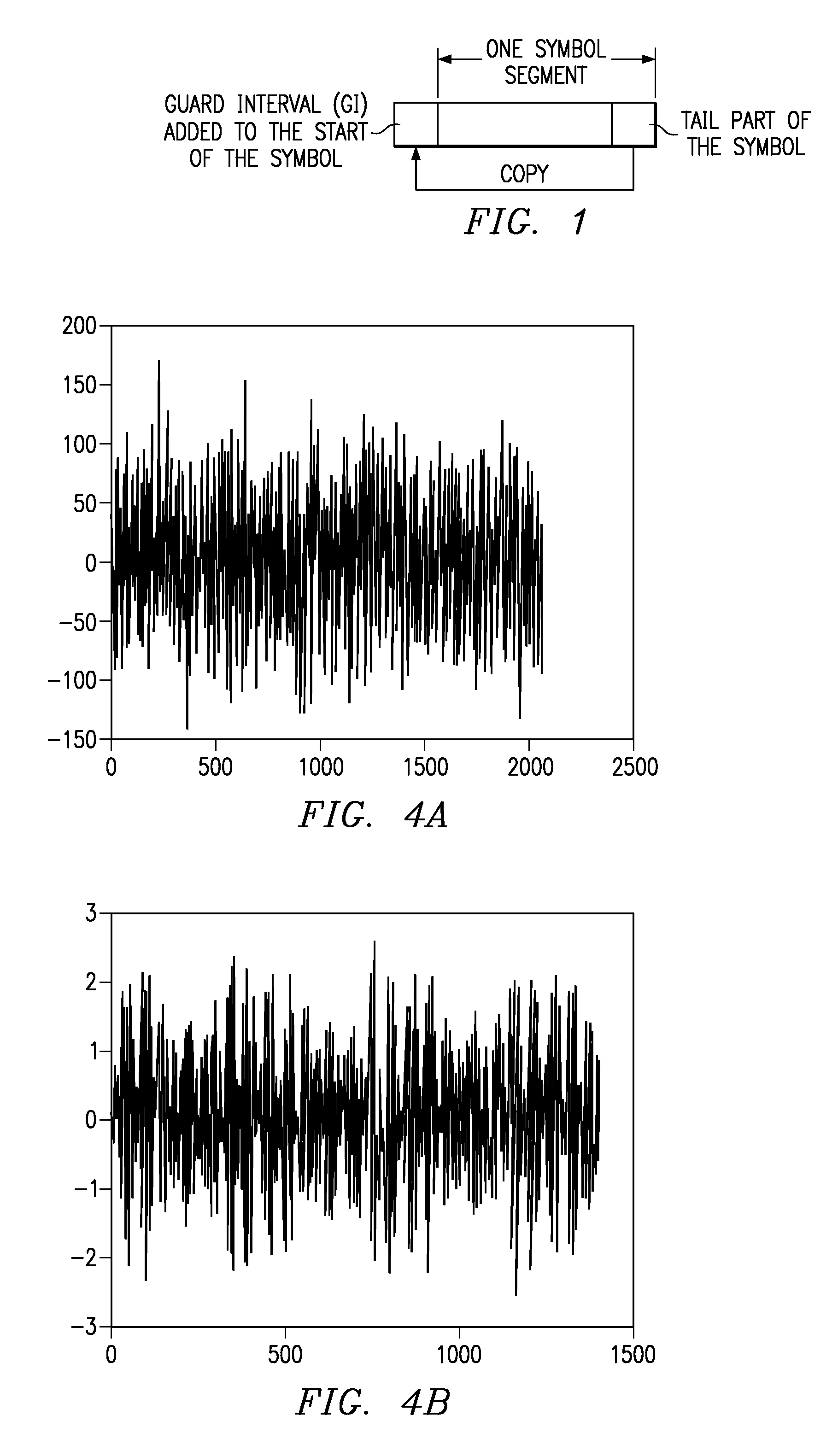
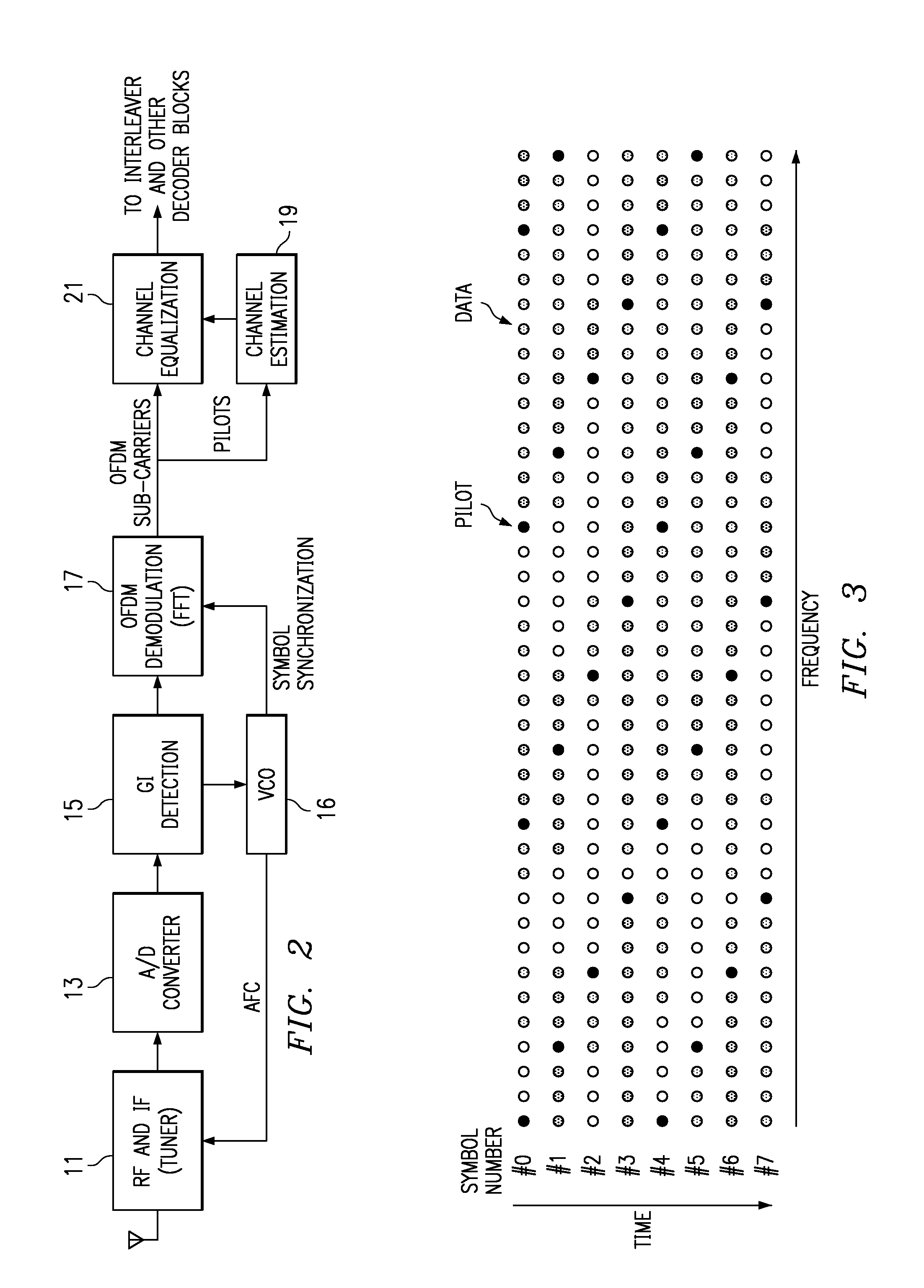
Patents
Literature
306 results about "Amplitude correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
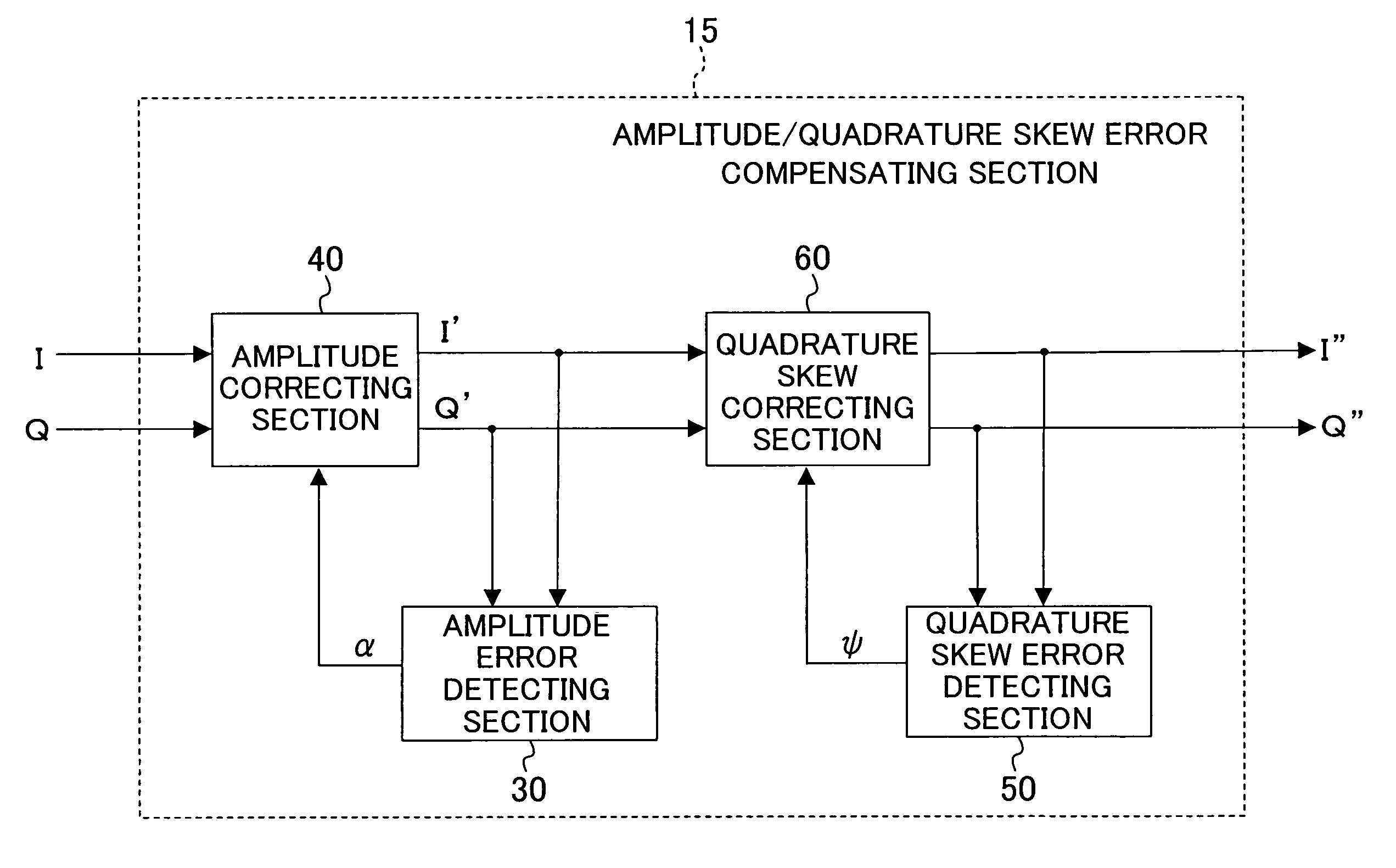
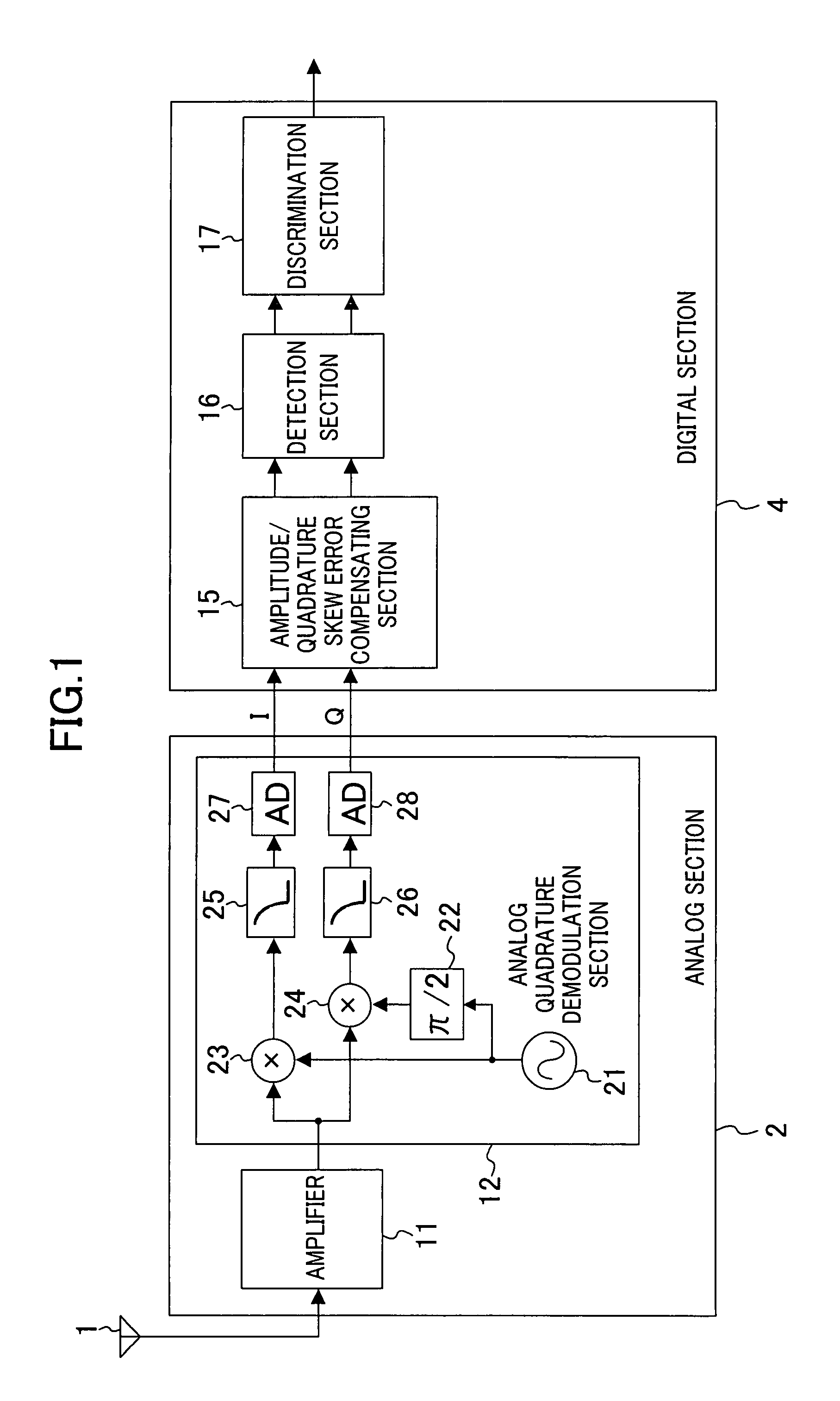
Amplitude error compensating device and quadrature skew error compensating device
InactiveUS7456683B2Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionInformation controlQuadrature demodulation
An amplitude error compensating device comprises an amplitude correcting section for performing amplitude correction with respect to an in-phase component and a quadrature component of a complex signal obtained by quadrature demodulation, based on amplitude error information, and outputting a resultant amplitude-corrected complex signal, and an amplitude error detecting section for obtaining the amplitude error information, depending on amplitudes of an in-phase component and a quadrature component of the amplitude-corrected complex signal. The amplitude error detecting section comprises a power difference calculating section for obtaining as a power error a difference in power between the in-phase component and the quadrature component of the amplitude-corrected complex signal, a rotation detecting section for detecting a rotation of a signal point of the amplitude-corrected complex signal, an error information control section for outputting the power error when a rotation of the signal point has been detected, and 0 when a rotation of the signal point has not been detected, and a smoothing section for smoothing an output of the error information control section, and outputting the result as the amplitude error information.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
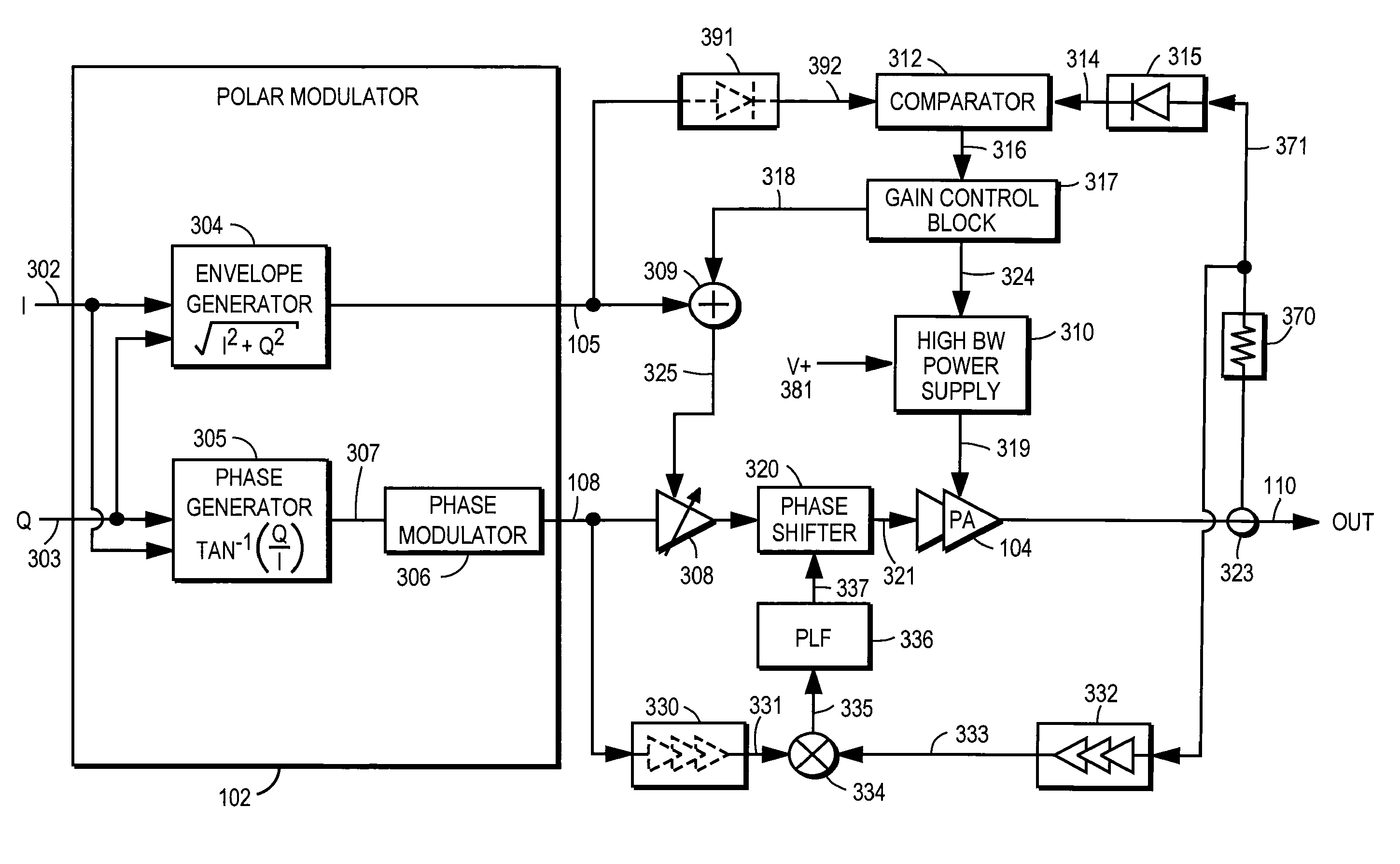
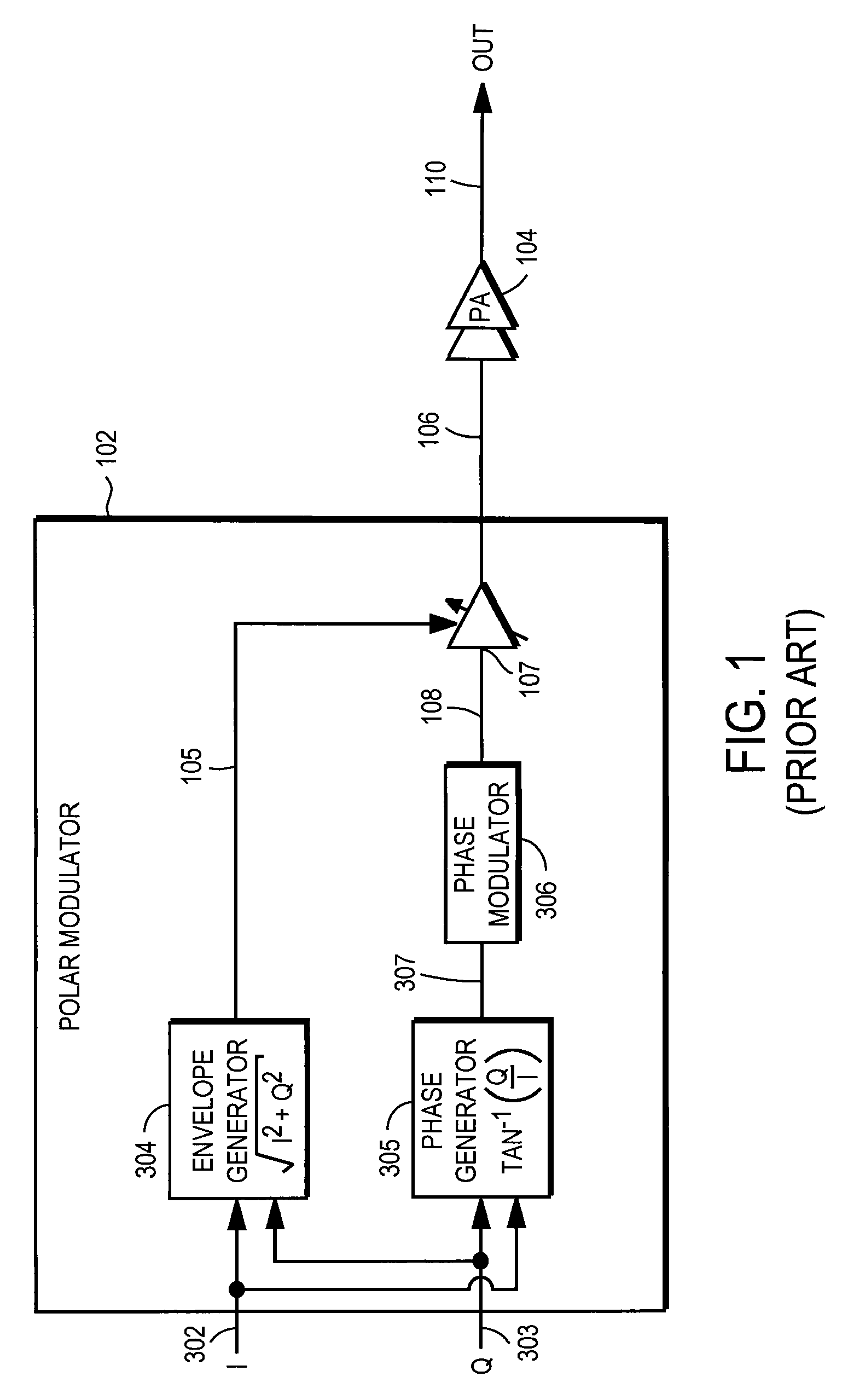
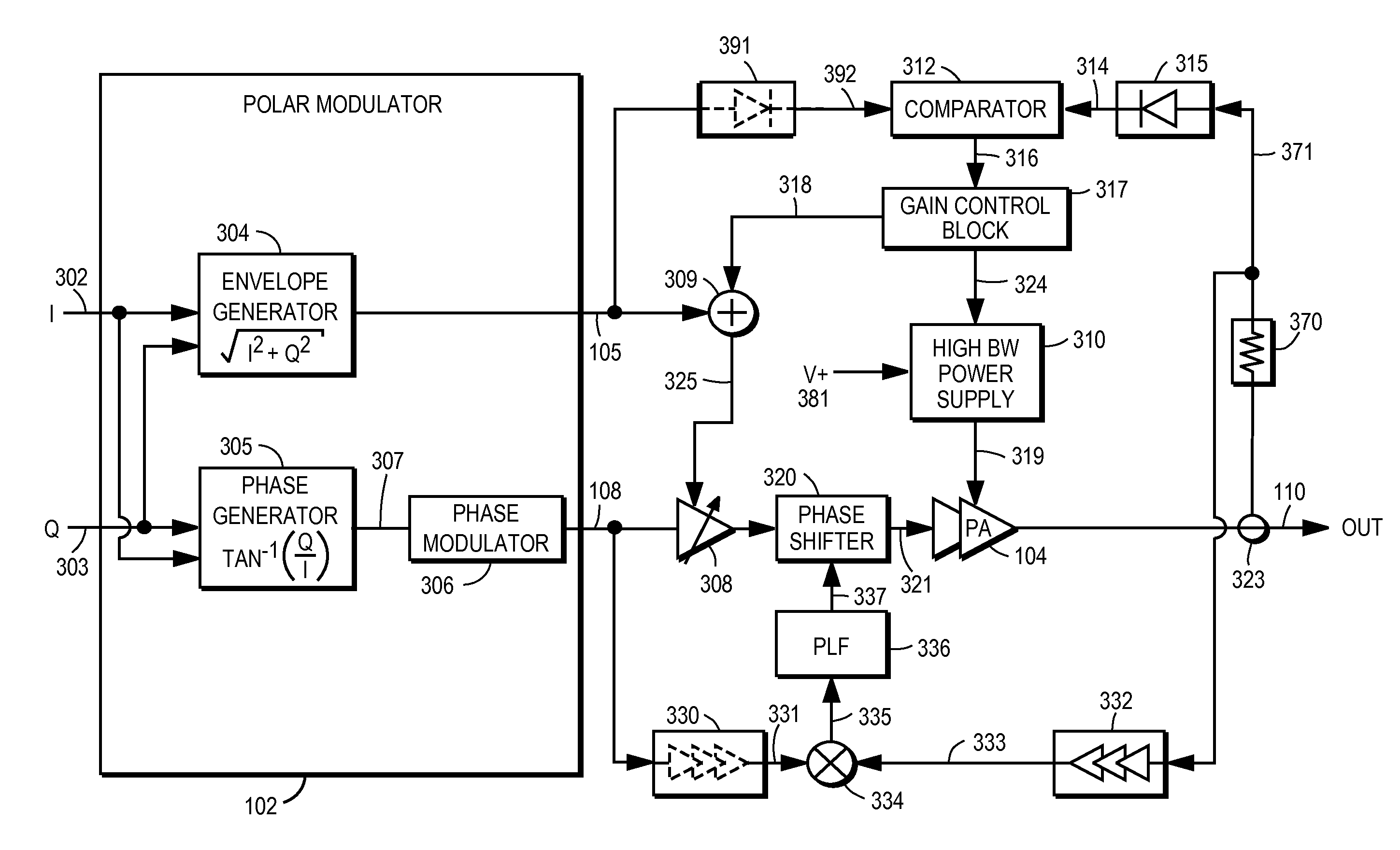
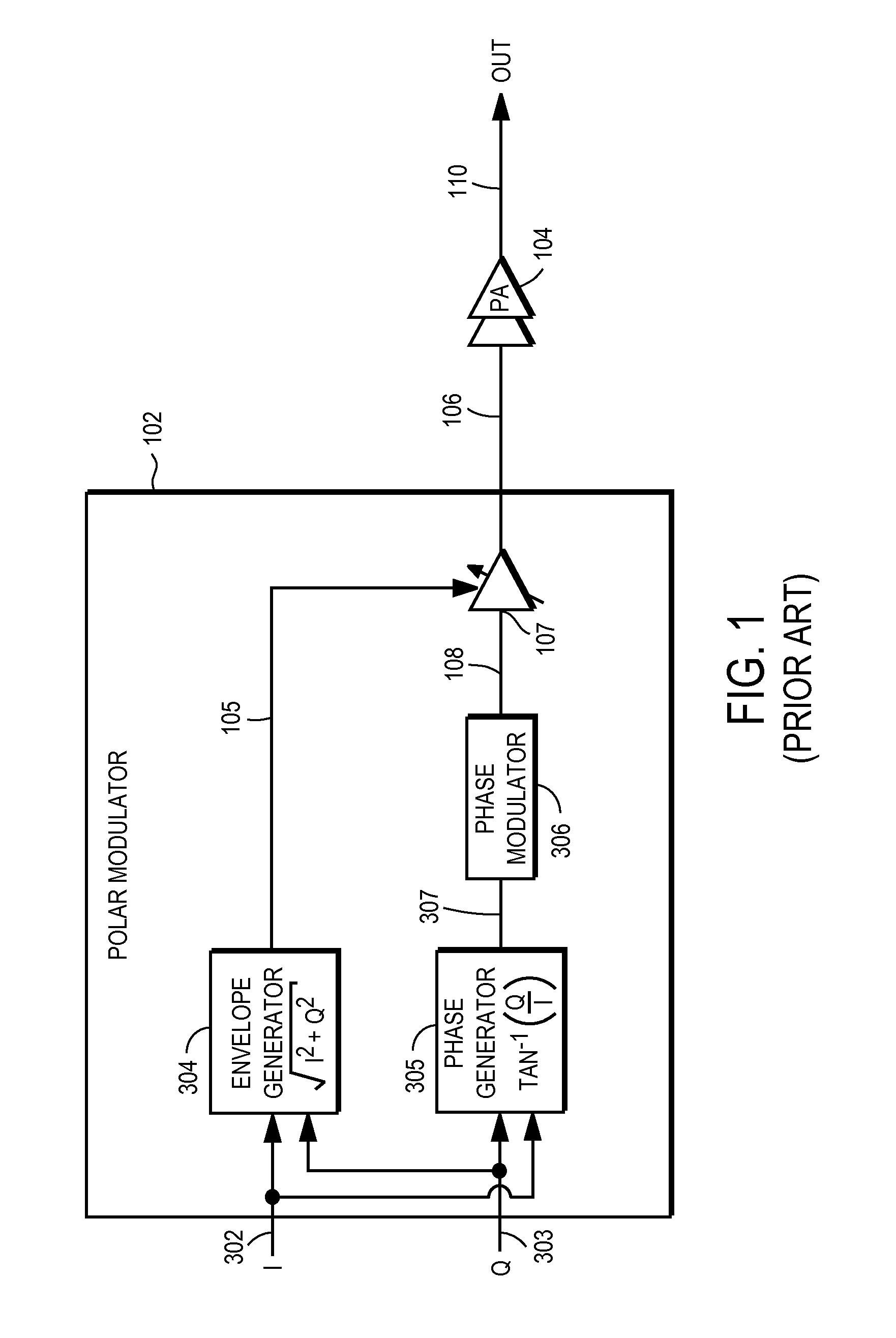
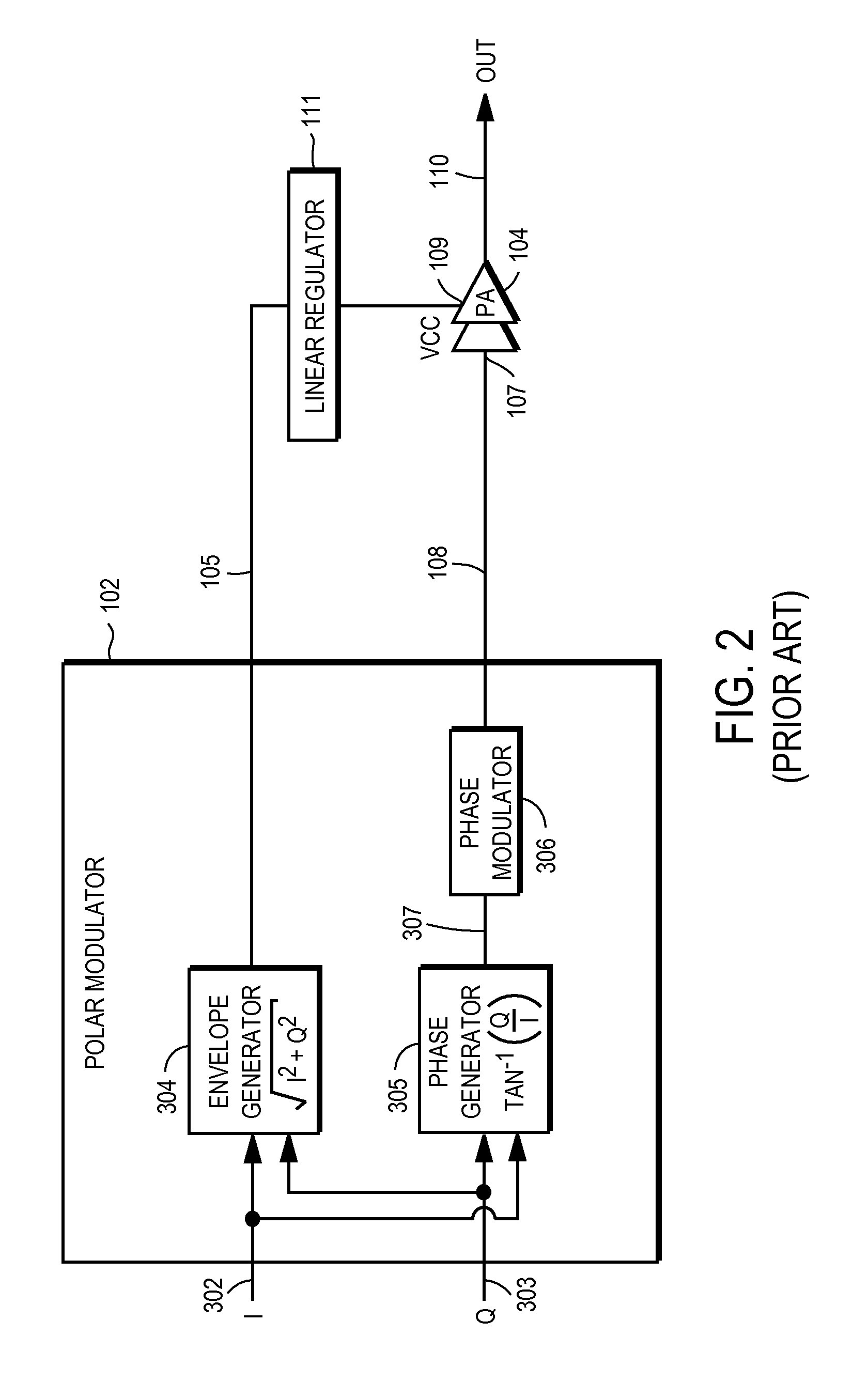
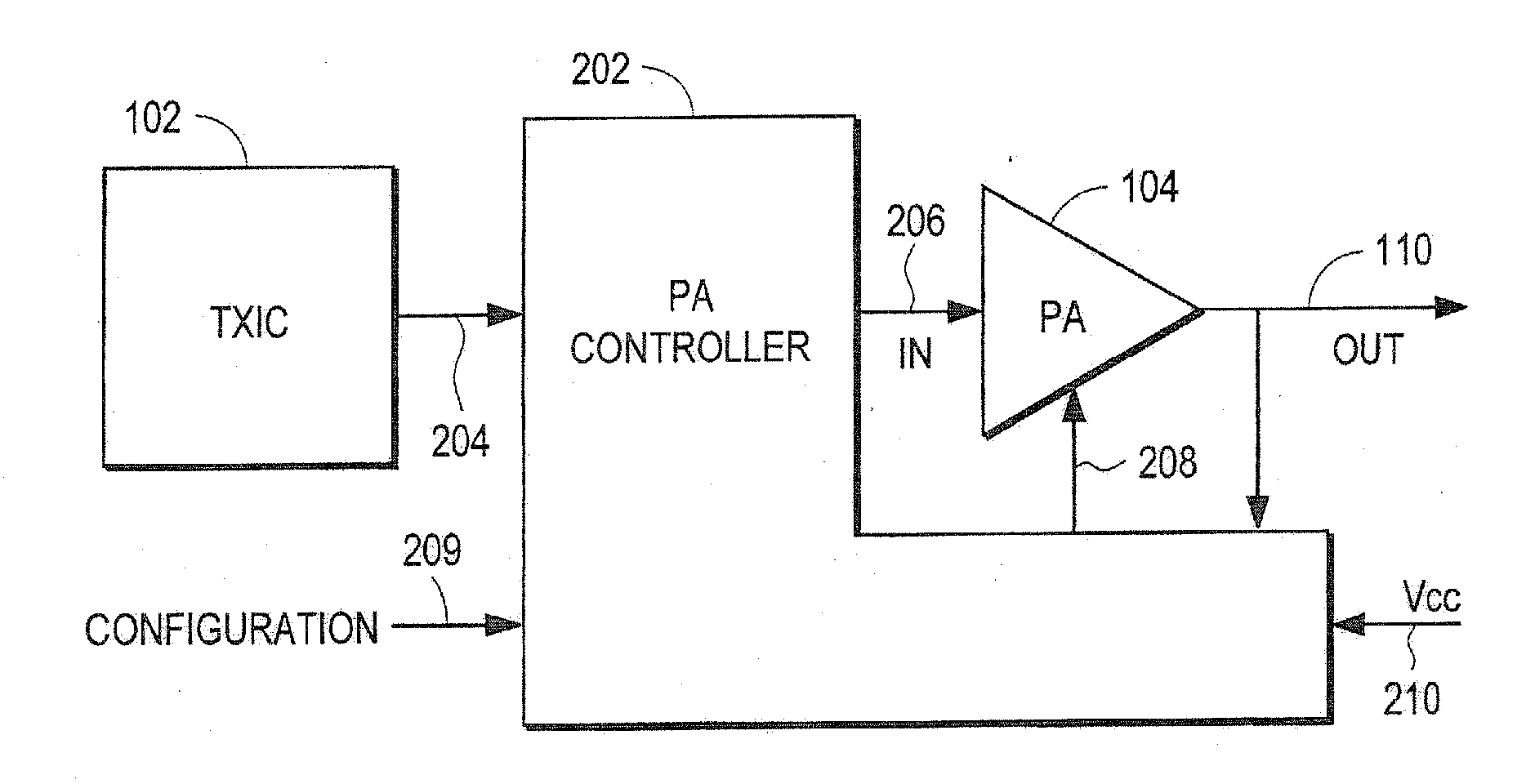
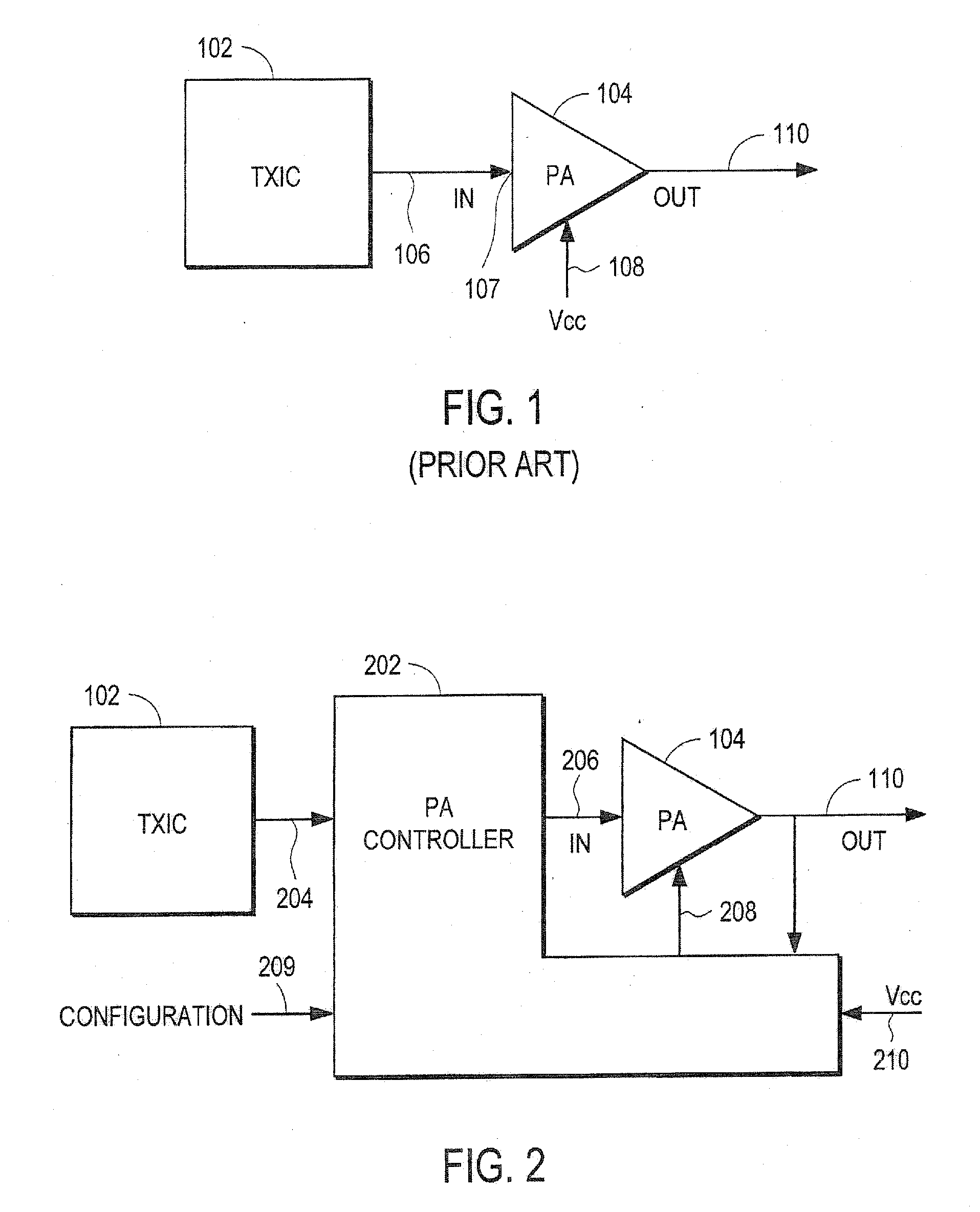
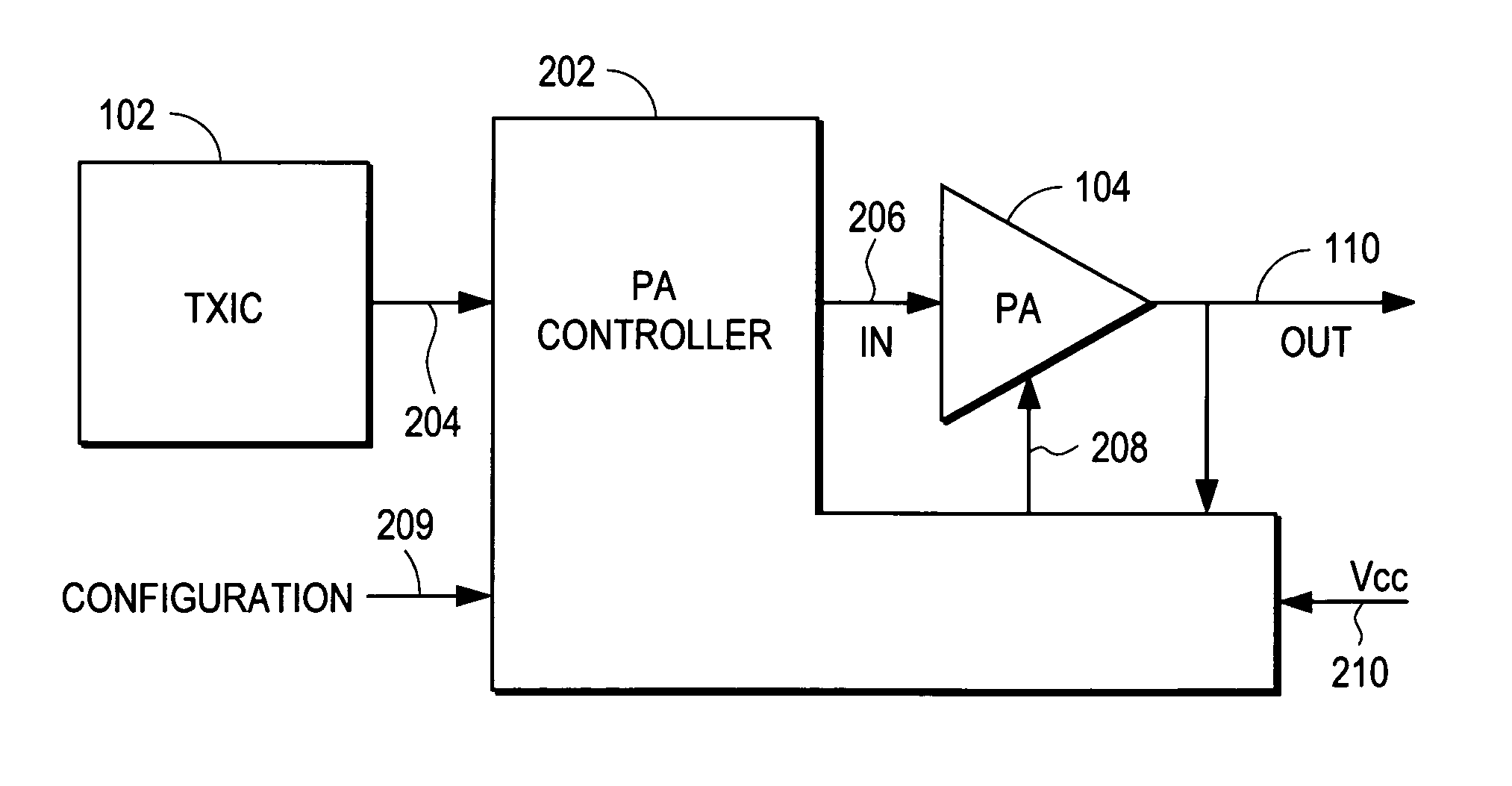
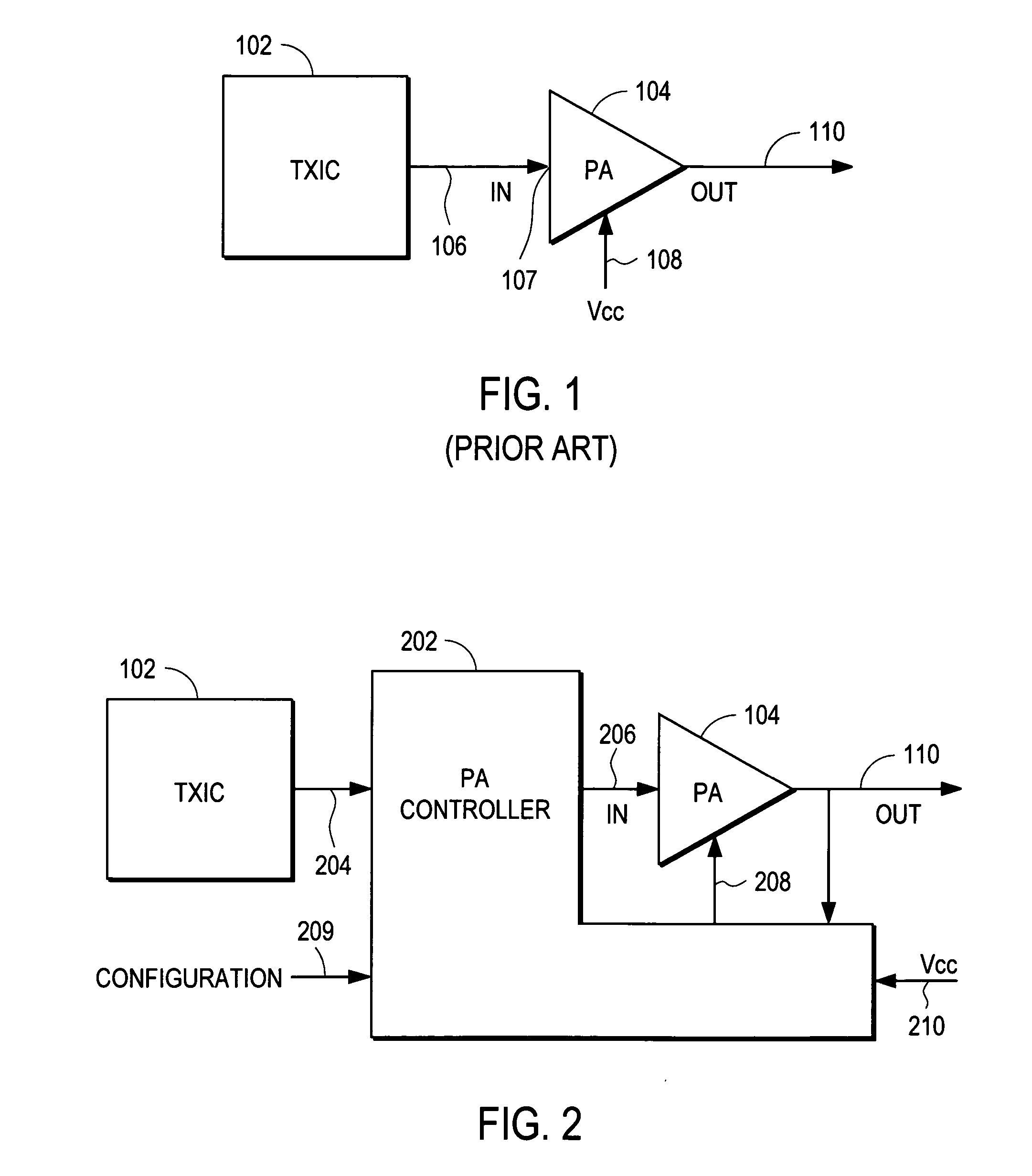
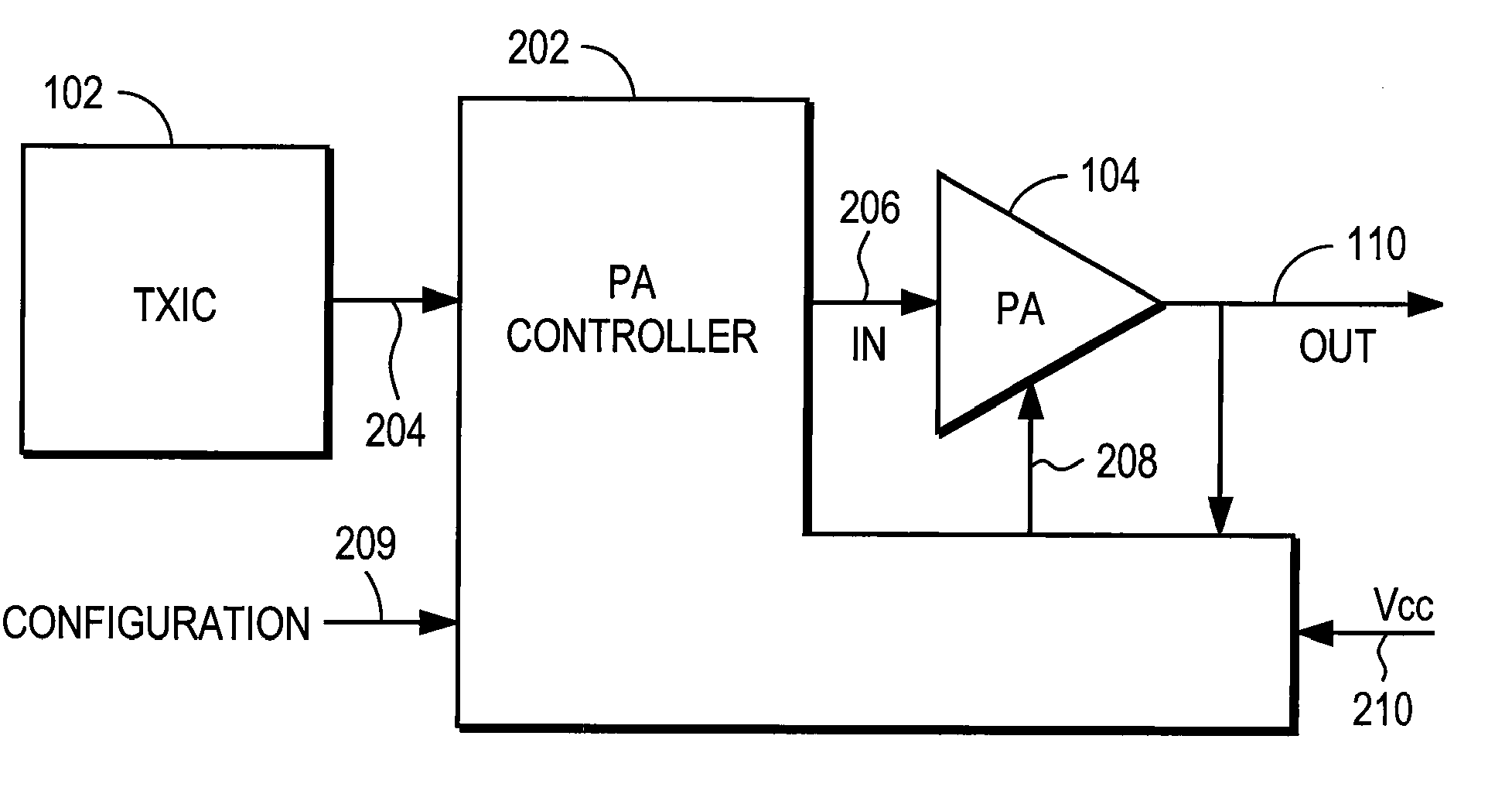
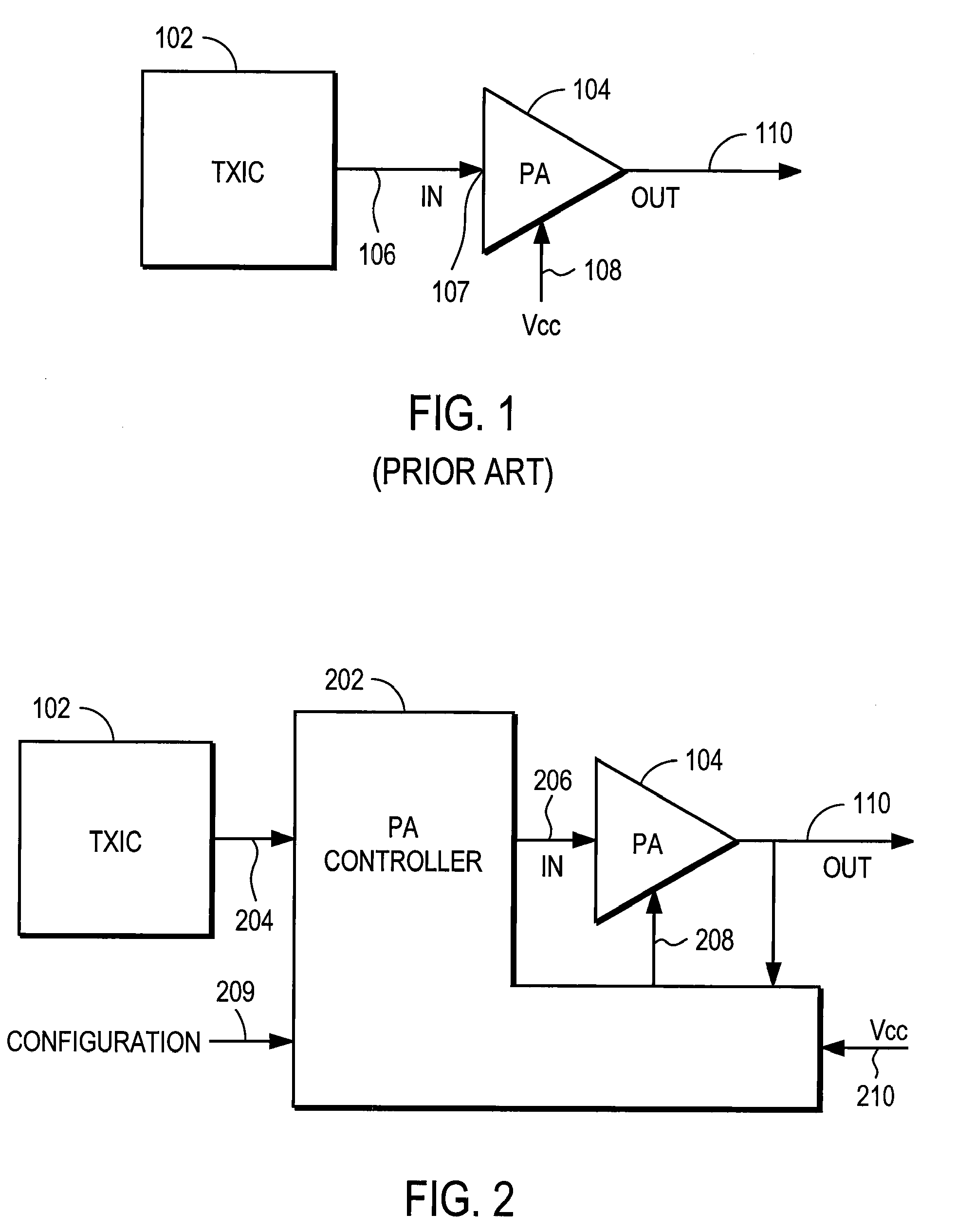
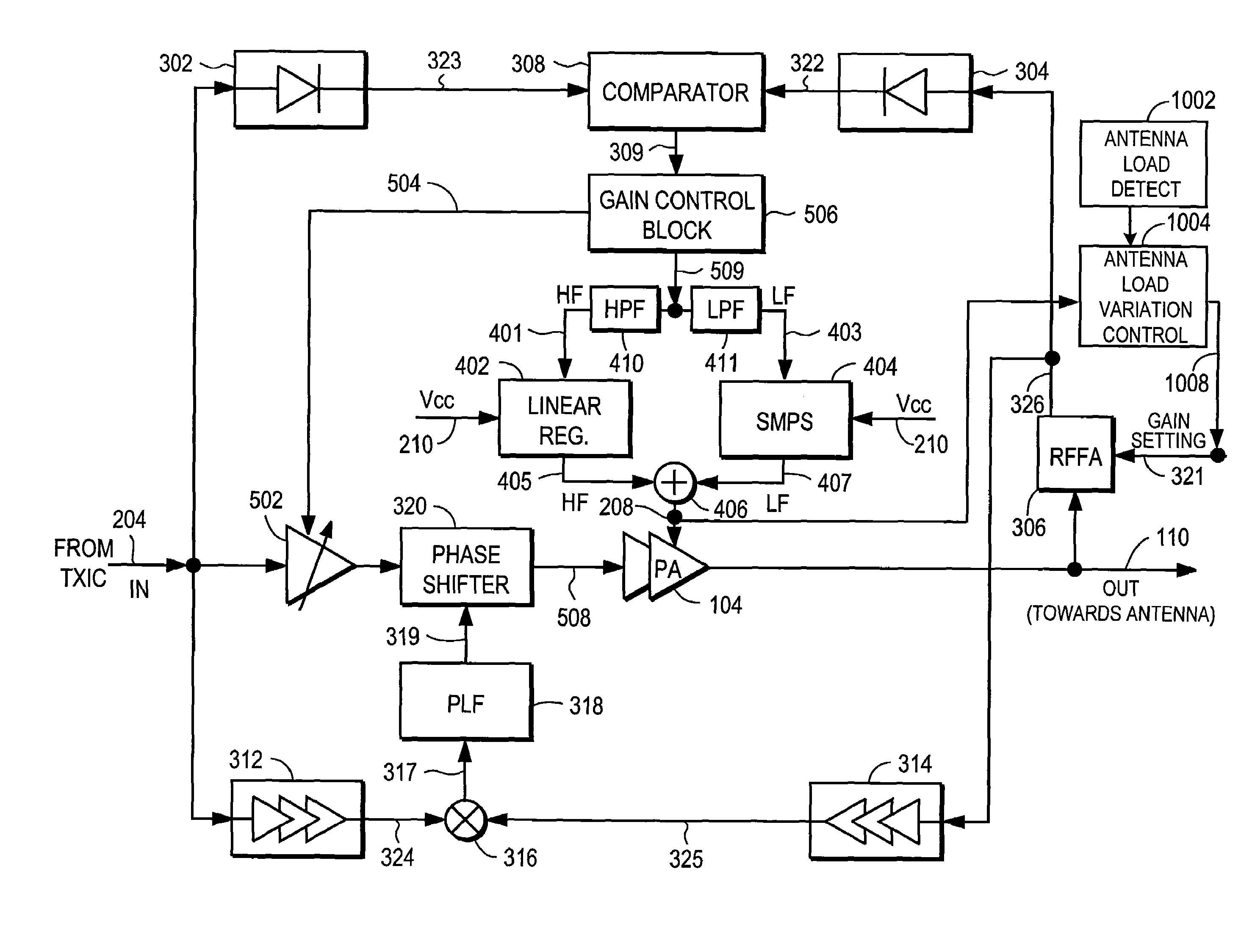
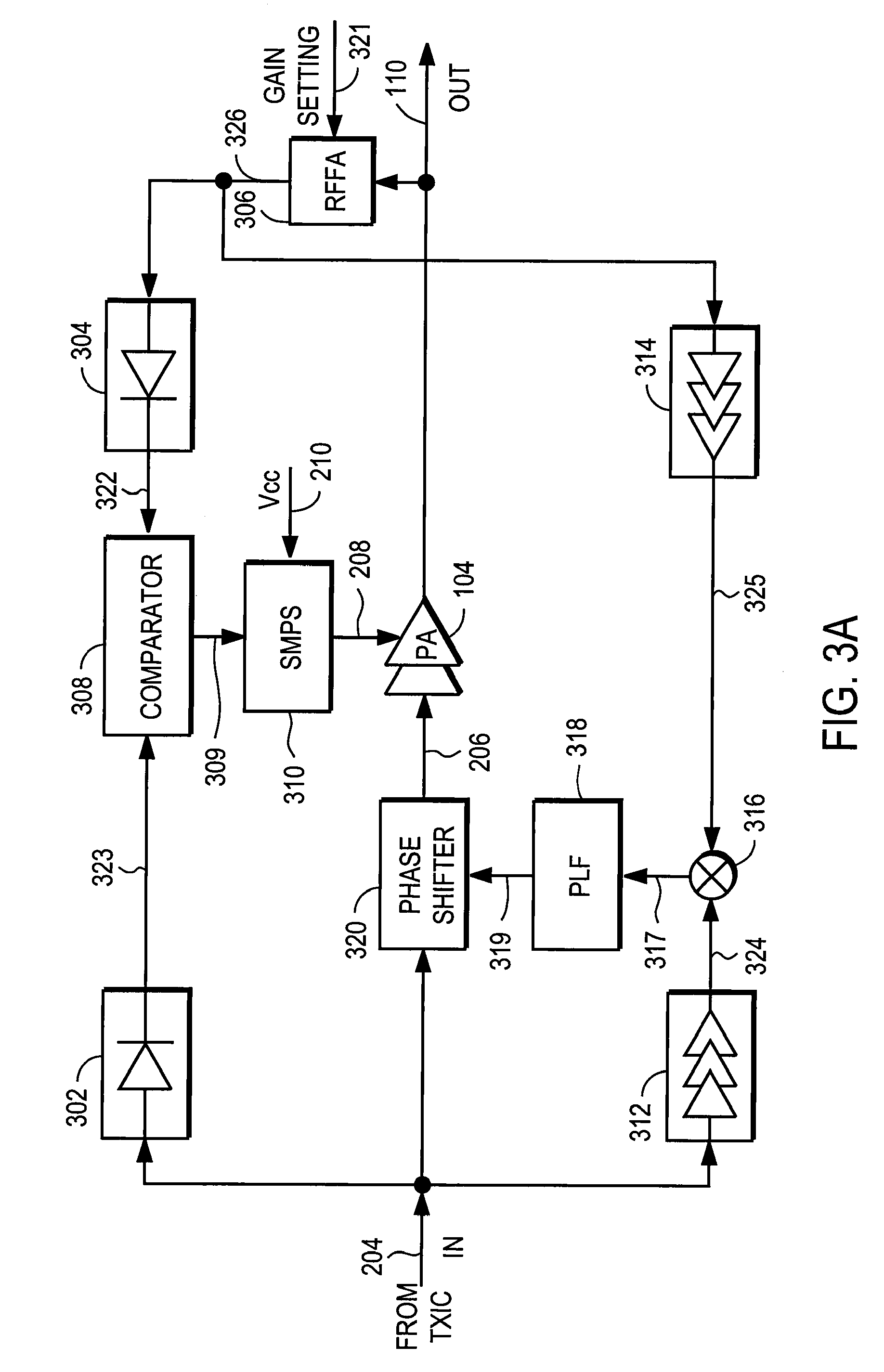
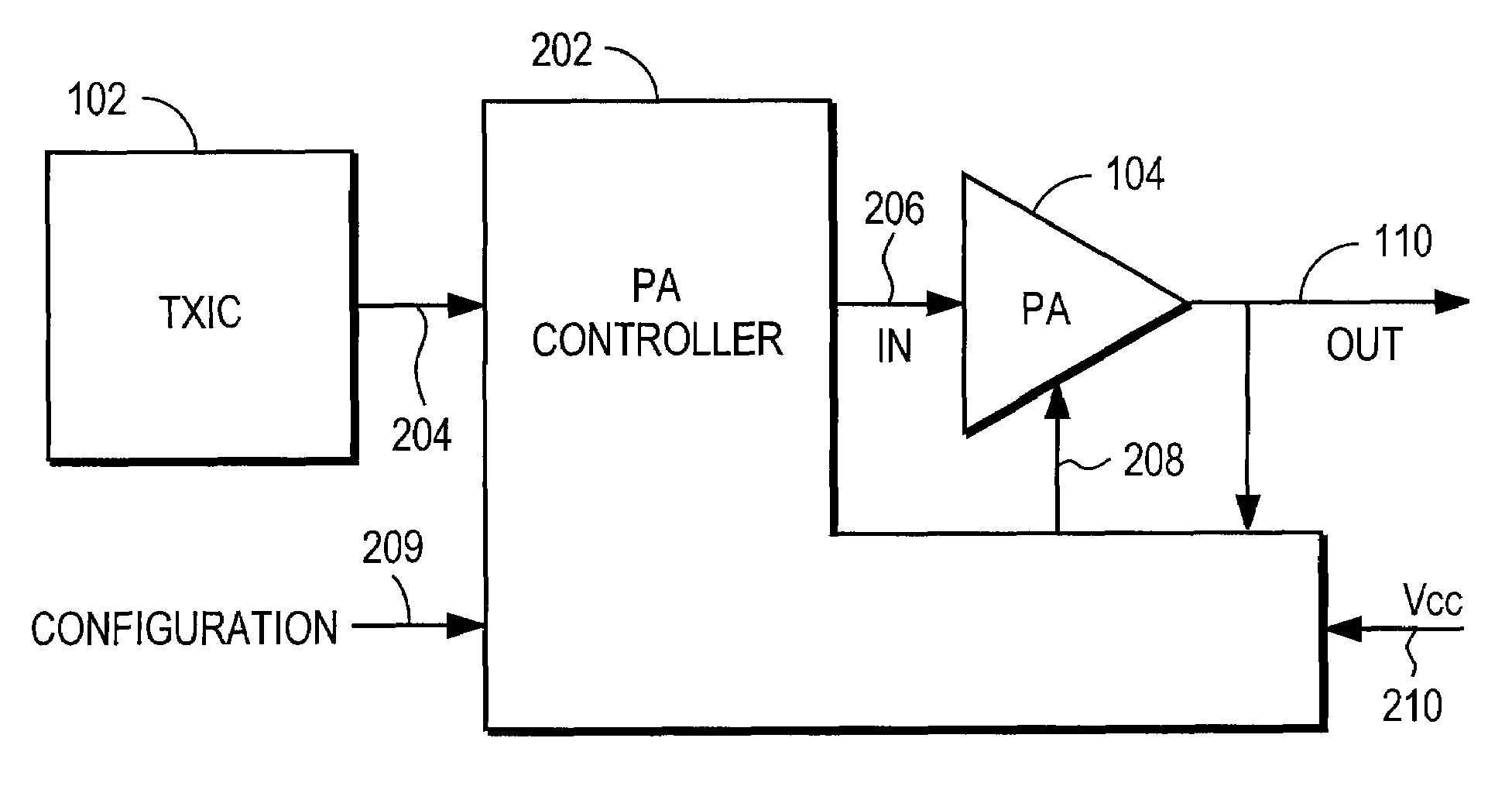
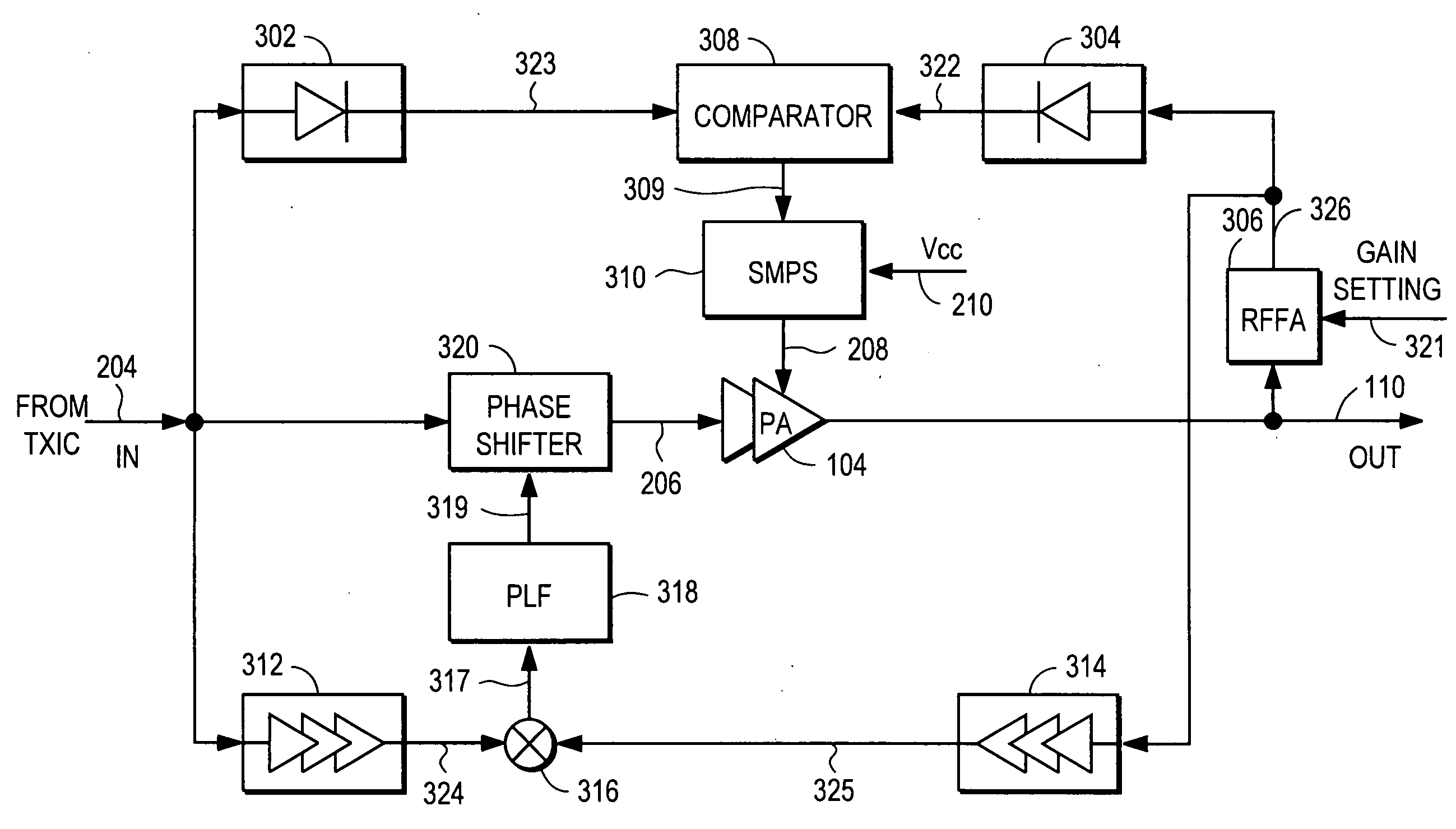
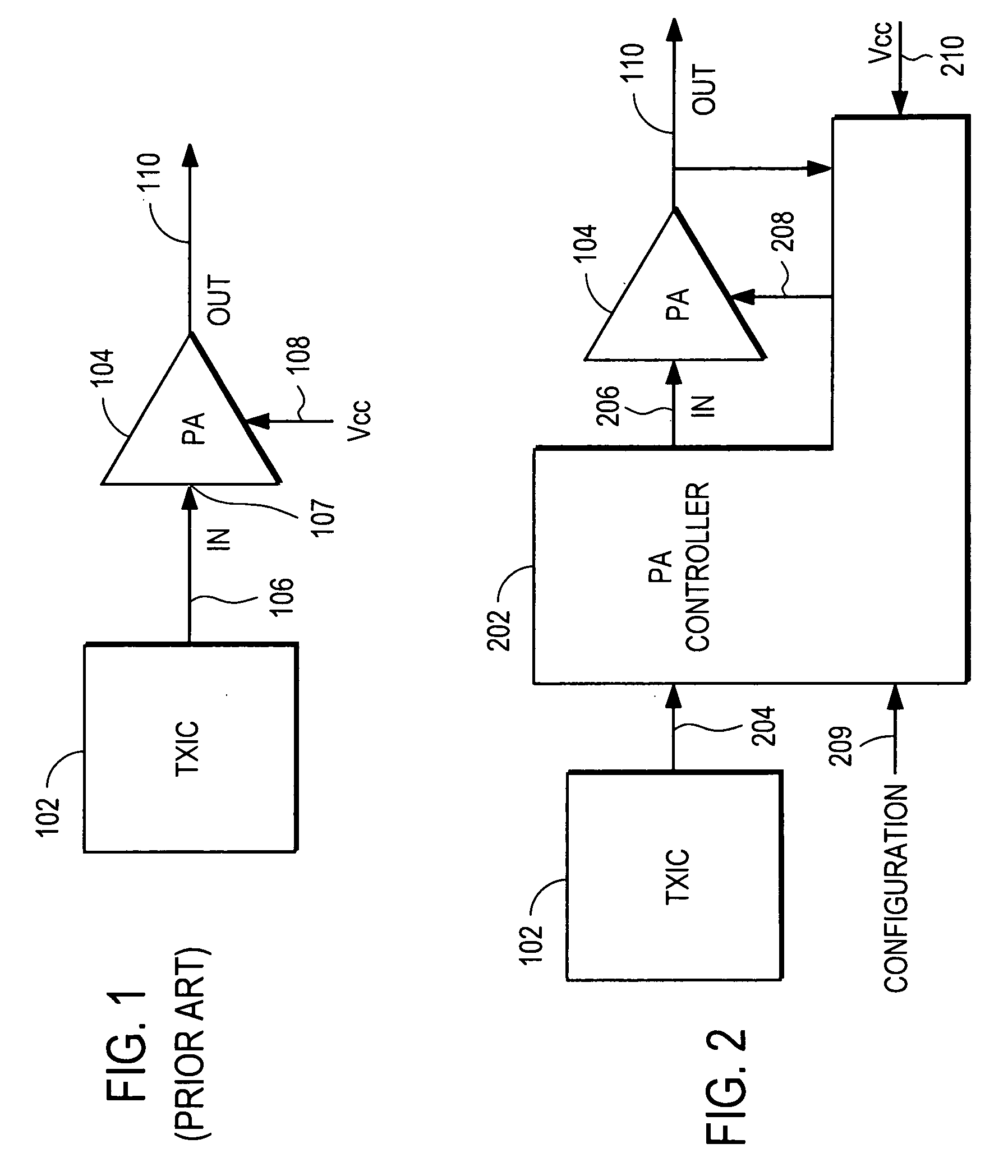
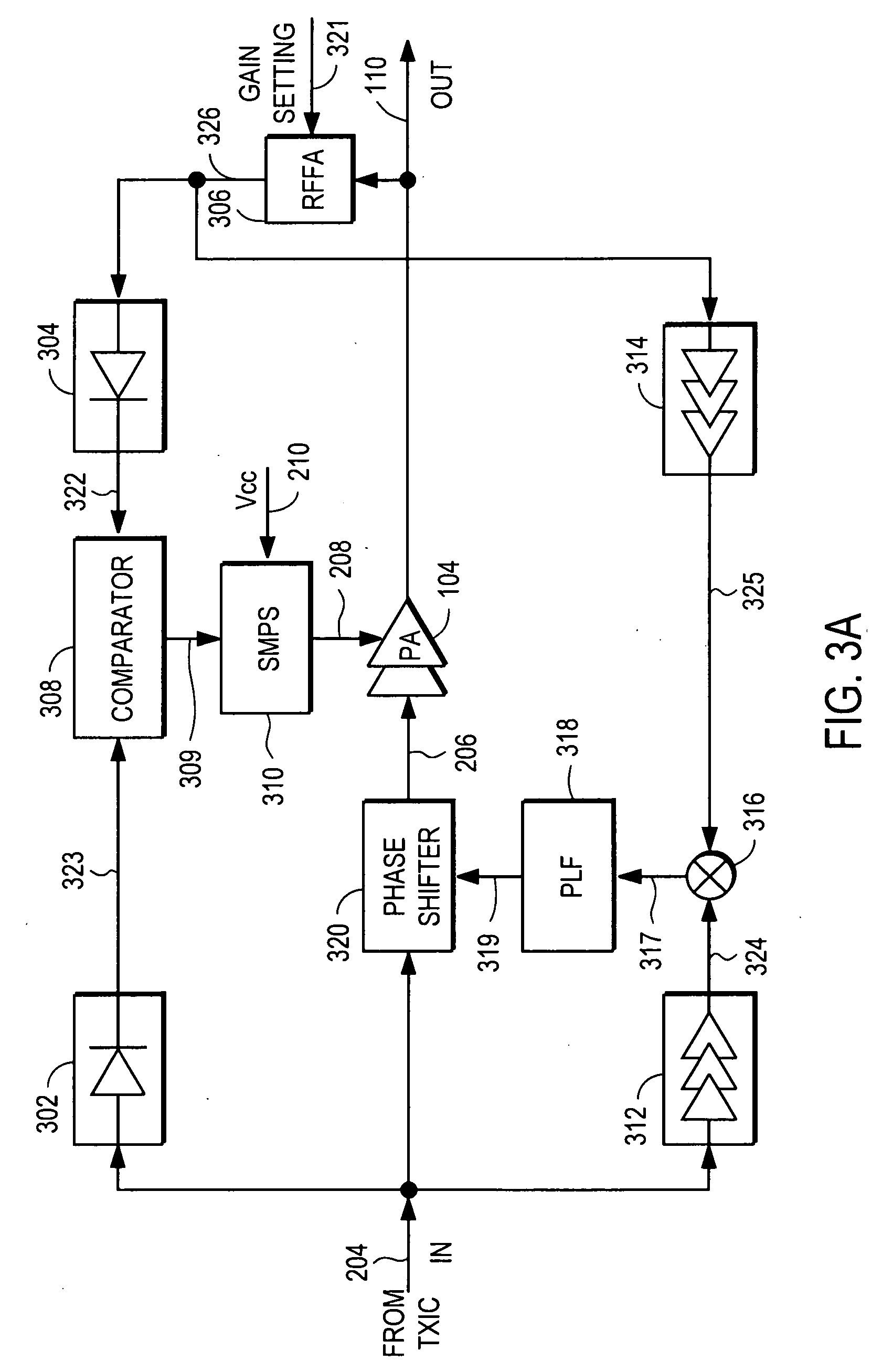
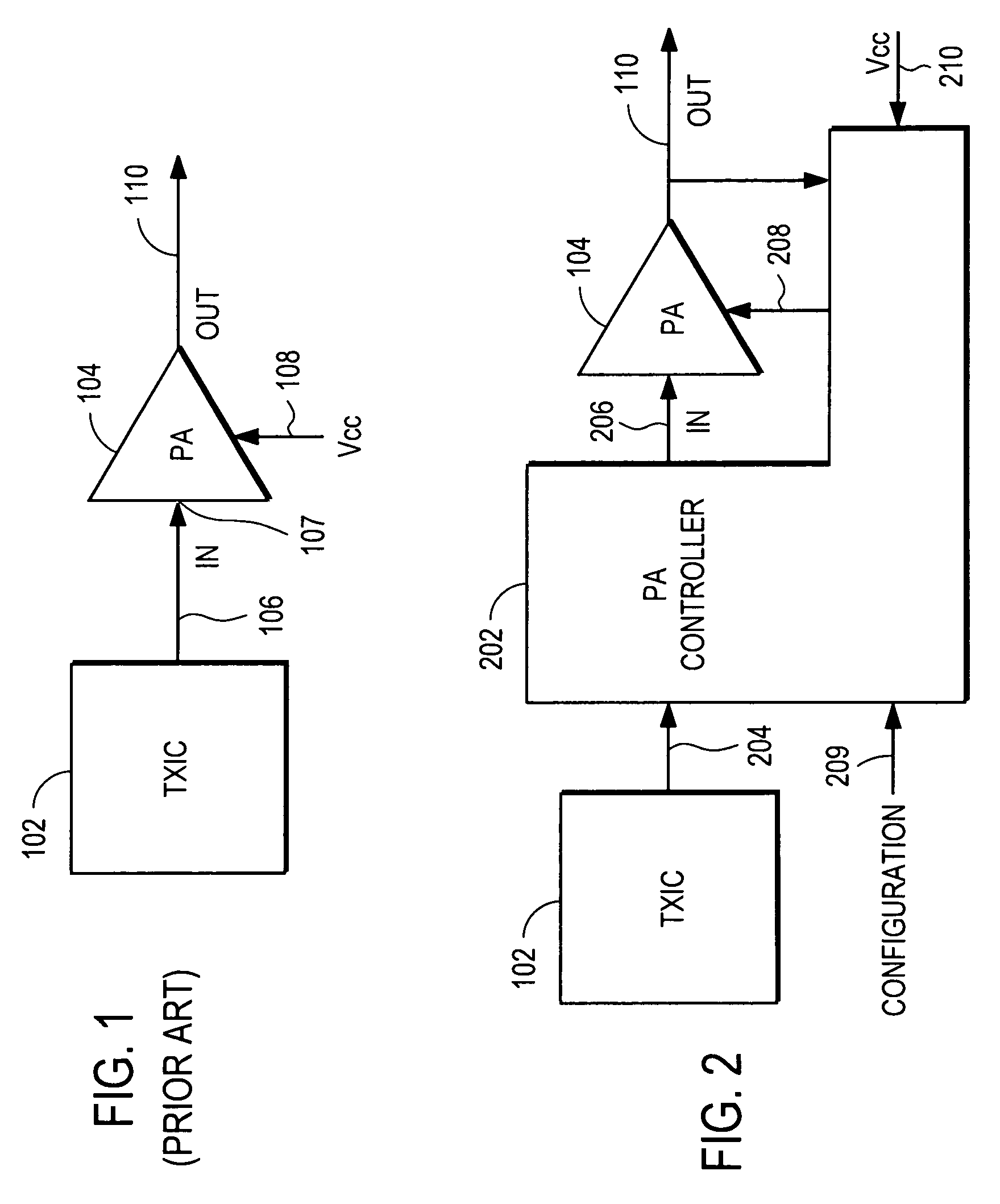
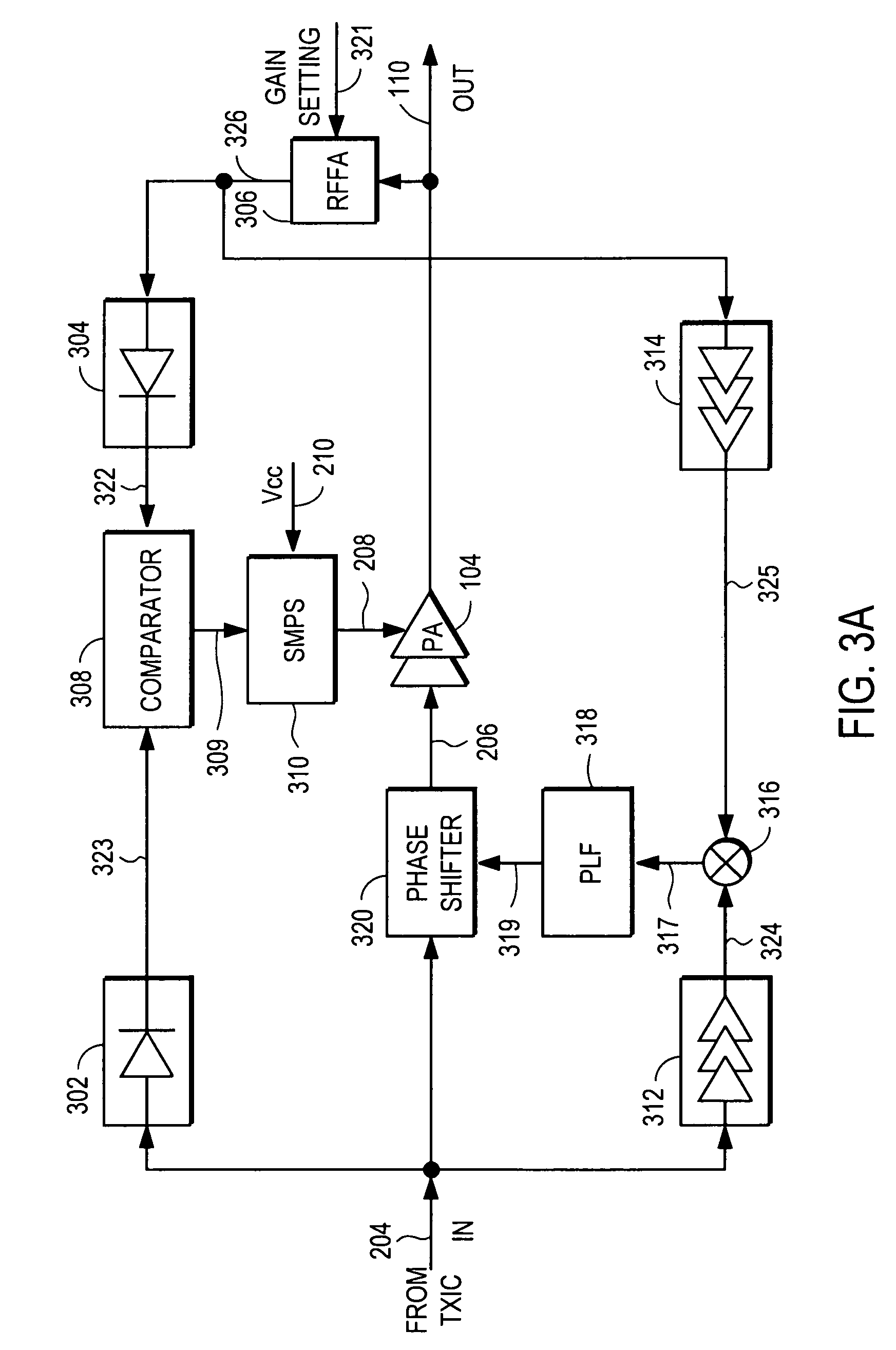
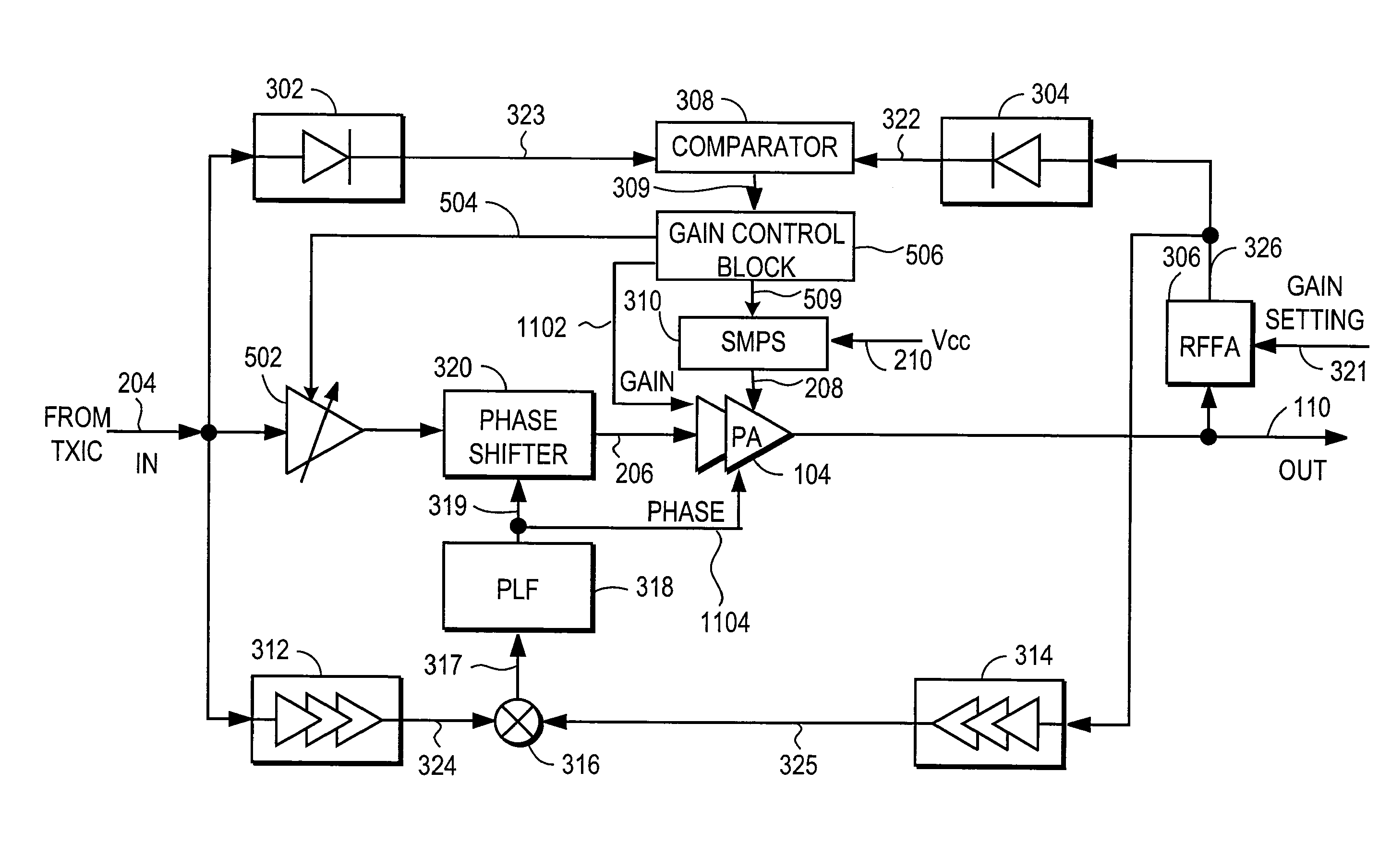
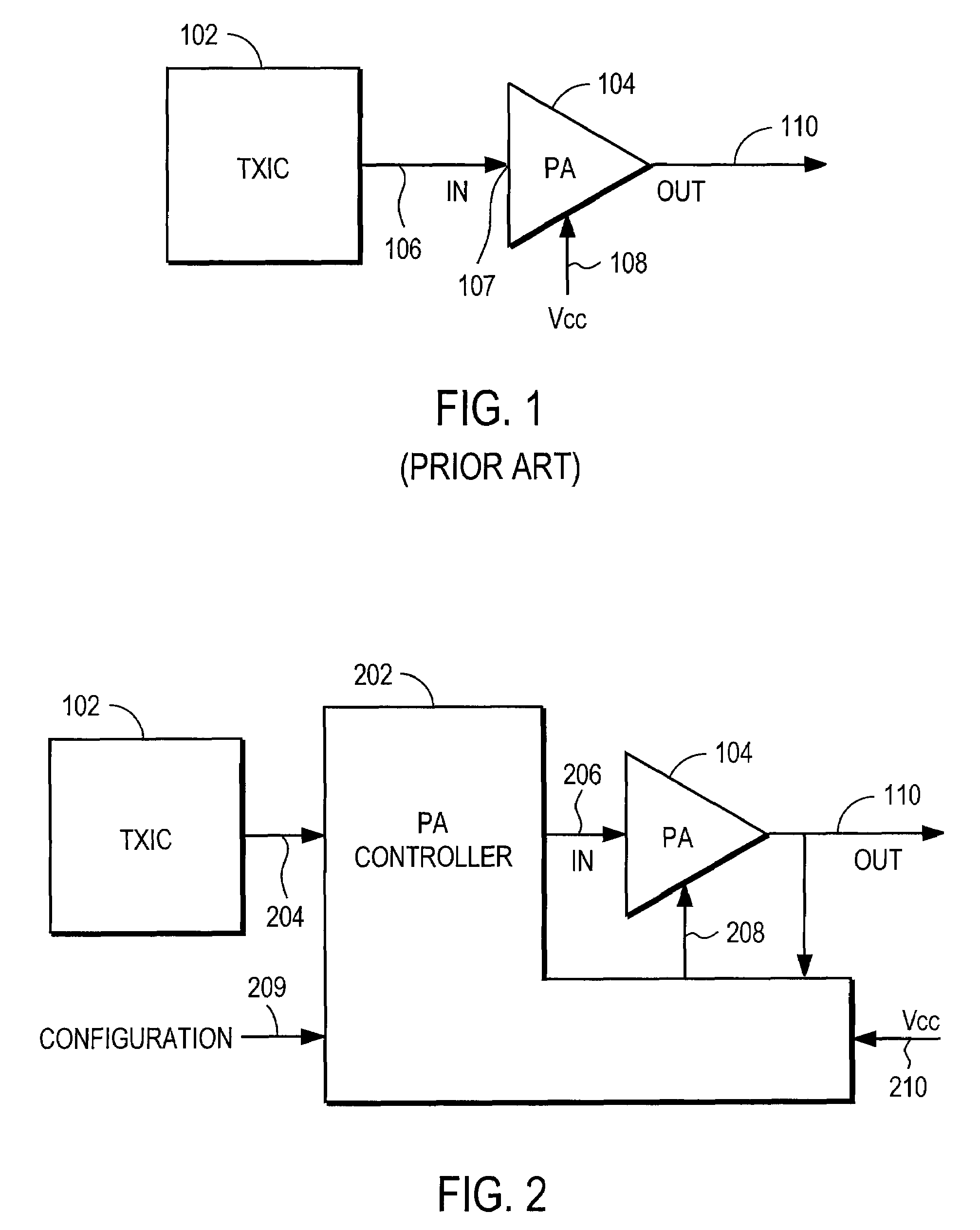
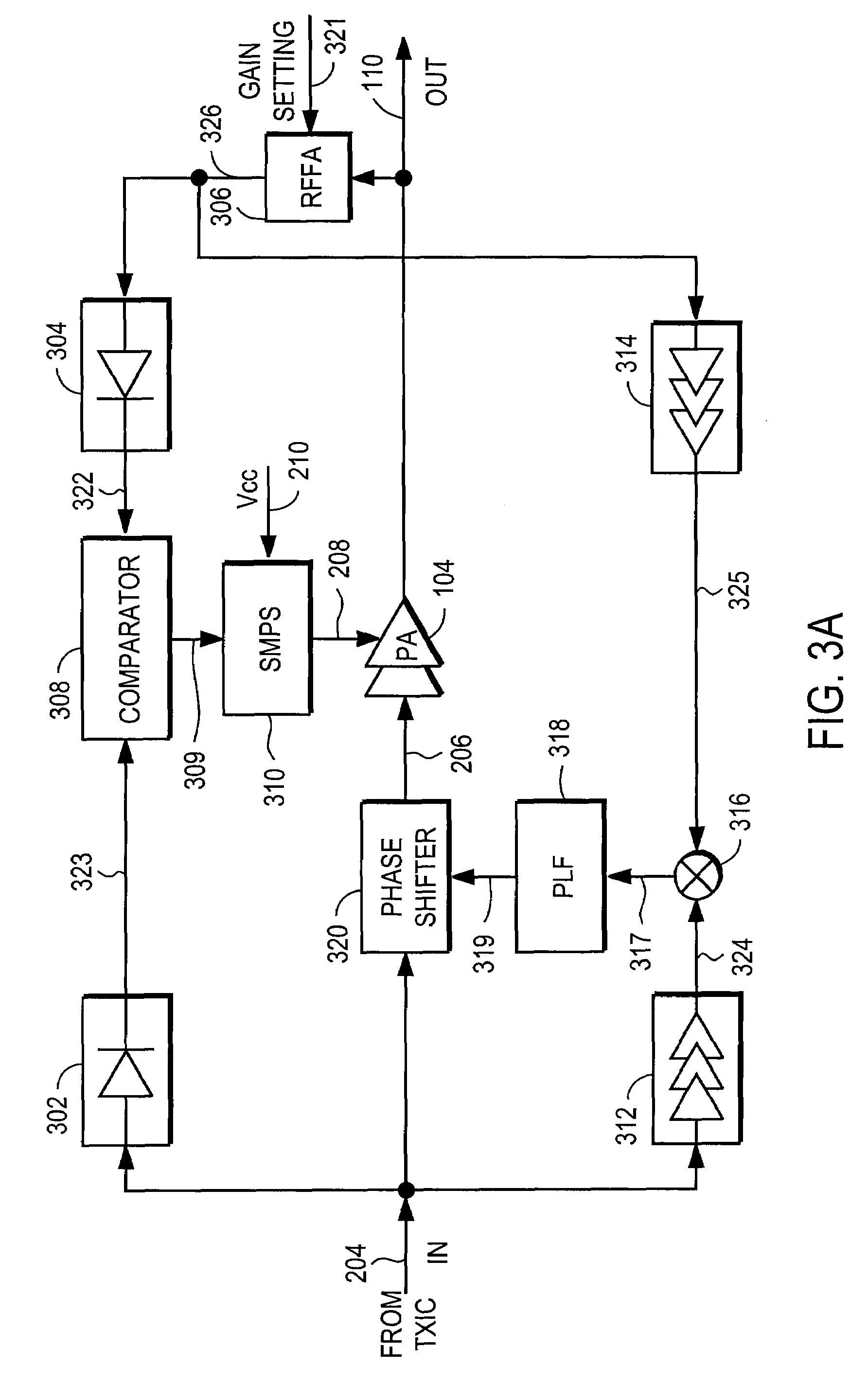
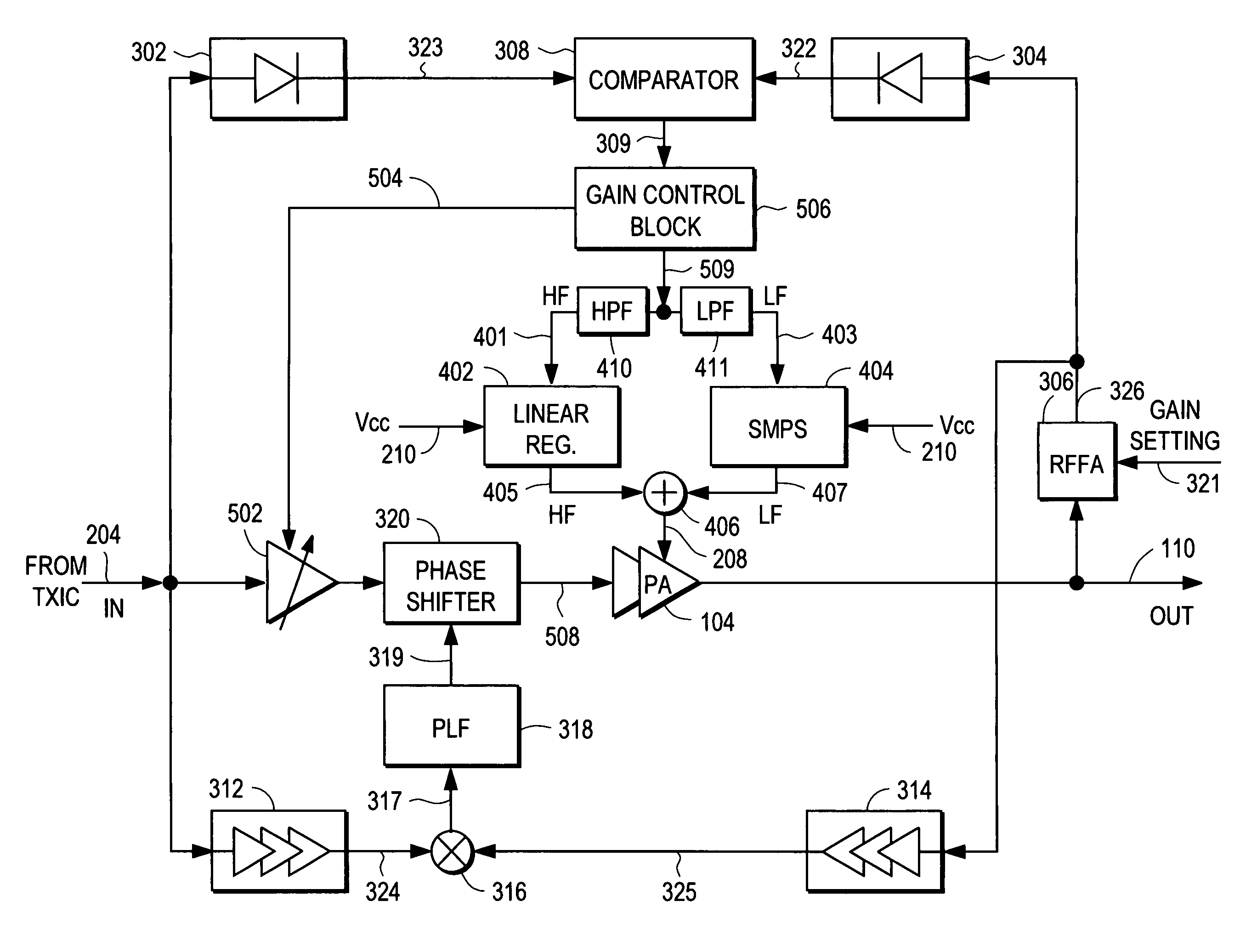
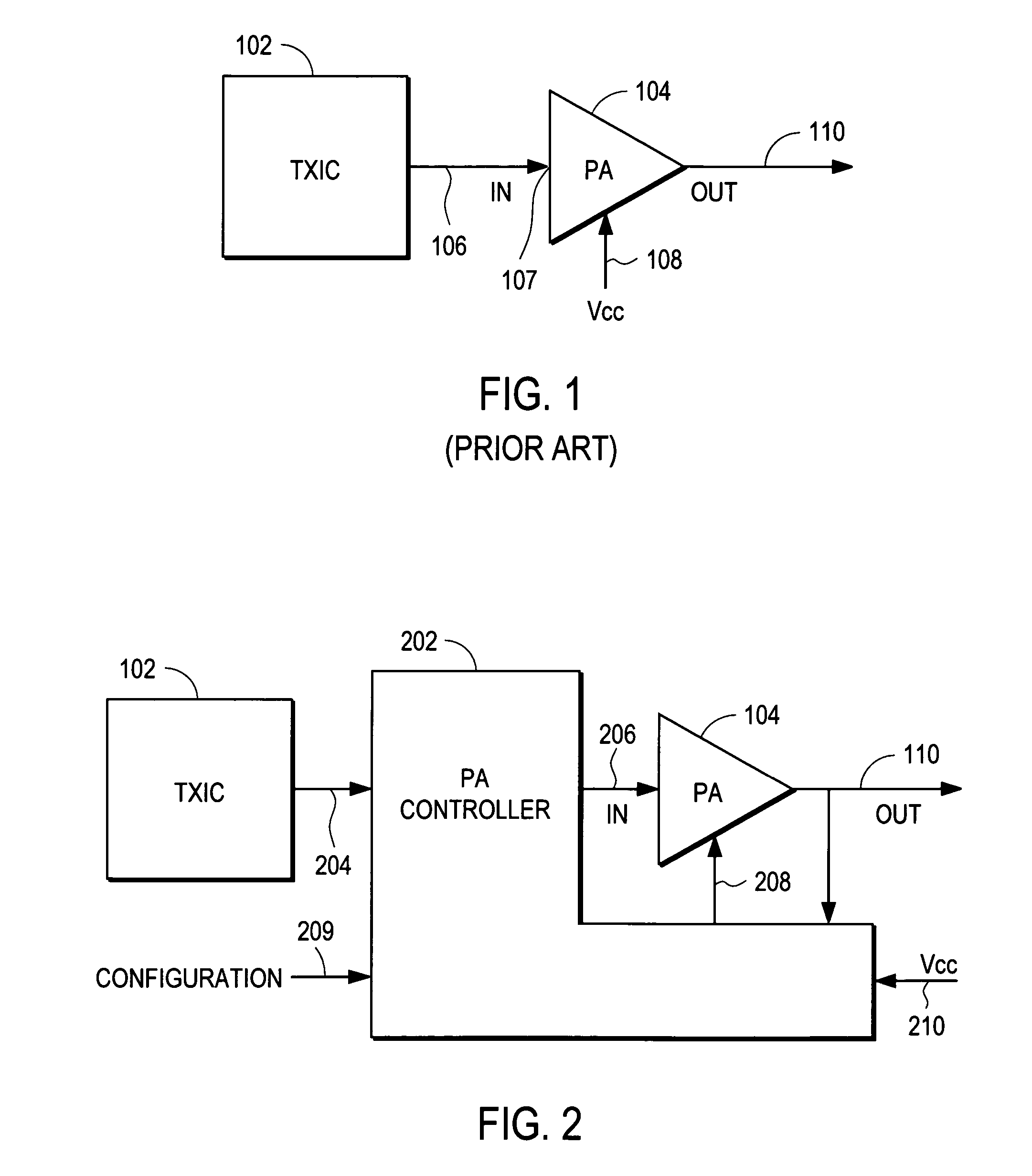
Power amplifier controller with polar transmitter
ActiveUS7783269B2Reduce glitchesImprove power efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierEngineering
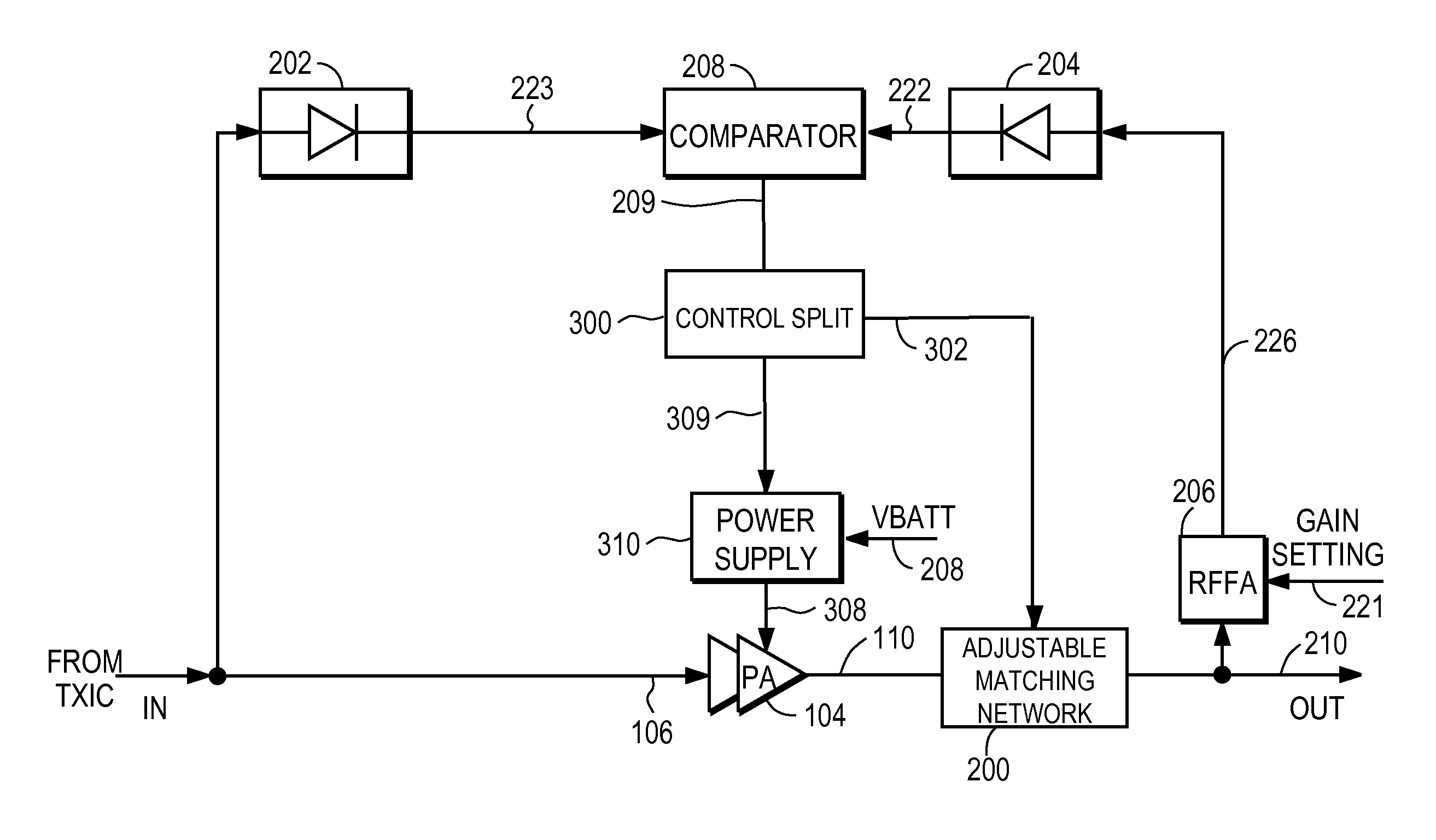
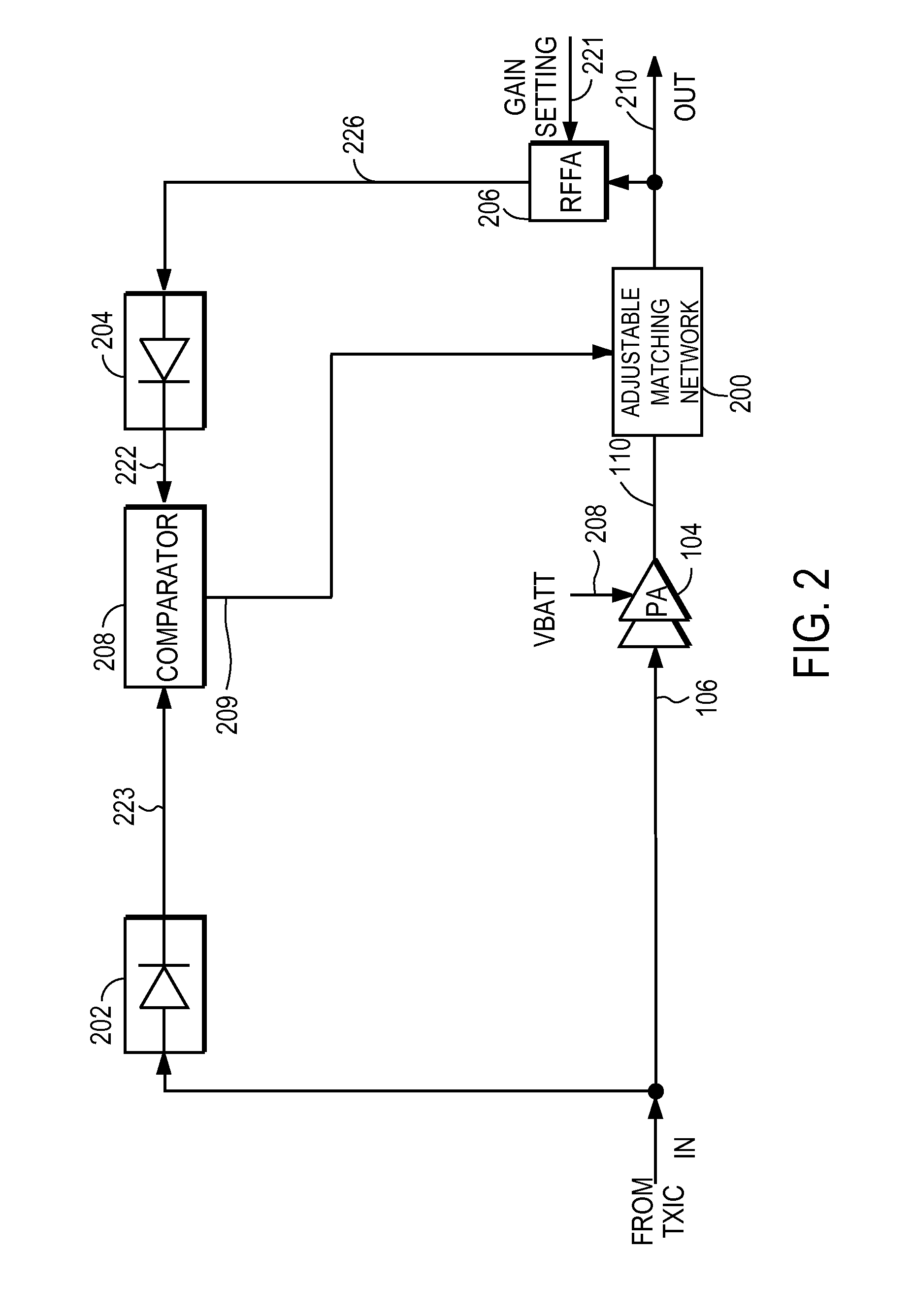
A power amplifier controller controls a power amplifier and is coupled to a polar modulator. The polar modulator generates an amplitude component and a phase-modulated component of the desired RF modulated signal, and outputs to the power amplifier controller. The power amplifier controller regenerates a combined phase and amplitude modulated RF signal to generate an input signal to a power amplifier by adjusting the gain of a VGA based on the amplitude component of the desired RF modulated signal. Concurrently, the power amplifier controller both controls an adjusted supply voltage to the PA and adjusts the gain of the VGA based upon an amplitude correction signal or amplitude error signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
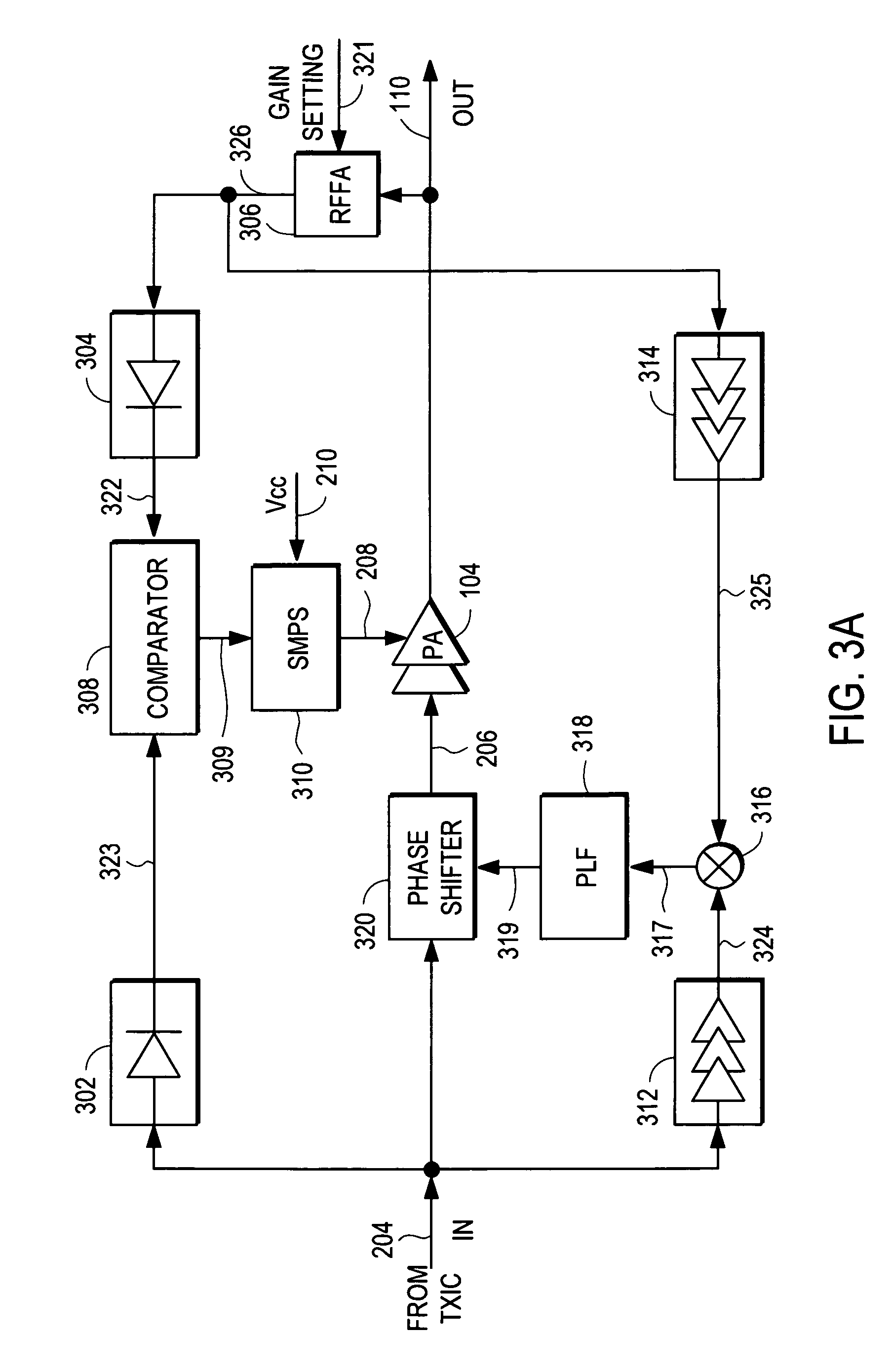
RF Power Amplifier Controller Circuit Including Calibrated Phase Control Loop
ActiveUS20070184794A1Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthResonant long antennasPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase difference
An RF power amplifier system comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal. The phase control loop may comprise one or more variable phase delays introducing a relative phase delay to allow the phase differences between the input and output signals of the PA circuit to be within a range compatible with a phase comparator generating the phase error signal, and a low frequency blocking module that removes the larger extent, lower frequency components of the phase error signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
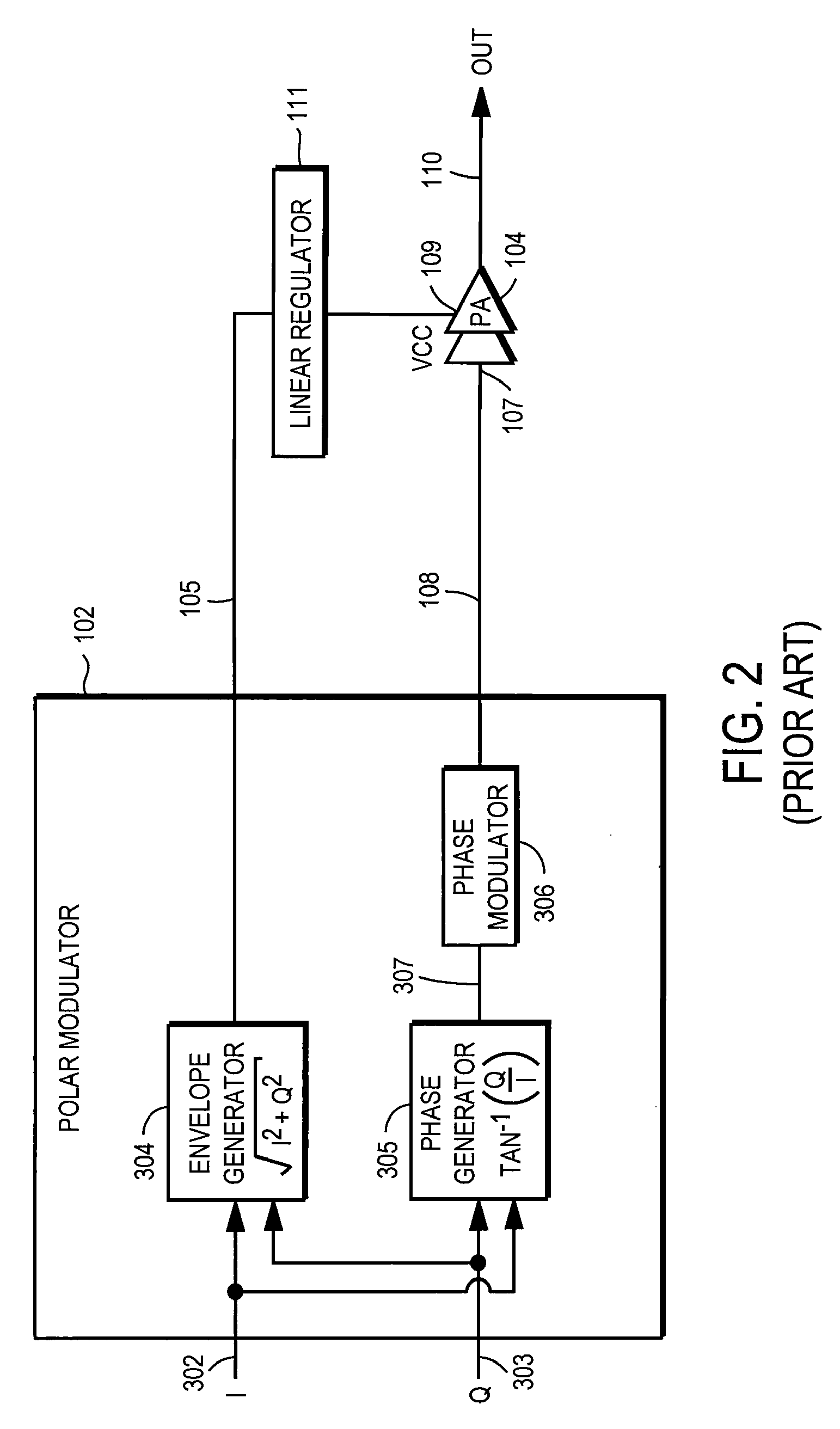
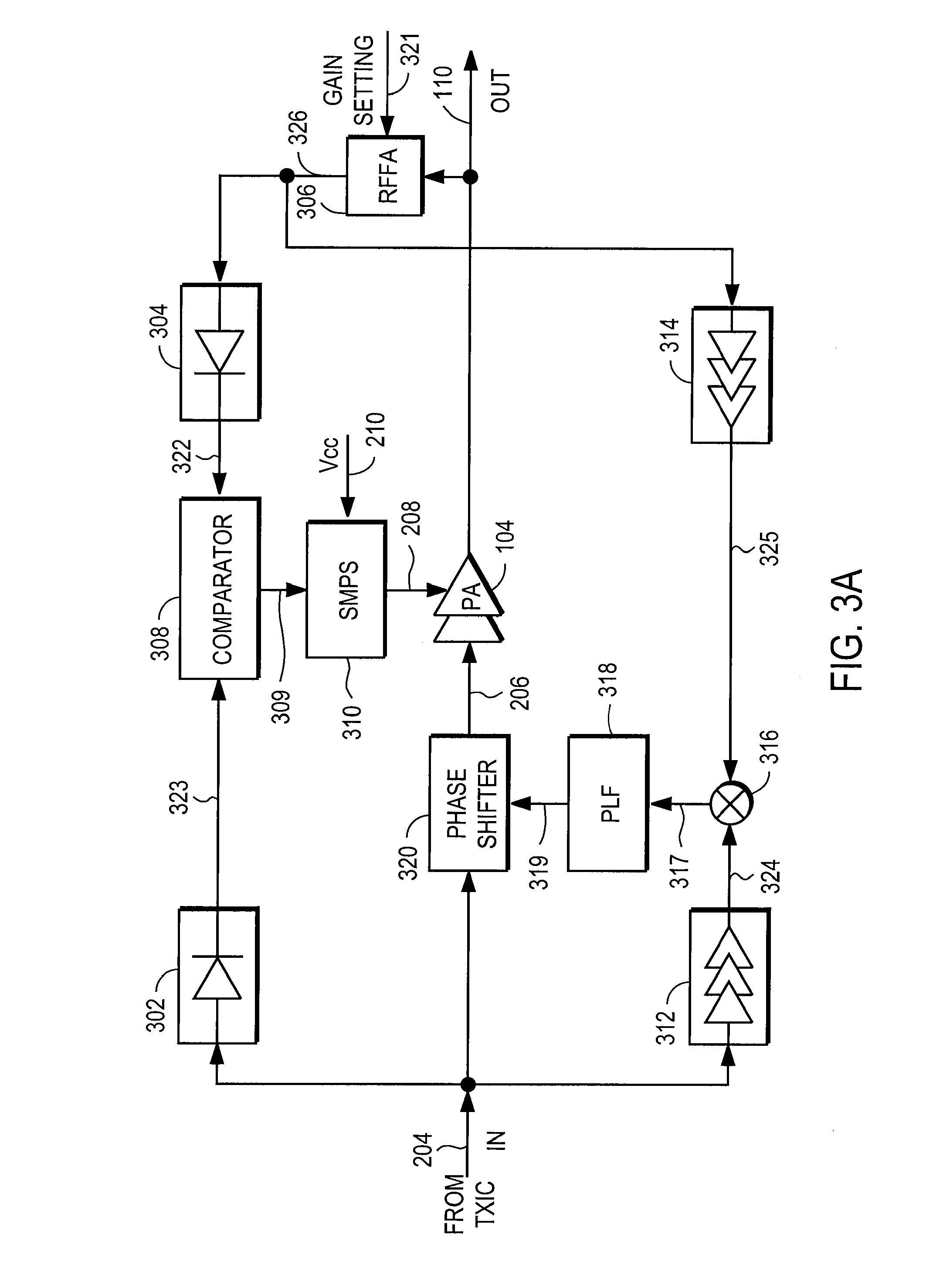
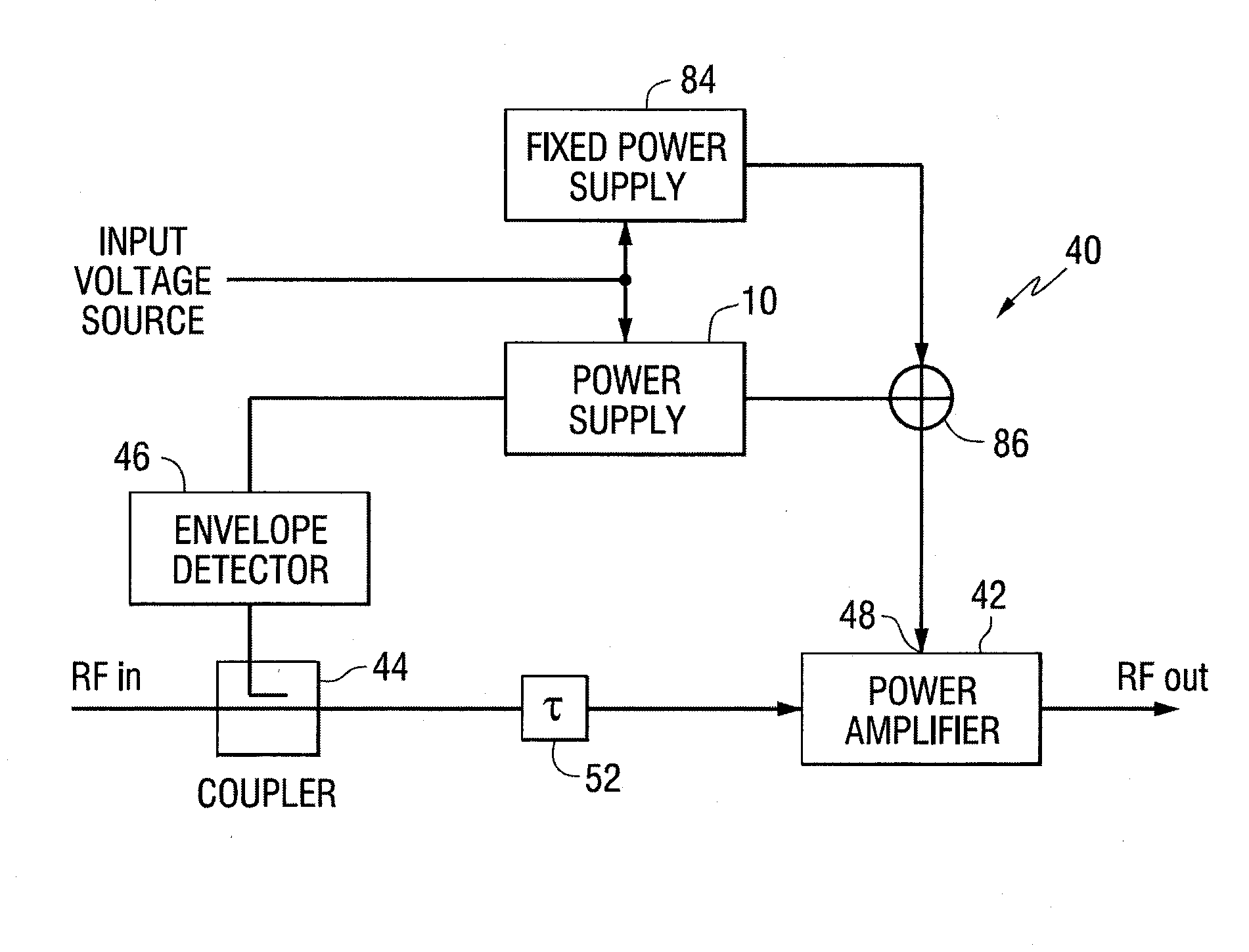
Power supply providing ultrafast modulation of output voltage
A circuit for use with a power amplifier that amplifies an input signal. The circuit may comprise an amplitude correction circuit and an open-loop switching regulator. The amplitude correction circuit may be configured to generate a corrected envelope signal from an input envelope signal that represents an envelope of the input signal. The open-loop switching regulator may be connected to the amplitude correction circuit and may be for powering the power amplifier based on the corrected envelope signal. According to various embodiments, the corrected envelope signal generated by the amplitude correction circuit is a function of the input envelope signal and an error voltage of the open-loop switching regulator.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
Power Amplifier Controller With Polar Transmitter
ActiveUS20100311365A1Reduce phase distortionMinimize the differenceAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierEngineering
A power amplifier controller controls a power amplifier and is coupled to a polar modulator. The polar modulator generates an amplitude component and a phase-modulated component of the desired RF modulated signal, and outputs to the power amplifier controller. The power amplifier controller regenerates a combined phase and amplitude modulated RF signal to generate an input signal to a power amplifier by adjusting the gain of a VGA based on the amplitude component of the desired RF modulated signal. Concurrently, the power amplifier controller both controls an adjusted supply voltage to the PA and adjusts the gain of the VGA based upon an amplitude correction signal or amplitude error signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
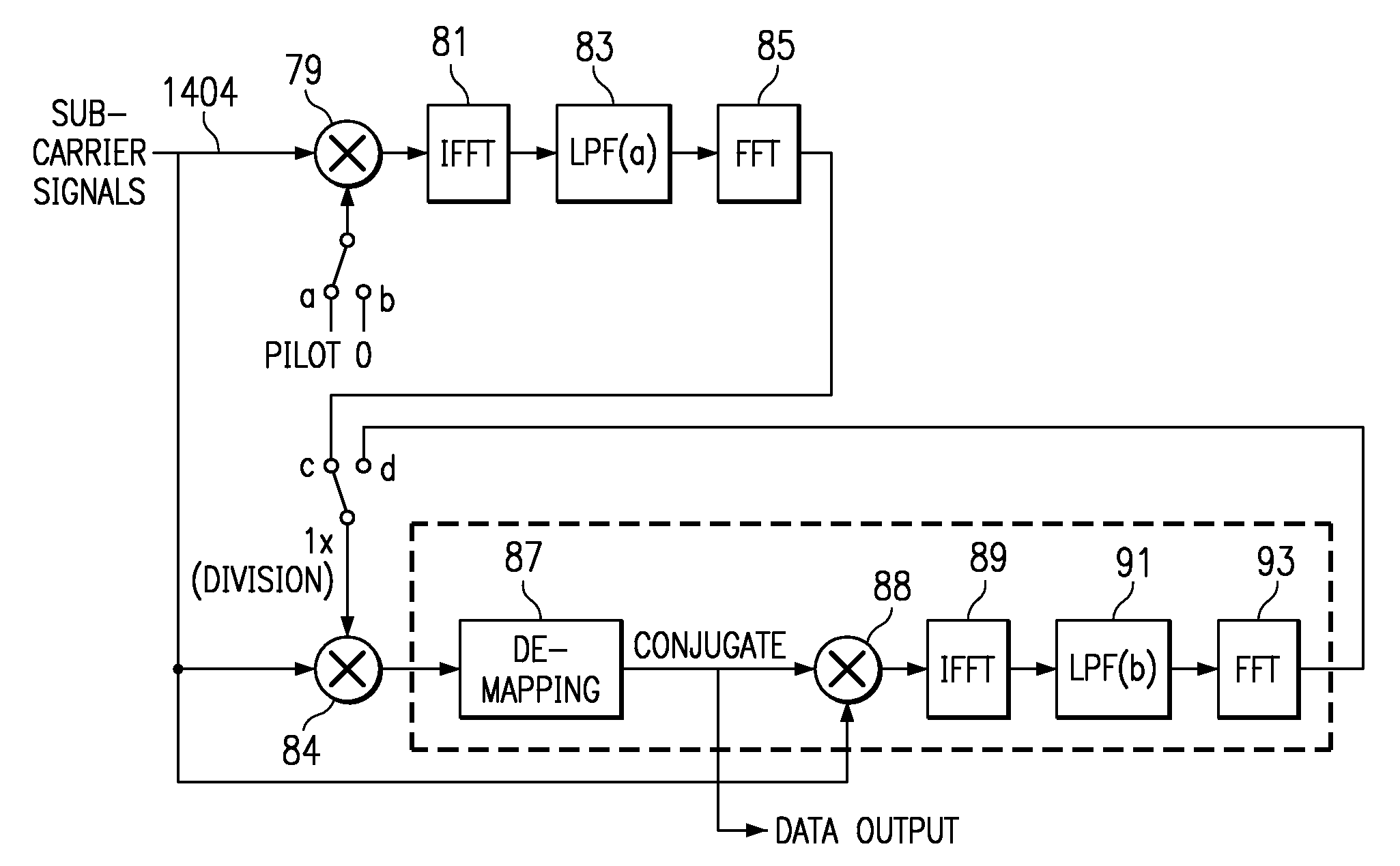
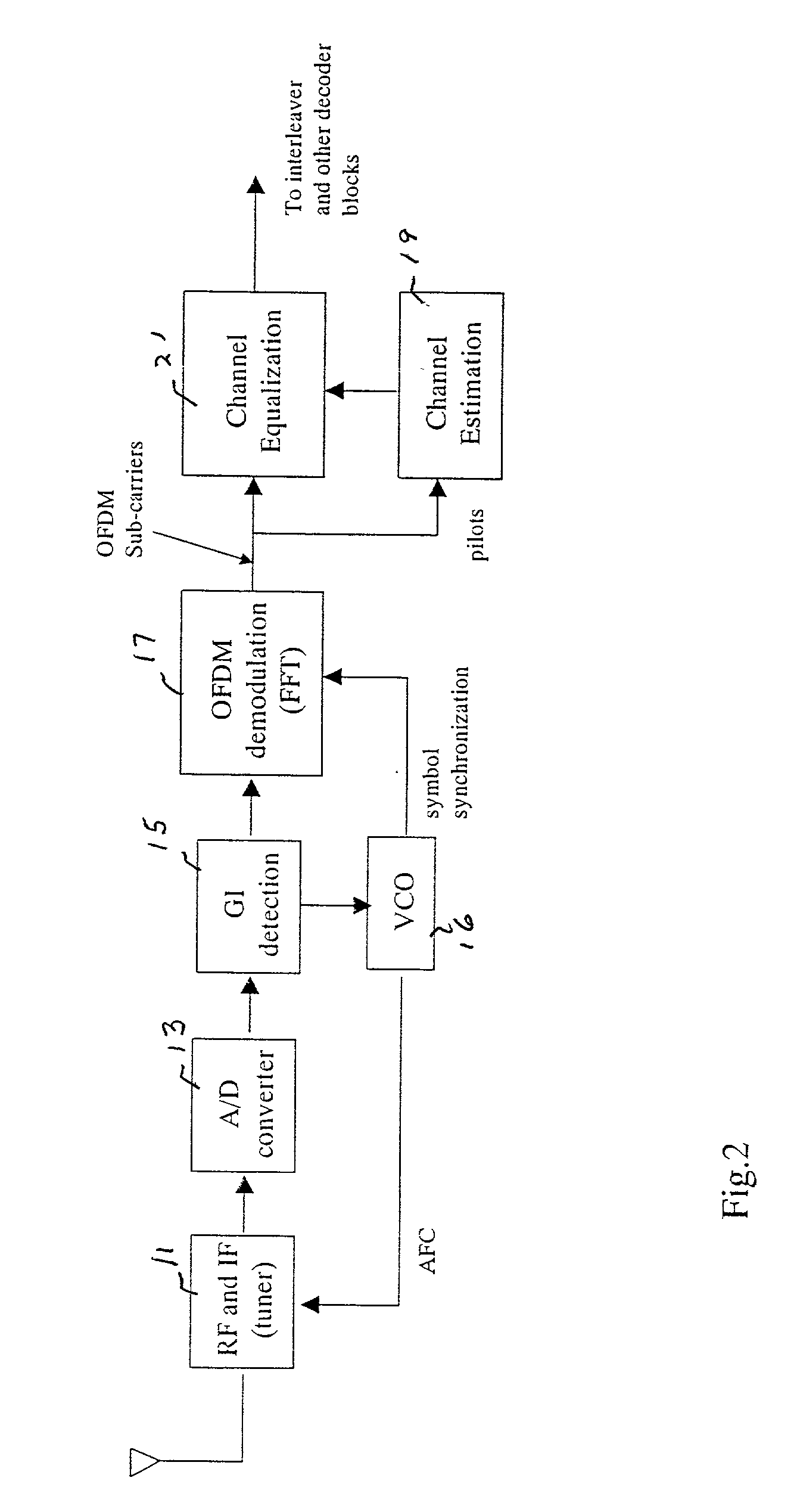
Multi-path equalization for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
ActiveUS7099270B2Transmission control/equalisingAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFourier transform on finite groupsEqualization
A multi-path equalization system for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication (OFDM) system includes a first estimator for estimating the channel characteristic using pilot signal. A divider is coupled to the estimator for dividing each sub-carrier with the channel characteristic to get the equalization to the data signal. A de-mapper uses the phase and amplitude correction of the channel estimate to recover the data signals. An improved channel estimation is provided by a repeat channel estimation feedback loop that includes the de-mapper a multiplier, an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT), a low pass filter and a fast Fourier transform (FFT). The improved channel estimation is obtained by multiplying at the multiplier the conjugate of the de-mapped data to the input sub-carriers and applying inverse FFT, low pass filtering and FFT to get the new channel estimate. Each sub-carrier is divided with new channel characteristic to get new equalization to the data signal. The channel estimation is repeated until there is convergence. The output is provided after the de-mapper. In the case of channel decoding to improve performance a Viterbi decoder and convolutional encoder is coupled in loop between the de-mapper and the multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multi-path equalization for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication system
ActiveUS20030227866A1Evenly goodTransmission control/equalisingAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsViterbi decoderCommunications system
A multi-path equalization system for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing communication (OFDM) system includes a first estimator for estimating the channel characteristic using pilot signal. A divider is coupled to the estimator for dividing each sub-carrier with the channel characteristic to get the equalization to the data signal. A de-mapper uses the phase and amplitude correction of the channel estimate to recover the data signals. An improved channel estimation is provided by a repeat channel estimation feedback loop that includes the de-mapper a multiplier, an inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT), a low pass filter and a fast Fourier transform (FFT). The improved channel estimation is obtained by multiplying at the multiplier the conjugate of the de-mapped data to the input sub-carriers and applying inverse FFT, low pass filtering and FFT to get the new channel estimate. Each sub-carrier is divided with new channel characteristic to get new equalization to the data signal. The channel estimation is repeated until there is convergence. The output is provided after the de-mapper. In the case of channel decoding to improve performance a Viterbi decoder and convolutional encoder is coupled in loop between the de-mapper and the multiplier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
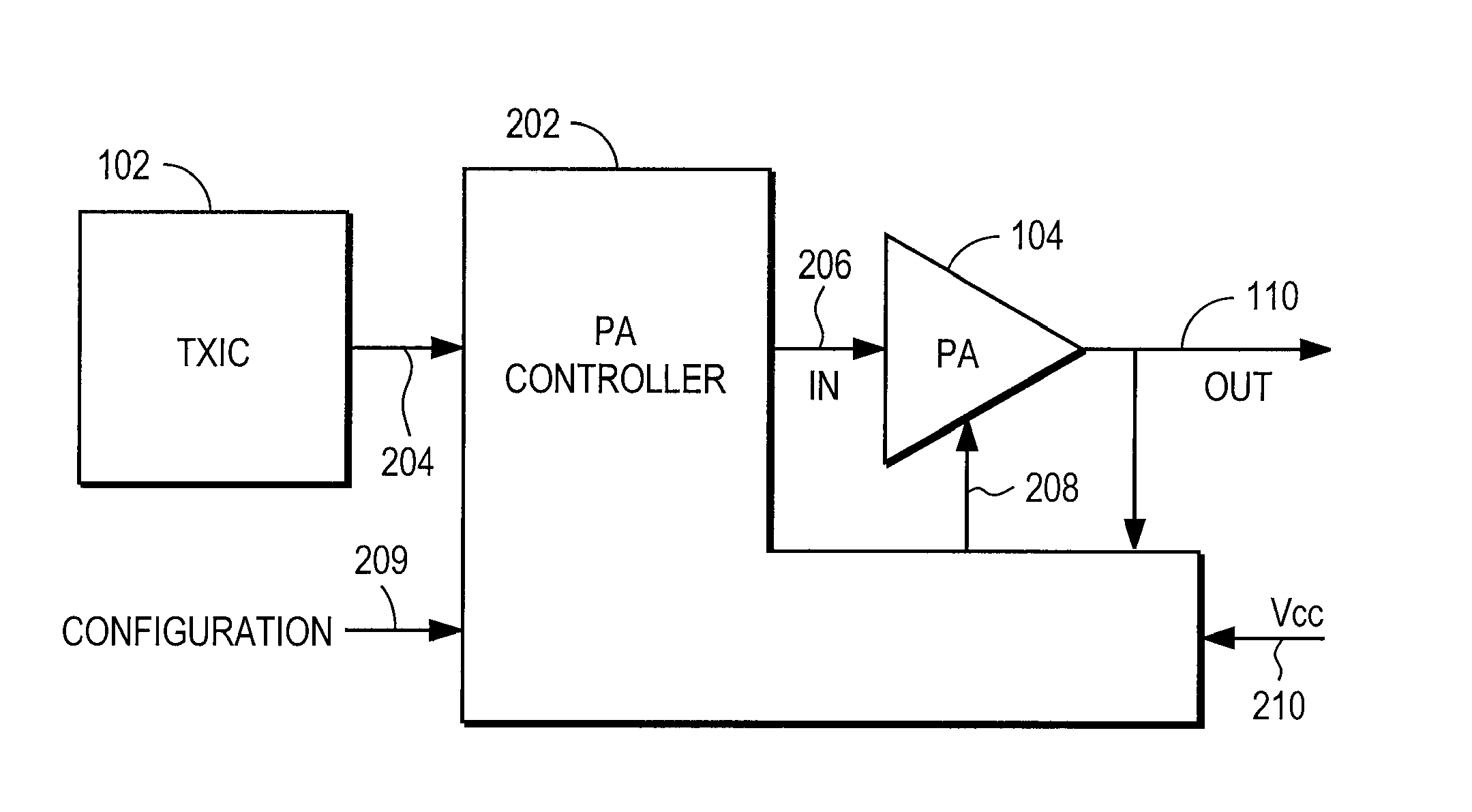
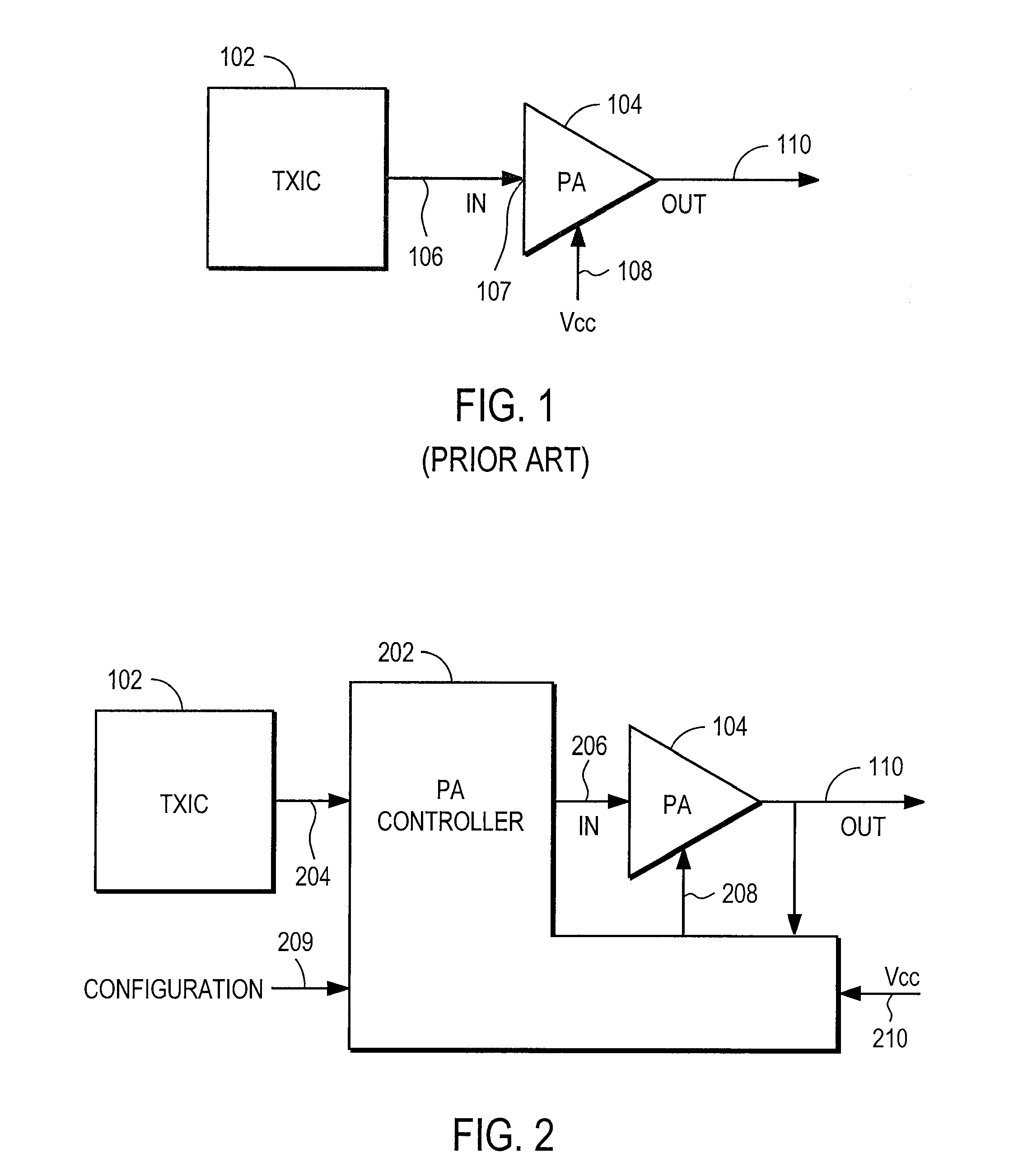
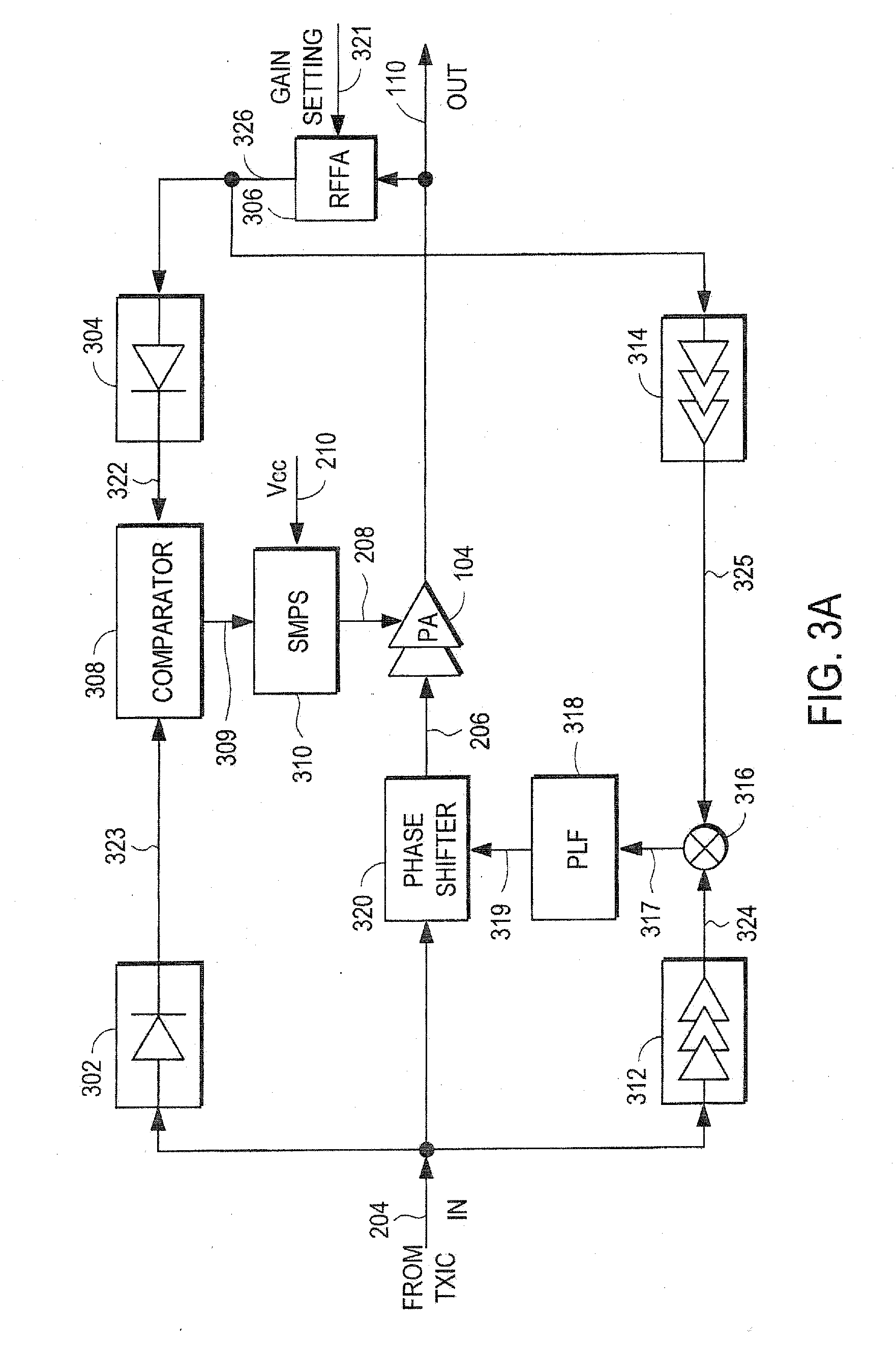
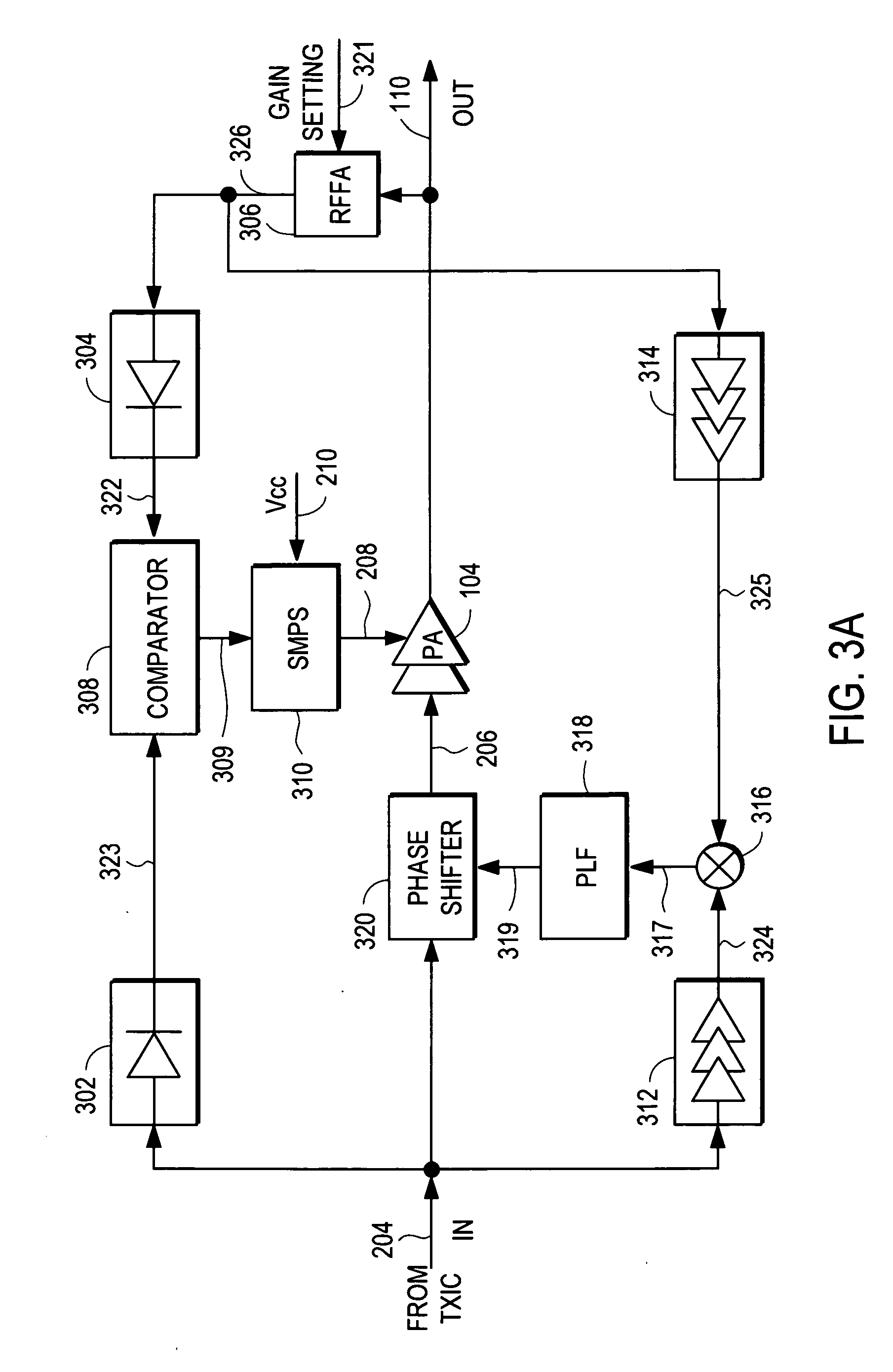
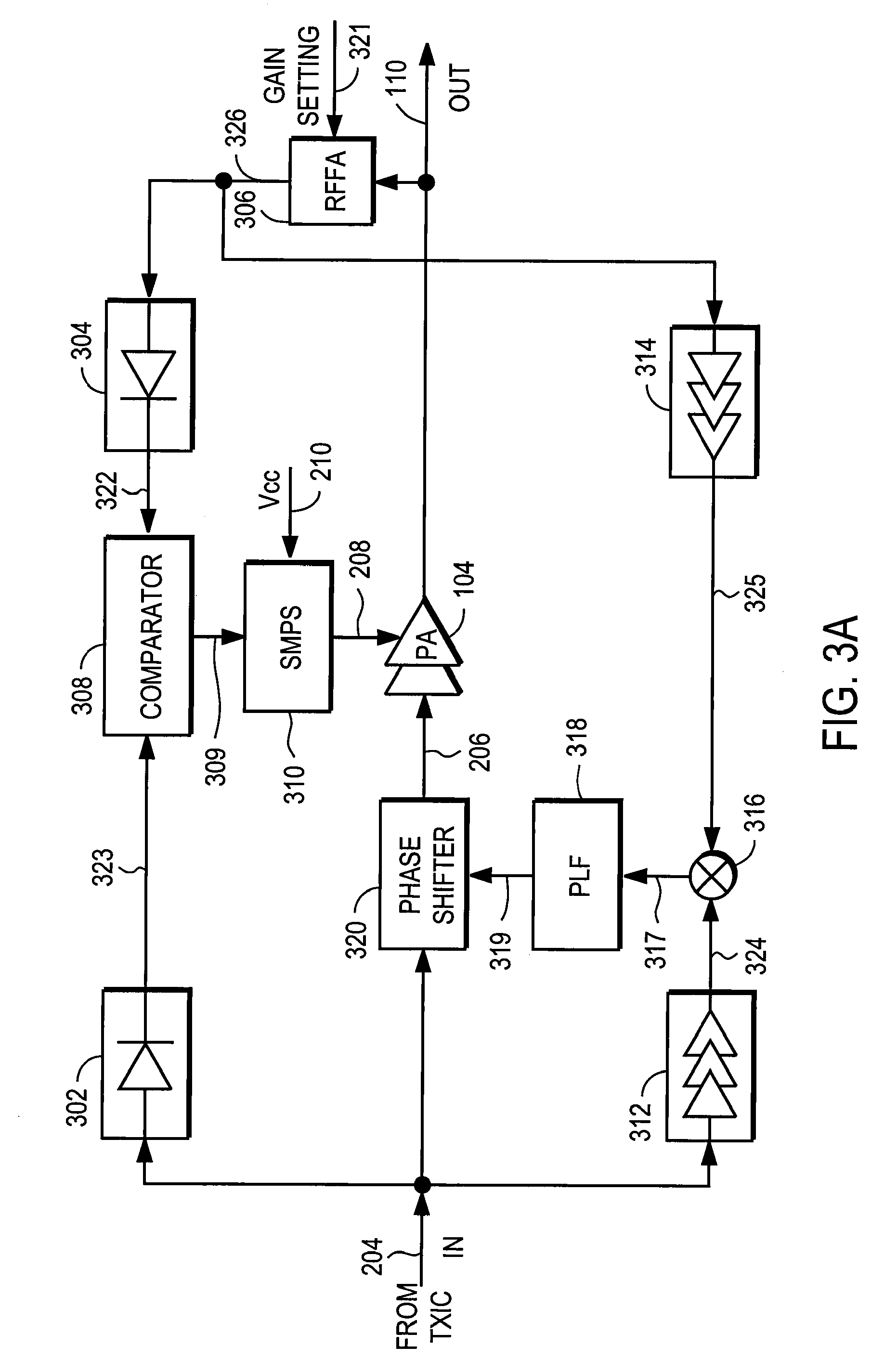
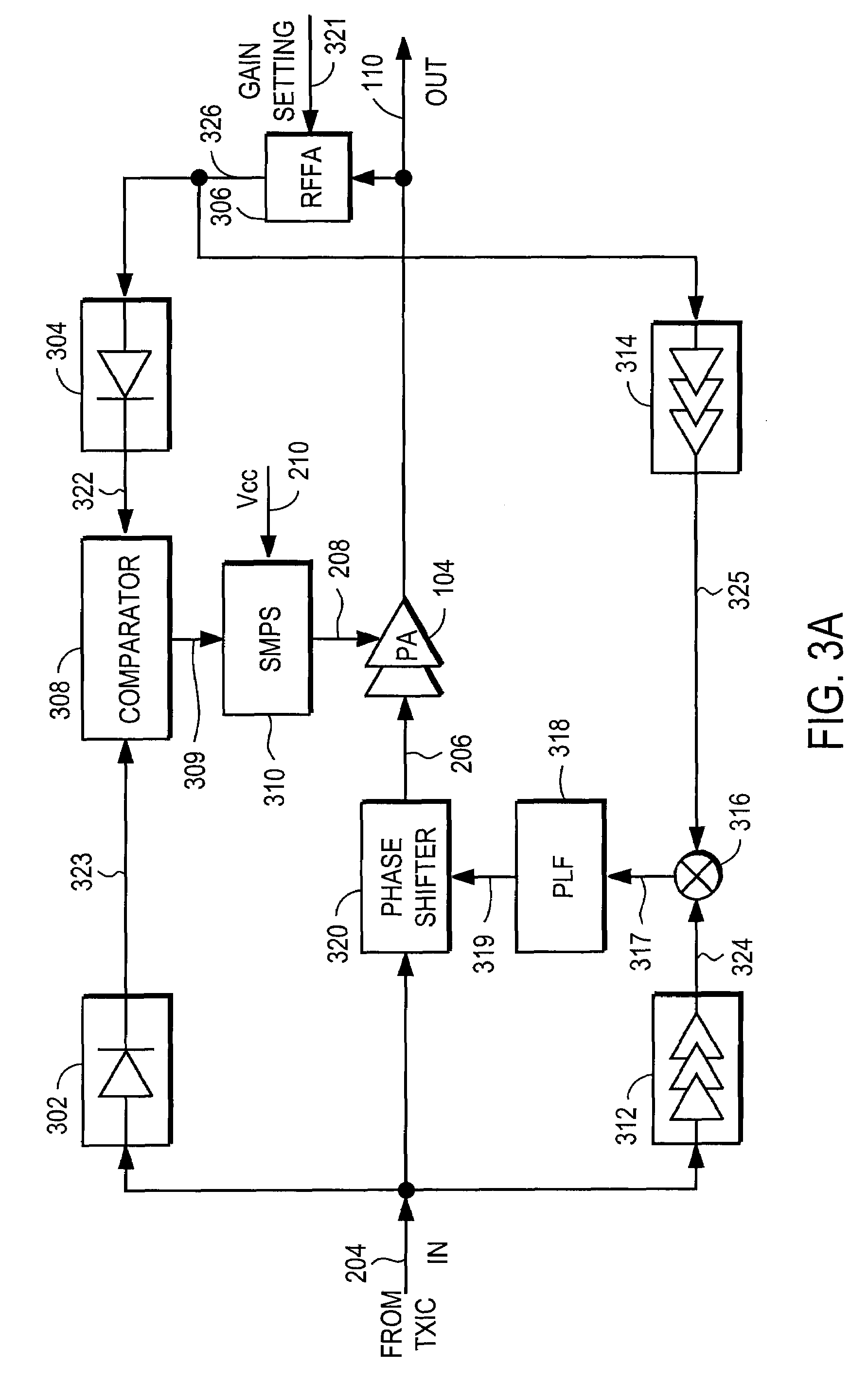
Amplifier compression controller circuit
ActiveUS20070184796A1Narrow bandwidthSacrificing efficiencyResonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
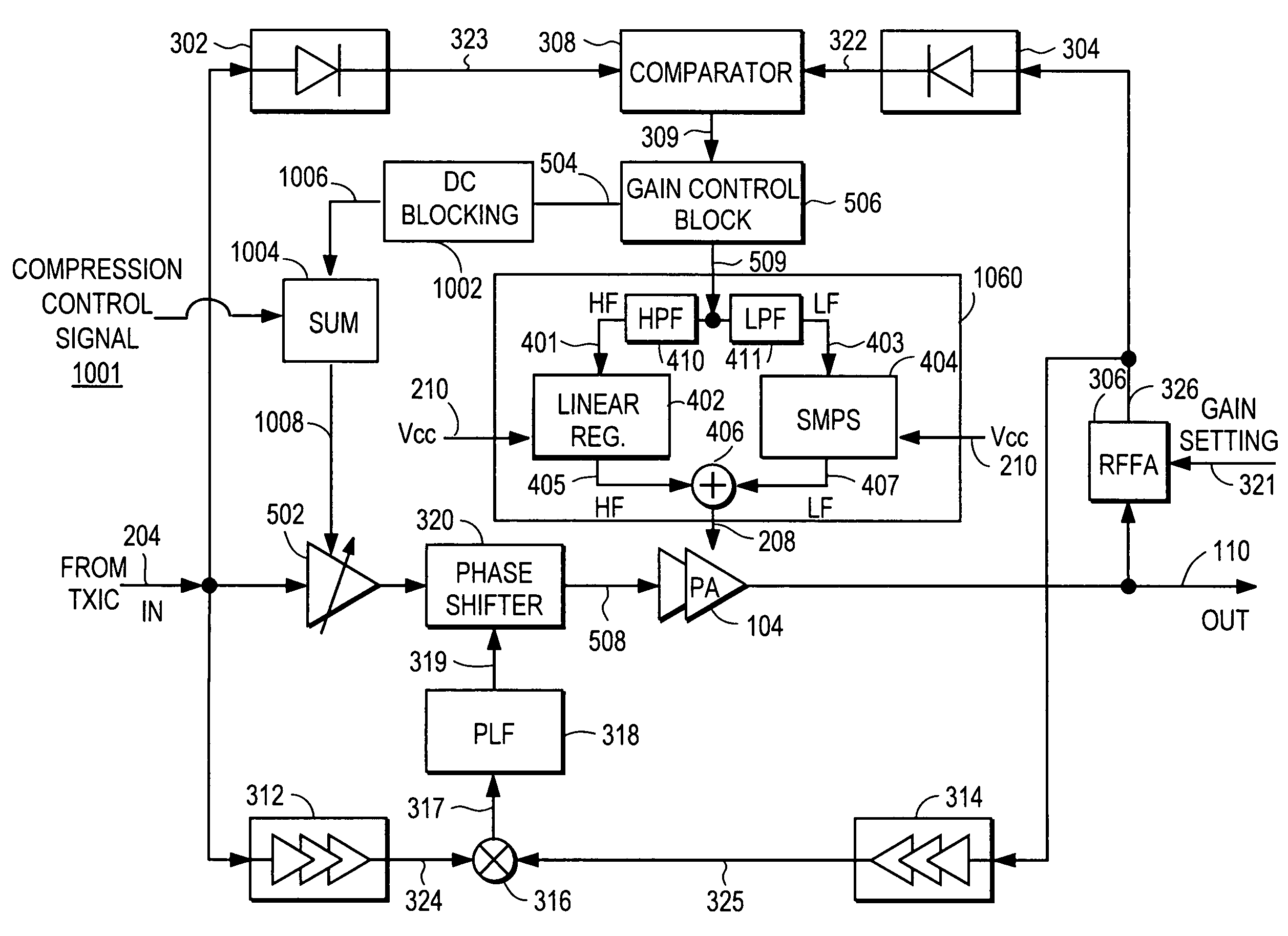
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude loop may include a variable gain amplifier adjusting the amplitude of the input signal. The amplitude loop can include a compression control block which may be configured either to adjust the gain in the variable gain amplifier or the voltage from the power supply based upon the operating level of the other, in addition to being based upon the amplitude correction signal, thus providing a way of maintaining the depth beyond the PA's compression point and allowing a control of the efficiency of the RF power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Power amplifier controller circuit
ActiveUS20070184791A1Narrow bandwidthSacrificing efficiencyResonant long antennasPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase distortion
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude correction signal may also be split into two or more signals with different frequency ranges and provided respectively to different types of power supplies with different efficiencies to generate the adjusted supply voltage to the power amplifier. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
RF Power Amplifier Controller Circuit With Compensation For Output Impedance Mismatch
ActiveUS20070184793A1Narrow bandwidthSacrificing efficiencyResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase distortion
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude control loop may also compensate for impedance mismatch with the load by increasing the power delivered from the power amplifier to the load, or decrease the output power of the power amplifier upon detection of excessive power dissipation in the power amplifier. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
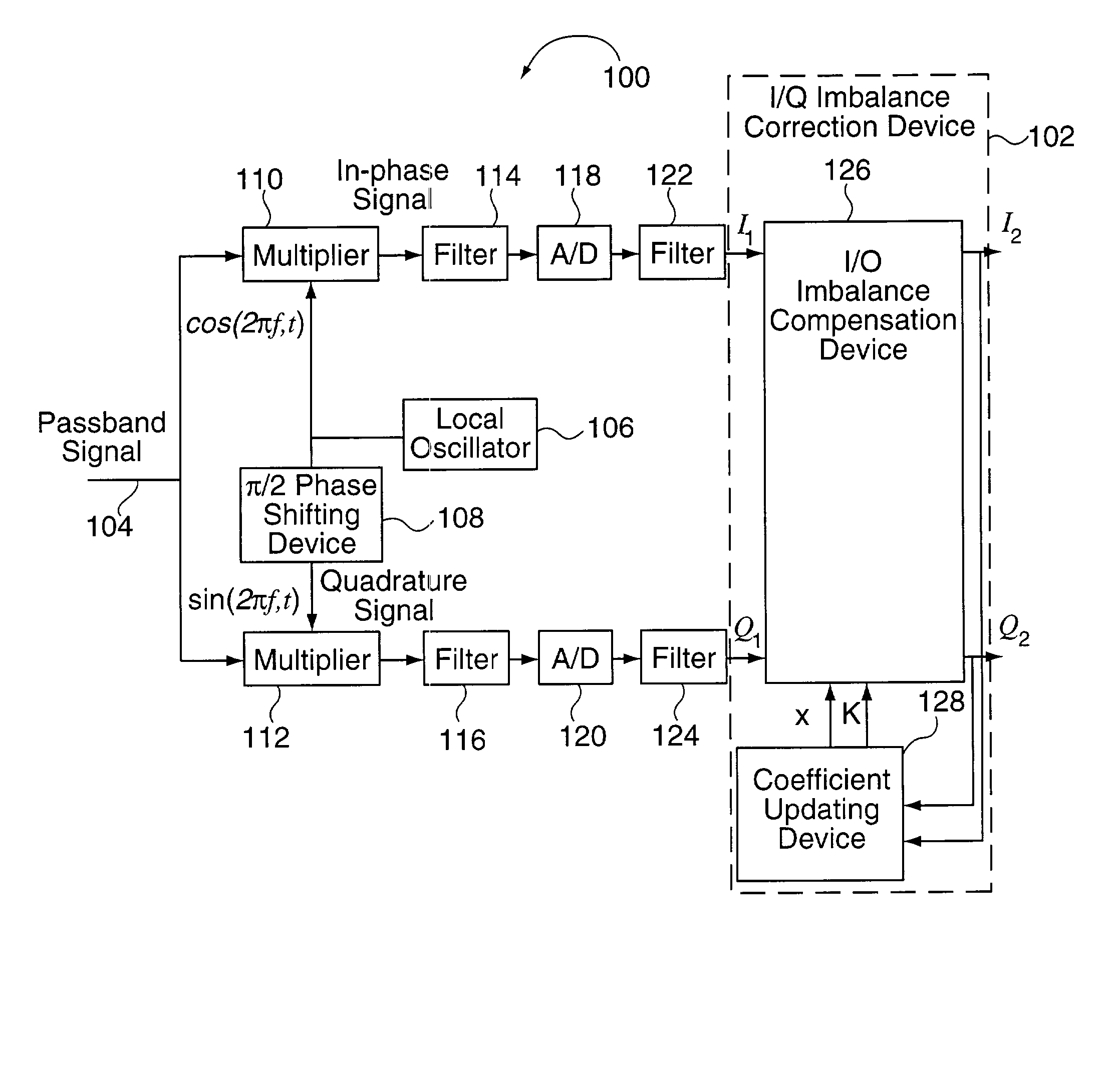
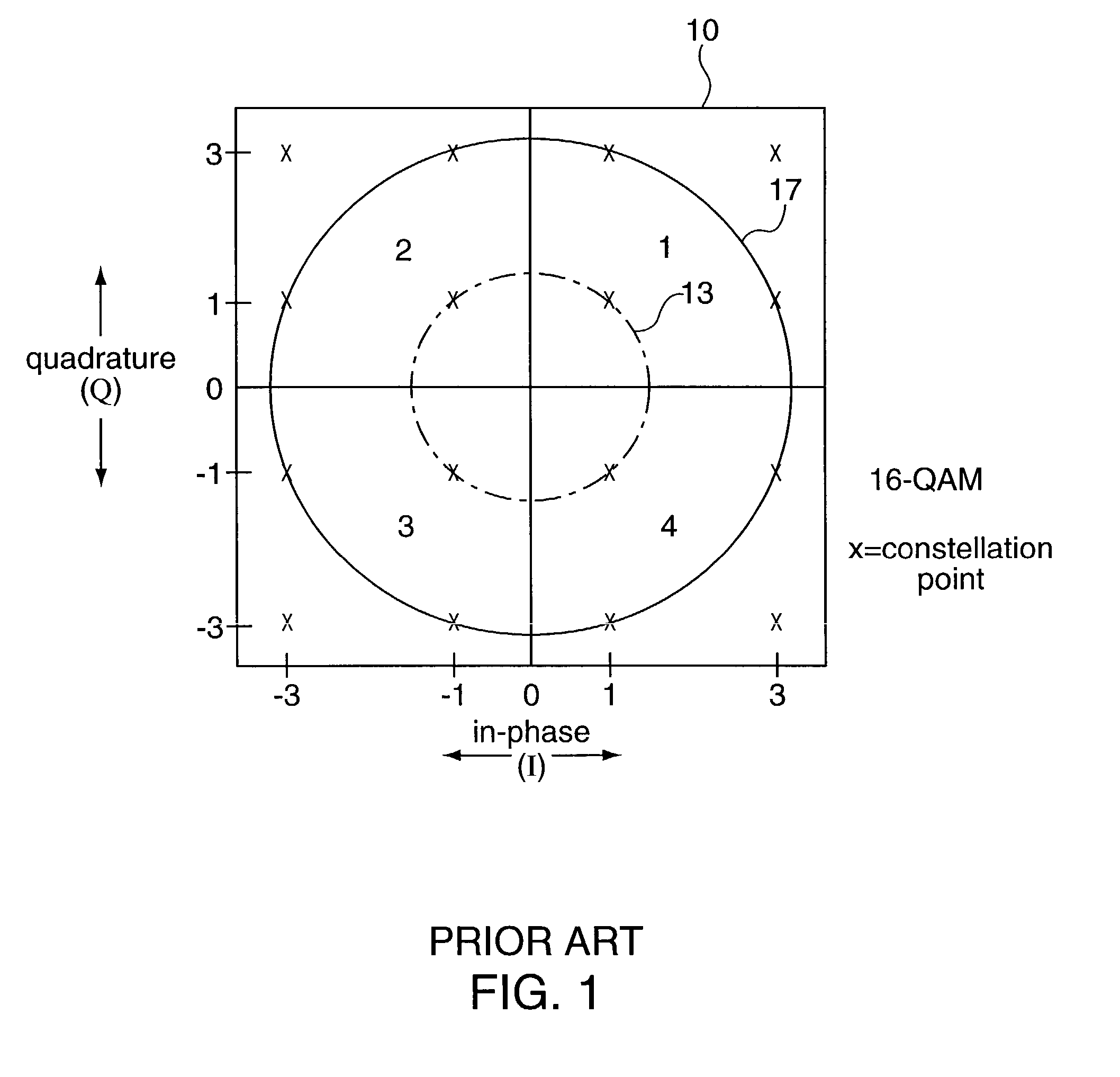
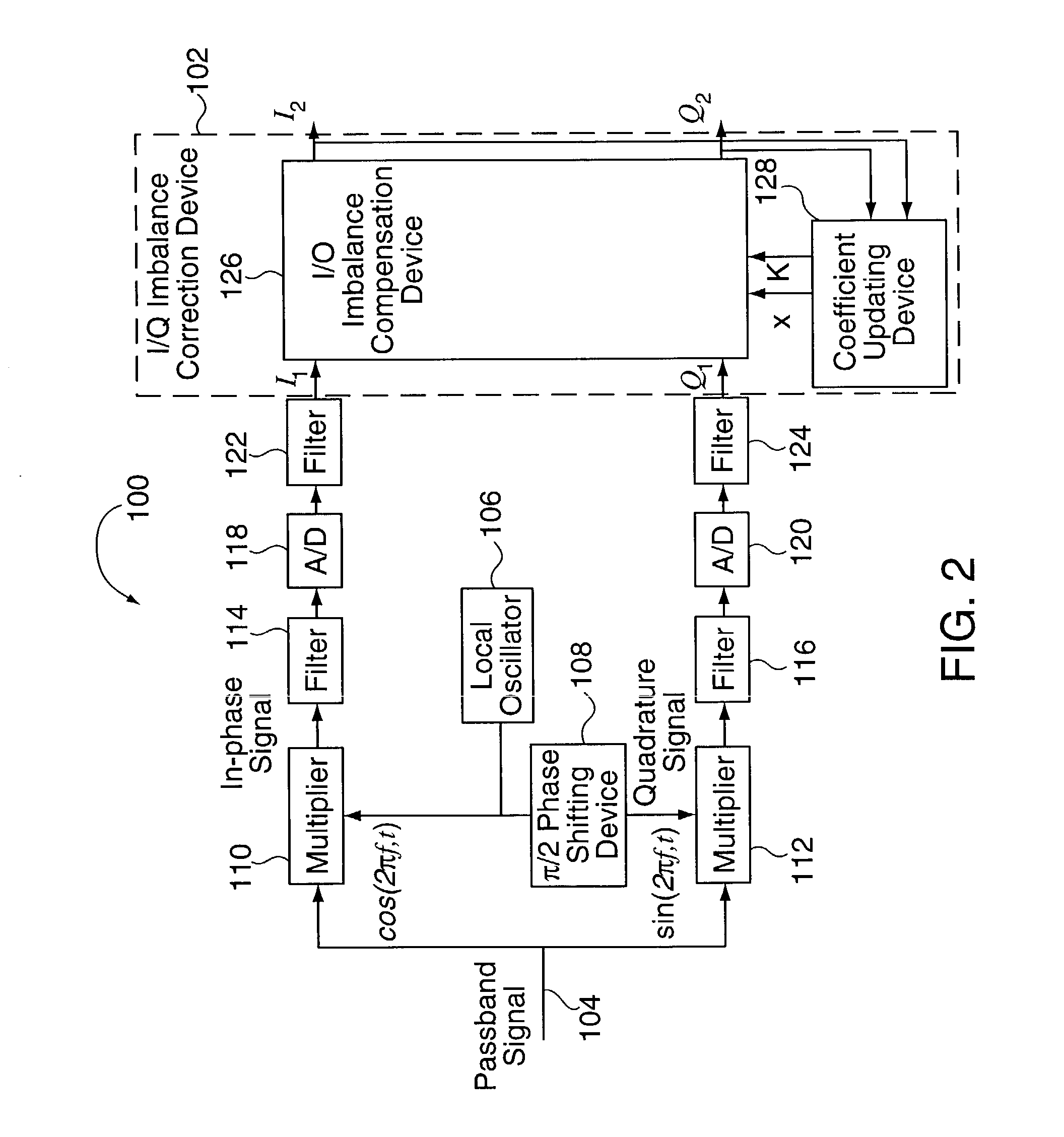
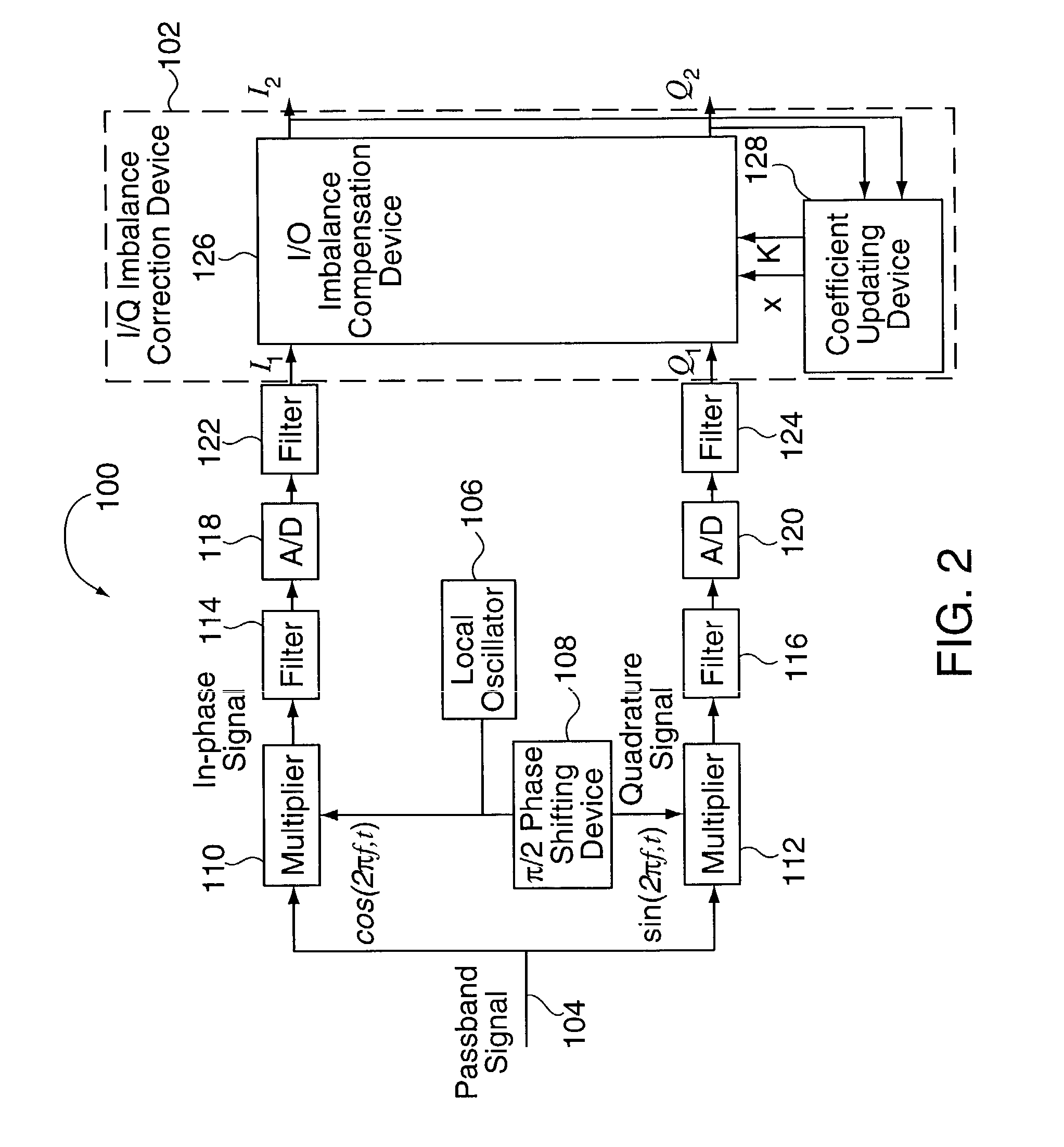
Methods and apparatus for I/Q imbalance compensation
InactiveUS20030007574A1Carrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase correctionPhase imbalance
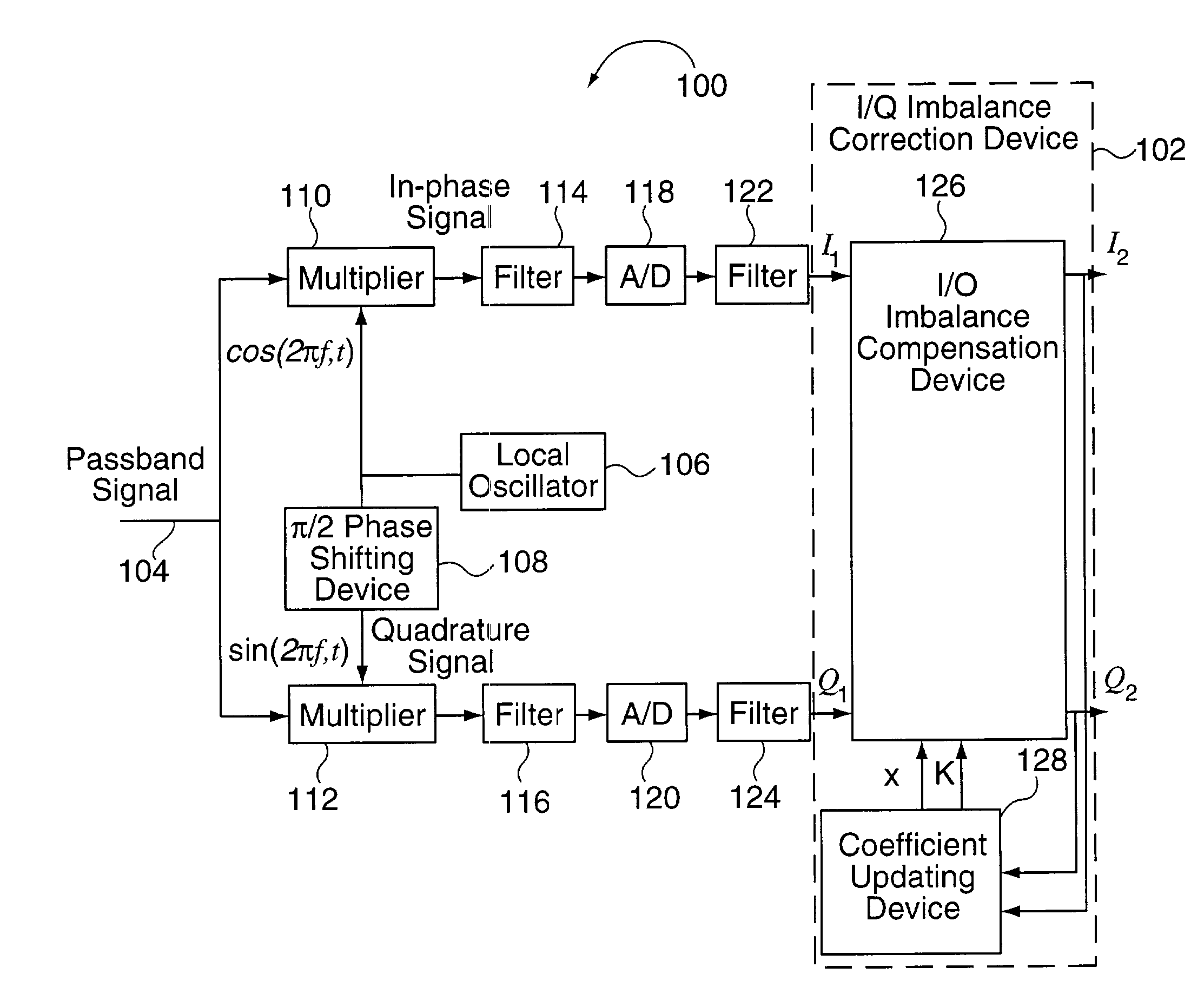
Methods and apparatus for performing amplitude and phase imbalance correction operations on in-phase and quadrature phase signal components corresponding to a received signal are described. The imbalance correction operations relay on the use of relatively simple to implement feedback loops. The phase imbalance feedback loop relies on the tendency of transmitted symbols to be distributed uniformly around the origin of the I / Q plane if proper phase balance is present in the processed signal. Phase correction coefficients are generated over time as a function of the negated product of the processed in-phase and quadrature phase signal components. Amplitude correction coefficients are generated over time as a function of the difference in the squared values of the I and Q processed signal components.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Power supply providing ultrafast modulation of output voltage
InactiveCN101669280AAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierVoltage
A circuit for use with a power amplifier that amplifies an input signal. The circuit may comprise an amplitude correction circuit and an open-loop switching regulator. The amplitude correction circuit may be configured to generate a corrected envelope signal from an input envelope signal that represents an envelope of the input signal. The open-loop switching regulator may be connected to the amplitude correction circuit and may be for powering the power amplifier based on the corrected envelope signal. According to various embodiments, the corrected envelope signal generated by the amplitudecorrection circuit is a function of the input envelope signal and an error voltage of the open-loop switching regulator.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
RF power amplifier controller circuit with compensation for output impedance mismatch
ActiveUS7761065B2Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthResonant long antennasHigh frequency amplifiersPhase distortionAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude control loop may also compensate for impedance mismatch with the load by increasing the power delivered from the power amplifier to the load, or decrease the output power of the power amplifier upon detection of excessive power dissipation in the power amplifier. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
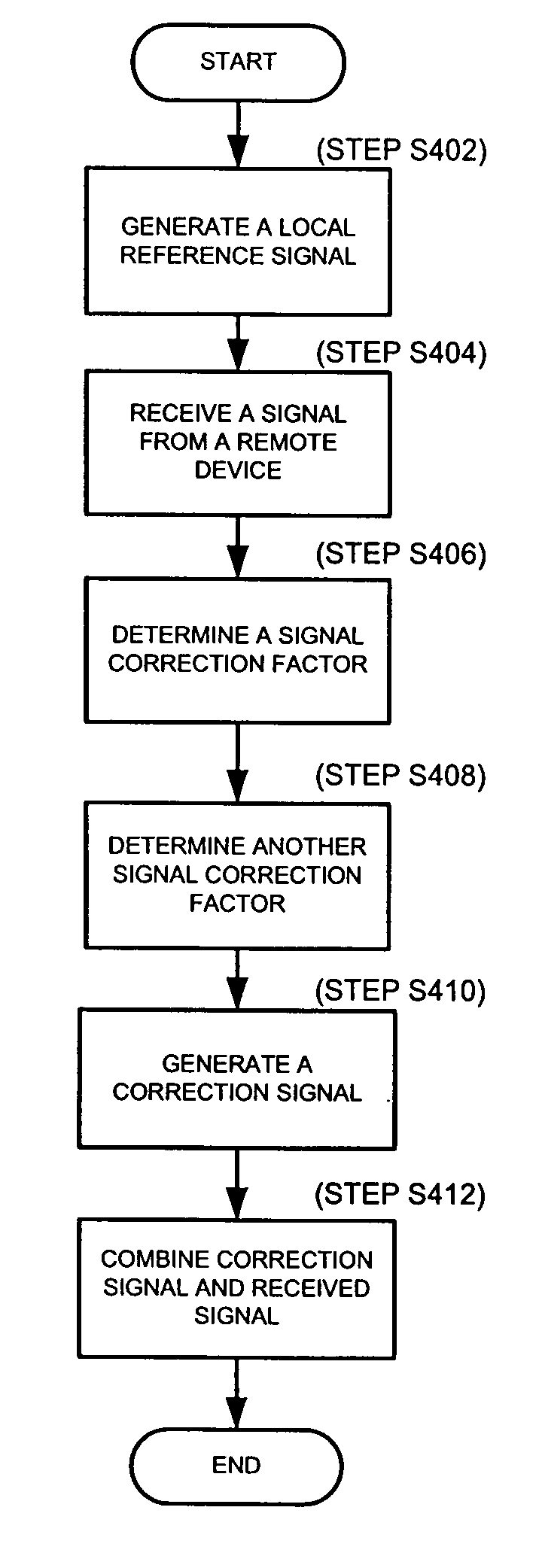
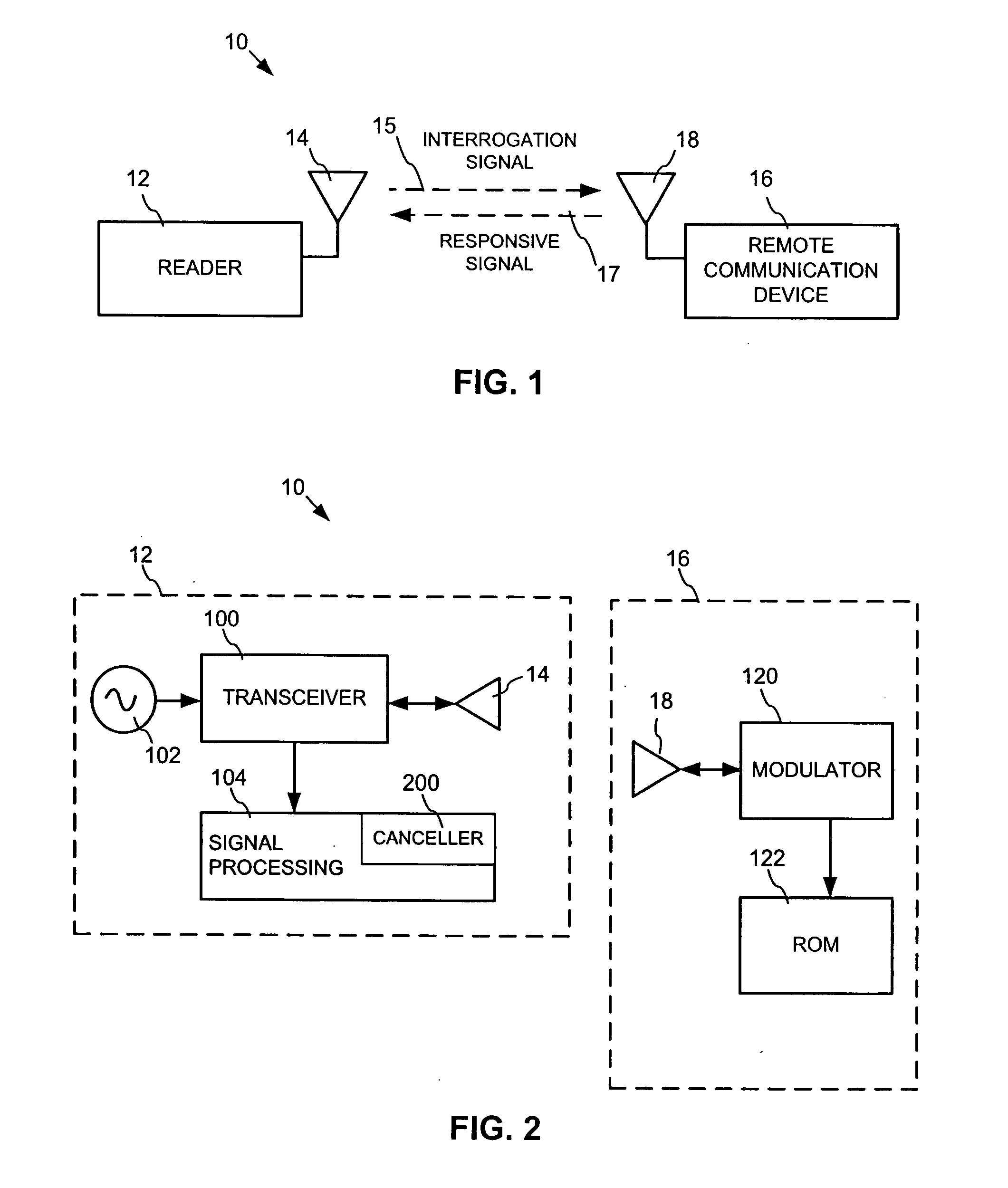
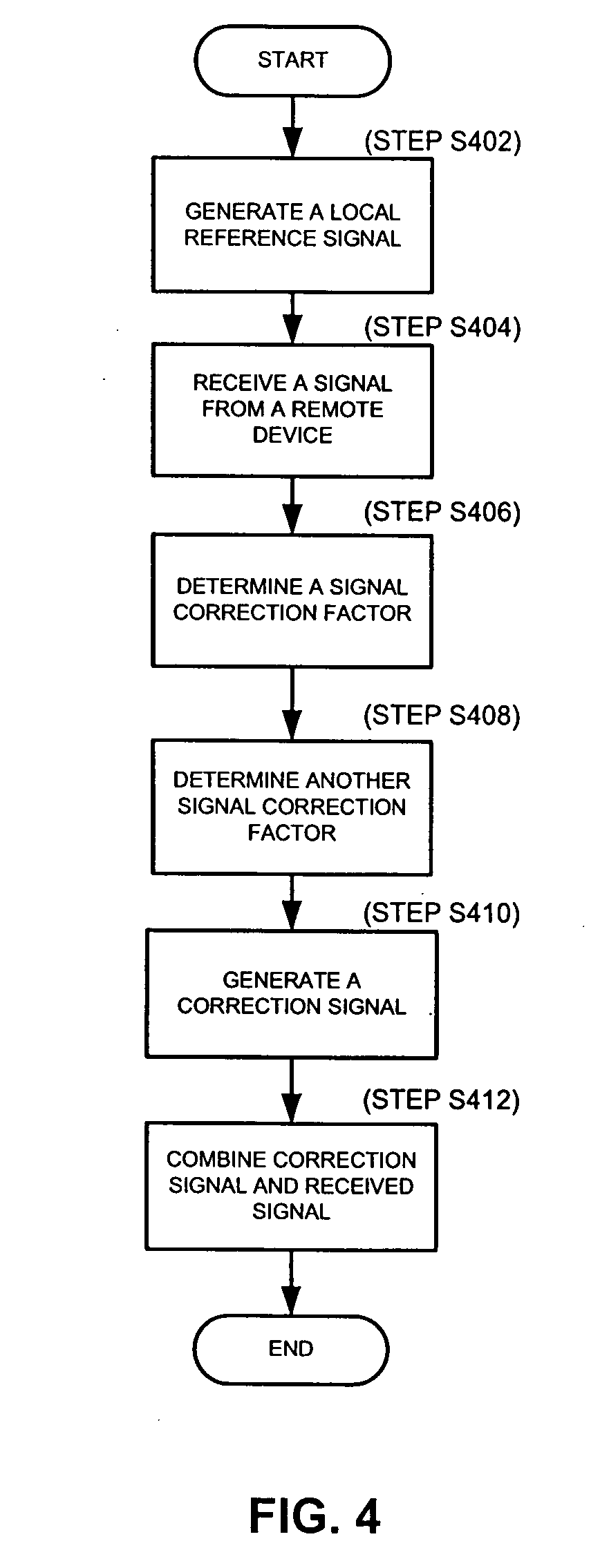
Radio frequency identification reader having a signal canceller and method thereof
InactiveUS20080079547A1Minimize and cancel out interferenceMinimize and cancel out and noiseMemory record carrier reading problemsSubscribers indirect connectionSignal cancellationEngineering
A method, system and apparatus for generating a cancellation signal in a RFID reader to isolate a transmit section and a receive section of a RFID reader, where the RFID reader generates a local reference signal from a broadcast transmit signal, receives a receive signal from a remote device, determines at least one correction factor, e.g., an amplitude correction factor, to generate a cancellation signal. The method, system and apparatus can further include combining a cancellation signal and a receive signal to minimize or cancel out interference and noise on the receive signal.
Owner:TYCO FIRE & SECURITY GMBH
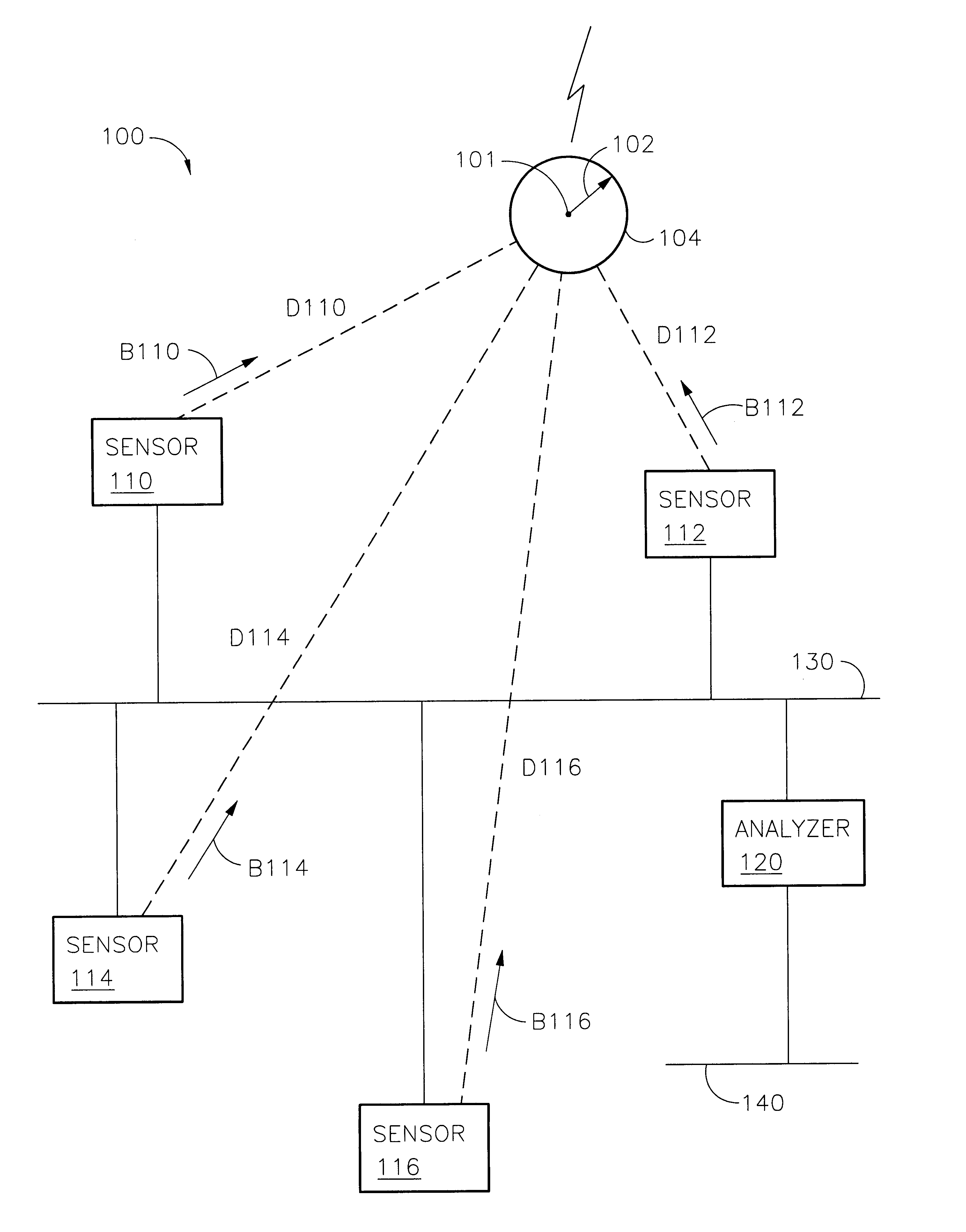
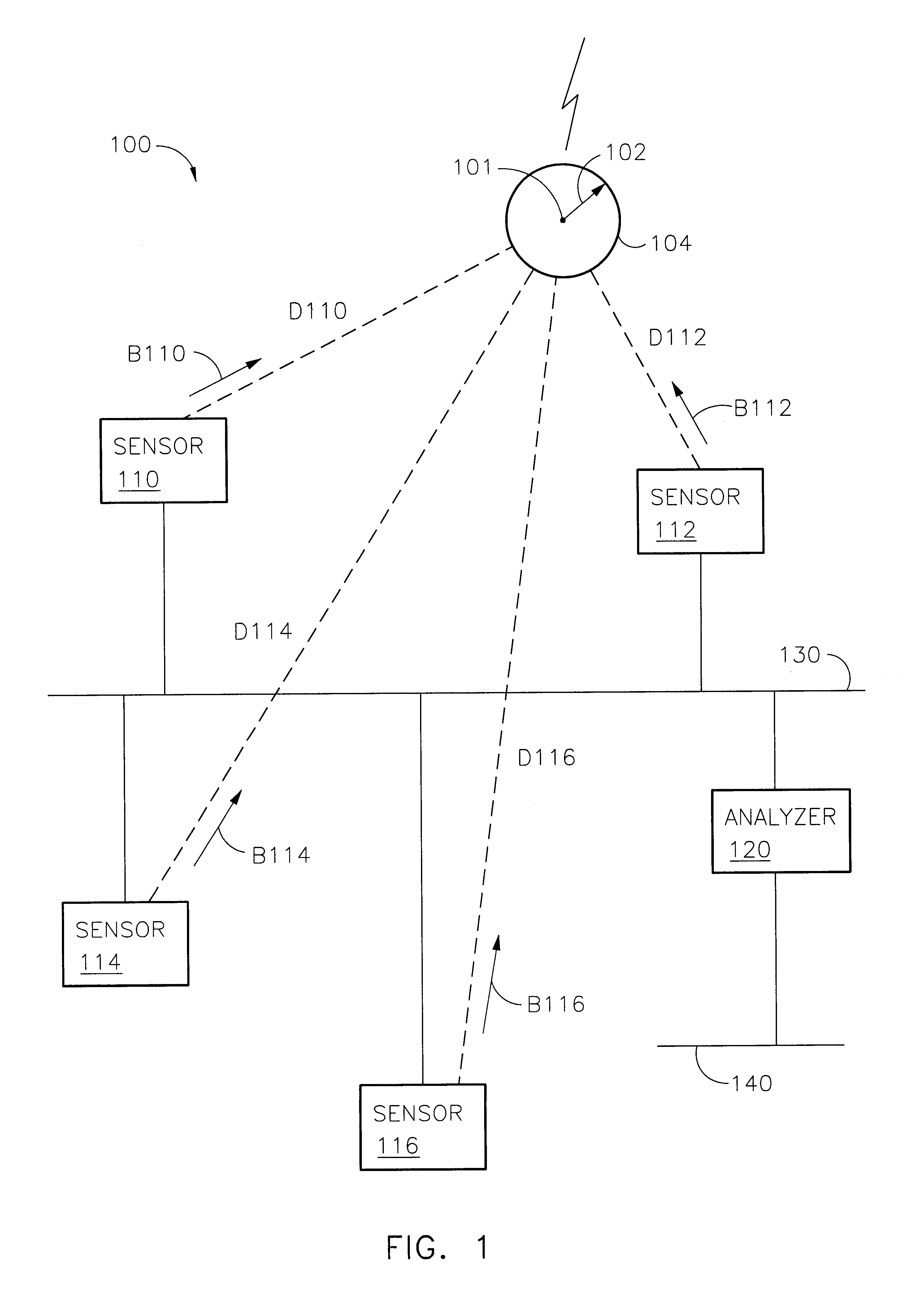
Systems and methods for time corrected lightning detection
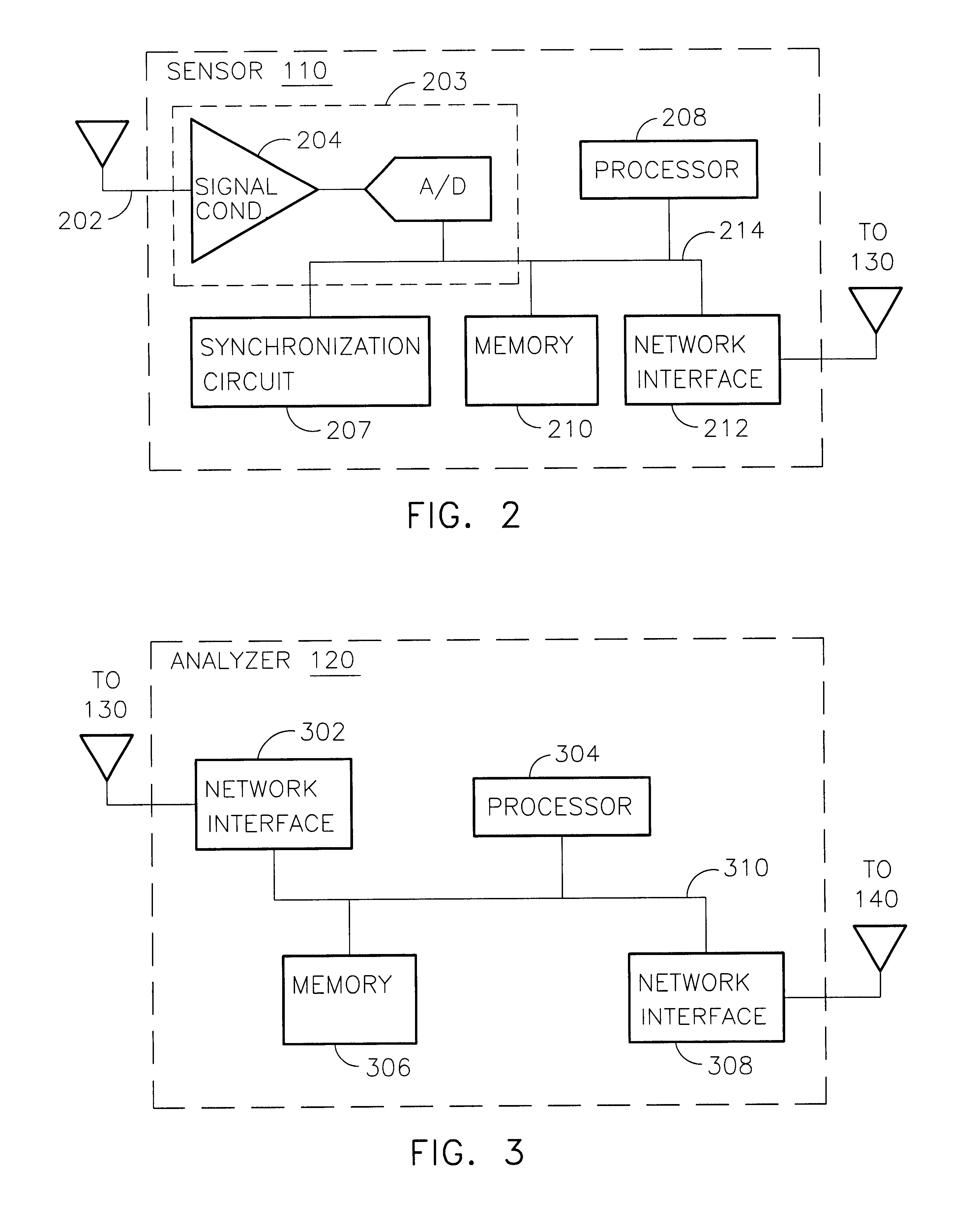
InactiveUS6868339B2Faster throughputEasy accessSpecial data processing applicationsAtmospheric potential difference measurementLightning strokesLongitude
A lightning detection system provides an estimated location of a lightning stroke. The system includes sensors, and an analyzer. Each sensor provides messages having sensor identification, an amplitude responsive to the lightning stroke, and a time of detecting the lightning stroke. The analyzer applies time corrections and amplitude corrections to improve the accuracy of determining the location of the lightning stroke. Time adjustments and amplitude adjustments for the time and amplitude corrections are recalled from a matrix accessed according to a suggested or estimated location. The matrix may be organized by coordinates of longitude and latitude.
Owner:VAISALA
RF Power Amplifier Controller Circuit
ActiveUS20070184792A1Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthResonant long antennasSupply voltage varying controlPhase distortionAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier. The amplitude control loop and the phase control loop may also adjust the gain and / or phase of the power amplifier, respectively.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Rotation-angle detection device, image processing apparatus, and rotation-angle detection method
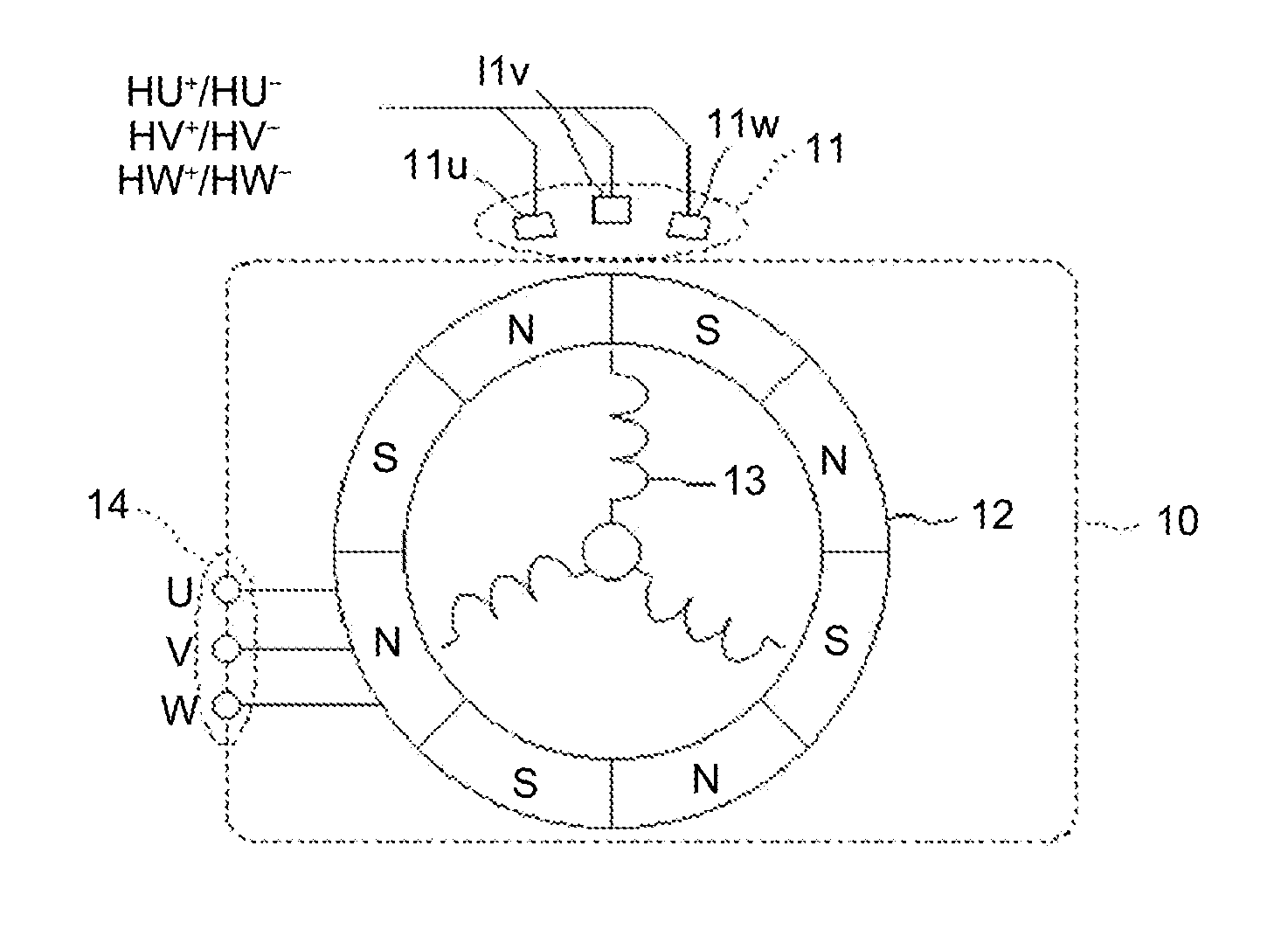
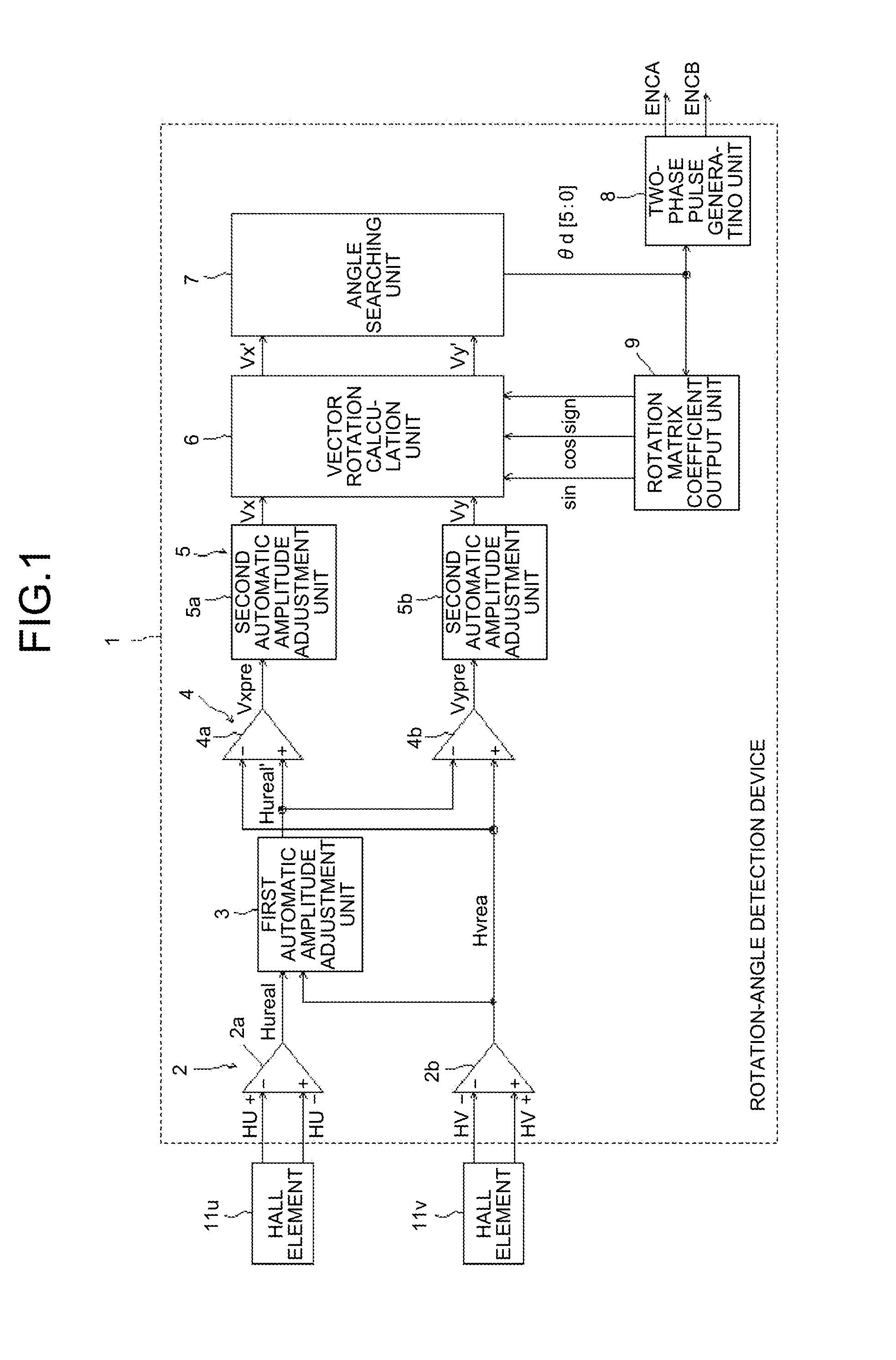
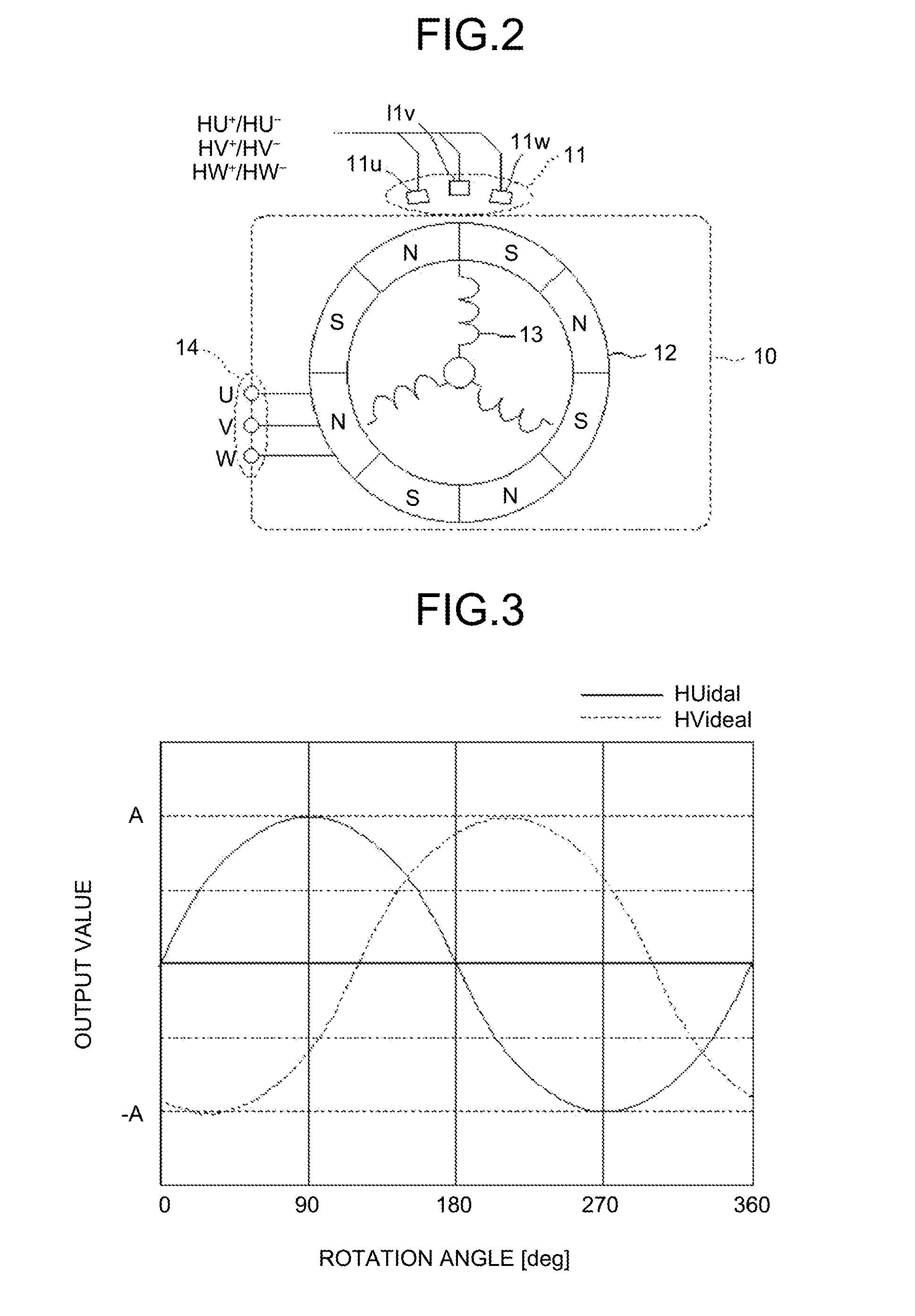
A rotation-angle detection device includes: an amplitude adjustment unit that performs correction to match amplitude values of multiple detection signals output from multiple rotation detection units to output corrected signals, the rotation detection units changing outputs in accordance with a rotation angle of a rotor and being provided such that the rotation detection units output the detection signals having different phases; a vector generation unit that performs addition and subtraction on two signals out of the corrected signals to generate two vector component signals that are perpendicular to each other; an amplitude correction unit that performs correction to match amplitudes of the two vector component signals to output corrected vector component signals; and a rotation-angle searching unit that searches for the rotation angle of the rotor on basis of a vector that is represented by the two corrected vector component signals to output a detection angle.
Owner:RICOH KK
Signal transmitter
InactiveUS20050118965A1Compensate for thermal characteristics of a radio frequency power amplifier efficiently and correctlyAccurate detectionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasAudio power amplifierFrequency spectrum
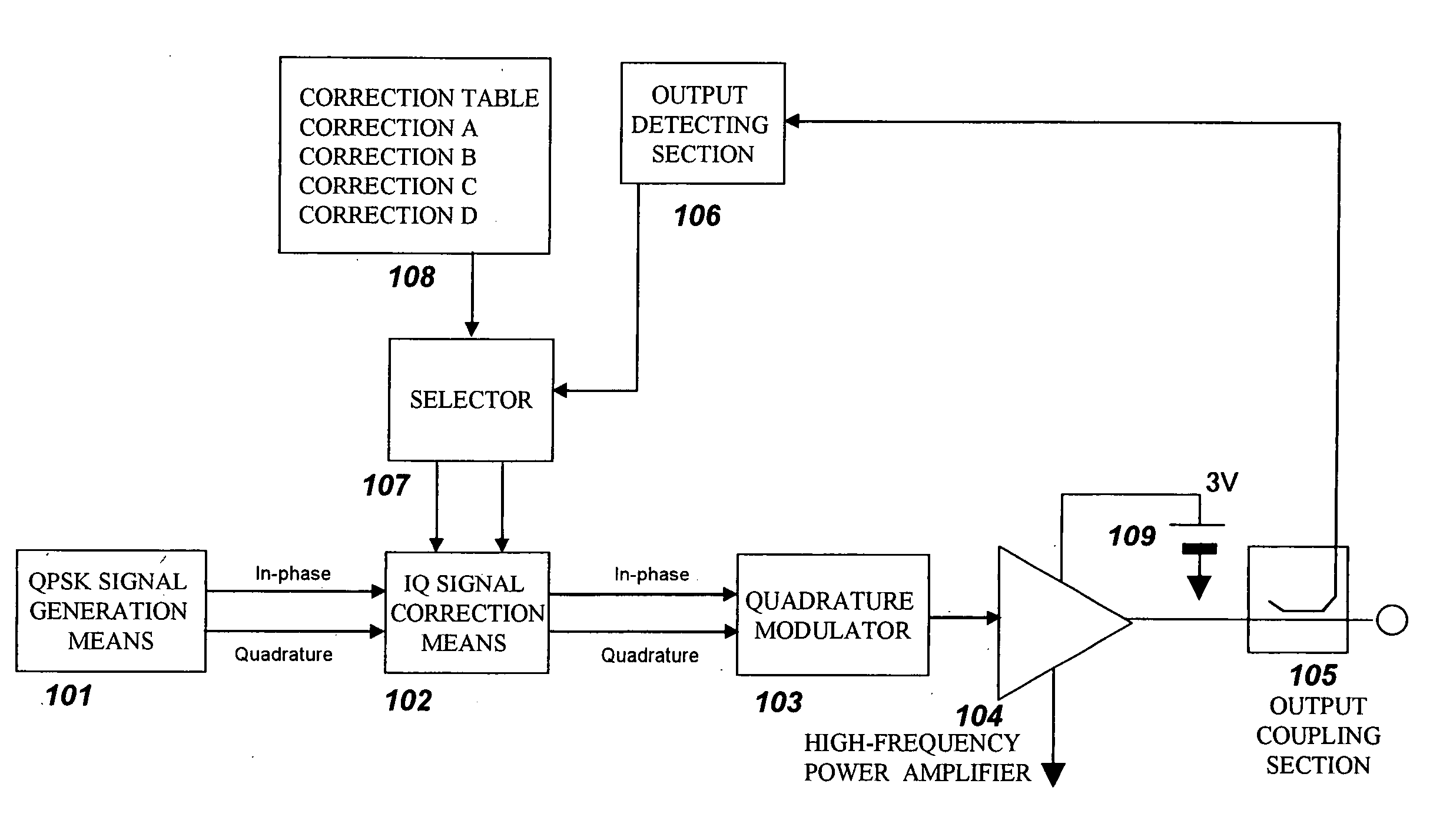
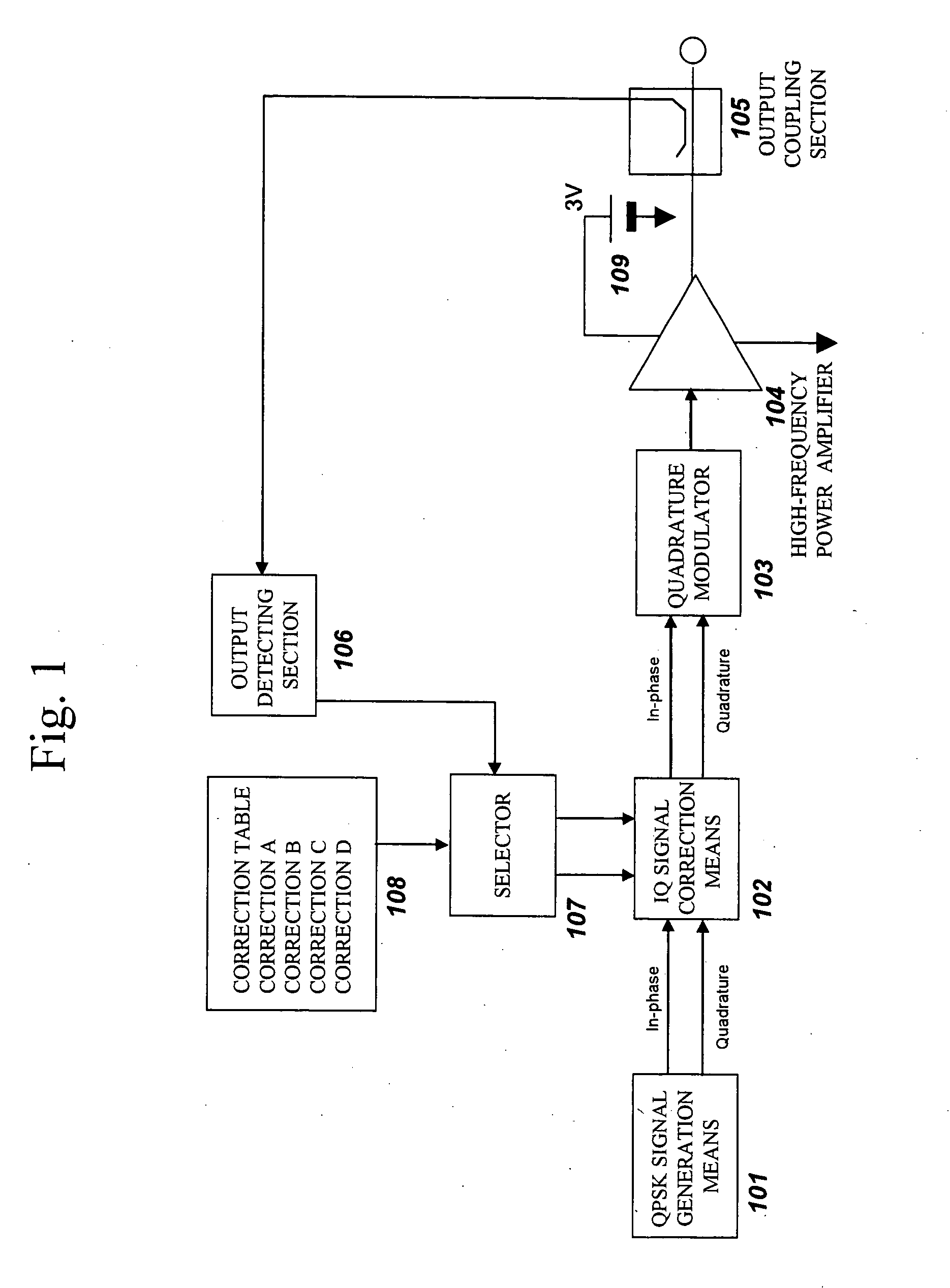
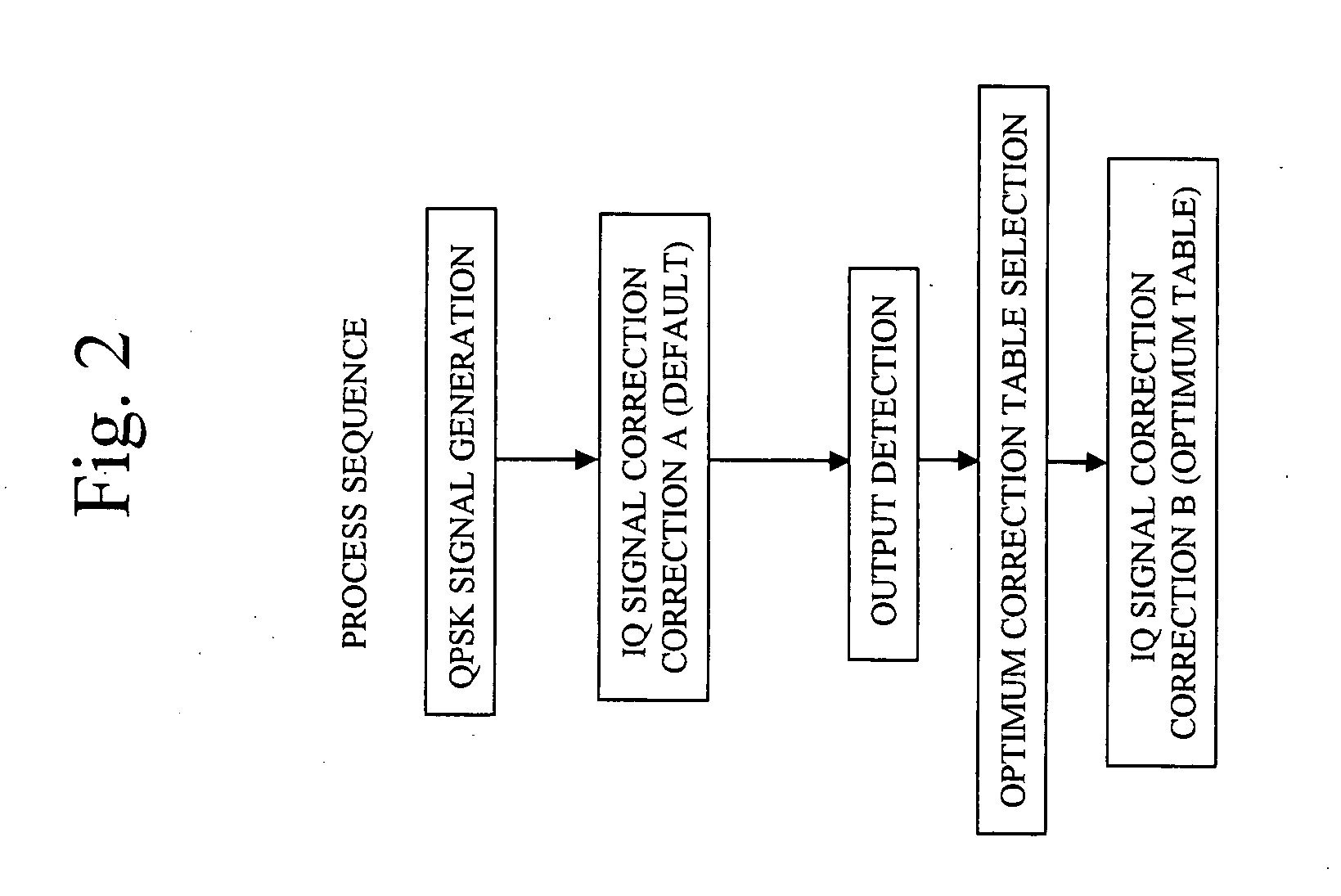
An amplitude component and a phase component among modulating signals are supplied into a radio frequency wave input terminal and a power supply terminal of a radio frequency power amplifier, respectively, and an original modulated wave is obtained from an output of the radio frequency power amplifier. The output of the radio frequency power amplifier is detected by an output detecting section, correction data to a detection voltage closest to the detection voltage among correction datatables which have been measured in various temperature environments and stored in advance are selected by a selector, and correction of an amplitude component and a phase component is performed by phase-amplitude correction means. Thereby enabling EER operation without spectrum degradation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Methods and apparatus for I/Q imbalance compensation
InactiveUS7061994B2Carrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase correctionPhase imbalance
Methods and apparatus for performing amplitude and phase imbalance correction operations on in-phase and quadrature phase signal components corresponding to a received signal are described. The imbalance correction operations relay on the use of relatively simple to implement feedback loops. The phase imbalance feedback loop relies on the tendency of transmitted symbols to be distributed uniformly around the origin of the I / Q plane if proper phase balance is present in the processed signal. Phase correction coefficients are generated over time as a function of the negated product of the processed in-phase and quadrature phase signal components. Amplitude correction coefficients are generated over time as a function of the difference in the squared values of the I and Q processed signal components.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
RF power amplifier system with impedance modulation
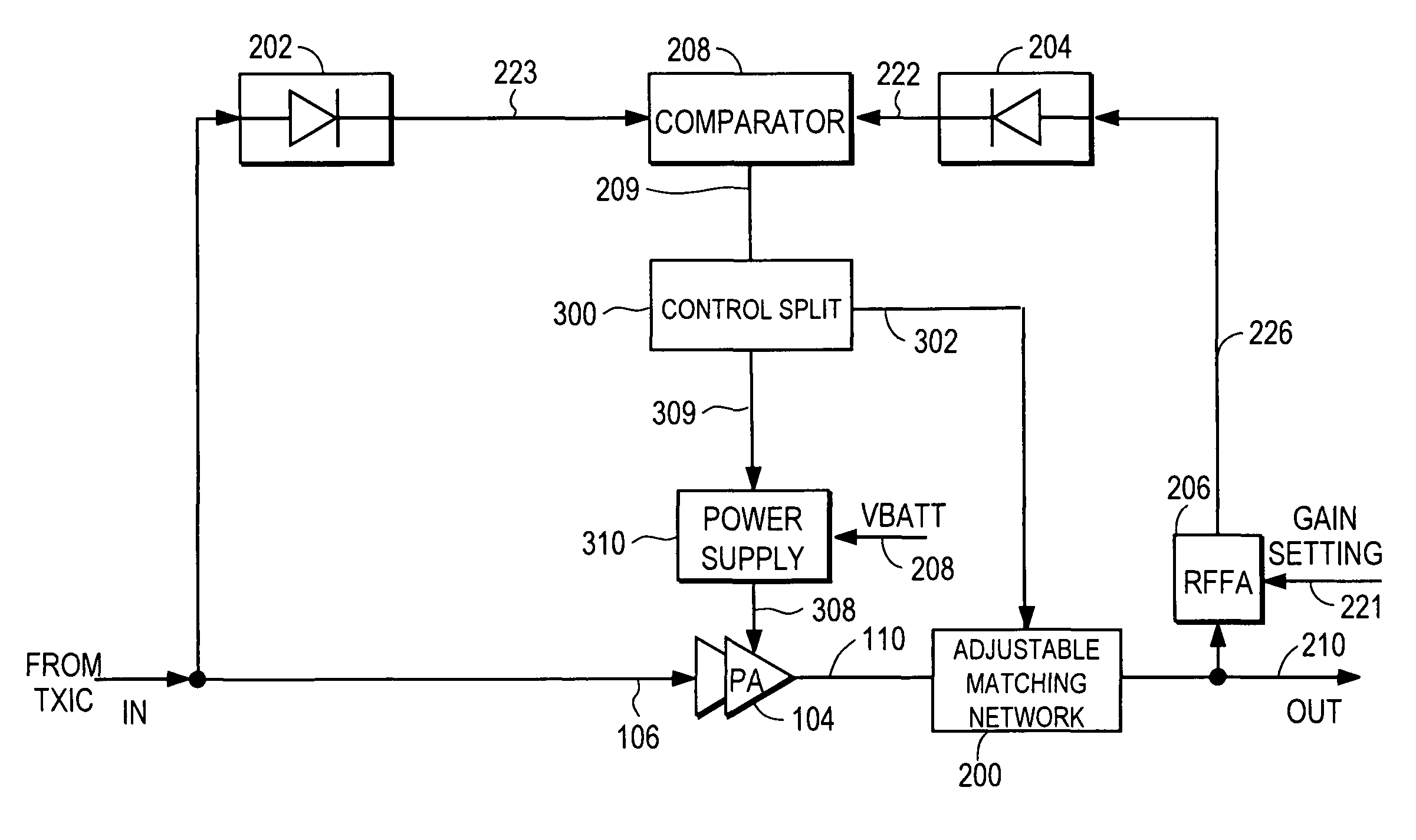
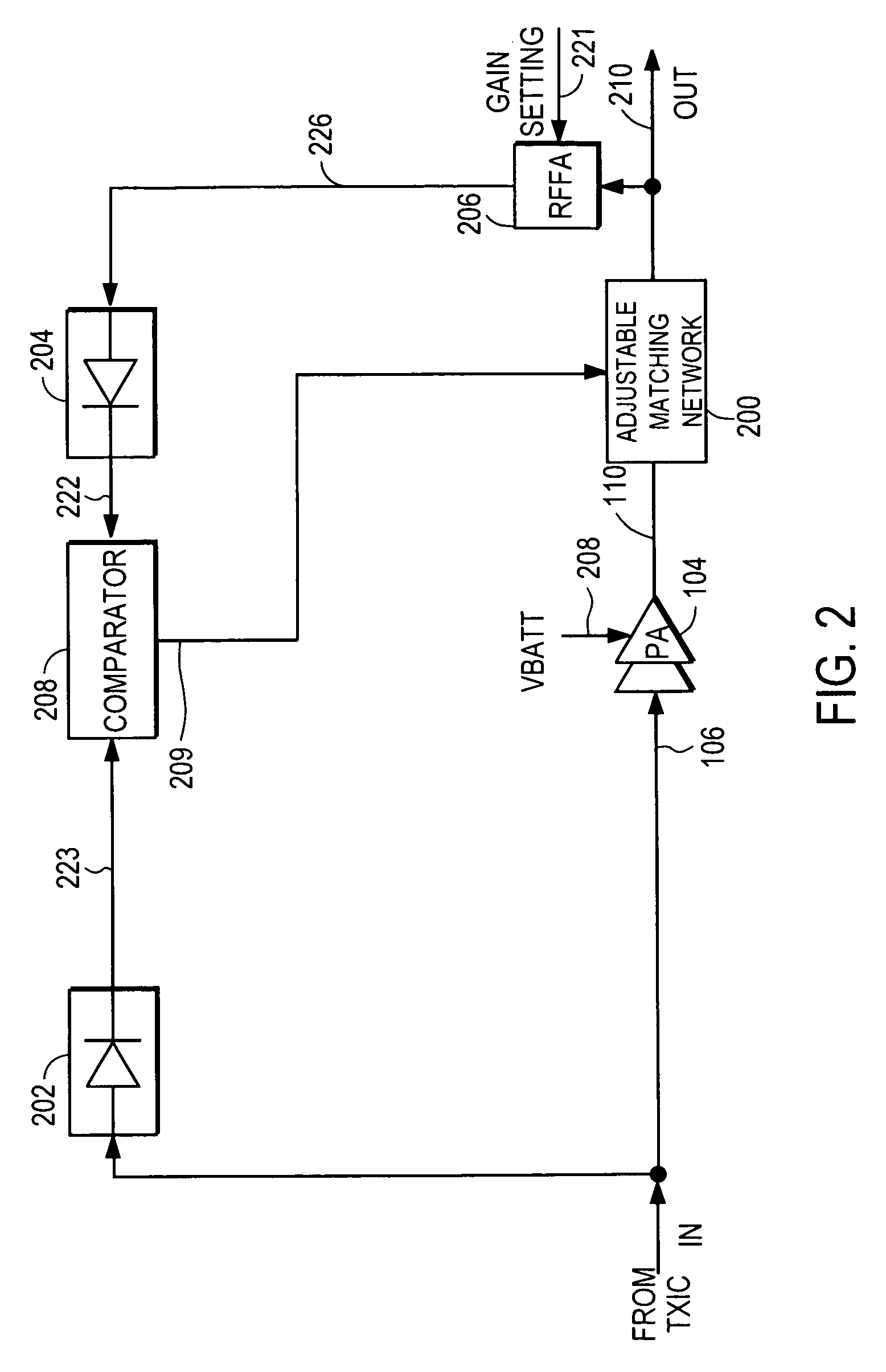
ActiveUS7782134B2Improve efficiencyReduce phase distortionHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
A power amplifier controller circuit controls an adjustable impedance matching network at the output of a power amplifier to vary its load line to improve the efficiency of the RF PA. The PA controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop that determines an amplitude correction signal. The amplitude loop is configured to control or correct for distortion from the adjustable matching network based upon the amplitude correction signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
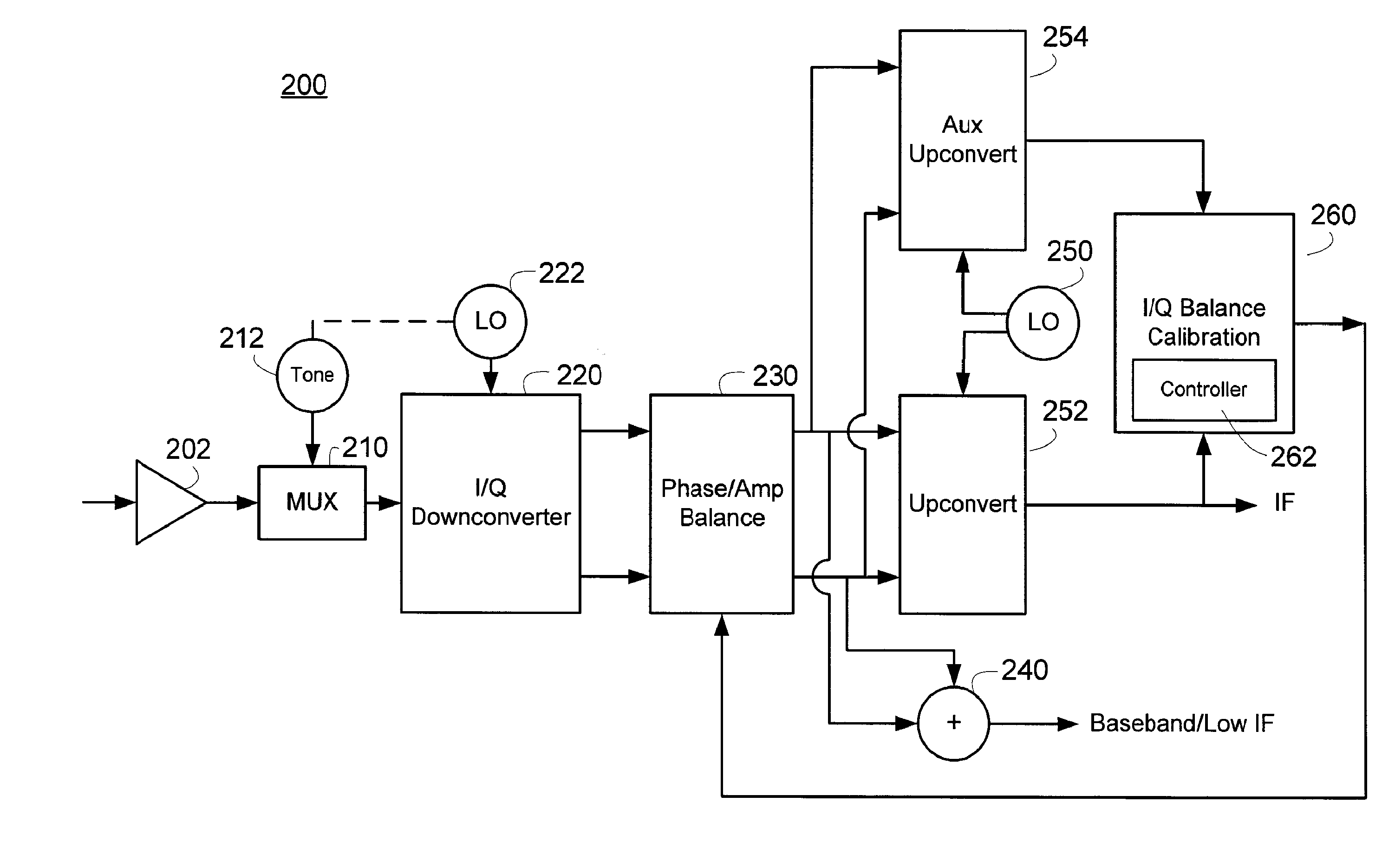
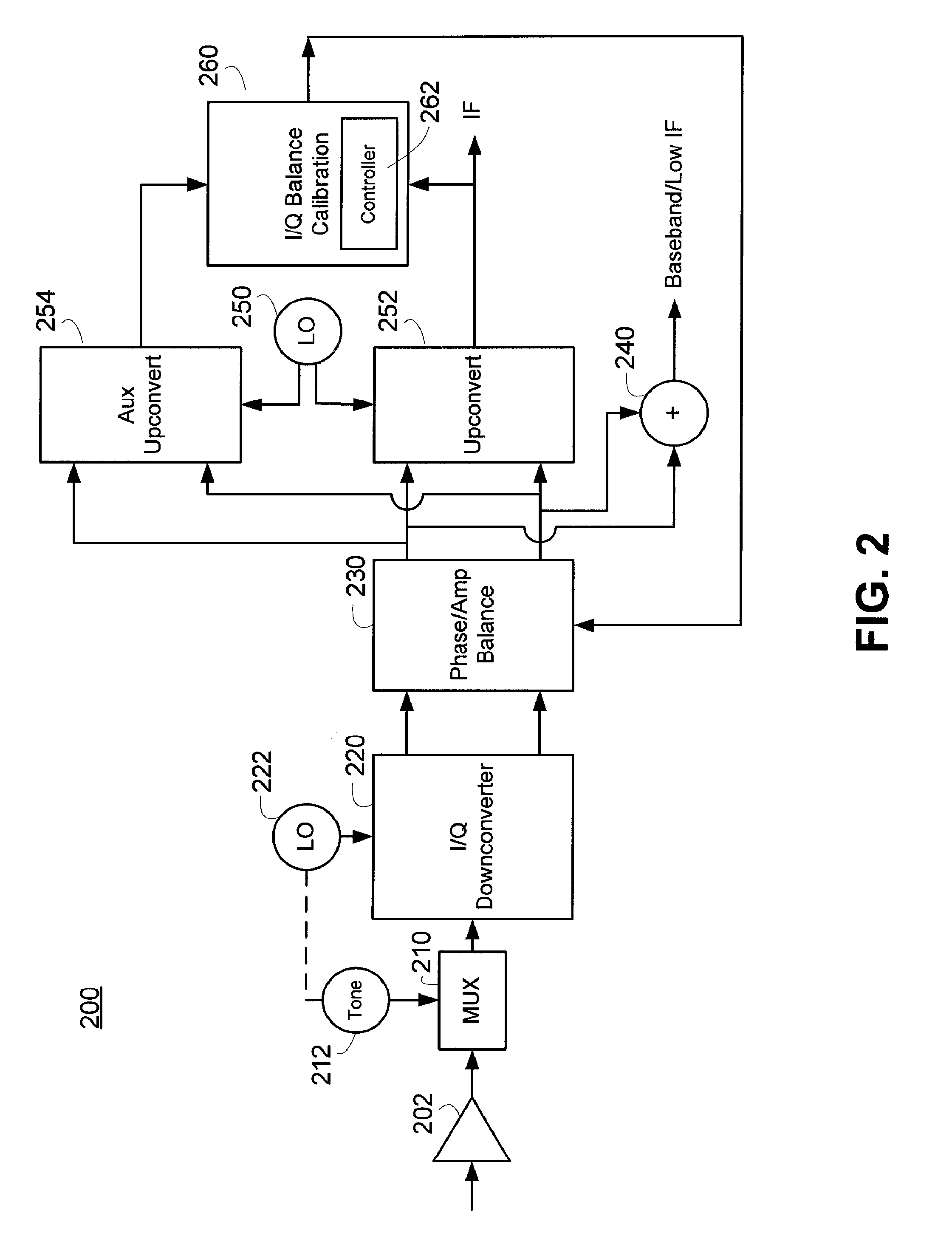
Method and Apparatus for Calibrating the Sideband Rejection of a Receiver
Methods and apparatus for calibrating In-phase and Quadrature imbalance within a receiver are described. A calibration process can inject a calibration tone to an RF or IF portion of a receiver. The receiver can frequency translate the tone to distinct I and Q calibration signals. The receiver upconverts the I and Q calibration signals to complementary sidebands or images using distinct and substantially matched upconverters. The complementary sidebands are mixed together to generate an error signal. The receiver determines a phase and amplitude correction based on the error signal.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
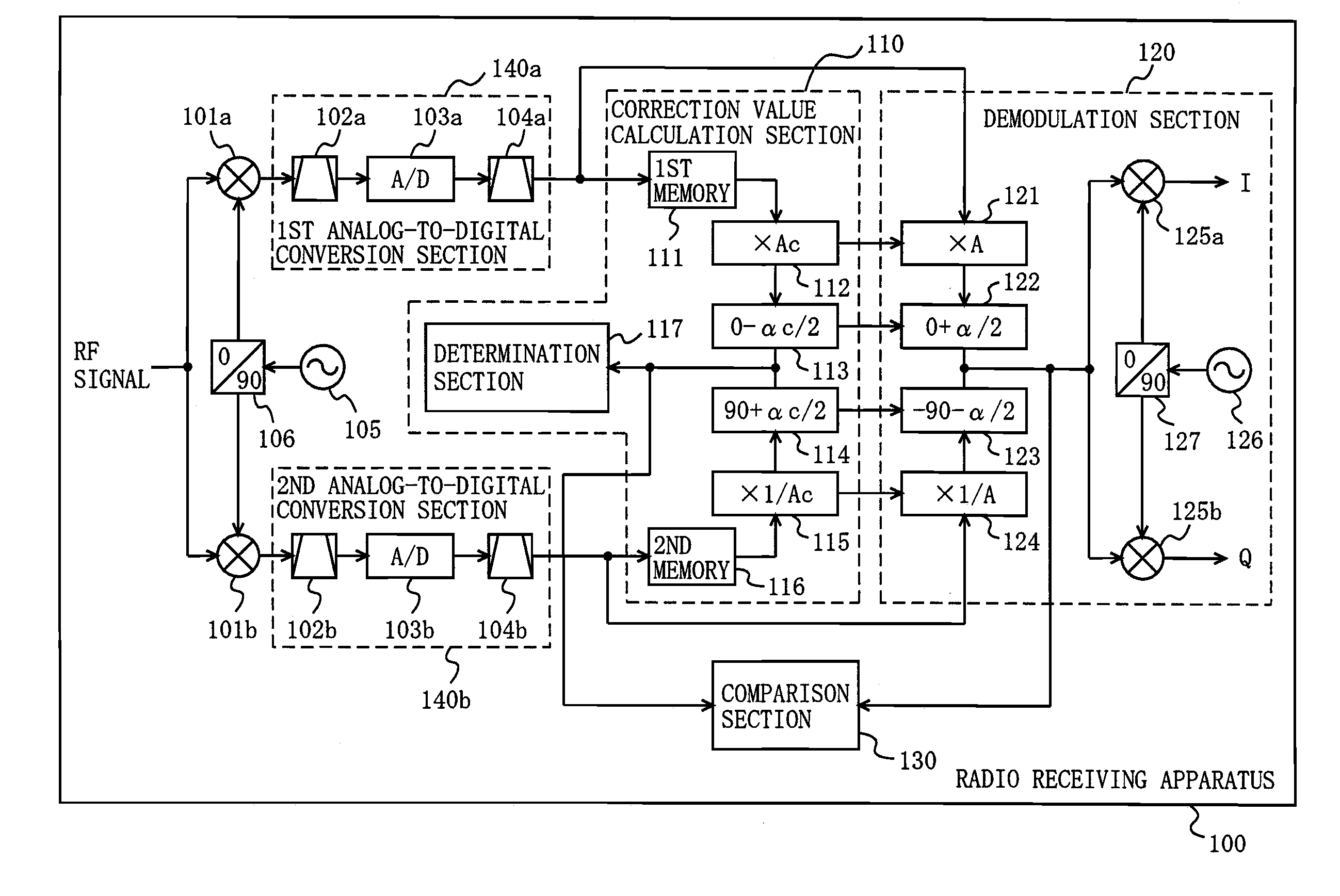
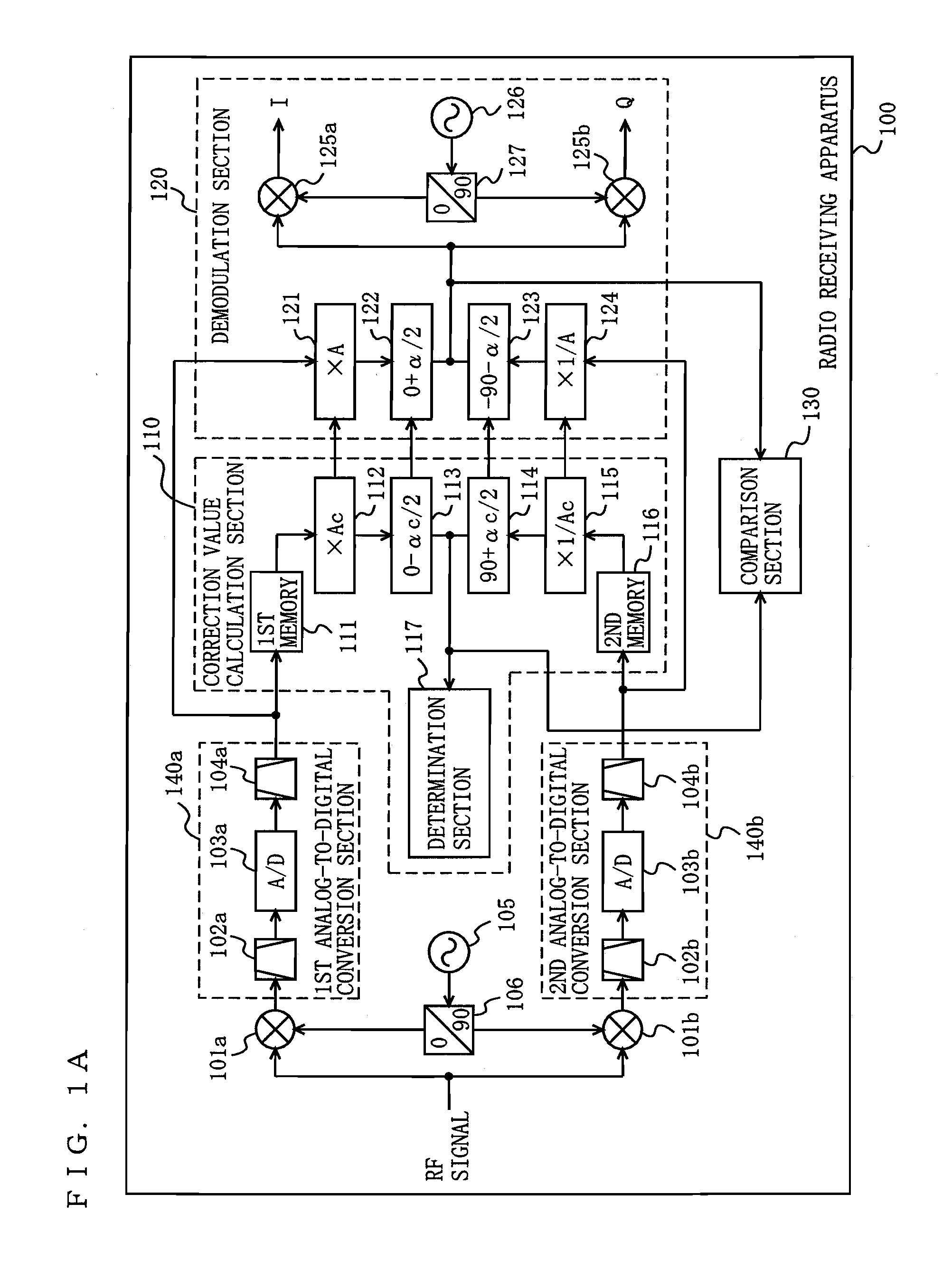
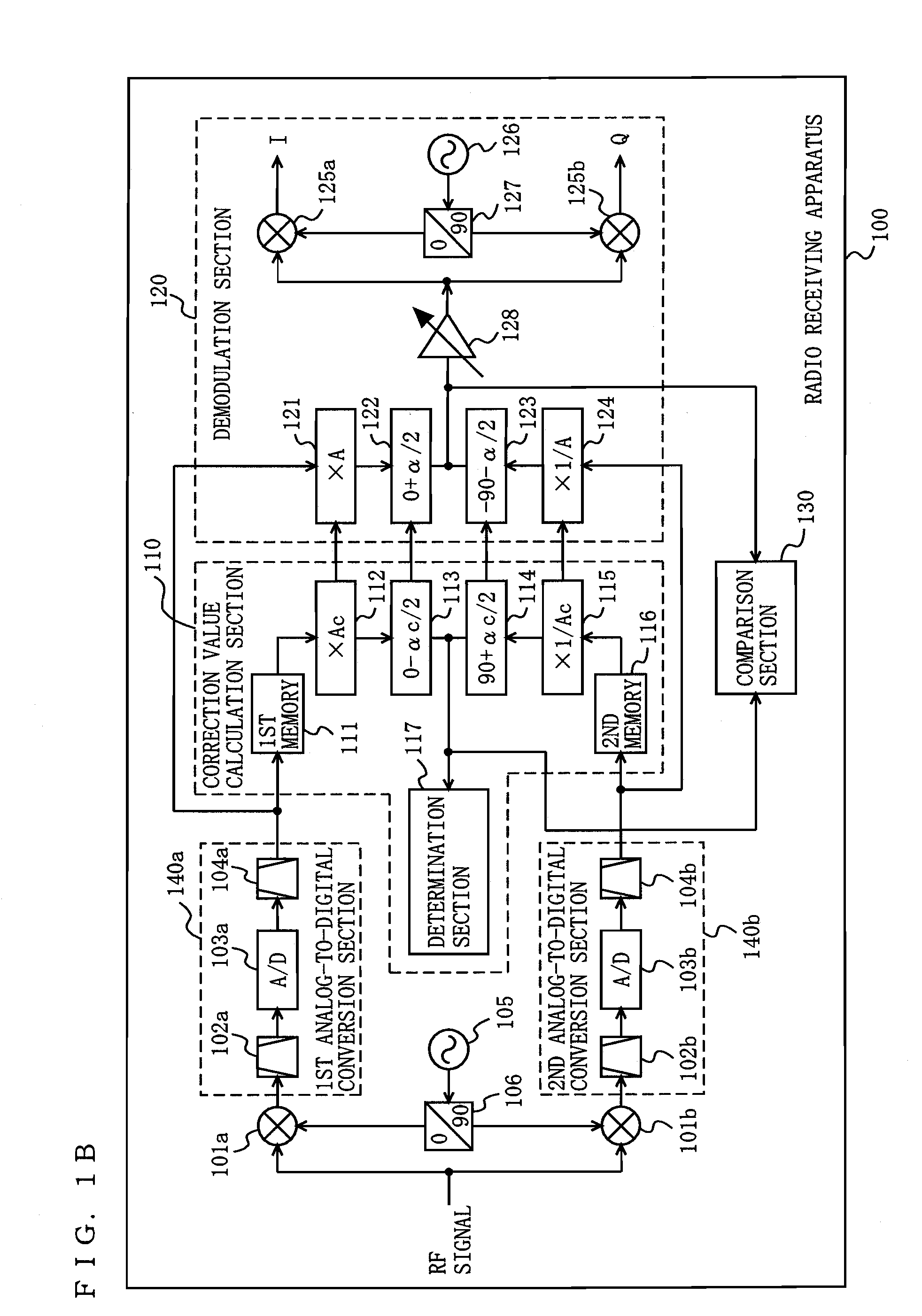
Radio receiving device
ActiveUS20100189197A1Suppress image noiseAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationPhase correctionPhase variation
A radio receiving apparatus capable of making compensation for both amplitude variations and phase variations and of suppressing image interference in a short period of time is provided.A correction value calculation section (110) combines a signal, obtained by multiplying a first digital signal by an amplitude correction candidate value and rotating the phase of the first digital signal, with a signal obtained by multiplying a second digital signal by a multiplicative inverse of the amplitude correction candidate value and performing, for the second digital signal, phase rotation which is in a quadrature relationship to phase rotation performed for the first digital signal, so as to obtain a first combined signal, obtain an inflection point of the first combined signal, and input, to a demodulation section (120), the amplitude correction candidate value and a phase correction candidate value, which correspond to the inflection point, as an amplitude correction value and a phase correction value, respectively. The demodulation section (120) makes compensation for the amplitudes and the phases and suppresses image interference, based on the amplitude correction value and the phase correction value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
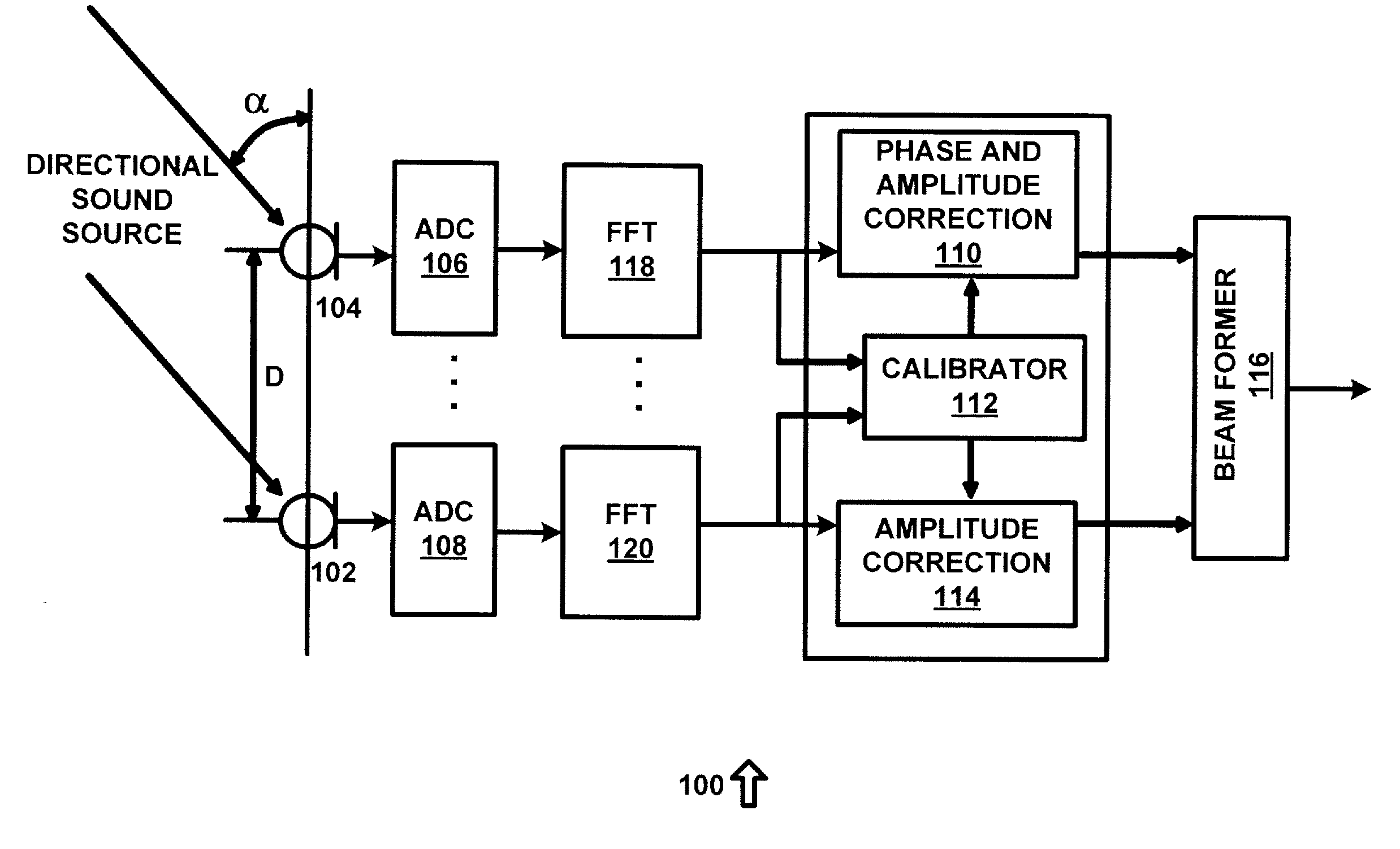
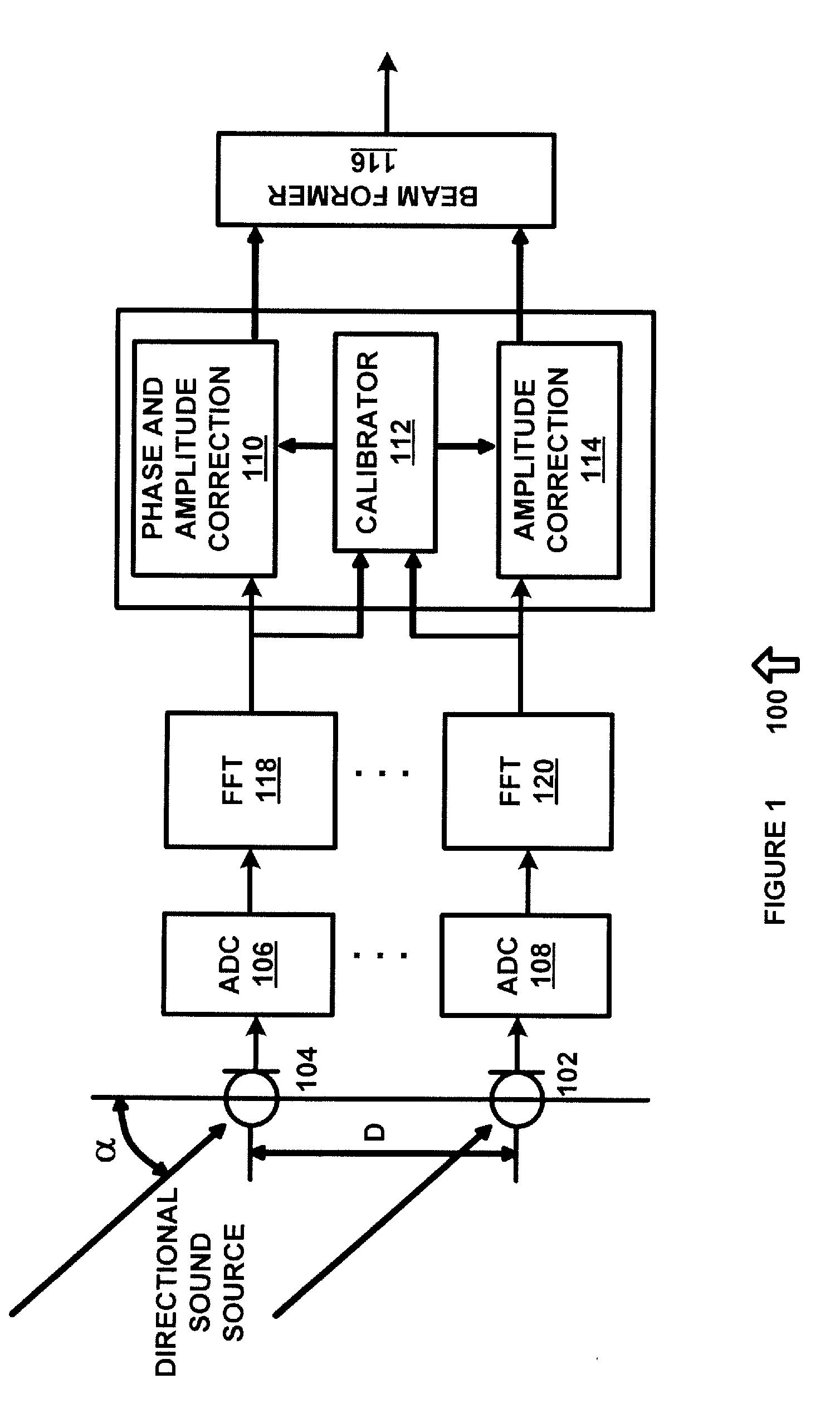
Microphone Array Calibration Method and Apparatus
ActiveUS20100158267A1Eliminate needMicrophones signal combinationTransmission noise suppressionPhase differenceEngineering
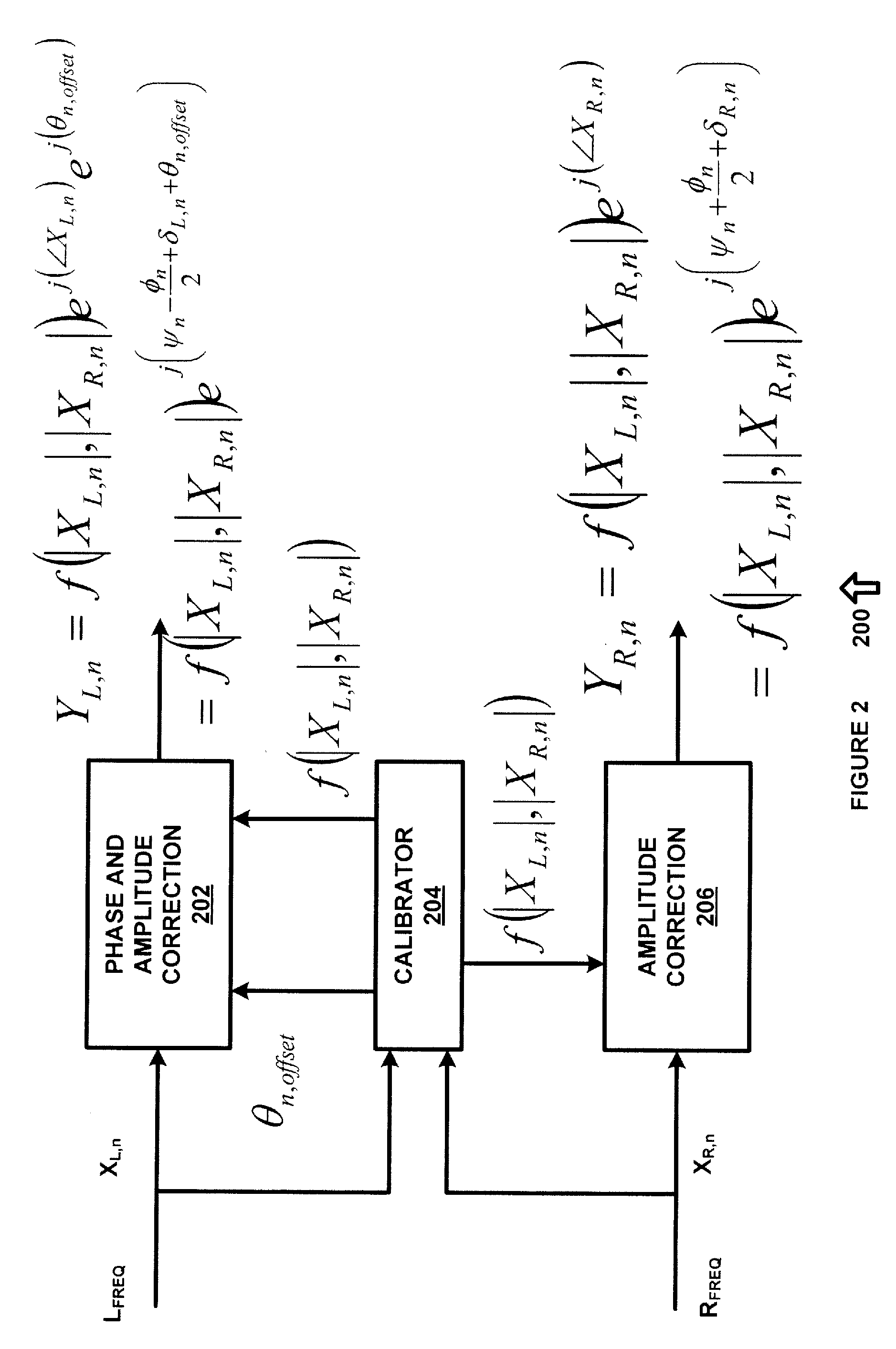
An apparatus for providing real-time calibration for two or more microphones. A calibrator for receiving a left microphone signal and a right microphone signal and generating phase difference data. A phase and amplitude correction system for receiving one of the left microphone signal or the right microphone signal the phase difference data and generating calibration data for a beamformer. The beamformer receiving the calibration data, the left microphone signal and the right microphone signal and generating a monaural beamformed signal.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
RF power amplifier system with impedance modulation
ActiveUS8018277B2Improve efficiencyReduce phase distortionHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierAmplitude control
Owner:QUANTANCE
Amplifier compression adjustment circuit
ActiveUS20100194476A1Narrow bandwidthSacrificing efficiencyGain controlPower amplifiersAc componentsVariable-gain amplifier
An RF power amplifier system adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the RF input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the RF output signal of the power amplifier. A variable gain amplifier (VGA) adjusts the amplitude of the RF input signal, thus providing a second means of adjusting the amplitude of the output of the power amplifier. The gain of the VGA or the supply voltage to the power amplifier is controlled based on the AC components of the amplitude correction signal, while the DC components of the amplitude correction signal are blocked from controlling the VGA or the supply voltage to the power amplifier. The DC level of the gain control of the VGA, the average supply voltage to the power amplifier, or the closed loop gain of the overall amplitude correction loop is controlled separately by a compression control signal.
Owner:QUANTANCE
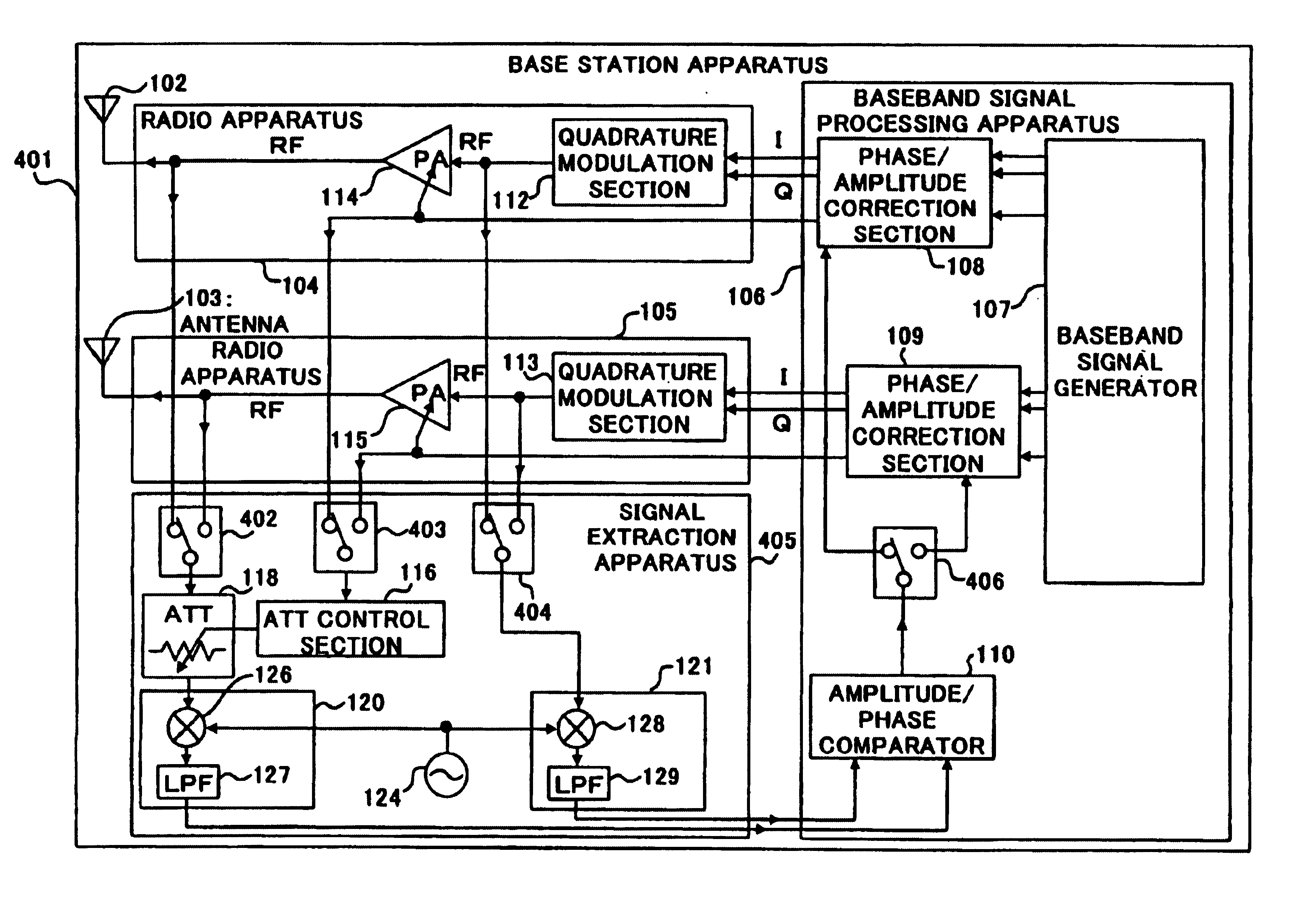
Communication apparatus and communication method
InactiveUS7058425B1Small sizeLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasPhase shiftedAudio power amplifier
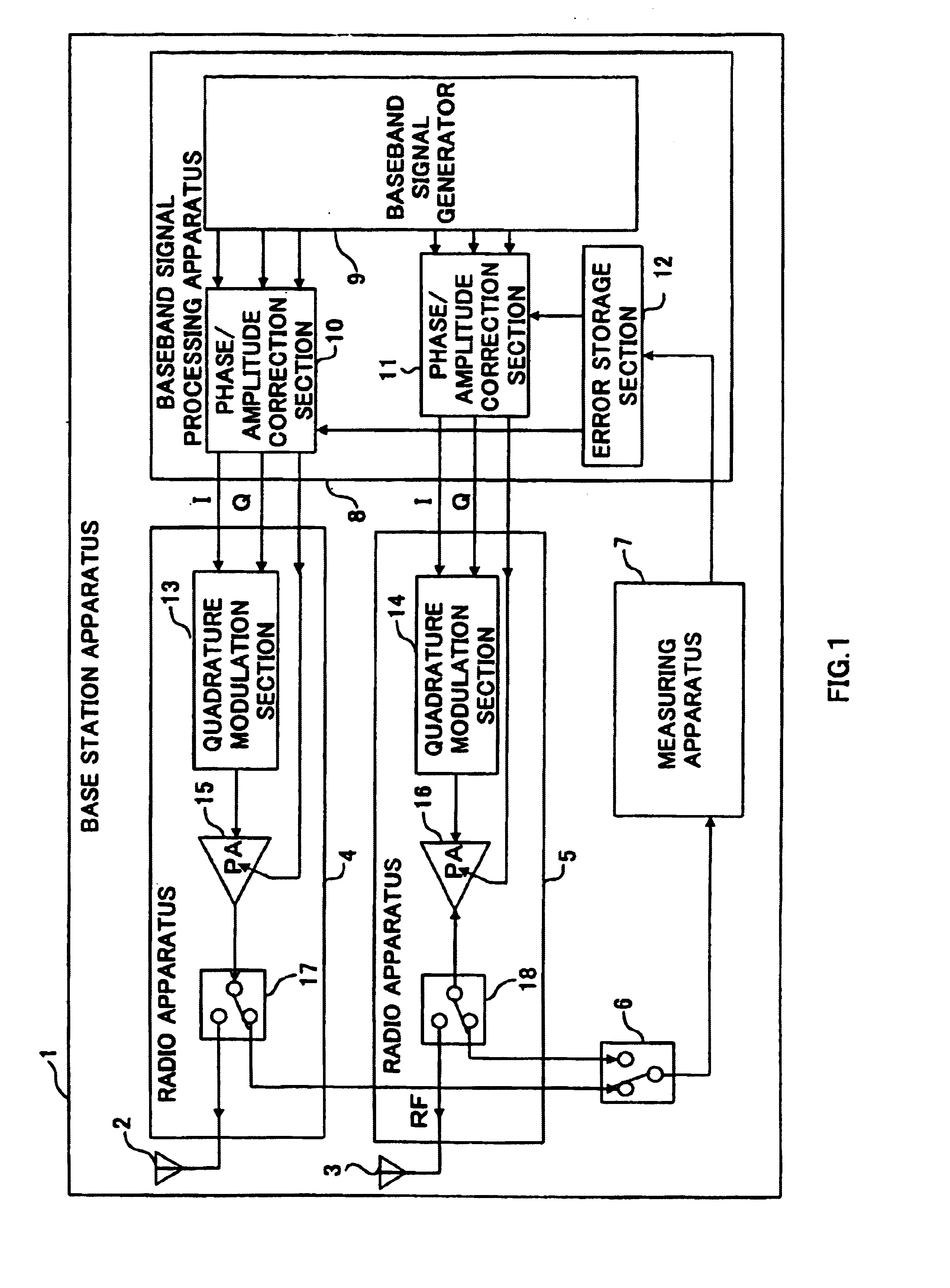
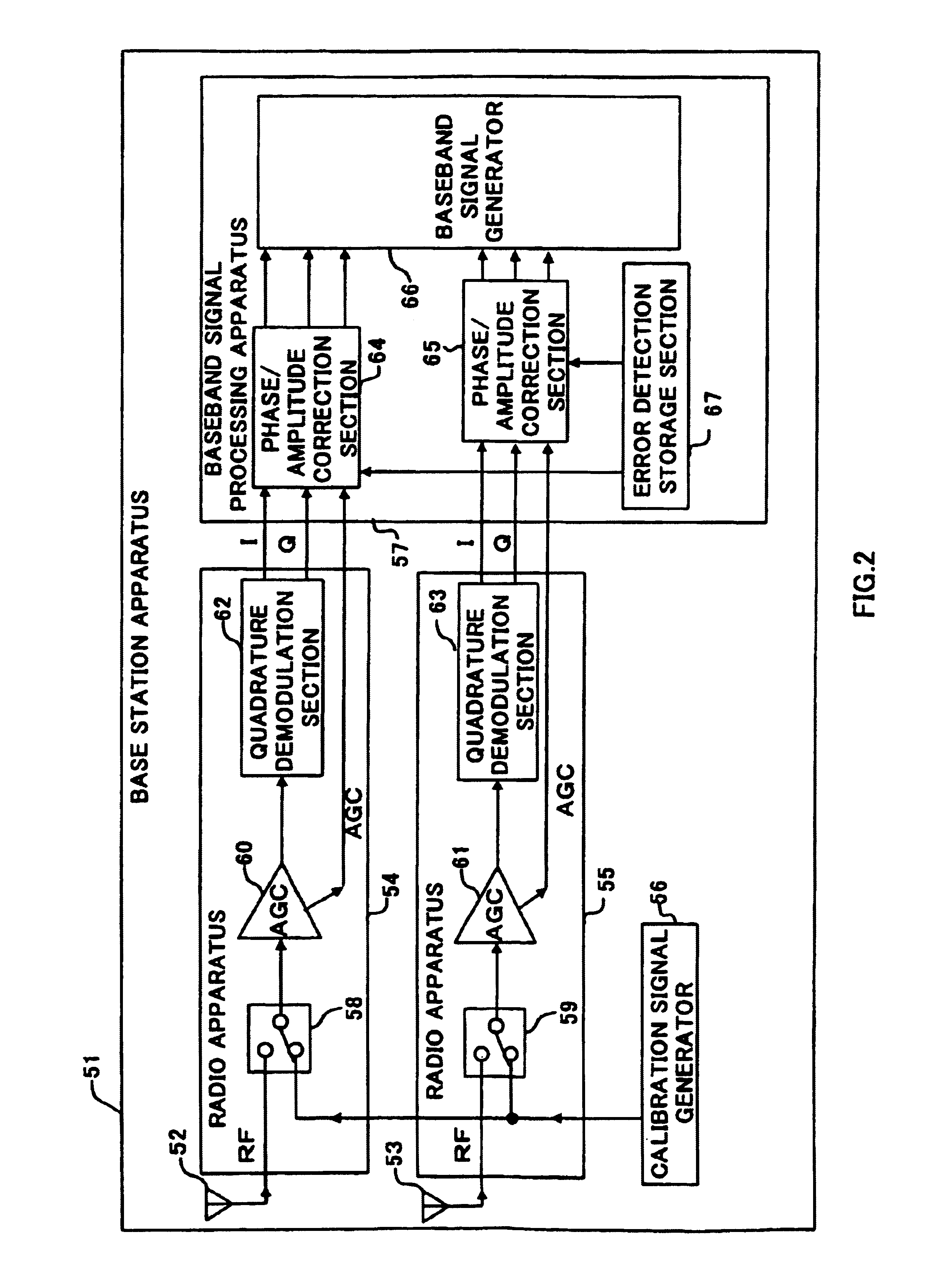
Baseband signal generator 107 outputs a transmission baseband signal with a coefficient for setting antenna directivity multiplied and a gain control signal to transmit power amplifier 114 and transmit power amplifier 114 amplifies the transmission baseband signal with a gain corresponding to the gain control signal and transmits the signal from antenna 102. ATT 118 attenuates the output signal of amplifier 114 according to the gain control signal, amplitude / phase comparator 110 calculates amplitude and phase errors between the attenuated signal with a frequency equalized by frequency conversion sections 120 and 121 and the input signal of amplifier 114 and phase / amplitude correction section 108 corrects the transmission baseband signal and gain control signal so as to eliminate the errors. This makes it possible to correct the amplitude and phase shifts of the transmission signal during a communication with other apparatuses and reduce the size and cost of the apparatus.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Amplifier compression adjustment circuit
ActiveUS7777566B1Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthGain controlPower amplifiersAc componentsAudio power amplifier
Owner:QUANTANCE
RF power amplifier controller circuit
ActiveUS8095090B2Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthResonant long antennasSupply voltage varying controlPhase distortionAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier. The amplitude control loop and the phase control loop may also adjust the gain and / or phase of the power amplifier, respectively.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Power amplifier controller circuit
ActiveUS7933570B2Reduce phase distortionNarrow bandwidthResonant long antennasPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase distortion
A power amplifier controller circuit controls a power amplifier based upon an amplitude correction signal indicating the amplitude difference between the amplitude of the input signal and an attenuated amplitude of the output signal. The power amplifier controller circuit comprises an amplitude control loop and a phase control loop. The amplitude control loop adjusts the supply voltage to the power amplifier based upon the amplitude correction signal. The amplitude correction signal may also be split into two or more signals with different frequency ranges and provided respectively to different types of power supplies with different efficiencies to generate the adjusted supply voltage to the power amplifier. The phase control loop adjusts the phase of the input signal based upon a phase error signal indicating a phase difference between phases of the input signal and the output signal to reduce phase distortion generated by the power amplifier.
Owner:QUANTANCE
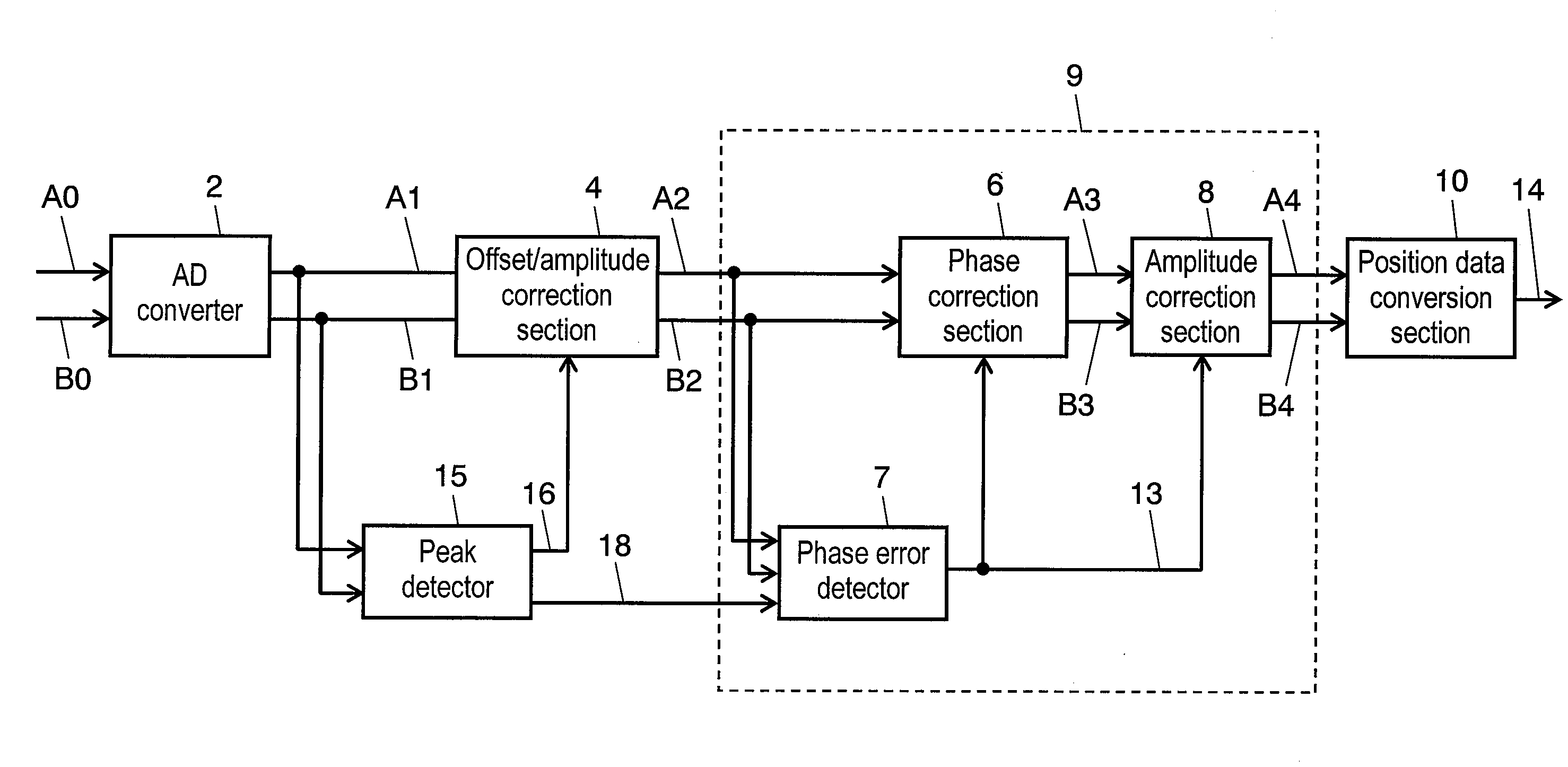
Phase correction circuit of encoder signal
ActiveUS20100091926A1Converting sensor output electrically/magneticallySynchronising arrangementPhase correctionPeak value
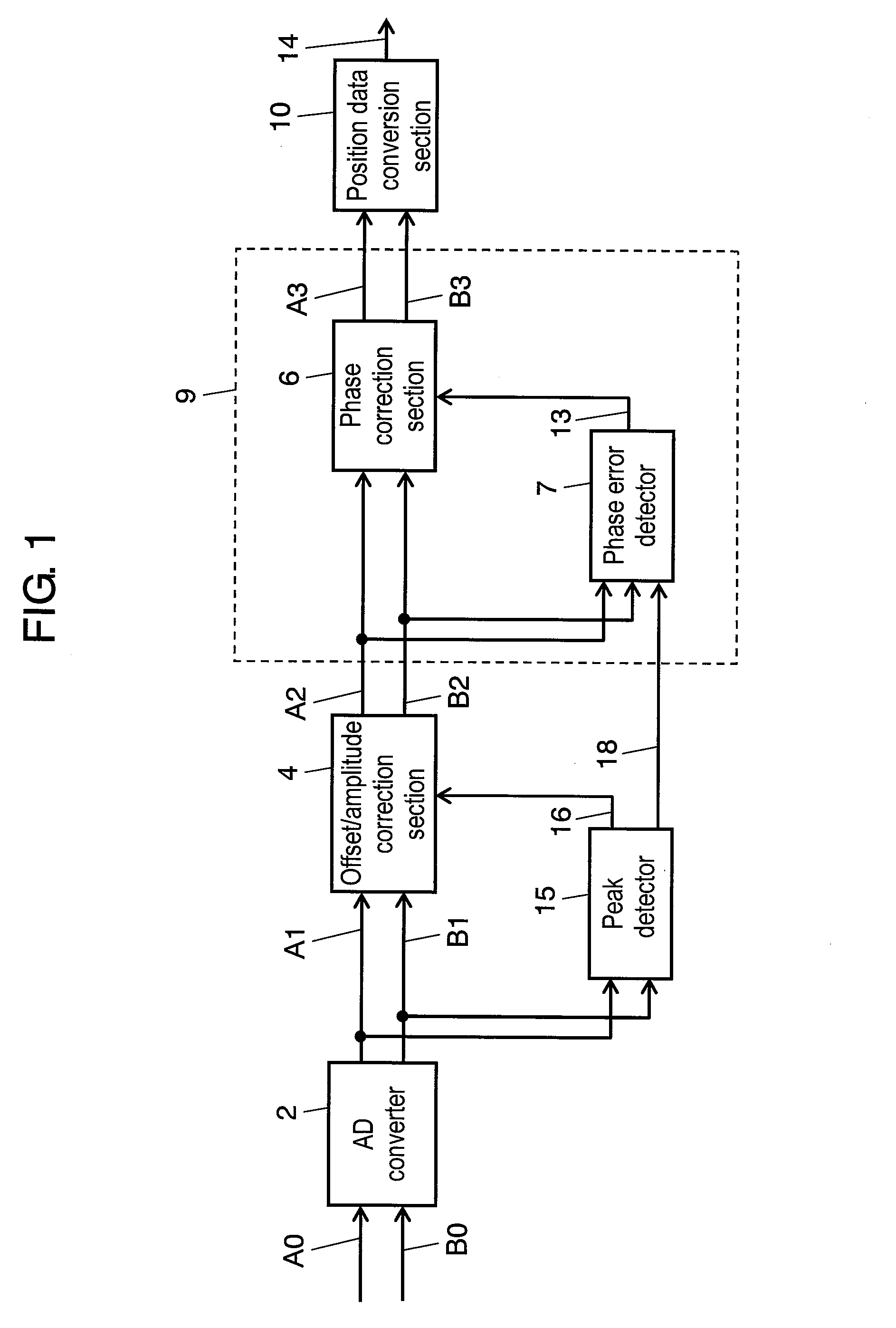
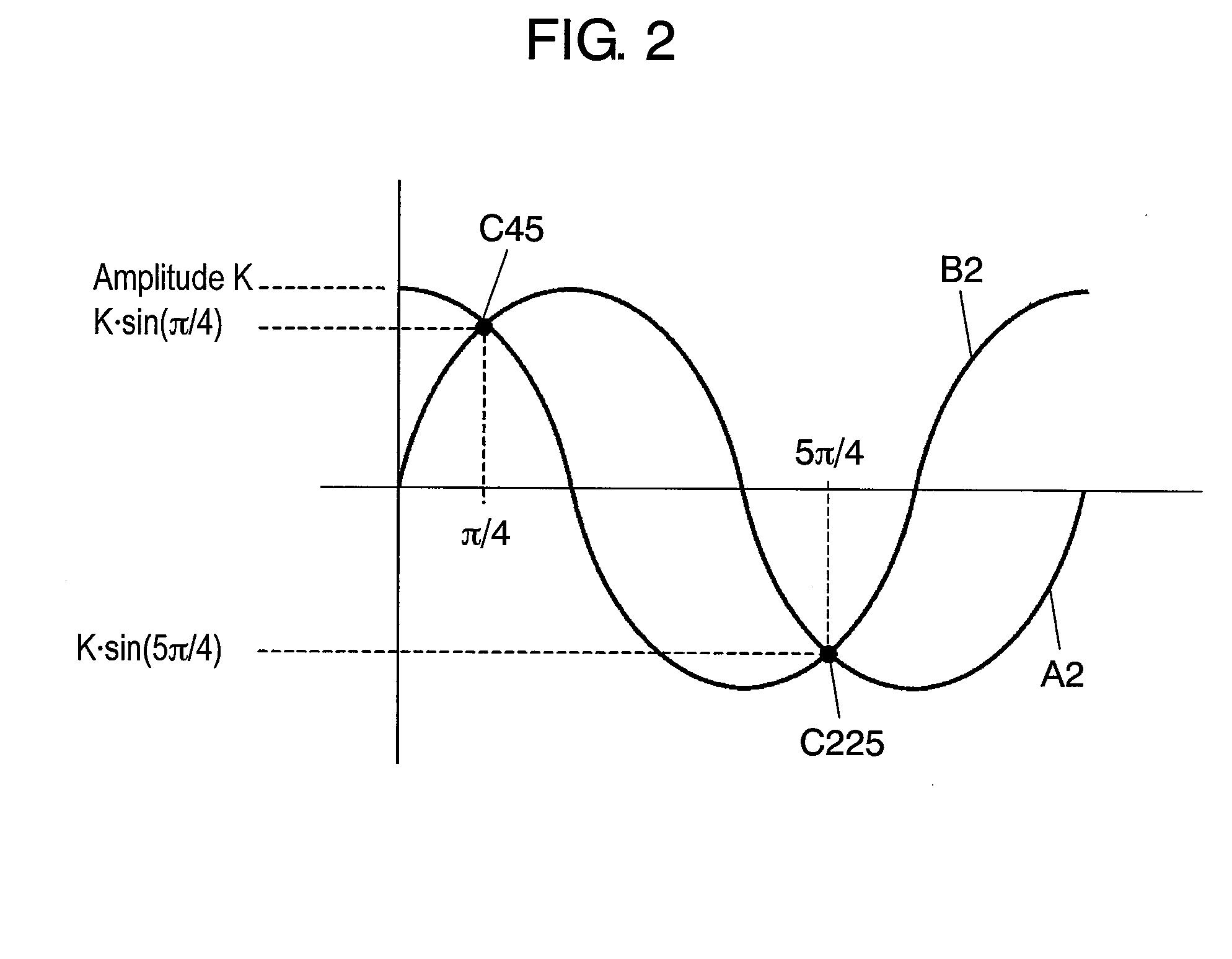
A position detector has a peak detector for detecting peak values of an A1 signal and a B1 signal serving as output signals of an analog to digital (AD) converter, an offset / amplitude correction section for generating an A2 signal and a B2 signal by correcting offsets and amplitude errors using the peak values detected by the peak detector, and a position data conversion section for converting the sinusoidal signals of an A phase and a B phase into position data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com