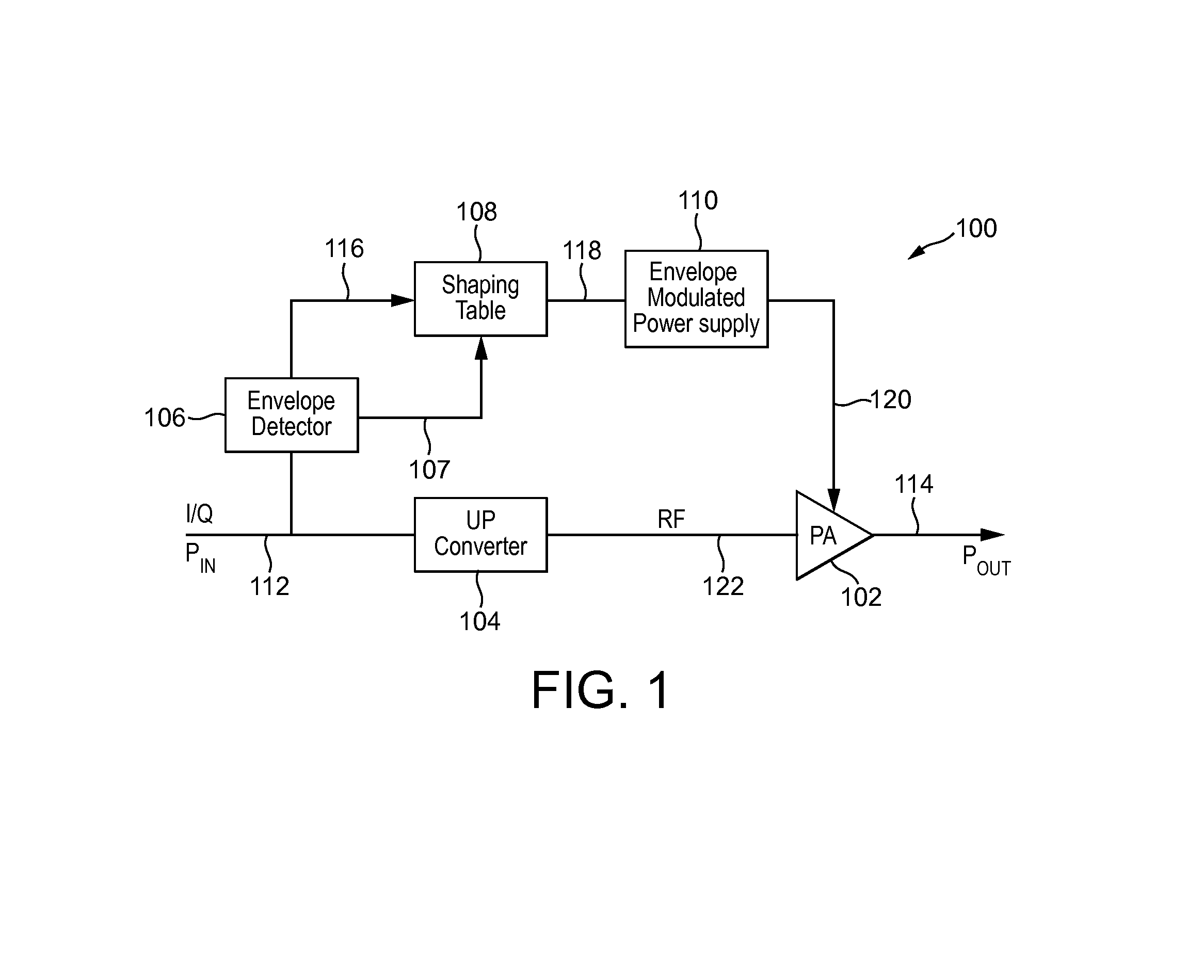
Crest Factor Reduction Applied To Shaping Table To Increase Power Amplifier Efficiency Of Envelope Tracking Amplifier
InactiveUS20140028370A1Reduction of crest factorIncrease powerPulse automatic controlHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
There is disclosed a method of controlling an input to an envelope modulated power supply of an envelope tracking amplification stage, comprising: generating an envelope signal representing the envelope of a signal to be amplified; applying a shaping function to the envelope signal to generate a shaped envelope signal, including: clipping the shaped envelope signal at high input envelope values; and providing the shaped envelope signal as an input signal to the envelope modulated power supply.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Power supply arrangement for multi-stage amplifier
There is disclosed a multi-stage amplifier comprising: a first amplifier stage; a second amplifier stage; a first voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the first amplifier in dependence on an average power of a signal to be amplified; and a second voltage supply stage arranged to provide a supply voltage to the second amplifier in dependence on an instantaneous power of a signal to be amplified.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Integrated RF front end
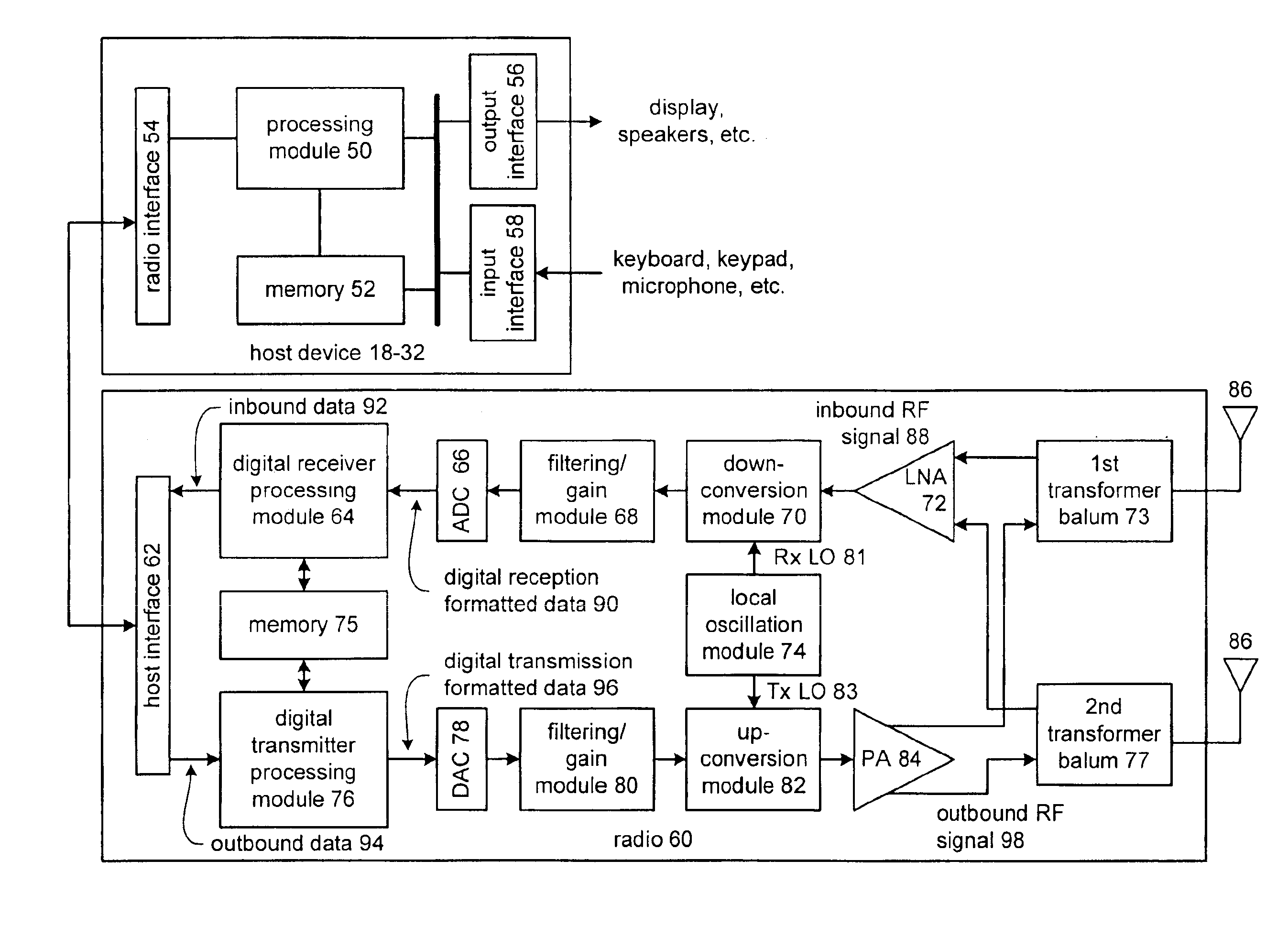
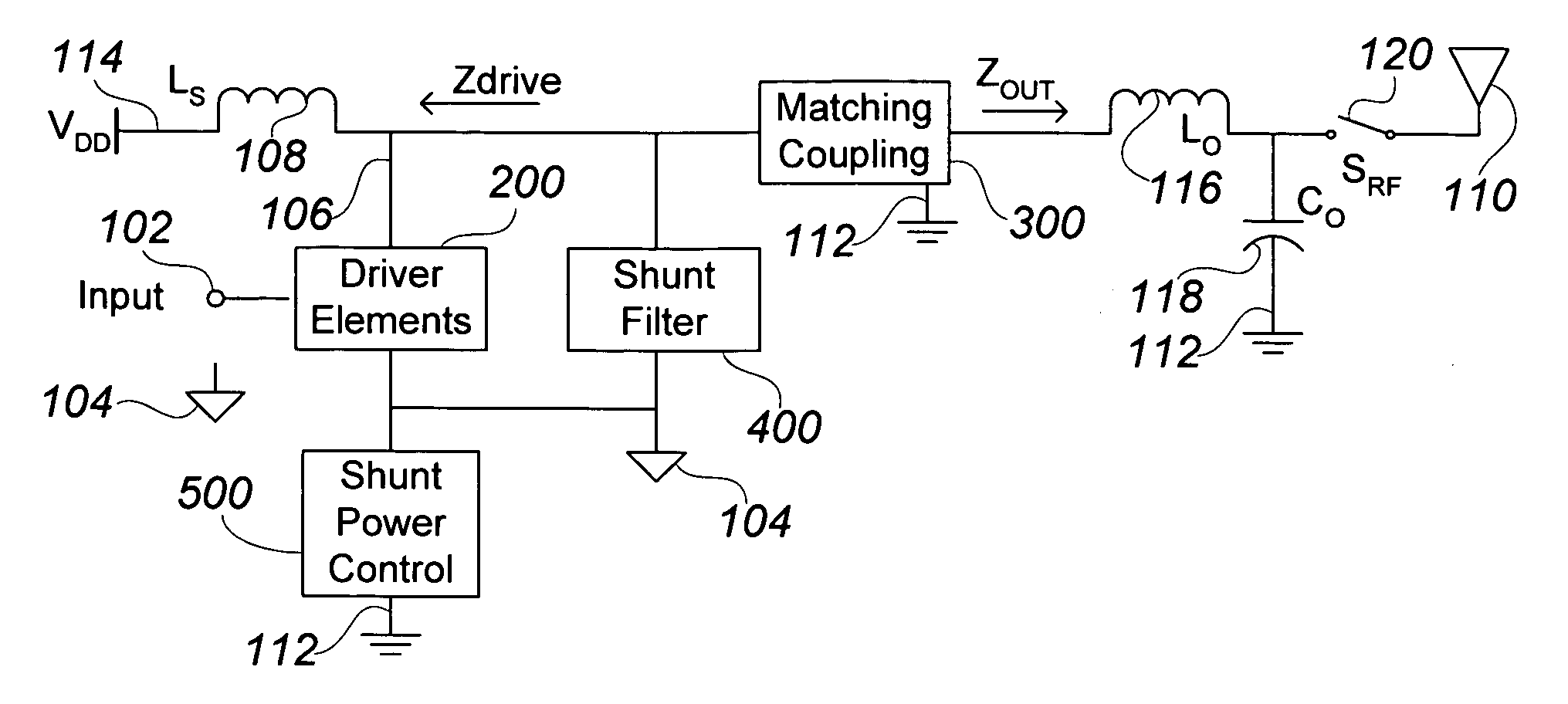
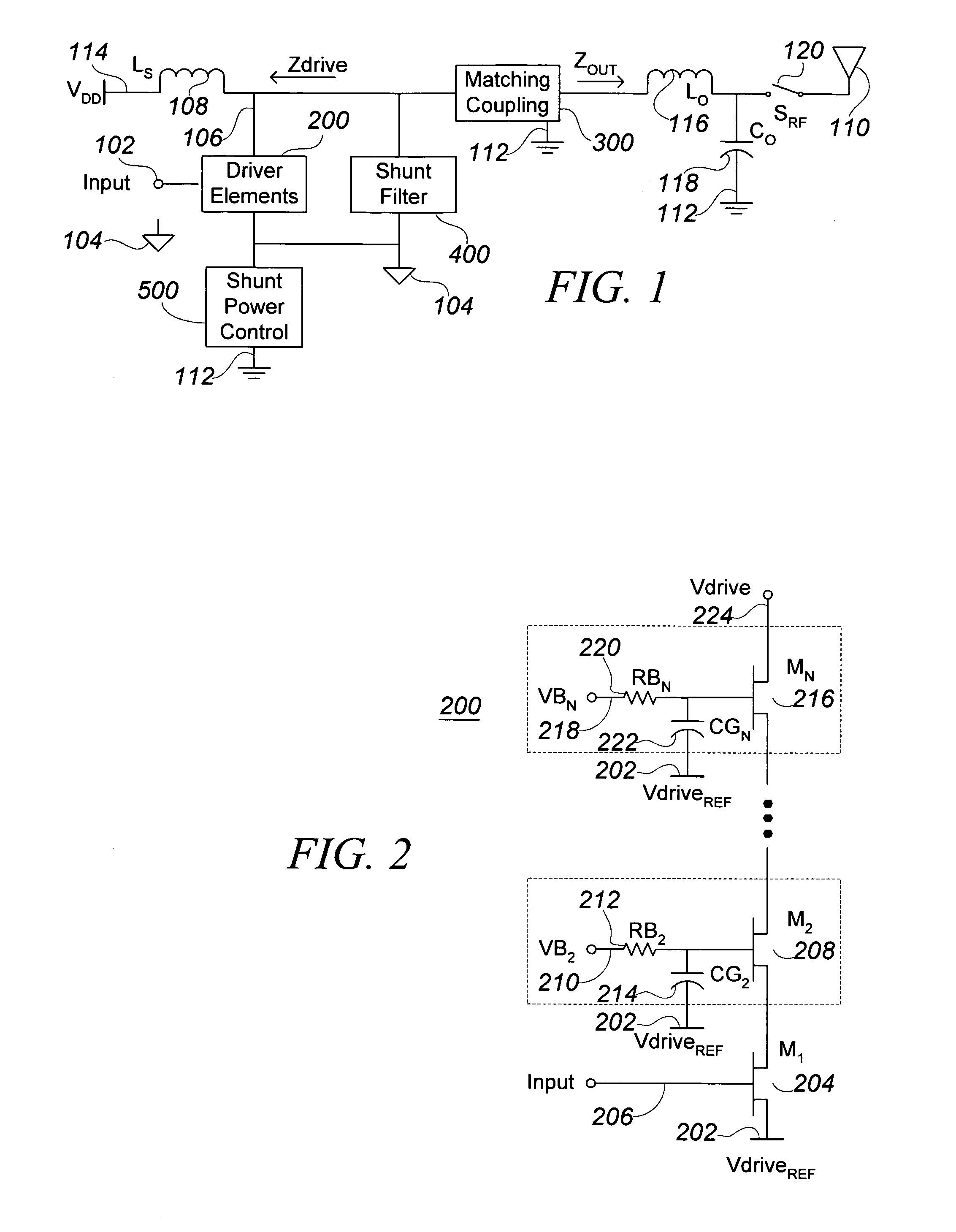
ActiveUS7088971B2Effective protectionResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersVoltage amplitudeTransceiver
A monolithic integrated circuit (IC), and method of manufacturing same, that includes all RF front end or transceiver elements for a portable communication device, including a power amplifier (PA), a matching, coupling and filtering network, and an antenna switch to couple the conditioned PA signal to an antenna. An output signal sensor senses at least a voltage amplitude of the signal switched by the antenna switch, and signals a PA control circuit to limit PA output power in response to excessive values of sensed output. Preferred fabrication techniques include stacking multiple FETs to form switching devices. An iClass PA architecture is described that dissipatively terminates unwanted harmonics of the PA output signal. A preferred embodiment of the RF transceiver IC includes two distinct PA circuits, two distinct receive signal amplifier circuits, and a four-way antenna switch to selectably couple a single antenna connection to any one of the four circuits.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Multi-band low noise amplifier, multi-band low noise amplifier module, wireless integrated circuit and multi-band RF module
InactiveUS20060189286A1Small sizeSpatial transmit diversitySimultaneous amplitude and angle demodulationMulti bandAudio power amplifier
A multi-band radio module for selectively supplying received signals in a plurality of frequency bands to a low noise amplifier via an input impedance matching circuit by switching over the operation mode of the low noise amplifier is comprised of: a pre-stage amplification unit including a plurality of fundamental amplifiers connected to one another in parallel, the fundamental amplifiers sharing a load impedance connected to a source voltage and a grounded degeneration impedance and having input signal lines commonly connected to an input impedance matching circuit; a post-stage amplifier to which the output signals of the plurality of fundamental amplifiers are commonly inputted; and a bias control unit for selectively turning on the fundamental amplifiers, wherein the input impedance of the low noise amplifier is selectively optimized for the matching circuit depending on the RF band to be received.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Power level controlling of first amplification stage for an integrated RF power amplifier
A power amplifier circuit is disclosed having a first amplification stage and a second amplification stage. The first amplification stage is biased using a controllable current source that provides a variable bias current thereto. A control circuit is provided for controlling the variable bias current in dependence upon the supply voltage and temperature of the power amplifier circuit. The control signal varies the variable bias current in dependence upon the supply voltage varying between first and second potential, where each potential supplies sufficient potential for operation of the power amplifier circuit.
Owner:SIGE SEMICON
Adaptive radio transceiver with floating MOSFET capacitors
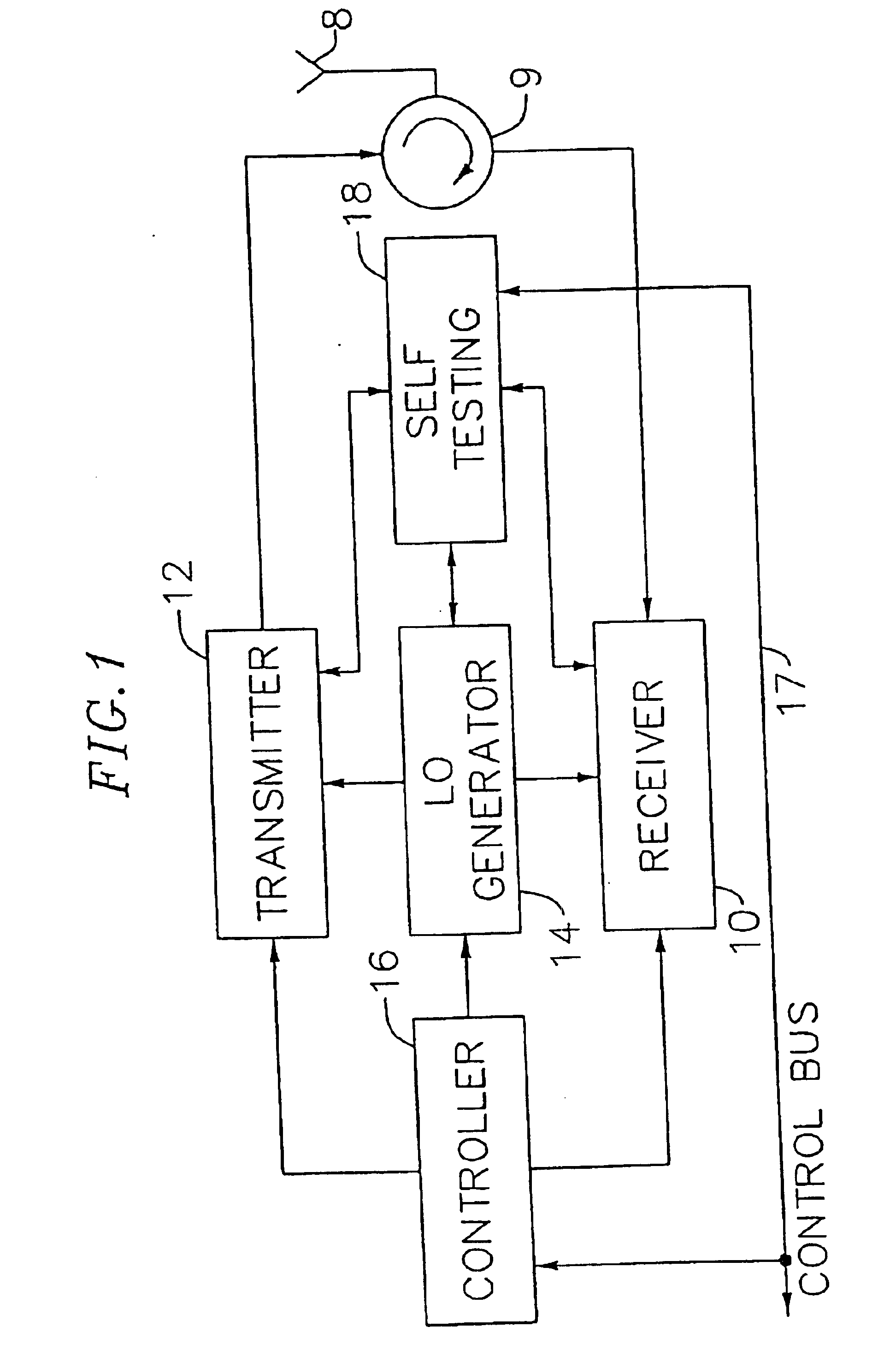
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multiwire linear equalizer for vector signaling code receiver
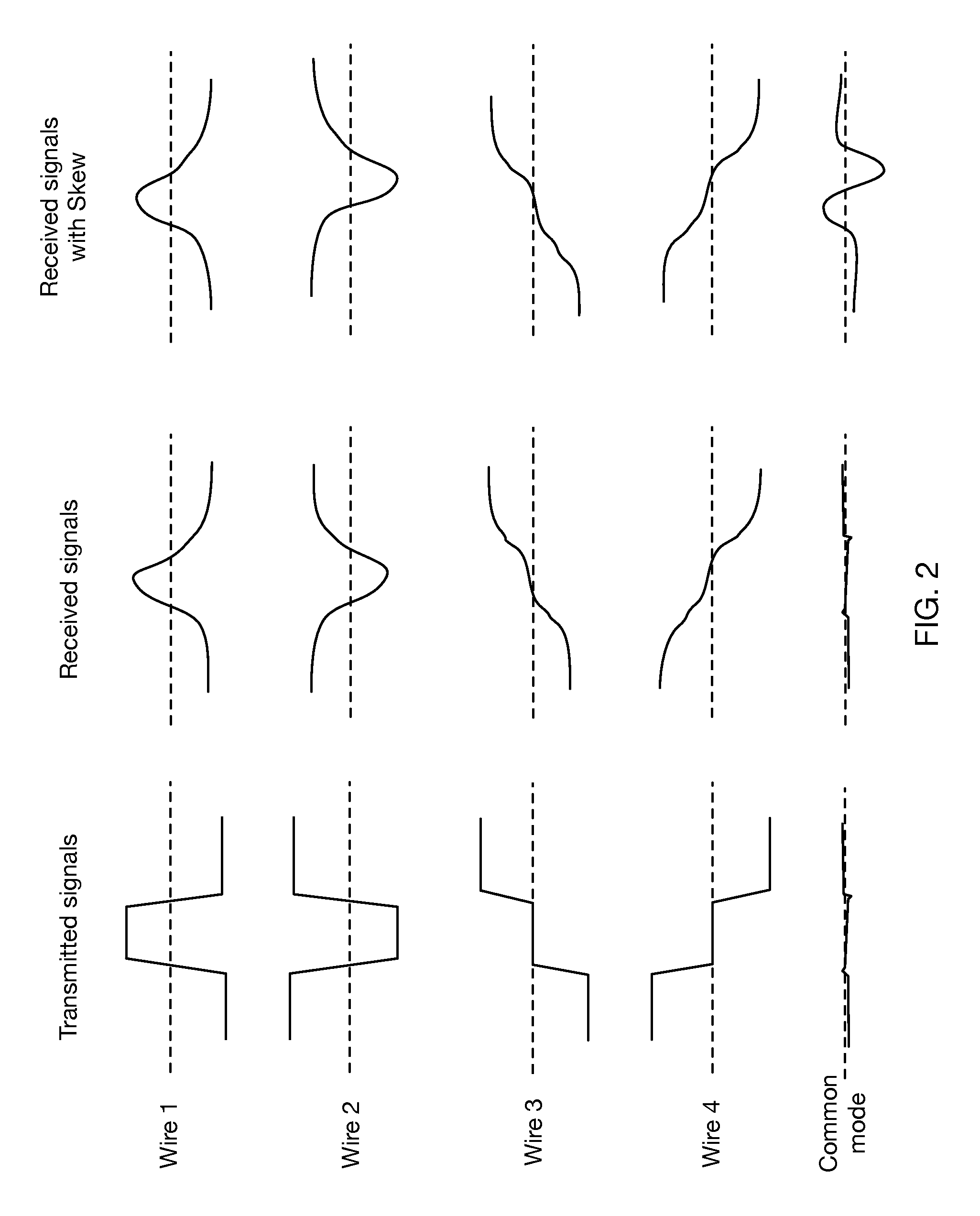
ActiveUS9106465B2Improve efficiencyReduce power consumptionMultiple-port networksHigh frequency amplifiersSignal onEqualization
Continuous-time linear equalization of received signals on multiple wire channels while maintaining accurate common mode signal values. Multiwire group signaling using vector signaling codes simultaneously transmits encoded values on multiple wires, requiring multiple receive signals to be sampled simultaneously to retrieve the full transmitted code word. By misaligning transitions on multiple wires, skew introduces a transient common mode signal component that is preserved by using frequency-selective common mode feedback at the receiver to obtain accurate sampling results.
Owner:KANDOU LABS
Method and system for reconfiguring private cellular networks for resolving frequency band conflicts with official government communication networks
InactiveUS20080227460A1Low bandpass insertion lossHigh selectivityError preventionTransmission systemsAudio power amplifierProgram planning
Disclosed herein is a system and method for achieving a government-imposed re-banding of communications frequencies within the cellular telecommunications industry that provides considerable advantages over options available in the prior art. Using a bi-directional amplifier means of the present invention, cellular service providers required to shift and otherwise adjust the frequency bands within which they are licensed to operate will be able to conform to government dictates in a manner that is cost effective and capable, without more, of implementing the government-imposed plan in multiple stages without resort to significant hardware upgrades or substitutions.
Owner:DAVID GREG +2
Multi-mode/multi-band power amplifier
InactiveUS6970040B1Impedance variesHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyMulti bandAudio power amplifier
Owner:QORVO US INC
Multiple bandwidth amplifier control systems for mobile stations and methods therefor
InactiveUS20020168025A1Resonant long antennasNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierControl signal
RF amplifier control circuits for transmitters in mobile communication devices, combinations thereof and methods therefor. The control circuits include generally proportional and integral control circuits having an output coupled to a control input of an amplifier. An initial control signal is applied to the amplifier before a vector modulator output coupled an input thereof is at full output power. The vector modulator output is ramped to full output after applying the initial control signal. Thereafter, the initial control signal applied to the amplifier during ramping is corrected by integrating an output of the amplifier relative to a second reference signal with an integral control circuit coupled to the control input of the amplifier, the second reference signal is proportional to the ramping vector modulator output.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com