Patents
Literature
418results about "Stray field compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
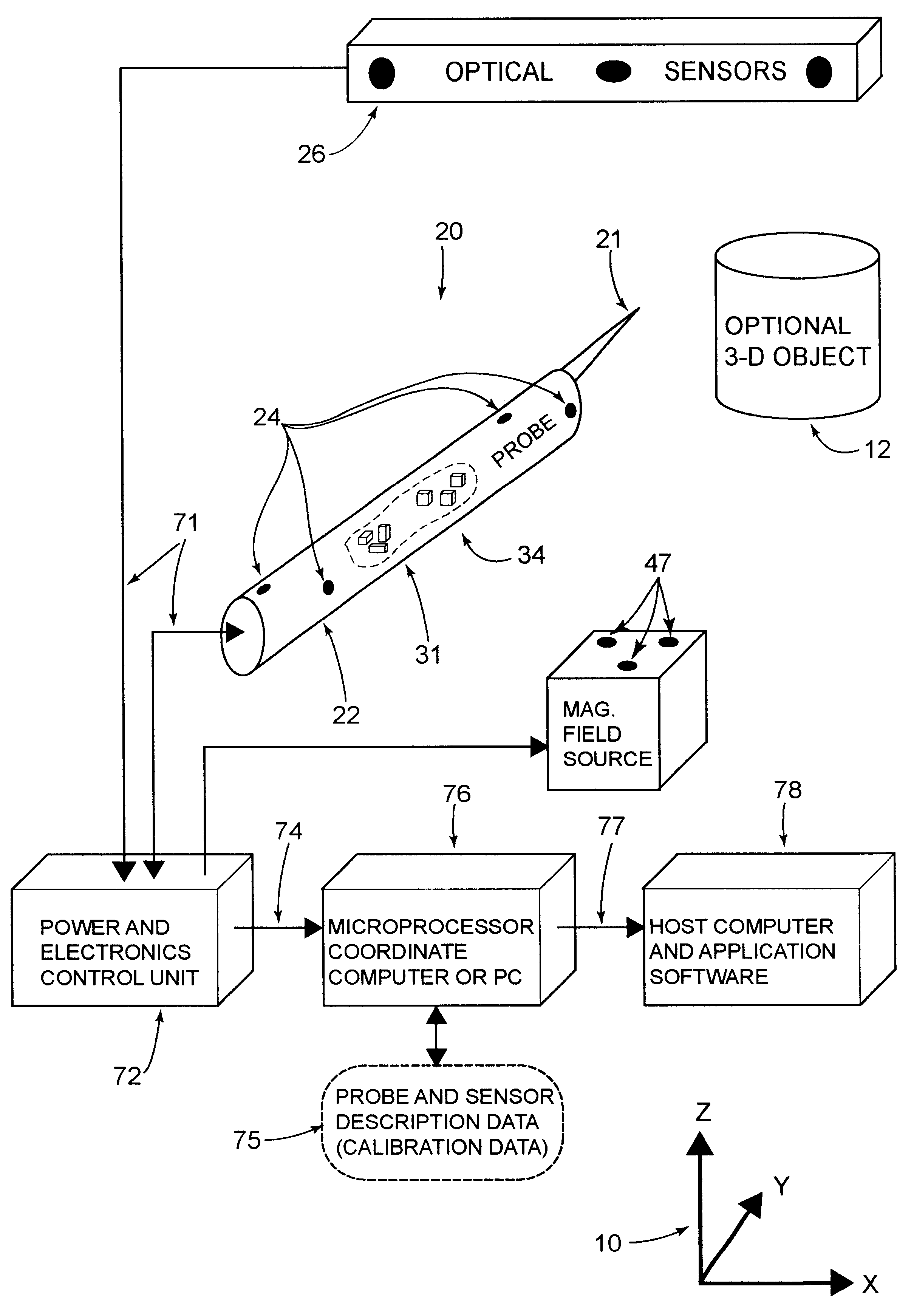
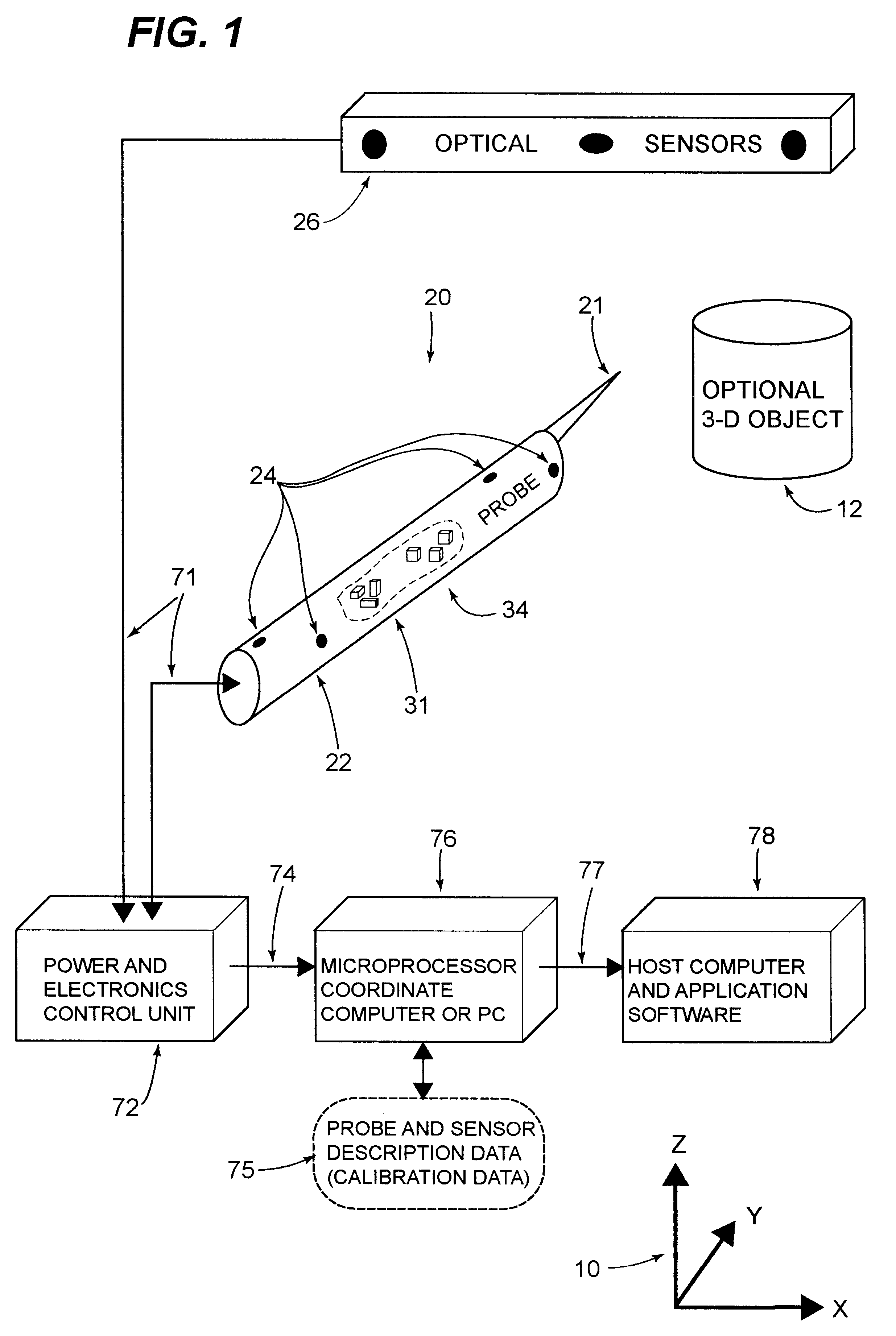
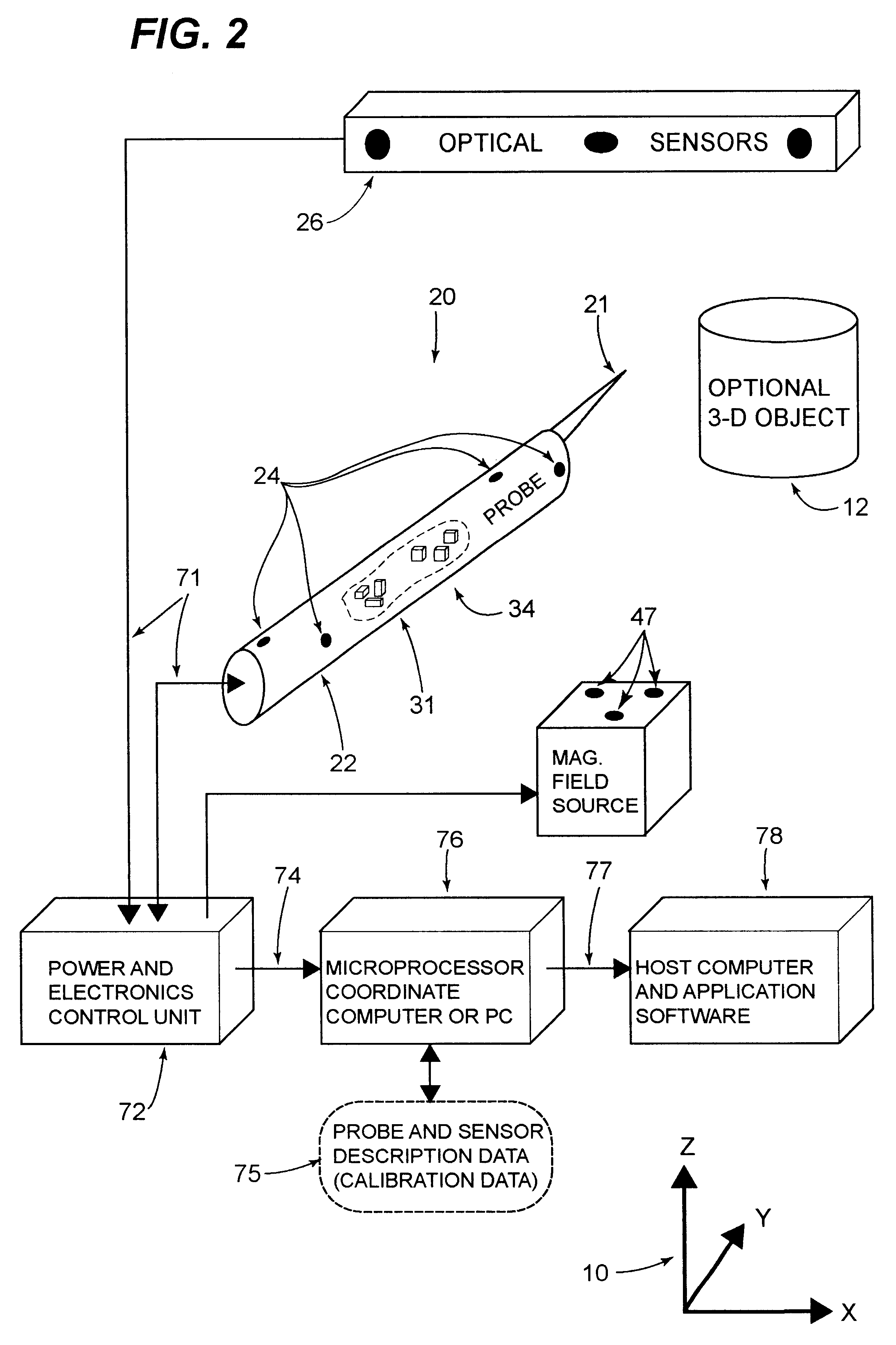
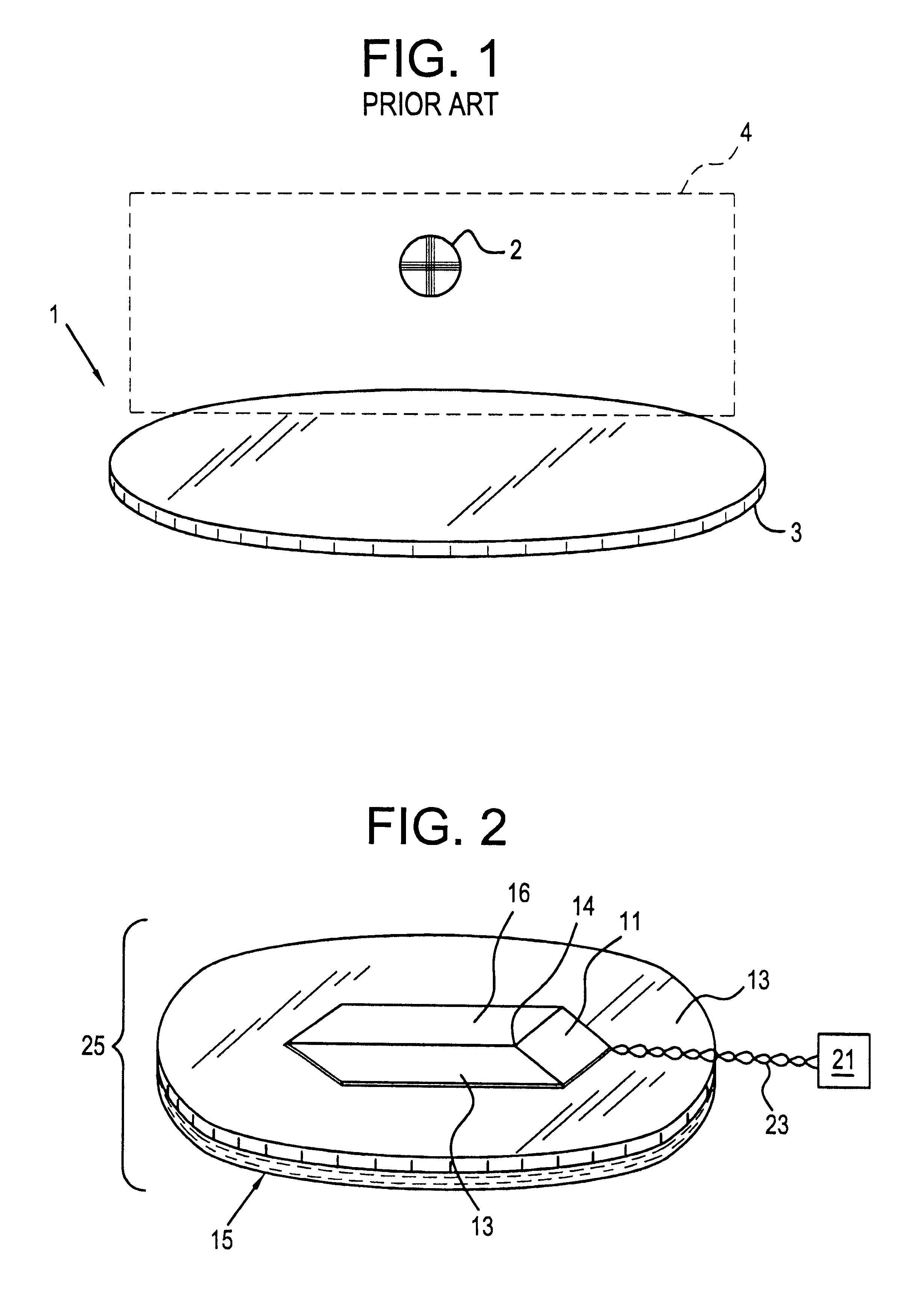
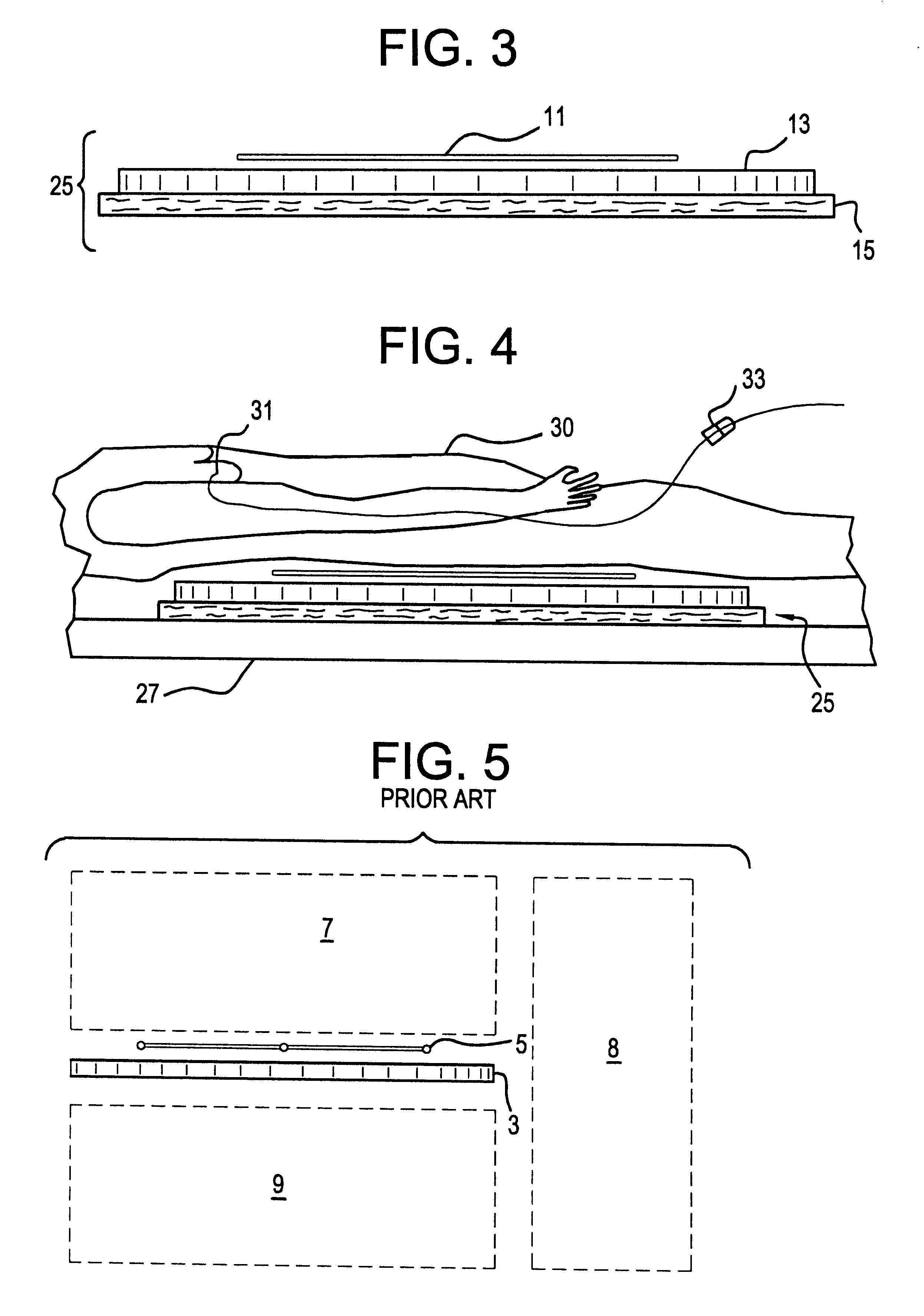
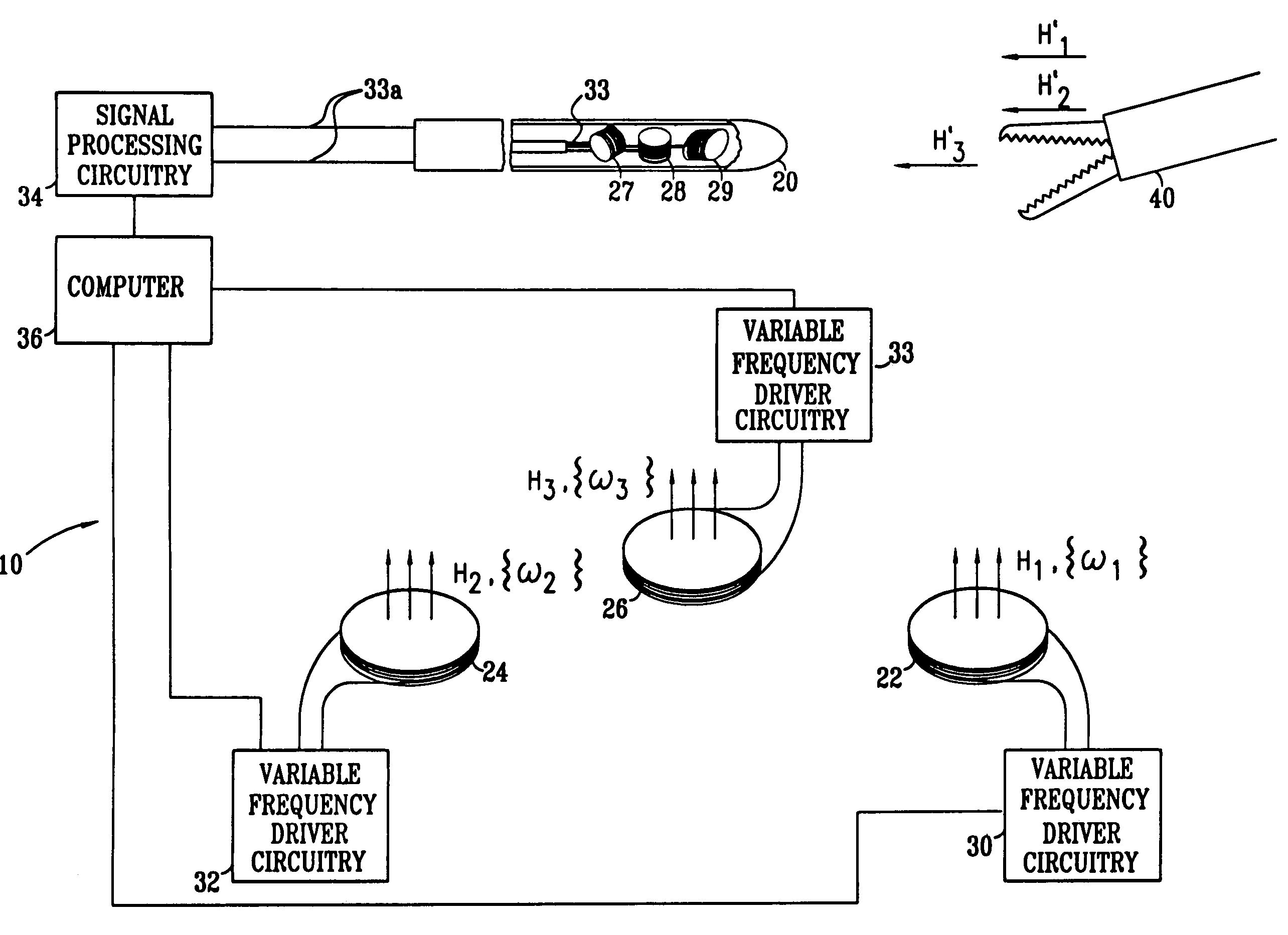
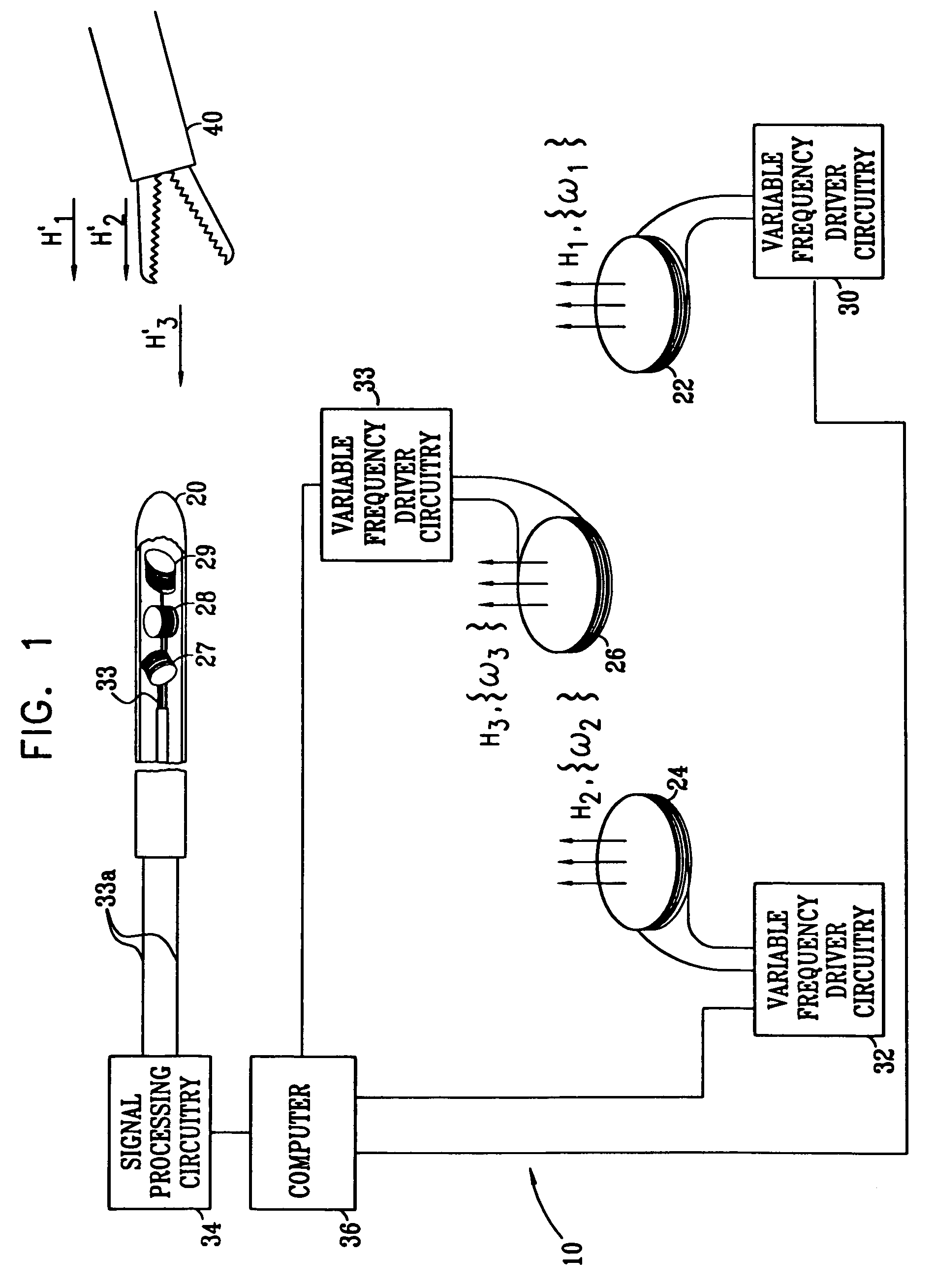
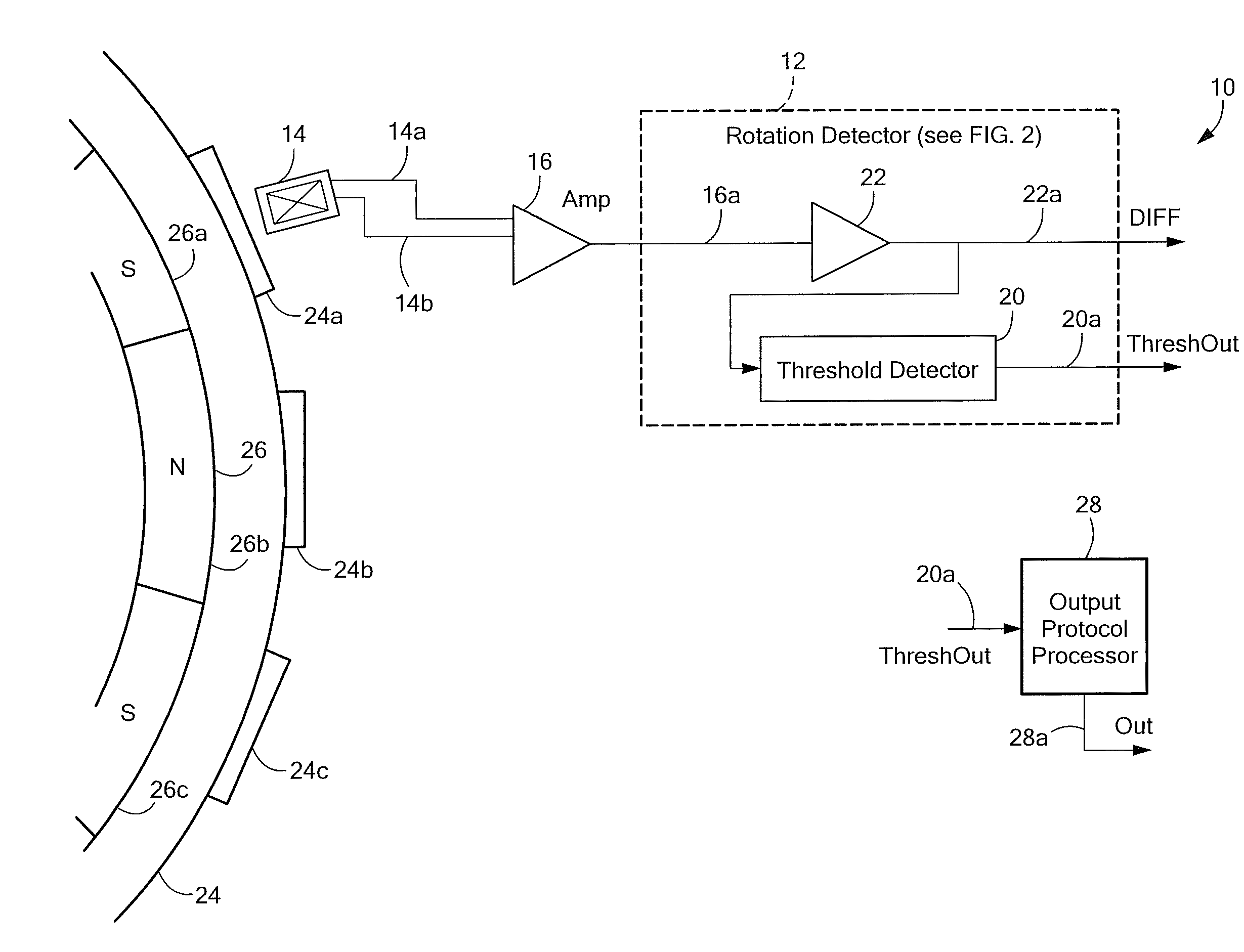
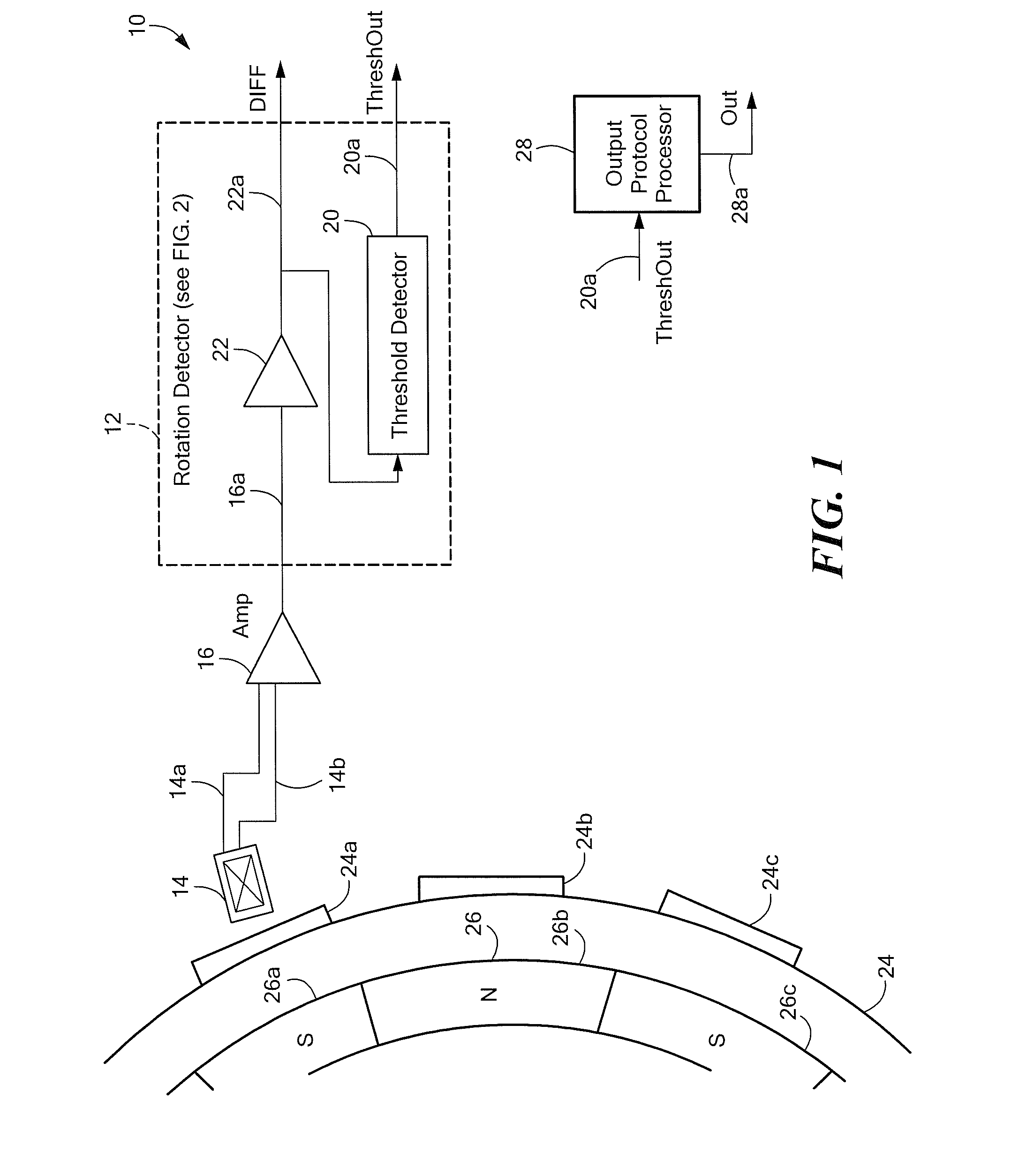
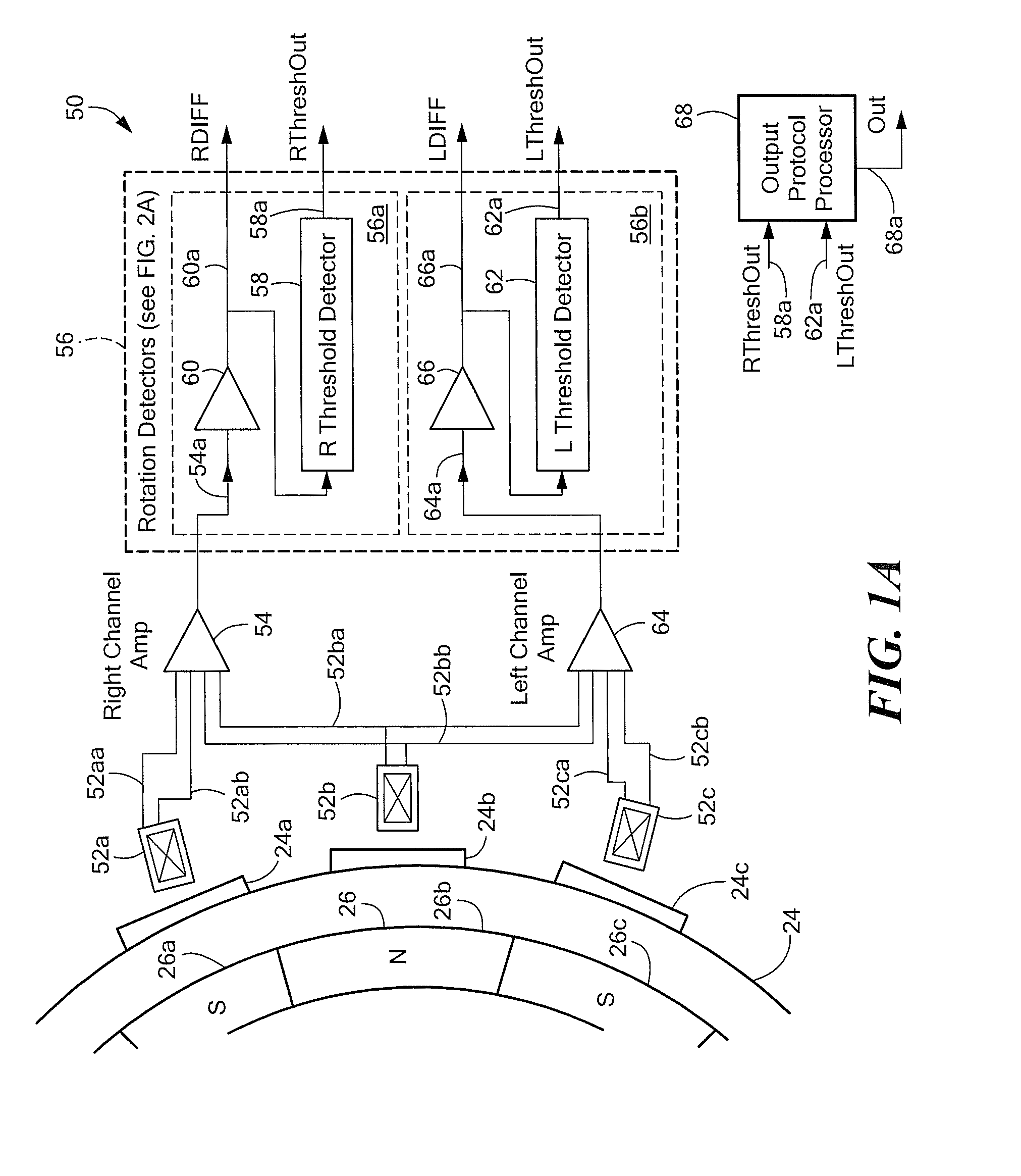
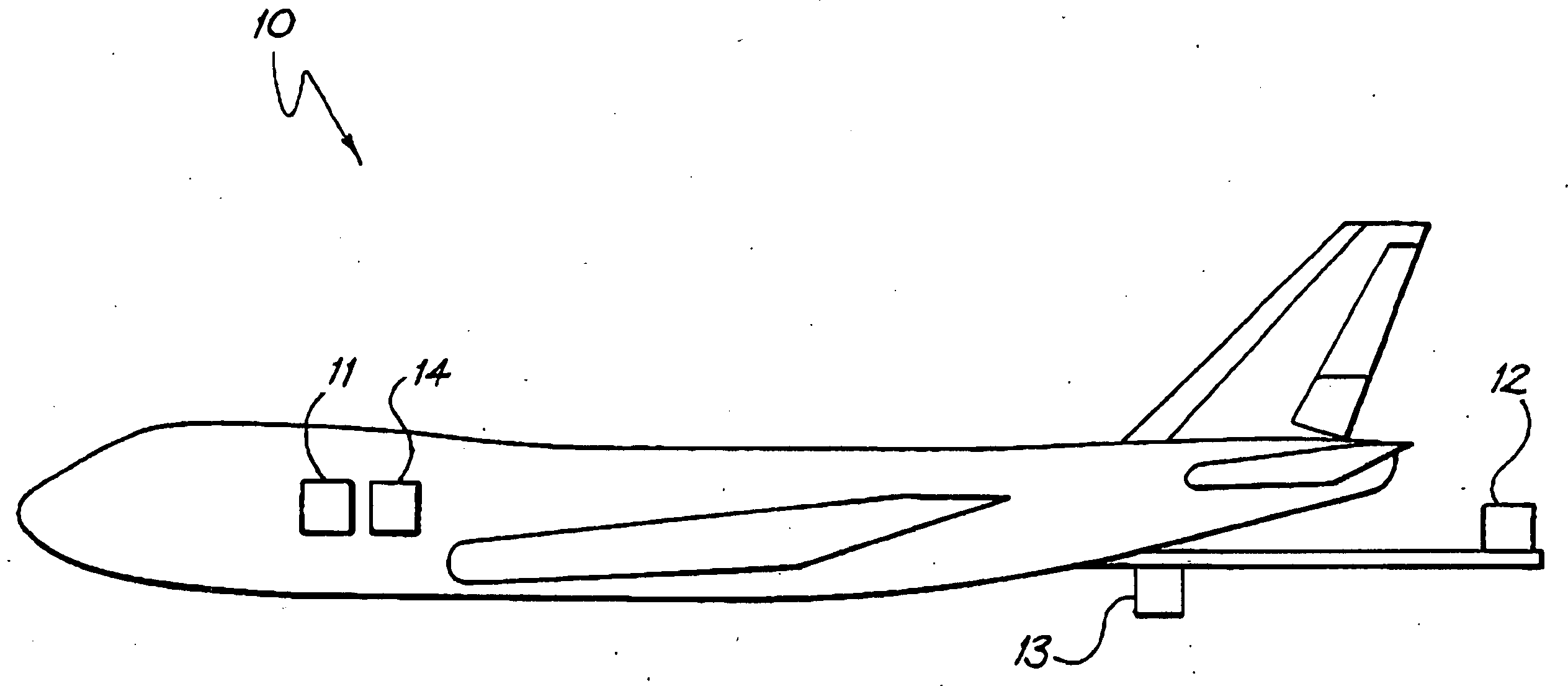
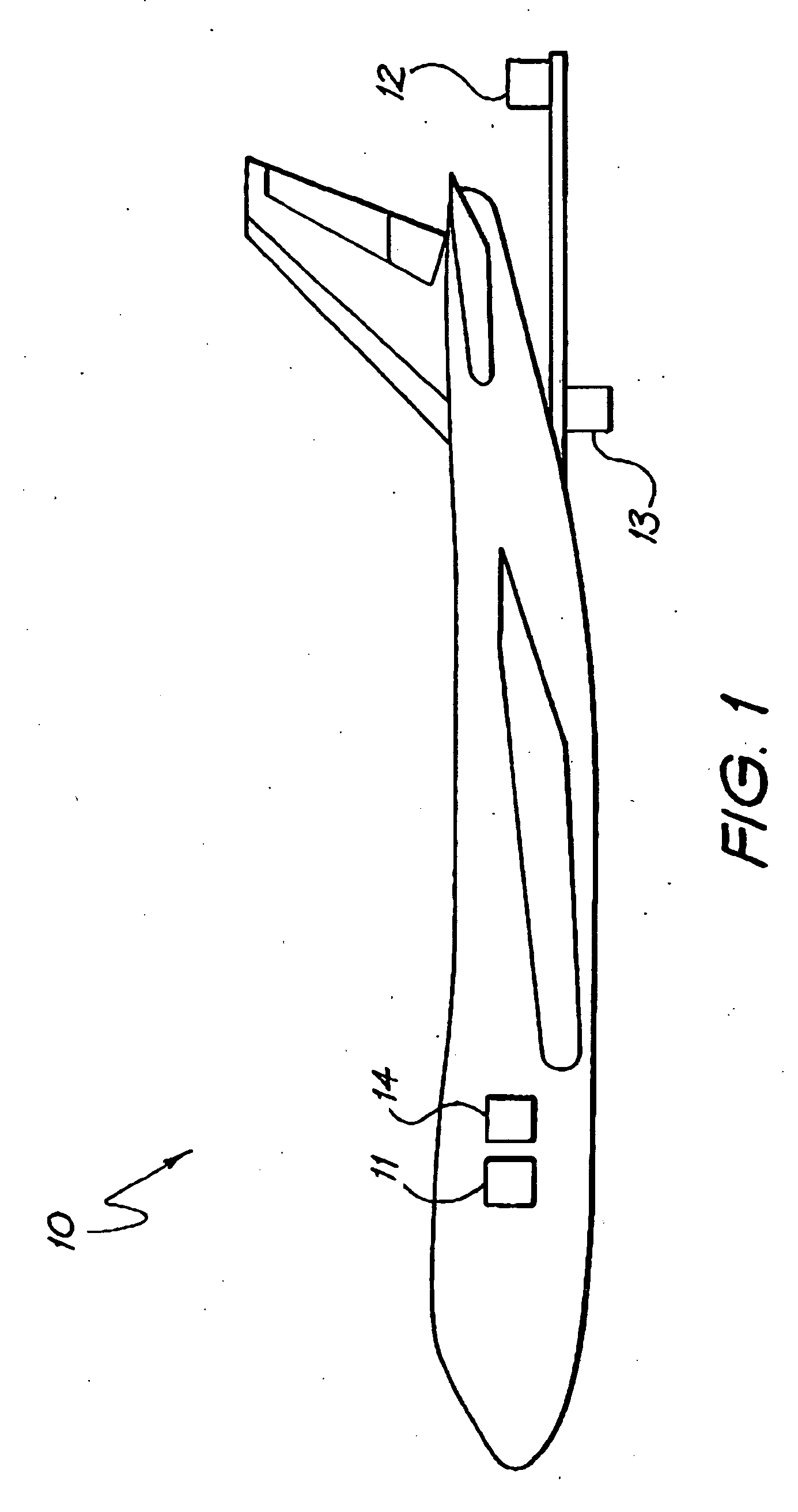
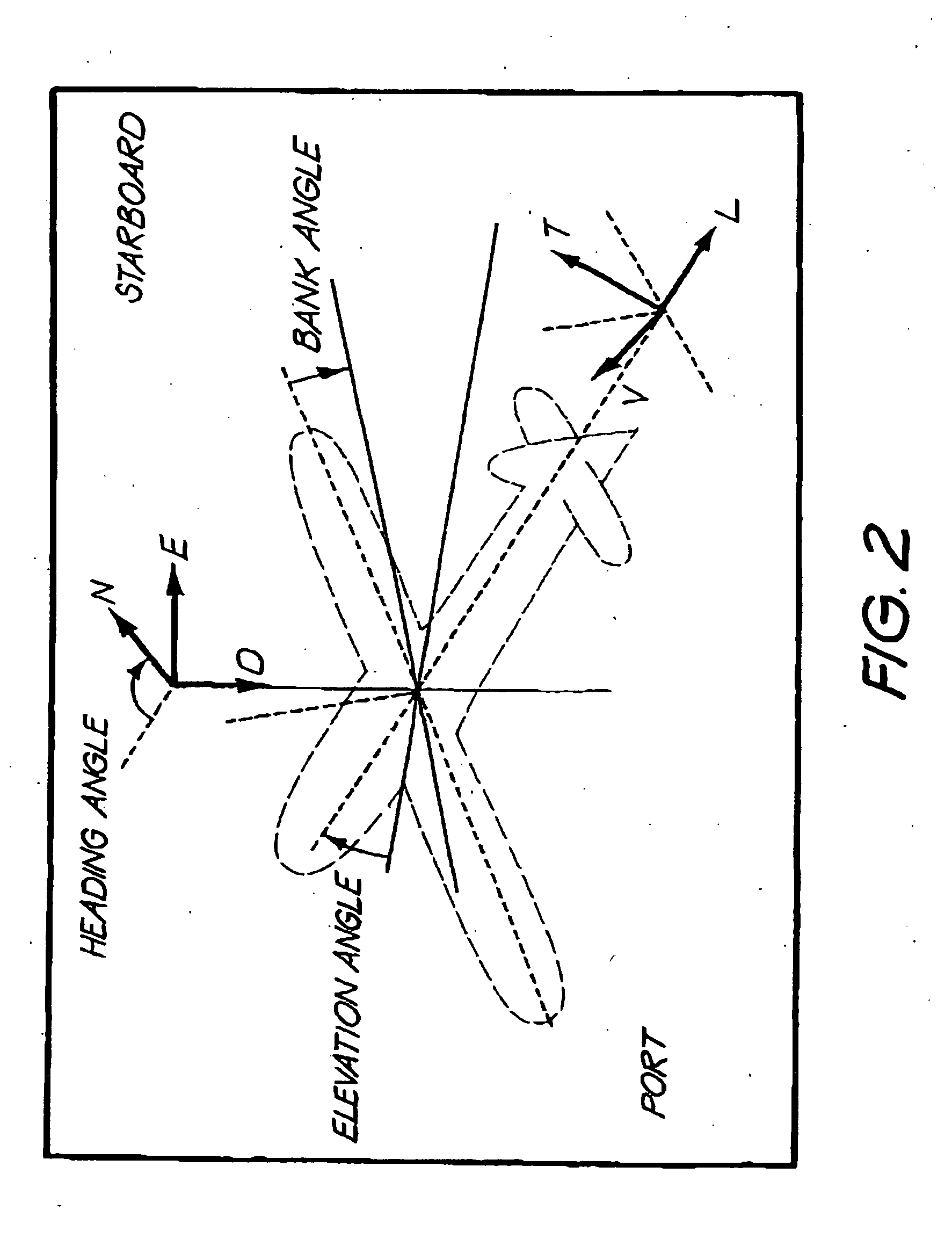
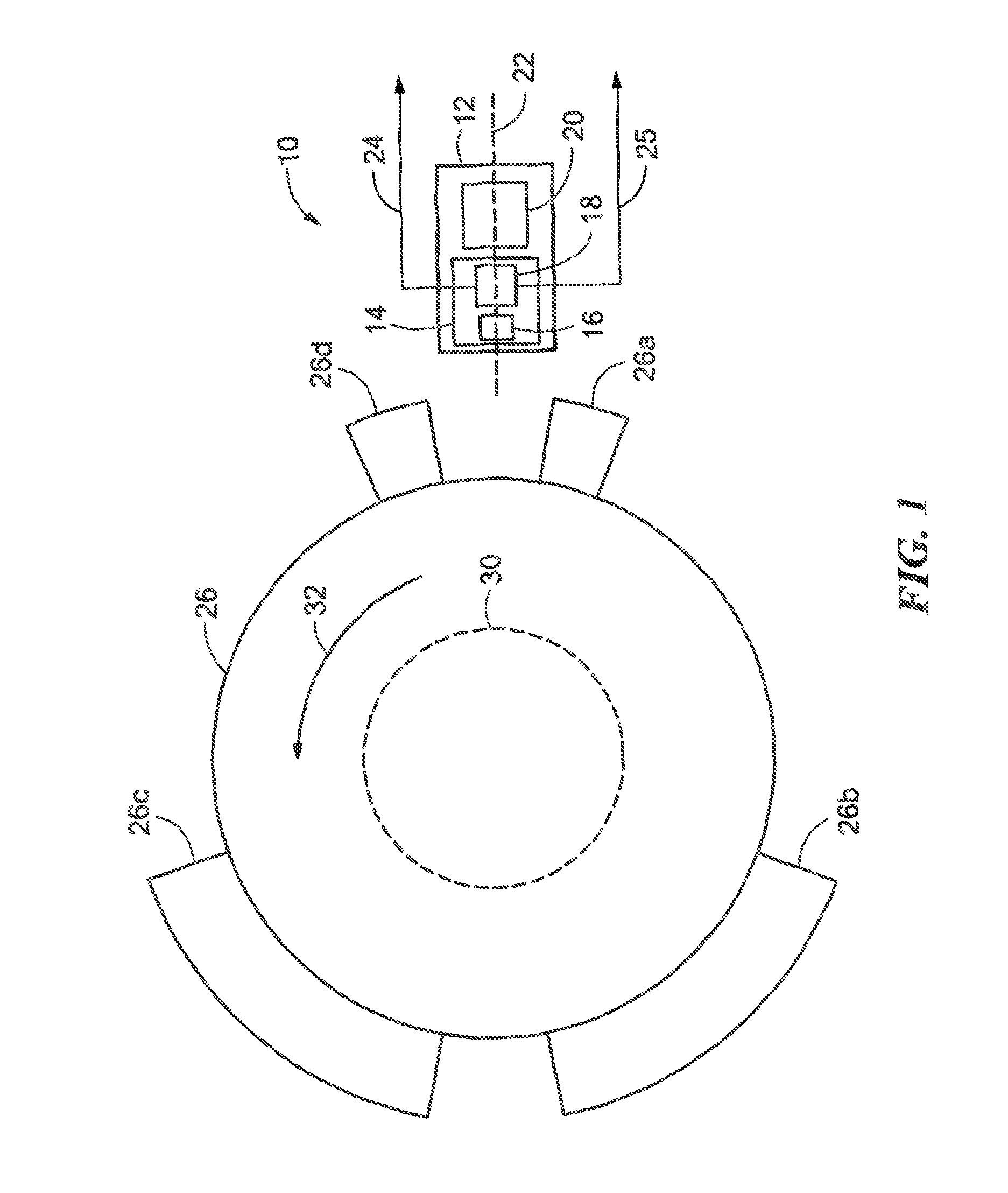
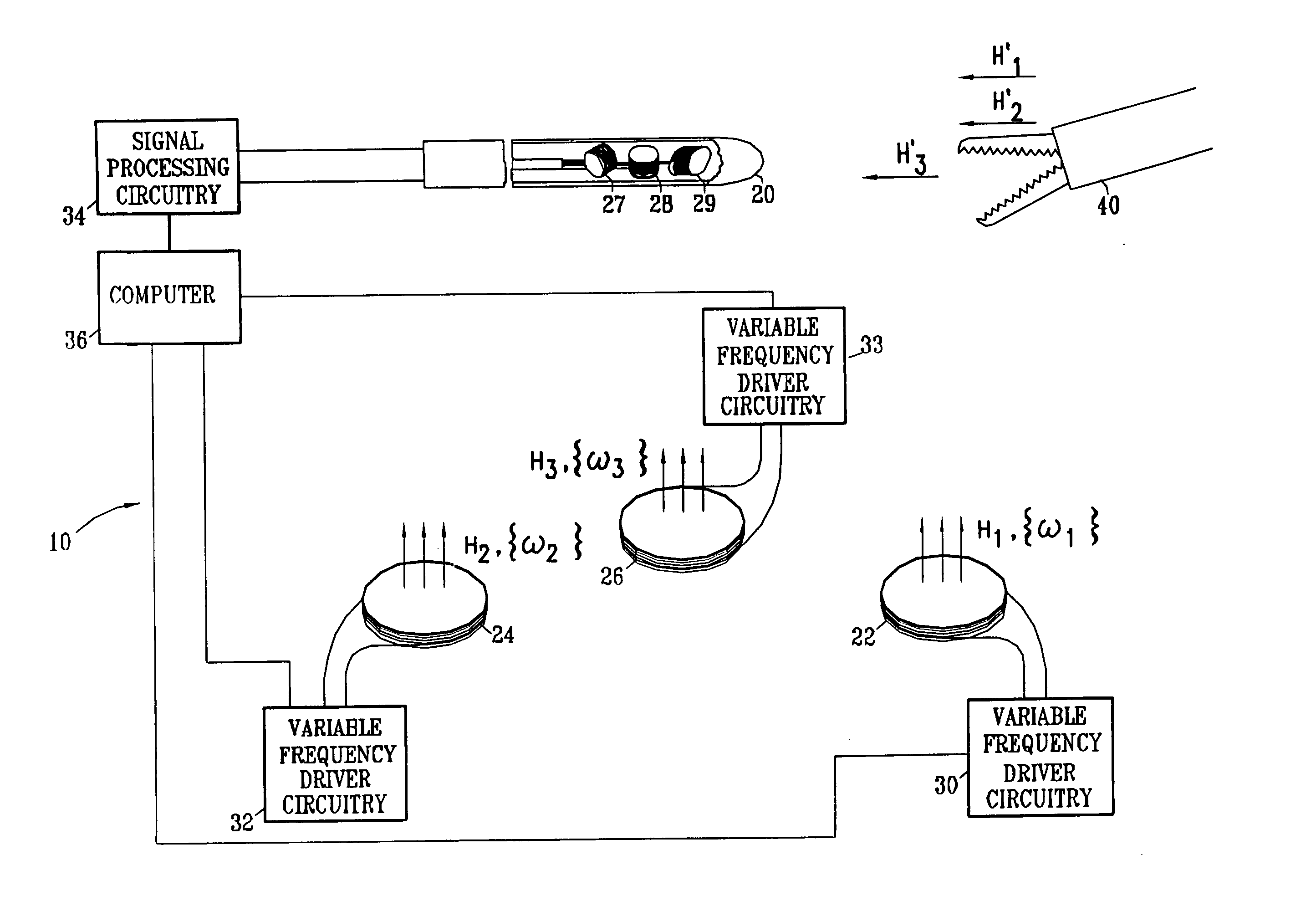
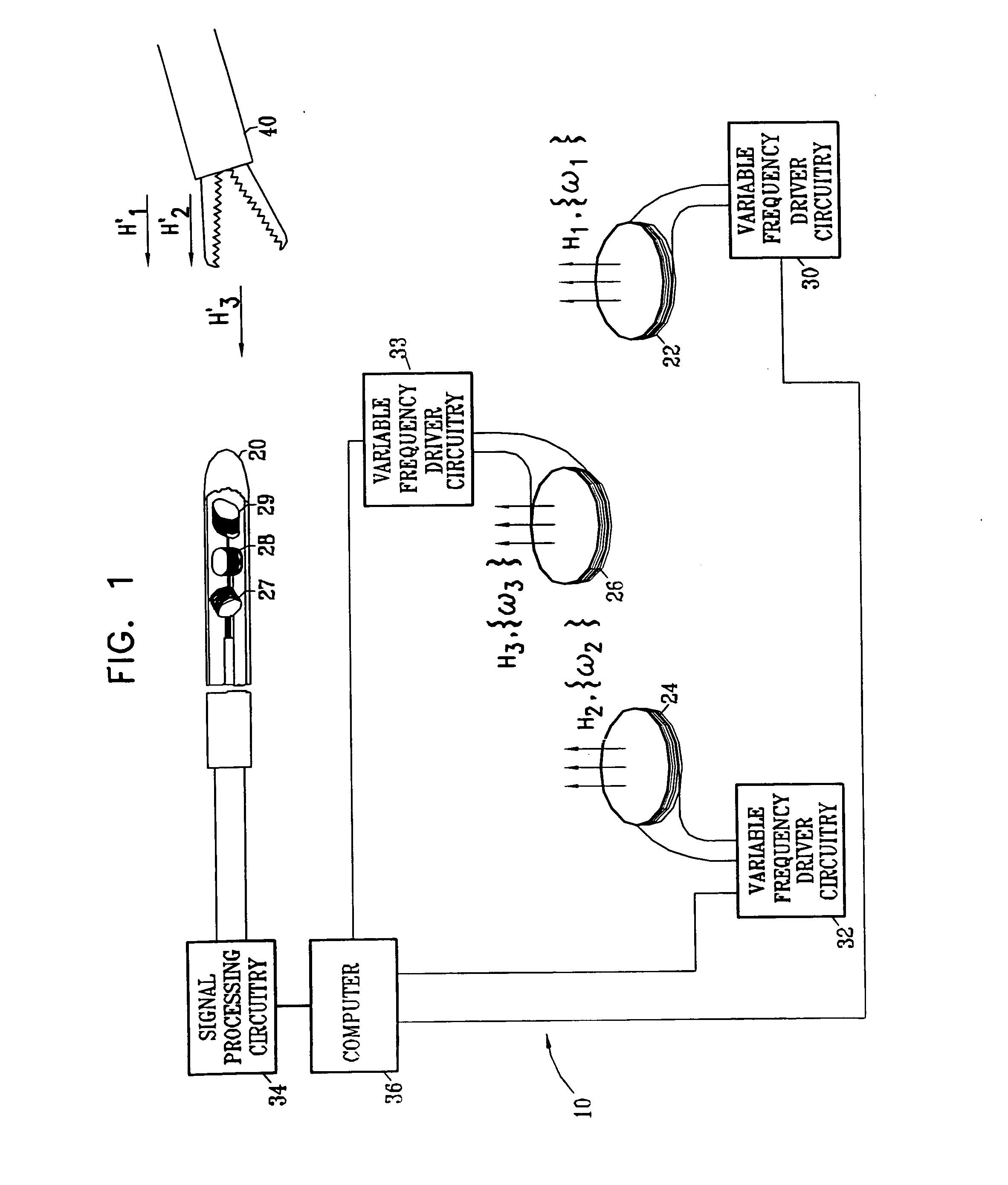
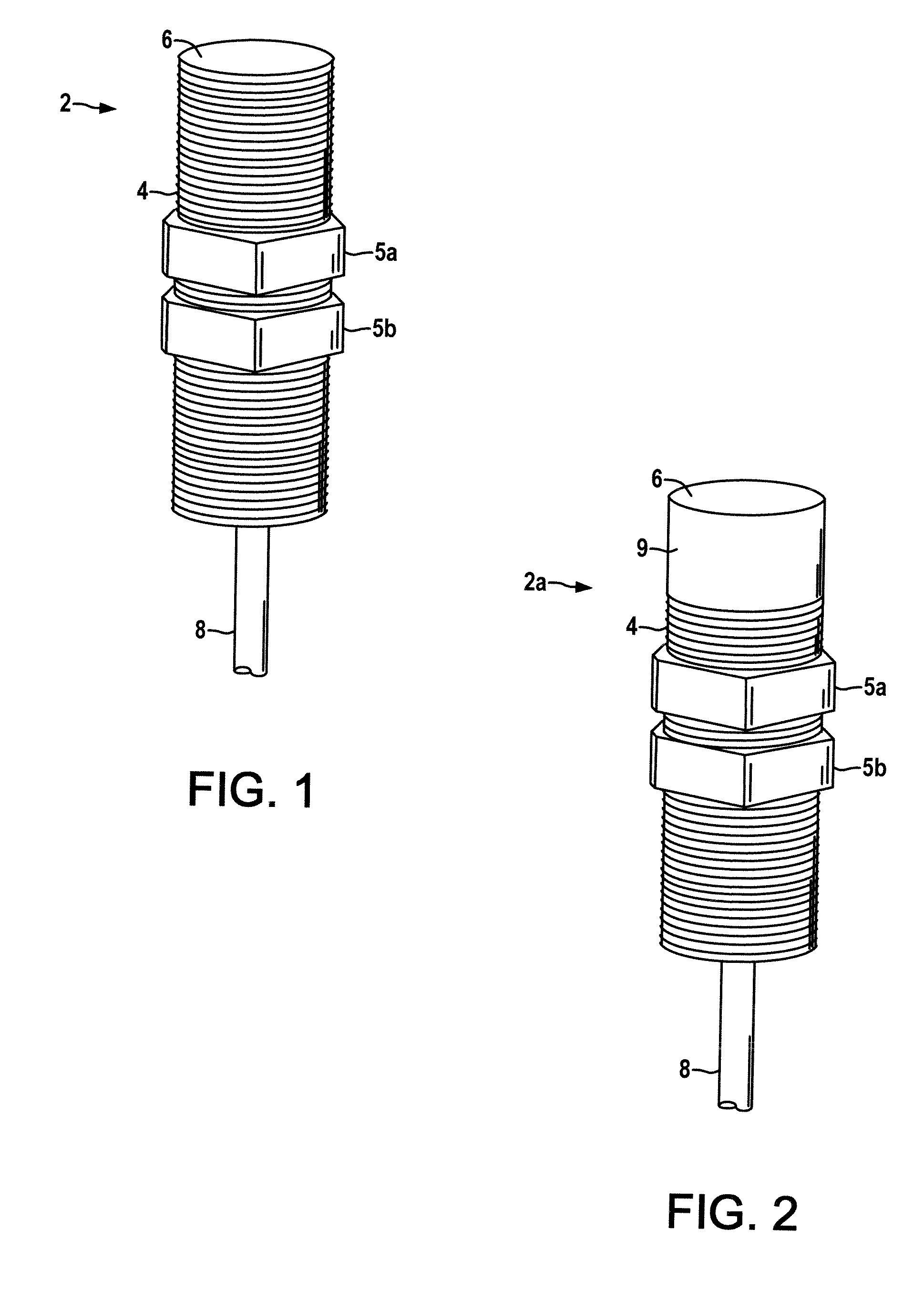
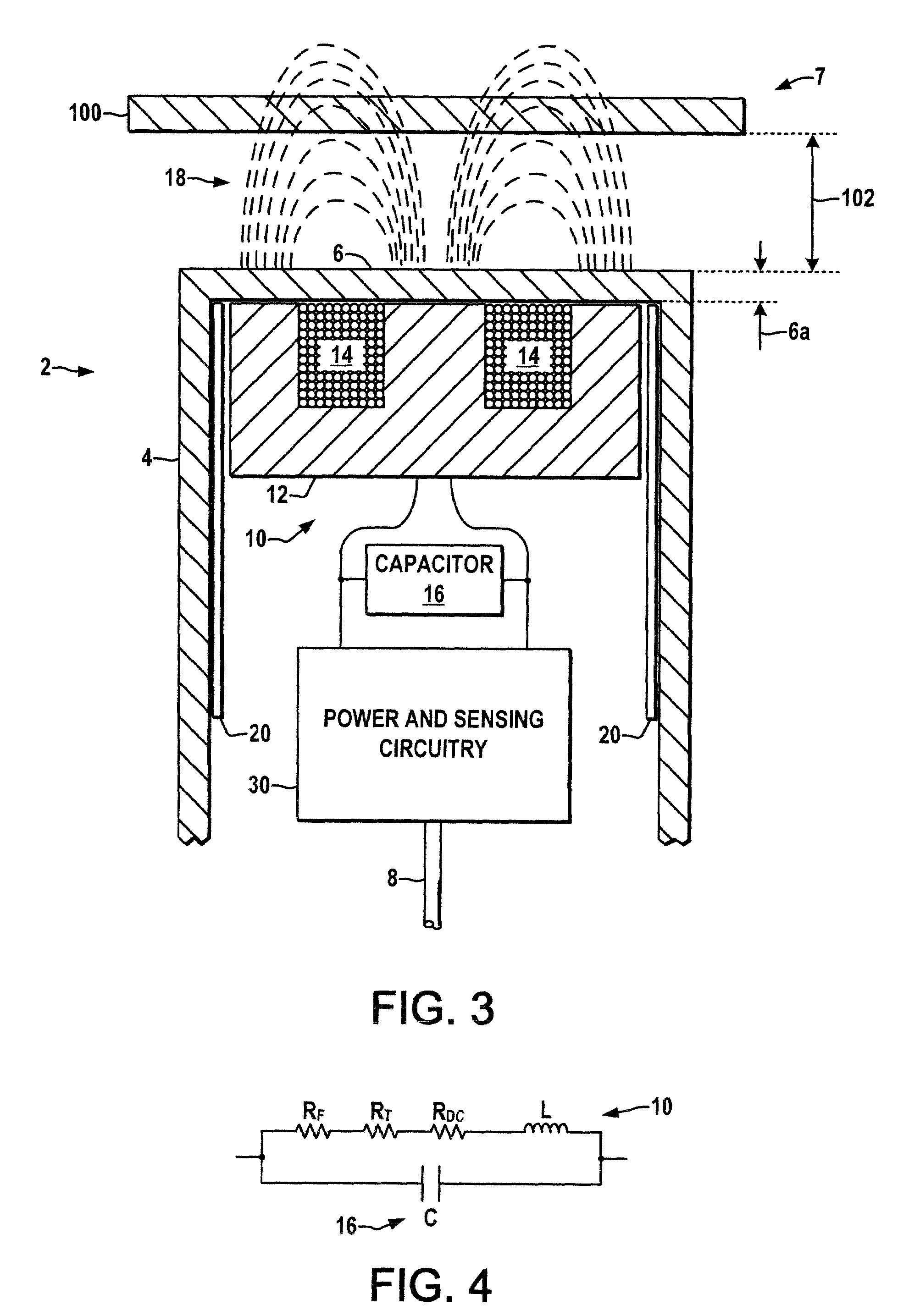
Hybrid 3-D probe tracked by multiple sensors
InactiveUS6611141B1Surgical navigation systemsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMultiple sensorQuantum system
This invention is a system that tracks the 3-dimensional position and orientation of one or more bodies (20) in a volume by a light based as well as at least one non-light based mensuration sub-system. This overcomes the limitation of light based mensuration systems to the necessity of the bodies (20) to be in constant line-of-sight of its light based position sensors (26). The invention possesses most of the accuracy and stability of its light based position measurement sub-system (24, 26, 72), but can also work without direct line of sight either for short periods of time or within certain parts of the volume. It does so by incorporating other sensors (31, 34), such as inertial or magnetic, which are frequently recalibrated against the light based sub-system (24, 26, 72) while the bodies (20) are visible by the light based sub-system (24, 26, 72).
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Magnetic field permeable barrier for magnetic position measurement system
InactiveUS6246231B1SurgeryElectric/magnetic position measurementsOrientation measurementMetallic Object
A magnetic field position and orientation measurement system contains, confines and re-directs the magnetic field from one or more transmitters such that the fields are attenuated in areas outside of the operating volume in areas where metallic objects are commonly found. A thin barrier made of a highly permeable material such as ferrite or mumetal is placed on top of a conductive plate. The thickness of the permeable layer is from 0.01 inches to 0.25 inches while the conductive plate, preferably made of an aluminum alloy, may preferably be from {fraction (3 / 16)} of an inch to ¼ inch in thickness. On top of the permeable barrier, a rhombic three axis transmitter is placed. In the preferred embodiment, the transmitter consists of a PC board carrying the transmitter. PC boards having thicknesses varying from 0.03125-0.125 inches may be employed. Thus, the entire "stack" including the transmitter, the permeable barrier and the conductive plate may only be from ½ inch to ⅝ of an inch in thickness. The permeable barrier may have a flat, planar configuration. Alternatively, it may be made to resemble, in cross-section, a cake pan having a flat central region with uplifted peripheral edges. Alternatively, the permeable barrier may have a generally flat configuration with peripheral edges that taper outwardly from the top surface thereof to the bottom surface thereof with the taper making an angle with the bottom surface in the range of, preferably, 30° to 85°.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
Detection of metal disturbance in a magnetic tracking system
InactiveUS7321228B2Improve accuracyPosition fixationDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic trackingComputational physics
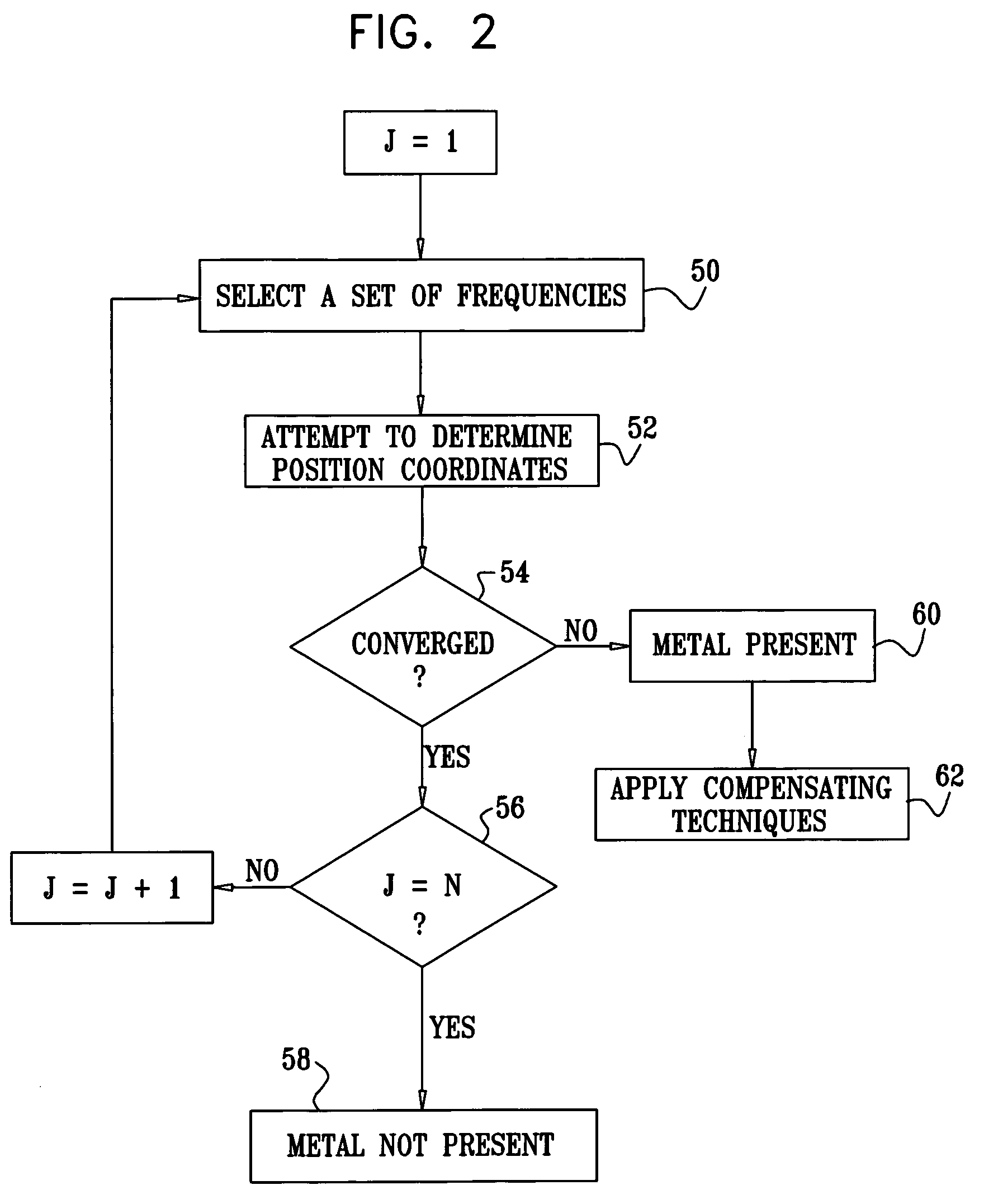
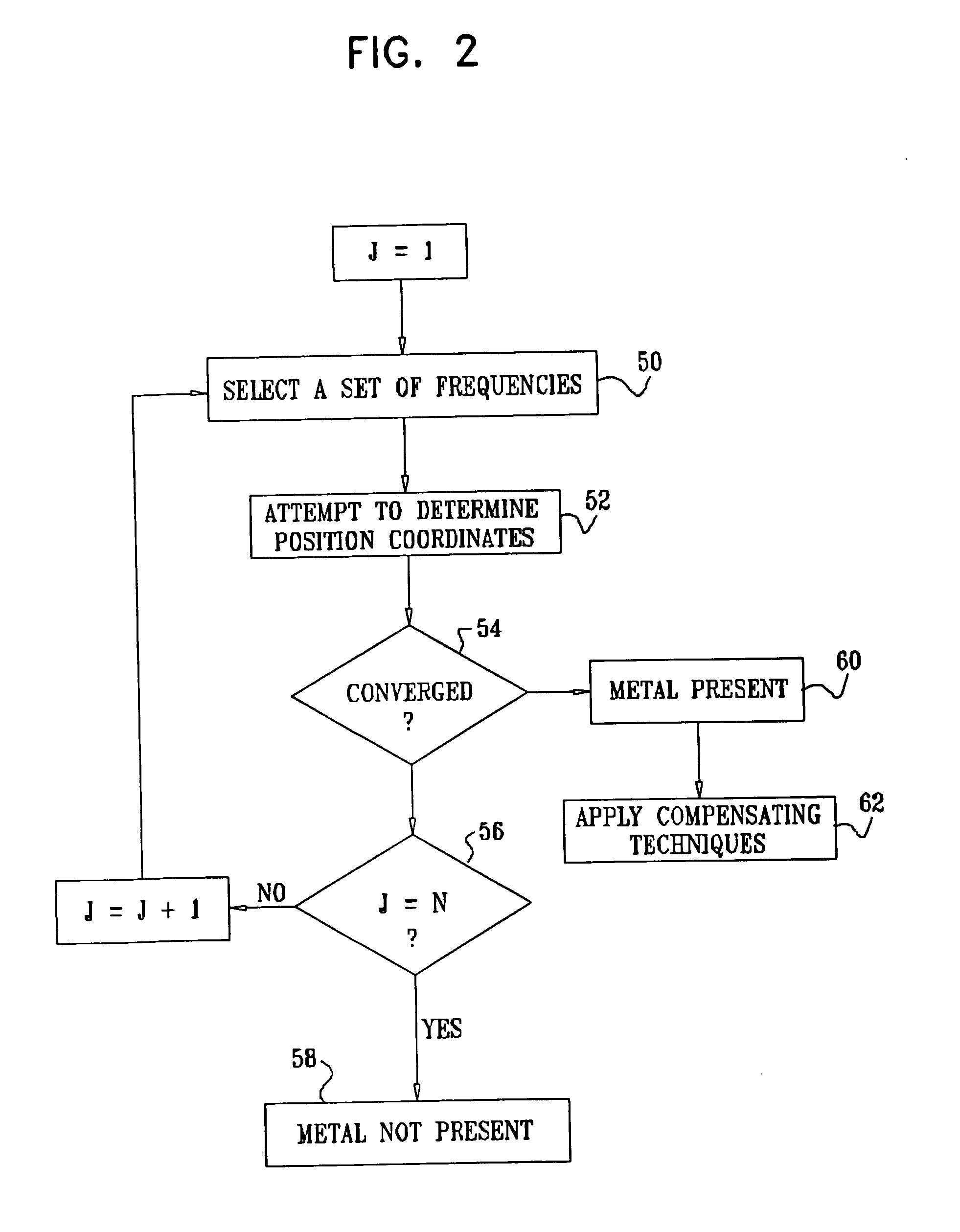
A method for tracking an object includes producing energy fields at a plurality of different frequencies in a vicinity of the object, and receiving signals that are generated at a location of the object at the different frequencies in response to the energy fields. Multiple computations are made of spatial coordinates of the object based on the signals received at the different frequencies. Convergence of the computations is tested in order to ascertain whether the energy fields have been perturbed by an article in the vicinity of the object.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Position detection using a spaced apart array of magnetic field generators and plural sensing loop circuits offset from one another in the measurement direction
InactiveUS6124708AReduce manufacturing costReduce sensitivityElectric signal transmission systemsUsing electrical meansElectrical conductorEngineering
Owner:SINNAPTIX
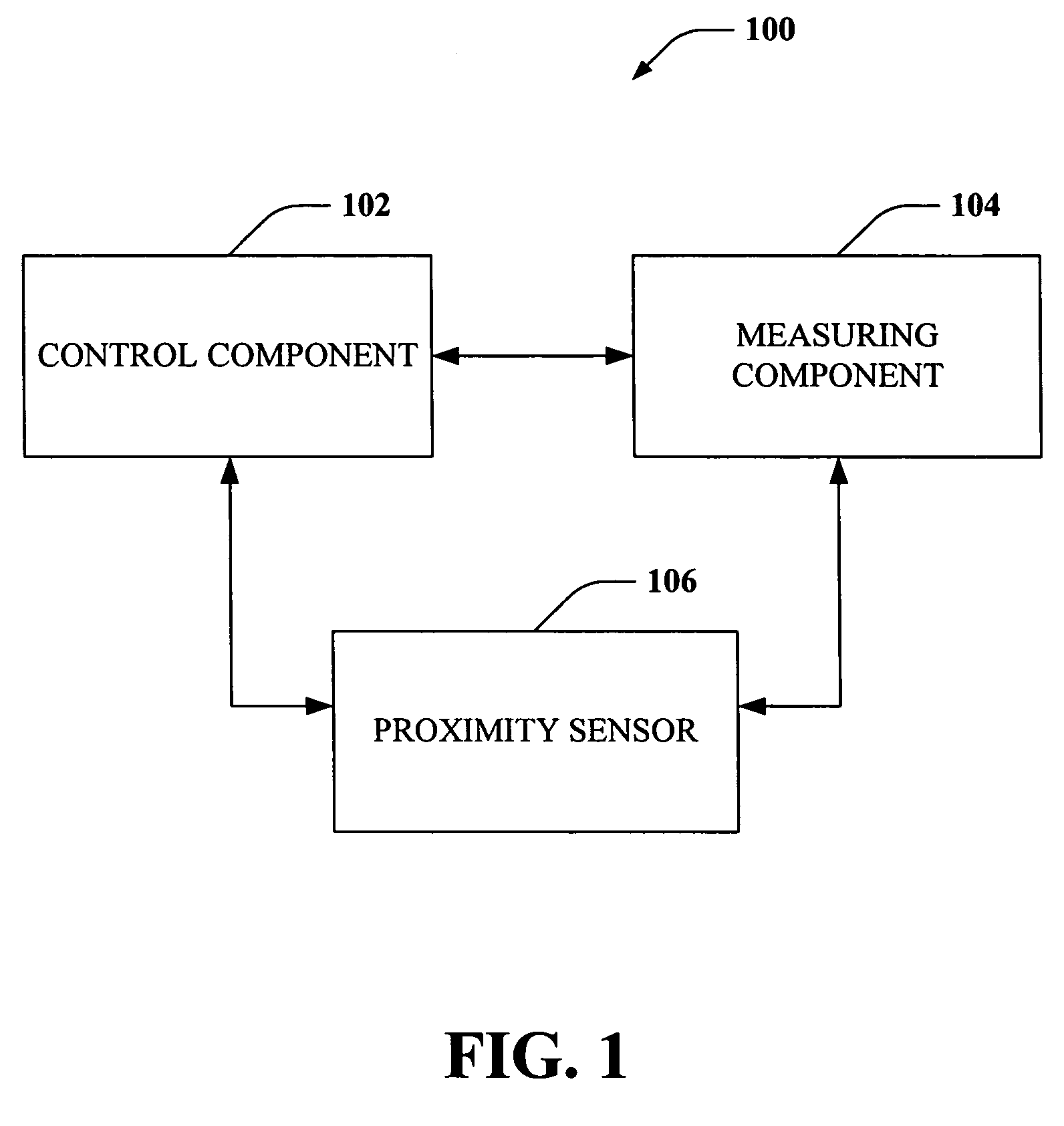
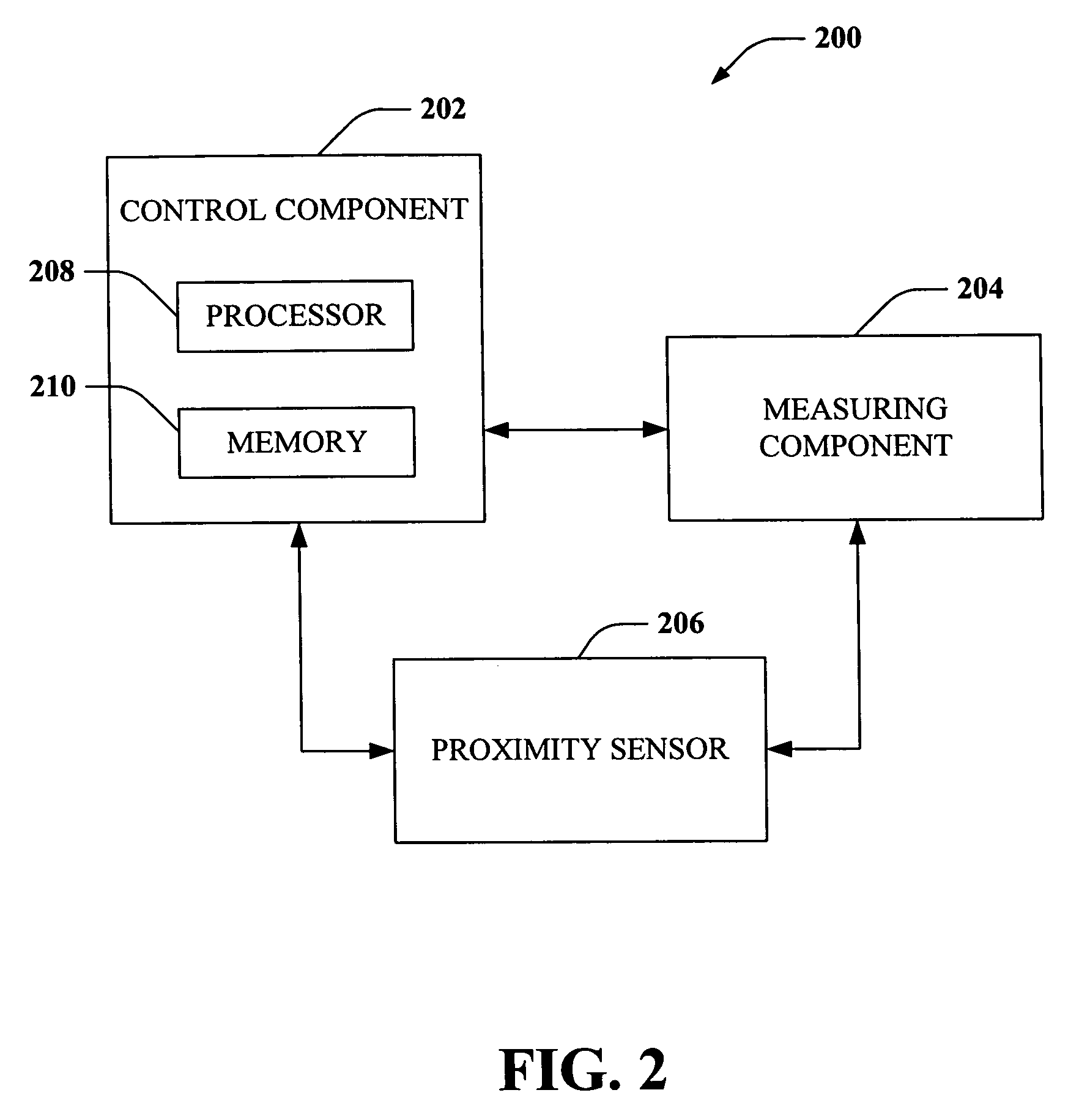
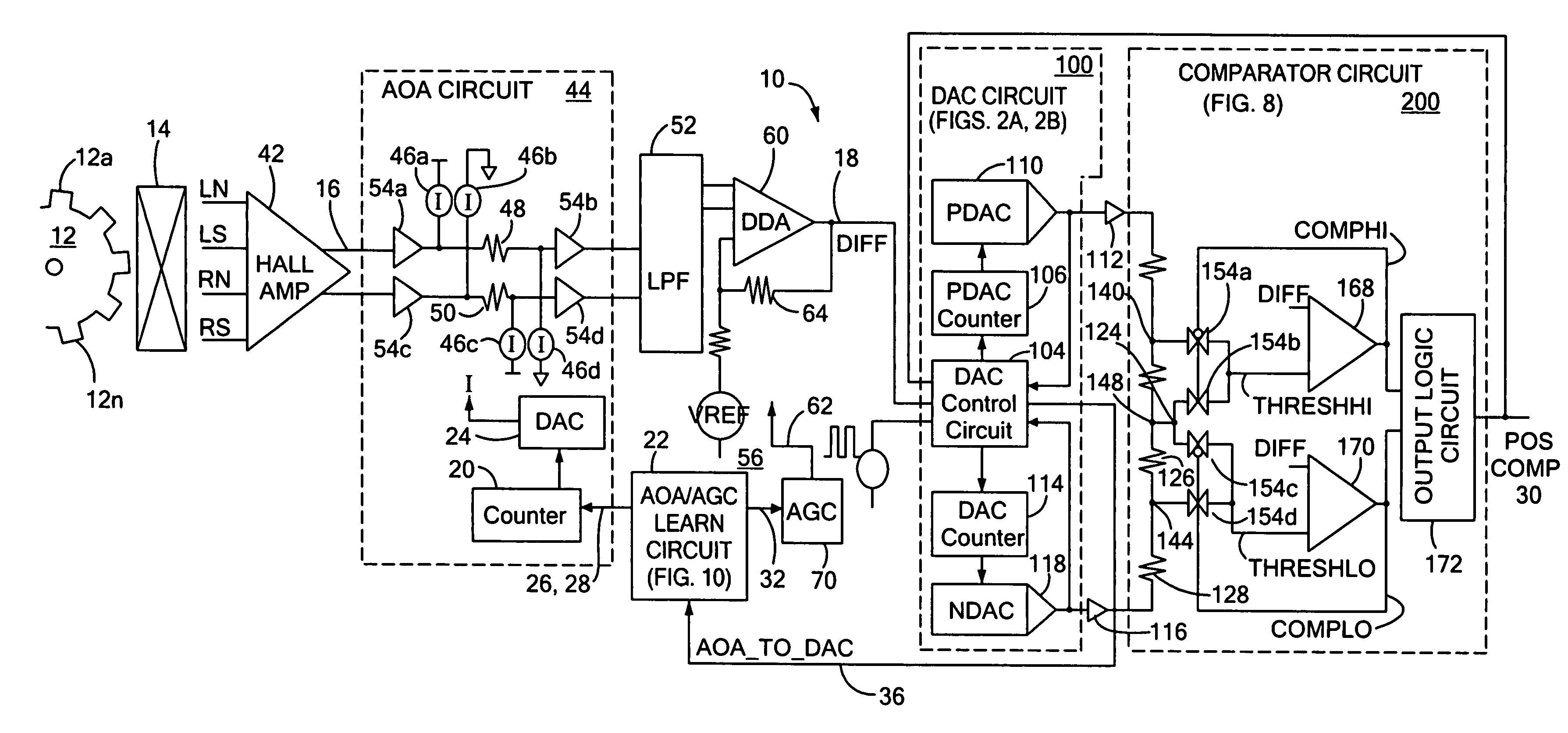
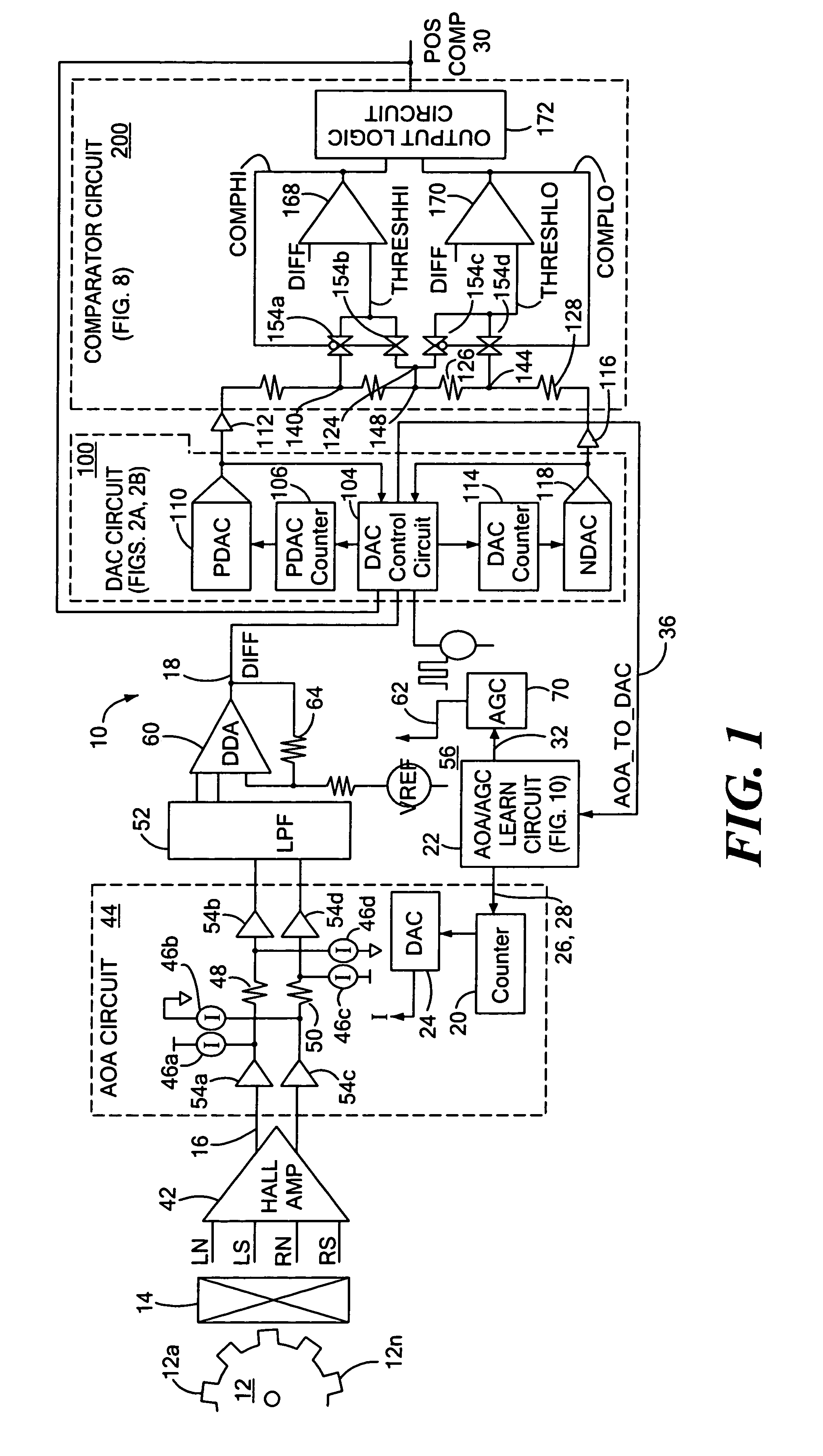
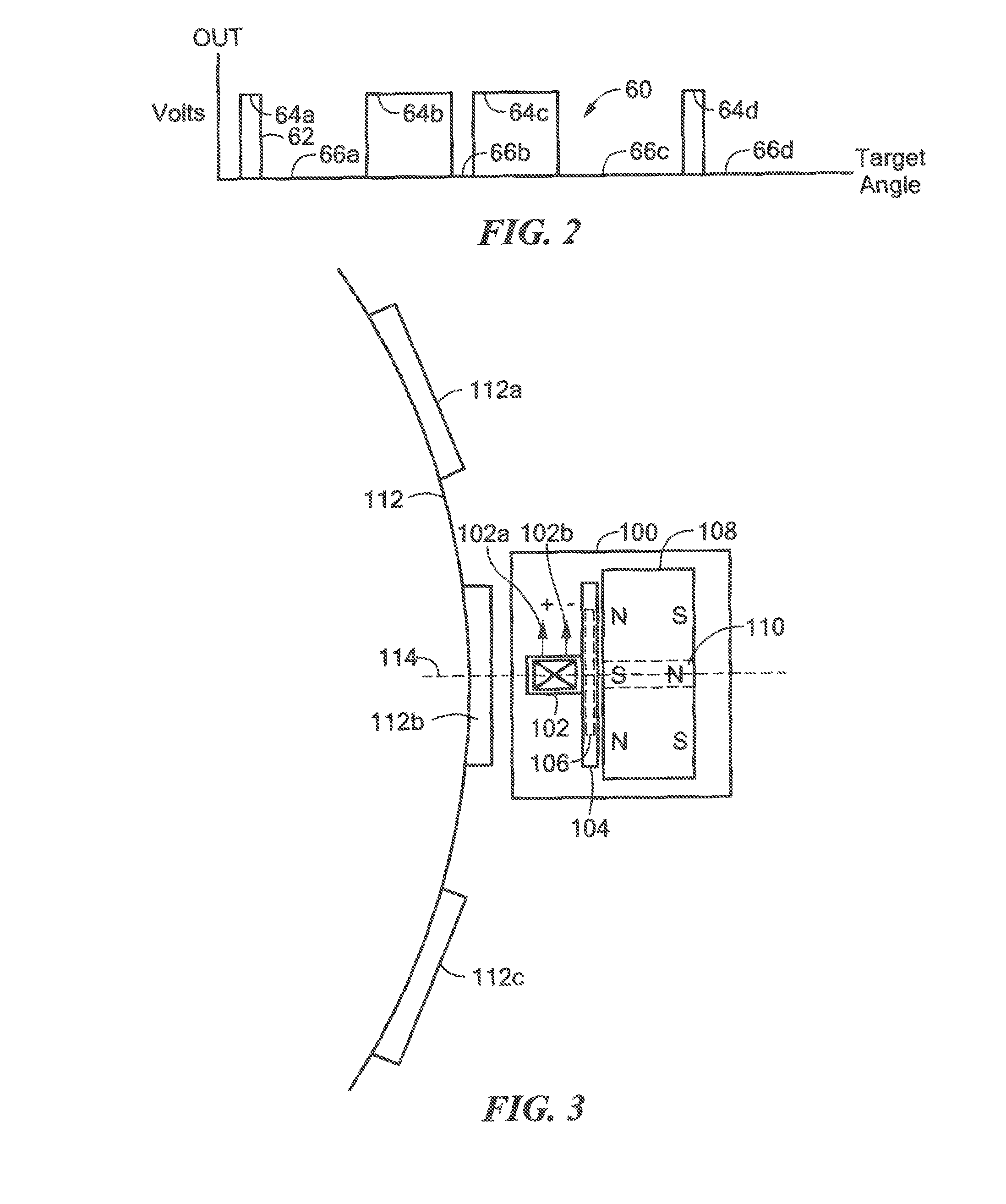
Proximity detector
ActiveUS7199579B2Accurate trackingReduce signalingMagnetic property measurementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringOperation mode
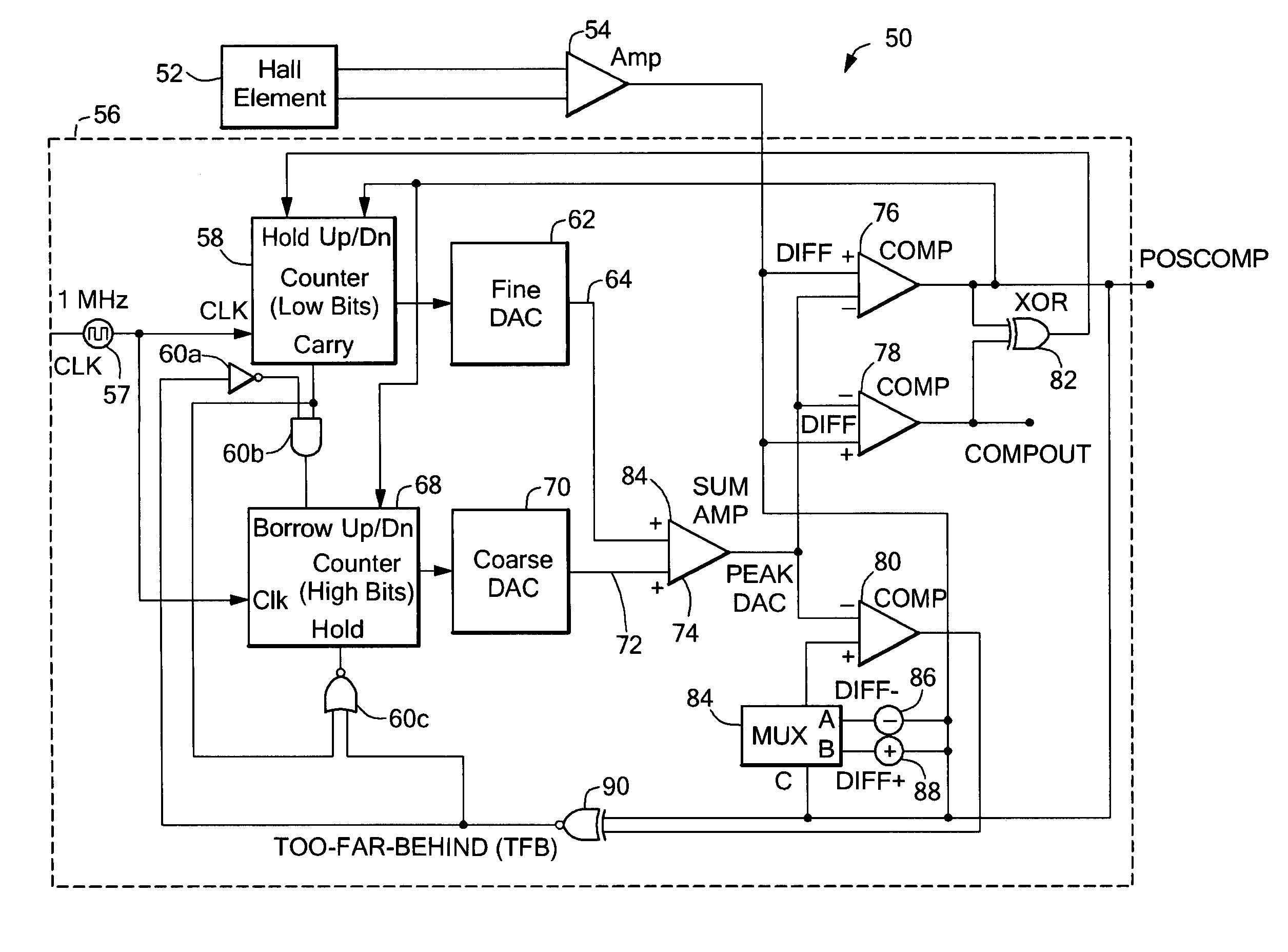
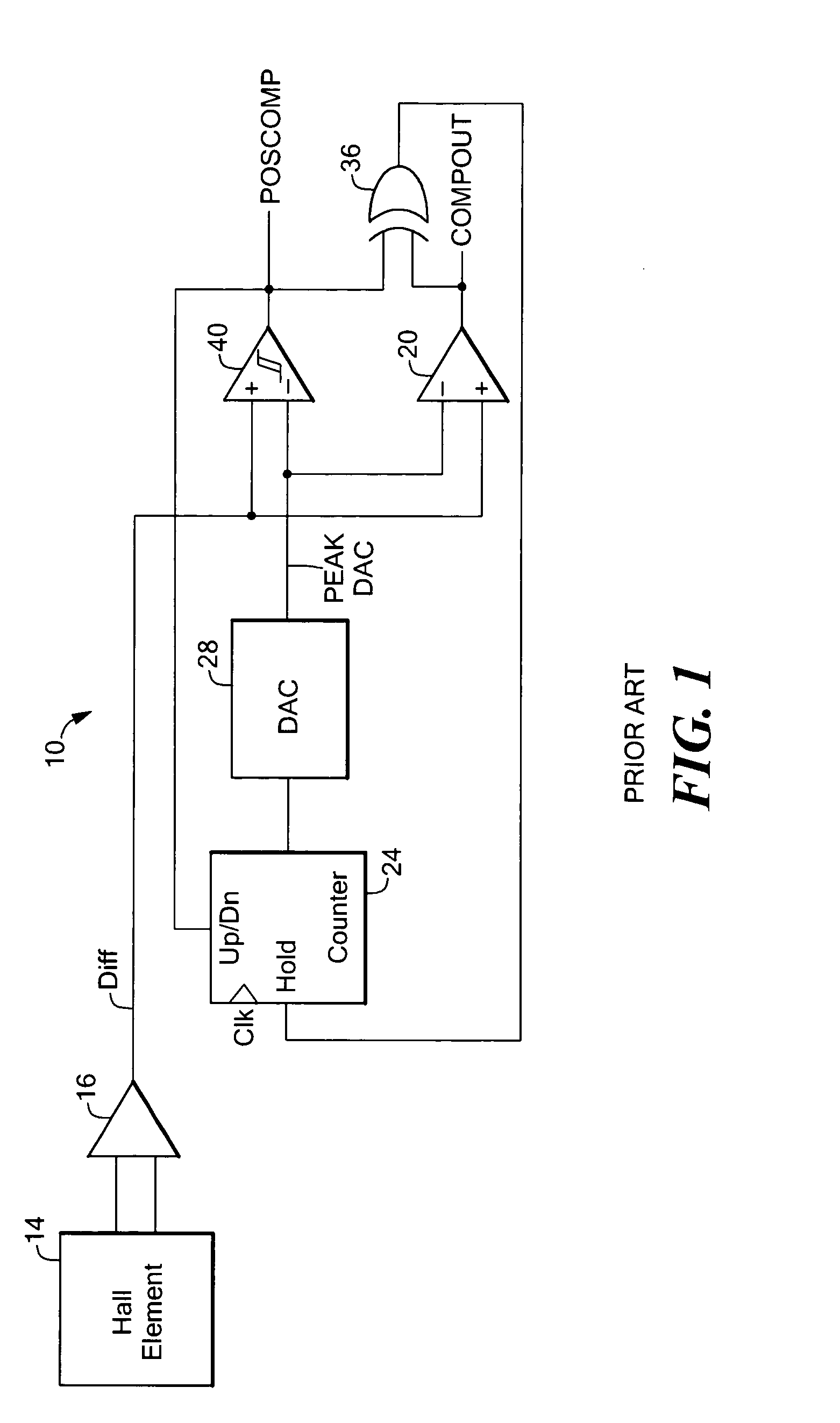
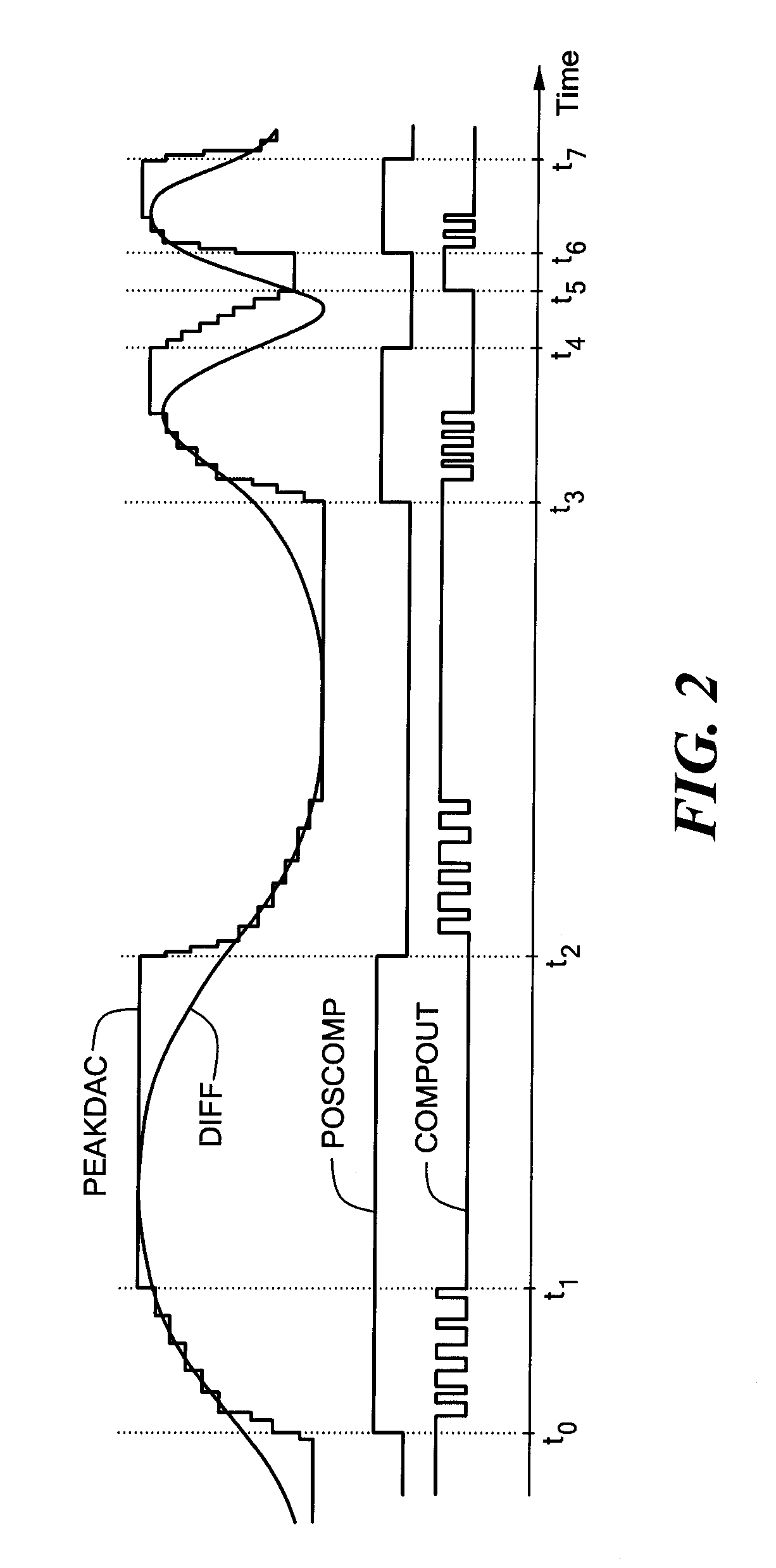
A proximity detector includes a fine DAC and a coarse DAC, outputs of which are summed to provide a tracking signal for tracking a magnetic field signal. The proximity detector provides two mode of operation. In a first mode of operation the coarse and fine DACs operate in combination as one higher order DAC. In a second mode of operation, the coarse DAC is provided with one or more extra counts, allowing the tracking signal to move more rapidly to track a rapidly changing magnetic field signal. In another embodiment, the proximity detector also includes an offset circuit for bringing at least one of the magnetic field signal and the tracking signal towards the other one of the magnetic field signal and the tracking signal.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
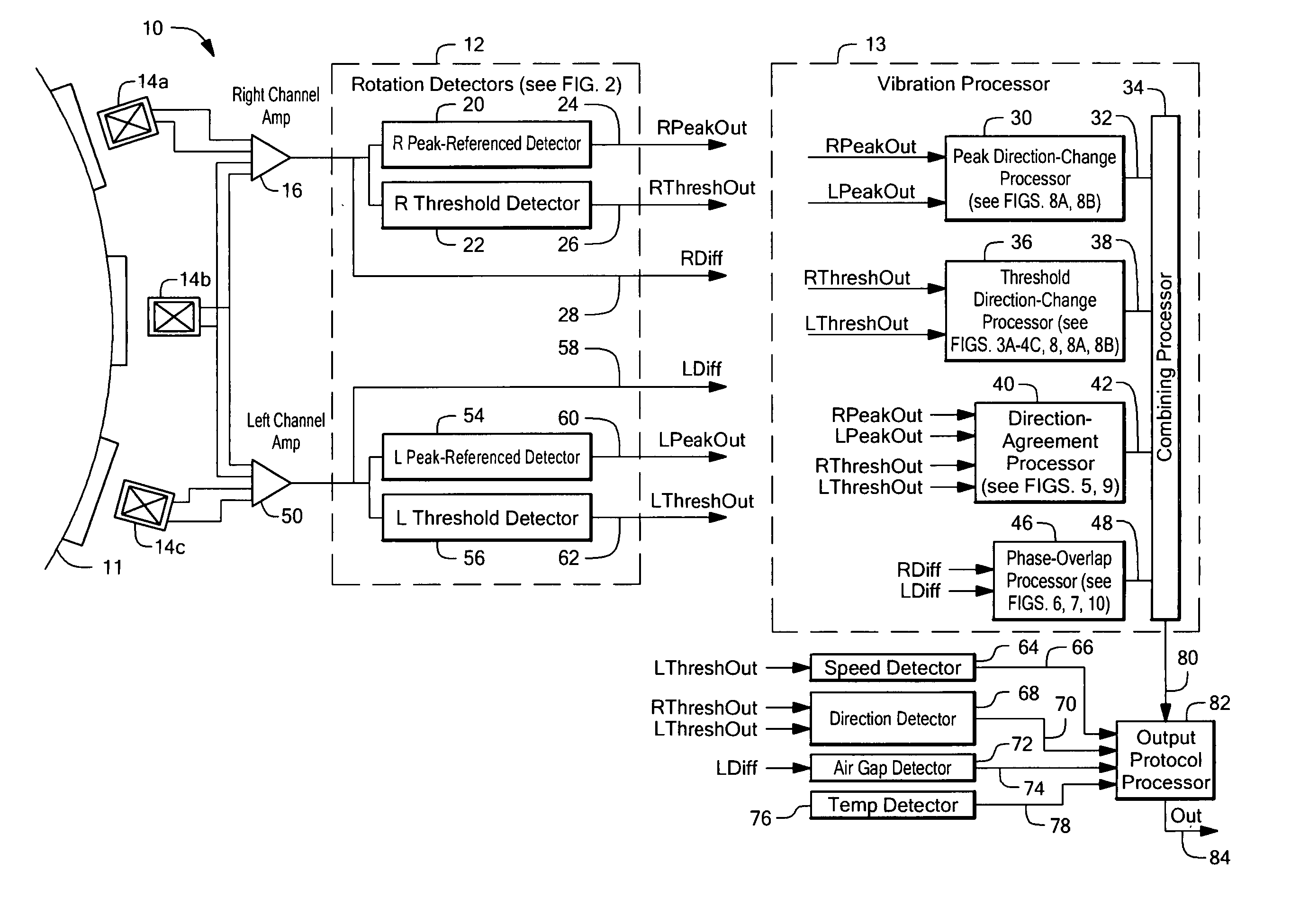
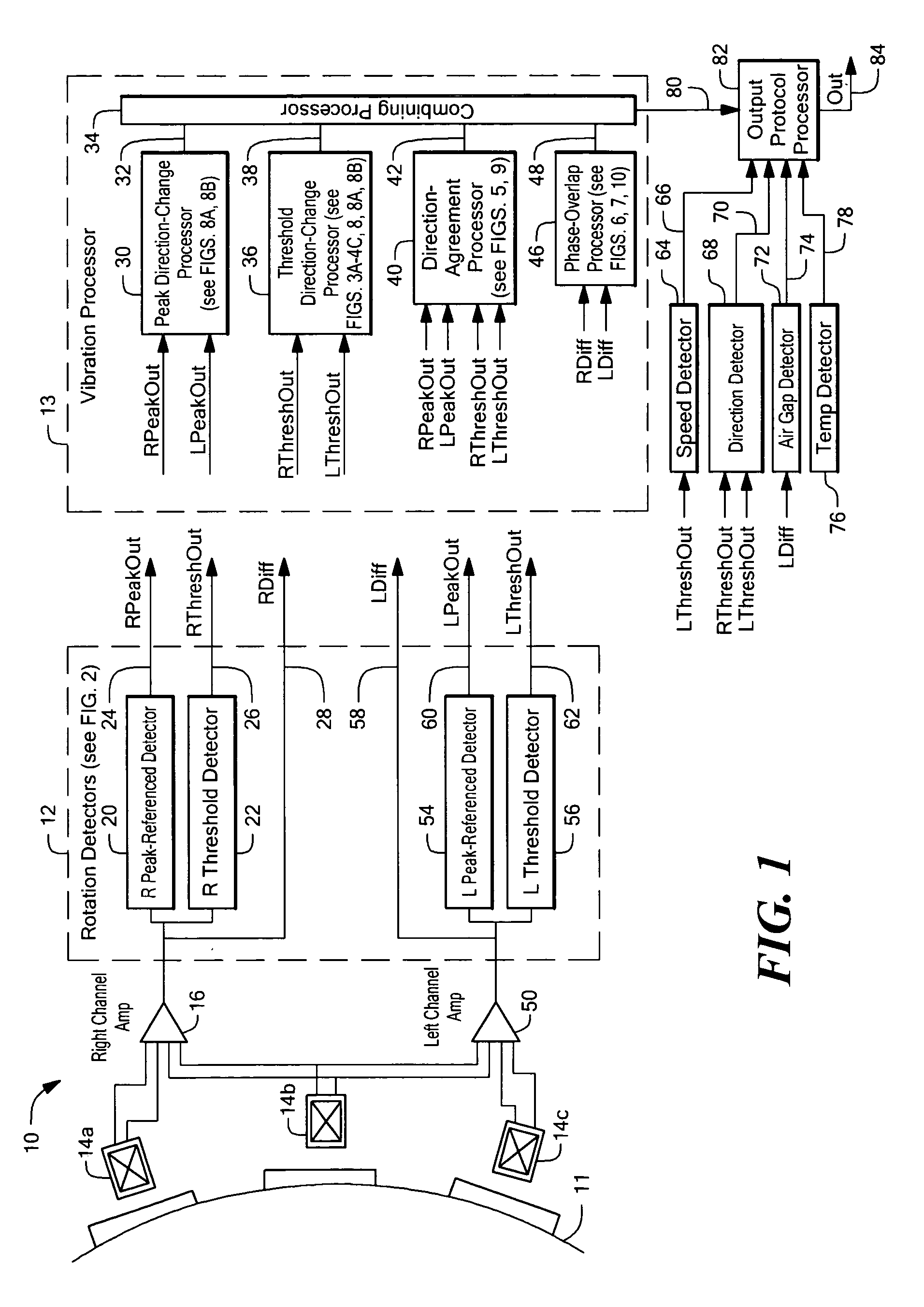
Method and apparatus for vibration detection
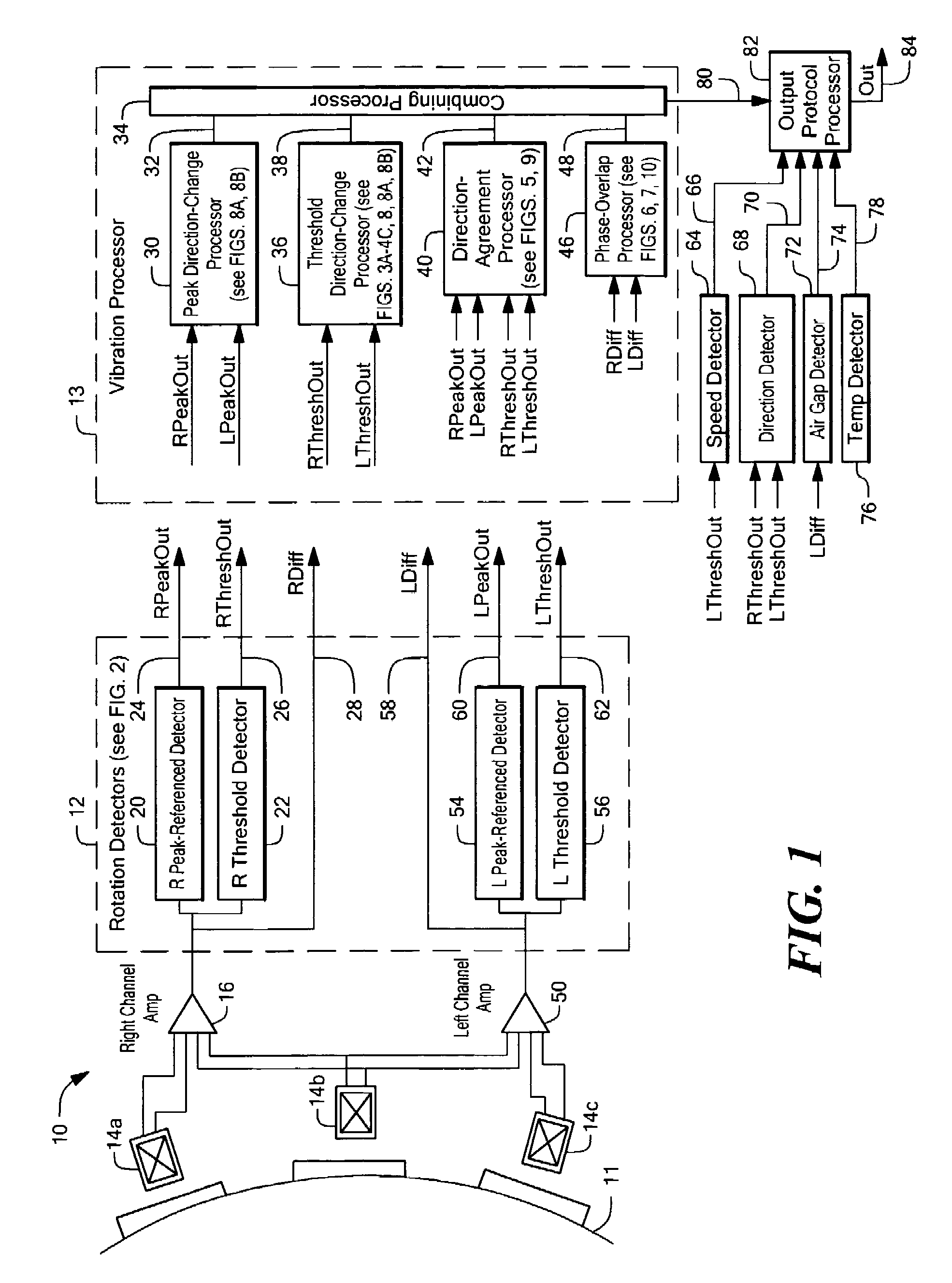
ActiveUS7365530B2Vibration measurement in solidsUsing electrical meansClassical mechanicsVibration detection
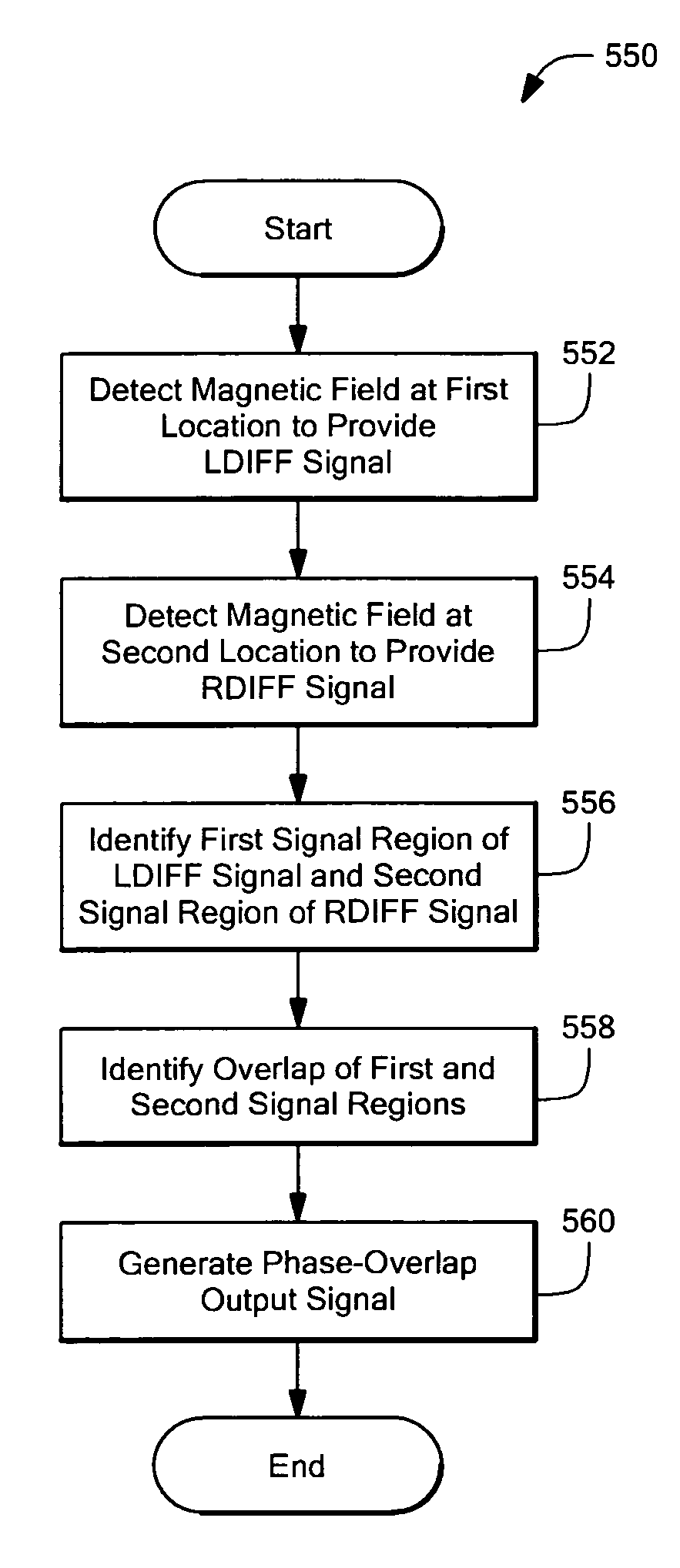
Apparatus for detecting vibration of an object adapted to rotate includes one or more vibration processors selected from: a direction-change processor adapted to detect changes in a direction of rotation of the object, a direction-agreement processor adapted to identify a direction of rotation of the object in at least two channels and identify an agreement or disagreement in direction of rotation identified by the at least two channels, a phase-overlap processor adapted to identify overlapping signal regions in signals associated with the rotation of the object, and a running mode processor adapted to identify an unresponsive output signal from at least one of the at least two channels. A method for detecting the vibration of the object includes generating at least one of a direction-change output signal with the direction-change processor, a direction-agreement output signal with the direction-agreement processor, a phase-overlap output signal with the phase-overlap processor, and a running-mode-vibration output signal with the running-mode processor, each indicative of the vibration the object.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
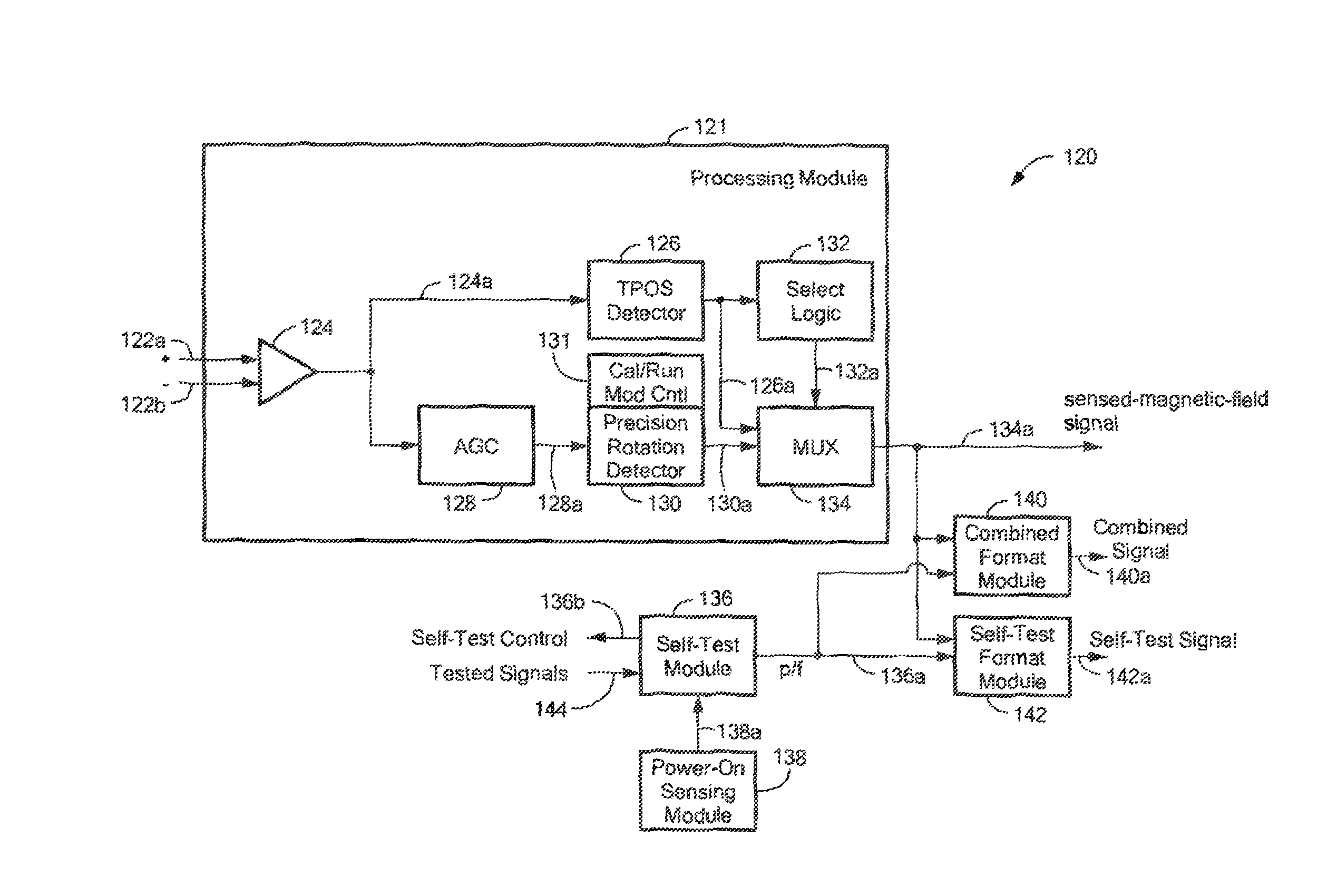
Magnetic Field Sensors and Related Techniques That Can Provide Self-Test Information in a Formatted Output Signal
A magnetic field sensor can provide an output signal indicative of a passing condition or a failing condition of the magnetic field sensor. The output signal has one of a variety of output signal formats.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Multi-sensor distortion detection method and system
InactiveUS20080183064A1Electric/magnetic position measurementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringFixed position
A method for detecting EM field distorting includes sampling a sensor assembly positioned within a volume of interest to acquire measurements of EM fields within the volume of interest, and monitoring the measurements to detect EM field distortion within the volume of interest. The sensor assembly includes a set of EM transmitters and a set of EM receivers fixed thereon. A system for detecting EM field distorting includes a sensor assembly for positioning within a volume of interest, wherein the EM sensor assembly comprises a set of EM receivers, and a set of EM transmitters, wherein the EM receivers and the EM transmitters are disposed at fixed locations on the sensor assembly. The system further includes a tracker configured to sample the sensor assembly to acquire measurements of EM fields generated by the EM transmitters, and monitor the measurements to detect EM field distortion within the volume of interest.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic field sensor and method for operating the magnetic field sensor
InactiveUS7259556B2Reduce core volumeWeaken energyMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMagnetizationElectrical current
A magnetic field sensor for the measurement of at least one component of a magnetic field comprises a ferromagnetic core that serves as a magnetic field concentrator, an excitation coil and a read-out sensor. The read-out sensor preferably comprises two sensors arranged in the vicinity of the outer edge of the ferromagnetic core and measures the at least one component of the magnetic field. The ferromagnetic core is ring-shaped or disc-shaped. On operation of the magnetic field sensor, a current is temporarily applied to the excitation coil in order to bring the ferromagnetic core into a state of predetermined magnetization in which the magnetization of the ferromagnetic core produces no signal in the read-out sensor.
Owner:MELEXIS TECH NV
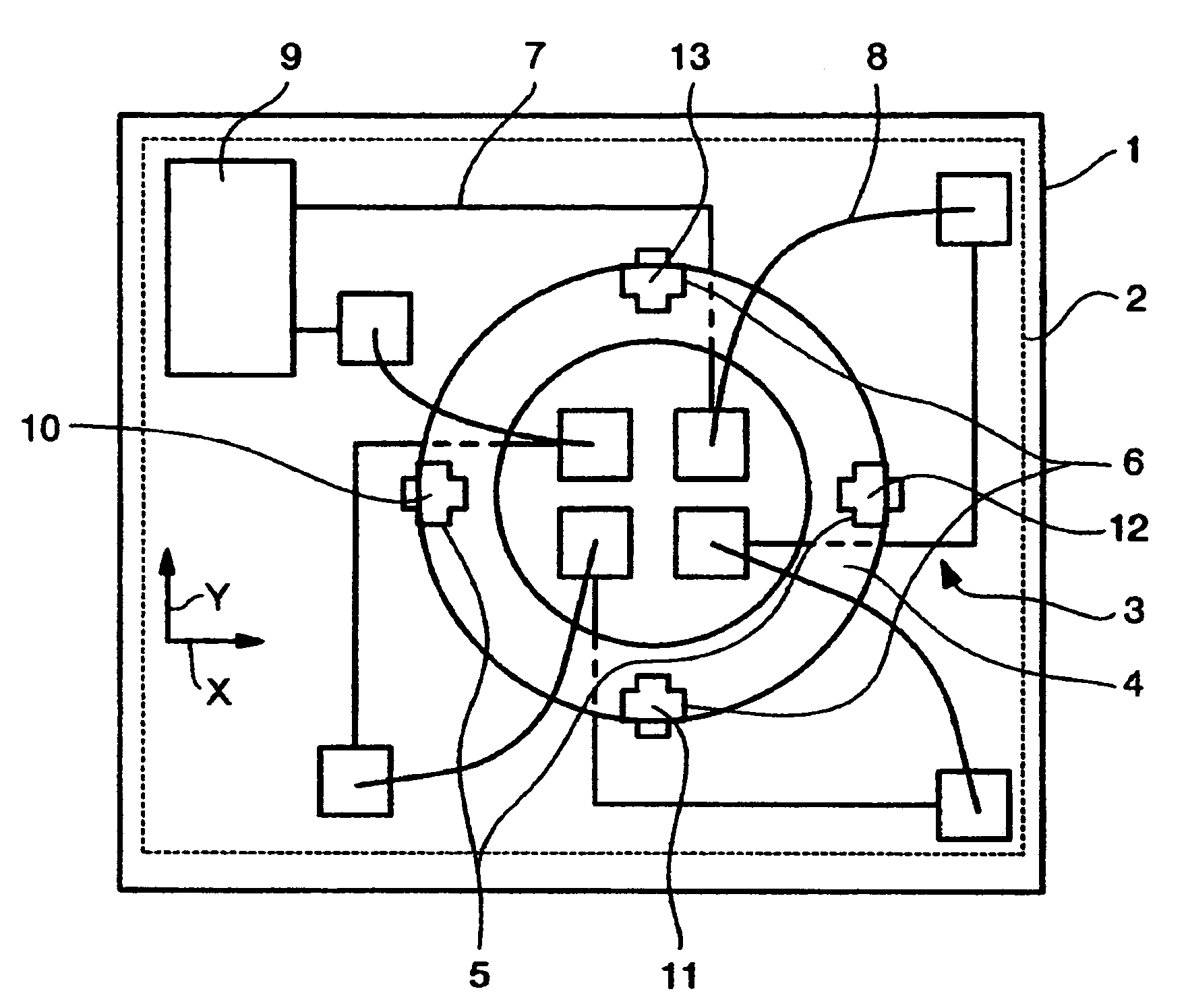
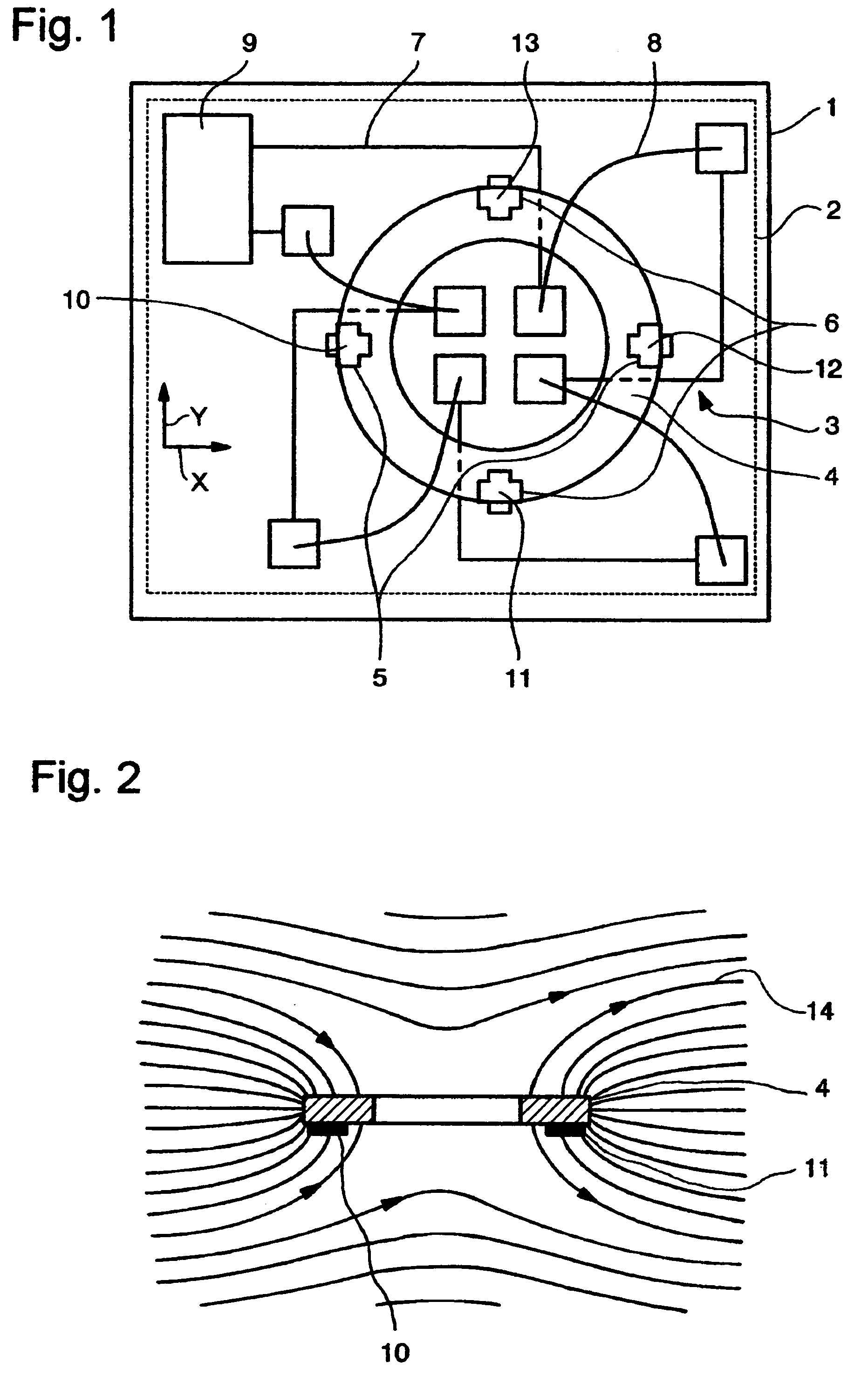
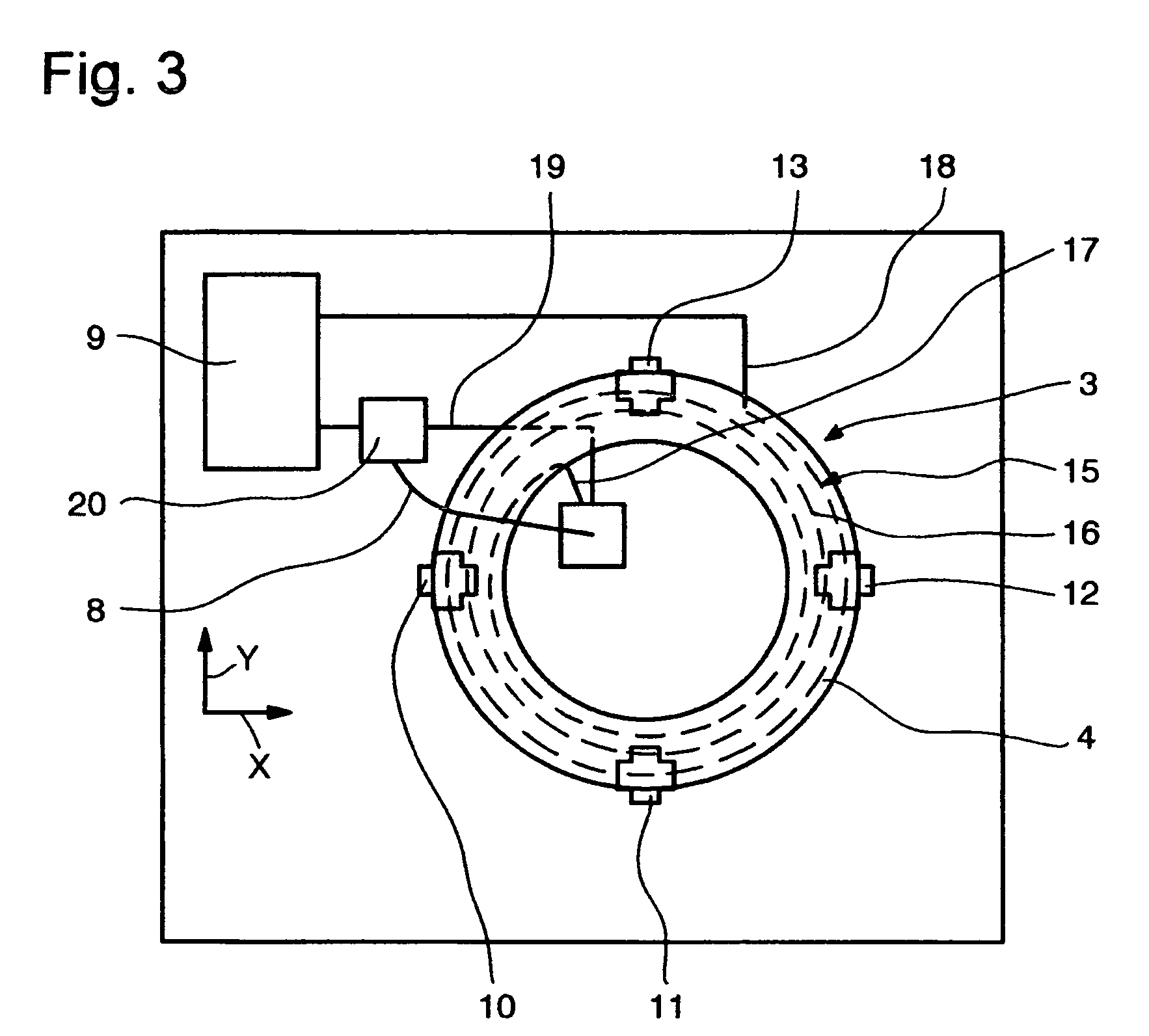
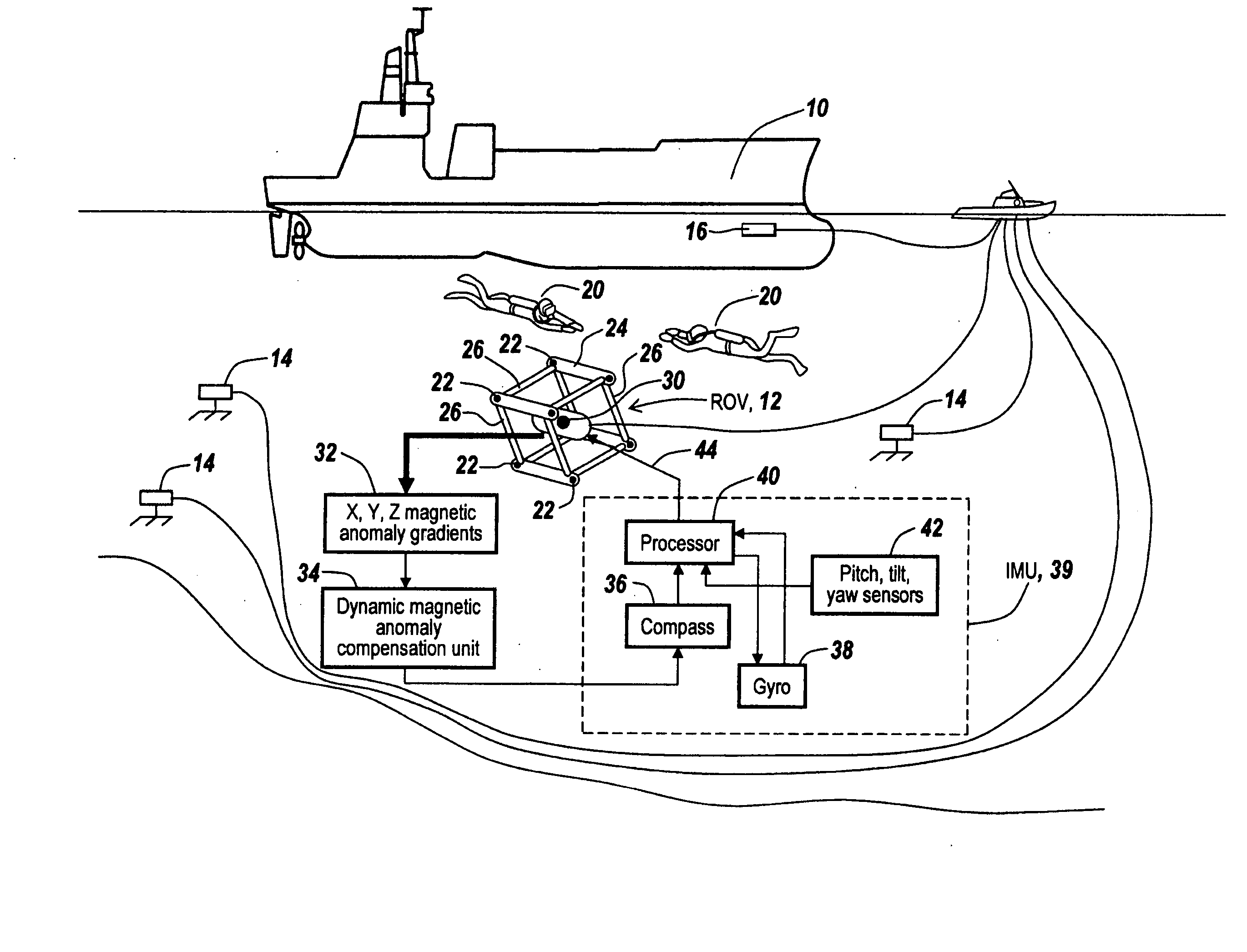
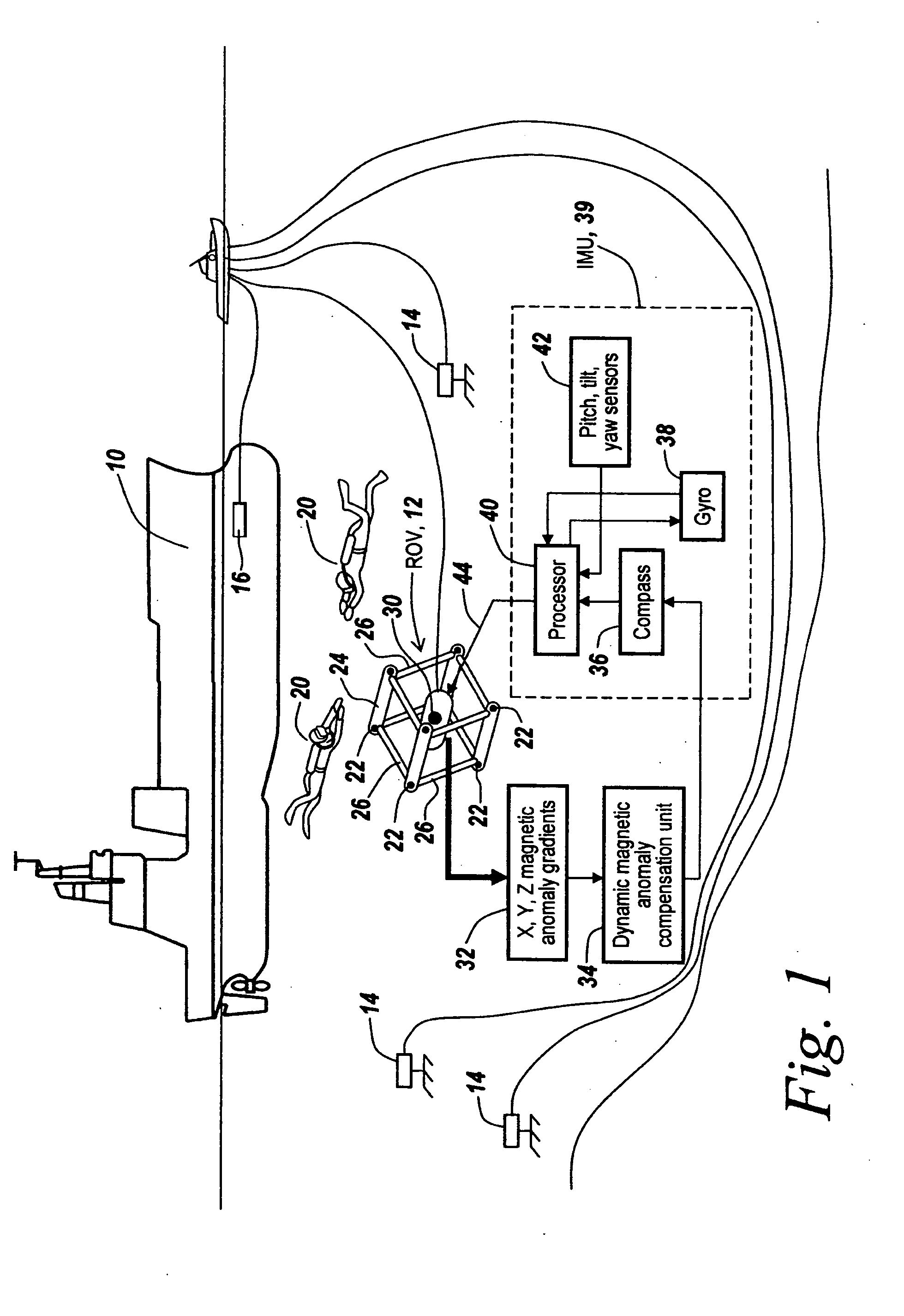
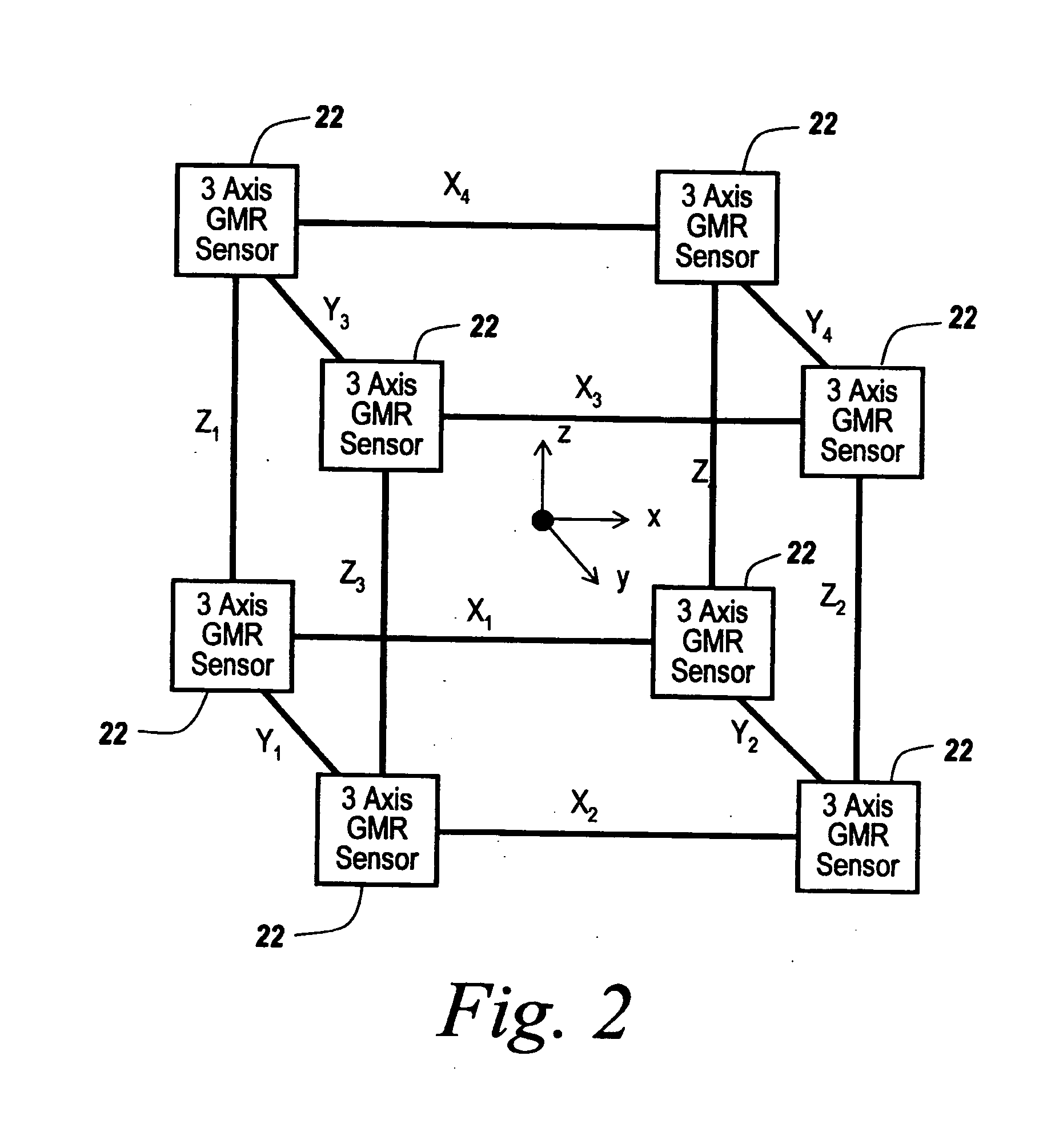
Dynamic magnetic anomaly compensation
InactiveUS20050099177A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionGyroscopeControl signal
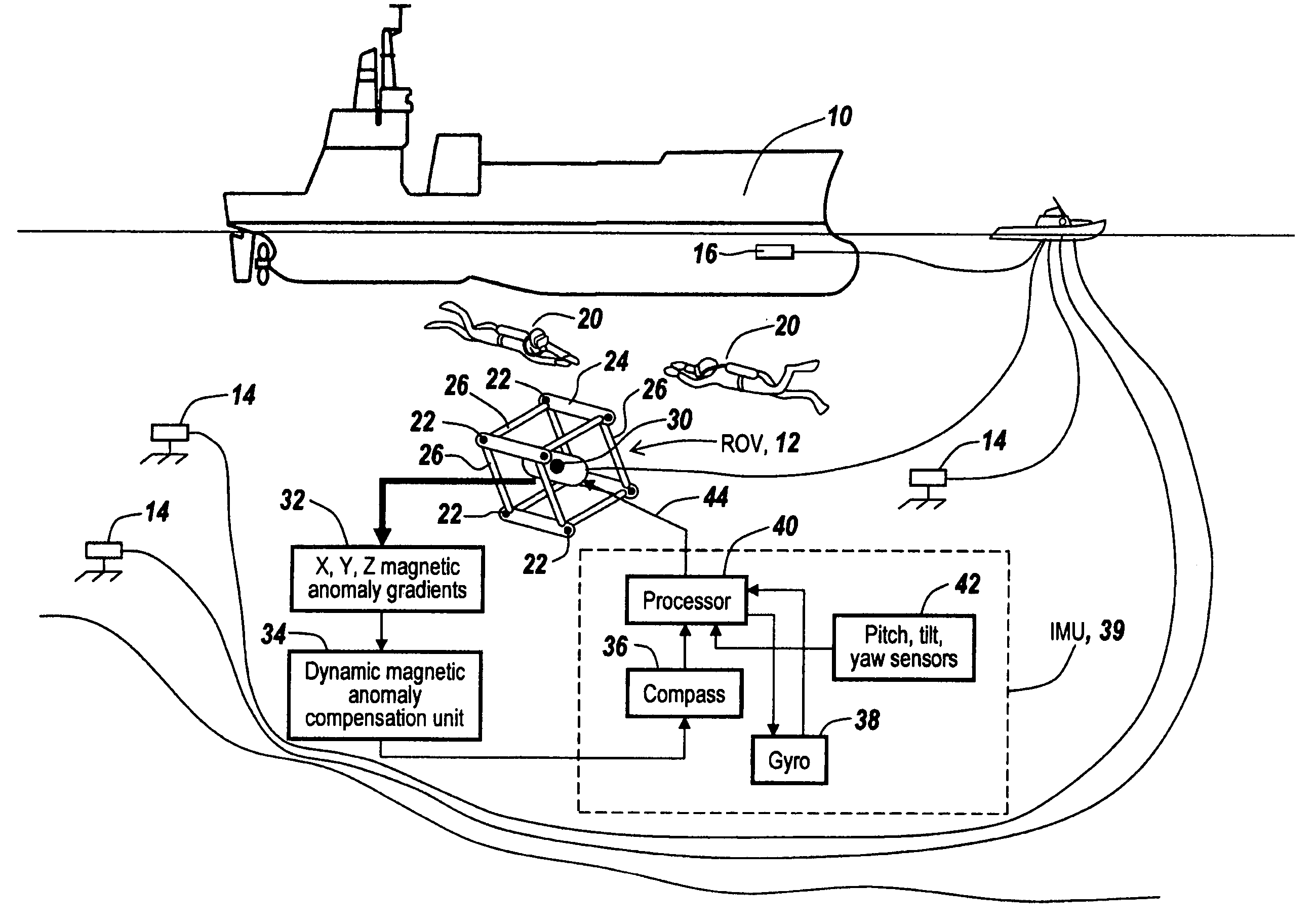
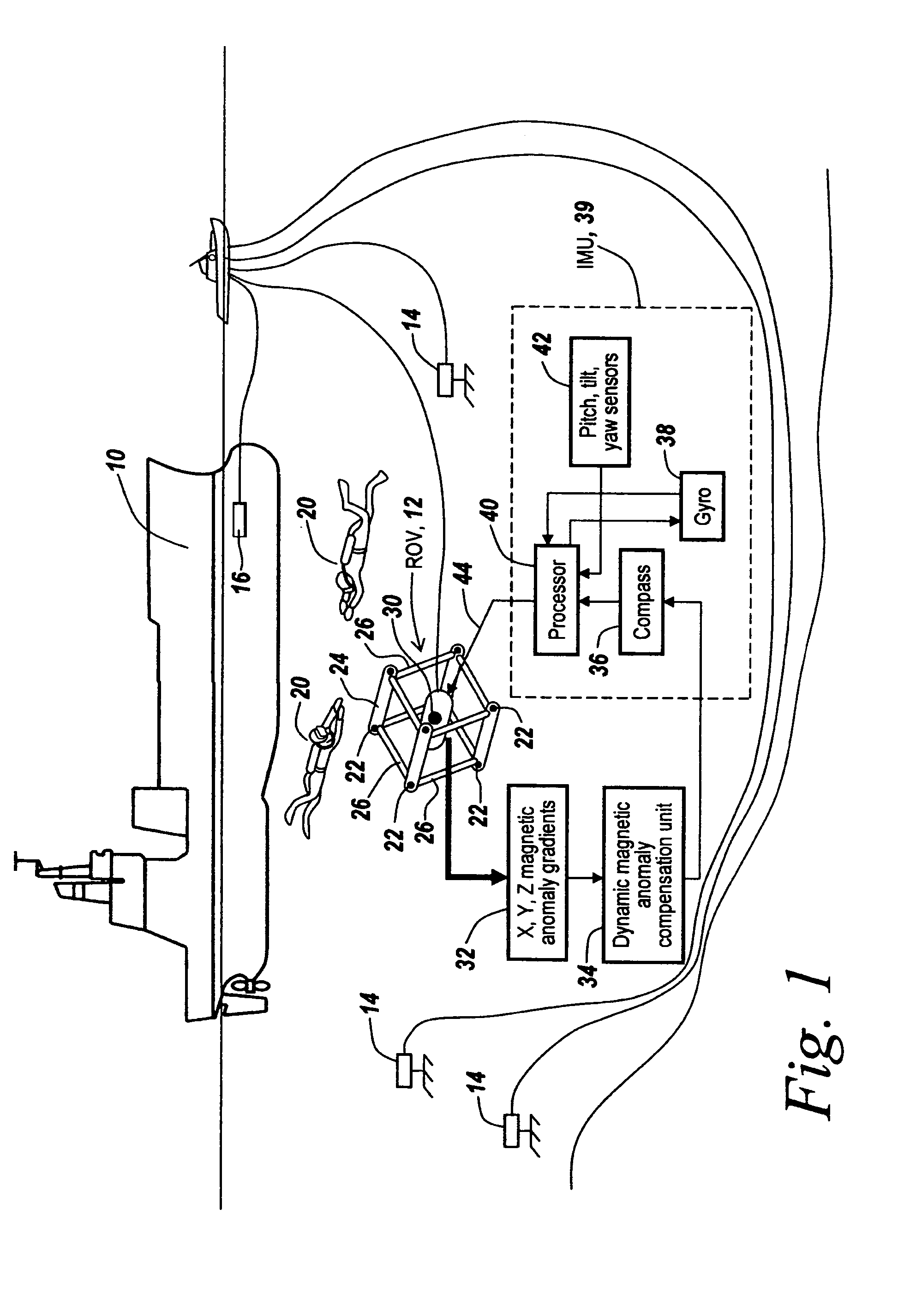
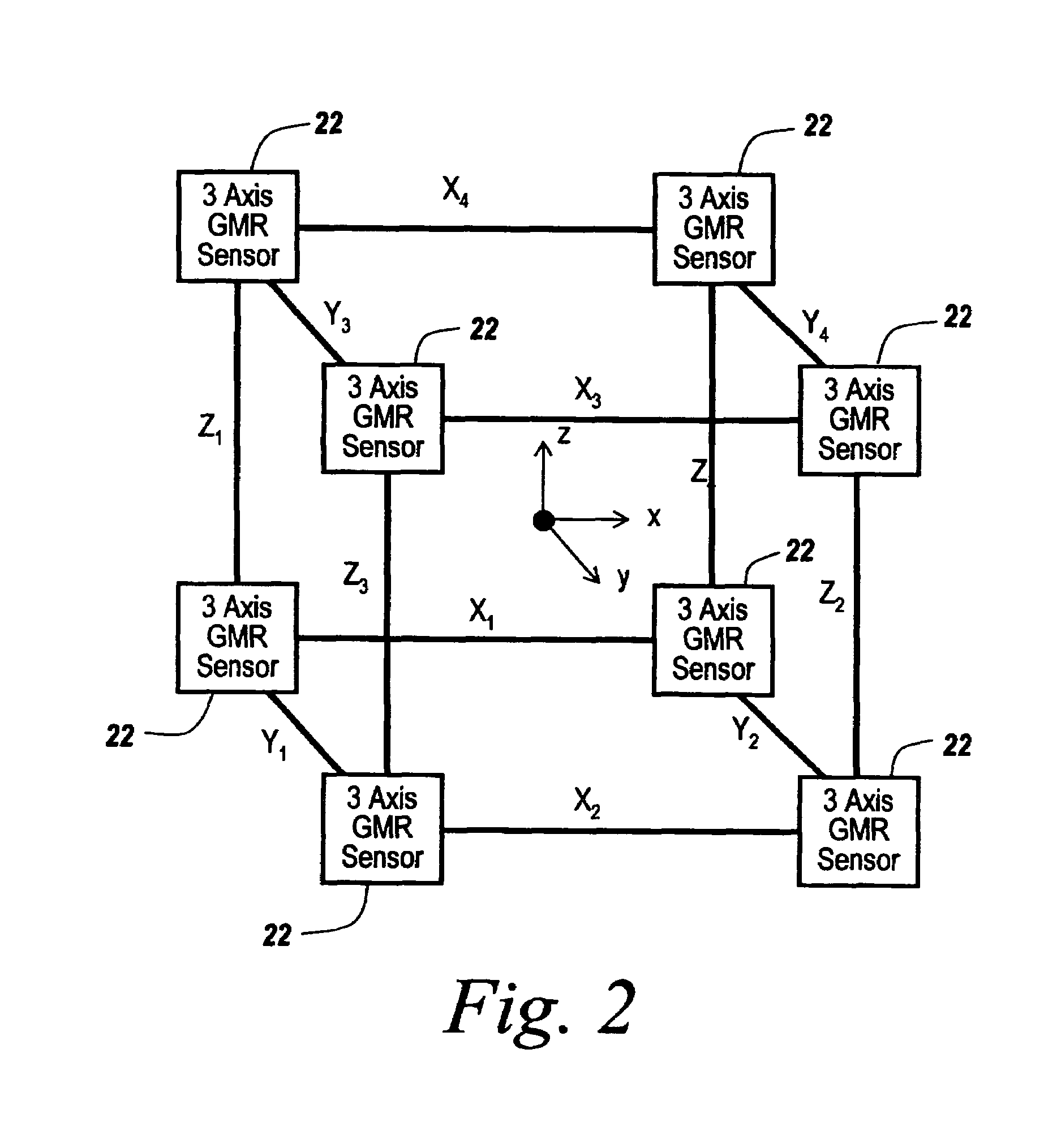
An array of three-axis magnetometers used for dynamic magnetic anomaly compensation are located at the corners of a parallelopiped, with pairs of magnetometer outputs used to derive a magnetic anomaly gradient vector used to compensate a compass and / or the output of a gyroscope in an inertial management unit. The system may be used in a neutrally buoyant remotely operated vehicle to permit ascertaining of course and position in the absence of surface control signals.
Owner:SONICWORKS
Methods and apparatus for vibration detection
InactiveUS20050225318A1Vibration measurement in solidsUsing electrical meansClassical mechanicsVibration detection
Apparatus for detecting vibration of an object adapted to rotate includes one or more vibration processors selected from: a direction-change processor adapted to detect changes in a direction of rotation of the object, a direction-agreement processor adapted to identify a direction of rotation of the object in at least two channels and identify an agreement or disagreement in direction of rotation identified by the at least two channels, and a phase-overlap processor adapted to identify overlapping signal regions in signals associated with the rotation of the object. A method for detecting the vibration of the object includes generating at least one of a direction-change output signal with the direction-change processor, generating a direction-agreement output signal with the direction-agreement processor, and generating a phase-overlap output signal with the phase-overlap processor, each indicative of the vibration of the object.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Circuits and Methods for Calibration of a Motion Detector
ActiveUS20110048102A1Accurate identificationUsing electrical meansUsing mechanical meansMotion detectorTime segment
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
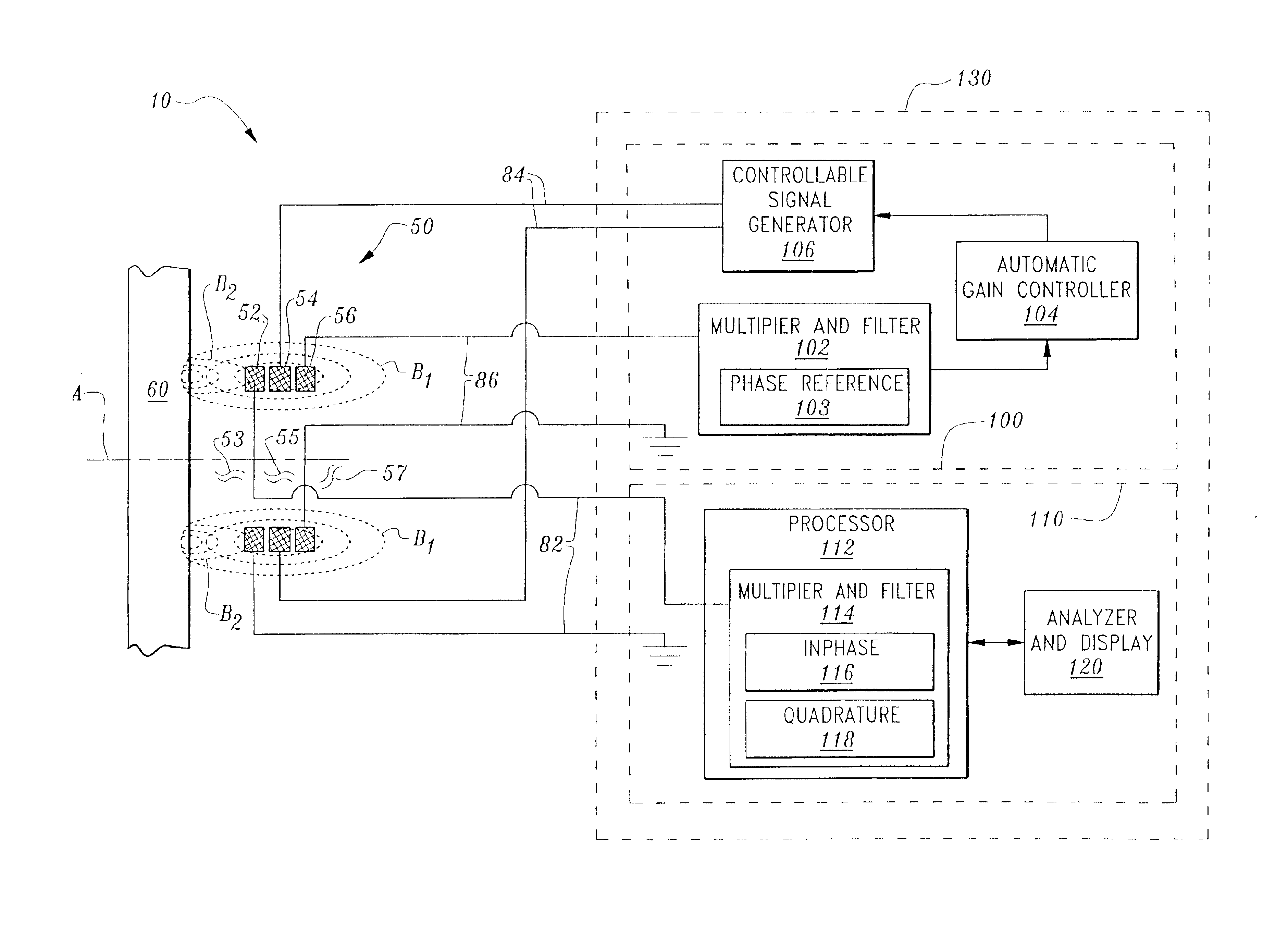
Airborne vector magnetic surveys
InactiveUS20050116717A1Reduce noiseImprove performanceStray field compensationAcoustic wave reradiationMagnetic tension forceMagnetic effect
An aircraft equipped for airborne vector magnetic exploration surveys comprising three magnetometers orthogonally mounted to measure the components of the earth's vector magnetic field; two rotation sensors mounted to measure the angular orientation of the aircraft; and a recording system to record the measurements of the magnetometers, and rotation sensors. The measured angular orientation is used to orientate the measured components of the earth's vector magnetic field to derive true vector acro-magnetic (VAM) data from airborne surveys. Also disclosed is a method for processing magnetic data by removing the permanent, induced, and eddy-current magnetic effects of the aircraft from the magnetic data.
Owner:FUGRO FINANCE
Current measuring device
ActiveUS20100237853A1Base element modificationsVoltage/current isolationElectrical conductorCurrent sensor
A current sensor is provided for non-invasively measuring electrical current in an electrical conductor. The current sensor includes a housing having a Hall effect device and circuitry for transmitting a signal indicative of the current flowing through the electrical conductor. The current sensor includes a base having a surface for supporting an electrical conductor. A magnetic shielding member is coupled to the surface to shield the Hall effect device from stray or external magnetic fields. A compliant member is coupled to the magnetic shielding member opposite the surface. The compliant member compresses to allow the current sensor to accommodate a large variety of electrical conductor sizes. The compliant member further acts to bias the electrical conductor against the Hall effect device.
Owner:CONSOL EDISON OF NEW YORK +1
Magnetic sensor with variable sensitivity
InactiveUS7046002B1Noise minimizationIncrease working frequencyMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesStray field compensationComb driveMicroelectromechanical systems
A microelectromechanical system (MEMS) device comprising a base structure; a magnetic sensor attached to the base structure and operable for sensing a magnetic field and allowing for a continuous variation of an amplification of the magnetic field at a position at the magnetic sensor; and for receiving a DC voltage and an AC modulation voltage in the MEMS device; a pair of flux concentrators attached to the magnetic sensor; and a pair of electrostatic comb drives, each coupled to a respective flux concentrator such that when the pair of electrostatic comb drives are excited by a modulating electrical signal, each flux concentrator oscillates linearly at a prescribed frequency; and a pair of bias members (mechanical spring connectors) connecting the flux concentrators to one another.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
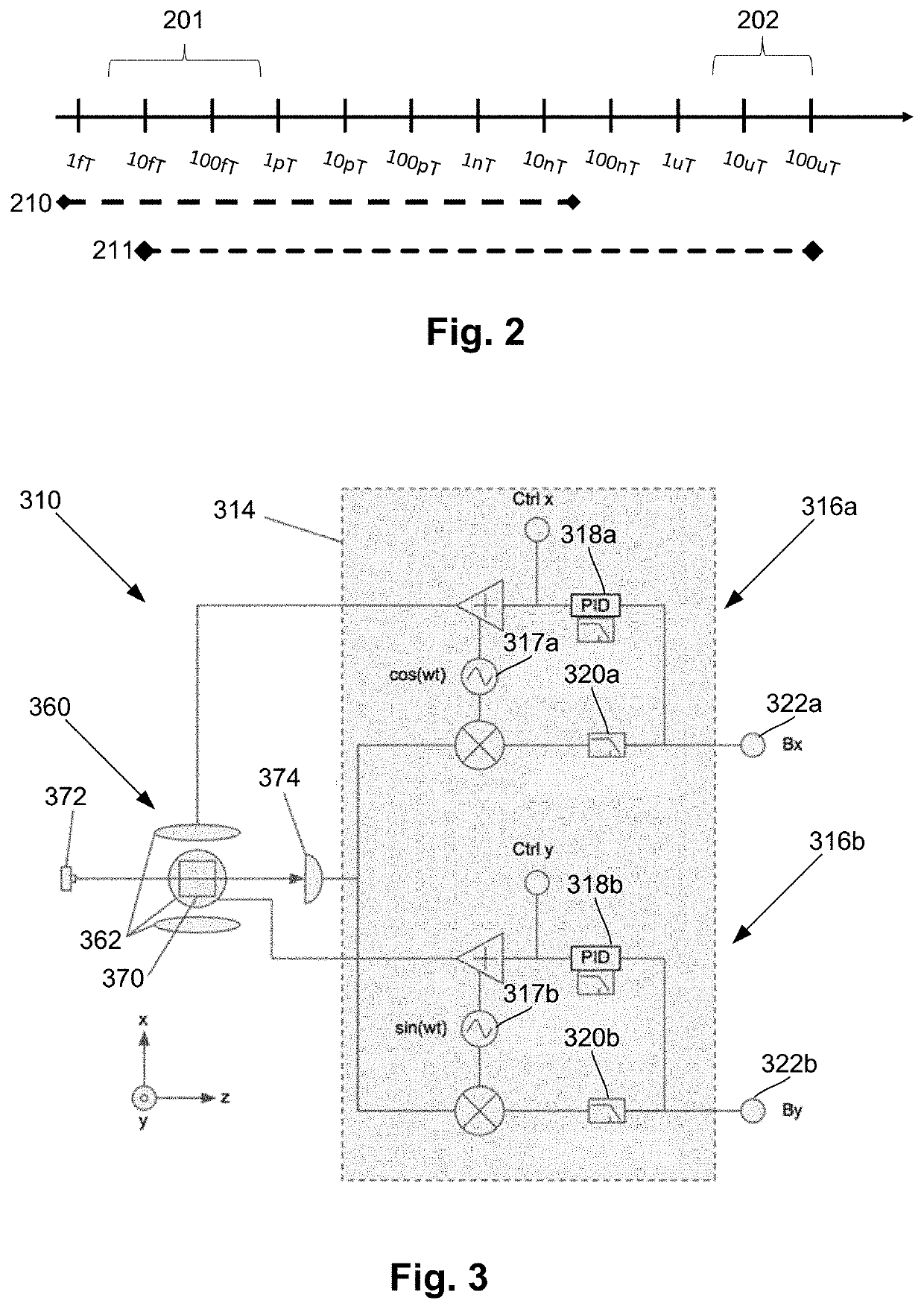
Magnetic field shaping components for magnetic field measurement systems and methods for making and using
ActiveUS20200057115A1High materialIncrease surface areaMagnetic field offset compensationMagnetic sensor packagingMagnetic fluxCondensed matter physics
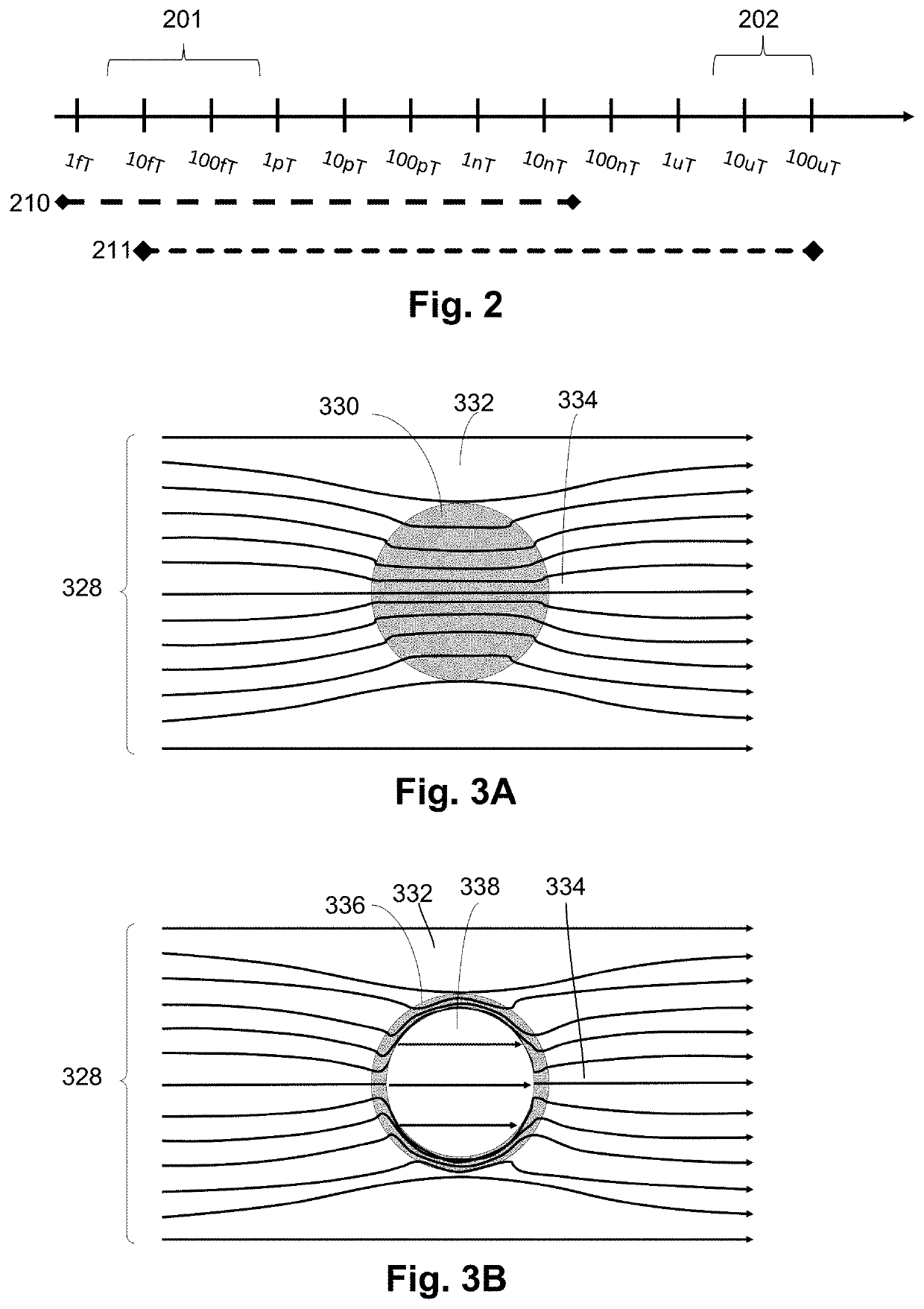
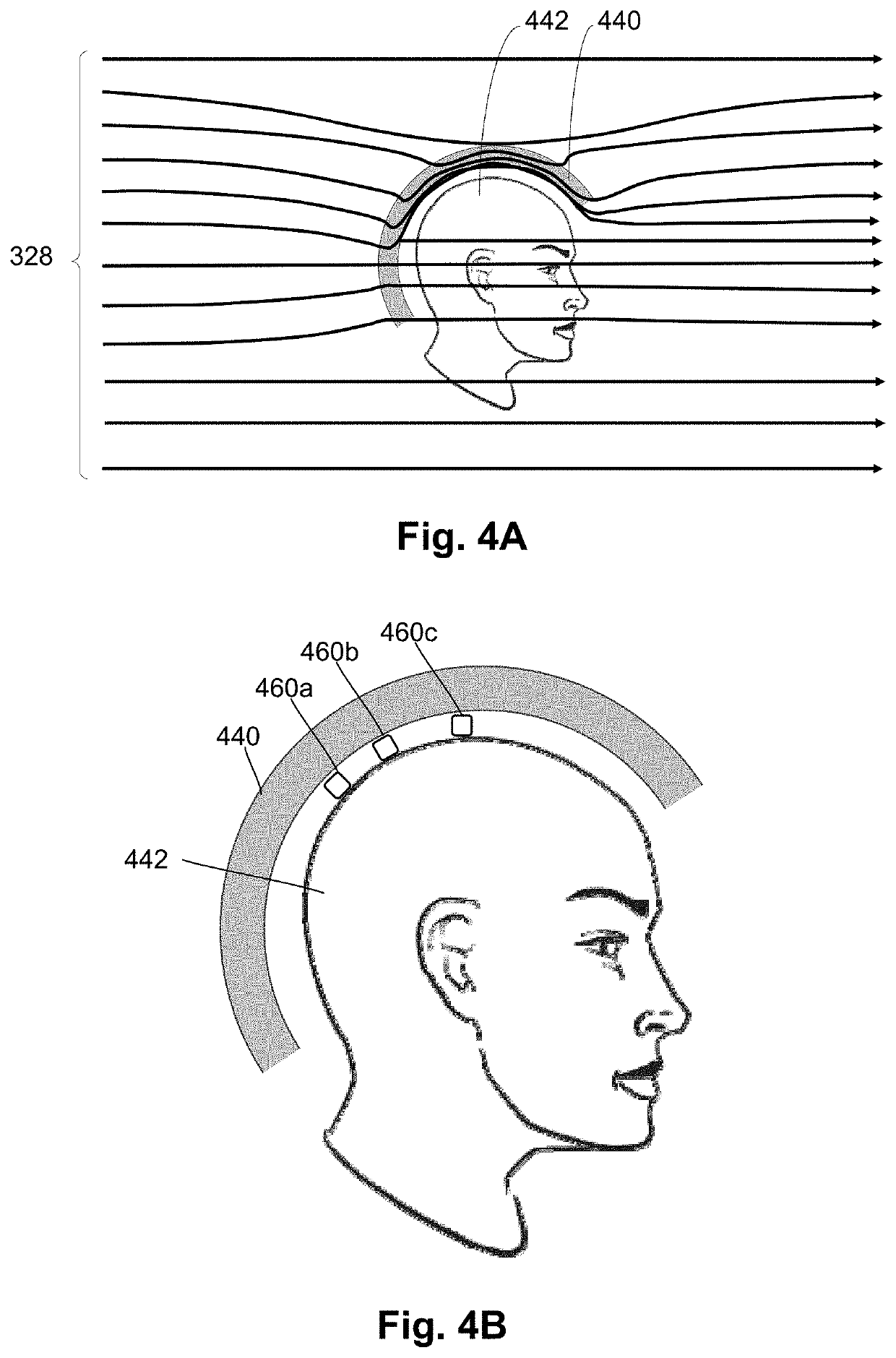
A magnetic field measurement system includes at least one magnetometer; and at least one flux concentrator made of a high magnetic permeability material and configured to receive magnetic field signals from a source, to concentrate the magnetic field signals or reorient the magnetic field signals in a preselected direction, and to direct the concentrated or reoriented magnetic field signals toward at least one of the at least one magnetometer. In addition to, or as an alternative to, the flux concentrator, the system can include a passive shield made of the high magnetic permeability material. The system may also include active shielding.
Owner:HI LLC
Probe for assessment of metal distortion
InactiveUS7688064B2Direction finders using radio wavesCurrent/voltage measurementAcousticsDistortion
Apparatus for assessing field distortion includes a probe and a processor. The probe includes a mechanical fixture for placement at a location to be tested, and one or more field generators, which are attached to the mechanical fixture and are arranged to generate respective magnetic fields. The probe further includes one or more field sensors, which are attached to the mechanical fixture at known positions with respect to the one or more field sensors and are arranged to sense the magnetic fields generated by the one or more field generators and to output signals responsively to the sensed magnetic fields. The processor is arranged to process the signals so as to assess a distortion of the magnetic fields sensed by the field sensors at the tested location.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
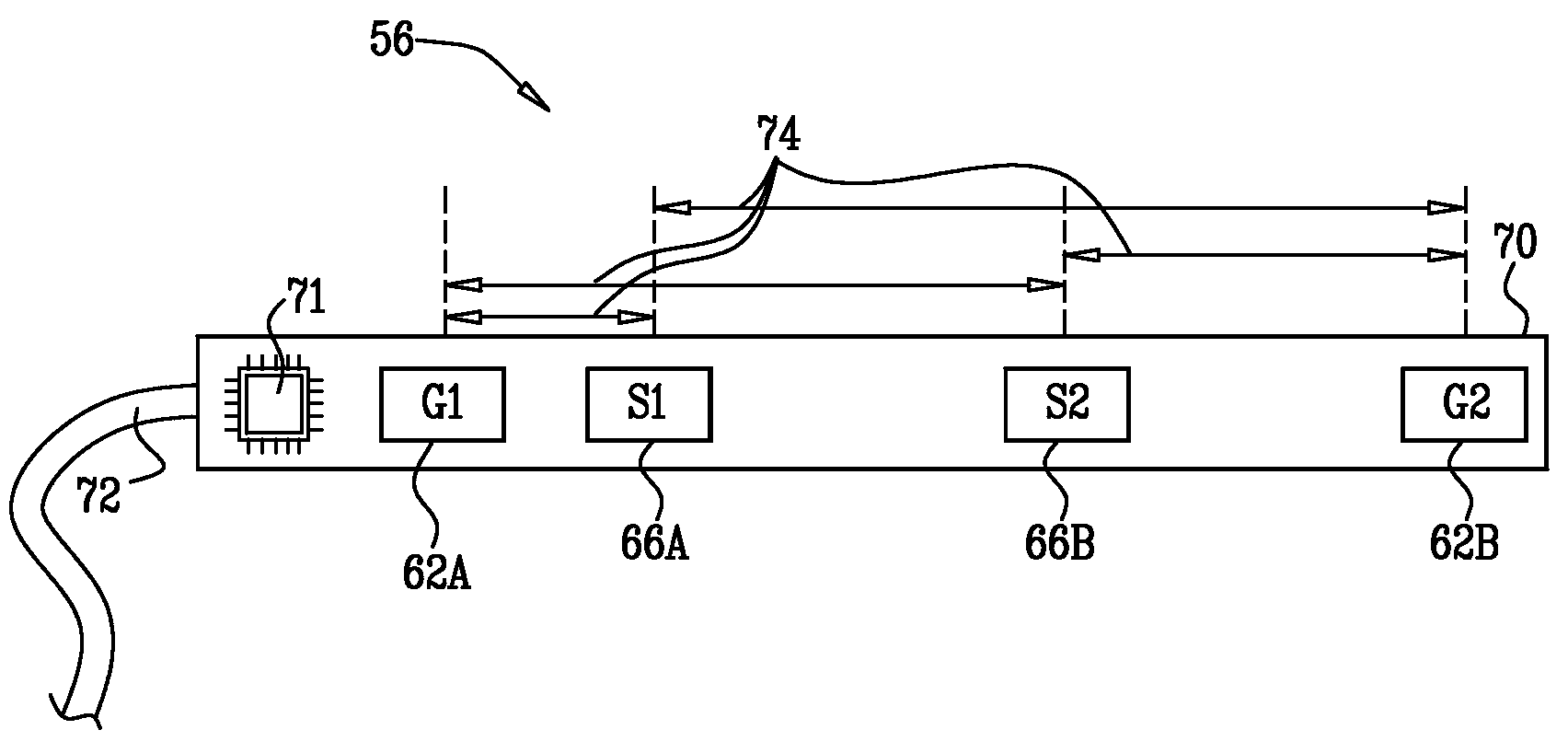
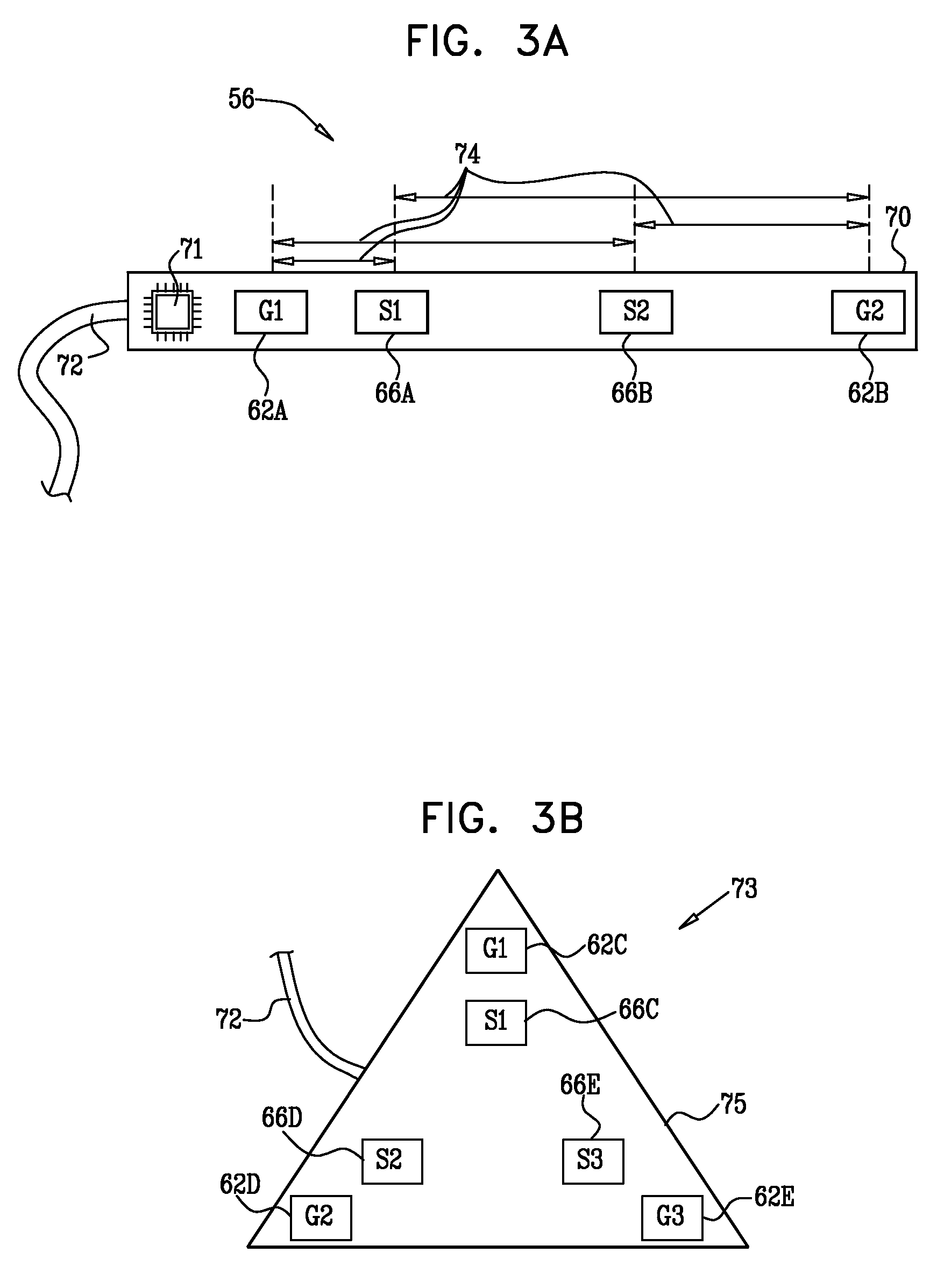
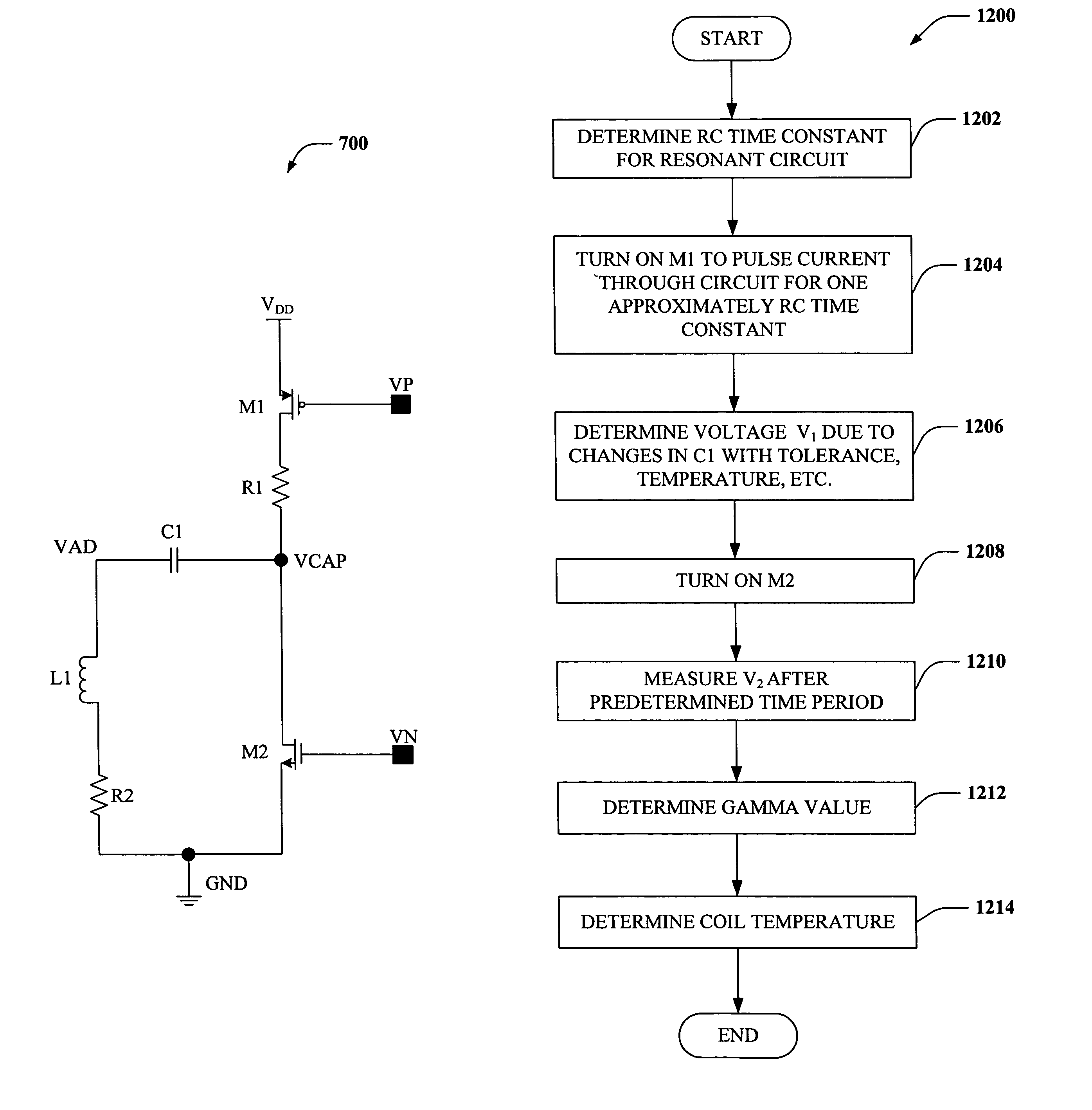
Inductive proximity sensor using coil time constant for temperature compensation
ActiveUS7173411B1Improve accuracyMitigates temperature drift effectUsing electrical meansElectronic switchingElectrical resistance and conductanceProximity sensor
Systems and methods are disclosed that facilitate determining coil temperature in a proximity sensor, such as an extended range inductive proximity sensor. Voltage measurements can be taken before, and during, damped oscillatory decay of a voltage in a resonant circuit in the proximity sensor to determine a value, γ, associated with an inductive time constant for the resonant circuit. The gamma value comprises information related to both inductance and resistance in the sensor coil, and can be employed to determine coil temperature. Derivation of the gamma value, and thus of coil temperature, can utilize a current pulse of a duration of approximately one RC time constant of the resonant circuit, thus mitigating current consumption by the proximity sensor during temperature assessment.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
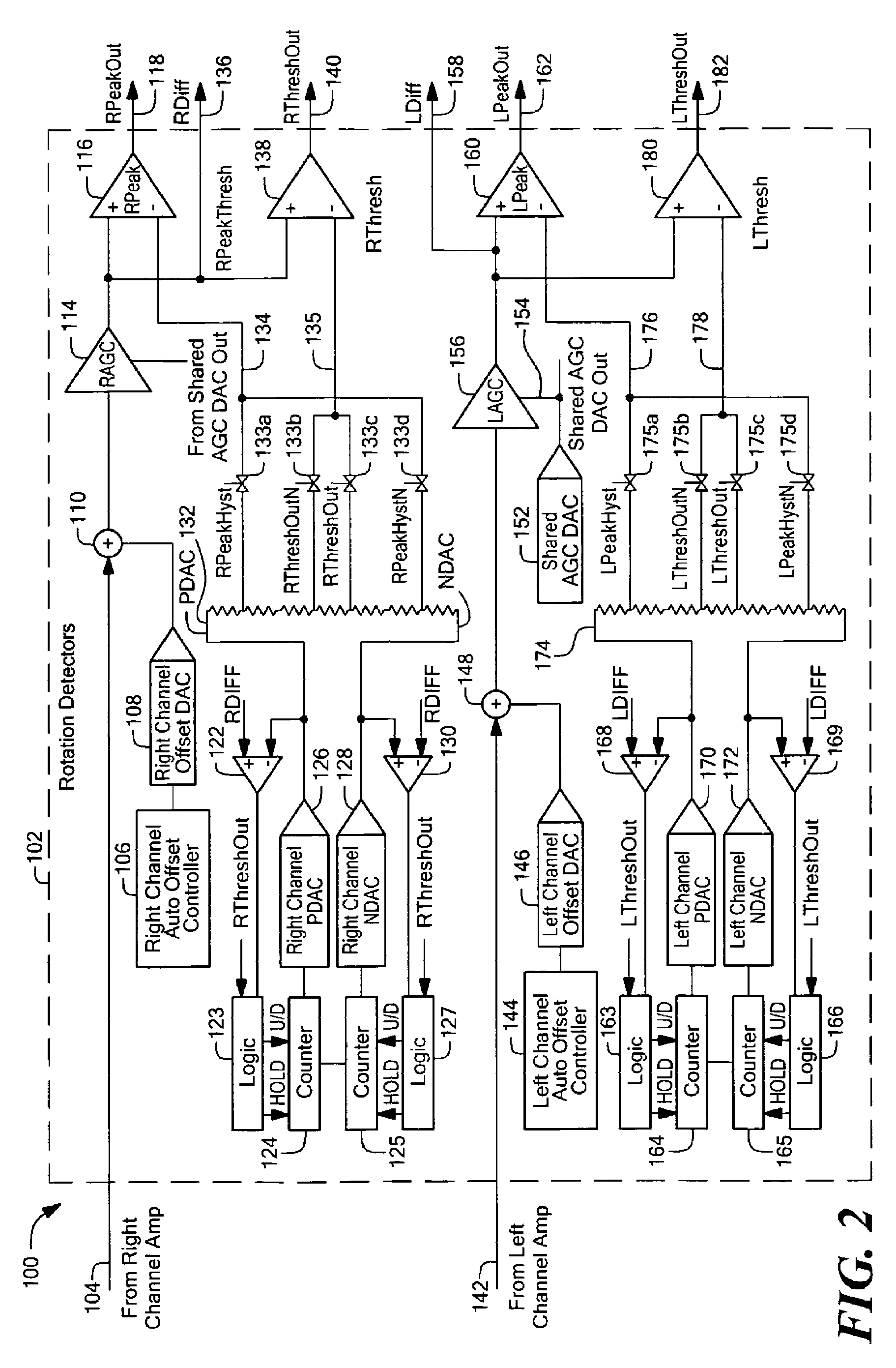
Methods and apparatus for dynamic offset adjustment in a magnetic article detector
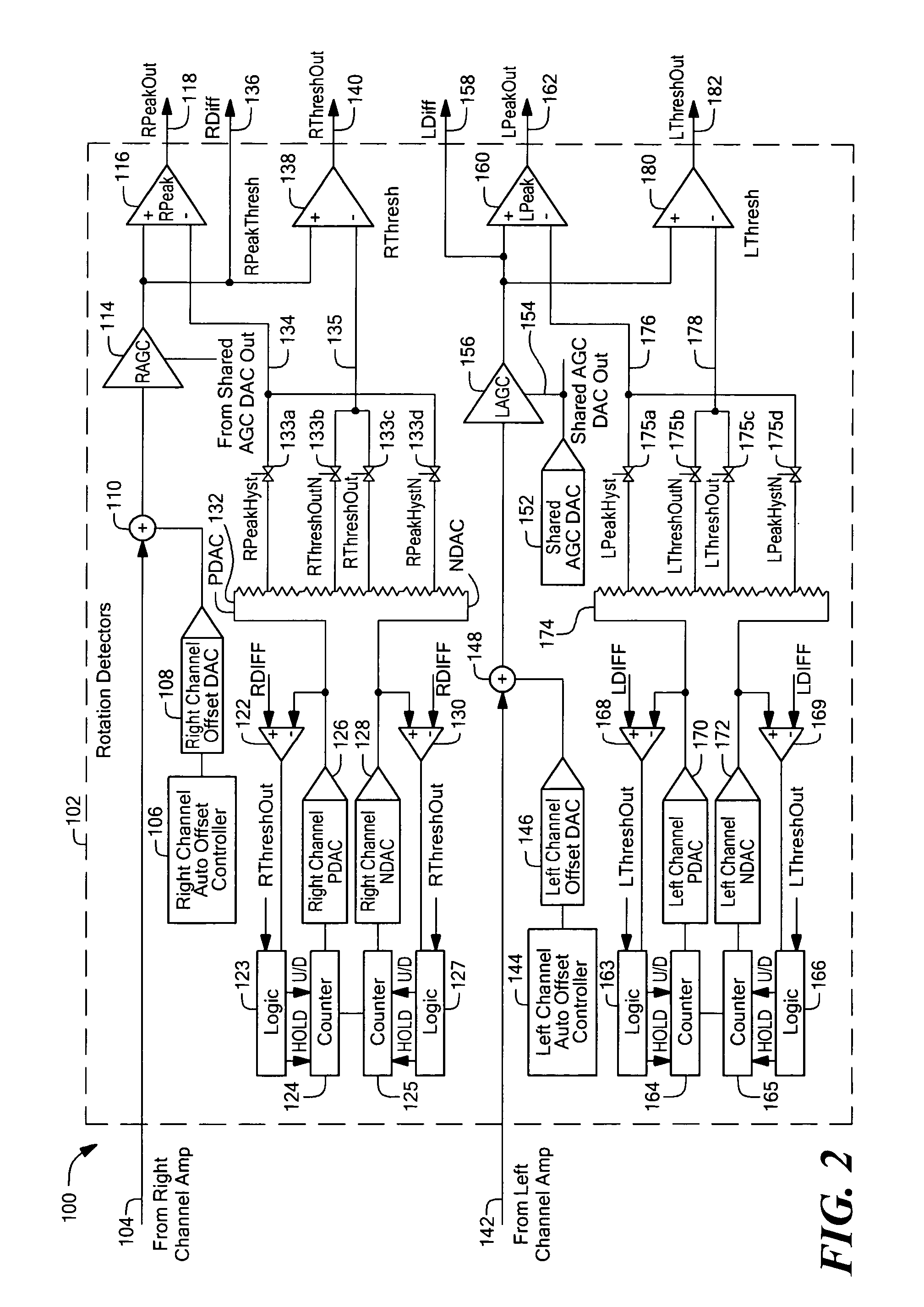
ActiveUS7138793B1Lower Level RequirementsUsing electrical meansDevices using electric/magnetic meansPeak valueNegative peak
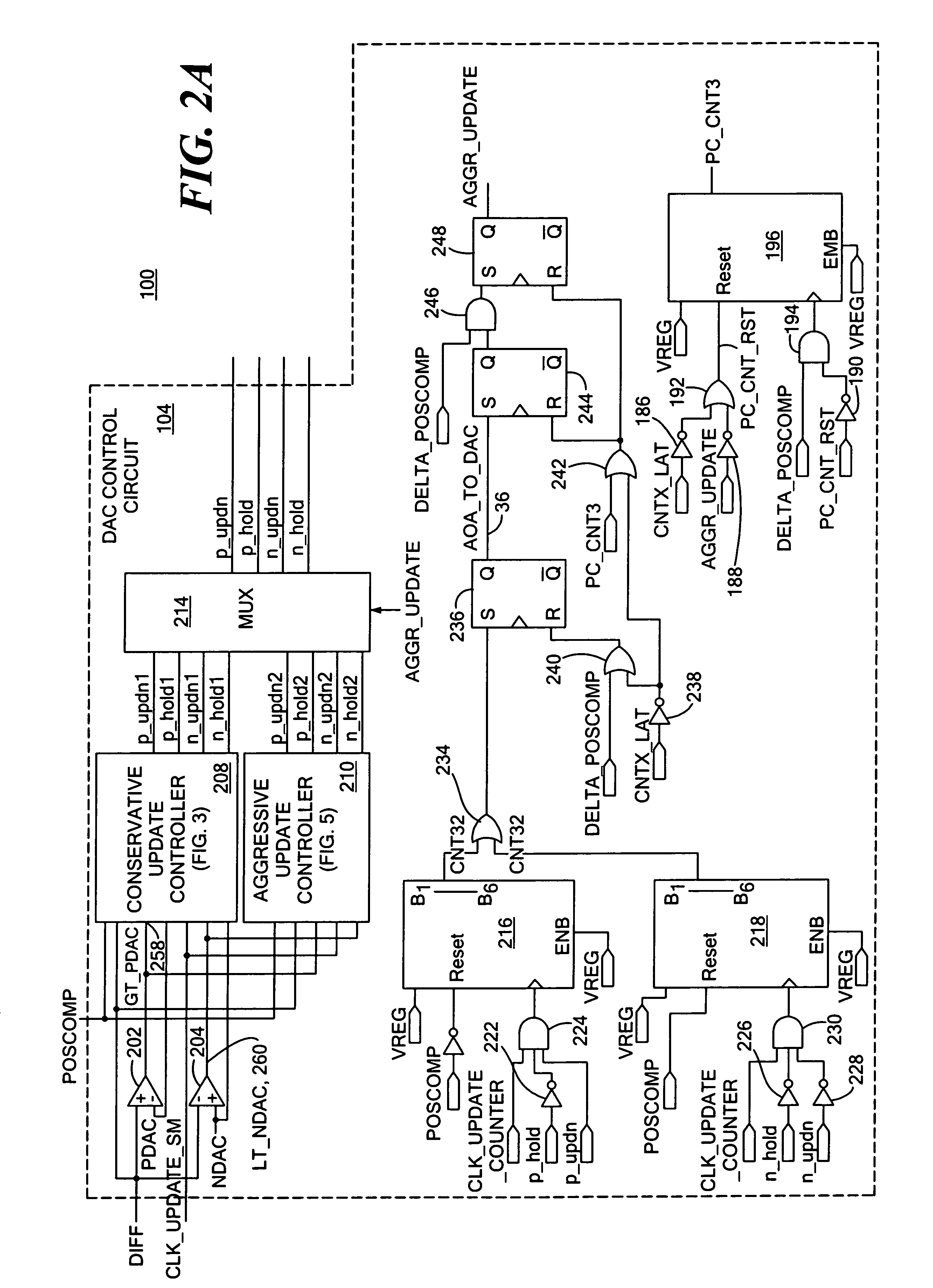
Apparatus and methods for detecting passing magnetic articles including an offset adjustment circuit for adjusting the DC level of the magnetic field signal based on a dynamically adjustable offset threshold signal. The detector includes a PDAC for tracking the positive peaks of a magnetic field signal and an NDAC for tracking the negative peaks of the magnetic field signal. In one embodiment, the offset threshold signal includes a positive offset threshold signal and a negative offset threshold signal that are initially set at fixed respective signal levels and that become the level of the PDAC signal and NDAC signals, respectively, in response to a counter, that counts a number of increments of the PDAC signal and decrements of the NDAC signal, reaching a predetermined count value.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Magnetoelastic torque sensor with ambient field rejection
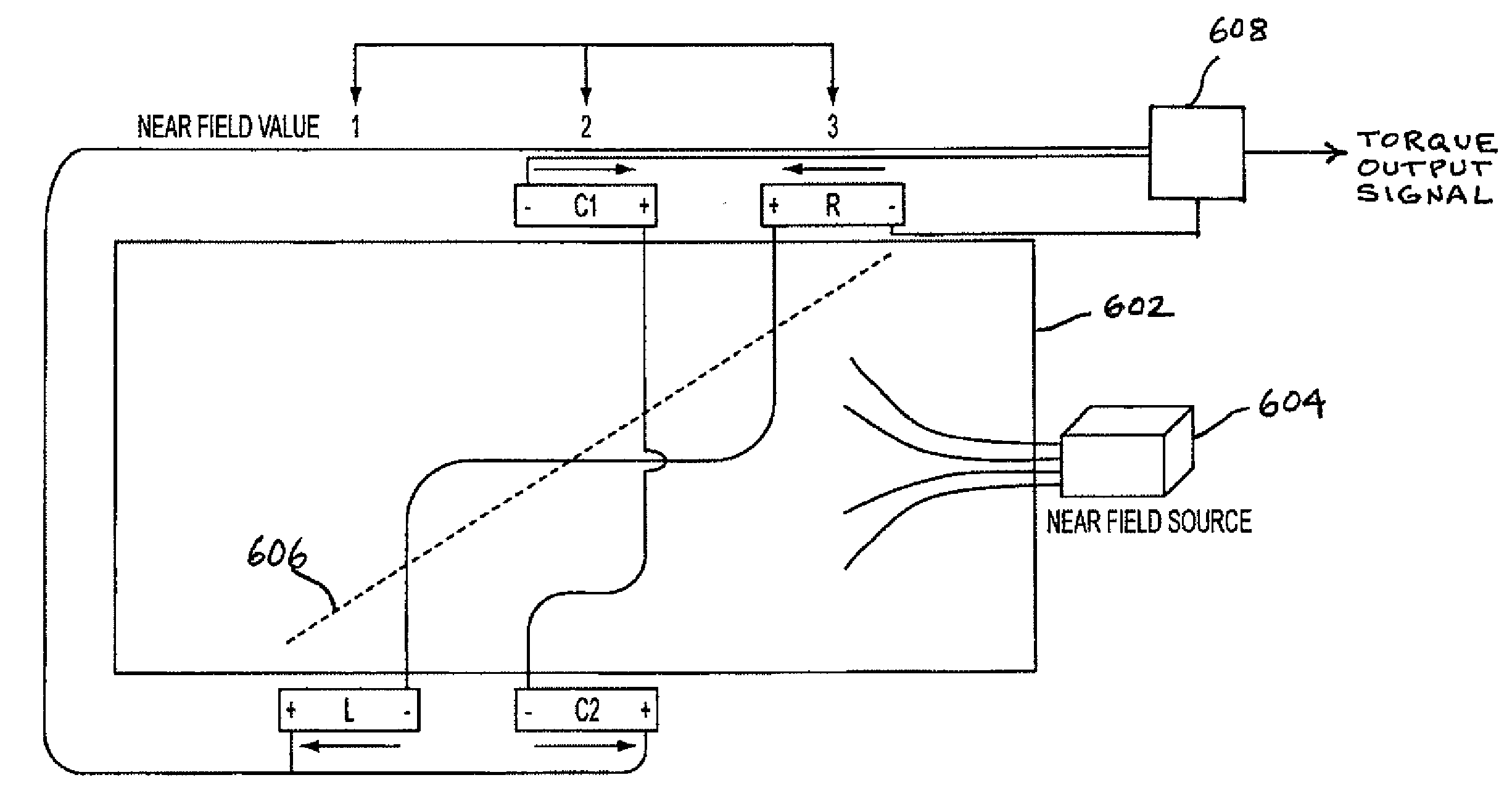
ActiveUS20090230953A1Cancellation effectEliminate the effects ofSolid-state devicesWork measurementCondensed matter physicsTorque sensor
The present invention involves a method and apparatus for canceling the effects of magnetic field noise in a torque sensor by placing three sets of magnetic field sensors around a shaft, the first set of field sensors being placed in the central region of the shaft and the second and third sets of field sensors being placed on the right side and left side of the field sensors placed at the central region, respectively. A torque-induced magnetic field is not cancelled with this arrangement of field sensors but a magnetic near field from a near field source is cancelled.
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
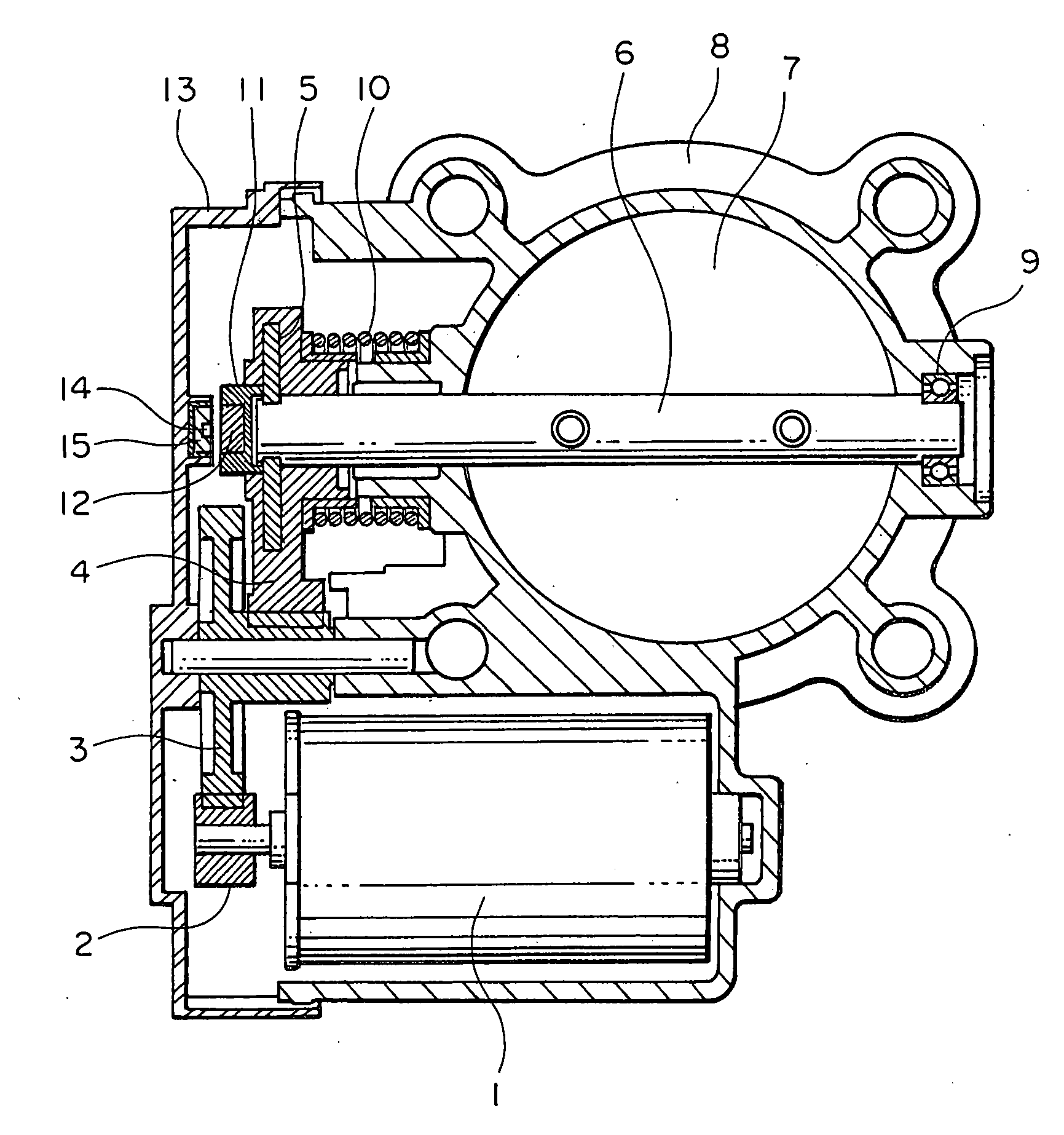
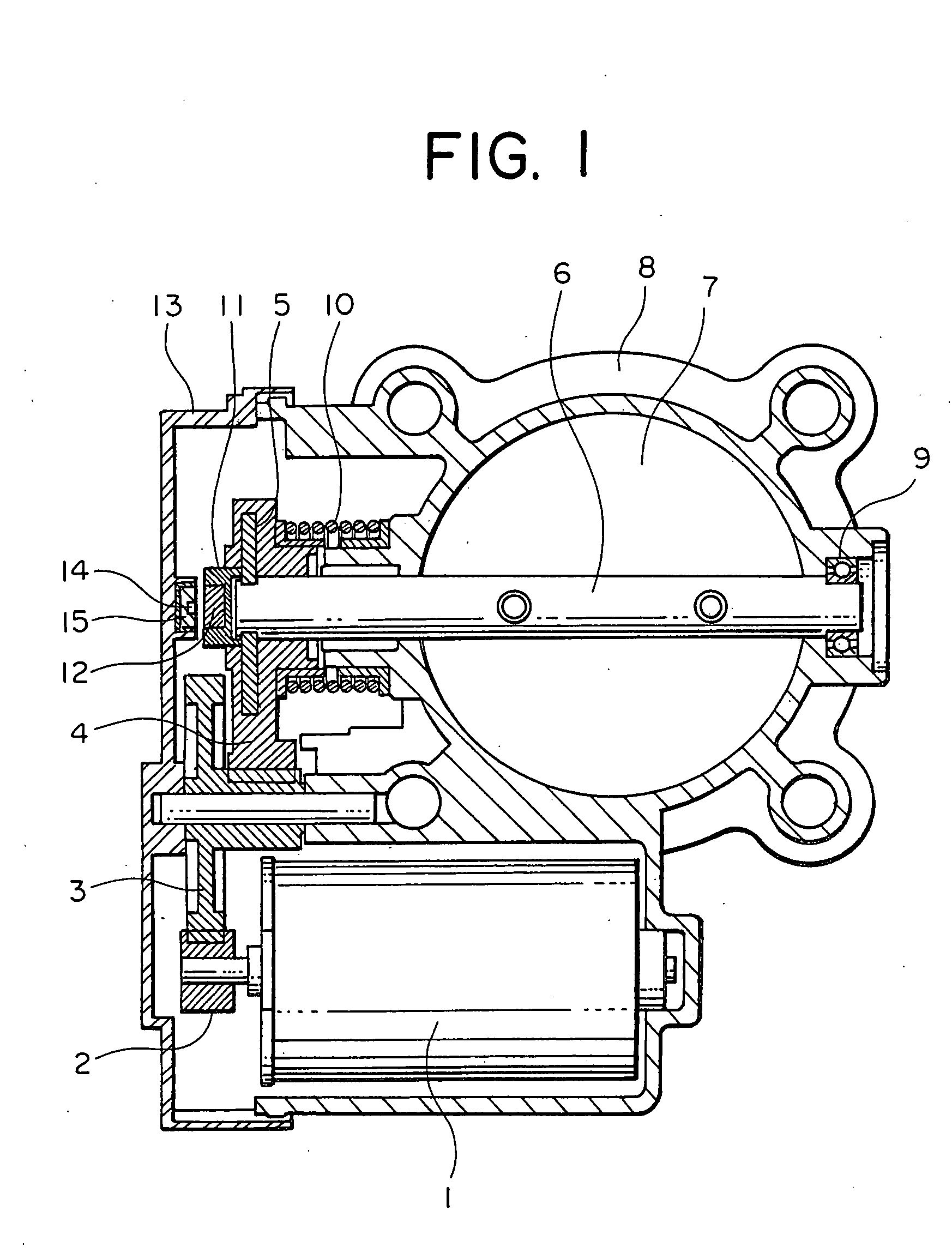
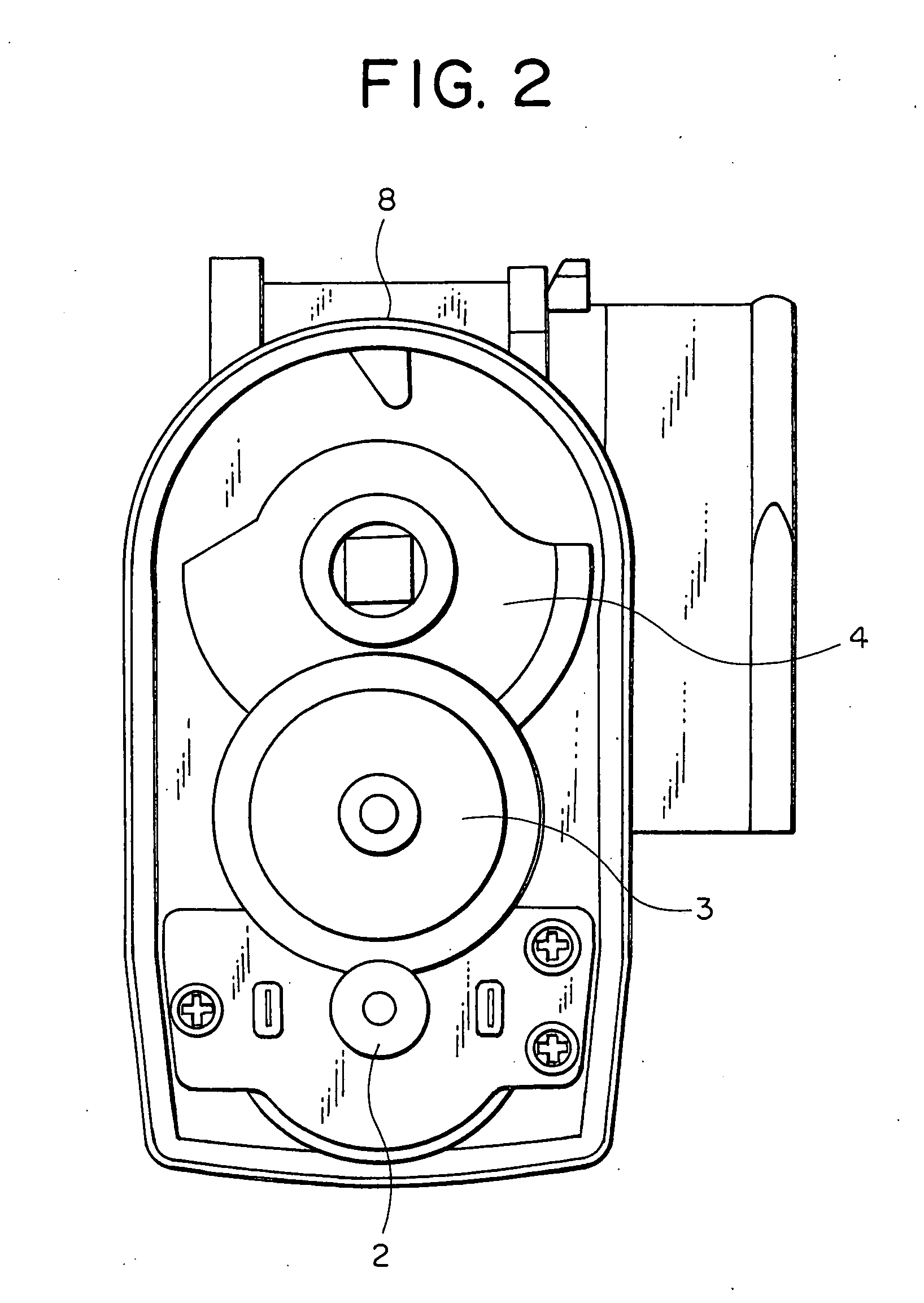
Intake air control apparatus for an engine
InactiveUS20050028871A1Prevent variation in outputInhibition effectElectrical controlMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic reluctanceEngineering
An intake air control apparatus for an engine is capable of suppressing the influence of external magnetic flux from outside thereby to prevent a variation in an output of a rotational angle detection sensor due to the external magnetic flux. A permanent magnet is provided on an end portion of a shaft. A rotational angle detection sensor is disposed in a spaced parallel relation with respect to the permanent magnet, and has a magnetoresistive element for detecting a change in direction of a magnetic flux of the permanent magnet thereby to detect a rotational angle of a throttle valve. A bypass member is disposed to enclose the rotational angle detection sensor with its side near the permanent magnet apertured to form an opening surface, the bypass member being made of a magnetic material which is adapted to form a bypass path for the magnetic flux from the permanent magnet.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
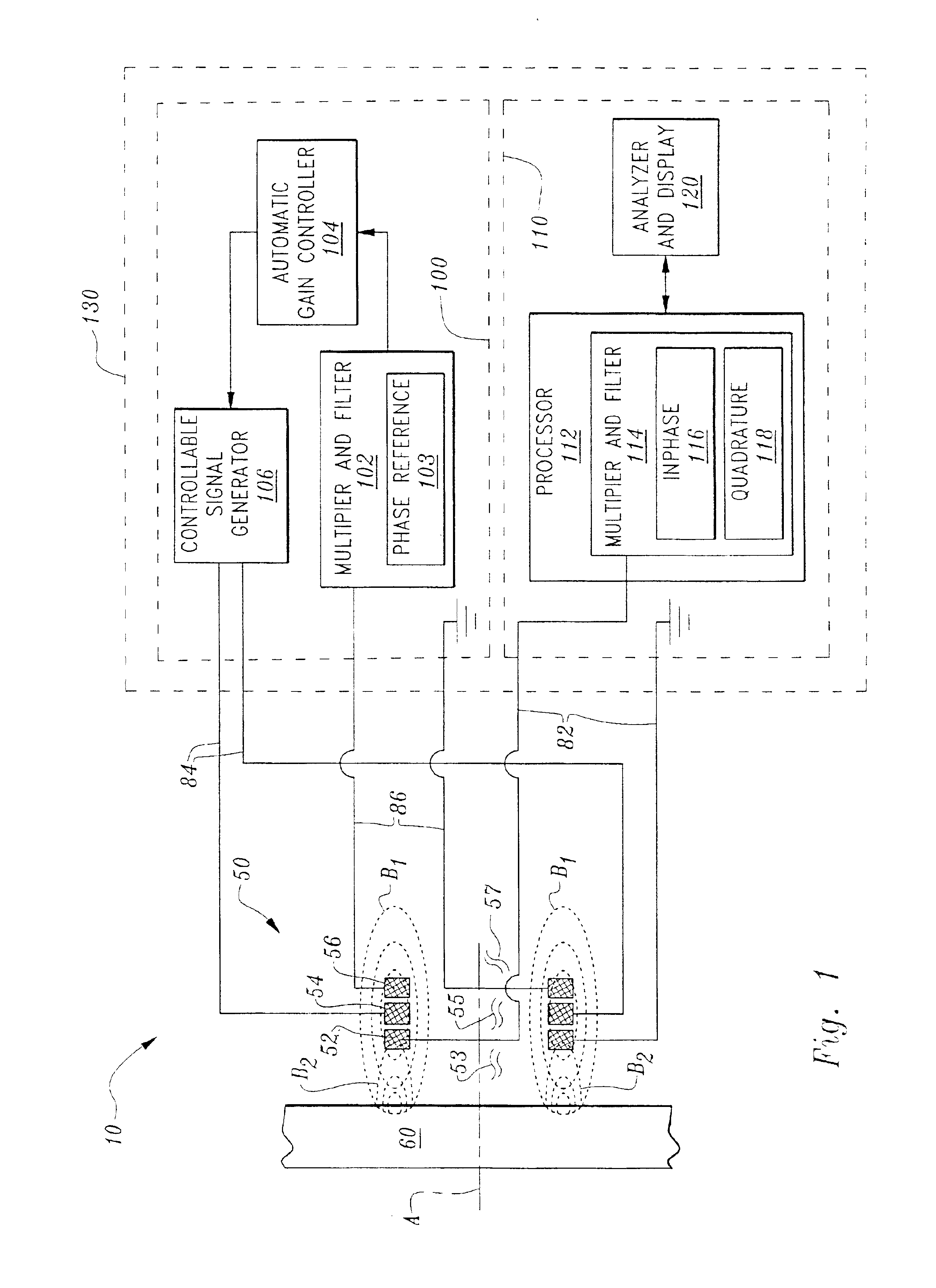
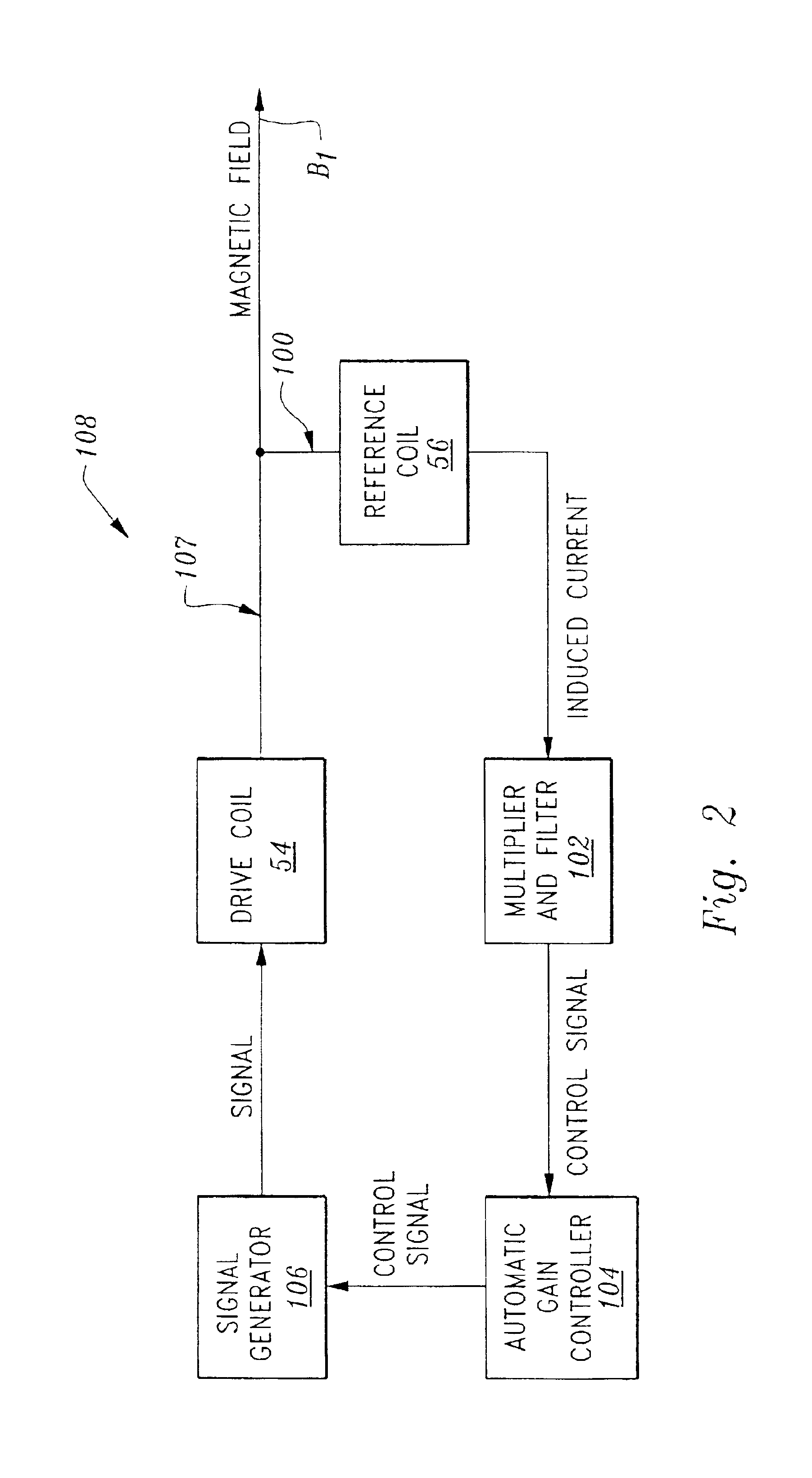
Multi-coil eddy current proximity probe system
InactiveUS6803757B2Elimination temperatureMagnetic property measurementsUsing electrical meansPosition dependentEddy current
A proximity probe system comprising a multi-coil proximity probe including a drive coil, a sense coil and a reference coil. The system includes a signal generator driving the drive coil with an alternating current for creating a magnetic field that induces eddy currents in a proximate conductive object resulting in an eddy current induced magnetic field emanating therefrom. The sense coil is interposed between the object and the drive coil for outputting an object induced alternating current that is detected by the system and correlated to a position of the object relative to the probe. The reference coil is positioned to be inductively coupled to the drive coil for carrying a drive coil induced alternating current that is detected, conditioned and feedback to the signal generator for controlling the magnetic field radiating from the drive coil while sensing the the object induced alternating current in the sense coil.
Owner:BENTLY NEVADA INC
Magnetic field sensors and related techniques that can provide self-test information in a formatted output signal
A magnetic field sensor can provide an output signal indicative of a passing condition or a failing condition of the magnetic field sensor. The output signal has one of a variety of output signal formats.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Distortion-immune position tracking using redundant measurements
ActiveUS20080033282A1Reduce measurement errorReduce impactElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringLocation trackingCondensed matter physics
A method for tracking a position of an object includes using a field sensor associated with the object to measure field strengths of magnetic fields generated by two or more field generators, wherein a measurement of at least one of the field strengths is subject to a distortion. Rotation-invariant location coordinates of the object are calculated responsively to the measured field strengths. Corrected location coordinates of the object are determined by applying to the rotation-invariant location coordinates a coordinate correcting function so as to adjust a relative contribution of each of the measured field strengths to the corrected location coordinates responsively to the distortion in the measured field strengths.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
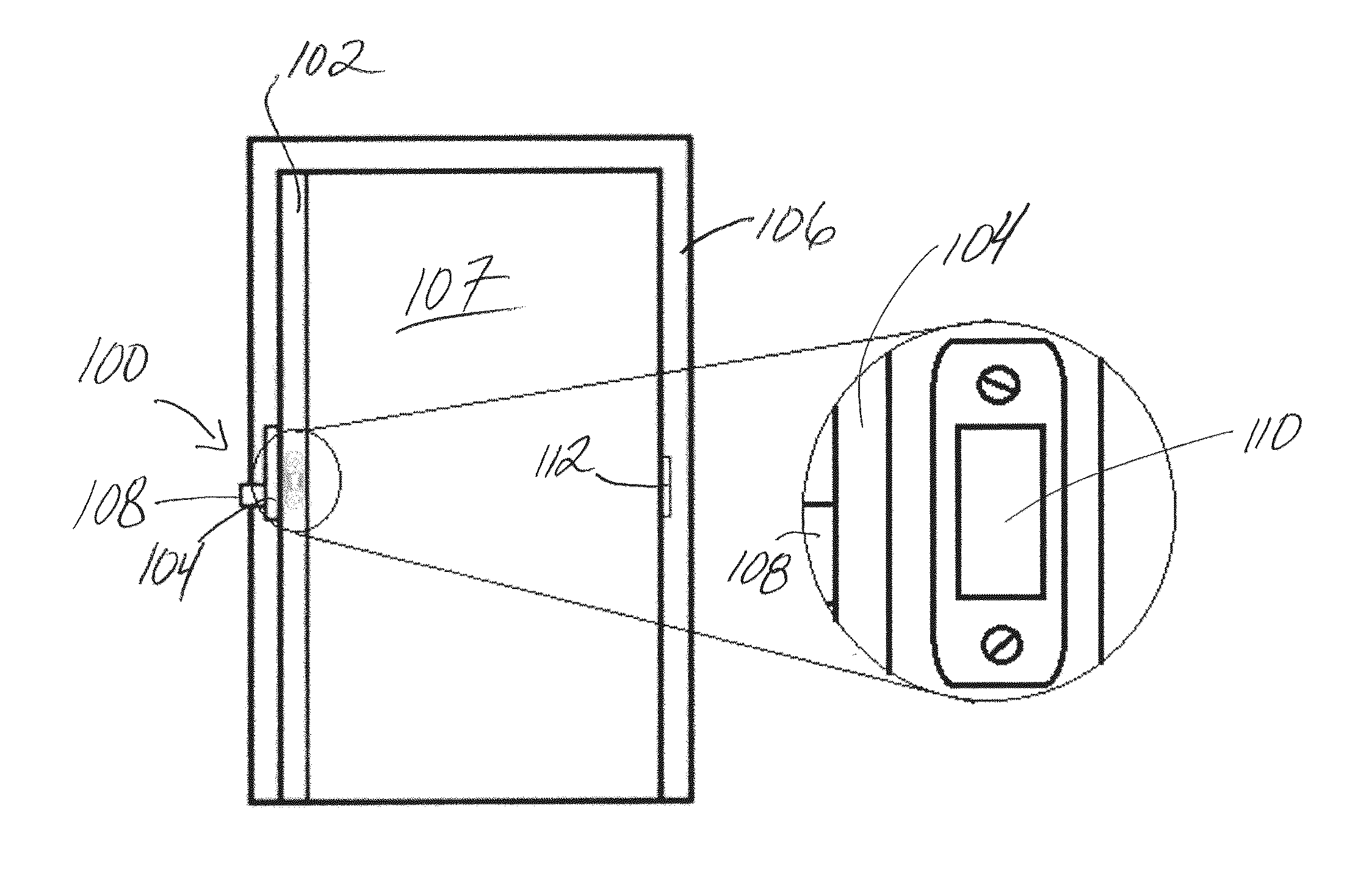
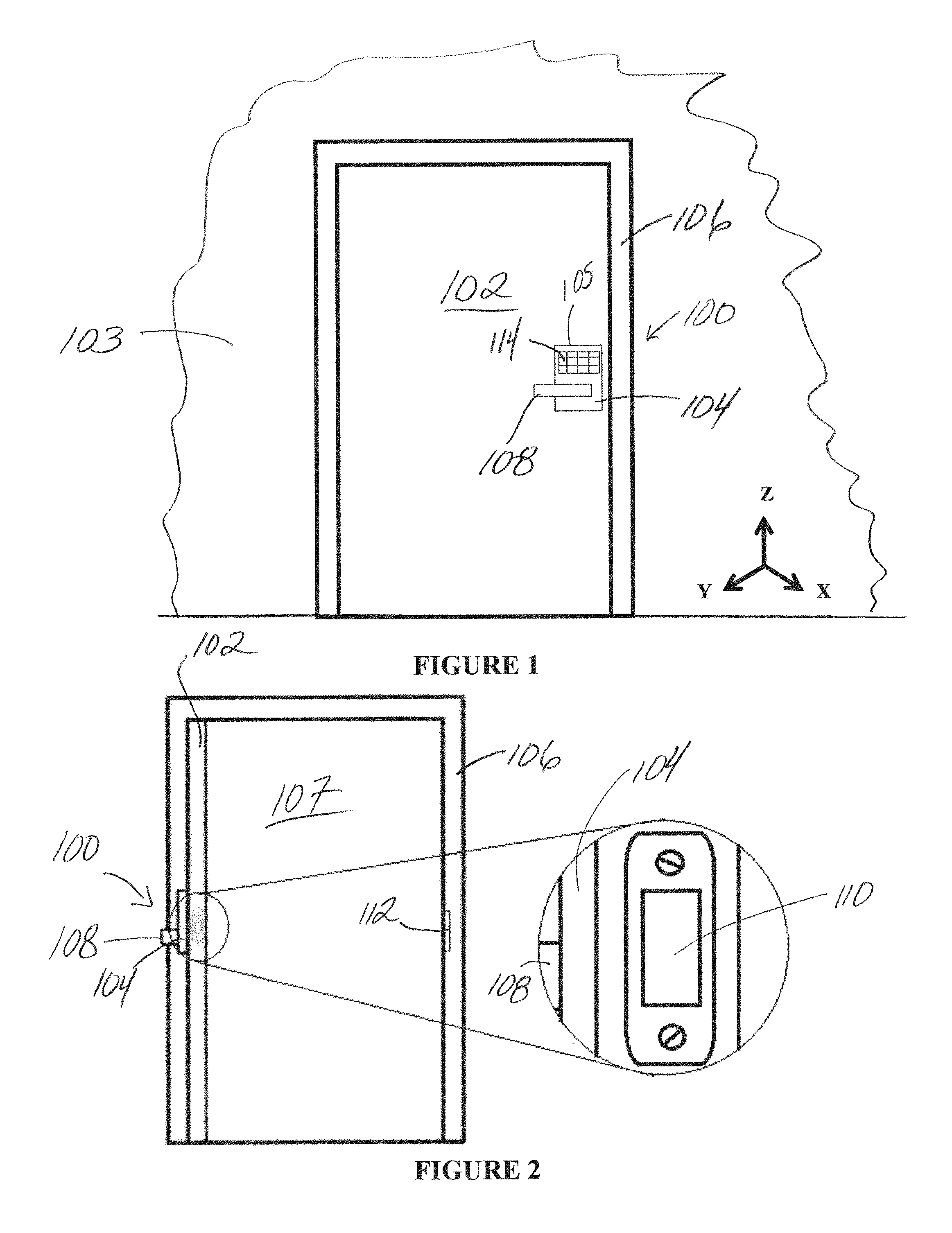
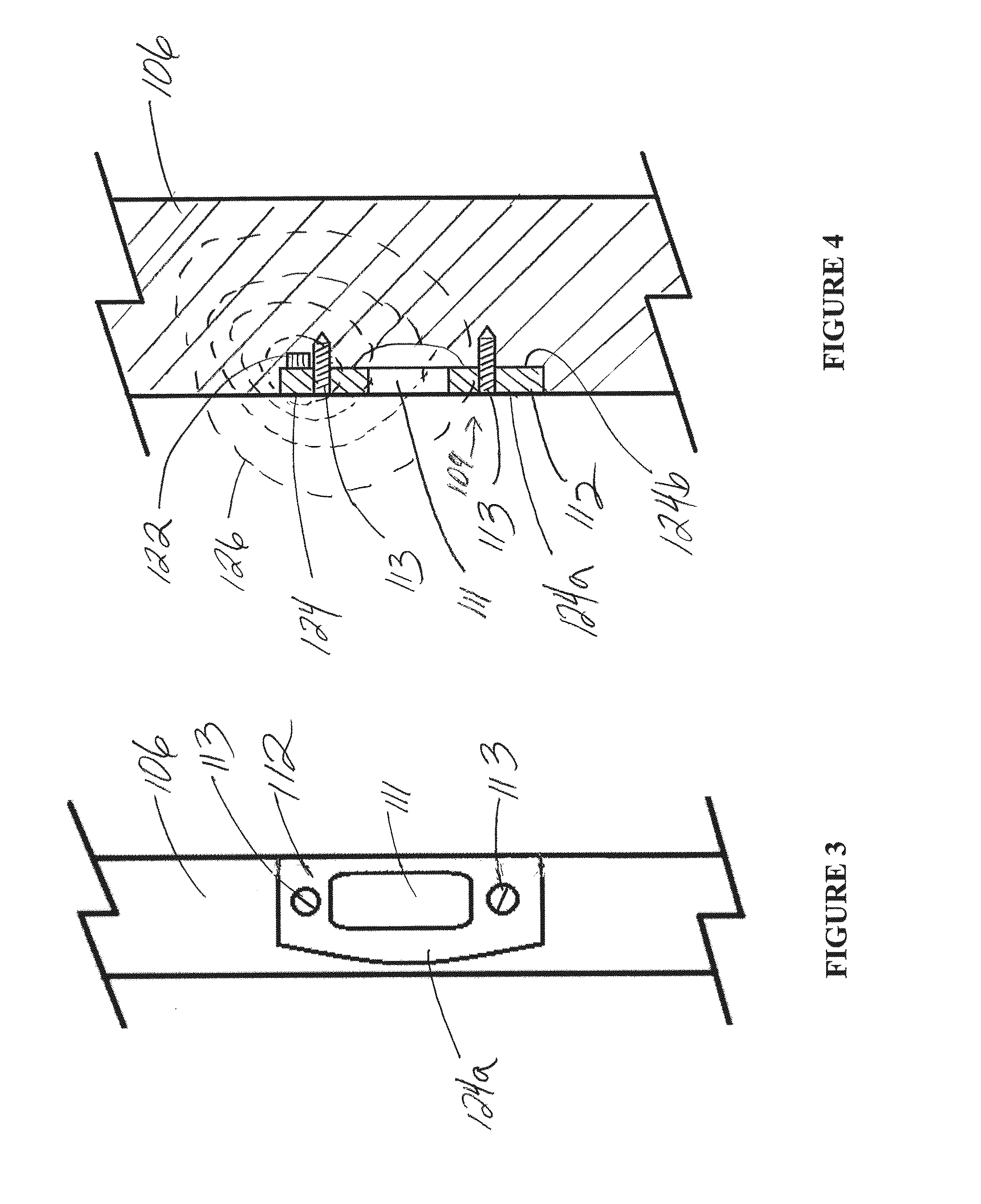
Lock device having position sensor
A position sensing system and method for detecting the displacement of a door from a reference position, such as, for example, from a closed position. The system includes a magnetometer that may be operably connected to the door, and which measures positional location relative to a reference magnetic field, such as, for example, a magnetic field provided by a magnet of a lock device. The system may also include an accelerometer that detects acceleration of the door, and thereby provides an indication of when location is to be measured by the magnetometer. Measurement information from the magnetometer is used to derive a position indicator that is compared to a reference indicator, the reference indicator being associated with the reference position. Differences between the position and reference indicators may provide an indication that the door has been moved from the reference position.
Owner:SCHLAGE LOCK
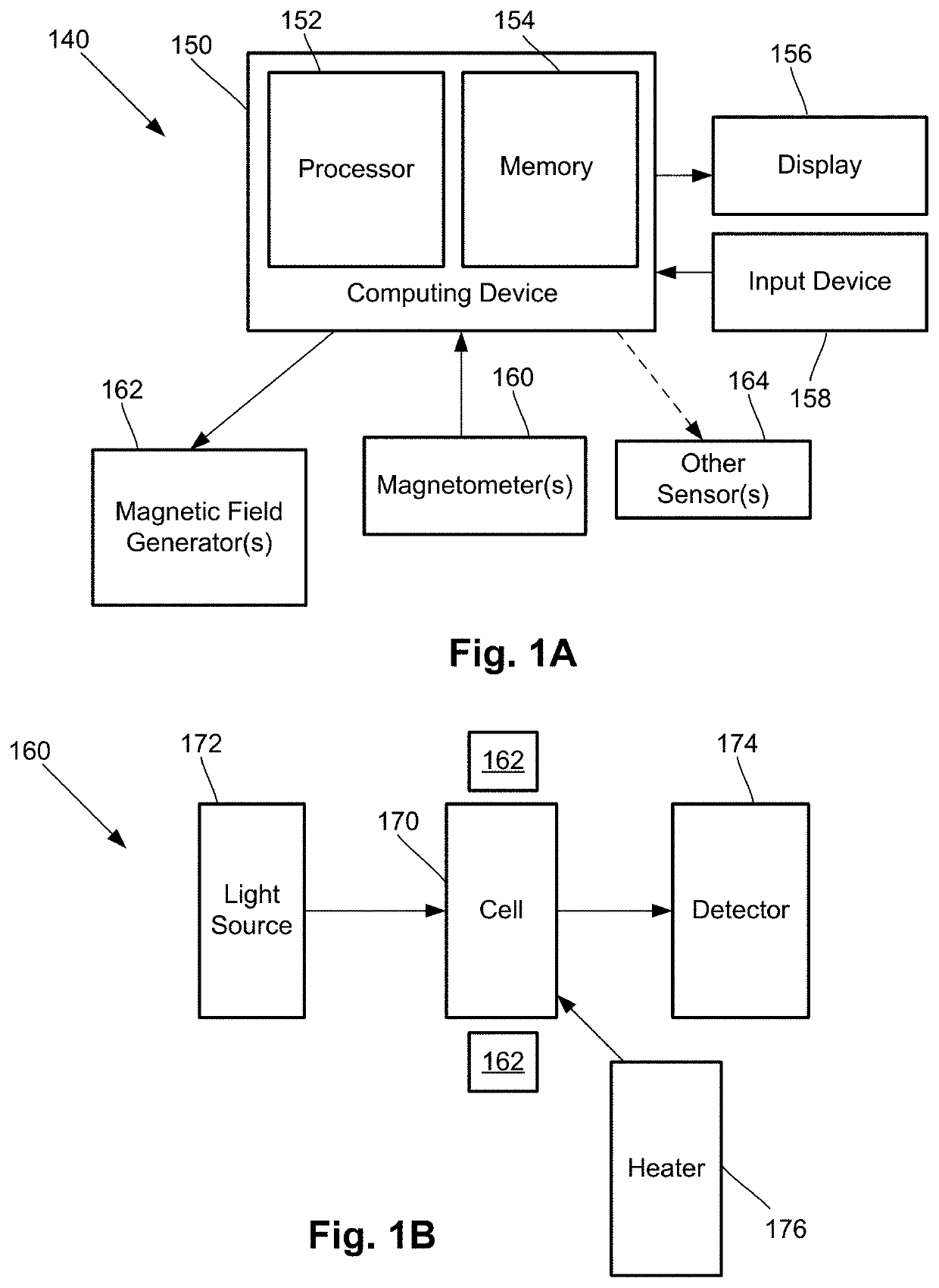
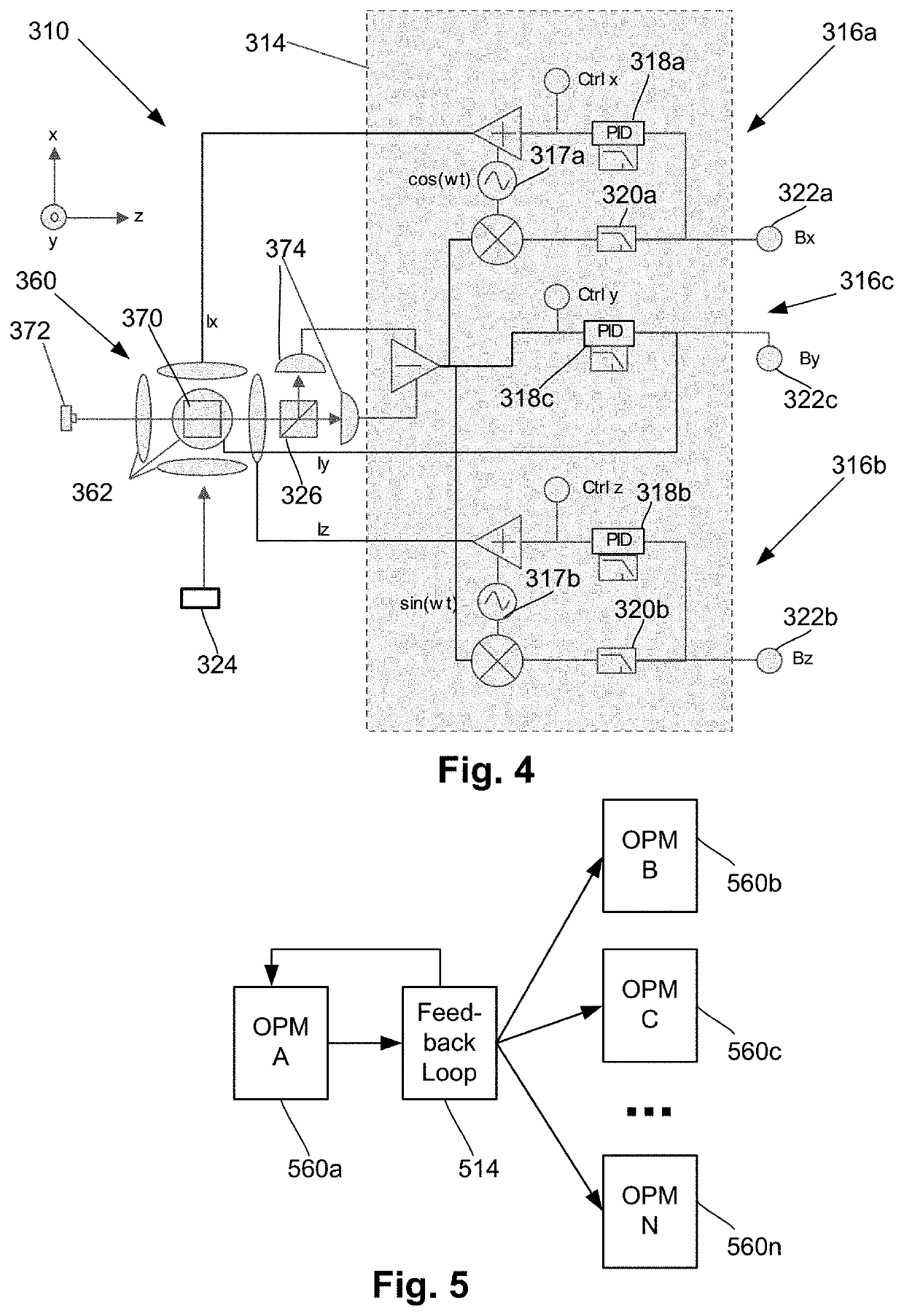
Neural feedback loop filters for enhanced dynamic range magnetoencephalography (MEG) systems and methods
ActiveUS20200256929A1Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringLow-pass filterSoftware engineering
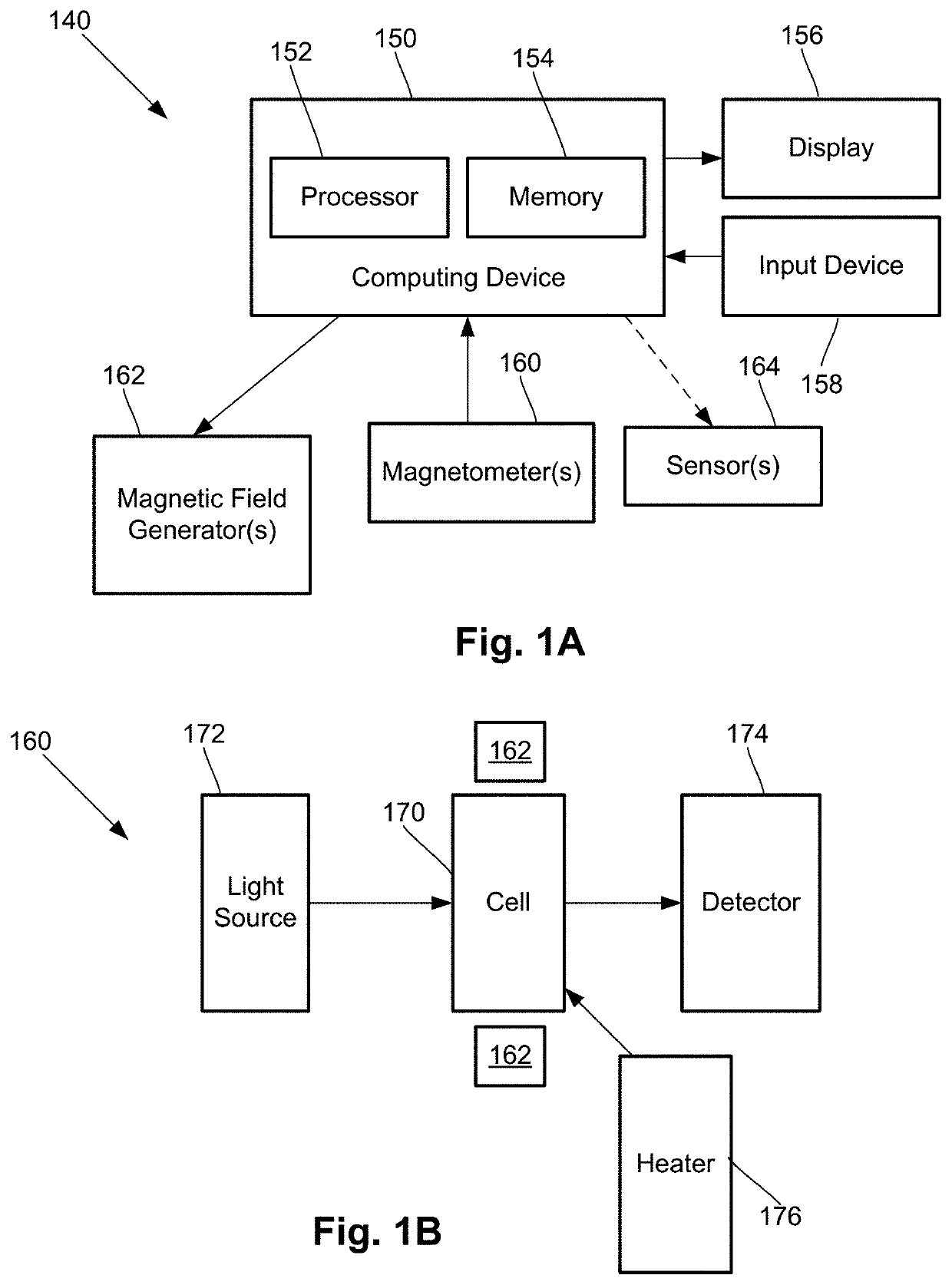
One embodiment is a magnetic field measurement system that includes at least one magnetometer having a vapor cell, a light source to direct light through the vapor cell, and a detector to receive light directed through the vapor cell; at least one magnetic field generator disposed adjacent the vapor cell; and a feedback circuit coupled to the at least one magnetic field generator and the detector of the at least one magnetometer. The feedback circuit includes at least one feedback loop that includes a first low pass filter with a first cutoff frequency. The feedback circuit is configured to compensate for magnetic field variations having a frequency lower than the first cutoff frequency. The first low pass filter rejects magnetic field variations having a frequency higher than the first cutoff frequency and provides the rejected magnetic field variations for measurement as an output of the feedback circuit.
Owner:HI LLC
Detection of metal disturbance in a magnetic tracking system
ActiveUS20050024043A1Improve accuracyPosition fixationDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic trackingObject based
A method for tracking an object includes producing energy fields at a plurality of different frequencies in a vicinity of the object, and receiving signals that are generated at a location of the object at the different frequencies in response to the energy fields. Multiple computations are made of spatial coordinates of the object based on the signals received at the different frequencies. Convergence of the computations is tested in order to ascertain whether the energy fields have been perturbed by an article in the vicinity of the object.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Dynamic magnetic anomaly compensation
InactiveUS7400142B2Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionManagement unitGyroscope
Owner:SONICWORKS
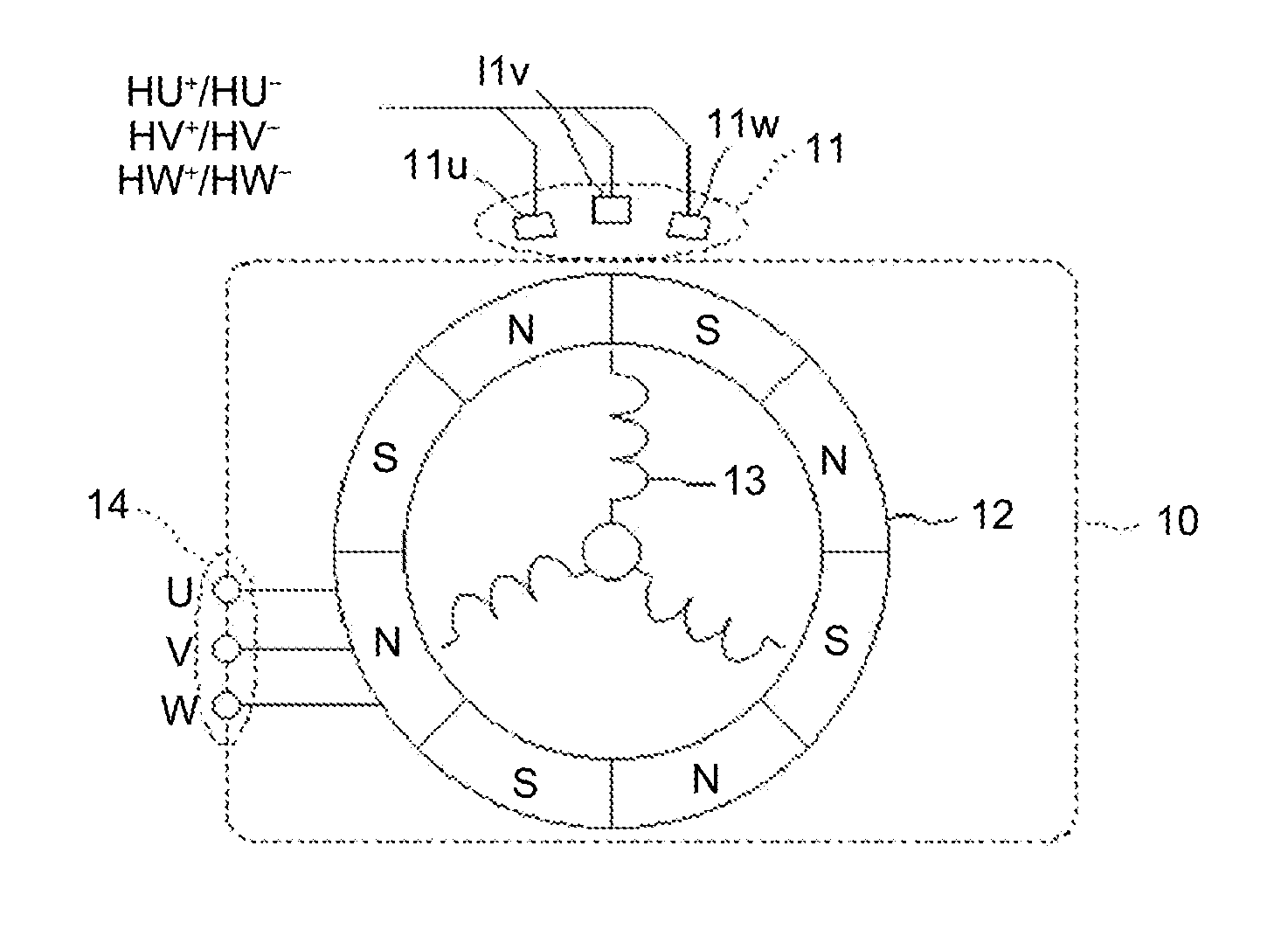
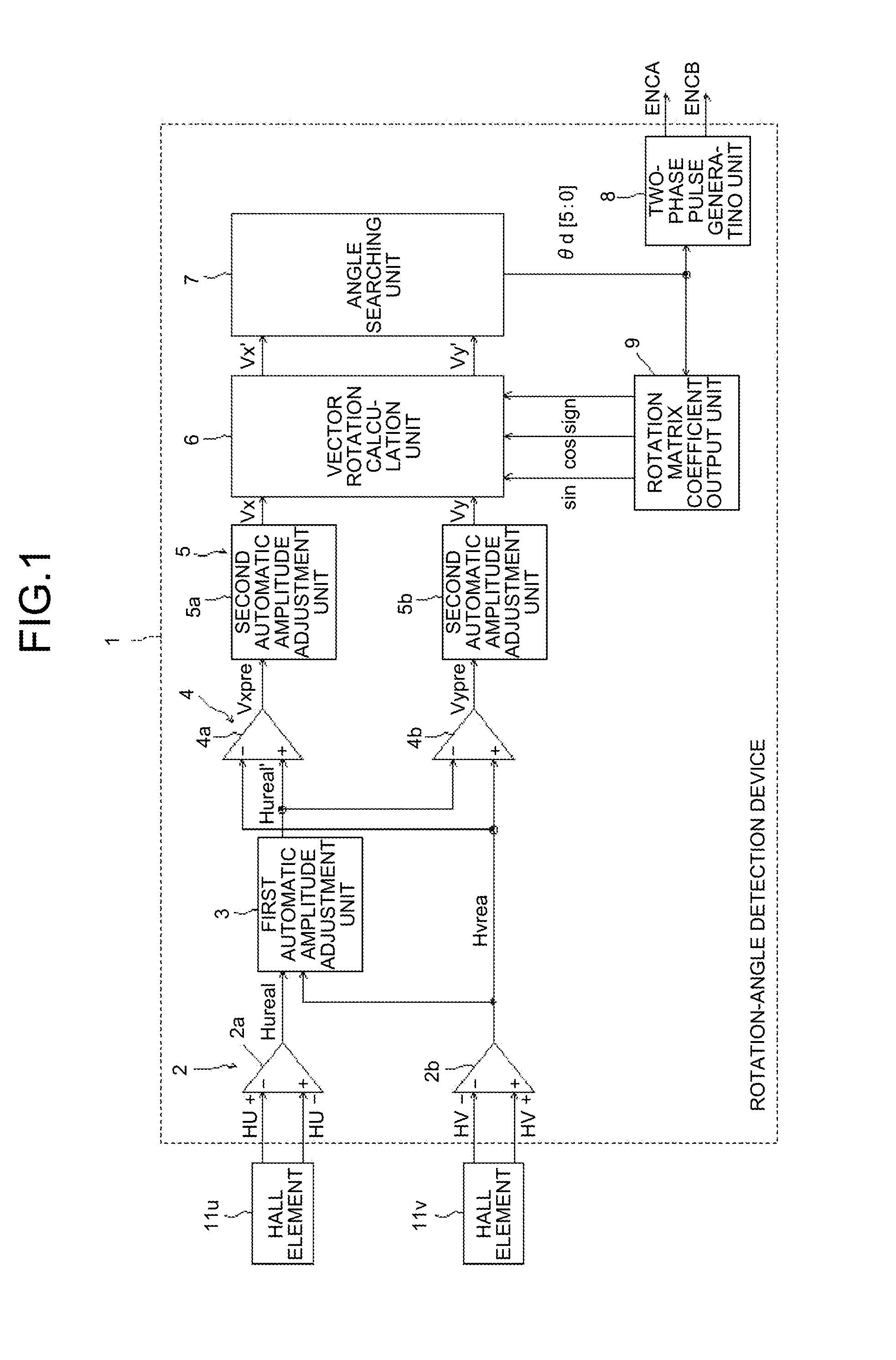
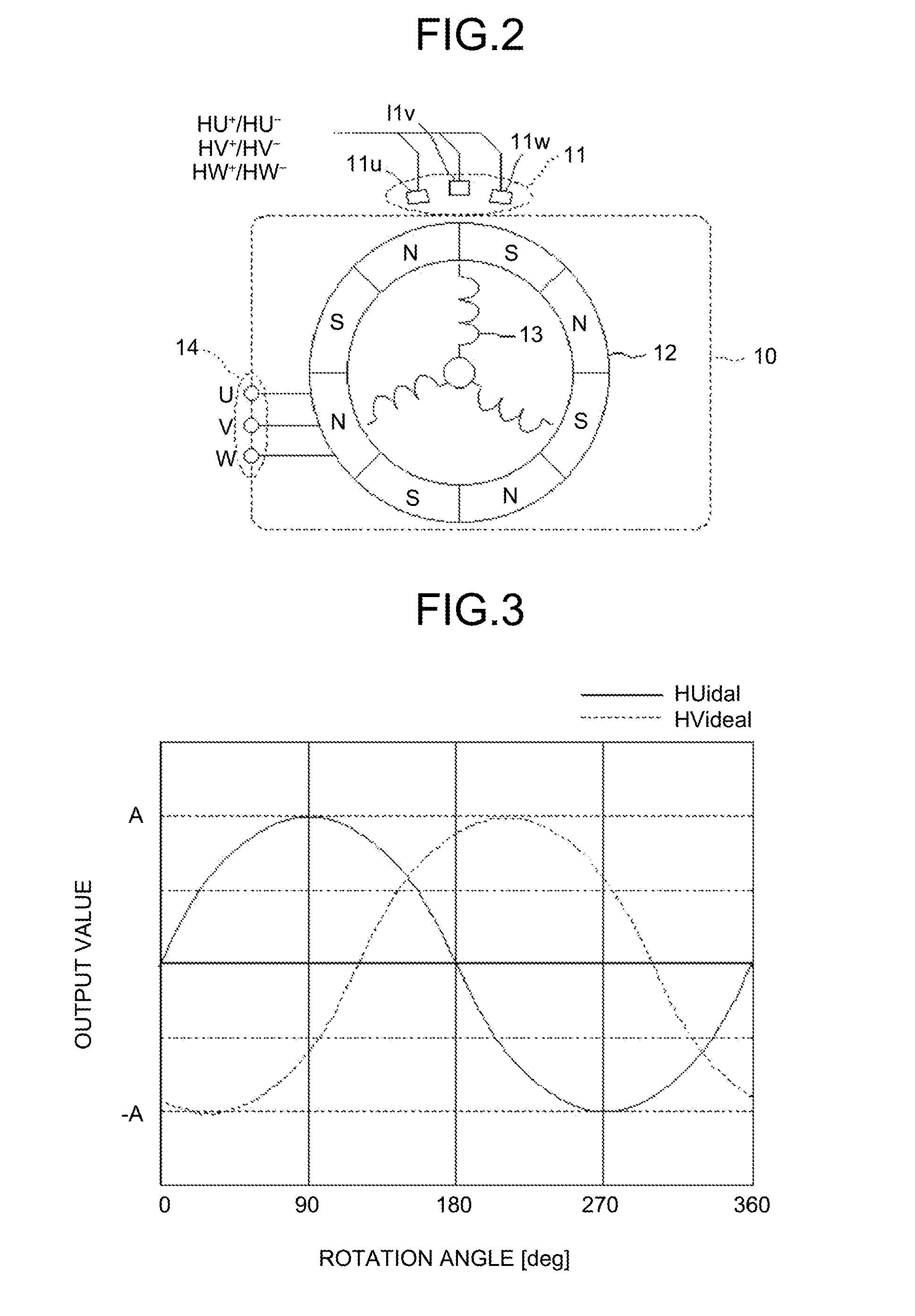
Rotation-angle detection device, image processing apparatus, and rotation-angle detection method
A rotation-angle detection device includes: an amplitude adjustment unit that performs correction to match amplitude values of multiple detection signals output from multiple rotation detection units to output corrected signals, the rotation detection units changing outputs in accordance with a rotation angle of a rotor and being provided such that the rotation detection units output the detection signals having different phases; a vector generation unit that performs addition and subtraction on two signals out of the corrected signals to generate two vector component signals that are perpendicular to each other; an amplitude correction unit that performs correction to match amplitudes of the two vector component signals to output corrected vector component signals; and a rotation-angle searching unit that searches for the rotation angle of the rotor on basis of a vector that is represented by the two corrected vector component signals to output a detection angle.
Owner:RICOH KK
Metal face inductive proximity sensor
ActiveUS20090189600A1To offer comfortReducing amount of field and energy lossMagnetic property measurementsUsing electrical meansProximity sensorEngineering
Metal face inductive proximity sensors and methods are presented for sensing the presence or absence of a target object in a target sensing area in which a coil system is operated to generate a magnetic field extending outward from the sensing face at a frequency in a range that maximizes a relative target effect for the sensing face area, material, and thickness, and a target material from which the target object is made to allow the protective advantages of metal sensing face materials while enhancing sensing distance by optimizing the ratio of the target energy loss to the energy loss in the metal face.
Owner:PEPPERL FUCHS GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com